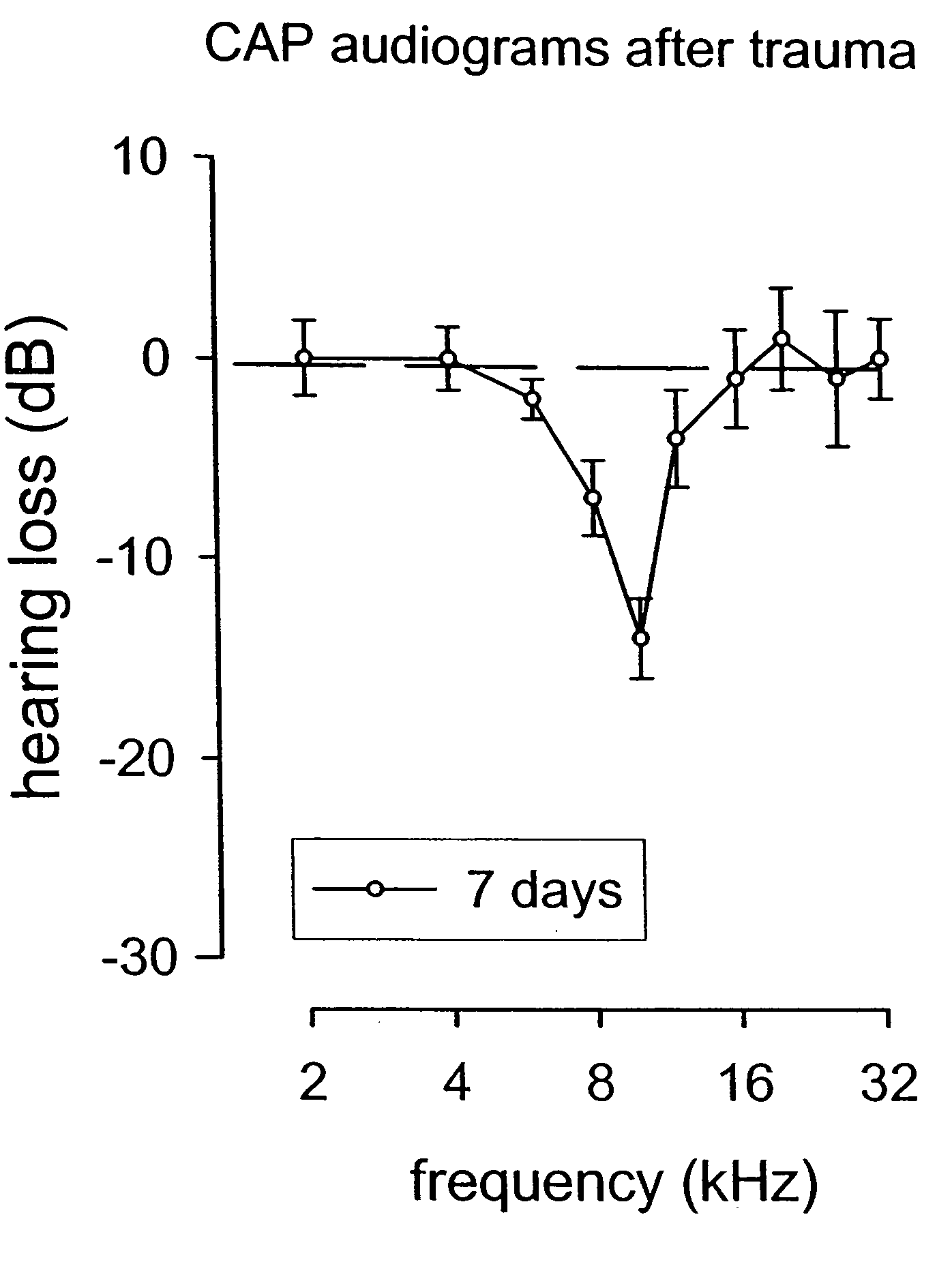
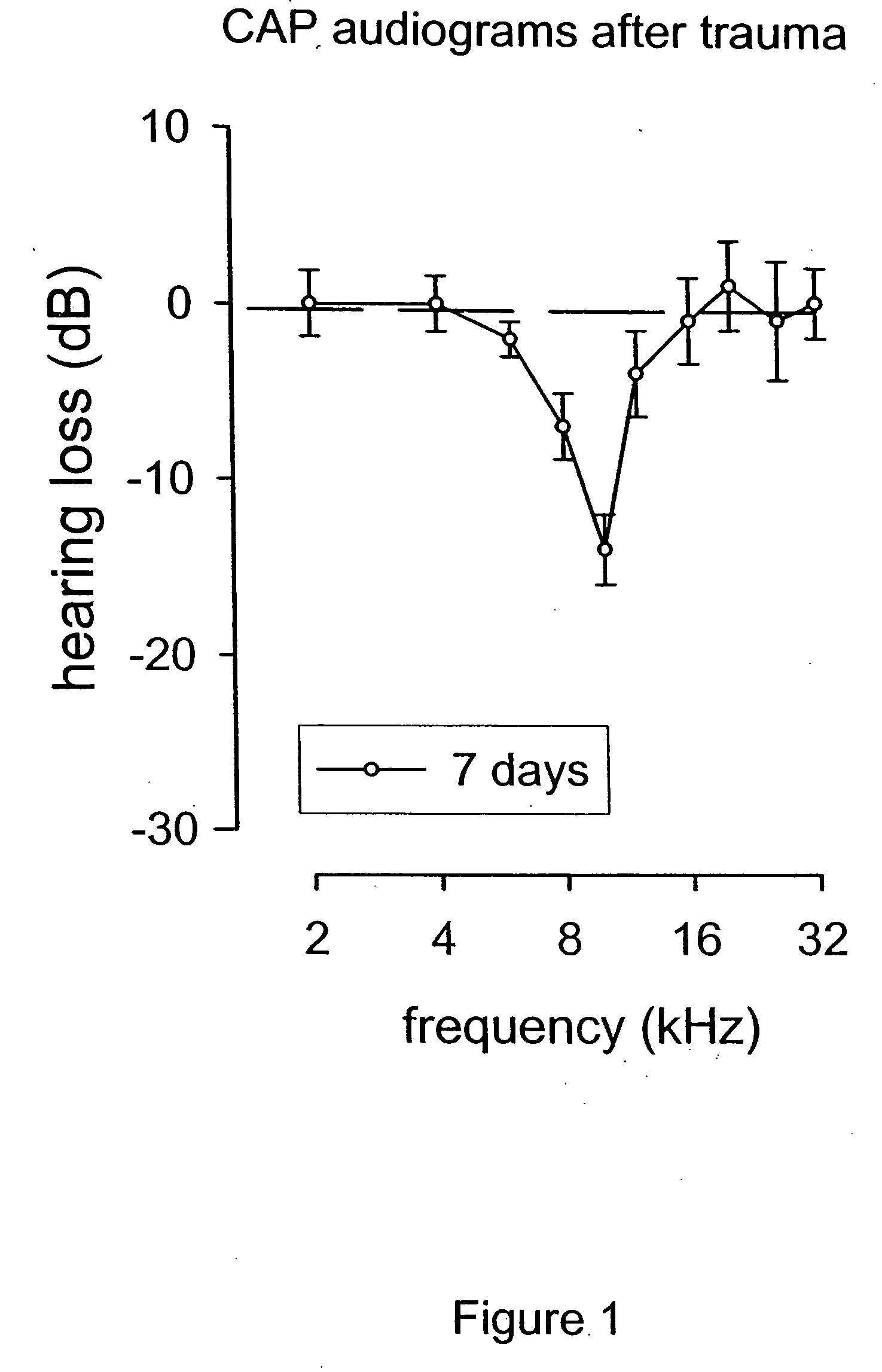
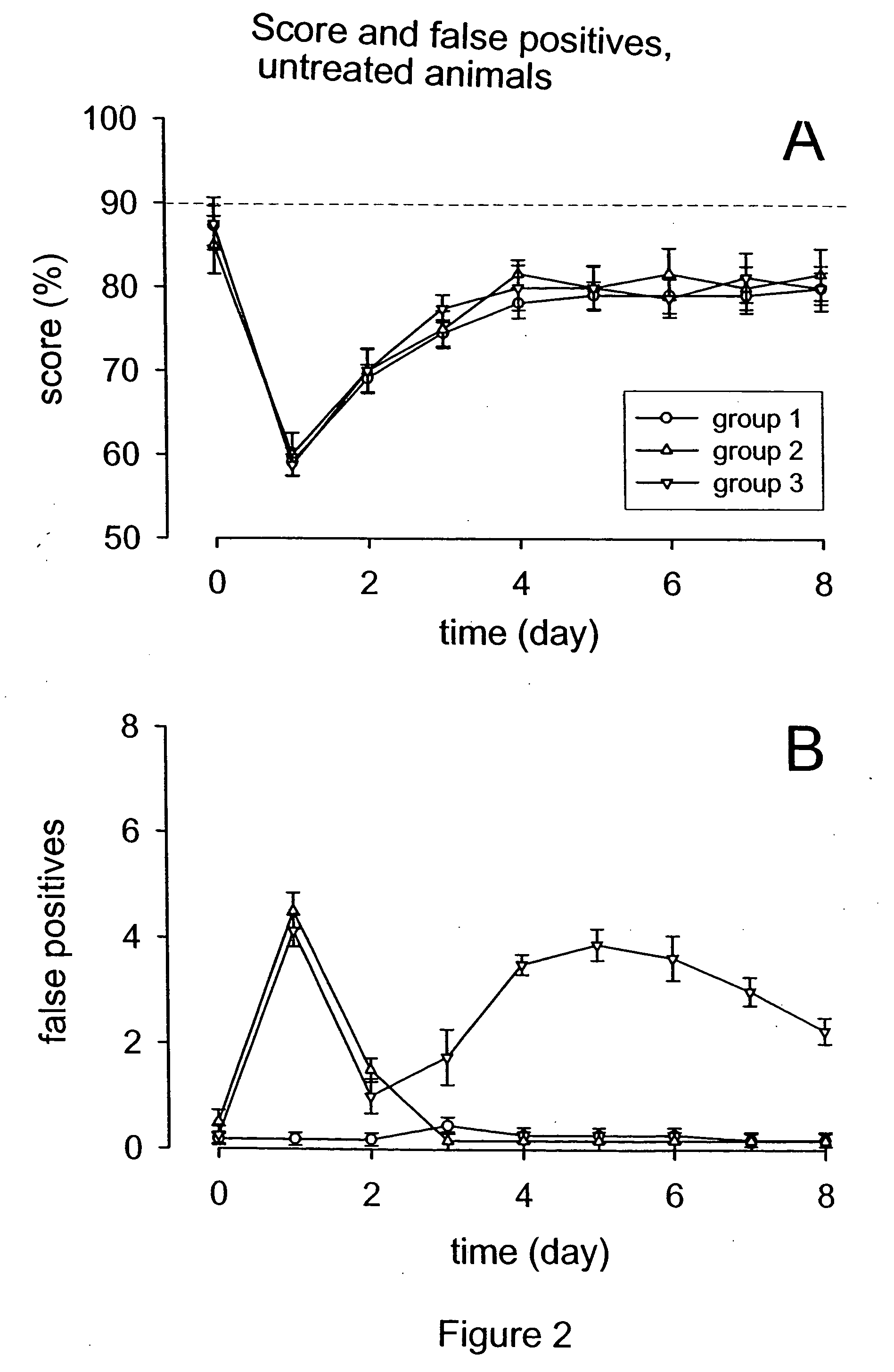
Patents
Literature
771 results about "Cochlea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
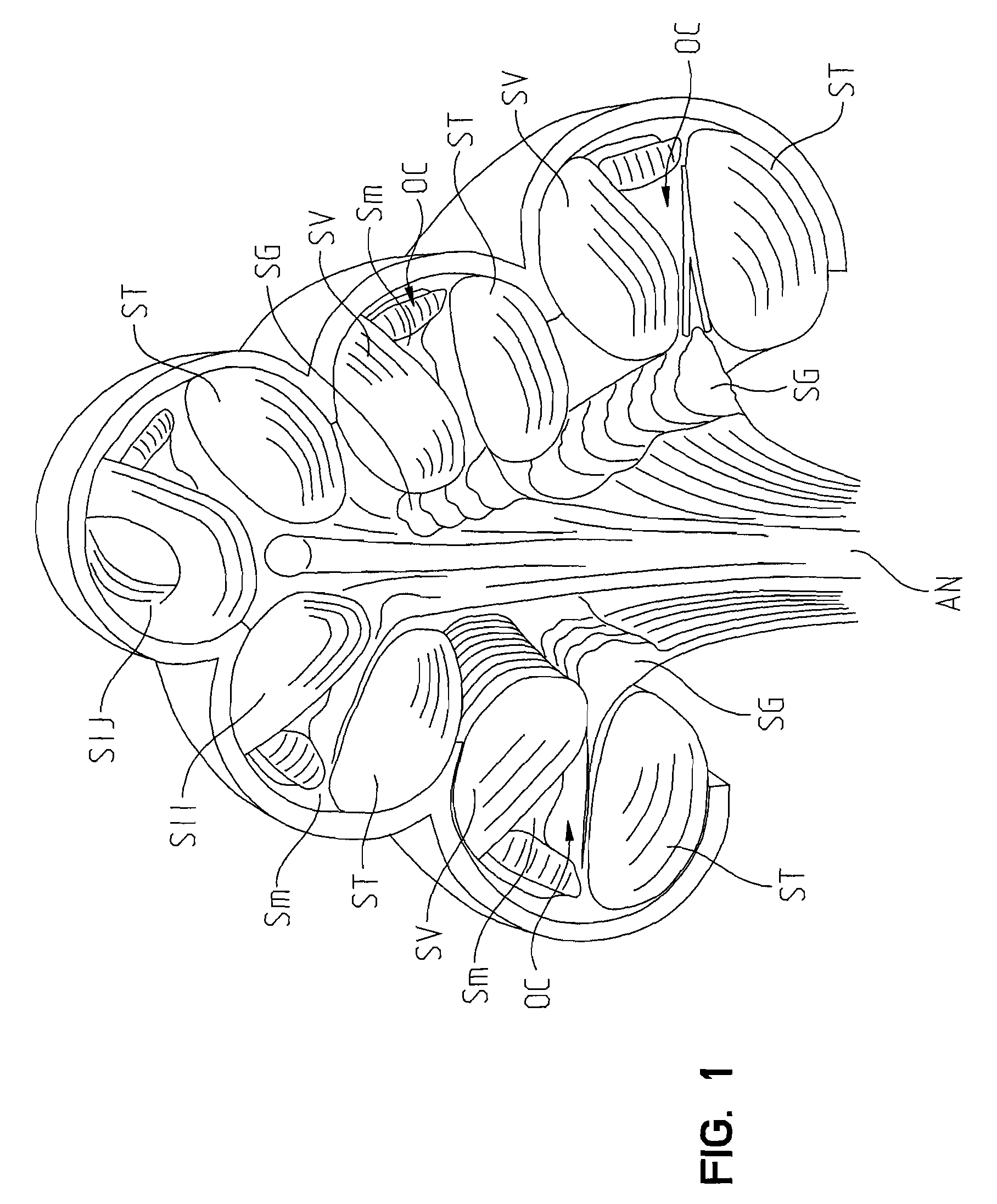
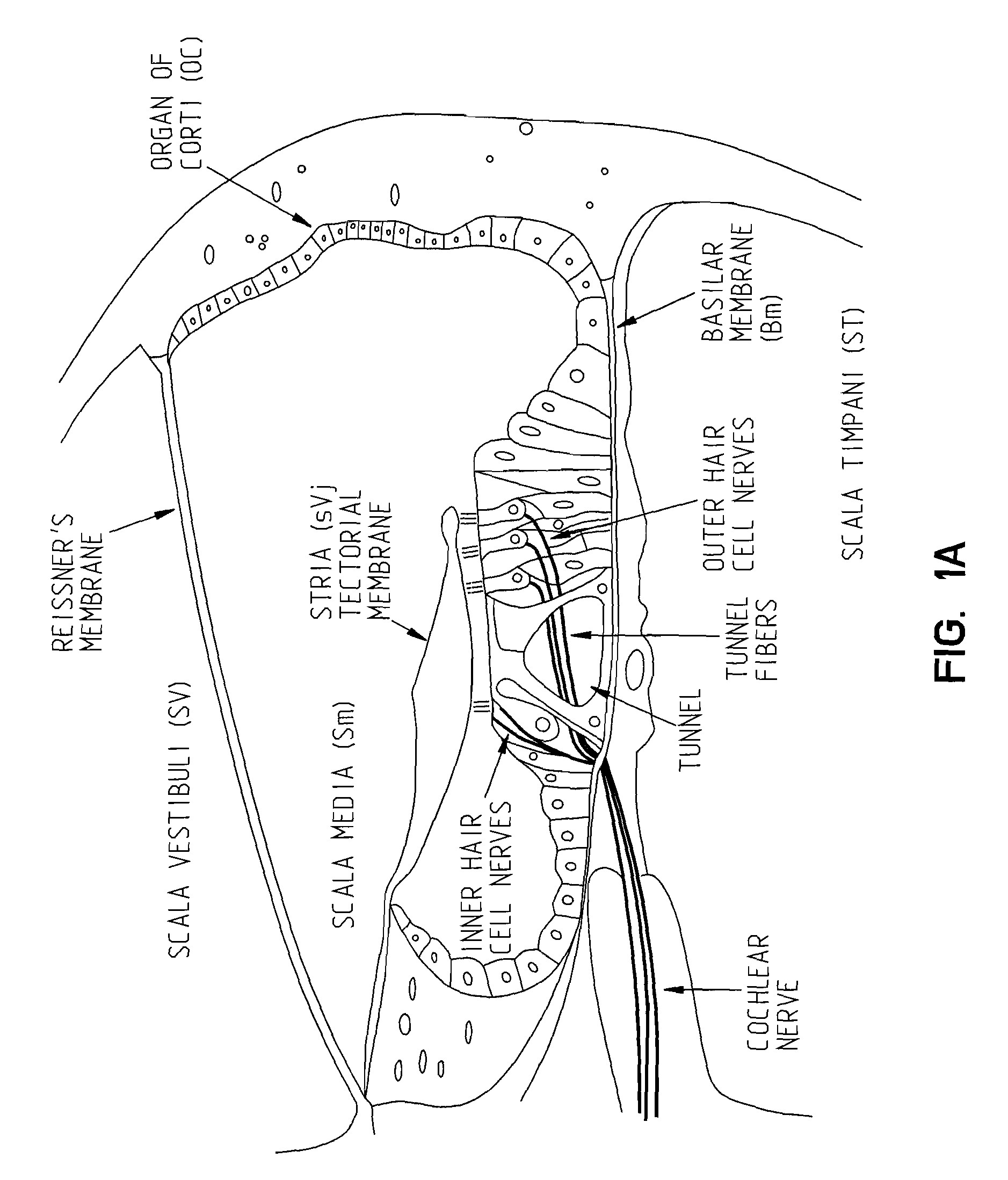
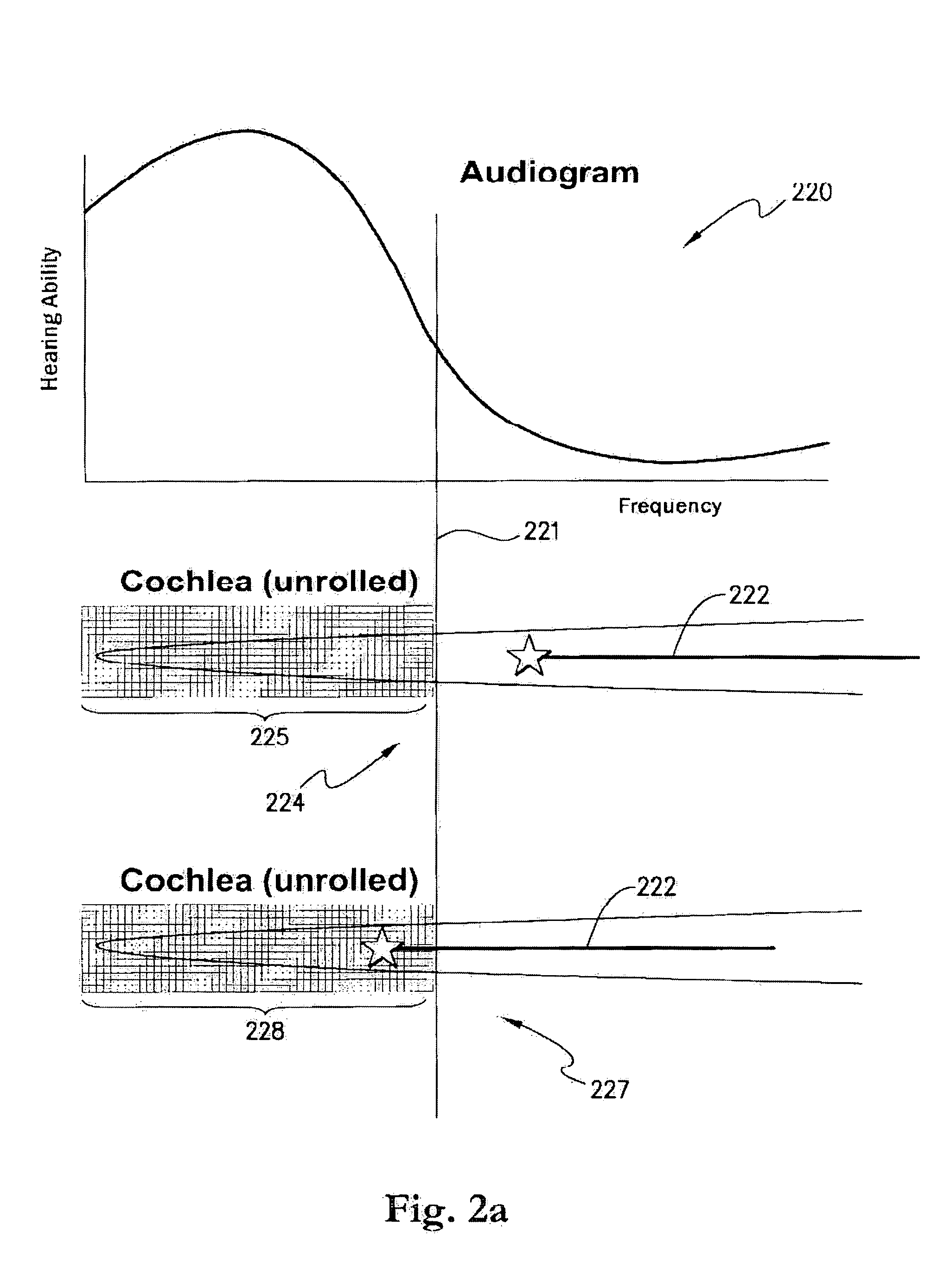
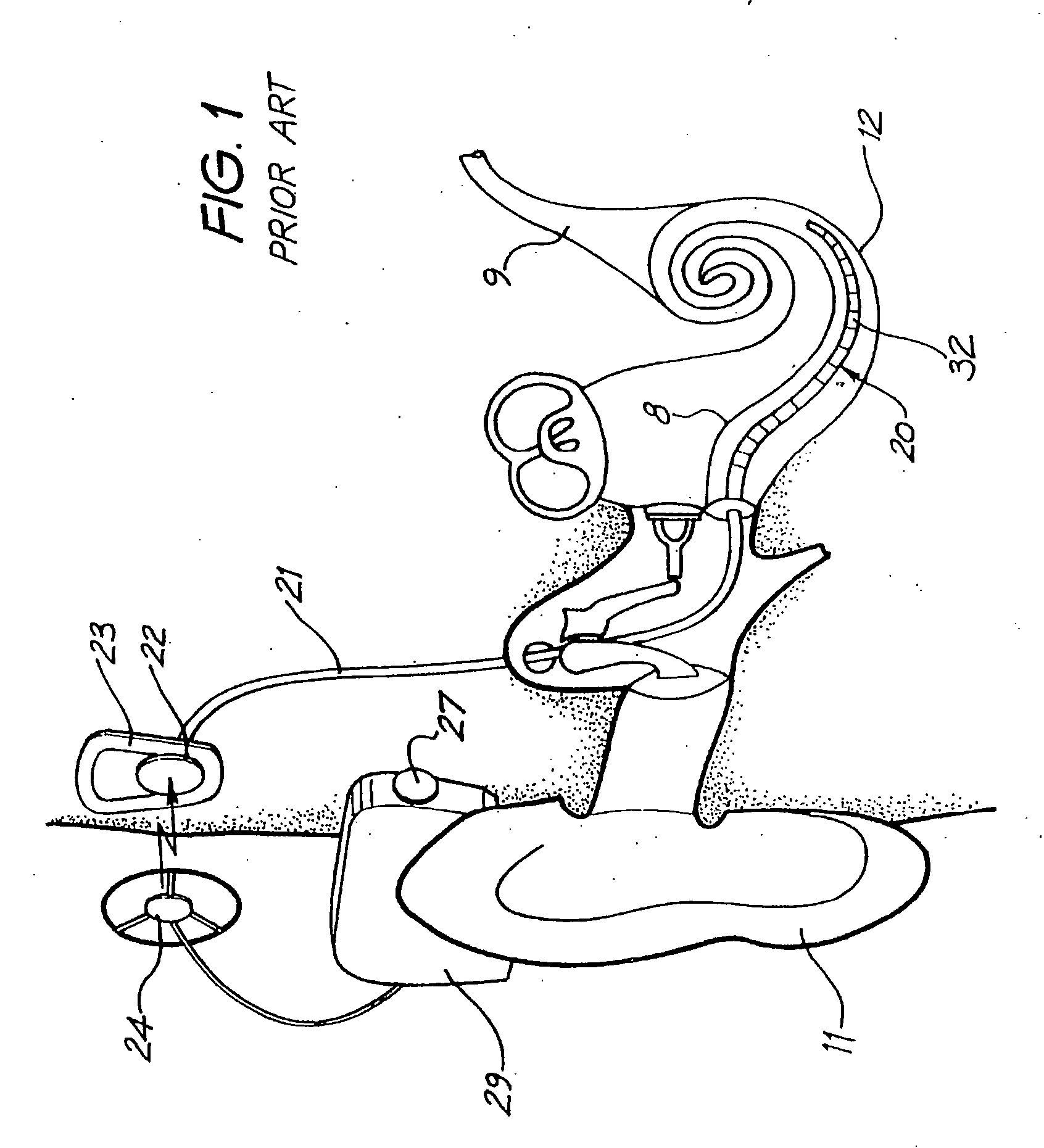
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea.
