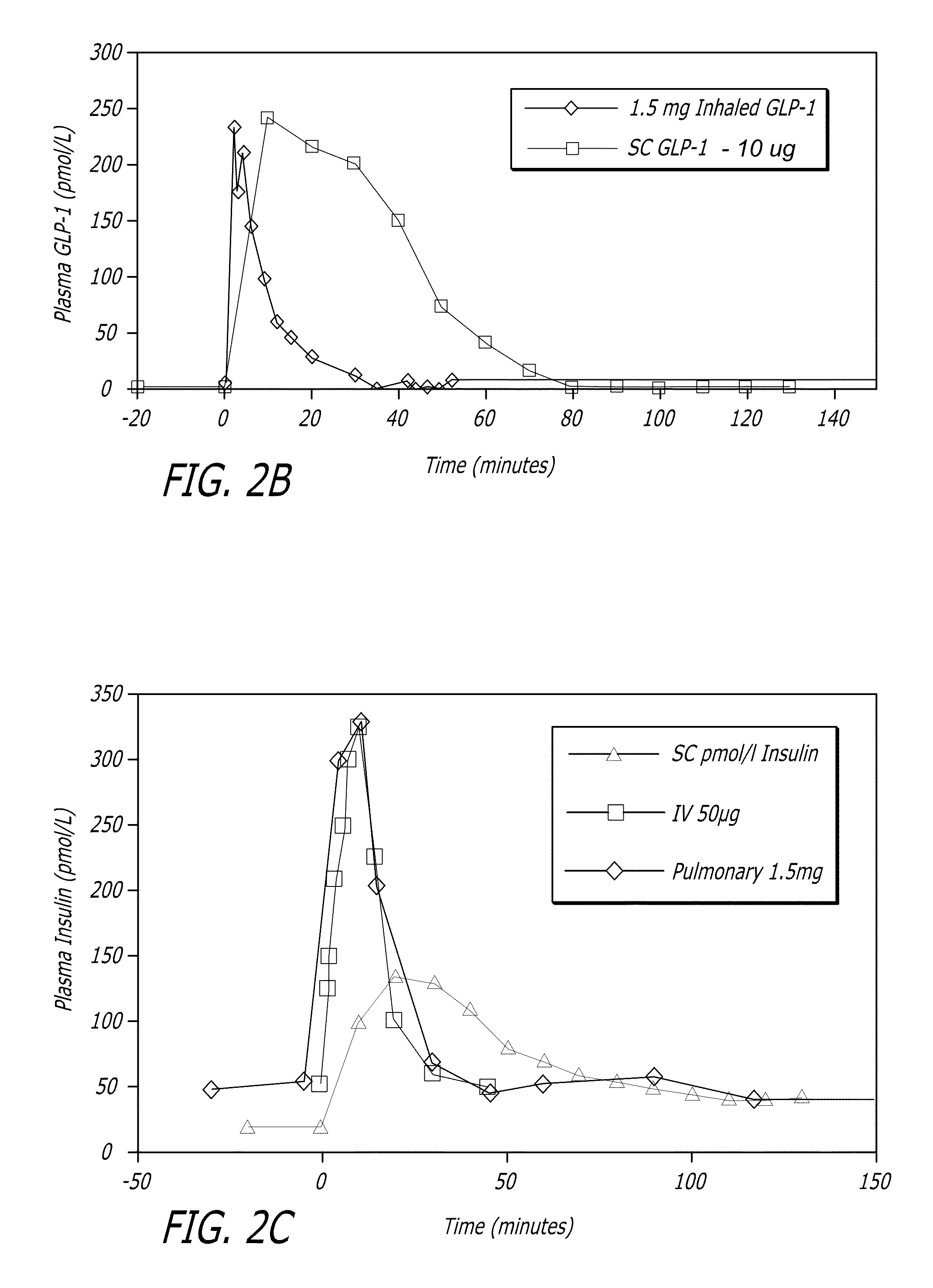
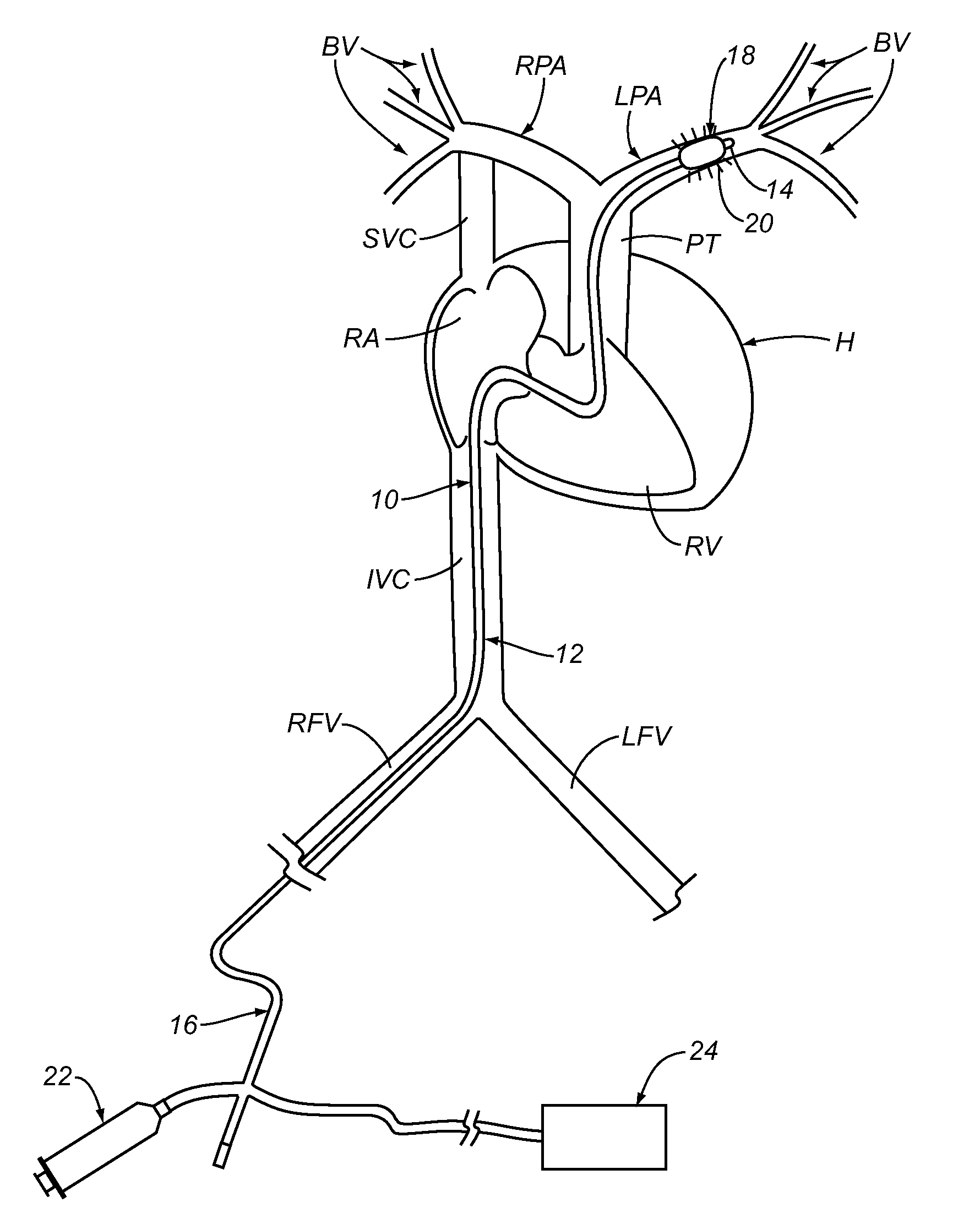
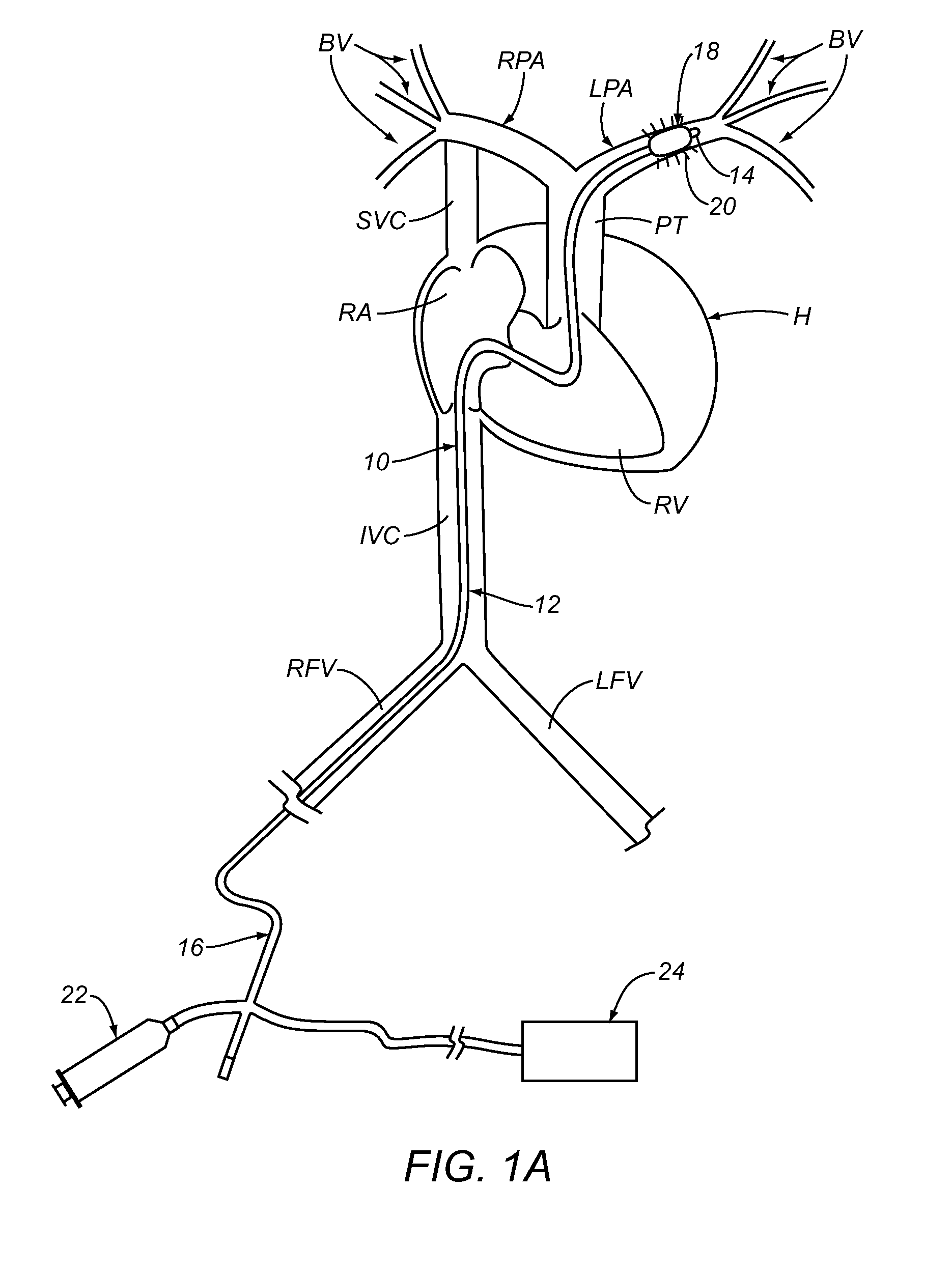
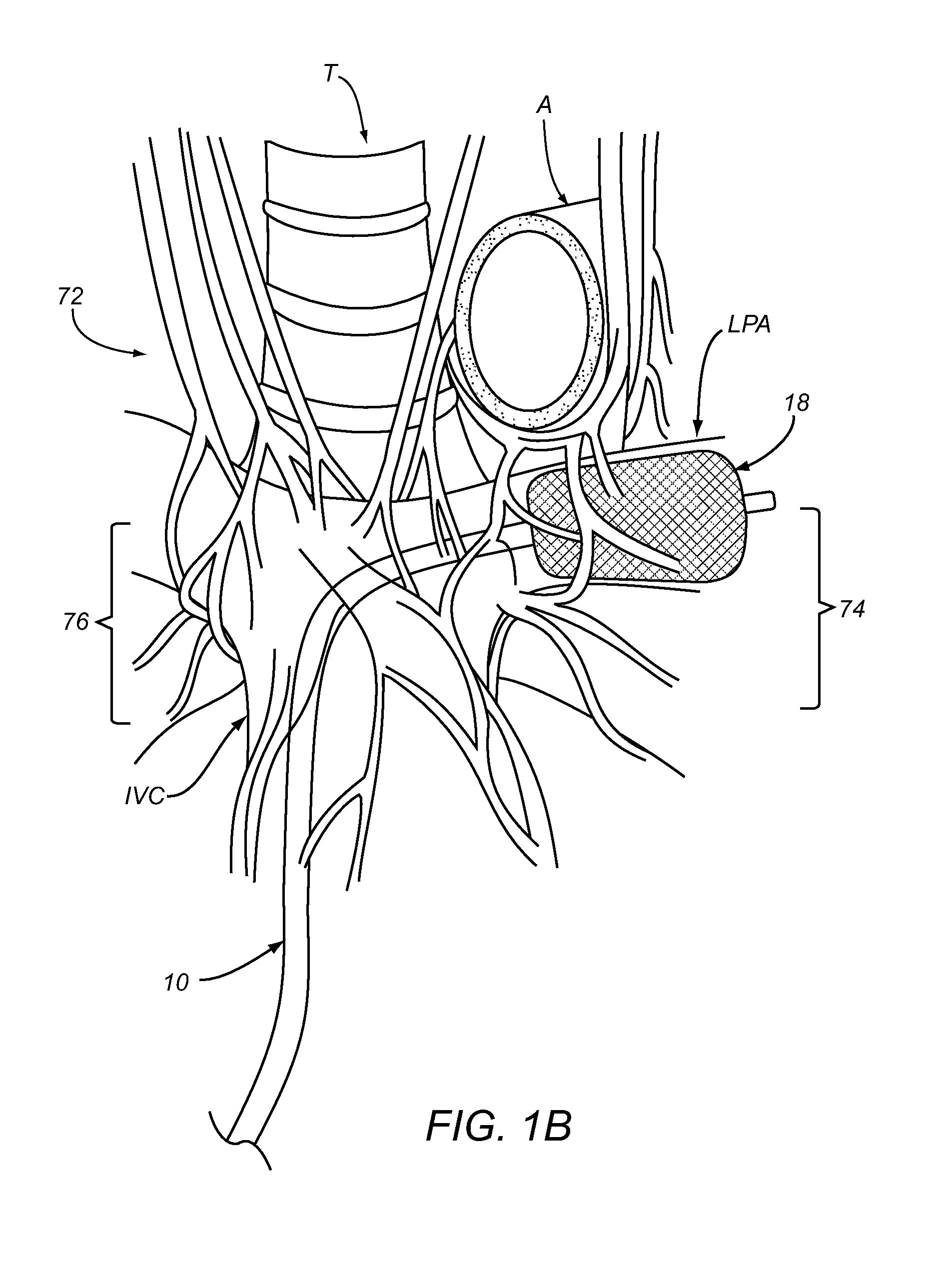
Patents
Literature
97 results about "Pulmonary vasculature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
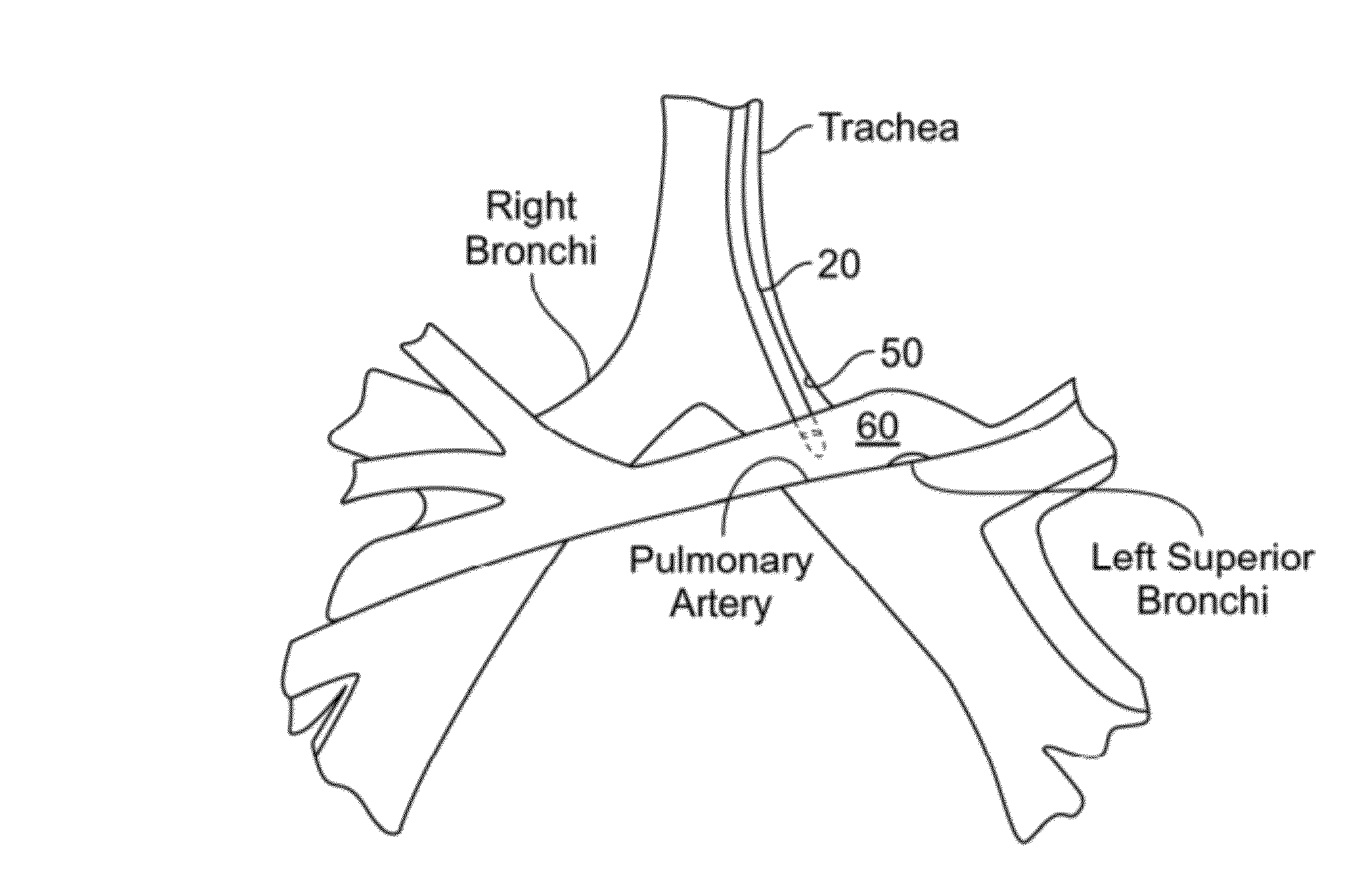
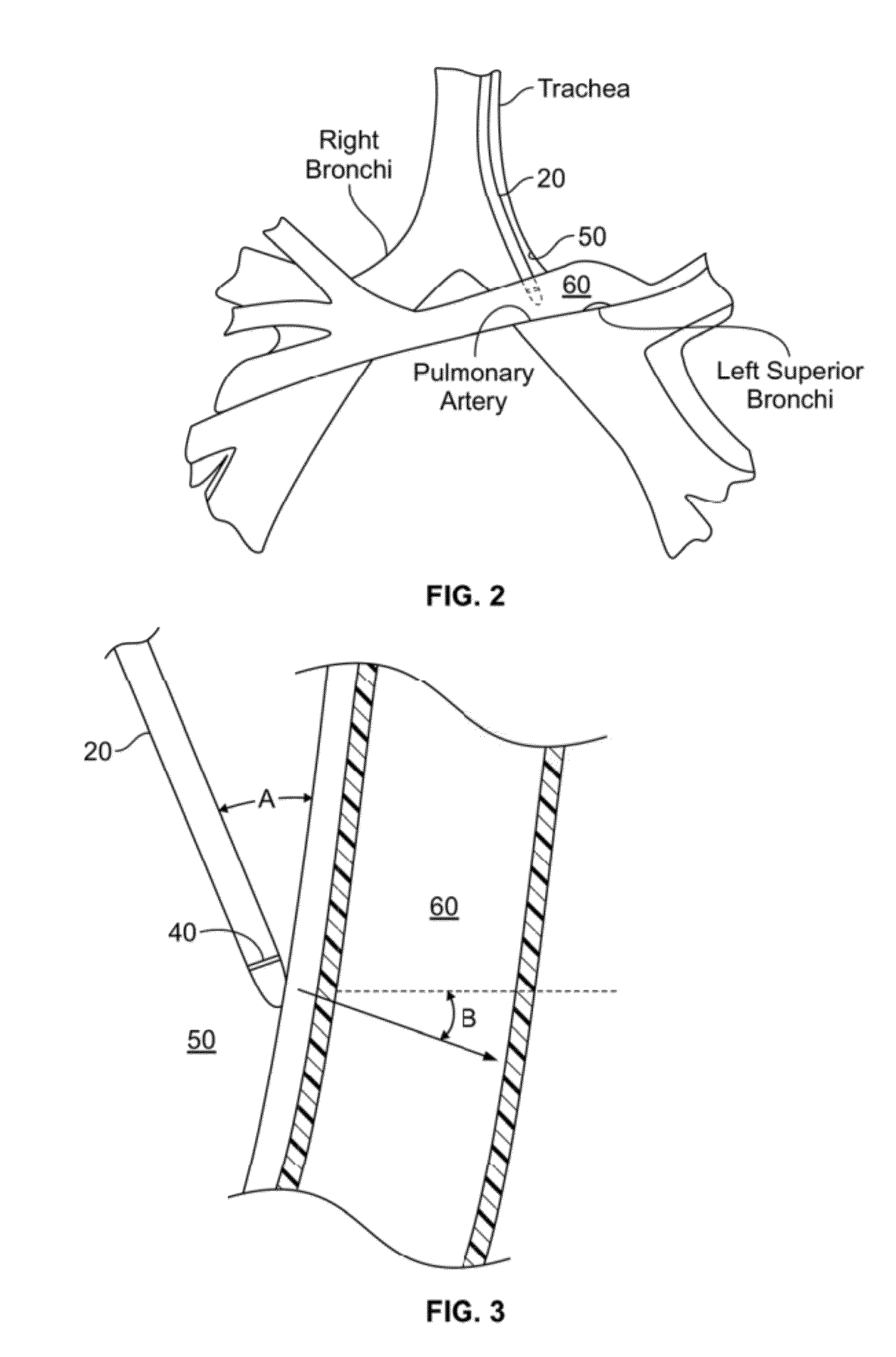
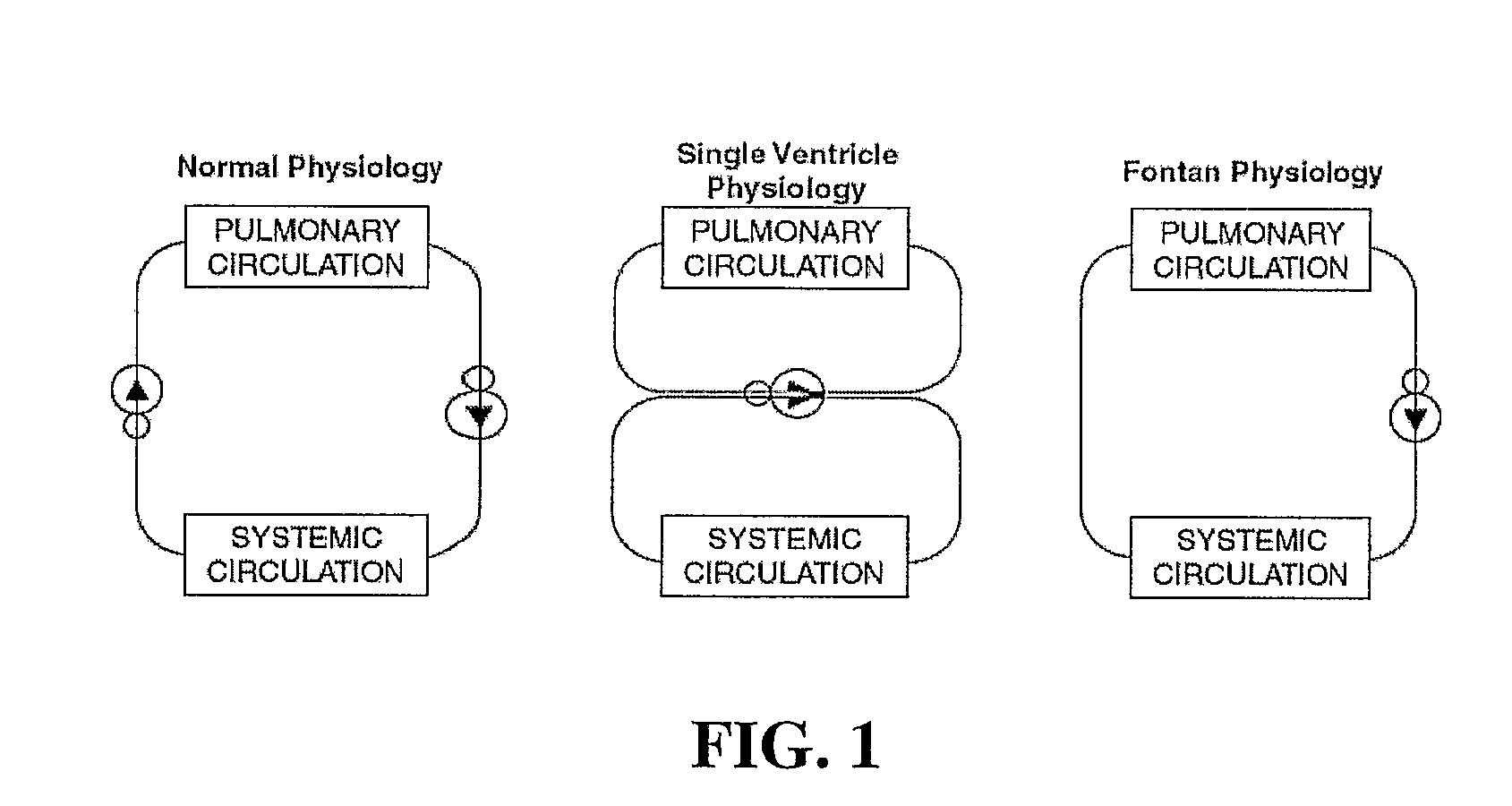
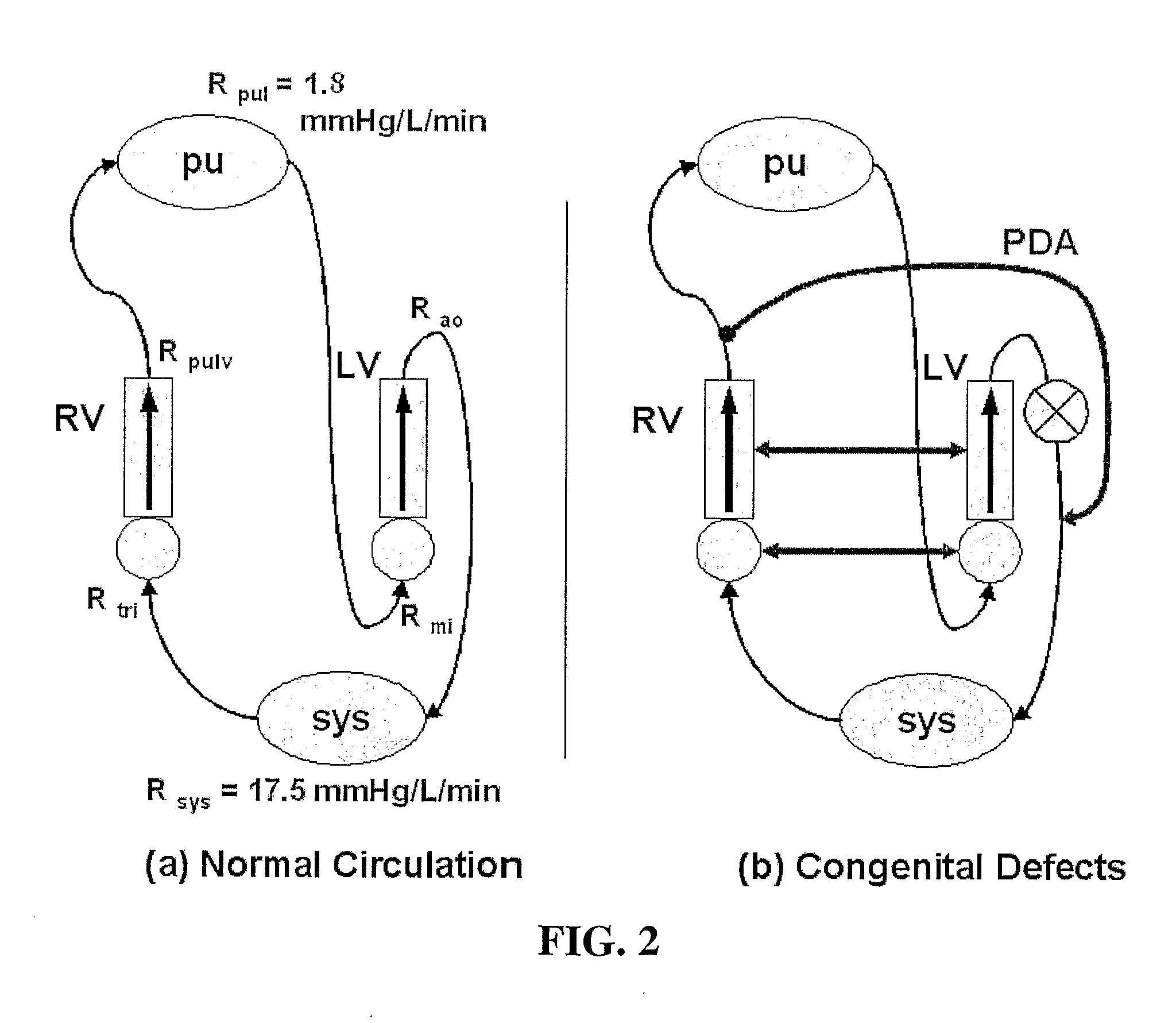
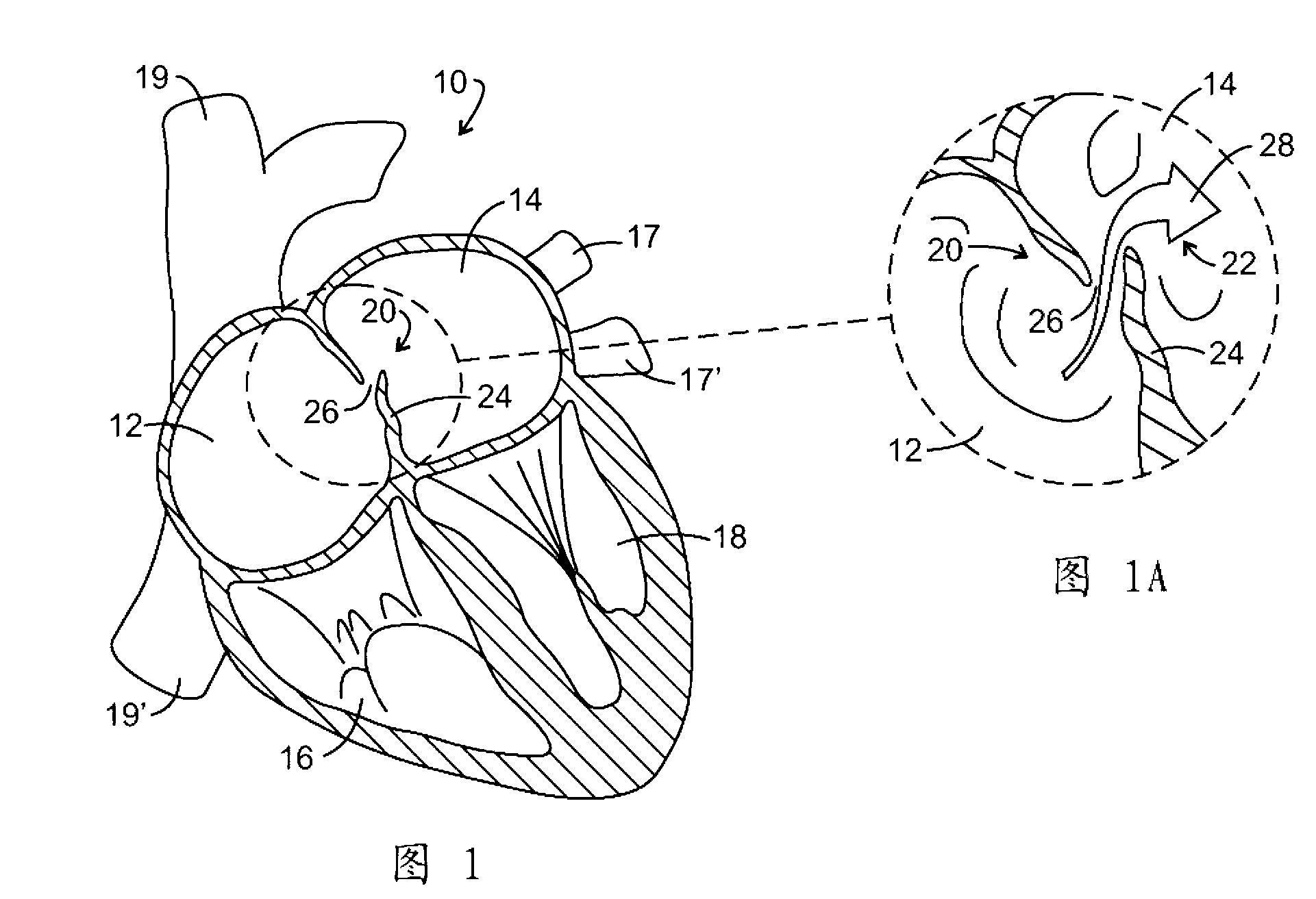
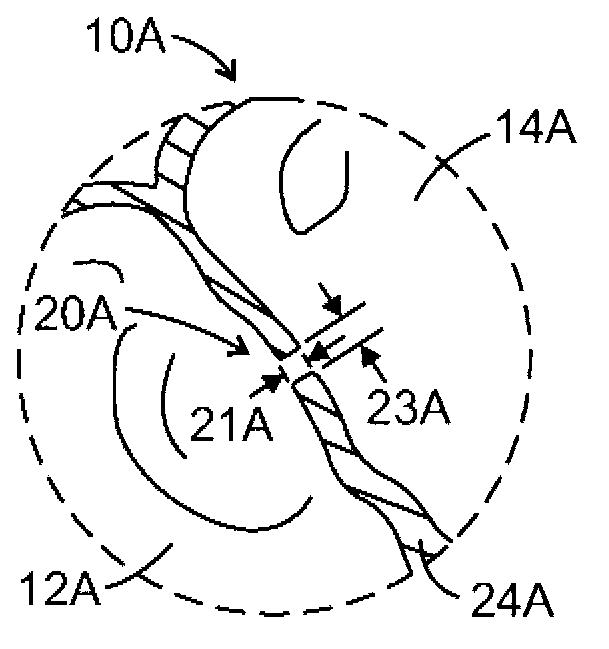
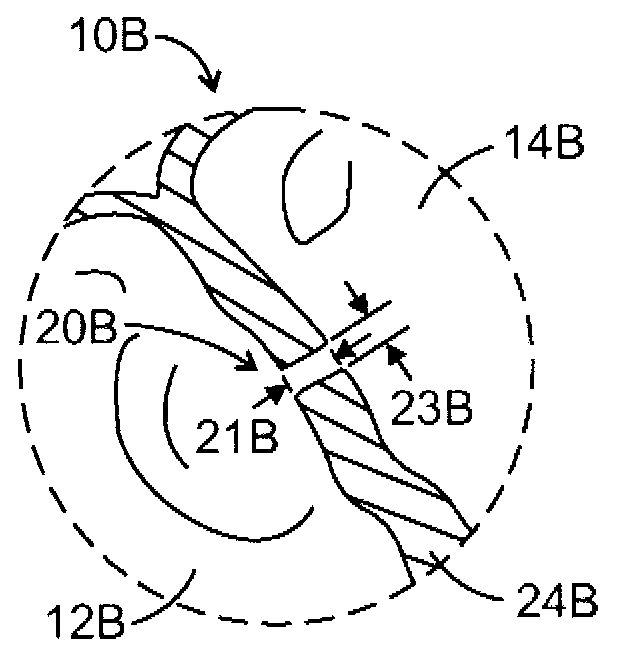
A number of medical conditions can affect the pulmonary circulation. Pulmonary hypertension describes an increase in resistance in the pulmonary arteries Pulmonary embolus is a blood clot, usually from a deep vein thrombosis that has lodged in the pulmonary vasculature.
