Patents
Literature
74 results about "Aortic wall" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
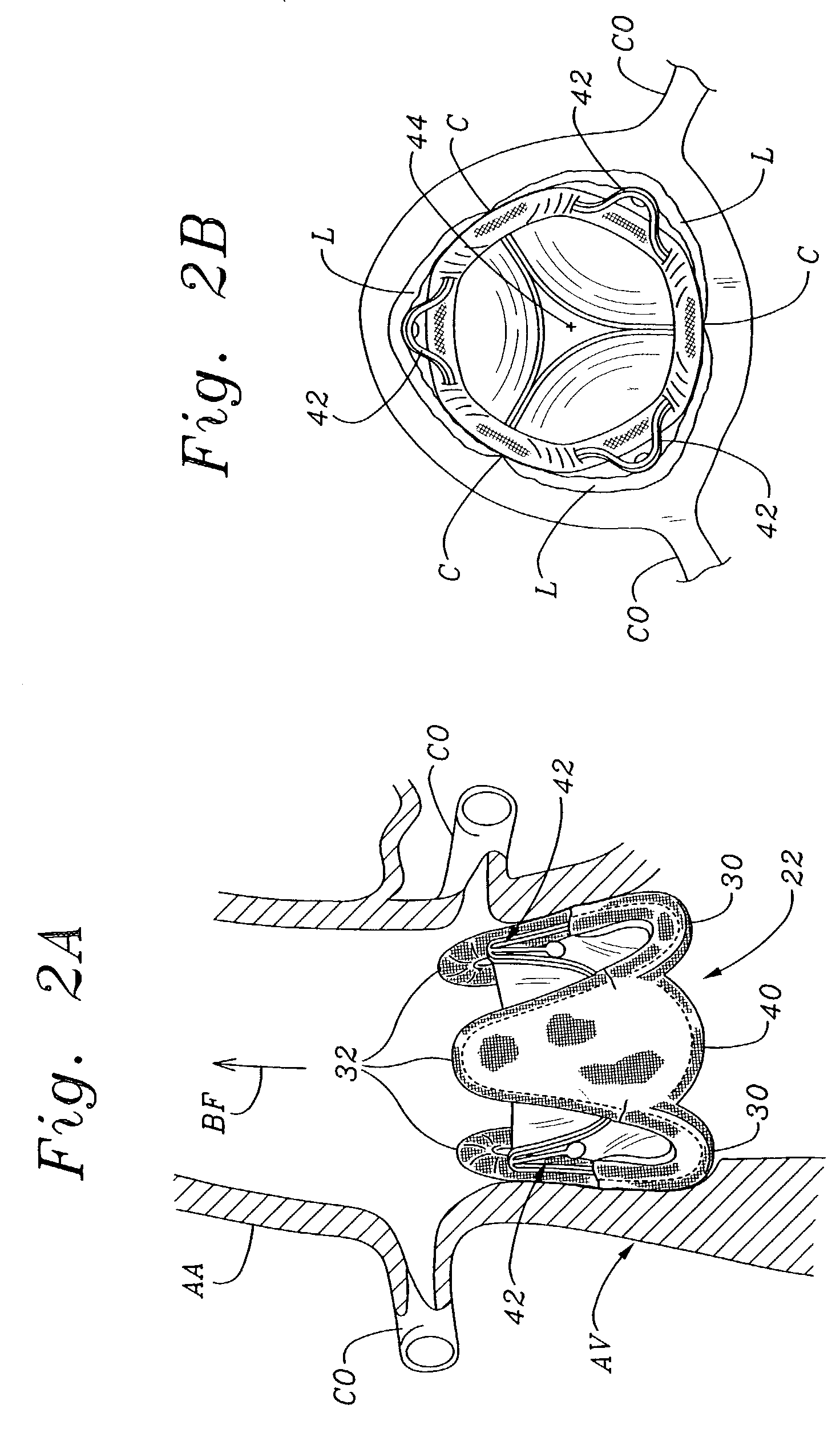
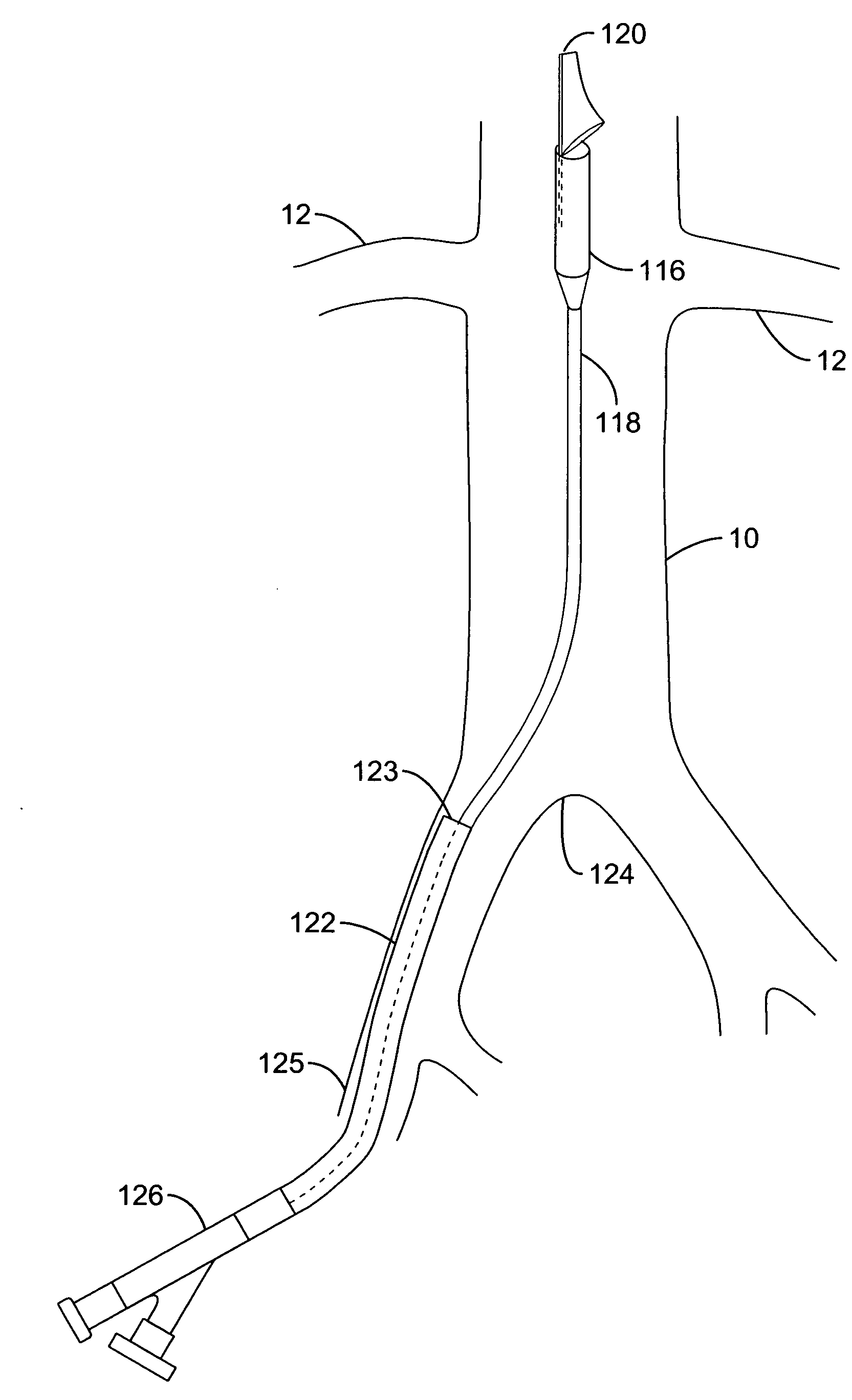
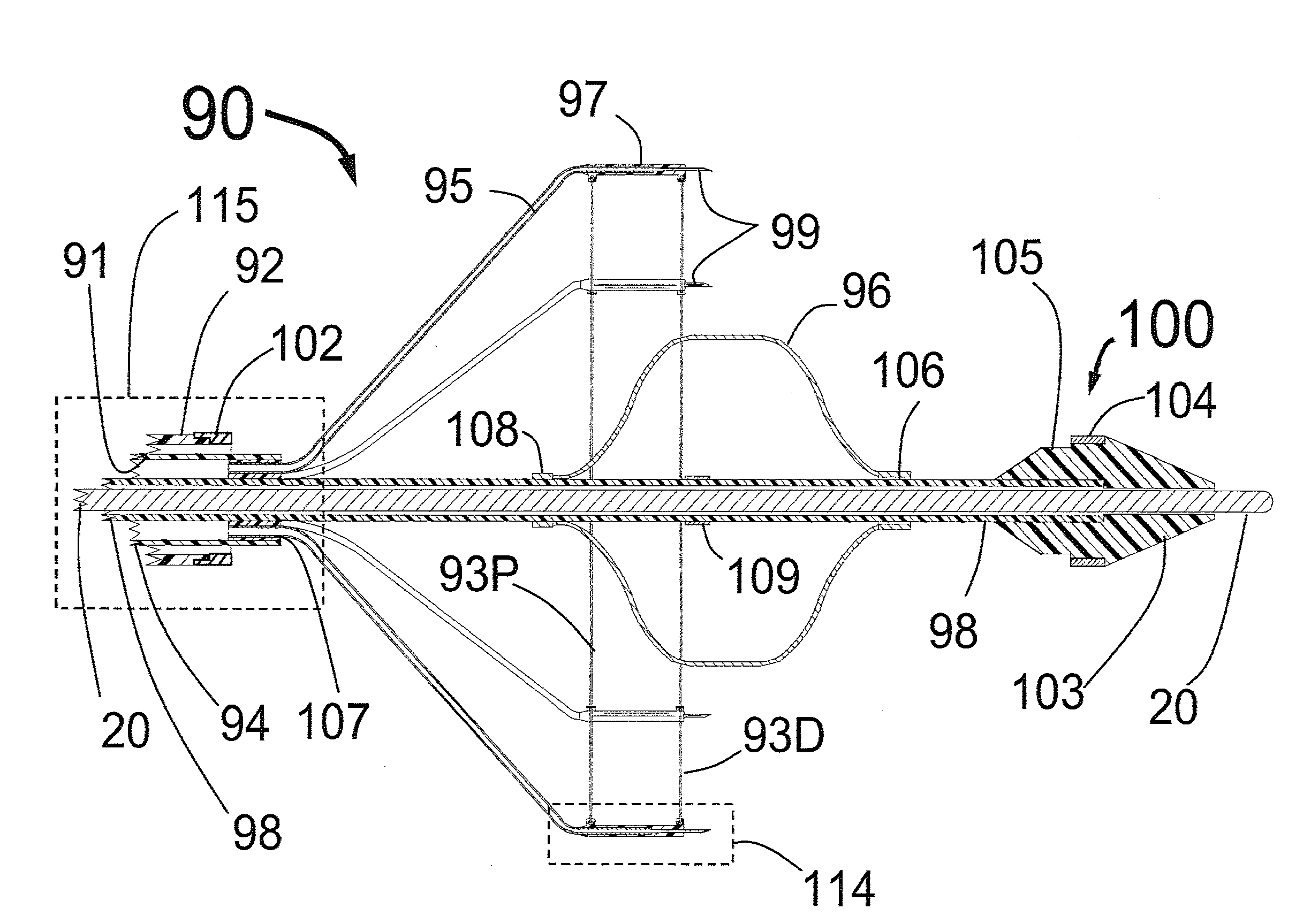
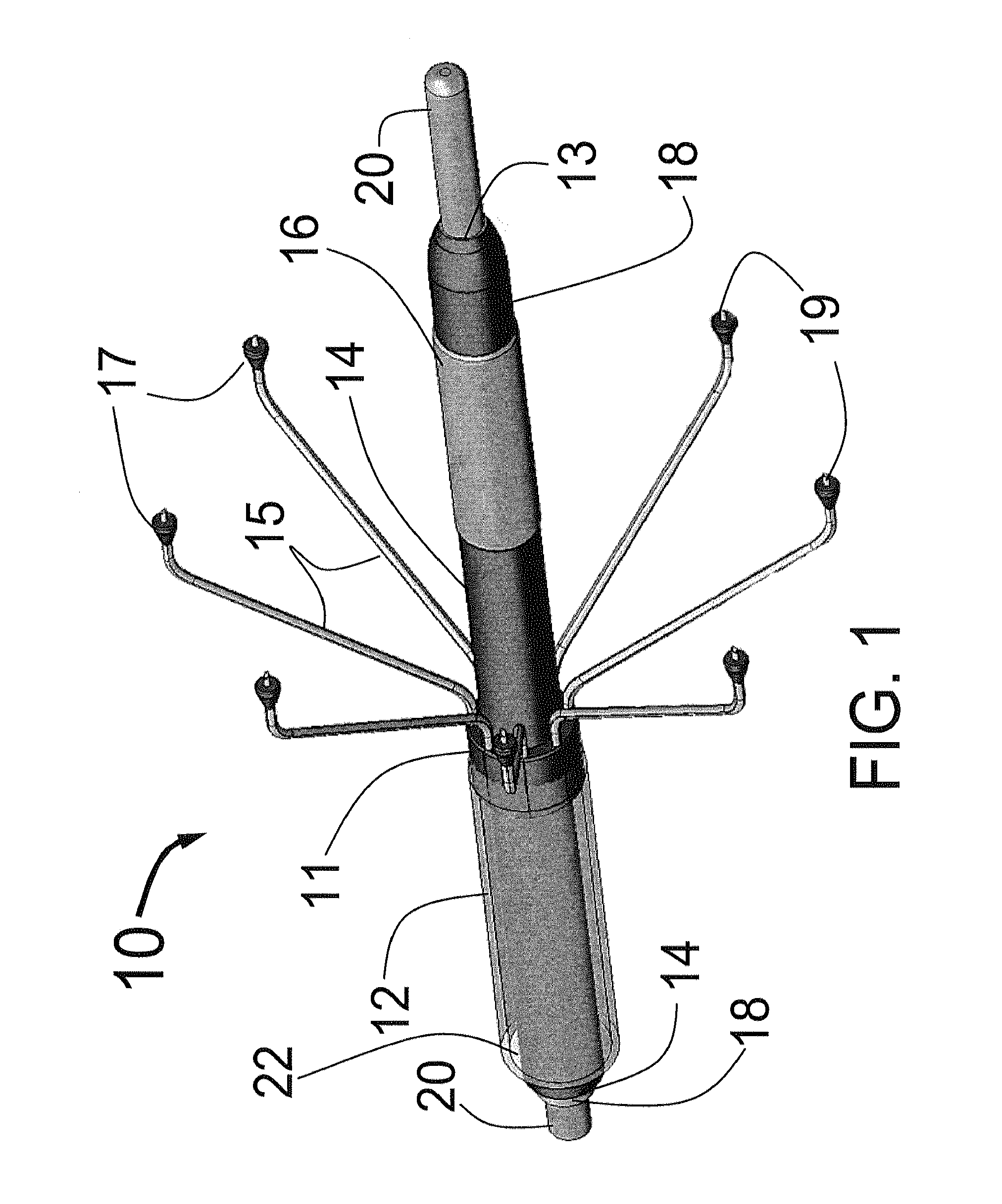
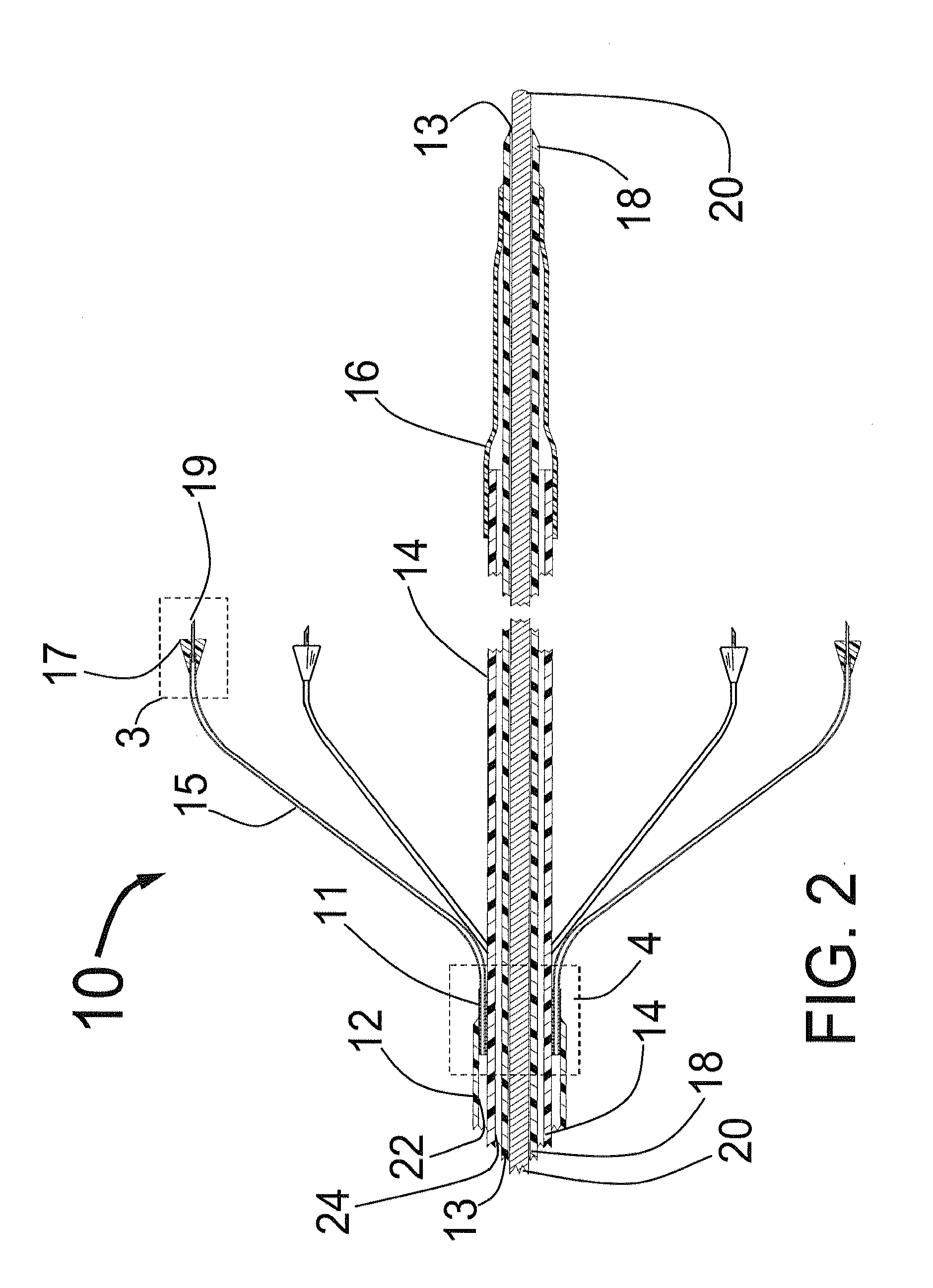
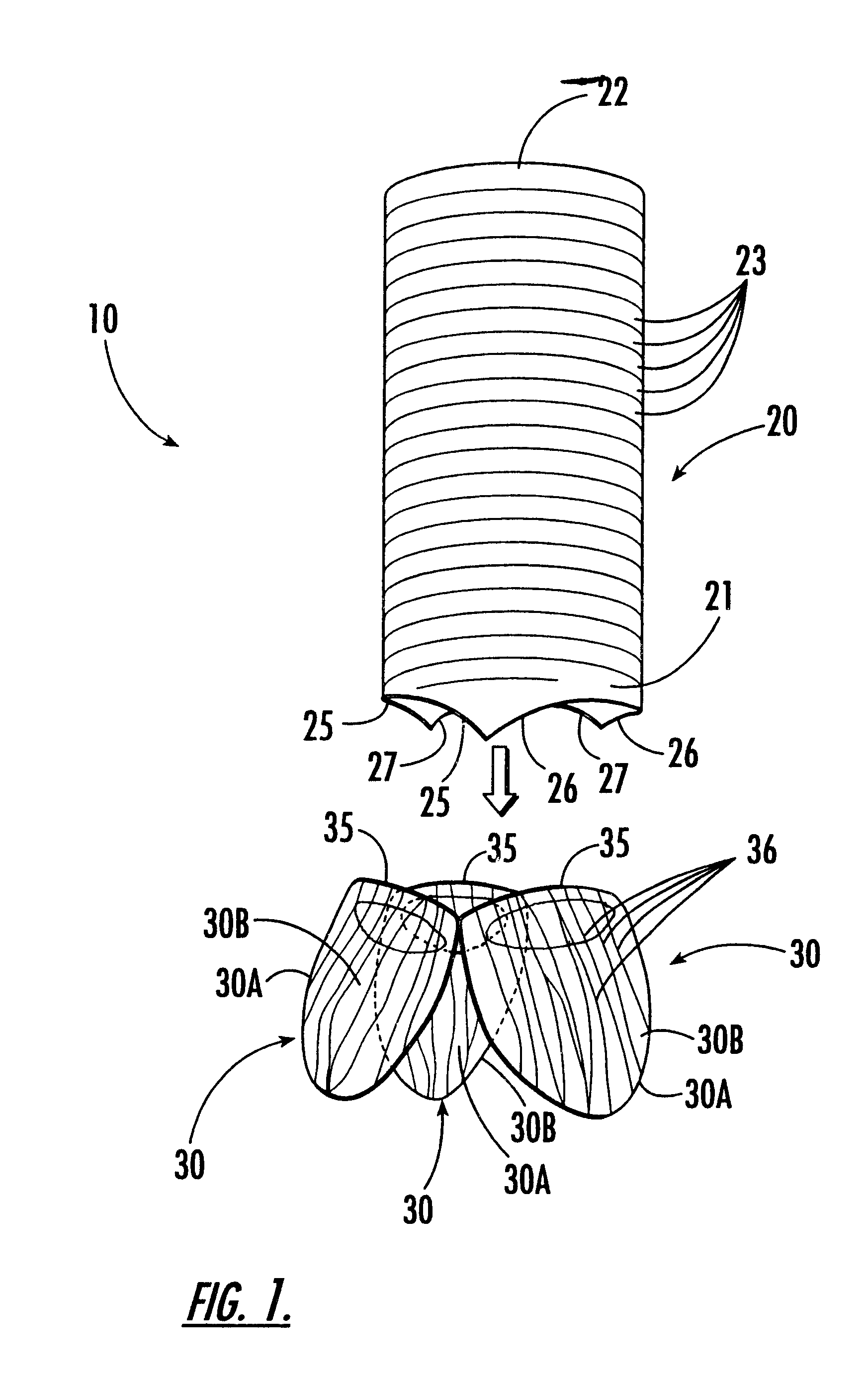
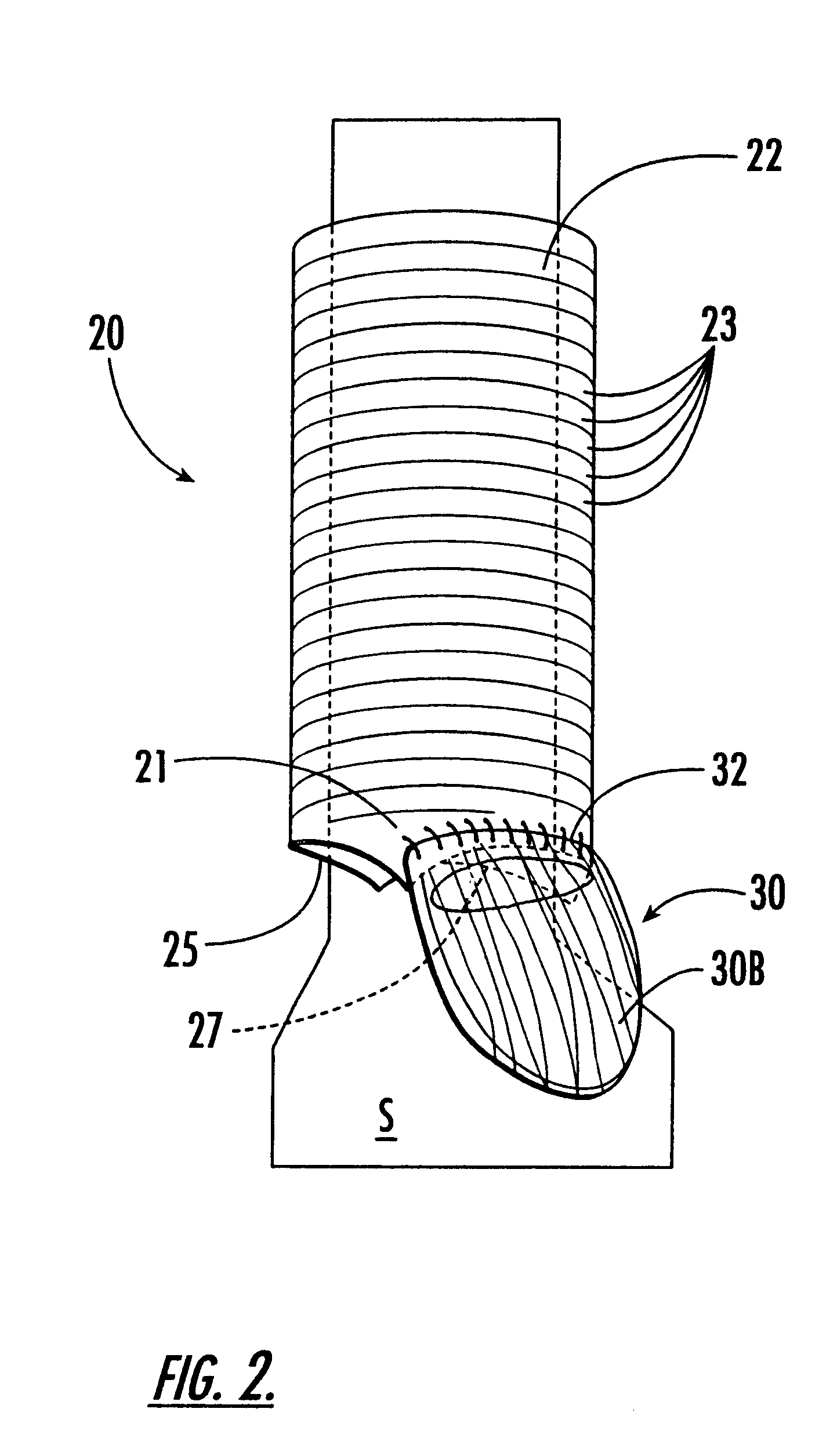
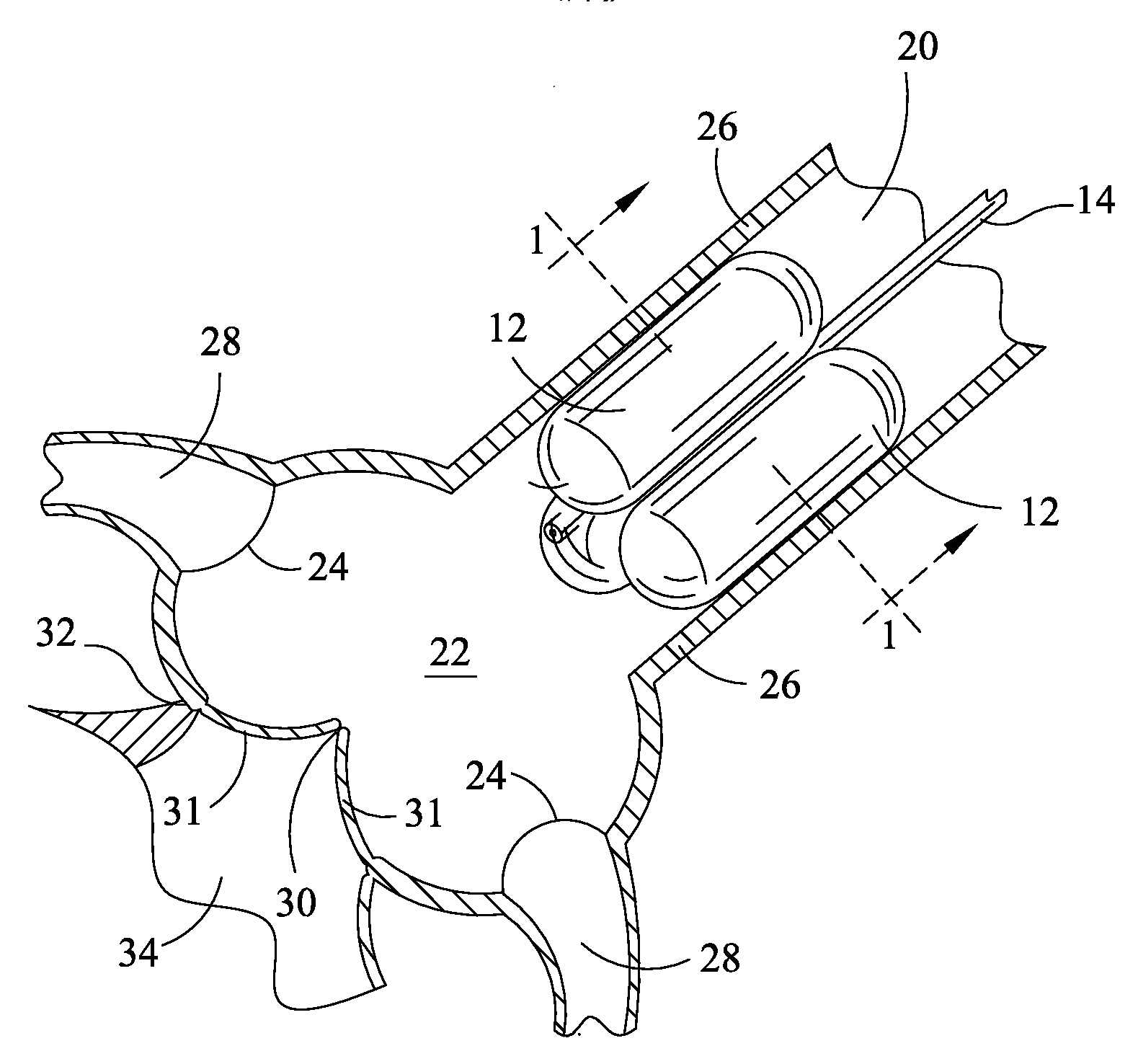
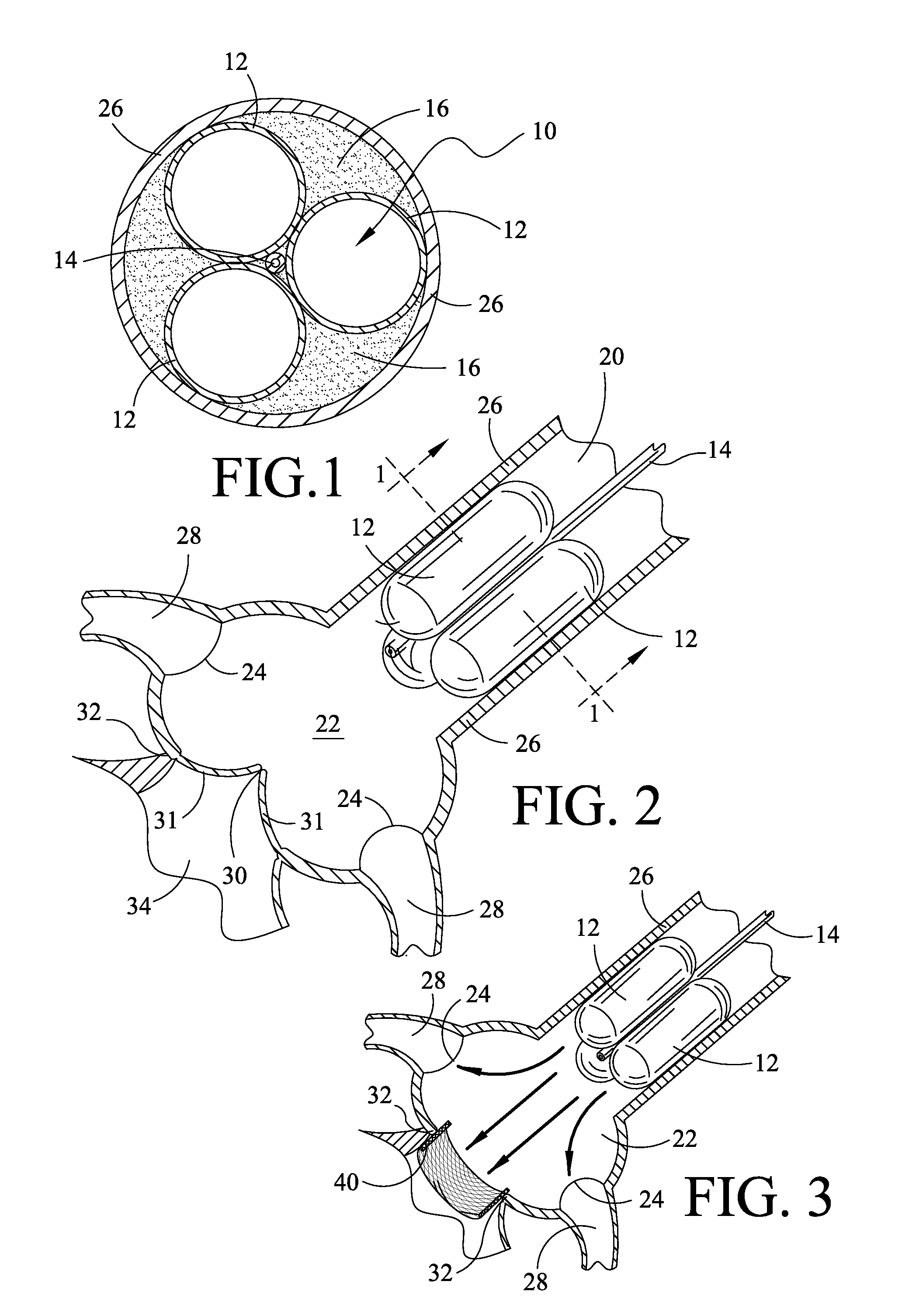
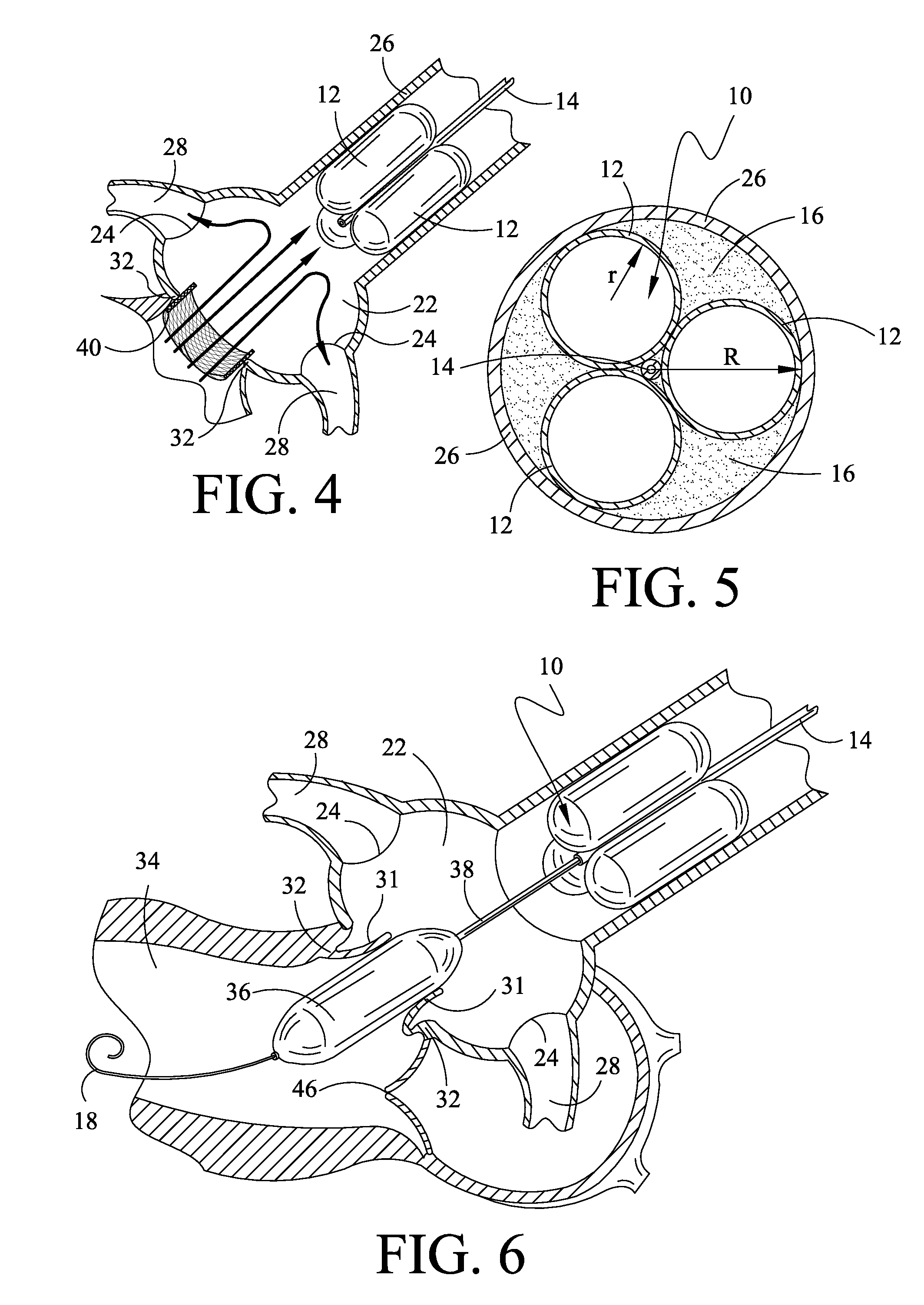
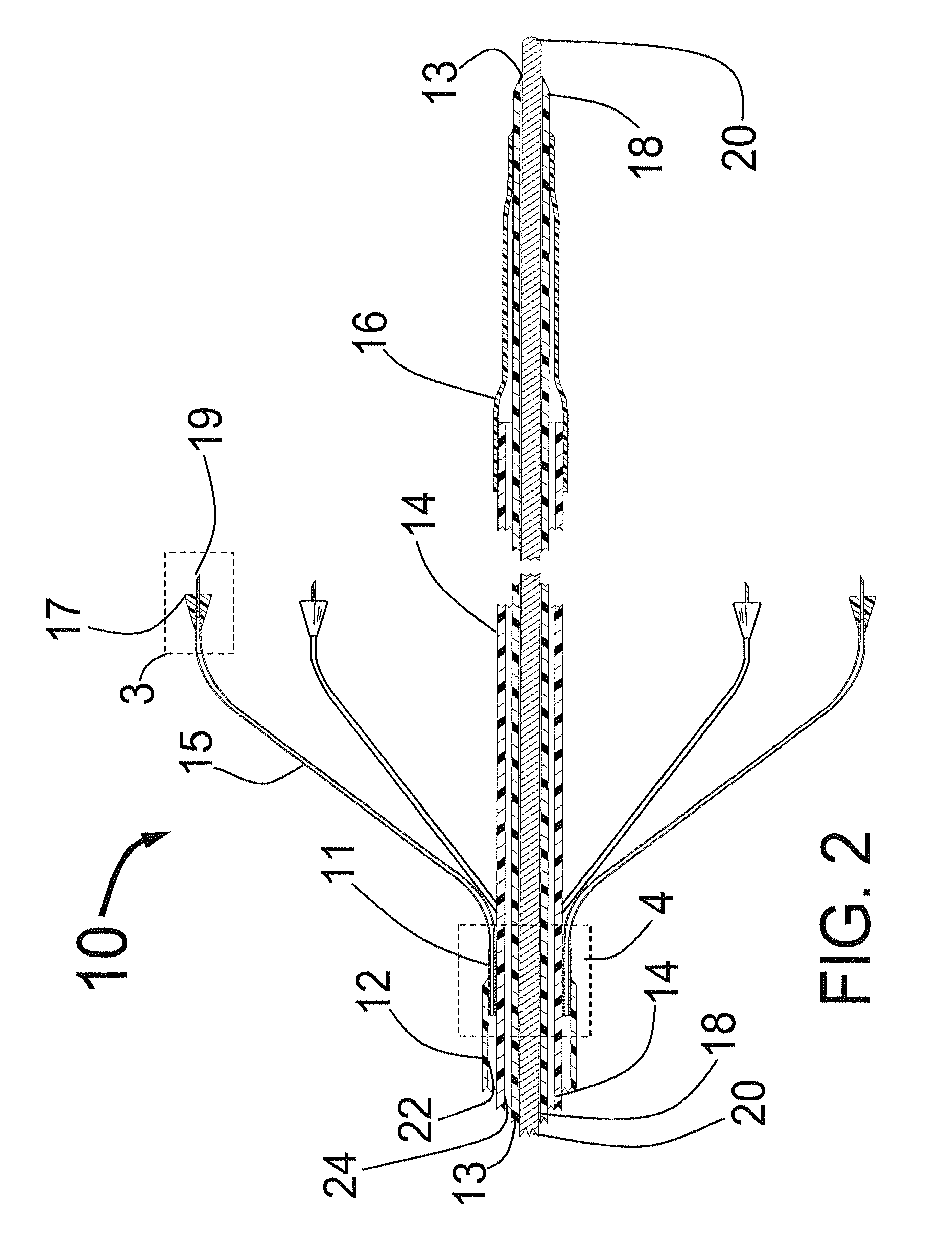
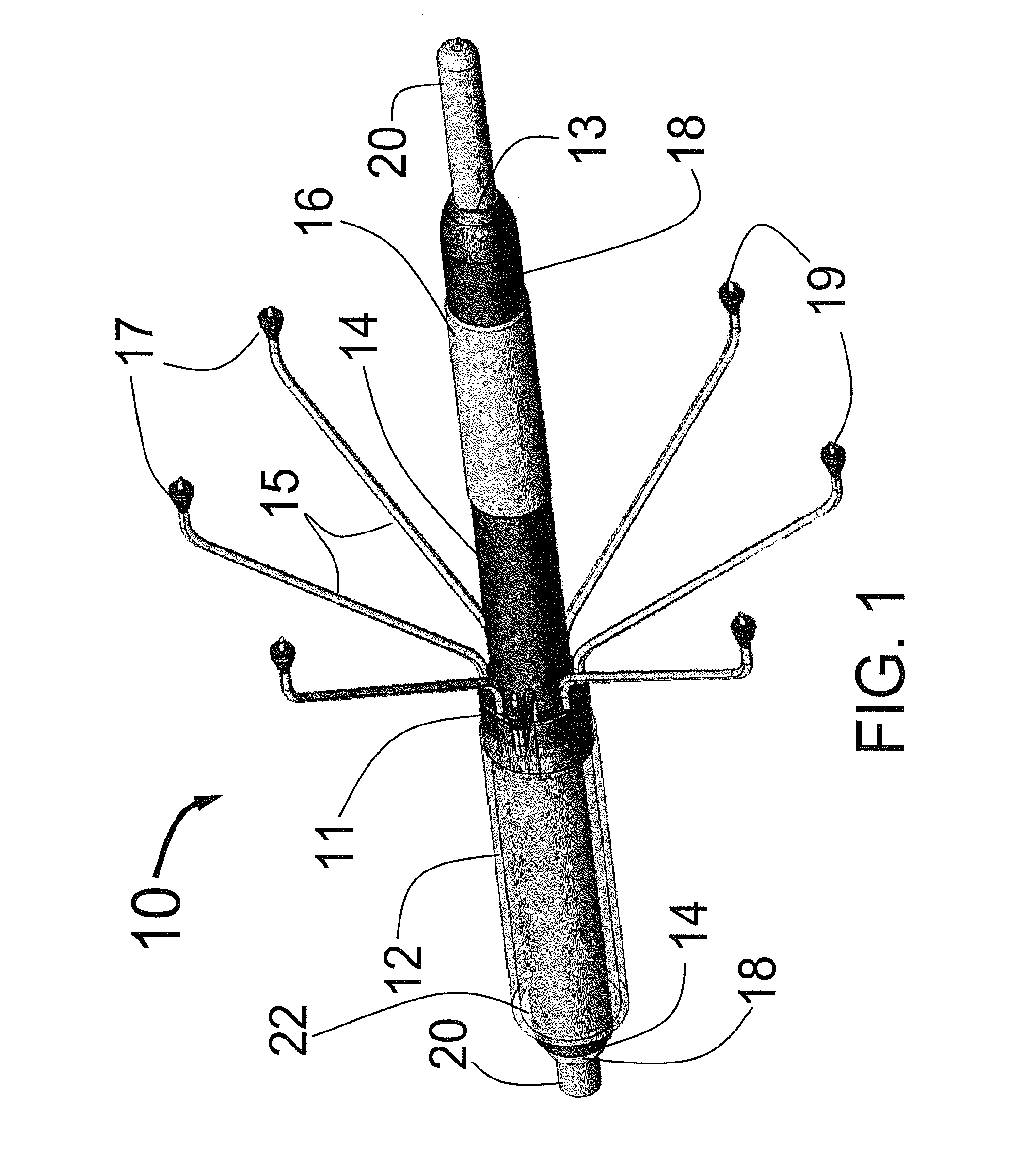
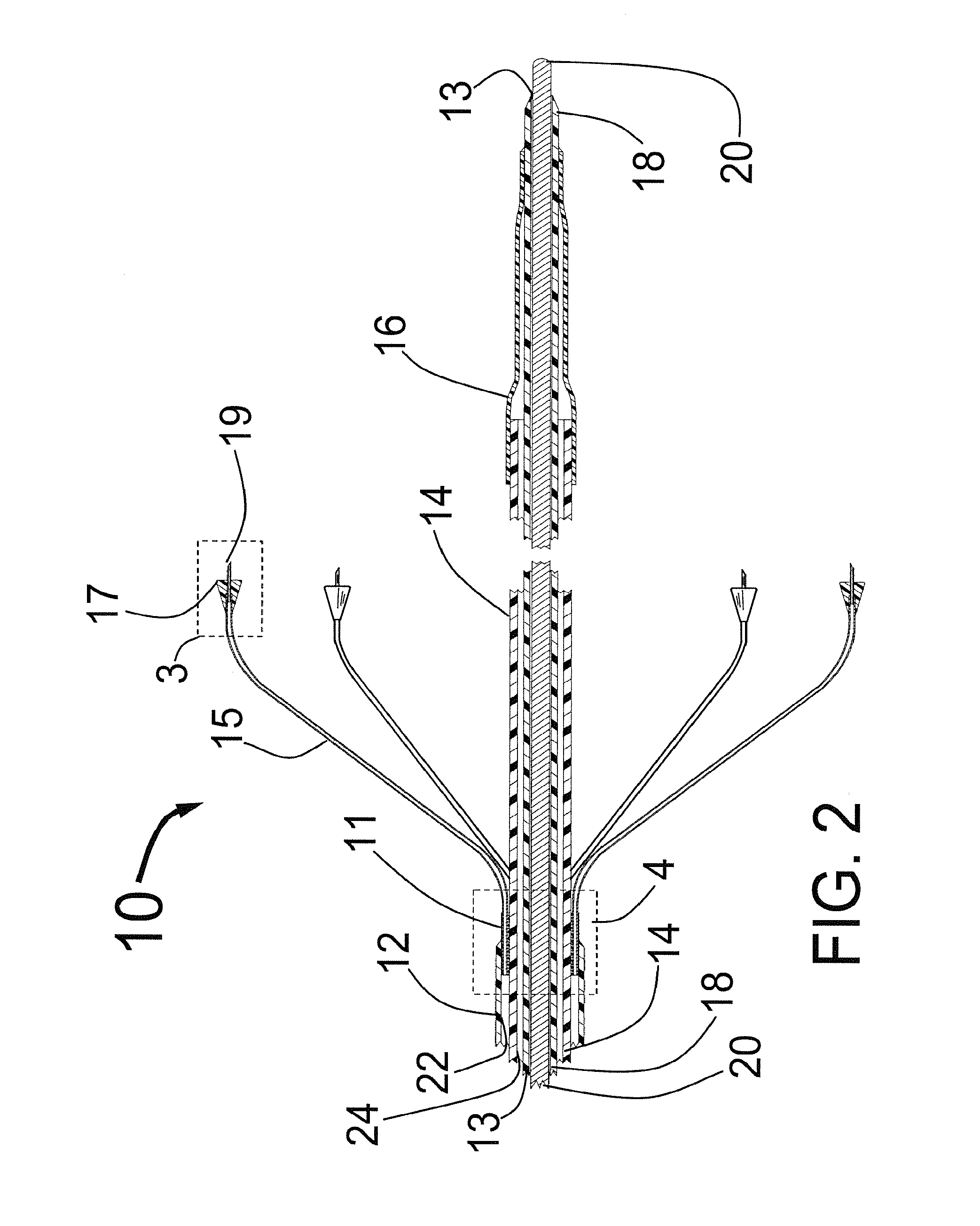
Valve prosthesis for implantation in the body and a catheter for implanting such valve prosthesis
InactiveUS7618446B2Inhibition of contractionEasy to shapeStentsBalloon catheterSurgical operationThoracic structure
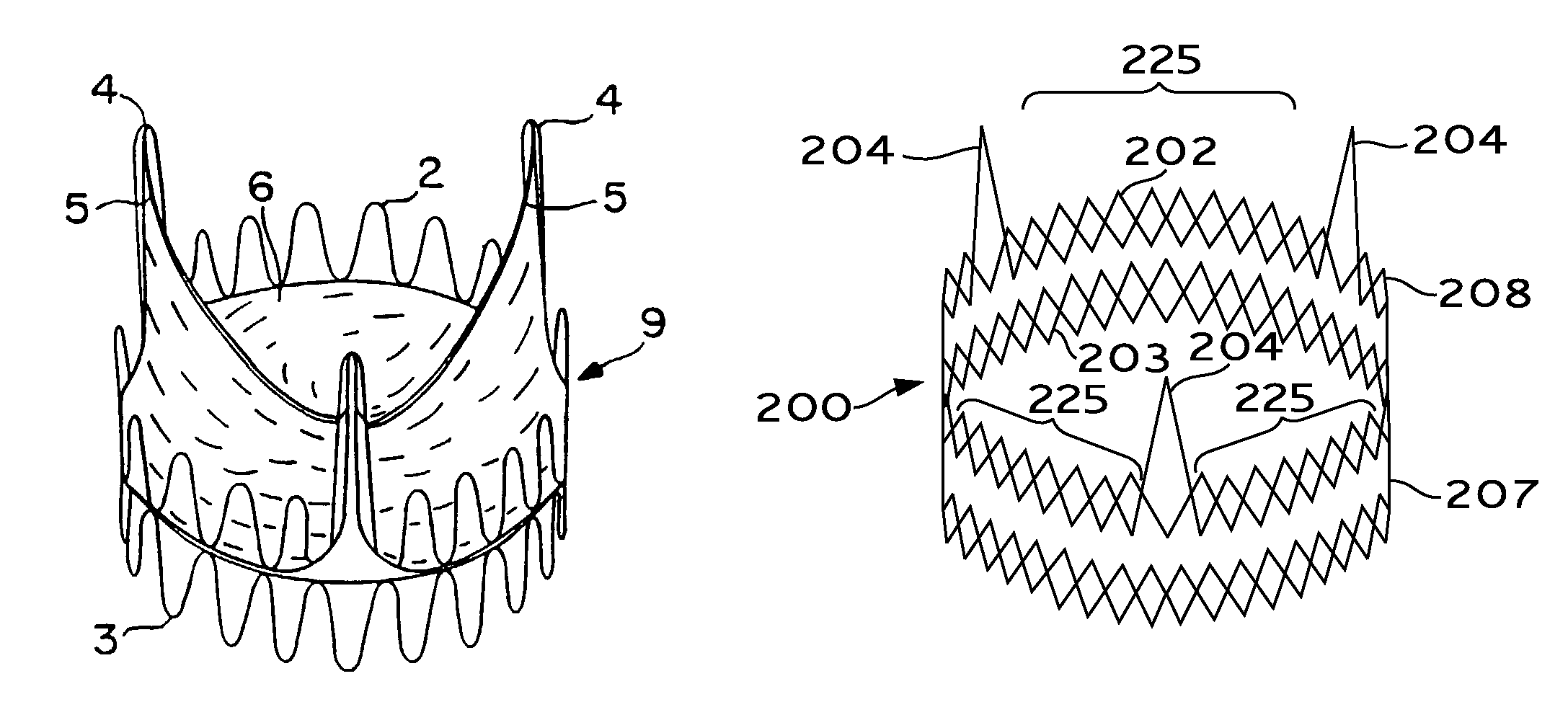
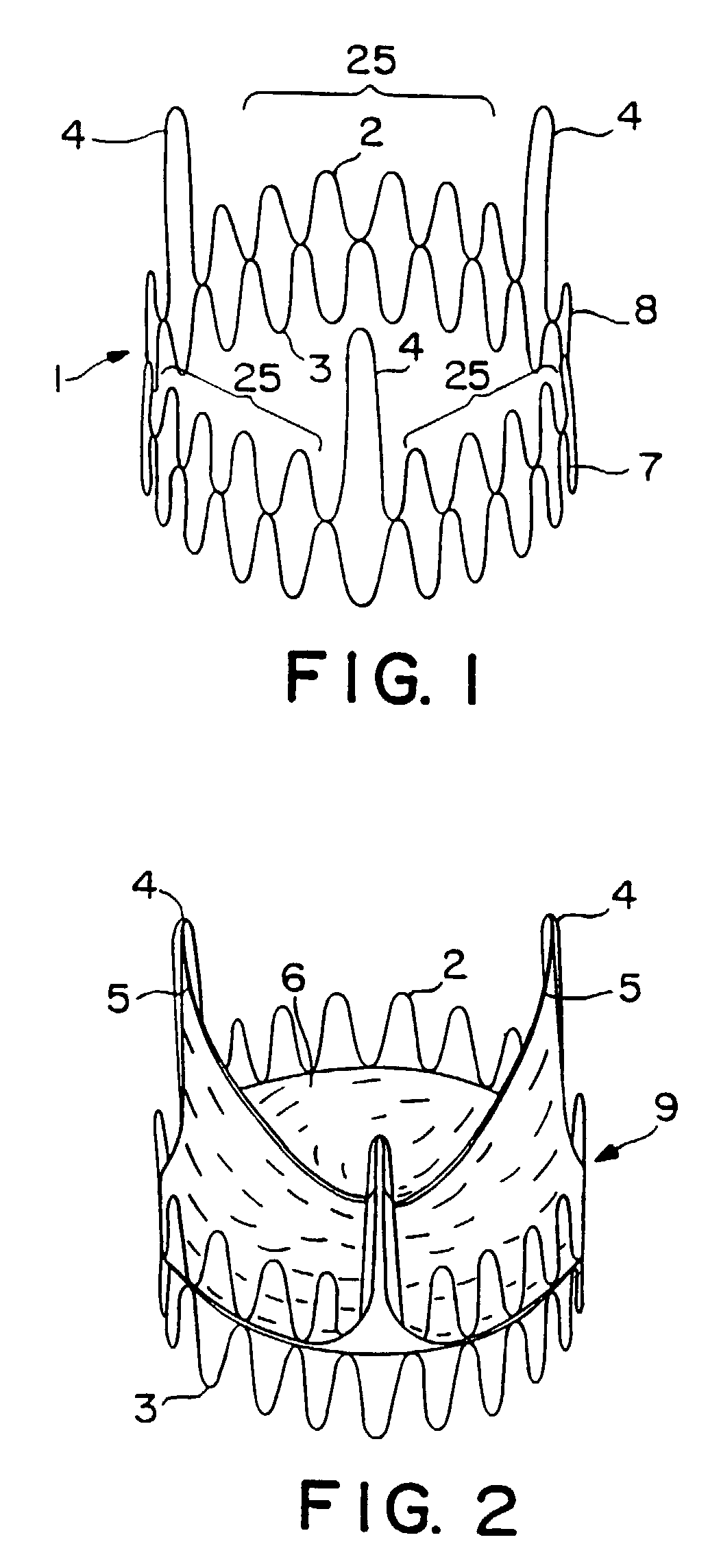
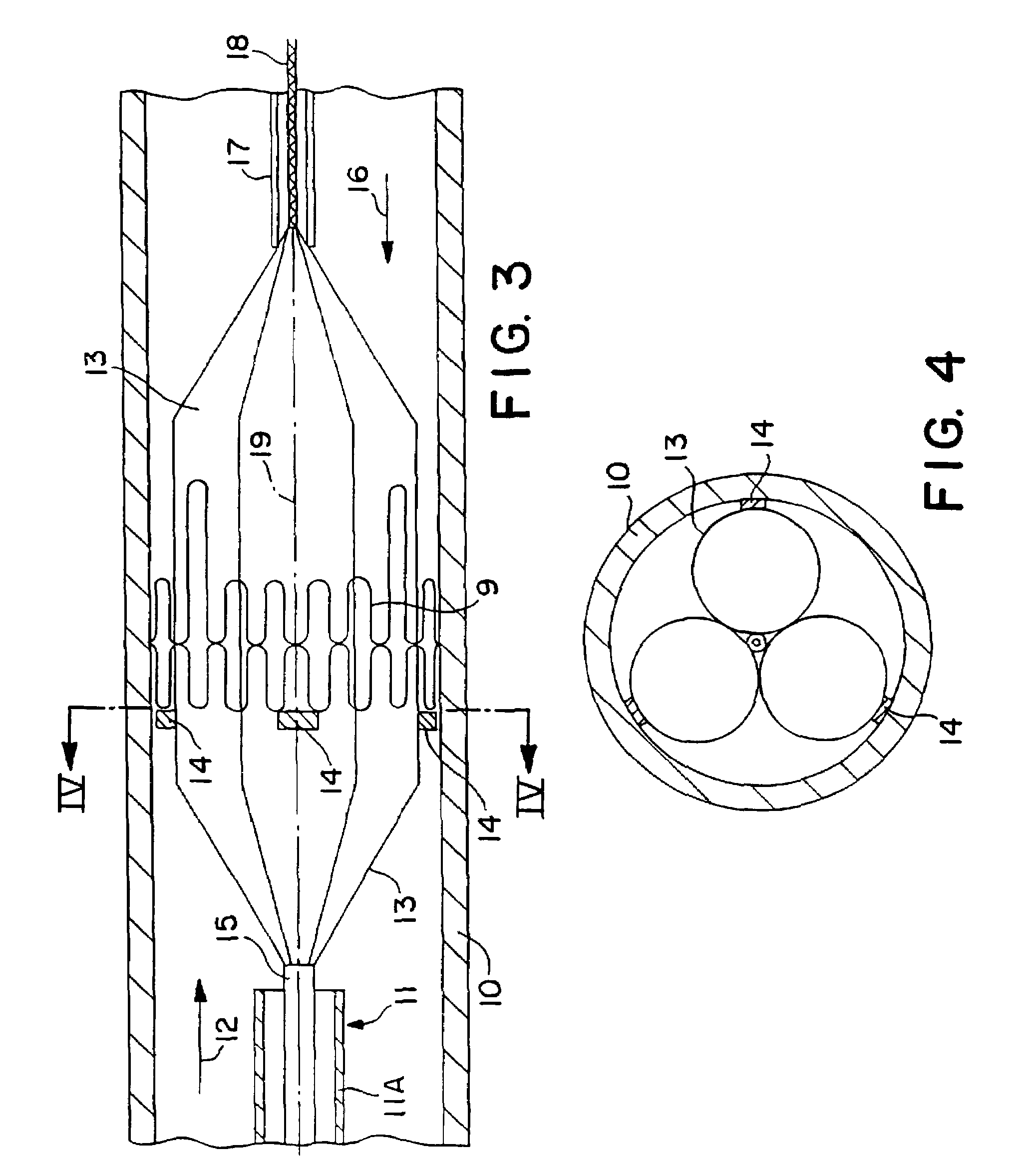
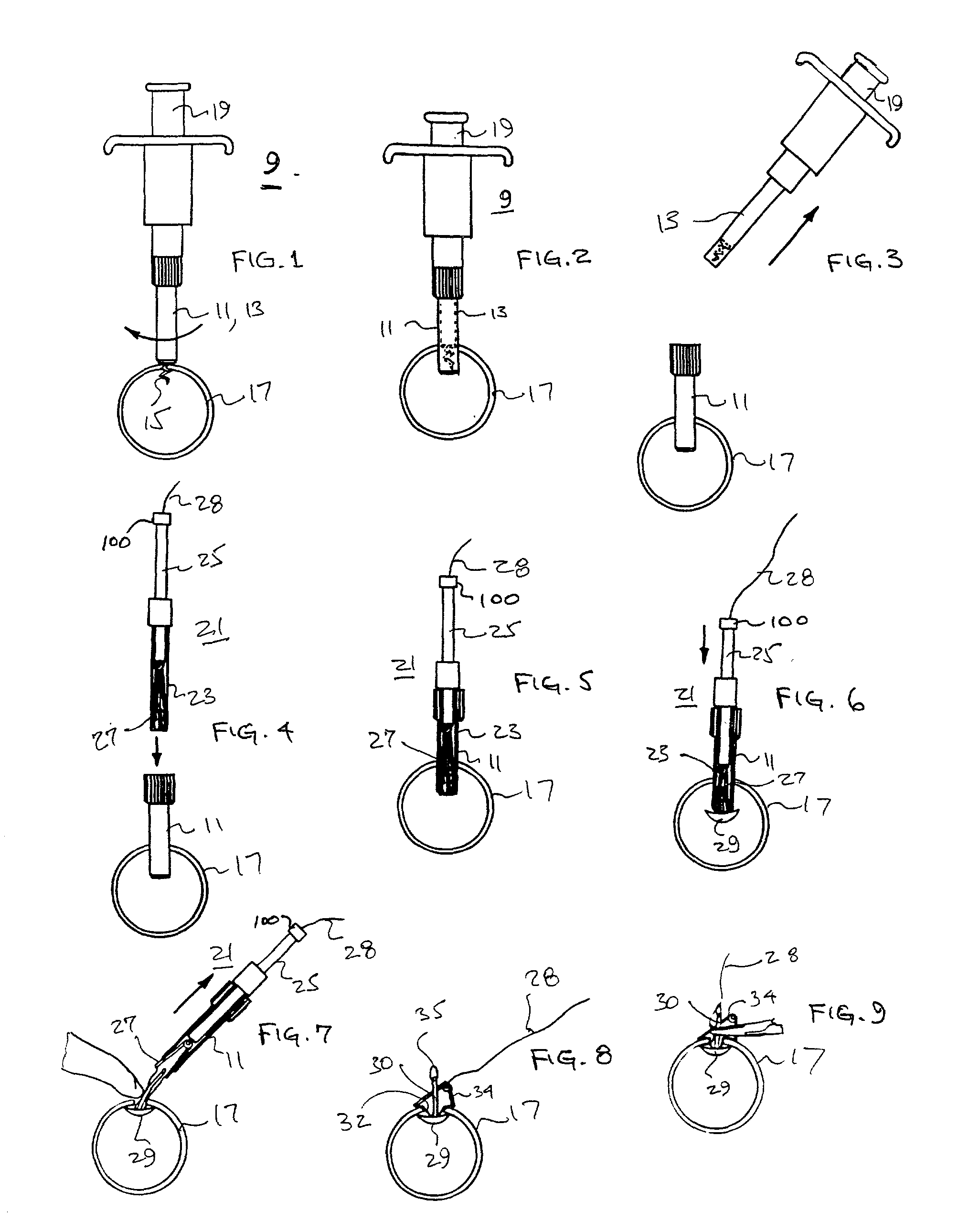
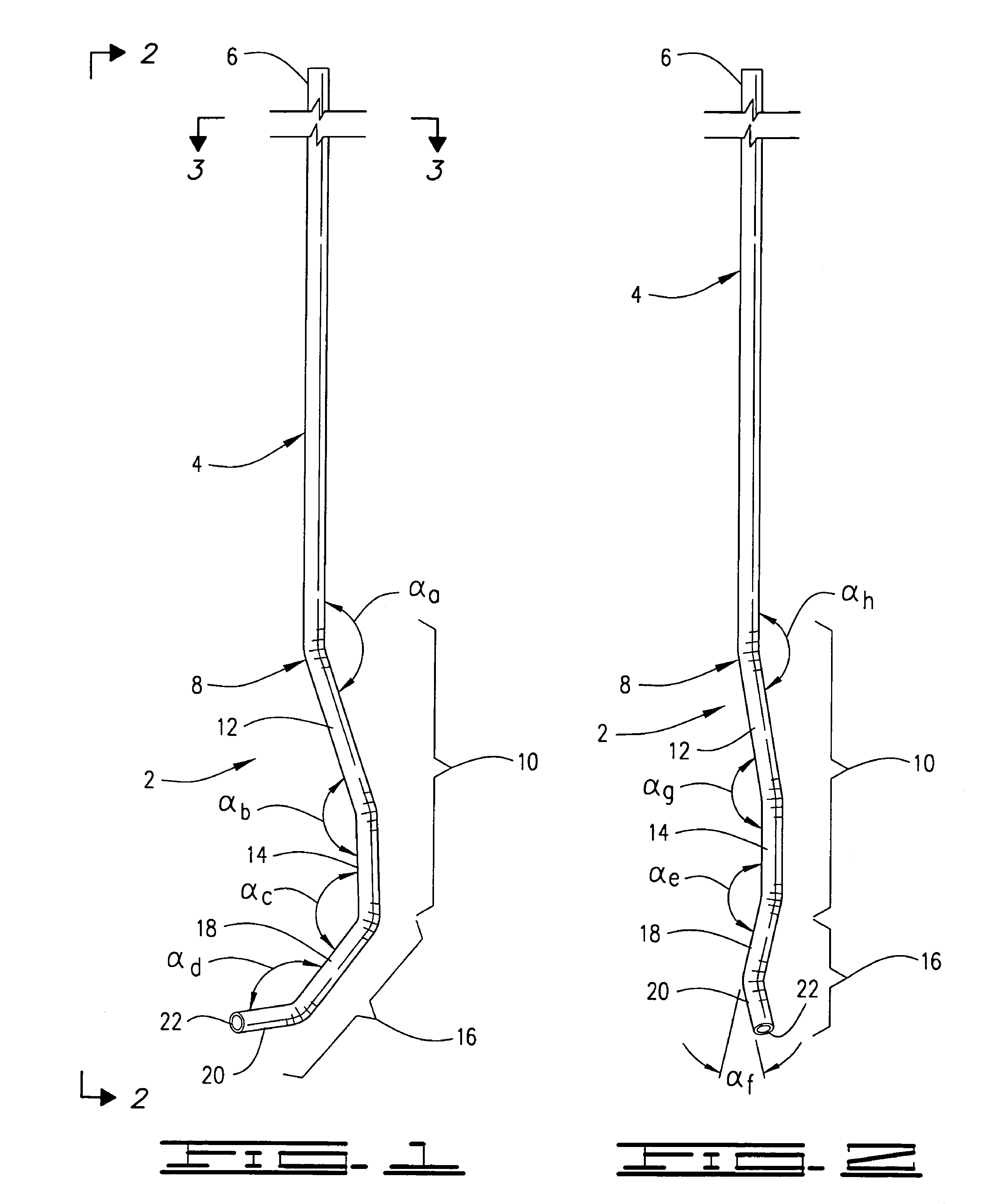
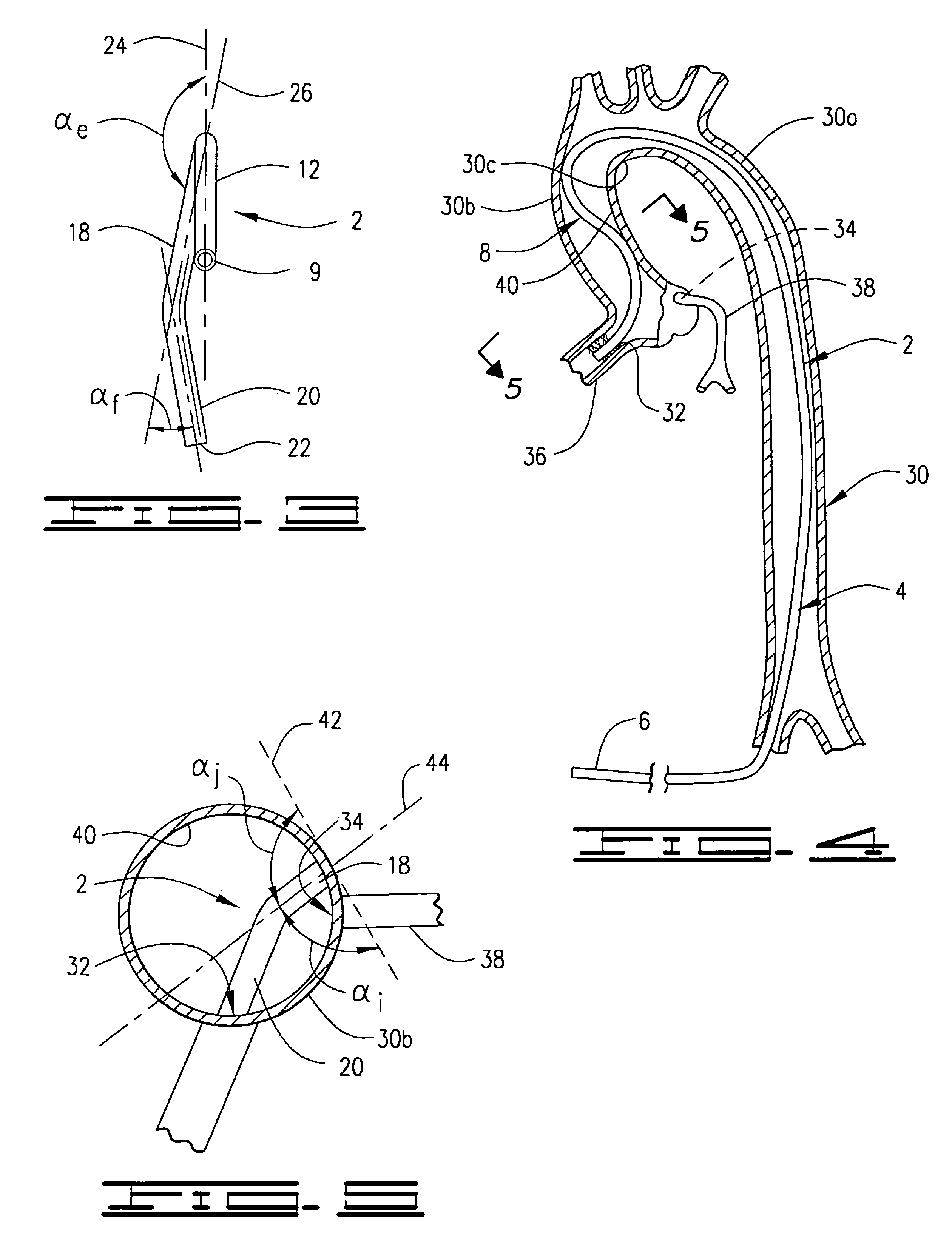
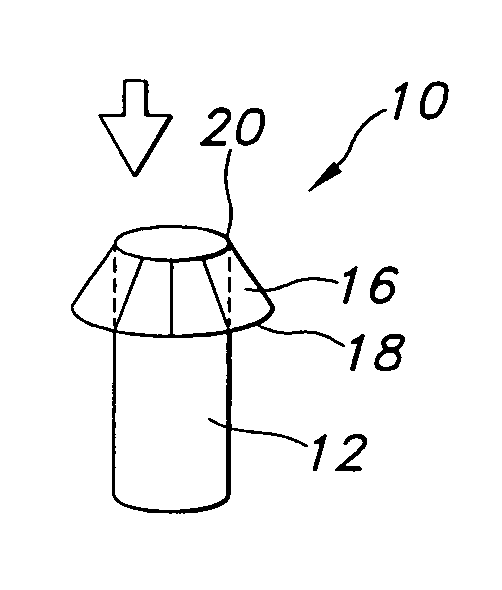
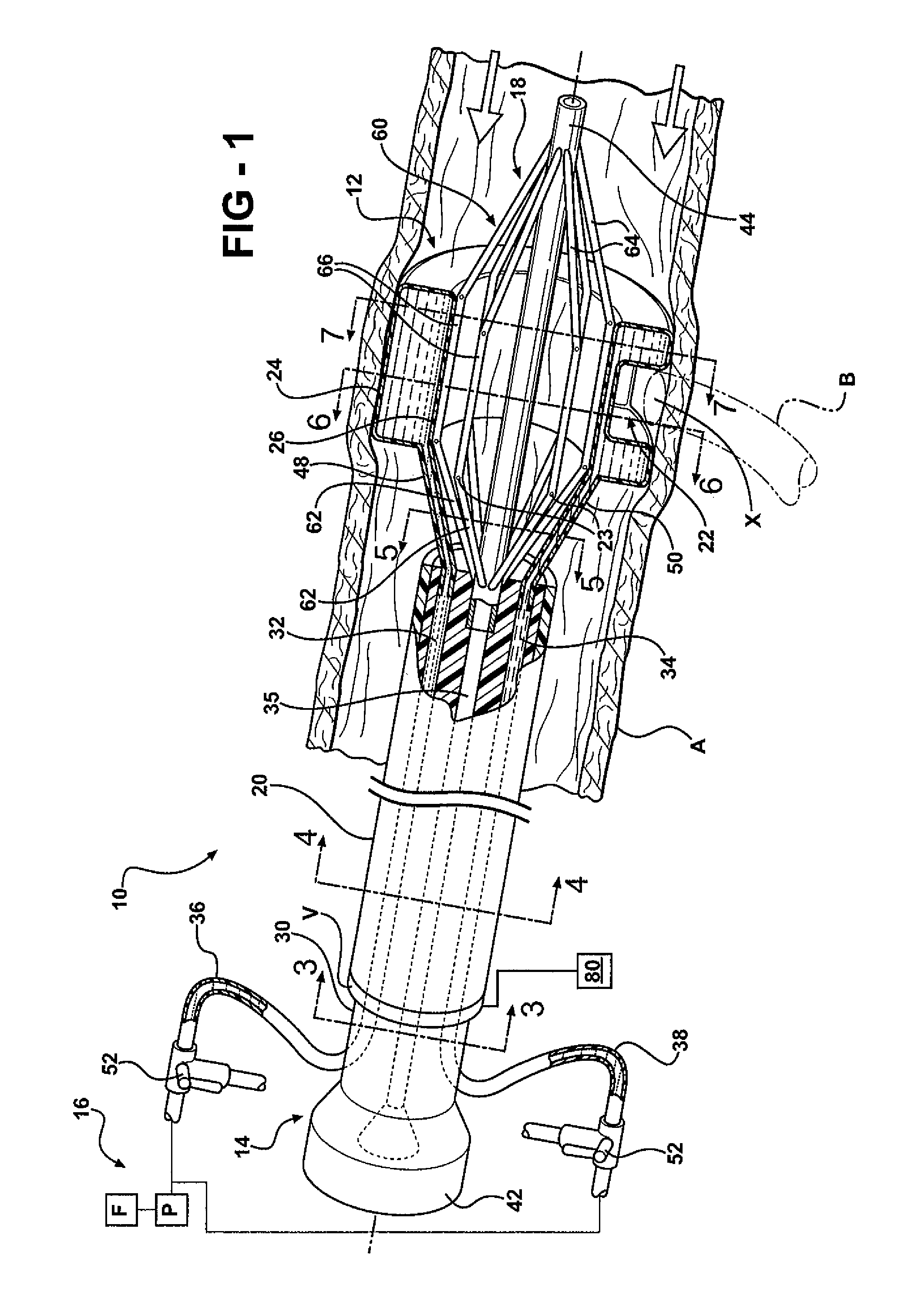
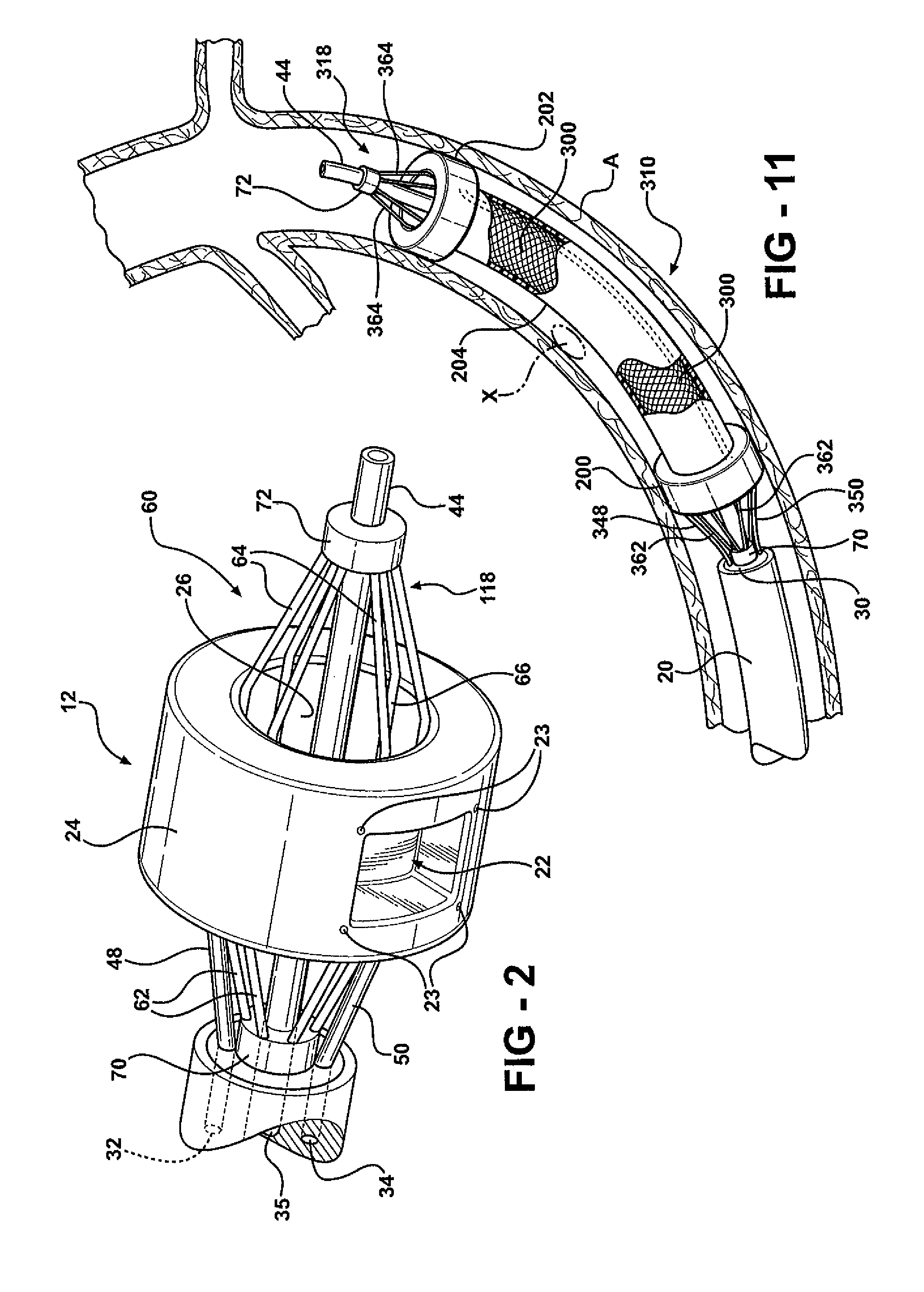
A valve prosthesis for implantation in the body by use of a catheter includes a stent made from an expandable cylinder-shaped thread structure including several spaced apices. The elastically collapsible valve is mounted on the stent as the commissural points of the valve are secured to the projecting apices. The valve prosthesis can be compressed around balloons of the balloon catheter and inserted in a channel, for instance, in the