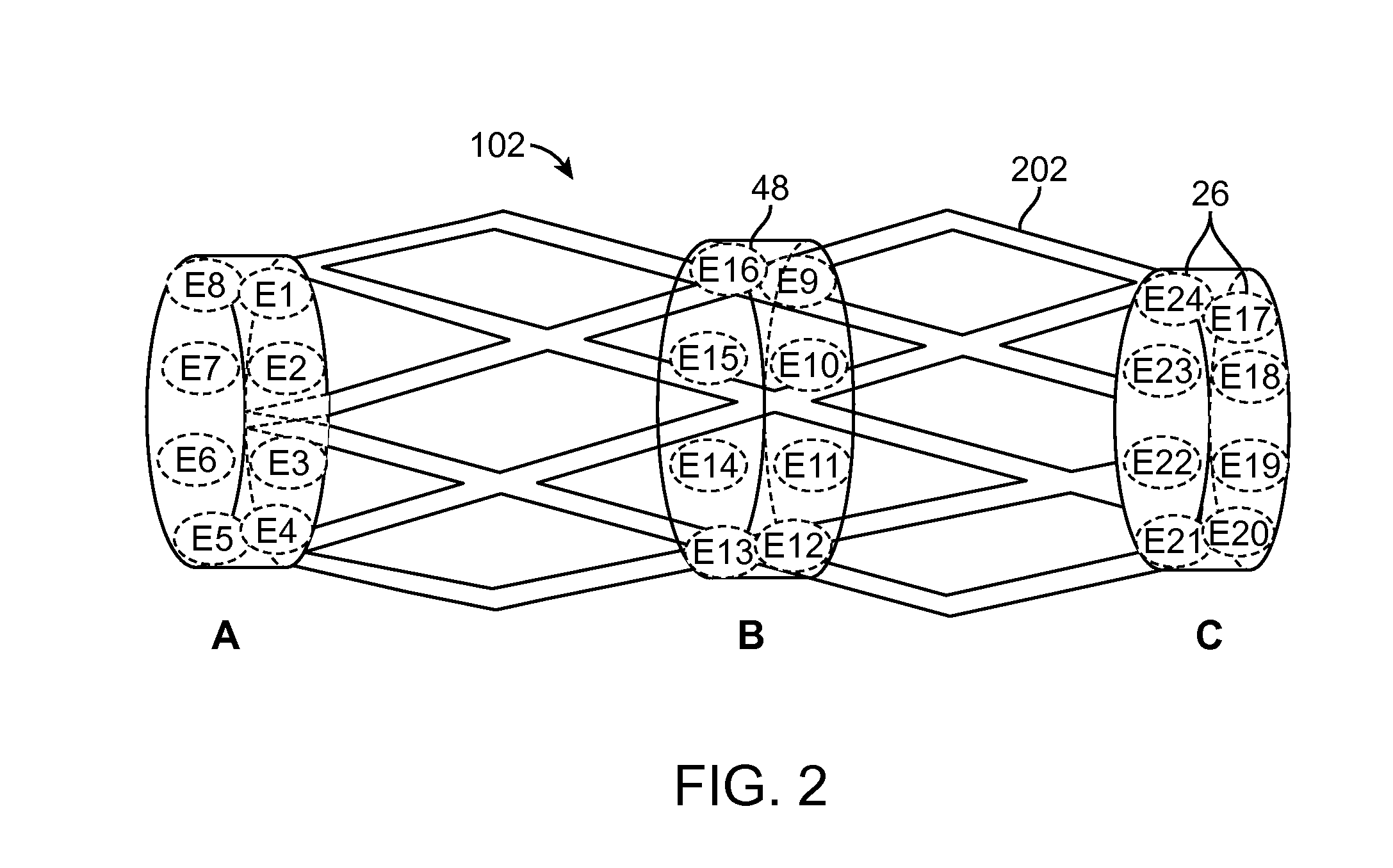
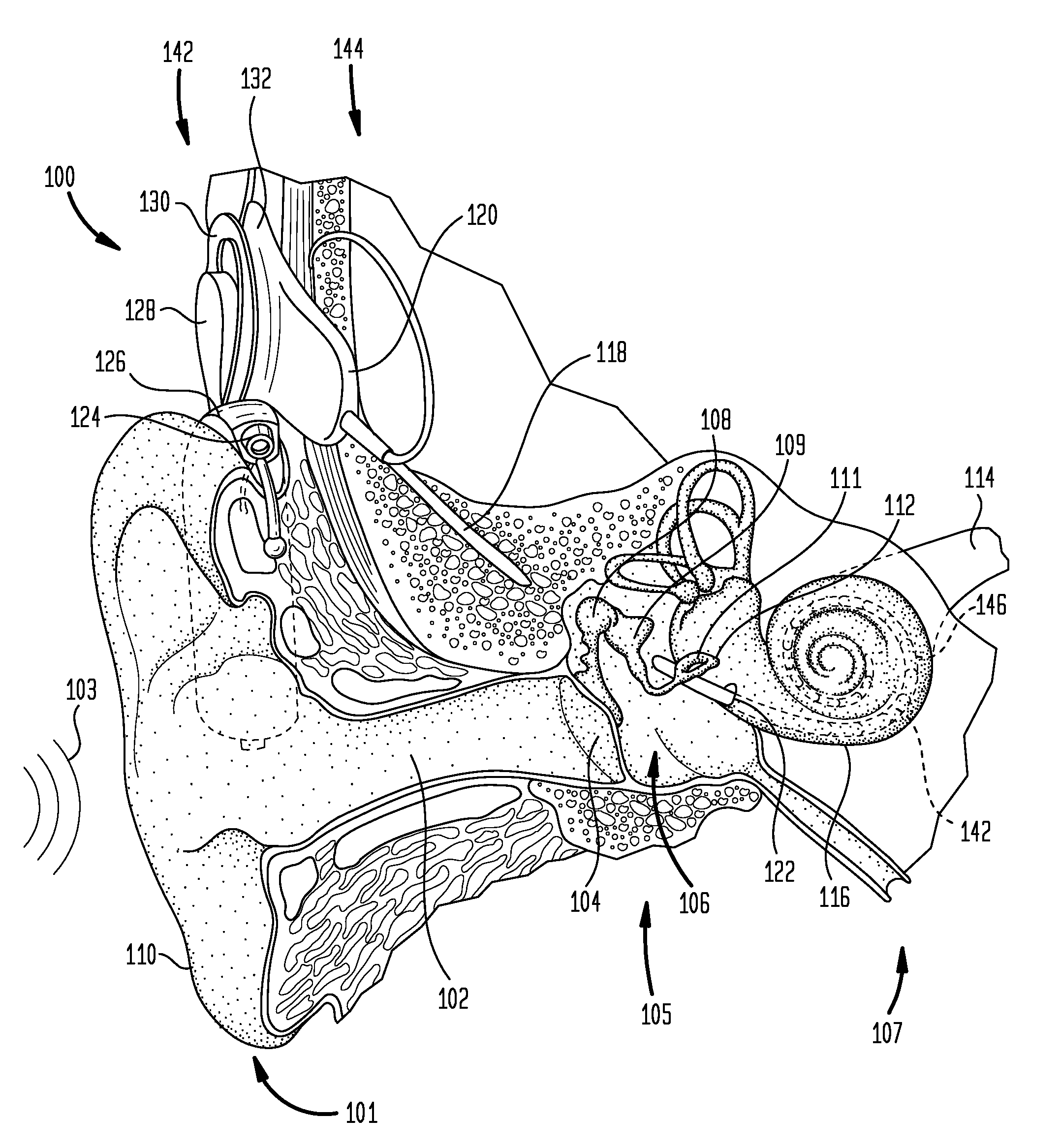
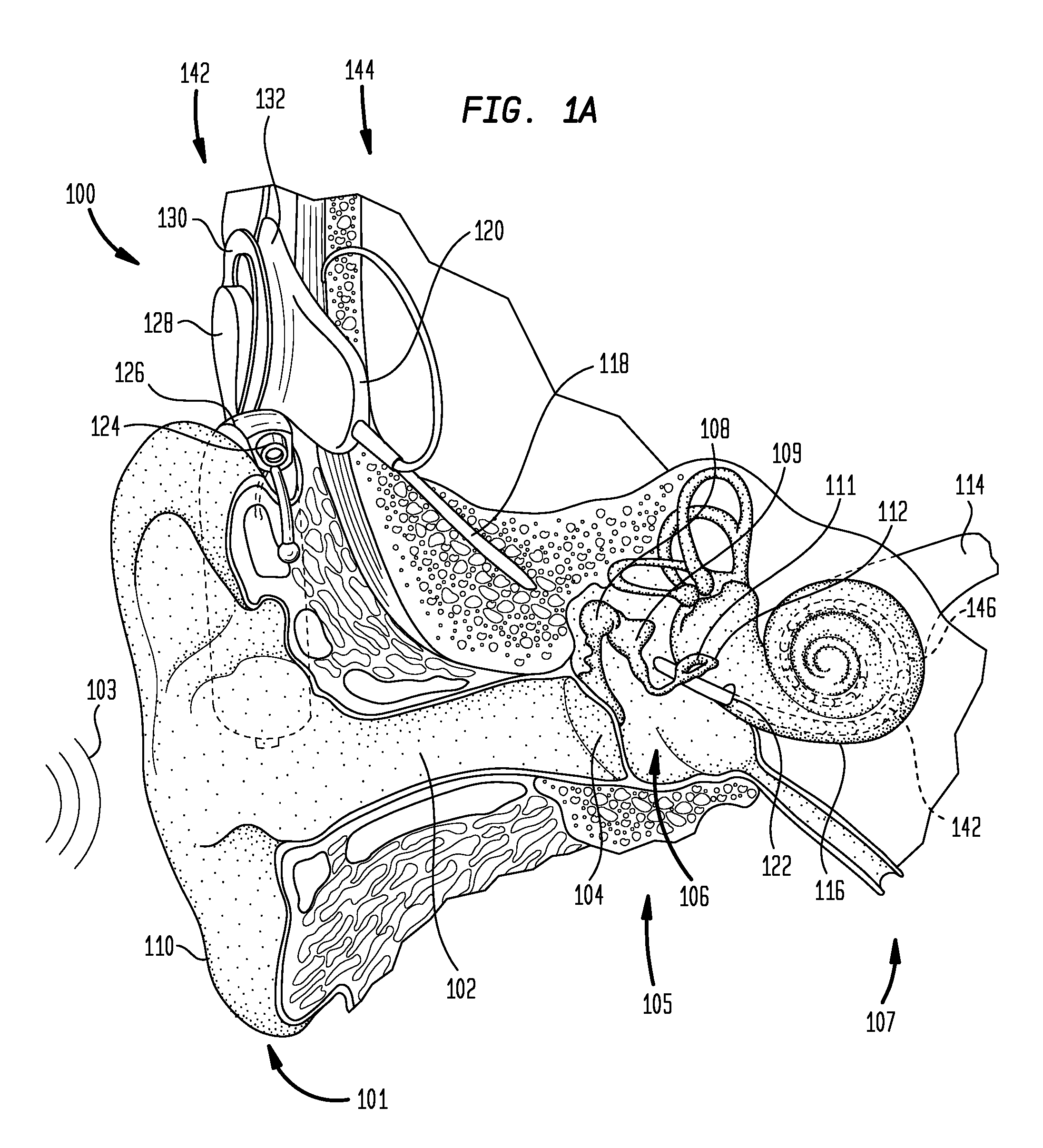
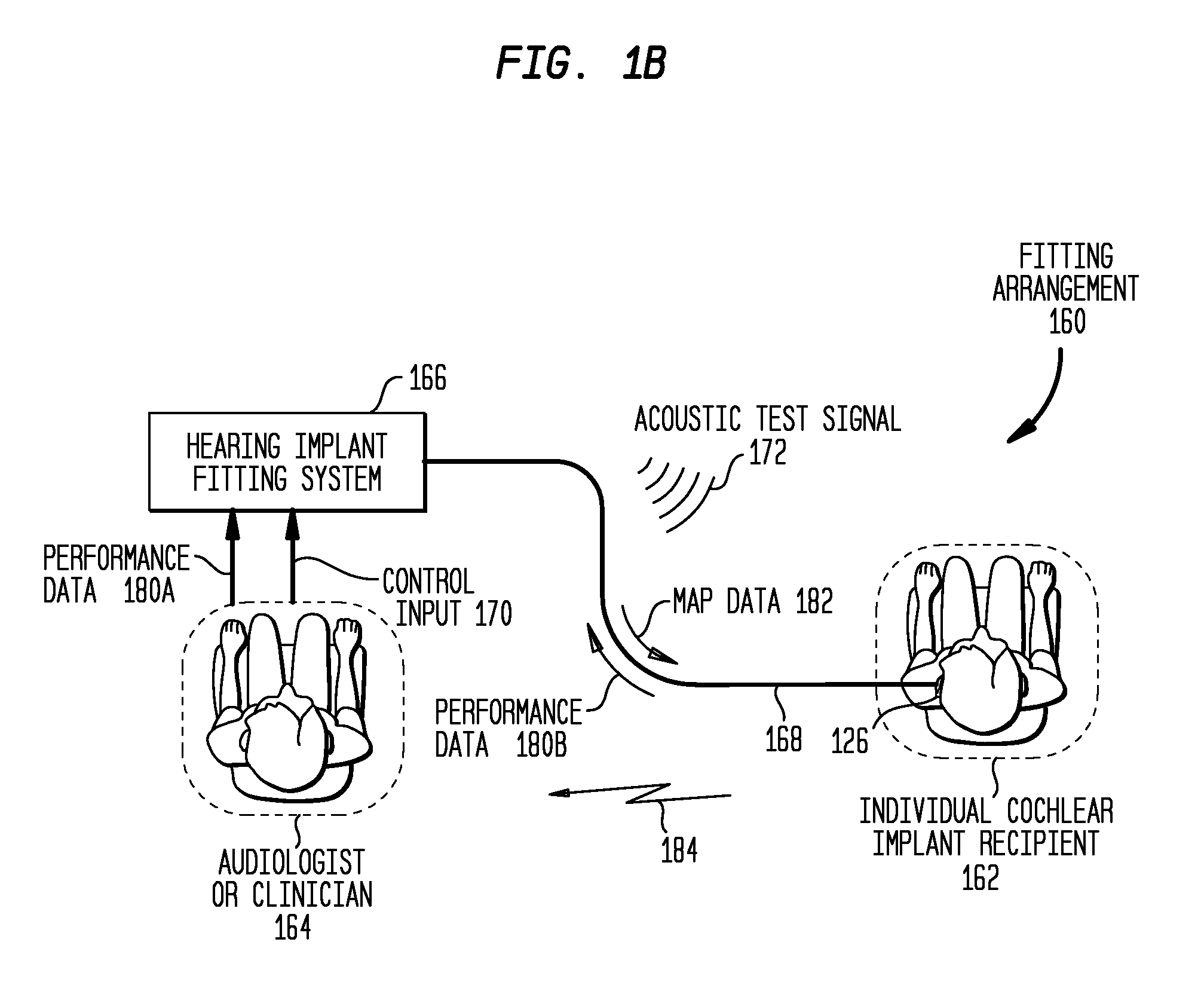
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Evoked compound action potential" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
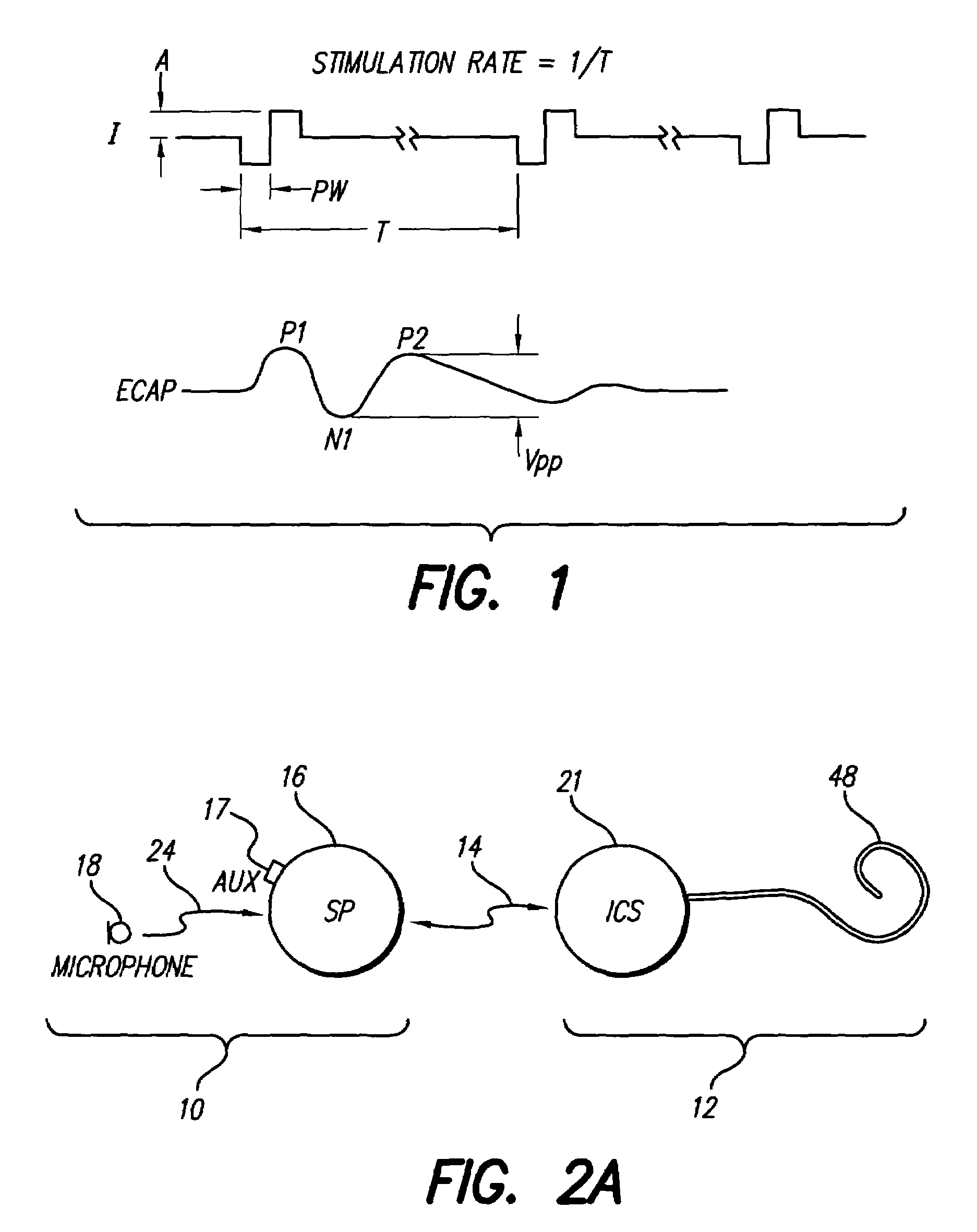
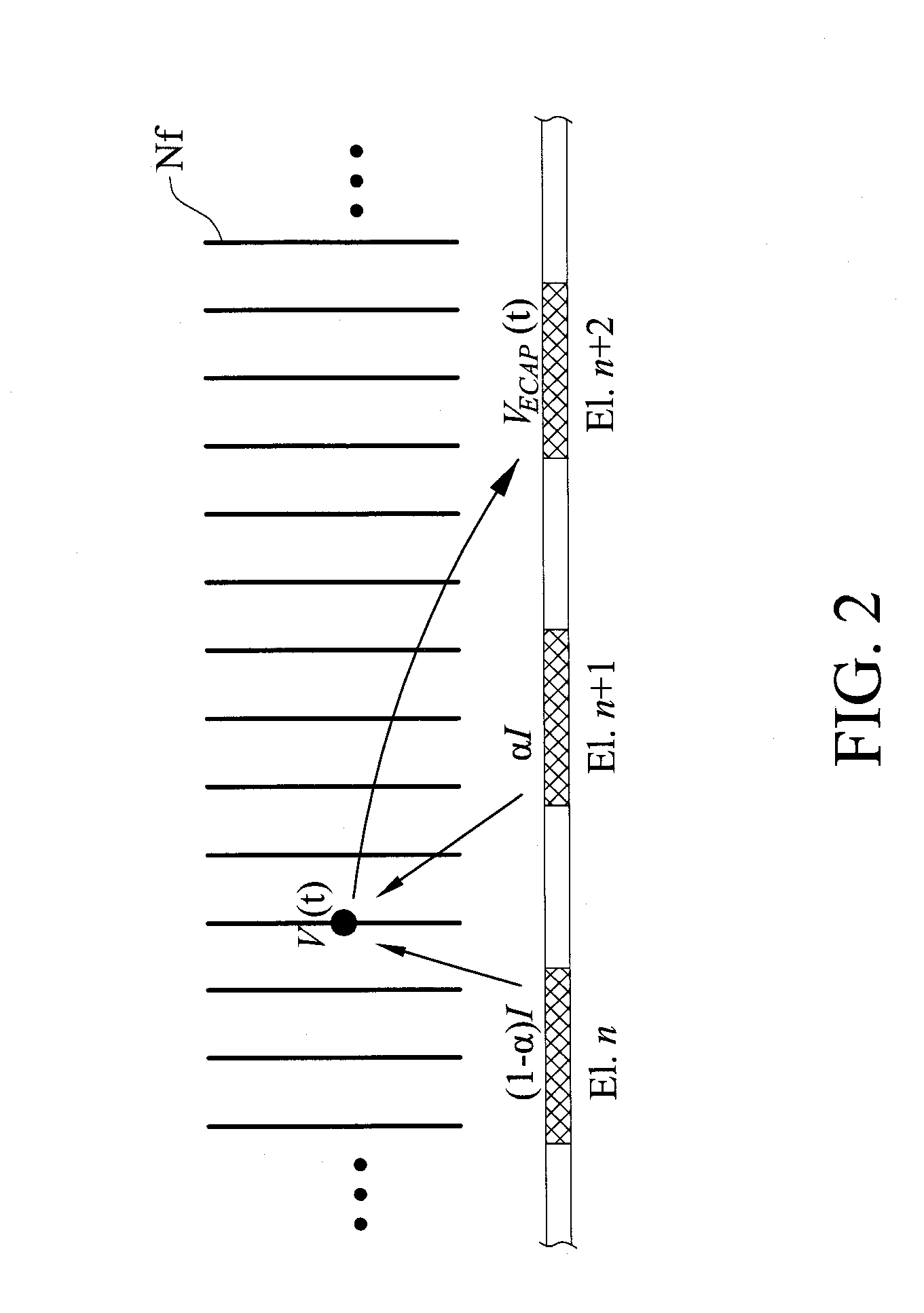
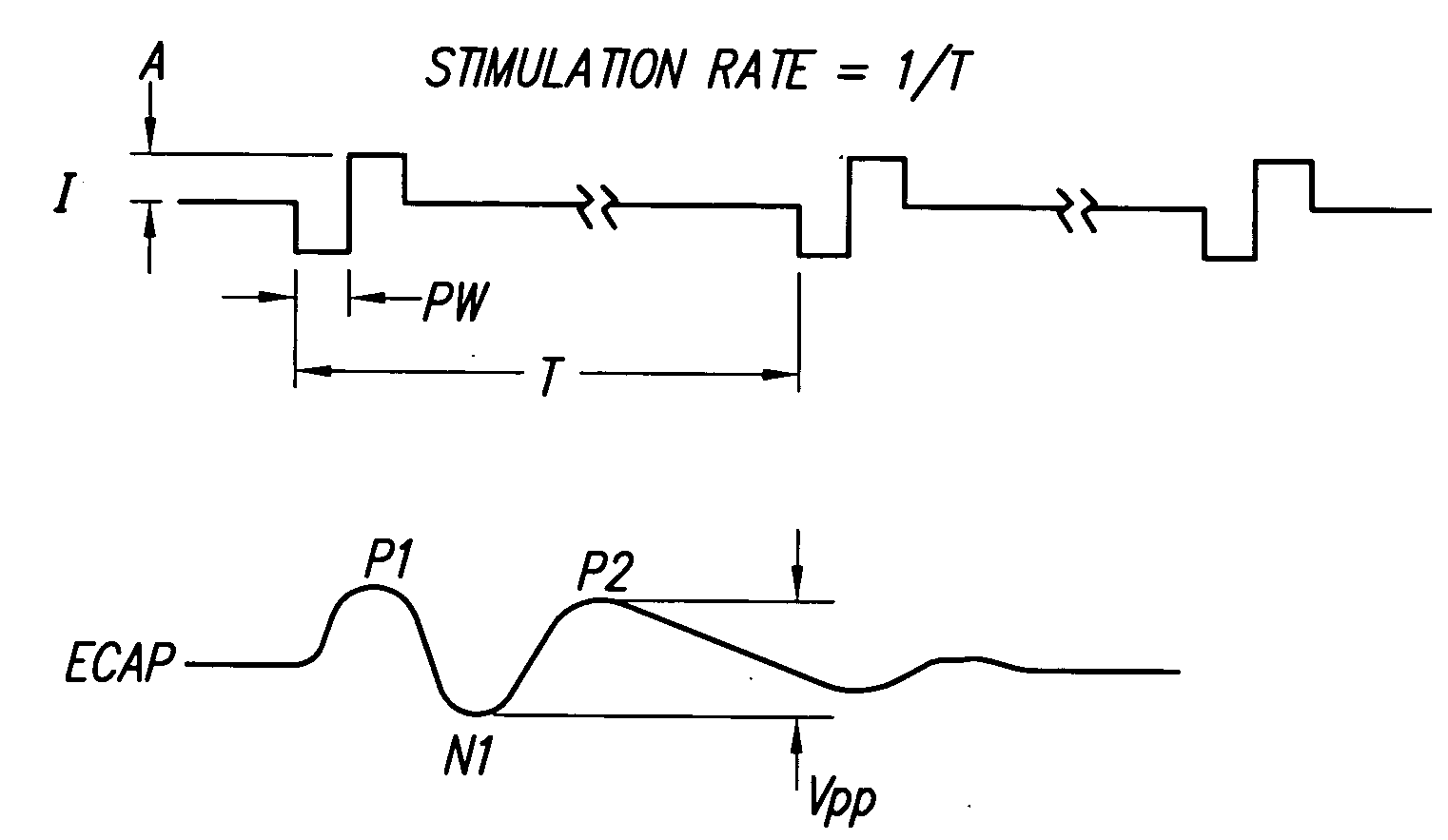
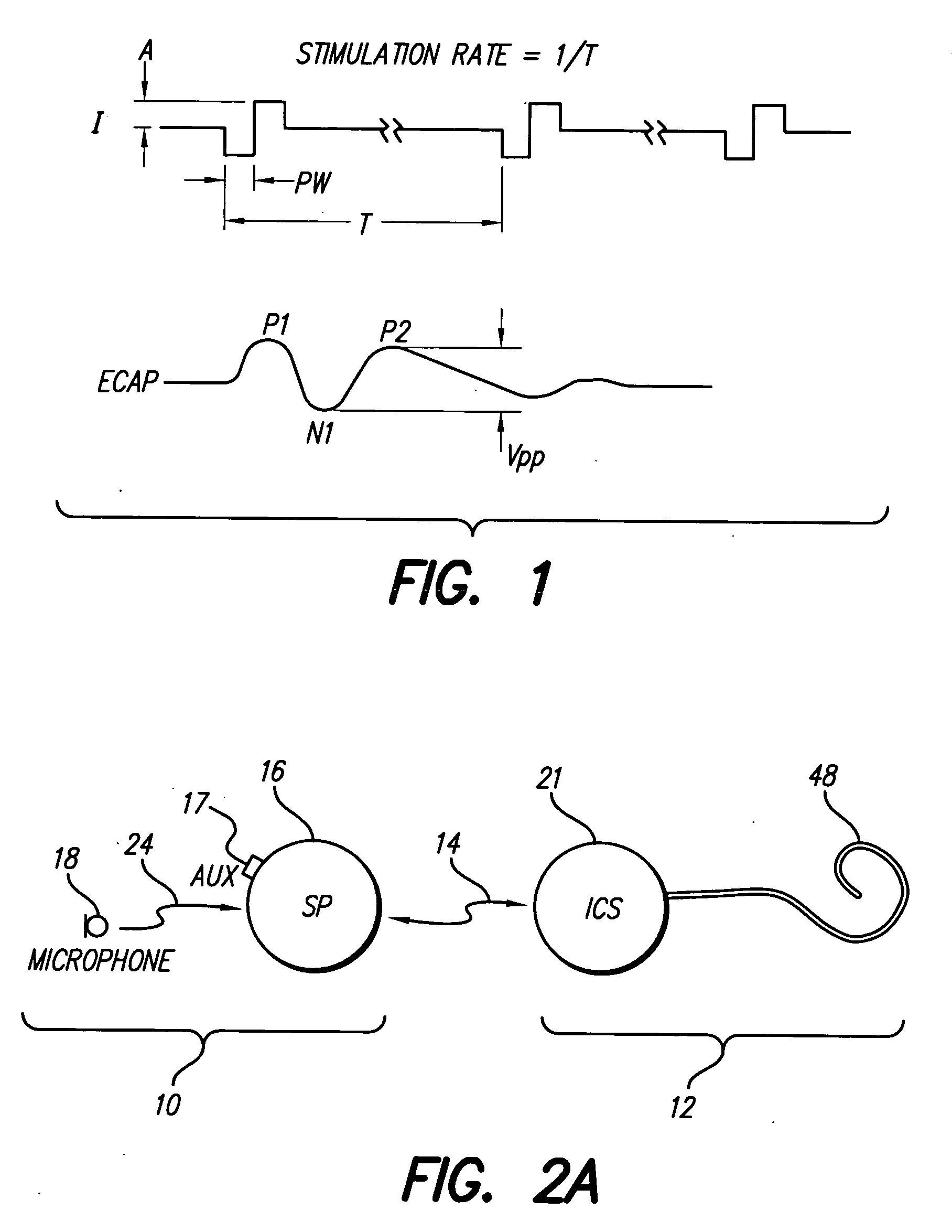
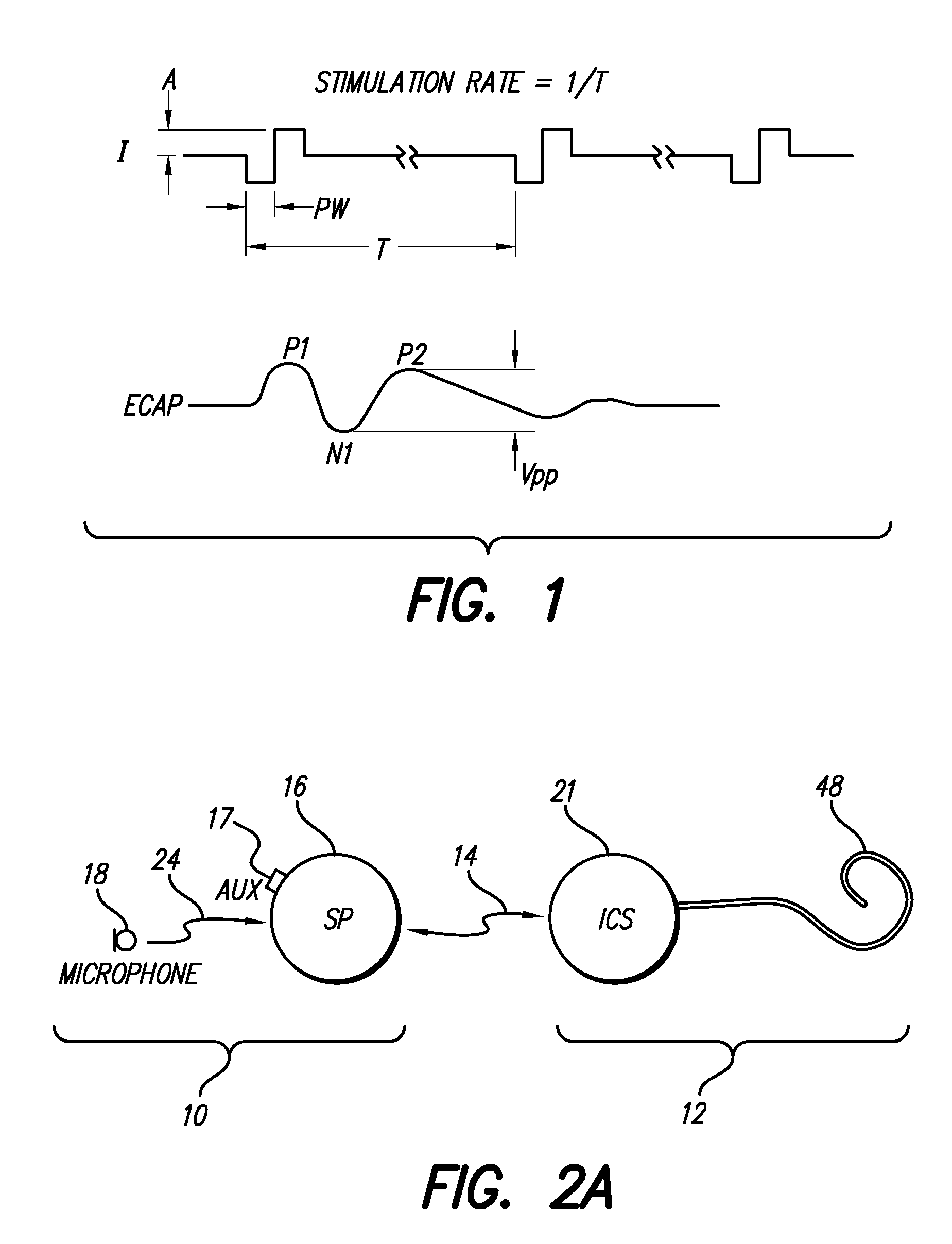
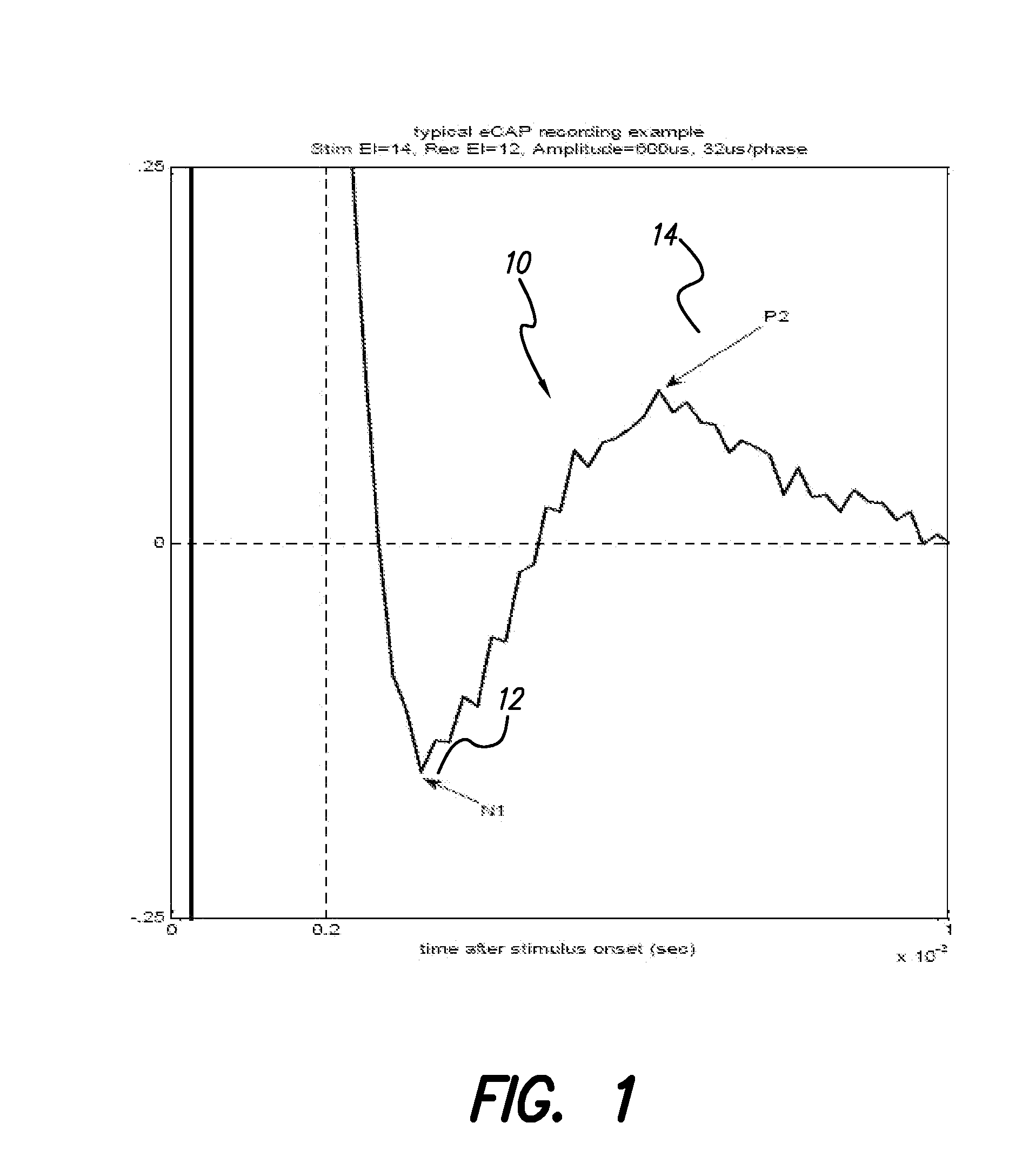
