Patents
Literature
236 results about "High Throughput Assay" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
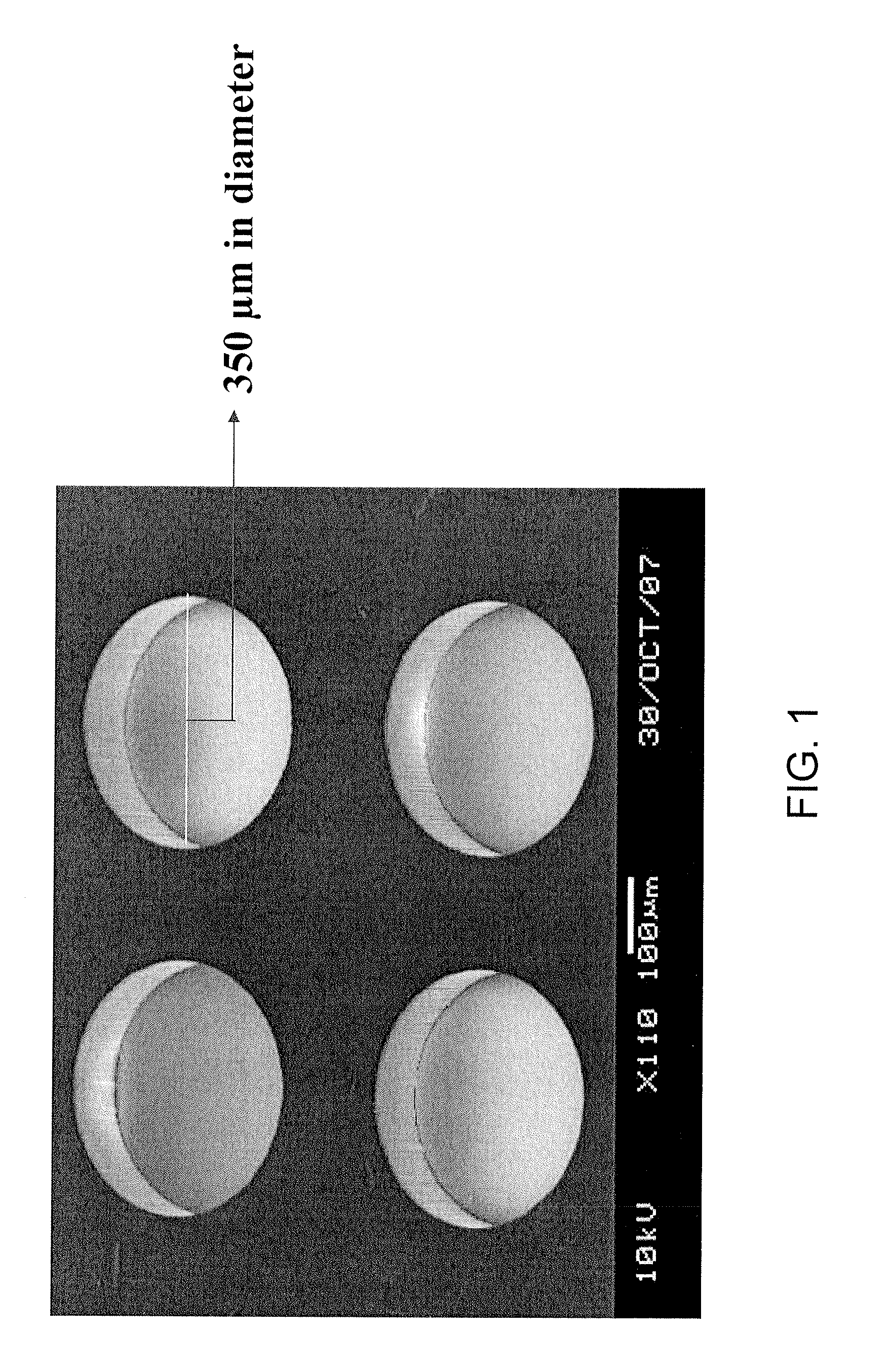
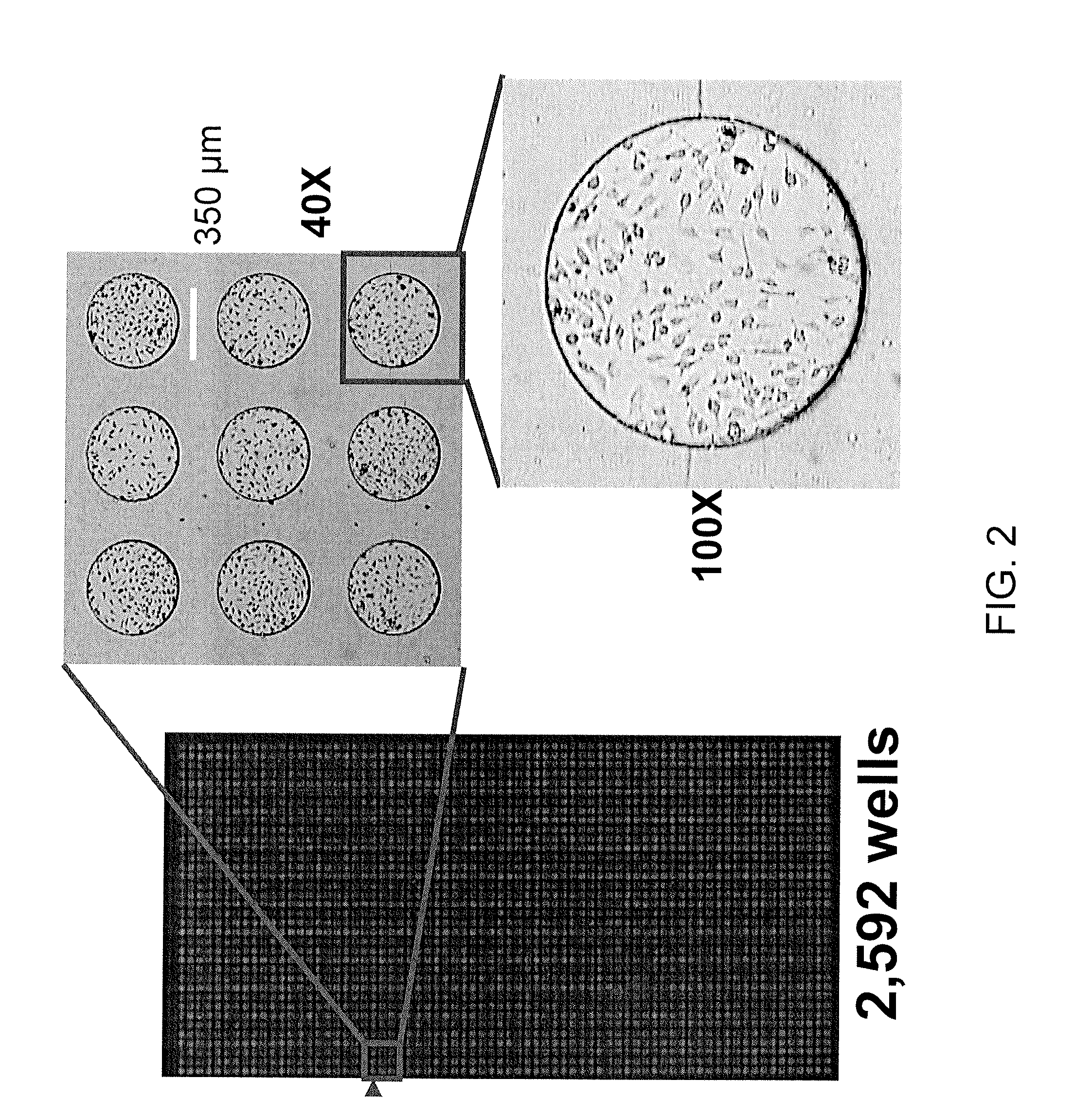
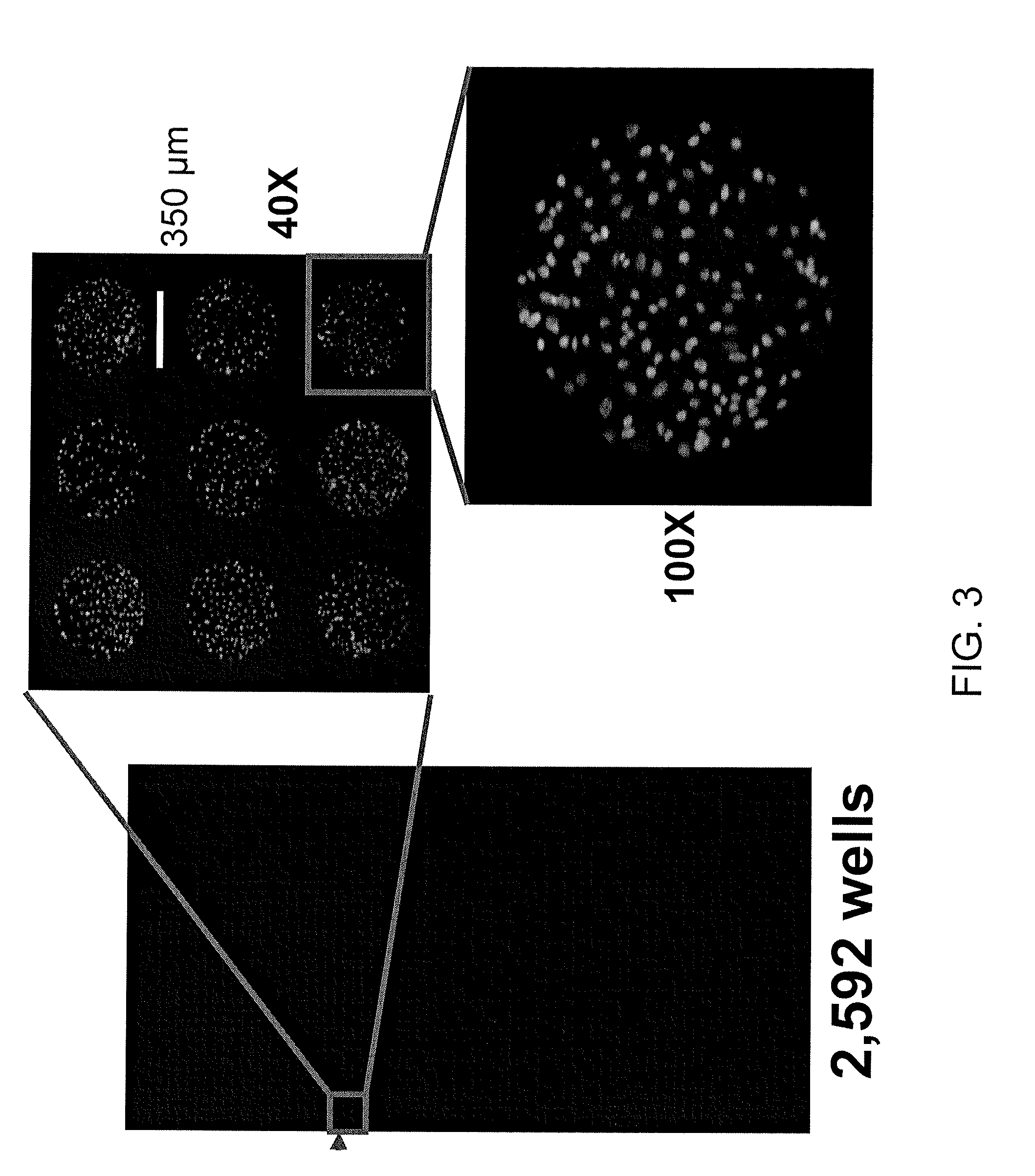
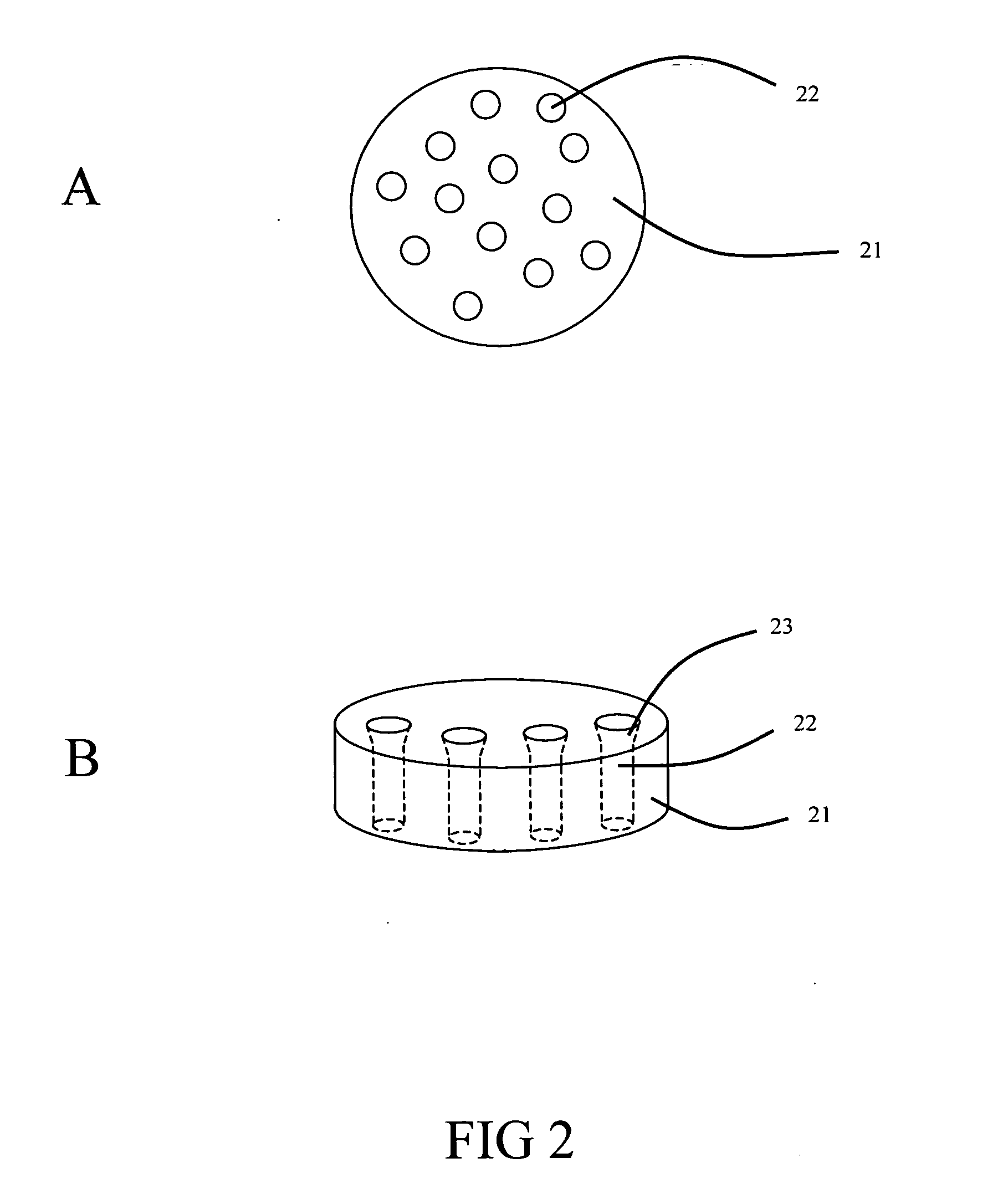
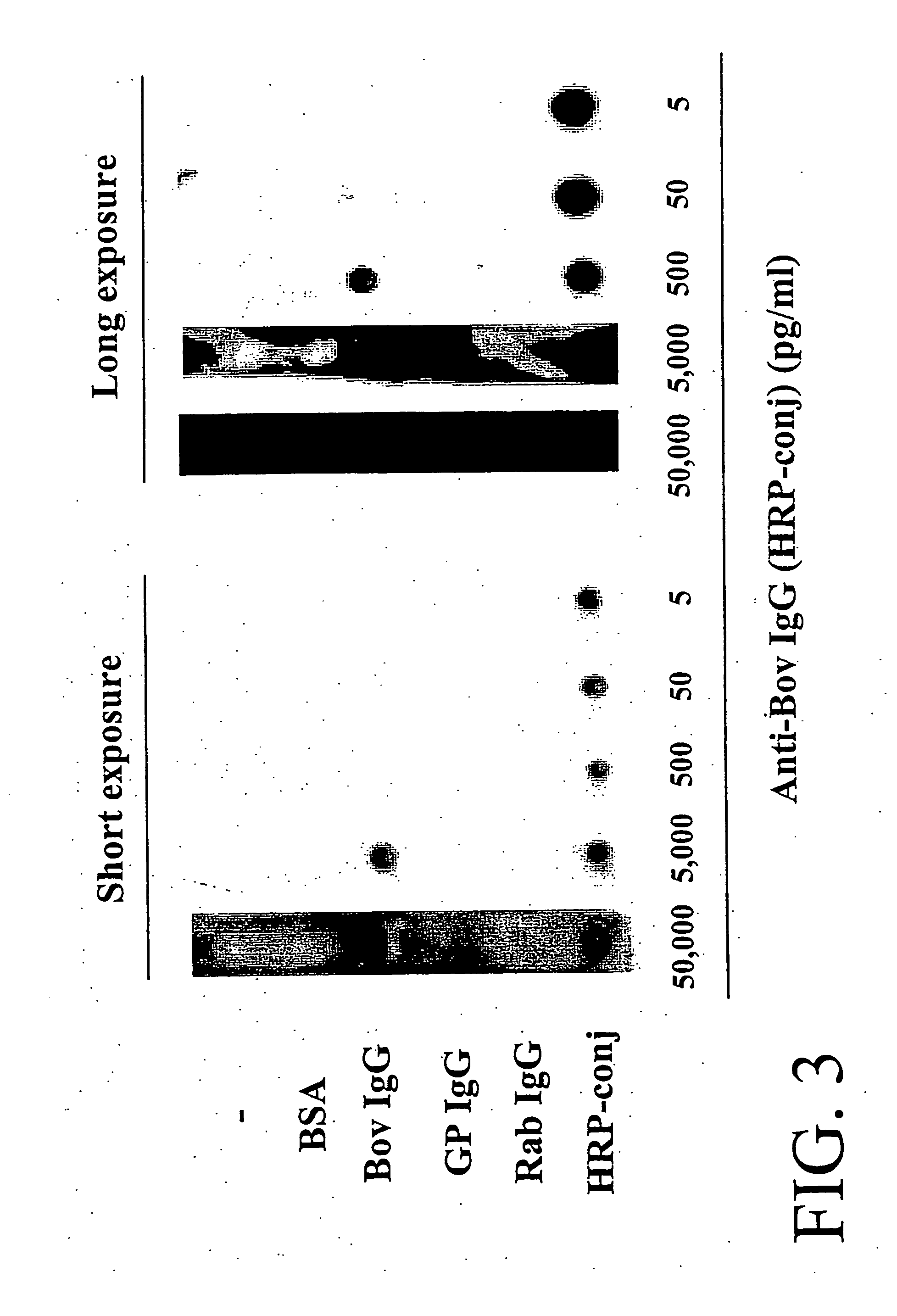
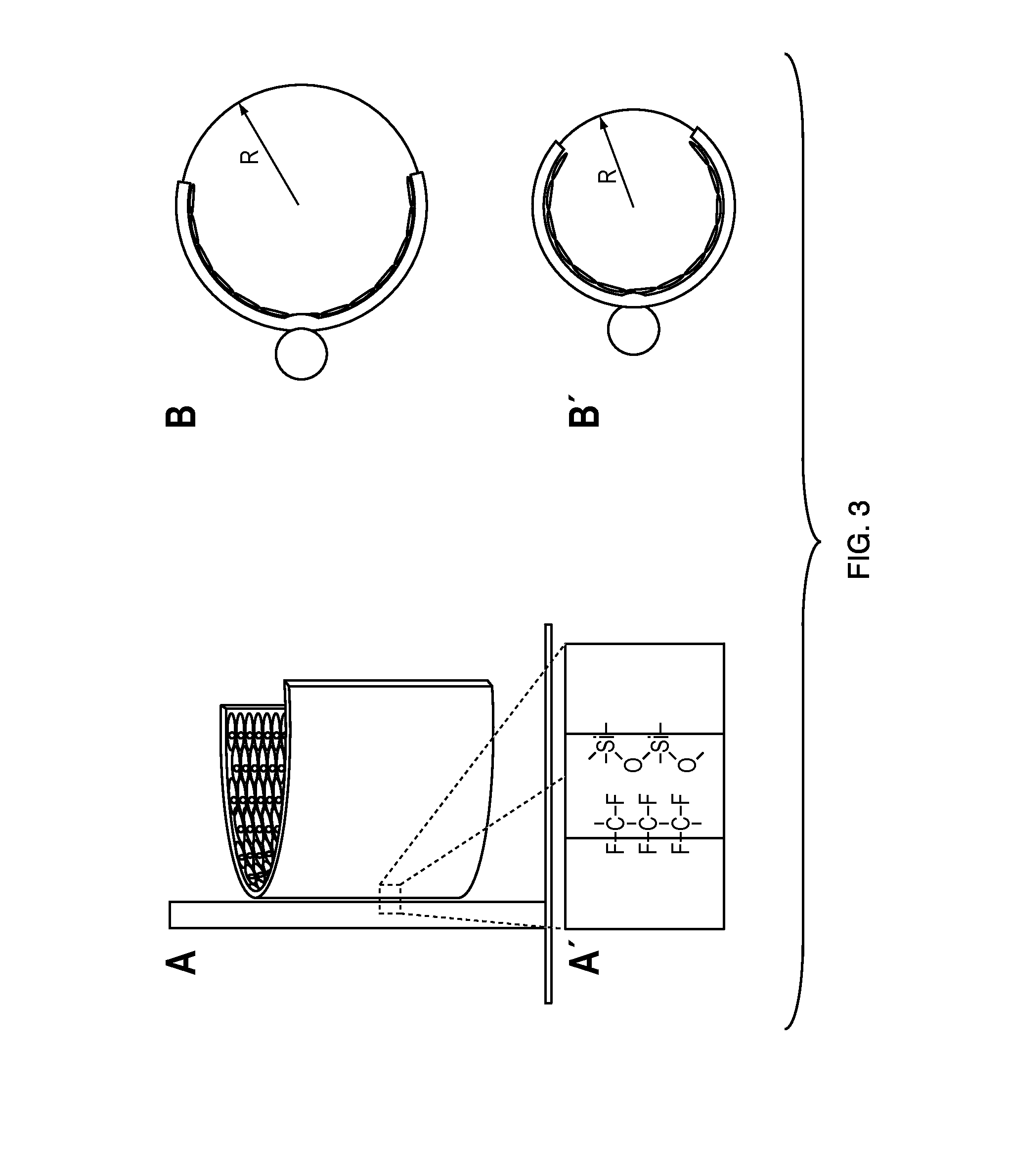
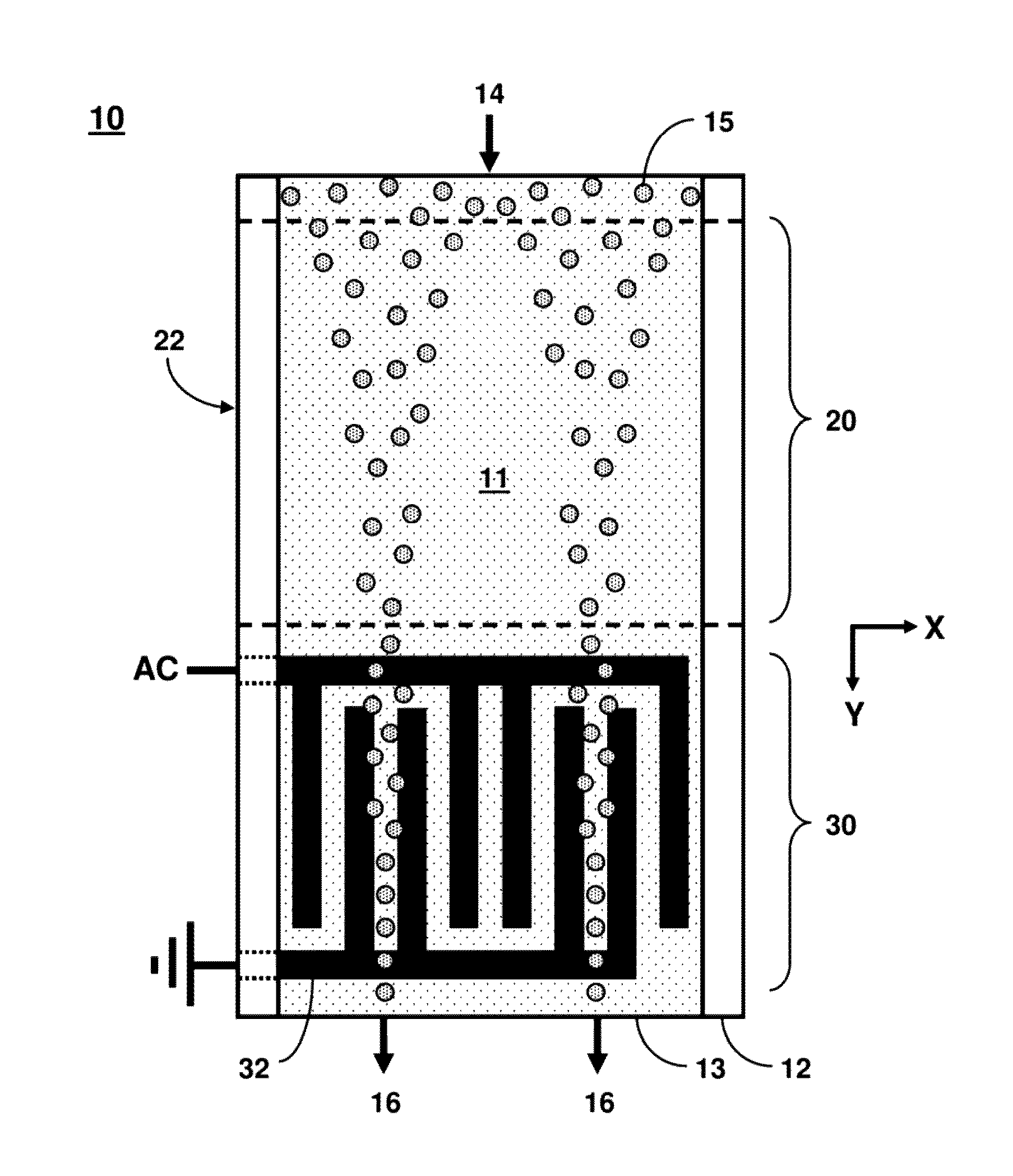
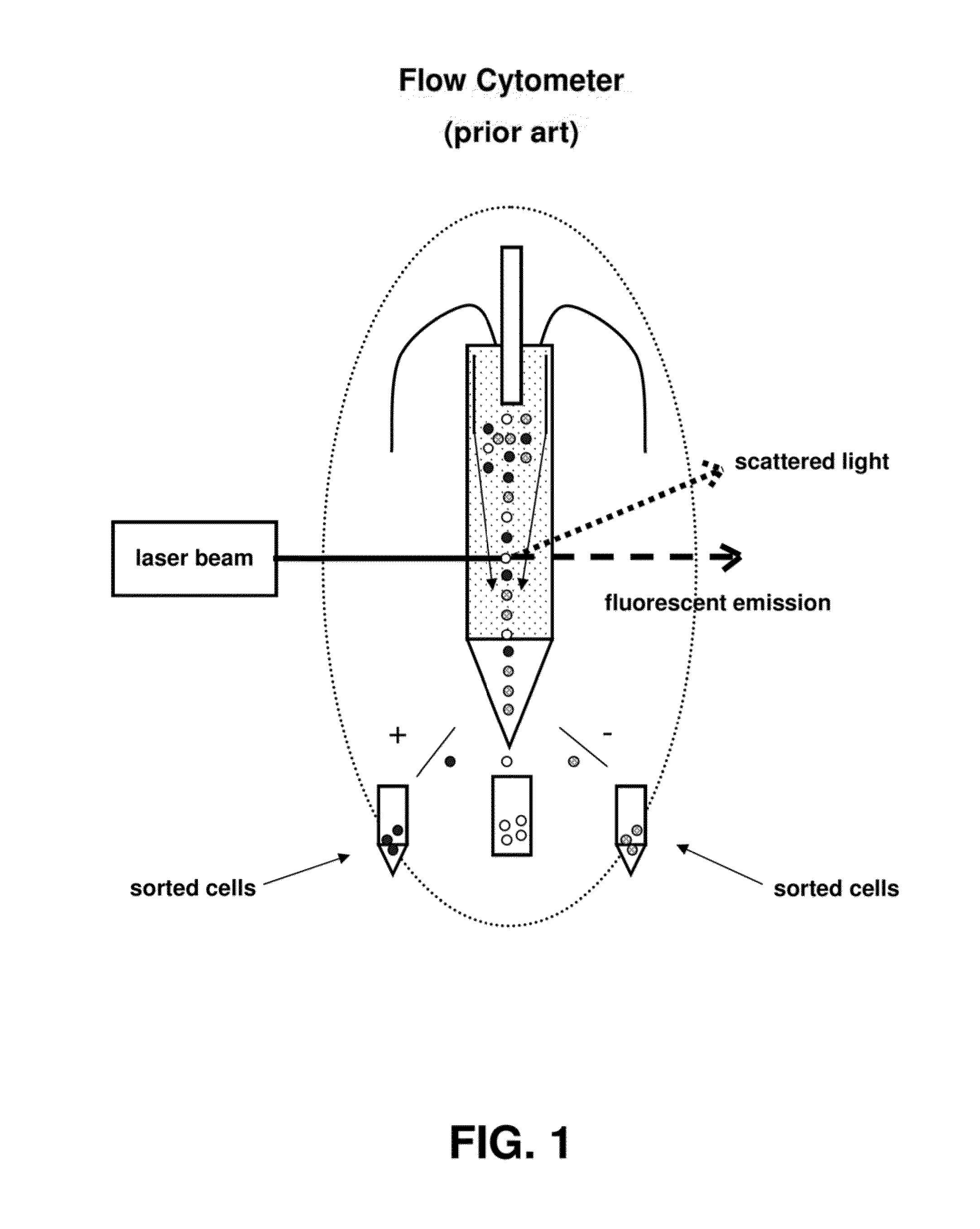