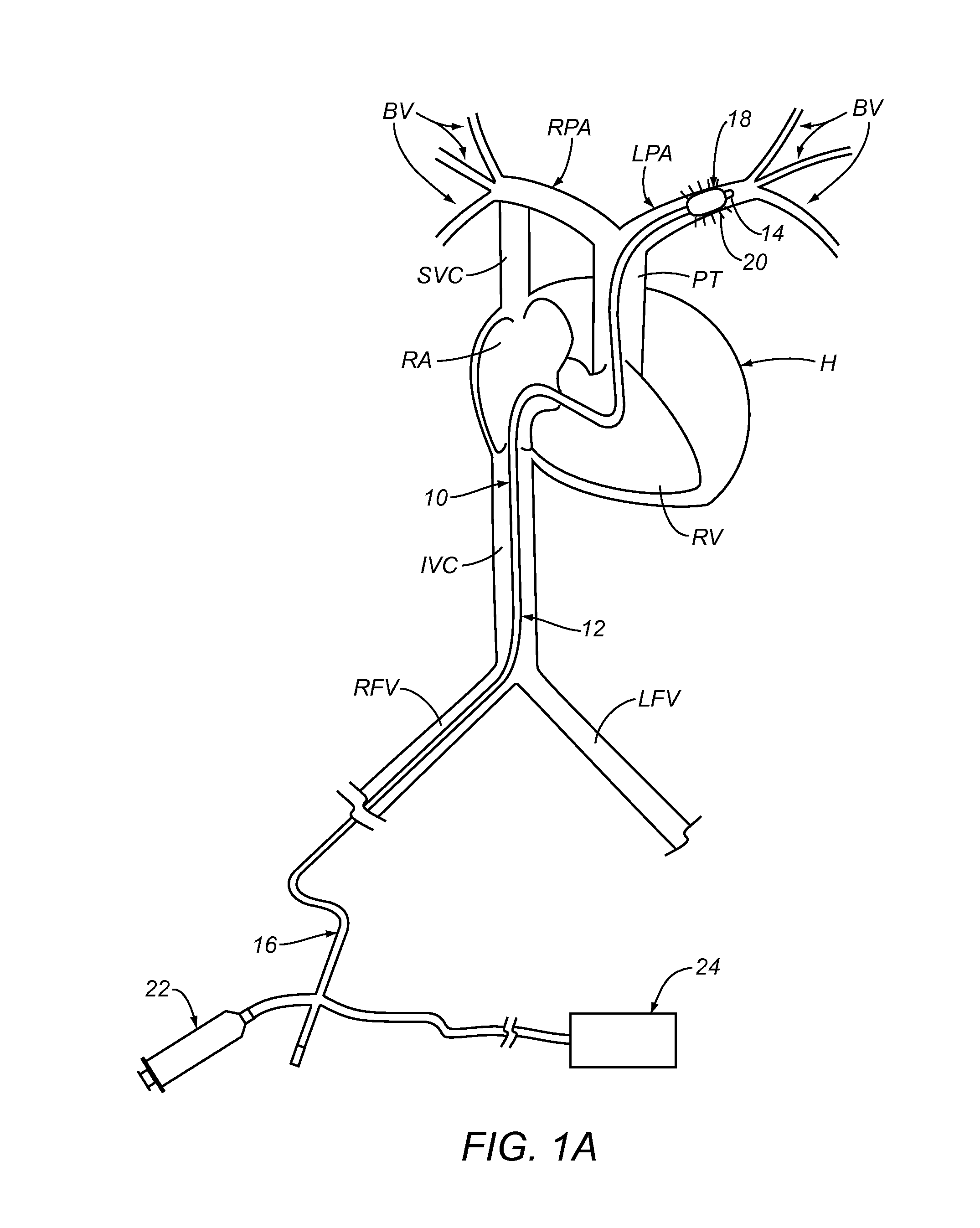
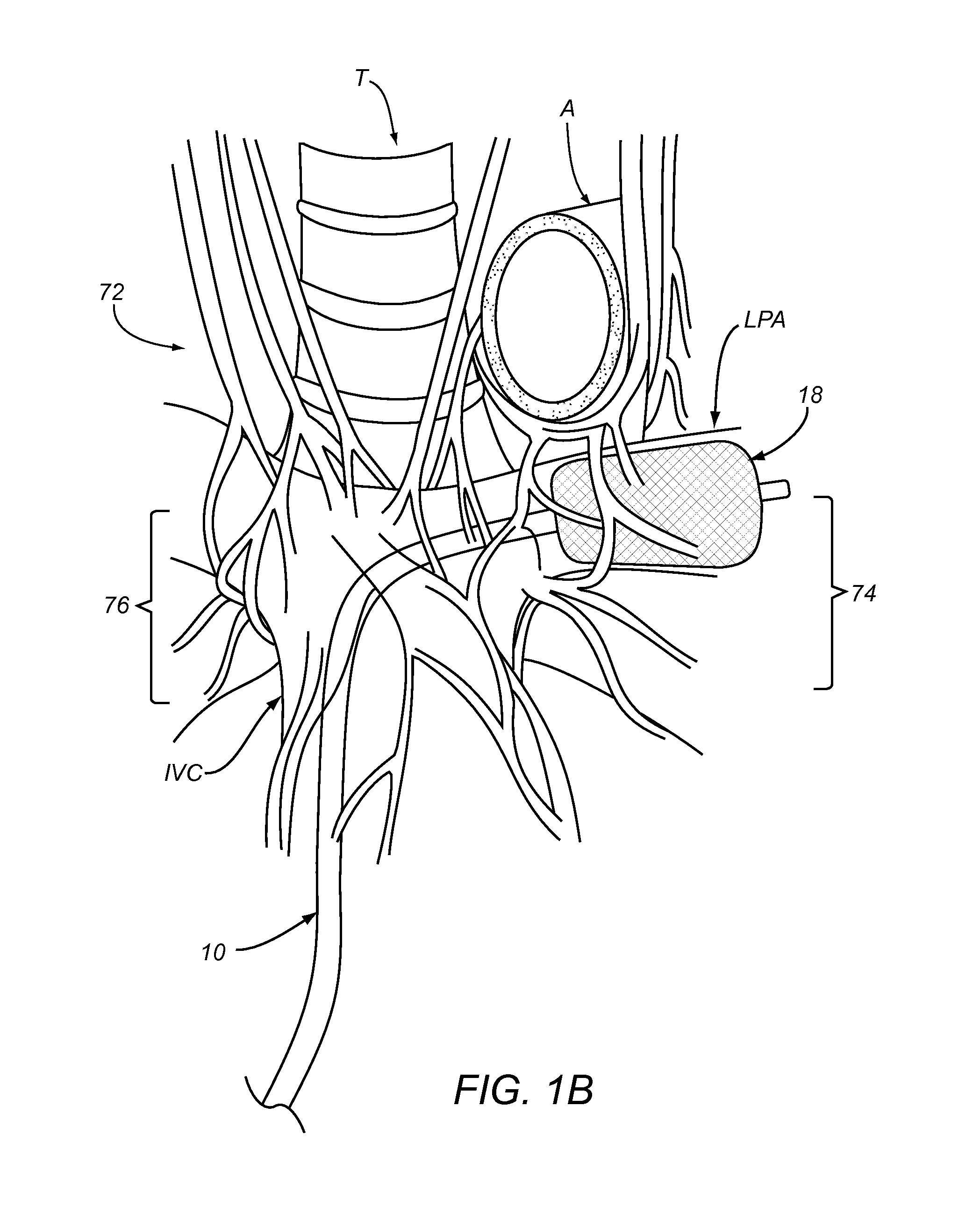
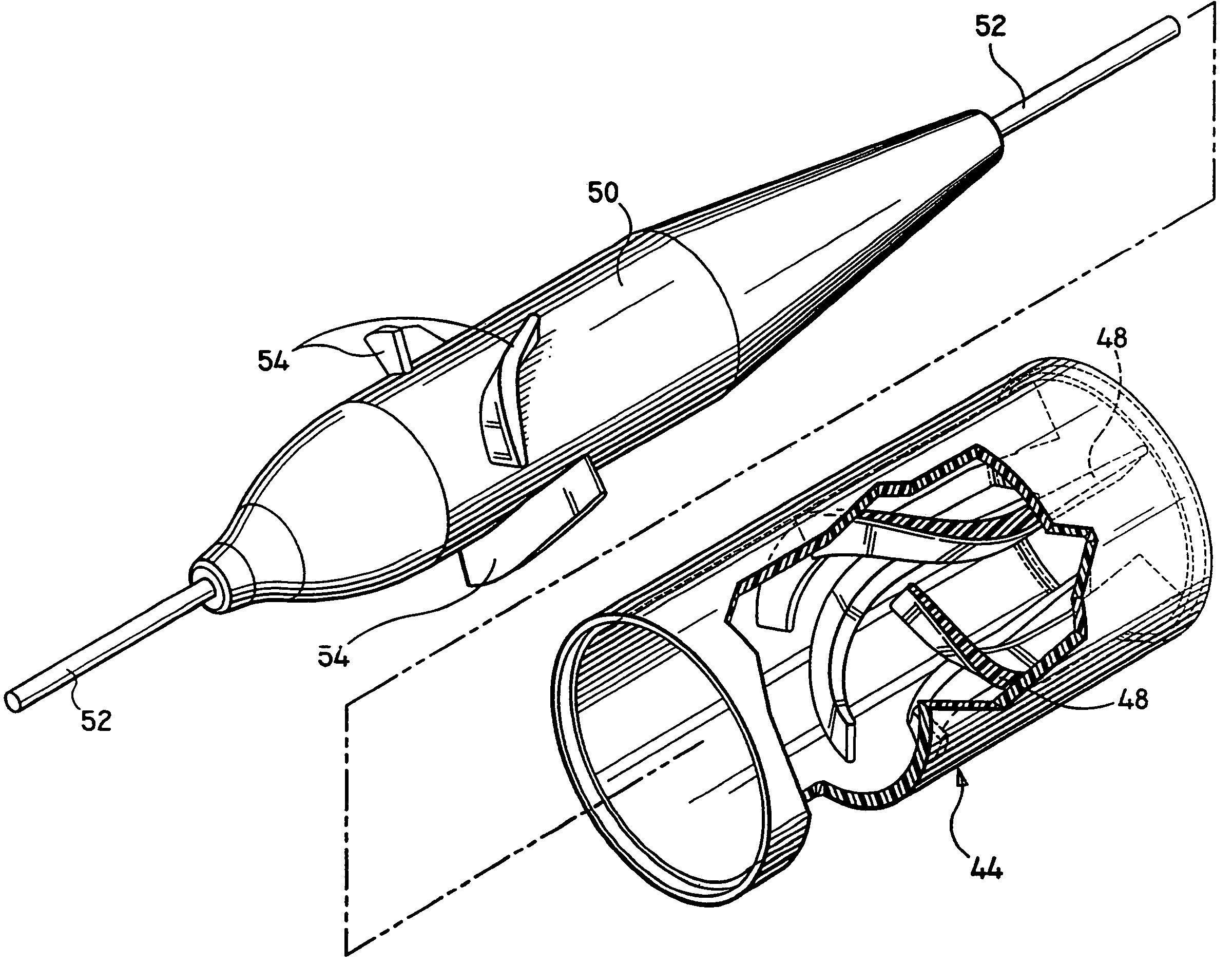
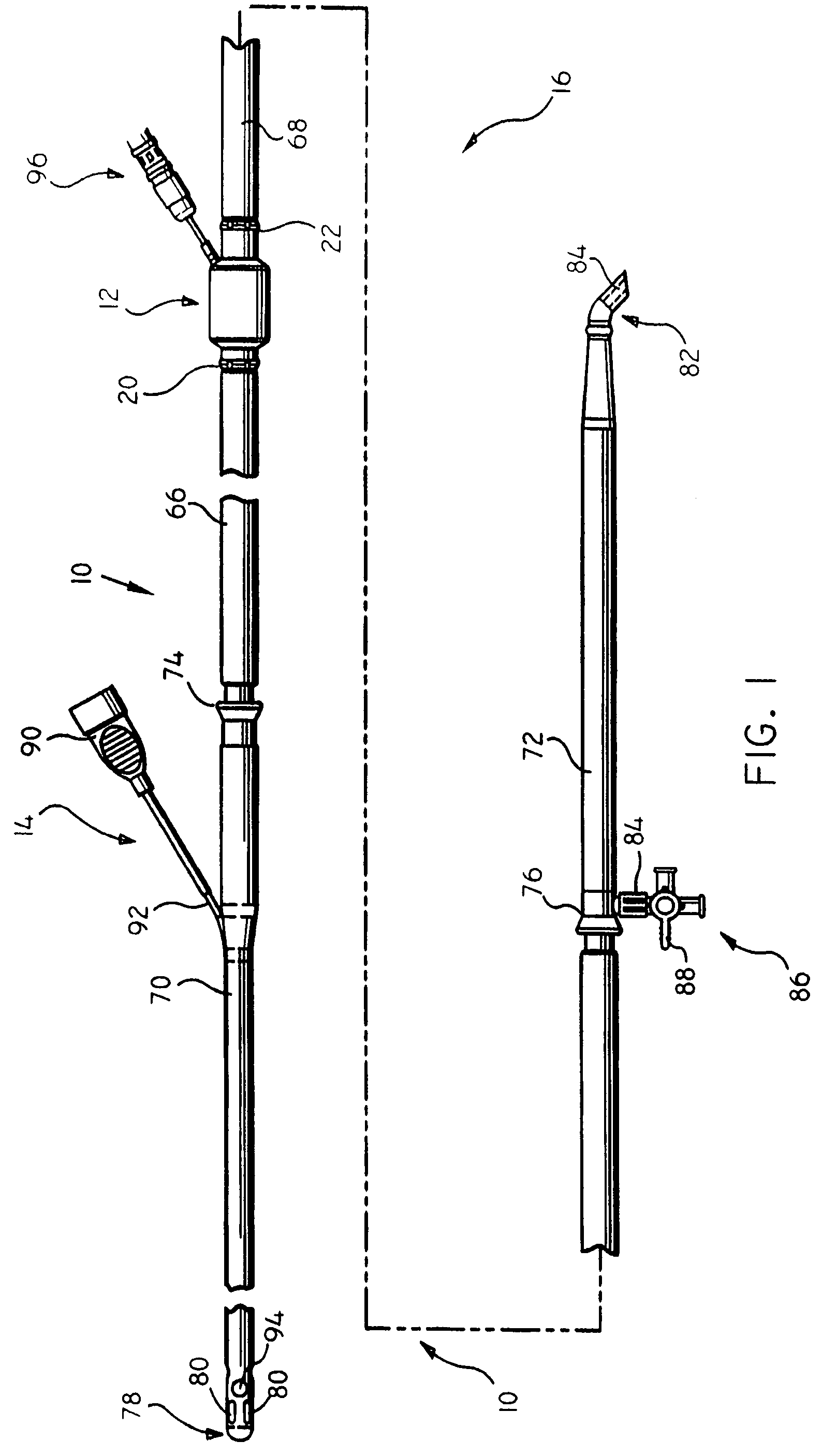
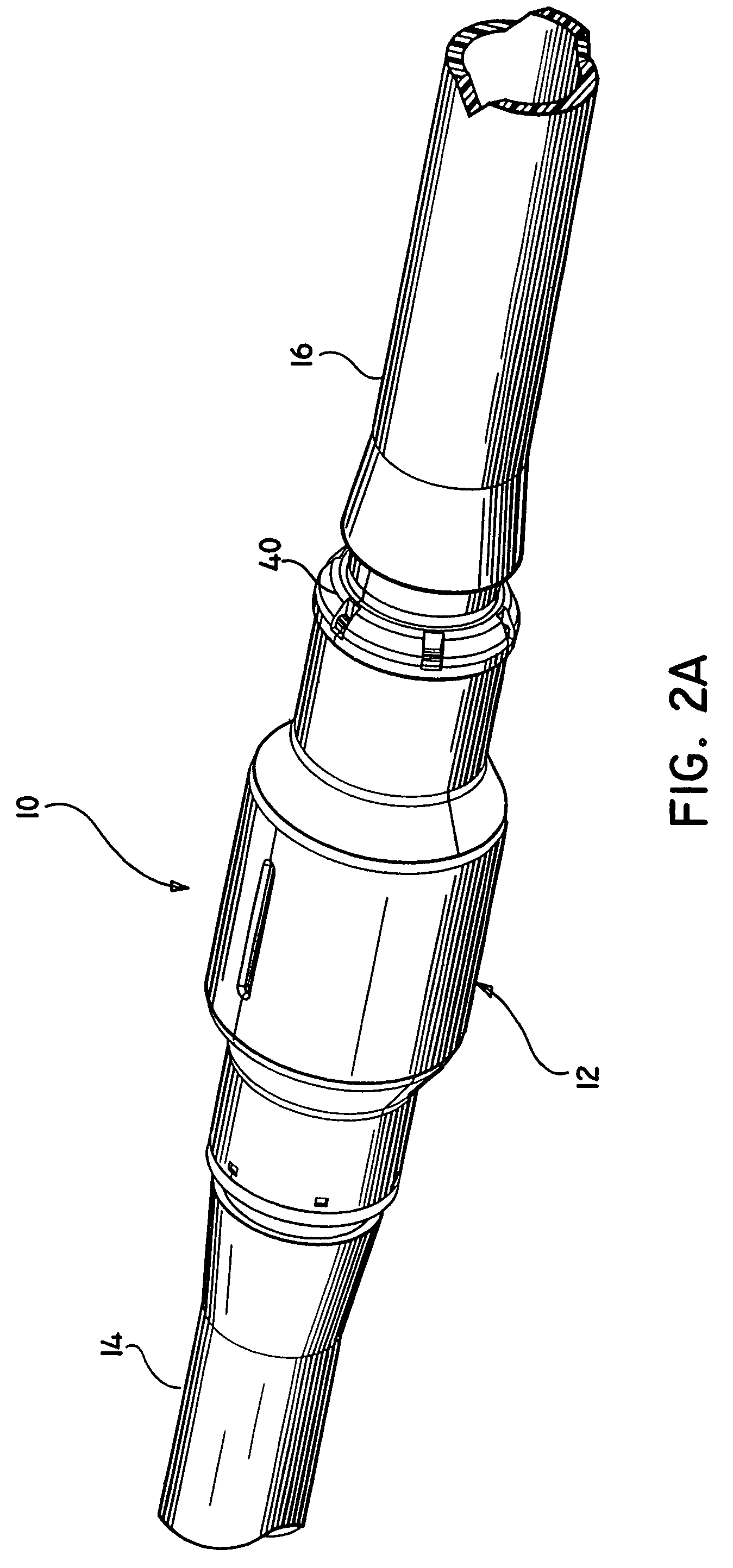
Pulmonary vein valve implant
InactiveUS20050273160A1Reduced likelihoodReduce severityStentsBronchiPulmonary vasculatureAtrial cavity
The present invention involves placing a valve between the left atrium and the lung to prevent regurgitant flow from increasing the pulmonary pressures, which may lead to pulmonary edema and congestion. Mitral stenosis or poor synchronization of the mitral valve may add additional pressures to the left atrium thus raising the pulmonary pressures and leading to congestion in the lung vasculature. By blocking the additional pressures from the mitral regurgitant flow from reaching the pulmonary circulation, the left atrium may act as a sealed vessel to allow additional aortic output. The valve placement can be intralumenal or attached to the ostium of the atrium. The device can be placed via the vascular conduits or through a surgical procedure into the pulmonary circulation. One or more devices may be placed in each of the four pulmonary veins. Additionally only one, two, three or all four veins may be implanted with the valve as desired by the physician.
