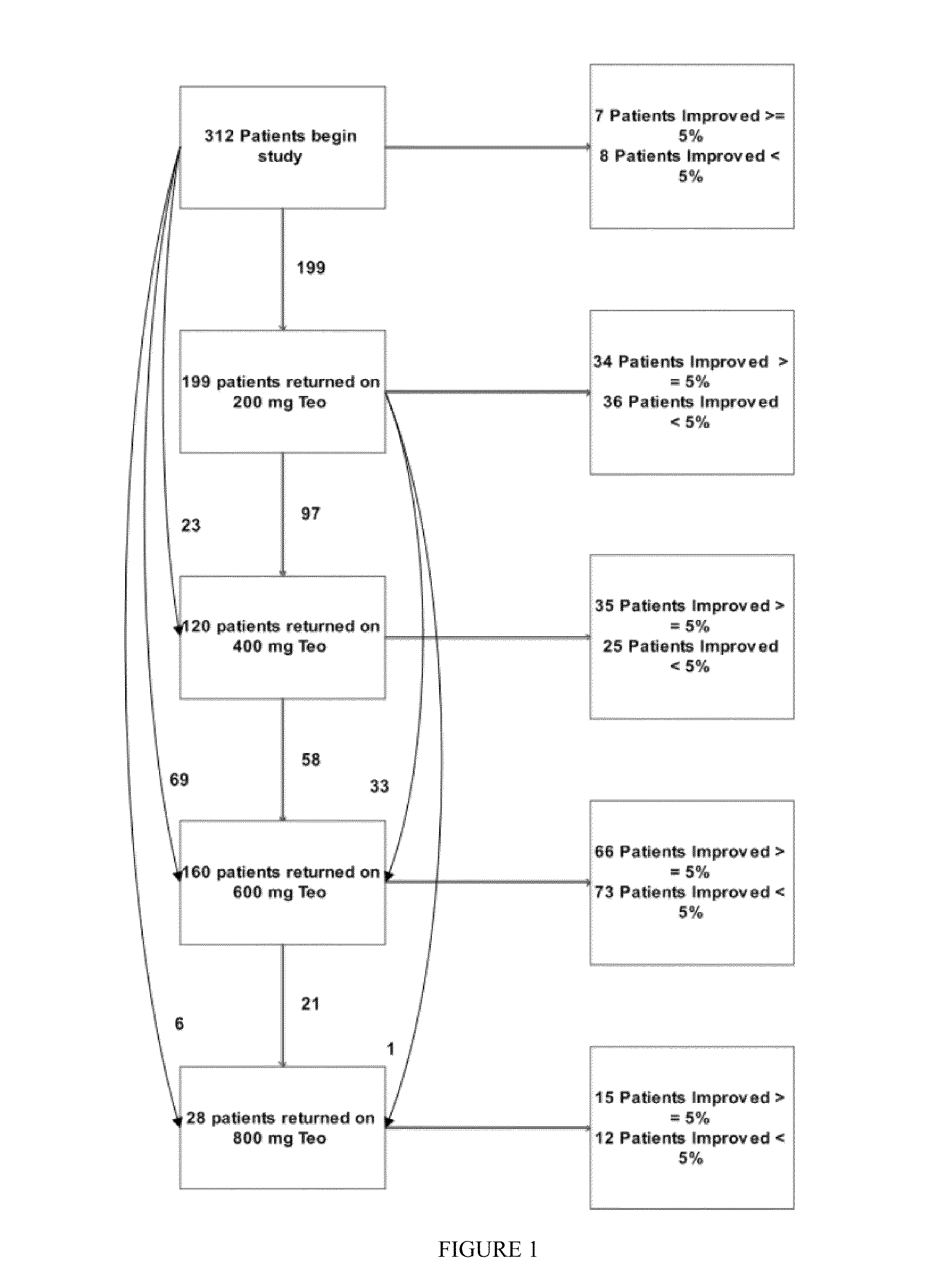
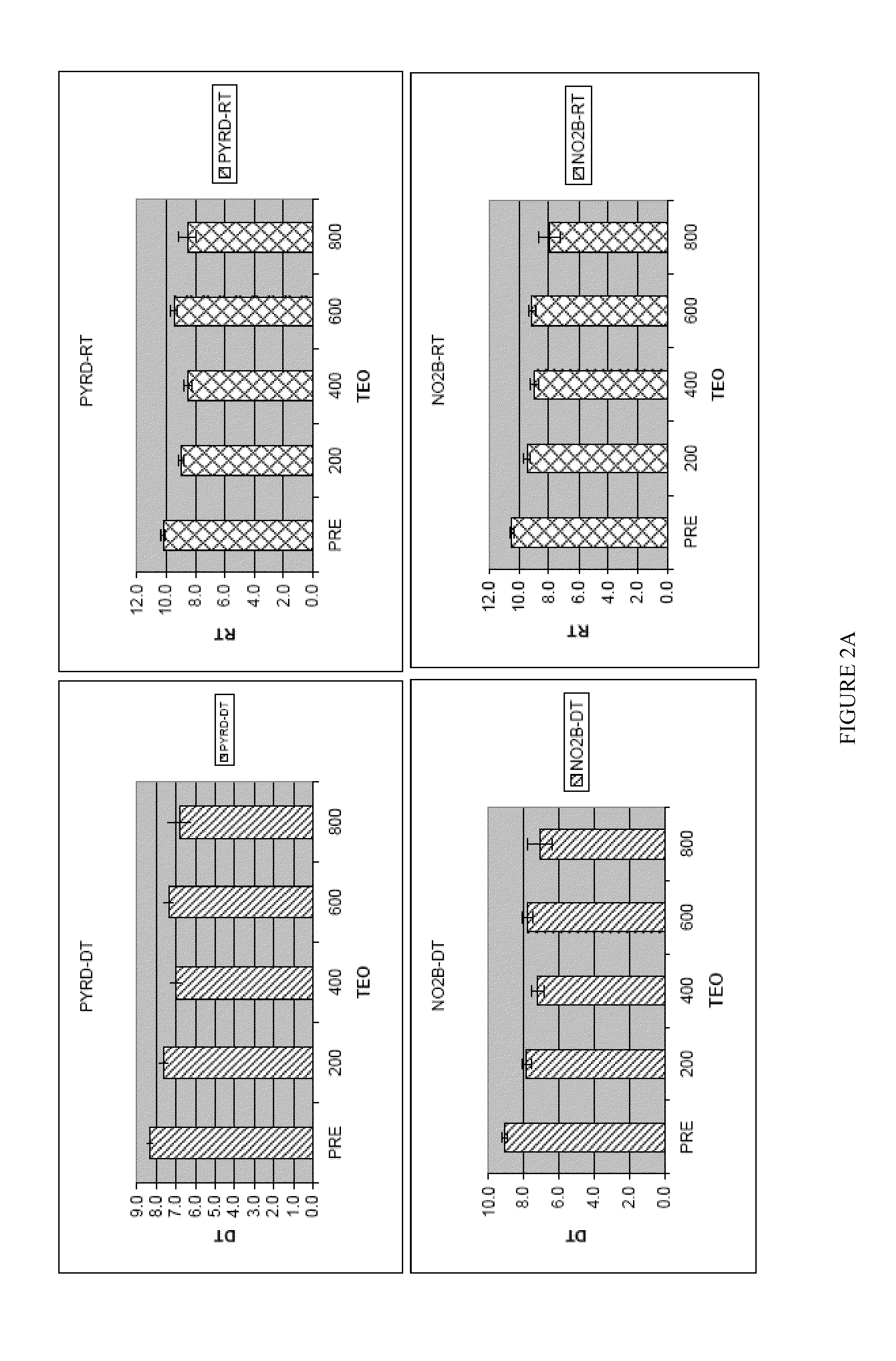
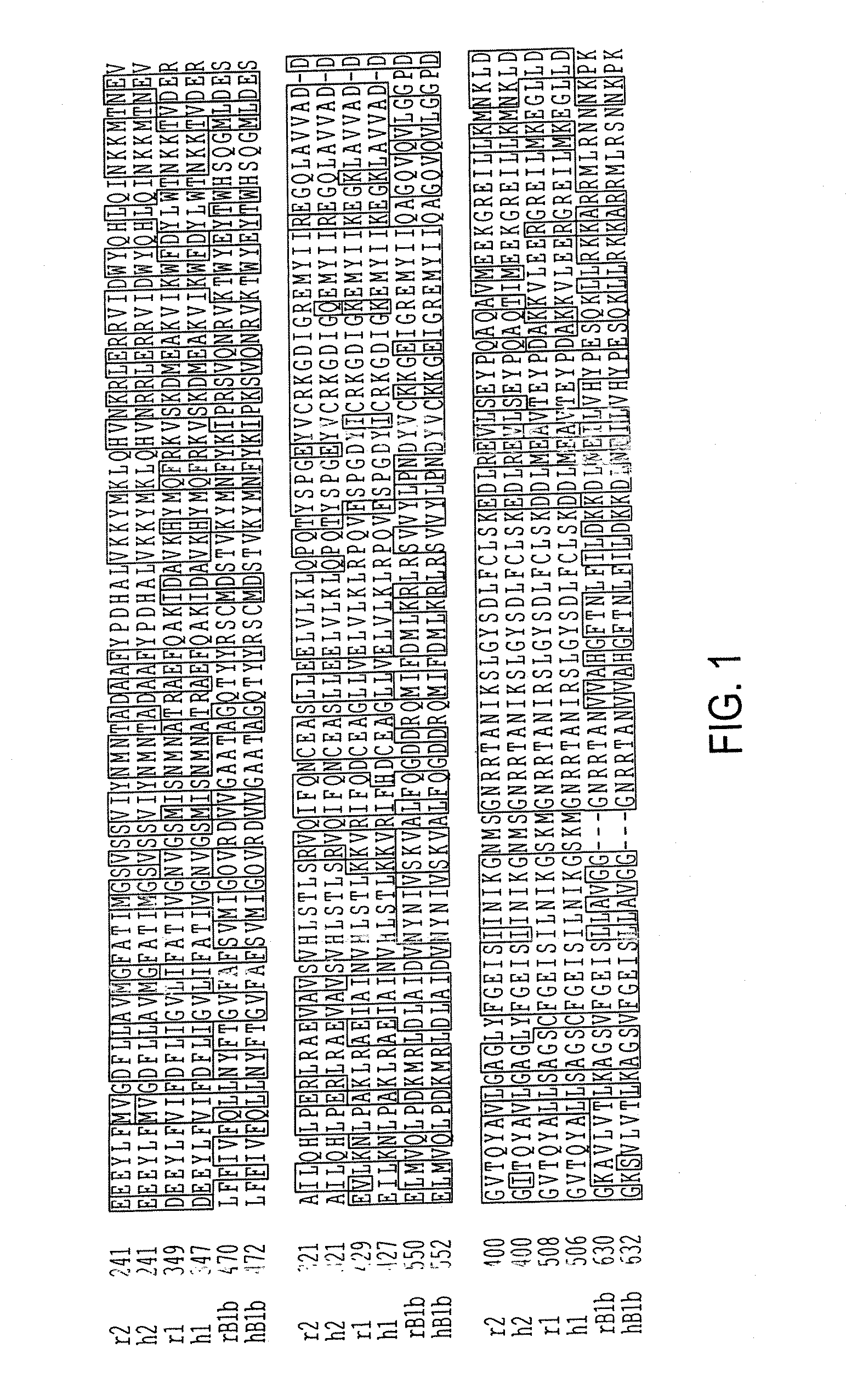
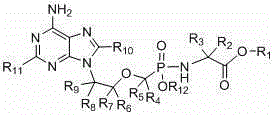
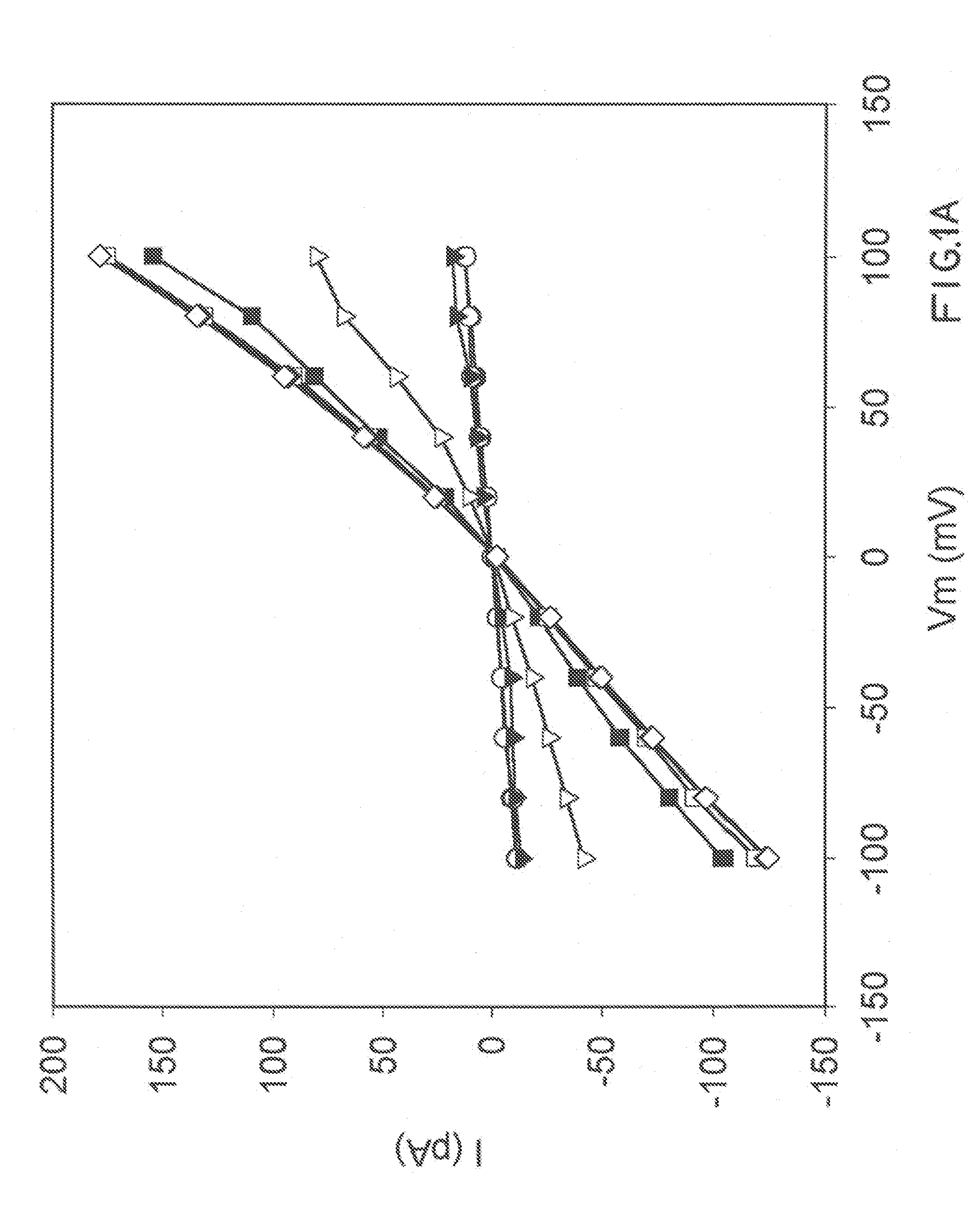
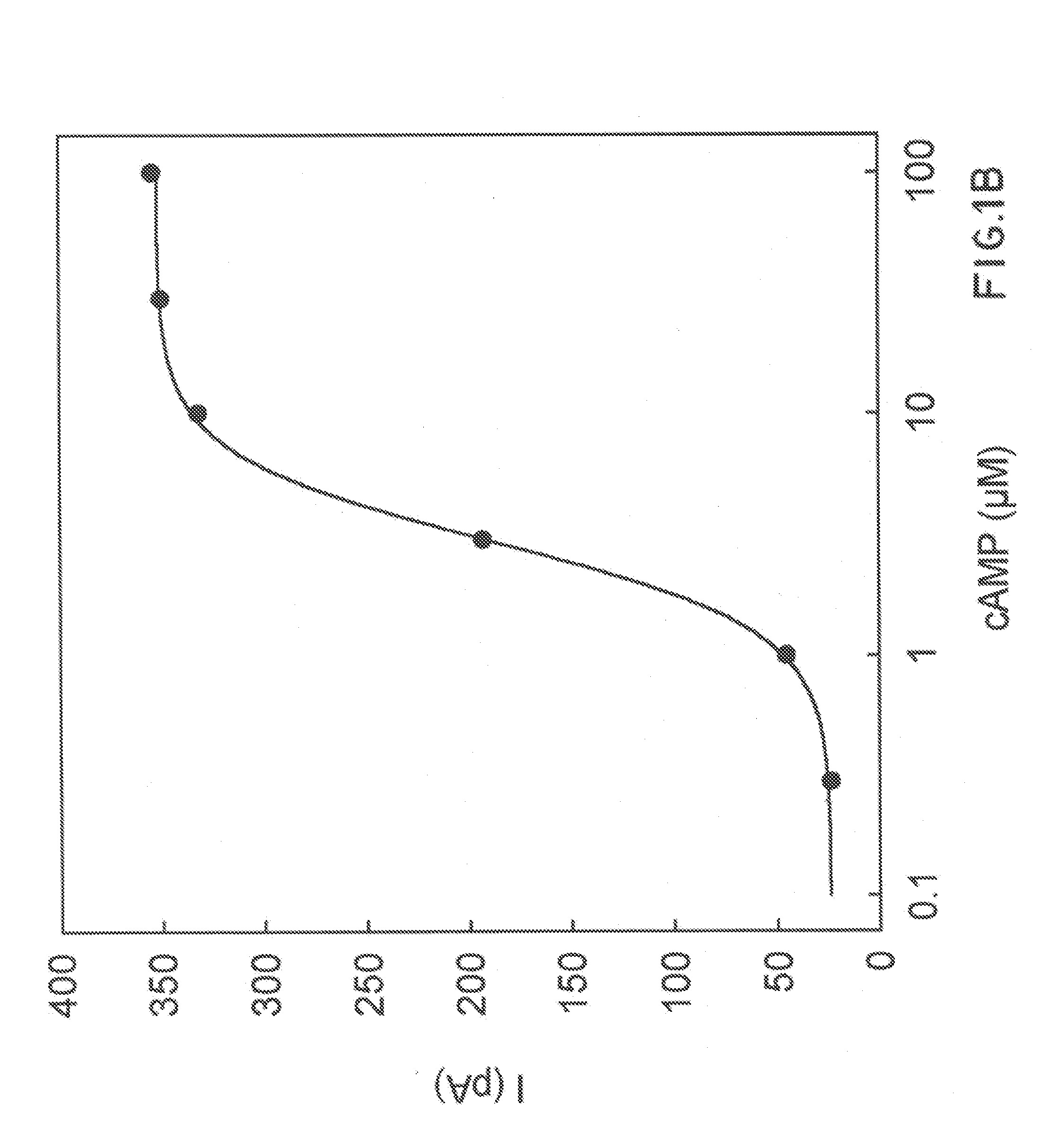
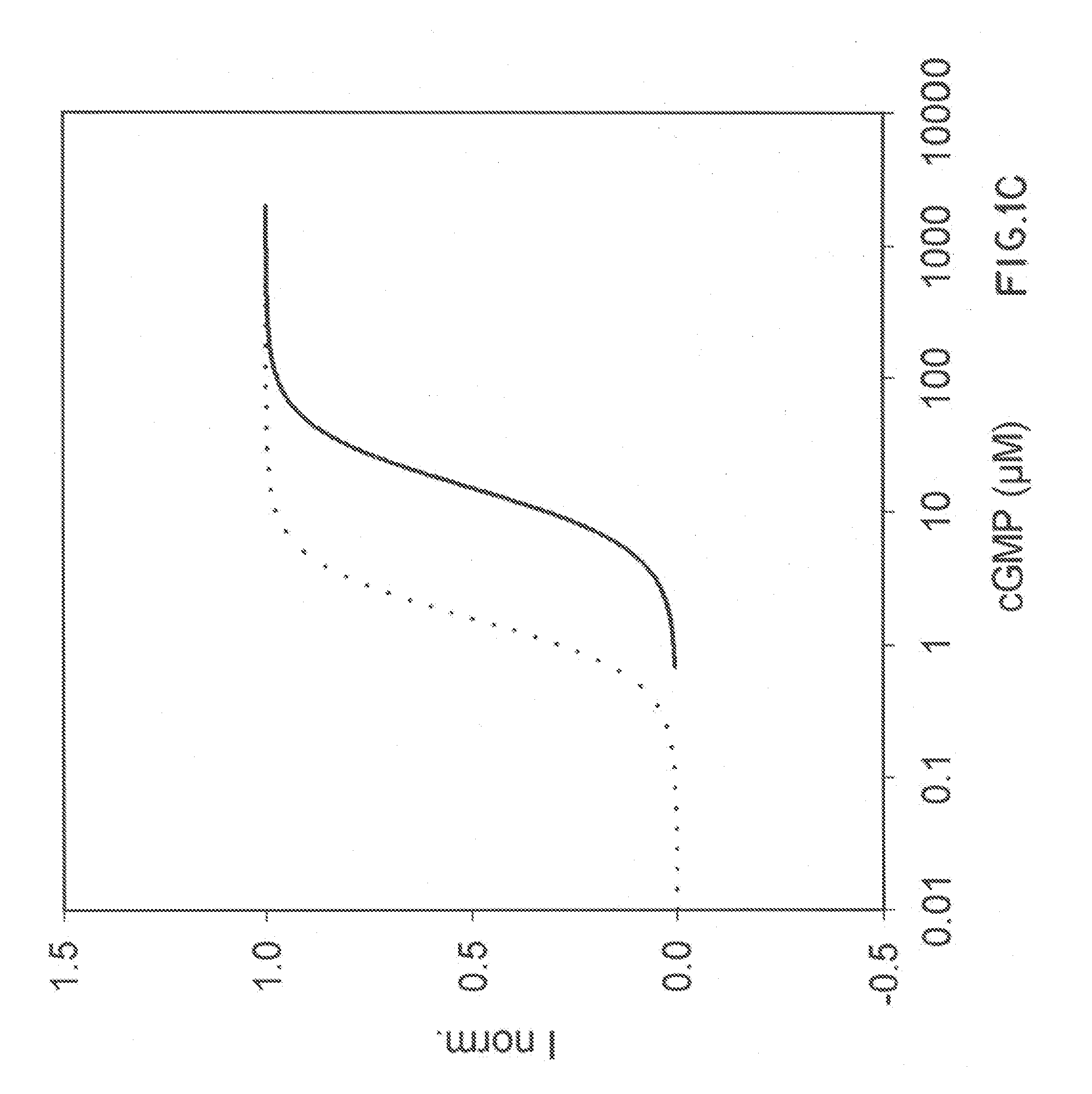
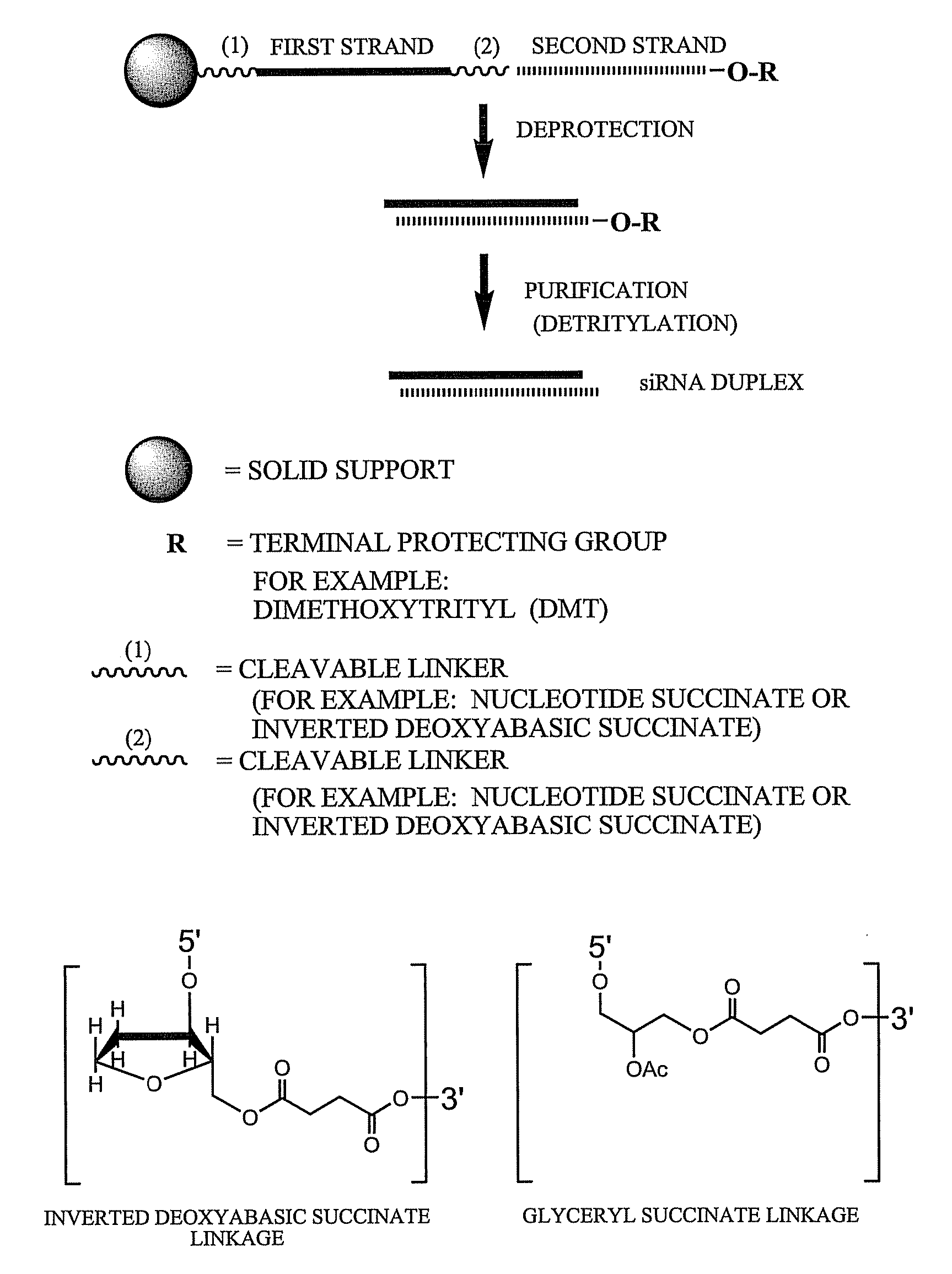
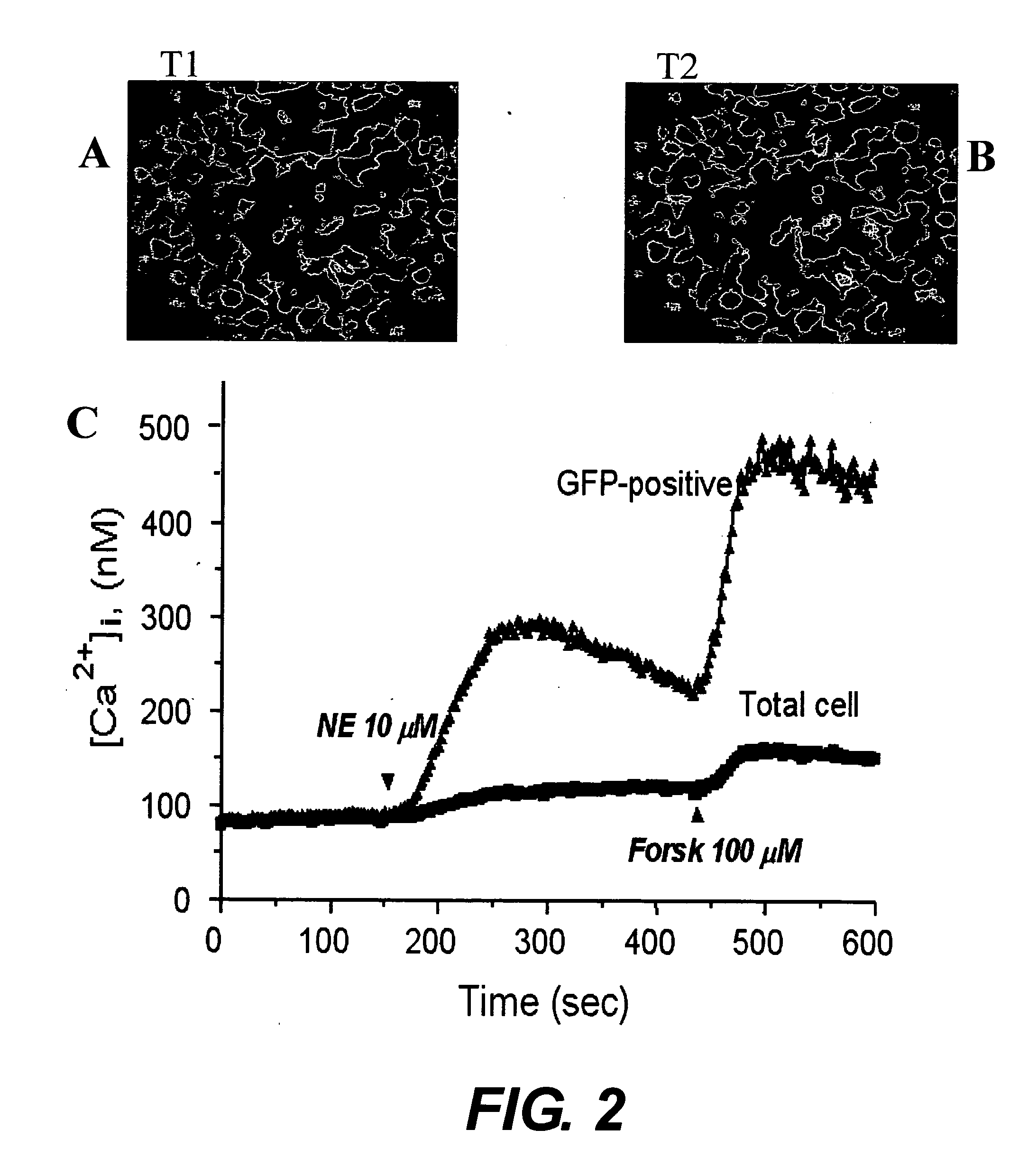
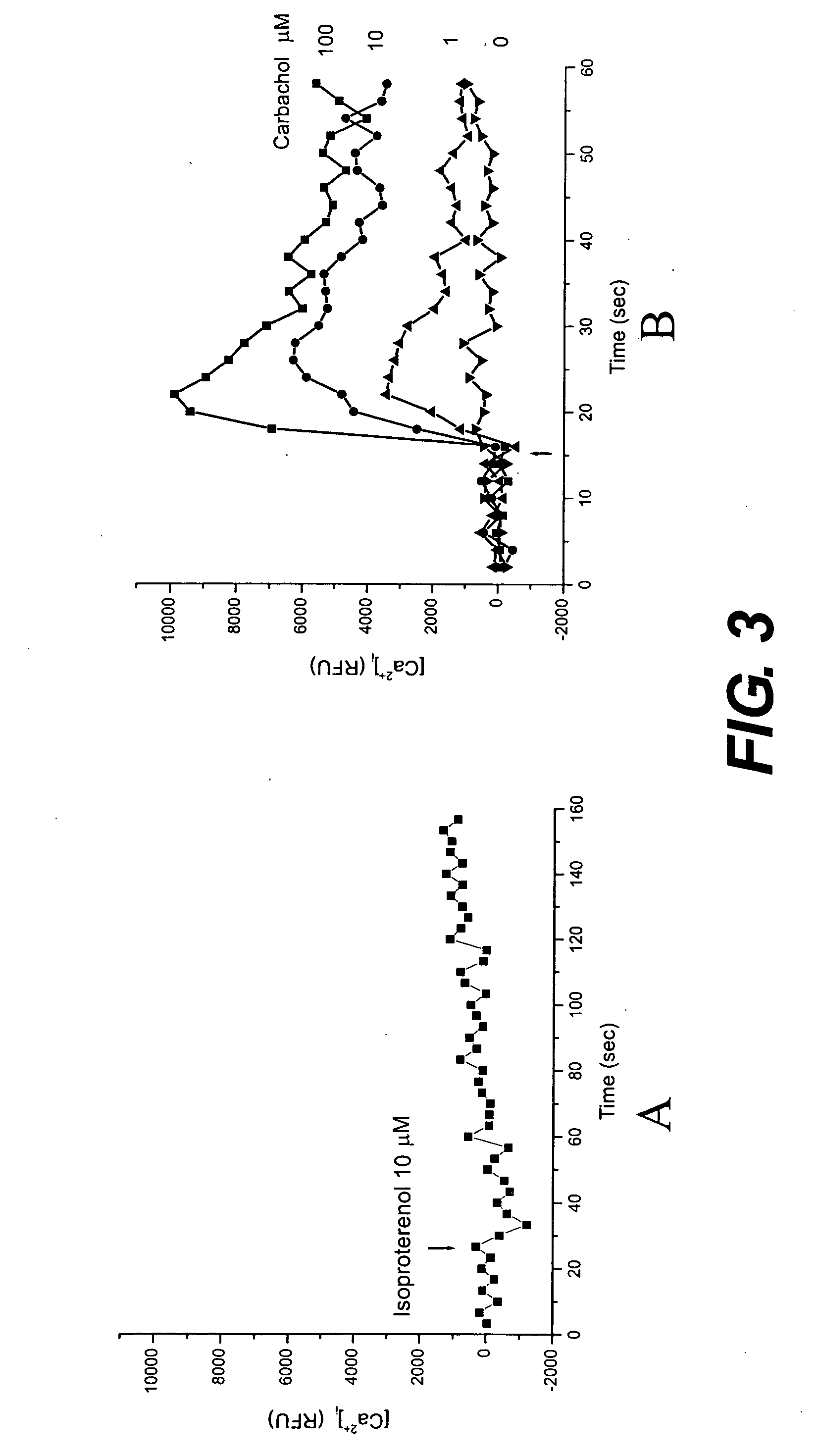
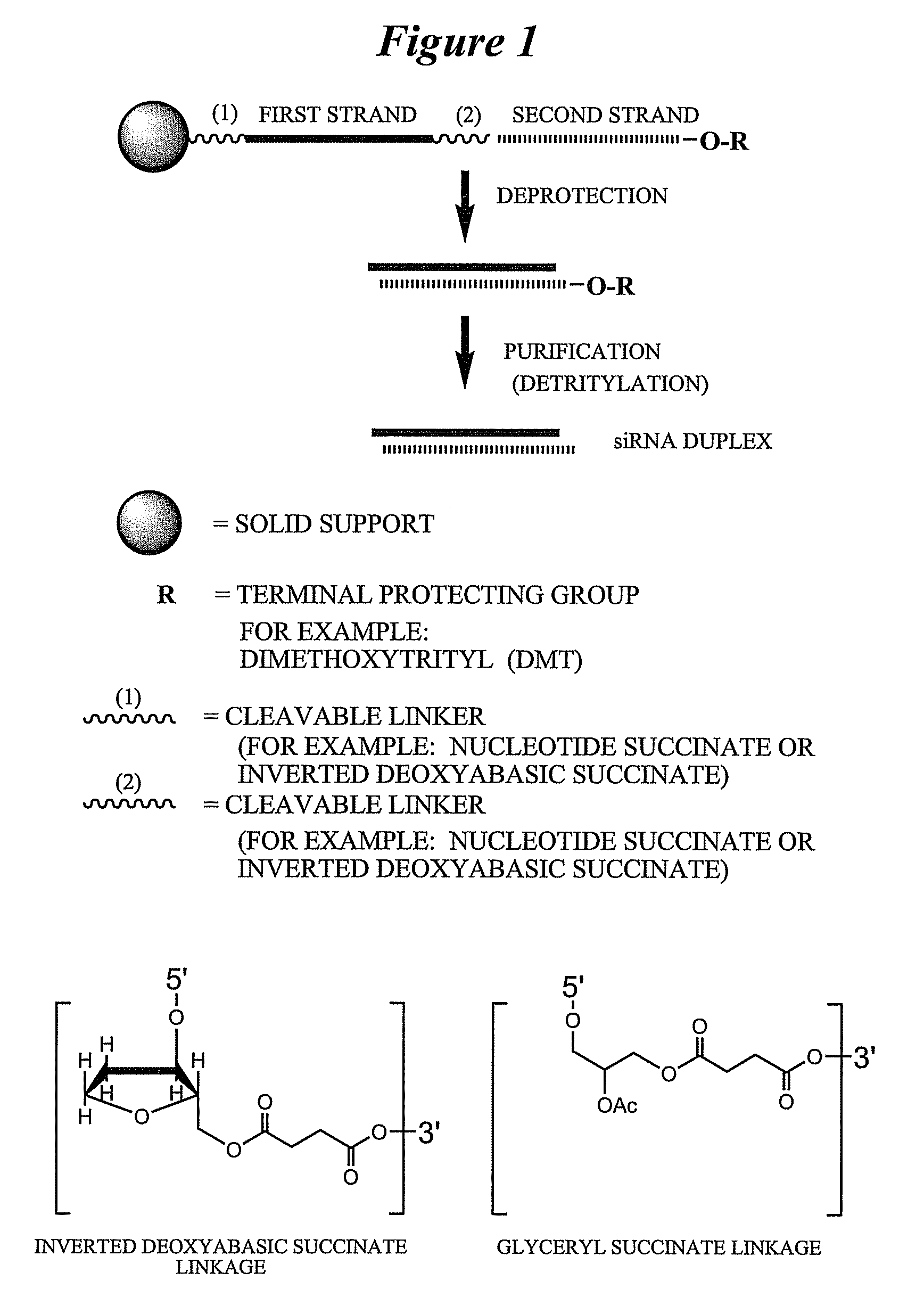
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Cyclic nucleotide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cyclic nucleotide (cNMP) is a single-phosphate nucleotide with a cyclic bond arrangement between the sugar and phosphate groups. Like other nucleotides, cyclic nucleotides are composed of three functional groups: a sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a single phosphate group. As can be seen in the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) images, the 'cyclic' portion consists of two bonds between the phosphate group and the 3' and 5' hydroxyl groups of the sugar, very often a ribose.
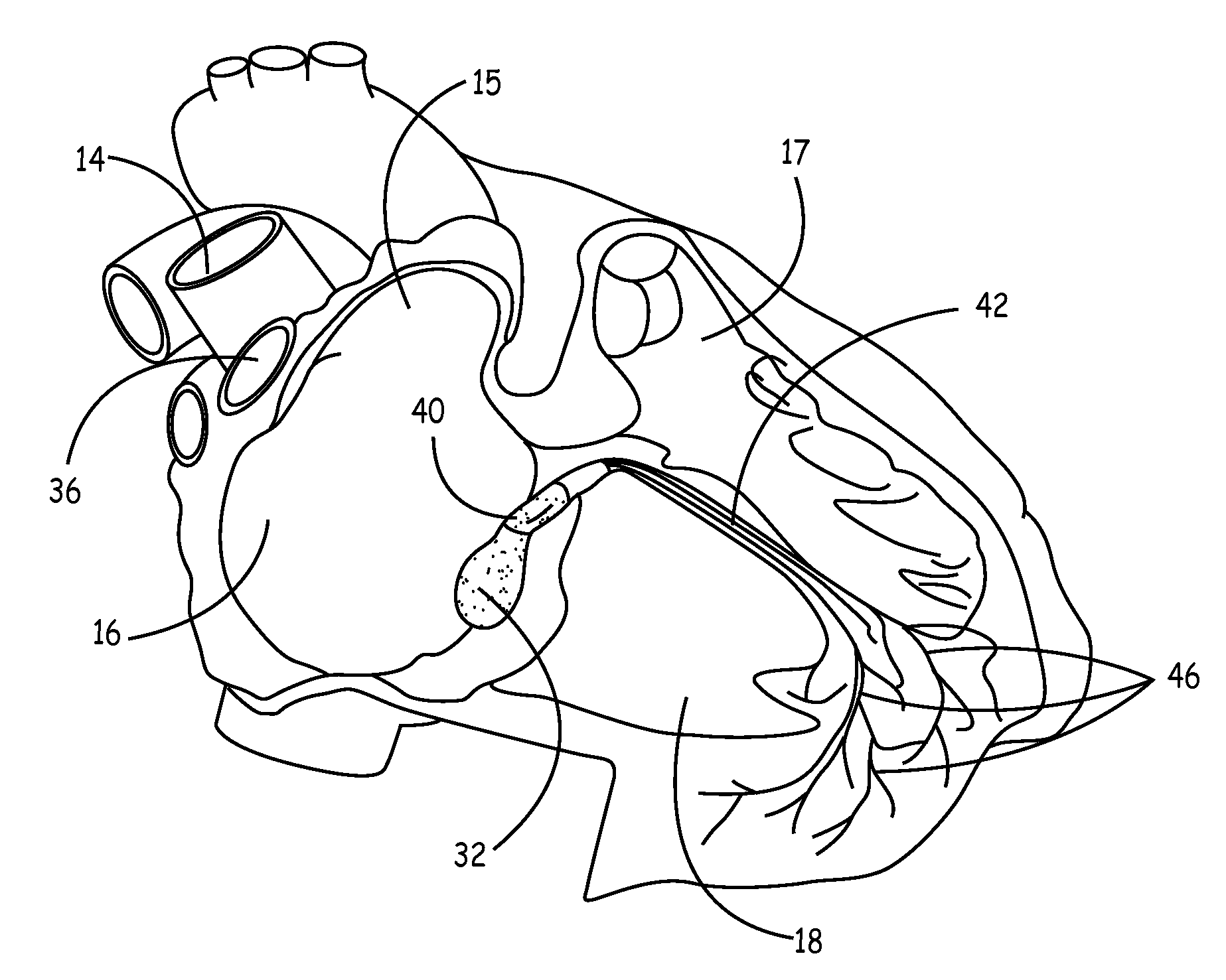
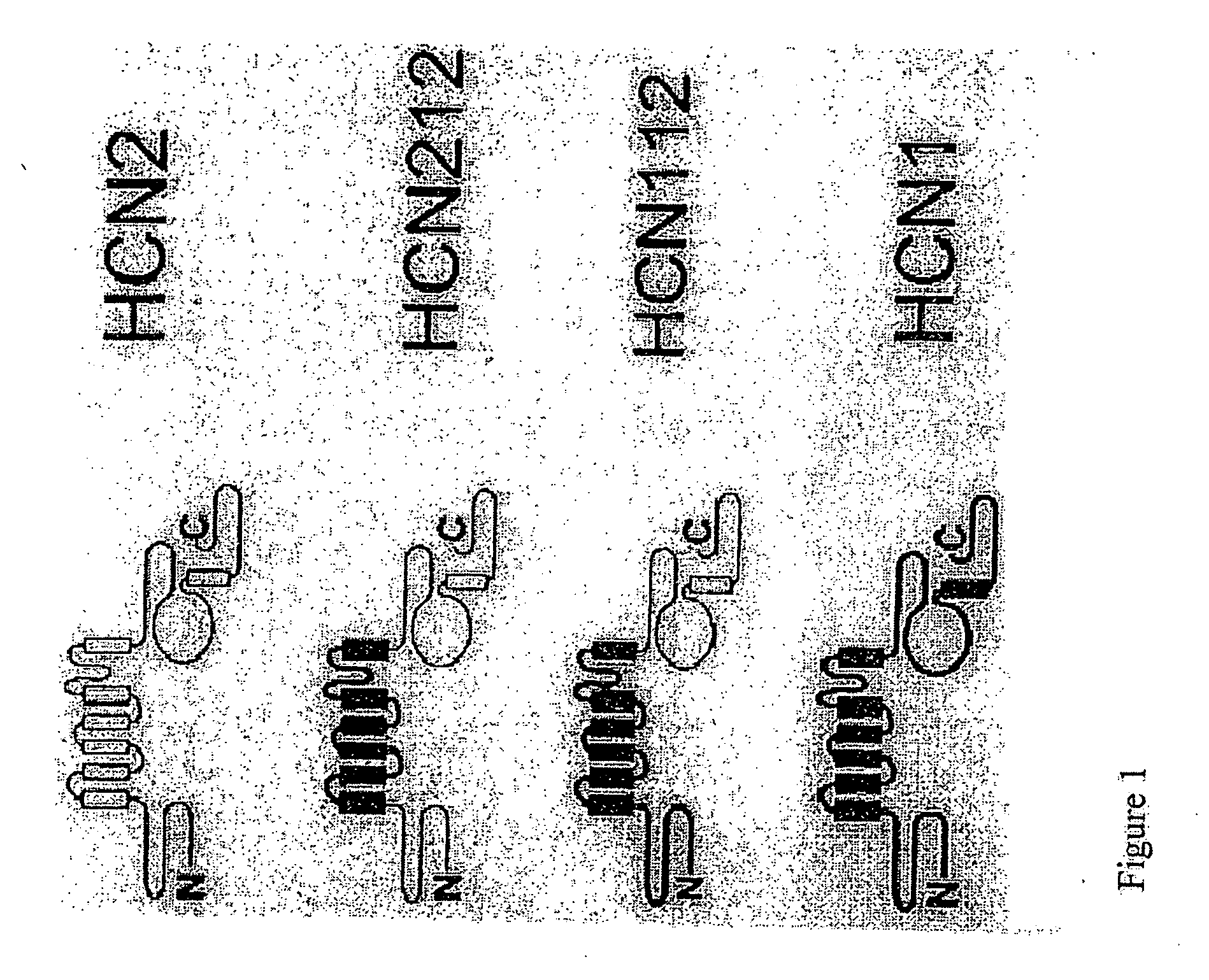
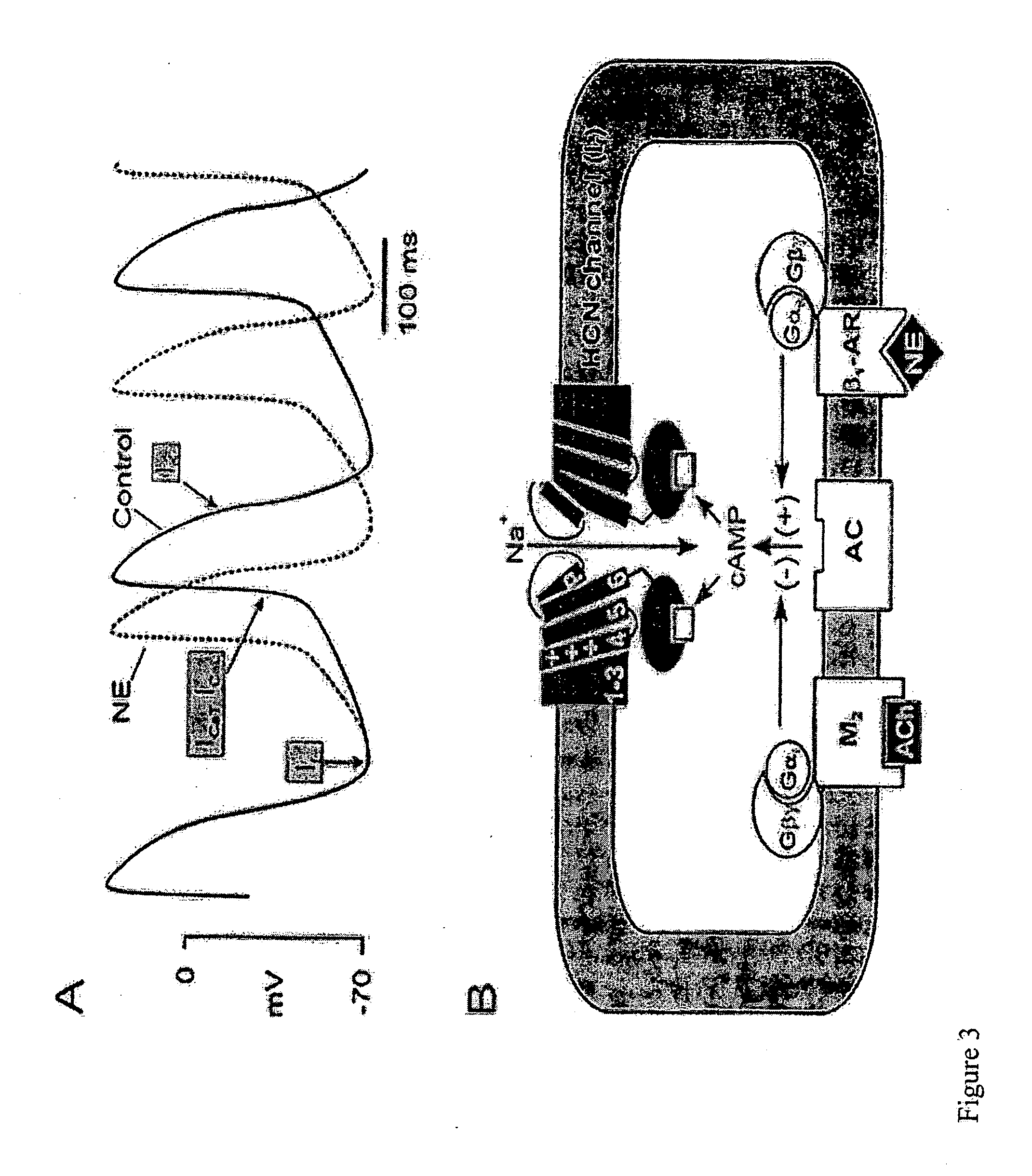
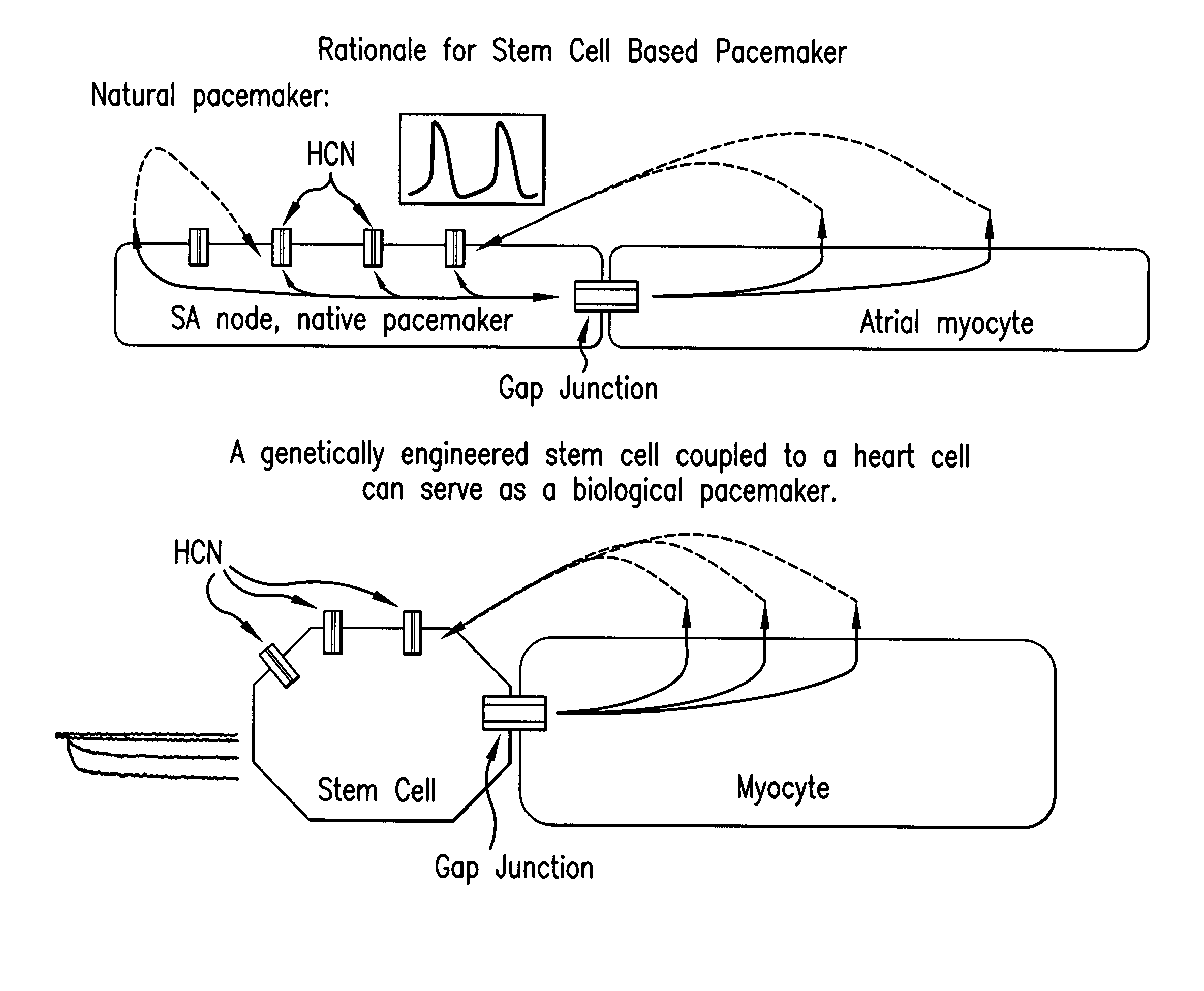
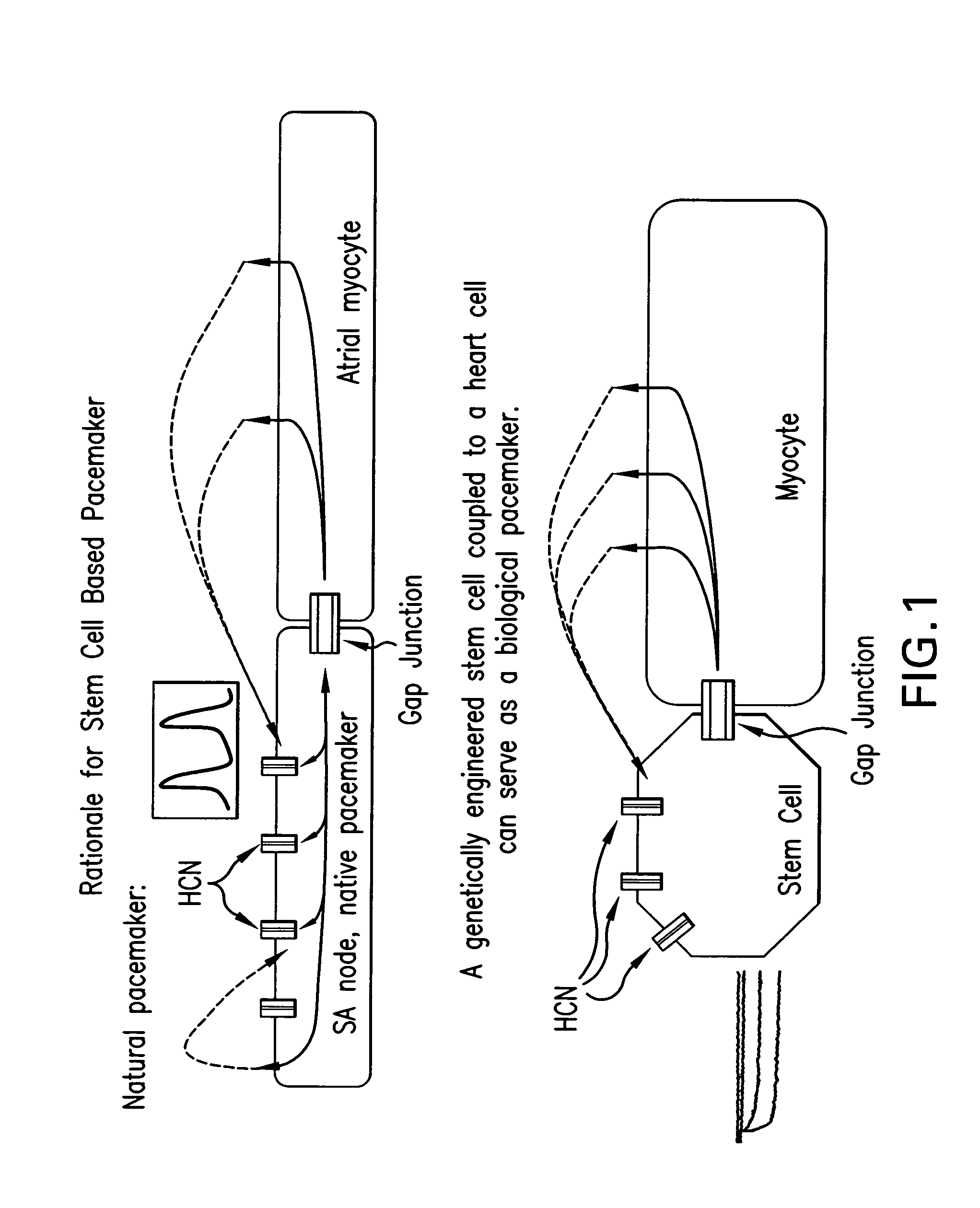
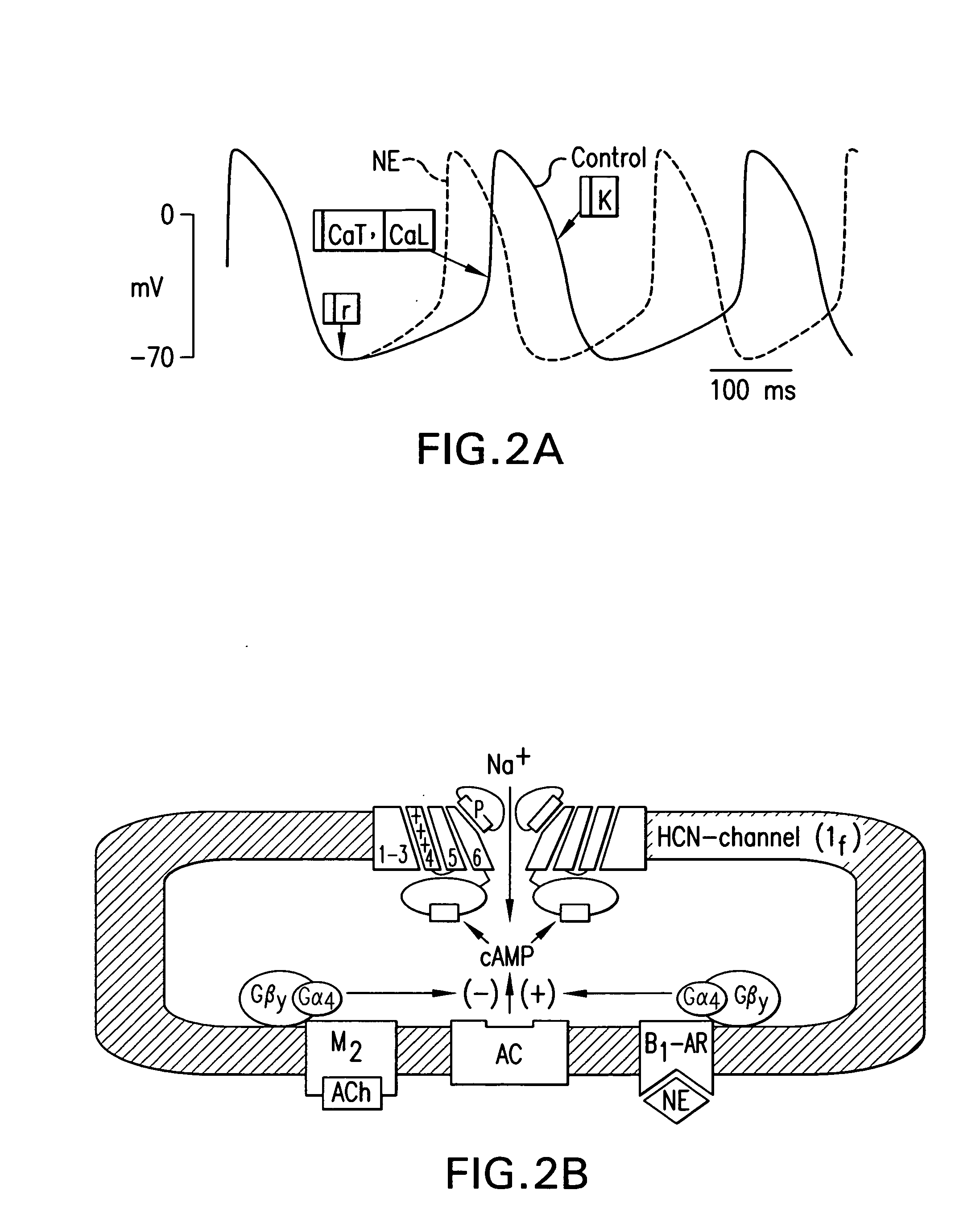
Biological pacemakers including mutated hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) channels
A composition for implantation into cardiac tissue includes a biological pacemaker that, when implanted, expresses an effective amount of a mutated hyperpolarization-activated and cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) isoform to modify Ih when compared with wild-type HCN. Methods for implementing each of the biological pacemakers include implanting each of biological pacemakers into cardiac tissue.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
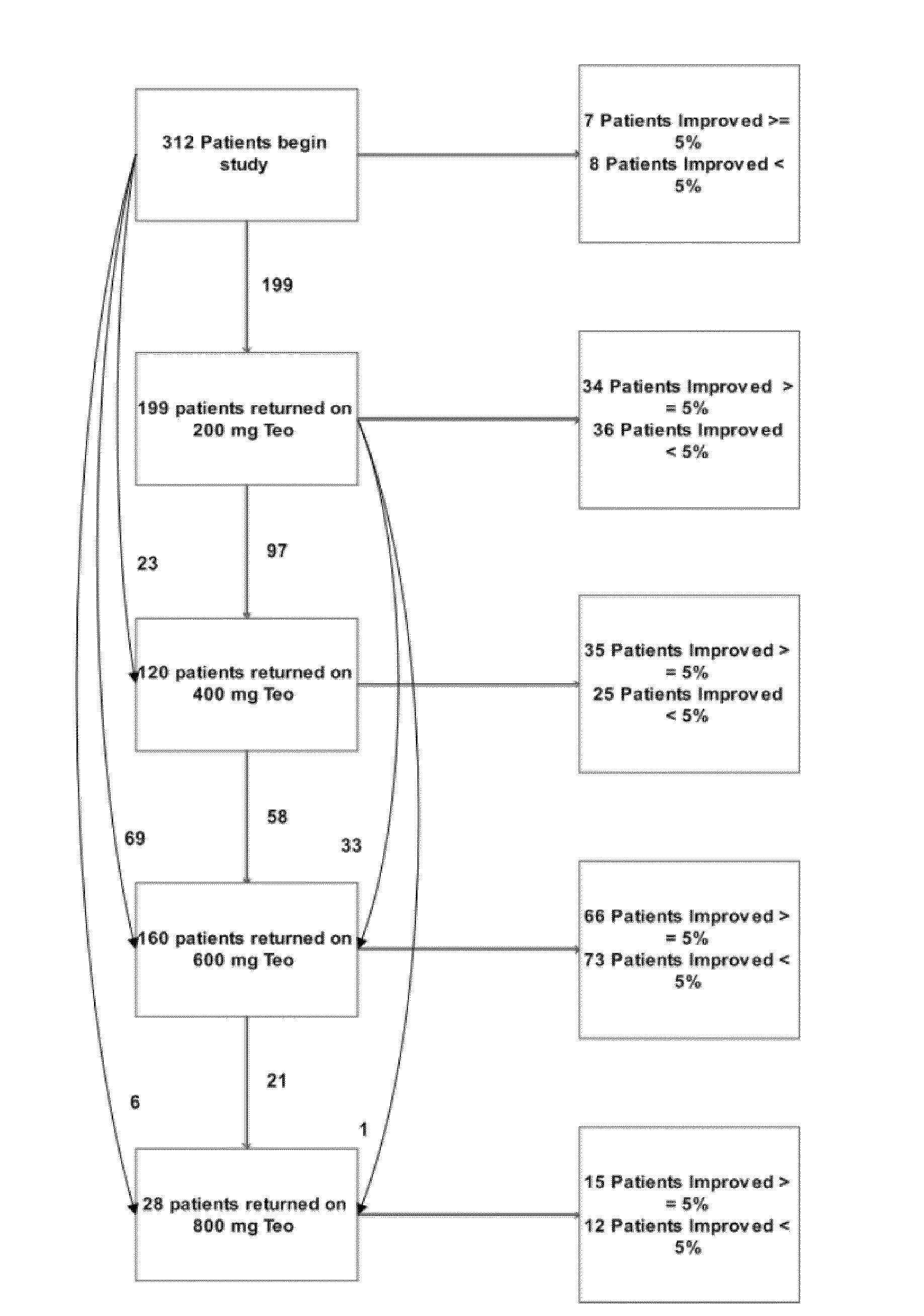
Phosphodiesterase inhibitor treatment
ActiveUS20100022563A1Great tasteImprove the level ofBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePhosphodiesterase inhibitor
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the treatment of diseases or conditions produced by or associated with low cyclic nucleotide levels. The compositions comprise phosphodiesterase inhibitors and are formulated for intranasal and pulmonary administration.
Owner:CYRANO THERAPEUTICS INC