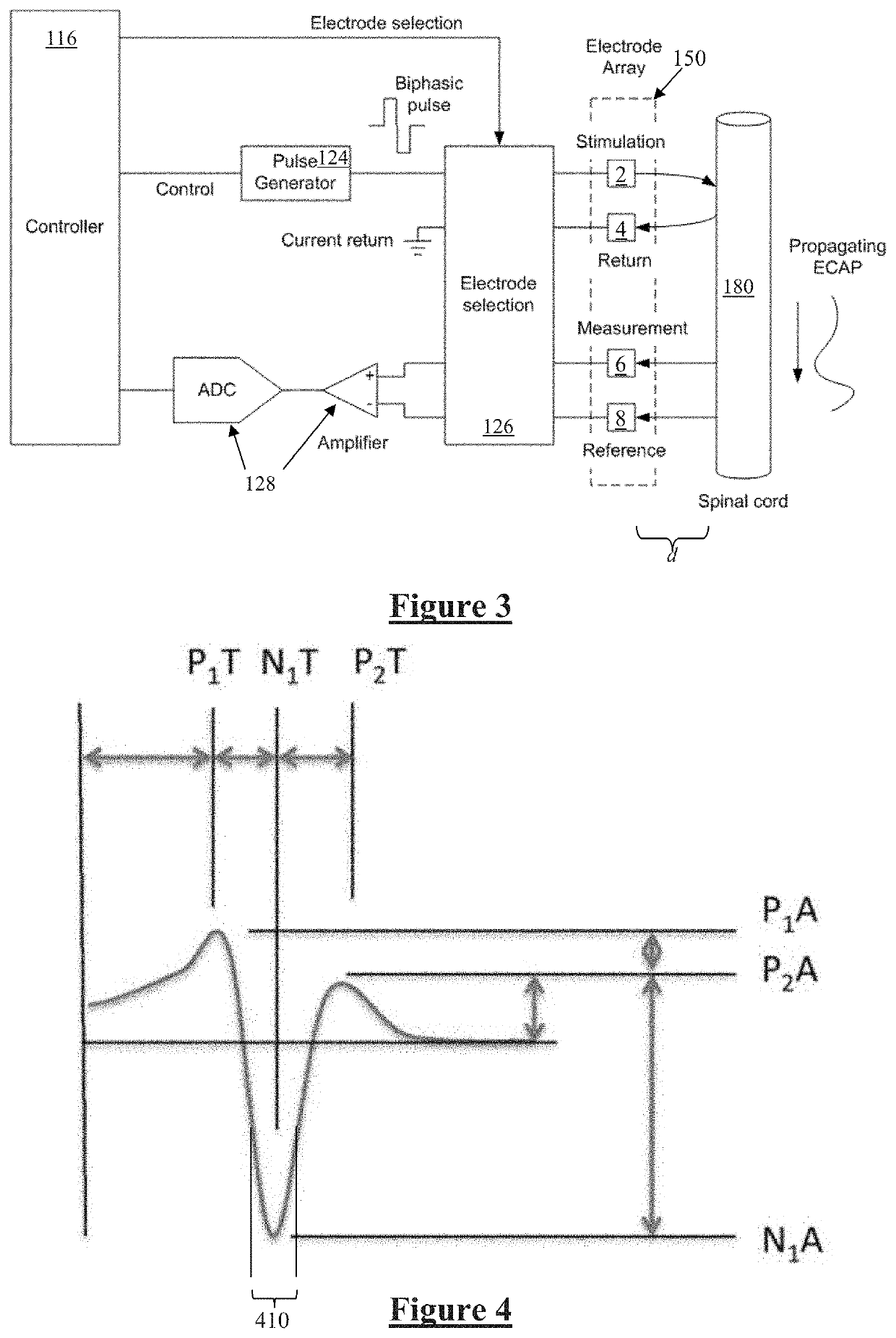
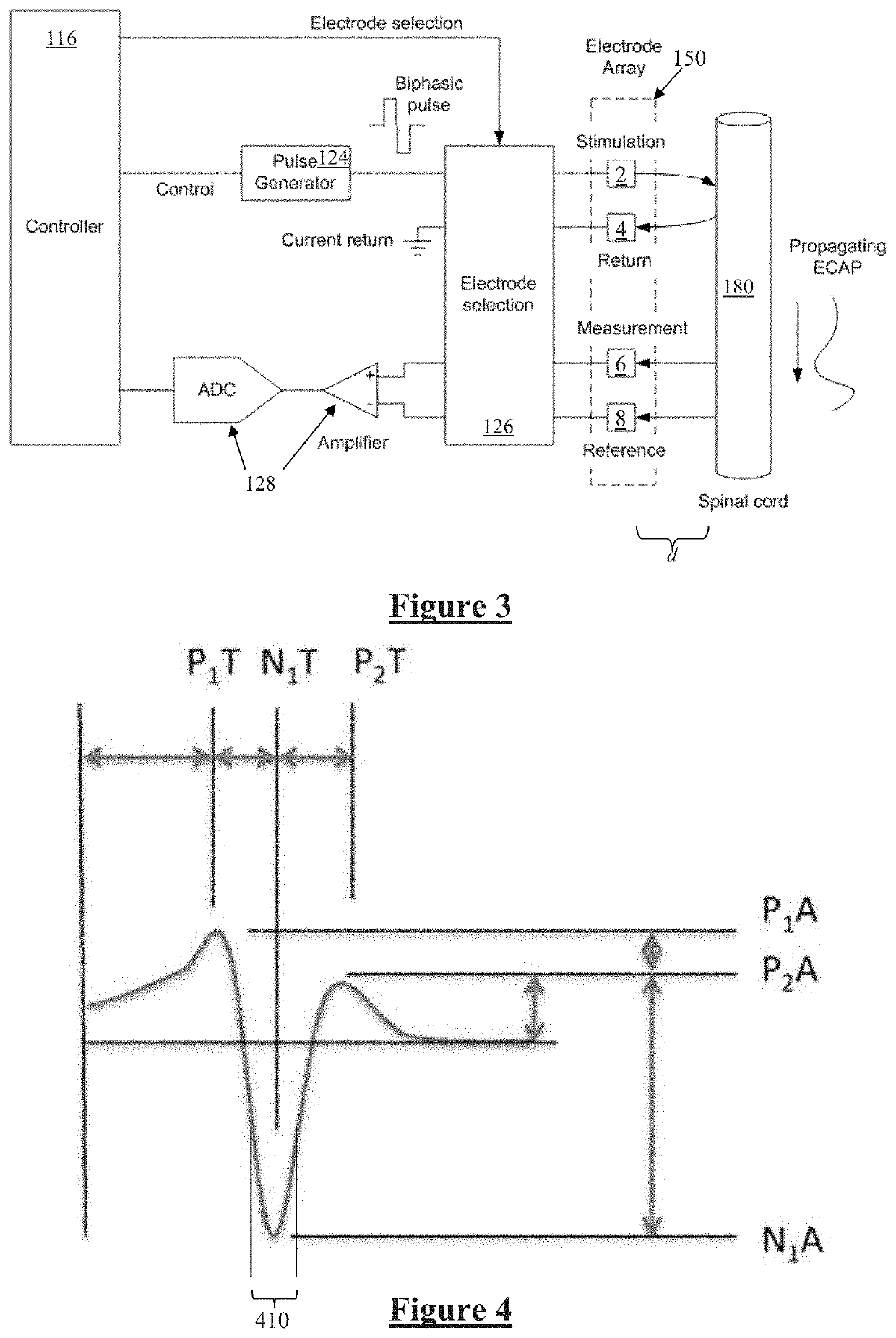
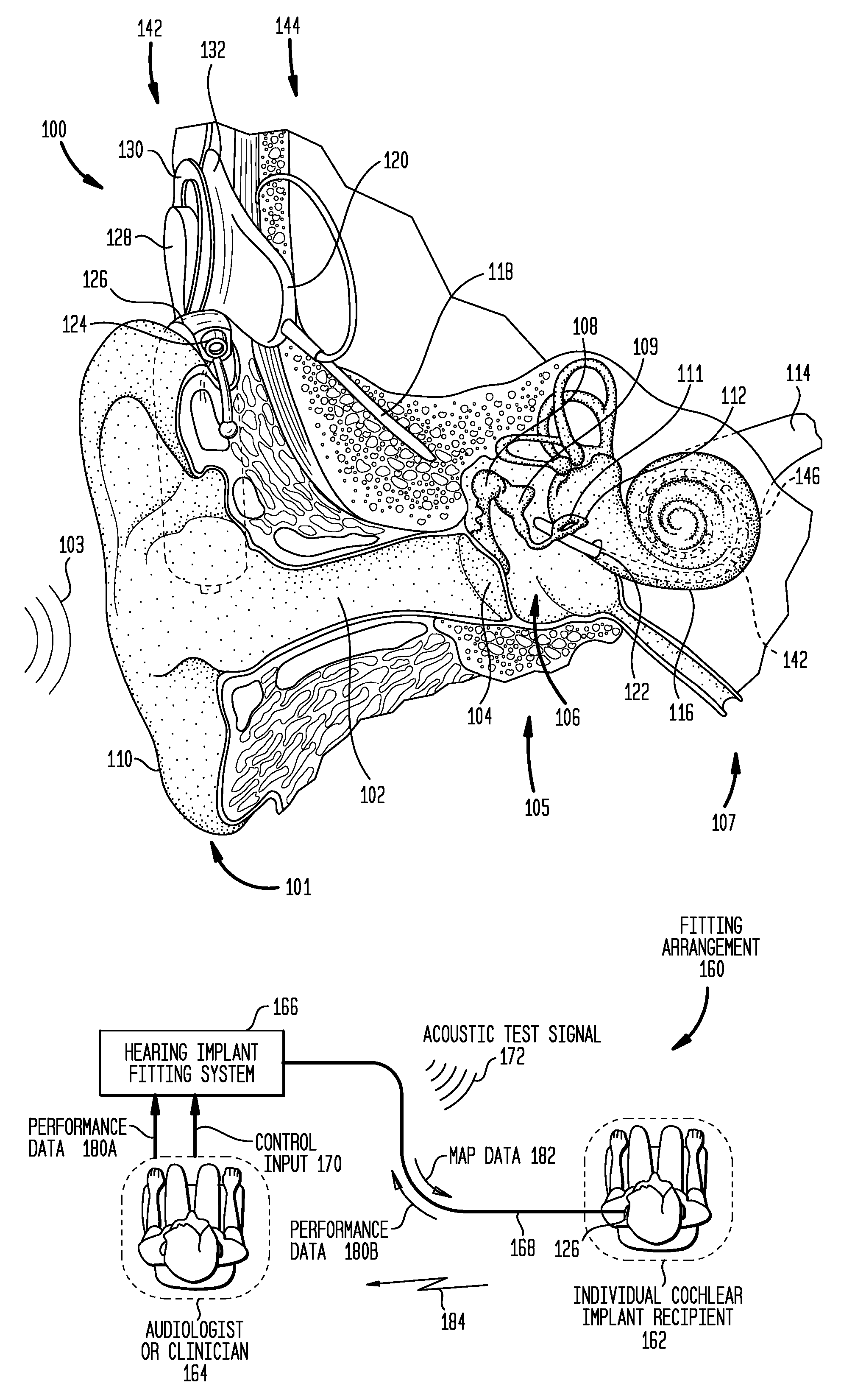
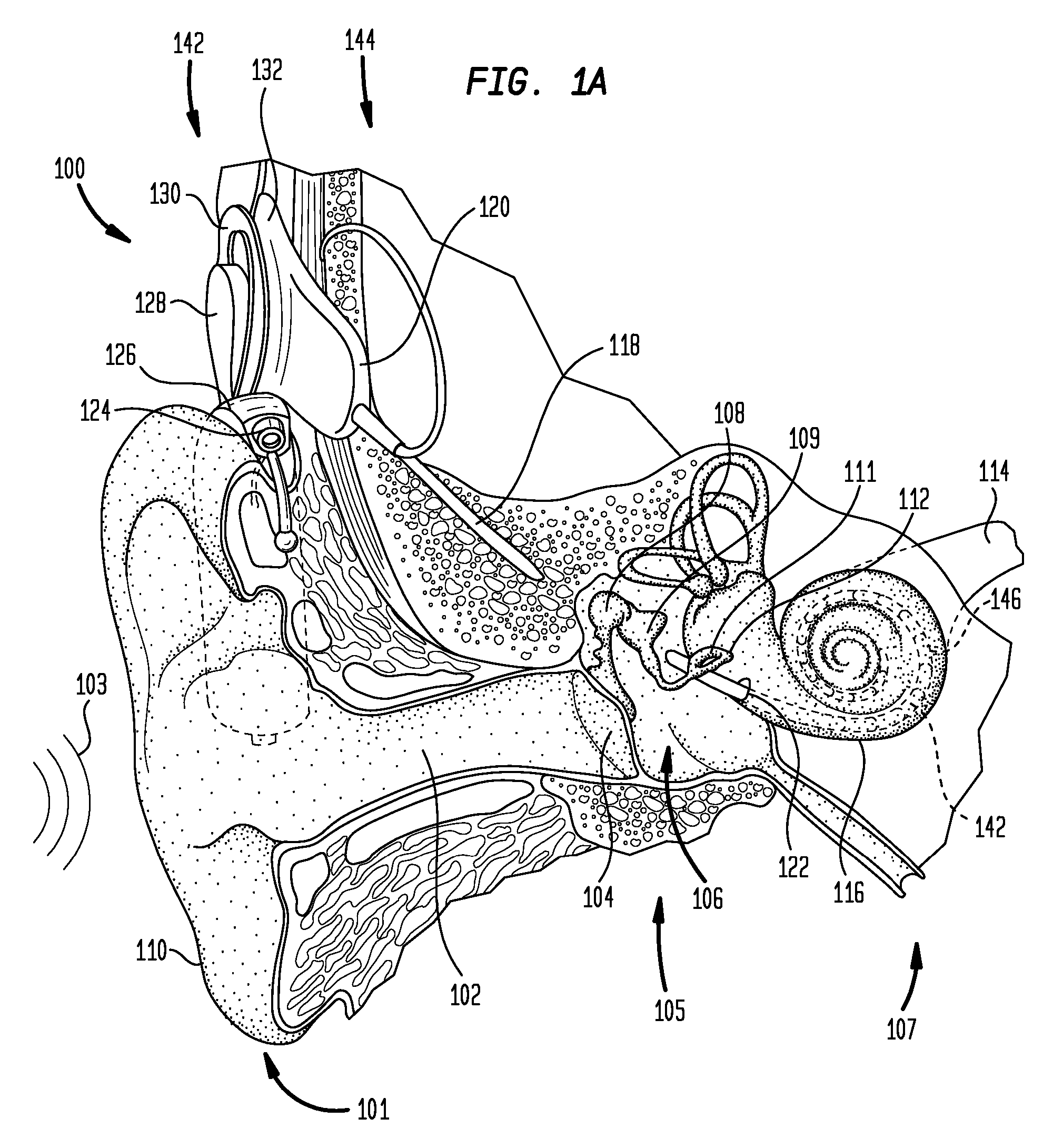
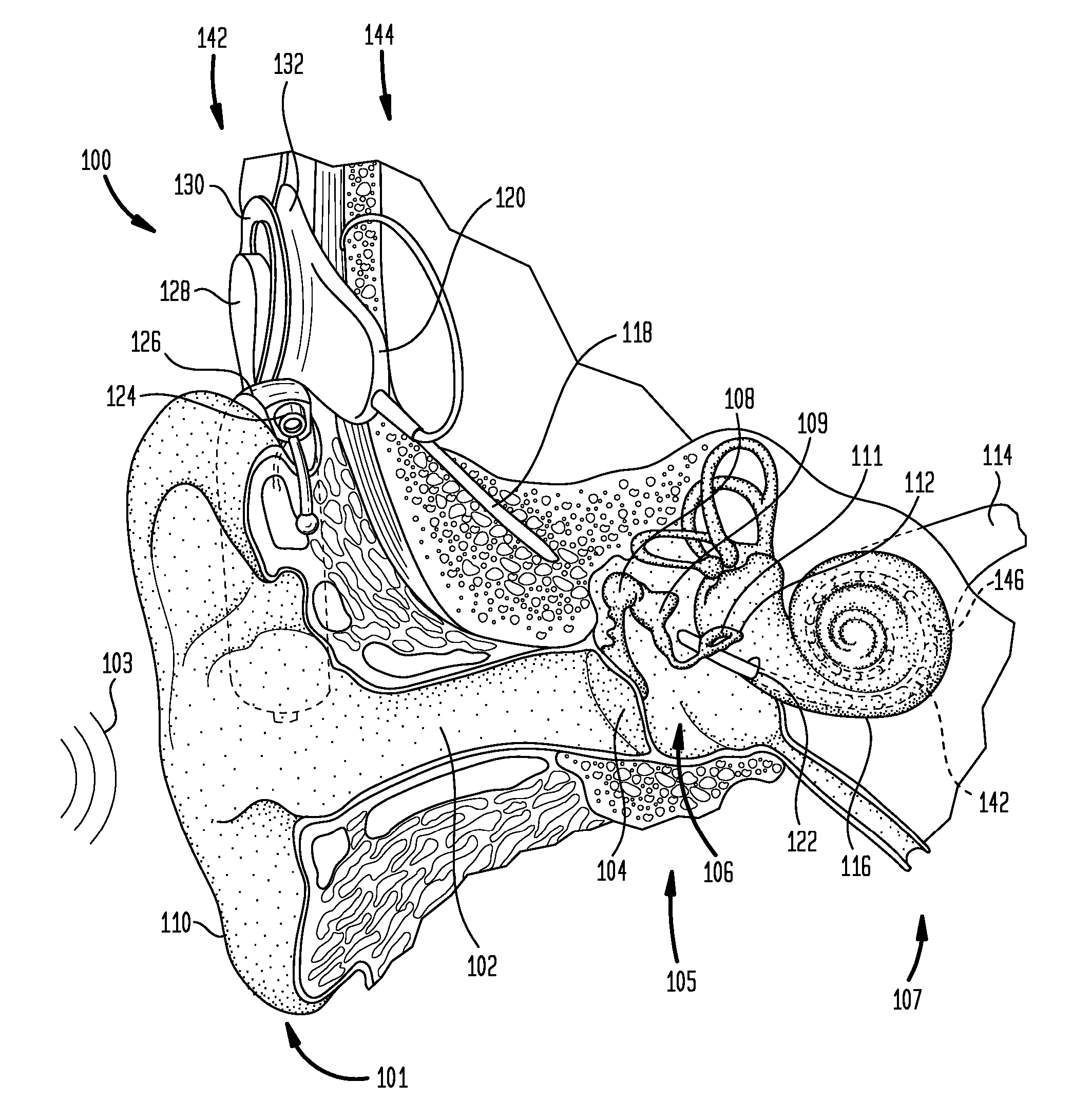
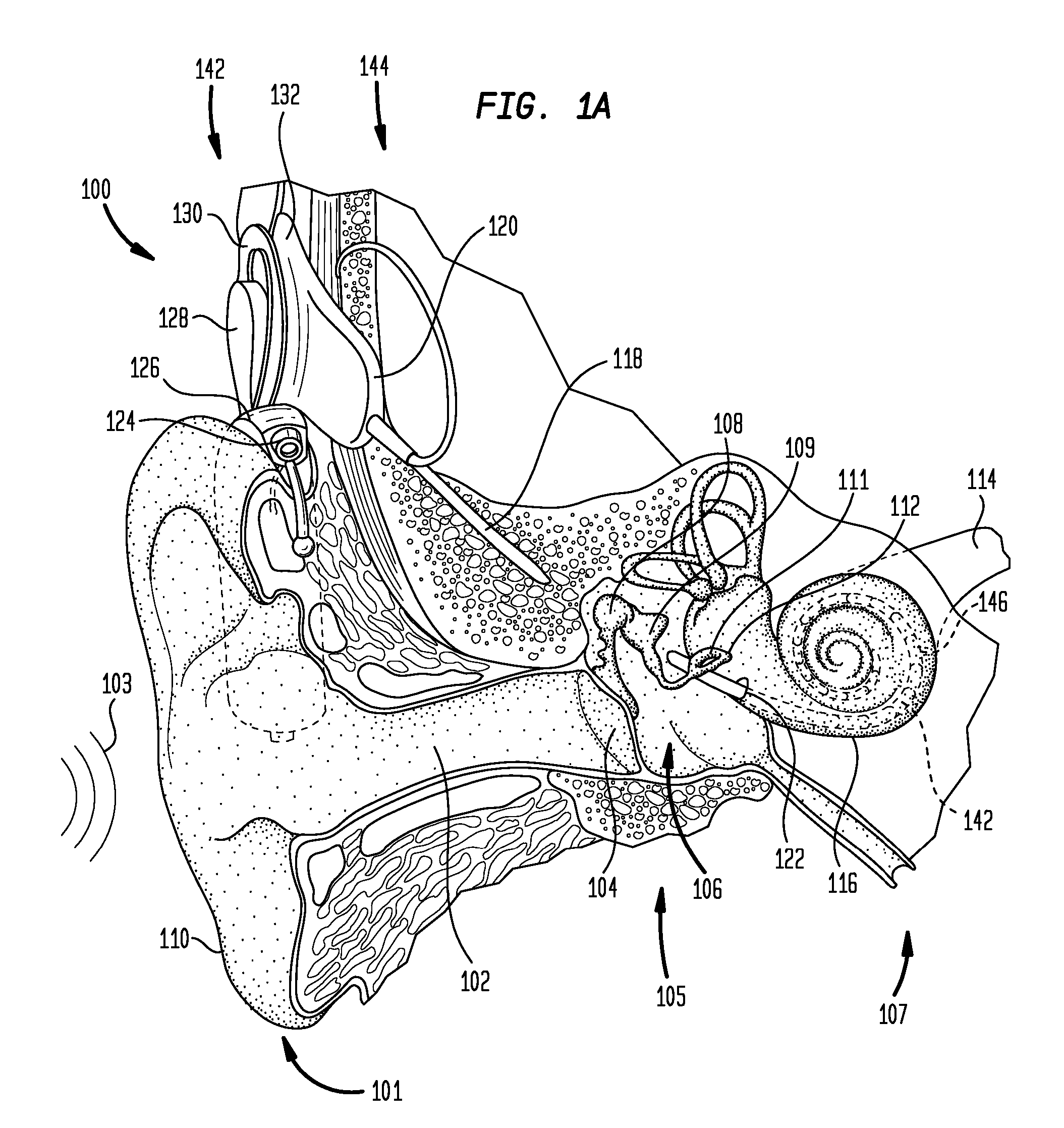
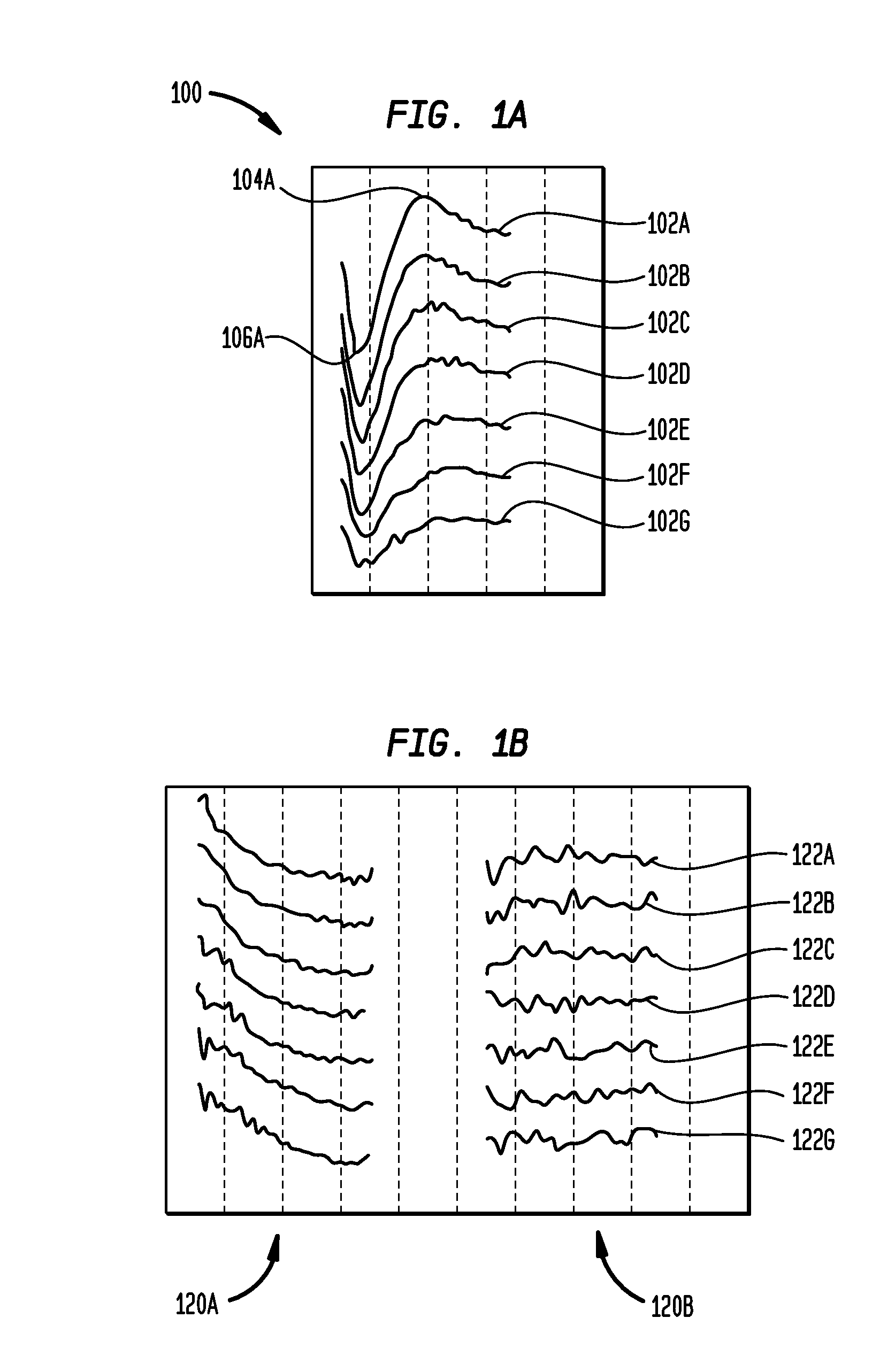
The electrically evoked compound action potential (eCAP) represents the synchronous firing of a population of electrically stimulated auditory nerve fibers. It can be directly recorded on a surgically exposed nerve trunk in animals or from an intra-cochlear electrode of a cochlear implant.
