Patents
Literature
74 results about "Central catheter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A central line catheter, also known as a central venous catheter, is a thin, flexible tube that inserted into a vein and threaded to the heart or central vein of the chest. This device allows a medical professional to administer medications and blood transfusions as well as obtaining blood samples.
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
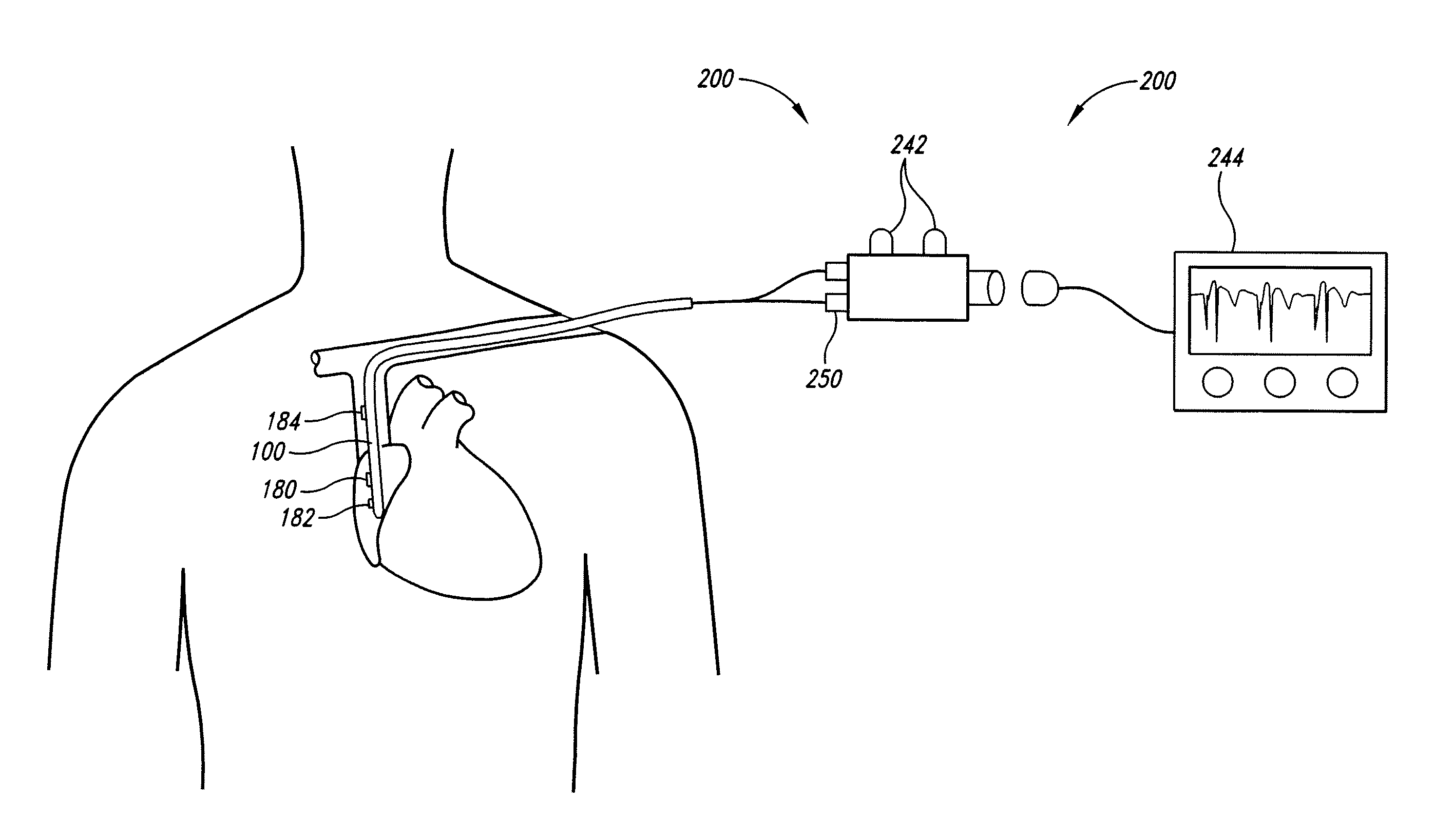
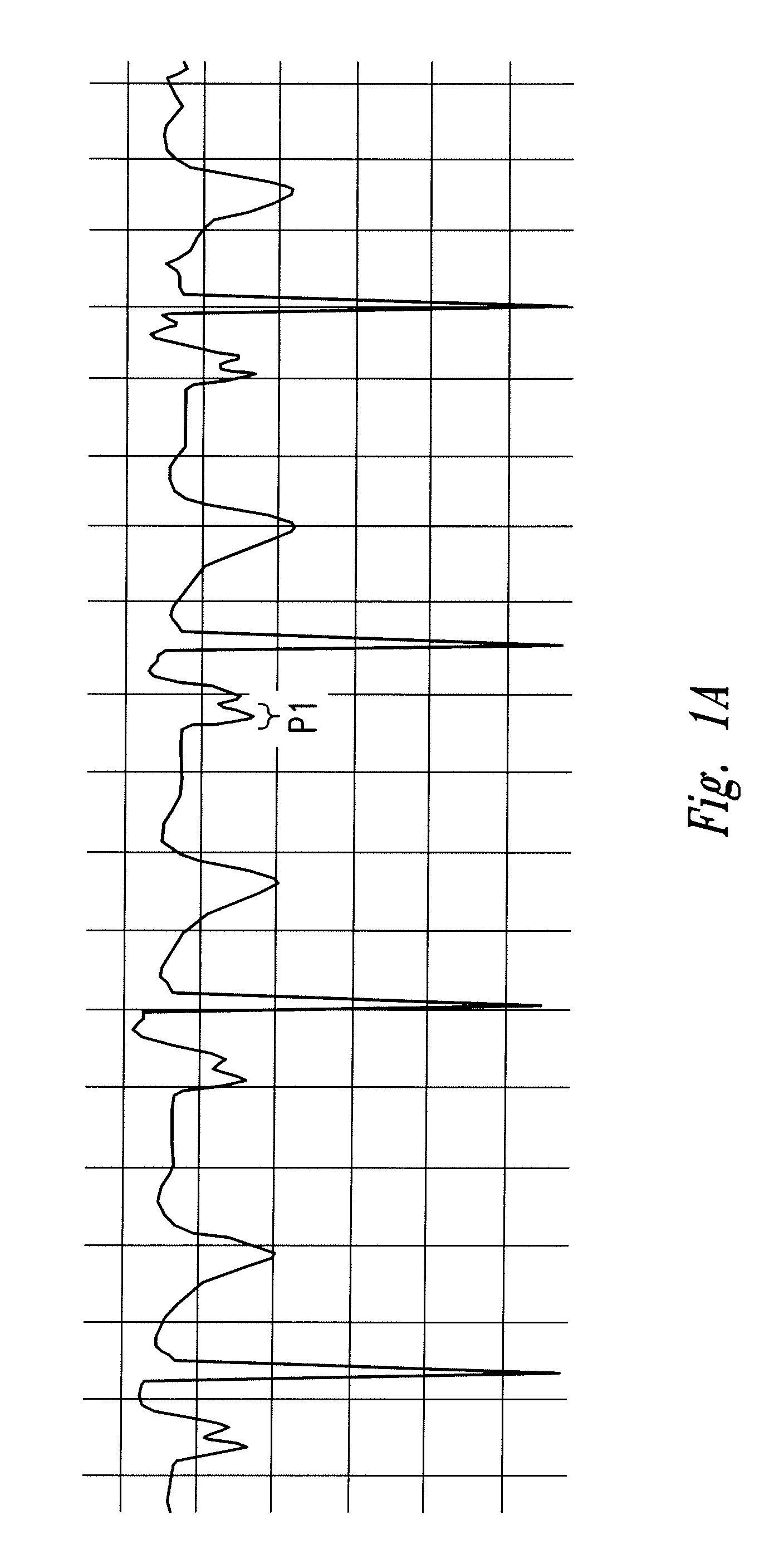
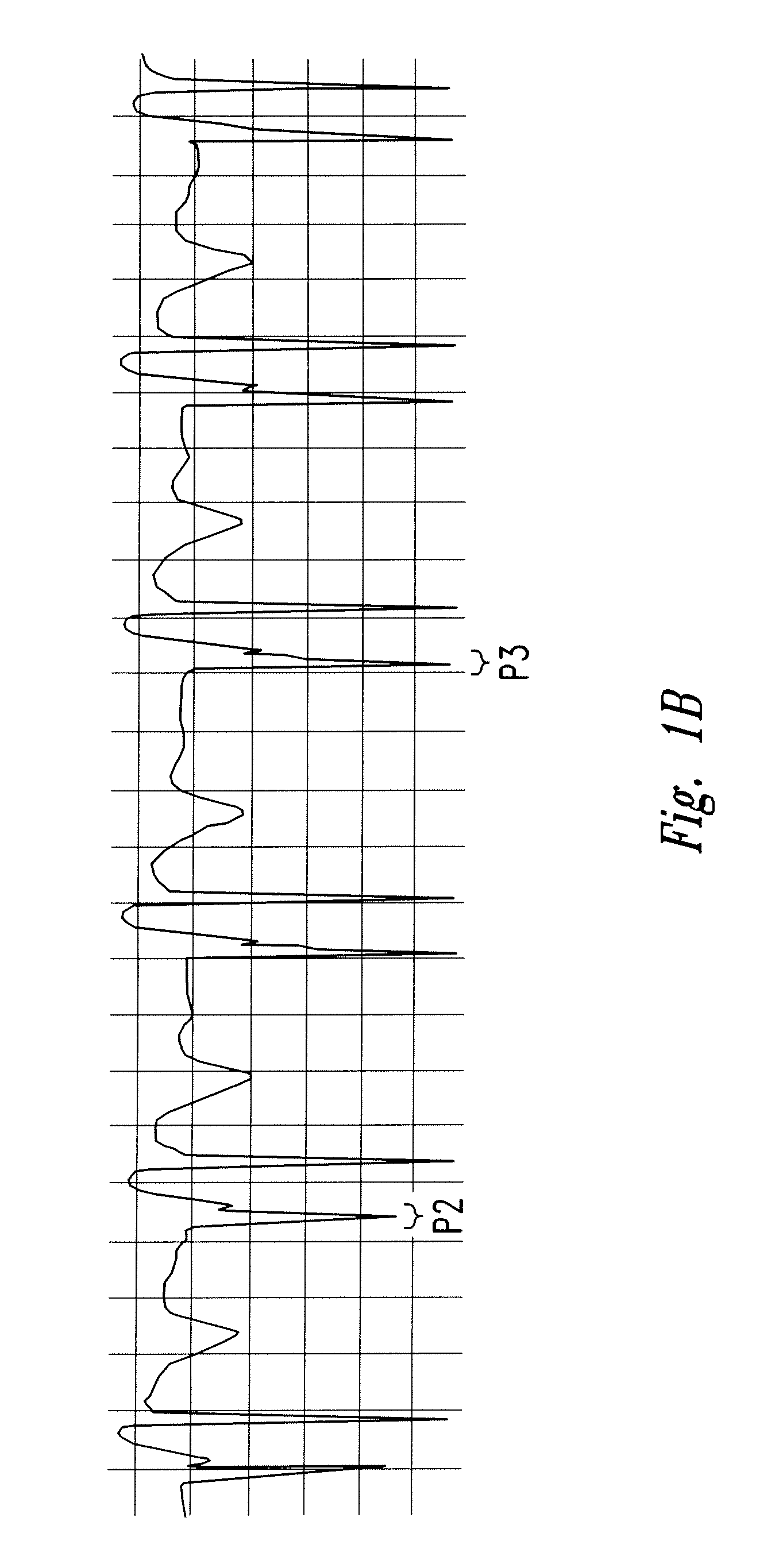
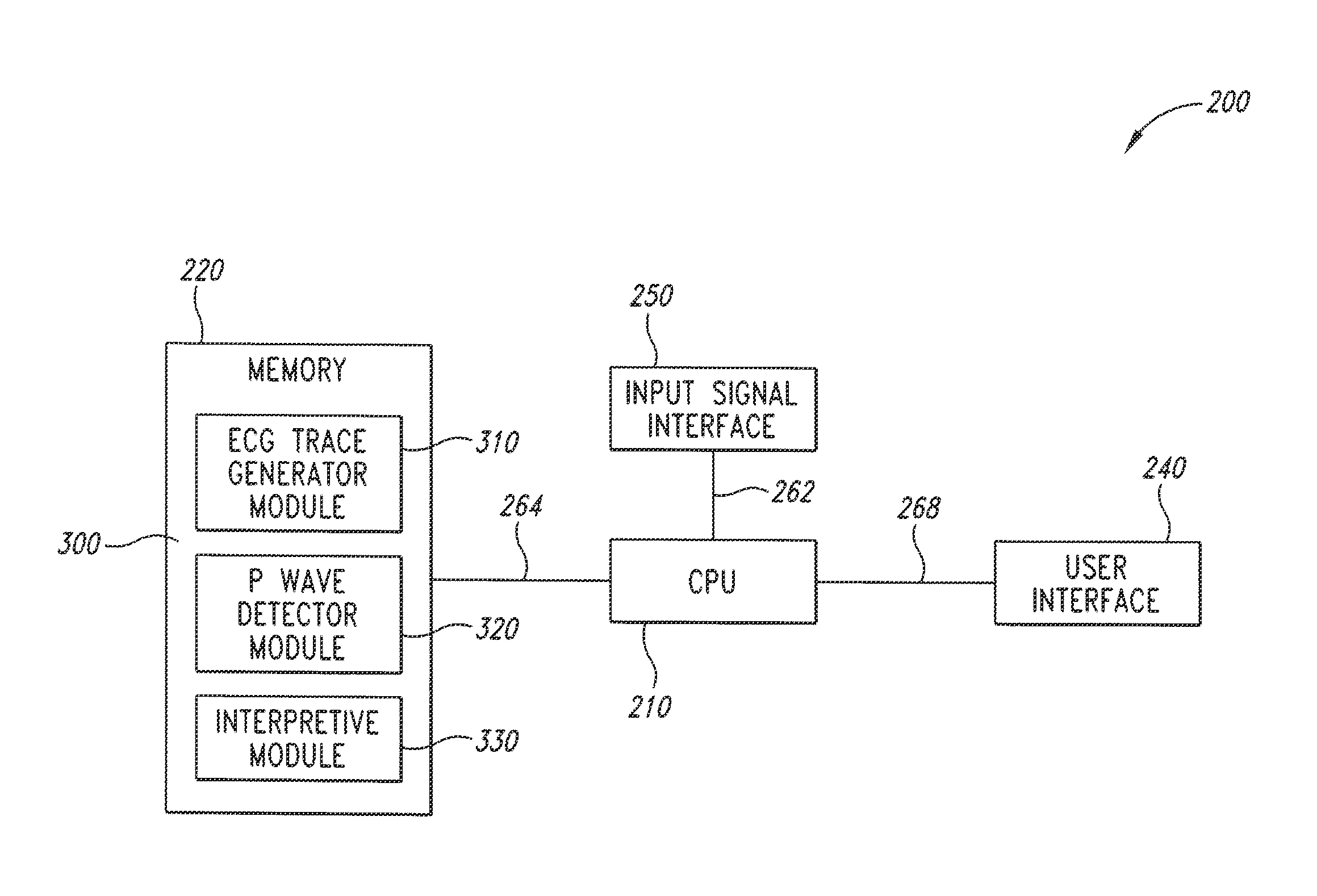
The invention includes a method of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) having a distal and proximal pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava, right atrium, and / or right ventricle. The method includes obtaining a distal and proximal electrical signal from the distal and proximal pair and using those signals to generate a distal and proximal P wave, respectively. A deflection value is determined for each of the P waves. A ratio of the deflection values is then used to determine a location of the tip of the CVC. Optionally, the CVC may include a reference pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava from which a reference deflection value may be obtained. A ratio of one of the other deflection values to the reference deflection value may be used to determine the location of the tip of the CVC.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
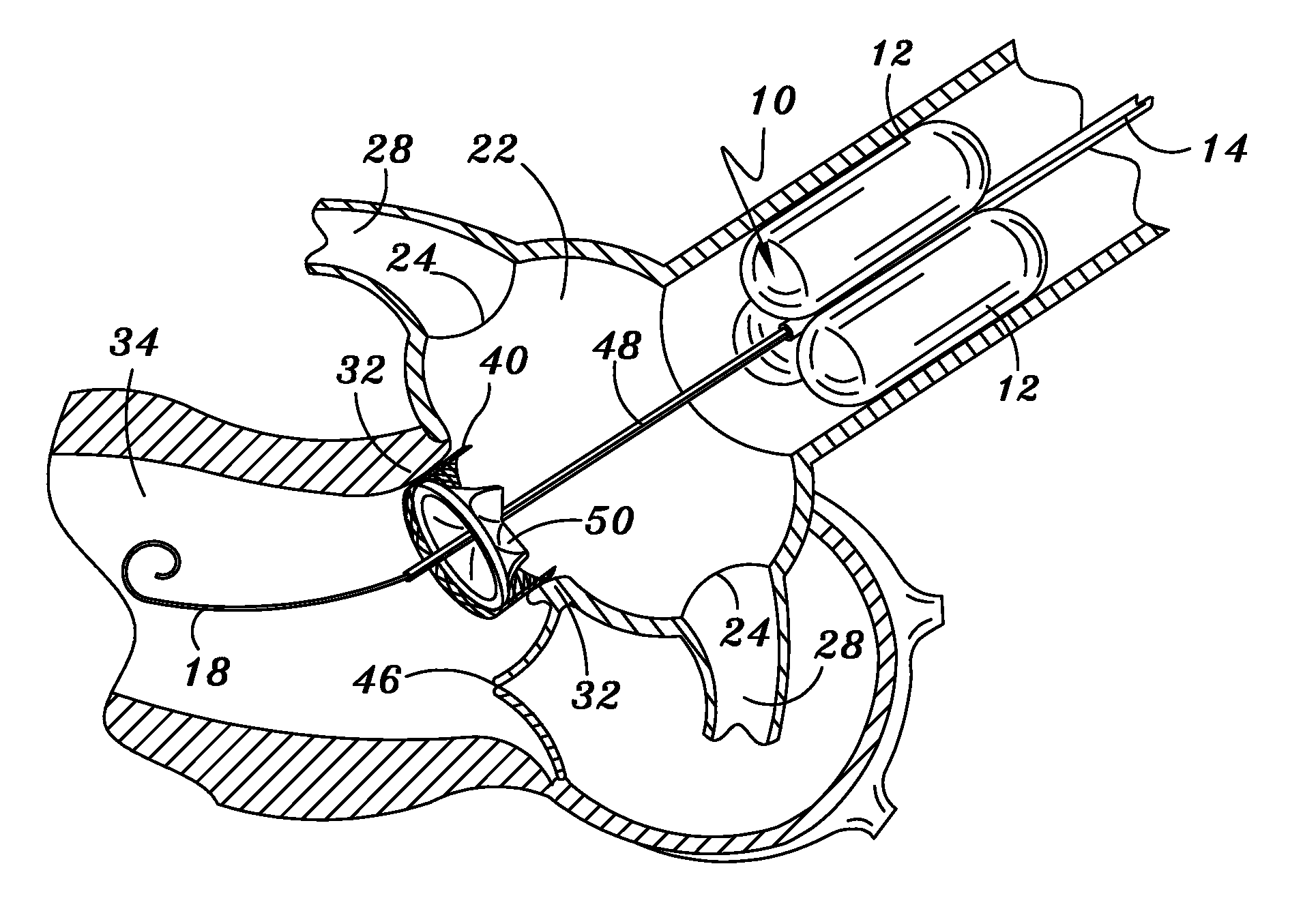
Methods and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS20090030510A1Optimize timingAccurate placementBalloon catheterHeart valvesVascular tissueCardiac cycle
A delivery system and method for percutaneous aortic valve (PAV) replacement and apparatus used therein. A temporary aortic valve comprised of a reversibly expandable occluding means, such as balloons, surrounds a central catheter mechanism. The temporary valve is positioned within the ascending aorta, just above and downstream from the coronary ostia. The occluding means is configured such that, when fully expanded against the aortic wall, gaps are left that promote continuous coronary perfusion during the cardiac cycle. The temporary valve with occluding means substitutes for the function of the native aortic valve during its replacement. The native aortic valve is next dilated, and then ablated through deployment of low profile, elongated, sequentially delivered stents. The ablation stent(s) displace the native valve tissues and remain within the aortic annulus to receive and provide a structure for retaining the PAV. The PAV is delivered, positioned and deployed within the ablation stent(s) at the aortic annulus with precision and relative ease. Ablation of the native aortic valve removes the structural obstacles to precise PAV placement. The temporary aortic valve mediates the hemodynamic forces upon the devices as encountered by the surgeon following native valve ablation. The temporary valve also promotes patient stability through continuous coronary perfusion and a moderated transvalvular pressure gradient and regurgitation. Sequential delivery of low profile PAV components minimize the risk of trauma and injury to vascular tissues. Mathematical considerations for determining the optimum cross-sectional area for the temporary valve blood perfusion gaps are also described.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Method and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS20090030503A1Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesCoronary artery ostiumCardiac cycle
A method for percutaneous aortic valve (PAV) replacement and a temporary aortic valve used to facilitate the same. The temporary valve is comprised of a reversibly expandable occluding means, such as balloons, surrounding a central catheter mechanism. The temporary valve is positioned within the ascending aorta, just above and downstream from the coronary ostia. The occluding means is configured such that, when fully expanded against the aortic wall, gaps are left that promote continuous coronary perfusion during the cardiac cycle. The native aortic valve is next dilated, and then ablated through deployment of an ablation stent. The ablation stent displaces the native valve tissues and remains within the aortic annulus to receive and retain the PAV. The PAV can then be positioned and deployed within the ablation stent with precision and ease. Ablation of the native aortic valve removes the structural obstacles to precise PAV placement. The temporary aortic valve mediates the hemodynamic forces encountered by the surgeon following native valve ablation. The temporary valve also promotes patient stability through continuous coronary perfusion and a moderated transvavlular pressure gradient. Mathematical considerations for determining the optimum cross-sectional area for the temporary valve blood perfusion gaps are also described.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Methods and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS8663319B2Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesCardiac cyclePerfusion
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Method and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS8663318B2Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesAscending aortaCoronary artery ostium
A catheter adapted for placement in the ascending aorta comprises a central catheter mechanism and a balloon structure or other occluding structure at its distal end. The catheter may be placed over the aortic arch such that the balloon structure is placed in the ascending aorta just above the Sinus of Valsalva and coronary ostia. Once in place, the balloon structure is inflated to control blood flow through the aorta during aortic valve ablation and replacement protocols.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Methods and devices for non-invasive cerebral and systemic cooling
ActiveUS20080215002A1Minimize neurologic deficitReduce perfusionInfusion devicesSurgeryNostrilNasal cavity
A method for cerebral and systemic cooling by circulating a cold liquid through a nasal catheter looped through the patient's nasal cavities and around the nasal septum. The nasal catheter is inserted into the patient's first nostril, advanced through the nasal cavity, around the nasal septum and out of the patient's second nostril. A cold fluid having a temperature between about −20° C. and about 37° C. is flowed though a lumen in the nasal catheter to cool the nasal cavity. The nasal catheter may have one or more flexible balloons mounted on the catheter such that when the catheter is looped around the nasal septum, the balloon(s) are positioned in a portion of the patient's first and second nasal cavities. When a cold liquid is circulated through the catheter lumen, the flexible balloons expand to a contact the inner walls of the nasal cavities and provide direct cooling of the nasal cavities.