aorta. When the valve prosthesis is placed correctly, the balloons are inflated to expand the stent and wedge it against the wall of the aorta. The balloons are provided with beads to ensure a steady fastening of the valve prosthesis on the balloons during insertion and expansion. The valve prosthesis and the balloon catheter make it possible to insert a cardiac valve prosthesis without a surgical operation involving opening the thoracic cavity.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
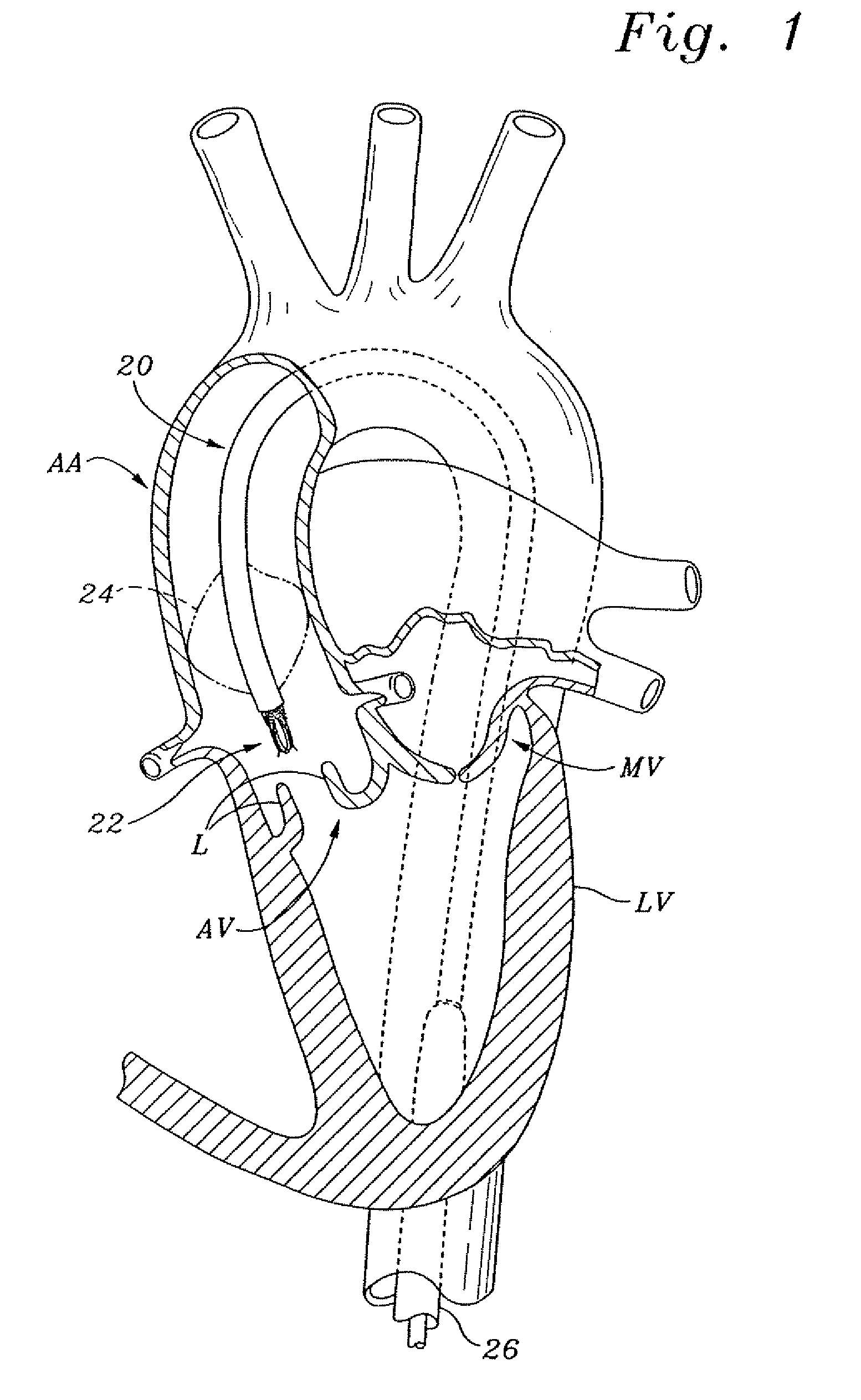
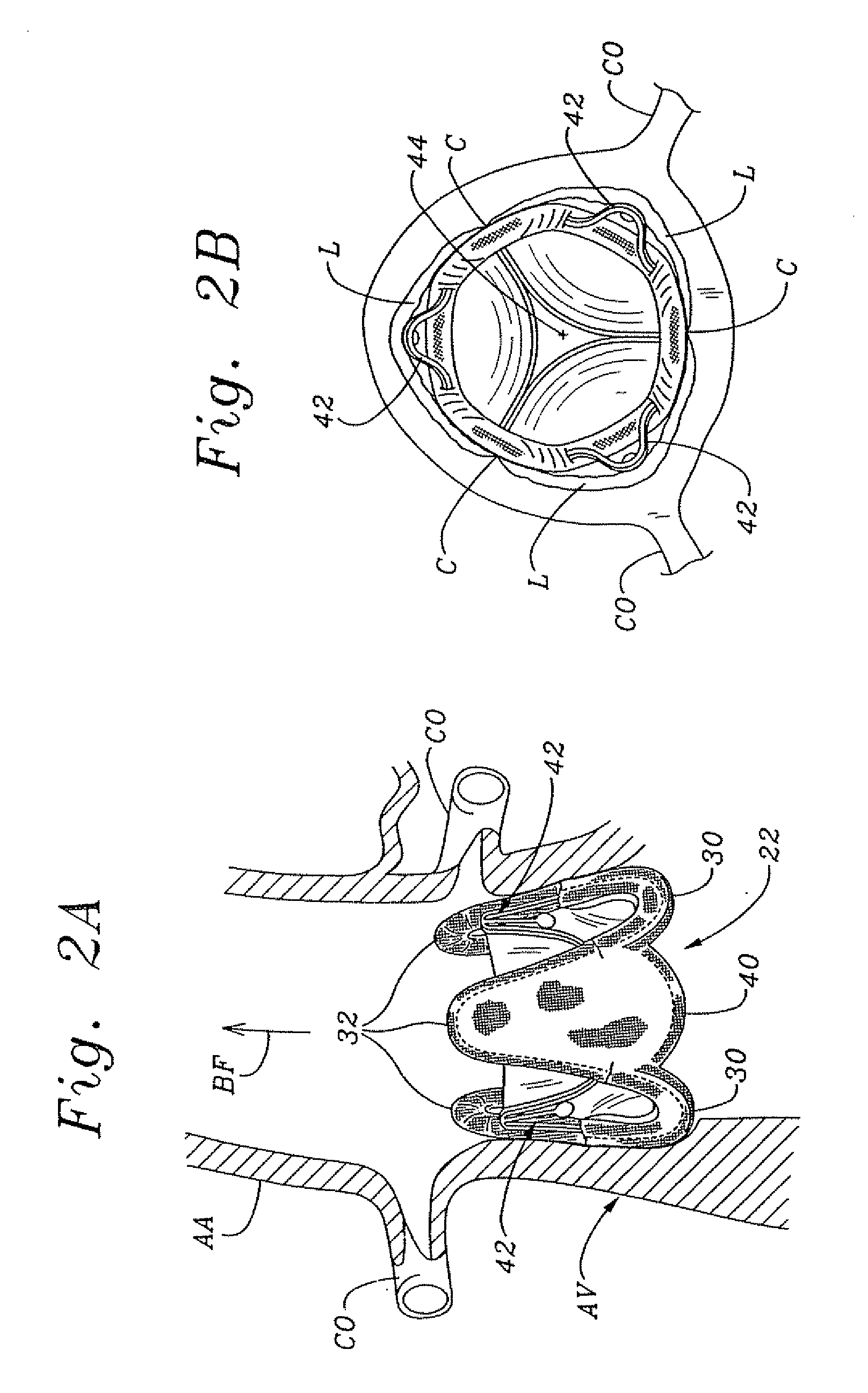
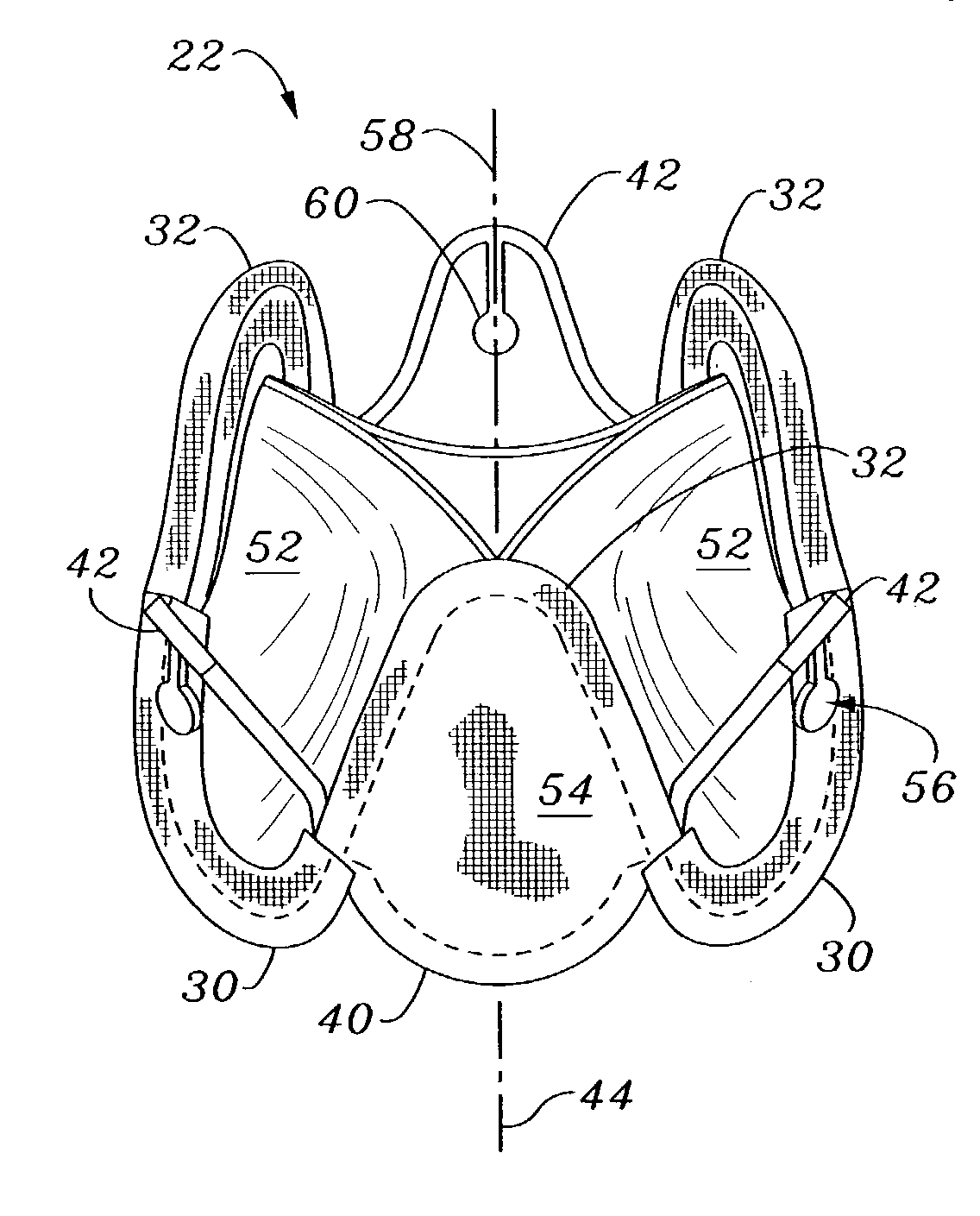
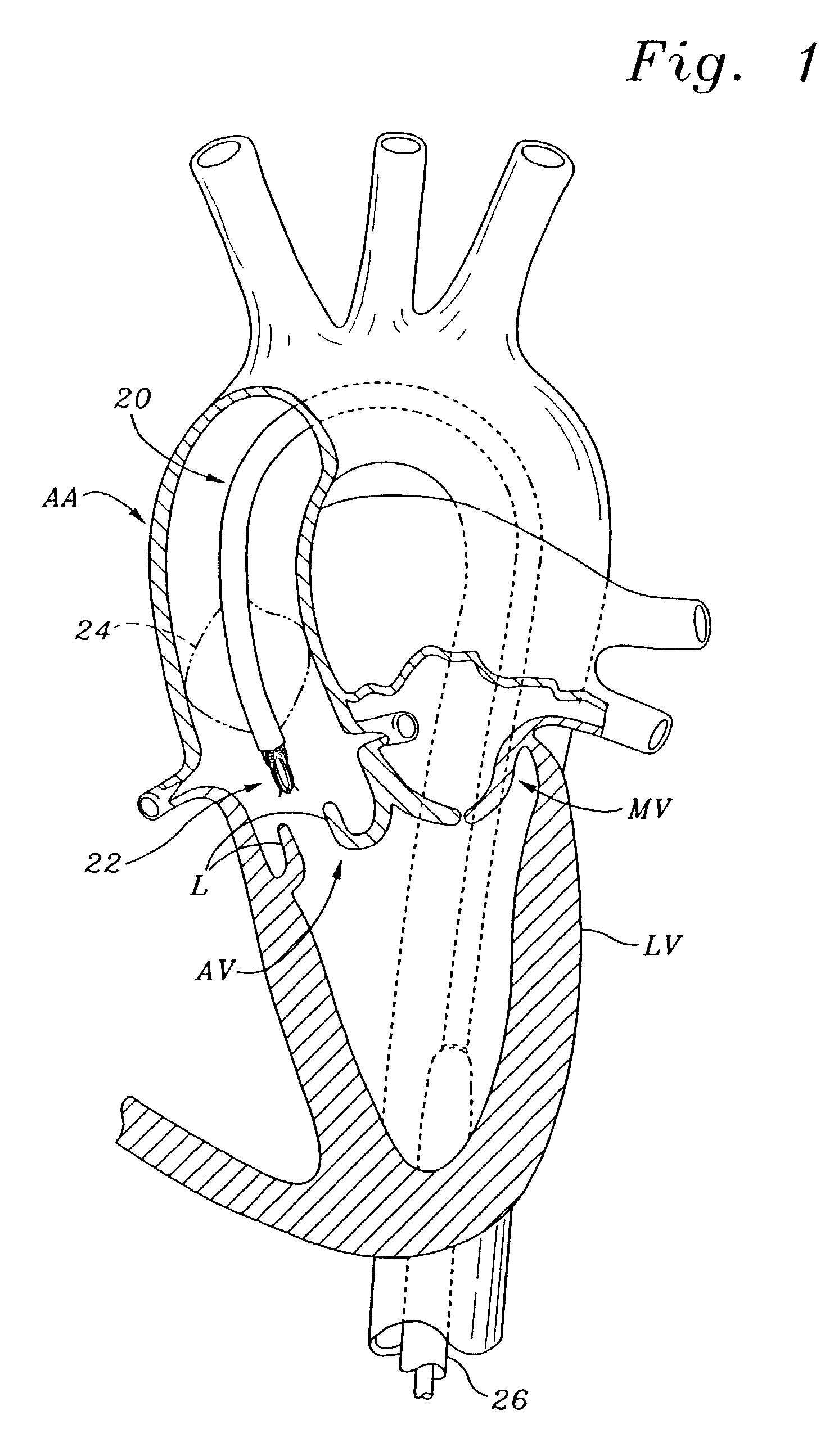
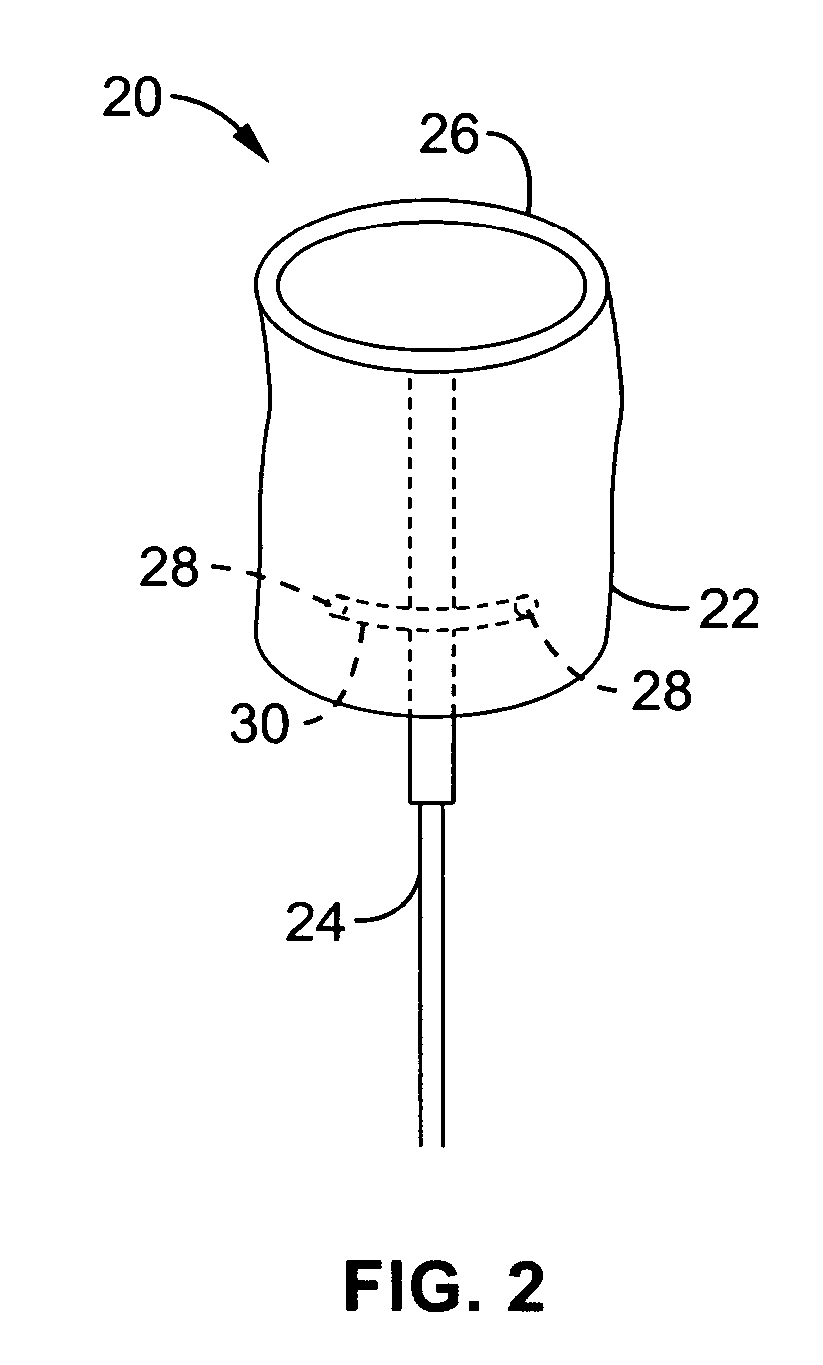
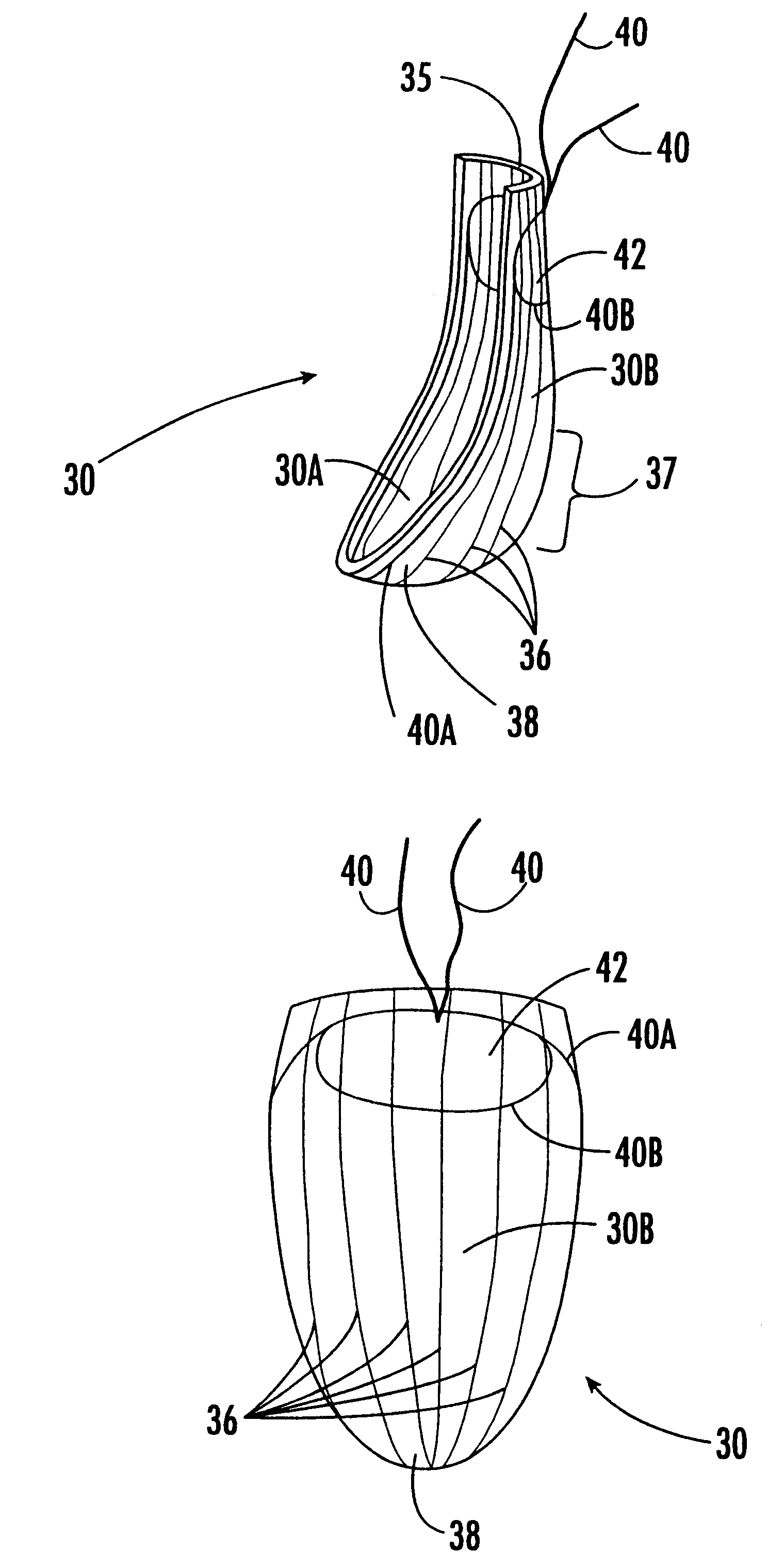
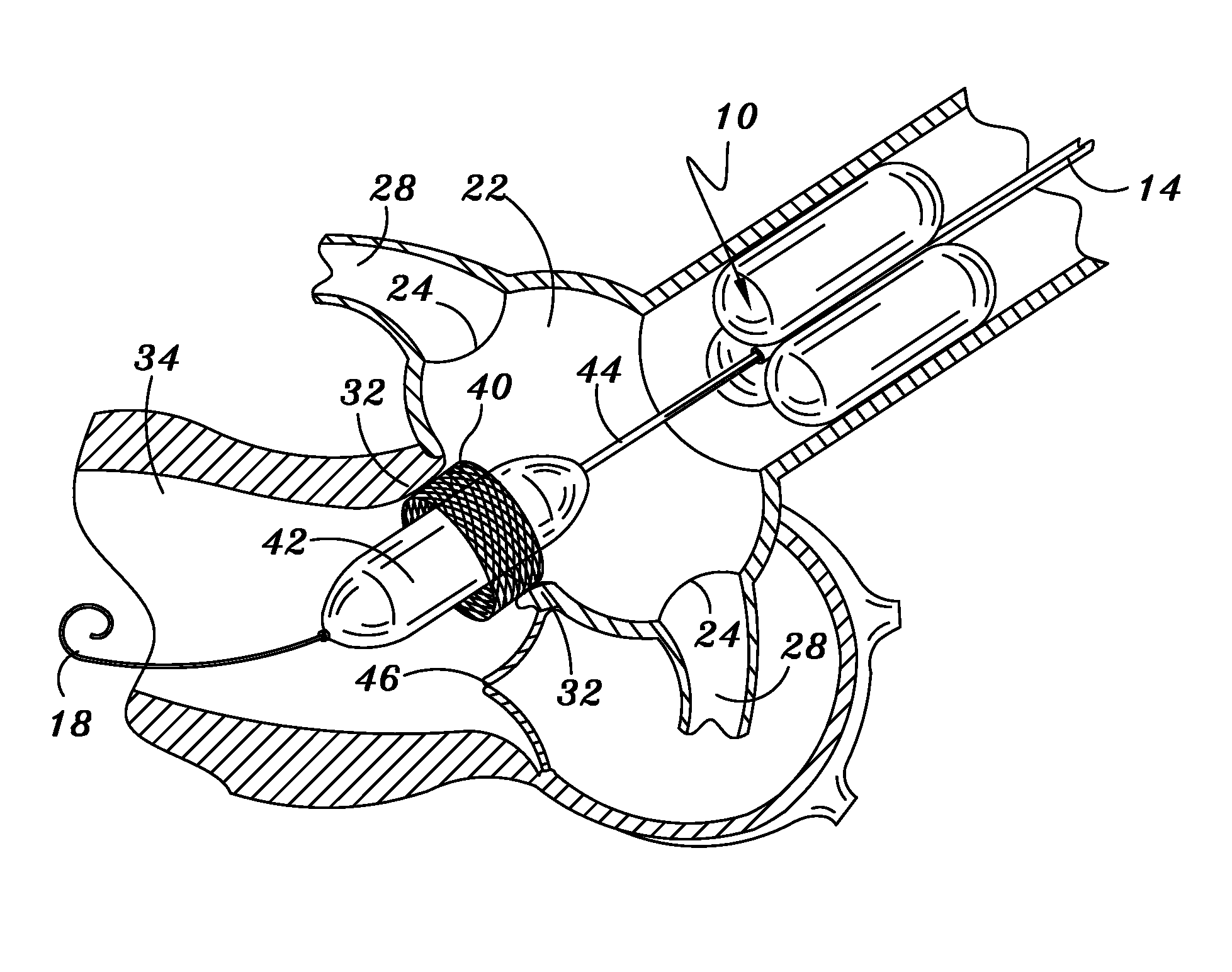
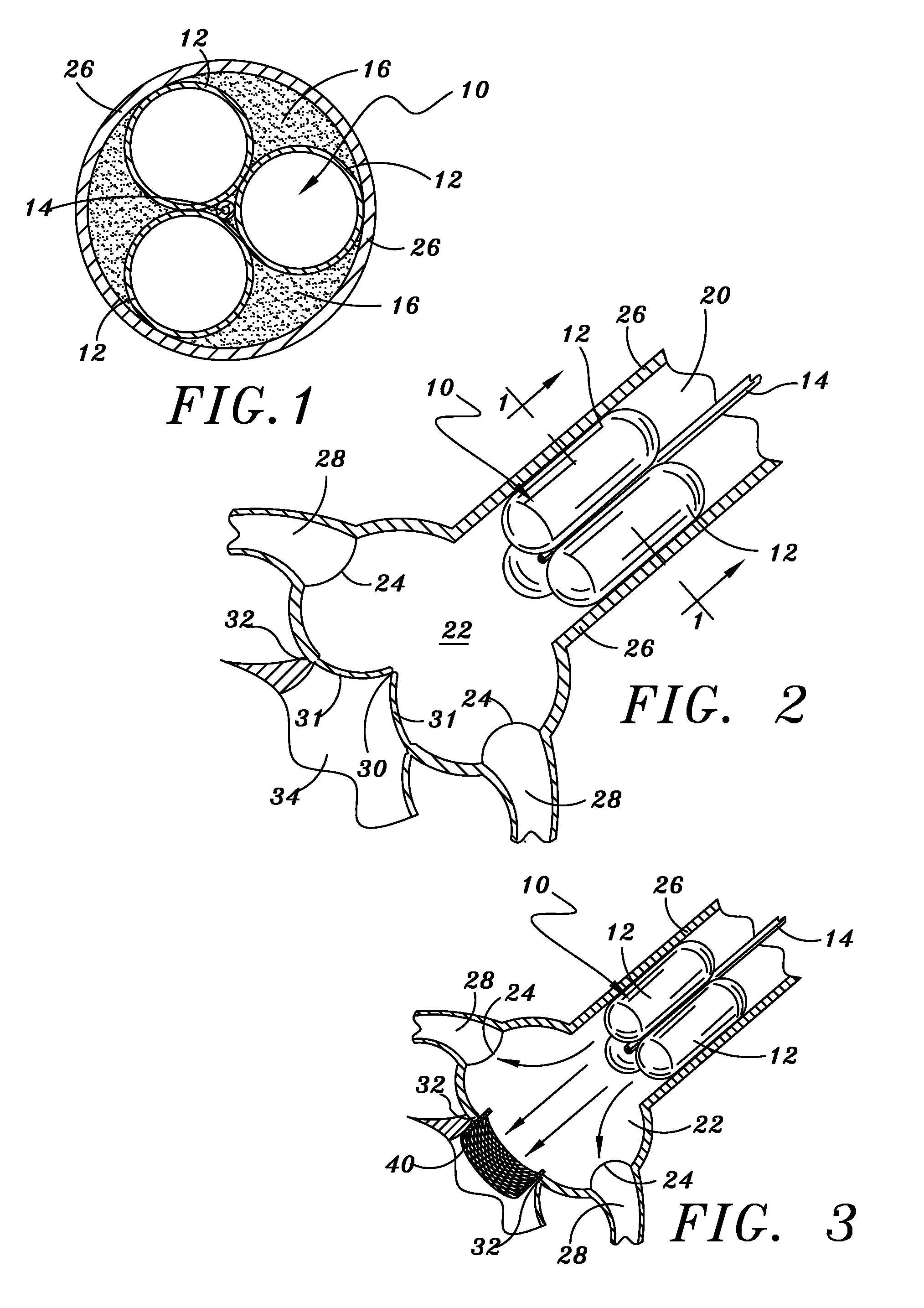
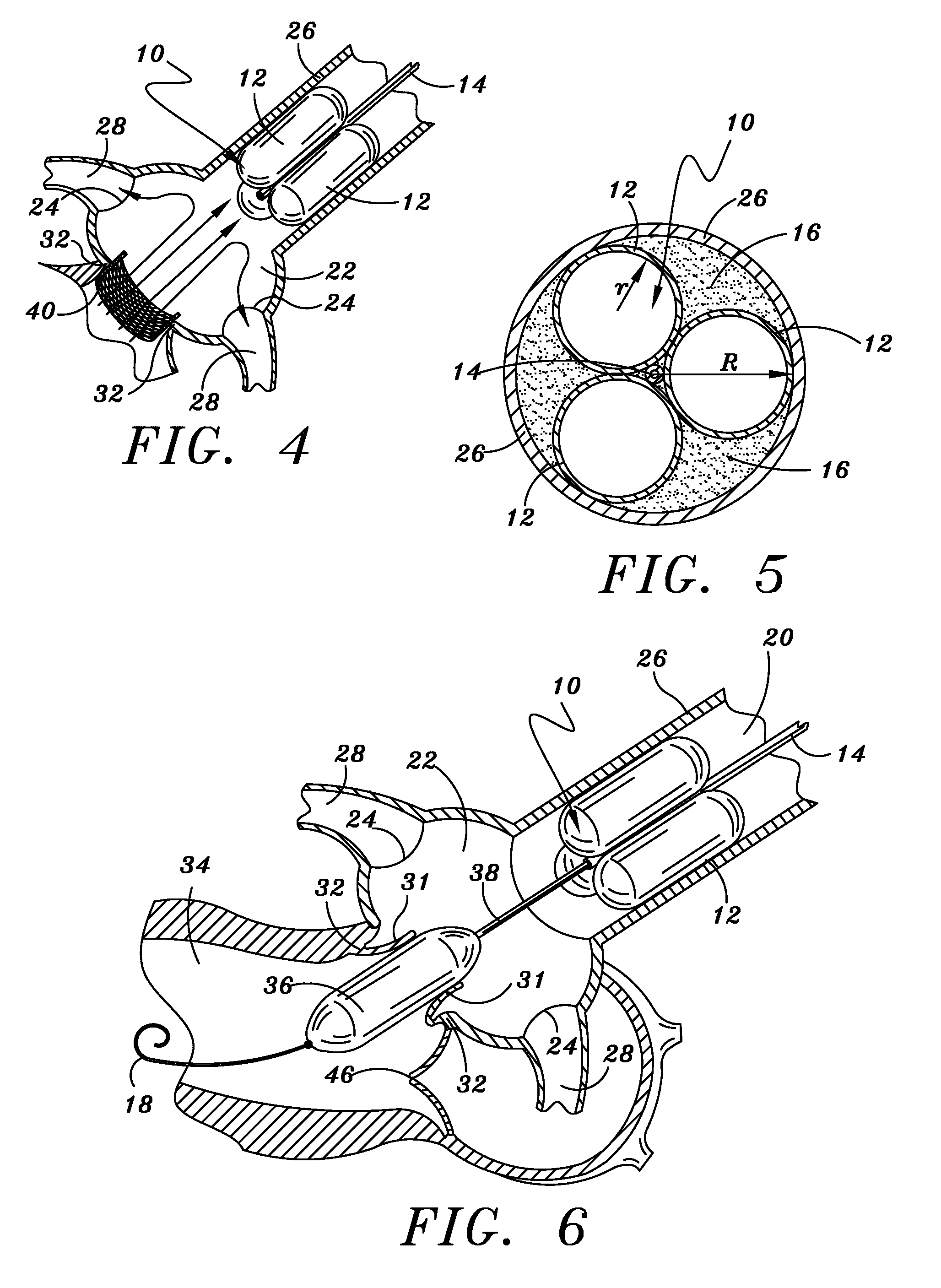
Minimally-invasive heart valve with cusp positioners
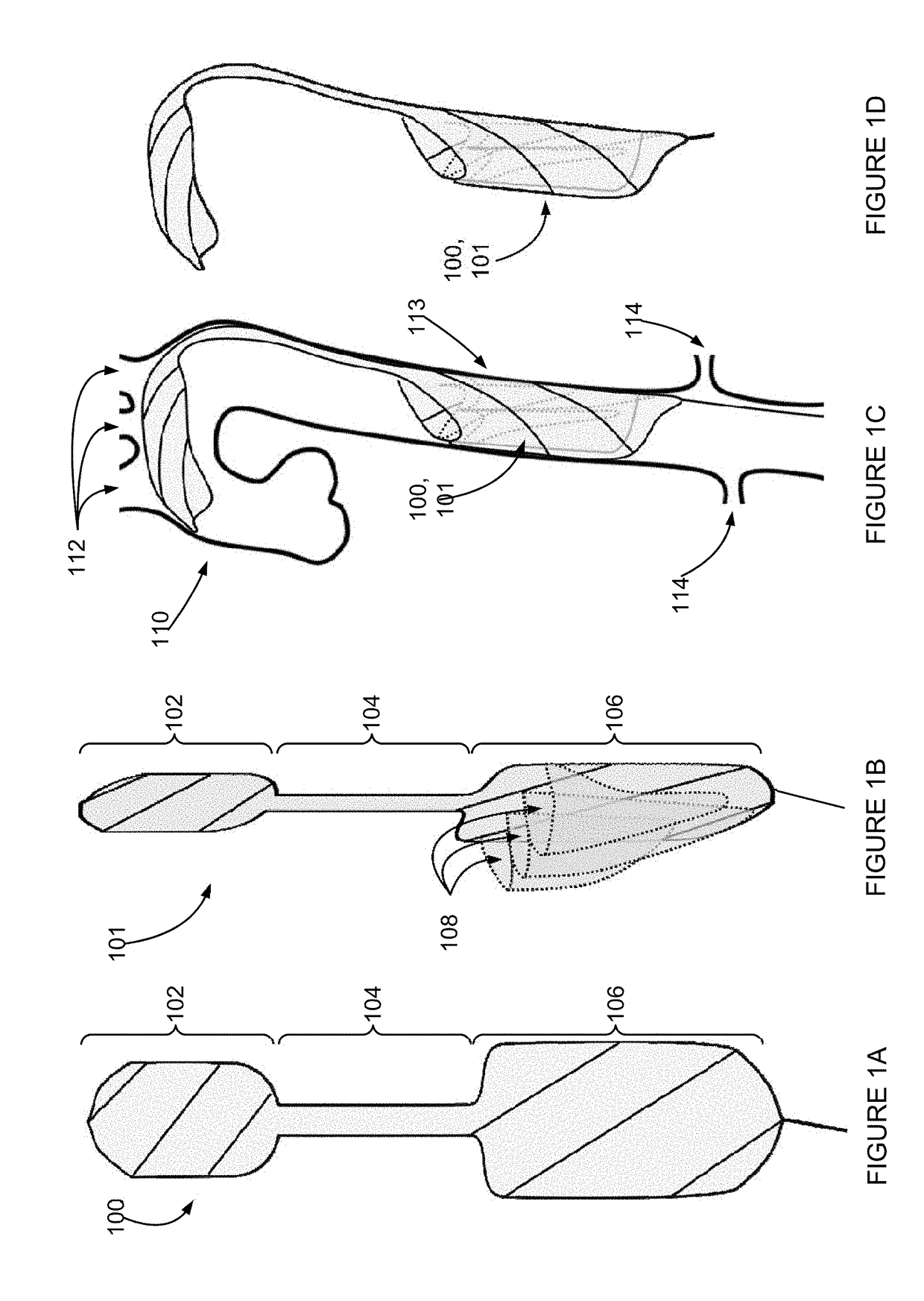
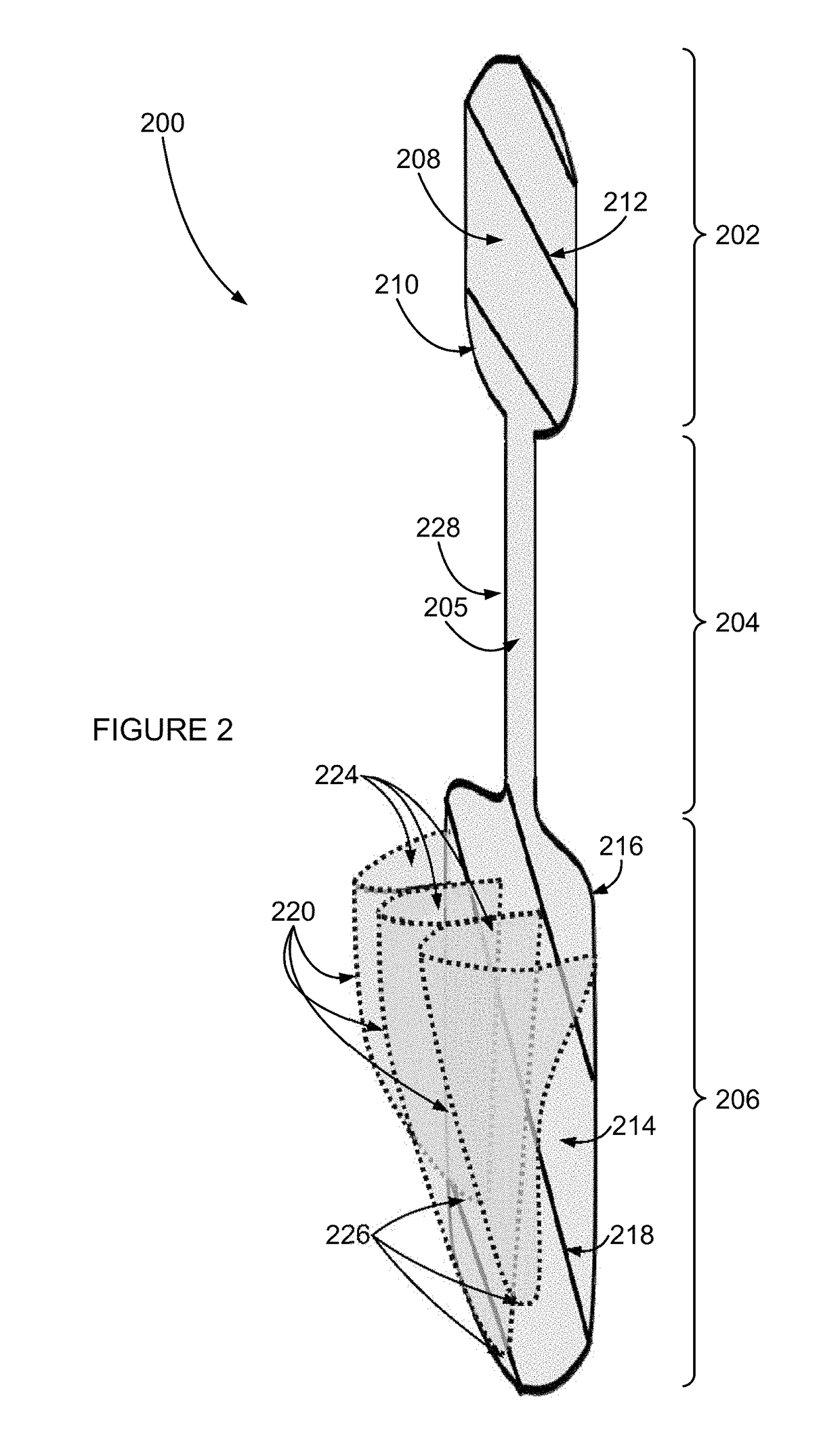
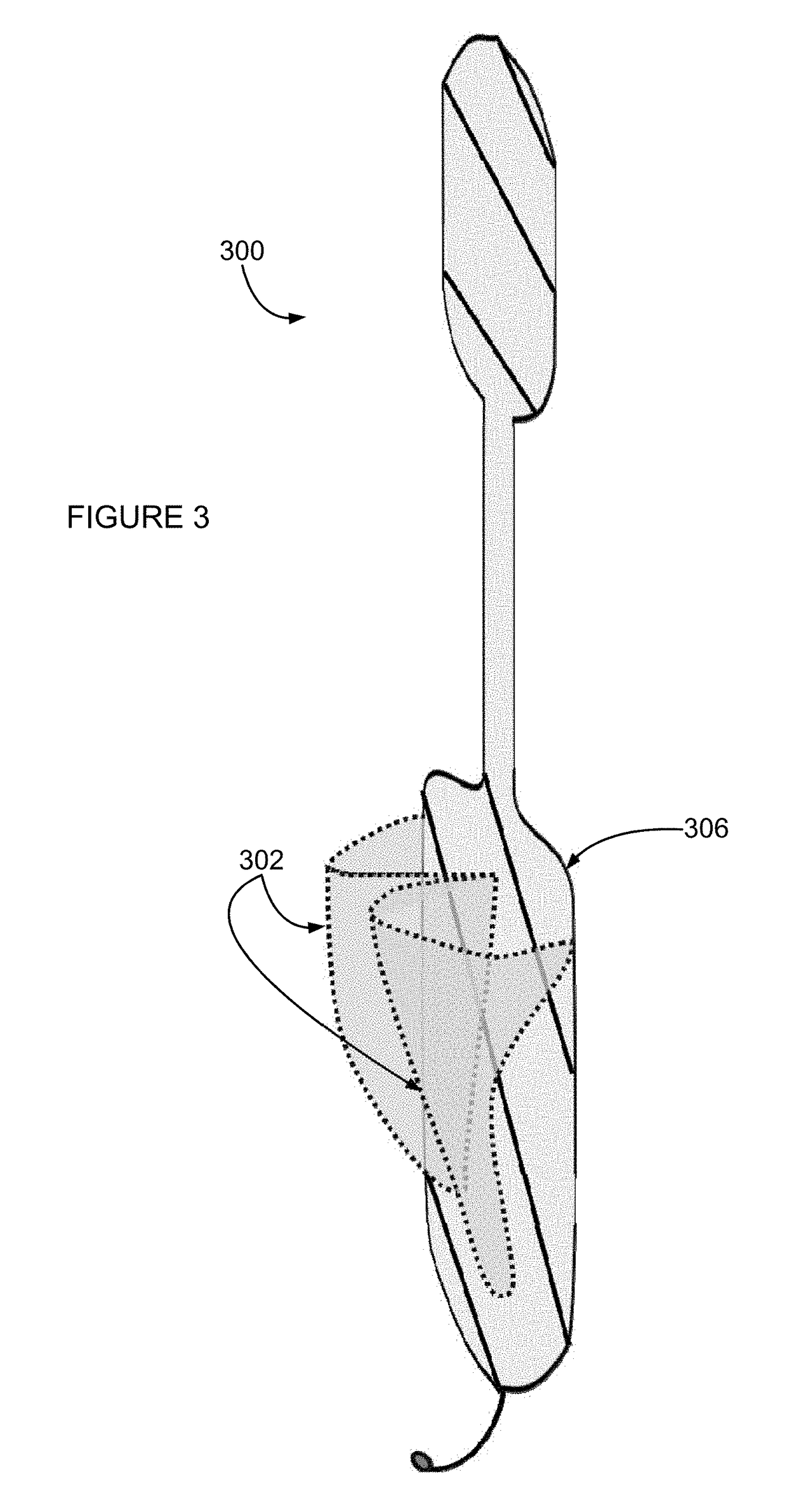
A prosthetic heart valve having an internal support frame with a continuous, undulating leaflet frame defined therein. The leaflet frame has three cusp regions positioned at an inflow end intermediate three commissure regions positioned at an outflow end thereof. The leaflet frame may be cloth covered and flexible leaflets attached thereto form occluding surfaces of the valve. The support frame further includes three cusp positioners rigidly fixed with respect to the leaflet frame and located at the outflow end of the support frame intermediate each pair of adjacent commissure regions. The valve is desirably