Patents
Literature
149 results about "Optical stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
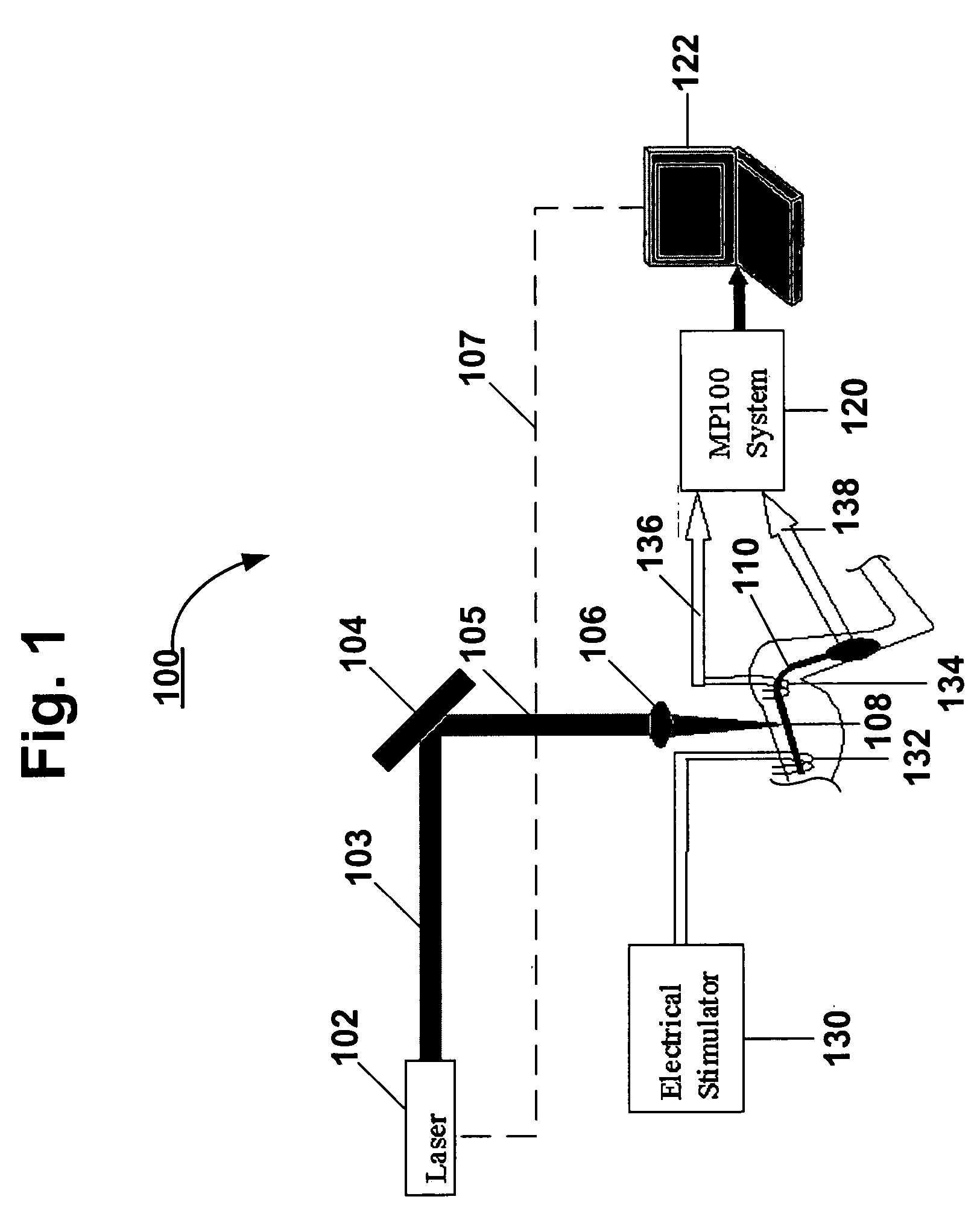
Methods and devices for optical stimulation of neural tissues
InactiveUS6921413B2Increasing electrical field sizeHighly specificElectrotherapySurgeryPHYSICAL MANIPULATIONSOptical stimulation
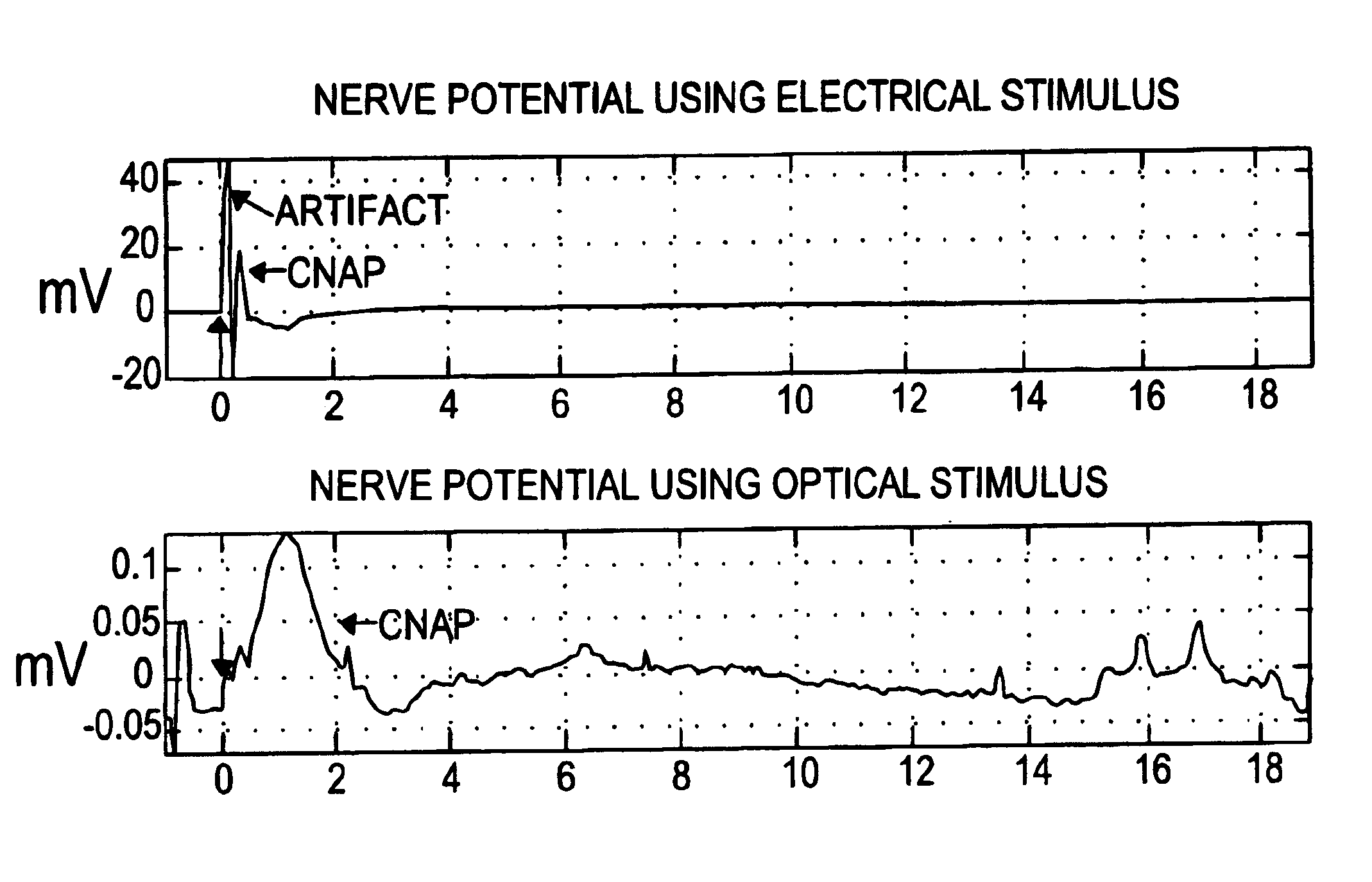
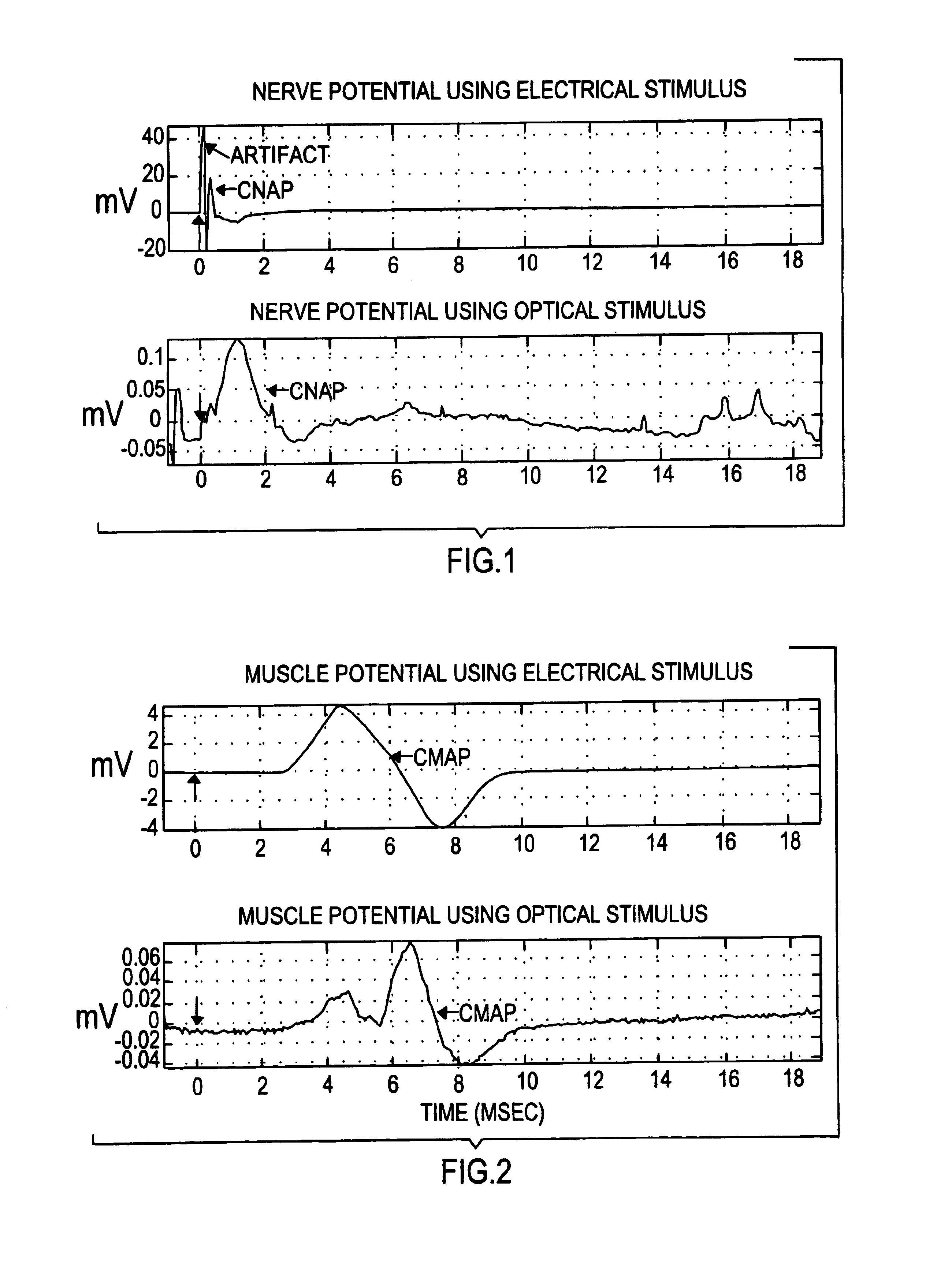
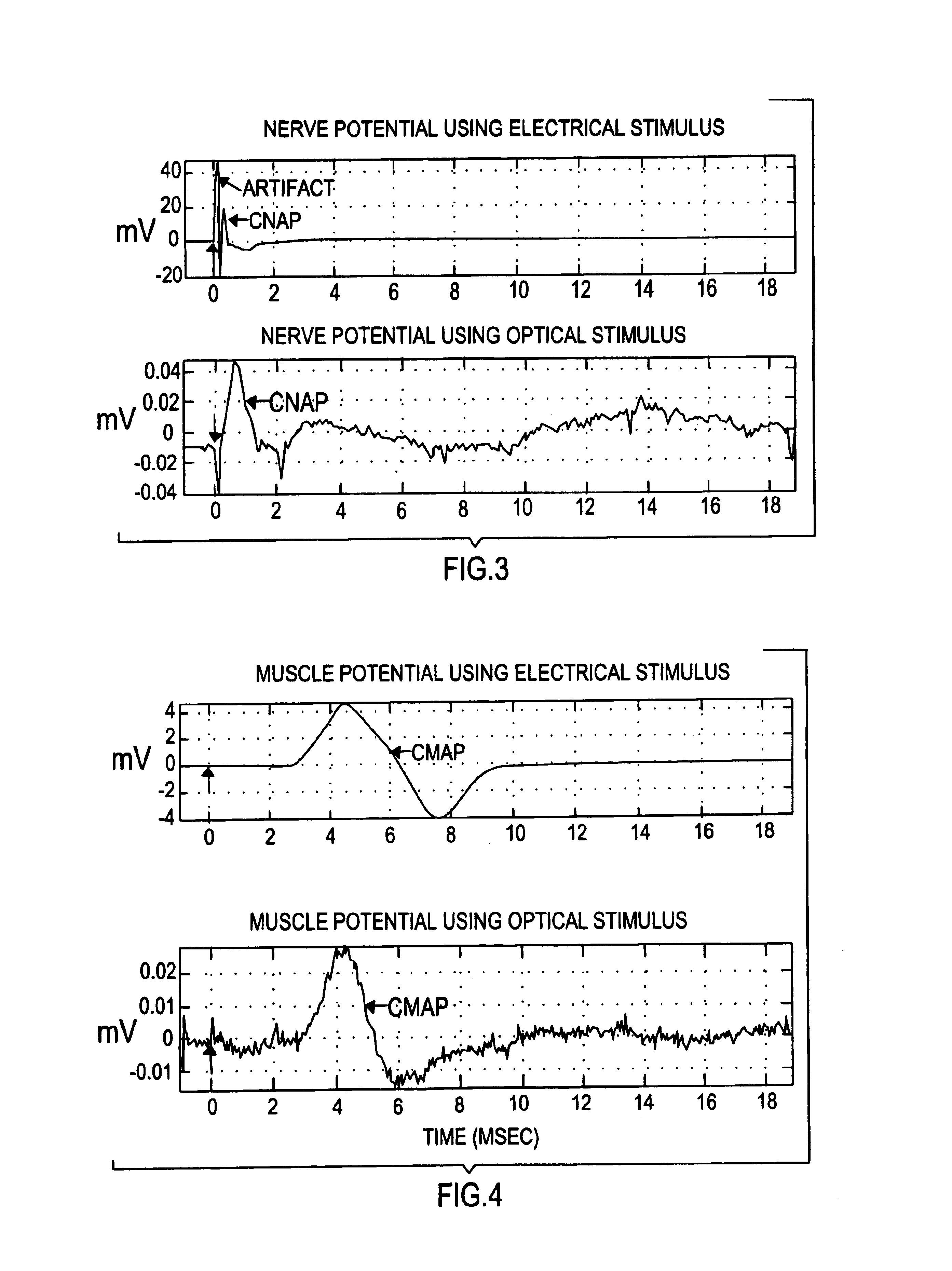
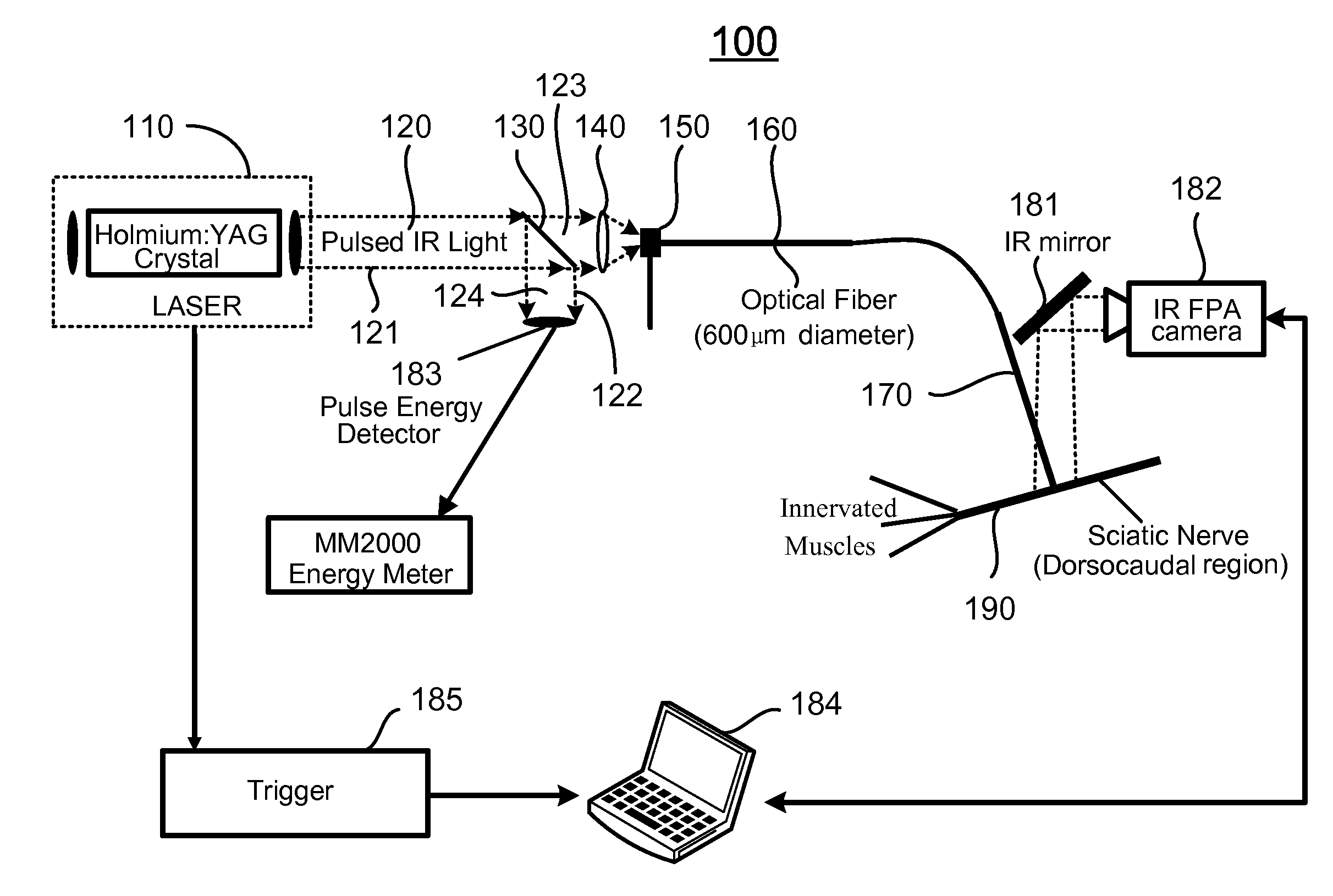
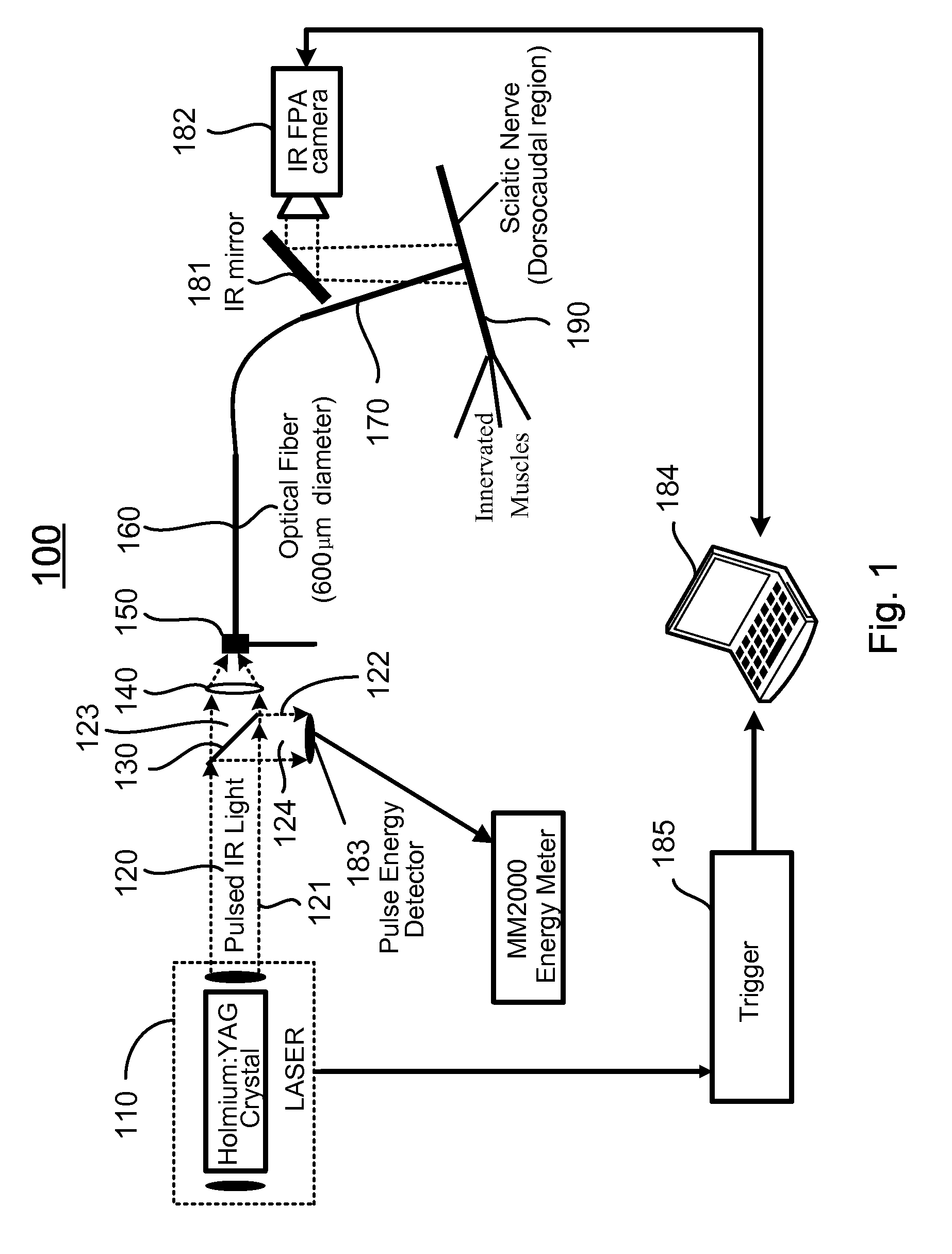
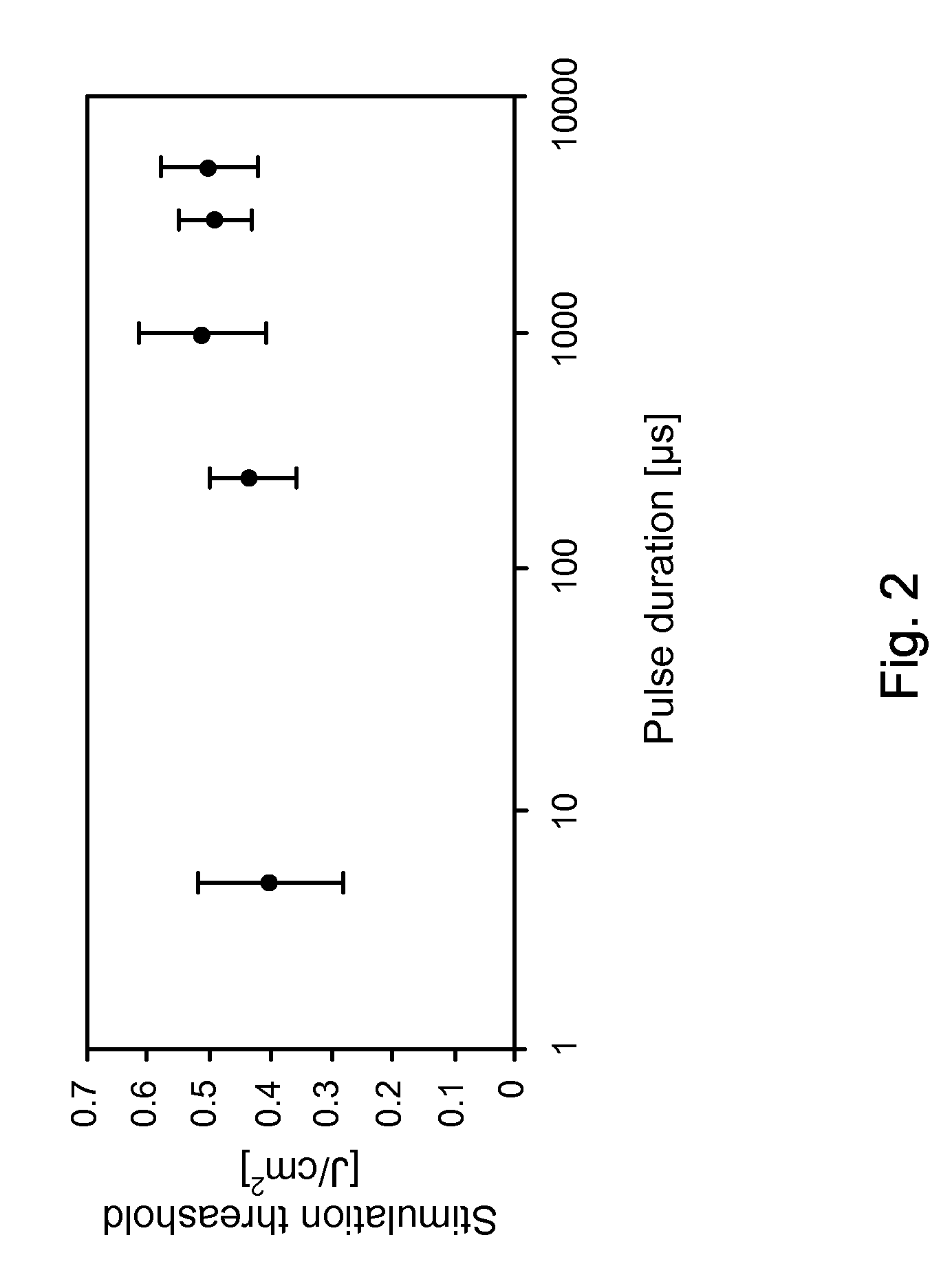
The present invention provides methods of directly stimulating neural tissue with optical energy. By stimulating neural tissue at wavelengths, laser pulses, and spot sizes disclosed herein, nerve stimulation may be used to uniquely stimulate neural tissue in way not afforded by other means of stimulation. It can allow basic scientists to study the properties of individual neurons or populations of neurons without piercing tissue with fragile microelectrodes. Furthermore, responses of neural tissue can be studied in a pure fashion without contamination by electrical artifact commonly seen with electrical stimulation. With respect to clinical uses, optical stimulation can be used to map function in subsections of peripheral nerves as an aid to operative repair. Finally, stimulation with optical energy does not require physical contact with the nerve which may be an advantage clinically when physical manipulation of neural tissue is not desired.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
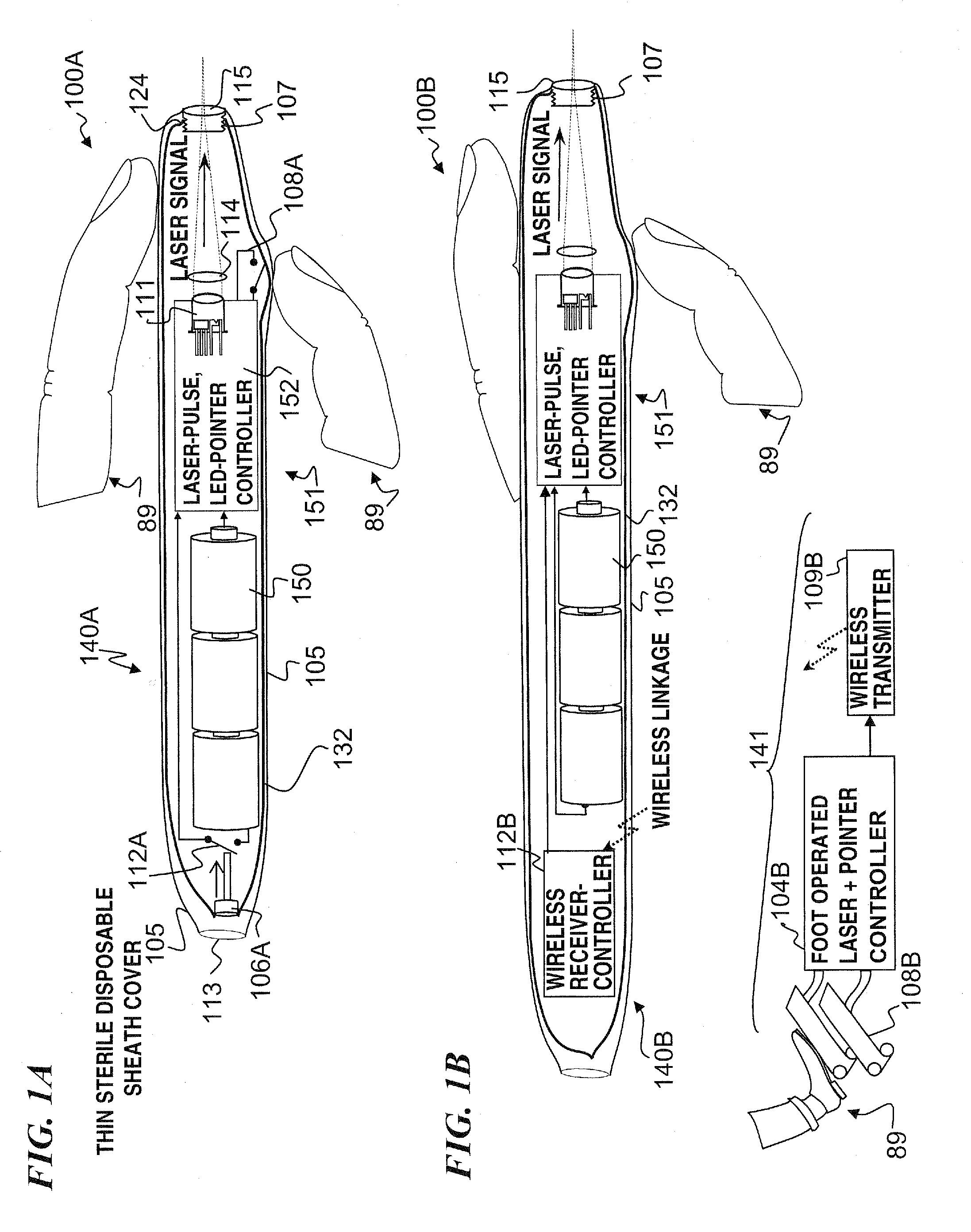
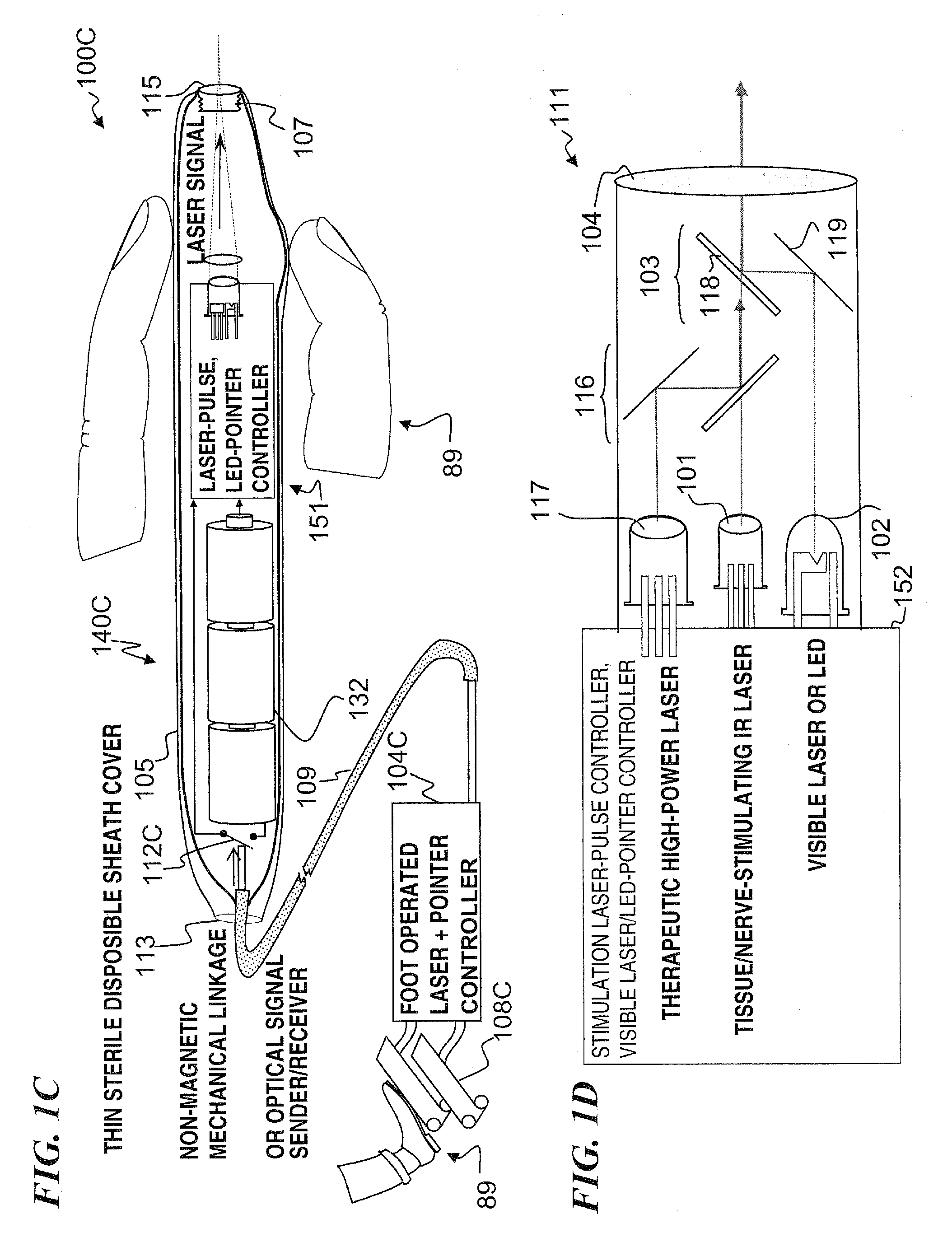
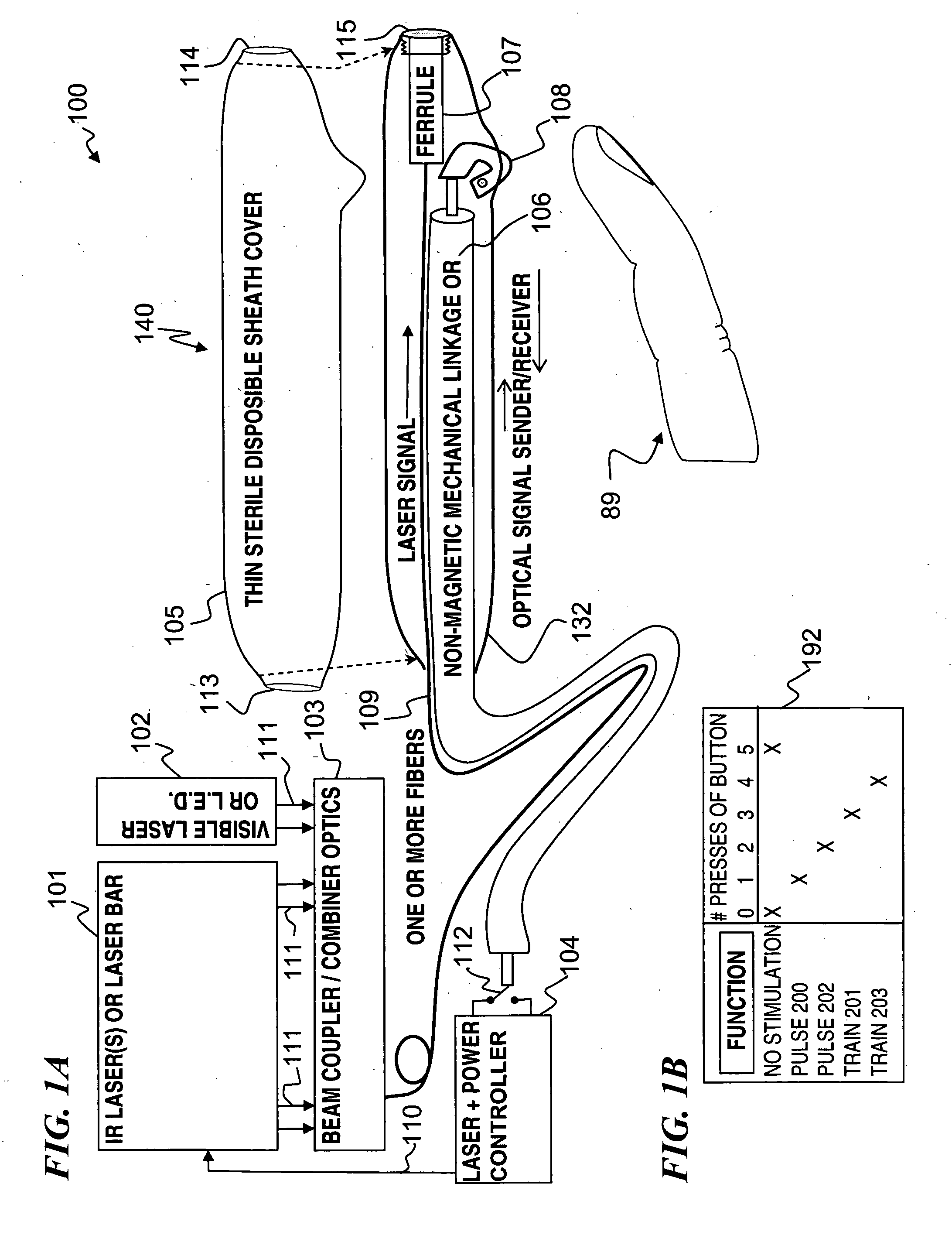
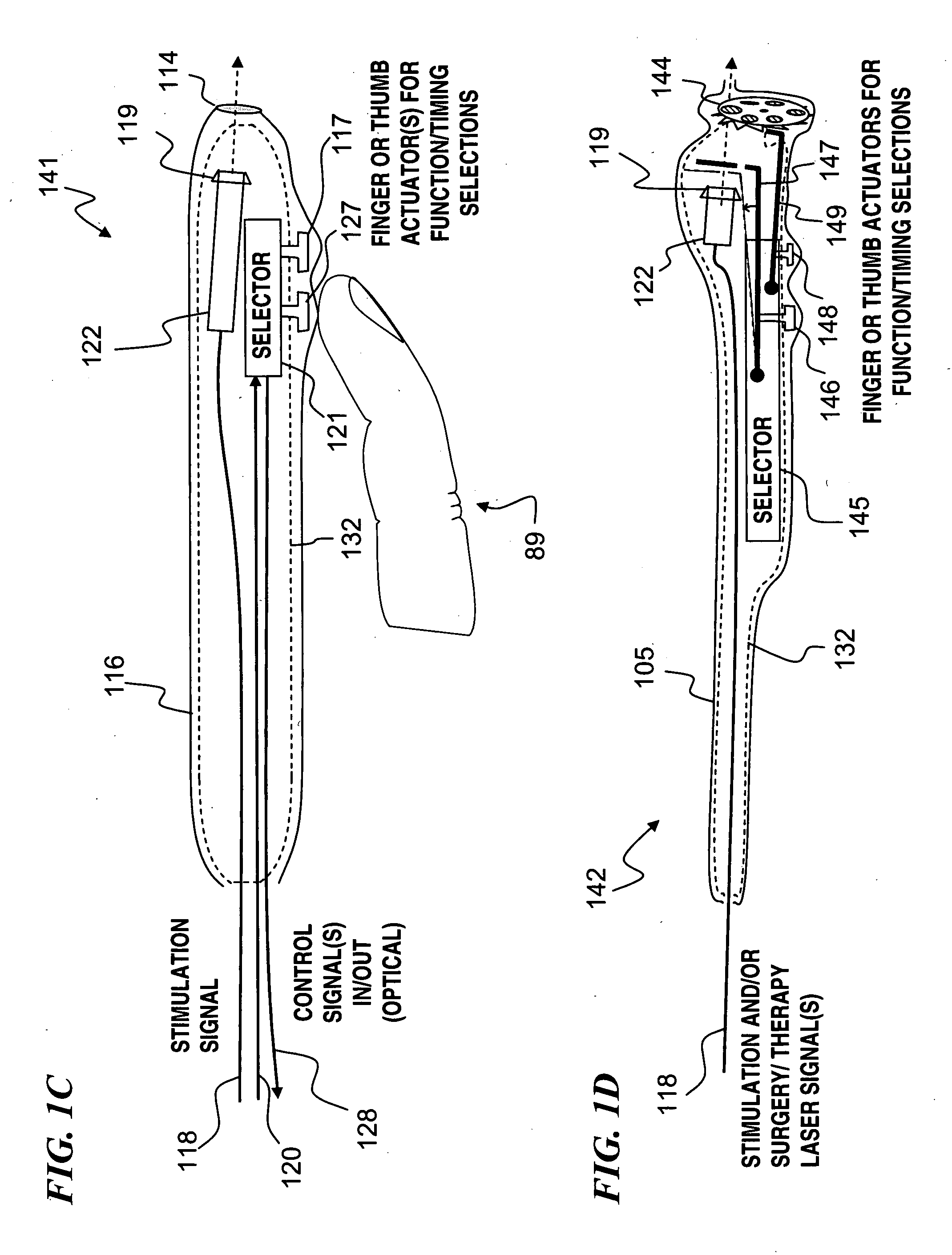
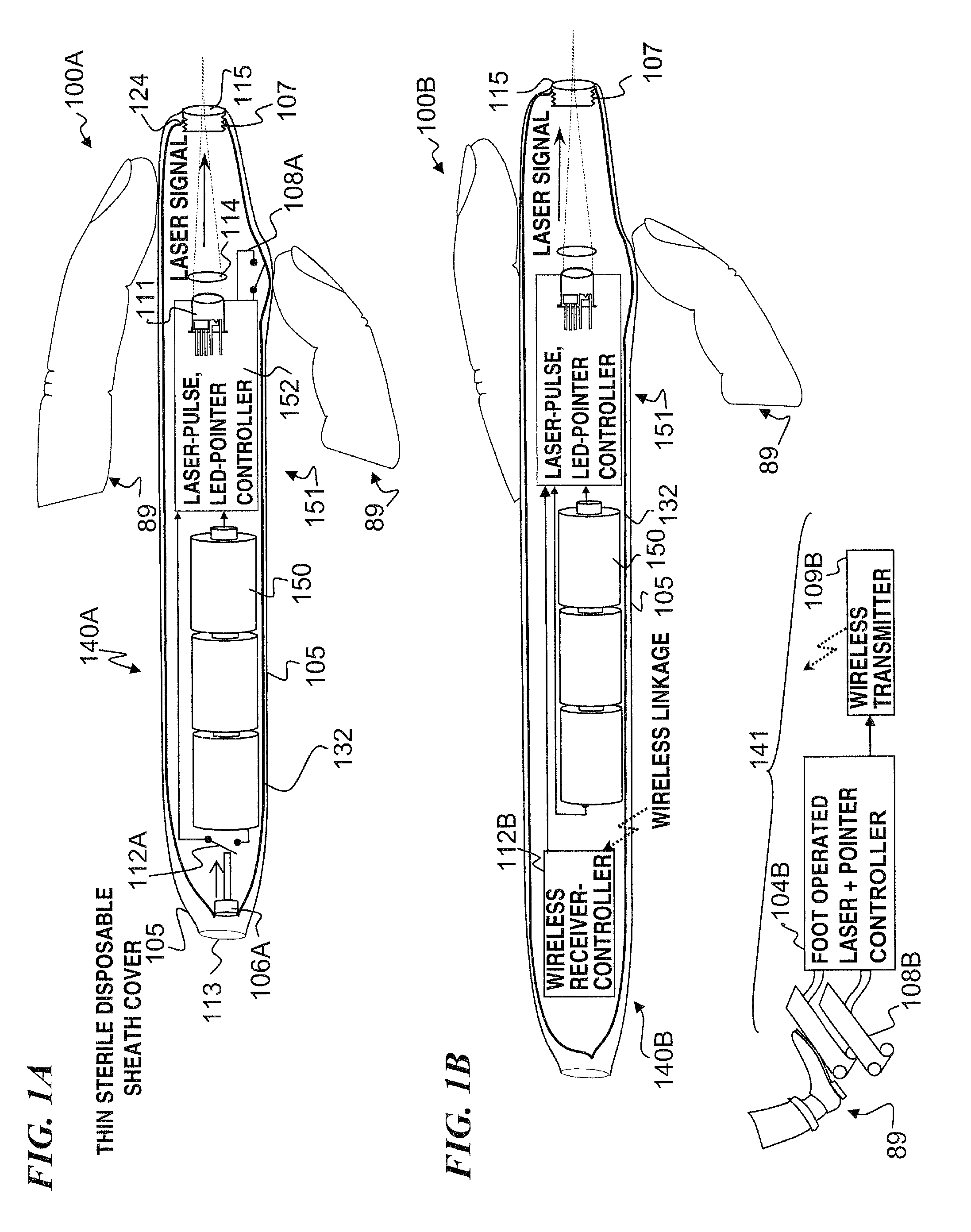
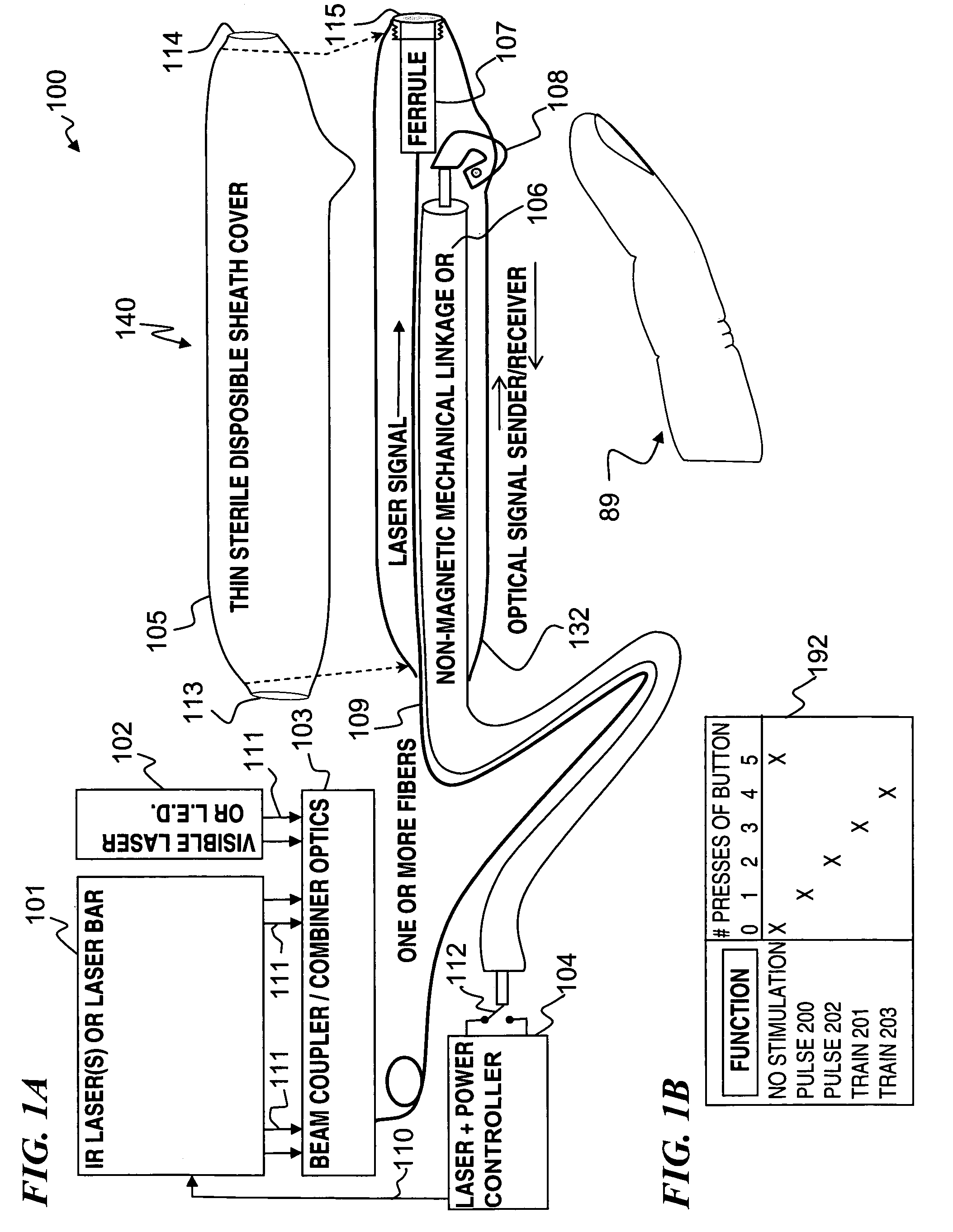
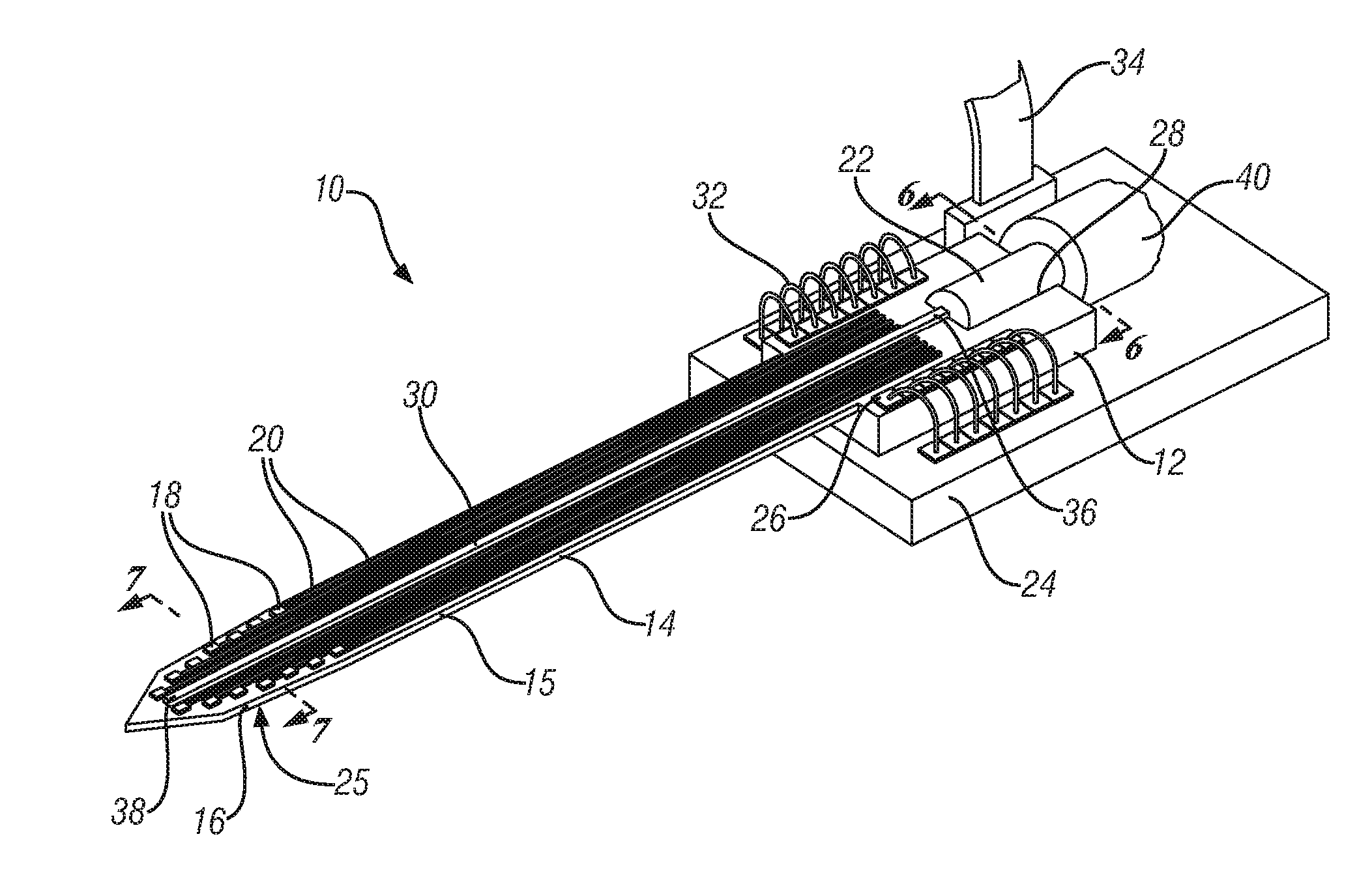
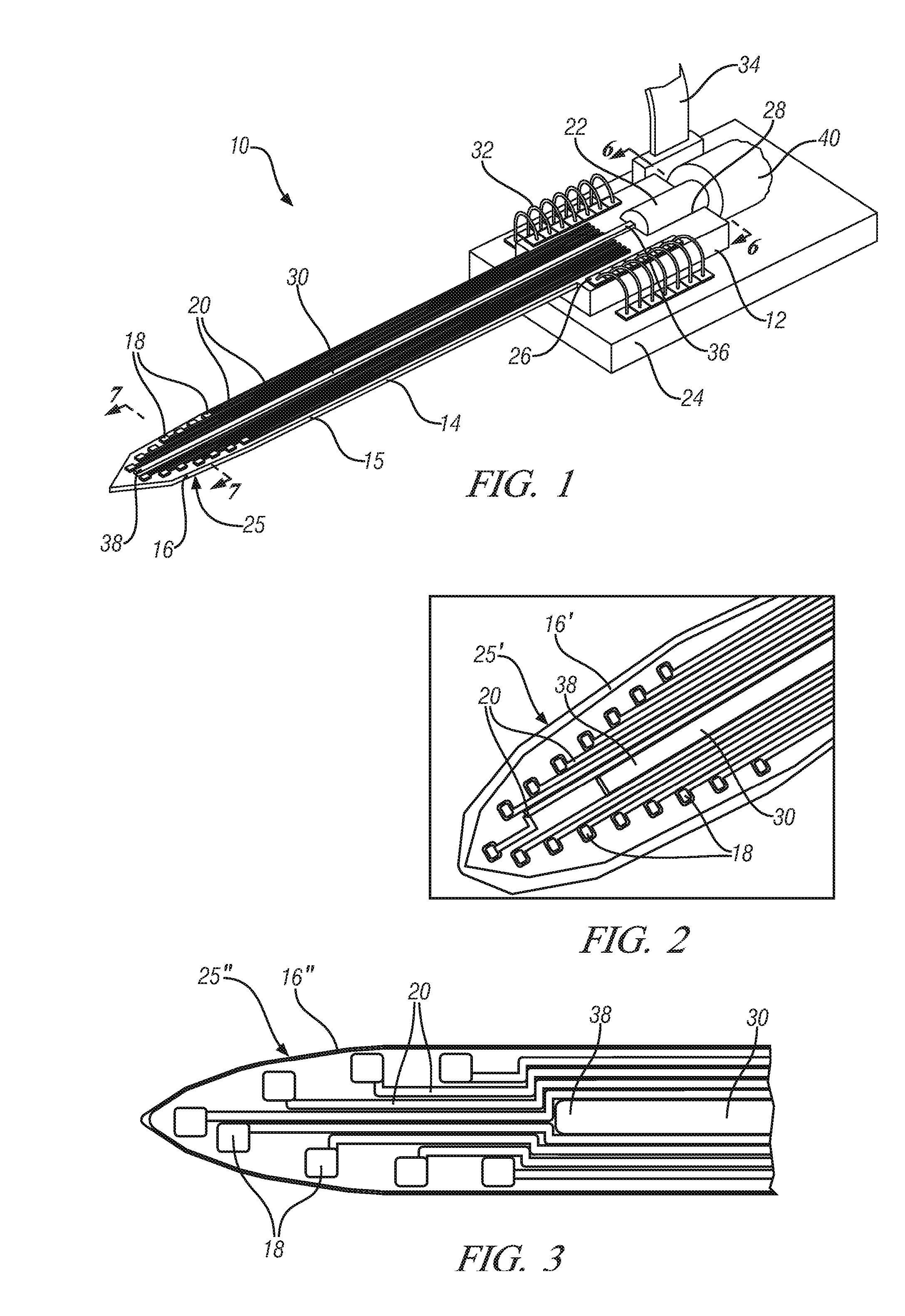
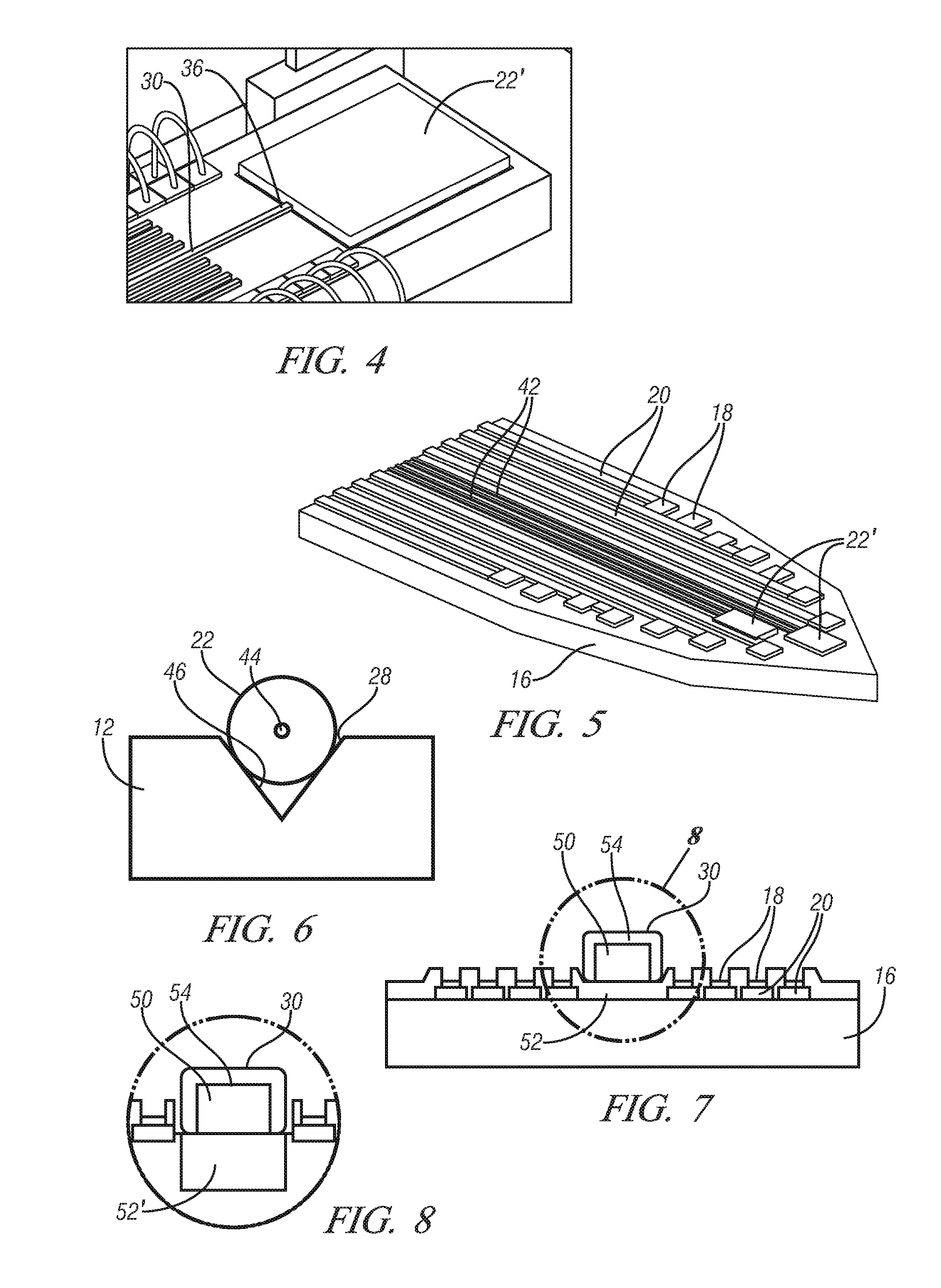
Miniature apparatus and method for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
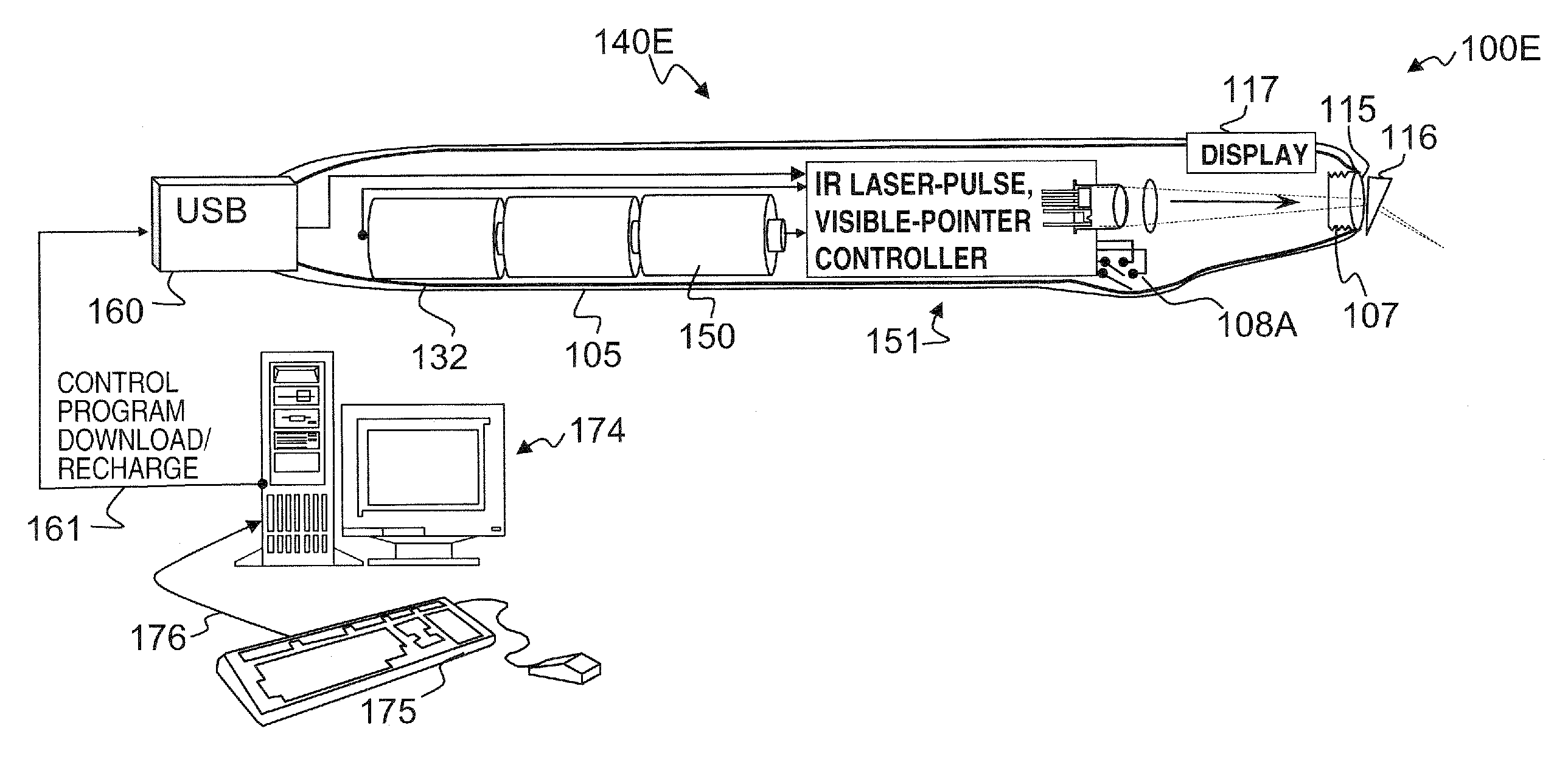