Owner:BRAINCOOL
Catheter with concentric balloons for radiogas delivery and booster radiosources for use therewith
InactiveUS7056274B2Reduce the amount requiredLower the volumeSurgeryDilatorsRadioactive gasExternal catheter
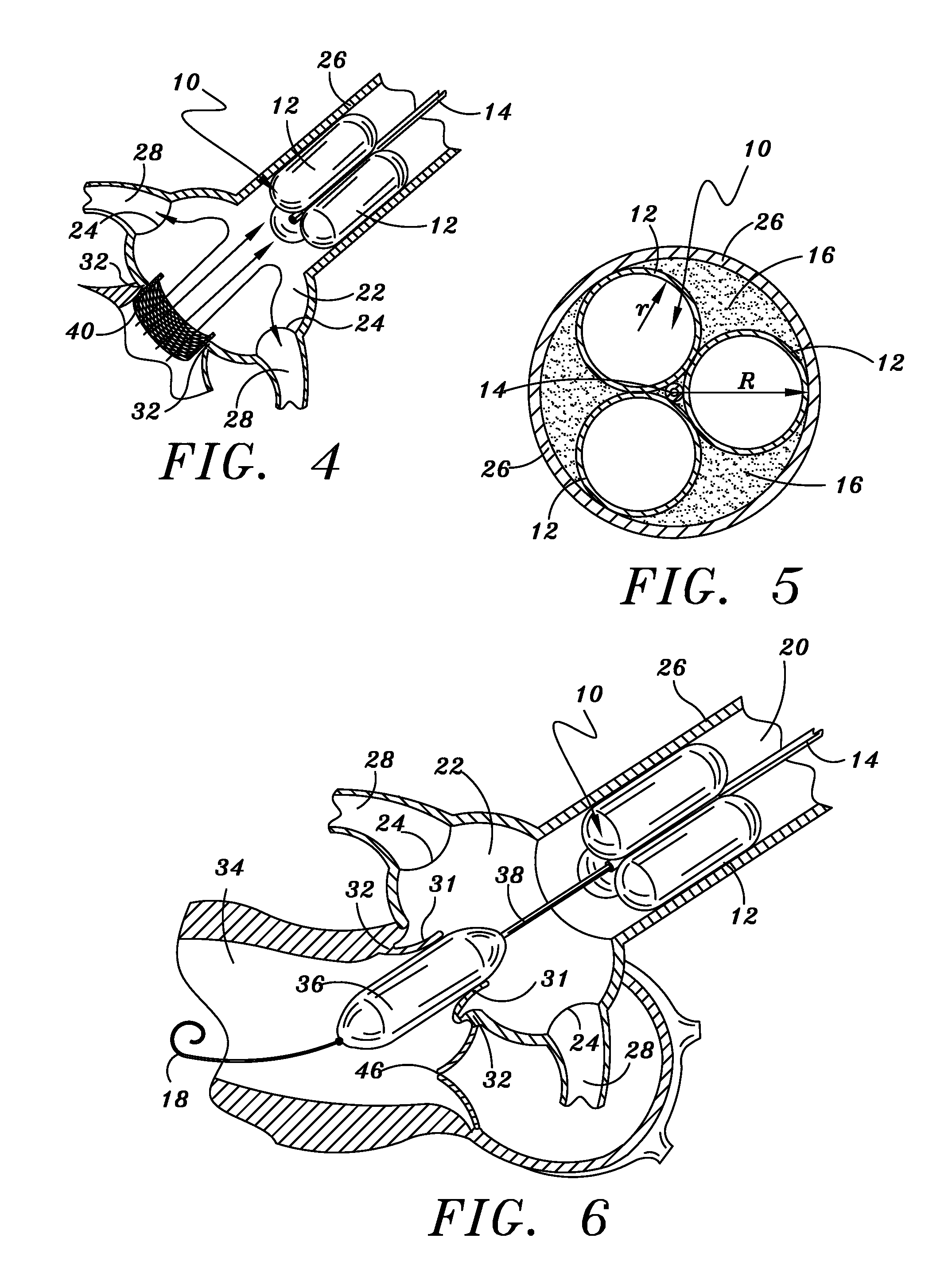
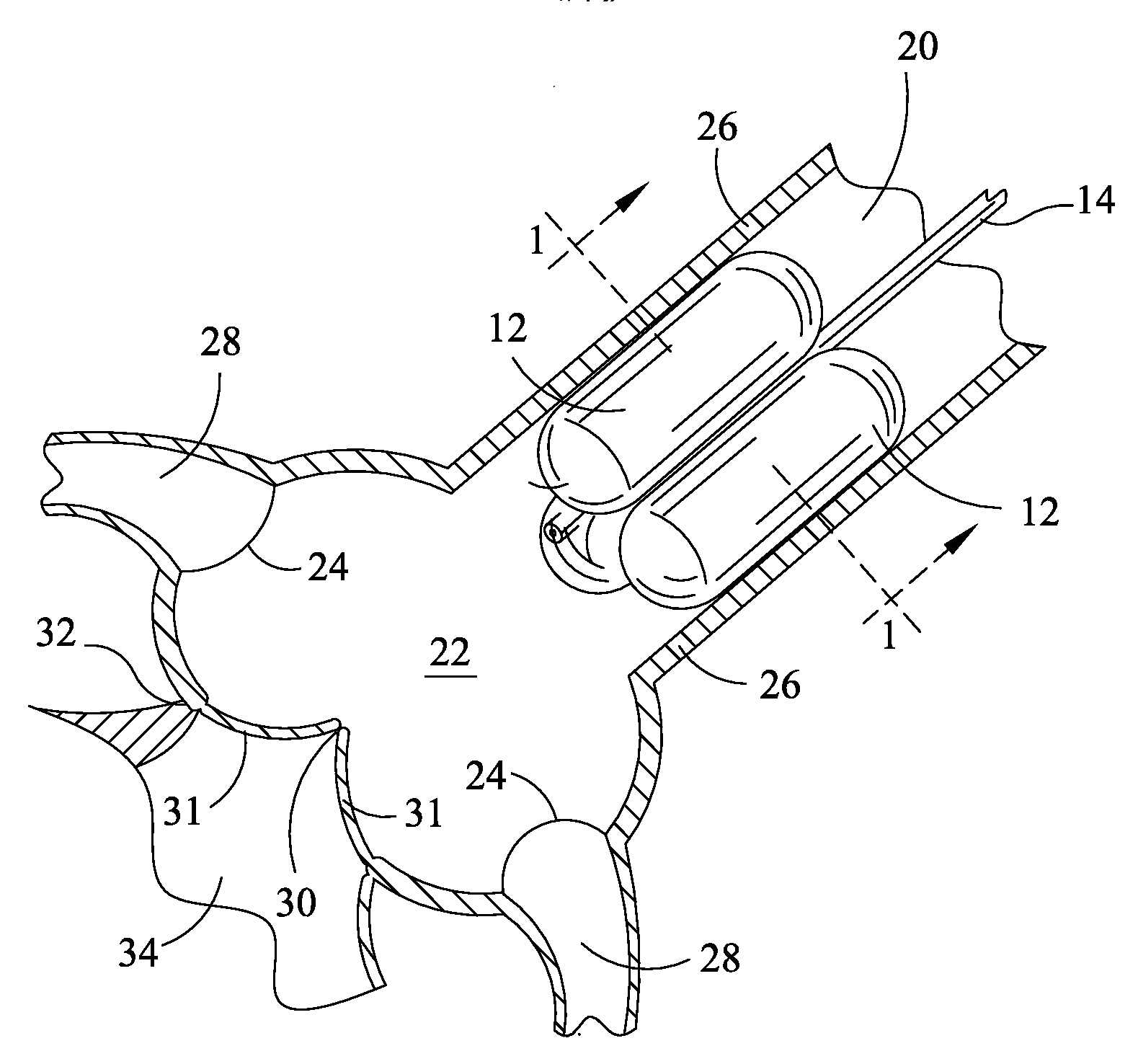
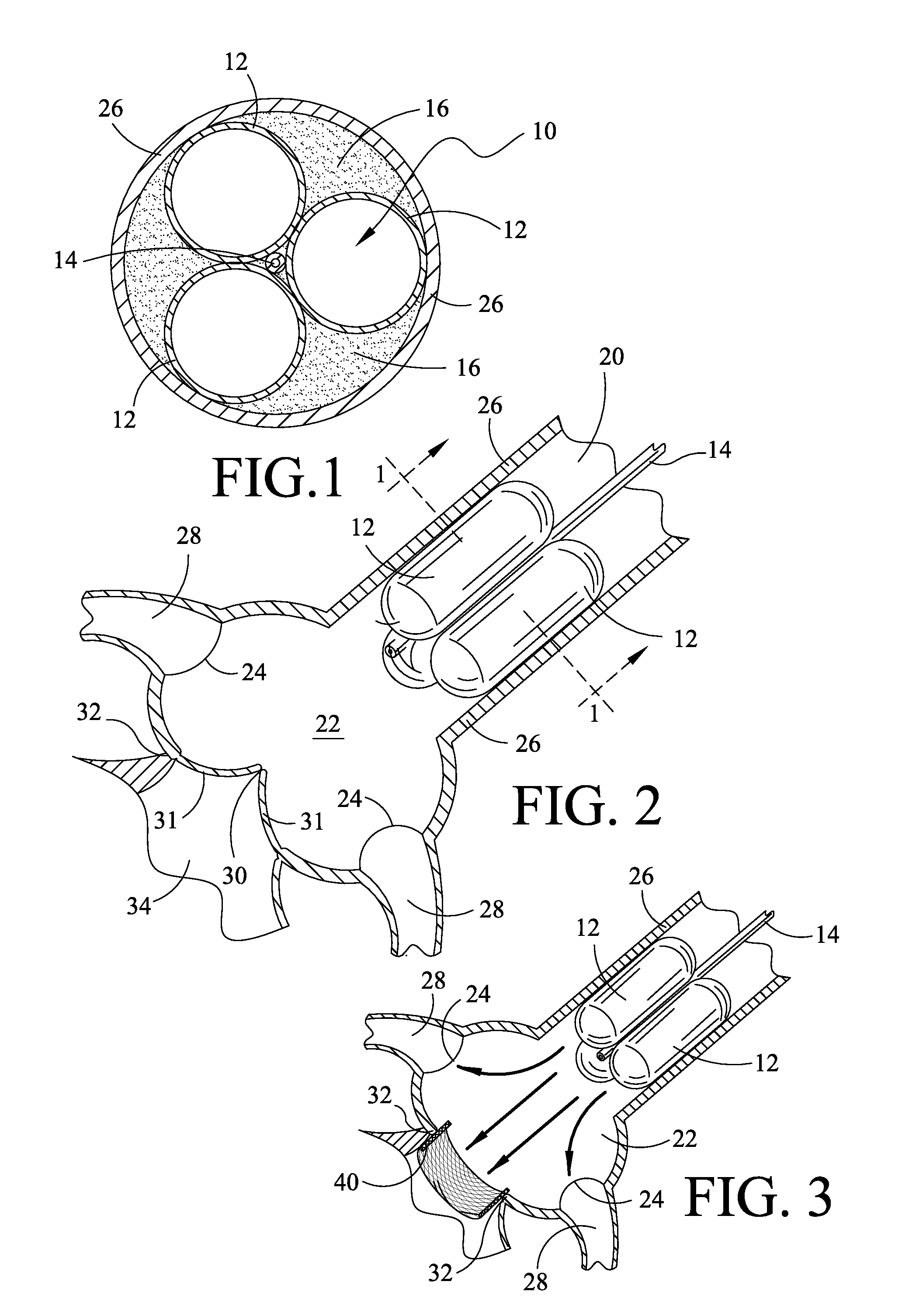
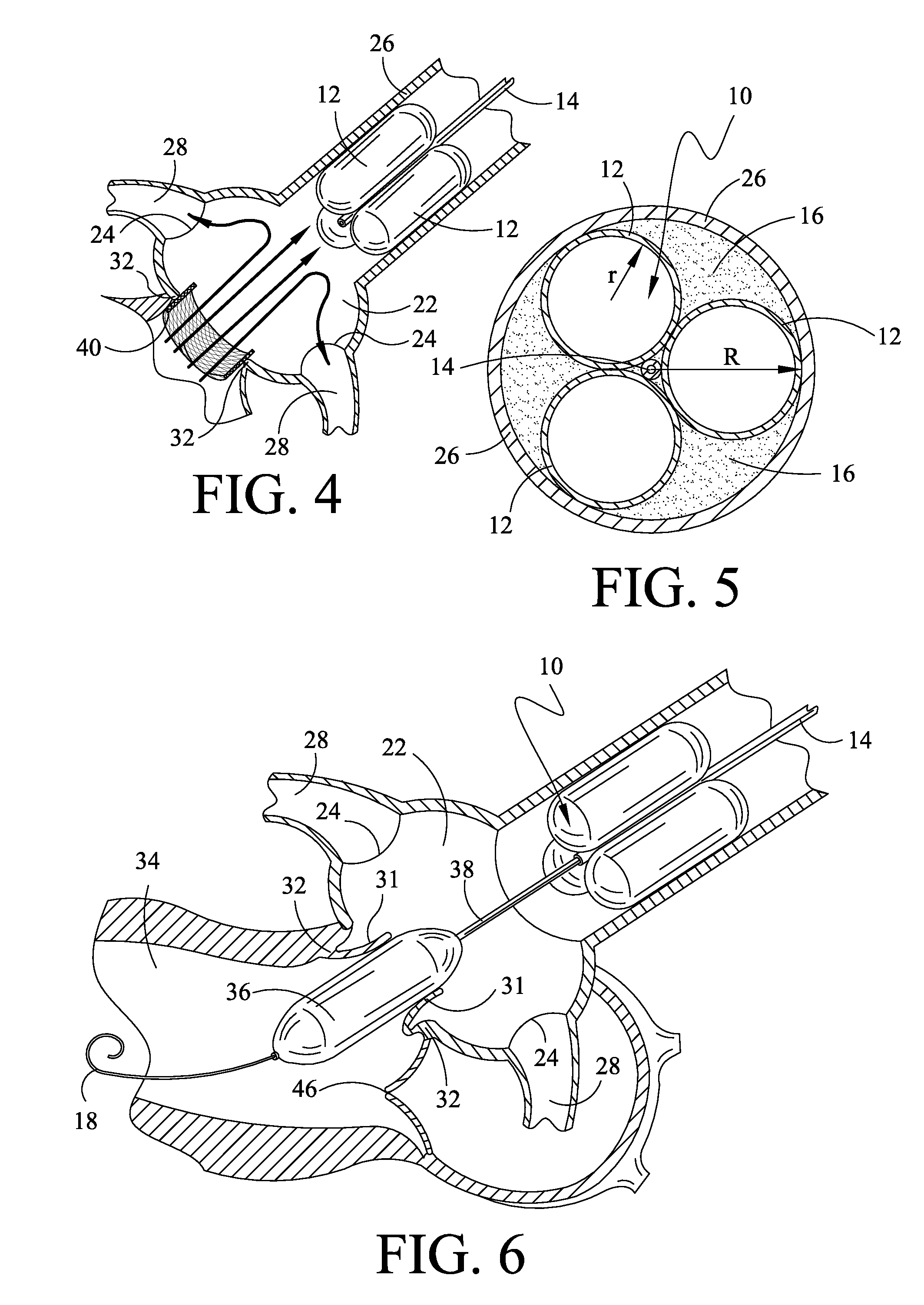
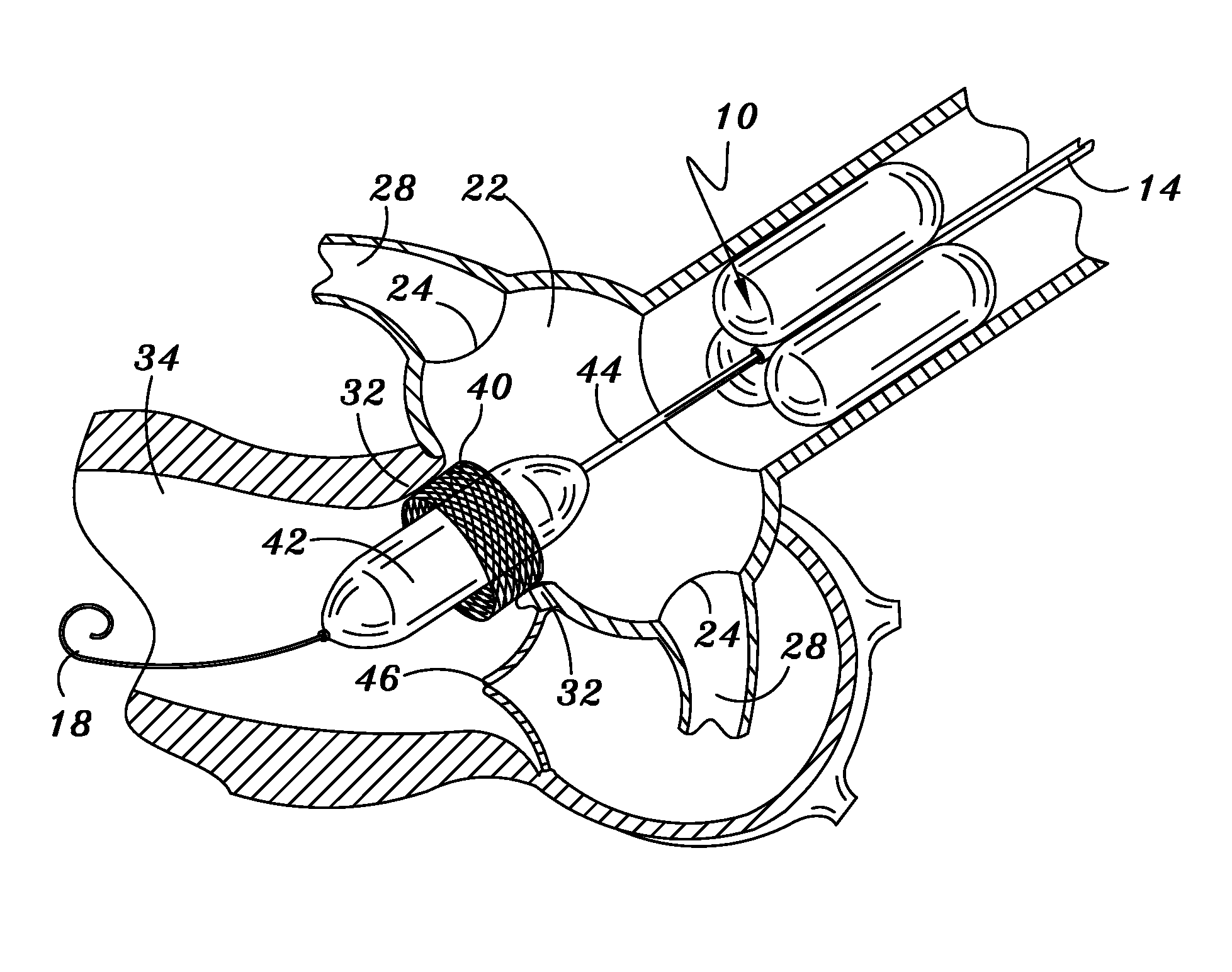
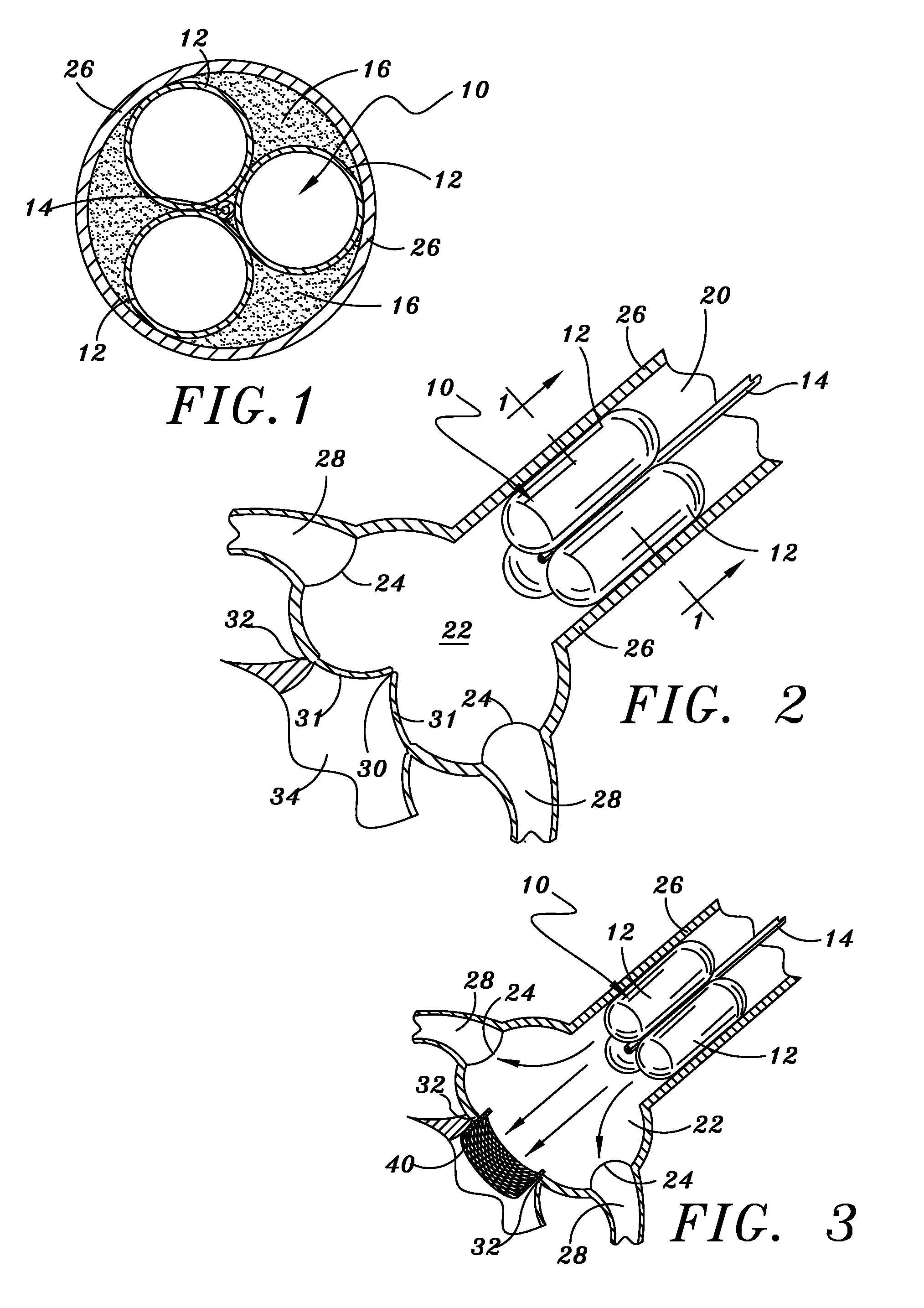
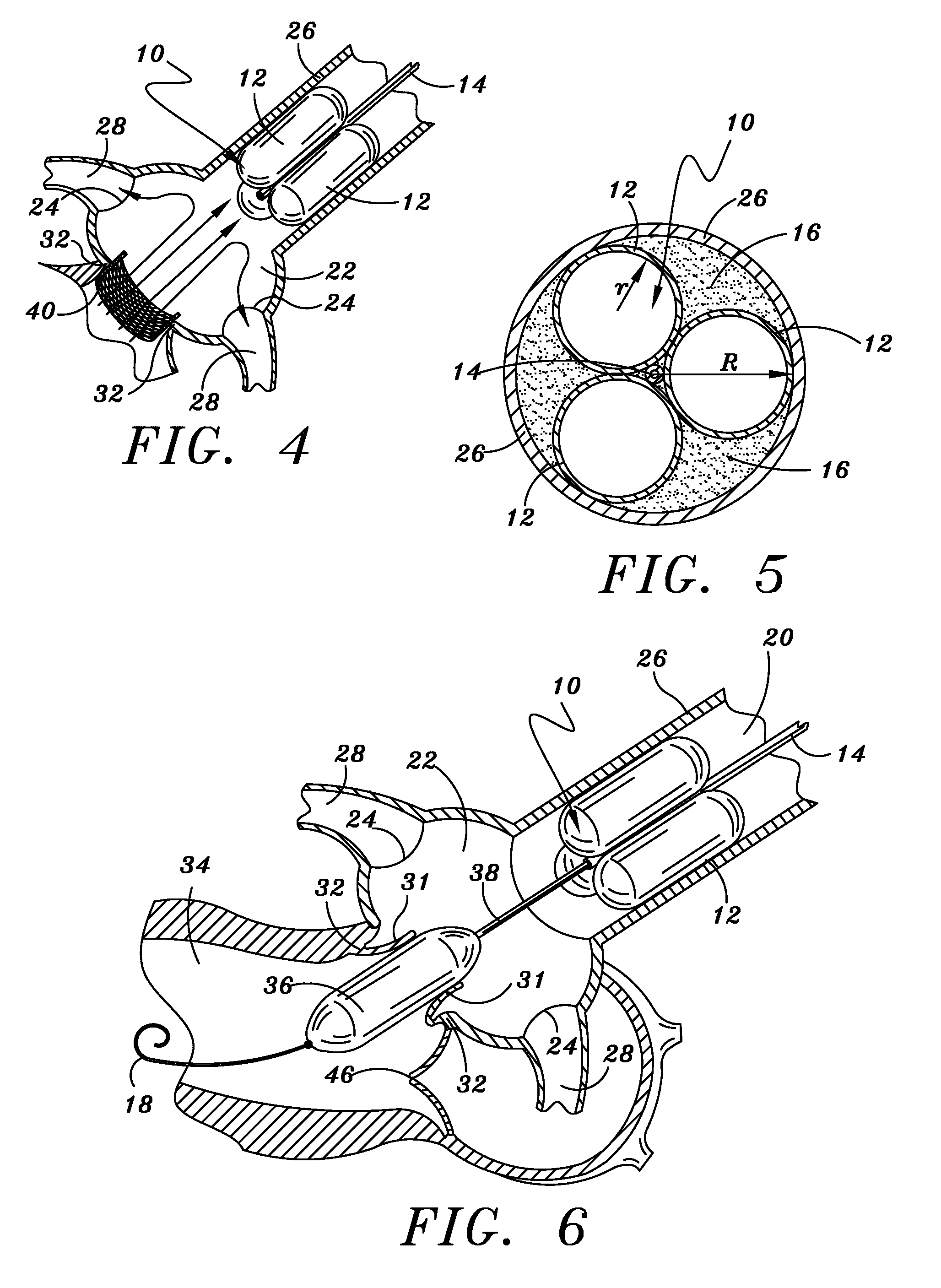
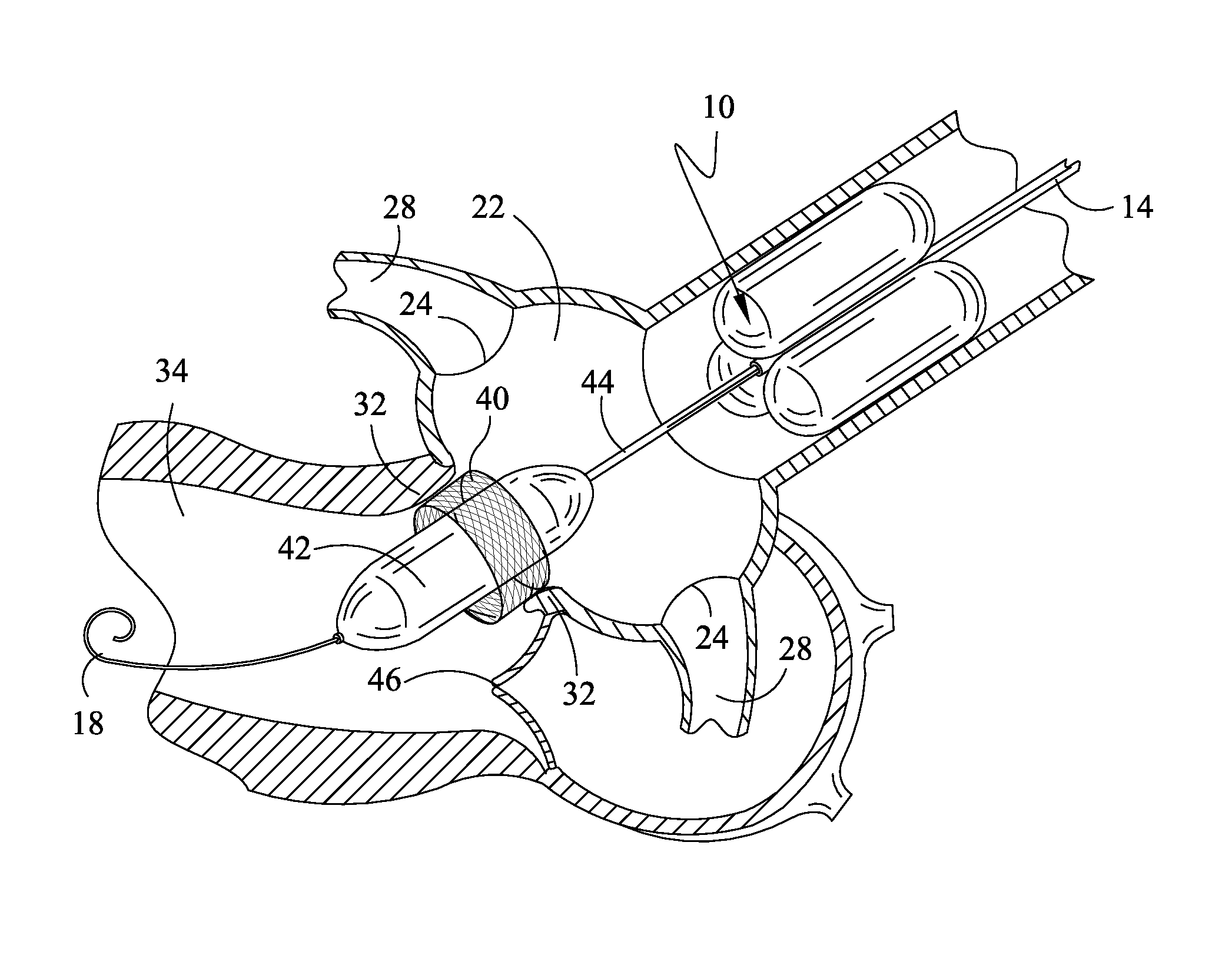
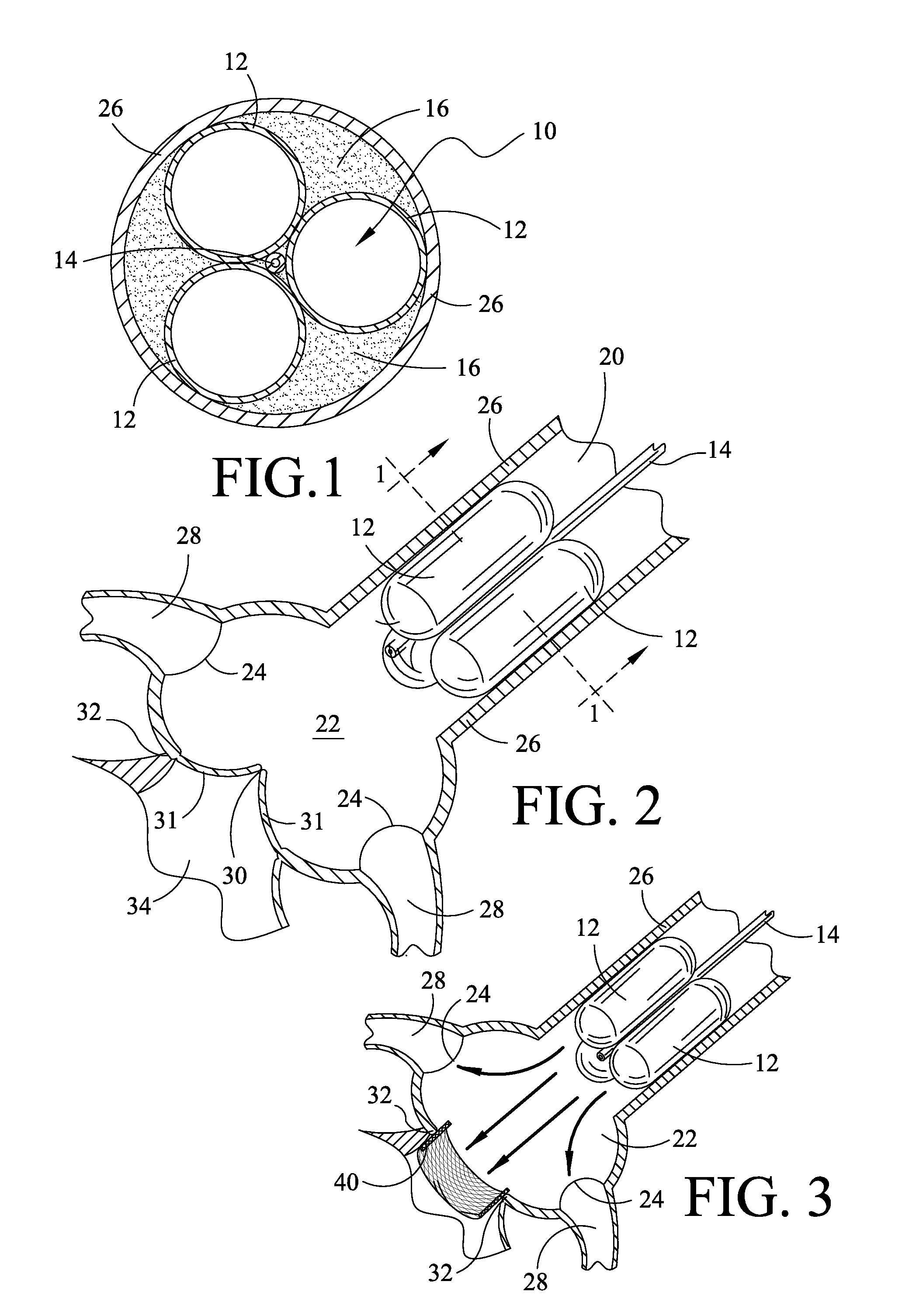
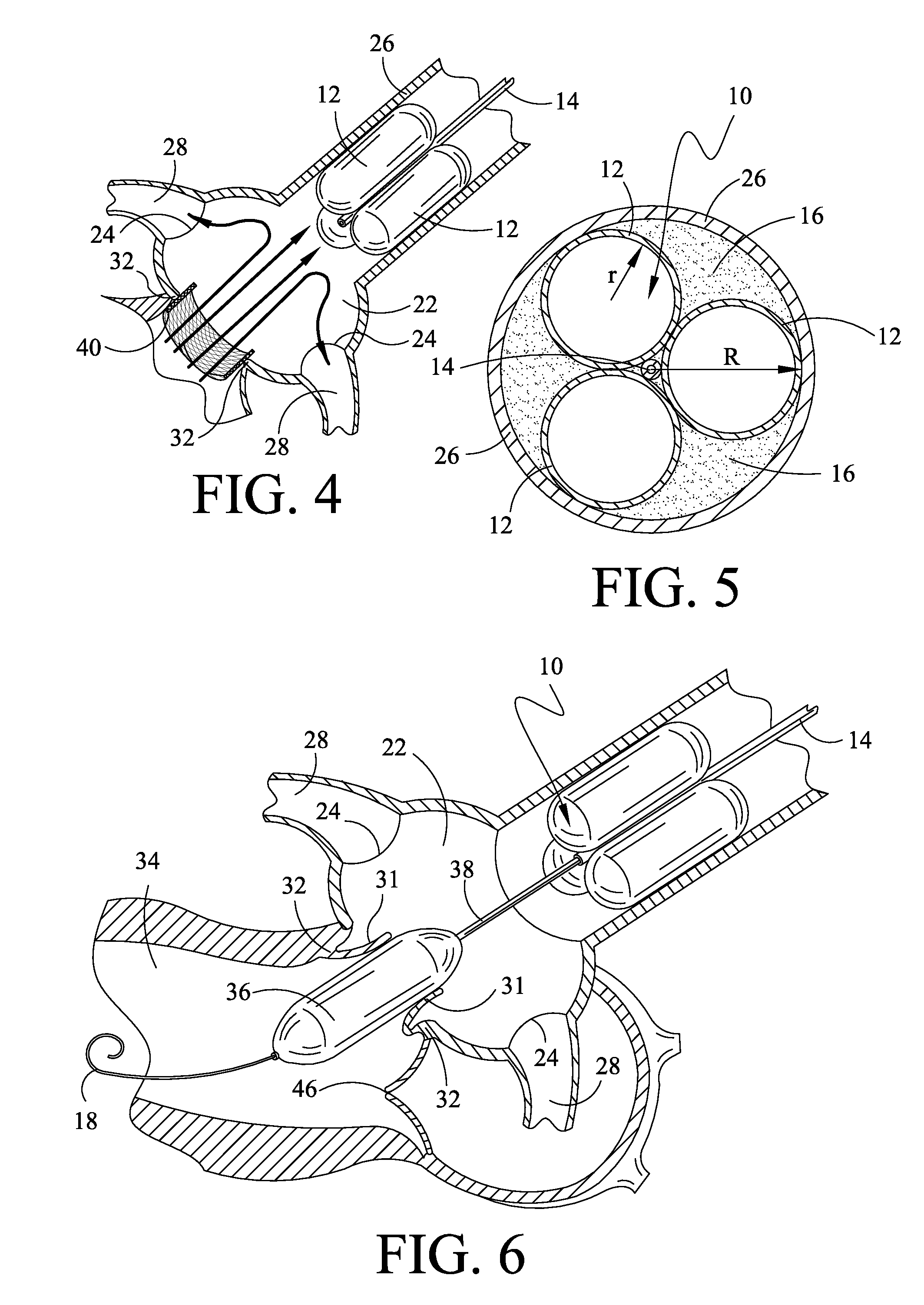
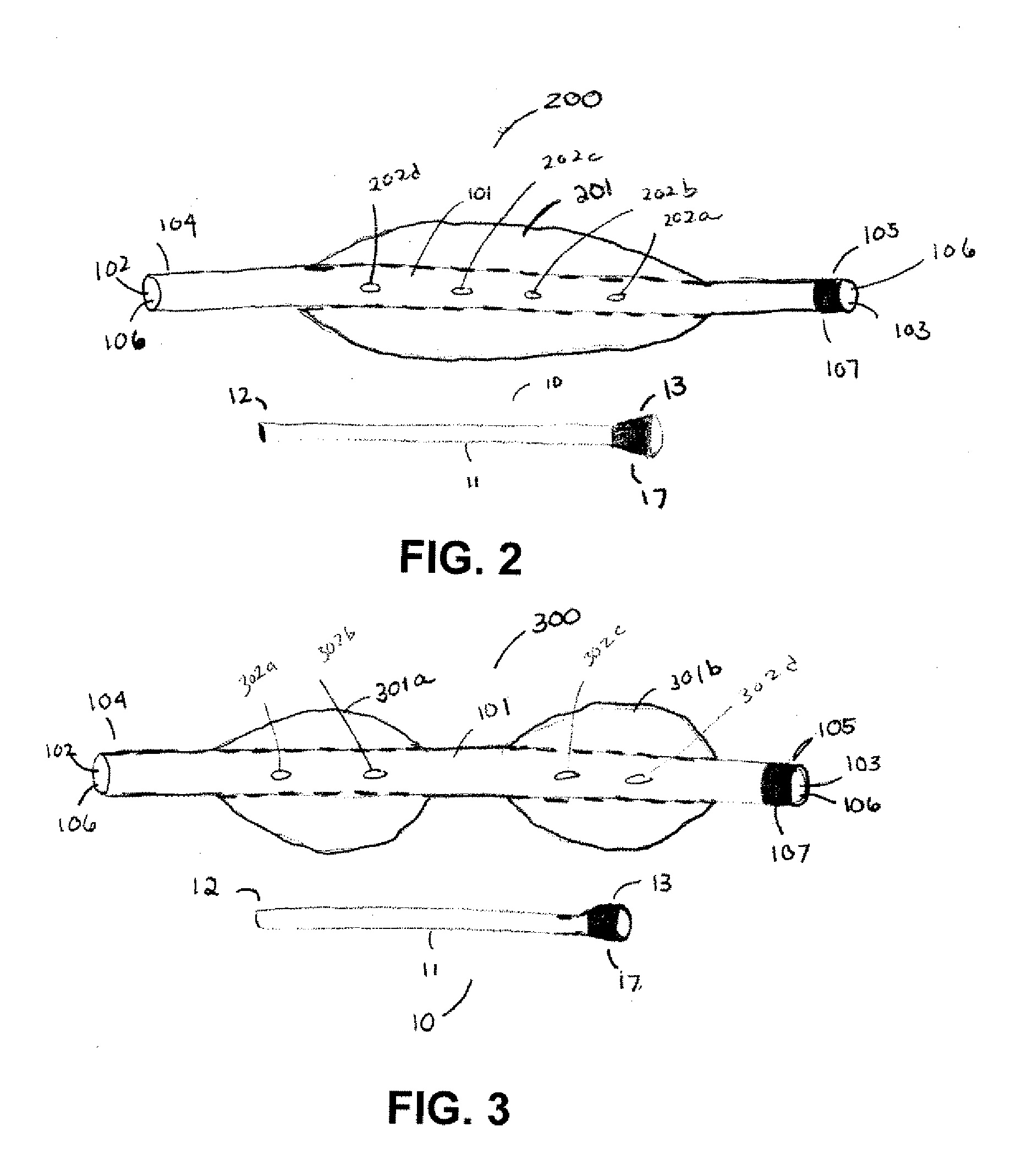
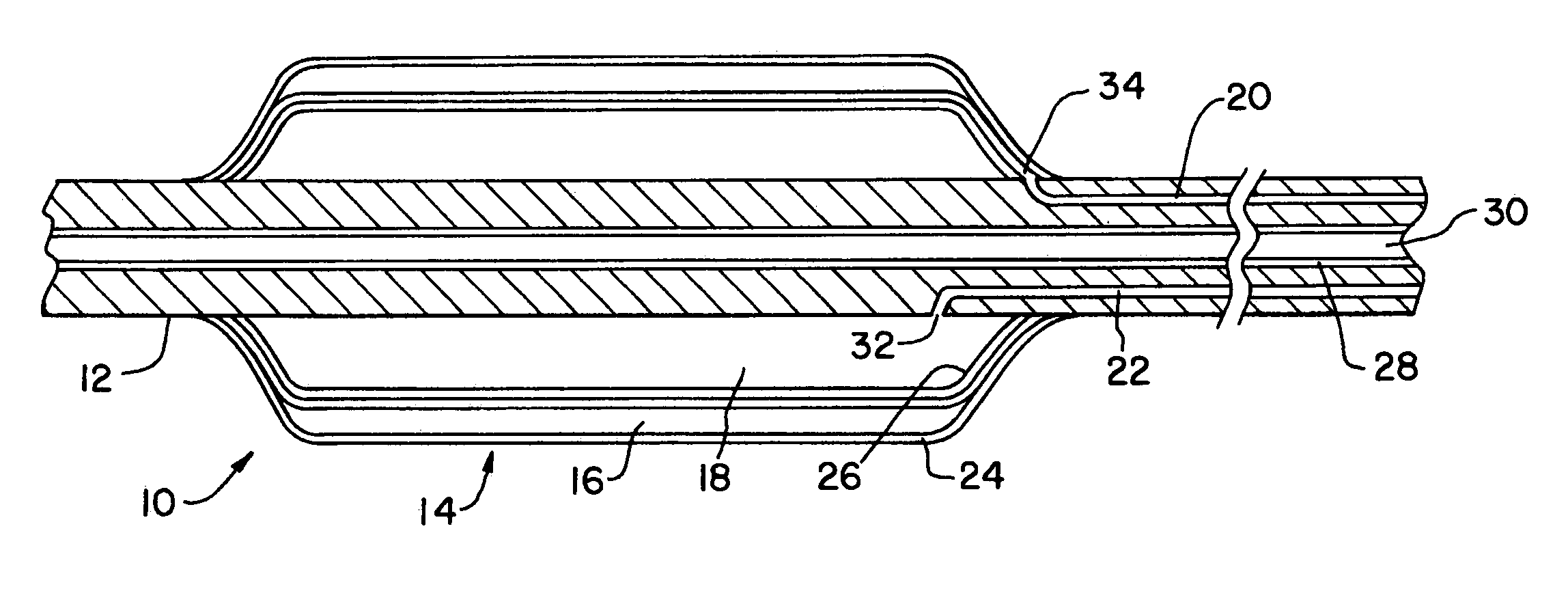
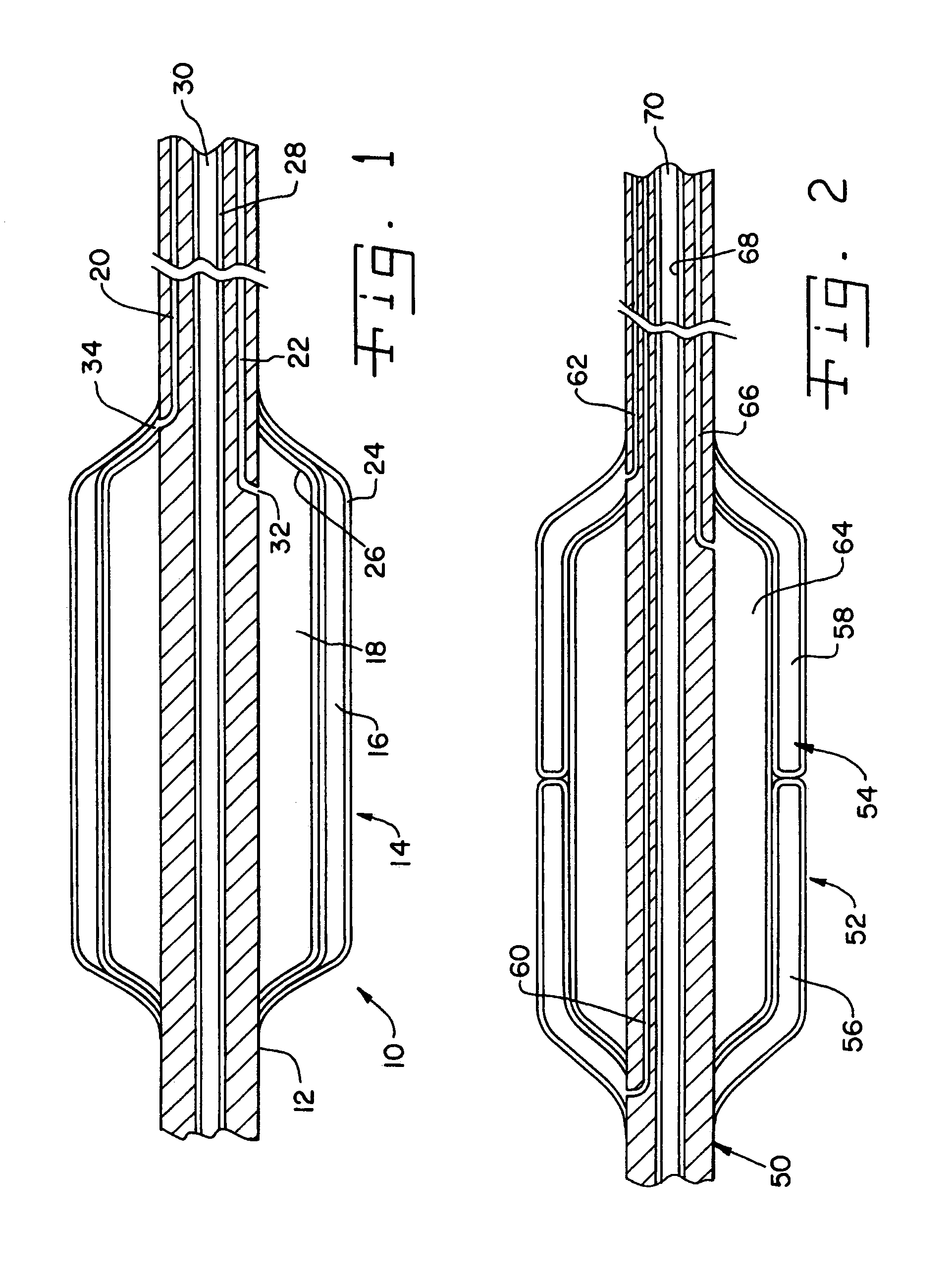
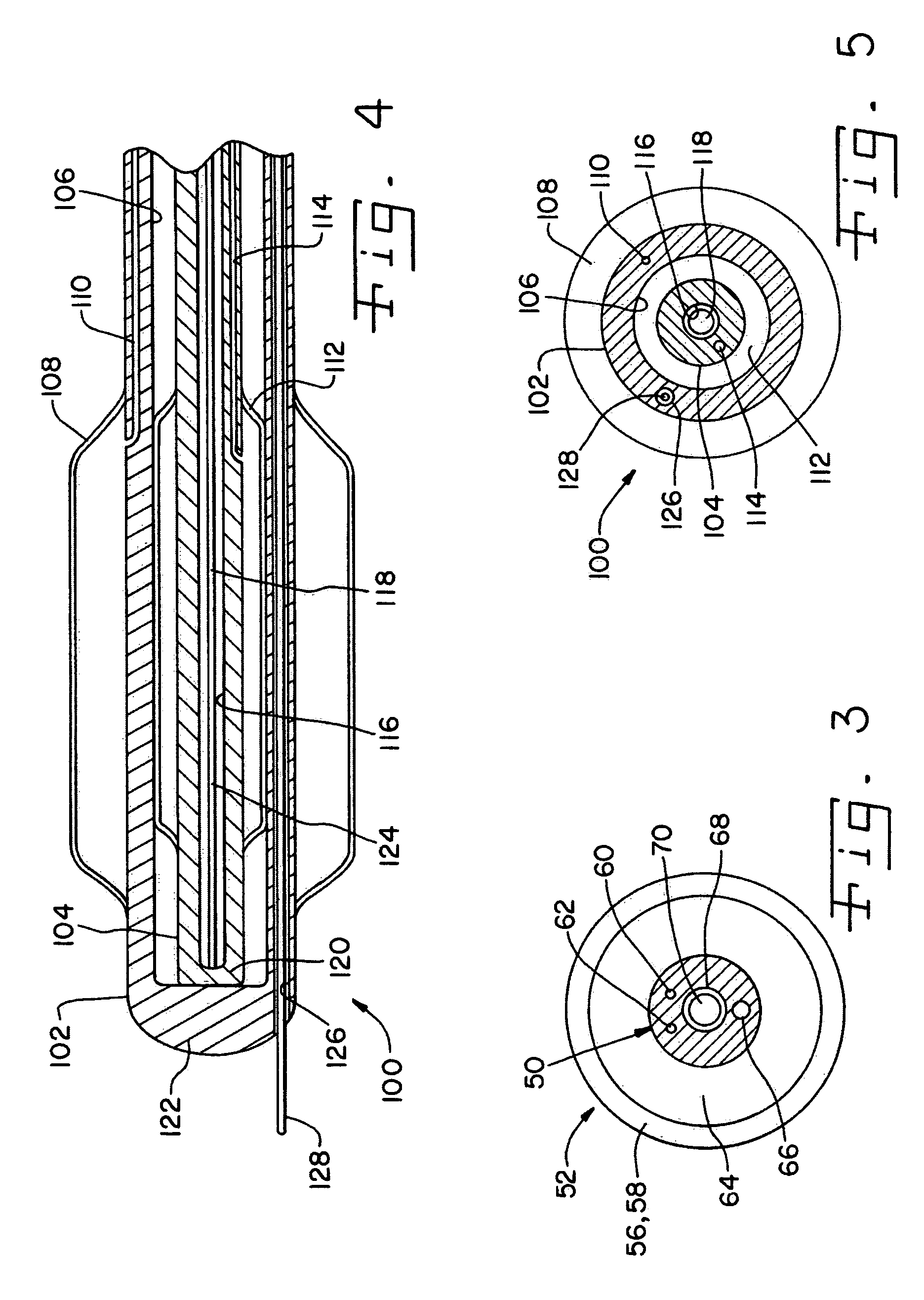
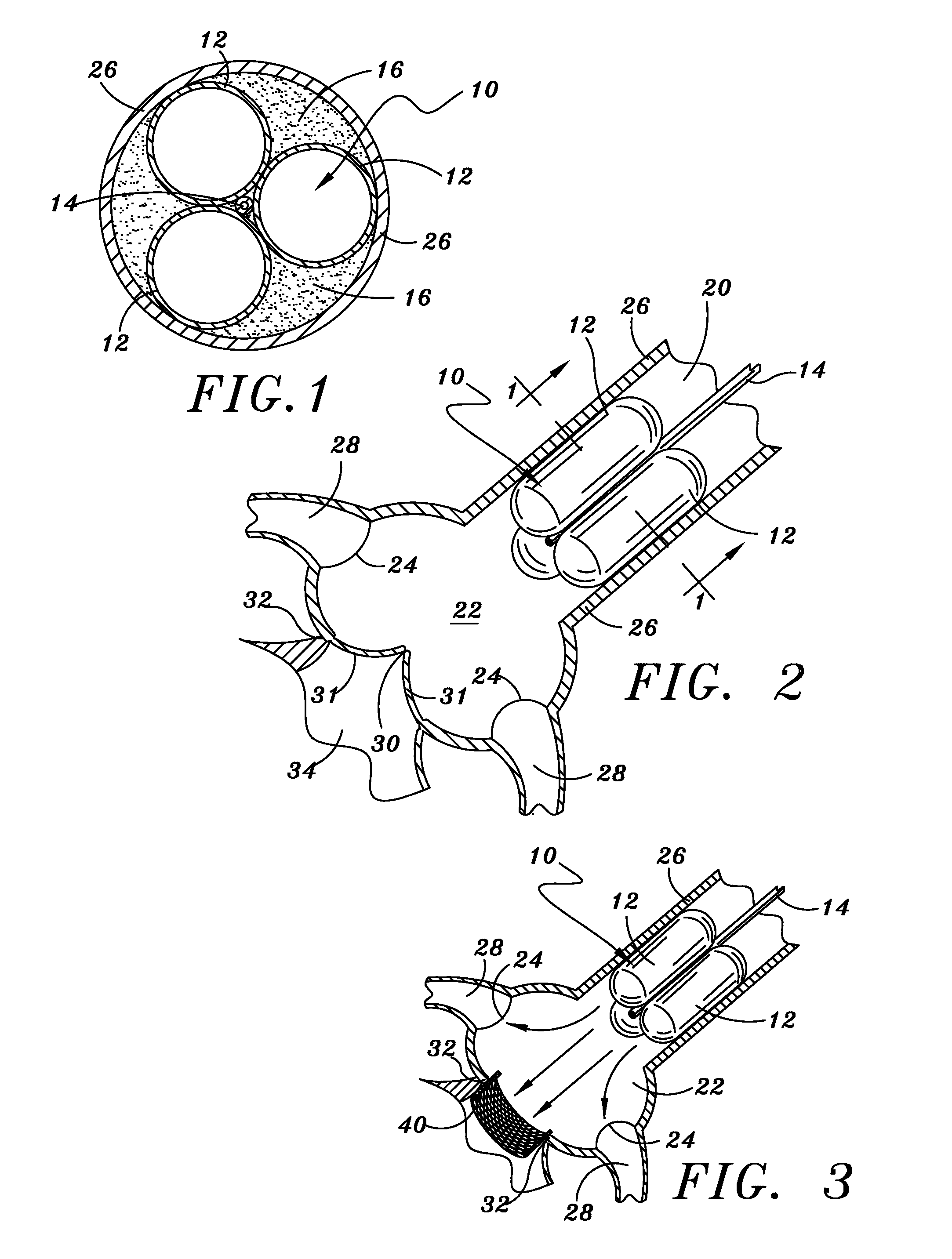
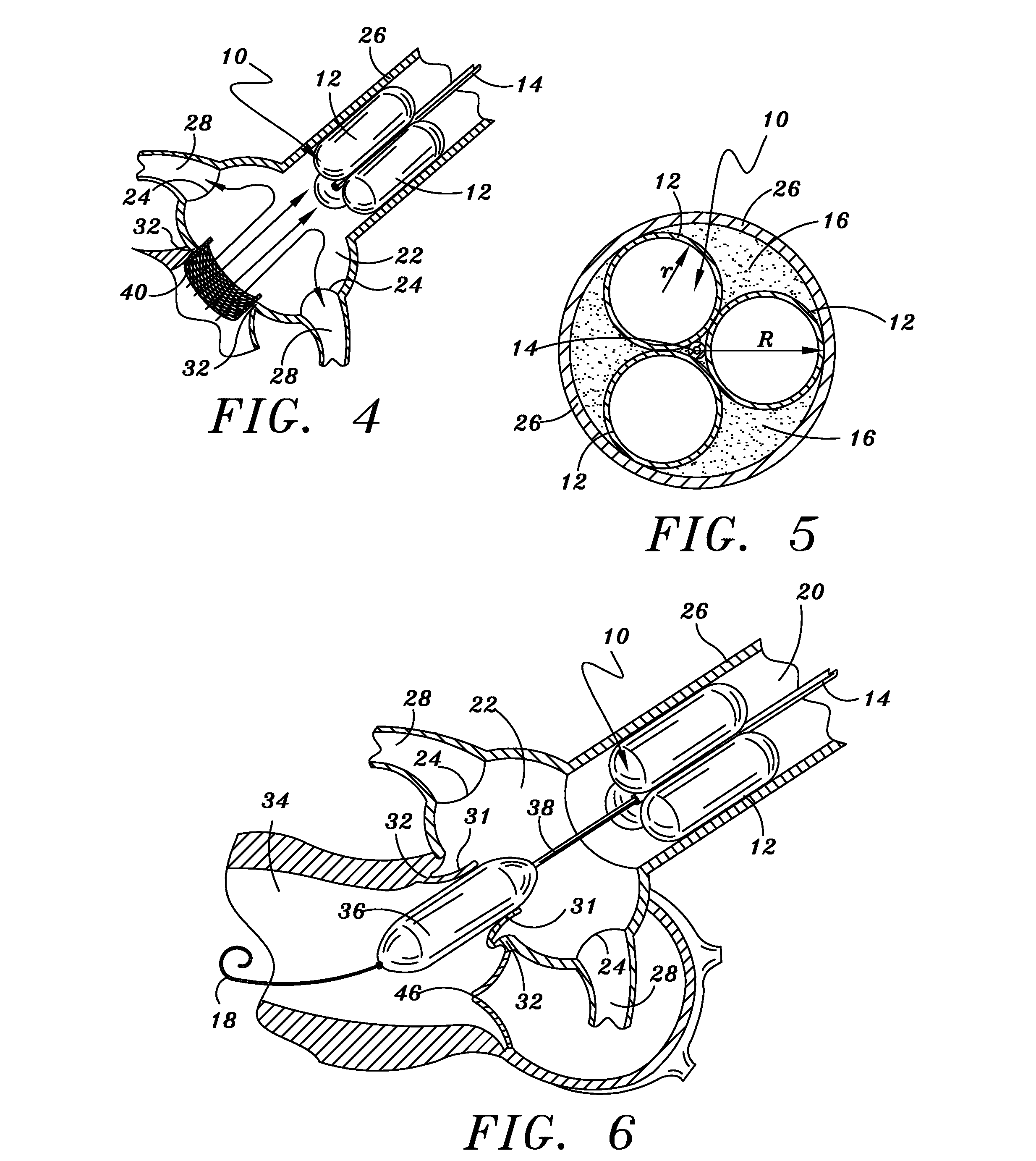
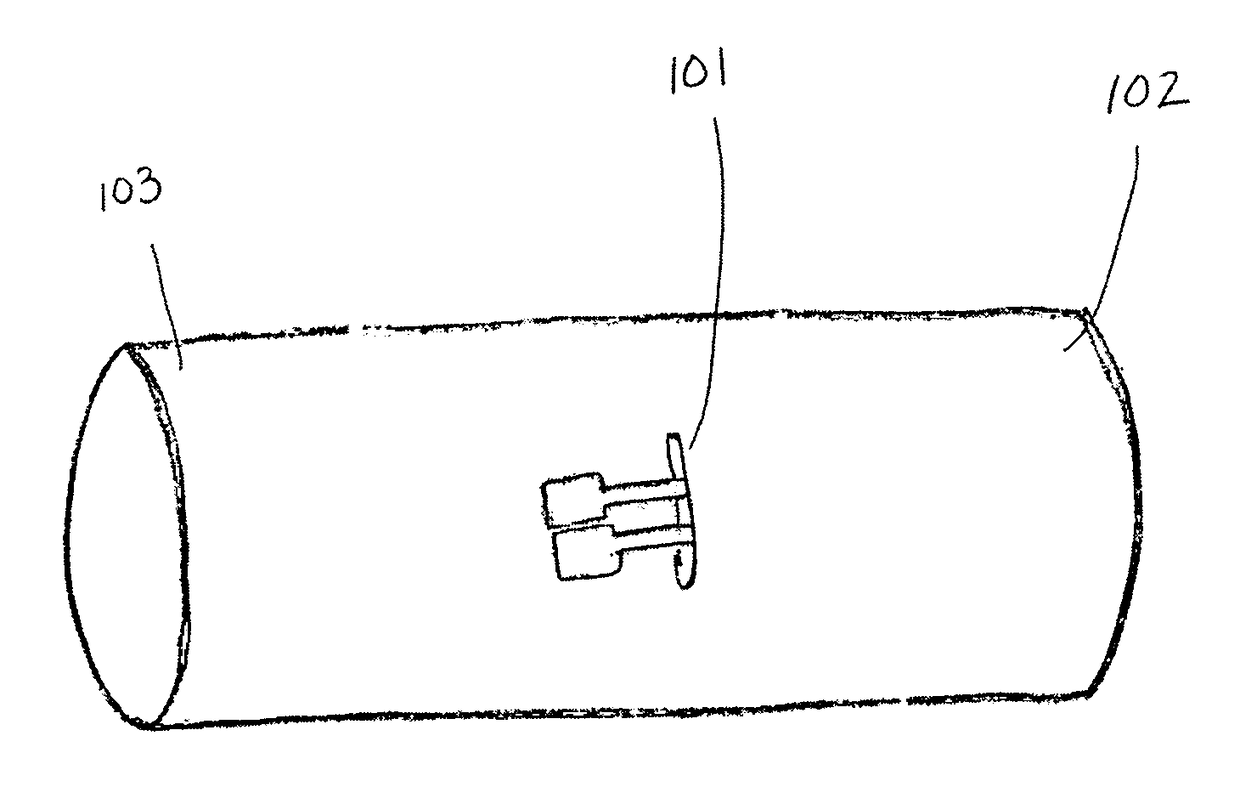
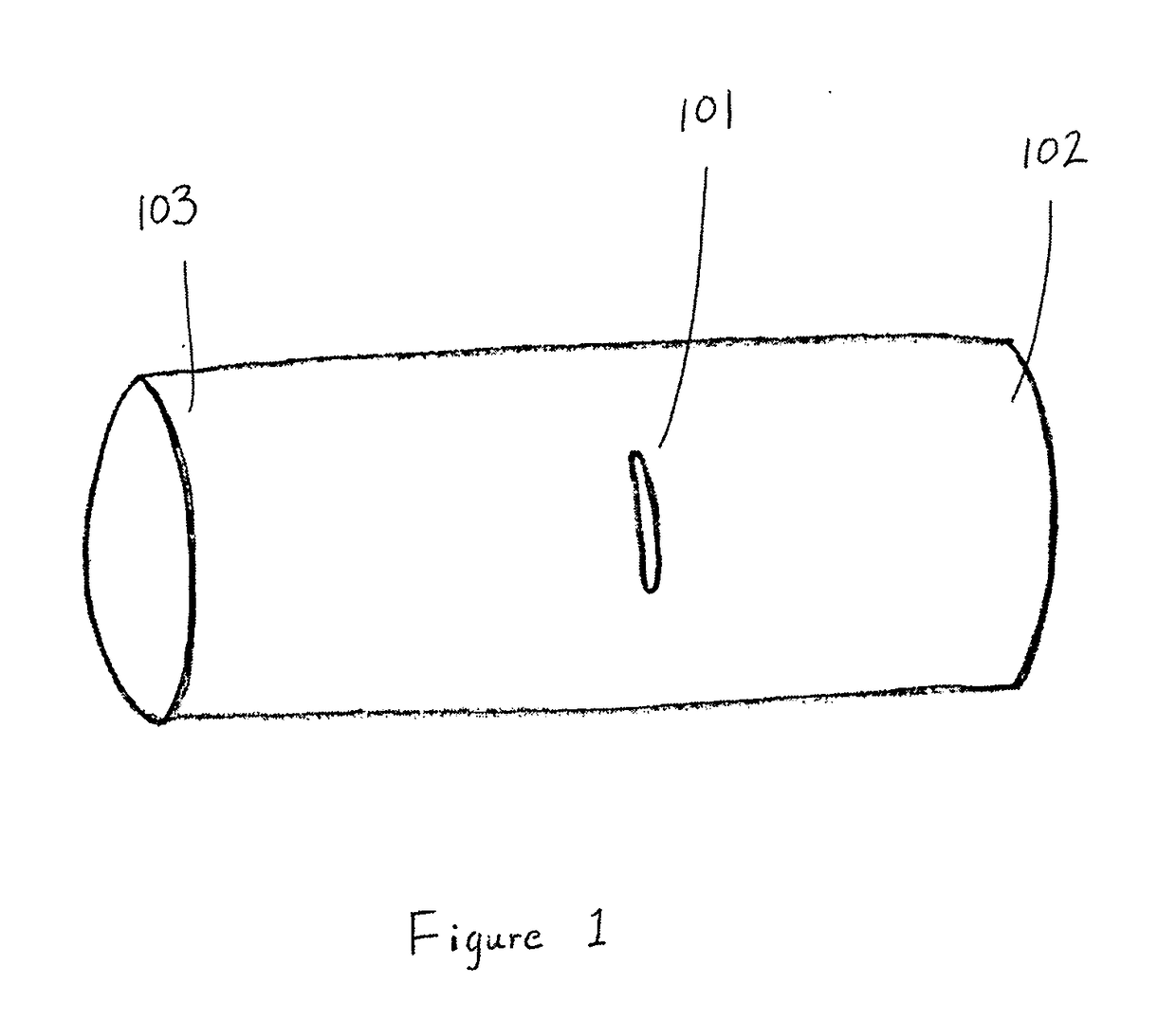
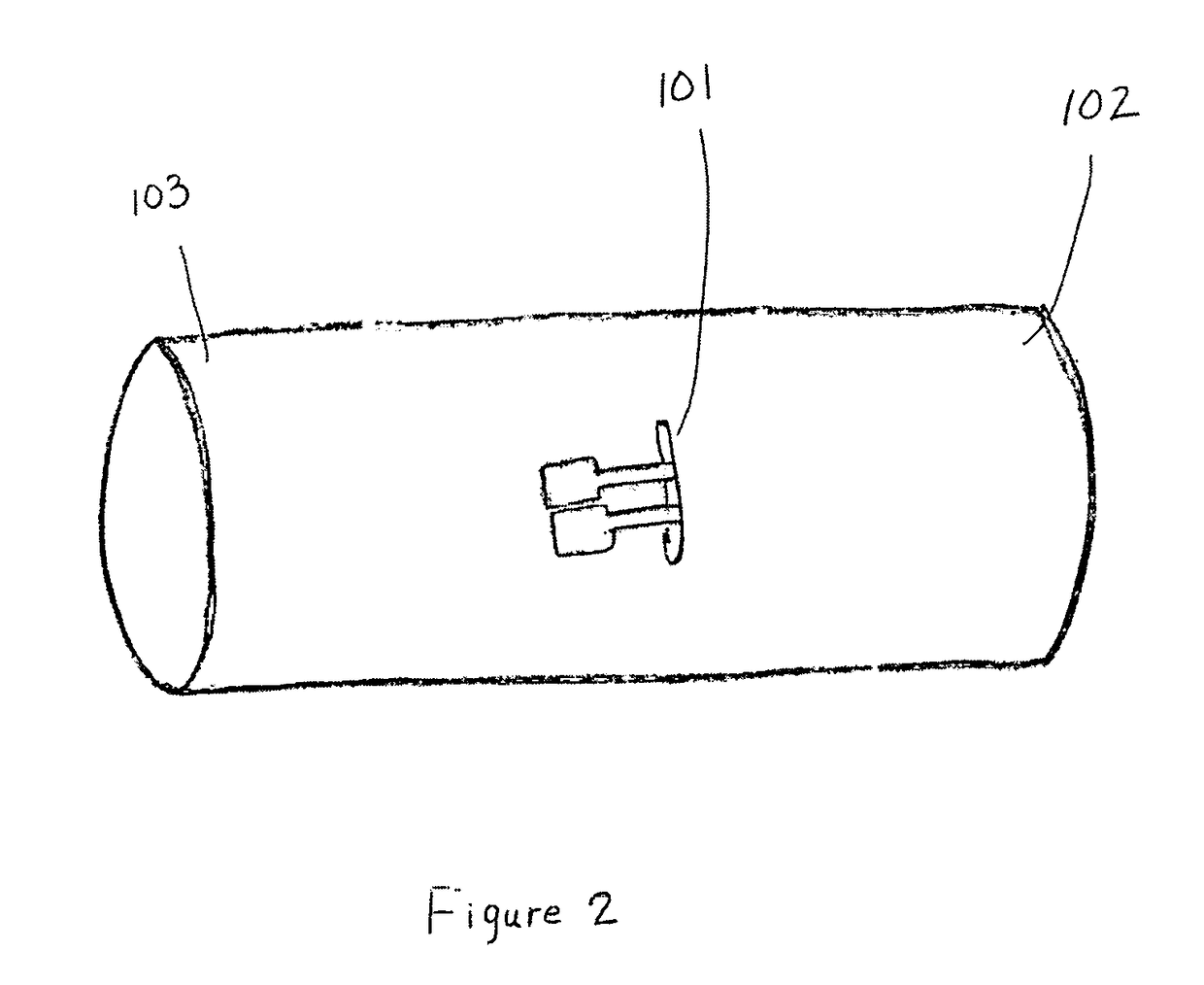
A catheter assembly for use in radiation therapy of a patient by insertion into a vessel, passageway or cavity to deliver radioactive material to a treatment site within the patient. The distal end of the catheter assembly (10) includes a noncompliant inner balloon (18) therearound that is inflatable with a non-radioactive fluid (such as CO2 or saline or contrast medium), and an outer balloon (16) therearound that is inflated with radioactive fluid (such as radiogas like xenon-133 ) and is noncompliant to conform the vessel wall to the balloon's shape at the treatment site for optimal distribution of dose. The inner balloon allows reduction in volume of the amount of radioactive fluid necessary to achieve a desired dose. The inner and outer balloons (112,108) may be affixed to inner and outer catheters (104,102), respectively. Further, a booster radioactive source, preferably removable from the catheter, may also be used to supplement the dose from the outer balloon, such as a radioactive line source (a wire or a seed train (118,234)) within the central catheter lumen (116,230) at the distal end, or a plurality of seeds (320) within flexible cylinders (318) spaced circumferentially around the inner balloon (308) but within the outer balloon (310), or a sleeve (402) around the inner balloon (406) that may be impregnated with iodine-125. A method of providing radiation therapy is disclosed.
Owner:APPLE DR MARC G
Suction catheter for thrombolysis and suction of thrombotic substance
InactiveCN105920720AEasy to handleAvoid the disadvantages of insufficient concentrationCatheterIntravenous devicesAspiration catheterThrombolysis
The invention relates to a suction catheter for thrombolysis and suction of thrombotic substance. The suction catheter comprises a central catheter, one end of the central catheter is connected with a suction connecting tube and an administration tube respectively, a liquid outlet of the suction connecting tube is connected with a middle tube, a liquid suction connecting head is arranged at each of two ends of the middle tube, the other end of the suction connecting tube is connected with a two-way valve, a liquid outgoing port end of the two-way valve is connected with a catheter joint, the other end of the catheter joint is connected with a rear-end suction catheter which is connected with a suction pump, a liquid incoming port end of the administration tube is connected with an administration one-way valve, and the other end of the administration one-way valve is connected with an administration injector. The suction catheter has the advantages of simple structure, convenience in operation, low manufacturing cost and convenience in clinical use.
