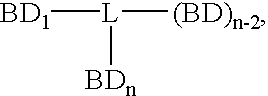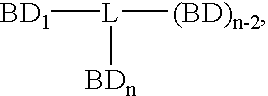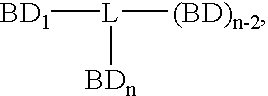Patents
Literature
476 results about "Neovascularization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
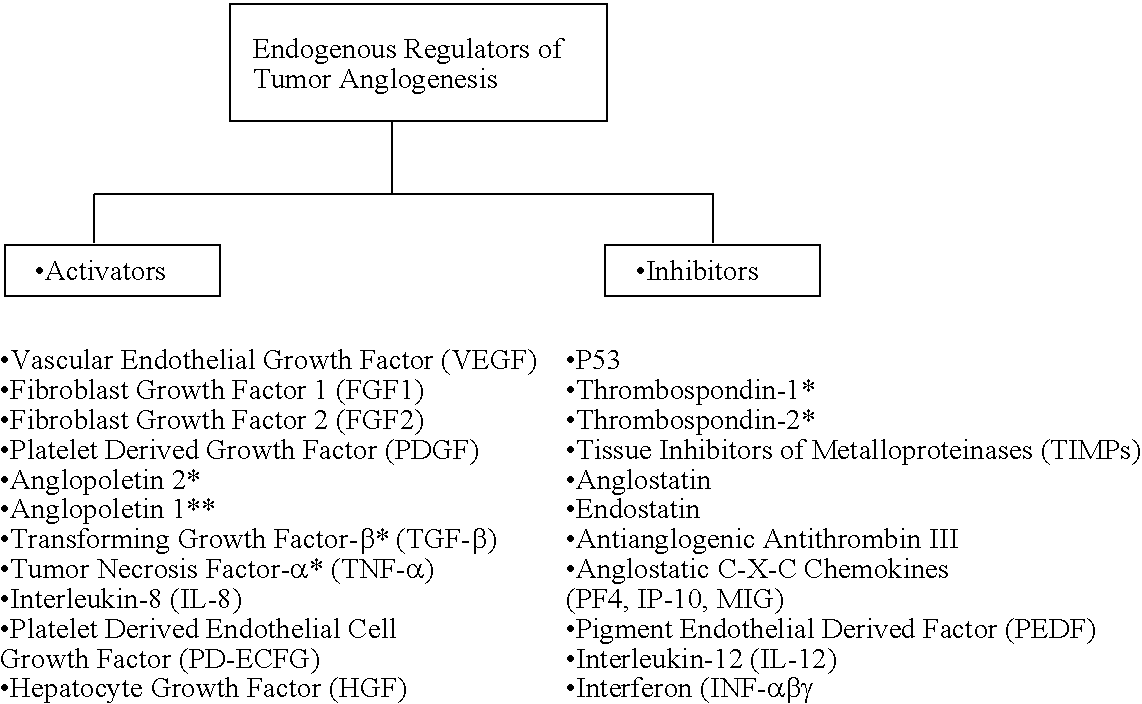
Neovascularization is the natural formation of new blood vessels (neo- + vascular + -ization), usually in the form of functional microvascular networks, capable of perfusion by red blood cells, that form to serve as collateral circulation in response to local poor perfusion or ischemia. Neovascularization is conventionally distinguished from angiogenesis in that angiogenesis is mainly characterized by the protrusion and outgrowth of capillary buds and sprouts from pre-existing blood vessels. Vasculogenesis can be synonymous with neovascularization but also often has reference instead to prenatal development and the initial embryologic formation of blood vessels. Growth factors that inhibit neovascularization include those that affect endothelial cell division and differentiation. These growth factors often act in a paracrine or autocrine fashion; they include fibroblast growth factor, placental growth factor, insulin-like growth factor, hepatocyte growth factor, and platelet-derived endothelial growth factor.
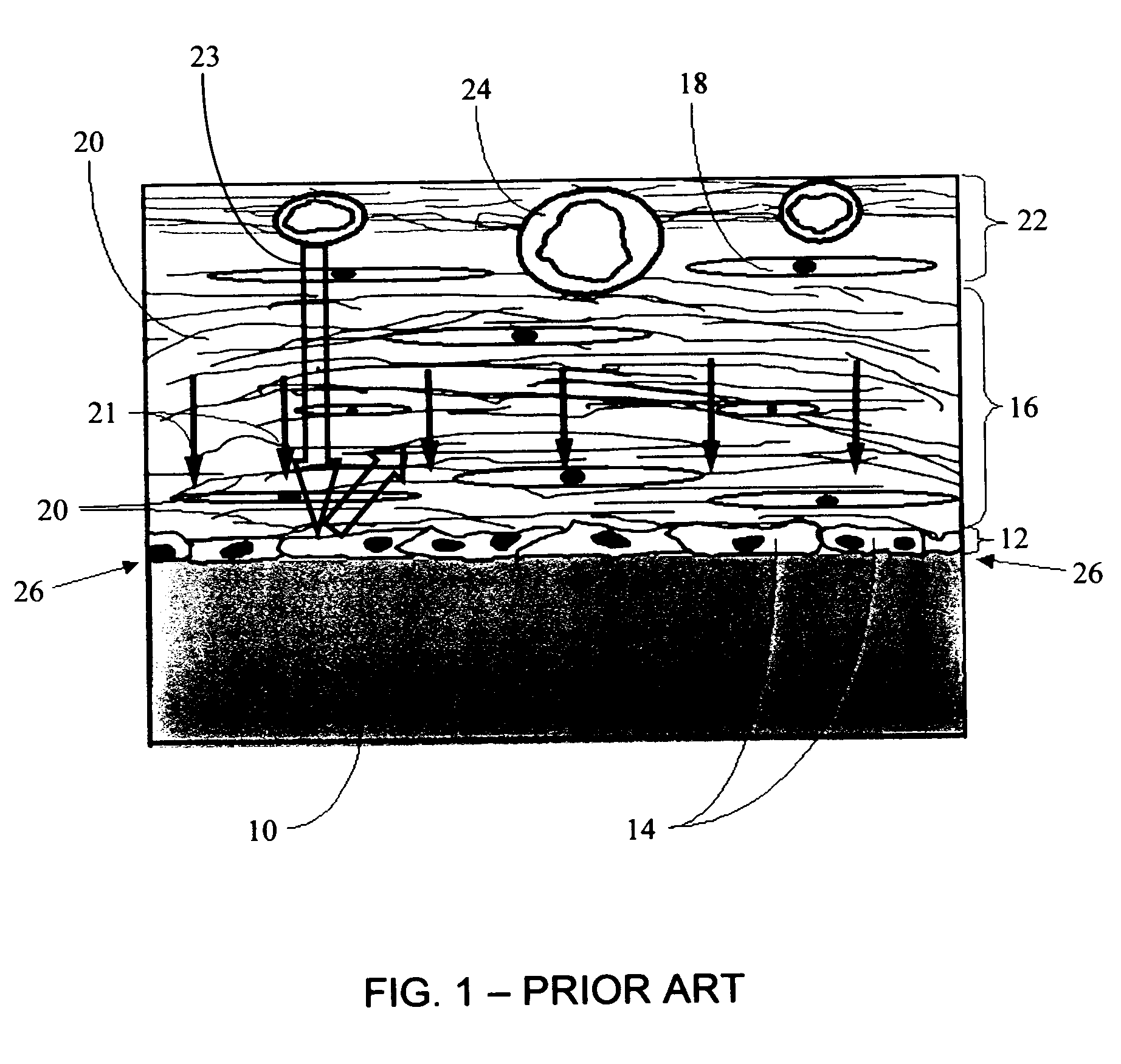
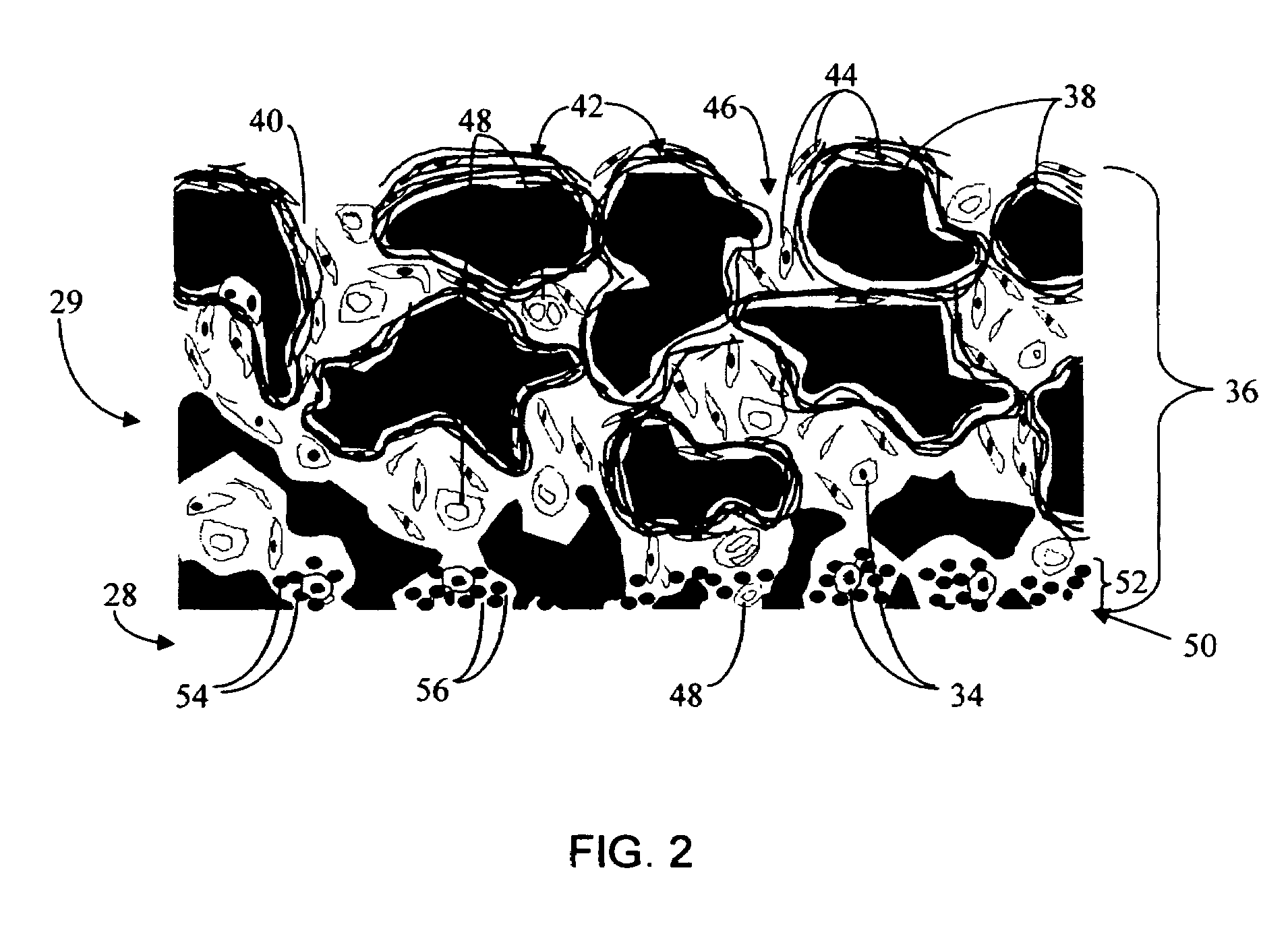
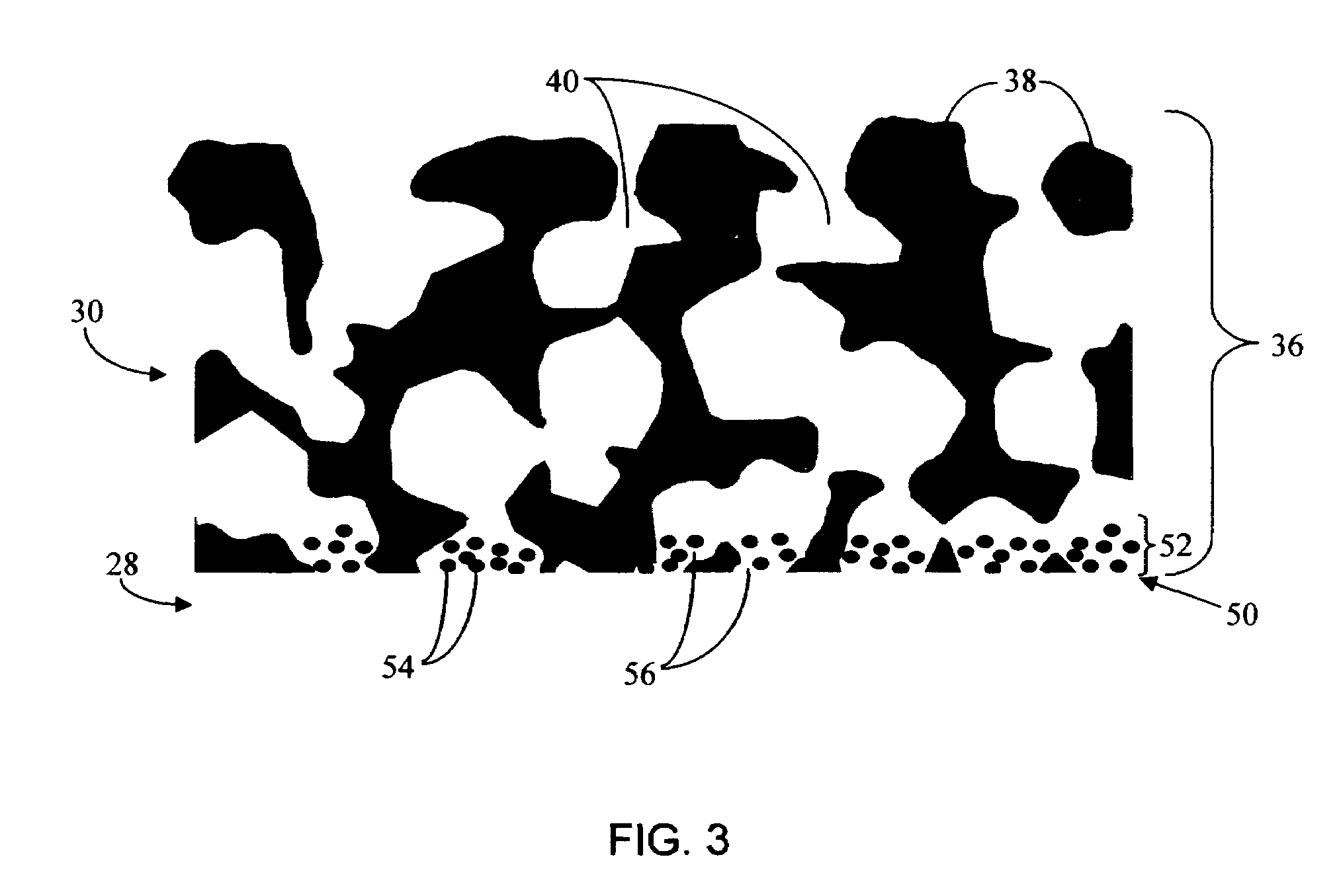
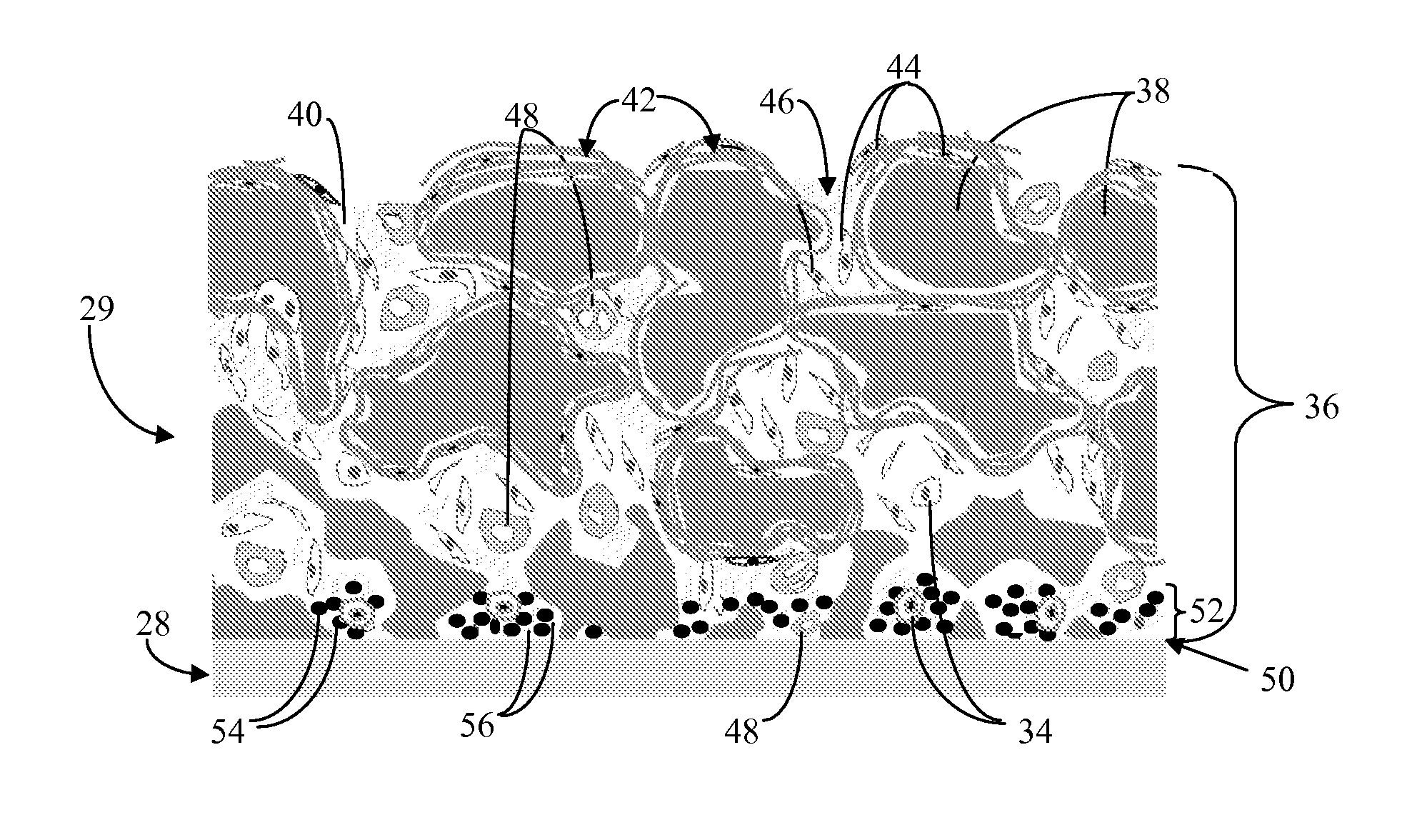