Expression of functional human olfactory cyclic nucleotide gated (CNG) channel in recombinant host cells and use thereof in cell based assays to identify smell modulators
ActiveUS20110224095A1High sensitivityFungiCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMammalG protein-coupled receptor
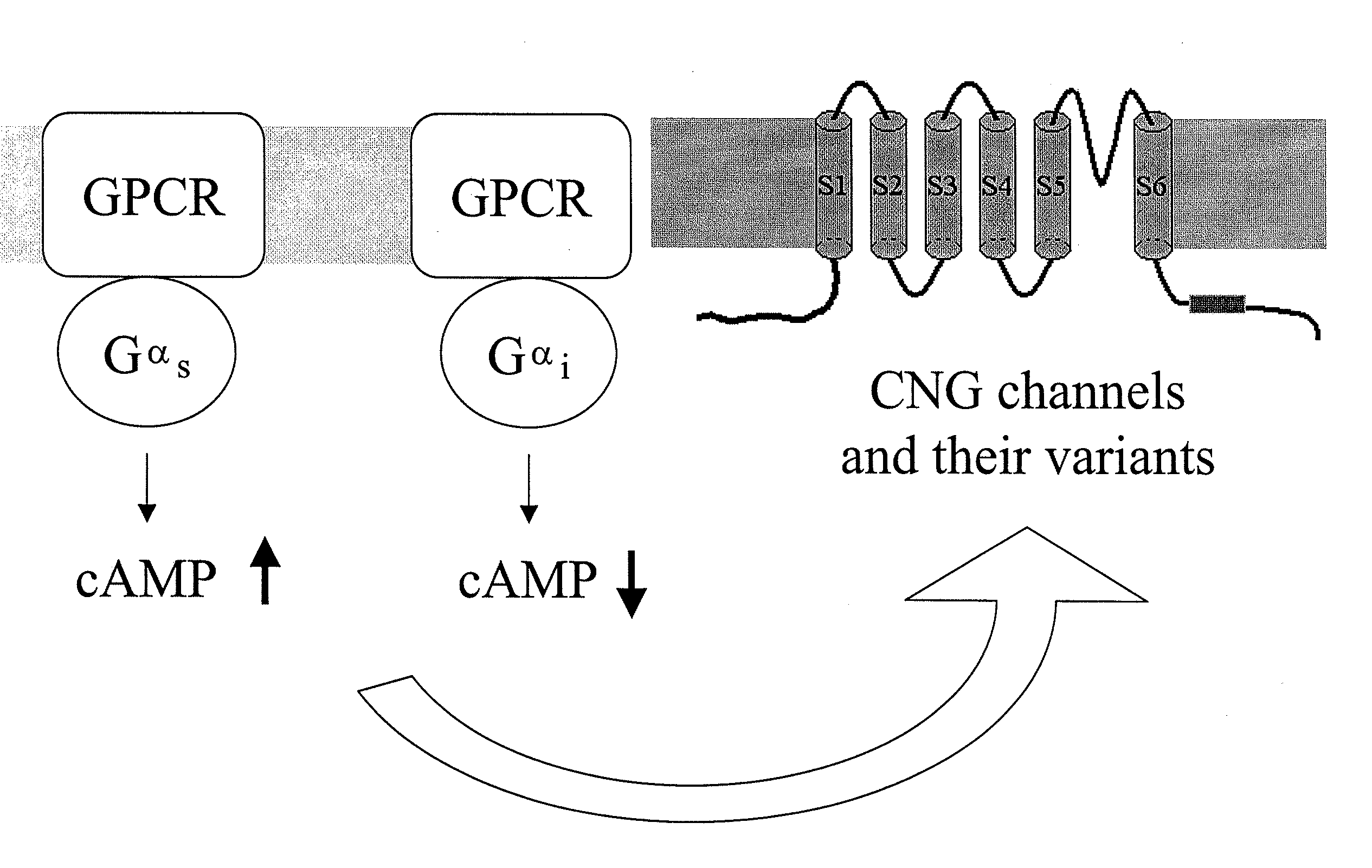
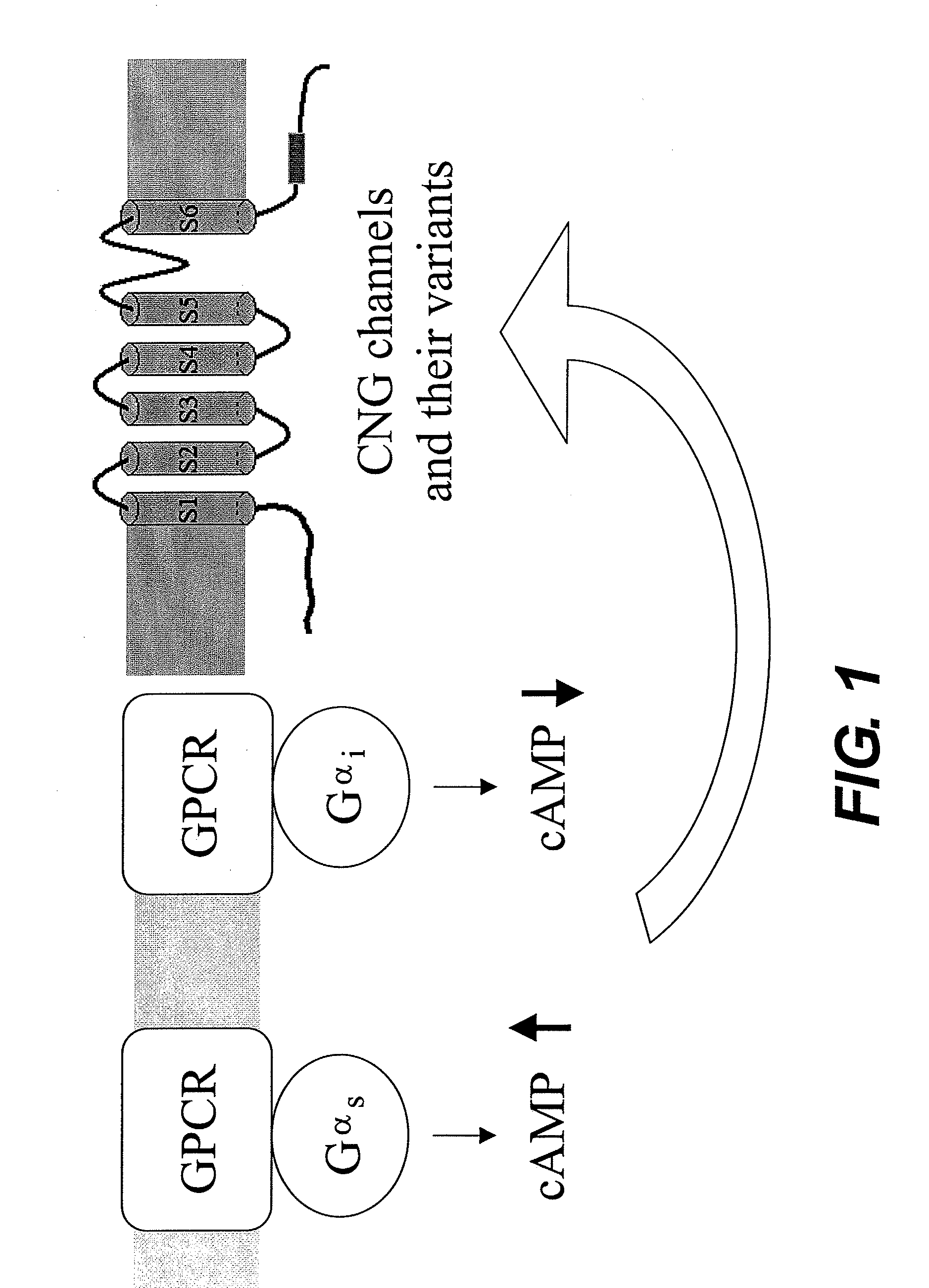
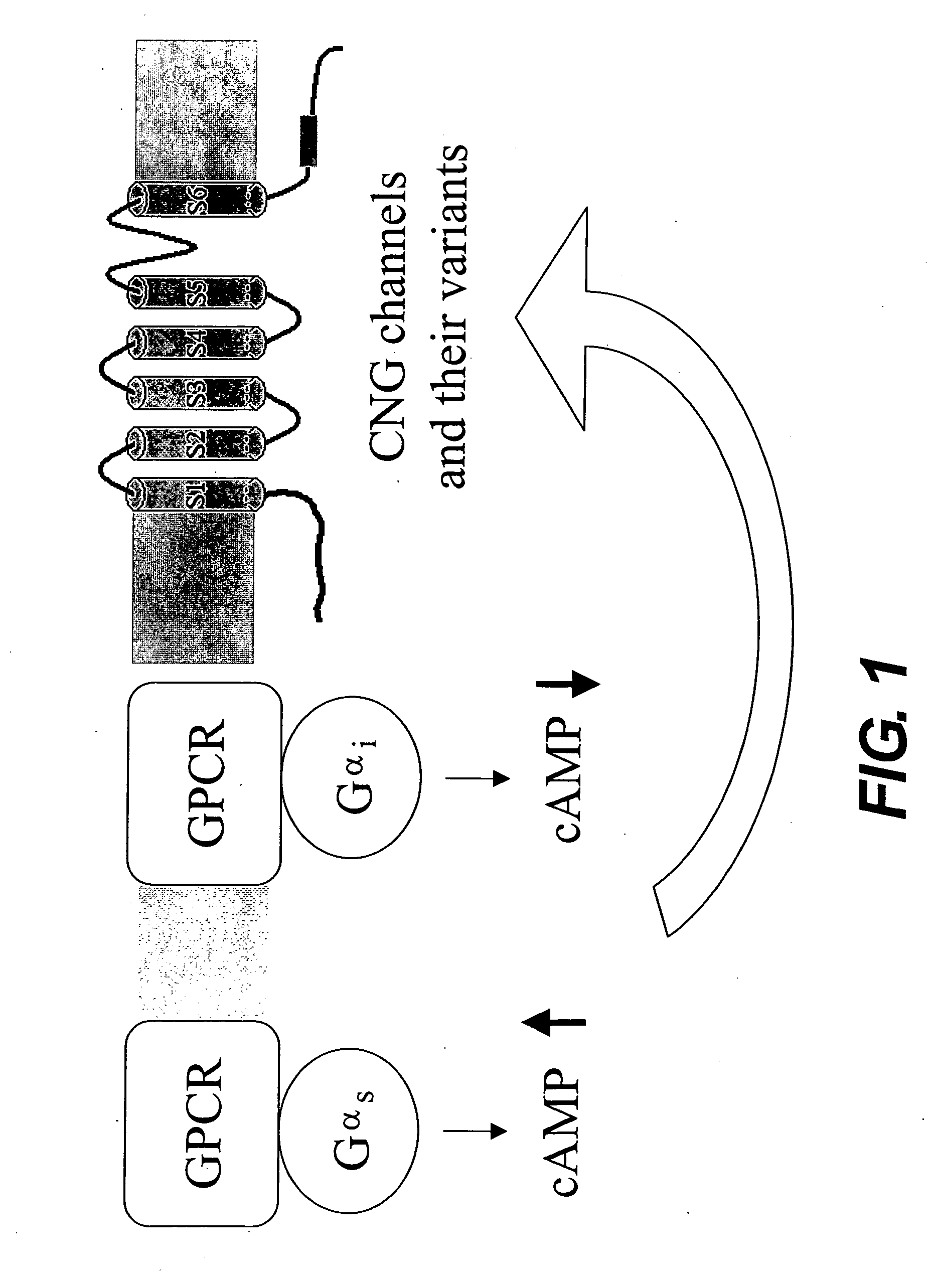
The present invention relates to isolated nucleic acid sequences that encode human olfactory cyclic nucleotide gated (CNG) channel subunits, and the corresponding polypeptides. The invention further relates to the use of human CNG channels to profile, screen for, and identify compounds that modulate the human olfactory CNG channel. More specifically, the invention relates to the expression of the human olfactory CNG channel in cells, preferably mammalian cells, and the use of these cells in high throughput cell-based assays to identify compounds that enhance or block human olfactory CNG function. Compounds that activate the olfactory CNG channel will enhance smell and can be used to make foods more palatable for individuals with attenuated olfactory function. Conversely, compounds that inhibit the olfactory CNG channel will inhibit smell and can be use to block malodors. Additionally, the invention relates to the use of cell-based olfactory CNG channel assays to identify modulates of G-protein coupled receptor (GPCRs) and other proteins that regulate cyclic nucleotide levels.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
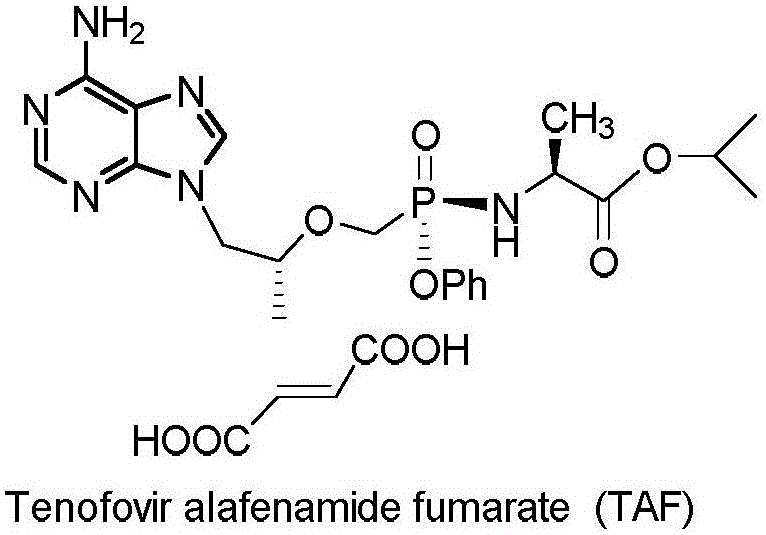
Preparation of non-cyclic nucleotide phosphoamides and salts thereof and application of non-cyclic nucleotide phosphoamides and salts thereof in aspect of antivirus
ActiveCN105669751AIntellectual property enhancementReduce exposureOrganic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsViral infectious diseaseSolvent
The invention belongs to the field of antivirus in medical chemistry, and relates to preparation of non-cyclic nucleotide phosphoamides and salts thereof and application of the non-cyclic nucleotide phosphoamides and salts thereof in treating human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B, hepatitis B virus (HBV) and other virus infection diseases. The non-cyclic nucleotide phosphoamides, and isomers, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates or crystals thereof have the general formula I of which the structure is disclosed in the