A hand-held self-contained nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light source is mounted to the handpiece. Light is passed from the light source through optical tip to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. In some embodiments, the handpiece contains a self-contained power source, such as batteries. In some embodiments, the handpiece is at least in part, activated by remote control in order to prevent moving the handpiece during activation. Some embodiments include a unit operable to sense a response of nerve stimulation and to suppress a laser-ablation surgery operation.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
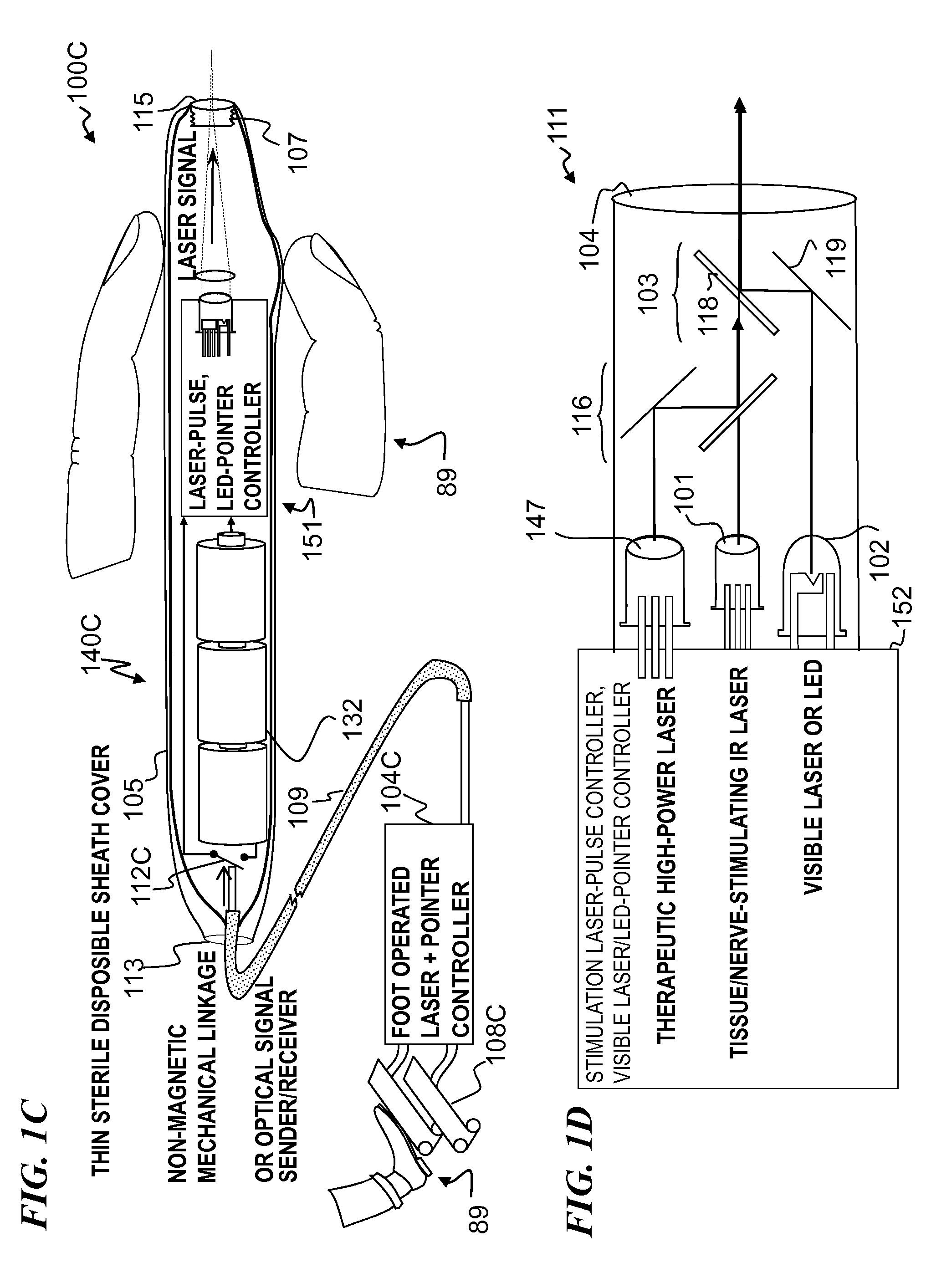
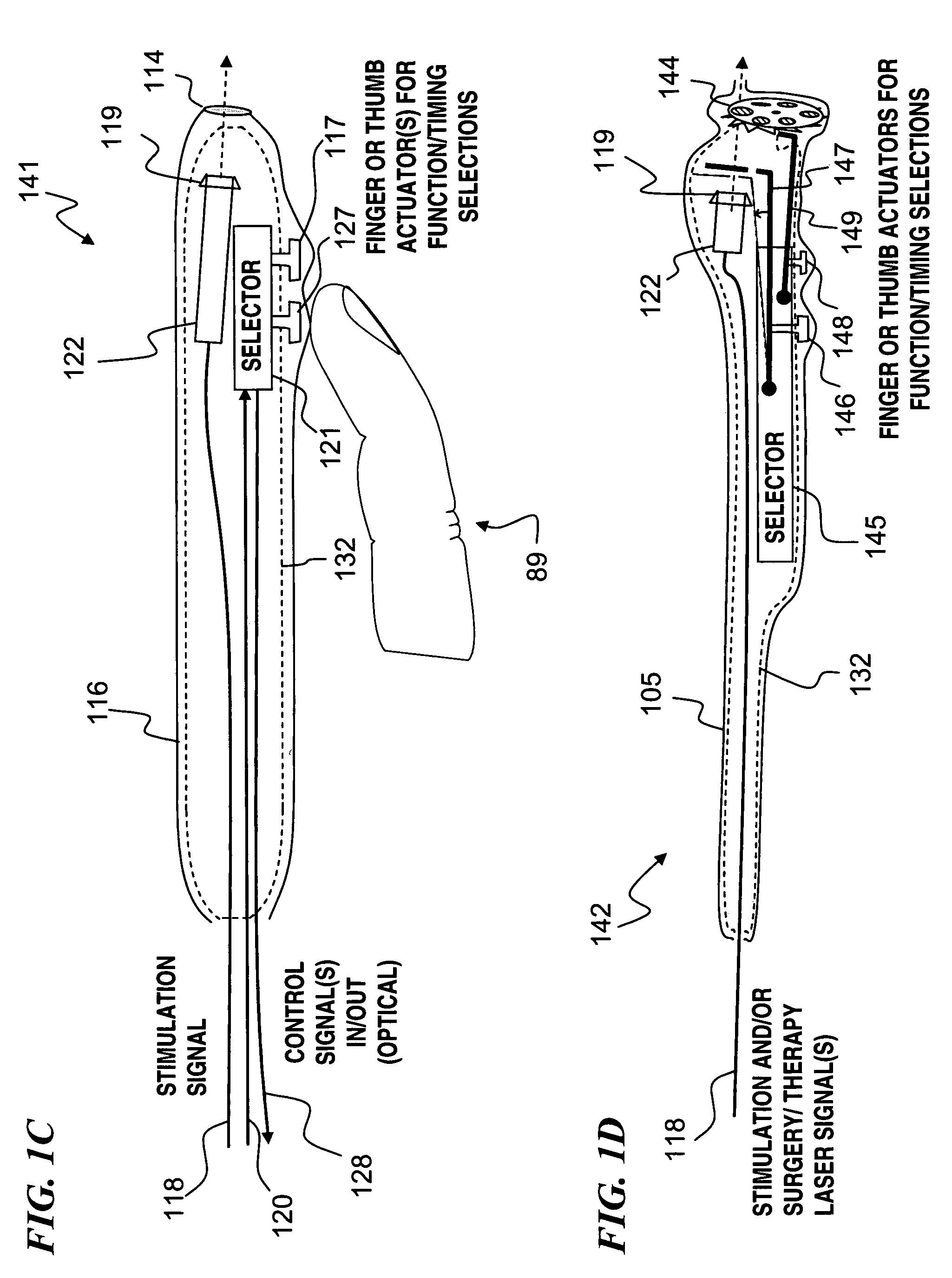
Apparatus and method for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
A nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light-generating source is operatively coupled to an optical fiber, which in turn is coupled to a plug in the end of a holder in a sheath. Light is then passed from the light source through the optical fiber to the holder and out a selected optical tip on the sheath to provide an efficacious amount of light to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. Some embodiments omit the fiber and use light directly from the laser diode.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
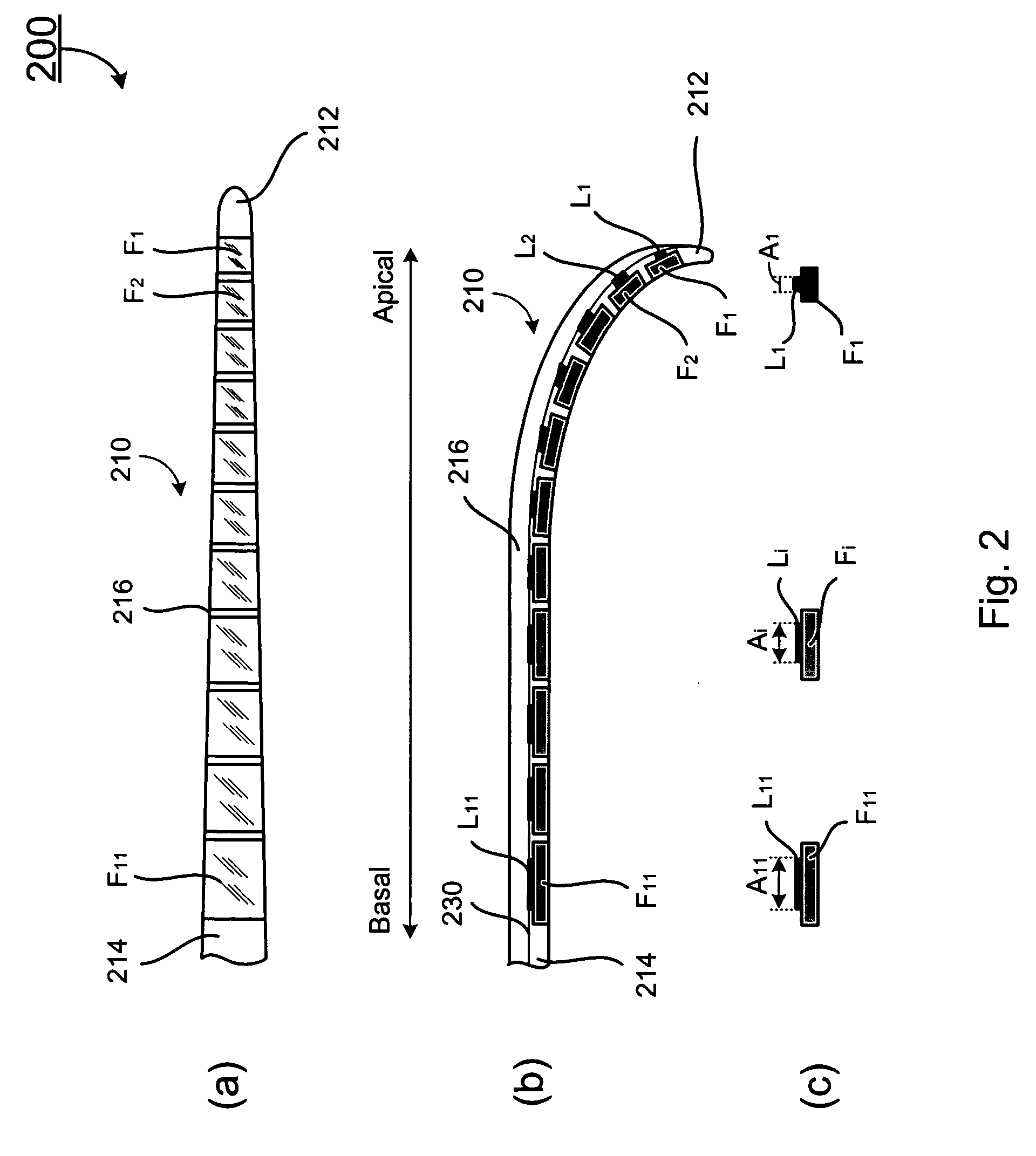
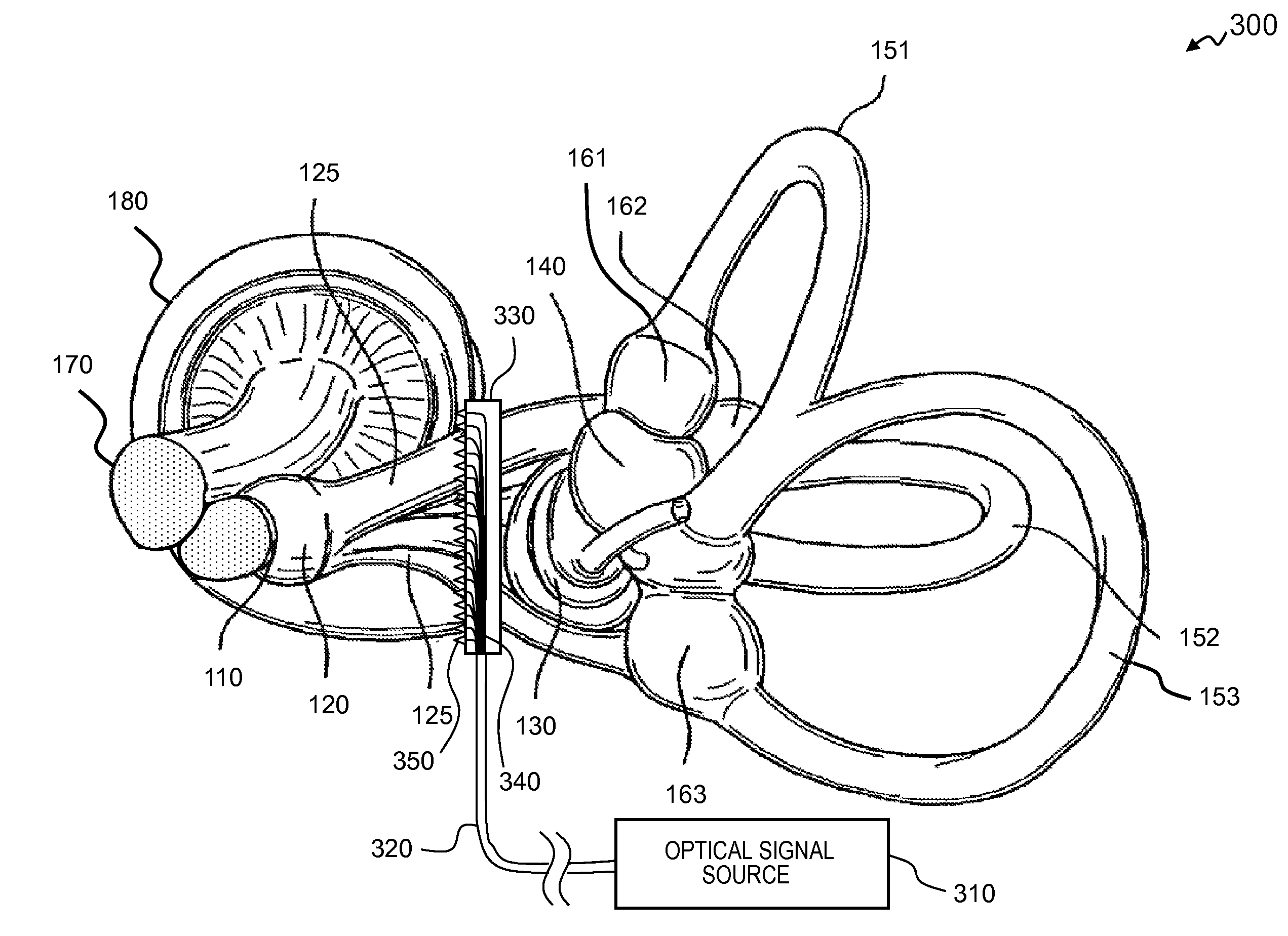
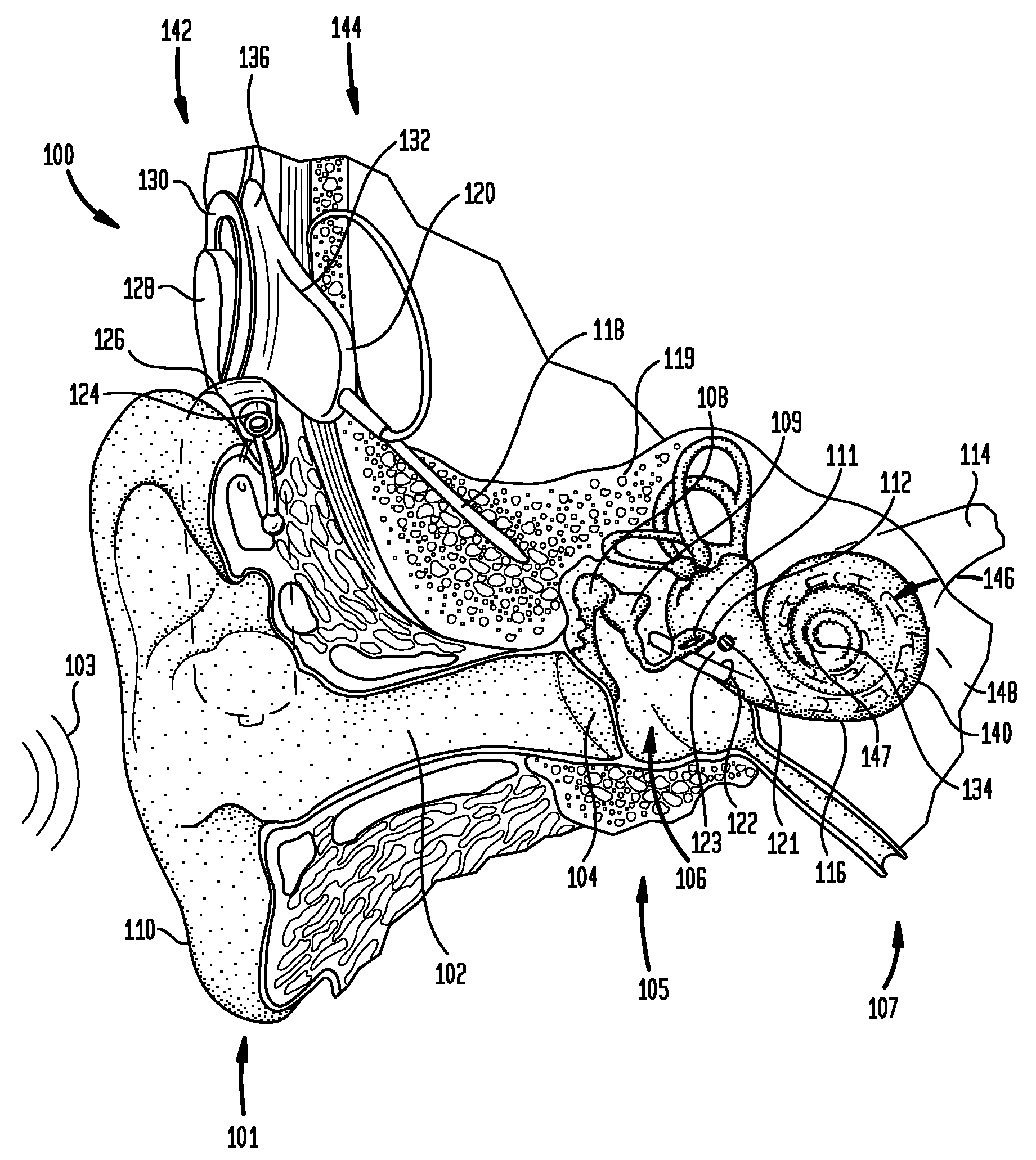
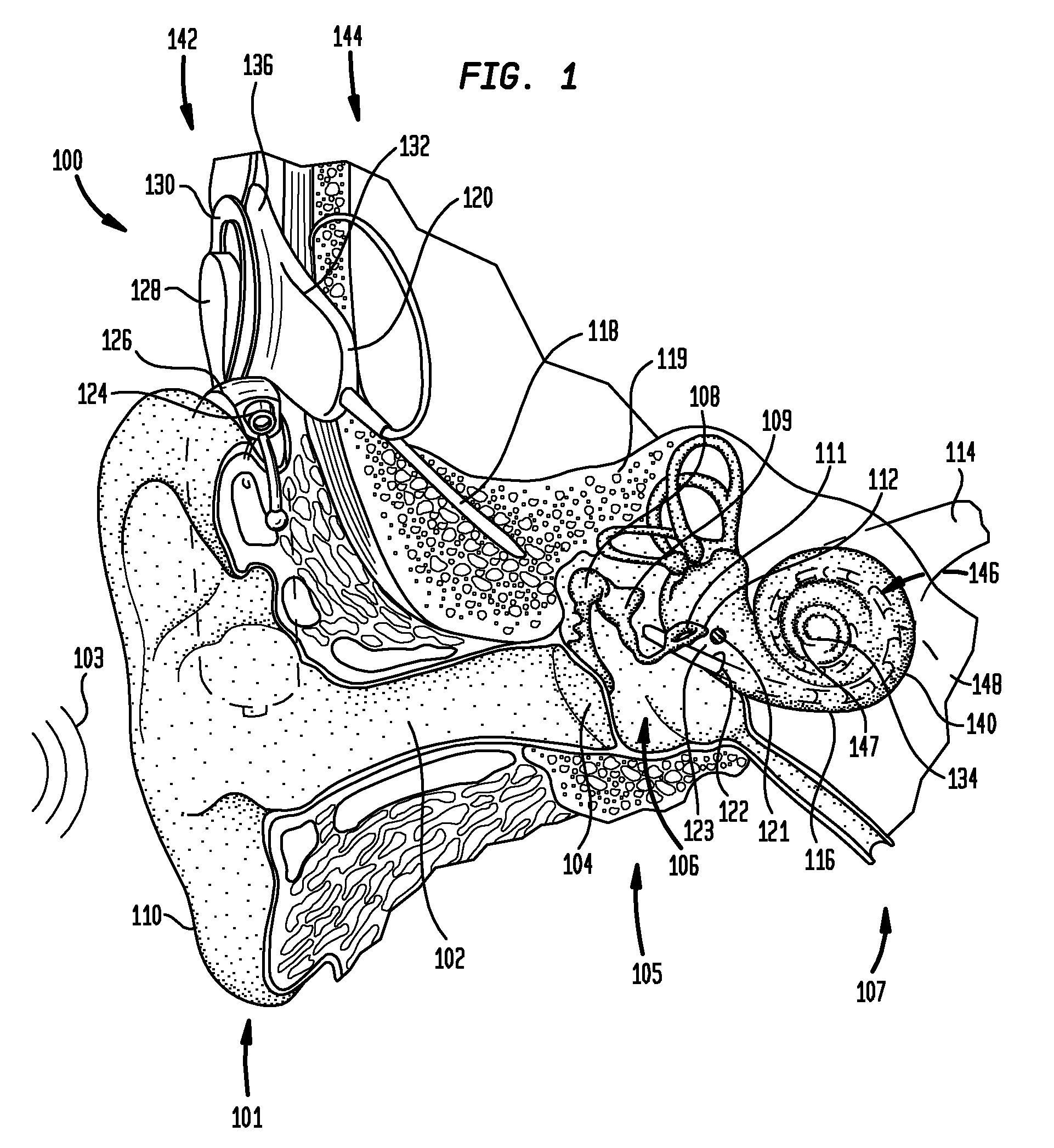
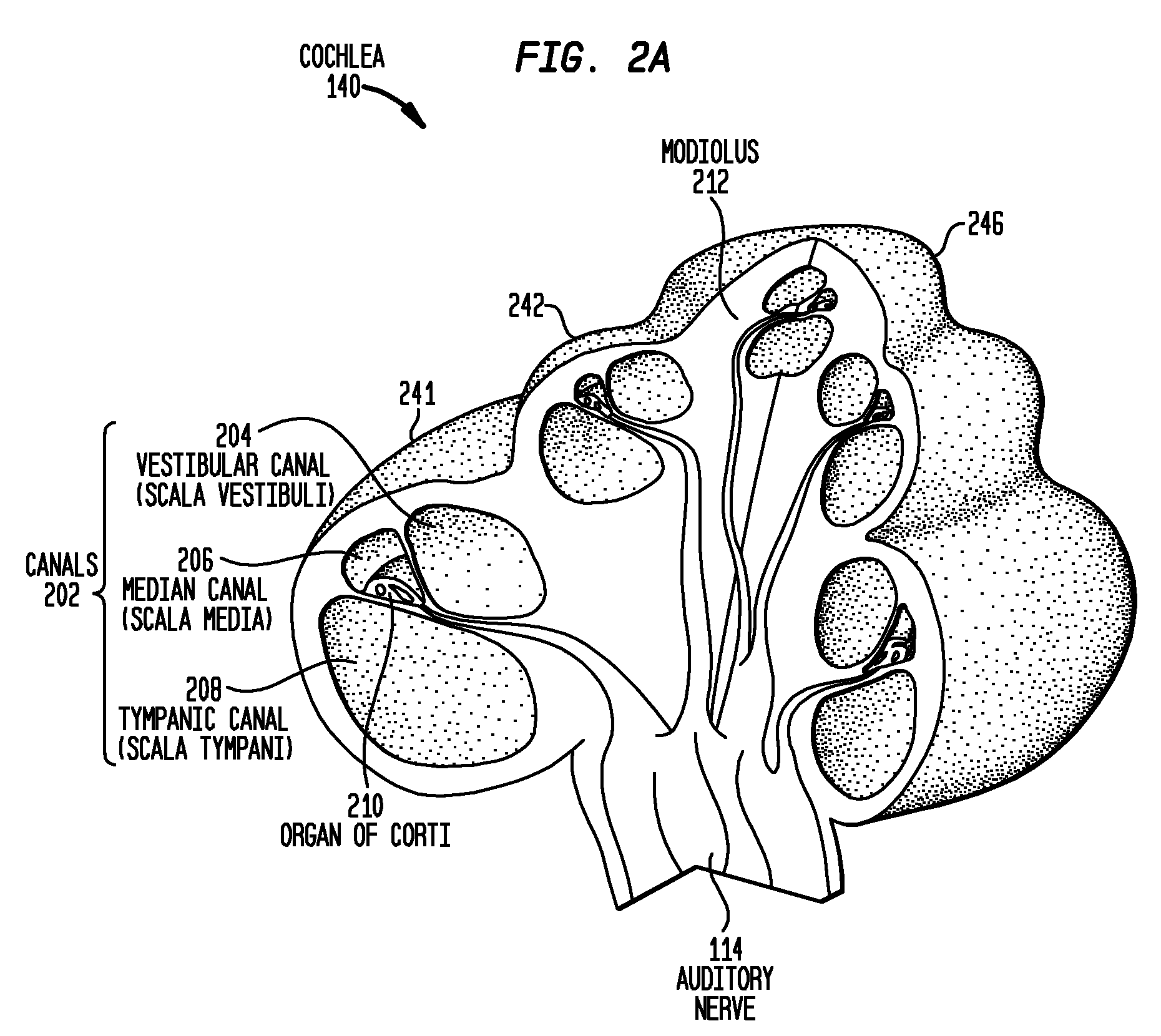
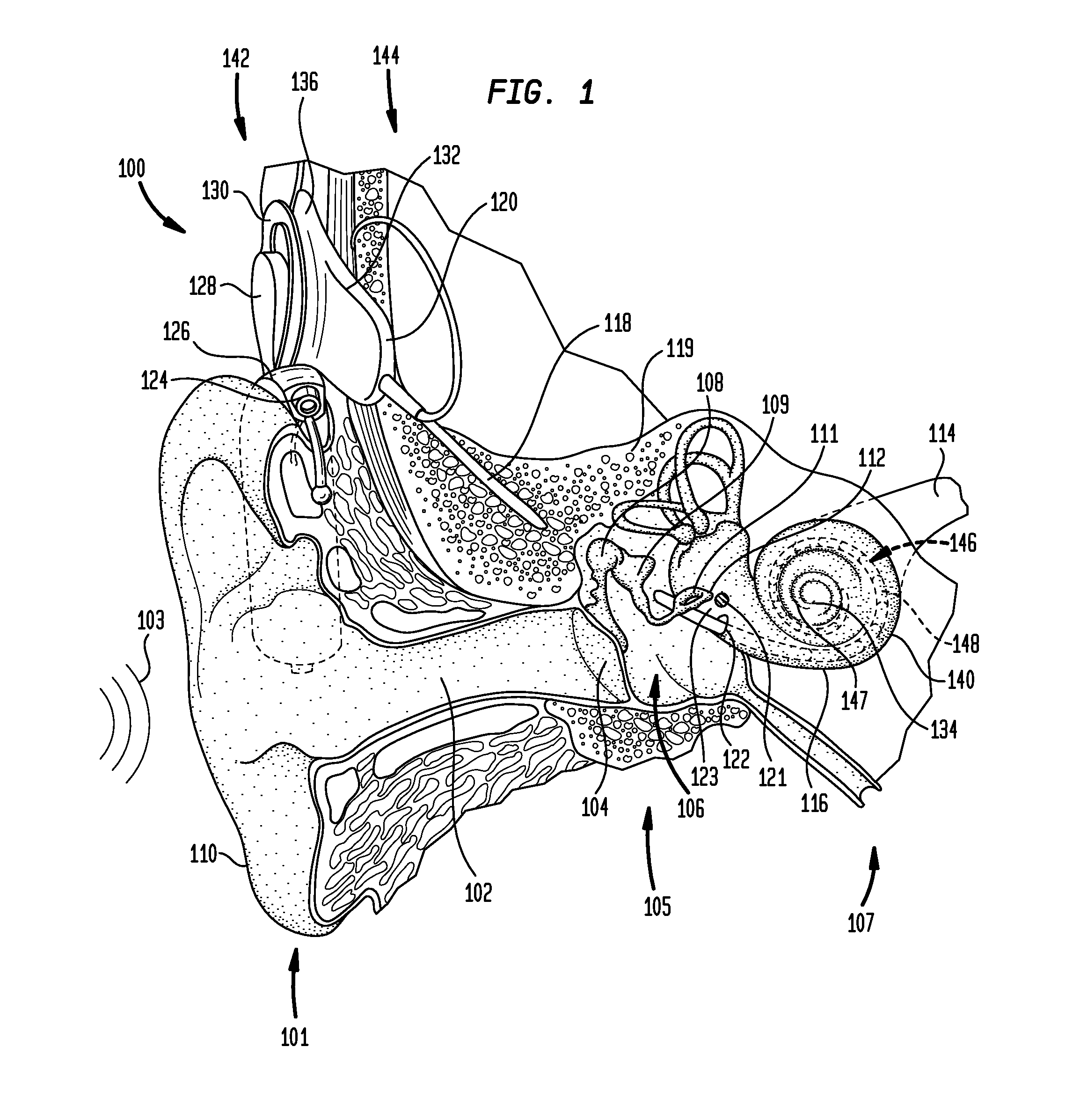
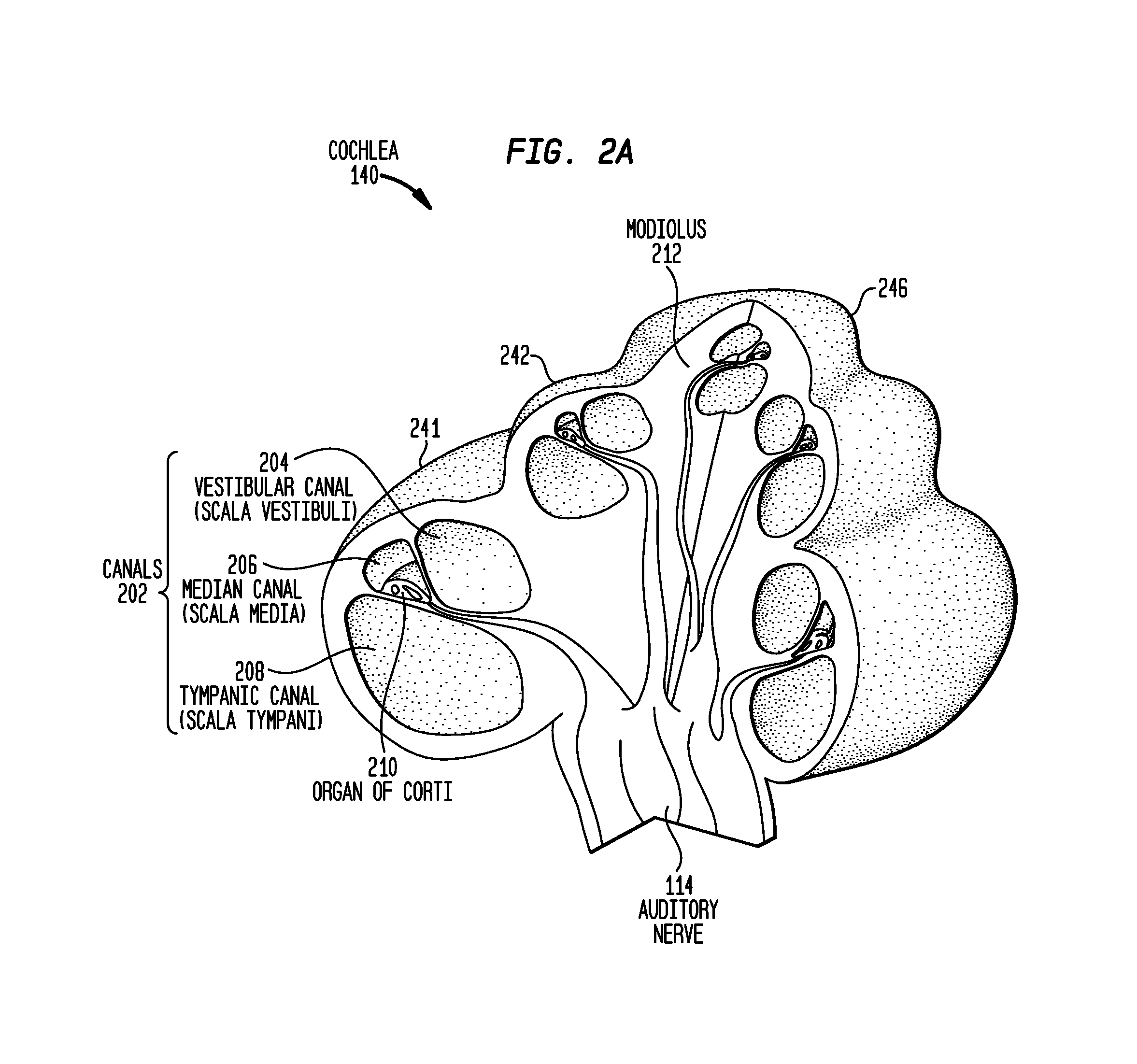
Apparatus and methods for optical stimulation of the auditory nerve
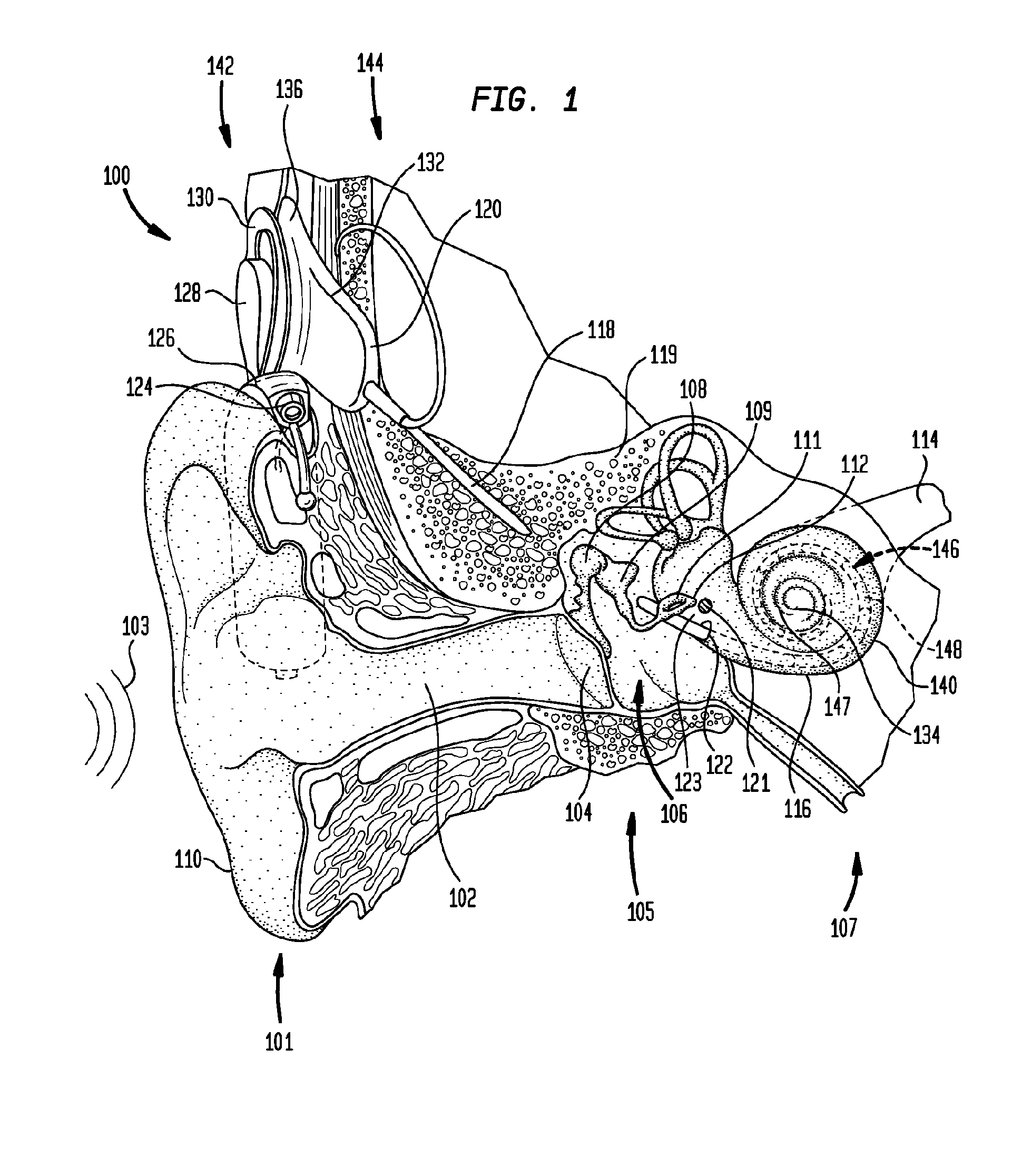
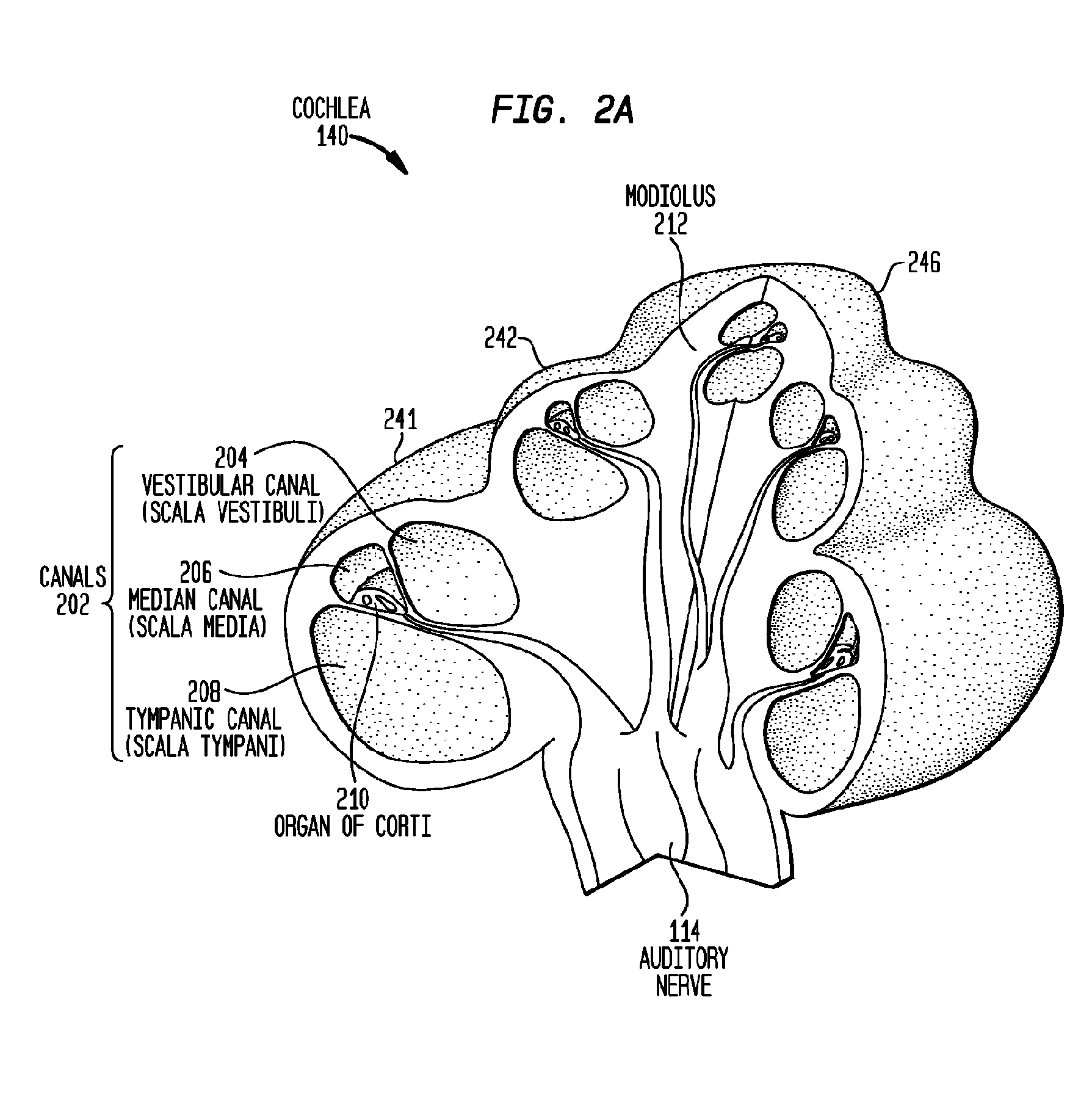
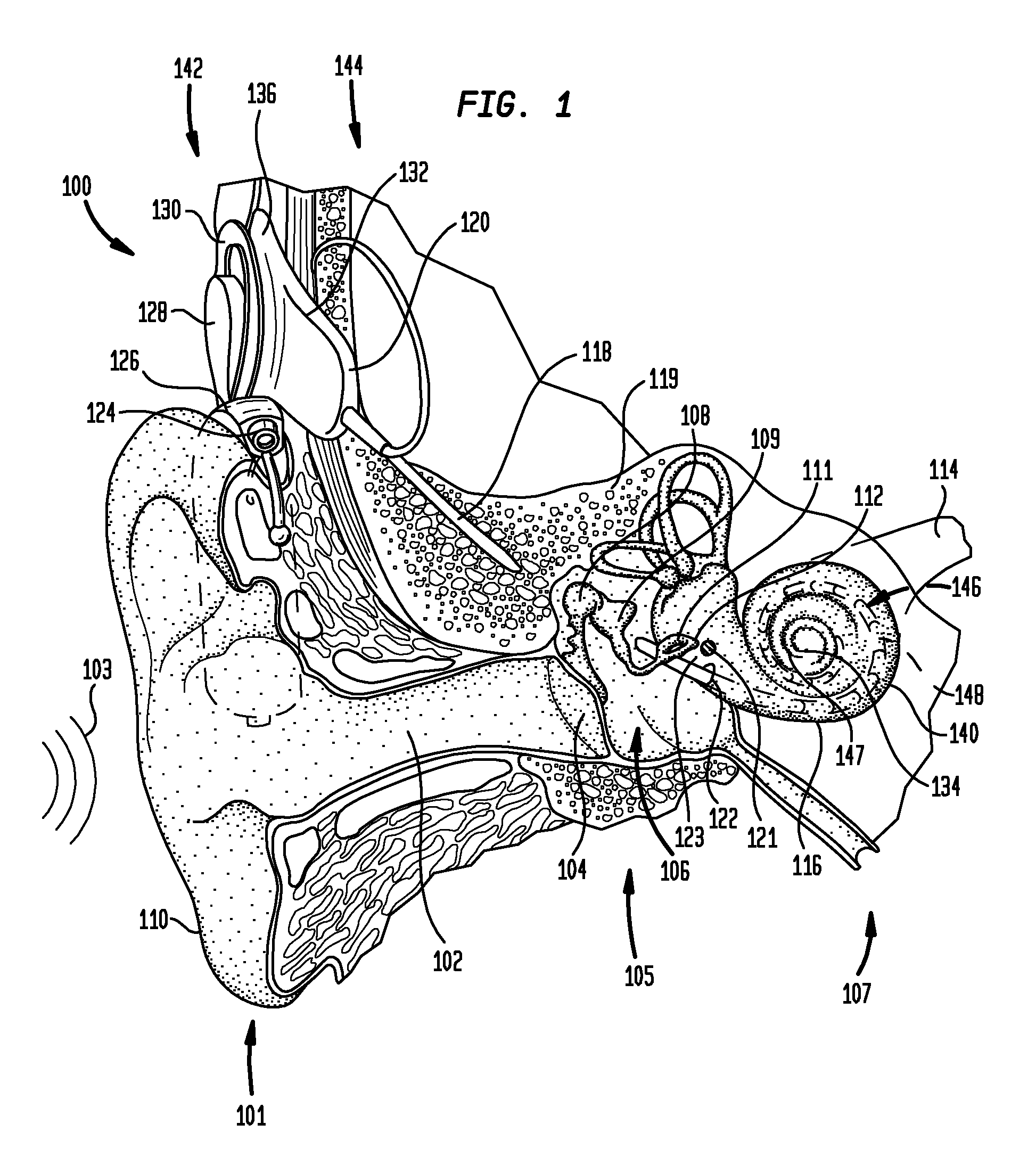
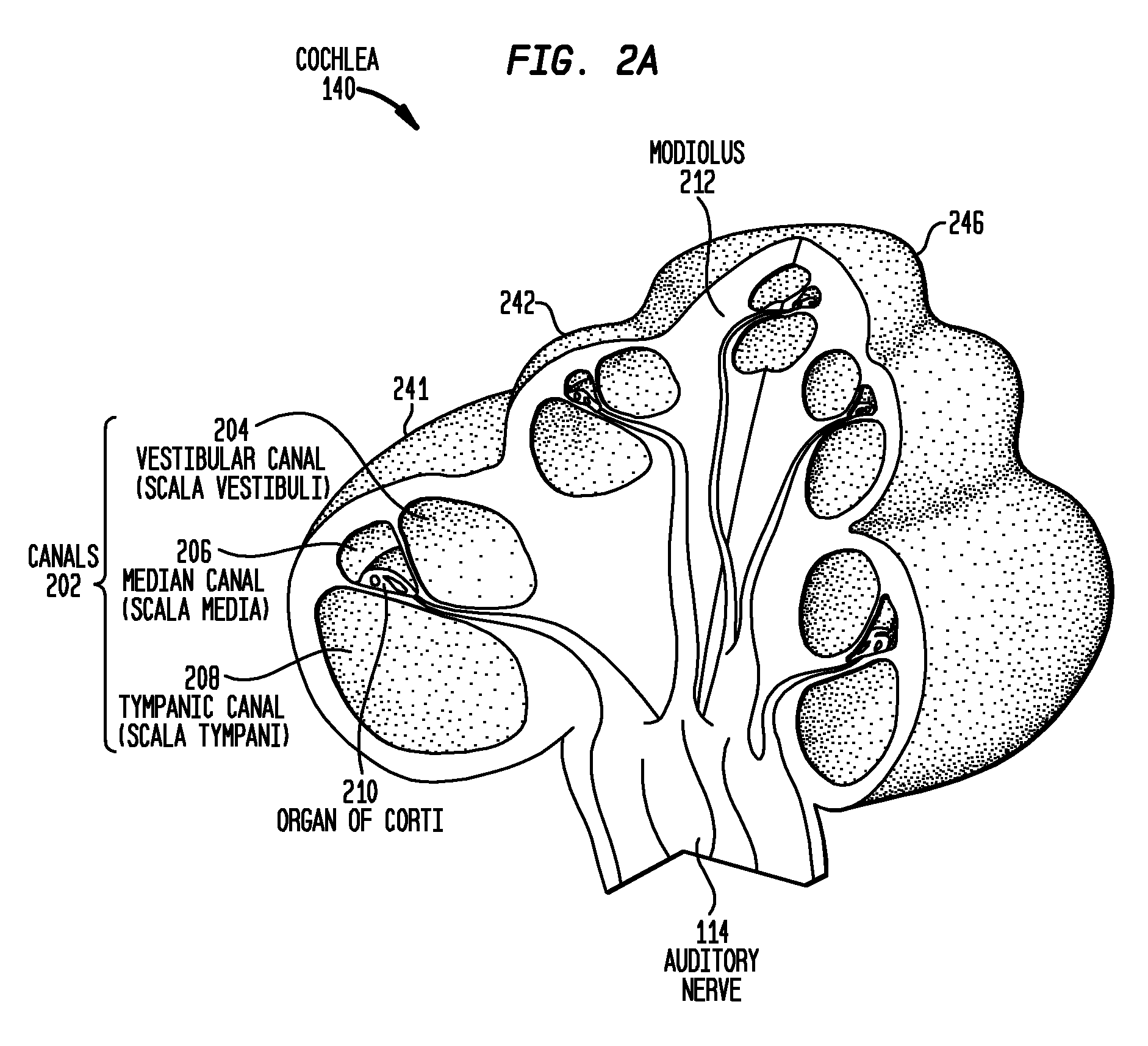
A cochlear implant placed in a cochlea of a living subject for stimulating the auditory system of the living subject, where the auditory system comprises auditory neurons. In one embodiment, the cochlear implant includes a plurality of light sources, {Li}, placeable distal to the cochlea, each light source, L1, being operable independently and adapted for generating an optical energy, Ei, wherein i=1, . . . , N, and N is the number