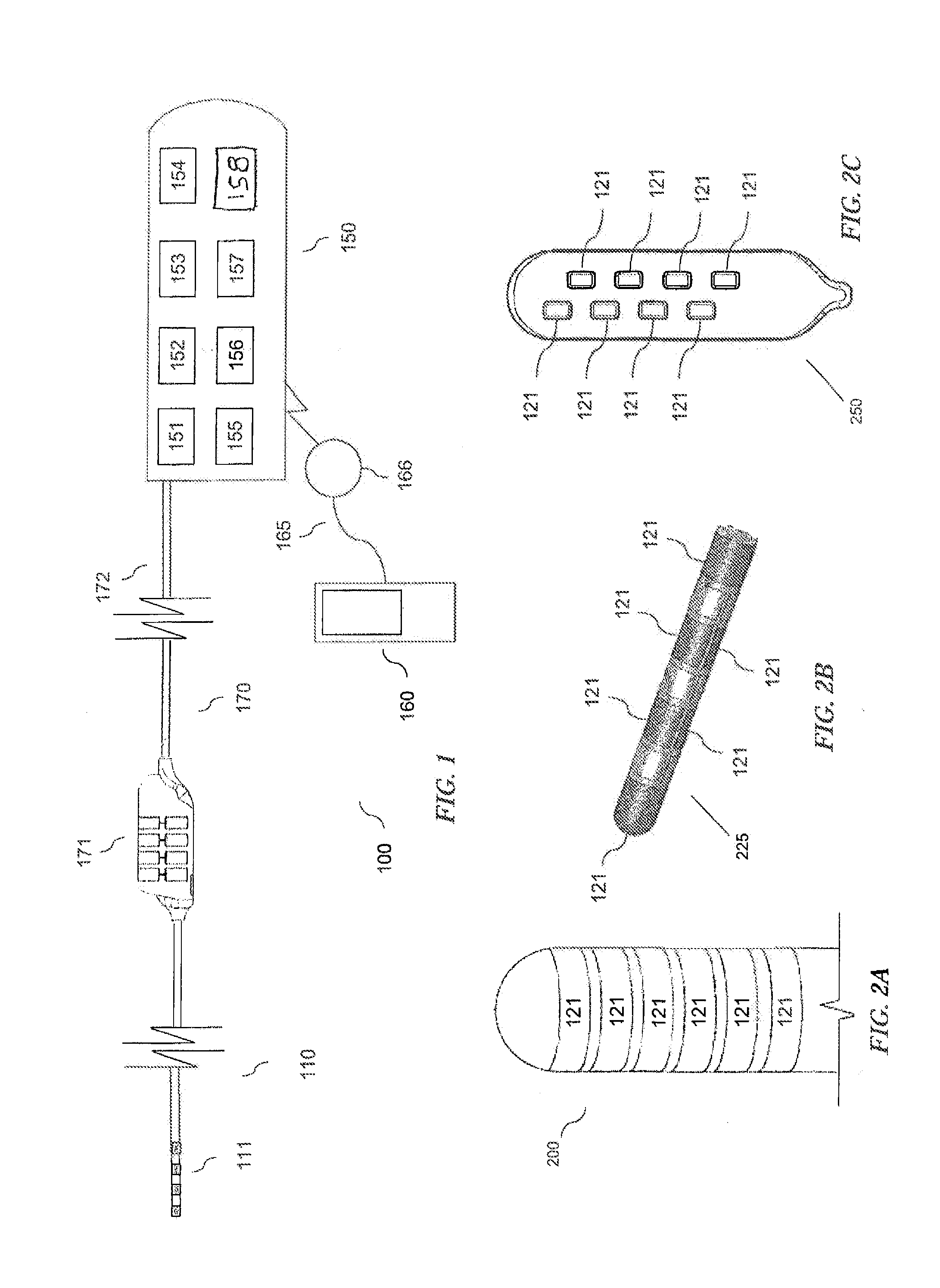
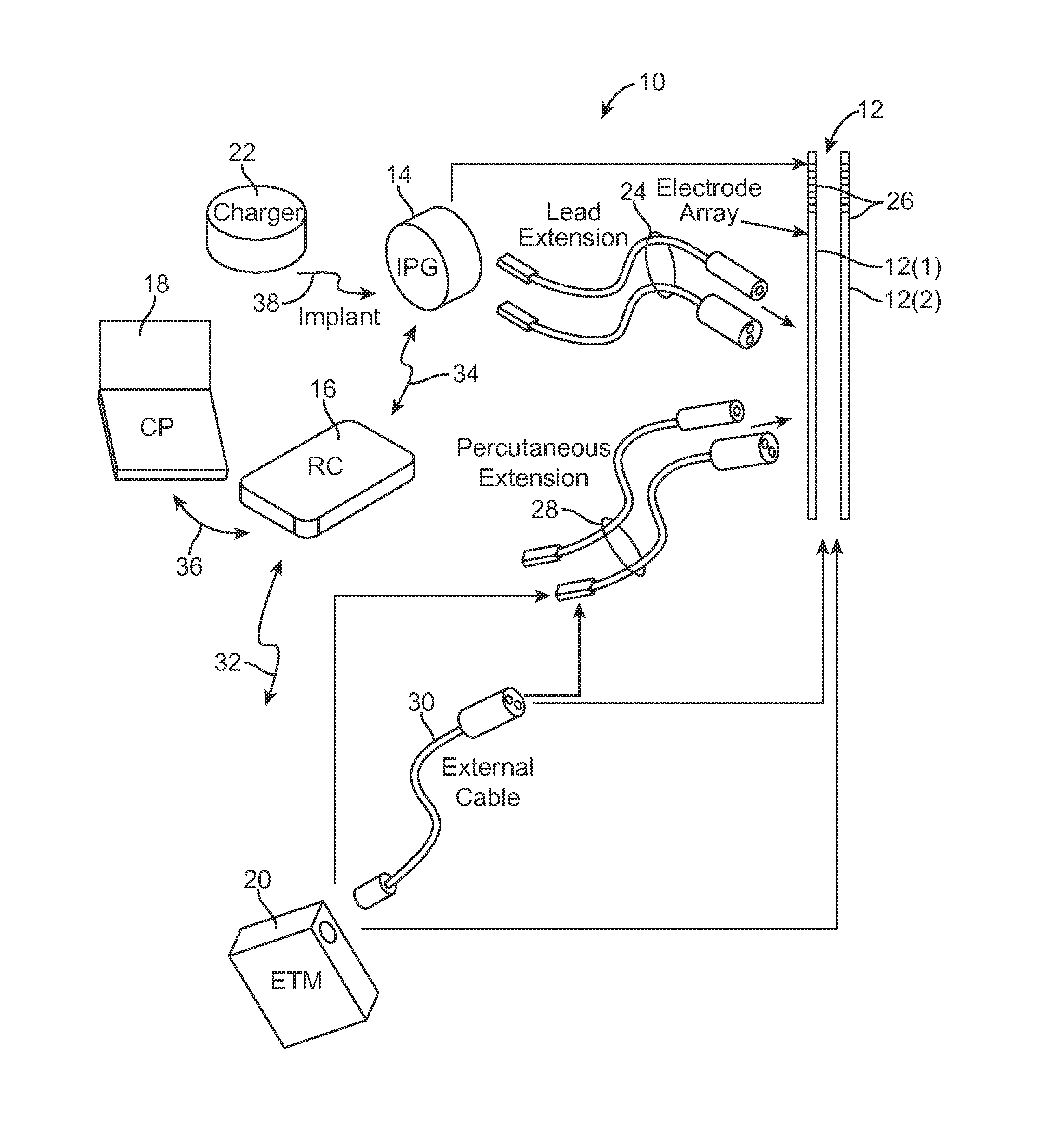
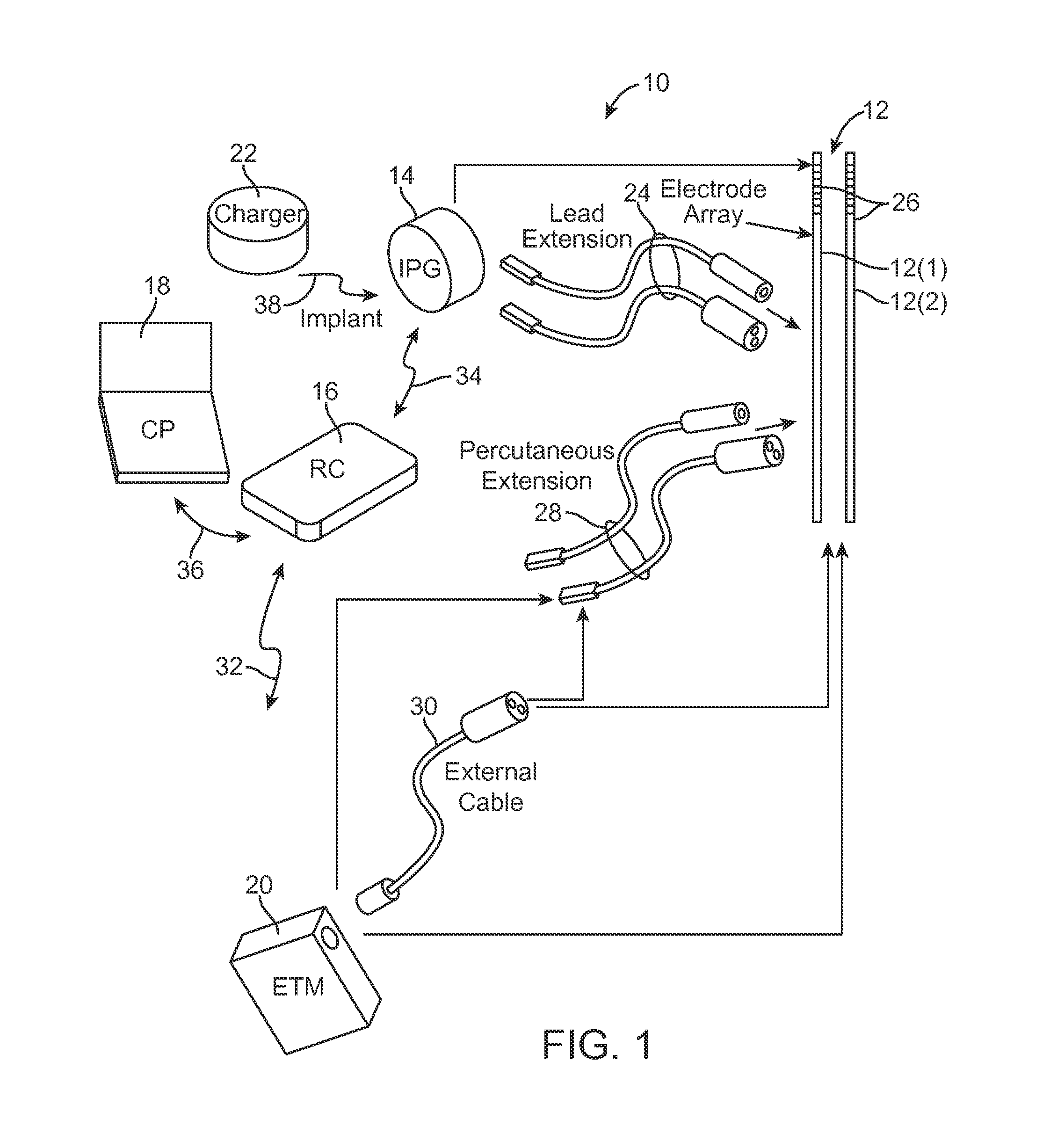
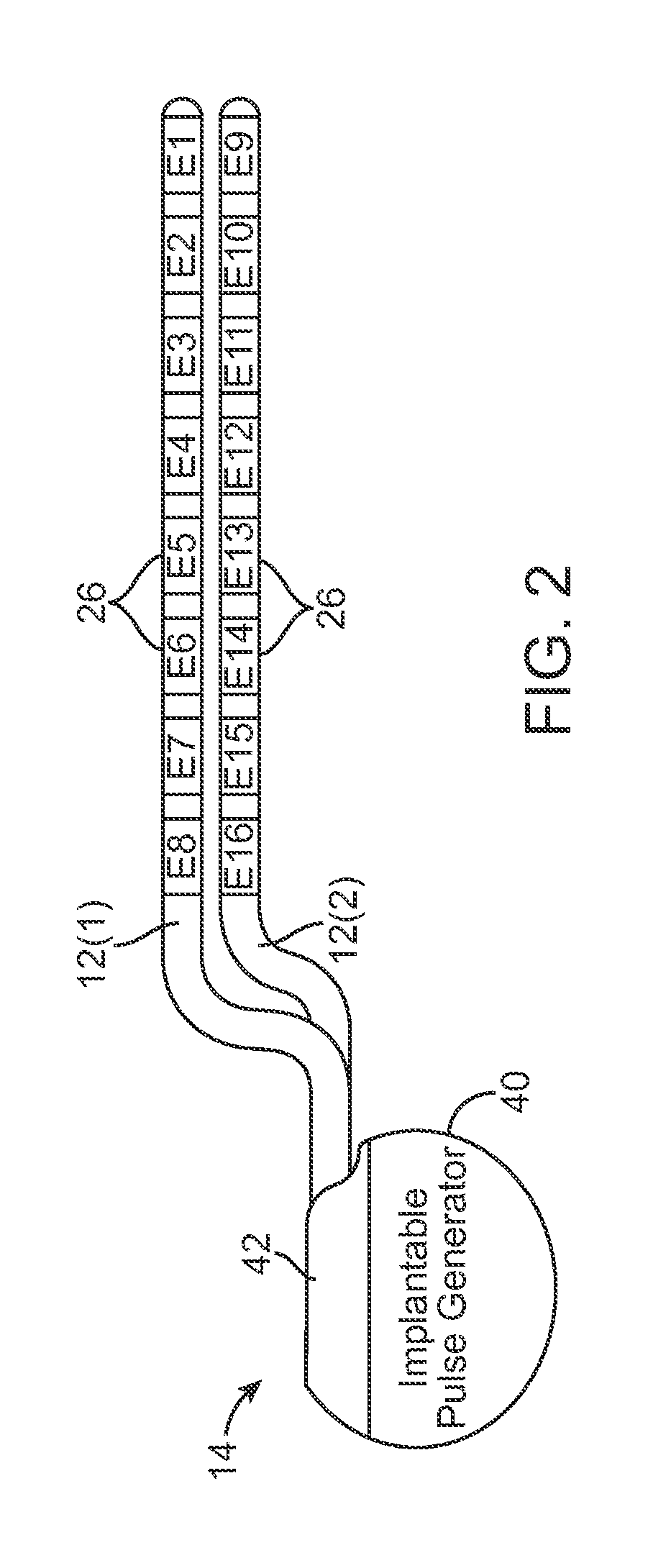
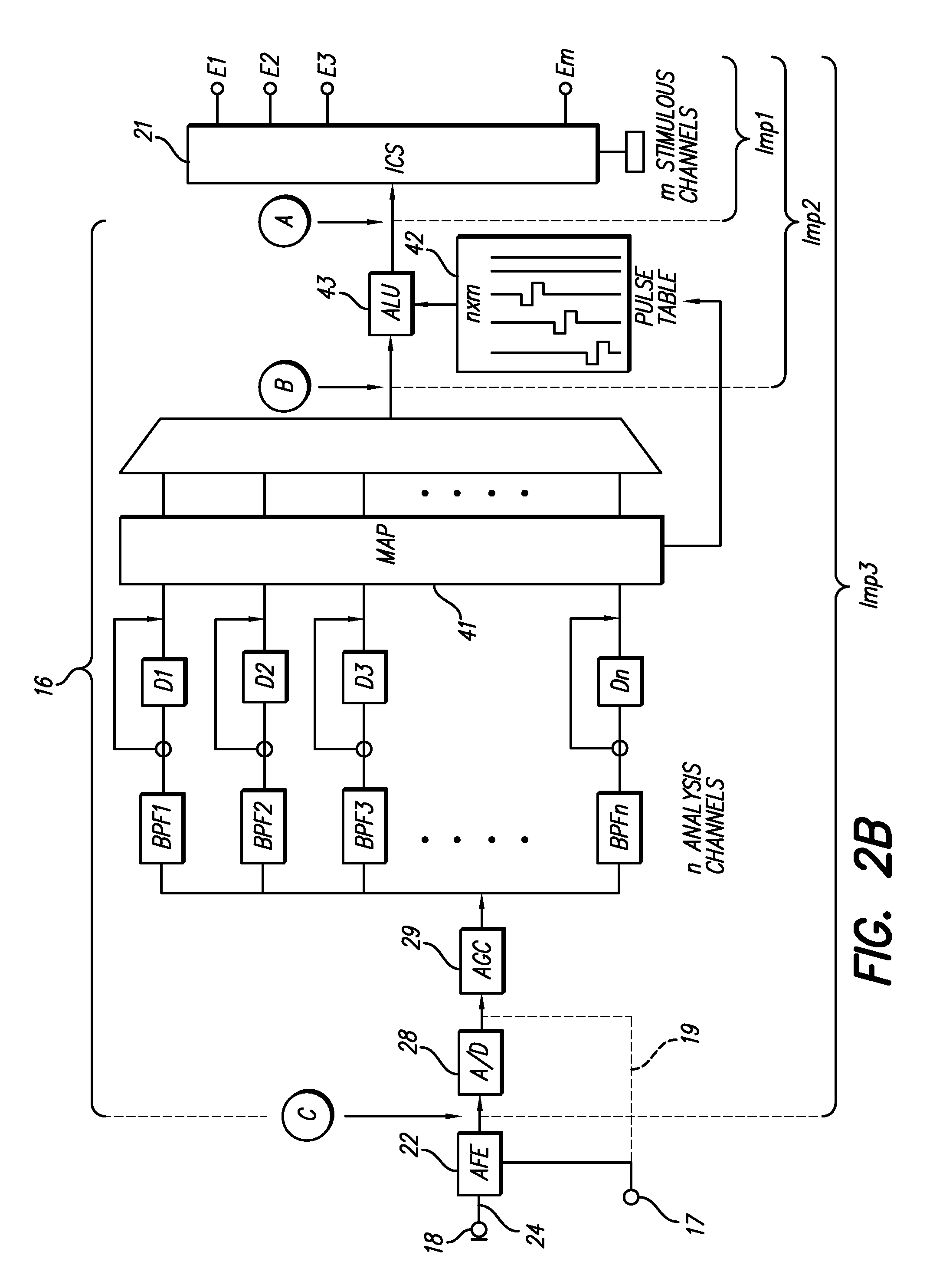
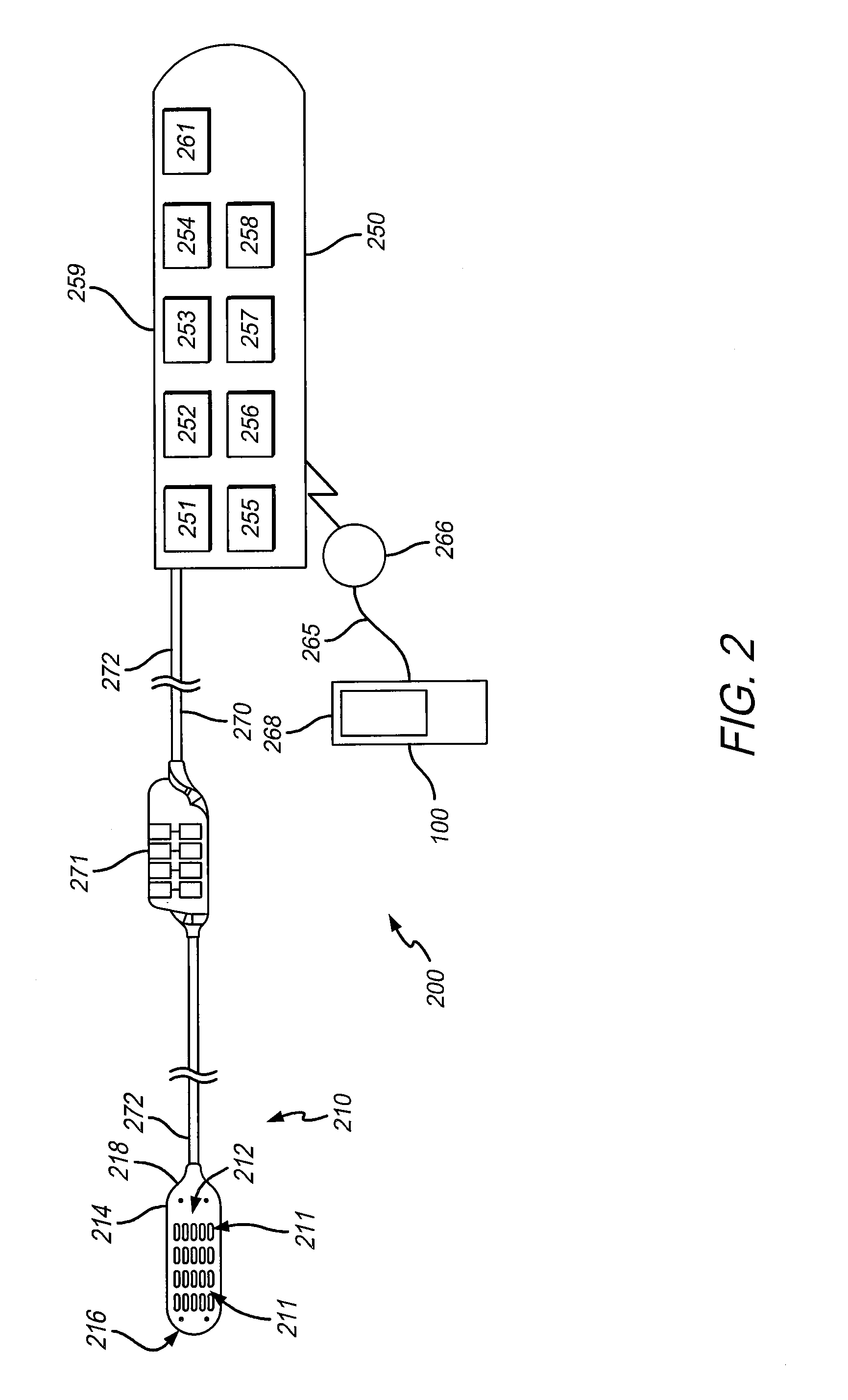
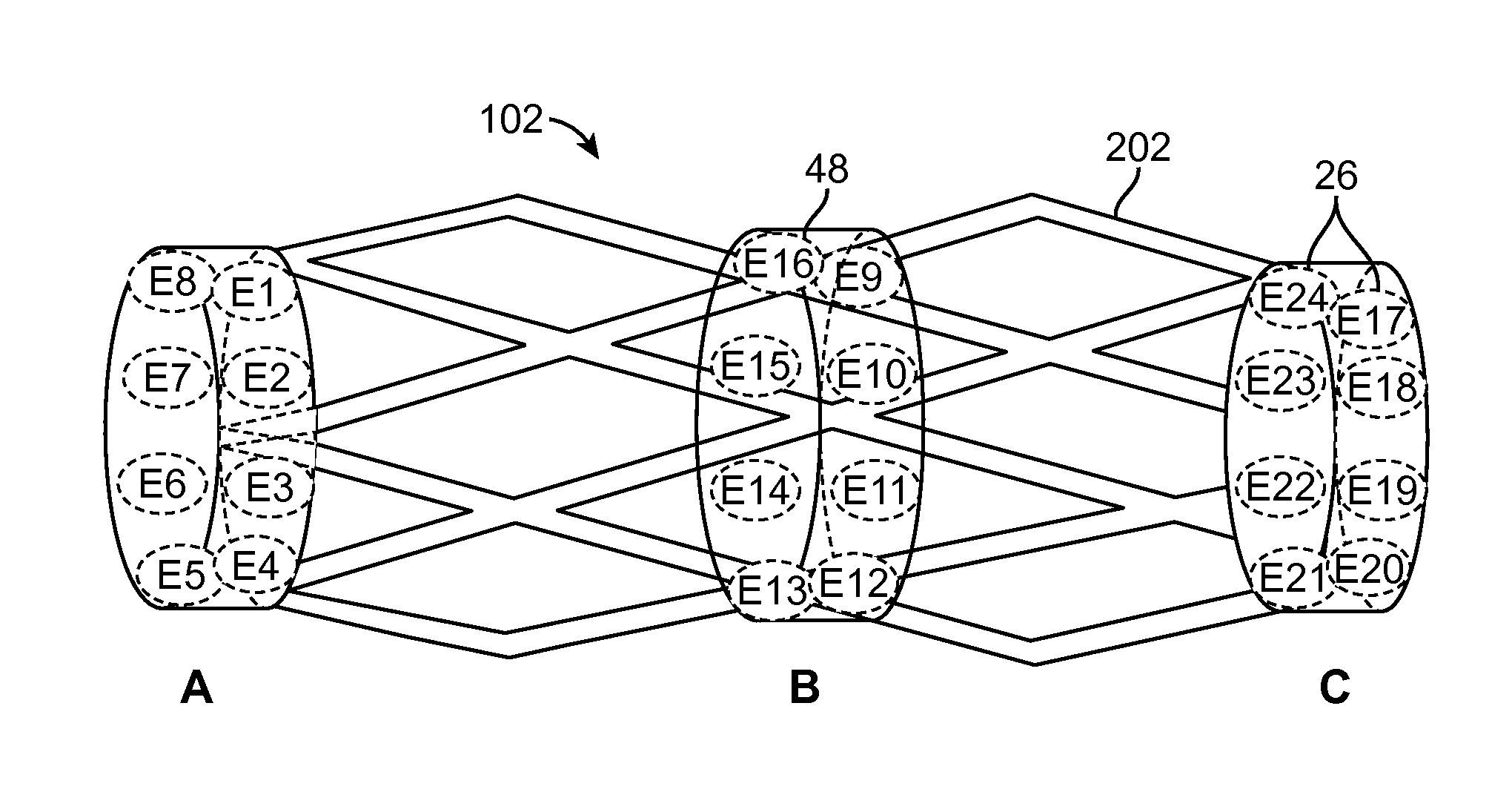
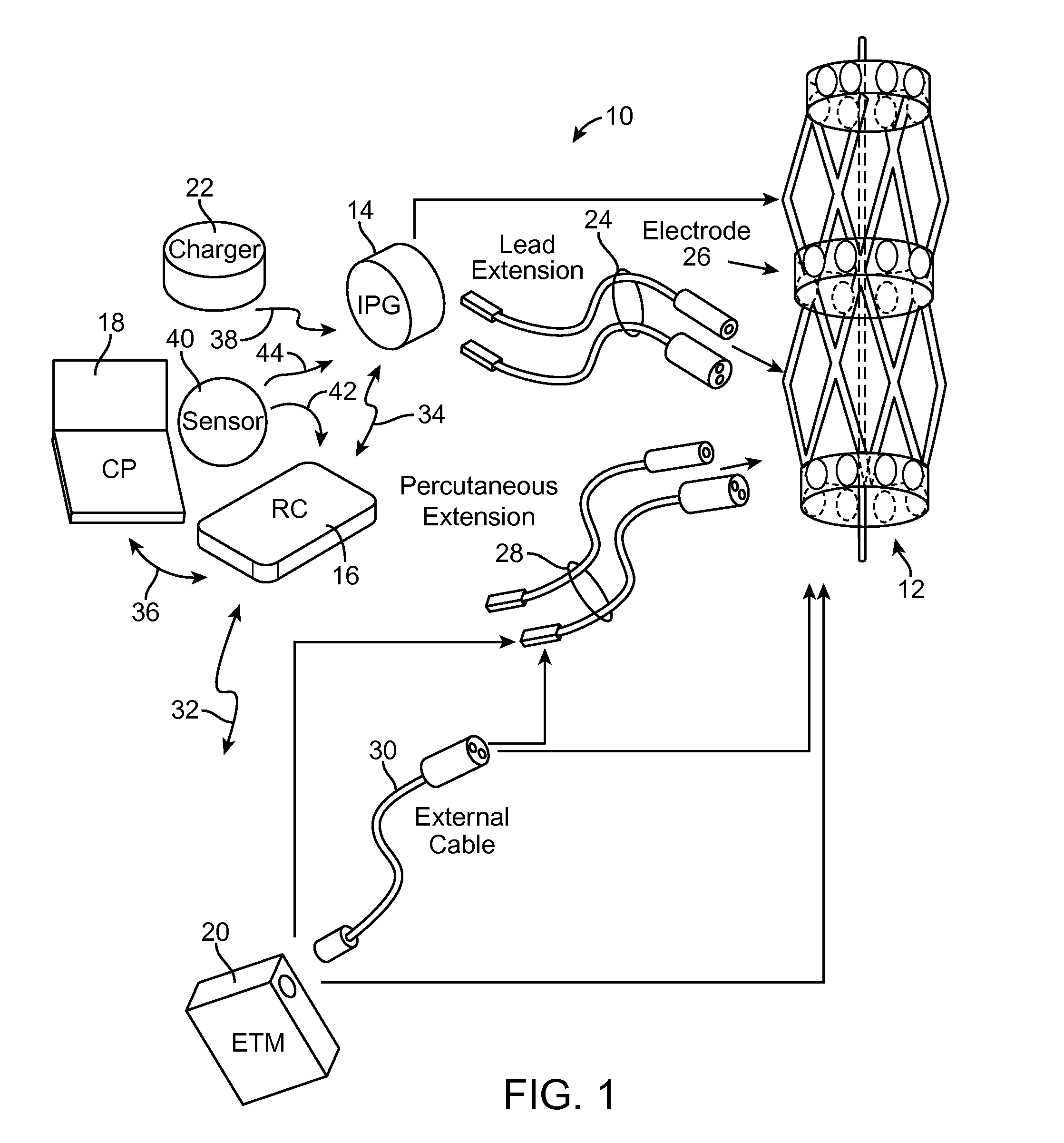
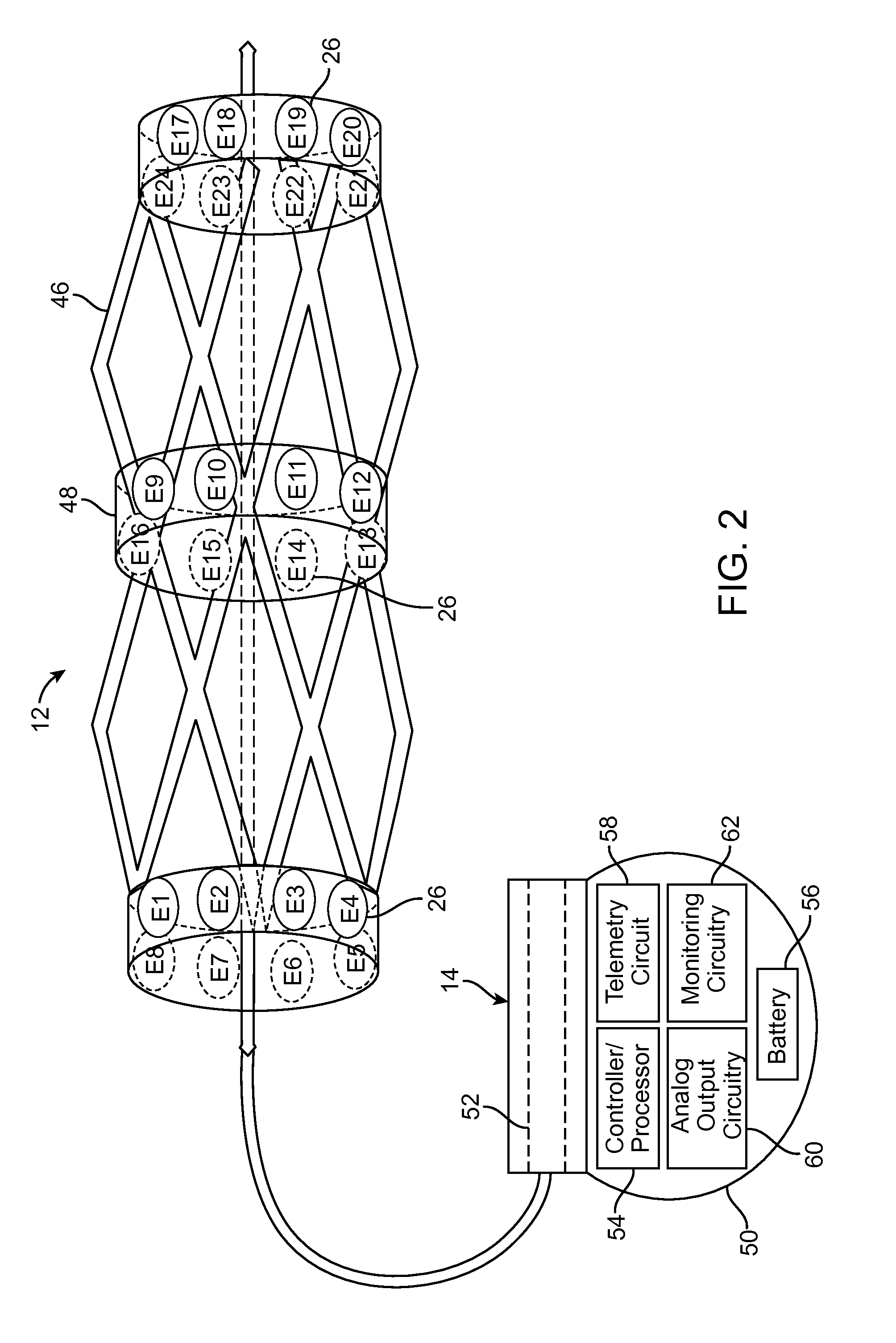
Method and system for generating a cochlear implant program using multi-electrode stimulation to elicit the electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS7206640B1Increase amplitudeConvenient recordingHead electrodesEvoked compound action potentialConfocal
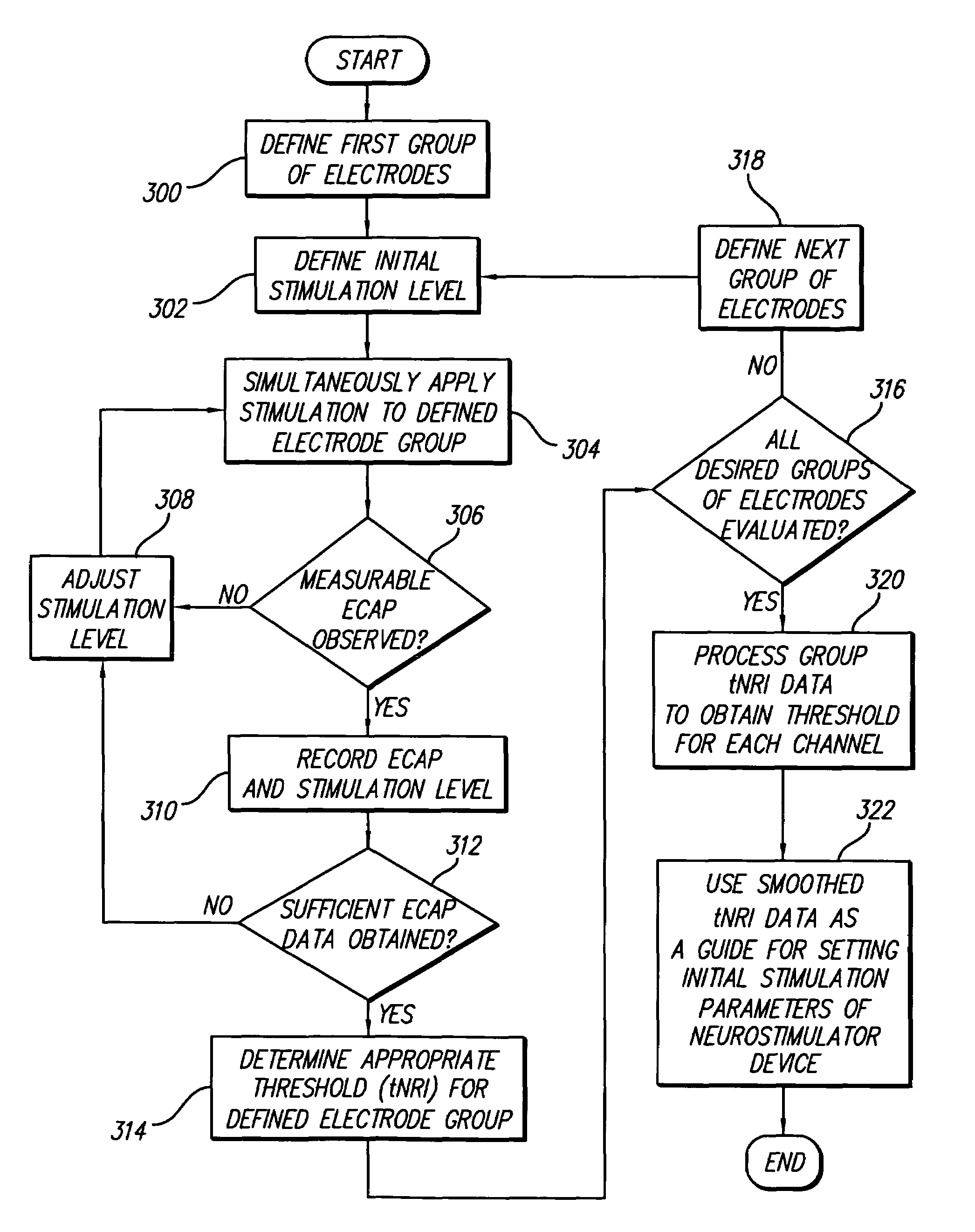
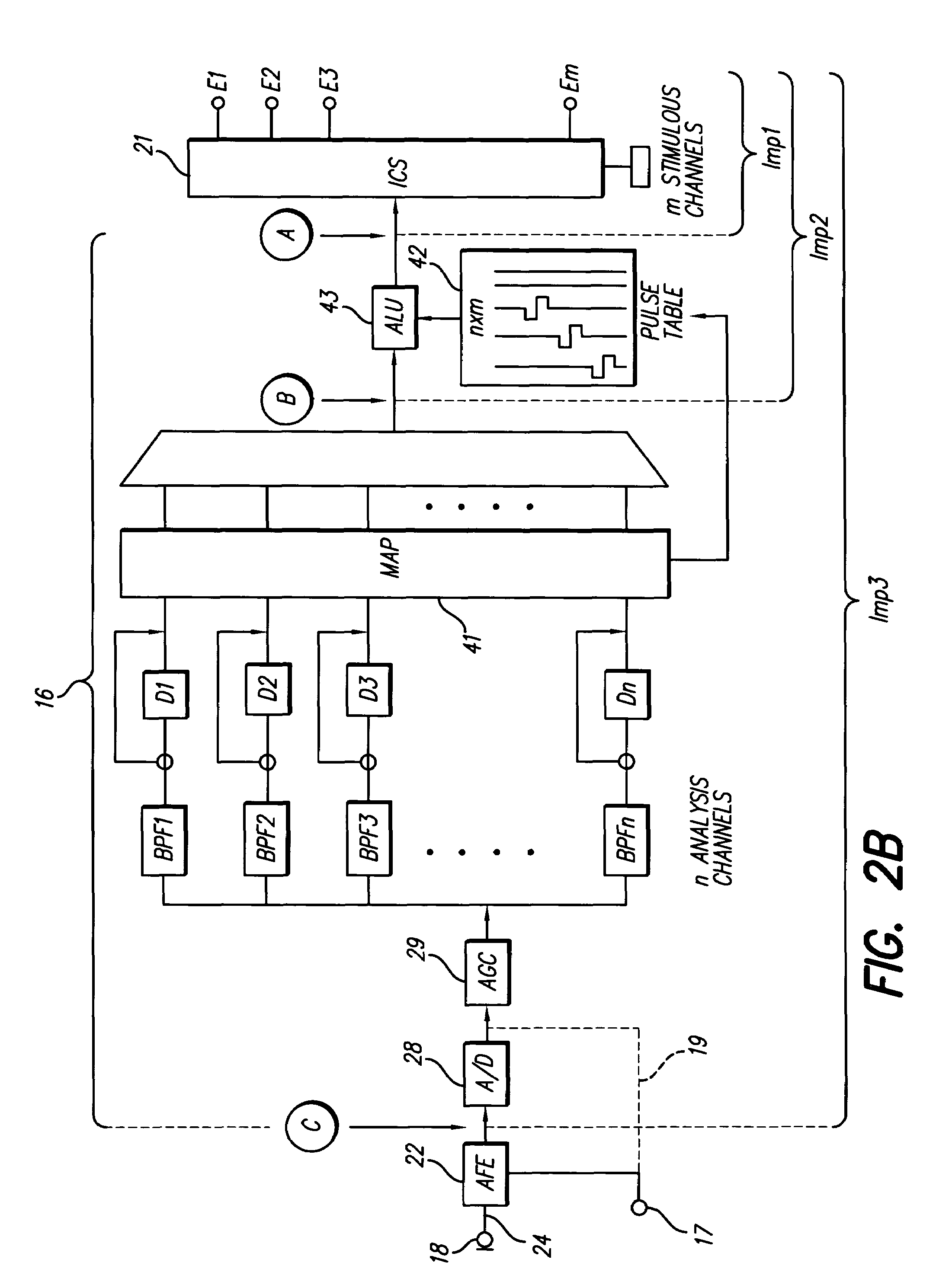
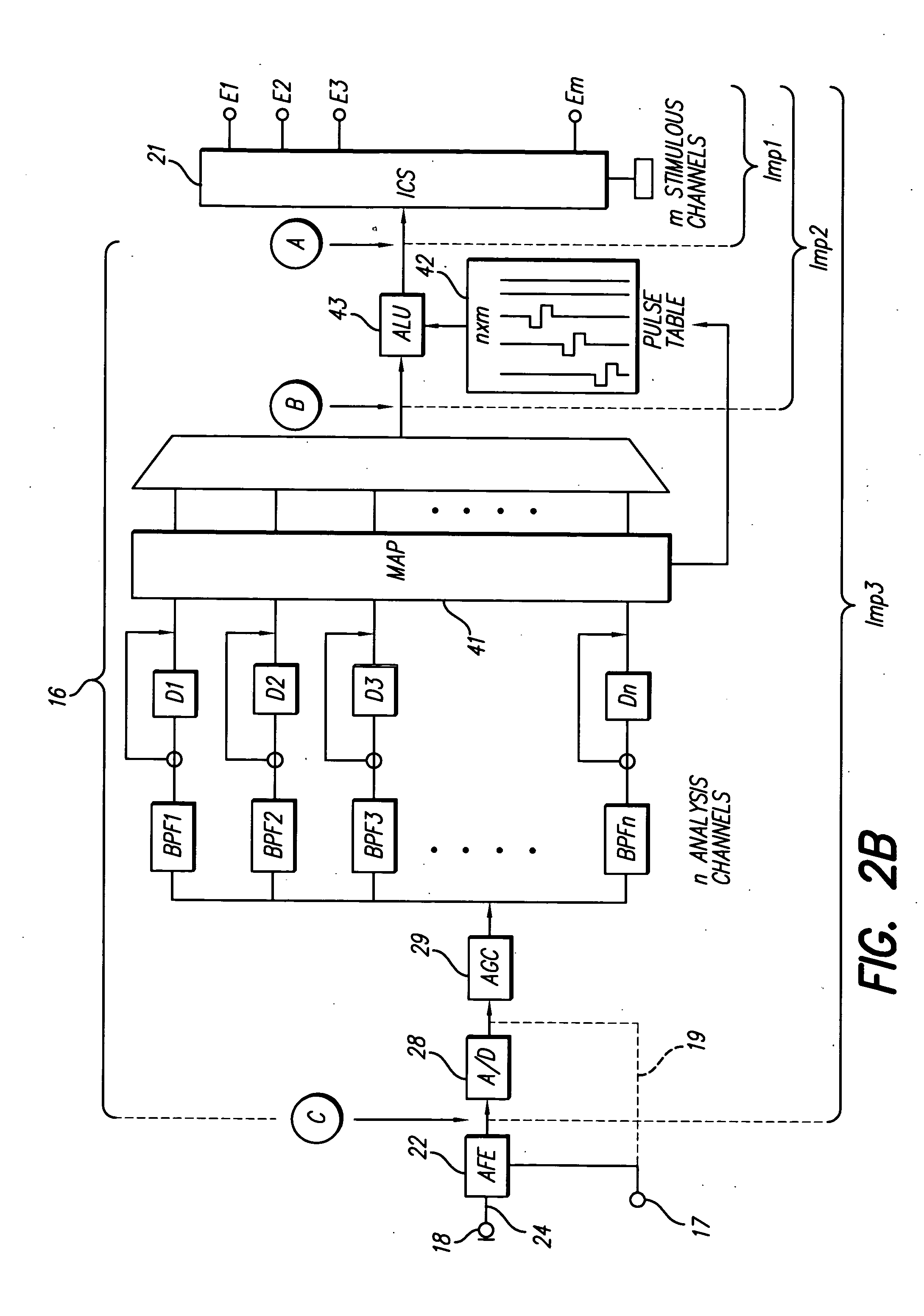
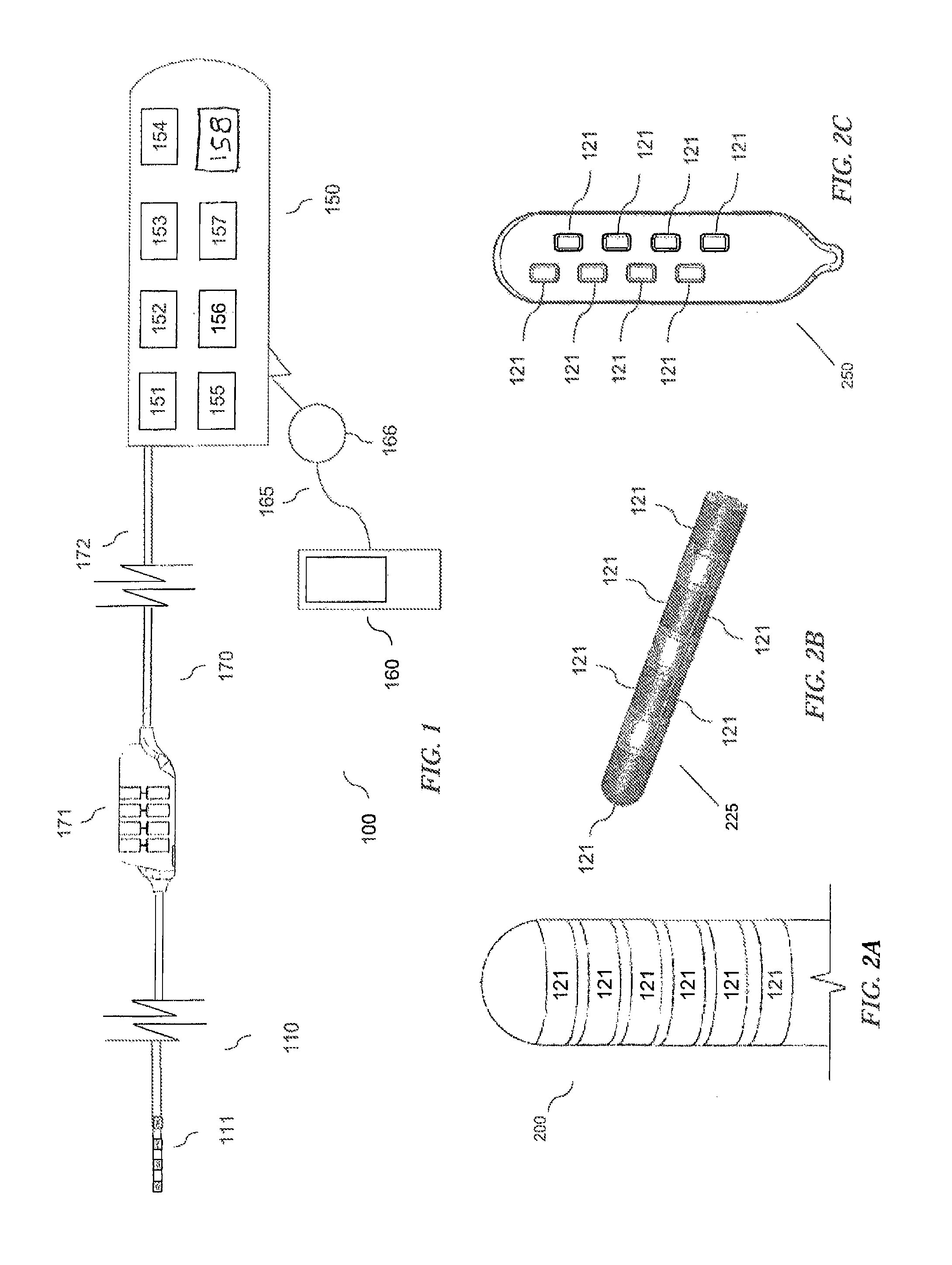
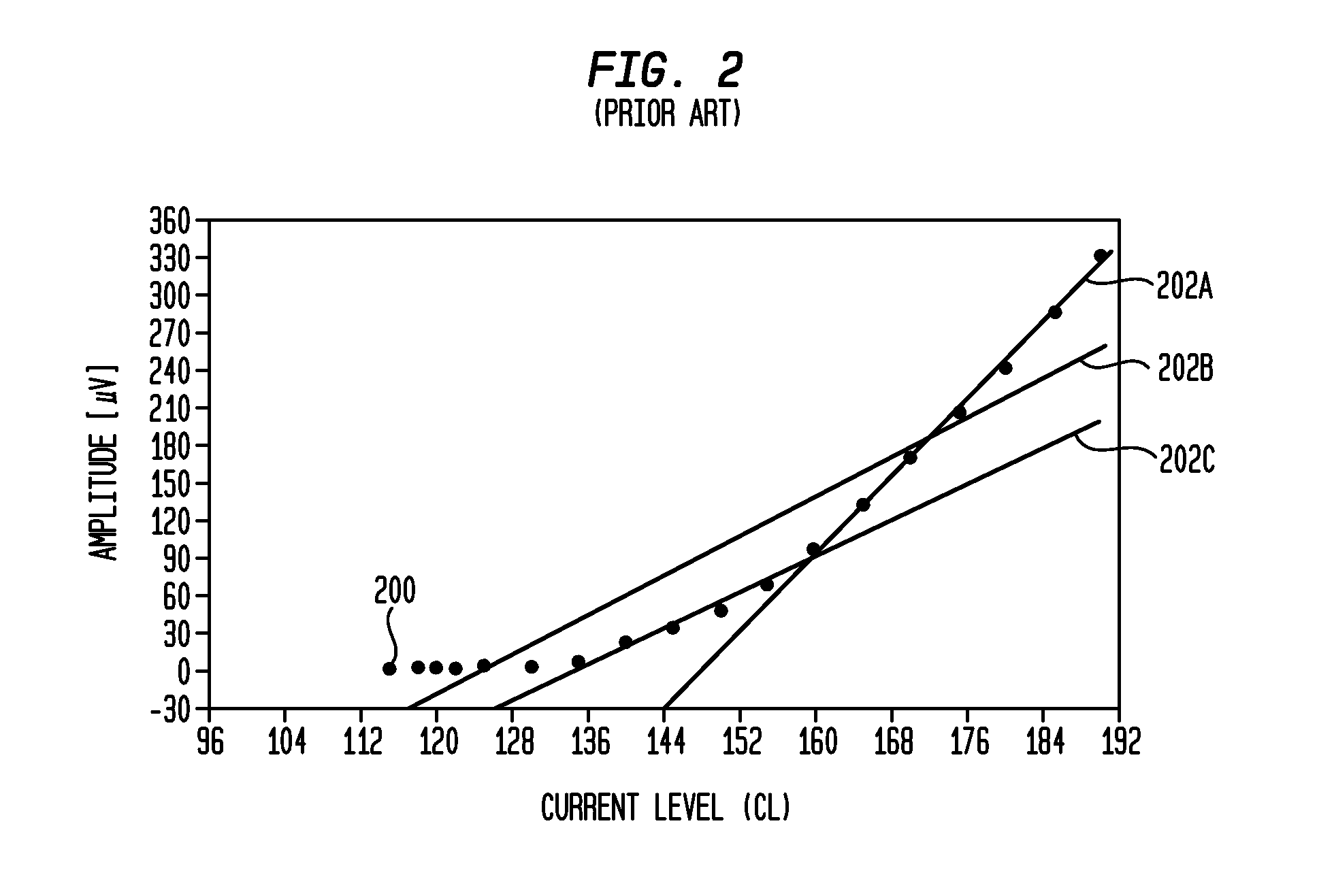
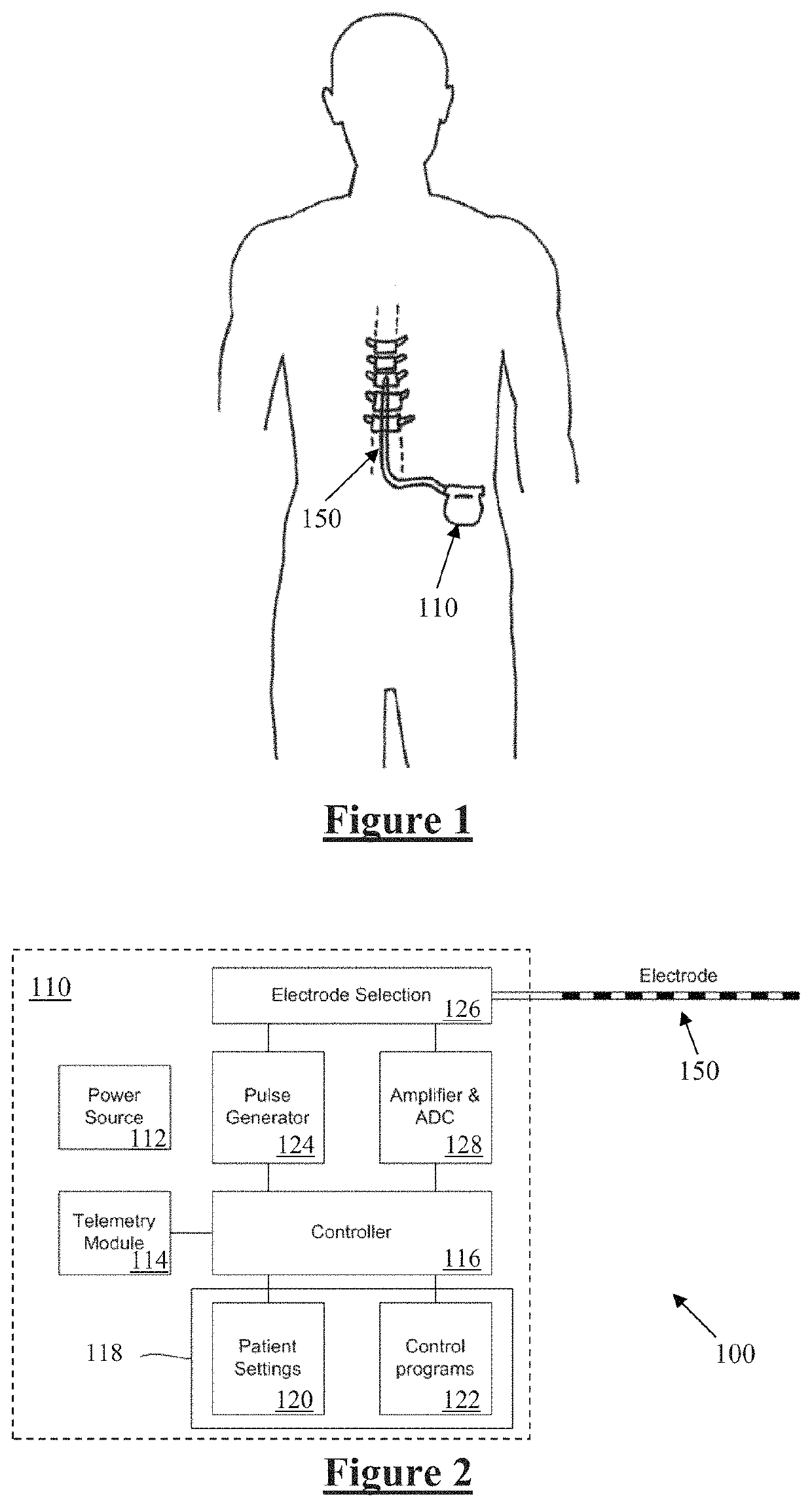
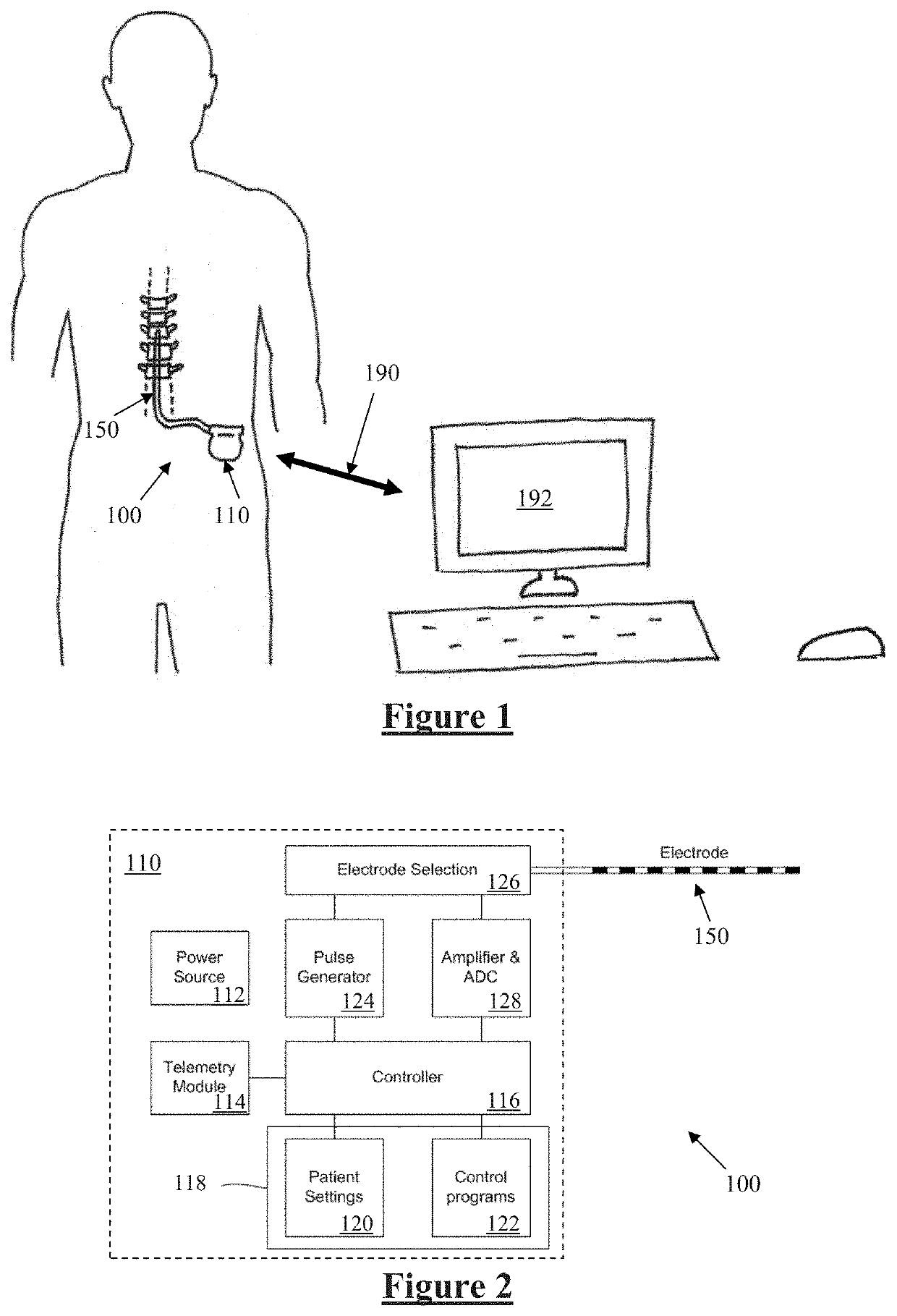
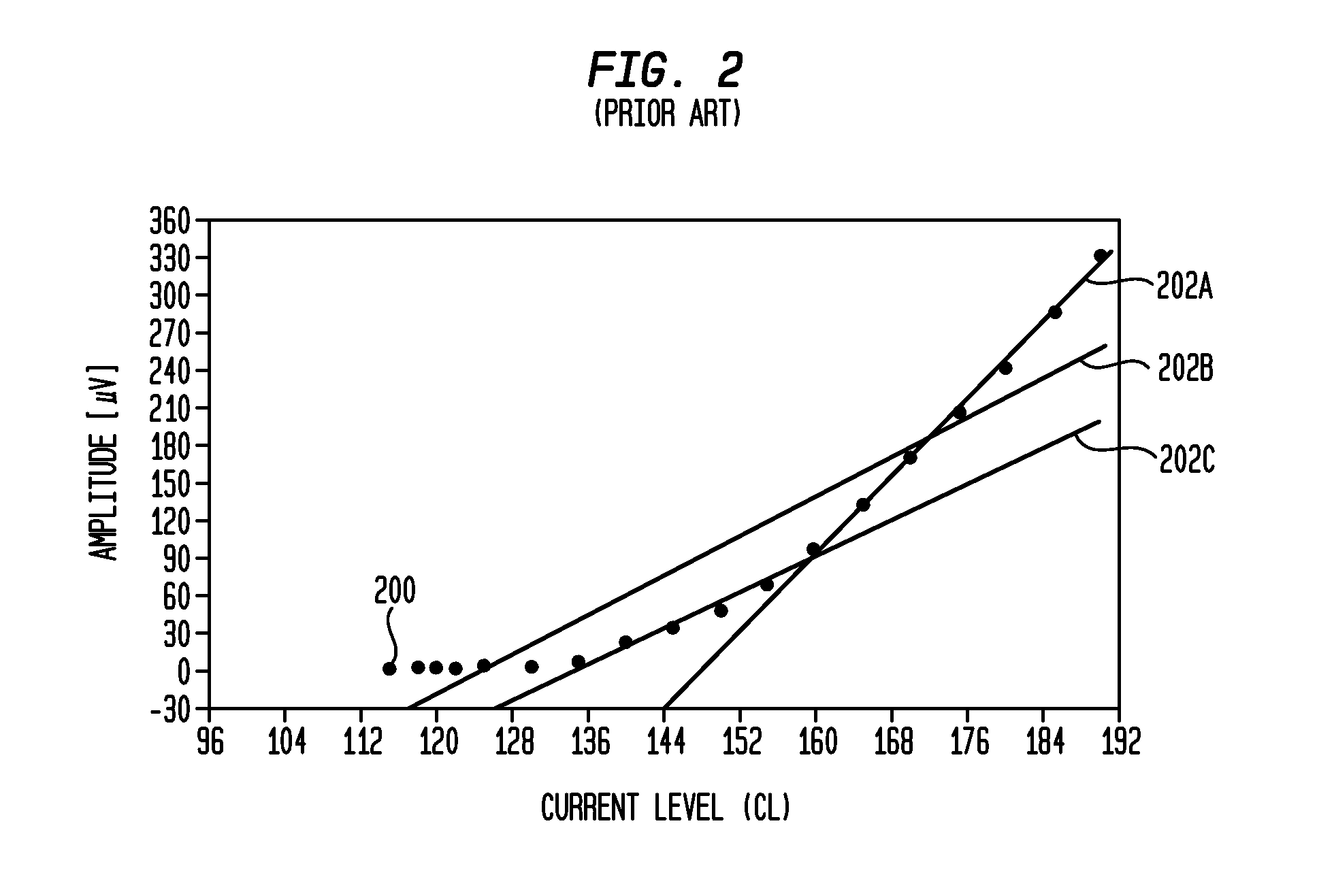
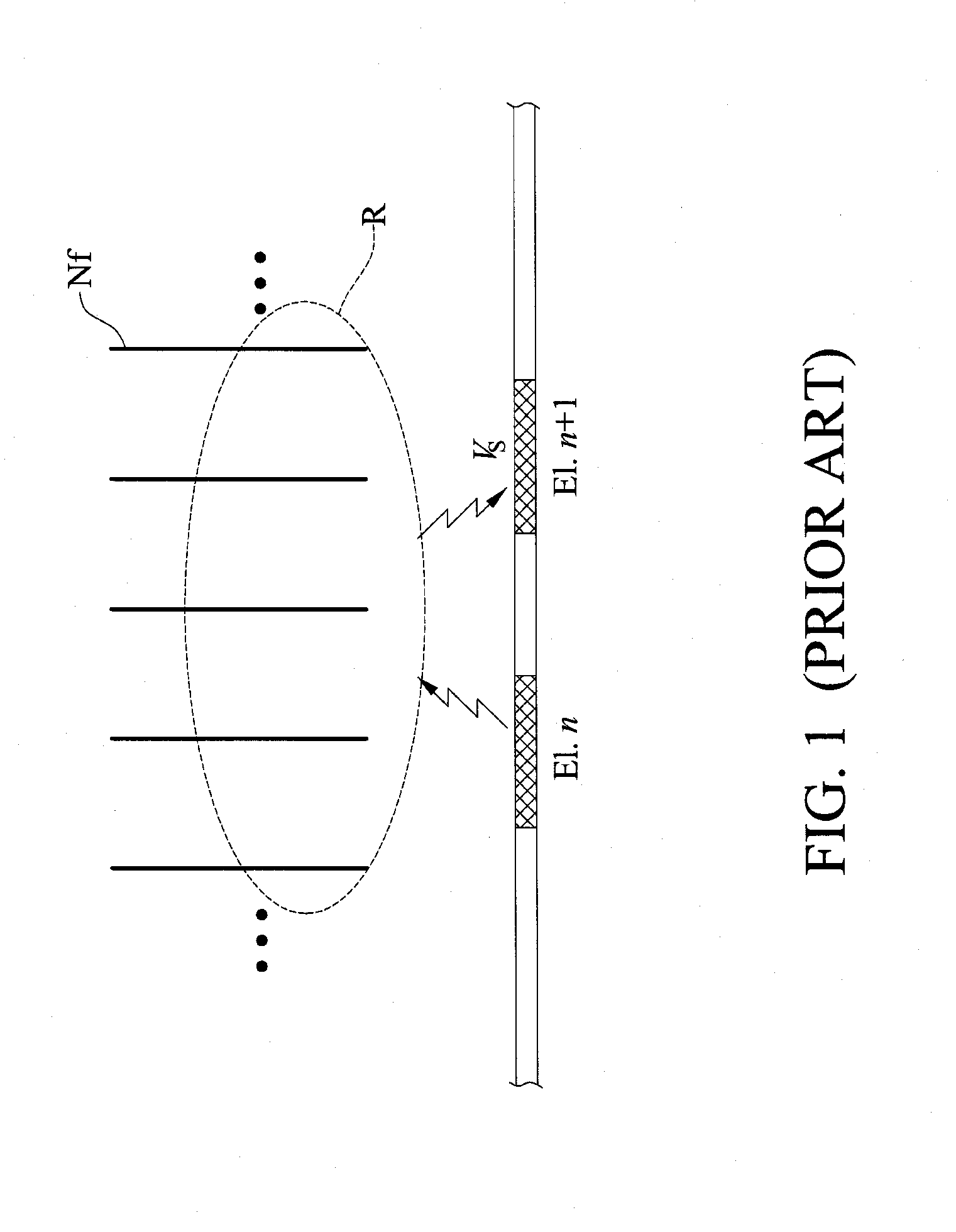
A multichannel cochlear implant system spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
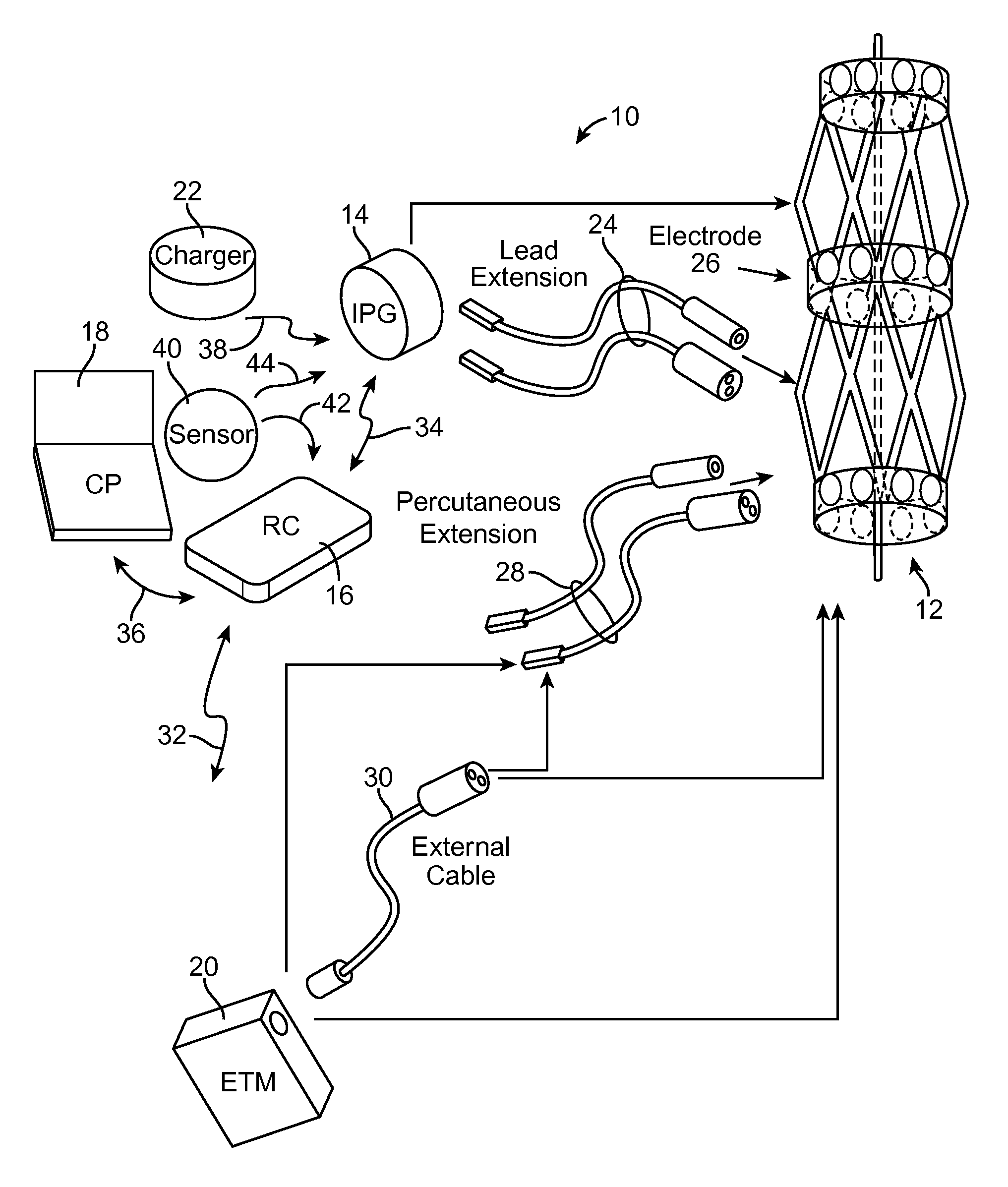
Method and system for non-linear feedback control of spinal cord stimulation
ActiveUS20150360031A1ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialSpinal column
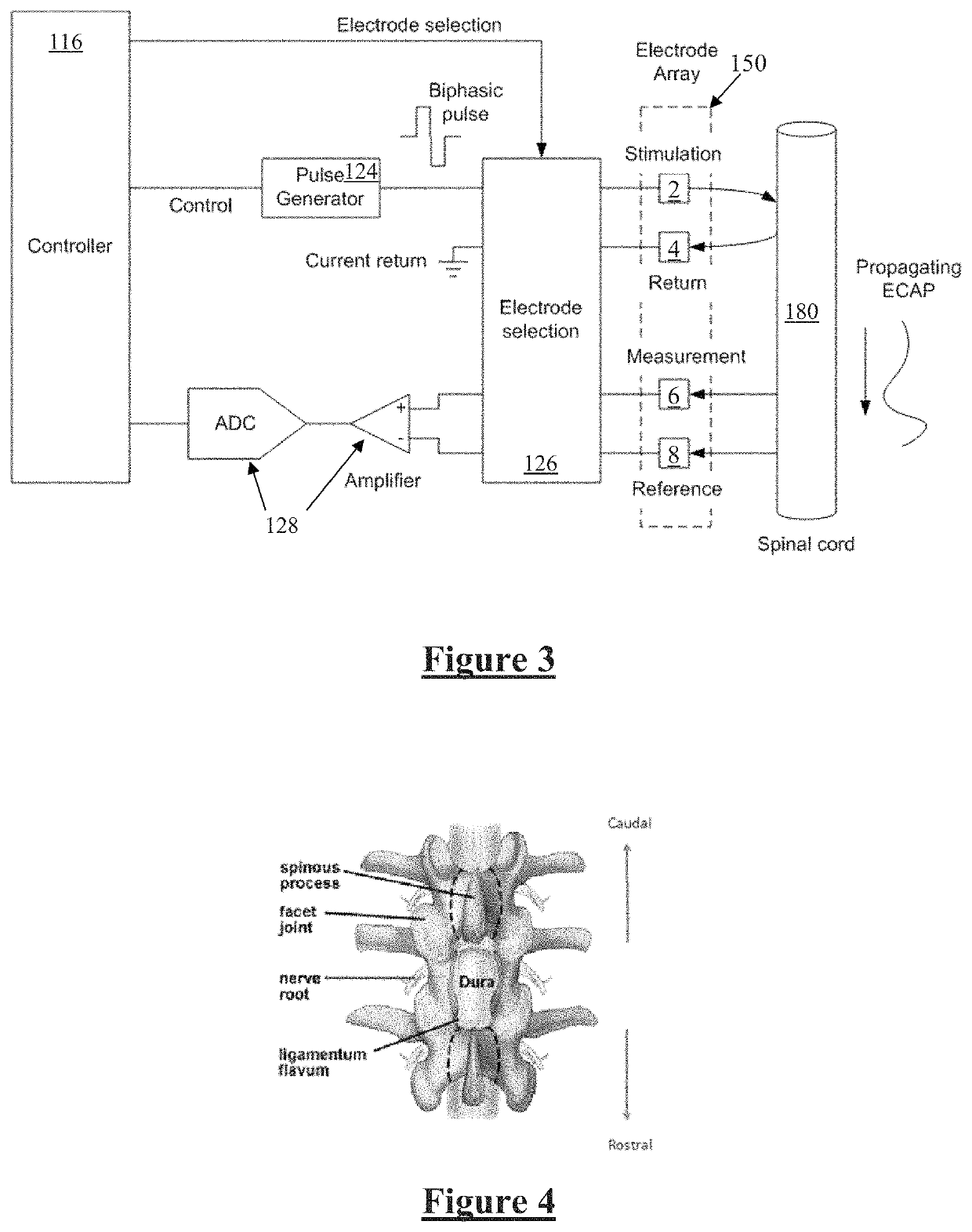
A system of non-linear feedback control for spinal cord stimulation is provided. The system comprises a lead adapted to be implanted within an epidural space of a dorsal column of a patients spine, and a pulse generator (PG) electrically coupled to the lead. The PG is configured to deliver spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapy. The system also comprises a sensing circuitry configured to sense an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) response that propagates along the neural pathway. The system also comprises a processor programmed to operation, in response to instructions stored on a non-transient computer-readable medium, to obtain a baseline ECAP response when the lead and spinal cord tissue properties are in baseline states; analyze ECAP responses relative to the baseline ECAP response to obtain an ECAP feedback difference indicative of a change in at least one of the baseline state of the lead and the baseline state of the spinal cord tissue properties. The processor is also programmed to adjust an SCS therapy based on the ECAP feedback.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method for analyzing nerve fiber distribution and measuring normalized evoked compound action electric potential
ActiveUS20140066803A1Rapidly and precisely and analyzingRapidly and precisely measuringHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringFiberEvoked compound action potential
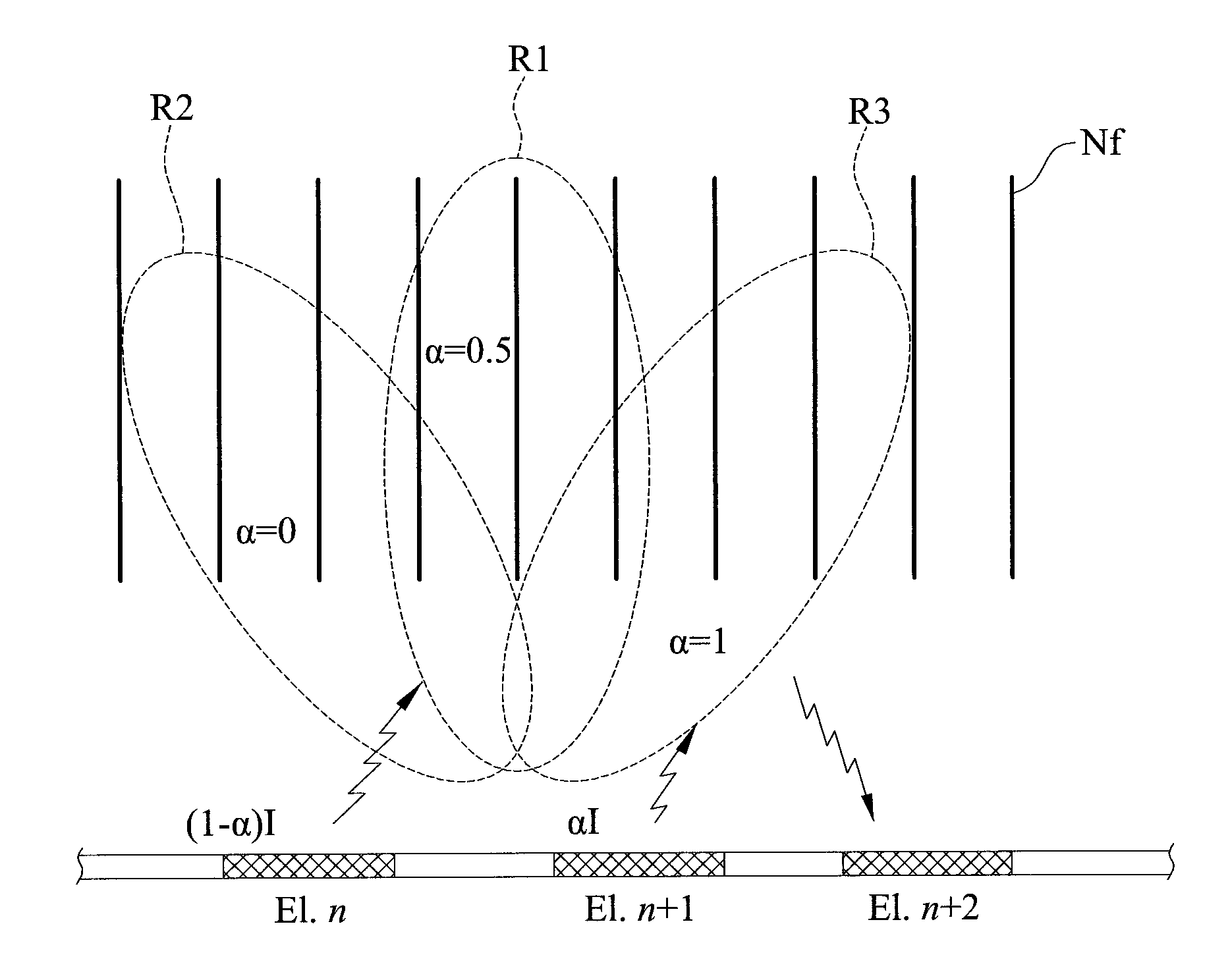
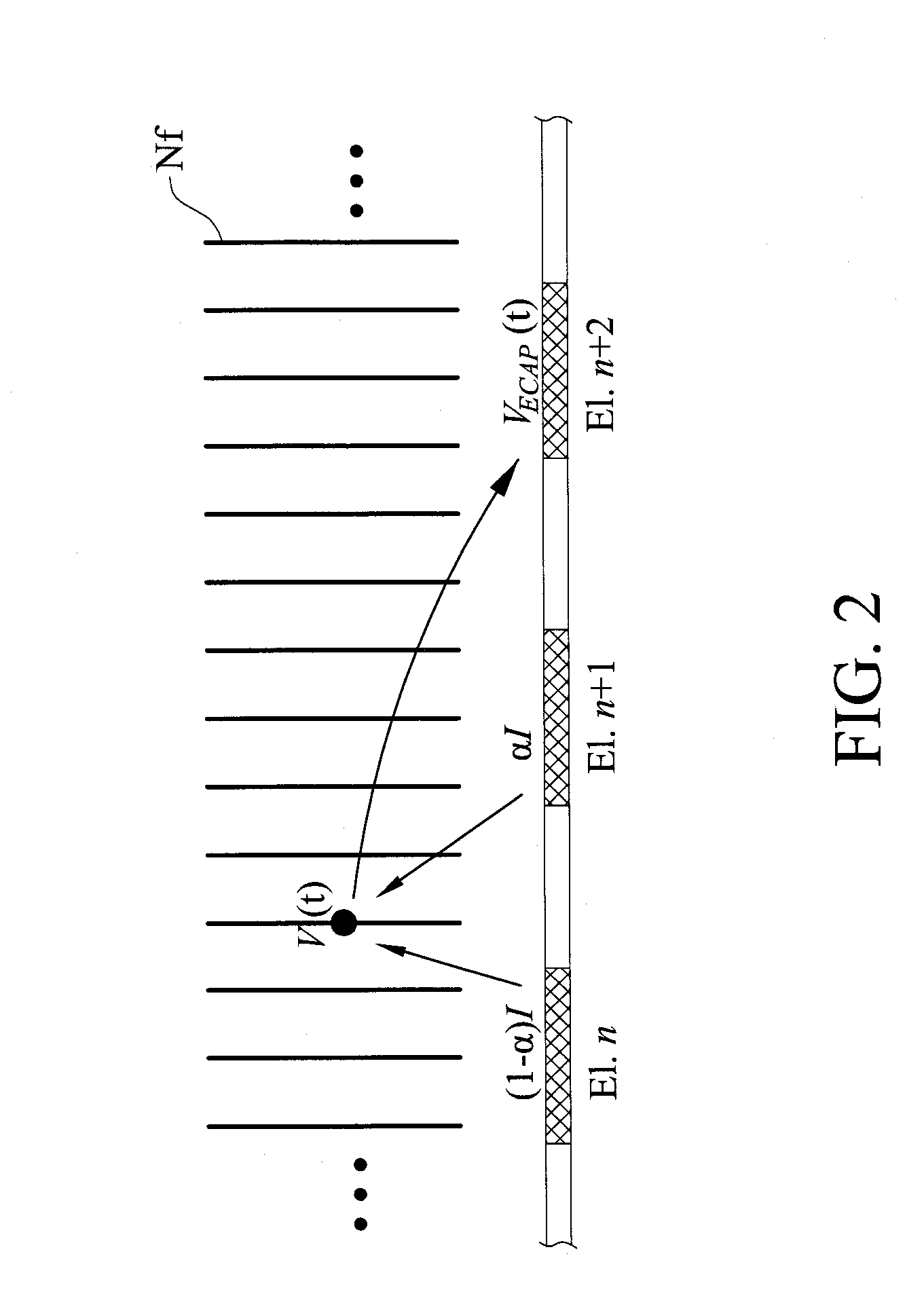
A method for analyzing nerve fibers distribution is provided, including inputting a stimulation signal into a nerve tissue through at least two sensing and conducting electrodes, applying a stimulation signal ratio to control the stimulation signal using an electric current steering technique to electrically stimulate a plurality of nerve fibers within a plurality of stimulations areas of the nerve tissue; receiving a plurality of evoked compound action potentials (ECAP) using at least two sensing and conducting electrodes due to the nerve fibers electrically stimulated and computing a distance between the nerve fiber and the conducting electrodes including eliminating non-ideal effect caused by an electric potential attenuation factor, wherein the electric potential attenuation factor is a function of the distance between each of the conducting electrodes and the nerve tissue; and integrating and comparing the received ECAPs and analyzing the nerve fibers distribution of the nerve tissue.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Systems and methods of providing modulation therapy without patient-perception of stimulation
InactiveUS20150032181A1Improve matchElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectricityEvoked compound action potential
A neuromodulation system and method of providing sub-threshold modulation therapy. Electrical modulation energy is delivered to a target tissue site of the patient at a programmed intensity value, thereby providing therapy to a patient without perception of stimulation. In response to an event, electrical modulation energy is delivered at incrementally increasing intensity values. At least one evoked compound action potential (eCAP) is sensed in a population of neurons at the target tissue site of the patient in response to the delivery of the electrical modulation energy at the incrementally increasing intensity values. One of the incrementally increased intensity values is selected based on the sensed eCAP(s). A decreased intensity value is automatically computed as a function of the selected intensity value. Electrical modulation energy is delivered to the target tissue site of the patient at the computed intensity value, thereby providing sub-threshold therapy to the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Multi-electrode stimulation to elicit electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS20080221640A1Good determine appropriate intensity threshold levelSimple technologyElectrotherapyEvoked compound action potentialSequential stimulation