Owner:HENAN YADU IND
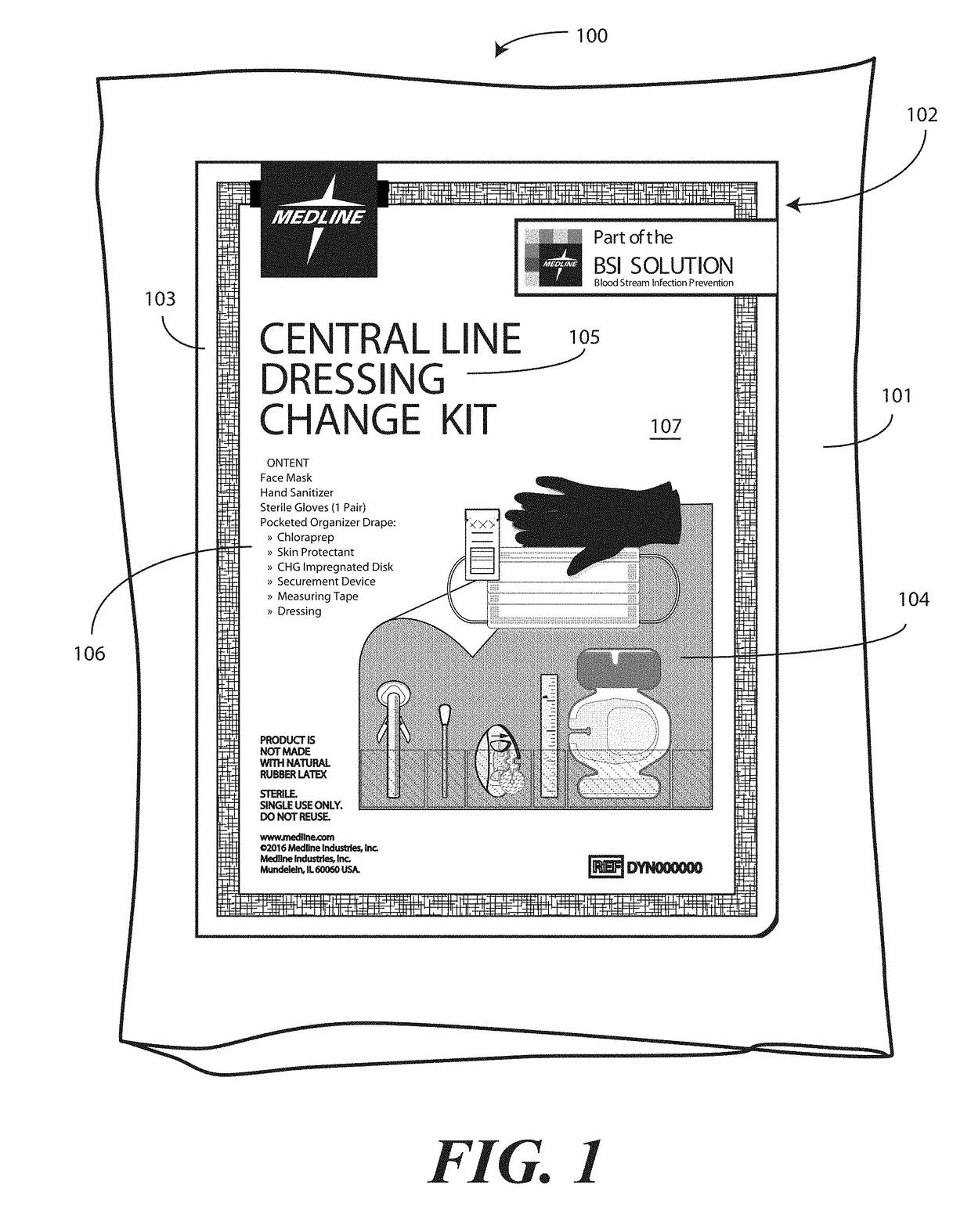
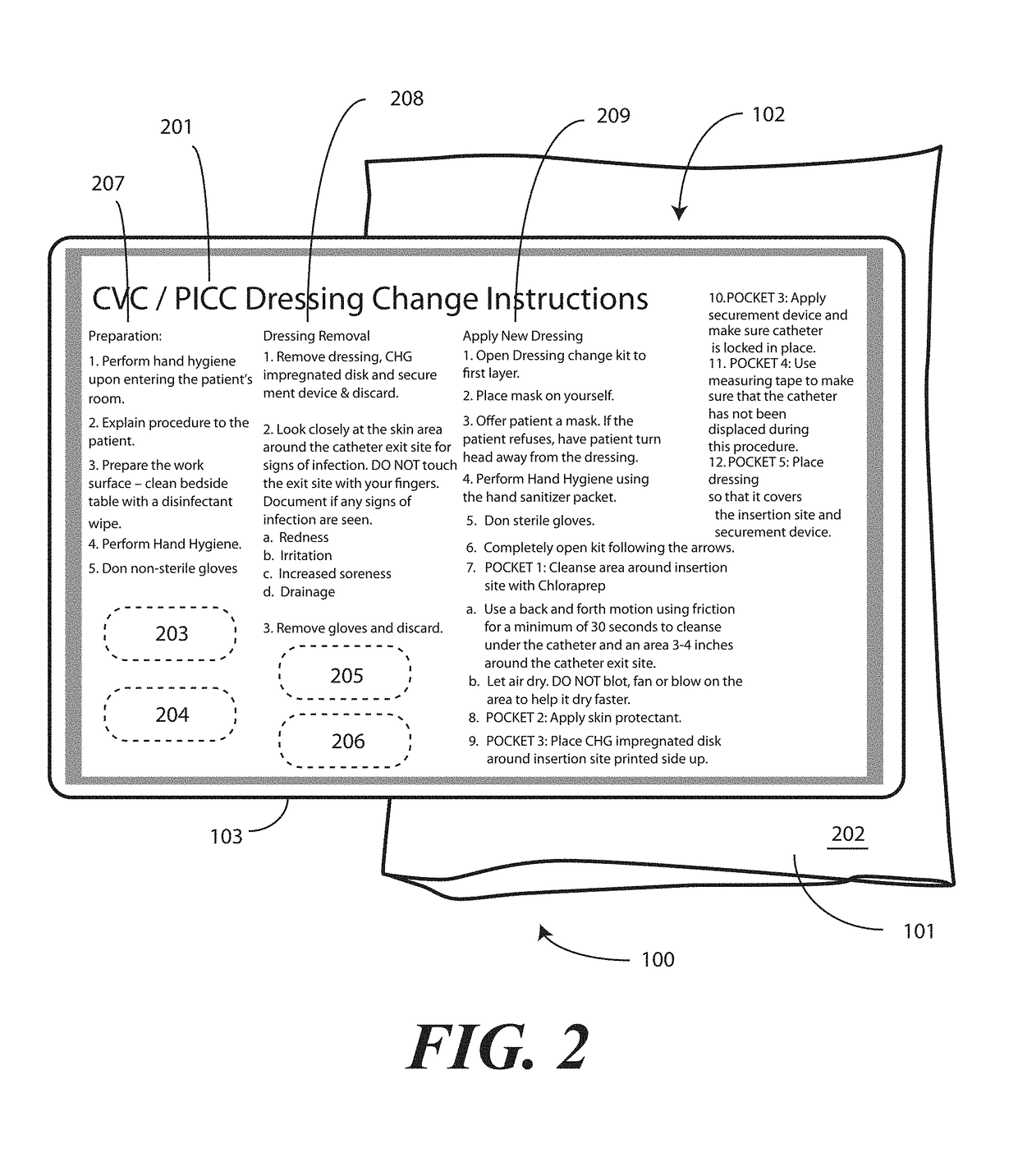
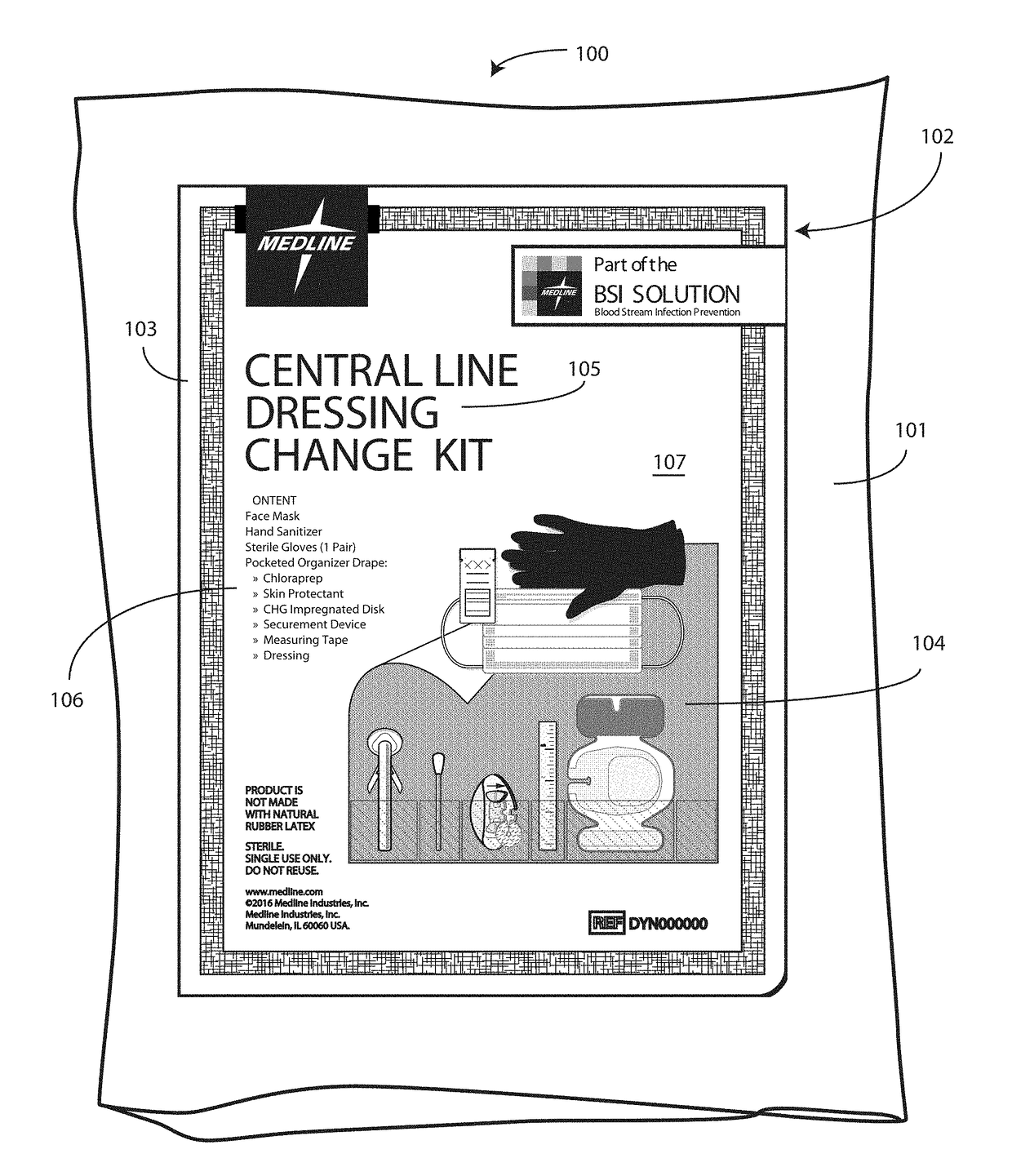
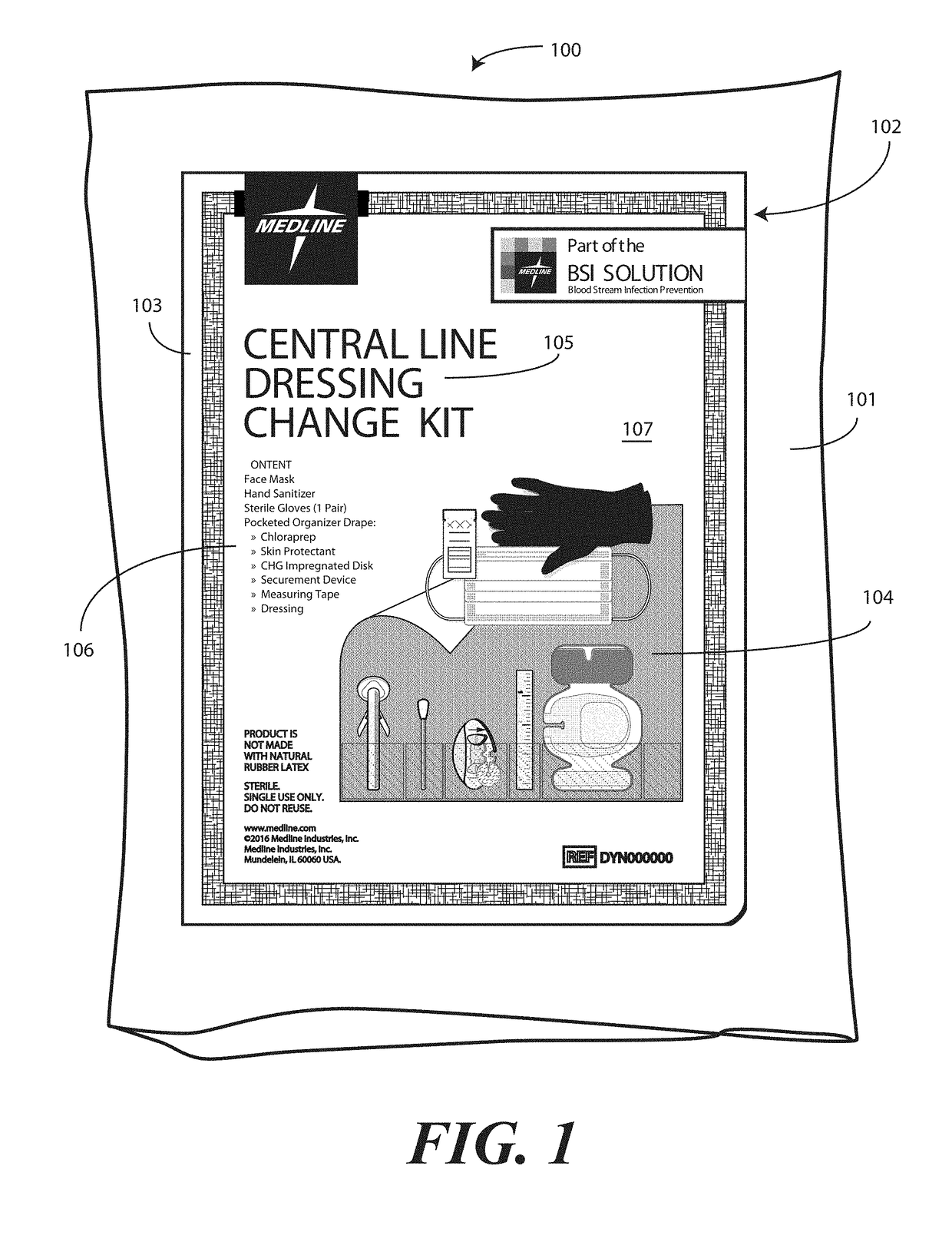
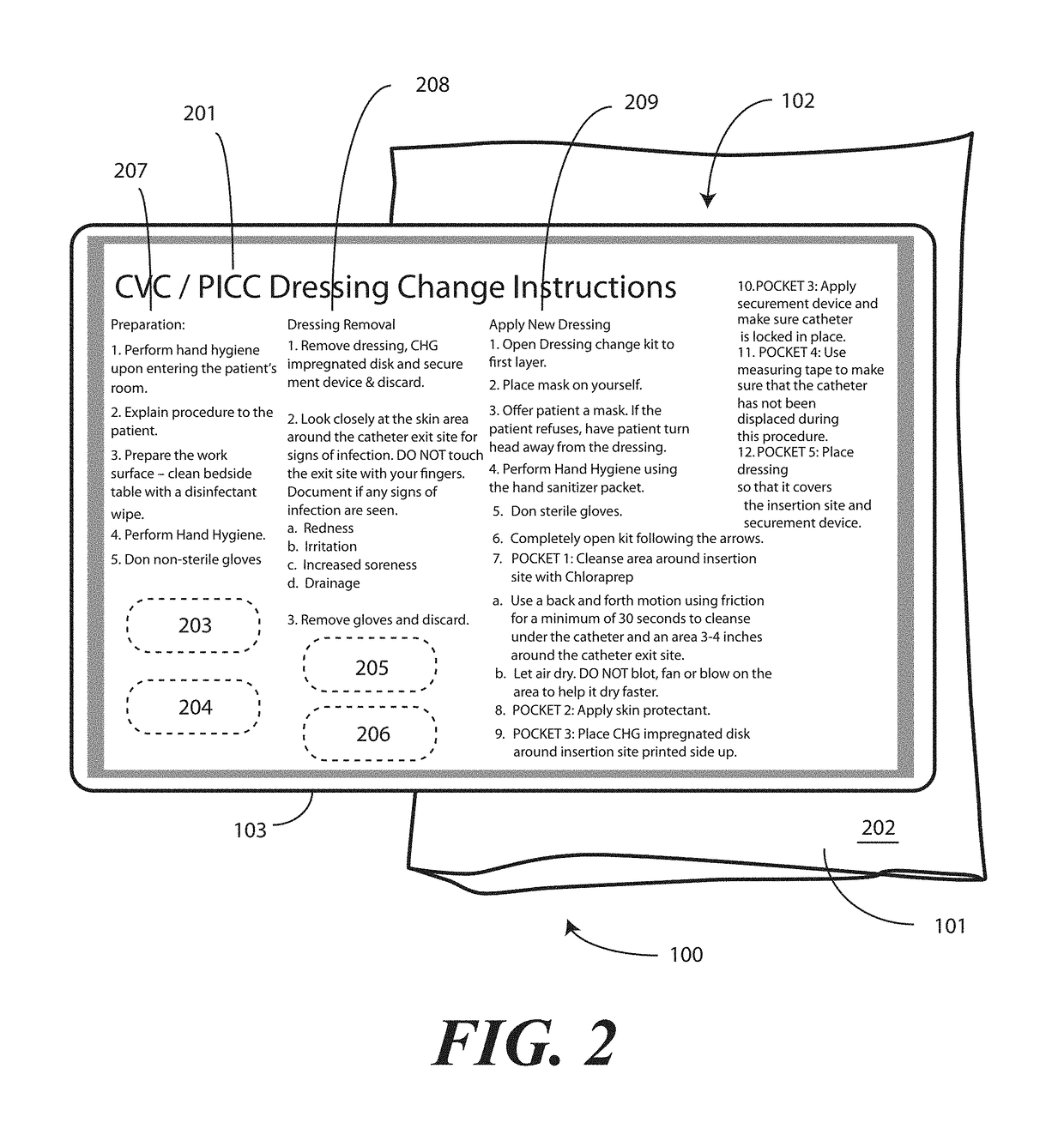
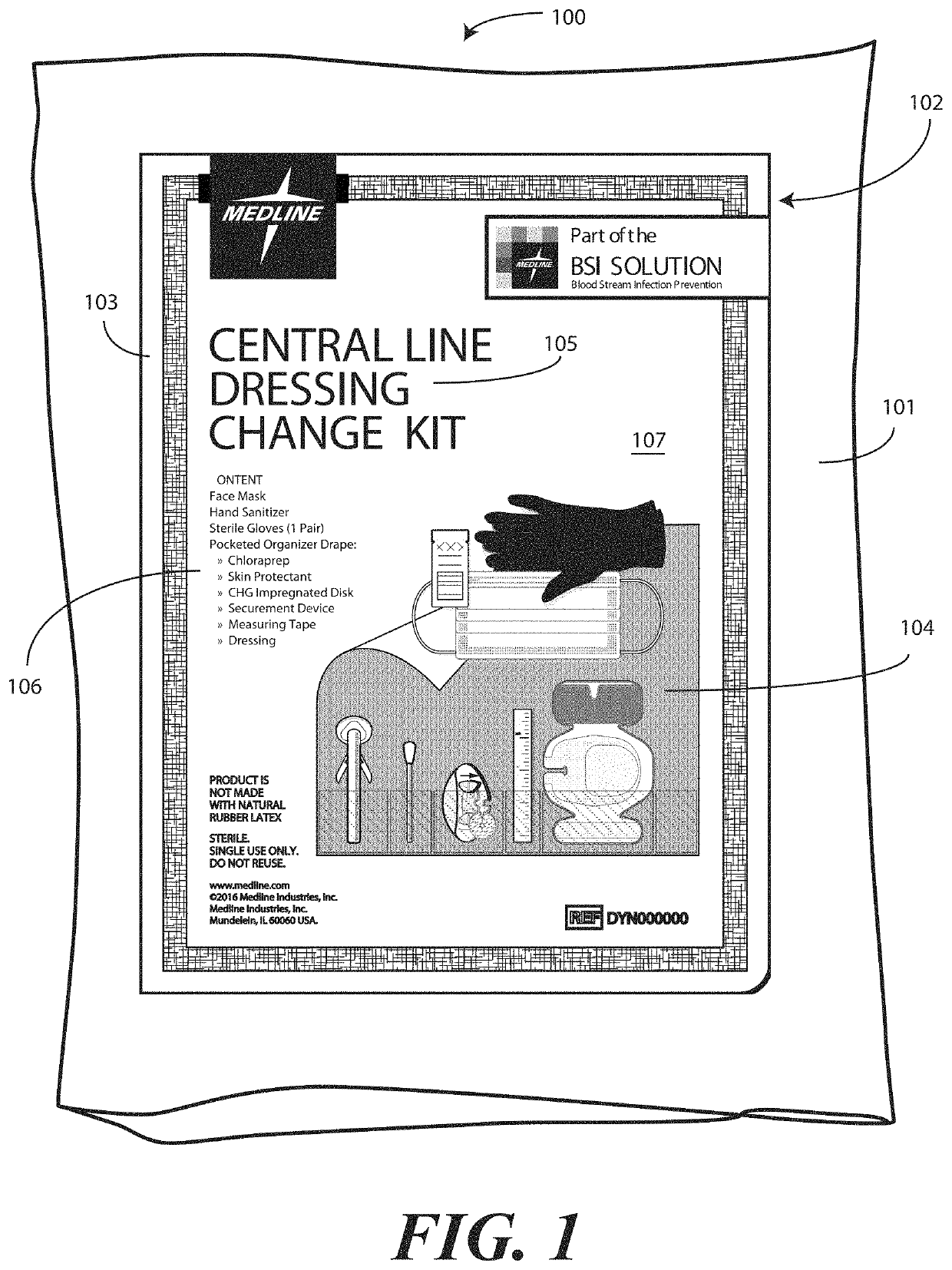
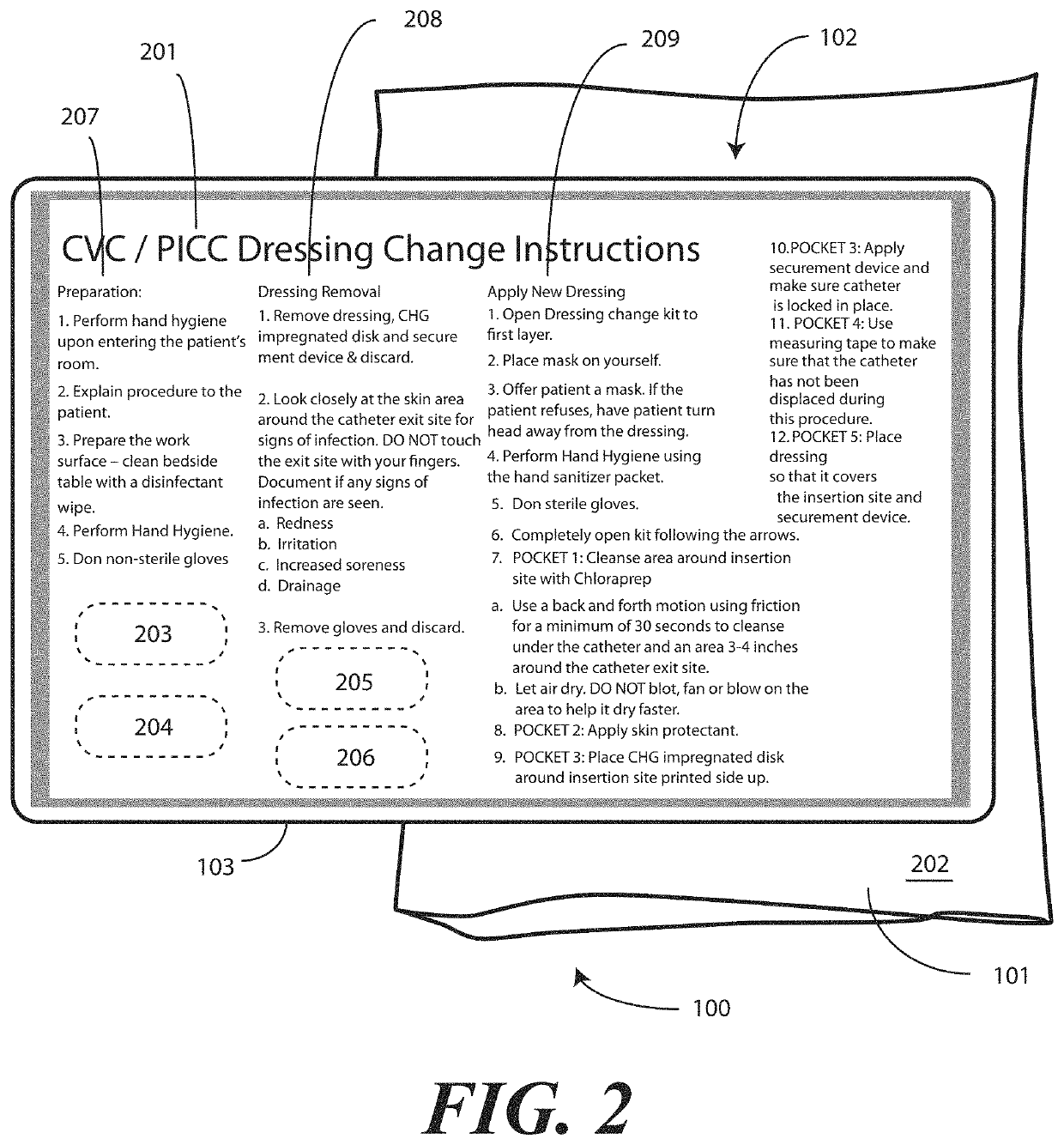
Medical Kit and Associated Systems and Methods for Preventing Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infection
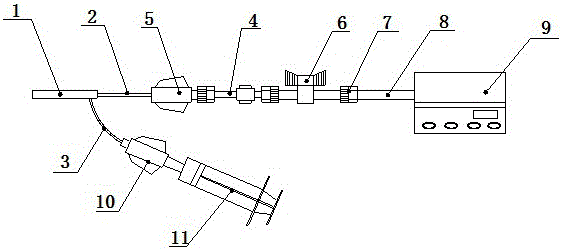
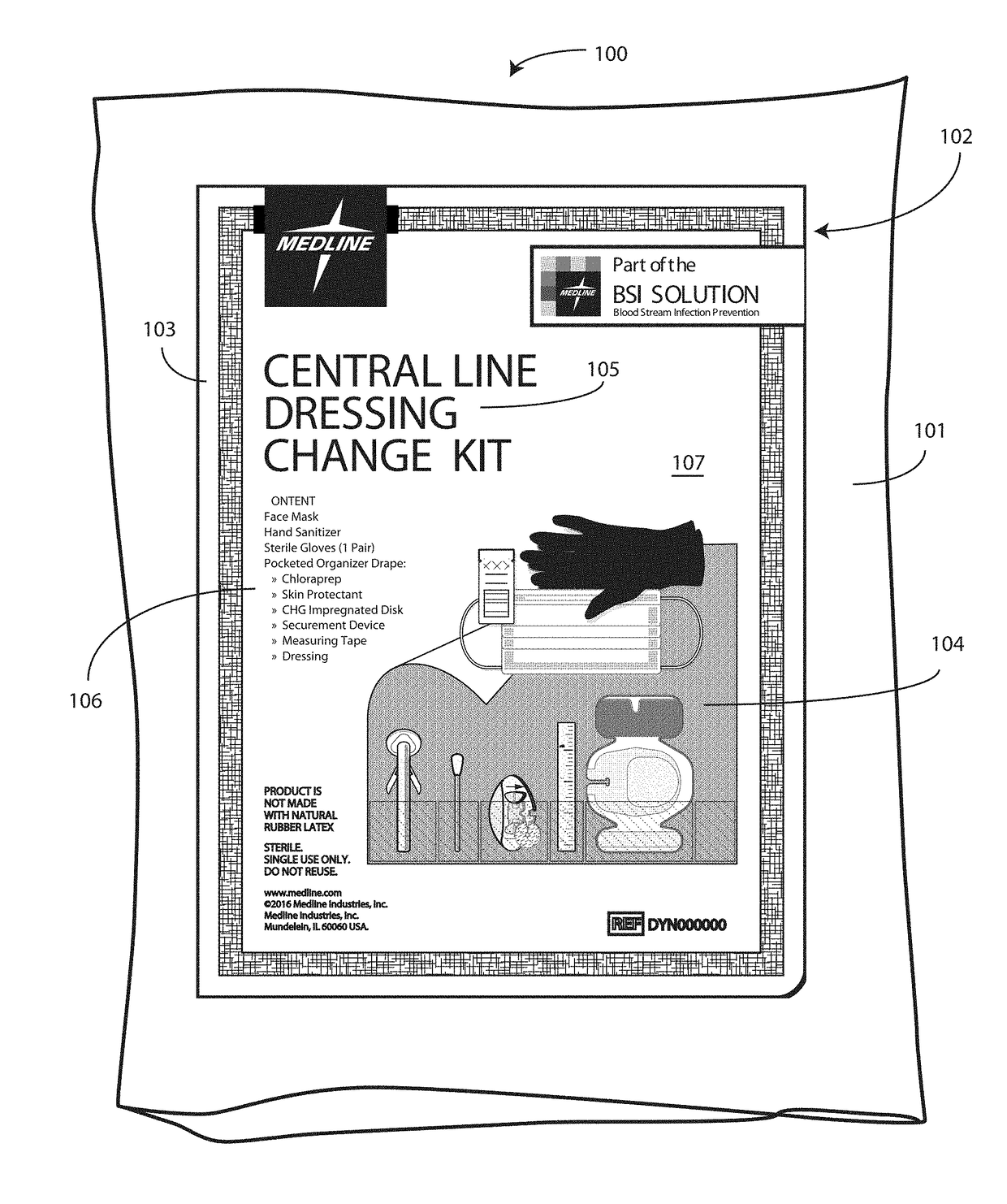
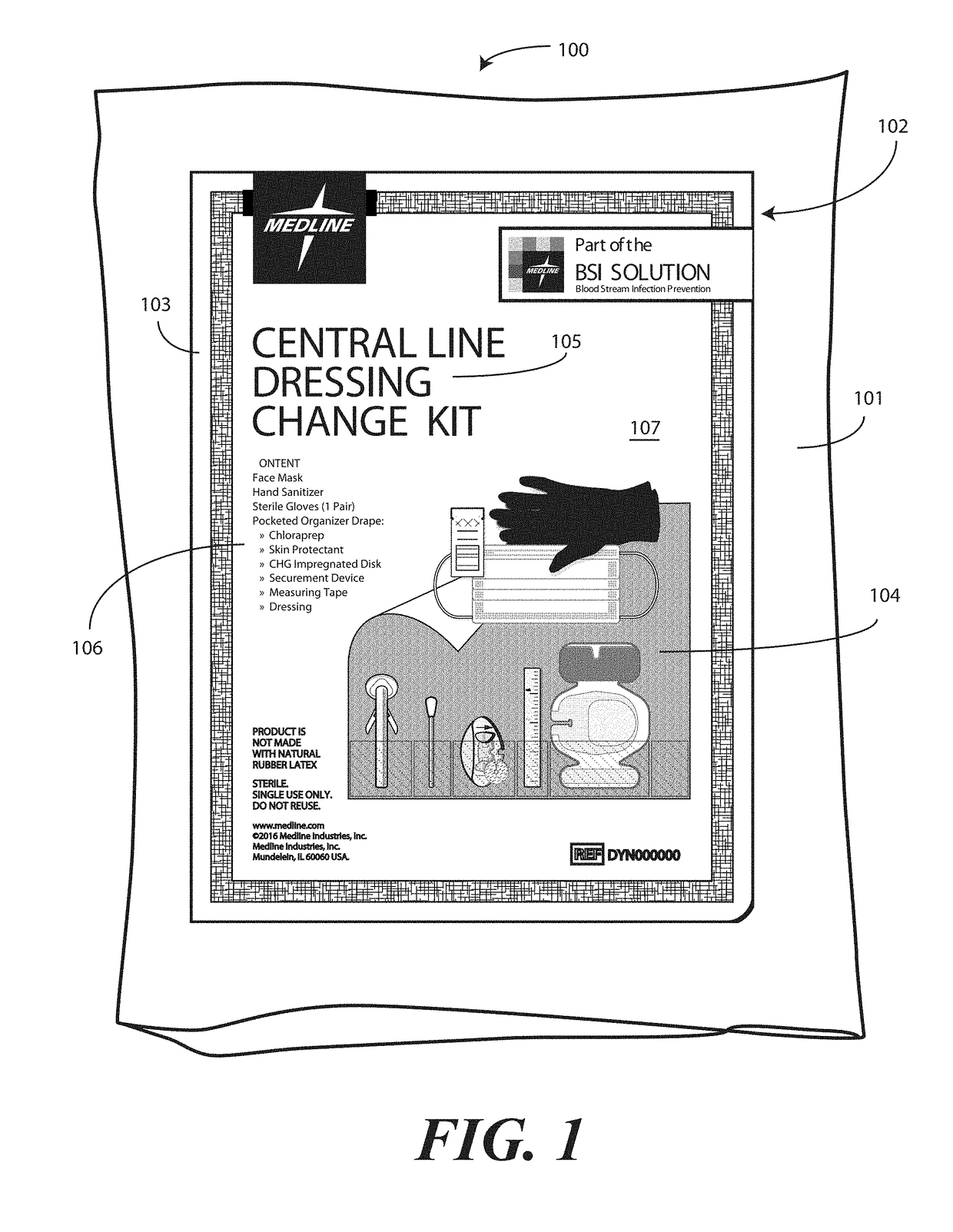
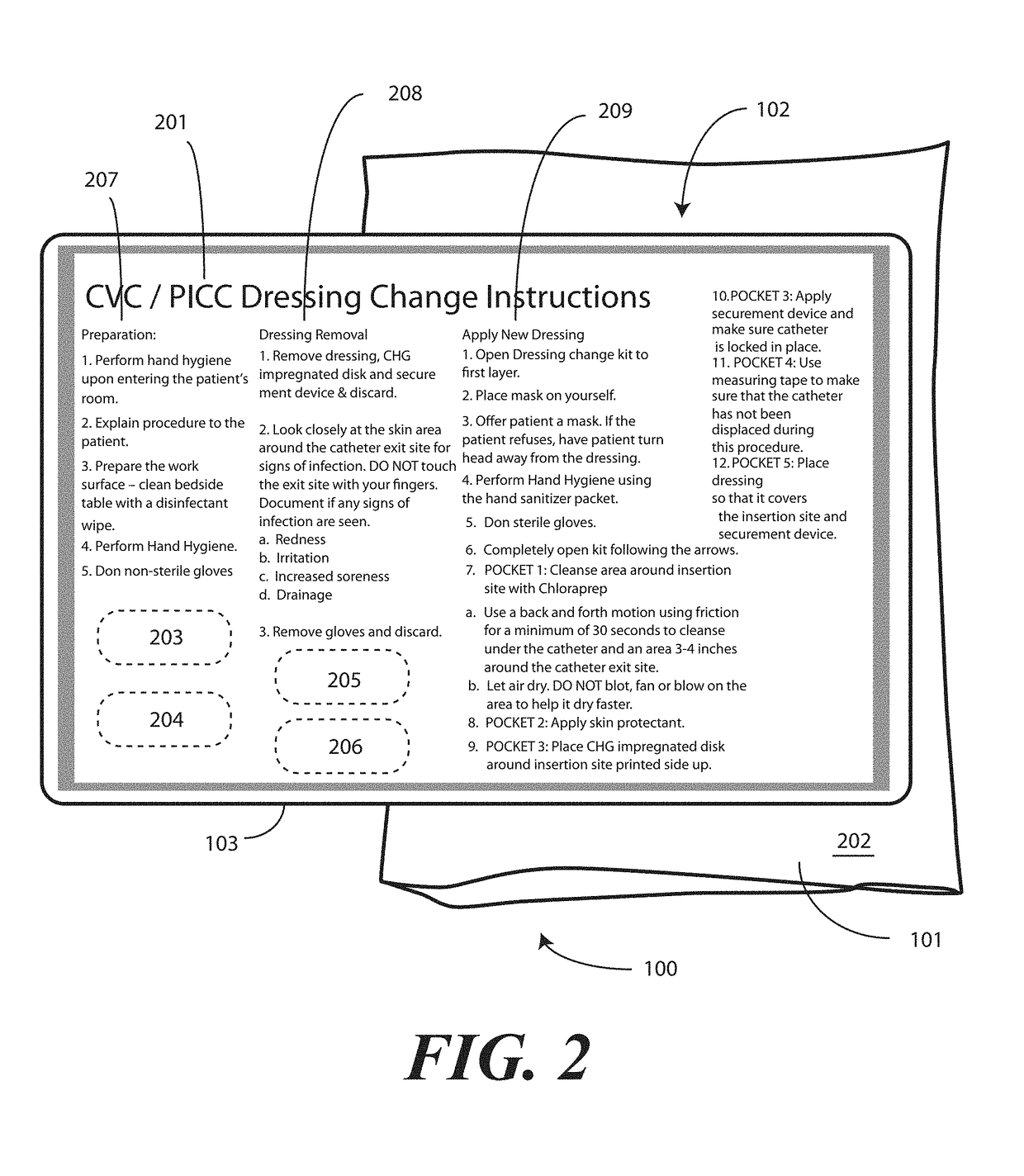
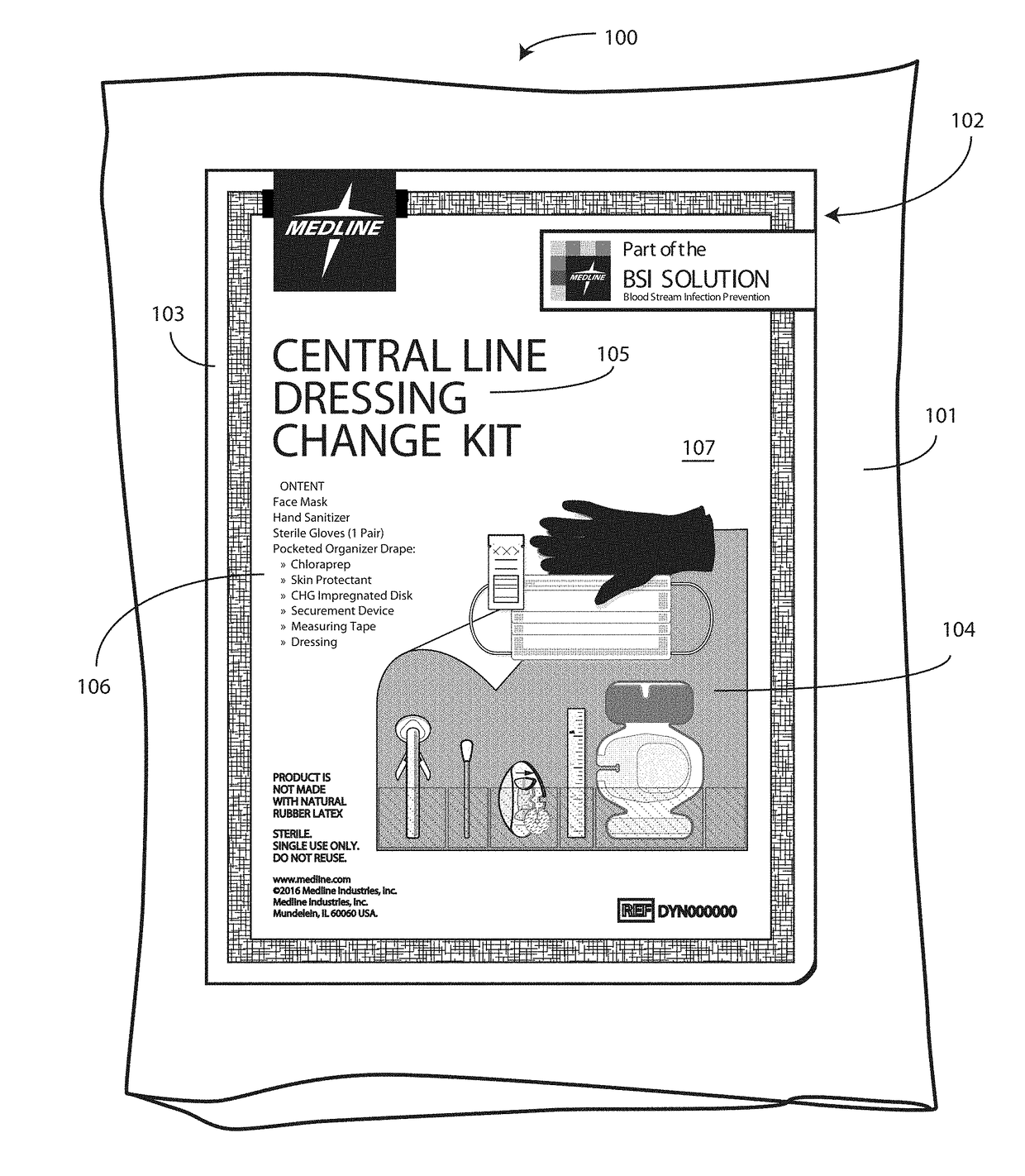
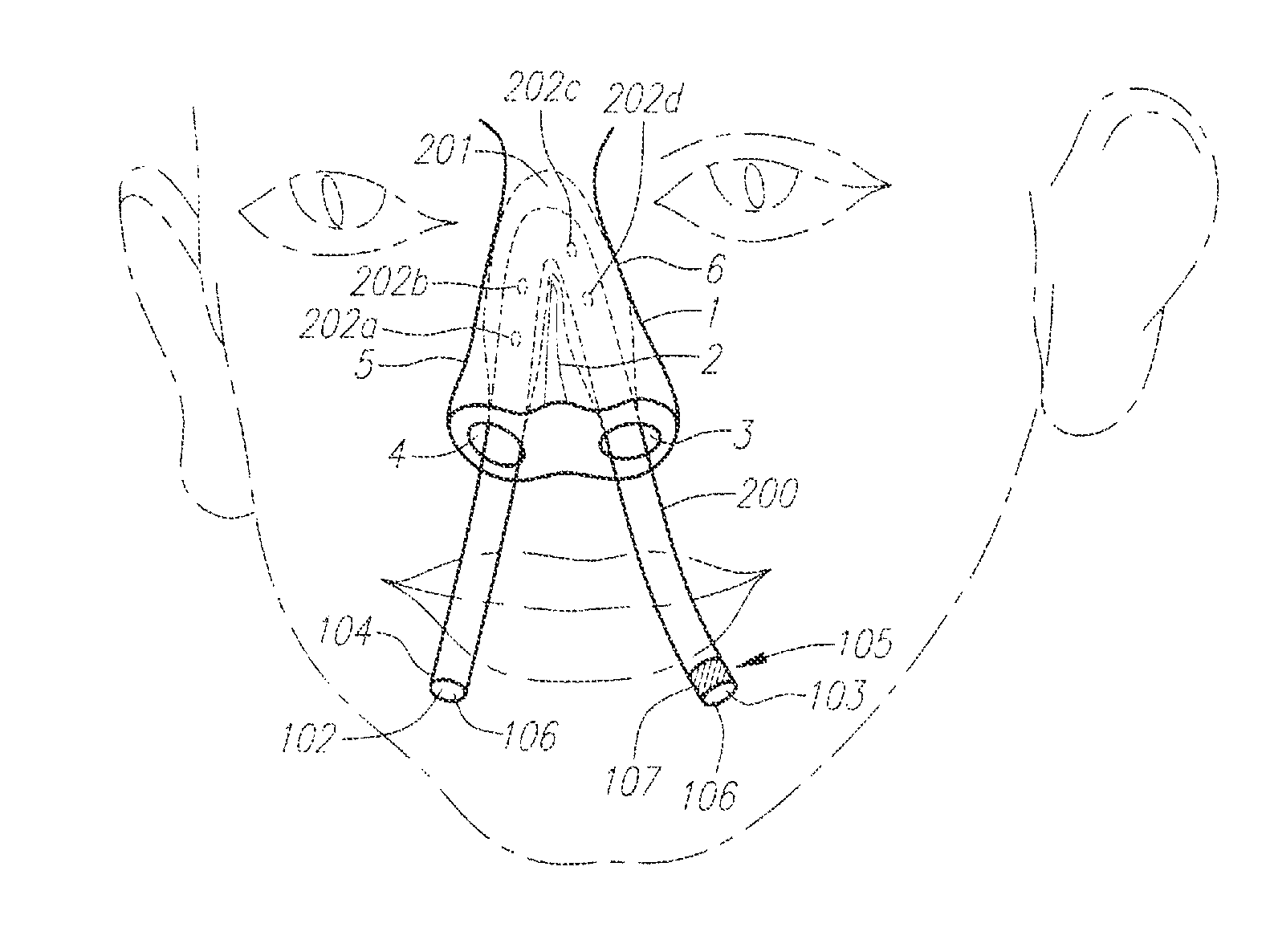
A medical kit 100 includes a drape 1323. A plurality of pockets (1302,1303,1304,1305, 1306,1307) are disposed along a bottom edge of the drape 1323 in a linear, side-by-side arrangement. A plurality of medical implements (1310,1311,1312,1313,1314,1315) are stowed in the plurality of pockets on a one-to-one basis. Medical indicia (1316,1317,1318,1319,1320,1321) is disposed along each pocket. The medical indicia can include comprising one or more educational prompts that instruct medical personnel how to use a particular medical implement disposed in a pocket to complete a central catheter dressing change.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Specialized catheter securement devices for peripherally inserted central catheters
ActiveUS20120109069A1Avoid problemsEasy to disassembleCatheterInfusion needlesCatheter hubCatheter securement device
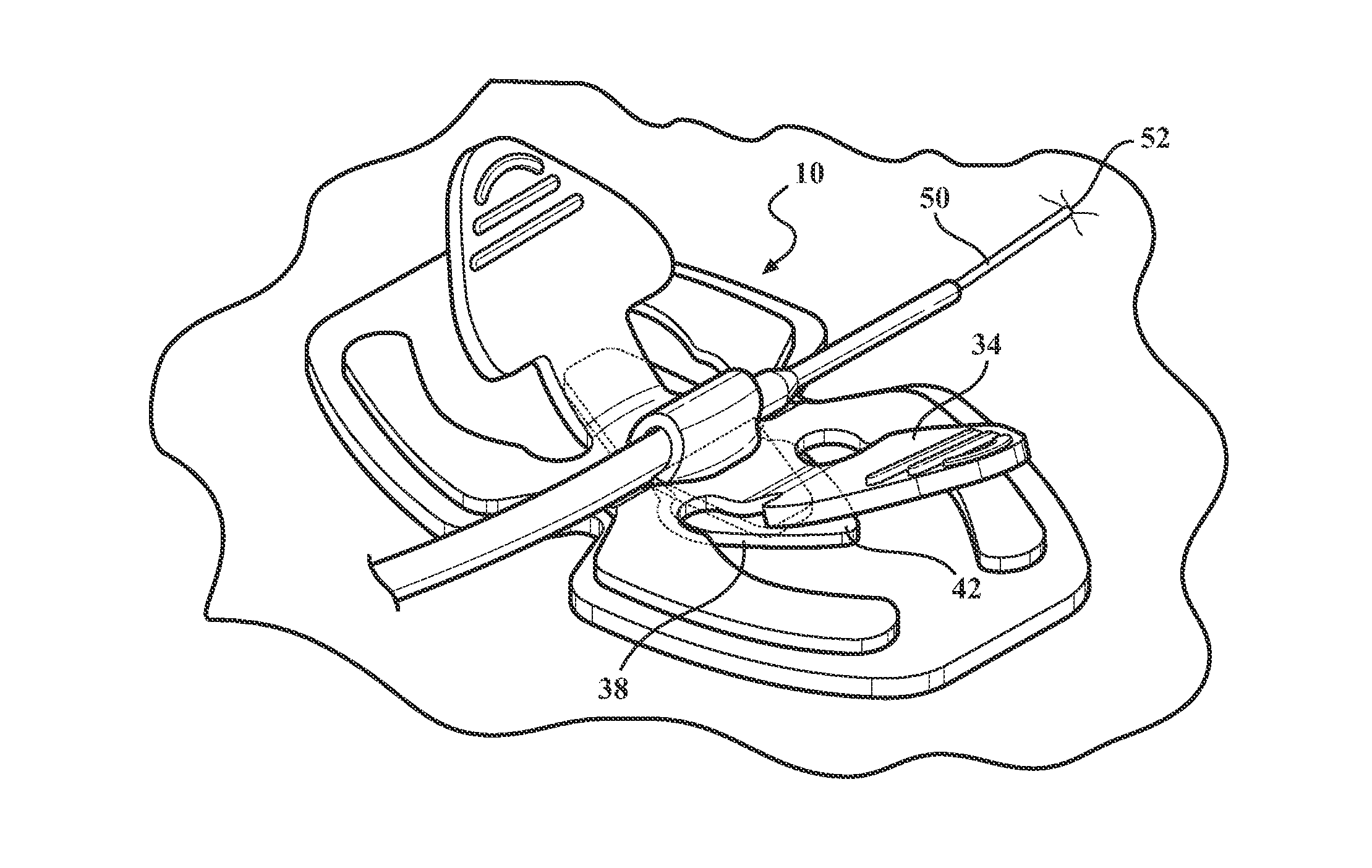
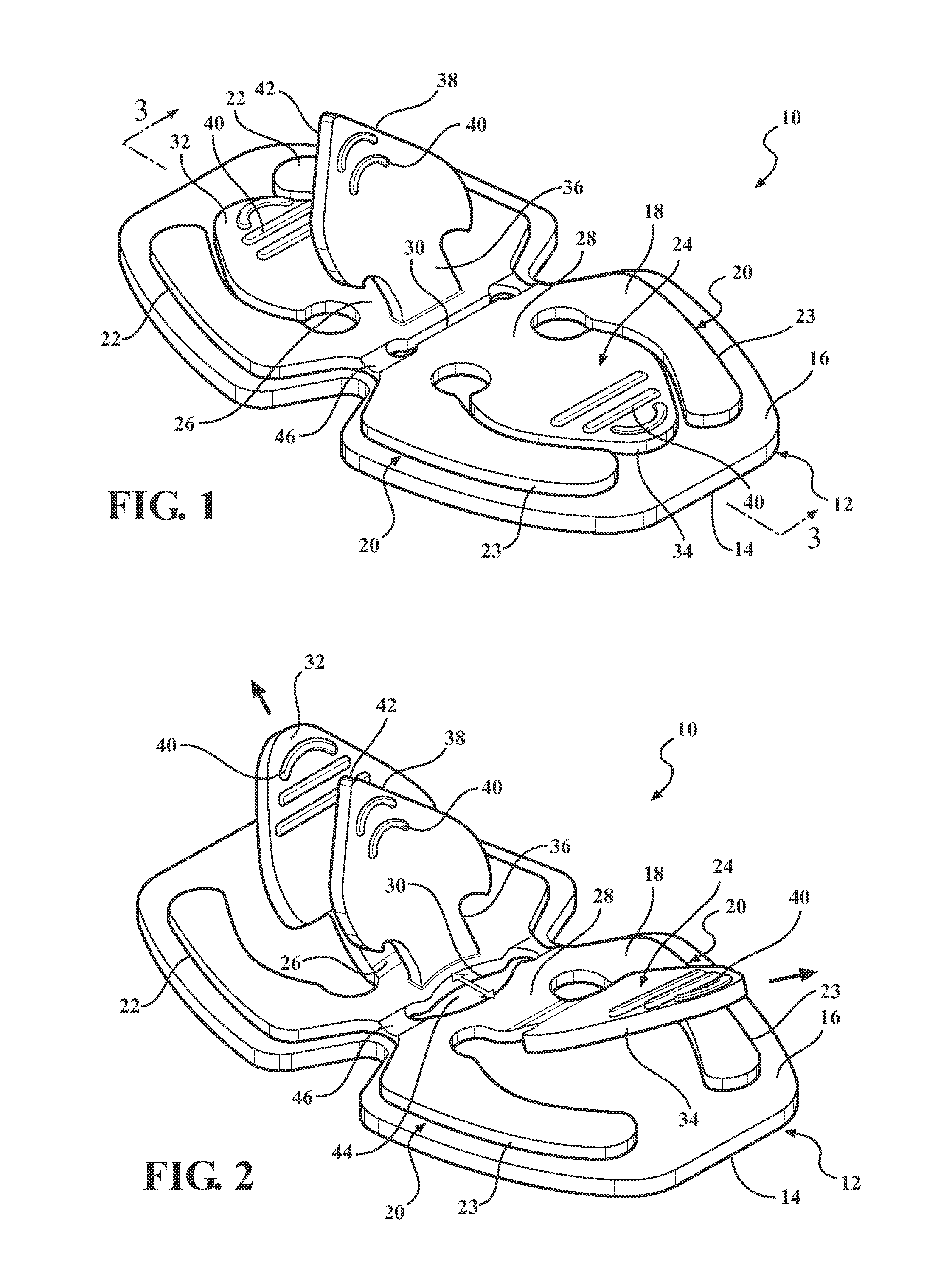
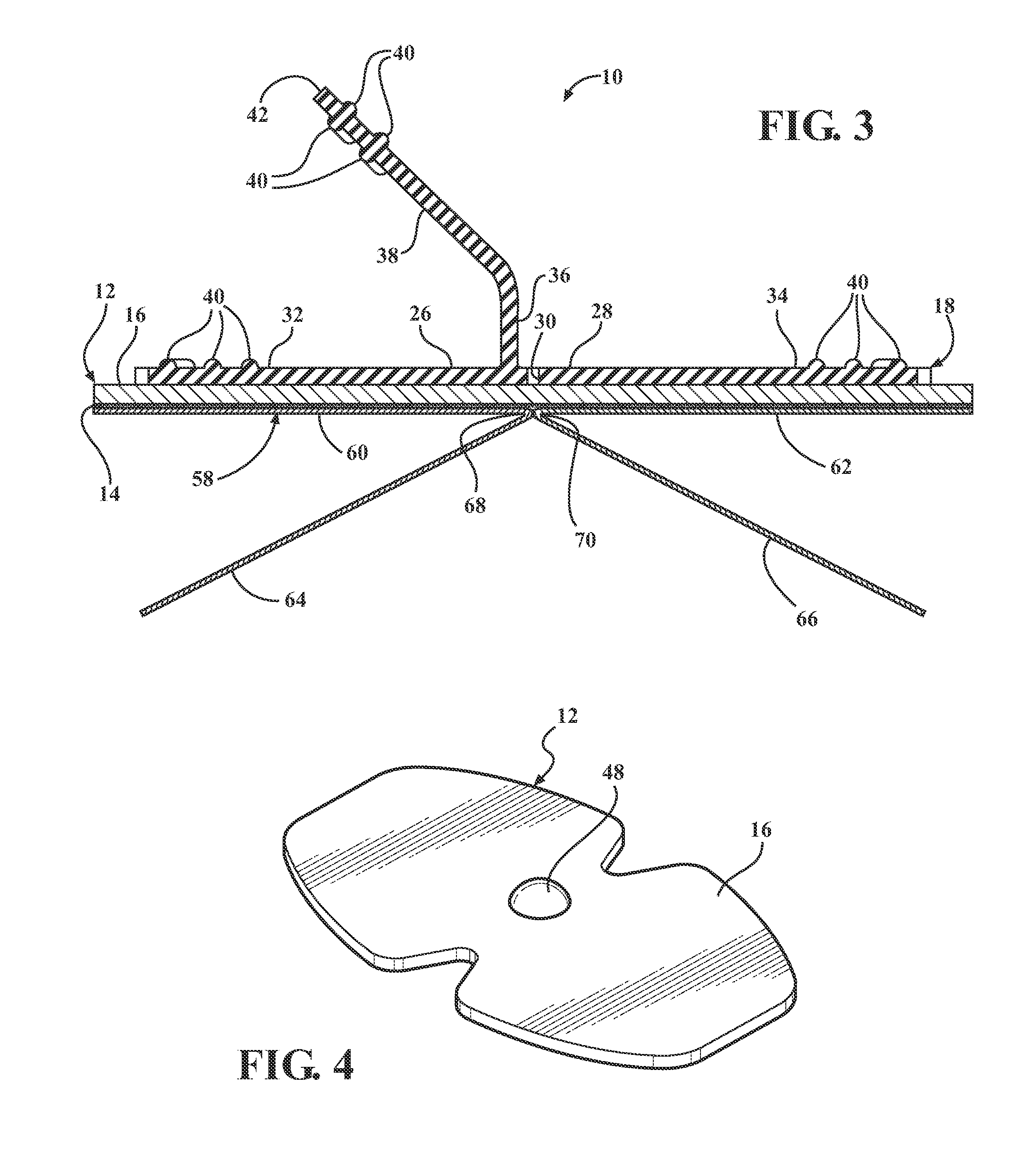
A catheter securement device in accordance with the present invention includes a flexible base member having an adhesive side and an opposite non-adhesive side. A single piece elastomeric anchoring member is mounted on the non-adhesive side of the base member. The anchoring member integrally includes a pair of opposing pull tabs, a slit disposed between the opposing pull tabs, and a third pull tab disposed between the slit and one of the opposing pull tabs. Pulling the opposing pull tabs opens the slit for receiving a catheter hub in the slit, and the third pull tab is insertable into the slit for securing the catheter hub between the anchoring member and the base member.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Medical Kit and Associated Systems and Methods for Preventing Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infection
A medical kit 100 includes a drape 1323. A plurality of pockets (1302,1303,1304,1305, 1306,1307) are disposed along a bottom edge of the drape 1323 in a linear, side-by-side arrangement. A plurality of medical implements (1310,1311,1312,1313,1314,1315) are stowed in the plurality of pockets on a one-to-one basis. Medical indicia (1316,1317,1318,1319,1320,1321) is disposed along each pocket. The medical indicia can include one or more educational prompts that instruct medical personnel how to use a particular medical implement disposed in a pocket to complete a central catheter dressing change.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Medical Kit and Associated Systems and Methods for Preventing Central Line Associated Blood Stream Infection
