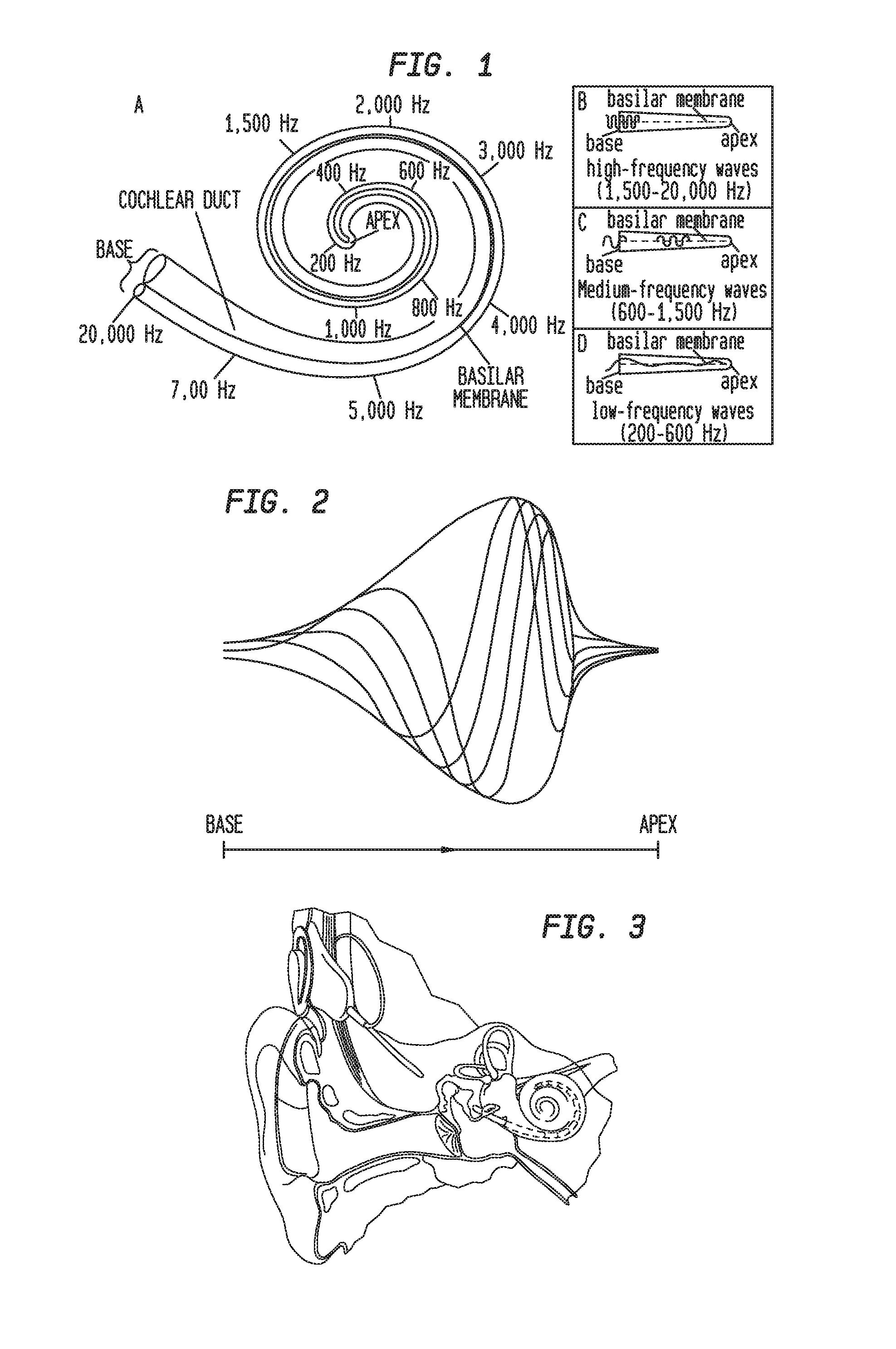
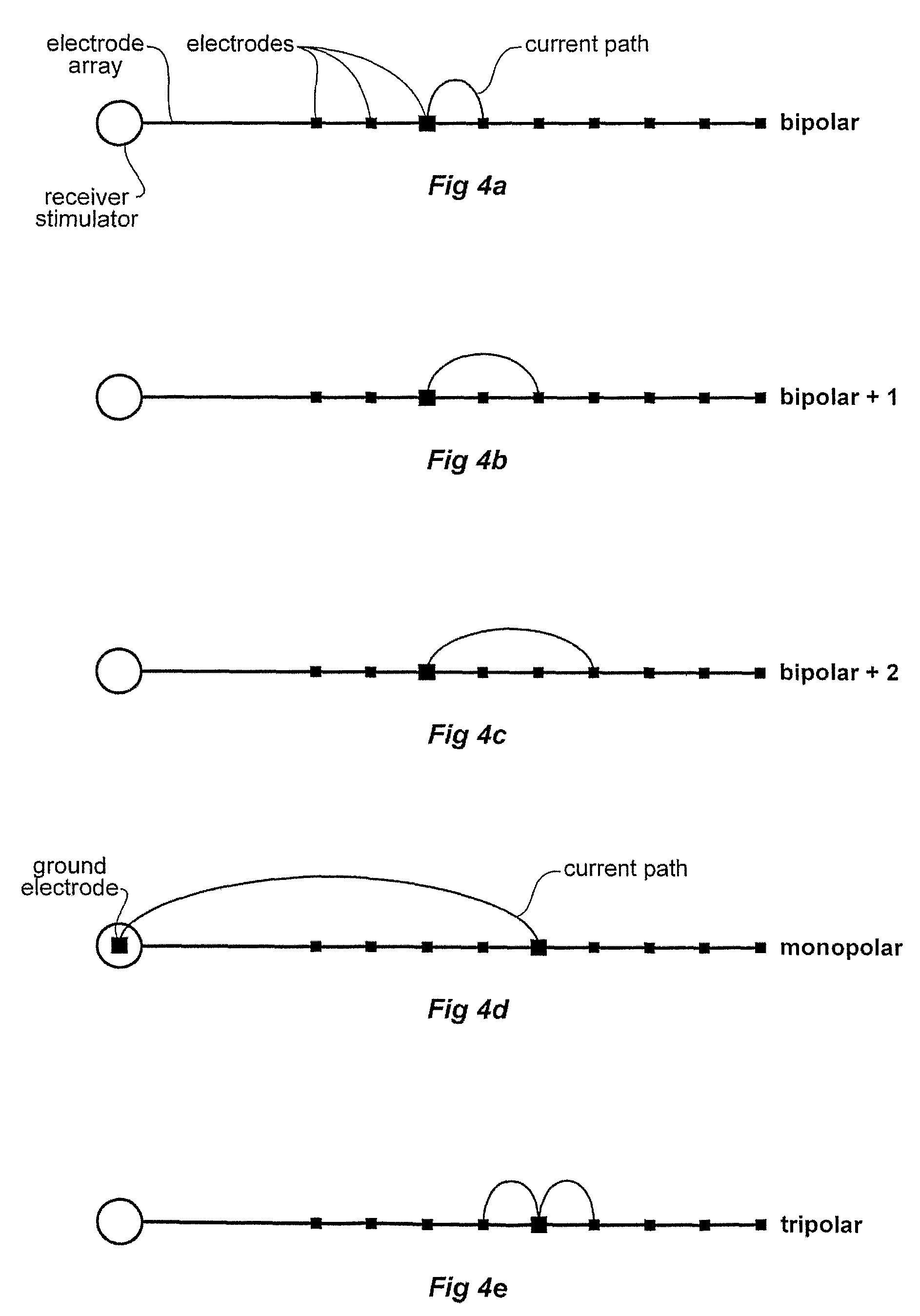
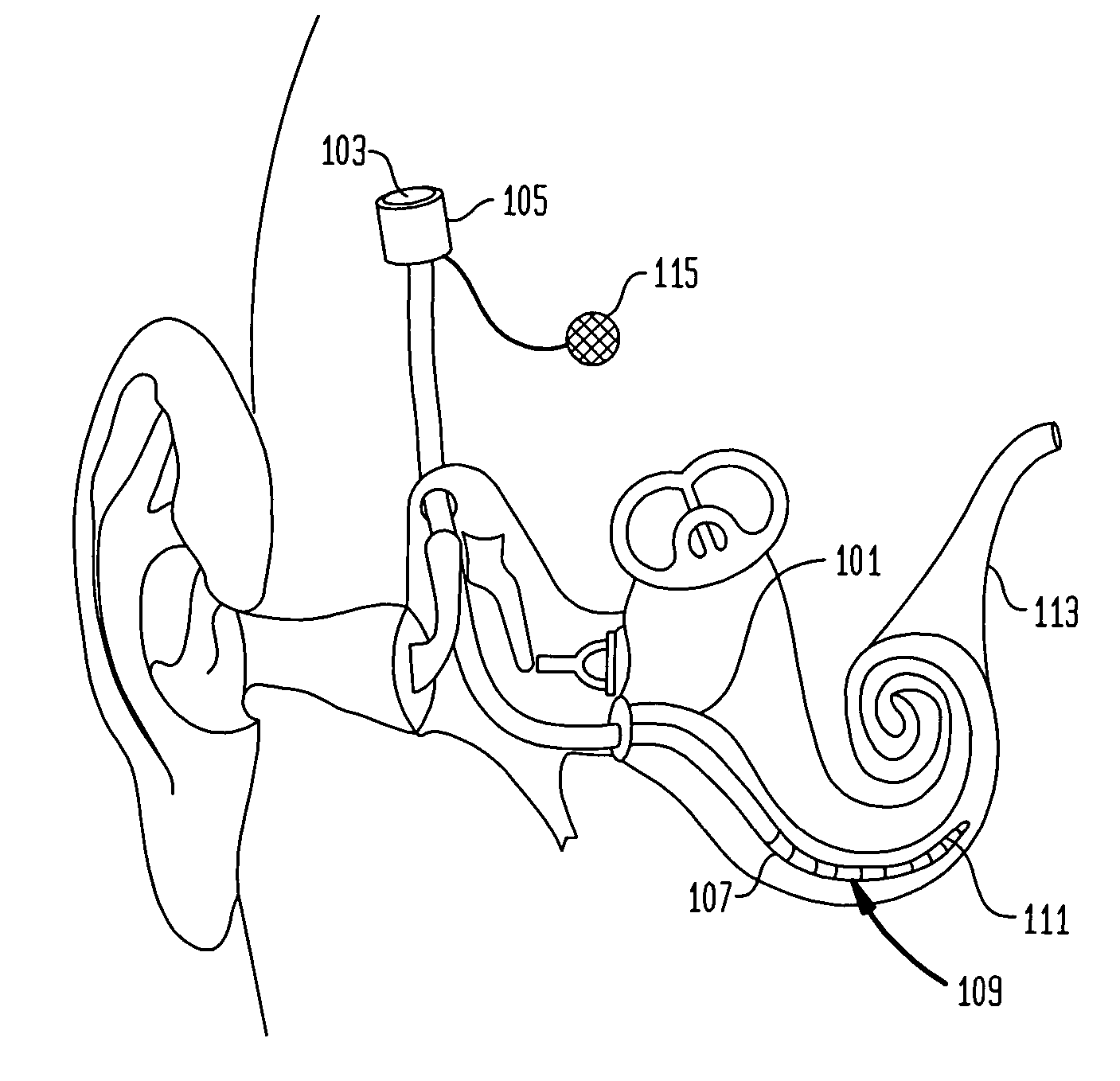
Patents
Literature
58 results about "Stimulation rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
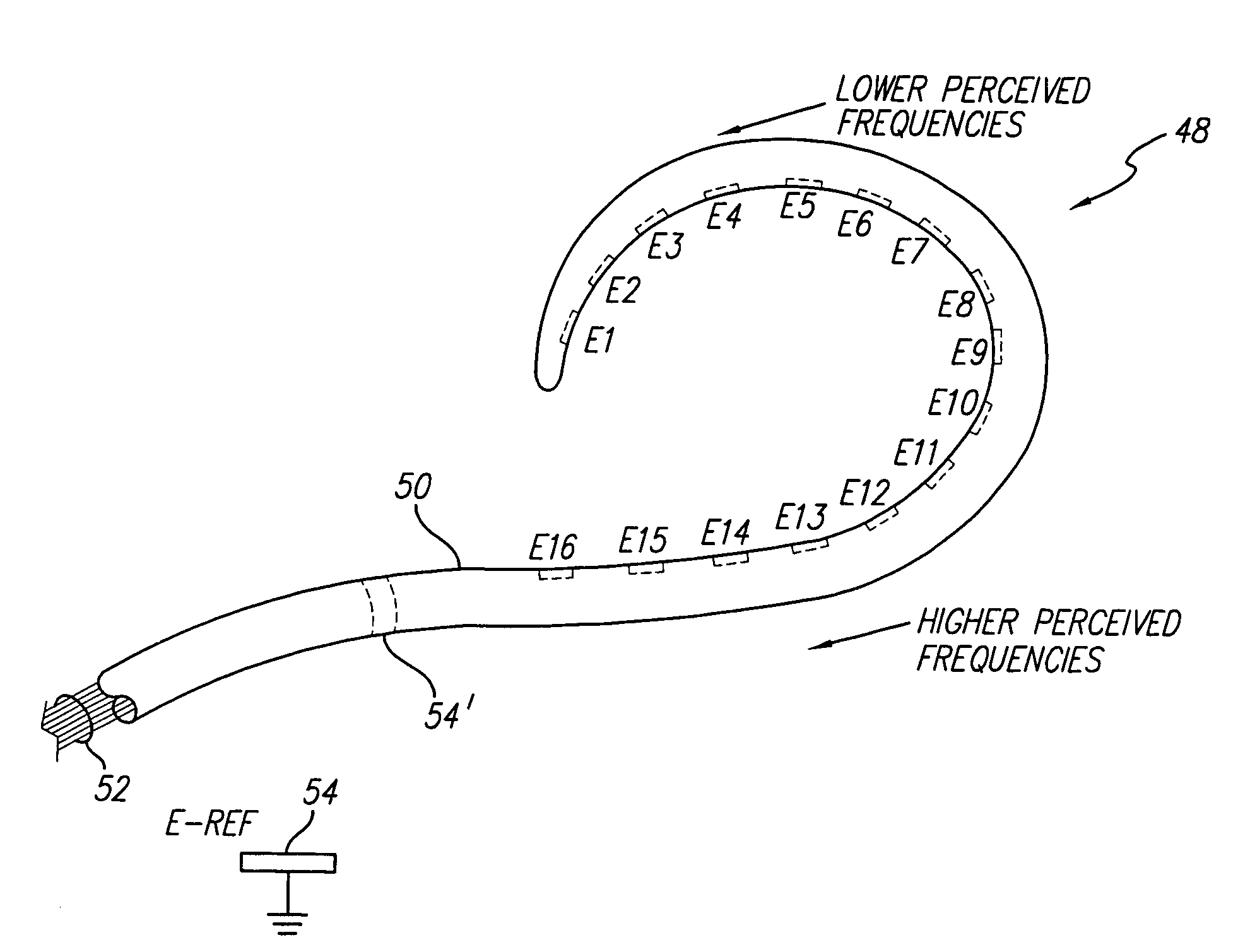
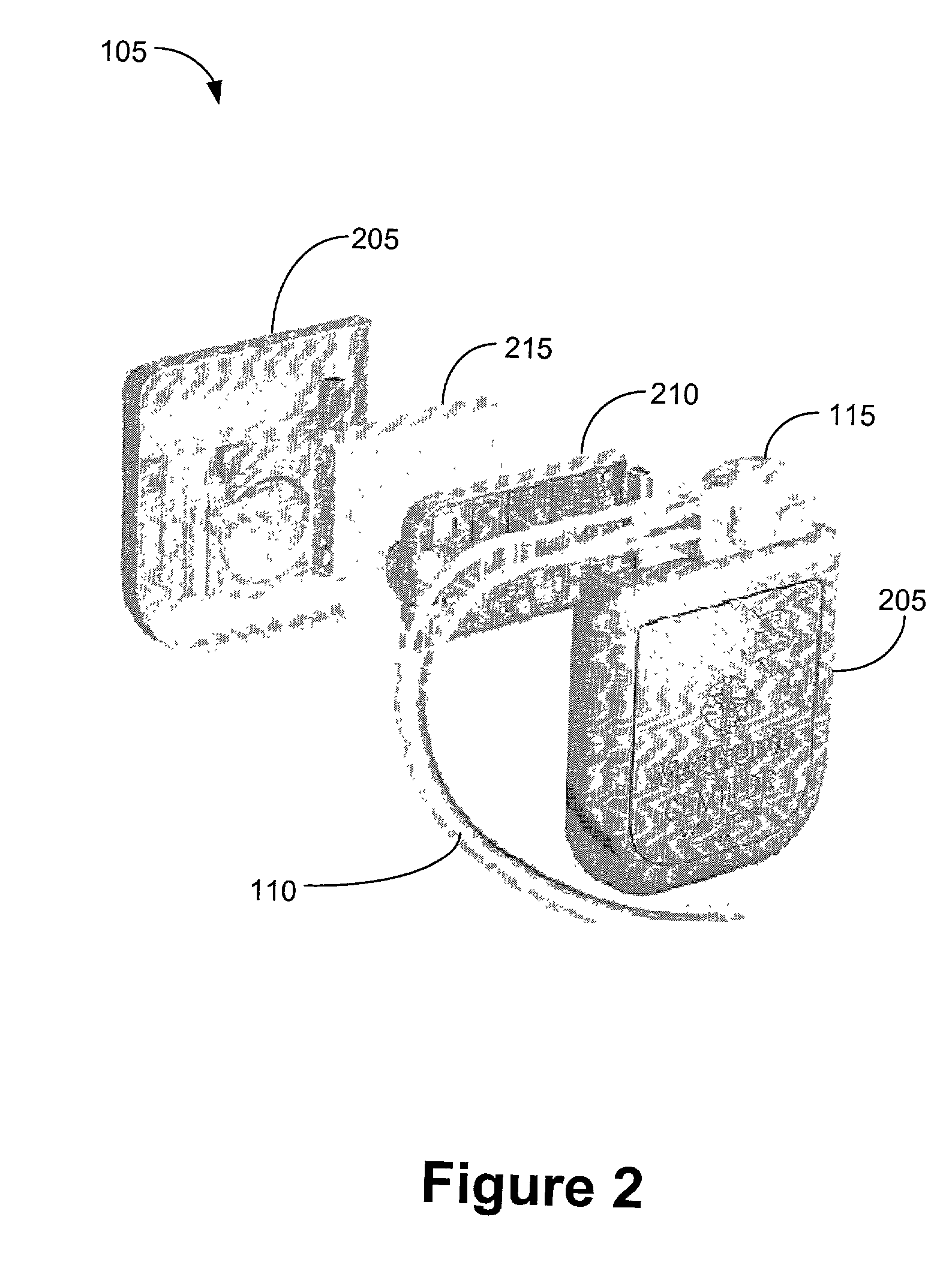
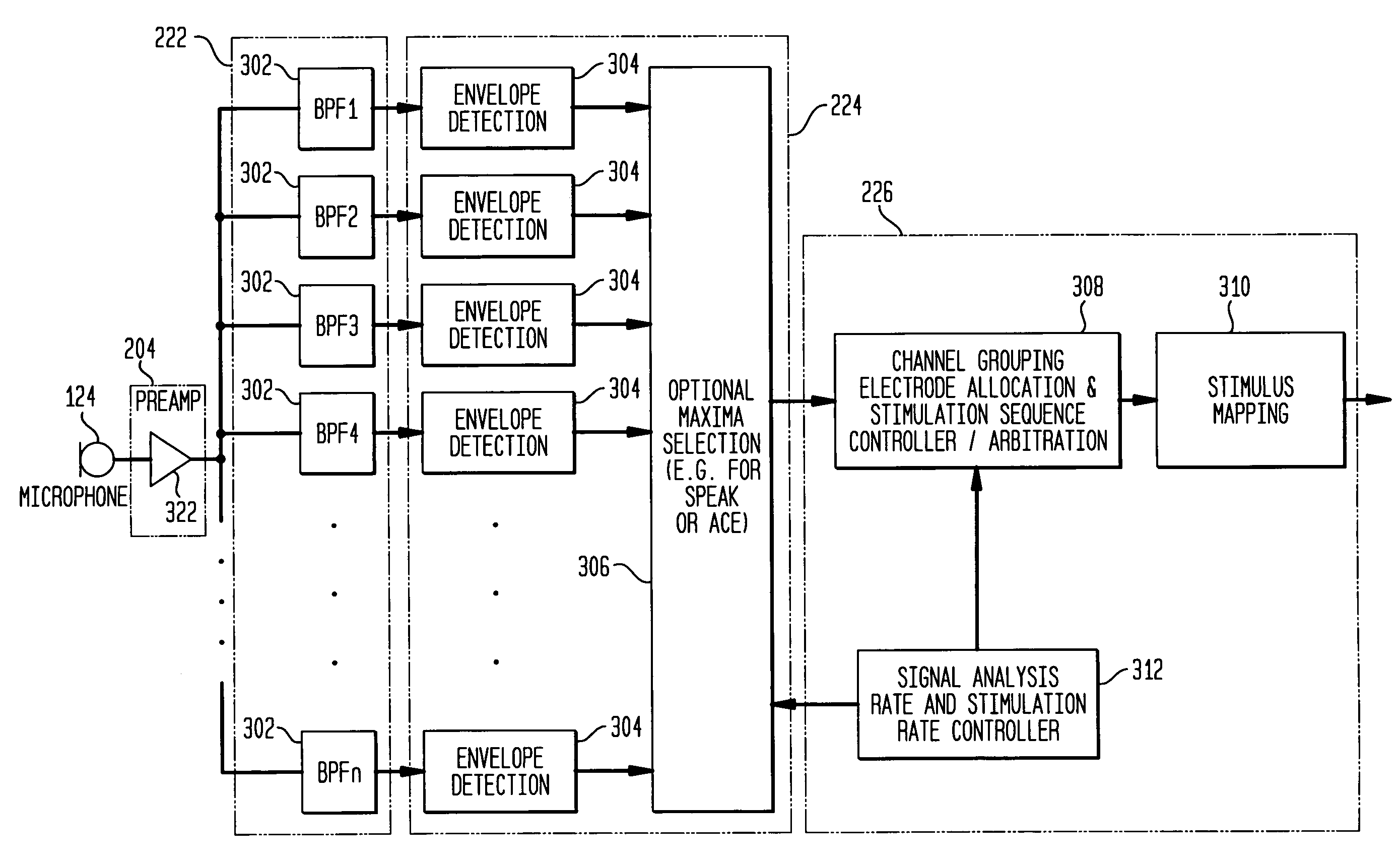
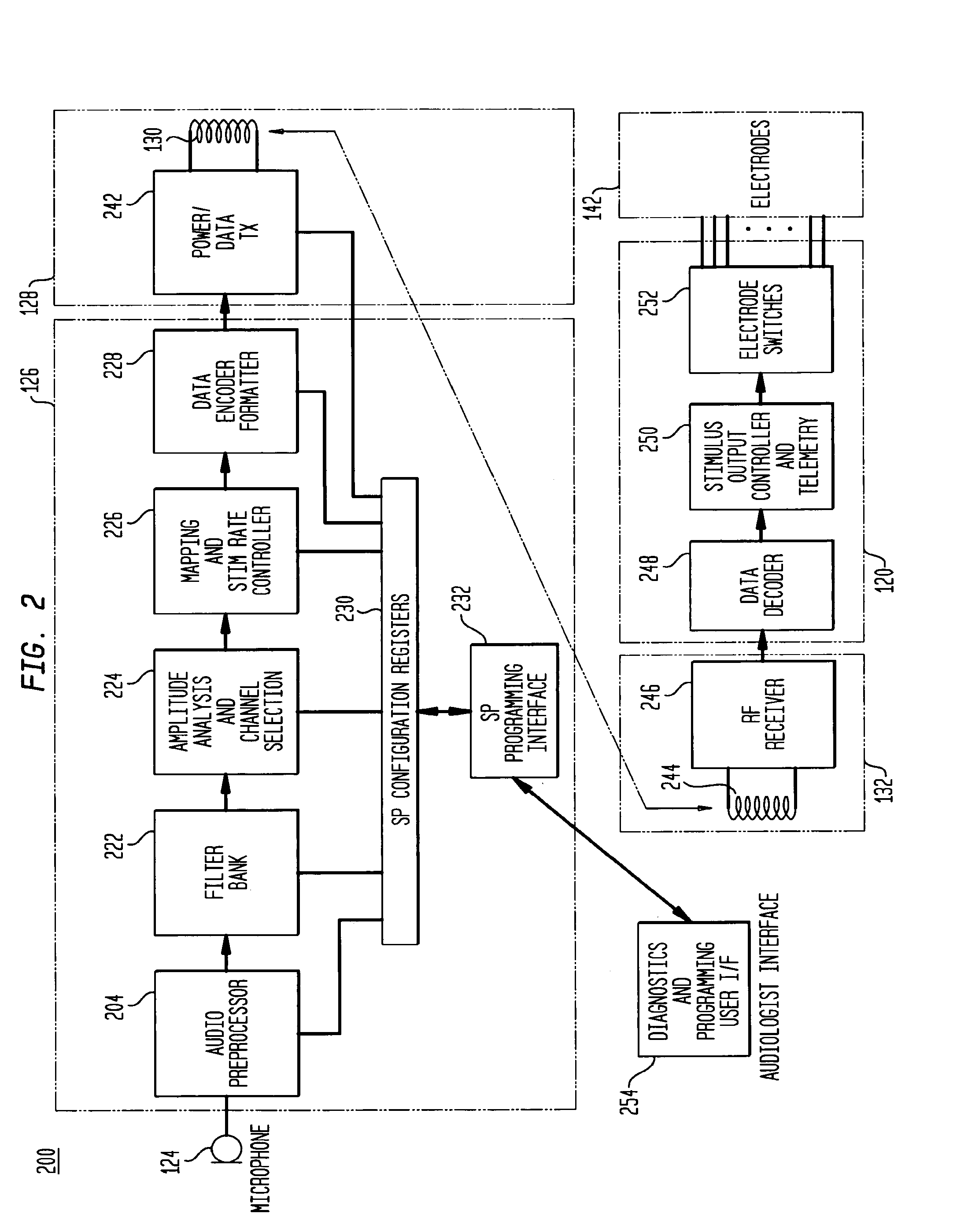
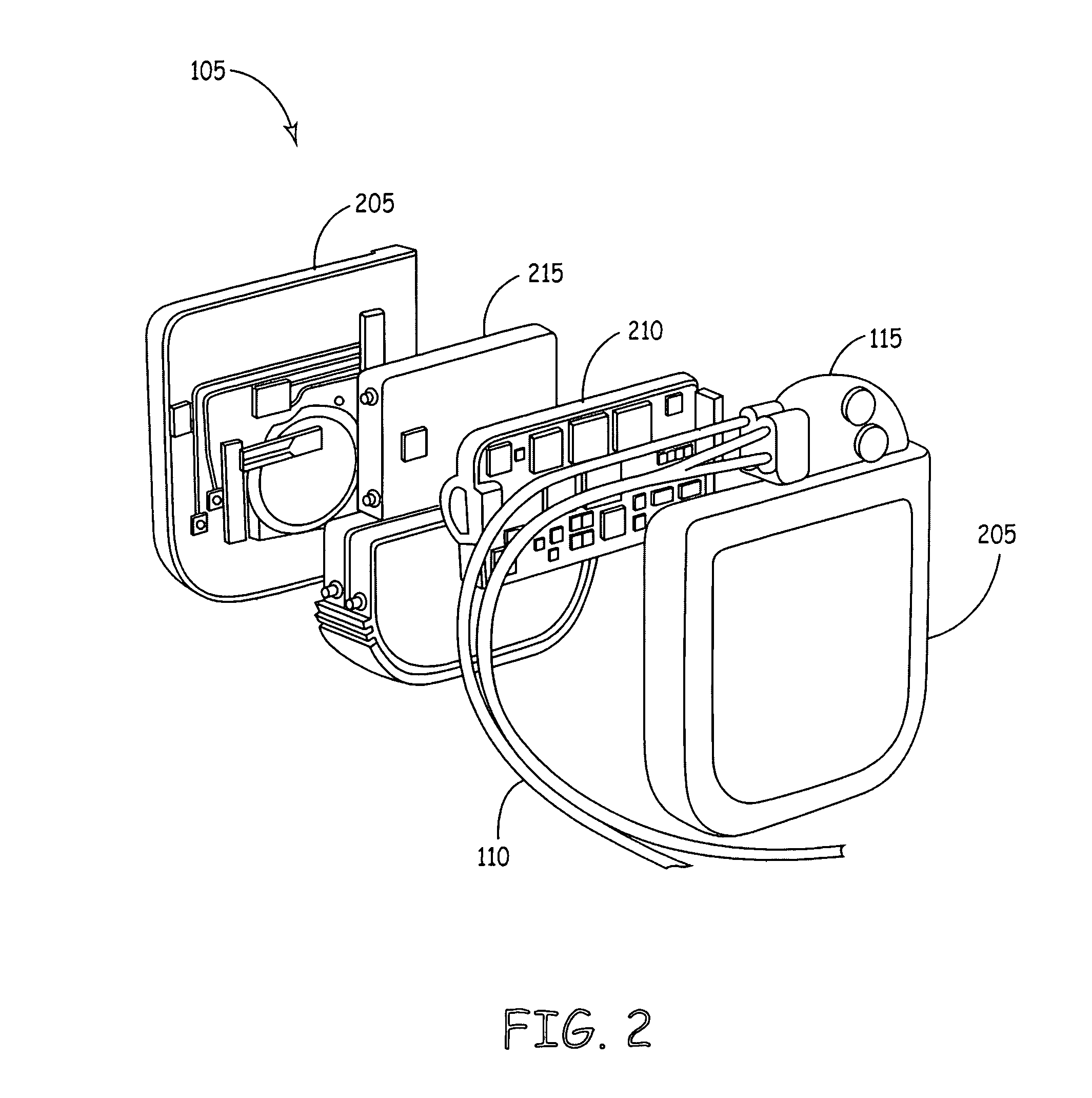
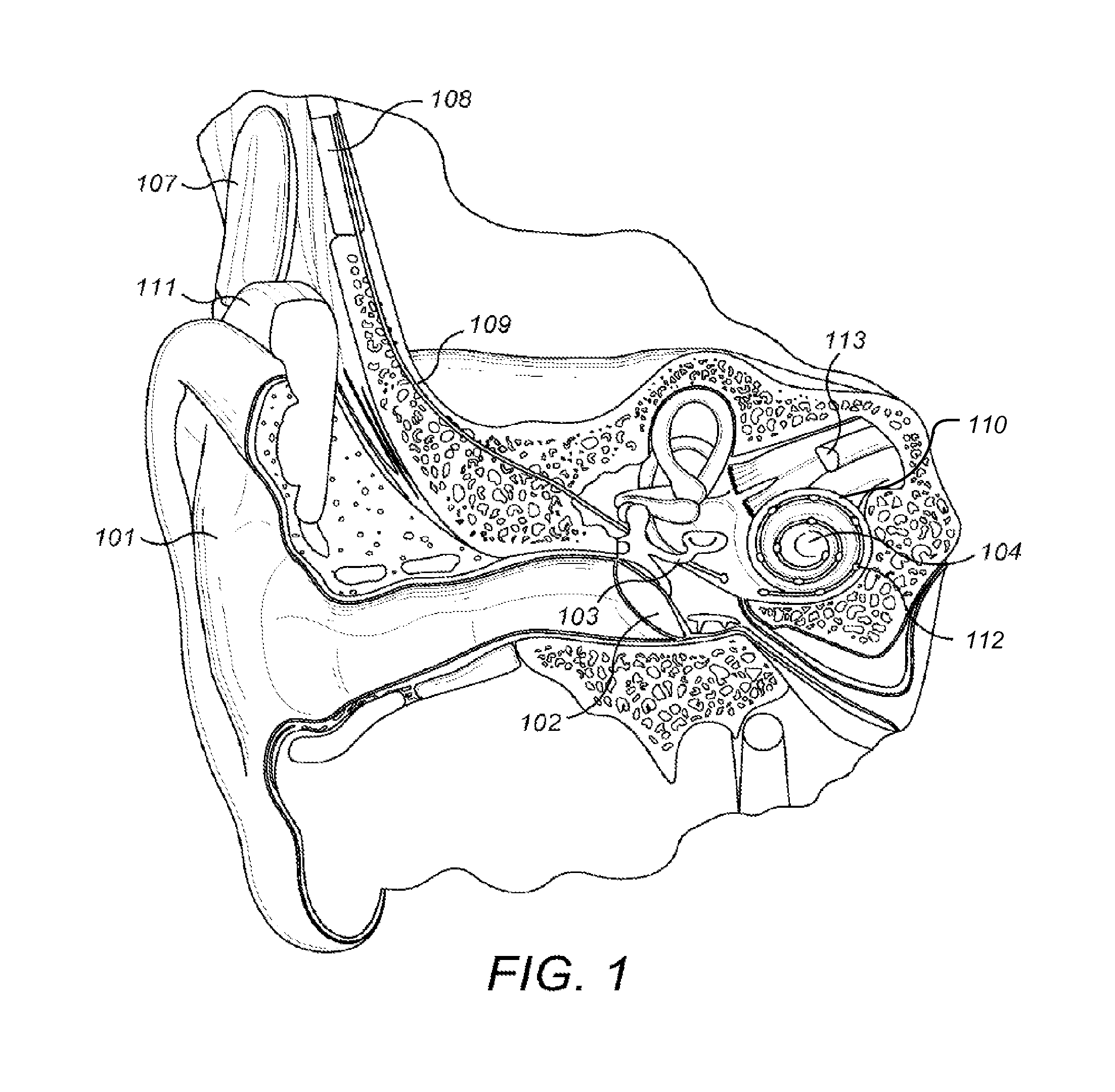
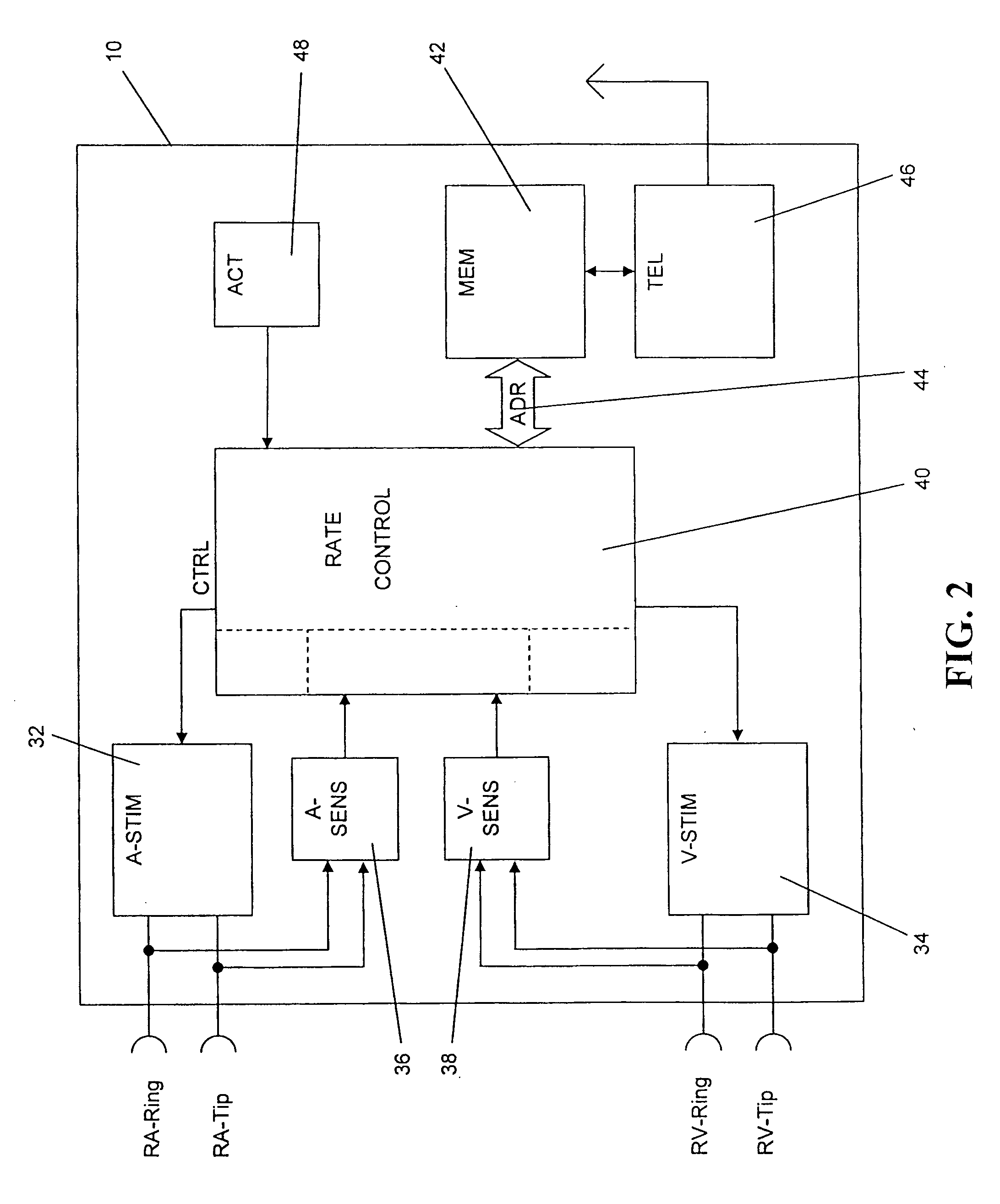
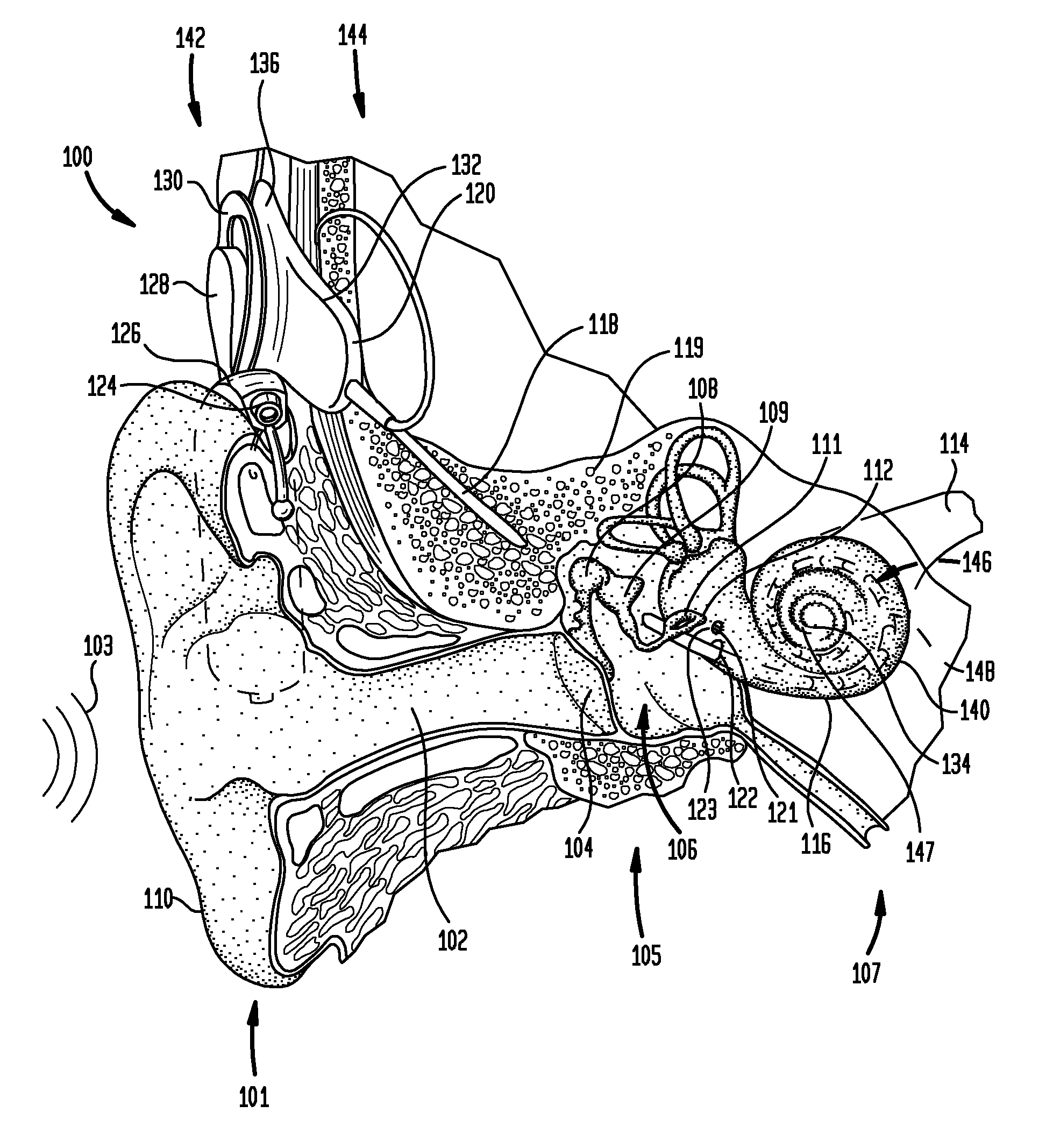
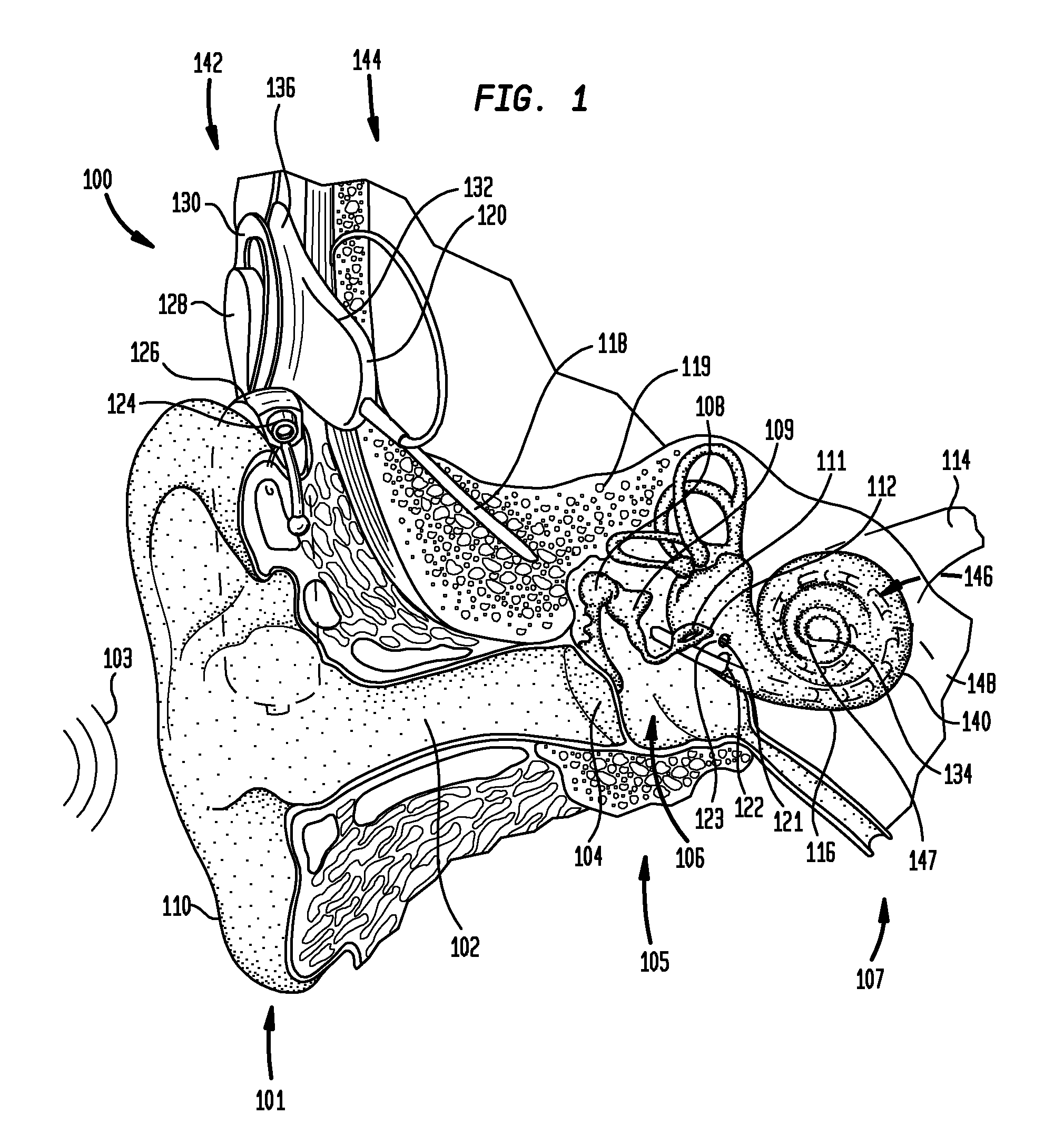
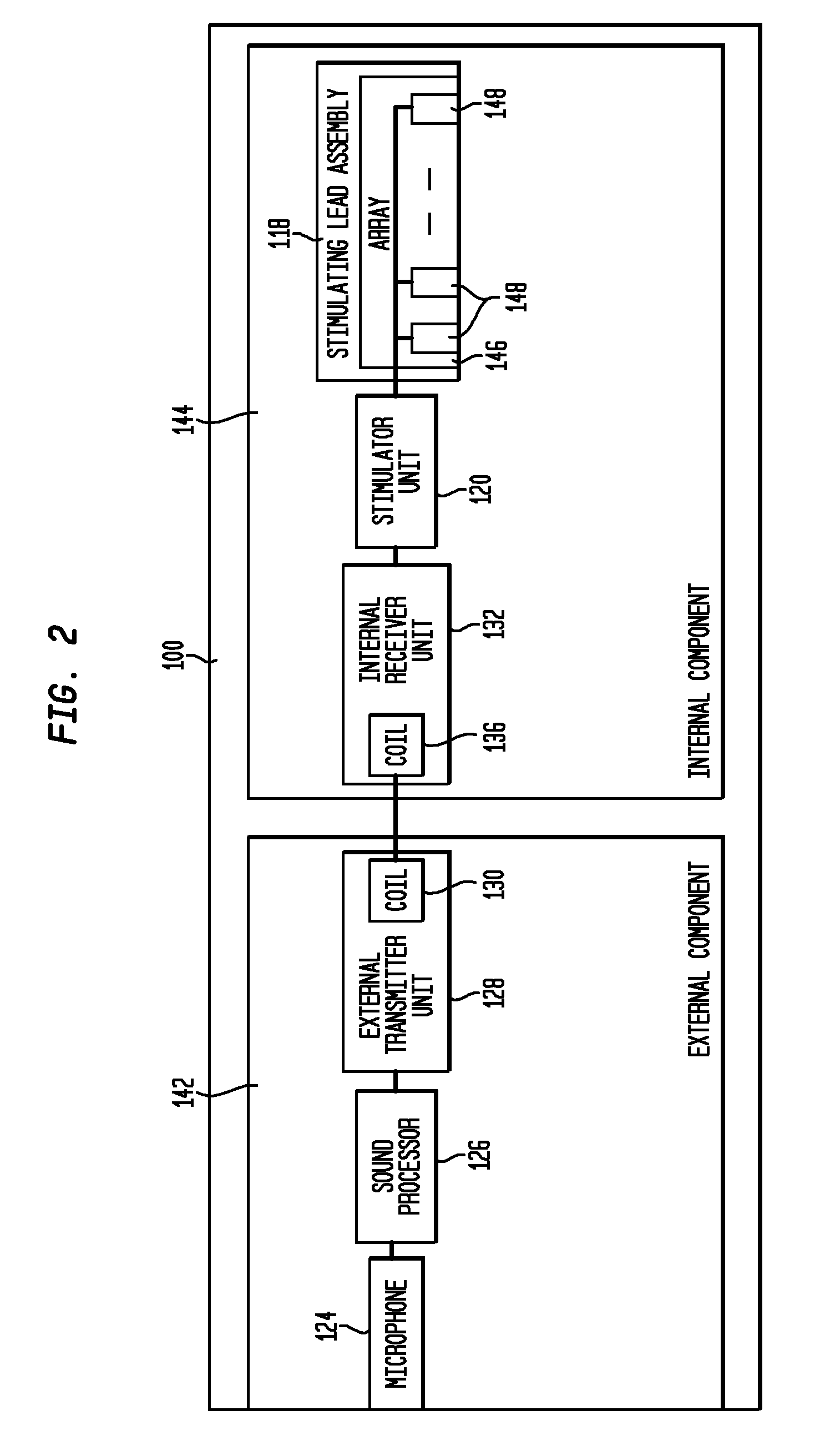
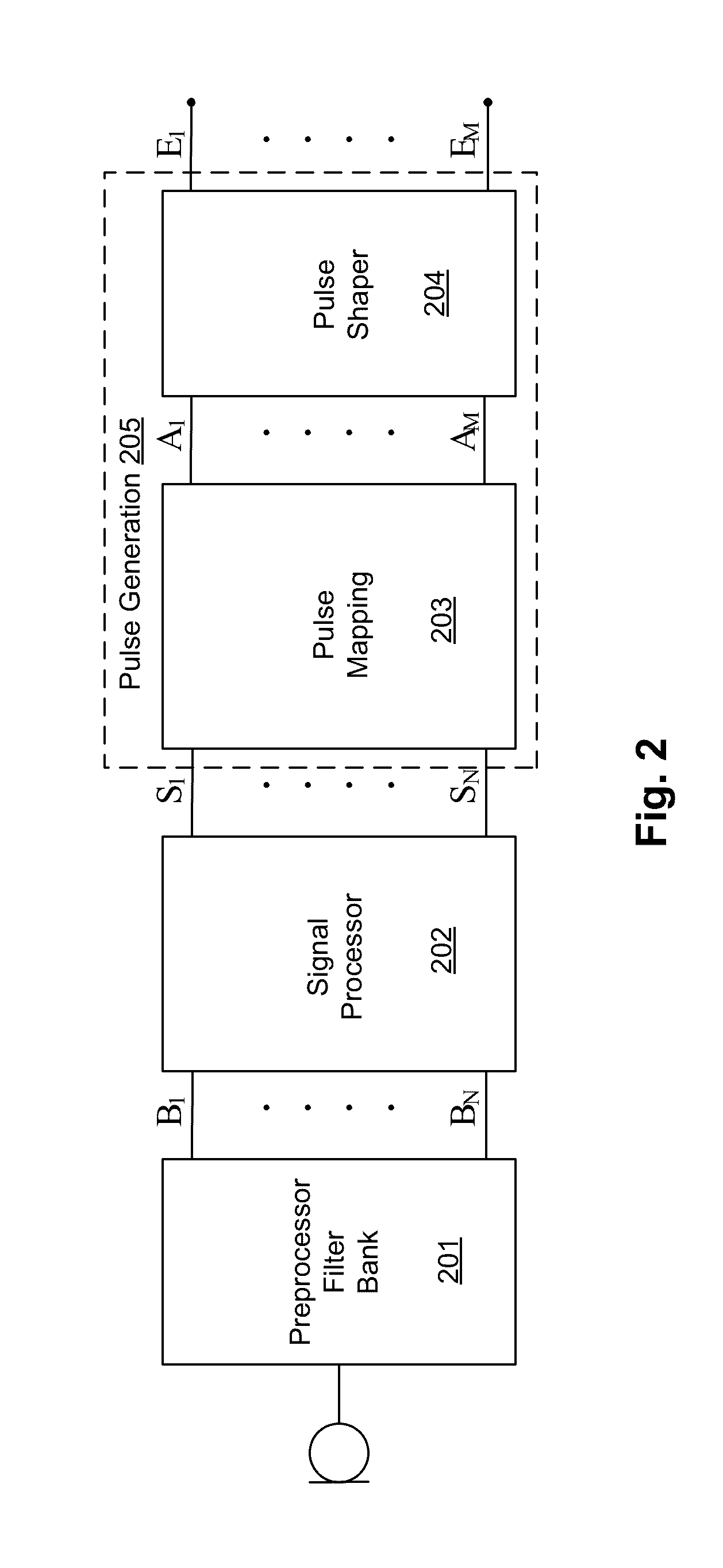
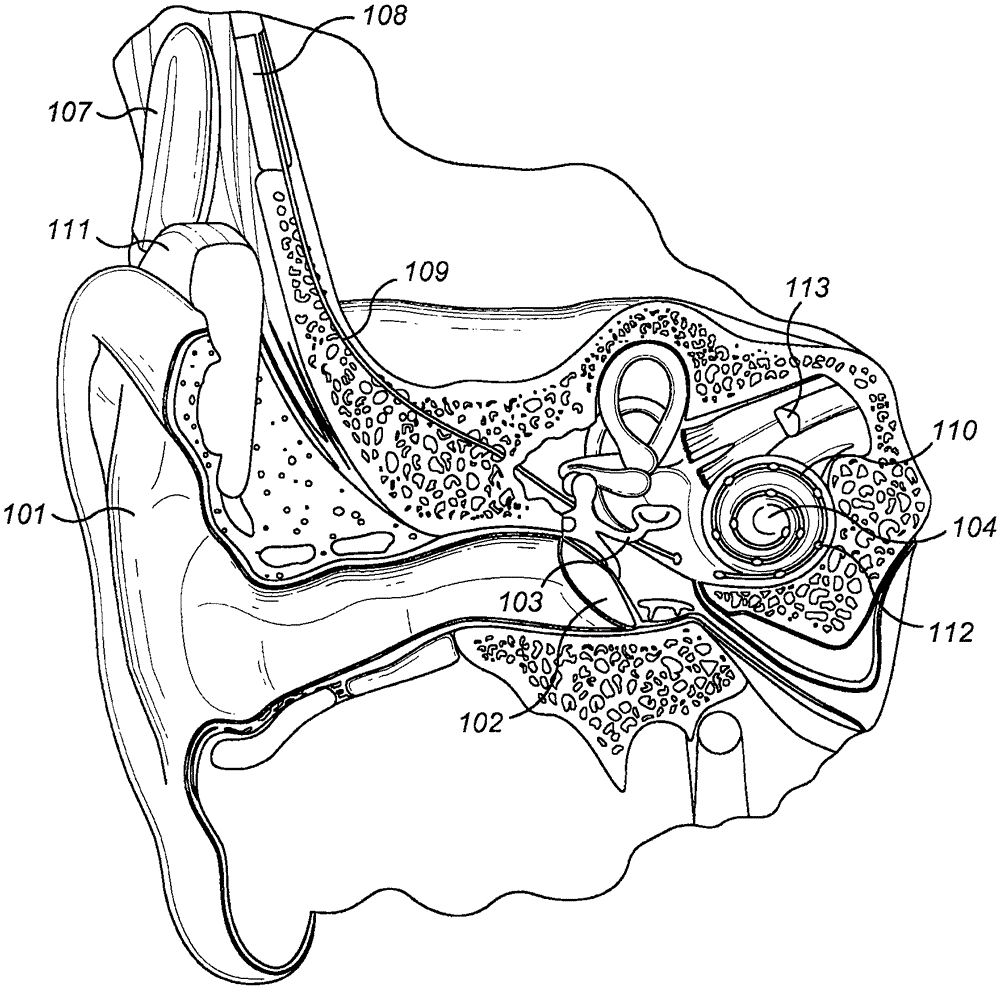
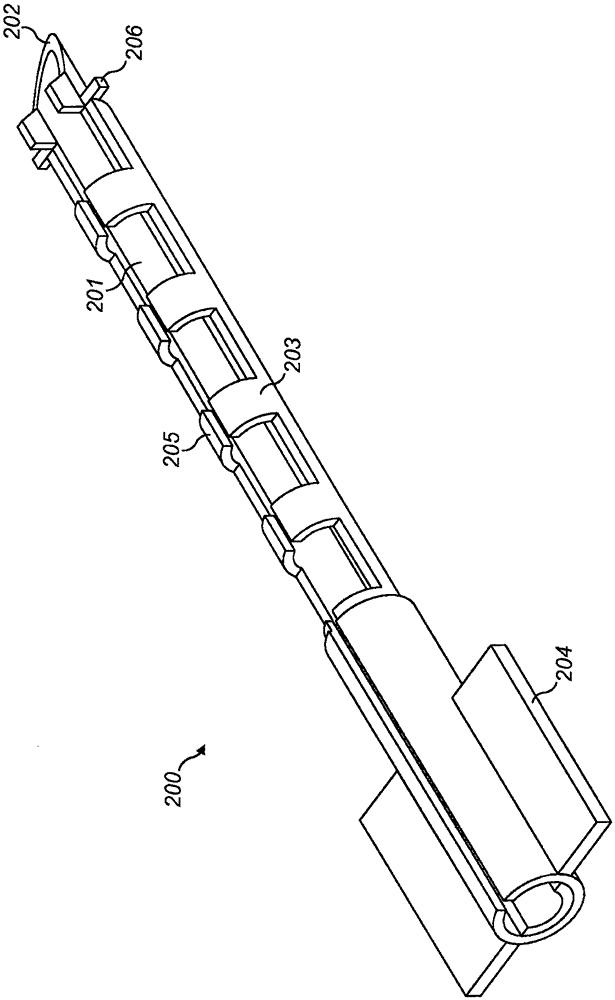
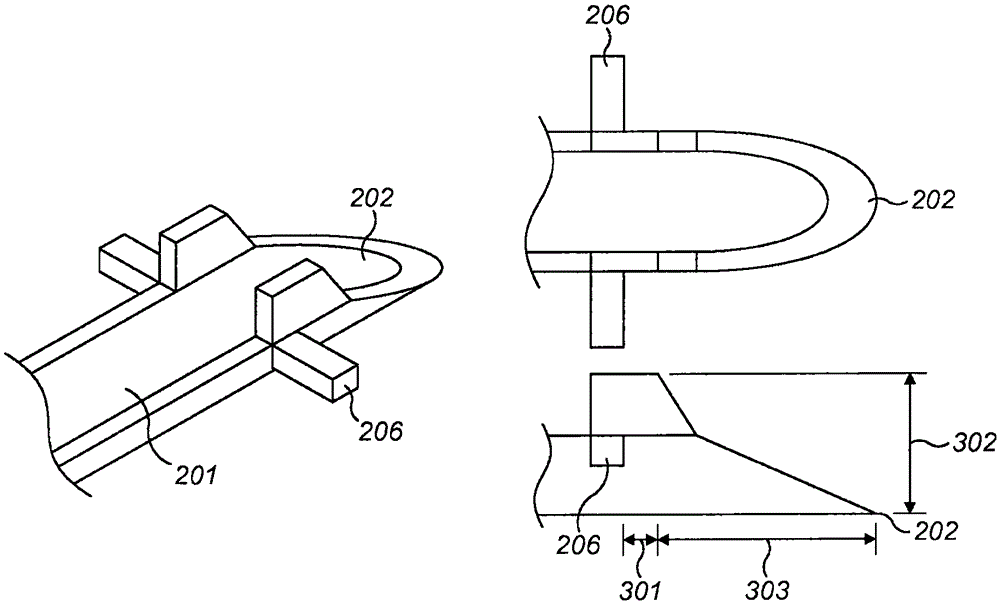
Multiple channel-electrode mapping
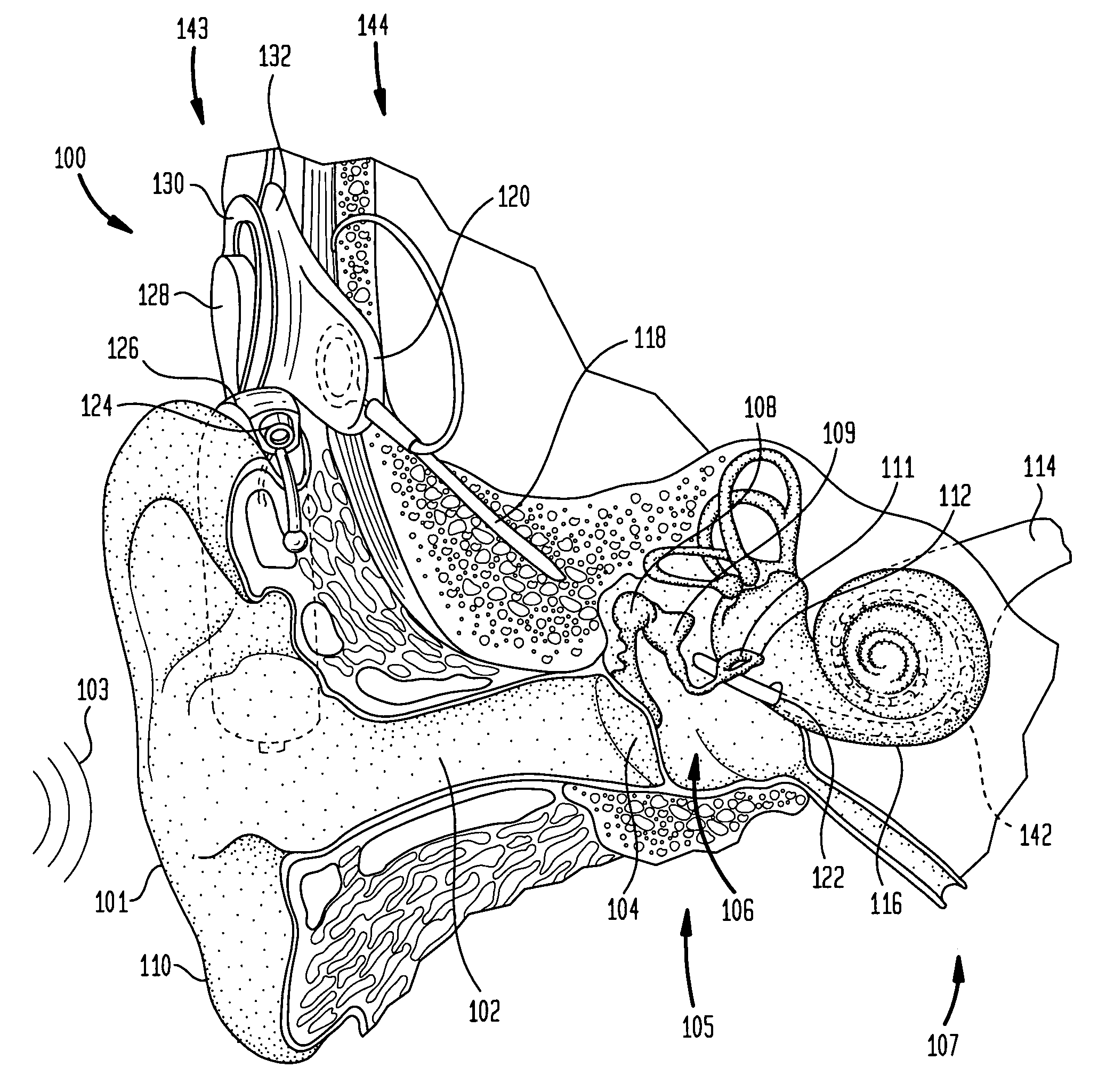
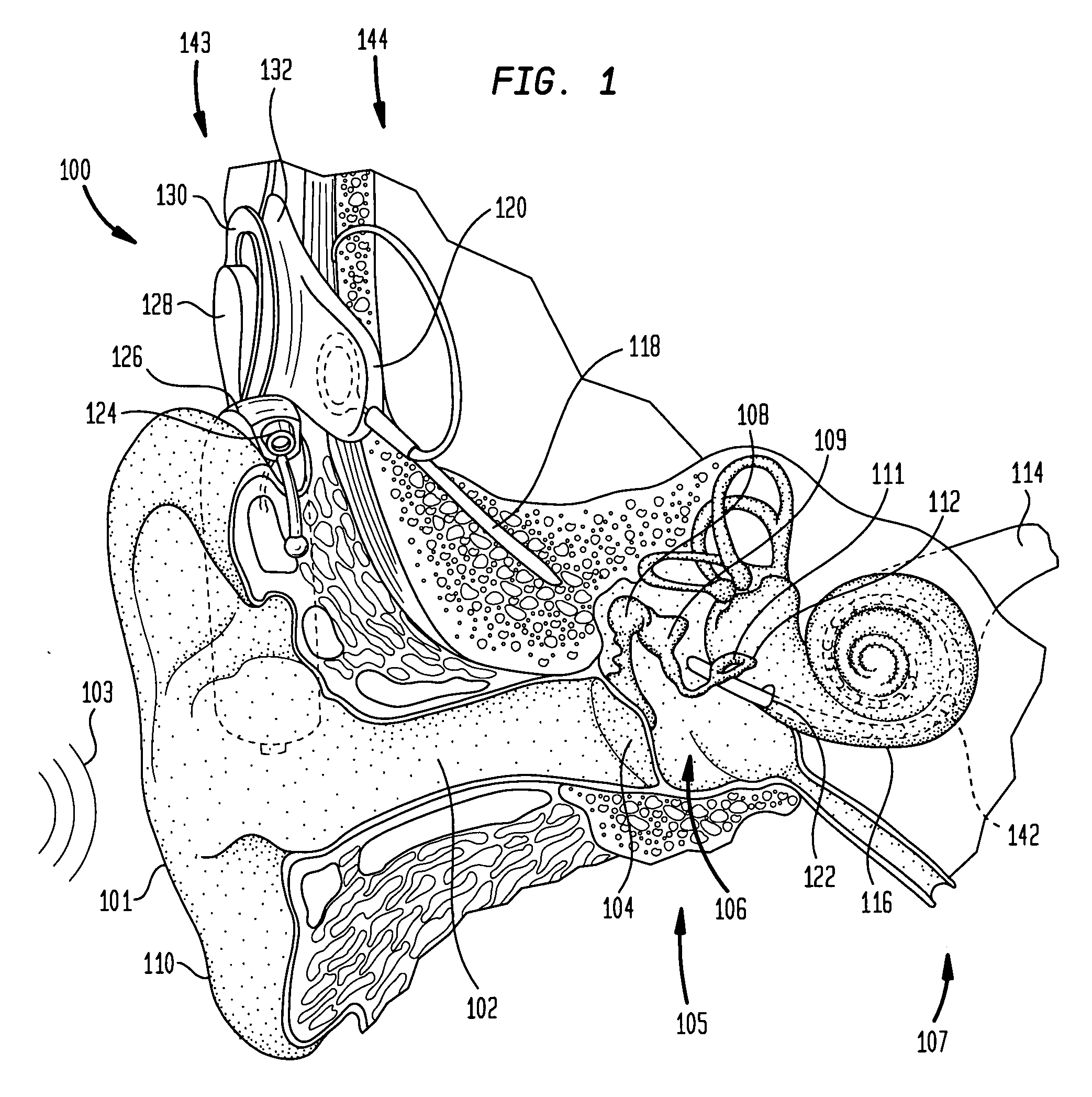
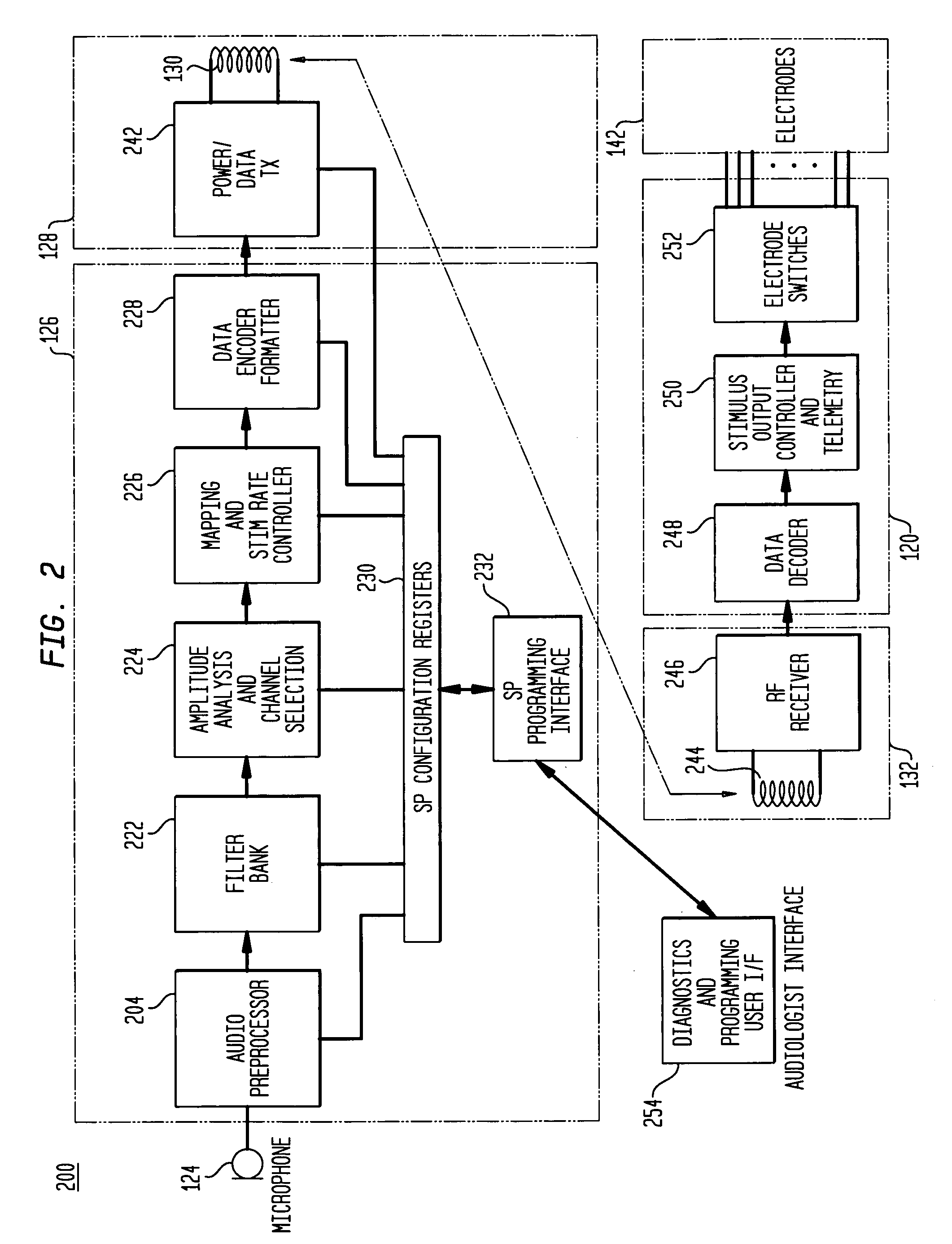
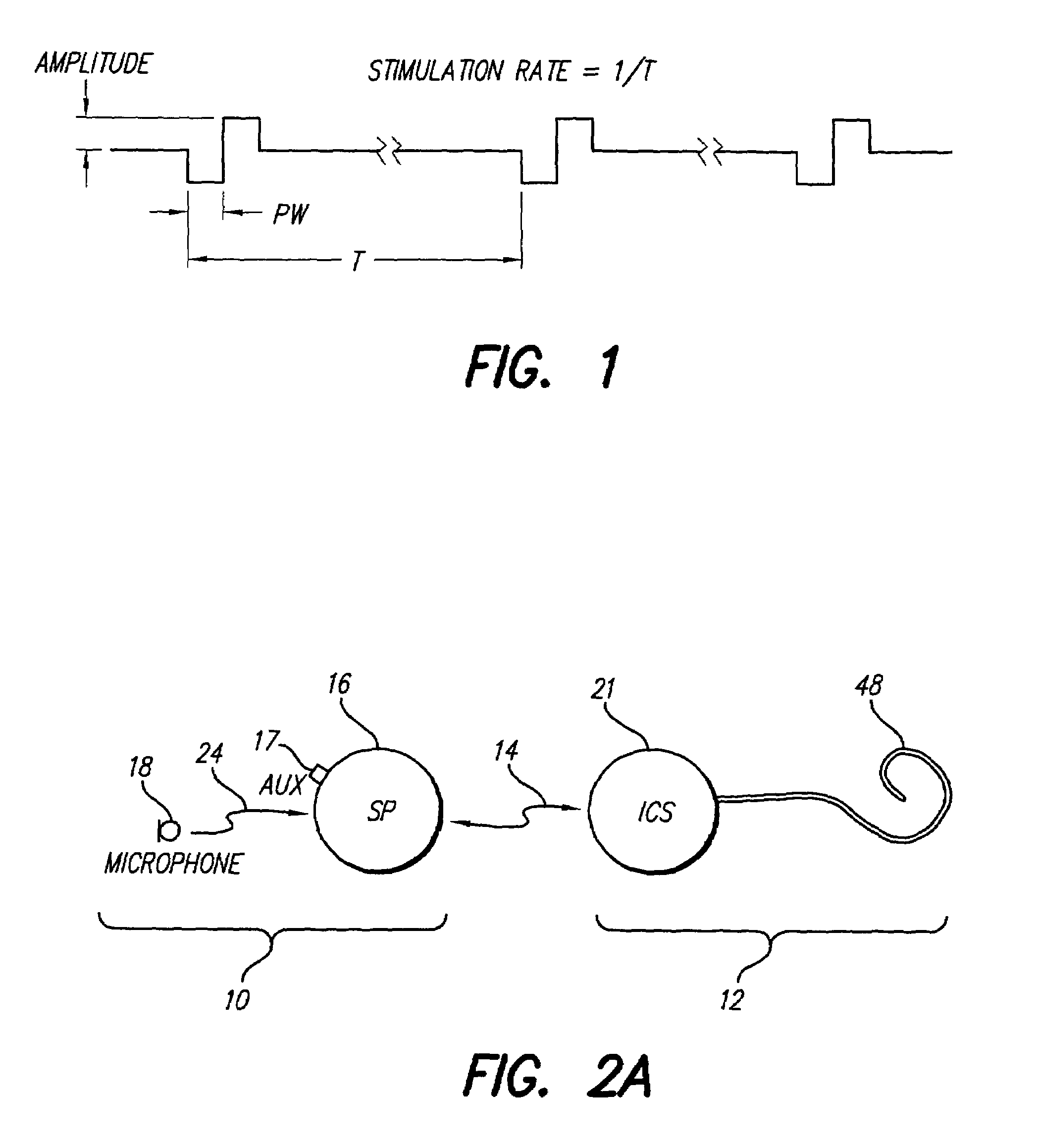
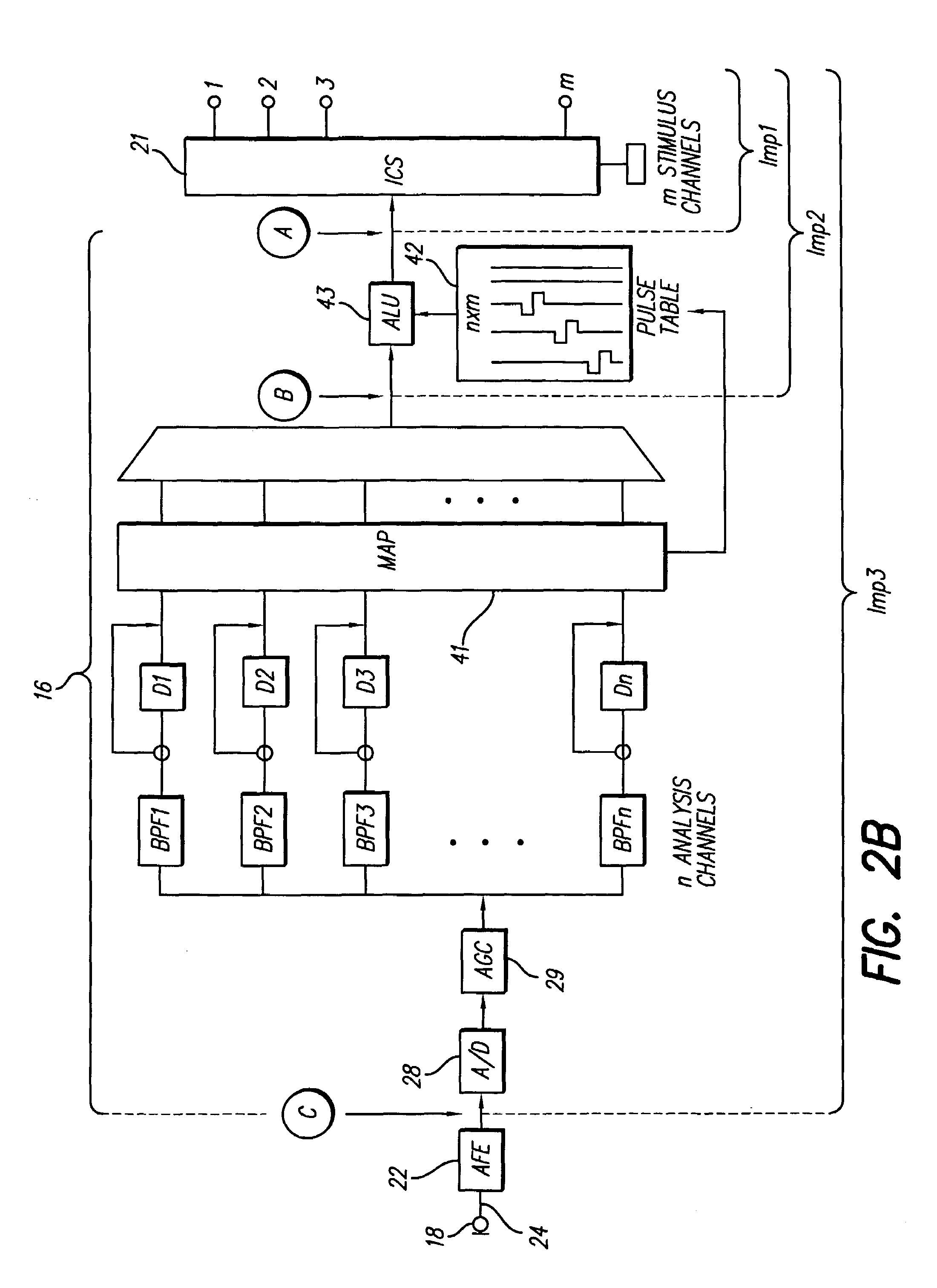
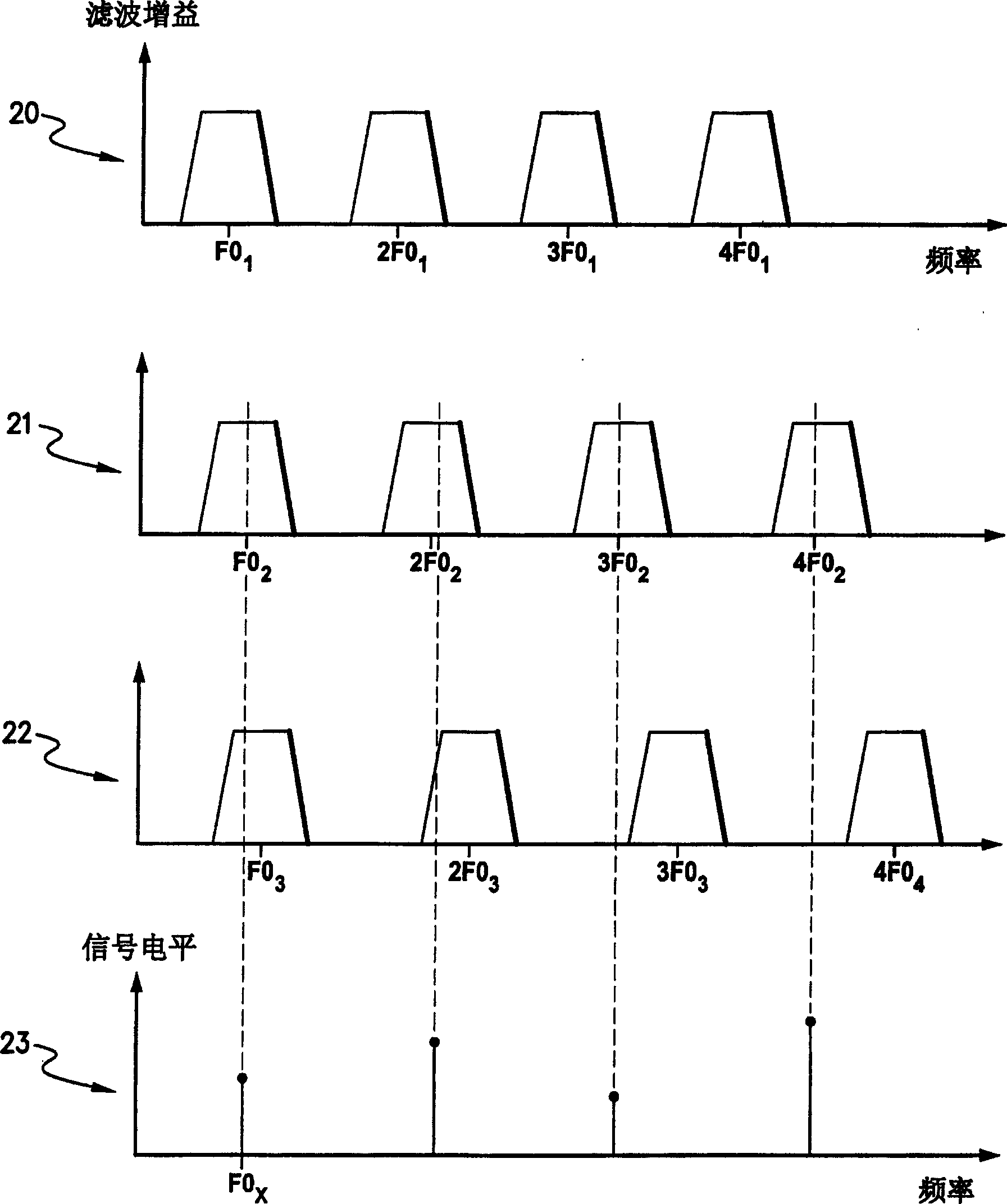
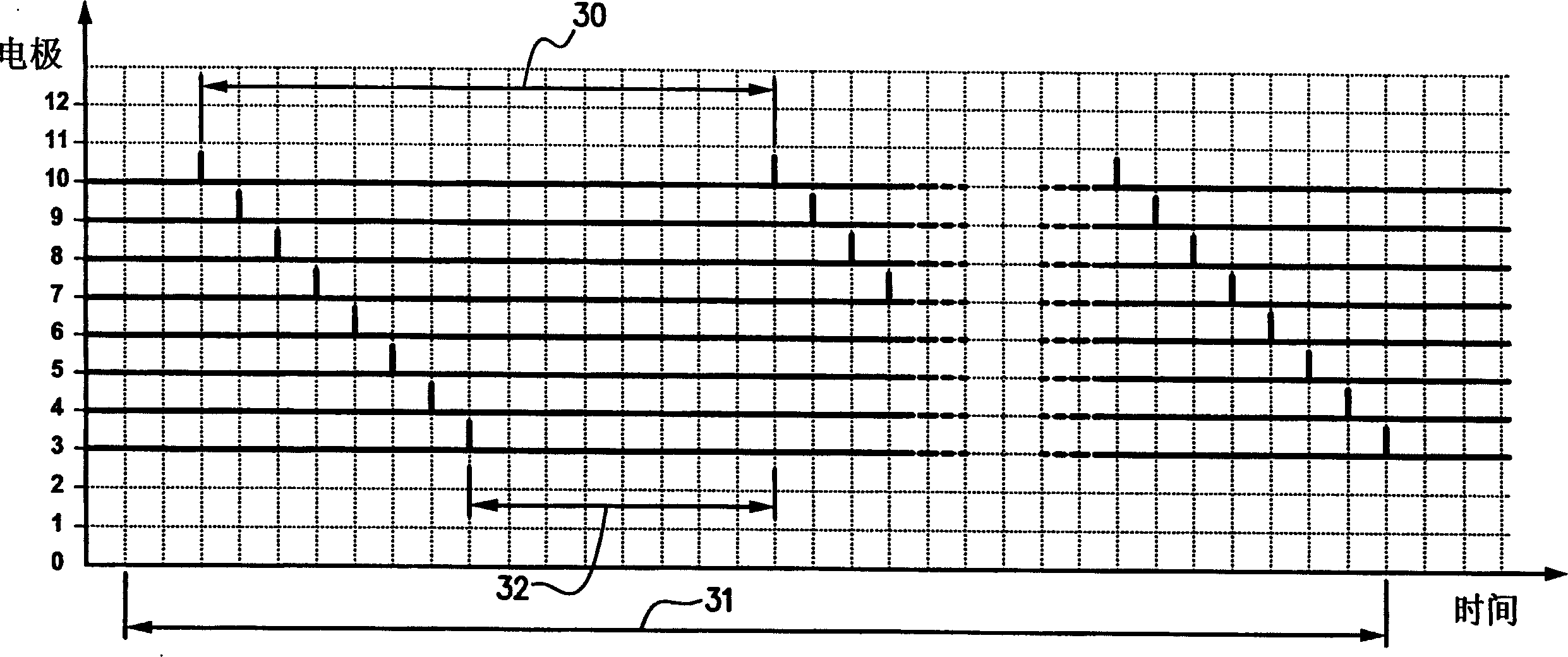
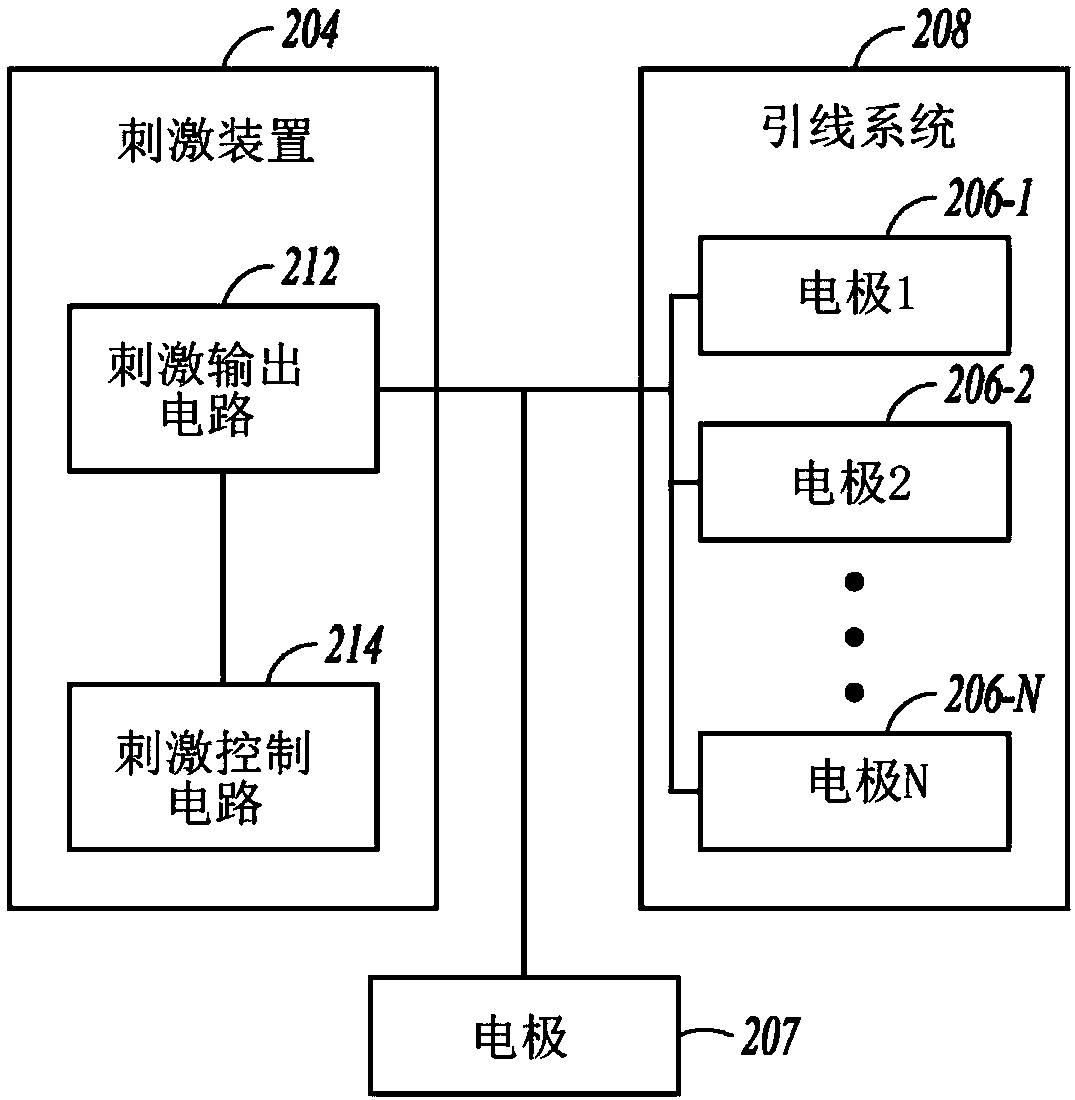
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, methods and systems are disclosed for delivering a stimulating signal by a stimulating medical device having a plurality of electrodes. Such methods and systems comprise receiving a signal; filtering the received signal to obtain a plurality of band pass filtered signals; delivering to each electrode of a first group of one or more electrodes, a first set of stimulation signals, wherein the first set of stimulation signals comprises stimulations signals for each of a first group of two or more band pass filtered signals; and delivering to each of electrodes of a second group of one or more electrodes, a second set of stimulation signals, wherein the second set of stimulation signals comprises stimulations signals for each of a second group of one or more band pass filtered signals; and wherein the first set of stimulation signals are delivered at a different effective stimulation rate than the second set of stimulation signals.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Spatial decimation stimulation in an implantable neural stimulator, such as a cochlear implant
ActiveUS7039466B1High rate stimulationReduce power levelElectrotherapyArtificial respirationCochlear implantationElectrode array
A cochlear implant system, or other neural stimulation system, has the capability to stimulate fast enough to induce stochastic neural firing so as to restore “spontaneous” neural activity. The stimulation rate applied to the more distally-located electrodes of an electrode array connected to the implant system is reduced from the stimulation rate applied to the more proximally-located electrodes. Thus, in the case of a cochlear implant system, the apically-located regions within the cochlea are stimulated at a reduced rate in order to conserve power. Pulse widths of the reduced-rate pulses may further be increased, and amplitudes reduced, to further conserve power. As needed, a low-level random conditioner stimulation signal may be applied to the apical regions of the cochlea in order to ensure the occurrence of random neural firings.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