Owner:DIRECT FLOW MEDICAL INC
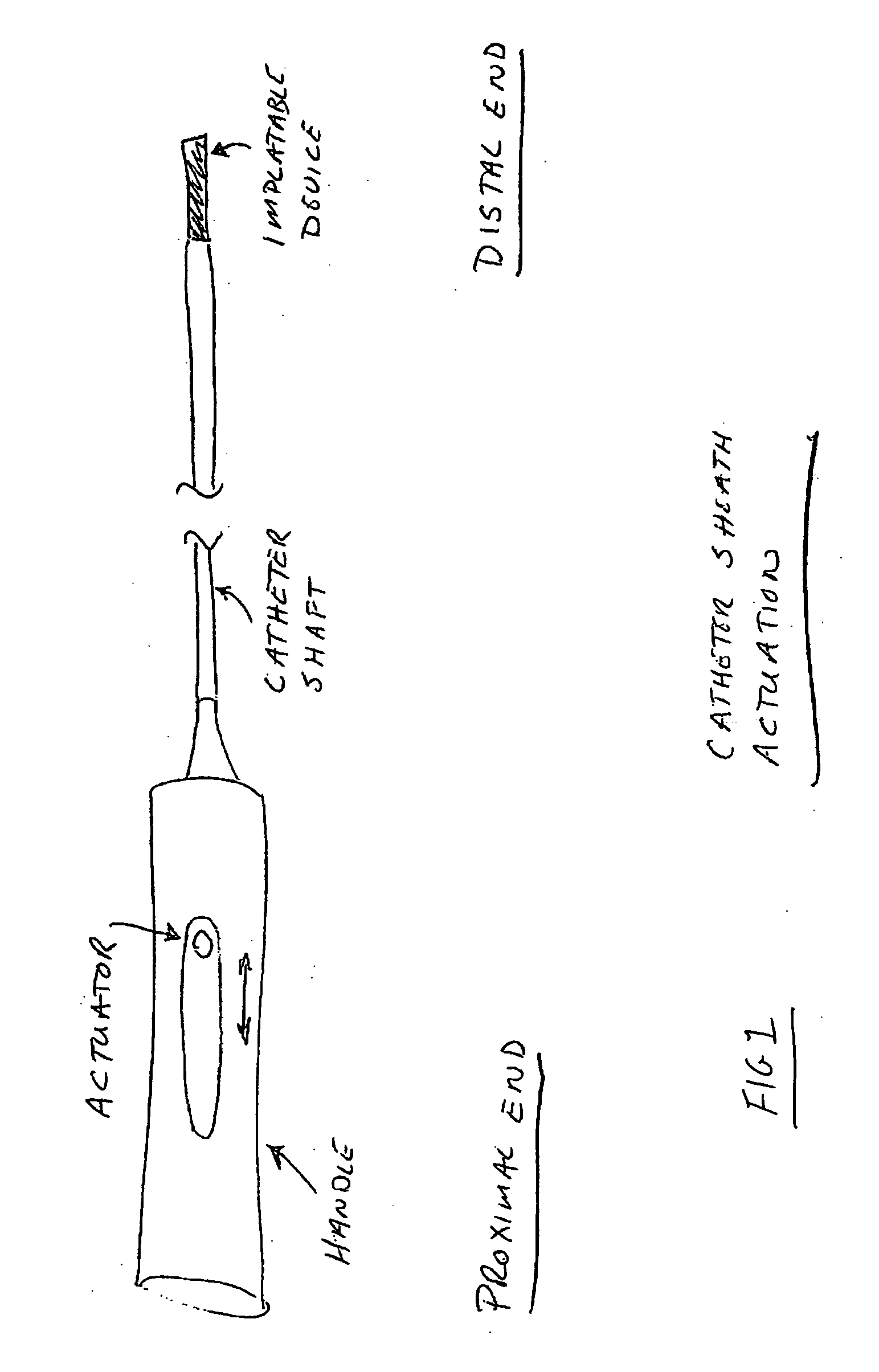
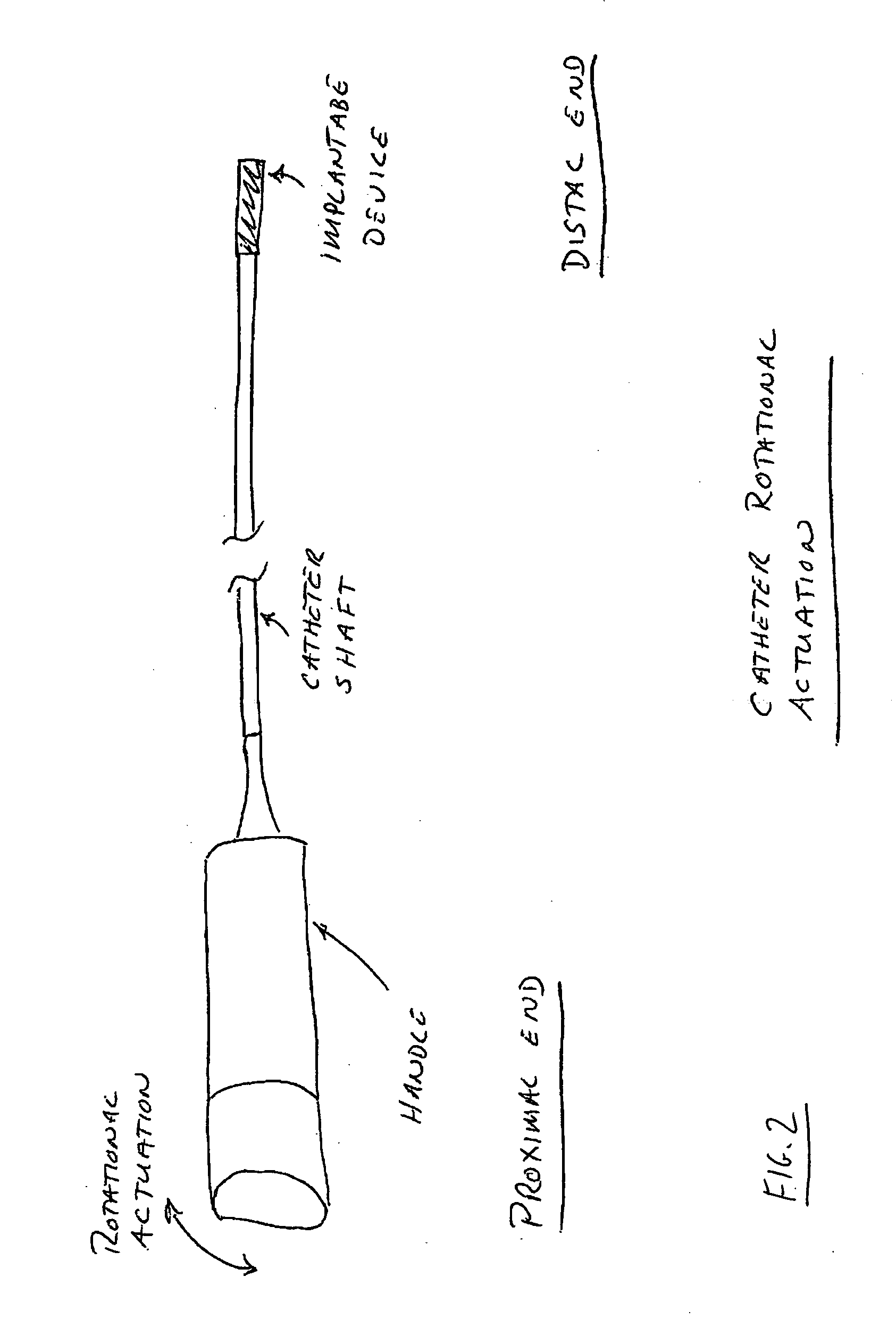
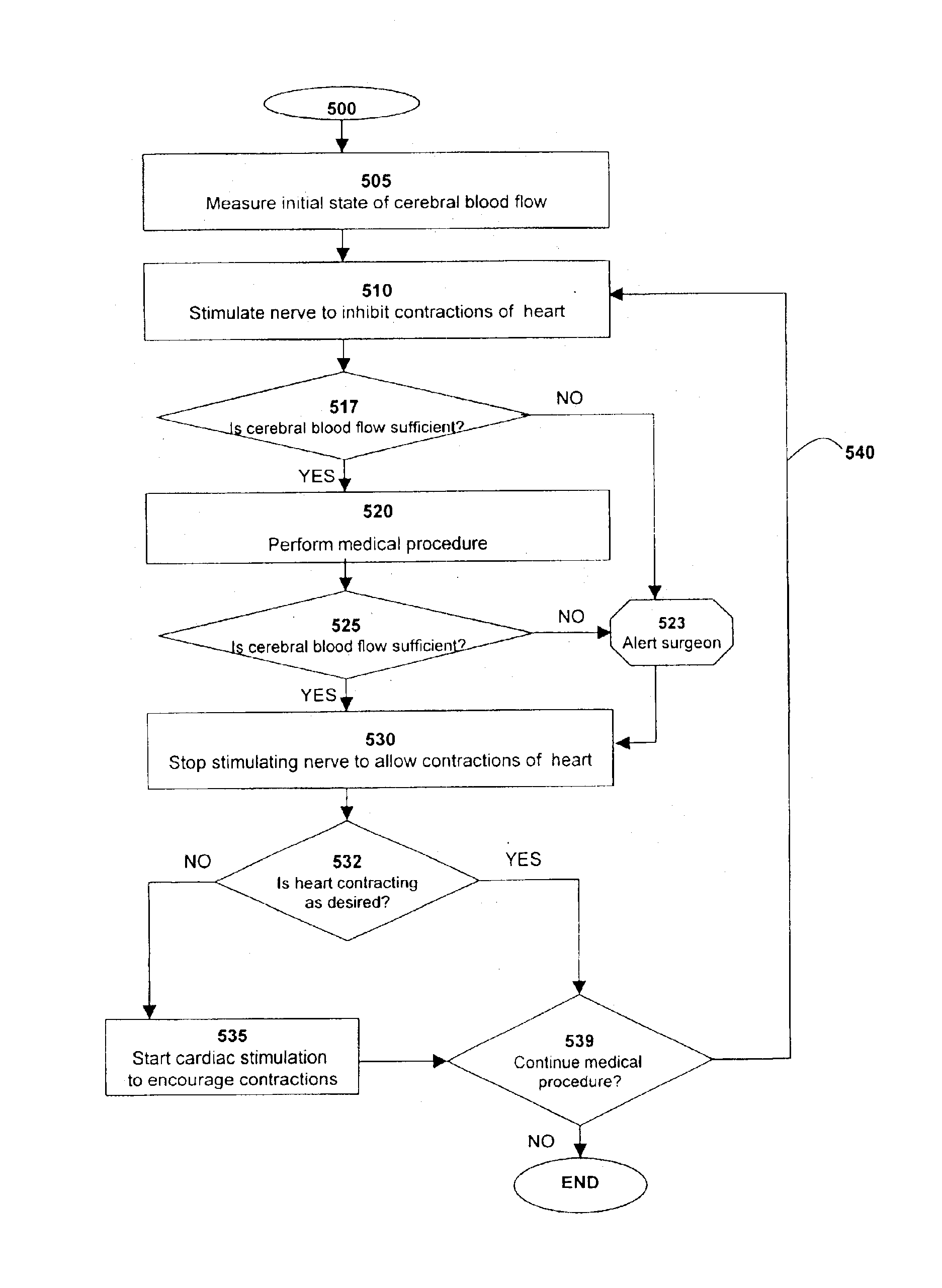
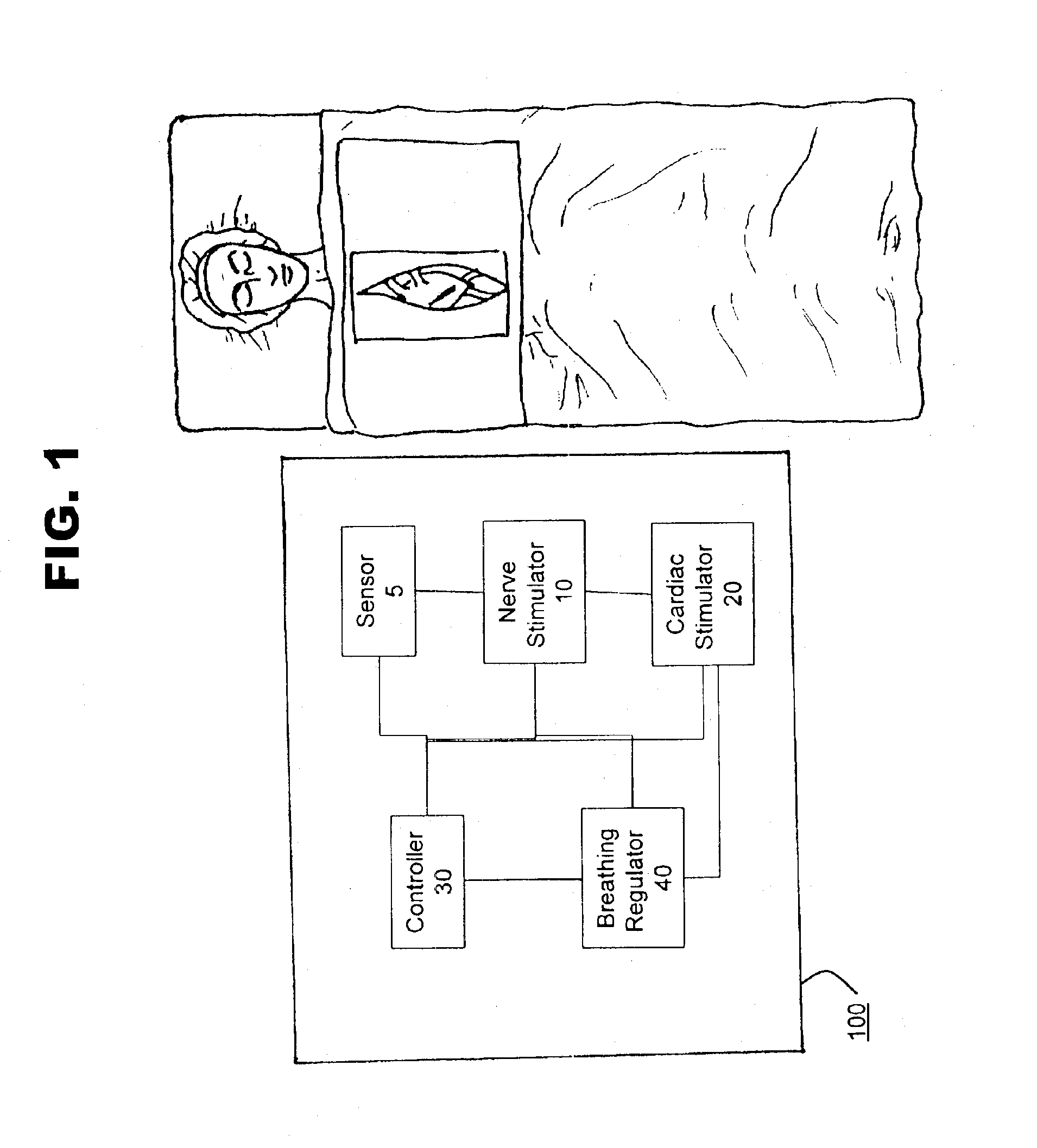
Method and system for monitoring and controlling systemic and pulmonary circulation during a medical procedure
A method of performing a medical procedure, such as surgery, is provided. The system comprises a sensor to sense a biological characteristic, such as a chemical, physical or physiological characteristic of a bodily tissue or fluid. The method also comprises a nerve stimulator in communication with the sensor to inhibit beating of a heart when the sensor senses the biological characteristic at a first value; and a cardiac stimulator in communication with the sensor to stimulate beating of the heart when the sensor senses the biological characteristic at a second value.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
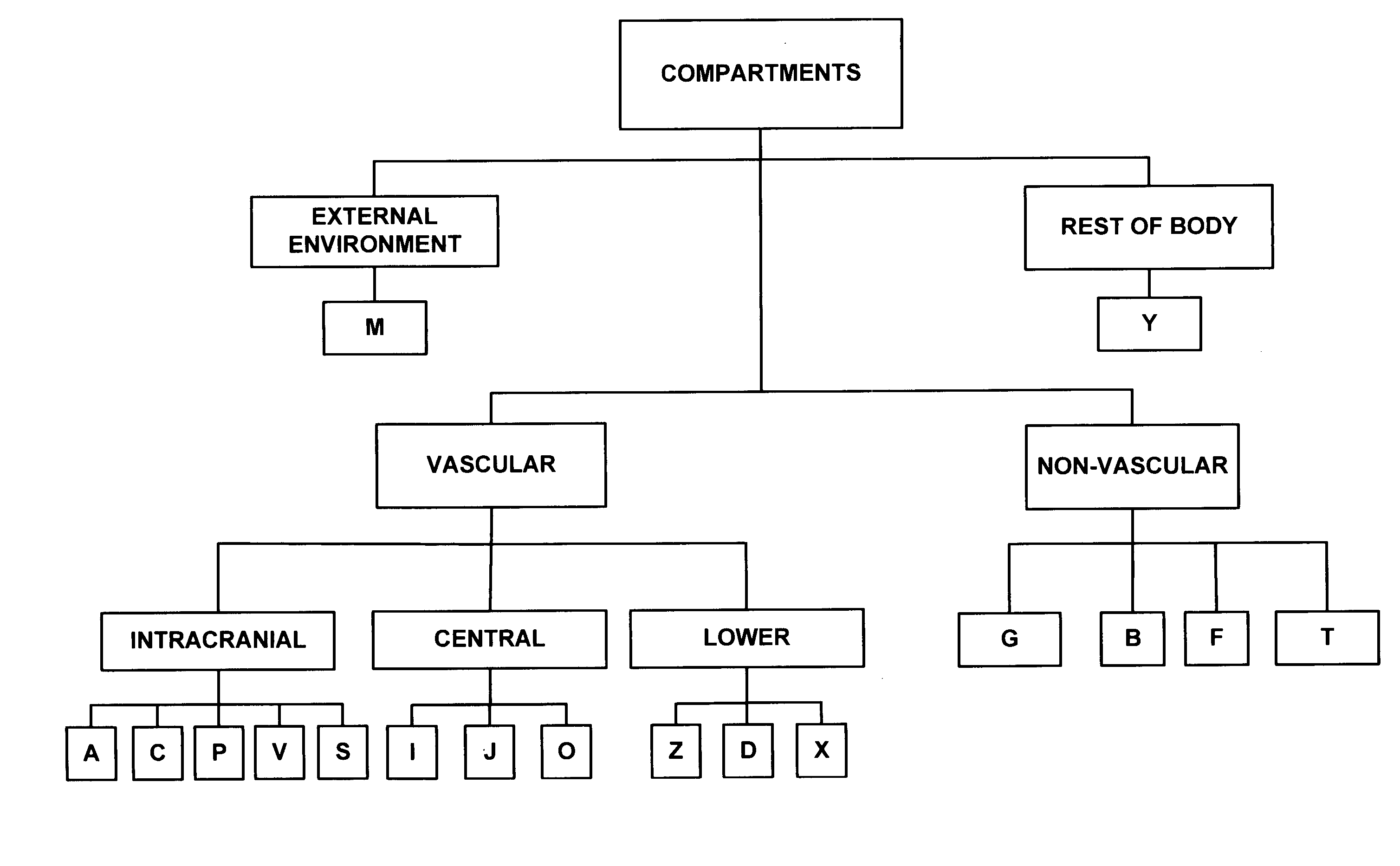
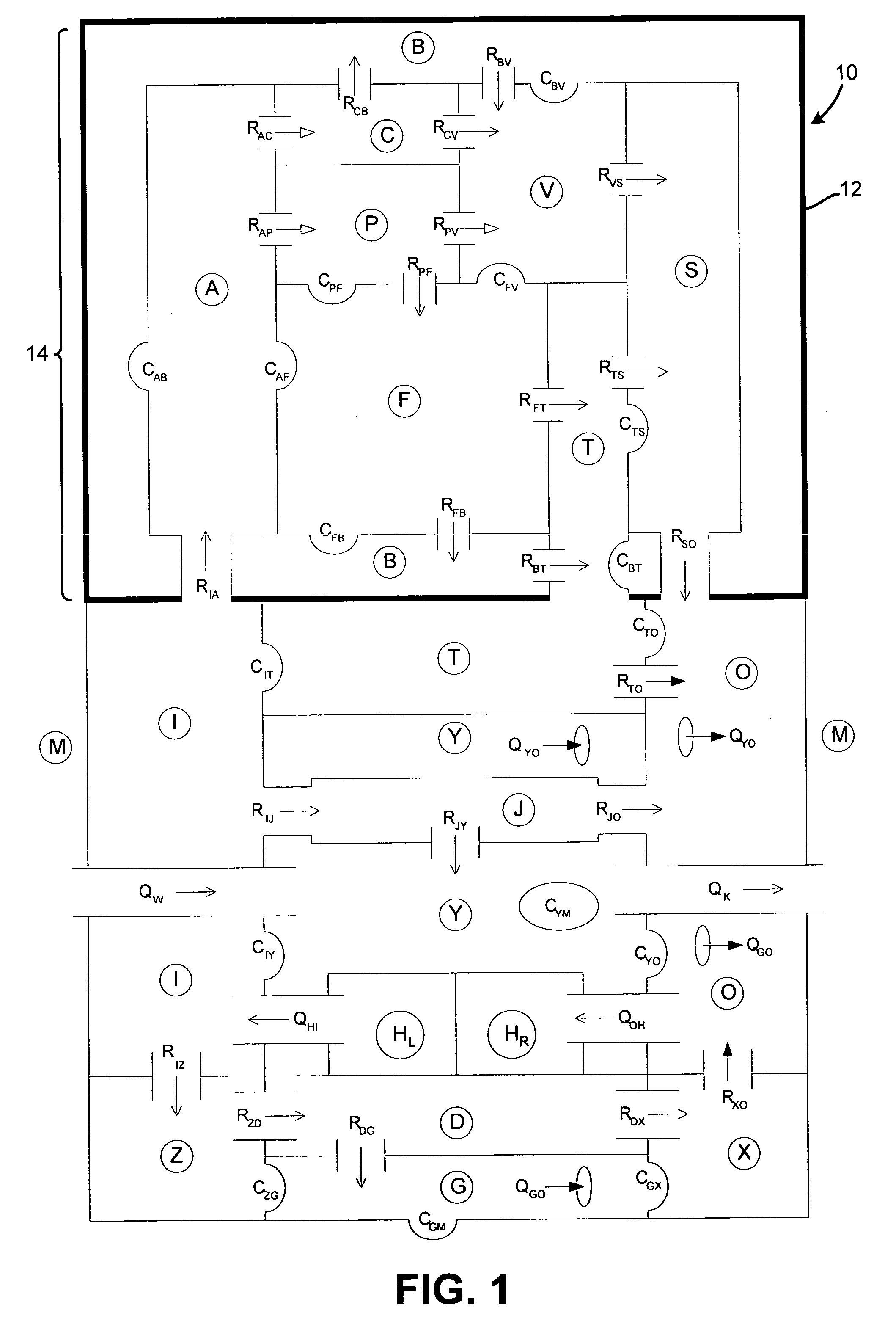
Whole-body mathematical model for simulating intracranial pressure dynamics
InactiveUS7182602B2Analogue computers for chemical processesEducational modelsPulmonary vasculatureVein
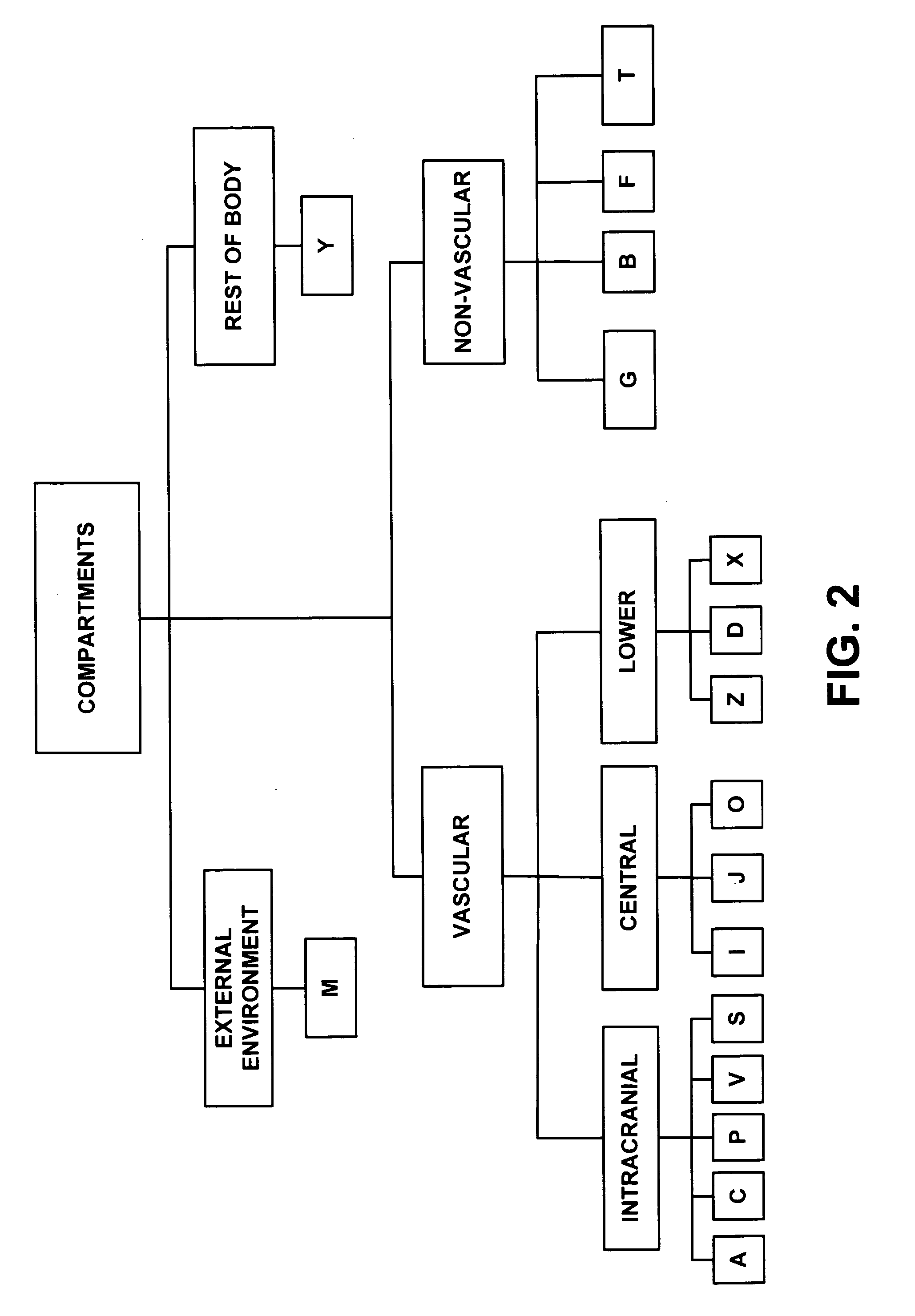
A whole-body mathematical model (10) for simulating intracranial pressure dynamics. In one embodiment, model (10) includes 17 interacting compartments, of which nine lie entirely outside of intracranial vault (14). Compartments (F) and (T) are defined to distinguish ventricular from extraventricular CSF. The vasculature of the intracranial system within cranial vault (14) is also subdivided into five compartments (A, C, P, V, and S, respectively) representing the intracranial arteries, capillaries, choroid plexus, veins, and venous sinus. The body's extracranial systemic vasculature is divided into six compartments (I, J, O, Z, D, and X, respectively) representing the arteries, capillaries, and veins of the central body and the lower body. Compartments (G) and (B) include tissue and the associated interstitial fluid in the intracranial and lower regions. Compartment (Y) is a composite involving the tissues, organs, and pulmonary circulation of the central body and compartment (M) represents the external environment.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
Apparatus and method for treating cardiovascular diseases
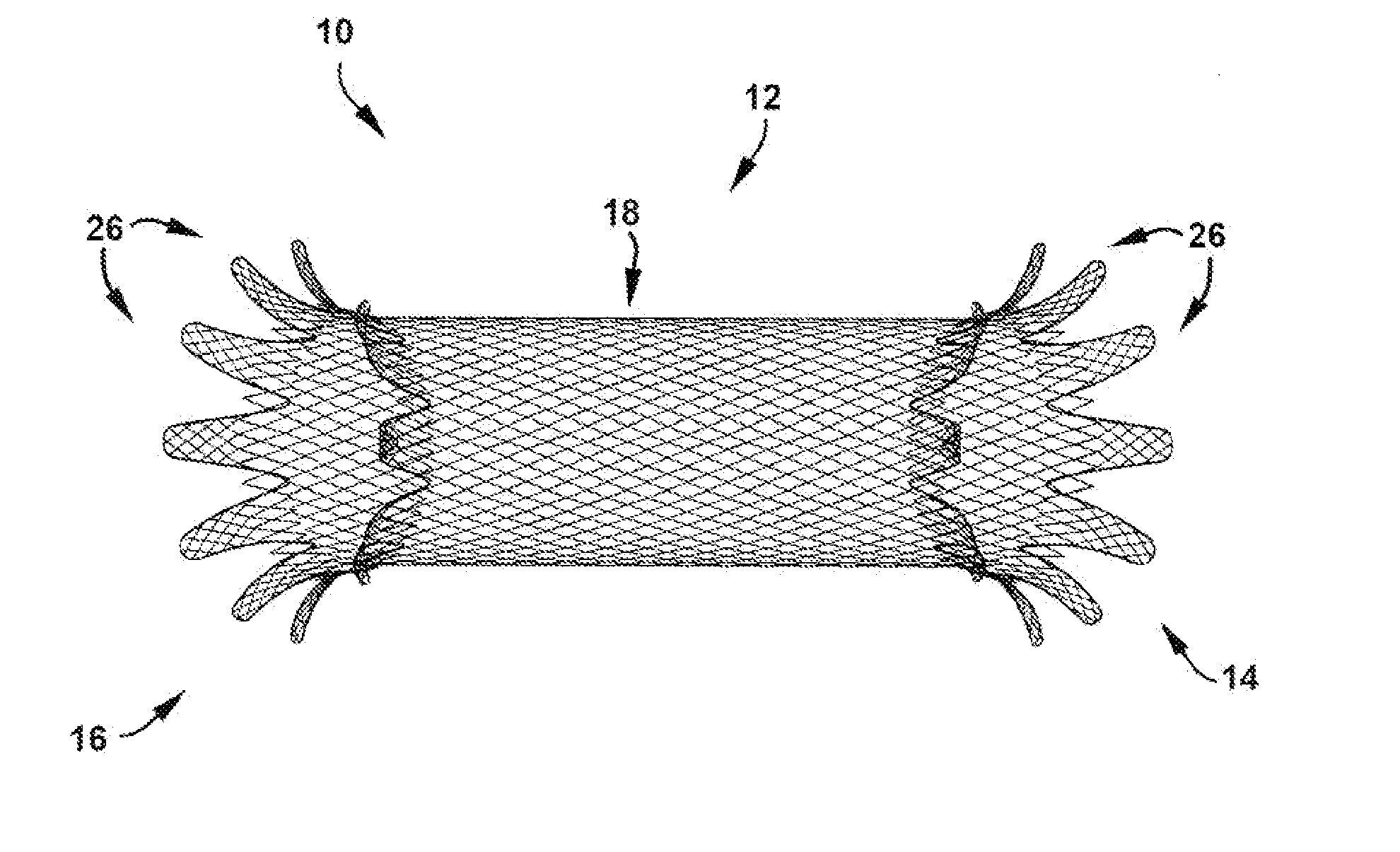
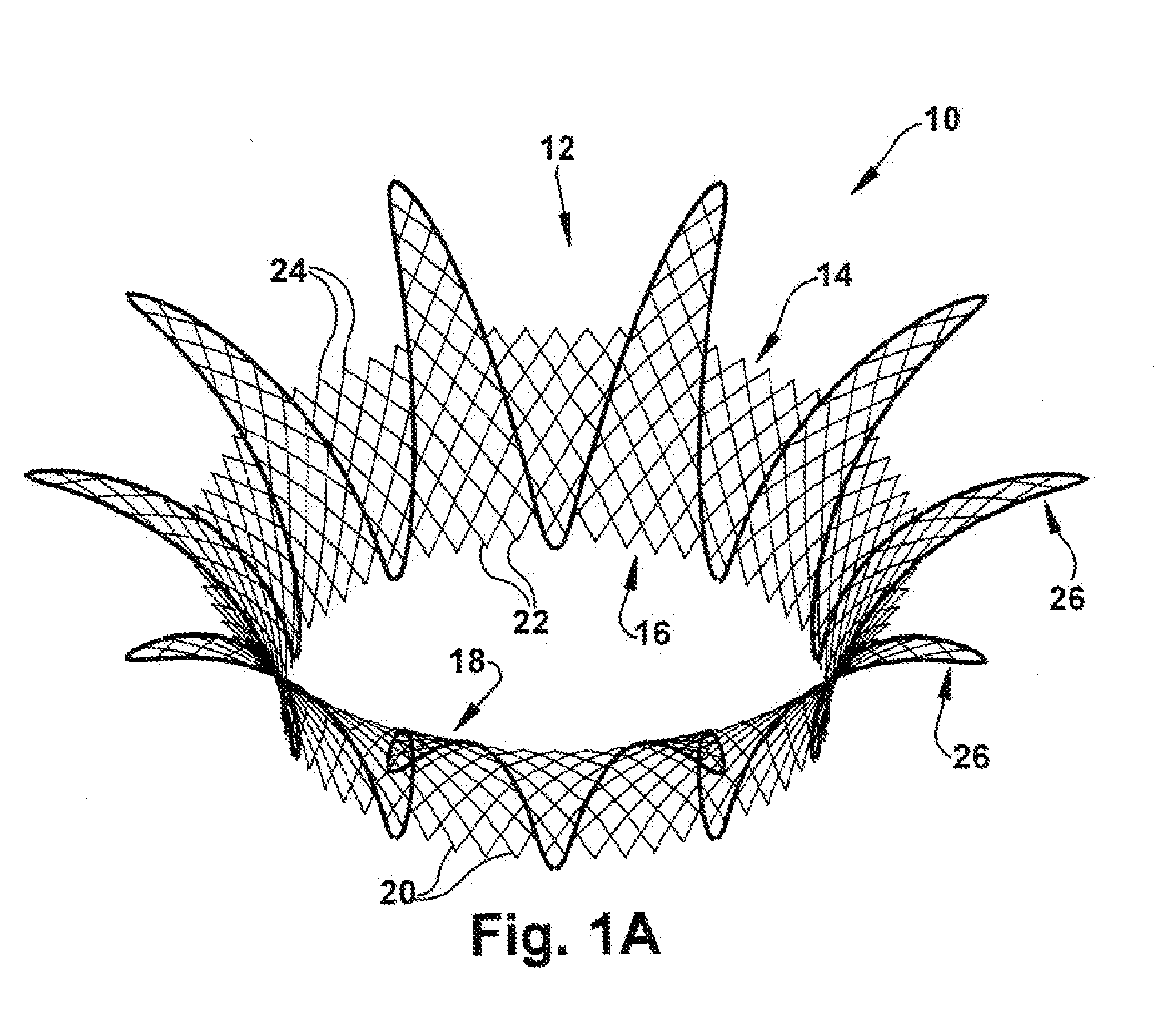
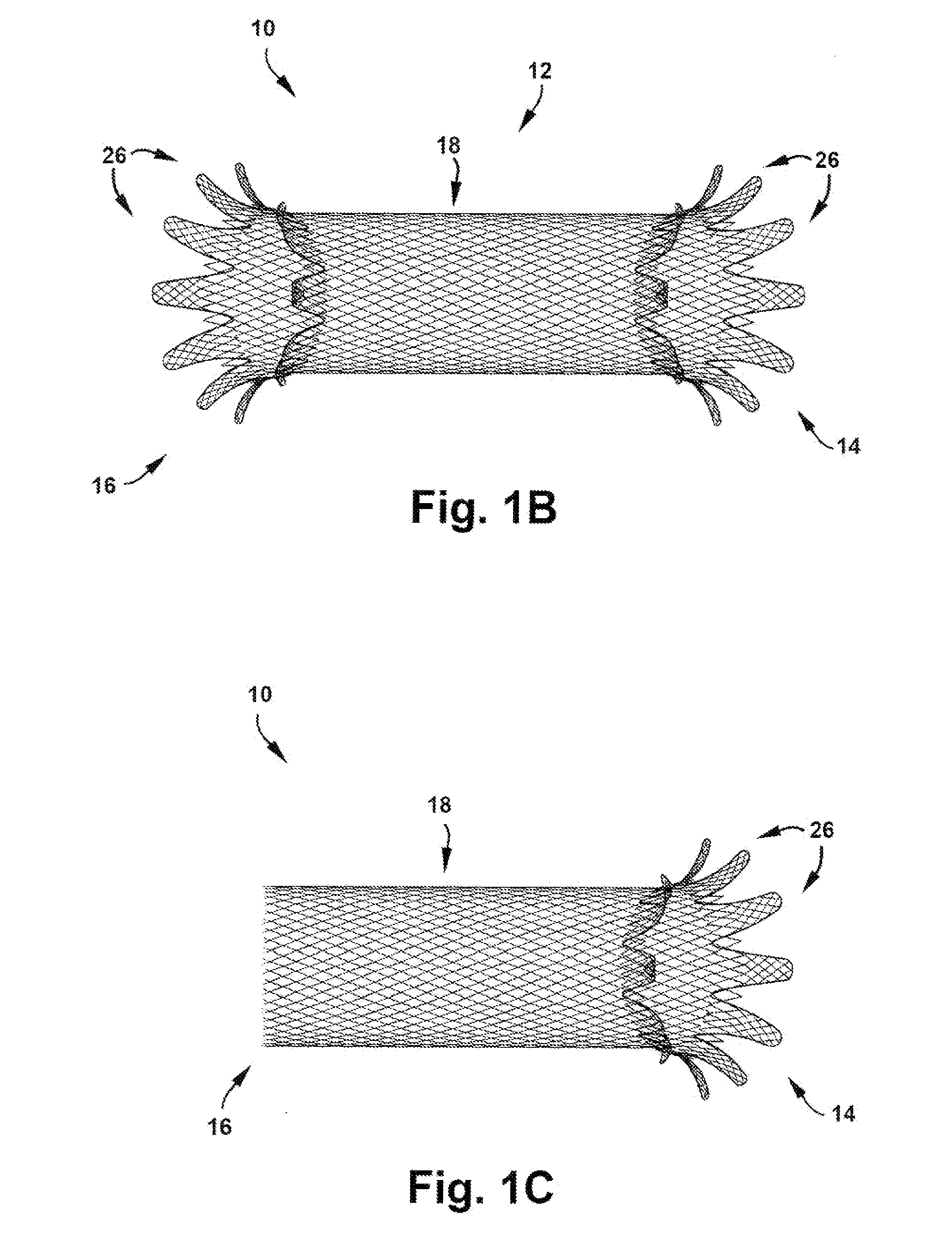
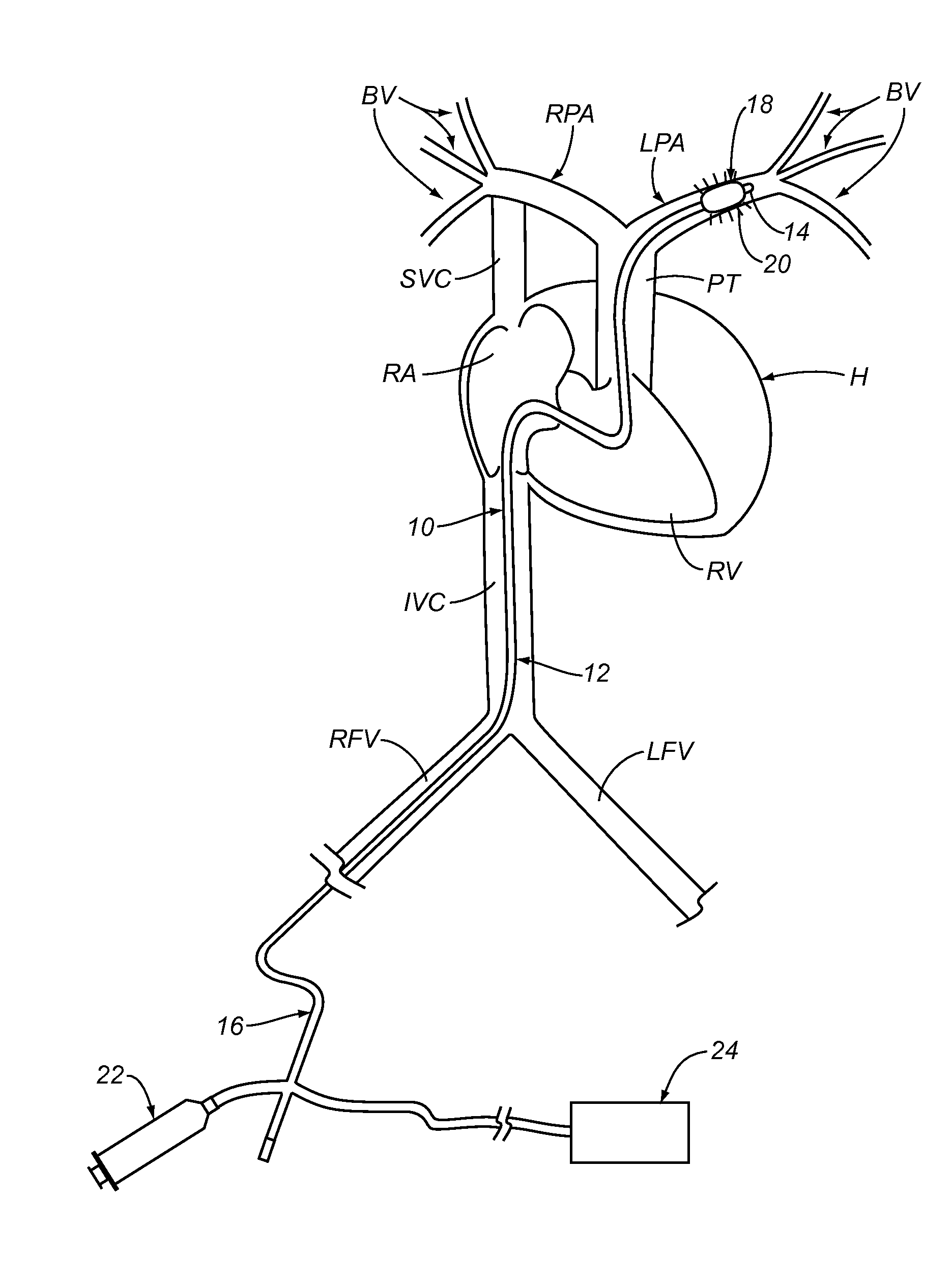
A method is provided for treating a cardiovascular disease, such as pulmonary arterial hypertension, an arrhythmia, or heart failure. One step of the method includes providing an apparatus. The apparatus includes an expandable support member having oppositely disposed proximal and distal end portions and a main body portion extending between the end portions. The proximal end portion includes a plurality of wing members extending from the main body portion. At least a portion of the expandable support member is treated with at least one therapeutic agent for eluting into a blood vessel. The expandable support member is inserted into the pulmonary vasculature and then advanced to a bifurcation in the pulmonary vasculature. The bifurcation includes the intersection of a first pulmonary vessel, a second pulmonary vessel, and a third pulmonary vessel. The expandable support member is secured at the bifurcation to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension, for example.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Apparatus and method for treating cardiovascular diseases
A method is provided for treating a cardiovascular disease, such as pulmonary arterial hypertension, an arrhythmia, or heart failure. One step of the method includes providing an apparatus. The apparatus includes an expandable support member having oppositely disposed proximal and distal end portions and a main body portion extending between the end portions. The proximal end portion includes a plurality of wing members extending from the main body portion. At least a portion of the expandable support member is treated with at least one therapeutic agent for eluting into a blood vessel. The expandable support member is inserted into the pulmonary vasculature and then advanced to a bifurcation in the pulmonary vasculature. The bifurcation includes the intersection of a first pulmonary vessel, a second pulmonary vessel, and a third pulmonary vessel. The expandable support member is secured at the bifurcation to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension, for example.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Apparatus and Methods For Treating Pulmonary Hypertension
ActiveUS20130204068A1Ameliorate pulmonary hypertensionReduced activityChiropractic devicesMedical devicesPulmonary vasculatureNerve fiber bundle