of the light sources, and delivering means placeable in the cochlea and optically coupled to the plurality of light sources, {Li}, such that in operation, the optical energies {Ei} generated by the plurality of light sources {Li} are delivered to target sites, {Gi}, of auditory neurons, respectively, wherein the target sites G1 and GN of auditory neurons are substantially proximate to the apical end and the basal end of the cochlea, respectively.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV +1
Optical stimulation therapy
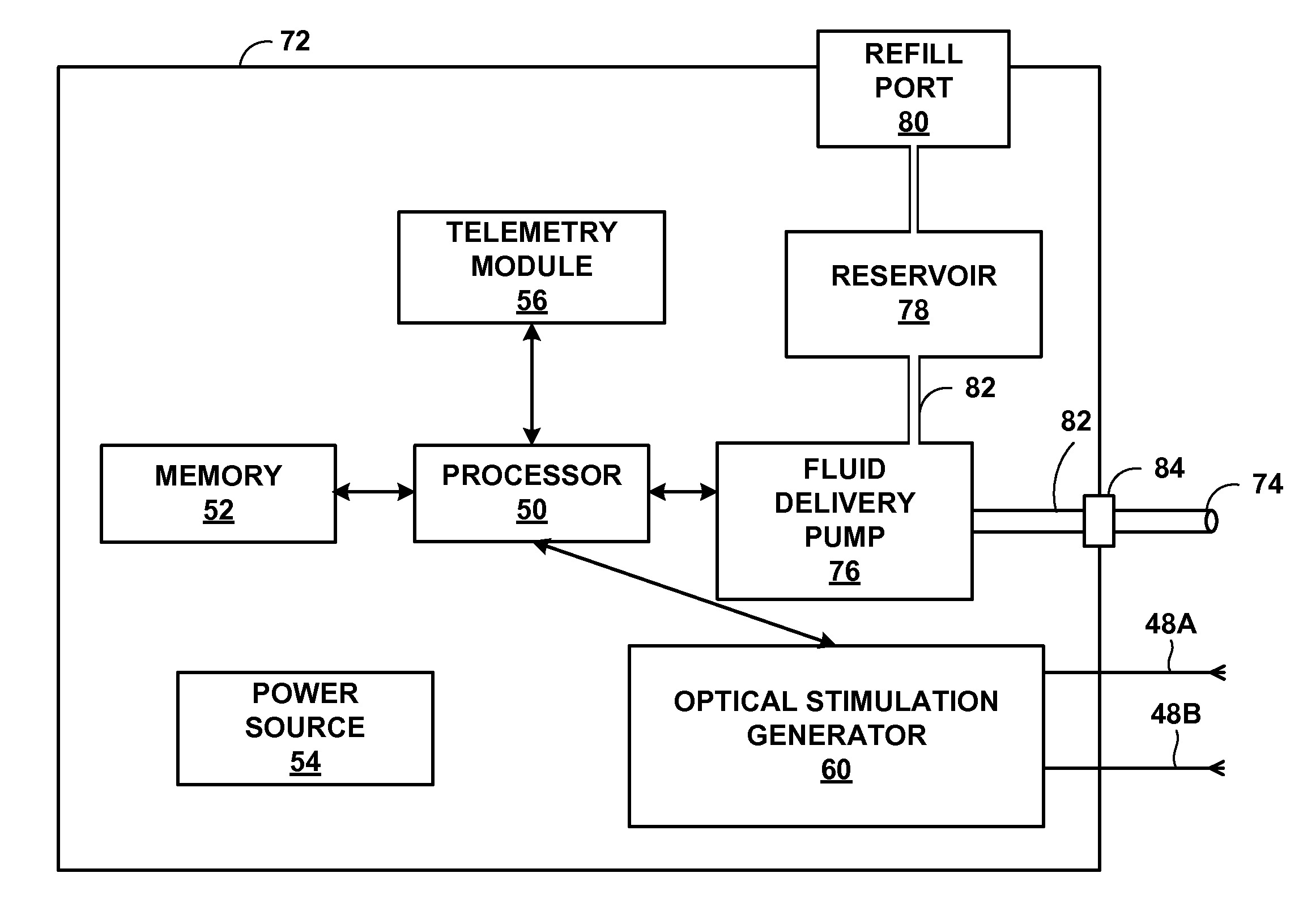
Methods of delivering optical stimulation to a target tissue from an optical stimulation device are provided. One method comprises sensing a temperature at the optical stimulation device or proximate to the optical stimulation device, and adjusting the delivery of light to the target tissue based on the sensed temperature. Another method comprises delivering the light to the target tissue with an optical light guide and sensing bioelectric signals with a sense electrode, wherein the optical light guide and the sense electrode each comprise a material that produces substantially no induced current in an electromagnetic field. Another method comprises delivering light from a light source of an optical stimulation device to a window of the optical stimulation device, delivering the light from the window to an optical light guide optically connected to the window, and delivering the light to a target tissue via the optical light guide.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Miniature apparatus and method for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
A hand-held self-contained nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light source is mounted to the handpiece. Light is passed from the light source through optical tip to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. In some embodiments, the handpiece contains a self-contained power source, such as batteries. In some embodiments, the handpiece is at least in part, activated by remote control in order to prevent moving the handpiece during activation. Some embodiments include a unit operable to sense a response of nerve stimulation and to suppress a laser-ablation surgery operation.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
