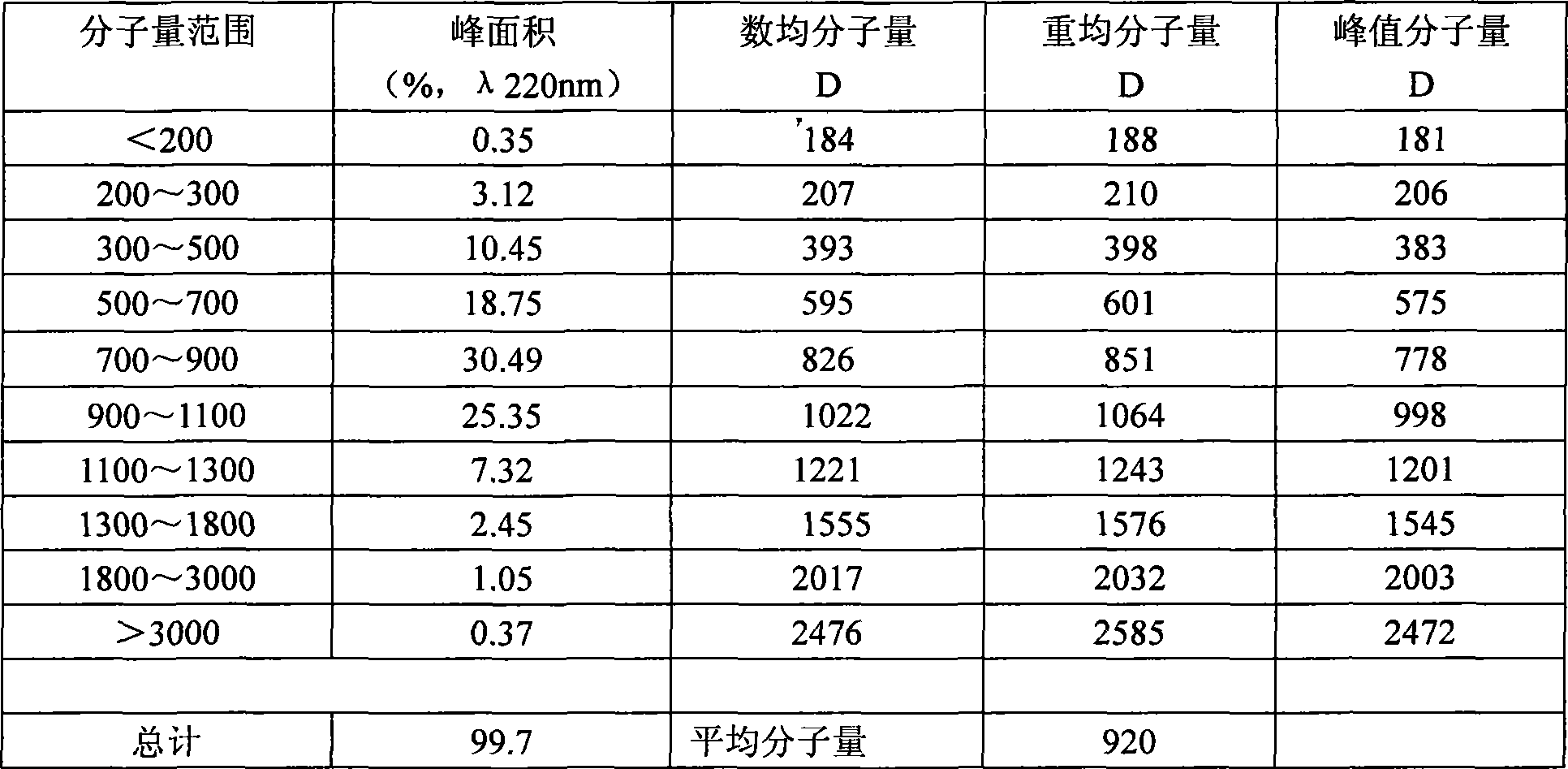
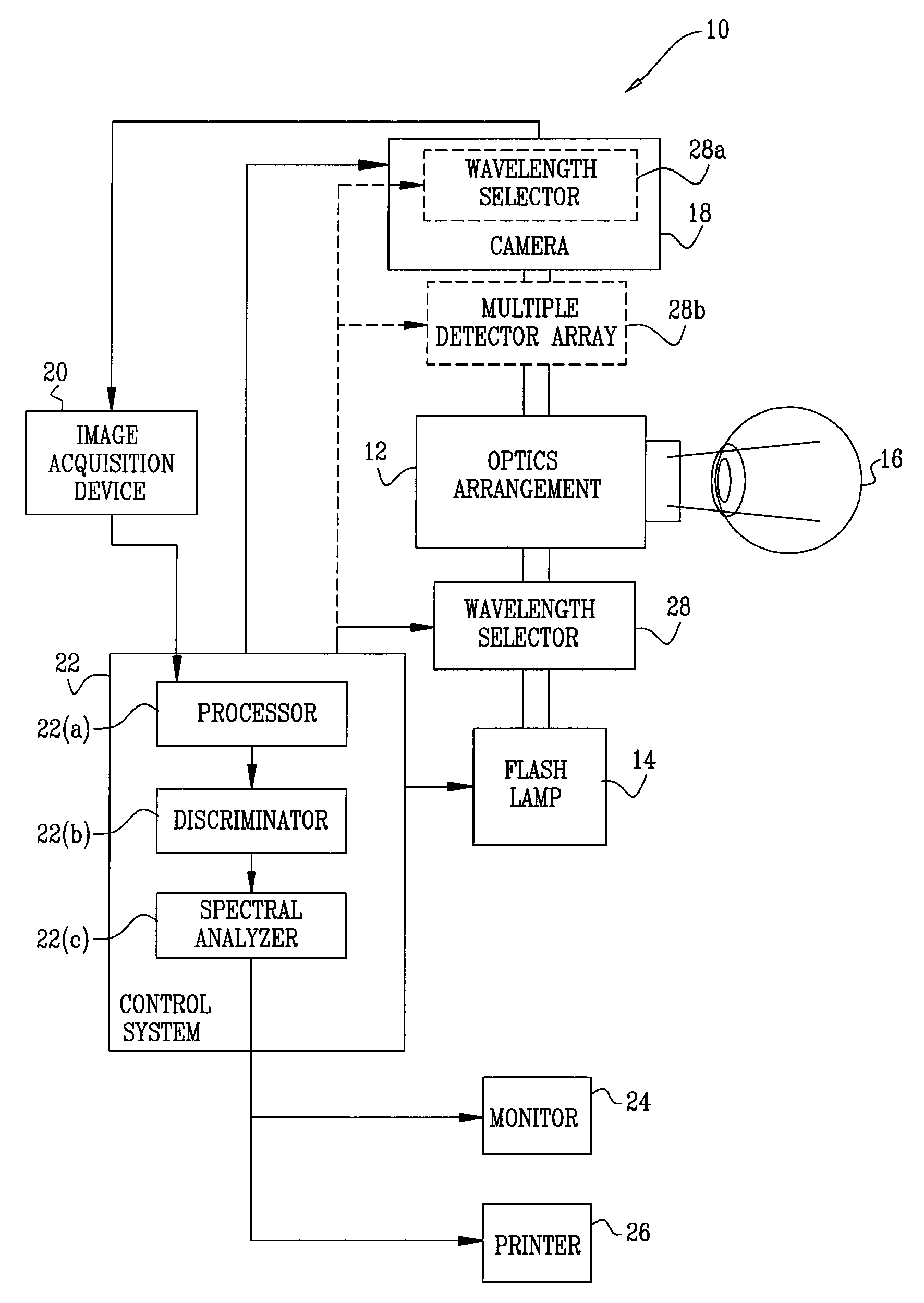
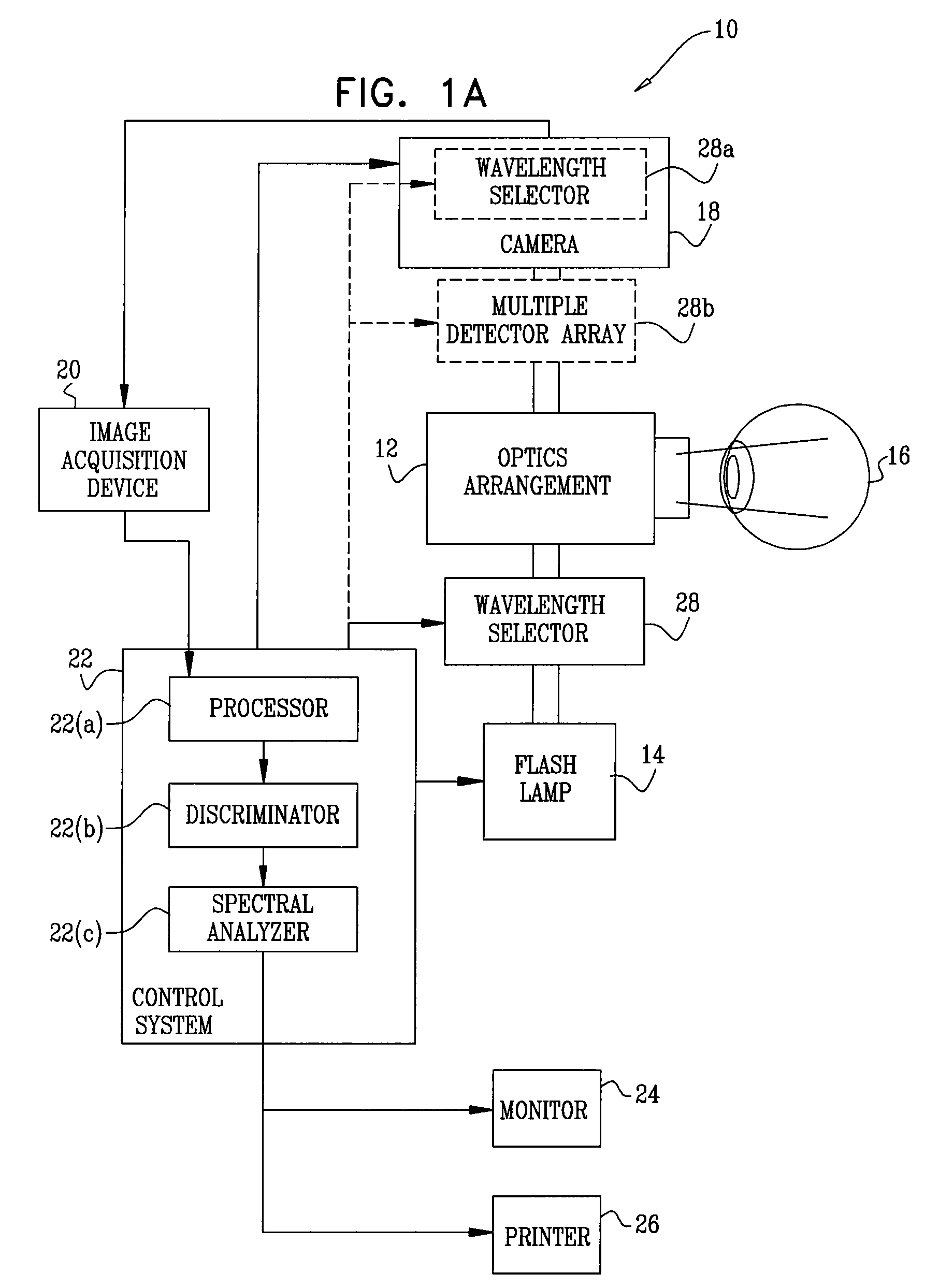
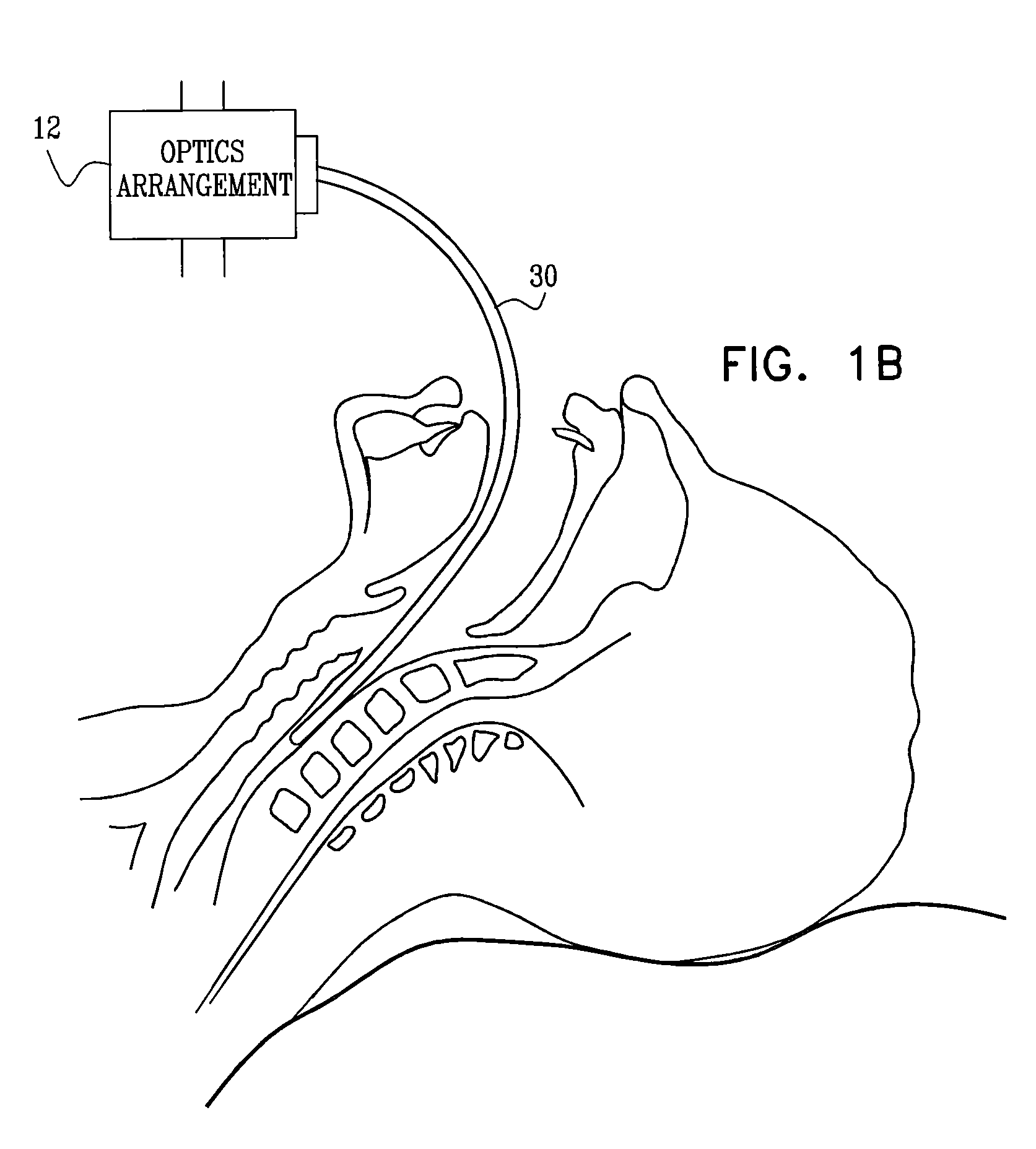
Patents
Literature
582 results about "Capillary vessels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Perfused three-dimensional cell/tissue disease models
ActiveUS20050260745A1Easy to primeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLymphatic SpreadPathology diagnosis
A system has been constructed that recapitulate the features of a capillary bed through normal human tissue. The system facilitates perfusion of three-dimensional (3D) cell monocultures and heterotypic cell co-cultures at the length scale of the capillary bed. A major feature is that the system can be utilized within a “multiwell plate” format amenable to high-throughput assays compatible with the type of robotics commonly used in pharmaceutical development. The system provides a means to conduct assays for toxicology and metabolism and as a model for human diseases such as hepatic diseases, including hepatitis, exposure-related pathologies, and cancer. Cancer applications include primary liver cancer as well as metastases. The system can also be used as a means of testing gene therapy approaches for treating disease and inborn genetic defects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Implantable biosensor
The invention consists of a sensor with multiple indicating (sensing) electrodes covered with a selectively permeable membrane for monitoring fluid concentrations in a biological environment. The indicating electrodes respond to changes in certain analytes, such as glucose, through an enzyme-mediated reaction. The currents generated from the enzyme-mediated reactions are transmitted through radio signals to an external receiver where the information is processed and recorded. Through the use of various biomaterials and biochemicals associated with the sensor, the monitoring accuracy is improved and the overall viability is prolonged. The process of foreign body fibrosis (formation of a scar capsule around the implanted sensor) eventually limits the functional life of the device. We teach methods of delivery of certain biochemicals that can increase the functional life of the sensor by inhibiting the formation of the foreign body capsule or by stimulating the growth of capillaries into the capsule.
Owner:LEGACY GOOD SAMARITAN HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENT
Implantable biosensor
ActiveUS20050107677A1Readily availableMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterForeign matterSurvivability
The invention consists of a sensor with multiple indicating (sensing) electrodes covered with a selectively permeable membrane for monitoring fluid concentrations in a biological environment. The indicating electrodes respond to changes in certain analytes, such as glucose, through an enzyme-mediated reaction. The currents generated from the enzyme-mediated reactions are transmitted through radio signals to an external receiver where the information is processed and recorded. Through the use of various biomaterials and biochemicals associated with the sensor, the monitoring accuracy is improved and the overall viability is prolonged. The process of foreign body fibrosis (formation of a scar capsule around the implanted sensor) eventually limits the functional life of the device. We teach methods of delivery of certain biochemicals that can increase the functional life of the sensor by inhibiting the formation of the foreign body capsule or by stimulating the growth of capillaries into the capsule.
Owner:LEGACY GOOD SAMARITAN HOSPITAL & MEDICAL CENT
Method and apparatus for calculating blood flow parameters
A method for determining tissue type includes quantitatively determining a tissue blood flow (TBF) by deconvoluting Q(t) and Ca(t), where Q(t) represents a curve of specific mass of contrast, and Ca(t) represents an arterial curve of contrast concentration, and quantitatively determining a tissue blood volume (TBV) by deconvoluting Q(t) and Ca(t). The method also includes quantitatively determining a tissue mean transit time (TMTT) by deconvoluting Q(t) and Ca(t), and quantitatively determining a tissue capillary permeability surface area product (TPS) by deconvoluting Q(t) and Ca(t). The method also includes determining a tissue type based on the TBF, the TBV, the TMTT, and the TPS.