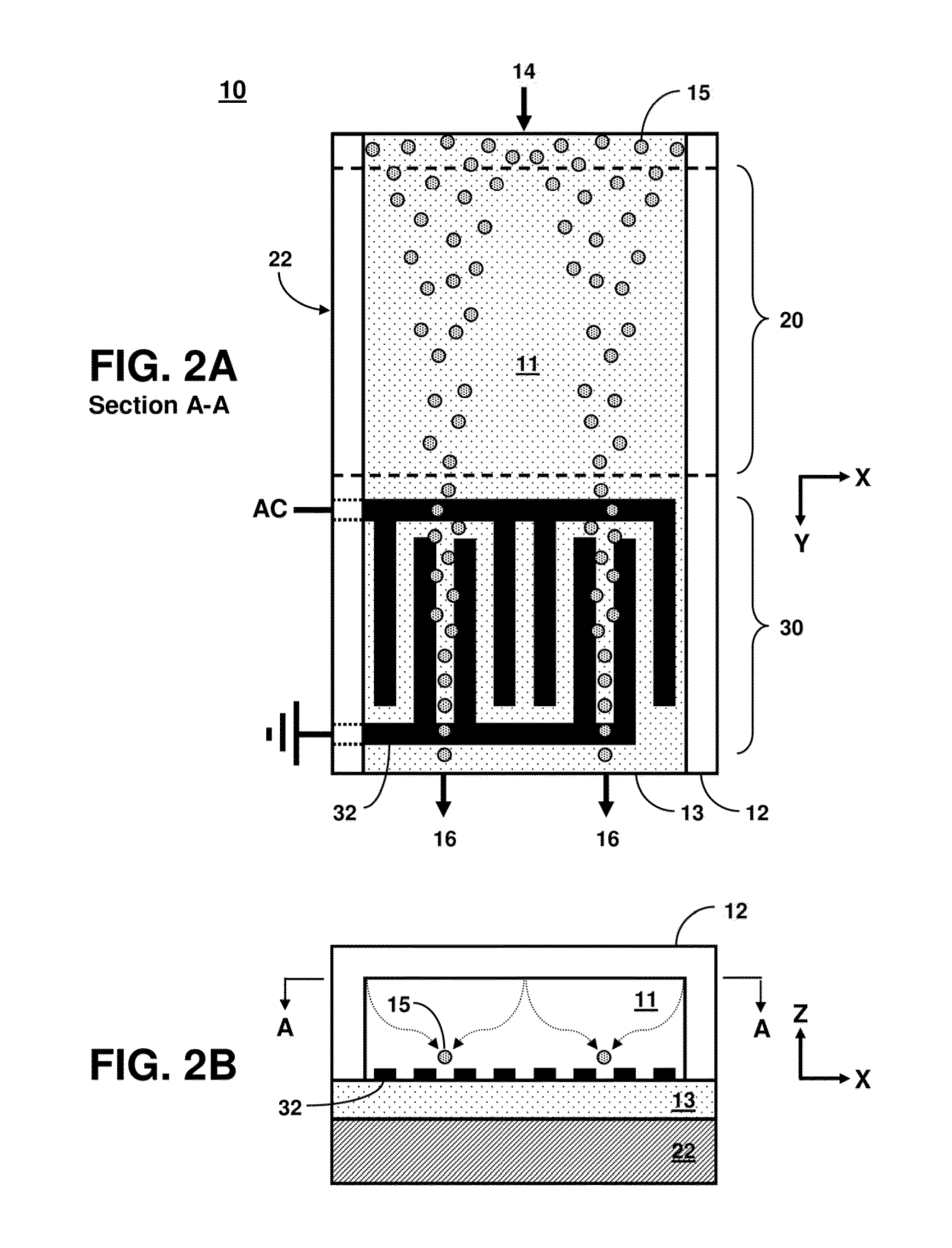
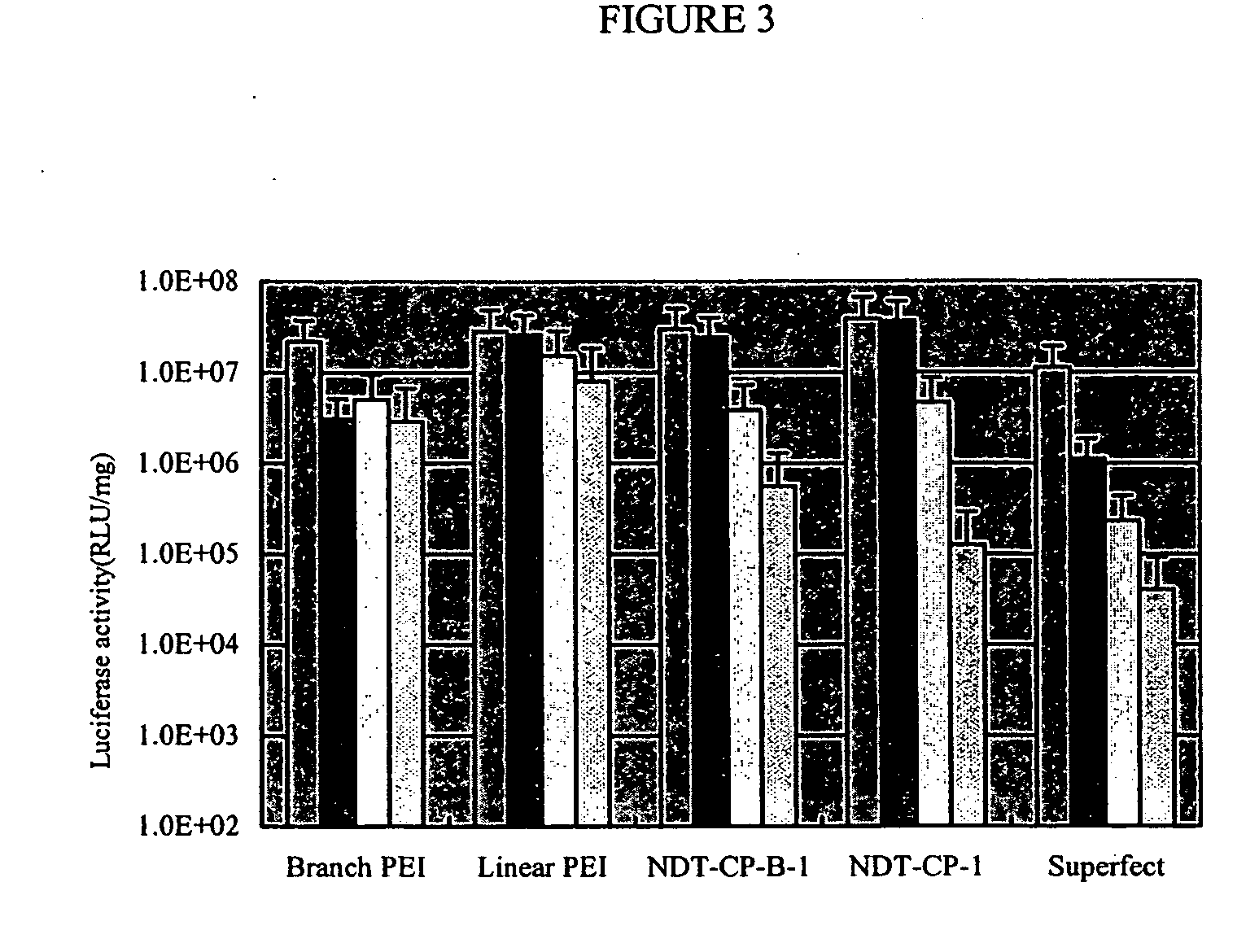
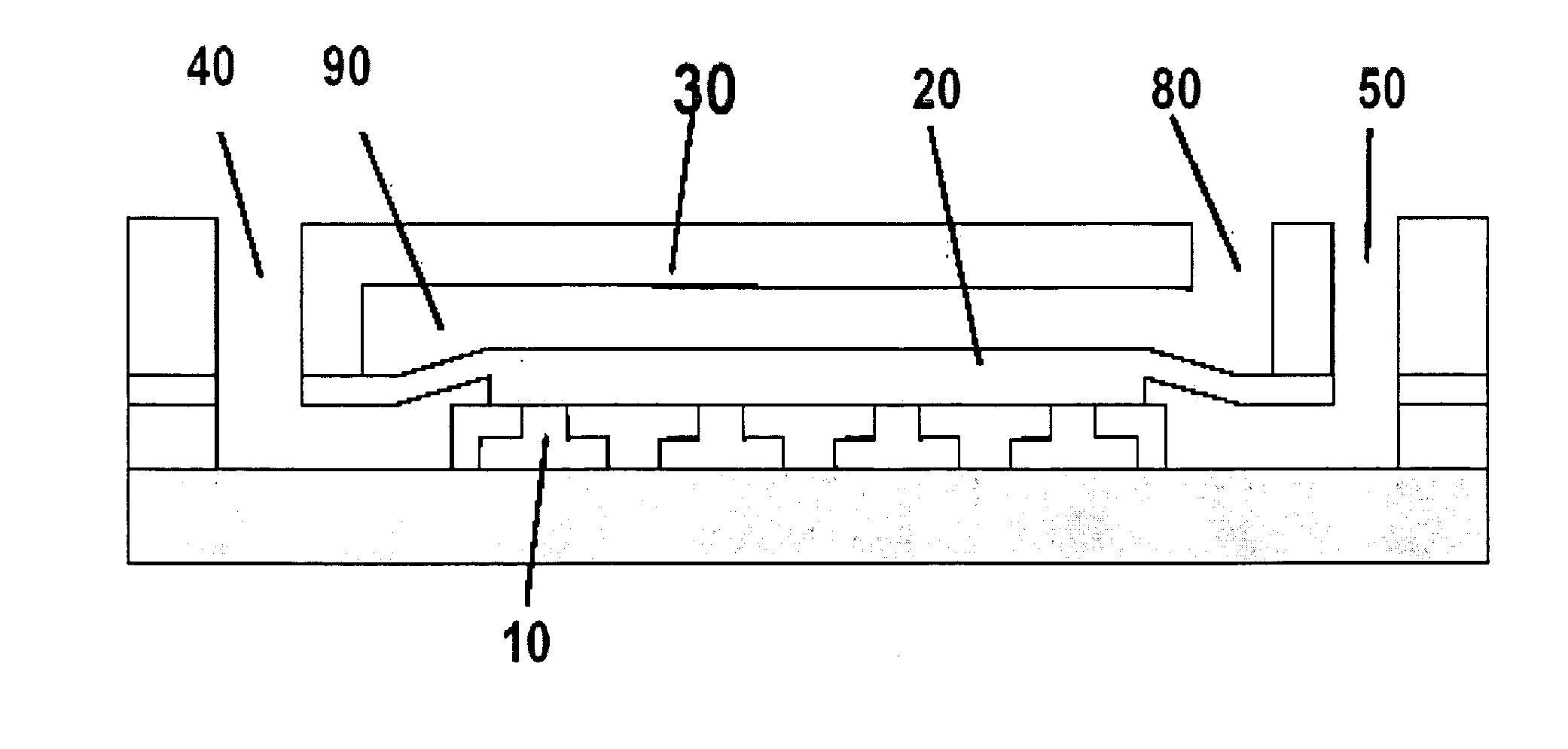
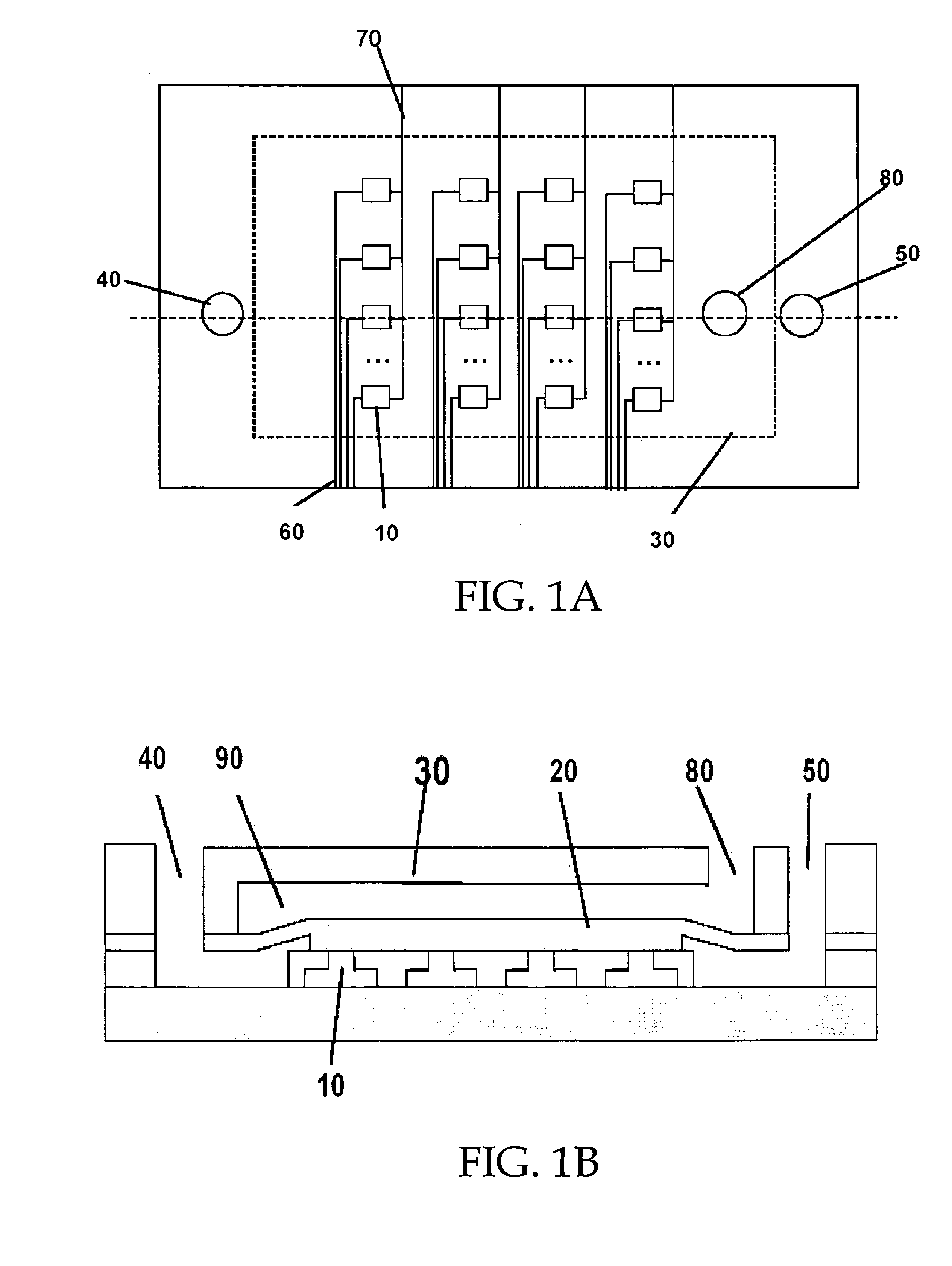
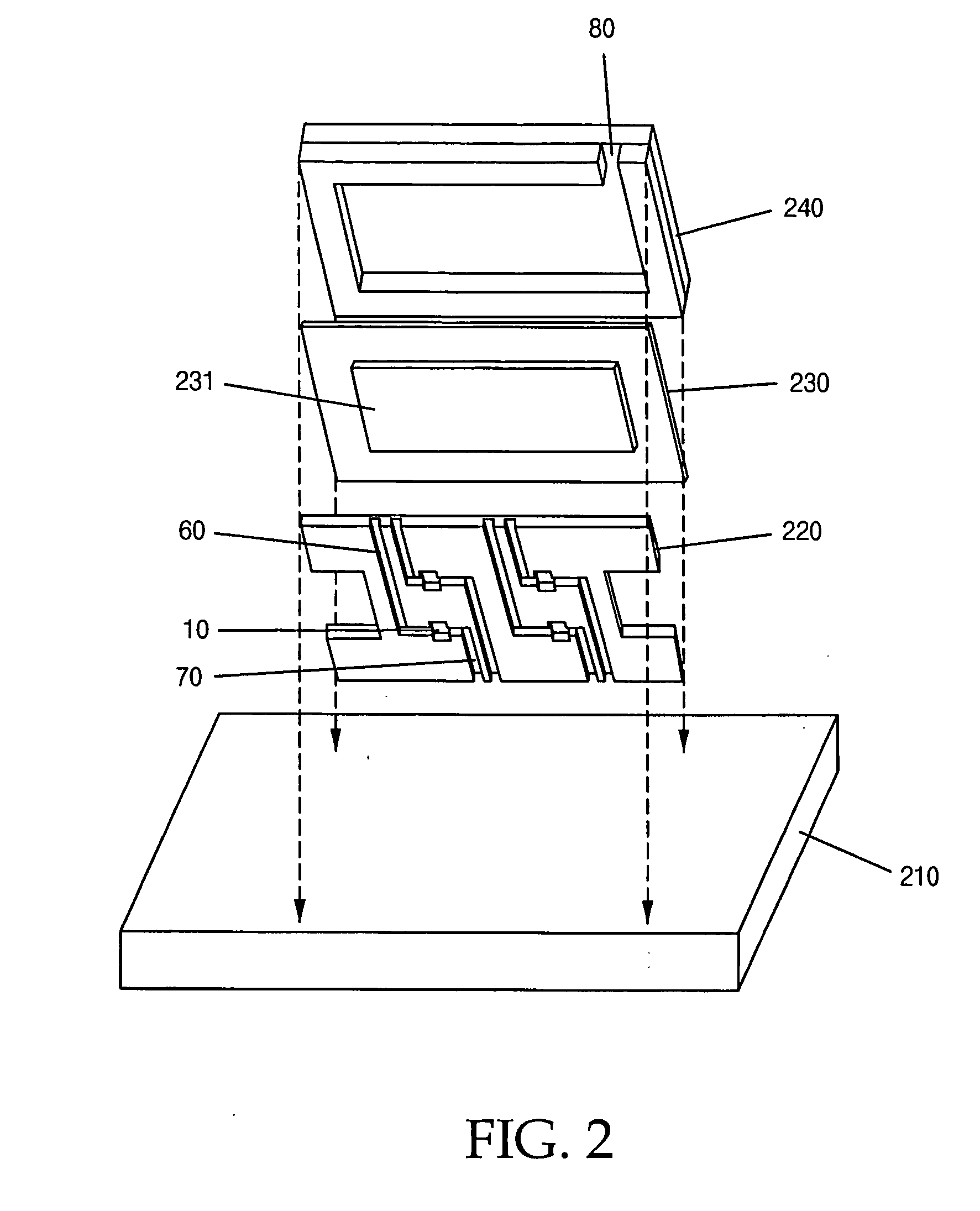
In vitro high throughput assays are usually conducted using a microtiter plate: a plate containing a grid with a large number of small divots called “wells.” The wells contain chemical and/or biological substrate (e.g., living cells or proteins).