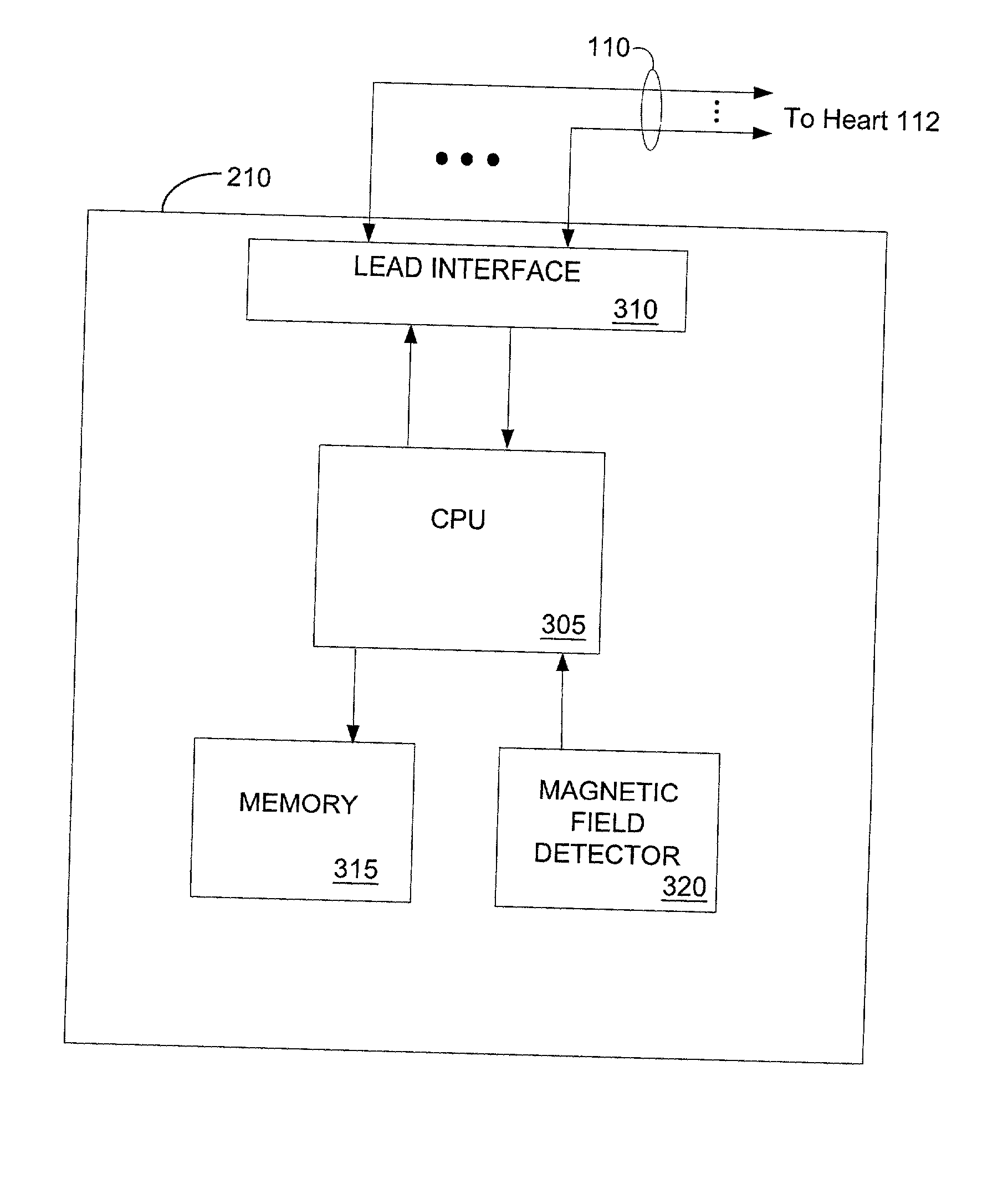
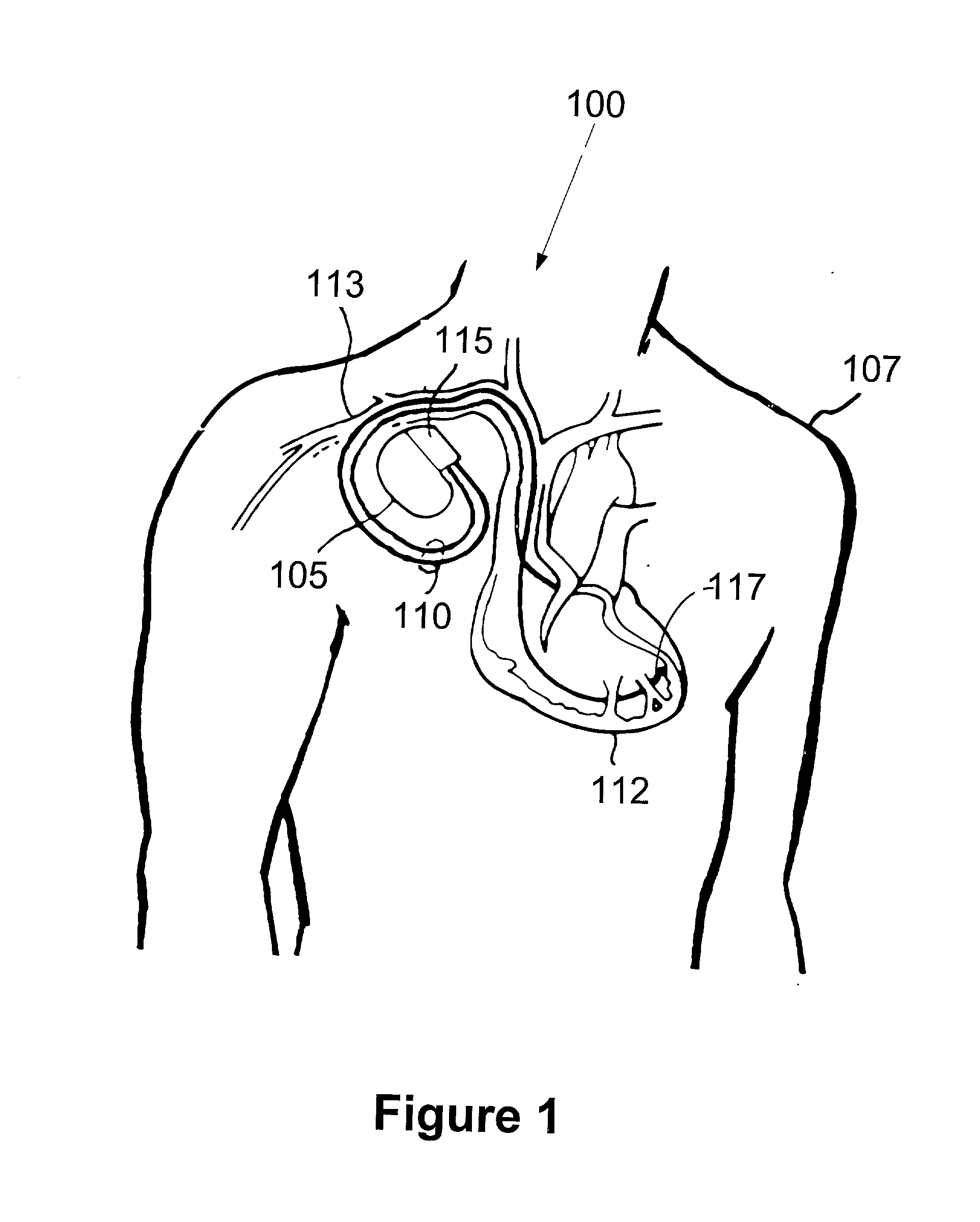
Method and apparatus for controlling an implantable medical device in response to the presence of a magnetic field and/or high frequency radiation interference signals
An implantable medical device includes a detector for detecting the presence of a magnetic field, where the presence of the magnetic field is detected in response to the strength of the magnetic field exceeding a first preselected magnetic field threshold. The device further includes a processor for adjusting a stimulation rate provided by the implantable medical device in response to determining that the strength of the detected magnetic field exceeds a second preselected magnetic field threshold. The second preselected magnetic field threshold is greater than the first preselected magnetic field threshold. In another embodiment, the implantable device includes a detector for detecting the presence of a high frequency (HF) radiation interference signal and a processor for adjusting a stimulation rate provided by the implantable medical device in response to determining that the strength of the detected HF radiation interference signal exceeds a preselected HF radiation threshold.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
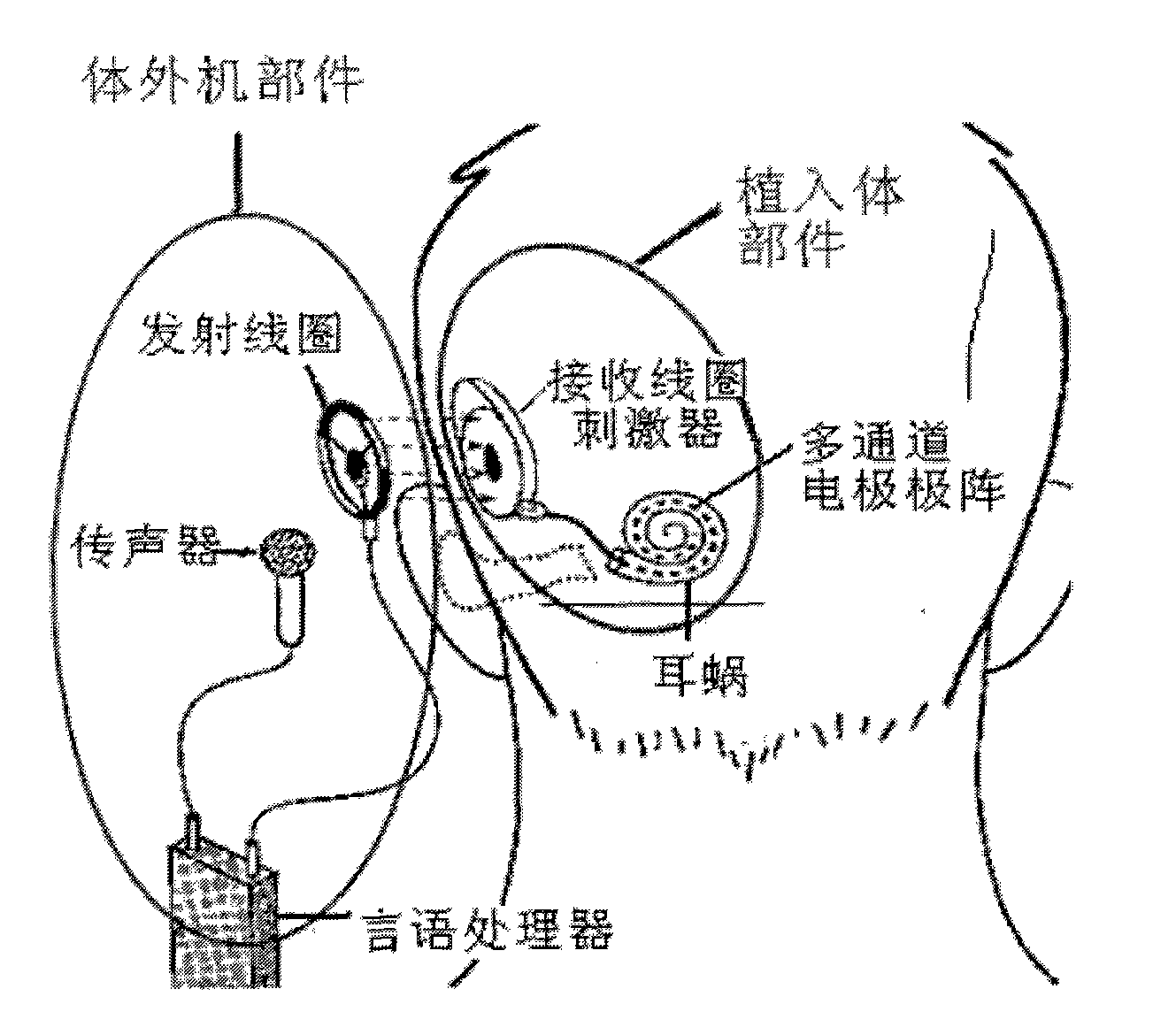
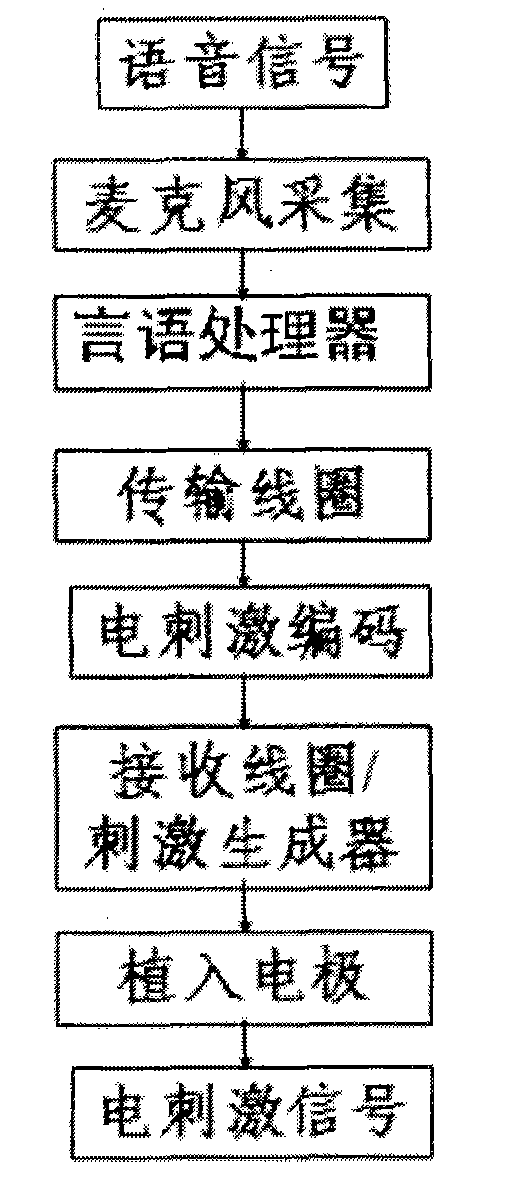
Sound processing method and system
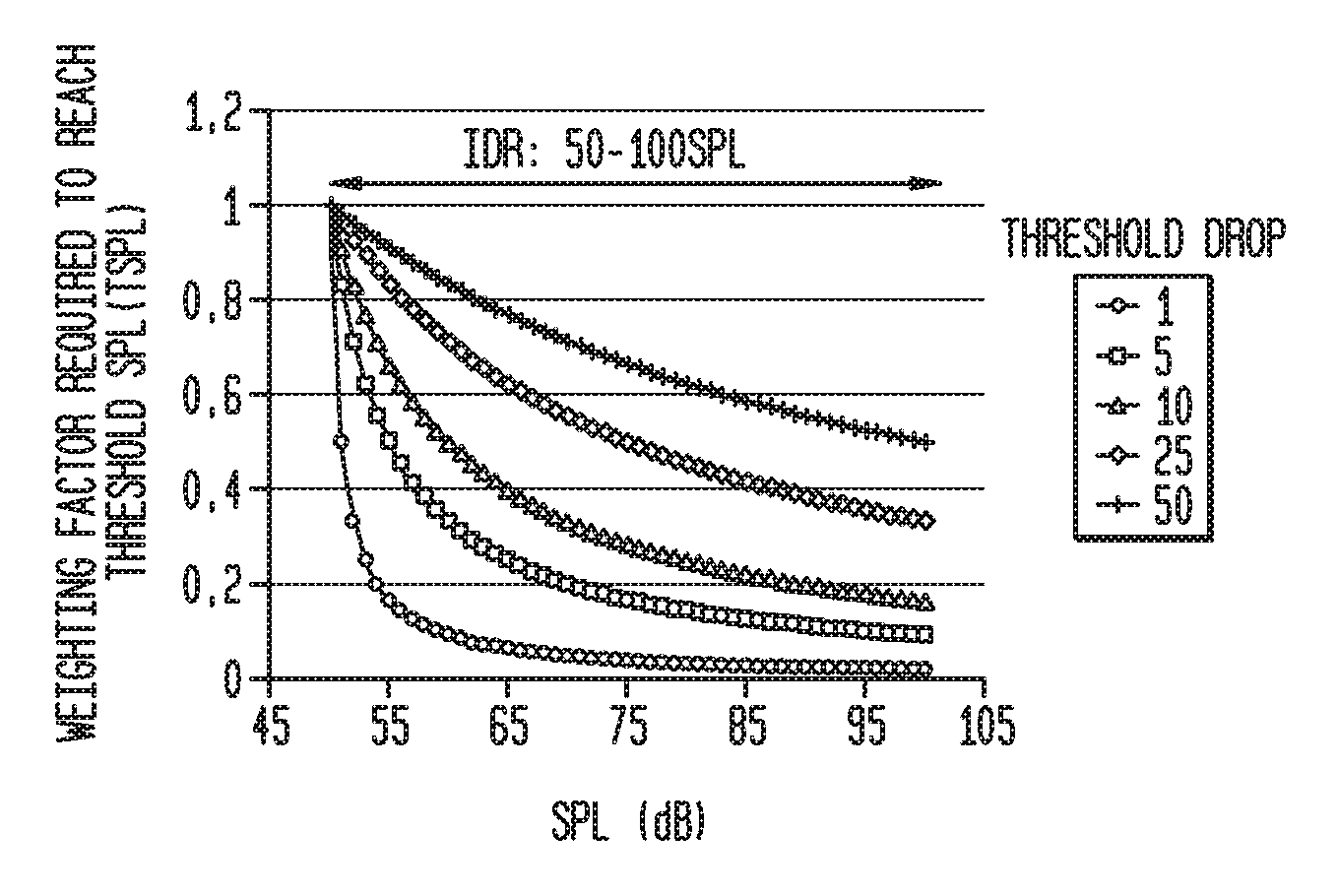
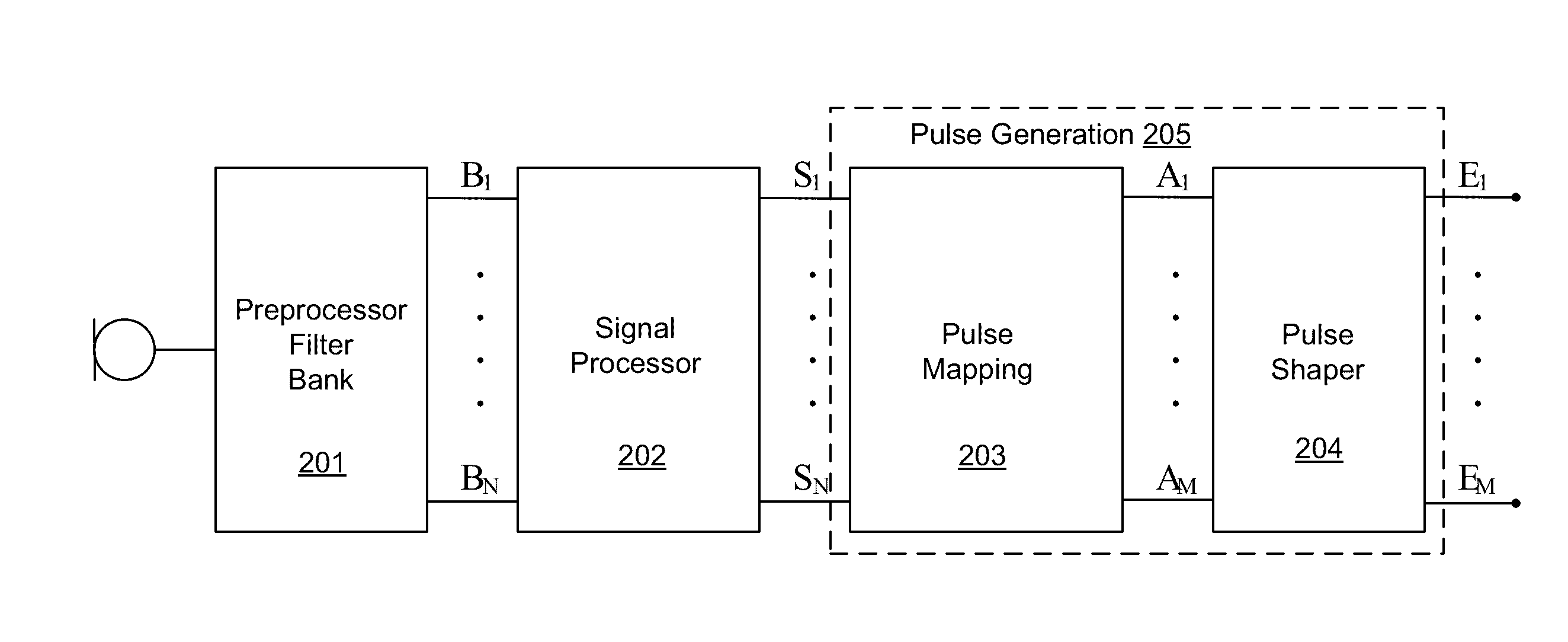
Coding of received audio signals and the resulting application of electrical stimuli applied to electrodes used in a cochlear implant system are disclosed together with a method of fitting this new coding strategy. One of the aims is to place specific stimulation representing pitch by applying near threshold electrical stimuli with limited and focussed excitation fields. A range of stimulation rates and a minimal range of current levels above threshold are used for creation of a dynamic loudness percept for a cochlear implant recipient. Another aim is to disclose a coding scheme based on a model of physiological measures (i.e. refractoriness, adaptation, spread of activation field, spatiotemporal acoustical cochlear activation patterns and spontaneous activity) to estimate the proportions of available excitable auditory neurons close to the electrodes available for stimulation. The spectral bands formed from the pre-processing of incoming audio signals are weighted by these proportions of excitability to control place, timing, rate and current level of electrical stimuli applied to the electrodes available in the array.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Flexible Communication and Control Protocol for a Wireless Sensor and Microstimulator Network
InactiveUS20080140154A1Improve performanceOptimize reliabilityInternal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringLine sensorMuscle force
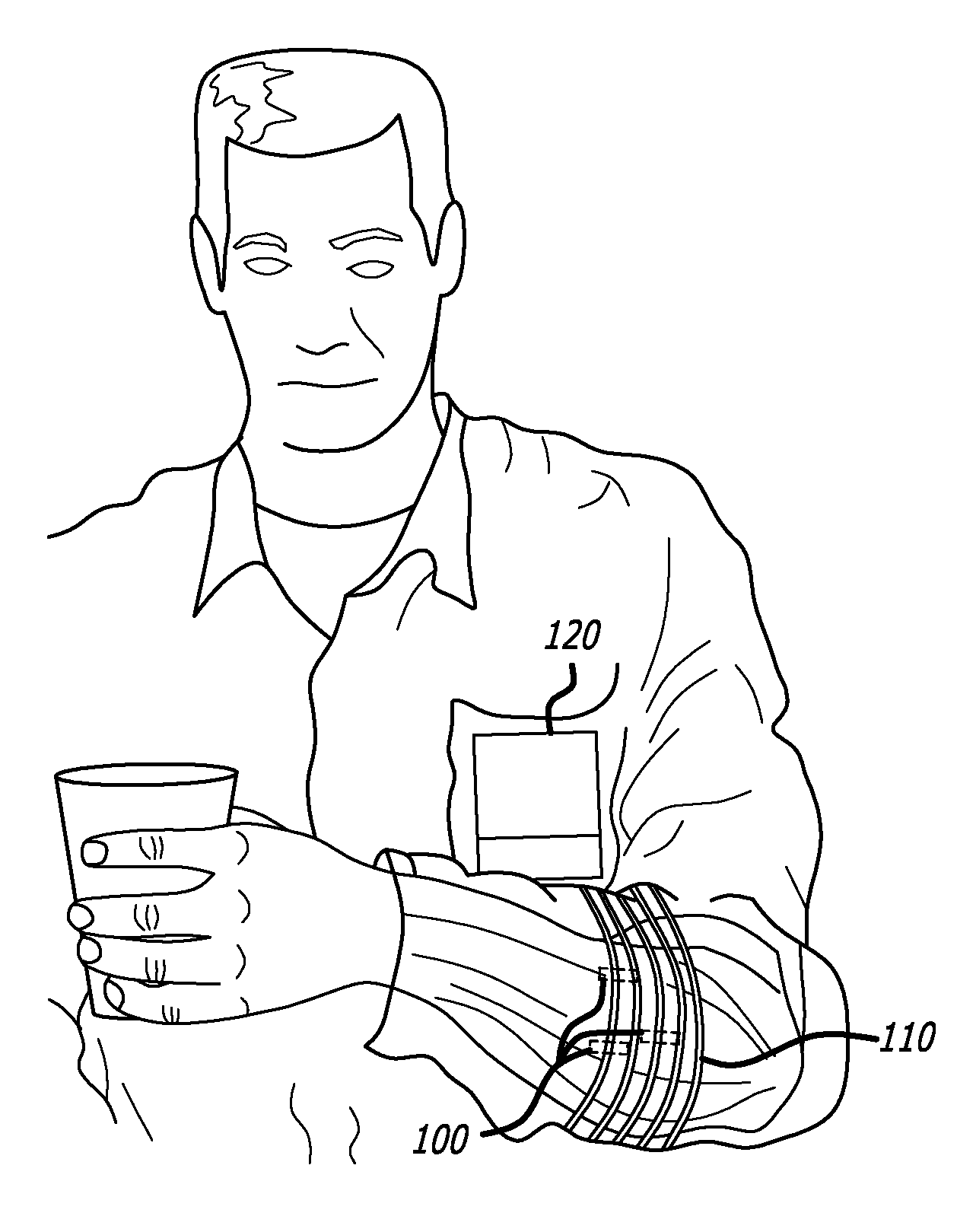
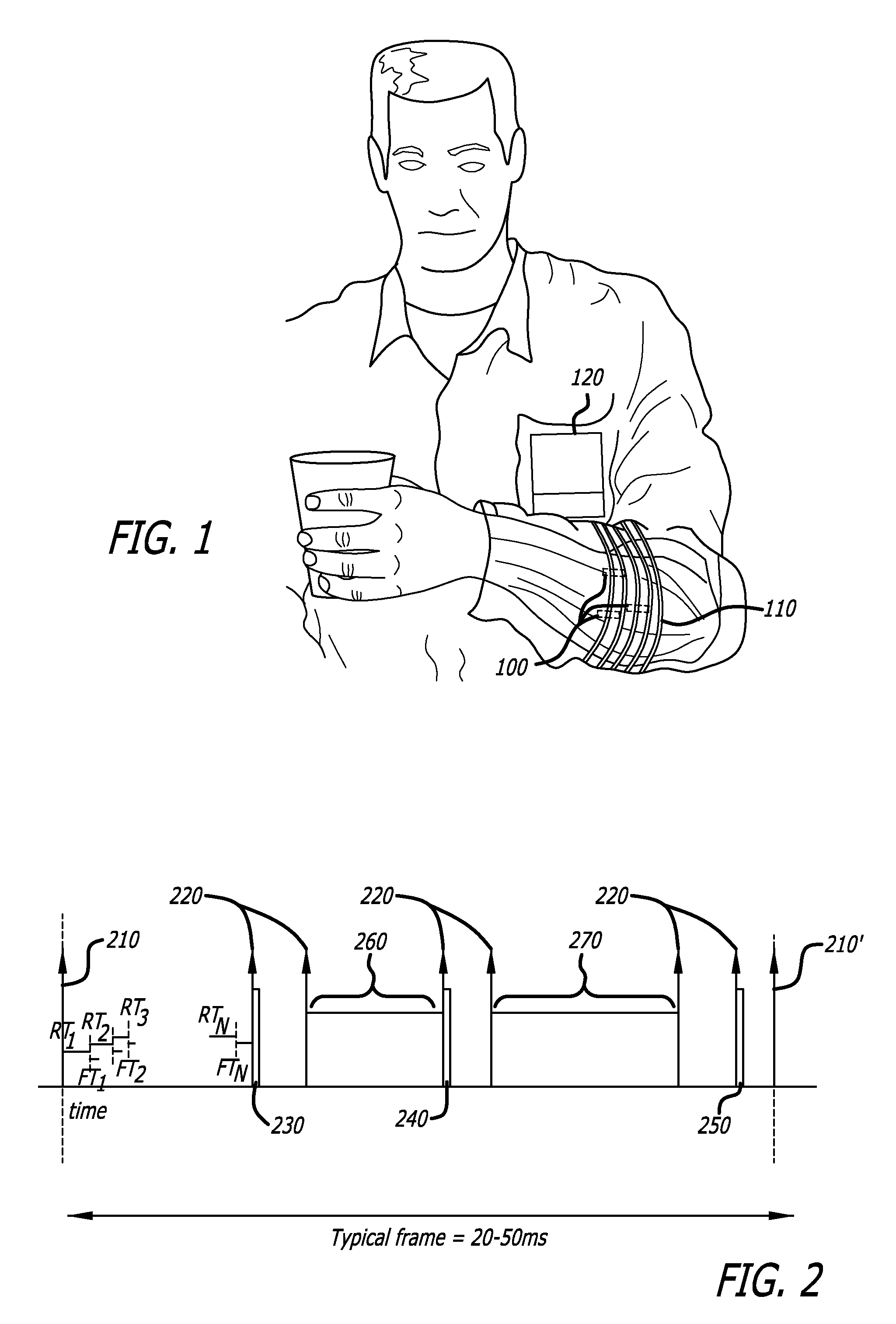
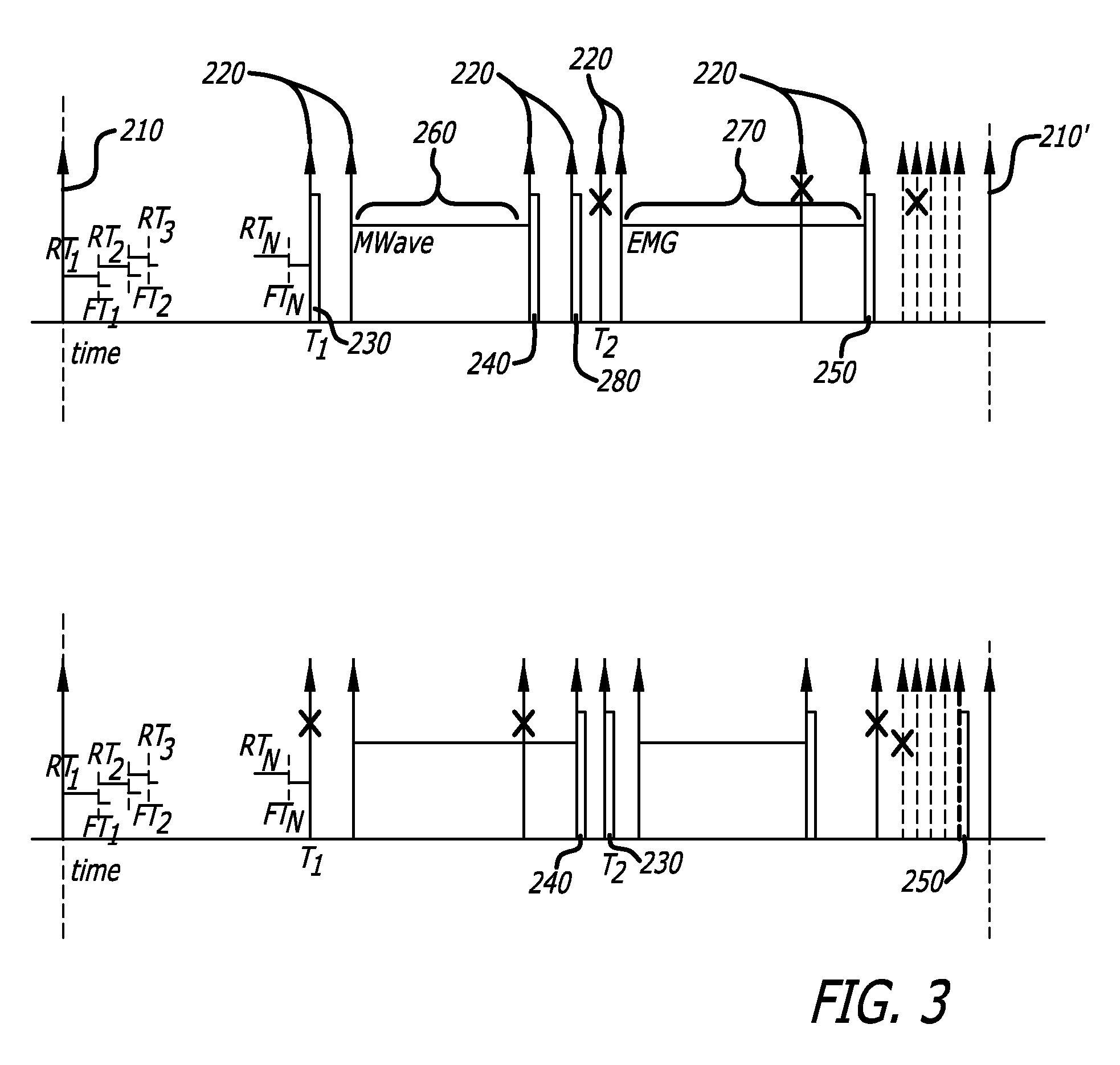