specification. The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition containing the compounds and isomers, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, hydrates, solvates or crystals thereof, and application of the compounds or composition in treating and / or preventing HIV and HBV infection. The compounds provided by the invention have the advantages of favorable anti-HIV and HBV activities, low oral dosage and low toxicity.
Owner:洛阳聚慧新材料科技有限公司
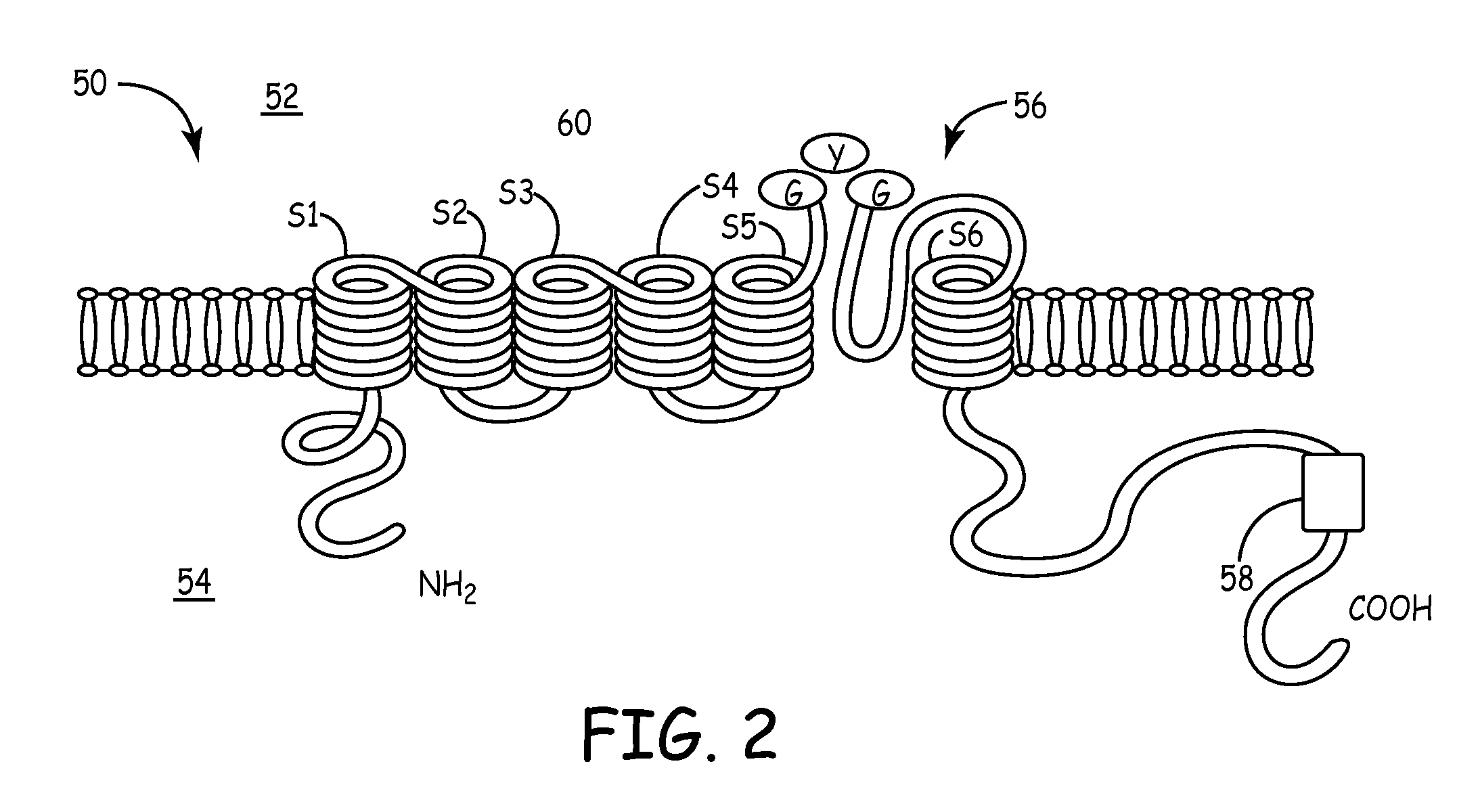
Chimeric HCN channels
InactiveUS20070099268A1Fast dynamicsMore positive activationCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCardiac pacemaker electrodeCyclic nucleotide
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
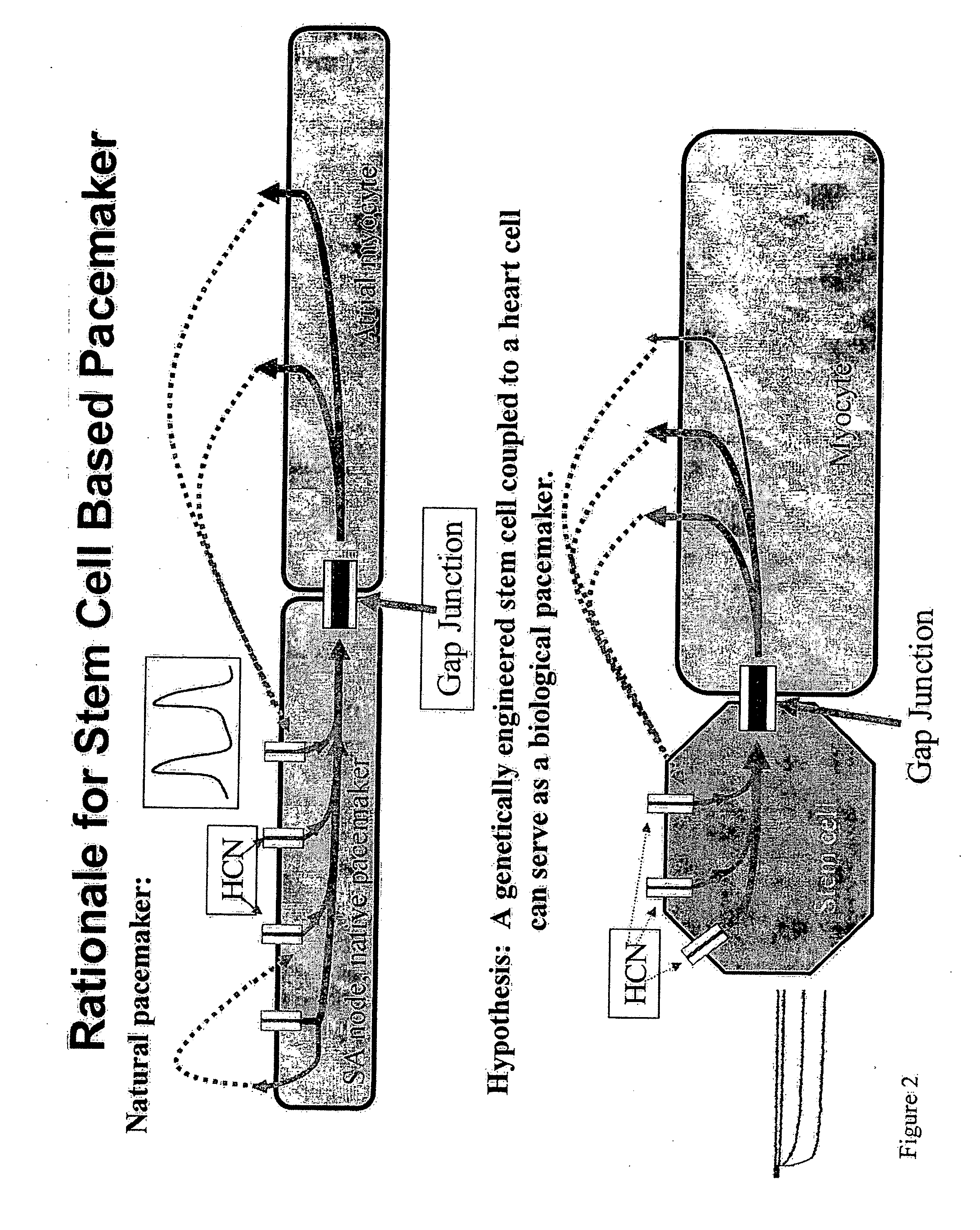
Tandem cardiac pacemaker system
InactiveUS20090053180A1High basal signal frequencyLess negative maximum diastolic potentialBiocideGenetically modified cellsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac pacemaker
This invention provides pacemaker systems comprising (1) an electronic pacemaker, and (2) a biological pacemaker, wherein the biological pacemaker comprises a cell that functionally expresses a chimeric hyperpolarization-activated, cyclic nucleotide-gated (HCN) ion channel at a level effective to induce pacemaker current in the cell. The invention also provides related biological pacemakers, atrioventricular bridges, methods of making same, and methods of treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac rhythm disorder.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +2
Separating and extracting method for date cyclic nucleotide syrup, dietary fibre and date wax
InactiveCN1408257AOvercome high sugarOvercome the disadvantage of high calorieSugar derivativesFood preparationWaxOrganic solvent
The pulp of ripe data, after being dried, cooled and crushed, is ethanol extracted; the residual dreg after ethanol extraction is steamed and dried to produce dietary fiber powder; the extracted liquid is concentrated to recover ethanol and extracted with organic solvent to separate data wax; and the raffinate is concentrated to obtain date cyclic nucleotide syrup. The said process can produce several kinds of data products of different active components and different physical and chemical property, and the data products include functional health dietary fiber and date cyclic nucleotide syrup as tonic for people with delicate constitution.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Tumor marker for ovarian cancer diagnosis