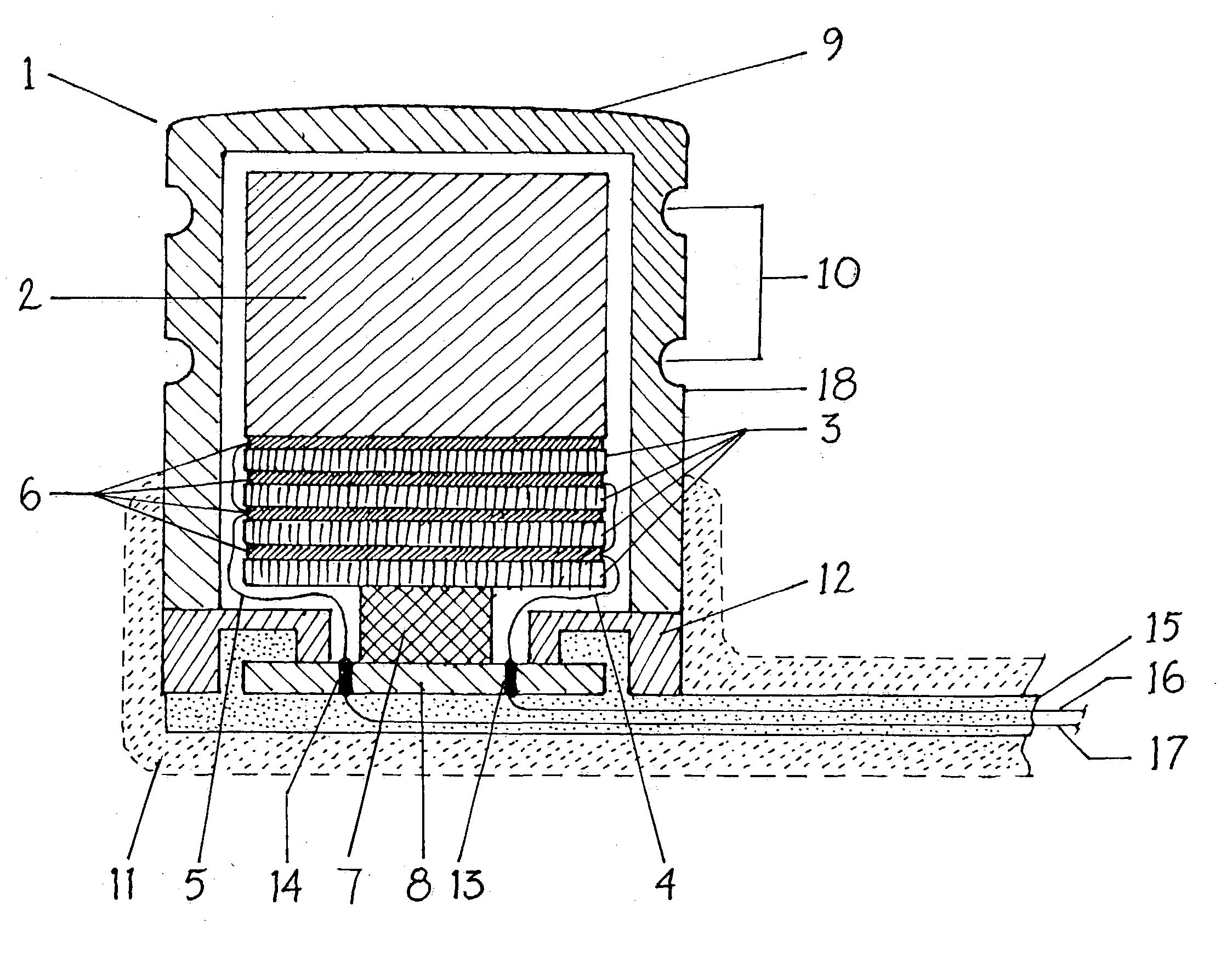
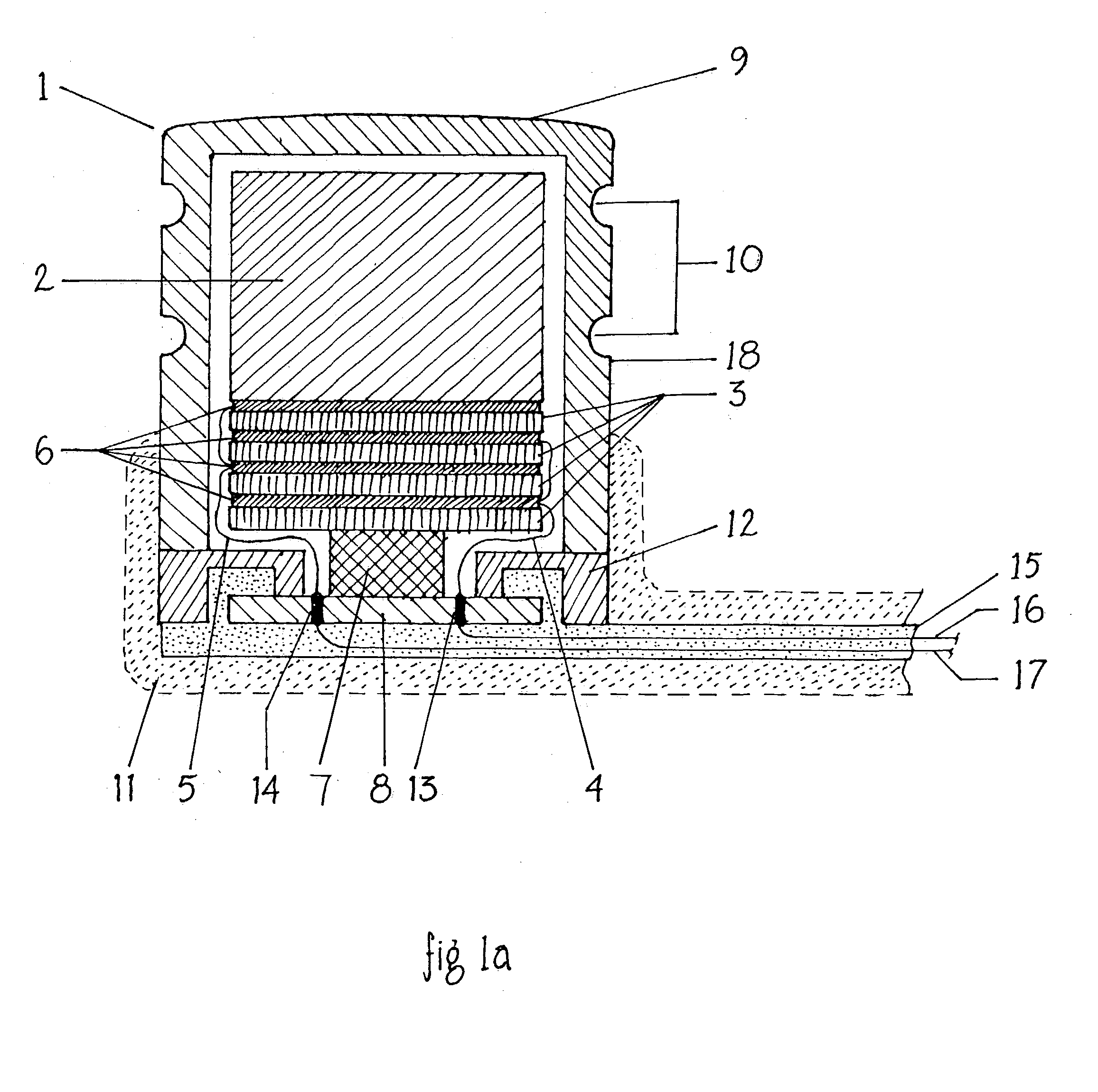
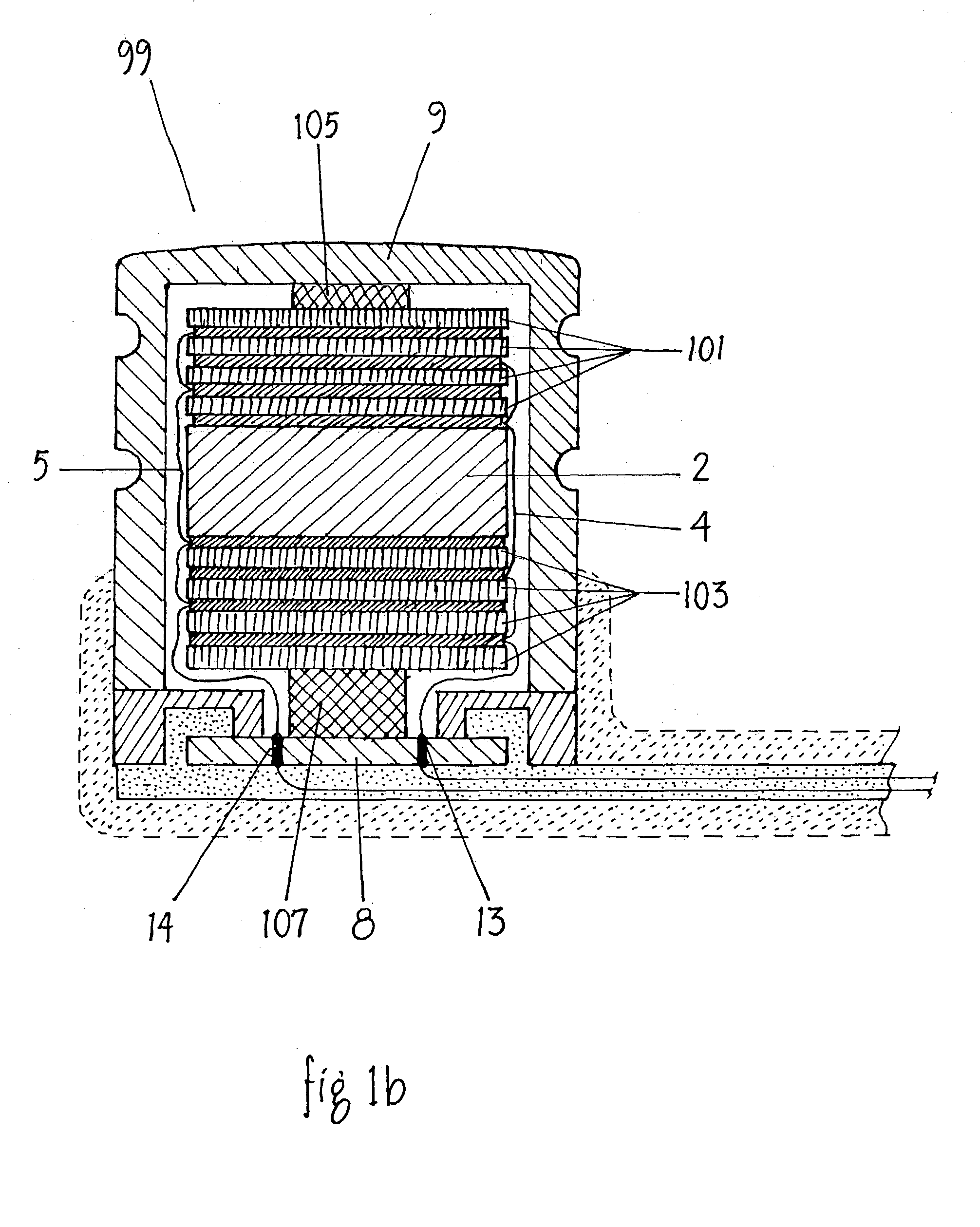
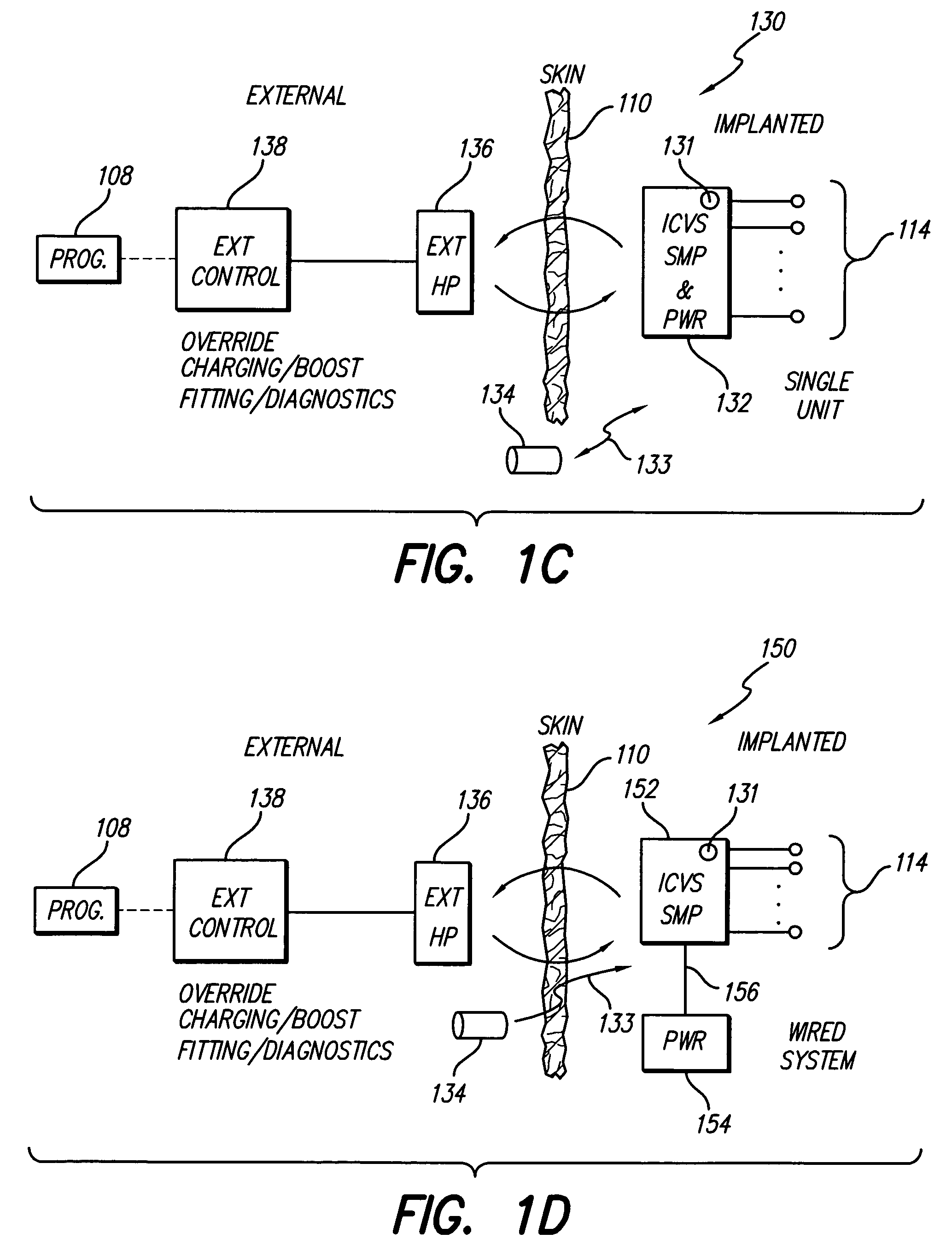
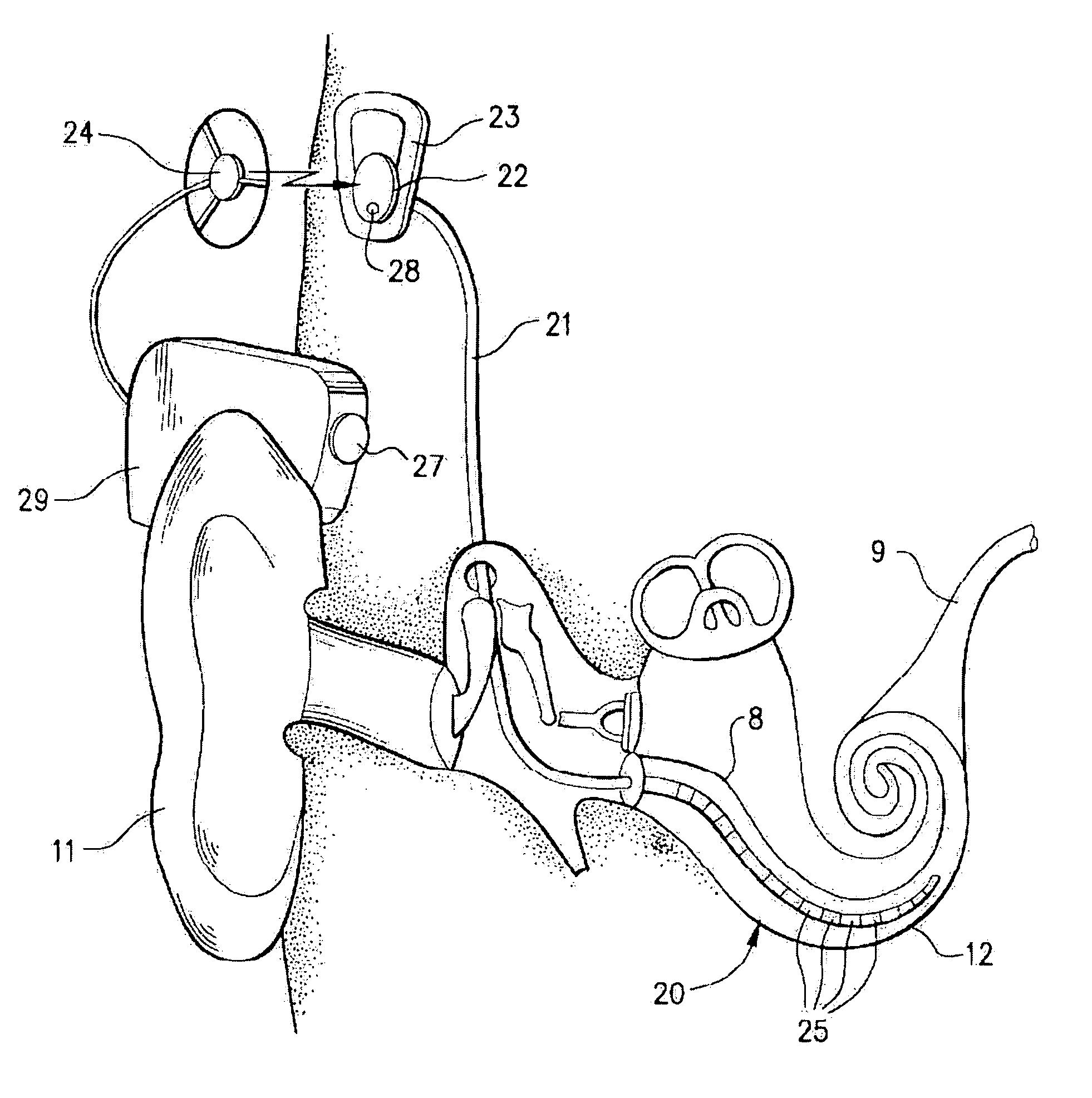
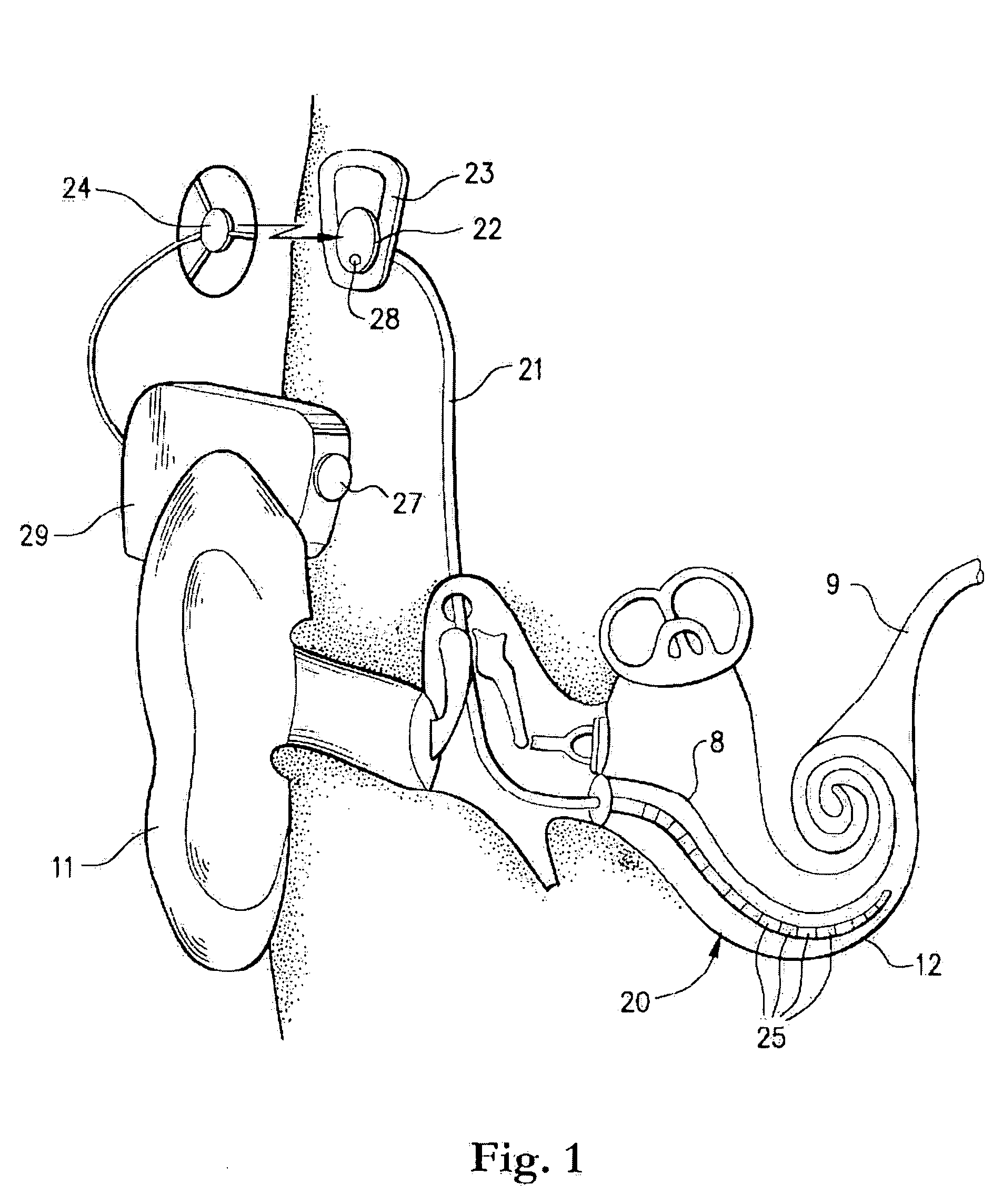
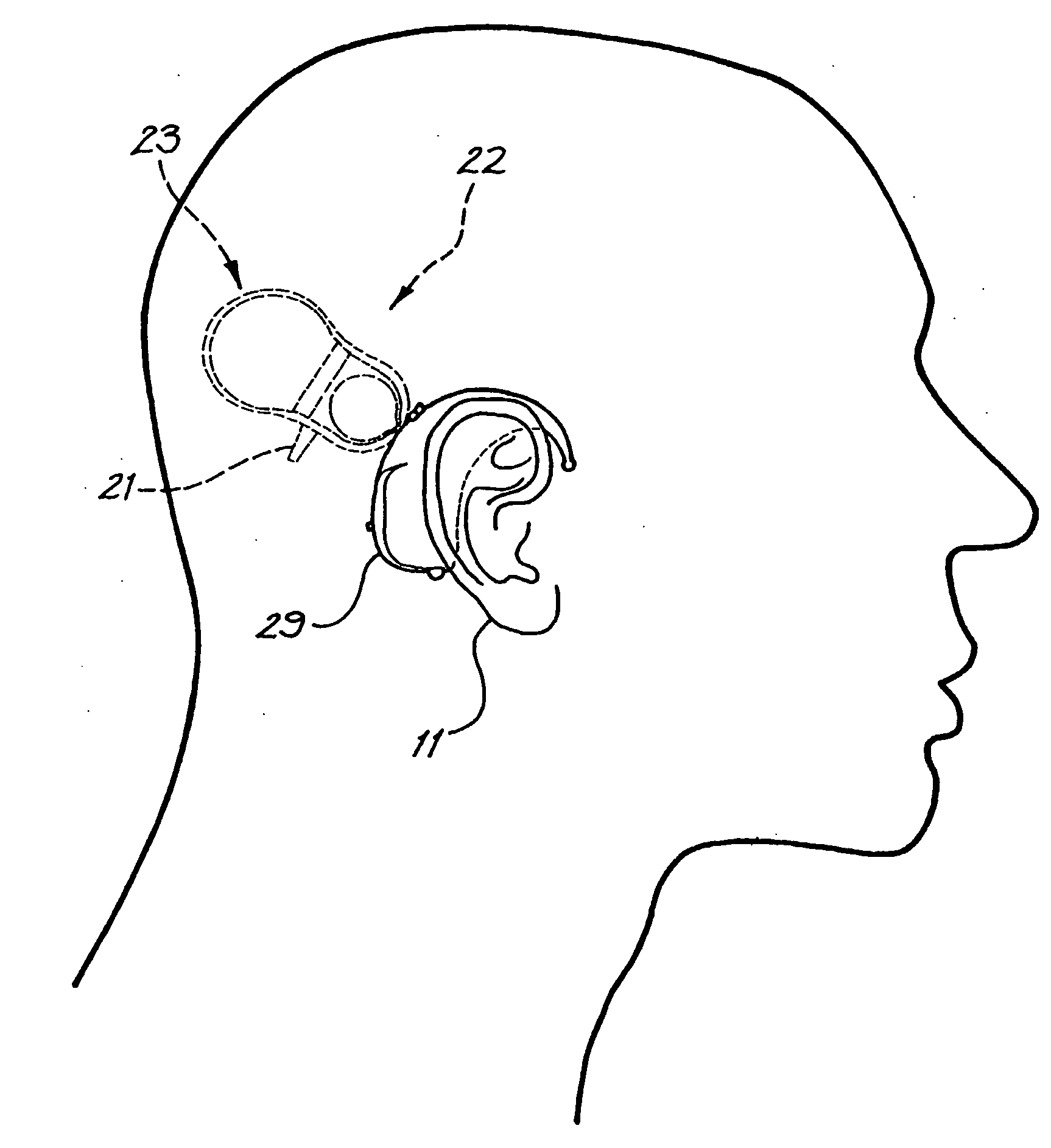
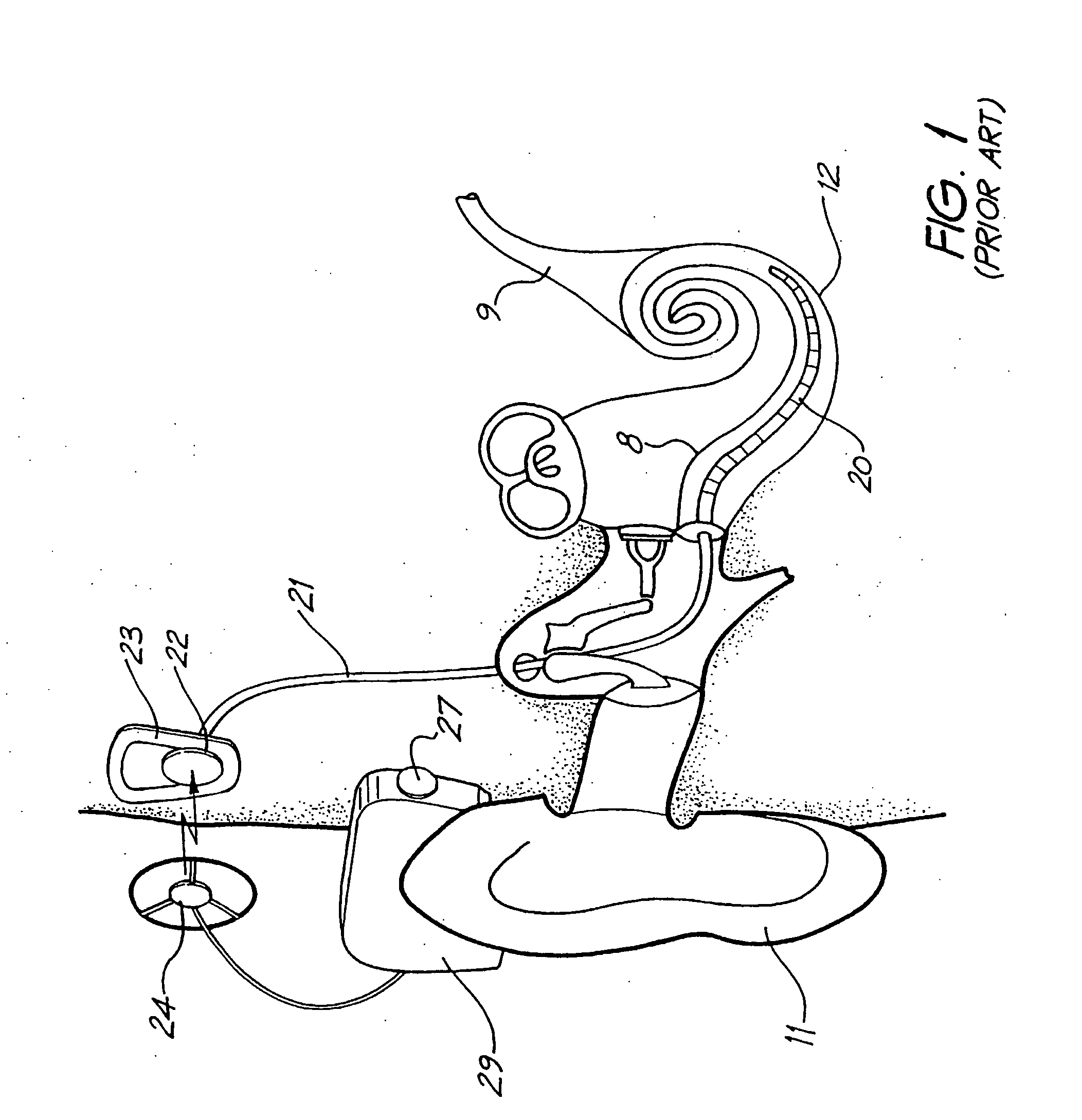
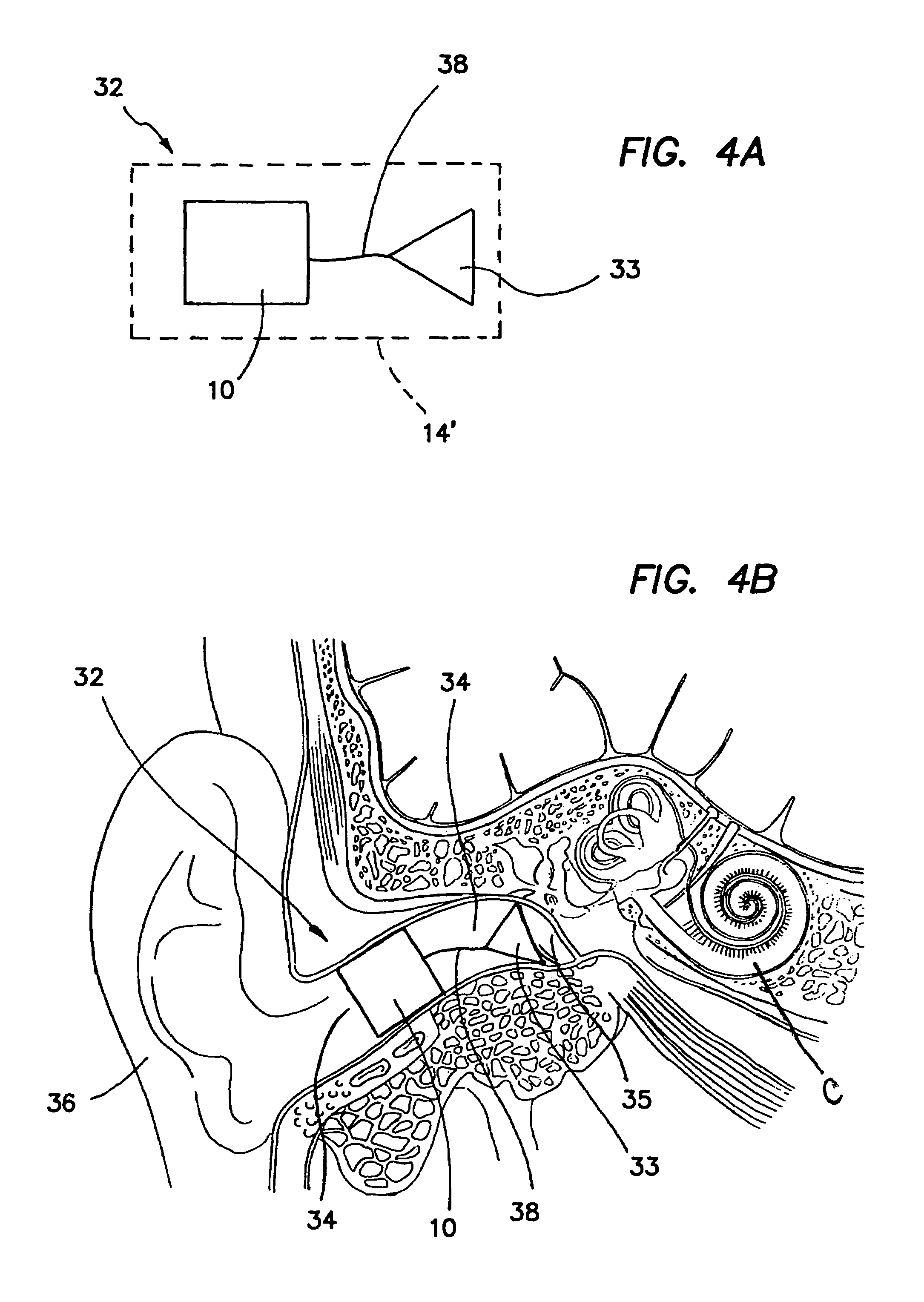
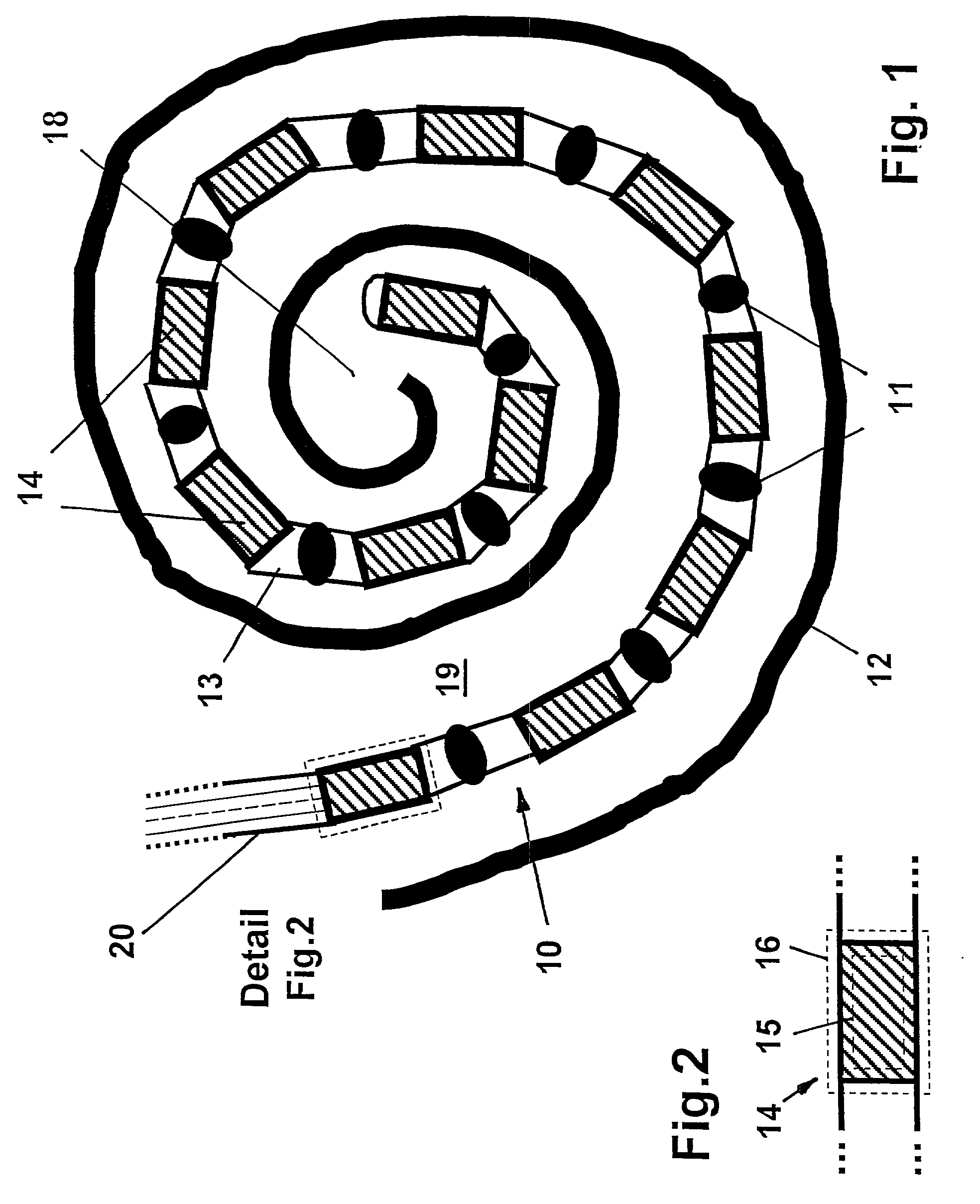
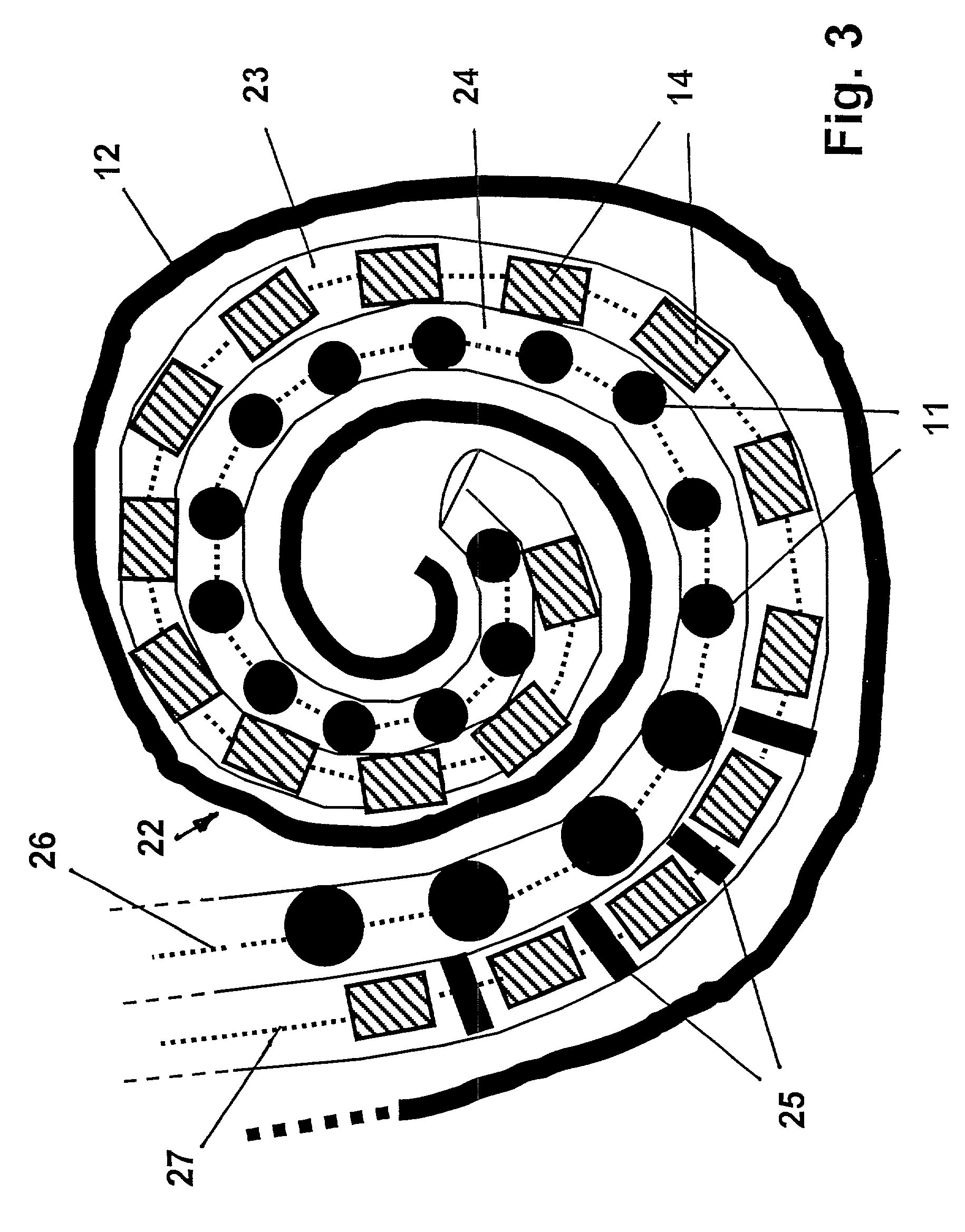
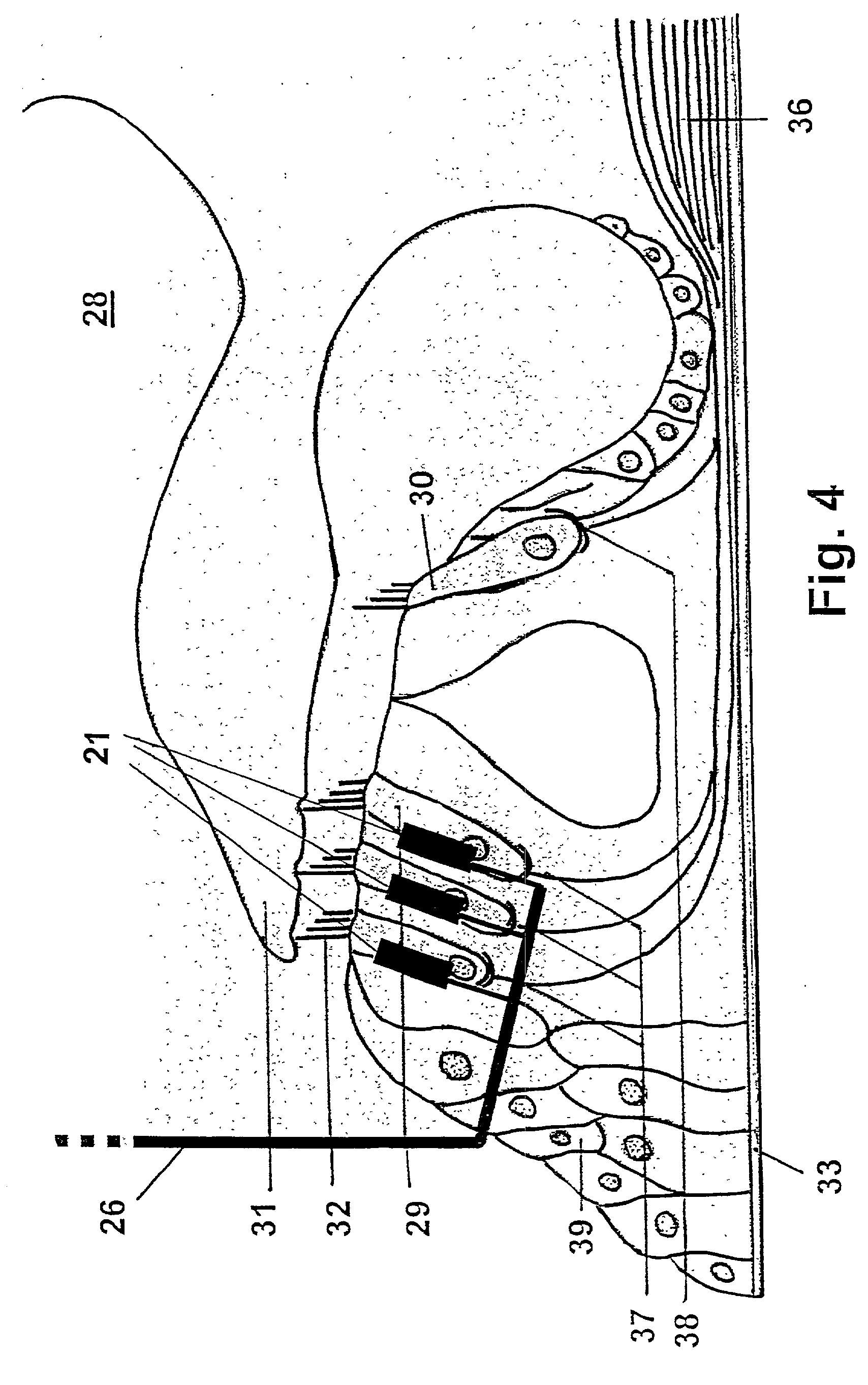
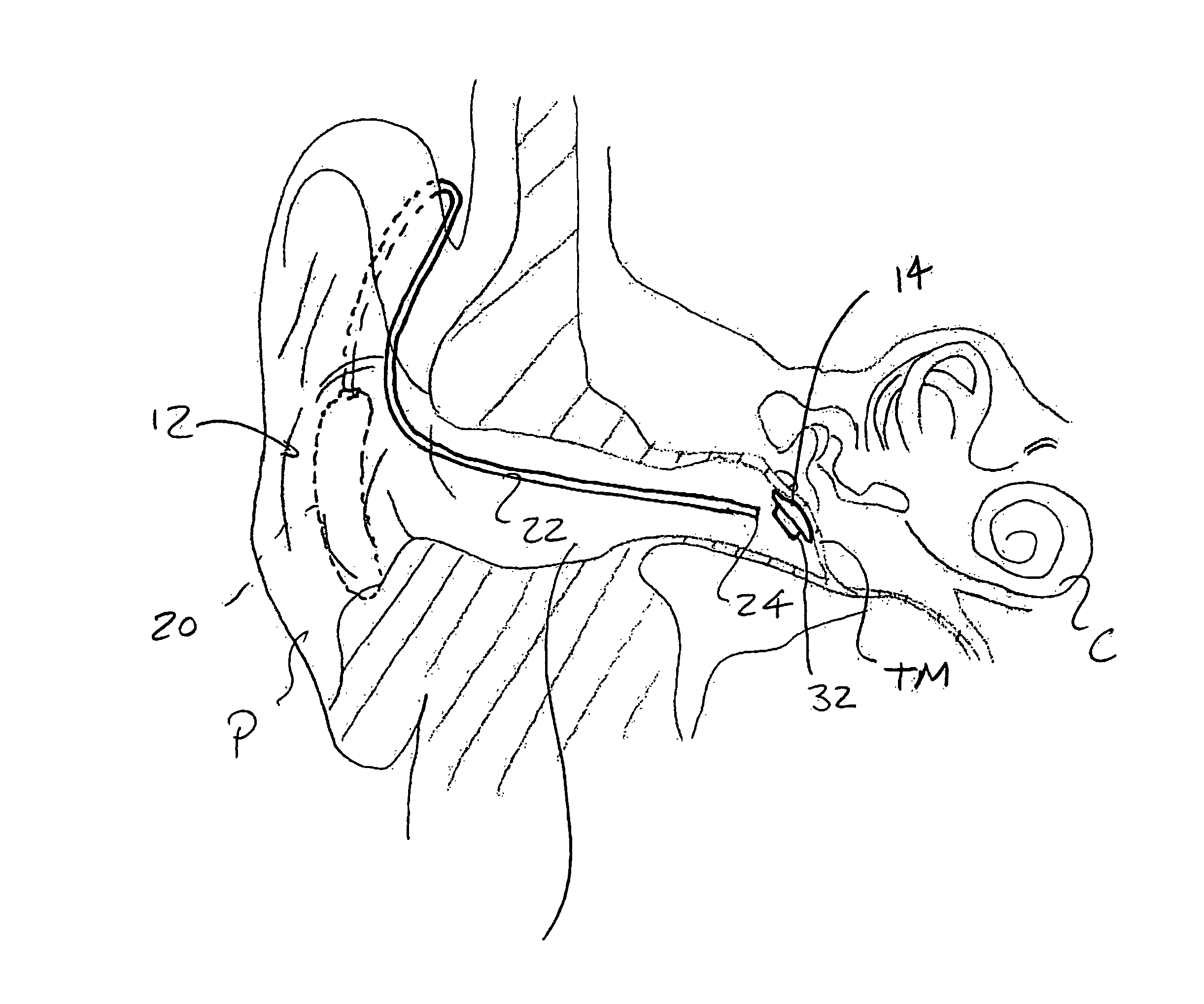
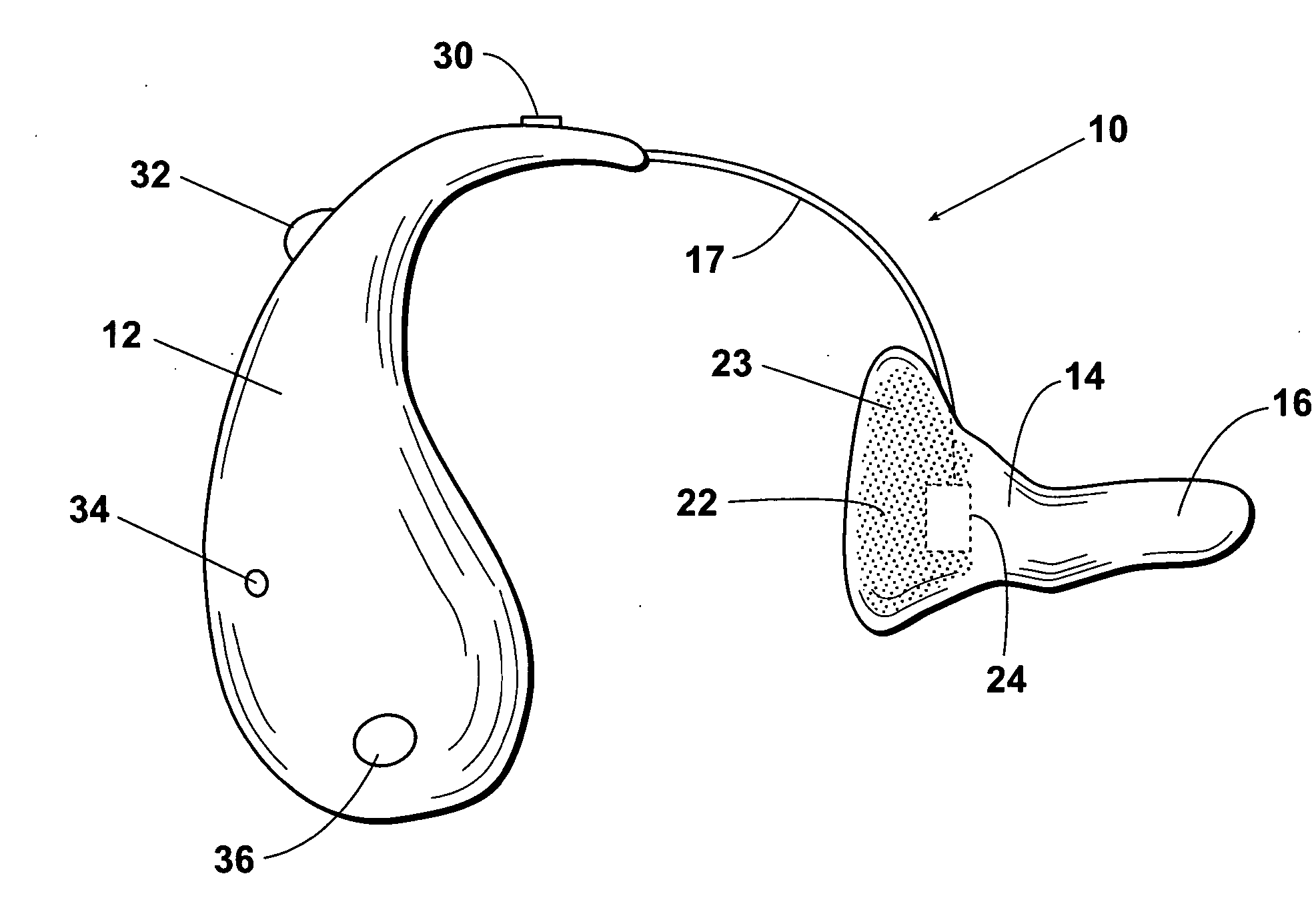
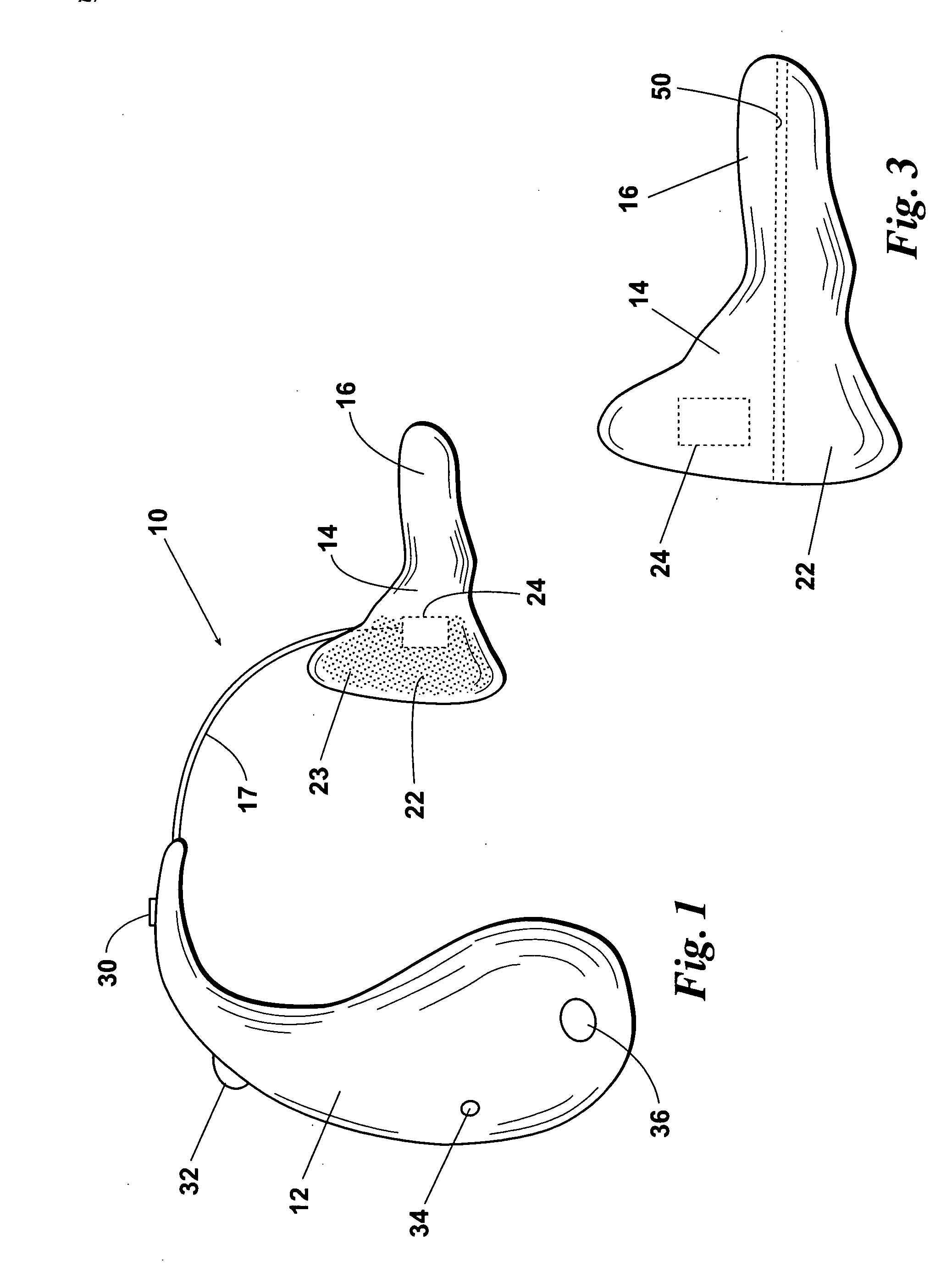
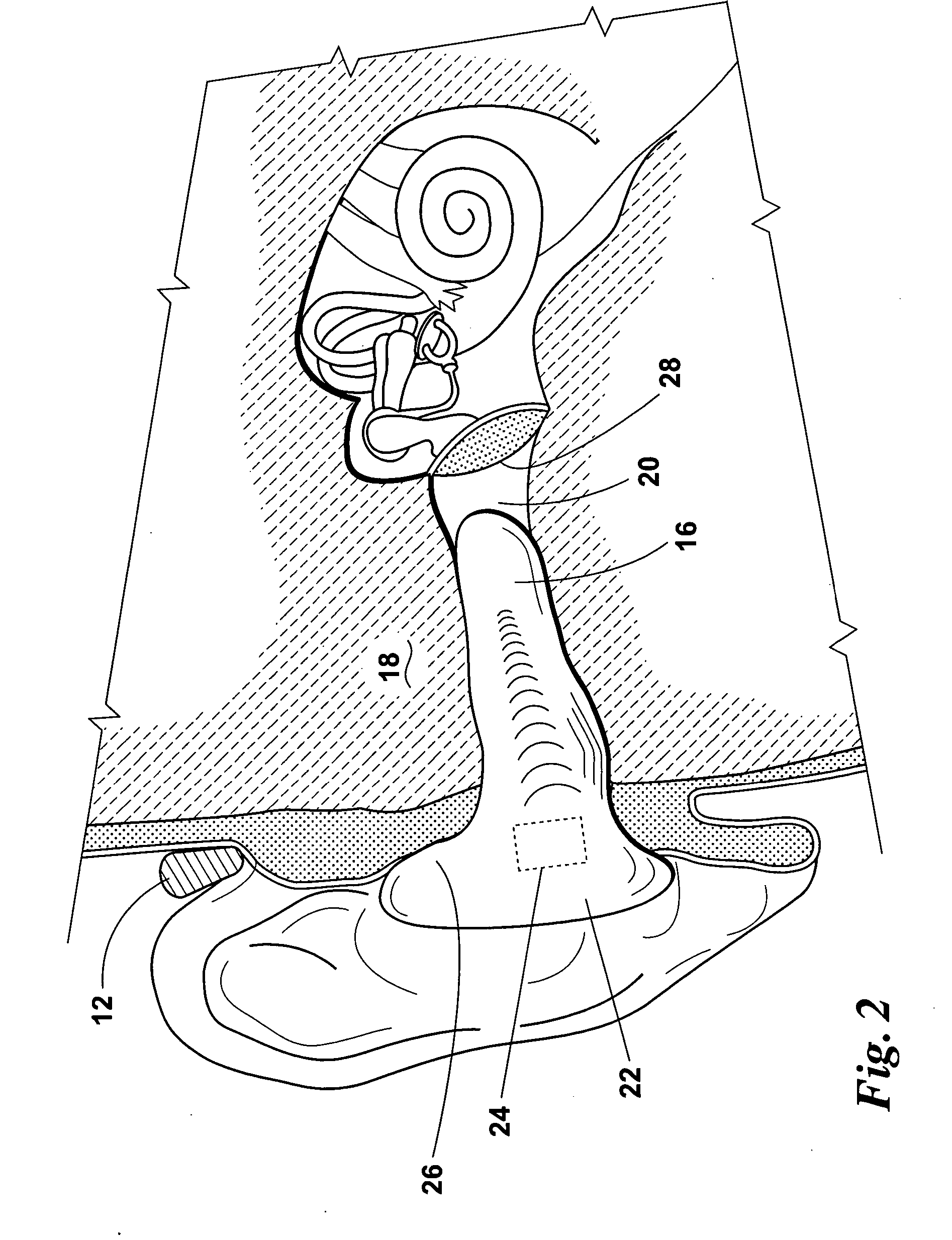
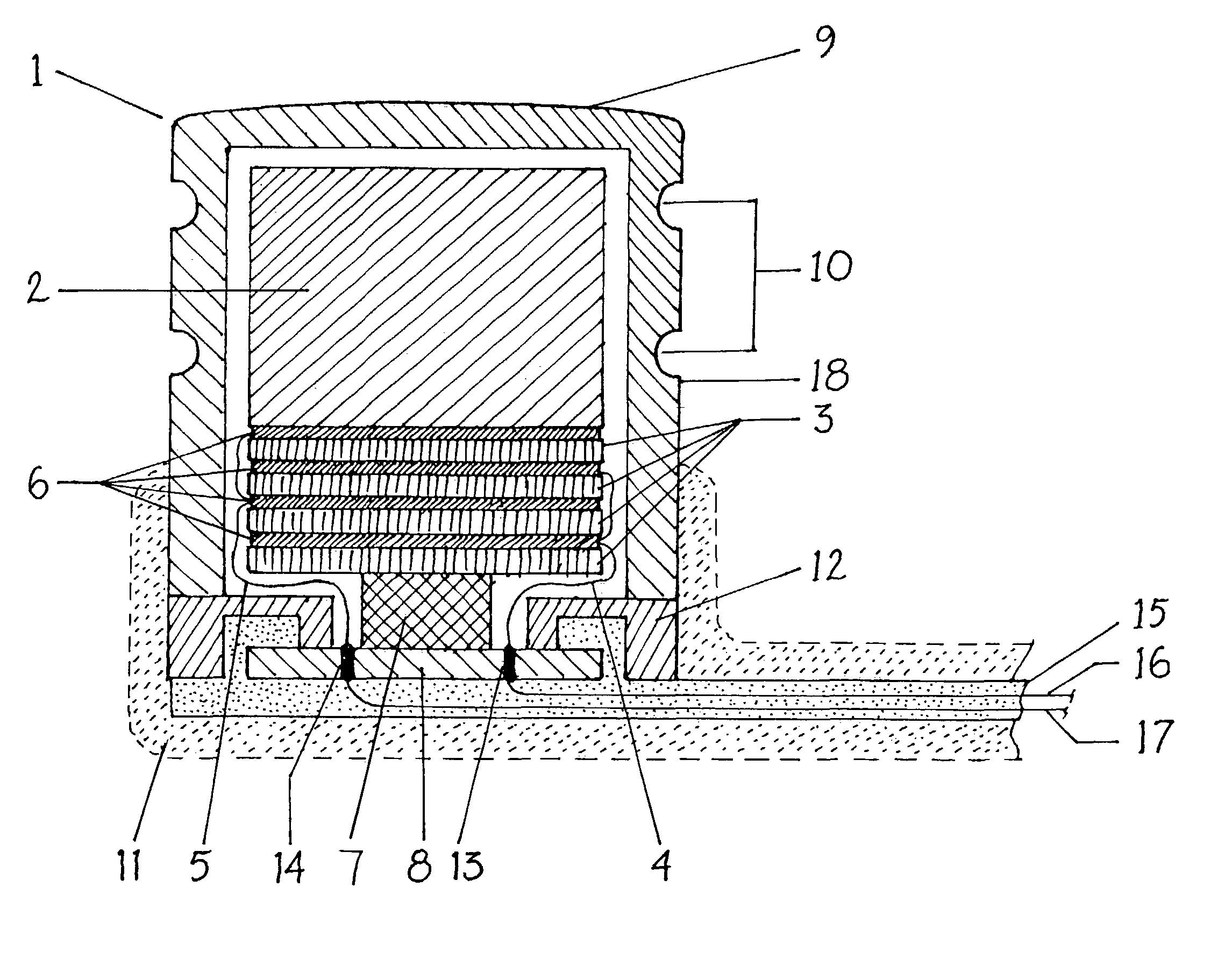
Totally implantable hearing prosthesis
ActiveUS20050020873A1Easy and safe to implantIncrease powerElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsCochlear implantationProsthesis
The invention comprises a totally implantable hearing prosthesis for hearing impaired persons. An inertial vibrational element is hermetically sealed and implanted in bone between the lateral and superior semicircular canals without breaching the integrity of the canals. The vibrational element is adapted to vibrate the walls of the canals and the fluids contained therein, thereby vibrating contiguous fluids within the cochlea thus stimulating hair cells and creating a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to be a tinnitus masking system, and / or used in combination with a coehlear implant hearing system.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
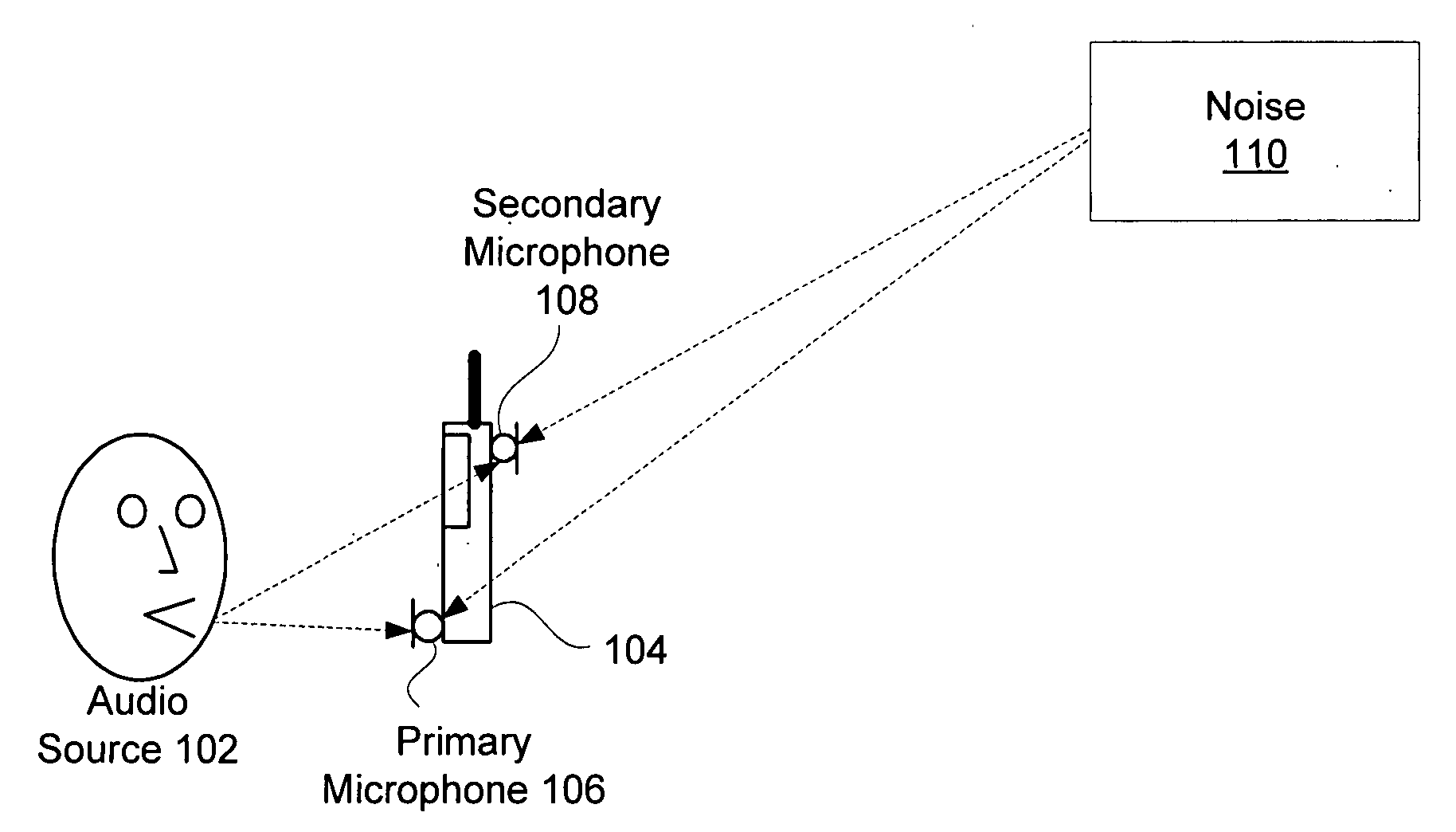
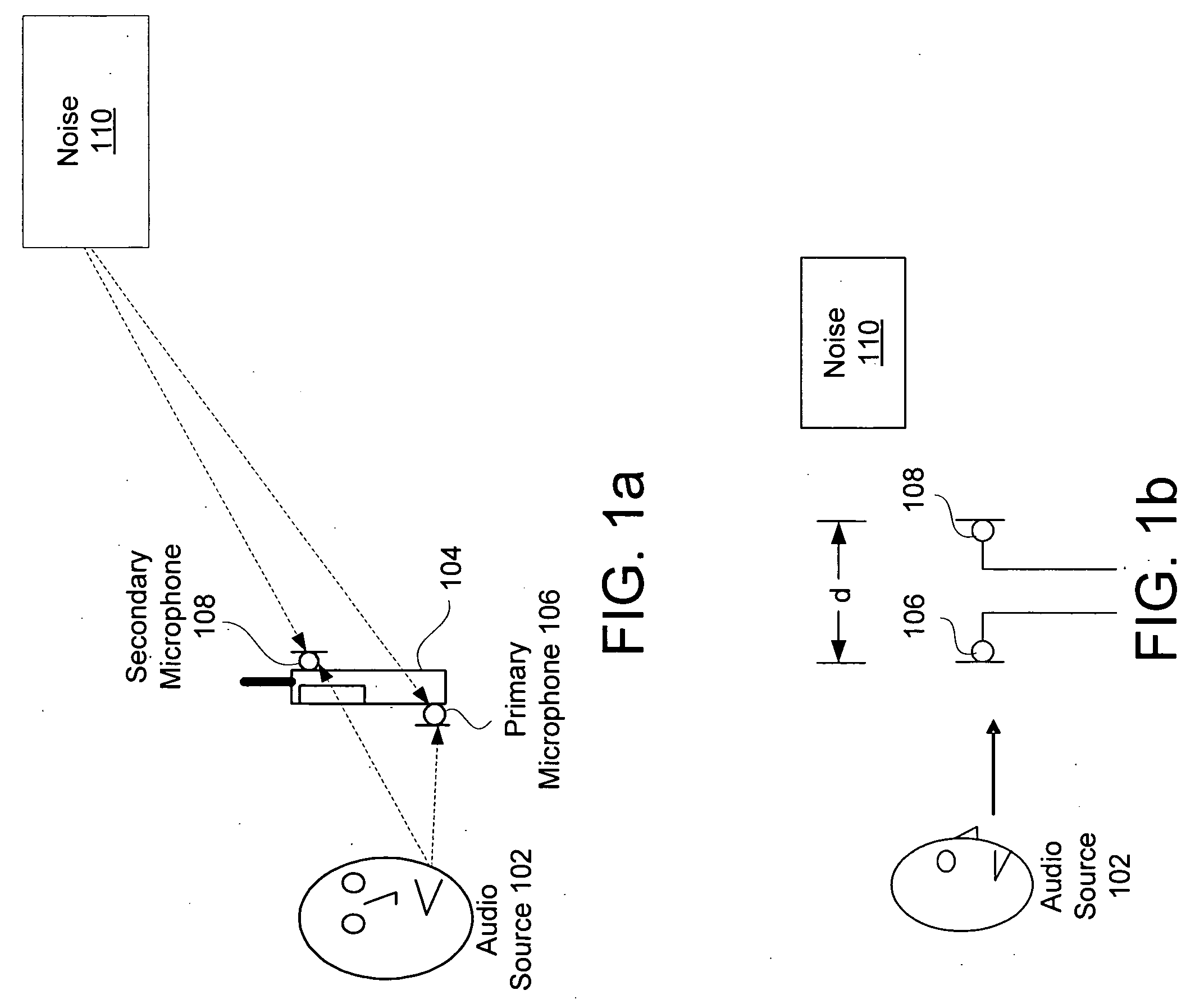