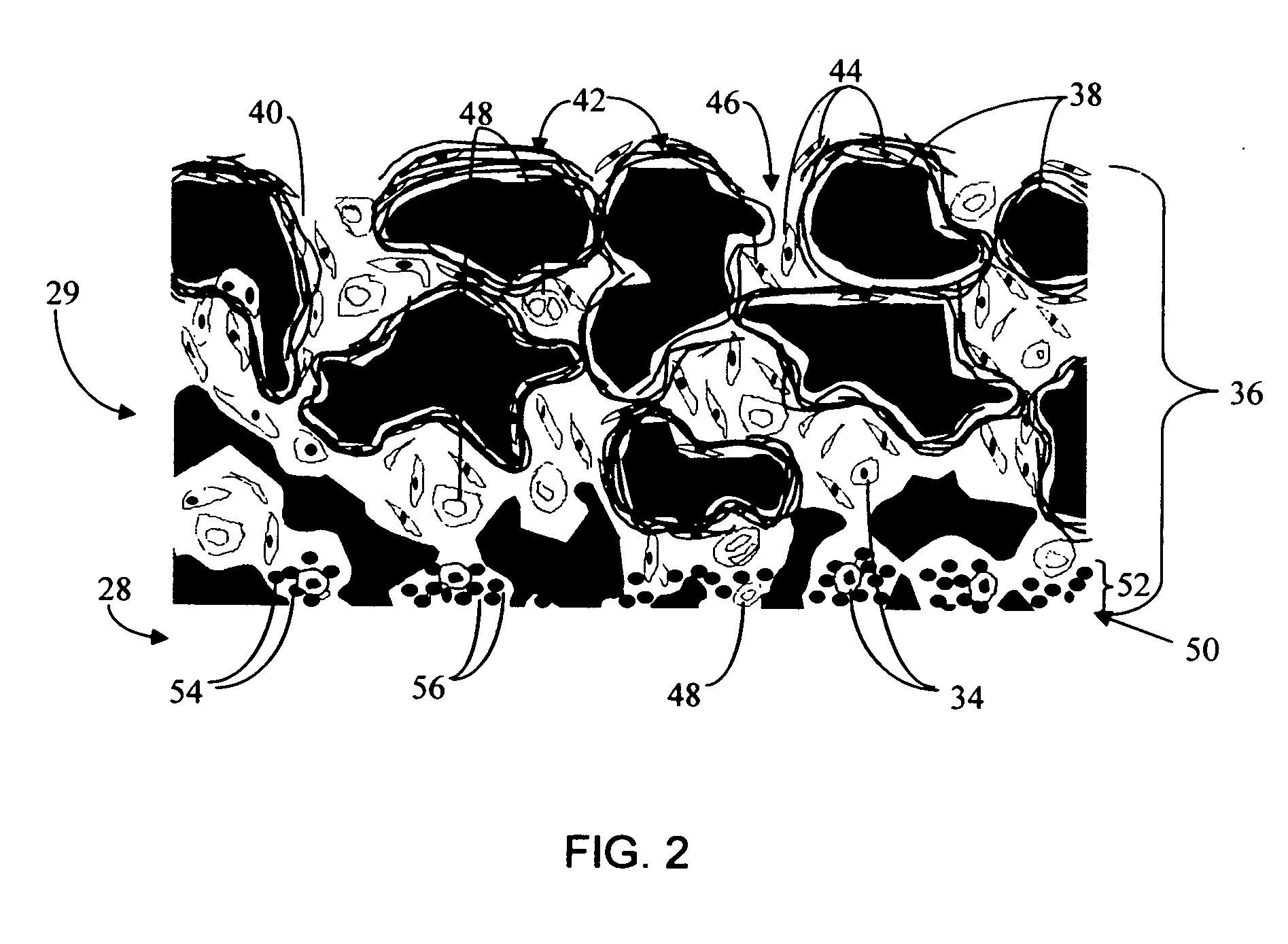
Biointerface membrane with macro-and micro-architecture
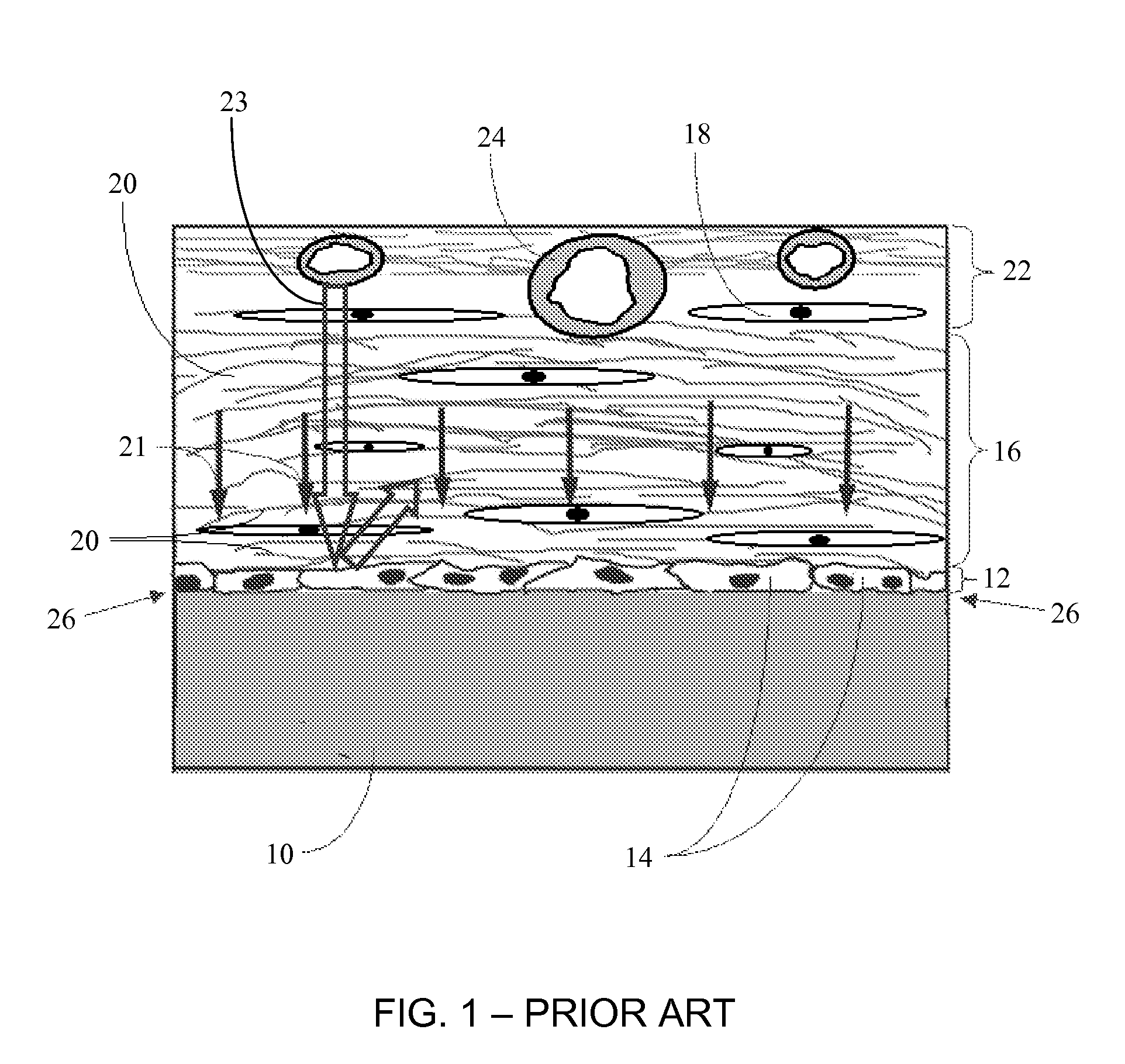
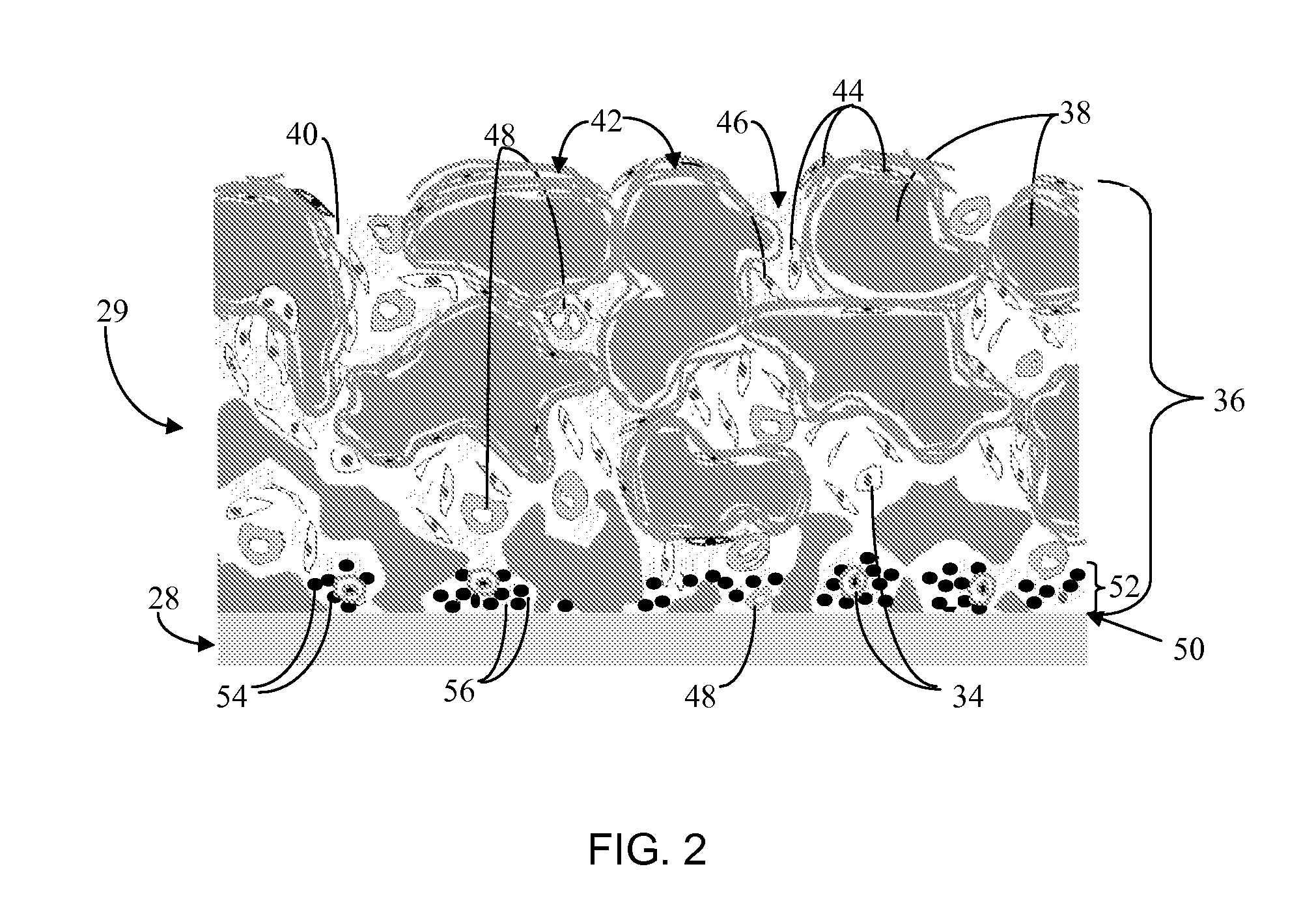
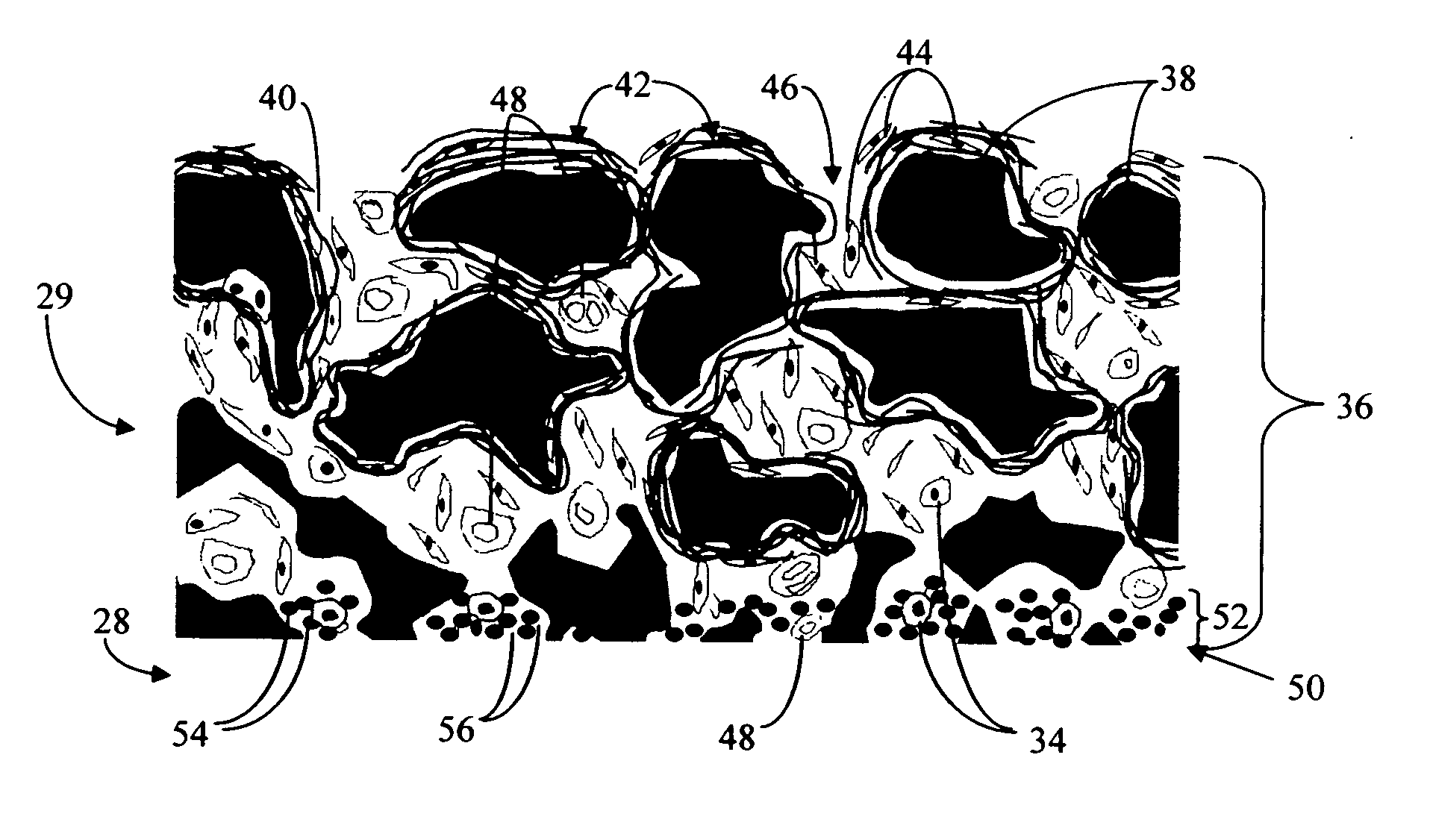
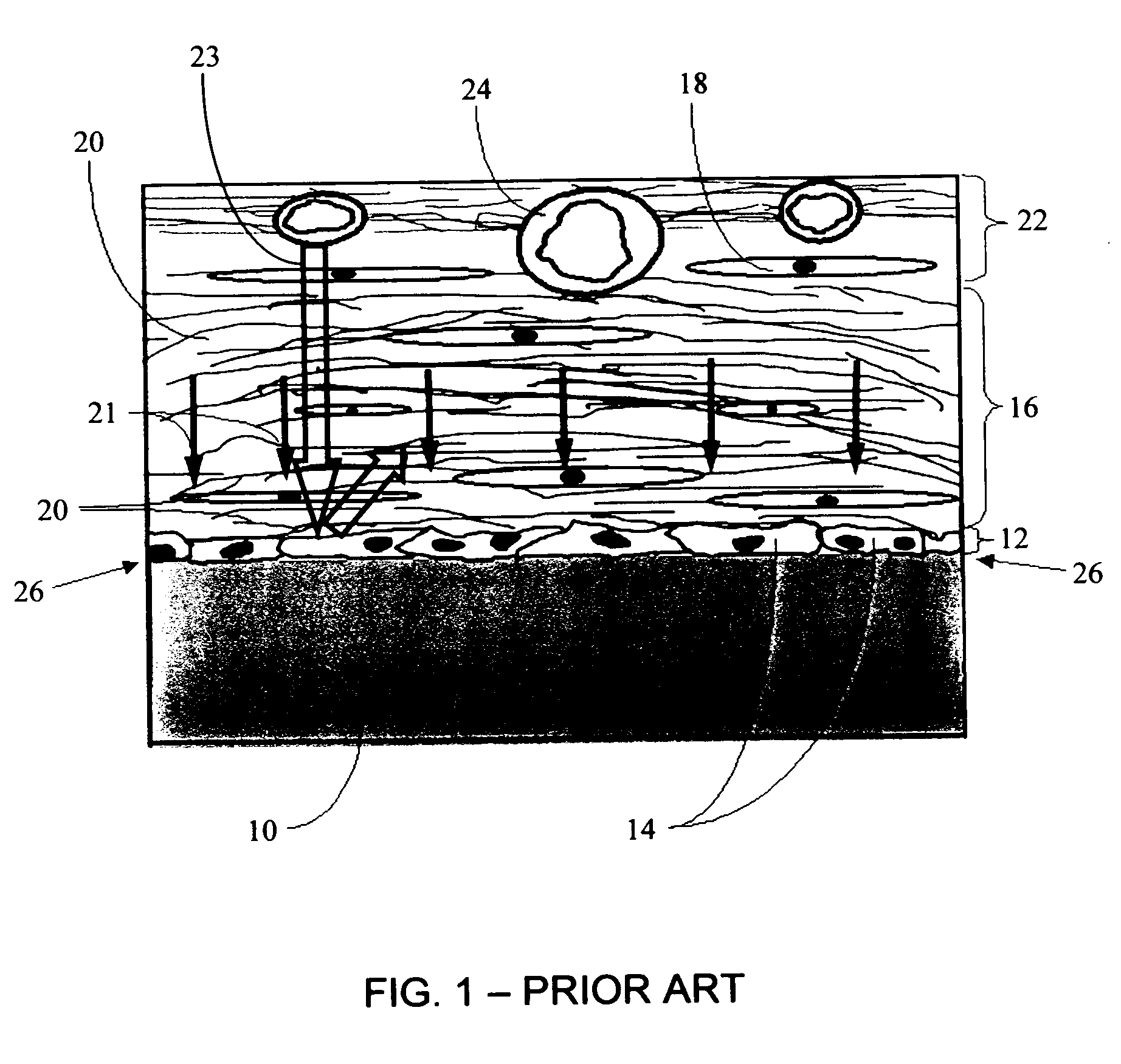
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
Biointerface with macro- and micro-architecture
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Biointerface with macro-and micro-architecture
Disclosed herein are biointerface membranes including a macro-architecture and a micro-architecture co-continuous with and bonded to and / or located within at least a portion of the macro-architecture. The macro- and micro-architectures work together to manage and manipulate the high-level tissue organization and the low-level cellular organization of the foreign body response in vivo, thereby increasing neovascularization close to a device-tissue interface, interfering with barrier cell layer formation, and providing good tissue anchoring, while reducing the effects of motion artifact, and disrupting the organization and / or contracture of the FBC. The biointerface membranes of the preferred embodiments can be utilized with implantable devices such as devices for the detection of analyte concentrations in a biological sample (for example, from a body), cell transplantation devices, drug delivery devices, electrical signal delivering or measuring devices, and / or combinations thereof.