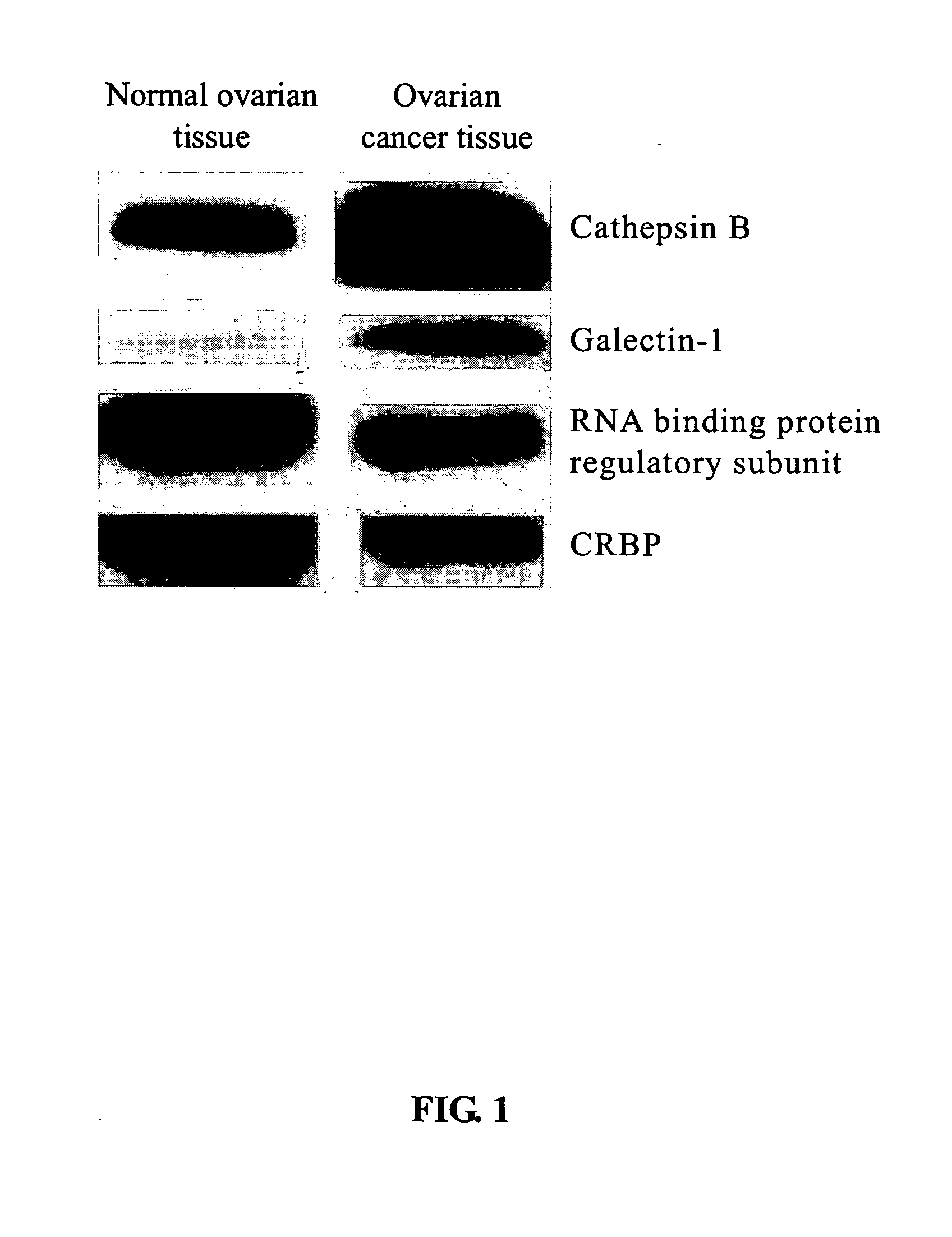
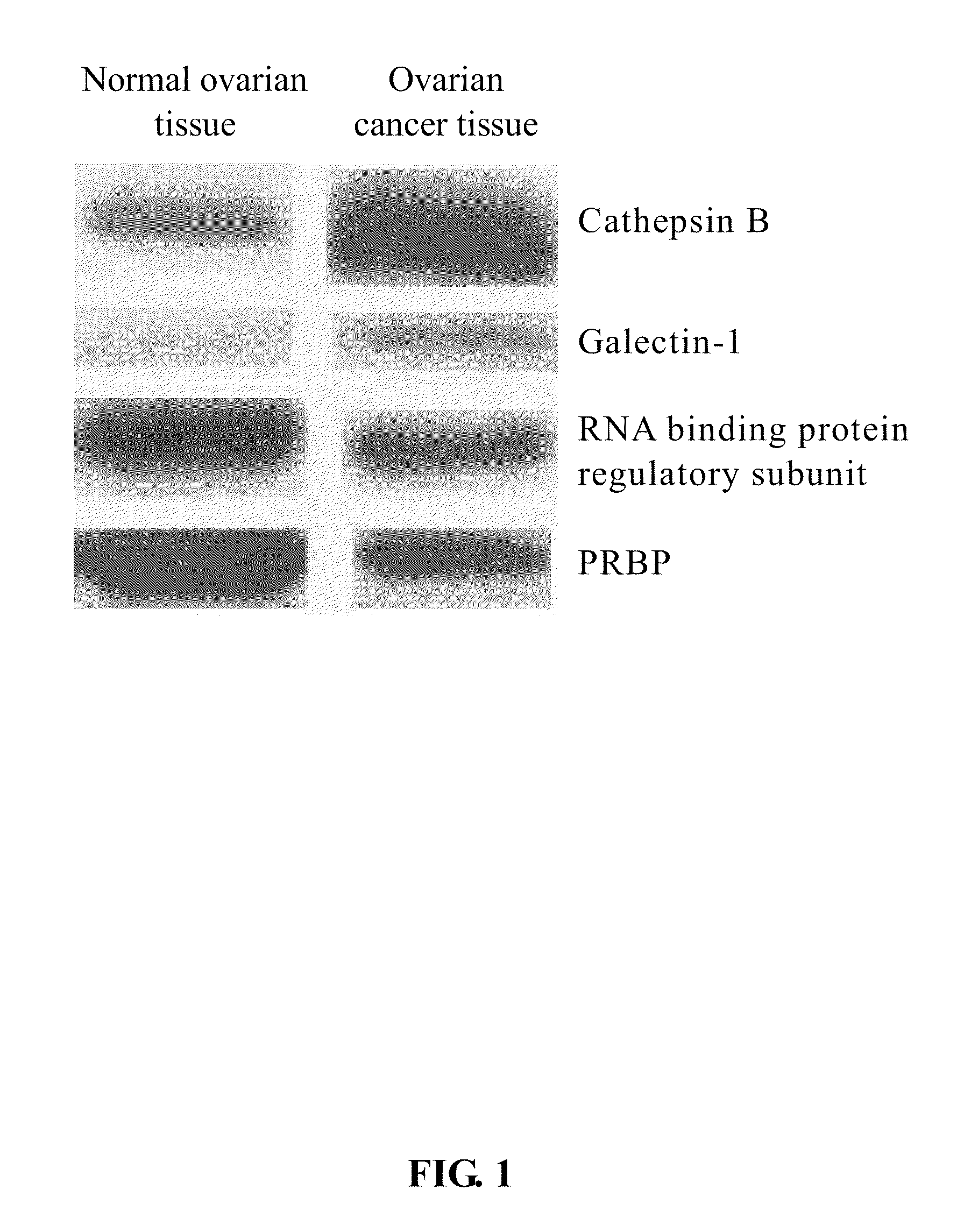
InactiveUS20070134689A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisAbnormal tissue growthCathepsin B
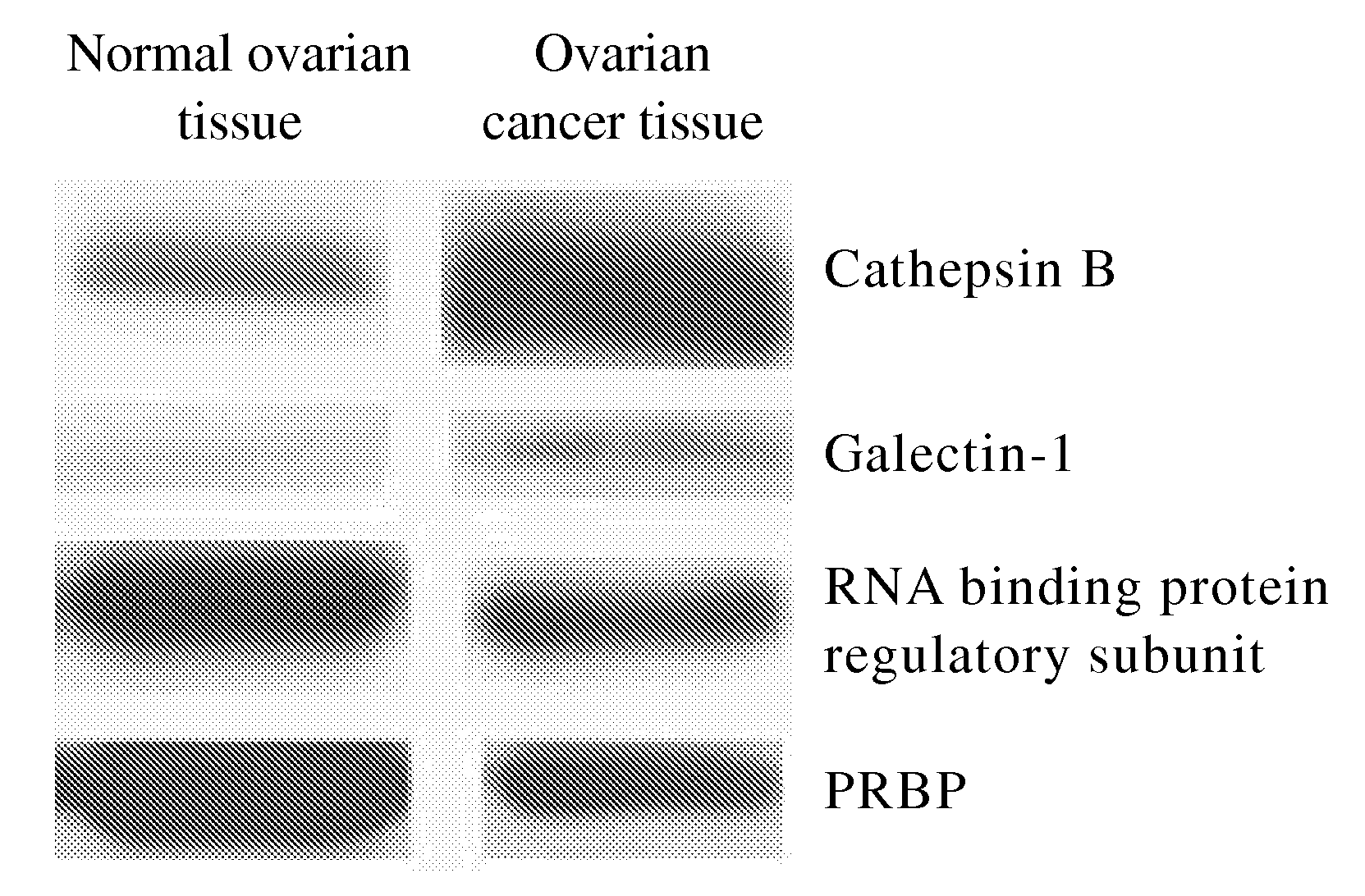
The present invention relates to a tumor marker for diagnosis of ovarian cancer, which is selected from the group consisting of alectin-1, cathepsin B, MHC class I antigen, heat shock protein (HSP) 27, ubiquitin carboxy-termal esterase L1, cellular retinol-binding protein (CRBP), transthyretin, SH3 binding glutamate-rich protein, tubulin-specific chaperone A, RNA binding protein regulatory subunit, γ-actin, tropomyosin and calcium / calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphatase. The ovarian cancer is diagnosed effectively and efficiently based on detecting the expression levels of the tumor markers in the invention from the ovarian tissue sample of an individual to be diagnosed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
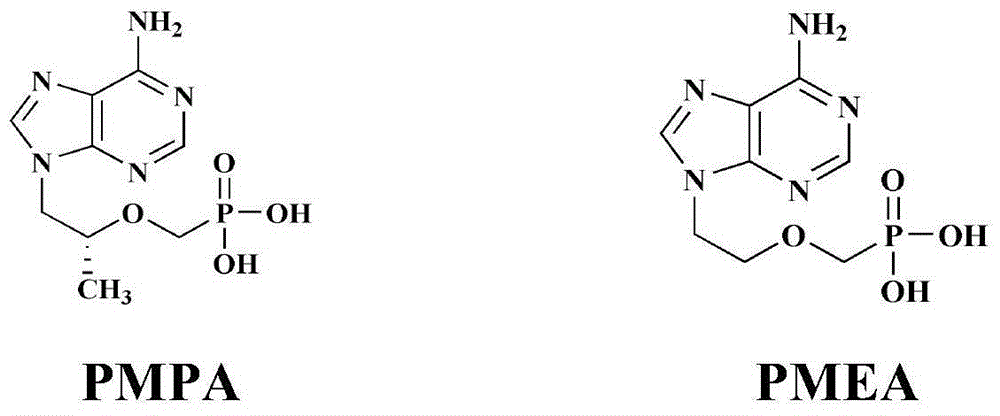
Novel acyclic nucleoside phosphonic acid and its ester derivatives and pharmaceutical use thereof
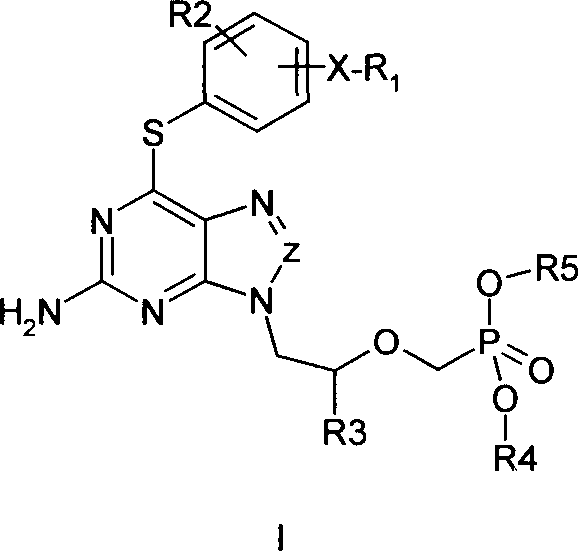
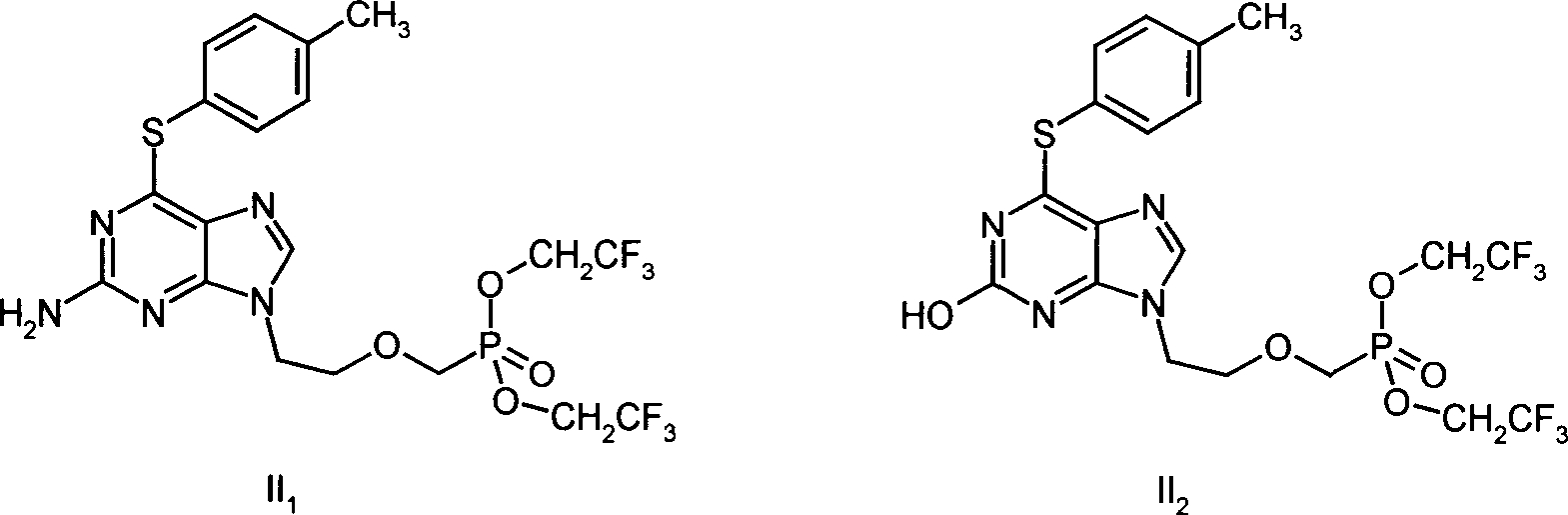
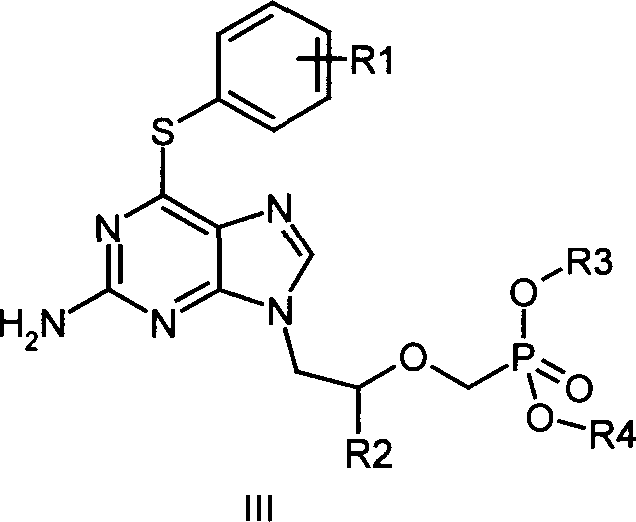
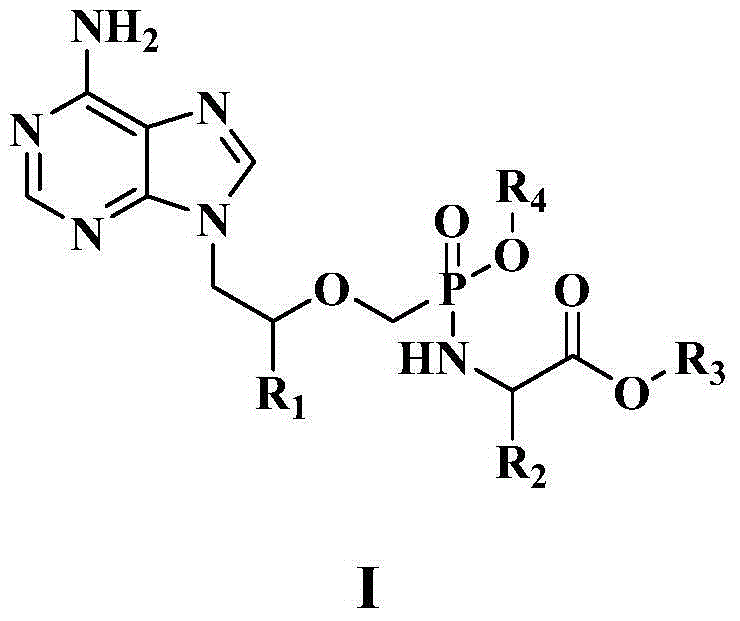
Disclosed is a non-cyclic nucleotide phosphonic acid represented by formula (I) and its ester derivative, its non-toxic pharmaceutically acceptable salts, or their hydrates or solvates, wherein R1 represents C1-C6 alkyl, X represents NH or S, R2 represents hydrogen, C1-C3 alkyl or halogen substituted alkoxy, C1-C3 alkyl or halogen substituted alkyl, halogen, R3 represents H, C1-C3 alkyl, C1-C3 hydroxyl substituted alkyl or C1-C3 alkyl substituted by more than one halogen atoms, R4 and R5 represent H, C1-C22 alkyl, phenyl, acylorxy or alkyl substituted by more than one halogen atoms. Z represents C or N.
Owner:广东京豪生物制药有限公司
Nucleotide analogs
ActiveUS9493493B2Cosmetic preparationsInorganic phosphorous active ingredientsCyclic nucleotideVirology
Disclosed herein, inter alia, are acyclic nucleotide analogs and methods of using an acyclic nucleotide analog for treating and / or ameliorating a papillomavirus infection.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
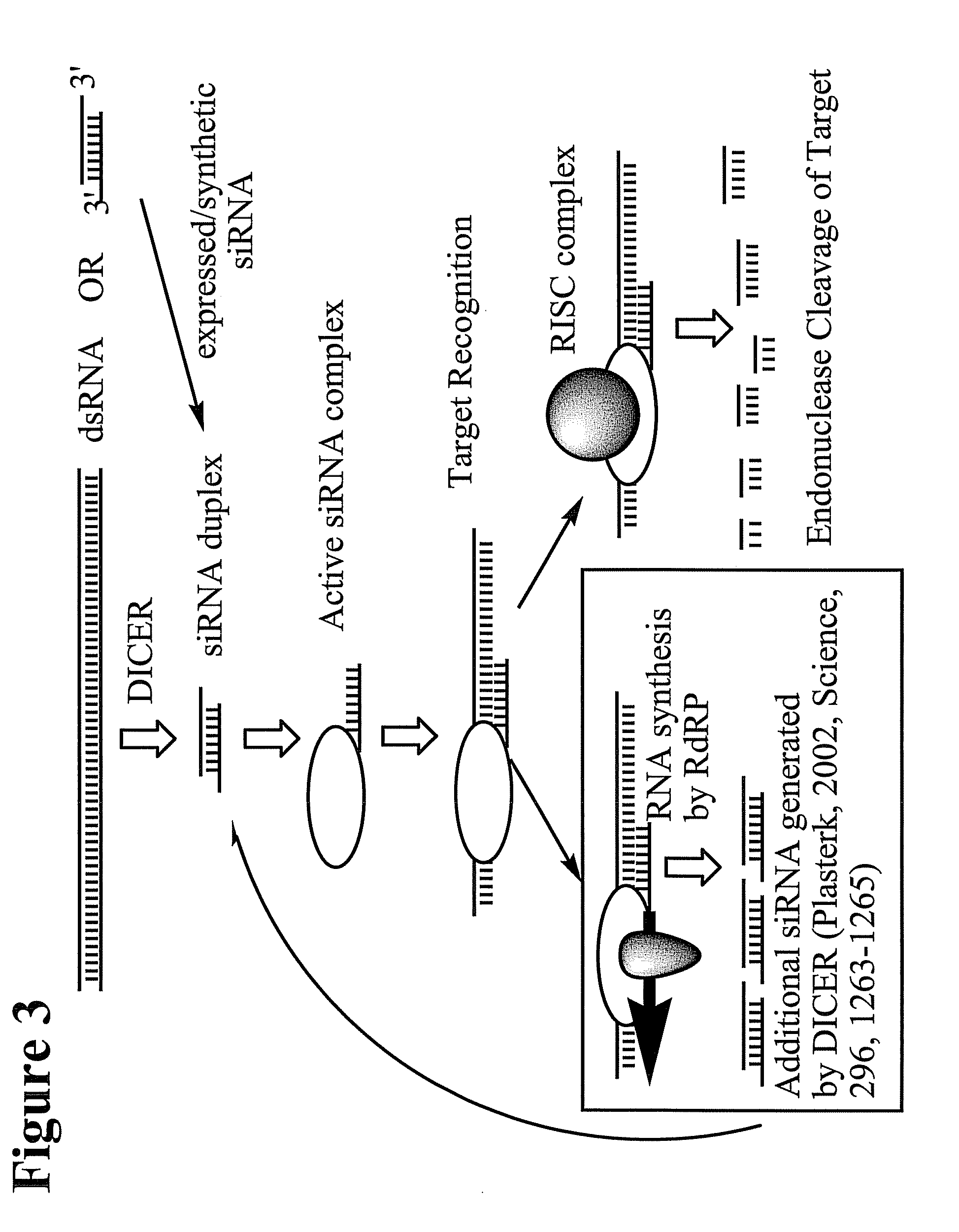