Owner:THE JOHN P ROBARTS RES INST
Whole-body mathematical model for simulating intracranial pressure dynamics
InactiveUS7182602B2Analogue computers for chemical processesEducational modelsPulmonary vasculatureVein
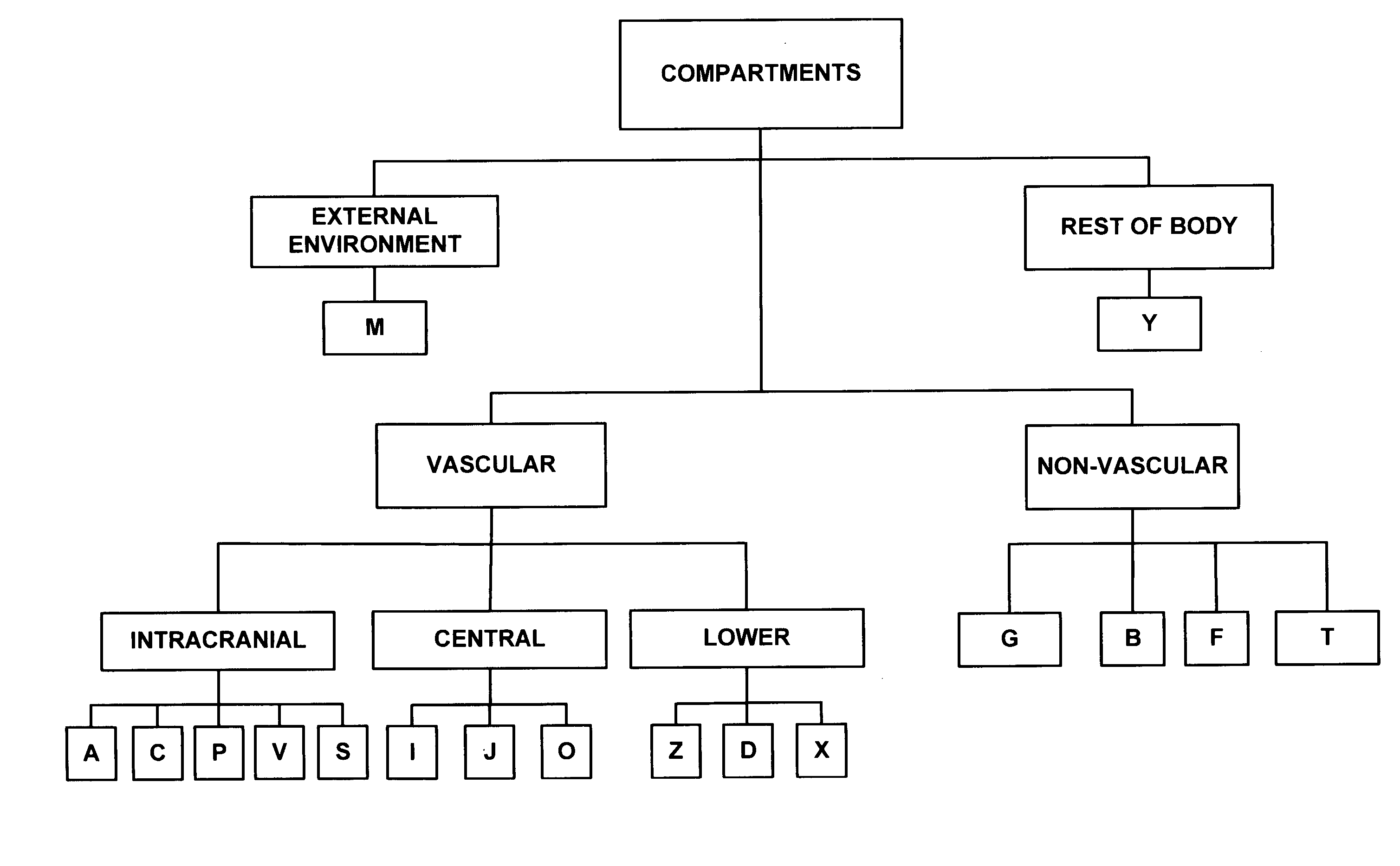
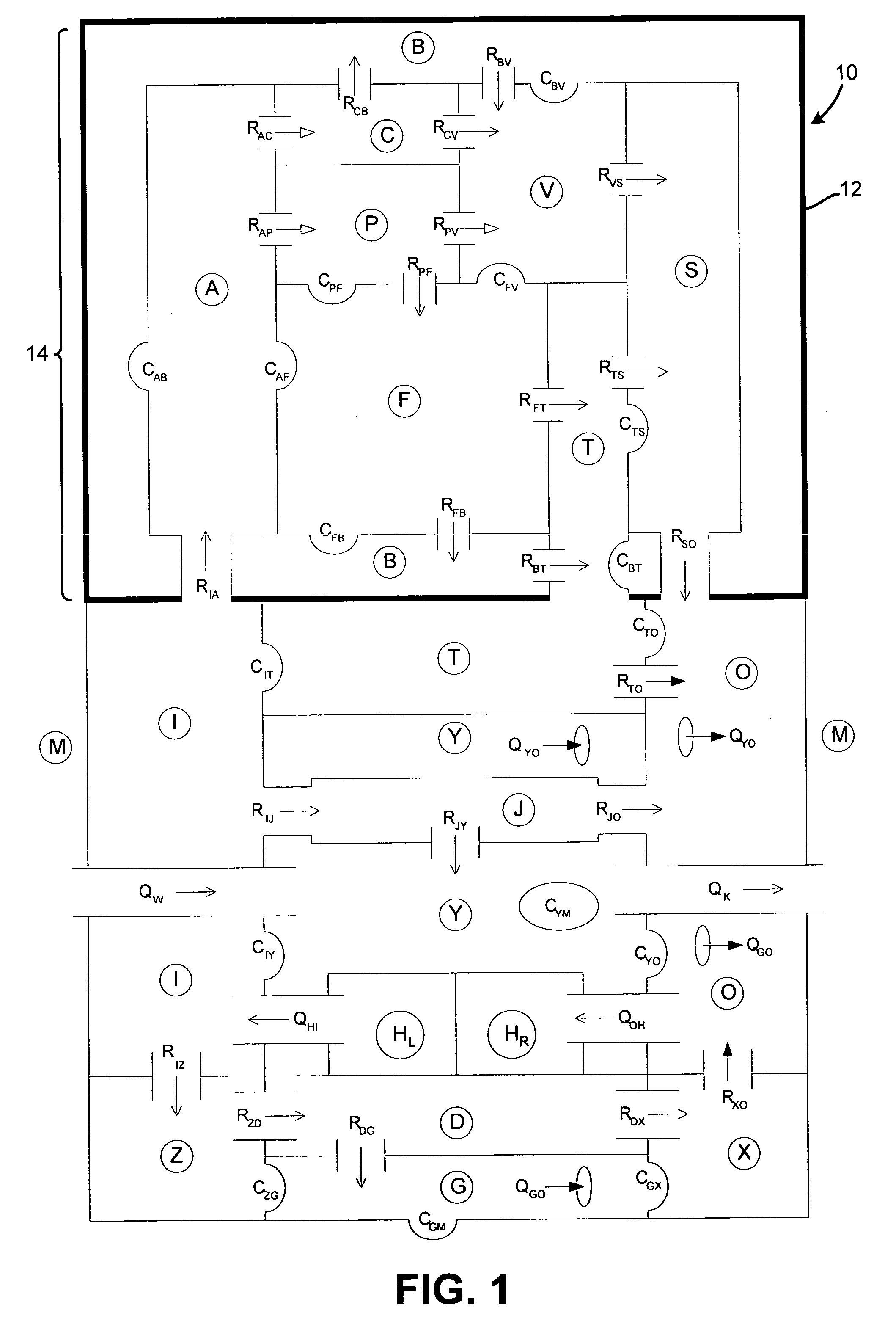
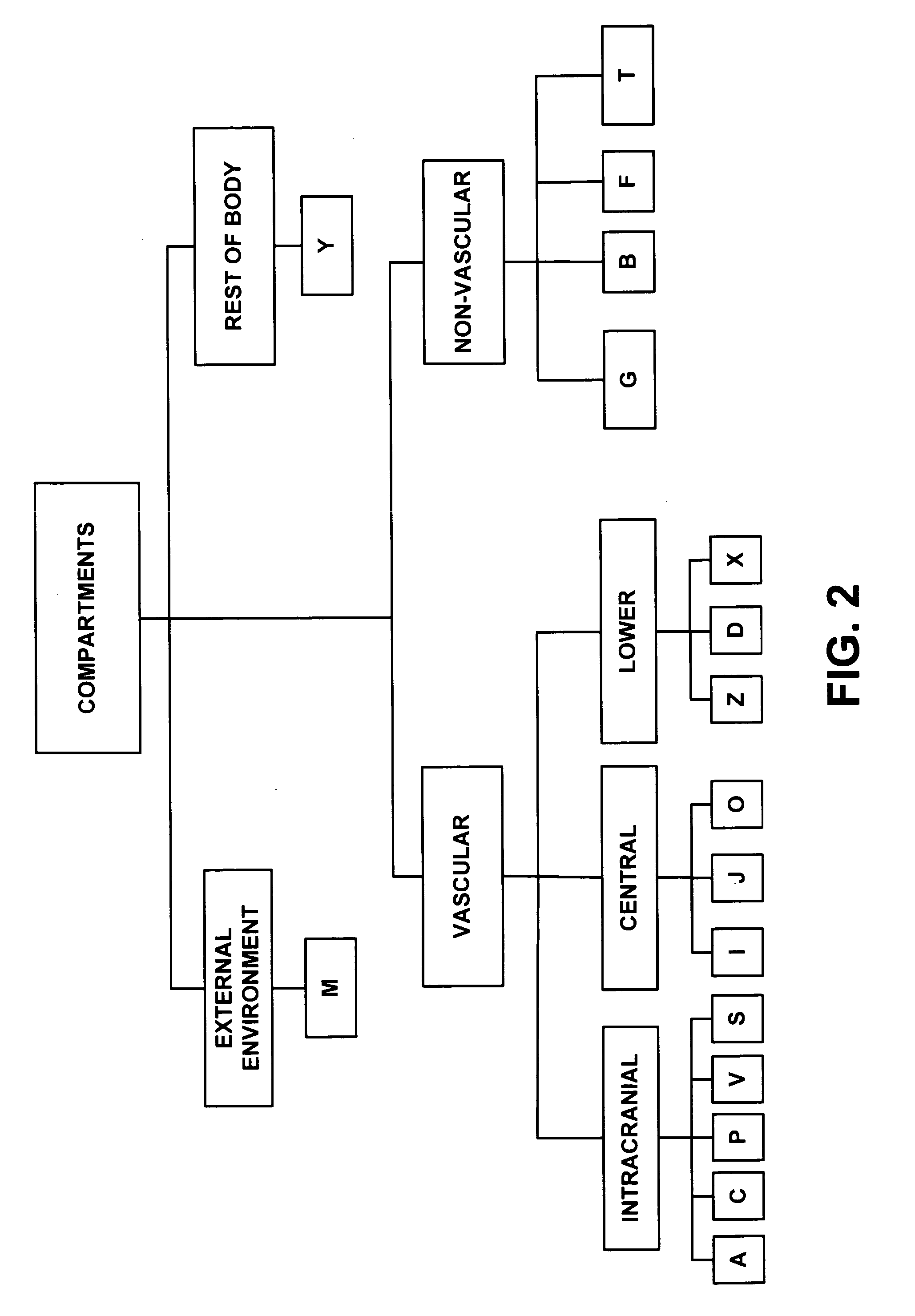
A whole-body mathematical model (10) for simulating intracranial pressure dynamics. In one embodiment, model (10) includes 17 interacting compartments, of which nine lie entirely outside of intracranial vault (14). Compartments (F) and (T) are defined to distinguish ventricular from extraventricular CSF. The vasculature of the intracranial system within cranial vault (14) is also subdivided into five compartments (A, C, P, V, and S, respectively) representing the intracranial arteries, capillaries, choroid plexus, veins, and venous sinus. The body's extracranial systemic vasculature is divided into six compartments (I, J, O, Z, D, and X, respectively) representing the arteries, capillaries, and veins of the central body and the lower body. Compartments (G) and (B) include tissue and the associated interstitial fluid in the intracranial and lower regions. Compartment (Y) is a composite involving the tissues, organs, and pulmonary circulation of the central body and compartment (M) represents the external environment.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
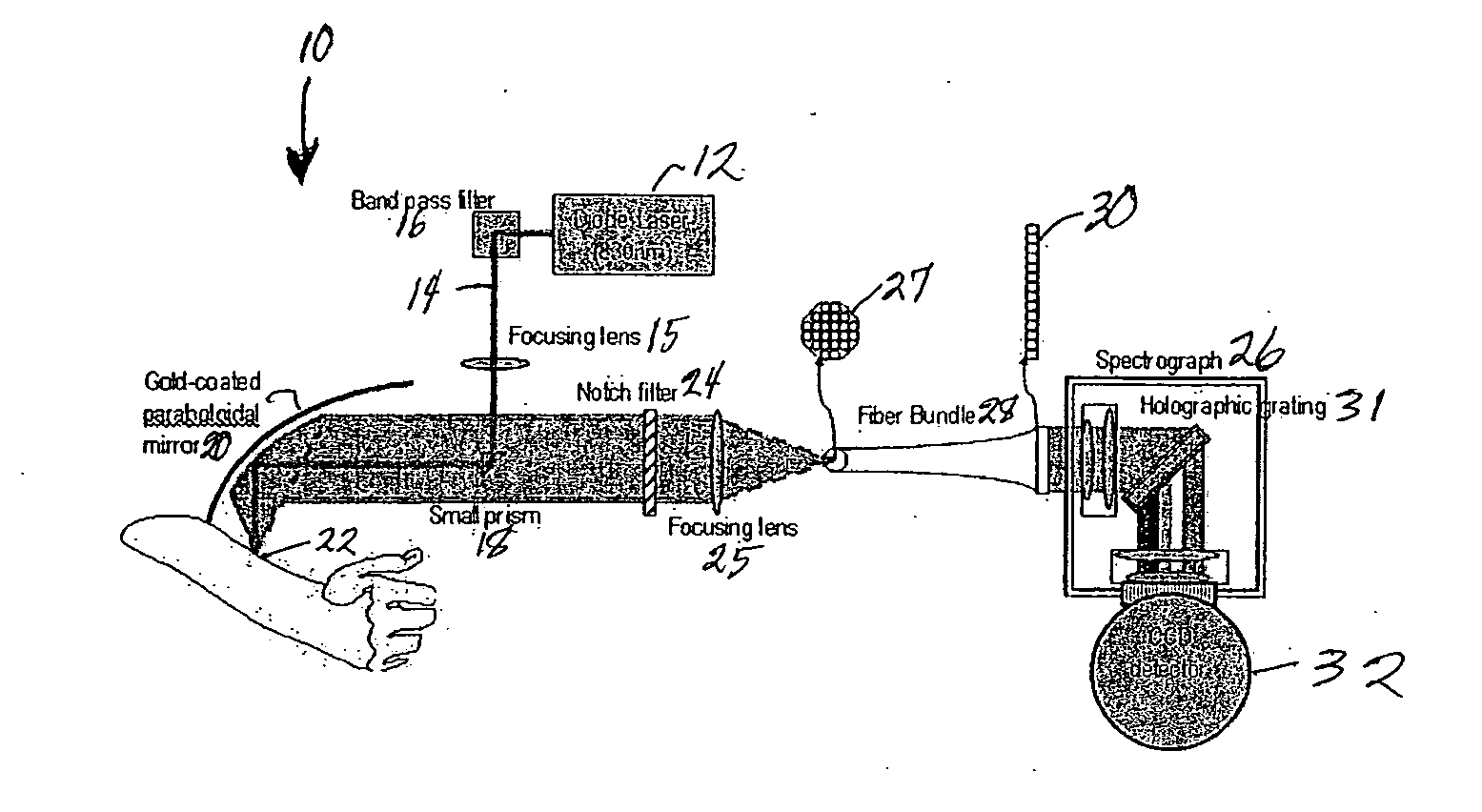
Raman spectroscopy for non-invasive glucose measurements
ActiveUS20070060806A1Error minimizationIncreased signal noiseRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringMonitor glucoseGlucose Measurement
The present invention relates to the use of Raman spectroscopy for quantitative, non-invasive transcutaneous measurement of blood analytes, such as glucose. Raman spectroscopy is used to measure glucose transcutaneously, in patients whose blood glucose levels were monitored. Raman spectra were collected transcutaneously along with glucose reference values provided by standard capillary blood analysis. A partial least squares calibration was created from the data from each subject and validated using leave-one-out cross validation.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Scaffold for tissue engineering, artificial blood vessel, cuff, and biological implant covering member
InactiveUS20050107868A1Reduce foreign body reactionsImprove patencyTissue cultureBlood vesselsSubcutaneous tissueTunnel infection
The invention provides a porous scaffold for tissue engineering which allows easy cell engraftment and cell culture and thus enables stable organization and an artificial blood vessel which exhibits high patency rate even if the inner diameter is small. The scaffold for tissue engineering is made of thermoplastic resin which forms a porous three-dimensional network structure having communication property, wherein the porous three-dimensional network structure has an average pore diameter of from 100 to 650 μm and an apparent density of from 0.01 to 0.5 g / cm3. The artificial blood vessel is composed of this scaffold. The invention provides a cuff which allows easy infiltration of cells from living subcutaneous tissues, easy engraftment of cells, and neovascularization of capillary vessels so as to obtain robust bonding with subcutaneous tissues and, as a result, ensures separation of a wounded portion from the outside, thereby blocking exacerbation factors such as bacterial infection on healing and inhibiting progression of downgrowth. That is, the invention provides a cuff with none or little infection trouble such as tunnel infection. The cuff comprises a porous three-dimensional network structure which is made of thermoplastic resin or thermosetting resin and has communication property, wherein the porous three-dimensional network structure has an average pore diameter of from 100 to 1000 μm and apparent density of from 0.01 to 0.5 g / cm3. The invention provides a biological implant covering member which allows easy infiltration of cells from living subcutaneous tissues, easy engraftment of cells, and organization, thereby obtaining robust bonding with native tissues and therefore protecting a living body from adverse effect which may occur due to the insertion of a biological implantation member into the living body. The biological implant covering member comprises a porous three-dimensional network structure which is made of thermoplastic resin or thermosetting resin and has communication property, wherein the porous three-dimensional network structure has an average pore diameter of from 100 to 1000 μm and apparent density of from 0.01 to 0.5 g / cm3.
Owner:JAPAN AS REPRESENTED BY PRESIDENT OF NAT CARDIOVASCULAR +2
Characterization of moving objects in a stationary background
InactiveUS20080021331A1Easy to detectPromote absorptionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringVascular compartmentVenule
A method and system for determination and mapping the quantity of chromophores having a distinct spectrum attached to moving objects in an spectrally rich environment that may include multiple chromophores attached to stationary objects. An area of inters is imaged at different times and different wavelengths, and the spectral properties of the or more chromophores attached to the moving objects are separated from the stationary spectral properties of the background, followed by spectral analysis of the moving objects to determine their quantity. Application to the retinal vasculature is illustrated, showing the imaging, analyzing and quantifying of the oxygen saturation of retinal blood, resolved for the different vascular compartments—capillaries, arterioles, venules, arteries, and veins. Changes in the structure of the vascular environment are also determined, whether growth of new vessels or the elimination of existing ones, by the generation of path maps based on analysis of differential images taken at a single wavelength of the moving components in the blood flow.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
System and method for assessing capillary vitality
ActiveUS20080183059A1Increase blood flowDecreased blood flowBlood flow measurement devicesEvaluation of blood vesselsMedicineMultiple criteria
A device for assessing capillary vitality comprises an inflatable cuff, a blood flow sensor and a pressure sensor in communication with the cuff, a pressure instrument in fluid communication with the cuff for inflation and deflation thereof, a microprocessor coupled to the pressure instrument for controlling airflow, at least one metabolic sensor for measuring a metabolic condition, and a computer program executable by the microprocessor. The pressure instrument includes a source of pressurized air and a conduit connecting the source of pressurized air to the cuff. The microprocessor is arranged to receive inputs from the blood flow, pressure and metabolic sensors. When executed by the microprocessor, the computer program causes the microprocessor to initiate an automatic inflation sequence resulting in a no flow condition, initiate an automatic deflation sequence, automatically qualify a perfusion measurement as an SPP value upon one or more conditions being met during the deflation sequence, and initiate the measurement of at least one metabolic factor.