Owner:DEXCOM
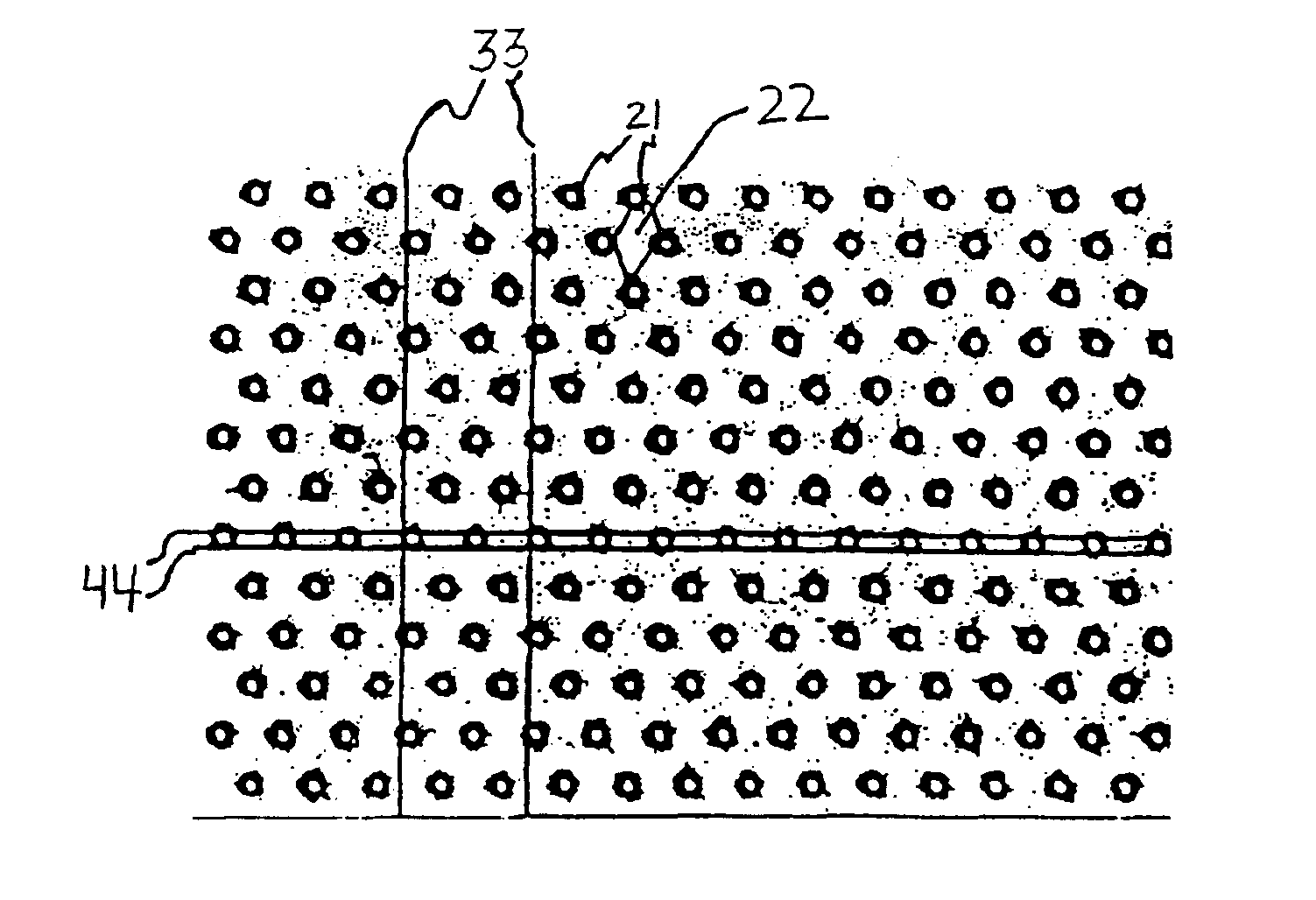
Neovascularization promoting membrane for bioimplants
A method of producing a biocompatible microporous membrane comprising the steps of providing a biocompatible membrane and using an energy beam to form a set of pores having a minor axis of less than 15 μm through the biocompatible membrane. One embodiment includes the steps of producing a first layer of material, defining a first set of pores; producing a second layer of material, defining a second set of pores and wherein the second set of pores is defined so as to cooperatively engage the first set of pores; and aligning and joining the first layer of material to the second layer of material to form a laminated membrane, having through-passageways formed by the first set of pores at least partially aligned with the second set of pores.
Owner:WAVEFORM TECH INC
Implant device for trans myocardial revascularization
InactiveUS6258119B1Direct accessPrevent implant detachmentStentsEar treatmentCardiac muscleAngiogenesis growth factor
A myocardial implant for insertion into a heart wall for trans myocardial revascularization (TMR) of the heart wall. The TMR implant provides for means to promote the formation of new blood vessels (angiogenesis), and has a flexible, elongated body that contains a cavity and openings through the flexible, elongated body from the cavity. The TMR implant includes a coaxial anchoring element integrally formed at one end for securing the TMR implant in the heart wall.
Owner:MYOCARDIAL STENTS
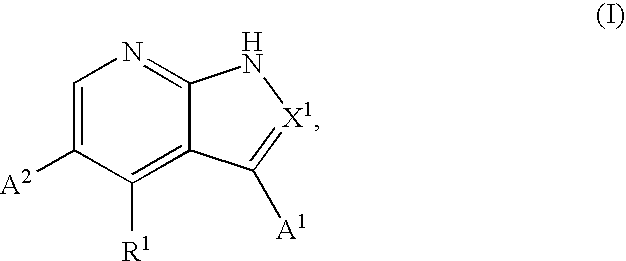
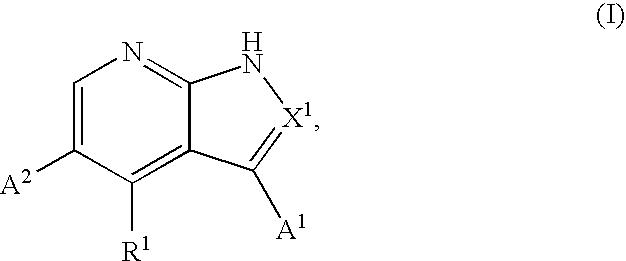
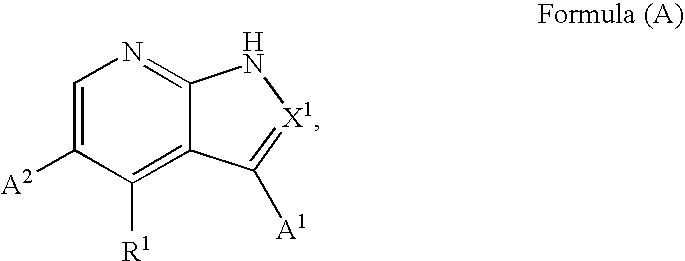
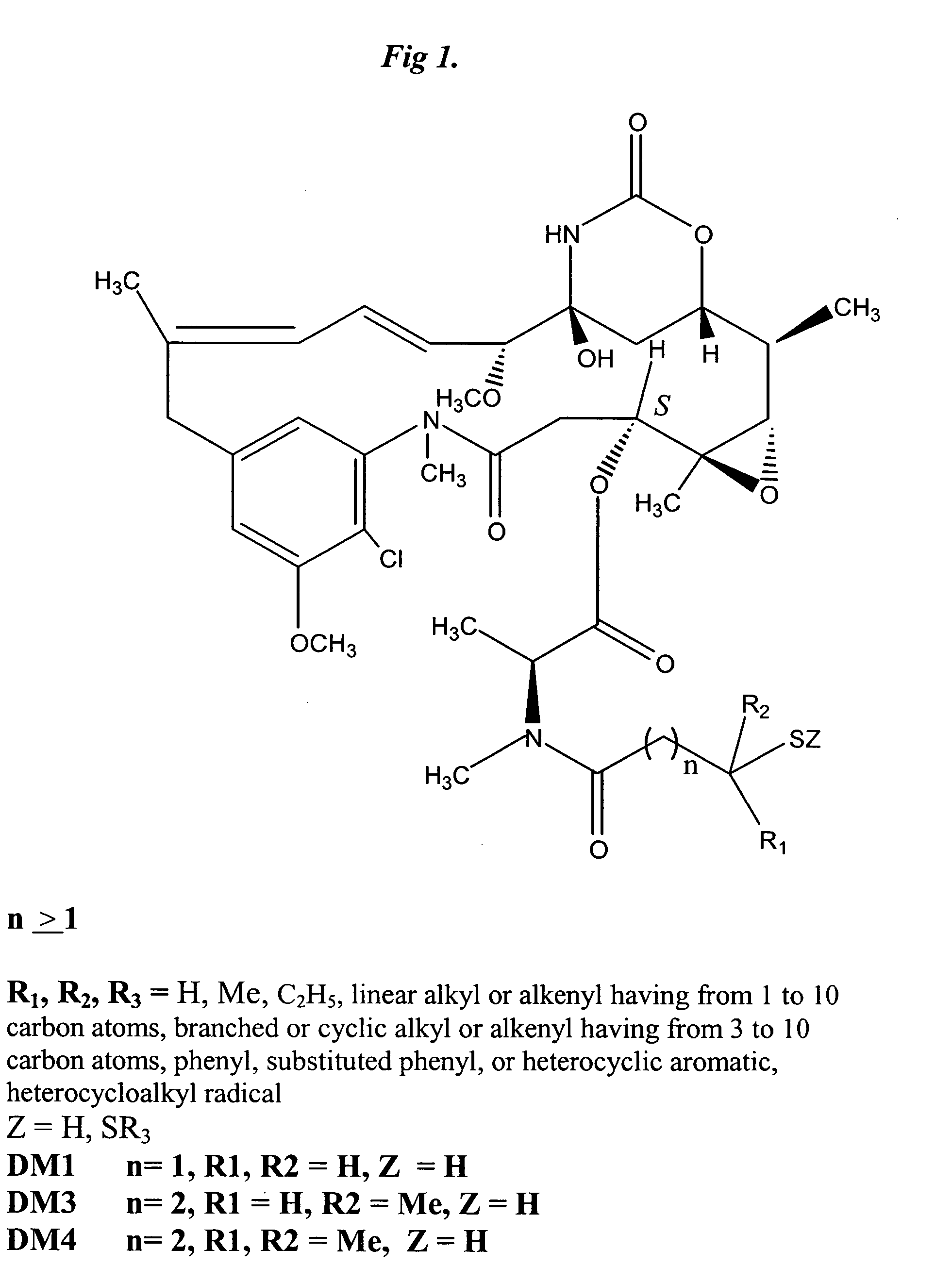
Substituted pyrrolopyridines and pyrazolopyridines as kinase modulators
Provided herein are substituted pyrrolopyridine heterocycles and substituted pyrazolopyridine heterocycles, pharmaceutical compositions comprising said heterocycles and methods of using said heterocycles in the treatment of disease. The heterocycles disclosed herein function as kinase modulators and have utility in the treatment of diseases such as cancer, allergy, asthma, inflammation, obstructive airway disease, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disease, infection, CNS disease, brain tumor, obesity, asthma, hematological disorder, degenerative neural disease, cardiovascular disease, or disease associated with angiogenesis, neovascularization, or vasculogenesis.
Owner:SGX PHARMA INC
System and method for tissue generation and bone regeneration
ActiveUS20070061015A1Promotes bone formationIncrease surface areaImpression capsBone implantDamages tissueActive agent
A system and method for the repair of damaged tissue and bones, congenitally missing tissue / cosmetic reconstruction of tissue is described. The system has a layered porous structure with a sufficiently large area of exposed pores to promote neo-vascularization as well as bone and tissue formation. The disclosed porous implant system can contain bioactive agents necessary for rapid tissue formation and keep ingrowth of unwanted tissue out of the implant surgical site. The implant can be reinforced with an additional, stronger polymer layer and / or may include an endoskeleton or exoskeleton for dimensional stability.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ARKANSAS
Injectable cross-linked polymeric preparations and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050003010A1Promote regenerationFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryCross-linkDamages tissue
A composition for promoting repair of damaged tissues, being a cross-linked alginate solution, which can be maintained in liquid form indefinitely (under constant conditions) and only gels in vivo. This cross-linked alginate solution is an ideal material to be used for tissue repair. Injection of said material into cardiac tissue post-myocardial infarct induced tissue regeneration. The invention provides such injectable solution, as well as compositions and method of preparation thereof. The invention also provides various methods and uses of the cross-linked alginate solution, for cardiac tissue regeneration, induction of neo-vascularization, enhancing SDF-1 expression and guiding stem cell chemotaxis, among others. A kit for tissue repair is also provided.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
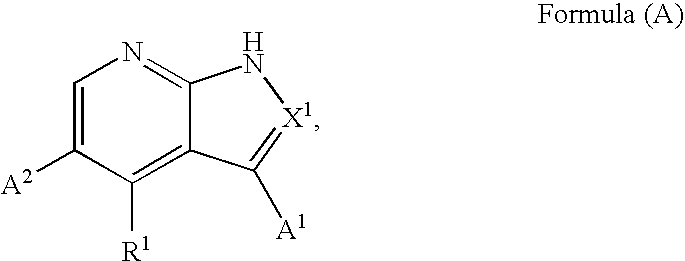
Substituted pyrrolopyridines and pyrazolopyridines as kinase modulators
Provided herein are substituted pyrrolopyridine heterocycles and substituted pyrazolopyridine heterocycles, pharmaceutical compositions comprising said heterocycles and methods of using said heterocycles in the treatment of disease. The heterocycles disclosed herein function as kinase modulators and have utility in the treatment of diseases such as cancer, allergy, asthma, inflammation, obstructive airway disease, autoimmune diseases, metabolic disease, infection, CNS disease, brain tumor, obesity, asthma, hematological disorder, degenerative neural disease, cardiovascular disease, or disease associated with angiogenesis, neovascularization, or vasculogenesis.