RNA Interference Mediated Inhibition of Cyclic Nucleotide Type 4 Phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) Gene Expression Using Short Interfering Nucleic Acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20100137405A1Improve stabilityGood treatment effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression and / or activity, including PDE4B1, PDE4B2, and PDE4B3 gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions, including but not limited to IL-6, IL-I, IL-8, IL-15, TNF-alpha and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), such as MMP-I, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9 and MMP-12. Specifically, the invention relates to double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and multifunctional siNA molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression, including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. The present invention also relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as siNA, siRNA, antisense and others that can inhibit the function of endogenous RNA molecules or RNAi pathway components (RNAi inhibitors), such as endogenous micro-RNA (miRNA) (e.g, miRNA inhibitors) or endogenous short interfering RNA (siRNA), (e.g., siRNA inhibitors) or that can inhibit the function of RISC (e.g., RISC inhibitors), to modulate PDE4B gene expression by interfering with the regulatory function of such endogenous RNAs or proteins associated with such endogenous RNAs (e.g., RISC) including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. Such small nucleic acid molecules are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or reduce inflammatory, respiratory, and autoimmune diseases, traits, and conditions, and / or other disease states associated with PDE4B gene expression or activity in a subject or organism.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Nucleoside phosphoramidate type compound with HBV/HIV resistance activity and salt and application of nucleoside phosphoramidate type compound
ActiveCN106565785AOrganic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsSolubilityPhosphoric acid
Owner:周雨恬
Phosphodiesterase inhibitor treatment
ActiveUS20120178768A1Improve acuityGreat tasteBiocideSenses disorderDiseasePhosphodiesterase inhibitor
Methods and compositions are disclosed for the treatment of diseases or conditions produced by or associated with low cyclic nucleotide levels. The compositions comprise phosphodiesterase inhibitors and are formulated for intranasal and pulmonary administration.