compressible so as to be delivered in a minimally invasive manner through a catheter to the site of implantation. Upon expulsion from catheter, the valve expands into contact with the surrounding native valve annulus and is anchored in place without the use of sutures. In the aortic valve position, the cusp positioners angle outward into contact with the sinus cavities, and compress the native leaflets if they are not excised, or the aortic wall if they are. The support frame may be formed from a flat sheet of Nitinol that is bent into a three-dimensional configuration and heat set. A holder having spring-like arms connected to inflow projections of the valve may be used to deliver, reposition and re-collapse the valve, if necessary.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Minimally-invasive heart valve with cusp positioners
A prosthetic heart valve having an internal support frame with a continuous, undulating leaflet frame defined therein. The leaflet frame has three cusp regions positioned at an inflow end intermediate three commissure regions positioned at an outflow end thereof. The leaflet frame may be cloth covered and flexible leaflets attached thereto form occluding surfaces of the valve. The support frame further includes three cusp positioners rigidly fixed with respect to the leaflet frame and located at the outflow end of the support frame intermediate each pair of adjacent commissure regions. The valve is desirably compressible so as to be delivered in a minimally invasive manner through a catheter to the site of implantation. Upon expulsion from catheter, the valve expands into contact with the surrounding native valve annulus and is anchored in place without the use of sutures. In the aortic valve position, the cusp positioners angle outward into contact with the sinus cavities, and compress the native leaflets if they are not excised, or the aortic wall if they are. The support frame may be formed from a flat sheet of Nitinol that is bent into a three-dimensional configuration and heat set. A holder having spring-like arms connected to inflow projections of the valve may be used to deliver, reposition and re-collapse the valve, if necessary.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
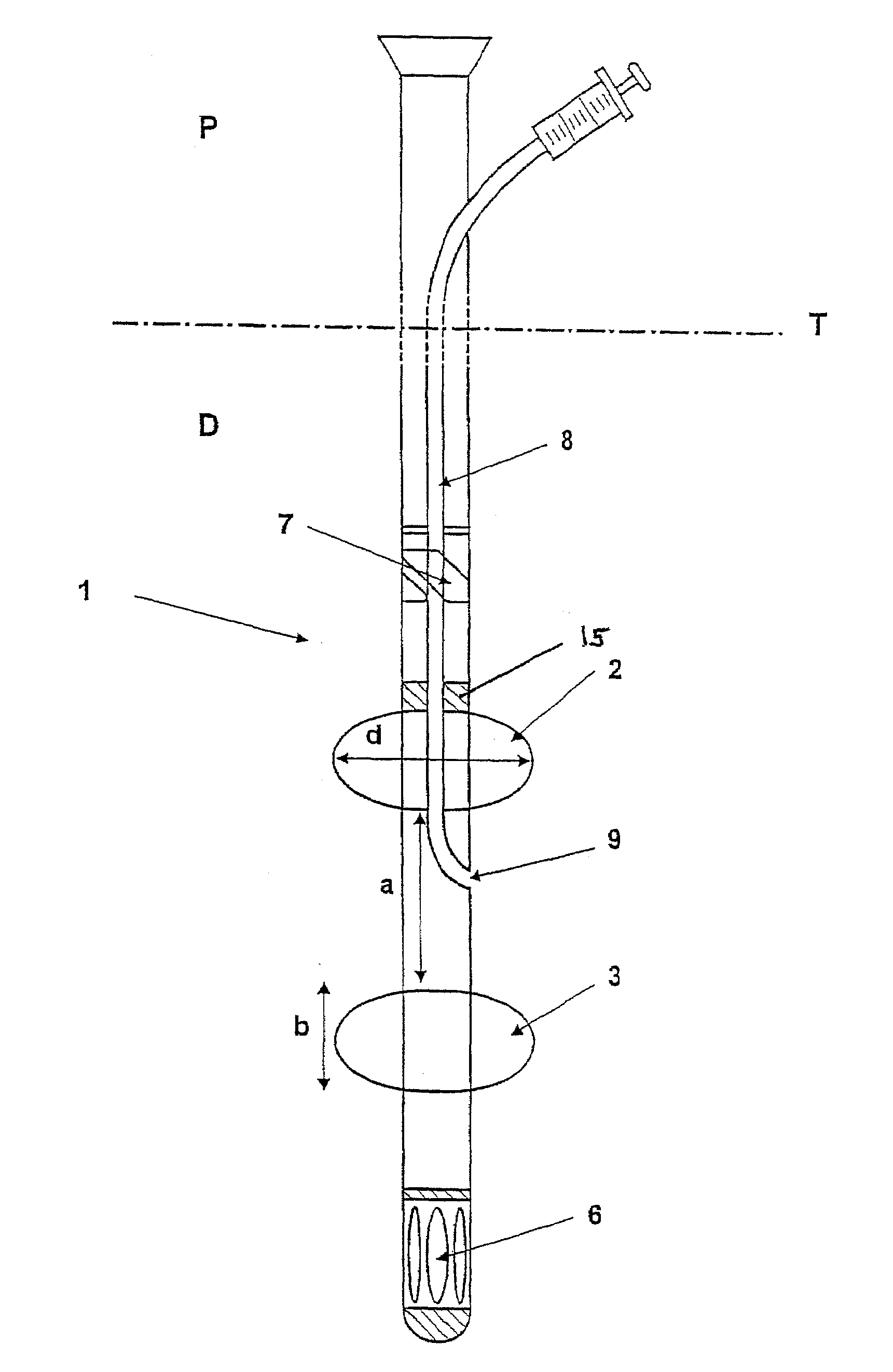
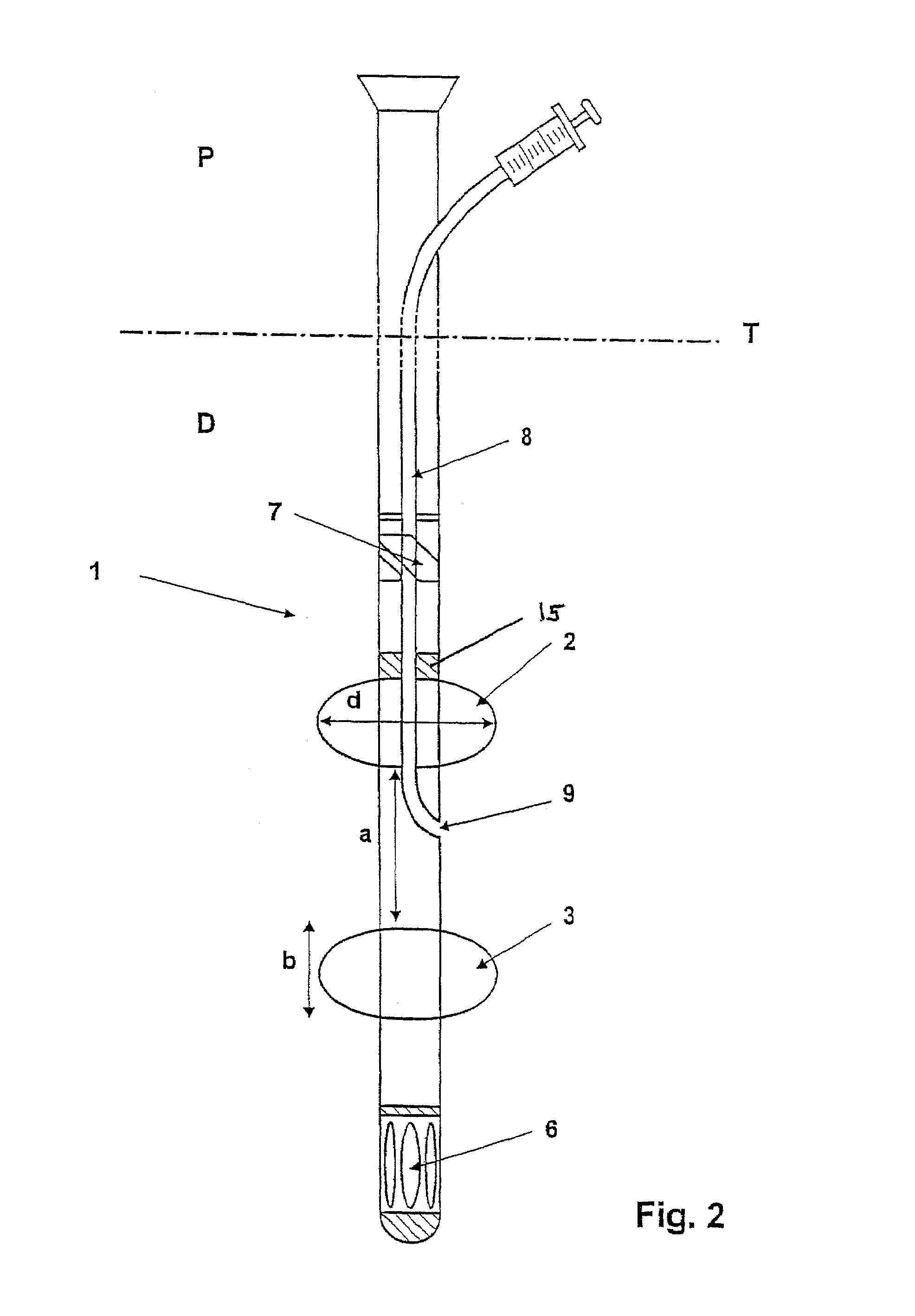
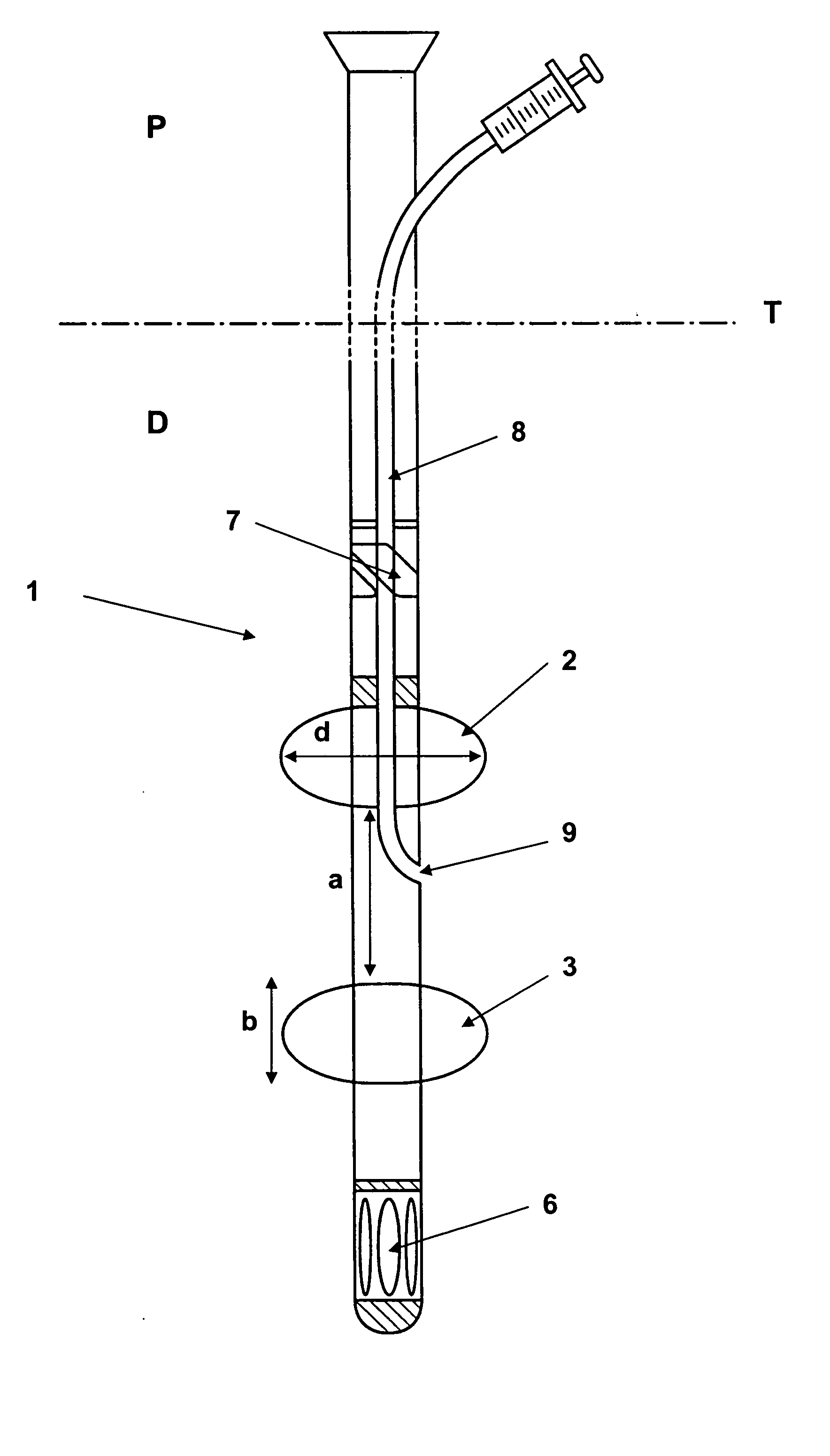
Device for minimally invasive intravascular aortic valve extraction
InactiveUS7338467B2Minimally invasiveThe equipment is easy to operateStentsMedical devicesPerfusionBlood vessel
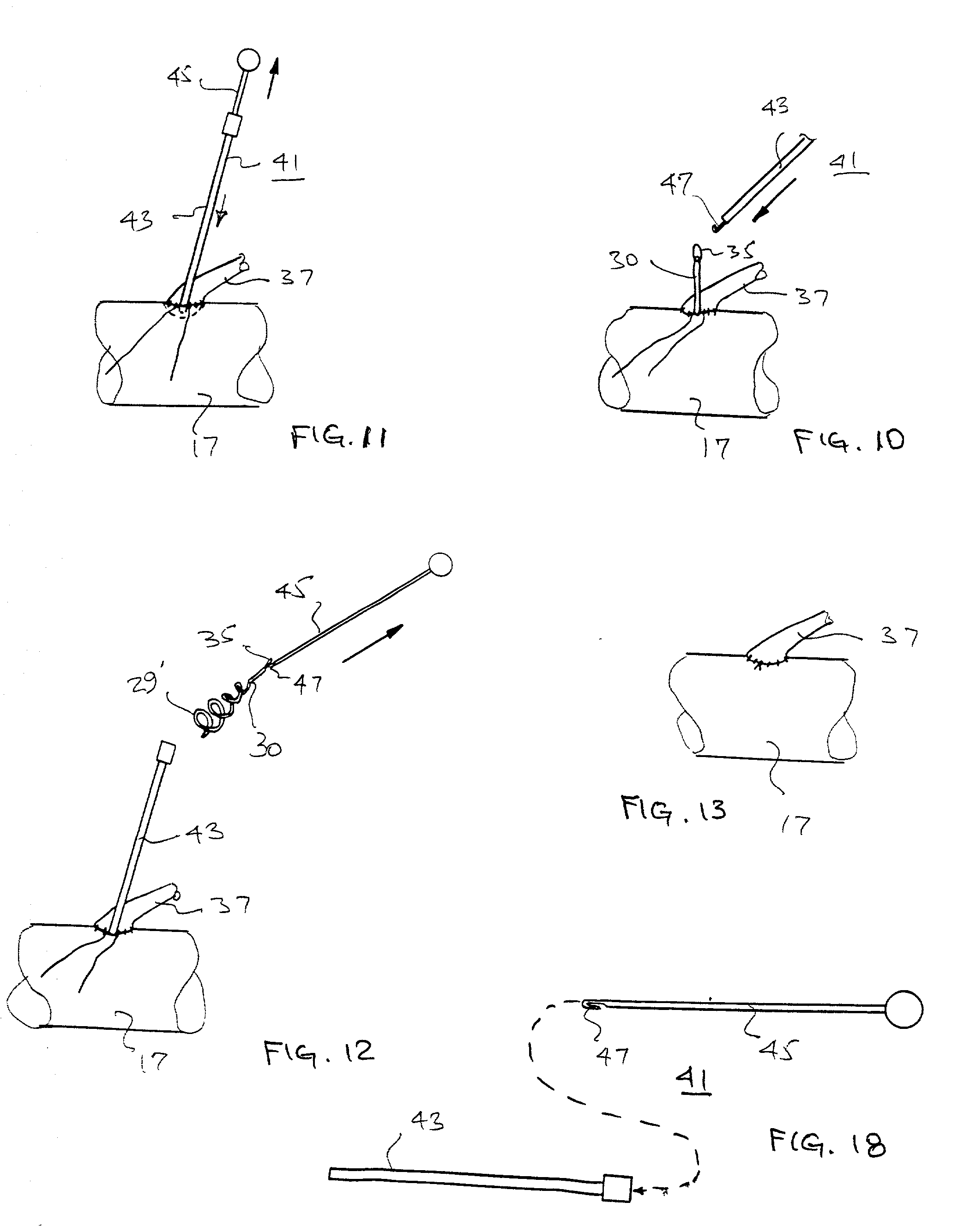
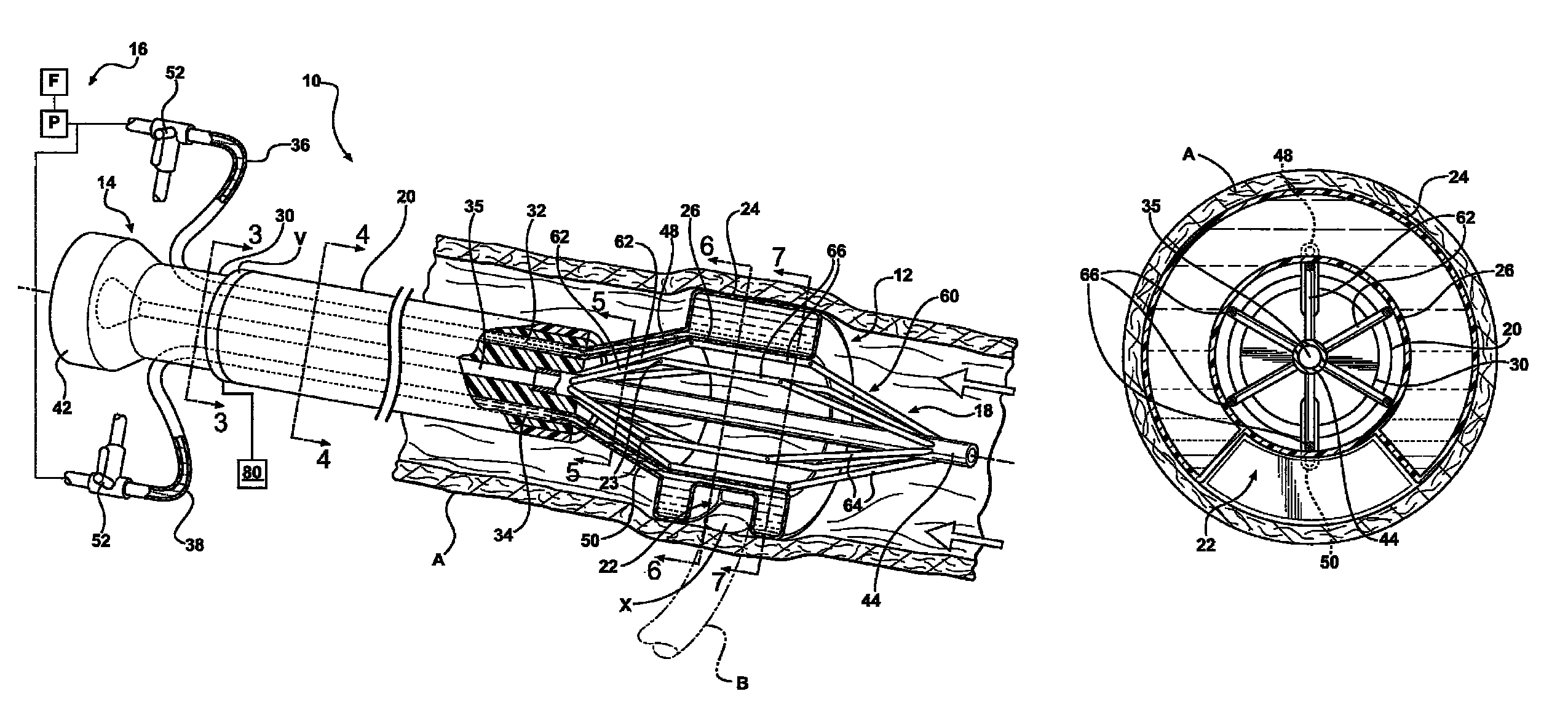
A perfusion catheter includes at least one perfusion channel and at least two dilation units disposed at a distance from each other at the distal catheter region in the longitudinal extension of the catheter. Both of the at least two dilation units are projected through by the perfusion catheter and form, in an inflated state, an at least practically fluid-tight occlusion with the aortic wall. At least the dilation unit disposed on the proximal side has at least one passage through which an auxiliary catheter can be introduced in a fluid-tight manner. The perfusion catheter may have a working channel with an outlet opening in the region between the two dilation units and through which at least one auxiliary catheter can be introduced for aortic valve ablation.