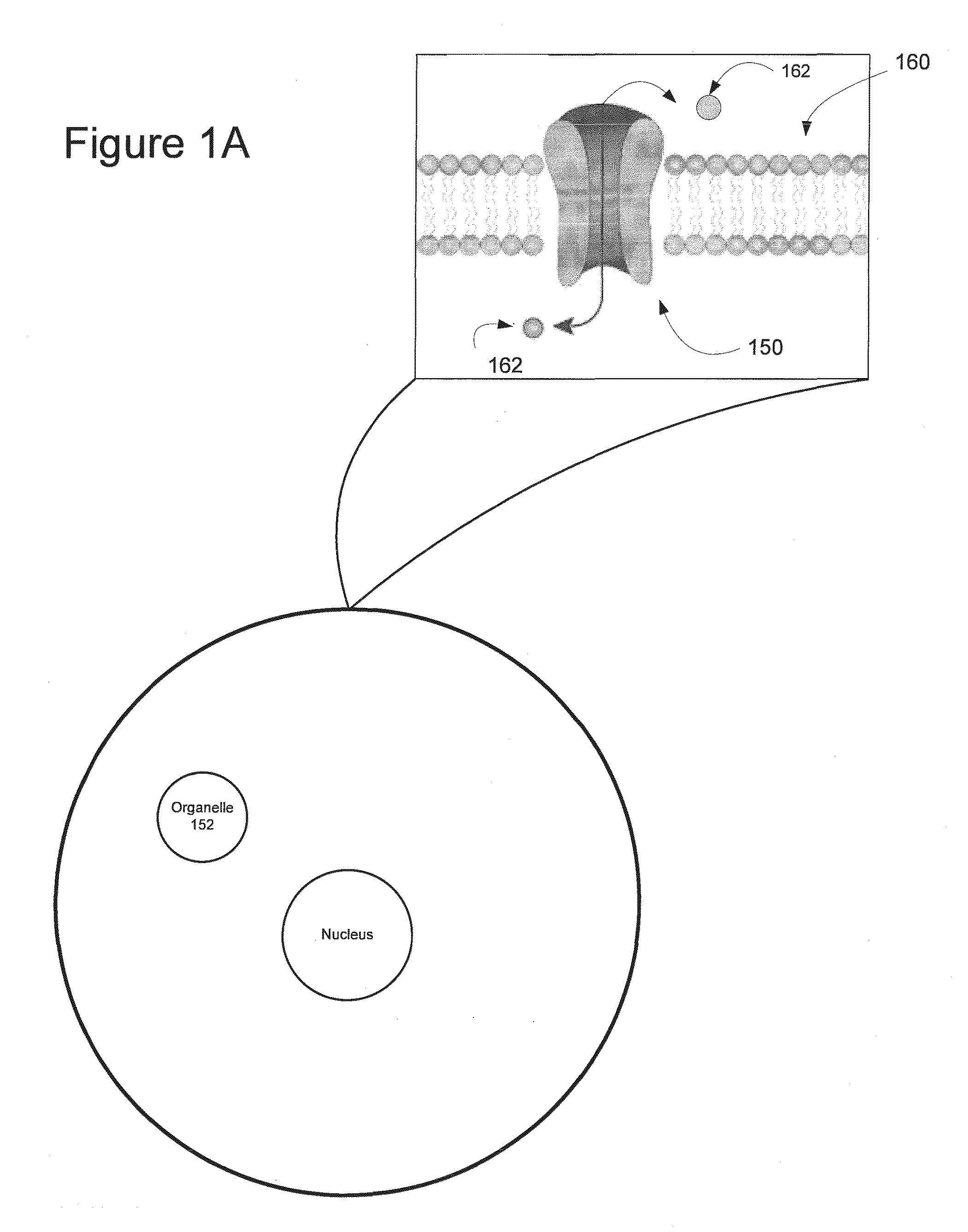
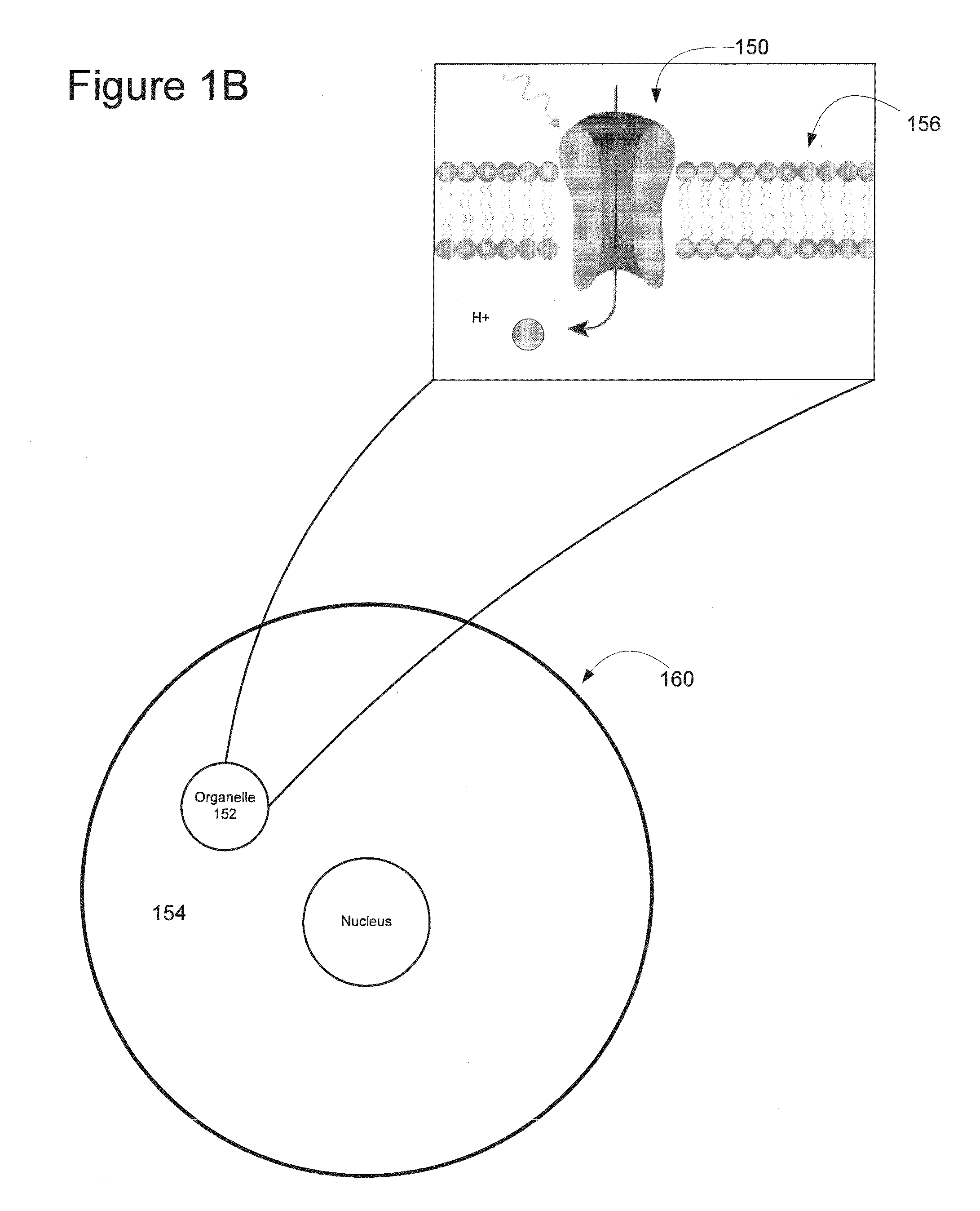
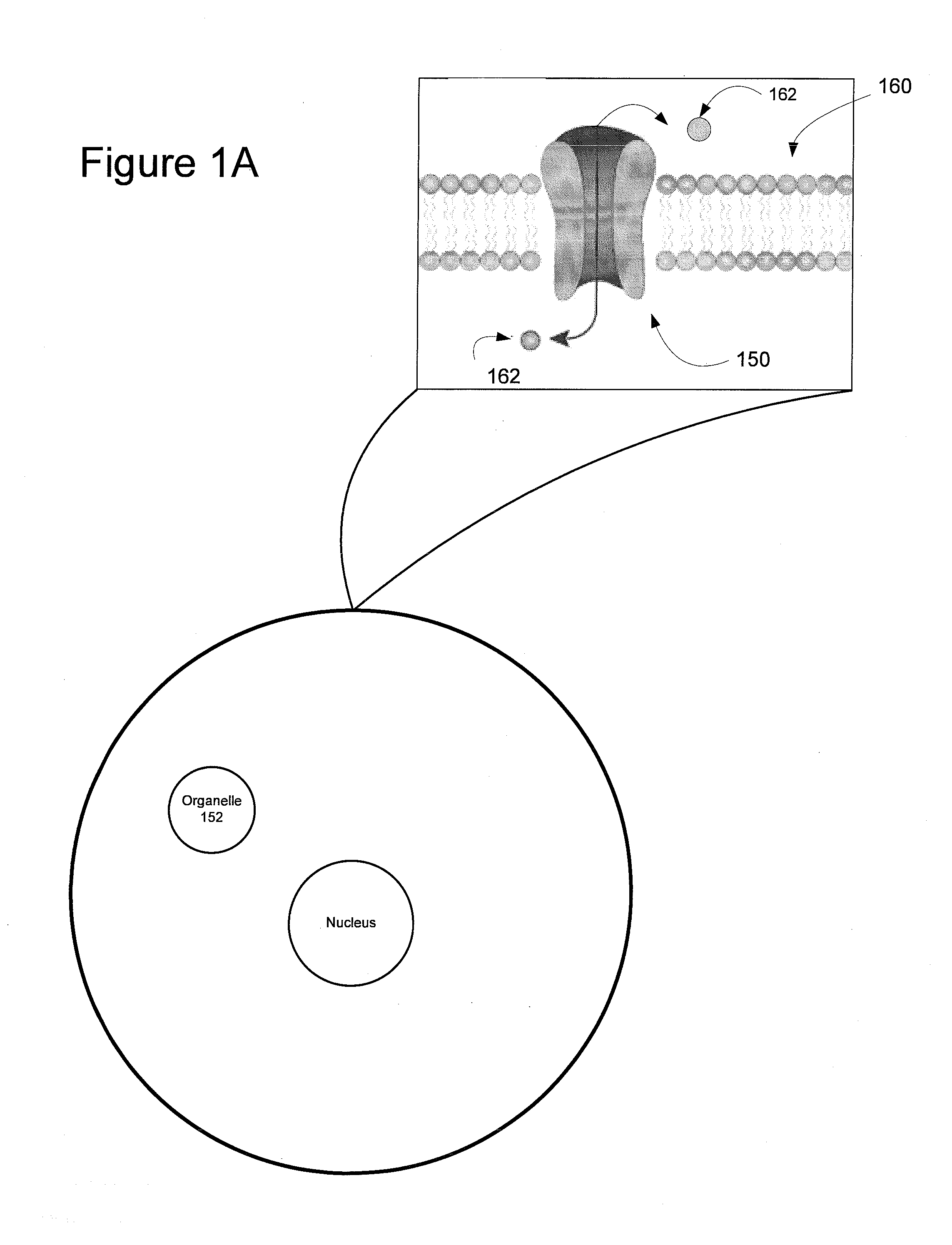
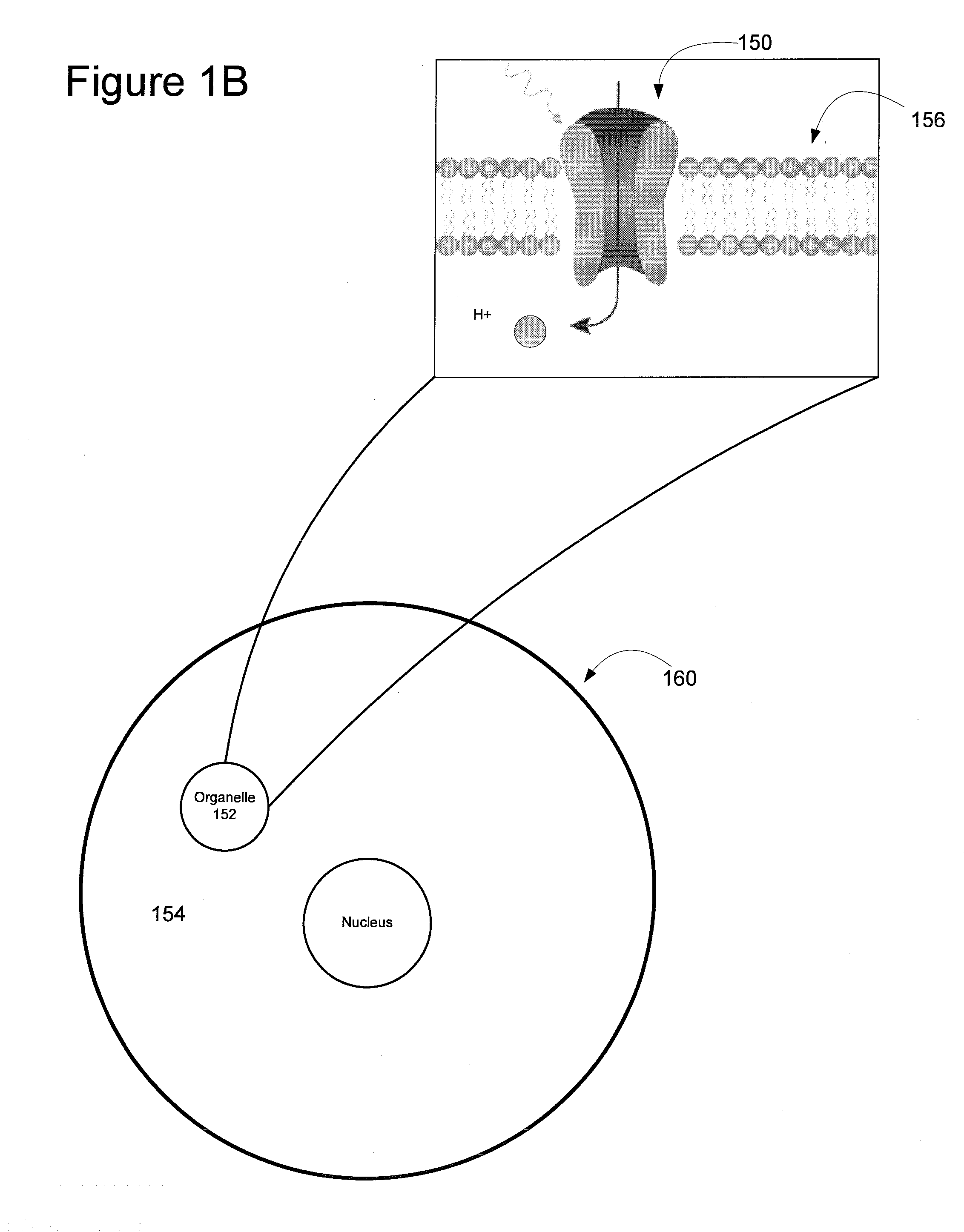
Light-Sensitive Ion-Passing Molecules
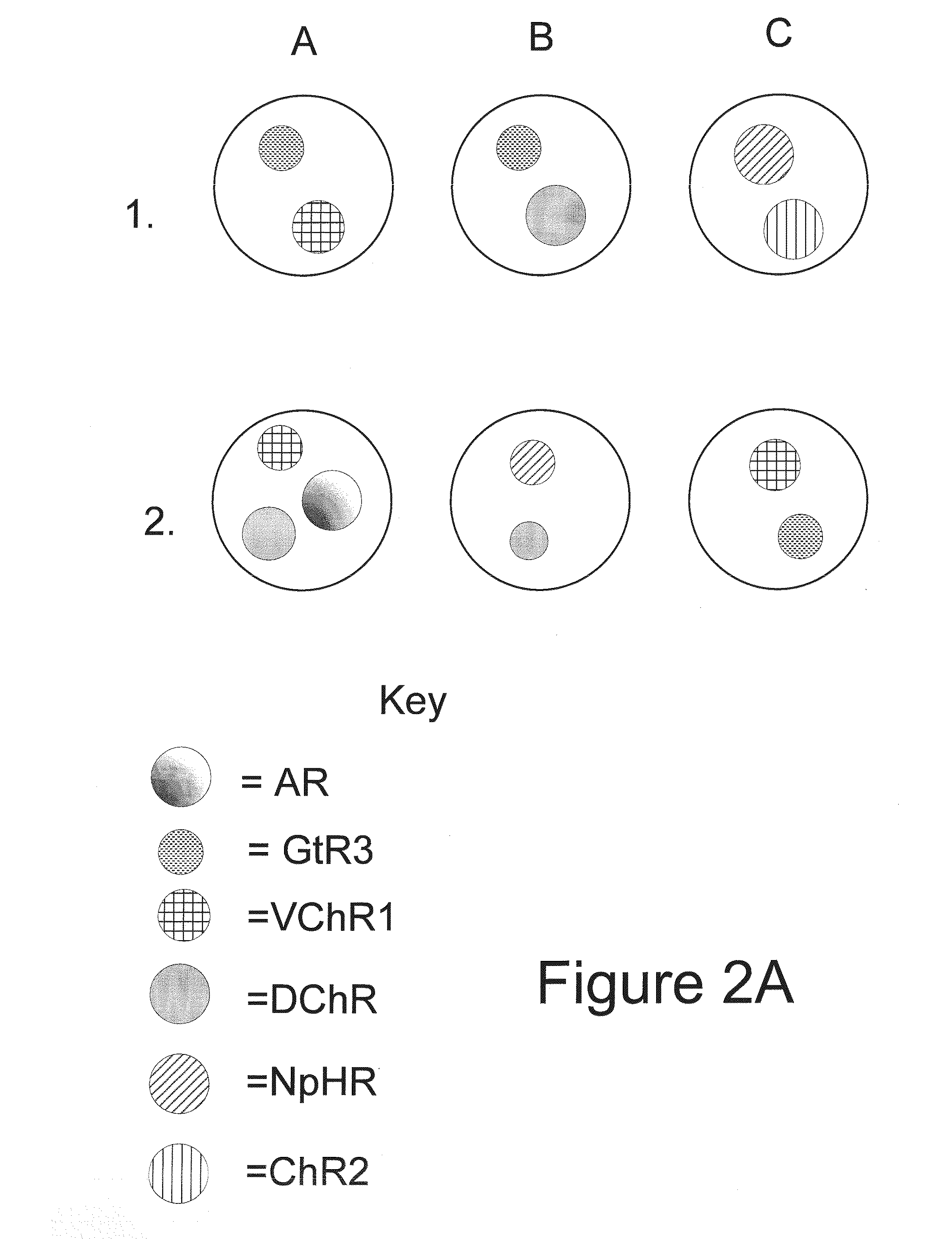
ActiveUS20130019325A1Dissuade depolarizationIncrease probabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsOptical stimulationLight activated
Disclosed are polynucleotides and methods for expressing light activated proteins in animal cells and altering an action potential of the cells by optical stimulation. The disclosure also provides animal cells and non-human animals comprising cells expressing the light-activated proteins.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Mapping retinal function using corneal electrode array
A system and method for obtaining information about the spatial distribution of photoreceptor activity and neural activity in the retina using simultaneously recorded multiple biopotential signals. The information thus gathered is used to assess retinal dysfunction due to trauma or disease. The biopotential signals are recorded from the surface of the eye and head using a plurality of electrodes, including those integral to a contact lens. The biopotential signals are recorded before, during and after the presentation of an optical stimulus to the subject eye. The recorded biopotential signals are then analyzed and interpreted to reveal the distribution of photoreceptor activity and neural activity across the retina. The analysis and interpretation of the biopotential signals is quantitative, and makes use of an electromagnetic model of the subject eye. The subject may be animal or human.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
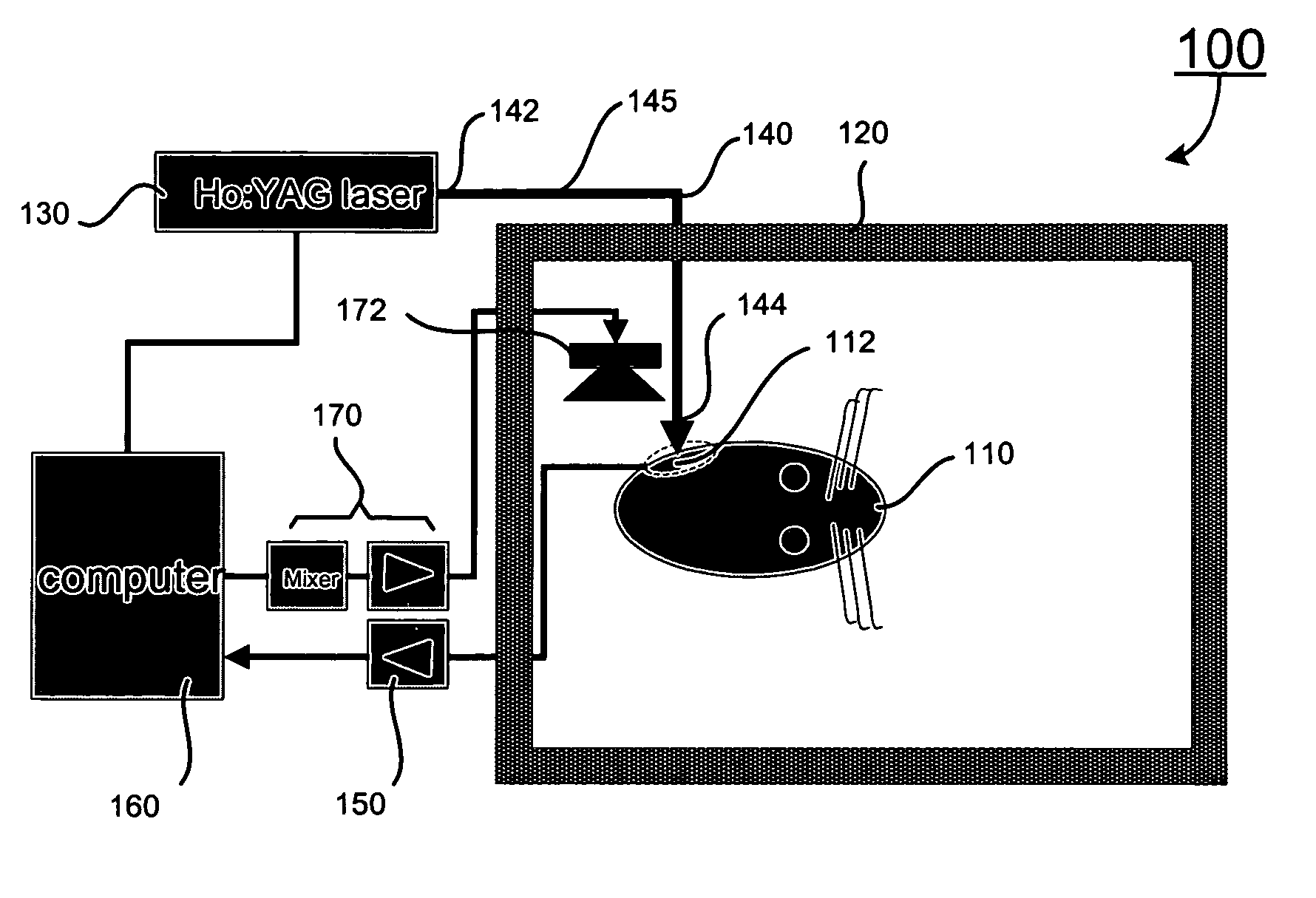
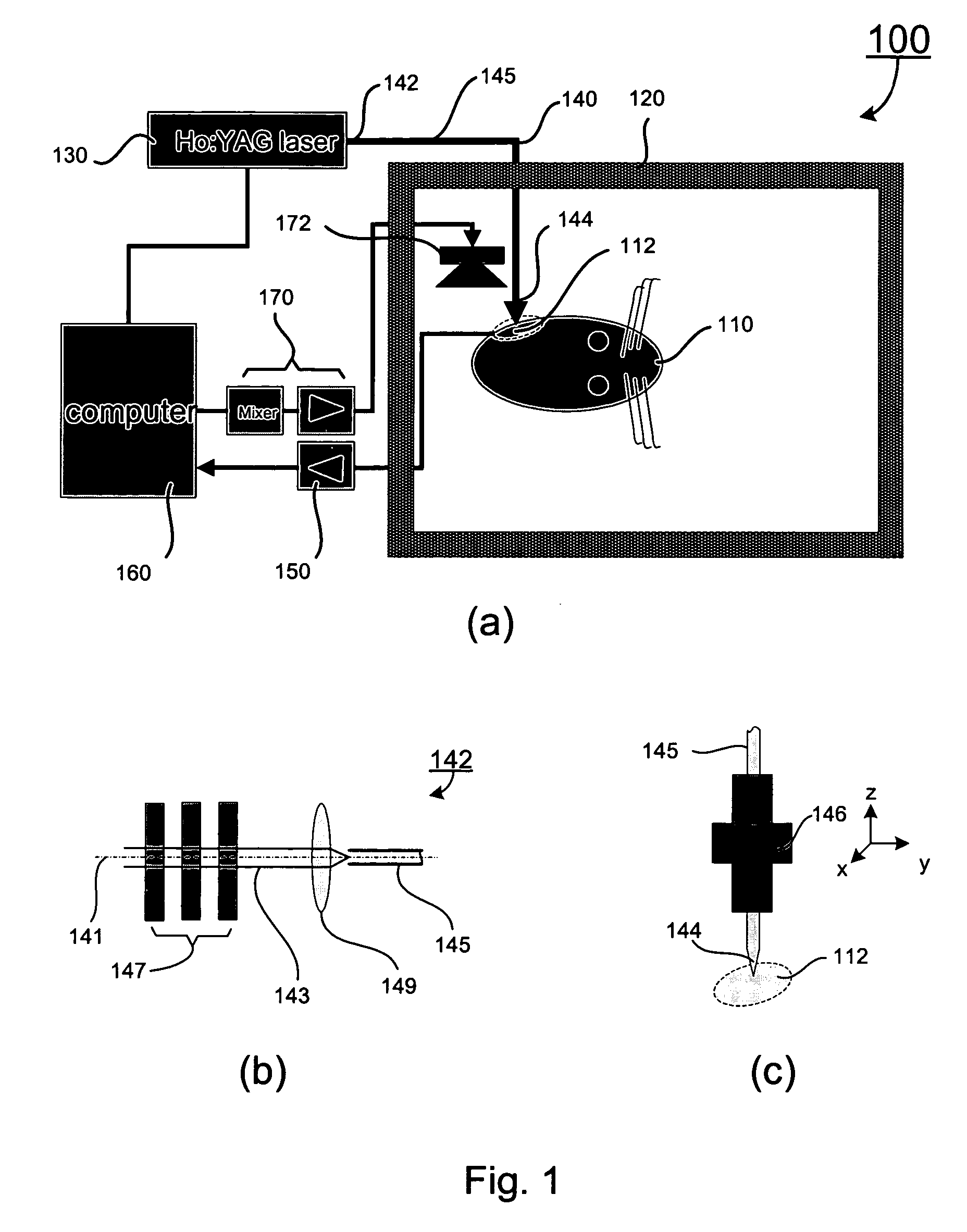
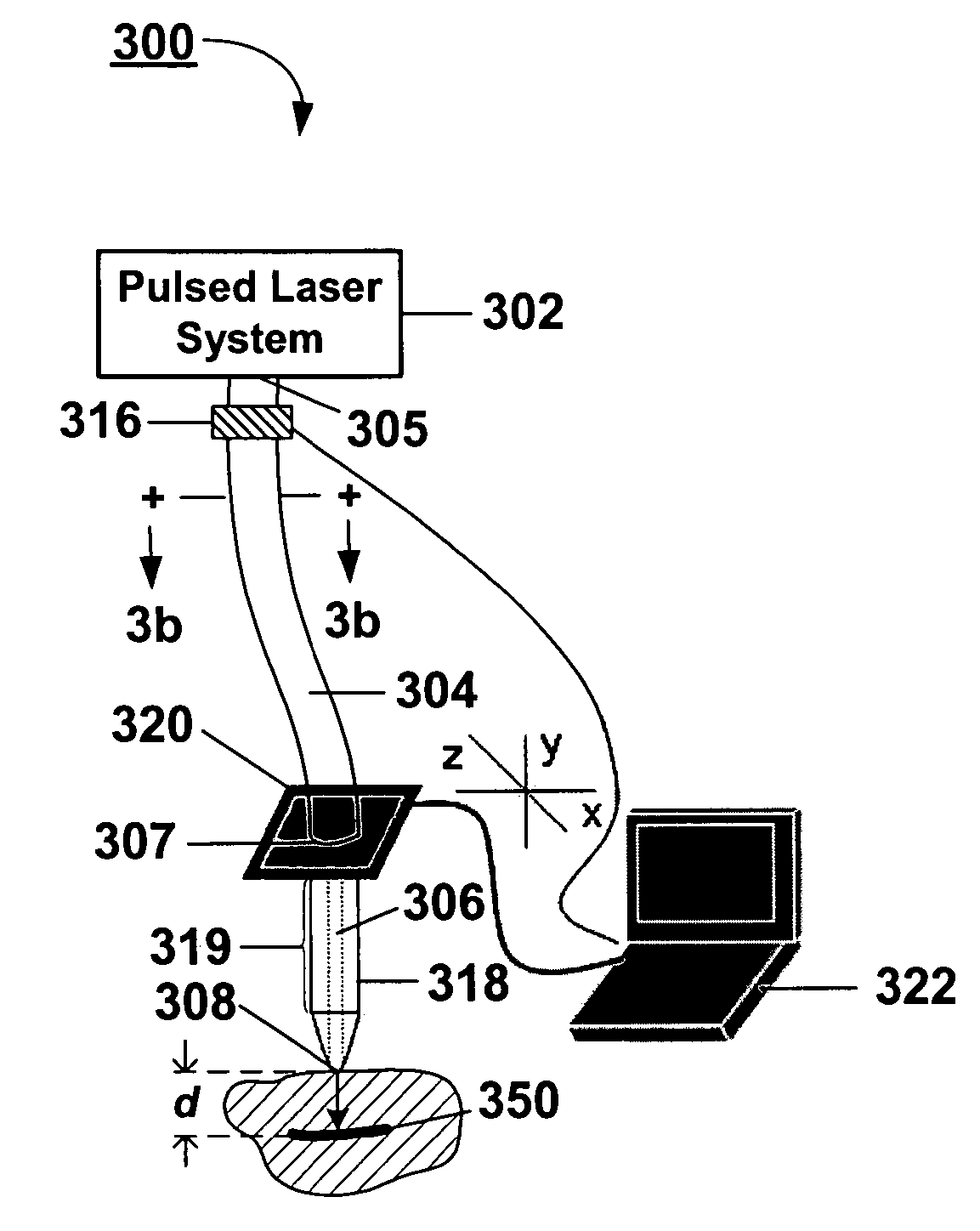
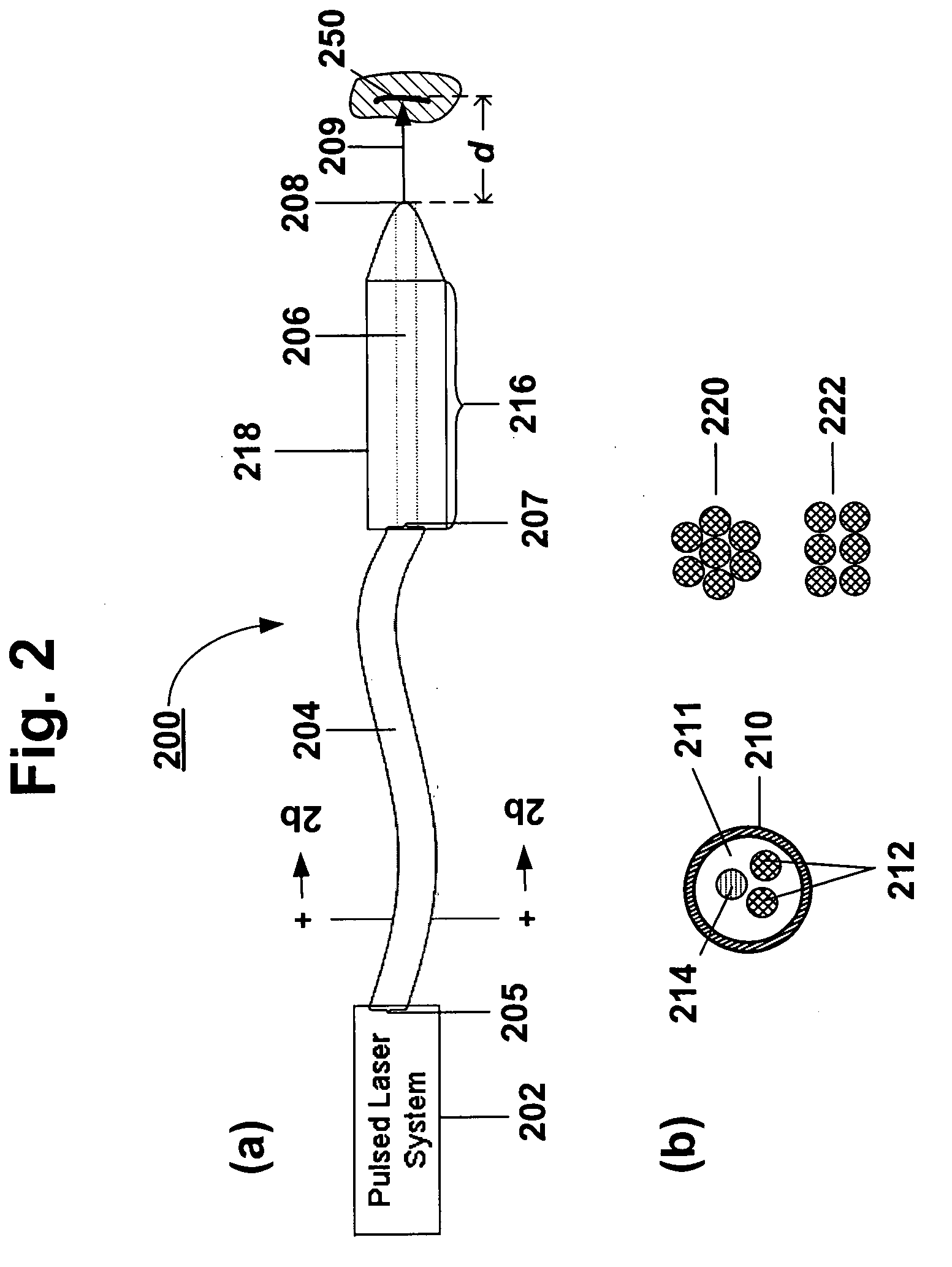
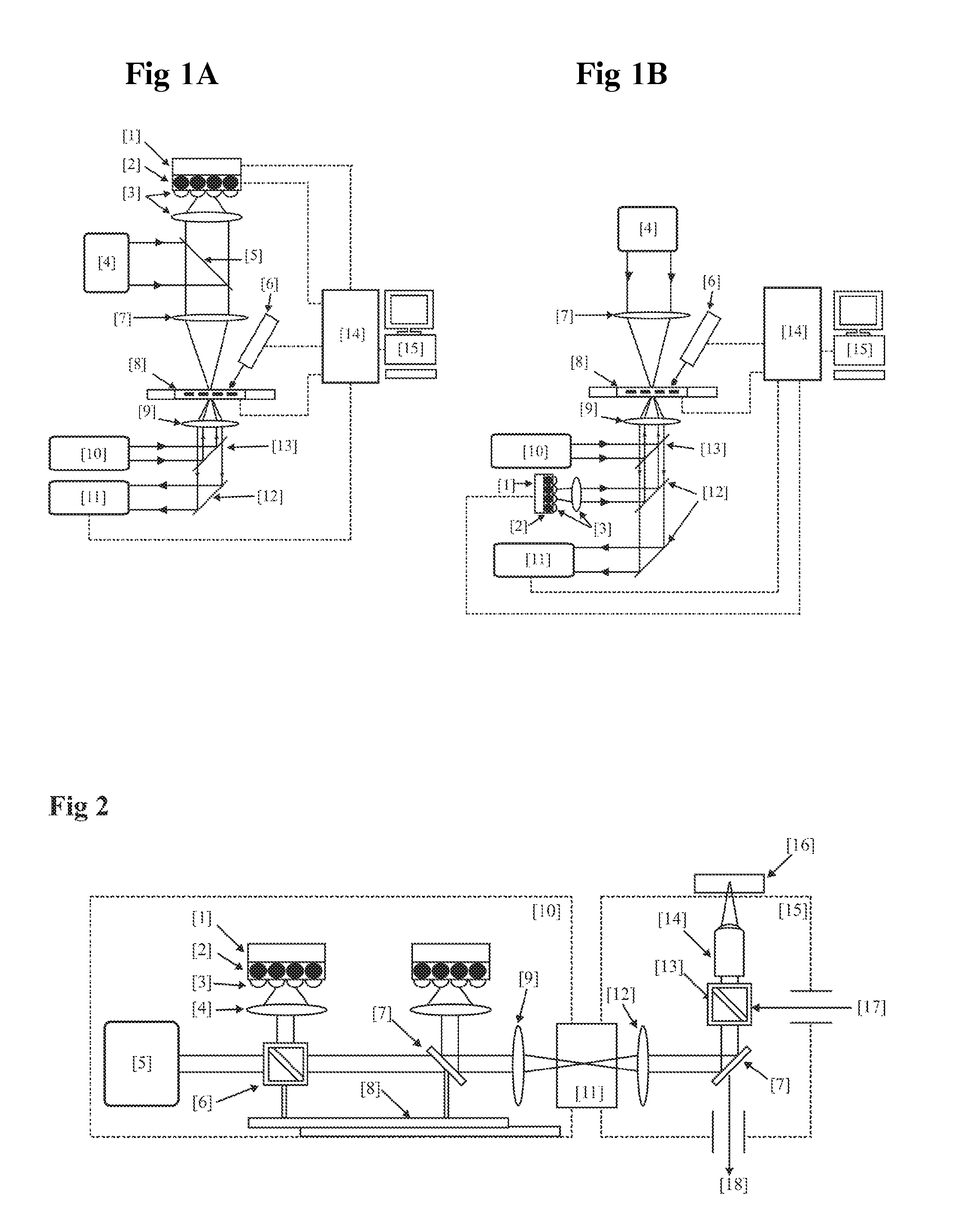
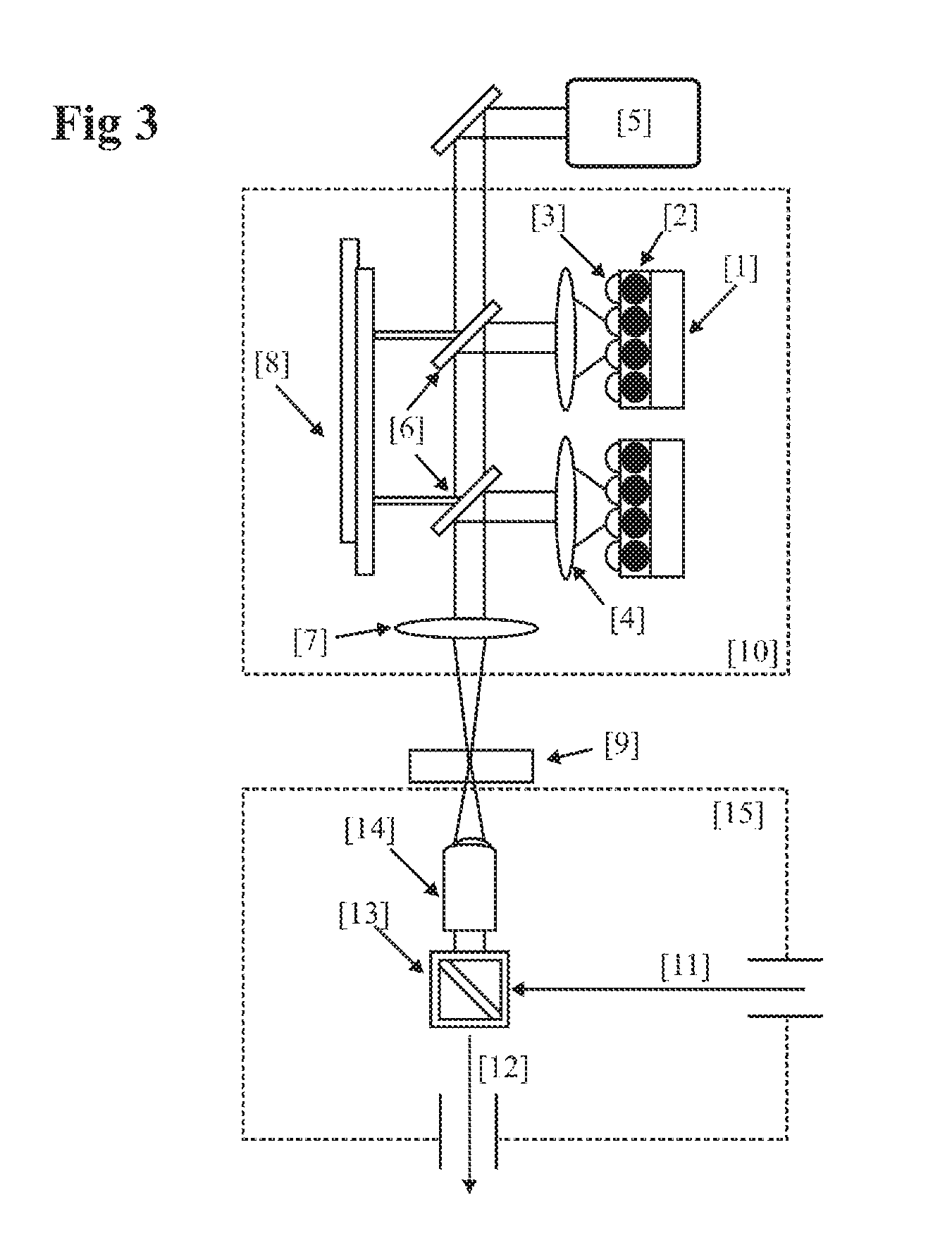
System and methods for optical stimulation of neural tissues