Owner:CYRANO THERAPEUTICS INC
Quantum dot labeled stem cells for use in providing pacemaker function
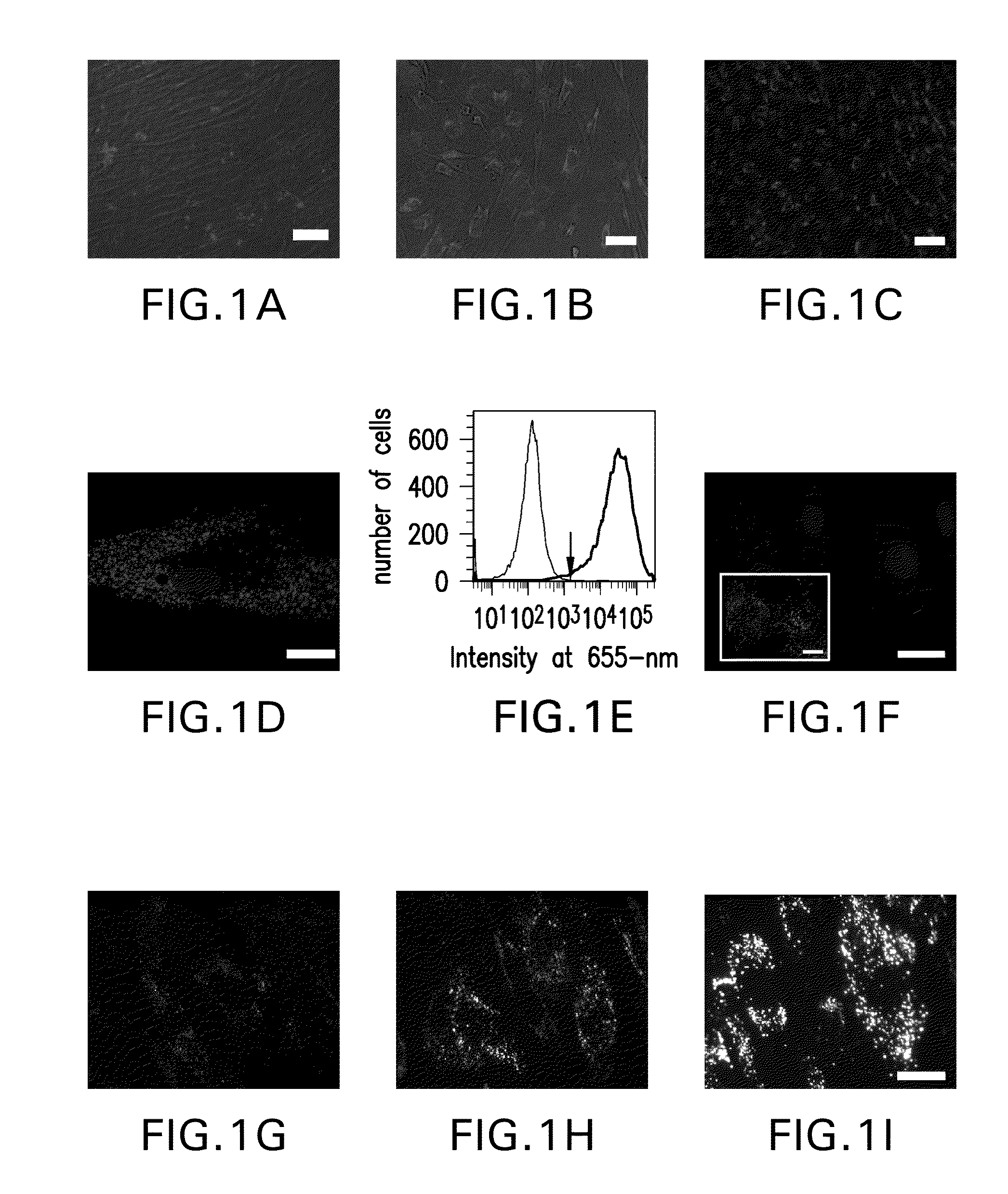
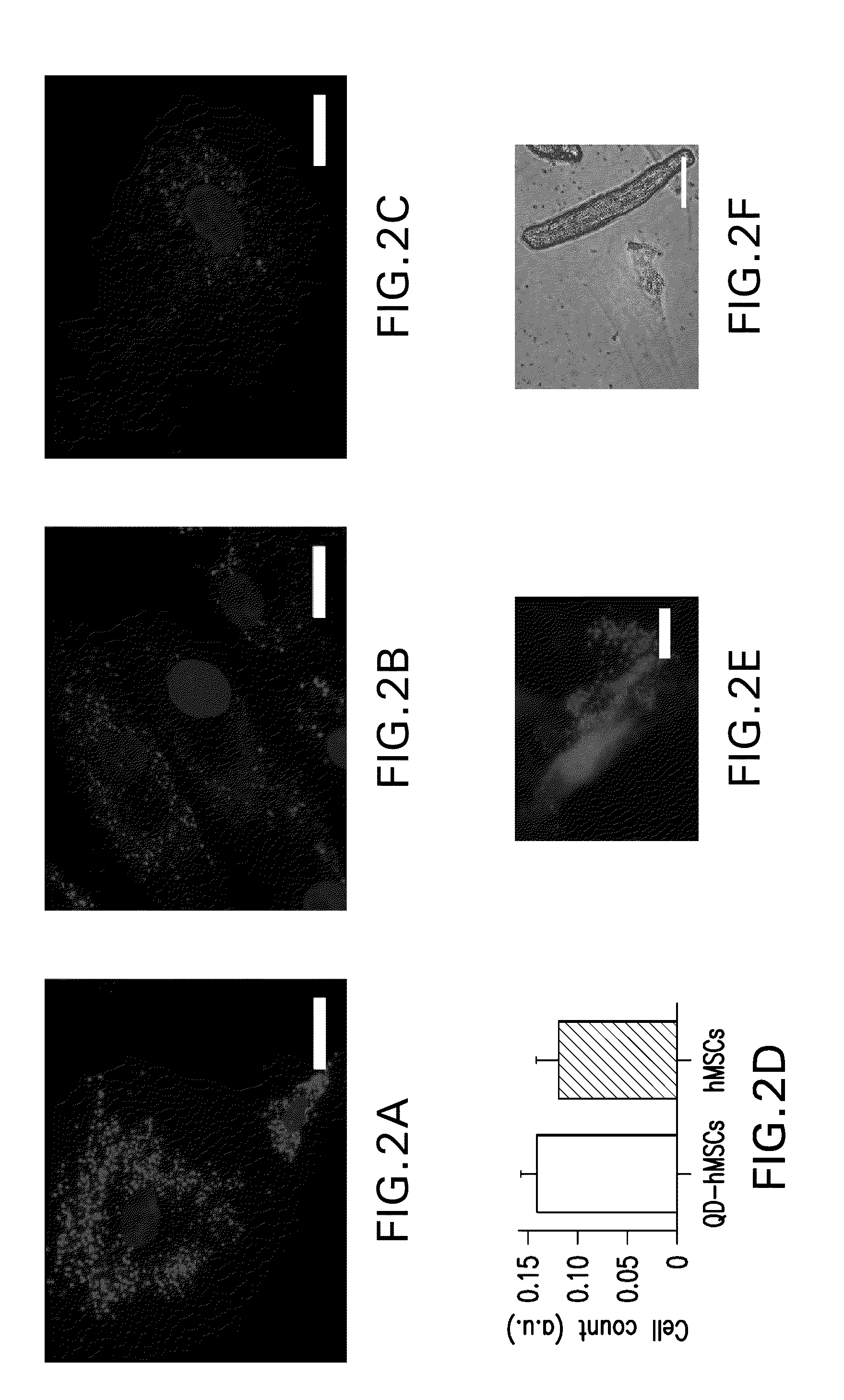
InactiveUS20090062876A1AbilityLack of perinuclear aggregationGenetically modified cellsBiological material analysisCardiac pacemaker electrodeFluorescence
The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to the labeling of target cells with nanometer scale fluorescent semiconductors referred to as quantum dots (QDs). Specifically, a delivery system is disclosed based on the use of negatively charged QDs for delivery of a tracking fluorescent signal into the cytosol of target cells via a passive endocytosis-mediated delivery process. In a specific embodiment of the invention the target cell is a stem cell, preferably a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC). Such labeled MSCs provide a means for tracking the distribution and fate of MSCs that have been genetically engineered to express, for example, a hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (“HCN”) channel and administered to a subject to create a biological pacemaker. The invention is based on the discovery that MSCs can be tracked in vitro for up to at least 6 weeks. Additionally, QDs delivered in vivo can be tracked for up to at least 8 weeks, thereby permitting for the first time, the complete 3-D reconstruction of the locations of all MSCs following administration into a host.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Quantum dot labeled stem cells for use in providing pacemaker function
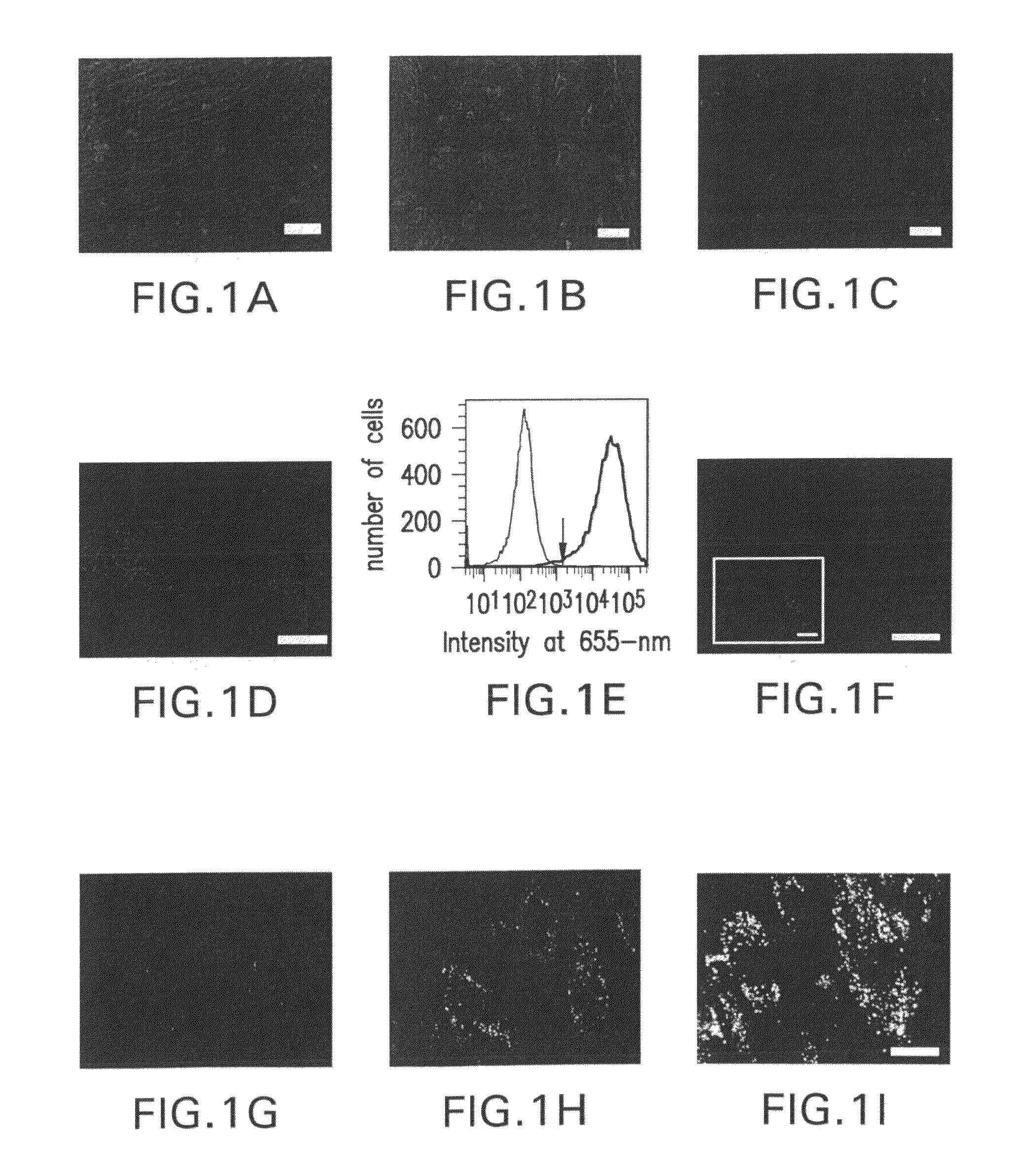
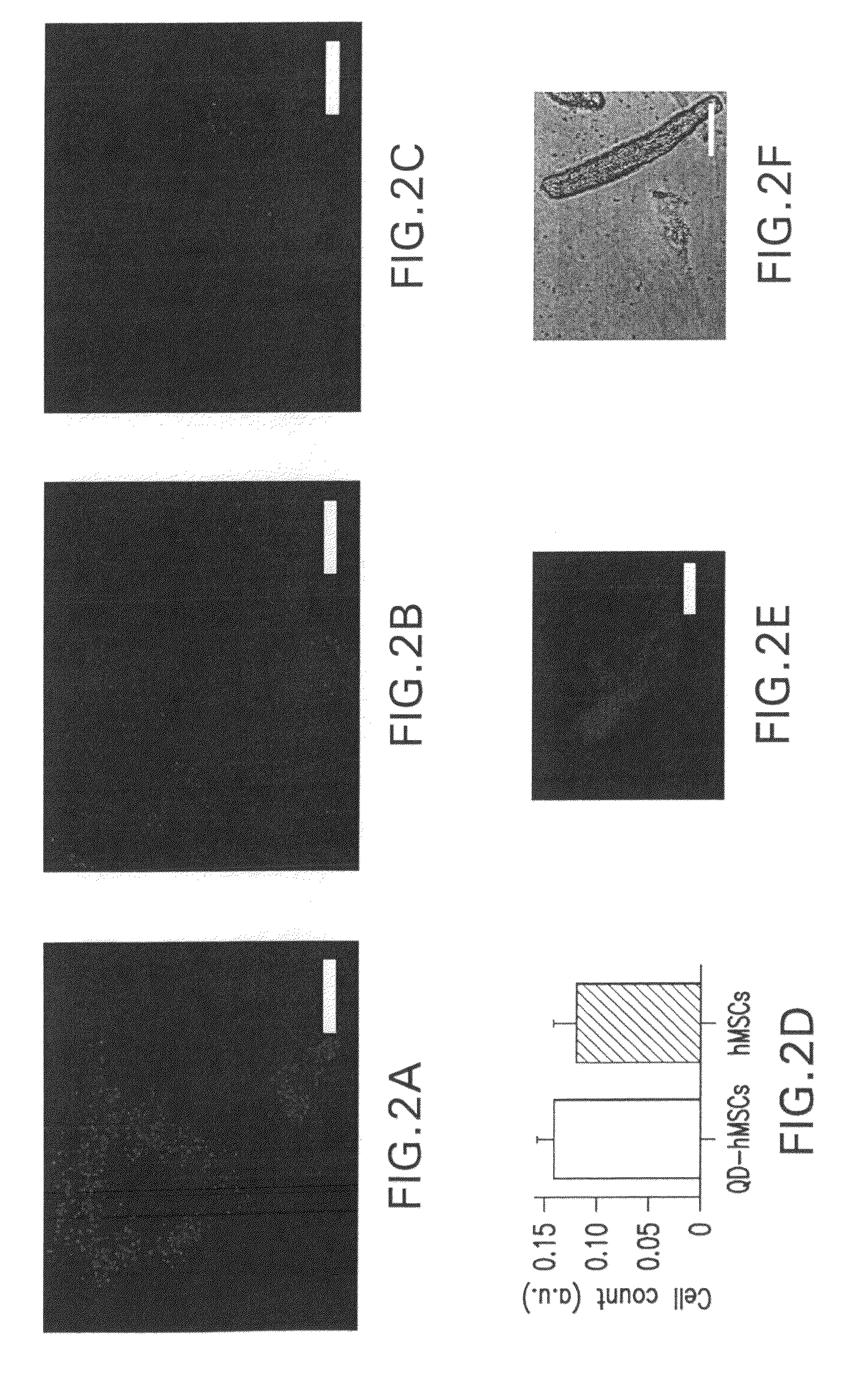
InactiveUS8170665B2AbilityLack of perinuclear aggregationElectrotherapyGenetically modified cellsCytosolCyclic nucleotide gated channels
The present invention provides methods and compositions relating to the labeling of target cells with nanometer scale fluorescent semiconductors referred to as quantum dots (QDs). Specifically, a delivery system is disclosed based on the use of negatively charged QDs for delivery of a tracking fluorescent signal into the cytosol of target cells via a passive endocytosis-mediated delivery process. In a specific embodiment of the invention the target cell is a stem cell, preferably a mesenchymal stem cell (MSC). Such labeled MSCs provide a means for tracking the distribution and fate of MSCs that have been genetically engineered to express, for example, a hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated (“HCN”) channel and administered to a subject to create a biological pacemaker. The invention is based on the discovery that MSCs can be tracked in vitro for up to at least 6 weeks. Additionally, QDs delivered in vivo can be tracked for up to at least 8 weeks, thereby permitting for the first time, the complete 3-D reconstruction of the locations of all MSCs following administration into a host.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Tumor markers for ovarian cancer diagnosis
The present invention relates to a tumor marker for diagnosis of ovarian cancer, which is selected from the group consisting of galectin-1, cathepsin B, MHC class I antigen, heat shock protein (HSP) 27, ubiquitin carboxy-termal esterase L1, plasma retinol-binding protein (PRBP), transthyretin, SH3 binding glutamate-rich protein, tubulin-specific chaperone A, RNA binding protein regulatory subunit, γ-actin, tropomyosin and calcium / calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphatase. The ovarian cancer is diagnosed effectively and efficiently based on detecting the expression levels of the tumor markers in the invention from the ovarian tissue sample of an individual to be diagnosed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Expression of functional human olfactory cyclic nucleotide gated (CNG) channel in recombinant host cells and use thereof in cell based assays to identify GPCR modulators
The present invention relates to isolated nucleic acid sequences that encode human olfactory cyclic nucleotide gated (CNG) channel subunits, and the corresponding polypeptides. The invention further relates to the use of human CNG channels to profile, screen for, and identify compounds that modulate the human olfactory CNG channel. More specifically, the invention relates to the expression of the human olfactory CNG channel in cells, preferably mammalian cells, and the use of these cells in high throughput cell-based assays to identify compounds that enhance or block human olfactory CNG function. Compounds that activate the olfactory CNG channel will enhance smell and can be used to make foods more palatable for individuals with attenuated olfactory function. Conversely, compounds that inhibit the olfactory CNG channel will inhibit smell and can be use to block malodors. Additionally, the invention relates to the use of cell-based olfactory CNG channel assays to identify modulates of G-protein coupled receptor (GPCRs) and other proteins that regulate cyclic nucleotide levels.
Owner:SENOMYX INC
Nucleotide phosphonate compound, pharmaceutical composition, preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN104804042AEffective against HBVGood prospects for drug applicationOrganic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsChemical industryViral infectious disease
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical and chemical industry, and relates to a nucleotide phosphonate compound, a pharmaceutical composition, a preparation method and uses thereof, particularly to a non-cyclic nucleotide phosphonate compound represented by a general formula, a pharmaceutically acceptable inorganic or organic salt, and a preparation method thereof, and a composition containing the compound represented by the general formula I. The compound of the present invention can be used as the active substance for treatment and / or prevention of viral infection diseases. The formula I is defined in the instruction.
Owner:QILU PHARMA HAINAN
Genetically modified cyclic-nucleotide controlled ion chan
InactiveUS20090104644A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementWild typeGene Modification
A genetically modified cyclic-nucleotide controlled ion channels where the subunits thereof are altered in such a manner that they have a higher sensitivity for cAMP in relation to cGMP in comparison with the Wildtype according to Seq ID No. 1 and 2.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
RNA Interference Mediated Inhibition of Cyclic Nucleotide Type 4 Phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) Gene Expression Using Short Interfering Nucleic Acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20100120895A1Good treatment effectHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression and / or activity, including PDE4B1, PDE4B2, and PDE4B3 gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions, including but not limited to IL-6, IL-7, IL-8, IL-15, TNF-alpha and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), such as MMP-I, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9 and MMP-12. Specifically, the invention relates to double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and multifunctional siNA molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression, including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. The present invention also relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as siNA, siRNA, antisense and others that can inhibit the function of endogenous RNA molecules or RNAi pathway components (RNAi inhibitors), such as endogenous micro-RNA (miRNA) (e.g, miRNA inhibitors) or endogenous short interfering RNA (siRNA), (e.g., siRNA inhibitors) or that can inhibit the function of RISC (e.g., RISC inhibitors), to modulate PDE4B gene expression by interfering with the regulatory function of such endogenous RNAs or proteins associated with such endogenous RNAs (e.g., RISC) including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. Such small nucleic acid molecules are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or reduce inflammatory, respiratory, and autoimmune diseases, traits, and conditions, and / or other disease states associated with PDE4B gene expression or activity in a subject or organism.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Separating and extracting method for date cyclic nucleotide syrup, dietary fibre and date wax
InactiveCN1175758CReduce heatIntestinal effect is obviousSugar derivativesFood preparationWaxOrganic solvent
The pulp of ripe data, after being dried, cooled and crushed, is ethanol extracted; the residual dreg after ethanol extraction is steamed and dried to produce dietary fiber powder; the extracted liquid is concentrated to recover ethanol and extracted with organic solvent to separate data wax; and the raffinate is concentrated to obtain date cyclic nucleotide syrup. The said process can produce several kinds of data products of different active components and different physical and chemical property, and the data products include functional health dietary fiber and date cyclic nucleotide syrup as tonic for people with delicate constitution.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
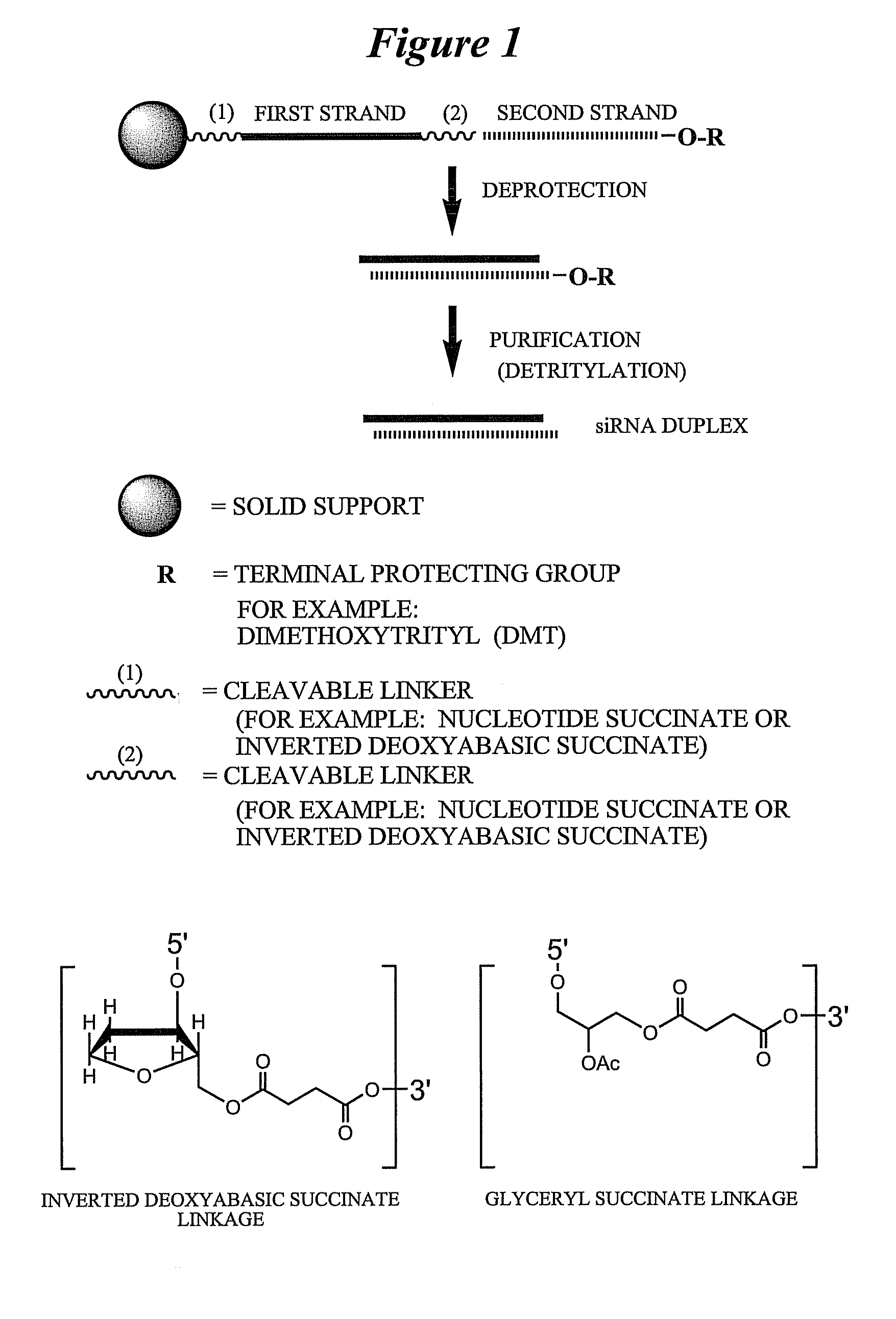
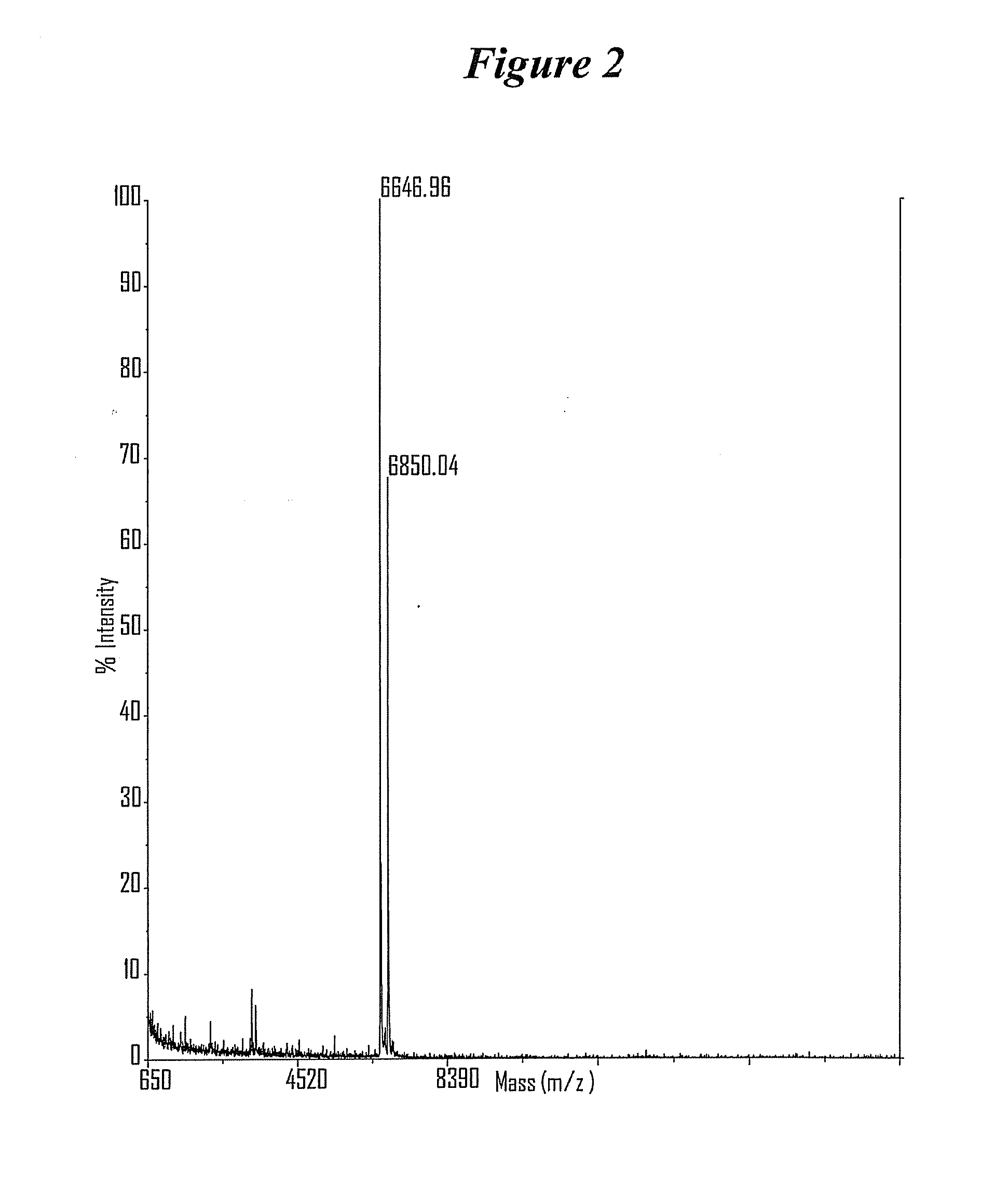
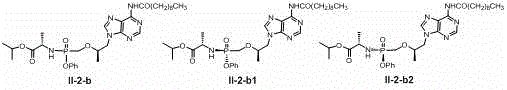
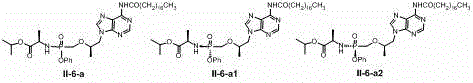
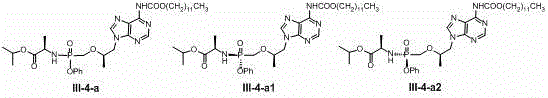
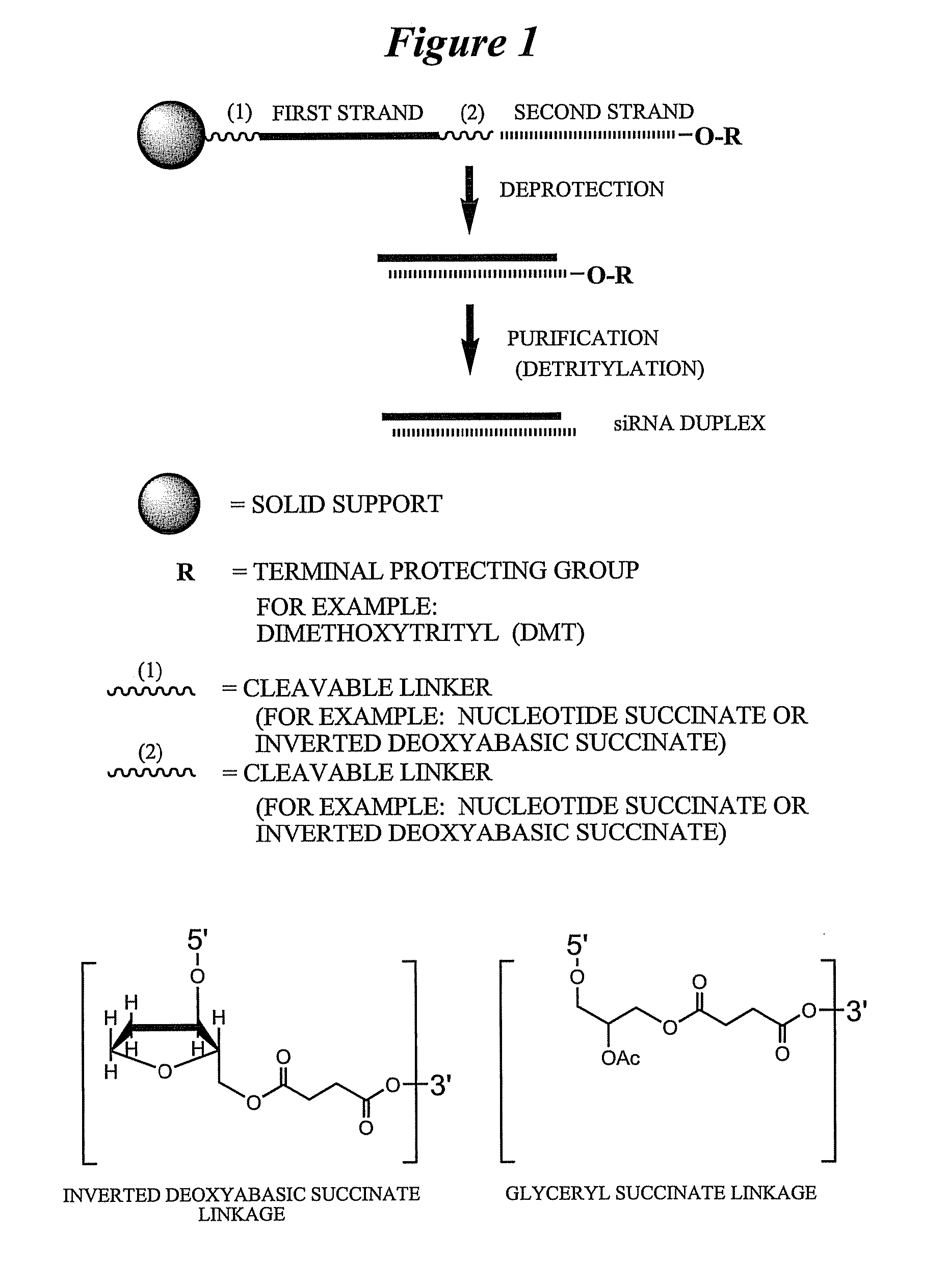
Synthesis and method of purification of cyclic nucleotide derivatives
The present invention relates to methods for the synthesis and purification of cyclic nucleotide derivatives. The present invention provides a method for separating a cyclic nucleotide derivative from a mixture resulting from a chemical reaction to produce a cyclic nucleotide derivative from a cyclic nucleotide. In one embodiment, this mixture may comprise a cyclic nucleotide derivative, a pyridine solvent, and at least one of an alkyl carboxylic acid, an alkyl acid halide, or an alkyl carboxylic acid anhydride. In another embodiment, this mixture may comprise a cyclic nucleotide derivative and at least one of an alkyl carboxylic acid, an alkyl acid halide, or an alkyl carboxylic acid anhydride.