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Method and apparatus for selective drug infusion via an intra-aortic flow diverter delivery catheter
A local renal delivery system includes a flow isolation assembly and a local injection assembly. The flow isolation assembly in one mode is adapted to isolate only a partial flow region along the outer circumference along the aorta wall such that fluids inject there are maintained to flow substantially into the renal arteries. Various types of flow isolation assemblies and local injection assemblies are described.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
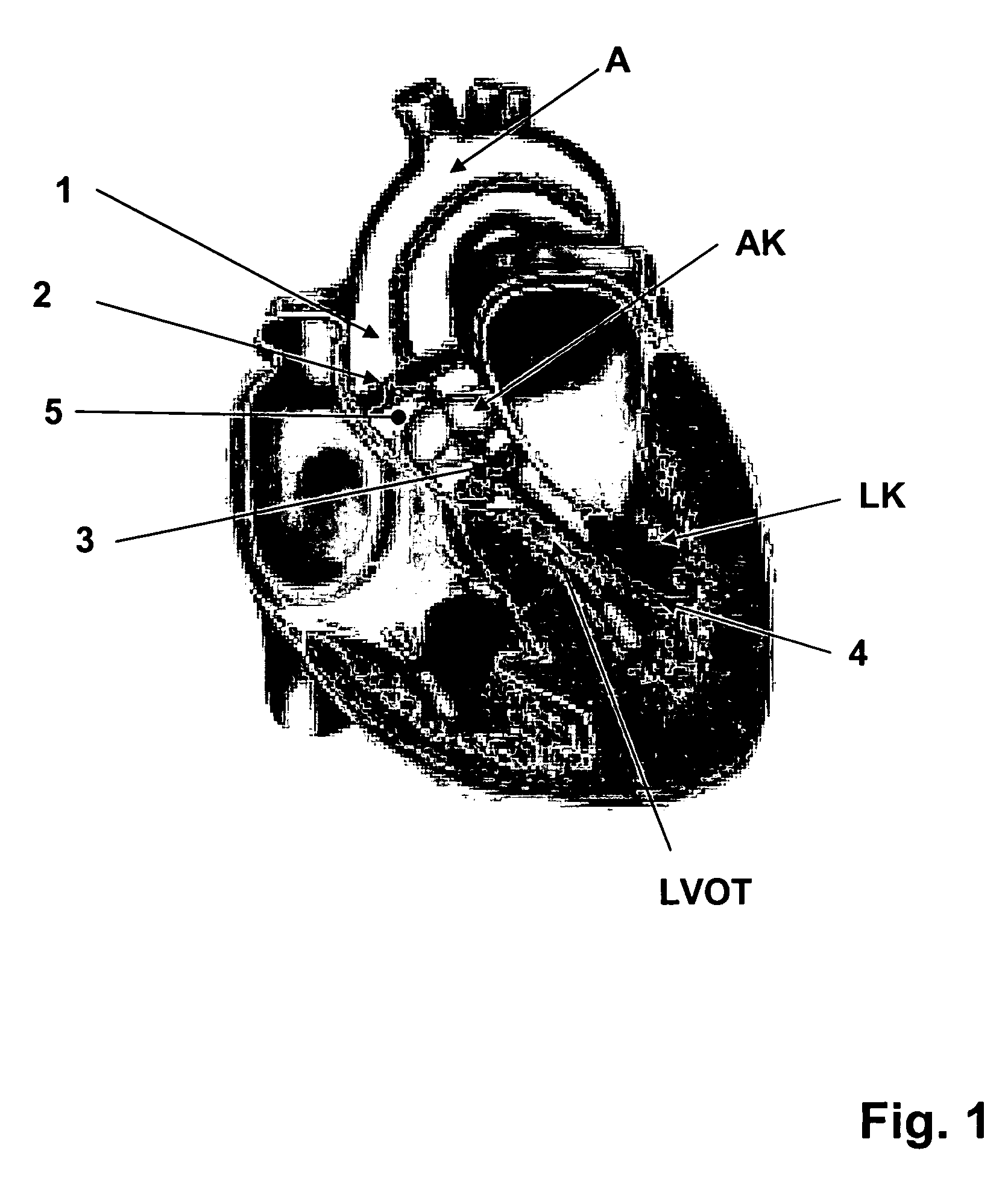
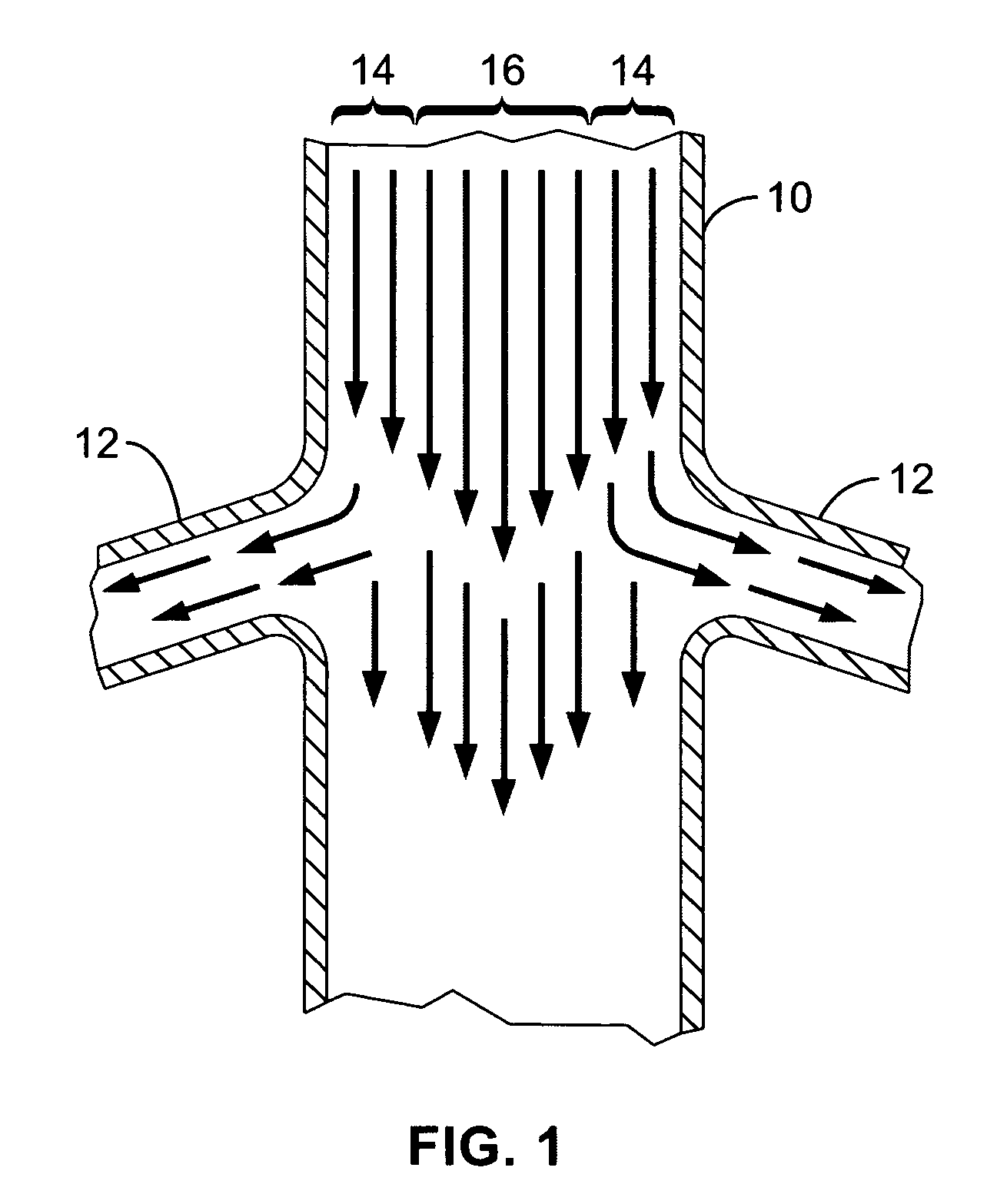
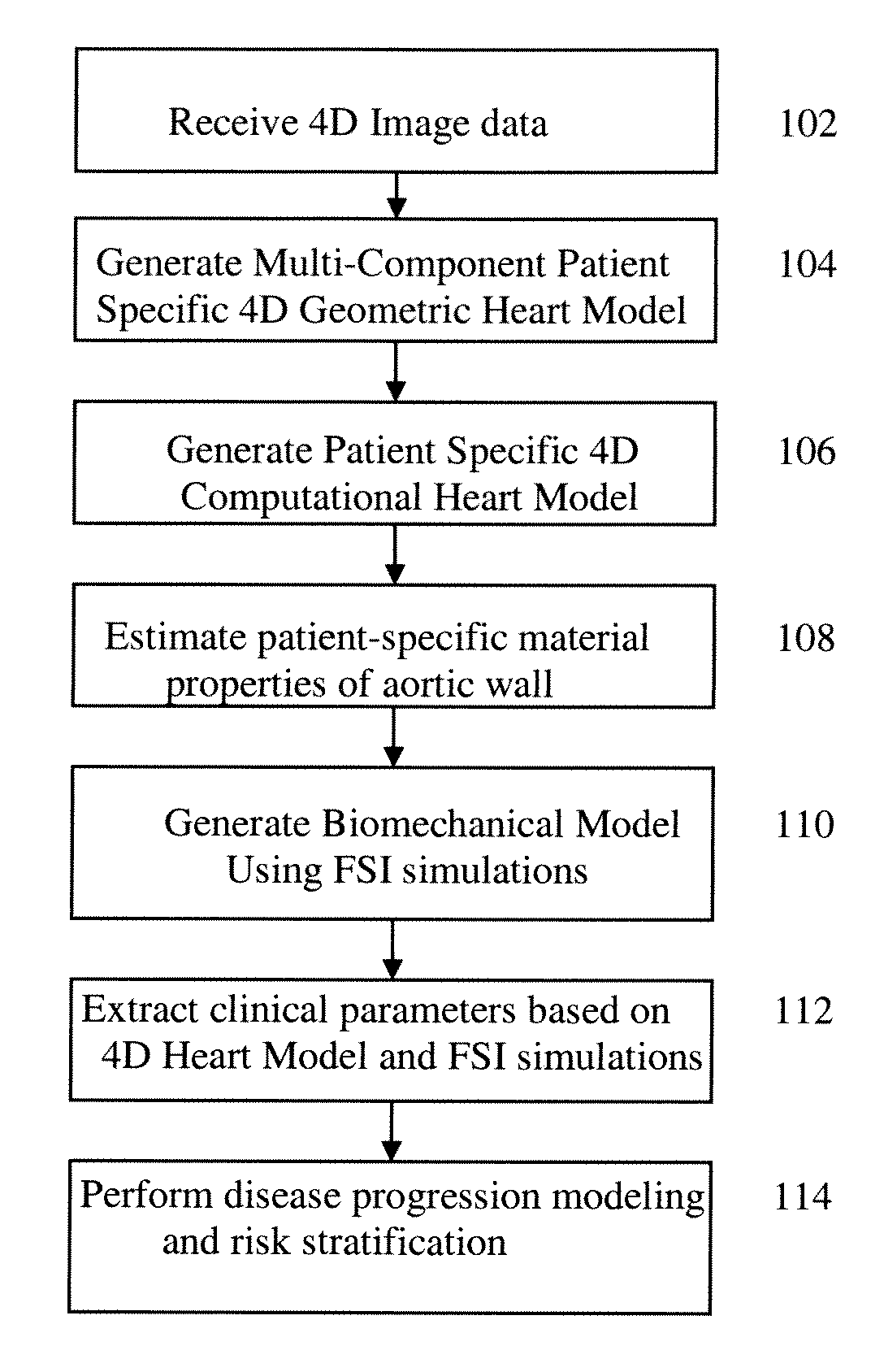
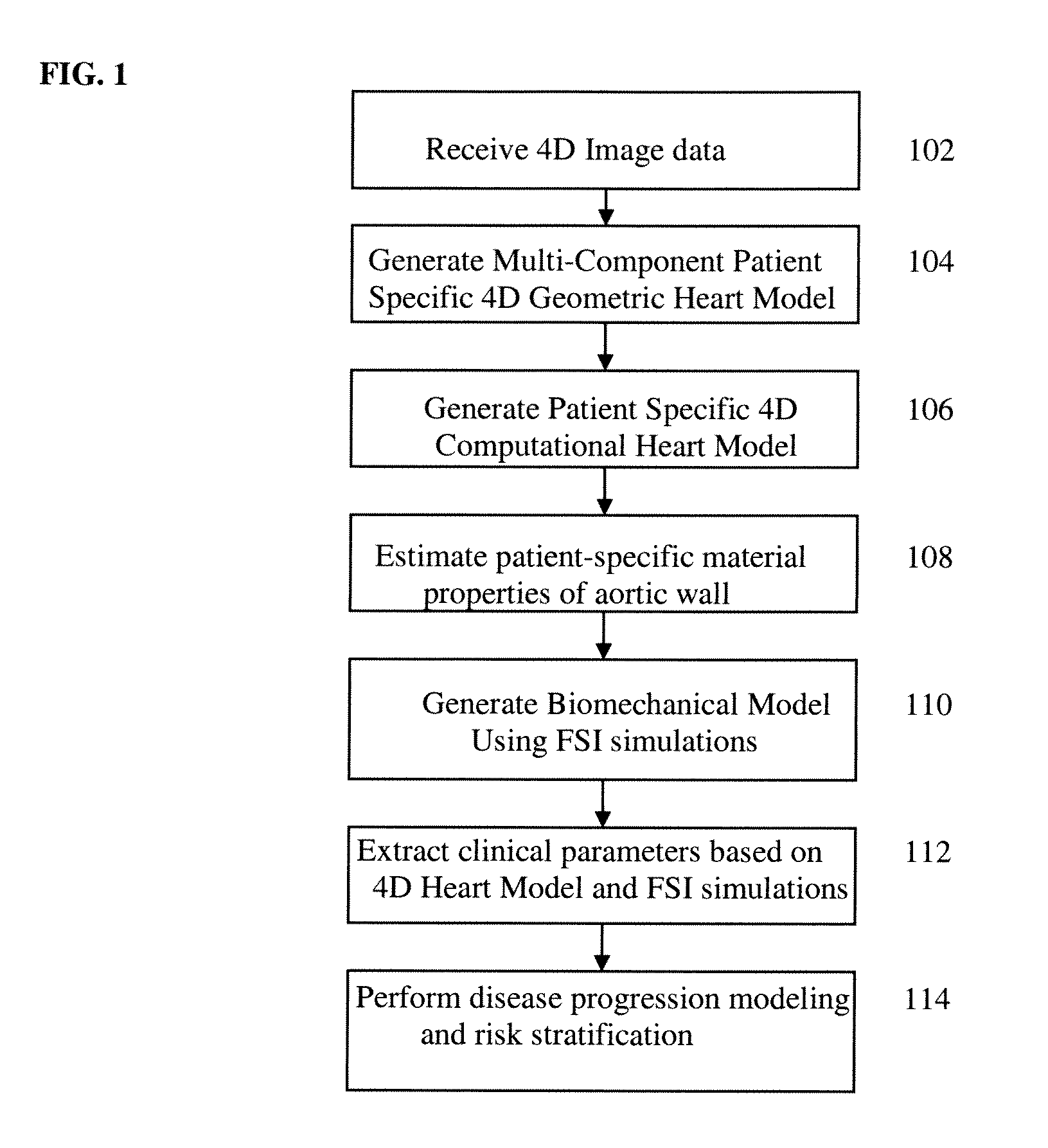
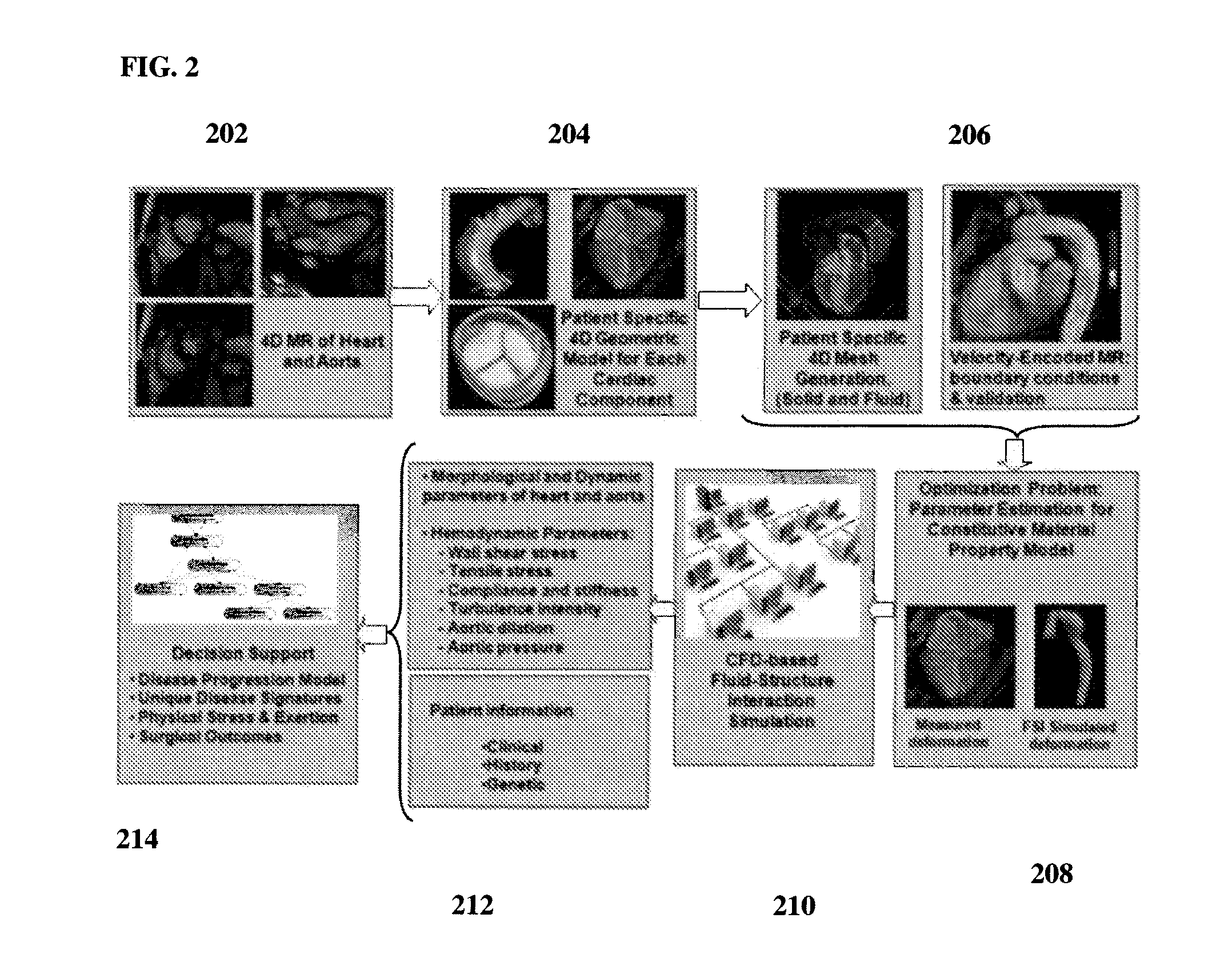
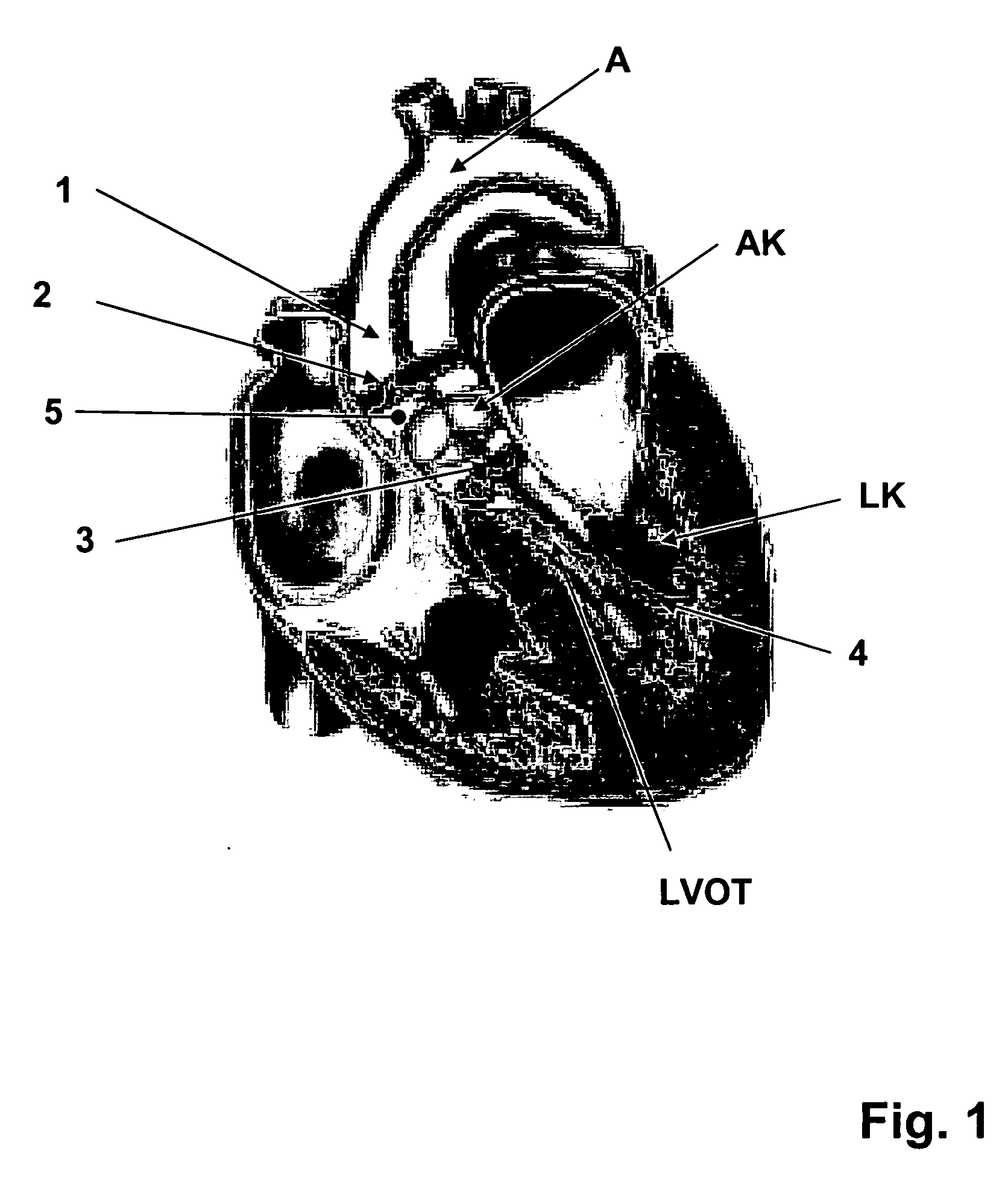
Method and System for Computational Modeling of the Aorta and Heart
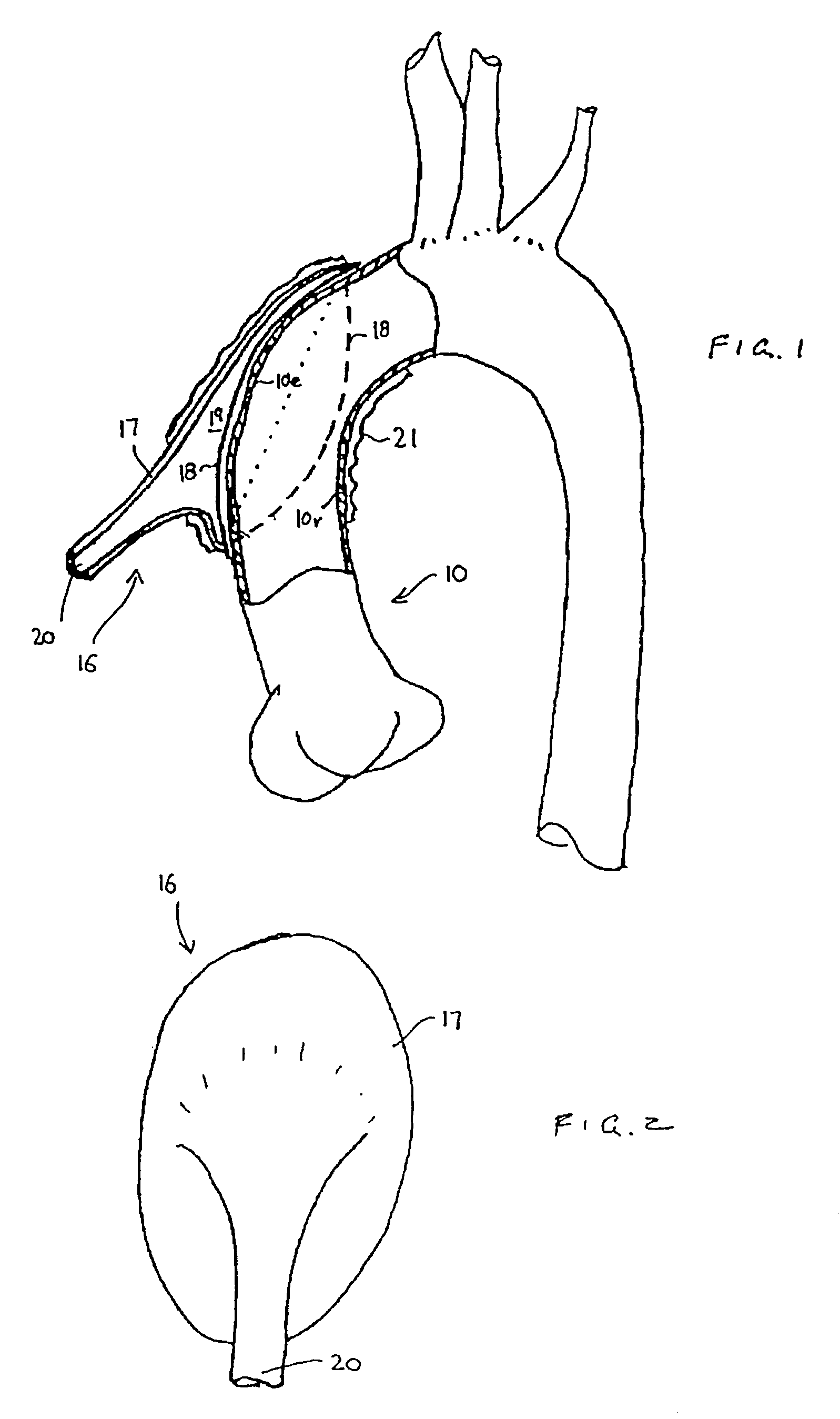
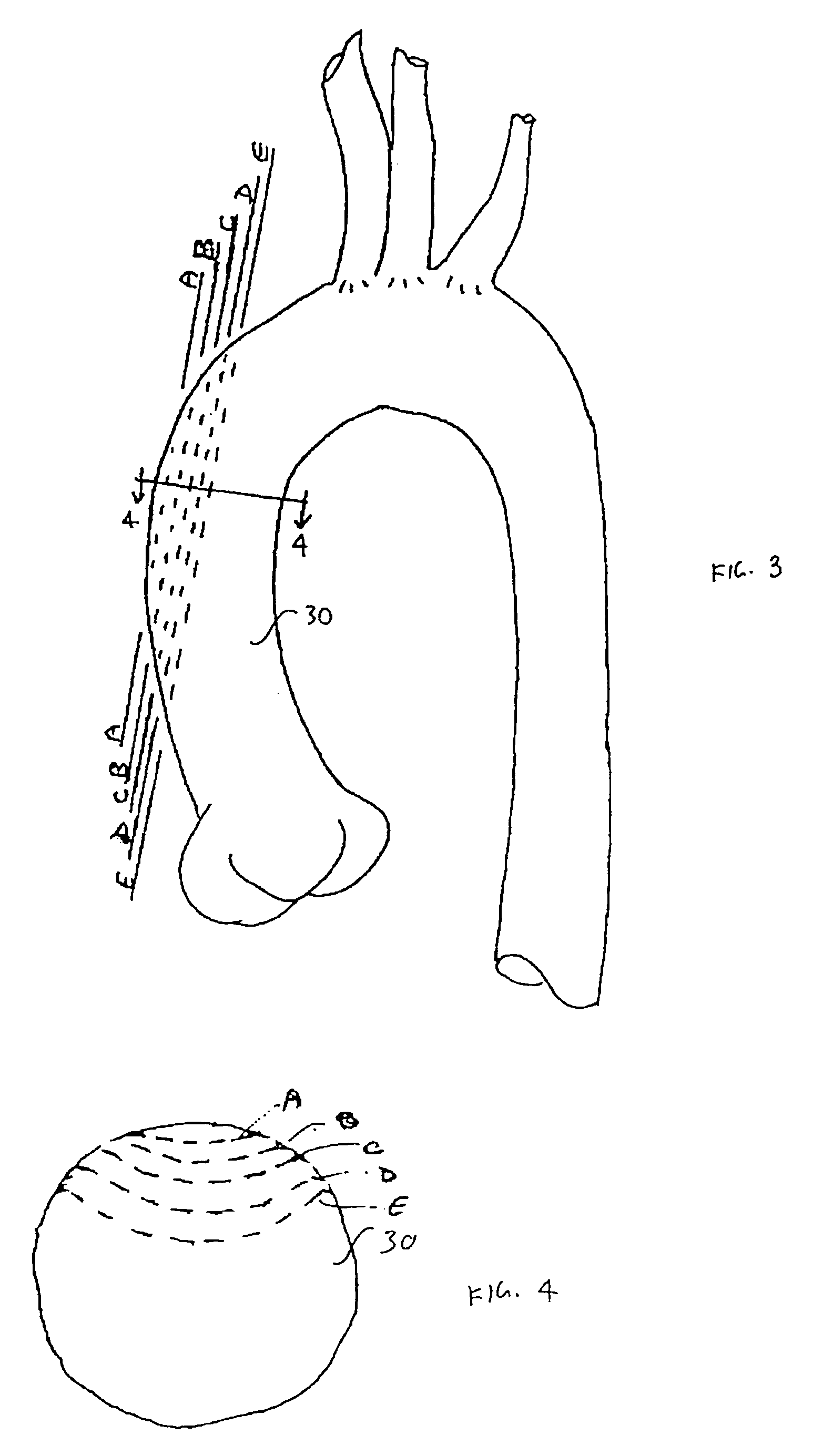
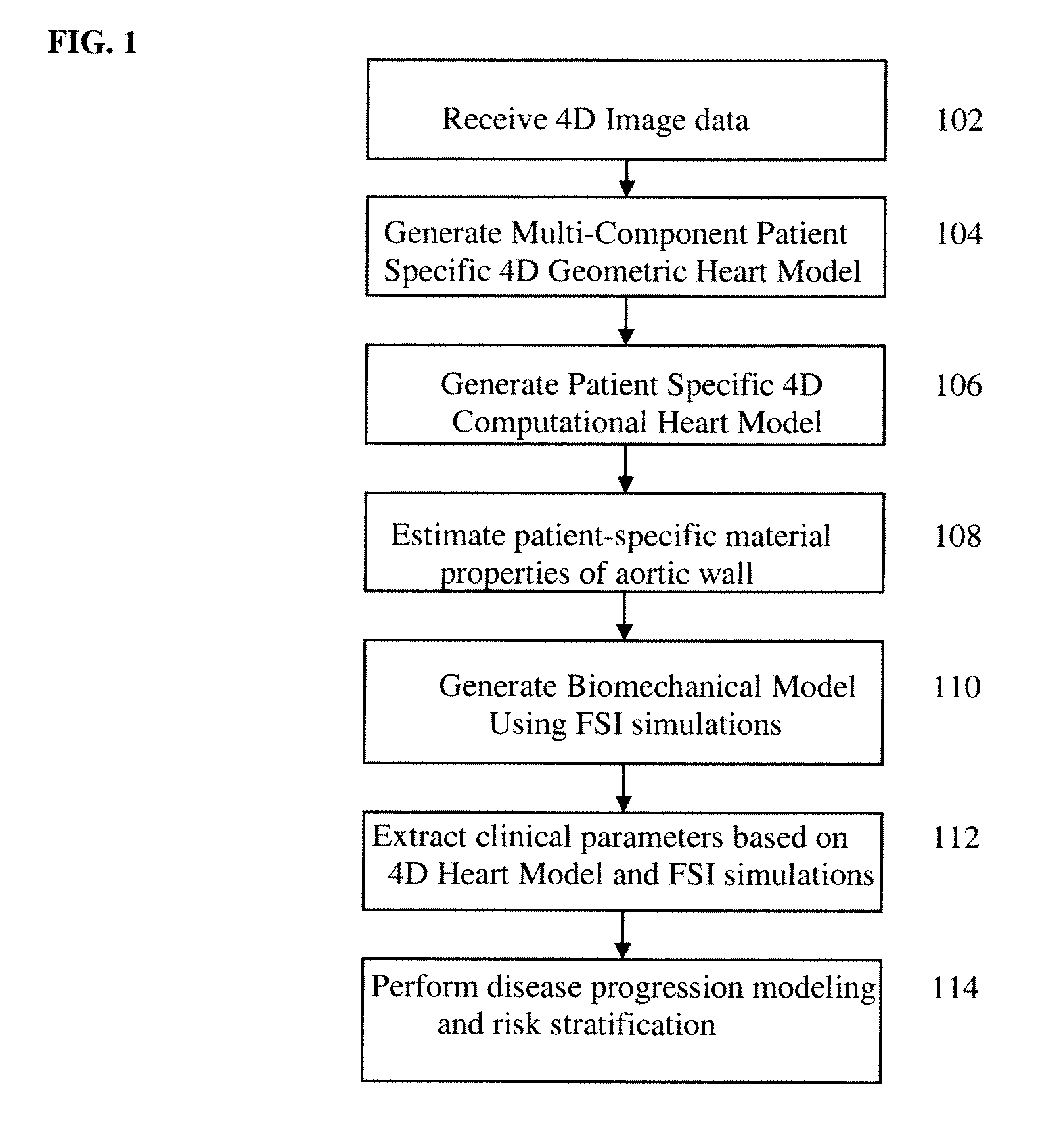
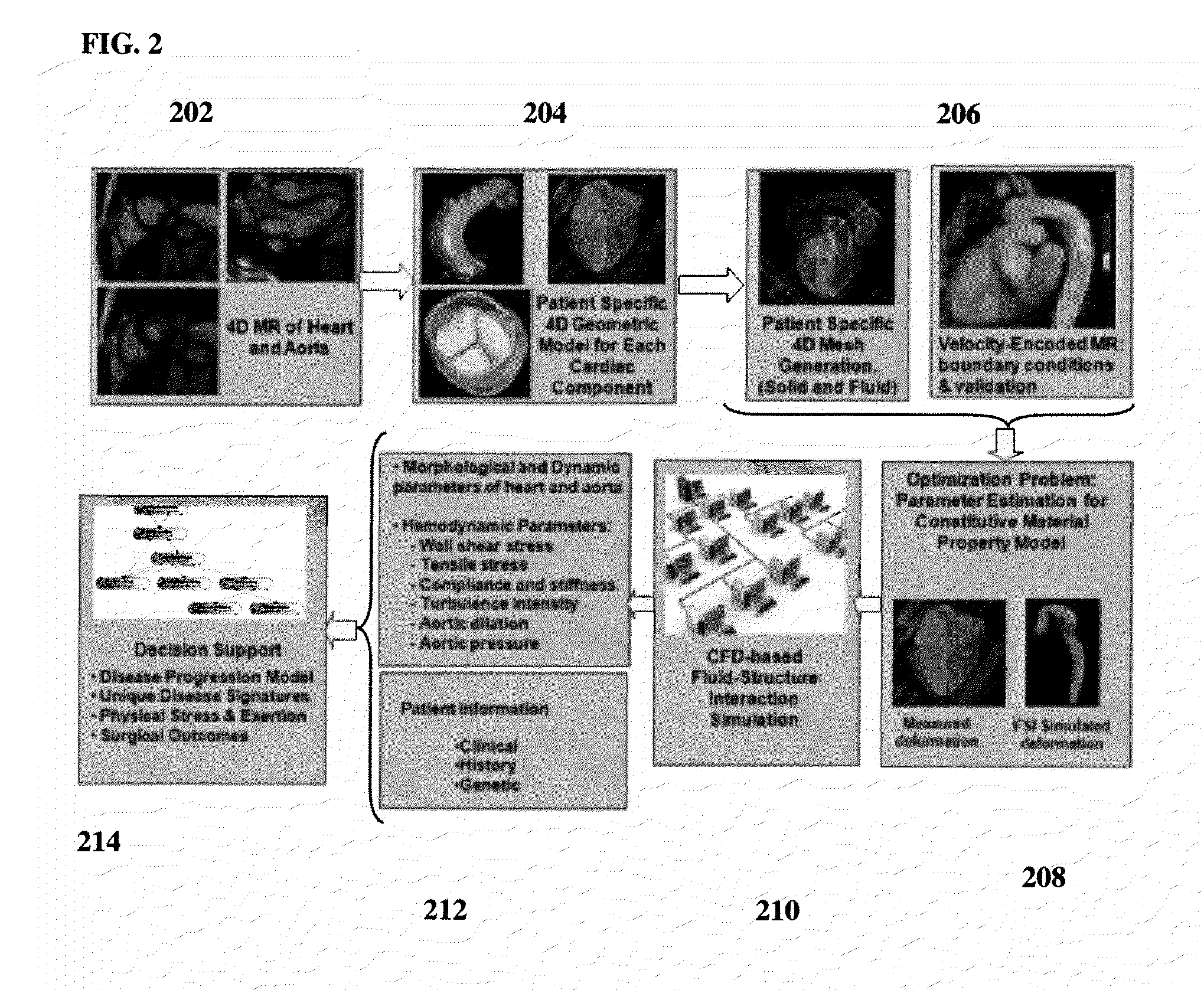
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. A sequence of volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT), echocardiography, or magnetic resonance (MR) image data of a patient's cardiac region is received. A multi-component patient specific 4D geometric model of the heart and aorta estimated from the sequence of volumetric cardiac imaging data. A patient specific 4D computational model based on one or more of personalized geometry, material