A method is described for decreasing activity of at least one sympathetic nerve, nerve fiber or neuron innervating at least one blood vessel in the pulmonary vasculature of a patient to ameliorate pulmonary hypertension. In one embodiment, the method may involve advancing an intravascular treatment device to a target location in a target blood vessel within the pulmonary vasculature of the patient and using the treatment device to decrease activity of at least one sympathetic nerve, nerve fiber or neuron innervating the target blood vessel at or near the target location to ameliorate pulmonary hypertension.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Circulatory support system
InactiveUS7264606B2Facilitate pumping functionFacilitate functioningOther blood circulation devicesBlood pumpsAxial-flow pumpPulmonary vasculature
A method for providing at least partial bypass of the heart to supplement the pumping function of the heart to thereby enable the surgeon to perform various surgical procedures thereon includes providing a circulatory assist system having a portable extracorporeal axial flow pump with a pump housing, a rotating pumping member disposed in the pump housing and inlet and outlet cannulated tubes respectively connected to inlet and outlet ports of the pump housing, accessing the patient's left atrium of the heart with the inlet cannulated tube, accessing the aorta with the outlet cannulated tube, actuating the rotating pumping member to draw oxygenated blood from the left atrium of the heart through the lumen of the inlet cannulated tube and into the inlet port of the pump housing whereby the pumping member imparts mechanical energy to the oxygenated blood passing through the pump housing and directs the oxygenated blood through the outlet port and through the lumen of the outlet cannulated tube to be transferred by the aorta to the systemic arteries and permitting the right side of the heart to function whereby oxygen-depleted blood returning through the systemic veins to the right atrium is directed through the right ventricle to the patient's lungs for oxygenation and subsequent pulmonary circulation.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
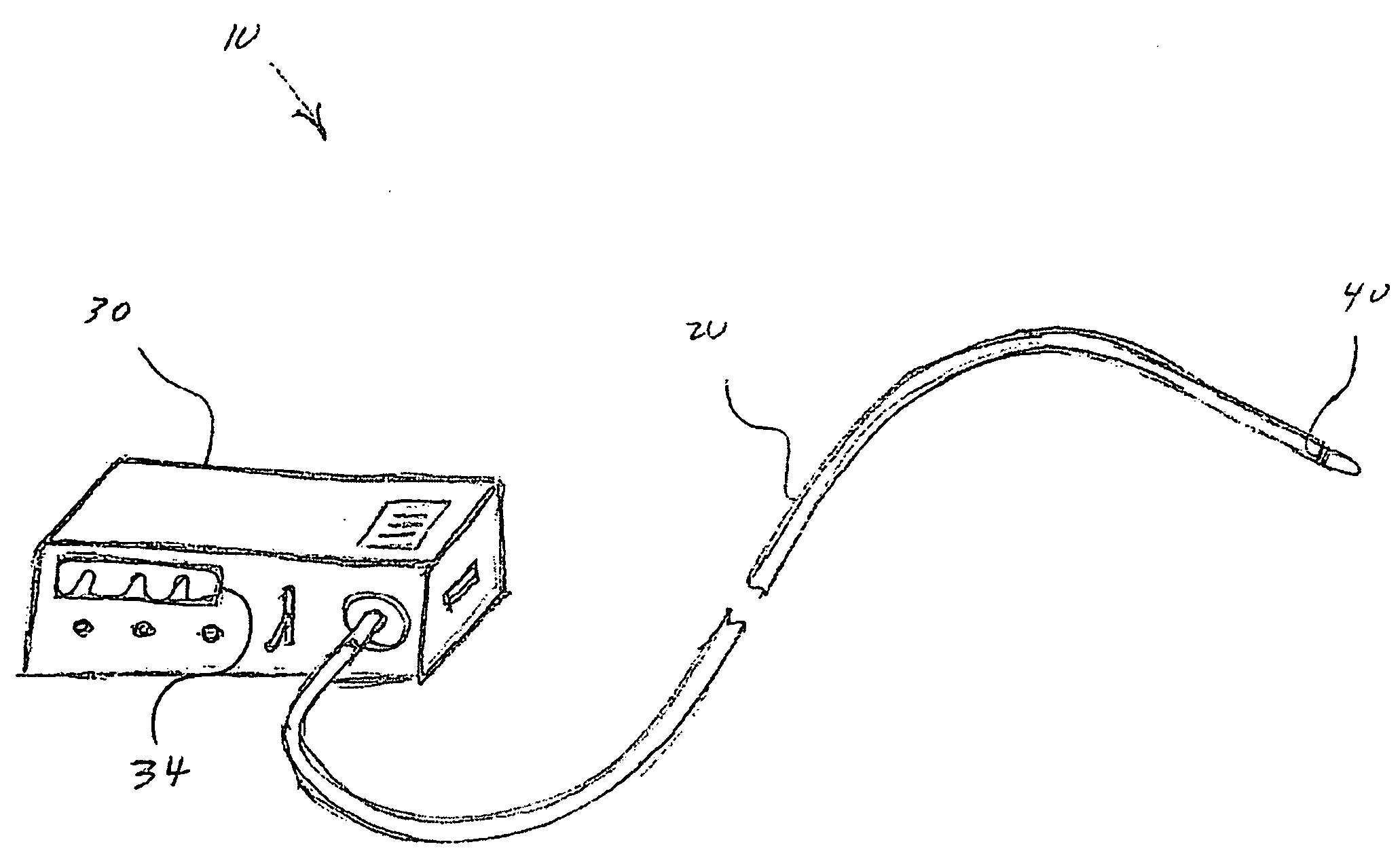
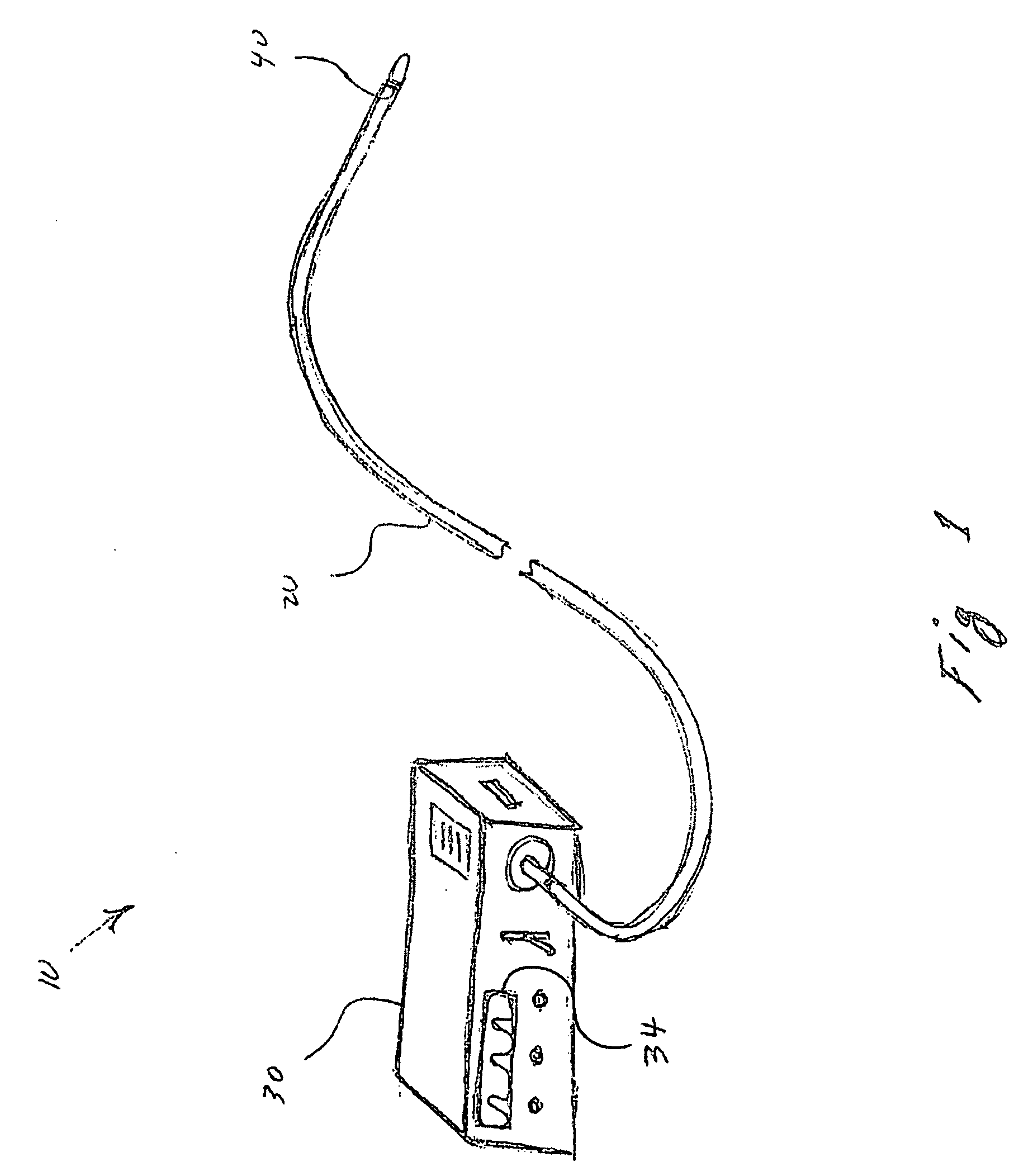
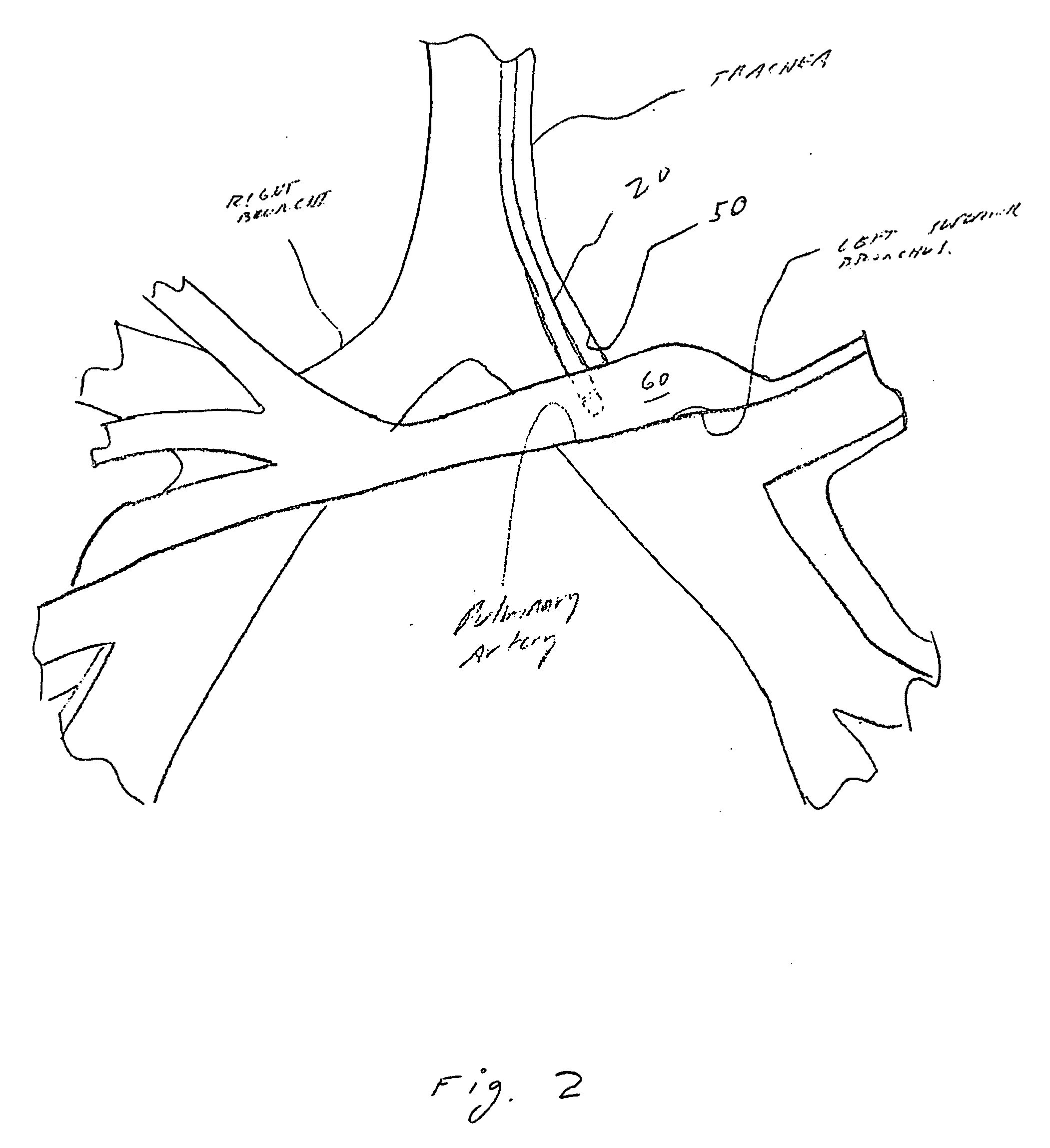
Method and system for measuring pulmonary artery circulation information
Minimally invasive systems and methods are described for measuring pulmonary circulation information from the pulmonary arteries. A transbronchial Doppler ultrasound catheter is advanced through the airways and in the vicinity of the pulmonary artery. Doppler ultrasound energy is sent through the airway wall and across the pulmonary artery to obtain velocity information of blood flowing through the artery. The velocity information is used to compute pulmonary circulation information including but not limited to flowrate.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Heart-lung preparation and method of use
InactiveUS20140370490A1Easy to produceMaintain activityDead animal preservationEducational modelsPulmonary vasculatureLung structure
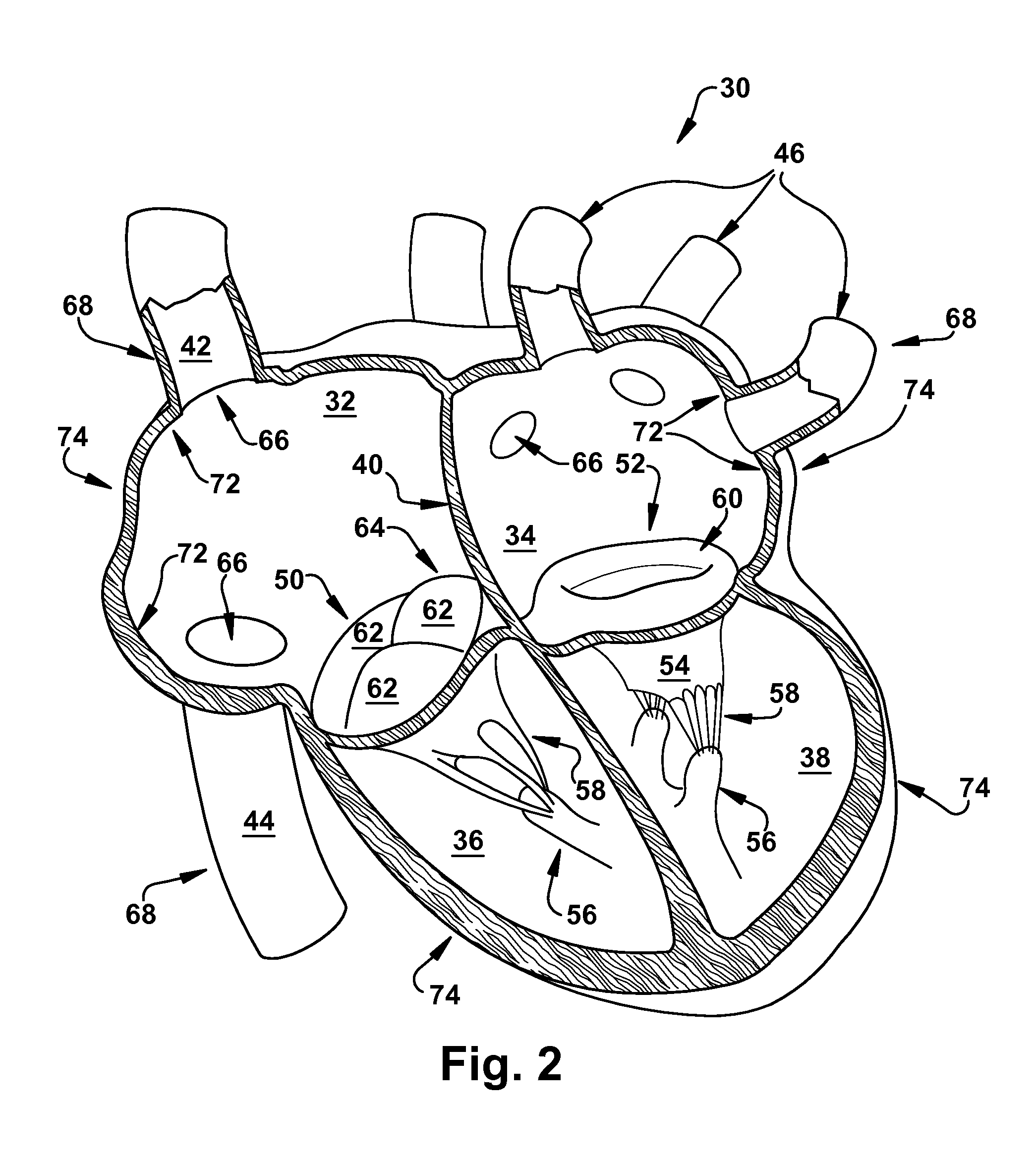
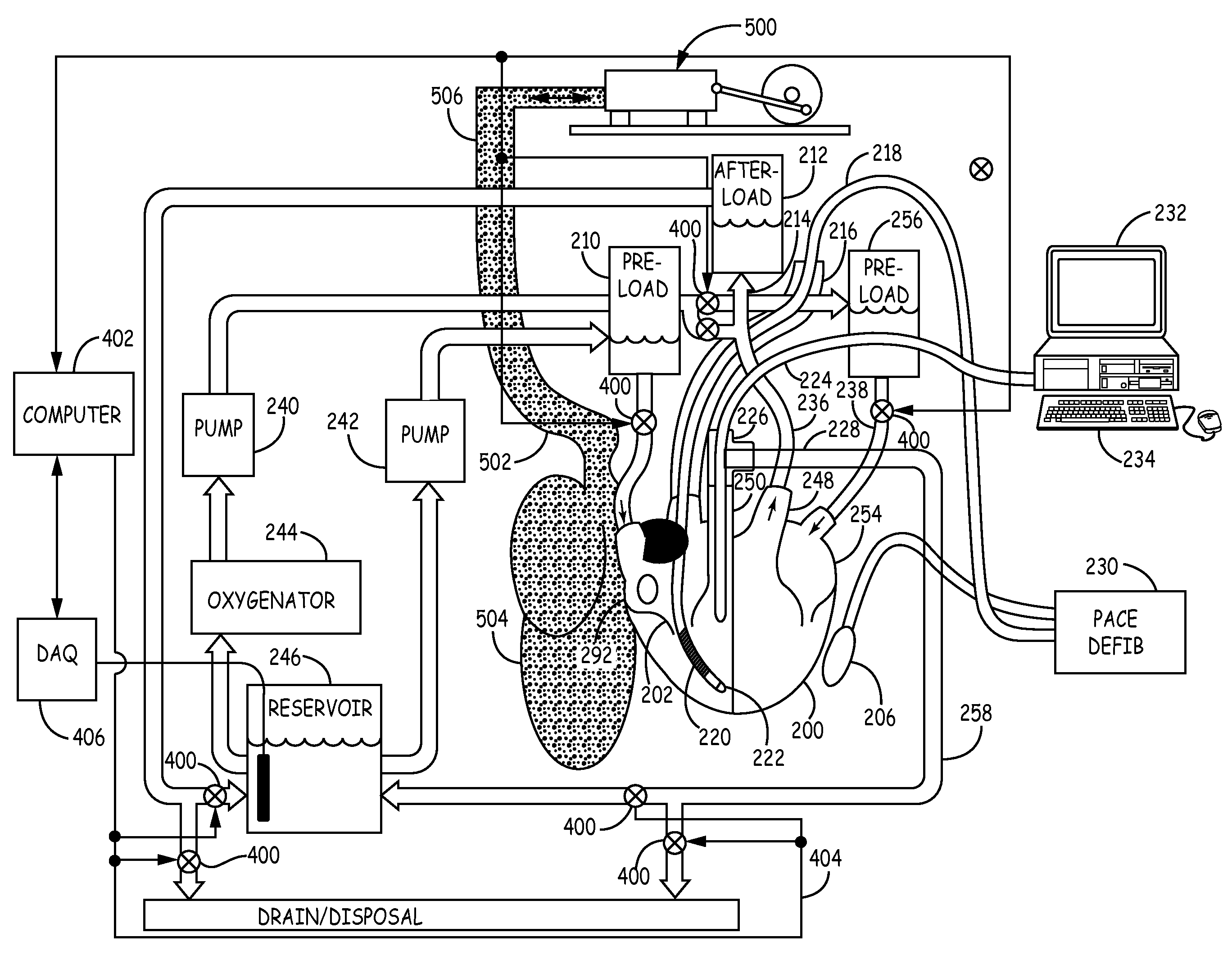
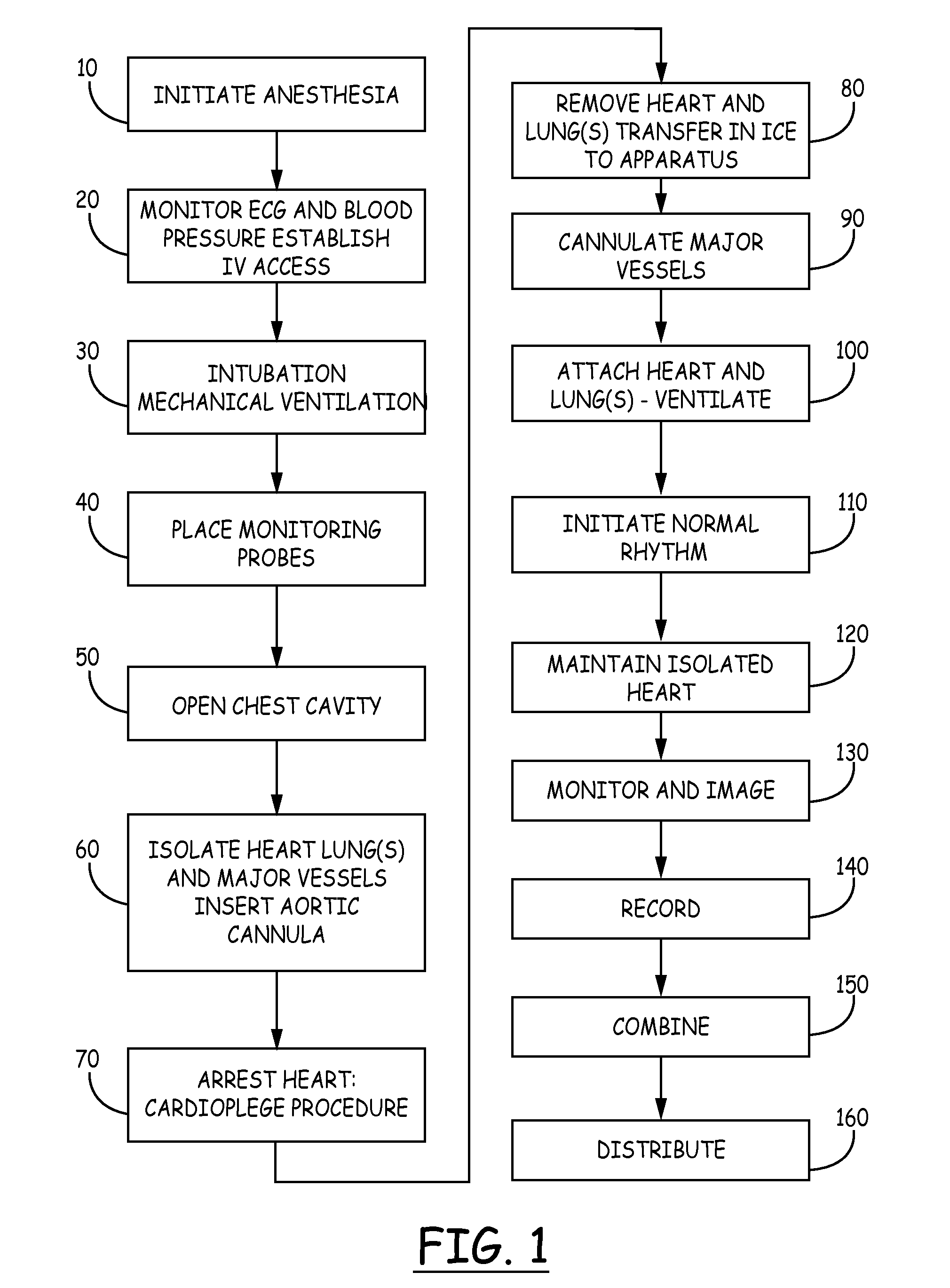
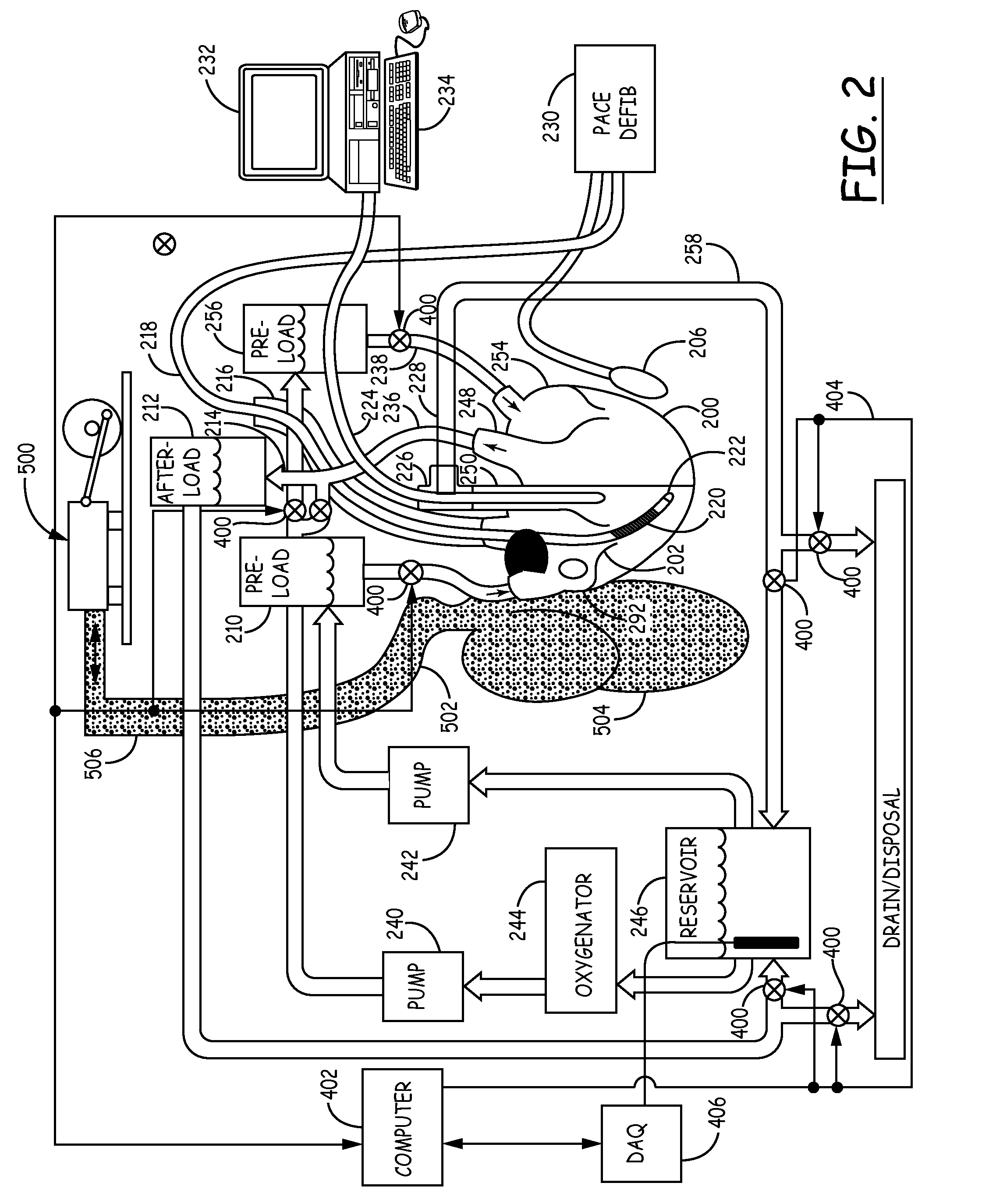
An isolated heart or heart-lung preparation in which essentially normal pumping activity of all four chambers of the heart is preserved, allowing for the use of the preparation in conjunction with investigations of electrode leads, catheters, ablation methods, cardiac implants and other medical devices intended to be used in or on a beating heart. The system can be designed to be used within a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) unit or a X-ray computed tomography (CT) scanner. The preparation may also be employed to investigate heart and lung functions, in the presence or absence of such medical devices. In order to allow comparative imaging visualizations of either or simultaneously the heart and / or lung structures and devices located within the chambers of the heart or vessels or bronchi within the lungs, a clear perfusate such as a modified Krebs buffer solution with oxygenation is circulated through all four chambers of the heart and thus the coronary and / or pulmonary vasculatures. A ventilator with intubation tube can be used to inflate / deflate the lungs and / or provide oxygen to the isolated organs. The preparation and recordings of the preparation may be used in conjunction with the design, development and evaluation of devices for use in or on the heart and / or lungs, as well as for use as an investigational and teaching aid to assist physicians and students in understanding the operation of the cardiopulmonary system.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and display apparatus for non-invasively determining pulmonary characteristics by measuring breath gas and blood gas
