Patents
Literature
338 results about "Nerve fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Group A nerve fibers are one of the three classes of nerve fiber as generally classified by Erlanger and Gasser. The other two classes are the group B nerve fibers, and the group C nerve fibers. Group A are heavily myelinated, group B are moderately myelinated, and group C are unmyelinated.
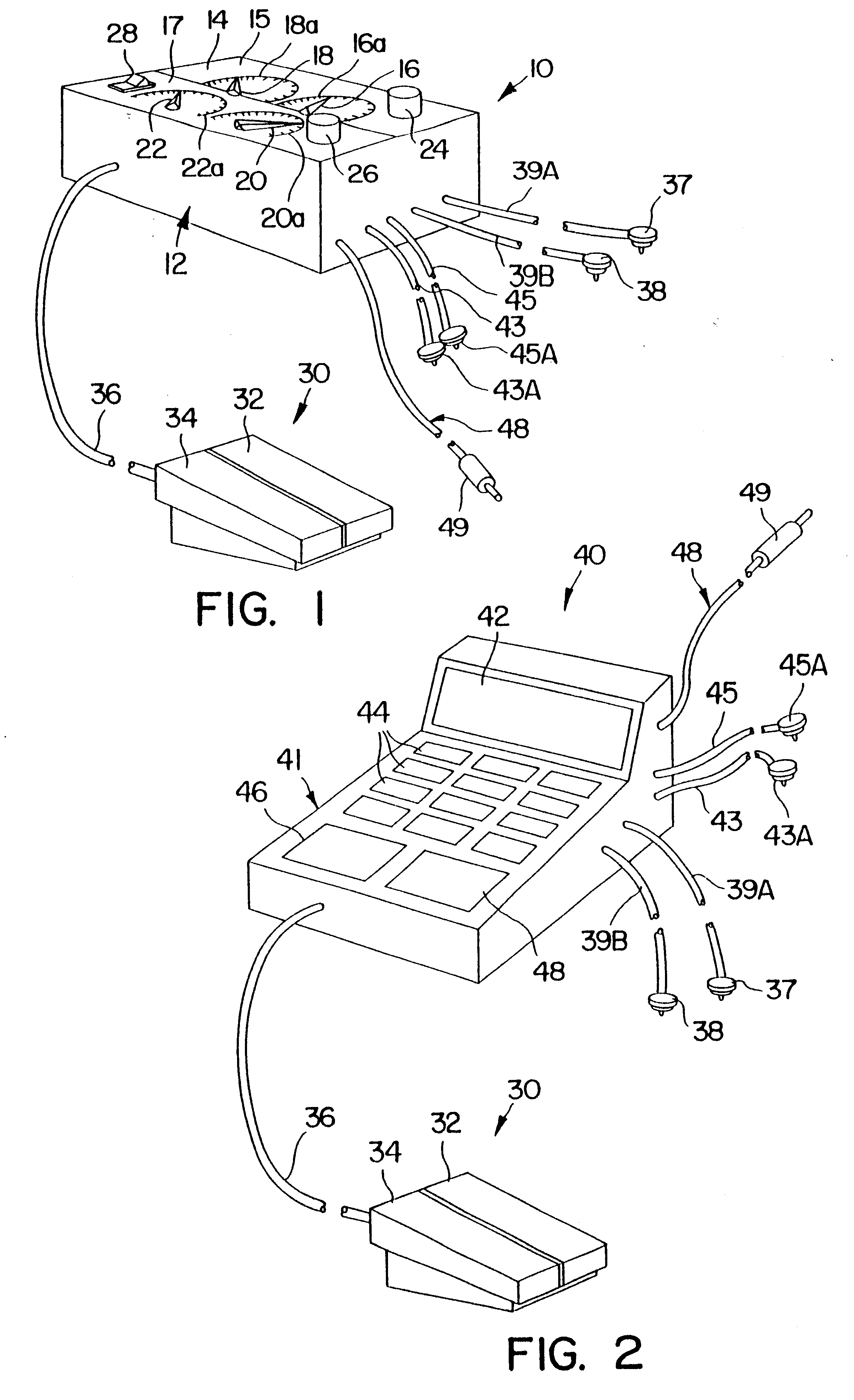
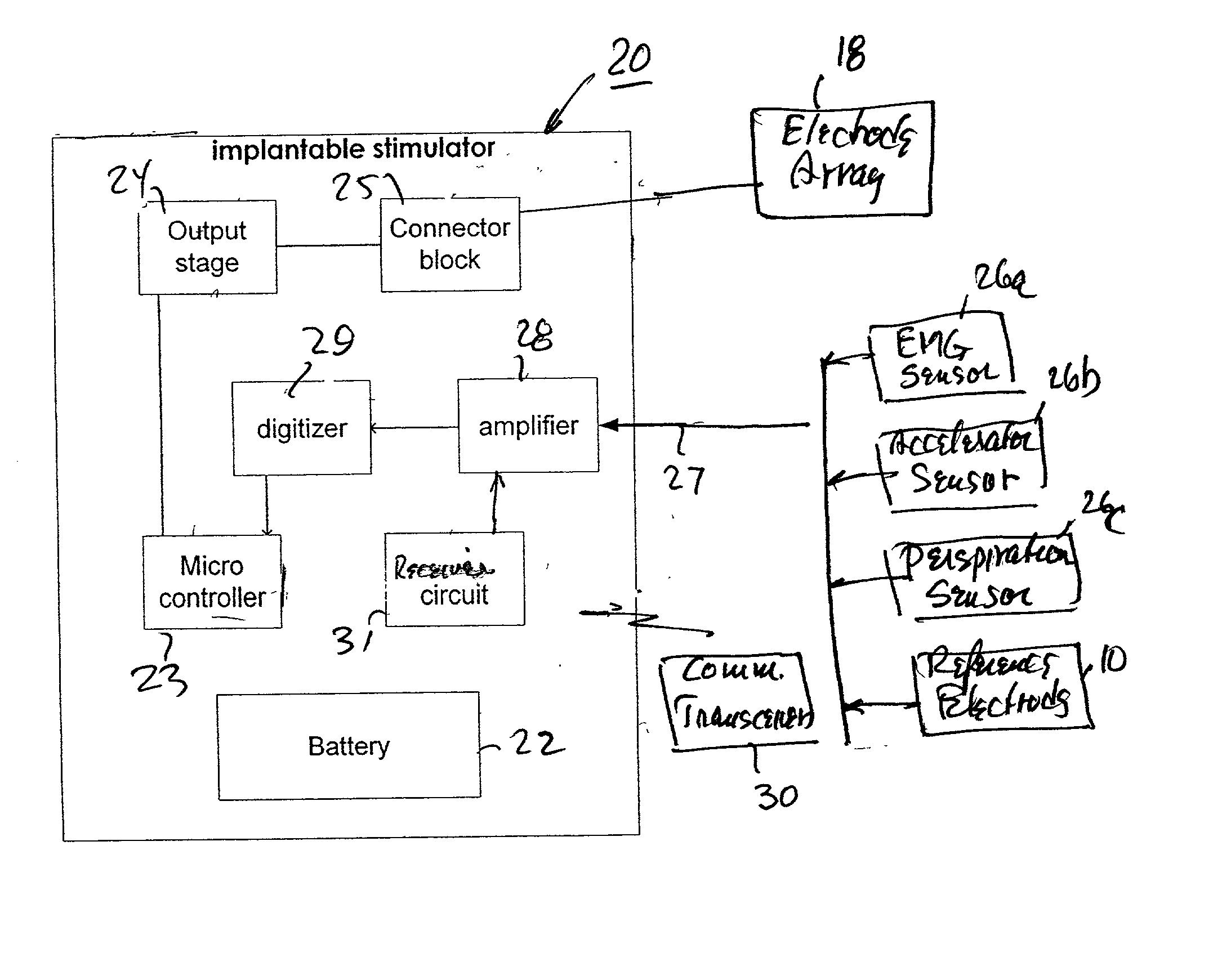
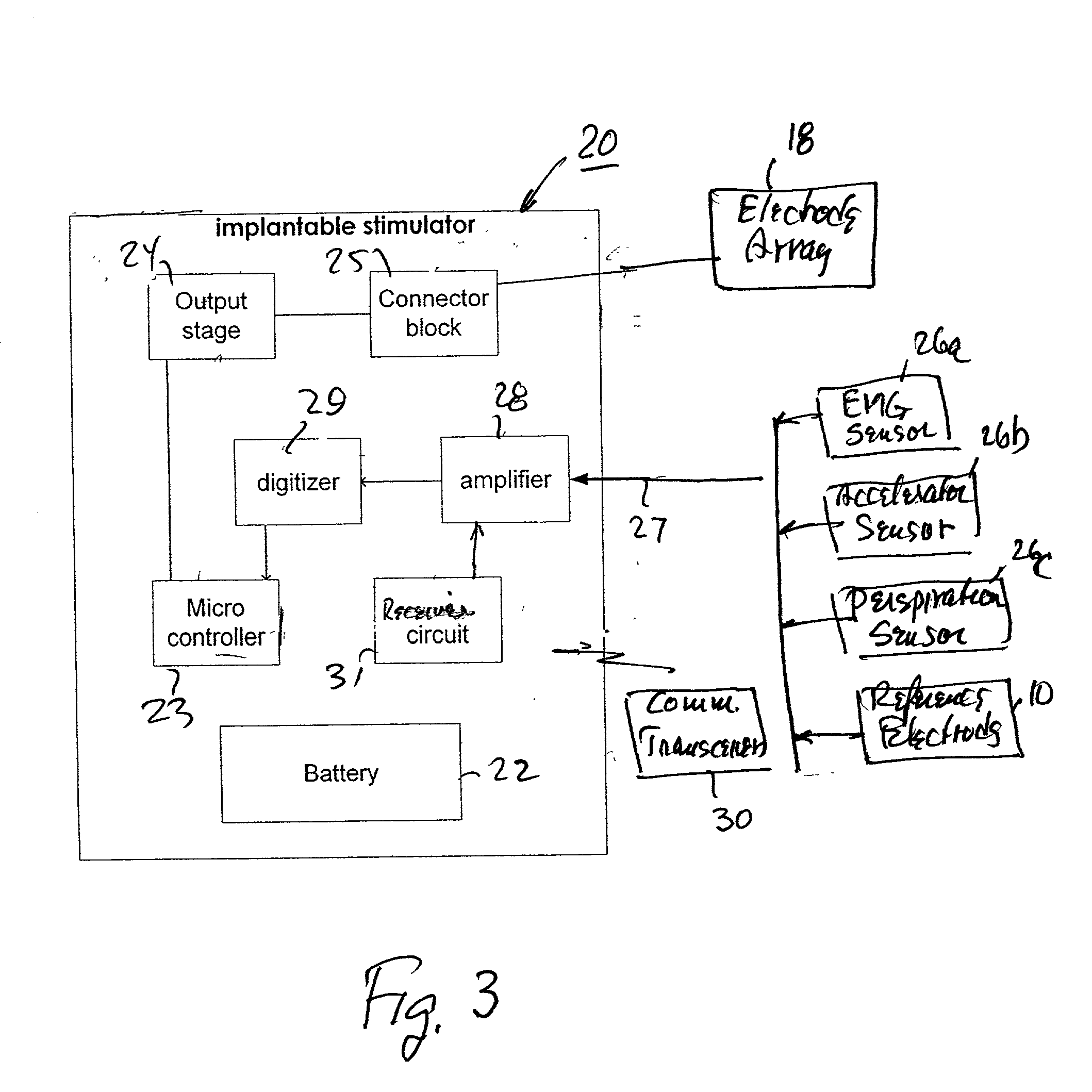
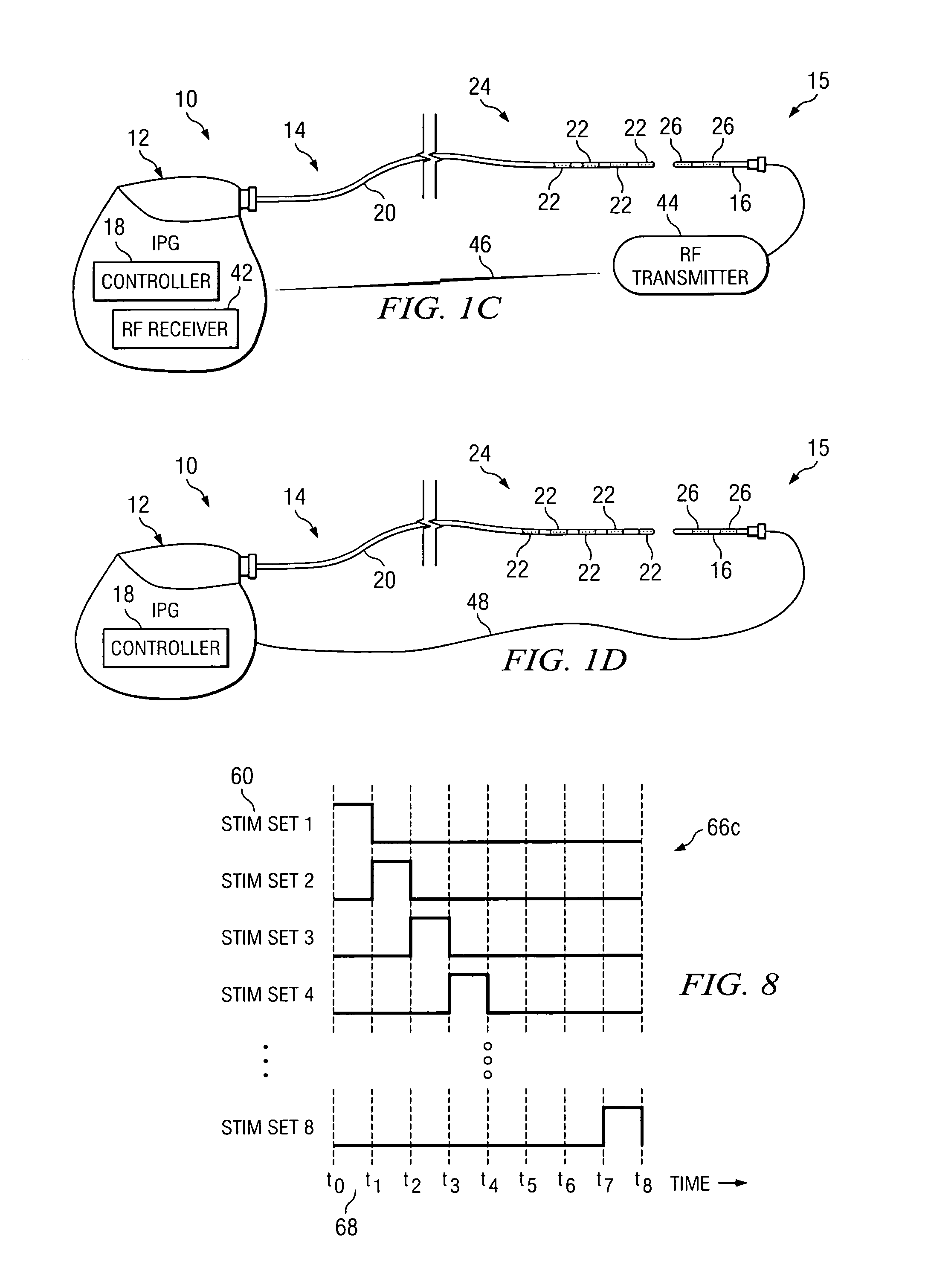
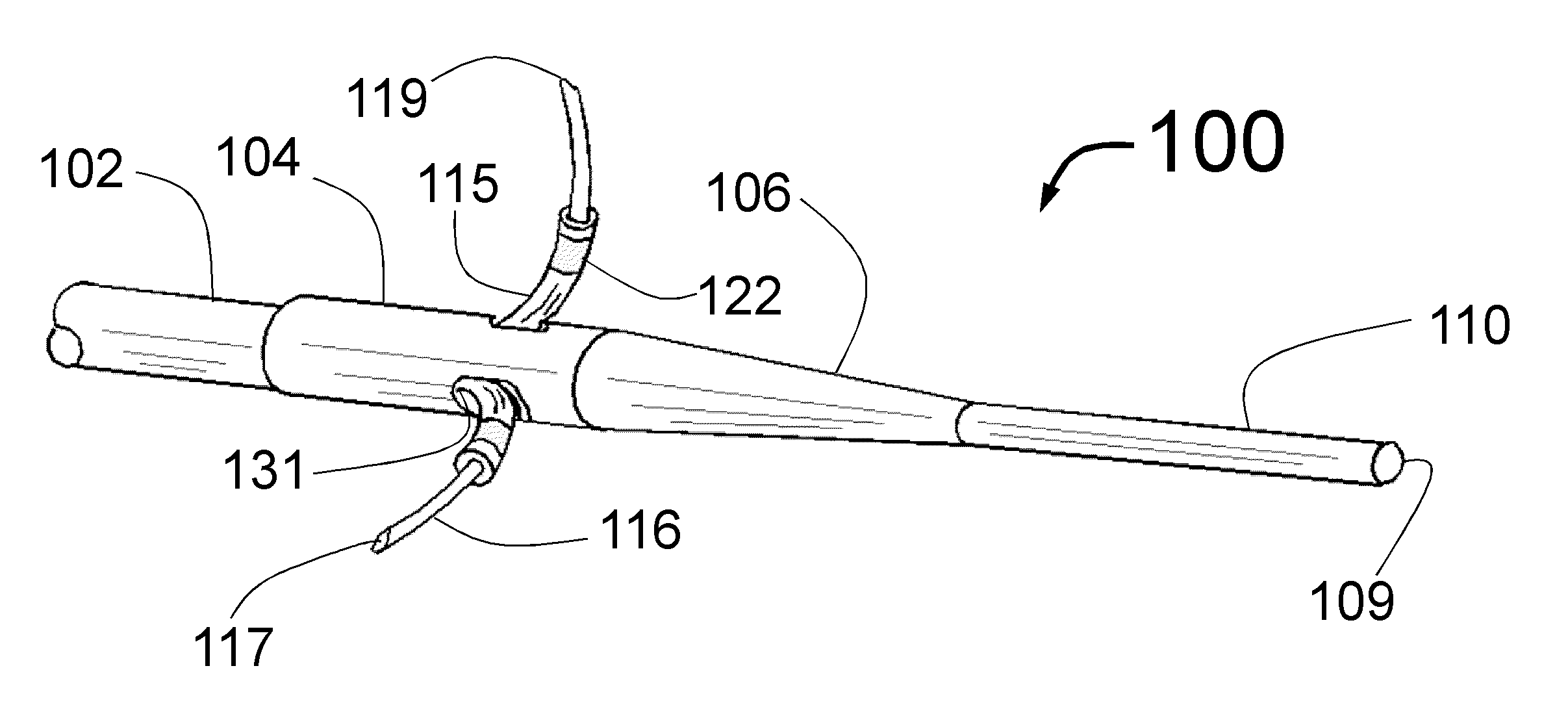
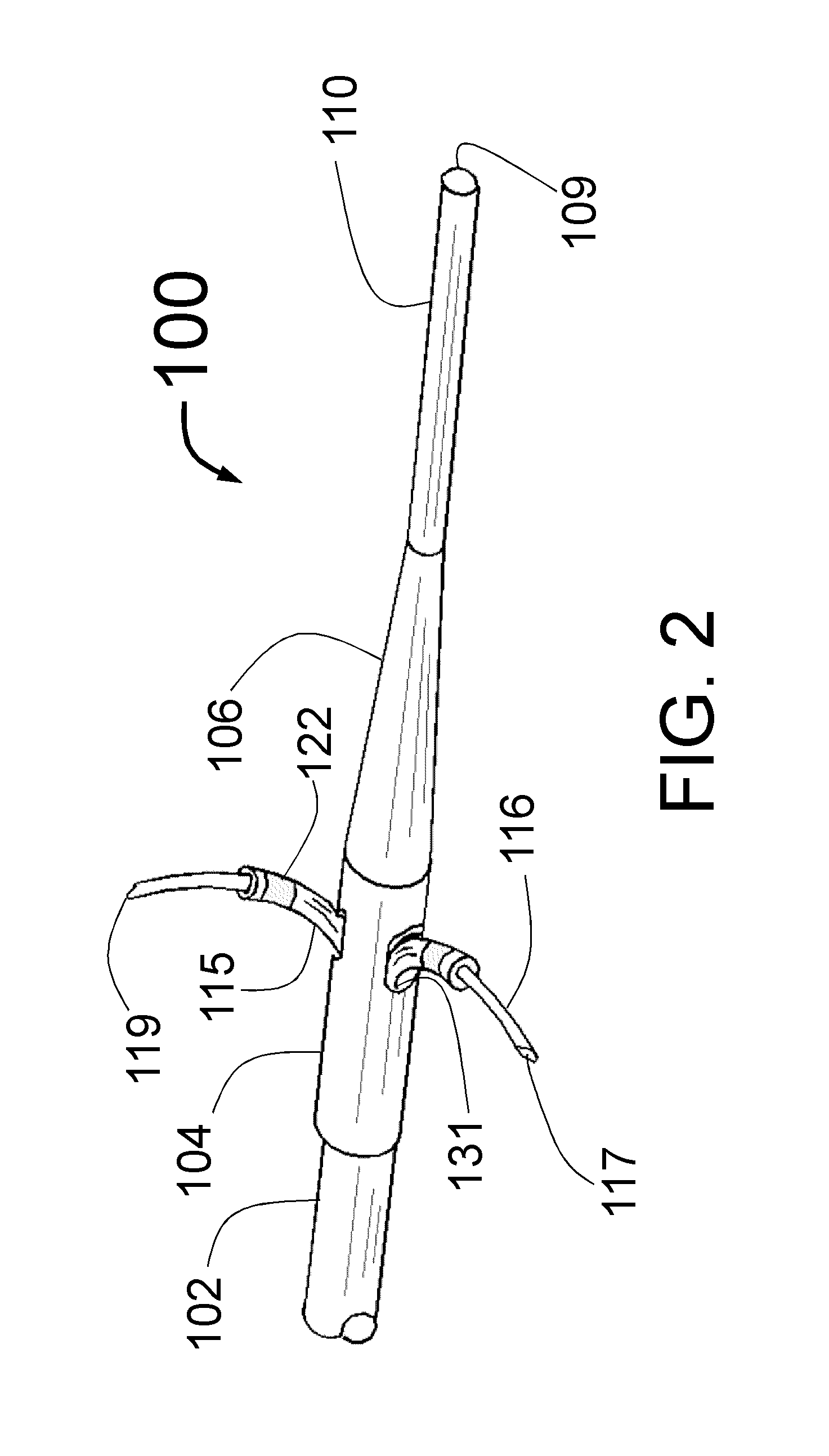
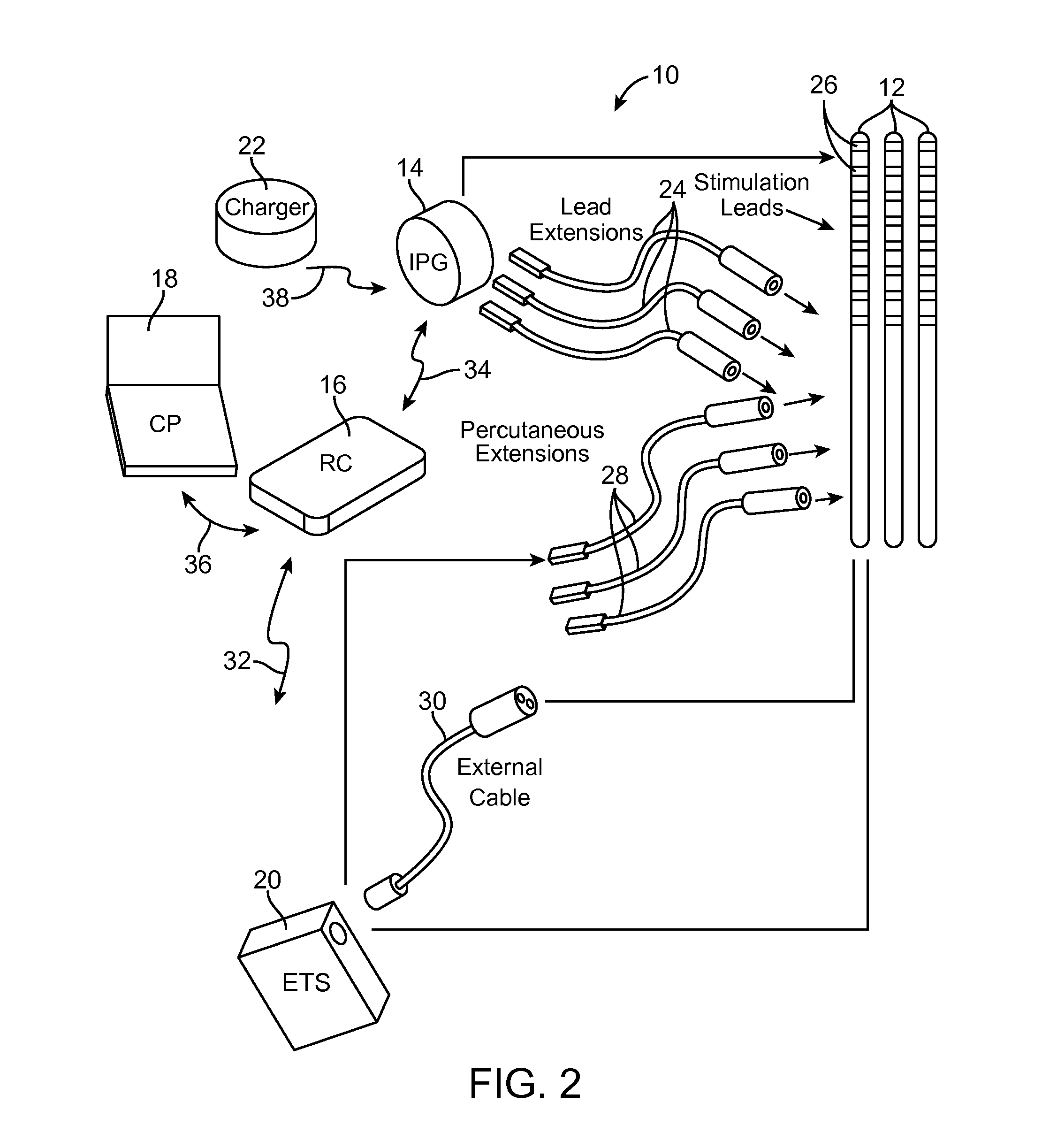
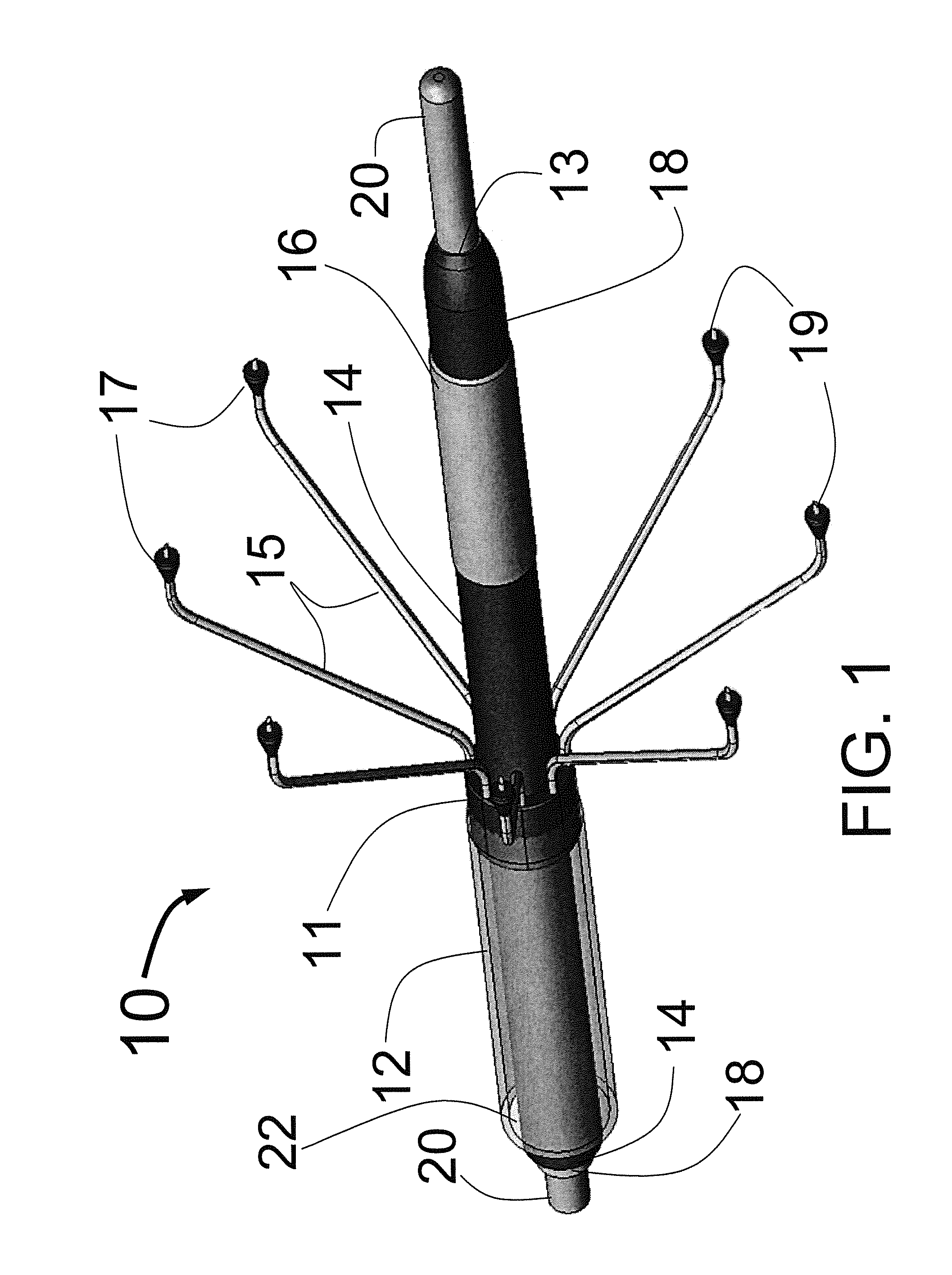
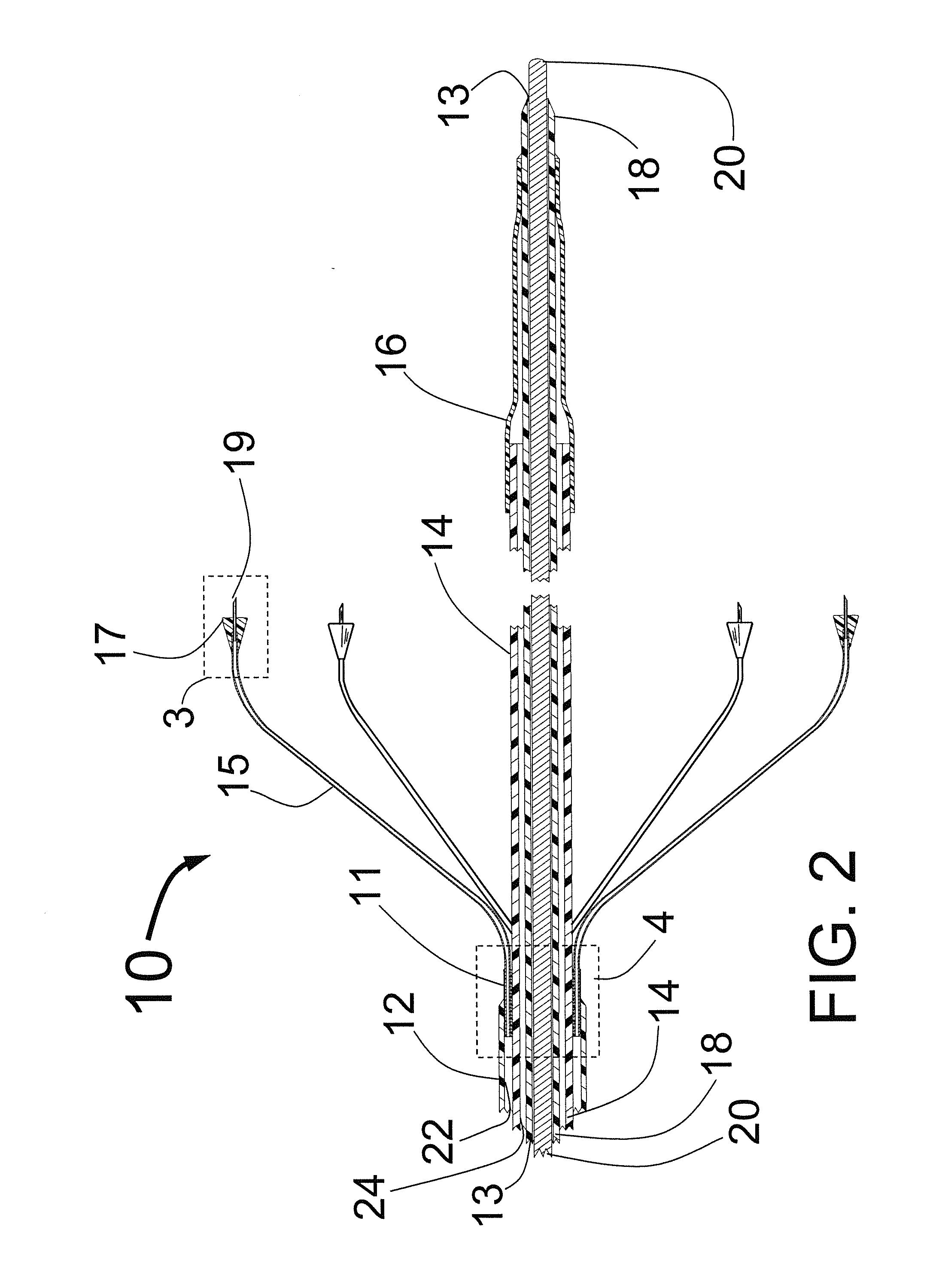
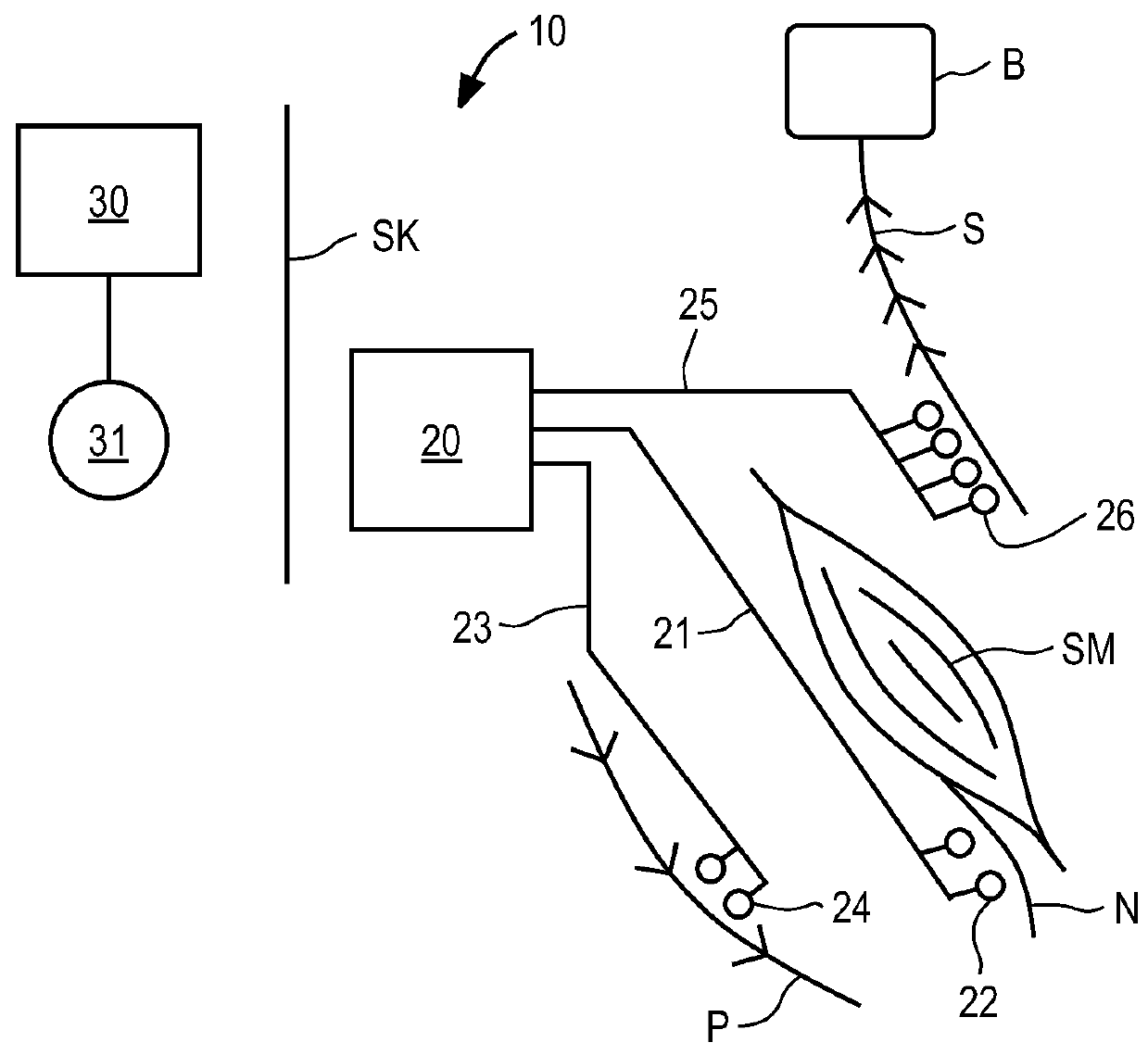
Method and apparatus for selective control of nerve fibers
InactiveUS6600954B2Pain reliefReduced sensationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationFiberNerve fiber bundle
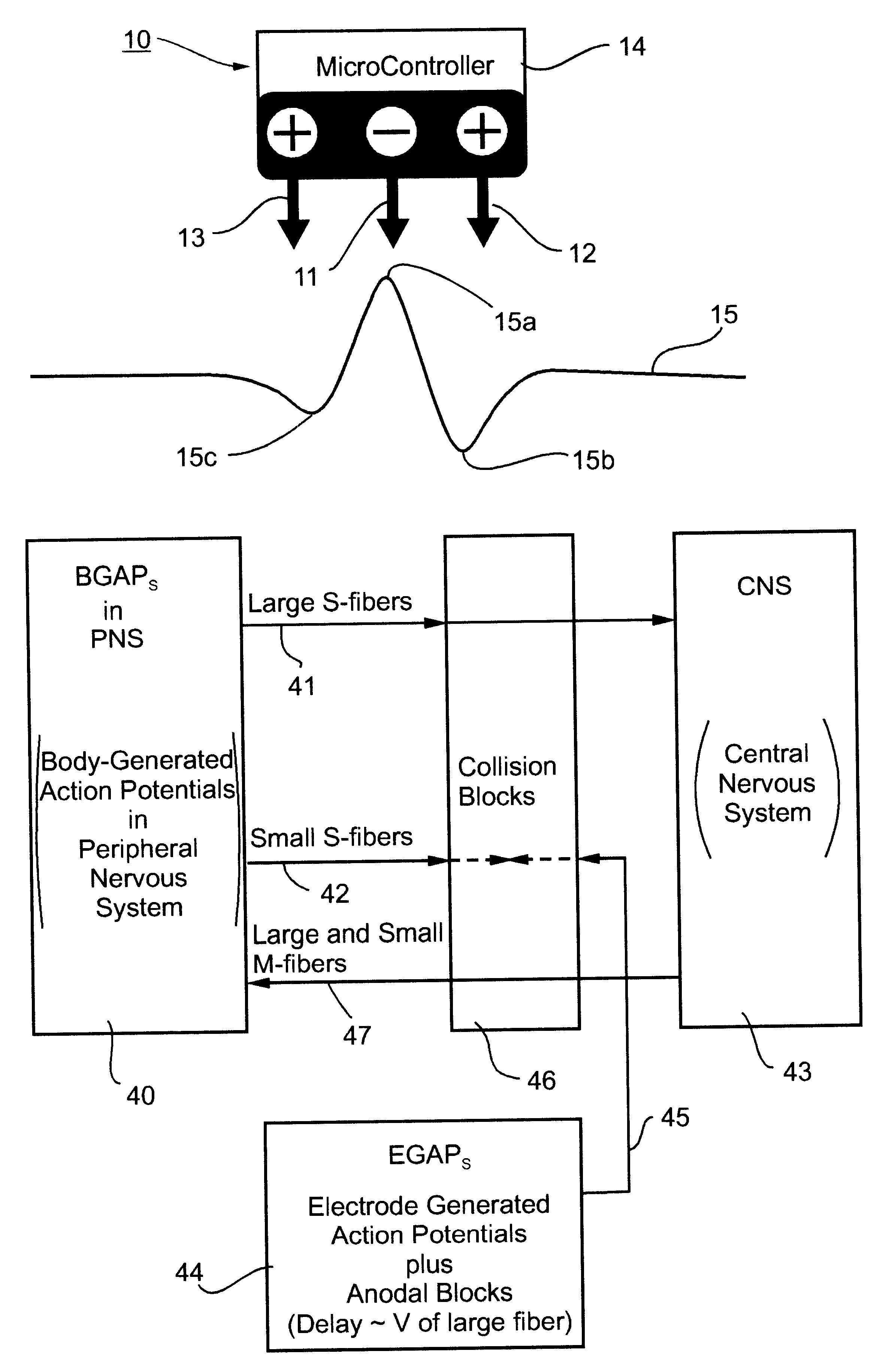
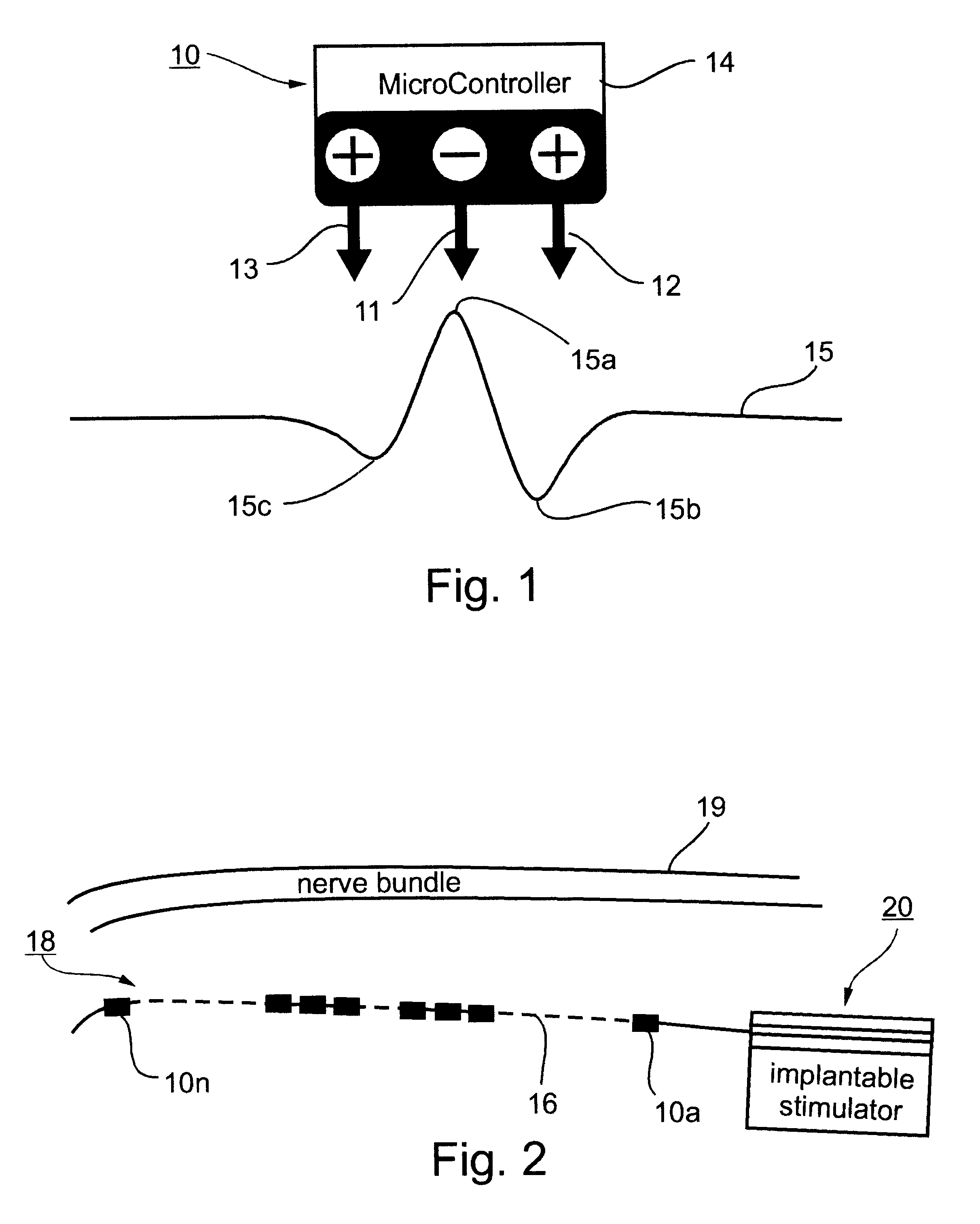
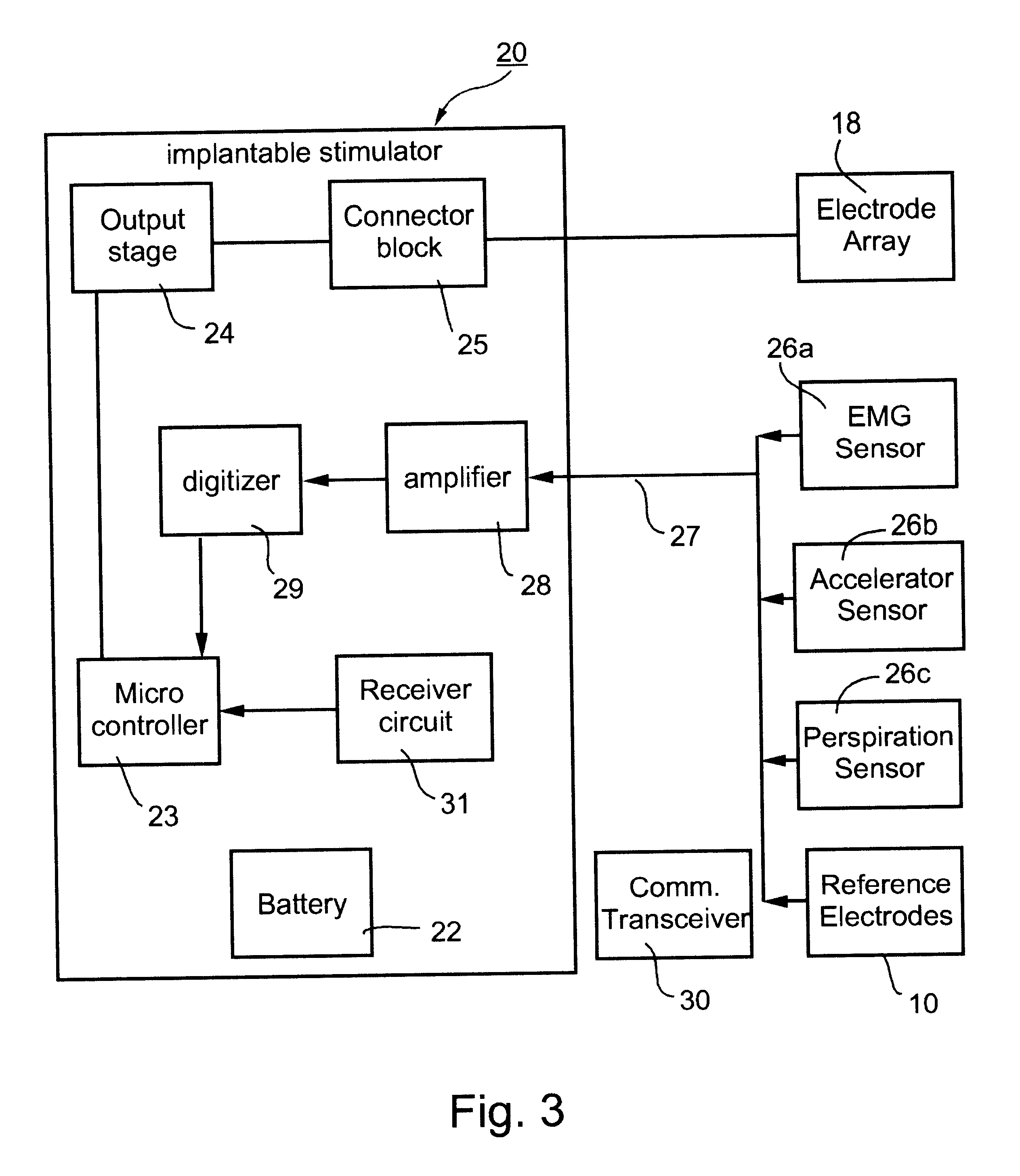
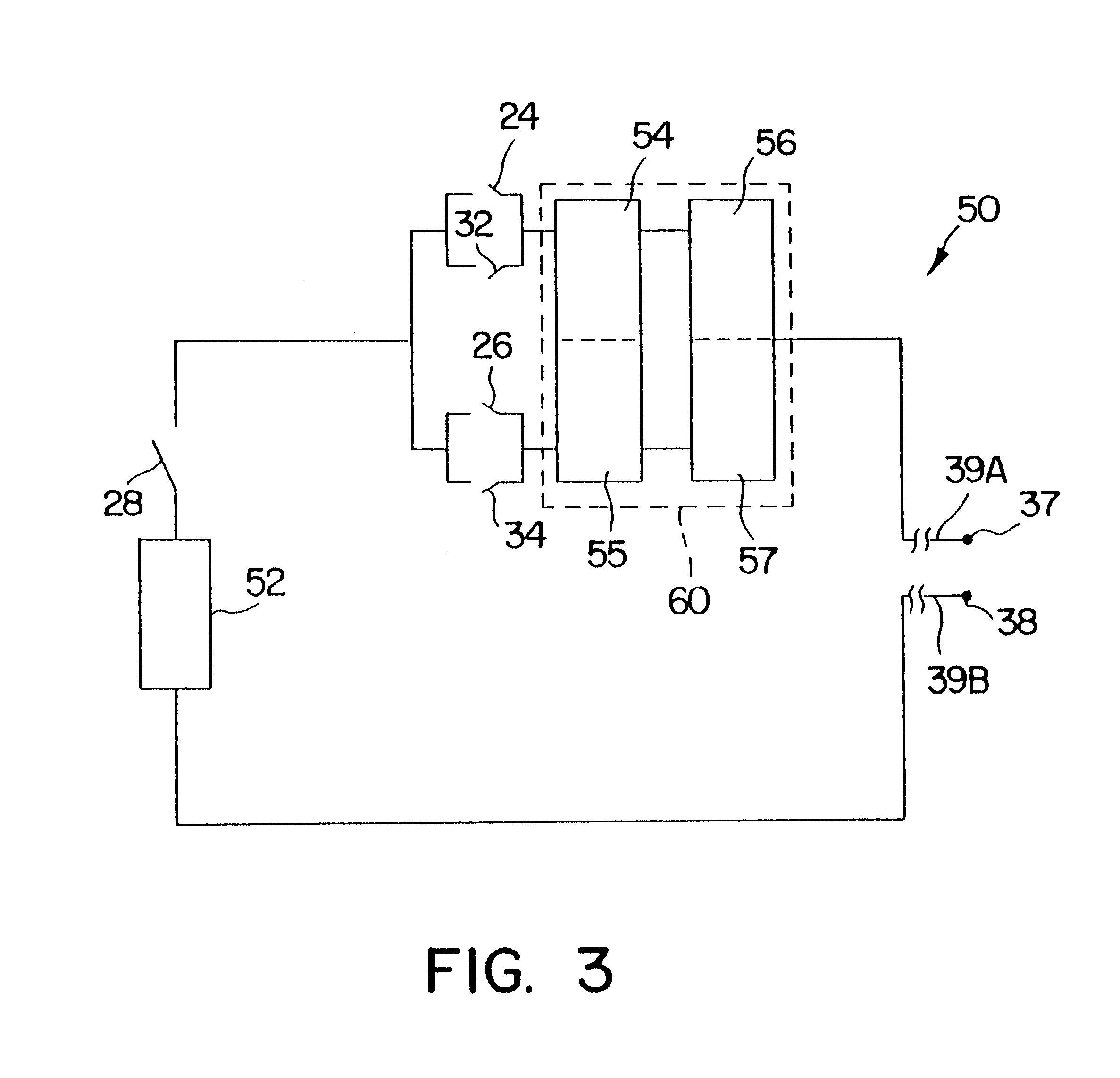
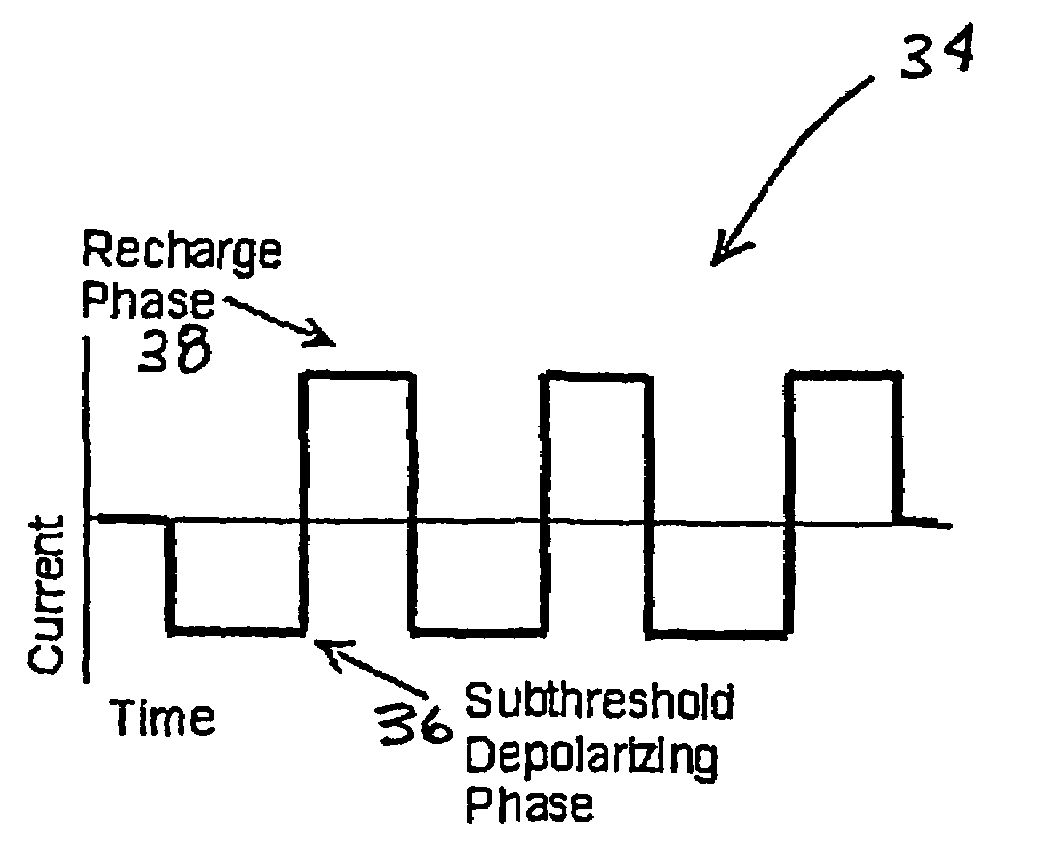
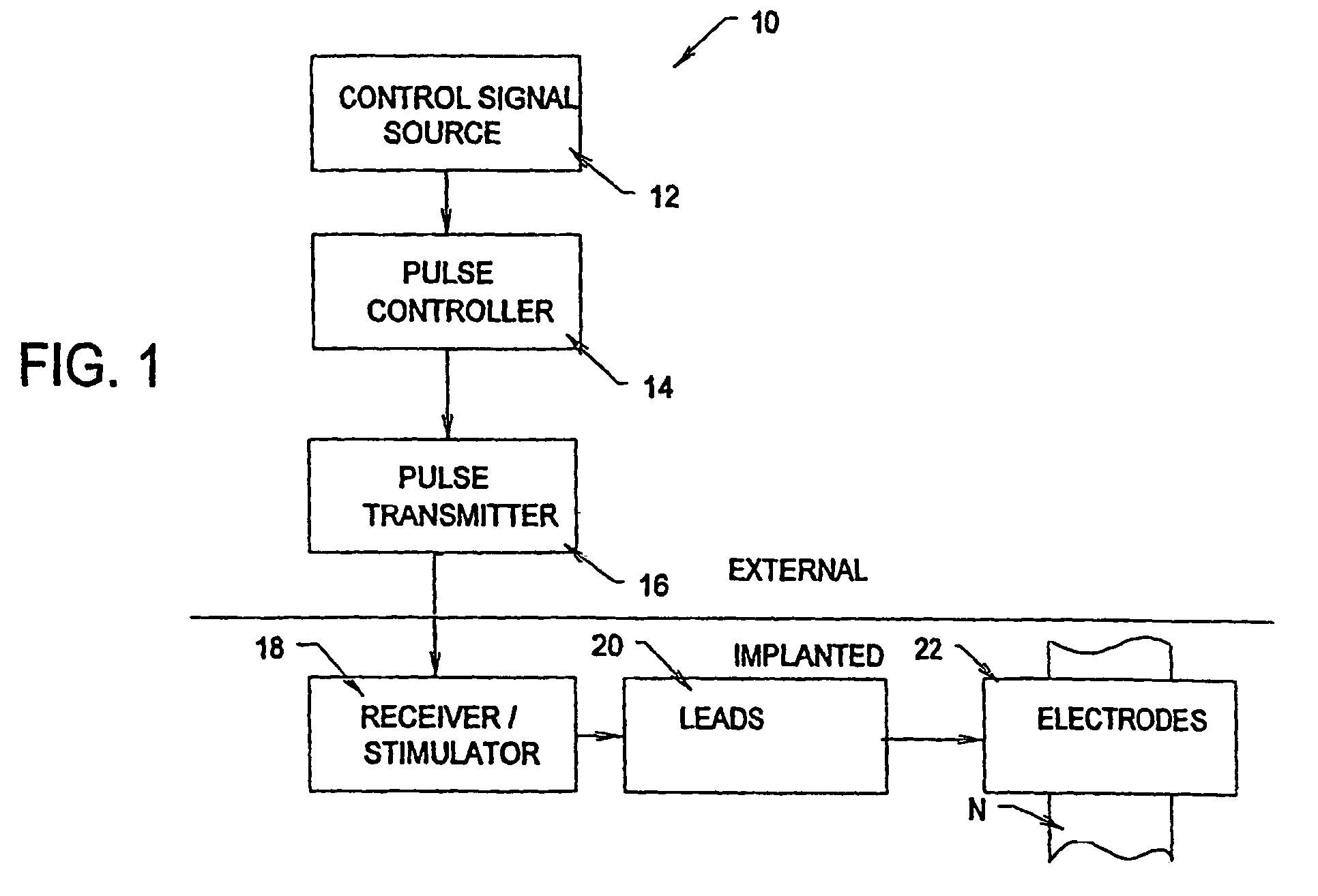
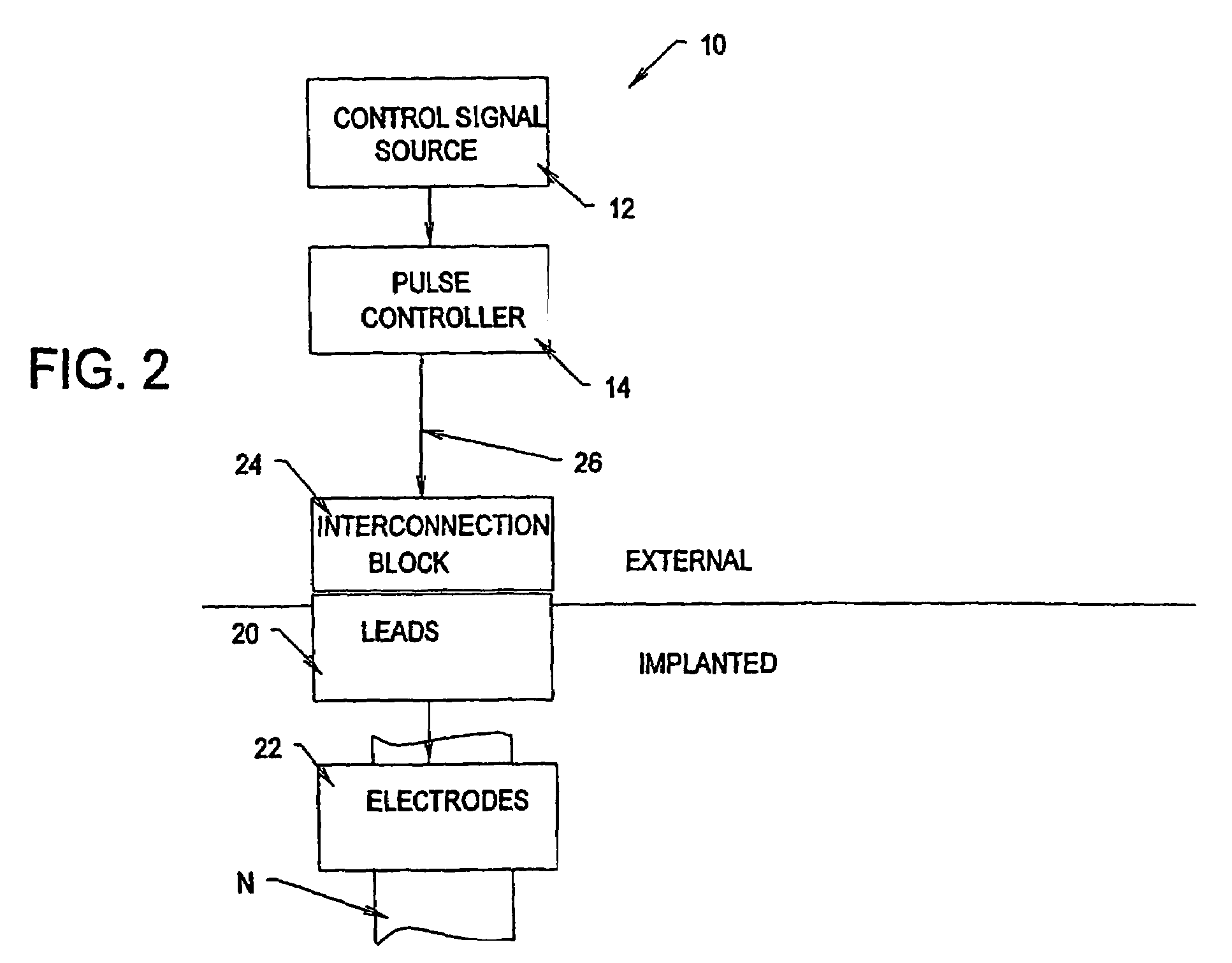
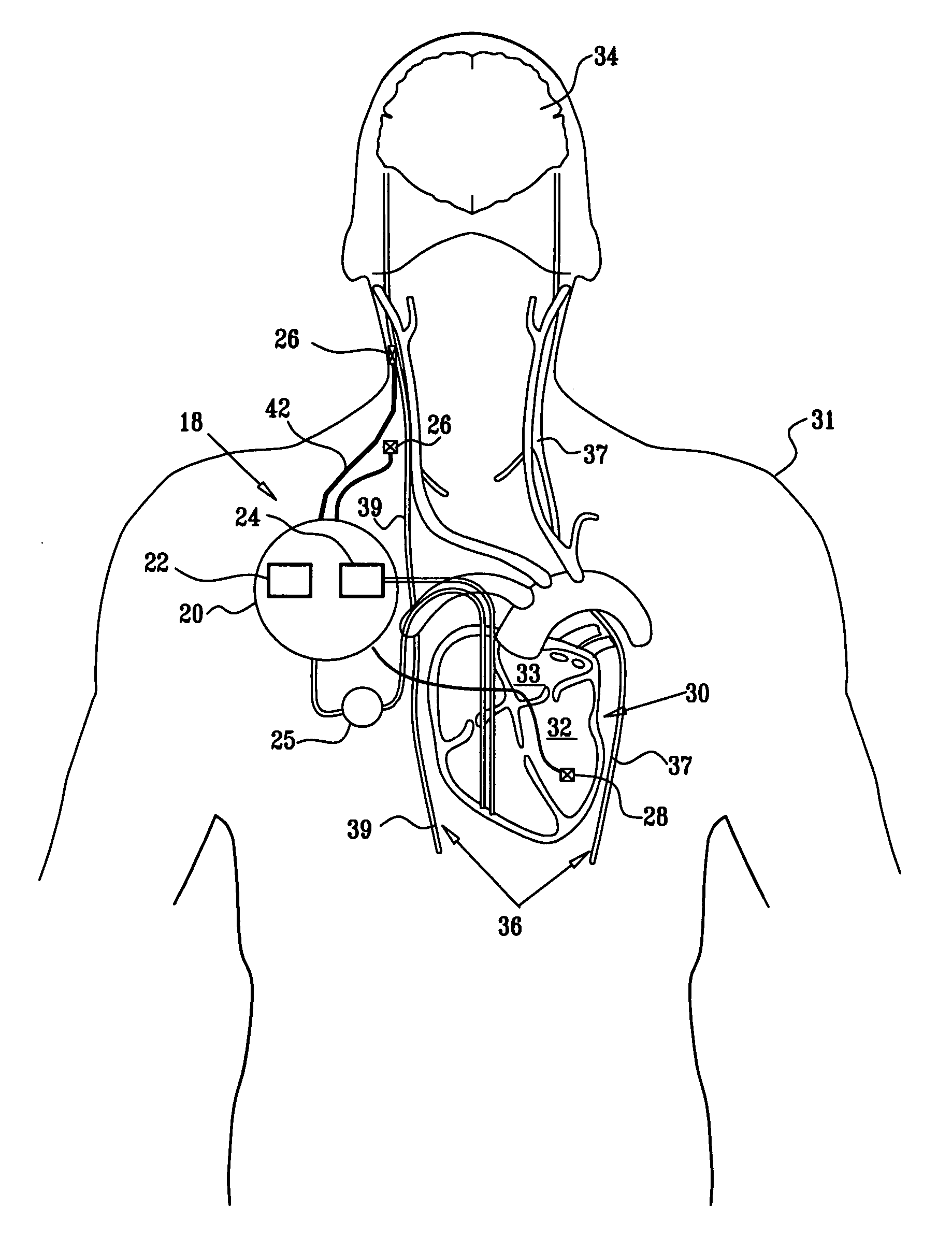
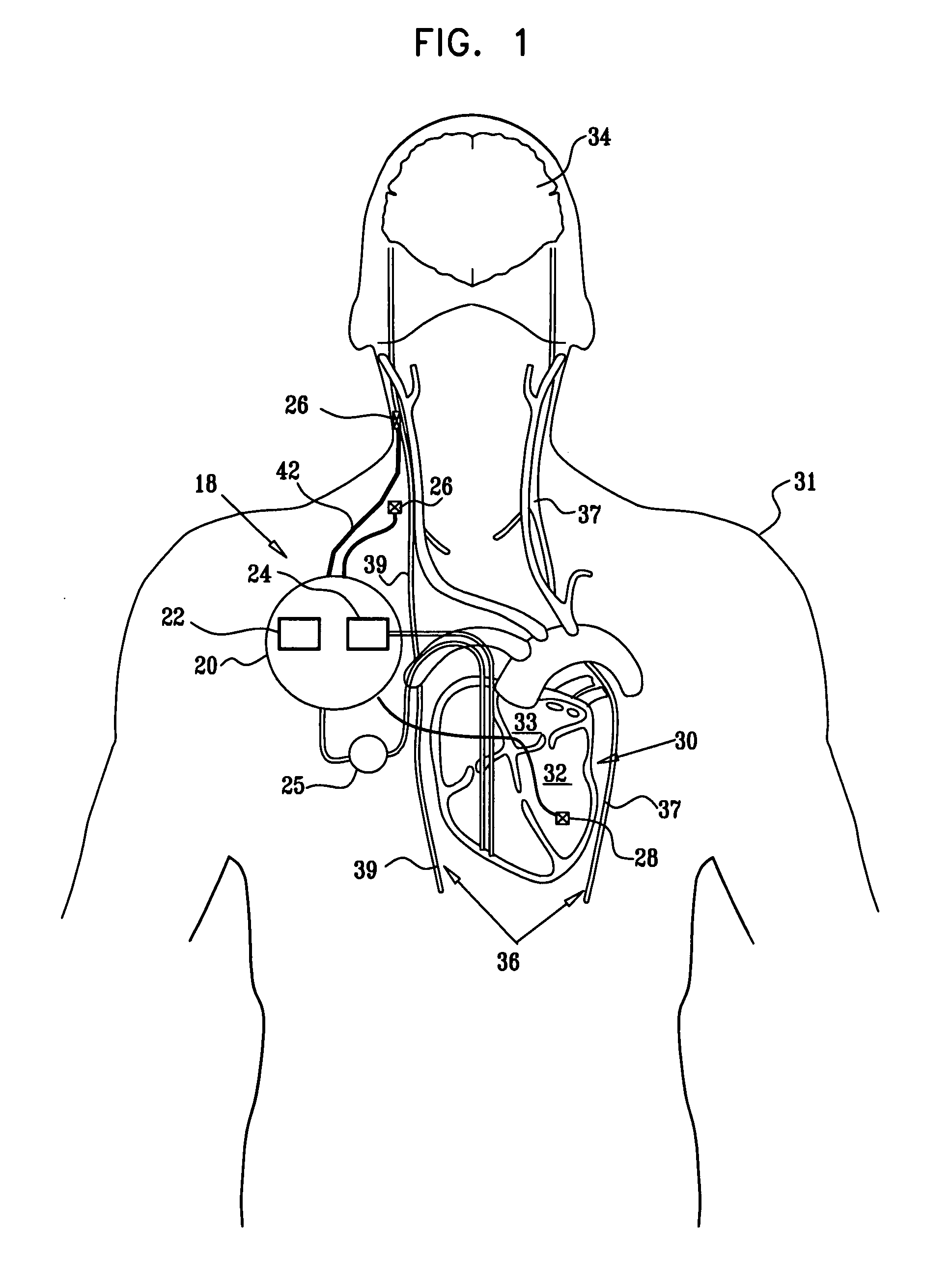
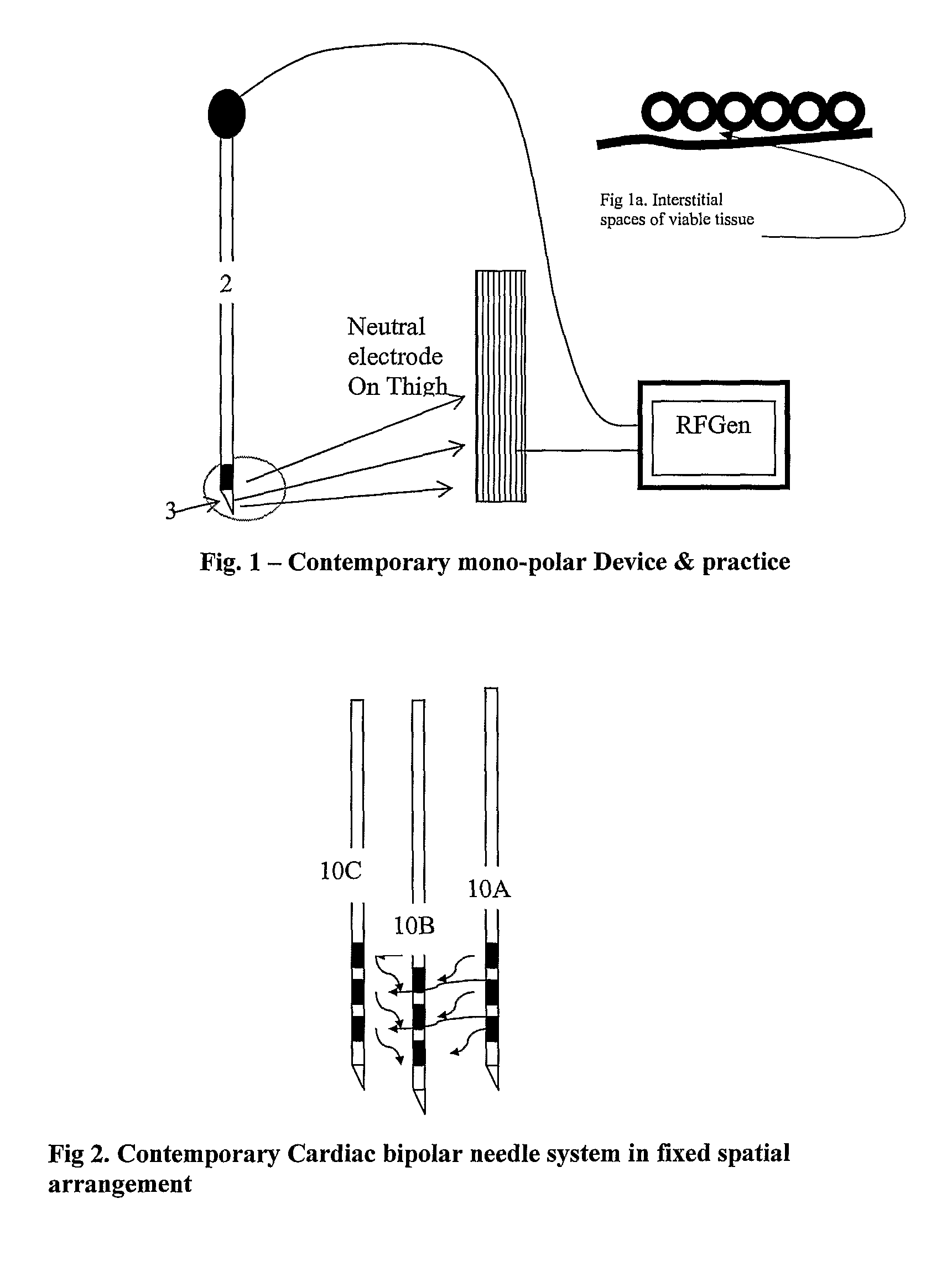
A method and apparatus particularly useful for pain control by selectively blocking the propagation of body-generated action potentials travelling through a nerve bundle by using a tripolar electrode device to generate unidirectional action potentials to serve as collision blocks with the body-generated action potentials representing pain sensations in the small-diameter sensory fibers. In the described preferred embodiments there are a plurality of electrode devices spaced along the length of the nerve bundle which are sequentially actuated with delays corresponding to the velocity of propagation of the body-generated action potentials through the large-diameter fibers to produce a "green wave" effect which minimizes undesired anodal blocking of the large-diameter fibers while maximizing the collision blocking of the small-diameter fibers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
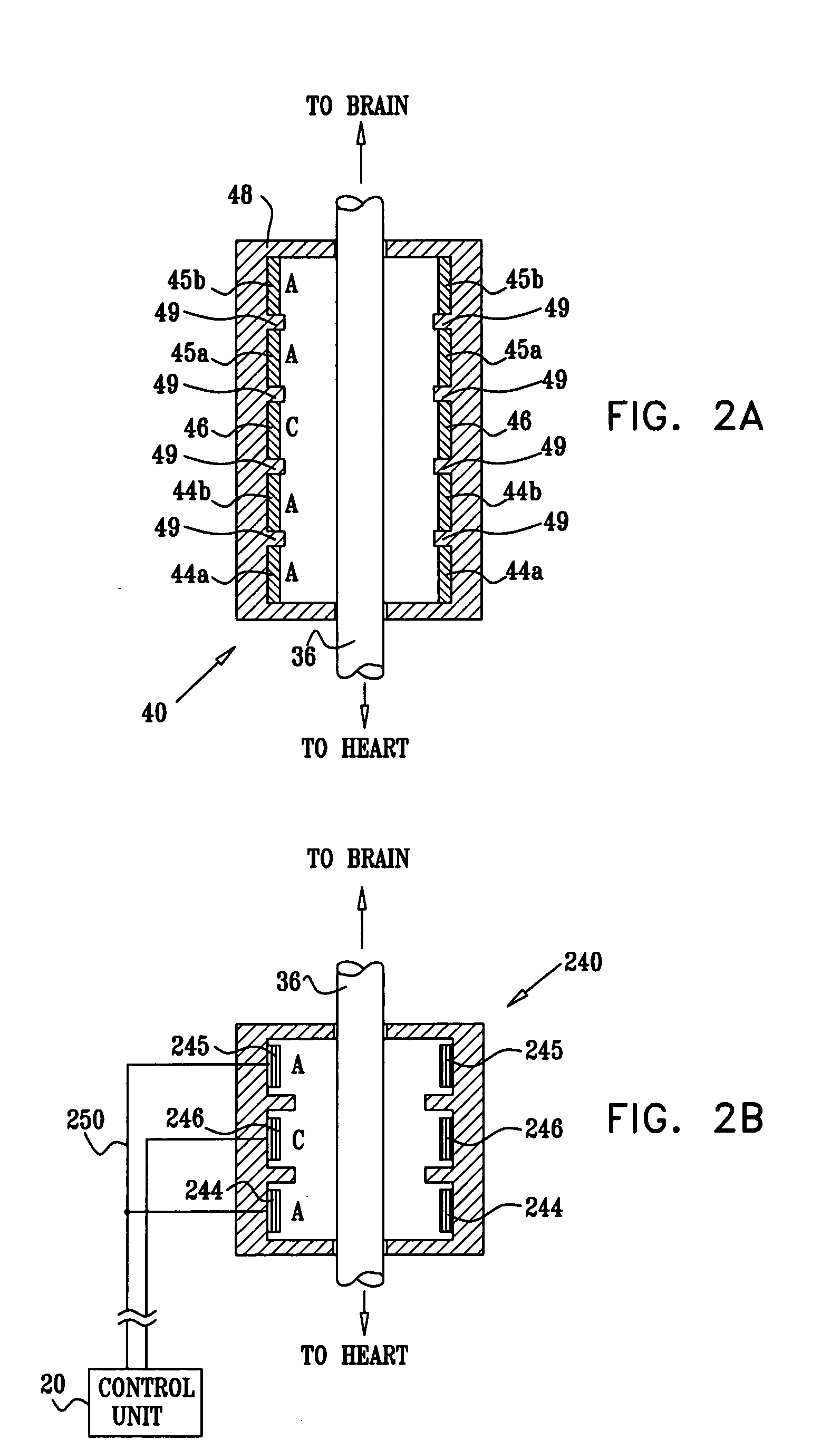
Techniques for applying, calibrating, and controlling nerve fiber stimulation
InactiveUS20050197675A1Reduce riskFew potential side effectSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsNerve fiber bundleFiber
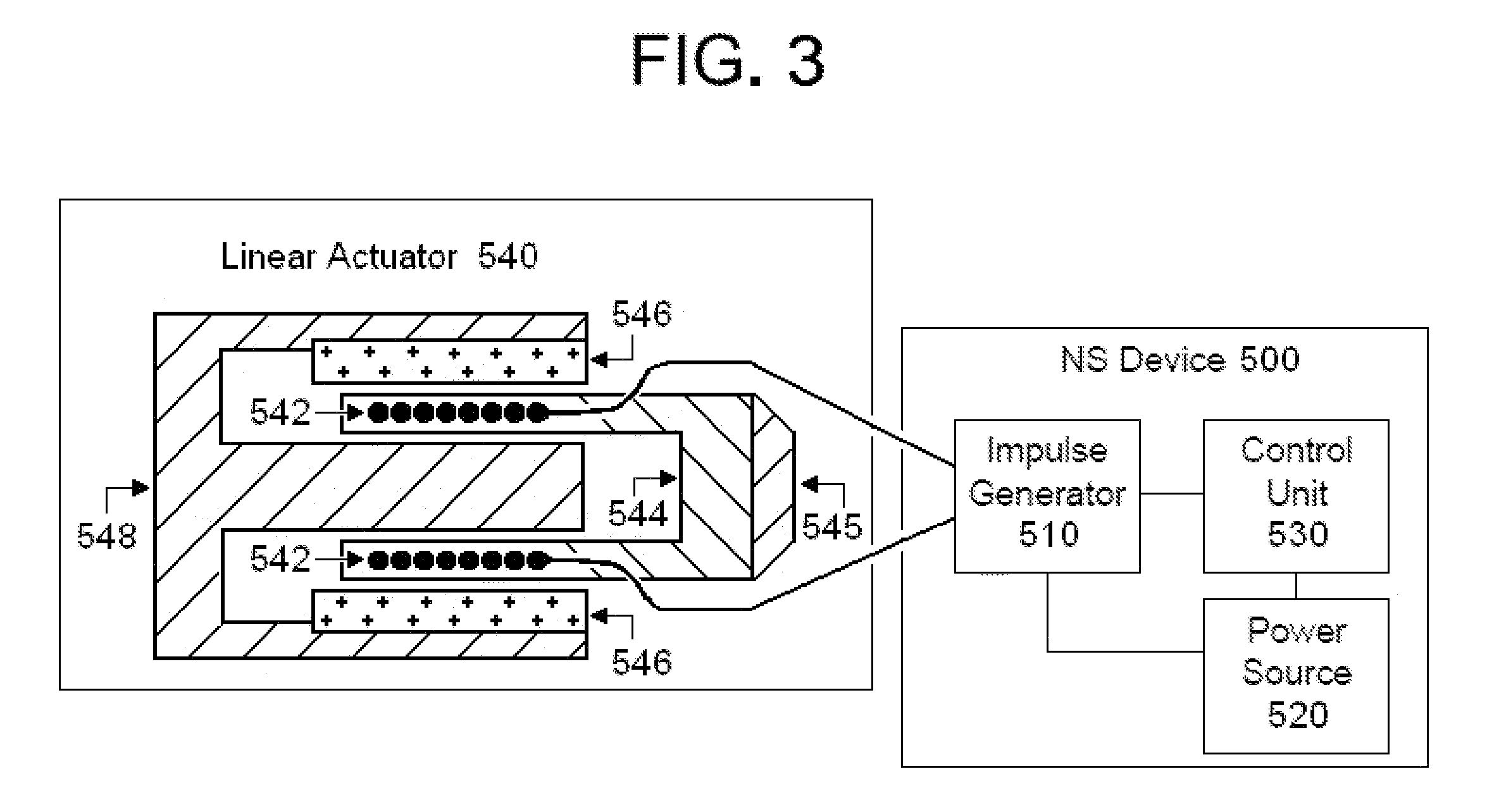
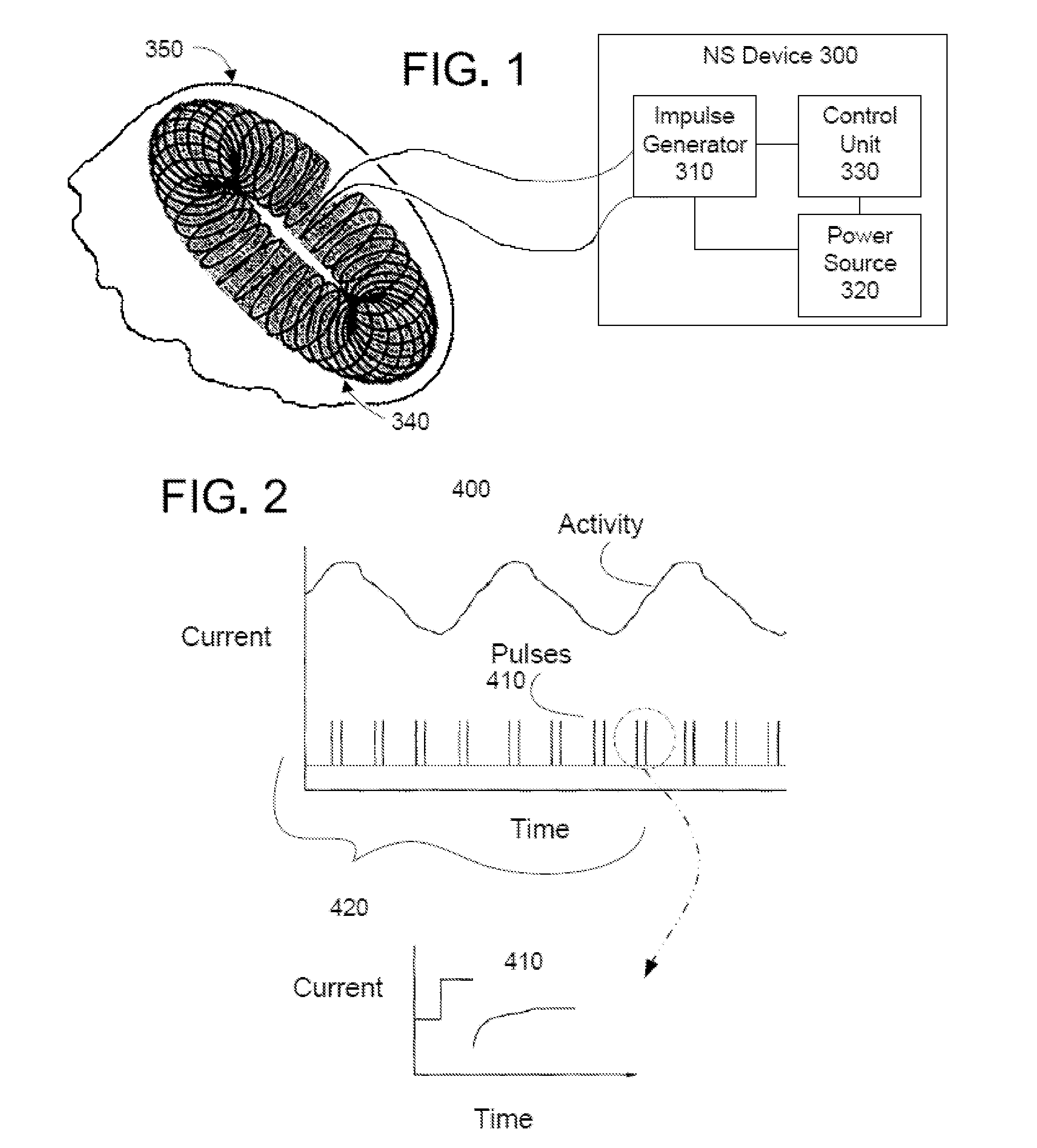