properties, fluid boundary conditions, and flow velocity measurements in the 4D geometric model is generated. Patient specific material properties of the aortic wall are estimated using the 4D geometrical model and the 4D computational model. Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations are performed using the 4D computational model and estimated material properties of the aortic wall, and patient specific clinical parameters are extracted based on the FSI simulations. Disease progression modeling and risk stratification are performed based on the patient specific clinical parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Prosthetic aortic valve
InactiveUS6951573B1Eliminating and minimizing riskHigh mechanical strengthHeart valvesBlood vesselsAscending aortaCoronary arteries
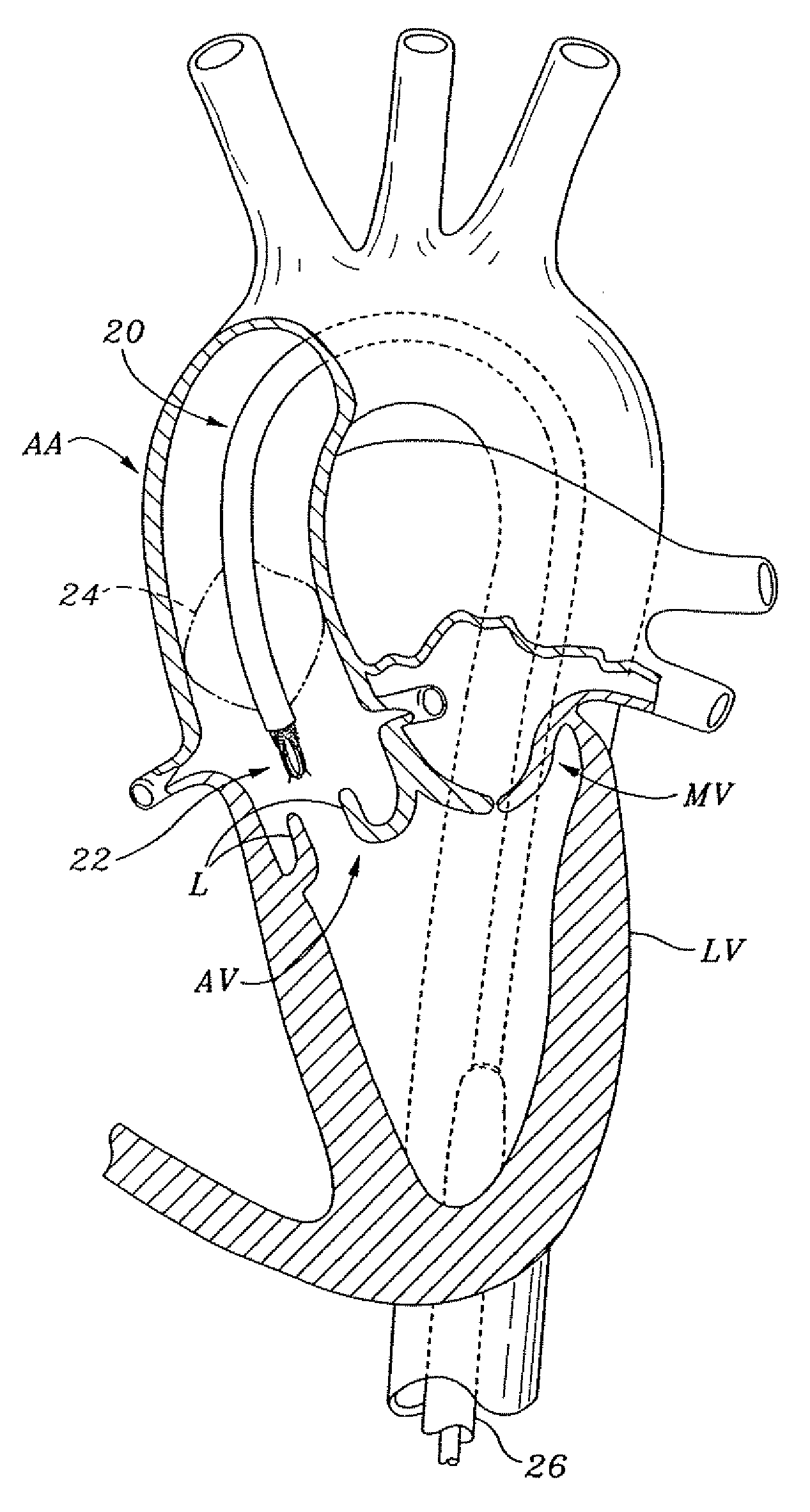
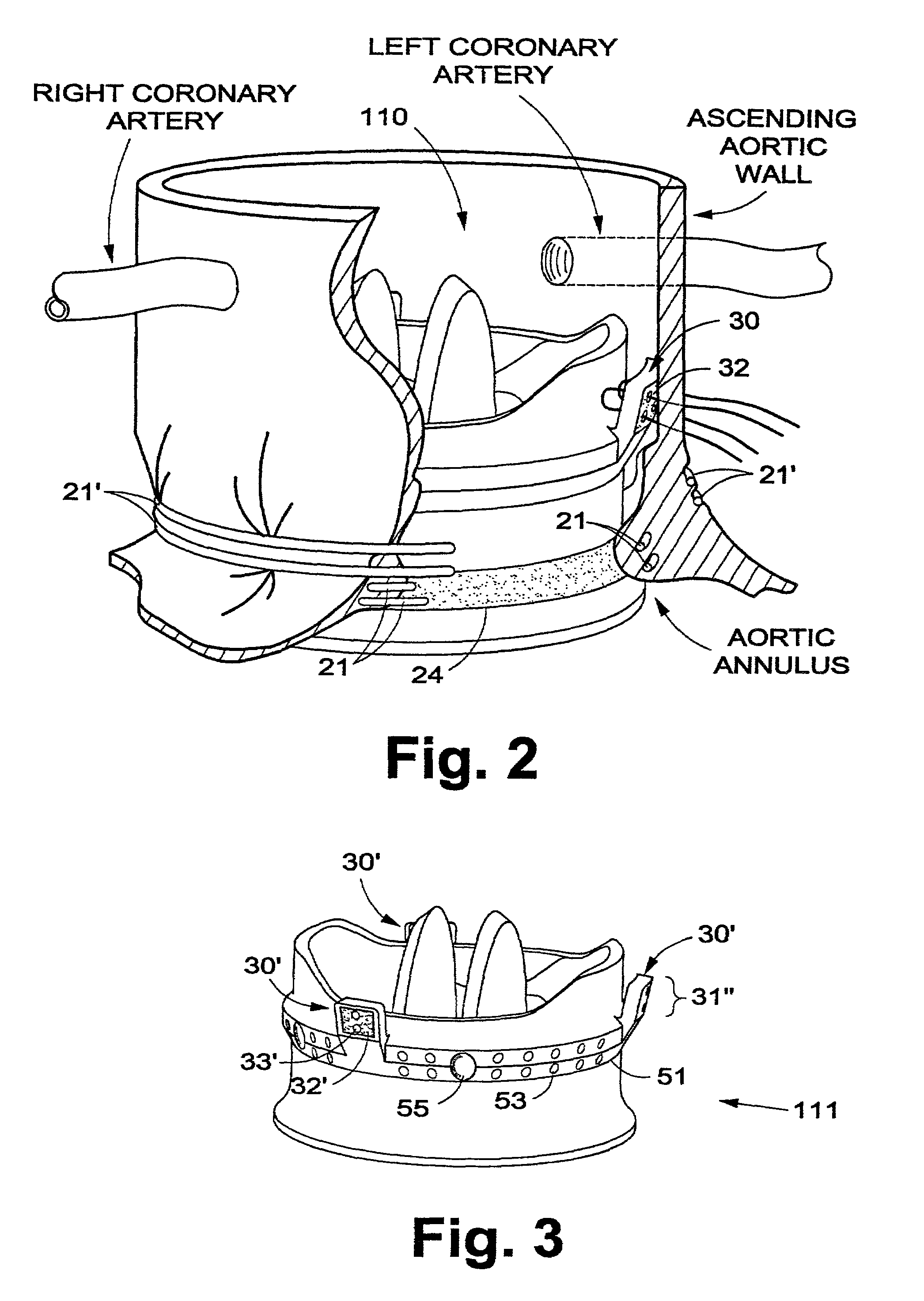
A prosthetic aortic valve is designed to be implanted in the natural aortic annulus and to extend into the ascending aorta to a point short of the right and left coronary arteries. Blood leakage around the valve is prevented by tension in one or more circumferential cords drawing annular tissue into sealing contact with an external sealing ring on the valve body. The security of the valve's attachment to a patient is assured with a plurality of interrupted sutures between a semirigid flange on the valve outer surface and the patient's aortic commissures and / or the patient's ascending aortic wall. The sutures are preferably attached to posts or cleats on the semirigid sewing flange, the flange being spaced apart from the valve inlet by the sealing ring.