Owner:SGX PHARMA INC
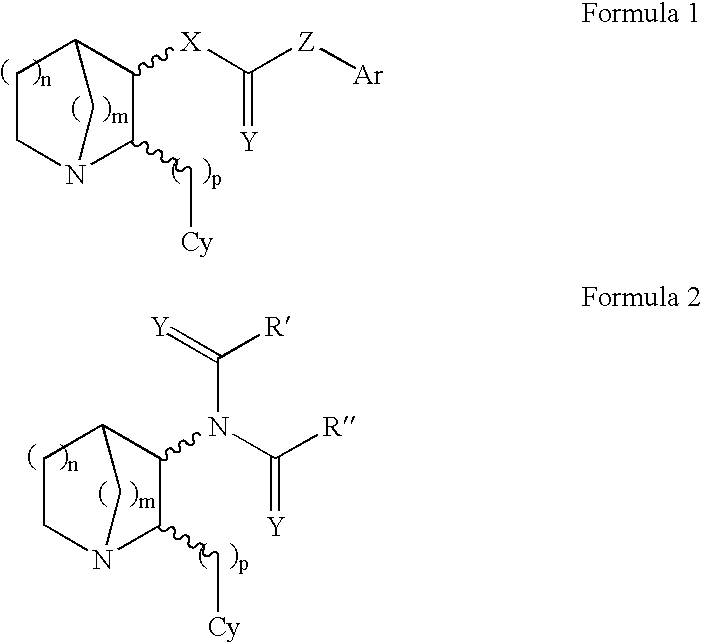
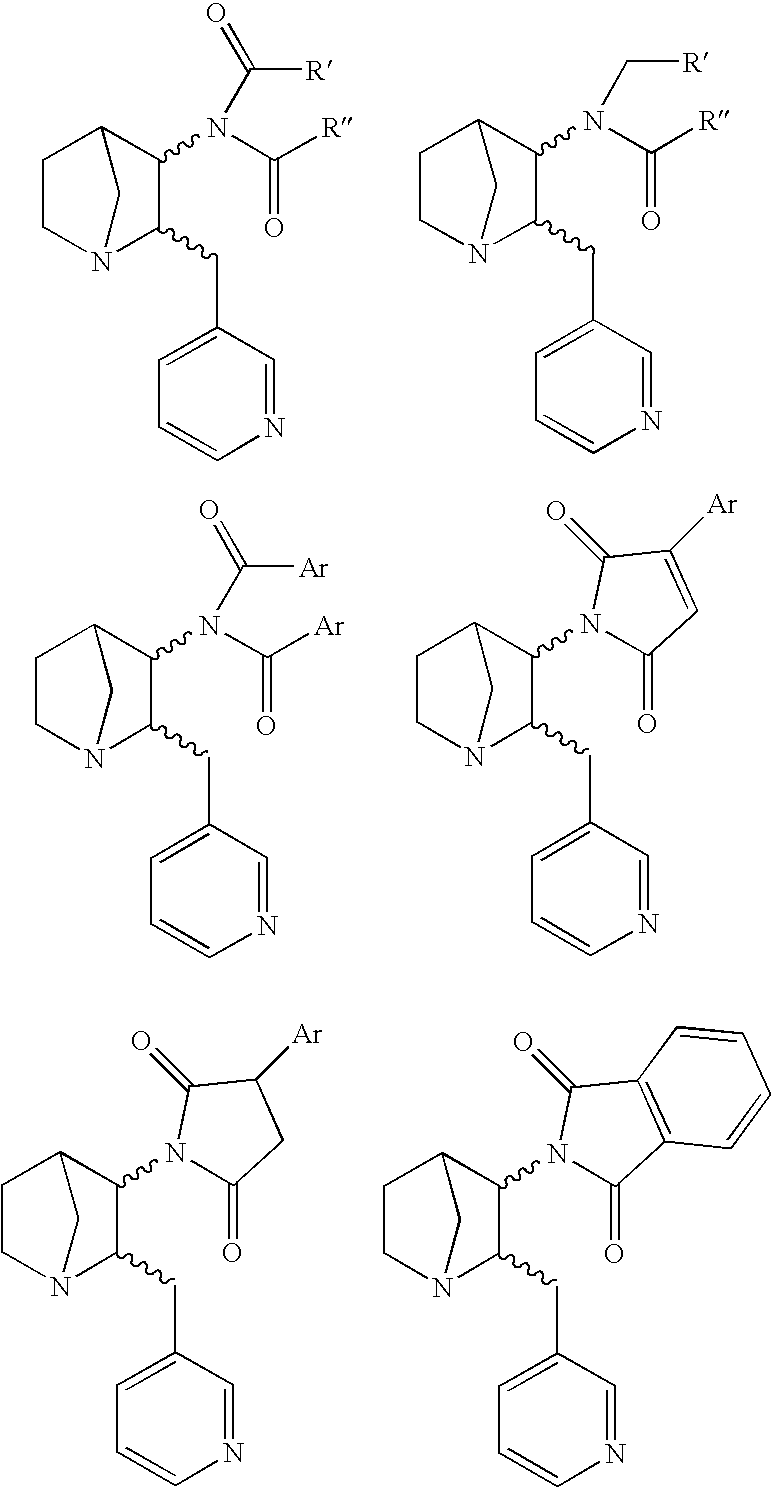
3-substituted-2(arylalkyl)-1-azabicycloalkanes and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS6953855B2Modulate activityWithout side effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseThiocarbamate
The present invention relates to 3-substituted-2-(arylalkyl)-1-azabicycloalkanes, methods of preparing the compounds and methods of treatment using the compounds. The azabicycloalkanes generally are azabicycloheptanes, azabicyclooctanes, or azabicyclononanes. The aryl group in the arylalkyl moiety is a 5- or 6-membered ring heteroaromatic, preferably 3-pyridinyl and 5-pyrimidinyl moieties, and the alkyl group is typically a C1-4 alkyl. The substituent at the 3-position of the 1-azabicycloalkane is a carbonyl group-containing moiety, such as an amide, carbamate, urea, thioamide, thiocarbamate, thiourea or similar functionality. The compounds exhibit activity at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), particularly the α7 nAChR subtype, and are useful towards modulating neurotransmission and the release of ligands involved in neurotransmission. Methods for preventing or treating conditions and disorders, including central nervous system (CNS) disorders, which are characterized by an alteration in normal neurotransmission, are also disclosed. Also disclosed are methods for treating inflammation, autoimmune disorders, pain and excess neovascularization, such as that associated with tumor growth.
Owner:ATTENUA INC
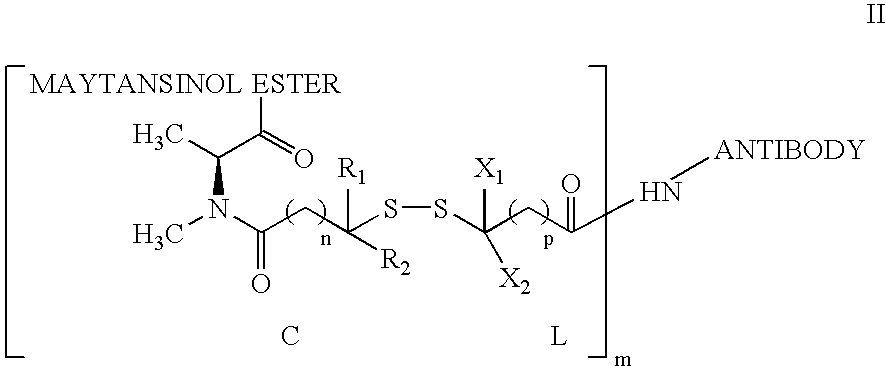
Anti-integrin immunoconjugates, methods and uses
The invention relates to conjugates of anti-integrin specific antibodies with cytotoxic compounds, the synthesis, selection, and use of such conjugates for use in cancer therapy or other diseases mediated by cell proliferation, cell migration, or inflammation and which pathology involves angiogenesis or neovascularization of new tissue. In addition the invention relates to combination therapy of such diseases wherein the treatment comprises use of said conjugates in combination with one or more other treatment modalities including but not limited to: chemotherapy, surgery or radiation therapy. The preferred conjugates contain maytansinoid compounds linked to the antibody by a disulfide linkage, and preferred chemotherapeutic agents are doxorubicin, a taxane, a camptothecin, a podophyllotoxin, a nucleoside analog, or a pyrimidine analog.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC +1
ANGIOSTATIC COMPOSITIONS COMPRISING TRUNCATED TYROSYL-tRNA SYNTHETASE POLYPEPTIDES AND METHODS OF USING SAME
InactiveUS20110104139A1Provide activitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTyrosyl-tRNA SynthetaseAngiogenesis growth factor
Angiostatic compositions are provided comprising truncated forms of tyrosyl tRNA synthetase polypeptides. Also provided are methods of using such compositions in the treatment of conditions that benefit from decreased angiogenesis and / or neovascularization.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
Drug delivery systems and methods for treating neovascularization
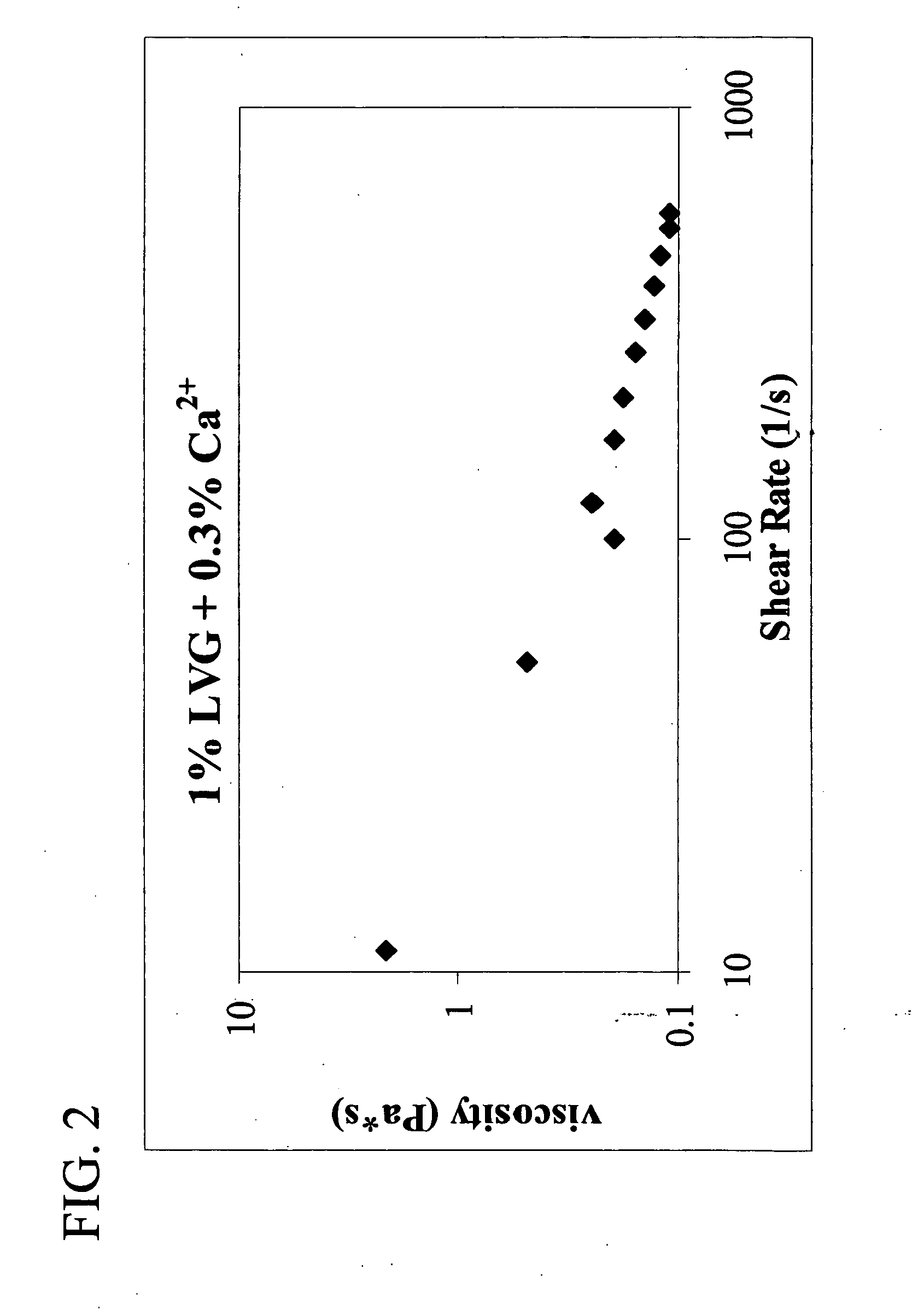
InactiveUS20100098772A1Effective treatmentImprove clarityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideShear rateNeovascularization