Owner:OPTICAL SENSORS
Method and apparatus for determining a property of a fluid which flows through a biological tubular structure with variable numerical aperture
InactiveUS20060181791A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioSmall detection volumeDiagnostics using lightMirrorsBlood flowIn vivo
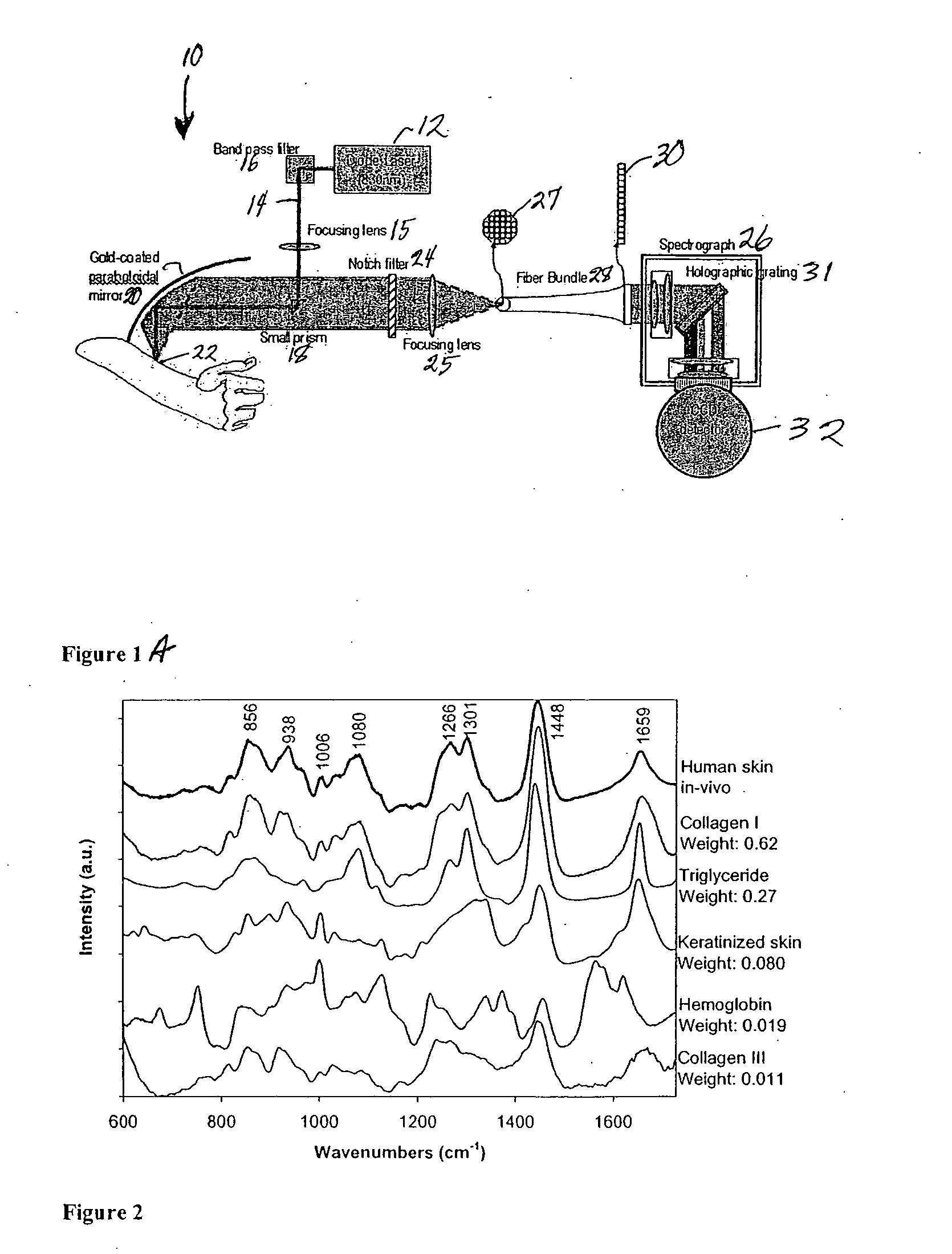
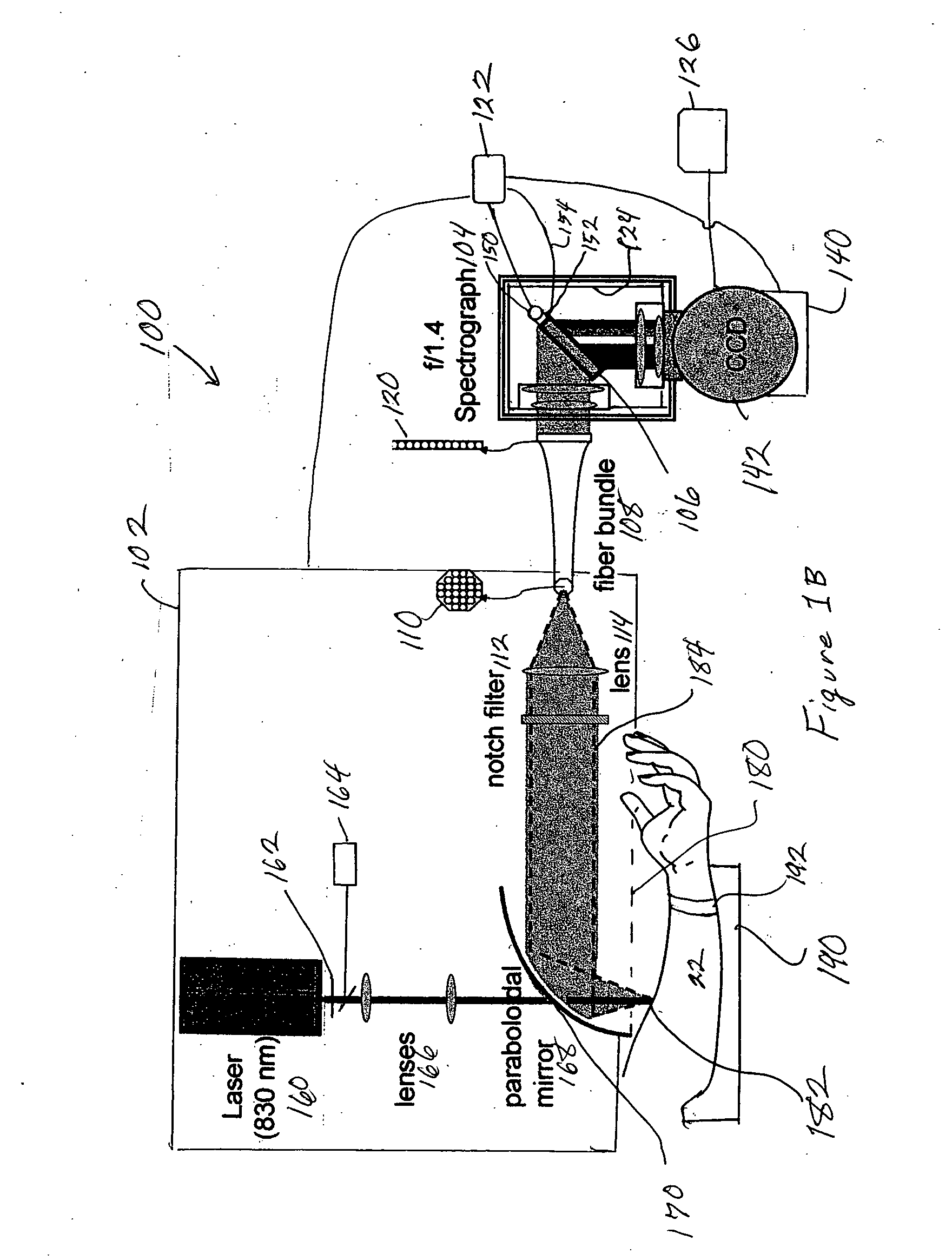
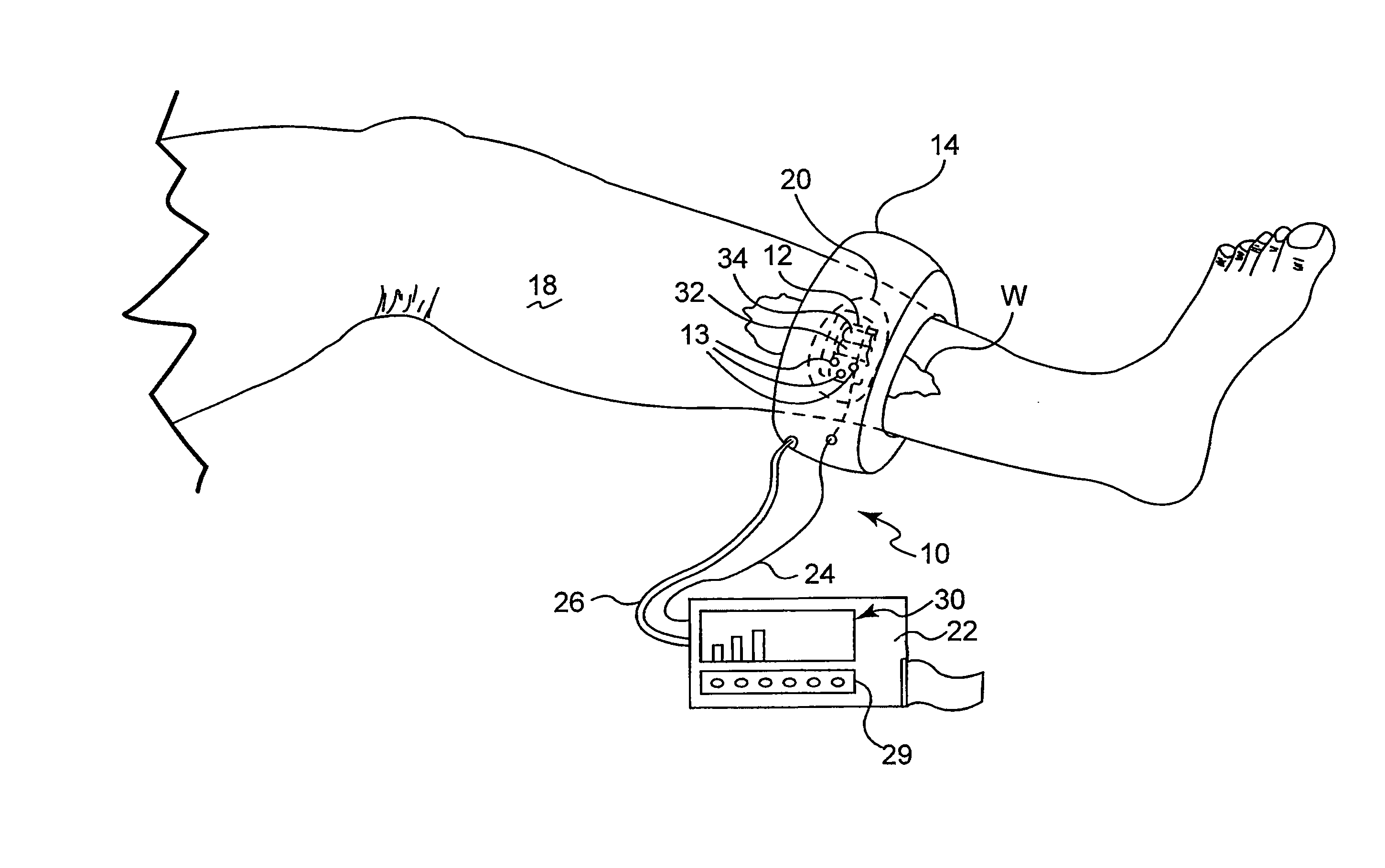
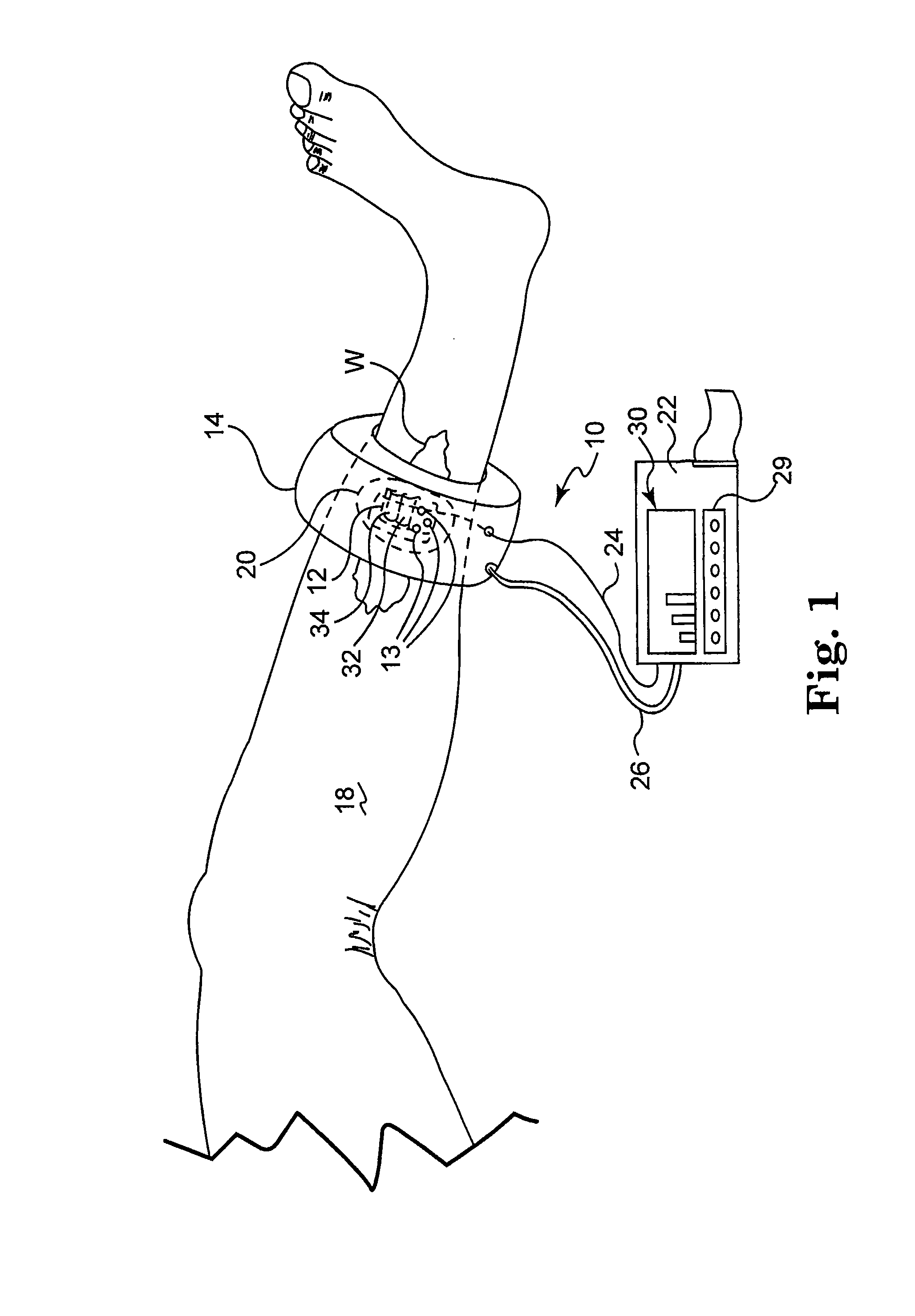
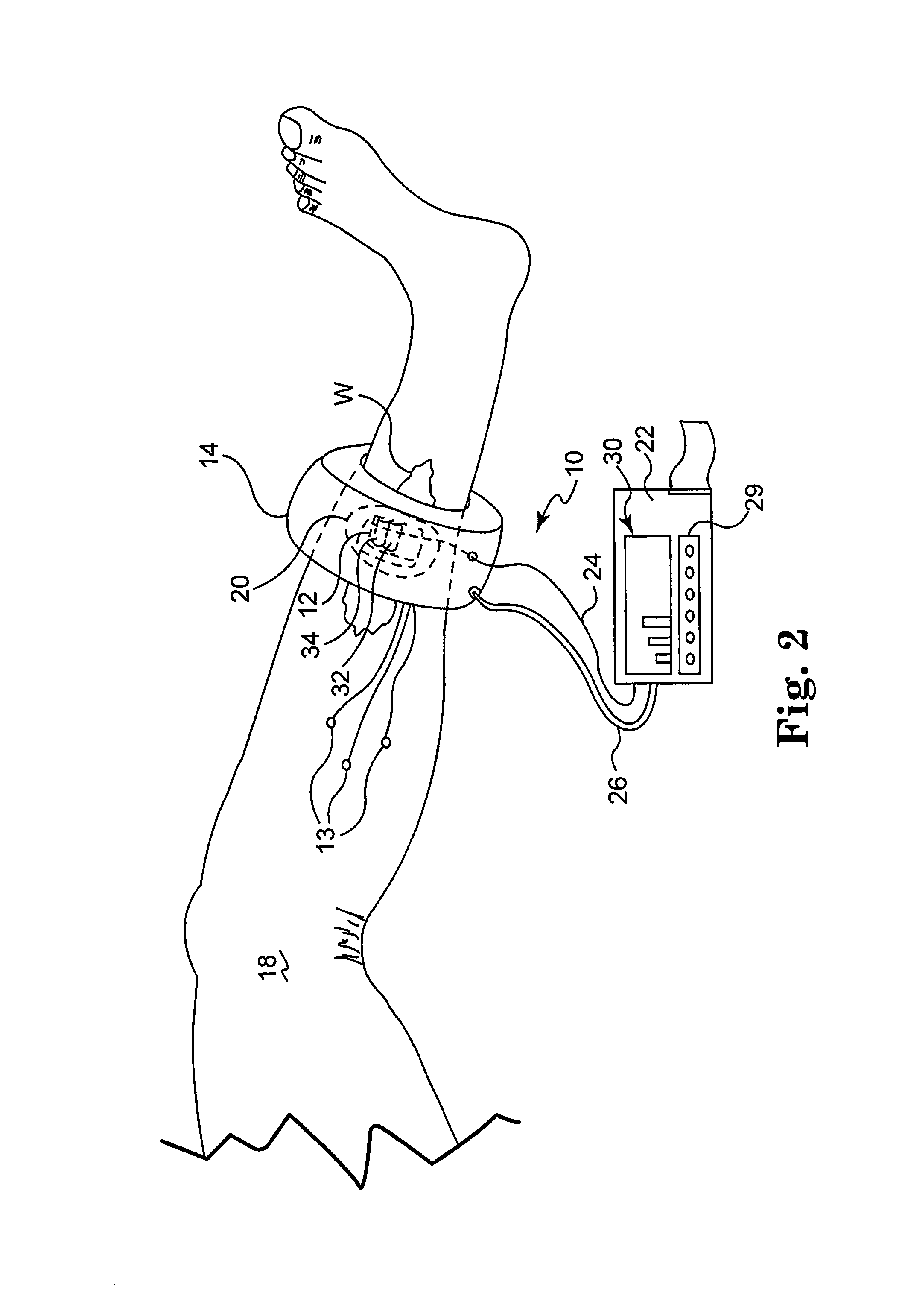
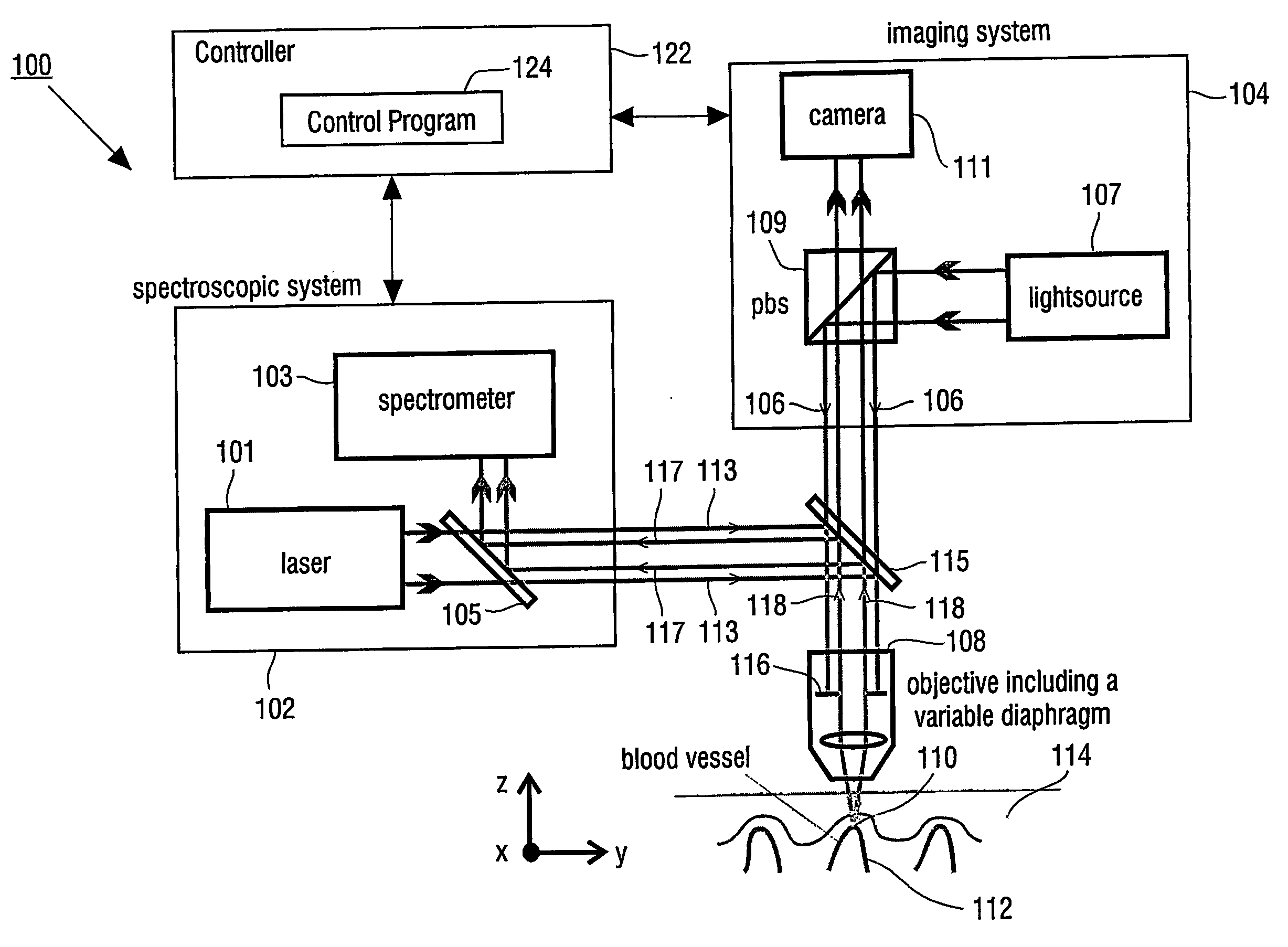
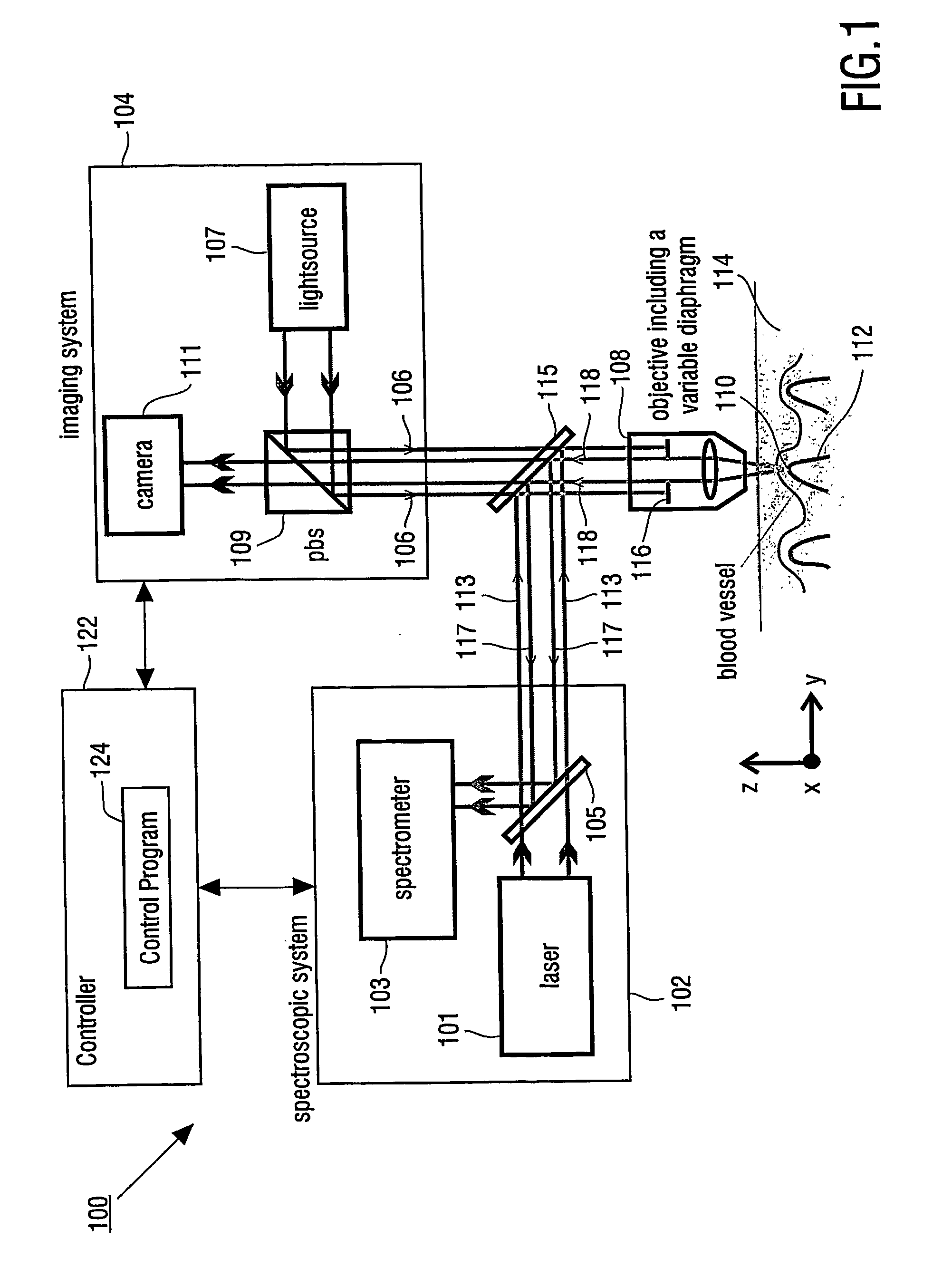
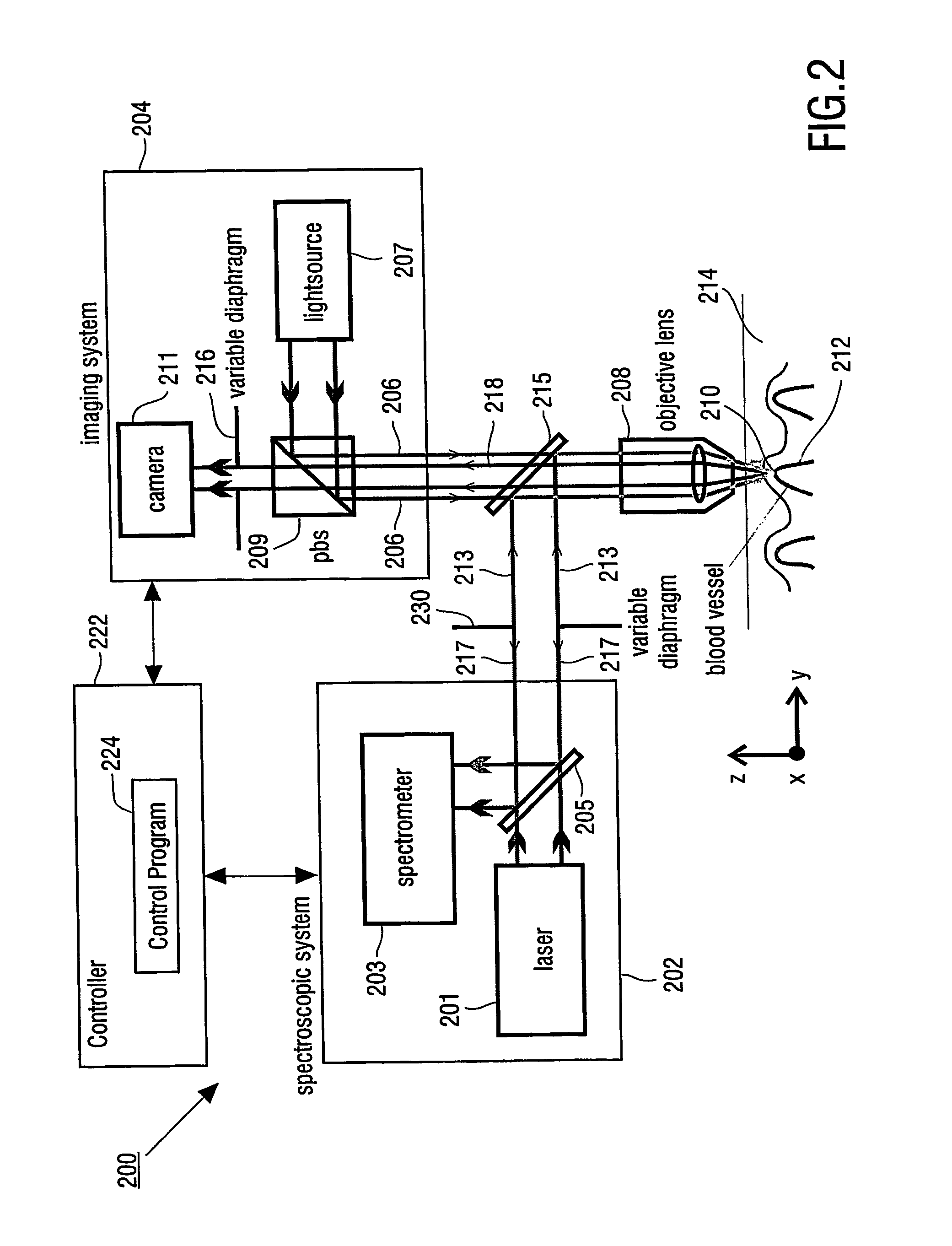
The present invention provides for an apparatus and a method for determining a property of a fluid which flows through a biological tubular structure, such as blood flowing through a capillary vessel (112) under the skin (114). This enables in vivo non-invasive blood analysis. An objective (108) having a variable numerical aperture (116) is used to enable automatic detection of a blood vessel (112) and to provide a high signal to noise ratio of the return radiation for the purposes of the spectroscopic analysis and to provide a small detection volume that fits completely within the target region.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
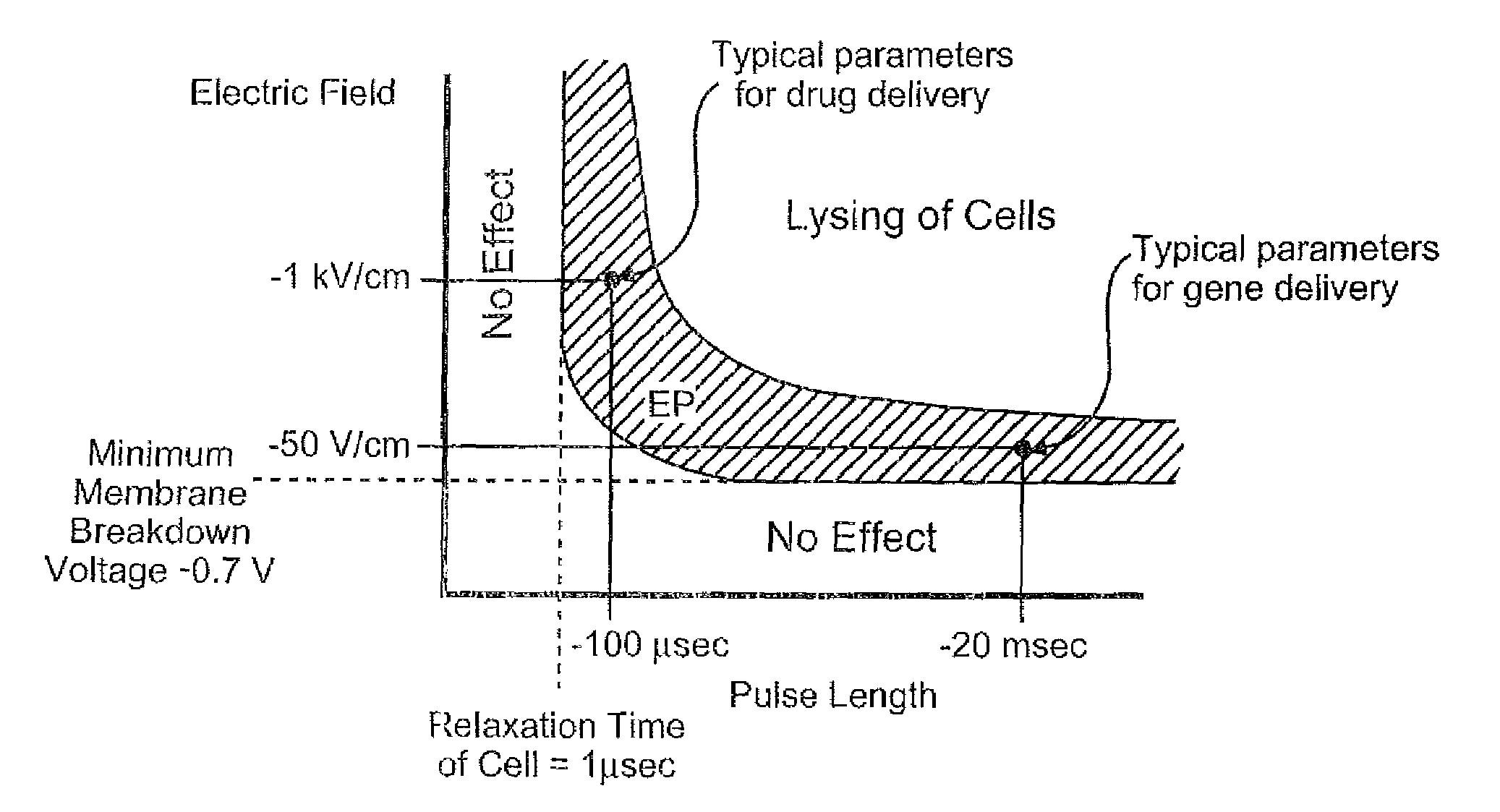
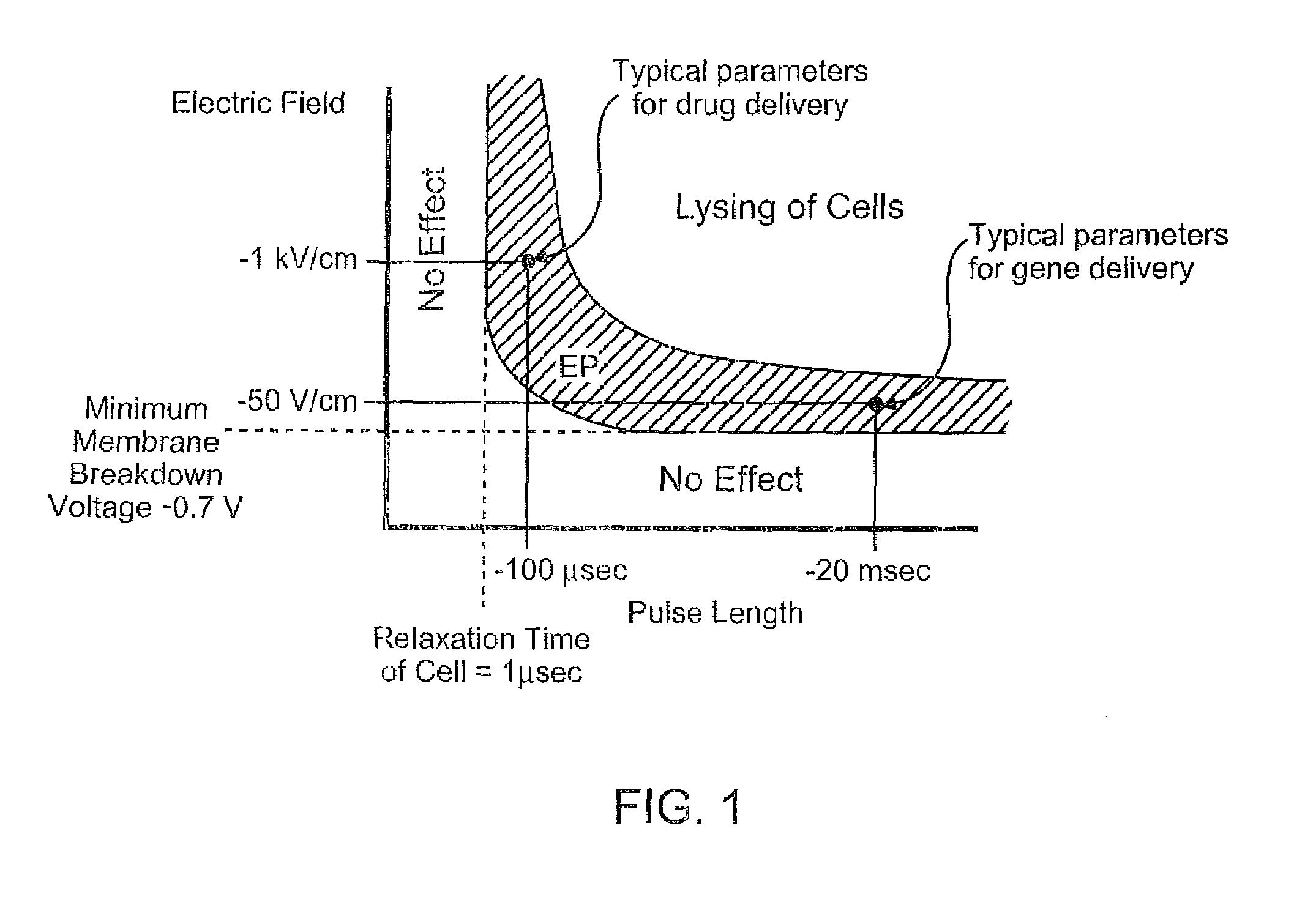
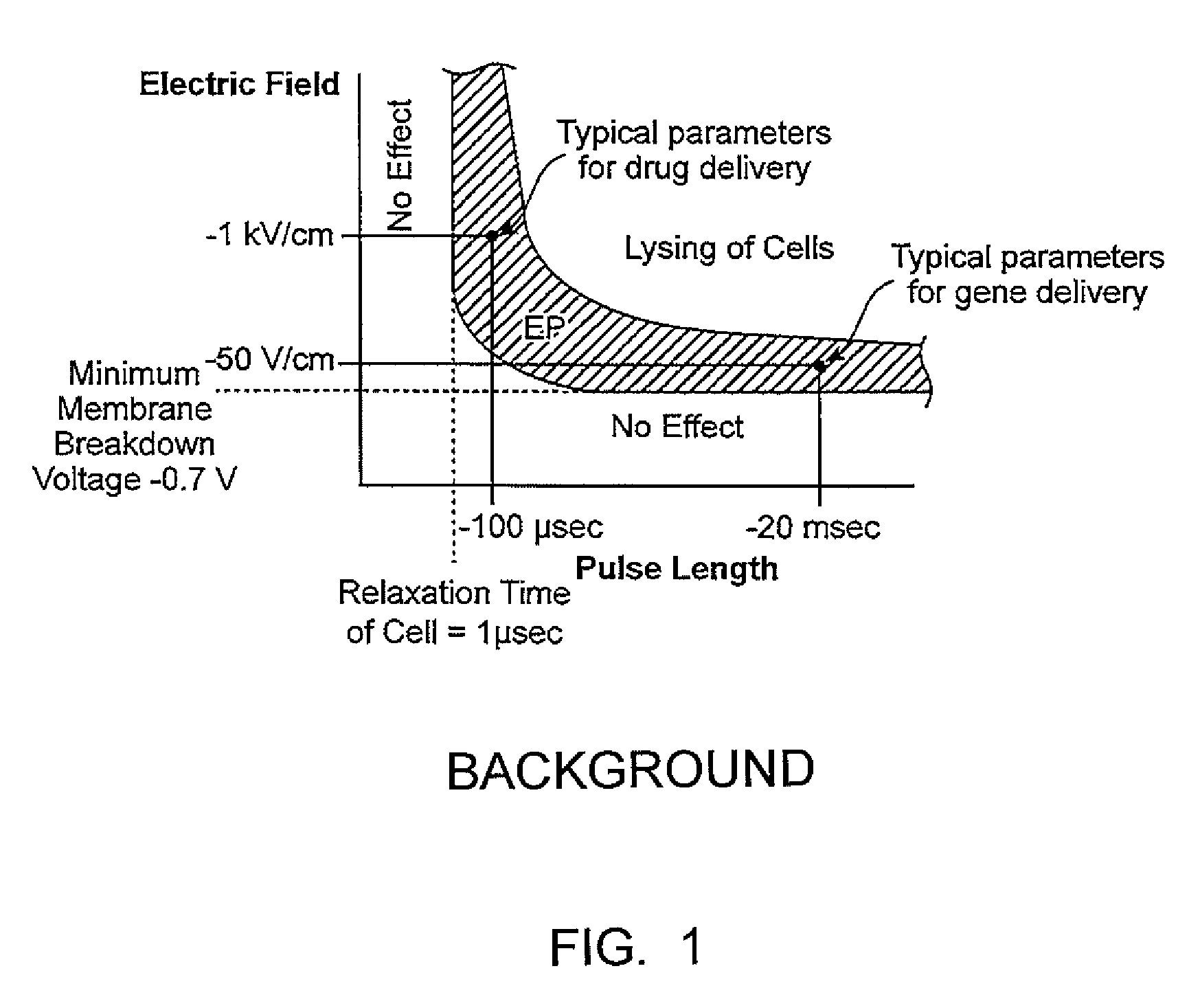
Electroporation to deliver chemotherapeutics and enhance tumor regression
ActiveUS20090326436A1Convenient introductionIncrease the number ofElectrotherapySurgical needlesAbnormal tissue growthCell membrane