Apparatus is provided including an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of a subject; and a control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply a current to the site intermittently during alternating “on” and “off”periods, each of the “on” periods having an “on” duration equal to between 1 and 10 seconds, and each of the “off” periods having an “off”duration equal to at least 50% of the “on” duration. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
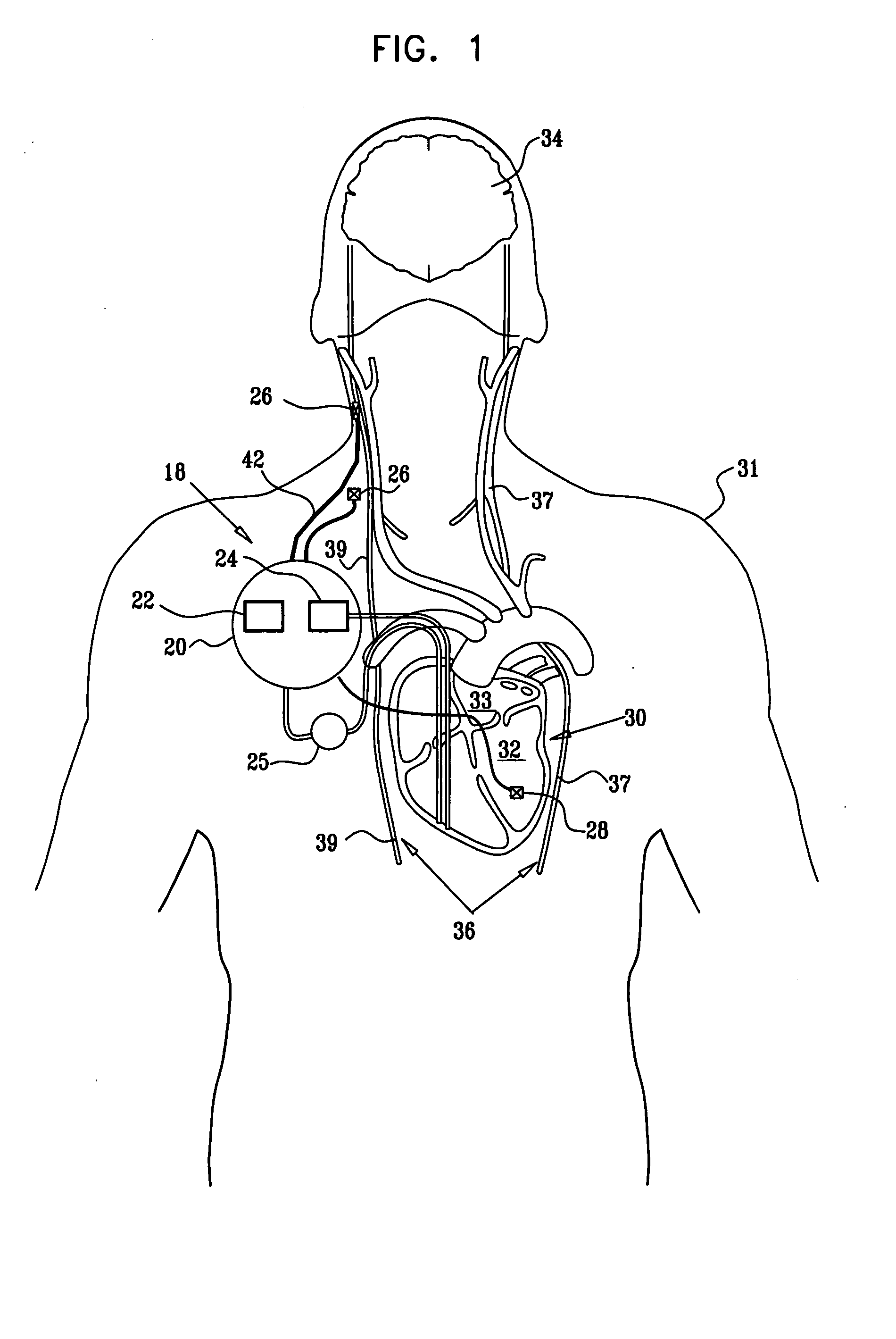
Method and device for electronically controlling the beating of a heart using venous electrical stimulation of nerve fibers
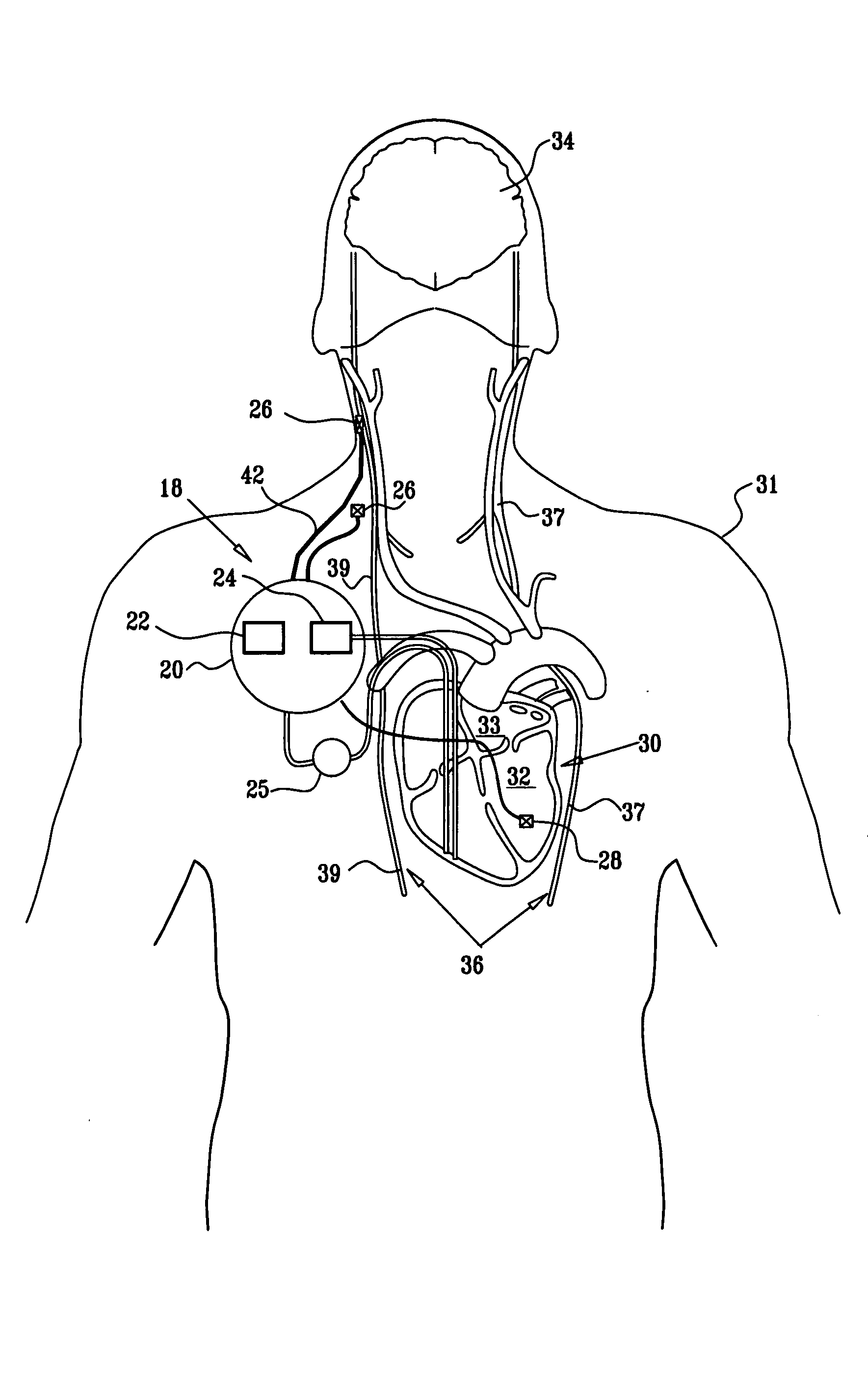
An electro-stimulation device includes a pair of electrodes for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The electro-stimulation device both electrically arrests the heartbeat and stimulates the heartbeat. A pair of electrodes are provided for connection to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat. The pair of electrodes may be connected to an intravenous catheter for transvenous stimulation of the appropriate nerve. A first switch is connected between a power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to augment any natural stimuli to the heart and thereby stop the heart from beating. A second switch is connected between the power supply and the electrodes for selectively supplying current from the power supply to the electrodes to provide an artificial stimulus to initiate heartbeating. In another aspect, the invention is directed to a method for arresting the beat of a heart in a living body comprising the steps of connecting the pair of electrodes to at least one location in the body that affects or regulates the heartbeat and supplying an electrical current to the electrodes of sufficient amplitude and duration to arrest the heartbeat. The device may also serve to still the lungs by input to a respirator or by stimulation of the phrenic nerve during surgical procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for reversibly blocking nerve activity
InactiveUS7389145B2Reduce the amplitudeRaise the possibilityElectrotherapyChronic conditionHigh likelihood
Systems and methods for blocking nerve impulses use an implanted electrode located on or around a nerve. A specific waveform is used that causes the nerve membrane to become incapable of transmitting an action potential. The membrane is only affected underneath the electrode, and the effect is immediately and completely reversible. The waveform has a low amplitude and can be charge balanced, with a high likelihood of being safe to the nerve for chronic conditions. It is possible to selectively block larger (motor) nerve fibers within a mixed nerve, while allowing sensory information to travel through unaffected nerve fibers.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