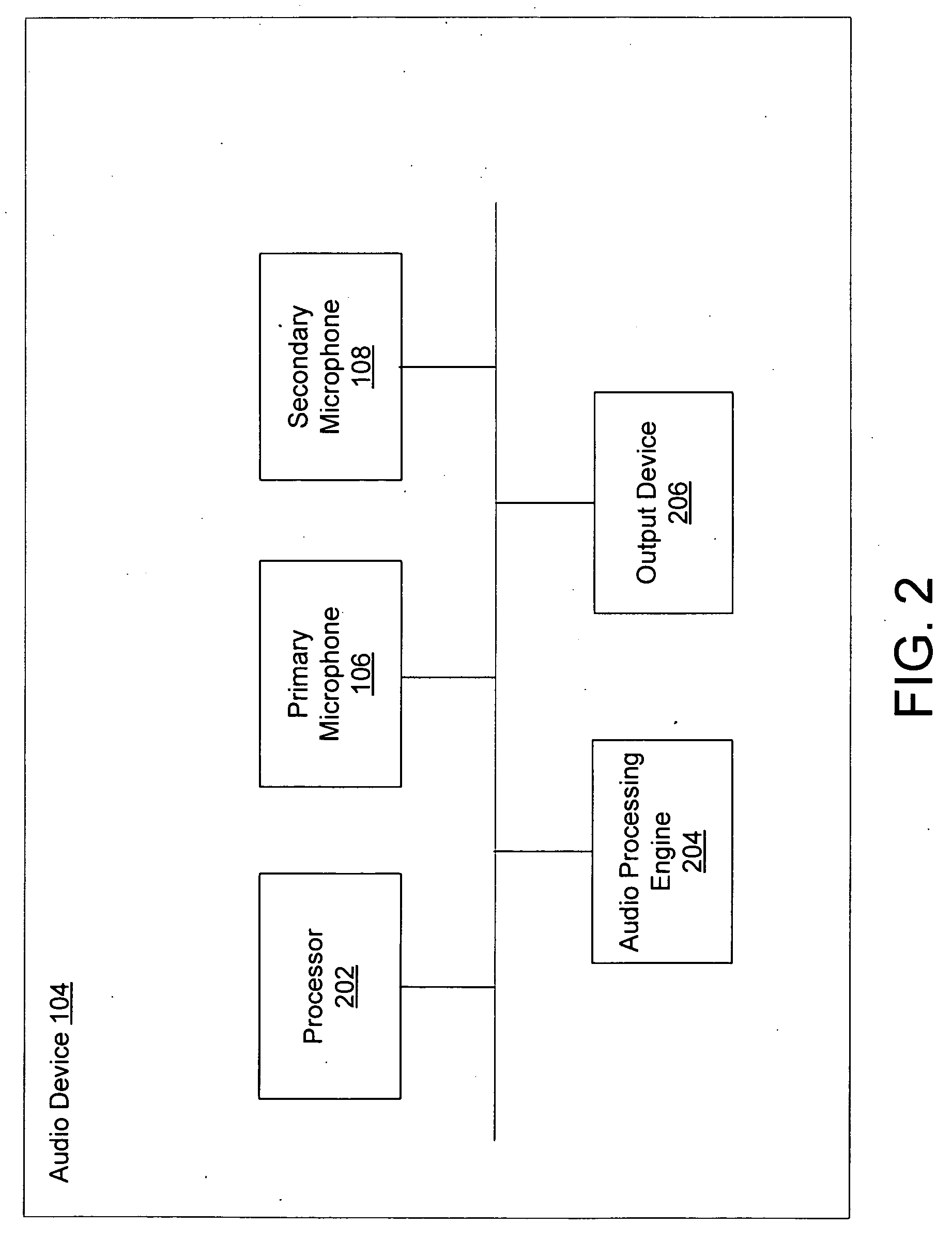
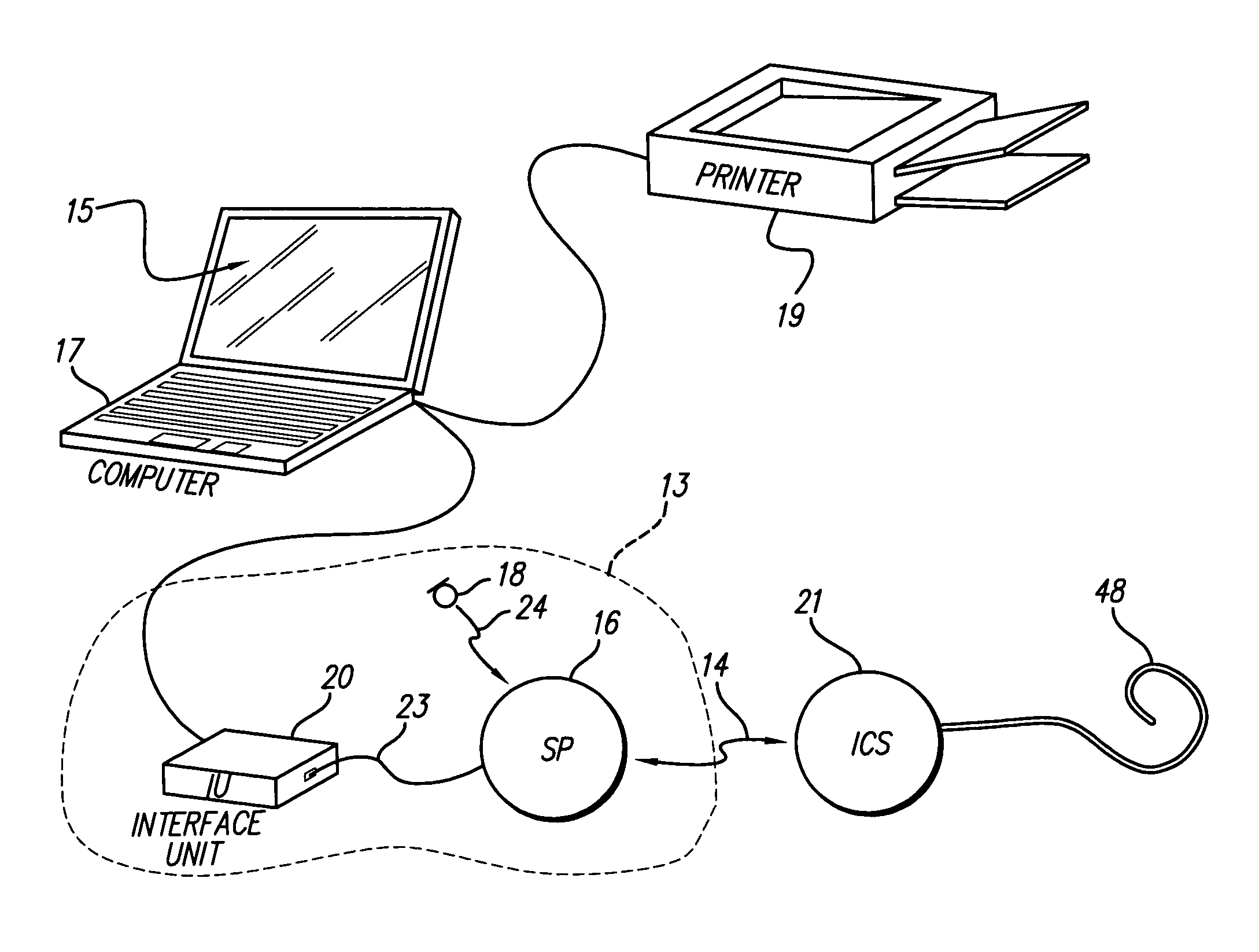
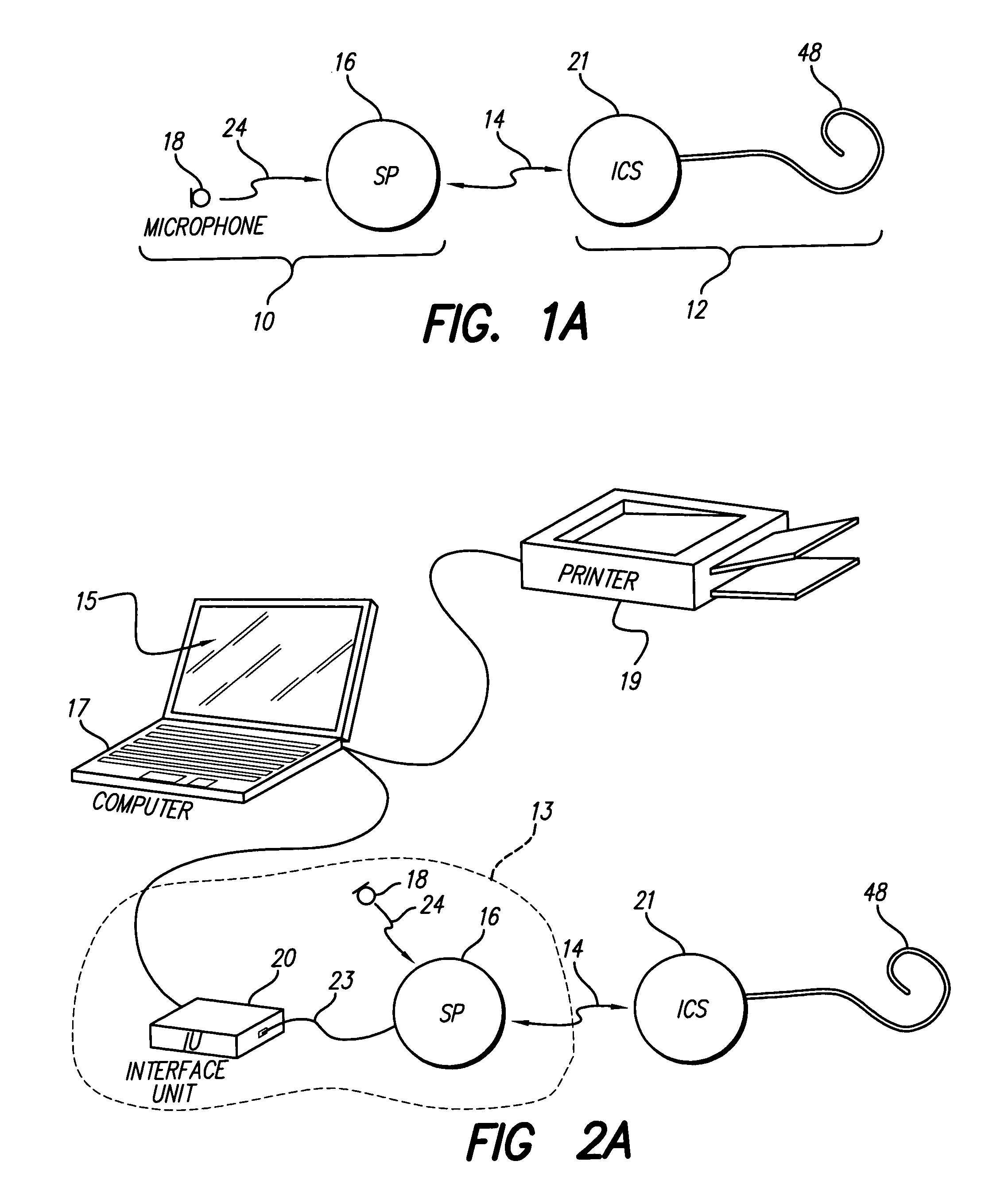
System and method for utilizing omni-directional microphones for speech enhancement
ActiveUS20080019548A1Suppression problemEnhance speechMicrophones signal combinationSpeech recognitionEngineeringOmni directional
Systems and methods for utilizing inter-microphone level differences (ILD) to attenuate noise and enhance speech are provided. In exemplary embodiments, primary and secondary acoustic signals are received by omni-directional microphones, and converted into primary and secondary electric signals. A differential microphone array module processes the electric signals to determine a cardioid primary signal and a cardioid secondary signal. The cardioid signals are filtered through a frequency analysis module which takes the signals and mimics a cochlea implementation (i.e., cochlear domain). Energy levels of the signals are then computed, and the results are processed by an ILD module using a non-linear combination to obtain the ILD. In exemplary embodiments, the non-linear combination comprises dividing the energy level associated with the primary microphone by the energy level associated with the secondary microphone. The ILD is utilized by a noise reduction system to enhance the speech of the primary acoustic signal.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
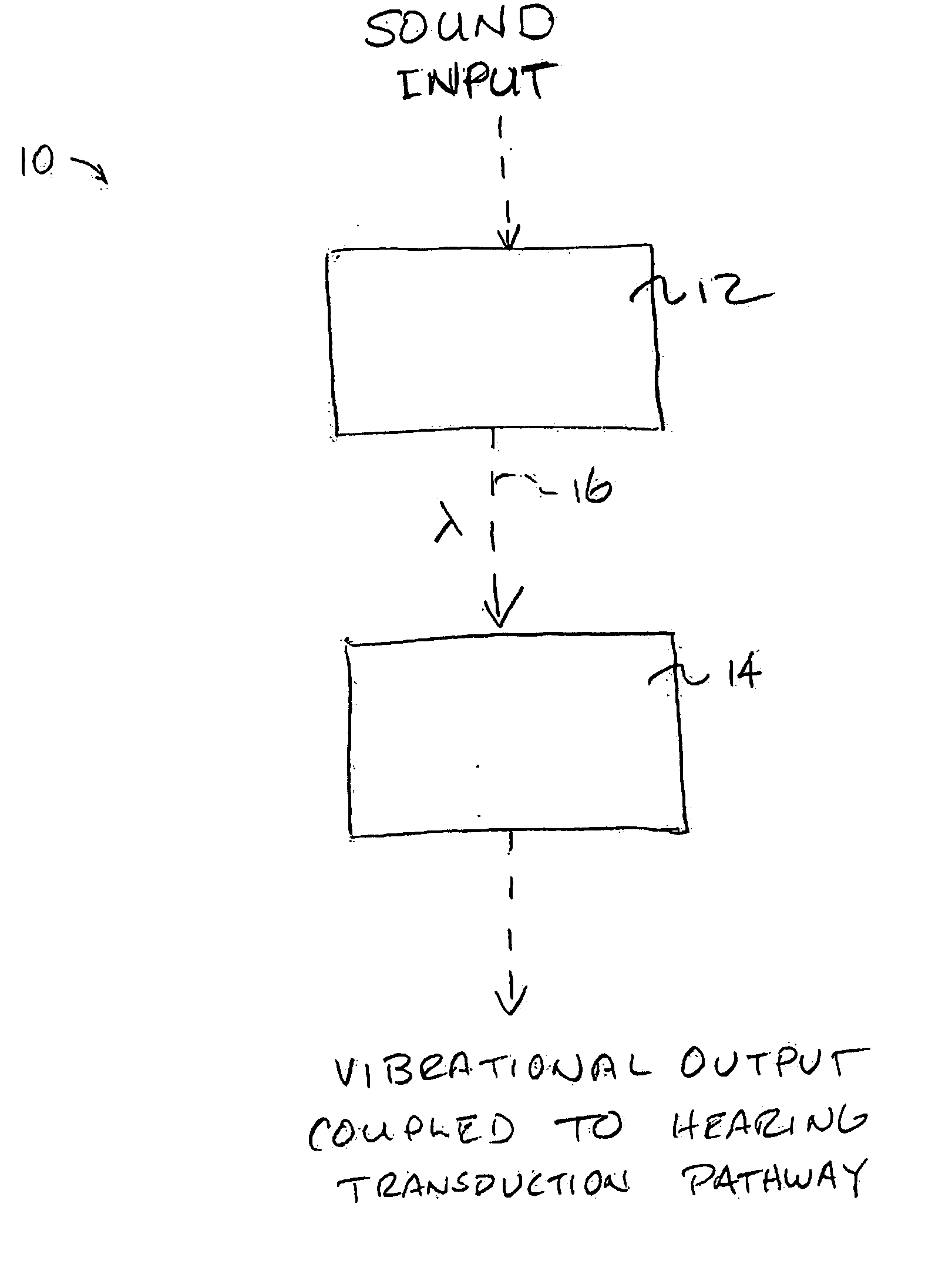
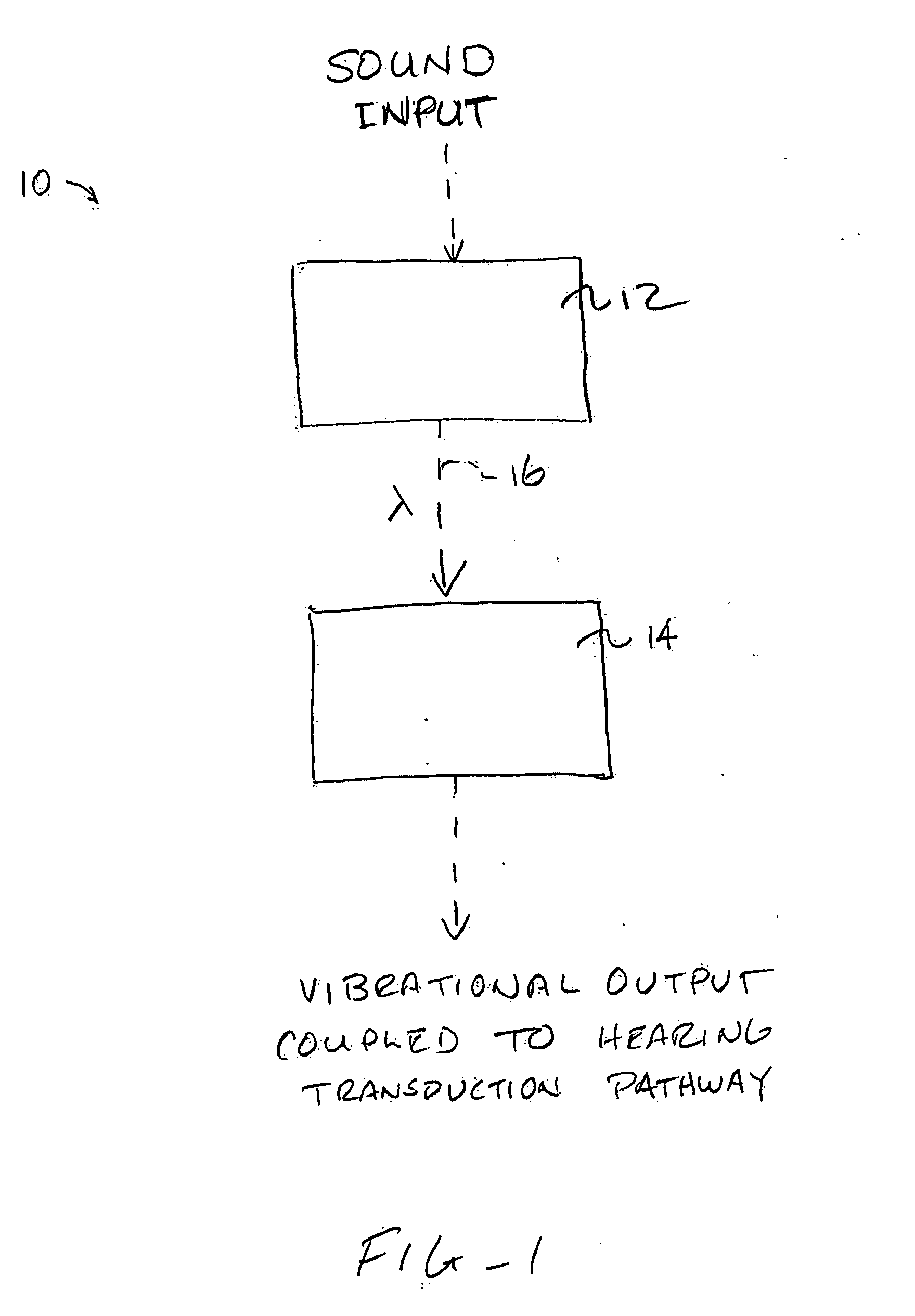
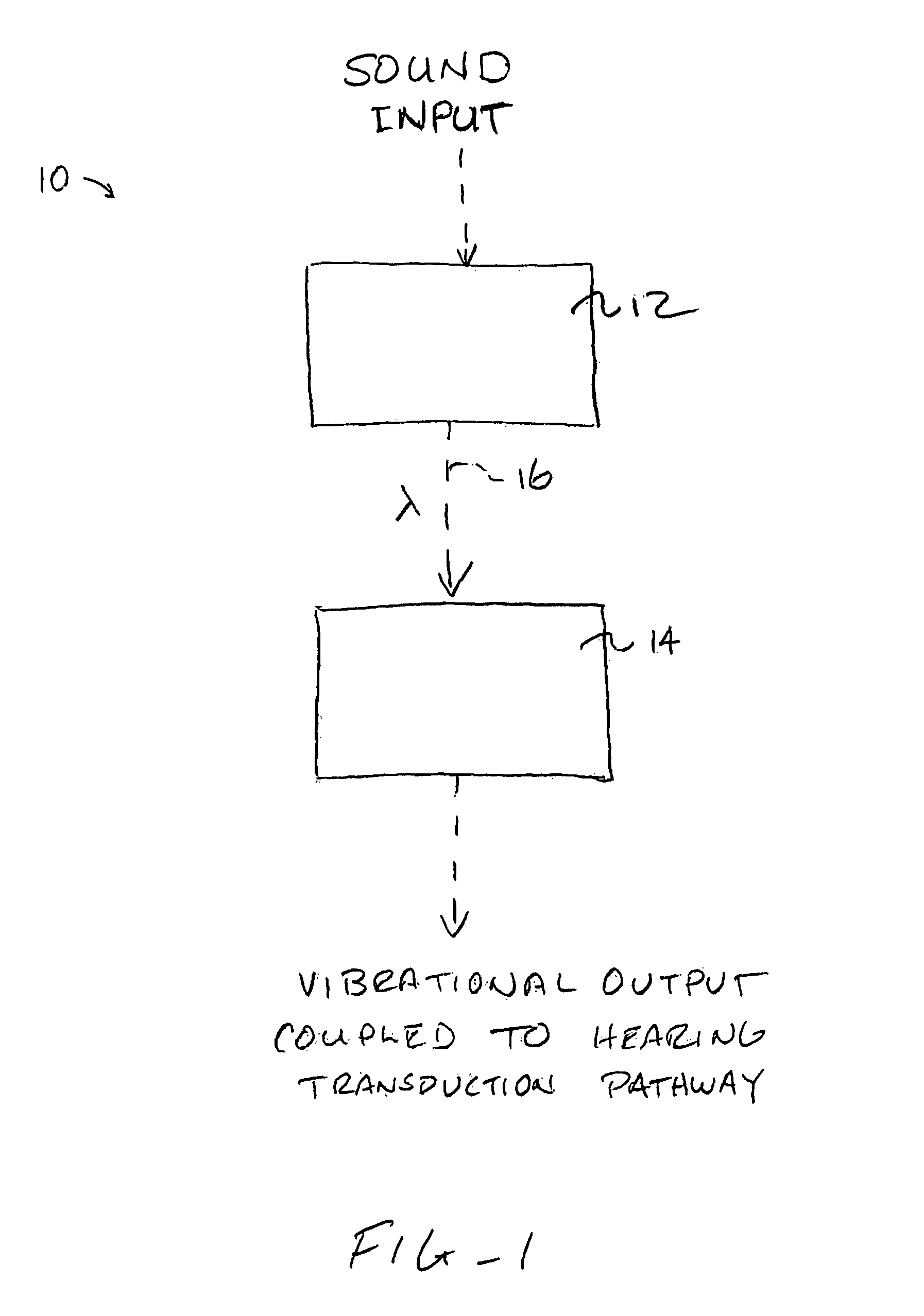
Systems and methods for photo-mechanical hearing transduction