Anti-angiogenesis compositions, and methods of using such compositions, useful for intraocular to treat neovascularization. The compositions can have viscosities at about 25° C. of at least about 10 cps or about 100 cps at a shear rate of 0.1 / second. In a preferred embodiment, the viscosity at 25° C. is in the range of from about 80,000 cps to about 300,000 cps.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
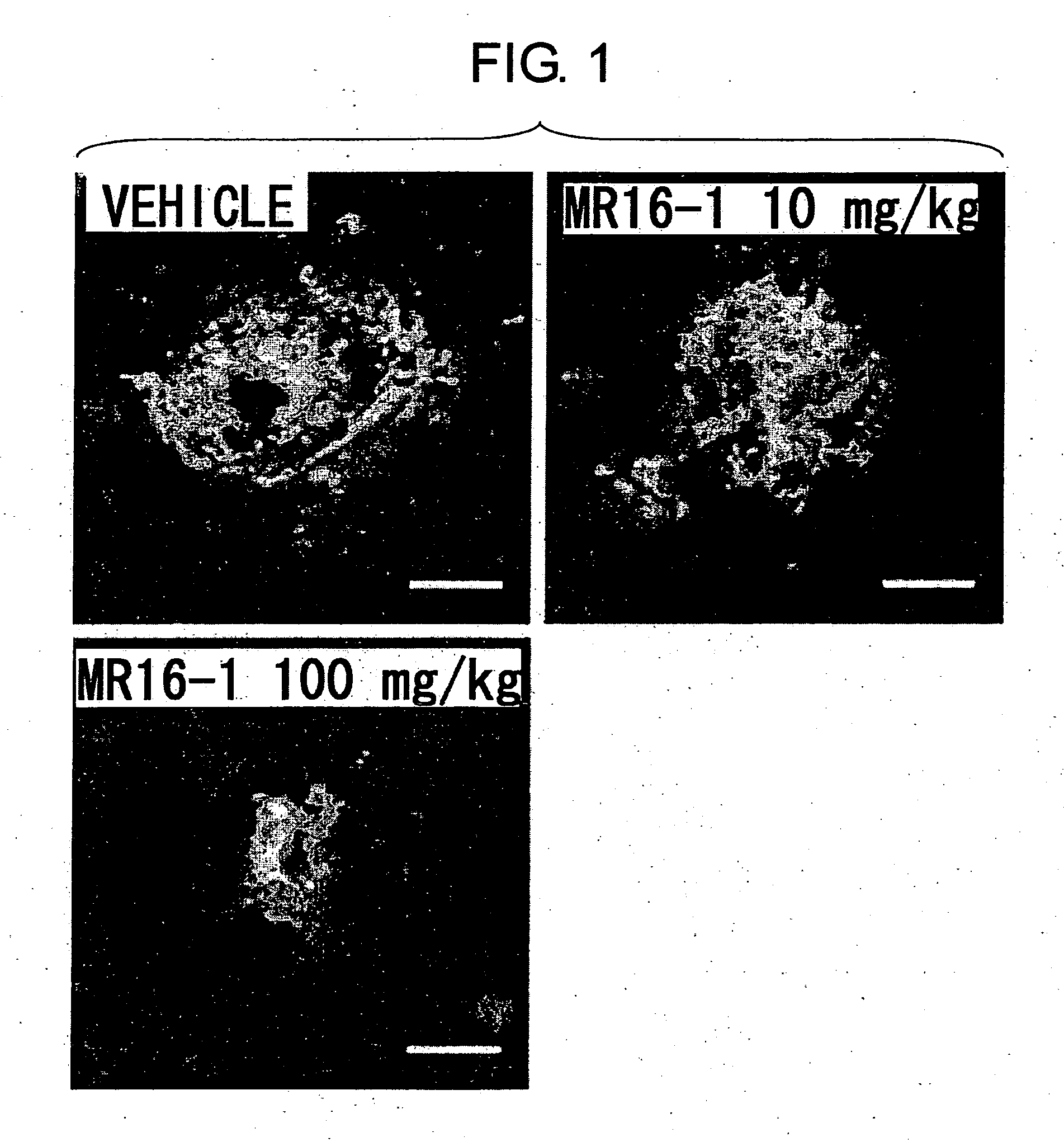
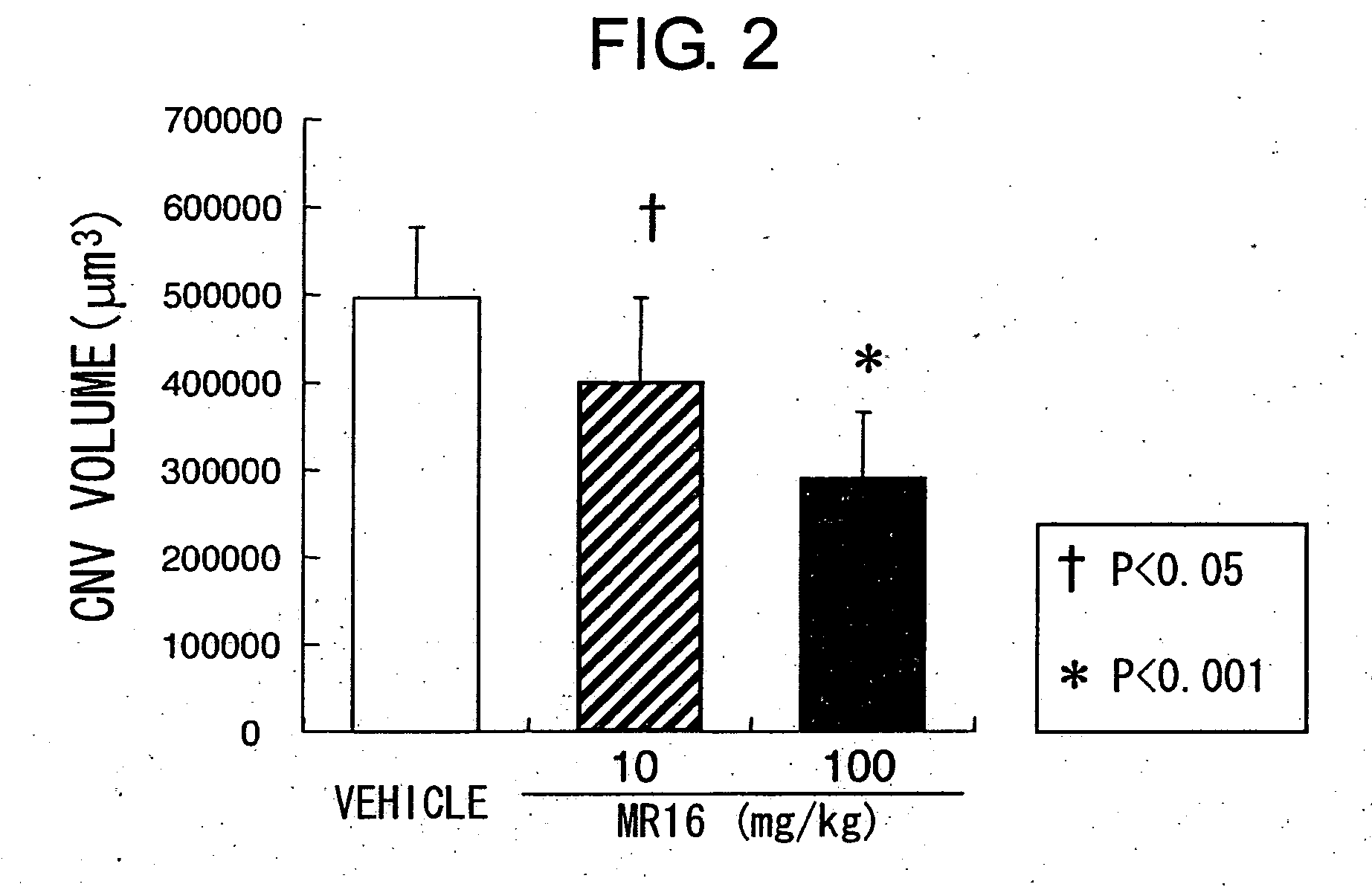
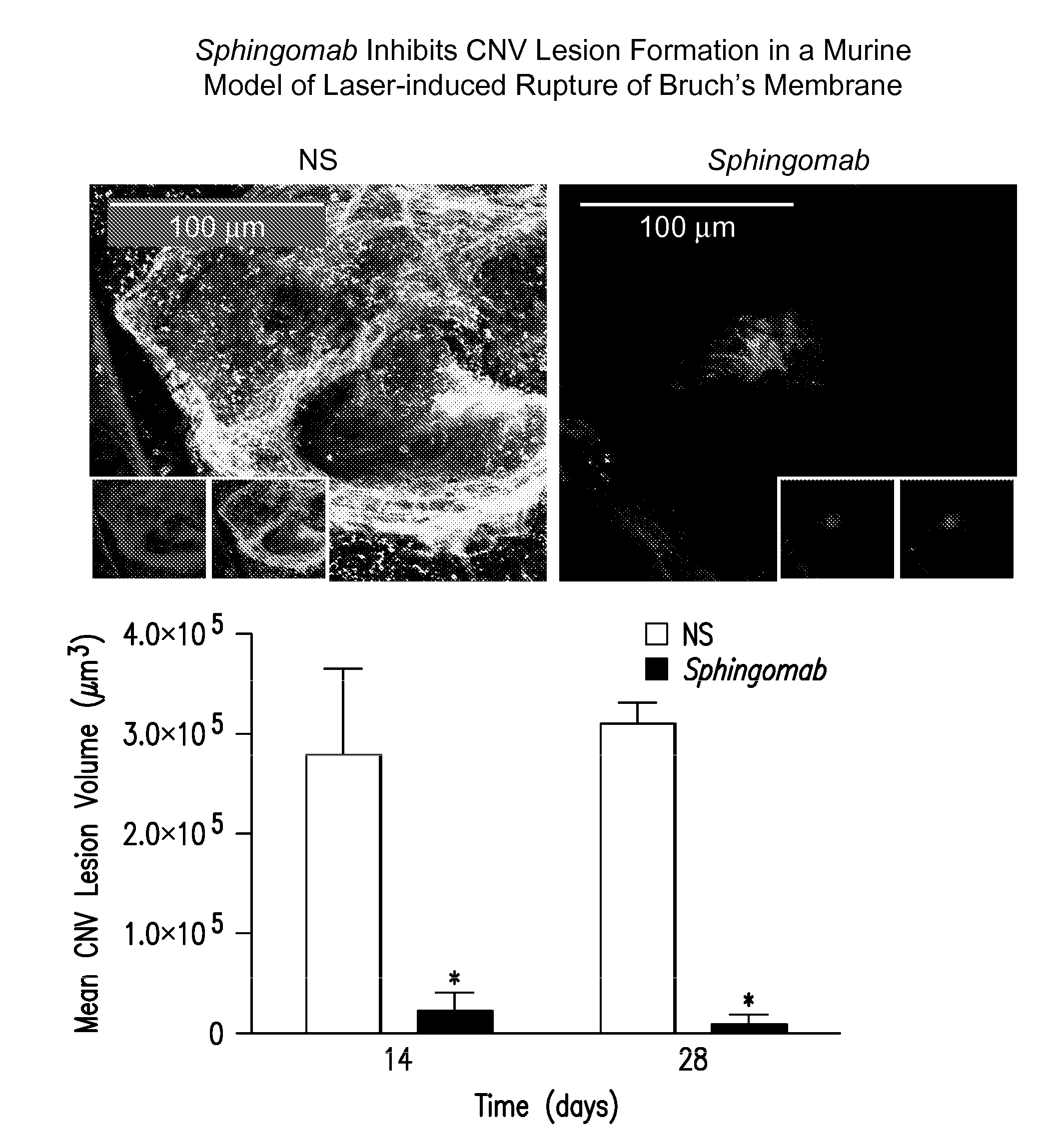
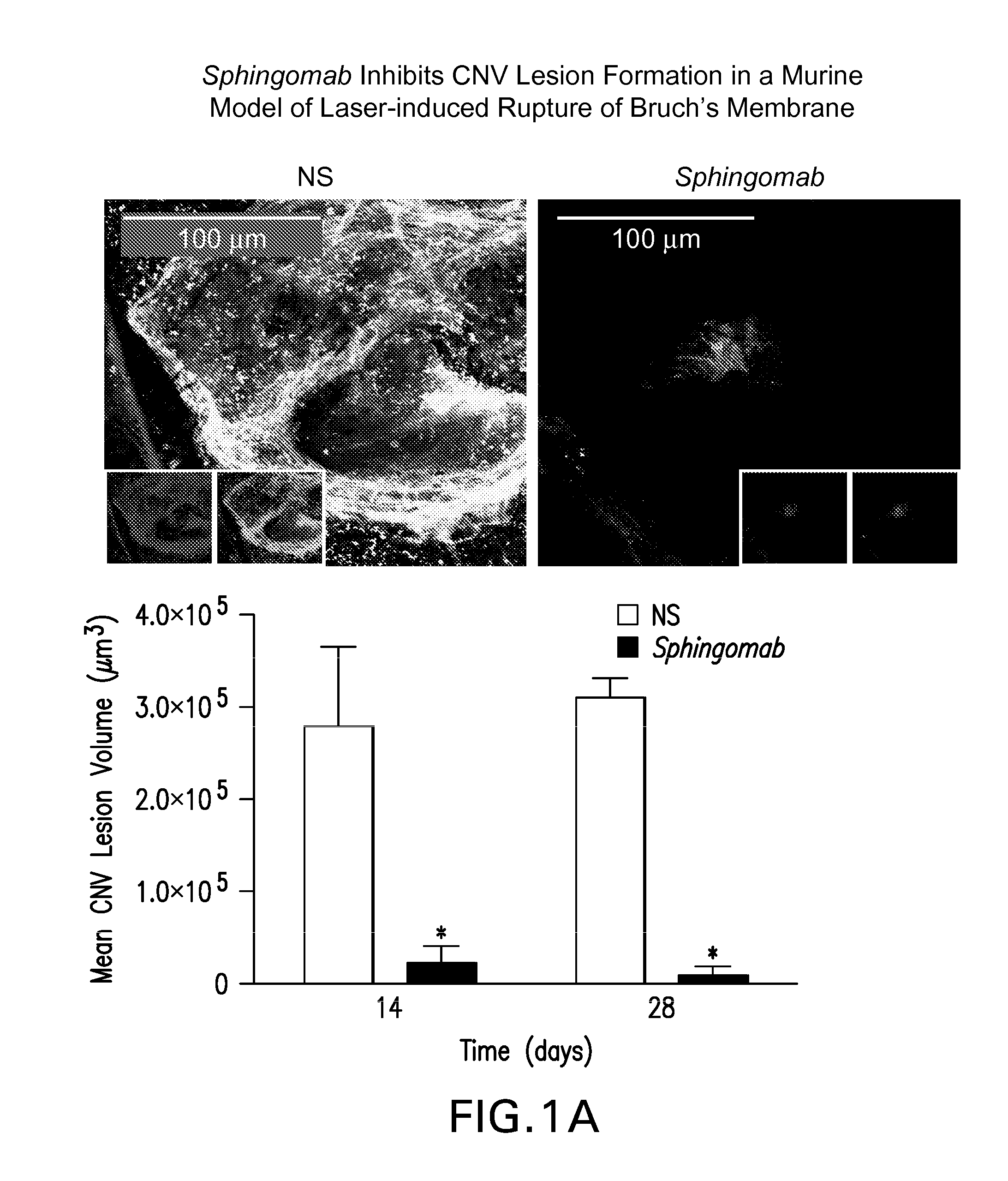
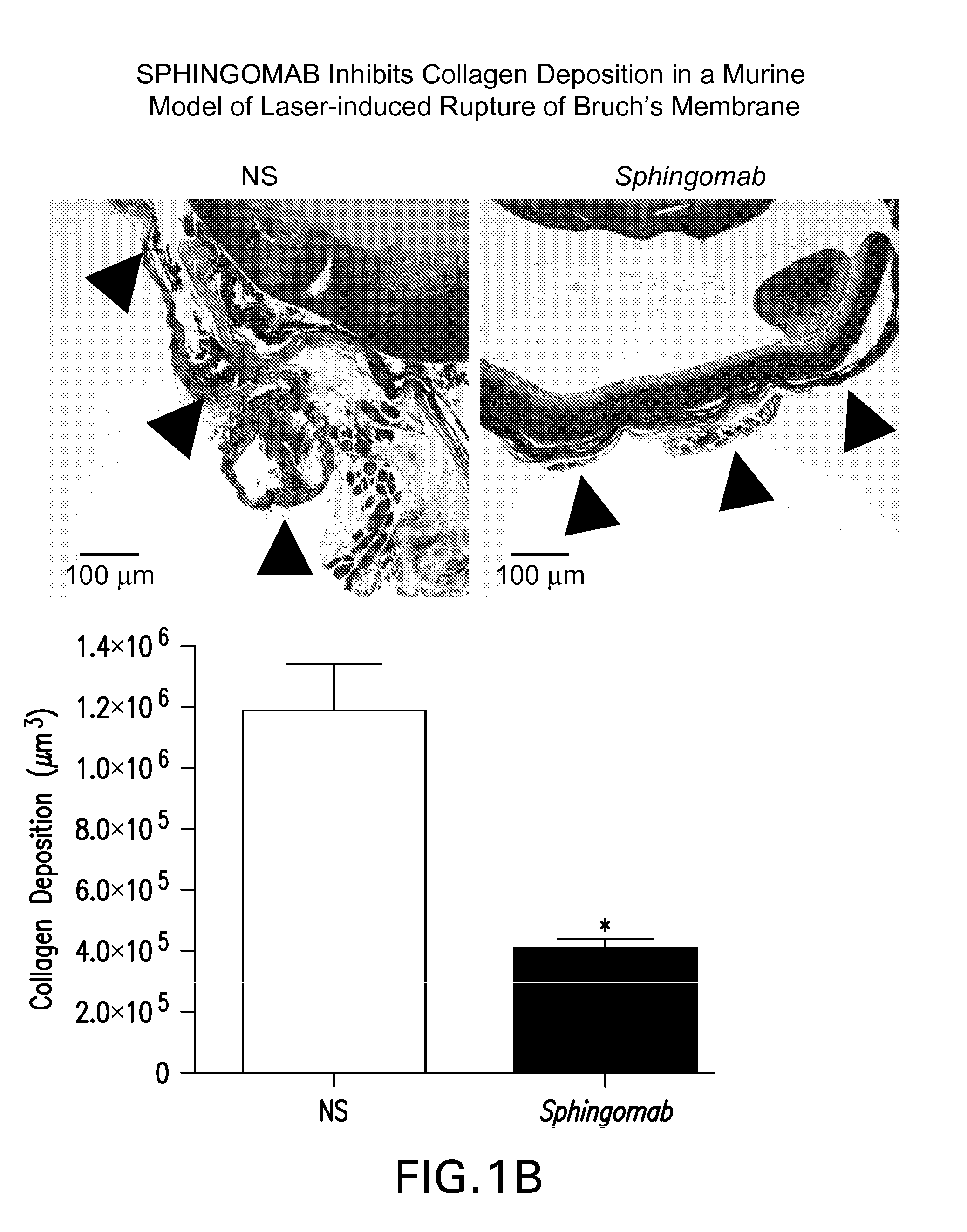
Method of inhibiting choroidal neovascularization
ActiveUS20050187241A1Reduce lossesQuick identificationBiocideSenses disorderAngiogenesis growth factorNeovascularization
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for inhibiting unwanted angiogenesis, particularly those of ocular tissues. The treatment, inhibition, and / or prevention of choroidal neovasculature (CNV) is provided, along with an animal model for CNV and imaging techniques that permit the screening of potential agents as anti-angiogenesis and anti-CNV agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Scaffold for tissue engineering, artificial blood vessel, cuff, and biological implant covering member
InactiveUS20050107868A1Reduce foreign body reactionsImprove patencyTissue cultureBlood vesselsSubcutaneous tissueTunnel infection
The invention provides a porous scaffold for tissue engineering which allows easy cell engraftment and cell culture and thus enables stable organization and an artificial blood vessel which exhibits high patency rate even if the inner diameter is small. The scaffold for tissue engineering is made of thermoplastic resin which forms a porous three-dimensional network structure having communication property, wherein the porous three-dimensional network structure has an average pore diameter of from 100 to 650 μm and an apparent density of from 0.01 to 0.5 g / cm3. The artificial blood vessel is composed of this scaffold. The invention provides a cuff which allows easy infiltration of cells from living subcutaneous tissues, easy engraftment of cells, and neovascularization of capillary vessels so as to obtain robust bonding with subcutaneous tissues and, as a result, ensures separation of a wounded portion from the outside, thereby blocking exacerbation factors such as bacterial infection on healing and inhibiting progression of downgrowth. That is, the invention provides a cuff with none or little infection trouble such as tunnel infection. The cuff comprises a porous three-dimensional network structure which is made of thermoplastic resin or thermosetting resin and has communication property, wherein the porous three-dimensional network structure has an average pore diameter of from 100 to 1000 μm and apparent density of from 0.01 to 0.5 g / cm3. The invention provides a biological implant covering member which allows easy infiltration of cells from living subcutaneous tissues, easy engraftment of cells, and organization, thereby obtaining robust bonding with native tissues and therefore protecting a living body from adverse effect which may occur due to the insertion of a biological implantation member into the living body. The biological implant covering member comprises a porous three-dimensional network structure which is made of thermoplastic resin or thermosetting resin and has communication property, wherein the porous three-dimensional network structure has an average pore diameter of from 100 to 1000 μm and apparent density of from 0.01 to 0.5 g / cm3.