A multichannel neurostimulation device spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Method and system for non-linear feedback control of spinal cord stimulation
A system of non-linear feedback control for spinal cord stimulation is provided. The system comprises a lead adapted to be implanted within an epidural space of a dorsal column of a patients spine, and a pulse generator (PG) electrically coupled to the lead. The PG is configured to deliver spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapy. The system also comprises a sensing circuitry configured to sense an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) response that propagates along the neural pathway. The system also comprises a processor programmed to operation, in response to instructions stored on a non-transient computer-readable medium, to obtain a baseline ECAP response when the lead and spinal cord tissue properties are in baseline states; analyze ECAP responses relative to the baseline ECAP response to obtain an ECAP feedback difference indicative of a change in at least one of the baseline state of the lead and the baseline state of the spinal cord tissue properties. The processor is also programmed to adjust an SCS therapy based on the ECAP feedback.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System for generating a cochlear implant program using multi-electrode stimulation to elicit the electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS20070179565A1Increase amplitudeConvenient recordingHead electrodesArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialSequential stimulation
A multichannel cochlear implant system spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
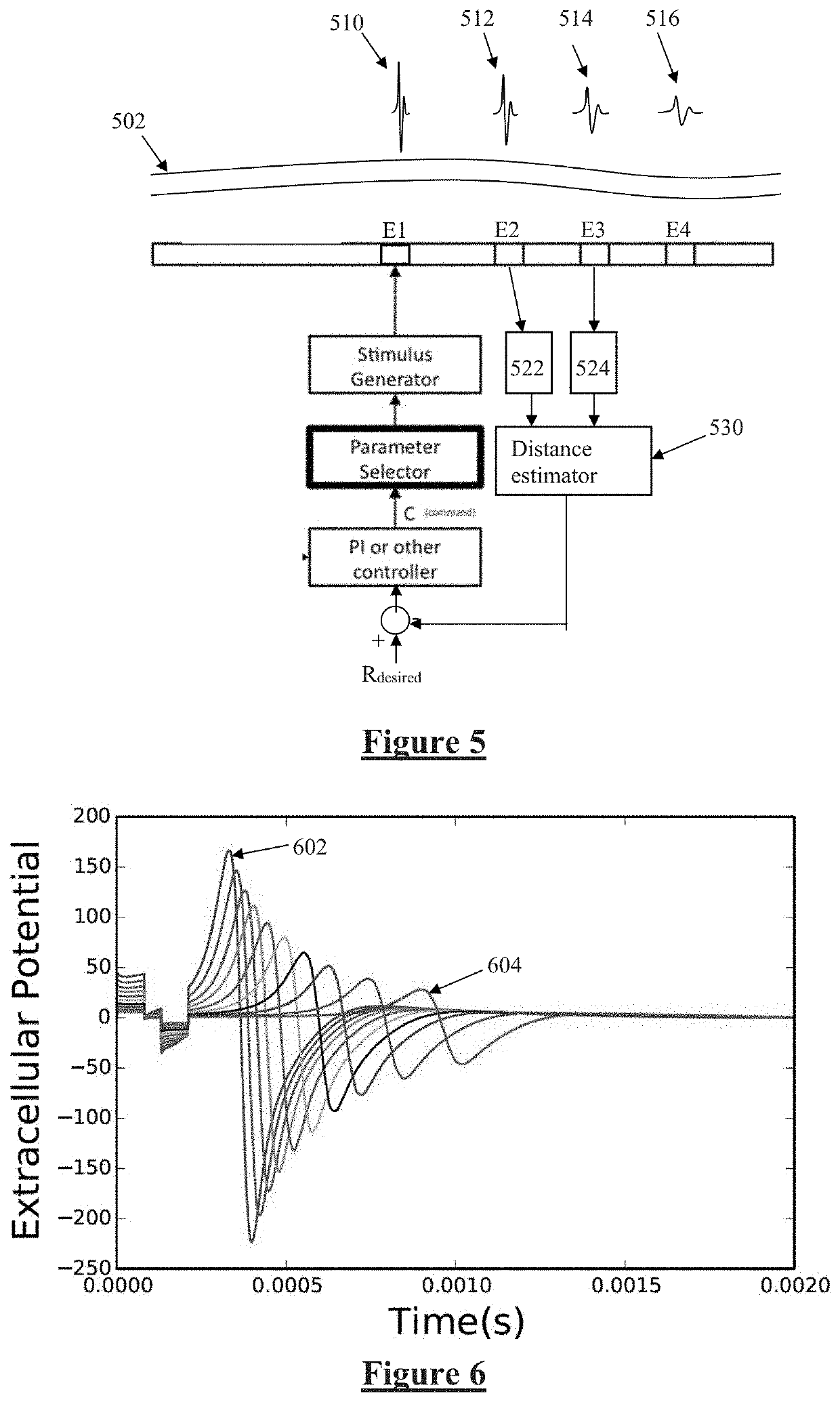
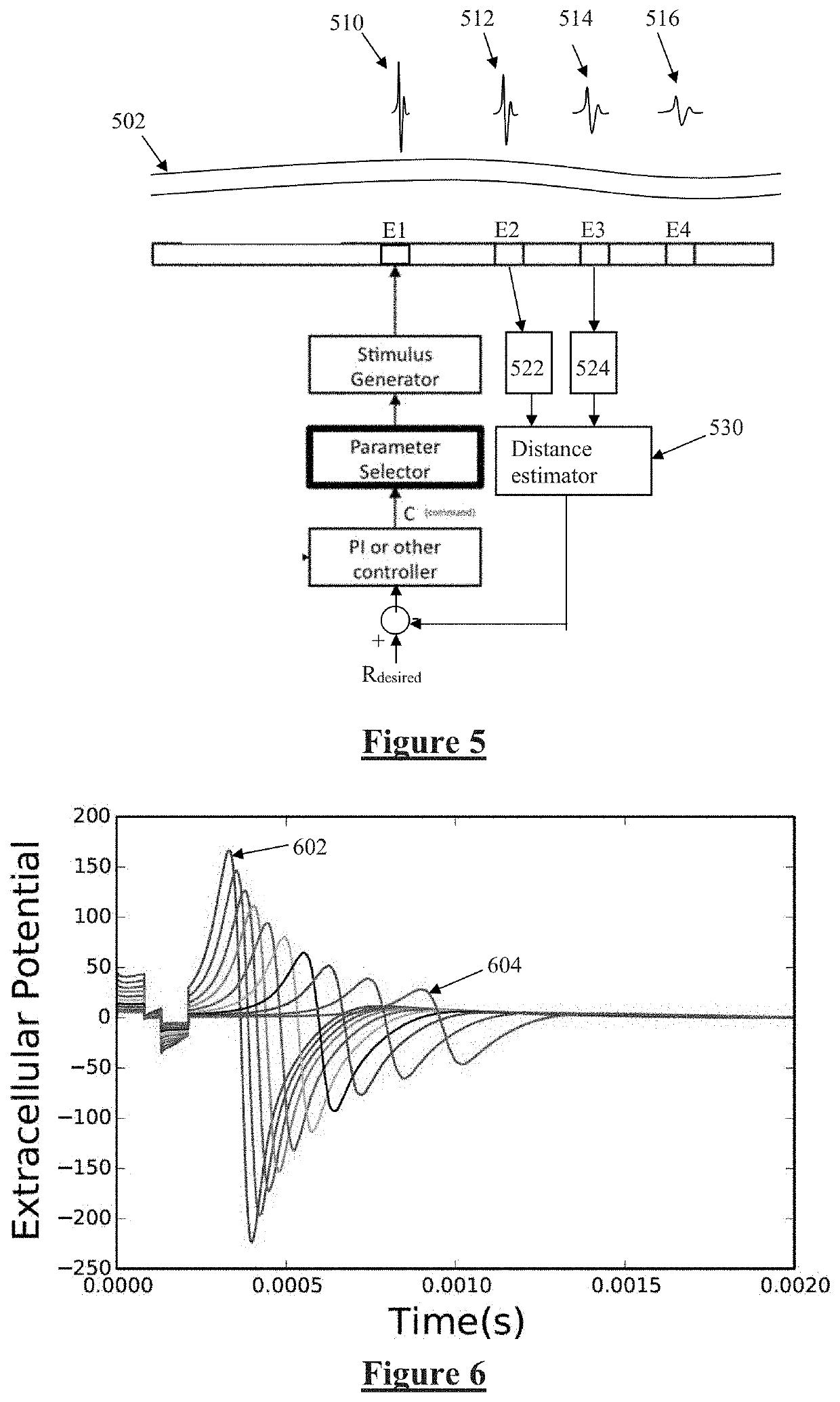
Electrode to Nerve Distance Estimation
ActiveUS20180110987A1Promote resultsComplicate to effectElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialMedicine
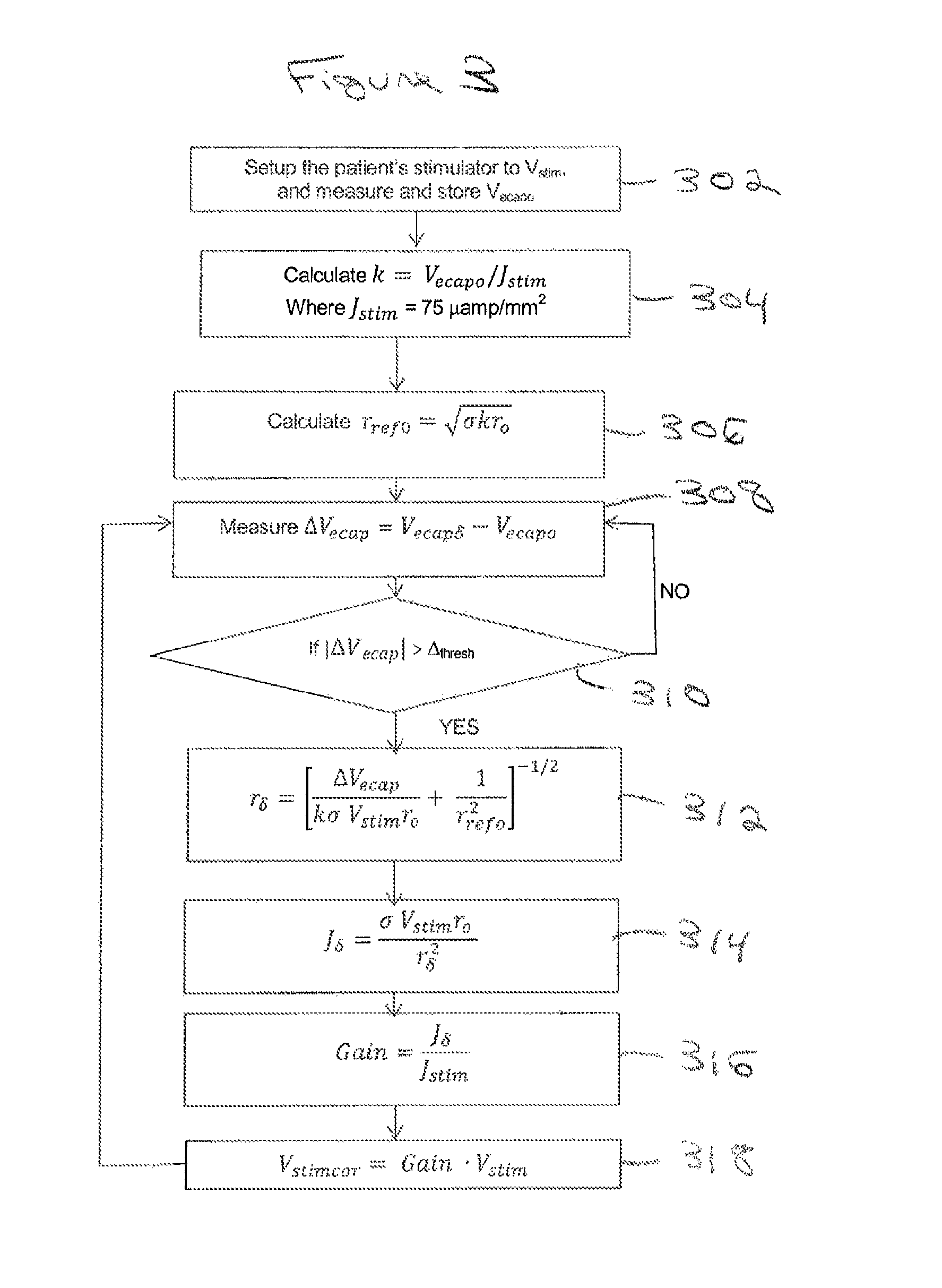
Estimating a nerve-to-electrode distance involves applying a stimulus from a stimulus electrode to a nerve. Neural measurements of at least one evoked compound action potential are obtained, and processed in order to estimate an originating state of stimulation exhibiting at least one characteristic defined by a single fibre size. A single fibre model is then applied to produce a measure of the nerve-to-electrode distance. Also provided for is estimation of a distribution of recruited fibres. Measurements of a compound action potential are obtained from sense electrodes spaced apart along a neural pathway. A conduction velocity of the compound action potential is determined from the latency between the measurements. From the conduction velocity a dominant recruited fibre diameter is determined. A rate of dispersion of the compound action potential between the sense electrodes is determined. From the rate of dispersion a distribution of diameters of the recruited fibre population is determined.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL
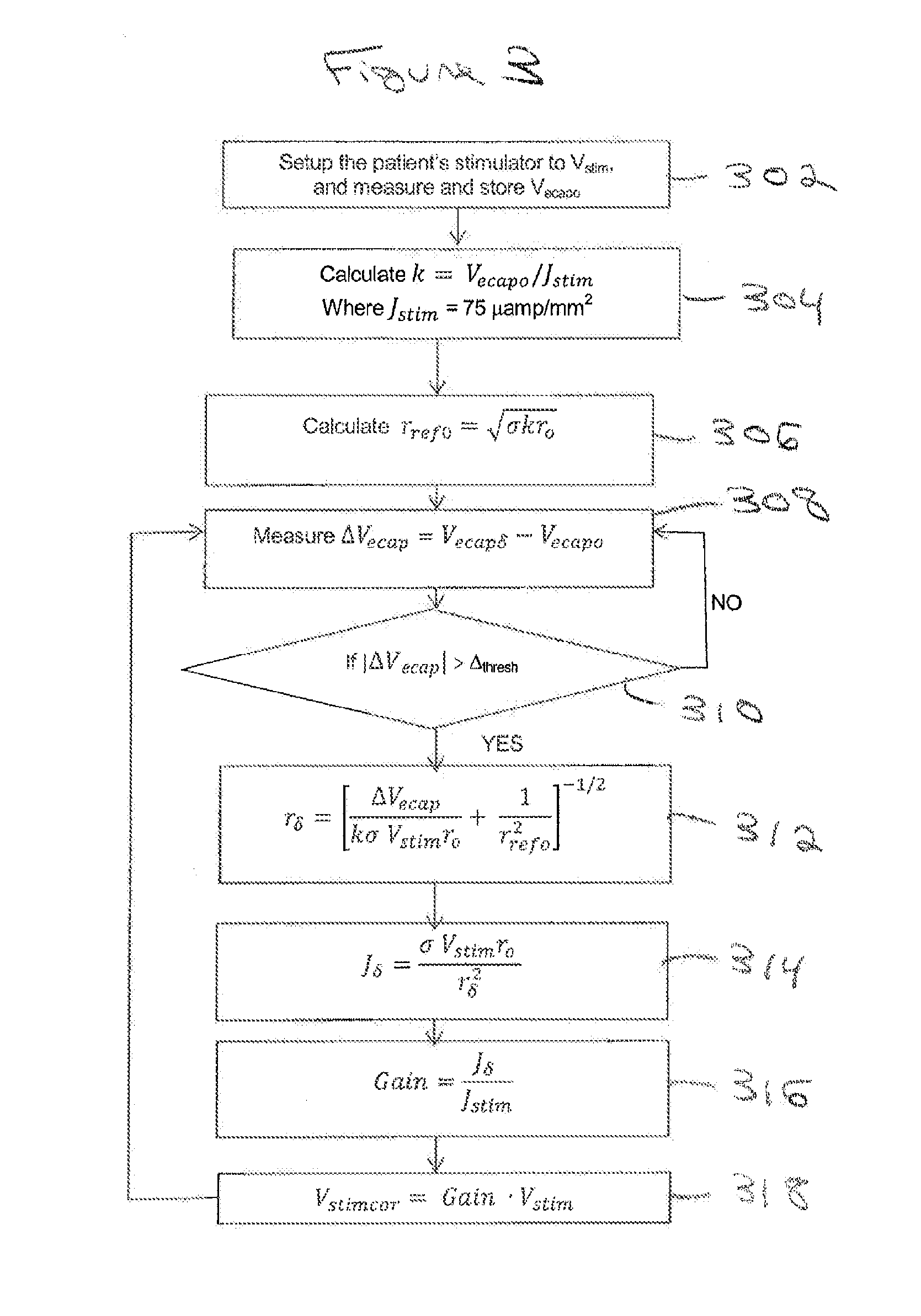
Removing Artifact in Evoked Compound Action Potential Recordings in Neural Stimulators
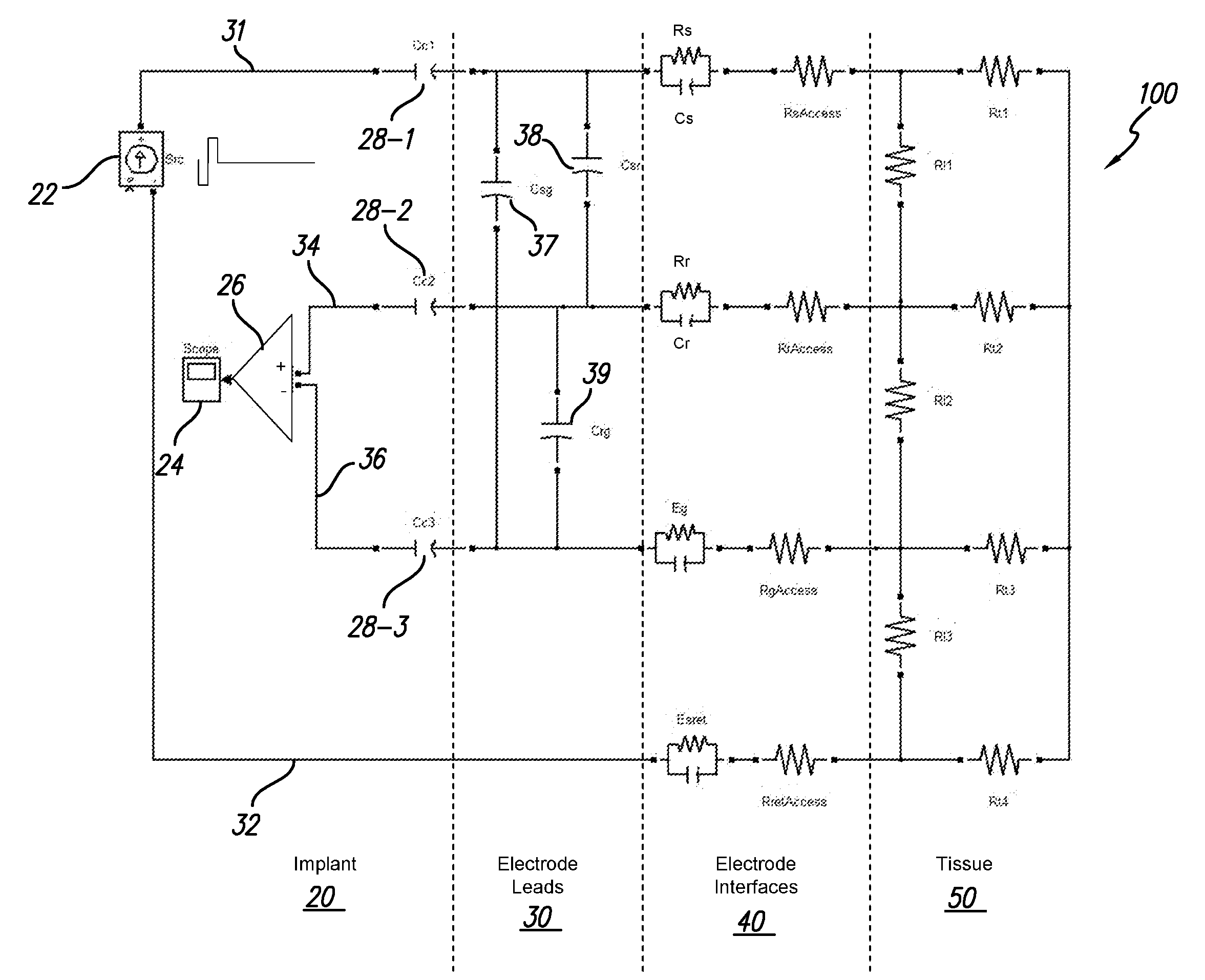
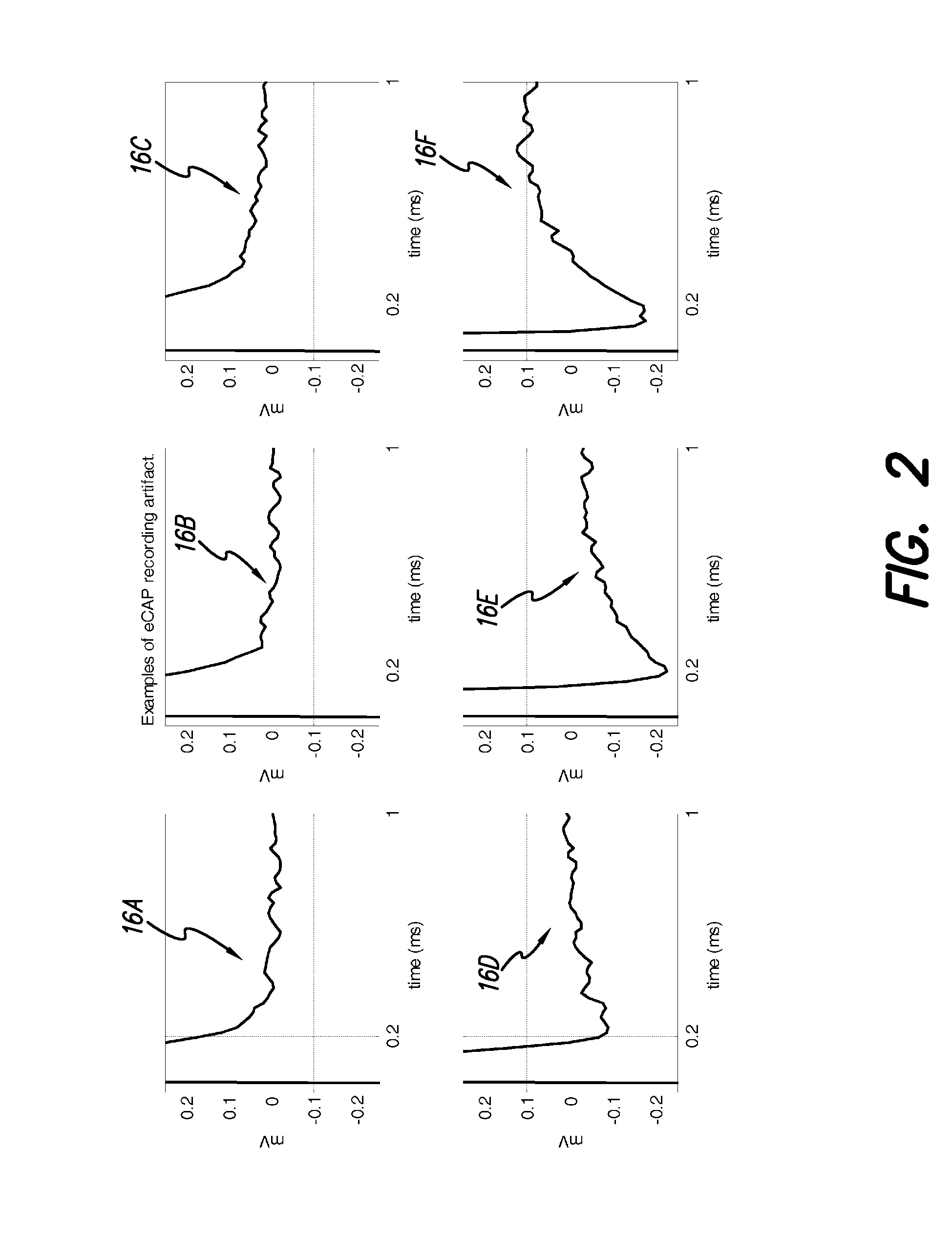
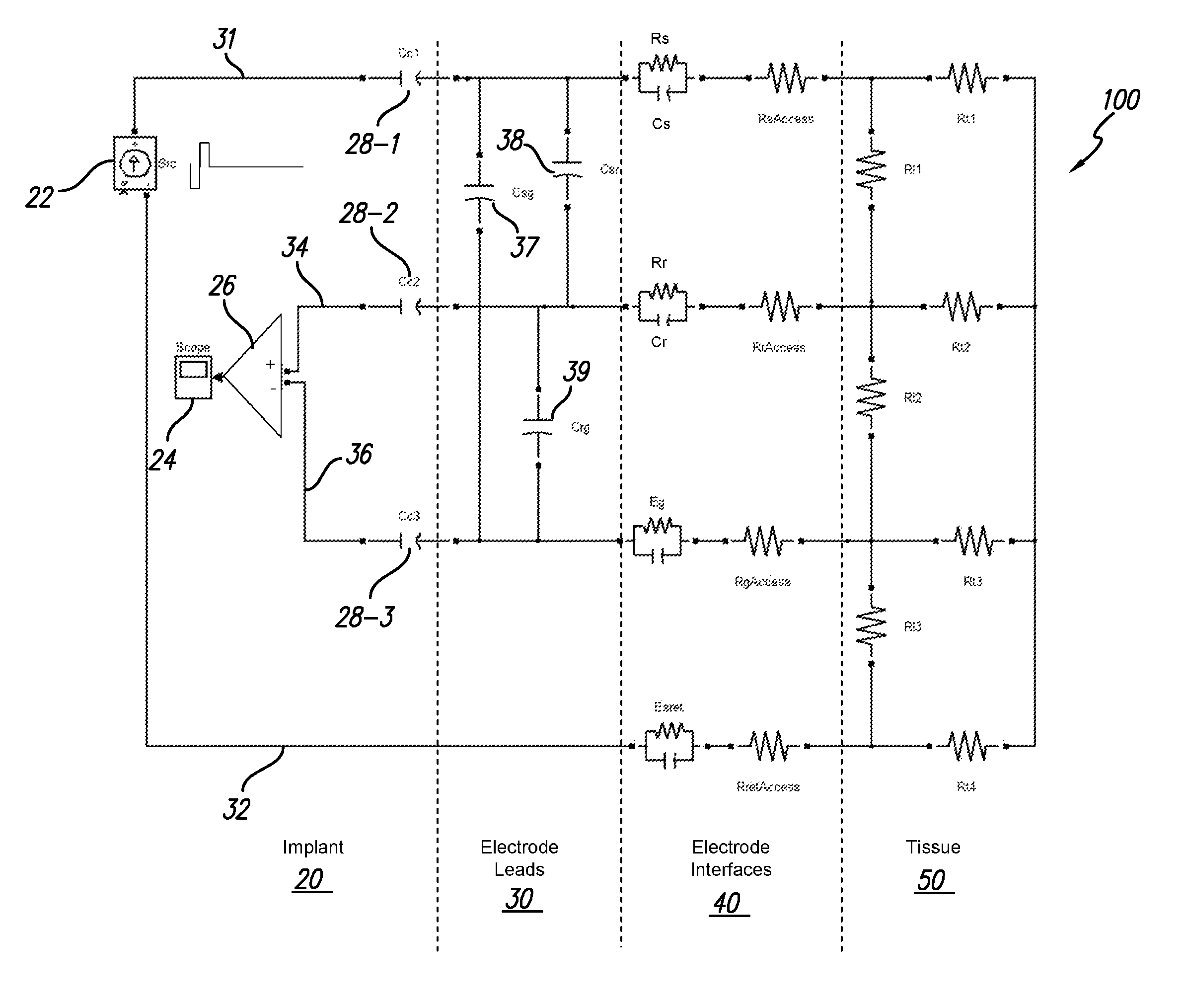
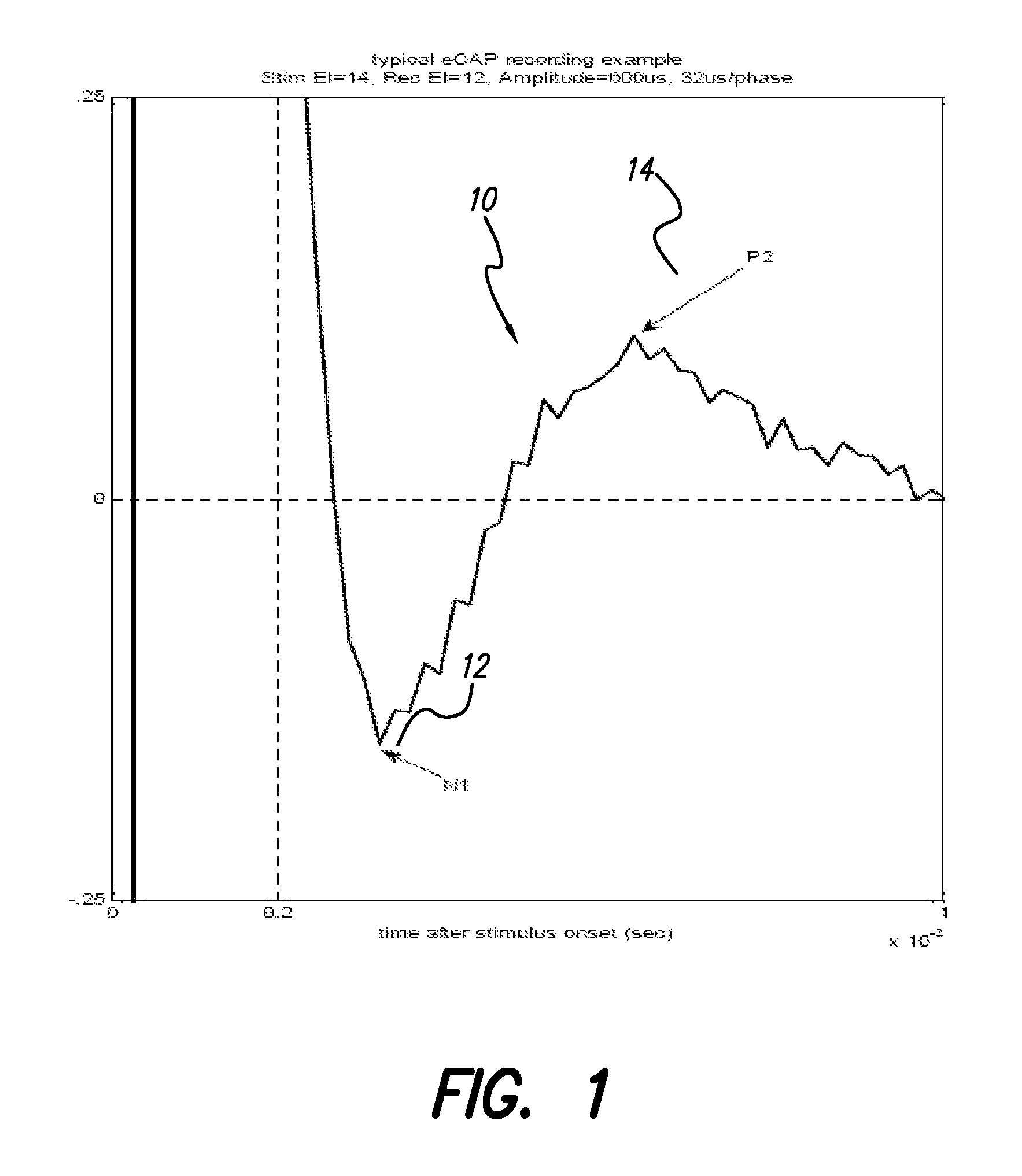
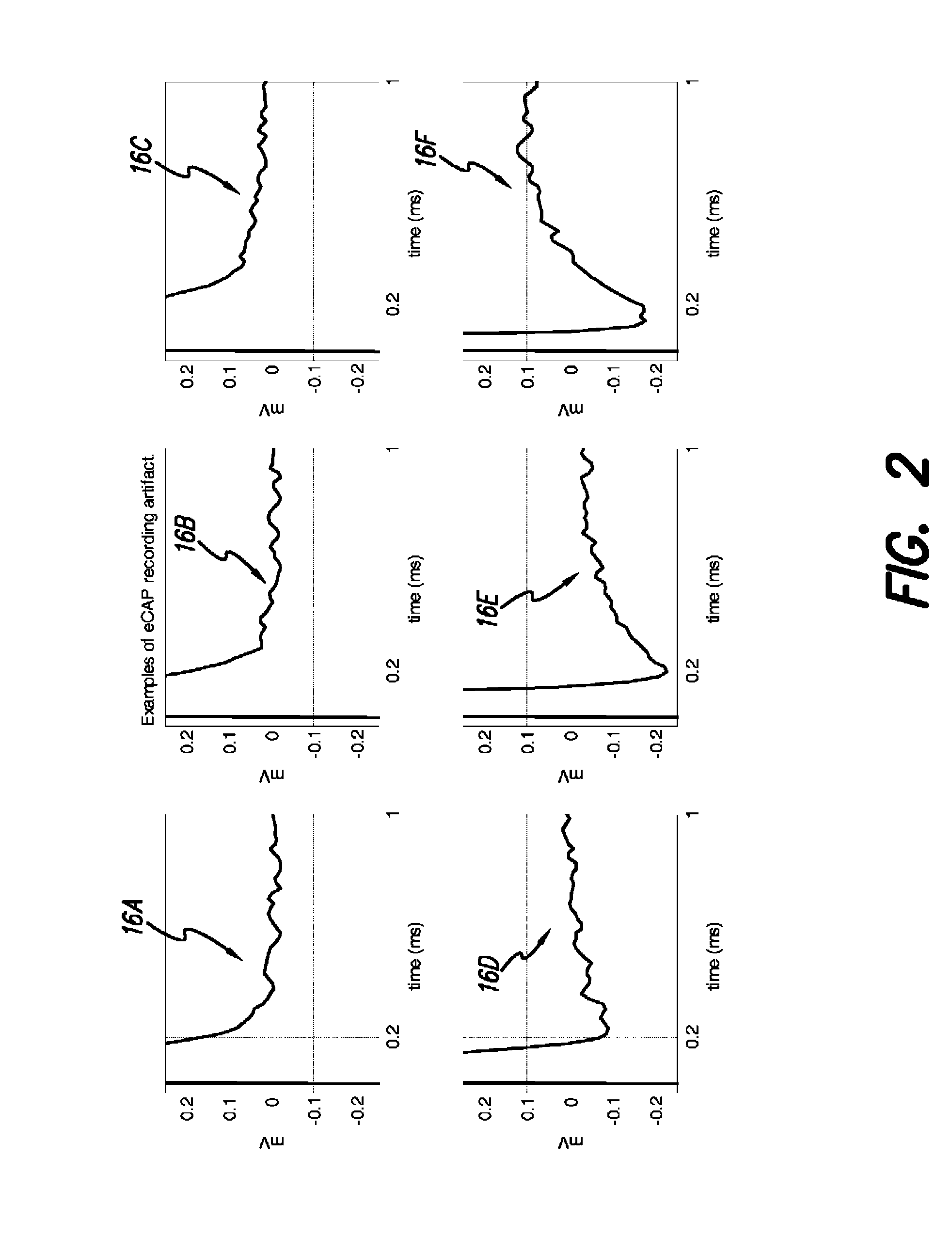
The accuracy of neural response recordings in neural stimulators, e.g., cochlear implants, is often degraded by a recording artifact. An idealized electrical-equivalent model of a neural stimulator is created to study, measure and compensate for artifact evoked compound action potential (eCAP). Using this model, the artifact is shown to occur even when the electrical components that make-up the neural stimulator are ideal. The model contains parasitic capacitances between the electrode wires. The model demonstrates that these small parasitic capacitances provide a current path during stimulation which can deposit charge on the electrode-tissue interfaces of the recording electrodes. The dissipation of this residual charge and the charge stored across the stimulating electrode is seen as the recording artifact. The proposed solution for eliminating the artifact problem is realized by utilizing a capacitive electrode material, e.g., TiO2, Ta2O5, or other dielectric coatings or films, instead of Faradaic electrode material, e.g., Platinum (Pt), Pt—Ir alloy or similar alloys, on the neural stimulator electrode lead.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Removing artifact in evoked compound action potential recordings in neural stimulators