Owner:DILLING EMERY W
Implantable prosthesis with displaceable skirt
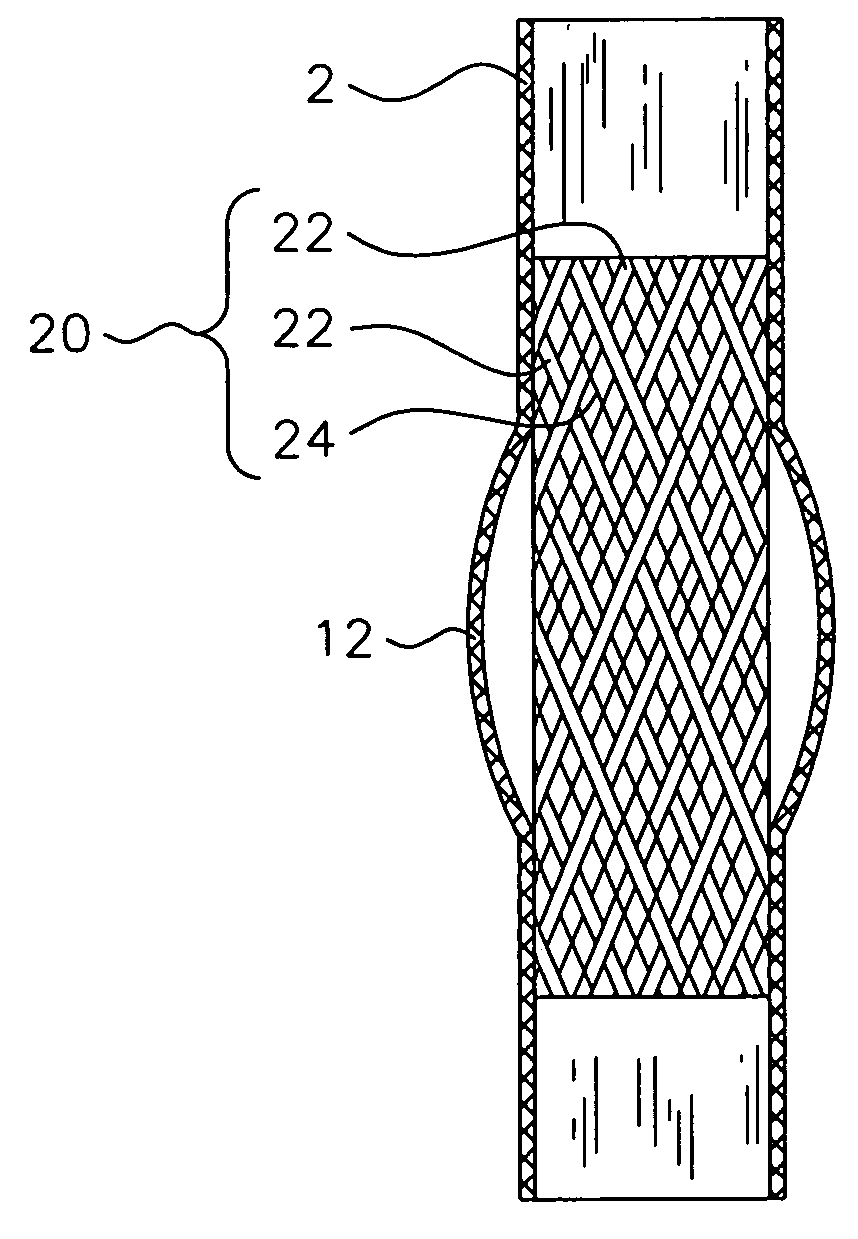
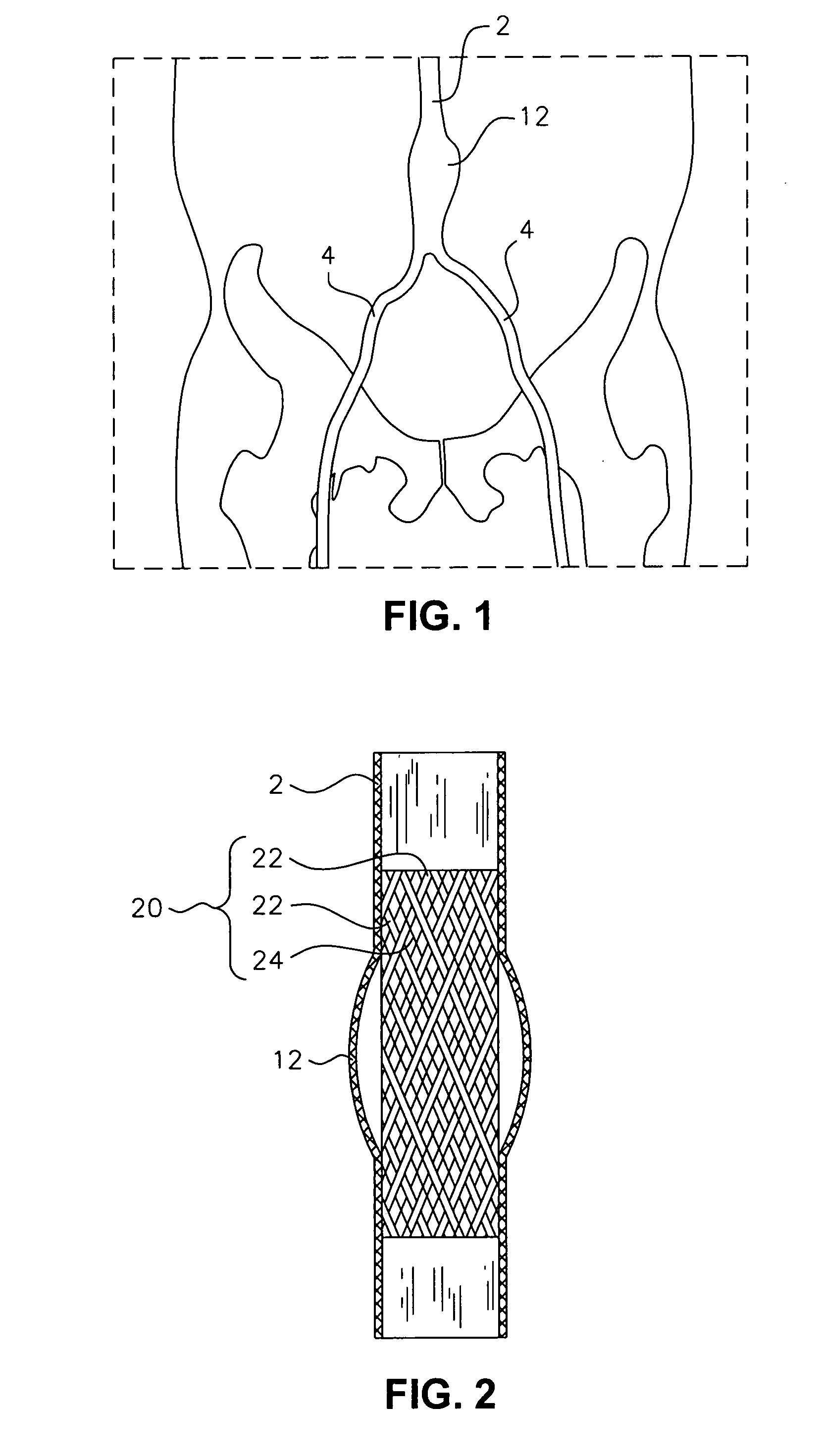
An implantable prosthesis is provided having a radially-expandable tubular body and at least one skirt extending therefrom. The skirt terminates in a peripheral edge, wherein at least portions of the peripheral edge are free and displaceable to a greater diameter of the tubular body. Thus, with the implantable prosthesis being a stent-graft used to treat an aortic aneurysm (e.g., abdominal aortic aneurysm (“AAA”)), the skirt may be used to inhibit Type I endoleaks upon its selective displacement in response to irregular aortic shaping and / or aneurysm neck expansion. The skirt may actively inhibit Type I endoleaks by forming a physical barrier against flow between the tubular body and the aortic wall. In addition, the skirt may passively inhibit endoleak formation by sufficiently restricting blood flow to allow coagulation and clot formation, which would act as a barrier against endoleakage.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20120271277A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Aortic root prosthesis with compliant sinuses
An aortic root prosthesis for being implanted into a patient during a valve sparing surgery as a replacement for a biological aortic root segment of an ascending aorta is disclosed. The aortic root prosthesis includes a hollow, annular tube having proximal and distal ends, and an inner and outer wall. The distal end is for being attached to the ascending aorta. A plurality of sinuses are circumferentially connected to the proximal end of the tube. Each of the sinuses is adapted for being attached to the aortic wall. Each of the sinuses also includes contouring means for imparting a convex contour to an outer wall of the sinus to thereby create a space between the open leaflet and its respective sinus to prevent impact between the leaflet of the valve and the inner wall of the sinus.
Owner:HEINEMAN MEDICAL RES
Device for minimally invasive intravascular aortic valve extraction
The present invention is distinguished by a perfusion catheter being provided comprising at least one perfusion channel designed as a hollow channel and at least two dilation units disposed at a distance from each other at the distal catheter region in the longitudinal extension of the catheter, both the dilation units being projected through by the perfusion catheter and forming in an inflated state an at least practically fluid-tight occlusion with the aortic wall, of which the dilation units at least said dilation unit disposed on the proximal side is provided with at least one passage through which at least one auxiliary catheter can be introduced aortic valve ablation in a fluid-tight manner and / or the perfusion catheter is provided with a working channel which is provided with an outlet opening in the region between the two dilation units and through which at least one auxiliary catheter can be introduced for aortic valve ablation.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
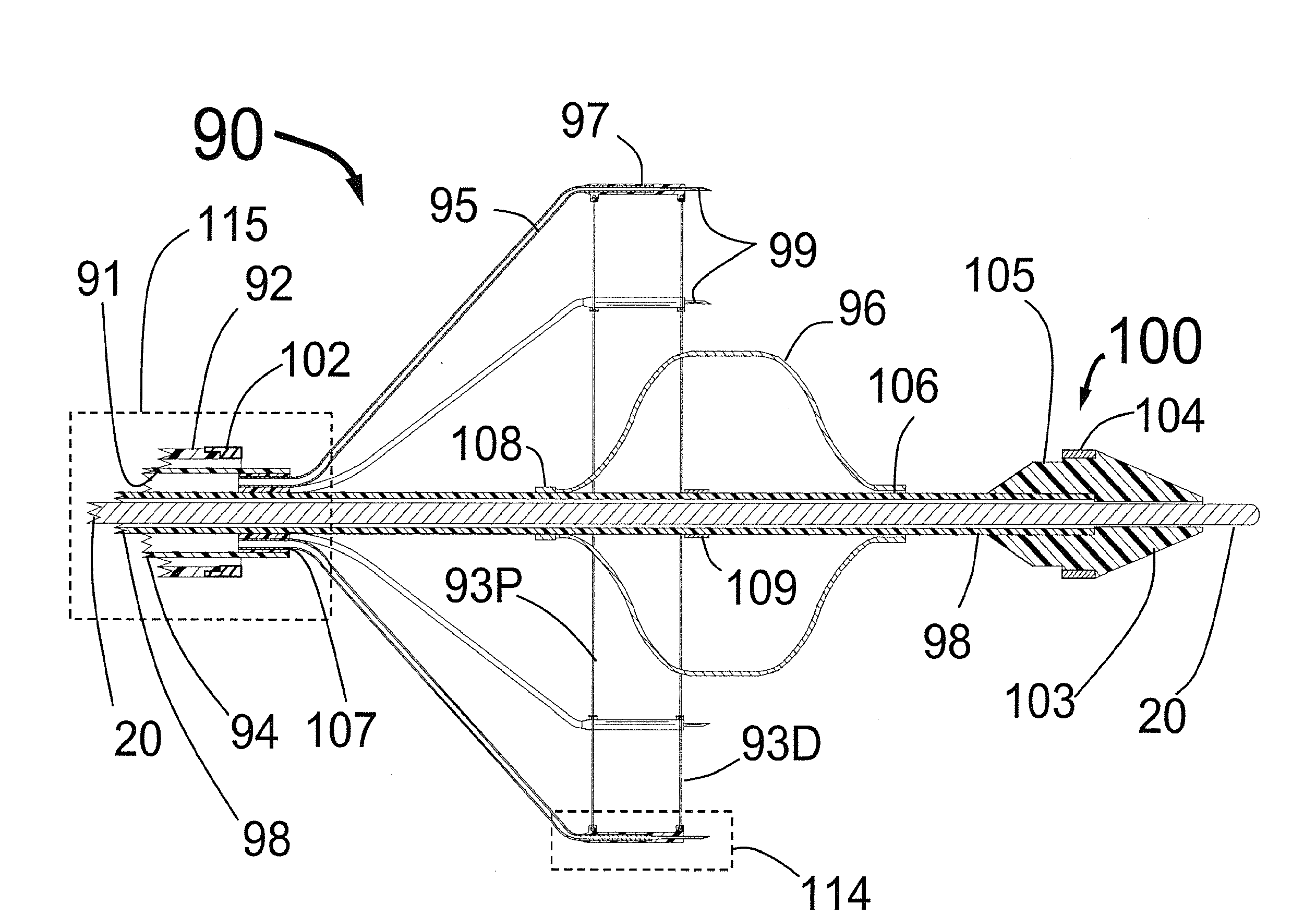
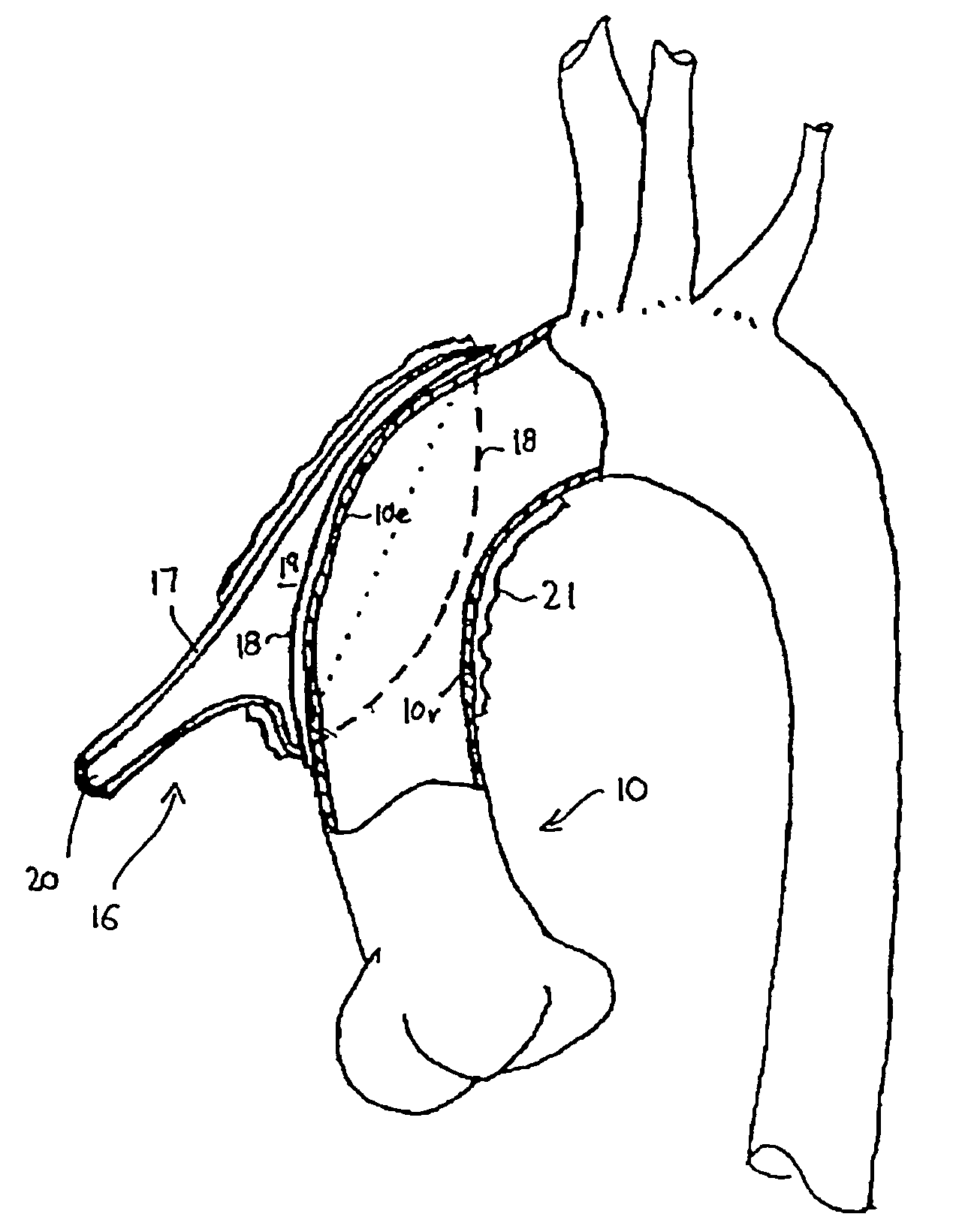
Methods and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS20090030510A1Optimize timingAccurate placementBalloon catheterHeart valvesVascular tissueCardiac cycle
A delivery system and method for percutaneous aortic valve (PAV) replacement and apparatus used therein. A temporary aortic valve comprised of a reversibly expandable occluding means, such as balloons, surrounds a central catheter mechanism. The temporary valve is positioned within the ascending aorta, just above and downstream from the coronary ostia. The occluding means is configured such that, when fully expanded against the aortic wall, gaps are left that promote continuous coronary perfusion during the cardiac cycle. The temporary valve with occluding means substitutes for the function of the native aortic valve during its replacement. The native aortic valve is next dilated, and then ablated through deployment of low profile, elongated, sequentially delivered stents. The ablation stent(s) displace the native valve tissues and remain within the aortic annulus to receive and provide a structure for retaining the PAV. The PAV is delivered, positioned and deployed within the ablation stent(s) at the aortic annulus with precision and relative ease. Ablation of the native aortic valve removes the structural obstacles to precise PAV placement. The temporary aortic valve mediates the hemodynamic forces upon the devices as encountered by the surgeon following native valve ablation. The temporary valve also promotes patient stability through continuous coronary perfusion and a moderated transvalvular pressure gradient and regurgitation. Sequential delivery of low profile PAV components minimize the risk of trauma and injury to vascular tissues. Mathematical considerations for determining the optimum cross-sectional area for the temporary valve blood perfusion gaps are also described.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Method and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS20090030503A1Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesCoronary artery ostiumCardiac cycle
A method for percutaneous aortic valve (PAV) replacement and a temporary aortic valve used to facilitate the same. The temporary valve is comprised of a reversibly expandable occluding means, such as balloons, surrounding a central catheter mechanism. The temporary valve is positioned within the ascending aorta, just above and downstream from the coronary ostia. The occluding means is configured such that, when fully expanded against the aortic wall, gaps are left that promote continuous coronary perfusion during the cardiac cycle. The native aortic valve is next dilated, and then ablated through deployment of an ablation stent. The ablation stent displaces the native valve tissues and remains within the aortic annulus to receive and retain the PAV. The PAV can then be positioned and deployed within the ablation stent with precision and ease. Ablation of the native aortic valve removes the structural obstacles to precise PAV placement. The temporary aortic valve mediates the hemodynamic forces encountered by the surgeon following native valve ablation. The temporary valve also promotes patient stability through continuous coronary perfusion and a moderated transvavlular pressure gradient. Mathematical considerations for determining the optimum cross-sectional area for the temporary valve blood perfusion gaps are also described.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Temporary anastomotic seal and method
Forming a proximal anastomosis on an aortic wall includes method and instrumentation and apparatus for forming an aortic puncture and inserting into the vessel through the puncture a fluid-impervious sealing element with a protruding retainer. An anastomosis of a graft vessel over the puncture is partially completed with the retainer of the sealing element protruding through the partial anastomosis. The retainer facilitates removal of the sealing element from the partial anastomosis prior to completion of the procedure.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS9237925B2Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesFiberCapital equipment
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Expandable catheter system for peri-ostial injection and muscle and nerve fiber ablation
ActiveUS20160235464A1Improve control and treatmentTime efficient and safeElectrocardiographySurgical needlesCapital equipmentLeft atrium
At the present time, physicians often treat patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) using radiofrequency (RF) catheter systems to ablate conducting tissue in the wall of the Left Atrium of the heart around the ostium of the pulmonary veins. These systems are expensive and take time consuming to use. The present invention circular ablation system CAS includes a multiplicity of expandable needles that can be expanded around a central axis and positioned to inject a fluid like ethanol to ablate conductive tissue in a ring around the ostium of a pulmonary vein quickly and without the need for expensive capital equipment. The expansion of the needles is accomplished by self-expanding or balloon expandable structures. The invention includes centering means so that the needles will be situated in a pattern surrounding the outside of the ostium of a vein. Also included are members that limit the distance of penetration of the needles into the wall of the left atrium, or the aortic wall. The present invention also has an important application to ablate tissue around the ostium of one or both renal arteries, for the ablation of the sympathetic nerve fibers and / or other afferent or efferent nerves going to or from each kidney in order to treat hypertension.