A medical kit 100 includes a drape 1323. A plurality of pockets (1302, 1303, 1304, 1305, 1306, 1307) are disposed along a bottom edge of the drape 1323 in a linear, side-by-side arrangement. A plurality of medical implements (1310, 1311, 1312, 1313, 1314, 1315) are stowed in the plurality of pockets on a one-to-one basis. Medical indicia (1316, 1317, 1318, 1319, 1320, 1321) is disposed along each pocket. The medical indicia can include one or more educational prompts that instruct medical personnel how to use a particular medical implement disposed in a pocket to complete a central catheter dressing change.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Medical kit and associated systems and methods for preventing central line associated blood stream infection
A medical kit 100 includes a drape 1323. A plurality of pockets (1302,1303,1304,1305, 1306,1307) are disposed along a bottom edge of the drape 1323 in a linear, side-by-side arrangement. A plurality of medical implements (1310,1311,1312,1313,1314,1315) are stowed in the plurality of pockets on a one-to-one basis. Medical indicia (1316,1317,1318,1319,1320,1321) is disposed along each pocket. The medical indicia can include one or more educational prompts that instruct medical personnel how to use a particular medical implement disposed in a pocket to complete a central catheter dressing change.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Methods and devices for non-invasive cerebral and systemic cooling via the nasal cavity
ActiveUS8308786B2Minimize neurologic deficitsReduce perfusionInfusion devicesMedical devicesNasal cavityNostril
A method for cerebral and systemic cooling by circulating a cold liquid through a nasal catheter looped through the patient's nasal cavities and around the nasal septum. The nasal catheter is inserted into the patient's first nostril, advanced through the nasal cavity, around the nasal septum and out of the patient's second nostril. A cold fluid having a temperature between about −20° C. and about 37° C. is flowed though a lumen in the nasal catheter to cool the nasal cavity. The nasal catheter may have one or more flexible balloons mounted on the catheter such that when the catheter is looped around the nasal septum, the balloon(s) are positioned in a portion of the patient's first and second nasal cavities. When a cold liquid is circulated through the catheter lumen, the flexible balloons expand to a contact the inner walls of the nasal cavities and provide direct cooling of the nasal cavities.
Owner:BRAINCOOL
Partition type tissue engineering spinal cord
InactiveCN101278865APromote repairPromote migrationMammal material medical ingredientsTissue cultureFiber bundleExternal catheter