A novel system and method for restoring functional movement of a paralyzed limb(s) or a prosthetic device. Stimulating one or more muscles of a patient using an implanted neuromuscular implants and sensing the response of the stimulated muscle by the implants, wherein the sensing the response is not limited to data related to patient's movement intention, the posture, muscle extension, M-Wave and EMG. A communication and control protocol to operate the system safely and efficiently, use of forward and reverse telemetry channels having a limited bandwidth capacity, and minimizing the adverse consequences caused by errors in data transmission and intermittent loss of power to the implants. Adjusting stimulation rates and phases of the stimulator in order to achieve an efficient control of muscle force while minimizing fatigue and therefore providing for smooth movements and dynamic increase of the strength in patient's muscle contraction.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
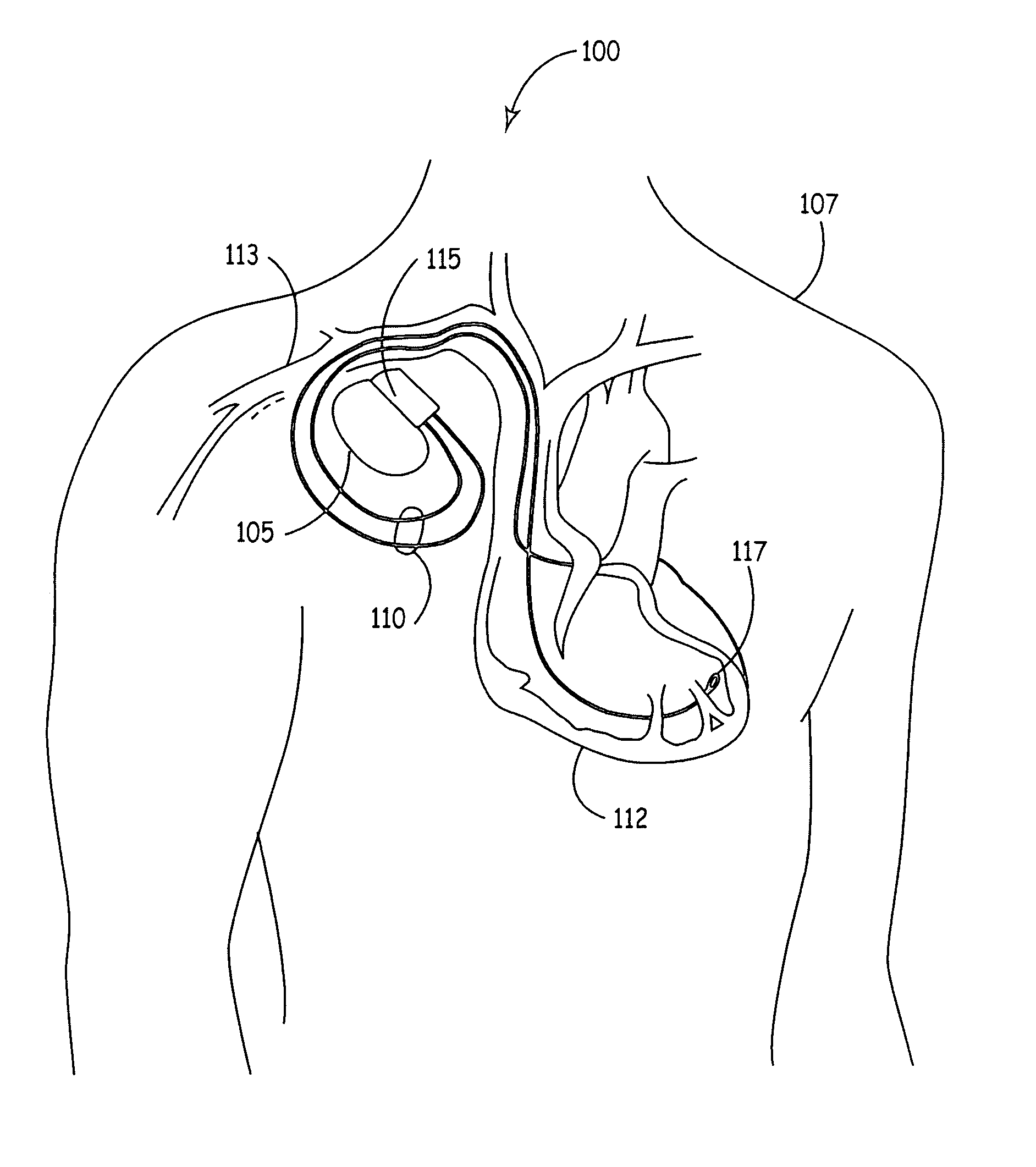
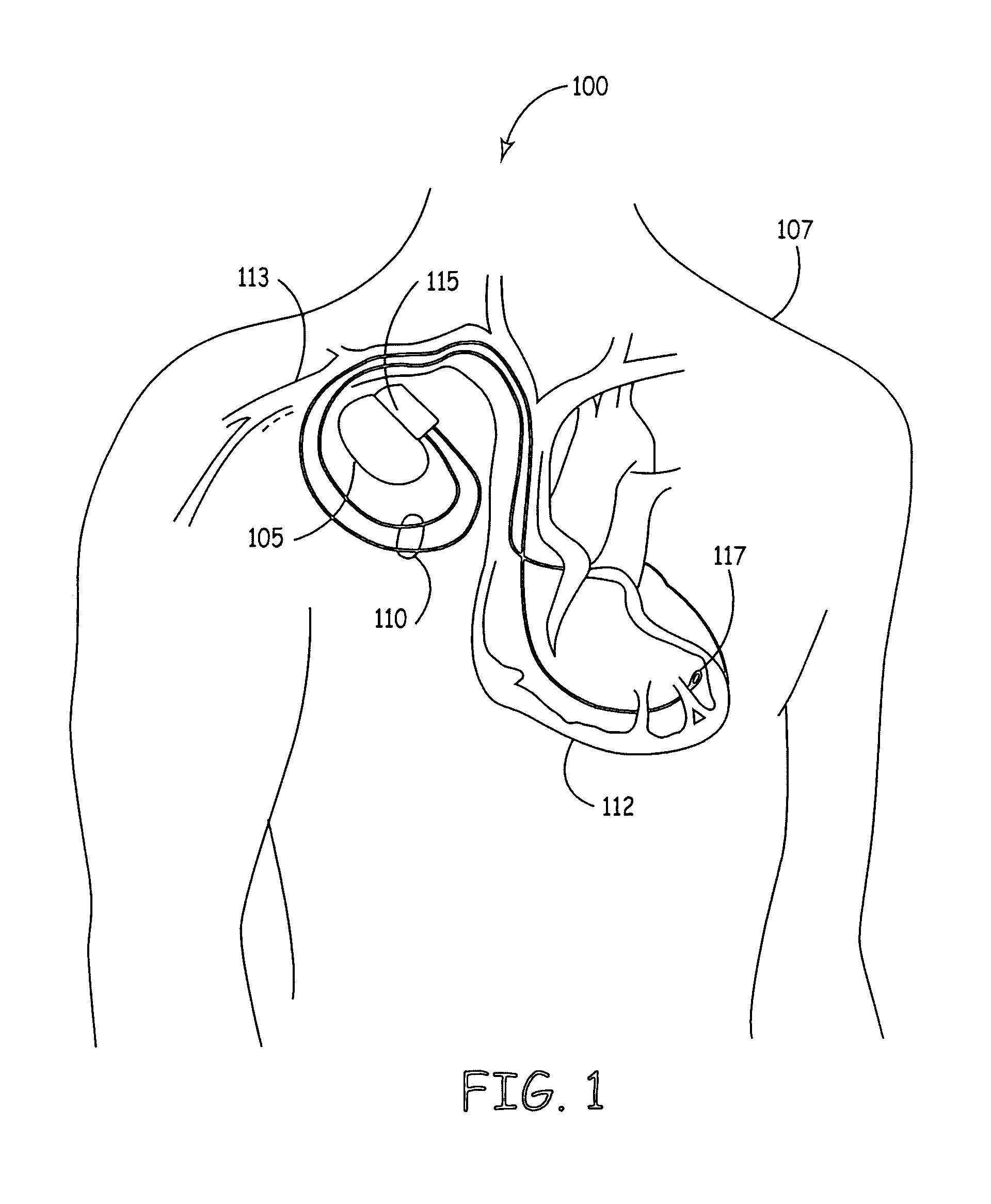
Heart stimulator using a Bezier function to define AV-delay values
Owner:BIOTRONIX CRM PATENT AG
Multi-site cardiac stimulation device for controlling inter-chamber stimulation delay
An implantable, multi-chamber cardiac stimulation device and method automatically adjust inter-chamber stimulation delays whenever stimulation rate is changed according to a patient's metabolic need. Inter-chamber stimulation delays include inter-atrial delays, inter-ventricular delays, and atrio-ventricular delays. Inter-chamber stimulation delays are defined according to whether the event which triggers the start of the delay is an intrinsic sensed event or the delivery of a stimulation pulse. Adjustment to inter-chamber stimulation delays is made as a function of the stimulation rate changes. By providing automatically adjustable inter-chamber stimulation delays optimal synchronization of heart chamber contractions may be maintained at all stimulation rates.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
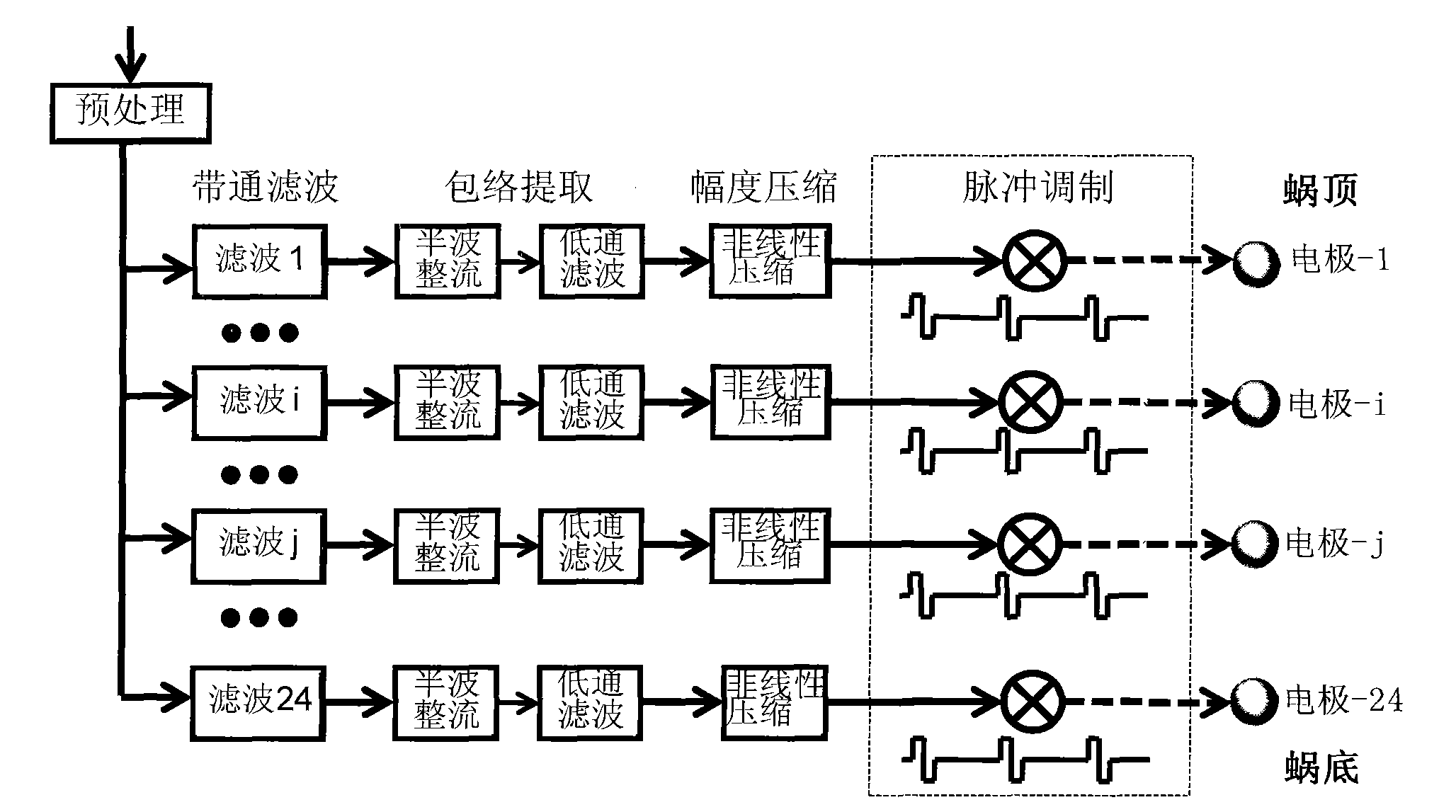
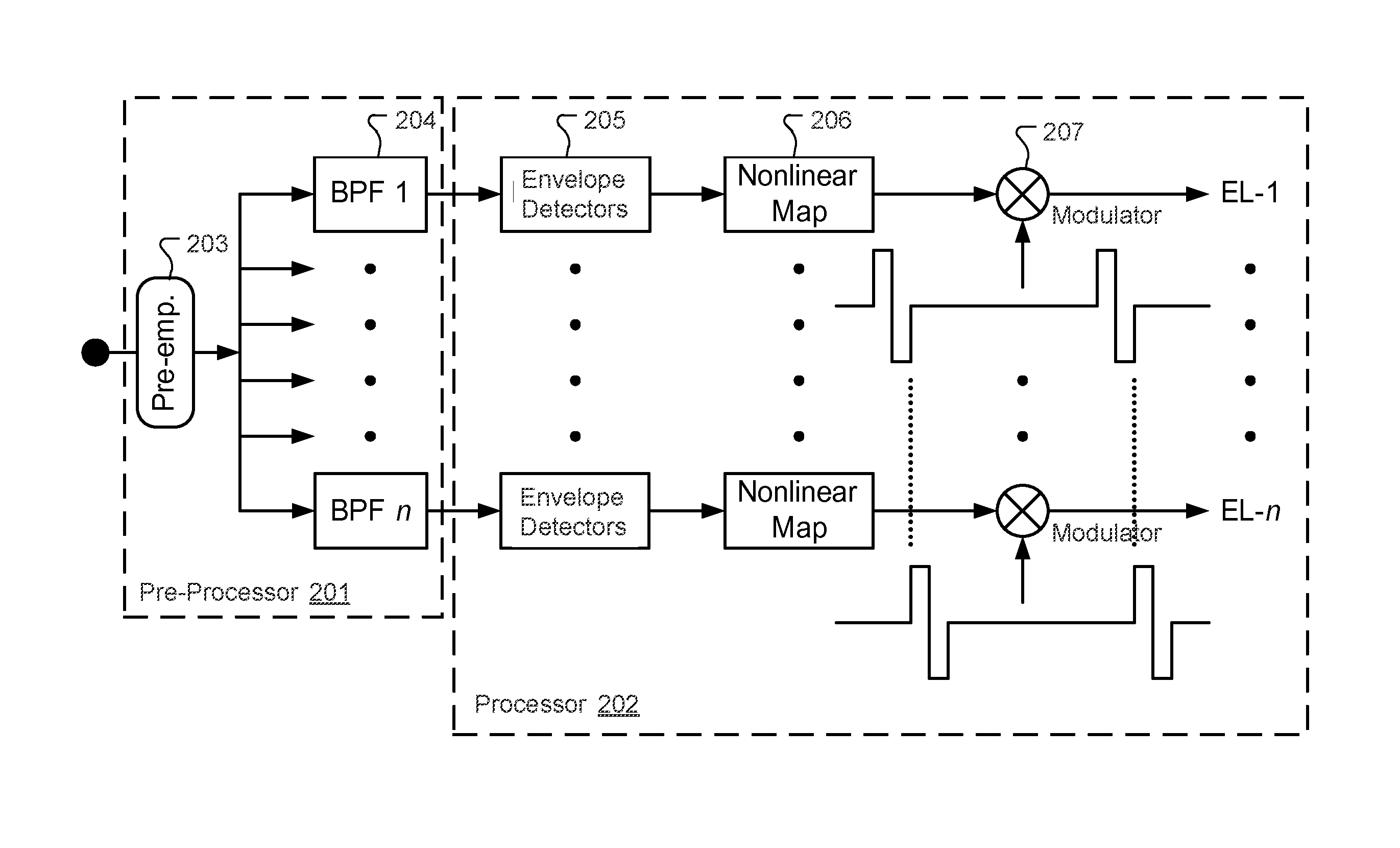
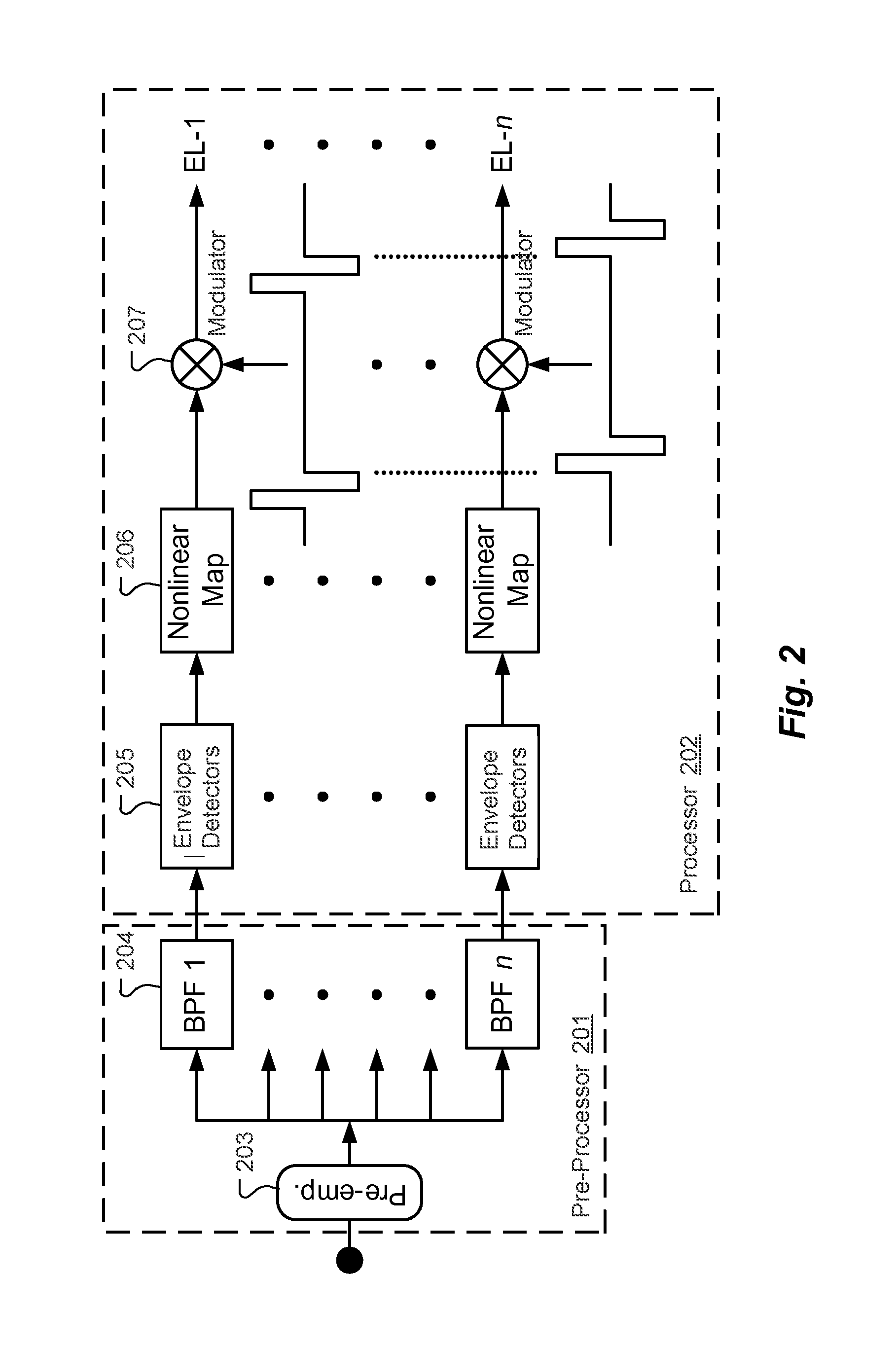
Voice processing method applied in electronic ear
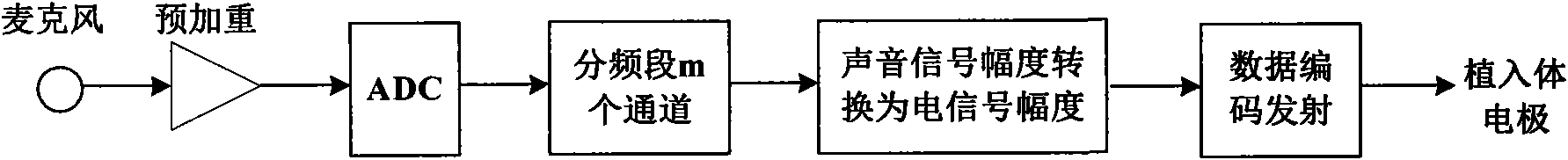
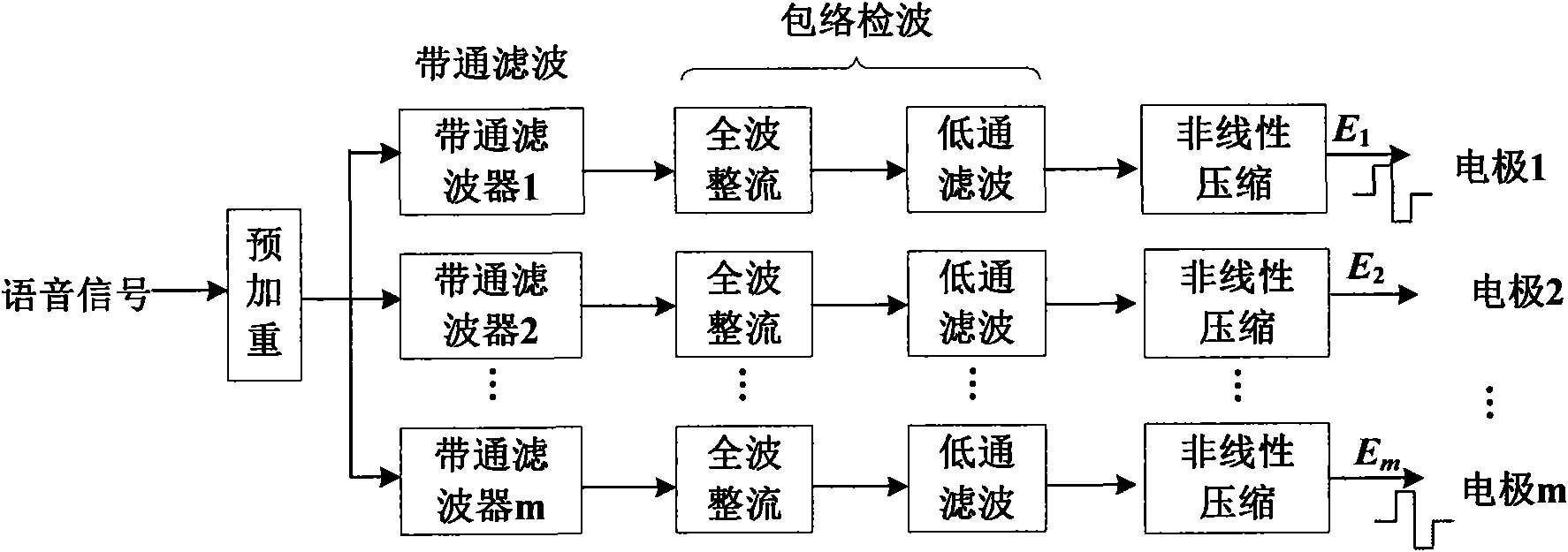
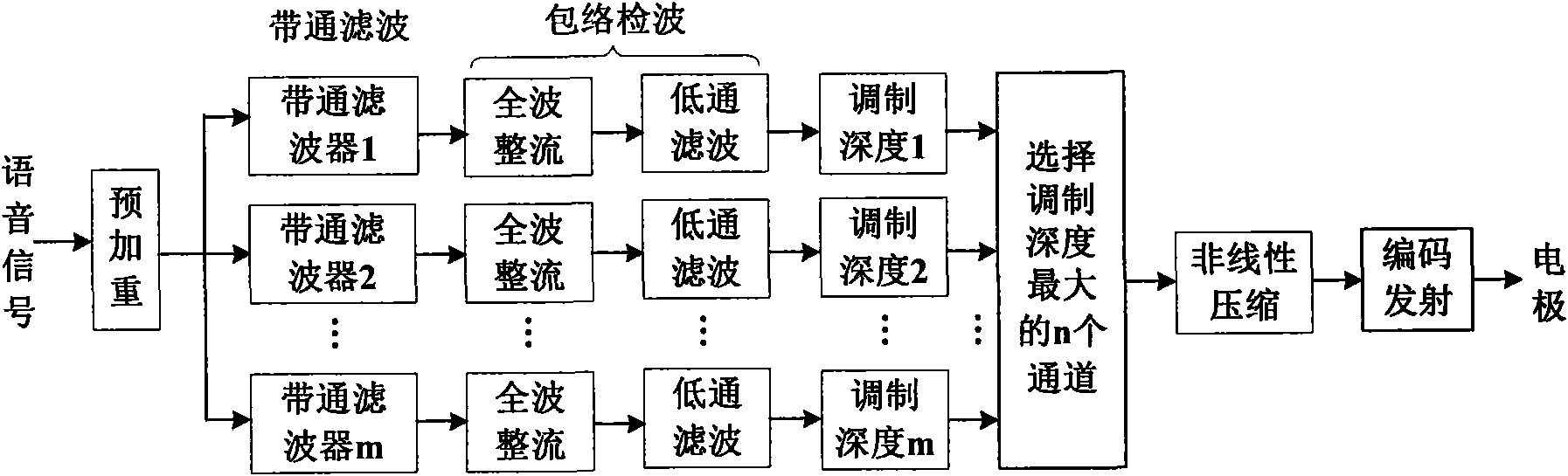
InactiveCN101645267AIncreased stimulation rateImprove accuracyEar treatmentSpeech recognitionFull waveFiltration
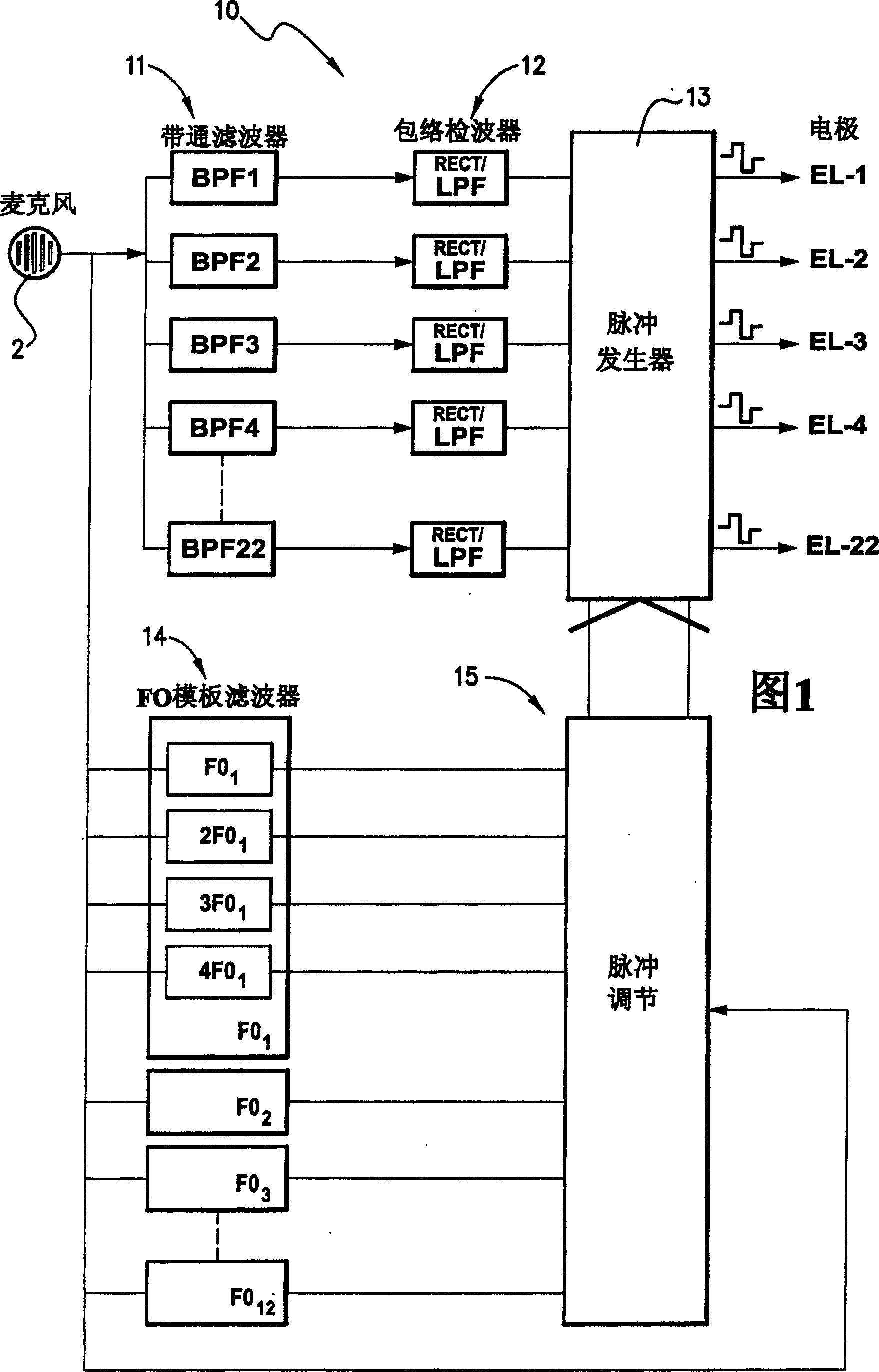
The invention provides a voice processing method applied in an electronic ear. The method comprises the steps of carrying out pre-emphasis treatment on an input voice signal by promoting high frequency components, then dividing the voice signal into m frequency bands through a filter group consisting of m band-pass filters, obtaining envelope signals of m channels by full-wave rectification and low-pass filtration, calculating the modulation depth of each channel, selecting n channels with greatest modulation depth, carrying out non-linear function compression on envelopes of the n channels for obtaining a relatively narrow dynamic range, using a symmetric dual-phase pulse sequence for carrying out modulation on envelope amplitude information after the compression