ActiveUS20060189841A1Least riskAvoid excessive distanceCompletely in canal hearing aidsOptical signal transducersTransducerLight signal
Hearing systems for both hearing impaired and normal hearing subjects comprise an input transducer and a separate output transducer. The input transducer will include a light source for generating a light signal in response to either ambient sound or an external electronic sound signal. The output transducer will comprise a light-responsive transducer component which is adapted to receive light from the input transducer. The output transducer component will vibrate in response to the light input and produce vibrations in a component of a subject's hearing transduction pathway, such as the tympanic membrane, a bone in the ossicular chain, or directly on the cochlea, in order to produce neural signals representative of the original sound.
Owner:EARLENS CORP
Method and apparatus for picking up auditory evoked potentials
InactiveUS6428484B1Avoid the needElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyImplanted deviceAuditory system
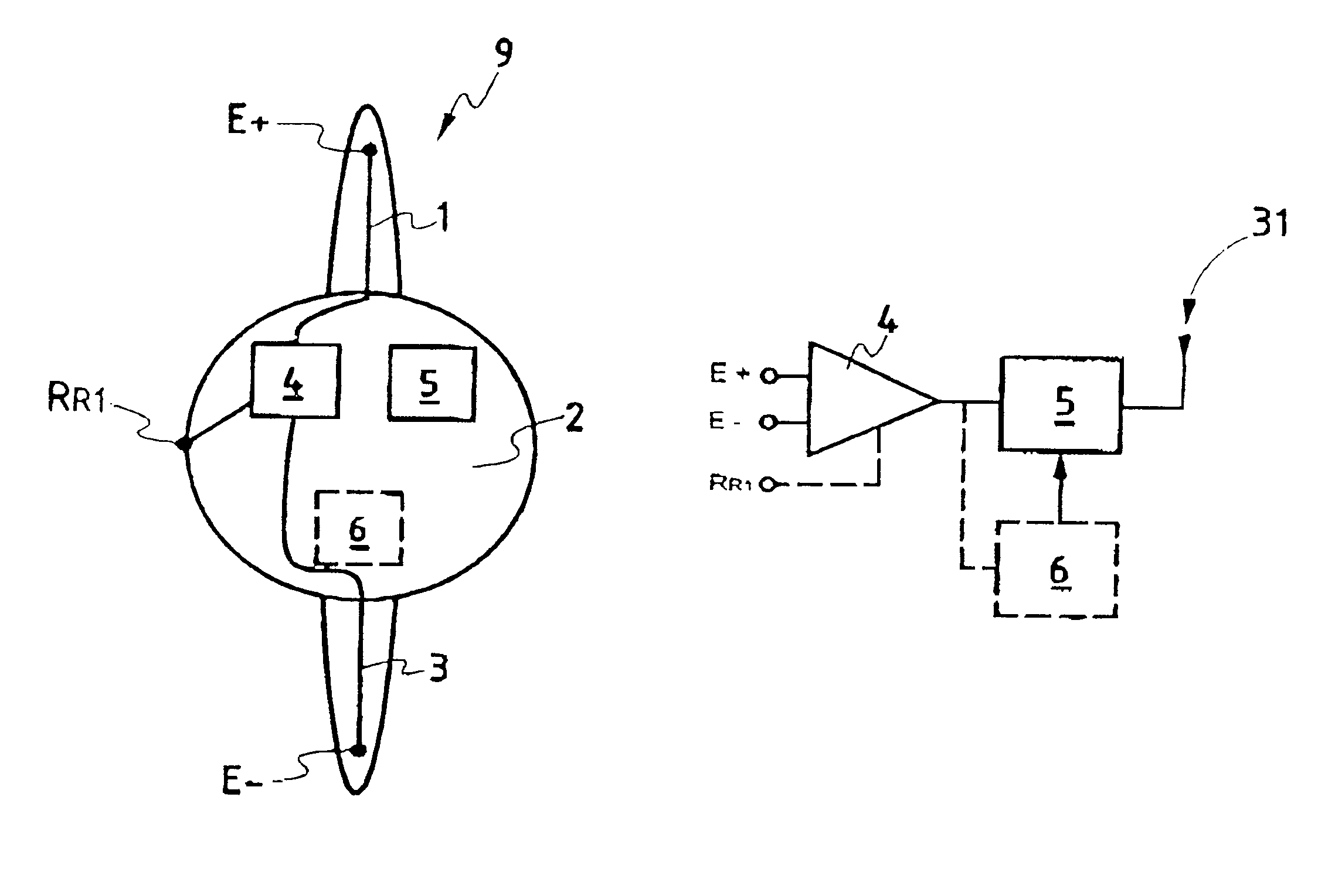
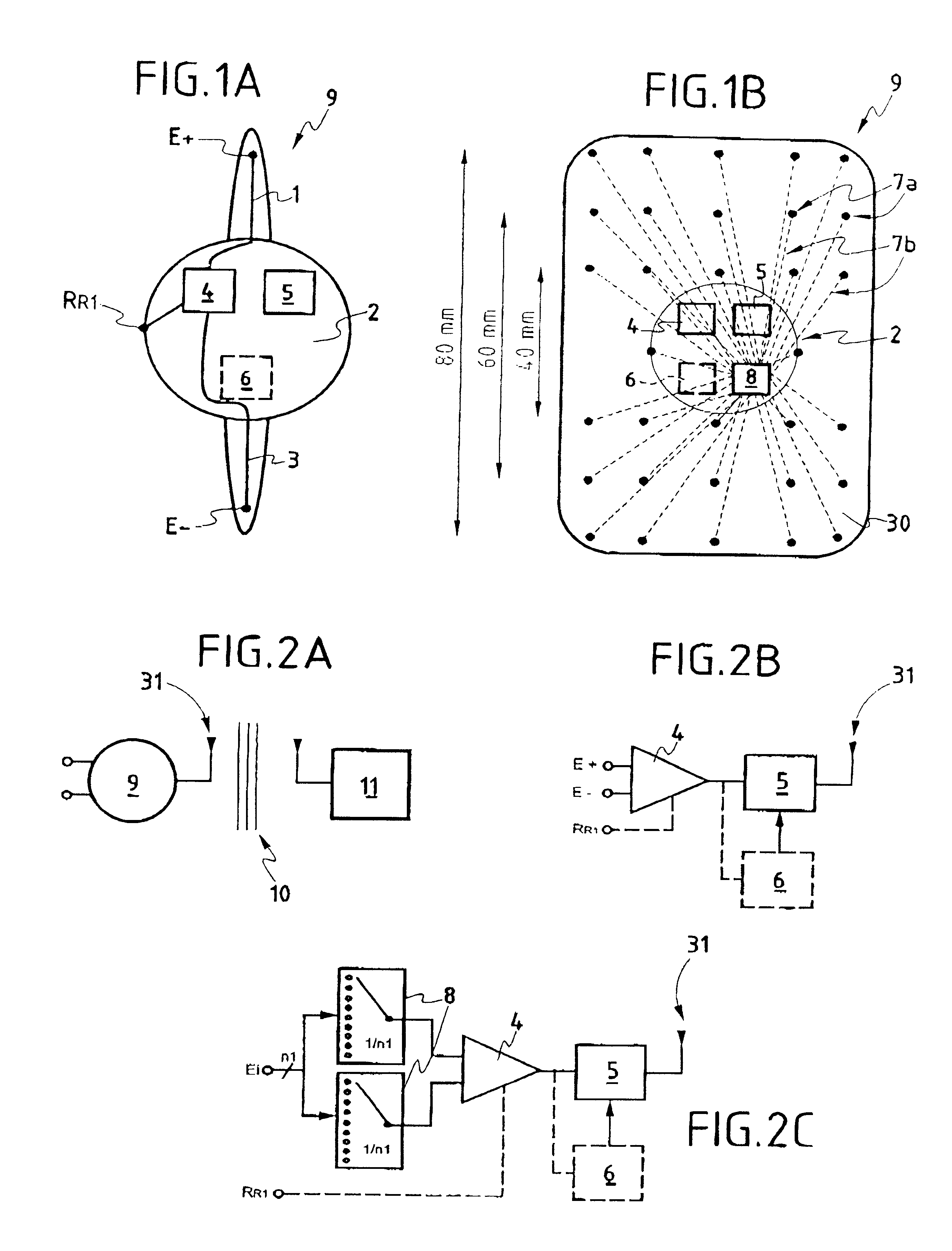
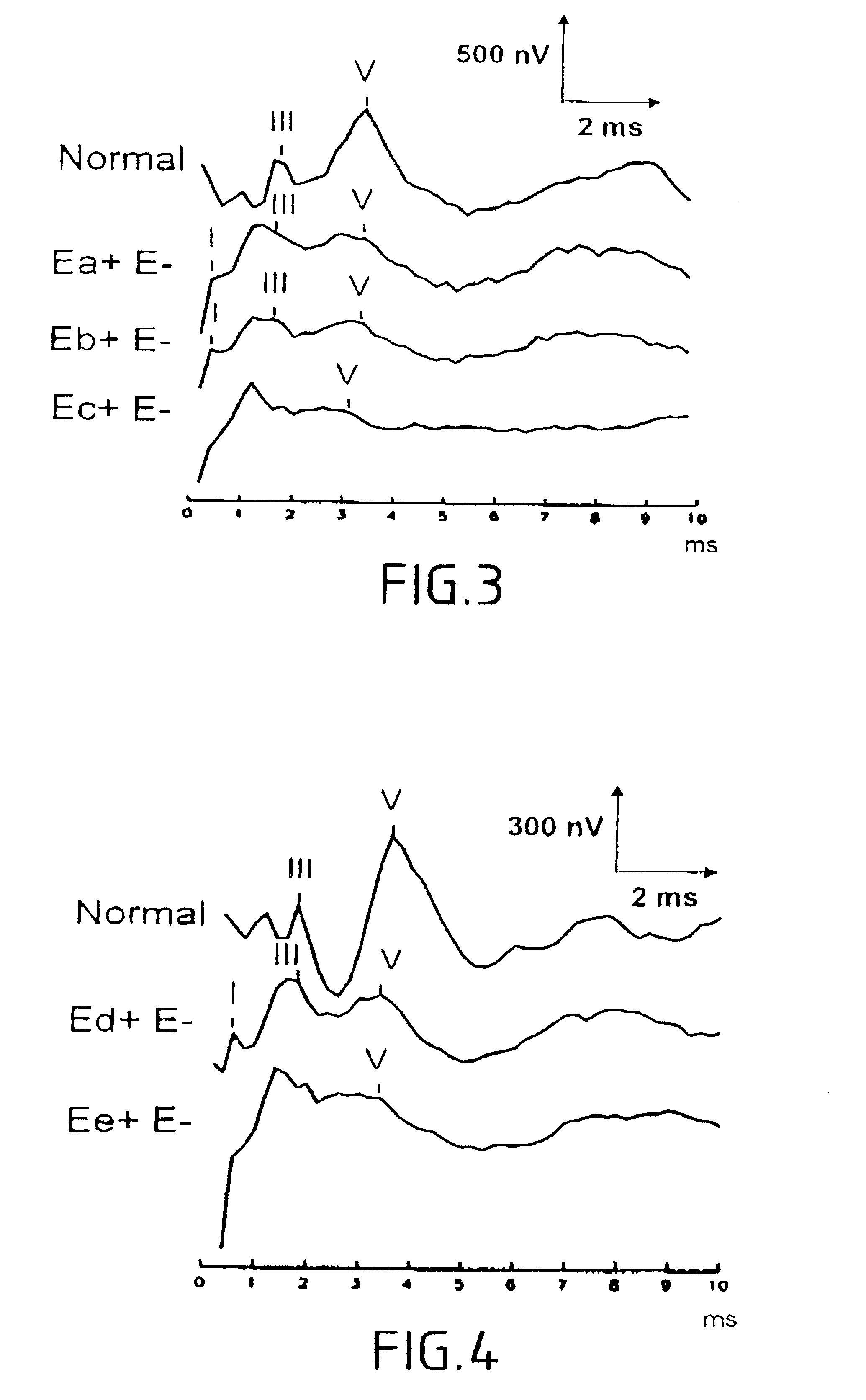
The present invention relates to a device for picking up biological electrical signals, and more precisely auditory evoked potentials generated by acoustic and / or electrical and / or mechanical stimulation of the cochlear, or of a portion of the auditory system in man or animal. The implantable device for measuring or picking up auditory evoked potentials comprises at least two extracochlear pickup electrodes connected to the inputs of a differential amplifier.