Owner:PHARMACORE
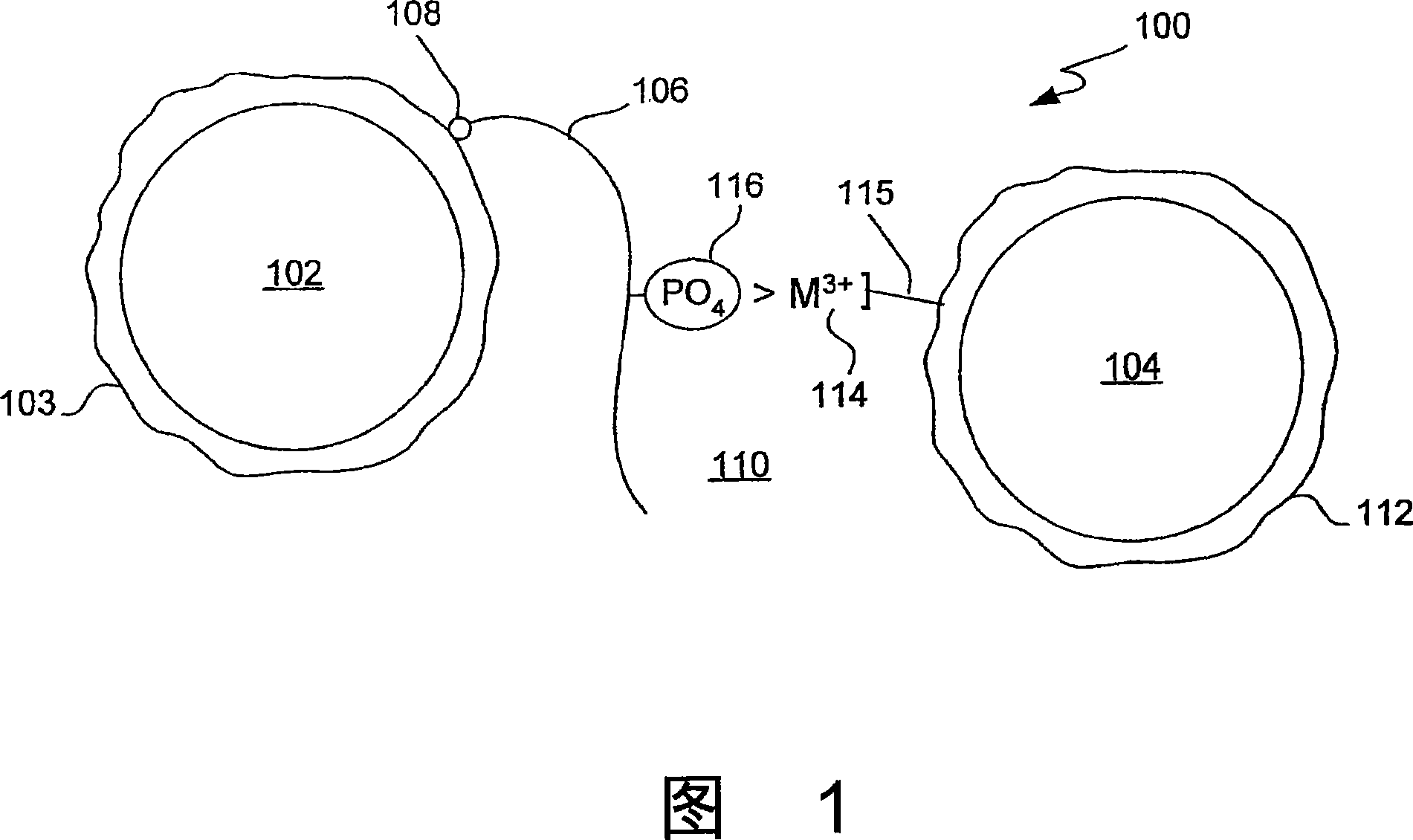
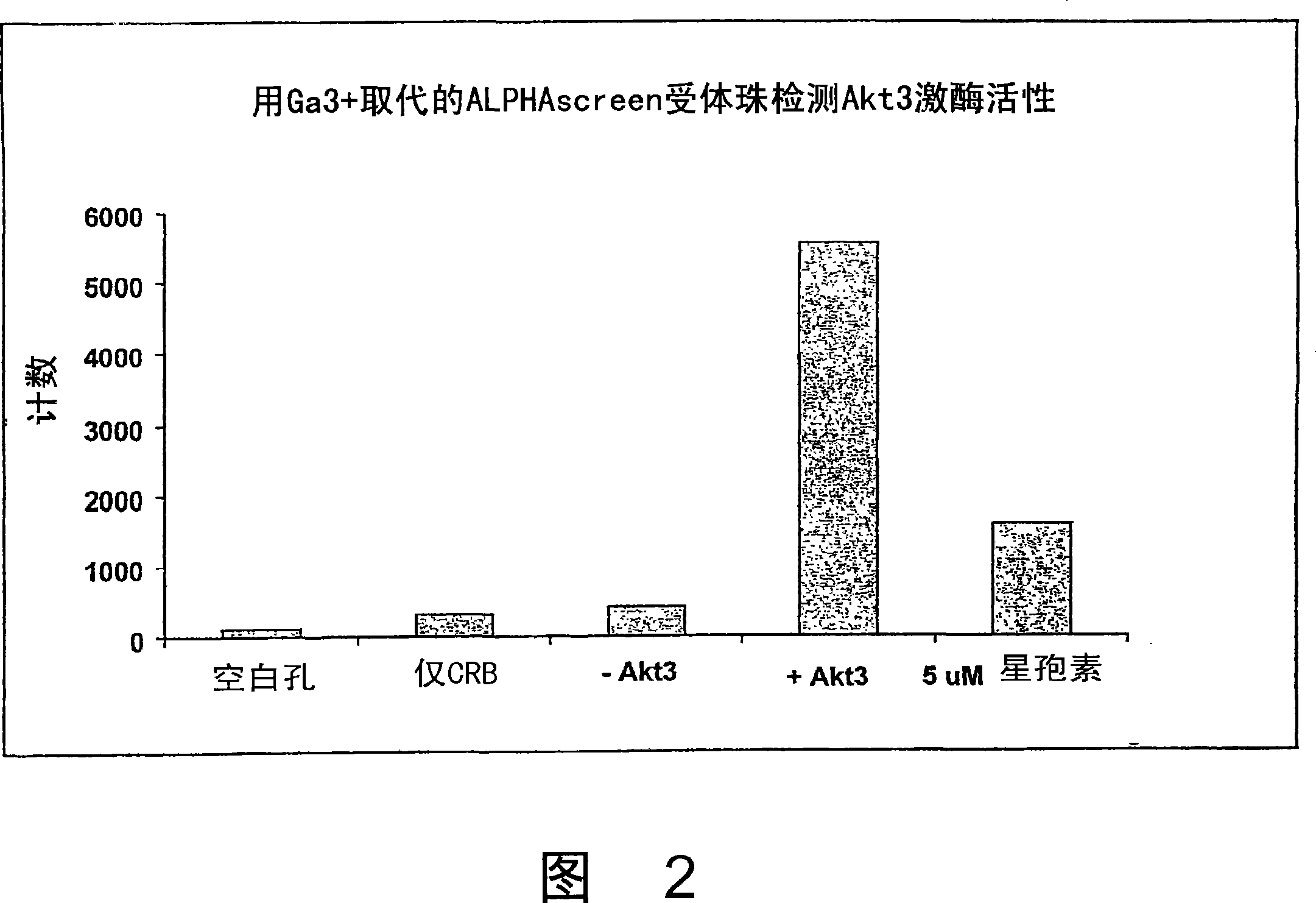
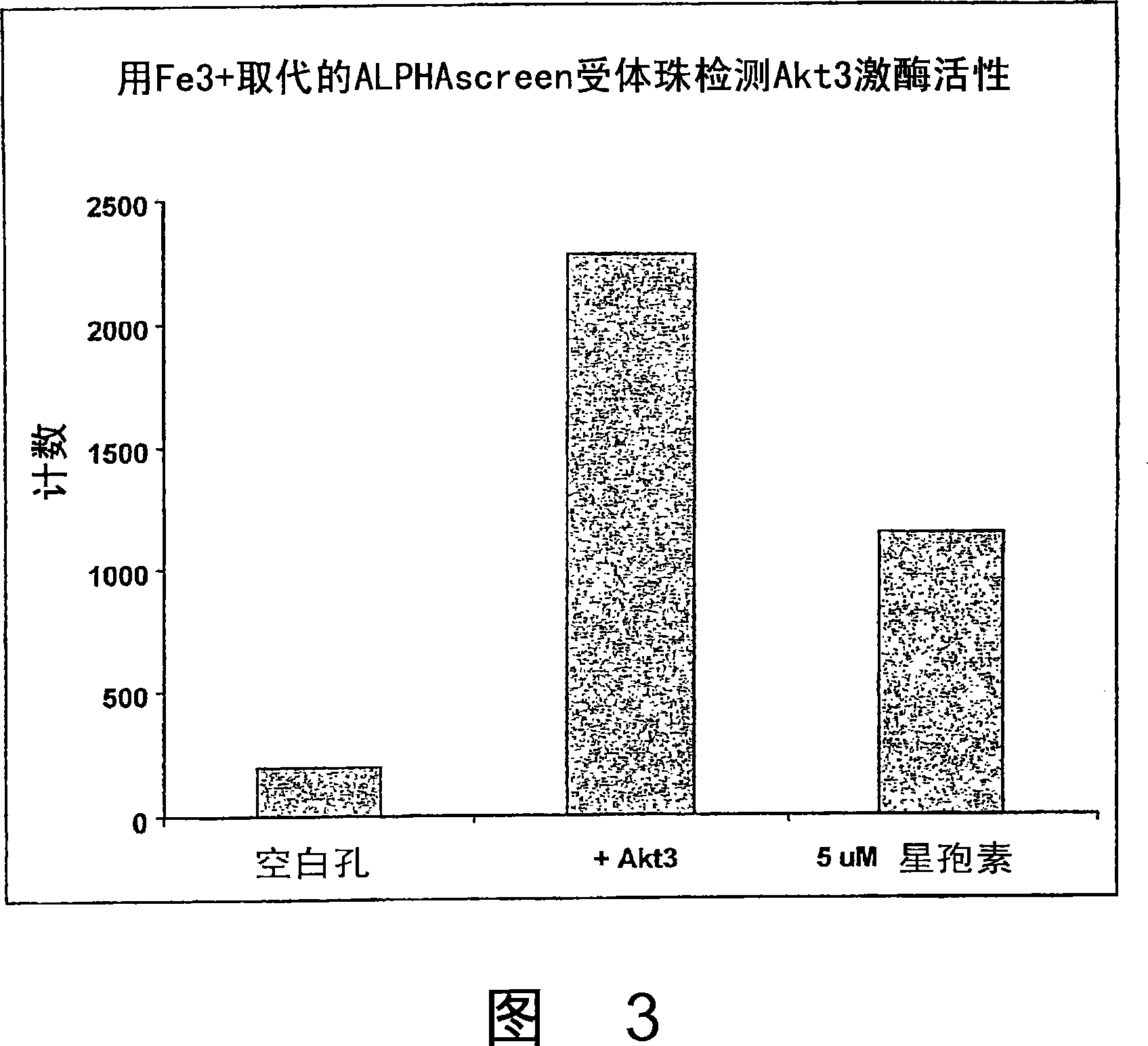
Trivalent metal mediated homogeneous luminescent proximity assay
An in vitro protein kinase assay technology that (1) exhibits a high assay signal to background ratio (S / B) and range (S-B); (2) is homogenous; (3) is non-radioactive; and (4) does not require a phospho-specific antibody involves complexing a trivalent metal ion (e.g. Ga<3+>, Fe<3+>, Al<3+>, In<3+>, Ru<3+>, Sc<3+>, Y<3+>) to the surface of amplified luminescent proximity assay acceptor or donor beads, e.g., via a suitable linker such as nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA; also referred to as carboxymethyl-lysine), iminodiacetic acid (IDA), or an appropriately substituted N-containing heterocycle, for example a triazoheterocycle, for example a triazocyclononaneononane, such as 1-propylamino-4-acetato-1,4,7-triazacyclononane. A protein (or constituent part) or other kinase substrate is bound to the surface of the other of an amplified luminescent proximity assay acceptor or donor bead and, if phosphorylated, brought into proximity with the trivalent metal ion-complexed acceptor bead to generate a luminescent signal. Presence of a kinase inhibitor inhibits phosphorylation and therefore signal generation and, in this way, is detectable. As the invention described herein recognizes the presence or absence of phosphate groups on a protein, (or constituent part), or other biological macromolecule (e.g., mono, di, or trinucleotides, cyclic nucleotides or phosphate substituted inositols), it is broadly applicable to any phosphorlylation or dephosphorylation reaction enzymes and provides a highly robust and flexible assay format for protein kinases and other enzyme classes, including lipid kinases, phosphatases, phosphodiesterases and others.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
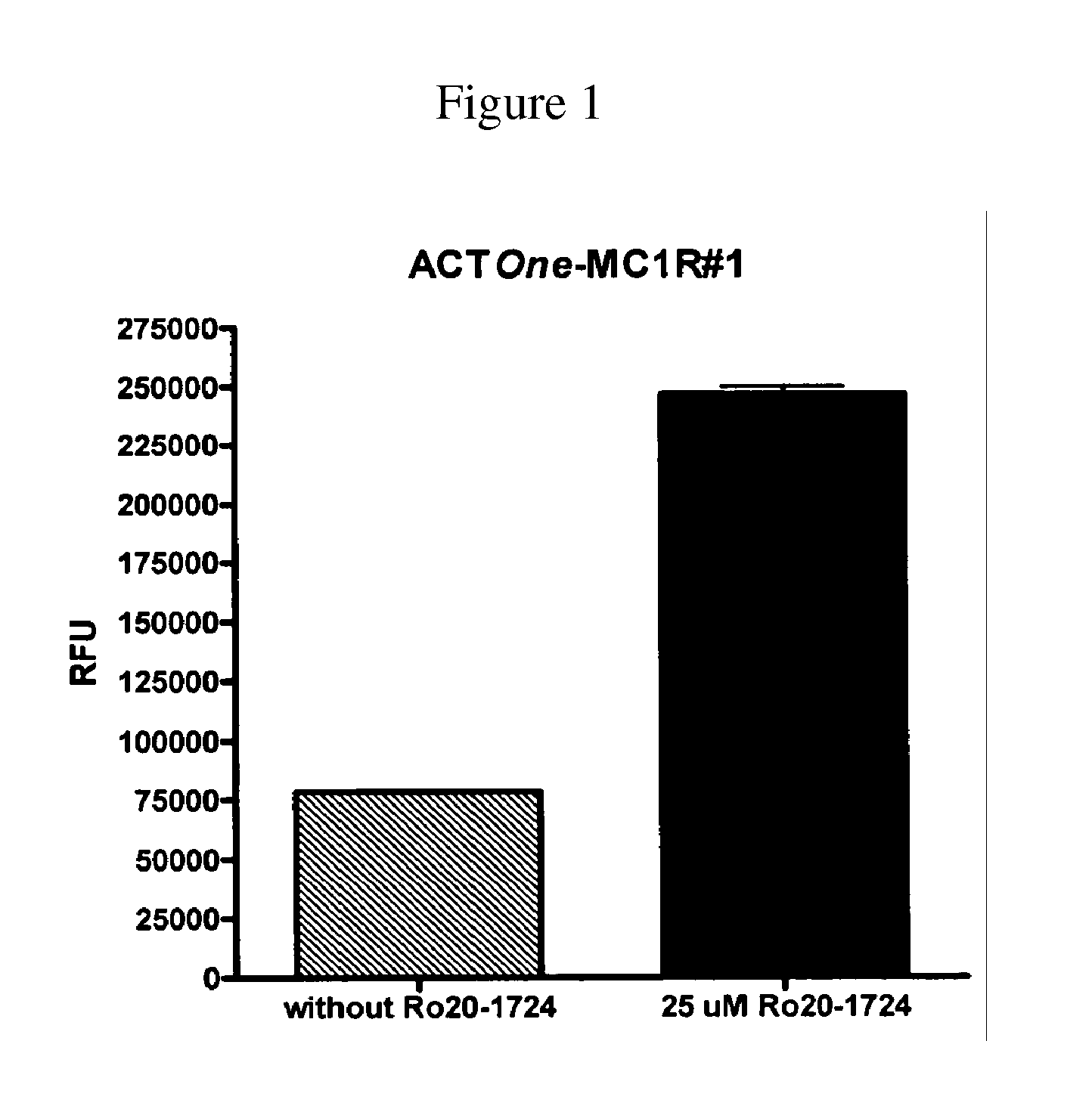
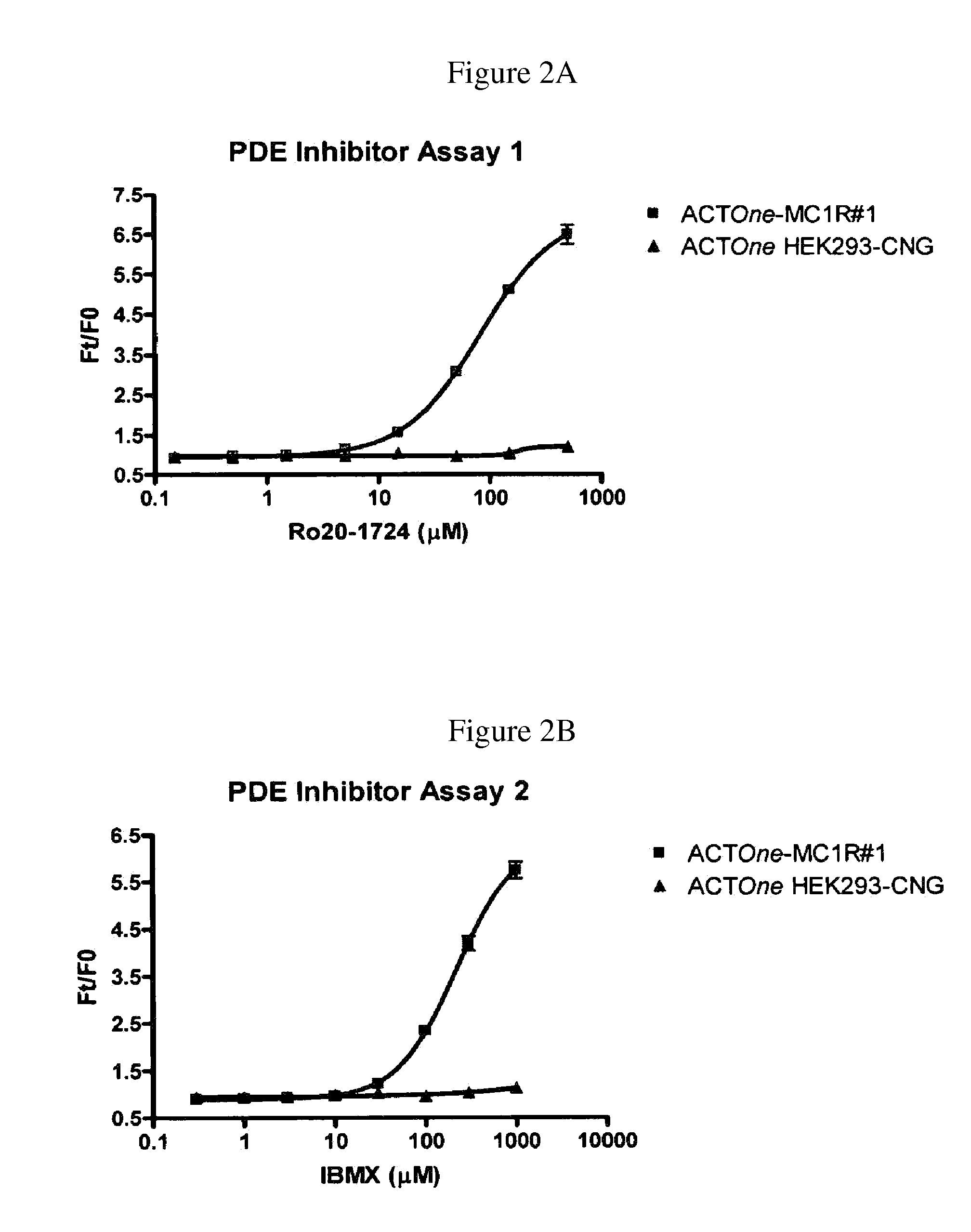
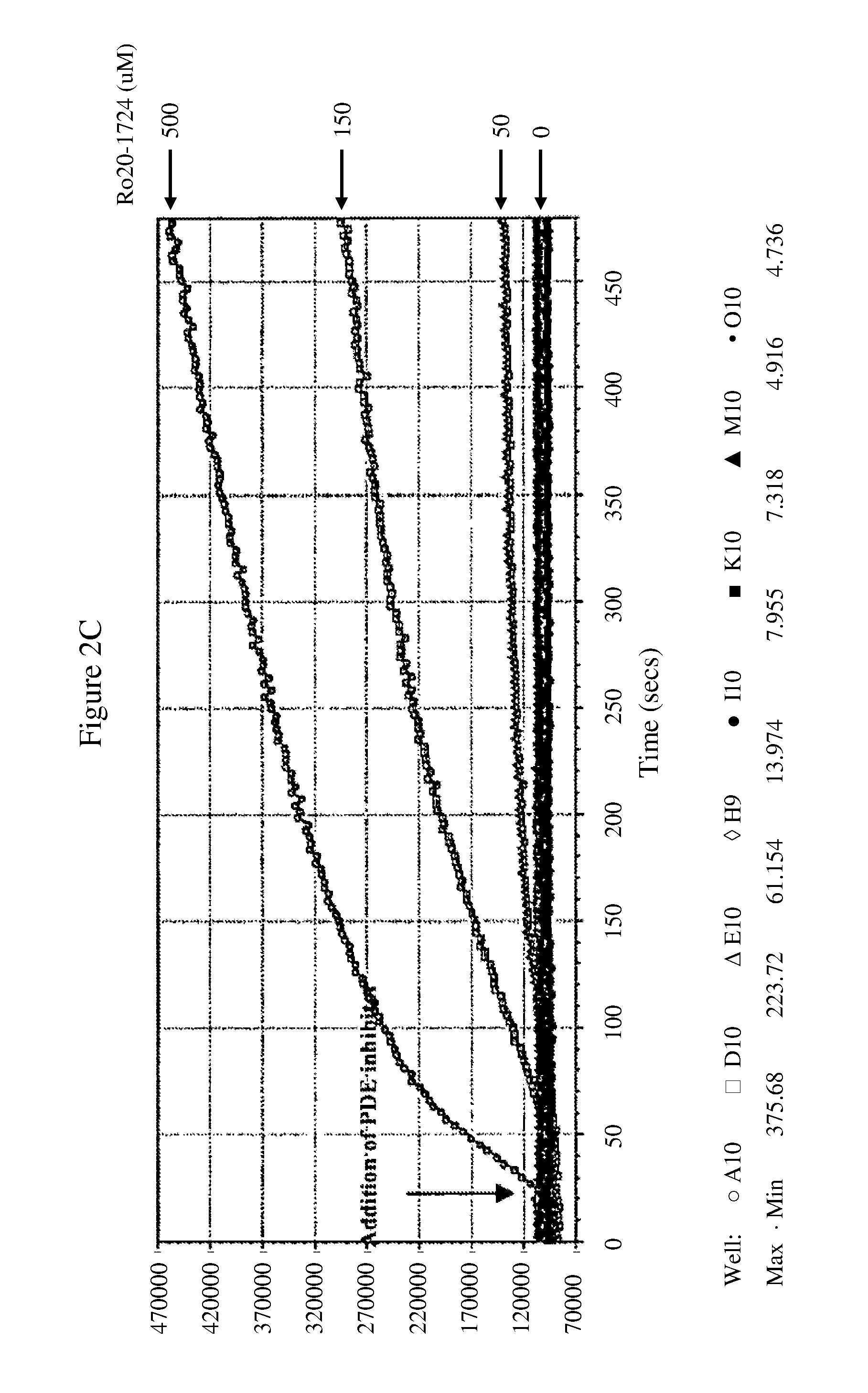
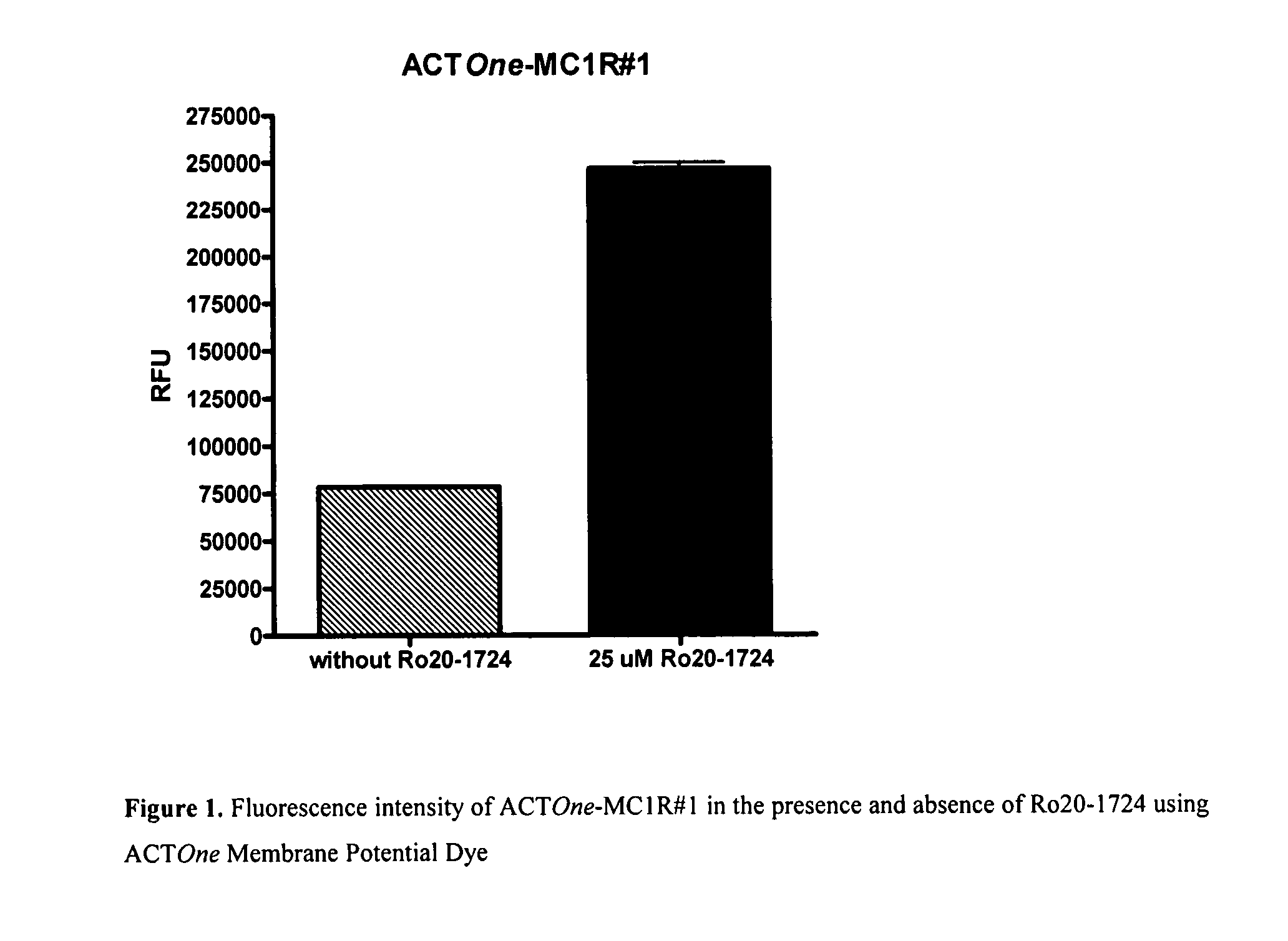
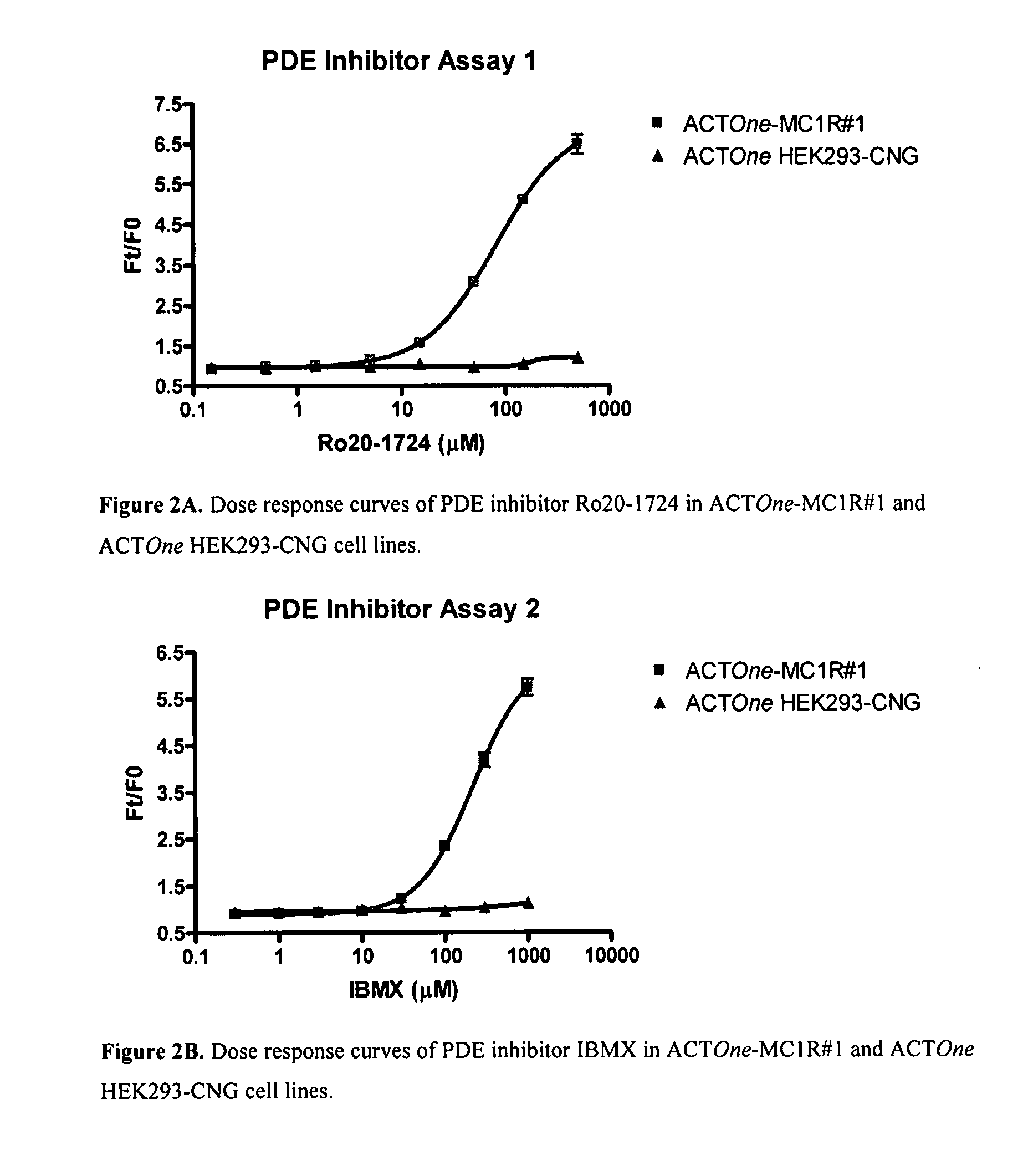
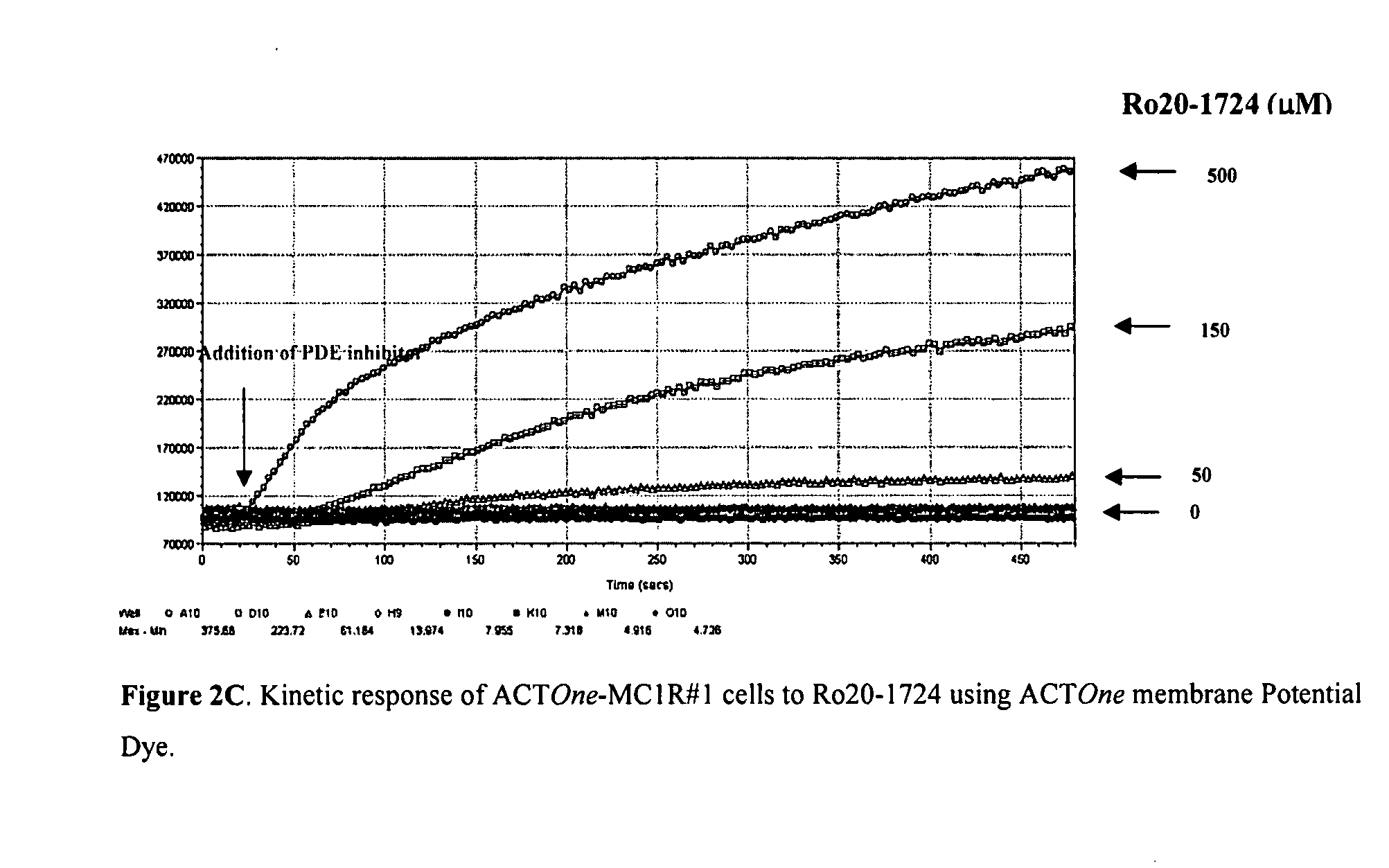
Novel Cell-Based Phosphodiesterase Assays
InactiveUS20110086374A1Improve the level ofHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphodiesteraseCyclic nucleotide gated channels
Owner:BD BIOSCI
Novel cell-based assays employing voltage and calcium dyes
InactiveUS20080166803A1Improve sensitivity and specificityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionIntracellularAssay
Disclosed are novel compositions and methods employing cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and fluorescence dyes and other indicators in detecting changes of intracellular cAMP levels, for instance in response to the stimulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. CNG mutants comprising one or more pore mutations that enhance sensitivity to cAMP and decrease divalent cation-mediated blockage are used in a variety of assays, including detection of the G-protein-coupled receptor activity. Also disclosed are novel dye quencher formulations that are particularly suited for cell-based assays of protein interactions.
Owner:XIAMEN AMOYTOP BIOTECH
Biomolecules involved in alzheimer's disease
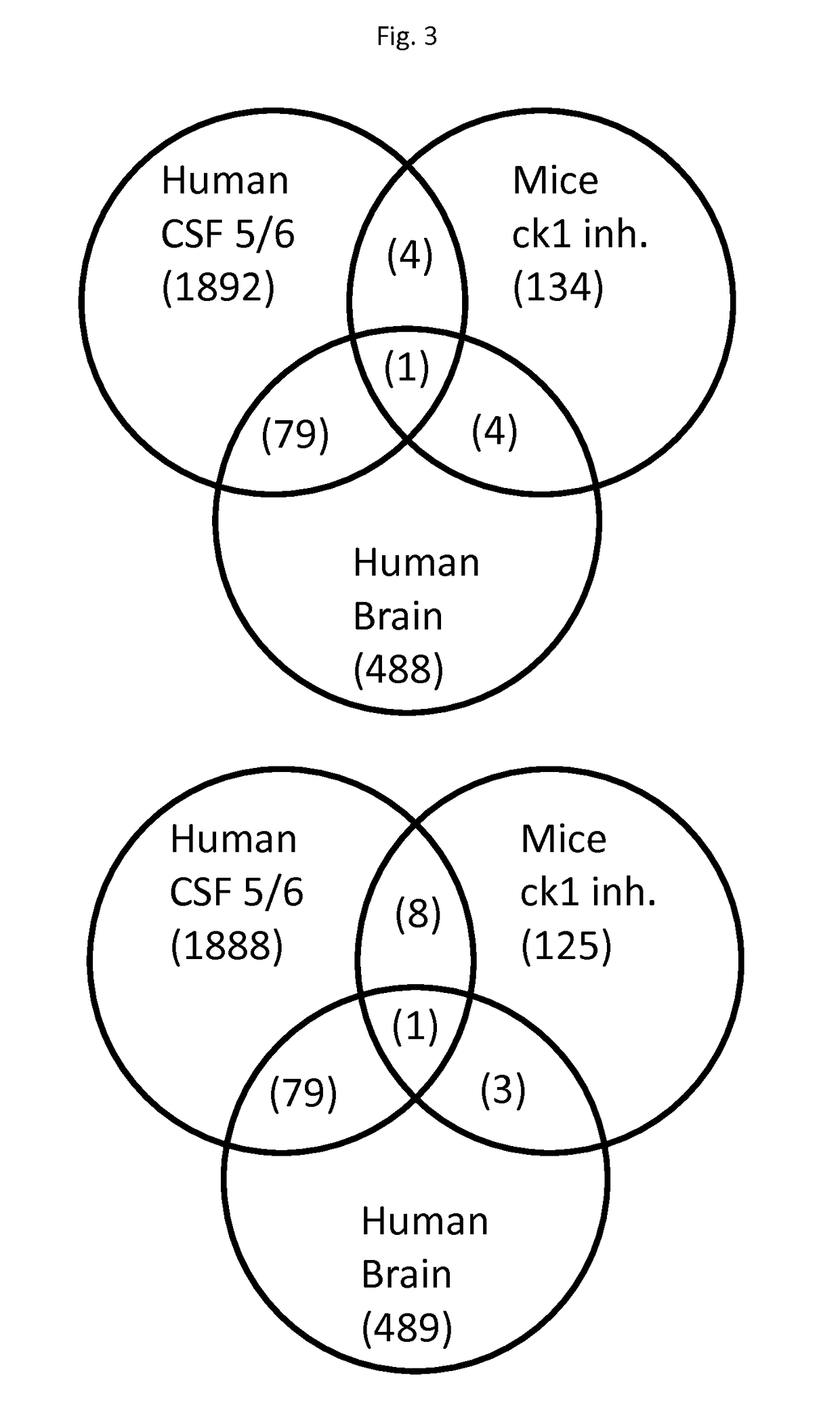
The invention relates to panels of biomarkers including proteins phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 14A and / or 2′,3′-cyclic-nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase and / or phosphorylated tau or fragments thereof and methods using thereof for diagnosing, staging, treating and assessing the response of a treatment for a neurocognitive disorder characterised by tau toxicity, in particular for Alzheimer's disease. The present invention shows that the biomarkers disclosed herein are elevated in the brain of subjects with an advanced stage of a neurocognitive disorder (Braak stage V / VI) and / or are regulated in the CSF of AD subjects in comparison to cognitively affected non-AD controls; and / or regulated in response to two casein kinase 1 delta inhibitors.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
Tumor Marker For Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis
InactiveUS20090098595A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsCathepsin BOvarian tissue
