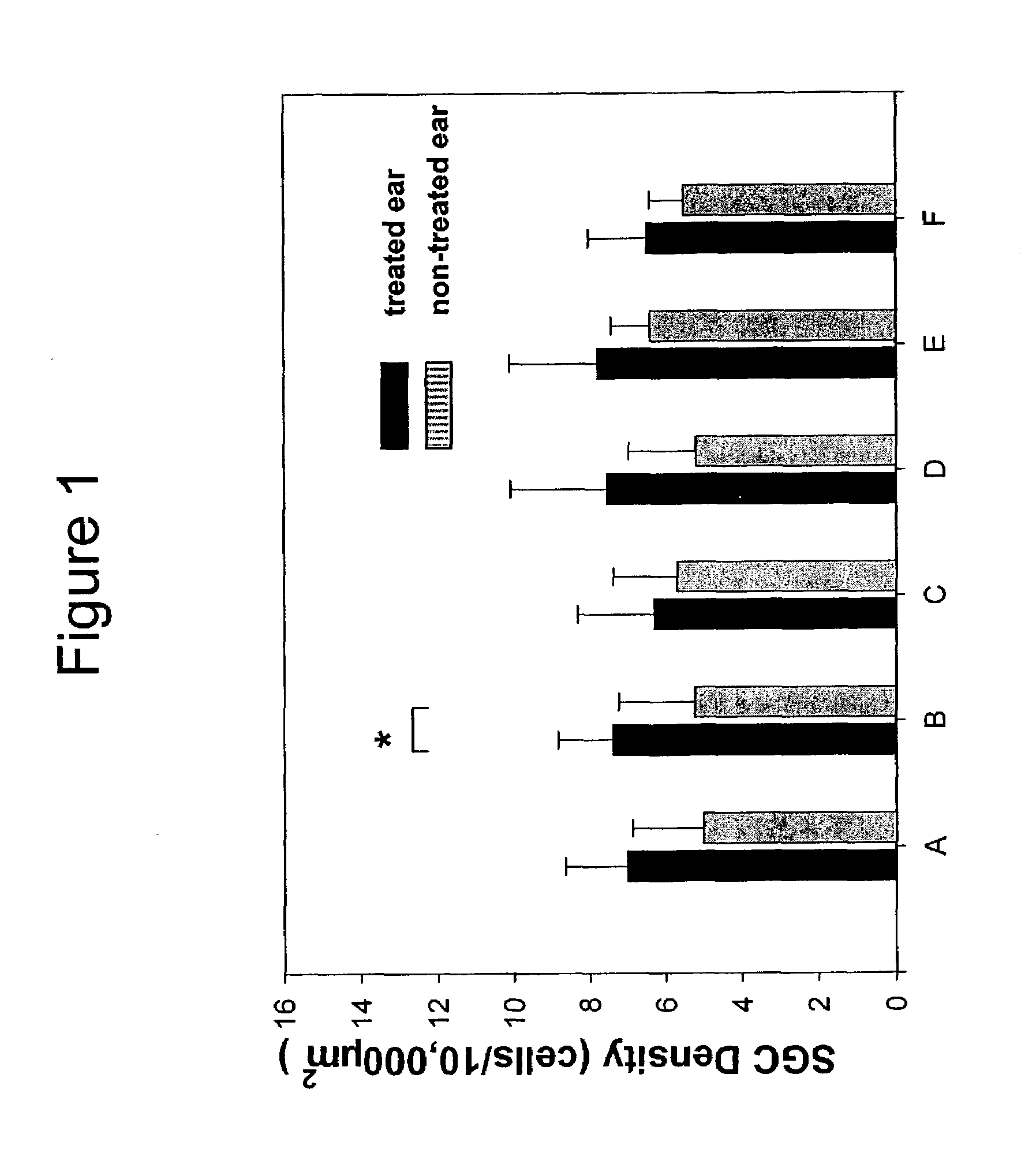
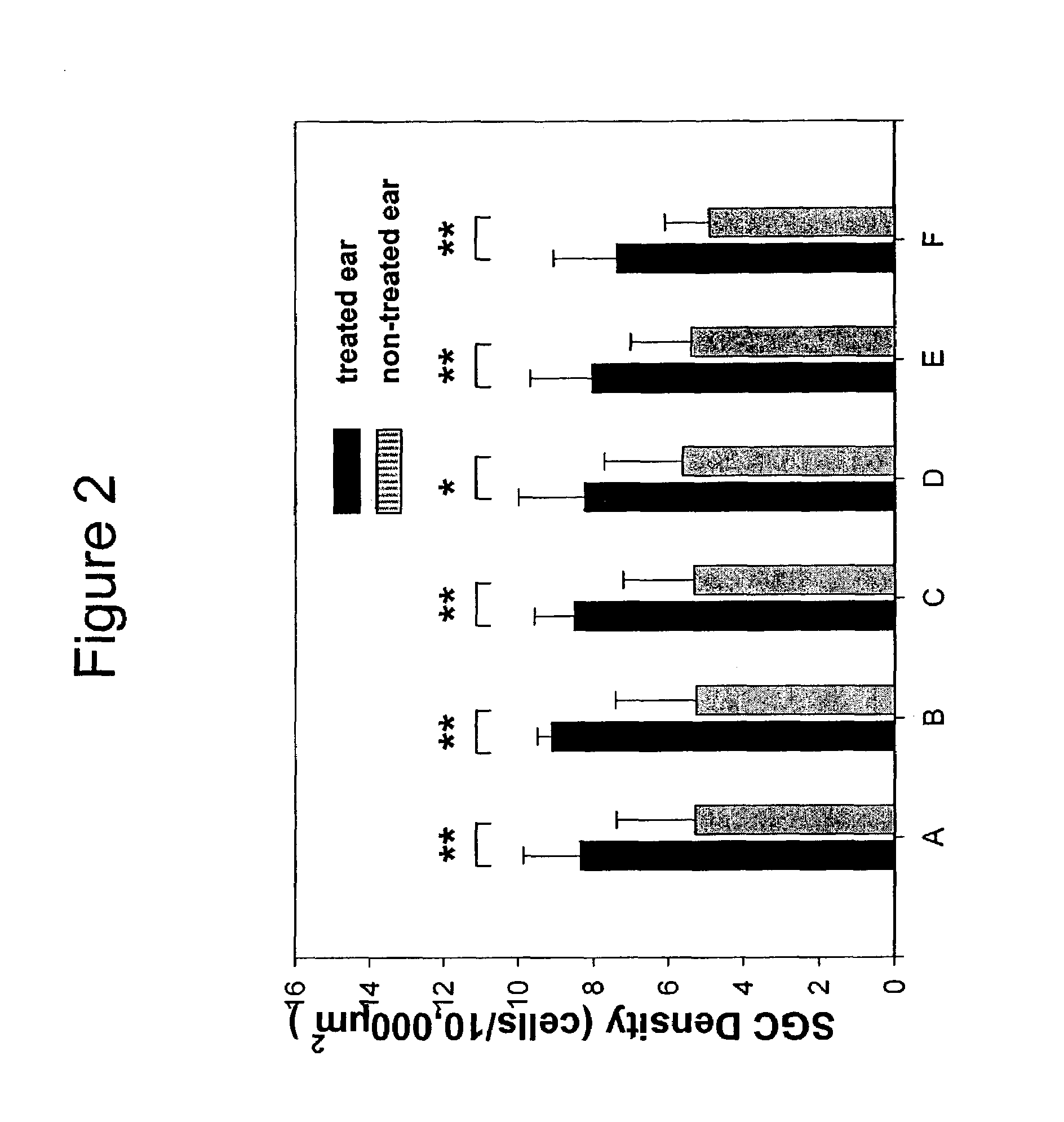
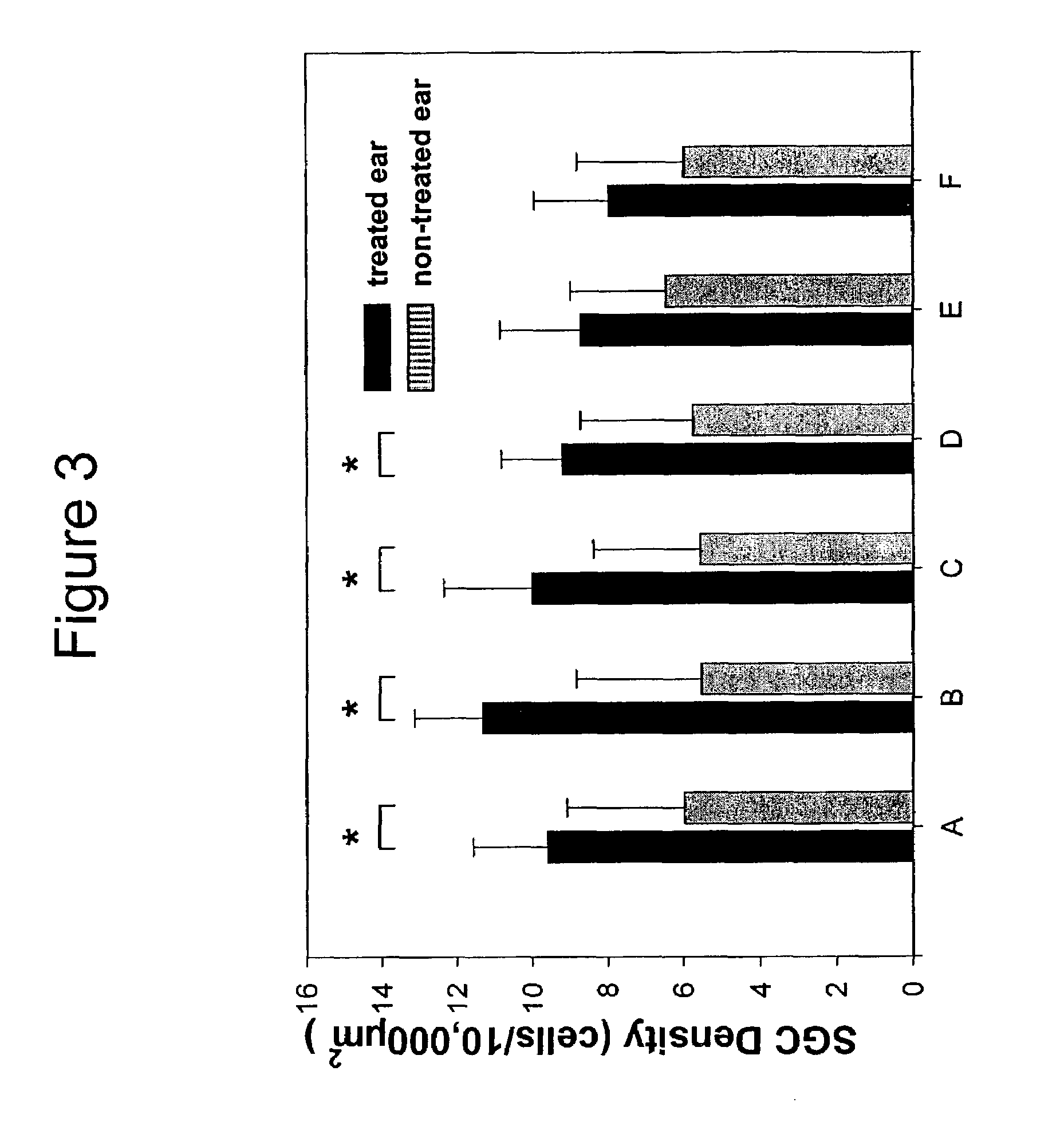
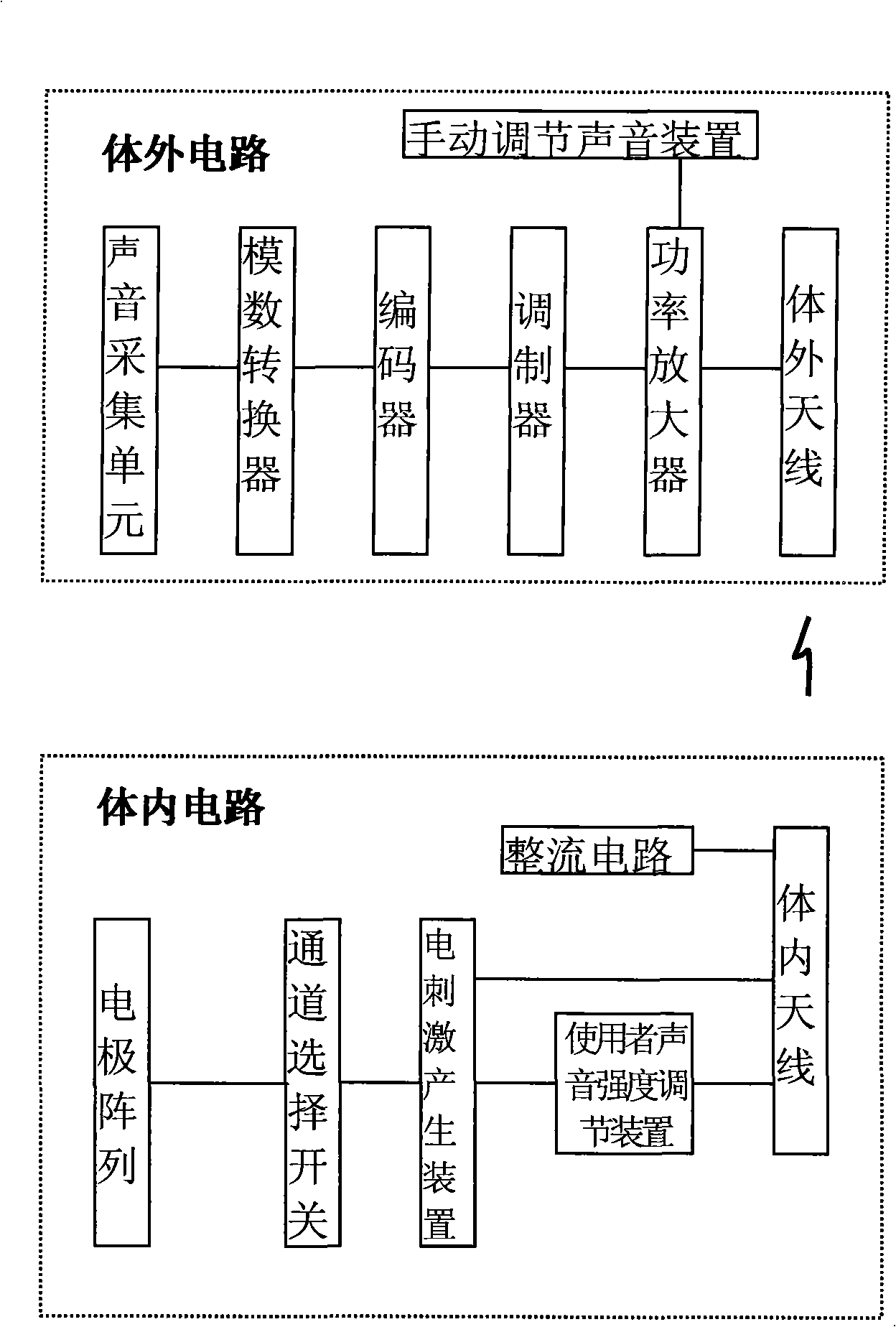
Patents
Literature
204 results about "Auditory nerves" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
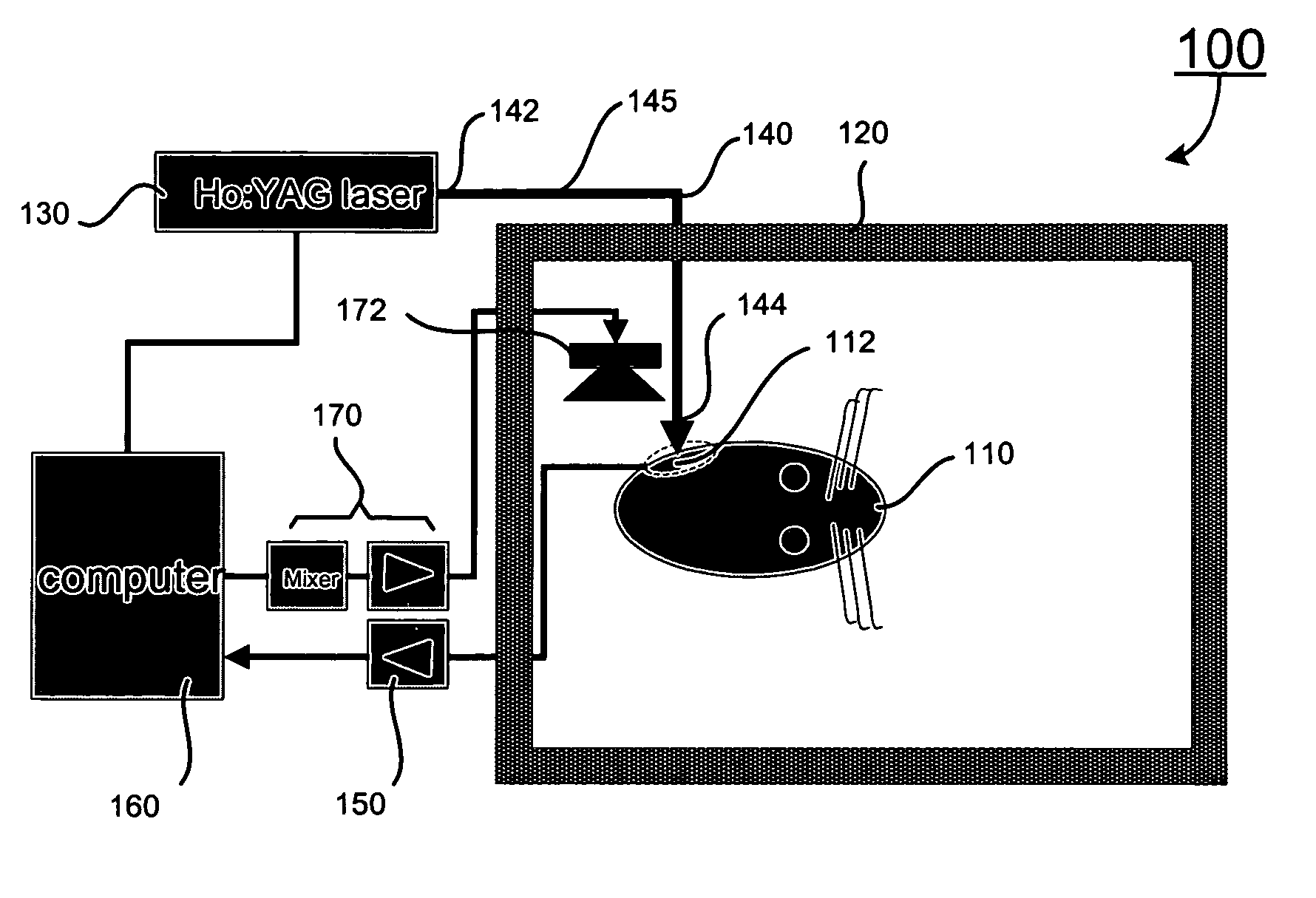
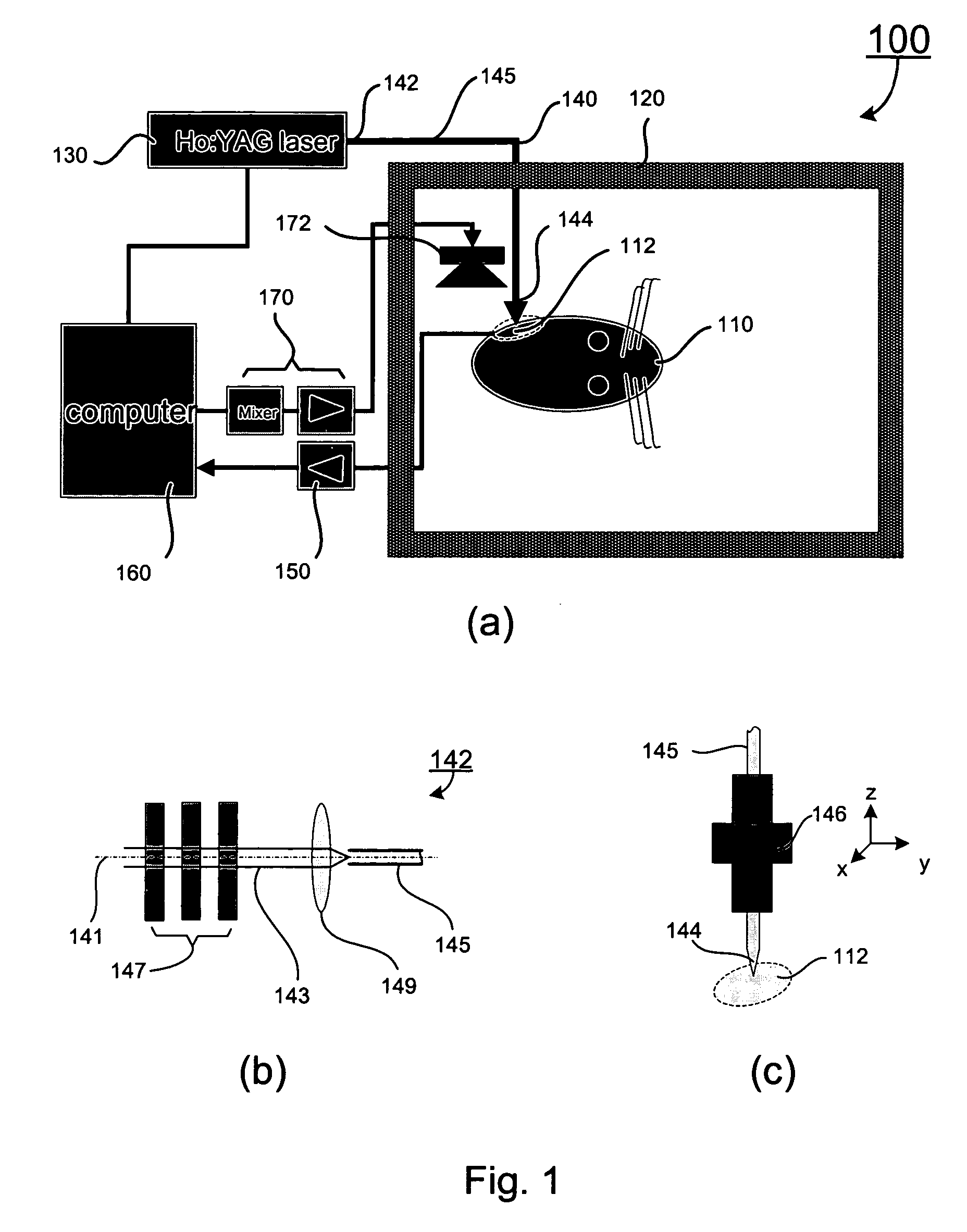
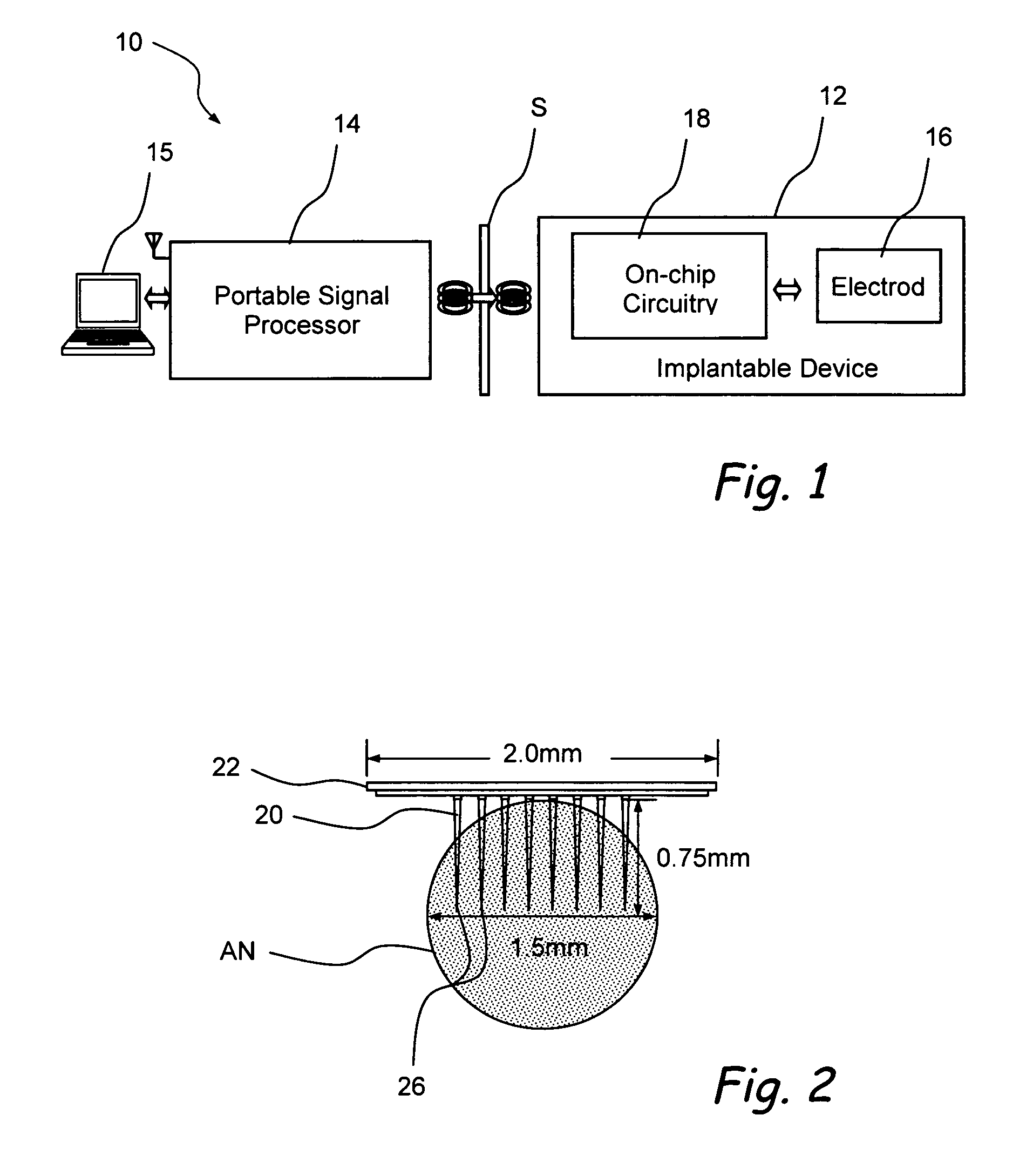
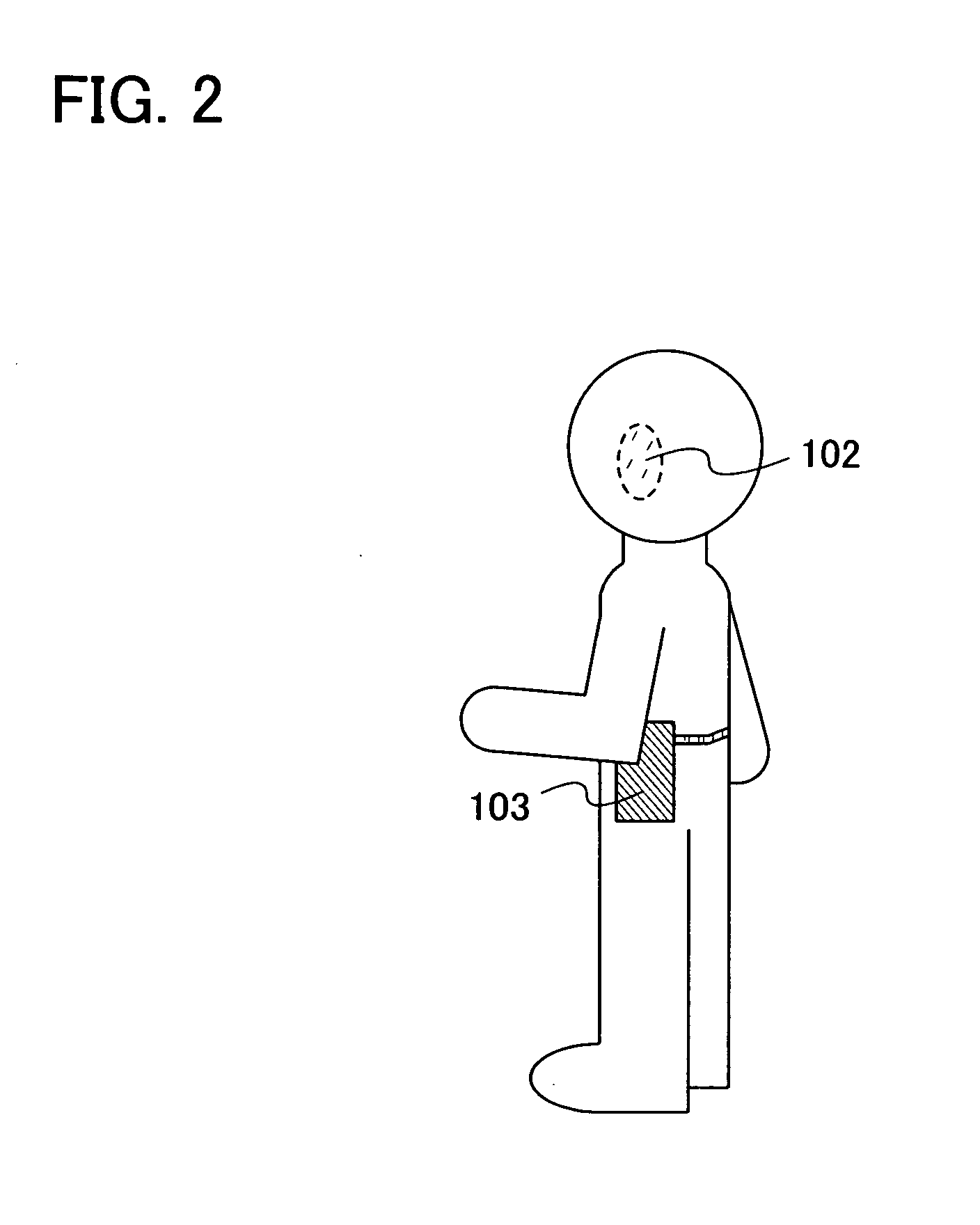
Apparatus and methods for optical stimulation of the auditory nerve
A cochlear implant placed in a cochlea of a living subject for stimulating the auditory system of the living subject, where the auditory system comprises auditory neurons. In one embodiment, the cochlear implant includes a plurality of light sources, {Li}, placeable distal to the cochlea, each light source, L1, being operable independently and adapted for generating an optical energy, Ei, wherein i=1, . . . , N, and N is the number of the light sources, and delivering means placeable in the cochlea and optically coupled to the plurality of light sources, {Li}, such that in operation, the optical energies {Ei} generated by the plurality of light sources {Li} are delivered to target sites, {Gi}, of auditory neurons, respectively, wherein the target sites G1 and GN of auditory neurons are substantially proximate to the apical end and the basal end of the cochlea, respectively.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Focused stimulation in a medical stimulation device
ActiveUS20060247735A1Narrowing of the stimulation regions minimizes or prevents this from occurringHead electrodesDeaf-aid setsCochlear implantationImplant electrode
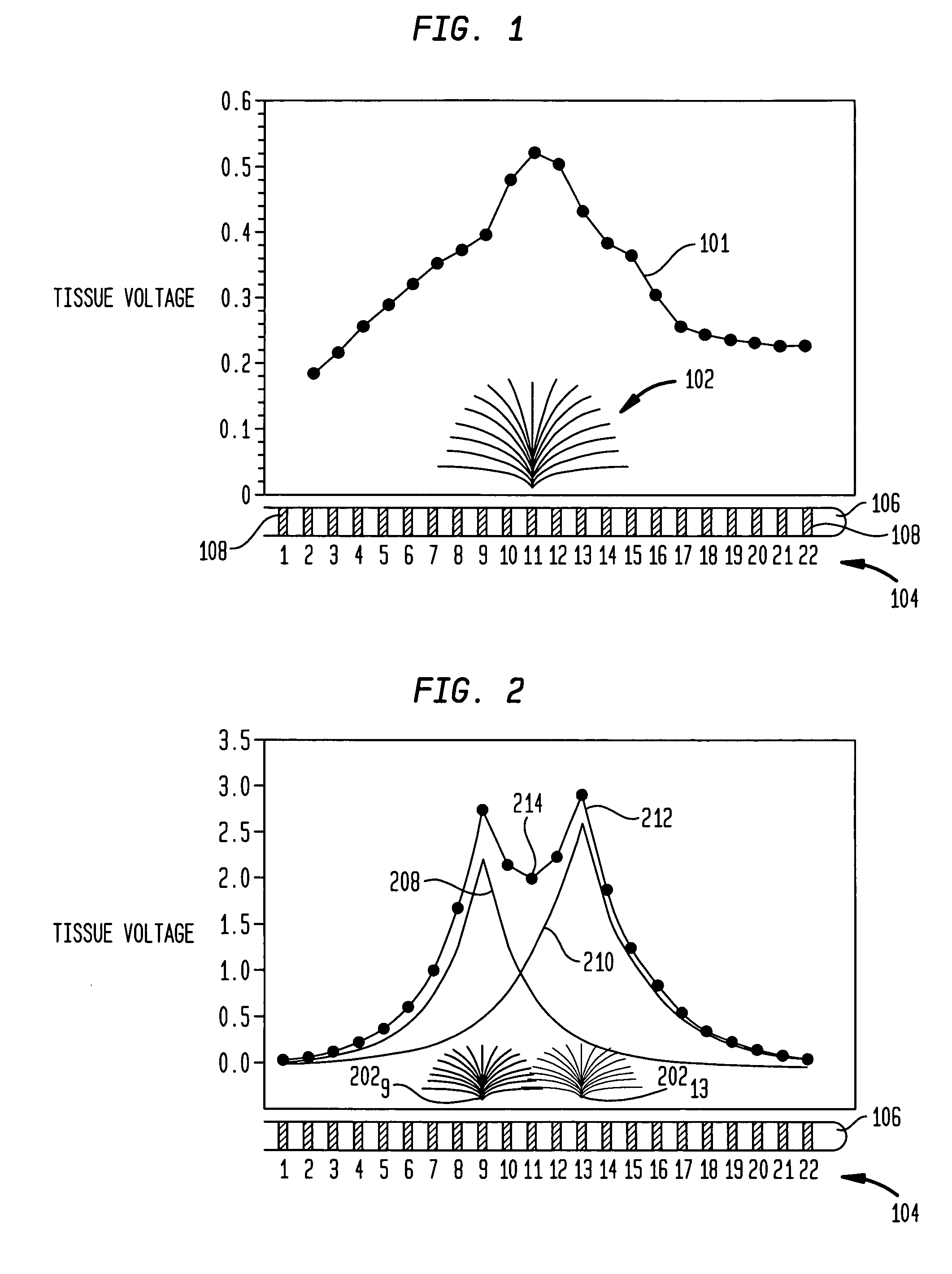
A medical stimulation device such as a cochlear implant configured to provide stimulation of one or more spatially-restricted contiguous portion(s) of the spiral array of auditory nerve fibers in the cochlear (“discrete stimulation regions”). Each discrete stimulation region is defined by the constructive and / or destructive interference of stimulating and limiting signals simultaneously applied to electrode channels of an implanted electrode array, the stimulating and limiting signals being determined based upon transimpedance measurements of intracochlear electrode channels of the implanted electrode