Methods for generating high titer helper-free preparations of released recombinant AAV vectors
InactiveUS6989264B2Genetic therapy composition manufactureGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGene deliveryHeterologous
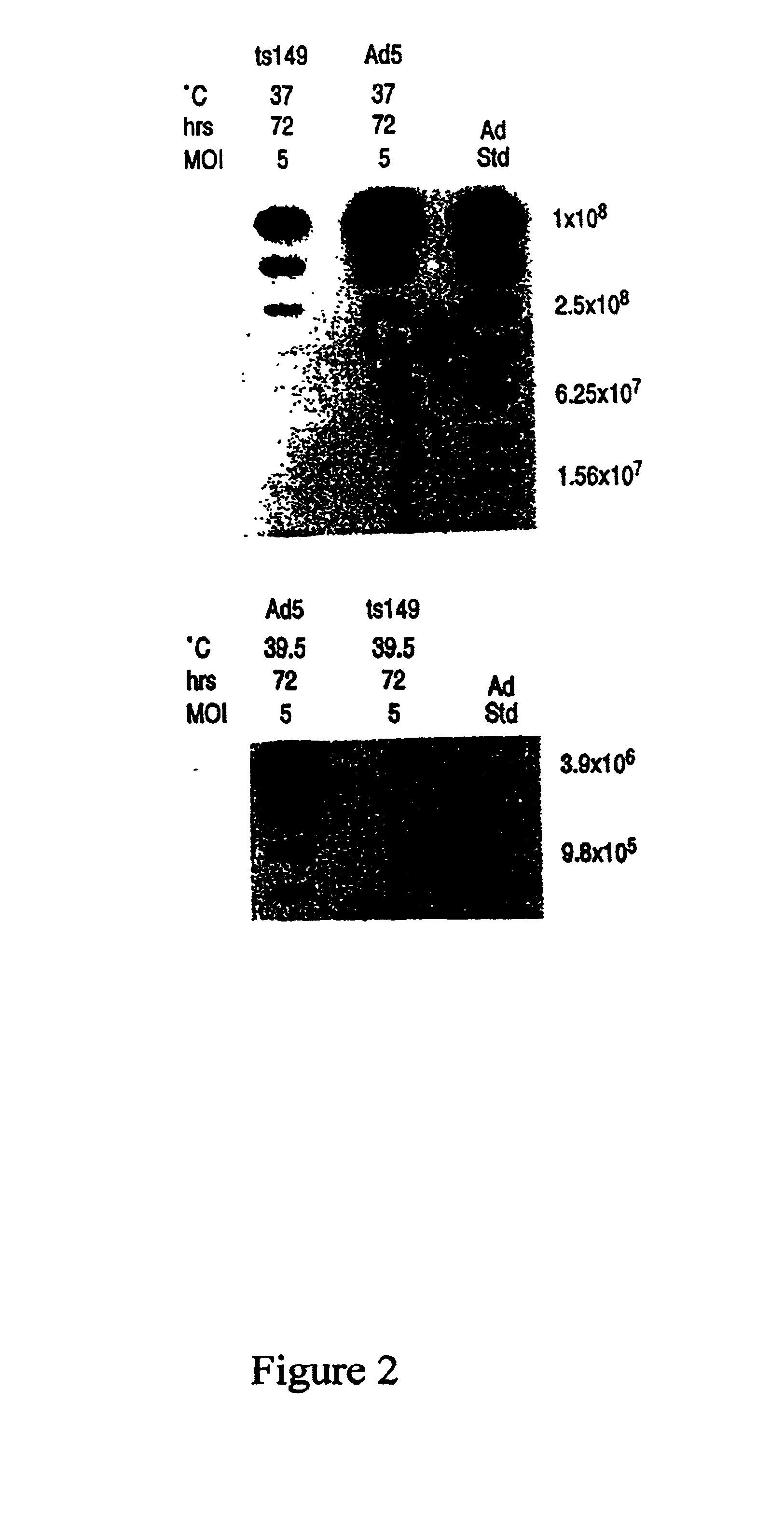
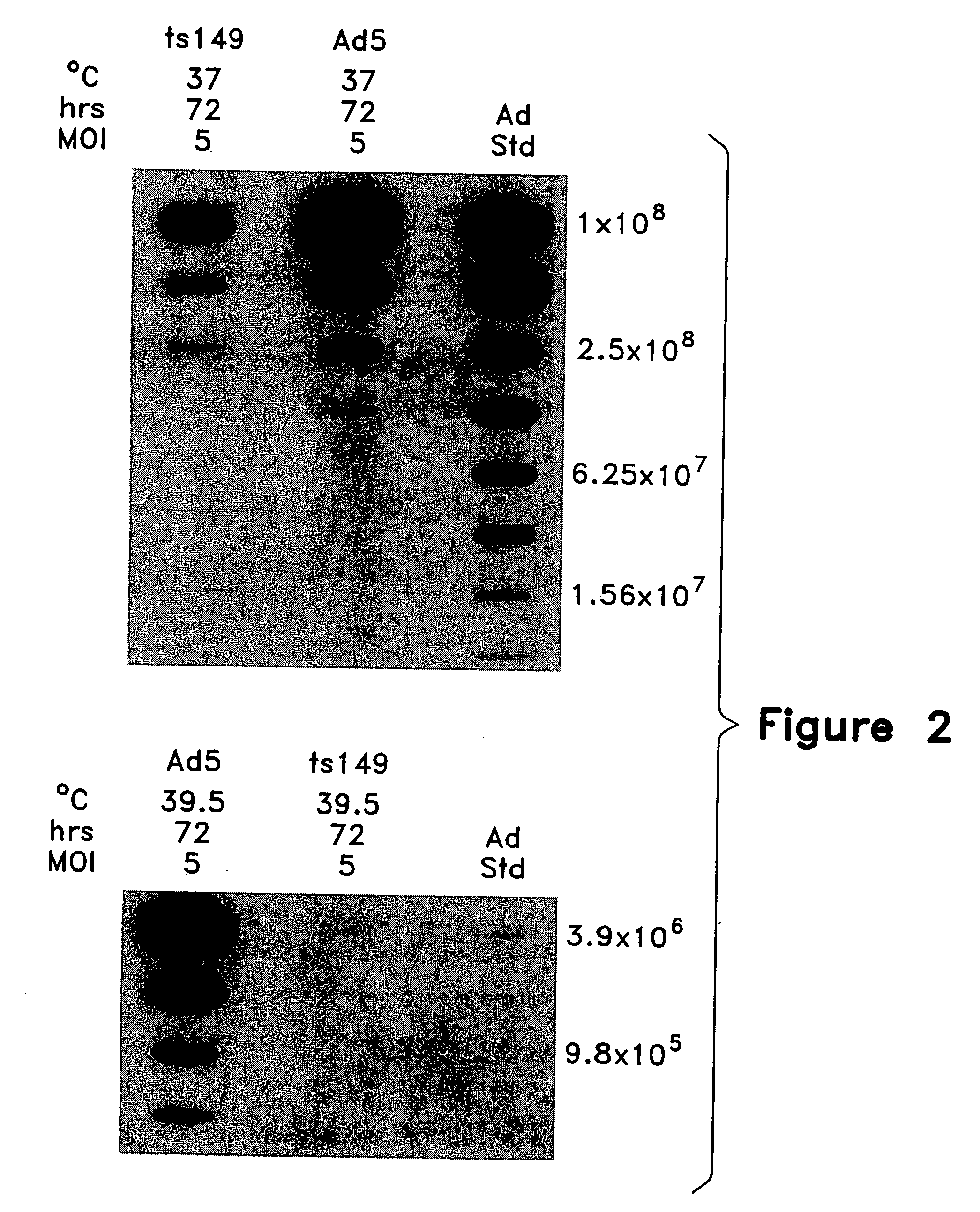
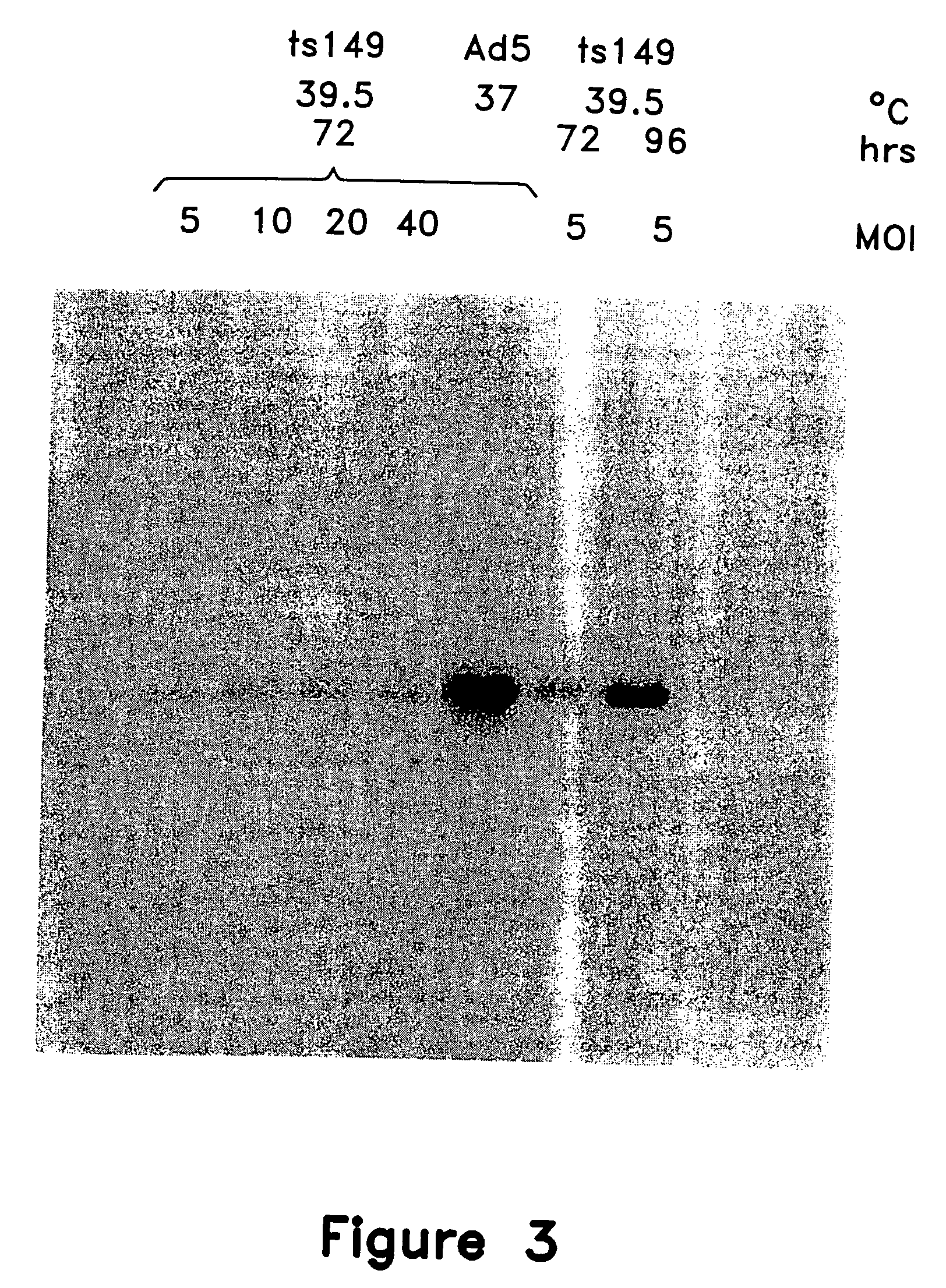
This invention provides methods and compositions for producing high titer, substantially purified preparations of recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that can be used as vectors for gene delivery. At the onset of vector production, AAV producer cells of this invention typically comprise one or more AAV packaging genes, an AAV vector comprising a heterologous (i.e. non-AAV) transgene of interest, and a helper virus such as an adenovirus. The AAV vector preparations produced are generally replication incompetent but are capable of mediating delivery of a transgene of interest (such as a therapeutic gene) to any of a wide variety of tissues and cells. The AAV vector preparations produced according to this invention are also substantially free of helper virus as well as helper viral and cellular proteins and other contaminants. The invention described herein provides methods of producing rAAV particles by culturing producer cells under conditions, such as temperature and pH, that promote release of virus. Also provided is a quantitative, high-throughput assay useful in the assessment of viral infectivity and replication, as well as in the screening of agent that affect viral infectivity and / or replication.
Owner:TARGETED GENETICS CORPORTION
Perfused three-dimensional cell/tissue disease models
ActiveUS20050260745A1Easy to primeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLymphatic SpreadPathology diagnosis
A system has been constructed that recapitulate the features of a capillary bed through normal human tissue. The system facilitates perfusion of three-dimensional (3D) cell monocultures and heterotypic cell co-cultures at the length scale of the capillary bed. A major feature is that the system can be utilized within a “multiwell plate” format amenable to high-throughput assays compatible with the type of robotics commonly used in pharmaceutical development. The system provides a means to conduct assays for toxicology and metabolism and as a model for human diseases such as hepatic diseases, including hepatitis, exposure-related pathologies, and cancer. Cancer applications include primary liver cancer as well as metastases. The system can also be used as a means of testing gene therapy approaches for treating disease and inborn genetic defects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Perfused three-dimensional cell/tissue disease models
ActiveUS8318479B2Easy to primeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLymphatic SpreadPathology diagnosis
A system has been constructed that recapitulate the features of a capillary bed through normal human tissue. The system facilitates perfusion of three-dimensional (3D) cell monocultures and heterotypic cell co-cultures at the length scale of the capillary bed. A major feature is that the system can be utilized within a “multiwell plate” format amenable to high-throughput assays compatible with the type of robotics commonly used in pharmaceutical development. The system provides a means to conduct assays for toxicology and metabolism and as a model for human diseases such as hepatic diseases, including hepatitis, exposure-related pathologies, and cancer. Cancer applications include primary liver cancer as well as metastases. The system can also be used as a means of testing gene therapy approaches for treating disease and inborn genetic defects.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
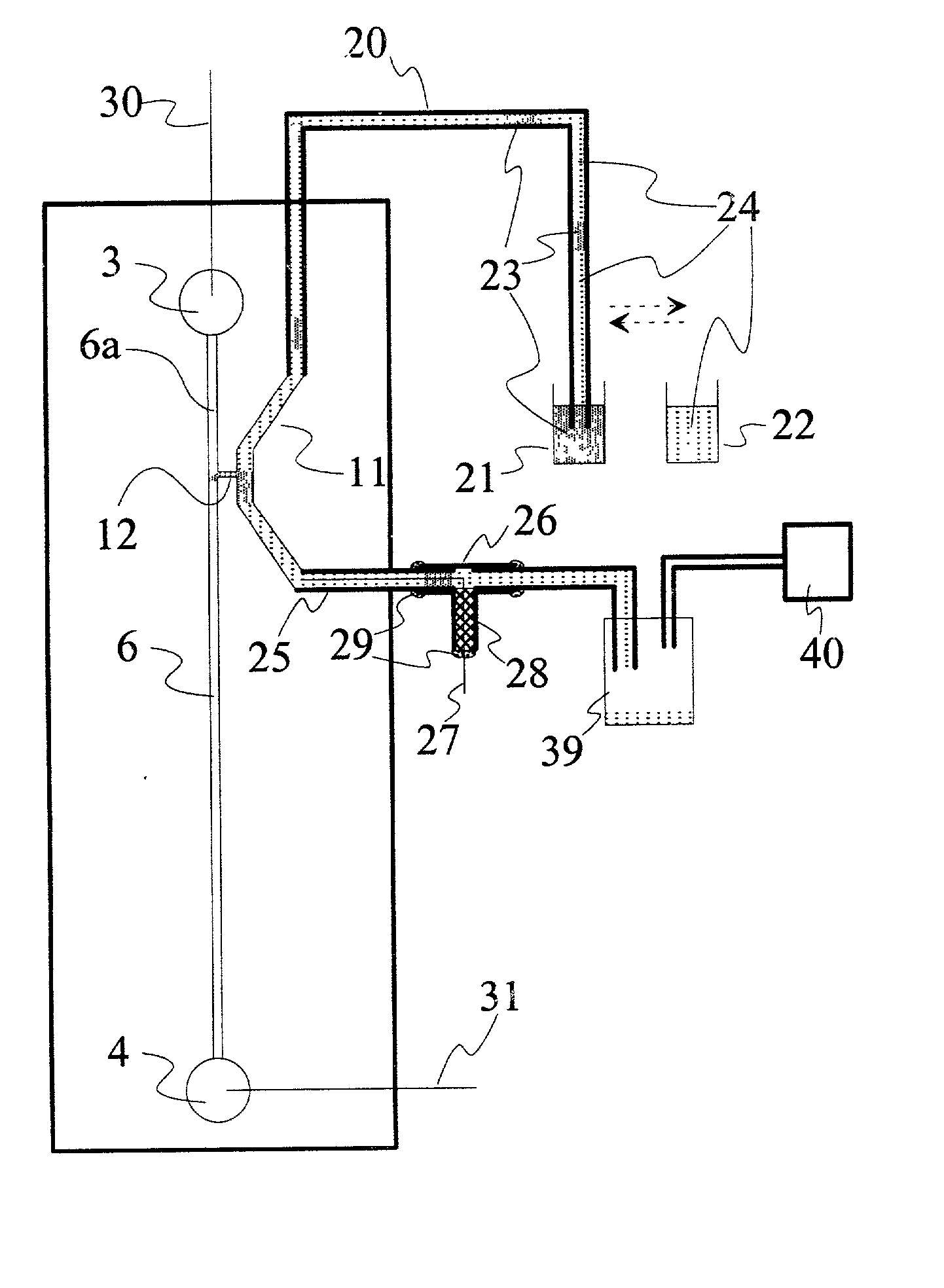
Method and apparatus for reproducible sample injection on microfabricated devices
InactiveUS6875403B2Small injectedGood reproducibilityImmobilised enzymesFixed microstructural devicesEngineeringFixed length
Fixed volumes of samples are metered into the reaction channel of a microfluidic device using one or more slidable blocks having at least one fixed-length sample metering channel. In another aspect of the present invention, fixed volumes of samples are metered into the reaction channel using one or more slidable blocks having at least one fixed-length sample metering channel. In another aspect of the present invention, a sample injection scheme based on injection time is implemented using relatively sliding blocks of separation channels and sample channels. In a further aspect of the present invention, separation channels are configured in relation to the slidable block in a manner that enables separations to be conducted continuously for high-throughput assays.
Owner:MICROCHEM SOLUTIONS
Apparatus, kits and methods for evaluating binding interactions, for detecting and quantifying binding molecules, and for sample preparation
InactiveUS20060019410A1Reduce amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProcess scaleProcess scaling
The present invention provides apparatus, kits and methods for evaluating binding between one or more binding molecules (e.g., a protein) and one or more ligands. The invention also provides apparatus, kits and methods for detecting and / or quantifying a binding molecule, for example, a protein. Also provided are apparatus, kits and methods for “stripping” a complex biological matrix of low molecular weight components. The invention can be carried out on a smaller process scale, and therefore be more efficient, than previously known methods. The present invention is particularly suitable for use in high-throughput assays, which can be partially or completely automated.