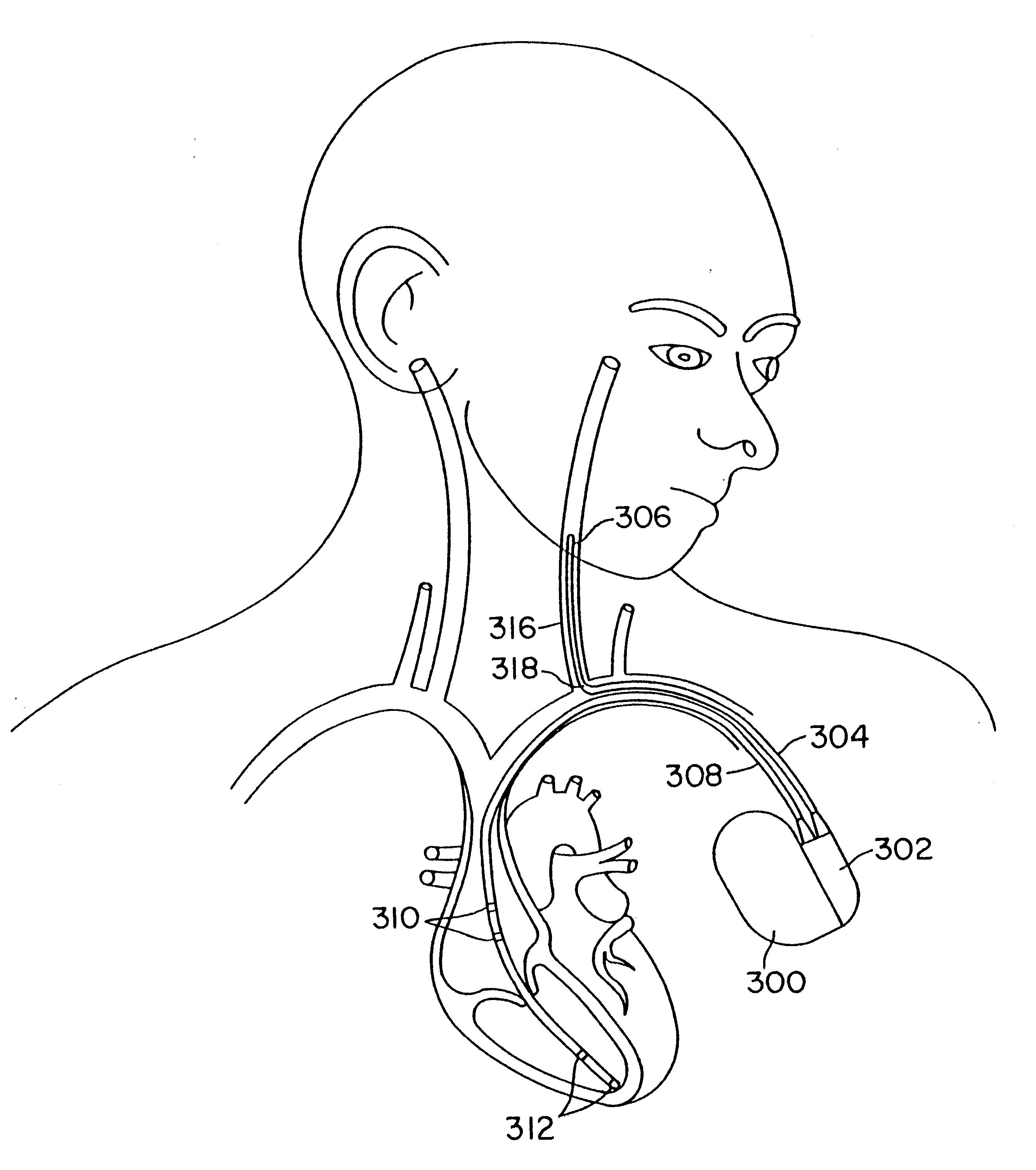
Techniques for applying, configuring, and coordinating nerve fiber stimulation
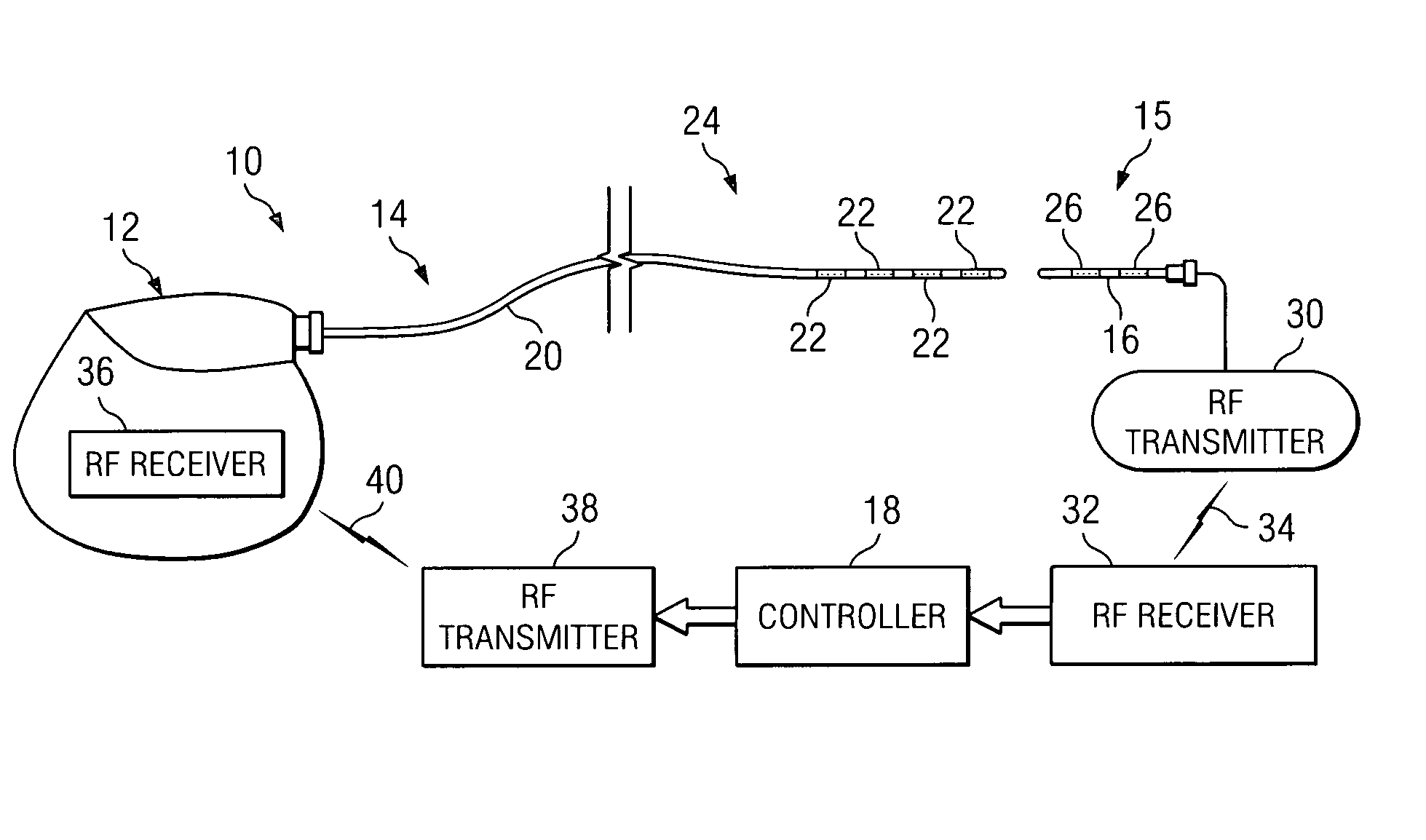
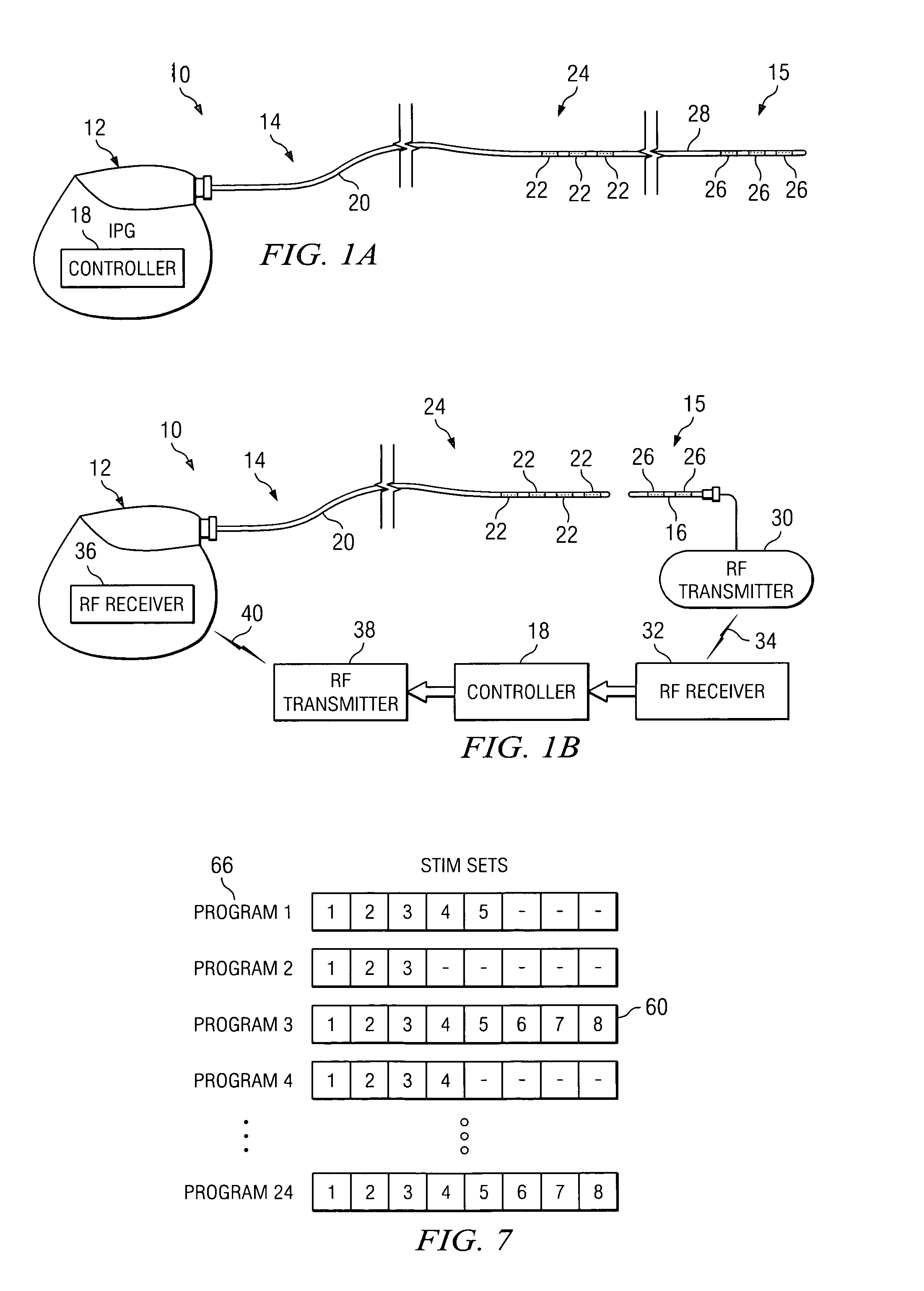
ActiveUS20050267542A1Decreased heart rateEliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsCardiac arrhythmiaCarotid sinus
Apparatus is provided including an implantable sensor, adapted to sense an electrical parameter of a heart of a subject, and a first control unit, adapted to apply pulses to the heart responsively to the sensed parameter, the pulses selected from the list consisting of: pacing pulses and anti-arrhythmic energy. The apparatus further includes an electrode device, adapted to be coupled to a site of the subject selected from the list consisting of: a vagus nerve of the subject, an epicardial fat pad of the subject, a pulmonary vein of the subject, a carotid artery of the subject, a carotid sinus of the subject, a coronary sinus of the subject, a vena cava vein of the subject, a right ventricle of the subject, and a jugular vein of the subject; and a second control unit, adapted to drive the electrode device to apply to the site a current that increases parasympathetic tone of the subject and affects a heart rate of the subject. The first and second control units are not under common control. At least one of the control units is adapted to coordinate an aspect of its operation with an aspect of operation of the other control unit. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Non-invasive treatment of bronchial constriction
ActiveUS20110046432A1Relieve spasmsDilation increaseUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyNerve fiber bundleSmooth muscle
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating bronchial constriction related to asthma, anaphylaxis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The treatment comprises transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers that are responsible for smooth muscle dilation. The transmitted energy impulses, comprising magnetic and / or electrical, mechanical and / or acoustic, and optical and / or thermal energy, stimulate the selected nerve fibers.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Non-invasive treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS20110152967A1Reduce neuroinflammationReduce inflammationElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsRetinoidPostoperative cognitive dysfunction