Owner:NEURELEC FIFTY PERCENT INTEREST
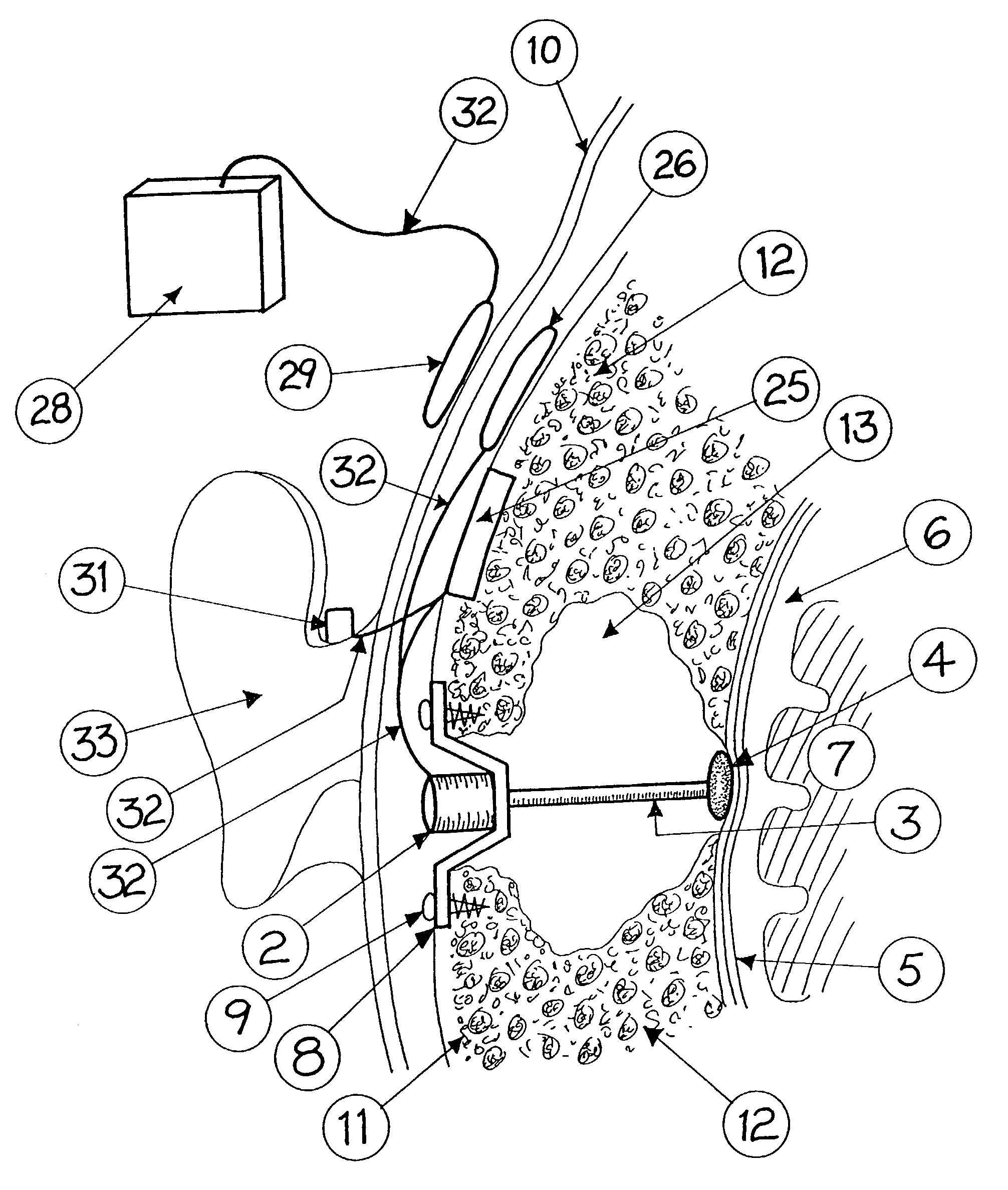
Cochlear drug delivery system and method
InactiveUS7206639B2Convenient, unobtrusive, and inexpensiveElectrotherapyEar treatmentDrug reservoirMiddle ear
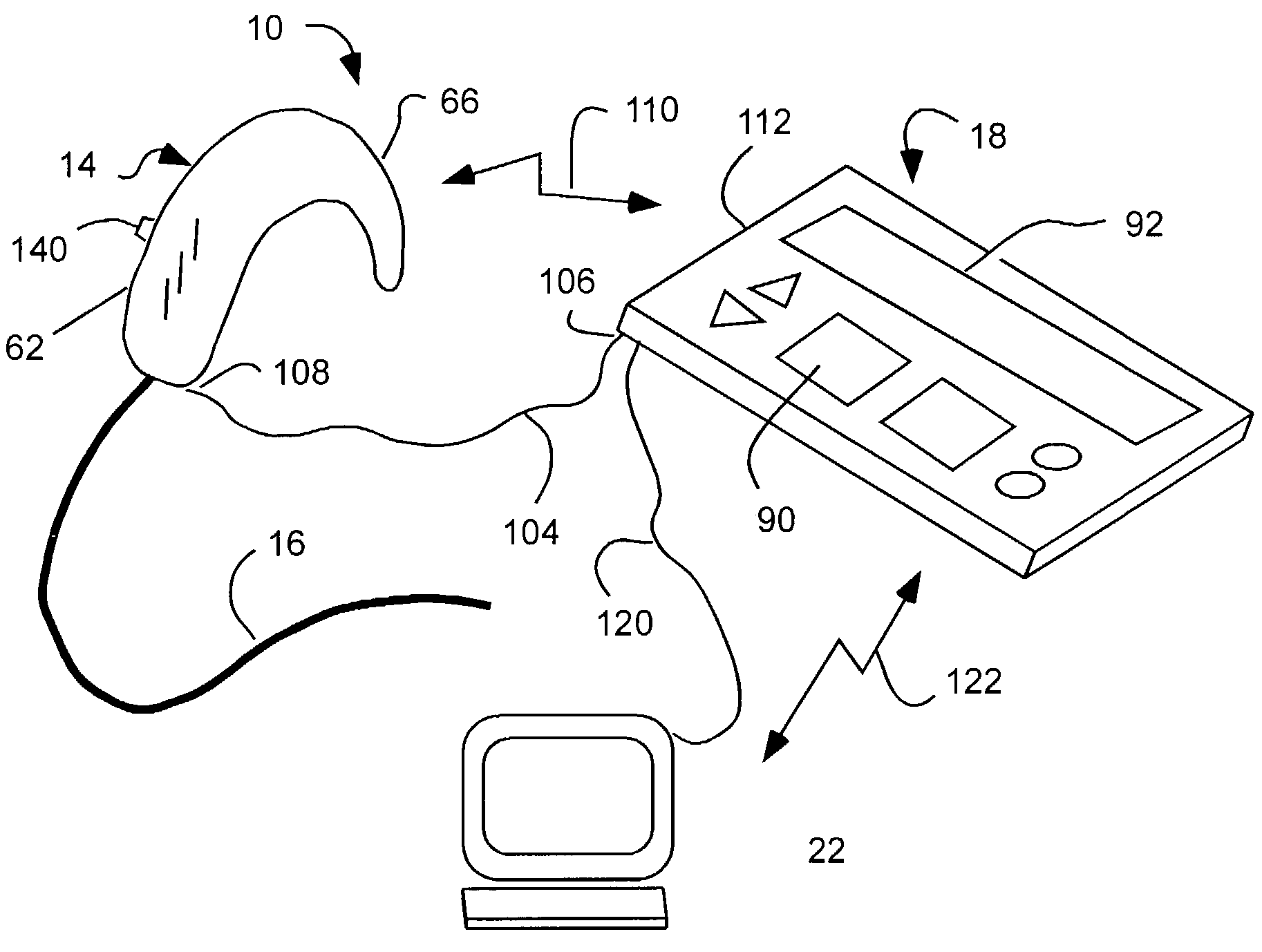
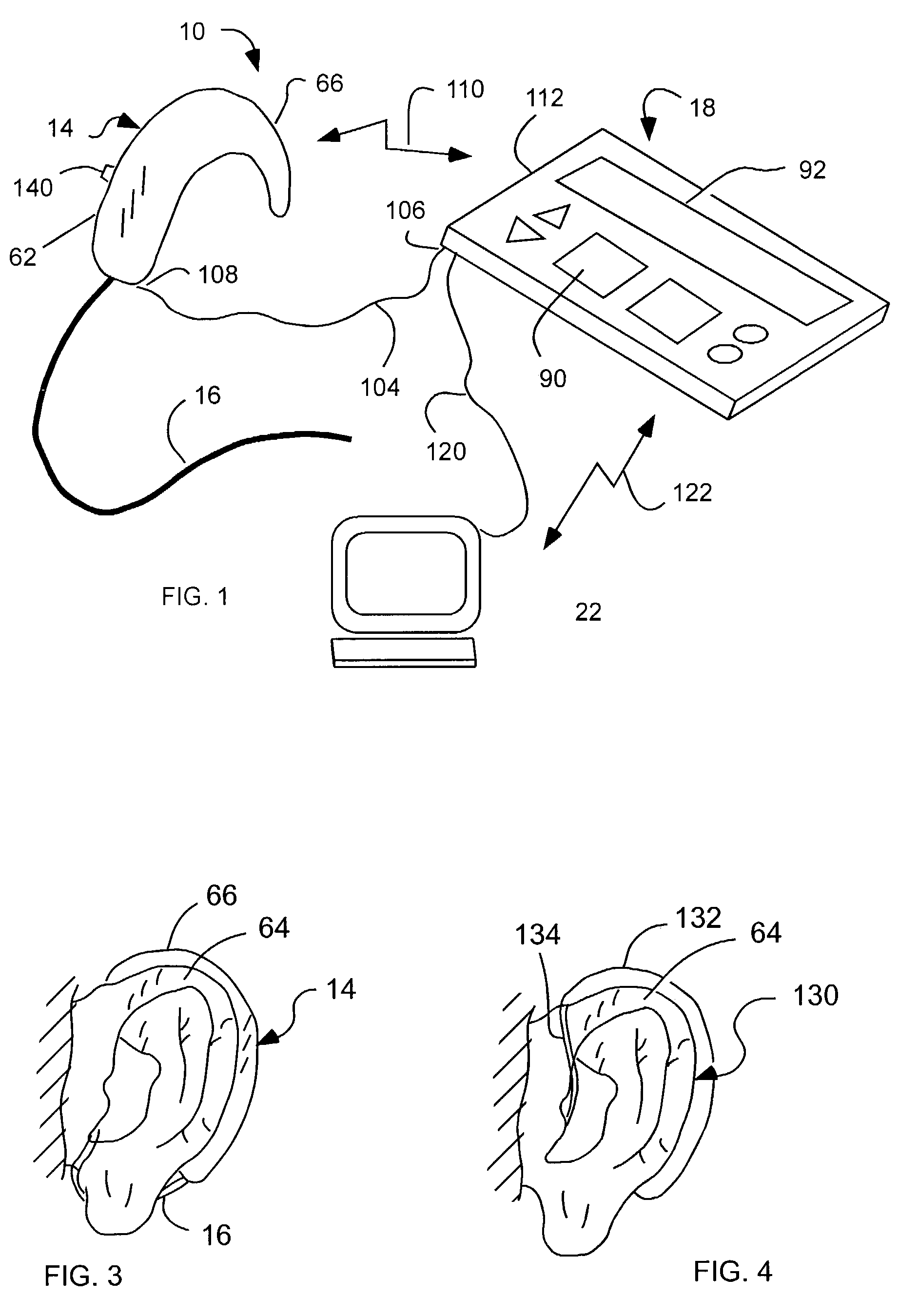
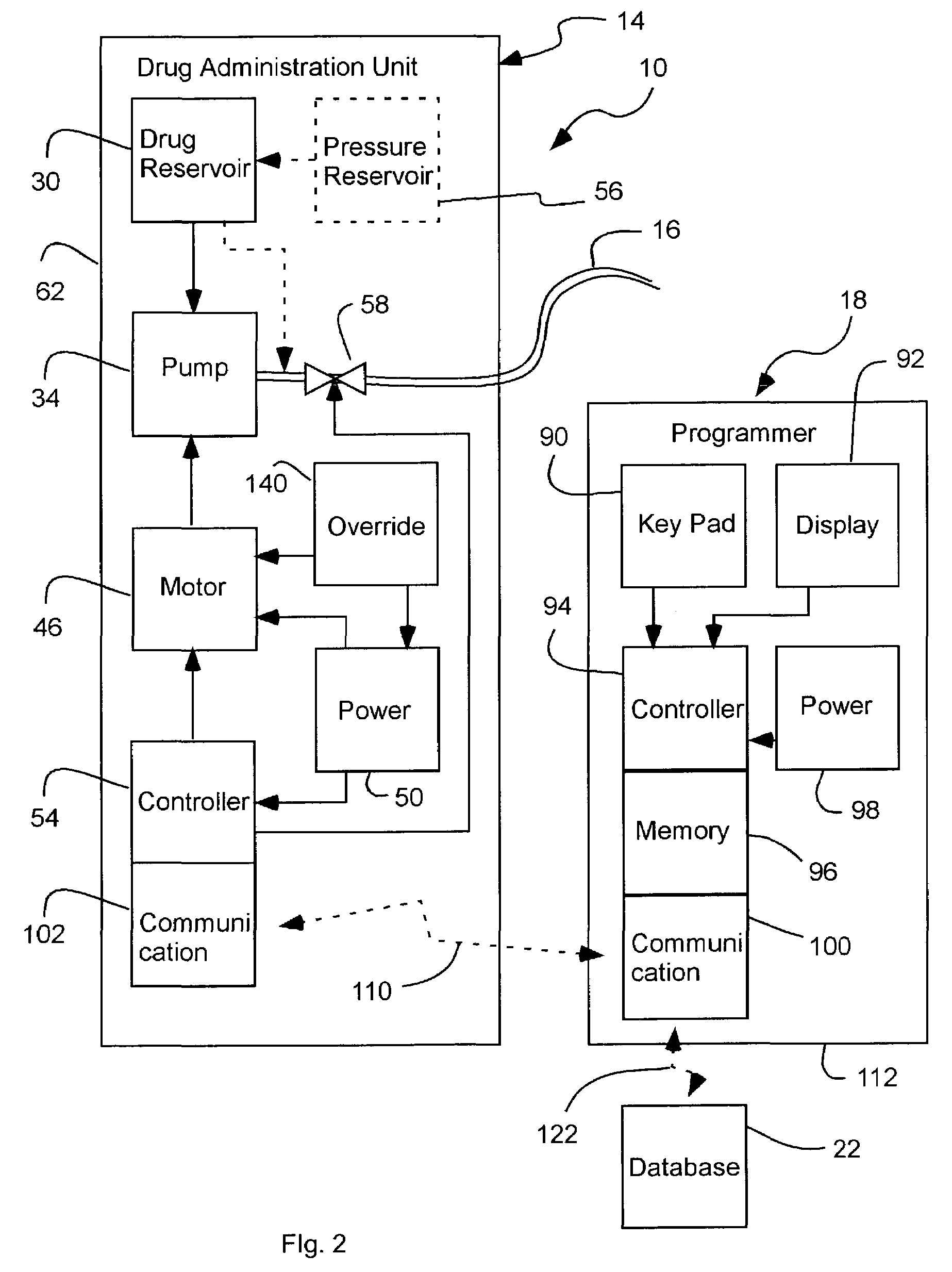
A drug administration system configured to administer a drug to a user's ear includes a housing, sized and shaped to substantially fit behind the user's ear, and configured to pump the drug in controlled amounts to the user's middle ear. A drug reservoir is disposed in the housing and includes a drug configured to treat an inner ear condition. A catheter is operatively coupled to the drug reservoir and is sized and shaped to extend from the drug administration unit into the user's middle ear.
Owner:STERLING INVESTMENTS LC
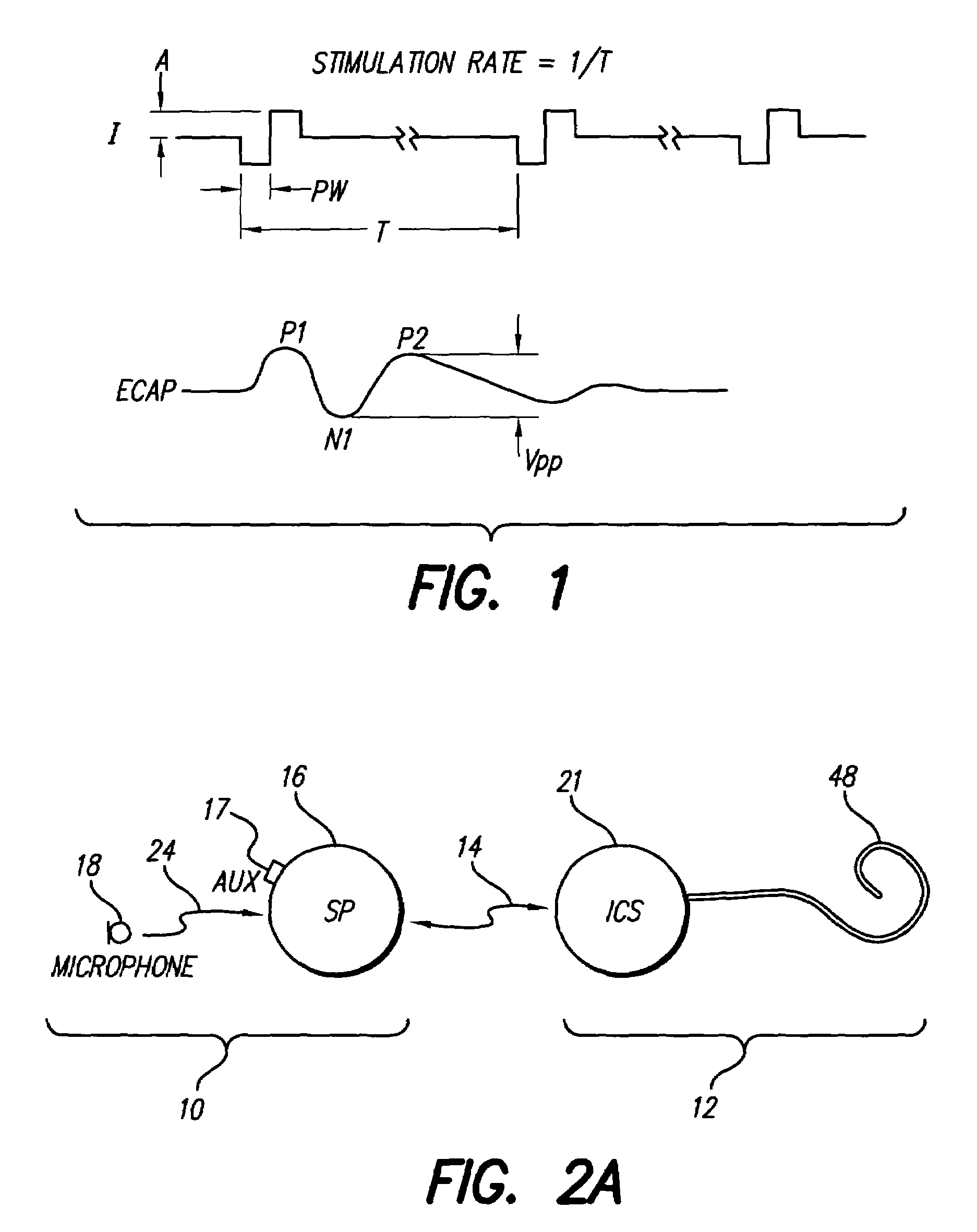
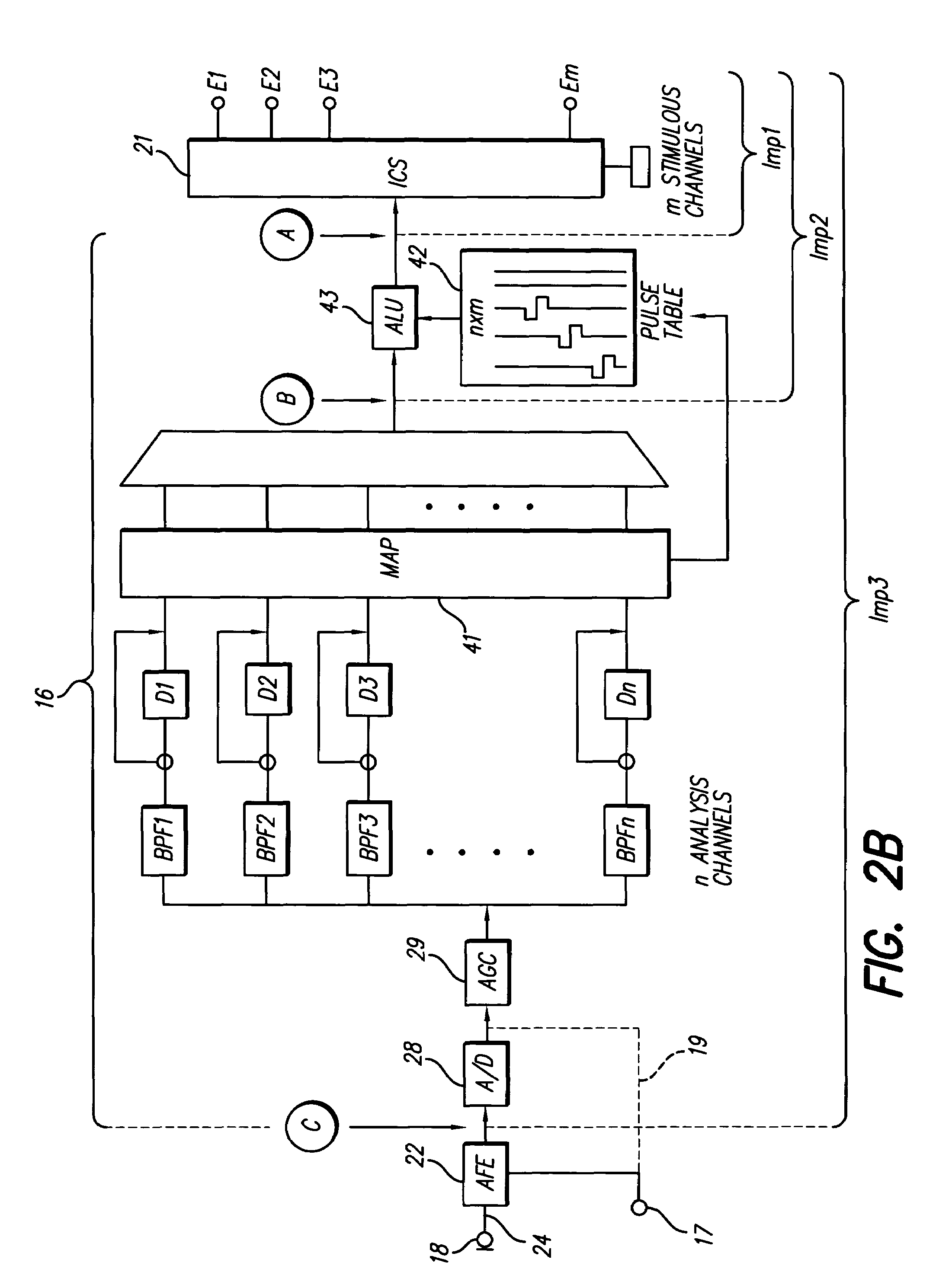
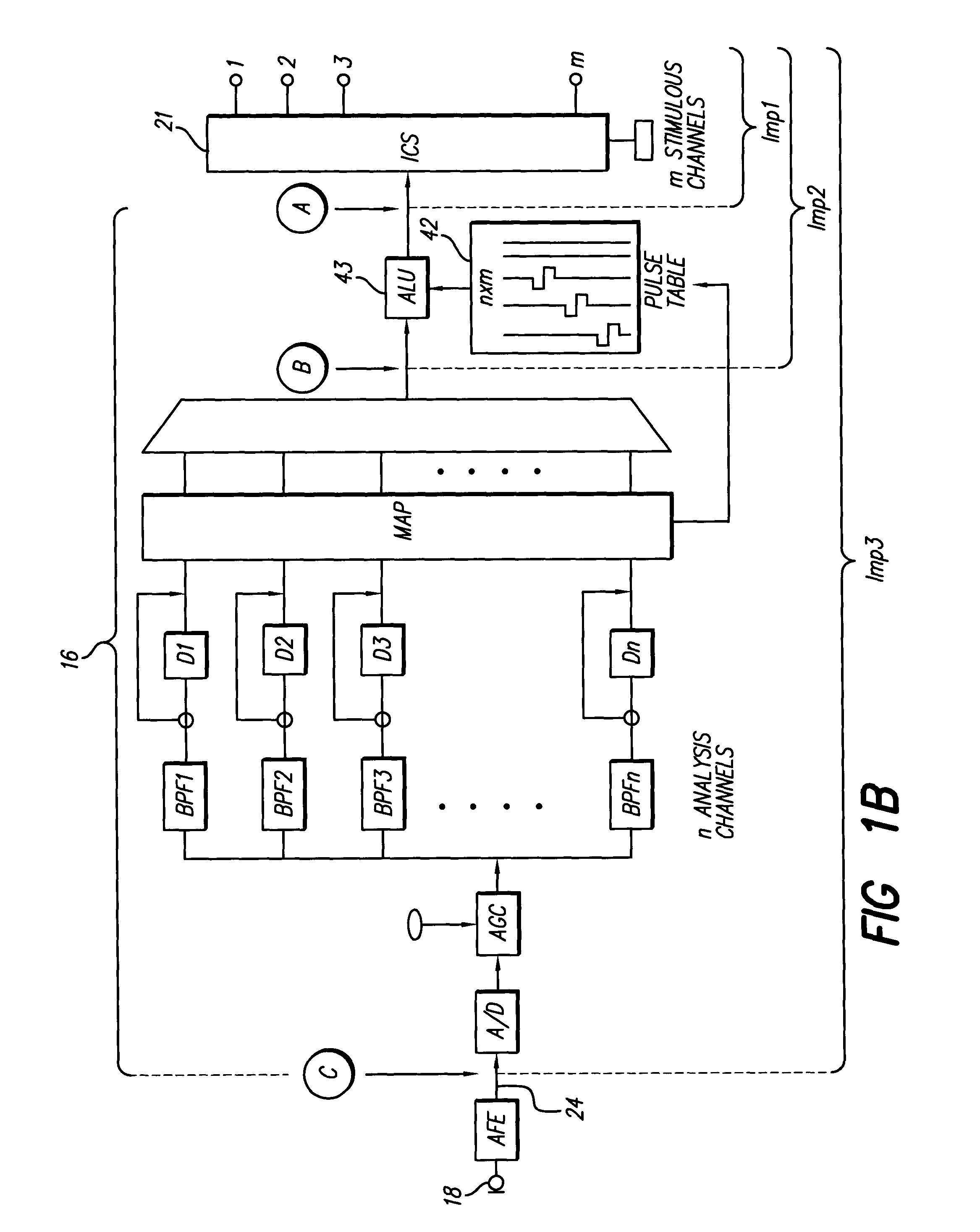
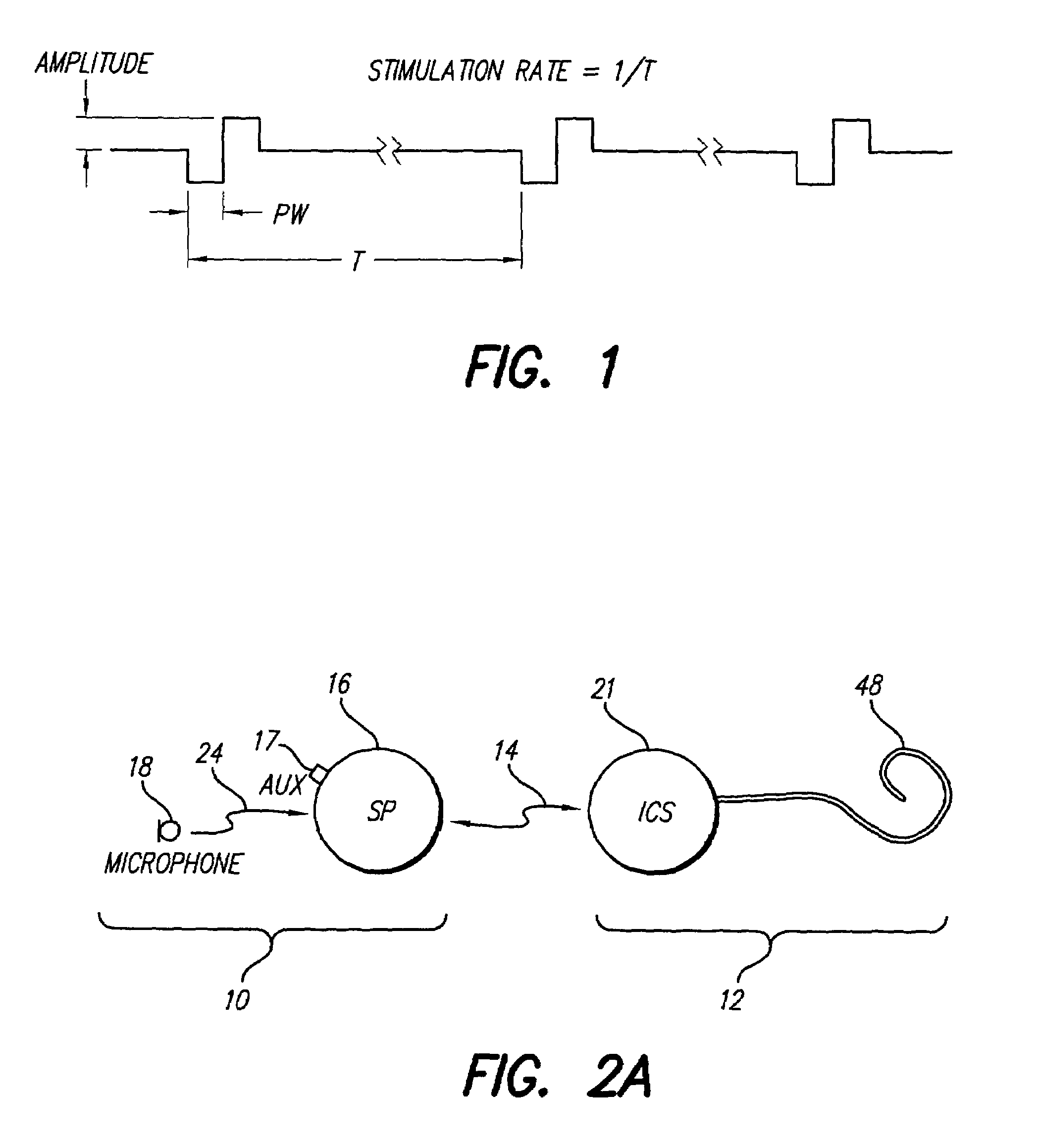
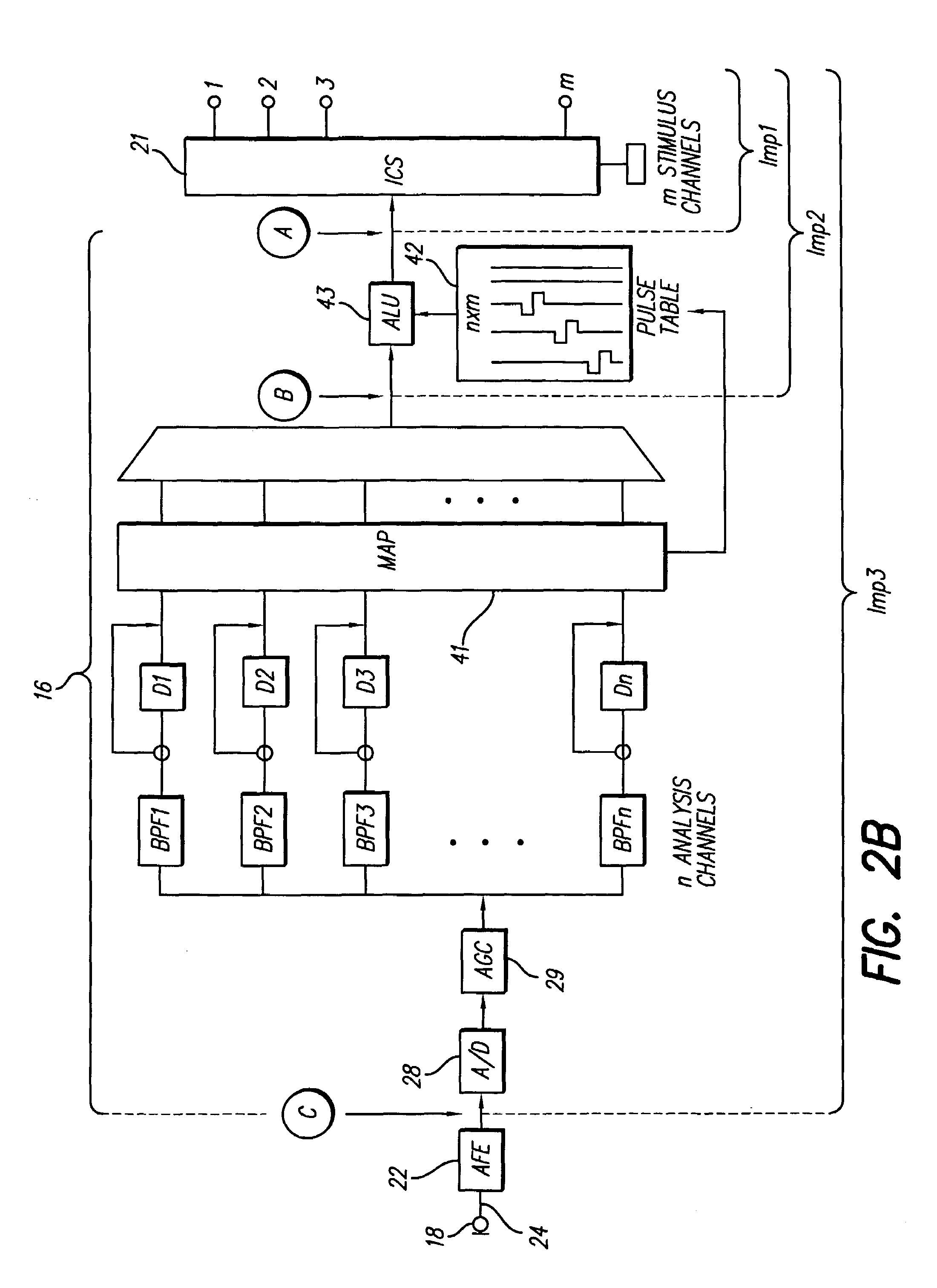
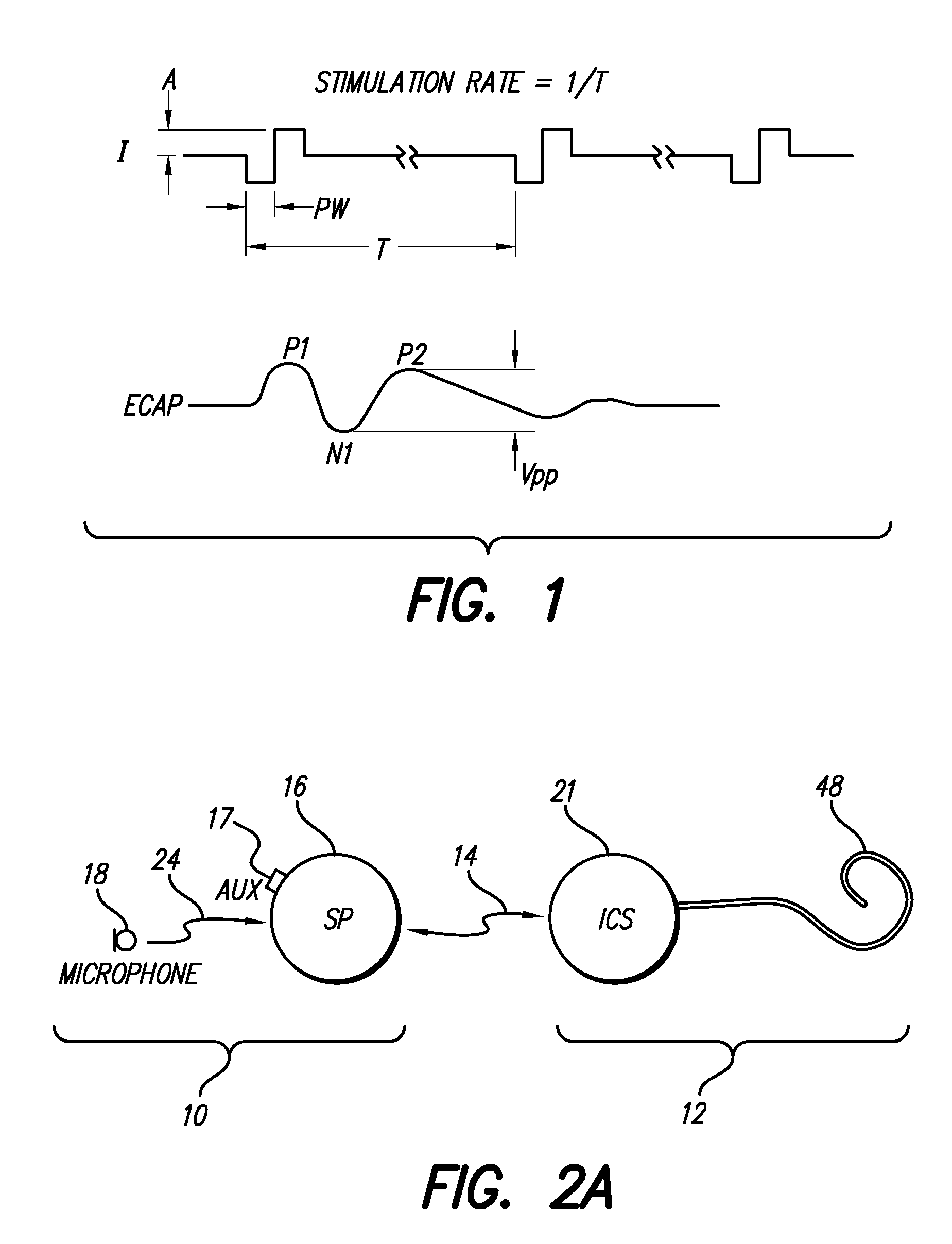
Method and system for generating a cochlear implant program using multi-electrode stimulation to elicit the electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS7206640B1Increase amplitudeConvenient recordingHead electrodesEvoked compound action potentialConfocal
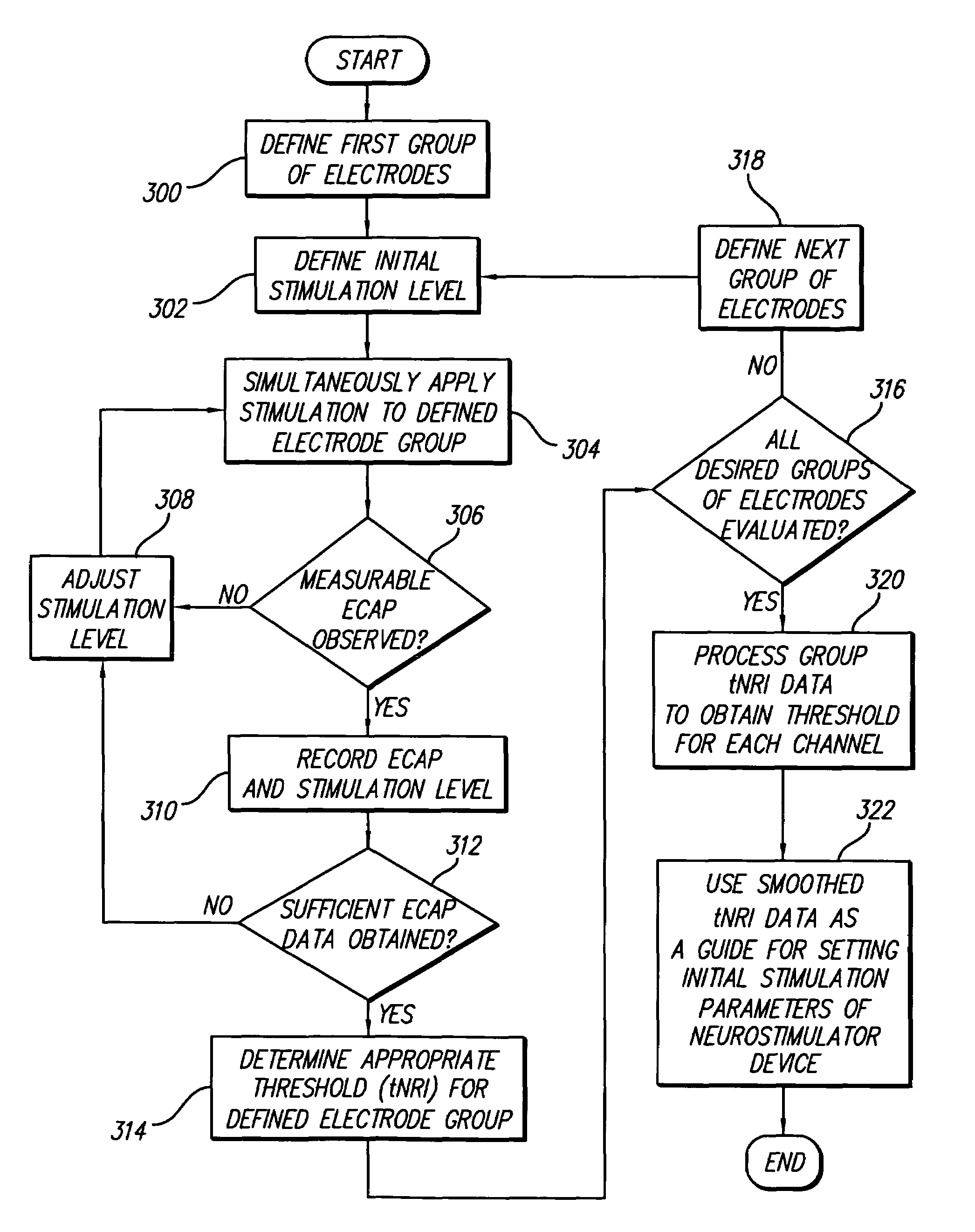
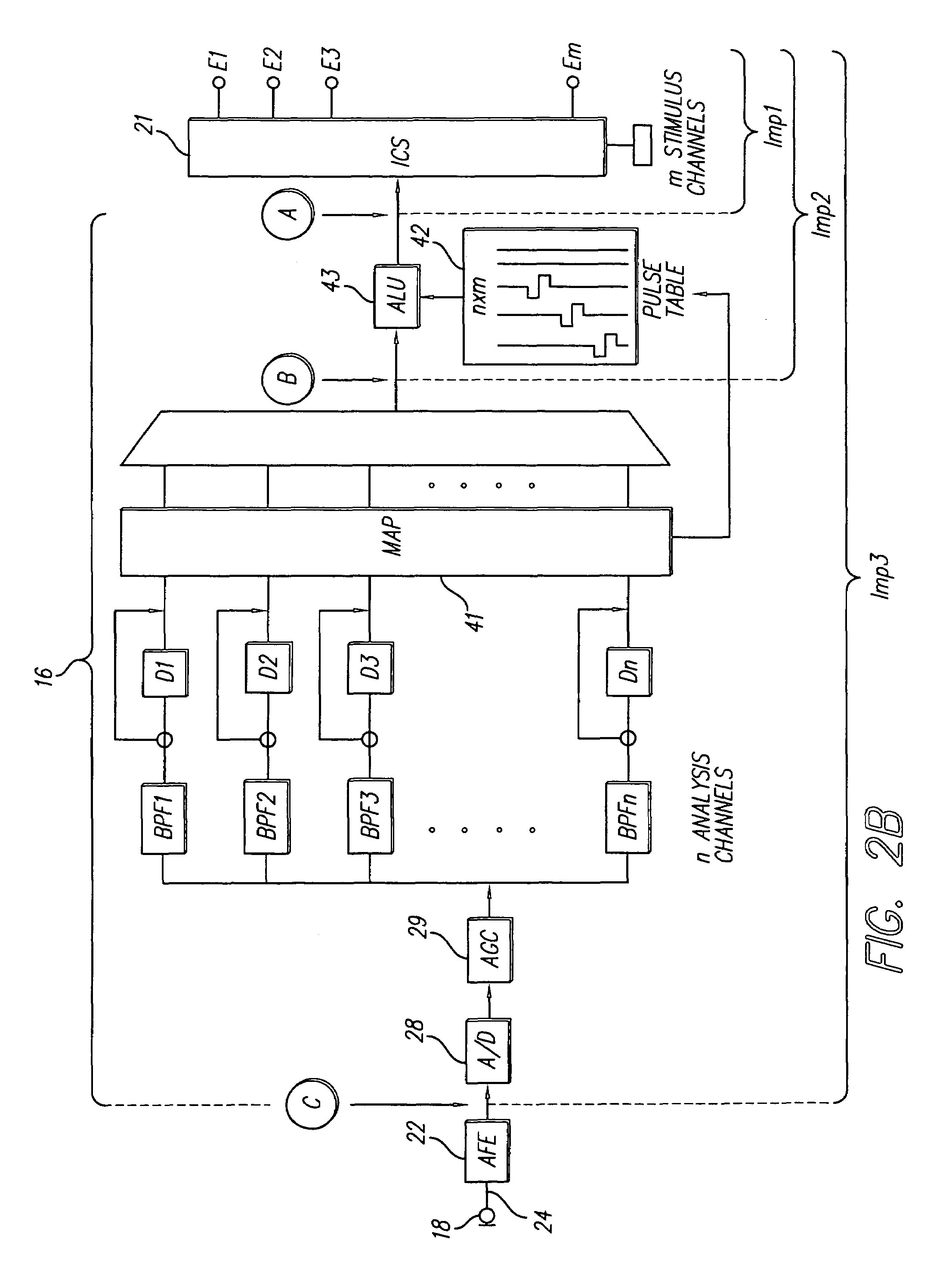
A multichannel cochlear implant system spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
Dual cochlear/vestibular stimulator with control signals derived from motion and speech signals
A system for treating patients affected both by hearing loss and by balance disorders related to vestibular hypofunction and / or malfunction, which includes sensors of sound and head movement, processing circuitry, a power source, and an implantable electrical stimulator capable of stimulating areas of the cochlea and areas of the vestibular system.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Enhanced methods for determining iso-loudness contours for fitting cochlear implant sound processors
InactiveUS7043303B1Simple processIncrease chanceElectrotherapyArtificial respirationHigh rateEqual-loudness contour
Methods are taught to simplify the cochlear implant fitting process for various cochlear prostheses and stimulation strategies, including high rate stimulation strategies. For instance, patient self-programming is made possible. In addition, auto-fitting is made possible (particularly useful for very young patients and other patients for whom it is challenging to obtain feedback) using iso-neural response contours which can be linearly transposed to arrive at iso-loudness contours. Furthermore, M iso-loudness contours (or iso-neural contours) can be linearly transposed to determine T iso-loudness contours. In addition, wider pulse widths can be used to generate an iso-loudness contour whose shape can be used (via linear transposition) to program high-rate, narrow pulse width stimulation.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