InactiveUS20100179392A1Solve the real problemSensorsBlood flow measurementPulmonary vasculatureLung structure
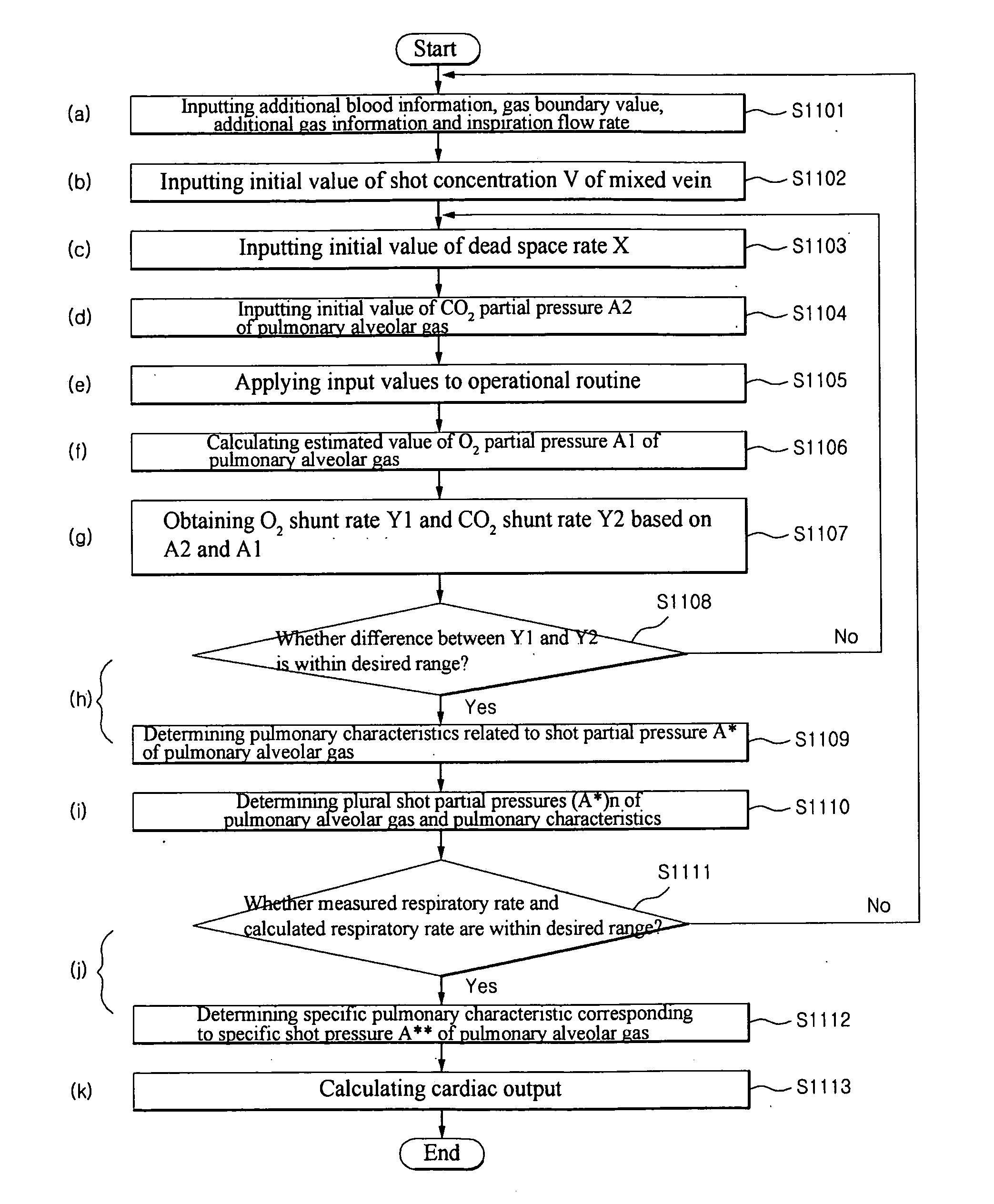
A method for non-invasively determining pulmonary characteristics by measuring breath gas and blood gas and a display apparatus for the same, and for estimating major physiological characteristics, such as respiratory characteristics of lungs-pulmonary circulation system, cardiac functional characteristics, structural characteristics of lungs, etc. by applying primary measurement parameters obtained from ventilation gas and blood during breathing; and a display apparatus useful for the same.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
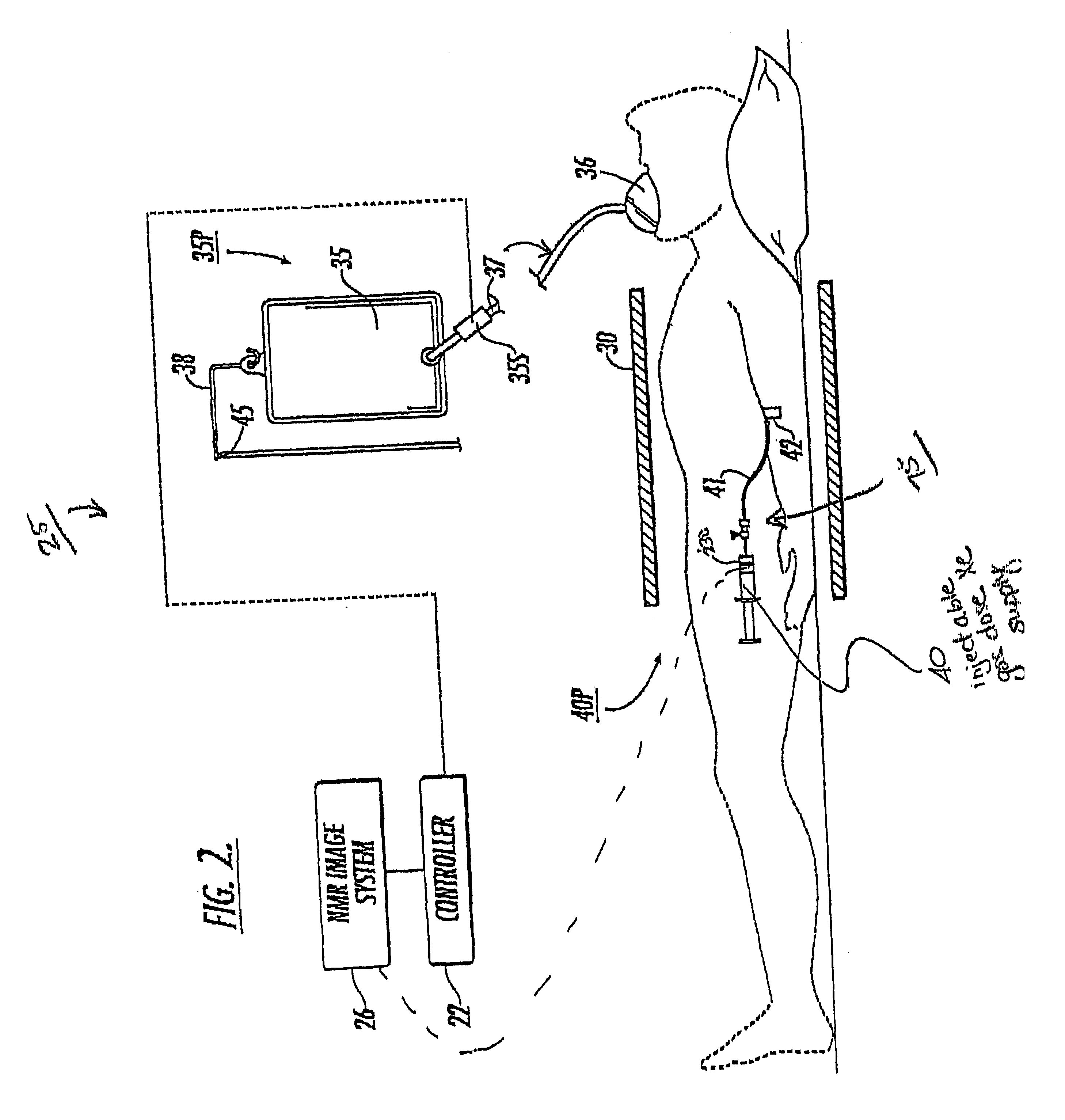
Diagnostic procedures using direct injection of gaseous hyperpolarized 129Xe and associated systems and products
InactiveUS6630126B2Prolong lifeConvenient lengthDispersion deliveryPressure infusionPulmonary vasculatureDual delivery
A method of screening for pulmonary embolism uses gaseous phase polarized <129>Xe which is injected directly into the vasculature of a subject. The gaseous <129>Xe can be delivered in a controlled manner such that the gas substantially dissolves into the vasculature proximate to the injection site. Alternatively, the gas can be injected such that it remains as a gas in the bloodstream for a period of time (such as about 8-29 seconds). The injectable formulation of polarized <129>Xe gas is presented in small quantities of (preferably isotopically enriched) hyperpolarized <129>Xe and can provide high-quality vasculature MRI images or NMR spectroscopic signals with clinically useful signal resolution or intensity. One method injects the polarized <129>Xe as a gas into a vein and also directs another quantity of polarized gas into the subject via inhalation. In this embodiment, the perfusion uptake allows arterial signal information and the injection (venous side) allows venous signal information. The dual delivery is used to generate a combined introduction path with a more complete image signal of both the arterial and venous side of the pulmonary vasculature. In this NMR imaging method, the pulmonary embolism screening method can use the same NMR chest coil for the excitation and detection of the <129>Xe signals. The direct injection of small quantities of gas at particular sites along the vasculature targets specific target regions to provide increased signal intensity NMR images. The disclosure also includes related methods directed to other diagnostic vasculature regions physiological and conditions. Associated delivery and dispensing systems and methods, containers, and quantitative formulations of the polarized gas are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
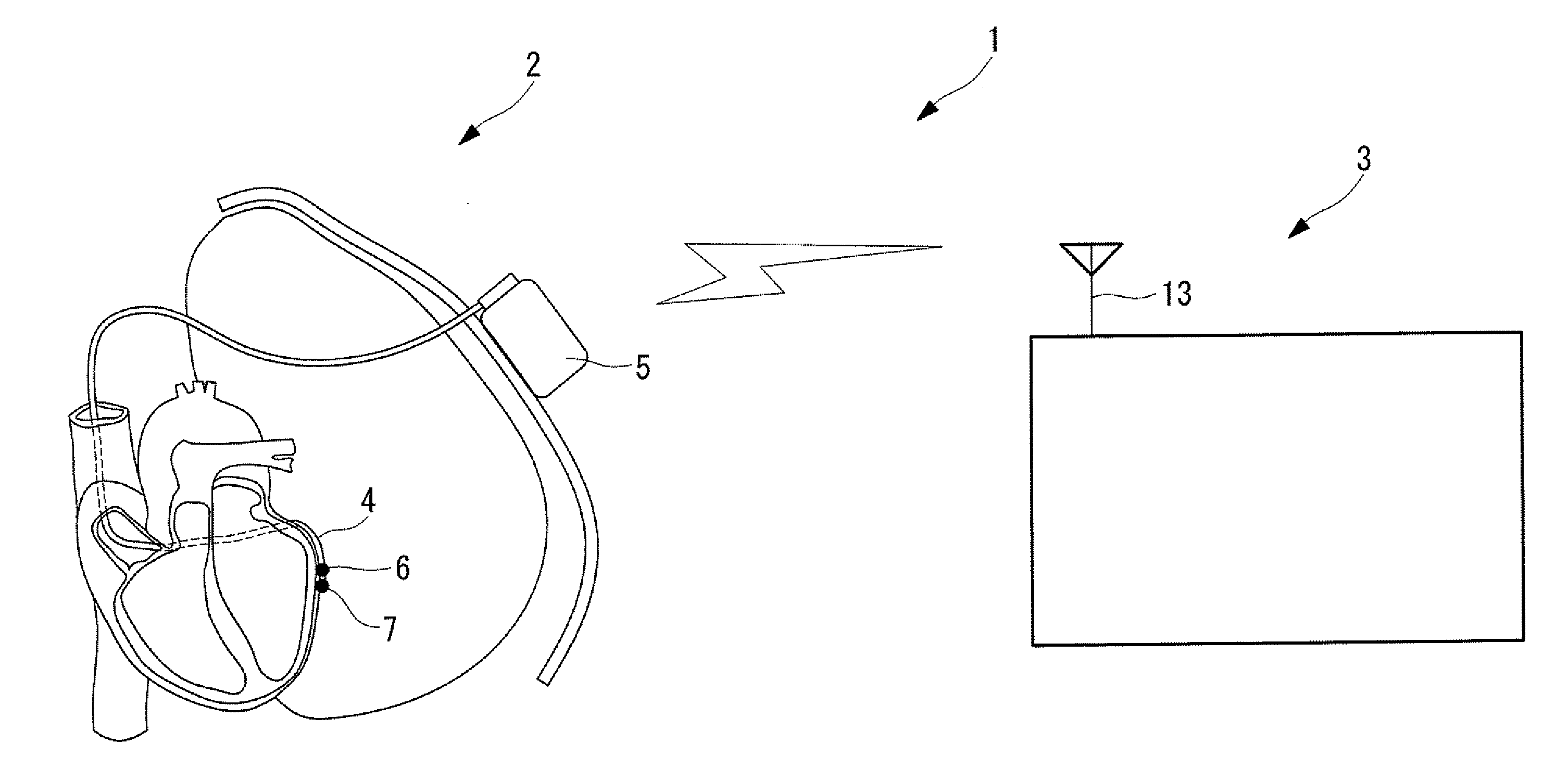
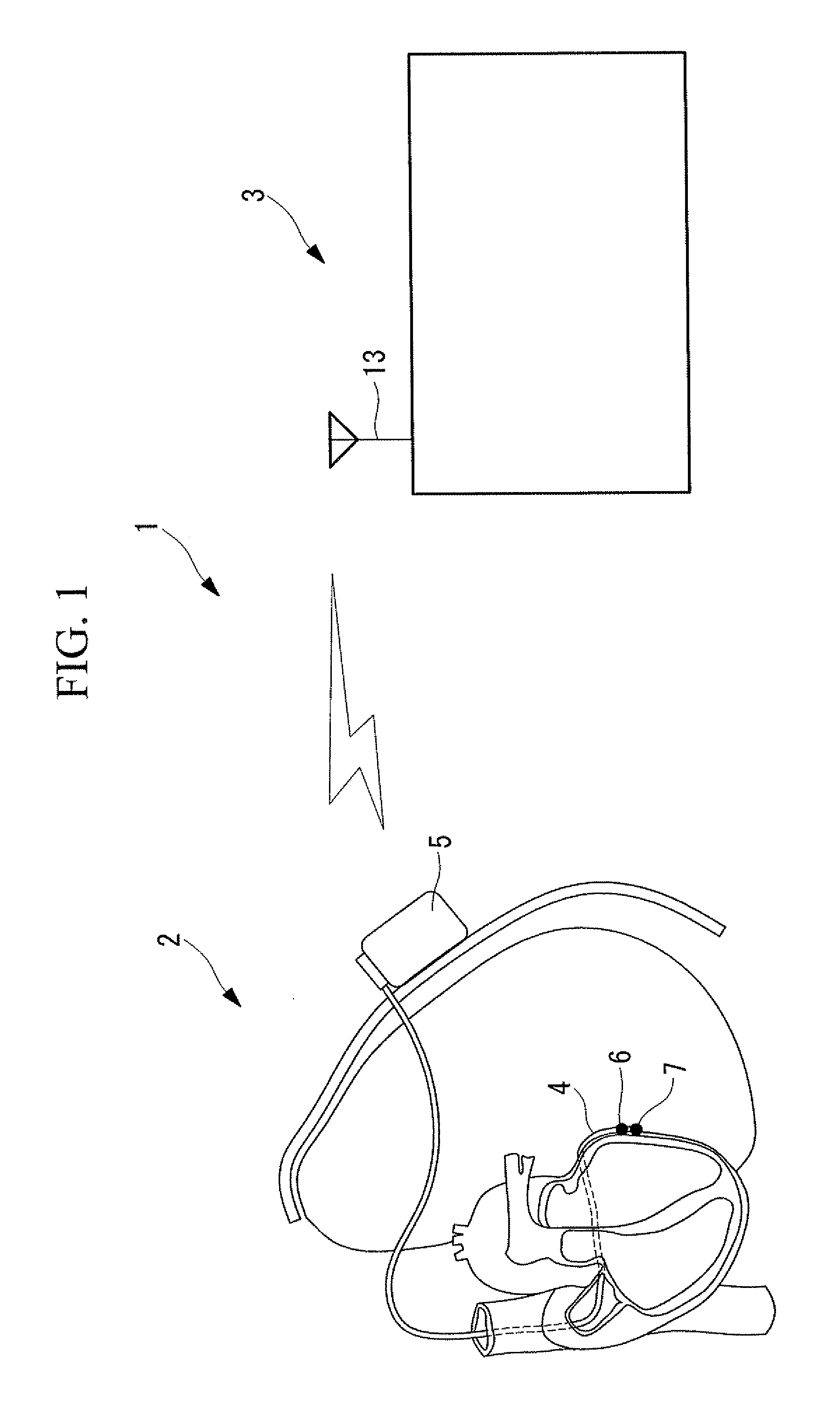
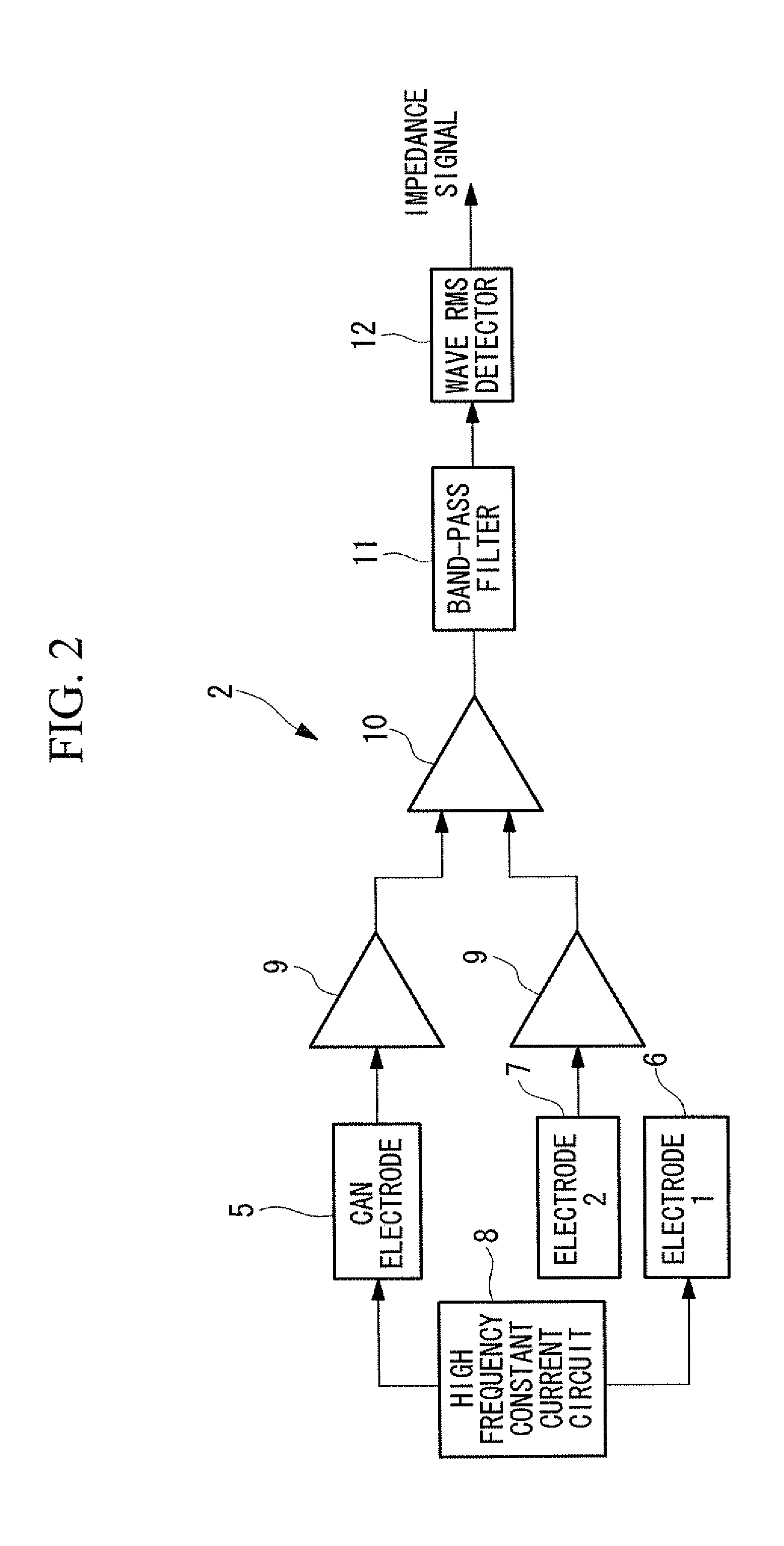
Solid tissue impedance estimating method, cardiac output calculating method, pulmonary artery wedge pressure calculating method, cardiac output monitoring device, cardiac output monitoring system, pulmonary artery wedge pressure monitoring device, and pulmonary artery wedge pressure monitoring system
A practical method for estimating cardiac output and pulmonary artery wedge pressure with good accuracy is provided. The present invention provides a method for estimating the impedance arising from solid tissue by determining the impedance at the intersection between the line of identity and the extrapolated regression line, where the regression line is obtained by linearly regressing the maximum value to the minimum value of the impedance signal of each of multiple data sets, where each data set contains the maximum value and the minimum value of the impedance signal during one cardiac cycle, where impedance signal is obtained between a can electrode implanted in the left thoracic wall and an electrode inserted into the coronary vein, over a specific period of time following the infusion of hypertonic saline into the pulmonary circulation.
Owner:NAT CEREBRAL & CARDIOVASCULAR CENT +1
Diagnostic procedures using direct injection of gaseous hyperpolarized 129Xe and associated systems and products
InactiveUS20020006382A1Quality improvementHigh-quality mammalianDispersion deliveryPressure infusionPulmonary vasculatureInjection site