Owner:QUALYST
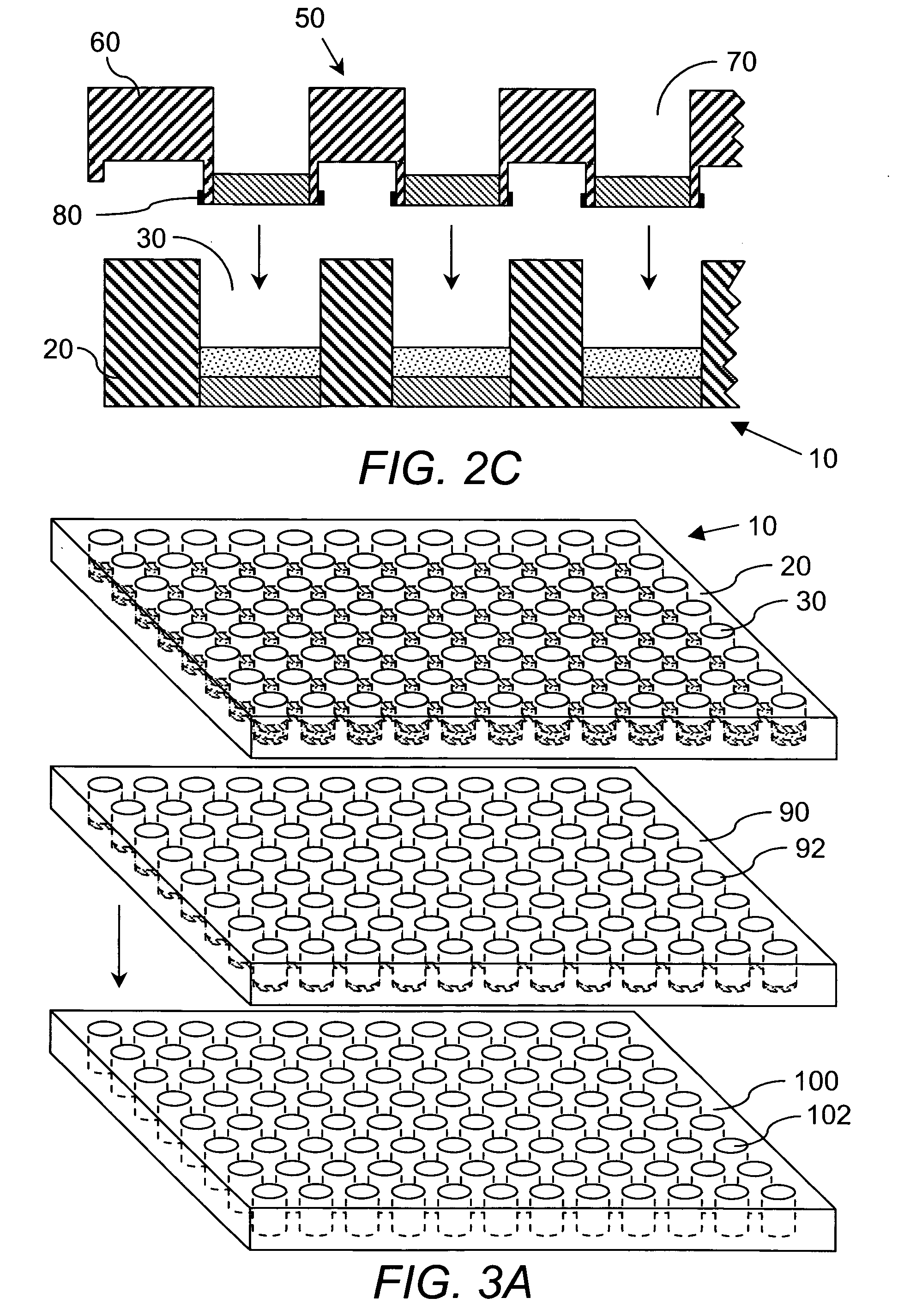
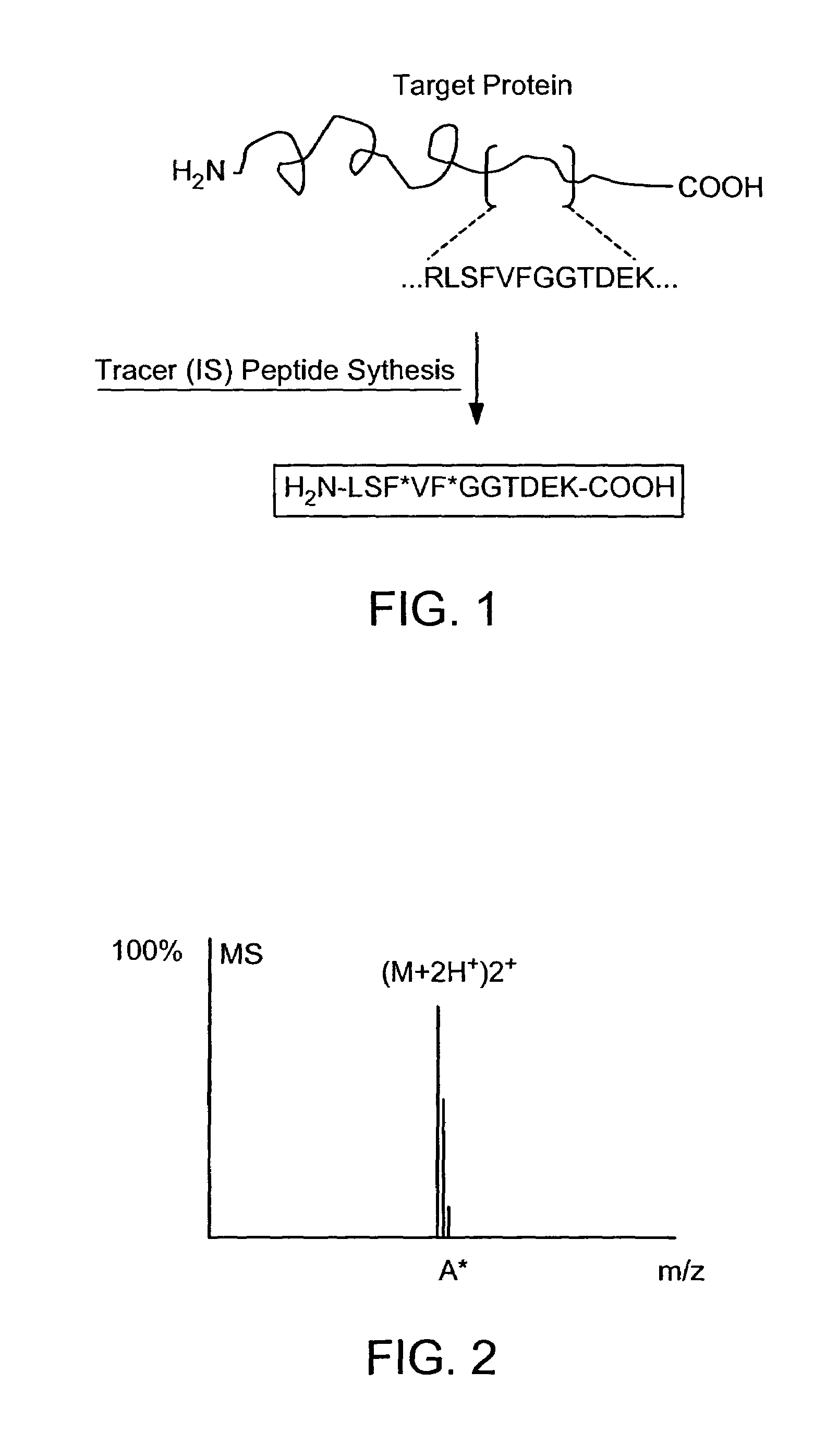
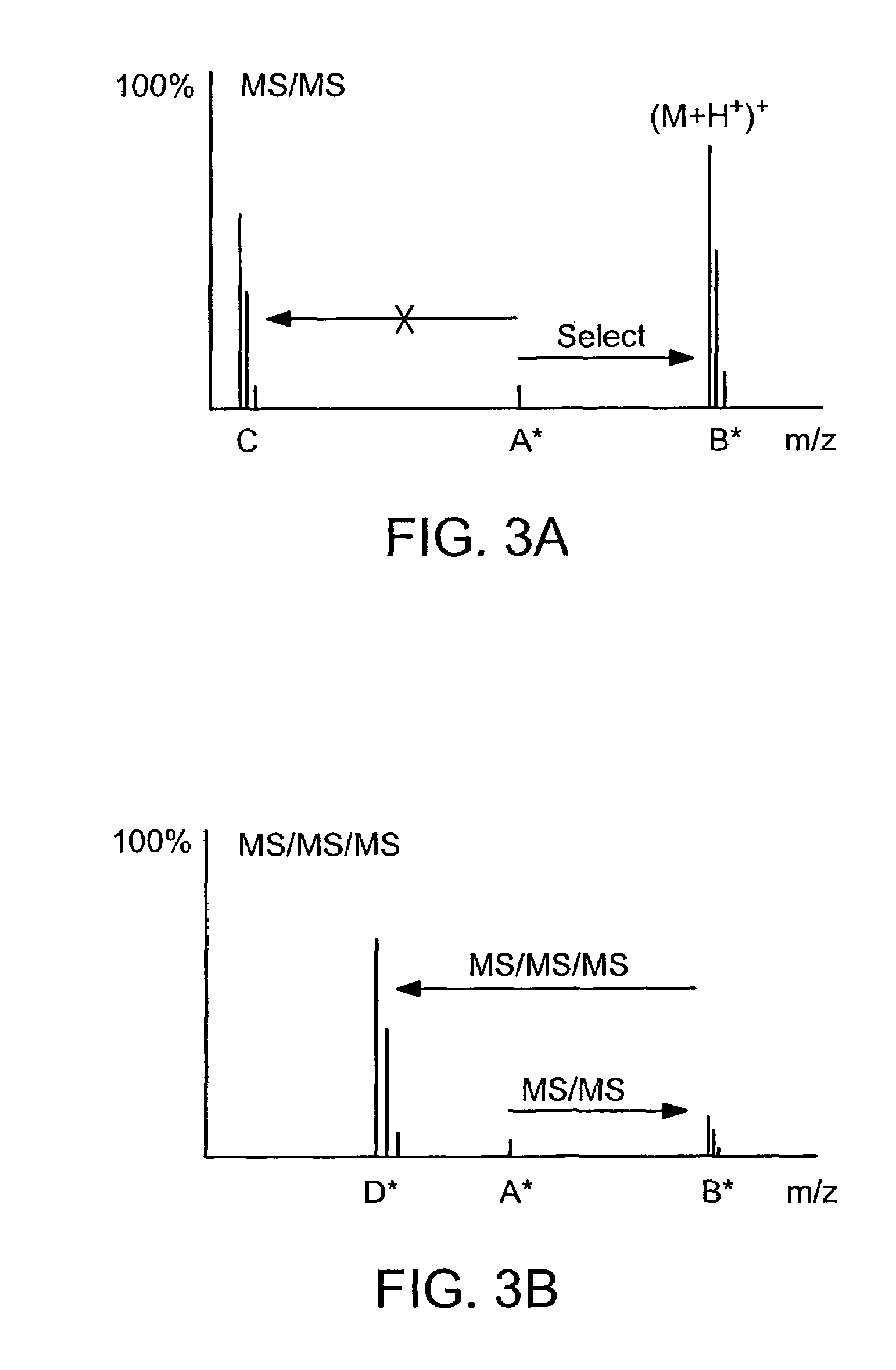
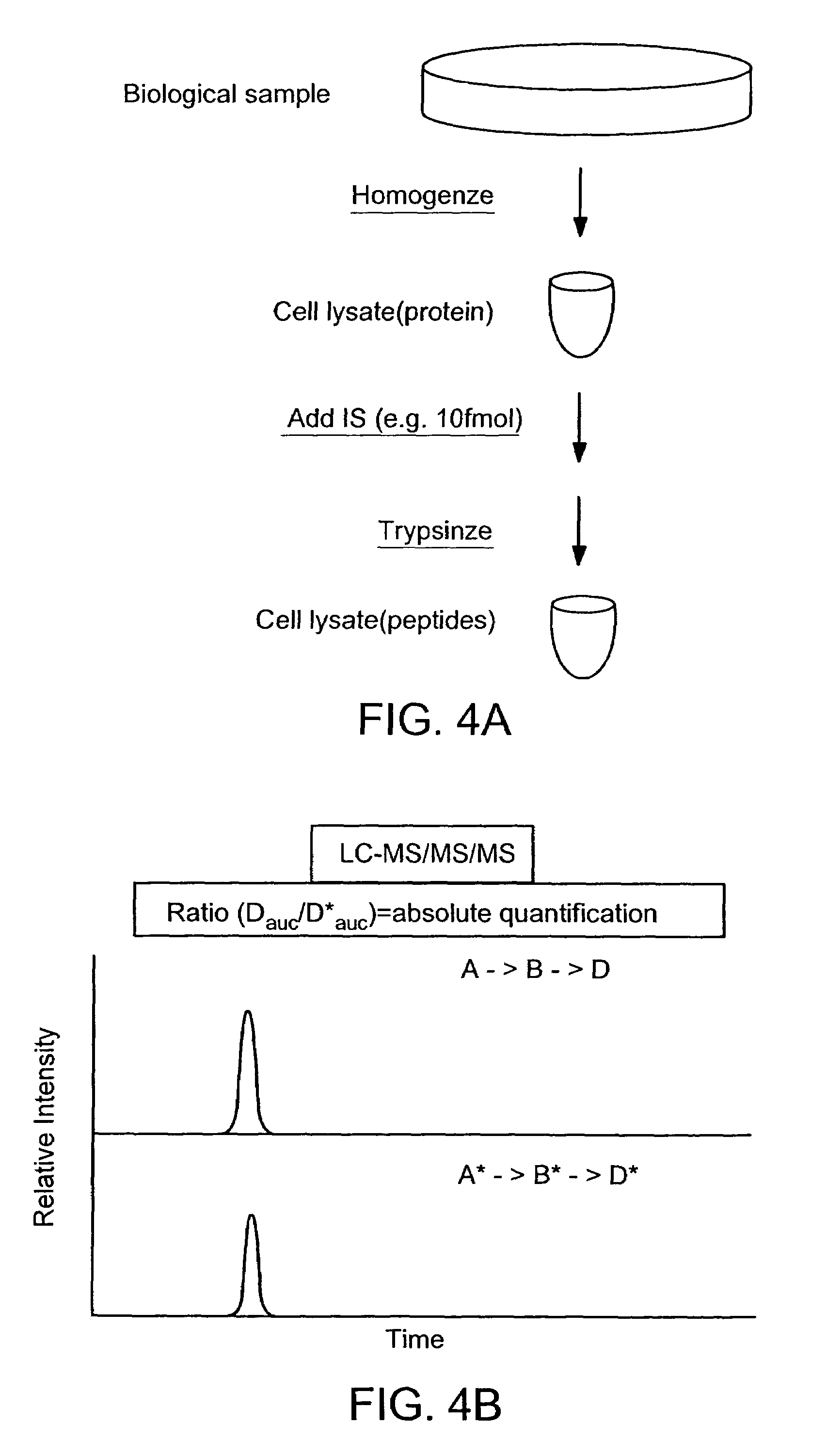
Absolute quantification of proteins and modified forms thereof by multistage mass spectrometry
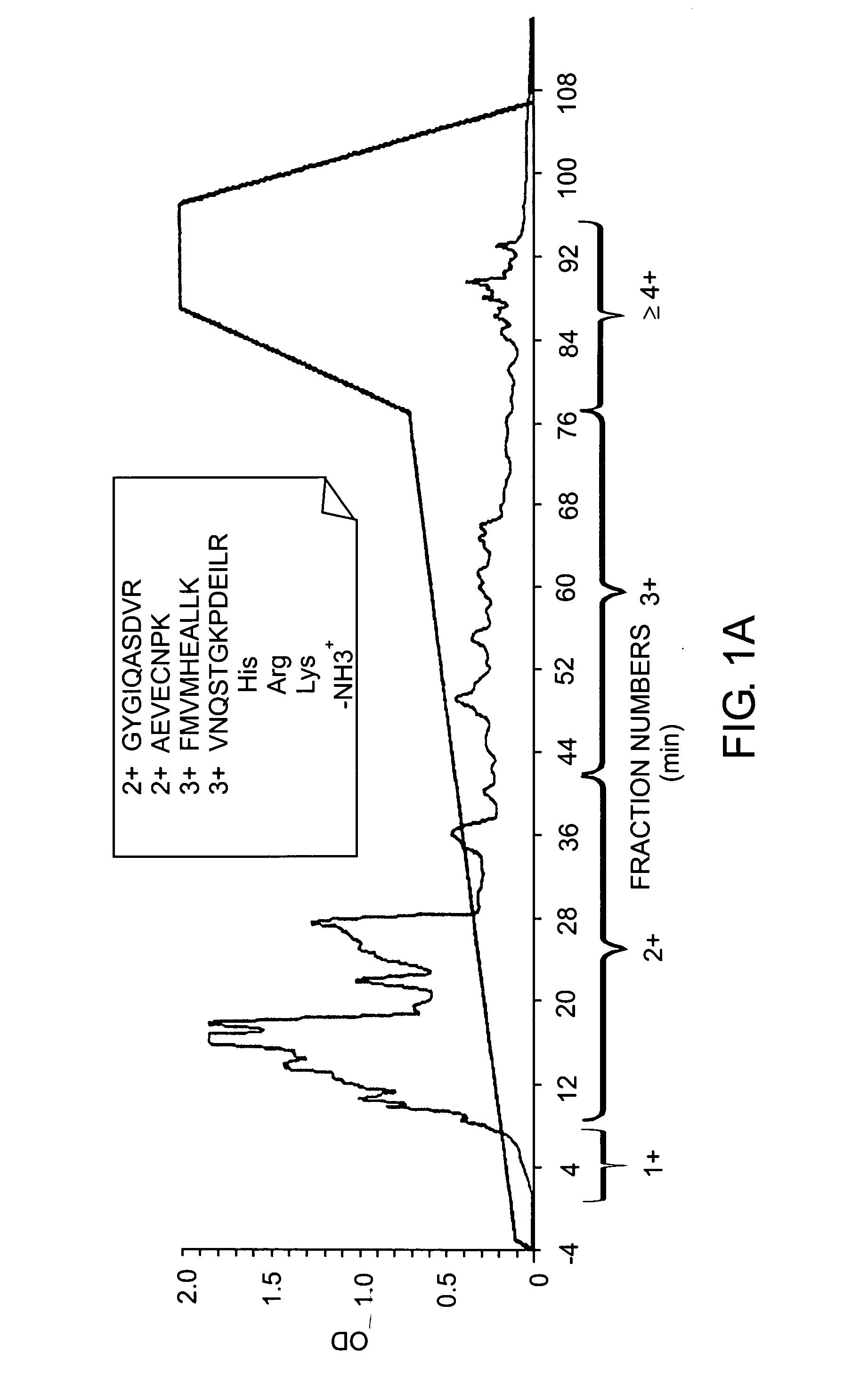
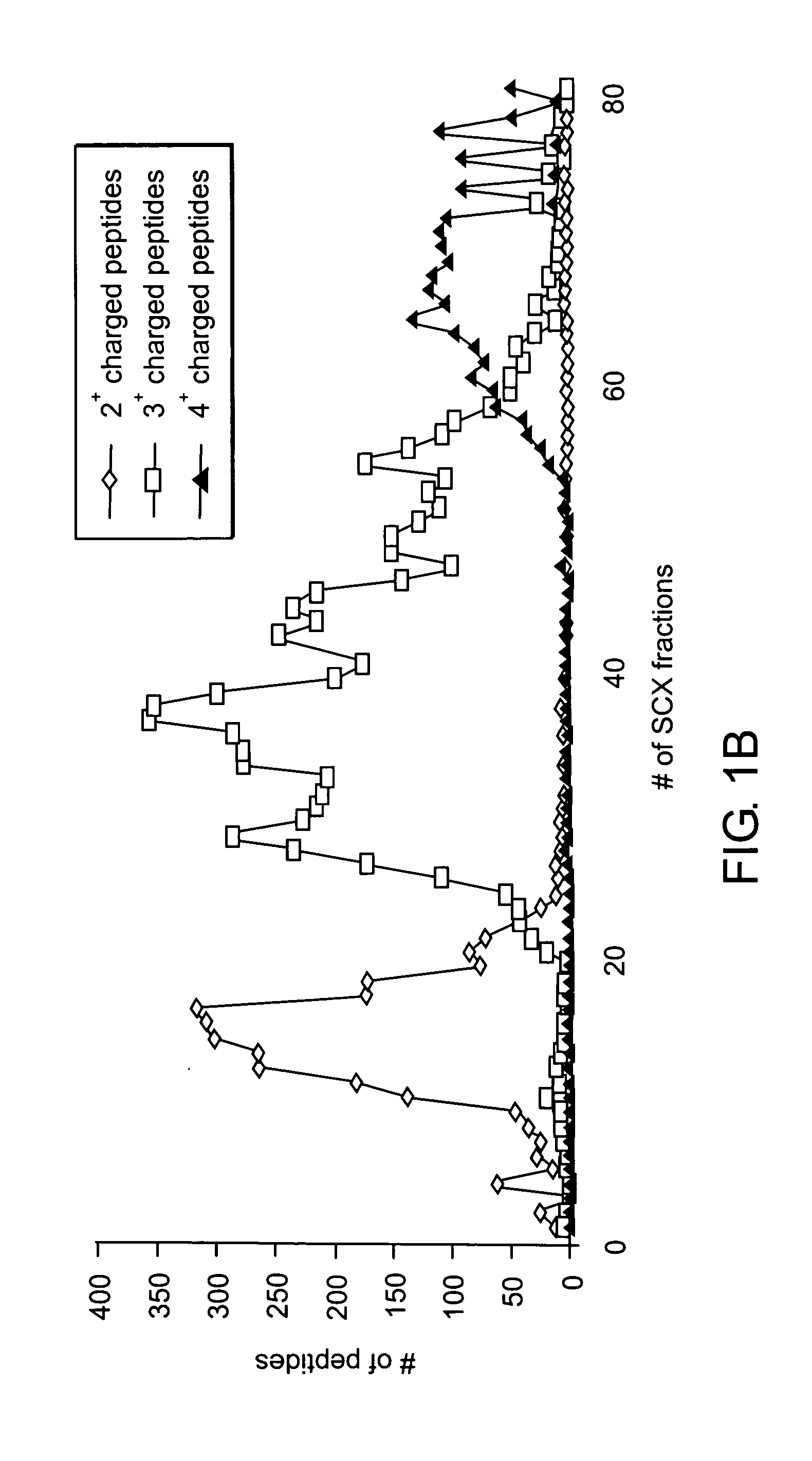
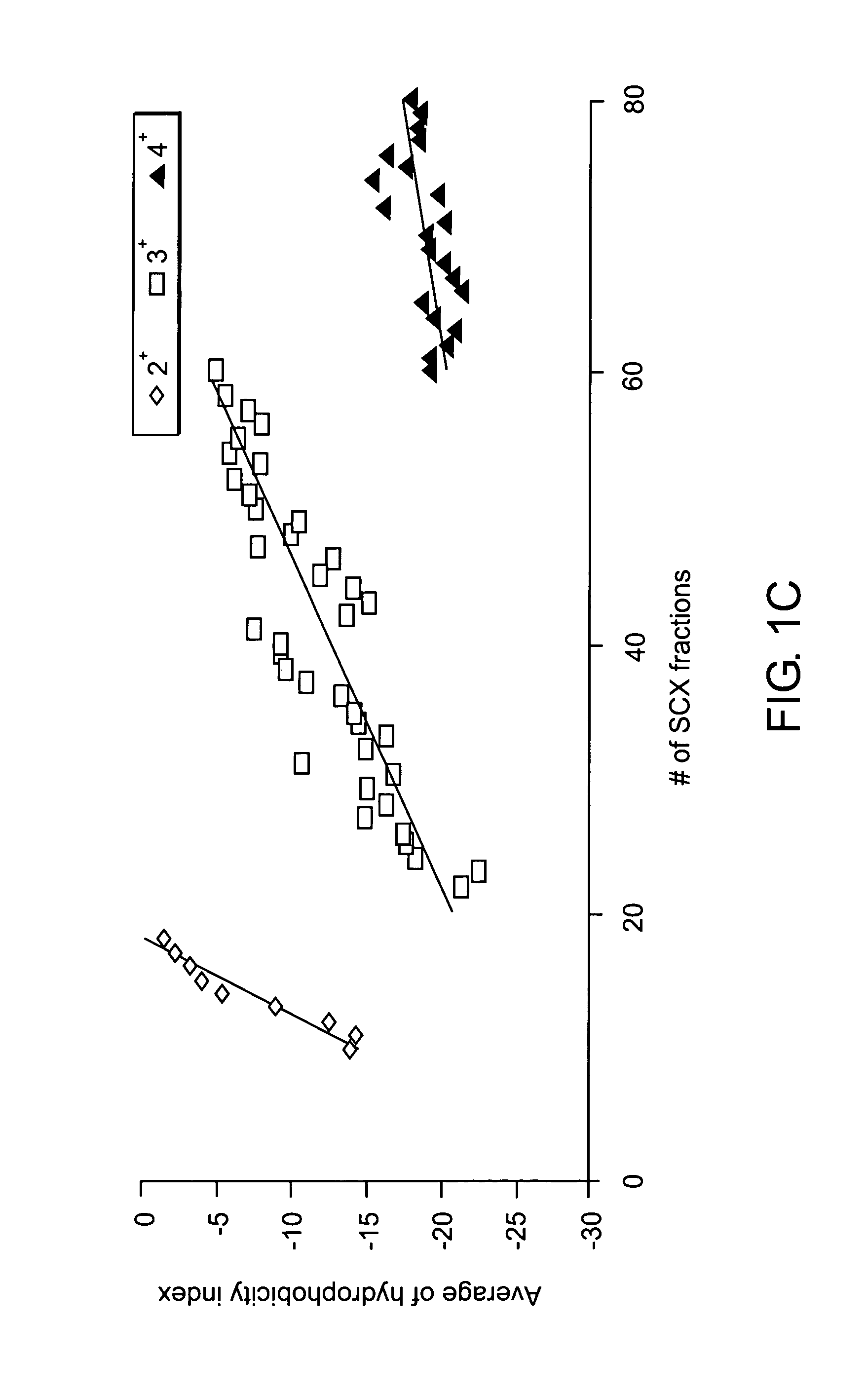
ActiveUS7501286B2Rapid and high throughput analysisQuantitative precisionDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsStable Isotope LabelingIsotope
The invention provides reagents, kits and methods for detecting and / or quantifying proteins in complex mixtures, such as a cell lysate. The methods can be used in high throughput assays to profile cellular proteomes. In one aspect, the invention provides a peptide internal standard labeled with a stable isotope and corresponding in amino acid sequence to the amino acid sequence of a subsequence of a target polypeptide. In another aspect, the peptide internal standard is labeled at a modified amino acid residue and is used to determine the presence of, and / or quantitate the amount of a particular modified form of a protein.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Microarray chip and method of fabricating for the same
The present invention provides a microarray chip for use in the analysis of various sample types. The microarray chips disclosed herein generally comprise a substrate covered with a coating material comprising a photoresist material, wherein the coating material is patterned to comprise a plurality of microstructures such as microwells and / or microcolumns. Methods for preparing and utilizing the microarray chips of the invention are further provided. The microarray chips of the instant invention find particular use in high-throughput assays.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
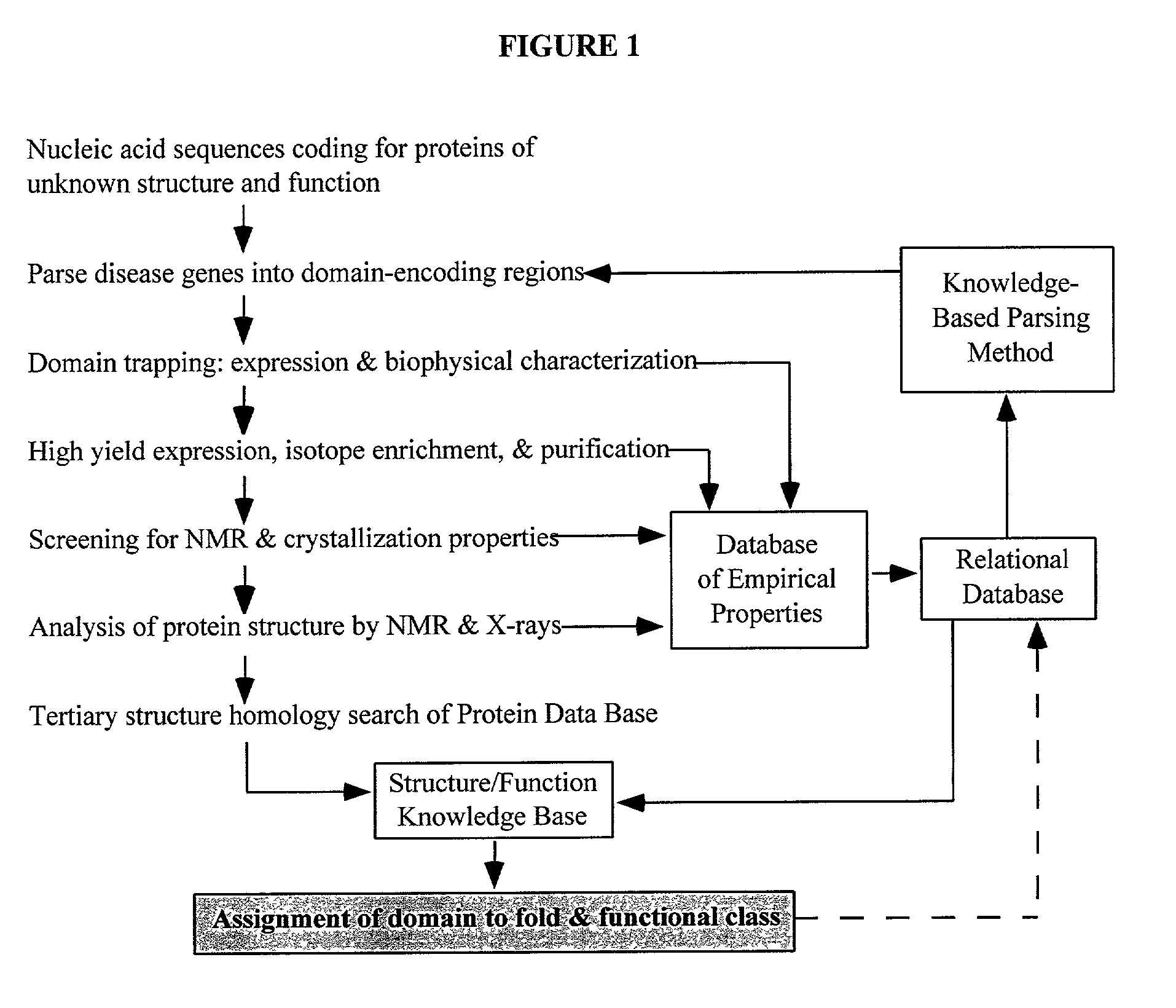
Linking gene sequence to gene function by three dimesional (3D) protein structure determination
InactiveUS20010016314A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFunctional profilingProtein structure
The present invention provides a structure-functional analysis engine for the high-throughput determination of the biochemical function of proteins or protein domains of unknown function. The present invention uses bioinformatics, molecular biology and nuclear magnetic resonance tools for the rapid and automated determination of the three-dimensional structures of proteins and protein domains.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
High-density ion transport measurement biochip devices and methods
InactiveUS20050196746A1Low costImprove production efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisFluidicsHigh density
The present invention provides novel biochips, biochip-based devices, and device configurations that can be used for ion transport measurement. The chips, devices, and designs of the present invention are particularly suited to high-throughput assays such as compound screening assays using patch clamping techniques. The invention includes high-density biochips made by novel methods and methods of making high density biochips, and also provides novel upper chamber configurations and fluidics designs for upper chambers of ion transport measurement devices that can be used in high throughput patch clamp assays. The present invention also includes methods of using ion transport measuring chips and devices of the present invention.