A method is disclosed for disrupting capillary blood flow and trapping materials such as chemotherapeutic agents in undesirable tissue, including cells of a cancerous or non-cancerous tumor. The method involves the placement of electrodes into or near the vicinity of capillary vessels supplying blood to capillaries in the undesirable tissue, and application of electrical pulses causing capillary blood flow disruption. In some cases, the electric pulses irreversibly permeate the cell membranes, thereby invoking cell death. The irreversibly permeabilized cells are left in situ and are removed by the body's immune system. The process may further comprise monitoring blood flow and / or infusion of a material such as a chemotherapeutic agent or marker into the blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
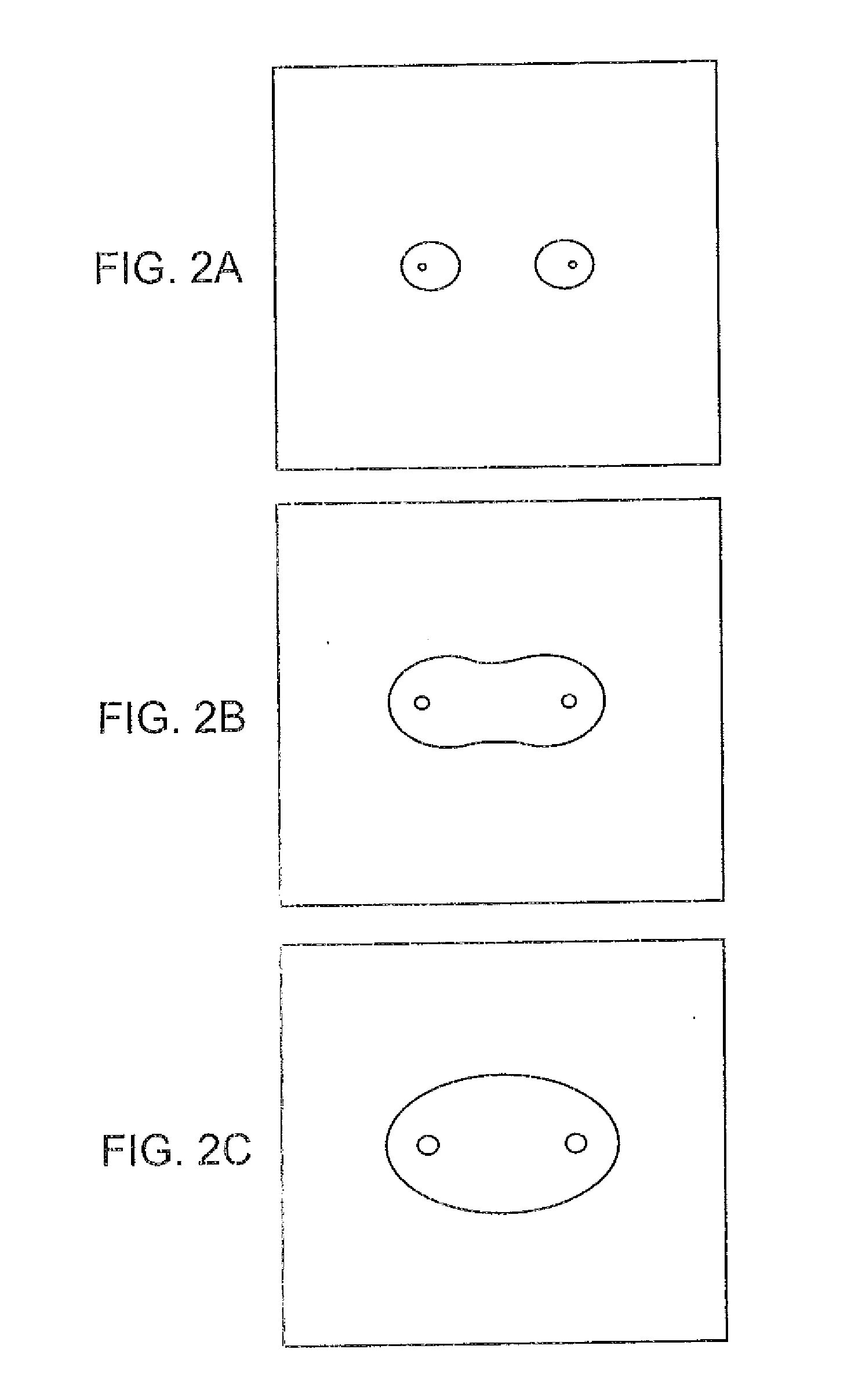
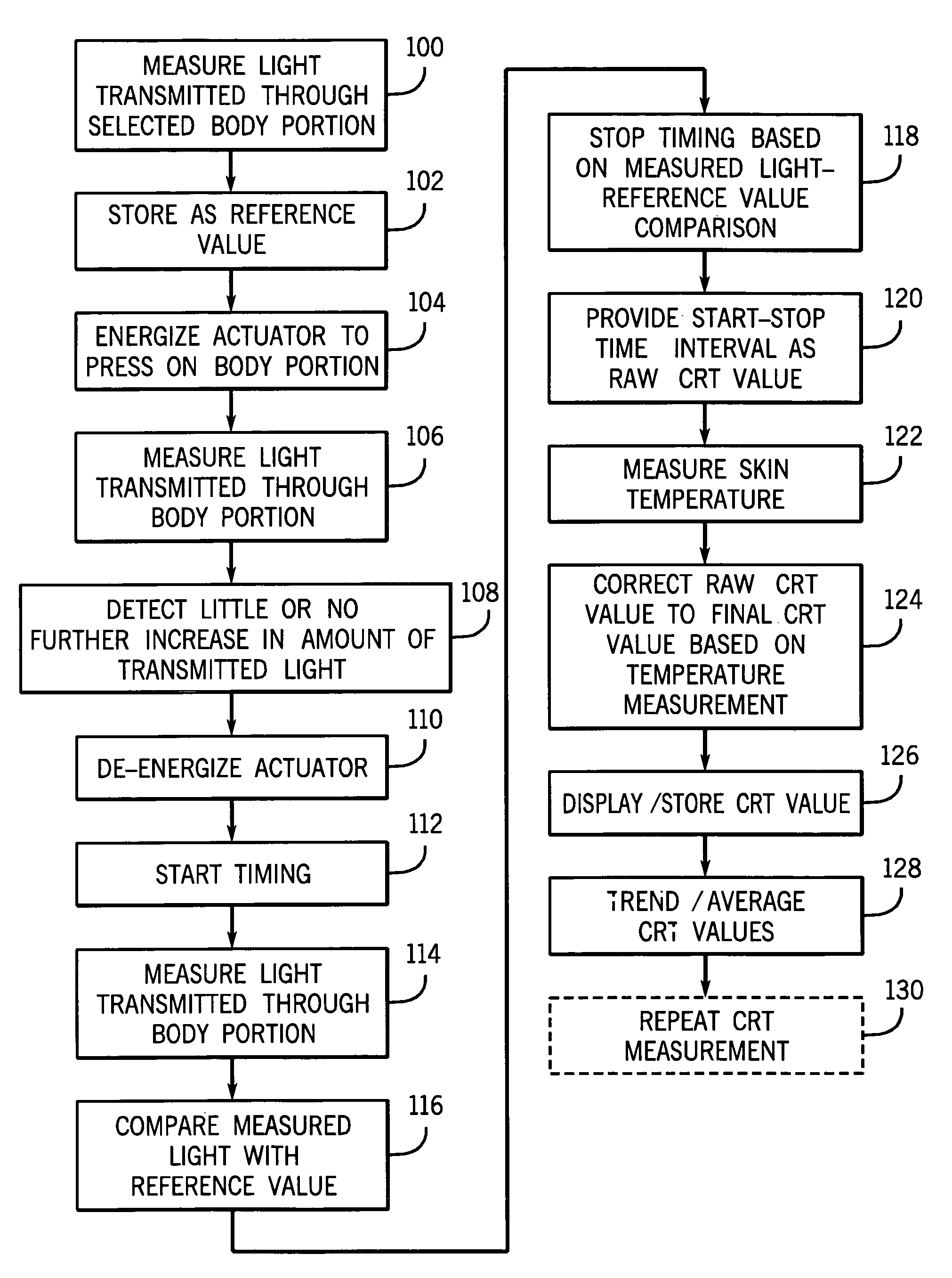
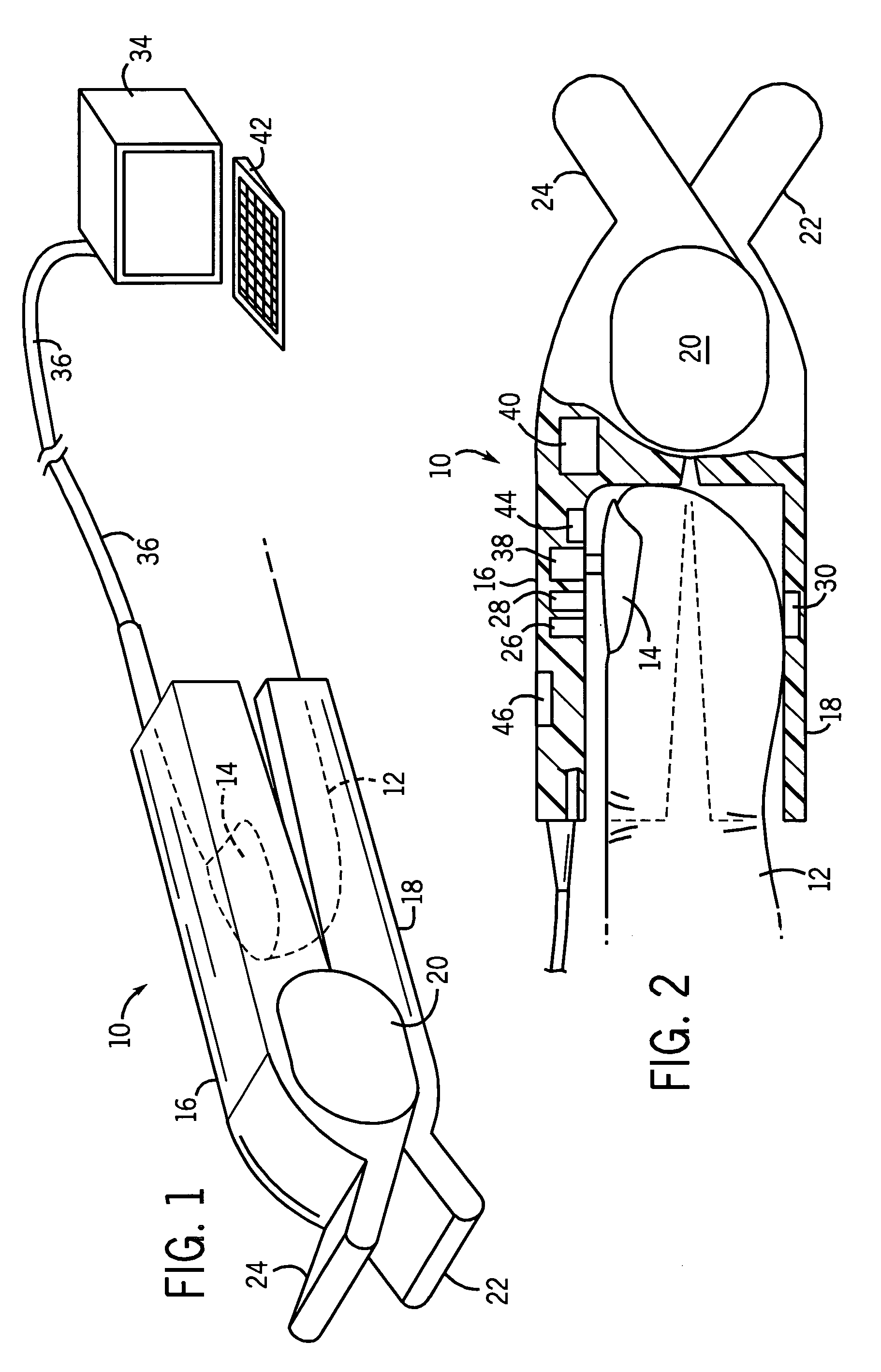
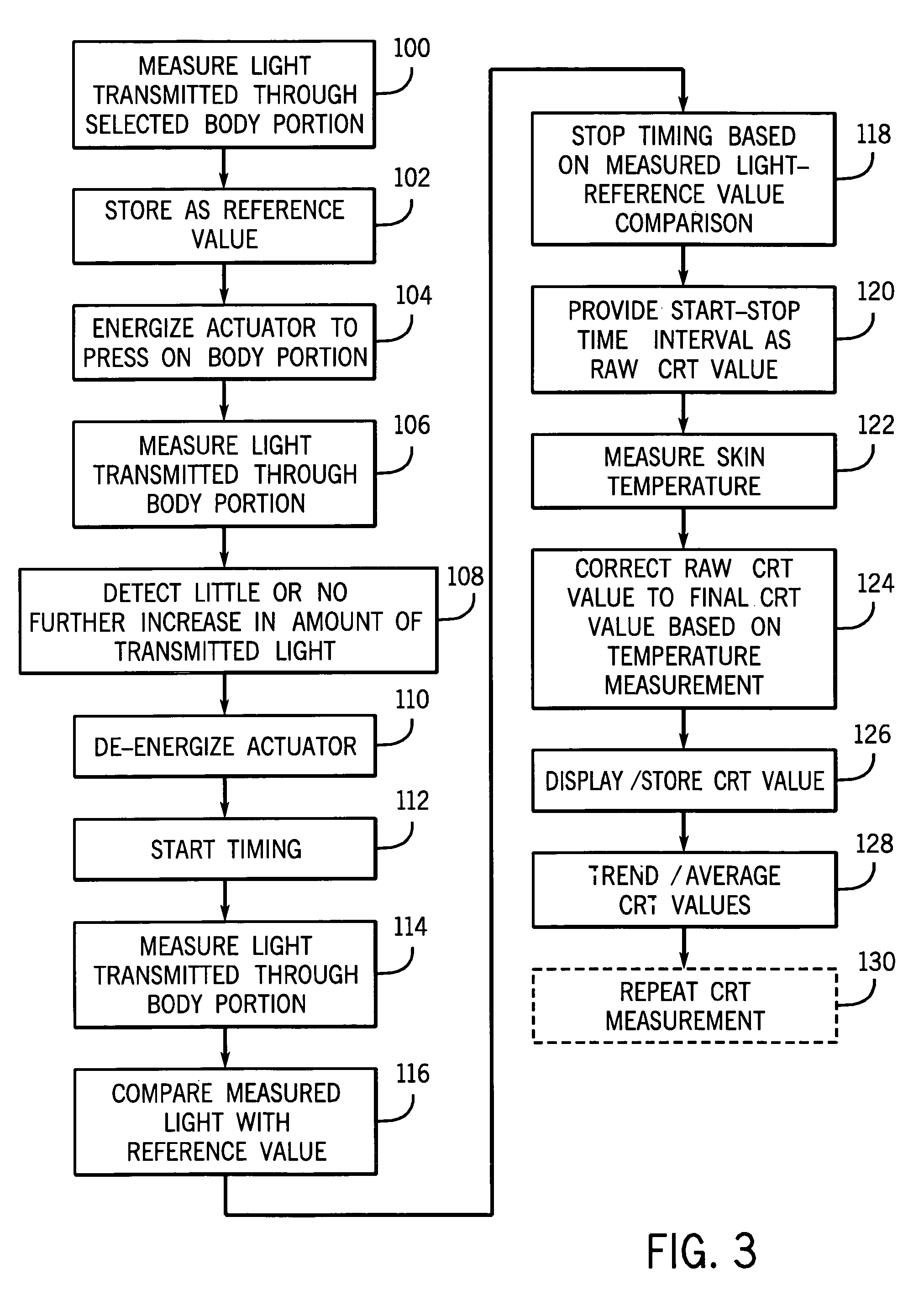
Method and apparatus for measuring capillary refill time and carrying out pulse oximetry with a single device
ActiveUS20070282182A1Simple and economical in construction and useEasy to carryDiagnostics using lightCatheterStart timeMedicine
A device for measuring the capillary refill time of a patient and for use in determining an amount of oxygen in the blood of the patient has light sources and a light detector for use in carrying out pulse oximetry. The device also includes an actuator for applying pressure to a selected portion of the body of the patient, such as the nail bed of a finger or toe of the patient, to cause the removal of blood from the nail bed when actuated. A timer commences a time interval with a deactuation of the actuator. The deactuation relieves the pressure applied by the actuator to the body portion of the patient and allows blood to return to the portion. The timing interval is terminated by a reduction in the amount of light received by the light detector as a result of the restoration of blood to the body portion. The time interval so determined comprises an indication of the capillary refill time of the patient. Compensation in accordance with a skin temperature measurement may be provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods and apparatus for measuring capillary pressure in a sample
ActiveUS20060116828A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioEliminate the effects ofAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsCapillary pressureCapillary Tubing
A method and apparatus are provided for measuring a parameter such as capillary pressure in porous media such as rock samples. The method comprises mounting a sample in a centrifuge such that different portions of the sample are spaced at different distances from the centrifuge axis, rotating the sample about the axis, measuring a first parameter in the different portions of the sample, and determining the value of a second parameter related to the force to which each portion is subjected due to rotation of the sample. In one embodiment, the first parameter is relative saturation of the sample as measured by MRI techniques, and the second parameter is capillary pressure.