A method of screening for pulmonary embolism uses gaseous phase polarized 129Xe which is injected directly into the vasculature of a subject. The gaseous 129Xe can be delivered in a controlled manner such that the gas substantially dissolves into the vasculature proximate to the injection site. Alternatively, the gas can be injected such that it remains as a gas in the bloodstream for a period of time (such as about 8-29 seconds). The injectable formulation of polarized 129Xe gas is presented in small quantities of (preferably isotopically enriched) hyperpolarized 129Xe and can provide high-quality vasculature MRI images or NMR spectroscopic signals with clinically useful signal resolution or intensity. One method injects the polarized 129Xe as a gas into a vein and also directs another quantity of polarized gas into the subject via inhalation. In this embodiment, the perfusion uptake allows arterial signal information and the injection (venous side) allows venous signal information. The dual delivery is used to generate a combined introduction path with a more complete image signal of both the arterial and venous side of the pulmonary vasculature. In this NMR imaging method, the pulmonary embolism screening method can use the same NMR chest coil for the excitation and detection of the 129Xe signals. The direct injection of small quantities of gas at particular sites along the vasculature targets specific target regions to provide increased signal intensity NMR images. The disclosure also includes related methods directed to other diagnostic vasculature regions physiological and conditions. Associated delivery and dispensing systems and methods, containers, and quantitative formulations of the polarized gas are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +1
System and methods for stress release and associated nitric oxide release for treatment of pain in specific parts of the body
InactiveUS20090124865A1Avoid painRelief the painChiropractic devicesMassageStress inducedPulmonary vasculature
This invention provides unique technology, systems and methods of treatment of stress induced afflictions in the musculoskeletal system, the vascular system or the nervous tissue. More specifically, the systems comprise diagnosis of a stress-induced consistent tightness on the right side of the cranial, cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral spine, referred herein as “The Twist”, and utilize “Stress Relief Methods” to reduce The Twist to resolve any afflictions associated with it. The invention comprises a coordinated series of untwisting dynamic motions, spinal manipulation and / or motion palpations that result in release of nitric oxide and relief from pain. The systems and methods of the invention therefore provide the benefits of increased nitric oxide release to maintain homeostasis in pulmonary vasculature. The invention also provides methods of training others in the correct use of the Stress Relief Methods to prevent and treat afflictions associated with the Twist.
Owner:KIERNAN JAMES E
Method and composition for treating migraines
ActiveUS8785396B2Avoid deactivationAvoid degradationBiocidePowder deliveryPulmonary vasculatureInhalation
A method for treating migraines is disclosed. The method utilizes a rapid drug delivery system which prevents deactivation or degradation of the active agent, including small molecules and peptides being administered to a patient in need of treatment. In particular, the drug delivery system is designed for inhalation for delivery of drugs to the pulmonary circulation in a rapid and therapeutically effective manner.
Owner:MANNKIND CORP
Apparatus and methods for treating pulmonary hypertension
ActiveUS20140221975A1Reduced activityPulmonary hypertensionSpinal electrodesUltrasound therapyPulmonary vasculatureNerve fiber bundle
A method is described for decreasing activity of at least one sympathetic nerve, nerve fiber or neuron innervating at least one blood vessel in the pulmonary vasculature of a patient to ameliorate pulmonary hypertension. In one embodiment, the method may involve advancing an intravascular treatment device to a target location in a target blood vessel within the pulmonary vasculature of the patient and using the treatment device to decrease activity of at least one sympathetic nerve, nerve fiber or neuron innervating the target blood vessel at or near the target location to ameliorate pulmonary hypertension.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and system for measuring pulmonary artery circulation information
Minimally invasive systems and methods are described for measuring pulmonary circulation information from the pulmonary arteries. A transbronchial Doppler ultrasound catheter is advanced through the airways and in the vicinity of the pulmonary artery. Doppler ultrasound energy is sent through the airway wall and across the pulmonary artery to obtain velocity information of blood flowing through the artery. The velocity information is used to compute pulmonary circulation information including but not limited to flowrate.
Owner:EKOS CORP
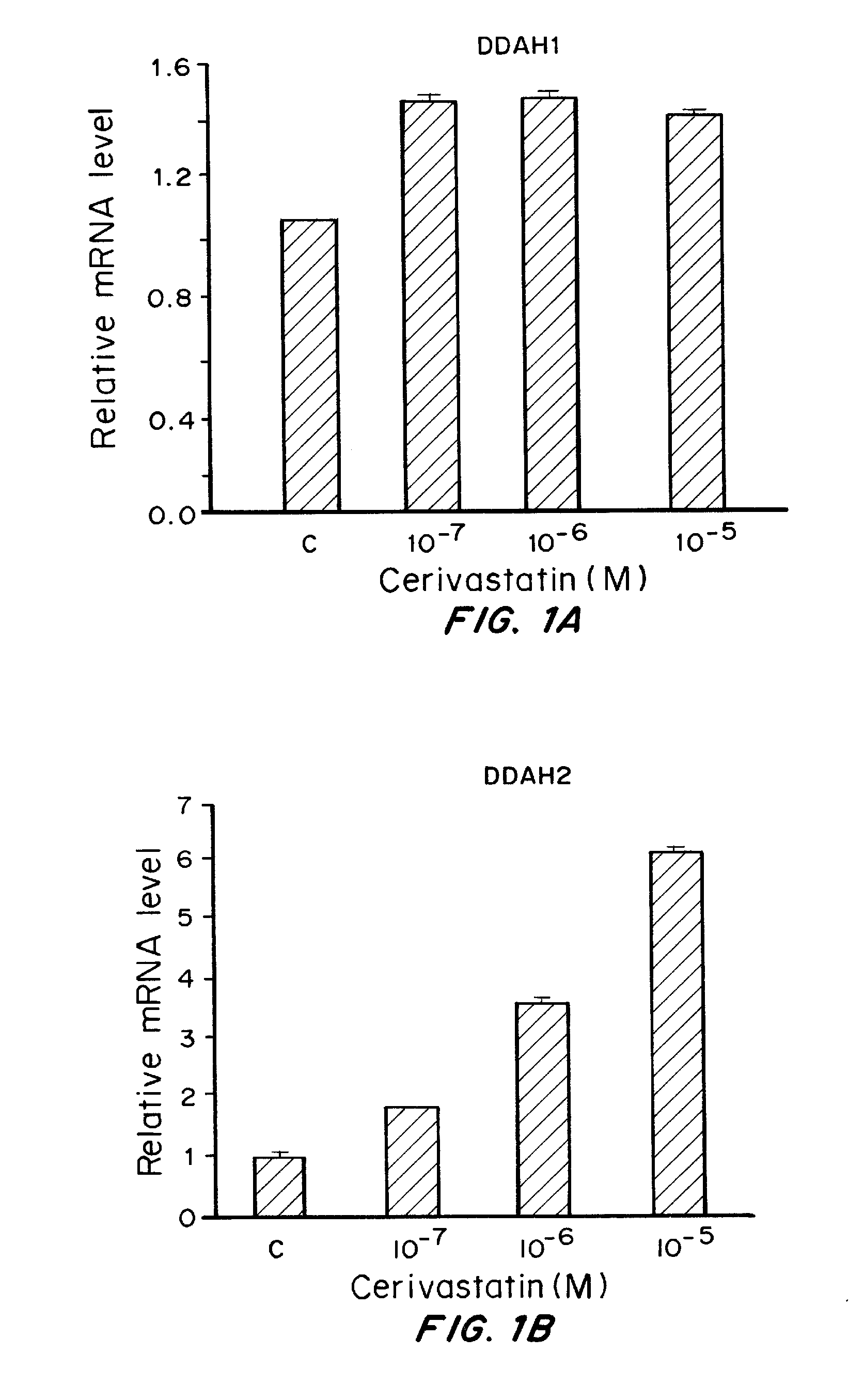
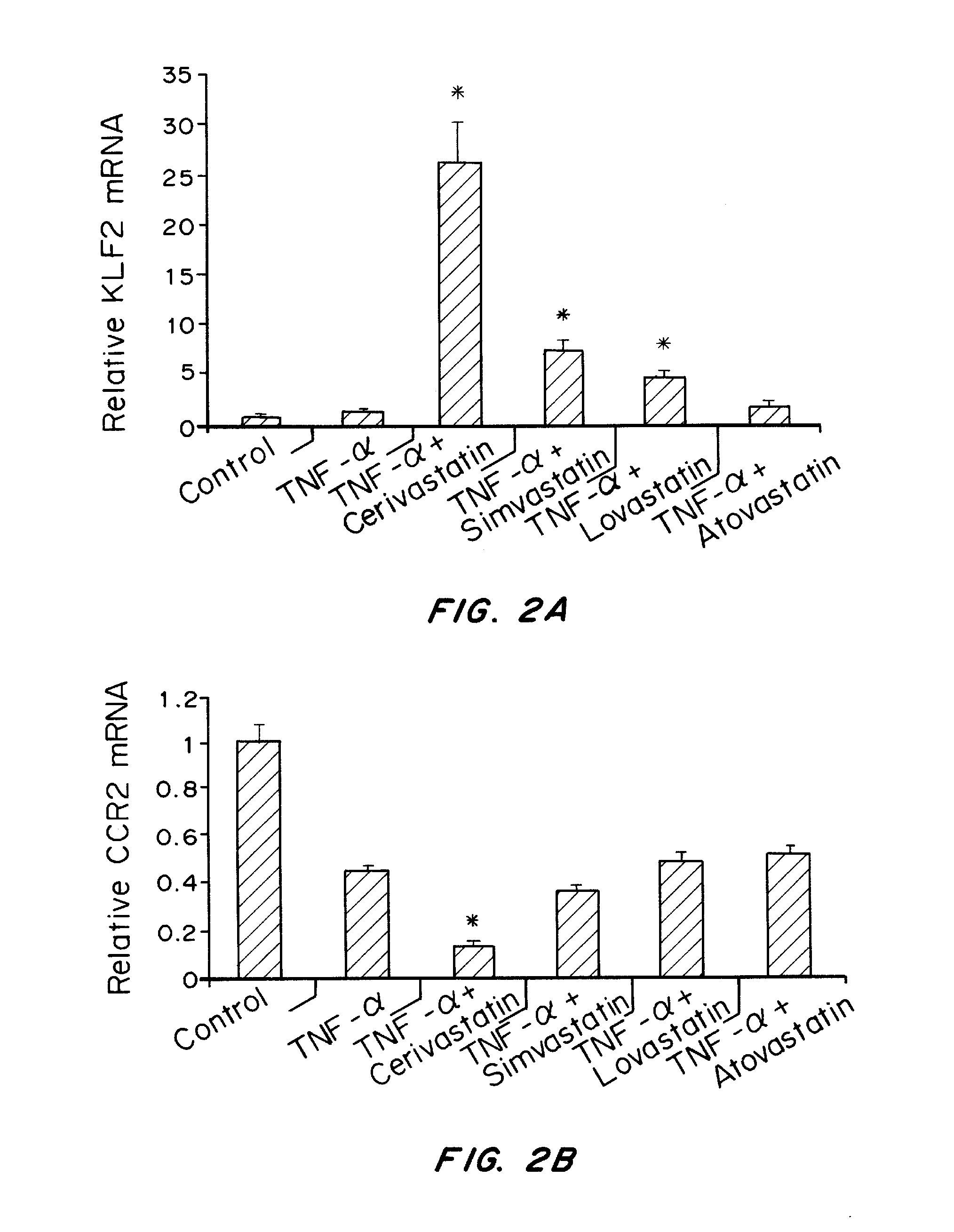
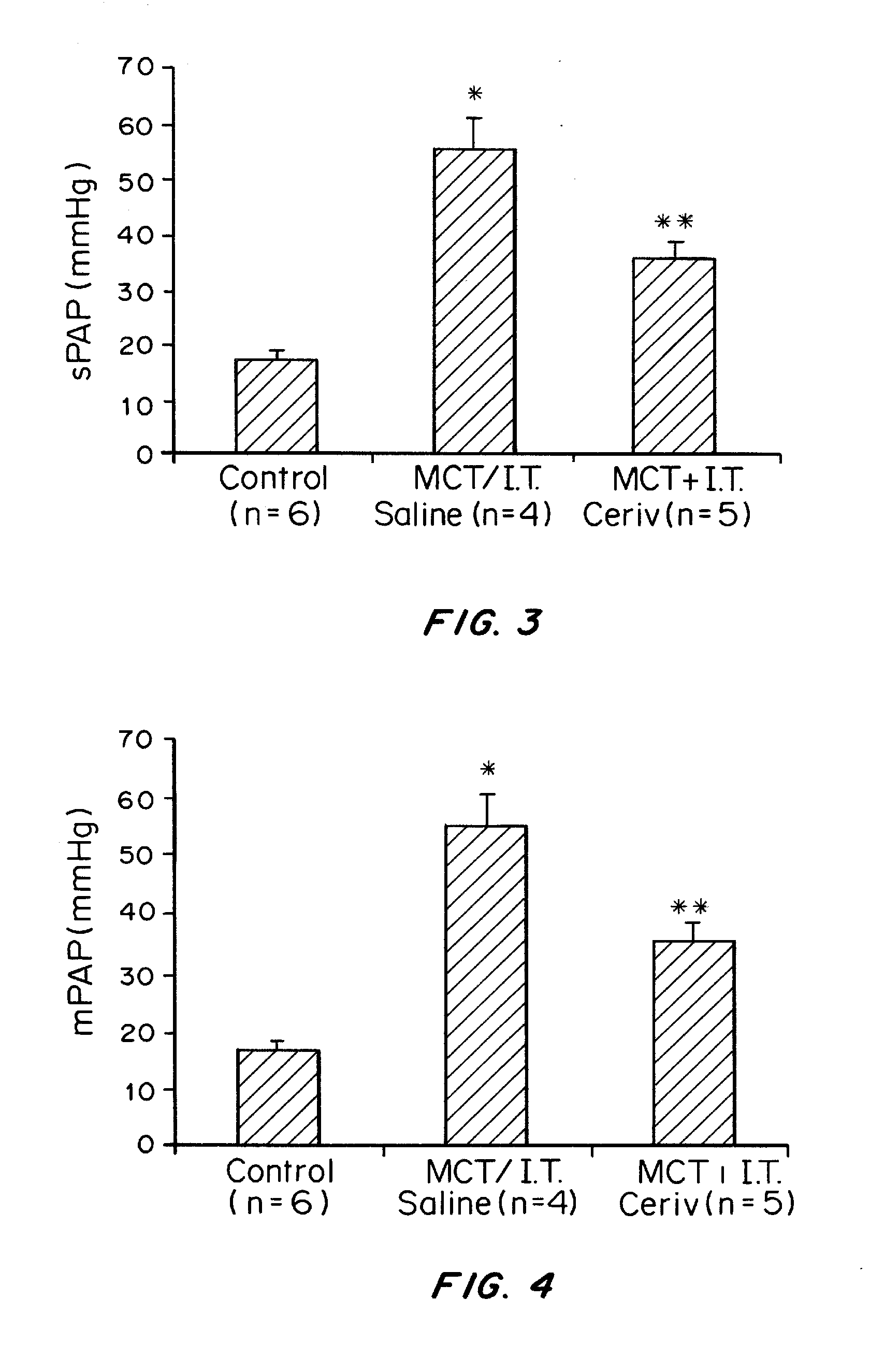
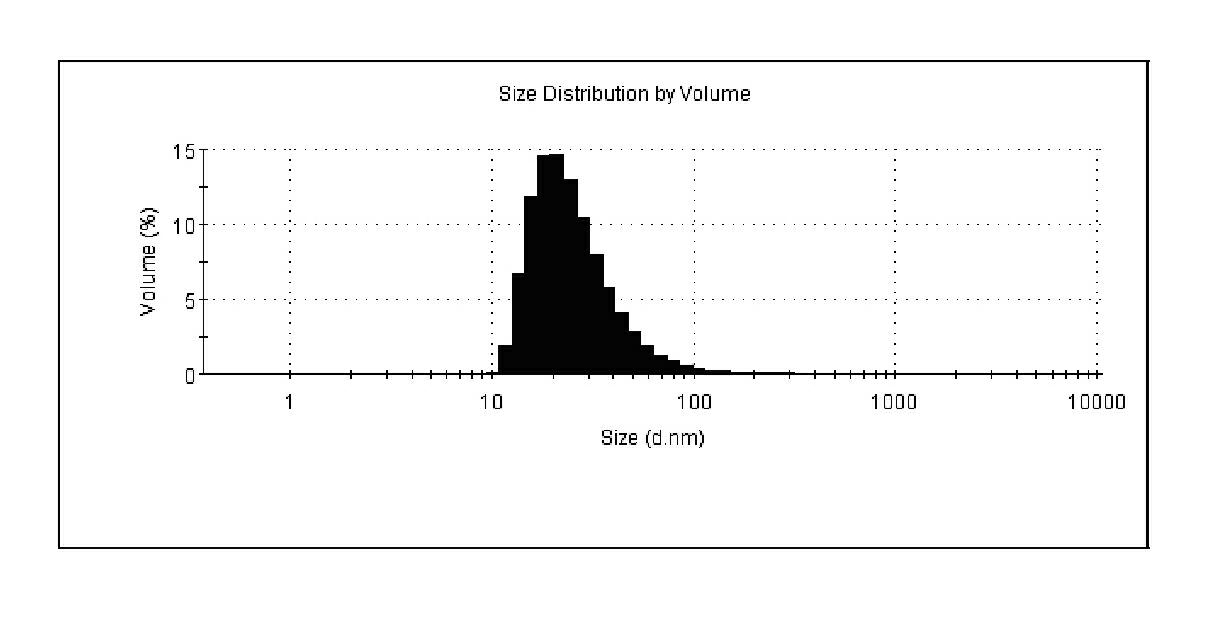
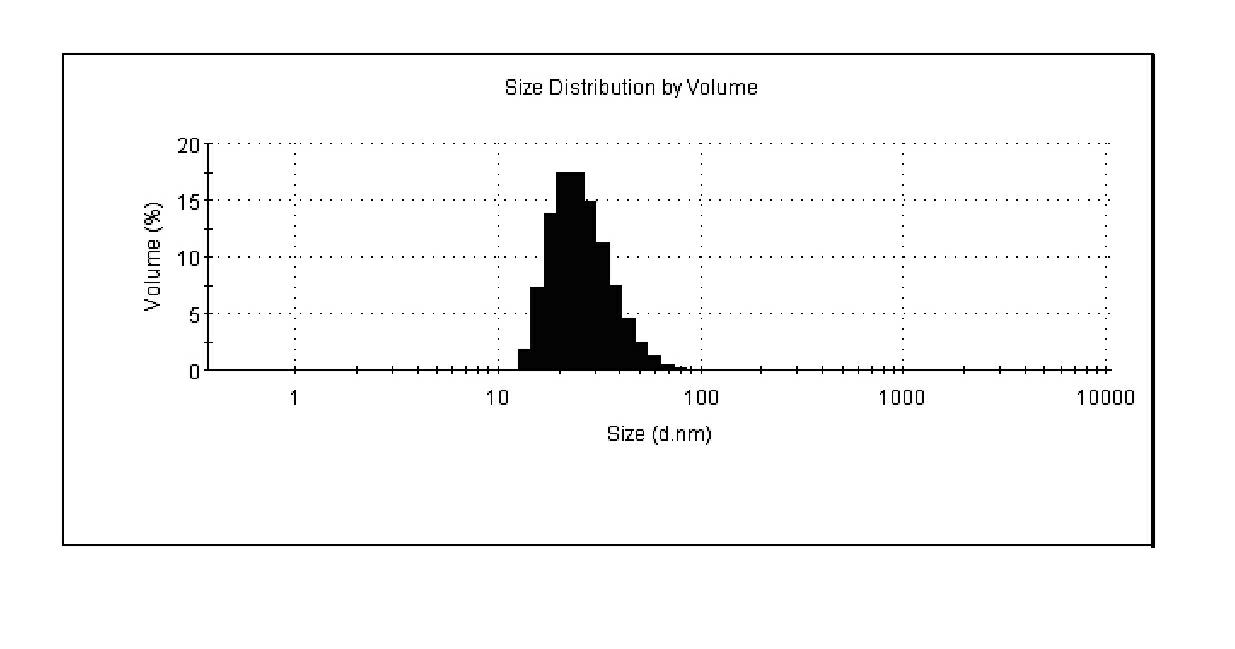
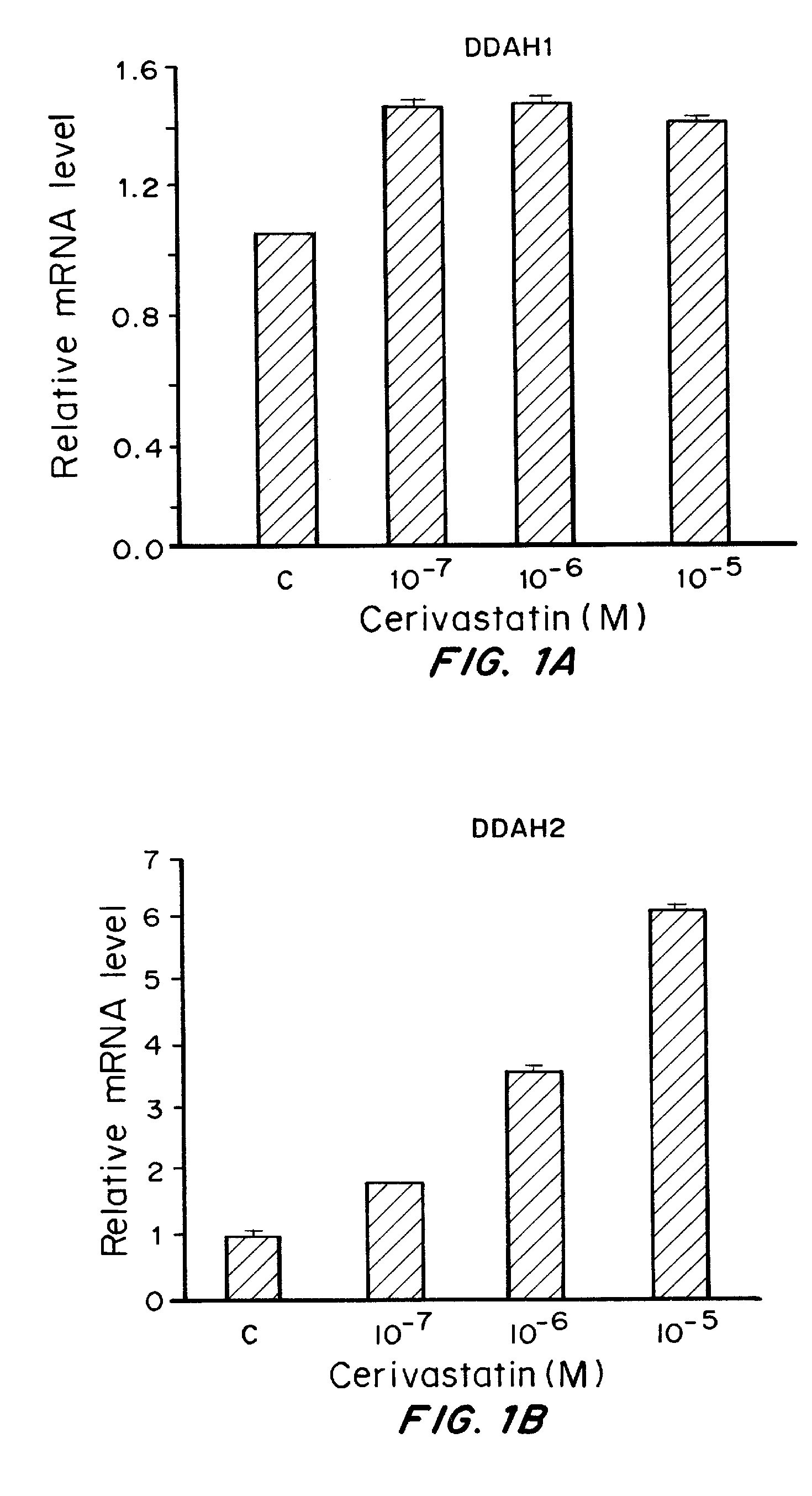