The invention discloses a zoning tissue engineering spinal cord which comprises a spinal external catheter and a central catheter. A gray matter catheter which is provided with the same shape as spinal gray matter is arranged in the spinal external catheter. Corresponding catheters are respectively arranged in a white matter region according to the geometric shapes of uplink fiber bundles and downlink fiber bundles. The zoning tissue engineering spinal cord can play the role of correct guidance and lead to the result that the spinal gray matter, white matter and the uplink fiber bundles and the downlink fiber bundles in the white matter respectively grow in different regions.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
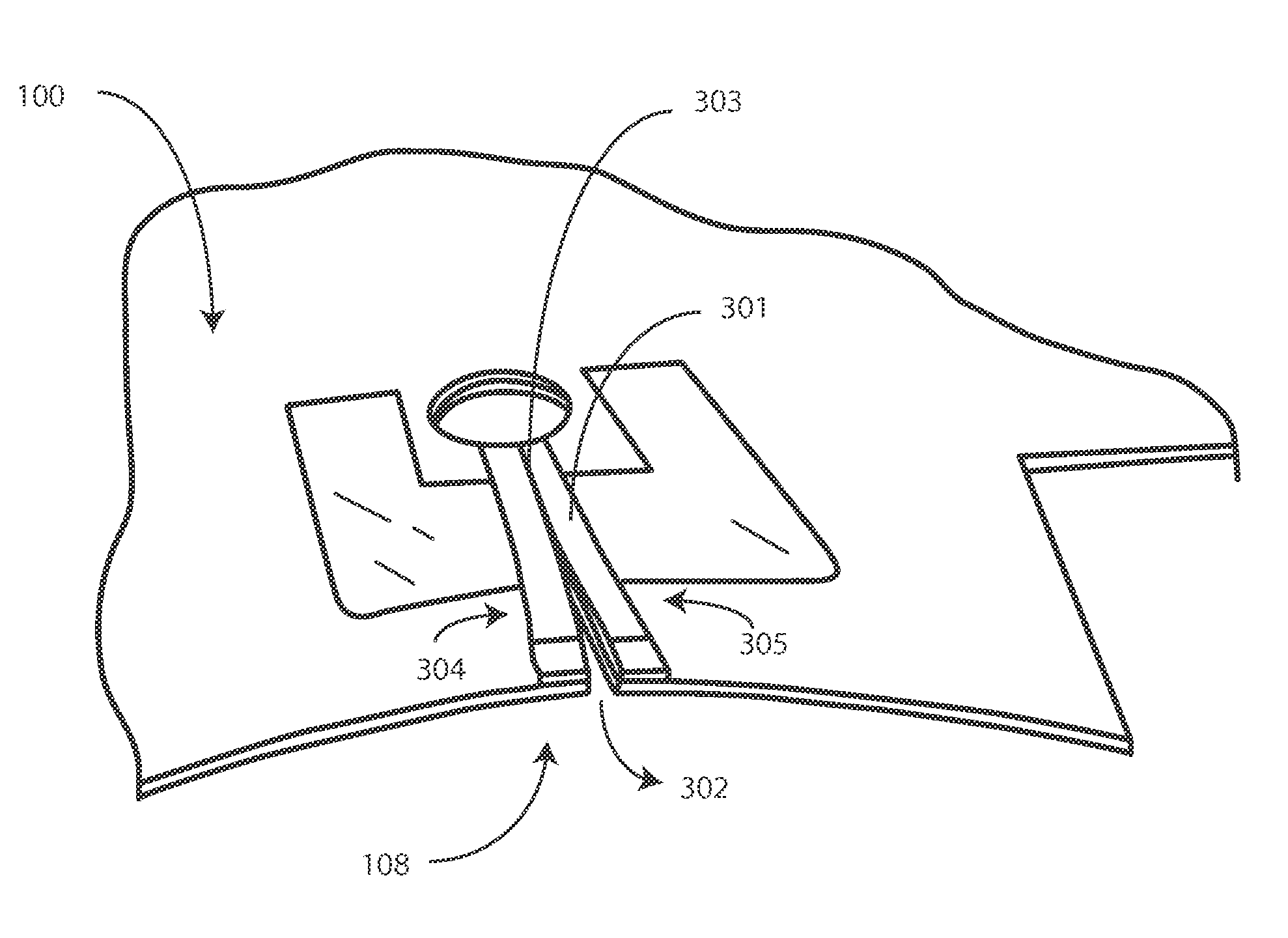
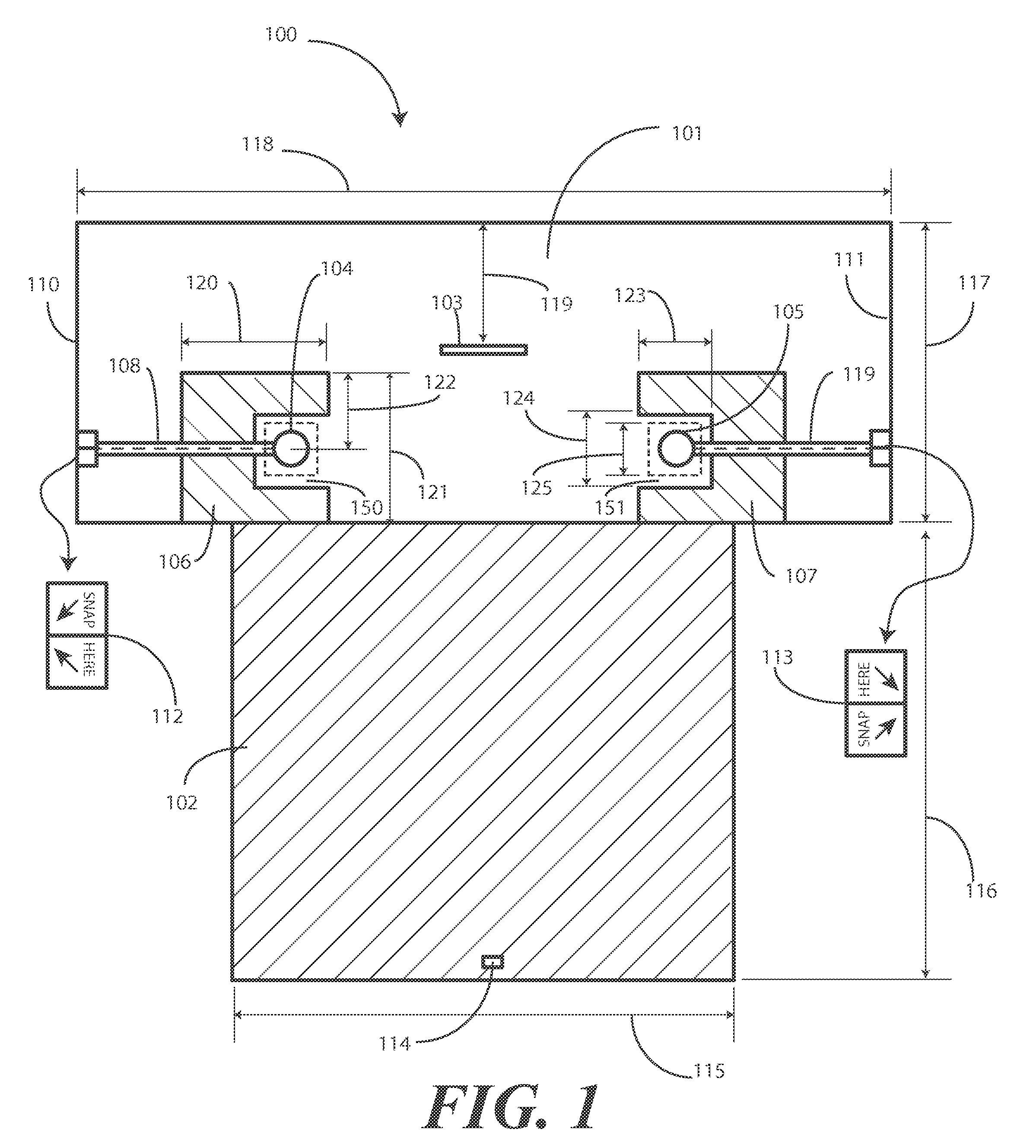
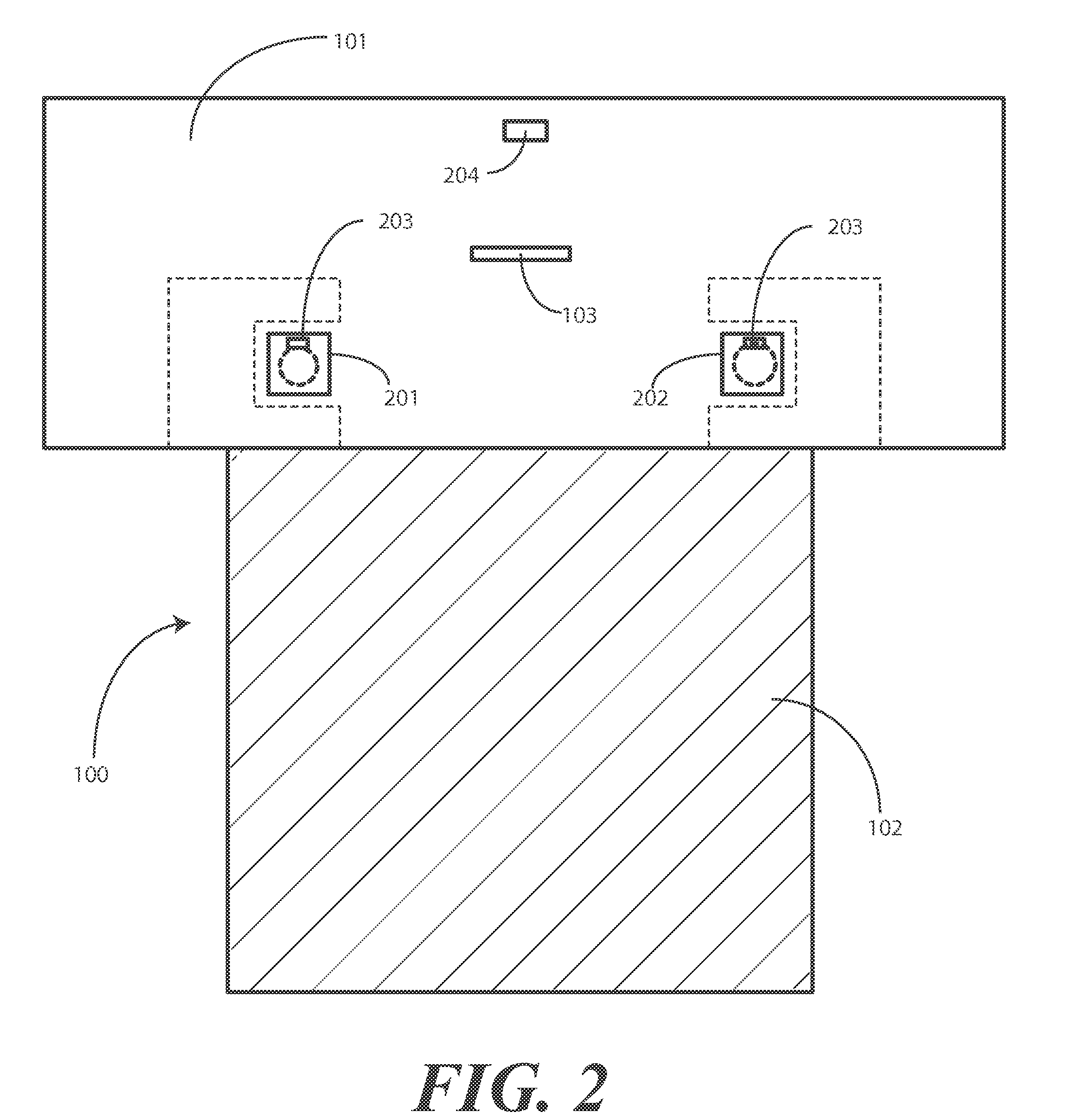
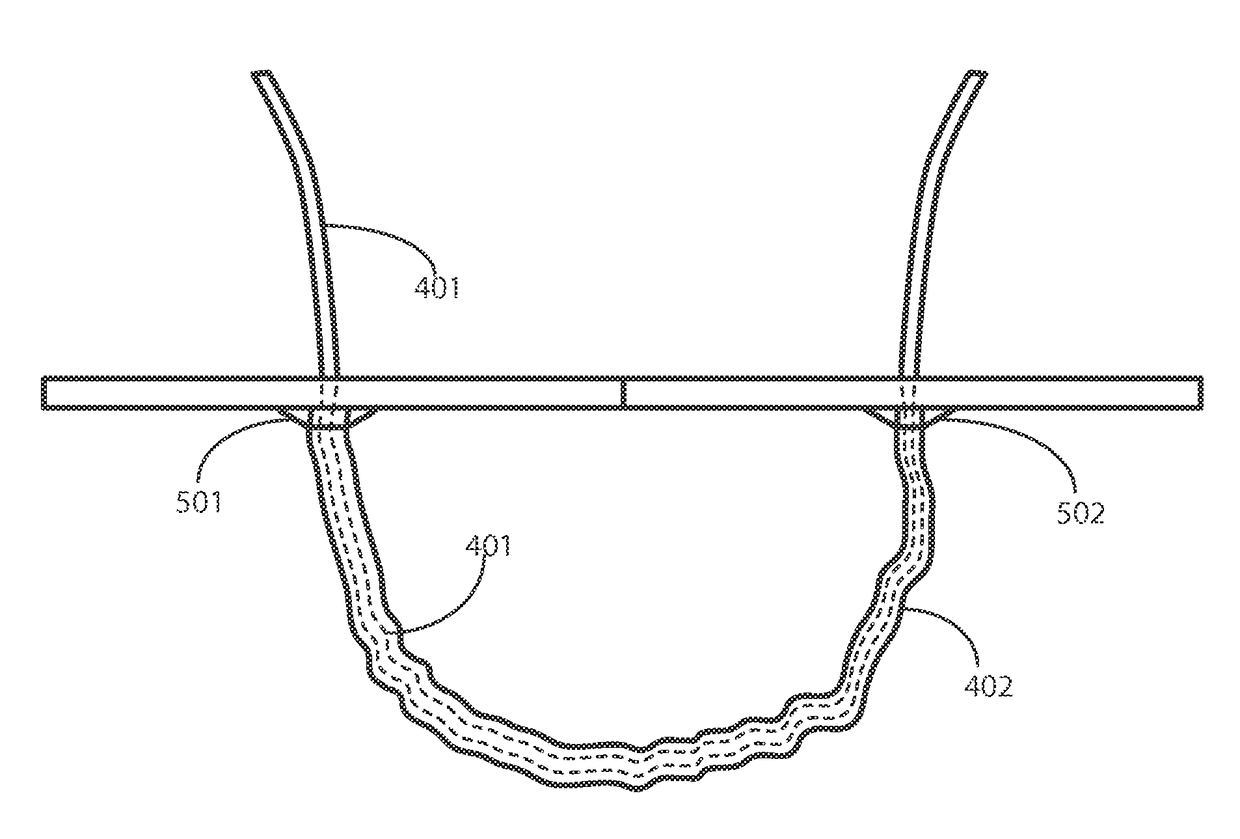
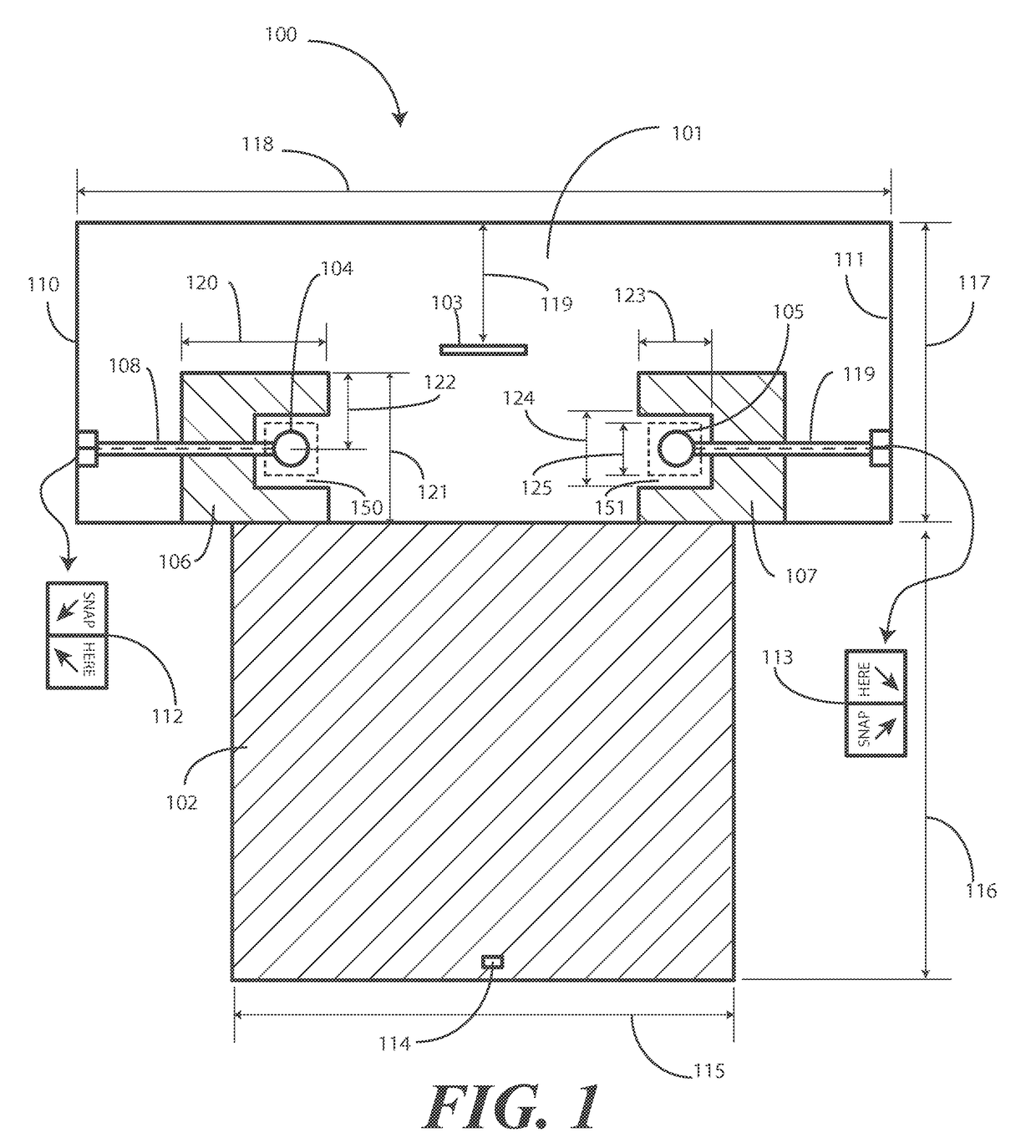
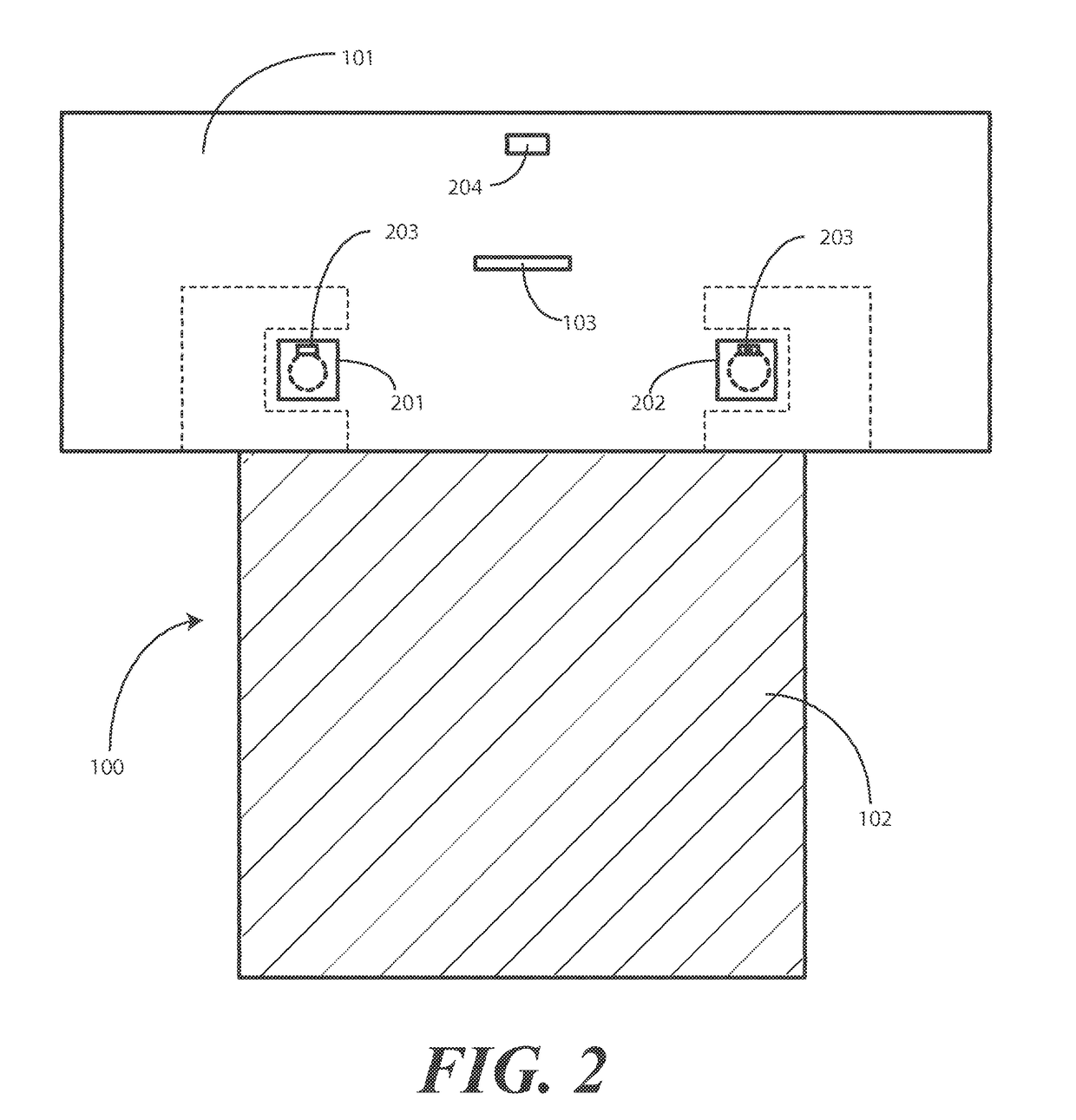
Surgical Drape Configured for Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter Procedures
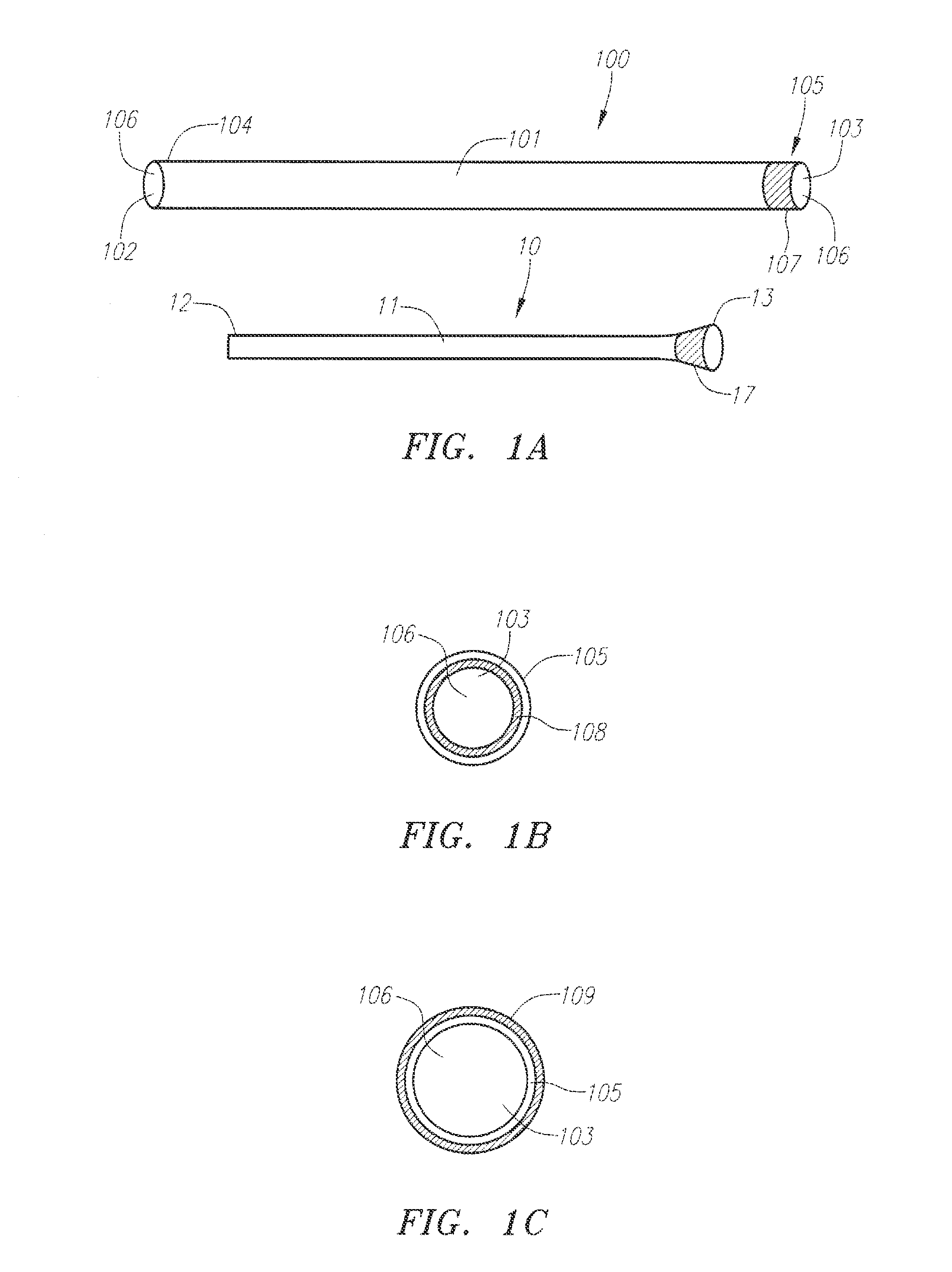
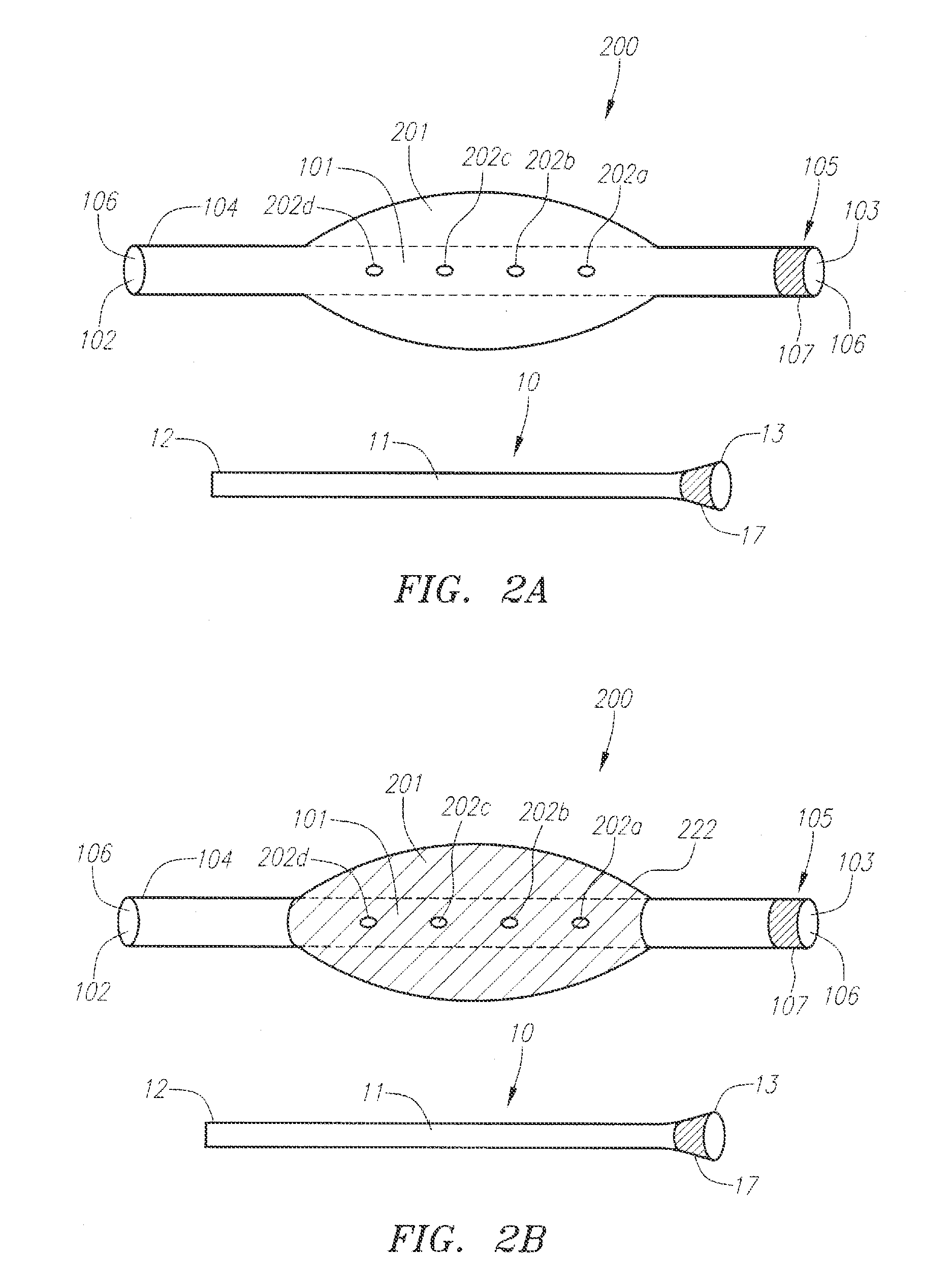
A medical drape (100) includes an upper portion (101) and a lower portion (102). The upper portion (101) can be pellucid, while the lower portion (102) can be opaque. To facilitate central catheter insertion, the upper portion (101) can define one or more apertures (104,105) through which a central line may be inserted. A tourniquet (401) may be integrated with the drape, as can one or more tool-less removal features (108,109).
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Method and Apparatus for Percutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement
ActiveUS20140200658A1Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesAscending aortaCoronary artery ostium
A catheter adapted for placement in the ascending aorta comprises a central catheter mechanism and a balloon structure or other occluding structure at its distal end. The catheter may be placed over the aortic arch such that the occluding structure is placed in the ascending aorta just above the Sinus of Valsalva and coronary ostia. Once in place, the occluding structure is inflated to control blood flow through the aorta during aortic valve ablation and replacement protocols.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Vesicle-type serial expansion balloon for valves
PendingCN111772876AIncrease pressureIncrease success rateBalloon catheterAnnuloplasty ringsProsthetic valveEngineering
The present invention relates to the technical field of medical device implants, and in particular to a vesicle-type serial expansion balloon for a valve. The expansion balloon comprises a central catheter and multiple split balloons serially connected in sequence along the axis of the central catheter, and the insides of the multiple split balloons respectively communicate with the cavity of thecentral catheter; and the central catheter is connected with an external fluid delivery device, and the multiple split balloons are inflated or decompressed through the external fluid delivery device.The vesicle-type serial expansion balloon for the valve has a simple manufacturing process and low manufacturing cost, the structure can be used to successfully locate the position of an aorta, and further increase the internal pressure of the balloon to expand the deformed or narrowed valve and destroy valve calcification to restore the elasticity of the valve; and the original valve is pre-expanded to prepare for the replacement of an artificial valve, at the same time, the matching degree of compliance is extremely high, adverse effects caused by balloon over-expansion and balloon slidingare reduced, and the possibility of occurrence of complications or injuries can be reduced, and the expansion balloon is convenient to operate and can increase the success rate of surgery.