array representing specific spread functions of an individual recipient. The stimulating signal is preferably applied through a targeted electrode channel; that is, one or more successive electrodes which is / are adjacent to the discrete stimulation region. The targeted electrode channel is selected to represent a sound based on the outputs of a sound processor to stimulate neural activity in the discrete stimulation region to thereby cause a percept of the represented sound. The size of the discrete stimulation region is defined by the limiting signal(s) applied to electrode channel(s) other than the targeted electrode channel, and which negate(s) current spread which would otherwise occur in response to the stimulating signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Integrated implantable hearing device, microphone and power unit
InactiveUS20060183965A1Easy accessAvoid difficultyElectrotherapyBehind the ear hearing aidsHearing apparatusElectric power
An implantable hearing unit is provided that includes an implantable microphone, a rechargeable power storage device and a speech signal processor. The hearing unit further includes a signal coupling device that is adapted for electrical interconnection to an implantable auditory stimulation device, which is operative to stimulate an auditory component of a patient. Such a stimulation device may include cochlear implants, brain stem stimulation systems, auditory nerve stimulation systems, and middle or inner ear transducer systems. The signal coupling device is operative to provide processed drive signals from the signal processor to the stimulation device as well provide power from the power storage device to operate the stimulation device. In one arrangement, the signal coupling device is a wireless coupling between first and second coils. In such an arrangement, the hearing unit may be utilized with an existing implanted stimulation device to make that device a fully implanted hearing system.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Method and apparatus for measurement of evoked neural response
