Vesicle-type serial expansion balloon for valves
A balloon and vesicle technology, which is applied to heart valve, valve annulus, balloon-shaped catheter and other directions, can solve the problems of high process precision, complex overall process and high manufacturing cost, and achieves low manufacturing cost, simple manufacturing process, Easy-to-use effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
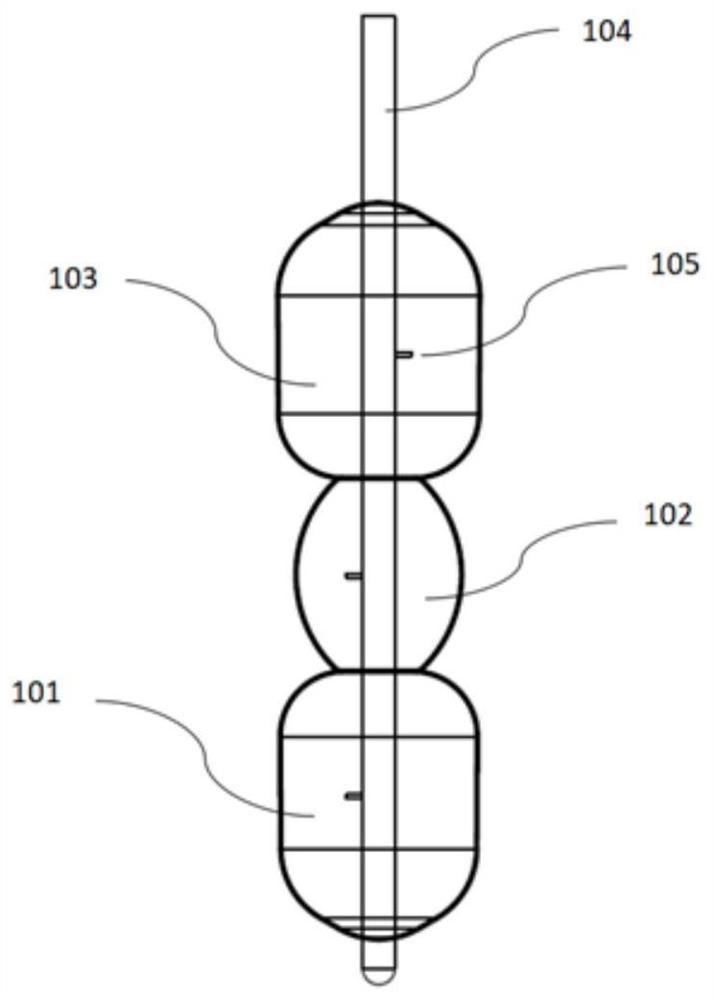
[0028] Such as Figure 1-3 As shown, the expansion balloon for the vesicular series valve of this embodiment includes a catheter and split balloons arranged in sequence along the catheter. Each balloon is not connected to each other and has an independent lumen. The balloon can be directly made of different materials to meet the material compliance requirements of different positions, and the process is simplified compared with the one-piece balloon.
[0029] Specifically, the split balloon includes a proximal balloon 103, an intermediate balloon 102, and a distal balloon 101. The proximal balloon 103 and the distal balloon 101 are made of non-compliant materials, and the non-compliant materials can be PET, PTFE, polyimide, polymer or fibrous materials can also be made relatively non-compliant by electron beam, chemical or other cross-linking methods using compliant or semi-compliant materials. The middle balloon 102 is made of a semi-compliant material, which can be nylon, r...