of the n channels, modulating the asynchronization of the pulse sequence on time sequence, appearing alternating pulses and eliminating interferences among the channels. The stimulation rate of each channel obtained by usingthe n channels for stimulating an electrode is larger than the simulation rate of each channel when using m channels for simulating the electrode under the condition of constant total stimulation rate, thereby transferring more time domain details of the voice signal and improving the accuracy of voice recognition.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple channel-electrode mapping
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, methods and systems are disclosed for delivering a stimulating signal by a stimulating medical device having a plurality of electrodes. Such methods and systems comprise receiving a signal; filtering the received signal to obtain a plurality of band pass filtered signals; delivering to each electrode of a first group of one or more electrodes, a first set of stimulation signals, wherein the first set of stimulation signals comprises stimulations signals for each of a first group of two or more band pass filtered signals; and delivering to each of electrodes of a second group of one or more electrodes, a second set of stimulation signals, wherein the second set of stimulation signals comprises stimulations signals for each of a second group of one or more band pass filtered signals; and wherein the first set of stimulation signals are delivered at a different effective stimulation rate than the second set of stimulation signals.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Sound processing method and system
Coding of received audio signals and the resulting application of electrical stimuli applied to electrodes used in a cochlear implant system are disclosed together with a method of fitting this new coding strategy. One of the aims is to improve place specific stimulation representing pitch by applying near threshold electrical stimuli with limited and focused excitation fields. A range of stimulation rates and a minimal range of current levels above threshold are used for creation of a dynamic loudness percept for a cochlear implant recipient. Another aim is to disclose a coding scheme based on a model of physiological measures (i.e. refractoriness, adaptation, spread of activation field, spatiotemporal acoustical cochlear activation patterns and spontaneous activity) to estimate the proportions of available excitable auditory neurons close to the electrodes available for stimulation. The spectral bands formed from the pre-processing of incoming audio signals are weighted by these proportions of excitability to control place, timing, rate and current level of electrical stimuli applied to the electrodes available in the array.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Multirate cochlear stimulation strategy and apparatus
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Flexible communication and control protocol for a wireless sensor and microstimulator network
InactiveUS7593776B2Improve performanceHigh dynamic strengthElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringMuscle forceMuscle contraction