Owner:ABLATIVE SOLUTIONS INC
Methods and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS8663319B2Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesCardiac cyclePerfusion
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Heart assist device utilising aortic deformation
The present invention relates to providing counter-pulsation heart assist by deforming the aorta. In a preferred embodiment, the deformation pressure is applied by cyclically, preferably in synchrony with the diastolic period of the heart. The deformation pressure may be applied to the outer wall of the aorta or to a patch covering a resected opening in the wall of the aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
Method and system for computational modeling of the aorta and heart
A method and system for generating a patient specific anatomical heart model is disclosed. A sequence of volumetric image data, such as computed tomography (CT), echocardiography, or magnetic resonance (MR) image data of a patient's cardiac region is received. A multi-component patient specific 4D geometric model of the heart and aorta estimated from the sequence of volumetric cardiac imaging data. A patient specific 4D computational model based on one or more of personalized geometry, material properties, fluid boundary conditions, and flow velocity measurements in the 4D geometric model is generated. Patient specific material properties of the aortic wall are estimated using the 4D geometrical model and the 4D computational model. Fluid Structure Interaction (FSI) simulations are performed using the 4D computational model and estimated material properties of the aortic wall, and patient specific clinical parameters are extracted based on the FSI simulations. Disease progression modeling and risk stratification are performed based on the patient specific clinical parameters.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for semi-automatic aortic aneurysm analysis
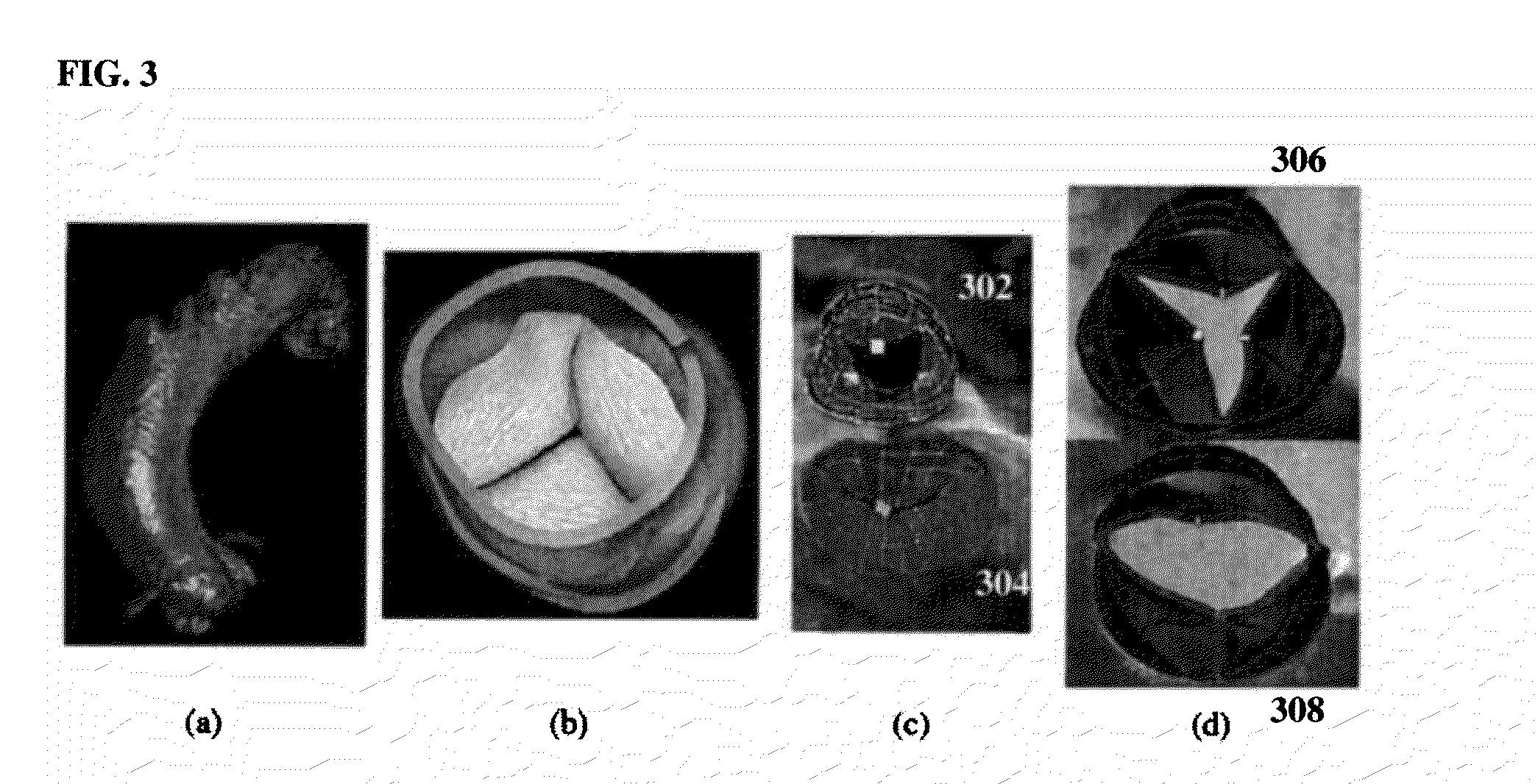
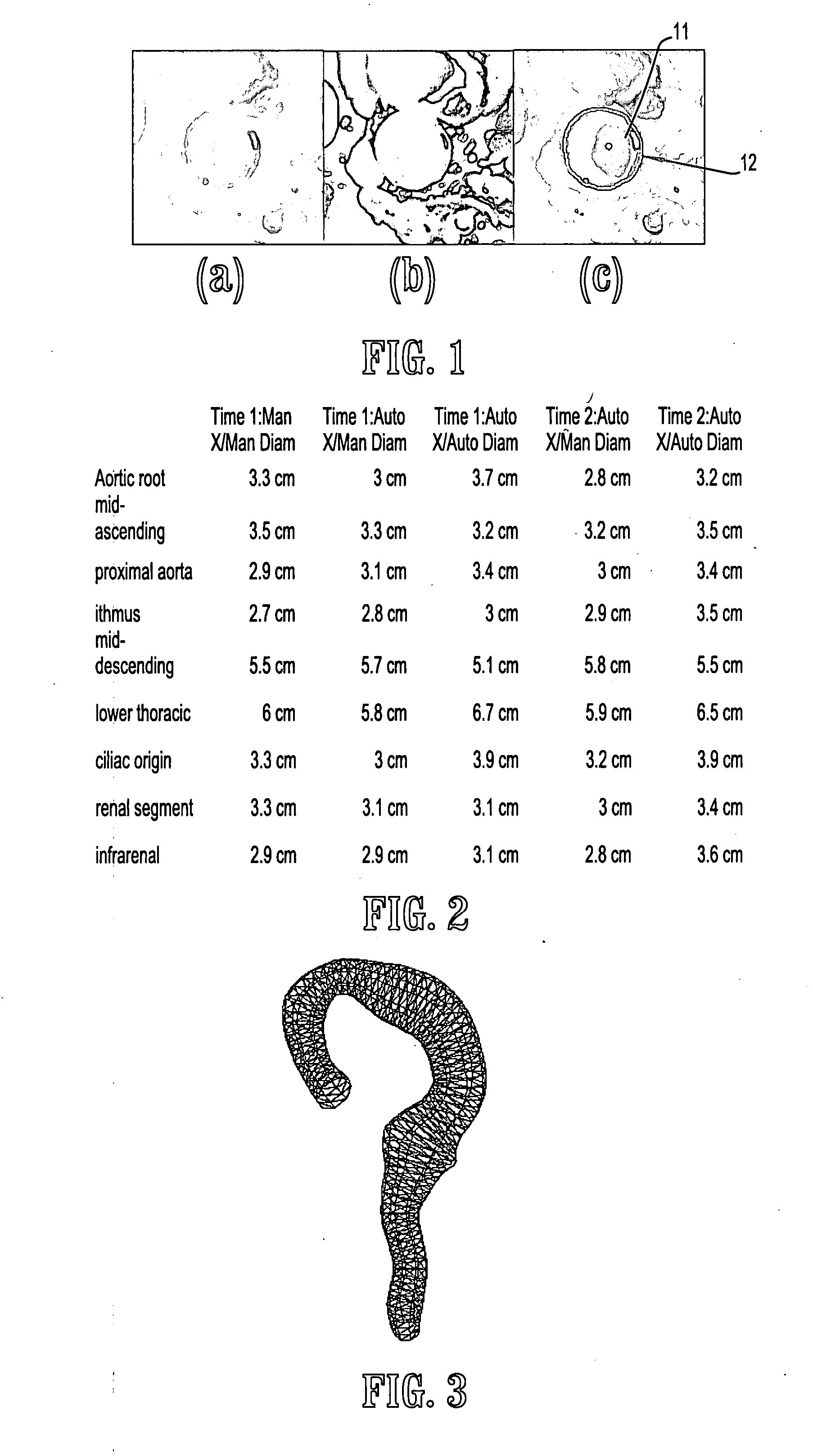
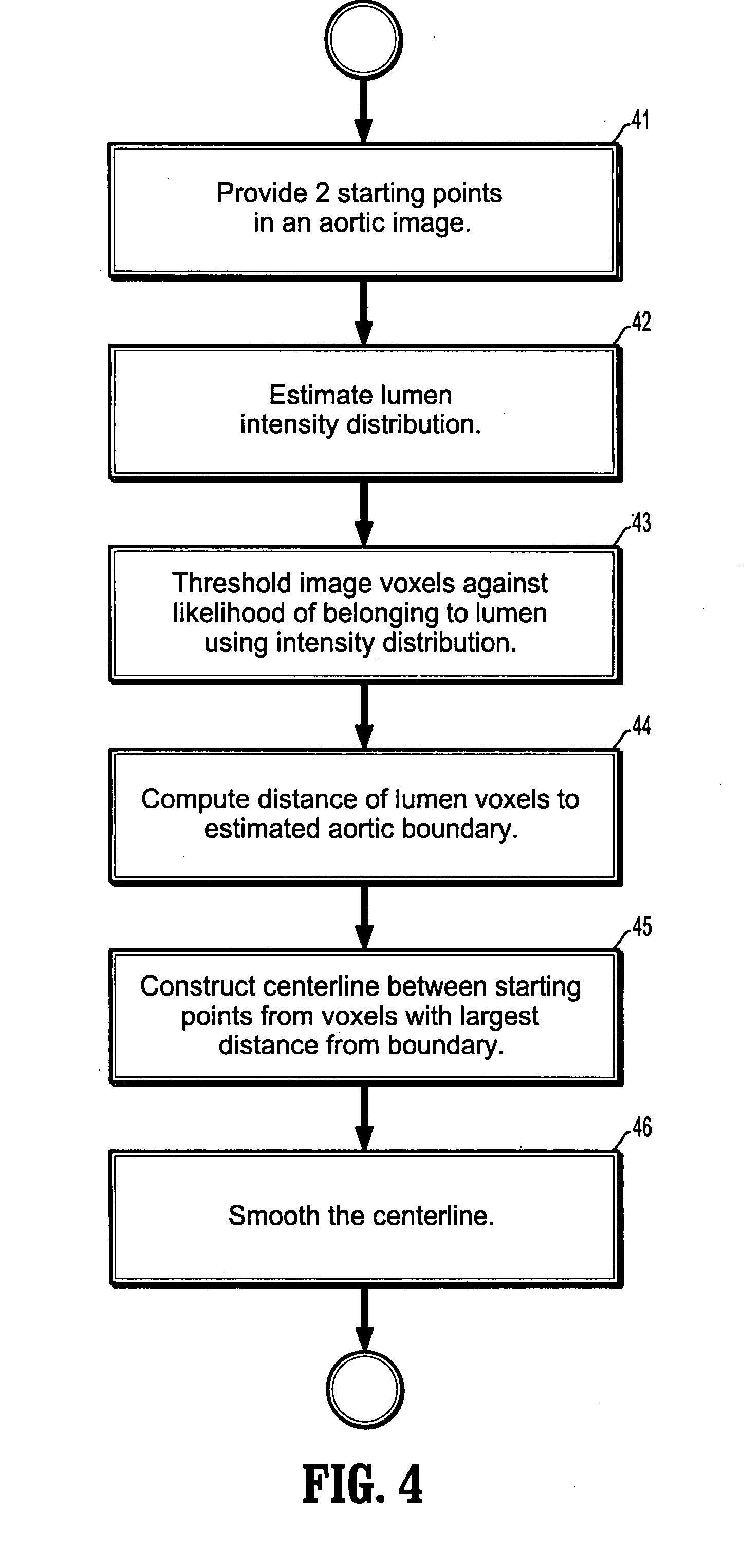
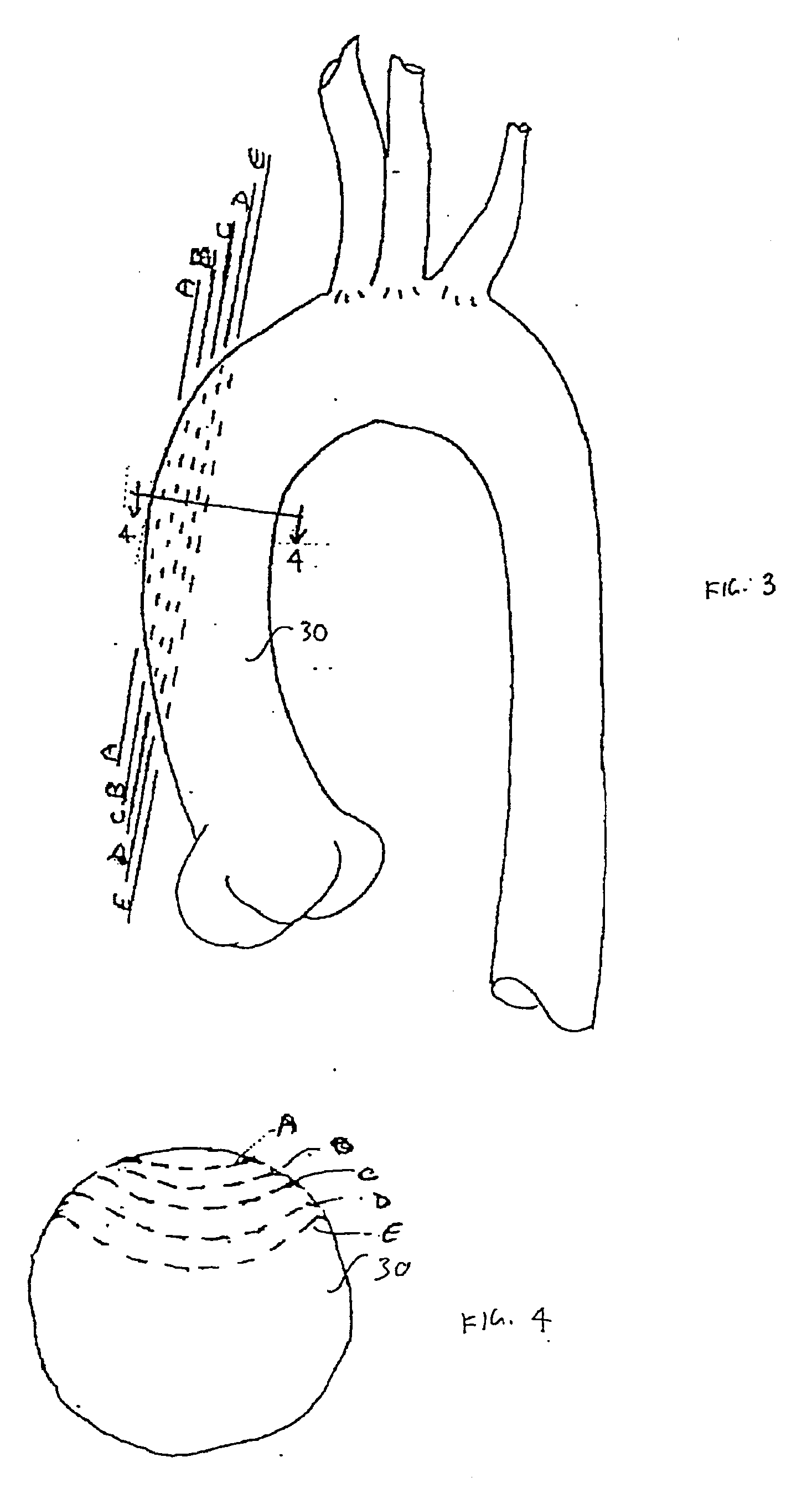
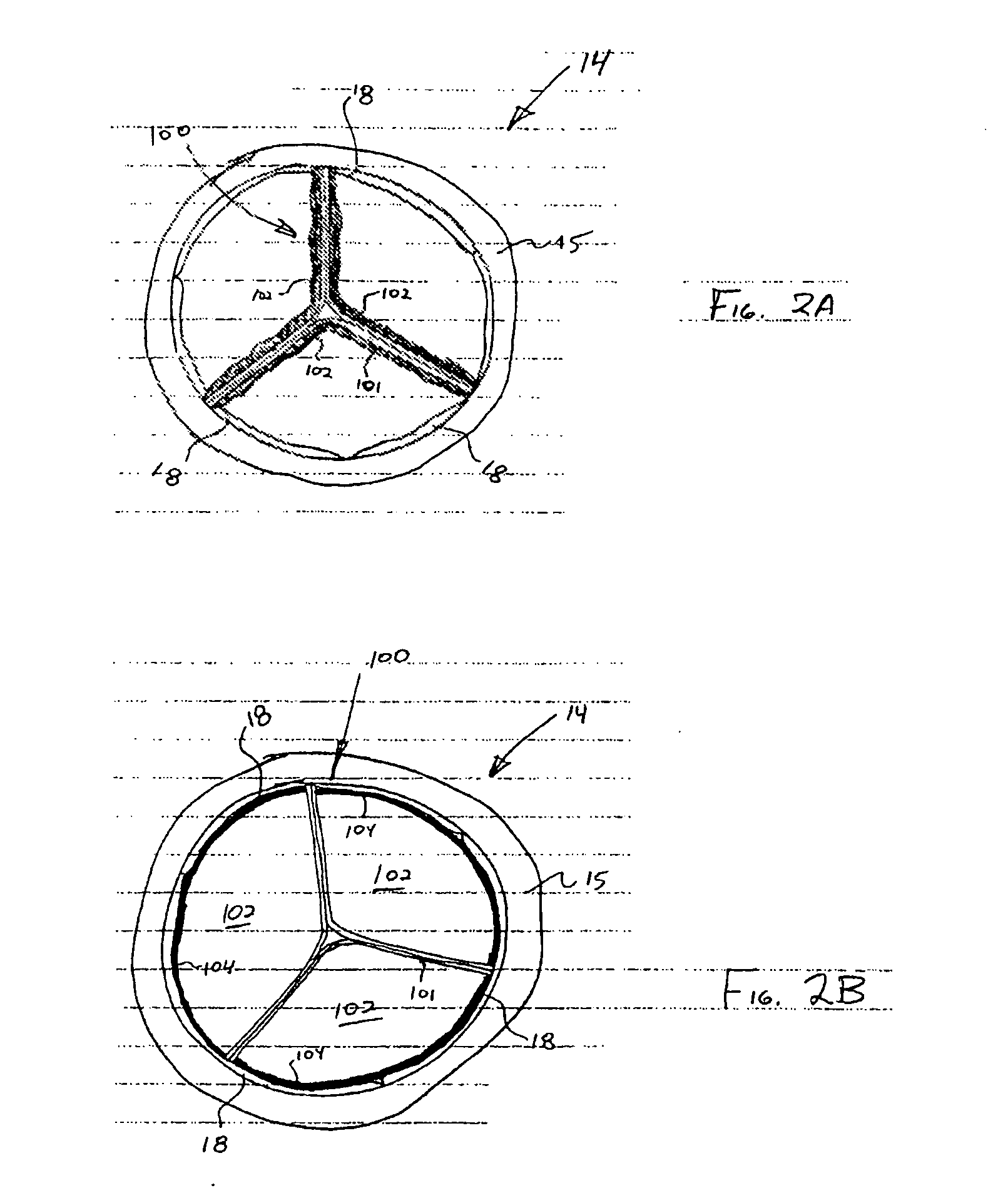
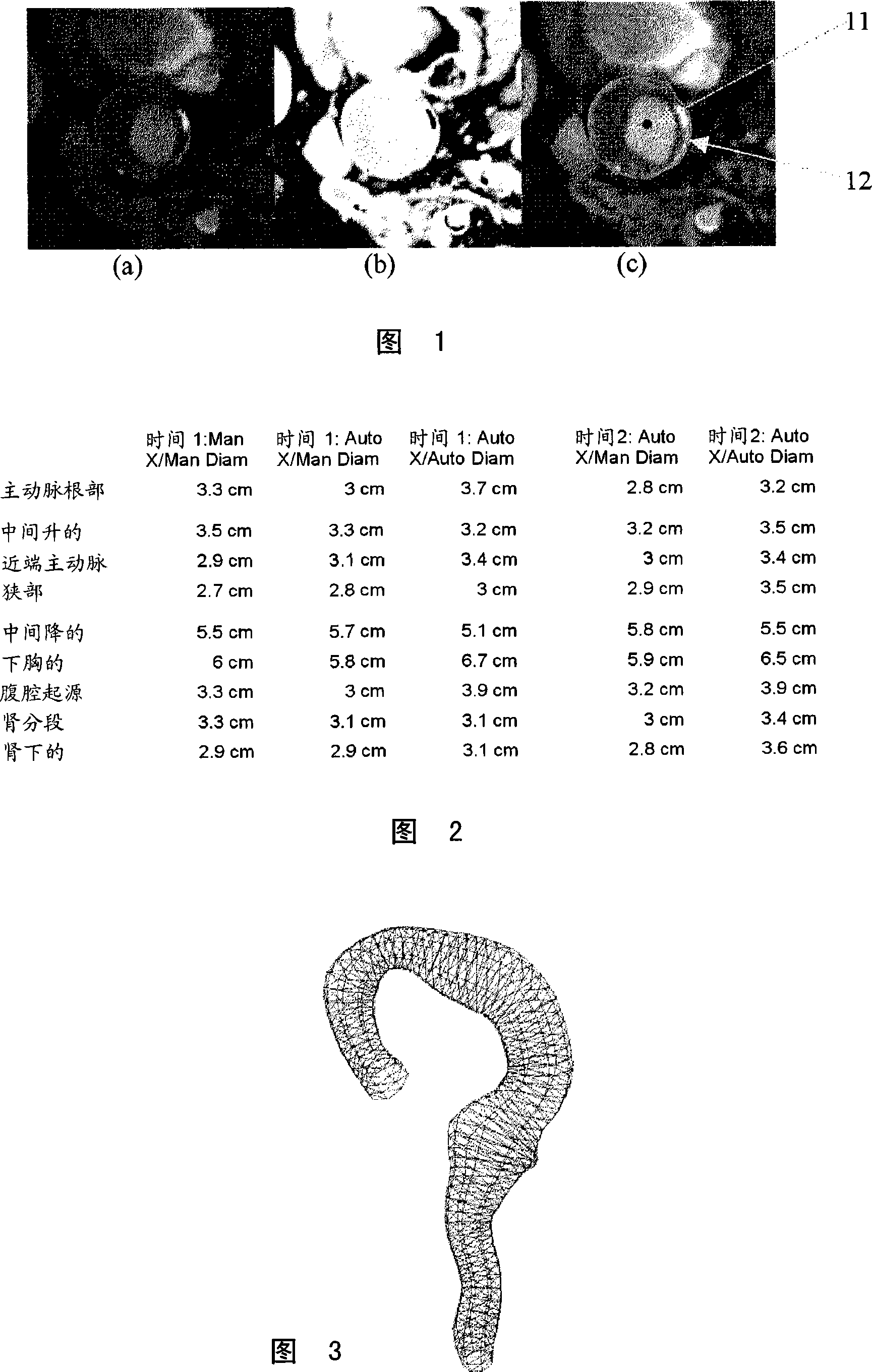
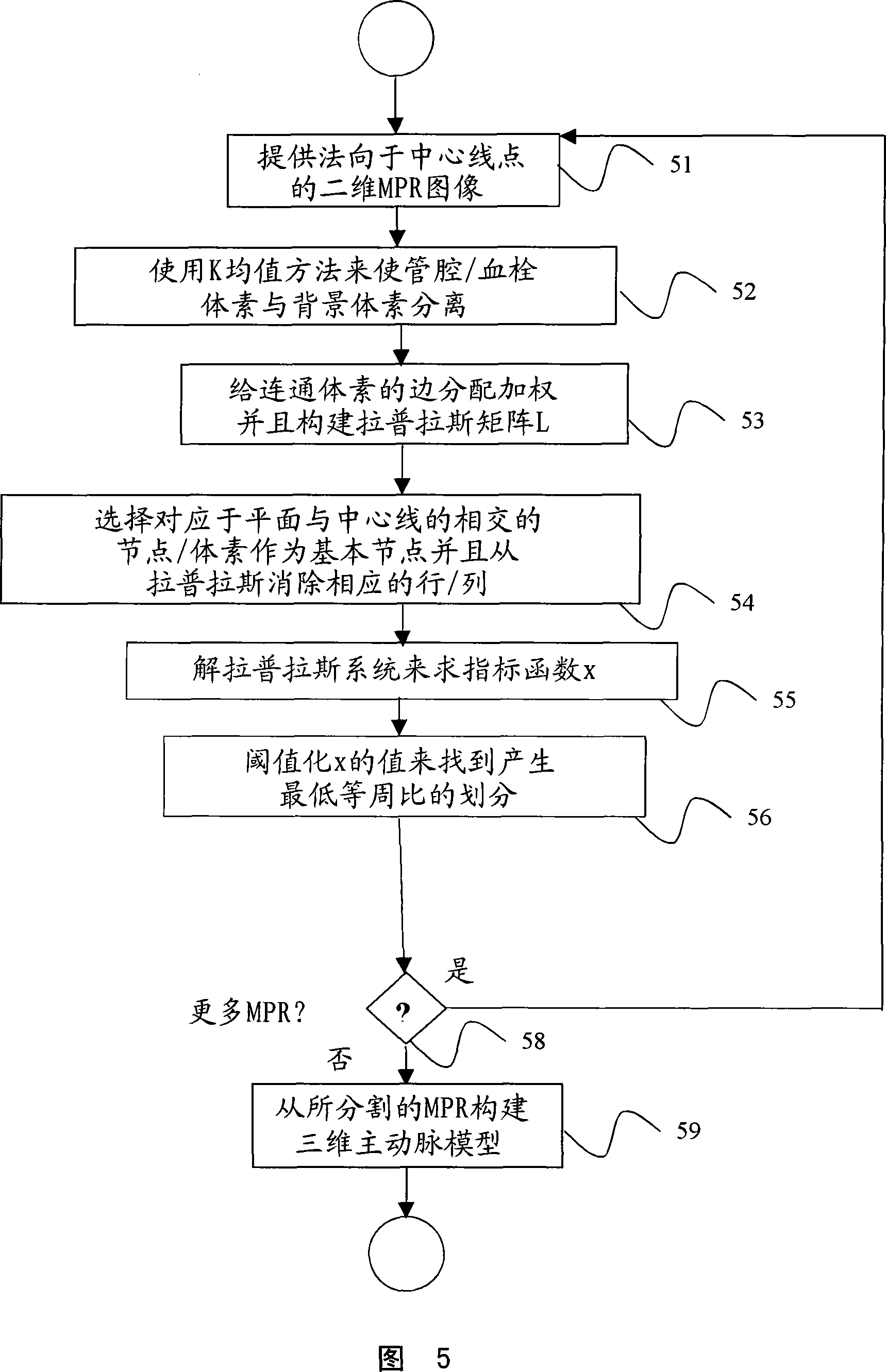
A method for automatically analyzing an aortic aneurysm includes providing a digitized 3-dimensional image volume of an aorta, determining which voxels in said image are likely to be lumen voxels, determining a distance of said lumen voxels from an aortic boundary, finding a centerline of the aorta in said image volume based on said lumen voxel distances, constructing a series of 2-dimensional multiplanar reformatted (MFR) image planes orthogonal to this centerline, segmenting aortic cross sections in each said MPR image plane wherein an aortic wall is located in each MPR image, and constructing from said aortic wall locations a 3D model of the aorta.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Temporary seal and method for facilitating anastomosis
Forming a proximal anastomosis on an aortic wall includes method and instrumentation and apparatus for forming an aortic puncture and inserting a fluid-impervious sealing element with a lateral flange and central stem into the vessel through the puncture. An anastomosis of a graft vessel over the puncture is partially completed with the central stem of the sealing element protruding through the partial anastomosis. A removal instrument attaches to the central stem and retrieves the sealing element that disassembles in helical disassociation of the flange and stem into a continuous strand that is withdrawn from the partial anastomosis prior to completion of the procedure.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Steerable catheter for right coronary artery
ActiveUS7867218B1Easy to placeEasy and less traumatic useCatheterIntravenous devicesAscending aortaGuide tube
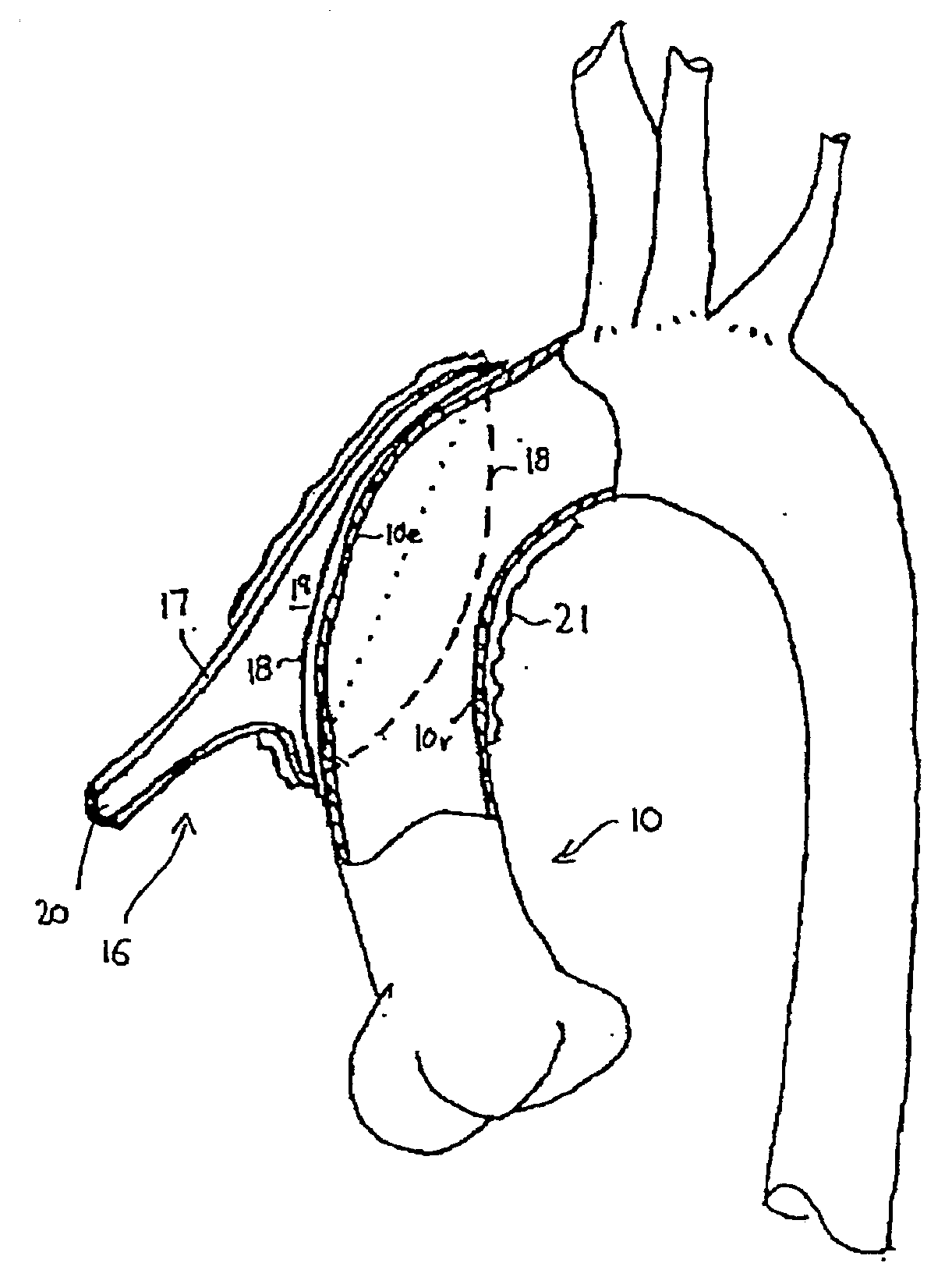
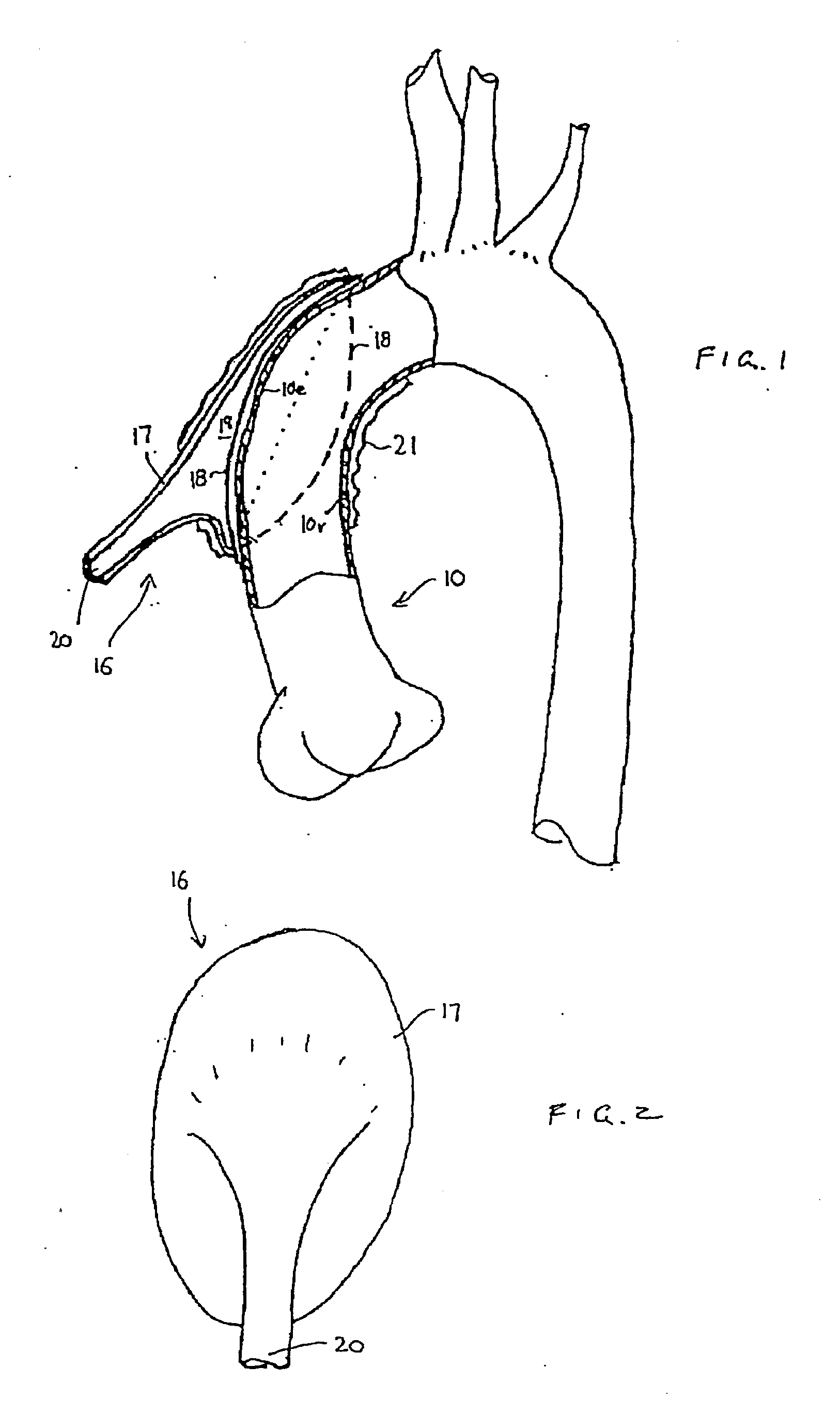
A steerable three dimensional catheter to engage the ostium of a right coronary artery in a patient includes: a torque-transmitting proximal shaft that receives manipulation by a user outside a patient in whom the catheter is used; and a distal shaft that is responsive to torque transmitted by the proximal shaft. The distal shaft includes a preformed support section having at least a segment that abuts a posterior or left lateral interior surface of the ascending aorta of the patient. The distal shaft also includes a preformed ostium entry section extending from the support section. In one implementation, the ostium entry section transitions from the support segment abutting the aortic wall to a distal tip end by way of at least two differently directed angles.
Owner:VODA HEART TECH
Heart Assist Device Utilising Aortic Deformation
The present invention relates to providing counter-pulsation heart assist by deforming the aorta. In a preferred embodiment, the deformation pressure is applied by cyclically, preferably in synchrony with the diastolic period of the heart. The deformation pressure may be applied to the outer wall of the aorta or to a patch covering a resected opening in the wall of the aorta.
Owner:NUWELLIS INC
Artificial endovascular stent and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the medical appliance field, particularly relates to an artificial endovascular stent and method for preparing thereof. The invention adopts tunica vasculosa made from varicosity Teflon and nickel-titanium alloy stent, and makes domestically produced artificial endovascular stents for the intracavity therapy of aneurism. The invention improves the performance of existing artificial endovascular stents, presents a small caliber, fits the windings of arteries, and improves the flexibility and biocompatibility. The stent is nontoxic, nonirritating for tissues, non-pyretogenic, non-sensitizing, non-teratogenic, and does not induce thrombosis in arteriae, thus reduces the direct damages to aorta walls.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV
Implantable prosthesis with displaceable skirt
InactiveUS20060184229A1Actively inhibitOvercomes shortcomingStentsSurgeryStent graftingAneurysm neck
An implantable prosthesis is provided having a radially-expandable tubular body and at least one skirt extending therefrom. The skirt terminates in a peripheral edge, wherein at least portions of the peripheral edge are free and displaceable to a greater diameter of the tubular body. Thus, with the implantable prosthesis being a stent-graft used to treat an aortic aneurysm (e.g., abdominal aortic aneurysm (“AAA”)), the skirt may be used to inhibit Type I endoleaks upon its selective displacement in response to irregular aortic shaping and / or aneurysm neck expansion. The skirt may actively inhibit Type I endoleaks by forming a physical barrier against flow between the tubular body and the aortic wall. In addition, the skirt may passively inhibit endoleak formation by sufficiently restricting blood flow to allow coagulation and clot formation, which would act as a barrier against endoleakage.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Prosthetic heart valves, support structures and systems and methods for implanting the same,
The implantable heart valve can have an inverted configuration and can include a support structure and at least two valve leaflets. Preferably, when the valve is placed in proximity with an aortic valve implantation site of a subject and engaged with the implantation site, the valve leaflets are configured to deflect towards the aortic wall into a first position for resisting the flow of blood towards the left ventricle and configured to deflect away from a aortic wall into a second position for allowing the flow of blood from a left ventricle, with the support structure configured to remain static during leaflet deflection.
Owner:AORTX
System and method for semi-automatic aortic aneurysm analysis
A method for automatically analyzing an aortic aneurysm includes providing a digitized 3-dimensional image volume of an aorta, determining which voxels in said image are likely to be lumen voxels, determining a distance of said lumen voxels from an aortic boundary, finding a centerline of the aorta in said image volume based on said lumen voxel distances, constructing a series of 2-dimensional multiplanar reformatted (MFR) image planes orthogonal to this centerline, segmenting aortic cross sections in each said MPR image plane wherein an aortic wall is located in each MPR image, and constructing from said aortic wall locations a 3D model of the aorta.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
Intra-aortic emboli protection filter device
ActiveUS20190000604A1More freedomBlood vesselsBlood vessel filtersEmbolic Protection DevicesEngineering
An embolic protection device including a porous deflector screen including a filter, arranged to expand and to conform to a wall of the aortic arch covering entrances to arteries branching from an aorta, an emboli collector including a cylinder arranged to expand and to lie along walls of a descending aorta, pushing against walls of the descending aorta and anchoring the porous deflector screen, and a connecting portion for connecting the porous deflector screen and the emboli collector, arranged to push the porous deflector screen against a wall of the aortic arch while anchoring against the emboli collector. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:FILTERLEX MEDICAL LTD
Clampless anastomotic device
Owner:WILSON DAVID B
Devices and methods for AAA management
A method of treating an abdominal aortic aneurysm is disclosed. The method includes the steps of providing an endovascular graft configured to be disposed within an aorta of a patient and to be attached to an aortic wall to channel aortic blood flow therethrough; advancing a temporary stent catheter endovascularly to a location of the aneurysm, the catheter being attached to a temporary stent, the temporary stent and the graft being constrained by one or more constraining devices during advancement of the graft; removing the one or more constraining devices from the graft and temporary stent, to allow the temporary stent to stabilize the graft against the aortic wall; fixing the graft to the aortic wall; reconstraining the temporary stent with one of the one or more constraining devices; and withdrawing the temporary stent catheter, temporary stent and the one or more constraining devices, releasing the graft.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com