The invention provides a method of electrical artefact compensation in measurement of a neural response. The neural response is evoked by a first stimulus, after which a compensatory stimulus is applied in order to counteract a stimulus artefact caused by the first stimulus. The invention also provides for short circuiting the stimulating electrode subsequent to the first stimulus. A system for implementing such steps is also provided. The invention may be of application in measurement of physiological responses, including neural responses and in particular a neural response of the auditory nerve.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Minimization of electrical stimulus artifact during measurement of evoked neural response
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
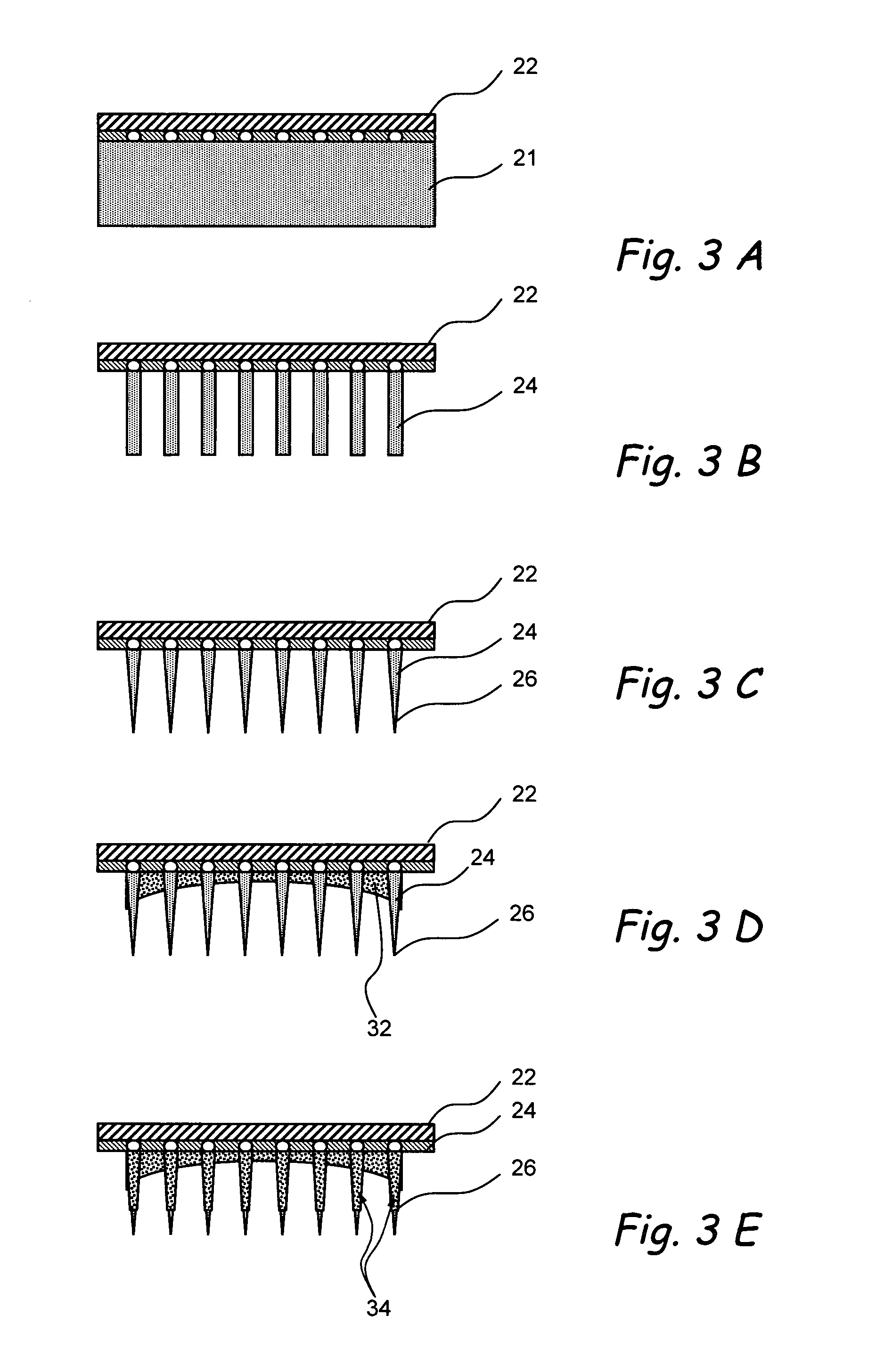
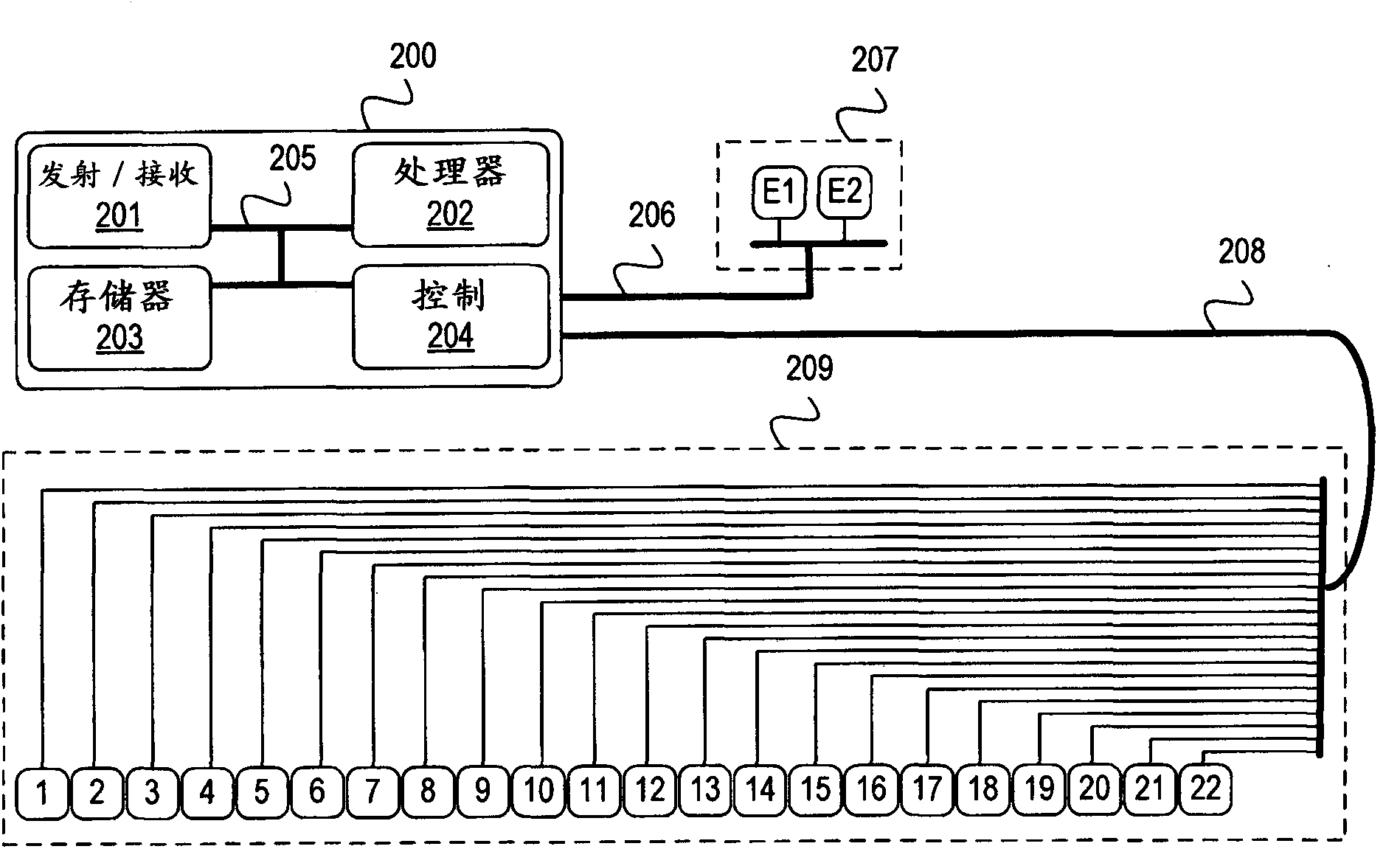
High density micromachined electrode arrays useable for auditory nerve implants and related methods
ActiveUS7991475B1Heat dissipationPrecise positioningHead electrodesSensorsImplantable ElectrodesHigh density
Devices, systems and methods that comprise or utilize implantable electrode arrays for neural stimulation and / or sensing. In some embodiments, the electrode array is implanted or inserted into the auditory nerve and is used to deliver electrical impulses to / receive data from the auditory nerve in the treatment of hearing disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
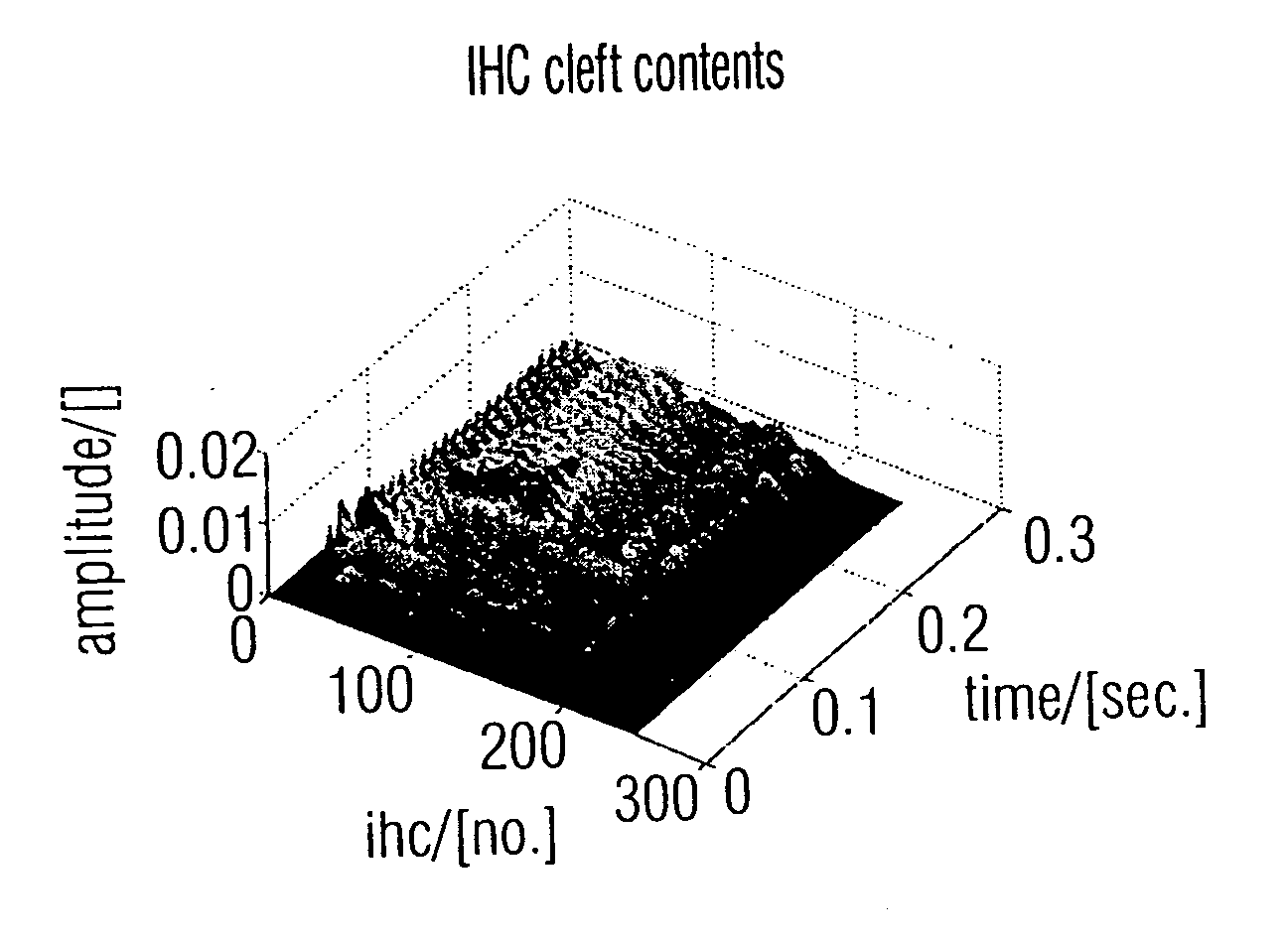
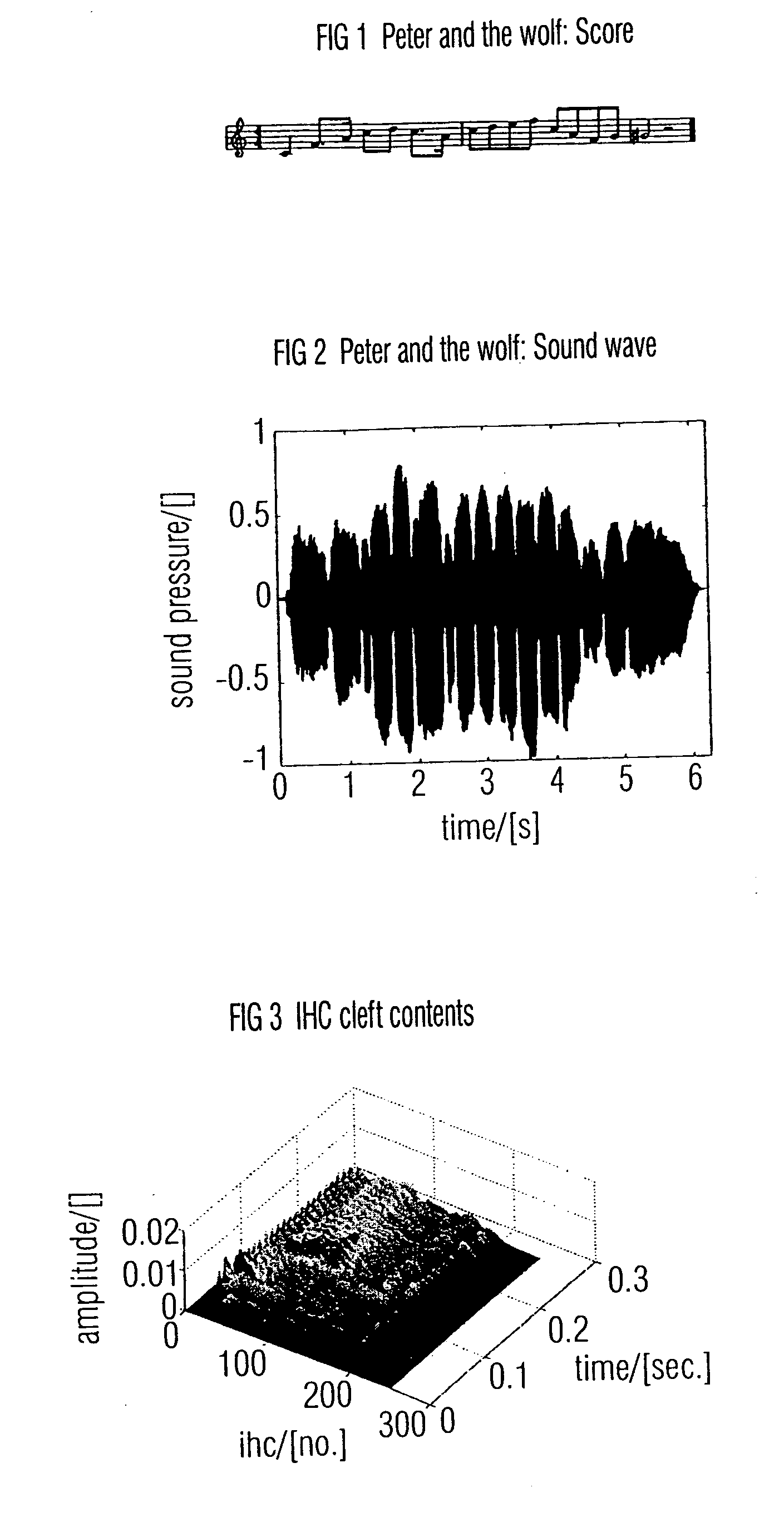
Apparatus and method for analyzing a sound signal using a physiological ear model
ActiveUS20050234366A1Improve performanceElectrophonic musical instrumentsElectrotherapyMedicineAuditory nerves
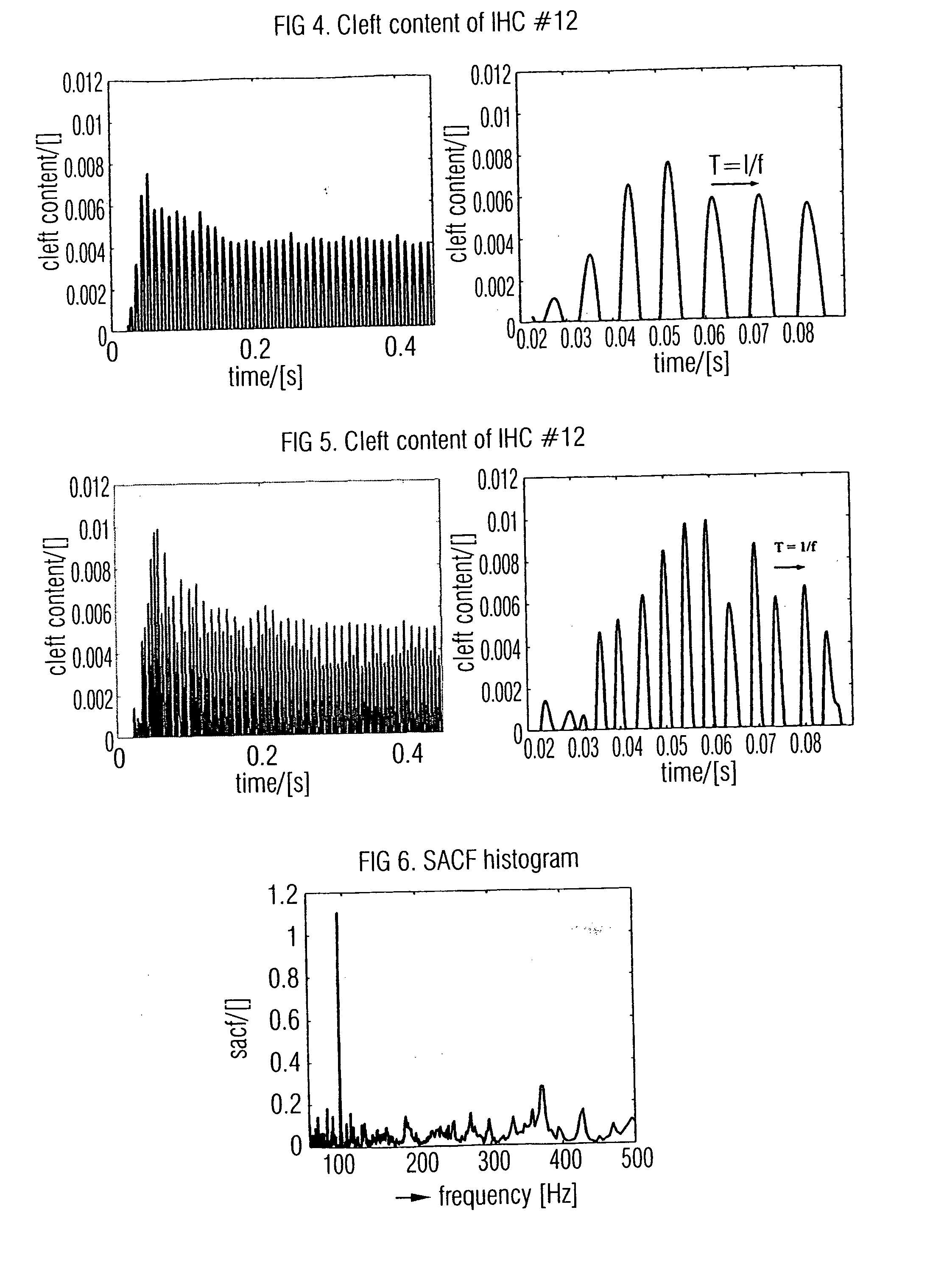
An apparatus for analyzing a sound signal is based on an ear model for deriving, for a number of inner hair cells, an estimate for a time-varying concentration of transmitter substance inside a cleft between an inner hair cell and an associated auditory nerve from the sound signal so that an estimated inner hair cell cleft contents map over time is obtained. This map is analyzed by means of a pitch analyzer to obtain a pitch line over time, the pitch line indicating a pitch of the sound signal for respective time instants. A rhythm analyzer is operative for analyzing envelopes of estimates for selected inner hair cells, the inner hair cells being selected in accordance with the pitch line, so that segmentation instants are obtained, wherein a segmentation instant indicates an end of the preceding note or a start of a succeeding note. Thus, a human-related and reliable sound signal analysis can be obtained.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