Owner:GREEN IMAGING TECH
Electroporation to deliver chemotherapeutics and enhance tumor regression
ActiveUS8298222B2Disruption in blood flowReducing minimal therapeutic doseElectrotherapySurgical needlesCell membraneTumor regression
A method is disclosed for disrupting capillary blood flow and trapping materials such as chemotherapeutic agents in undesirable tissue, including cells of a cancerous or non-cancerous tumor. The method involves the placement of electrodes into or near the vicinity of capillary vessels supplying blood to capillaries in the undesirable tissue, and application of electrical pulses causing capillary blood flow disruption. In some cases, the electric pulses irreversibly permeate the cell membranes, thereby invoking cell death. The irreversibly permeabilized cells are left in situ and are removed by the body's immune system. The process may further comprise monitoring blood flow and / or infusion of a material such as a chemotherapeutic agent or marker into the blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
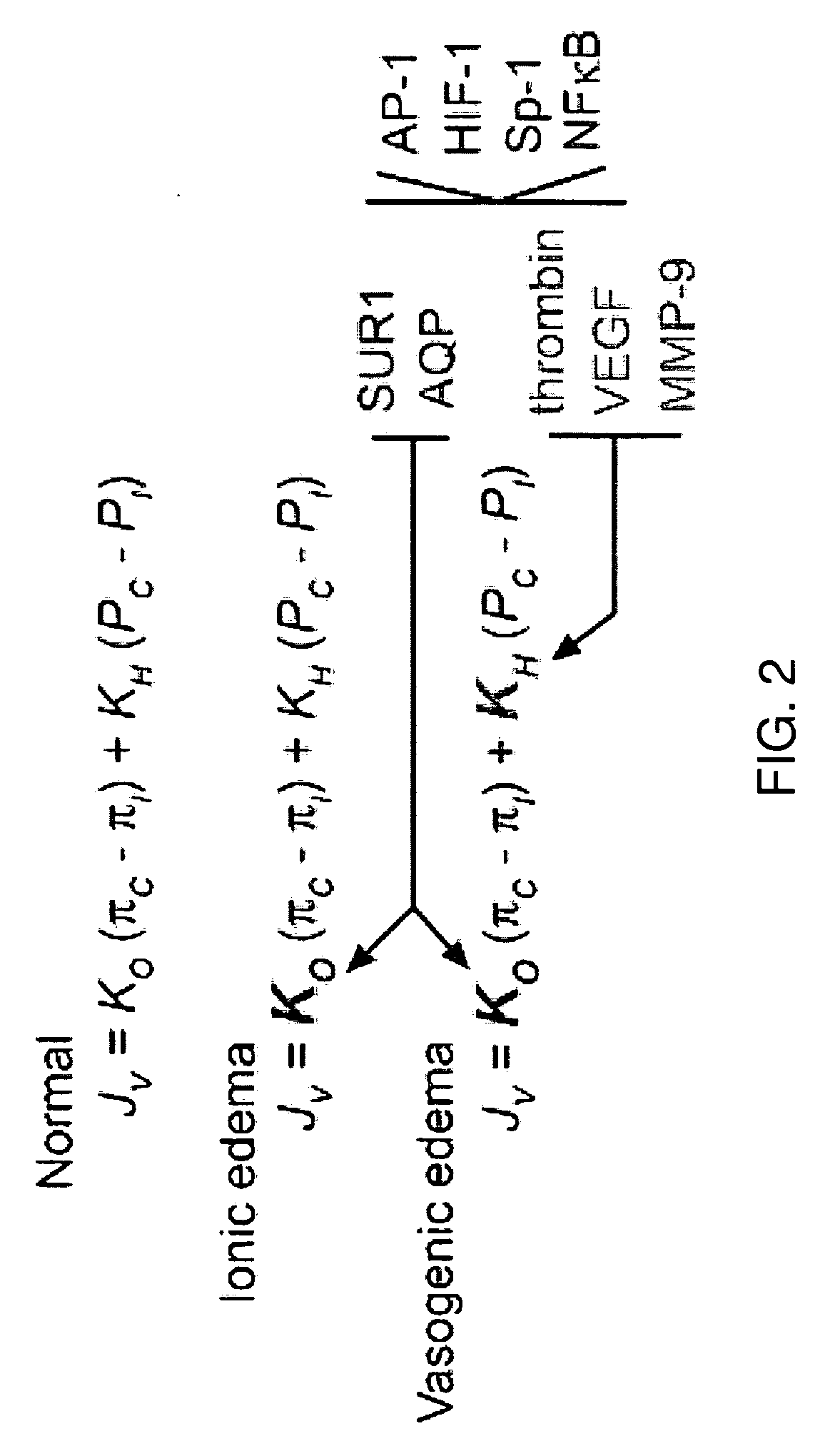
Antagonists of a non-selective cation channel in neural cells
InactiveUS20100092469A1Reduce mortalityReduces stroke sizeBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseNervous system
The present invention is directed to a combination of therapeutic compounds and treatment methods and kits using the combination. In particular, one of the combination affects the NCca-ATP channel of neural tissue, including neurons, glia and blood vessels within the nervous system. Exemplary SUR1 and / or TRPM4 antagonists that inhibit the NCca-ATP channel may be employed in the combination. The combination therapy also employs one or more of a non-selective cation channel blocker and / or an antagonist of VEFG, NOS, MMP, or thrombin. Exemplary indications for the combination therapy includes the prevention, diminution, and / or treatment of injured or diseased neural tissue, including astrocytes, neurons and capillary endothelial cells, that is due to ischemia, tissue trauma, brain swelling and increased tissue pressure, or other forms of brain or spinal cord disease or injury, for example. In other embodiments, there are methods and compositions directed to antagonists of TRPM4, including at least for therapeutic treatment of traumatic brain injury, cerebral ischemia, central nervous system (CNS) damage, peripheral nervous system (PNS) damage, cerebral hypoxia, or edema, for example.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Ultrasound-mediated drug delivery
InactiveUS20050283110A1Quick cureImproves transdermal penetrationElectrotherapySurgerySexual impotenceTopical treatment
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for treating physiological problems, and for providing rapid, efficacious transdermal treatment, for example, of muscle sprains, erectile dysfunction, or baldness, without requiring the use of needles or other invasive interventions. A topical therapeutic agent and ultrasound energy are applied to a tissue surface, e.g., the skin, such that the ultrasound enhances transdermal penetration of the agent. The invention is especially useful in localized delivery of a controlled dosage of a therapeutic agent to the small blood vessels and capillaries beneath the skin's surface.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Electrophoresis apparatus having at least one auxiliary buffer passage
ActiveUS20070111329A1Good loadabilityHigh sensitivityElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSingle sampleAnalyte
An electrophoresis apparatus is generally disclosed for sequentially analyzing a single sample or multiple samples having one or more analytes in high or low concentrations. The apparatus comprises a relatively large-bore transport capillary which intersects with a plurality of small-bore separation capillaries and includes a valve system. Analyte concentrators, having antibody-specific (or related affinity) chemistries, are stationed at the respective intersections of the transport capillary and separation capillaries to bind one or more analytes of interest. The apparatus allows the performance of two or more dimensions for the optimal separation of analytes. The apparatus may also include a plurality of valves surrounding each of the analyte concentrators to localize each of the concentrators to improve the binding of one or more analytes of interest.
Owner:PRINCETON BIOCHEM
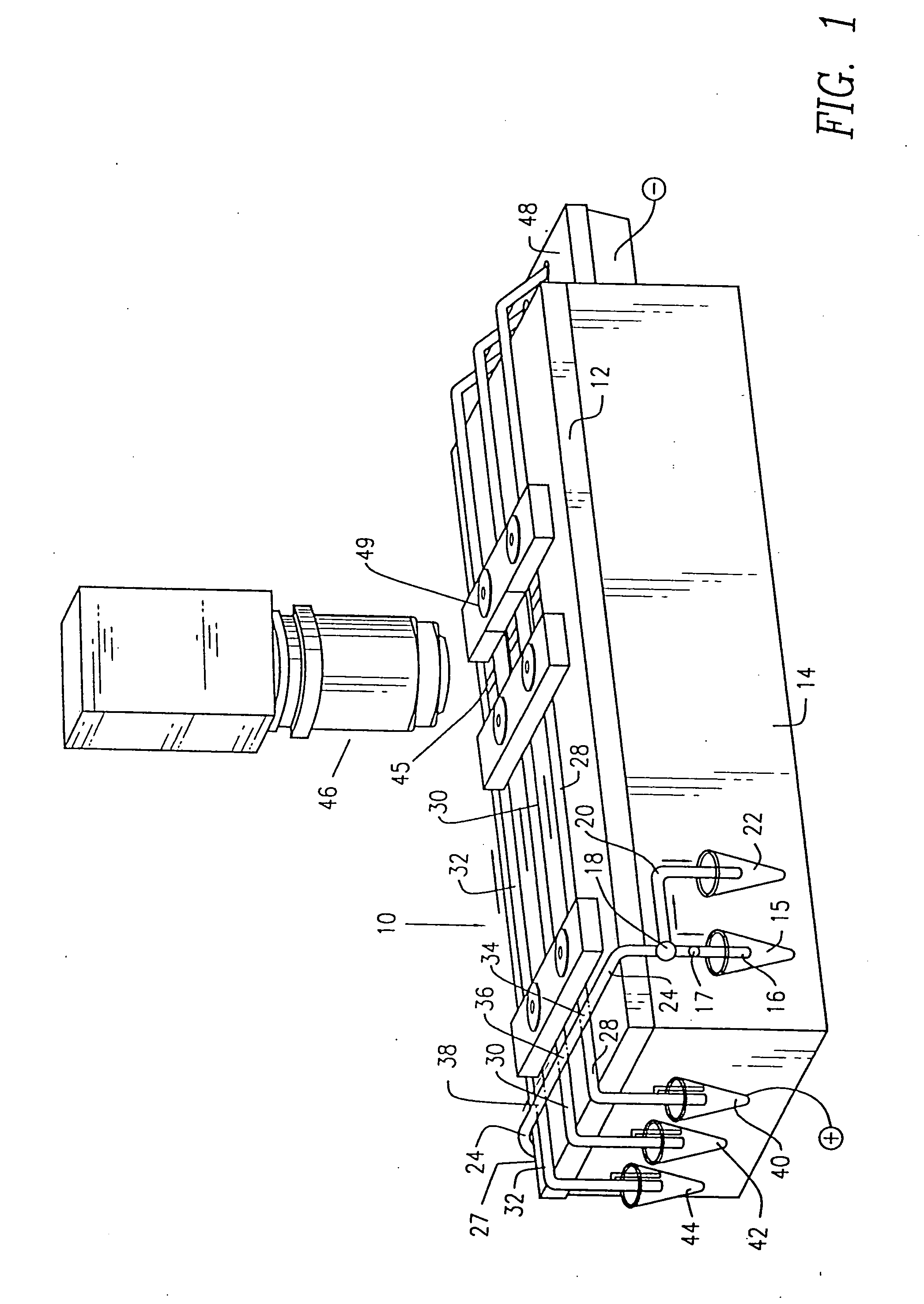
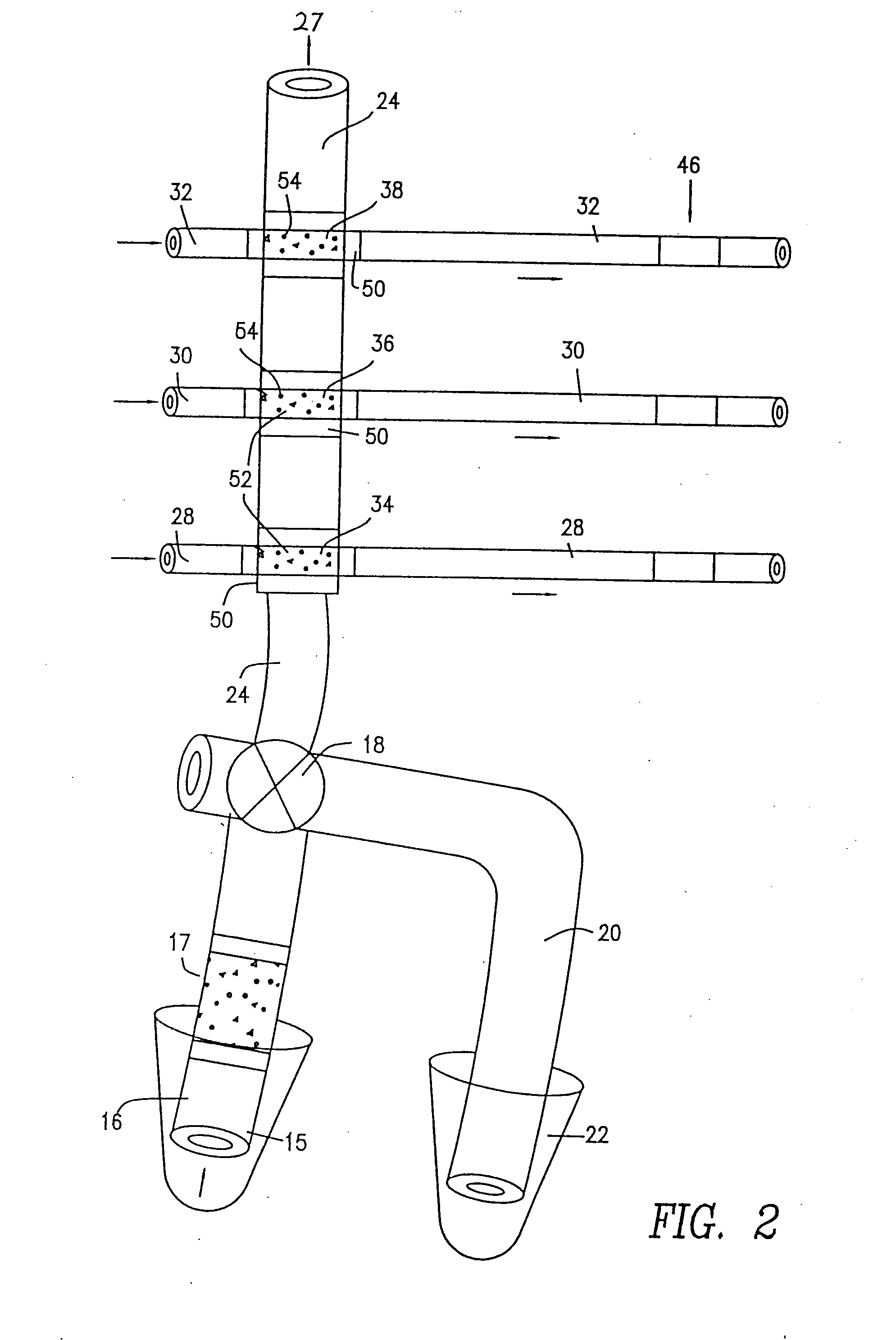
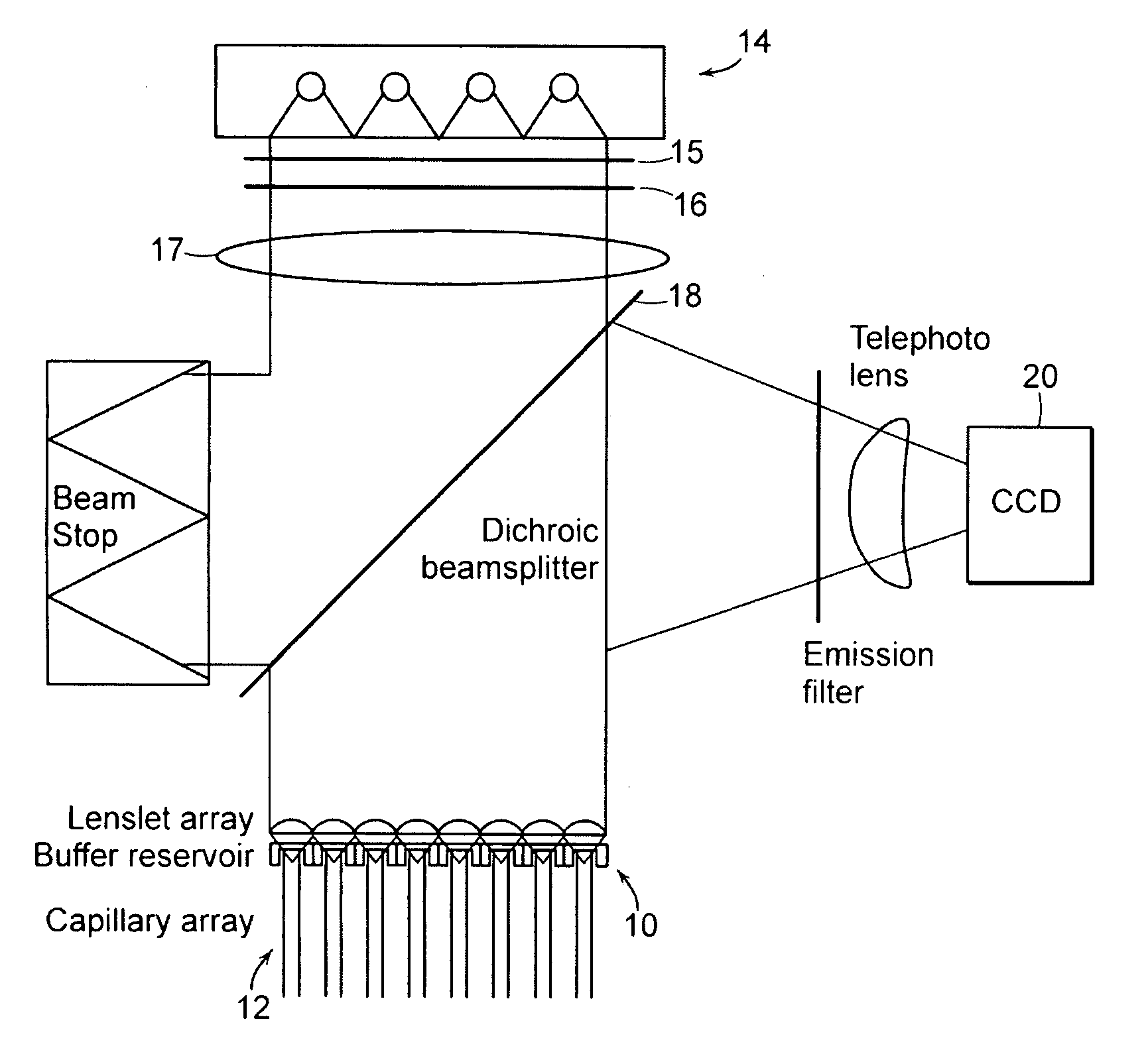
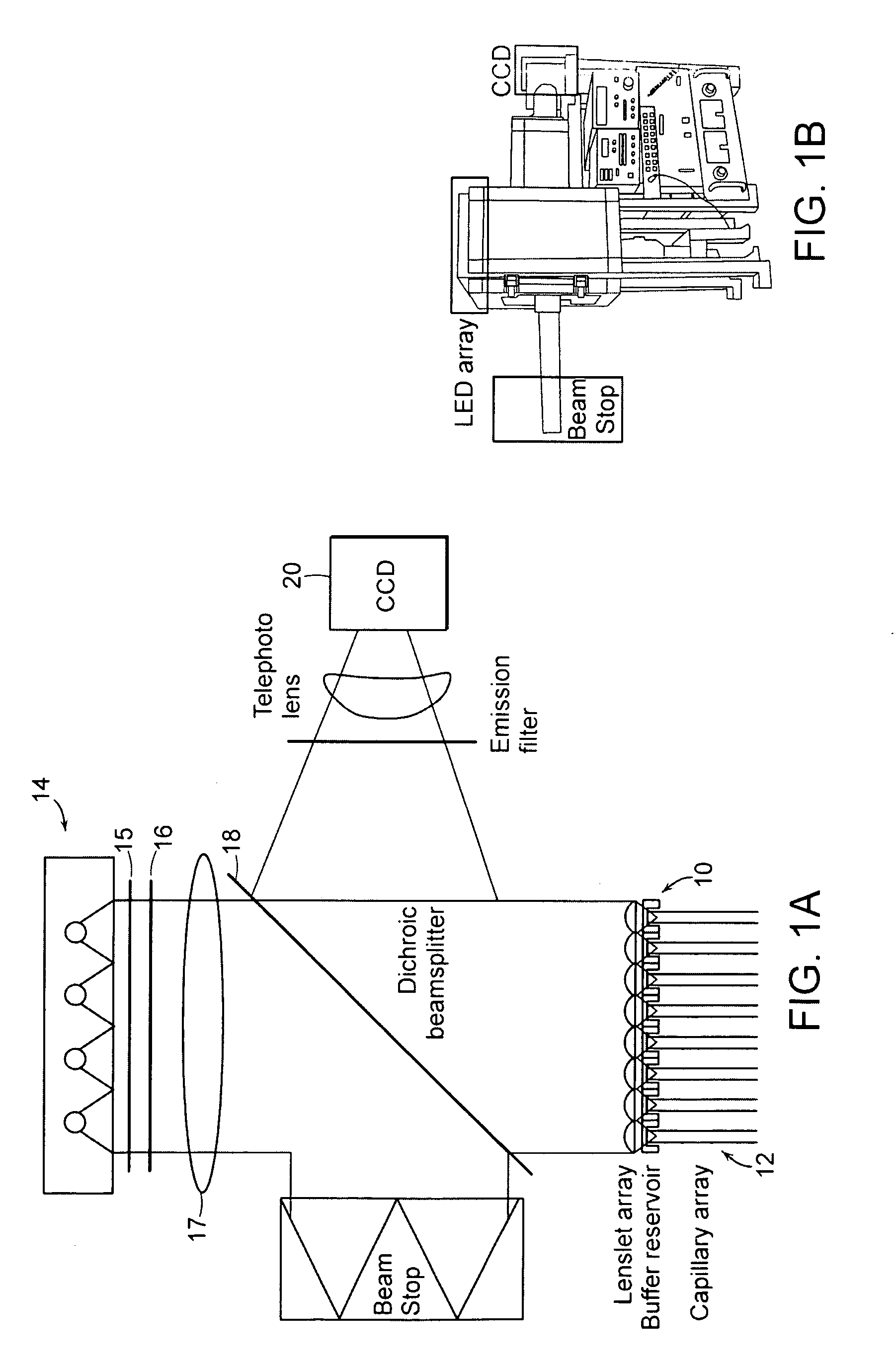
End-column fluorescence detection for capillary array electrophoresis
InactiveUS20060176481A1Easy to collectSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
A massively parallel electrophoresis system comprised of capillaries, with means for parallel imaging of the capillary ends. The capillaries are aligned with parallel longitudinal axes and a set of ends that are substantially coplanar. The electrophoresis system has a source of excitation radiation for illuminating the ends while an imaging optical arrangement places substantially coplanar loci, one per capillary, within a focal region of the imaging optical arrangement. A detector module receives electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by fluorophores within the capillaries upon excitation by the excitation radiation and transmitted to the detector module by way of the imaging optical arrangement. A manifold may terminate the array of electrophoresis capillaries, wherein the manifold has a platen with a plurality of recessions for receiving each of a the ends of the array of capillaries, and a septum disposed adjacent to the platen for penetration by the ends of the array of capillaries when inserted into the platen. Electrophoresis products may be separated by segregating effluent from one or more capillaries of the array.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Capillary array-based enzyme screening
InactiveUS6972183B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismExpression Library
A process for screening an expression library to identify clones expressing enzymes having a desired activity is provided. The process involves first generating from genomic DNA samples of one or more microorganisms an expression library comprising a plurality of recombinant cell clones, and then introducing into capillaries in a capillary array a substrate and at least a subset of the clones, either individually or as a mixture. Interaction of the substrate and a clone expressing an enzyme having the desired activity produces an optically detectable signal, which can then be spatially detected to identify capillaries containing clones producing such a signal. The signal-producing clones can then be recovered from the identified capillaries.