Owner:AVIVA BIOSCI
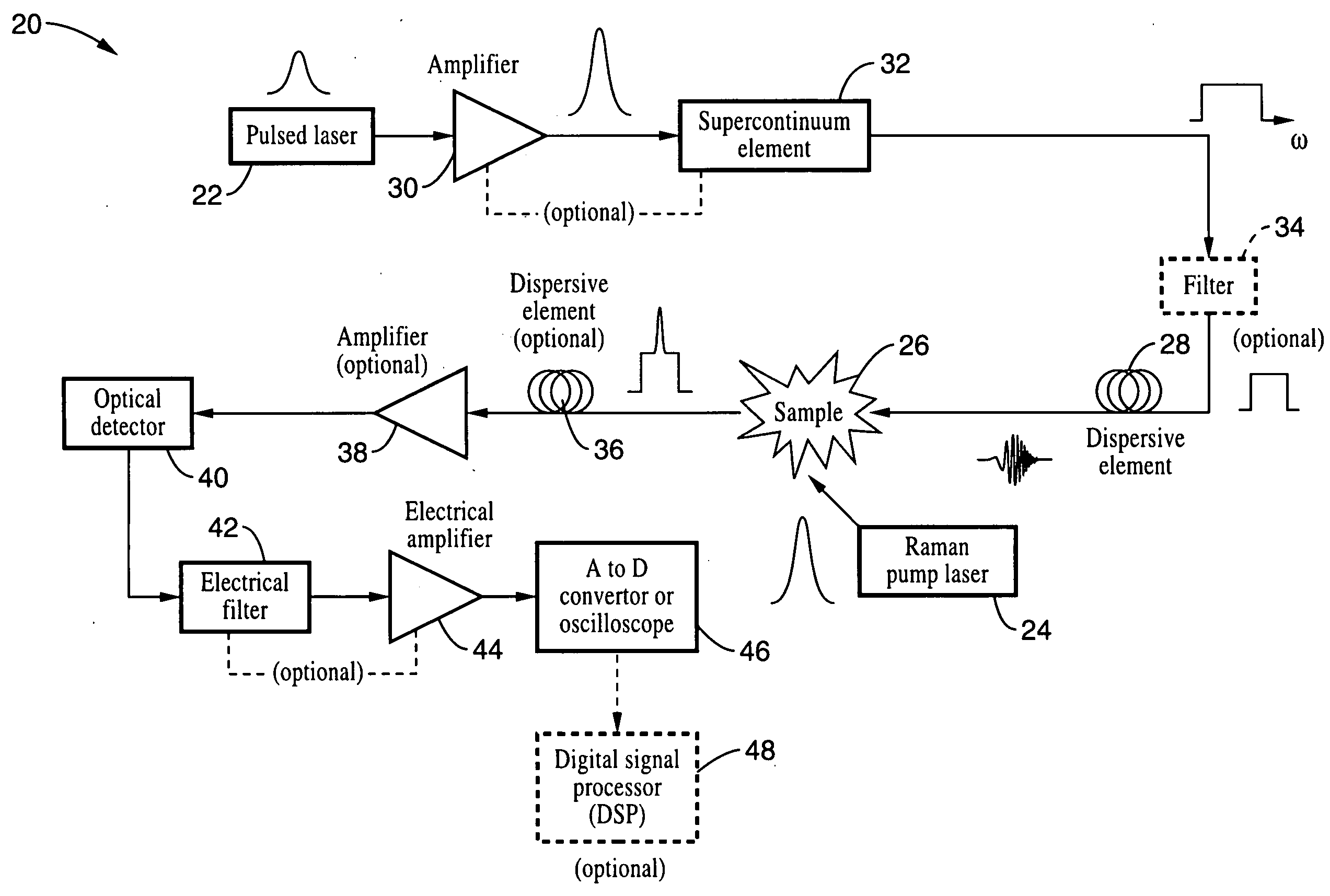
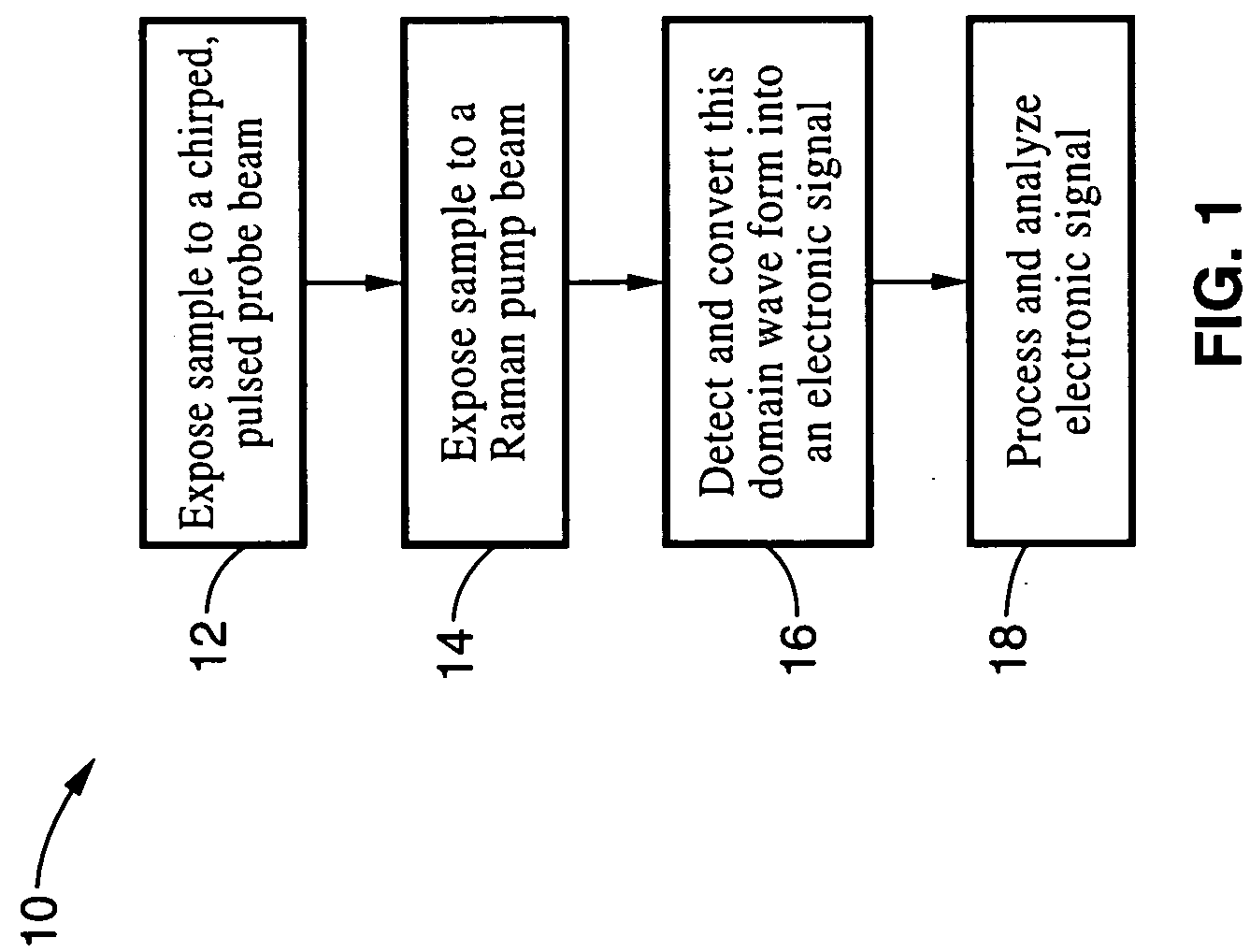
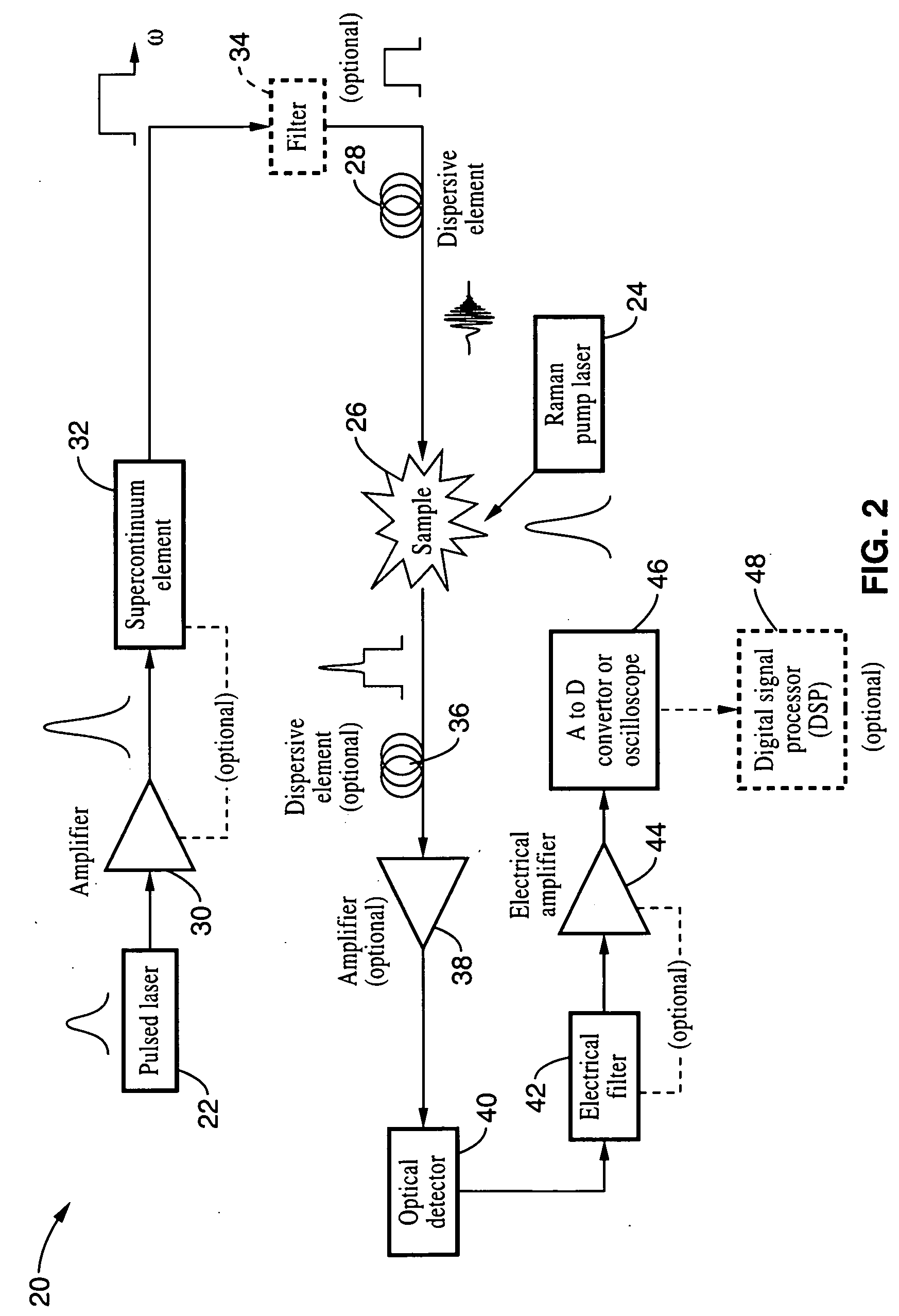
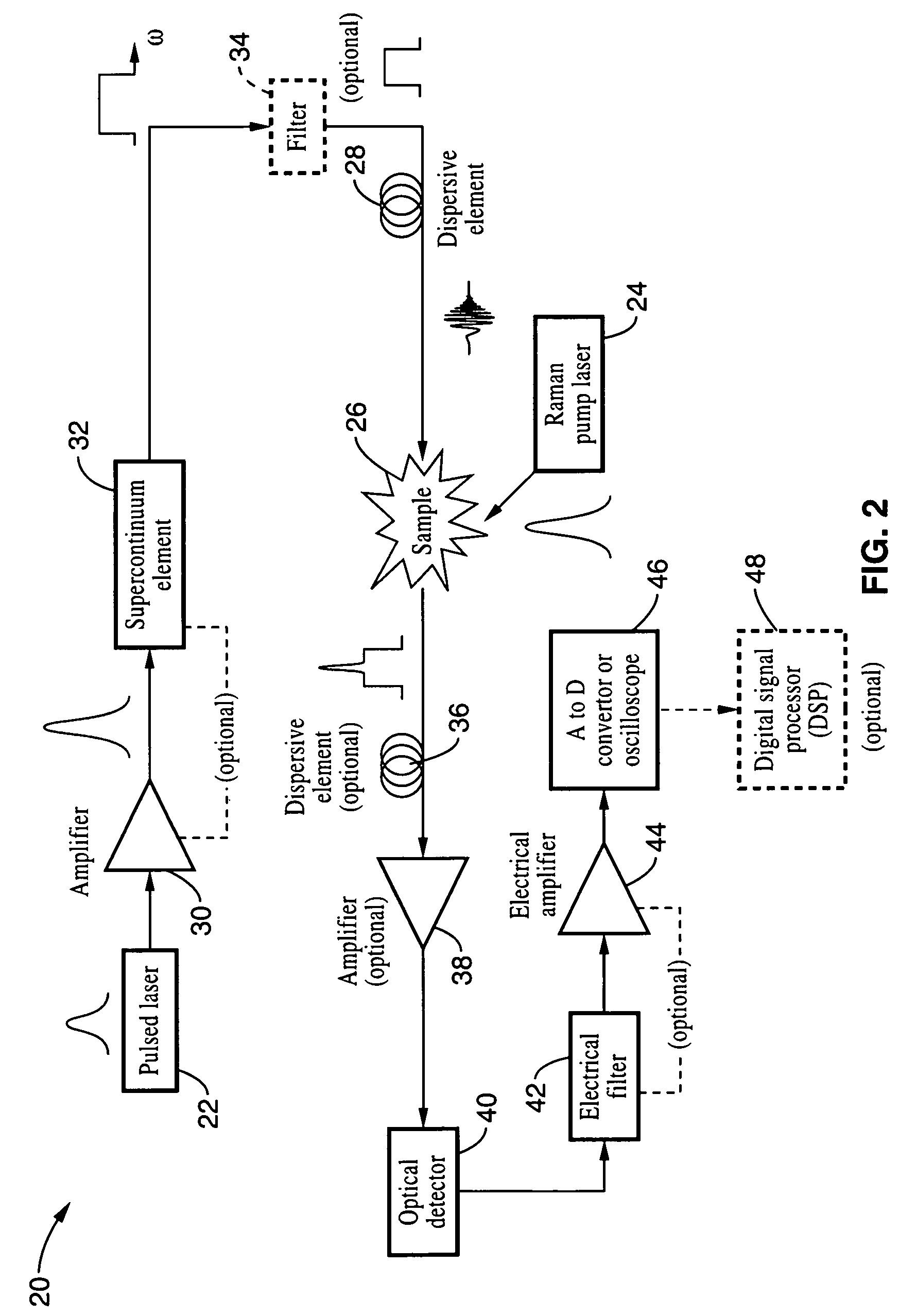
Apparatus and method for raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS20090073432A1Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometrySpectroscopySpectrometer
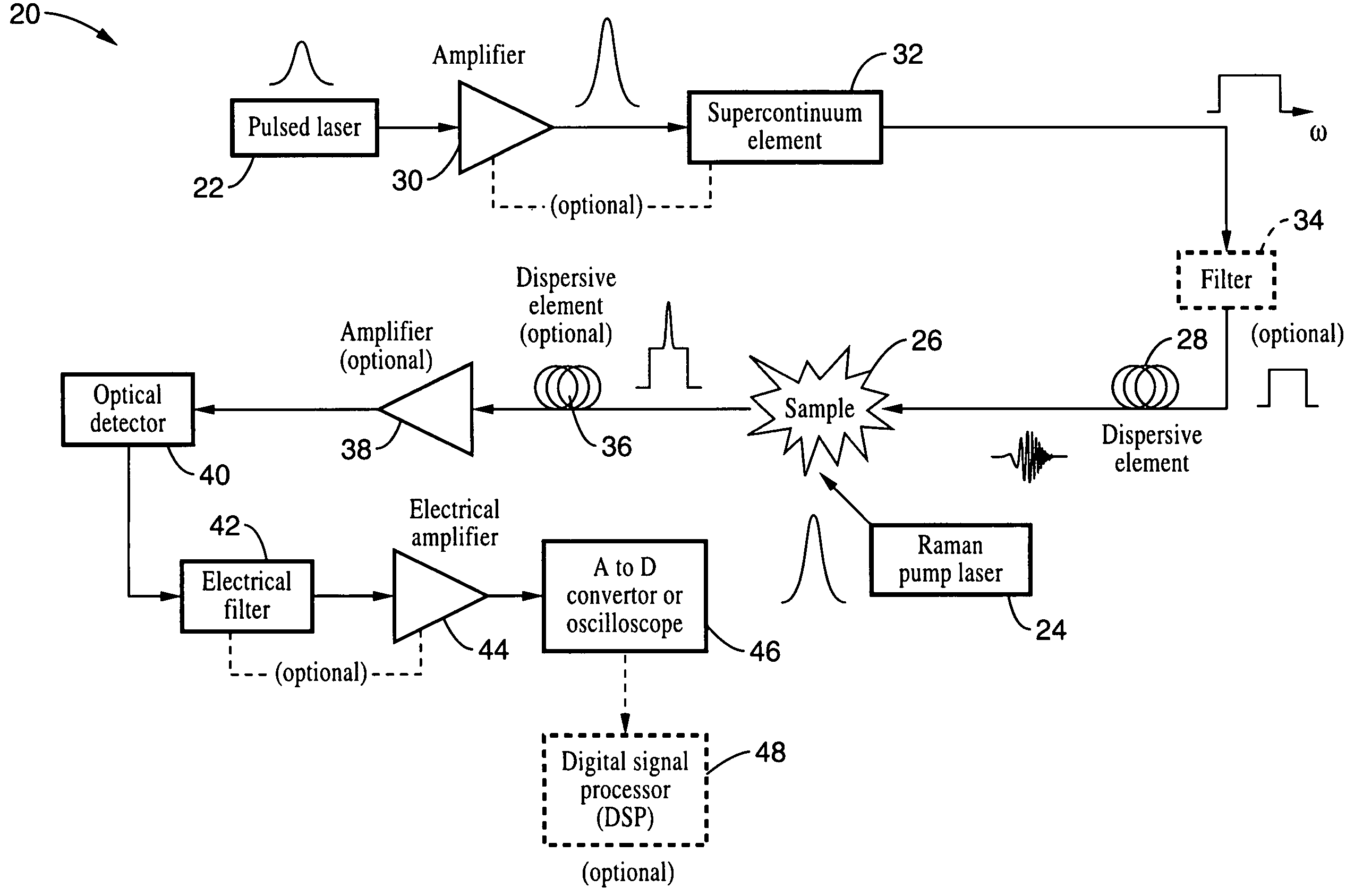
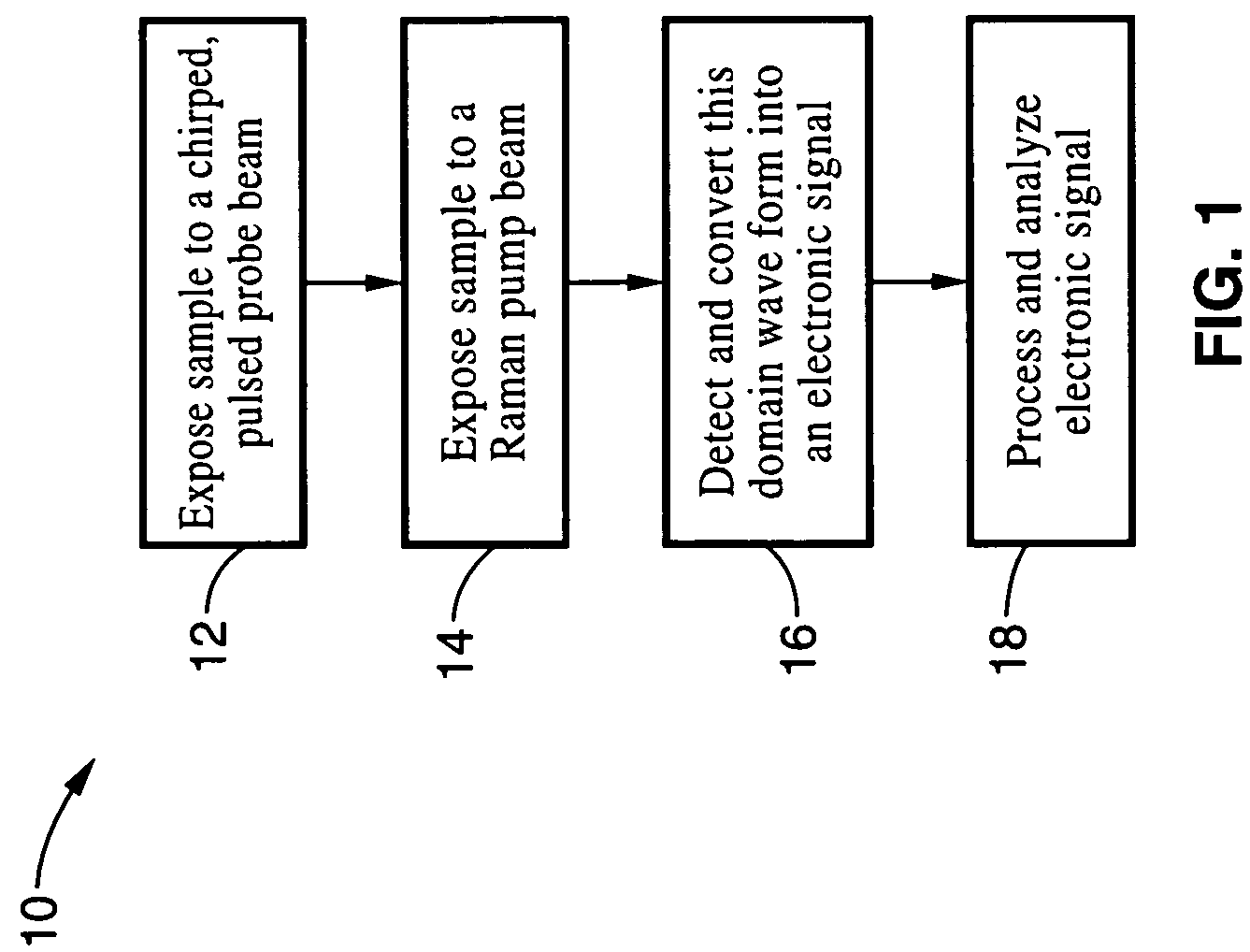
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Virtual wells for use in high throughput screening assays
InactiveUS20040018615A1Improve throughputRapid responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
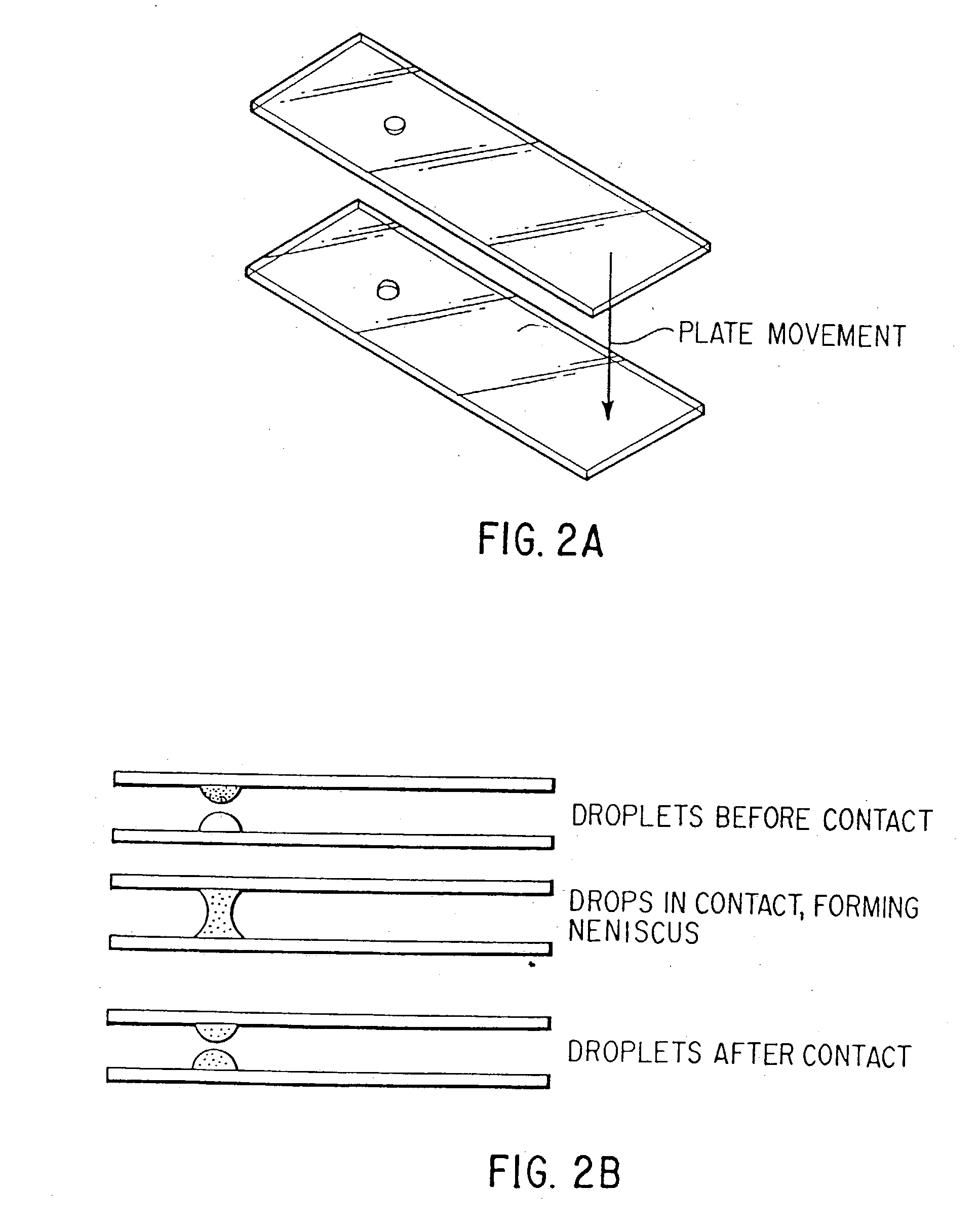
Microtiter-like plates containing virtual wells formed by an arrangement of relatively hydrophilic domains within relatively hydrophobic fields are provided. Assay mixtures are confined to the hydrophilic domains of the virtual wells by the edges of the hydrophobic fields. The use of virtual wells allows one to perform homogeneous and capture and wash high throughput screening assays with assay mixtures having volumes on the order of about 100 nl to 10 mu. Virtual wells also provide a means of easily moving fluids, which is particularly useful for simultaneous additions needed for kinetic studies and flash detection and washing. Methods for controlling evaporation during the dispensing of reagents as well as during incubation of high throughput screening utilizing microtiter-like plates containing virtual wells are also provided. The present invention also provides an inexpensive, disposable device for transferring small volumes of an entire array of compounds from a first microtiter-like plate to a second microtiter-like plate, preserving the spatial arrangement of the compounds. Methods of manufacturing and using the device are also provided.
Owner:GARYANTES TINA K
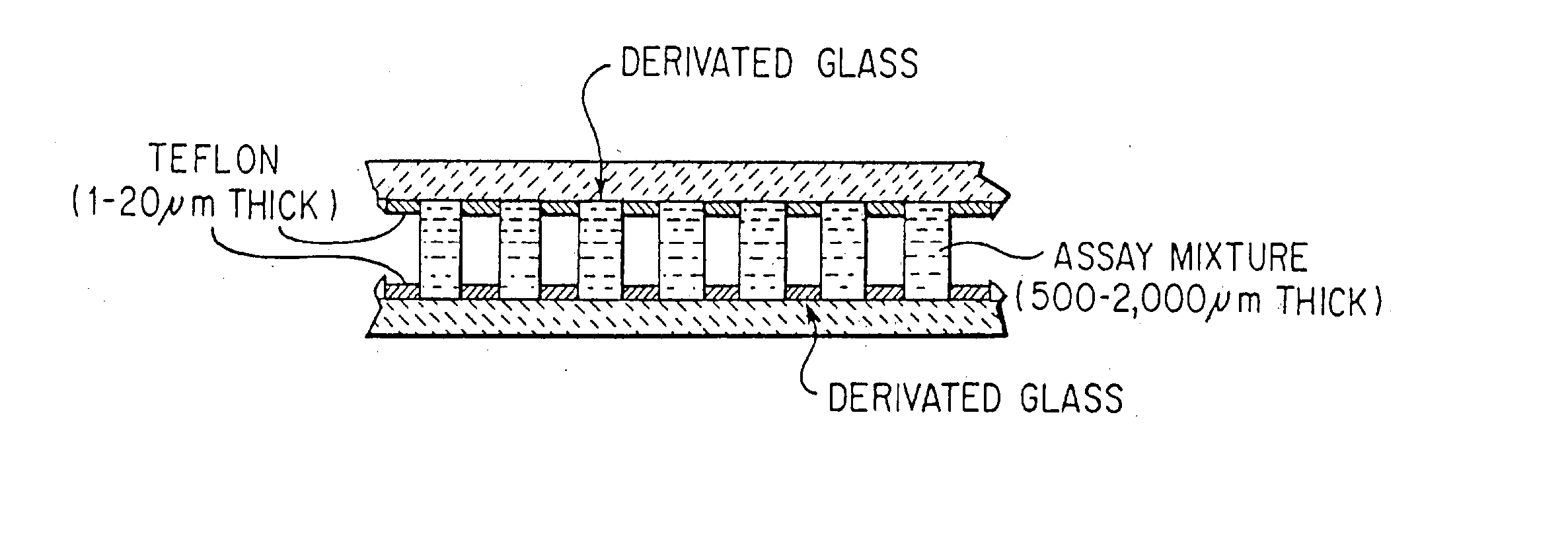
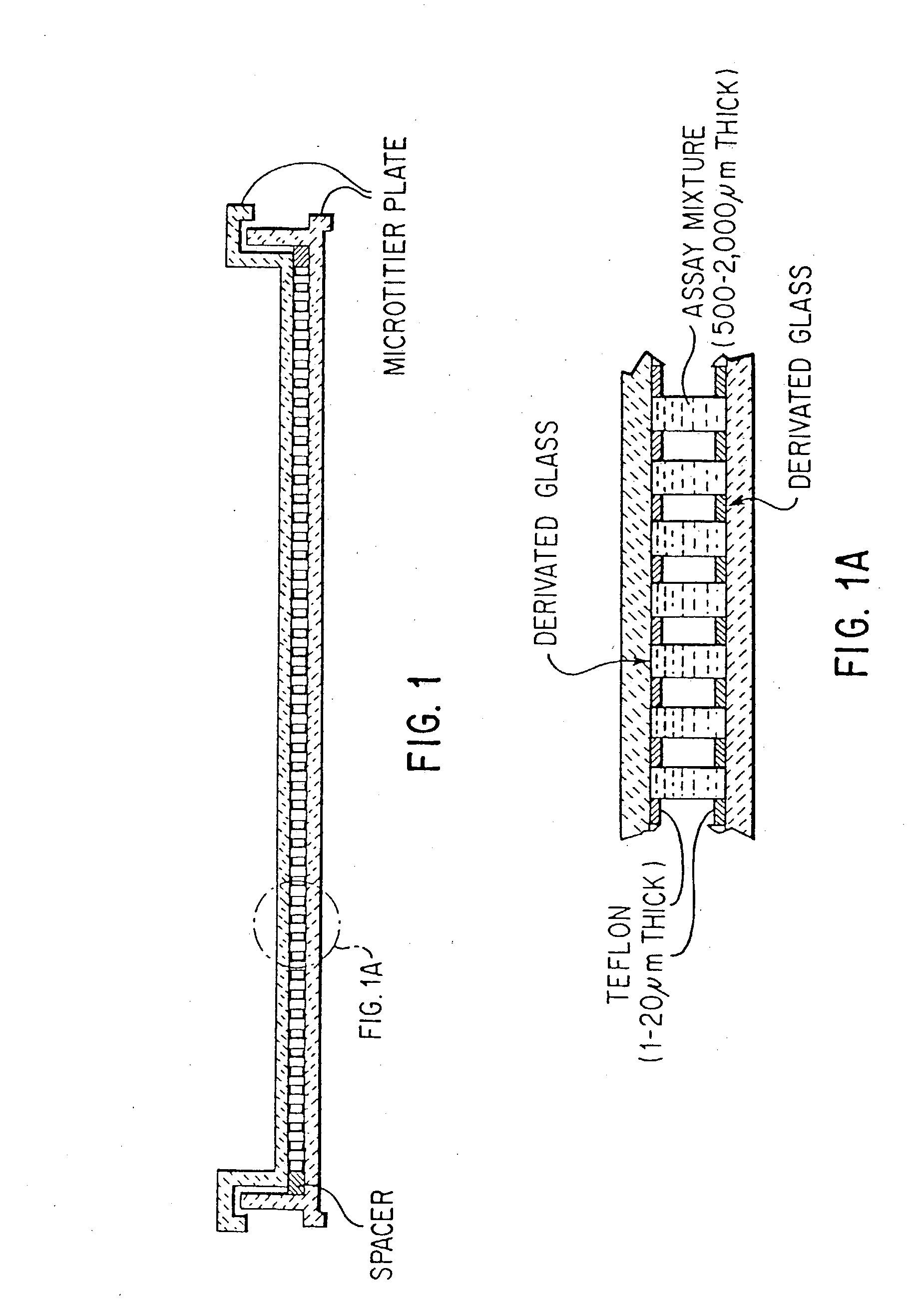
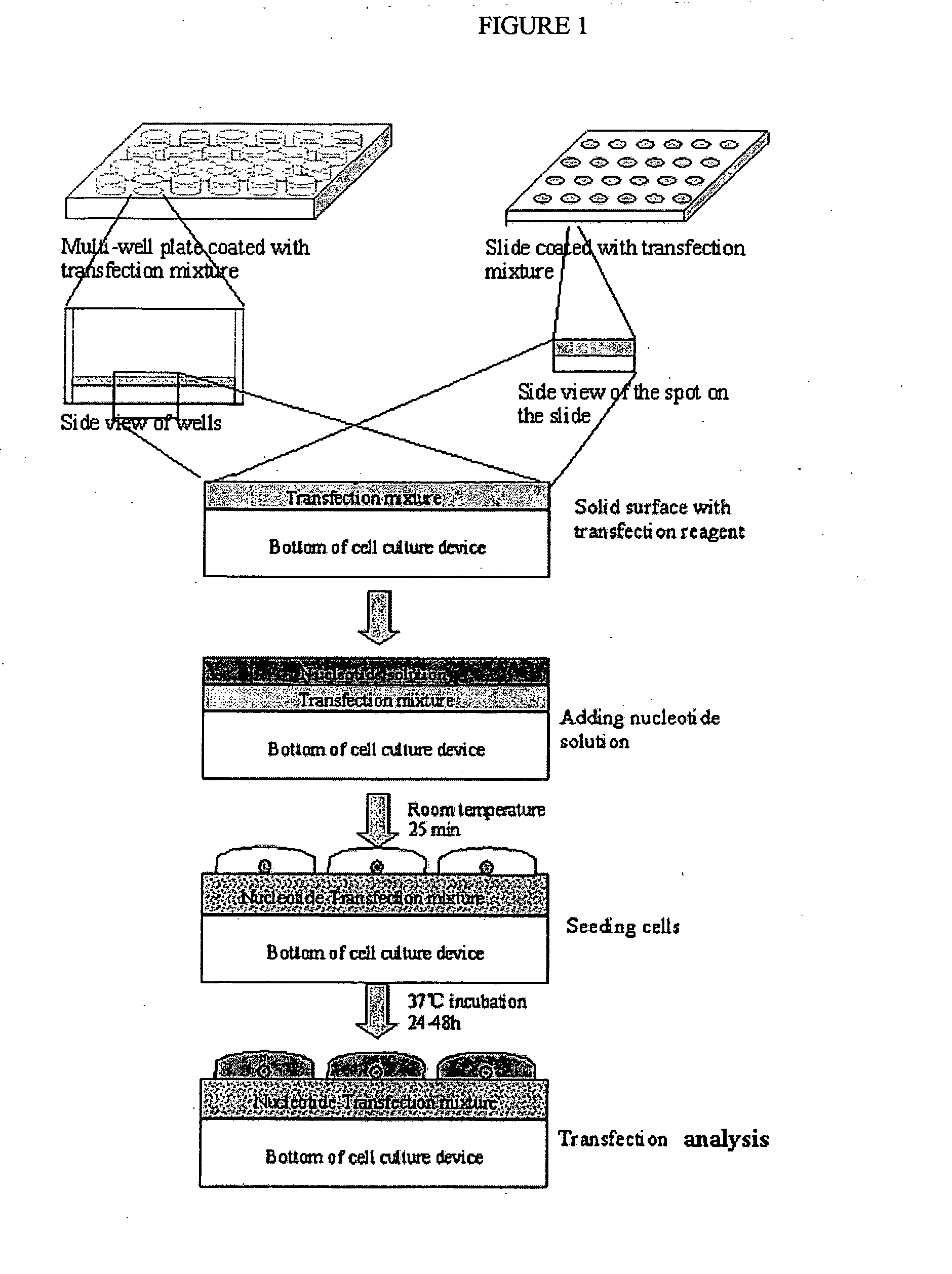
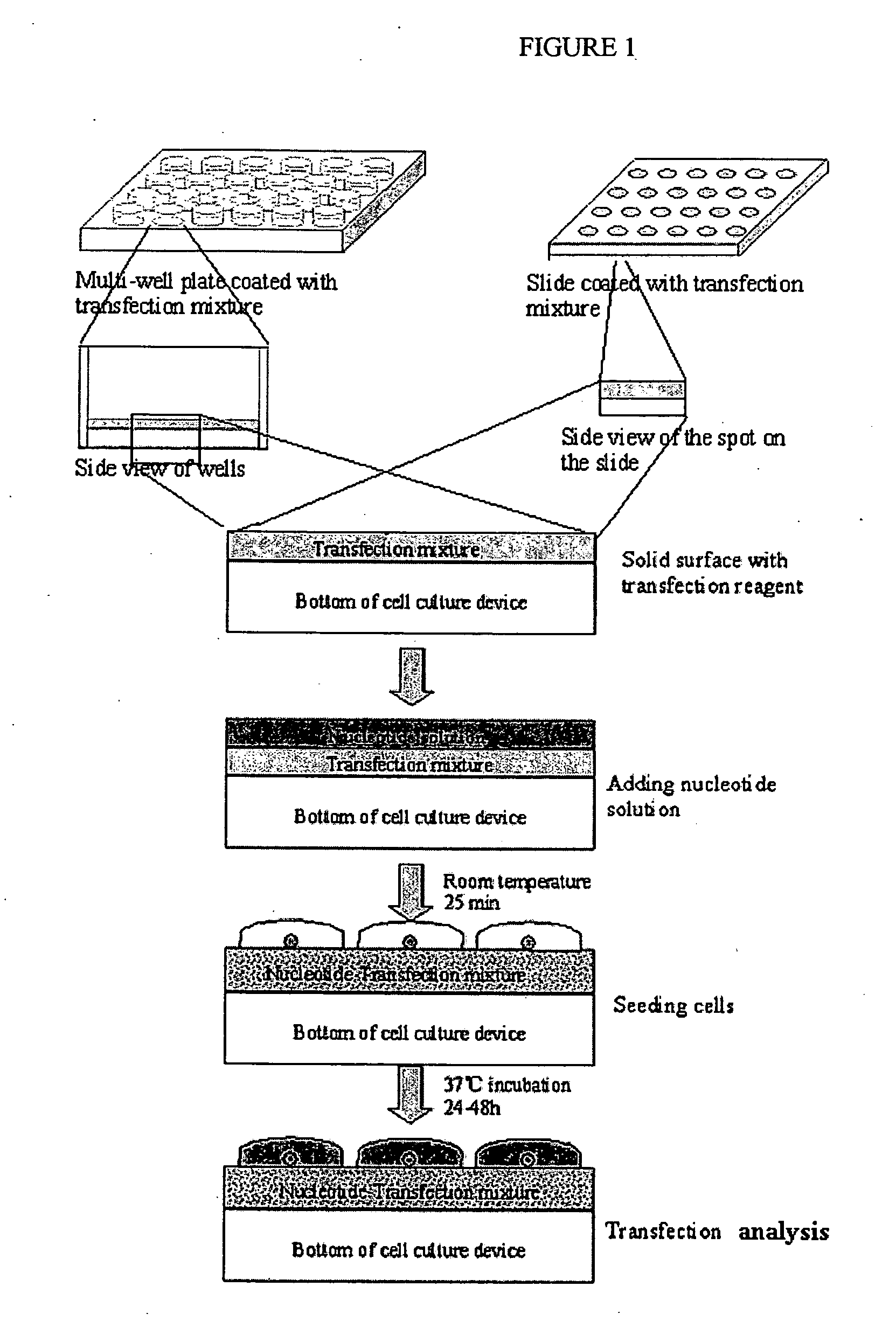
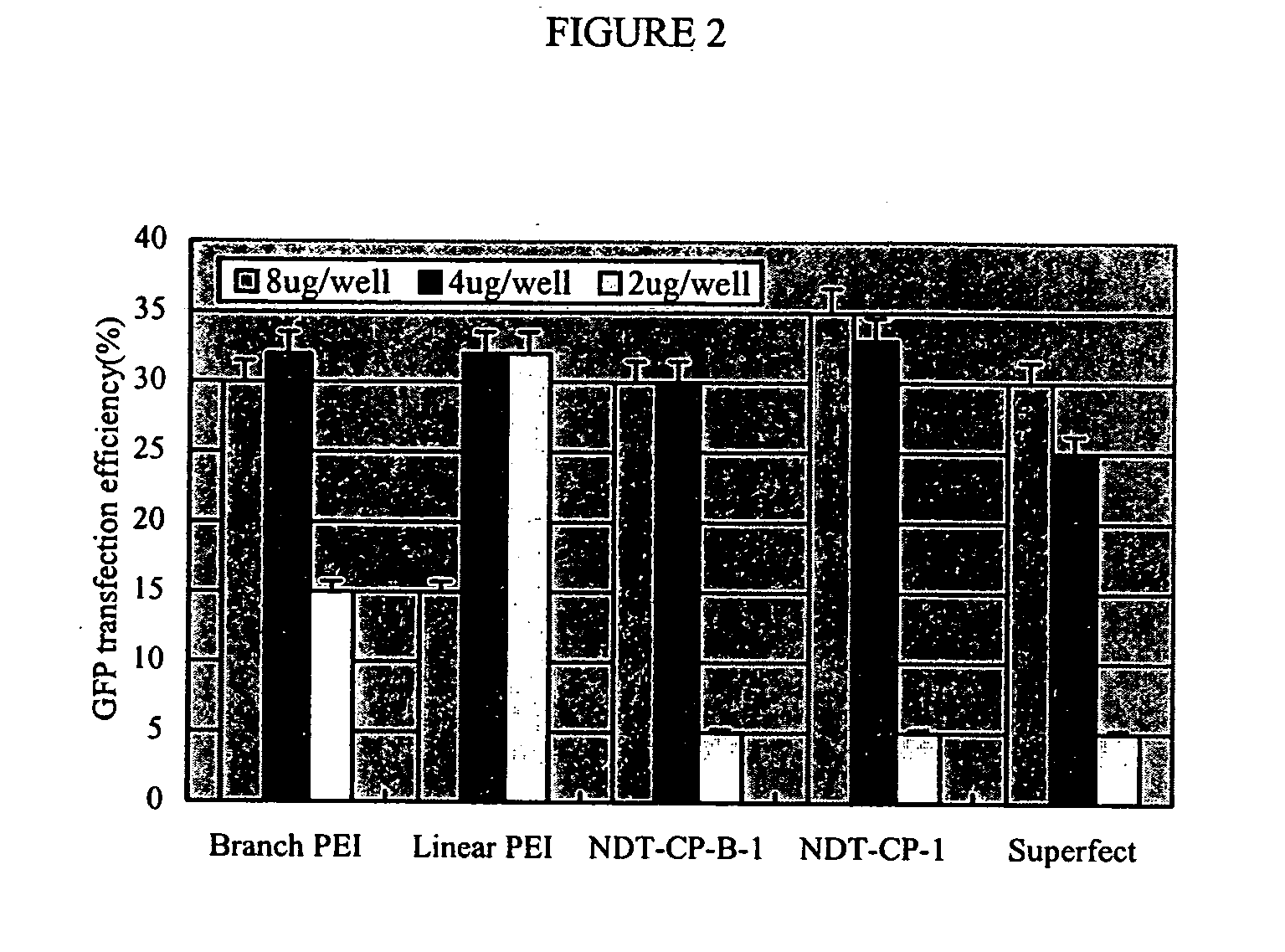
Solid surface for biomolecule delivery and high-throughput assay
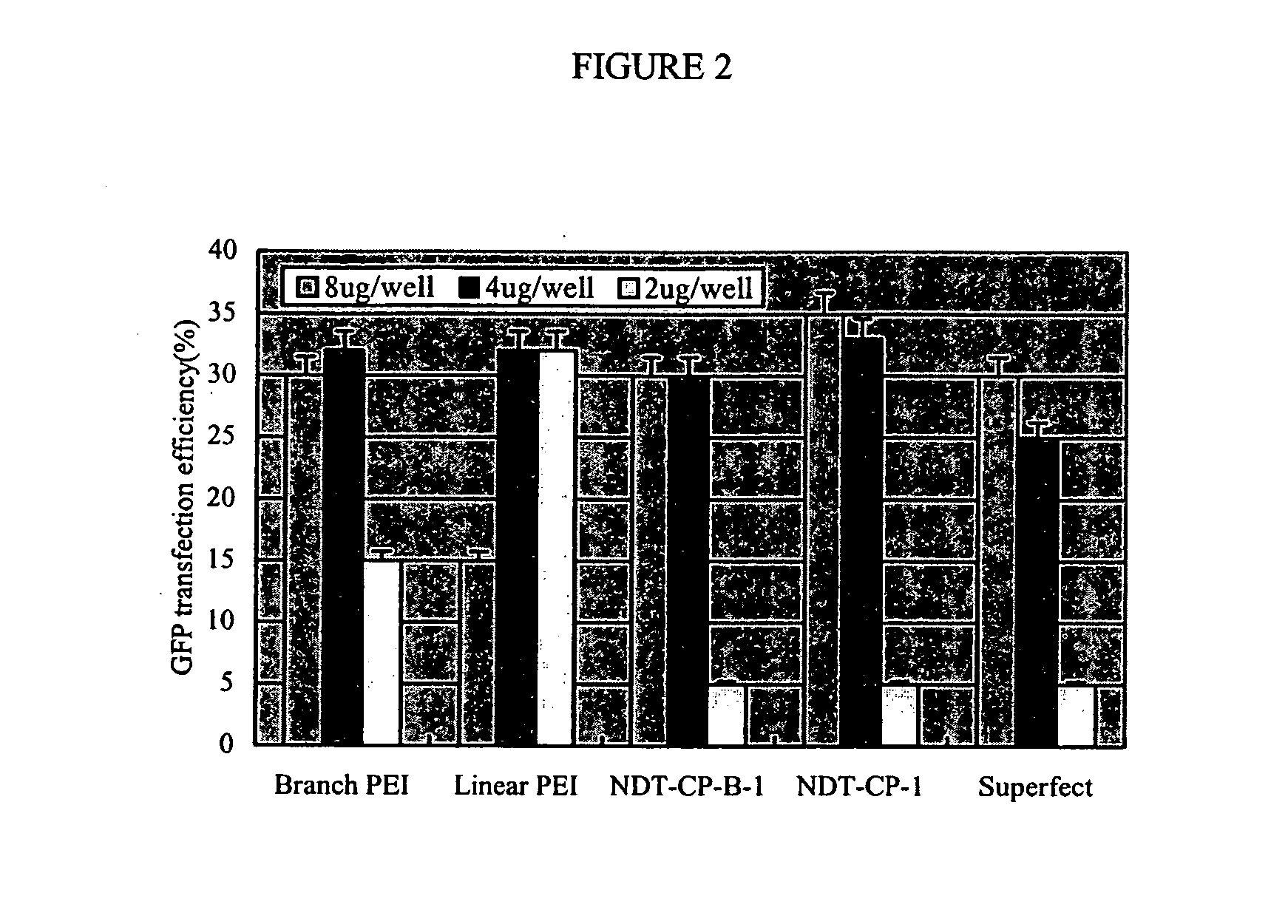
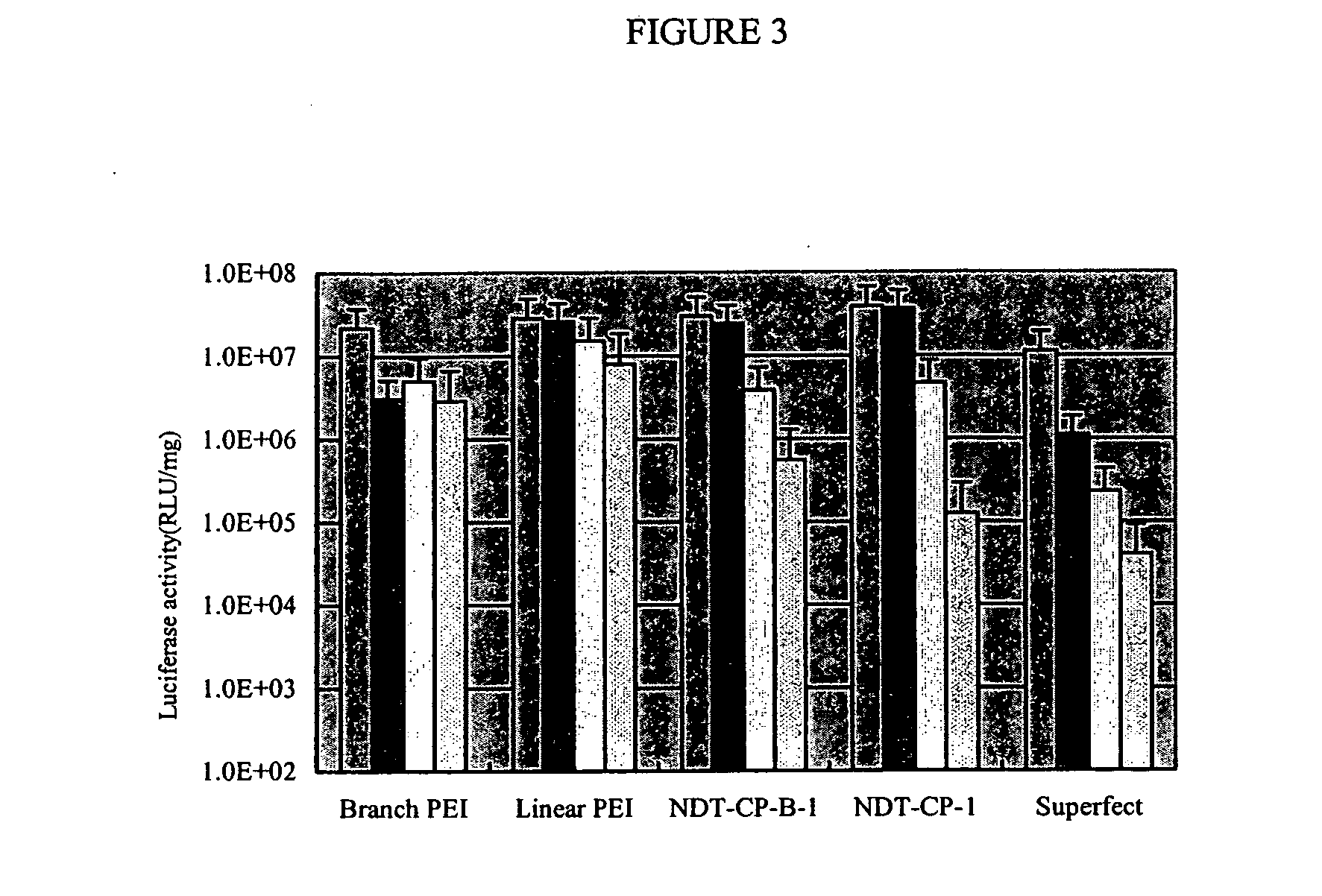
The present invention is related to a method for introducing biomolecules, such as nucleic acids, into cells by culturing cells on a solid surface which is coated with a transfection reagents and biomolecules.
Owner:YU LEI +3
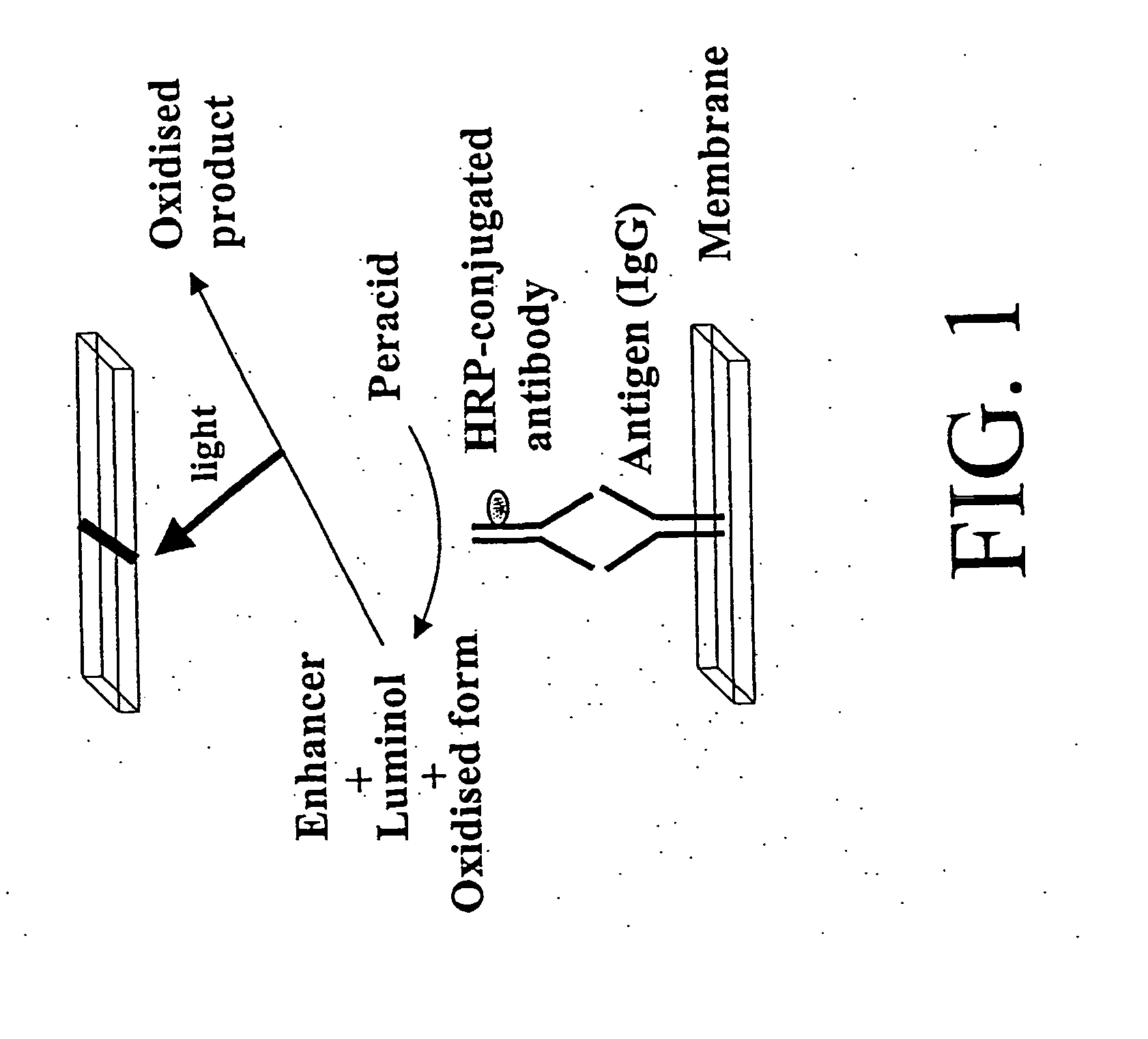
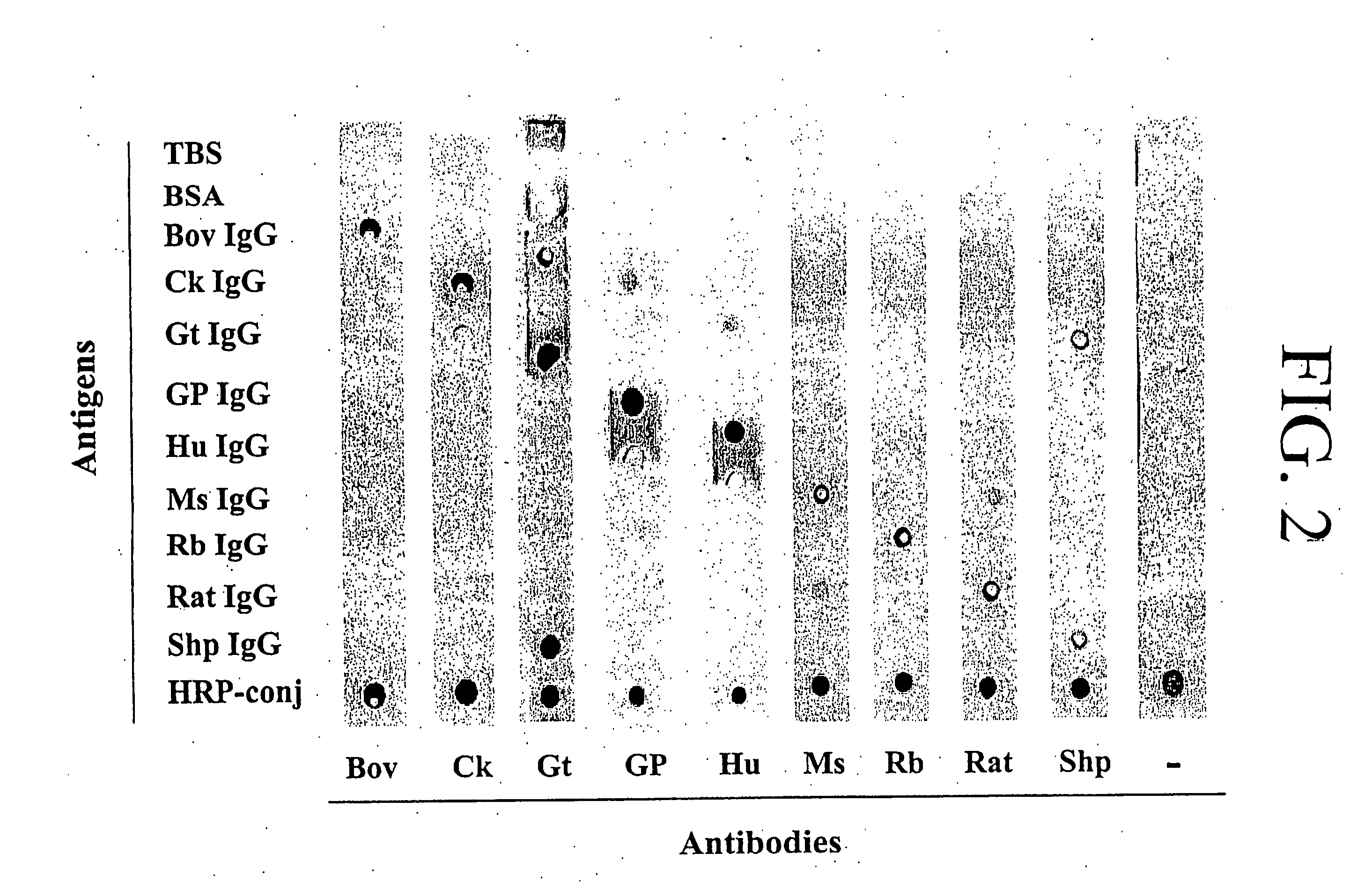
Antibody-based protein array system
InactiveUS20070054326A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenAnalyte
The invention of novel protein microarrays and protein microarray-based techniques to determine the presence and amounts of proteins of interest are described. These microarrays and methods of use can be used for the simultaneous detection of a multiplicity of antigens or antibodies in a high throughput assay based upon the differential affinity of molecules for one another. The microarrays can be formed by immobilizing capture proteins in an array on a membrane. Analytes of interest can be bound by the capture proteins and can be detected either by the position to which they are immobilized or by the identity of detecting proteins or agents which bind to the analytes of interest. The interactions that can be detected using the present invention can also be used to characterize proteins of unknown identity or character.
Owner:HUANG RUO PAN
High throughput assays for determining contractile function and devices for use therein
The present invention provides high throughput assays for identifying compounds that modulate a contractile function, as well as devices suitable for use in these assays.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Systems, methods and kits for characterizing phosphoproteomes
InactiveUS20050164324A1Quick filterImprove developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementIsotope separationPhosphorylationSystems approaches
The invention provides systems, software, methods and kits for detecting and / or quantifying phosphorylatable polypeptides and / or acetylated polypeptides in complex mixtures, such as a lysate of a cell or cellular compartment (e.g., such as an organelle). The methods can be used in high throughput assays to profile phosphoproteomes and to correlate sites and amounts of phosphorylation with particular cell states.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method and apparatus for sample injection in microfabricated devices
InactiveUS20020168780A1Fixed microstructural devicesVolume/mass flow measurementSample poolThroughput
An off-column sample injection scheme for introducing samples into micro-reaction channels in microfabricated devices. In one aspect of the present invention, off-column sample injection is effected by introducing sample from a sample reservoir provided on the substrate of the microfabricated device into a reaction channel via a constricted channel or opening interface, e.g., a narrow connection-channel and / or a pinhole. In another embodiment of the present invention, off-column sample injection is effected by introducing sample from a sample reservoir that is provided outside the substrate of the microfabricated device. A through-hole is provided in the substrate to facilitate sample introduction into the reaction channel. In a further aspect of the present invention, the free-end of a capillary tube connected to the sample-channel is moved alternatively to a sample and an auxiliary solution to bring multiple samples in series to the vicinity of a reaction channel for convenient sample introduction and high-throughput assays.