Owner:KOKA NANTONG LIFESCIENCES CO LTD
Cover for a peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC) line
InactiveUS20180015258A1Easy to slipWithout restricting freedomMedical devicesCatheterPeripheral catheterPeripherally inserted central catheter
A protective cover for use with peripheral inserted central catheters (PICC) to secure the outer portion of the catheter lines. The device is an elasticated sleeve so as to snugly fit over the extremity that has the exposed peripheral catheter lines.
Owner:SHEN HSIU CHIN
Surgical drape configured for peripherally inserted central catheter procedures
A medical drape (100) includes an upper portion (101) and a lower portion (102). The upper portion (101) can be pellucid, while the lower portion (102) can be opaque. To facilitate central catheter insertion, the upper portion (101) can define one or more apertures (104,105) through which a central line may be inserted. A tourniquet (401) may be integrated with the drape, as can one or more tool-less removal features (108,109).
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
Infusion support capable of automatically splicing medicine bottles and convenient to adjust
InactiveCN112274723AEasy to adjustReduce work intensityInfusion devicesMedical devicesApparatus instrumentsFluid administration
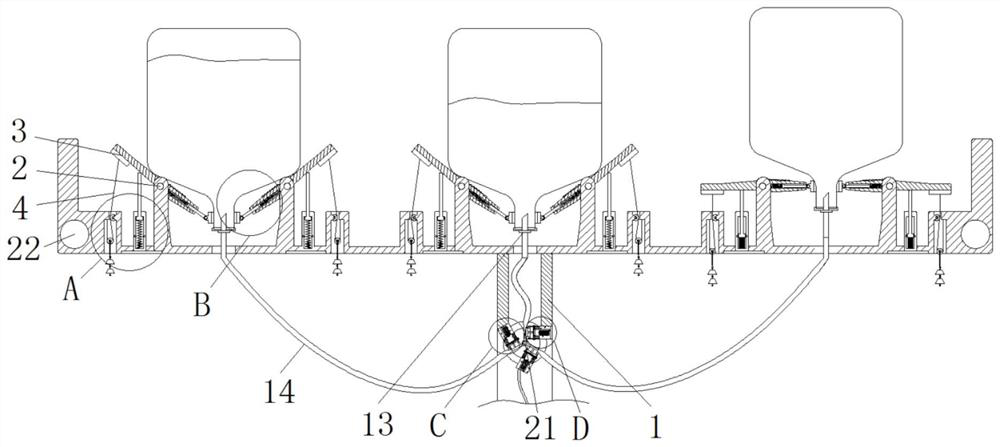
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and discloses an automatic medicine bottle continuing and convenient-to-adjust infusion support. The infusion support comprises a support body, wherein a lever is rotatably connected to the top of the support body, a balancing weight is fixedly connected to the left end of the lever, and a pull rope is fixedly connected to the bottom end of the balancing weight; the bottom end of the balancing weight is in transmission connection with a balancing weight through a pulley block, and the interior of the right end of the lever ismovably connected with a telescopic rod. According to the infusion support capable of automatically splicing the medicine bottles and convenient to adjust, the lever rotates upwards to enable the contacts to be communicated, the corresponding electromagnets are excited to be communicated, and the next infusion bottle and the central catheter are communicated, so the effect of automatically splicing the medicine bottles to reduce working intensity of medical staff is achieved, and medicine changing efficiency is improved; balance weight is selected according to infusion bottles of different specifications, alarm and medicine adding positions of the different infusion bottles can be adjusted conveniently, and universality of the device is improved.
Owner:李朝霞
Tube placing bed for placing central venous catheter through peripheral vein