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
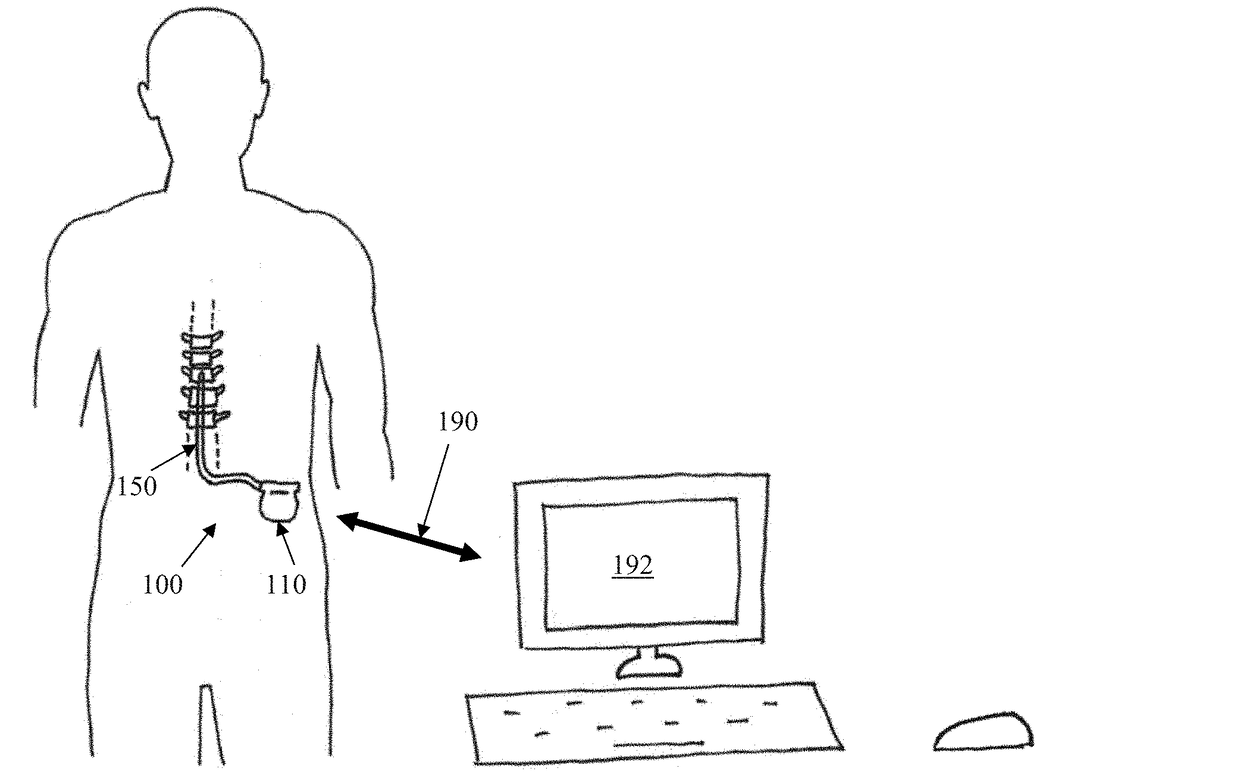
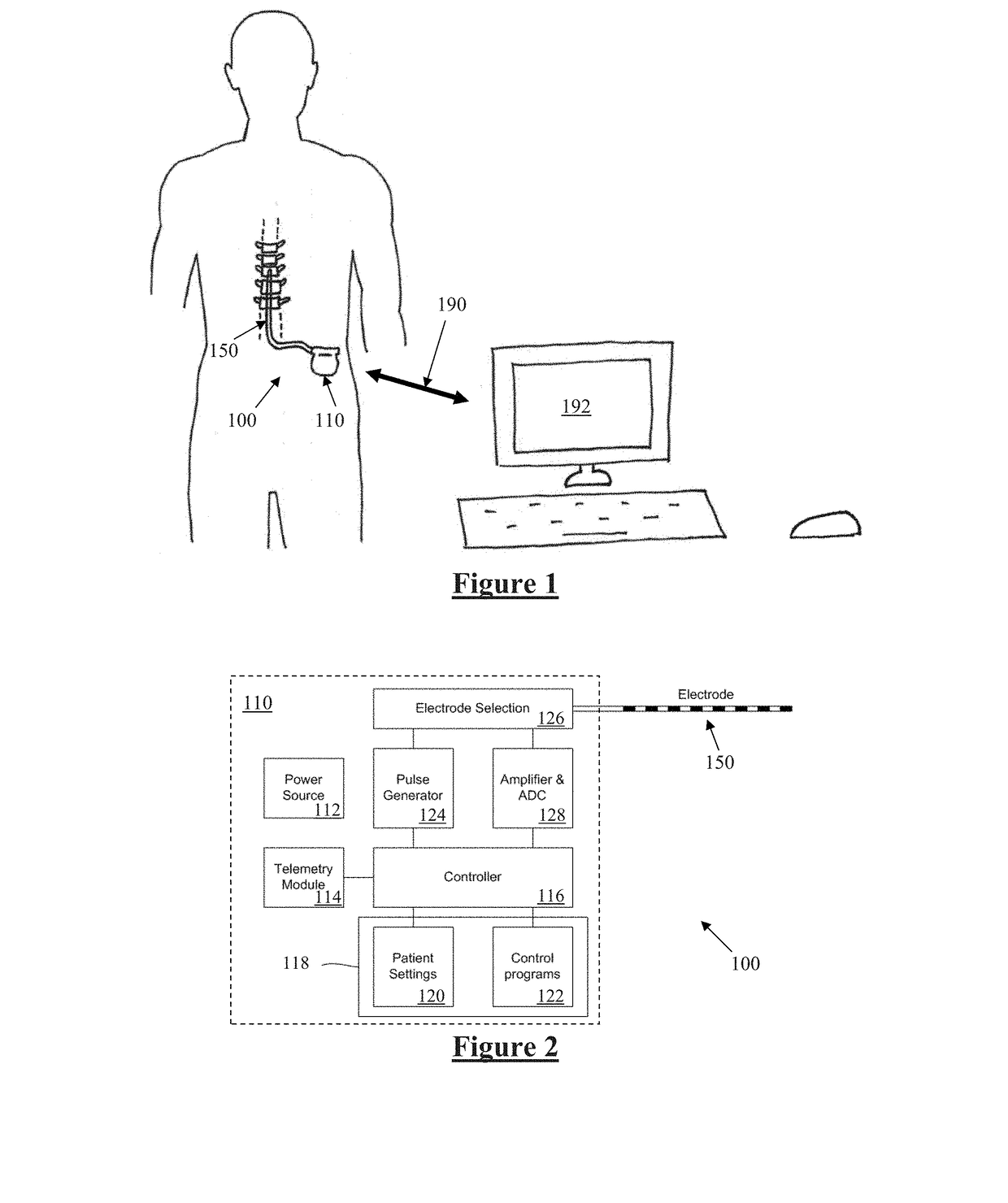
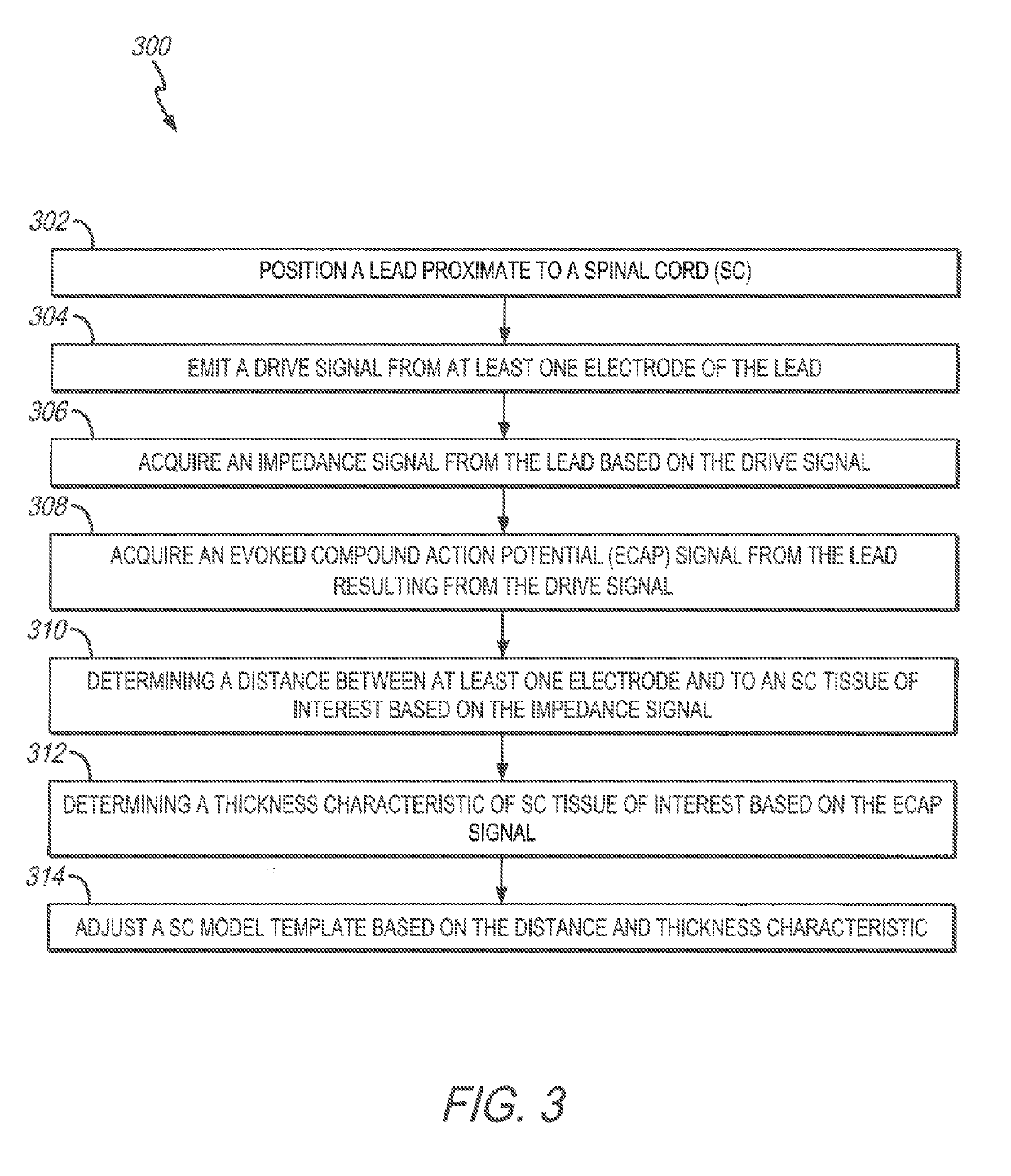
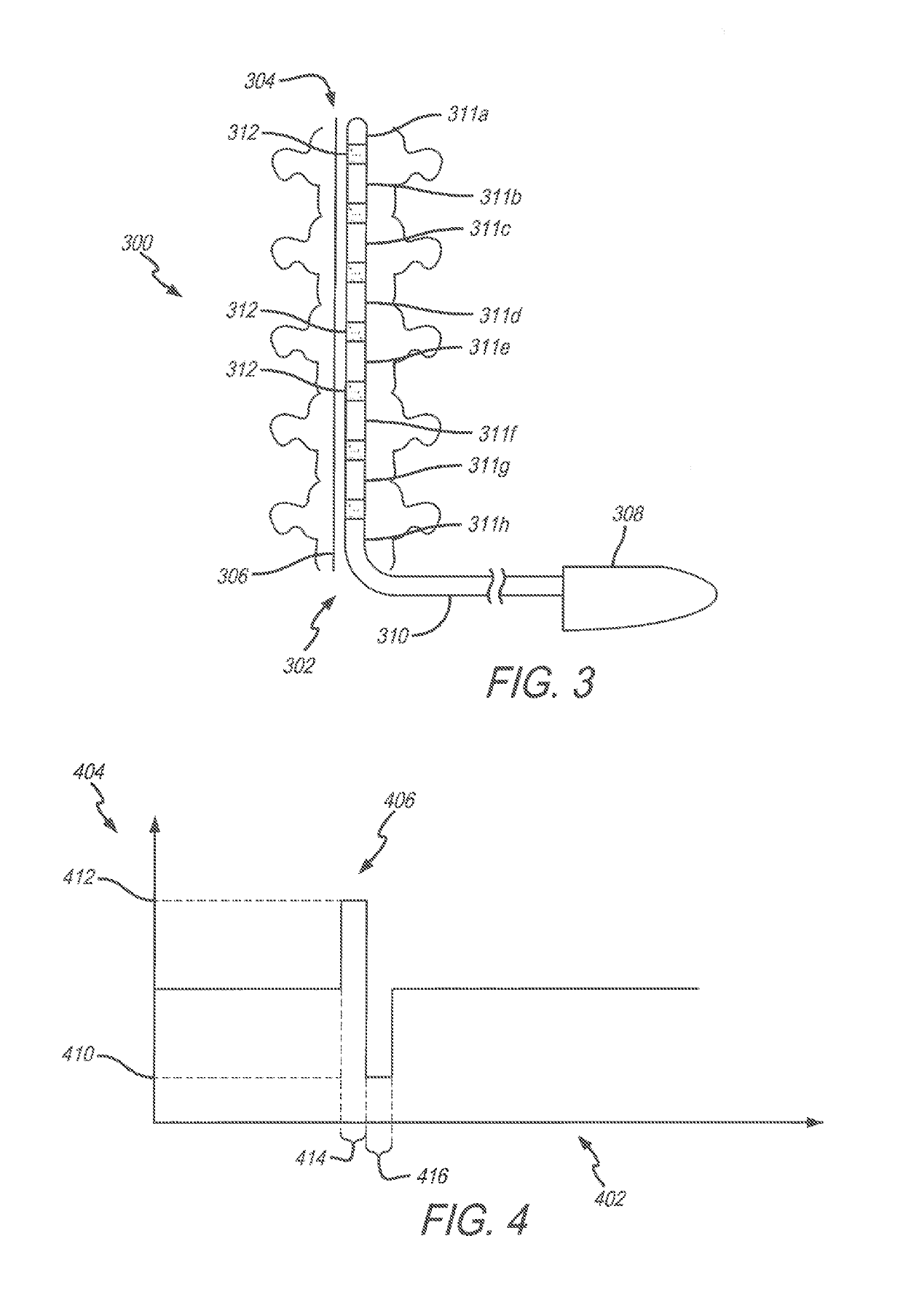
Spinal cord stimulation guidance system and method of use
ActiveUS20160157769A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationEvoked compound action potentialGuidance system
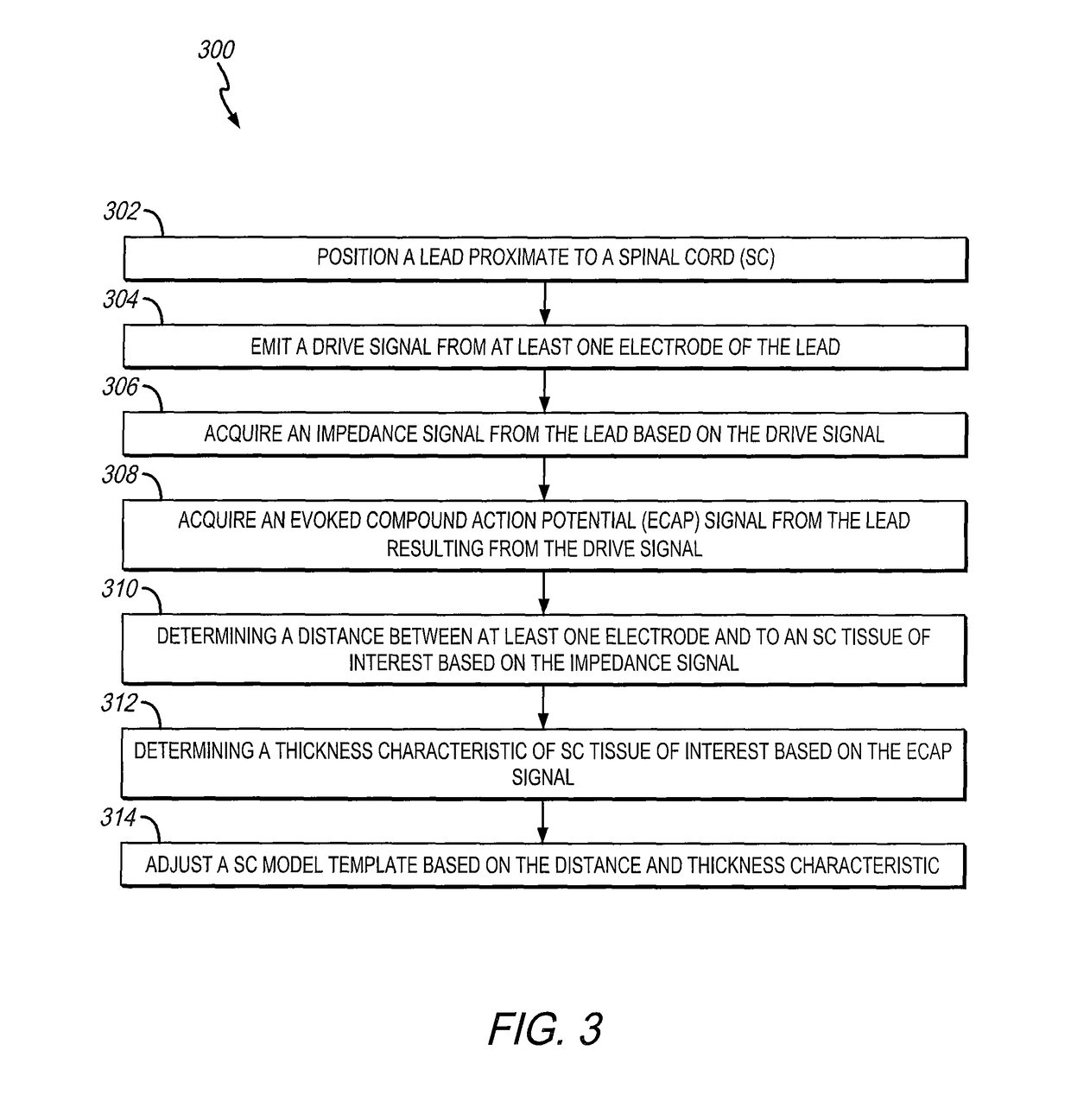
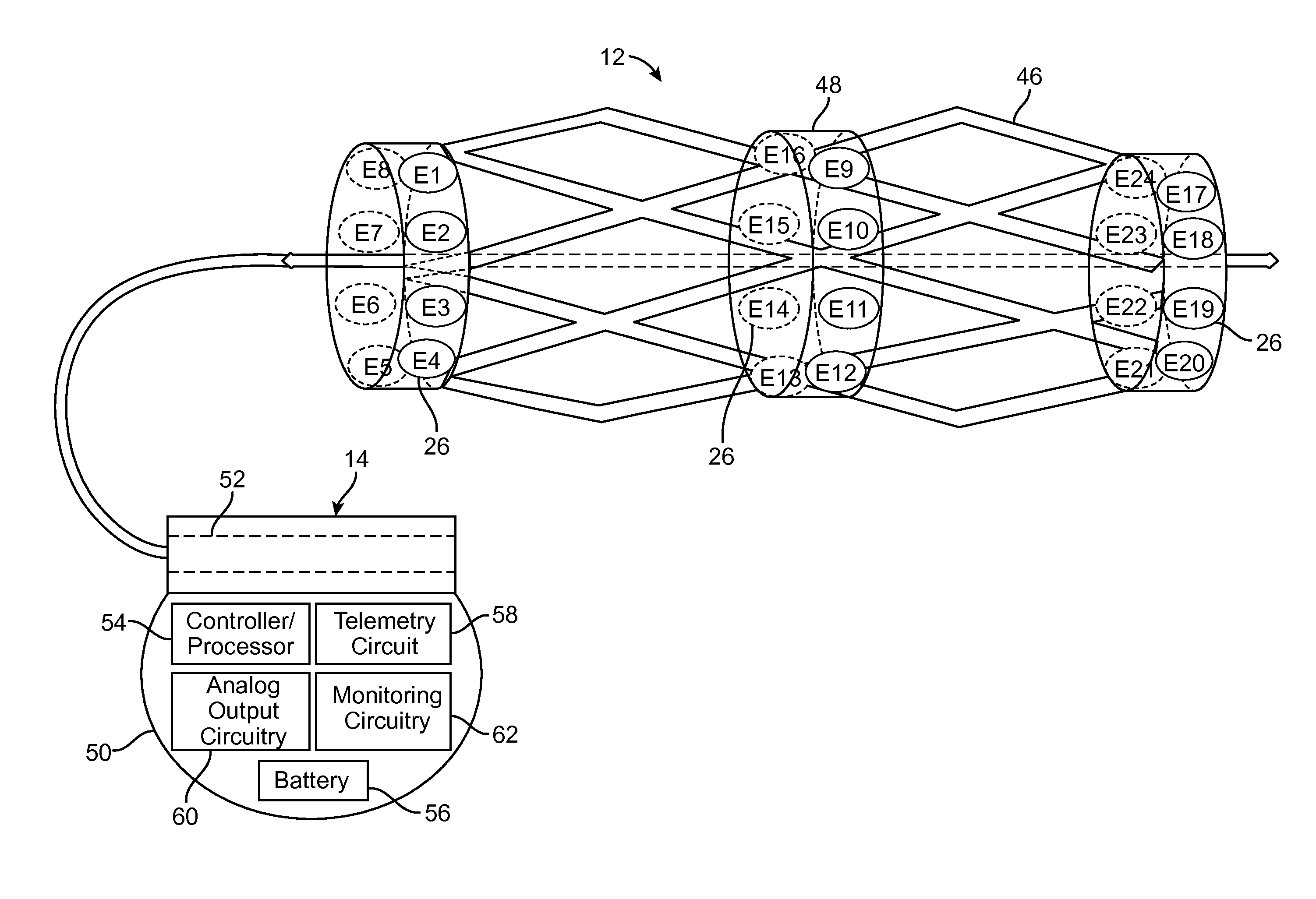
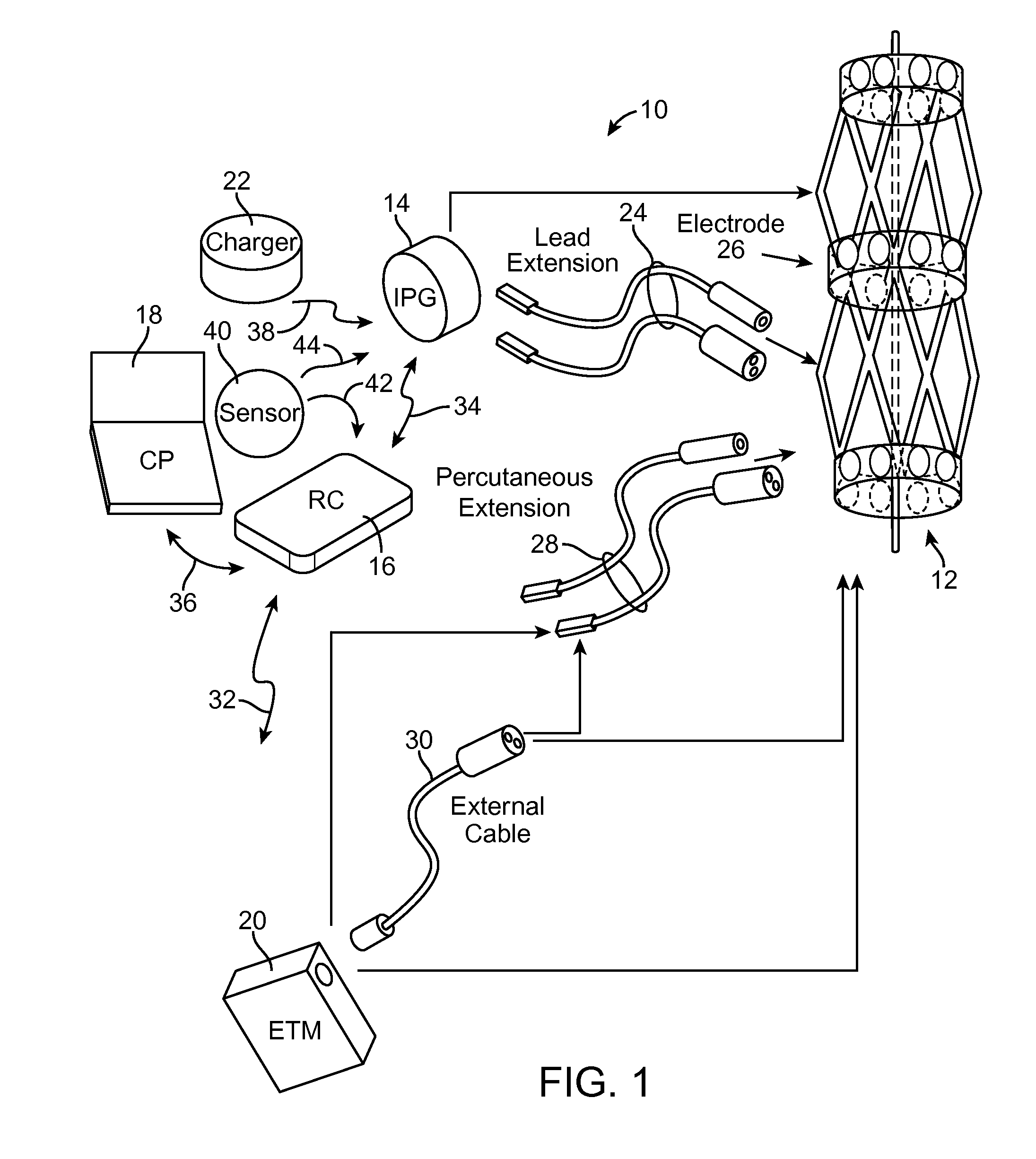
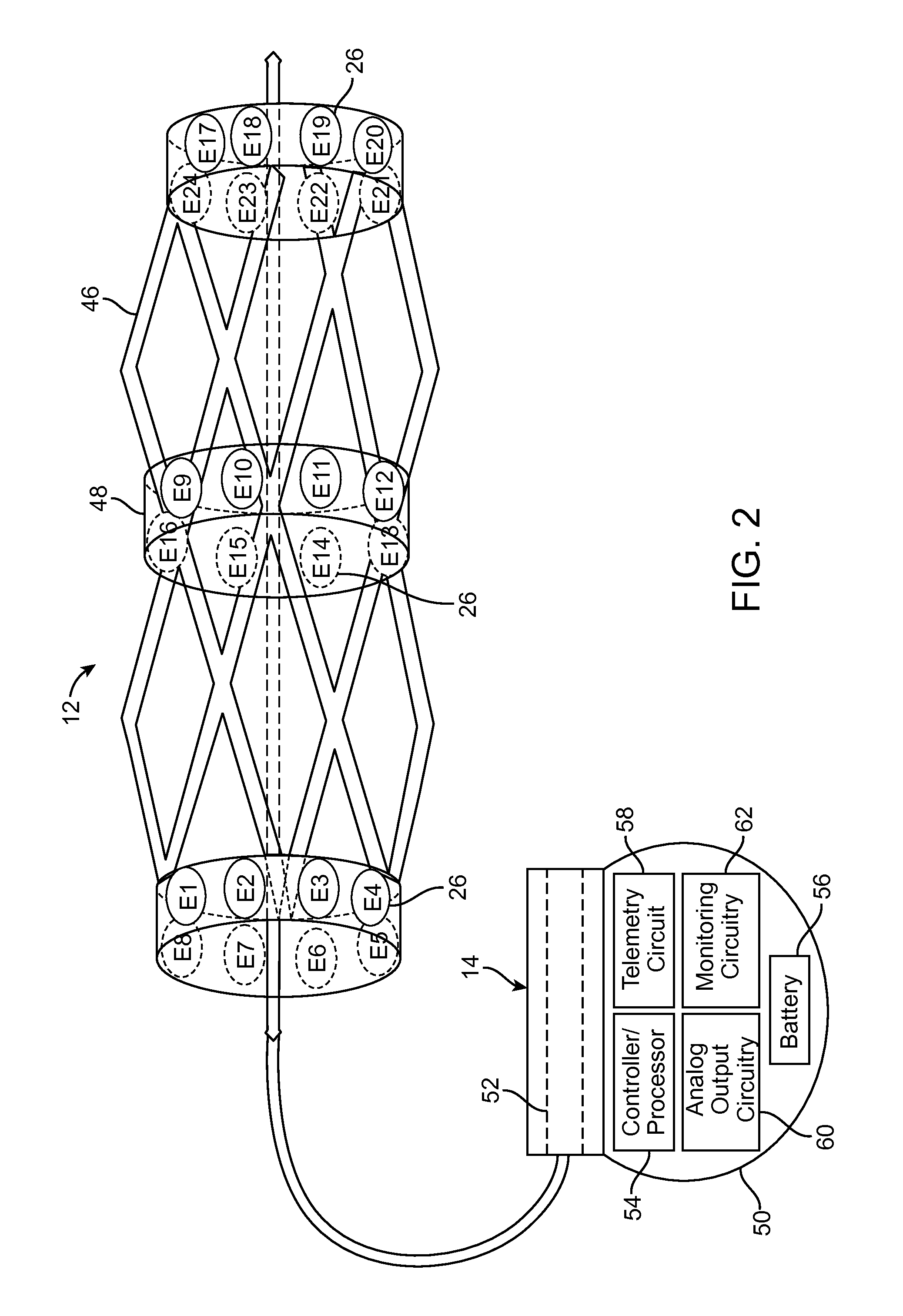
A system and method for modeling patient-specific spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is disclosed. The system and method acquire impedance and evoked compound action potential (ECAP) signals from a lead positioned proximate to a spinal cord (SC). The lead includes at least one electrode. The system and method determine a patient-specific anatomical model based on the impedance and ECAP signals, and transform a dorsal column (DC) map template based on a DC boundary of the patient-specific anatomical model. Further, the system and method map the transformed DC map template to the patient-specific anatomical model. The system and method may also include the algorithms to solve extracellular and intracellular domain electrical fields and propagation along neurons. The system and method may also include the user interfaces to collect patient responses and compare with the patient-specific anatomical model as well as using the patient-specific anatomical model for guiding SCS programming.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
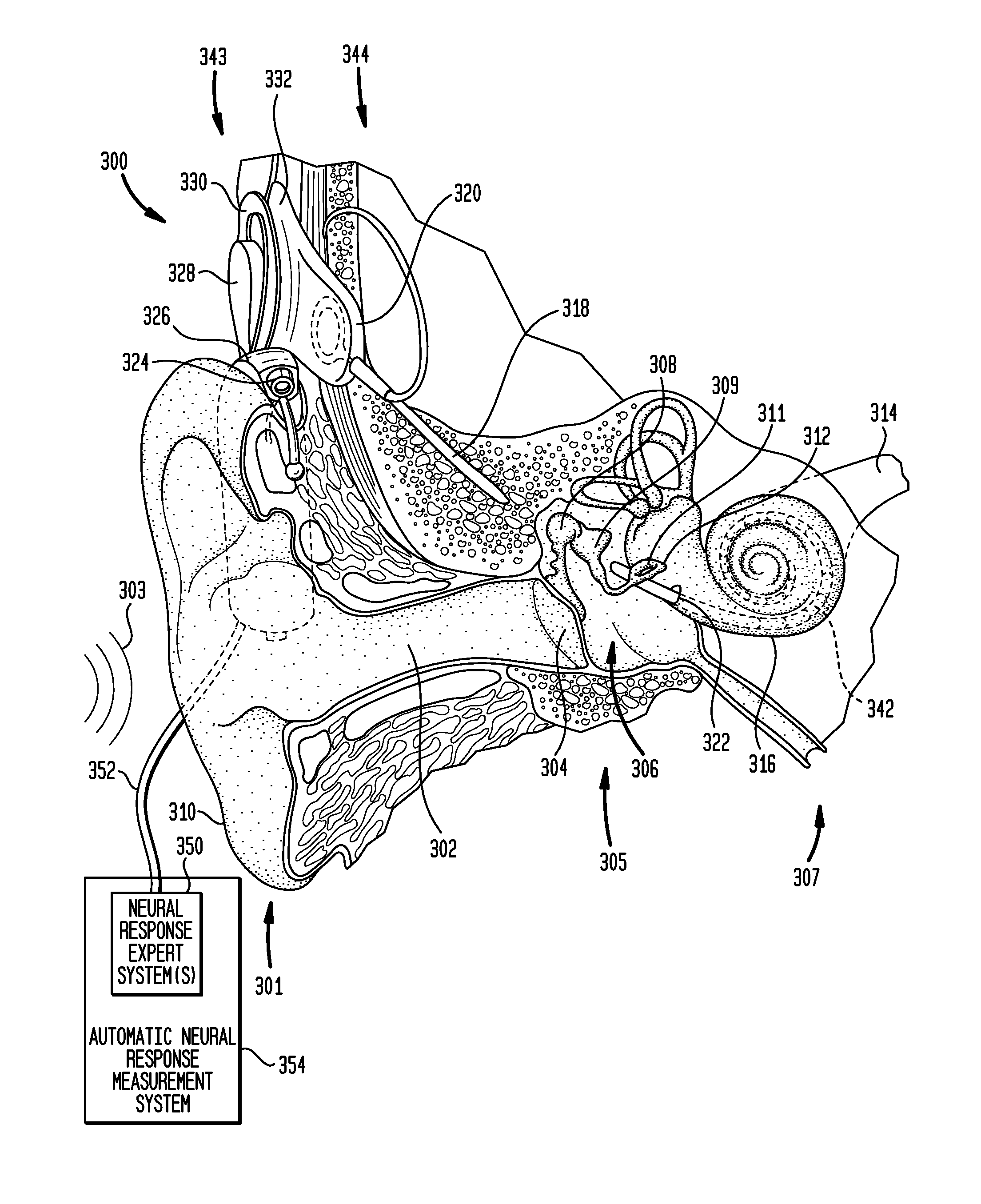
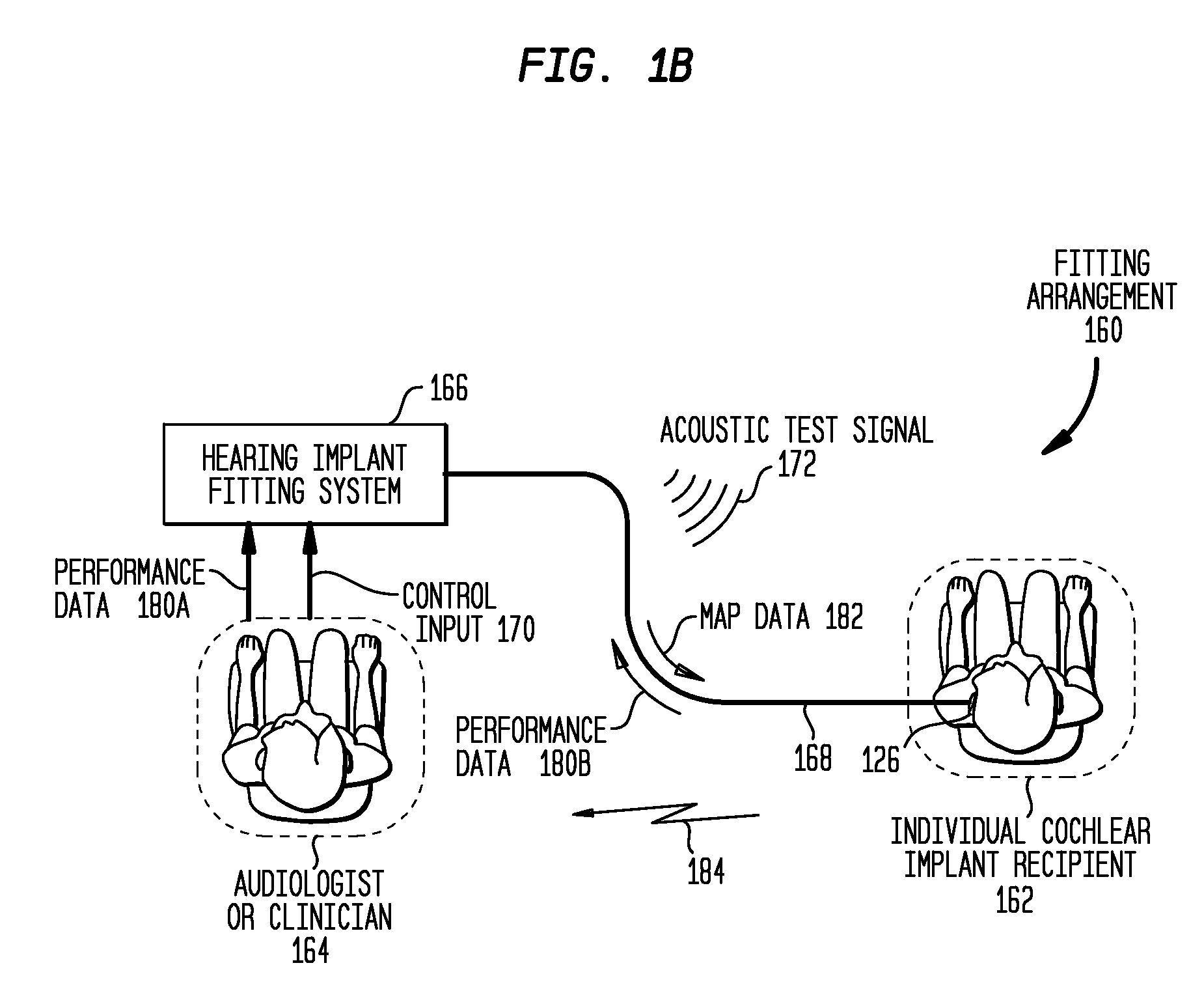
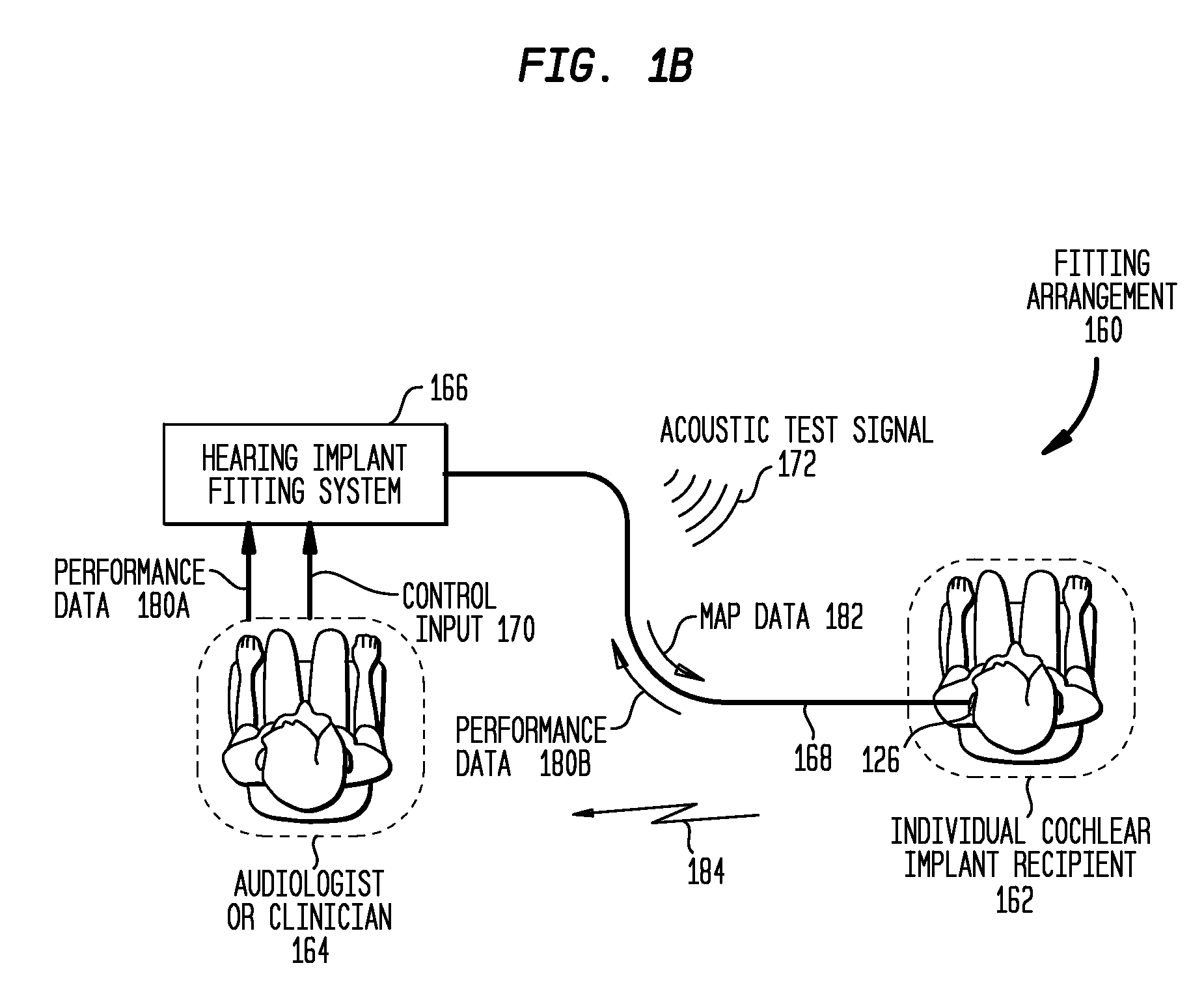
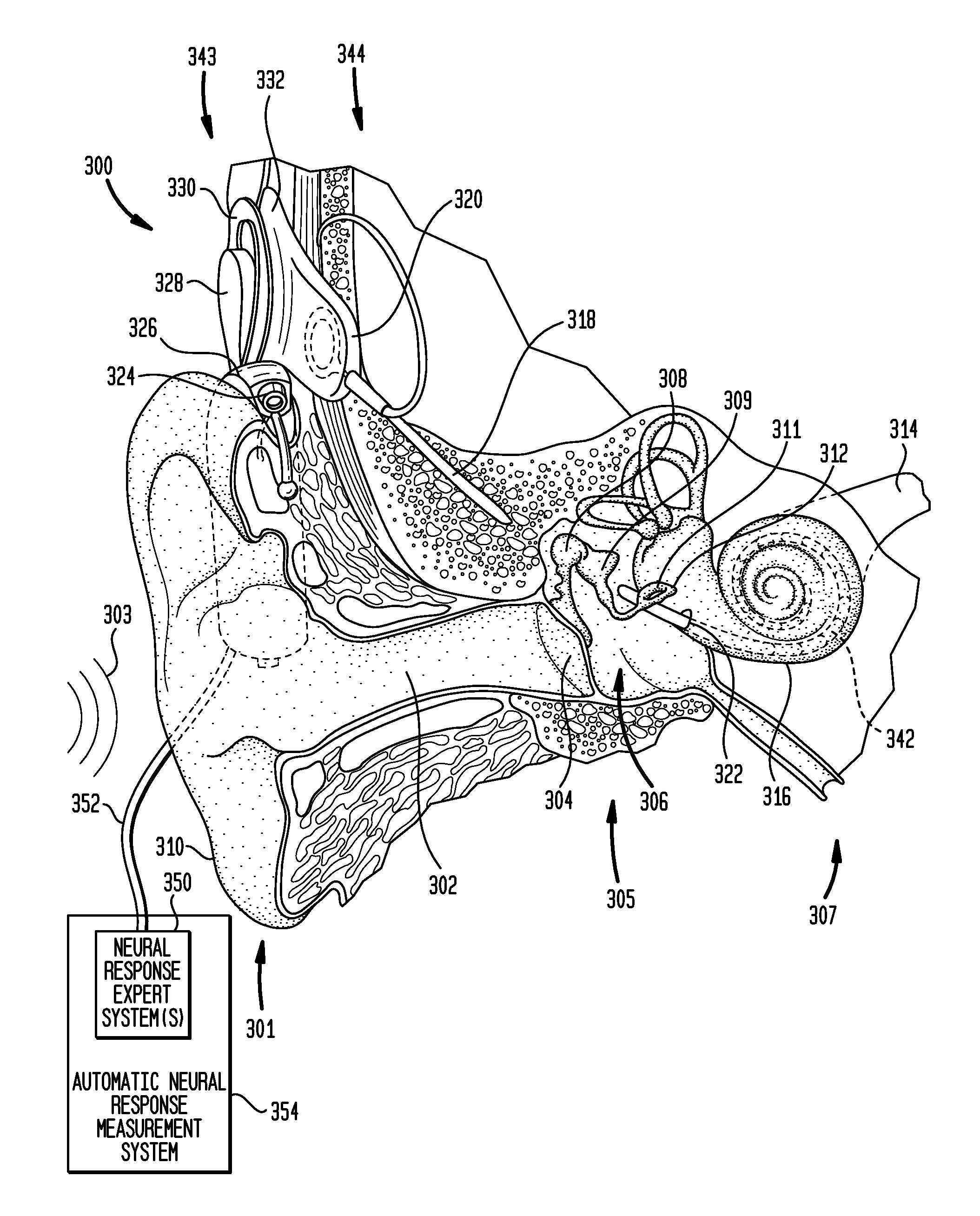
Automatic measurement of an evoked neural response concurrent with an indication of a psychophysics reaction
A method of fitting to a recipient a cochlear implant including a plurality of stimulation channels. The method comprises applying to at least one stimulation channel of the cochlear implant a first stimulus signal comprising a neural response component and a psychophysics signal component, automatically measuring a strength of an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) of the recipient evoked in response to the application of the neural response component of the first stimulus signal, and simultaneously providing to a user an indication of the automatically measured strength of the ECAP and a value of the applied psychophysics signal component.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
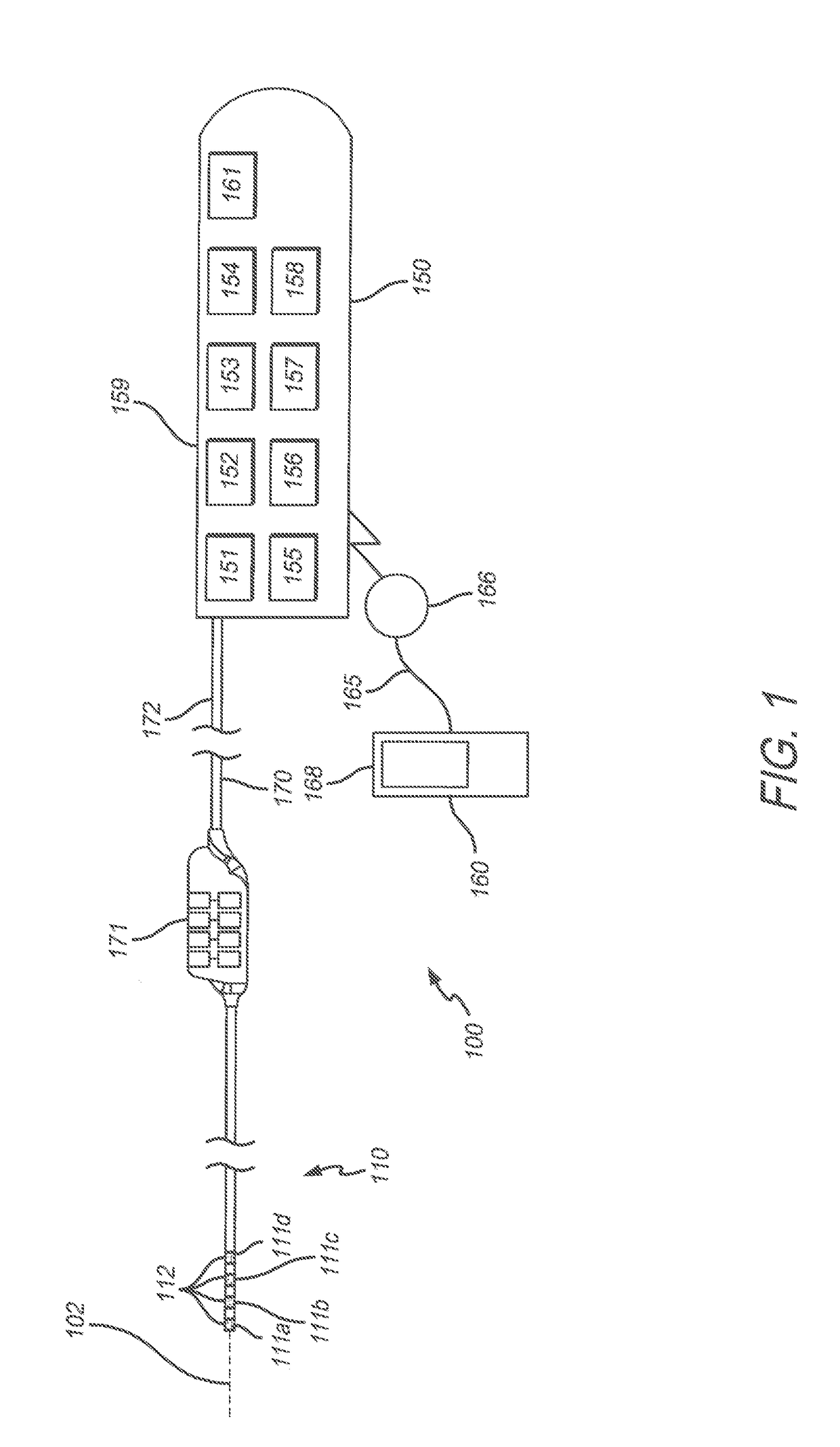
Implantable electrode positioning
ActiveUS10588698B2Maximize sensitivitySpinal electrodesSurgical navigation systemsEvoked compound action potentialImplantable Electrodes
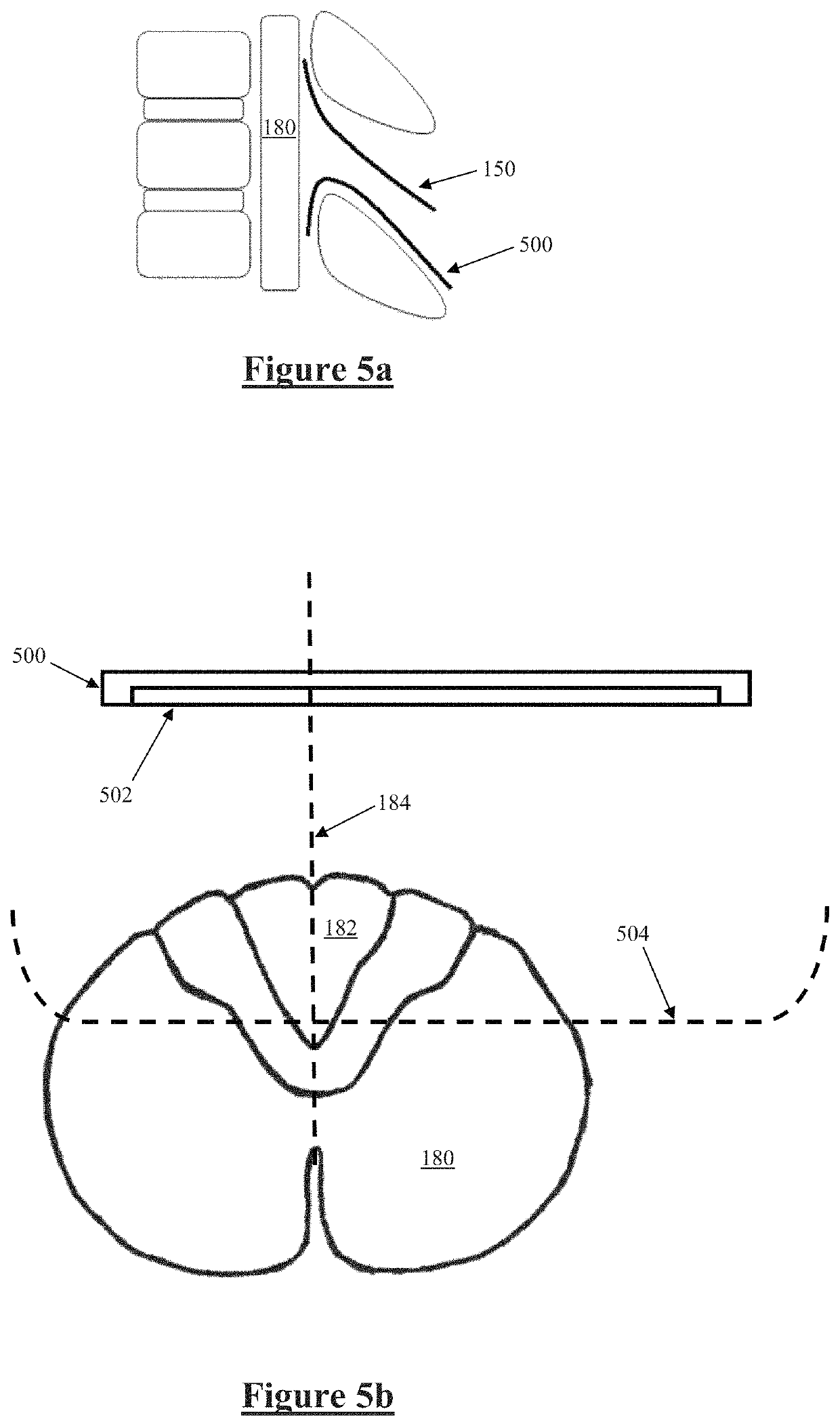
A method of surgically positioning an electrode array at a desired implantation location relative to a nerve. A temporary probe electrode is temporarily positioned adjacent to the nerve and at a location which is caudorostrally separate to the desired implantation location of the electrode array. The implanted position of the probe electrode is temporarily fixed relative to the nerve. During implantation of the electrode array, electrical stimuli are applied from one of the temporarily fixed probe electrode and the electrode array, to evoke compound action potentials on the nerve. Compound action potentials evoked by the stimuli are sensed from at least one electrode of the other of the temporarily fixed probe electrode and the electrode array. From the sensed compound action potentials a position of the electrode array relative to the nerve is determined.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Electrode to Nerve Distance Estimation
ActiveUS20210162214A1Complicate to effectPromote resultsElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialPhysical therapy
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Electrode to nerve distance estimation
ActiveUS10894158B2Complicate to effectPromote resultsElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialPhysical therapy
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
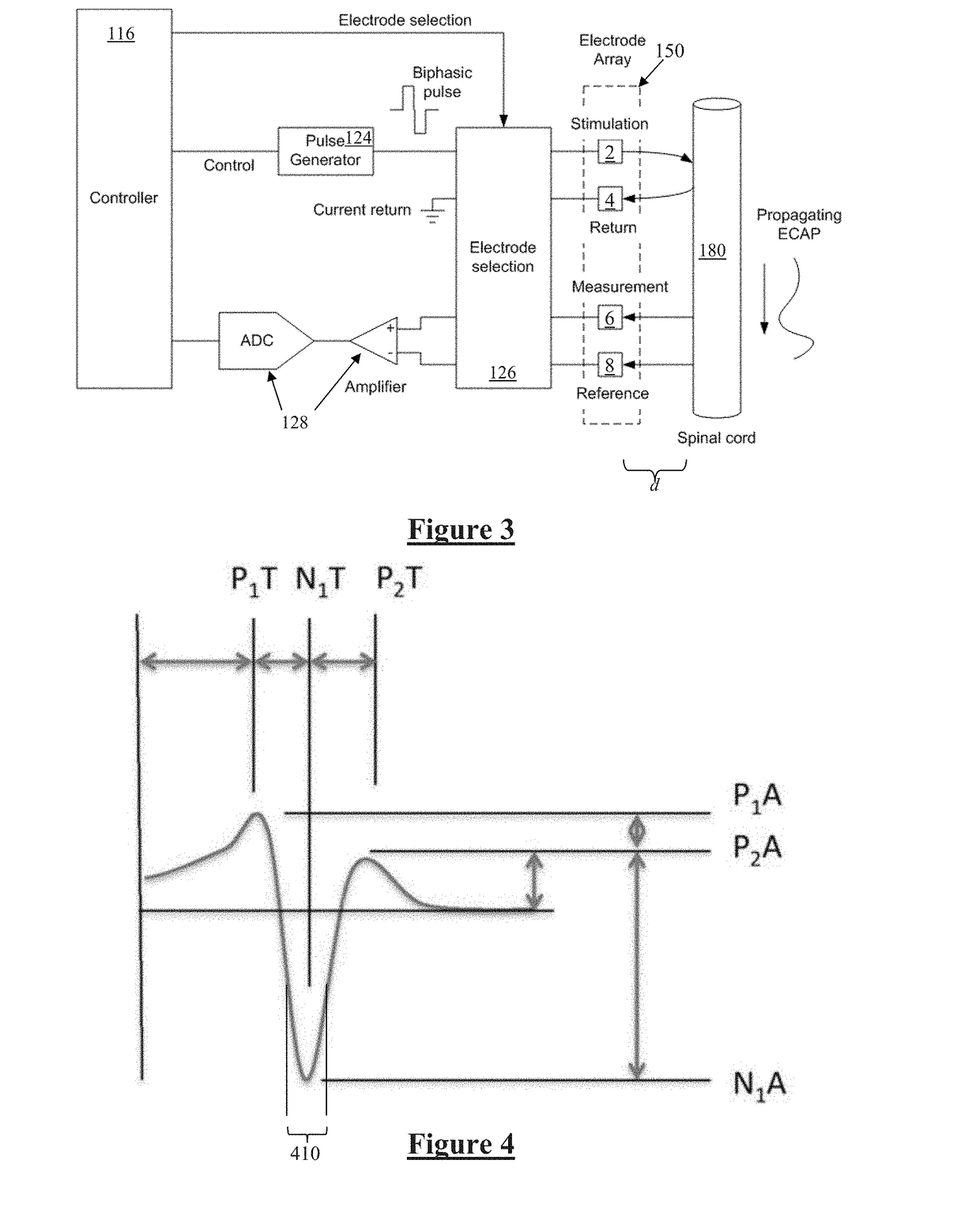
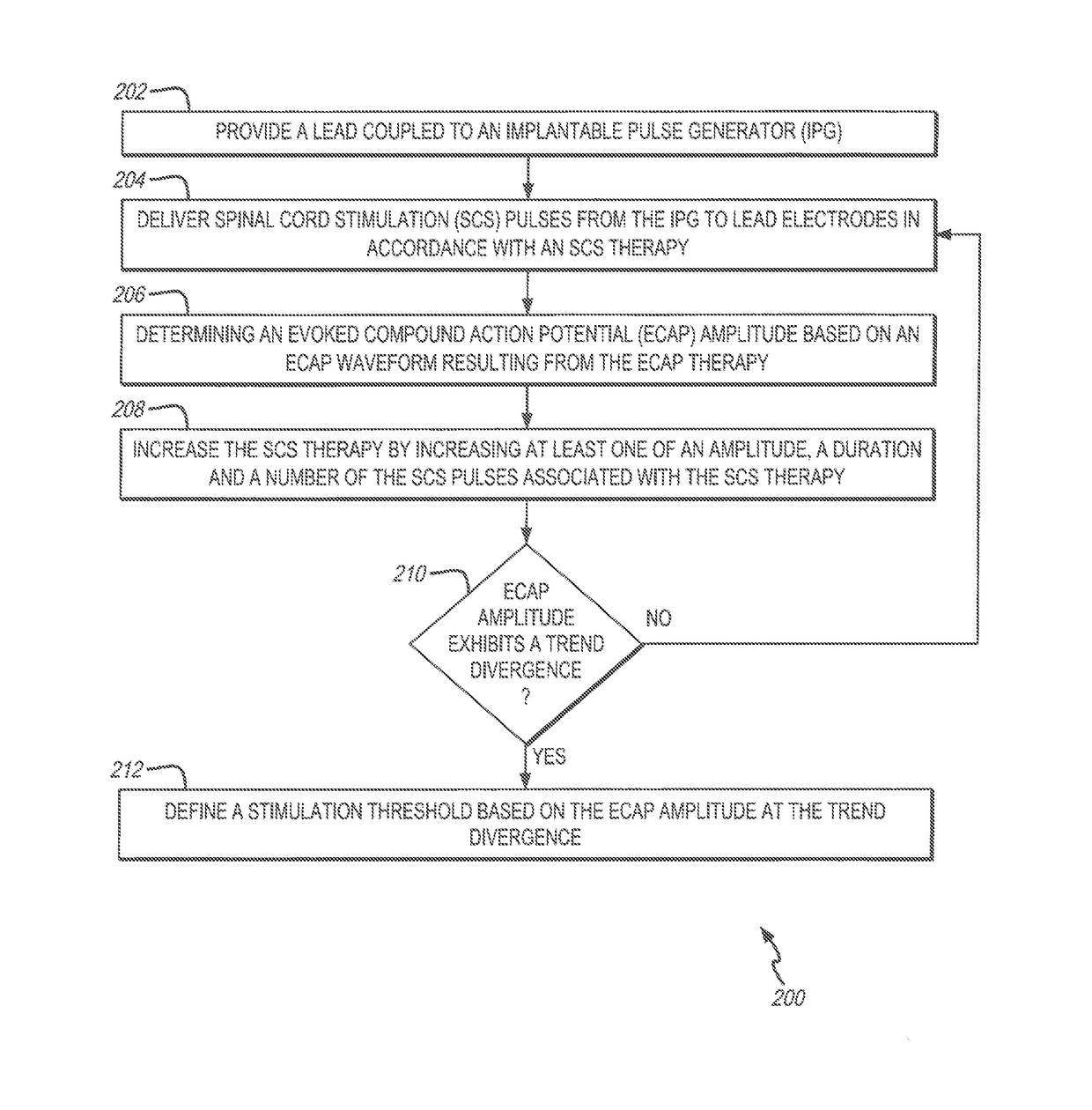
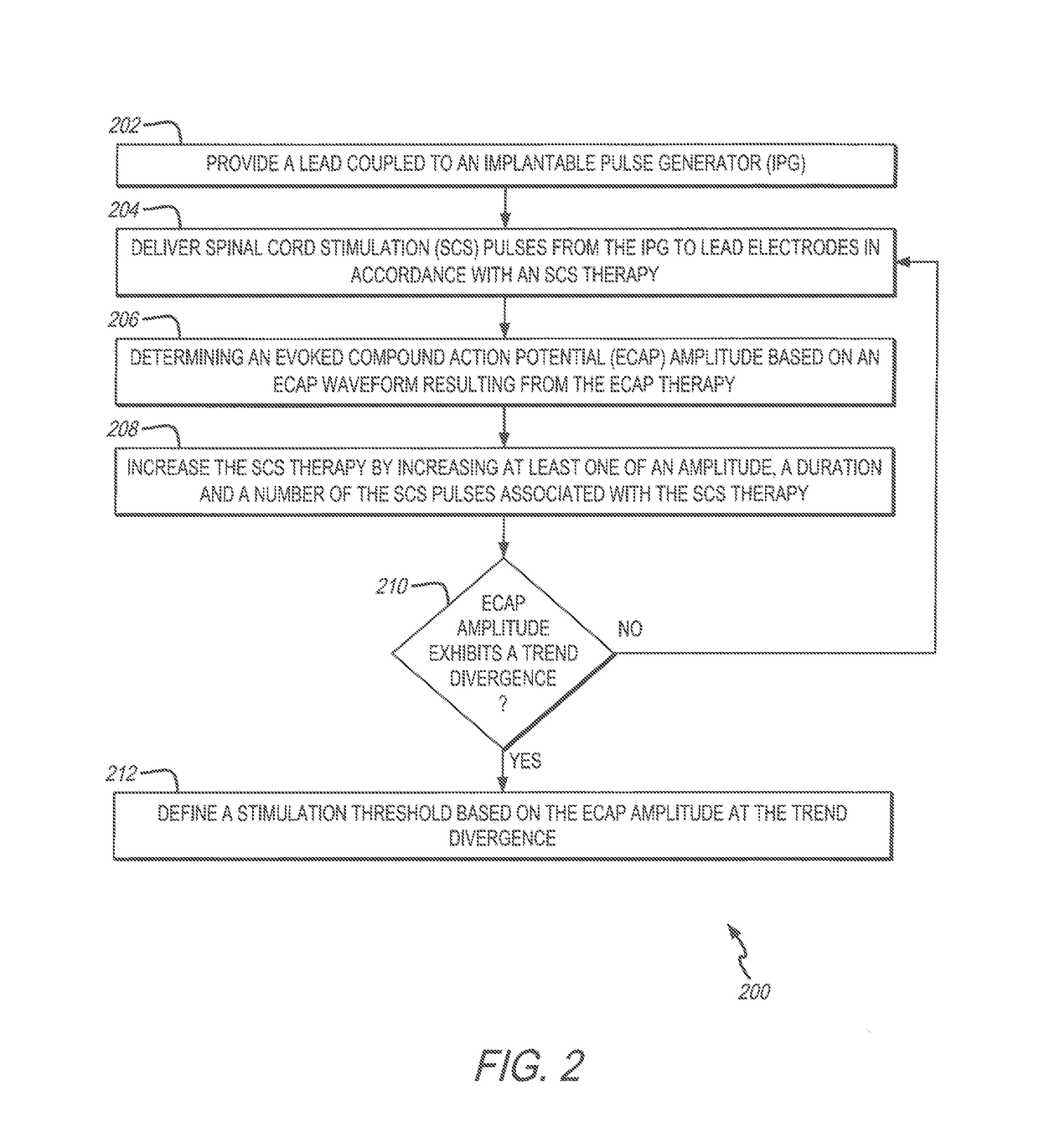
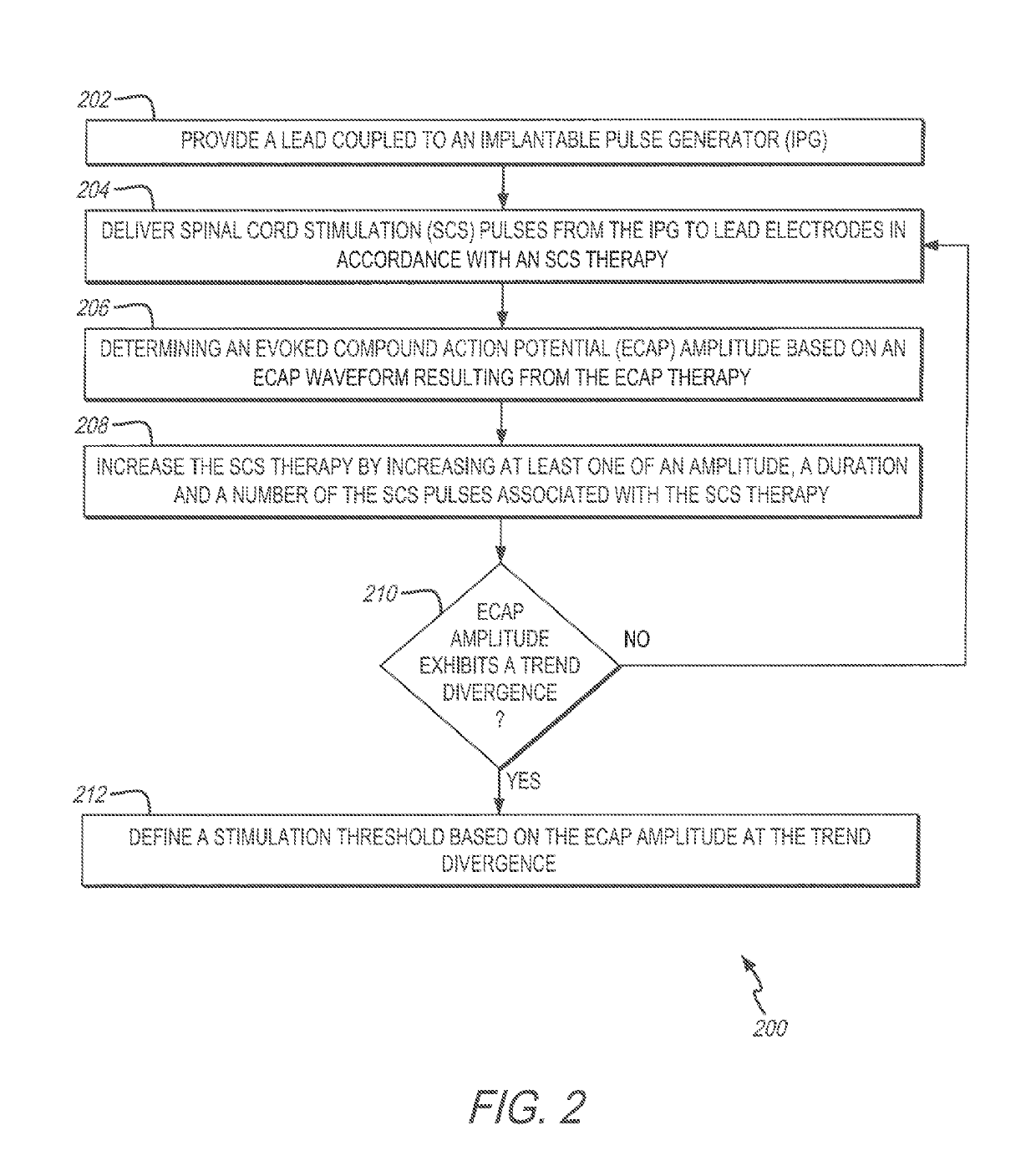
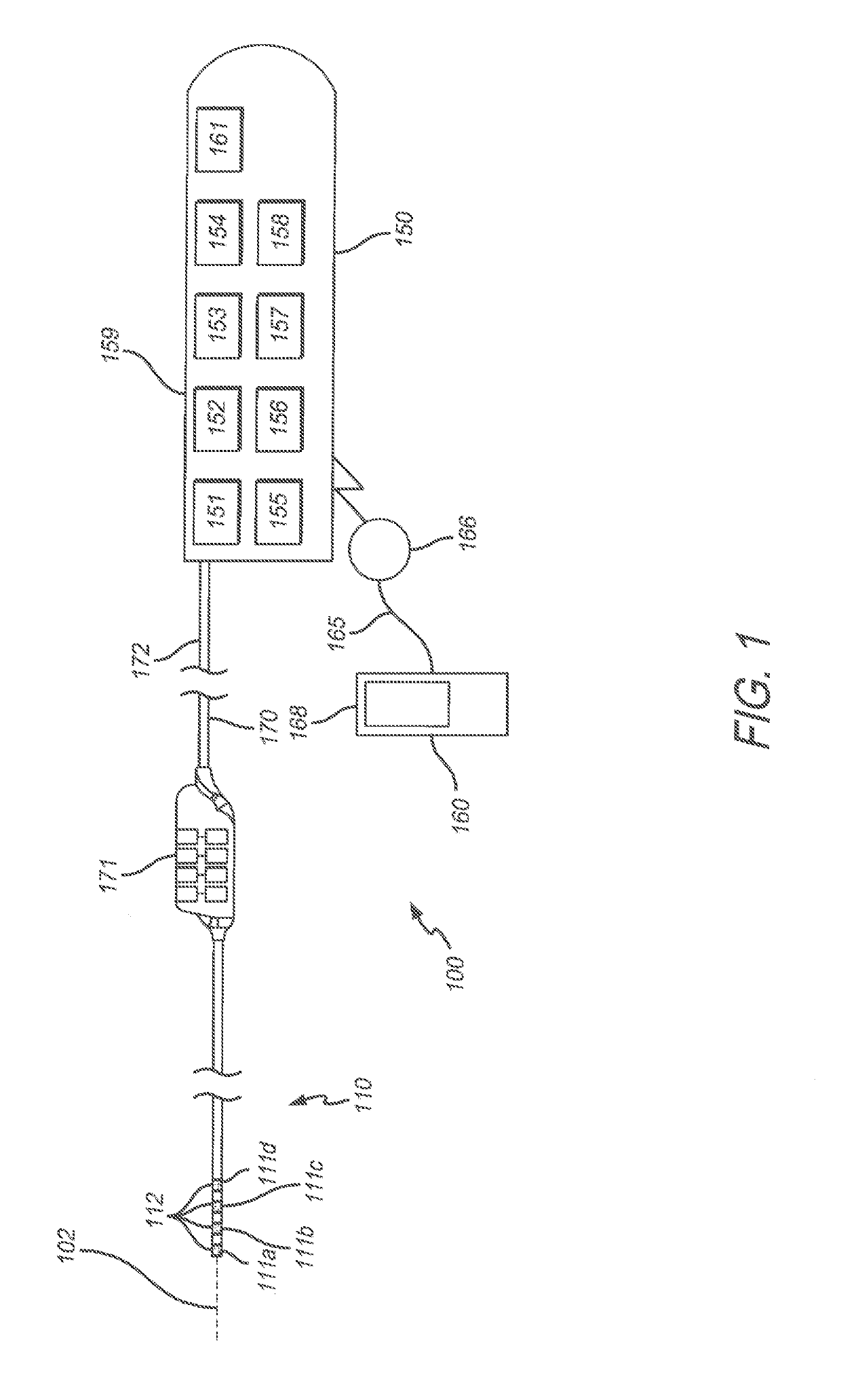