A novel system and method for restoring functional movement of a paralyzed limb(s) or a prosthetic device. Stimulating one or more muscles of a patient using an implanted neuromuscular implants and sensing the response of the stimulated muscle by the implants, wherein the sensing the response is not limited to data related to patient's movement intention, the posture, muscle extension, M-Wave and EMG. A communication and control protocol to operate the system safely and efficiently, use of forward and reverse telemetry channels having a limited bandwidth capacity, and minimizing the adverse consequences caused by errors in data transmission and intermittent loss of power to the implants. Adjusting stimulation rates and phases of the stimulator in order to achieve an efficient control of muscle force while minimizing fatigue and therefore providing for smooth movements and dynamic increase of the strength in patient's muscle contraction.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Electrical stimulation audition tone perception testing and estimating system
InactiveCN102058453AAccurate and effective measurementAccurate and effective evaluationEar treatmentAudiometeringElectricityPattern perception
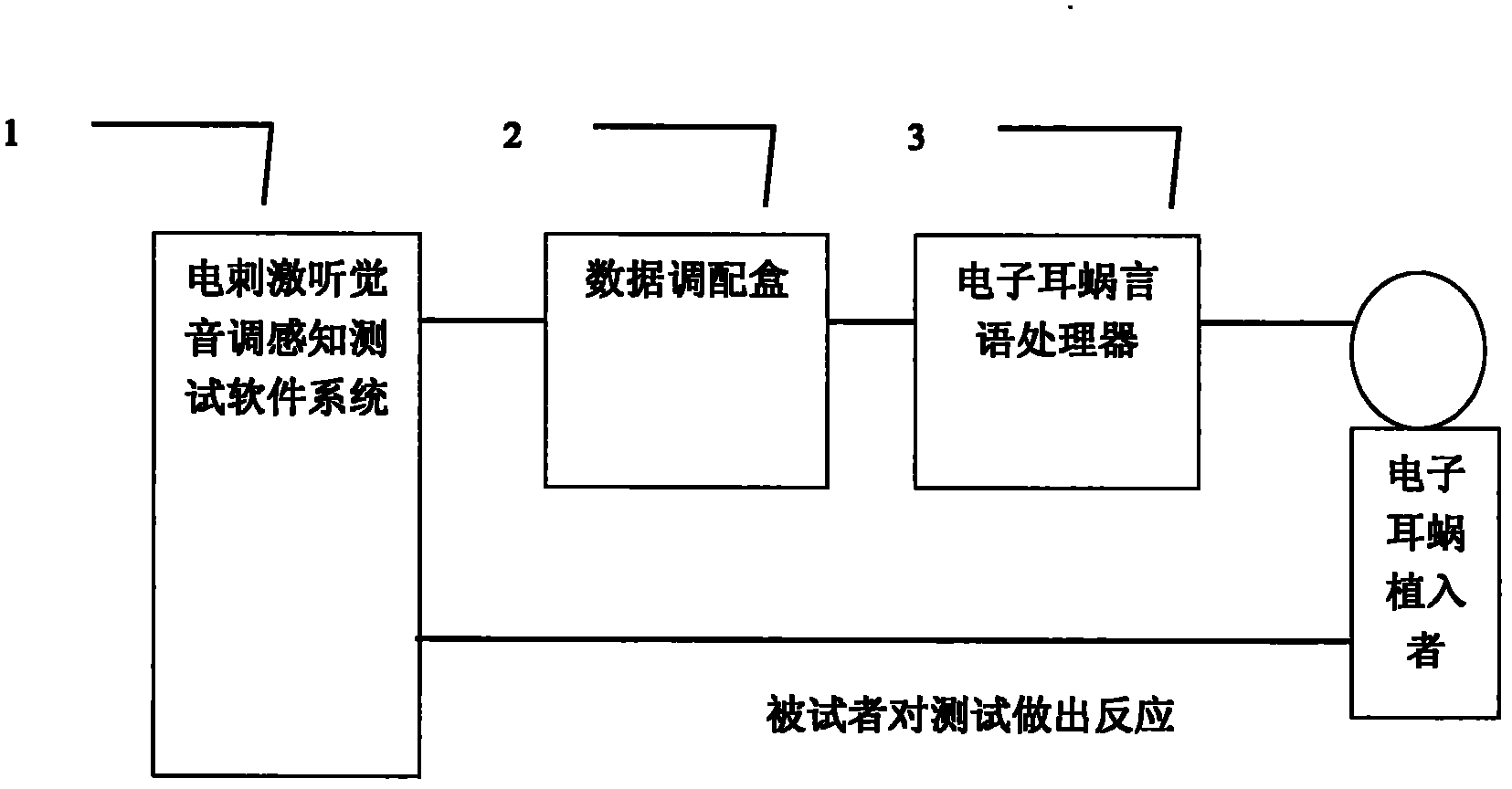
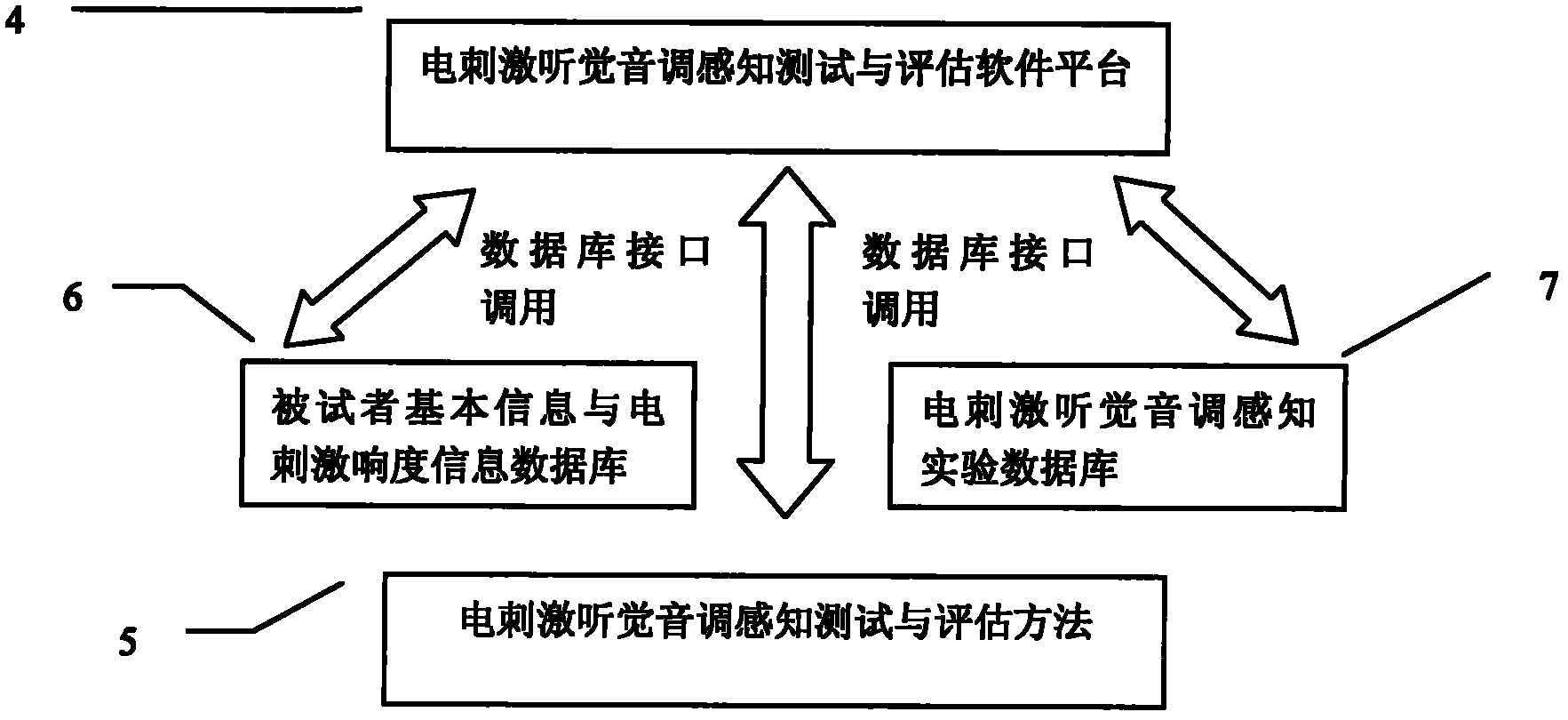
The invention relates to an electrical stimulation audition tone perception testing and estimating system. By selecting a part tone testing and estimating module (8), a time tone testing and estimating module (9) or a part-time combined tone perception testing and estimating module (10), the testing and estimation are carried out by combining a testee basic information and electrical stimulation loudness information database (6) with an electrical stimulation audition tone perception experimental database (7); the part tone testing and estimating module (8) is used for testing the correlationbetween an implanted electrode position and electrical stimulation audition tone perception; the time tone testing and estimating module (9) is used for testing the correlation between an electric pulse stimulation rate and tone perception; and the part-time combined tone perception testing and estimating module (10) is used for testing the correlation between electrode position-electric pulse stimulation rate combination and tone perception. The method is accurate and effective.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Audio processing method and system implantted cochlea
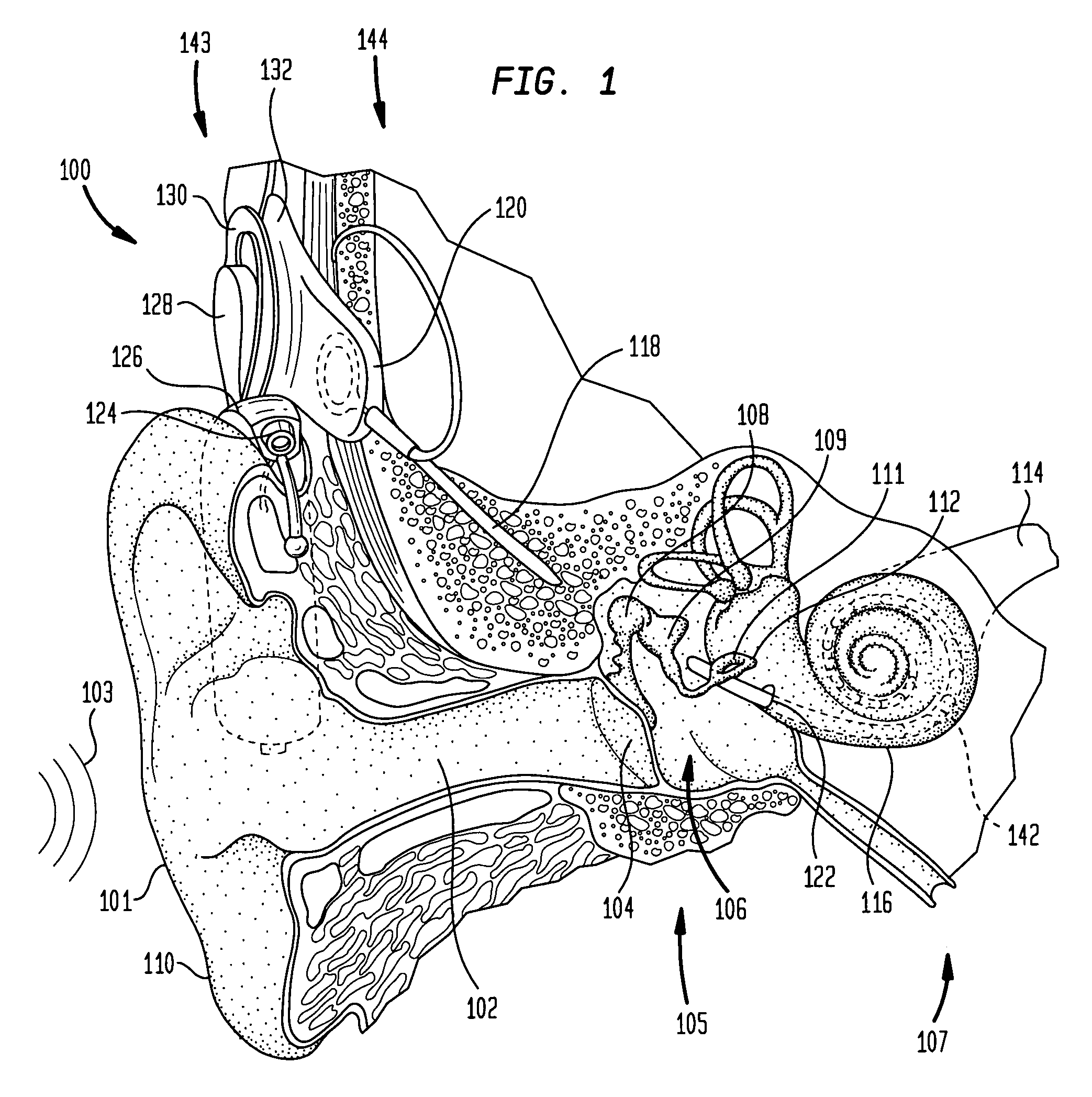
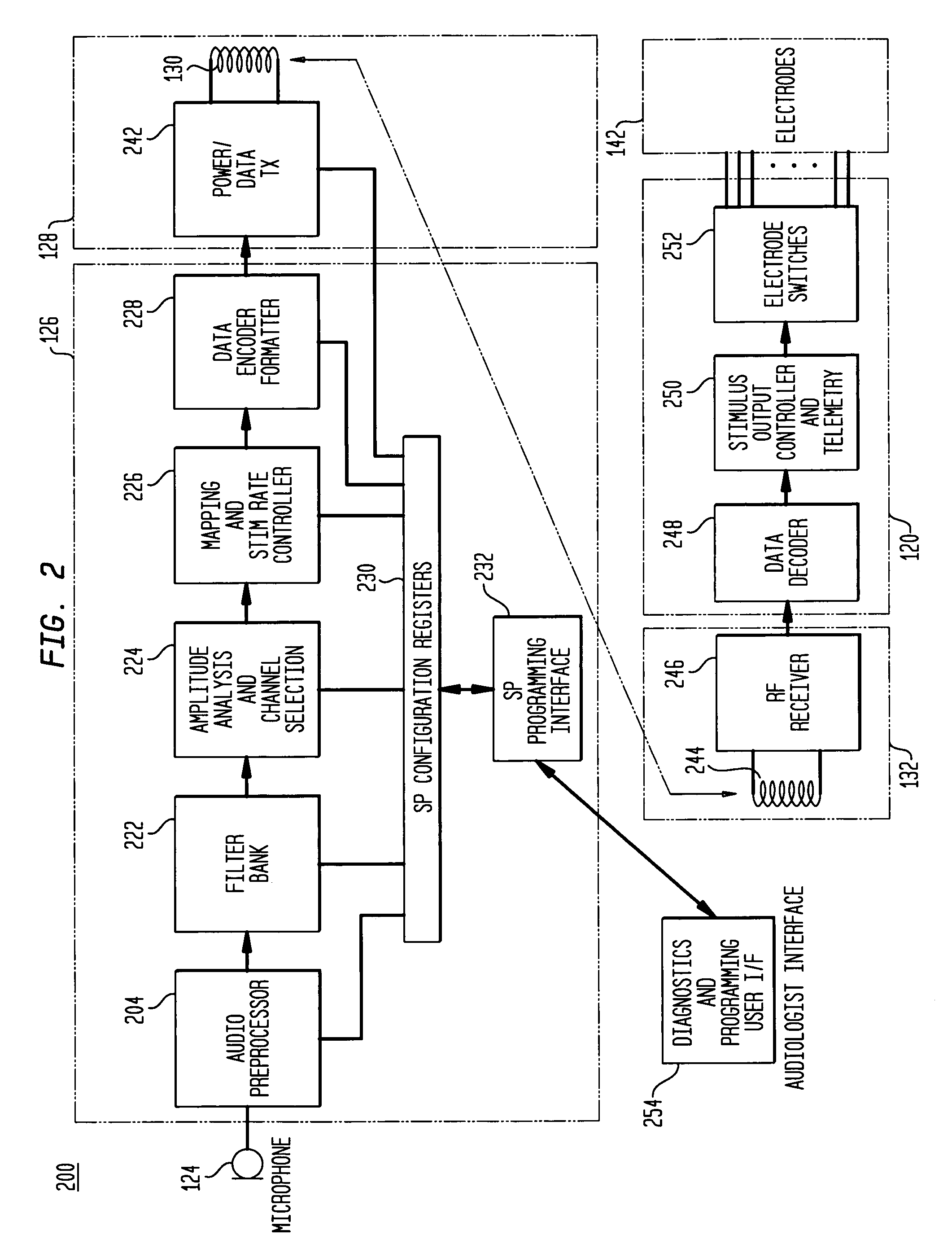
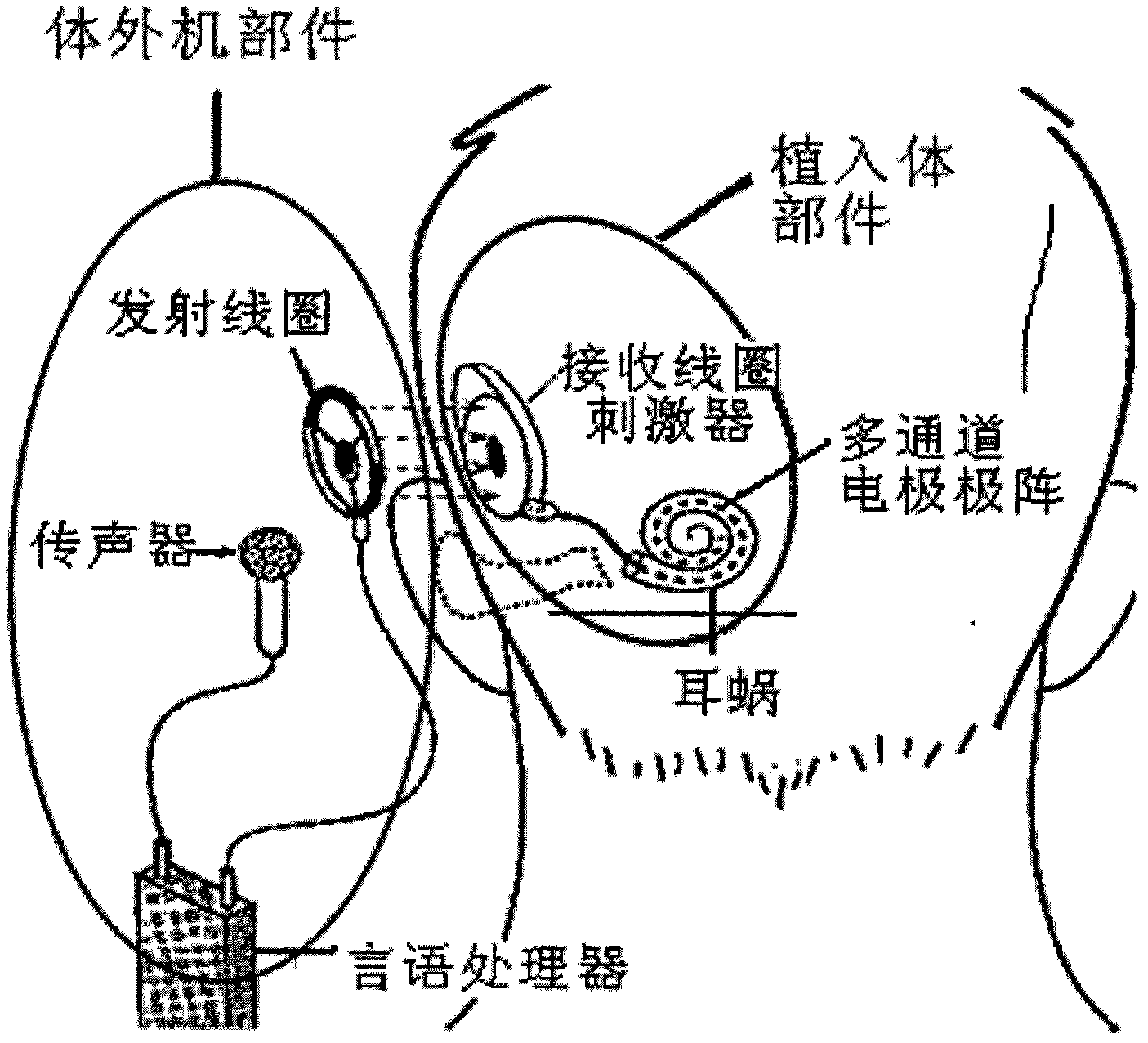
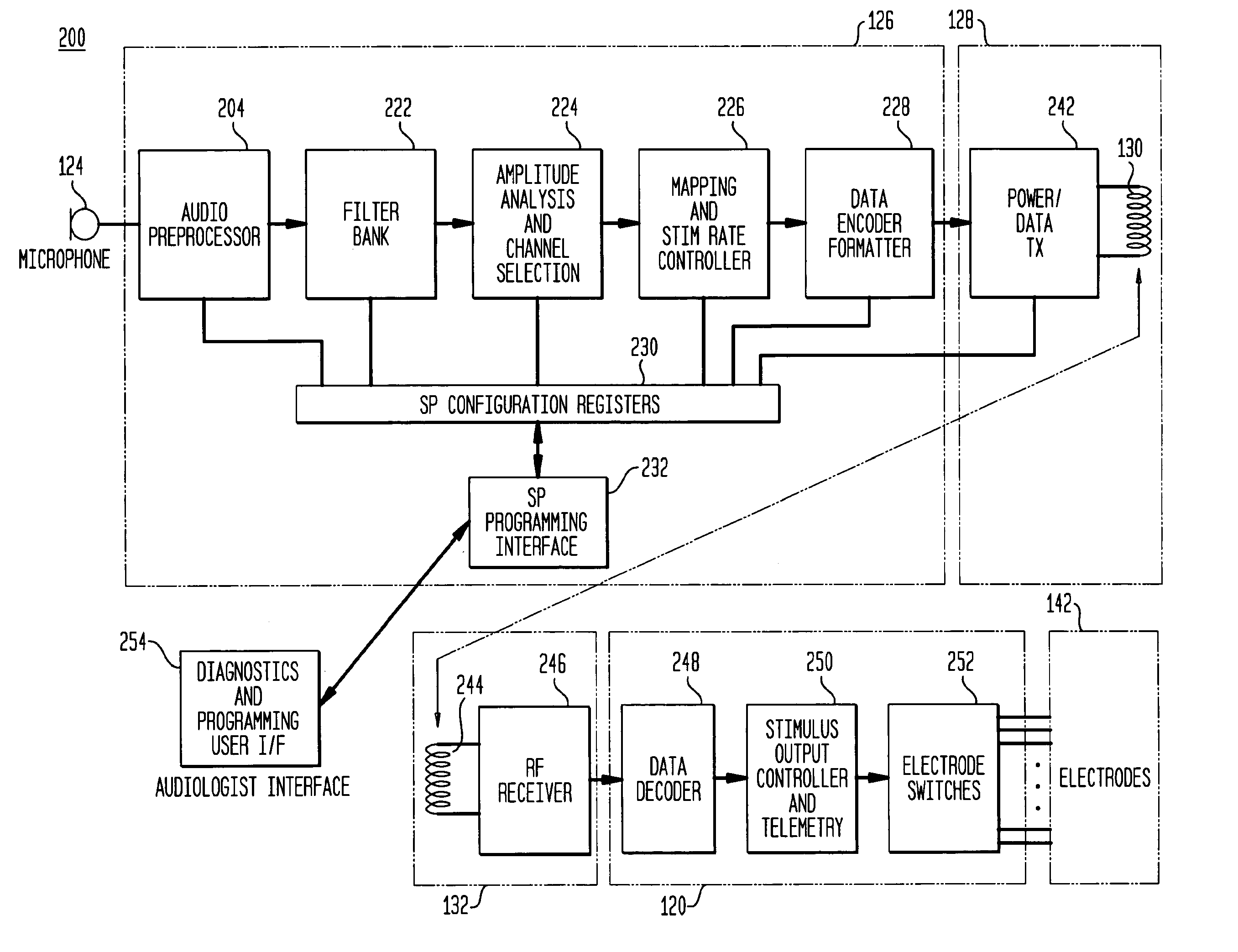
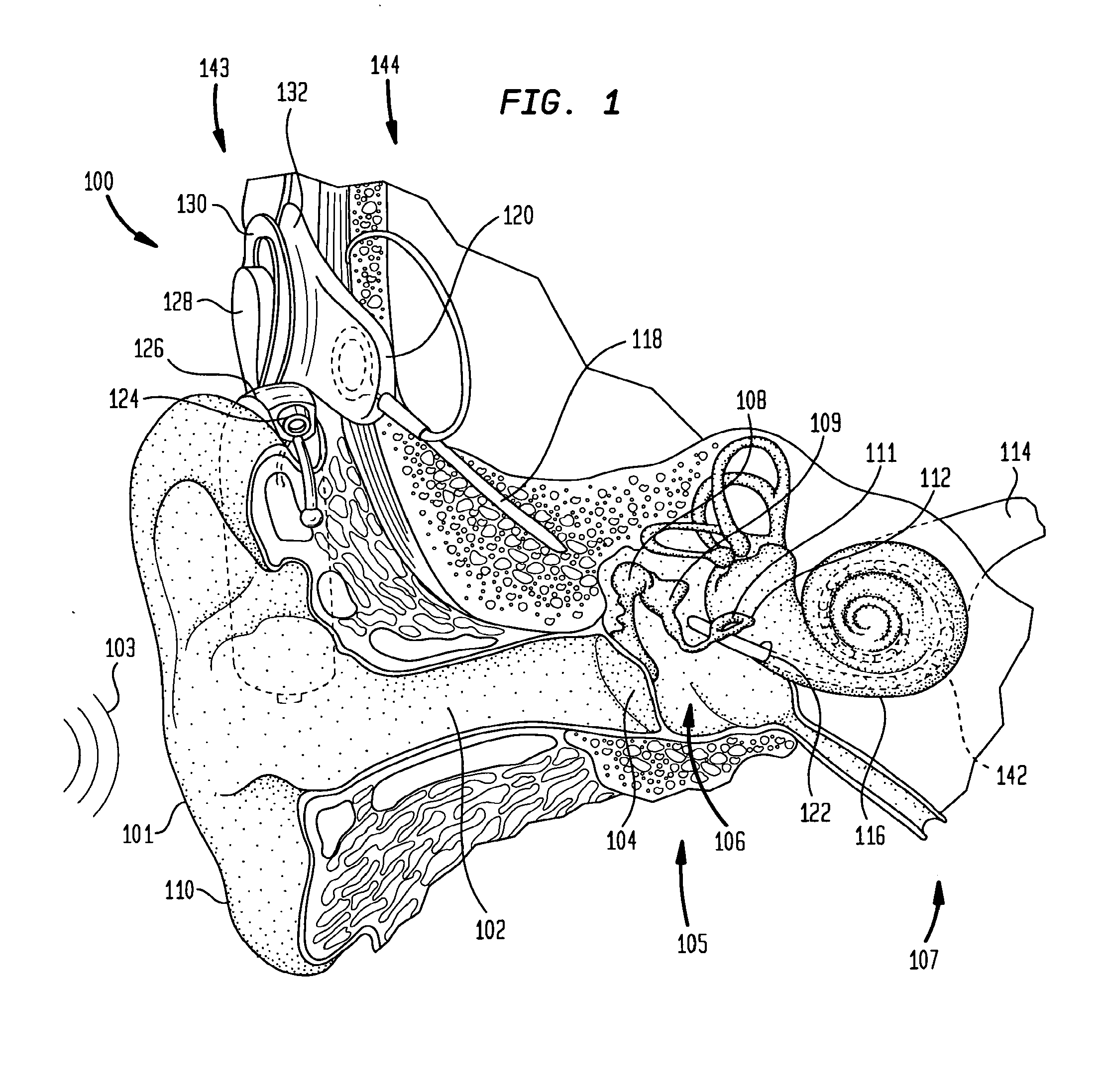
An auditory prosthesis device for selectively stimulating electrodes within an auditory prosthesis electrode array, comprising a transducer ( 2 ) for converting a complex acoustic sound into an electrical signal; signal processing means ( 13 ) responsive to an electrical signal and generating a temporal pattern of stimulation pulses to selected electrodes within the electrode array, the stimulation pulses being applied to each electrode at an electrode stimulation rate; feature extraction means ( 14 ) for deriving an estimate of at least one fundamental frequency of the electrical signal; and stimulation pulse adjustment means ( 15 ) for adjusting the stimulation pulses in accordance with the estimated fundamental frequency.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Multiple channel-electrode mapping