The invention discloses a tube placing bed for placing a central venous catheter through a peripheral vein, which comprises a bed body and a support plate, wherein the support plate is positioned below the bed body; support rods are fixedly arranged on both sides of the upper end of the support plate; the upper end of each support rod is fixedly connected with the lower end of the bed body; the upper end face of the support plate is provided with a first sliding plate which can slide along the length direction of the support plate; a second sliding plate is arranged on the upper end surface ofthe first sliding plate and can be connected with the first sliding plate in a sliding way along the width direction of the support plate; a supporting plate is positioned above the second sliding plate, and two sides of the lower end of the supporting plate are connected with the second sliding plate through a telescopic device. According to the tube placing bed, the supporting plate is arranged, so that the arm of a patient can be straightened and placed on the supporting plate during tube placing; the upper position, the lower position, the front position and the rear position of the supporting plate are adjustable, so that the tube placing bed can be suitable for patients of different sizes; the arm of the patient can be positioned at the most proper position as much as possible whenthe arm of the patient is straightened and placed on the supporting plate, thereby reducing the pain.
Owner:神农架林区人民医院
Determining and displaying the 3D location and orientation of a cardiac-ablation balloon
ActiveUS20180317864A1Shorten the length of timeImprove insightsElectrocardiographyBalloon catheterFluoroscopic imageRespiratory phase
A method for generating and displaying a 3D visualization of a cardiac-ablation balloon in a region of a living heart within a predefined 3D space, the method using single-plane fluoroscopic images and comprising: (1) placing, inflating and positioning the balloon into the region, the balloon having a radio-opaque location marker and central catheter portion; (2) capturing a burst of first-view digitized 2D images of the region from a fluoroscope positioned at a first angle; (3) capturing a burst of second-view digitized 2D images of the region from the fluoroscope positioned at a second angle different from the first angle; (4) selecting first-view and second-view images from the bursts such that the difference between measures of the cardio-respiratory phases of the selected first-view and second-view images is minimized; (5) identifying the location marker in each of the two selected images; (6) placing first and second orientation markers in the selected first-view and second view images, respectively, where the central catheter portion intersects the projected image of the inflated balloon at a farthest point from the location marker; (7) associating the location marker and the second orientation marker in the selected second-view image with the location marker and first orientation marker in the selected first-view image; (8) determining 3D location and orientation of the balloon in the region using the selected first-view and second-view images; (9) based on the determined location and orientation, inserting a 3D balloon model into the predefined space to generate the 3D visualization; and (10) displaying the 3D visualization on a display device, whereby a user can visualize where cardiac ablation was applied within the region.