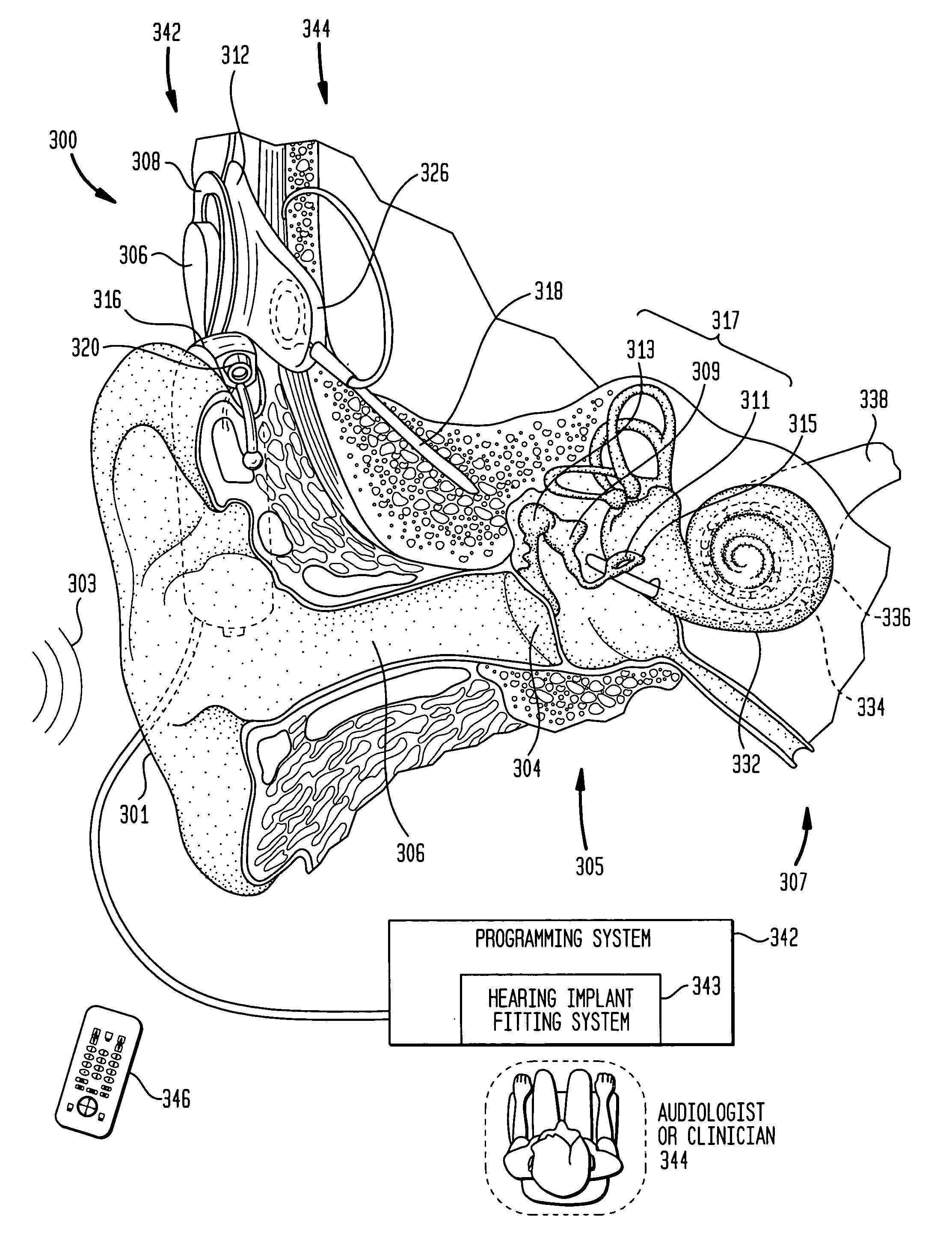
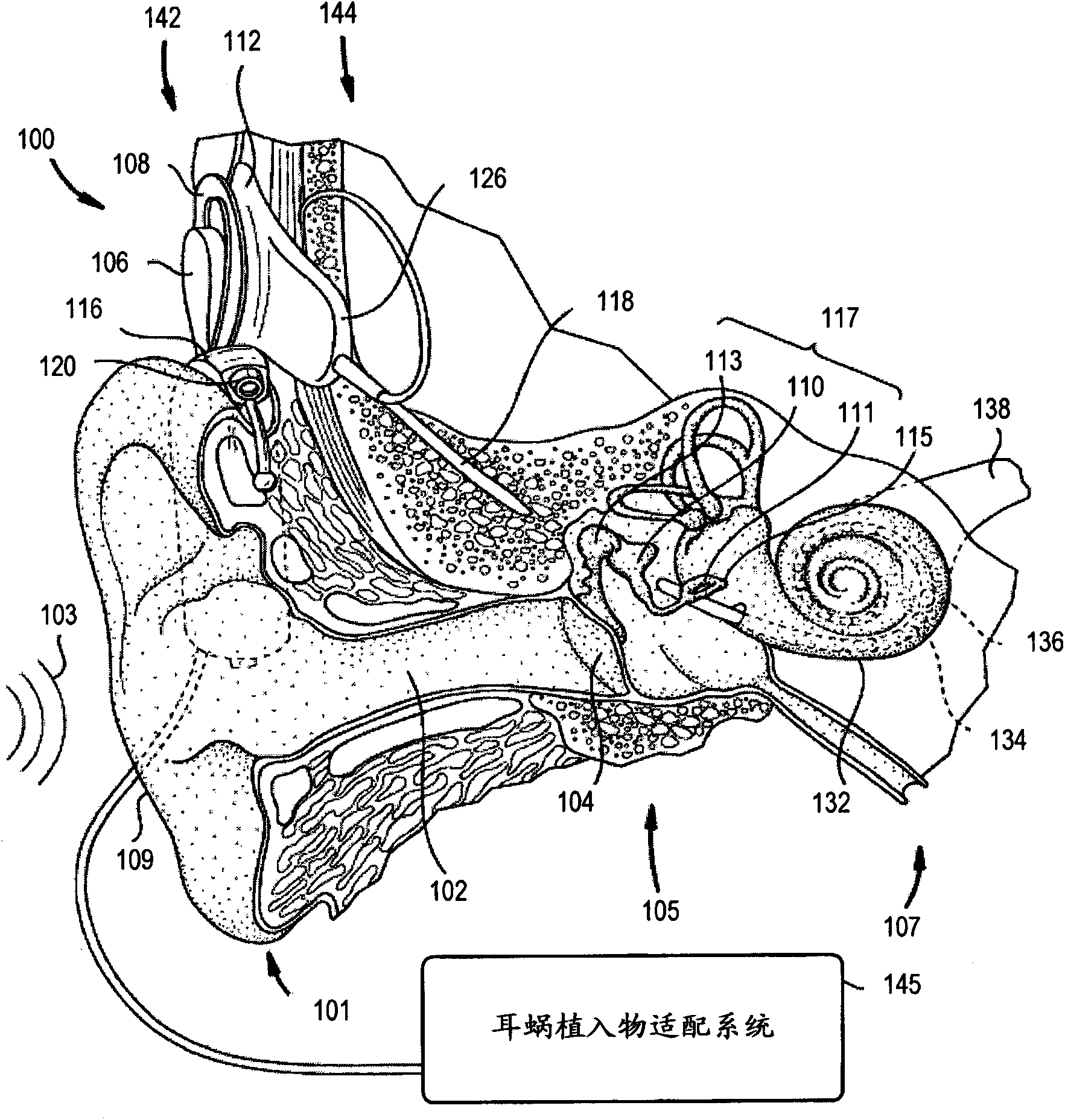
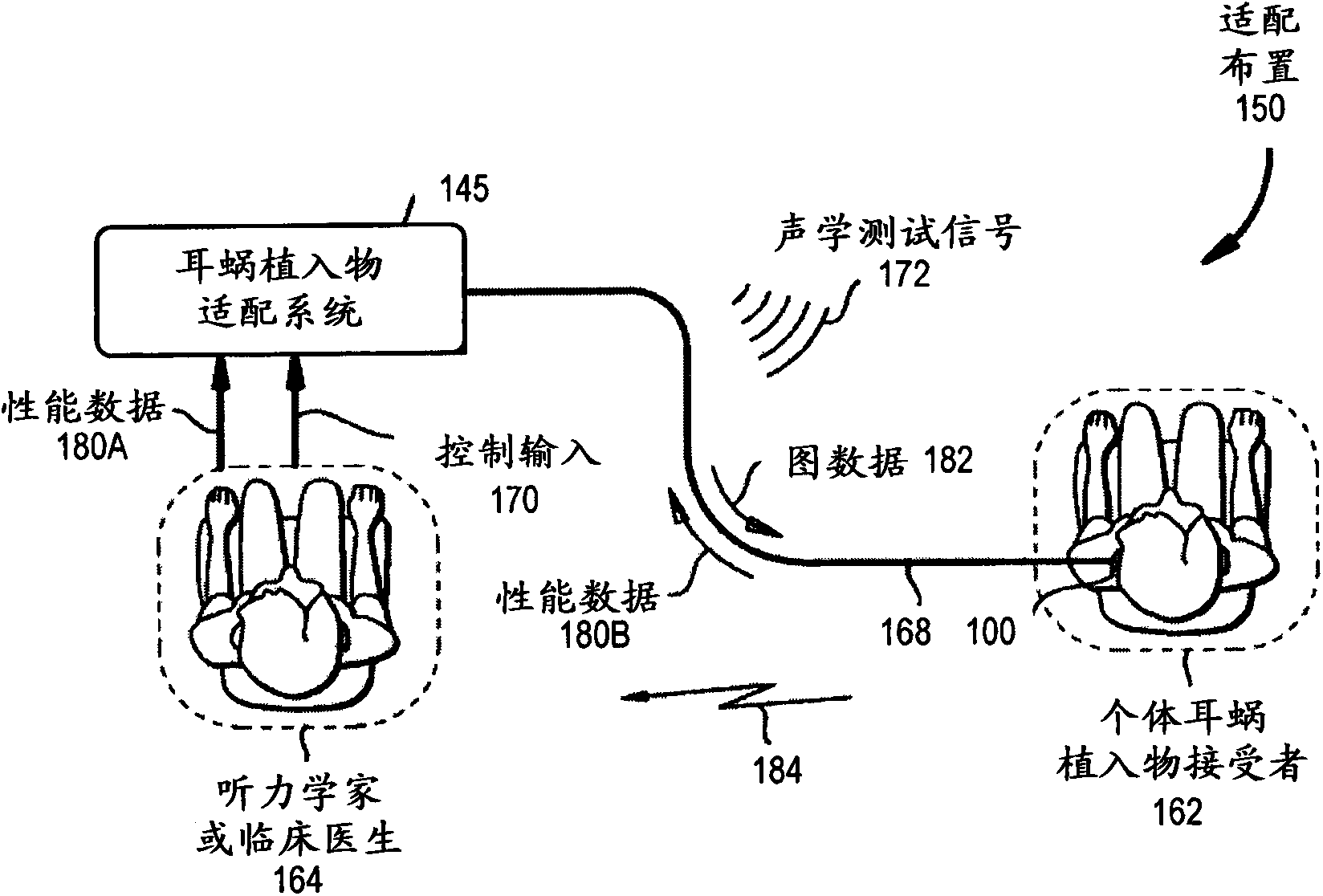
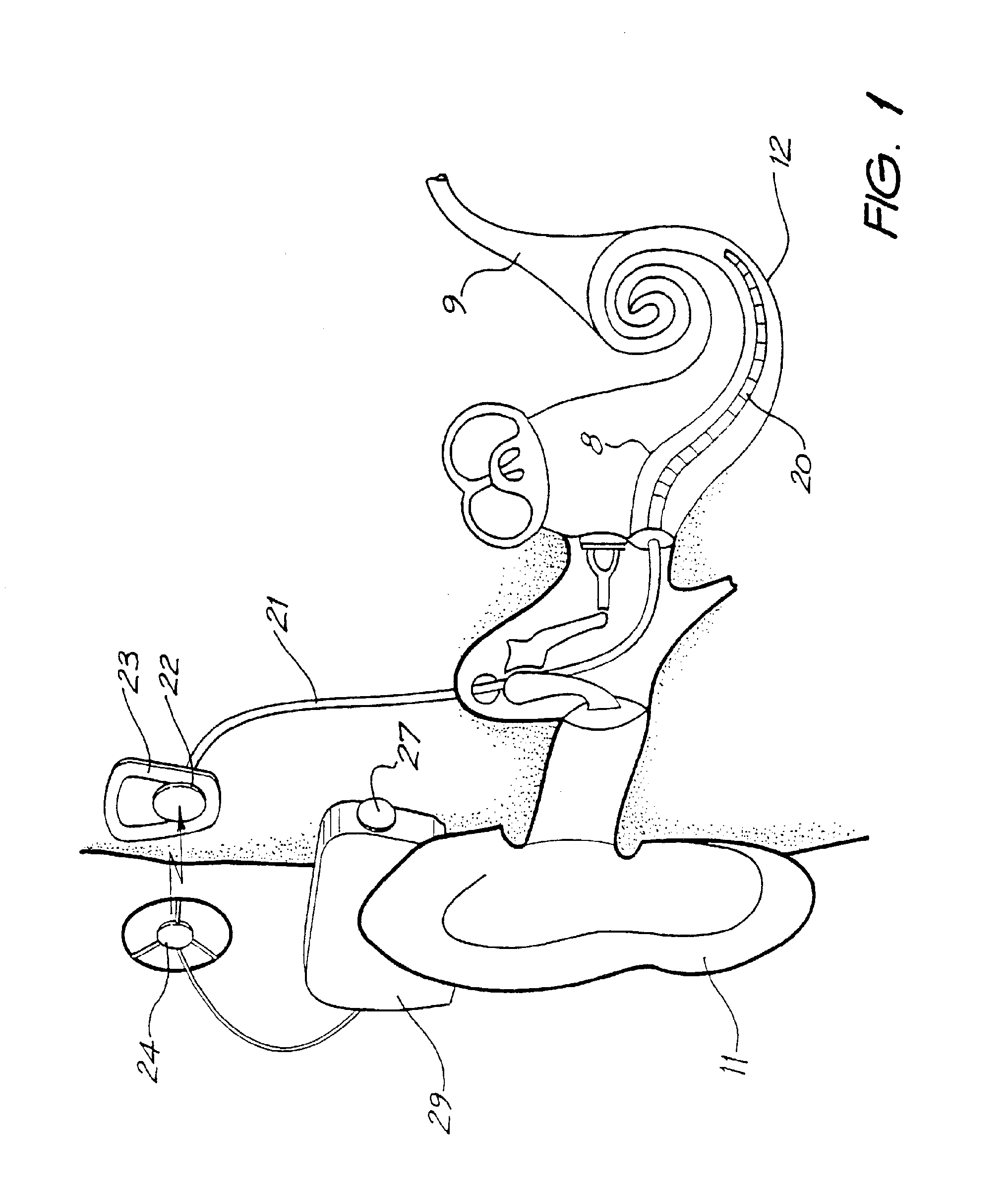
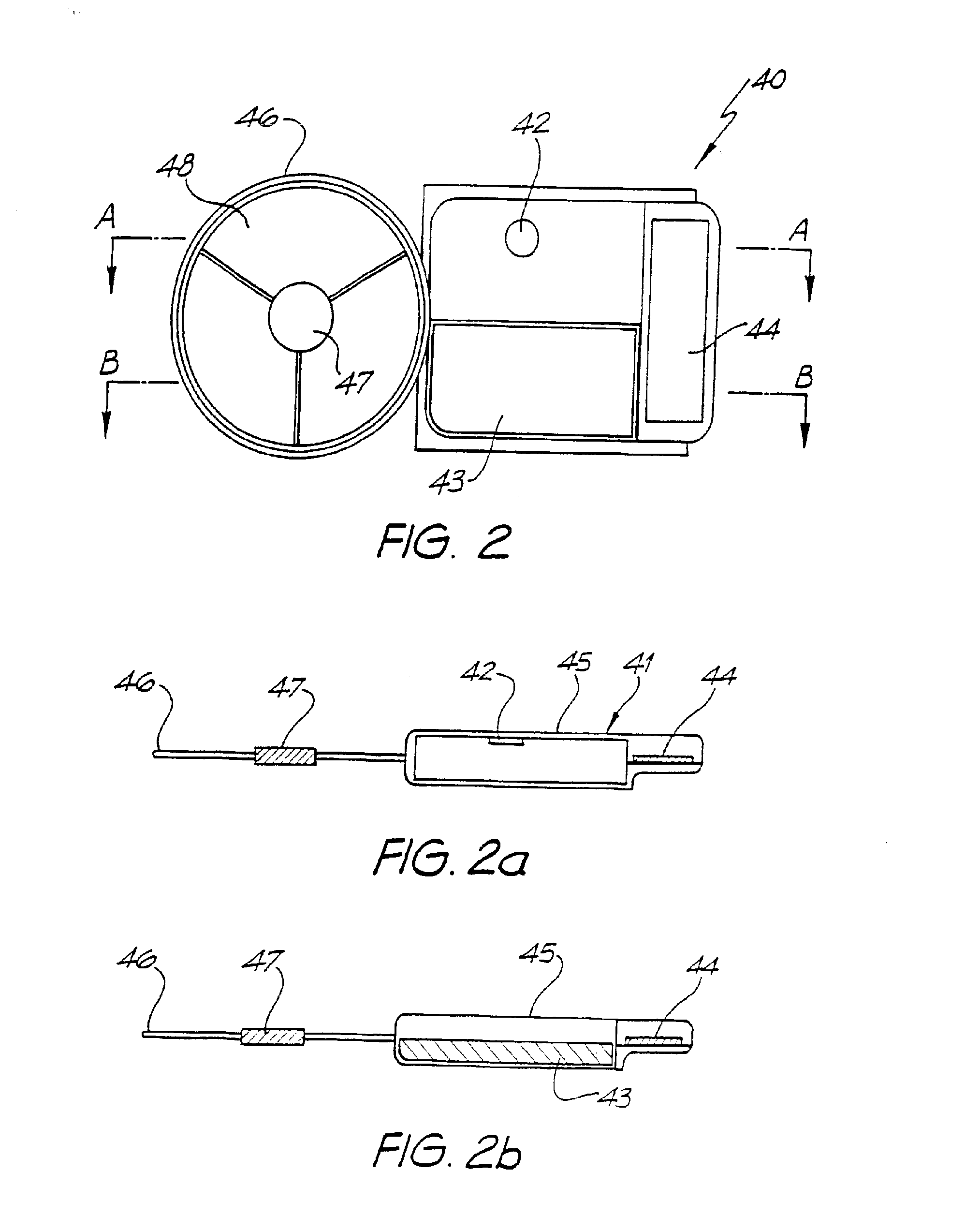
Cochlear implant
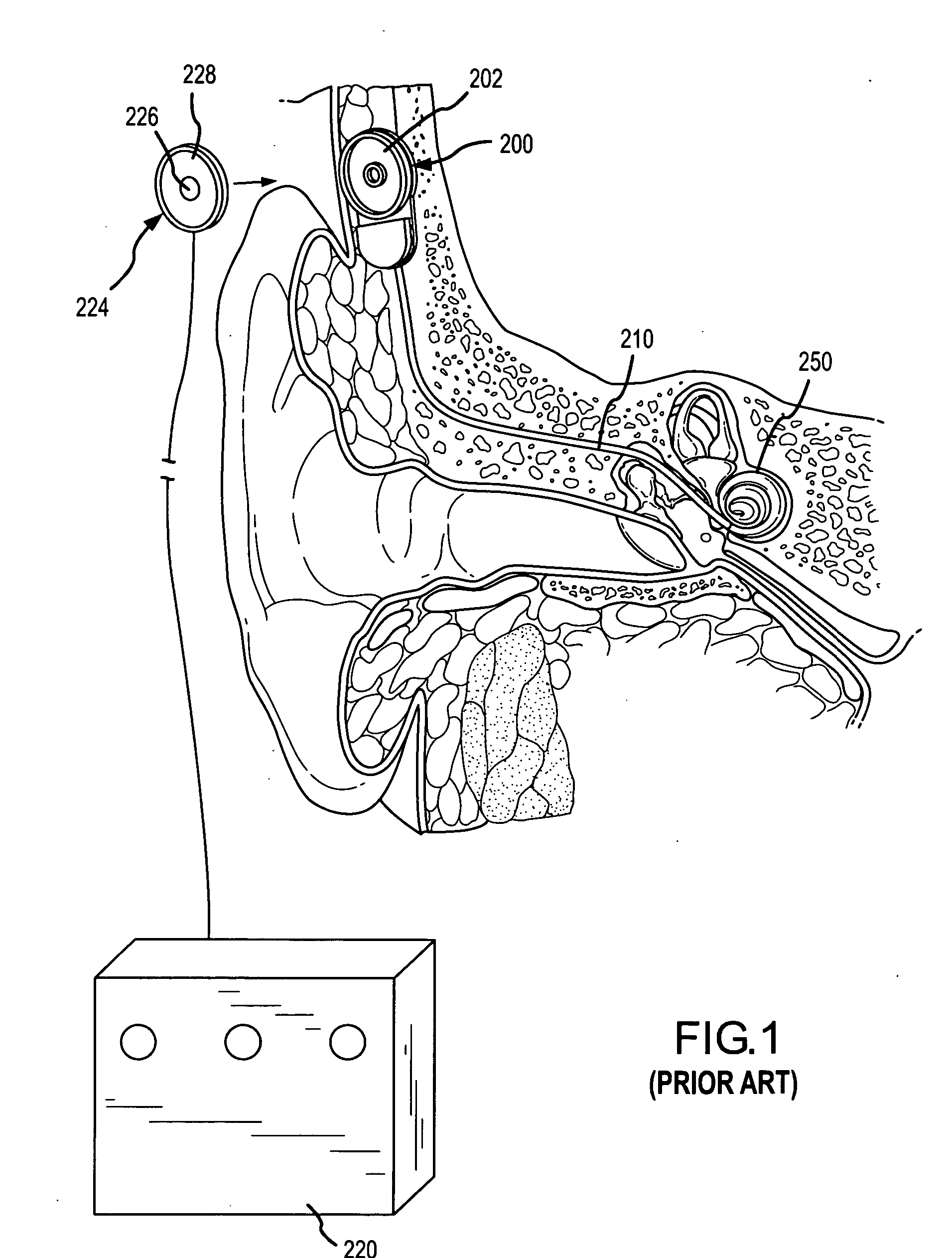
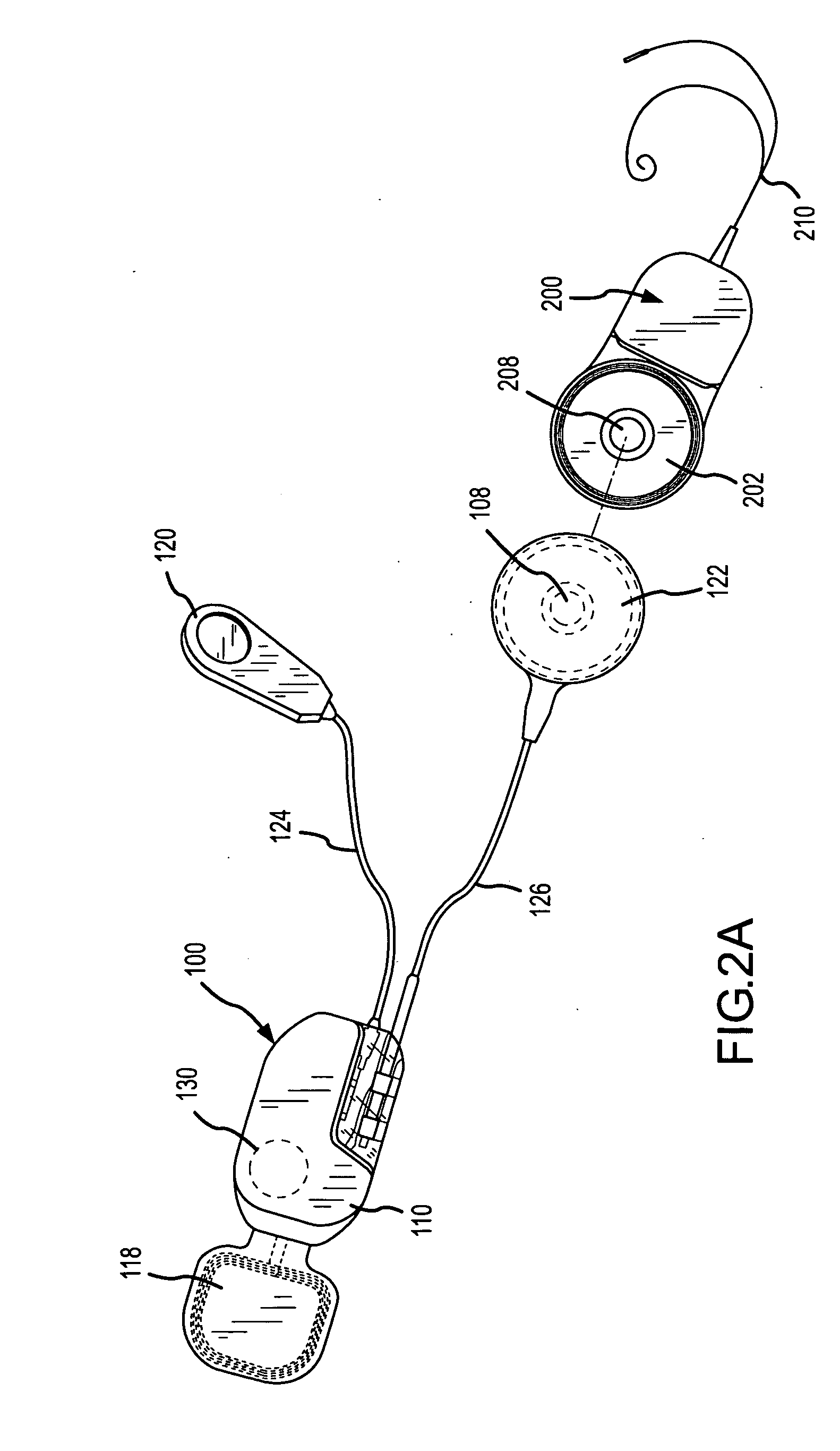
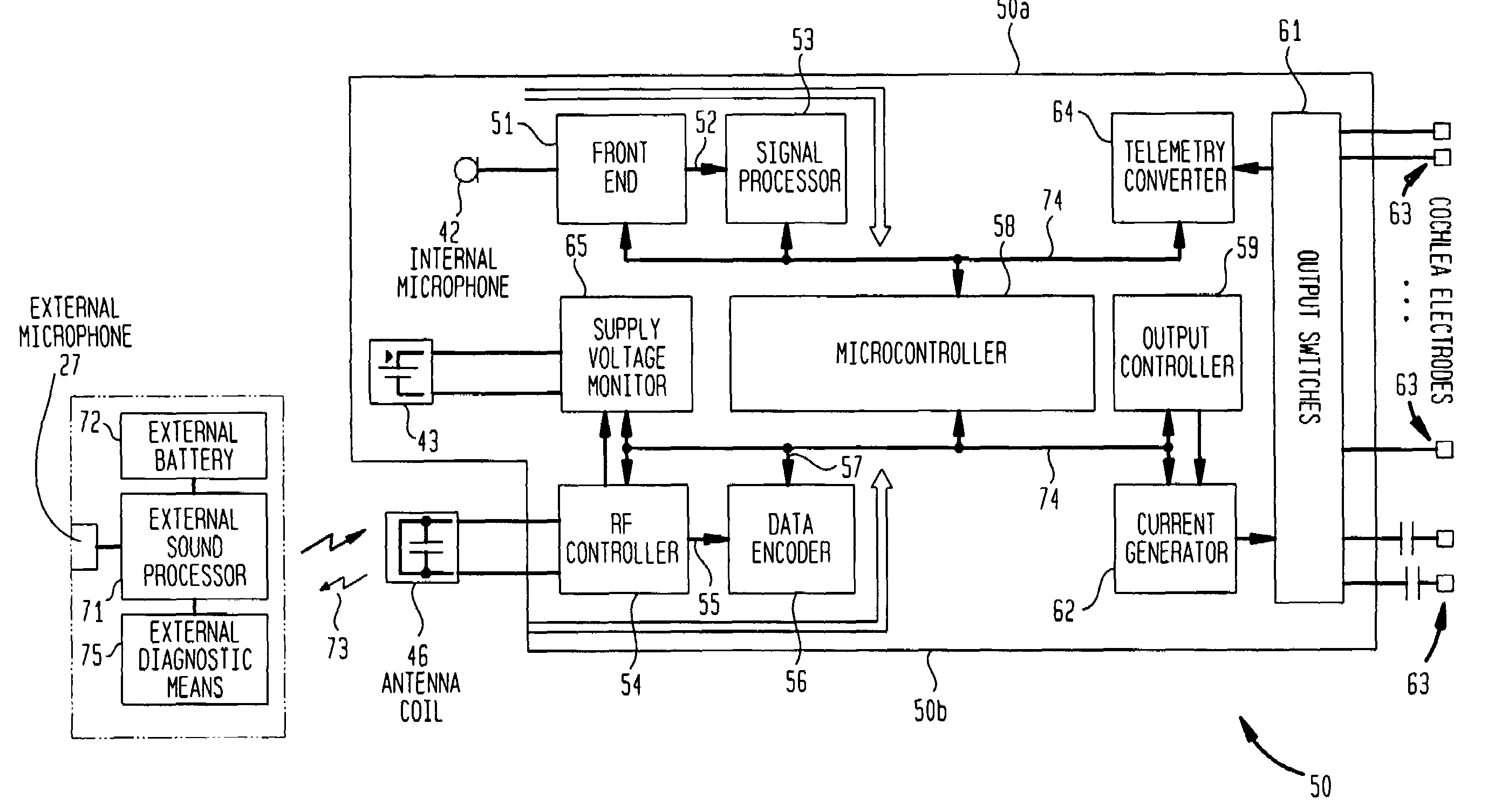
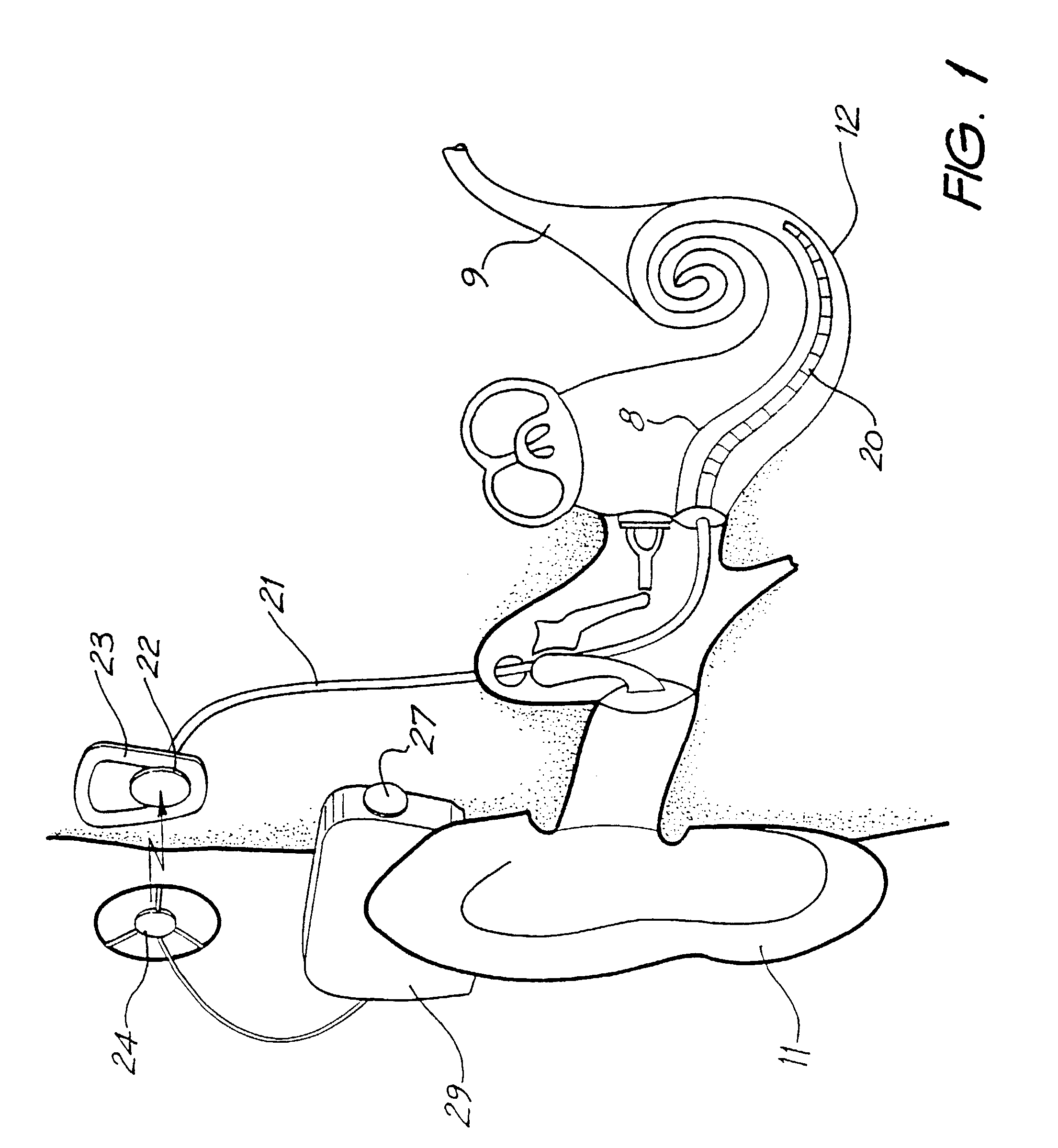
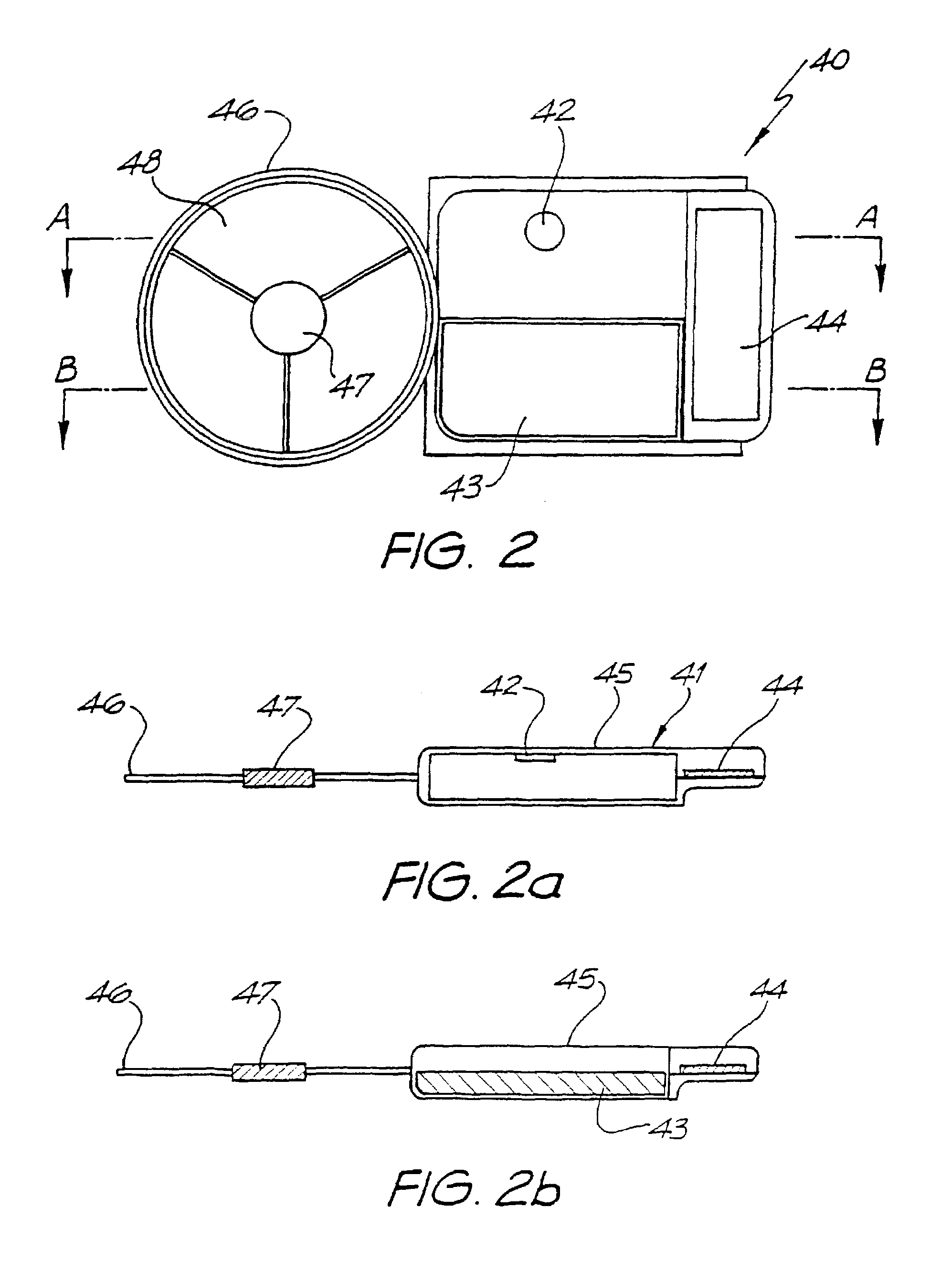
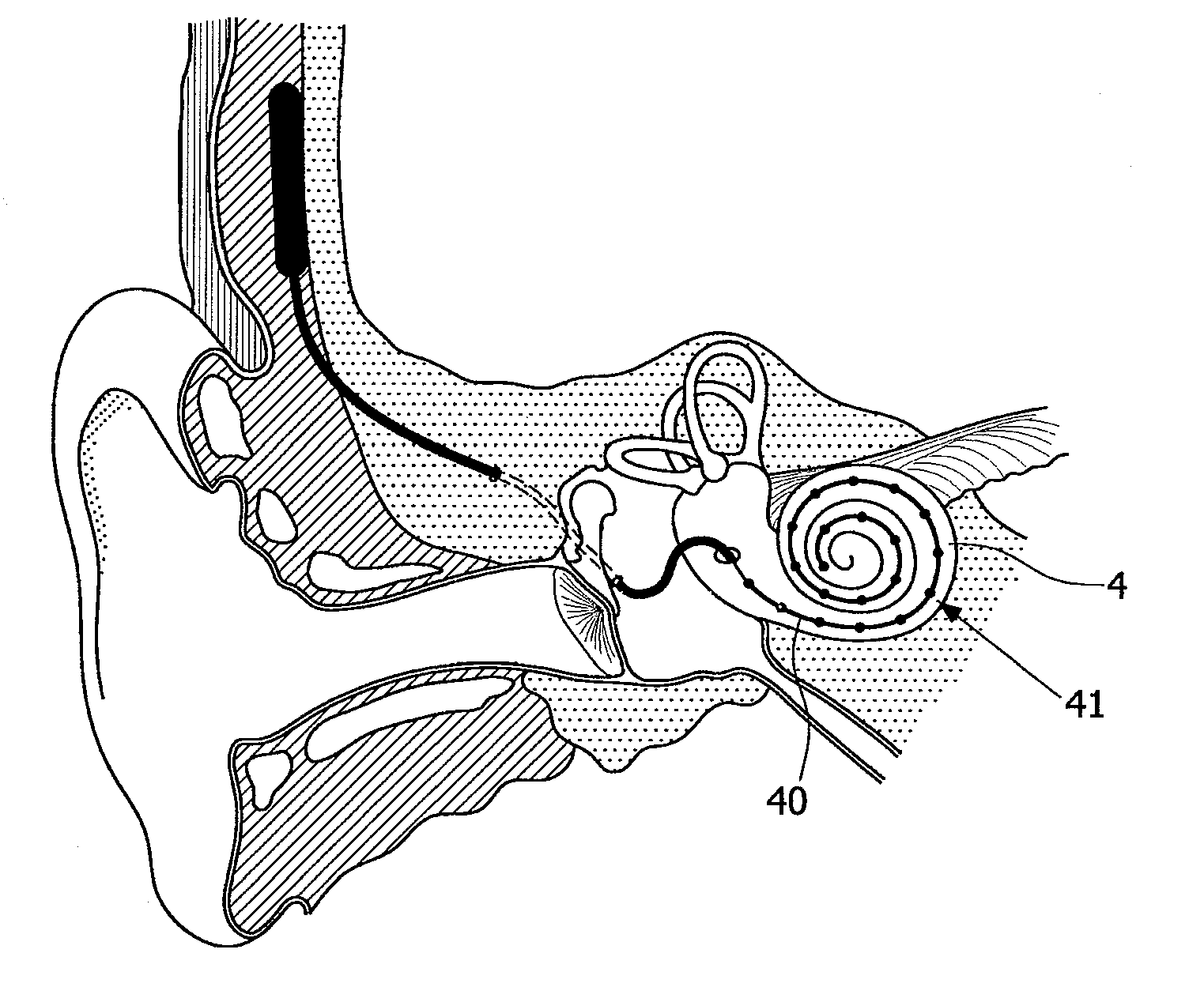
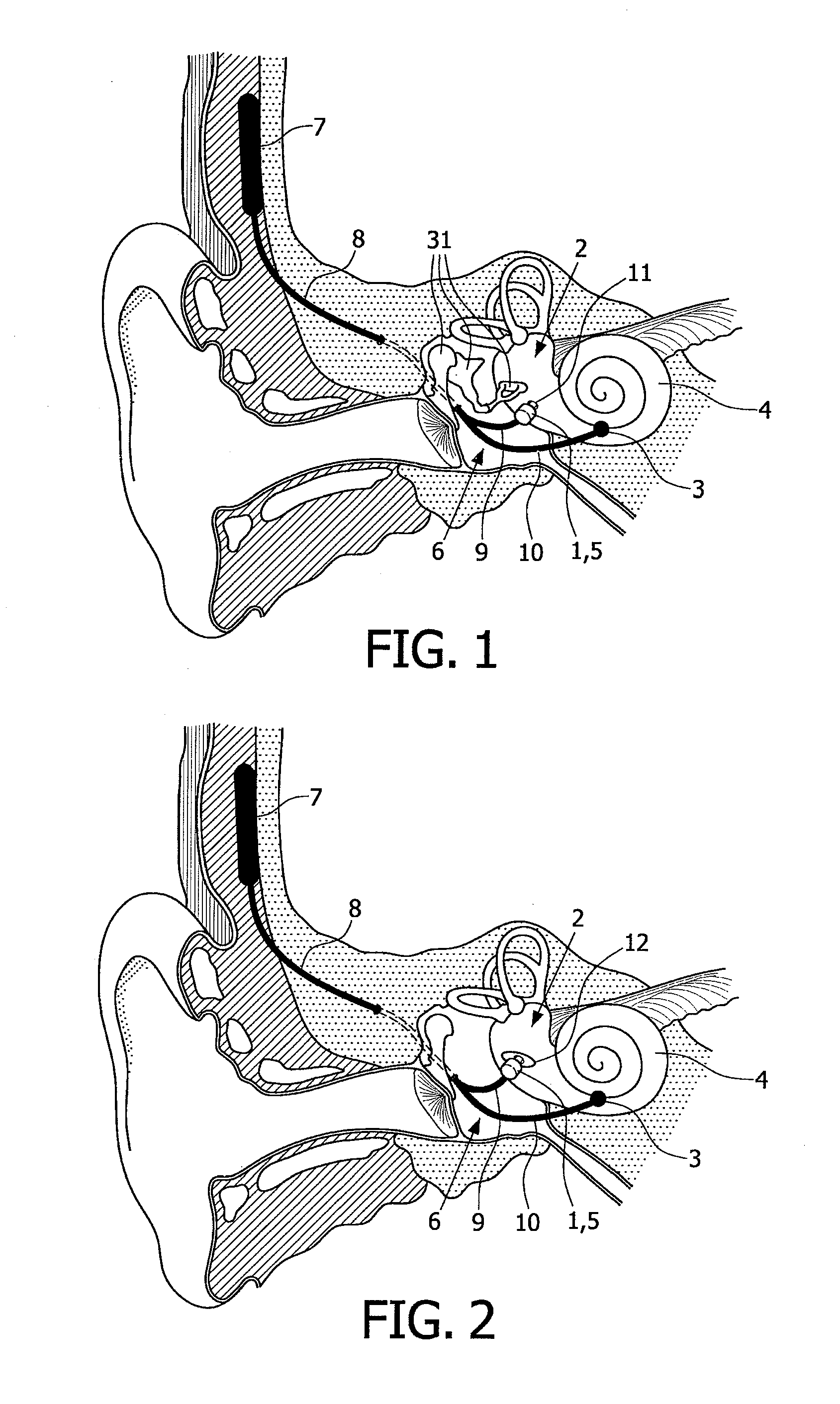
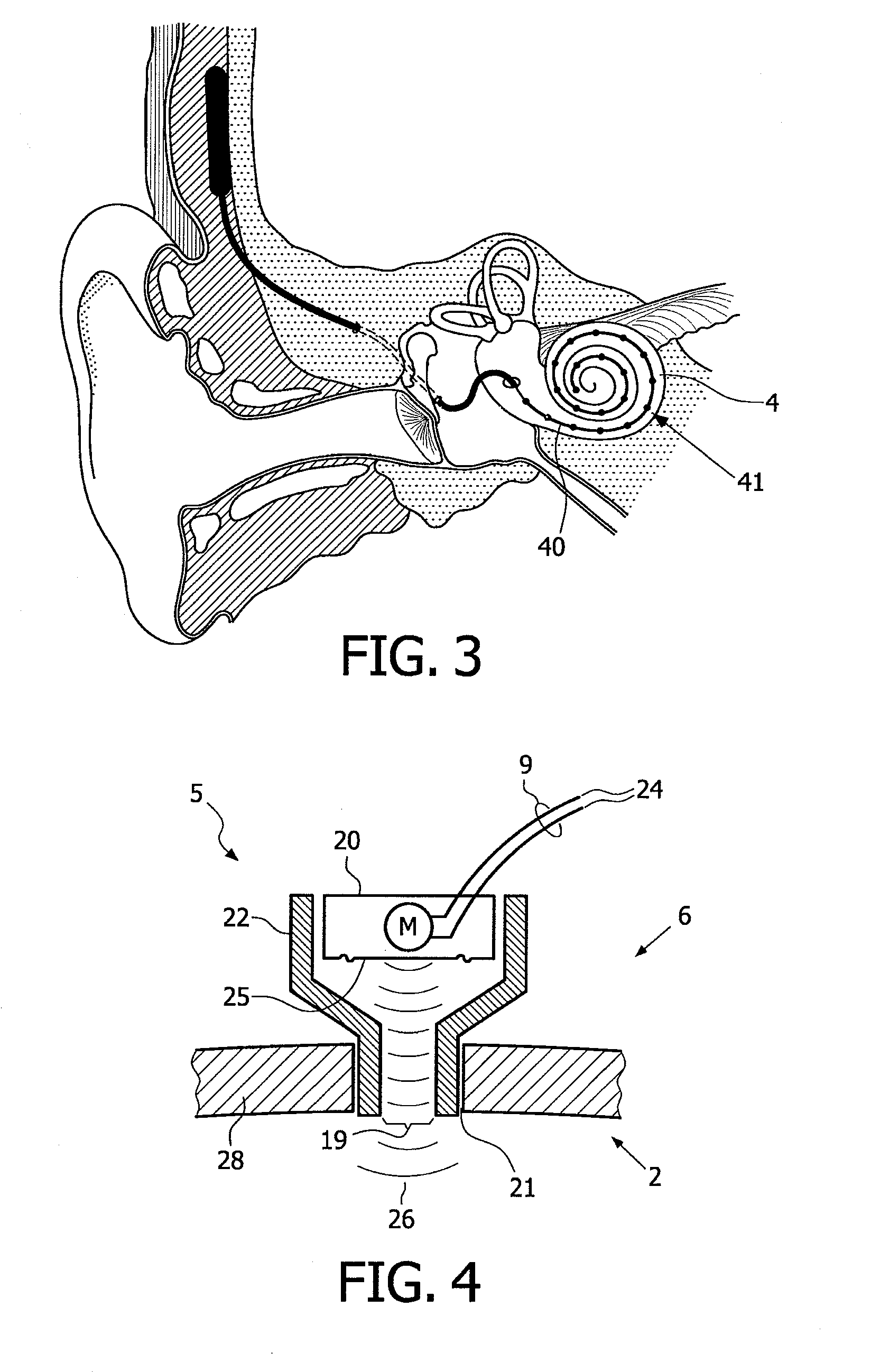
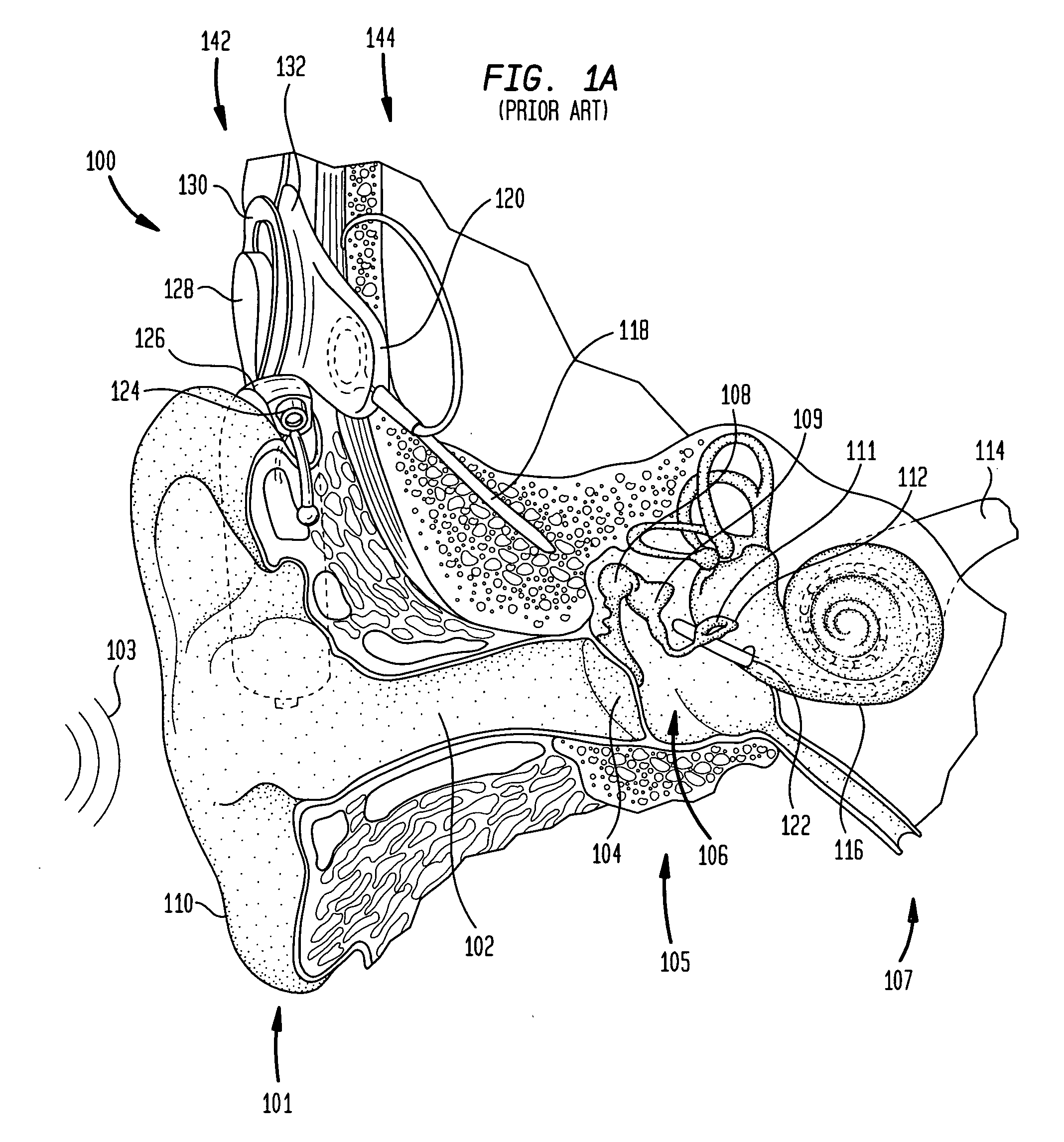
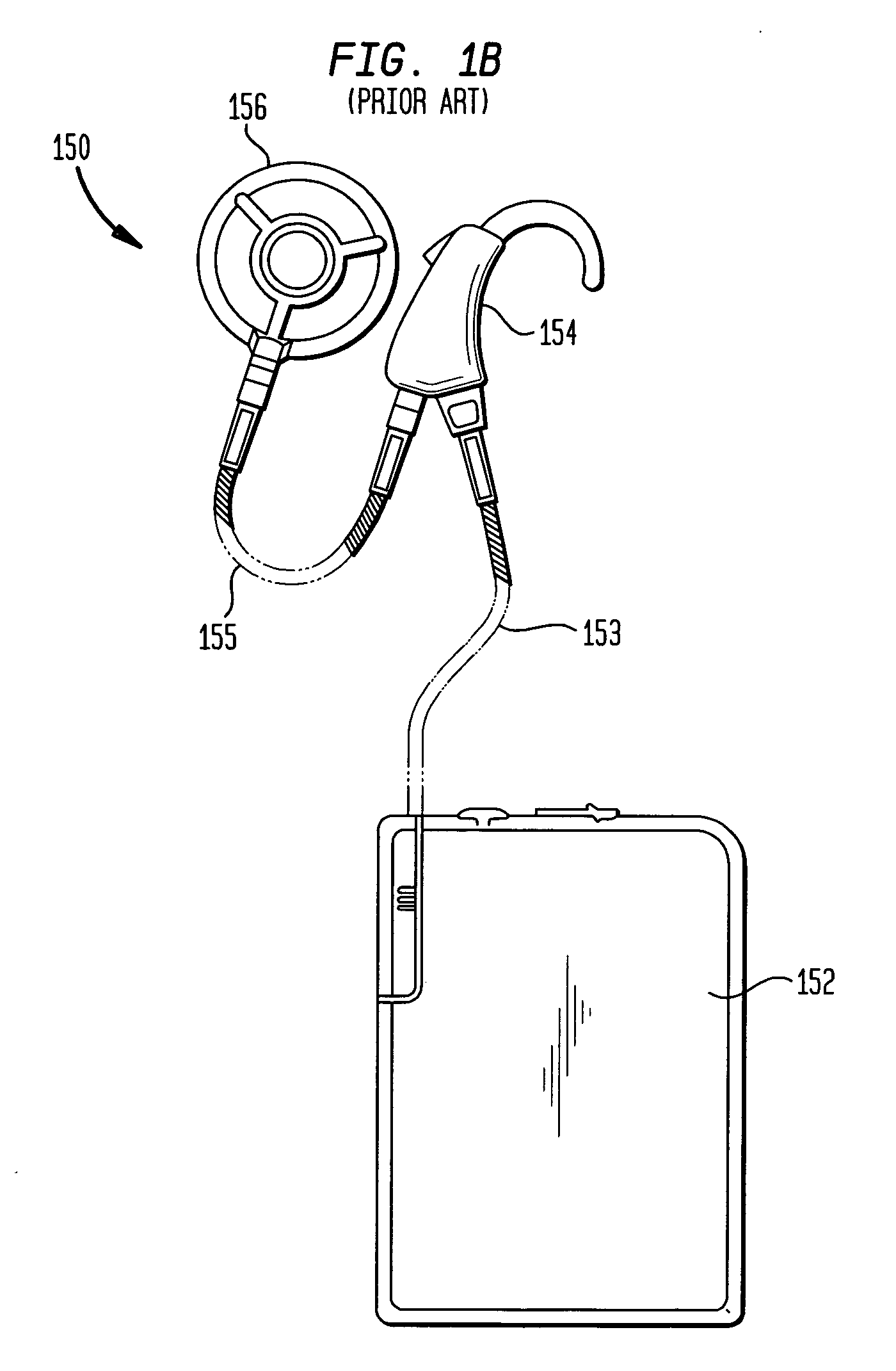
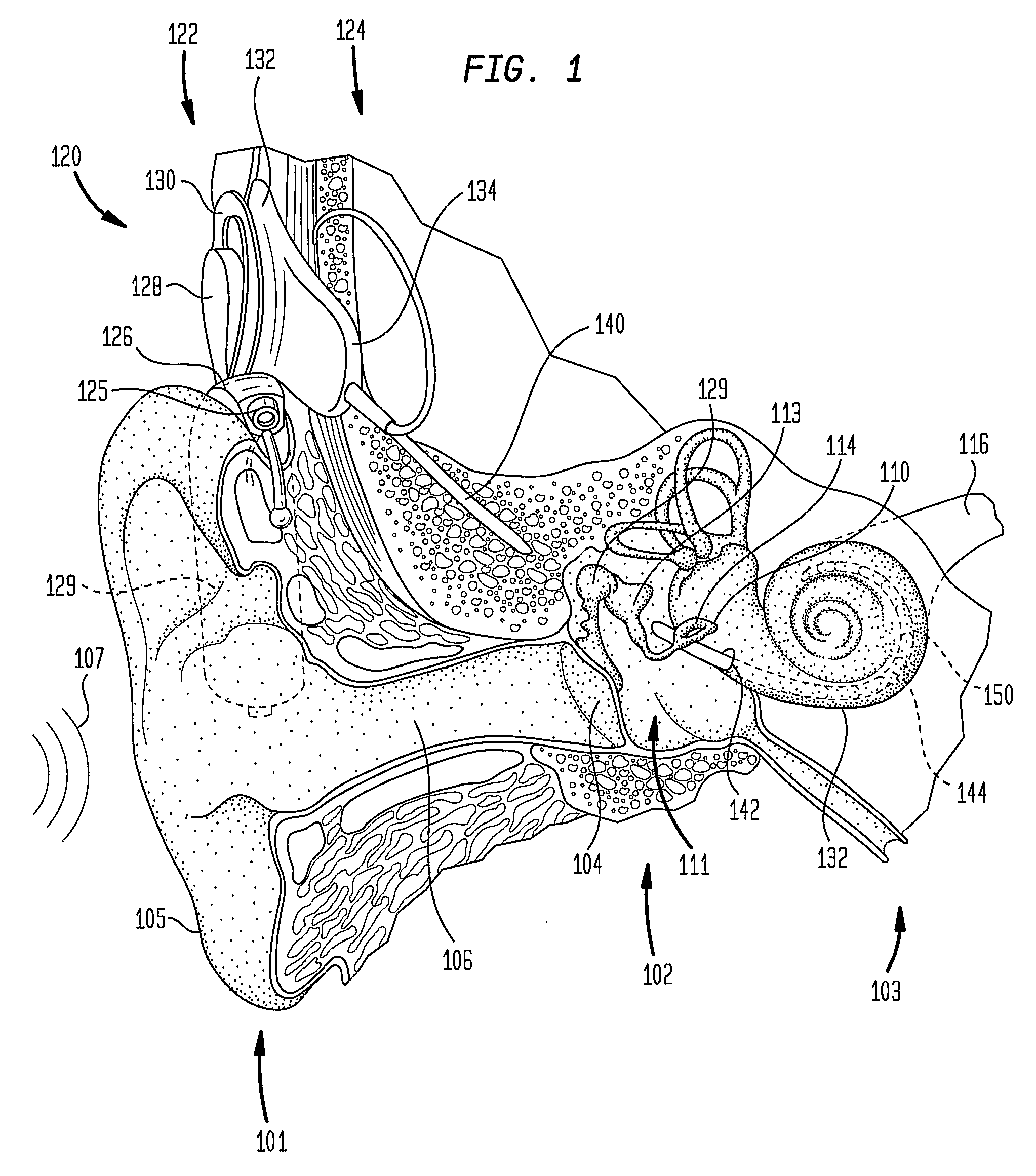
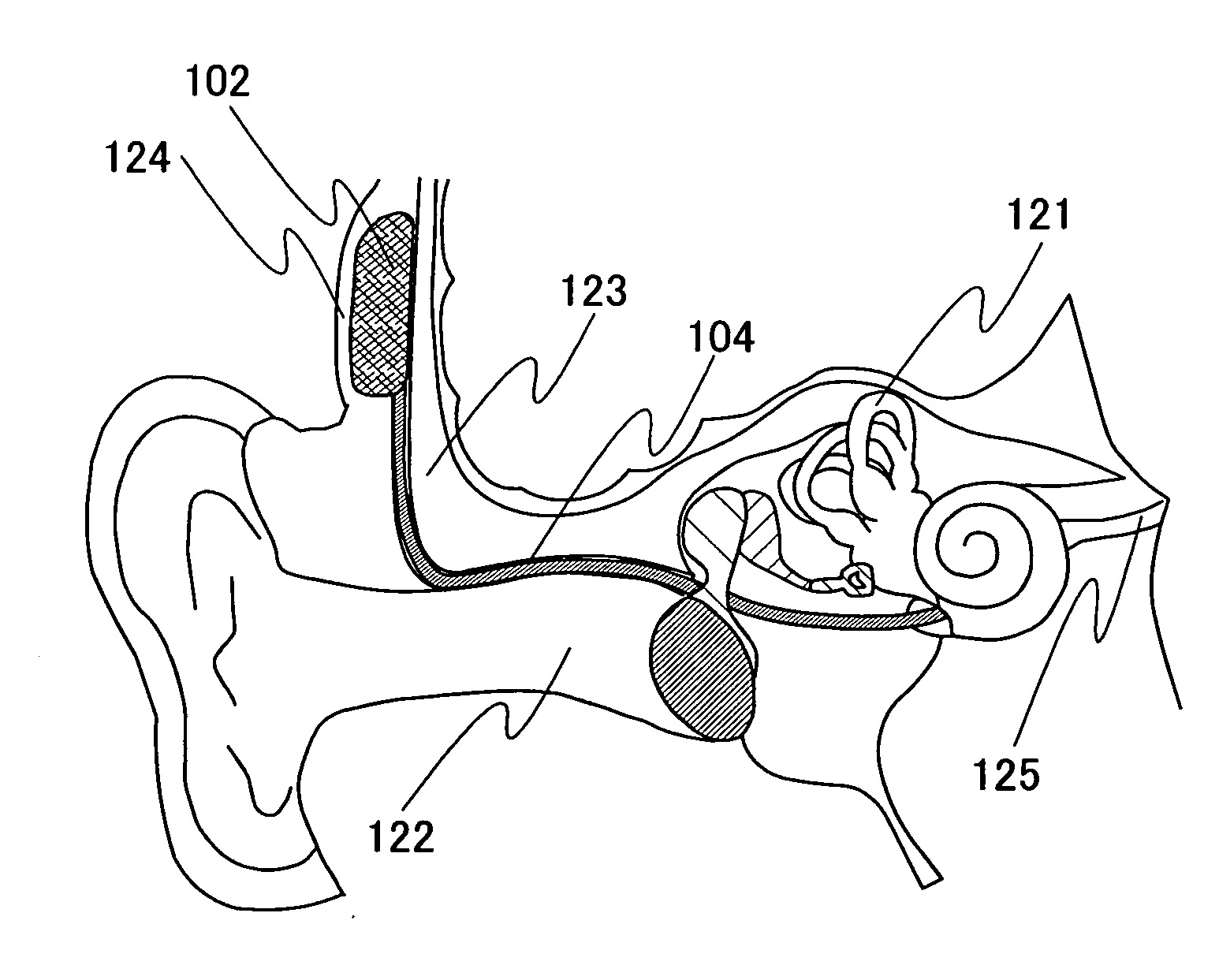
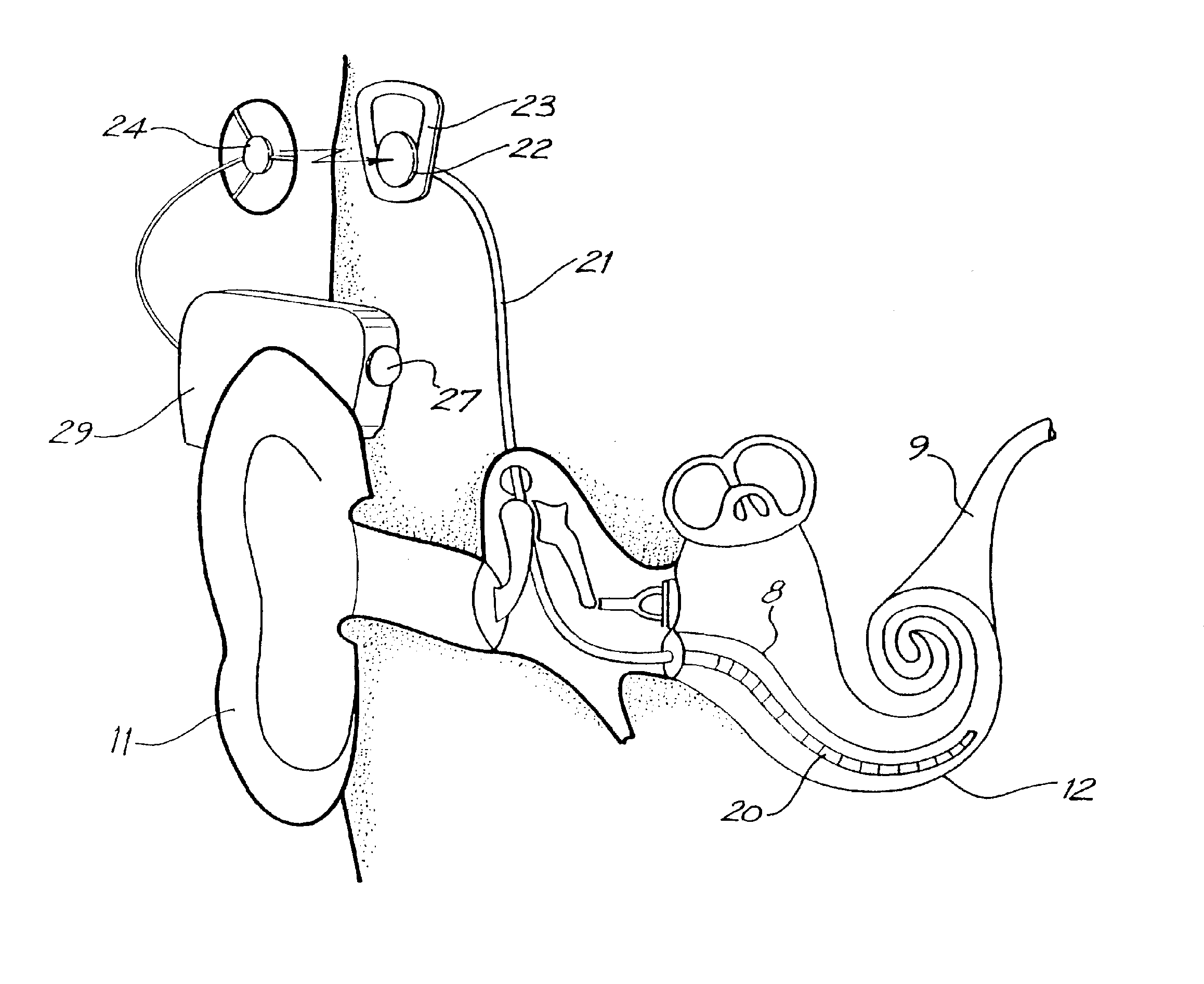
A totally implantable cochlear implant system forming a single implantable unit (40). The unit (40) has an implantable power source (43) that provides the power requirements of the implantable unit (40). The unit (40) also has an on-board microphone (42) that detects external sounds, such as speech, and outputs acoustic signals representative of the detected sounds. The unit further includes speech processor circuitry (44) that directly receives the acoustic signals from the microphone (42) and converts the signals into stimulation signals representative of the detected sounds. An electrode array (20) suitable for insertion of the cochlea (12) of an implantee receives the stimulation signals and transmits electrical stimulations to the implantee'auditory nerve (9).
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Device and method for improving hearing
An implantable device for improving hearing is provided. The device includes a vibration generator including an output region configured to apply vibrational stimulation to an inner ear fluid, a proximal electrode configured to physically attach to a wall enclosing an inner ear at a location proximal to the output region of the vibration generator, and a separate distal electrode configured to make electrical contact with an auditory nerve.