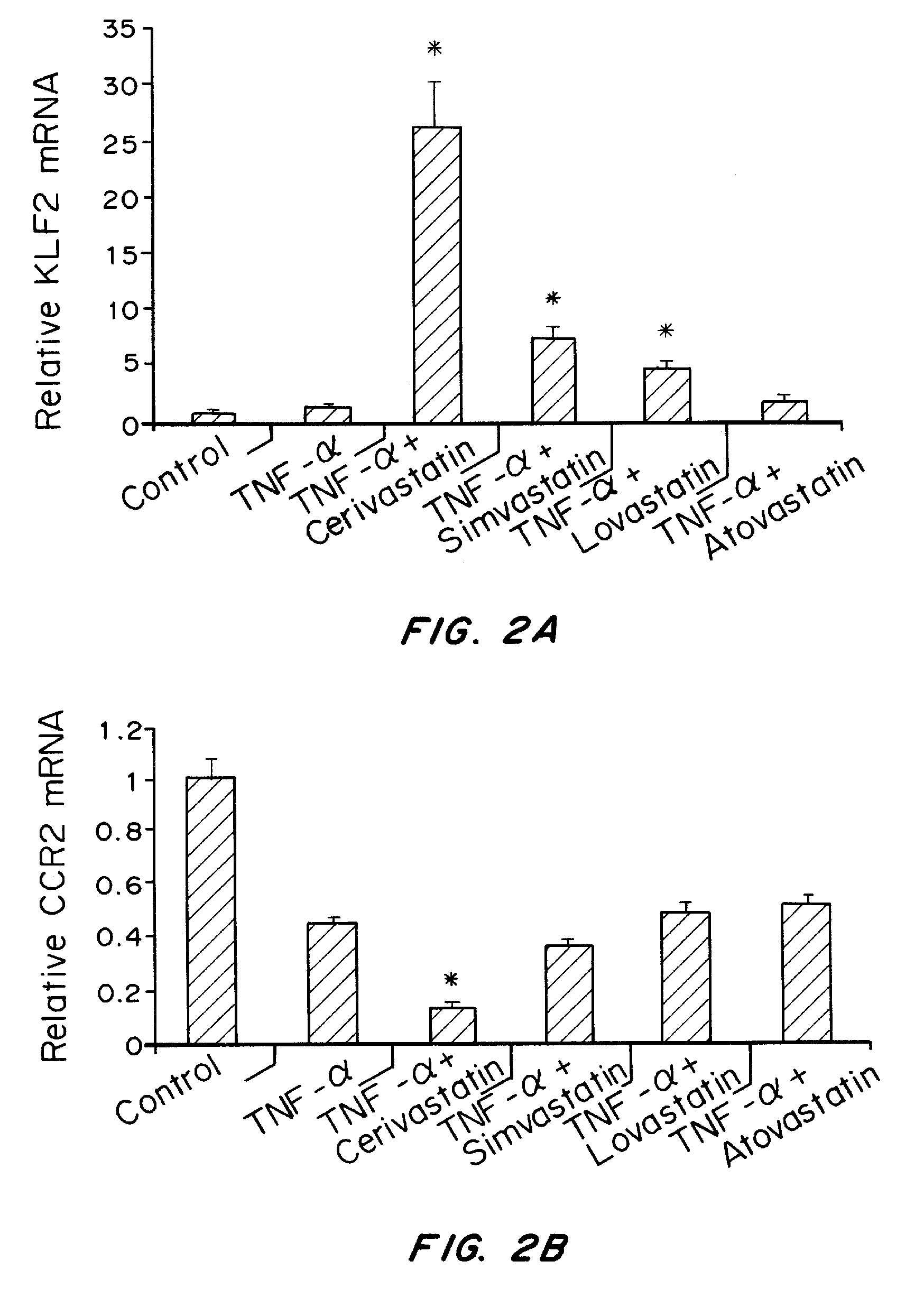
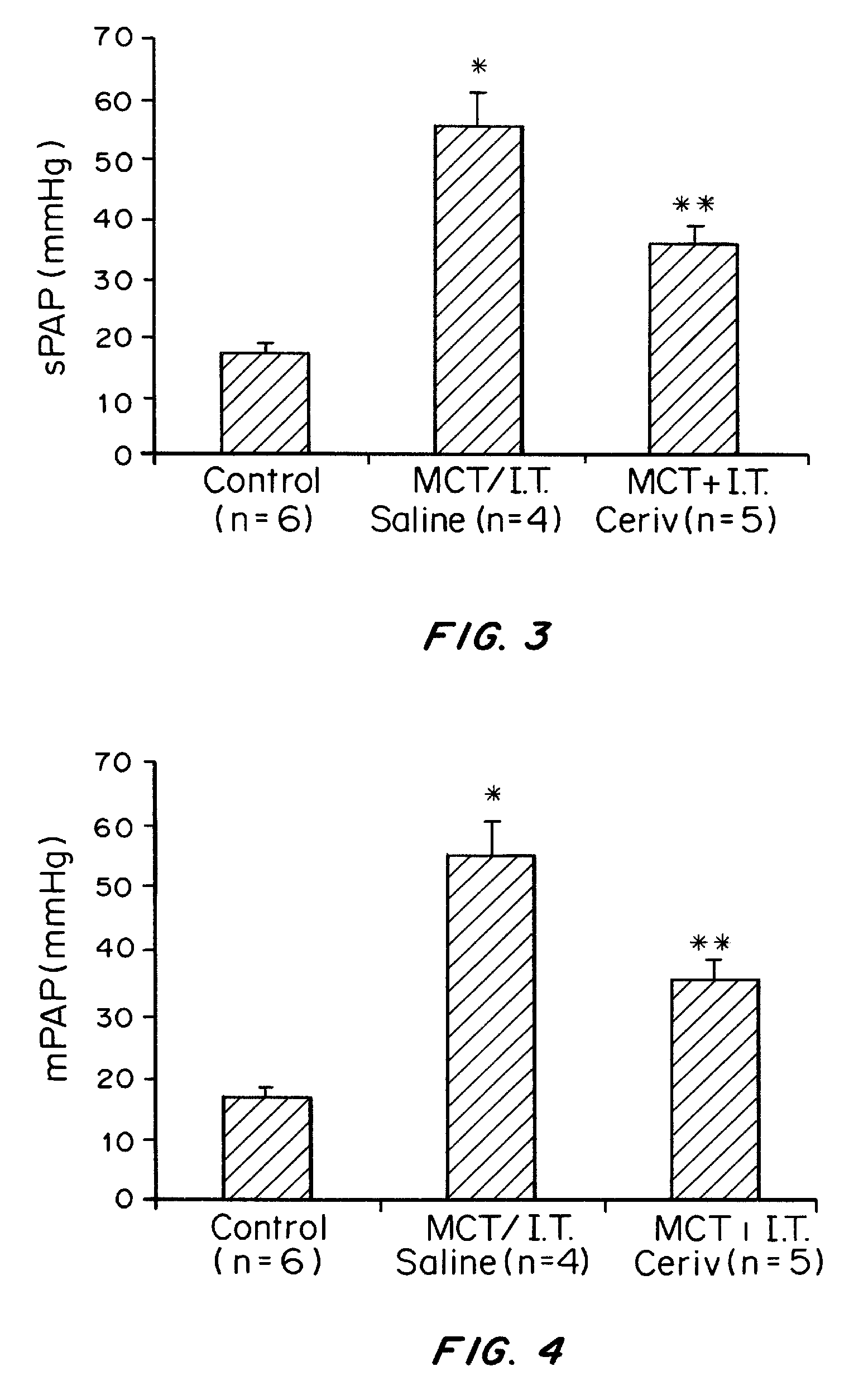
Cerivastatin to treat pulmonary disorders
InactiveUS20130098357A1Improve the level ofSuppress high blood pressureCompounds screening/testingBiocidePulmonary vasculatureInflammation Process
Pharmaceutical formulations and methods of using thereof for the treatment and prevention of pulmonary arterial hypertension are provided. The formulations contain one or more agents to simultaneously reduce ADMA levels in a patient and reduce inflammatory processes in the pulmonary vasculature of a patient. The formulations contain a therapeutically effective amount of cerivastatin, a cerivastatin analog, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug, clathrate, or solvate thereof in a carrier suitable for pulmonary administration.
Owner:SINGH JAI PAL
Registration method for projections in dual energy
ActiveUS20080247626A1Reduce computational complexityReduce usageRecognition of medical/anatomical patternsPulmonary vasculatureImaging processing
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
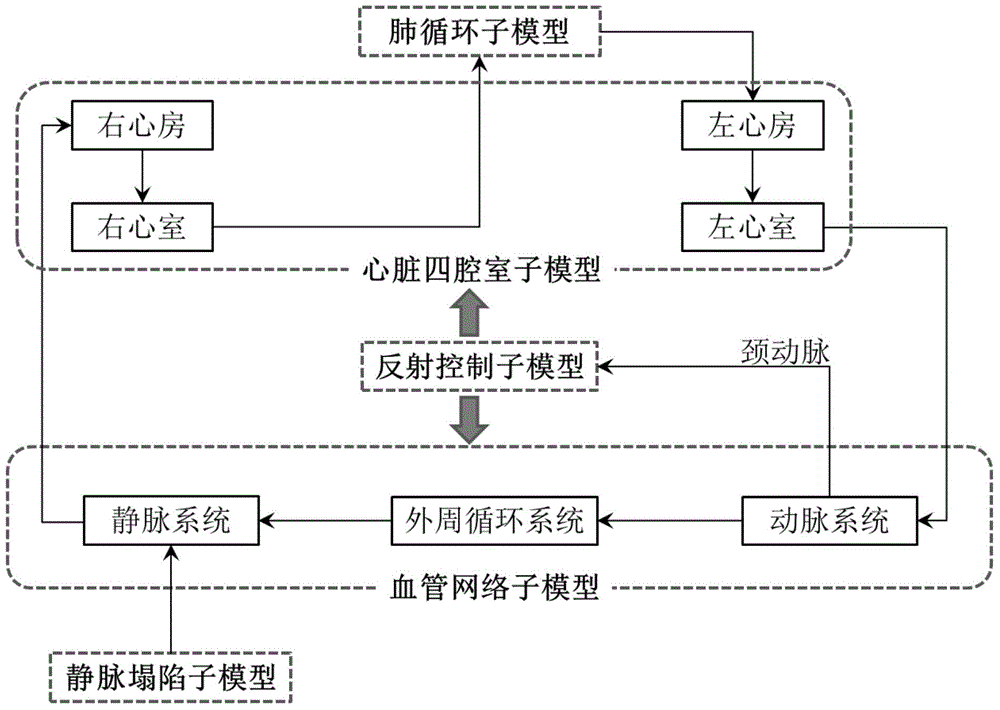
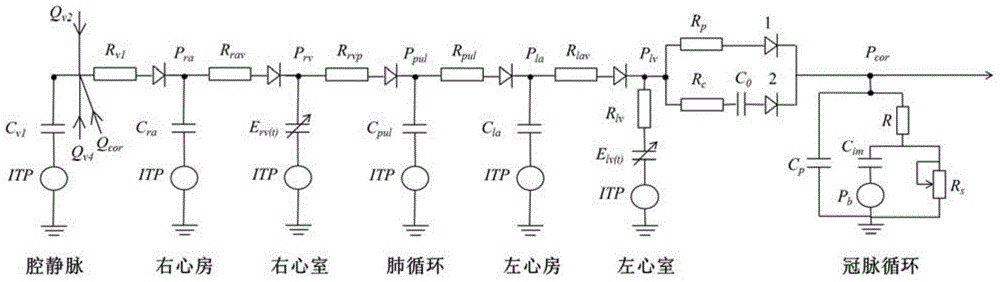
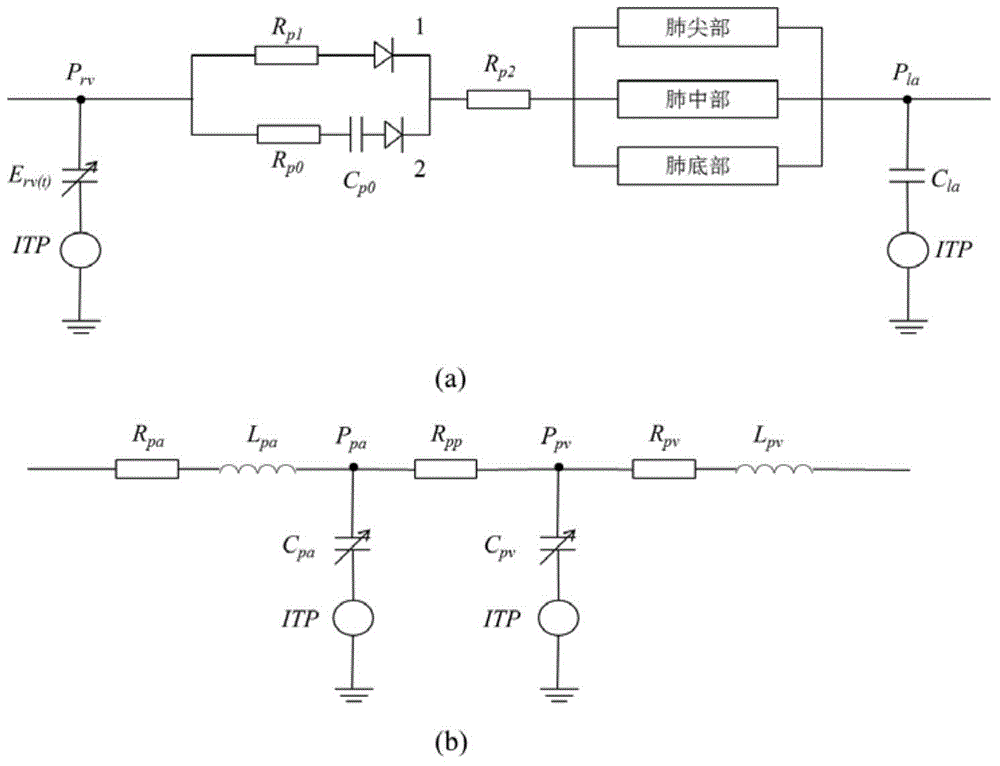
Distributed-type cardiovascular system simulation model
InactiveCN104794973AIncrease reflectionIn-depth analysisEducational modelsPulmonary vasculatureModel system
The invention discloses a distributed-type cardiovascular system simulation model. The distributed-type cardiovascular system simulation model is characterized by comprising a cardiac four-cavity sub-model, a pulmonary circulation sub-model, a blood vessel network sub-model, a reflection control sub-model and a vein collapse sub-model, the cardiac cavity sub-model is provided with a left ventricle connected with a left atrium and a right ventricle connected with a right atrium, the left ventricle and the right ventricle drive systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation, the blood vessel network sub-model comprises an arterial system, a peripheral circulation system and a venous system which are connected sequentially, an input end of the arterial system is connected with an output end of the left ventricle, an output end of the venous system is connected with an input end of the right ventricle, the vein collapse sub-model is connected with another input end of the venous system, an output end of the arterial system is connected with the reflection control sub-model through a carotid artery, and the reflection control sub-model controls blood pressure fluctuation of a model system through heart rate and heart contractility effectors arranged on the cardiac four-cavity model and arterial resistance, venous volume and vascular tone effectors arranged in the blood vessel network model.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary disorders
InactiveUS20050130928A1Preferentially modulatingIncrease and decrease midkine expression levelVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePulmonary vasculature
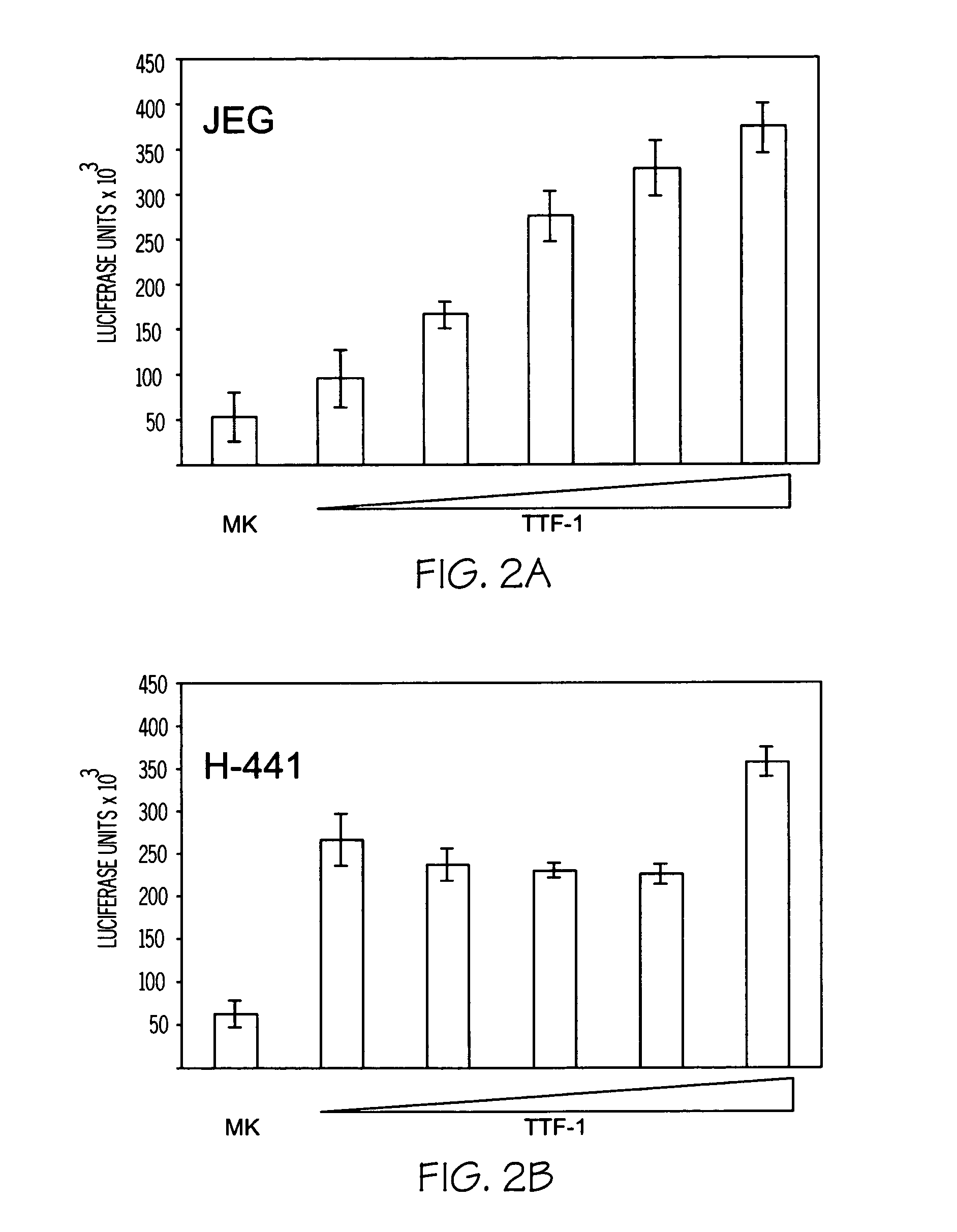
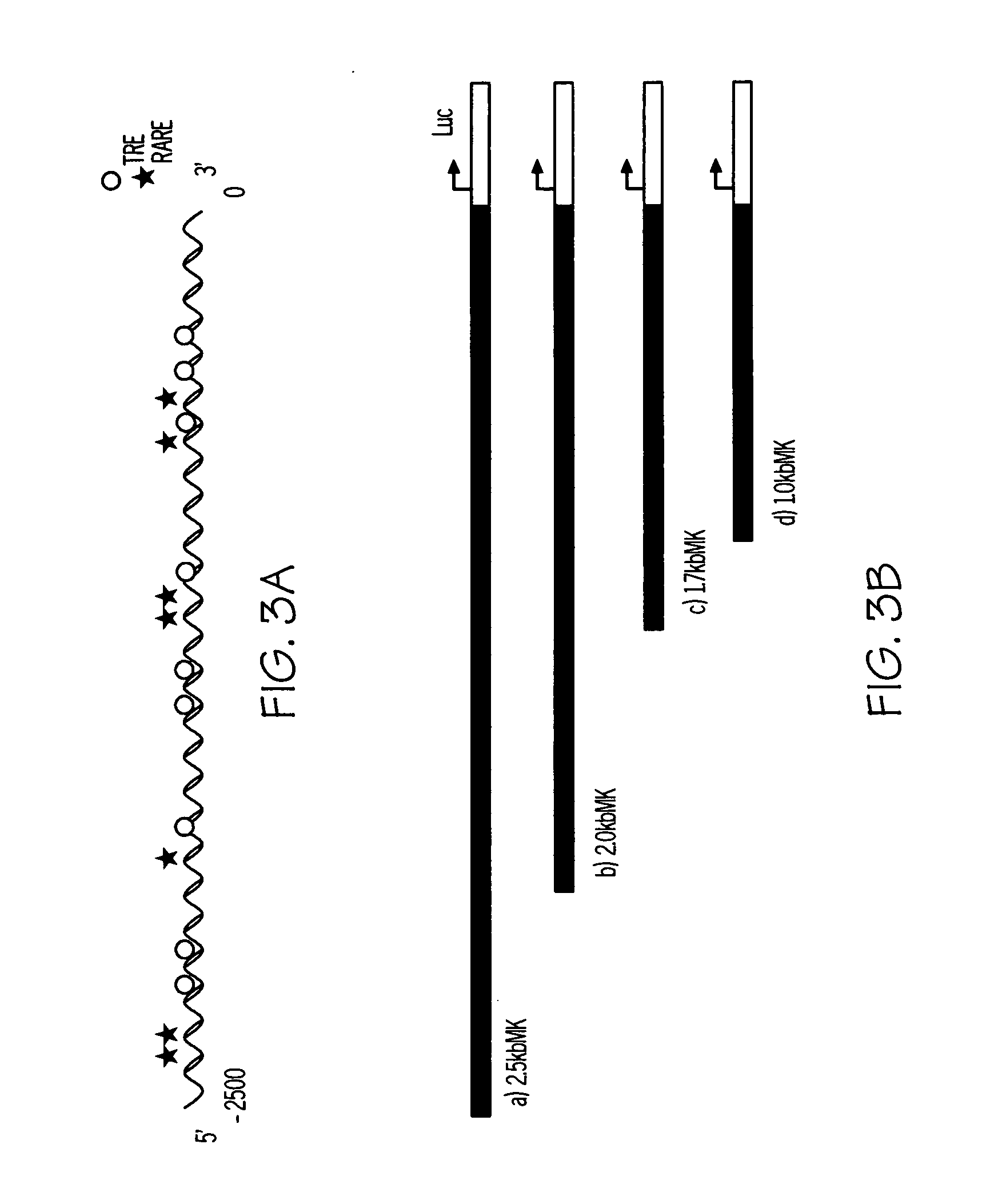
This invention relates to the discovery that midkine modulates pulmonary vasculature development and smooth muscle cell development. Modulation of midkine activity thus alters pulmonary vasculature development and smooth muscle cell development. The invention provides methods of modulating pulmonary disorders, smooth muscle cell related disorders, and pulmonary smooth muscle cell disorders. Disorders of particular interest include, but are not limited to, asthma and pulmonary hyperplasia. Further the invention relates to the discovery that TTF1 and HIF1 -α exhibit midkine modulating activity. The invention pertains to the discovery that midkine modulates myocardin activity.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell separation and culturing method and application of same
InactiveCN102168062AConducive to survivalAvoid damageArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsDiseaseCell survival
The invention relates to a method of separating and culturing human pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells from strips of PTE and the cells' application in studies of diseases related to lung circulation. The method comprises treating cell membranes by single enzymic digestion method to decrease damage degree of the cells, thereby benefiting survival of the cells. The culturing method has stable technology and good repeatability, the cultured cells have uniform forms, and the growth of the cells is good. At the same time, the cells obtained provide rich material source with strong singularity for further study on lung circulation diseases, particularly for experiments on Chronic Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension patients' pathogenesis, diseases generation and development processes and PTE prognosis.