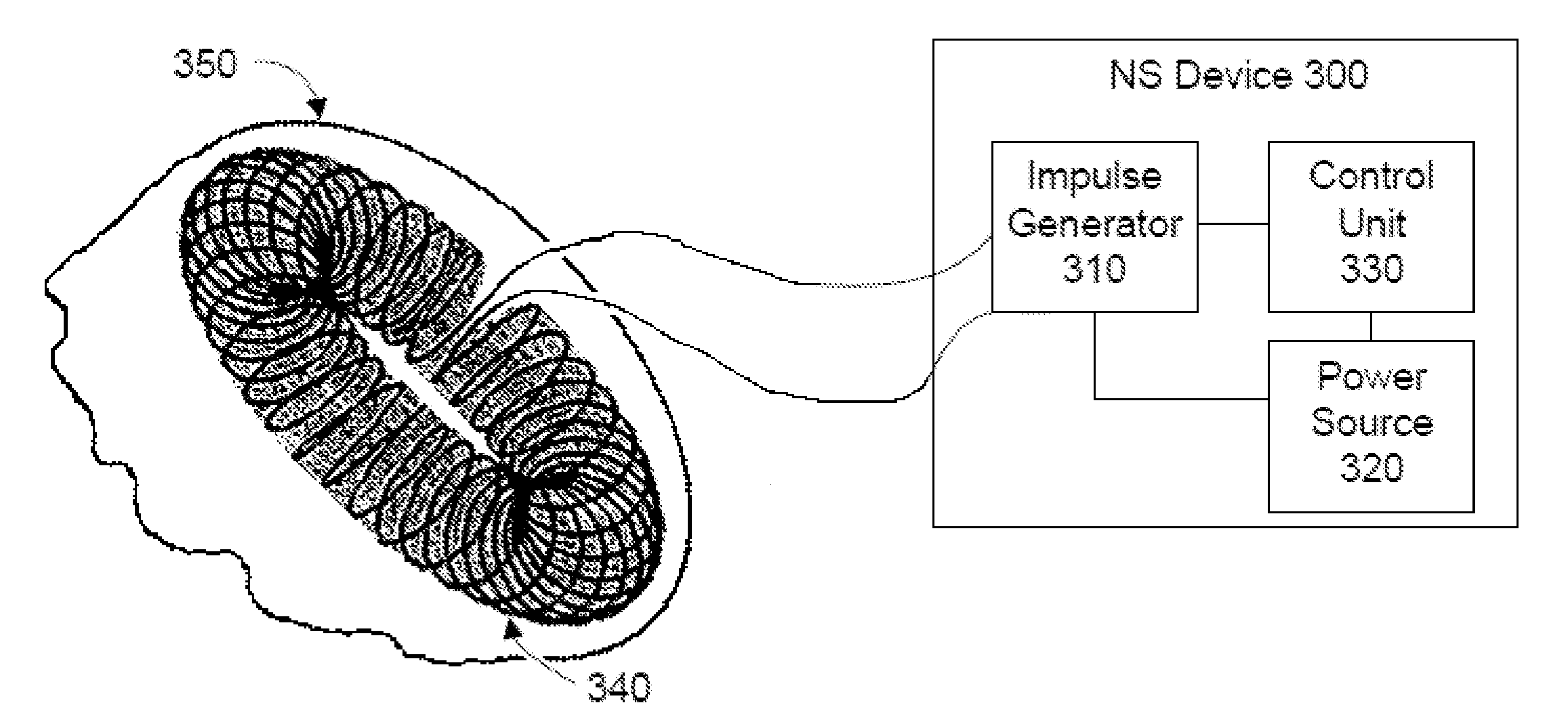
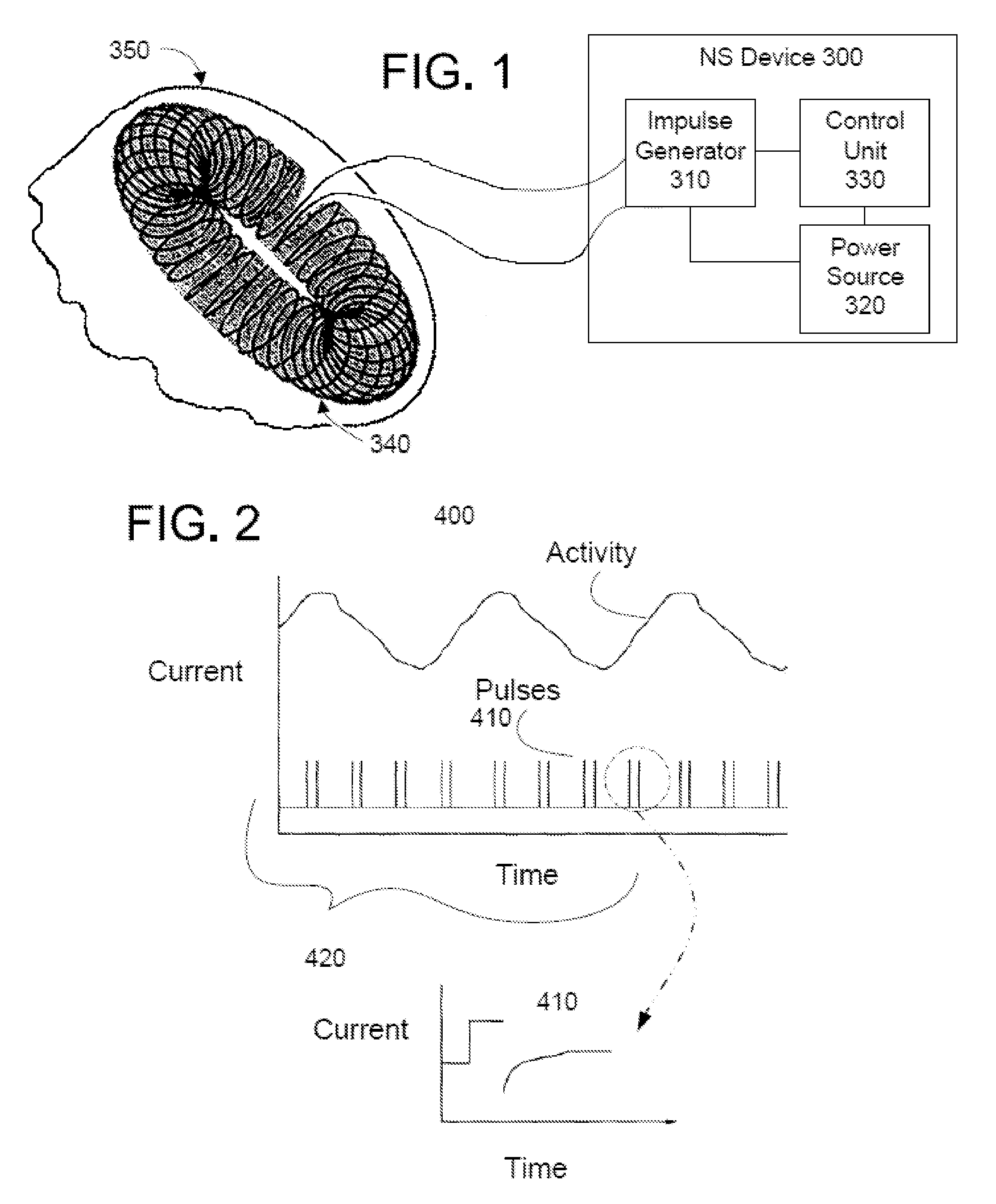
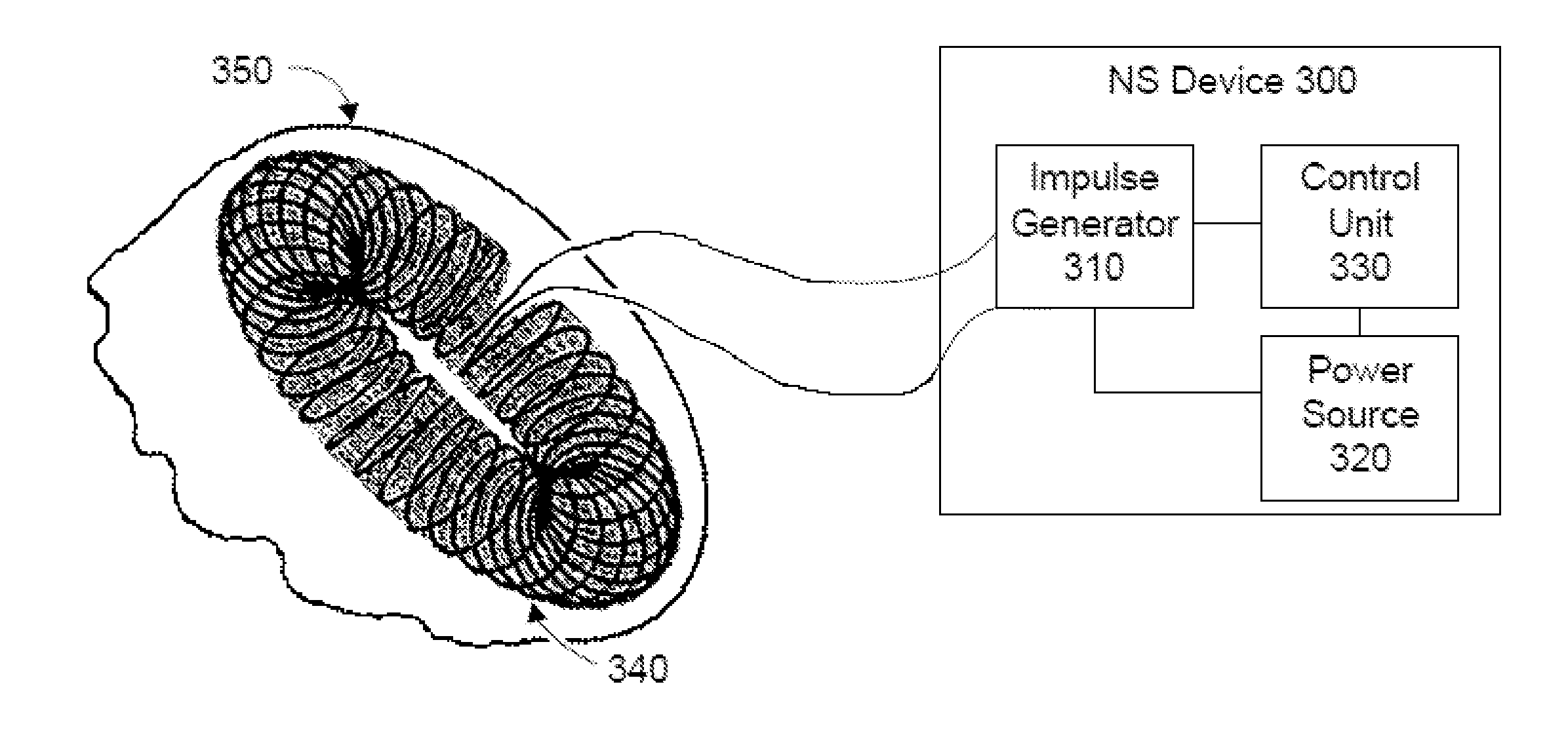
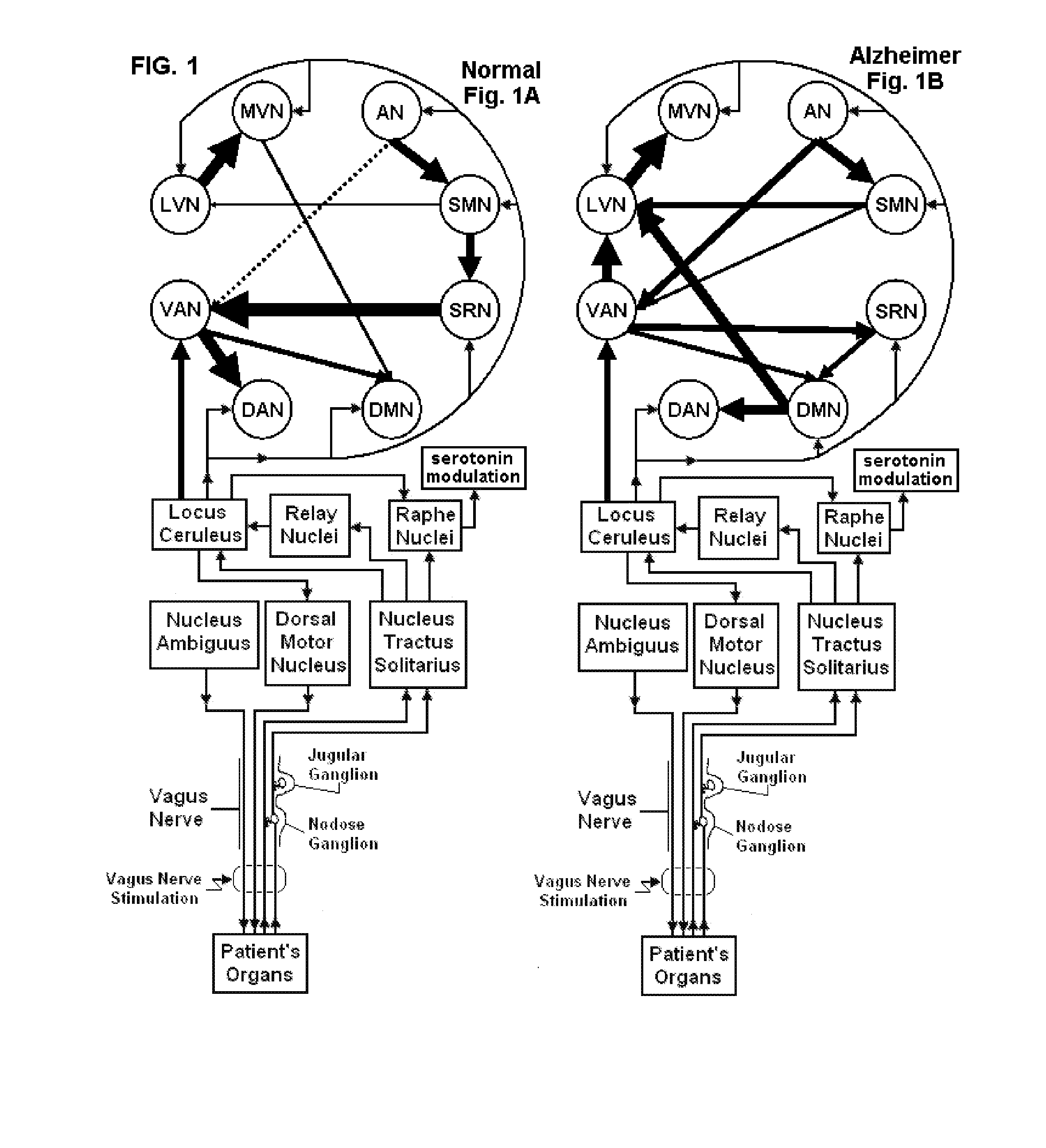
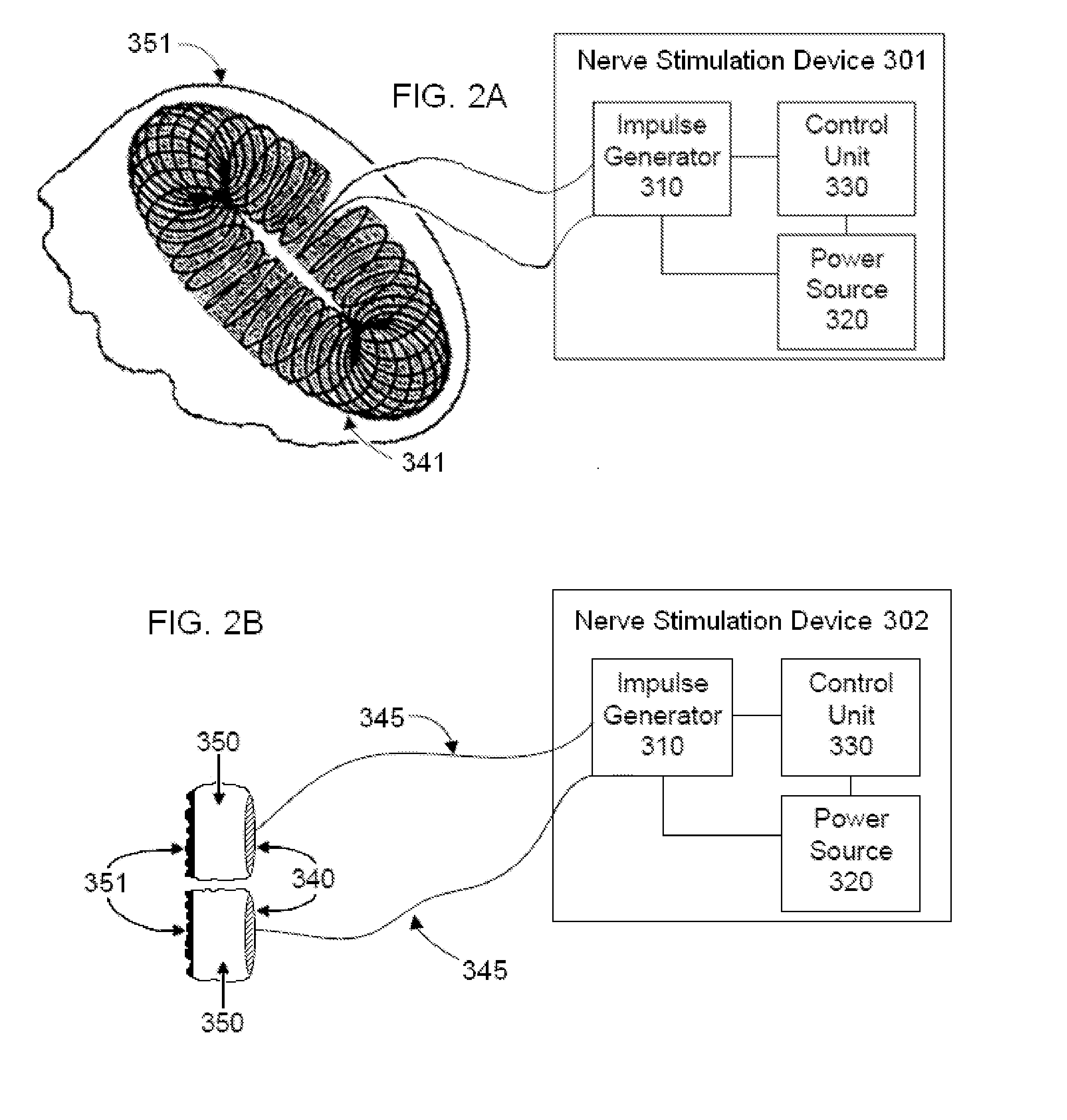
Methods and devices are disclosed for the non-invasive treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through delivery of energy to target nervous tissue, particularly the vagus nerve. The devices include a magnetic stimulator having coils with toroidal windings, which are in contact with an electrically conducting medium that is adapted to conform to the contour of a target body surface of a patient. The coils induce an electric current and / or an electric field within the patient, thereby stimulating nerve fibers within the patient. The stimulation brings about reduction of neuroinflammation in patients suffering from conditions comprising Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, postoperative cognitive dysfunction and postoperative delirium. Reduction in inflammation is effected by enhancing the anti-inflammatory competence of cytokines such as TGF-beta, wherein a retinoid or components of the retinoic acid signaling system provide an anti-inflammatory bias, by enhancing anti-inflammatory activity of a neurotrophic factor such as NGF, GDNF, BDNF, or MANF, and / or by inhibiting the activity of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-alpha.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Therapeutic device for pain management and vision
ActiveUS20100036488A1Increase moistureRelieve painSenses disorderEye implantsEpitheliumTherapeutic Devices
A therapeutic lens for the treatment of an epithelial defect comprises a layer of therapeutic material disposed over the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane to inhibit water flow from the tear liquid to the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane, such that corneal deturgescence can be restored to decrease corneal swelling and light scattering. The layer may cover and protect nerve fibers to decrease pain. The layer may comprise an index of refraction to inhibit light scatter from an anterior surface of the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane. The lens may comprise a curved anterior surface that provides functional vision for the patient when the epithelium regenerates. The layer of therapeutic material can be positioned on the eye in many ways, for example with a spray that is cured to adhere the layer to the exposed surface of the stroma and / or Bowman's membrane.