Owner:3WIN
Cochlear endosteal electrode carrier member
InactiveUS20060079950A1Head electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedial surfaceAnatomical structures
An elongate electrode carrier member for implantation in a location external to the cochlear canals to position at least one, and likely many, electrodes sufficiently proximate to the organ of Corti to effectively deliver stimulation signals to the auditory nerve fibers of the cochlear. Generally, the carrier member is dimensioned to be implanted in a crevice, channel or pocket formed between the spiral ligament and bony capsule of the cochlear. Embodiments of the carrier member preferably have a minimized volume to accommodate insertion into such a crevice. In addition, embodiments of the carrier member comprise an elongate bulbous central region having electrodes disposed on the medial surface thereof, and elongate tapered side regions laterally extending from the central region. The side regions have rounded edges and are preferably flexible, while the carrier is configured to coil or turn toward the medial surface. This construction facilitates implantation of the carrier member: the carrier member has sufficient longitudinal strength to maintain its form and direction while being pushed into the surgically-formed crevice, and coils in a longitudinal plane to follow the contour of the cochlear, while the side regions serve to guide the direction of travel, flexing out of the lateral plane as necessary to avoid damaging anatomical structures. Once implanted, embodiments of the carrier member are urged to remain in its implanted position due to one or more of either the side regions extending into the corners of the crevice, and / or due to the curved lateral surface of the carrier member which approximates the curvature of the endosteum along the basal turn of the cochlea.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
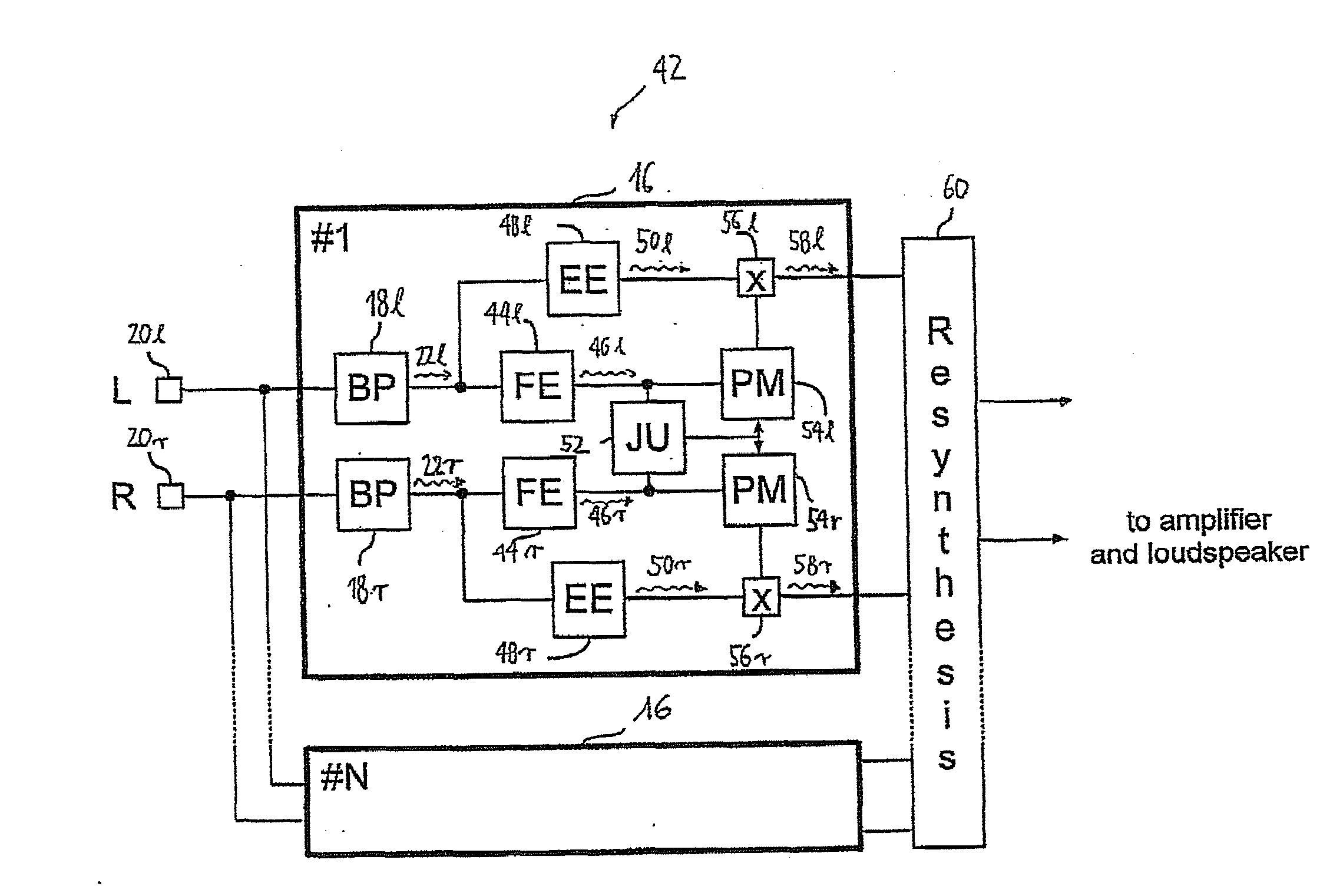
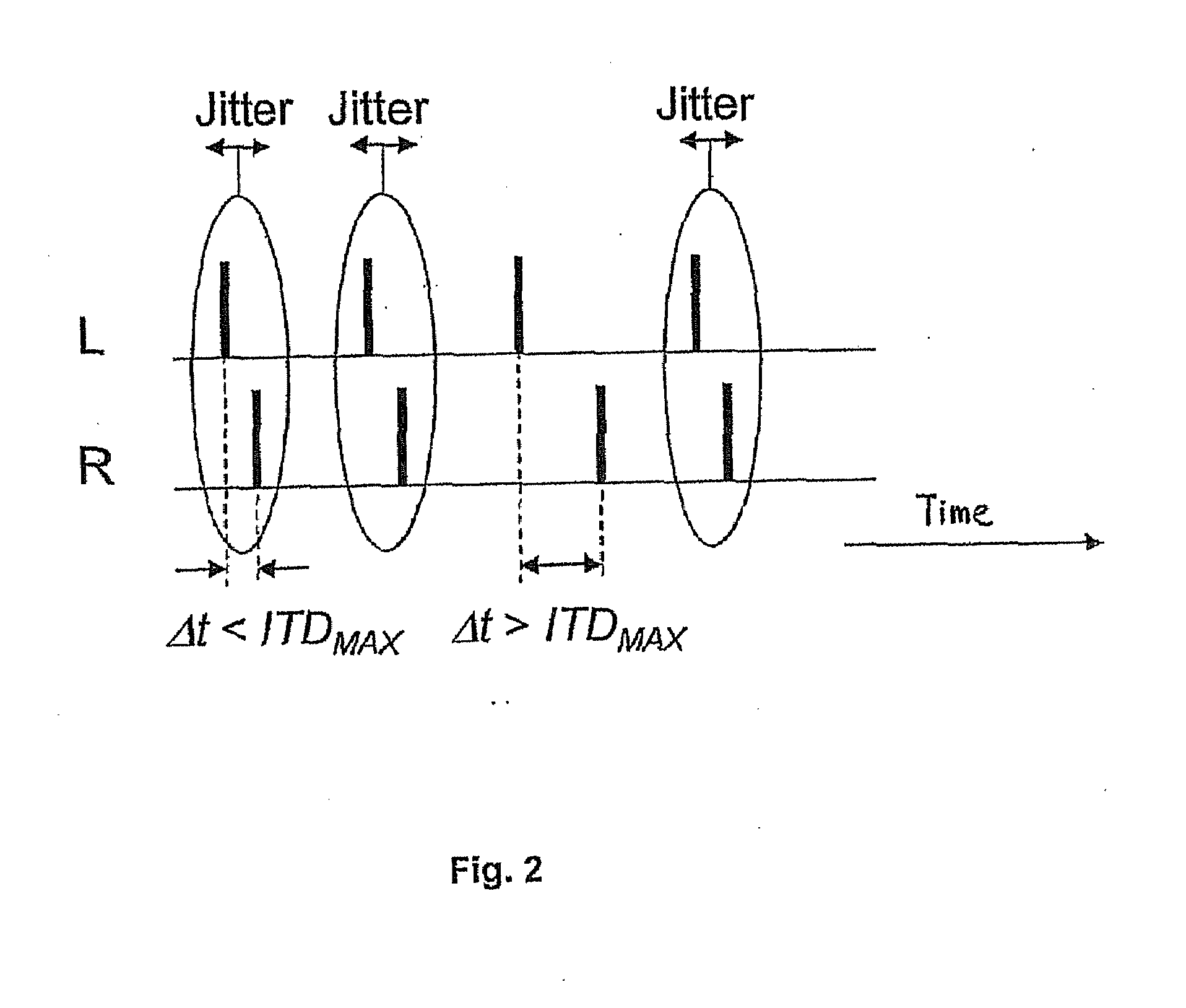
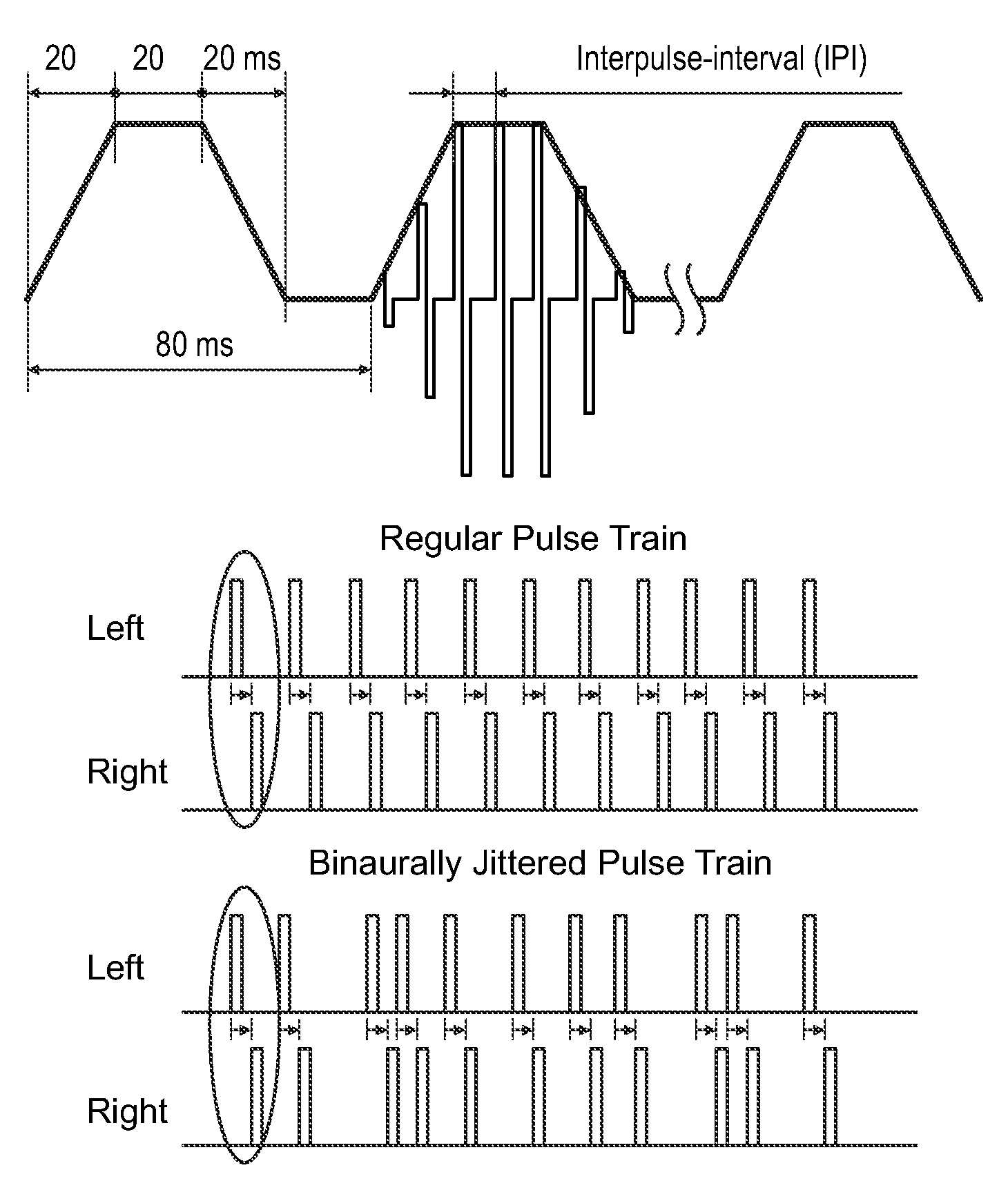
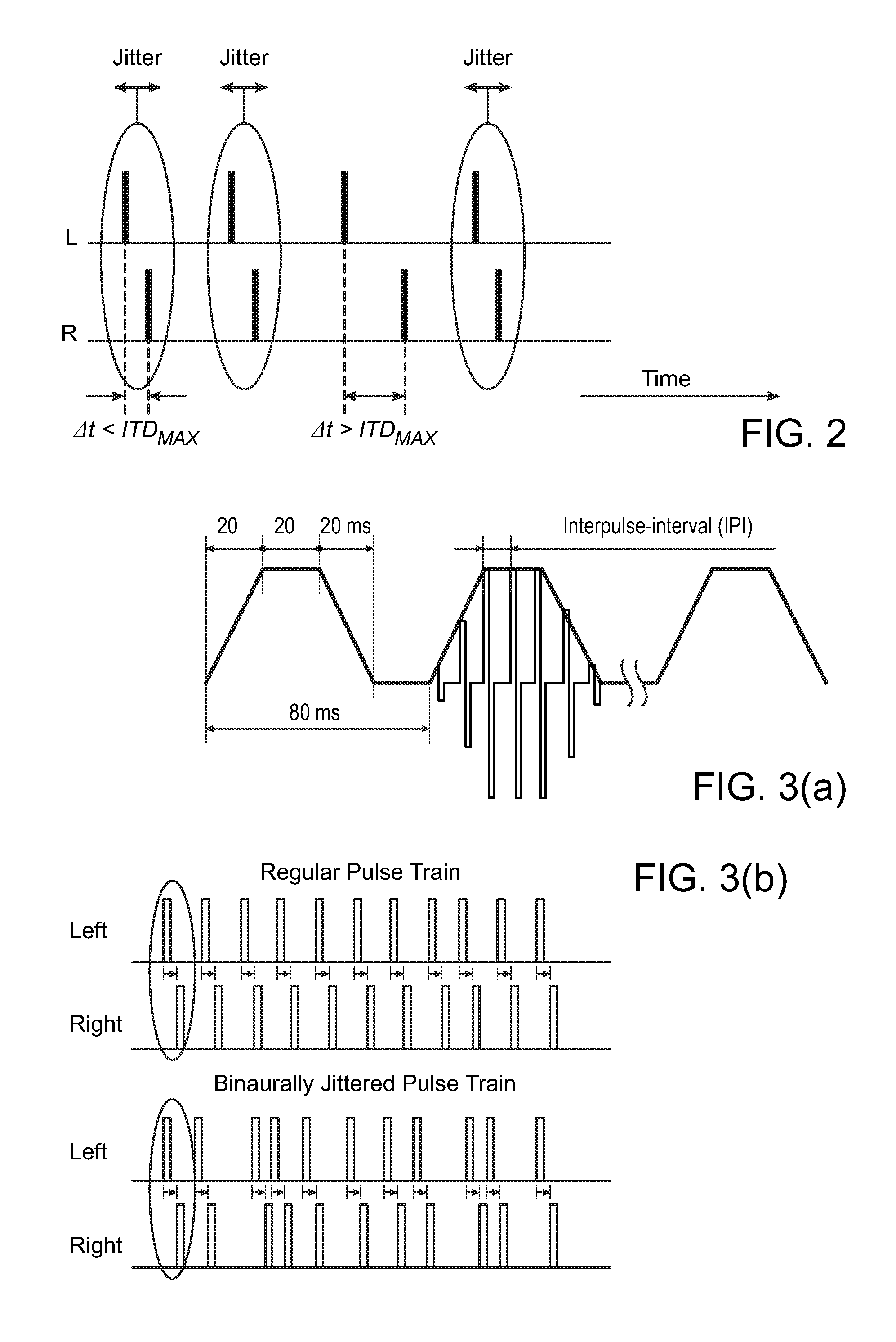
Binaural Stimulation in Neural Auditory Prostheses or Hearing Aids
ActiveUS20080319509A1Avoid time-overlapElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsInteraural time differenceFine structure
The present invention discloses of binaural stimulation in a neural auditory prosthesis. Binaural acoustic signals are generated that represent sound associated with a user's left and right ears respectively. Based on the binaural acoustic signals, corresponding binaural stimulation signals are generated for electrical stimulation of auditory nerve tissue of the user, wherein the binaural stimulation signals each include a fine structure component with periodic characteristics and interaural time difference (ITD) information. A phase jitter component is added to the binaural stimulation signals to reduce the periodic characteristics of the fine structure component while preserving the interaural time difference (ITD) information.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
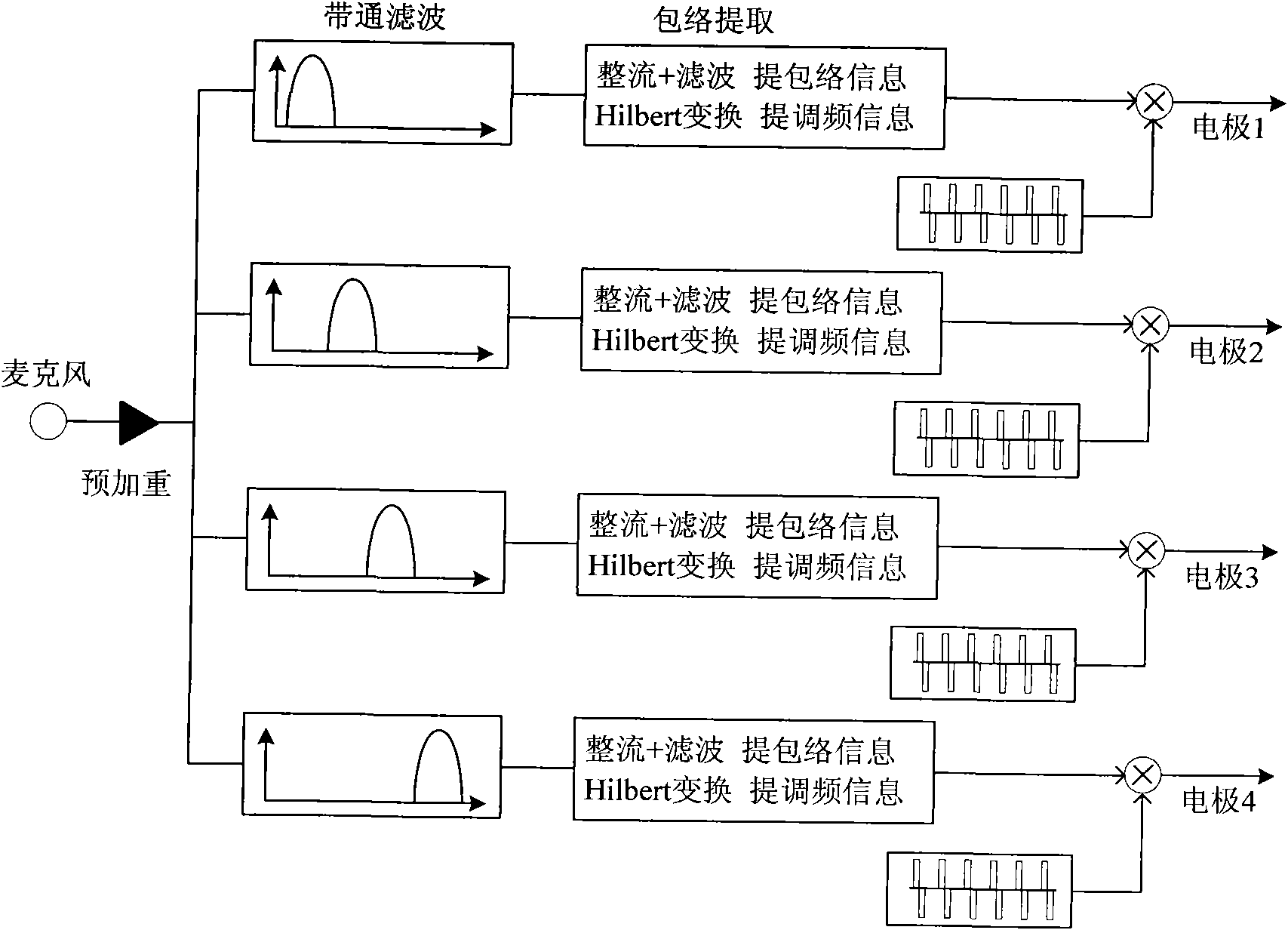
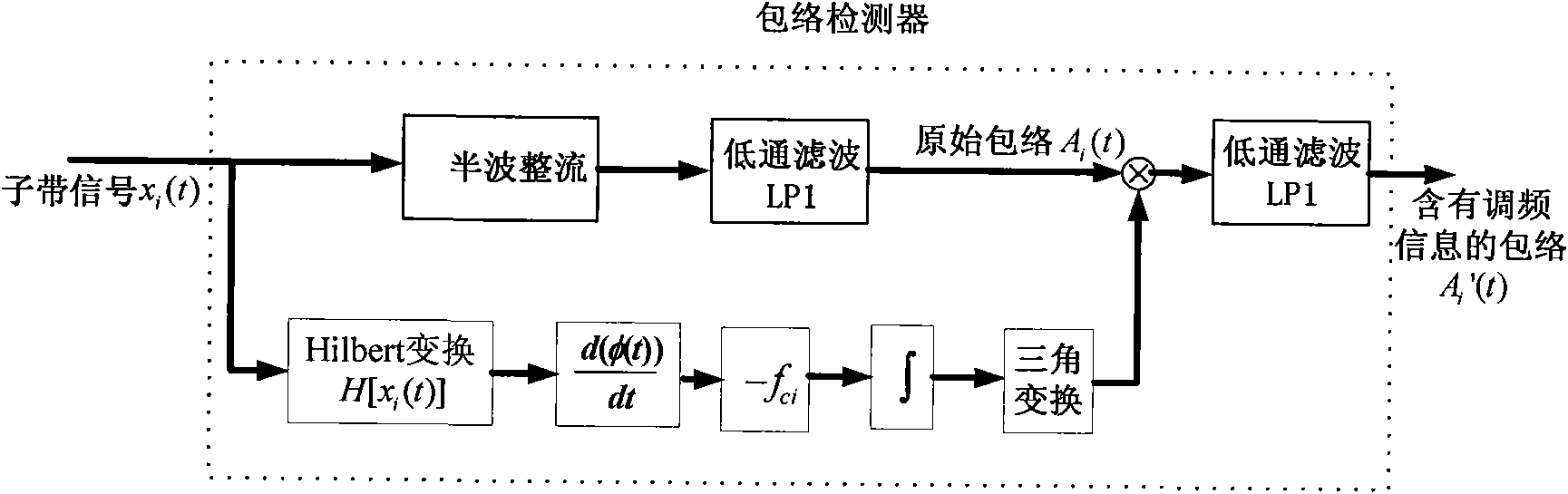
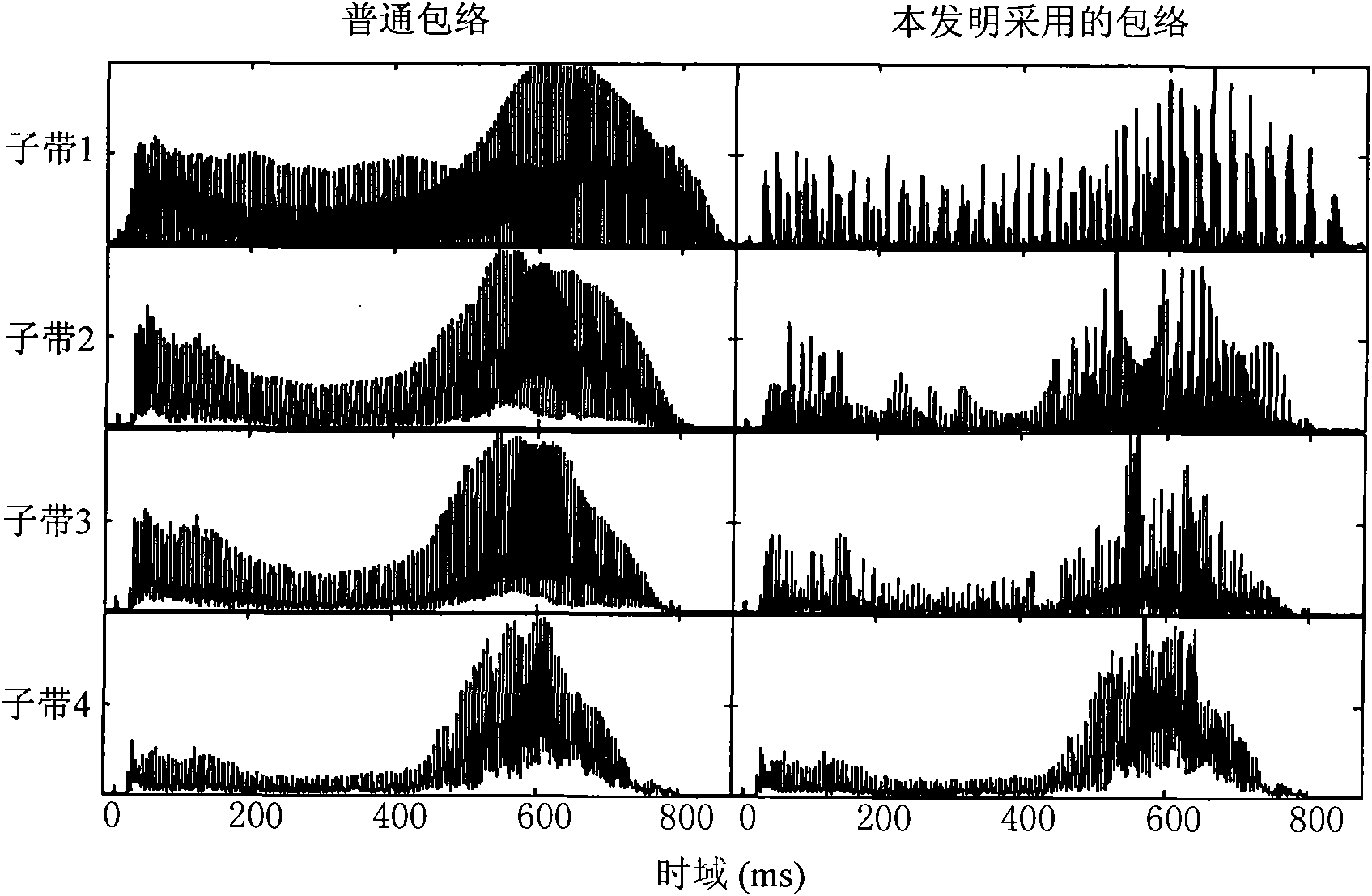
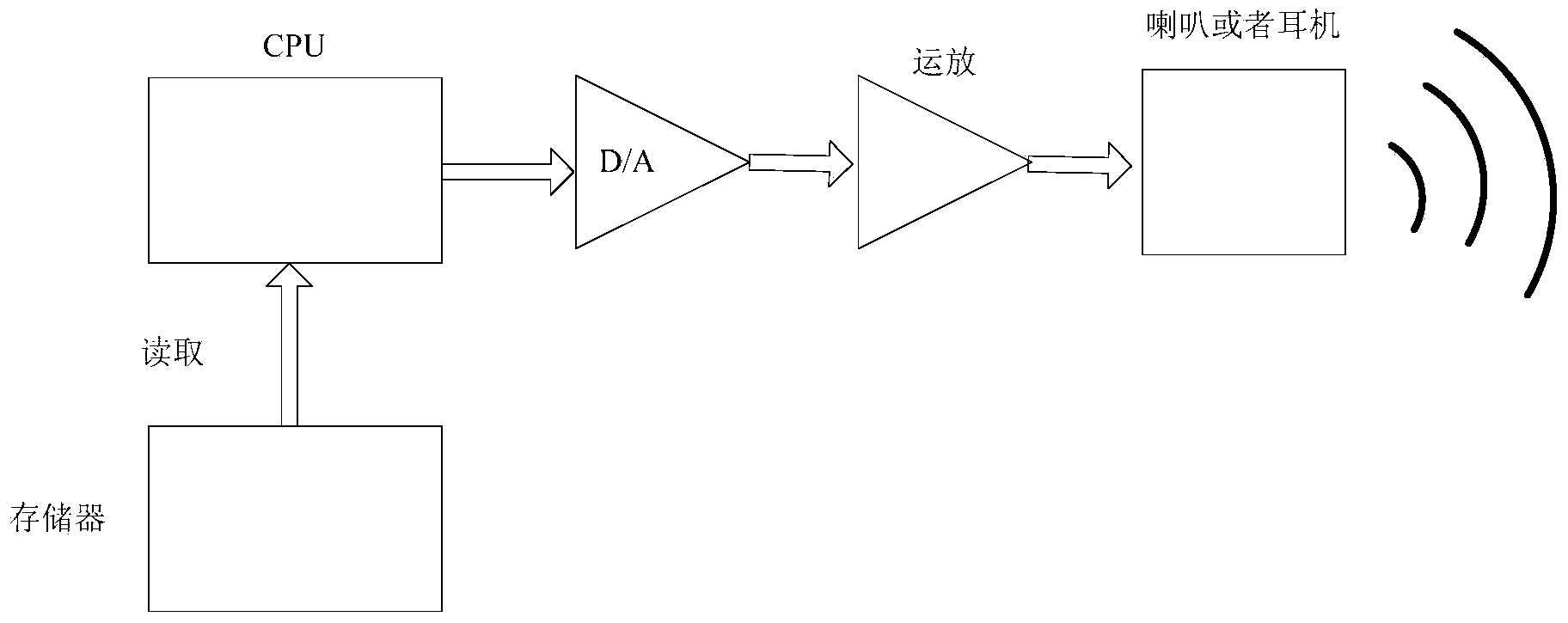
Artificial cochlea speech processing method based on frequency modulation information and artificial cochlea speech processor
ActiveCN101642399AImprove speech recognition performanceGood effectEar treatmentSpeech analysisSpeech ProcessorElectrical impulse
The invention provides an artificial cochlea speech processing method based on frequency modulation information and an artificial cochlea speech processor. The artificial cochlea speech processing method comprises the following steps: pre-emphasizing a speech signal; decomposing the speech signal by an analysis filter into a plurality of sub frequency bands; then, extracting the time-domain envelope information of each sub frequency band signal; adopting a Hilbert transform method to extract the frequency modulation information of a low-frequency part to multiple by time-domain envelopes so asto acquire a synthetic time-domain envelope containing the frequency modulation information; utilizing various acquired time-domain envelopes of the sub frequency bands to modulate a pulse sequence by a pulse generator; adding modulated pulses of various sub frequency bands to acquire a finally synthesized stimulus signal; and sending the stimulus signal to an electrode to generate an electric pulse to stimulate the auditory nerve. The artificial cochlea speech processor is suitable for deafness patients speaking Chinese as a native language to recognize speeches in a noise environment and has noise robustness, thereby enabling the deafness patients to feel more fine speech structure information, enhancing the speech recognition abilities of the deafness patients in the noise environmentand benefiting the tone recognition.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
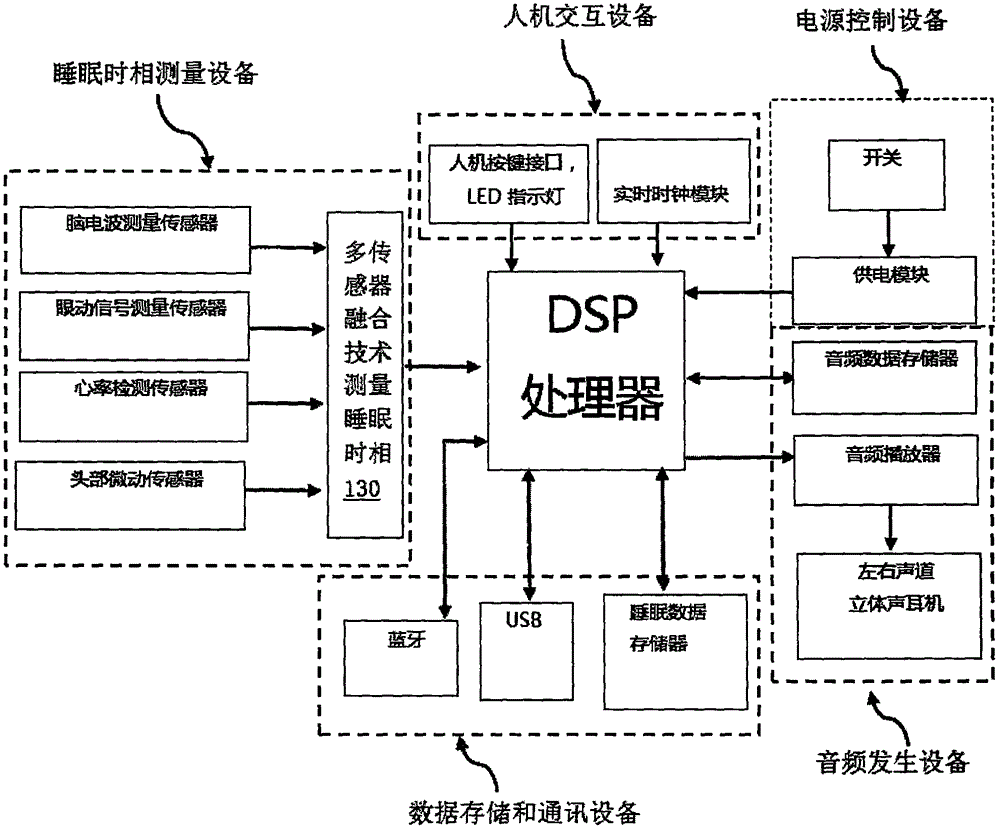
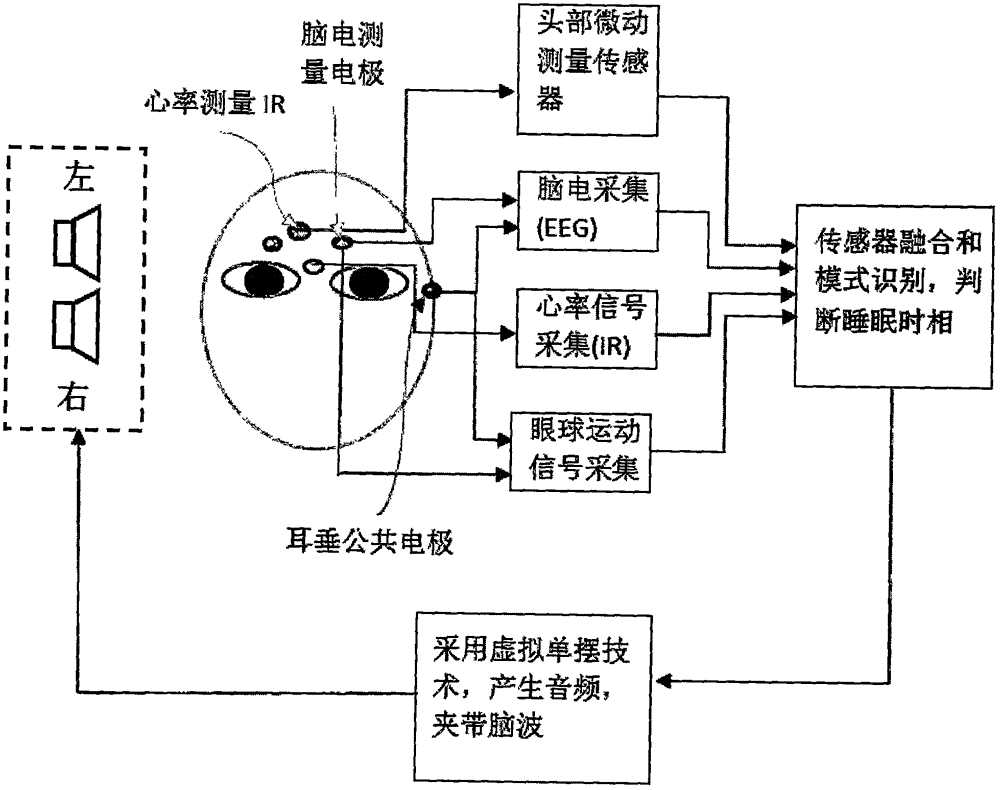
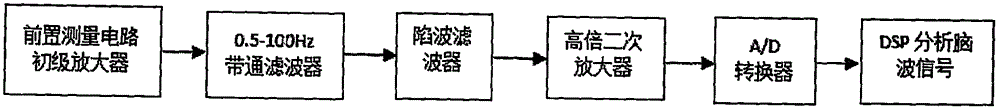
Novel intelligent sleeping-aiding and natural wakening method and device
InactiveCN105833411AImprove comfortImprove stabilitySleep inducing/ending devicesSleep/relaxation inducing devicesEngineeringAudio frequency
The invention relates to the technical field of sleeping aiding and wakening, in particular to a novel intelligent sleeping-aiding and natural wakening method and device, and concretely provides an intelligent sleeping-aiding and natural wakening system based on virtual swinging rhythm and electroencephalogram signal biofeedback. According to the method, firstly, the actual frequency of the current brain waves is measured; then, the swinging frequency similar to the current brain wave frequency is determined; for the swinging frequency, two voice frequencies with the frequency difference are respectively transmitted to two ears of the human body to cause the impression of swinging of a single voice frequency between the two ears in the brain through the integration by auditory nerves, so that the swinging voice frequency, i.e., the swinging frequency is formed in the brain; the swinging frequency is similar to the frequency of the brain waves, so that the swinging frequency carries the brain wave frequency to gradually reduce or increase the current brain wave frequency until the brain wave frequency reaches the target frequency required for sleeping or wakening; and finally, a sleeper can sufficiently fall asleep or can be naturally wakened. The method and the device provided by the invention are mainly applied to the sleeping aspect.