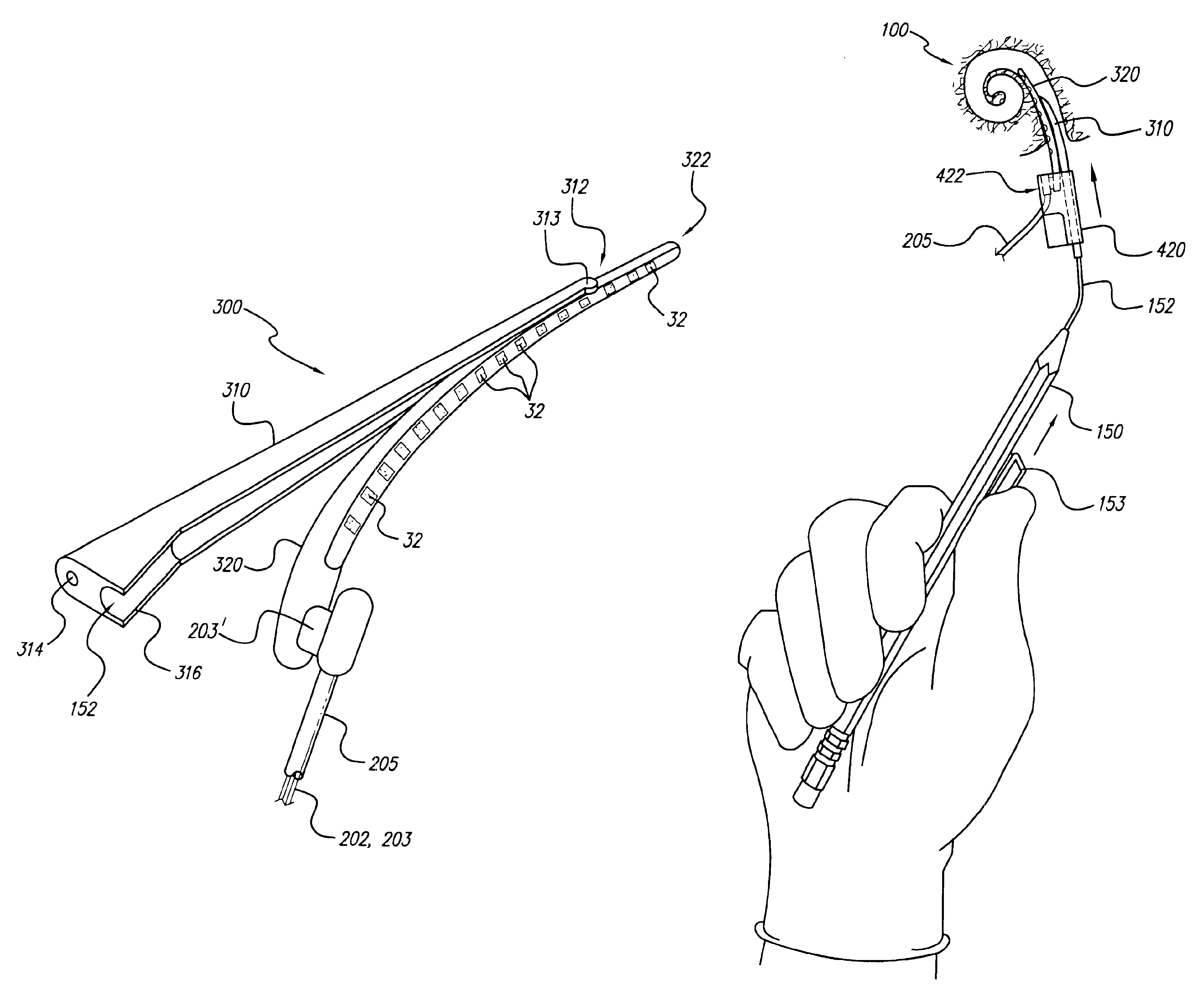
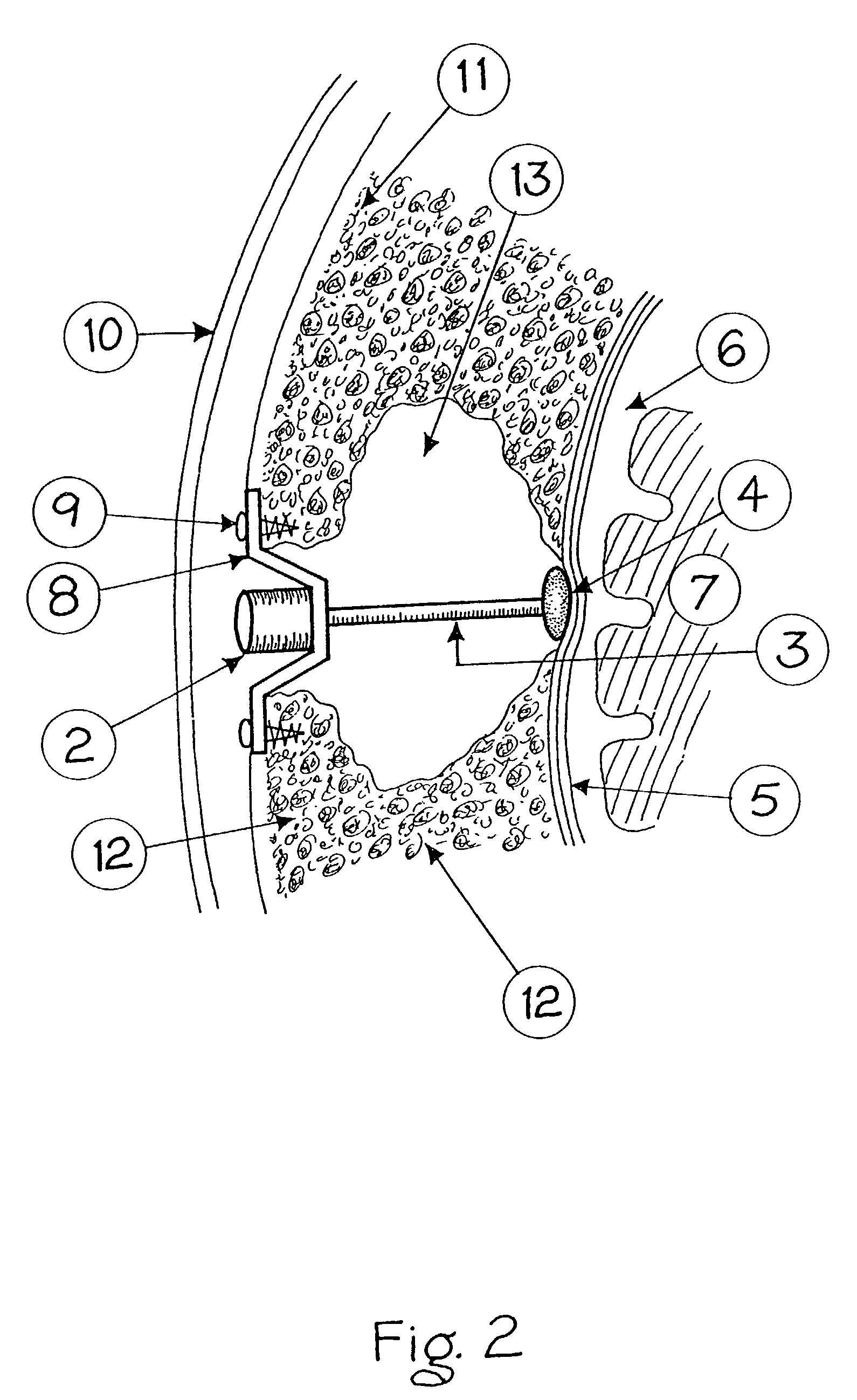
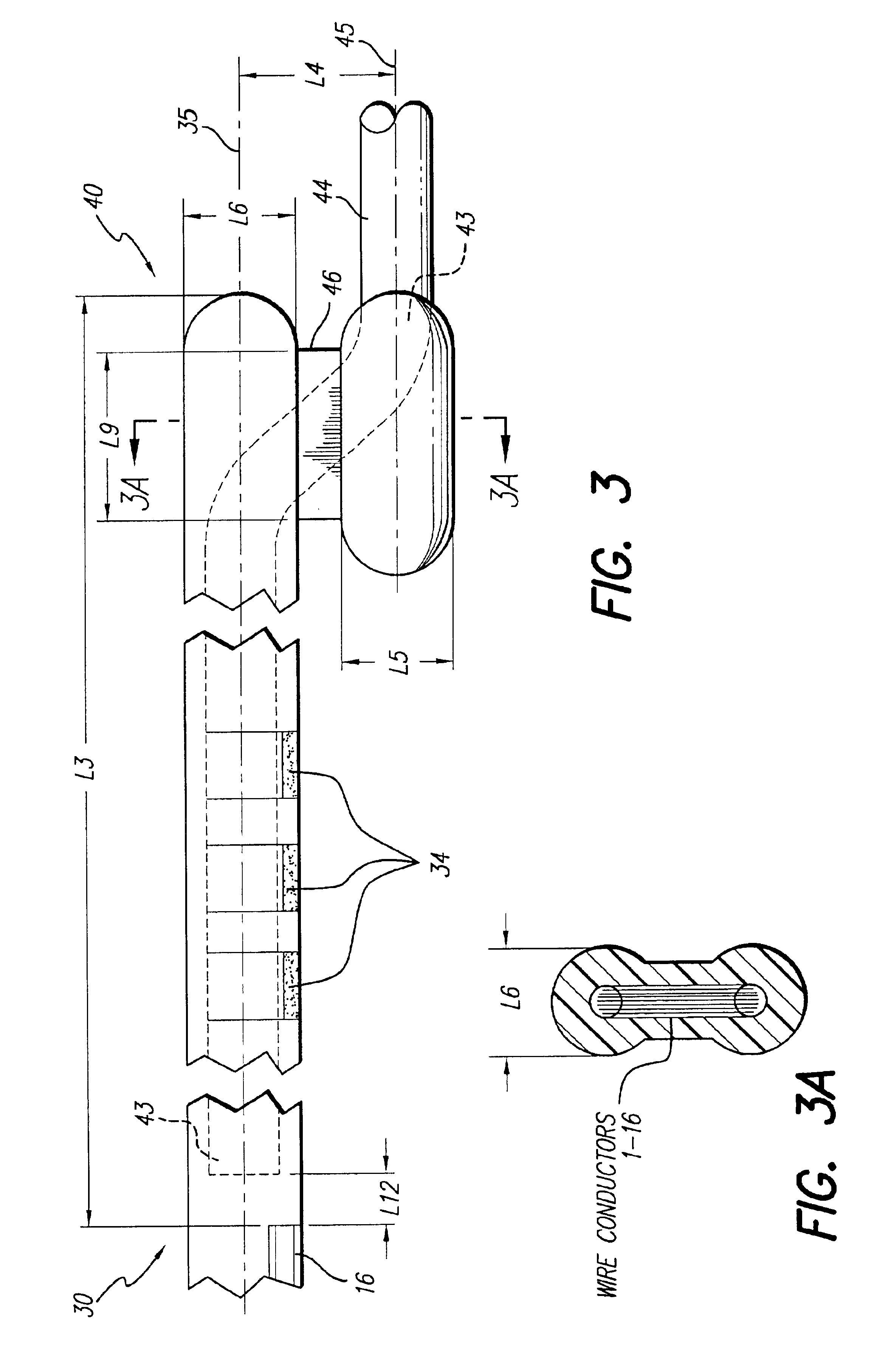
Method for inserting cochlear electrode and insertion tool for use therewith
InactiveUS6968238B1Minimal effortEasy to insertHead electrodesSurgical needlesImplantable ElectrodesCatheter
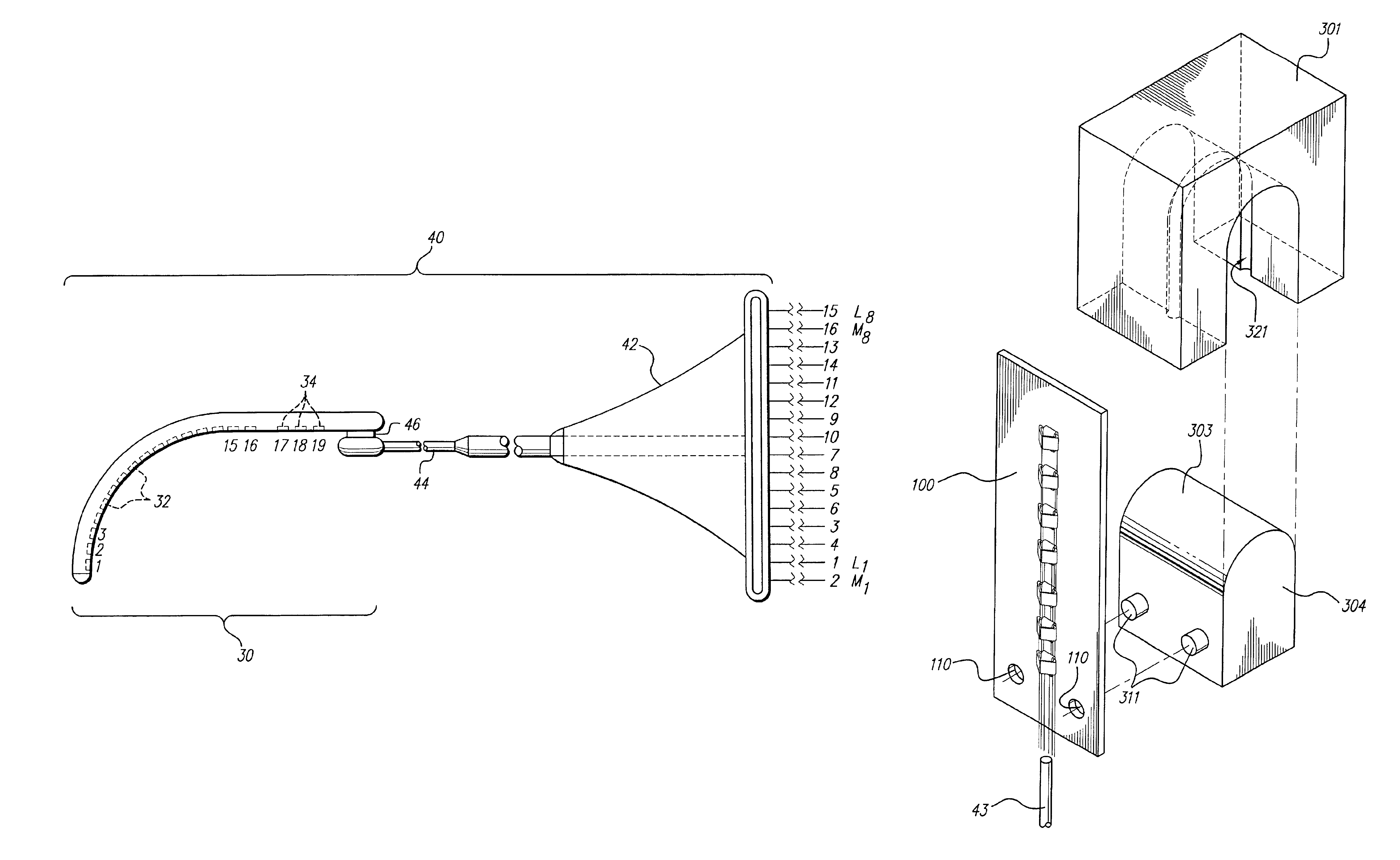
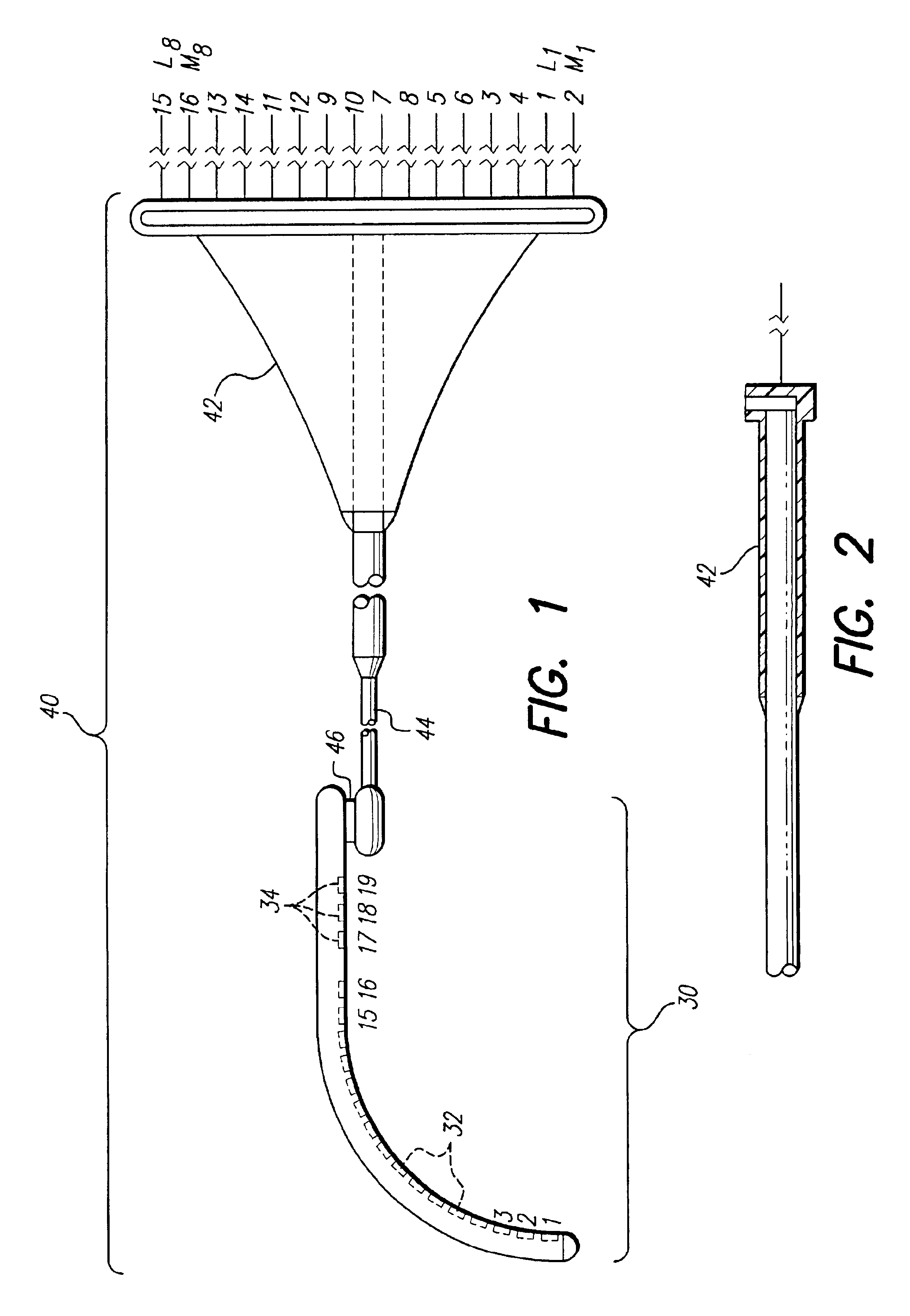
An implantable electrode system, adapted for insertion into a cochlea, includes an elongate electrode array stored within a sheath. The electrode array has a multiplicity of electrode contacts carried on a flexible elongate carrier, which carrier is adapted for insertion into one of the spiraling ducts, e.g., the scala tympani, of the cochlea, and further has longitudinal channel or lumen that passes therethrough. 3-6 mm from the distal end of the electrode array. To insert the electrode system into the cochlea, a stylet wire is inserted into the channel or lumen of the electrode array while the electrode array is held within the sheath. The sheath is then removed, and the electrode array is then gently guided and pushed through a cochleostomy into the cochlea by extending the stylet wire to a desired depth. As the electrode array is thus inserted into the cochlea, the stylet wire is retracted and the electrode array remains implanted within the cochlea.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Intracochlear Nanotechnology and Perfusion Hearing Aid Device
An intra-cochlear implant is provided for aiding in the hearing of a patient. The implant includes a body portion implantable within an interior of a cochlea of a patient. The body portion has a proximal end, a distal end and a primary axis. A plurality of signal carrying electrodes extends along the body portion. The electrodes have proximal ends and distal ends, with the proximal ends being capable of receiving a signal from a signal generator, and the distal ends being capable of delivering the received signal to an anatomical receptor within a cochlea. At least several of the plurality of electrodes have a nanoelectrode-sized portion. The implant also may include a fluid delivery system of tubules, reservoirs, and pumps for the delivery of chemicals and cells to activate regeneration of neural elements lost during the hearing loss process.