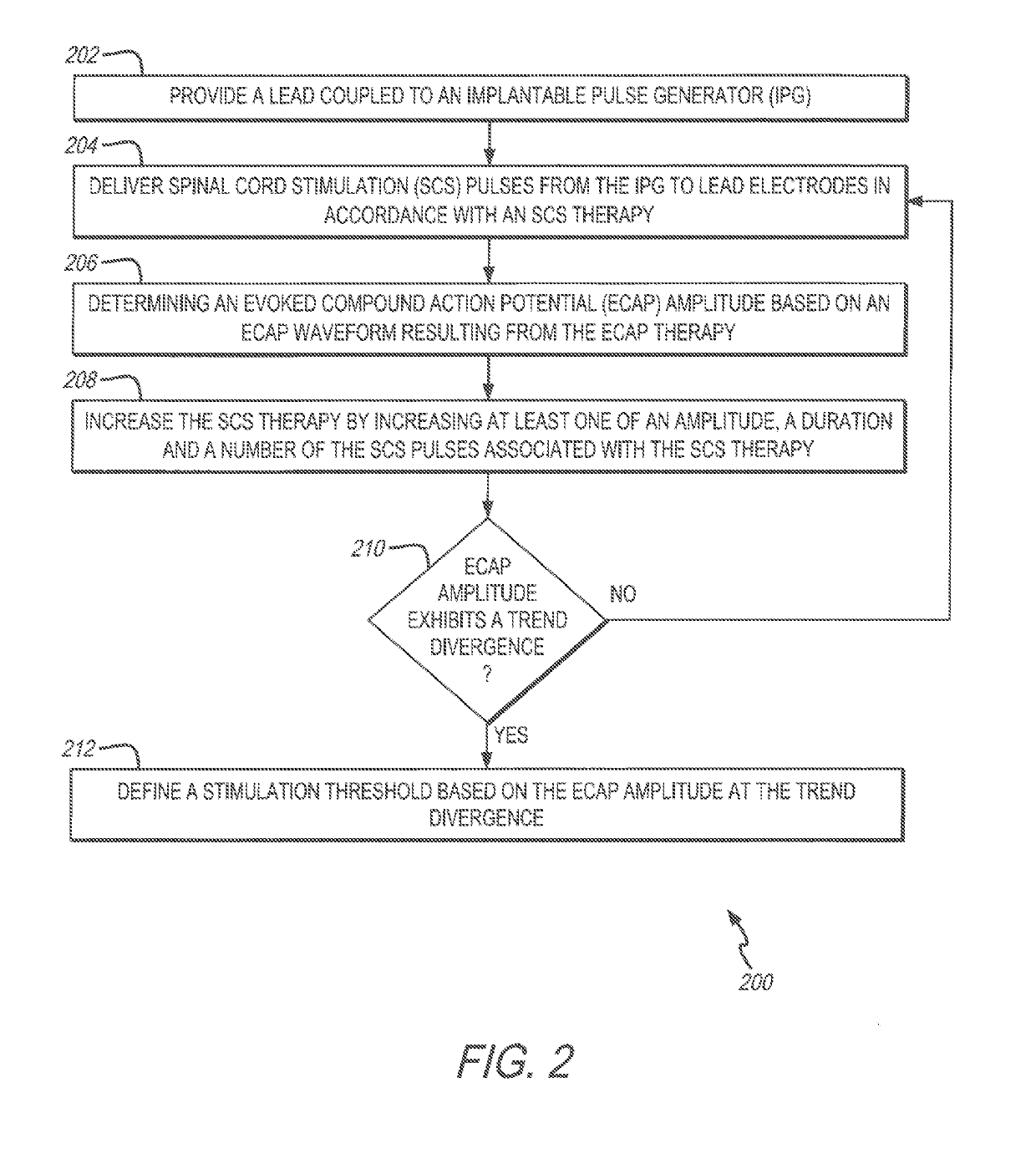
System and method for determining a stimulation threshold for closed loop spinal cord stimulation
ActiveUS20180126169A1Increases SCS therapySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesCardiologyEvoked compound action potential
System and methods are provided for determining a stimulation threshold for closed loop spinal cord stimulation (SCS). The system and methods provide a lead coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The system and methods deliver SCS pulses from the IPG to the lead electrodes in accordance with an SCS therapy, and determine an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) amplitude based on an ECAP waveform resulting from the SCS therapy. The system and methods increase the SCS therapy by increasing at least one of an amplitude, a duration, and number of the SCS pulses associated with the SCS therapy. The system and methods also include iteratively repeat the delivering, determining and increasing operations until the ECAP amplitude exhibits a downward trend divergence. The system and methods define a stimulation threshold based on the ECAP amplitude at the trend divergence.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Automatic measurement of neural response concurrent with psychophysics measurement of stimulating device recipient
The automatic measurement of evoked compound action potential (ECAP) thresholds of the auditory nerve; that is, a neural response, concurrently with the performance of psychophysics measurements of a prosthetic hearing implant recipient. During the fitting process, a stimulus signal comprising two components is applied to each stimulation channel. One signal component is configured to elicit an ECAP neural response, referred to herein as a neural response signal component. The other component is configured to elicit a response to a psychophysics stimulation, referred to herein as a psychophysics signal component. Indications of the psychophysics measurement and the concurrently obtained neural response measurements are provided to the user. For the psychophysics measurement, this includes the selected characteristics of the psychophysics signal component since the results of the applied stimulation is a recipient behavioral or auditory response.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Automatic Measurement Of Neural Response Concurrent With Psychophysics Measurement Of Stimulating Device Recipient
The automatic measurement of evoked compound action potential (ECAP) thresholds of the auditory nerve; that is, a neural response, concurrently with the performance of psychophysics measurements of a prosthetic hearing implant recipient. During the fitting process, a stimulus signal comprising two components is applied to each stimulation channel. One signal component is configured to elicit an ECAP neural response, referred to herein as a neural response signal component. The other component is configured to elicit a response to a psychophysics stimulation, referred to herein as a psychophysics signal component. Indications of the psychophysics measurement and the concurrently obtained neural response measurements are provided to the user. For the psychophysics measurement, this includes the selected characteristics of the psychophysics signal component since the results of the applied stimulation is a recipient behavioral or auditory response.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
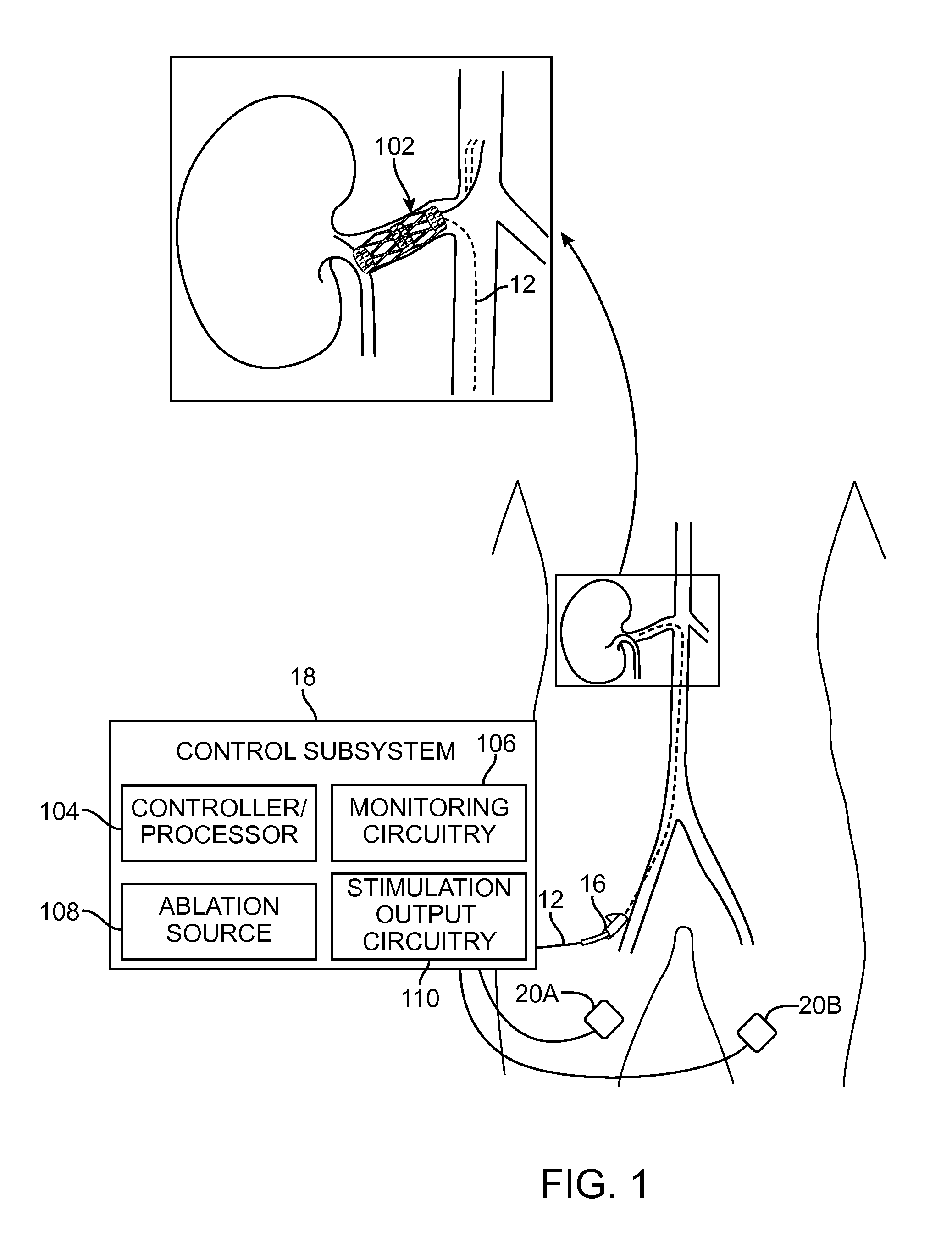
System and method of using evoked compound action potentials to minimize vessel trauma during nerve ablation
InactiveUS20140276707A1Lower blood pressureImprove signal-to-noise ratioCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringEvoked compound action potentialElectricity
A therapy system for use with a patient and a method of treating a medical condition of a patient. Electrical stimulation energy is delivered to a stimulation site on the wall of a blood vessel, thereby evoking at least one compound action potential in a nerve branch associated with the blood vessel. The evoked compound action potential(s) is sensed at a sensing site on the wall of the blood vessel. A circumferential location of the nerve branch is identified as being adjacent one of the stimulation site and the sensing site based on the sensed compound action potential(s). Ablation energy is delivered to an ablation site on the wall of the blood vessel adjacent the circumferential location of the nerve branch, thereby ablating the nerve branch and treating the medical condition.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Provision of stimulus components having variable perceptability to stimulating device recipient