Owner:TAIYUAN TEMARU ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
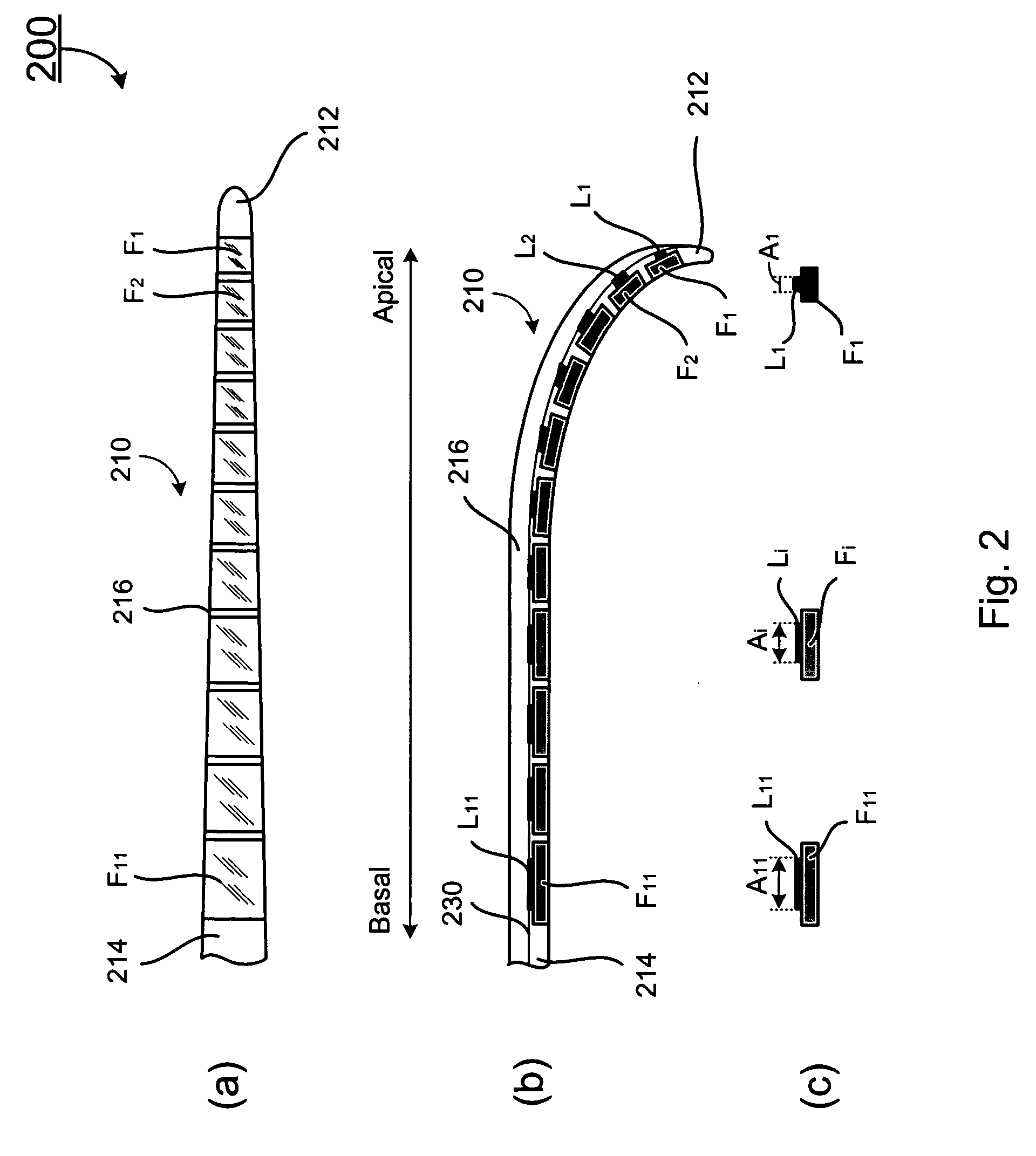
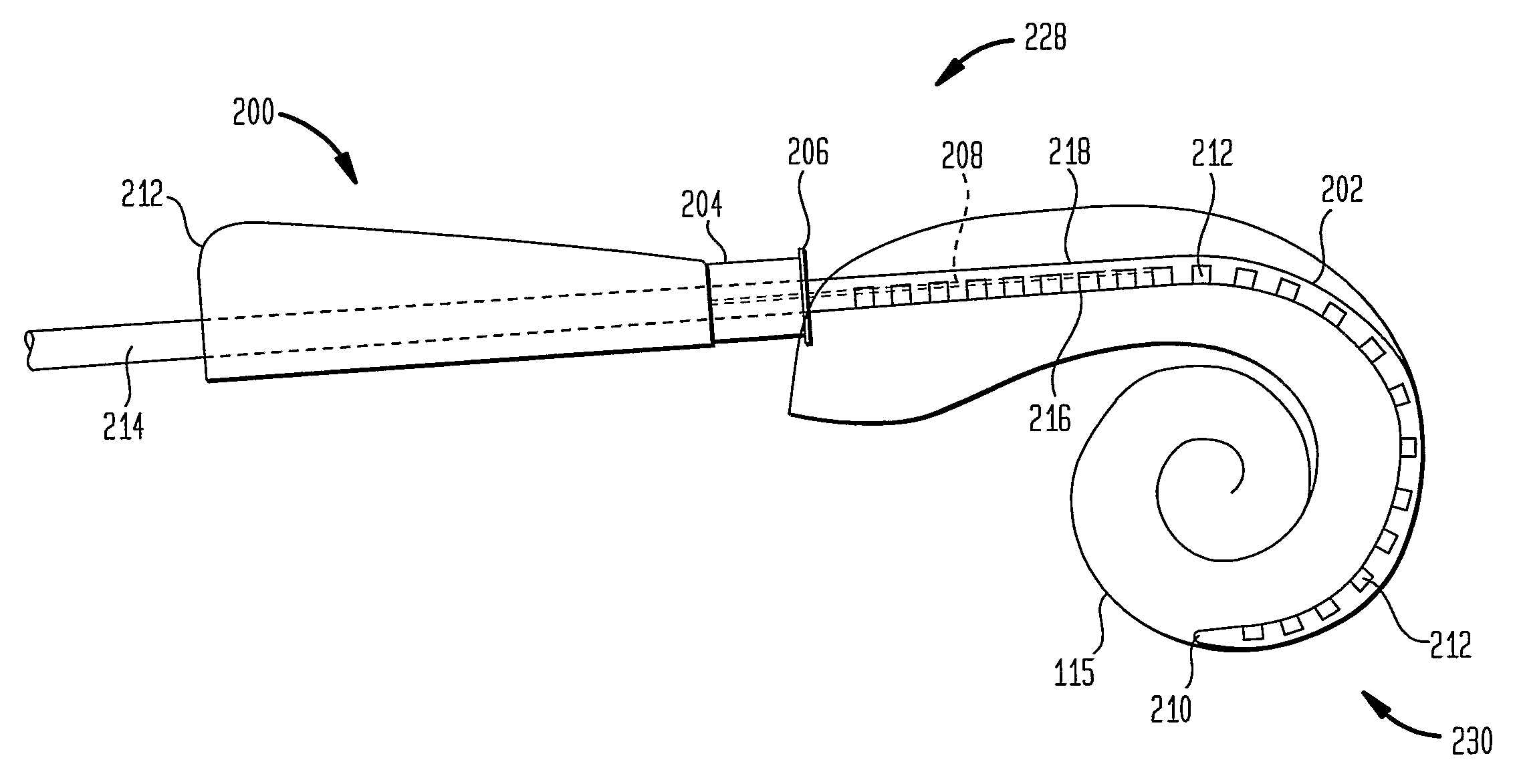
Elongate implantable carrier member having an embedded stiffener
ActiveUS20090030483A1Reduced flexibilityAvoid deformationHead electrodesEar treatmentCochlear implantationAuditory nerves
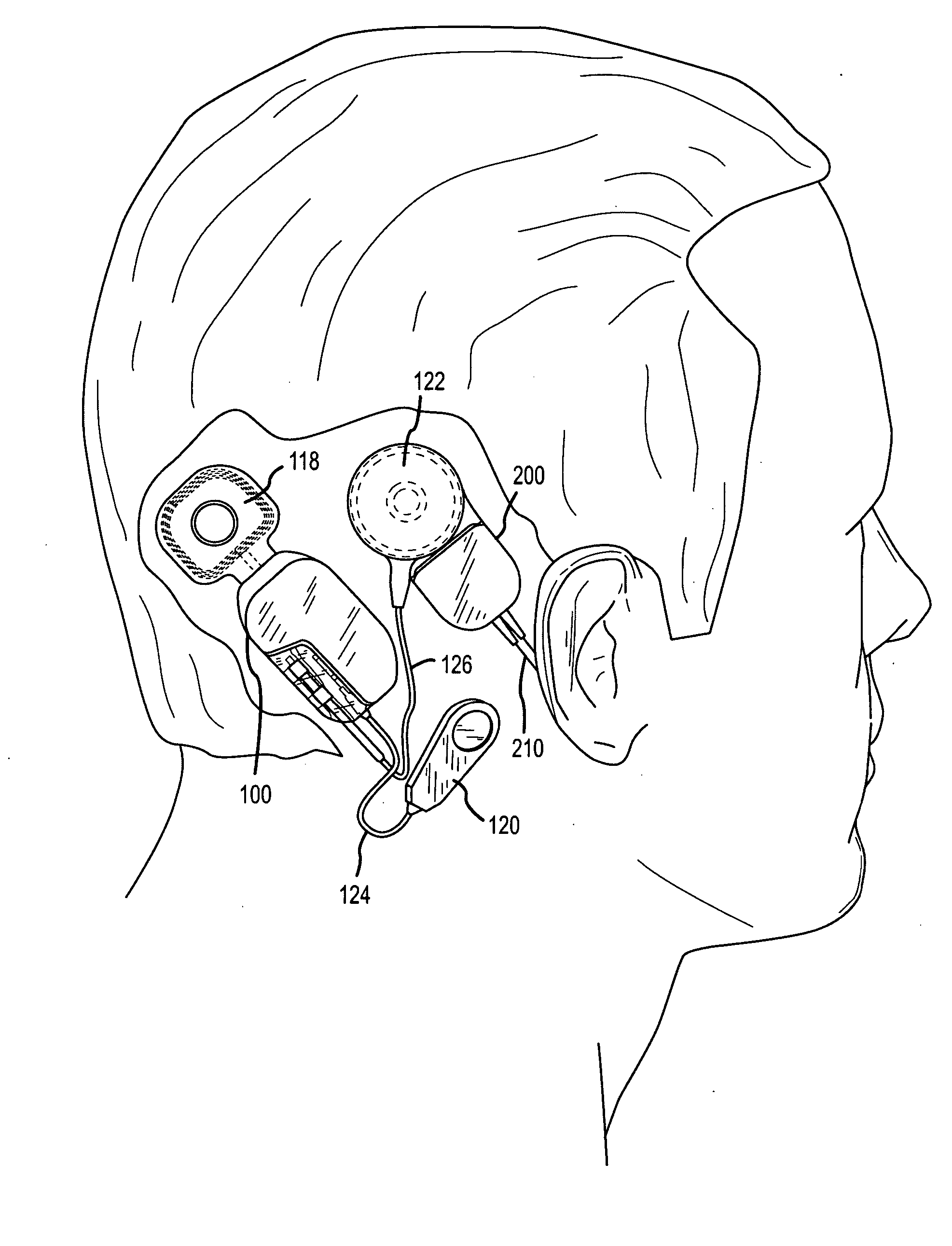
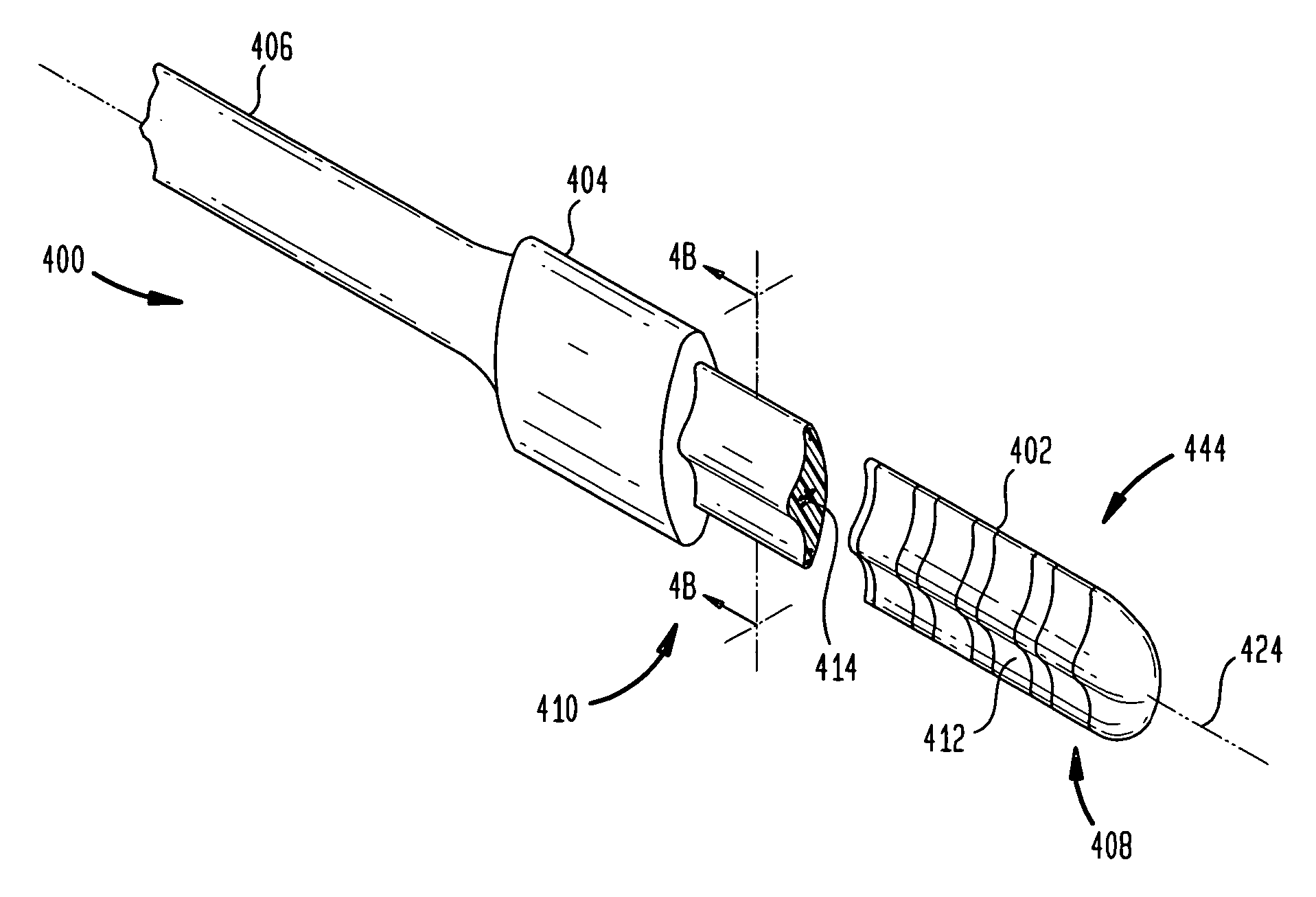
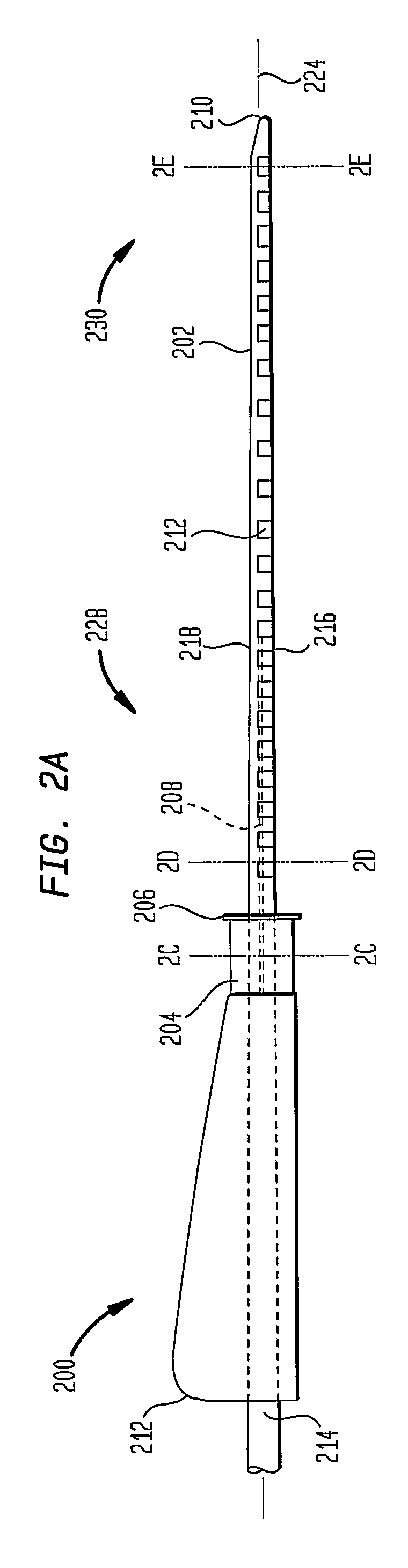
A cochlear implant comprising: a speech processor for processing received sounds to generate coded stimulation control signals; a stimulator unit configured to generate stimulation signals in response to the control signals; and an electrode assembly (200). The electrode assembly in turn comprises: a flexible elongate carrier member (202) having a plurality of electrodes (212) disposed thereon, the electrodes configured to stimulate auditory nerves of the cochlea; and a stiffening member (208), permanently embedded in and longitudinally extending through at least a first region of carrier member, configured to decrease the flexibility of the carrier member region so as to prevent deformation of the first region during implantation.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Cochlear implant device, extracorporeal sound collector, and cochlear implant system having the same
InactiveUS20080177353A1Improve communication distanceConvenient for daily lifeHead electrodesSolid-state devicesInformation processingElectrical battery
An object is to provide a cochlear implant system (also known as an artificial inner ear system) which is easy to use with little interference with daily activities. A cochlear implant device (or artificial inner ear device) includes an inner ear electrode, an information processing circuit, a transmitter / receiver circuit, a charging circuit, and a battery; and the battery is charged with electromagnetic waves received by the transmitter / receiver circuit through the charging circuit. In addition, the power stored in the battery is supplied to the cochlear implant device. Further, the electromagnetic waves received by the transmitter / receiver circuit are converted into a signal by the information processing circuit, and the signal is provided from the inner ear electrode to stimulate the auditory nerve.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
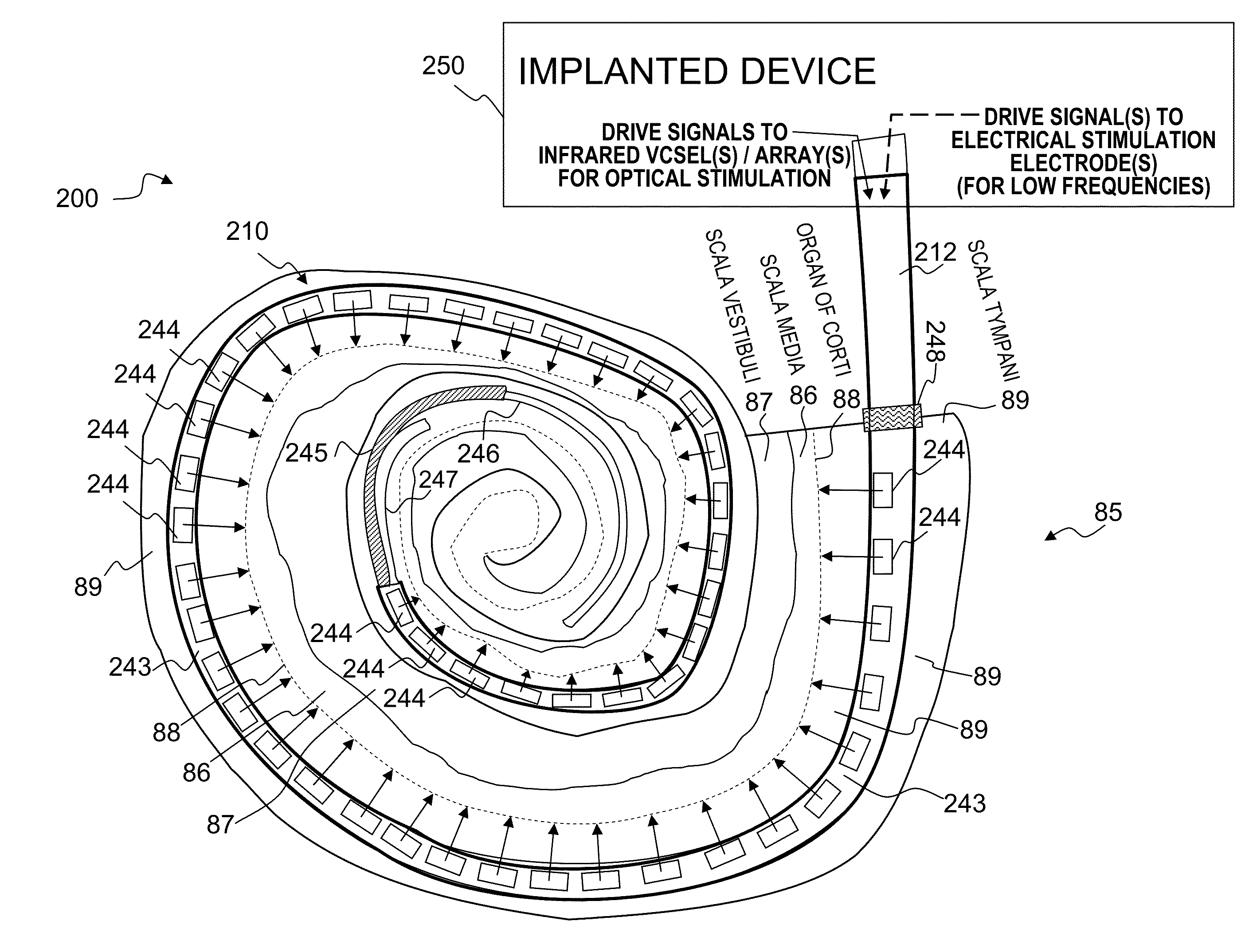
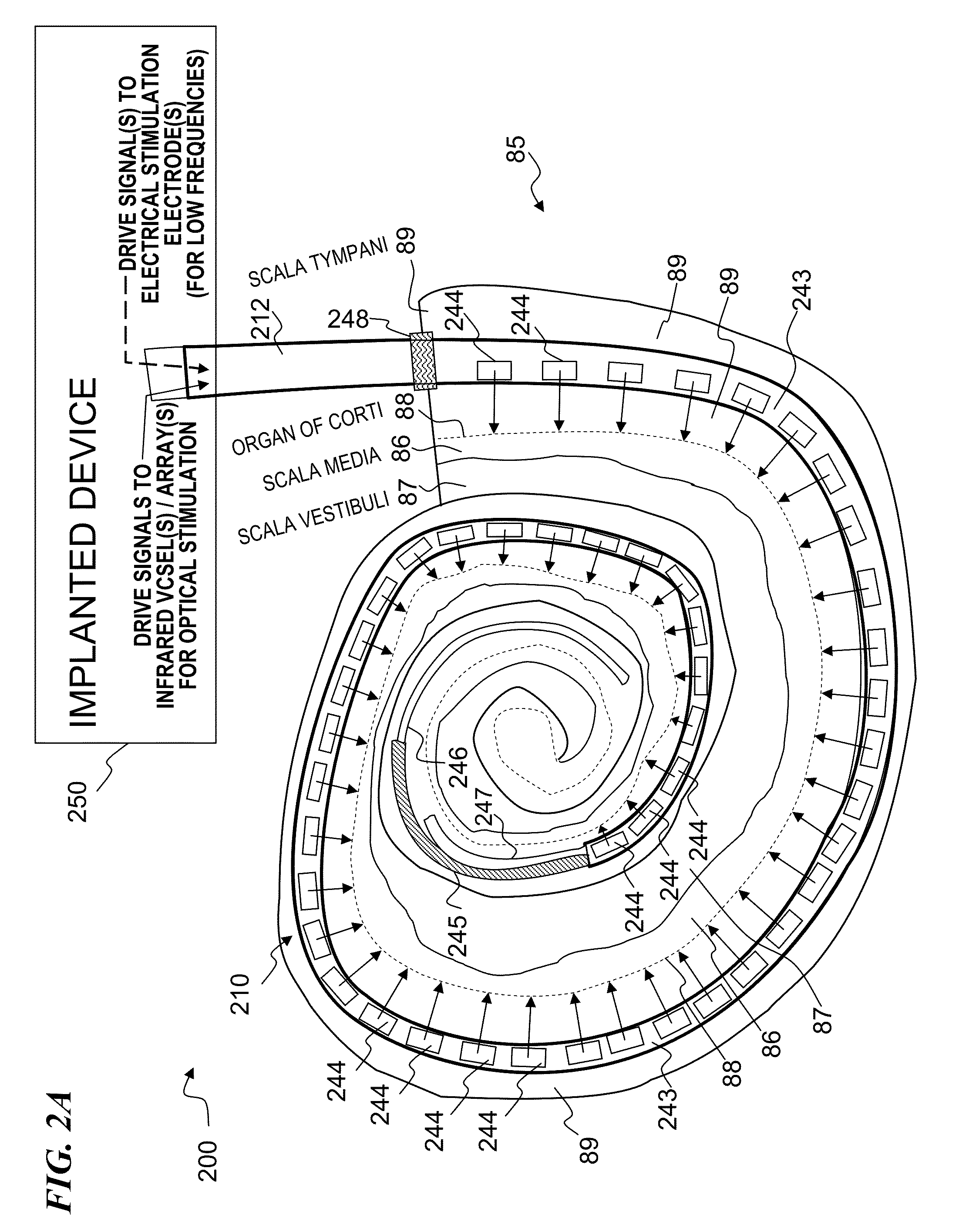
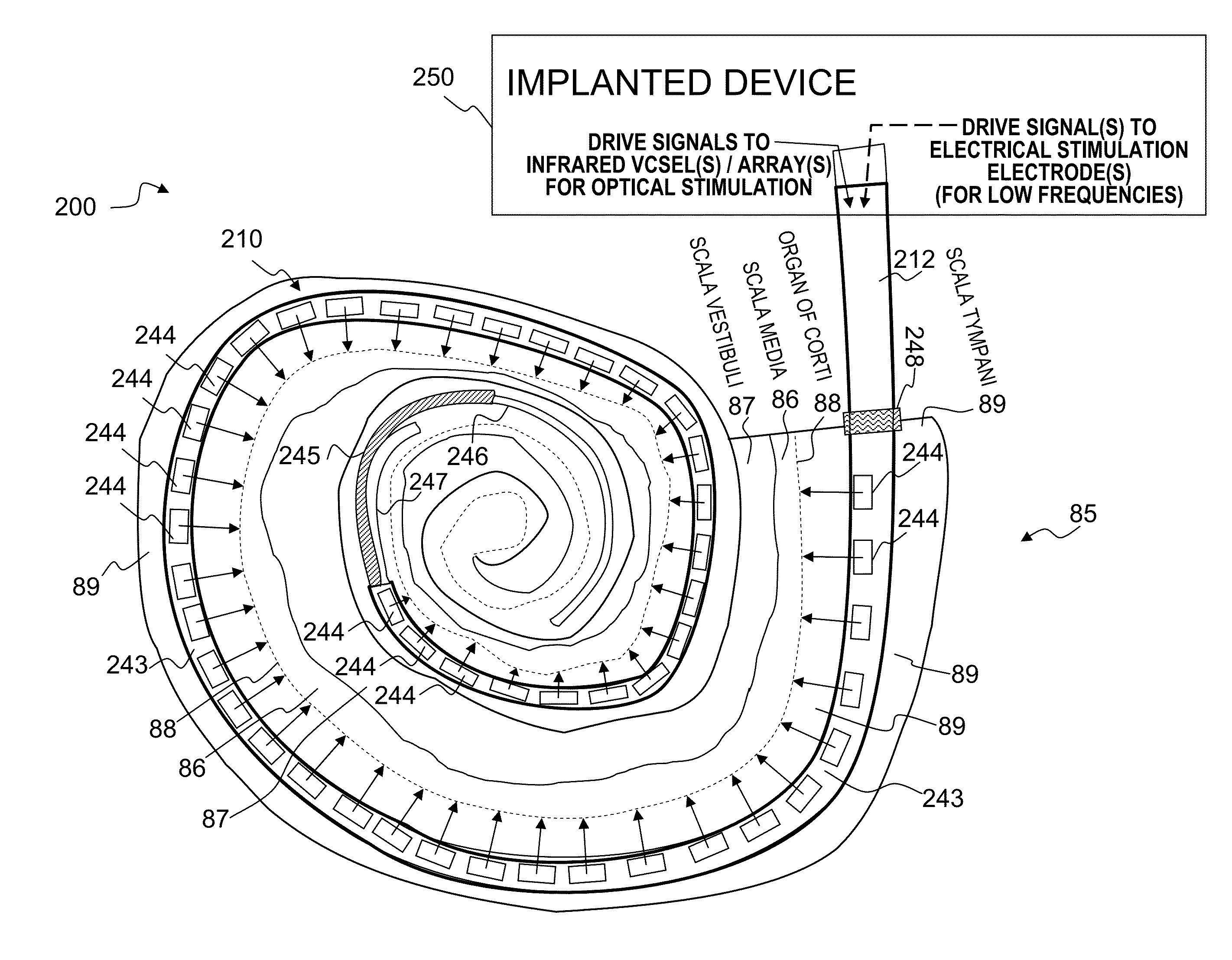
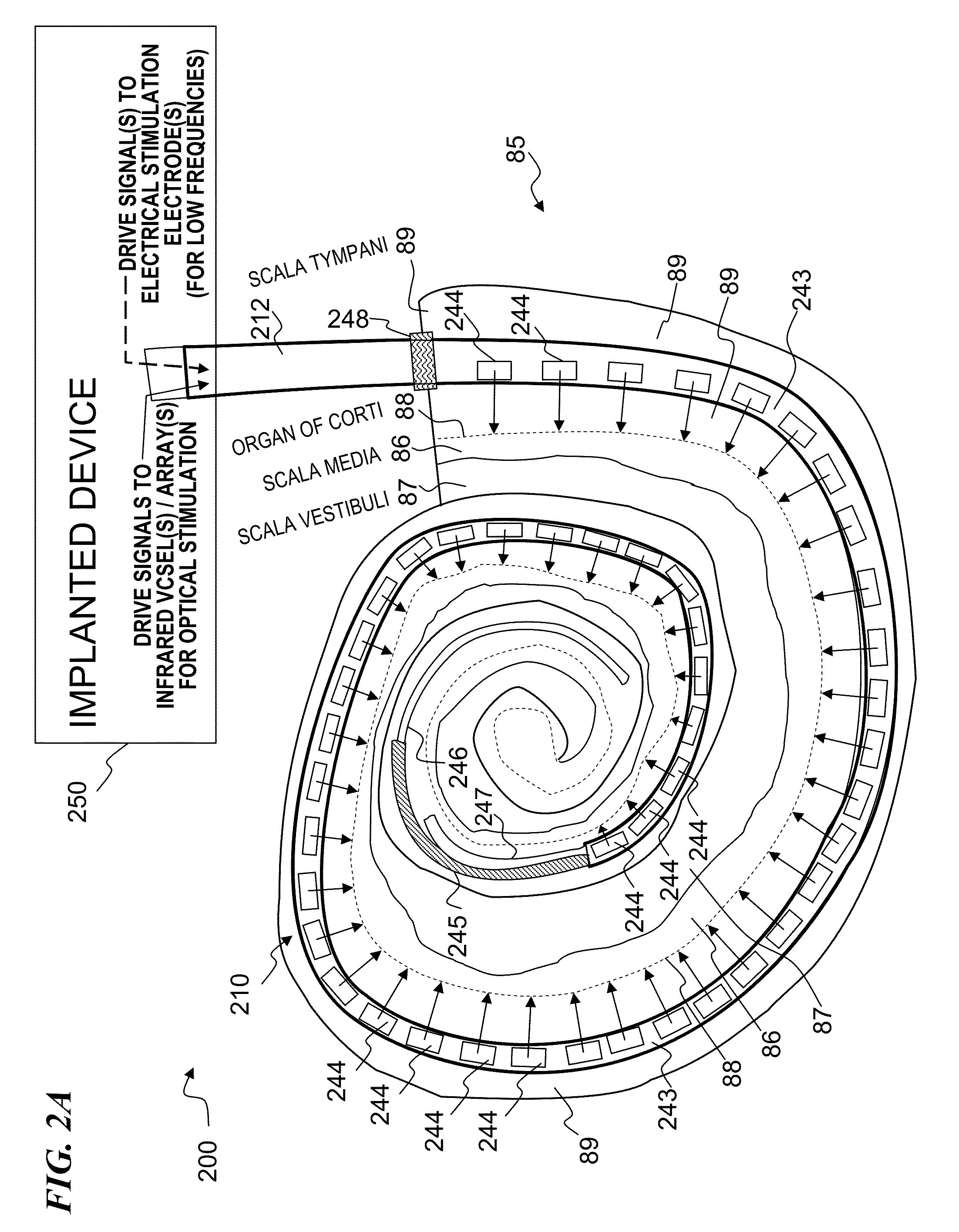
Optical-stimulation cochlear implant with electrode(s) at the apical end for electrical stimulation of apical spiral ganglion cells of the cochlea
ActiveUS20130023967A1Increased frequency rangeSpeech recognitionHead electrodesEar treatmentOptical stimulationElectrical stimulations
Method and apparatus for optically and electrically stimulating neurons of auditory nerve pathways of a person to provide auditory sensations for the person including generating a plurality of pulsed light signals having one or more successive pulses, delivering the plurality of pulsed light signals to one or more auditory nerve pathways of the cochlea of the person and selectively controlling the plurality of light signals to optically stimulate and trigger nerve action potentials (NAPs) in the one or more auditory nerve pathways. In some embodiments, the present invention also includes one or more electrical stimulation electrodes used to stimulate the low frequency portions of the auditory nerves.