In accordance with one aspect of the invention, methods and systems are disclosed for delivering a stimulating signal by a stimulating medical device having a plurality of electrodes. Such methods and systems comprise receiving a signal; filtering the received signal to obtain a plurality of band pass filtered signals; delivering to each electrode of a first group of one or more electrodes, a first set of stimulation signals, wherein the first set of stimulation signals comprises stimulations signals for each of a first group of two or more band pass filtered signals; and delivering to each of electrodes of a second group of one or more electrodes, a second set of stimulation signals, wherein the second set of stimulation signals comprises stimulations signals for each of a second group of one or more band pass filtered signals; and wherein the first set of stimulation signals are delivered at a different effective stimulation rate than the second set of stimulation signals.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Artificial electronic cochlea and method for processing speech with double stimulation rates
ActiveCN101773429AImprove speech recognition performanceSolve the problem of missing low-amplitude envelope informationEar treatmentSpeech ProcessorElectrical impulse
The invention discloses an artificial electronic cochlea, a speech processor and a method for processing a speech with double stimulation rates. The speed processor and the method are applied to the artificial electronic cochlea, and the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, performing preprocessing, band-pass filtering, half-wave rectification and low-pass filtering on speech signalsto acquire the envelope amplitude of each channel, and adjusting the current amplitude to a working amplitude range; secondly, selecting a plurality of channels of which the envelope amplitudes are more than or equal to a threshold value to form a first part (high-amplitude) channel, and performing pulse sequence modulation with a first (high) stimulation rate on the first part channel; selectinga plurality of channels of which the envelop amplitudes are smaller than the threshold value to form a second part (low-amplitude) channel, and performing pulse sequence modulation with a second (low) stimulation rate on the second part channel; and adopting electronic pulse sequences of the first and second part channels after modulation to stimulate corresponding stimulating electrodes. The artificial electronic cochlea, the speech processor and the method realize the aim of transmitting information on the envelope amplitudes of all the channels to an artificial electronic cochlea patient, and effectively improve the speech recognition effect of the artificial electronic cochlea.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NUROTRON BIOTECH
Methods and apparatus for reducing spurious signals in implantable medical devices caused by x-ray radiation