The present invention relates to a tumor marker for diagnosis of ovarian cancer, which is selected from the group consisting of galectin-1, cathepsin B, MHC class I antigen, heat shock protein (HSP) 27, ubiquitin carboxy-termal esterase L1, plasma retinol-binding protein (PRBP), transthyretin, SH3 binding glutamate-rich protein, tubulin-specific chaperone A, RNA binding protein regulatory subunit, γ-actin, tropomyosin and calcium / calmodulin-stimulated cyclic nucleotide phosphatase. The ovarian cancer is diagnosed effectively and efficiently based on detecting the expression levels of the tumor markers in the invention from the ovarian tissue sample of an individual to be diagnosed.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Novel cell-based assays employing voltage and calcium dyes
InactiveUS20050221426A1High sensitivityStrong specificityRecord information storagePhotomechanical treatmentCyclic nucleotide gated channelsFluorescence
Disclosed are novel compositions and methods employing cyclic nucleotide-gated channels and fluorescence dyes and other indicators in detecting changes of intracellular cAMP levels, for instance in response to the stimulation of G-protein-coupled receptors. CNG mutants comprising one or more pore mutations that enhance sensitivity to cAMP and decrease divalent cation-mediated blockage are used in a variety of assays, including detection of the G-protein-coupled receptor activity. Also disclosed are novel dye quencher formulations that are particularly suited for cell-based assays of protein interactions.
Owner:XIAMEN AMOYTOP BIOTECH
RNA Interference Mediated Inhibition of Cyclic Nucleotide Type 4 Phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) Gene Expression Using Short Interfering Nucleic Acid (siNA)
InactiveUS20100137406A1Good treatment effectHigh activityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
The present invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression and / or activity, including PDE4B1, PDE4B2, and PDE4B3 gene expression and / or activity. The present invention is also directed to compounds, compositions, and methods relating to traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of expression and / or activity of genes involved in cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression pathways or other cellular processes that mediate the maintenance or development of such traits, diseases and conditions, including but not limited to IL-6, IL-I, IL-8, IL-15, TNF-alpha and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), such as MMP-1, MMP-2, MMP-3, MMP-9 and MMP-12. Specifically, the invention relates to double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and multifunctional siNA molecules capable of mediating RNA interference (RNAi) against cyclic nucleotide type 4 phosphodiesterase (PDE4B) gene expression, including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. The present invention also relates to small nucleic acid molecules, such as siNA, siRNA, antisense and others that can inhibit the function of endogenous RNA molecules or RNAi pathway components (RNAi inhibitors), such as endogenous micro-RNA (miRNA) (e.g., miRNA inhibitors) or endogenous short interfering RNA (siRNA), (e.g., siRNA inhibitors) or that can inhibit the function of RISC (e.g., RISC inhibitors), to modulate PDE4B gene expression by interfering with the regulatory function of such endogenous RNAs or proteins associated with such endogenous RNAs (e.g., RISC) including cocktails of such small nucleic acid molecules and lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations of such small nucleic acid molecules. Such small nucleic acid molecules are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or reduce inflammatory, respiratory, and autoimmune diseases, traits, and conditions, and / or other disease states associated with PDE4B gene expression or activity in a subject or organism.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Novel cell-based phosphodiesterase assays
InactiveUS20070224645A1Improve the level ofMicroorganismsArtificial cell constructsPhosphodiesteraseCyclic nucleotide gated channels
The present invention relates to improved cell-based assays for the in vivo assessment of phosphodiesterase (PDE) activity using cyclic nucleotide-gated channels as cyclic nucleotide sensors, and for the assessment of the effect of PDE modulating compounds.
Owner:BD BIOSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com