Owner:JAPAN AS REPRESENTED BY PRESIDENT OF NAT CARDIOVASCULAR +2
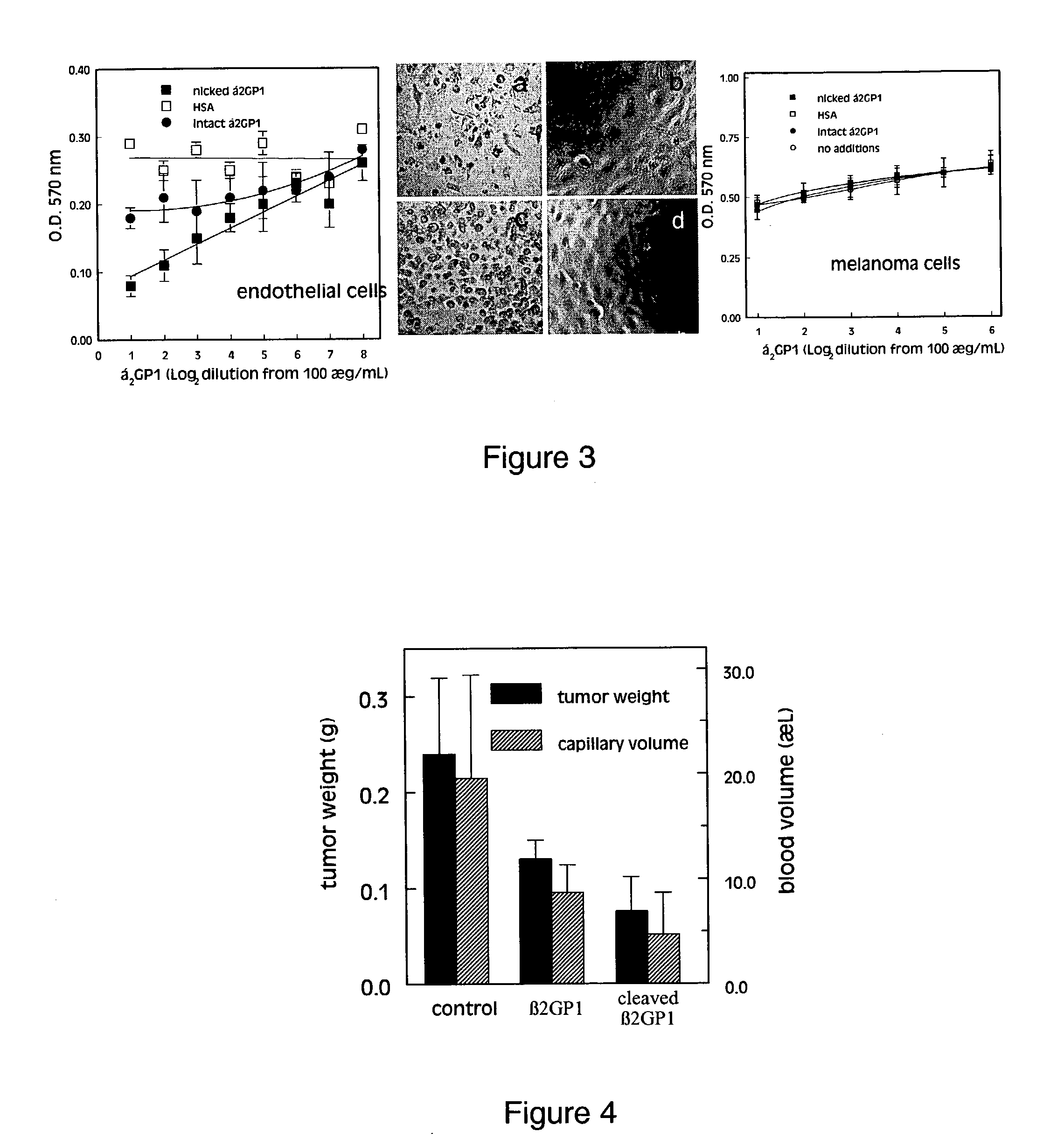
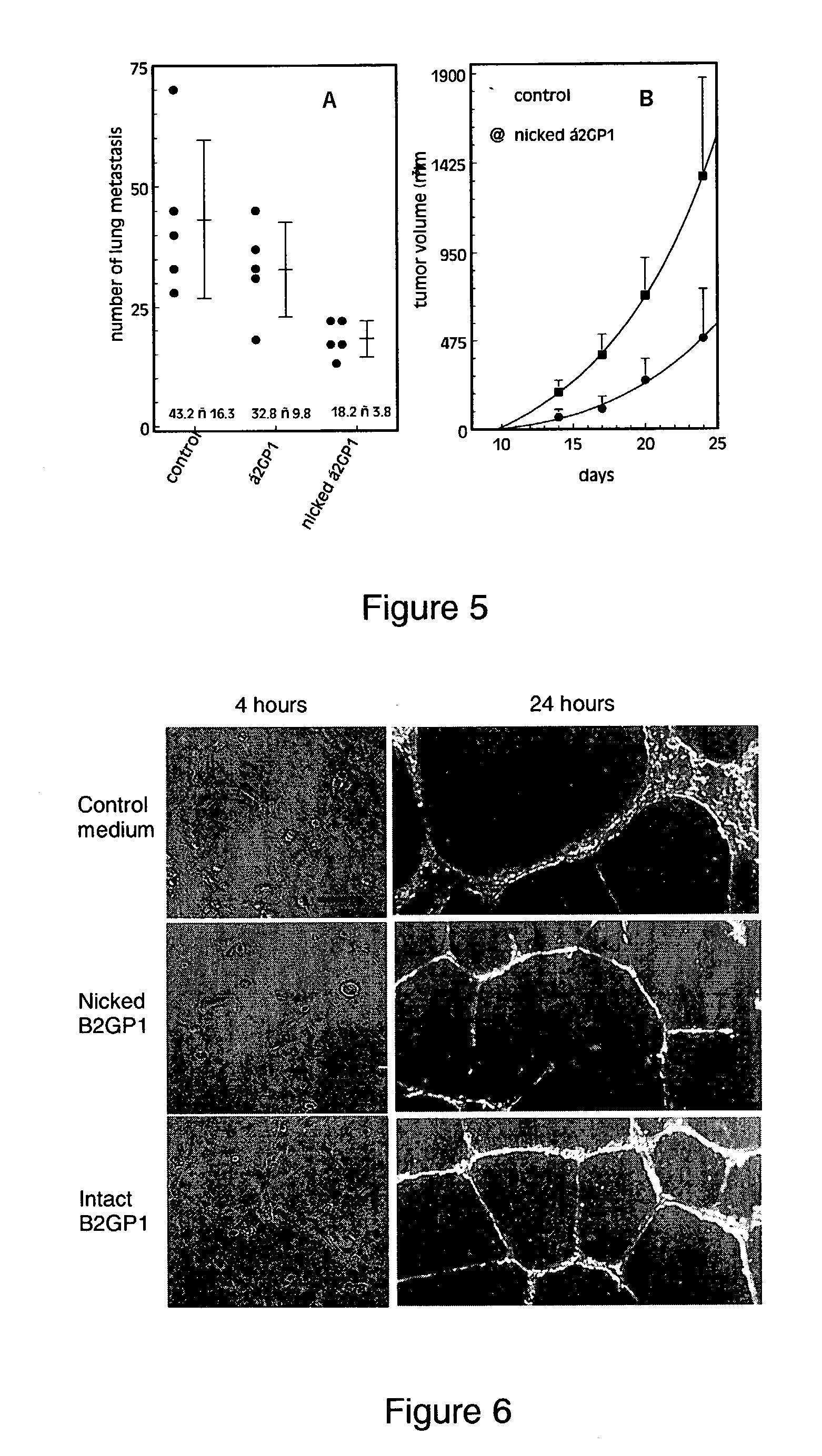
Beta-2-glycoprotein is an inhibitor of angiogenesis
The present disclosure provides a method of inhibiting angiogenesis within a tissue of interest by providing either intact or nicked beta2-Glycoprotein 1 (beta2GP1) to cells associated with the tissue. The presence of beta2GP1 inhibits angiogenesis within the tissue, in part by preventing neovascularization into the tissue. The disclosure also provides a method for treating tumors by providing beta2GP1 to the tumor.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Promoters exhibiting endothelial cell specificity and methods of using same for regulation of angiogenesis
Isolated polynucleotide sequences exhibiting endothelial cell specific promoter activity, novel cis regulatory elements and methods of use thereof enabling treatment of diseases characterized by aberrant neovascularization or cell growth are disclosed.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
Multivalent protein conjugate with multiple ligand-binding domains of receptors
InactiveUS20030064053A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifPeptide/protein ingredientsWound healingAbnormal cell
The present invention provides compositions and methods for treating abnormal cell proliferation and for regulating angiogenesis. In particular, multivalent protein conjugates (MVPs) are constructed to include multiple ligand-binding domains of different receptors and utilized to target multiple, different ligands that are involved in regulation of cell growth and neovascularization. The MVPs of the present invention can be used to treat various conditions associated with abnormal cell proliferation and angiogenesis such as cancer and cardiovascular disorders, as well as to promote wound healing.
Owner:ABMAXIS
Novel methods, compositions and devices for inducing neovascularization
The invention provides methods of inducing neovascularization in a subject in need thereof. The invention further provides compositions, devices and implantable products generated from conditioned media, and in particular, from conditioned media from cultured umbilical cord populations. These compositions are useful for inducing neovascularization. The invention also provides methods of distributing compositions, devices and products to health care professionals.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
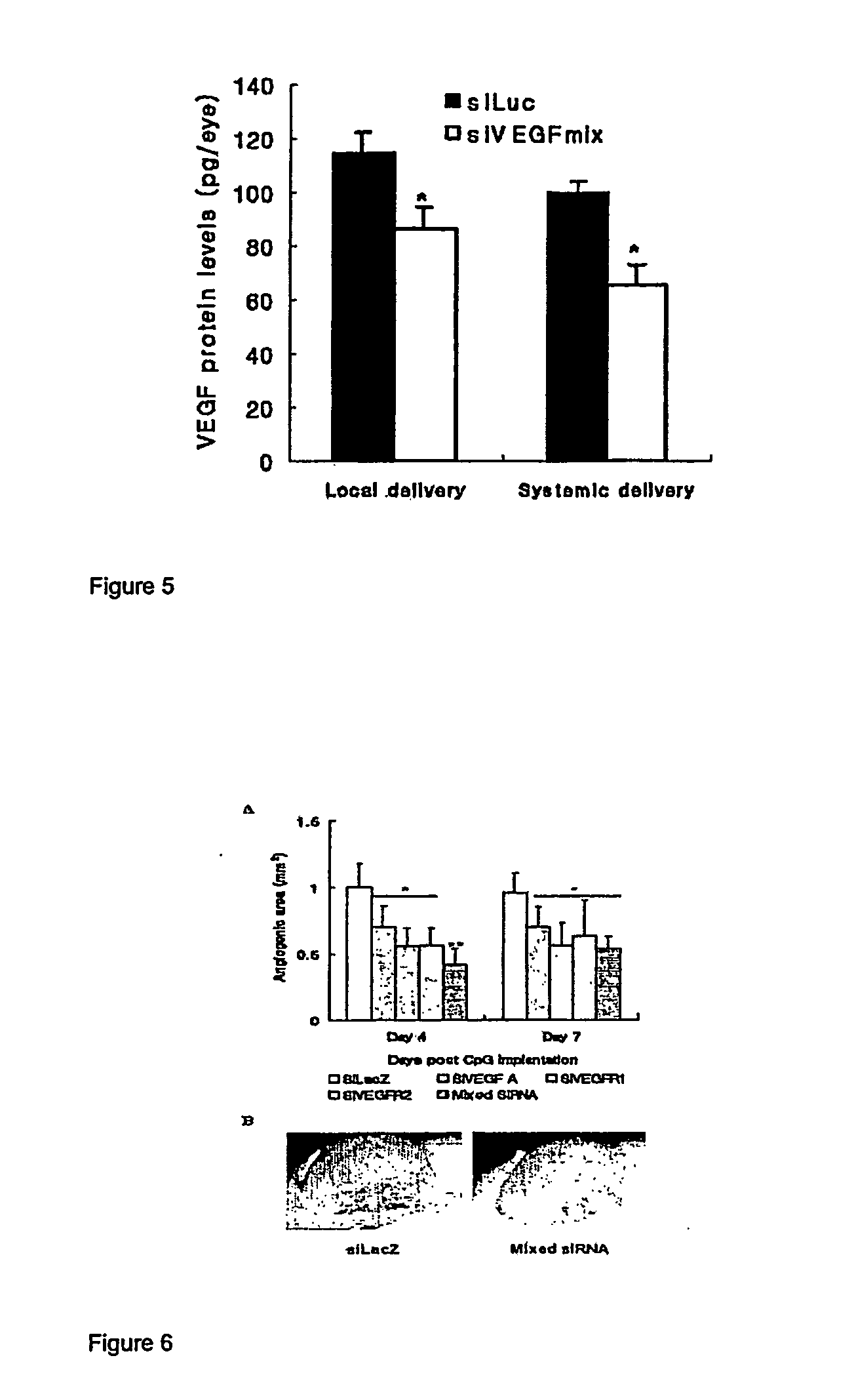
RNAi Therapeutics for Treatment of Eye Neovascularization Diseases
InactiveUS20090247604A1Inhibit expressionInhibit ocular NV diseaseCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsVascular diseaseRNAi Therapeutics
Compositions and methods for treating ocular disease are provided. Specifically, siRNA molecules and mixtures of siRNA molecules are provided that inhibit angiogenesis and / or neovascularization. The compositions and methods are suitable for treating ocular diseases associated with angiogenesis and / or neovascularization.
Owner:INTRADIGM CORP
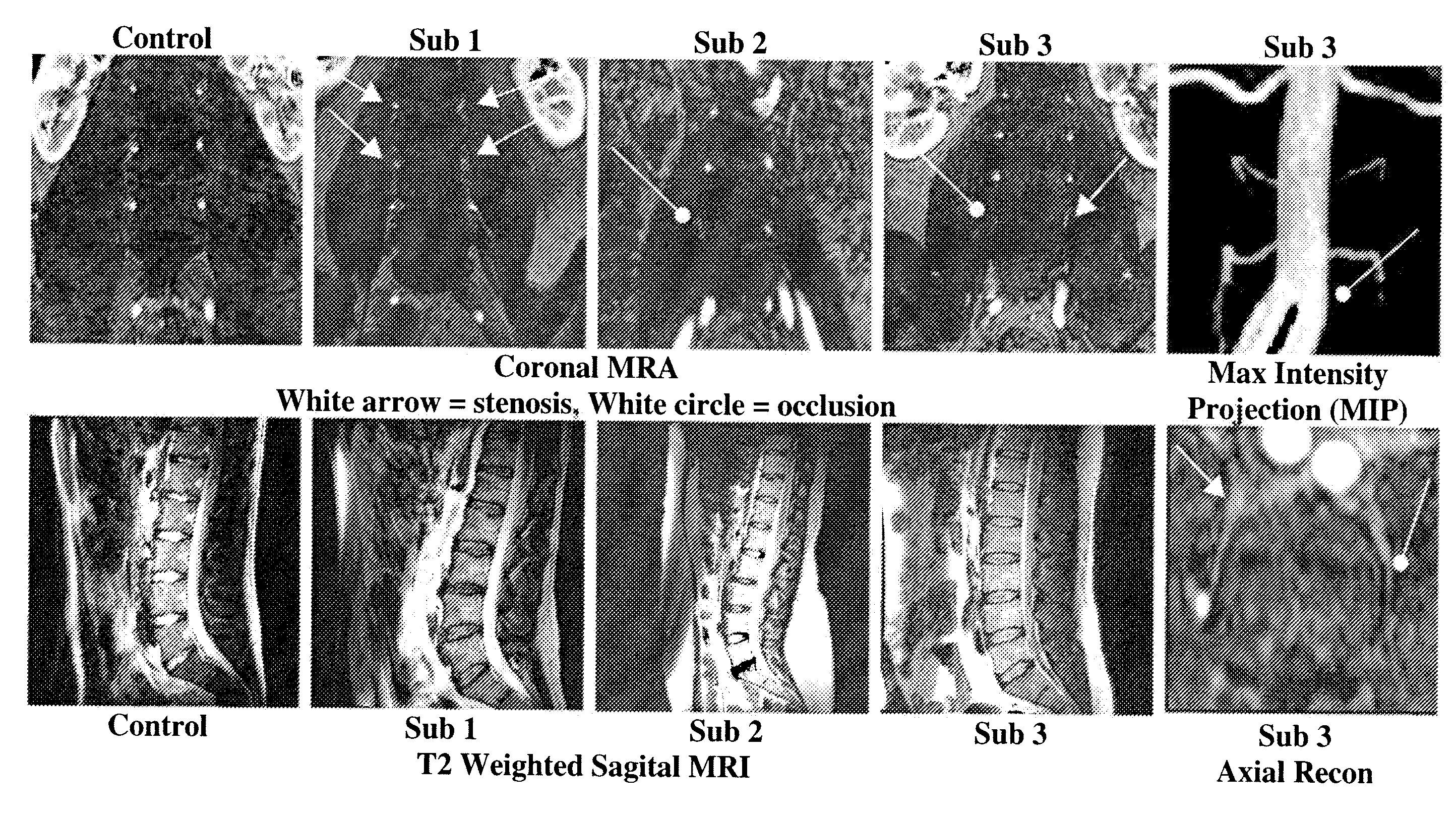
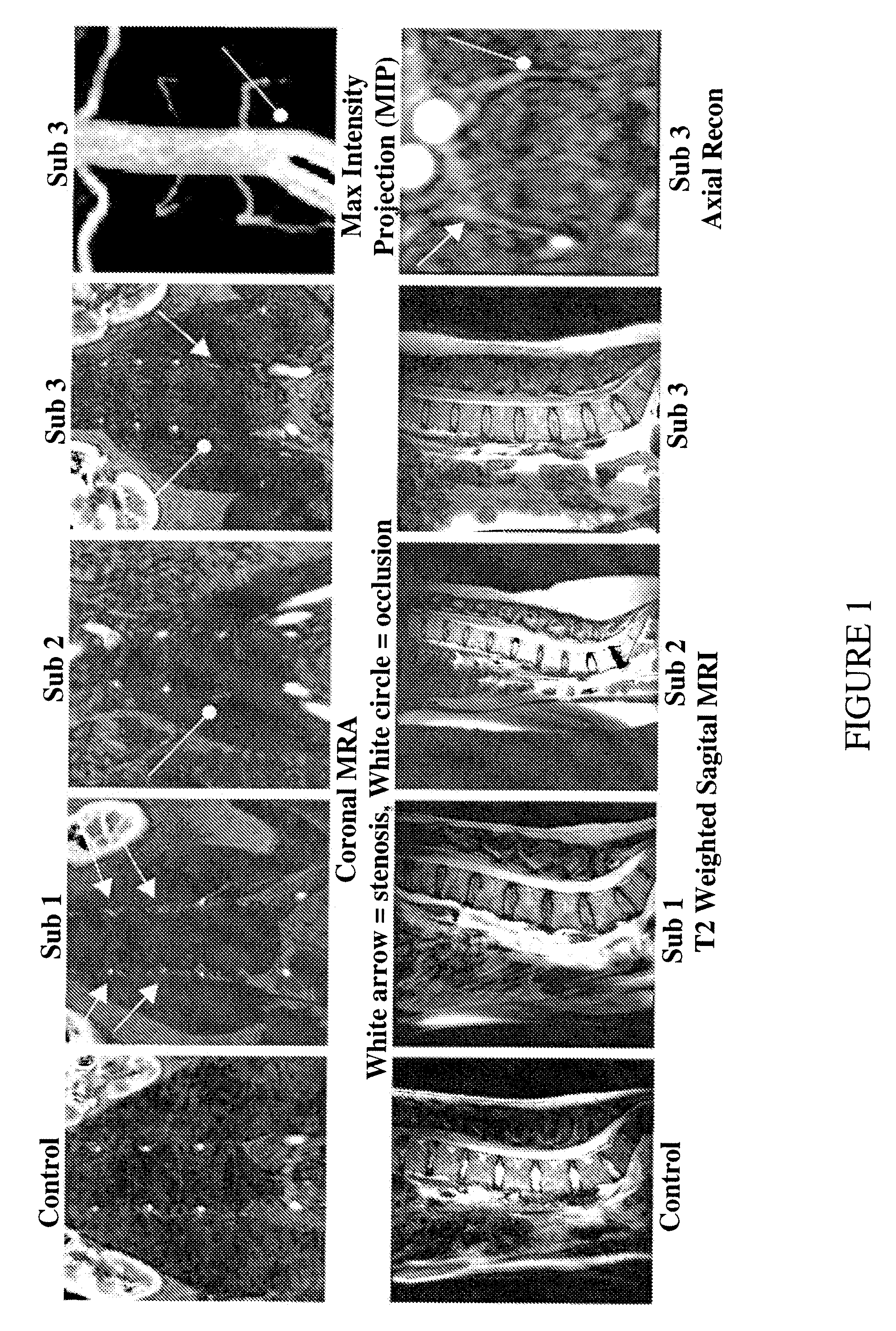
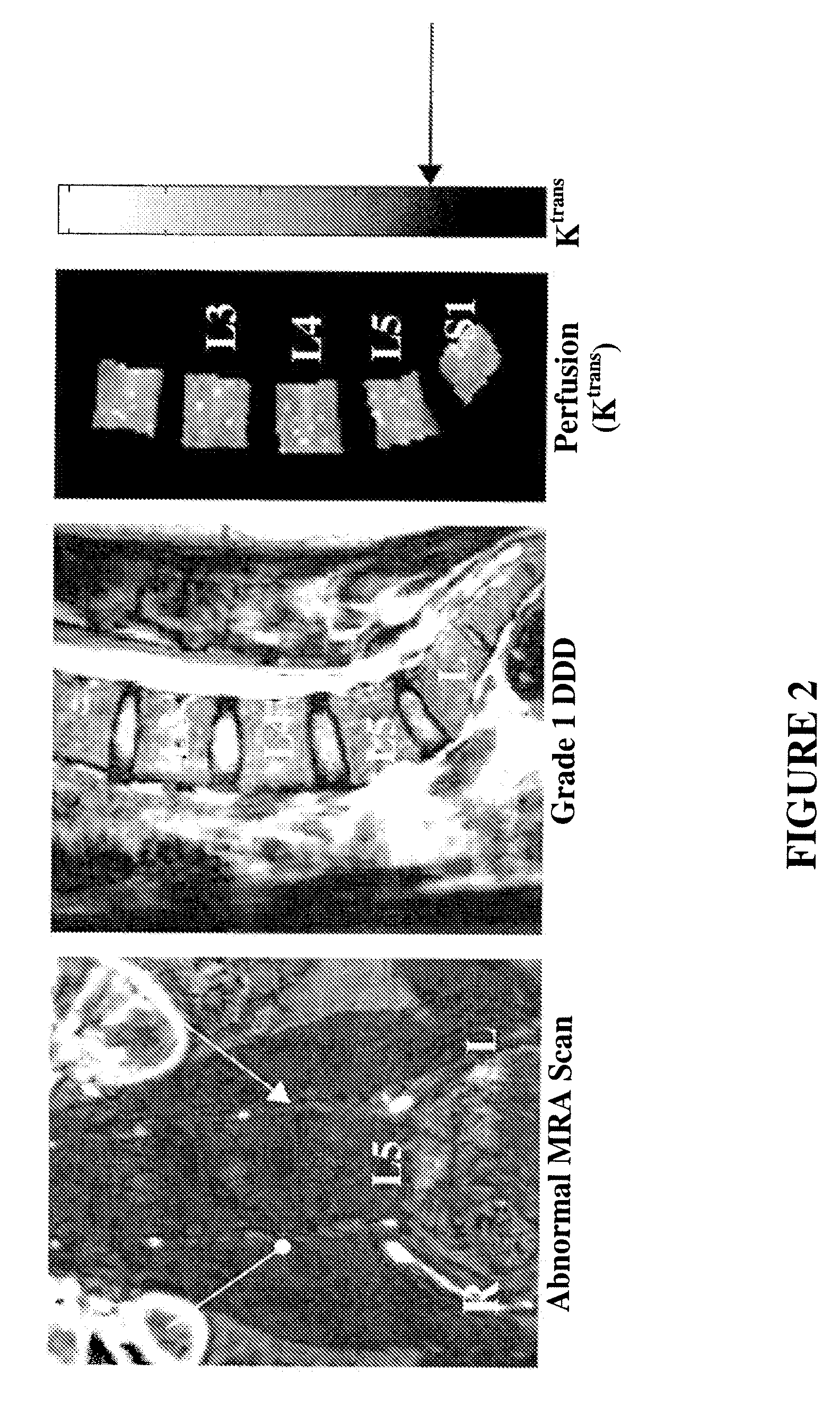
Therapeutic angiogenesis for treatment of the spine
ActiveUS20090076481A1Increase perfusionPeptide/protein ingredientsMedical devicesMuscular abnormalityNeovascularization
The invention relates to methods for the diagnosis, amelioration, and treatment of back pain, particularly lumbar back pain, in particular, back pain caused by muscular abnormalities, vertebral body osteoporosis, and disc degeneration. Patients with back pain are categorized into specific subsets that are deemed to have potential to respond to therapy. In particular, the invention includes a therapy involving stimulation of neovascularization so as to increase perfusion of various spine compartments.