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a system for stimulating neural tissue of a living subject. The system comprises an energy source capable of generating optical energy, a connector having a first end and a second end capable of transmitting optical energy, and a probe operably coupled to the second end of the connector and having an end portion for delivering optical energy to a target neural tissue. In one embodiment, the energy source comprises a tunable laser.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Apparatus for optical stimulation of nerves and other animal tissue
A nerve-stimulation device and method using light to provide a source of precise stimulation on one or more nerve fibers. In some embodiments, this simulation is provided through a device and method wherein a laser- or LED-light-generating source is operatively coupled to an optical fiber, which in turn is coupled to a plug in the end of a holder in a sheath. Light is then passed from the light source through the optical fiber to the holder and out a selected optical tip on the sheath to provide an efficacious amount of light to simulate nerves. In some embodiments, the device is constructed from non-magnetic material such as glass, plastic or ceramics. In some embodiments, the light emanating from the optical tip can be controlled manually or automatically. Some embodiments omit the fiber and use light directly from the laser diode.
Owner:NERVESENSE LTD
Method and vestibular implant using optical stimulation of nerves
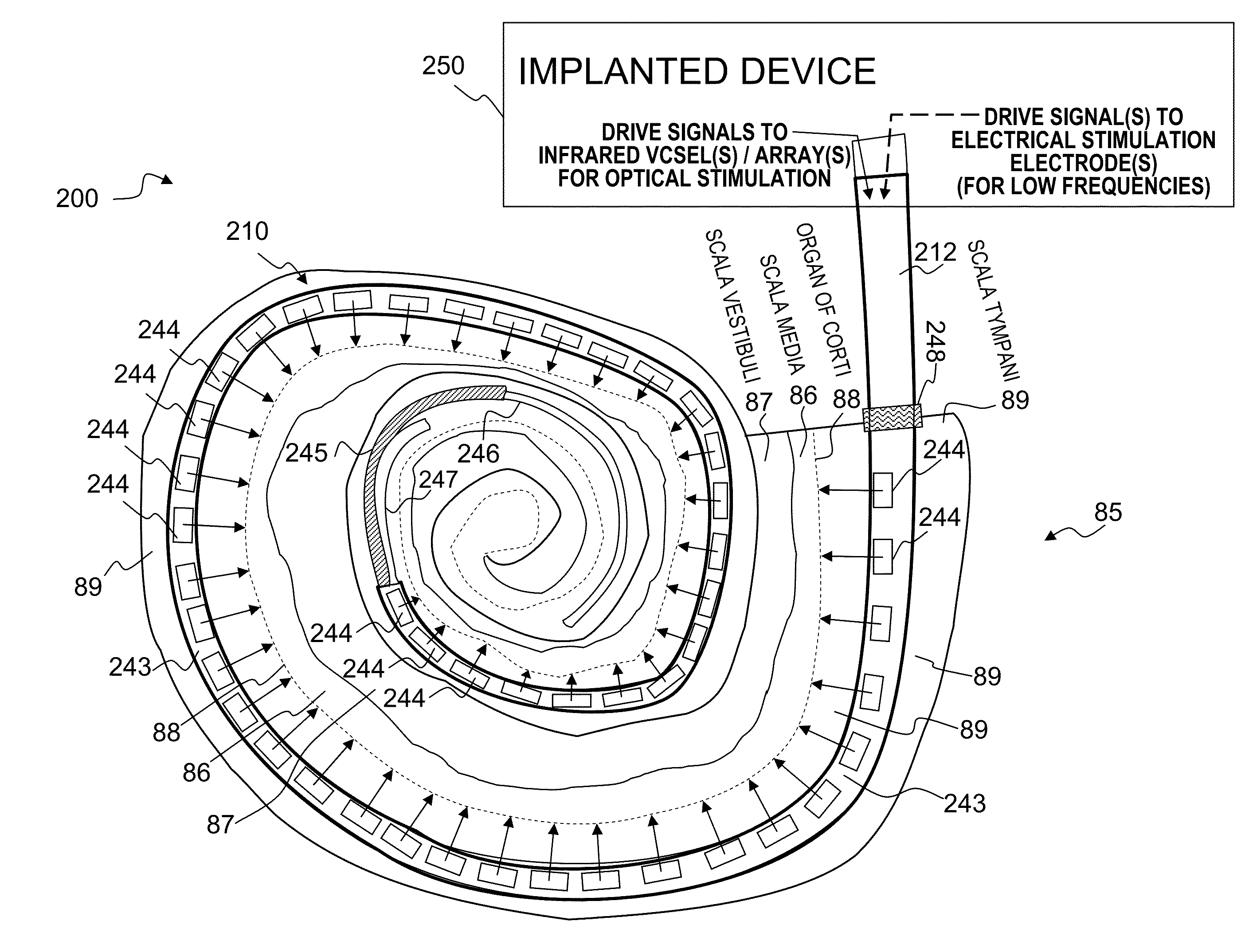
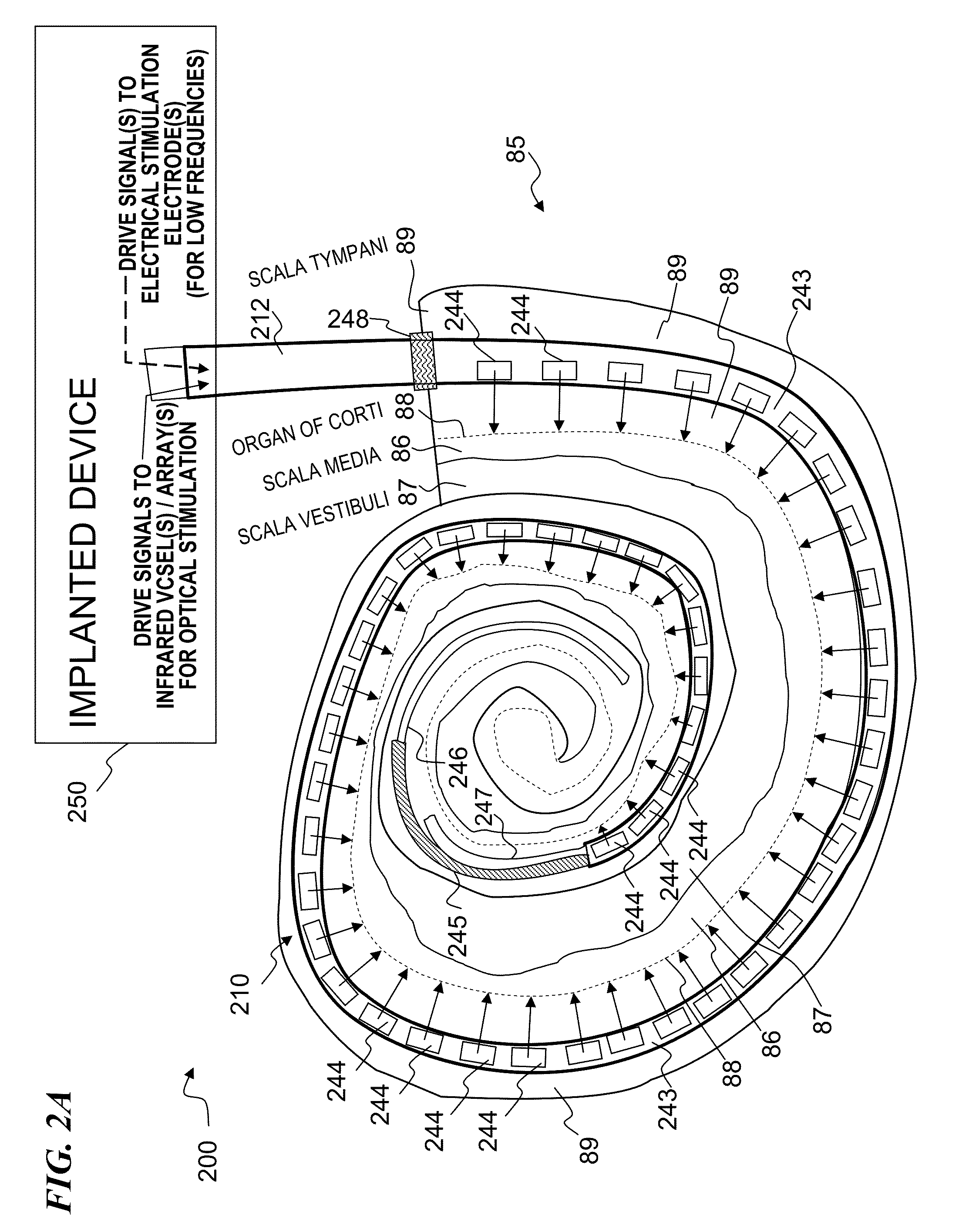
ActiveUS8012189B1Restore vestibular functionImprove balanceLight therapyImplanted deviceOptical stimulation
An optical-signal vestibular-nerve stimulation device and method that provides different nerve stimulation signals to a plurality of different vestibular nerves, including at least some of the three semicircular canal nerves and the two otolith organ nerves. In some embodiments, balance conditions of the person are sensed by the implanted device or external device, and based on the sensed balance conditions, varying laser nerve-stimulation signals are sent to a plurality of the different vestibular nerves.