Owner:BEIJING CHAOYANG HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV +1
Alprostadil lipid nanosphere freeze-drying injection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102228446AStable physical stabilityImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryPulmonary vasculatureDisease
The invention discloses an alprostadil lipid nanosphere freeze-drying injection and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The alprostadil lipid nanosphere freeze-drying injection is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 0.0005 to 0.1 part of alprostadil, 15 to 60 parts of medium-chain oil, 3.0 to 35 parts of emulsifier, 8.5 to 48 parts of polyethylene glycol-12-hydroxy stearate, 22 parts of glycerol, 20 to 200 parts of trehalose, and 20 to 300 parts of cyclodextrin. The particle size of the alprostadil lipid nanosphere freeze-drying injection after redissolution is less than 100nm; and an aseptic filtration way can be used for sterilization, so that the disadvantage of thermal instability of the alprostadil is overcome, and the stability of products is improved. Meanwhile, lipid nanospheres have smaller particle sizes which are less than 100nm, so the alprostadil lipid nanosphere freeze-drying injection is more favorable for the distribution of the alprostadil in in-vivo non-reticuloendothelial system (RES) tissues, reduces pulmonary circulation inactivation and blood clearance, is favorable for circulating in vivo for a long time, and is suitable for the treatment of cardiac and neurosurgical diseases.
Owner:SHENYANG WANJIA INST OF BIOLOGICAL TECH RES
Cerivastatin to treat pulmonary disorders
InactiveUS8586527B2Improve the level ofSuppress high blood pressureCompounds screening/testingBiocidePulmonary vasculatureDisease
Pharmaceutical formulations and methods of using thereof for the treatment and prevention of pulmonary arterial hypertension are provided. The formulations contain one or more agents to simultaneously reduce ADMA levels in a patient and reduce inflammatory processes in the pulmonary vasculature of a patient. The formulations contain a therapeutically effective amount of cerivastatin, a cerivastatin analog, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, prodrug, clathrate, or solvate thereof in a carrier suitable for pulmonary administration.
Owner:SINGH JAI PAL
Alprostadil nano granule formulation and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101322712AReduce chance of regroupingOvercoming chemistryPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsDiseasePulmonary vasculature
The invention relates to an alprostadil nanoparticle preparation and a preparation method thereof. The preparation is essentially used for transdermal administration and used for treating diseases such as diabetic ulcer, ischemia of extremity end, burn and the like, and belongs to the technical field of medicine. The preparation consists of the raw materials by the following weight ratio that alprostadil:lipid component: emulsifier: excipient matrix: water is 0.01-0.1:0.5-10:0.5-5:550-950:5. The alprostadil nanoparticle preparation has the advantages of overcoming the chemical and physiological instability of the alprostadil, strengthening in vitro stability, reducing degradation of the alprostadil caused by inactivation effect of in vivo pulmonary circulation, enhancing concentration of the preparation on the local affected parts, being more easy to aggregate at the affected part, sustained release and long effect, and reducing irritation of the preparation.
Owner:SHENYANG WANJIA INST OF BIOLOGICAL TECH RES
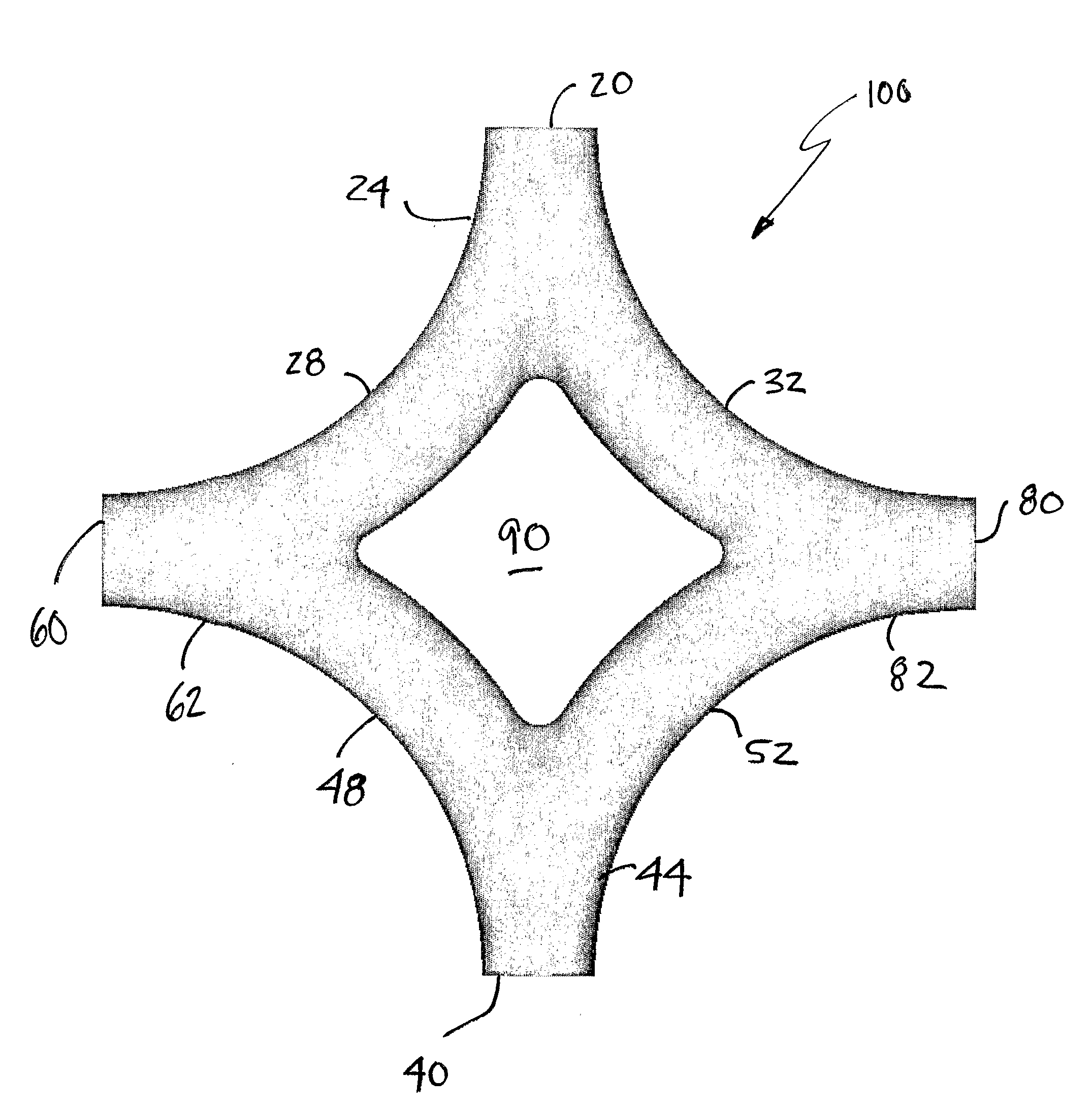
Anatomical Connection
InactiveUS20080021368A1Minimize momentum lossCatheterMultiple way valvesPulmonary vasculatureWhole body
A device for use in the total cavopulmonary connection (TCPC) in order to optimize its hemodynamics. Although the current procedure of choice for single ventricle heart repairs, the TCPC has reduced the post-operative mortality to the level of simpler types of congenital heart disease repairs, Fontan patients are still subjected to serious long-term complications. The TCPC procedure, which restores the vital separation between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, also leads to an increased workload for the remaining single ventricle, as it is now responsible for pumping the blood through both the systemic and pulmonary circulation. The present device reduces this workload by altering the surgically created design of the TCPC. Improved fluid mechanics and reduced energy dissipation at the connection site translates into less work for the single ventricle and improved transport of deoxygenated blood to the lungs, which may in turn contribute to improved post-operative results and quality of life.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
System for improved hemodynamic detection of circulatory anomalies
InactiveCN102933140AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterPulmonary vasculaturePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention generally relates to a system, and apparatus for detection of circulatory anomalies in the mammalian body. Particularly, apparatus is provided that allows the clinician to quantitatively determine the extent of any anomalies in the pulmonary circulation. Specifically a quantifiable agent is injected into a peripheral location, and the transit of the indicator agent is monitored. Aberrant circulation is then quantified. The preferred indicator is an injection of indocyanine green dye, detected and measured by fluorescence at a sensor location. Sensor arrays are provided that allow for optimization of detection of circulatory anomalies Quantification is carried out by a monitor / controller providing visual cues to the patient and operator, said monitor / controller actuable for carrying out a Valsalva maneuver, and a displaying shunt conductance index.
Owner:CARDOX
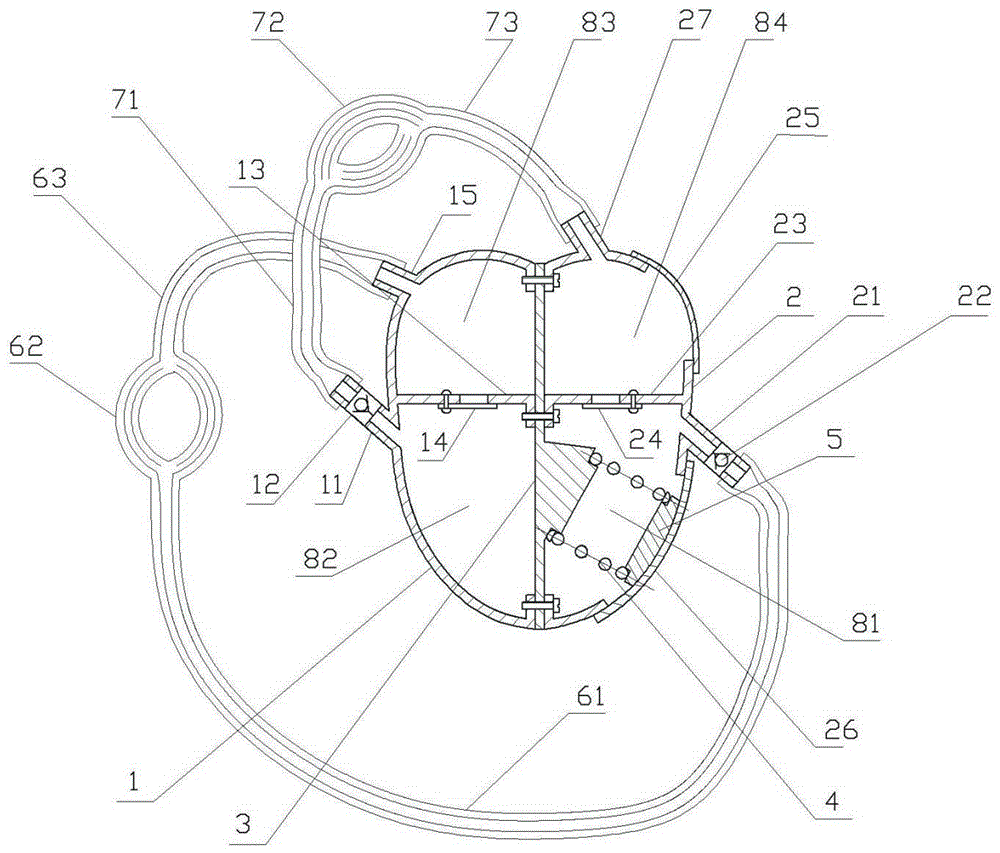
Dynamic model of human heart and blood systemic circulation system
InactiveCN105206156ADeepen memoryDeepen understandingEducational modelsPulmonary vasculatureAnatomical structures
The invention discloses a dynamic model of a human heart and blood systemic circulation system. The dynamic model is mainly used for classroom teaching in a medical college, is realistic in structure and convenient to use, and deeply impress classmates with the pressing of a simulated heart to push blood to flow in the whole circulation system. The dynamic model comprises the simulated heart, simulated blood vessels and simulated organ vascular nets, wherein the simulated heart comprises a right half shell, an intermediate partition and a left half shell; the right half shell and the left half shell are arranged on the right and left sides of the simulated heart; two partitions are respectively arranged in the middles of the right half shell and the left half shell. The dynamic model has the benefits that the structure is simple and realistic; blood circulation can be simulated without utilizing an external pressurizing device; through the dynamic model, the heart anatomical structure can be understood in a visible and operable manner, and systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation can be simulated; the dynamic model can serve as an intuitional teaching aid for showing the heat structure to students, simulating the pathways and directions of heart blood circulation, helping to understand pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation, and facilitating memory deepening and book knowledge understanding.
Owner:赵菁
Method and system for imaging
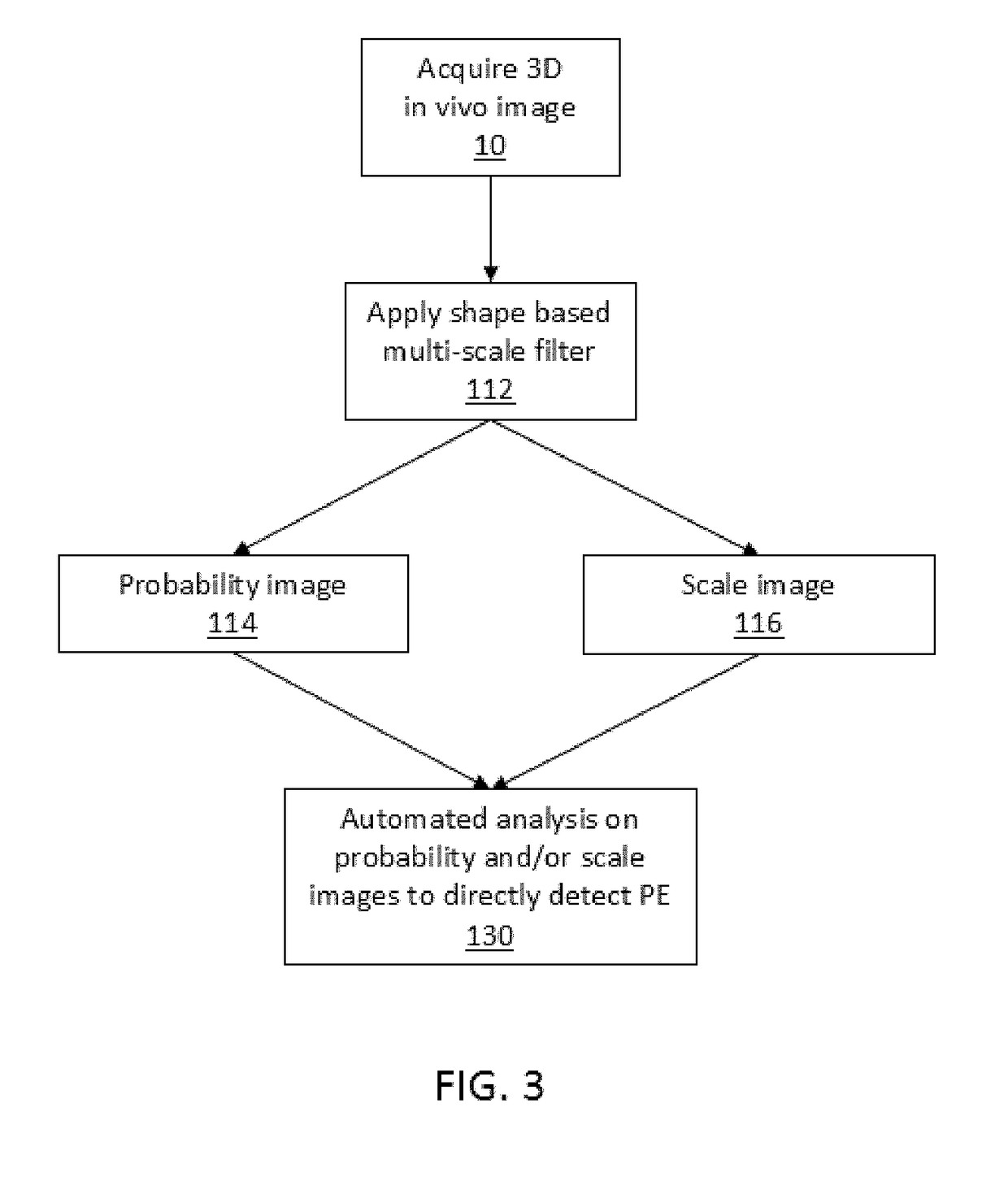
ActiveUS20190059840A1Low densityHigh densityImage enhancementMedical imagingPulmonary vasculatureImaging processing
The present invention relates to the field of medical imaging in the absence of contrast agents. In one form, the invention relates to the field of imaging vessels, particularly blood vessels such as the pulmonary vasculature and is suitable for use as a technique for detecting pulmonary embolism (PE), such as acute PE. Embodiments of the present invention provide improved image processing techniques having the capability to extract and use image data to overcome the need for contrast agents to distinguish between different types of tissue. Furthermore, it has also been realised that the image data accessed by the improved image processing can be used to identify irregularities in vessels.
Owner:4DMEDICAL LTD
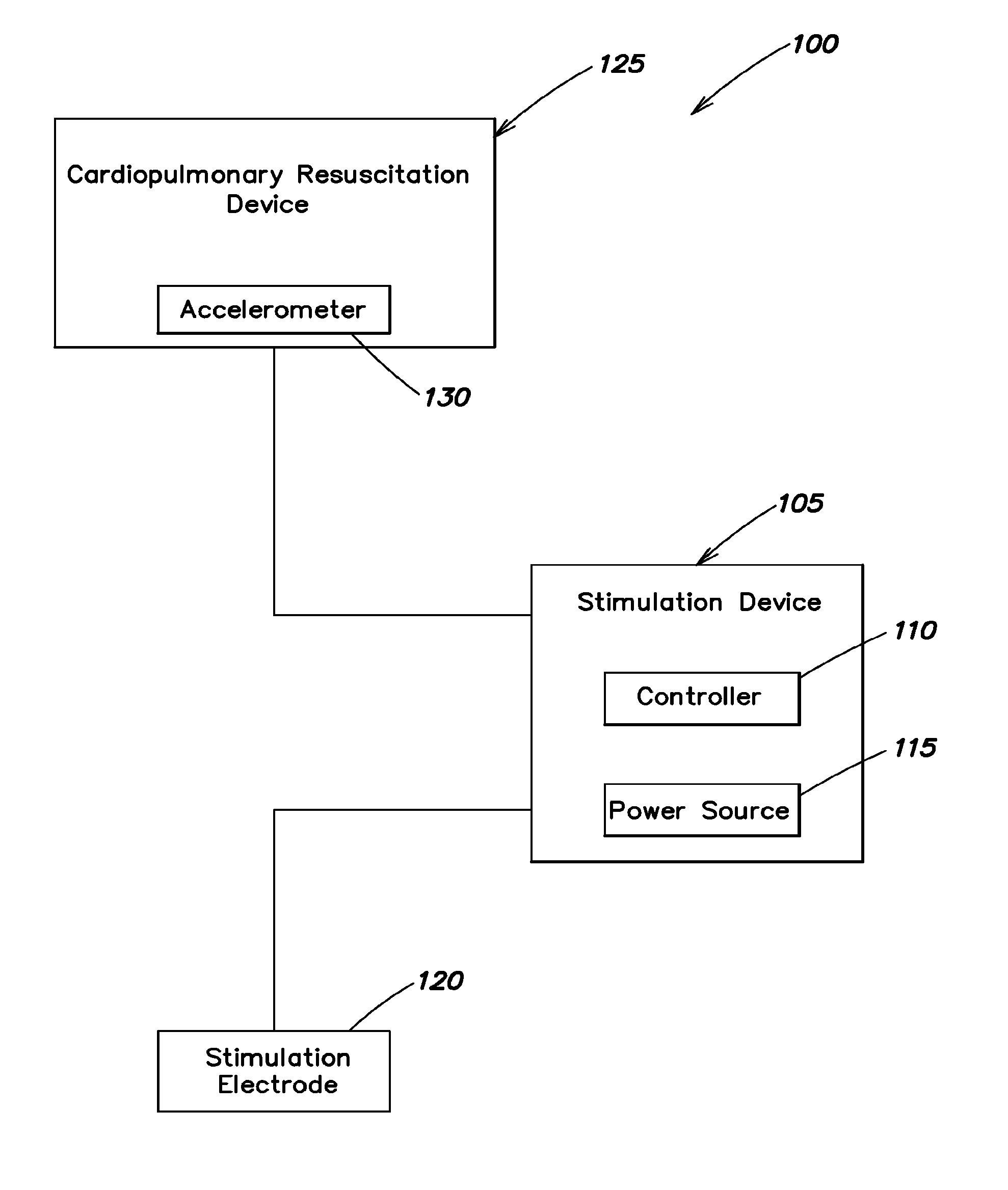
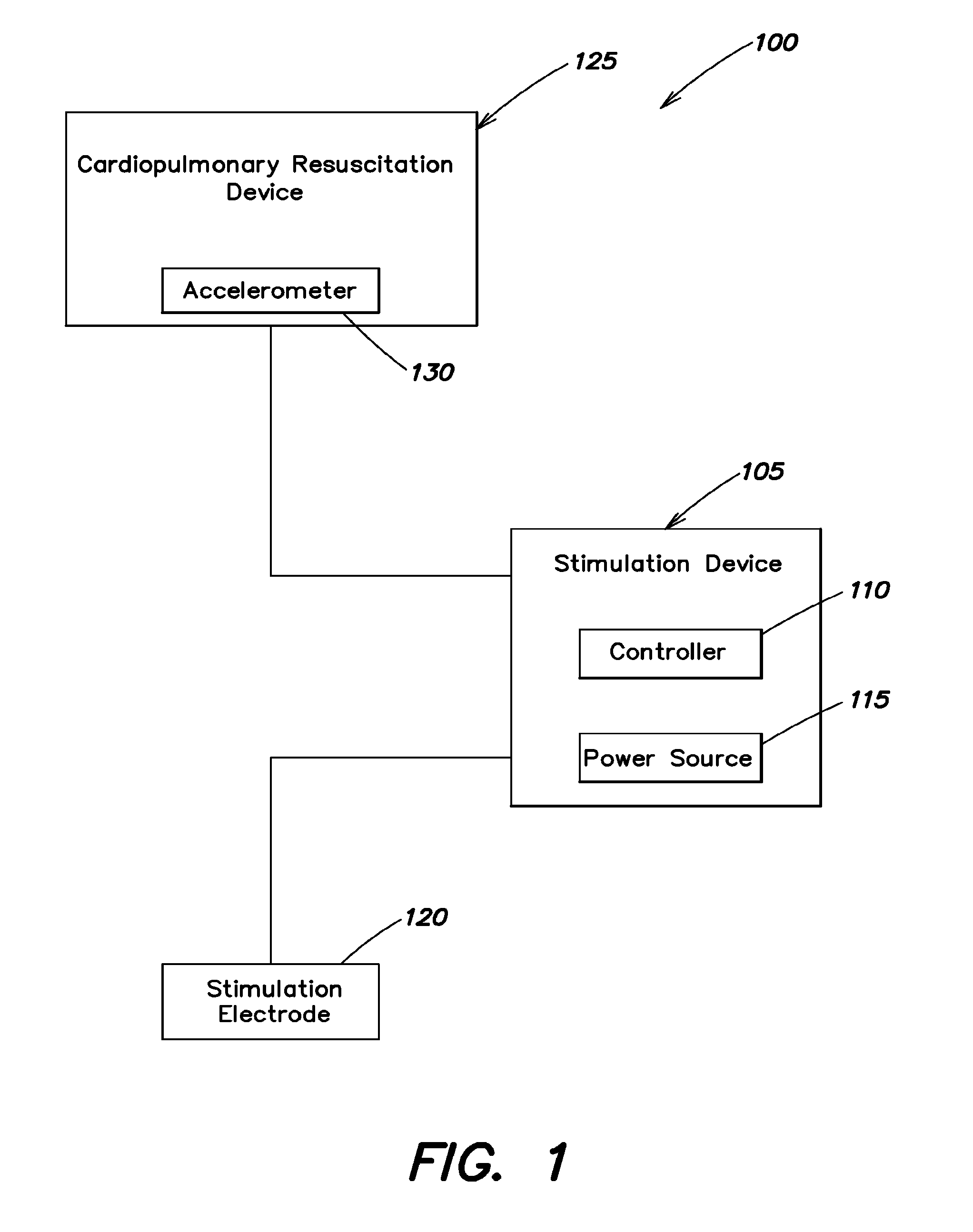
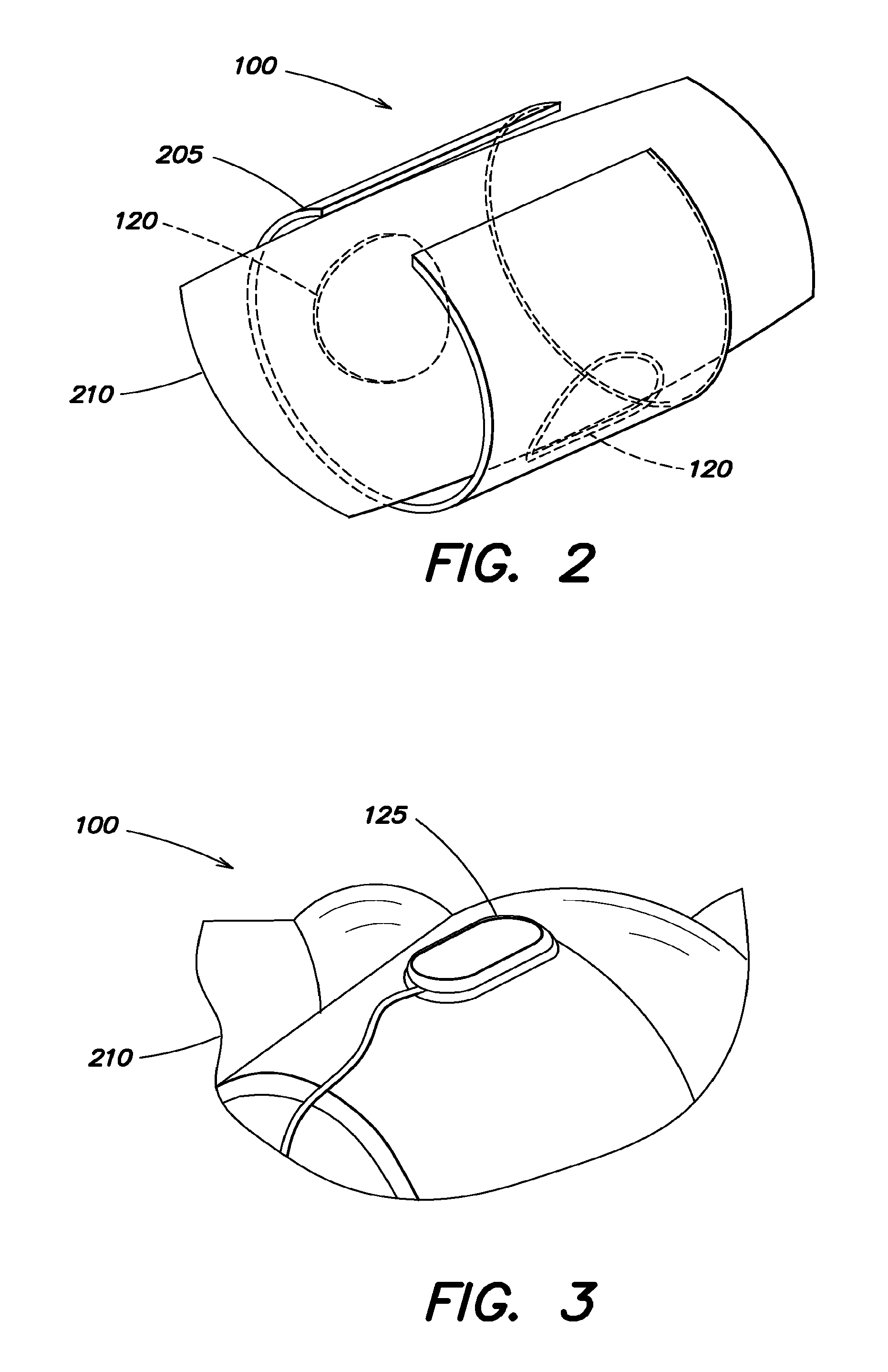
Systems and methods for enhanced venous return flow during cardiac event
InactiveUS8527043B2Enhancing cardiopulmonary circulationIncrease volumeCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPulmonary vasculatureVein
Systems and methods of enhancing cardiopulmonary circulation in a subject during resuscitation are provided. A signal is received responsive to an induced heart compression that is applied to the subject, for example during ventricular fibrillation, an asystolic condition, or cardiac arrest. Responsive to receipt of the signal, a muscle distal subject's heart is electrically stimulated to contract and expel blood into the venous blood flow toward a heart of the subject.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com