Owner:NEXIS VISION LIQUIDATING TRUST +2
Method and apparatus for selective control of nerve fibers
InactiveUS20020099419A1Pain reliefReduced sensationElectrotherapyArtificial respirationFiberNerve fiber bundle
A method and apparatus particularly useful for pain control by selectively blocking the propagation of body-generated action potentials travelling through a nerve bundle by using a tripolar electrode device to generate unidirectional action potentials to serve as collision blocks with the body-generated action potentials representing pain sensations in the small-diameter sensory fibers. In the described preferred embodiments there are a plurality of electrode devices spaced along the length of the nerve bundle which are sequentially actuated with delays corresponding to the velocity of propagation of the body-generated action potentials through the large-diameter fibers to produce a "green wave" effect which minimizes undesired anodal blocking of the large-diameter fibers while maximizing the collision blocking of the small-diameter fibers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
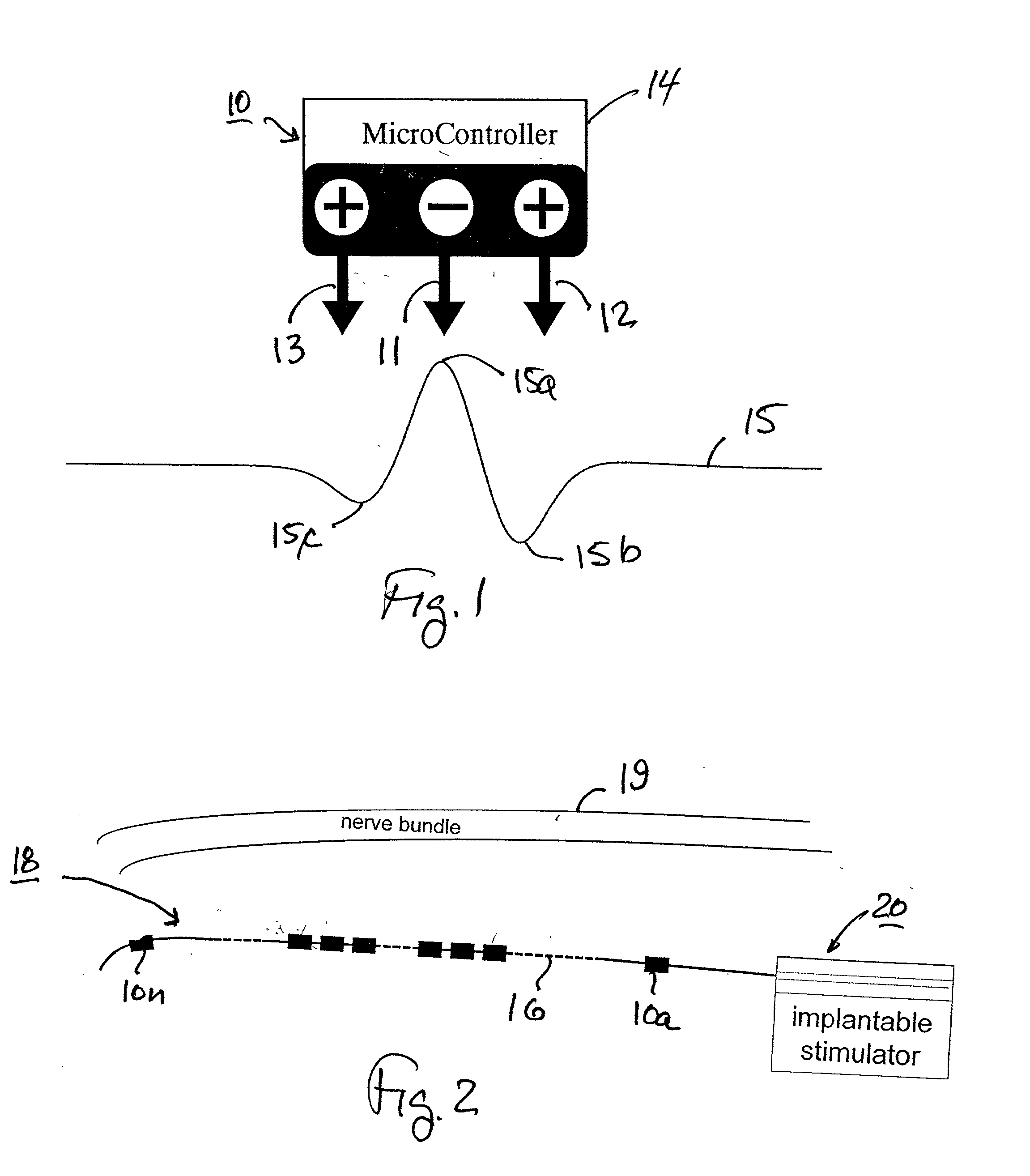
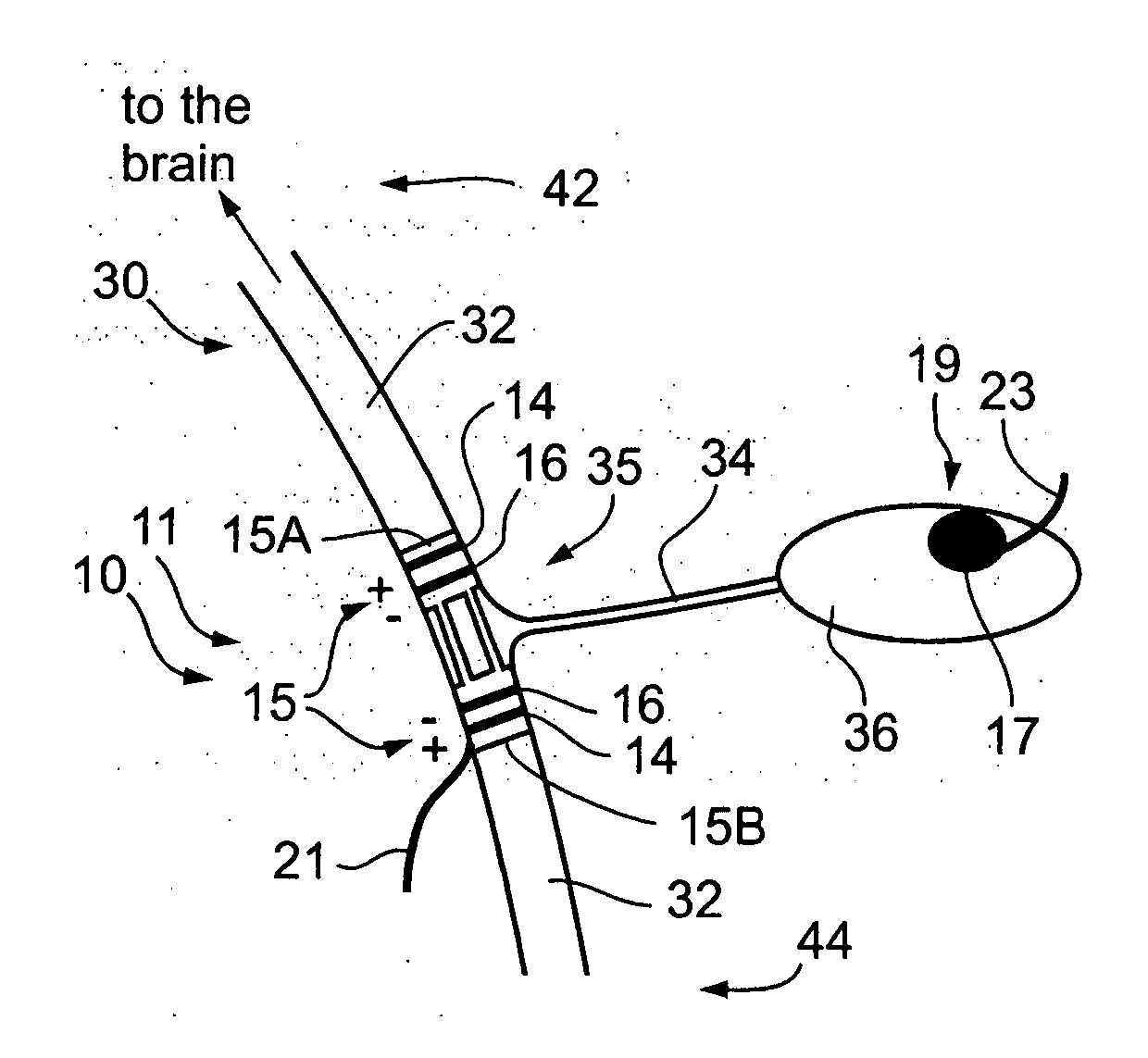
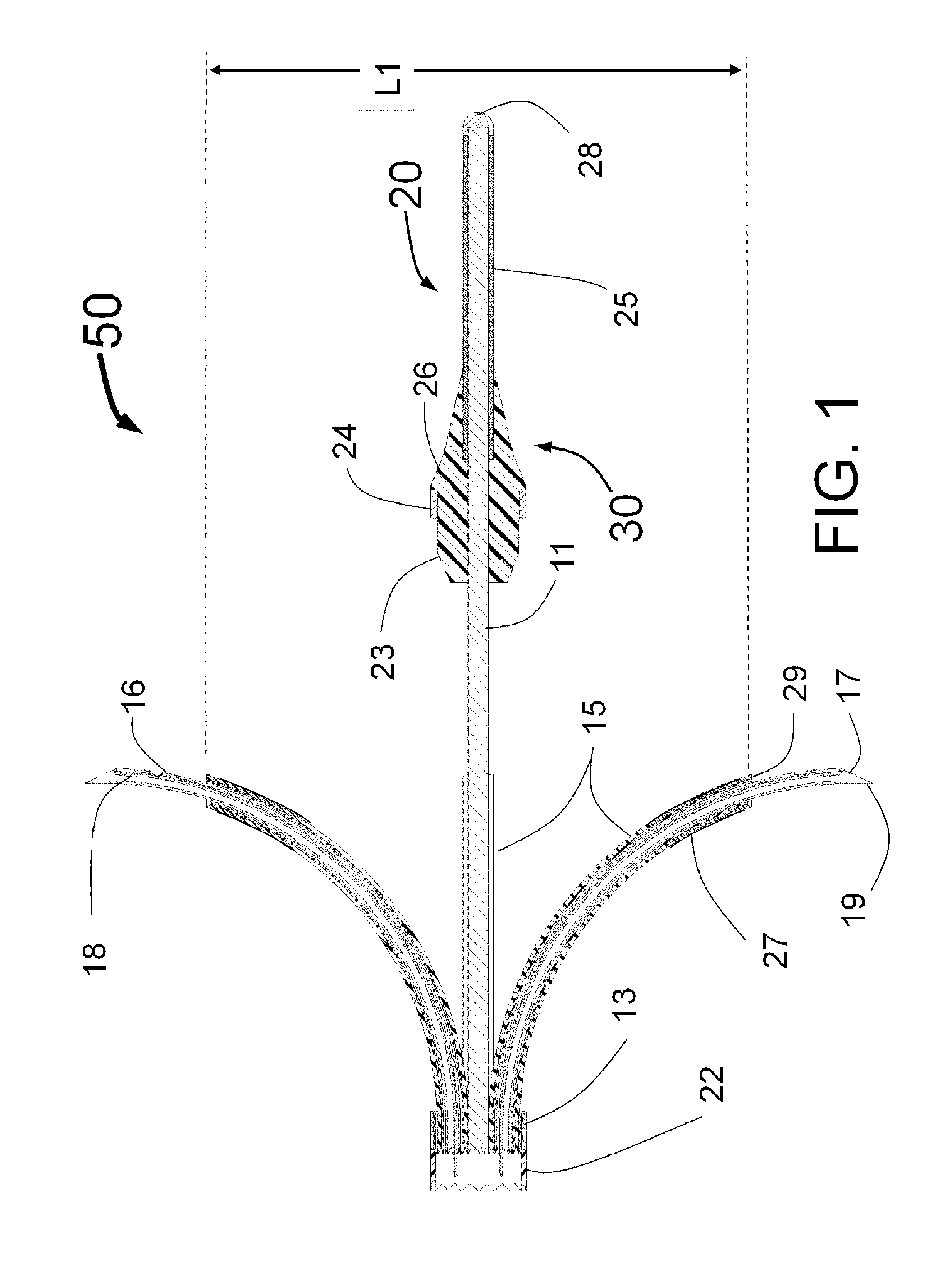
Nerve-branch-specific action-potential activation,inhibition, and monitoring
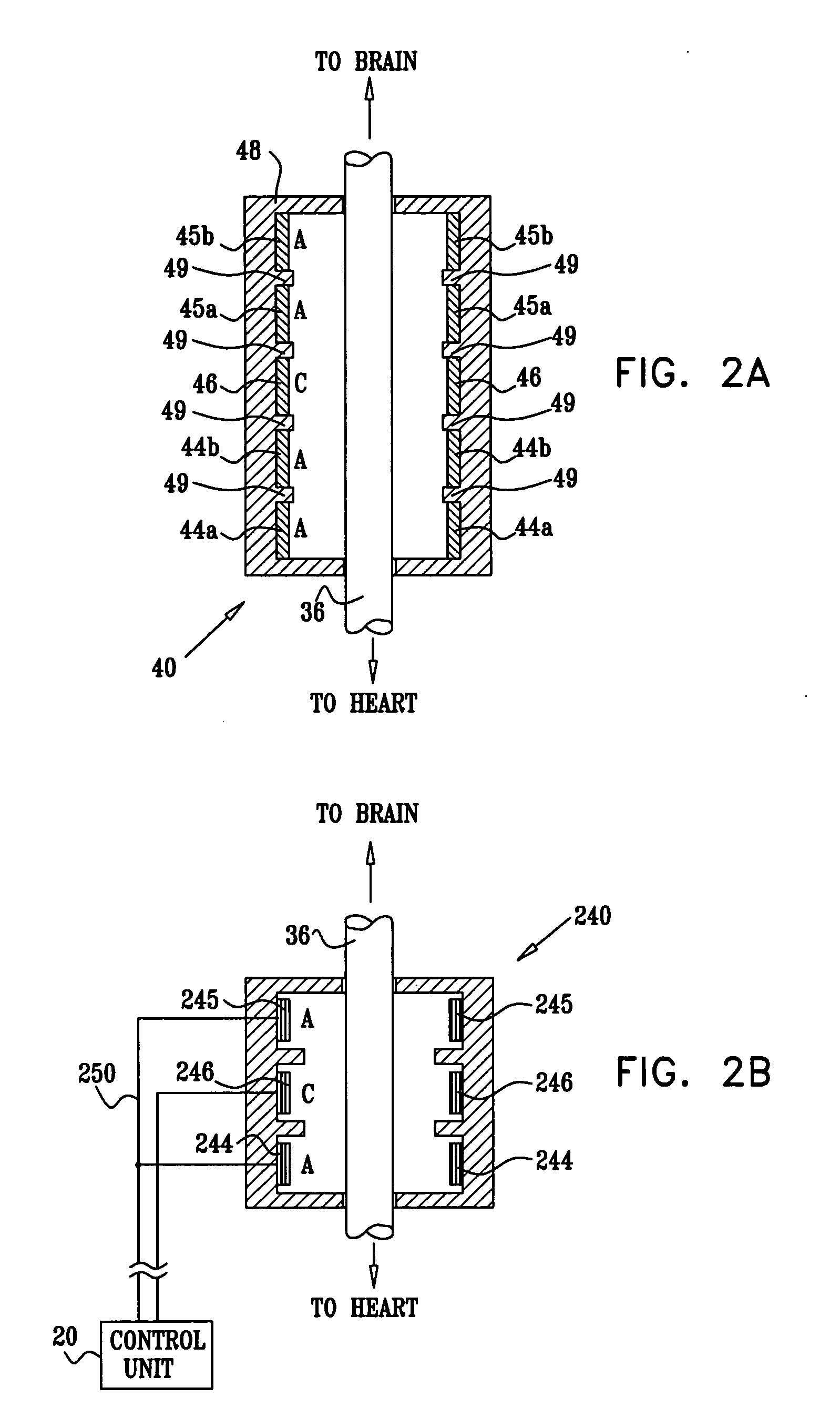
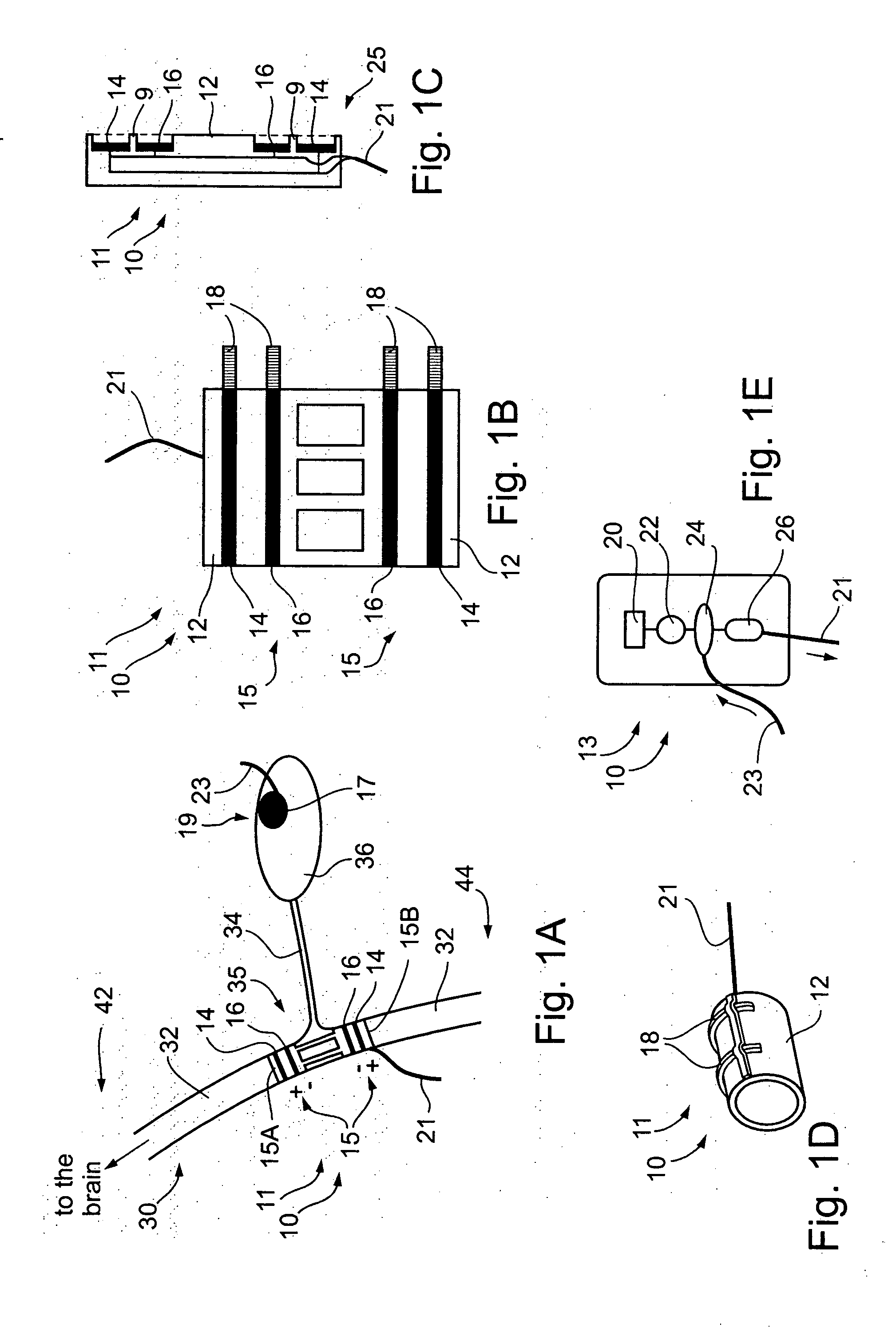
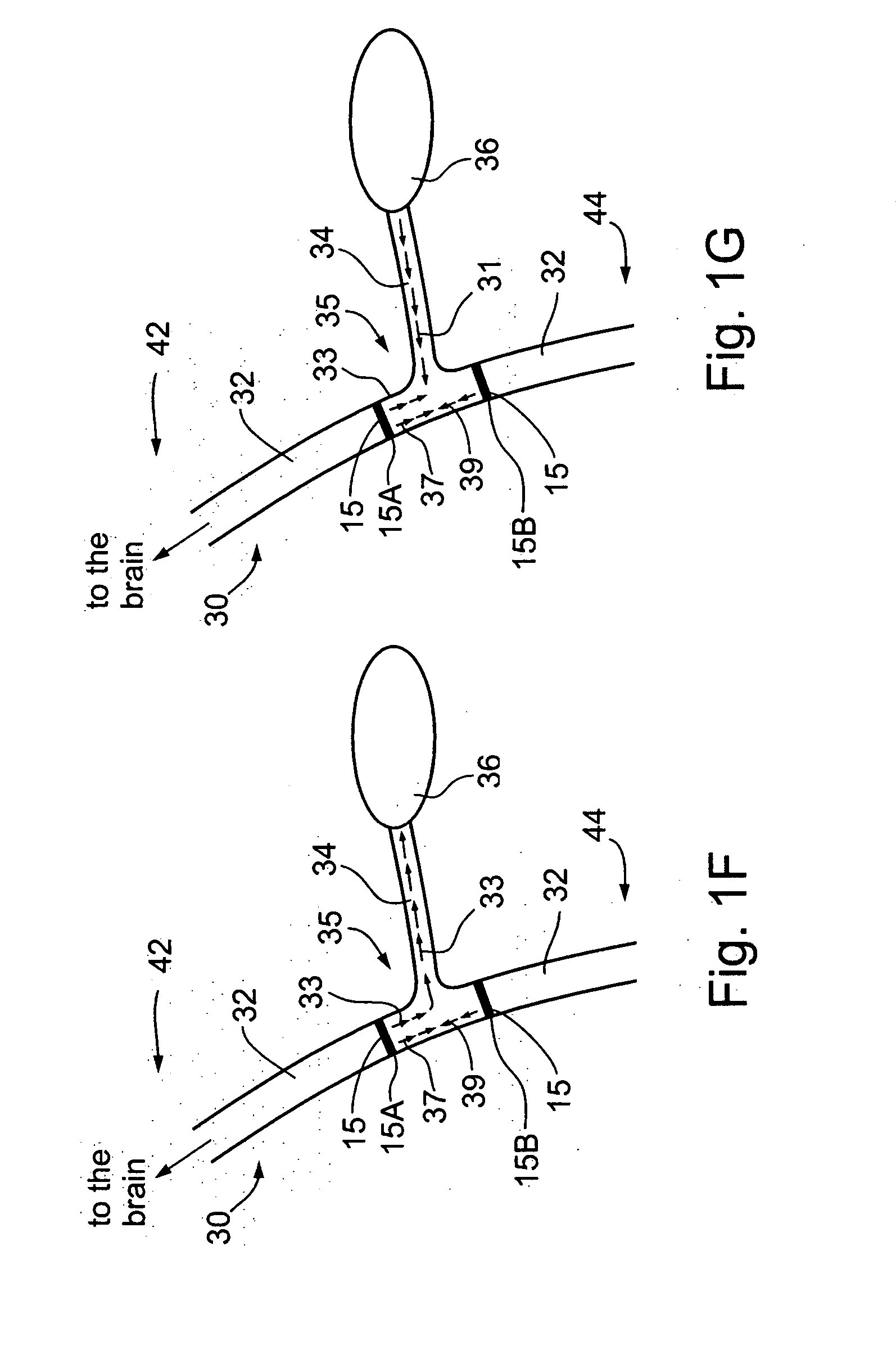
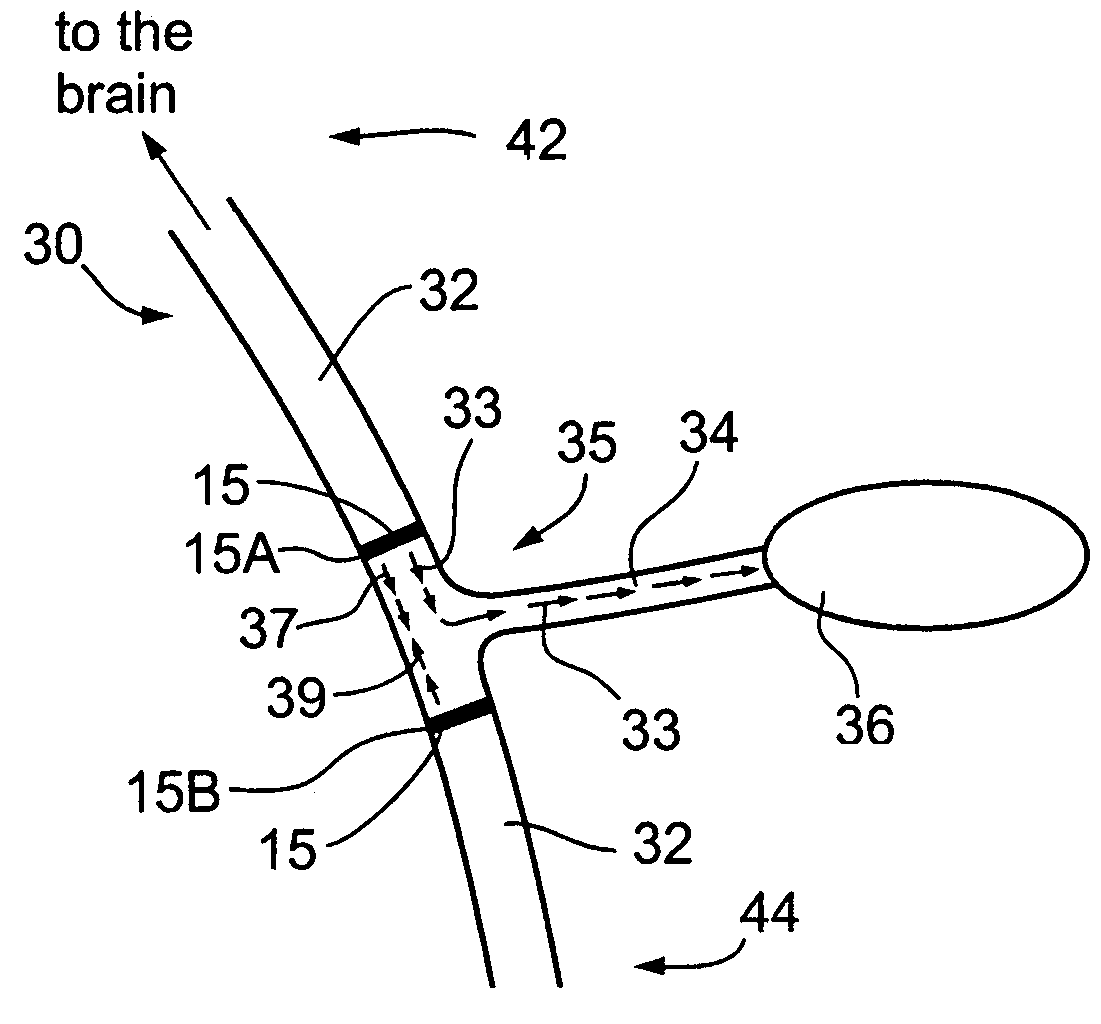
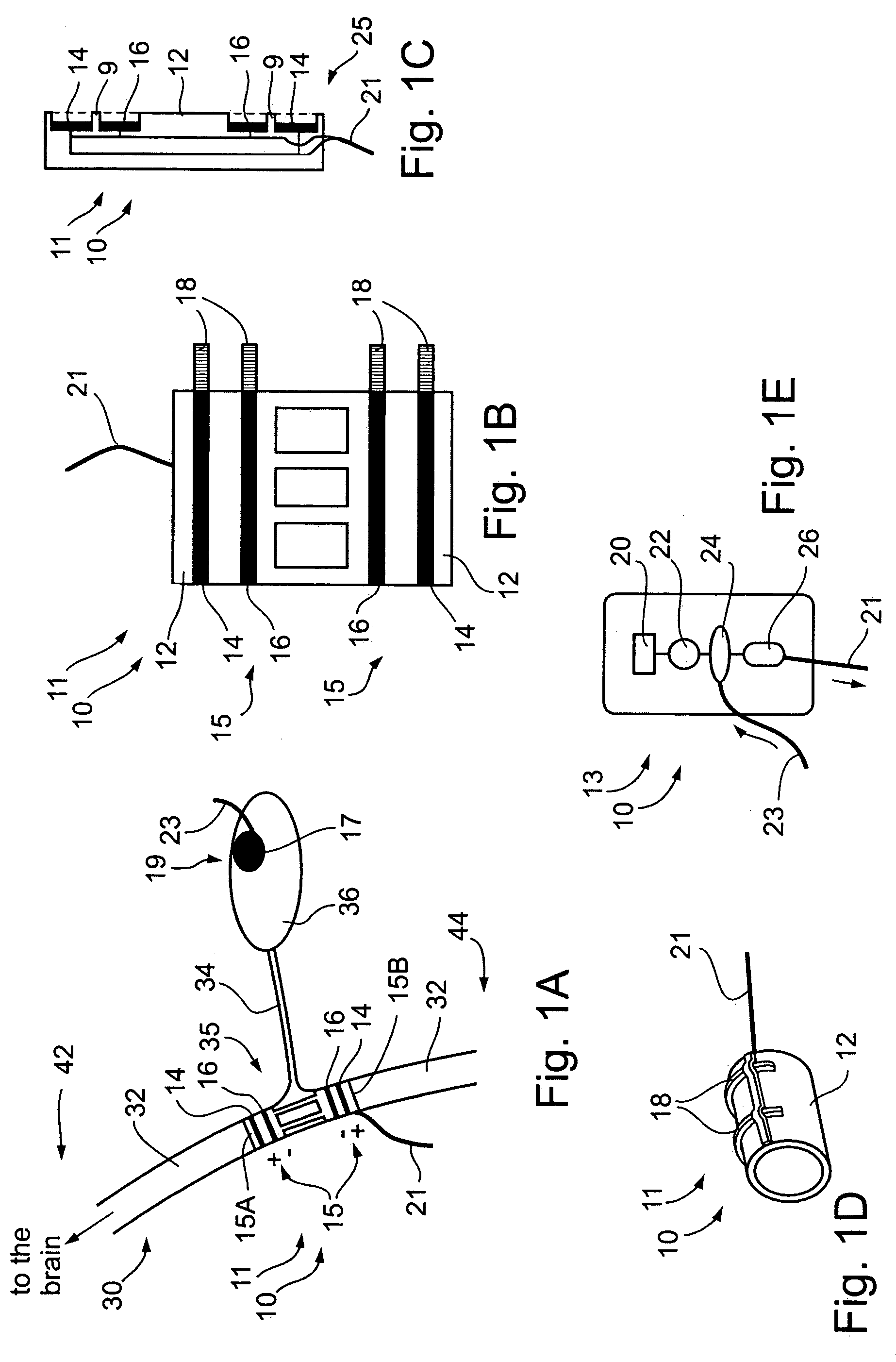
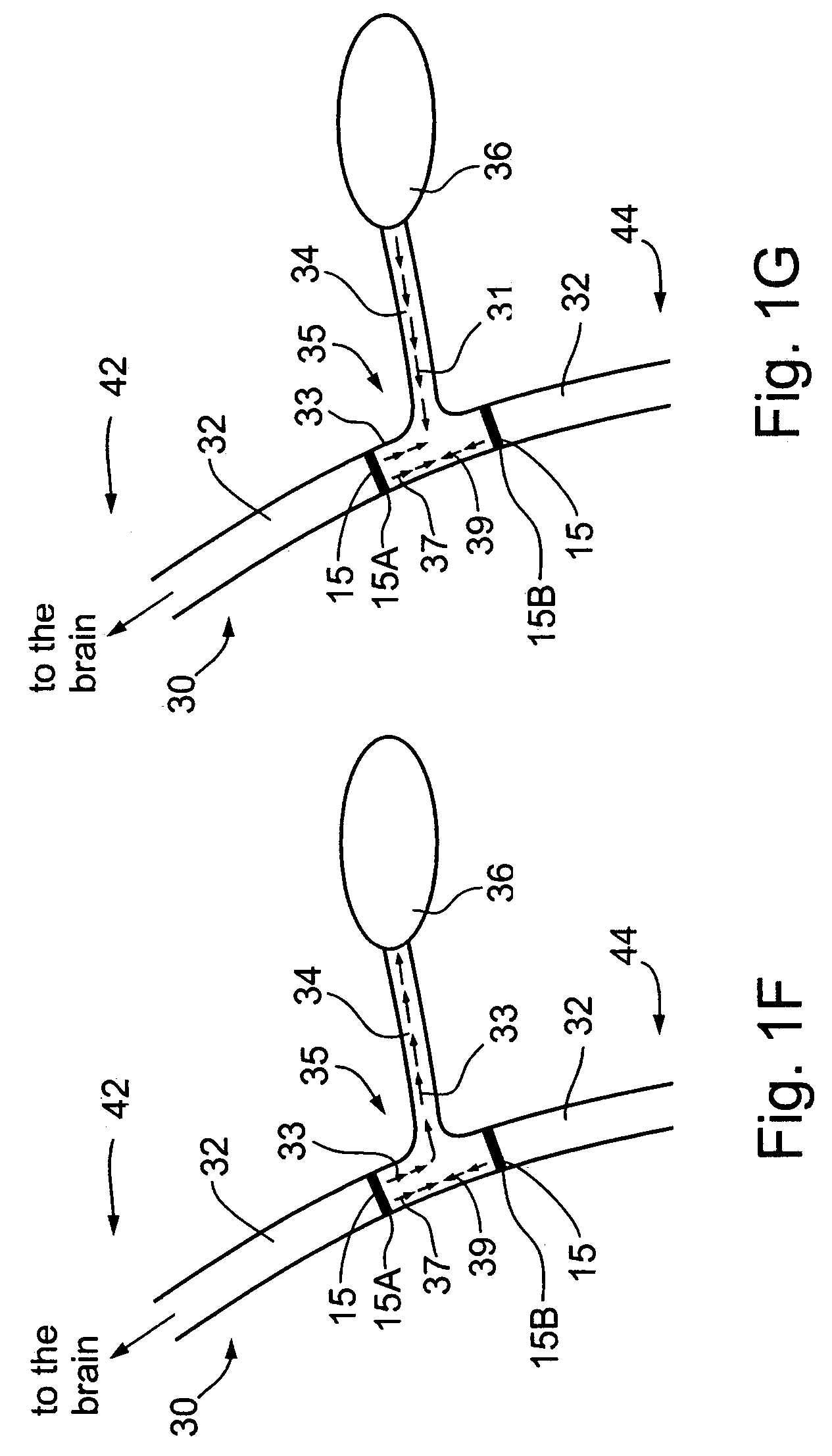
A dual electrode arrangement, is provided, wherein two, preferably unidirectional, electrode configurations flank a nerve junction from which a preselected nerve branch issues, proximally and distally to the junction, with respect to the brain. The arrangement is conducive to the following: generating efferent action-potential propagations, substantially restricted to the preselected nerve branch, inhibiting afferent action-potential propagations, from the preselected nerve branch, selectively generating action-potential propagations, in a subset of nerve fibers of a predetermined diameter range, substantially restricted to the preselected nerve branch, and selectively inhibiting action-potential propagations, in a subset of nerve fibers of a predetermined diameter range, substantially restricted to the preselected nerve branch. The dual electrode arrangement is further conducive to monitoring naturally-occurring, efferent action-potential propagations, heading towards the preselected nerve branch, and monitoring naturally-occurring, afferent action-potential propagations, from the preselected nerve branch. The unidirectional electrode configurations may be monopolar, bipolar, tripolar, or multipolar. Communication with extracorporeal stations, and closed loop operations are also provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Minimal device and method for effecting hyperthermia derived anesthesia
InactiveUS9031667B2Improve comfortLess chance of physical damageElectrotherapySurgical needlesFiberMammal
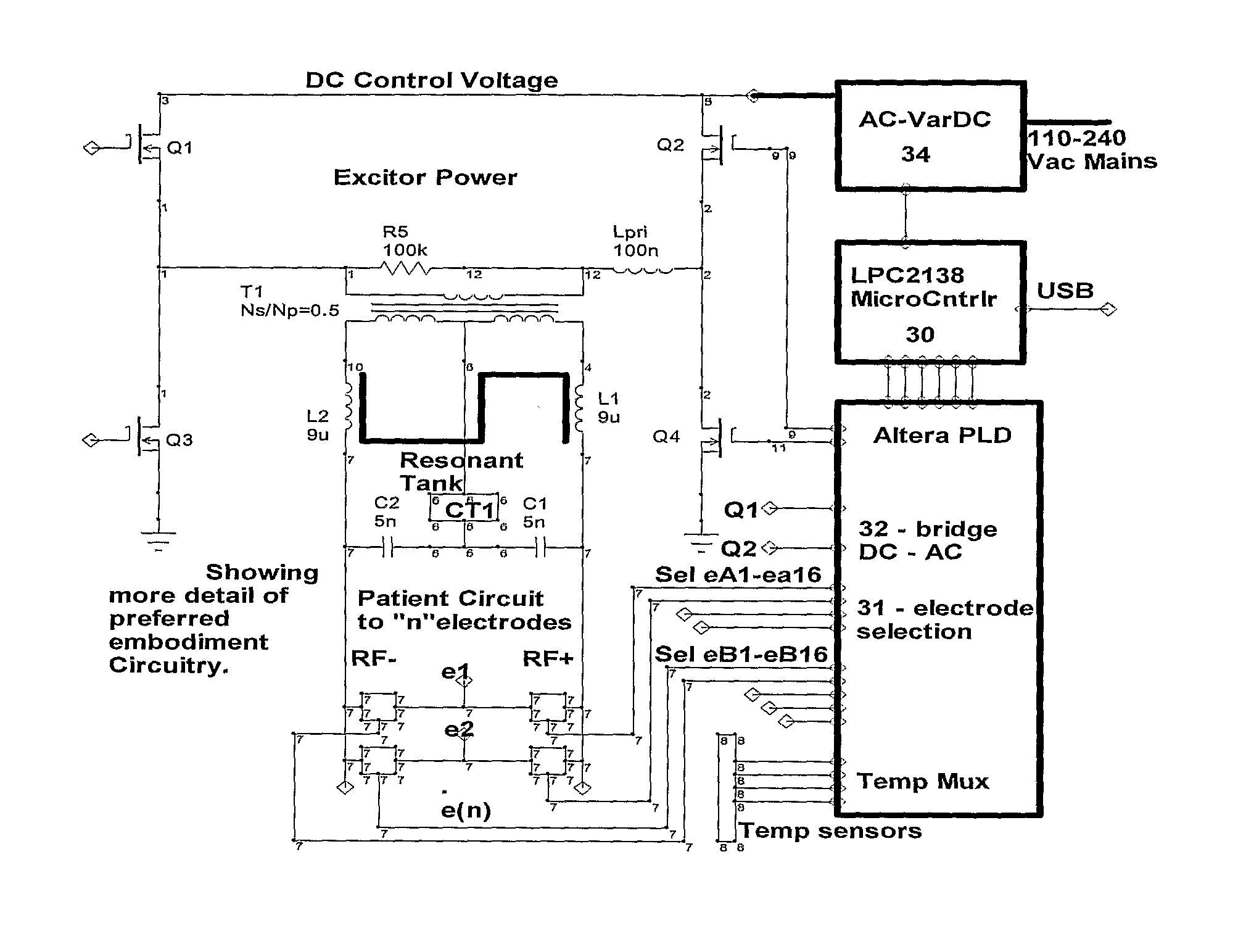
A method and device for inducing anaesthesia in mammals by the application of RF energy to create hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia. An RF generator drives a plurality of electrodes placed in tissue surrounding the target nerve fiber to desiccate the desired length of nerve fiber to be desiccated in a single deployment. The device allows high-speed selection / de-selection of bipolar electrode pairs or sets under continuous RF excitation. Activation of electrode pairs is adapted in response to sensed current density and temperature (by electrodes not in the current discharge activation phase) in order to create lesions of complex and well defined shape necessary for the production of hyperthermia derived neural anaesthesia.