Owner:NUROTONE MEDICAL LTD
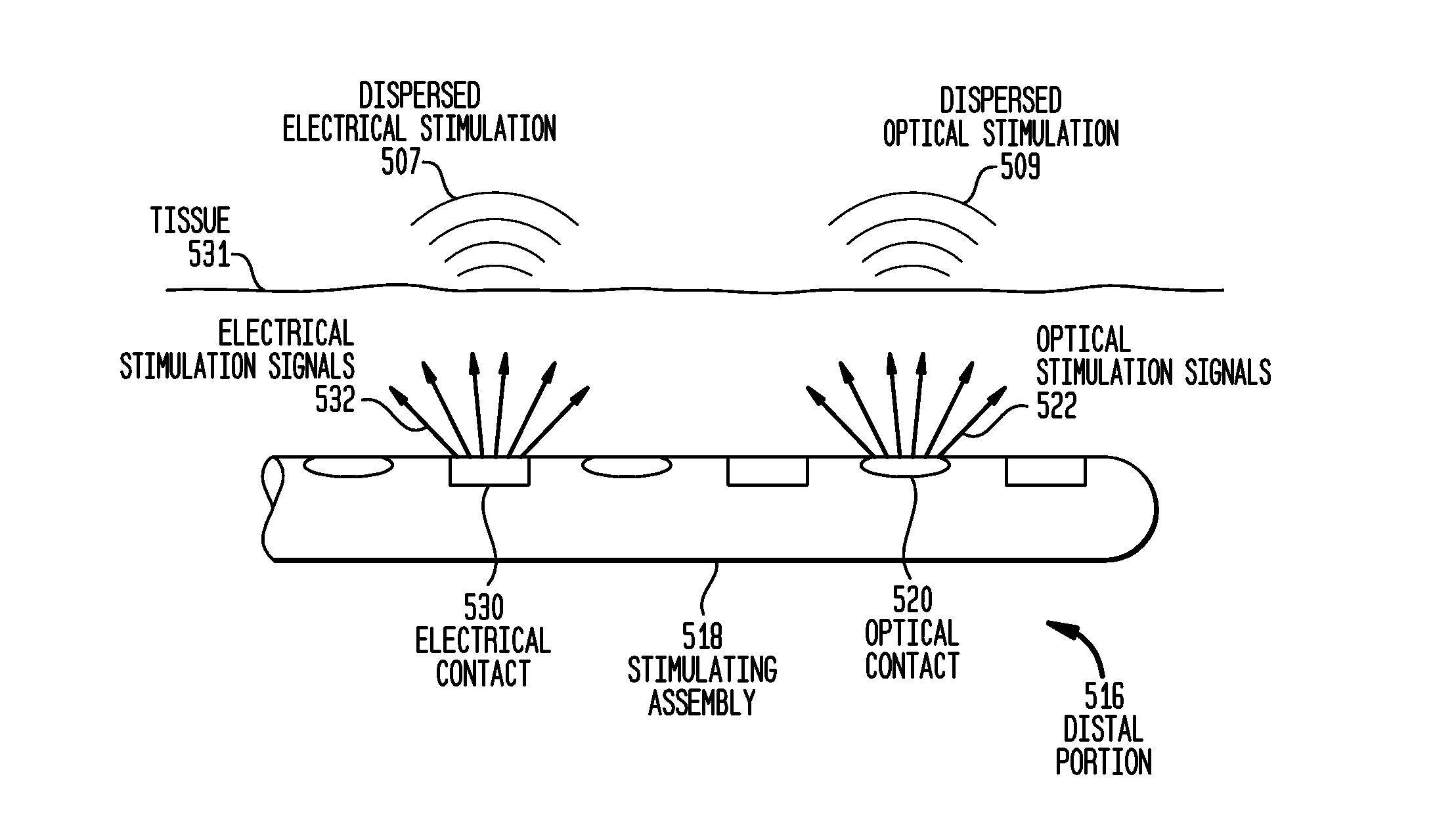
Combined optical and electrical neural stimulation
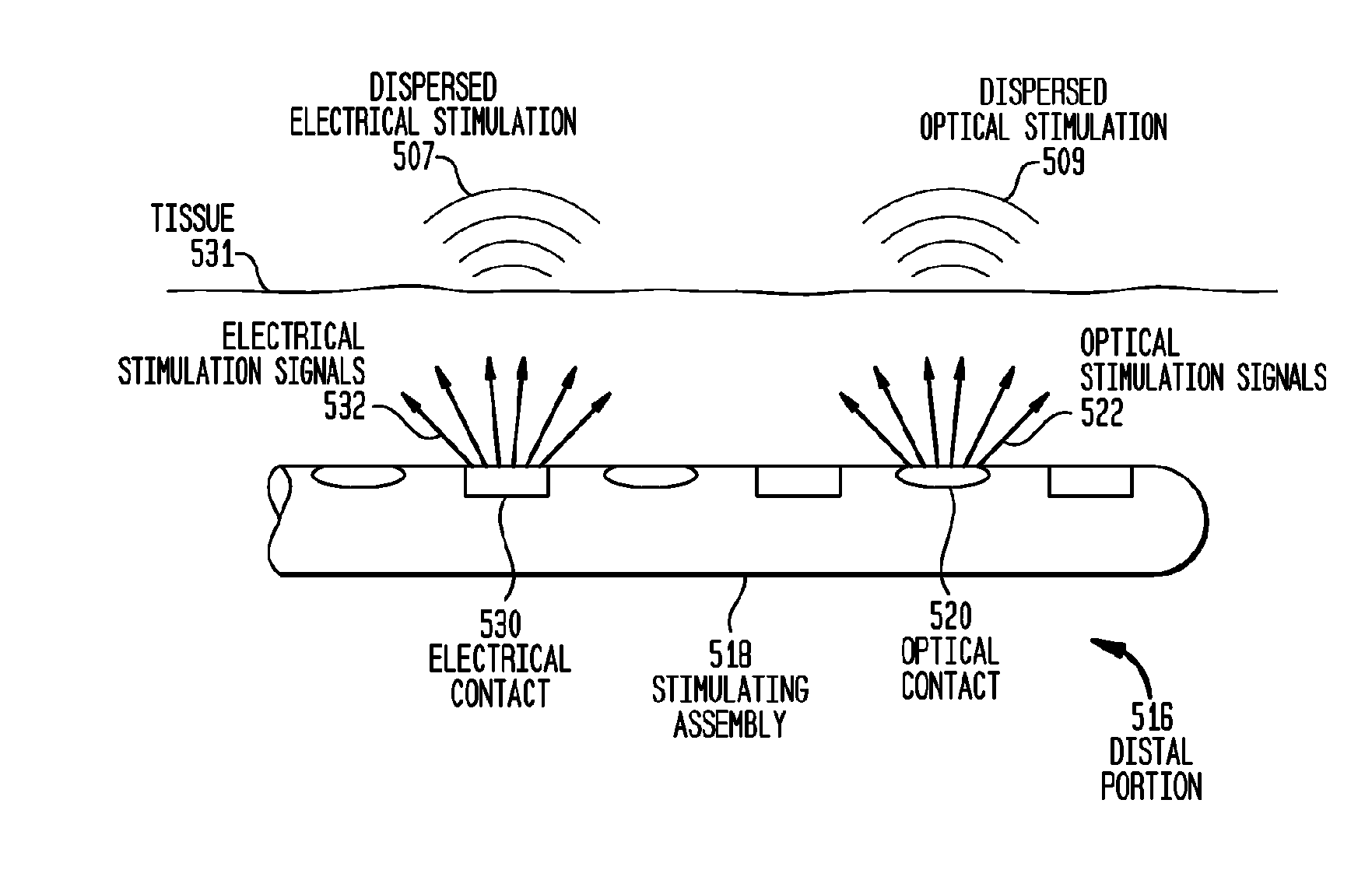
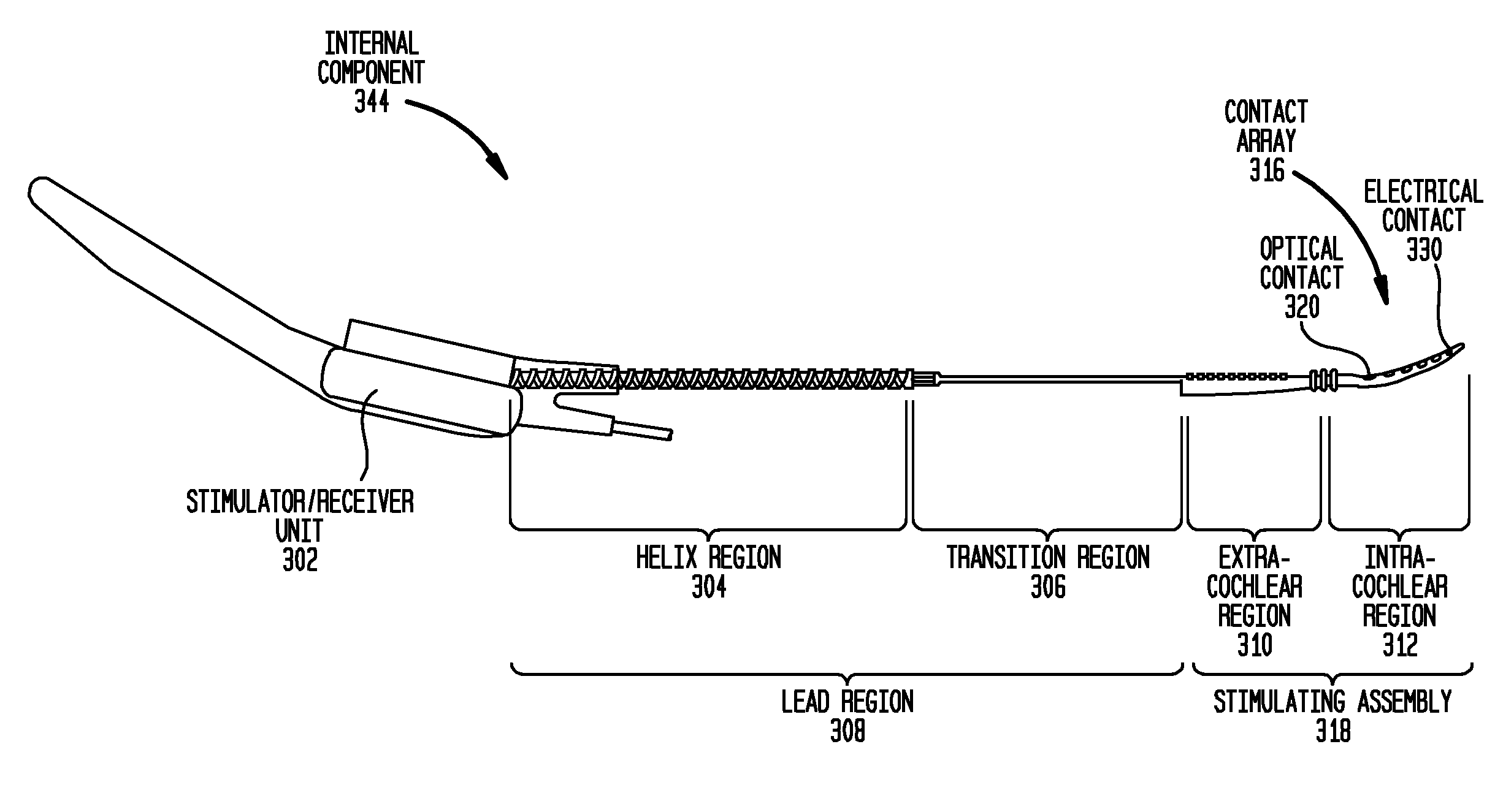
A neural-stimulating device for stimulating nerve cells of a recipient is provided. The neural-stimulating device comprises an electromagnetic radiation source configured to generate one or more optical stimulation signals and an electrical stimulation generator configured to generate electrical stimulation signals. The neural-stimulating device also comprises an implantable stimulating assembly configured to be implanted in the recipient, and having disposed thereon an optical contact to deliver the one or more optical stimulation signals to the nerve cells, and an electrical contact to deliver the electric stimulation signals to the nerve cells.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Apparatus and methods for optical stimulation of neural tissues
InactiveUS20090069871A1Minimal tissue damageSubstantial temperature increaseDiagnosticsSurgeryFluenceOptical stimulation
The present invention, in one aspect, relates to a method for stimulating neural tissue of a living subject. In one embodiment, the method has the steps of generating at least one beam of radiation; introducing at least one of one or more chromophores and one or more optical agents to a target neural tissue; and delivering the at least one beam of radiation to the target neural tissue, wherein the at least one beam of radiation is delivered with a radiant exposure that causes a thermal gradient in the target neural tissue, thereby stimulating the target neural tissue.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Optical neural stimulating device having a short stimulating assembly
A cochlear implant is provided. The cochlear implant comprises a stimulator unit configured to generate electrical stimulation signals based on sound processor-encoded signals, and to generate one or more optical stimulation signals, and an implantable stimulating assembly. The implantable stimulating assembly is configured to be implanted into a basal region of a recipient's cochlea such that when the stimulating assembly is fully implanted, a distal end of the assembly extends to the basal turn of the cochlea. The stimulating assembly also comprises: an optical contact to deliver the one or more optical stimulation signals to the cochlea, and an electrical contact to deliver the electric stimulation signals to a basal region of the cochlea so as to cause perception by the recipient of one or more frequency components of the acoustic sound signal.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
System and method for autonomic blood pressure regulation
InactiveUS20140067003A1Improve complianceReduce cardiovascular riskSpinal electrodesCatheterCervical vertebral bodyEfferent
A system for regulating blood pressure by stimulating an afferent pathway to the brain which produces an efferent output in kidneys includes a electrode device adapted for implantation in the cervical region, a stimulator generator, a cable connecting the electrode device and the stimulator generator, wherein the cervical region is generally located between a pair of common carotid arteries, above an aortic arch and in front of cervical vertebrae C2 and C3. A method of implantation includes placing the electrode device in the cervical region, selectively energizing the device in accordance with a stimulation scheme, assessing any changes in the patient's blood pressure, selectively energizing the device in accordance with another stimulation scheme, and assessing any changes in the patient's blood, for determining an optical stimulation scheme, wherein stimulation scheme involves parameters including, for example, position, placement and configuration of the electrode device in relation to surrounding tissue and / or organs, selection of electrodes energized, width, frequency and amplitude of stimulation current.
Owner:VASE ABHI +1
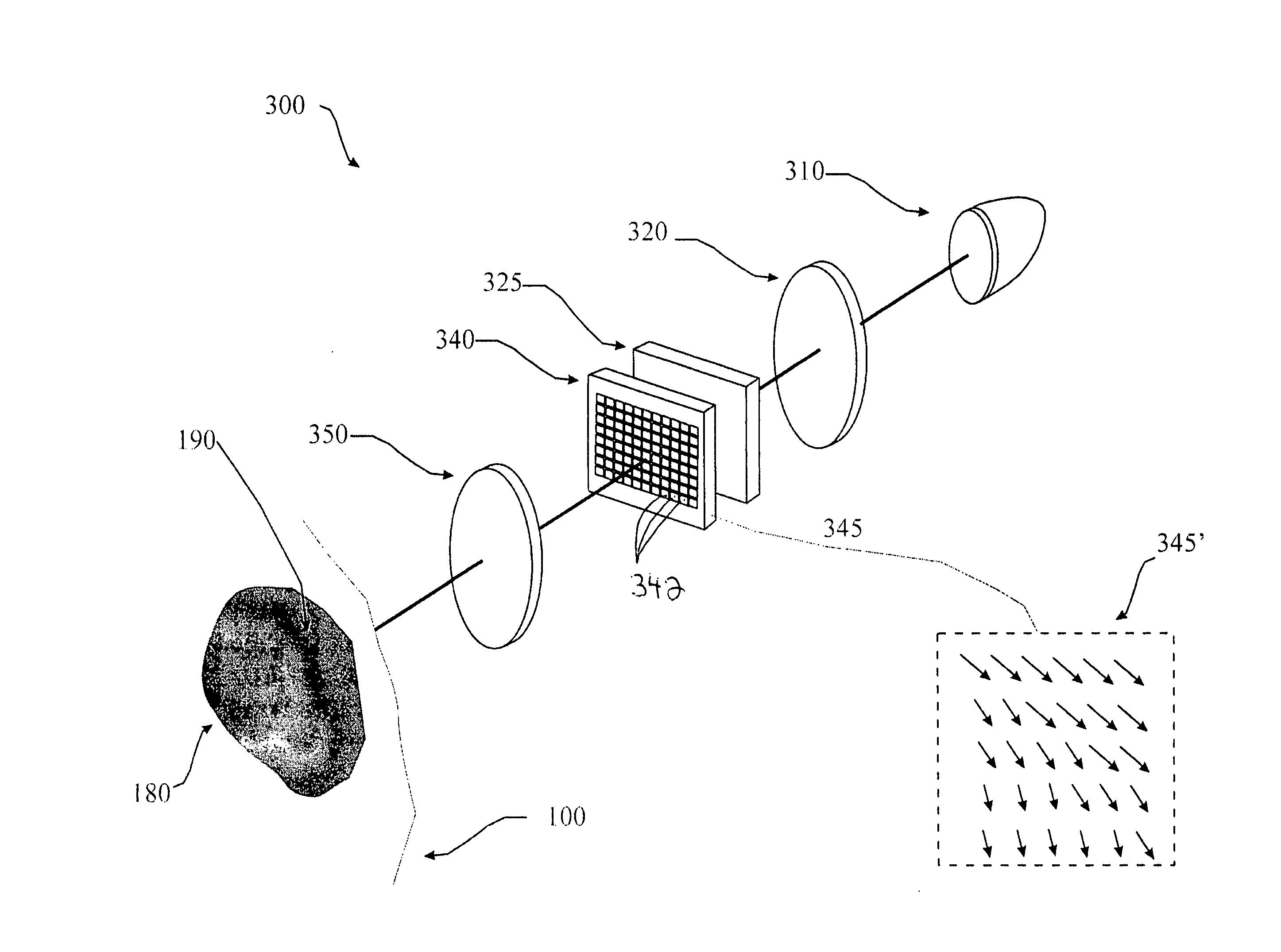
Device for optically stimulating collagen formation in tissue
A polarization based medical device (300) for optically stimulating the formation of collagen in tissue (100) comprises a light source (310) for providing a beam of light. A polarizer polarizes the beam of light. A first beam shaping optics (320) directs the polarized beam of light to a spatial light modulator (340). A second beam shaping optics (350) directs the polarized beam from the spatial light modulator to an area of interest within the tissue. A spatially controlled pattern of polarized light is directed onto the tissue, thereby affecting the orientation of formation of collagen within the tissue.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Combined Stimulation with Controlled Light Distribution for Electro-Optical Cochlear Implants
An implantable stimulation device is described which includes an implantable stimulation source carrier for insertion into or adjacent to target tissue. The stimulation source carrier includes stimulation contacts for delivering neural stimulation signals to nearby target tissue. At least one of the stimulation contacts is an optical stimulation element having multiple individual optical stimulation sub-elements for delivering optical stimulation signals to the nearby target tissue with controlled shape and direction.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Neural-stimulating device for generating pseudospontaneous neural activity
A neural-stimulating device for stimulating nerve cells of a recipient is provided. The neural-stimulating device comprises an electromagnetic radiation (EMR) generator configured to generate one or more optical stimulation signals configured to cause pseudospontaneous activity; and an implantable stimulating assembly having an optical contact coupled to the EMR generator, the stimulating assembly configured to be implanted in the recipient such that the one or more optical stimulation signals are applied to the nerve cells via the optical contact.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Beam Scanner for Autonomous Vehicles
ActiveUS20180217262A1Reduce power consumptionLarge field of regardElectromagnetic wave reradiationElectricityWavefront
A light beam steering transmissive element with an arbitrarily sized aperture comprising at least one layer of a insulating matrix modified for increased polarizability under electrical, magnetic or optical stimulation, between two or more substrates that can be electrically configured to provide signal modulation (optical, magnetic or electrical) that will control the wavefronts of incident light, thereby taking off-axis electromagnetic signals and aligning them to the aperture of a receiving element positioned near the device, or the reverse, sending signals originating behind the steering device to a variety of user-defined angles in two or more dimensions.
Owner:ALBELO JEFFREY +1
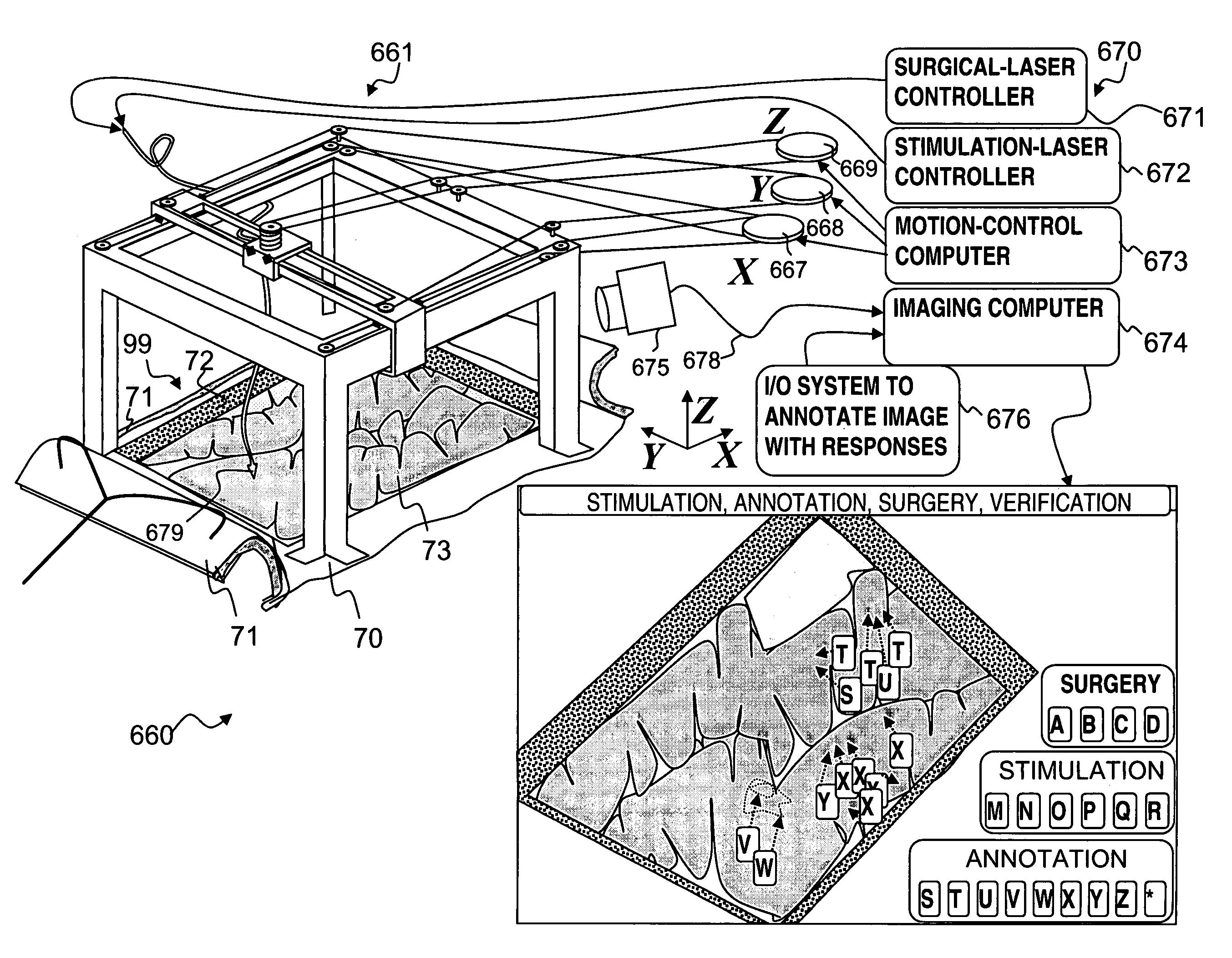
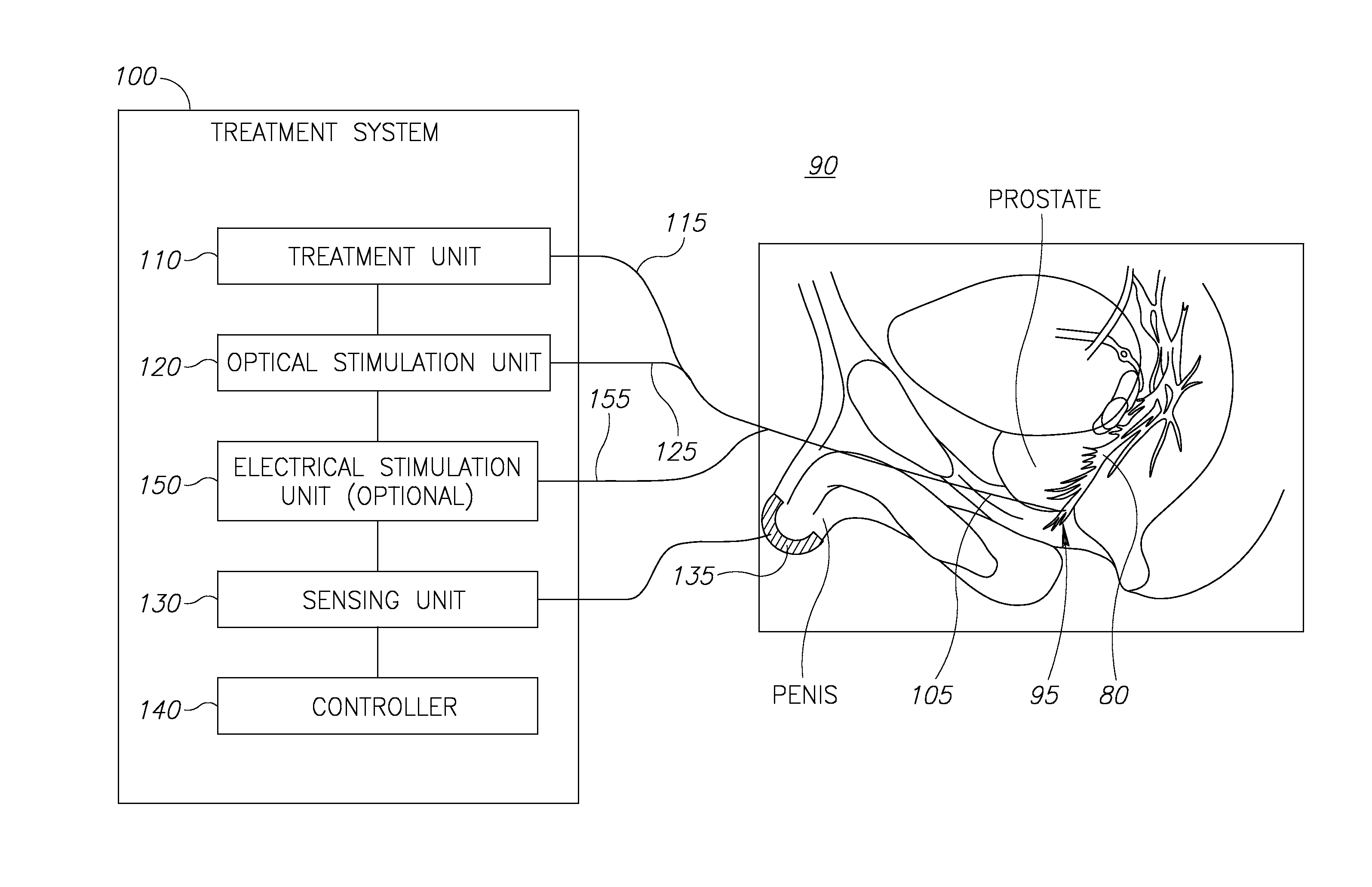
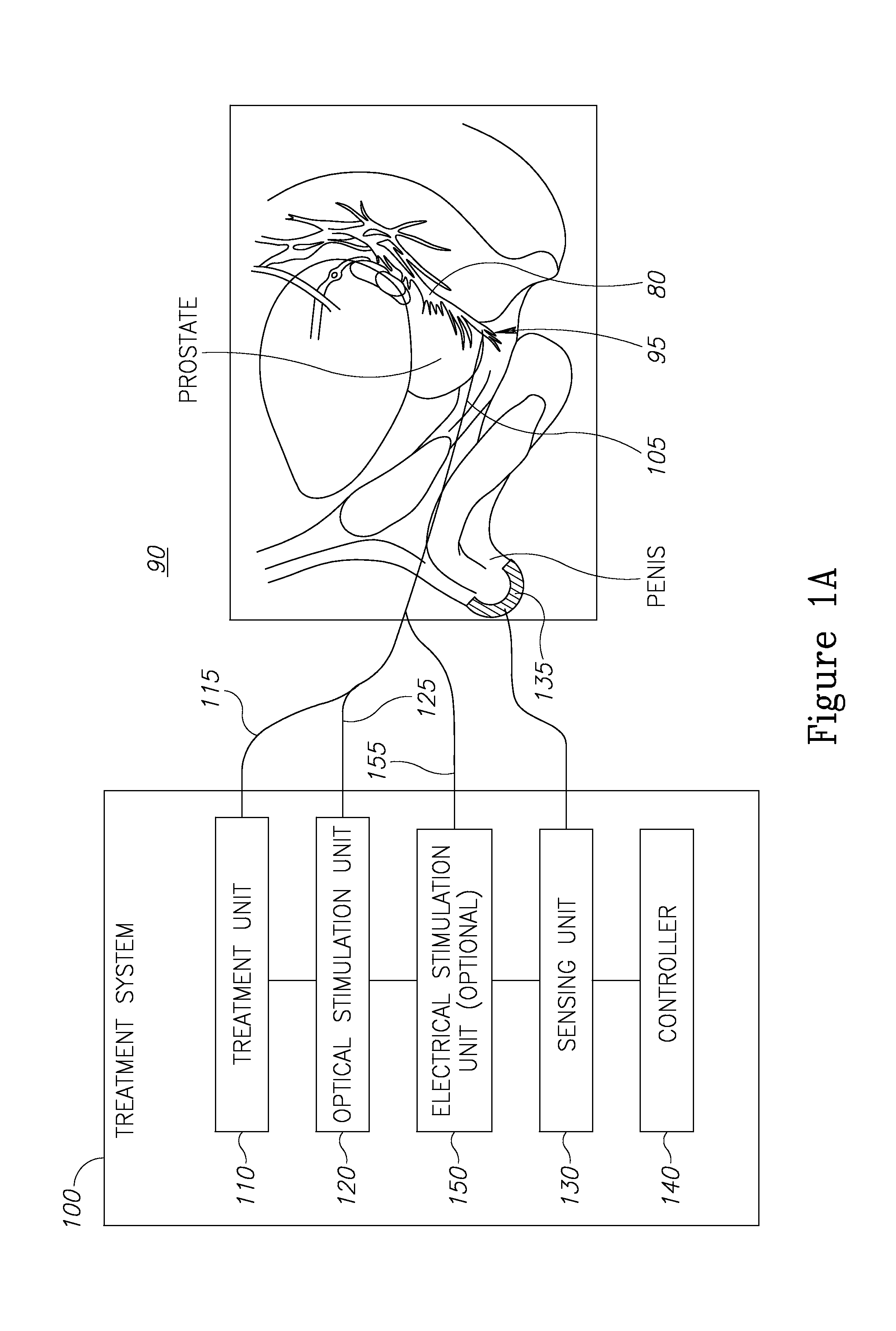
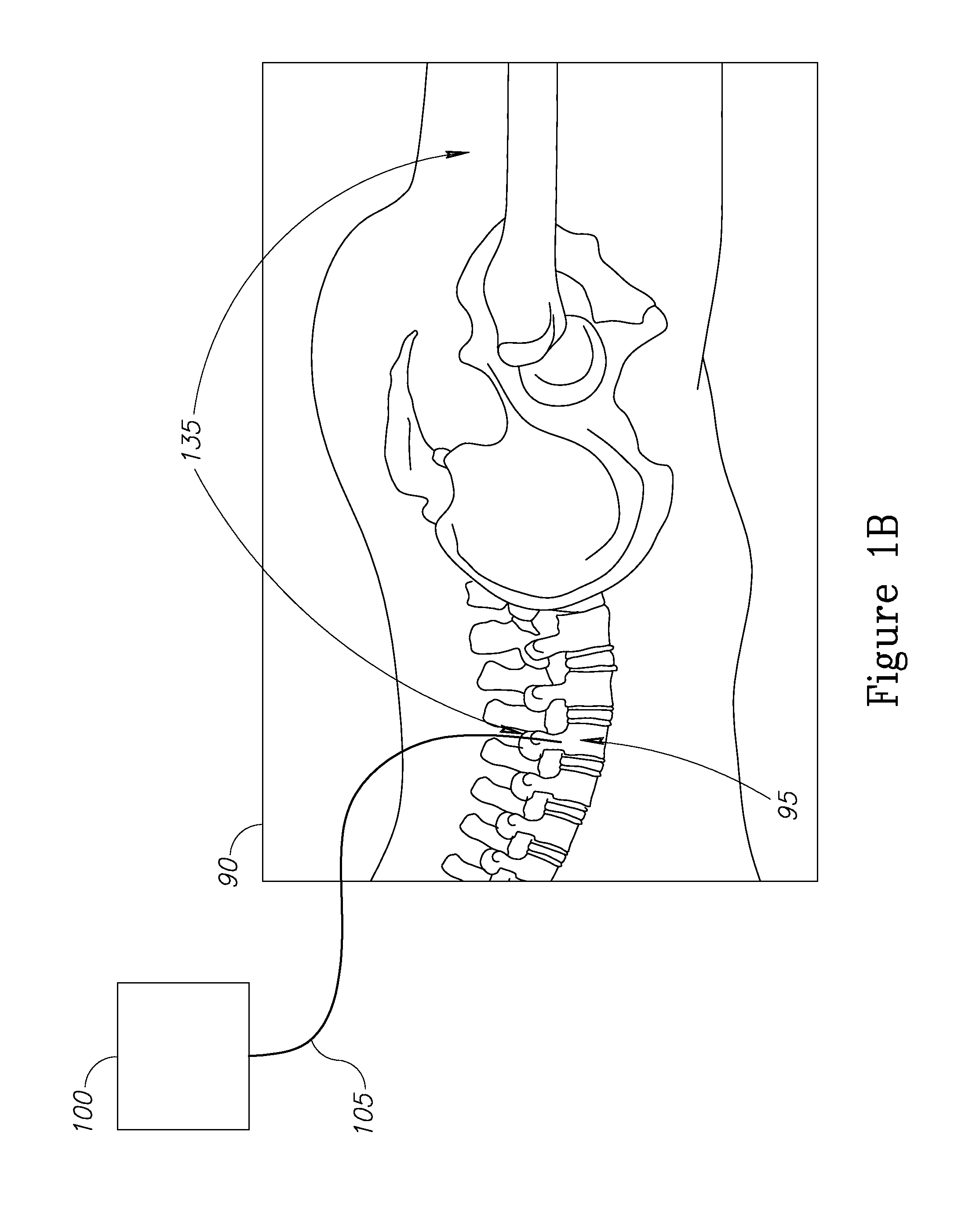
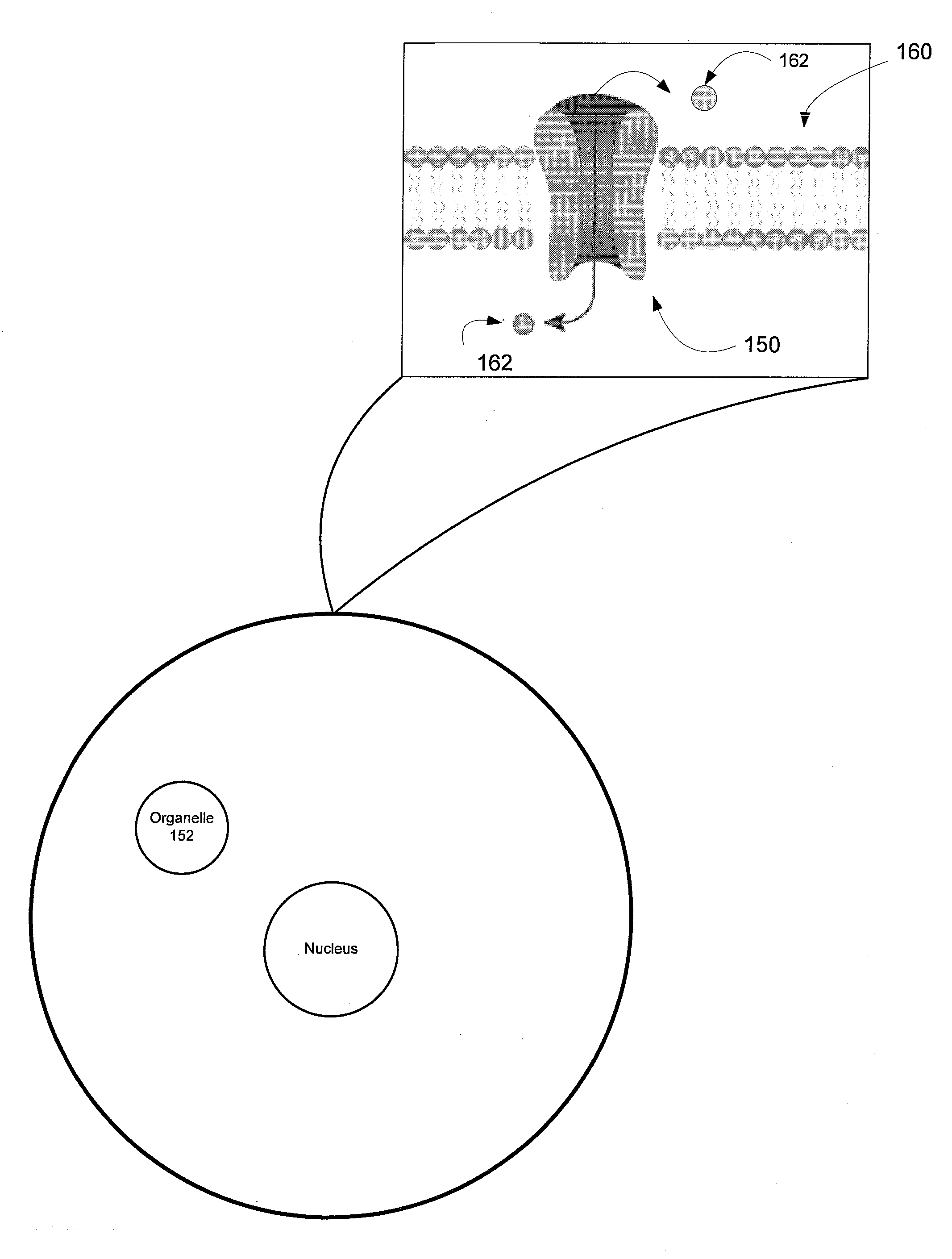
Nerve sparing treatment systems and methods
InactiveUS20150238259A1Controlling energy of instrumentDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityClosed loop
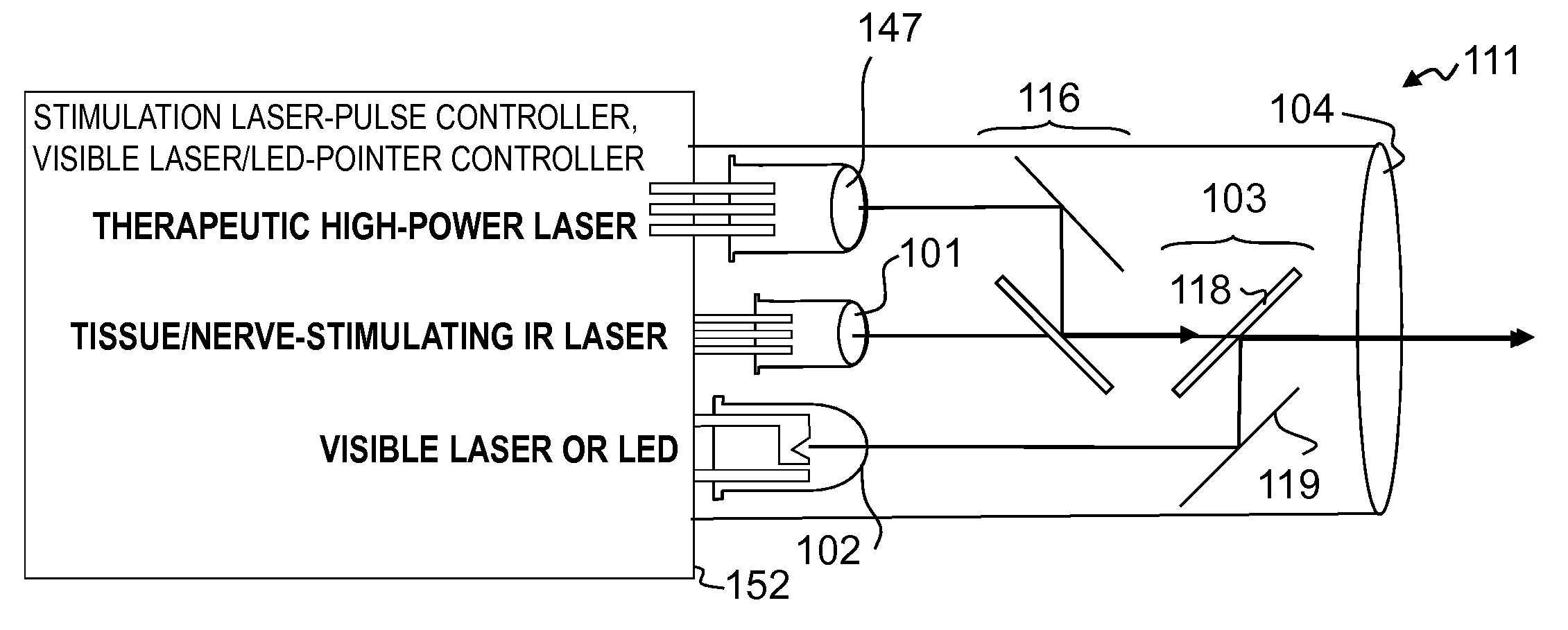
Treatment systems are provided, which comprise a treatment element applying a treatment to a tissue, a stimulation element optically stimulating nerves in the tissue, a sensing unit sensing an electrical signal produced by nerves in the tissue in response to the optical stimulation, and a control unit controlling the application of the treatment according to the sensed signal. The systems and methods are used to avoid damaging nerves by sensing them during operation and immediately before local treatment application and preventing energy emission when the treatment tool is too close to specified nerves. Additional electric stimulation may be provided to enable avoidance of nerve damages on a larger scale, the treatment may be applied by a cold laser, and the control unit may control the treatment in realtime and in a closed loop and immediate prevent further treatment upon sensing optically stimulated nerves.