Owner:VENTURIS THERAPEUTICS INC
Therapeutic agents for diseases involving choroidal neovascularization
ActiveUS20100034811A1Advancement of CNV could be suppressedSenses disorderAntibody ingredientsDiseaseNeovascularization
The present inventors focused on the fact that inflammation at the subretinal macular area enhances choroidal neovascularization, and developed pharmaceutical agents that suppress initiation or advancement of neovascularization by angiogenic factors such as VEGF. More specifically, the present inventors revealed that administering anti-IL-6 receptor monoclonal antibodies to mice treated with laser photocoagulation inhibits the development of choroidal neovascularization.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Promoters exhibiting endothelial cell specificity and methods of using same for regulation of angiogenesis
InactiveUS20050186179A1Down-regulating angiogenesisSenses disorderVirusesCell specificPromoter activity
Isolated polynucleotide sequences exhibiting endothelial cell specific promoter activity, novel cis regulatory elements and methods of use thereof enabling treatment of diseases characterized by aberrant neovascularization or cell growth are disclosed.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
Promoters exhibiting endothelial cell specificity and methods of using same for regulation of angiogenesis
Isolated polynucleotide sequences exhibiting endothelial cell specific promoter activity, novel cis regulatory elements and methods of use thereof enabling treatment of diseases characterized by aberrant neovascularization or cell growth are disclosed.
Owner:VASCULAR BIOGENICS
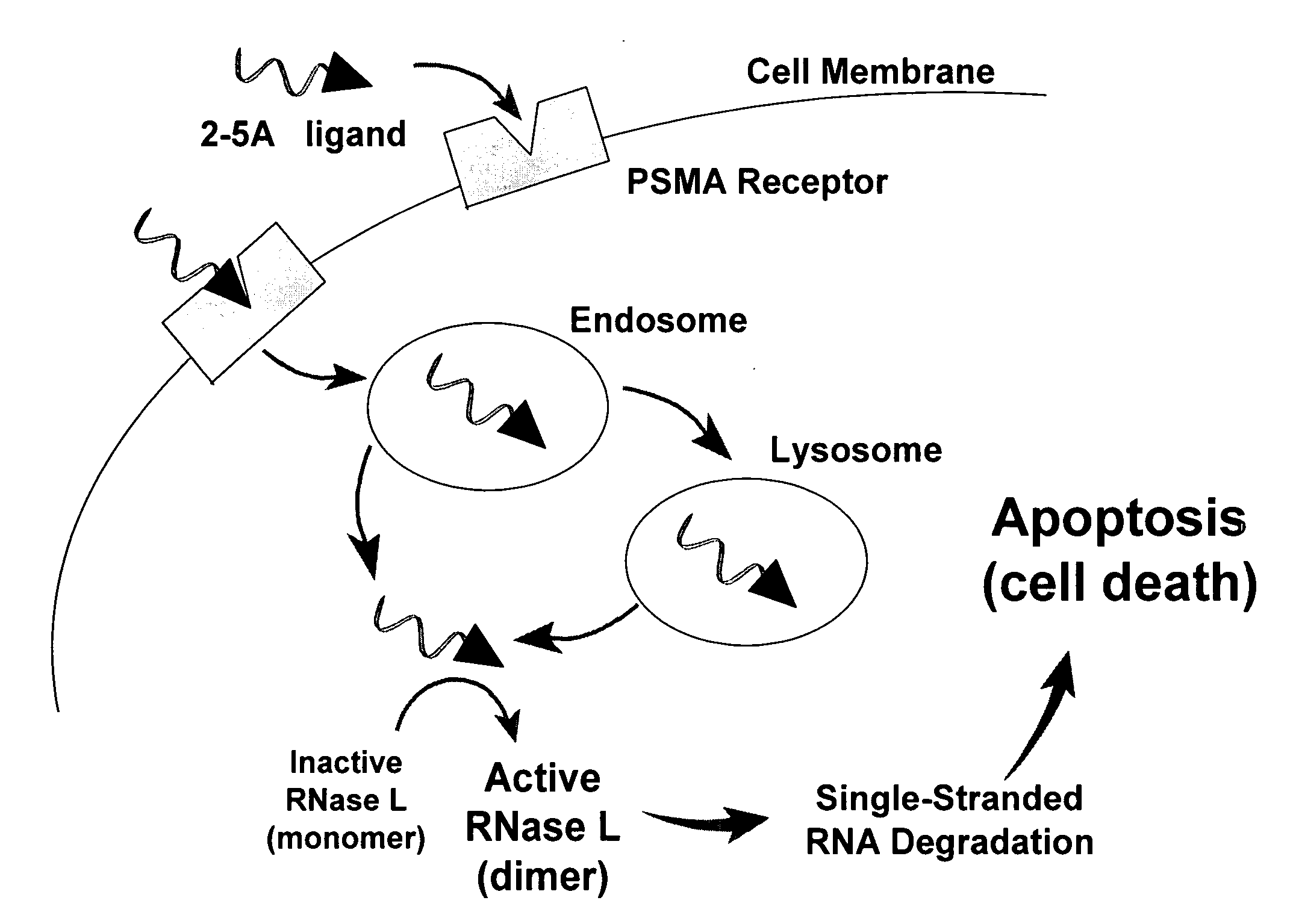
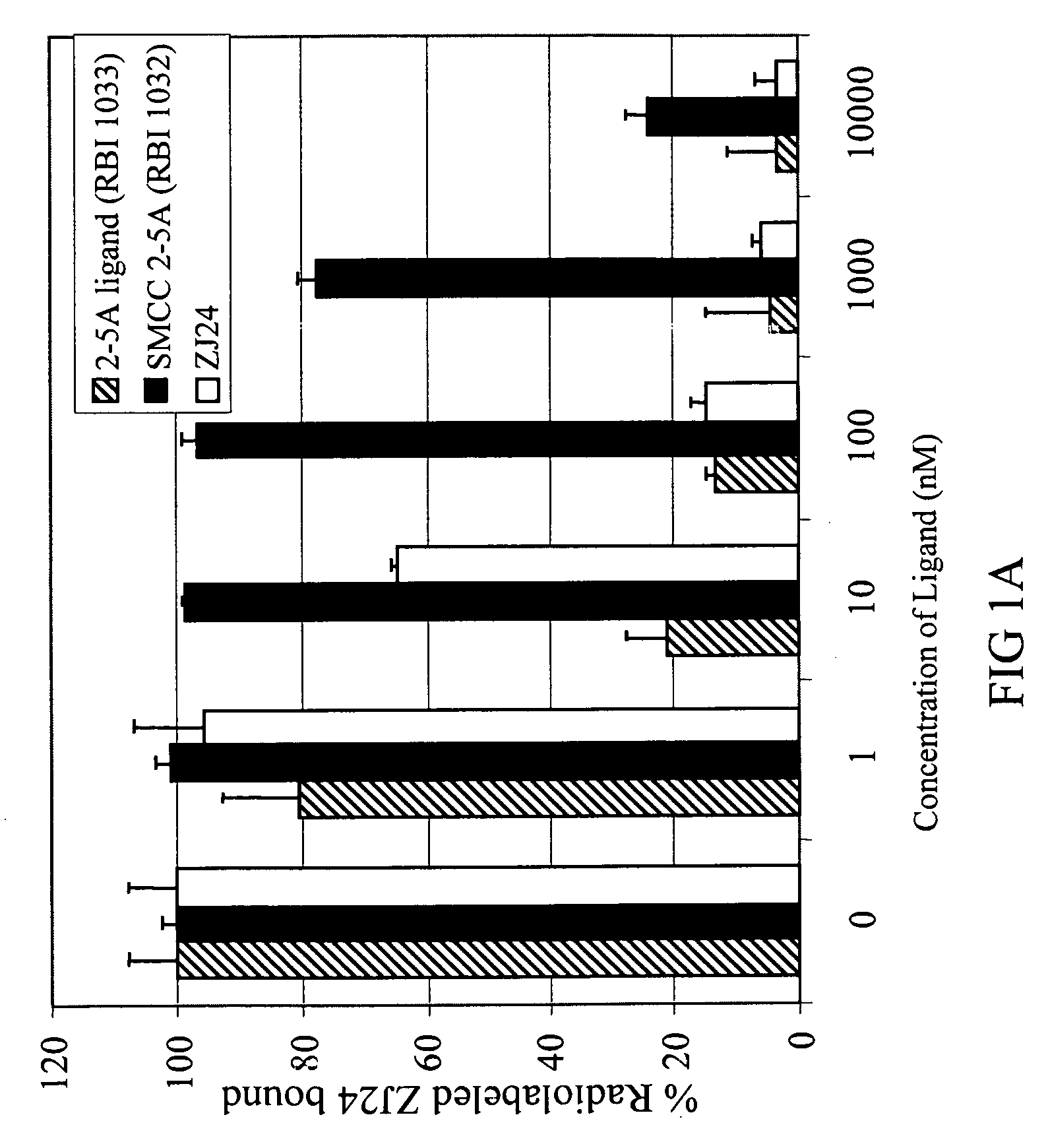
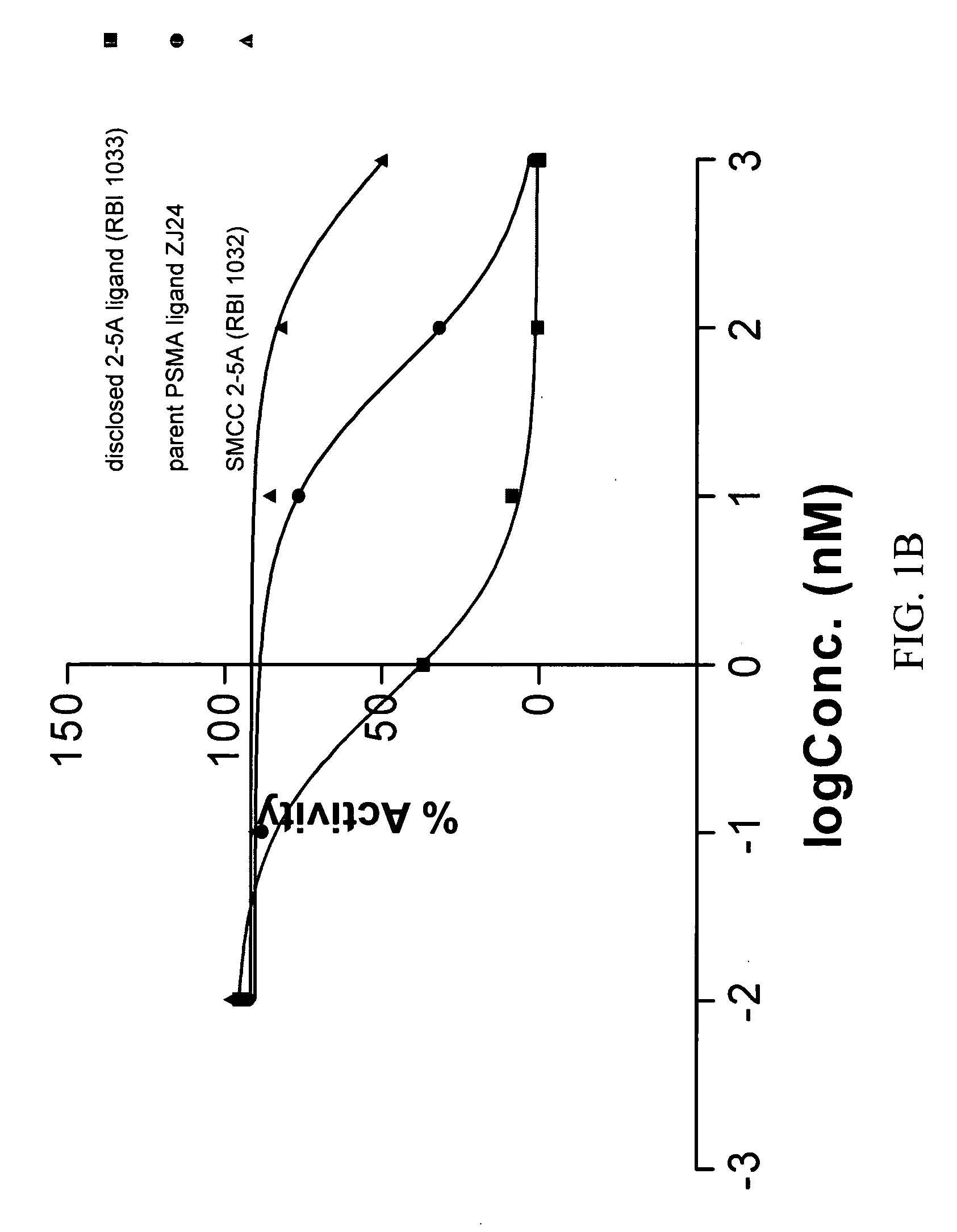
Compounds which bind PSMA and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080311037A1InhibitionInduced differentiationMaterial nanotechnologyBiocideAntigenDisease
A compound is represented by Structural Formula A1:C—B-L-A A1or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof.A is a prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) ligand;L is an optionally substituted aliphatic or heteroaliphatic linking group;B includes at least one optionally substituted moiety selected from the group consisting of a sugar, a charged group, an aryl ring, and a heteroaryl ring, wherein B optionally includes a drug or a labeling agent; andC is H, a drug, or a labeling agent, wherein CB together comprises the drug or the labeling agent.The compounds are useful as PSMA agents and in pharmaceutical compositions, methods for treating and detecting diseases such as cancer in a subject, methods for identifying cancer cells in a sample, methods for inhibiting tumor neovascularization, methods for identifying drugs that can treat cancer, and the like.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
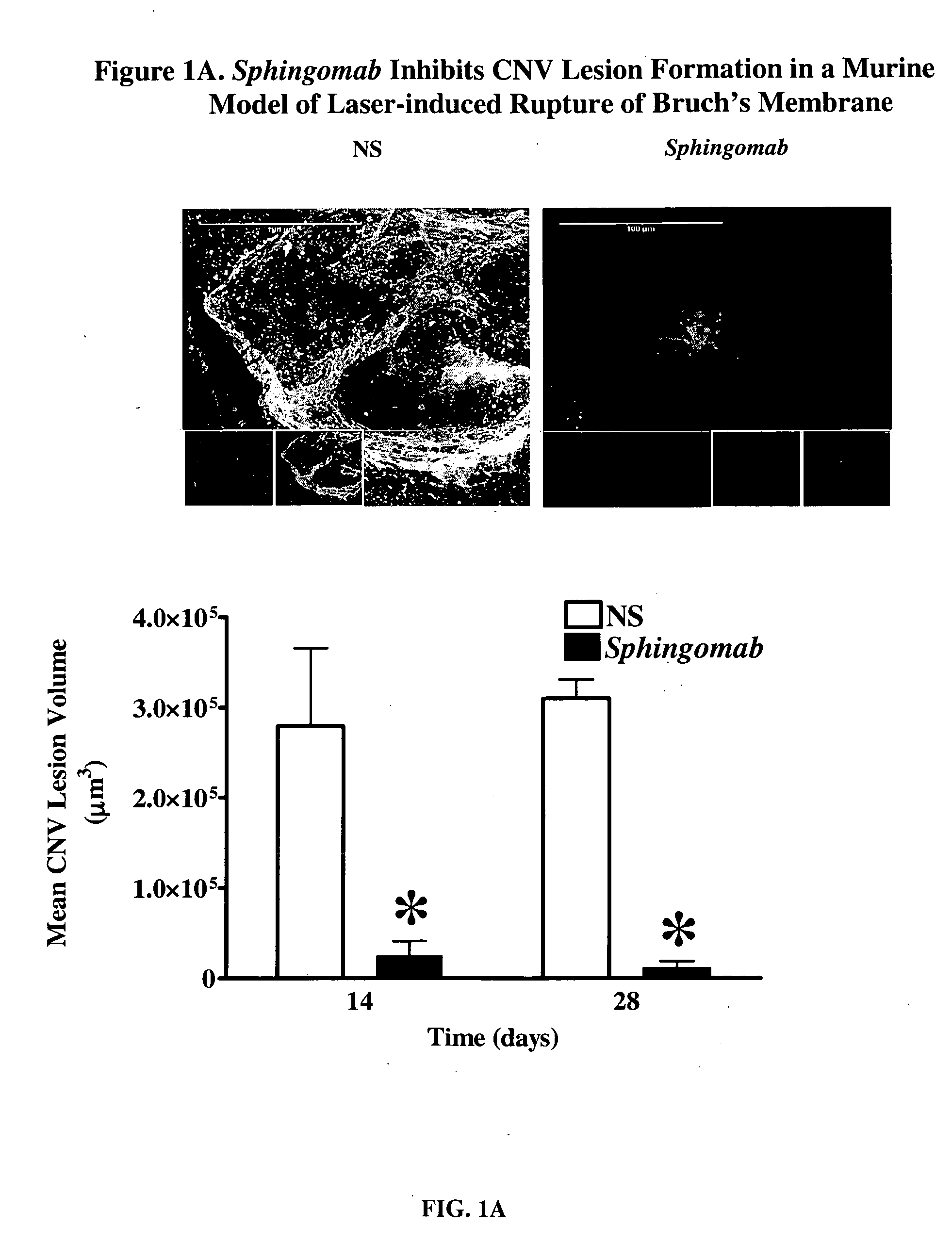
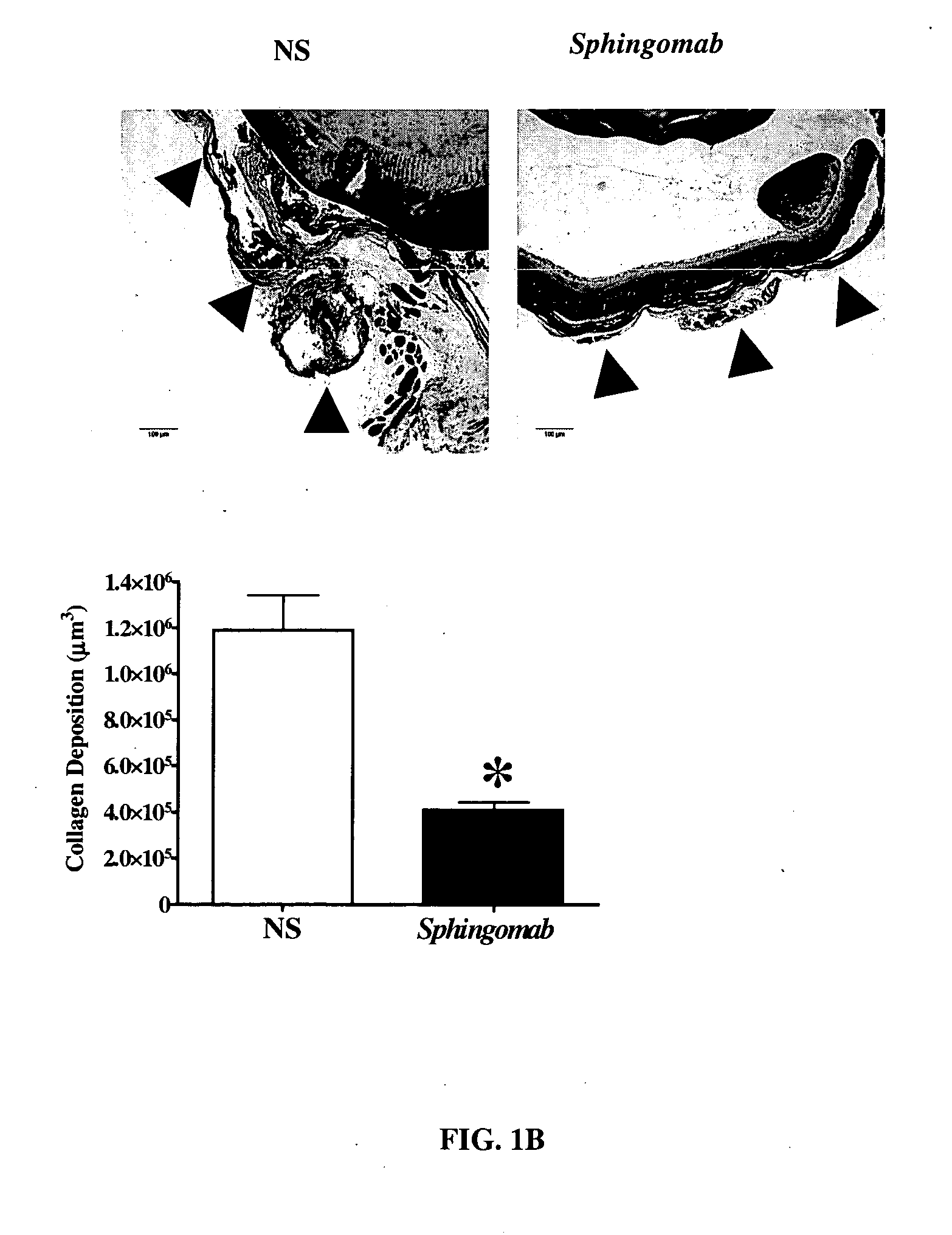
Compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of fibrotic, inflammatory and neovascularization conditions
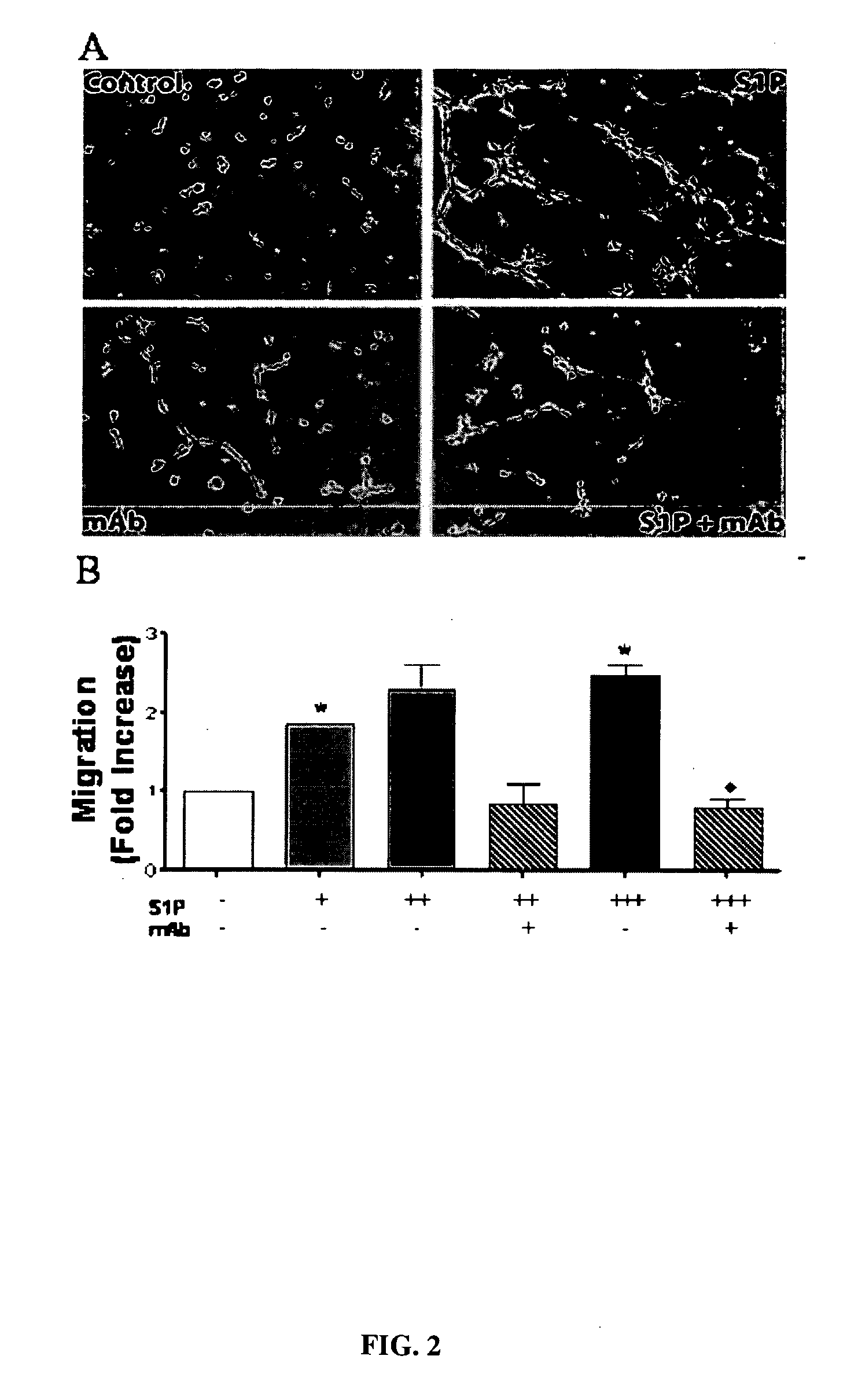