Owner:INTERVENTION TECH
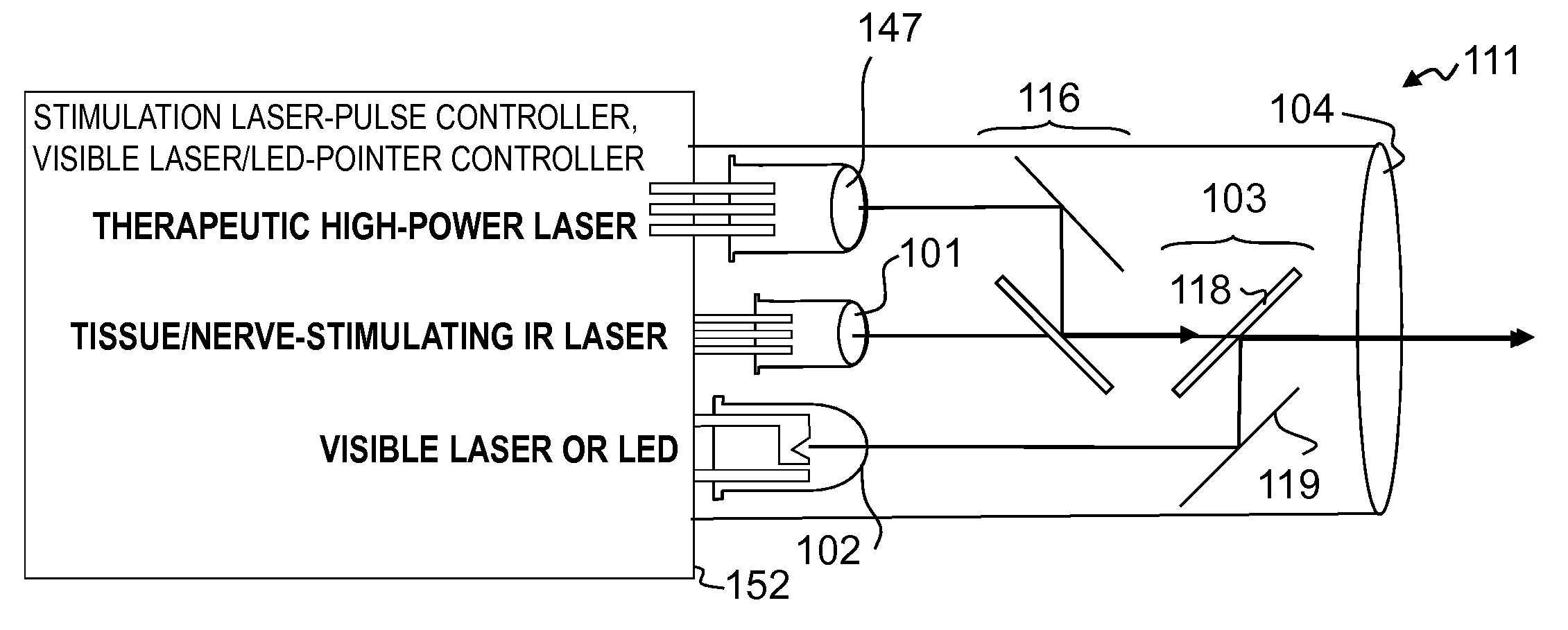
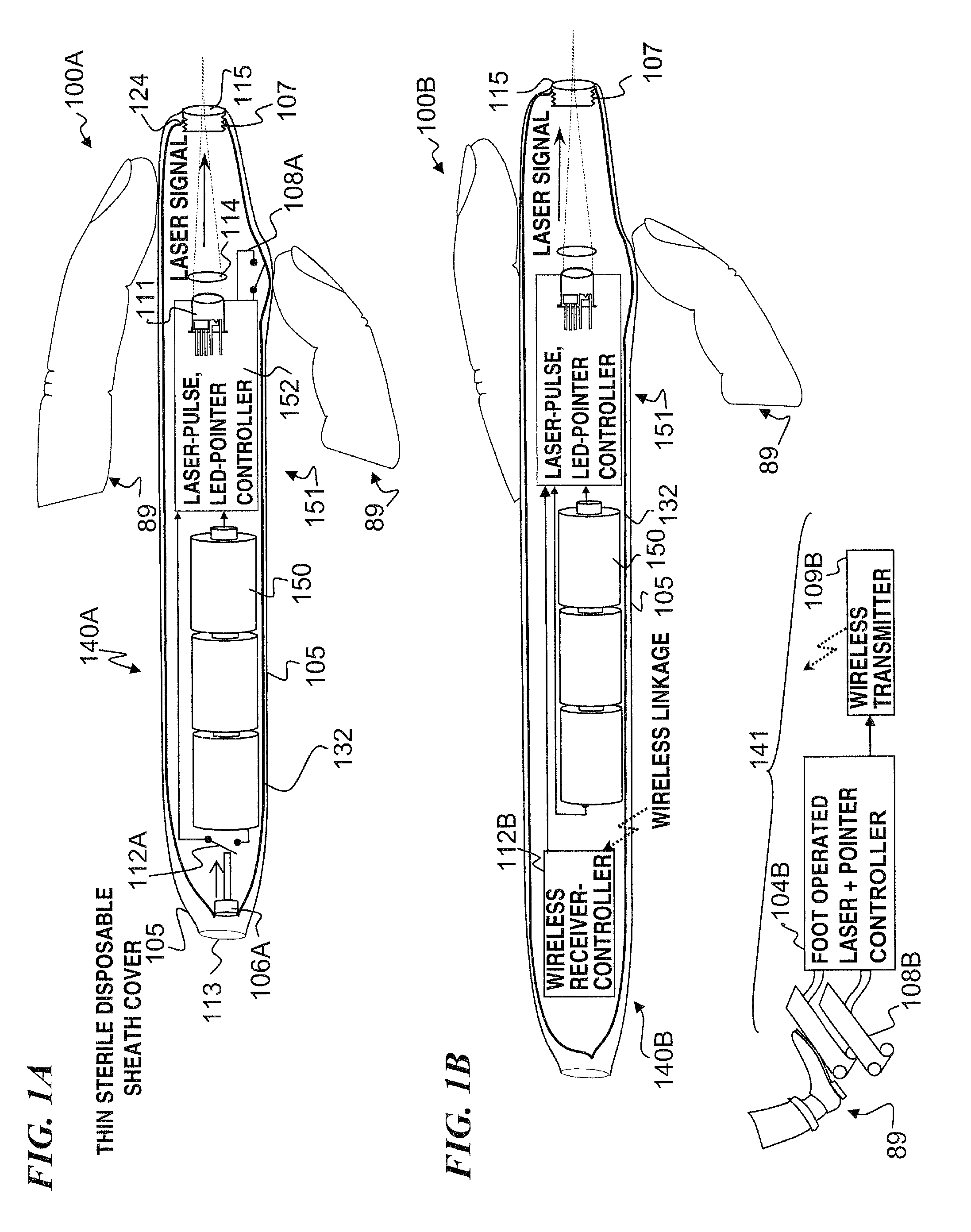
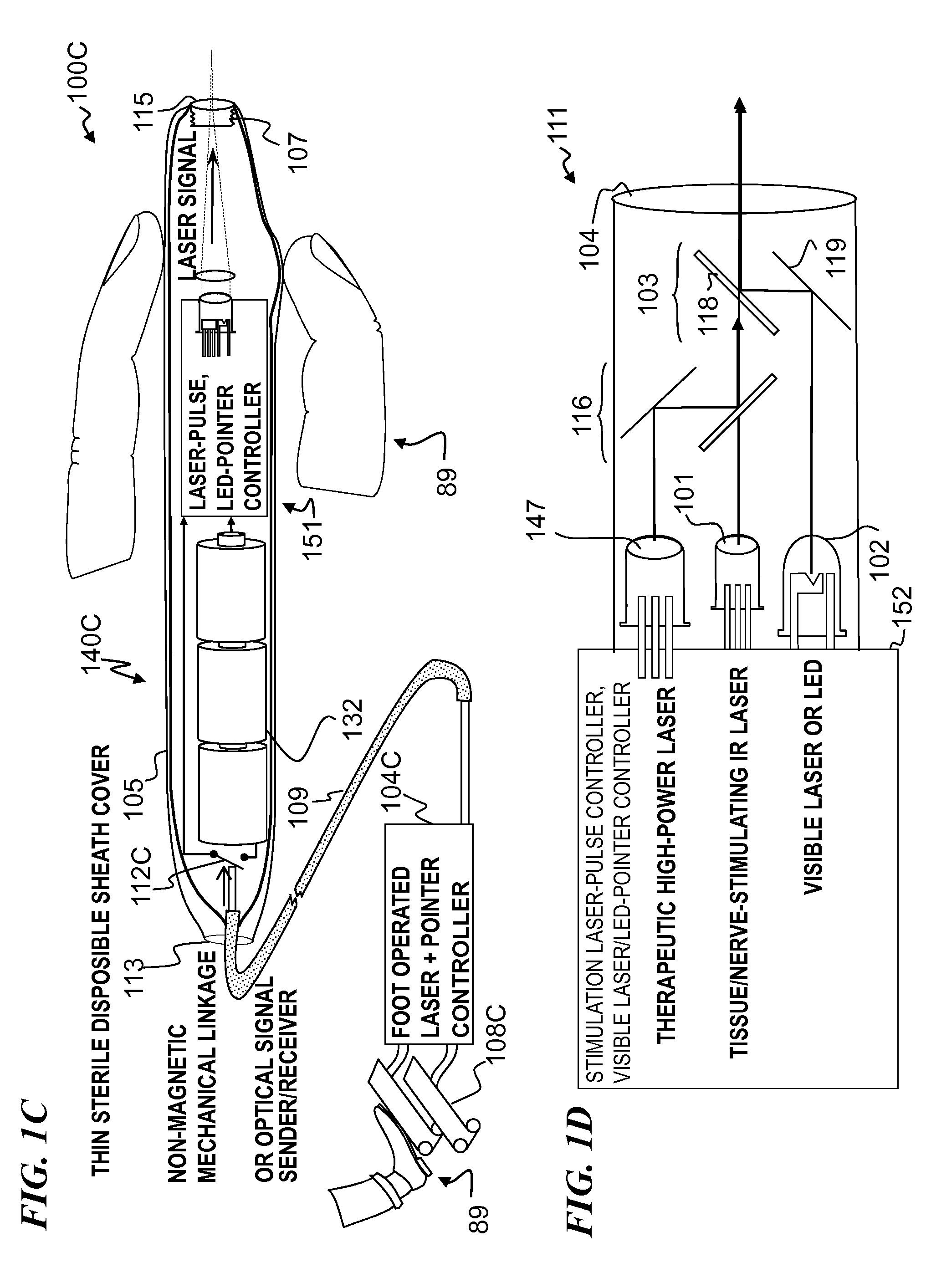
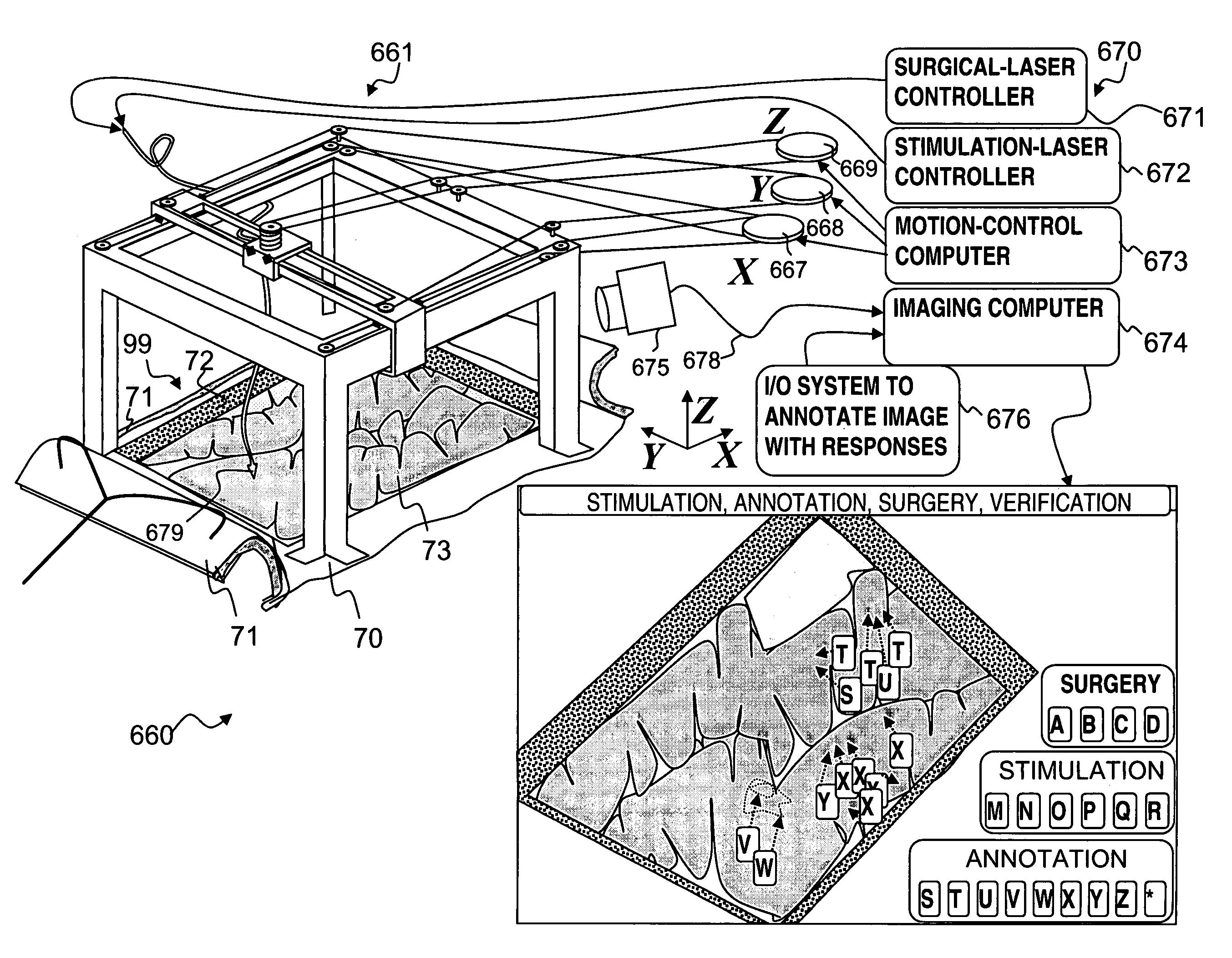
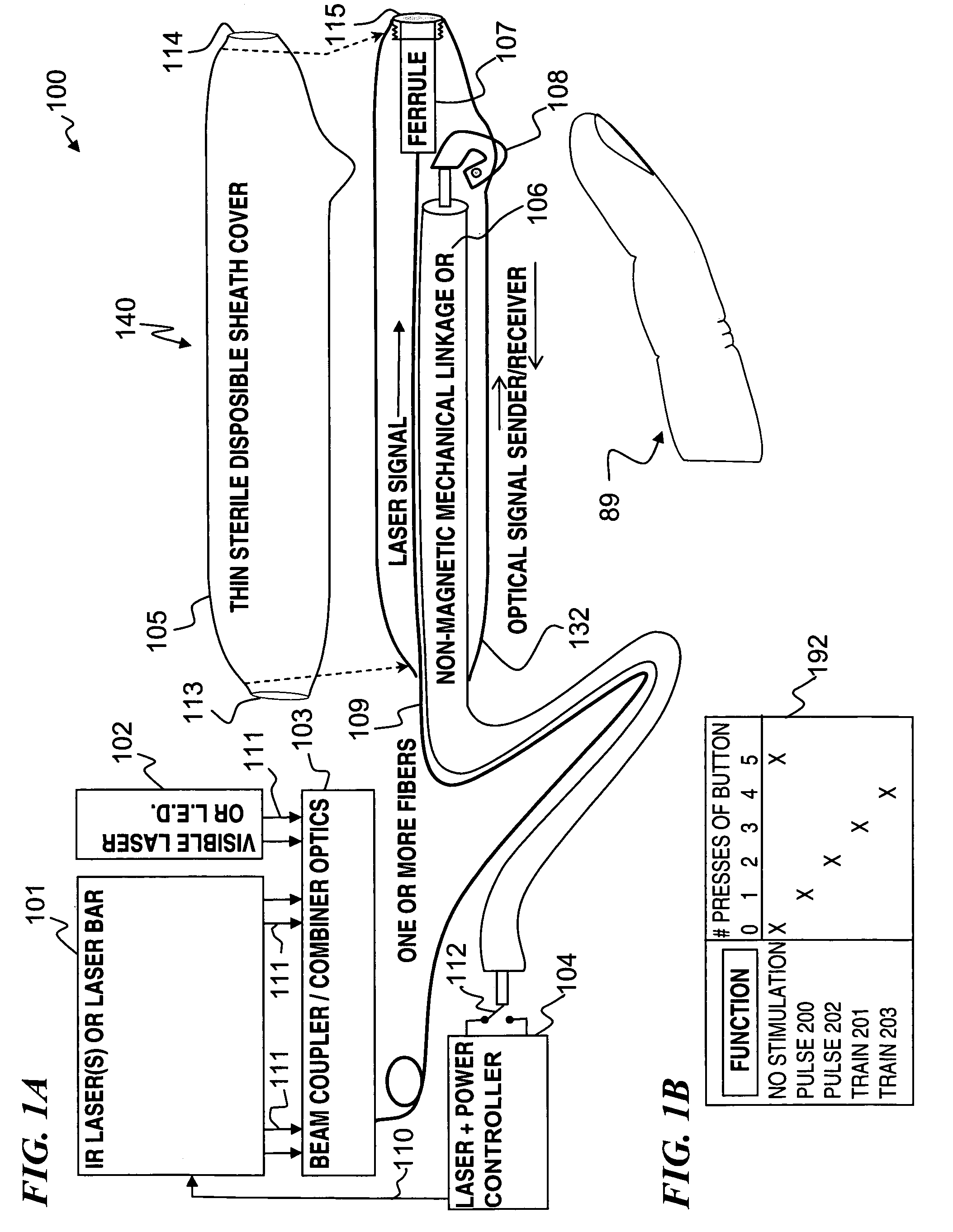
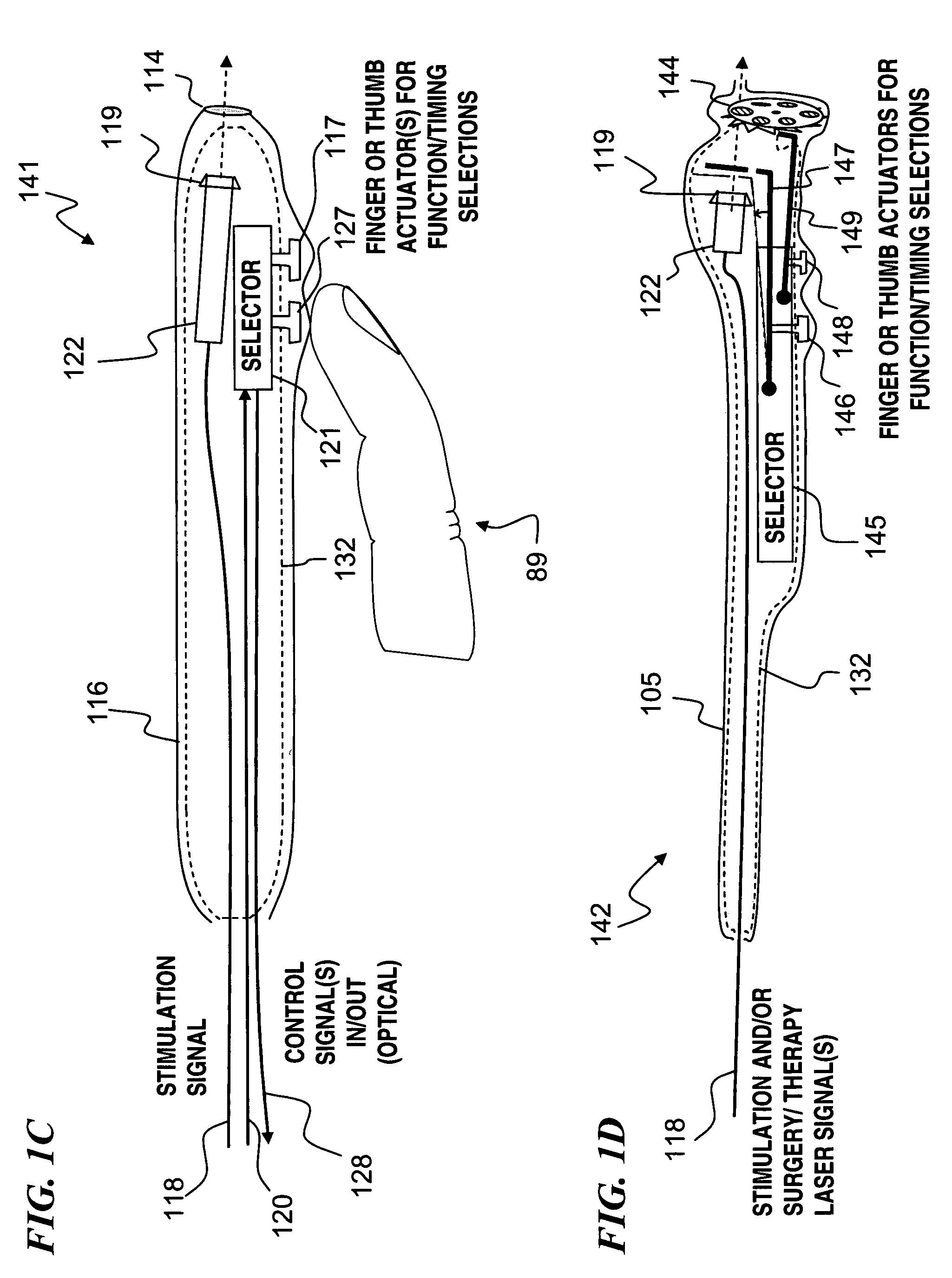
Miniature apparatus and method for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
A hand-held self-contained nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light source is mounted to the handpiece. Light is passed from the light source through optical tip to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. In some embodiments, the handpiece contains a self-contained power source, such as batteries. In some embodiments, the handpiece is at least in part, activated by remote control in order to prevent moving the handpiece during activation. Some embodiments include a unit operable to sense a response of nerve stimulation and to suppress a laser-ablation surgery operation.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
Non-invasive magnetic or electrical nerve stimulation to treat or prevent dementia
ActiveUS20130066392A1Inhibition of excitementAvoid stimulationElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyAdrenergicMedicine
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing dementia, such as Alzheimer's disease. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve, that modulate the activity of a patient's locus ceruleus. The transmitted energy impulses, comprising magnetic and / or electrical energy, stimulate the selected nerve fibers to cause the locus ceruleus to release norepinephrine into regions of the brain that contain beta-amyloids. The norepinephrine counteracts neuroinflammation that would damage neurons in those regions and the locus ceruleus, thereby arresting or slowing the progression of the disease in the patient.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
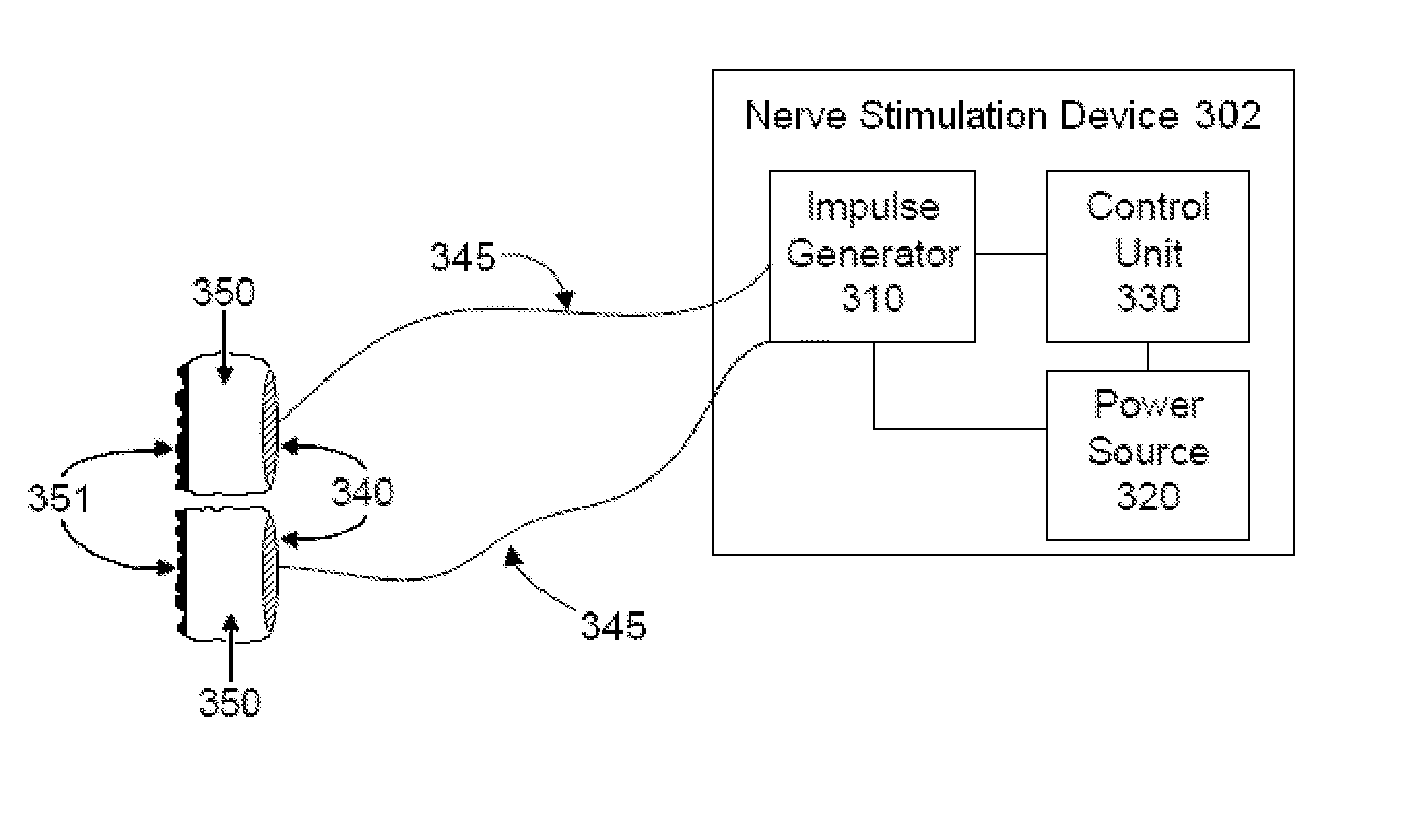
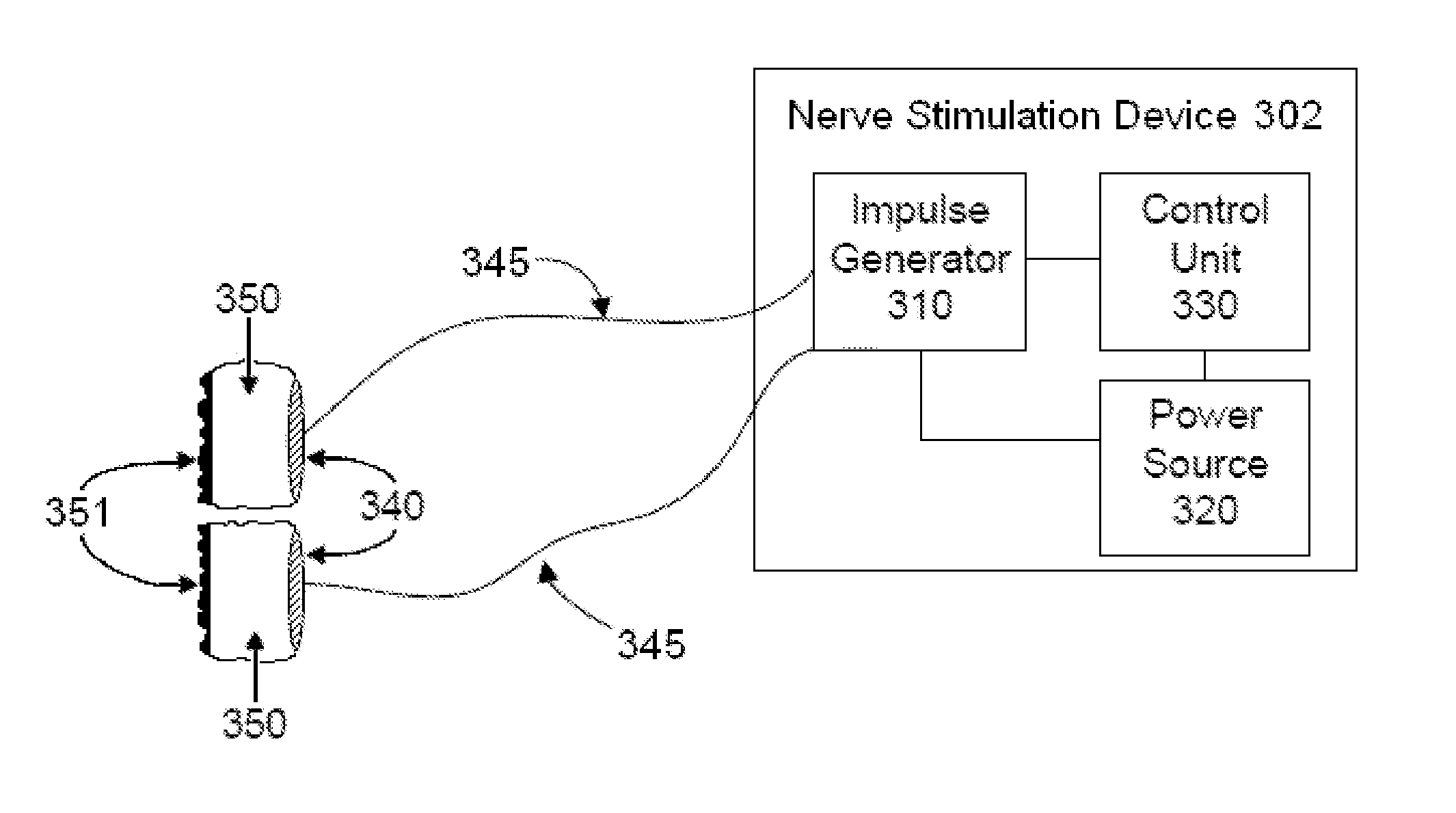
Method for controlling or regulating therapeutic nerve stimulation using electrical feedback
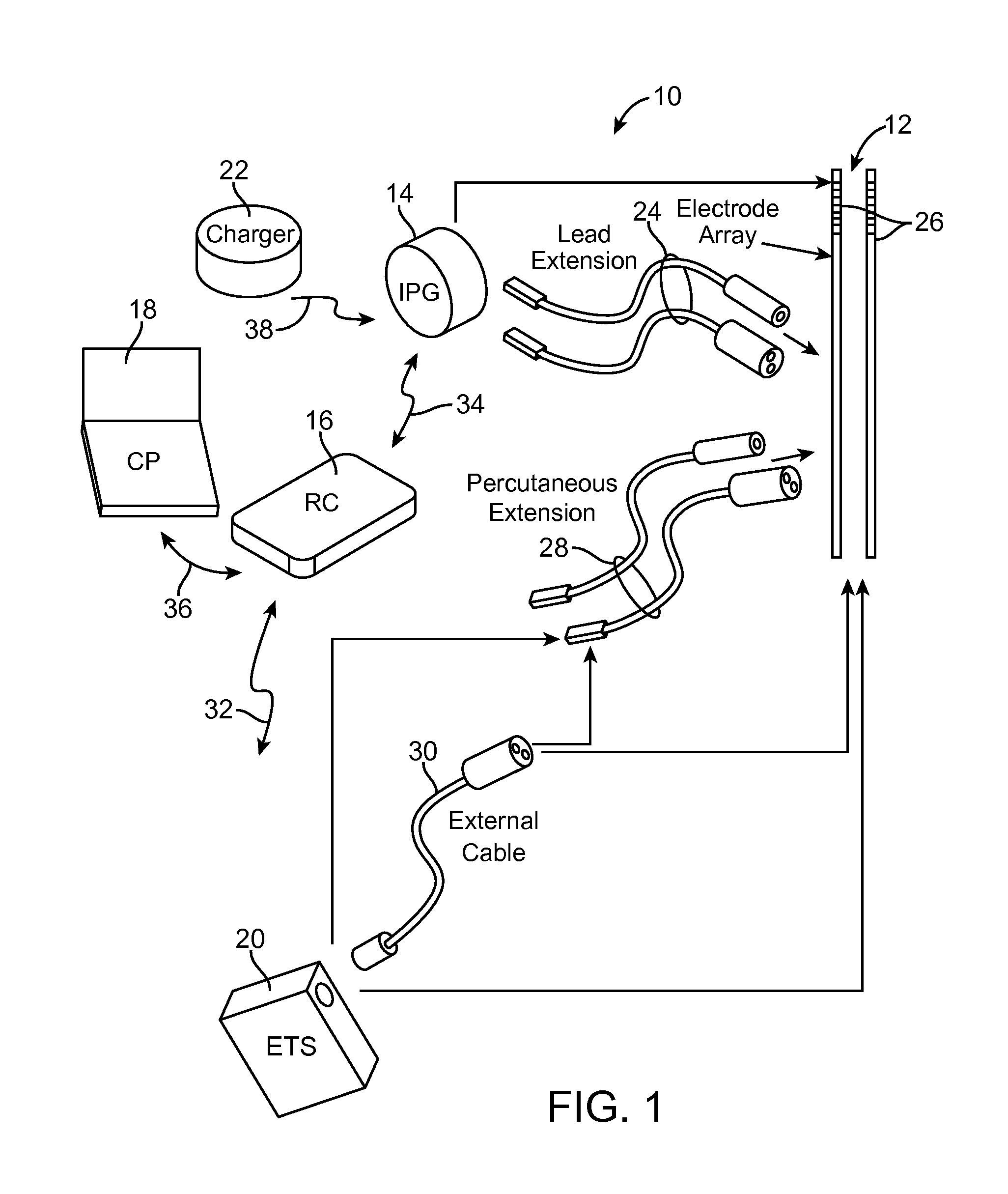
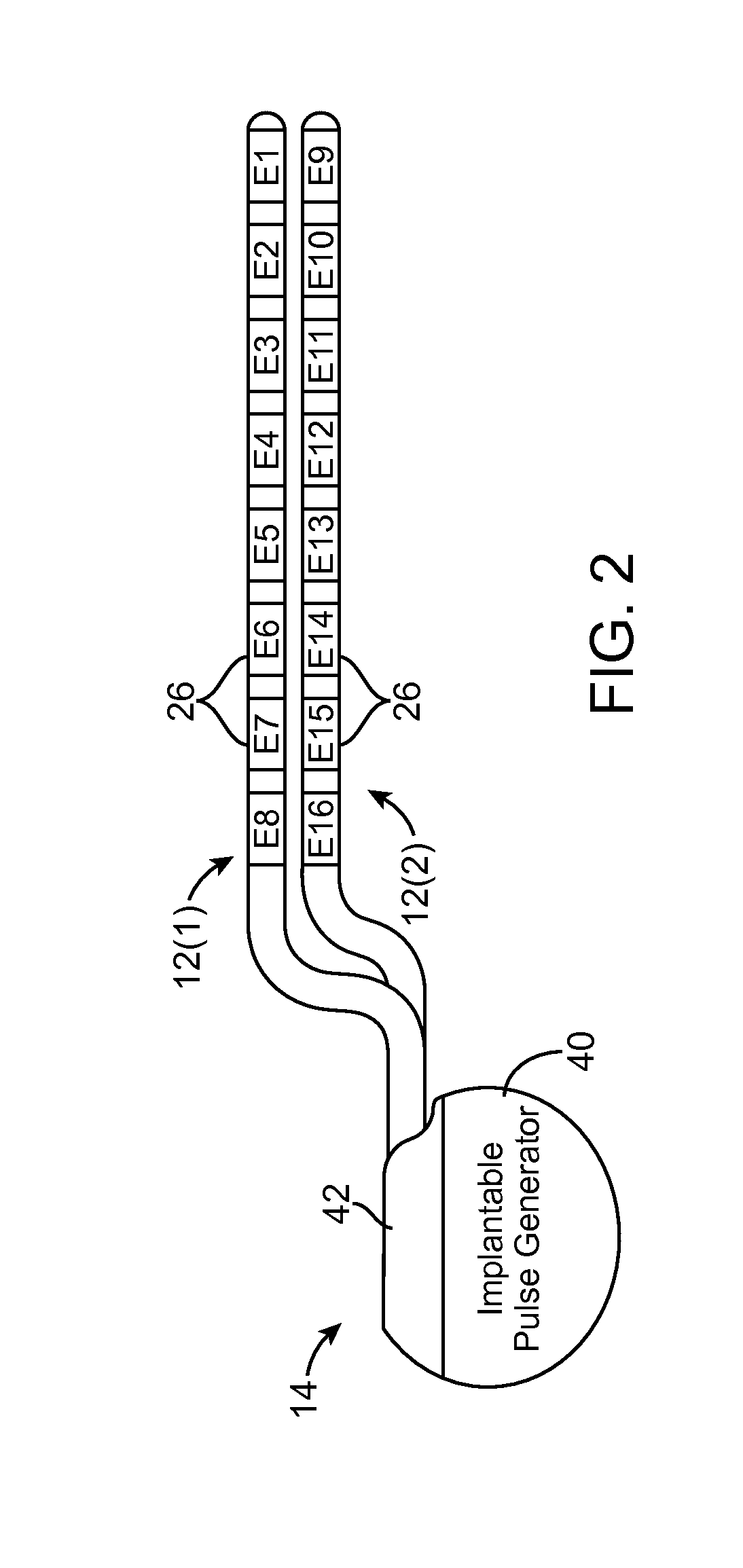
A stimulation system includes a stimulation source, an implantable stimulation lead, an implantable sensing device, and a controller. The stimulation source generates and transmits stimulation pulses to stimulation electrodes on the stimulation lead. The stimulation electrodes deliver the stimulation pulses to target nerve tissue in a nerve pathway to cause paresthesia in a portion of the person's body. Each stimulation pulse induces an action potential in a number of nerve fibers in the nerve pathway. The sensing device includes sensing electrodes positioned proximate the nerve pathway that detect compound action potentials of nerve fibers stimulated by the stimulation pulses. The controller modifies the stimulation pulses generated by the stimulation source and delivered to the target nerve tissue by the stimulation electrodes based on the detected compound action potentials to maintain a substantially constant level of paresthesia in the portion of the person's body.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
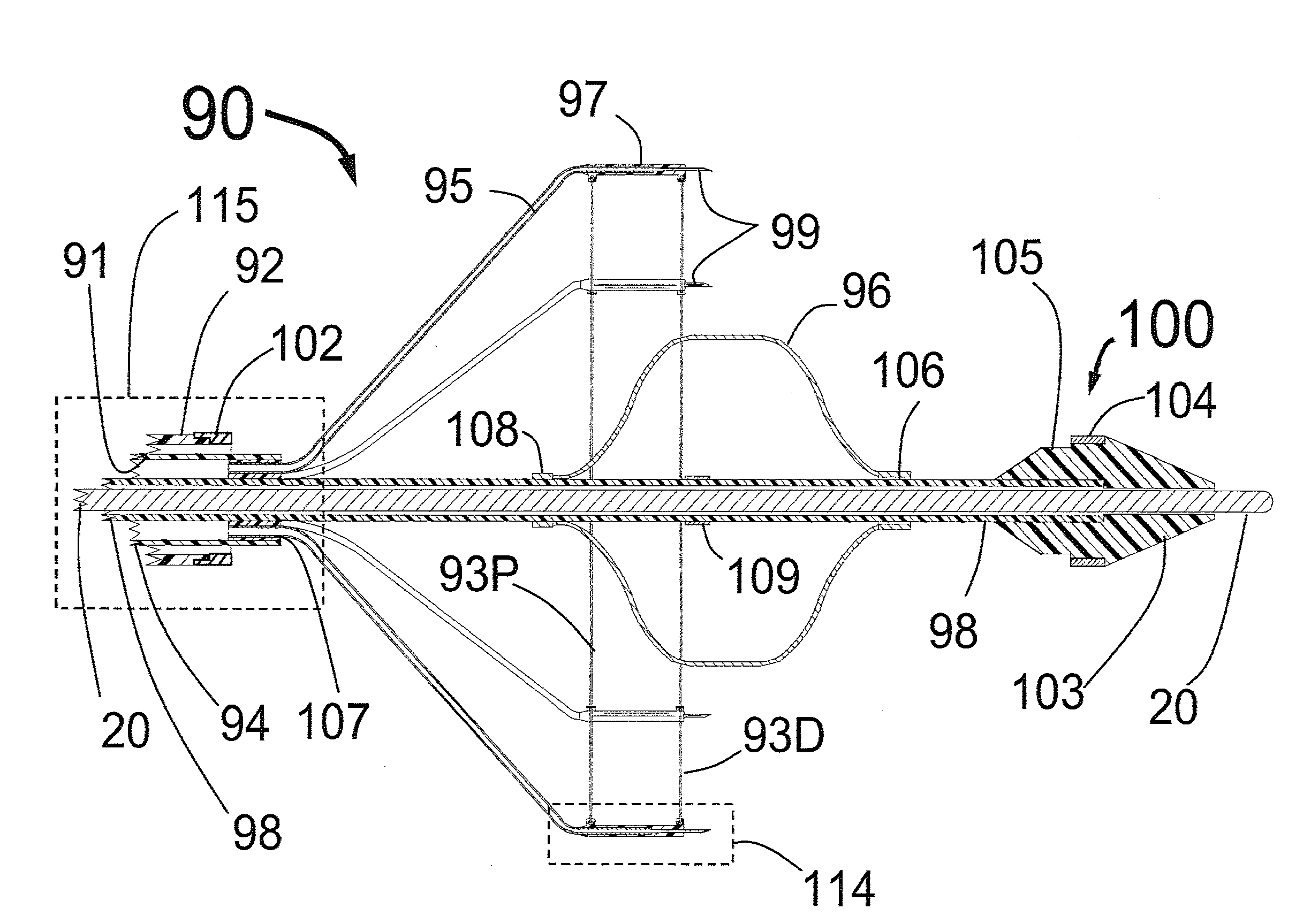
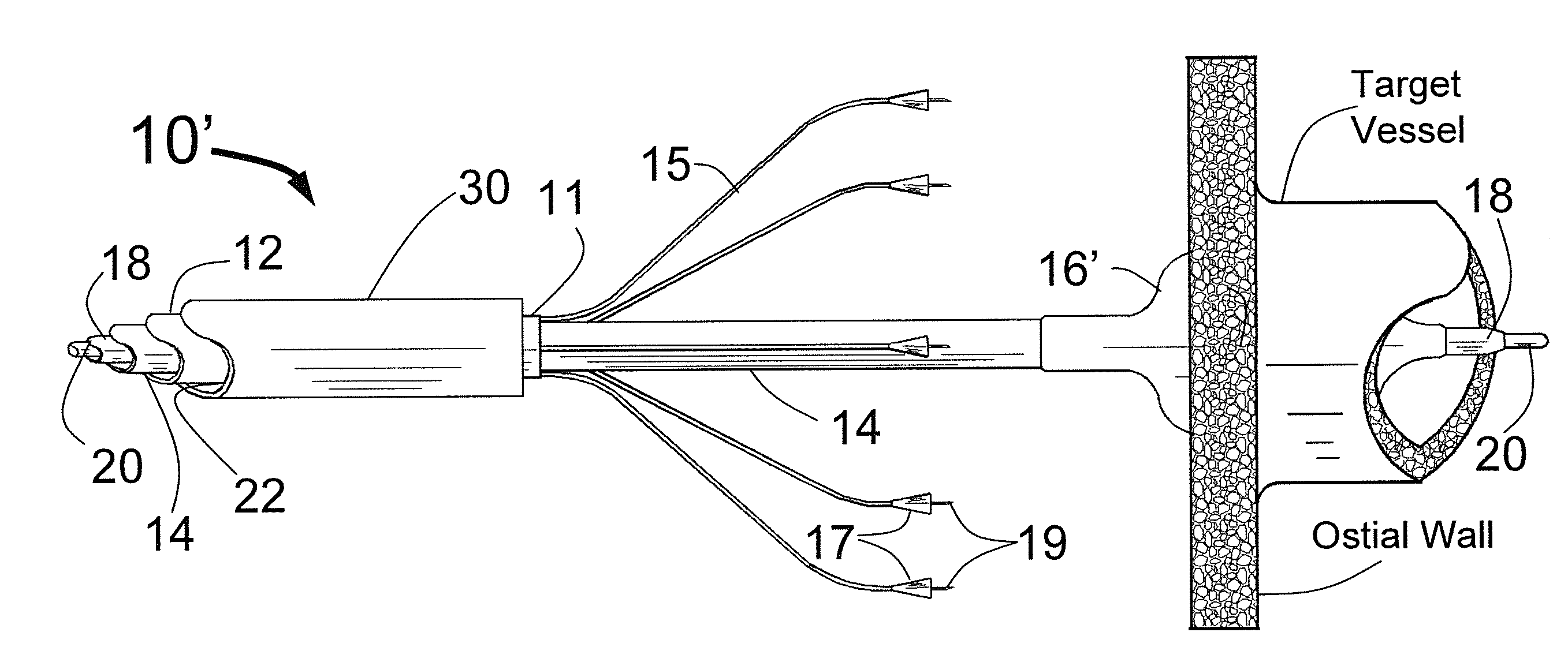
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20120271277A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Method of biochemical treatment of persistent pain
InactiveUS20050152905A1Reduce releaseAvoid exposureBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInterleukin 6Interleukin-1beta
This invention relates to a method for the biochemical treatment of persistent pain disorders by inhibiting the biochemical mediators of inflammation in a subject comprising administering to said subject any one of several combinations of components that are inhibitors of biochemical mediators of inflammation. Said process for biochemical treatment of persistent pain disorders is based on Sota Omoigui's Law, which states: ‘The origin of all pain is inflammation and the inflammatory response’. Sota Omoigui's Law of Pain unifies all pain syndromes as sharing a common origin of inflammation and the inflammatory response. The various biochemical mediators of inflammation are present in differing amounts in all pain syndromes and are responsible for the pain experience. Classification and treatment of pain syndromes should depend on the complex inflammatory profile. A variety of mediators are generated by tissue injury and inflammation. These include substances produced by damaged tissue, substances of vascular origin as well as substances released by nerve fibers themselves, sympathetic fibers and various immune cells. Biochemical mediators of inflammation that are targeted for inhibition include but are not limited to: prostaglandin, nitric oxide, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin 1-alpha, interleukin 1-beta, interleukin-4, Interleukin-6 and interleukin-8, histamine and serotonin, substance P, Matrix Metallo-Proteinase, calcitonin gene-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide as well as the potent inflammatory mediator peptide proteins neurokinin A, bradykinin, kallidin and T-kinin.
Owner:OMOIGUI OSEMWOTA SOTA
Neurostimulation system and method for providing therapy to patient with minimal side effects