Owner:NUROTONE MEDICAL LTD
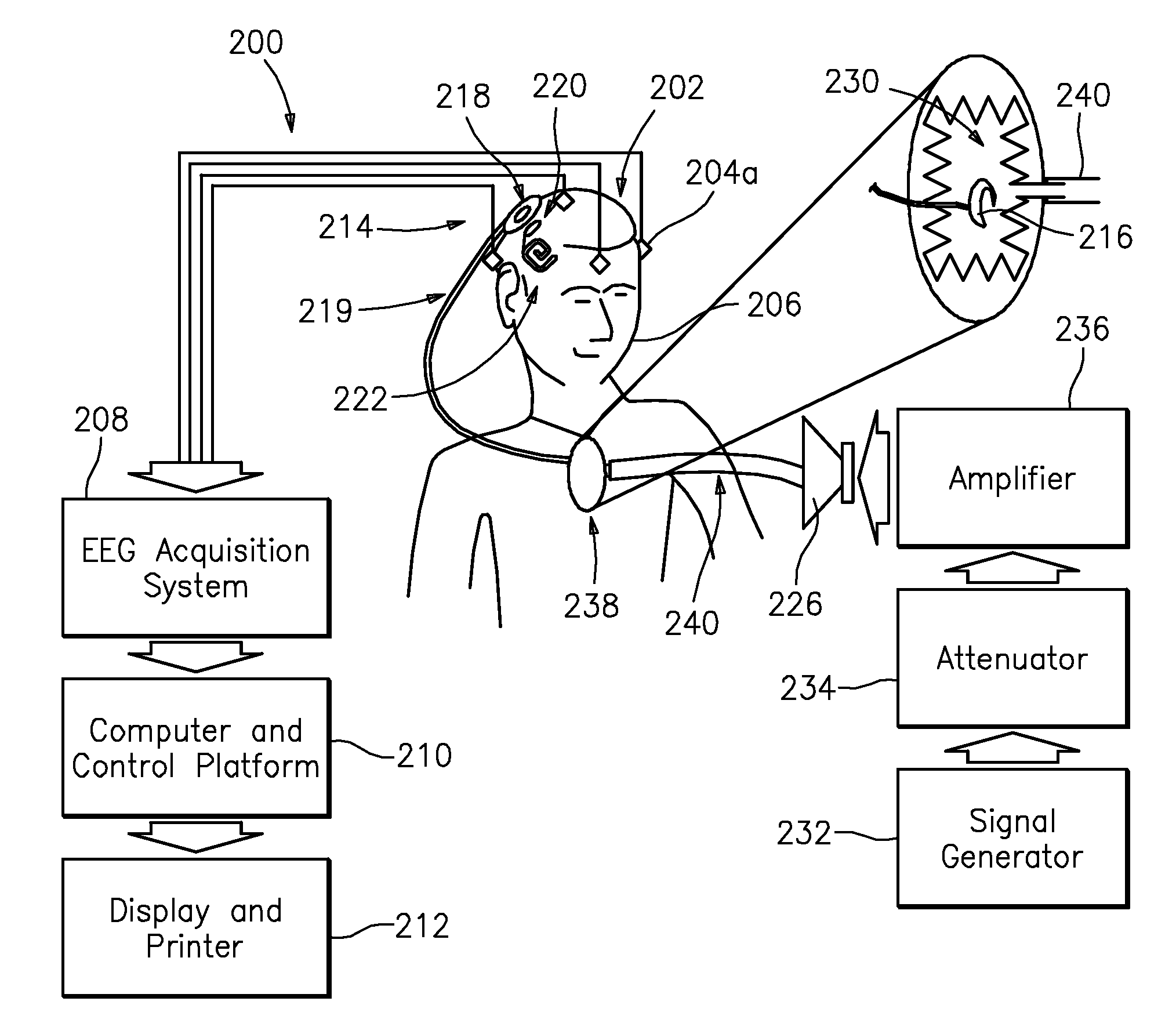
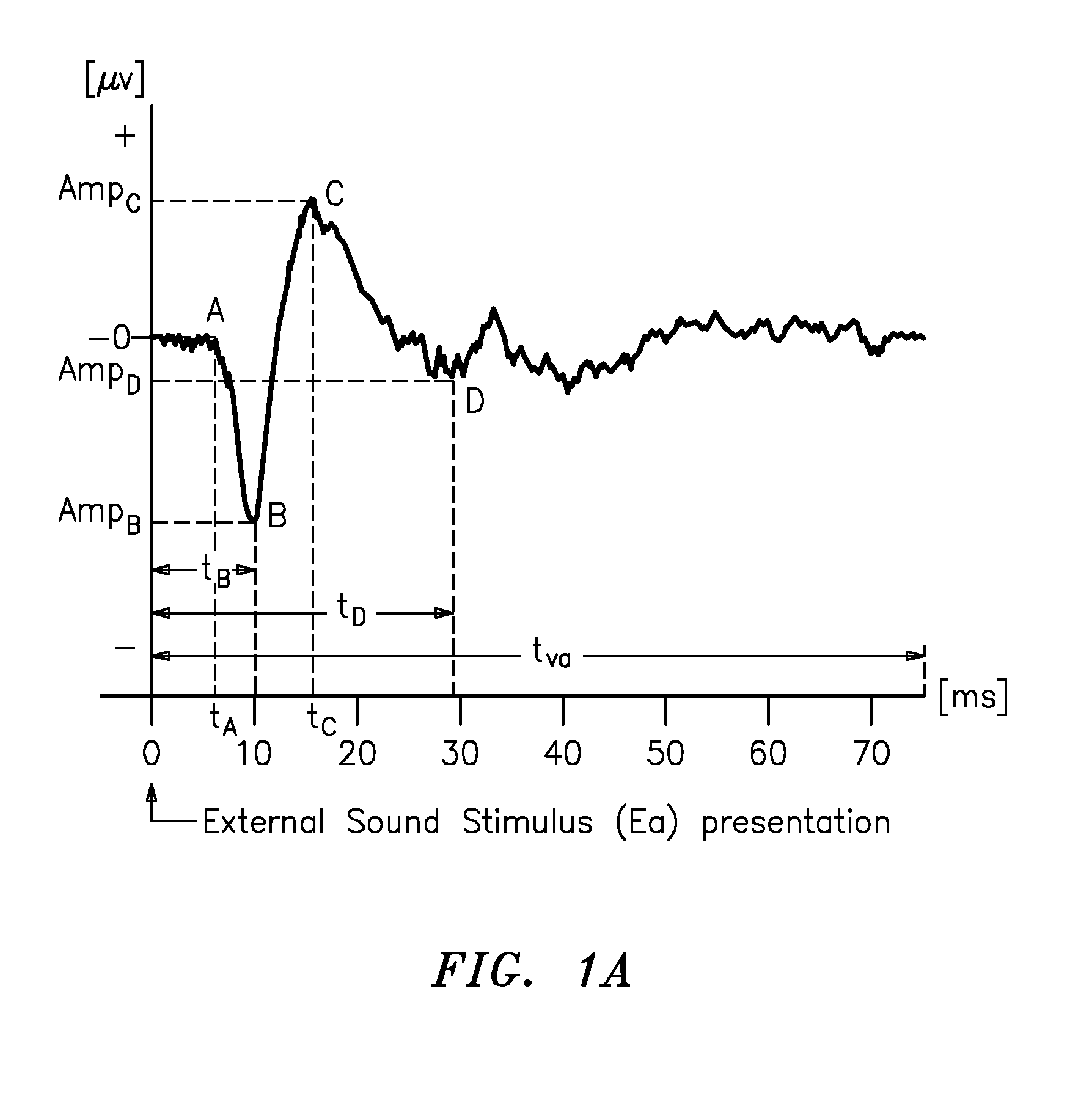
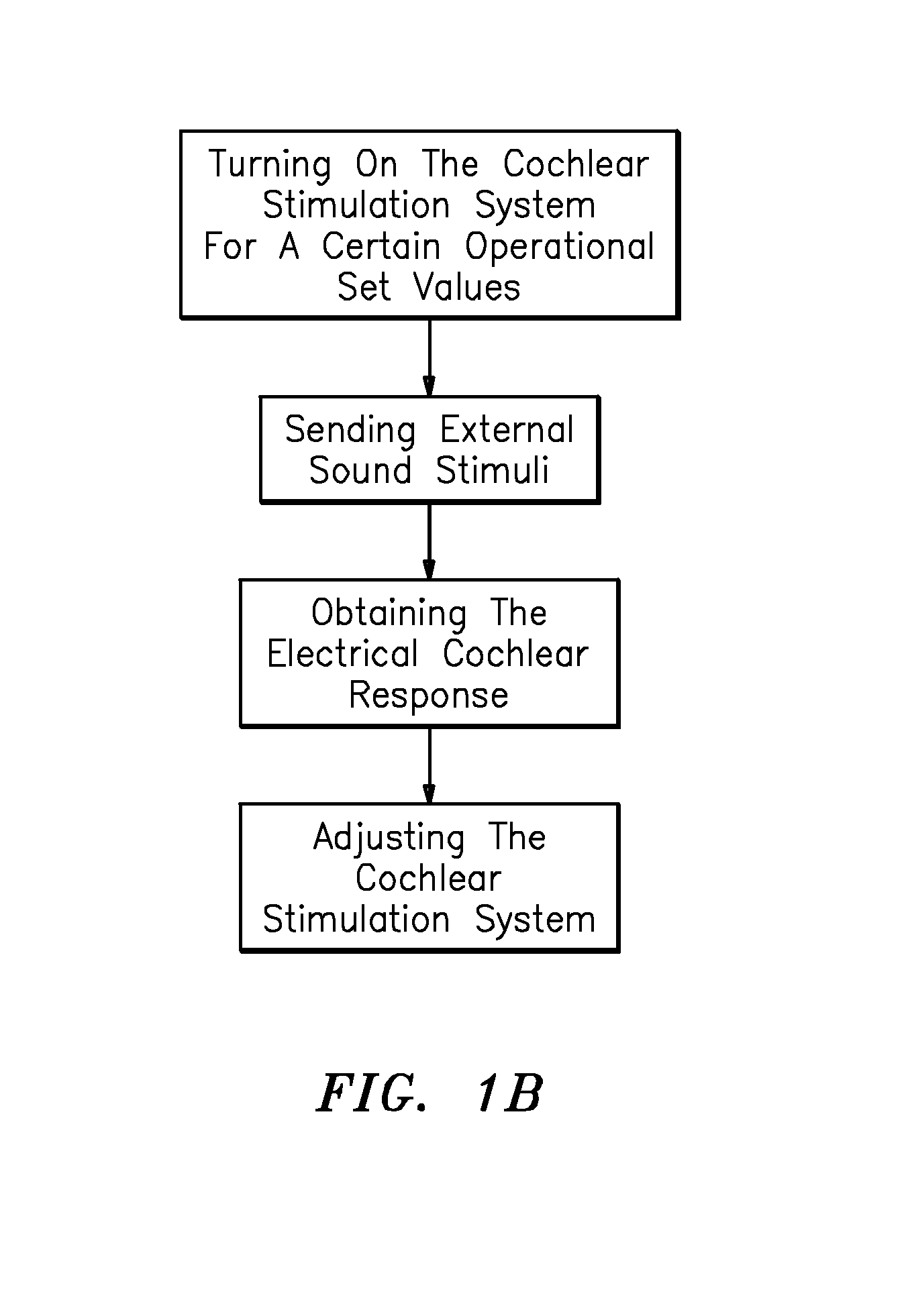
Method and apparatus for obtaining and registering an electrical cochlear response ("ecr")
This invention relates to a method and apparatus for obtaining and registering the Electrical Cochlear Response (“ECR”). Particularly, the ECR refers to the electrical activity of the auditory nerve and the intracochlear residual tissue located in the neighborhood of an intracochlear stimulation electrode, when an external sound is presented to a Cochlear Implant user, human or animal. Applicants recognize that an ECR can be thought of as a far-field electrical potential registered on the scalp of an implanted patient. Applicants, through their method and apparatus, can extract that potential from the patient's spontaneous electroencephalographic activity (EEG) and measure it by using an averaging algorithm. The Electrical Cochlear Response can be applied for adaptation, calibration, performance evaluation and failure detection of the Cochlear Implant of the implanted patient. Also Applicants' method can be applied to estimate the audiometric thresholds of the Cochlear Implant even without the implanted patient's knowledge.
Owner:UNIV AUTONOMA METROPOLITANA UNIDAD IZTAPALAPA
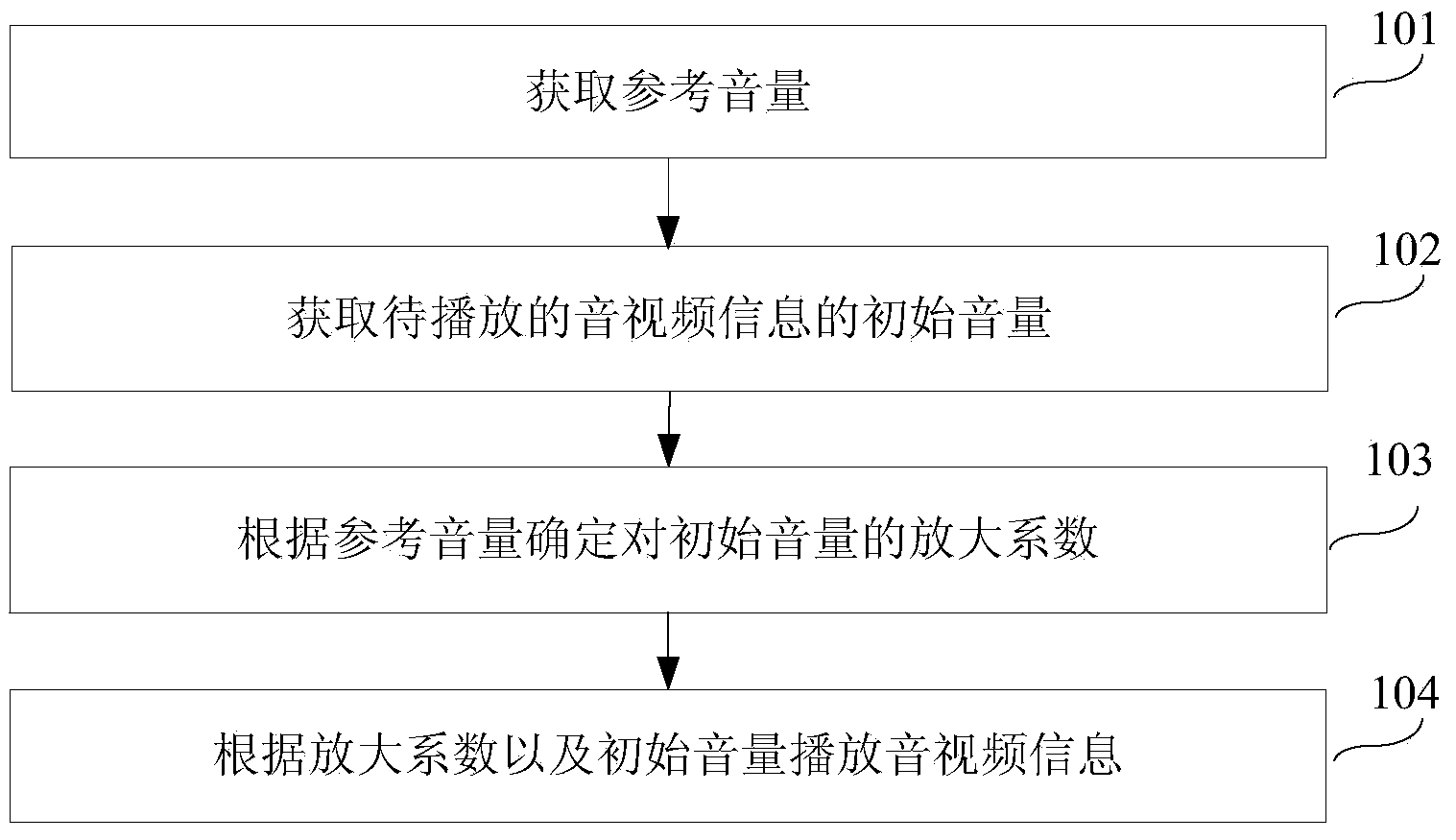
Volume adjustment method, device and electronic equipment
InactiveCN103618514AReduce operational complexityAvoid harmVolume compression/expansionElectric equipmentAuditory nerves
The invention discloses a volume adjustment method, a volume adjustment device and electronic equipment and belongs to the computer technical field. The volume adjustment method includes the following steps that: reference volume is obtained; initial volume of audio and video information to be played is obtained; the amplification coefficient of the initial volume is determined according to the reference volume; and the audio and video information is played according to the amplification coefficient and the initial volume. With the volume adjustment method, the volume adjustment device and the electronic equipment of the invention adopted, problems of high operational complexity of users and harm to auditory nerves of the users in the prior art can be solved; volume that is the same with the reference volume can be automatically adopted to play the audio and video information, such that the users do not need to manually adjust the volume, and the operational complexity of the users can be decreased; and at the same time, the same volume is adopted to play the audio and video information, and therefore, the harm to the auditory nerves of the users caused by too large or too small playing volume can be avoided.