An implantable medical device (IMD) includes a detector for detecting the presence of x-ray radiation, where the presence of x-ray radiation is detected in response to the strength of the x-ray radiation exceeding a first threshold. In one embodiment, the IMD includes a processor for adjusting a cardiac stimulation rate IMD in response to determining that the strength of the detected x-ray radiation exceeds a second threshold. The second pre-selected x-ray radiation threshold is greater than the first pre-selected x-ray radiation threshold. In another embodiment, the implantable device includes a detector for detecting the presence of any amount x-ray radiation and a processor for adjusting a stimulation rate provided by the IMD in response to detected x-ray radiation to reduce the chance of over-sampling artifacts or inappropriate therapy delivery.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Auditory Prosthesis Using Stimulation Rate as a Multiple of Periodicity of Sensed Sound
ActiveUS20150051668A1Enhances prominent frequencyImprove representationCompletely in canal hearing aidsHead electrodesStimulus frequencyProsthesis
A method is described for an auditory prosthesis system to generate electrical stimulation signals to stimulation contacts on an outer surface of an implanted electrode array. An input audio signal having a prominent sensed frequency is pre-processed to produce multiple representative frequency band signals. Each of the frequency band signals is then processed to generate corresponding electric stimulation signals for the stimulation contacts. Each of the electric stimulation signals has an associated stimulation frequency, and for at least one of the electric stimulation signals, the stimulation frequency is varied to maintain an integer ratio between the stimulation frequency and the prominent sensed frequency of the input audio signal.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
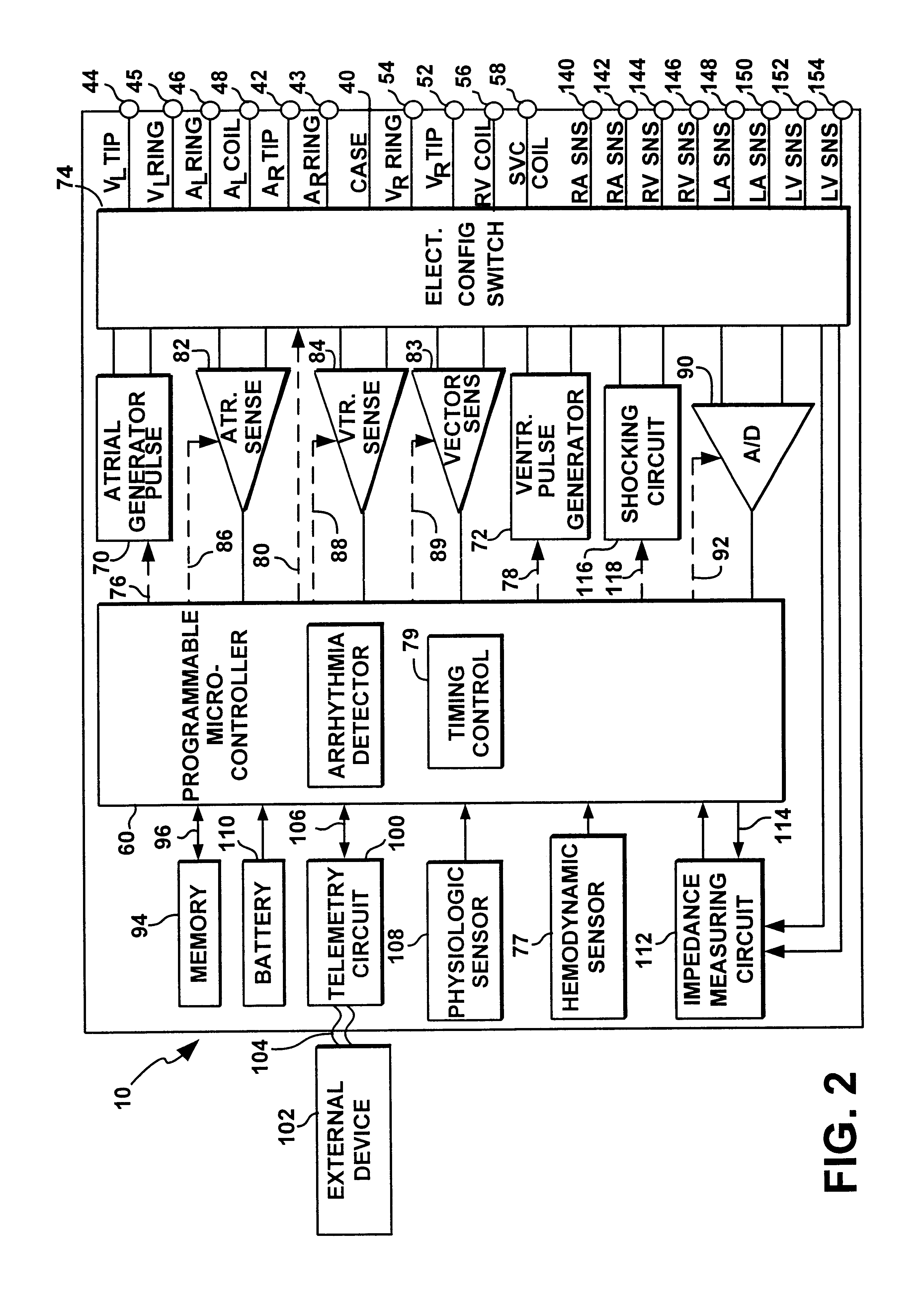
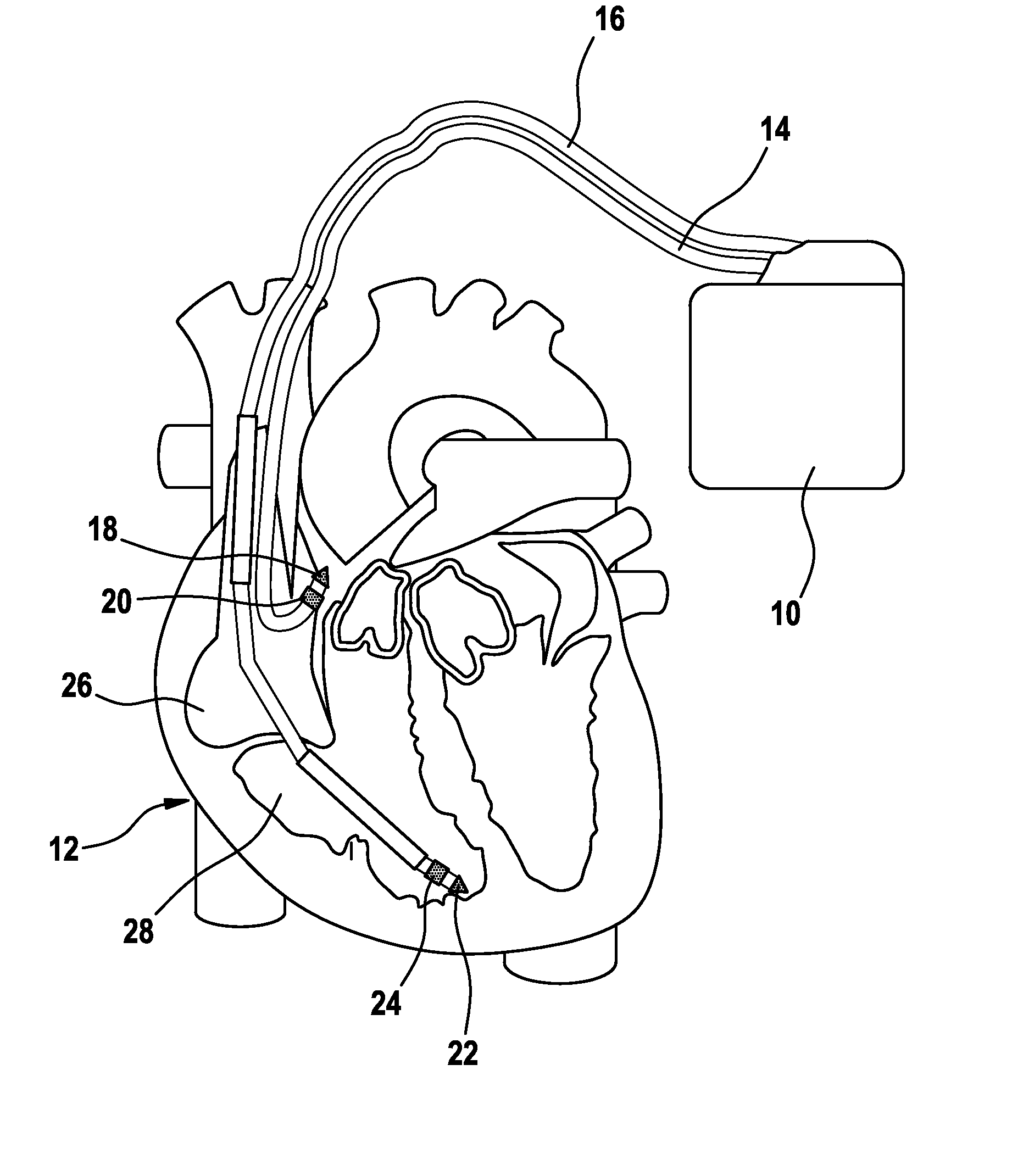
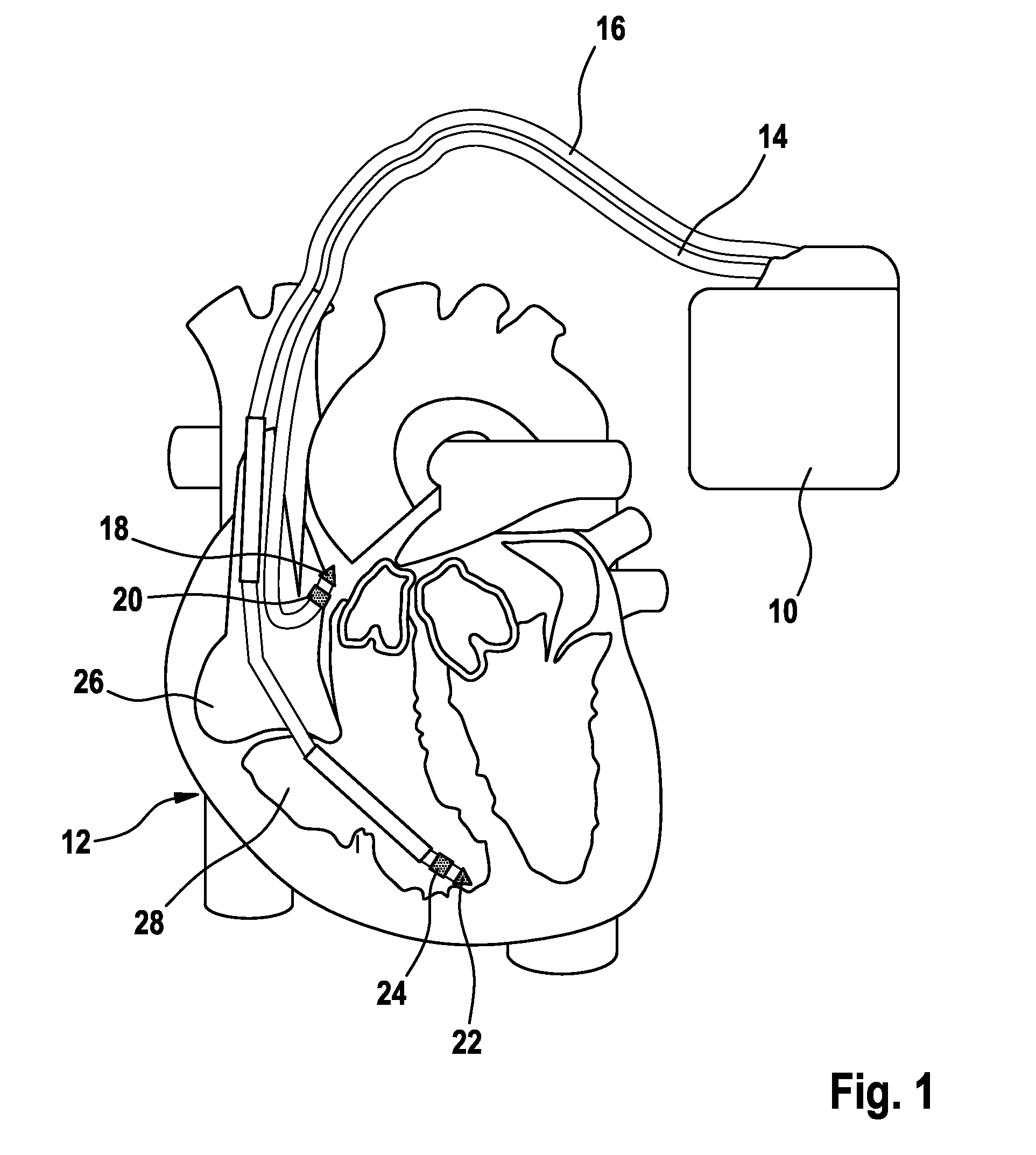
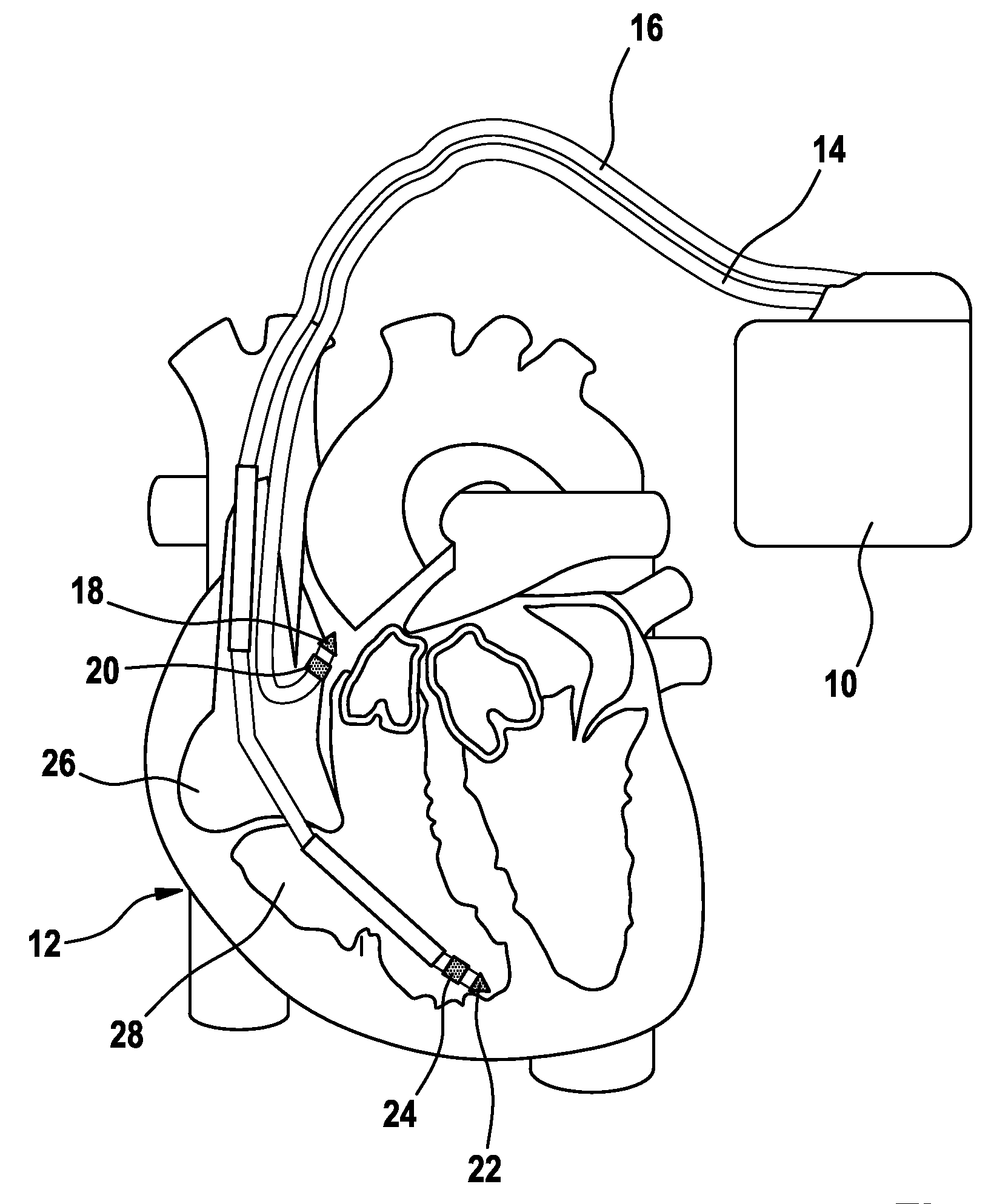
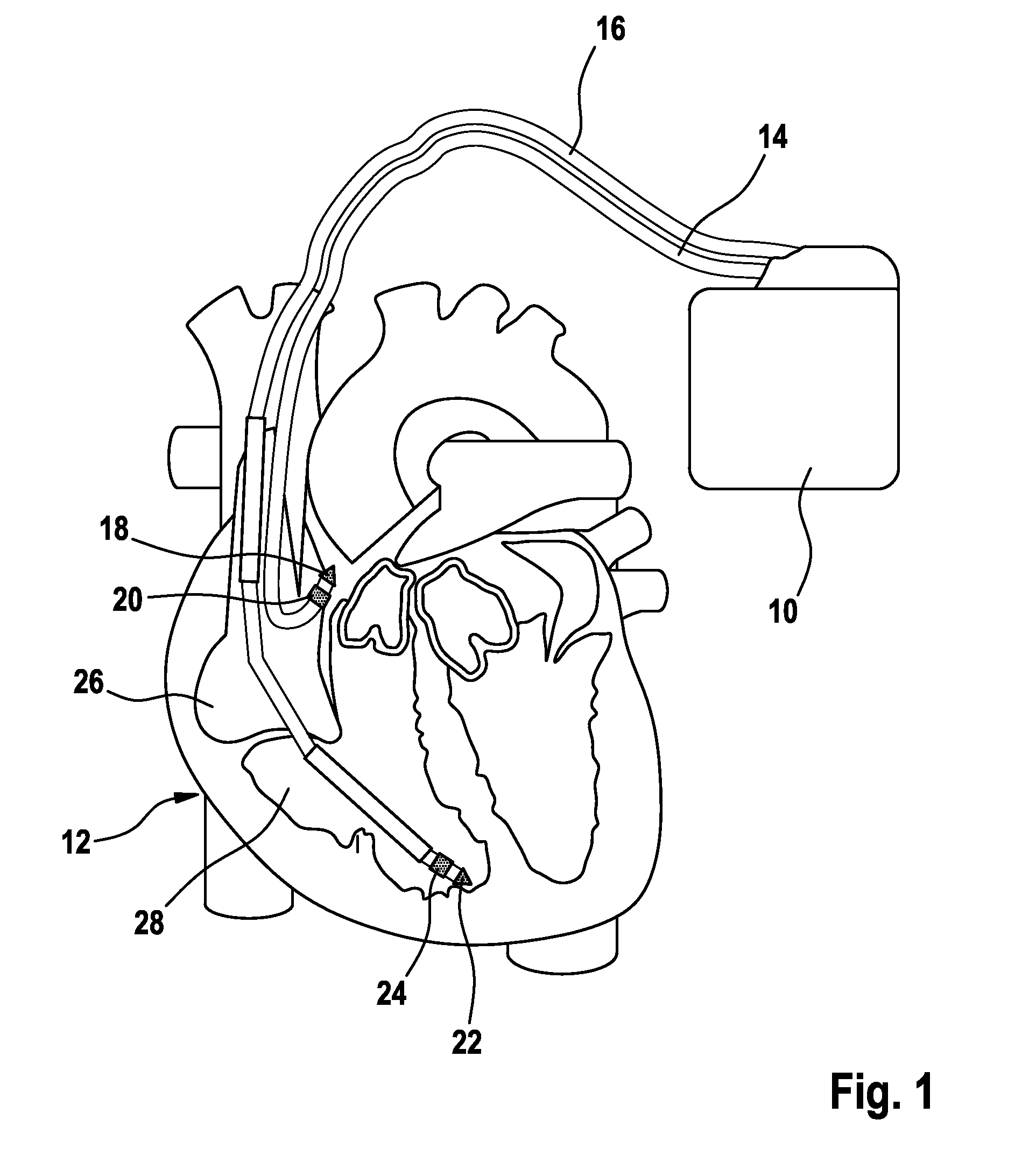
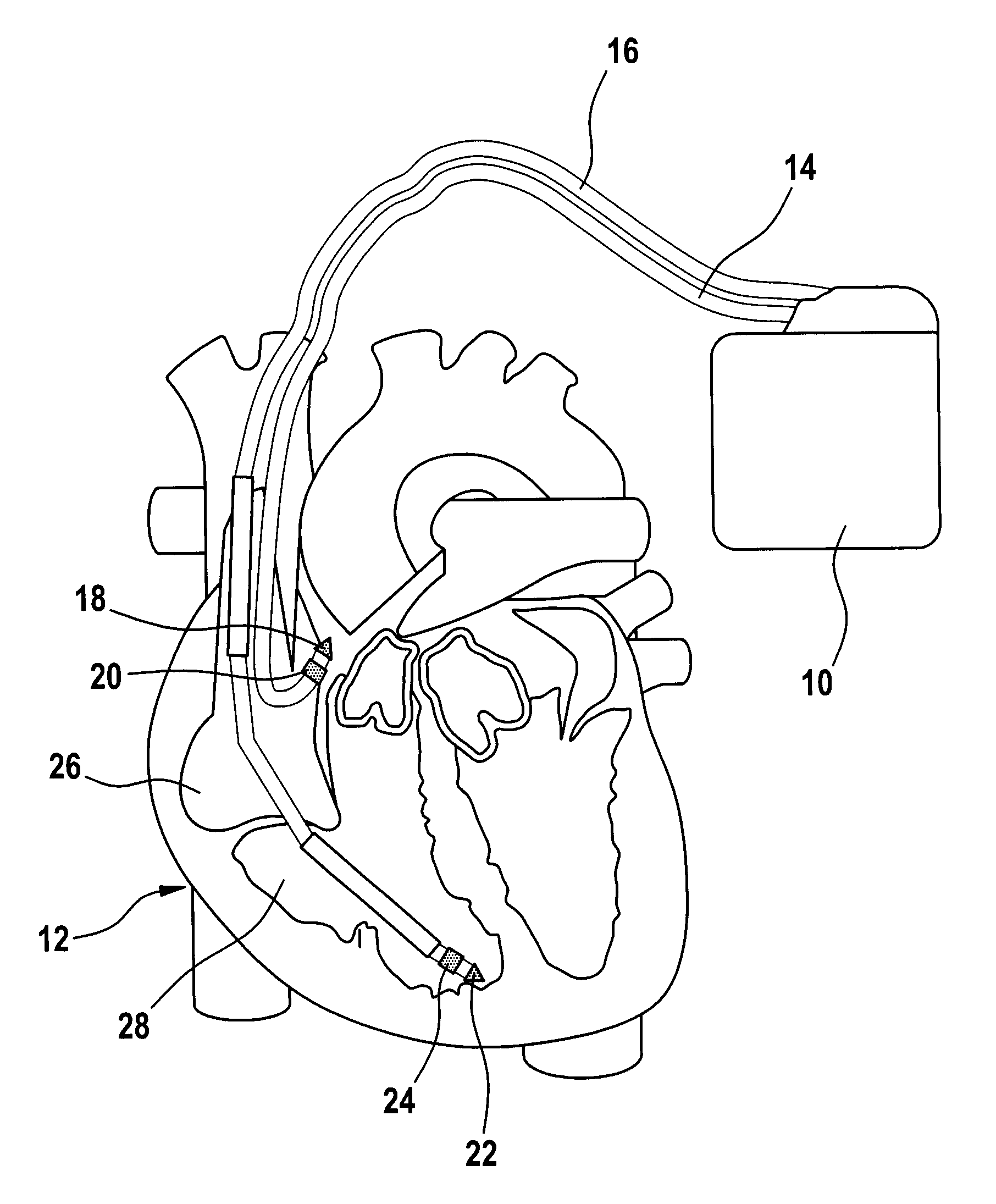
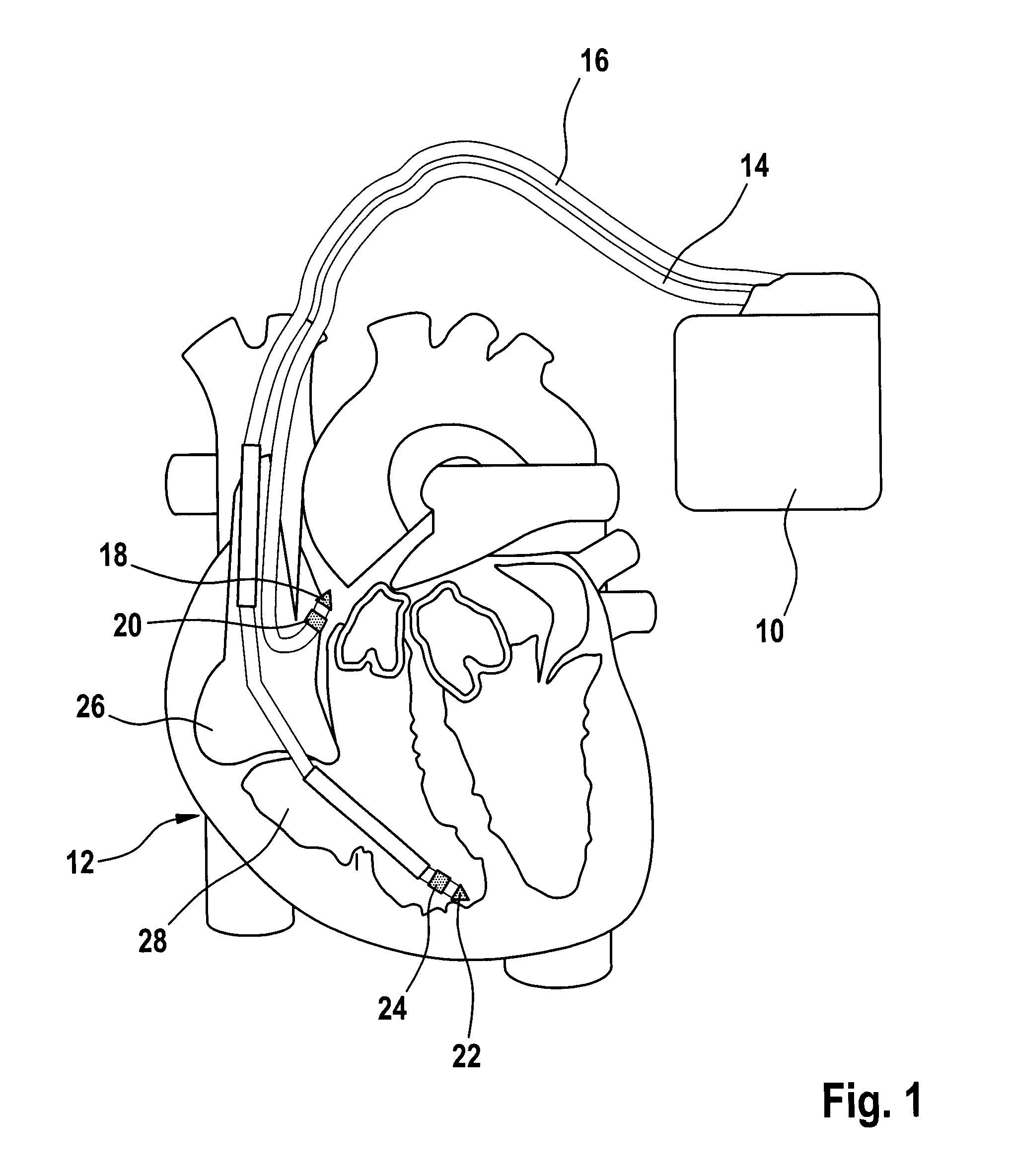
Heart Stimulator
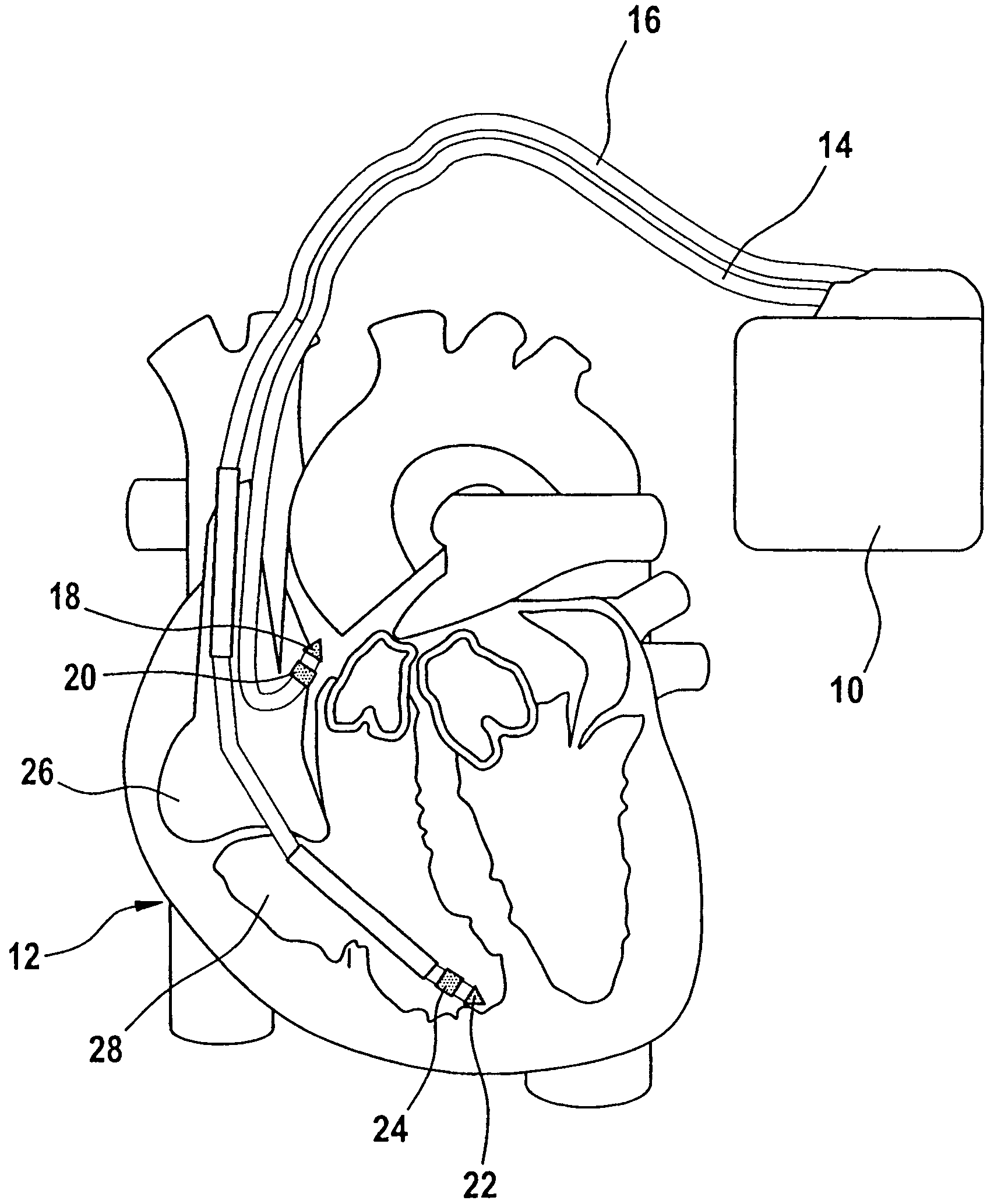
A heart stimulator provides for a more appropriate yet simple setting of the AV-delay. The heart stimulator comprises a stimulation pulse generator adapted to generate electric stimulation pulses and connected to a ventricular stimulation electrode for delivering electric stimulation pulses. A sensing stage connected to an electrode for picking up electric potentials inside a ventricle is adapted to sense an excitation or a contraction of a heart chamber. A memory is adapted to store parameters defining a Bezier function determining the relationship between AV-delay values and heart rate and a control unit connected to said memory, said sensing stage and to said stimulation pulse generator, is adapted to determine an actual AV-delay based on an actual intrinsic heart rate or an actual stimulation rate and a non-linear smoothing interpolation between said parameters stored in said memory.