Owner:BASF ENZYMES
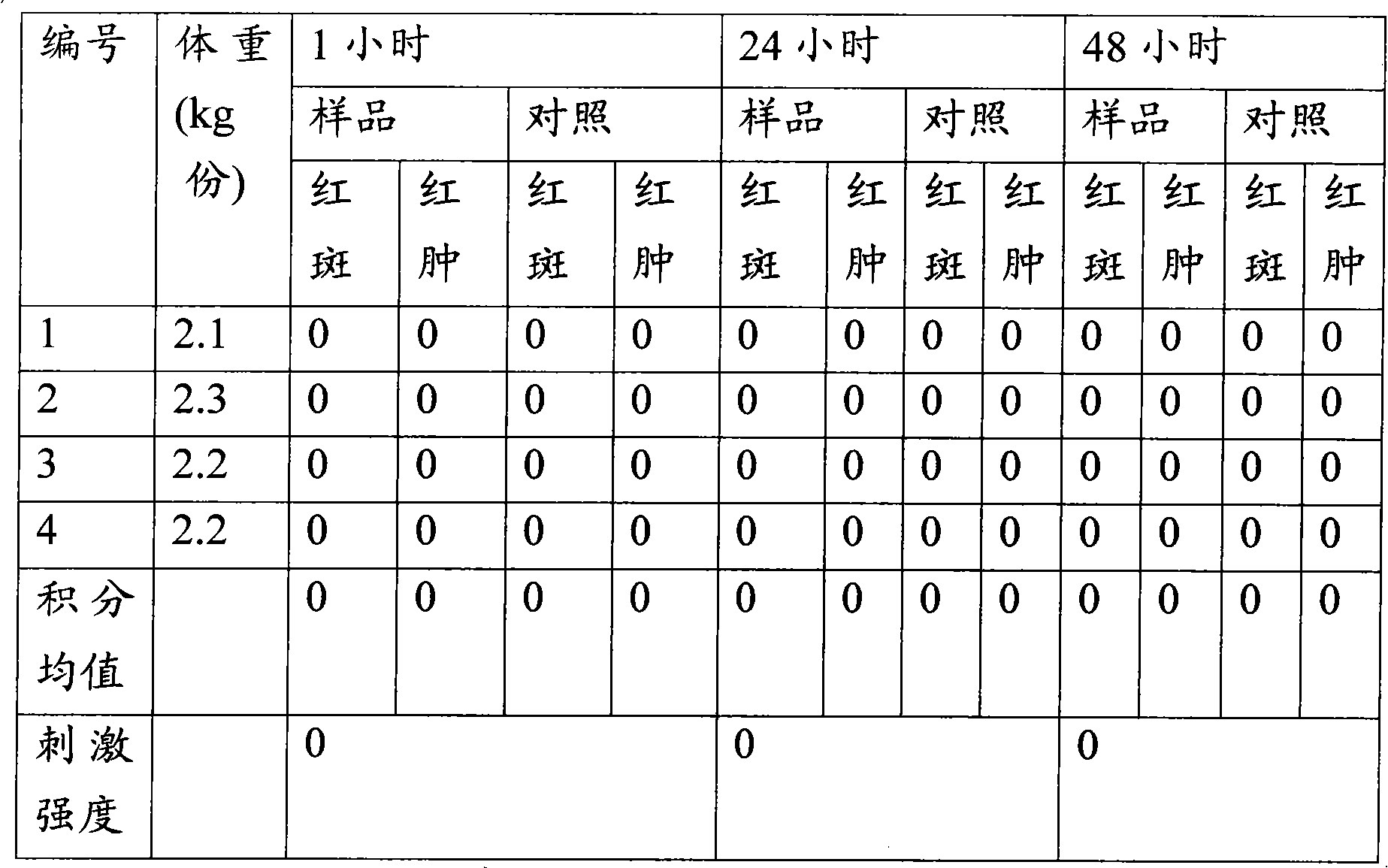
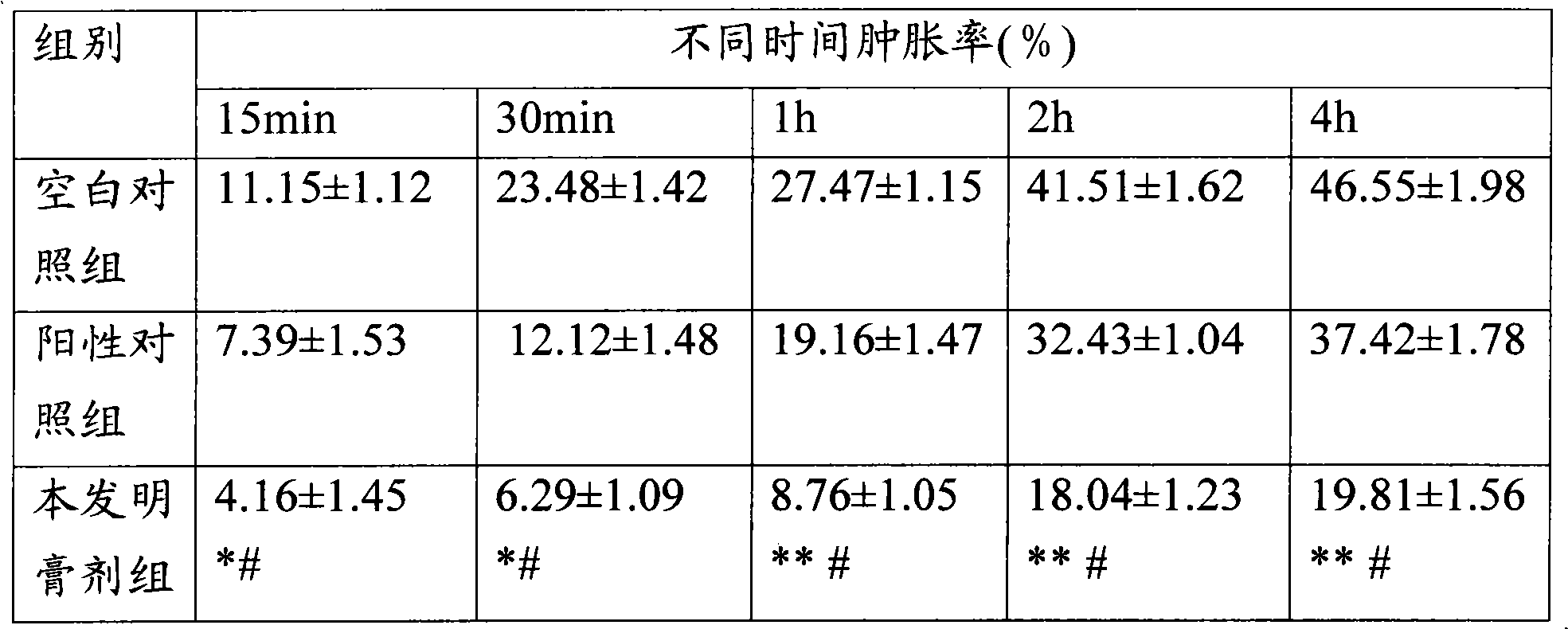
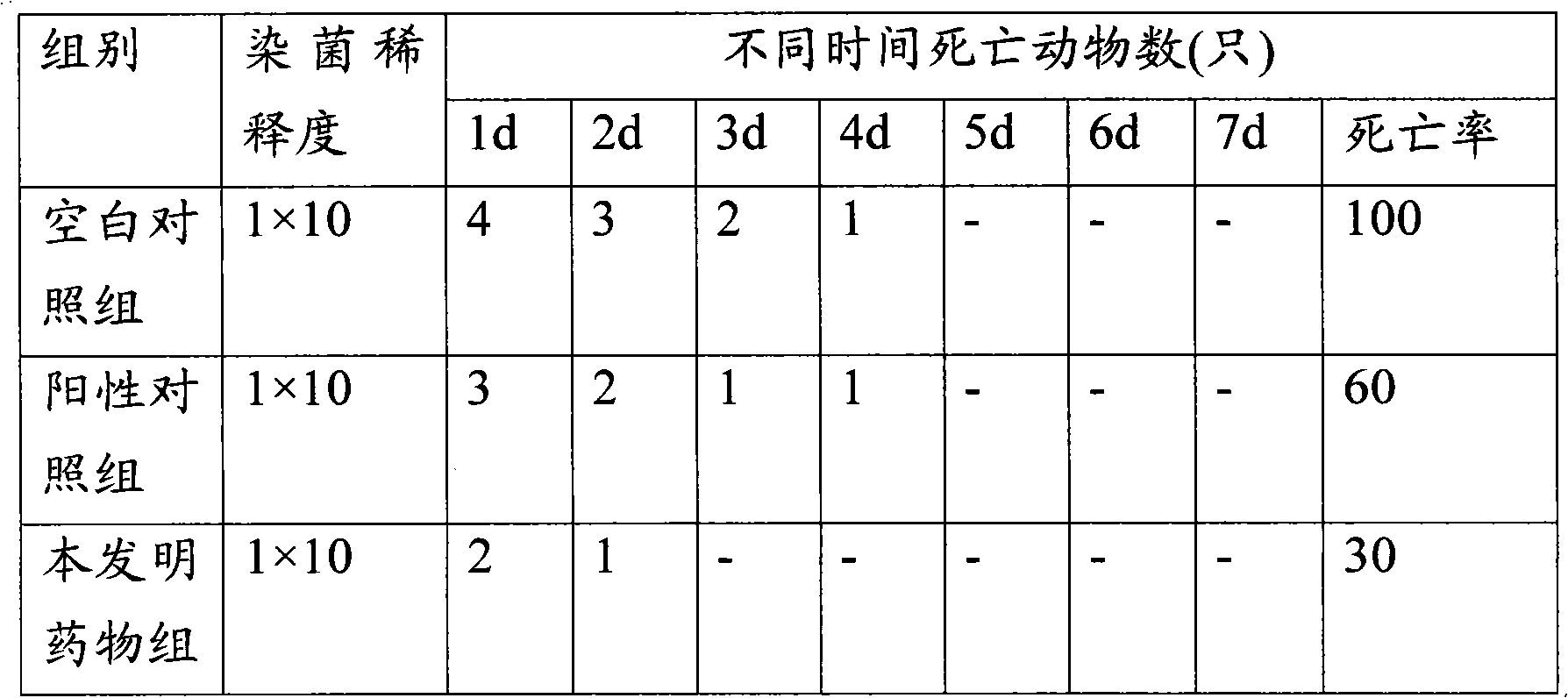
External traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating chronic wounds and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102091203AEasy to useEasy to wash offHydroxy compound active ingredientsDermatological disorderMyrrhGynecology
The invention provides an external traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating chronic wounds, which is prepared from the following raw medicines in parts by weight: 10-20 parts of draconis sanguis, 10-20 parts of chuanxiong rhizome, 10-20 parts of notoginseng, 10-20 parts of fried sanguisorba, 10-20 parts of safflower, 10-20 parts of spatholobus stem, 10-20 parts of giant knotweed, 10-20 parts of oldenlandia, 10-20 parts of red sage root, 10-20 parts of herba patriniae, 10-20 parts of moutan bark, 10-20 parts of myrrh, 10-20 parts of mastic, 10-20 parts of rhubarb, 10-20 parts of natural indigo, 10-20 parts of gromwell, 10-20 parts of catechu, 10-20 parts of borneol, 10-20 parts of phellodendron bark and 10-20 parts of boneset. The external traditional Chinese medicine preparation provided by the invention can promote healing of infectious wounds, increase pus, enhance qualitative viscosity and regenerate granulation to enable the wounds to quickly heal, has an obvious effect on treating wound infection, and can be used for treating partial ulcer, removing necrotic tissue and promoting granulation, accelerating the degeneration process of the necrotic tissue, promoting dilation of capillary vessels, accelerating microcirculation of the capillary vessels and filling the wounds.
Owner:李惠斌
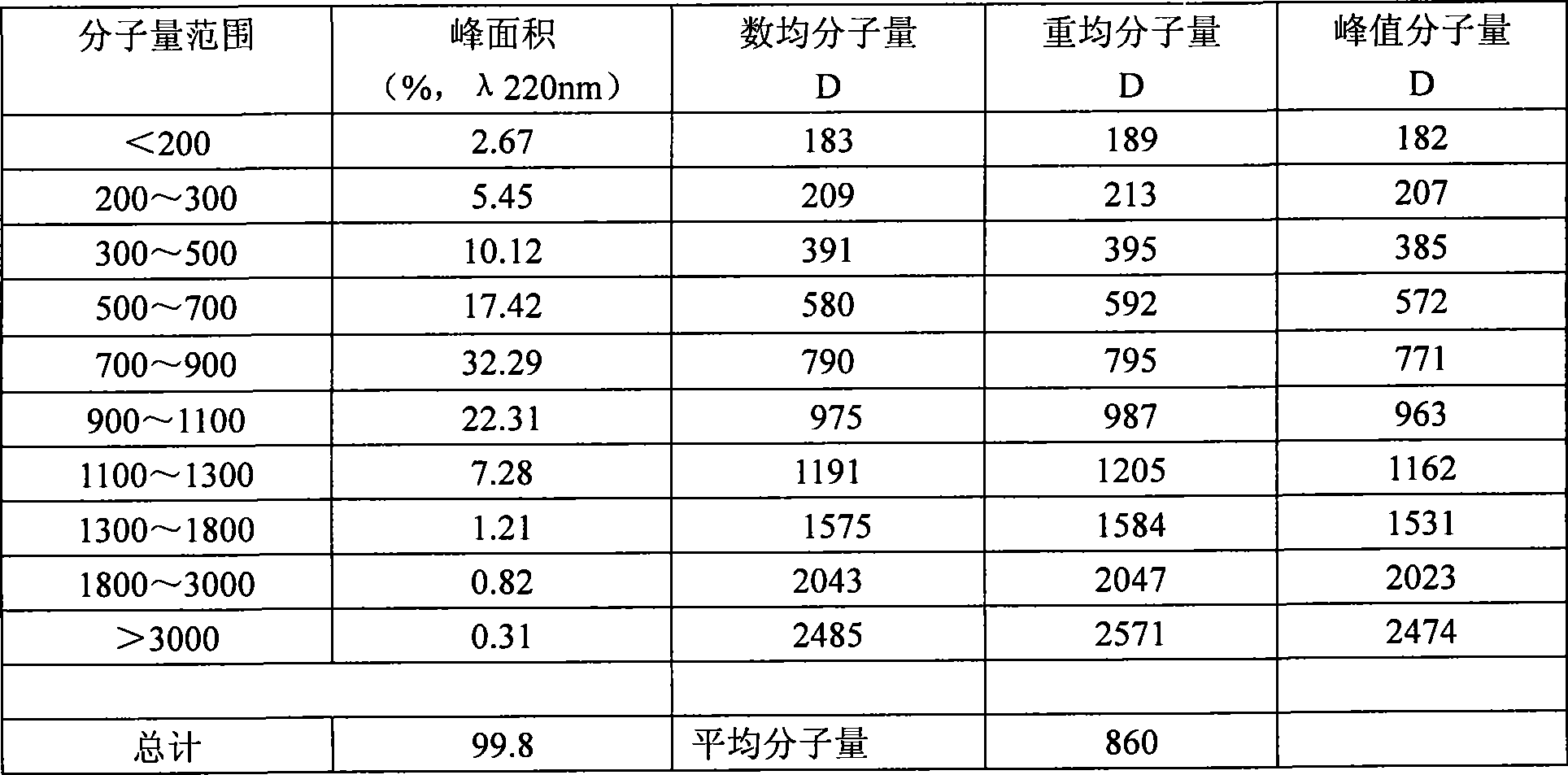
Nano micromolecule hyaluronic acid and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101507733AHigh affinityImprove permeabilityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsOligomerHydrolysis
The invention relates to a method for preparing nanometer low molecular hyaluronic acid, which comprises the following steps that: ultralow molecular weight hyaluronic acid with an average molecular weight less than 1,000D, namely nanometer hyaluronic acid oligomer, is obtained from hyaluronic acid with a molecular weight from tens of thousands to millions through hydrolysis methods such as enzyme and the like. The nanometer low molecular hyaluronic acid obtained by the method has functional characteristics of promoting the formation of capillary vessels, promoting the healing of wounds, having remarkable skin affinity and permeability and the like which are remarkably different from common hyaluronic acid, and can be taken as a high-grade raw material for cosmetology, health care food, and medicine.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF OLIGO PEPTIDE BIOLOGY
Characterization of moving objects in a stationary background
ActiveUS7912534B2Promote absorptionImprove reflectivityCatheterColor/spectral properties measurementsVascular compartmentOphthalmology
A method and system for determination and mapping the quantity of chromophores having a distinct spectrum attached to moving objects in an spectrally rich environment that may include multiple chromophores attached to stationary objects. Au area of interest is imaged at different times and different wavelengths, and the spectral properties of the chromophores attached to the moving objects are separated from the stationary spectral properties of the background, followed by spectral analysis of the moving objects to determine their quantity. Application to the retinal vasculature is illustrated, showing the imaging, analyzing and quantifying of the oxygen saturation of retinal blood, resolved for the different vascular compartments, including capillaries, arterioles, venules, arteries, and veins.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Characterization of moving objects in a stationary background
ActiveUS20050131284A1Easy to detectPromote absorptionCatheterColor/spectral properties measurementsVascular compartmentBlood flow
A method and system for determination and mapping the quantity of chromophores having a distinct spectrum attached to moving objects in an spectrally rich environment that may include multiple chromophores attached to stationary objects. An area of inters is imaged at different times and different wavelengths, and the spectral properties of the or more chromophores attached to the moving objects are separated from the stationary spectral properties of the background, followed by spectral analysis of the moving objects to determine their quantity. Application to the retinal vasculature is illustrated, showing the imaging, analyzing and quantifying of the oxygen saturation of retinal blood, resolved for the different vascular compartments—capillaries, arterioles, venules, arteries, and veins. Changes in the structure of the vascular environment are also determined, whether growth of new vessels or the elimination of existing ones, by the generation of path maps based on analysis of differential images taken at a single wavelength of the moving components in the blood flow.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Optical fingerprint identification device with living body scanning function and identification method
InactiveCN102103685AAdd comparison featuresImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionIdentification deviceSilica gel
The invention discloses an optical fingerprint identification device with living body scanning function and an optical fingerprint identification method for identifying fingerprint characteristics of a living body and stably and securely performing fingerprint authentication. Two kinds of different colored light with different penetrability are alternately used for assisting in capturing the characteristics of a finger to identify the truth of the finger and capturing fingerprint images of the same finger on different levels to further assist the identification; a red light source can be used for assisting in capturing a surface image of the fingerprints, and a blue-green light source can be used for assisting in capturing a capillary vessel image on the lower layer of the surface of the fingerprints, so that the fingerprints are from the living body or counterfeited silica gel fingerprints can be judged according to the capillary vessel image and the fingerprint surface image; and on the other hand, because more than two images of the same finger can be captured, the comparison characteristics of the same finger can be increased, and the accuracy of identification is increased.
Owner:MOREDNA TECH
Artificial nerve scaffold and preparation method and application thereof
The invention discloses an artificial nerve scaffold capable of inducing nerve regeneration active. The artificial nerve scaffold includes a dual-nerve catheter, oriented nano fiber beams and a natural polymer adhesive; the dual-nerve catheter is directly prepared outside the oriented nano fiber beams; and the natural polymer adhesive is poured into clearances of the oriented nano fiber beams to acquire the artificial nerve scaffold. the oriented nano fiber beams are rolled by a dual-component nano fiber film; the nano fiber beams are sparsely arranged, thereby facilitating growth of nerve cells; the outer layer of the nerve catheter is formed by a compact nano fiber film pipe having excellent hydrophobicity and can prevent growth of connective tissues; the inner layer of the nerve catheter is formed by a dual-component nano fiber film pipe, and is conductive to reconstruction of capillary vessels; and the natural polymer adhesive is an aqueous solution prepared by a natural polymer material, and stem cells can be added into the natural polymer adhesive. The invention discloses a preparation method of the artificial nerve scaffold, and application of the artificial nerve scaffold to peripheral nerve injury repairing.