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for prevention and treatment of diseases and conditions, including ocular diseases and conditions, characterized by aberrant fibrogenesis or scarring, inflammation and / or aberrant neovascularization or angiogenesis. The compositions and methods of the invention utilize immune-derived moieties that are specifically reactive against bioactive lipids and which are capable of decreasing the effective concentration of said bioactive lipid. In some embodiments, the immune-derived moiety is a monoclonal antibody that is reactive against sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) or lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).
Owner:LPATH
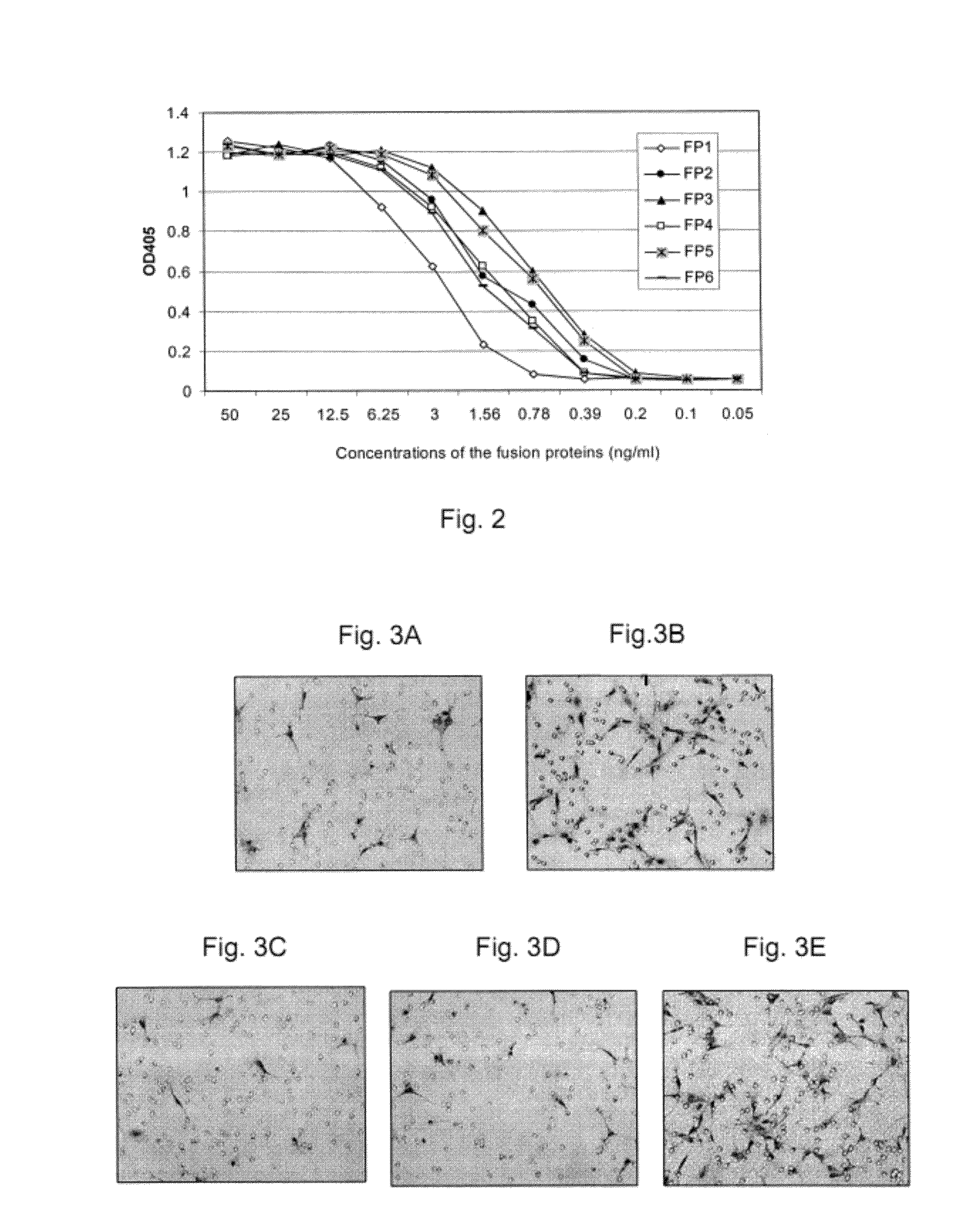
Inhibition of neovascularization with a soluble chimeric protein comprising VEGF FLT-1 and KDR domains
ActiveUS8216575B2Reduce neovascularizationImprove acuitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsChimerin ProteinsEndothelial NOS
Described herein are novel soluble chimeric fusion proteins comprising amino acid sequences derived from the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors flt-1 and KDR, including domain 4 of KDR. The claimed chimeric fusion proteins antagonize the endothelial cell proliferative and angiogenic activity of VEGF and are useful in the treatment of neovascularization-related disease.
Owner:CHENGDU KANGHONG BIOTECH
Purified populations of endothelial progenitor cells
The invention is directed to a purified population of mammalian endothelial stem cells. The invention further provides methods for isolating such populations of cells, methods for using such populations of cells for treating mammals in need of neovascularization and for making vectors for gene therapy, and methods for carrying out gene therapy with such vectors.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +2
Compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of fibrotic, inflammatory, and neovascularization conditions of the eye
InactiveUS20080213274A1Low effective concentrationHealing woundSenses disorderImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDiseaseAngiogenesis growth factor
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for prevention and treatment of ocular diseases and conditions characterized by aberrant fibrogenesis or scarring, inflammation and / or aberrant neovascularization or angiogenesis. The compositions and methods of the invention utilize immune-derived moieties that are specifically reactive against bioactive lipids and which are capable of decreasing the effective concentration of said bioactive lipid. In some embodiments, the immune-derived moiety is a monoclonal antibody that is reactive against sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) or lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).
Owner:LPATH
Quinazolinone containing pharmaceutical compositions for prevention of neovascularization and for treating malignancies
InactiveUS6028075AInhibit angiogenesisInhibit cell proliferationBiocideNervous disorderHydrogenNeovascularization
The invention provides a composition for attenuating neovascularization and treating malignancies, including a pharmaceutically effective amount of a compound having a formula: wherein: R1 is a member of the group consisting of hydrogen, halogen, nitro, benzo, lower alkyl, phenyl and lower alkoxy; R2 is a member of the group consisting of hydroxy, acetoxy, and lower alkoxy, and R3 is a member of the group consisting of hydrogen and lower alkenoxy carbonyl; as active ingredient therein, in combination with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:HADASIT MEDICAL RES SERVICES & DEVMENT +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com