Owner:ALBECK DAN DAVID +1
Light-Sensitive Ion-Passing Molecules
ActiveUS20130089503A1Dissuade depolarizationIncrease probabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman animalNucleotide
The invention provides polynucleotides and methods for expressing light-activated proteins in animal cells and altering an action potential of the cells by optical stimulation. The invention also provides animal cells and non-human animals comprising cells expressing the light-activated proteins.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
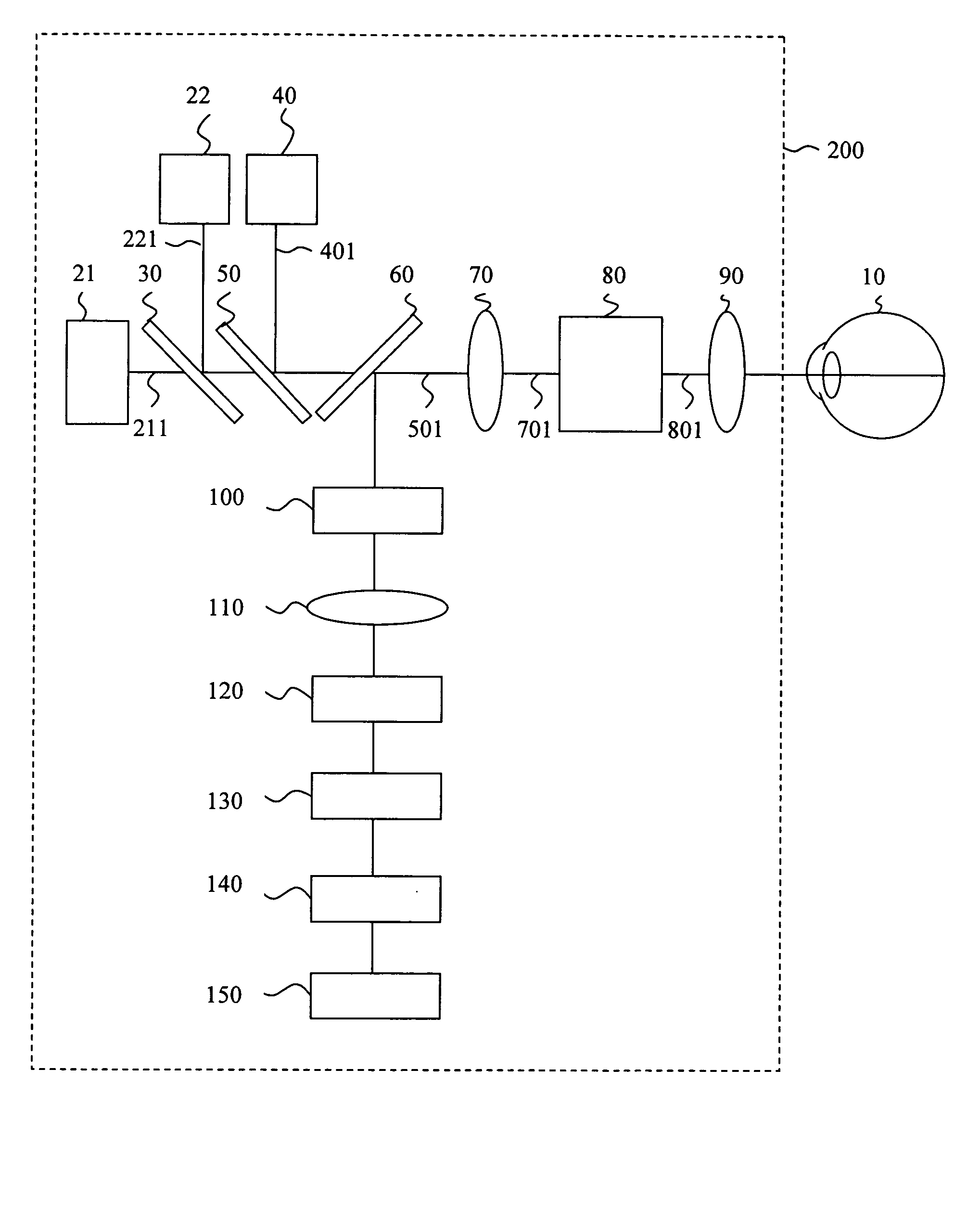
Display device
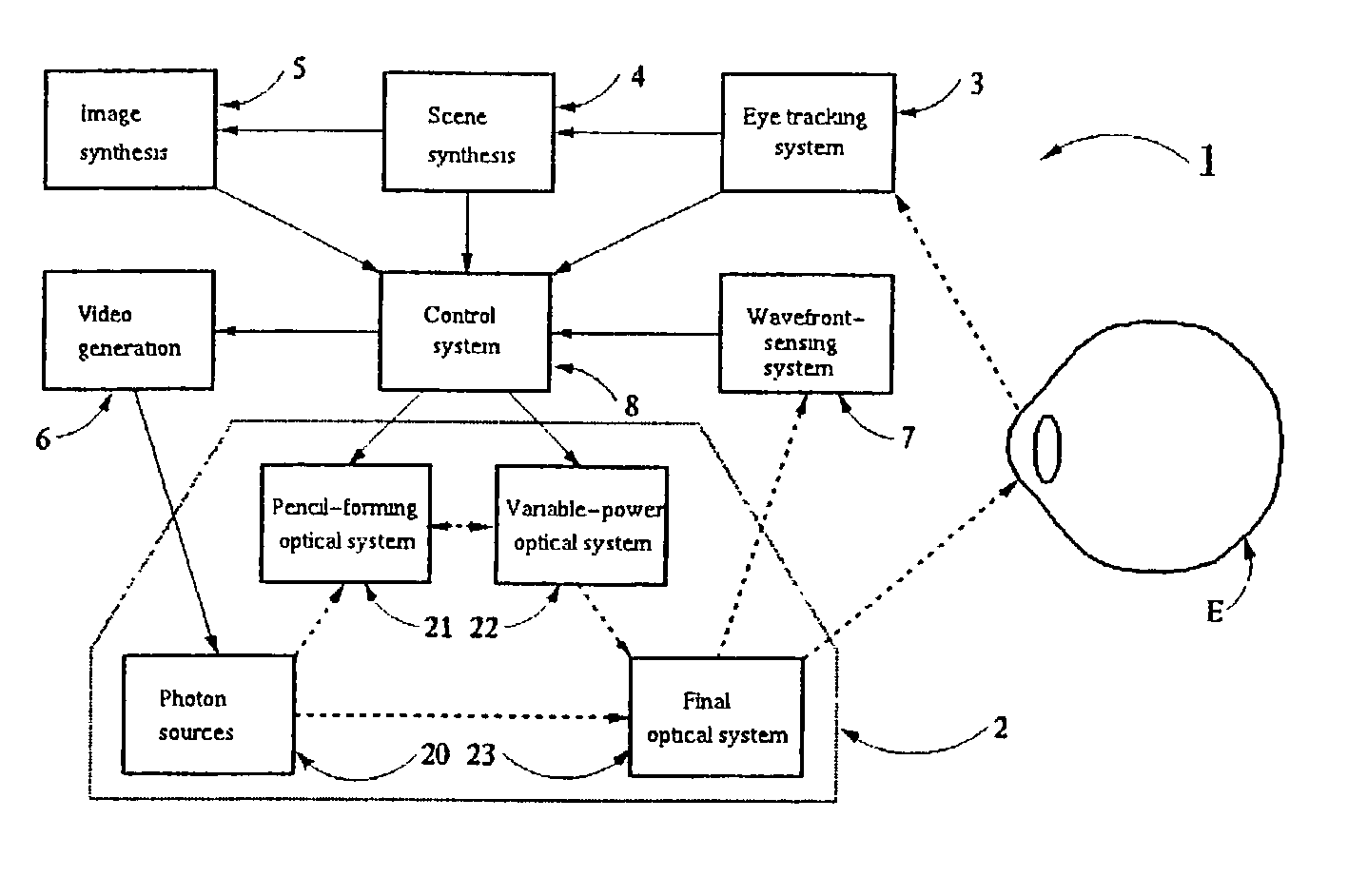
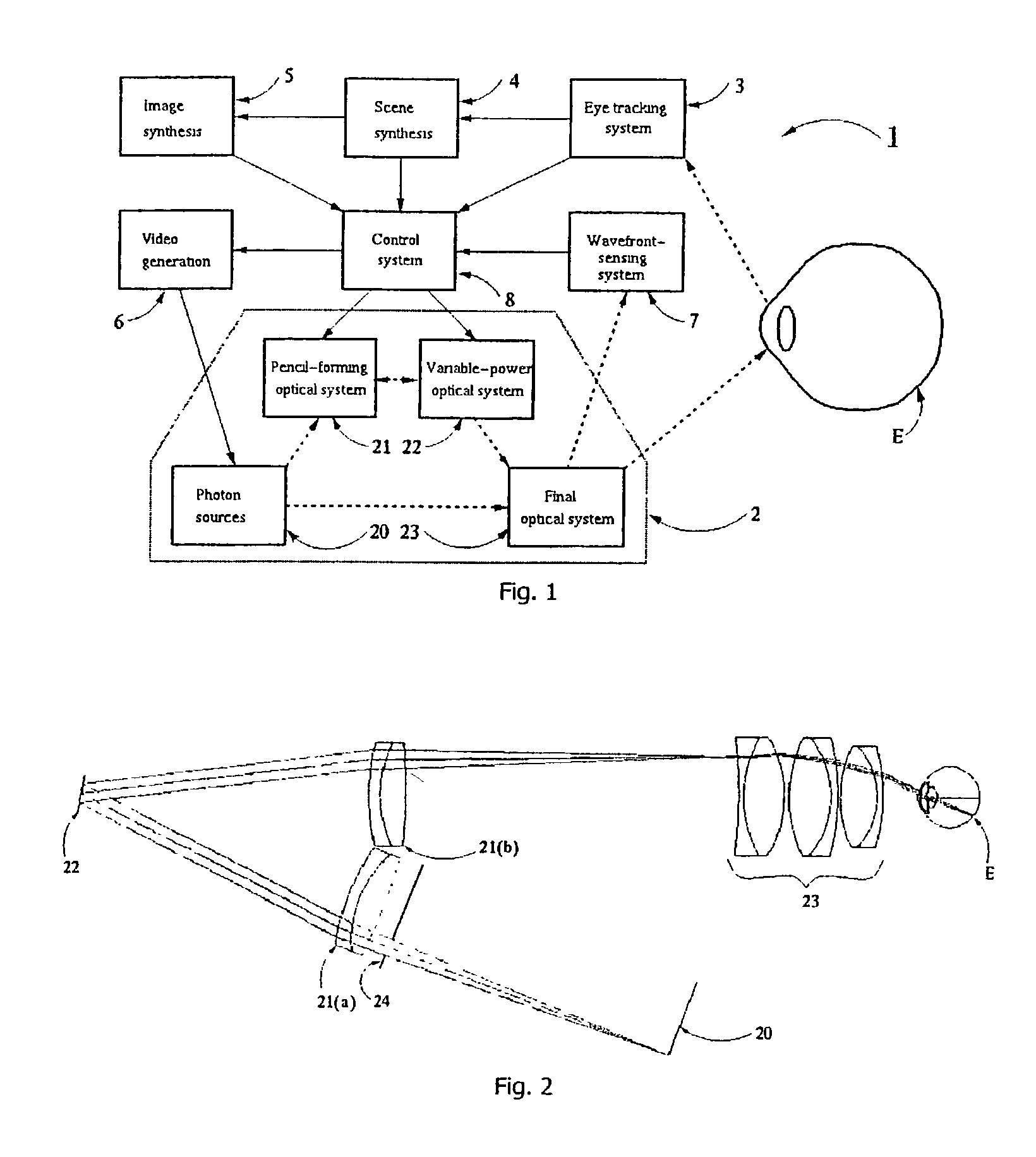
InactiveUS20020154272A1Magnitude is minimisedEye diagnosticsSteroscopic systemsControl systemDisplay device
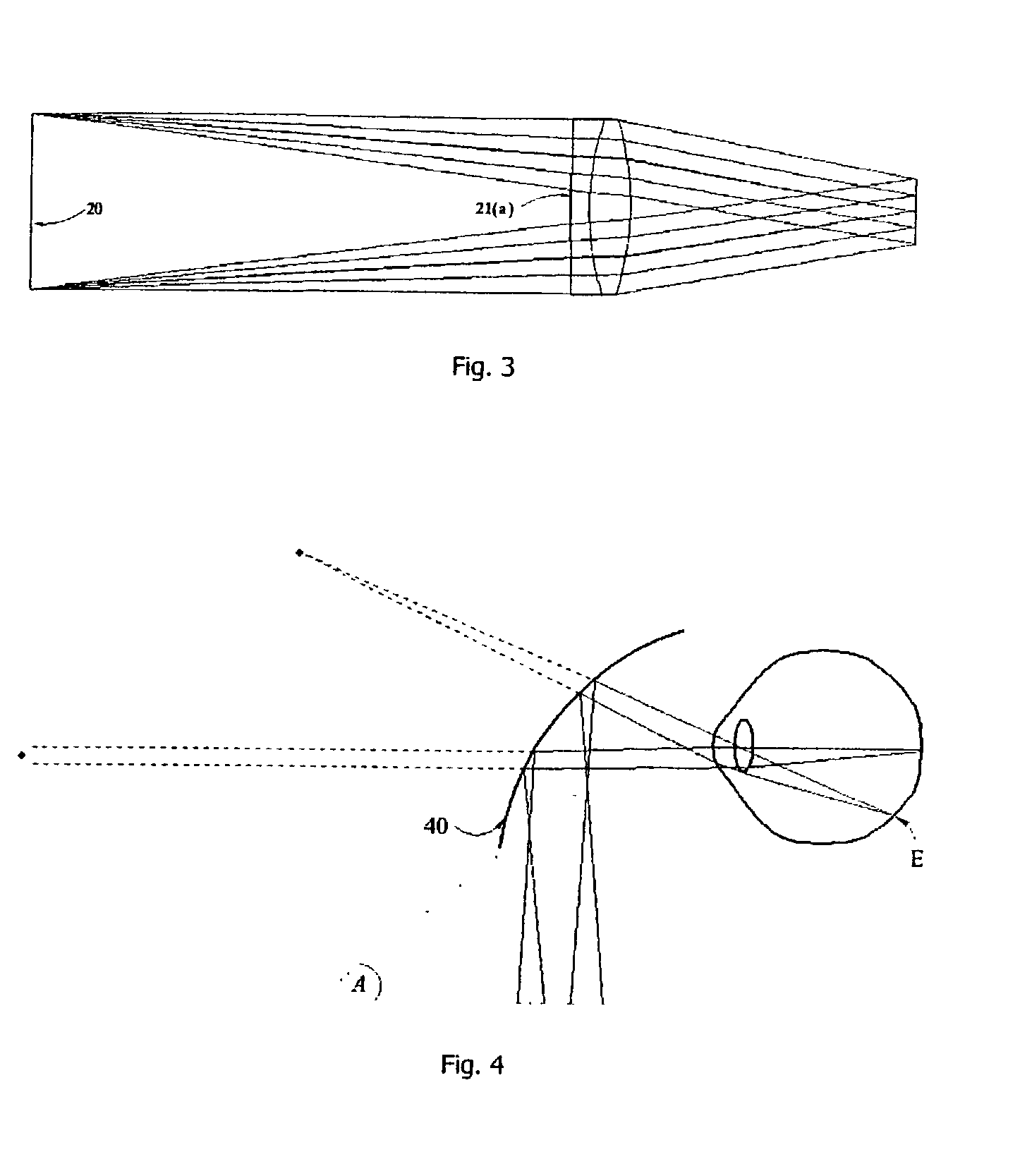
A display device (1) has a photon source (20) that displays an image scene in which the user perceives points at differents distances, resulting in optical stimulation of the eye's accommodative response. This is achieved by an intermediate optical system (21) forming the photons into pencils and a variable power optical system (22) positioned for convergence of the pencils. A control system (8) controls the variable power optical system (22) to modulate photon wavefront curvature according to image pixel co-ordinate and intensity data and data representing required perceived pixel distance.
Owner:SHEVLIN TECH
Optical-stimulation cochlear implant with electrode(s) at the apical end for electrical stimulation of apical spiral ganglion cells of the cochlea
ActiveUS20130023967A1Increased frequency rangeSpeech recognitionHead electrodesEar treatmentOptical stimulationElectrical stimulations
Method and apparatus for optically and electrically stimulating neurons of auditory nerve pathways of a person to provide auditory sensations for the person including generating a plurality of pulsed light signals having one or more successive pulses, delivering the plurality of pulsed light signals to one or more auditory nerve pathways of the cochlea of the person and selectively controlling the plurality of light signals to optically stimulate and trigger nerve action potentials (NAPs) in the one or more auditory nerve pathways. In some embodiments, the present invention also includes one or more electrical stimulation electrodes used to stimulate the low frequency portions of the auditory nerves.
Owner:NUROTONE MEDICAL LTD
Neural probe with optical stimulation capability
A neural probe is disclosed for optically stimulating or silencing neurons and recording electrical responses to the stimulus. Using patterning techniques, an integral optical waveguide may be fabricated on the probe for transmitting neuron-affecting light from a light source to a probe tip. The probe tip may include one or more electrodes to receive electrical responses from stimulated neurons for recording or further processing. According to various embodiments, the disclosed neural probes may utilize multiple light sources simultaneously, switch between multiple light sources, or utilize a single light source to stimulate or silence multiple neuron locations simultaneously via multiple probe tips or via multiple light-emitting sites located along the length of the probe. Neural probes are thereby provided that have sufficient spatial resolution to accurately target, stimulate, and record the reaction of neurons, or as few as a single neuron, utilizing a slim, compact structure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Analysis of retinal metabolism over at least a portion of a cardiac cycle
Retinal metabolism is analysed with a retinal function camera over at least a portion of a cardiac cycle by first illuminating a portion of a retina of an eye 10 with light of a first wavelength and producing a first image. The portion of the retina is subsequently illuminated with light of a second wavelength, the first and second wavelengths being selected such that absorptivity of light of the first wavelength by oxygenated blood is greater than absorptivity of light of the second wavelength and the absorptivity of light of the first wavelength by deoxygenated blood is less than absorptivity of light of the second wavelength, to produce a second image. The first and second images are processed to map relative oxygenation of the portion of the retina as an indication of retinal metabolic function of the portion of the retina. The procedure is repeated over at least a portion of a cardiac cycle to analyse metabolic function changes of the portion of the retina within the at least a portion of a cardiac cycle. In some embodiments at least a portion of the retina is subjected to optical stimulation and effects of the optical stimulation on retinal metabolic function analysed.