The automatic measurement of evoked compound action potential (ECAP) thresholds of the auditory nerve; that is, a neural response, concurrently with the performance of psychophysics measurements of a prosthetic hearing implant recipient. During the fitting process, a stimulus signal comprising two components is applied to each stimulation channel. One signal component is configured to elicit an ECAP neural response, referred to herein as a neural response signal component. The other component is configured to elicit a response to a psychophysics stimulation, referred to herein as a psychophysics signal component. Indications of the psychophysics measurement and the concurrently obtained neural response measurements are provided to the user. For the psychophysics measurement, this includes the selected characteristics of the psychophysics signal component since the results of the applied stimulation is a recipient behavioral or auditory response.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Spinal cord stimulation guidance system and method of use
ActiveUS20190142325A1Medical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesEvoked compound action potentialGuidance system
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for determining a stimulation threshold for closed loop spinal cord stimulation
InactiveUS20190275334A1Spinal electrodesExternal electrodesEvoked compound action potentialClosed loop
System and methods are provided for determining a stimulation threshold for closed loop spinal cord stimulation (SCS). The system and methods provide a lead coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The system and methods deliver SCS pulses from the IPG to the lead electrodes in accordance with an SCS therapy and determine an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) amplitude based on an ECAP waveform resulting from the SCS therapy. The system and methods increase the SCS therapy by increasing at least one of an amplitude, a duration, and number of the SCS pulses associated with the SCS therapy. The system and methods also include iteratively repeat the delivering, determining and increasing operations until the ECAP amplitude exhibits a downward trend divergence. The system and methods define a stimulation threshold based on the ECAP amplitude at the trend divergence.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Automatic measurement of an evoked neural response concurrent with an indication of a psychophysics reaction
A method of fitting to a recipient a cochlear implant including a plurality of stimulation channels. The method comprises applying to at least one stimulation channel of the cochlear implant a first stimulus signal comprising a neural response component and a psychophysics signal component, automatically measuring a strength of an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) of the recipient evoked in response to the application of the neural response component of the first stimulus signal, and simultaneously providing to a user an indication of the automatically measured strength of the ECAP and a value of the applied psychophysics signal component.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Systems and methods of providing modulation therapy without patient-perception of stimulation
ActiveUS20190217092A1ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectricityEvoked compound action potential
A neuromodulation system and method of providing sub-threshold modulation therapy. Electrical modulation energy is delivered to a target tissue site of the patient at a programmed intensity value, thereby providing therapy to a patient without perception of stimulation. In response to an event, electrical modulation energy is delivered at incrementally increasing intensity values. At least one evoked compound action potential (eCAP) is sensed in a population of neurons at the target tissue site of the patient in response to the delivery of the electrical modulation energy at the incrementally increasing intensity values. One of the incrementally increased intensity values is selected based on the sensed eCAP(s). A decreased intensity value is automatically computed as a function of the selected intensity value. Electrical modulation energy is delivered to the target tissue site of the patient at the computed intensity value, thereby providing sub-threshold therapy to the patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
System and method for determining a stimulation threshold for closed loop spinal cord stimulation