Owner:XIAOMI INC
System and method for detecting nerve stimulation with an implanted prosthesis
The present application discloses systems and methods for detecting non-auditory nerve stimulation with an implant having a plurality of electrodes configured to electrically stimulate a target nerve of the implant recipient. One embodiment includes generating an electrical stimulation signal with a first set of electrodes of the implant, measuring a response to the electrical stimulation signal with a second set of electrodes of the implant, and determining whether the electrical stimulation signal stimulated at least one non-target nerve of the implant recipient based on the measured response.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Multi-channel light stimulation-based cochlear implant device
InactiveCN101926693AImprove spatial resolutionRealize contactless stimulationProsthesisHearing perceptionLIGHT STIMULATION
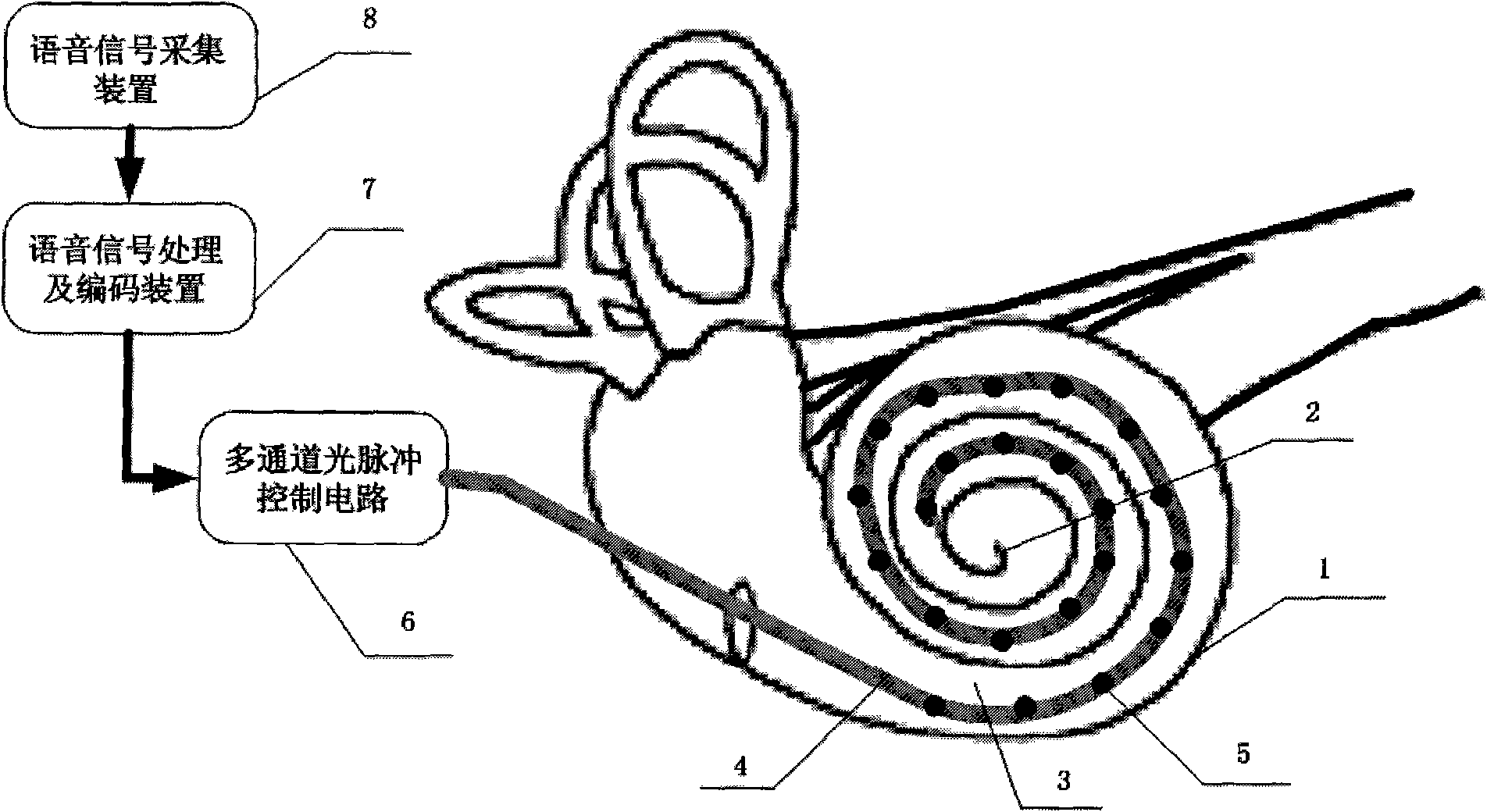
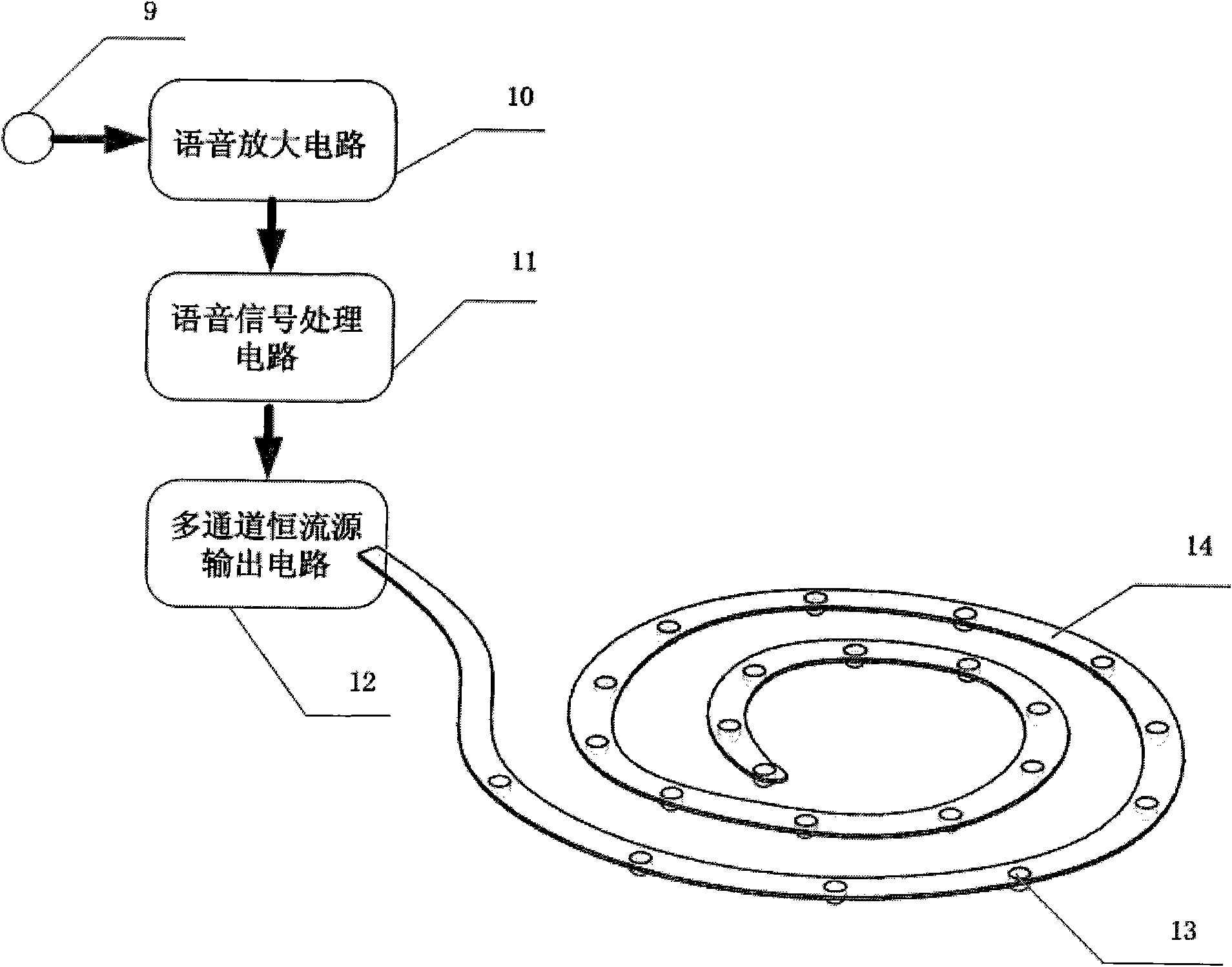
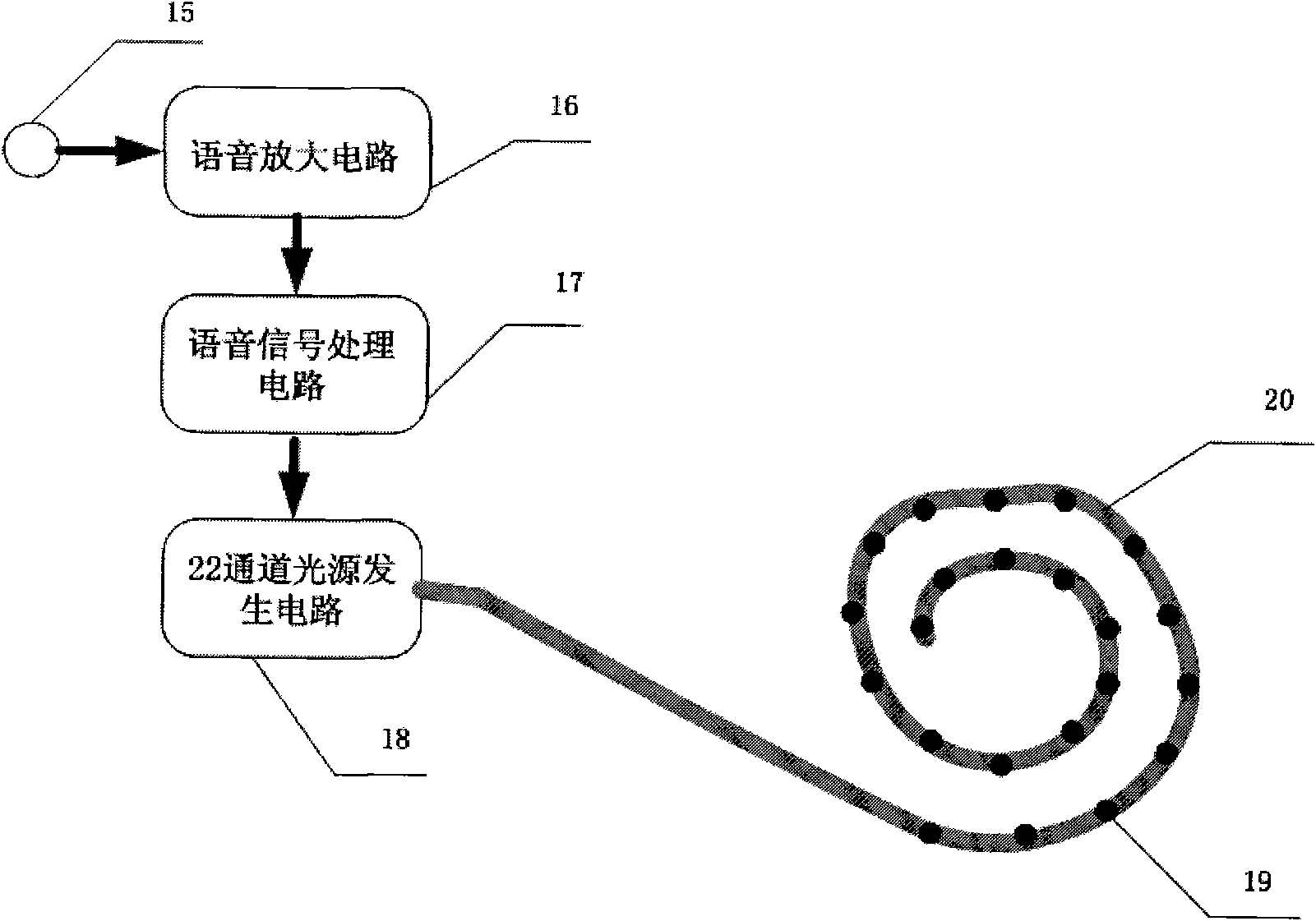
The invention relates to a multi-channel light stimulation-based cochlear implant device. The device comprises a multi-channel light stimulation device, a multi-channel light pulse control circuit, a voice signal acquisition deice and a voice signal processing and encoding device, wherein the device acquires a voice signal and encodes the voice signal into a light stimulation signal; and the light stimulation signal stimulates cochlear auditory nerve through a cochlea-implanted multi-channel light pulse output port to cause nerve impulse so as to form hearing in a central nervous system. The multi-channel light stimulation-based cochlear implant solves the problem of compatibility of a stimulating electrode and biological tissue in the electronic cochlear implant and also solves the problem of mutual interference between stimulating channels caused by current diffusion in the tissue.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Multifunctional piezoelectric bone conduction earphone and touch force feedback system integrated with glasses
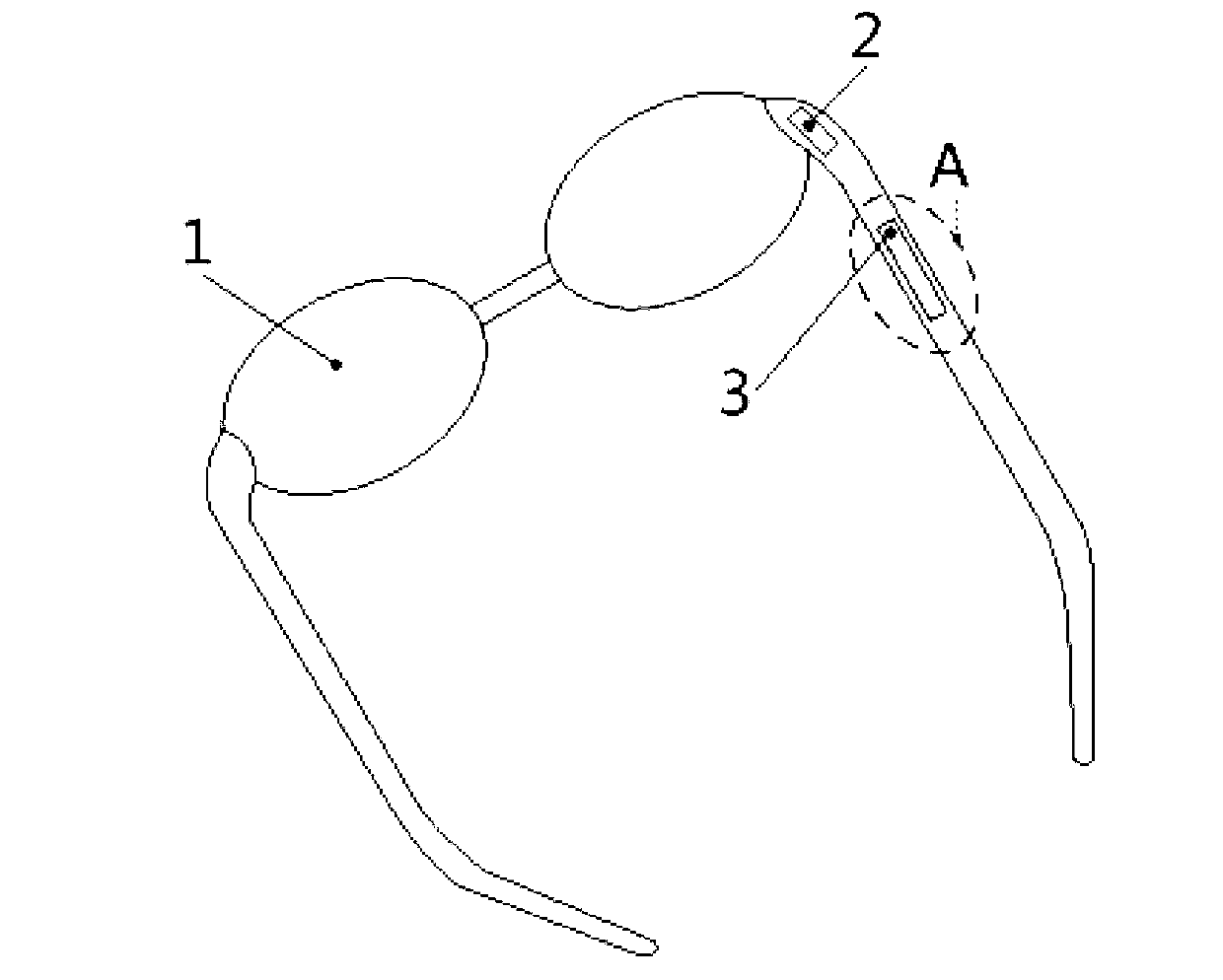
ActiveCN103002388AImprove space utilizationLittle external interferenceNon-optical adjunctsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive transducersFrame basedSignal processing circuits
The invention relates to the technical field of bone conduction earphones and touch force feedback, in particular to a multifunctional piezoelectric bone conduction earphone and touch force feedback system integrated with glasses. The system comprises a glasses frame base body, an integrated piezoelectric driving and force feedback signal processing circuit board, a power supply module, a piezoelectric material, an upper electrode layer, a lower electrode layer and a flexible circuit, wherein the integrated piezoelectric driving and force feedback signal processing circuit board and the power supply module are arranged at the roots of glasses legs, the piezoelectric material is fixed in a groove of one glasses leg, the upper electrode layer and the lower electrode layer are coated on the surface of the piezoelectric material, and the flexible circuit is connected with the electrode layers and the circuit board. The circuit board receives audio signals and applies voltage signals to the electrode layers of the piezoelectric material. By the aid of inverse piezoelectric effect, the piezoelectric material generates vibration identical to sound electric signals in frequency so as to drive the glasses legs to vibrate together, vibration of the glasses legs is transmitted into a human body face contacting with the glasses legs, sound is sensed by auditory nerves of a human body through bone conduction, and accordingly sense of hearing is generated. When the piezoelectric material is subjected to external force, corresponding induction electrical signals are generated and are processed by the circuit board to corresponding feedback touch signals which are used for achieving control functions of function selection, switching and the like.
Owner:KINGTONE INNOVATION BEIJING TECH
Light activated hearing aid device
ActiveUS20100197995A1Low transparencyEffectively generate mechanical vibrationElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsHearing perceptionPhysics
The invention relates to a hearing aid device for humans with impaired hearing, who have an at least partially functional cochlea and a functional nervous signalling pathway from the cochlea via the auditory nerve to the brain. The hearing aid device contains a receiver, a transducer of the sound or other acoustic signals into electrical current serving as a signal representing a sound, a pulsed irradiation source connected to the transducer for receiving the electrical current and for generating modulated pulsed irradiation in dependence from the electrical current, and preferably one or more optical fibres optically coupled to the exit of the pulsed irradiation source, wherein the optical path for conduction of irradiation within the device ends directly opposite a functional element of the natural vibration transduction pathway, e.g. adjacent the skull, the tympanic membrane, the hammer, the incus, the stapes, the outside of the cochlea, the otic capsule, the round window membrane, or the oval window membrane.
Owner:MEDIZINISCHE HOCHSCHULE HANNOVER
Focused stimulation in a medical stimulation device
ActiveUS7860573B2Narrowing of the stimulation regions minimizes or prevents this from occurringHead electrodesDeaf-aid setsPower flowDiffusion function
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Auditory nerve protection and re-growth
InactiveUS7700111B2Maintain their viabilityBiocideElectrotherapyIntervention measuresHearing perception
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for the protection and restoration of hearing. In particular, the present invention relates to treatments to facilitate the protection and re-growth of the auditory nerve. The present invention further provides methods of preventing hair cell loss and the accompanying loss in hearing. The present invention thus provides novel interventions for a variety of hearing impairments.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Artificial cochlea device
Owner:上海耳蜗医学科技有限公司
System and method for animal-human neural interface
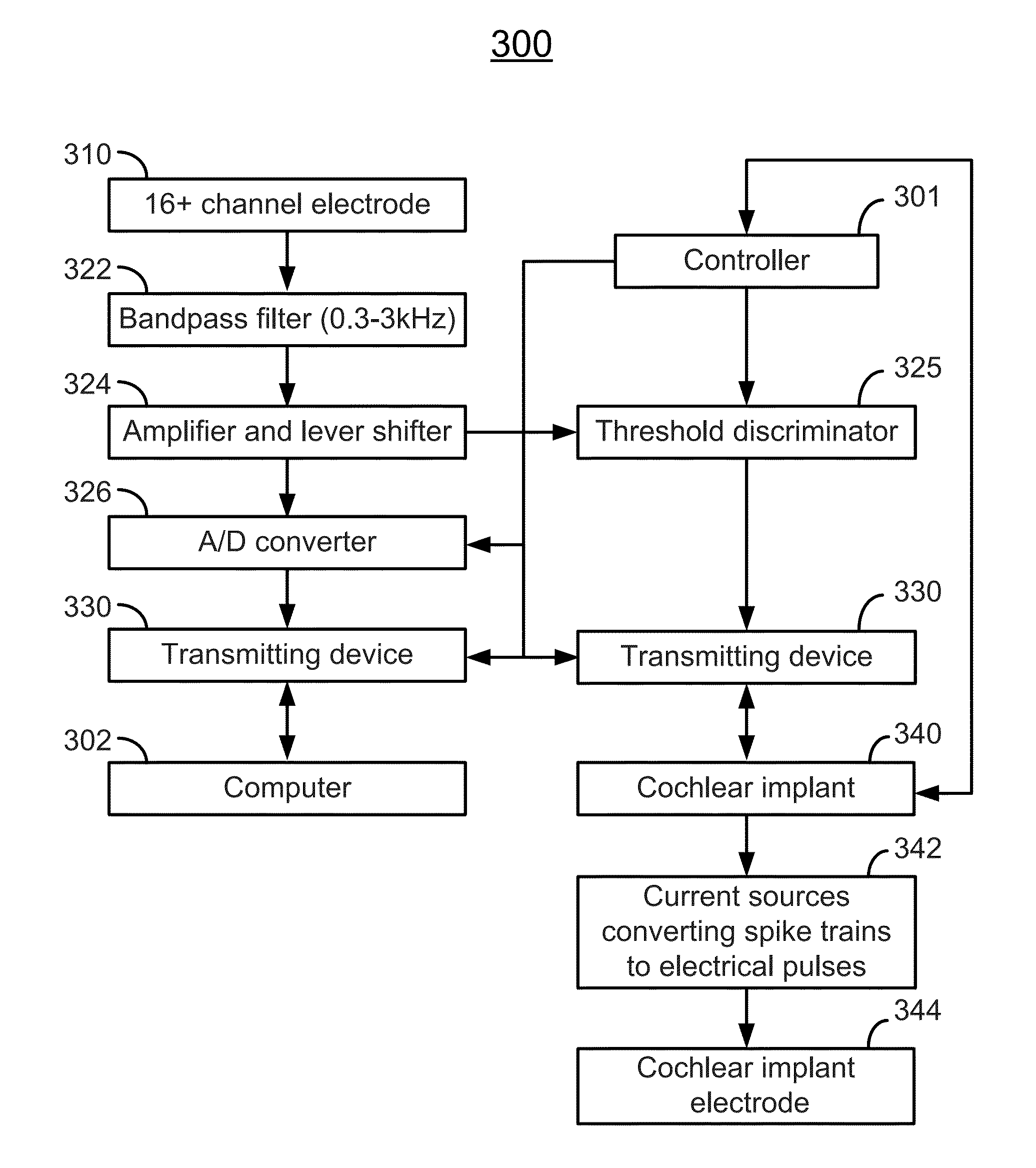
Aspects of the invention include system and method for transmitting neural data extracted from an electrical signal of a non-human mammal to a human. The system includes an electrode implantable into the animal auditory nerve, brainstem, or midbrain of the non-human mammal, configured to record the electrical signal of the non-human mammal, the electrical signal being in the form of sequences of pulses or pulse trains encoding frequency information of the non-human mammal, a processing device electrically coupled with the electrode, configured to process the electrical signal and convert the processed electrical signal into a digital signal, a transmitting device electrically coupled with the processing device, configured to transmit the digital signal, and a receiving device electrically coupled with the transmitting device, configured to receive the transmitted digital signal, convert the received digital signal into a sensory output perceptible to the human, and apply the sensory output to the human.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Cochlear implant
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Binaural stimulation in neural auditory prostheses or hearing aids
ActiveUS7920923B2Avoid time-overlapElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsInteraural time differenceFine structure
The present invention discloses of binaural stimulation in a neural auditory prosthesis. Binaural acoustic signals are generated that represent sound associated with a user's left and right ears respectively. Based on the binaural acoustic signals, corresponding binaural stimulation signals are generated for electrical stimulation of auditory nerve tissue of the user, wherein the binaural stimulation signals each include a fine structure component with periodic characteristics and interaural time difference (ITD) information. A phase jitter component is added to the binaural stimulation signals to reduce the periodic characteristics of the fine structure component while preserving the interaural time difference (ITD) information.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Optical-stimulation cochlear implant with electrode(s) at the apical end for electrical stimulation of apical spiral ganglion cells of the cochlea
ActiveUS8834545B2Speech recognitionImprove overall senseHead electrodesMachines/enginesOptical stimulationElectrical stimulations
Method and apparatus for optically and electrically stimulating neurons of auditory nerve pathways of a person to provide auditory sensations for the person including generating a plurality of pulsed light signals having one or more successive pulses, delivering the plurality of pulsed light signals to one or more auditory nerve pathways of the cochlea of the person and selectively controlling the plurality of light signals to optically stimulate and trigger nerve action potentials (NAPs) in the one or more auditory nerve pathways. In some embodiments, the present invention also includes one or more electrical stimulation electrodes used to stimulate the low frequency portions of the auditory nerves.
Owner:NUROTONE MEDICAL LTD
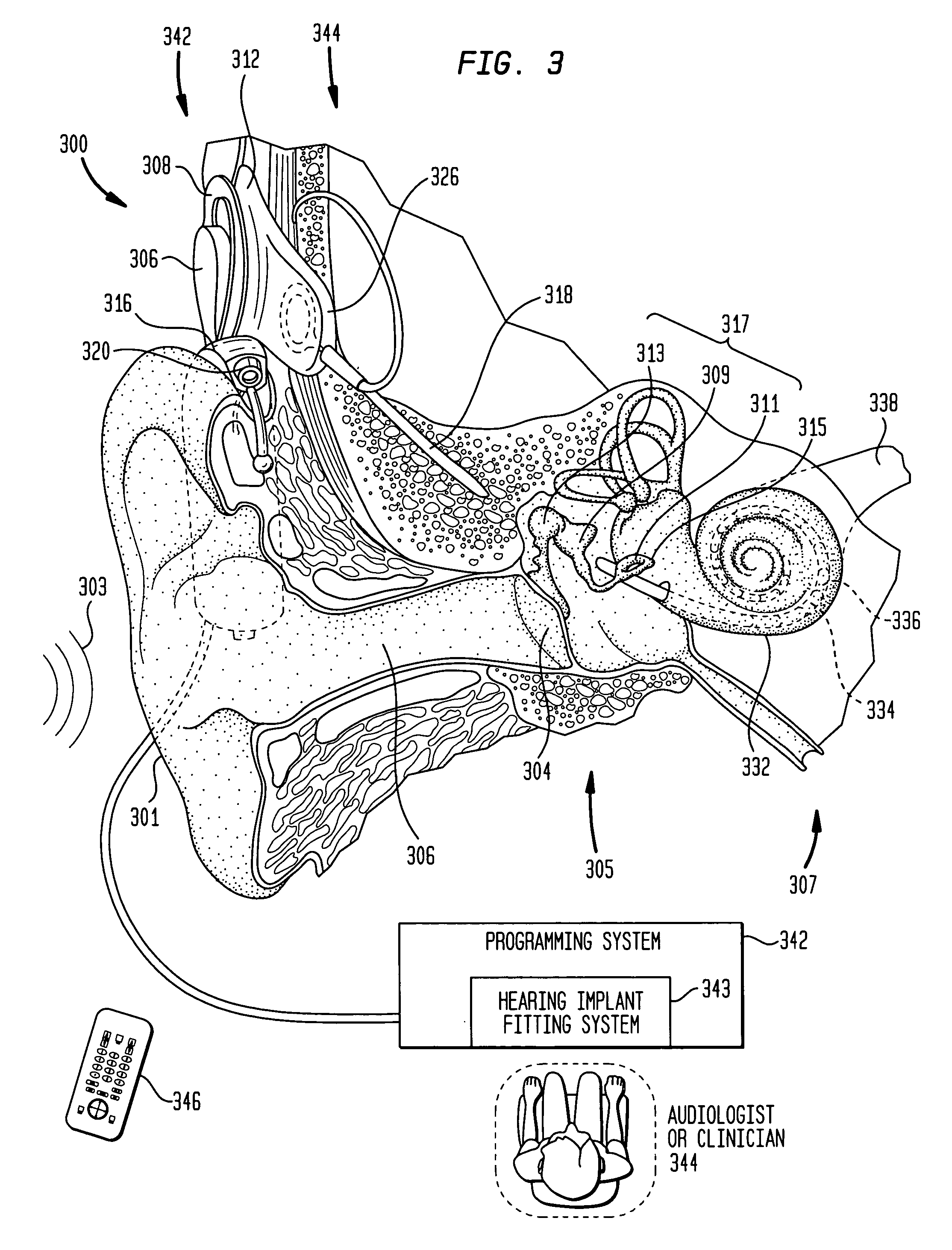
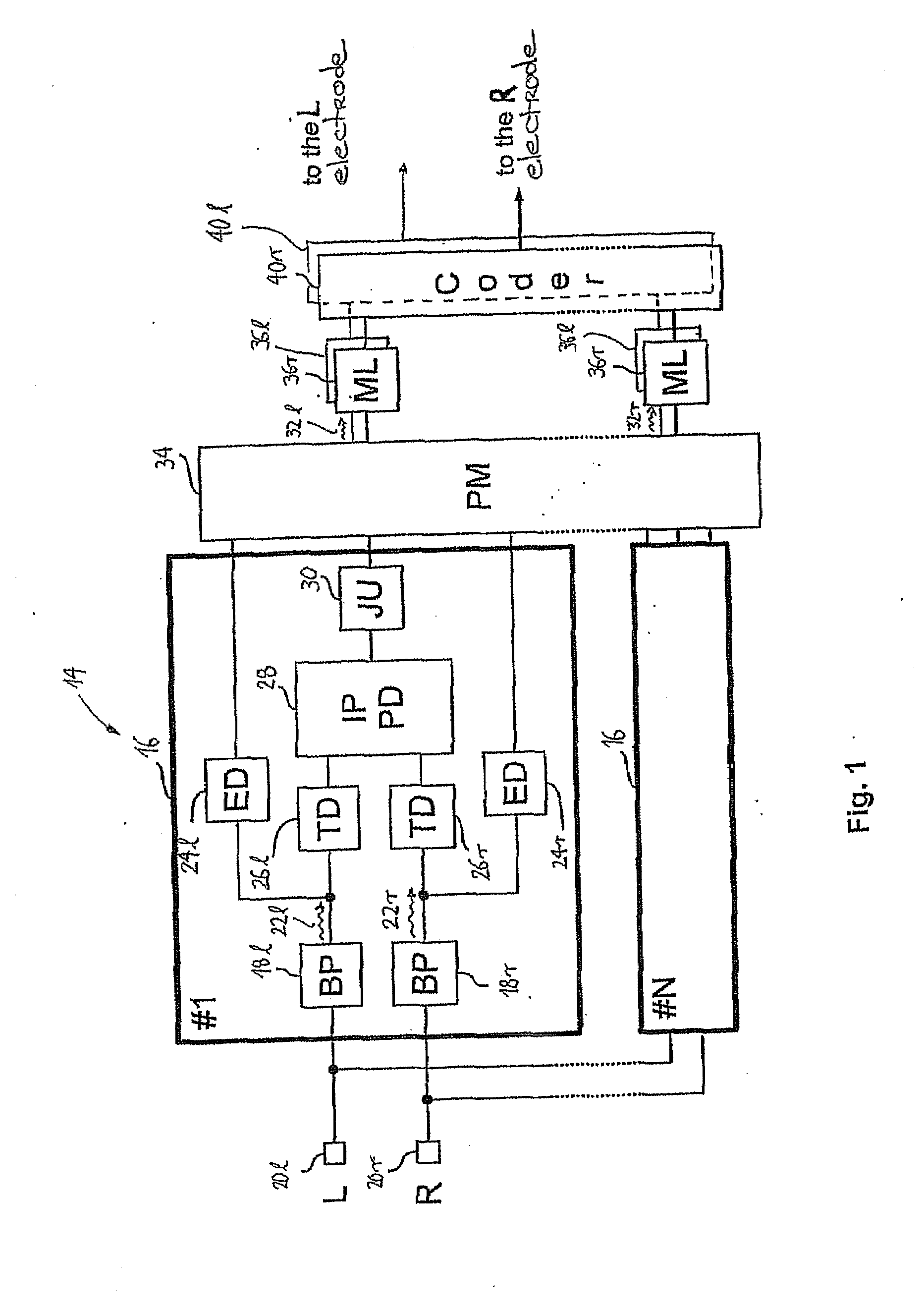
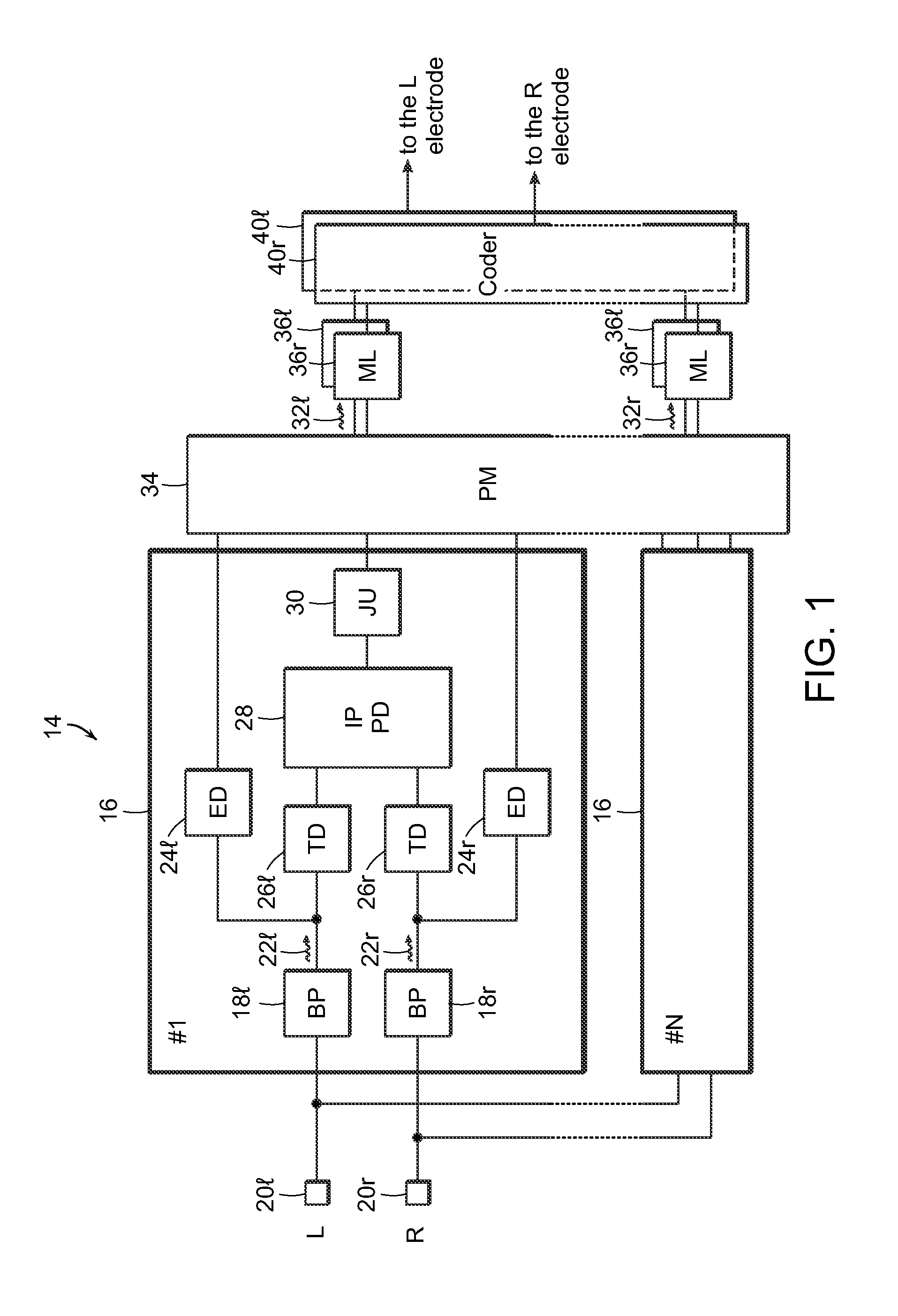
A hearing assistance device comprising an implanted part for measuring and processing electrically evoked nerve responses
The application relates to a hearing assistance device comprising an implanted part adapted for being implanted at a user's ear. The application further relates to a method of operating a hearing assistance device. The object of the present application is to improve identification and processing of recorded nerve response data in an implanted part of a hearing assistance device. The problem is solved in that the implanted part comprises a) A multitude of electrodes adapted for being located in the cochlea in proximity of an auditory nerve of the user; b) Stimulation circuitry electrically coupled to a stimulation electrode during a stimulation time period and configured for applying a stimulation signal to the stimulation electrode; c) Measurement circuitry electrically coupled to a recording electrode during a measurement time period and configured to measure a signal picked up by the recording electrode in response to said stimulation signal and providing a measured signal; d) A control unit configured to control the timing of the application of the stimulation signal in the stimulation time period and to control the measurement time period relative to the stimulation time period; and e) A processing unit configured to record the measured signal in the measurement time period and to identify a response from the auditory nerve based on said measured signal. This has the advantage of reducing the bandwidth requirement of a communication link to an external part during fitting. The invention may e.g. be used for cochlear implant type hearing aids, in particular during the fitting of such hearing aid to a particular user.
Owner:OTICON MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com