Owner:MICROCHEM SOLUTIONS
Muscle chips and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20140342394A1Improve throughputHigh content measurementCompound screeningBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHigh Throughput Assay
The present invention provides high throughput assays for identifying compounds that modulate a contractile function, as well as devices suitable for these assays.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Microfabricated particle focusing device
A microfabricated particle focusing device comprises an acoustic portion to preconcentrate particles over large spatial dimensions into particle streams and a dielectrophoretic portion for finer particle focusing into single-file columns. The device can be used for high throughput assays for which it is necessary to isolate and investigate small bundles of particles and single particles.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +1
Method for high throughput cell-based assays using versatile living microarrays
InactiveUS20050255445A1Lower the volumeImprove throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningCellular componentCell based assays
The present invention relates to methods for screening of cellular responses of cellular components comprising: (a) providing cellular components on the surface of a substrate, said substrate having immobilized thereon an array of detector molecules; (b) delivering test compounds to positions on the substrate corresponding to the arrayed detector molecules on the surface of said solid substrate; (c) incubating said test compounds with said cellular components on the surface of the solid support, under conditions allowing the induction of cellular responses; (d) assaying said cellular responses; and, identifying and characterizing the cellular responses induced by said test compounds. The present invention further relates to the uses of said methods as well as microarrays and kits for carrying out said methods.
Owner:PAMGENE
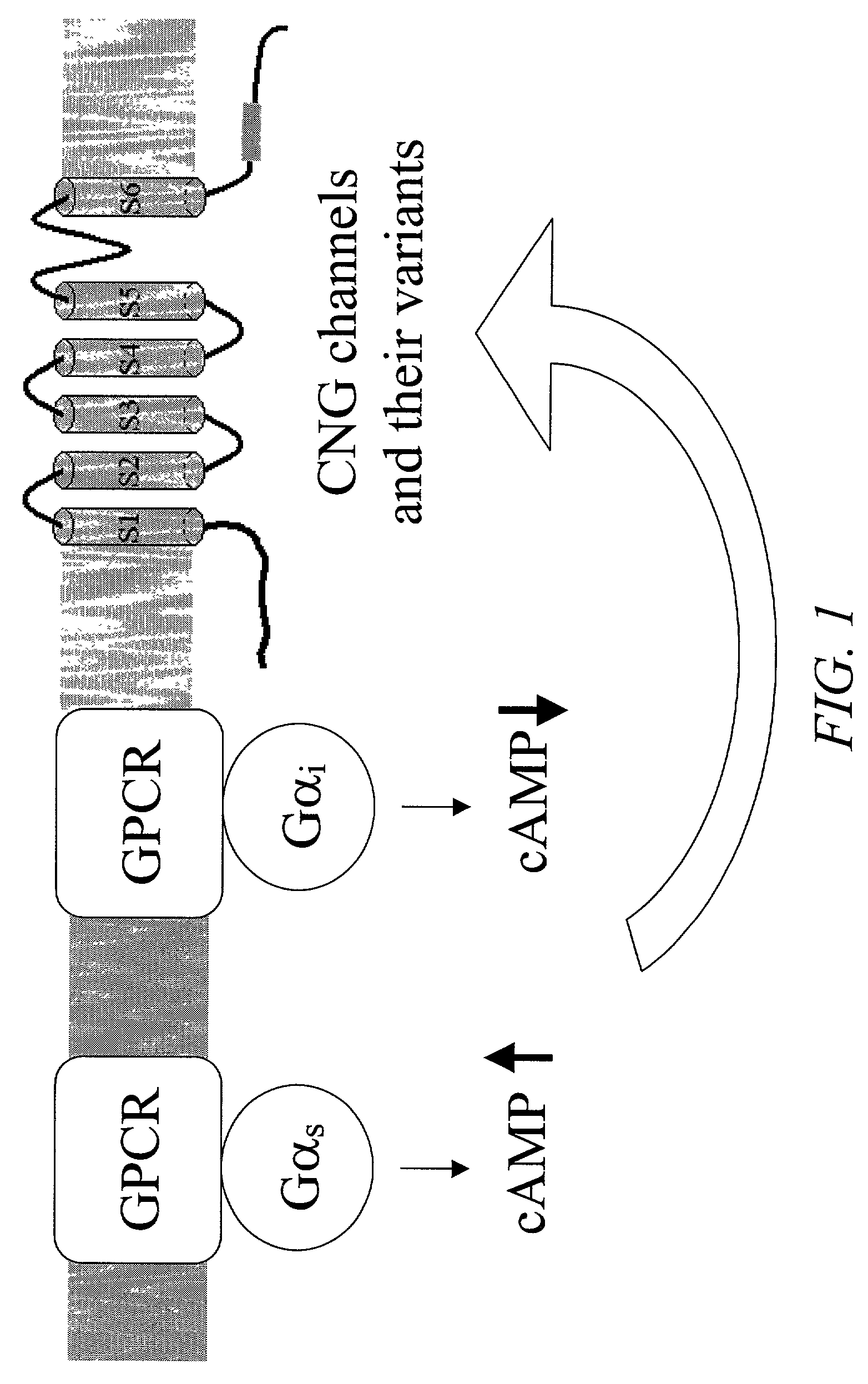
Cell-based assays for G-protein-coupled receptor-mediated activities
InactiveUS7115377B2Compound screeningApoptosis detectionCyclic nucleotide gated channelsCell based assays
Disclosed are compositions and methods for their use, such as in identifying G-protein-coupled receptors, ligands and compounds that modulate the activities of G-protein-coupled receptors. The compositions and methods employ cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and fluorescence dyes in detecting changes of intracellular cAMP levels in response to the stimulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. Activation of the G-protein-coupled receptors can be detected in a variety of assays, including cell-based imaging assays with fluorescence microscopes and high throughput assays with multi-well plates and fluorescence plate readers.