ActiveUS20120089200A1Decrease their propagationEliminate side effectsSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationSide effectMedicine
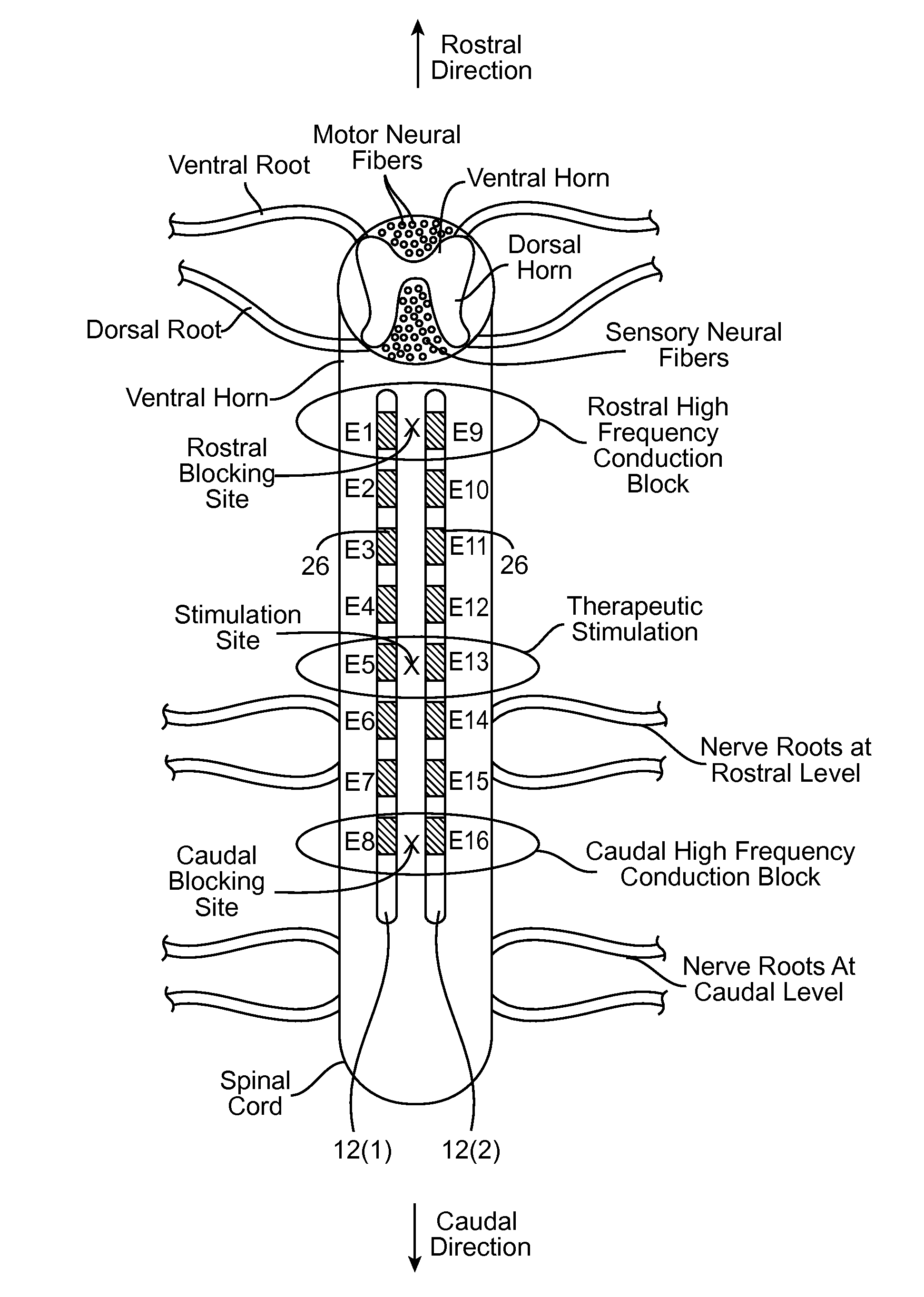
A method comprises conveying a pulsed waveform between an electrode and a stimulation site of a spinal cord, thereby evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a first sensory neural fiber creating a therapeutic effect in the tissue region, evoking the orthodromic propagation of action potentials along the first sensory neural fiber potentially creating paresthesia corresponding to the tissue region, and evoking the antidromic propagation of action potentials along a second sensory neural fiber potentially creating a side-effect in another tissue region. The method further comprises conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site rostral to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the first sensory neural fiber and reducing the paresthesia, and conveying electrical energy between an electrode and a blocking site caudal to the stimulation site, thereby blocking the action potentials propagated along the second sensory neural fiber and reducing the side-effect.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method for controlling the pain from injections or minor surgical procedures and apparatus for use therewith
InactiveUS6902554B2Reducing and eliminating painReduce and eliminate painSurgeryMedical devicesFiberNerve fiber bundle
The pain associated with an injection or minor surgical procedure at a site on the skin of a patient is reduced by urging a skin engaging surface of a pressure member against the skin proximate the site, thereby stimulating the large diameter afferent sensory nerve fibers in the skin proximate the site and at least partially blocking pain signals from the small diameter afferent pain nerve fibers in the skin proximate the site. An apparatus for use in this method comprises a pressure member having a skin engaging surface adapted to be pressed against the skin of a patient proximate the site to stimulate the large diameter afferent sensory nerve fibers in the skin proximate the site. In certain embodiments, the skin engaging surface is comprised of a plurality of projections extending from the pressure member. Various embodiments include a syringe retainer adapted to be secured to a syringe, and a least one resilient member, such as a spring, resiliently securing the pressure member to the syringe retainer.
Owner:BIONIX DEVMENT
Peri-vascular tissue ablation catheter with support structures
ActiveUS8740849B1Add supportImprove uniformityHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiagnosticsVascular tissueGuide tube
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through supported guide tubes which expand with open ends around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The system also includes means to limit and / or adjust the depth of penetration of the ablative fluid into and beyond the tissue of the vessel wall. The preferred embodiment of the catheter includes structures which provide radial and lateral support to the guide tubes so that the guide tubes open uniformly and maintain their position against the interior surface of the vessel wall as the sharpened injection needles are advanced to penetrate into the vessel wall.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Electrical Treatment Of Bronchial Constriction
ActiveUS20090281593A9Dilation increaseFunction increaseSpinal electrodesHead electrodesNerve fiber bundleSmooth muscle
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Transvascular catheter for extravascular delivery
ActiveUS20140121641A1Reduce or eliminate patient discomfort and painReduces potential traumaBalloon catheterSurgical needlesHuman bodyPerfusion
An intravascular catheter for peri-vascular and / or peri-urethral tissue ablation includes multiple needles advanced through guide tubes which may be supported by an expandable balloon. The guide tubes expand with open ends around a central axis to engage the interior surface of the wall of the renal artery or other vessel of a human body allowing the injection an ablative fluid for ablating tissue, and / or nerve fibers in the outer layer or deep to the outer layer of the vessel, or in prostatic tissue. The diameter of the inflated balloon is less than the inside diameter of the vessel, allowing perfusion across the inflated balloon and guide tubes.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Pattern analysis of retinal maps for the diagnosis of optic nerve diseases by optical coherence tomography
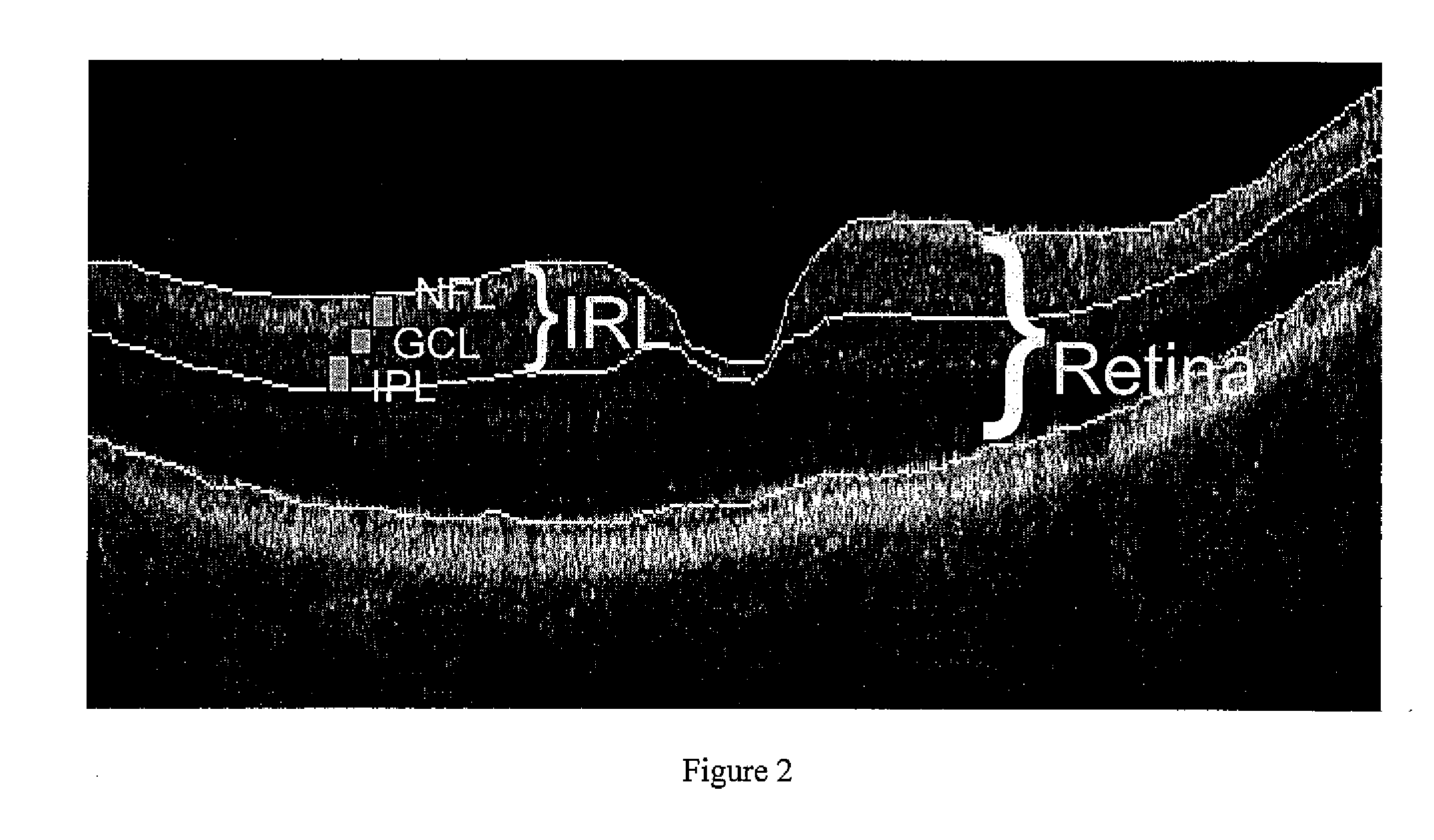
Methods for analyzing retinal tomography maps to detect patterns of optic nerve diseases such as glaucoma, optic neuritis, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy are disclosed in this invention. The areas of mapping include the macula centered on the fovea, and the region centered on the optic nerve head. The retinal layers that are analyzed include the nerve fiber, ganglion cell, inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers and their combinations. The overall retinal thickness can also be analyzed. Pattern analysis are applied to the maps to create single parameter for diagnosis and progression analysis of glaucoma and optic neuropathy.