Embodiment 2
[0040] The dilatation balloon for the vesicular series valve of this embodiment differs from that of Embodiment 1 in that:
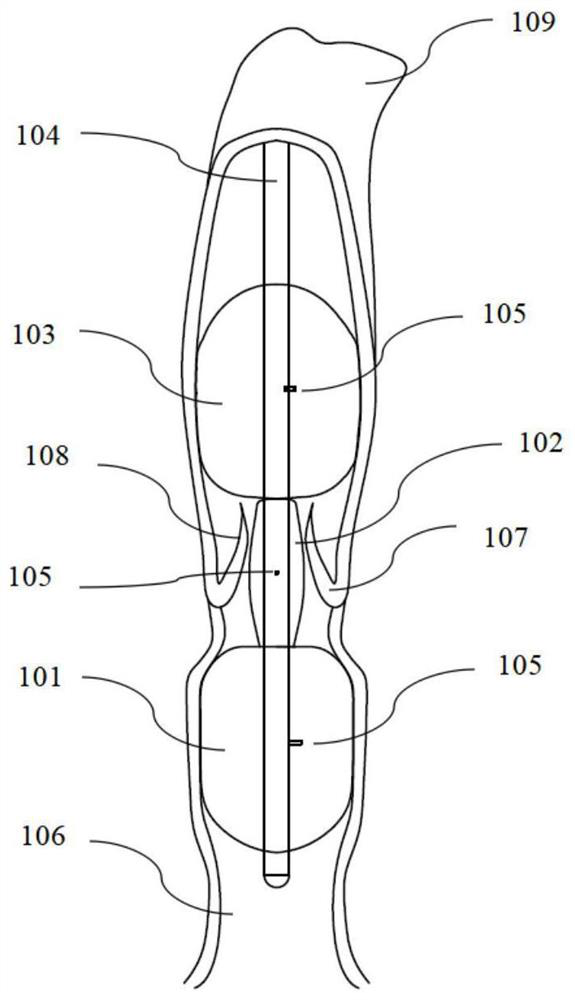
[0041] Such as Figure 4-6 As shown, the internal structure of the central catheter 104 in this embodiment adopts a rotary valve structure, and the interior of the proximal balloon 103, the distal balloon 101, and the middle balloon 102 communicate with the lumen 111 of the central catheter 104 through valve ports, respectively. The rotary valve 112 includes an input end and an output end. The input end is connected to an external fluid delivery device. By rotating the rotary valve 112, when the output end coincides with the valve port, the output end communicates with the valve port; when the output end does not coincide with the valve port , the output end is not connected to the valve port. That is, by rotating the inner tube 110 at the output end of the rotary valve 112, each valve port is aligned with the valve port on the central catheter 104, and...
Embodiment 3
[0047] The dilatation balloon for the vesicular series valve of this embodiment differs from that of Embodiment 1 in that:
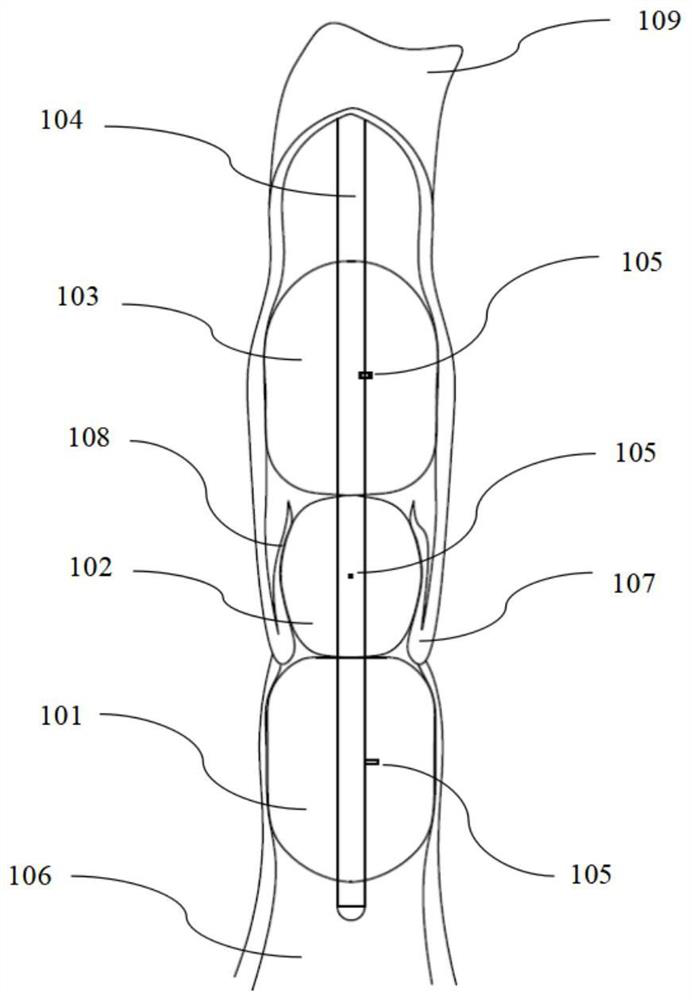
[0048] Such as Figure 7 As shown, the split balloon of this embodiment adopts the method of nesting additional balloons in the balloon to form a double-layer balloon. At the same time, the inner and outer double-layer balloons are respectively equipped with separate capillaries 105 for partial pressure control. Taking the distal balloon 101 as an example, a distal inner balloon 101a is nested inside, and the distal balloon 101 and the distal inner balloon 101a The internal pressure is controlled through different capillaries 105 respectively. The inner balloon has semi-compliance, and its maximum diameter is slightly larger than that of the outer balloon under fully expanded conditions, such as under a pressure of 1-3 atm. Compared with Embodiment 1, increasing the number of layers of the balloon can increase the pressure resistance inside a single ba...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com