Owner:XIAMEN AMOYTOP BIOTECH
Methods For The Delivery Of Toxins Or Enzymatically Active Portions Thereof
InactiveUS20100209955A1Increase the number of cellsIncrease rangeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCell based assaysToxin
The present invention relates to methods, systems, and kits for intoxicating cells, neuronal and non-neuronal cells, with a toxin or fragment thereof. This is done by subjecting toxin substrate and a lipid or polymeric carrier (e.g., DNA uptake facilitating agent) to one or more cells for use in cell based assays. In an aspect, the methods of the present invention allow for high throughput assays and, as such, for the evaluation of drug candidates.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
cAMP reporters and high throughput assays
ActiveUS20070111270A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesImage resolutionBioinformatics
cAMP reporters useful for obtaining measurements of cAMP levels with high spatial and temporal resolution and in high throughput assays.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods for generating high titer helper-free preparations of released recombinant AAV vectors
InactiveUS20050266567A1Genetic therapy composition manufactureGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGene deliveryHeterologous
This invention provides methods and compositions for producing high titer, substantially purified preparations of recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) that can be used as vectors for gene delivery. At the onset of vector production, AAV producer cells of this invention typically comprise one or more AAV packaging genes, an AAV vector comprising a heterologous (i.e. non-AAV) transgene of interest, and a helper virus such as an adenovirus. The AAV vector preparations produced are generally replication incompetent but are capable of mediating delivery of a transgene of interest (such as a therapeutic gene) to any of a wide variety of tissues and cells. The AAV vector preparations produced according to this invention are also substantially free of helper virus as well as helper viral and cellular proteins and other contaminants. The invention described herein provides methods of producing rAAV particles by culturing producer cells under conditions, such as temperature and pH, that promote release of virus. Also provided is a quantitative, high-throughput assay useful in the assessment of viral infectivity and replication, as well as in the screening of agent that affect viral infectivity and / or replication.
Owner:ATKINSON EDWARD M +5
Apparatus and method for Raman spectroscopy and microscopy with time domain spectral analysis
InactiveUS7821633B2Eliminate needHigh speed moldingRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopySpectroscopySpectrometer
An apparatus and method for measuring Raman-type spectra using optical dispersion to convert an optical spectrum into a waveform which can be detected directly in the time domain without the use of a conventional spectrometer. In the example of stimulated Raman spectroscopy, the apparatus and method exposes a sample to a chirped, pulsed probe beam and a Raman pump beam and the resulting Raman spectra is detected by an optical detector in the time domain, and analyzed. Alternatively, the Raman spectra from the probe and pump beams is chirped with a dispersive element prior to detection and analysis. Each probe pulse provides a snapshot of the Raman spectrum that is sampled in time so that neither repetitive waveforms nor static samples are required. Therefore, high speed acquisitions and high throughput assays can be conducted. To facilitate detection, these spectral signals can also be amplified using distributed Raman amplification directly in the dispersive element.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
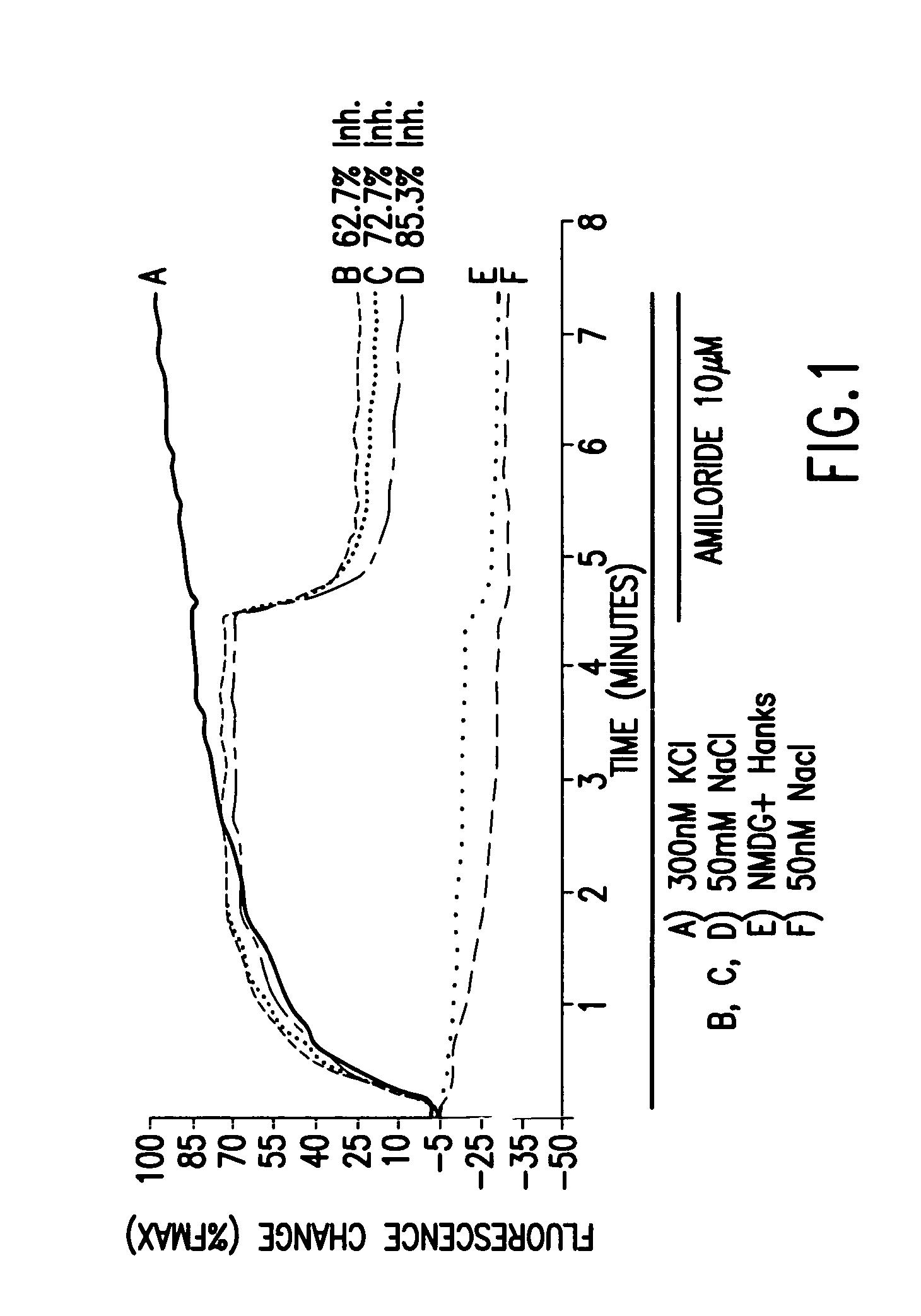
Electrophysiological assay using oocytes that express human ENaC and the use phenamil to improve the effect of ENaC enhancers in assays using membrane potential reporting dyes
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a mammalian cell-based high-throughput assay for the profiling and screening of human epithelial sodium channel (hENaC) cloned from a human kidney c-DNA library and is also expressed in other tissues including human taste tissue. The present invention further relates to amphibian oocyte-based medium-throughput electrophysiological assays for identifying human ENaC modulators, preferably ENaC enhancers. Compounds that modulate ENaC function in a cell-based ENaC assay are expected to affect salty taste in humans. The assays described herein have advantages over existing cellular expression systems. In the case of mammalian cells, such assays can be run in standard 96 or 384 well culture plates in high-throughput mode with enhanced assay results being achieved by the use of a compound that inhibits ENaC function, preferably an amiloride derivative such as Phenamil. In the case of the inventive oocyte electrophysiological assays (two-electrode voltage-clamp technique), these assays facilitate the identification of compounds which specifically modulate human ENaC. The assays of the invention provide a robust screen useful to detect compounds that facilitate (enhance) or inhibit hENaC function. Compounds that enhance or block human ENaC channel activity should thereby modulate salty taste in humans.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
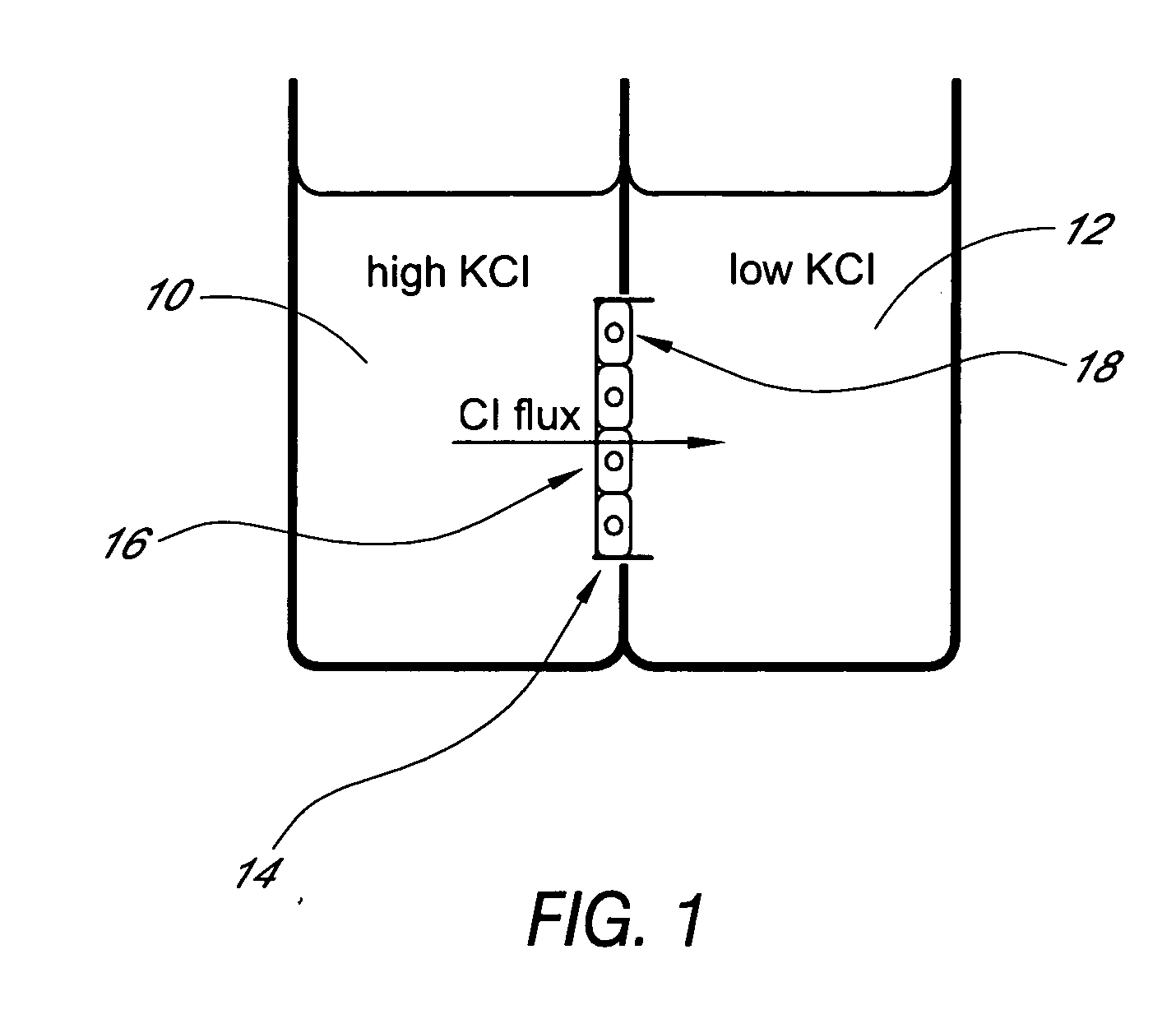
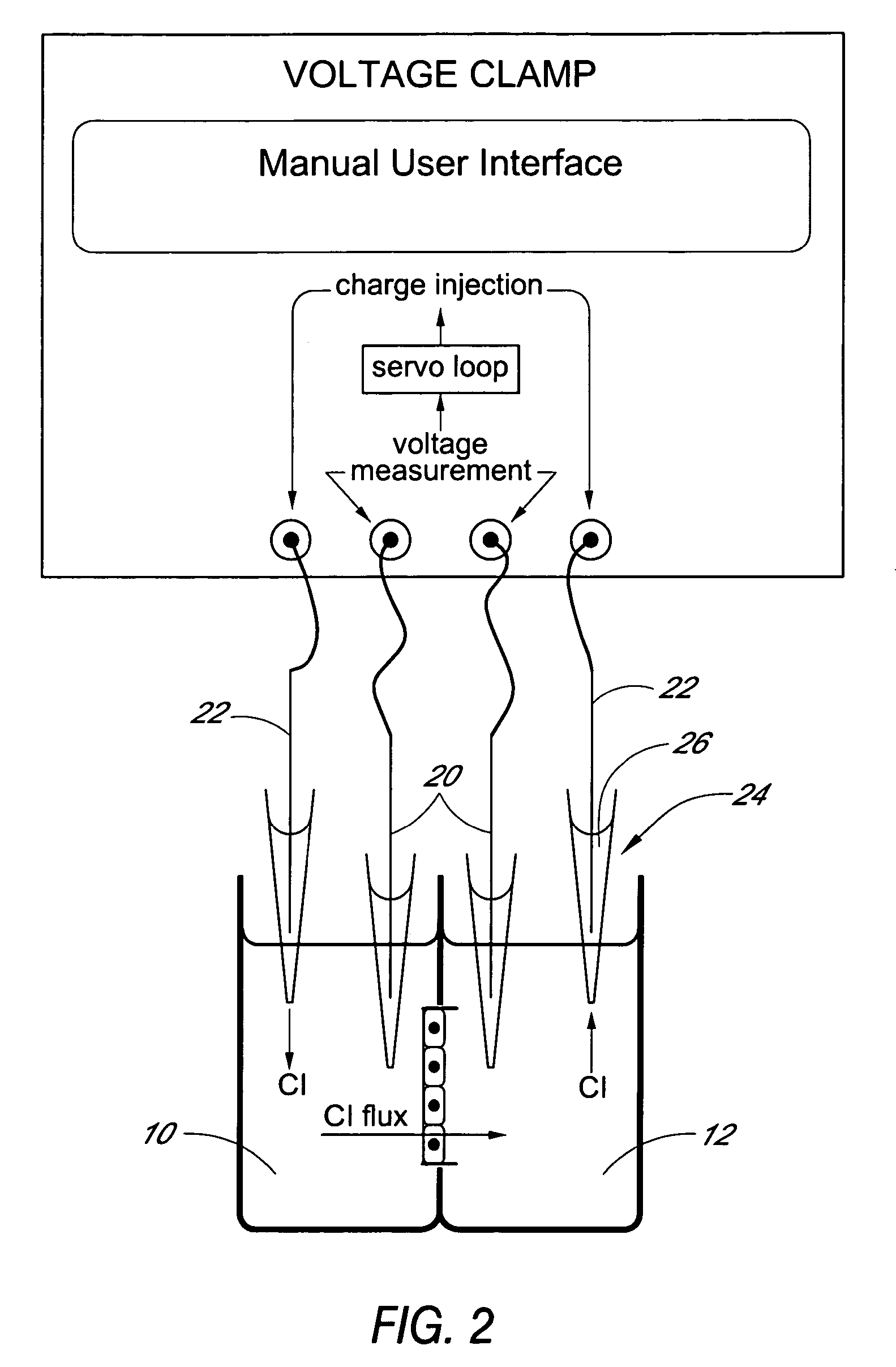
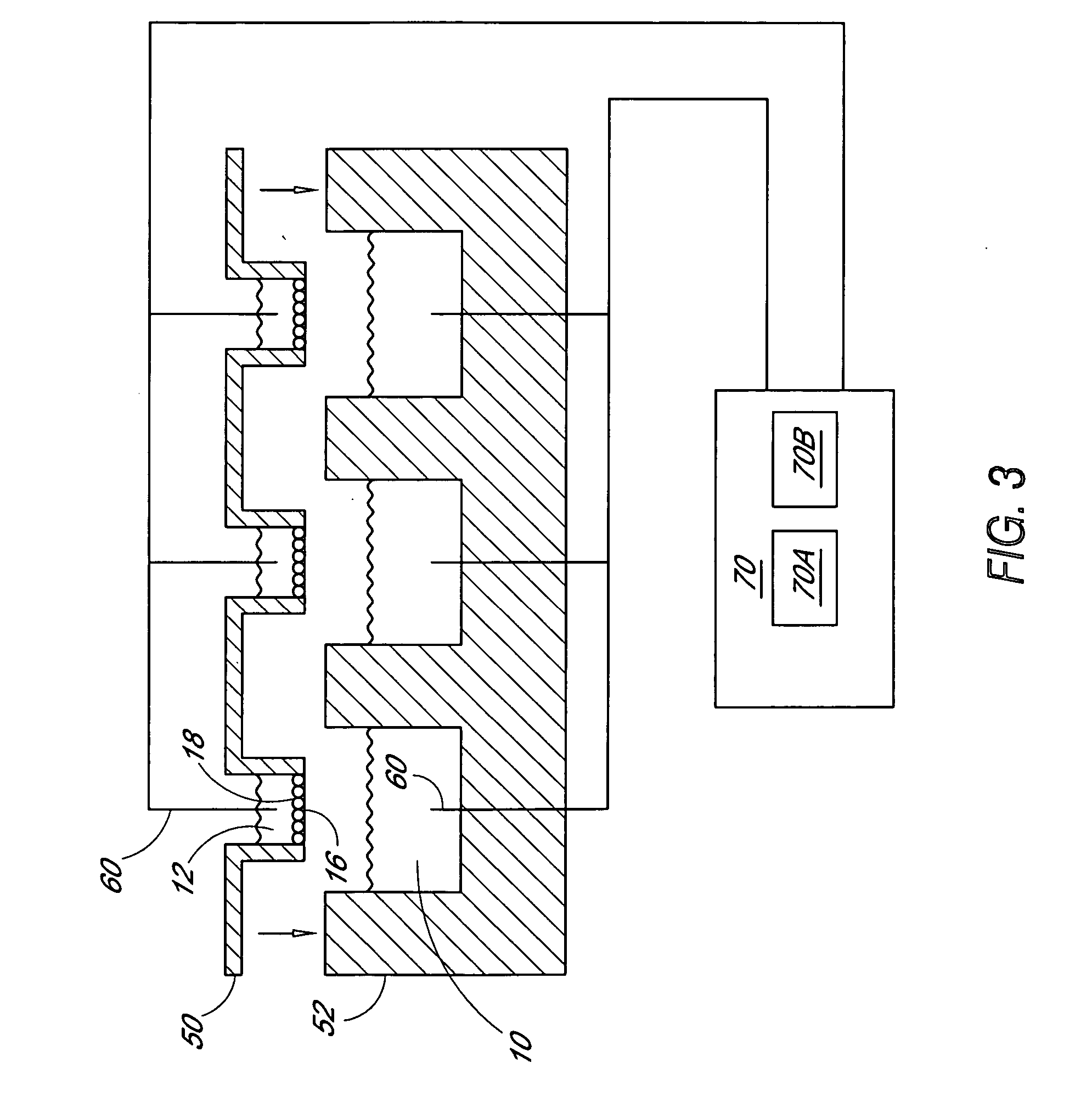
Multiwell plate assembly for use in high throughput assays
ActiveUS20050221274A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological propertyAssay
A device for characterizing the biological properties of cells can include a plurality of dual-compartment assay chambers wherein the compartments of each chamber are separated by a cell layer across which ions can flow. The biological properties of the cell layer in the presence or absence of experimental compounds can be determined by measuring an electrical gradient across the layer. A individual dual-compartment chamber of this type may be referred to as an “Ussing chamber.”
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
High-throughput assay for sugar-mediated drug transport
The invention provides a rapid, quantitative assay to directly assess the impact of a diverse range of sugars upon the sugar-mediated uptake of corresponding sugar-conjugates into various cell types.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Solid surface for biomolecule delivery and high-throughput assay
The present invention is related to a method for introducing biomolecules, such as nucleic acids, into cells by culturing cells on a solid surface which is coated with a transfection reagents and biomolecules.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Microfluidic chip for high-throughput screening and high-throughput assay
ActiveUS20050226781A1Highly integratedEasy injectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsHigh flux
Disclosed is a micro-fluidic chip for high-throughput screening and high-throughput assay, in which its structure is improved, thereby enhancing the efficiency of high-throughput screening and high-throughput assay. The micro-fluidic chip includes a well for isolating a specimen. The well can be arranged in a one- or two-dimension. A specimen-isolating means is disposed above the well and is movable upwards and downwards. An opening and closing means for moving the specimen-isolating means upwards and downwards is disposed above the specimen-isolating means. An inlet for injection the specimen and an outlet for discharging an excess of the injected specimen are provided. A reagent-injecting passage for injecting a reagent and a reagent-discharging passage for discharging the reagent are also provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Cellulase activity determination method based on micropore plate method
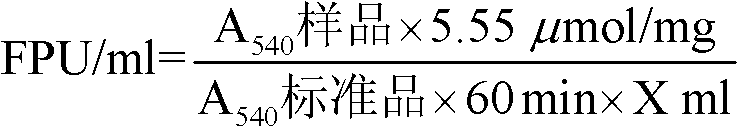
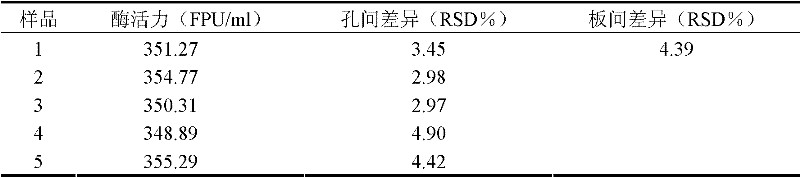
InactiveCN102230887AImprove stabilityHigh precisionColor/spectral properties measurementsAlgluceraseHigh flux
A cellulase activity determination method based on a micropore plate method relates to the field of biochemistry, and specifically relates to a cellulase activity high flux determination method based on a micropore plate method. The method comprises steps of 1) establishing a glucose standard curve; 2) determining a sample enzyme activity; 3) checking out corresponding glucose content from the glucose standard curve according to an absorbance of the sample enzyme, and calculating an enzyme activity value according to a gram weight of generated glucose. The method is suitable for activity determination of filter paper enzyme, endo-cellulase, exo-cellulase and beta-glucosidase, and has characteristics of convenient operation, rapidness, simple equipment requirement and easiness for popularization, etc.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com