Owner:烟台蓝创生物技术有限公司
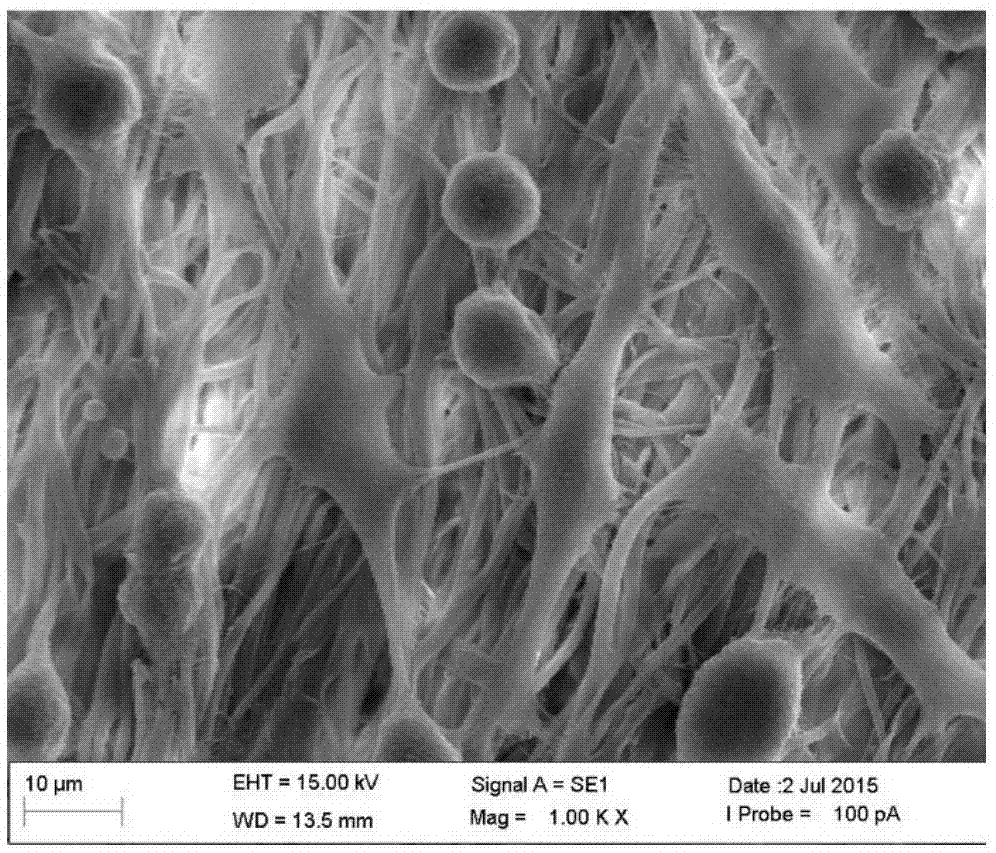
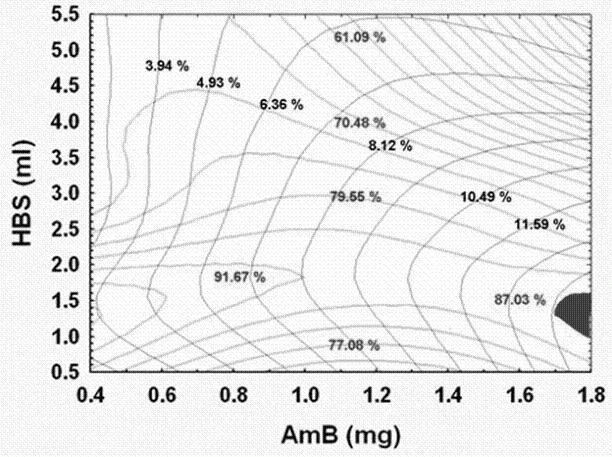
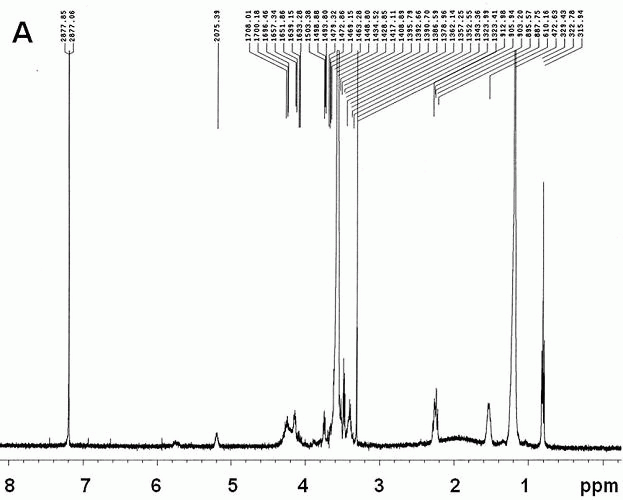
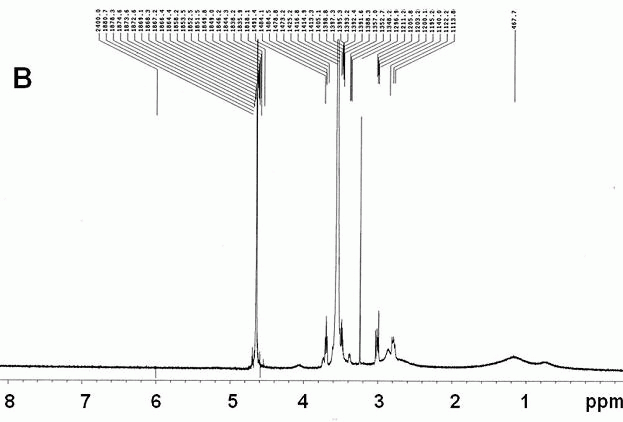
Brain targeted amphotericin B (AmB) polymer micelle administration system
InactiveCN102614105AAvoid effluxPromote accumulationOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBrain targetingPharmacology
The invention which belongs to the biotechnical field concretely relates to a brain targeted AmB polymer micelle administration system. The brain targeted AmB polymer micelle administration system is prepared by utilizing brain targeted head base Angiopep-2 modified polymer micelles extremely having a clinical application potential, and entrapping micromolecular hydrophobic drugs. The prepared brain targeted AmB polymer micelle administration system can effectively improve the uptaking of the hydrophobic drugs on brain capillary endothelial cells, and can effectively improve the accumulation amount of the drugs in the brain and the brain entrance efficiency of the drugs especially in a noninvasive intravenous injection mode; compared with present clinical preparations of the drugs, such as AmB for injection, the system of the invention has a substantially improved brain targeting efficiency; and the constructed polymer micelle administration system can obviously reduce the hemolyticity and the cytotoxicity of the AmB. The Angiopep-2 modified brain targeted AmB polymer micelle administration system of the invention can be used to promote the accumulation of hydrophobic drugs with low brain entrance efficiencies in the brain.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Methods of generating functional human tissue
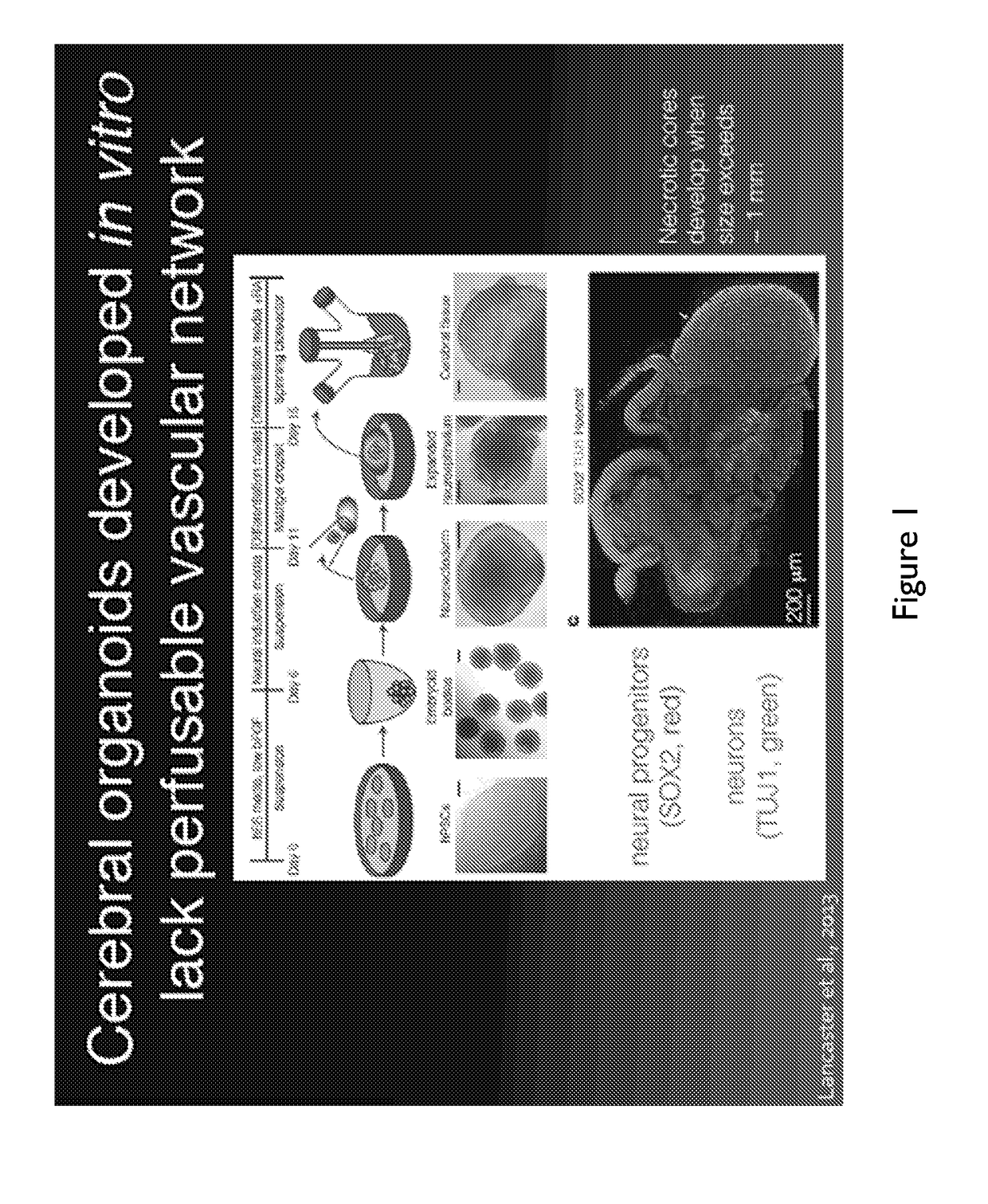
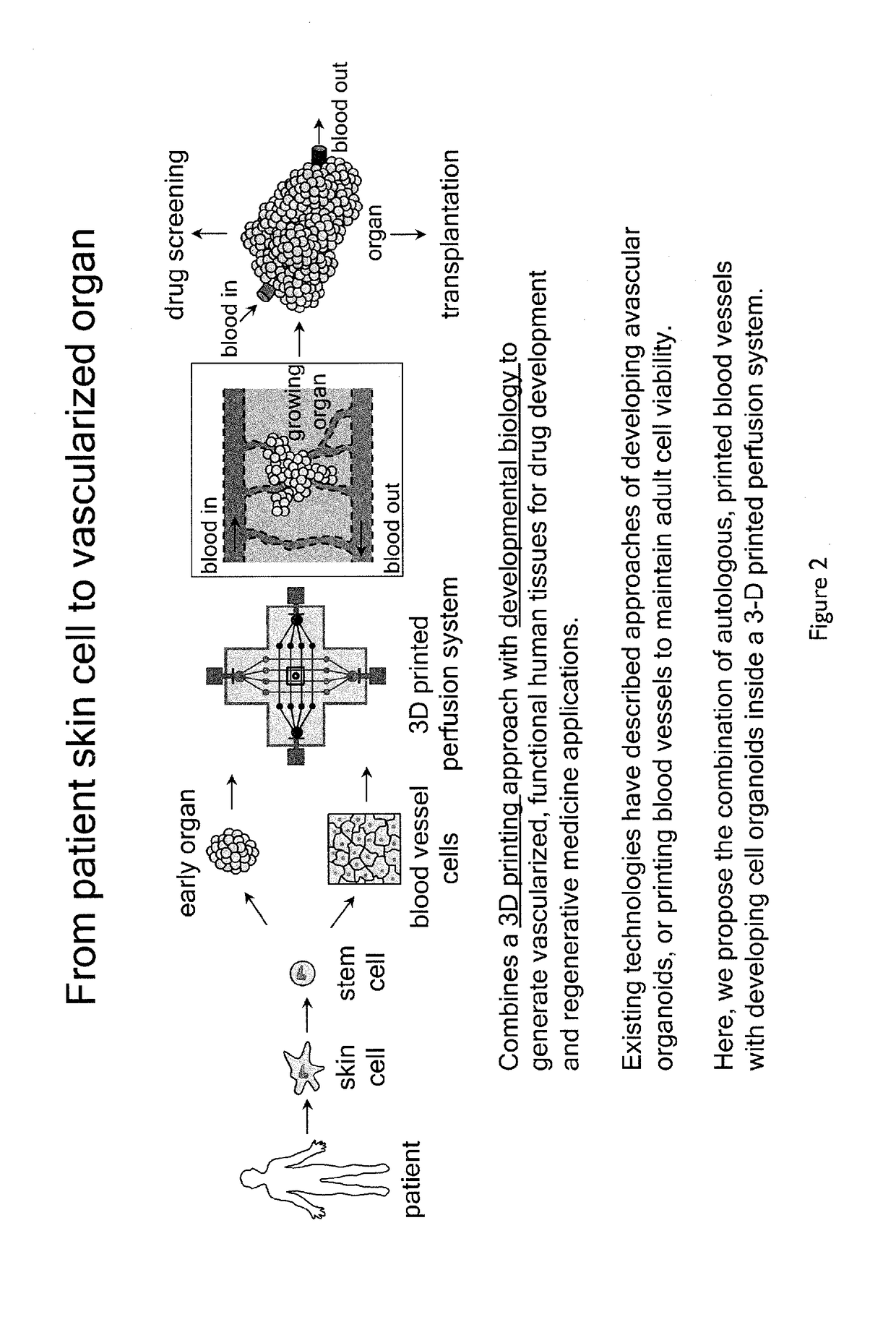
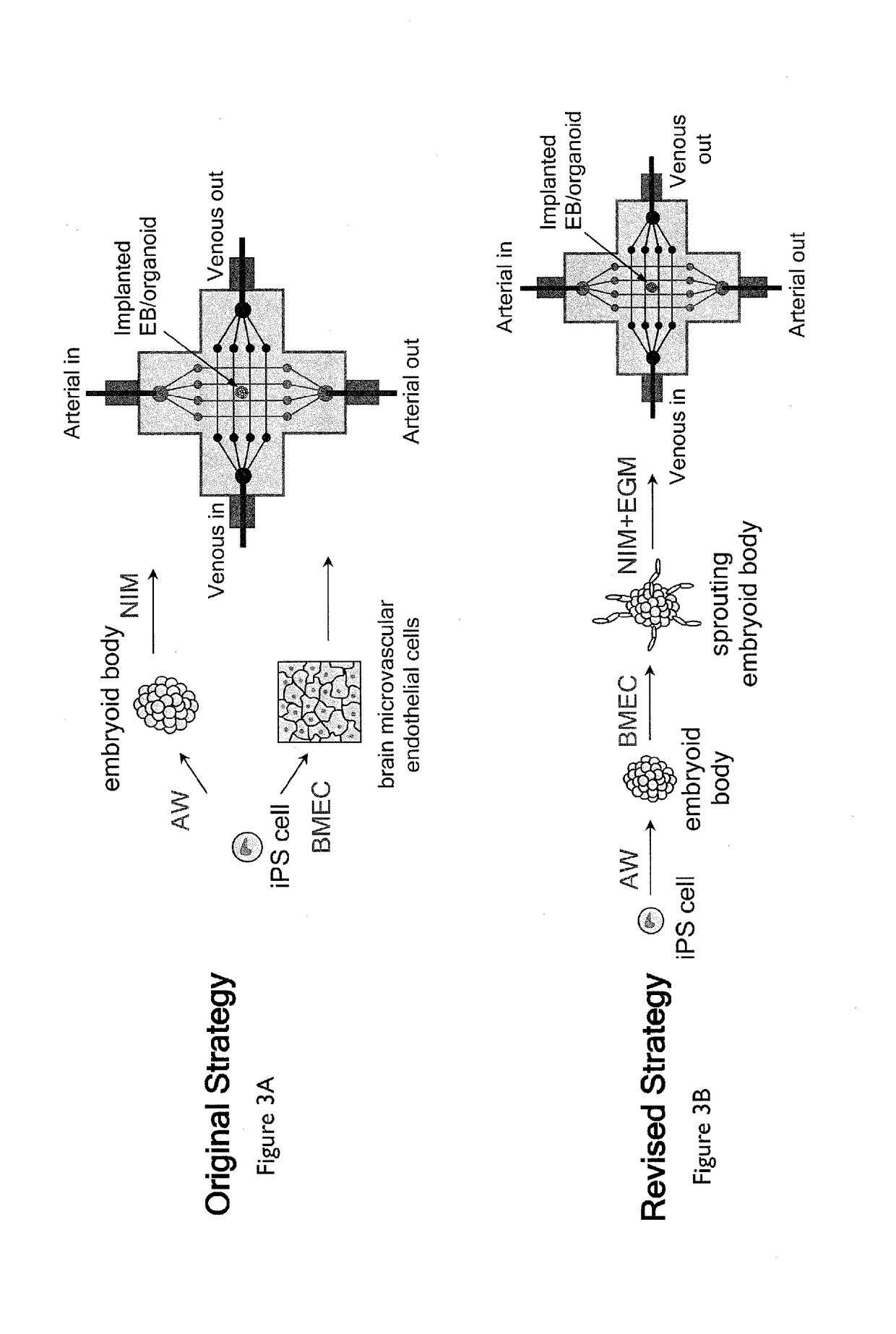
Methods of tissue engineering, and more particularly methods and compositions for generating various vascularized 3D tissues, such as 3D vascularized embryoid bodies and organoids are described. Certain embodiments relate to a method of generating functional human tissue, the method comprising embedding an embryoid body or organoid in a tissue construct comprising a first vascular network and a second vascular network, each vascular network comprising one or more interconnected vascular channels; exposing the embryoid body or organoid to one or more biological agents, a biological agent gradient, a pressure, and / or an oxygen tension gradient, thereby inducing angiogenesis of capillary vessels to and / or from the embryoid body or organoid; and vascularizing the embryoid body or organoid, the capillary vessels connecting the first vascular network to the second vascular network, thereby creating a single vascular network and a perfusable tissue structure.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Gadolinium-containing silicon dioxide nanosphere magnetic resonance contrast agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101745124AReduce distractionsIncreased sensitivityNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryMicrosphereEntrapment
The invention relates to a gadolinium-containing silicon dioxide nanosphere magnetic resonance contrast agent for lymphatic system specific imaging and a preparation method thereof. The contrast agent is nanosphere suspend liquid or powder formed by using water-soluble silicon dioxide to cover preparation containing gadolinium, wherein the particle size ranges from 50nm to 200nm; the weight ratio of the preparation containing gadolinium to the water-soluble silicon dioxide is between 1.86X10<-4> and 0.592. The nanosphere prepared by the invention has relatively high entrapment efficiency, can selectively enter Lymphatic capillaries but not capillary vessel, thereby being used for the lymphatic system specific imaging, reducing the interference of the capillary vessel, improving the sensitivity and specificity of the lymphatic qualitative diagnosis, as well as reducing the harm thereof to human body, therefore, the nanosphere magnetic resonance contrast agent is a new gadolinium-containing magnetic resonance contrast agent with high target.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Product for treating myocardial infarction based on chitosan aquagel and growth factor
InactiveCN101574514APromote formationFunction increasePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCardiac functioningFactor ii
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Inhibition of microtubule protrusion in cancer cells
ActiveUS20090137473A1Reduce microtentaclesImprove the level ofBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellCancer stem cell
The present invention generally concerns microtubule protrusions in cancer cells, including detached cancer cells, and inhibition of the protrusions. In particular aspects, the inhibition of the protrusions interferes with attachment of the cell to a vessel wall, and in further aspects the cell is killed by forcing it to enter capillaries and be destroyed, for example by shearing. Inhibition by a variety of agents and methods is contemplated.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com