Owner:DOMESTIC ASSET LLP
Cochlear implant fitting
ActiveUS20050261748A1Avoid applicationElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringHearing perceptionElectrical stimulations
A method for fitting a cochlear prosthesis to a cochlea having residual acoustic hearing capability, in order to exploit the residual acoustic hearing capability to the extent possible. A portion of the cochlea having residual acoustic hearing capability is determined by measuring the neural response to acoustic and / or electrical stimulations. Electrical stimulations are applied only to the portions of the cochlea lacking acoustic hearing capability, or possessing only partial acoustic hearing capability. Surgical implantation depth may be optimised by the method, and / or a patient map may be suitably defined to implement the method.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Cochlear implant drug delivery device
ActiveUS20060287689A1Small dimensionReduce frictionHead electrodesEar treatmentMedicineBiomedical engineering
Devices for the delivery of a bioactive substance to a cochlea and methods of delivery thereof. The devices include means to allow the release of the bioactive substance within a cochlea.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
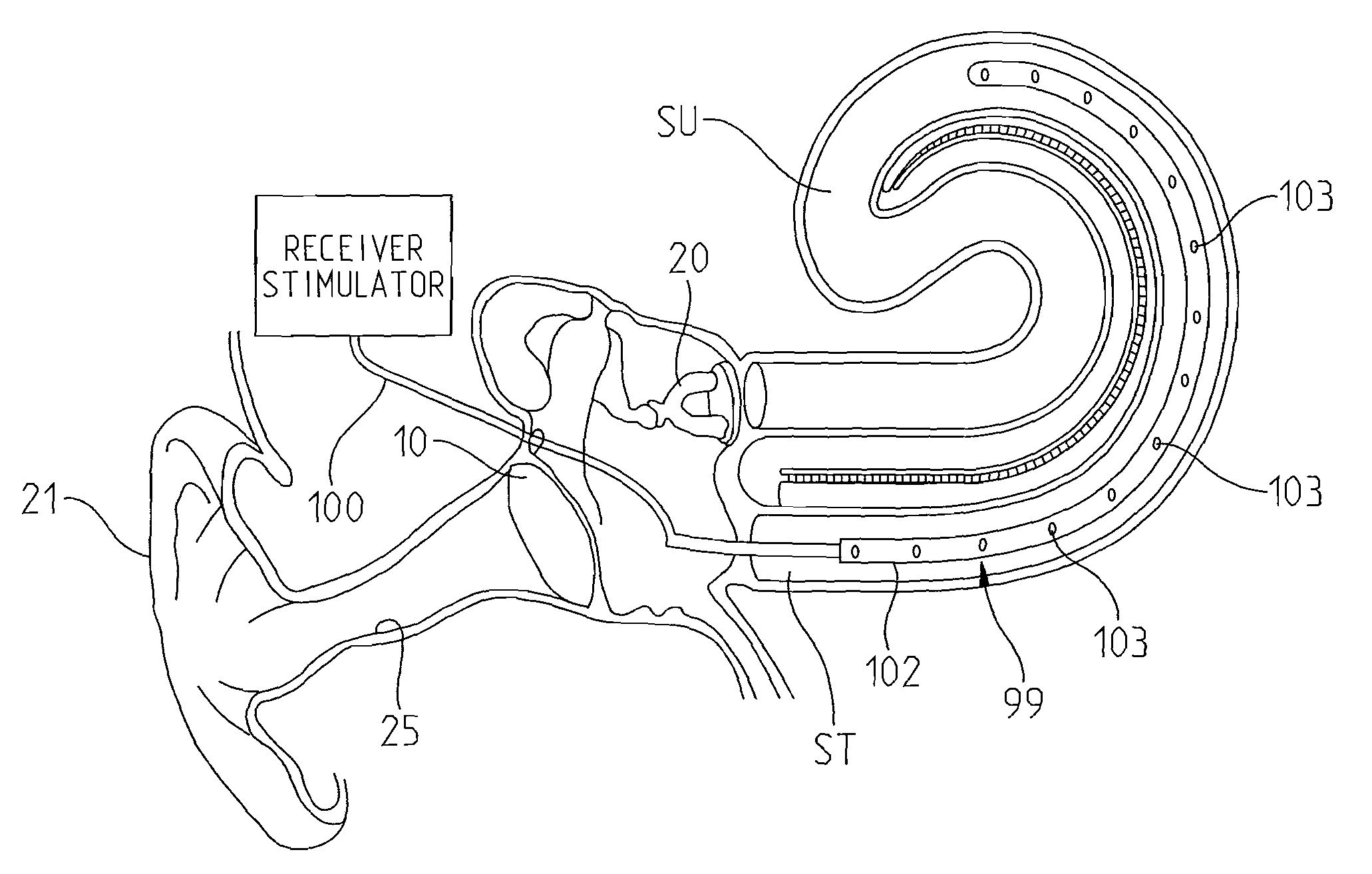
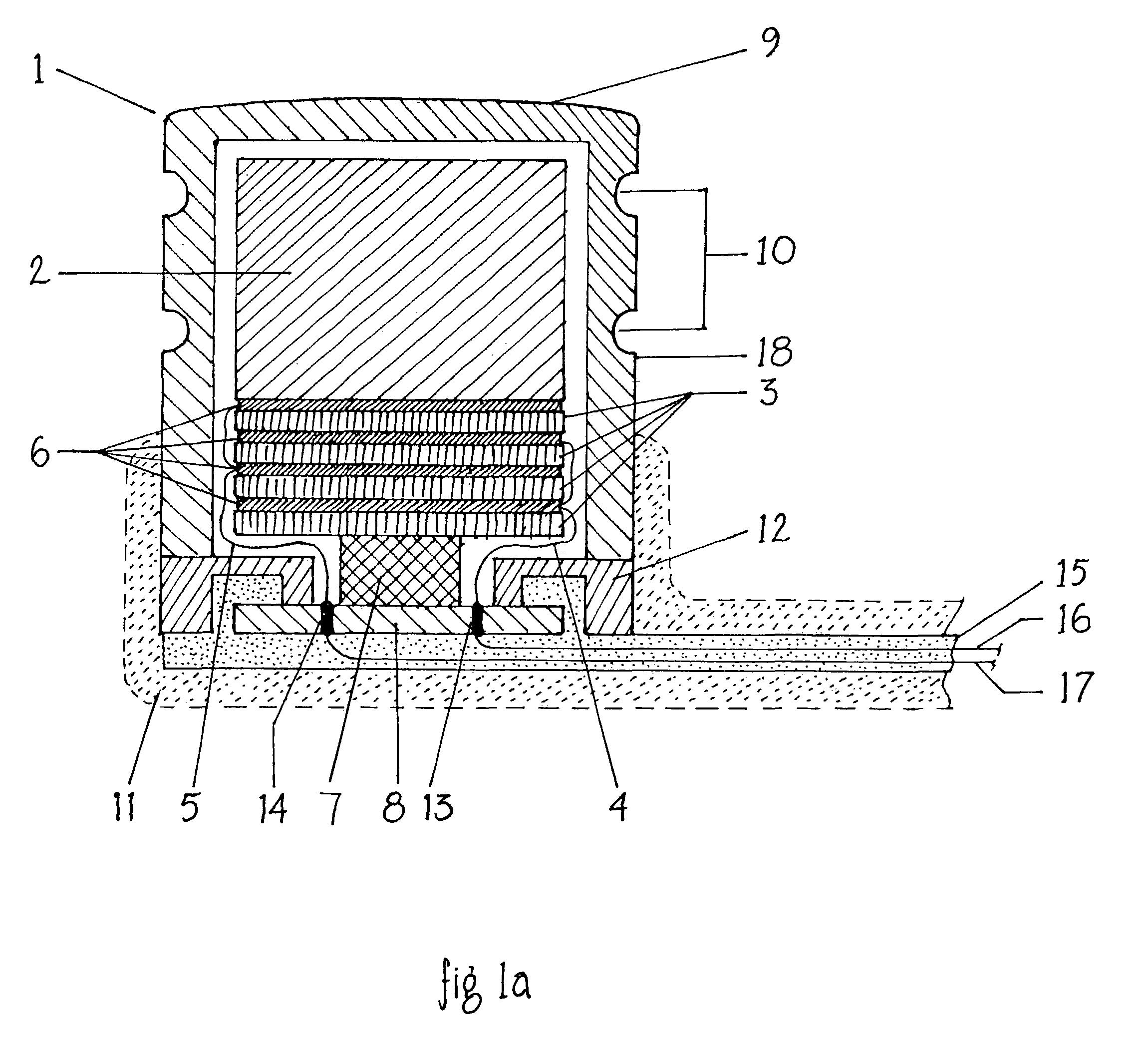
Cochlear implant
An implantable component (30) of a cochlear implant system comprising a housing for a stimulator unit (31) that is adapted to output one or more stimulation signals and an electrode assembly (30) adapted to apply electrical stimulation in accordance with the output of the stimulator unit (31). On implantation, the housing is positionable such that the electrode assembly (20) extends from the housing at least initially in a downward orientation toward the mastoid cavity before entering the cochlea. An external component (50, 60 or 70) of a cochlear implant system comprising a support for mounting to the ear of an recipient and an external signal transmitter coil (53) wherein the signal transmitter coil (53) is movably mounted to at least a portion of the support.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Methods for the treatment of tinnitus induced by cochlear excitotoxicity
InactiveUS20060063802A1Suppress and reduce NMDA receptor mediated aberrant activityPreventing and treating tinnitusCompounds screening/testingBiocideNR1 NMDA receptorTotal Deafness
The invention relates to methods for the prevention and / or treatment of tinnitus induced by cochlear excitotoxicity. In these methods, a pharmaceutical composition comprising an NMDA receptor antagonist is administered to an individual in need of such treatment by appropriate devices and / or formulations for local administration to the inner ear. The tinnitus to be prevented and / or treated may be provoked by acoustic trauma, presbycusis, ischemia, anoxia, treatment with one or more ototoxic medications, sudden deafness, or other cochlear excitotoxic-inducing occurrence. The invention also relates to method for the identification of compounds effective in the treatment and prevention of tinnitus by a novel screening method incorporating an electrophysiological test method.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Optical waveguide vibration sensor for use in hearing aid
InactiveUS7444877B2Vibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPolymer optical waveguideLoudspeaker
A directionally-sensitive device for detecting and processing vibration waves includes an array of polymeric optical waveguide resonators positioned between a light source, such as an LED array, and a light detector, such as a photodiode array. The resonators which are preferably oriented substantially perpendicularly with respect to incoming vibration waves, vibrate when a wave is detected, thus modulating light signals that are transmitted between the light source and the light detector. The light detector converts the modulated light into electrical signals which, in a preferred embodiment, are used to drive either the speaker of a hearing aid or the electrode array of a cochlear implant. The device is manufactured using a combination of traditional semiconductor processes and polymer microfabrication techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
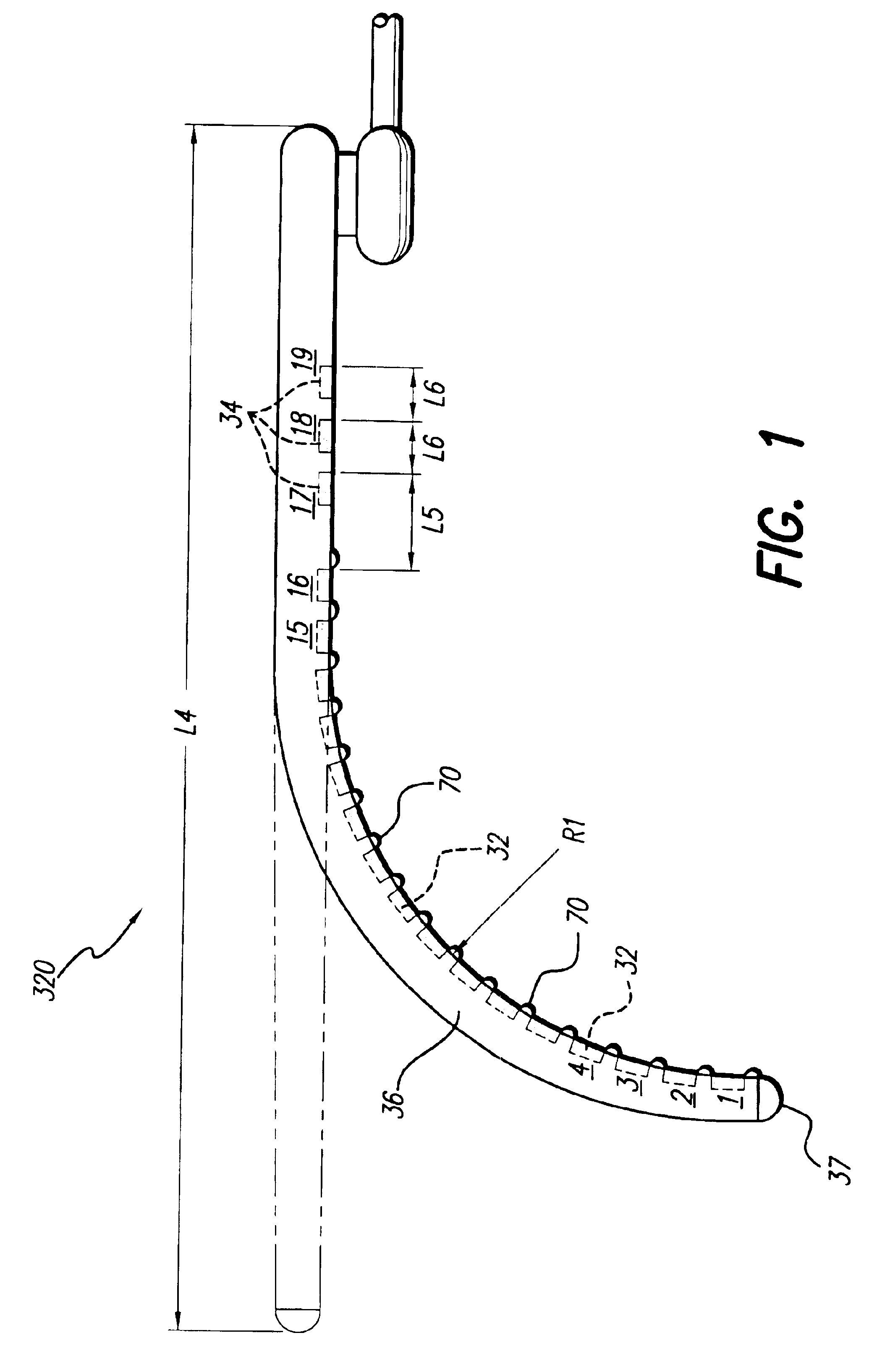
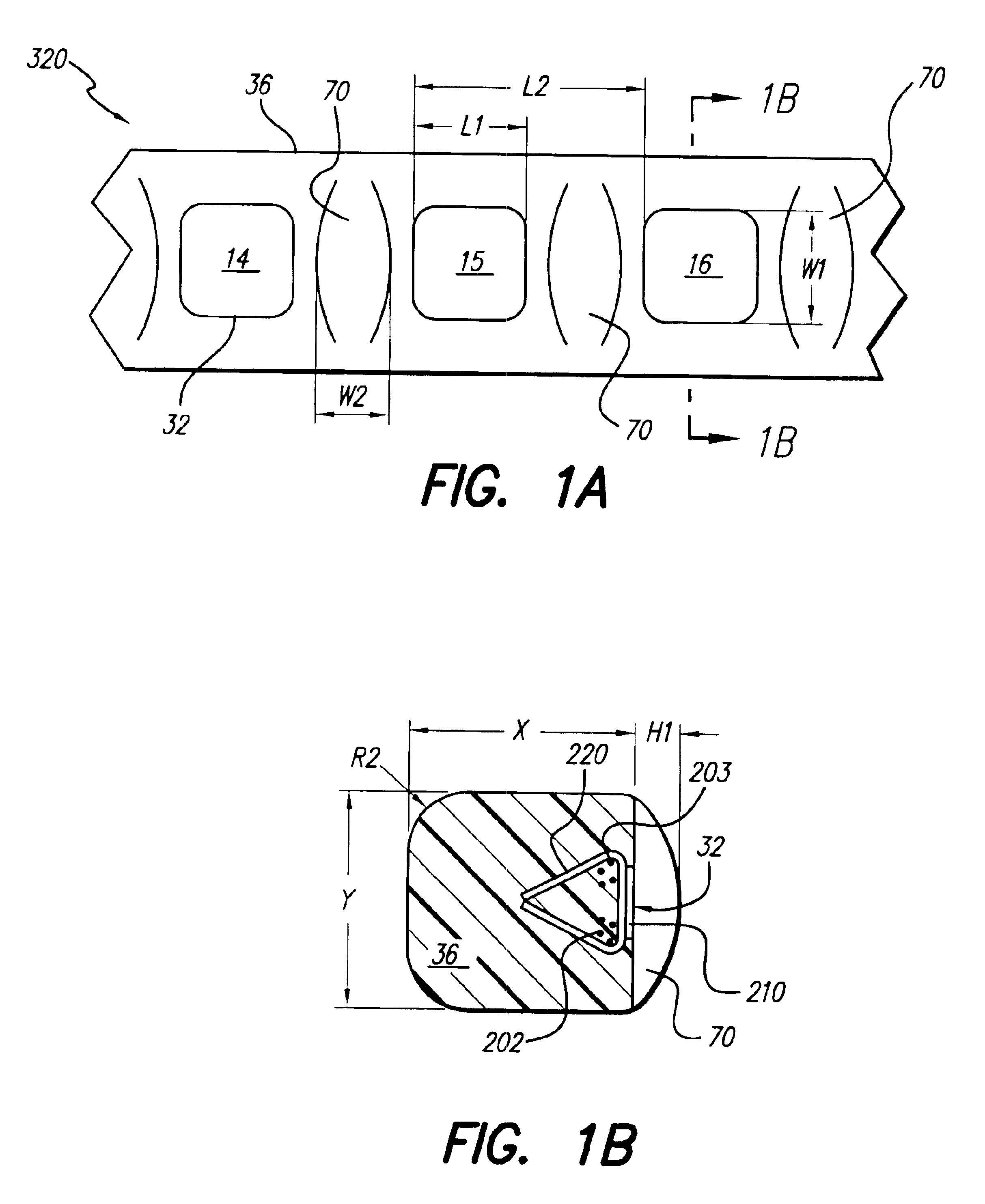
Cochlear implant electrode and method of making same
ActiveUS7319906B2Increase stiffnessImprove complianceHead electrodesExternal electrodesFilling materialsCochlear implantation
A cochlear stimulation lead and method of making an aggressively curved electrode array are provided. In one embodiment of the lead, while the curved section of the lead is curled further beyond the originally molded curvature and held in this position, a filling channel is filled up with a filling material that is hardened or cured in this held position. The resulting lead has a tip curvature that is more curved than the originally molded curvature.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
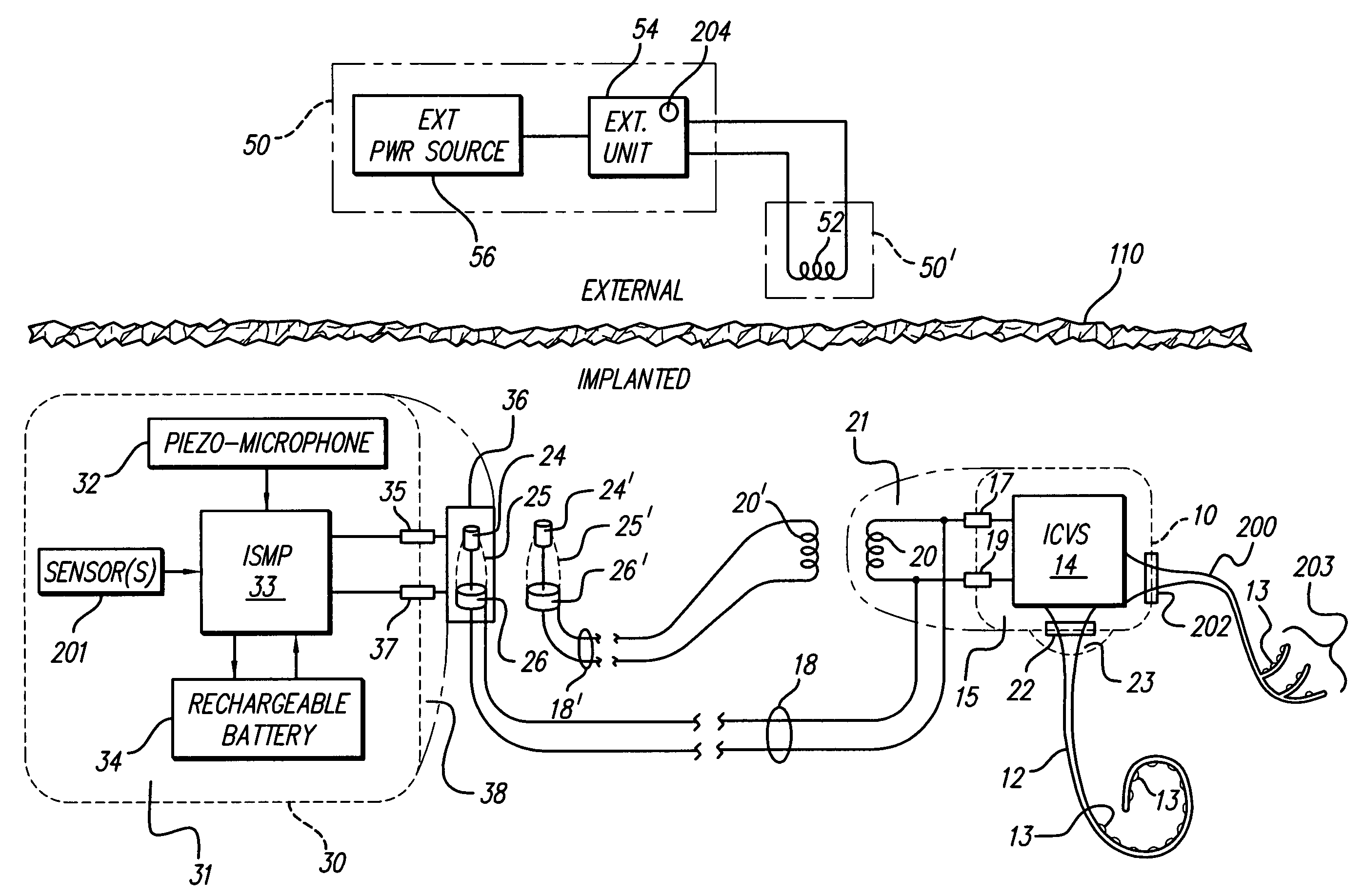
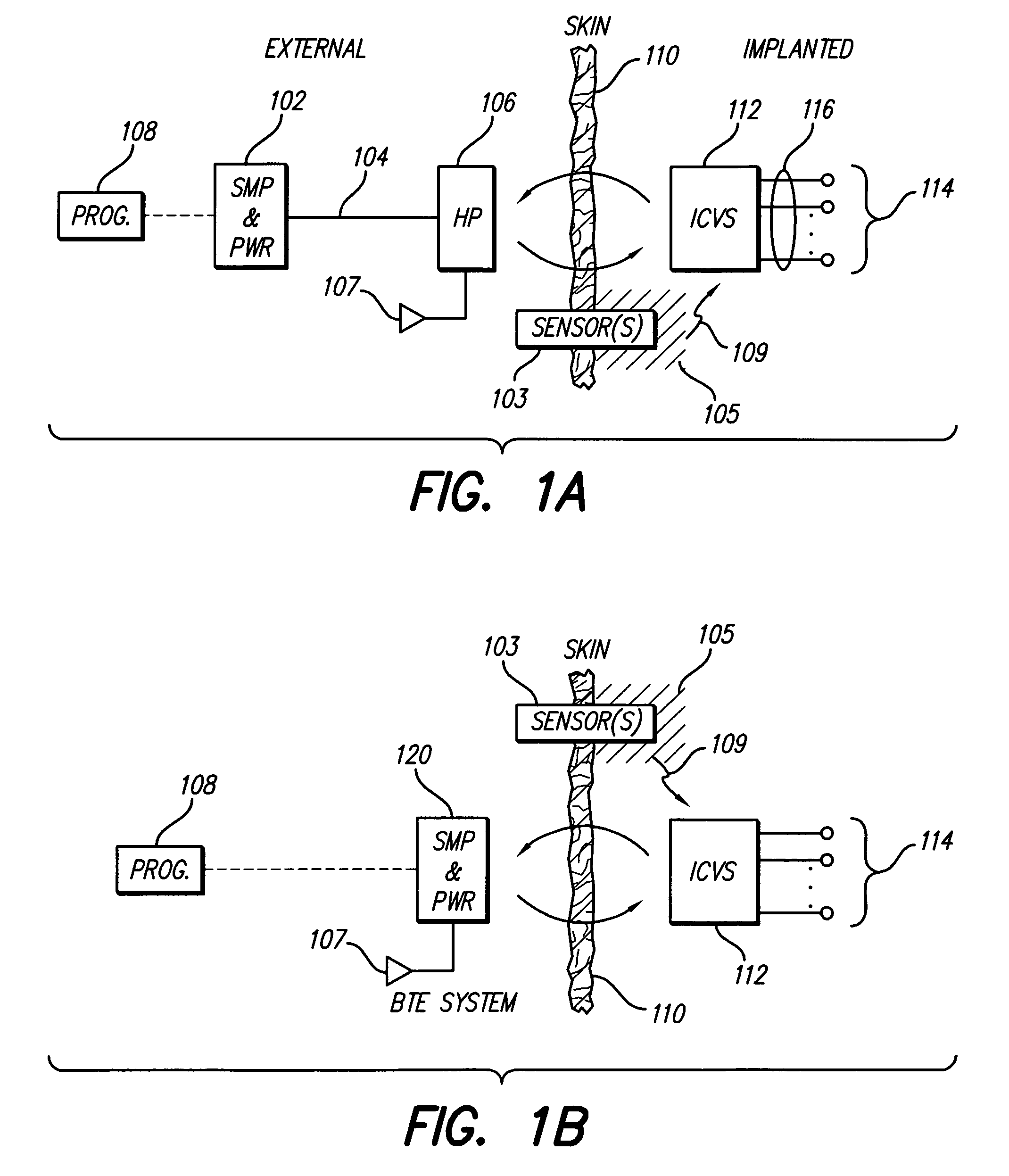
At least partially implantable system for rehabilitation of hearing disorder
InactiveUS20010049466A1Long and longer service lifeExtended stayHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringEngineeringActuator
An at least partially implantable system for rehabilitation of a hearing disorder with at least one acoustic sensor (microphone) for picking up an acoustic sensor signal and converting the acoustic sensor signal into corresponding electrical signals, an electronic signal processing unit for audio signal processing and amplification, an electrical power supply unit which supplies individual components of the system with energy, and an output-side actuator stimulation arrangement, the actuator stimulation arrangement has a dual intracochlear arrangement in combination with a stimulator arrangement with at least one stimulator element for at least indirect mechanical stimulation of a damaged inner ear and one electrically acting stimulation electrode arrangement with at least one cochlear implant electrode for electrical stimulation of the inner ear.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Systems and methods for photo-mechanical hearing transduction
ActiveUS7867160B2Least riskAvoid excessive distanceCompletely in canal hearing aidsEar supported setsTransducerLight signal
Hearing systems for both hearing impaired and normal hearing subjects comprise an input transducer and a separate output transducer. The input transducer will include a light source for generating a light signal in response to either ambient sound or an external electronic sound signal. The output transducer will comprise a light-responsive transducer component which is adapted to receive light from the input transducer. The output transducer component will vibrate in response to the light input and produce vibrations in a component of a subject's hearing transduction pathway, such as the tympanic membrane, a bone in the ossicular chain, or directly on the cochlea, in order to produce neural signals representative of the original sound.
Owner:EARLENS CORP
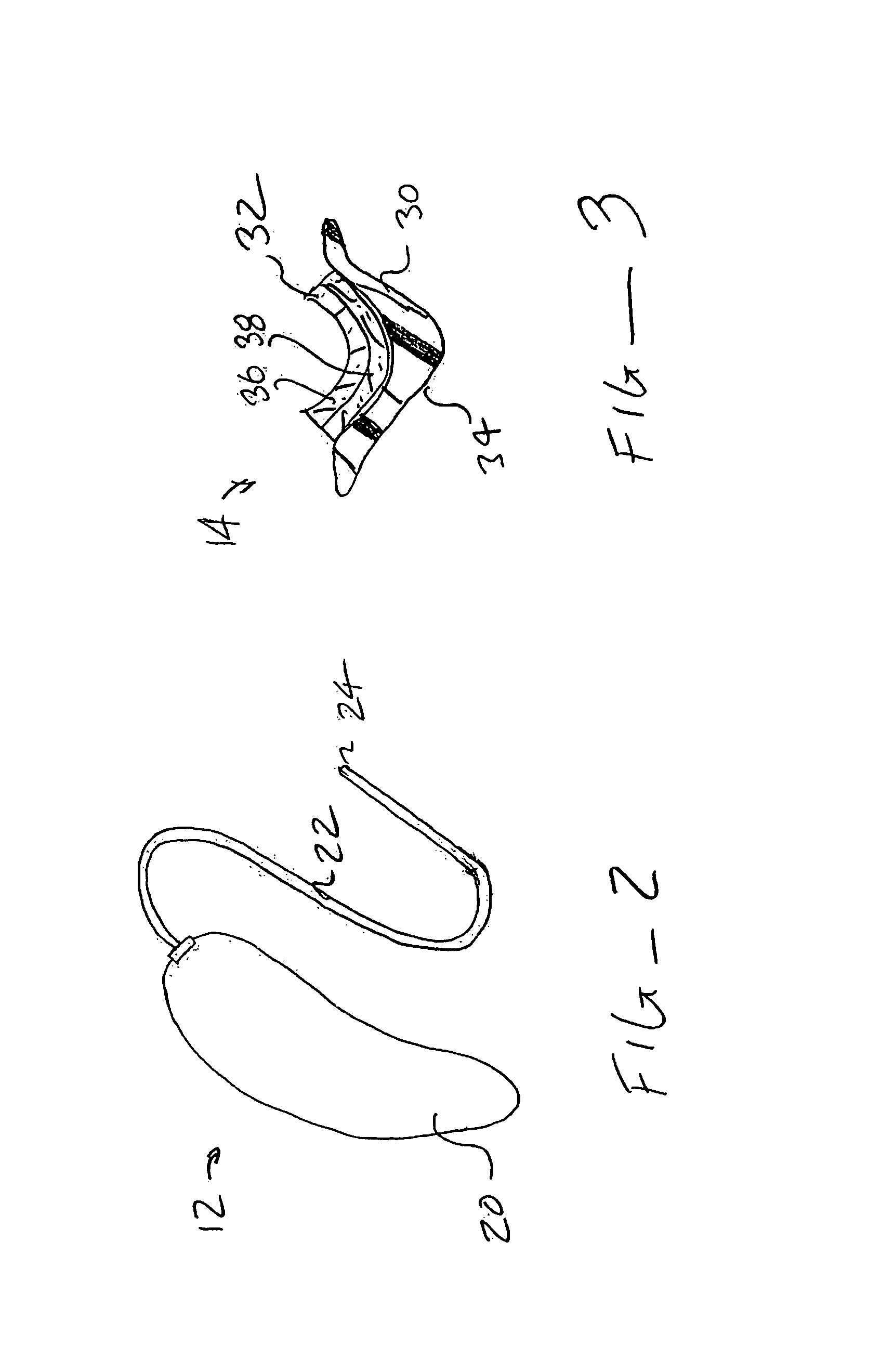
Surgically implantable hearing aid
InactiveUS7033313B2Negligible riskSurgery is simpleEar treatmentDeaf-aid setsDura materCochlear implantation
The invention comprises a surgically implantable hearing aid for hearing impaired persons. The hearing aid includes a vibrational element which is vibrated by sound waves and attached to the skull of the person, and a connector which crosses the mastoid cavity and delivers the sound waves to the dura mater of the patient thereby vibrating the dura mater, the cerebrospinal fluids, and the brain to create a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to act as a tinnitus masker or used in conjunction with a cochlear implant. It can also be used in a modified form to connect directly through the skull of the person.