Owner:USC STEVENS UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
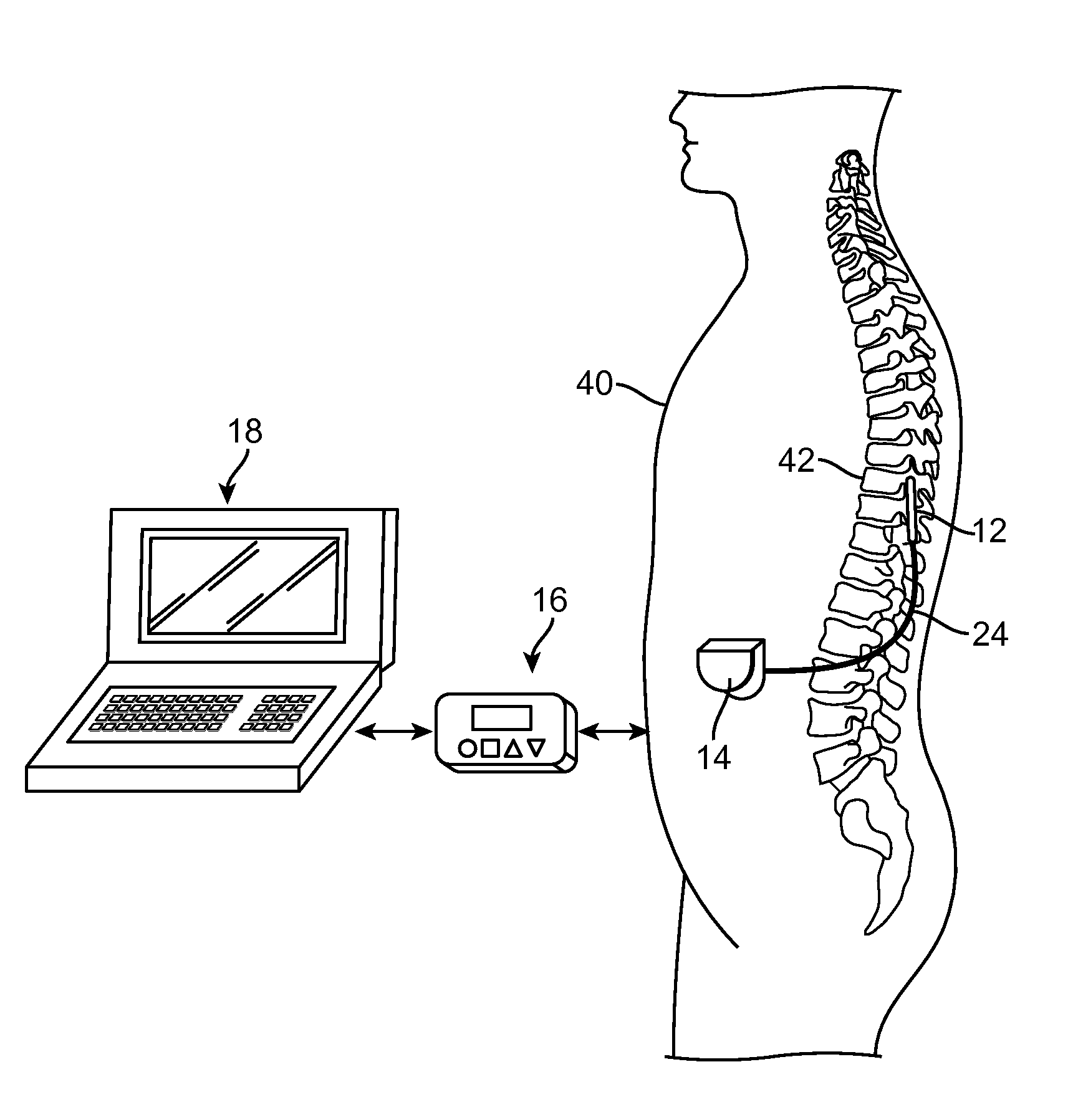
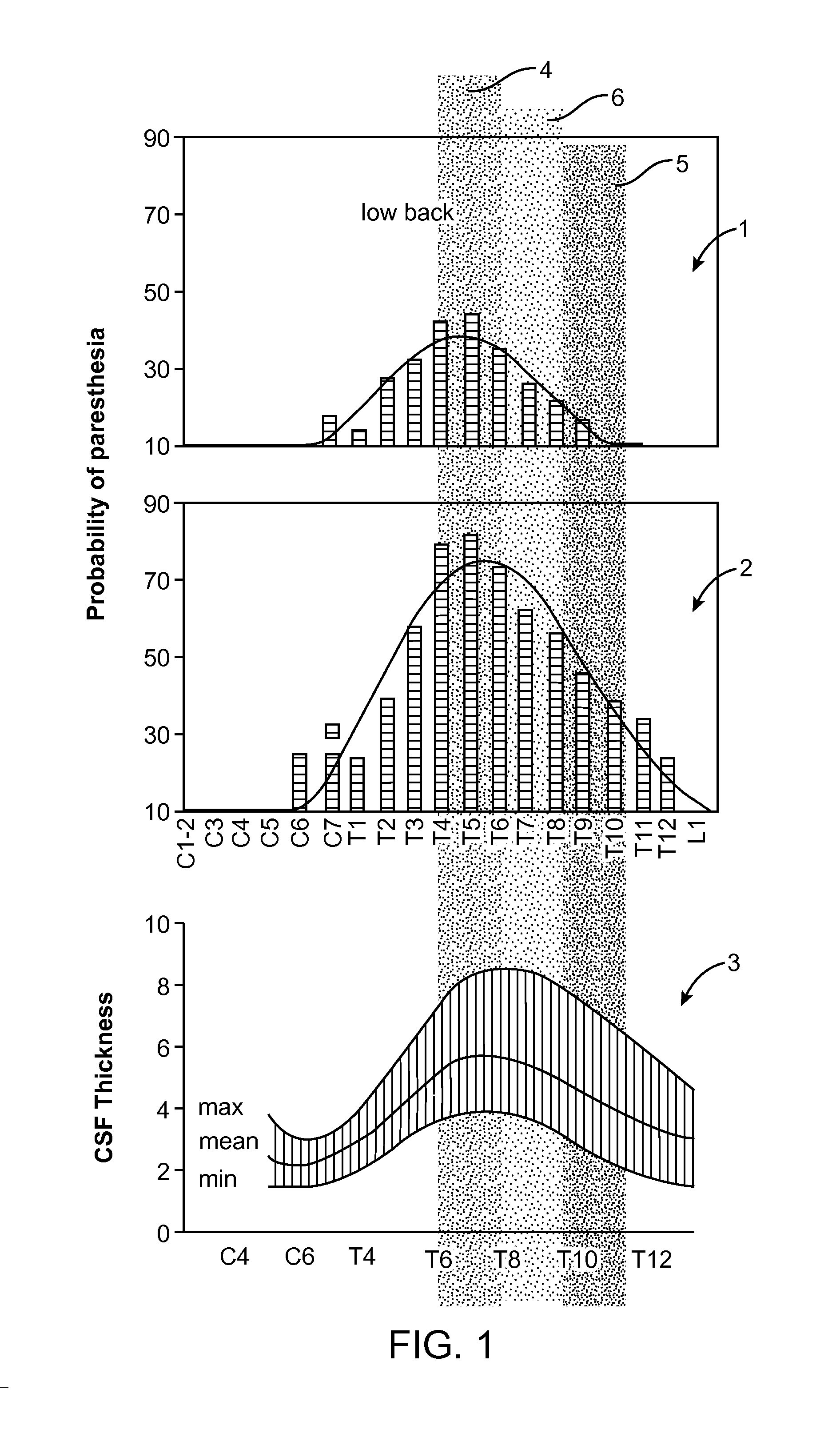
Method for achieving low-back spinal cord stimulation without significant side-effects
ActiveUS20130268021A1Increasing activation thresholdIncreased activationSpinal electrodesArtificial respirationSpinal columnNerve fiber bundle
A method for treating an ailment of a patient using at least one electrode implanted within a spinal column of the patient at a T4-T6 spinal nerve level. The method comprises increasing an activation threshold of a side-effect exhibiting neural structure relative to the activation threshold of a dorsal column (DC) nerve fiber of the patient, and applying electrical stimulation energy to the DC nerve fiber via the at least one electrode while the activation threshold of the neural structure is increased, thereby treating the ailment while minimizing stimulation of the neural structure. Another method comprises applying electrical stimulation energy to the spinal column of the patient via the plurality of electrodes, thereby generating a medio-lateral electrical field relative to the spinal column of the patient and treating the ailment.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
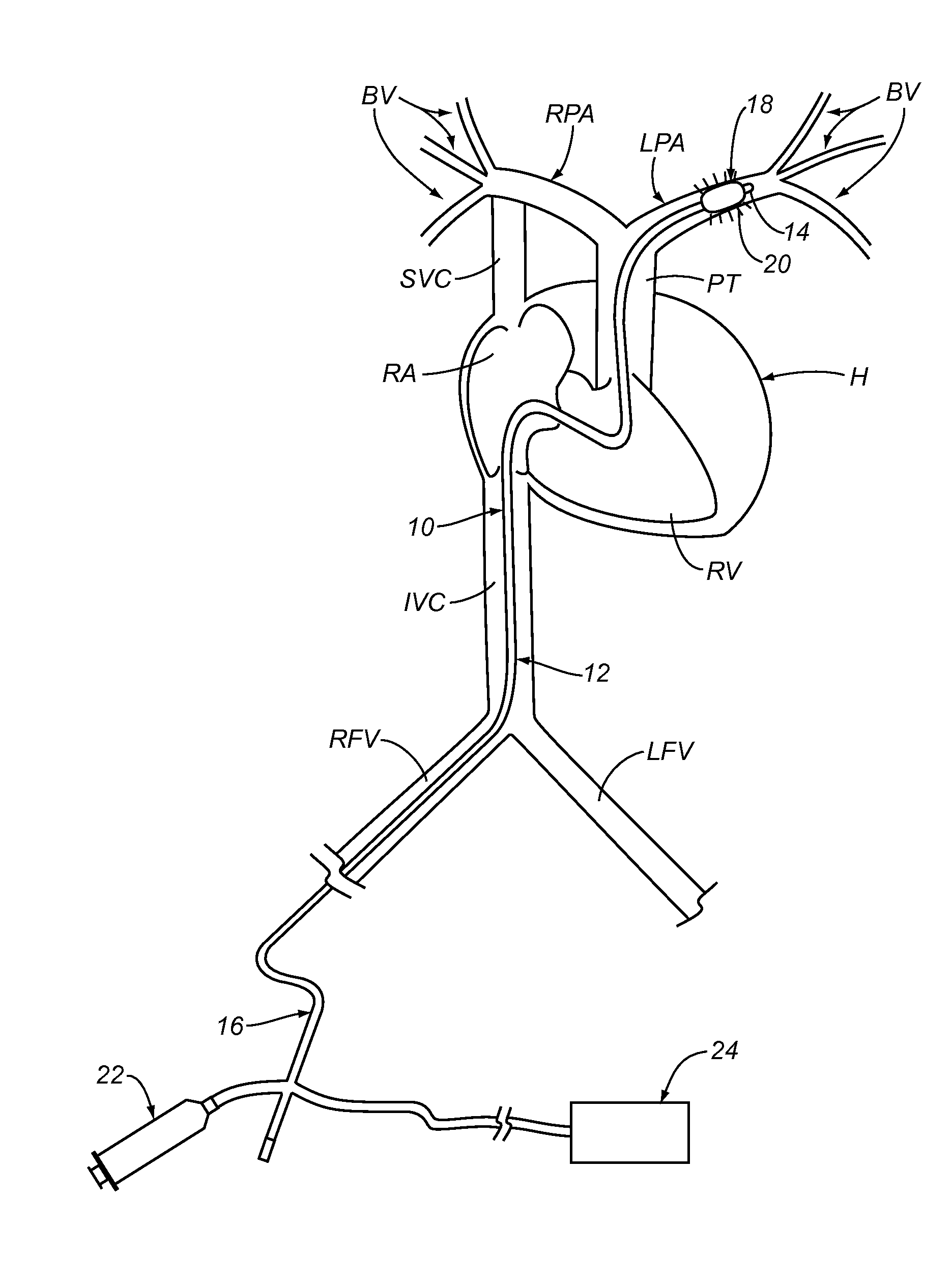
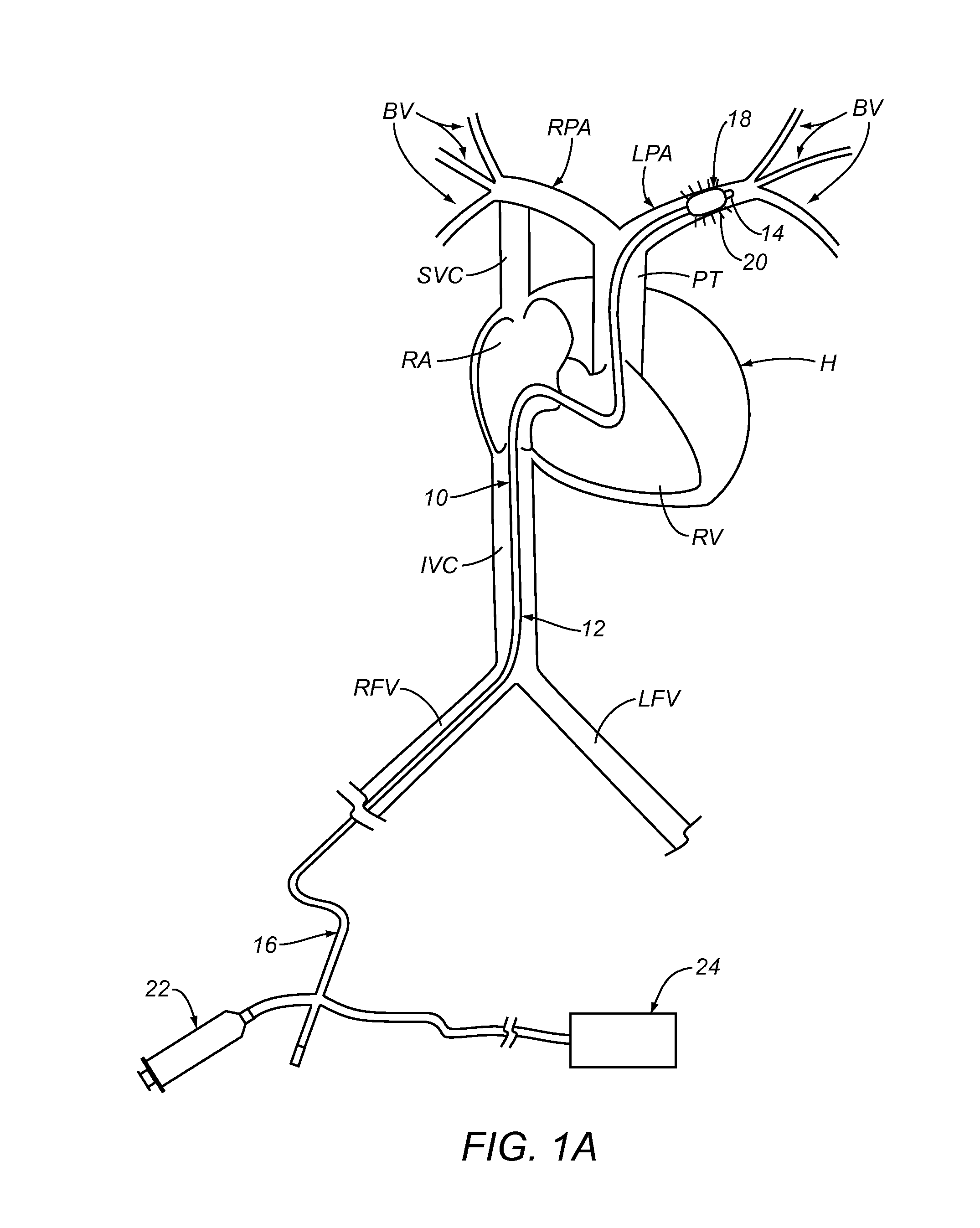
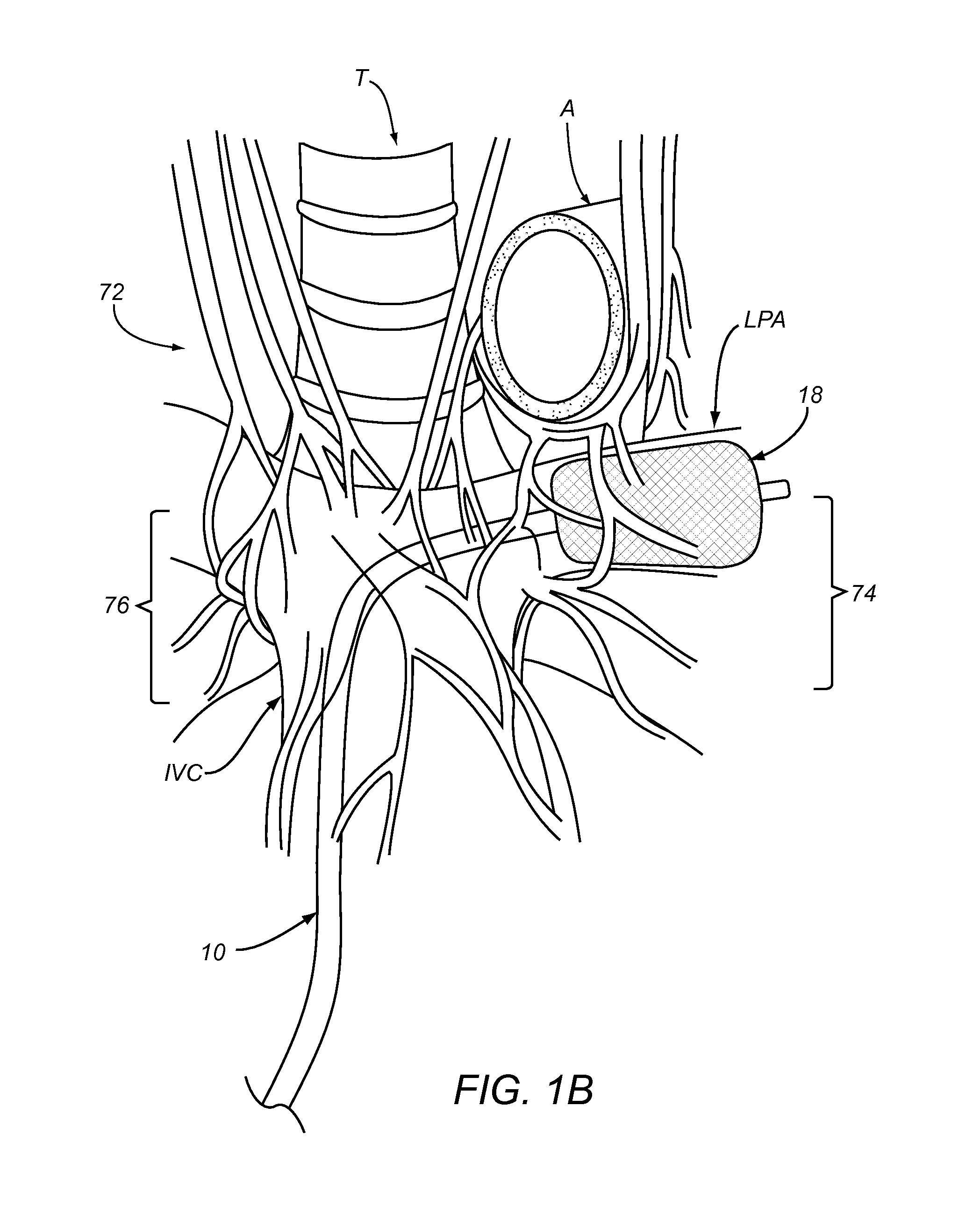
Apparatus and Methods For Treating Pulmonary Hypertension
ActiveUS20130204068A1Ameliorate pulmonary hypertensionReduced activityChiropractic devicesMedical devicesPulmonary vasculatureNerve fiber bundle
A method is described for decreasing activity of at least one sympathetic nerve, nerve fiber or neuron innervating at least one blood vessel in the pulmonary vasculature of a patient to ameliorate pulmonary hypertension. In one embodiment, the method may involve advancing an intravascular treatment device to a target location in a target blood vessel within the pulmonary vasculature of the patient and using the treatment device to decrease activity of at least one sympathetic nerve, nerve fiber or neuron innervating the target blood vessel at or near the target location to ameliorate pulmonary hypertension.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20120271301A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeIntravenous devicesSurgical instruments for heatingCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium. The present invention also has application to ablating tissue around the ostium of a renal artery for the treatment of hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
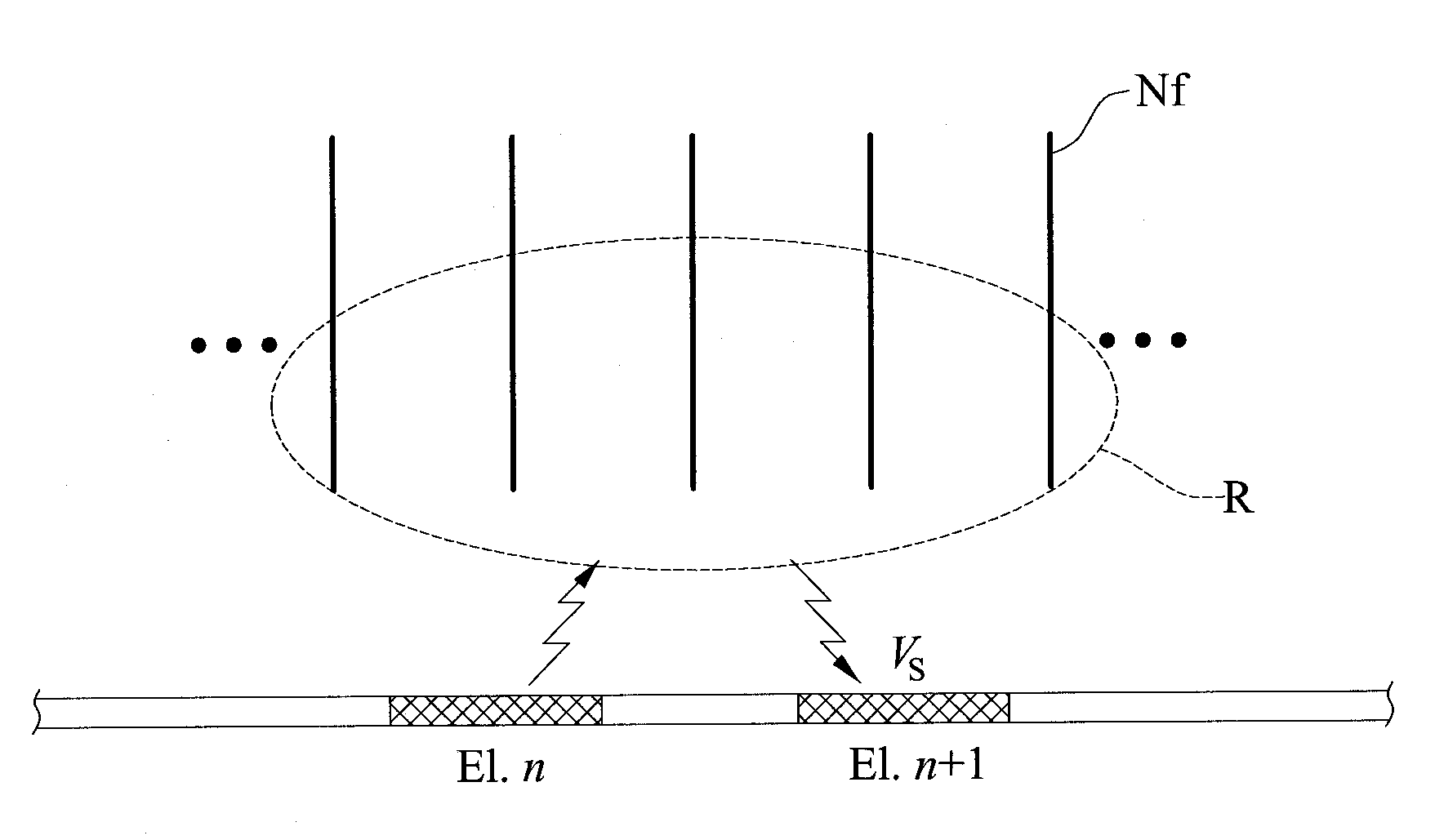
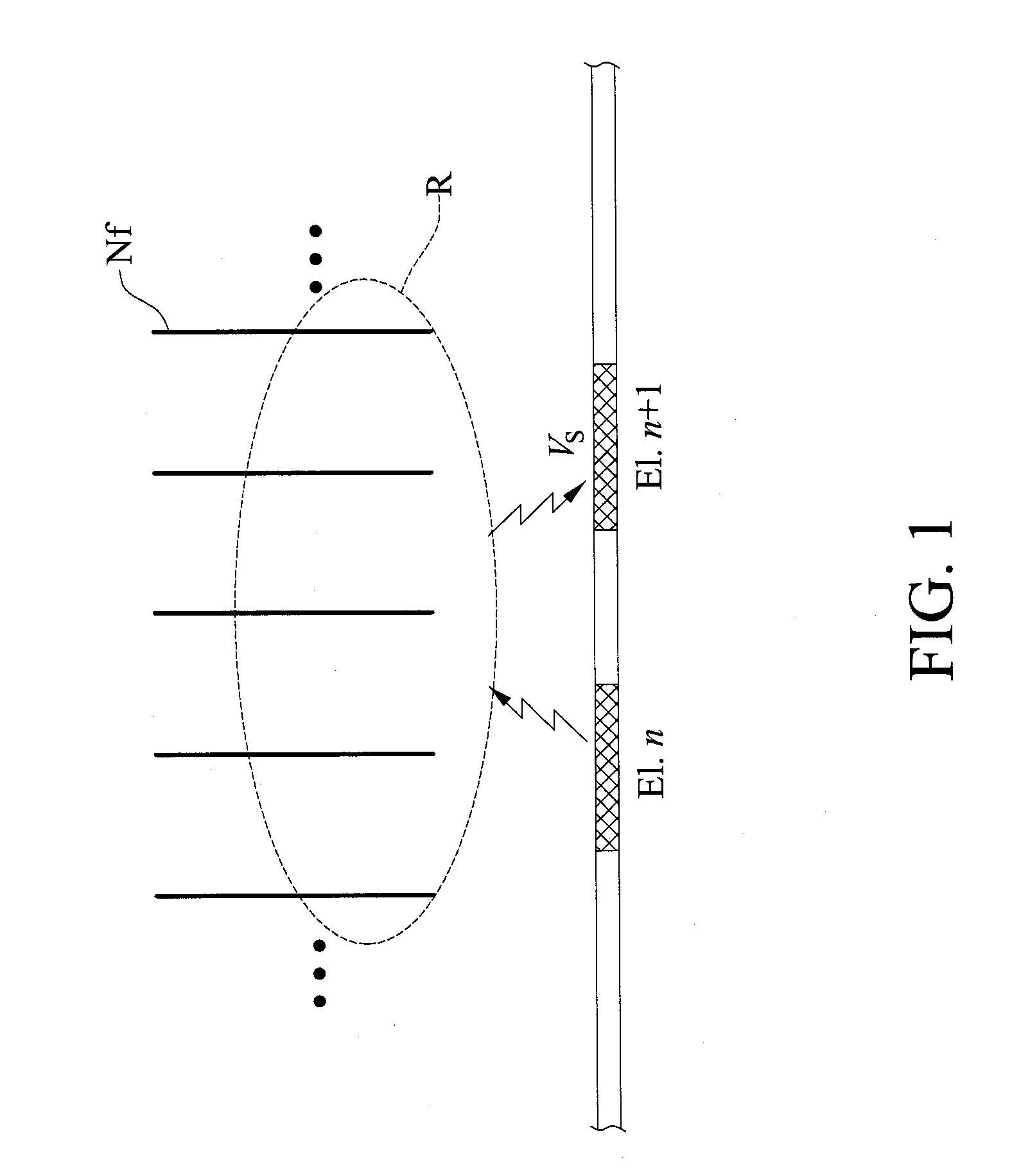
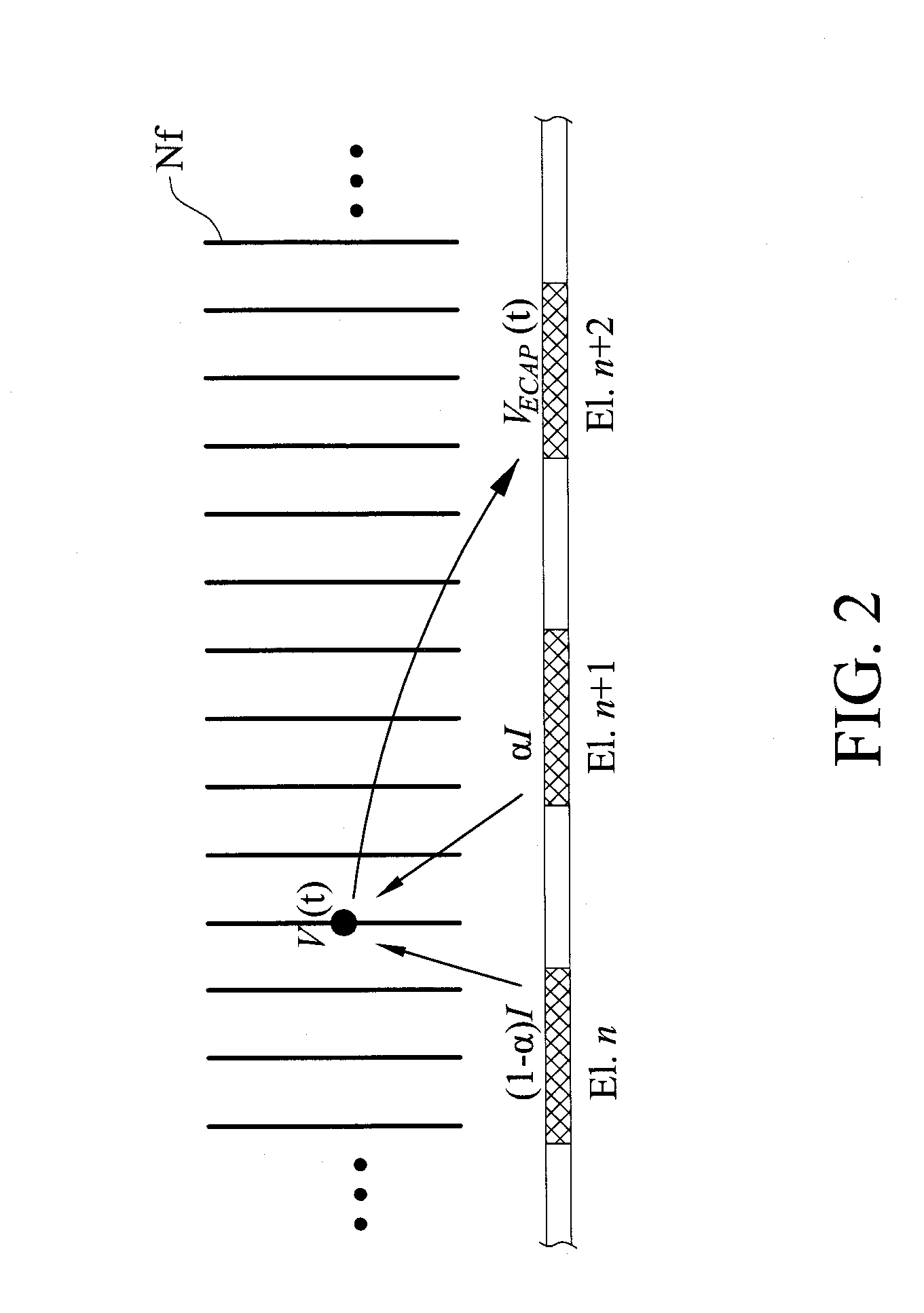
Method for analyzing nerve fiber distribution and measuring normalized evoked compound action electric potential
ActiveUS20140066803A1Rapidly and precisely and analyzingRapidly and precisely measuringHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberEvoked compound action potential
A method for analyzing nerve fibers distribution is provided, including inputting a stimulation signal into a nerve tissue through at least two sensing and conducting electrodes, applying a stimulation signal ratio to control the stimulation signal using an electric current steering technique to electrically stimulate a plurality of nerve fibers within a plurality of stimulations areas of the nerve tissue; receiving a plurality of evoked compound action potentials (ECAP) using at least two sensing and conducting electrodes due to the nerve fibers electrically stimulated and computing a distance between the nerve fiber and the conducting electrodes including eliminating non-ideal effect caused by an electric potential attenuation factor, wherein the electric potential attenuation factor is a function of the distance between each of the conducting electrodes and the nerve tissue; and integrating and comparing the received ECAPs and analyzing the nerve fibers distribution of the nerve tissue.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Vagal nerve stimulation to avert or treat stroke or transient ischemic attack
ActiveUS20130317580A1Improve the level ofInhibition of excitementSpinal electrodesMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsSerotoninRisk stroke
Devices, systems and methods are disclosed for treating or preventing a stroke and / or a transient ischemic attack in a patient. The methods comprise transmitting impulses of energy non-invasively to selected nerve fibers, particularly those in a vagus nerve. Vagus nerve stimulation is used to modulate the release of GABA, norepinephrine, and / or serotonin, thereby providing neuroprotection to the patient; to modulate the activity of resting state neuronal networks, particularly the sensory-motor network or resting state networks containing the insula; and to avert a stroke or transient ischemic attack that has been forecasted.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Apparatus for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
A nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light-generating source is operatively coupled to an optical fiber, which in turn is coupled to a plug in the end of a holder in a sheath. Light is then passed from the light source through the optical fiber to the holder and out a selected optical tip on the sheath to provide an efficacious amount of light to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. Some embodiments omit the fiber and use light directly from the laser diode.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
Modular stimulator for treatment of back pain, implantable RF ablation system and methods of use
ActiveUS9248278B2Rehabilitate spinal stabilityRestore neural driveSpinal electrodesDiagnosticsNerve fiber bundleElectricity
Apparatus and methods for treating back pain are provided, in which an implantable stimulator is configured to communicate with an external control system, the implantable stimulator providing a neuromuscular electrical stimulation therapy designed to cause muscle contraction to rehabilitate the muscle, restore neural drive and restore spinal stability; the implantable stimulator further including one or more of a number of additional therapeutic modalities, including a module that provides analgesic stimulation; a module that monitors muscle performance and adjusts the muscle stimulation regime; and / or a module that provides longer term pain relief by selectively and repeatedly ablating nerve fibers. In an alternative embodiment, a standalone implantable RF ablation system is described.
Owner:MAINSTAY MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com