System and methods are provided for determining a stimulation threshold for closed loop spinal cord stimulation (SCS). The system and methods provide a lead coupled to an implantable pulse generator (IPG). The system and methods deliver SCS pulses from the IPG to the lead electrodes in accordance with an SCS therapy, and determine an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) amplitude based on an ECAP waveform resulting from the SCS therapy. The system and methods increase the SCS therapy by increasing at least one of an amplitude, a duration, and number of the SCS pulses associated with the SCS therapy. The system and methods also include iteratively repeat the delivering, determining and increasing operations until the ECAP amplitude exhibits a downward trend divergence. The system and methods define a stimulation threshold based on the ECAP amplitude at the trend divergence.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Neuromodulation of renal nerve for treatment of hypertension
ActiveUS9233247B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioLower blood pressureHeart stimulatorsArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialSurgery
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Spinal cord stimulation guidance system and method of use
ActiveUS10213148B2Medical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesEvoked compound action potentialGuidance system
A system and method for modeling patient-specific spinal cord stimulation (SCS) is disclosed. The system and method acquire impedance and evoked compound action potential (ECAP) signals from a lead positioned proximate to a spinal cord (SC). The lead includes at least one electrode. The system and method determine a patient-specific anatomical model based on the impedance and ECAP signals, and transform a dorsal column (DC) map template based on a DC boundary of the patient-specific anatomical model. Further, the system and method map the transformed DC map template to the patient-specific anatomical model. The system and method may also include the algorithms to solve extracellular and intracellular domain electrical fields and propagation along neurons. The system and method may also include the user interfaces to collect patient responses and compare with the patient-specific anatomical model as well as using the patient-specific anatomical model for guiding SCS programming.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Neuromodulation of renal nerve for treatment of hypertension
ActiveUS20140277253A1Lower blood pressureImprove signal-to-noise ratioElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialRenal nerve
A system and method for treating a patient suffering from chronic hypertension. Electrical therapeutic energy is delivered to a nerve branch of a renal artery of the patient, thereby treating the chronic hypertension. Another system and method for treating a medical condition of a patient. Electrical stimulation energy is delivered to a stimulation site on the wall of a blood vessel, thereby evoking a compound action potential in a nerve branch associated with the blood vessel, sensing the evoked compound action potential at a sensing site on the wall of the blood vessel, identifying a circumferential location of the nerve branch as being adjacent the stimulation site or sensing site based on the sensed compound action potential(s), and delivering therapeutic energy to a therapeutic site on the wall of the blood vessel adjacent the circumferential location of the nerve branch, thereby modulating the nerve branch and treating the medical condition.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method for analyzing nerve fiber distribution and measuring normalized evoked compound action electric potential
ActiveUS9314202B2Rapidly and precisely and analyzingRapidly and precisely measuringHead electrodesSensorsFiberEvoked compound action potential
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
ECAP-based transient overstimulation
PendingCN114761073AElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialPhysical therapy
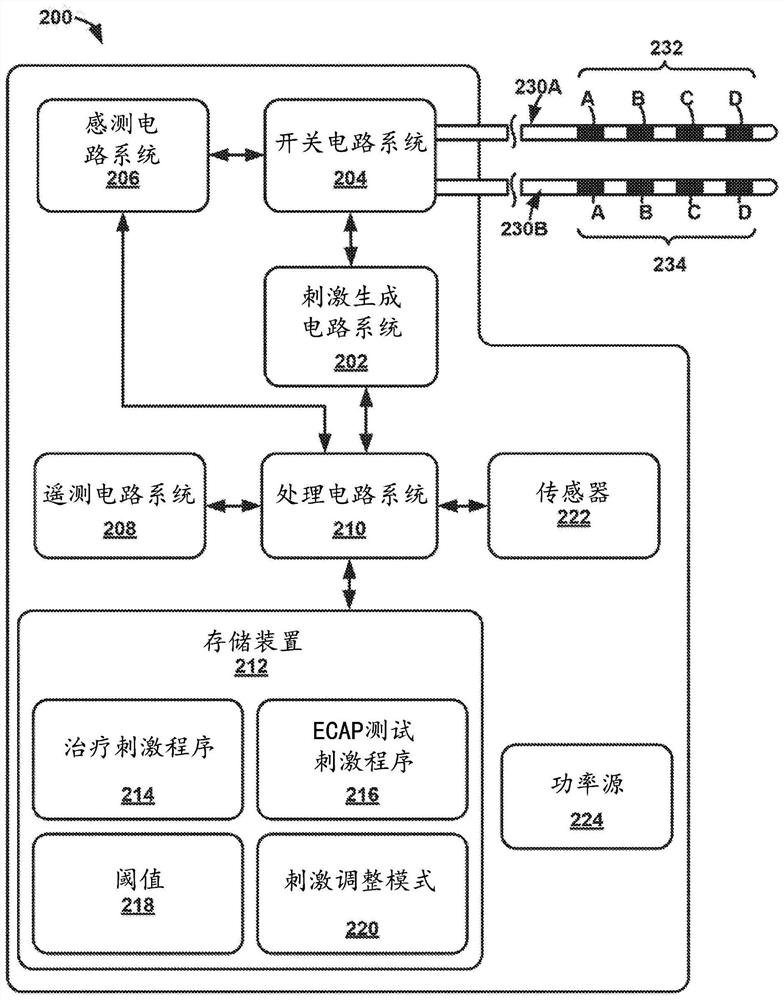
Treatment can be determined using evoked compound action potential (ECAP). For example, a medical device includes stimulation generation circuitry and processing circuitry. The processing circuitry is configured to determine whether a characteristic of the first ECAP is greater than a threshold ECAP characteristic value. Based on the characteristic of the first ECAP being greater than the threshold ECAP characteristic value, the processing circuitry is configured to reduce a parameter of a first set of pulses delivered by the stimulus generating circuitry after the first ECAP. Further, the processing circuitry is configured to determine whether a characteristic of a second ECAP is less than the threshold ECAP characteristic value, and based on the characteristic of the second ECAP being less than the threshold ECAP characteristic value, increase a parameter of a second set of pulses delivered by the stimulus generation circuitry after the second ECAP.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com