Owner:APN HEALTH
Methods and Apparatus for Percutaneous Aortic Valve Replacement
ActiveUS20140142692A1Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesCardiac cyclePerfusion
A delivery system and method for percutaneous aortic valve (PAV) replacement and apparatus used therein. A temporary aortic valve including a reversibly expandable occluding means surrounds a central catheter mechanism. The temporary valve is positioned within the ascending aorta, just above and downstream from the coronary ostia. The occluding means is configured such that, when fully expanded against the aortic wall, gaps are left that promote continuous coronary perfusion during the cardiac cycle. The temporary valve substitutes for the function of the native aortic valve during its replacement. The native aortic valve is next dilated, and then ablated through deployment of low profile, elongated, sequentially delivered stents. The stent(s) displace the native tissues and remain within the aortic annulus to receive and provide a structure for retaining the PAV. The PAV is delivered, positioned and deployed within the stent(s) at the aortic annulus with precision and relative ease.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECHNOLOGIES LLC
Surgical drape configured for peripherally inserted central catheter procedures
ActiveUS9937015B2Easily apply and use and removeDiagnosticsRestraining devicesTourniquet timeCoupling
A medical drape includes a patient drape (100) and a radial drape attachment (200). The radial drape attachment can be coupled to the patient drape by way of an adhesive coupling (202). The radial drape attachment includes defines one or more fenestrations (205) or apertures through which a central line may be inserted. Some or all of the radial drape attachment (200)can be transparent or pellucid. Portions of the radial drape attachment can be opaque as well. A support layer can be configured to be absorptive, fluid impenetrable, or both. A tourniquet (1801) may be integrated with the radial drape attachment, as can one or more tool-less removal features (209). Pouches (901,902) can be added to catch fluids or hold medical implements during a procedure.
Owner:MEDLINE IND LP
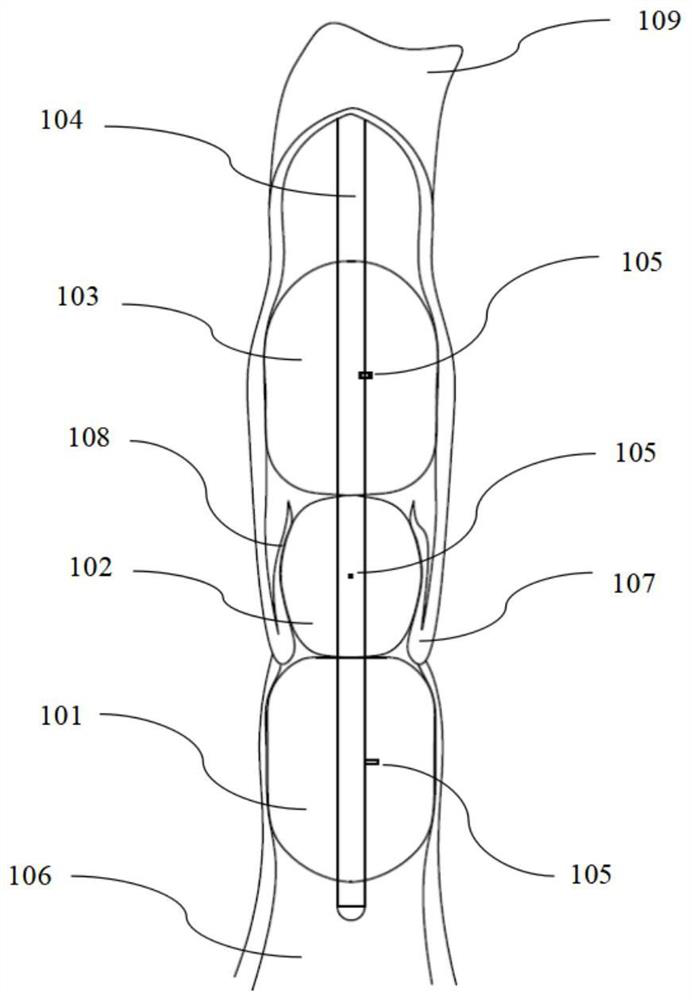
Central venous catheter with wall adherence preventing device for dialysis
InactiveCN102861373ASimple preparation processLow costBalloon catheterDialysis systemsCritically illVenous vessel
The invention discloses a central venous catheter with a wall adherence preventing device for dialysis. The central venous catheter comprises a catheter body, an outlet, a blood inlet and a blood outlet, an air bag which is close to the blood inlet is sleeved at a position of the upper portion of the blood inlet, the air bag comprises an air bag body and an air bag channel which is connected with the air bag body, the other end of the air bag channel extends to a position of the outlet of the upper end of the catheter to form an air vent, and the air bag body comprises at least three same air bag pouches which are uniformly distributed on a same horizontal plane. By means of the central venous catheter with the wall adherence preventing device for the dialysis, the problems that the blood inlet adheres to the wall when a dialysis catheter is placed in vein for a long time, and wall adherence can occur due to conditions of low blood pressure and the like of critically ill patients can be excellently solved, when blood flow is blocked caused by the fact that a fibrin sheath forms and wraps the tip end of the catheter, the air bag is opened to open up the fibrin sheath, thereby a part of space is reserved to enable blood to pass, the manufacturing process is simple, the cost is low, and the clinical practicability is high.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL XIAMEN UNIV
Graft for segmental bone defect repair
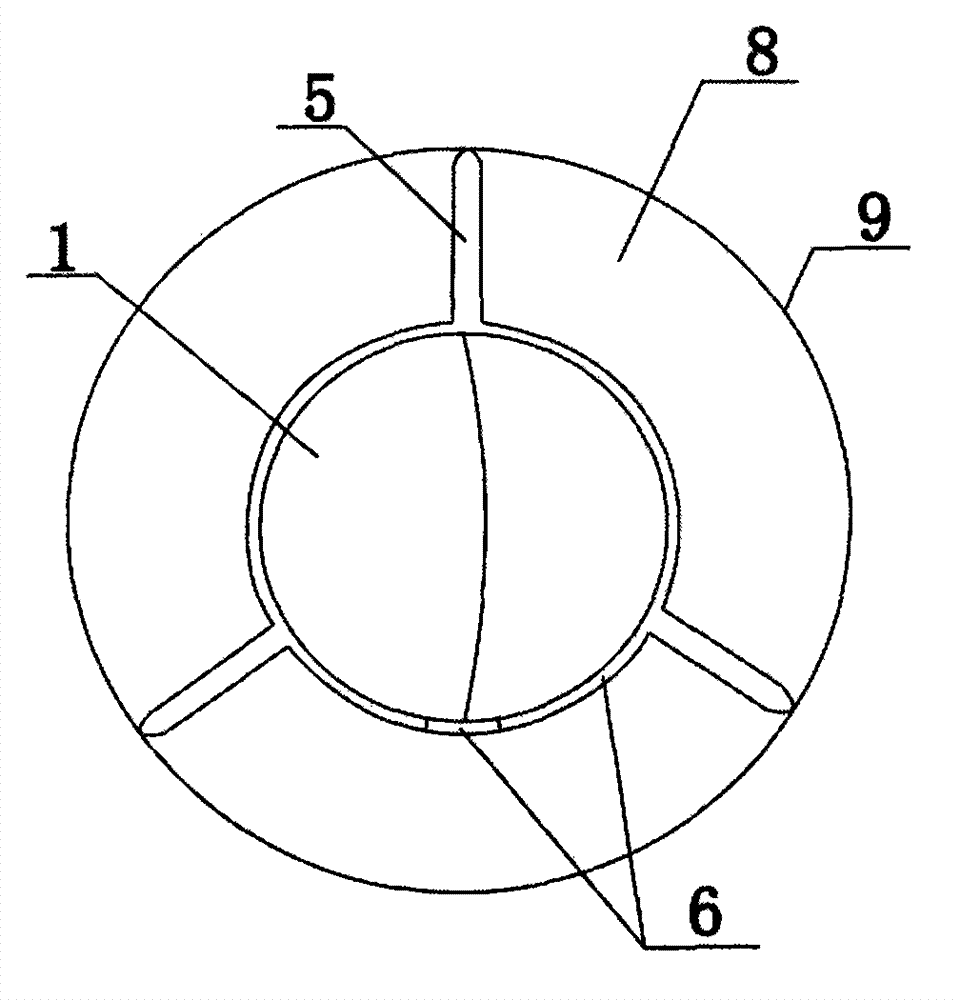
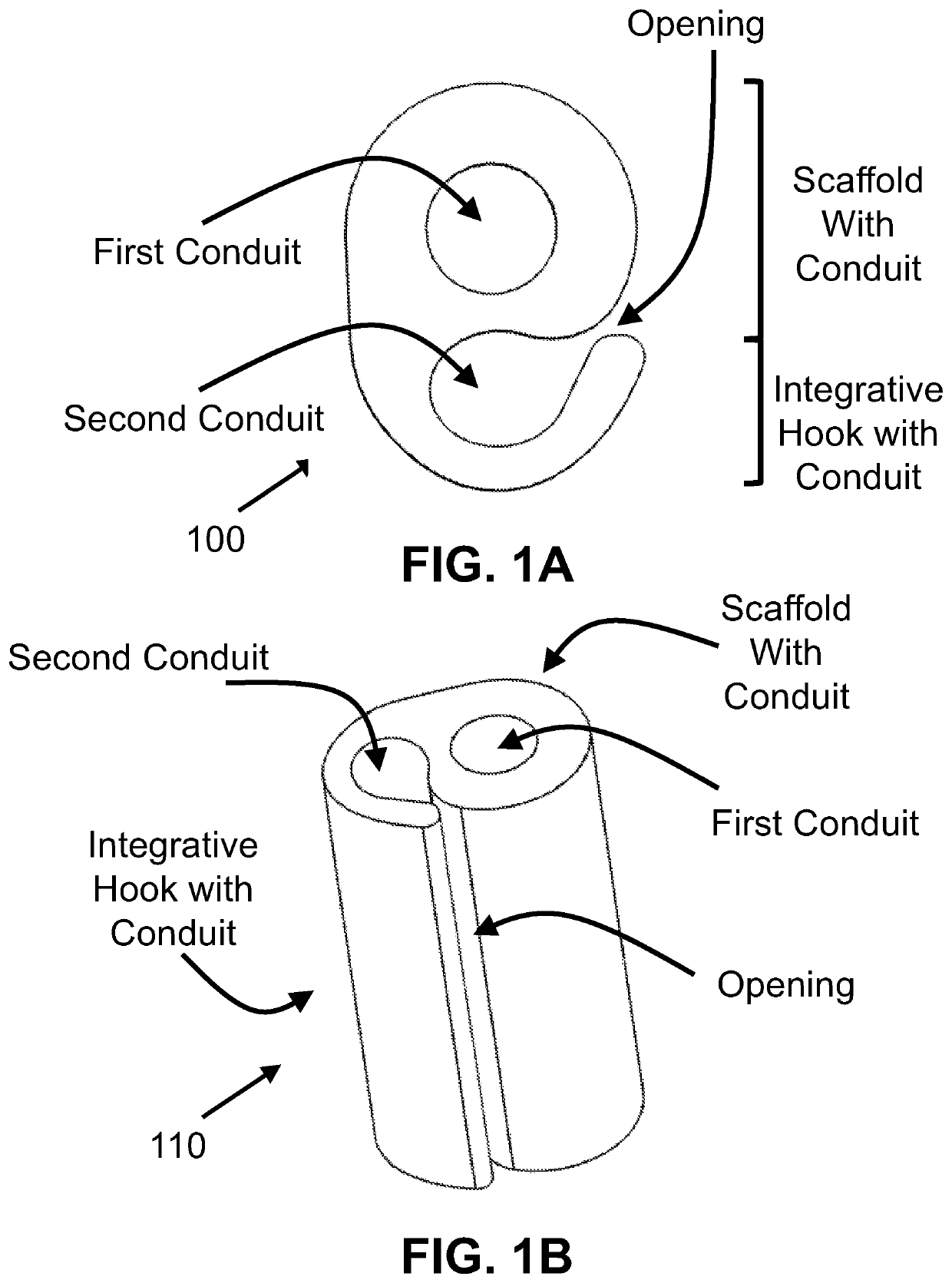
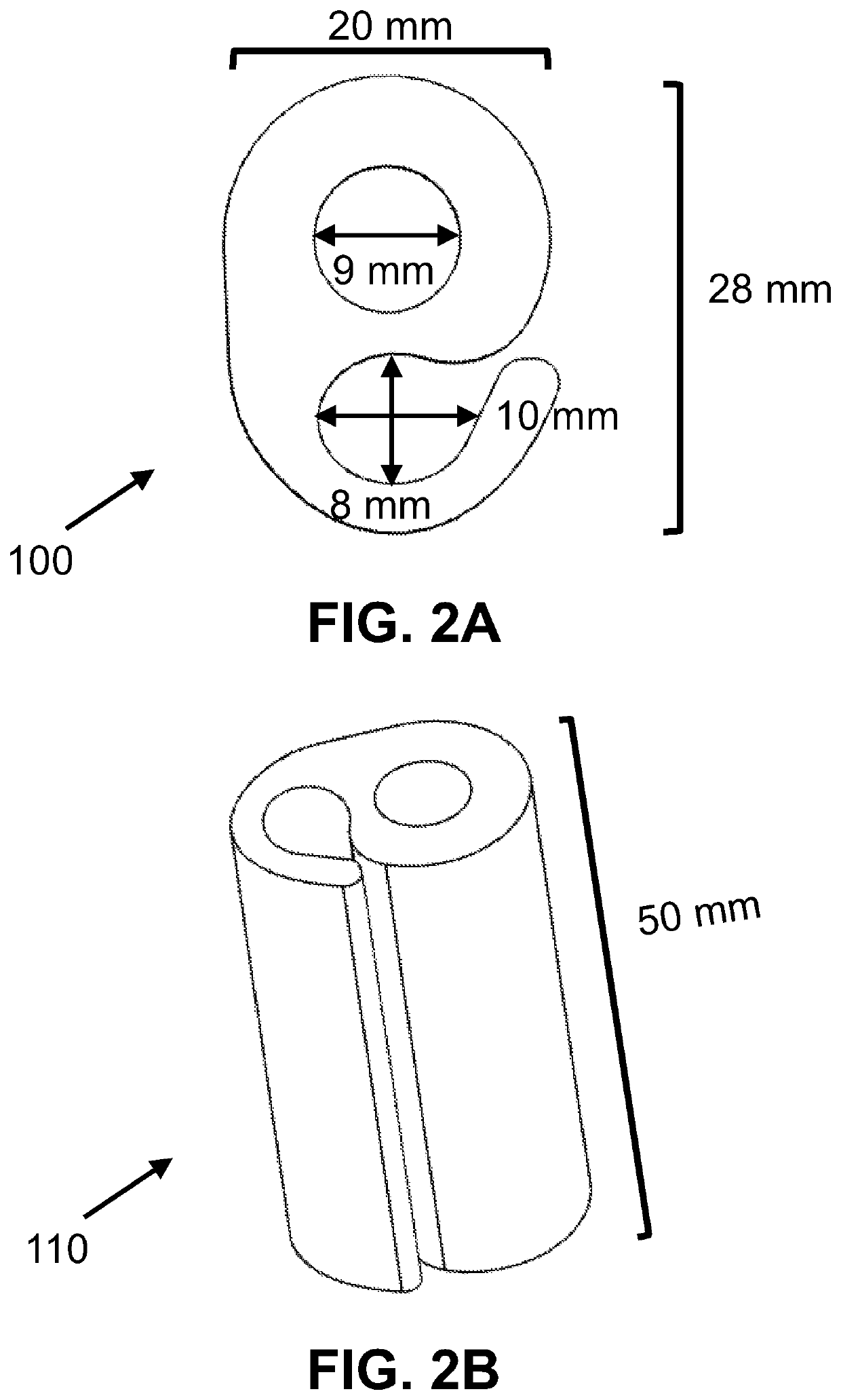
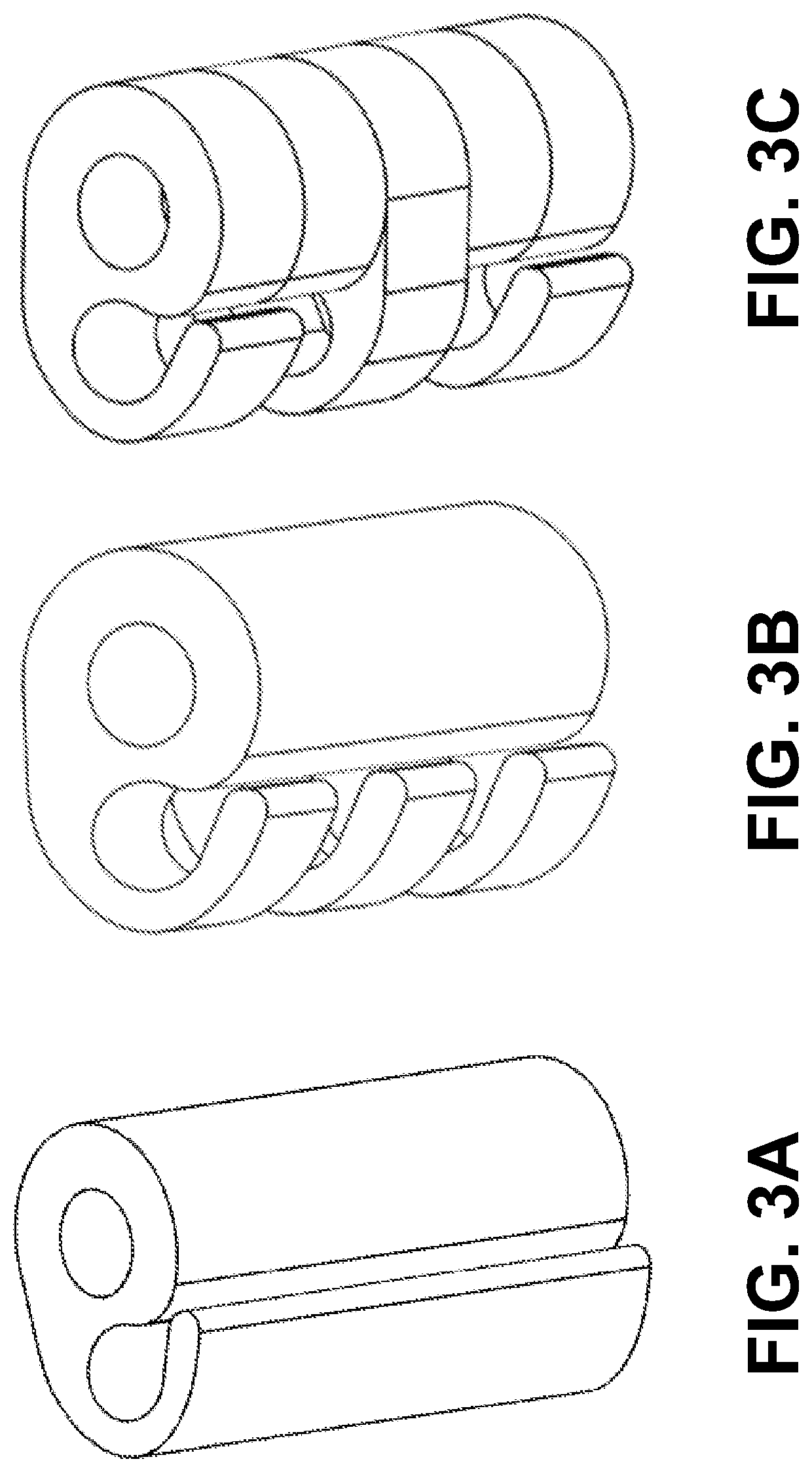
A graft scaffold geometry is provided for use in the repair of segmental large bone defect. The scaffold geometry has a first (central) conduit with one or several hook-shaped chamber, which form a second conduit, integrated to the lateral side of the scaffold. The purpose of the hook-shaped chamber(s) is three-fold: 1) to facilitate the insertion and containment of biological augmentation constructs, such as growth factor-impregnated carrier devices; 2) stabilize the local surrounding soft tissue envelope to allow ingrowth of new blood vessels; and 3) to improve the manipulation of the composite bone free flap during implantation. Whether one or all of these mechanisms are active in a given situation, the overall result is that the hook chamber enables enhanced containment of graft-augmenting synthetic osteoinductive constructs, prevents their displacement, and maintains their proximity to the scaffold, thus improving the chances of success of the graft.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System and method for determining cardiac output
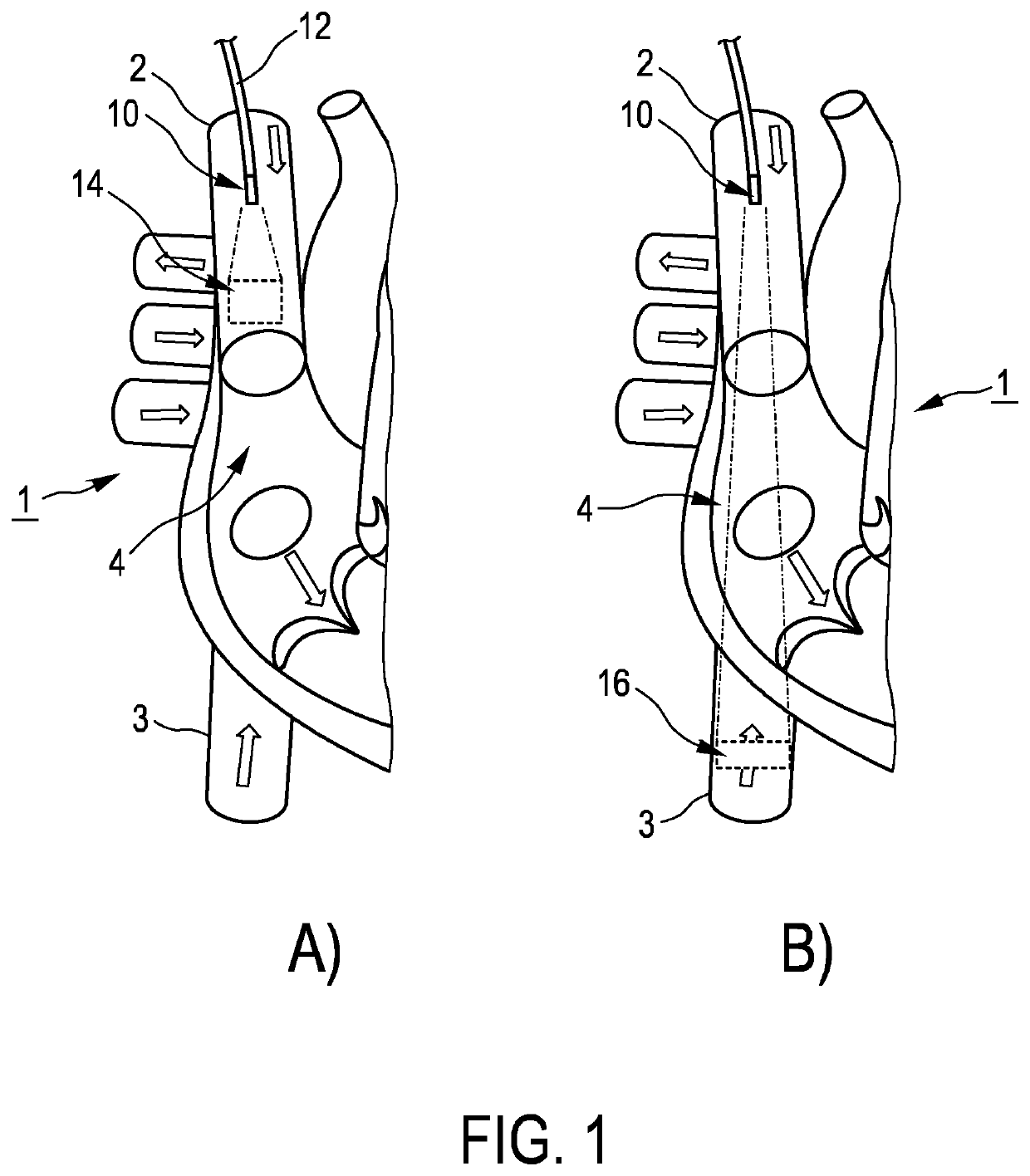
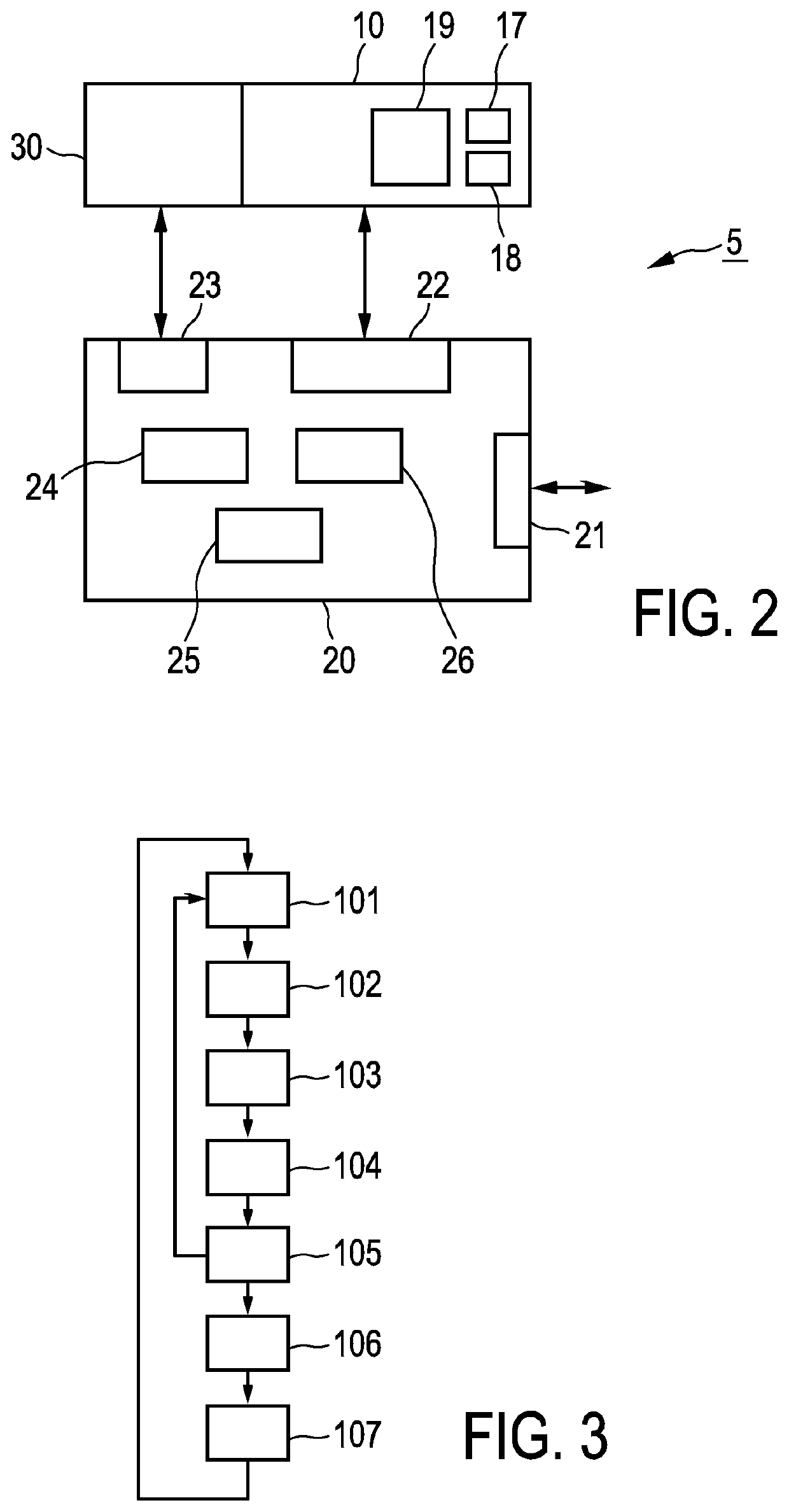
InactiveUS20210298714A1Reduce decreaseSimple methodBlood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic sensorSuperior vena caval
The invention relates to determining a representation of cardiac output in a patient. Provided are a method and a system for monitoring a cardiac output using a single device inserted into a Central Venous Catheter (CVC) or Peripheral Inserted Central Catheters (PICC) line. In an embodiment, the device contains an elongated body that fits the lumen of a Central Venous Cava or Peripheral Inserted Central Catheters line and has an ultrasound transducer at the tip. By operating the device such that the velocity in both the Superior Vena Cava and Inferior Vena Cava can be sampled continuously the CO is monitored.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Peripherally inserted central catheter
Owner:SHANDONG WEIGAO GROUP MEDICAL POLYMER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com