Owner:KERR PATRICK
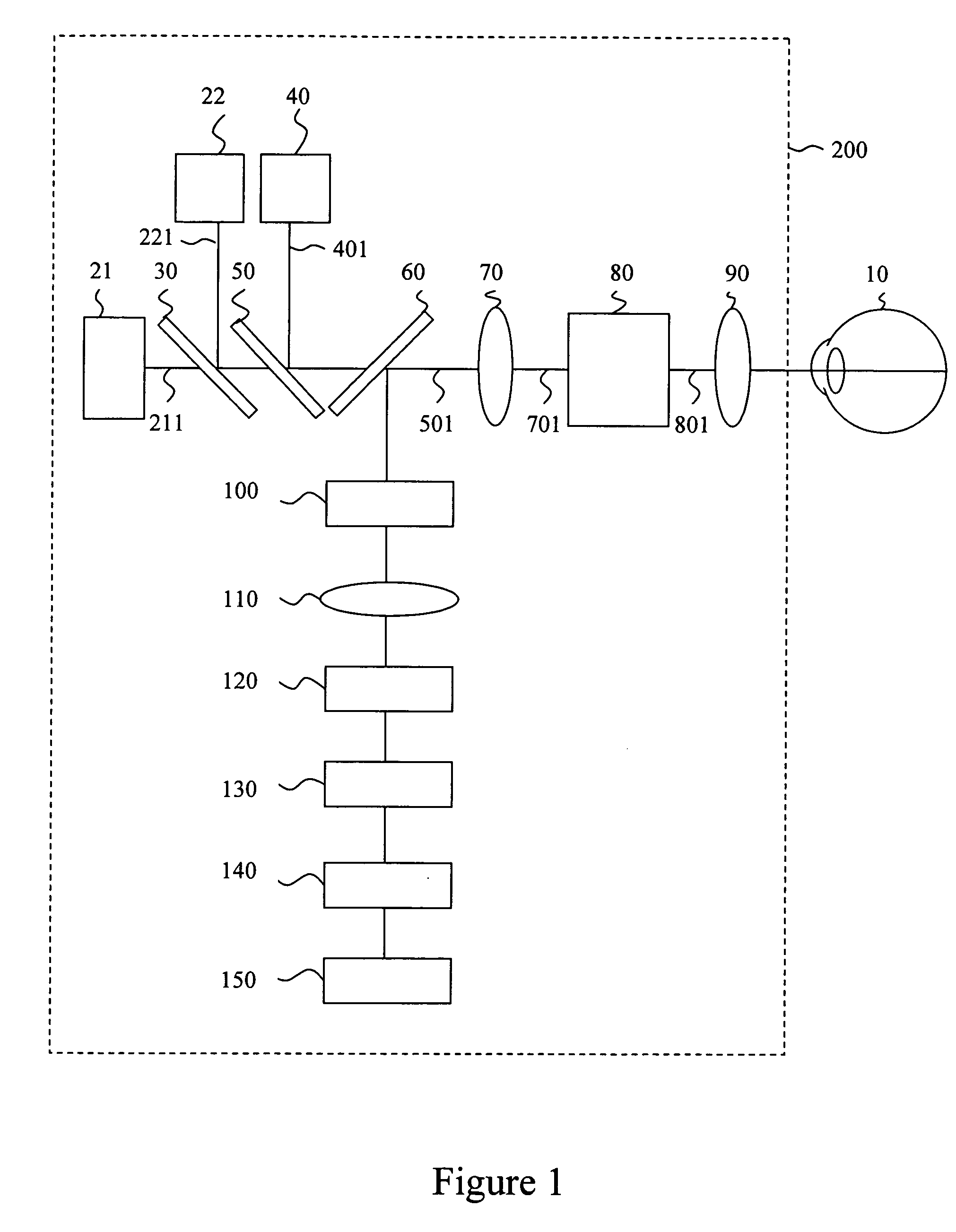
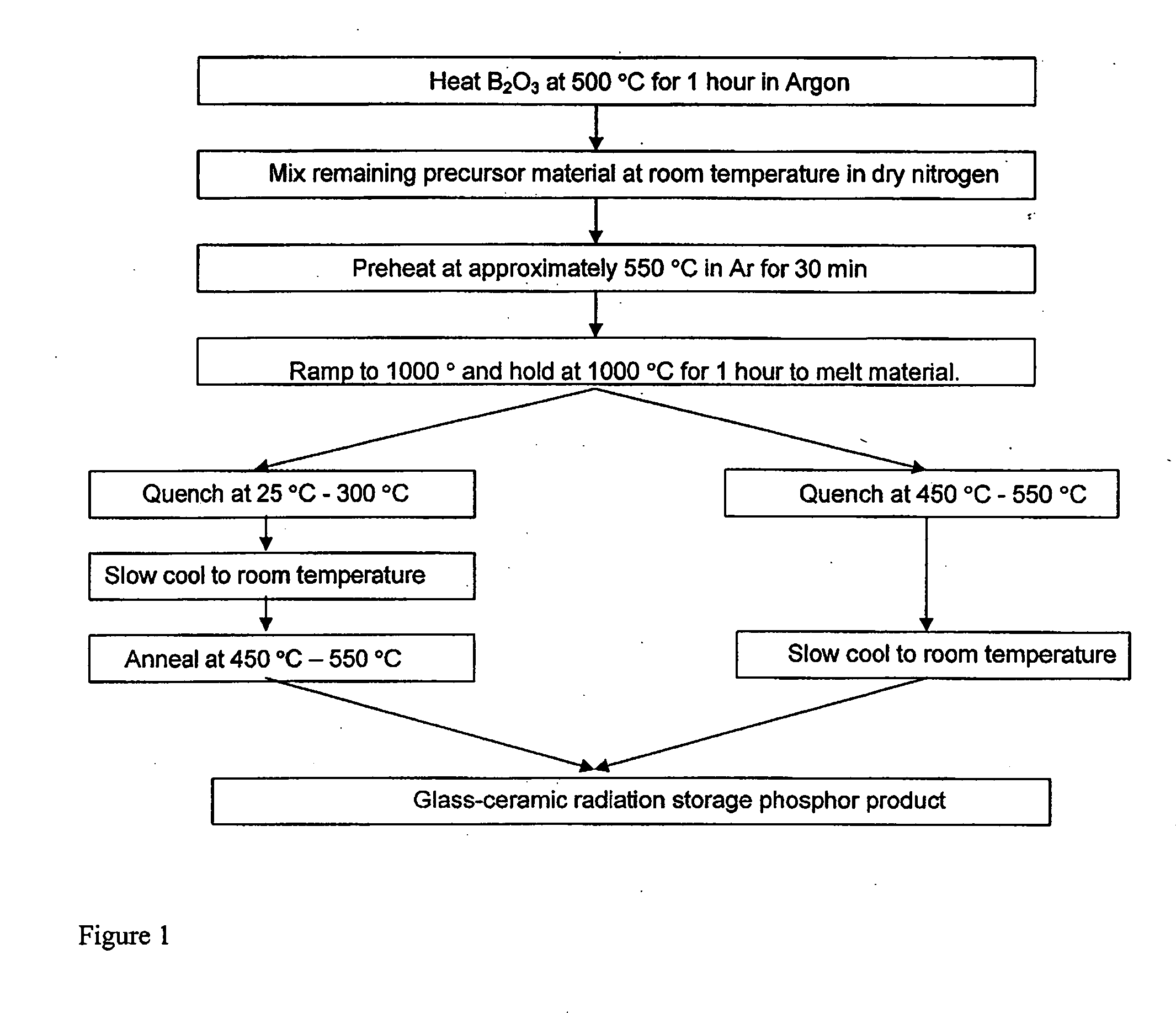
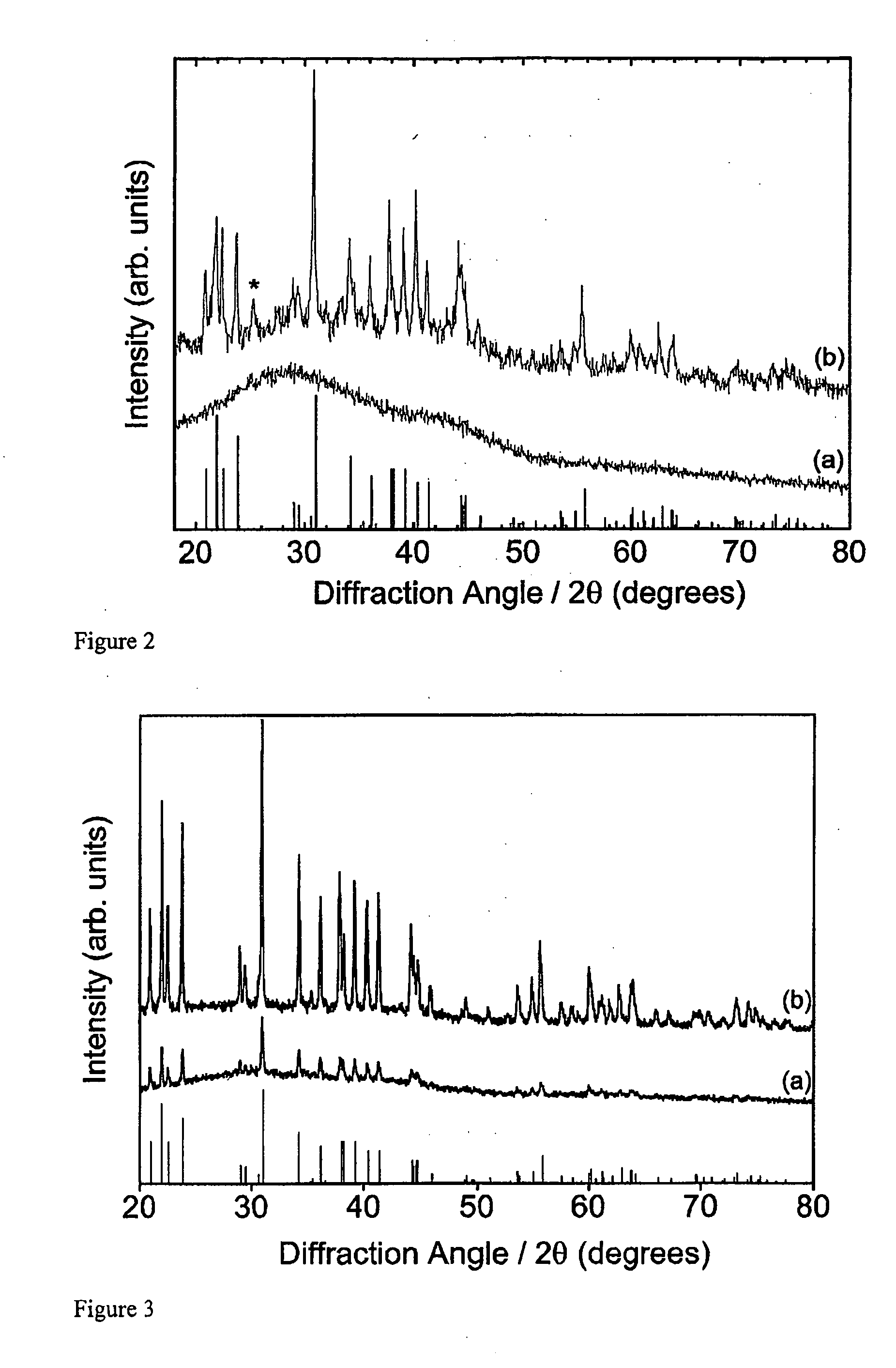
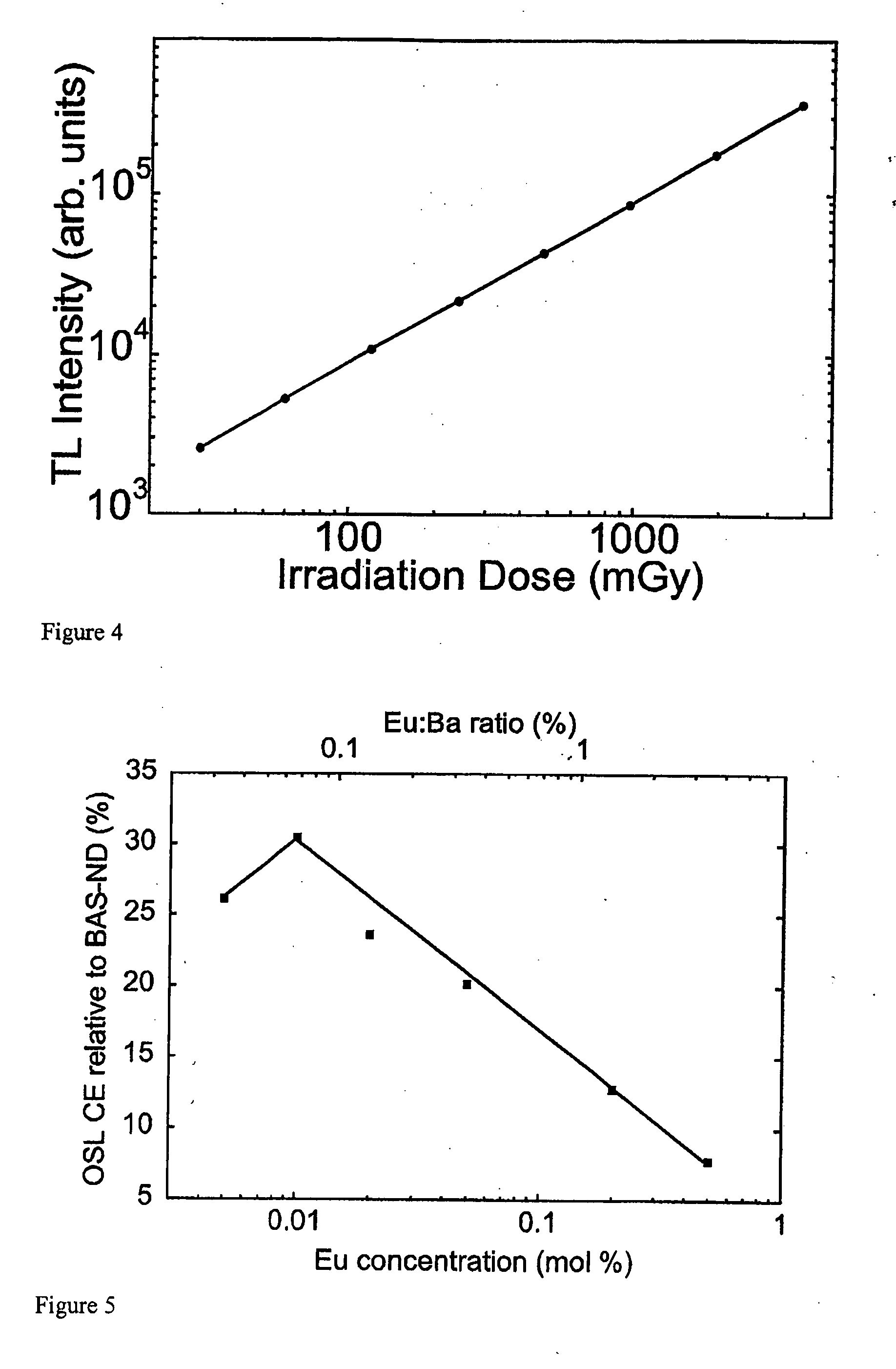
Photostimulable glass ceramic
A glass-ceramic material containing phosphor-doped crystallites suitable for thermal neutron detection is disclosed, the glass-ceramic material being capable of storing at least part of the energy of incident thermal neutrons, and releasing at least part of the energy by optical stimulation. A method for preparation of the glass-ceramic material is also disclosed.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Optical control of cardiac function
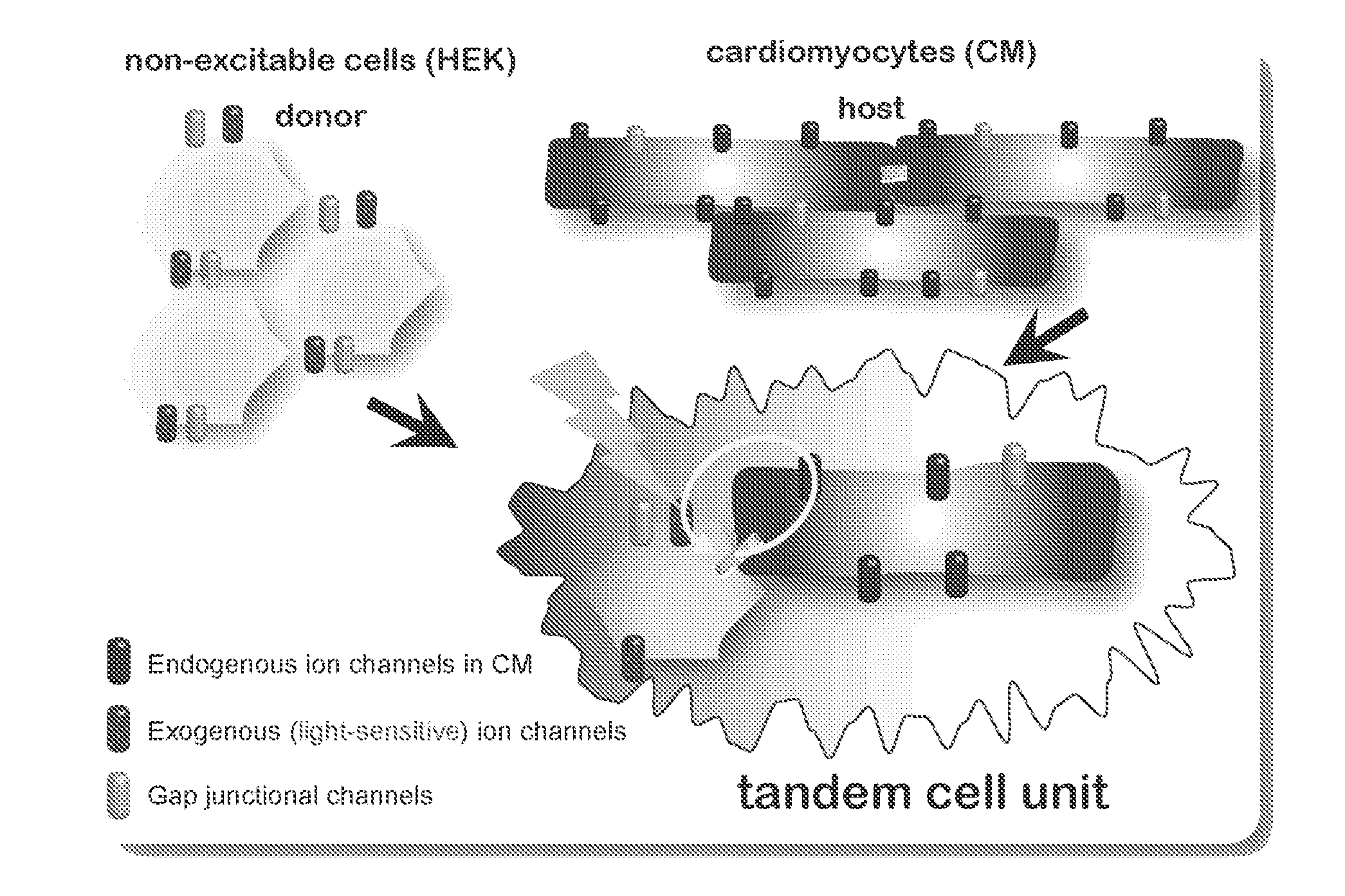
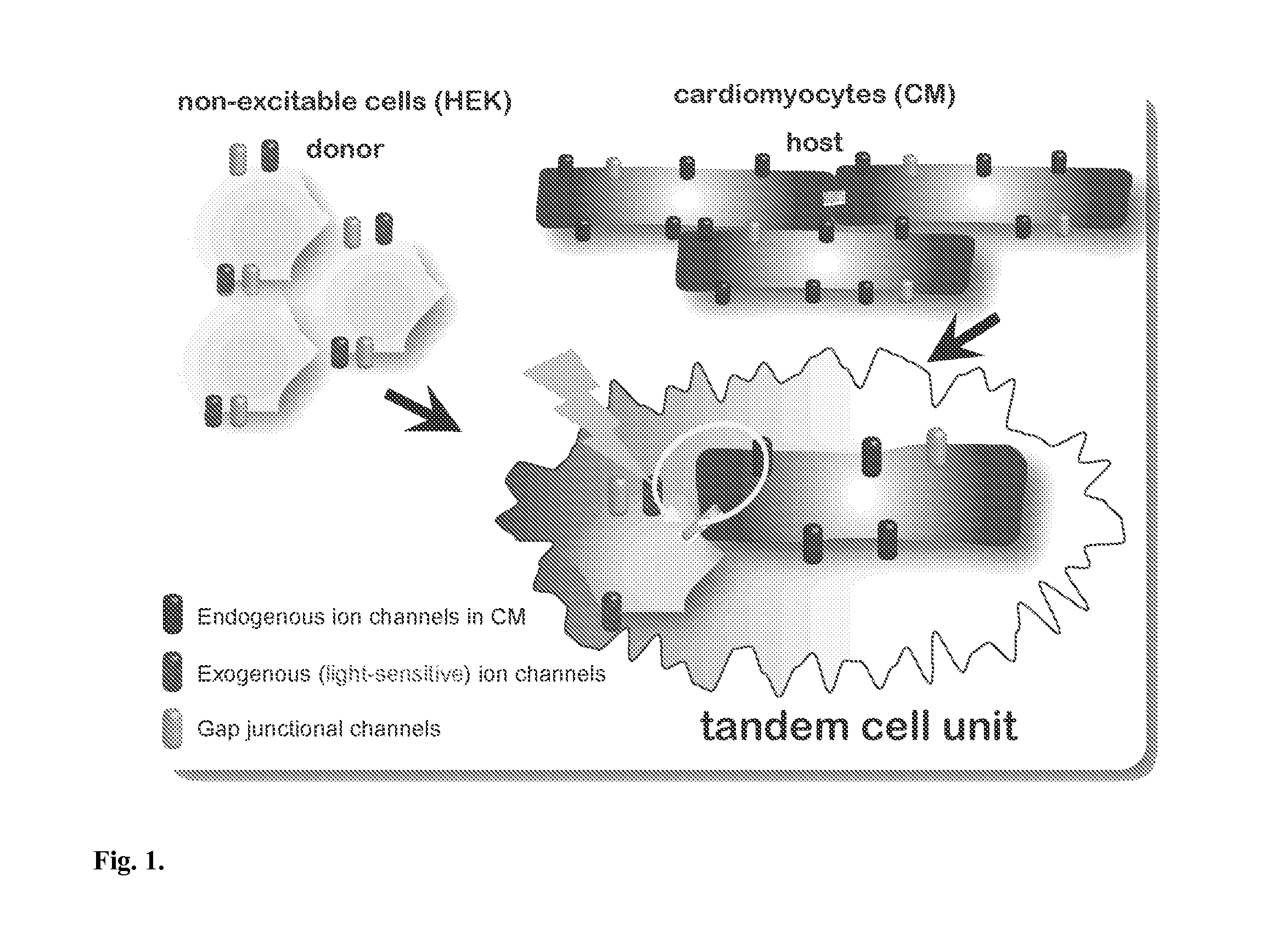
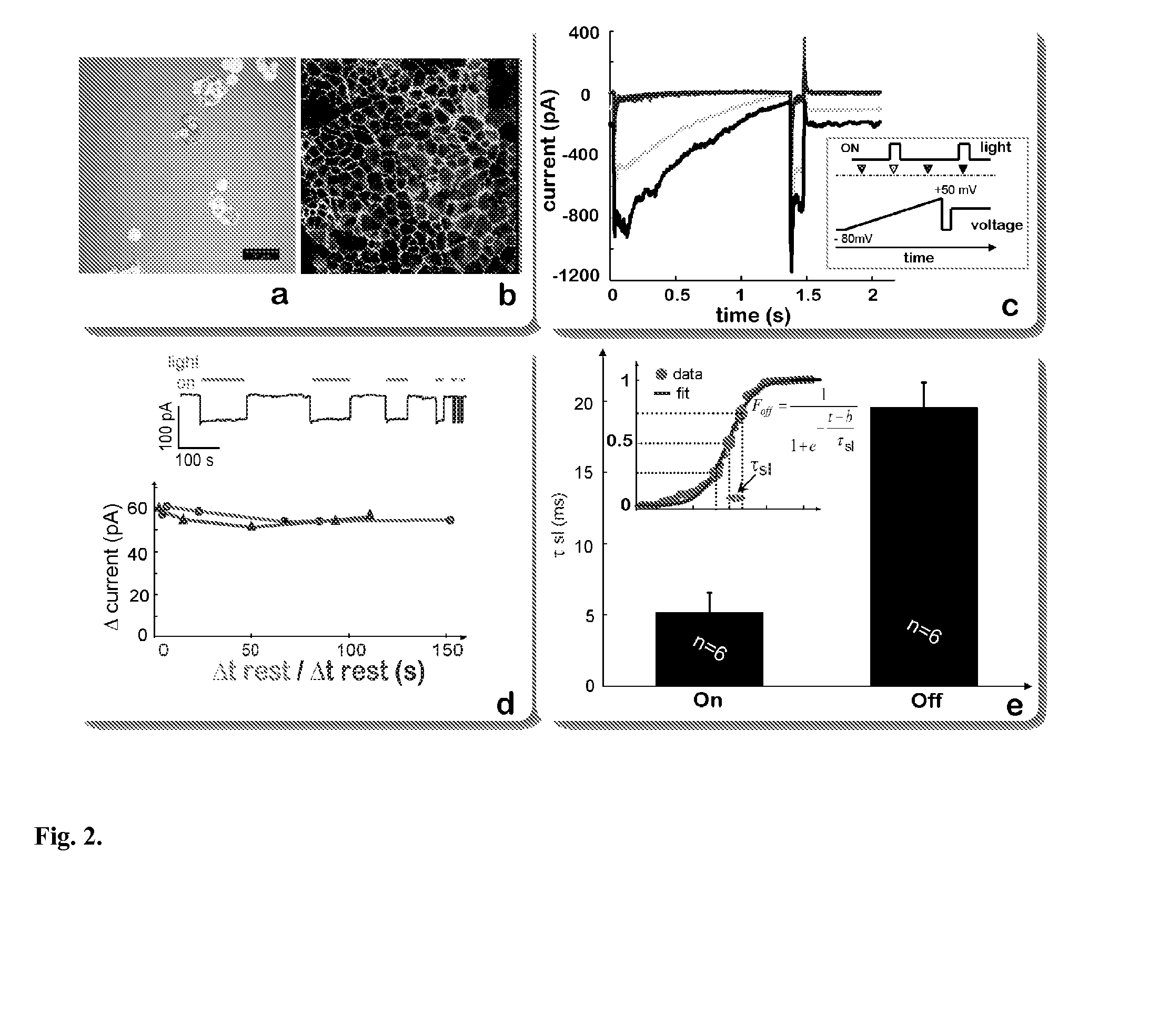
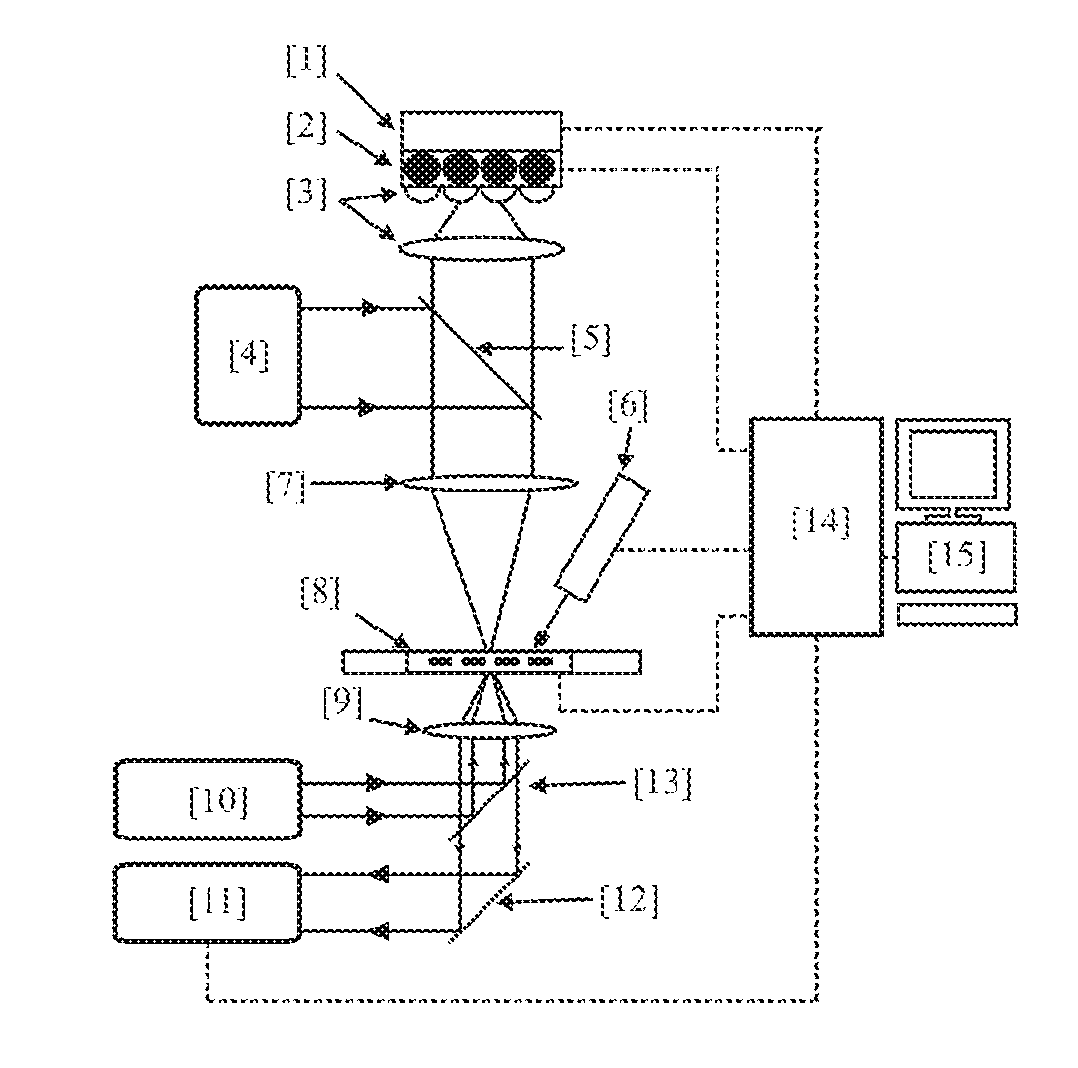
InactiveUS20130274838A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImplantable neurostimulatorsIon Channel ProteinIonic Channels
The invention features an optically-controlled biological device that includes a biological component comprising a non-excitable cell expressing a light-gated ion channel protein and capable of forming gap junction channels with a target cell, and an optical stimulation unit.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Optical stimulation of photosensitized cells
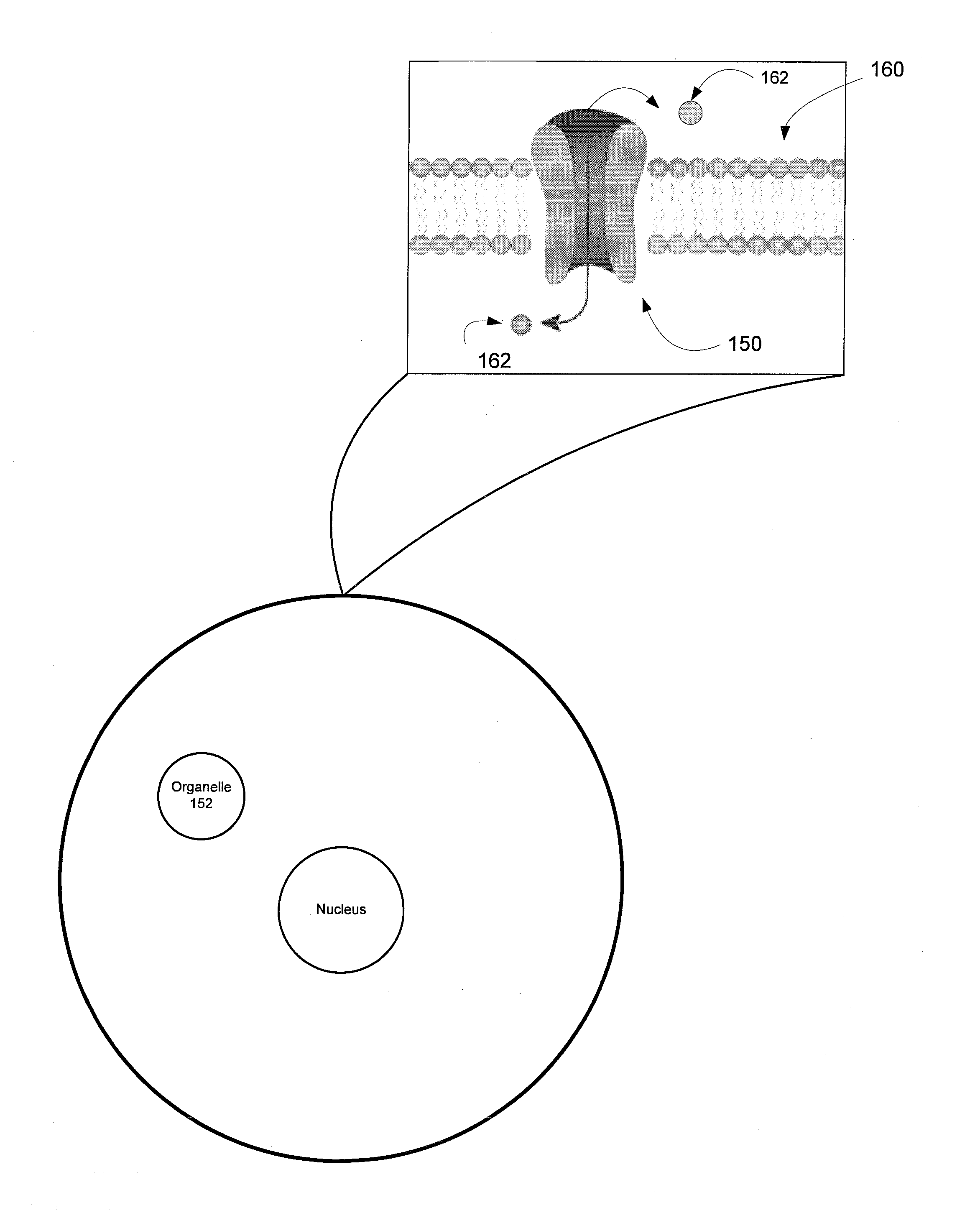
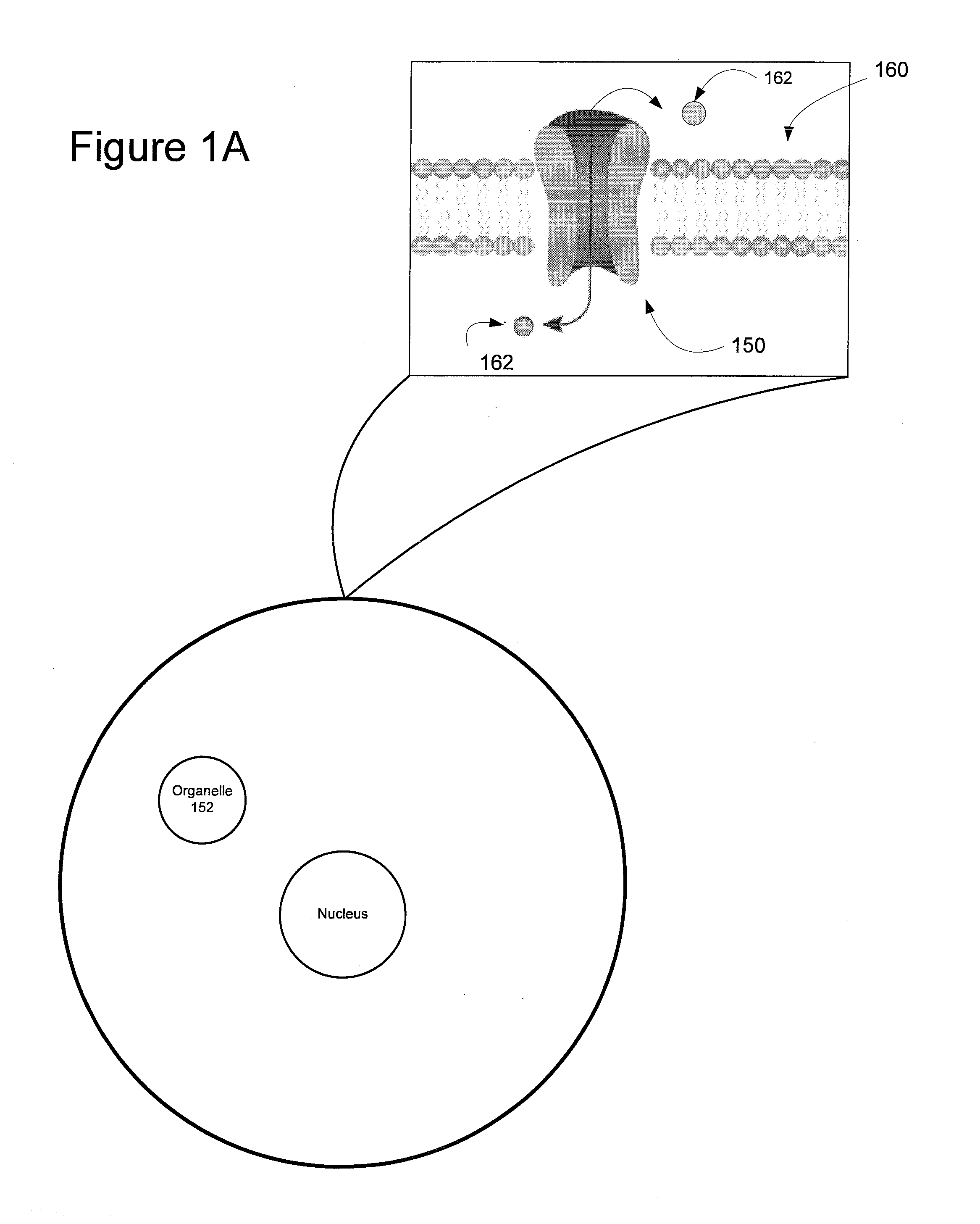
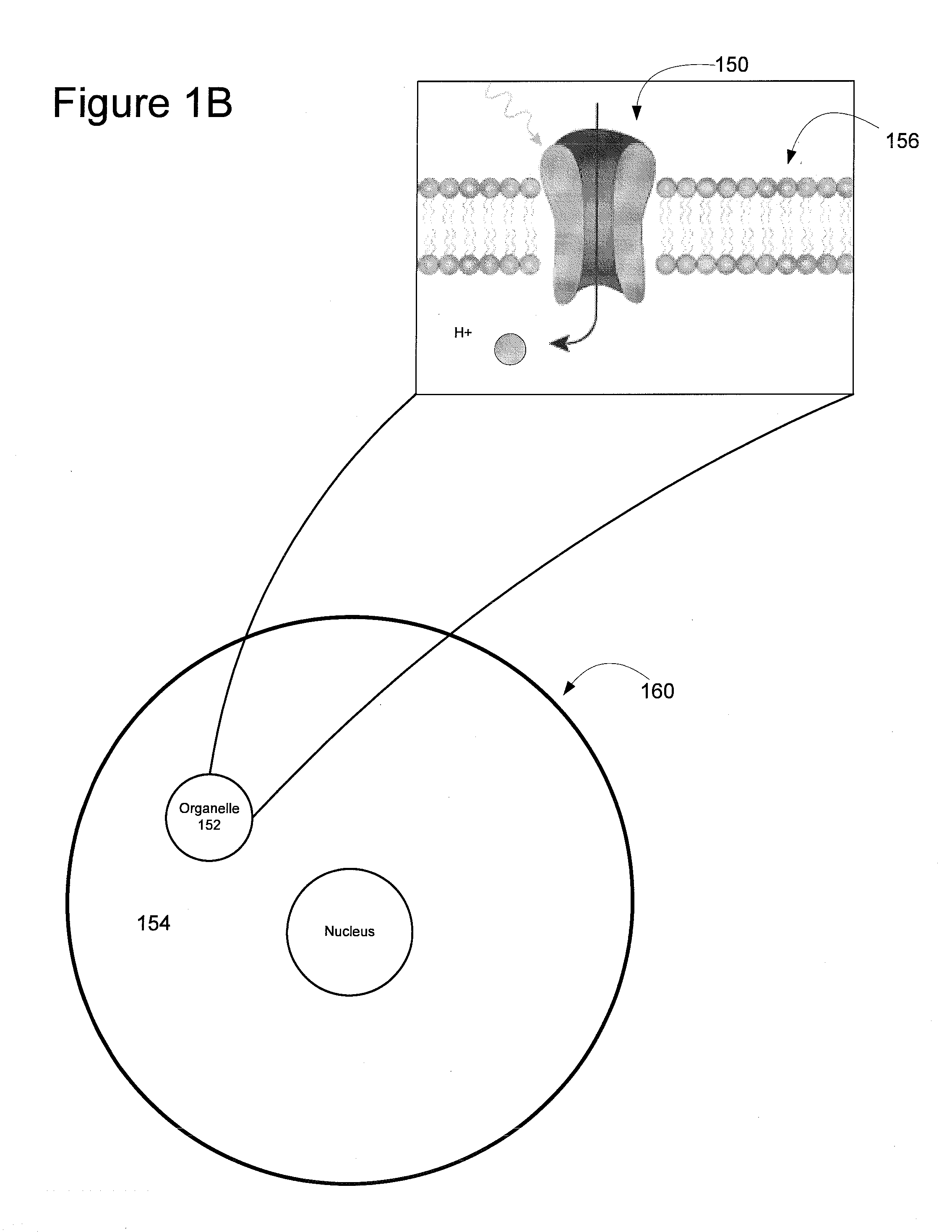
InactiveUS20110127405A1Improved kineticsImprove the kinetics of the photosensitized cellsPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical stimulationNeuron
This invention describes a device for optical stimulation of cells and other biological structures. It has an ability to target multiple cells and / or multiple sub-cellular targets. The stimulation optical pattern on each cell can be independently controlled with individual frequencies. The light sensitivity of the cells can be imparted as a result of genetic expression of surface and / or subsurface proteins, chemical modification of existing proteins, or via the release of caged entities which in turn act to stimulate the cell through chemical means. The embodiment is capable of functioning on neurons but can also be used for other cells. It can perform optimal stimulation with sub-cellular resolutions, record the activity of the targeted cells and perform processing to ensure calibration.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
Combined optical and electrical neural stimulation
A neural-stimulating device for stimulating nerve cells of a recipient is provided. The neural-stimulating device comprises an electromagnetic radiation source configured to generate one or more optical stimulation signals and an electrical stimulation generator configured to generate electrical stimulation signals. The neural-stimulating device also comprises an implantable stimulating assembly configured to be implanted in the recipient, and having disposed thereon an optical contact to deliver the one or more optical stimulation signals to the nerve cells, and an electrical contact to deliver the electric stimulation signals to the nerve cells.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Light-Sensitive Ion-Passing Molecules
ActiveUS20130090454A1Dissuade depolarizationIncrease probabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideOptical stimulation
The invention provides polynucleotides and methods for expressing light-activated proteins in animal cells and altering an action potential of the cells by optical stimulation. The invention also provides animal cells and non-human animals comprising cells expressing the light-activated proteins.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com