Owner:ALAN J LUPIN
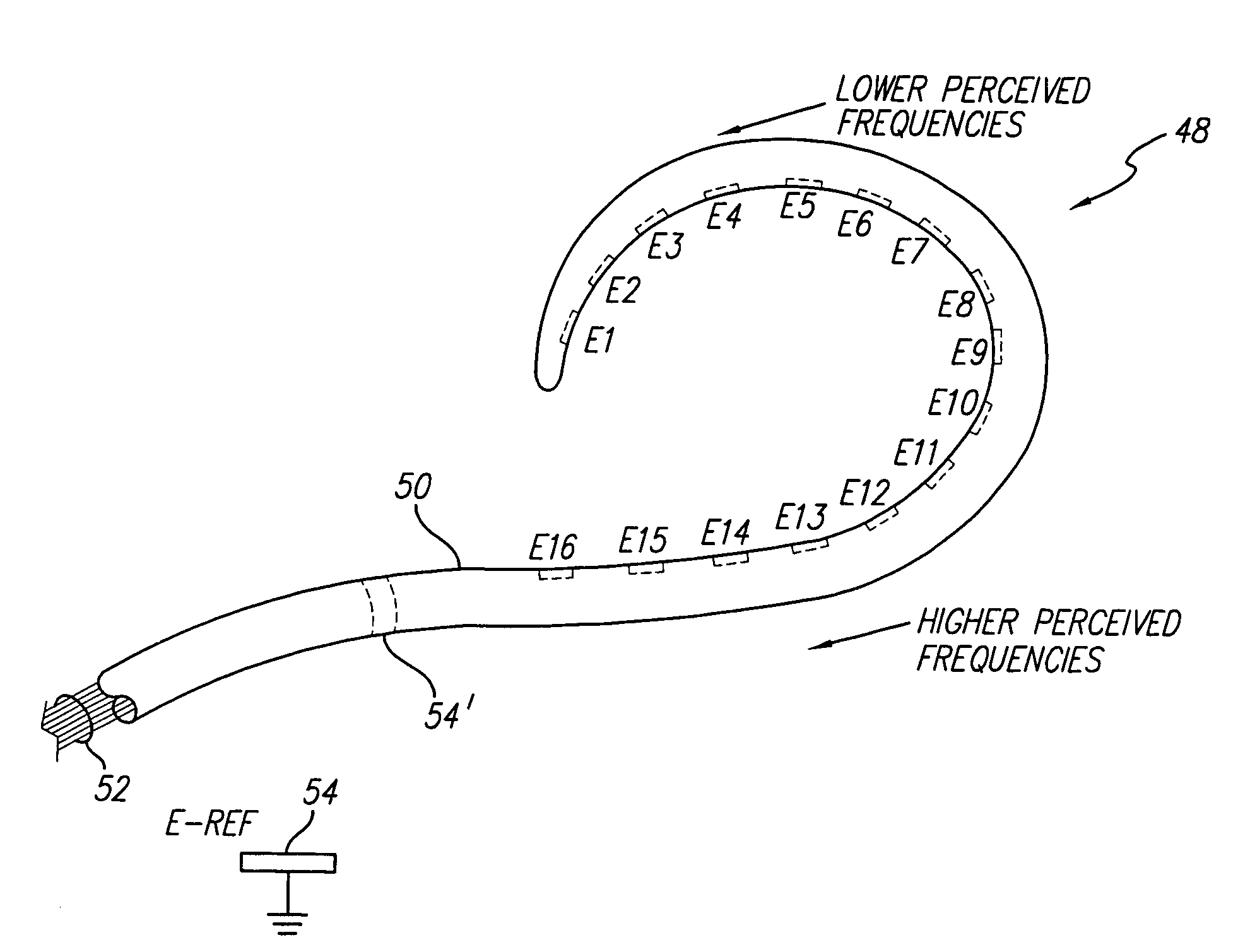
Spatial decimation stimulation in an implantable neural stimulator, such as a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7039466B1High rate stimulationReduce power levelElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCochlear implantationElectrode array
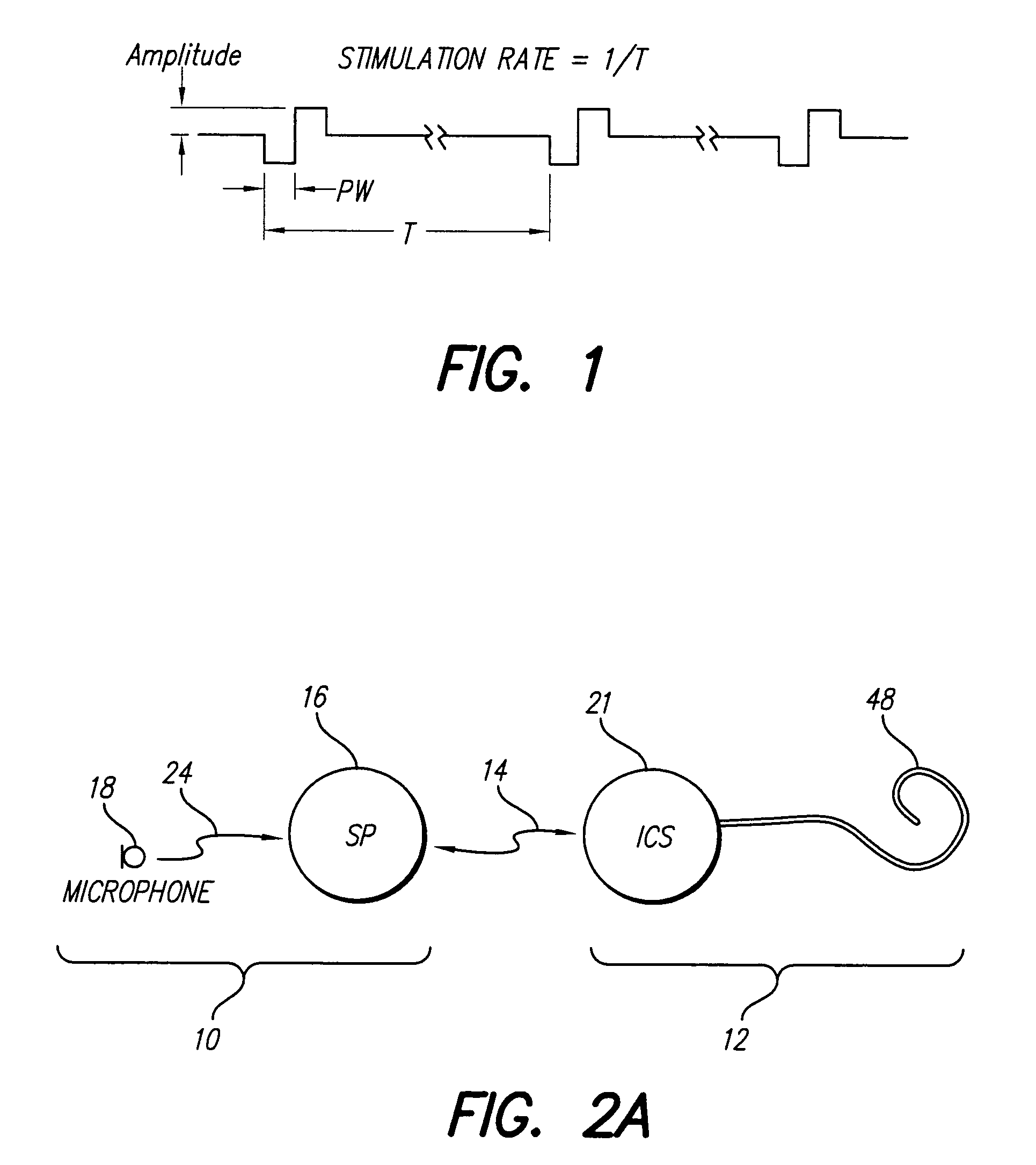
A cochlear implant system, or other neural stimulation system, has the capability to stimulate fast enough to induce stochastic neural firing so as to restore “spontaneous” neural activity. The stimulation rate applied to the more distally-located electrodes of an electrode array connected to the implant system is reduced from the stimulation rate applied to the more proximally-located electrodes. Thus, in the case of a cochlear implant system, the apically-located regions within the cochlea are stimulated at a reduced rate in order to conserve power. Pulse widths of the reduced-rate pulses may further be increased, and amplitudes reduced, to further conserve power. As needed, a low-level random conditioner stimulation signal may be applied to the apical regions of the cochlea in order to ensure the occurrence of random neural firings.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Dual Cochlear/Vestibular Stimulator with Control Signals Derived from Motion and Speech Signals
ActiveUS20070208403A1Internal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringHead movementsBalance disturbances
A system for treating patients affected both by hearing loss and by balance disorders related to vestibular hypofunction and / or malfunction, which includes sensors of sound and head movement, processing circuitry, a power source, and an implantable electrical stimulator capable of stimulating areas of the cochlea and areas of the vestibular system.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC +1
Optimizing pitch and other speech stimuli allocation in a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7251530B1Easy to controlImprove sound qualityElectrotherapyAudiometeringOctaveCochlear implantation
Errors in pitch (frequency) allocation within a cochlear implant are corrected in order to provide a significant and profound improvement in the quality of sound perceived by the cochlear implant user. In one embodiment, the user is stimulated with a reference signal, e.g., the tone “A” (440 Hz) and then the user is stimulated with a probe signal, separated from the reference signal by an octave, e.g., high “A” (880 Hz). The user adjusts the location where the probe signal is applied, using current steering, until the pitch of the probe signal, as perceived by the user, matches the pitch of the reference signal, as perceived by the user. In this manner, the user maps frequencies to stimulation locations in order to tune his or her implant system to his or her unique cochlea.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Method of making a cochlear electrode array having current-focusing and tissue-treating features
InactiveUS6862805B1Improve stabilityEasy to bendLine/current collector detailsHead electrodesImplantable ElectrodesElectrode Contact
A method of making an implantable electrode array, adapted for insertion into a cochlea, includes the steps of: (a) forming electrode contact pieces made from a precious, biocompatible material into a desired shape; (b) attaching the electrode contact pieces to a foil sheet made from a non-toxic but chemically-active metal; (c) connecting a wiring system to the metal contact pieces; (d) molding a flexible polymer carrier around the electrode contact pieces and wiring system while such are held in place by the foil sheet; and (e) etching away the foil sheet, leaving the electrode contact pieces exposed at a surface of the molded polymer carrier. The exposed electrode contacts are made so as to have a shape, geometry, or makeup that aids in controlling the current flow and current density associated with the electrode contact as a function of position on the electrode contact.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
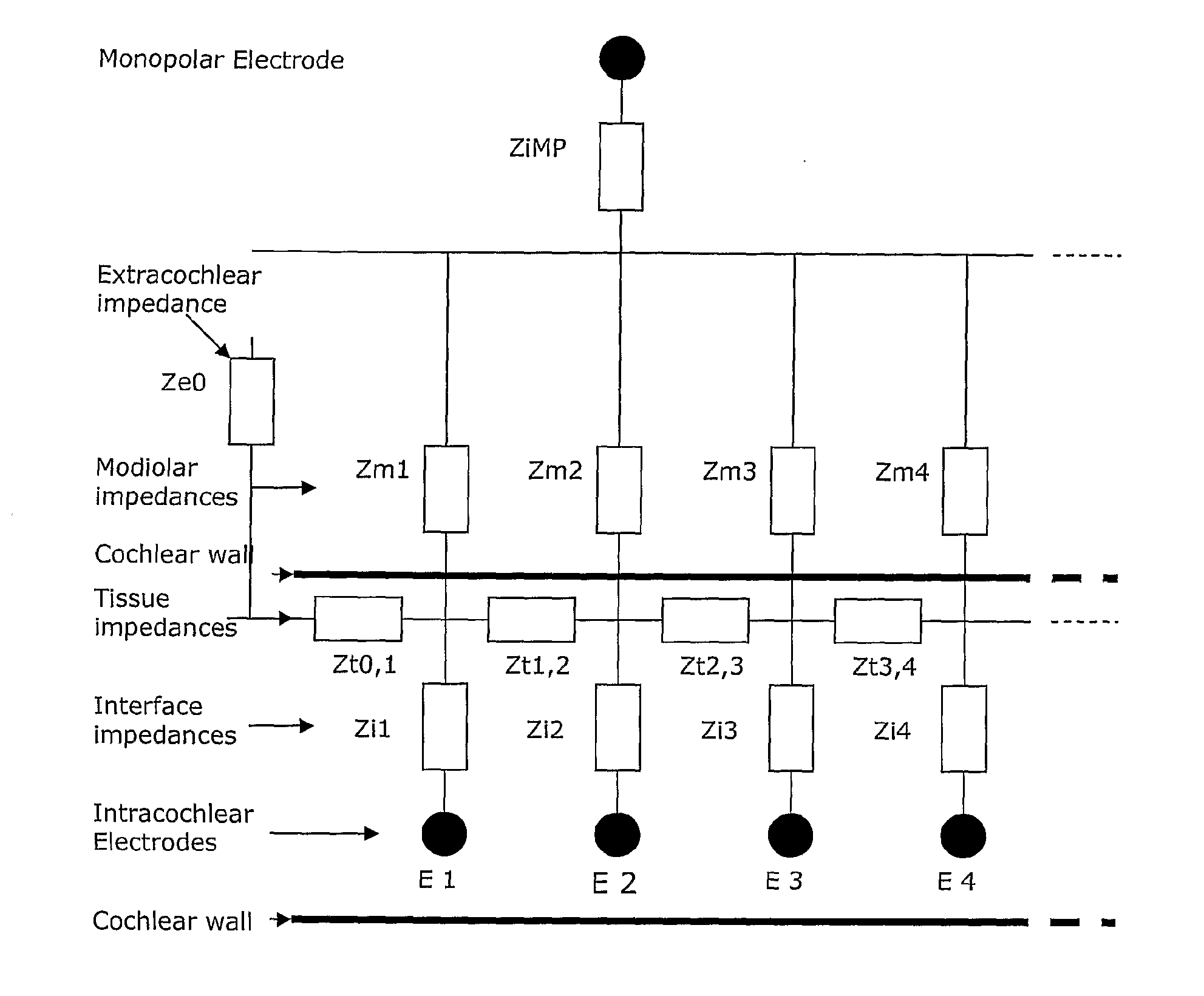
Method and device for intracochlea impedance measurement
ActiveUS20110087085A1Head electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMonopolar stimulationTissue characterization
This method of determining an intracochlea tissue impedance comprises using at least two stimulating electrodes to apply an electrical stimulus to intracochlea tissue. A voltage caused by the stimulus is measured between two measuring electrodes distinct from the stimulating electrodes. From the voltage a stimulus-response characteristic of tissue between the two measuring electrodes is determined. This allows the tissue / electrode interface impedance and potential and the tissue impedance and potential to be uniquely determined. In turn, modiolus currents can be estimated in monopolar stimulation mode. Also provided is automated initiation of re-mapping of the device when tissue characteristics change
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Bone conduction hearing assistance device
InactiveUS20060056649A1Reduce and eliminate feedbackBone conduction transducer hearing devicesTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsBone conduction hearingHearing perception
A bone conduction hearing aid includes an in-the-ear (ITE) component and a behind-the-ear (BTE) component. A bone vibrator is carried by the ITE component and positioned in the concha of the ear when in use. A vibrationally conductive structural member of the ITE component conducts vibration produced by the vibrator into the ear canal. From there, the vibration is transferred to a cochlea of the user by way of the mastoid bone, enabling enhanced hearing perception in patients with hearing loss.
Owner:SCHUMAIER DANIEL R
Totally implantable hearing prosthesis
ActiveUS7442164B2Easy and safe to implantMinimize power consumptionElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsHermetic sealProsthesis
The invention comprises a totally implantable hearing prosthesis for hearing impaired persons. An inertial vibrational element is hermetically sealed and implanted in bone between the lateral and superior semicircular canals without breaching the integrity of the canals. The vibrational element is adapted to vibrate the walls of the canals and the fluids contained therein, thereby vibrating contiguous fluids within the cochlea thus stimulating hair cells and creating a hearing percept. The invention can also be adapted to be a tinnitus masking system, and / or used in combination with a cochlear implant hearing system.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
System for generating a cochlear implant program using multi-electrode stimulation to elicit the electrically-evoked compound action potential
InactiveUS20070179565A1Increase amplitudeConvenient recordingHead electrodesArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialSequential stimulation
A multichannel cochlear implant system spatially spreads the excitation pattern in the target neural tissue by either: (1) rapid sequential stimulation of a small group of electrodes, or (2) simultaneously stimulating a small group of electrodes. Such multi-electrode stimulation stimulates a greater number of neurons in a synchronous manner, thereby increasing the amplitude of the extra-cellular voltage fluctuation and facilitating its recording. The electrical stimuli are applied simultaneously (or sequentially at a rapid rate) on selected small groups of electrodes while monitoring the evoked compound action potential (ECAP) on a nearby electrode. The presence of an observable ECAP not only validates operation of the implant device at a time when the patient may be unconscious or otherwise unable to provide subjective feedback, but also provides a way for the magnitude of the observed ECAP to be recorded as a function of the amplitude of the applied stimulus. From this data, a safe, efficacious and comfortable threshold level can be obtained which may be used thereafter as the initial setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device, or to guide the setting of the stimulation parameters of the neurostimulation device.
Owner:ADVNACED BIONICS LLC
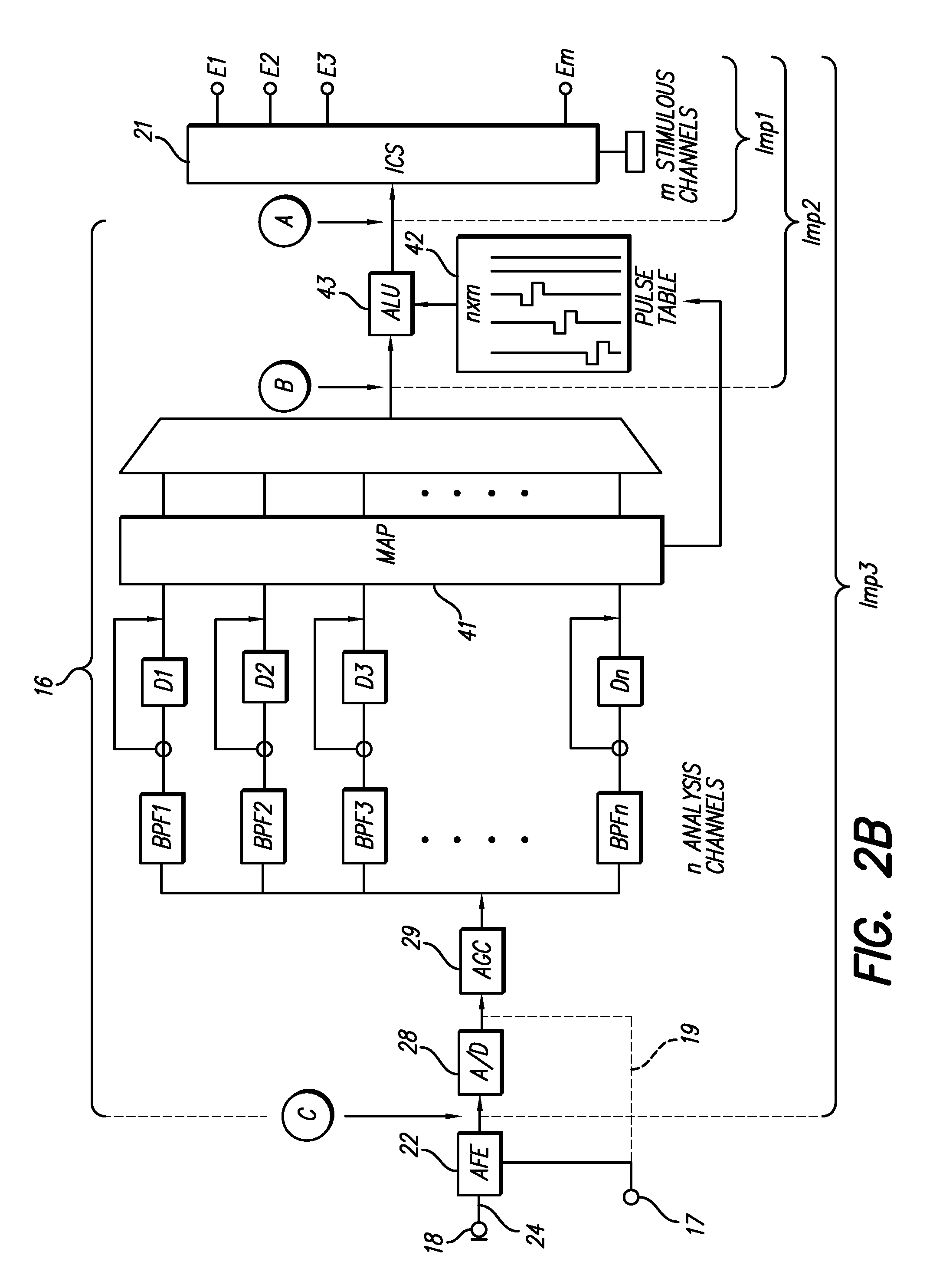
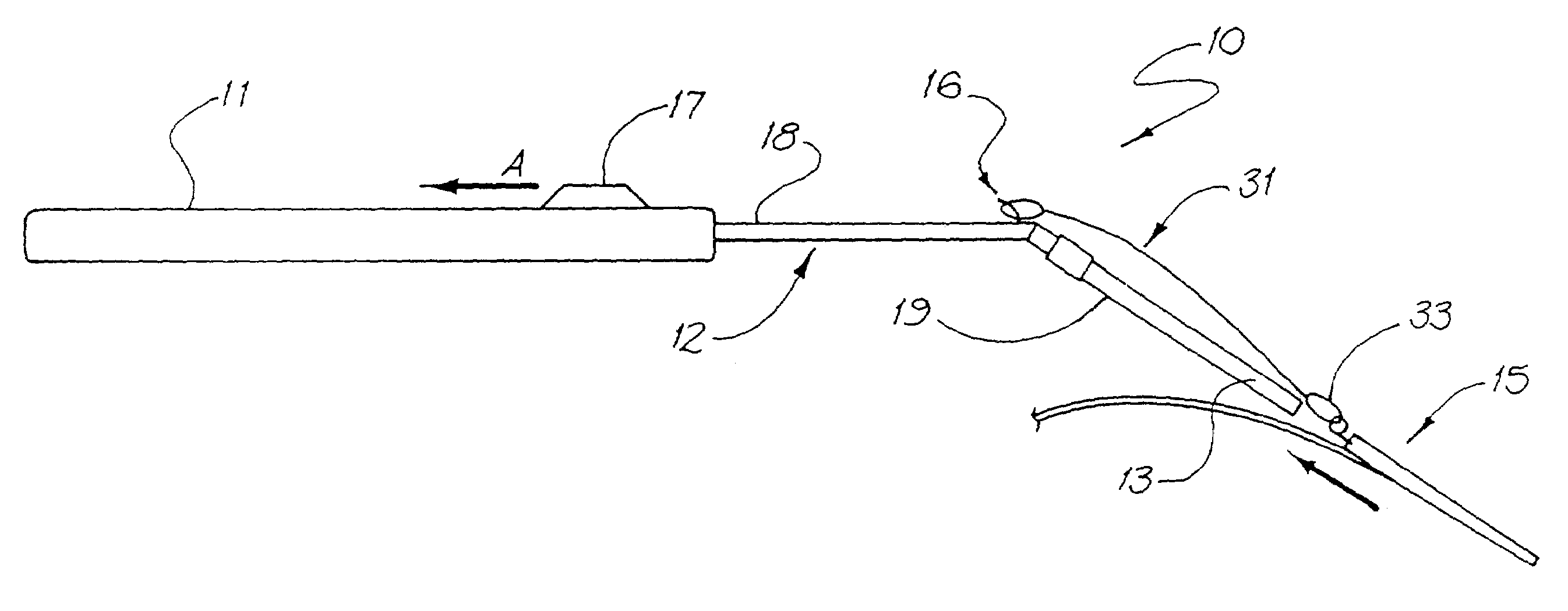
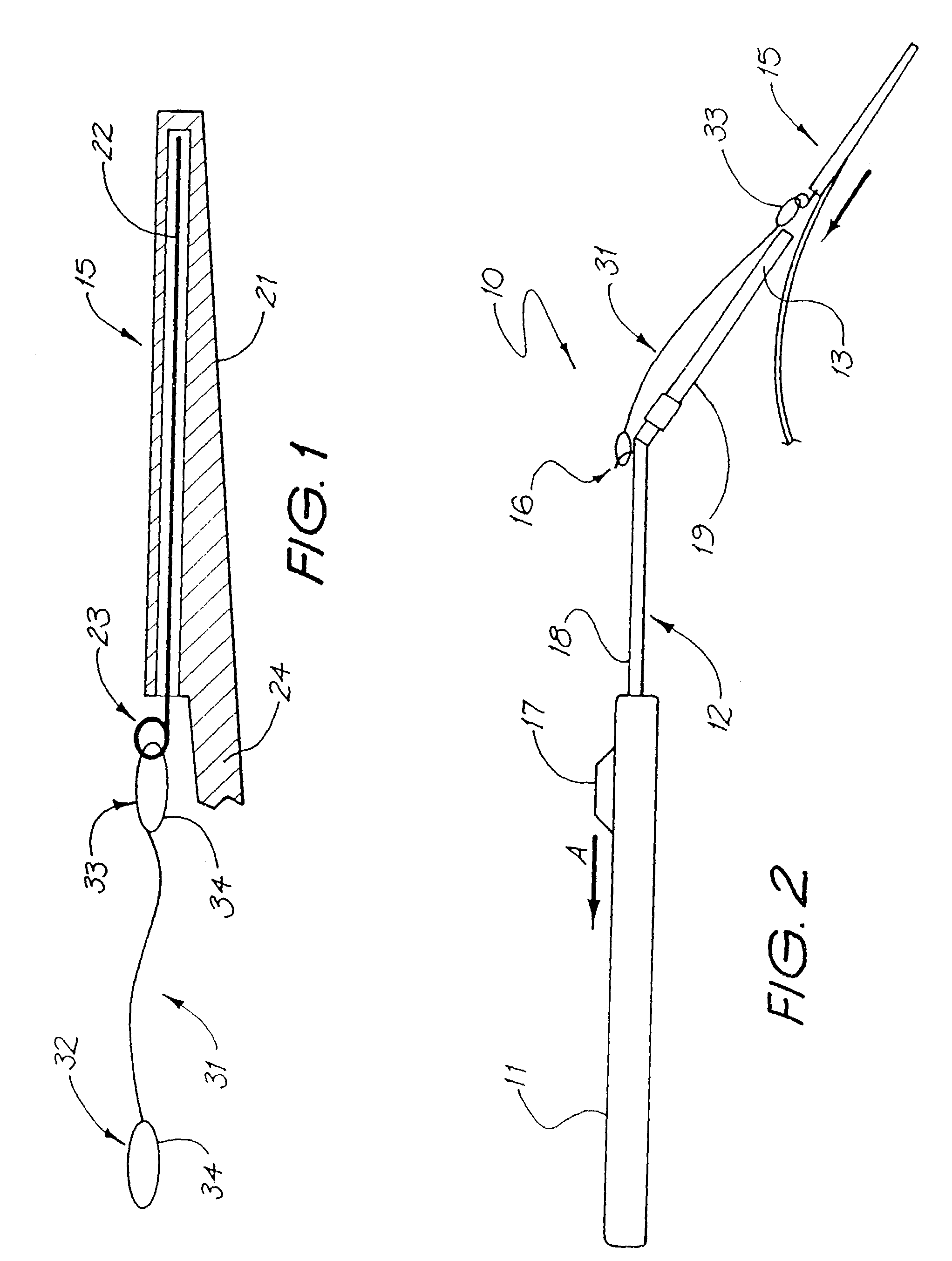
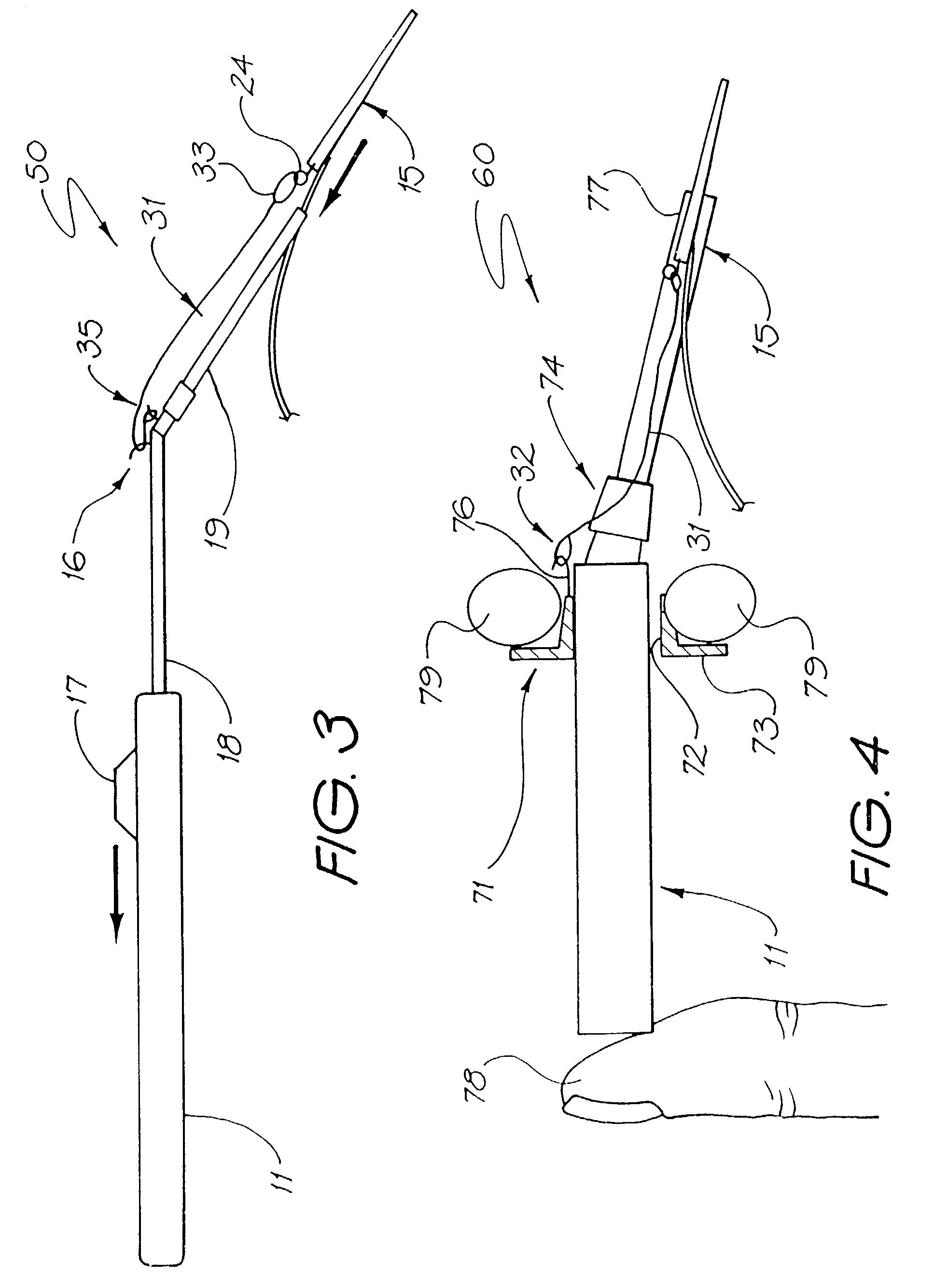
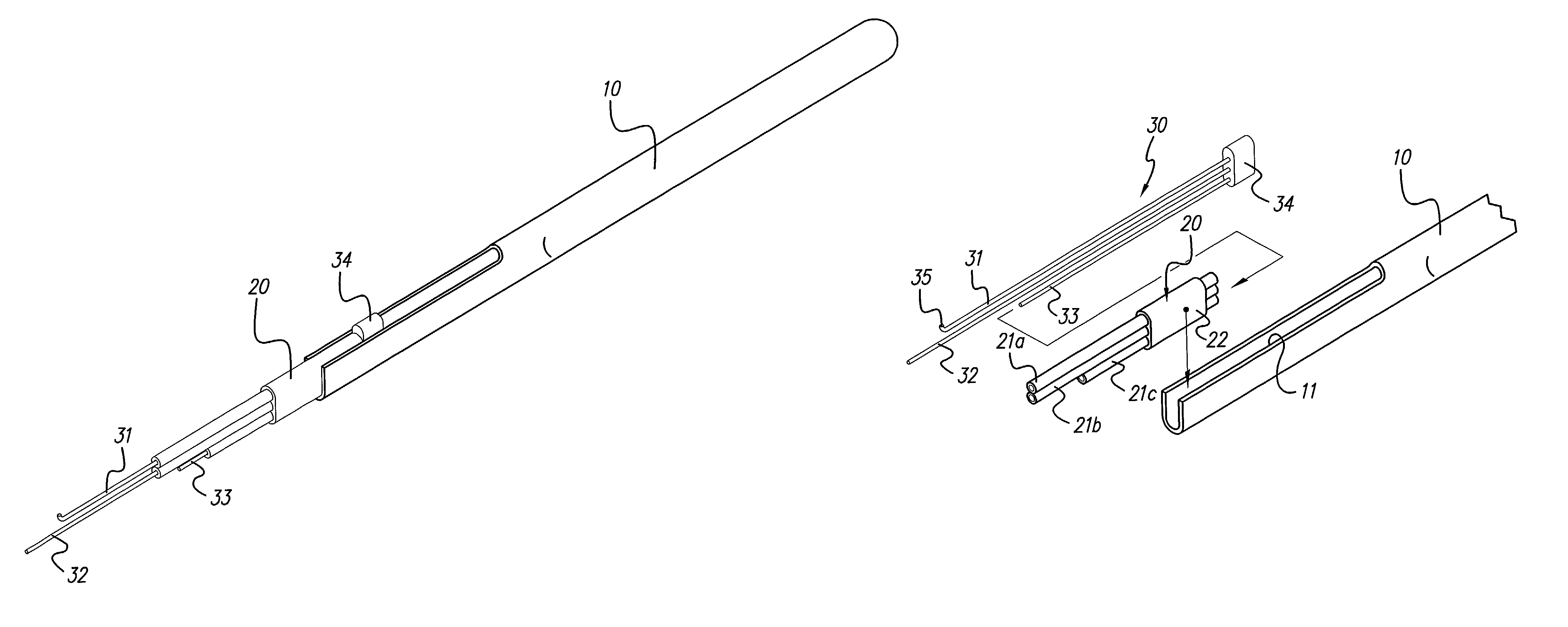
Insertion tool system for an electrode array
A device (10) used for inserting an electrode array (15) into a cochlea of a subject. Particularly, the device (10) is adapted for insertion of electrode arrays (15) having an elongate carrier member (21) and a removable stylet (22) extending through the carrier member (21). The device includes a handle (11), an elongate positioning member (12) mounted to the handle (11), an actuator member (17) movable relative to the elongate positioning member (12), and at least one anchor member (16) connected to the actuator member (17) and engageable with the removable stylet (22). On insertion of the electrode array (15) into a subject's cochlea, the actuator member (17) can be moved relative to the elongate positioning member (12) to withdraw the removable stylet (22) from the carrier member.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Methods for the treatment of tinnitus induced by cochlear excitotoxicity
ActiveUS20050214338A1Suppress and reduce NMDA receptor mediated aberrant activityPreventing and treating tinnitusBiocideHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsNR1 NMDA receptorTotal Deafness
The invention relates to methods for the prevention and / or treatment of tinnitus induced by cochlear excitotoxicity. In these methods, a pharmaceutical composition comprising an NMDA receptor antagonist is administered to an individual in need of such treatment by appropriate devices and / or formulations for local administration to the inner ear. The tinnitus to be prevented and / or treated may be provoked by acoustic trauma, presbycusis, ischemia, anoxia, sudden deafness, or other cochlear excitotoxic-inducing occurrence.
Owner:AURIS MEDICAL AG
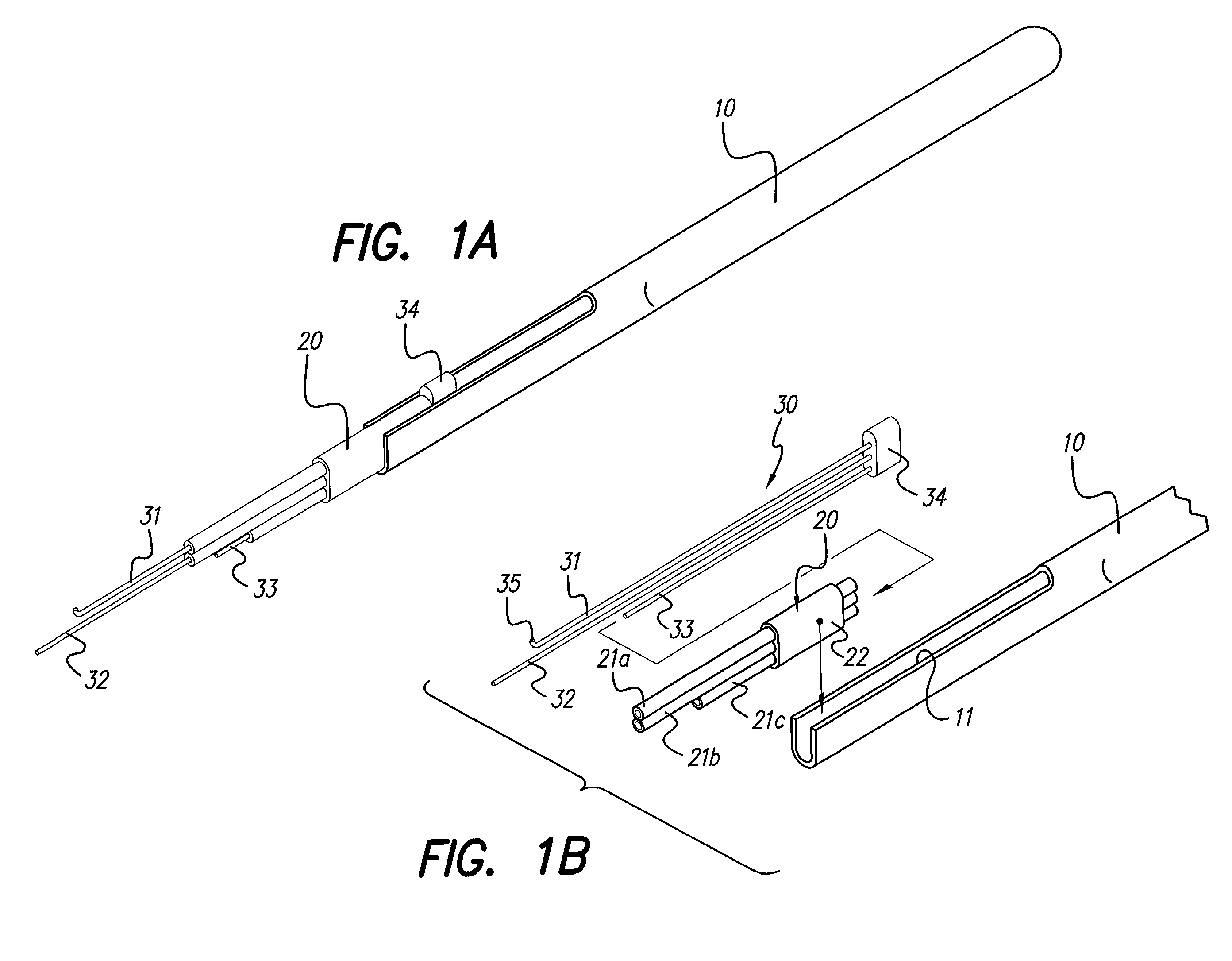
Insertion tool for placement of electrode system inside the cochlear lumen
An insertion tool uses a stylet wire to help guide an electrode system into a cochlea. The insertion tool includes three main elements or parts: a handle, a guide and a slider. The handle is made from light stainless steel tube flattened in front with a machined slot. The guide consists of a plurality of metal tubes, fixed to each other within a holding bracket. In one embodiment, the slider includes a stabilizer wire, a long stylet wire, and a short stylet wire. During the assembly process, the stabilizer and stylet wires are inserted into respective tubes of the guide and the end of the stabilizer wire is bent to form an offset. The electrode system is loaded onto the tool by inserting the short stylet wire into a holder that supports the electrode lead.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com