Owner:BIOTRONIX CRM PATENT AG
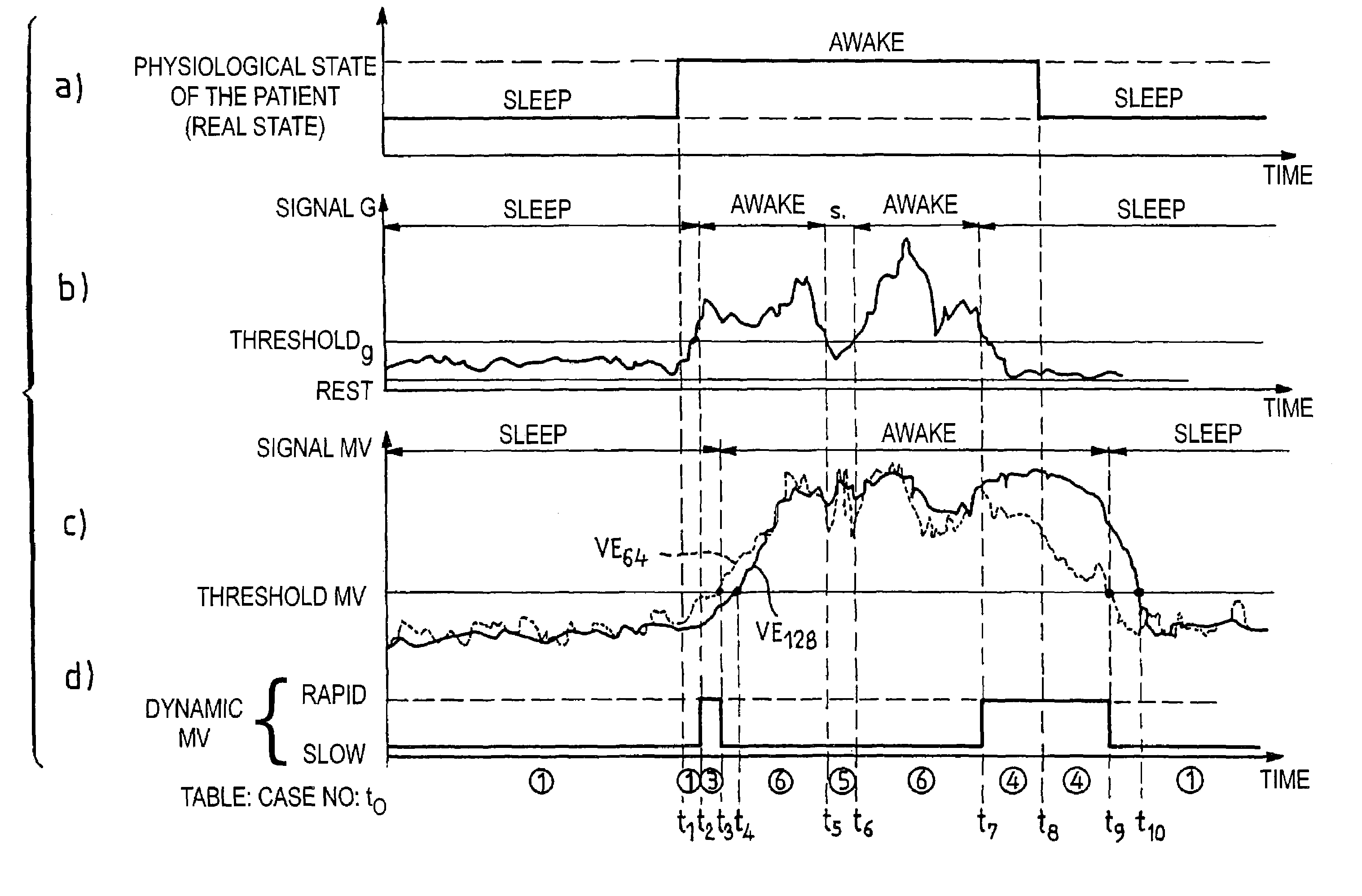
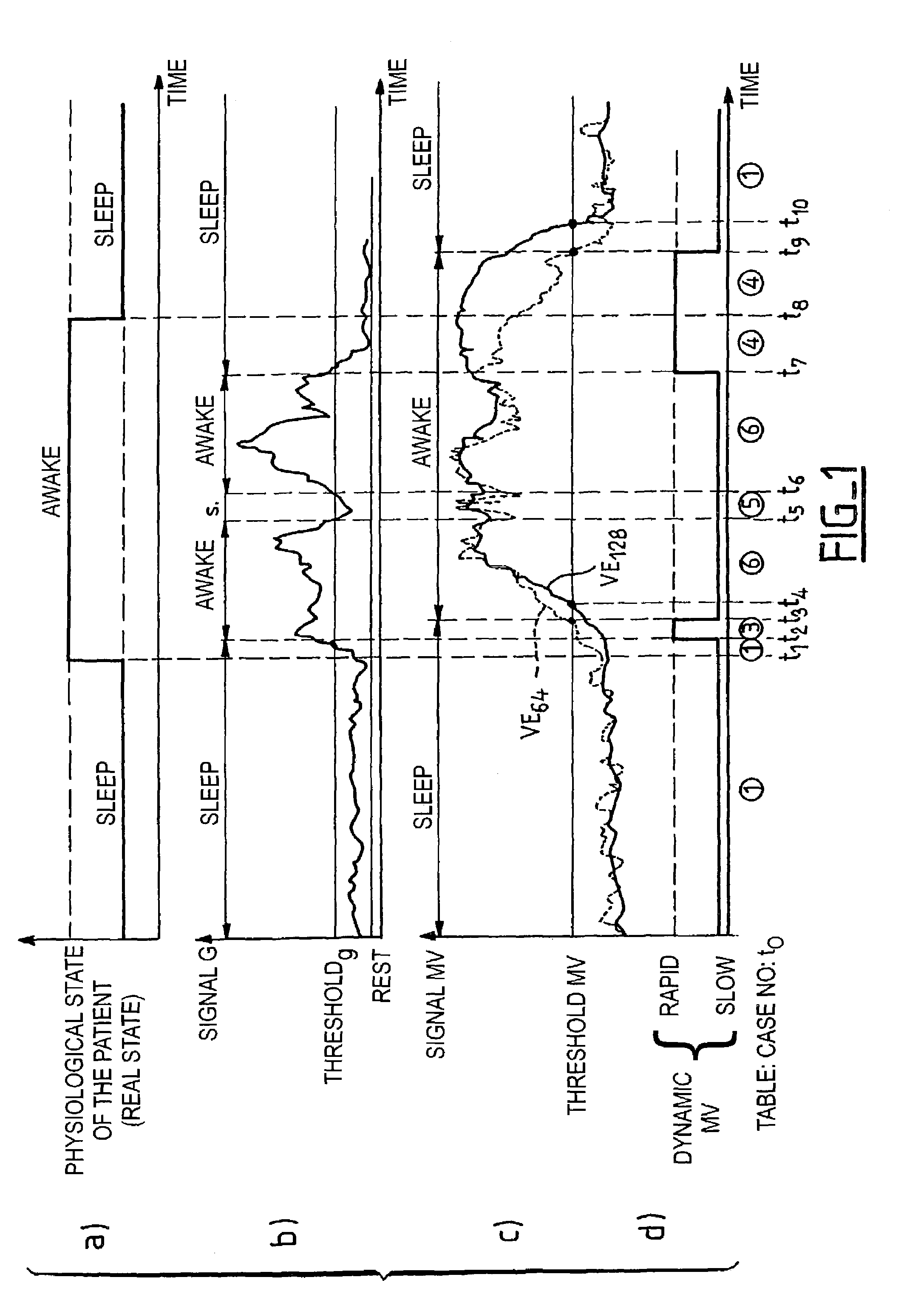
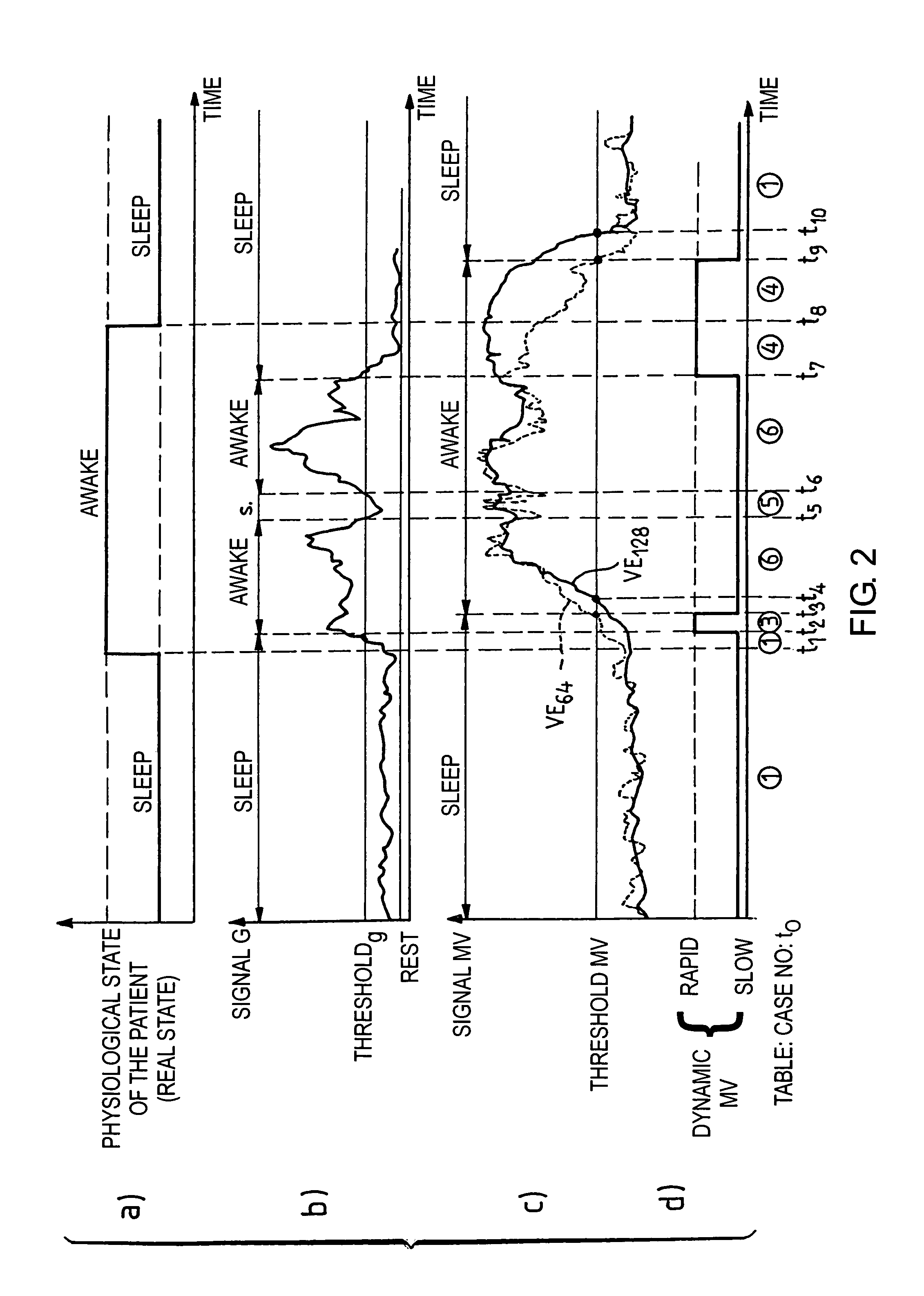
Detection and the treatment of ventilatory disorders during sleep for an active implantable medical device, in particular a pacemaker
InactiveUS7395115B2Inhibiting consequenceHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringHypopneaMedicine
An active medical device that is able to detect and treat ventiliatory activity disorders during sleep. This device measures the patient's respiratory activity, delivers a signal of the ventiliatory activity of the patient, analyzes the ventiliatory activity signal, and detects the occurrence of hypopneas. The analysis includes calculating at regular intervals a sliding average of the signal of ventiliatory activity, comparing the values of the successive sliding averages thus calculated, and detecting an occurrence of an hypopnea when, for two successive sliding averages, the difference between the averages crosses a predetermined threshold of comparison. When the device is one that also delivers cardiac stimulation pulses, it is advantageously envisaged to modify an operating parameter, in particular the stimulation rate based on the detected hypopnea, to treat the hypopnea.
Owner:ELA MEDICAL
Rate matching for a stimulating medical device
Methods and systems are disclosed for rate matching in a stimulating medical device, such as a cochlear implant or an auditory brain stimulator. In embodiments, the stimulating medical device applies a fast Fourier transform (FFT) at an analysis rate to the received signal to obtain a plurality frequency bin output signals. The stimulating medical device then applies a rate matching through interpolation function to the frequency bin output signals to match the stimulation rate for the stimulating medical device. This rate matching through interpolation function may apply a common interpolation filter to each frequency bin output to obtain a plurality of outputs distributed in time across the time period between executions of the FFT. The values of the frequency bin output signals at the time most closely matching the time for which stimulation is to be applied may then be selected and used in applying the stimulation.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
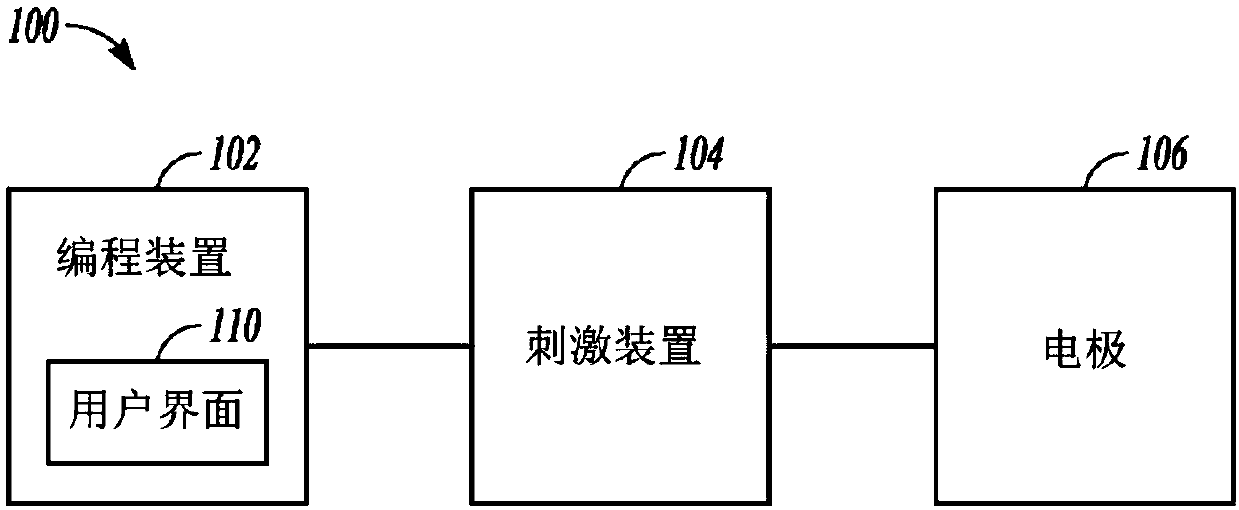
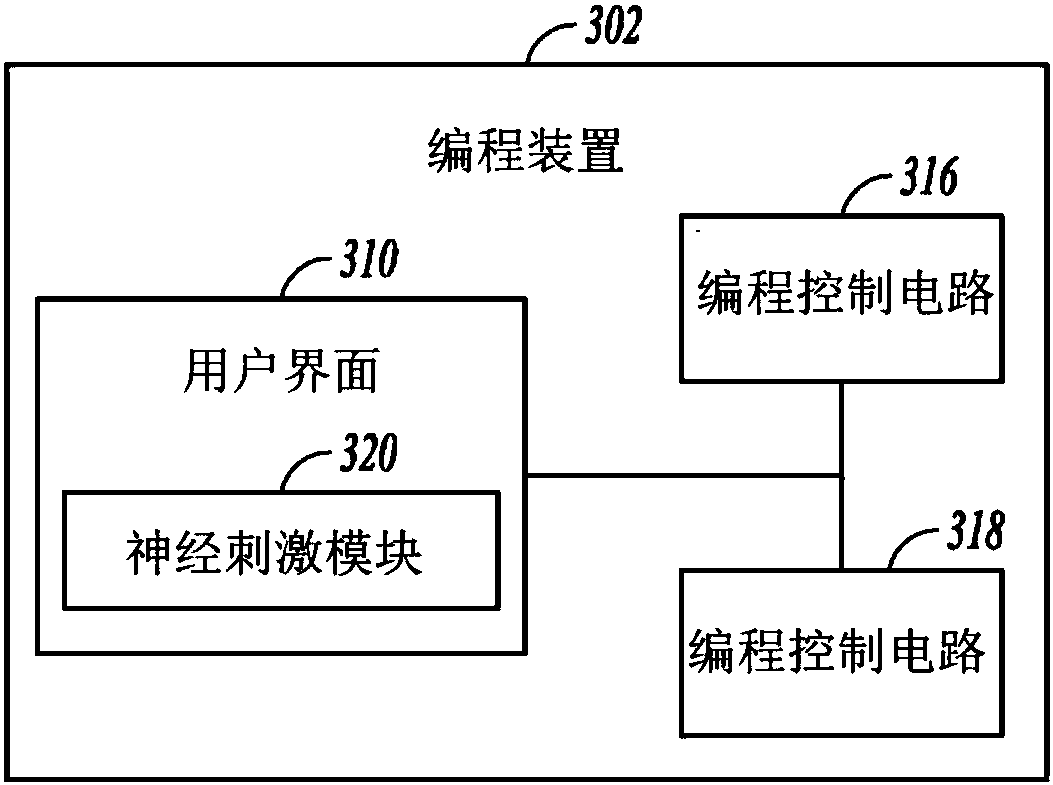
Systems for programming neuromodulation devices
An example of a system for delivering neurostimulation may include a programming control circuit and a user interface. The programming control circuit may be configured to generate stimulation parameters controlling delivery of neurostimulation pulses according to one or more stimulation waveforms associated with areas of stimulation each defined by a set of electrodes. The neurostimulation pulsesare each delivered to an area of stimulation. The user interface may include a display screen and an interface control circuit. The interface control circuit may be configured to define the one or more stimulation waveforms and the areas of stimulation, and may include a stimulation frequency module configured to display a stimulation rate table on the display screen. The stimulation rate table may present stimulation frequencies associated with each of the areas of stimulation for selection by a user.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Rate and Place of Stimulation Matched to Instantaneous Frequency
ActiveUS20160279414A1Head electrodesDetails for specific frequency responseElectricityTemporal change
A signal processing arrangement generates electrical stimulation signals to stimulation contacts in an implanted cochlear implant array. An input sound signal is decomposed into dominant psychophysically relevant frequency components, with each frequency component changing over time in frequency and level. Each frequency component is coded as a patient-specific, frequency-specific function of stimulation location, rate, and level to produce a sequence of requested stimulation events having an instantaneous frequency and level. And the electrical stimulation signals are generated from the requested stimulation events for delivery by the stimulation contacts to adjacent auditory neural tissue.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
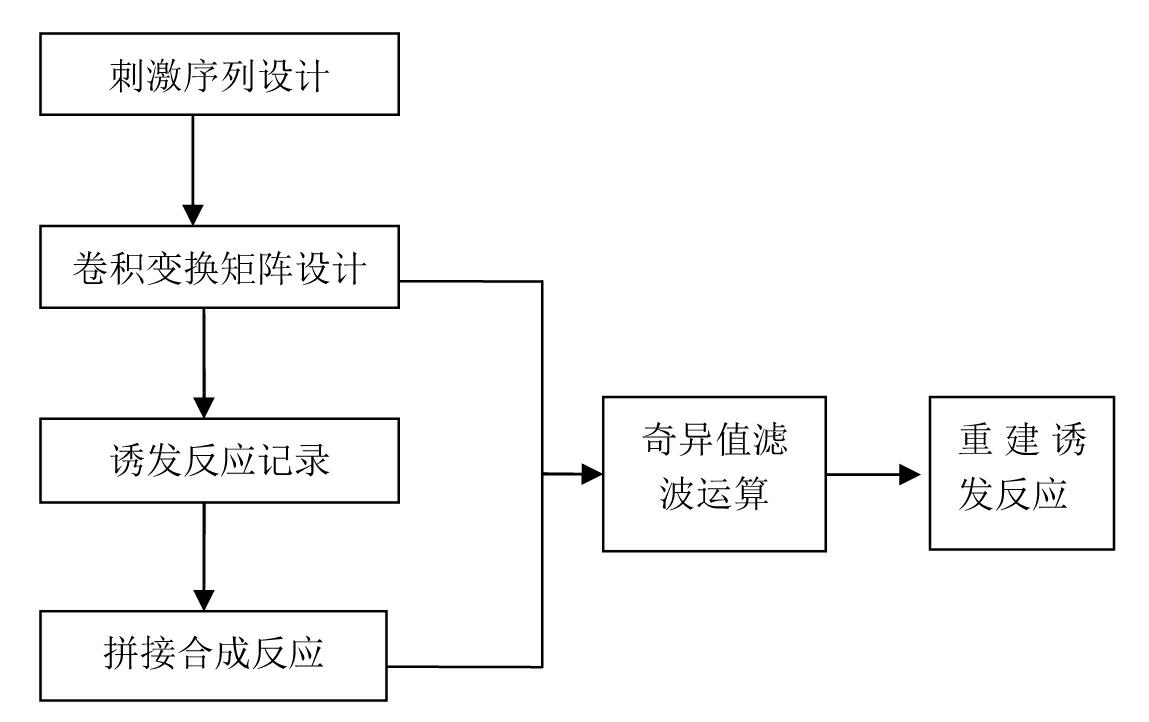
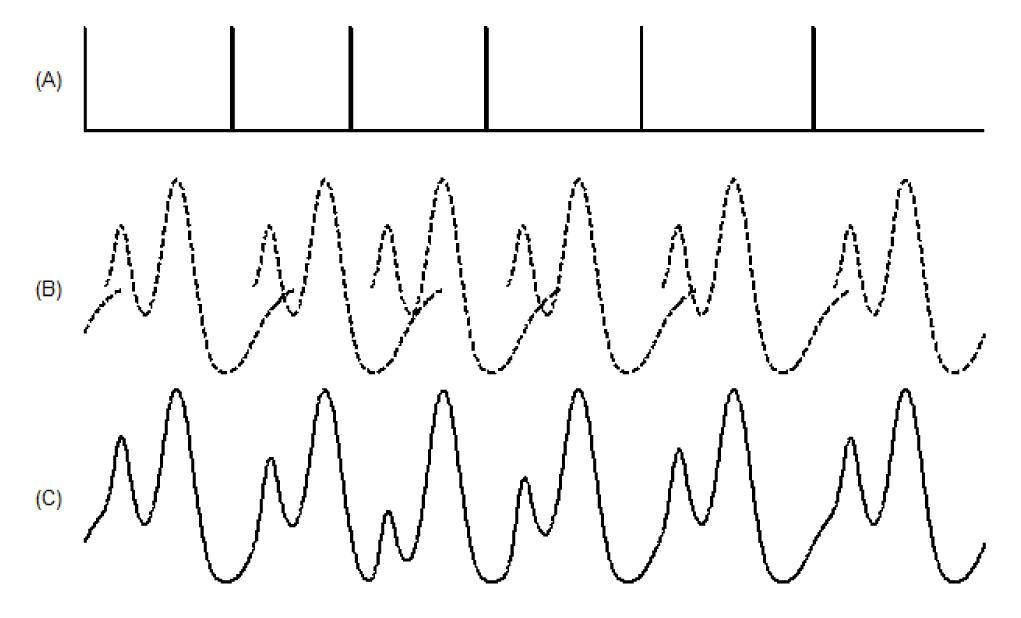
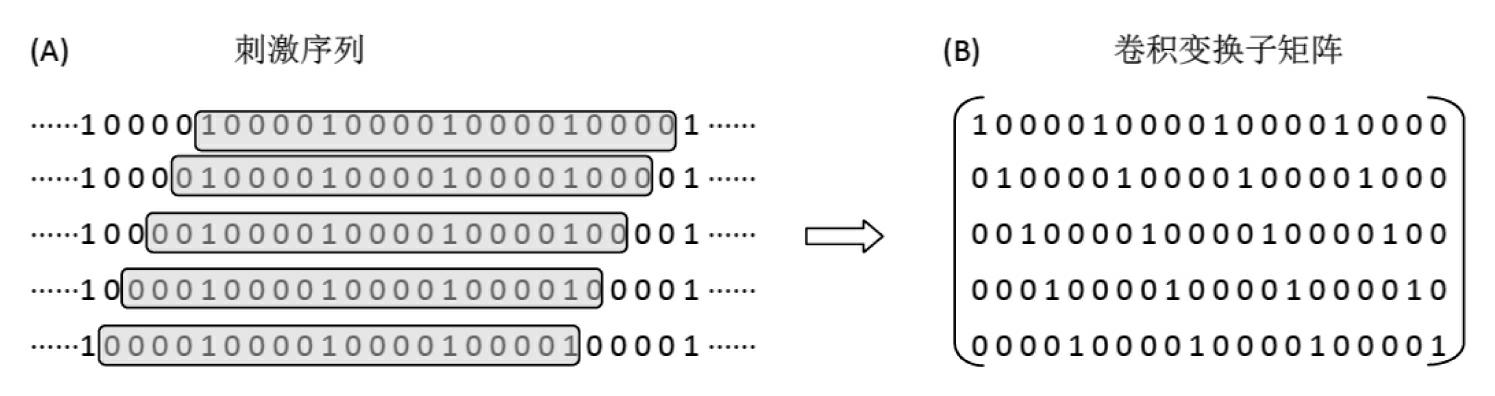
Deconvolution method for extracting evoked potential at high stimulation ratio
InactiveCN102631192APromote reconstructionOvercome the interference amplification problemDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSeptal stimulationConvolution
The invention discloses a deconvolution method for extracting an evoked potential at a high stimulation ratio. The deconvolution method comprises the following steps of: acquiring EP (Evoked Potential) waveform signals of a plurality of stimulation periods by adopting an equal-interval stimulation shake-free stimulation sequence according to a stacking average calculation method; generating a convolution conversion sub matrix according to a stimulation sequence parameter of each stimulation period, and further obtaining convolution conversion matrixes of N periods; splicing the average EP signals corresponding to the stimulation periods into a synthesized reaction based on corresponding stimulation ratios; and finally, calculating a transient reaction according to a singular value filter method, and estimating the transient EP according to the transient reaction. The method utilizes same experimental record mode and equipment as the conventional method, special requirements on hardware are eliminated, and an operator is not required to be trained; a singular value filter processing technology is introduced into an EP recovery stage, so that the problem that interference introduced by directly adopting an inverse filter process is enlarged is solved; and the reconstruction effect of the transient EP is improved obviously.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Auditory prosthesis stimulation rate as a multiple of intrinsic oscillation
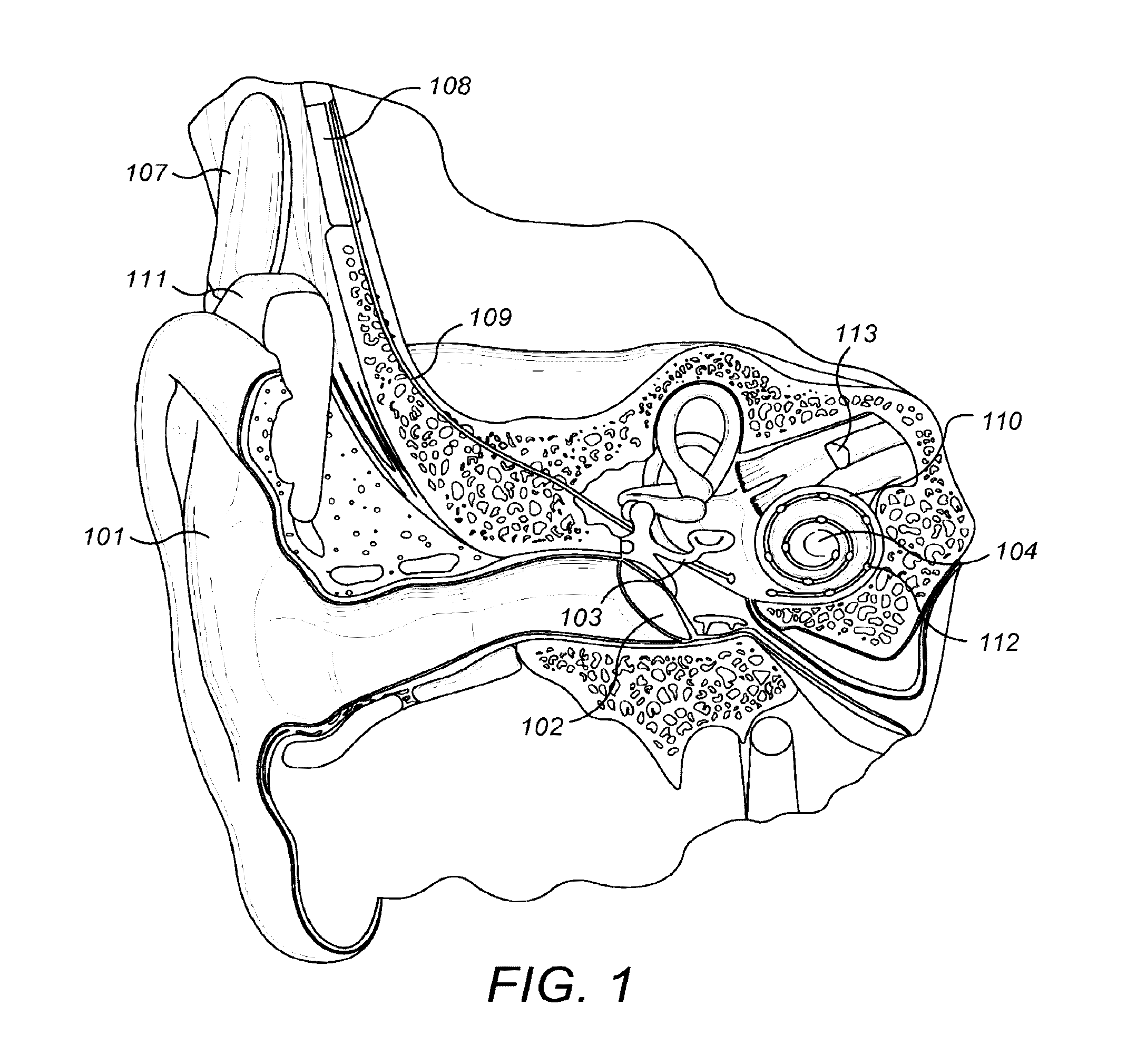
An electrode insertion support device is used for inserting a cochlear implant electrode into a cochlea scala of a patient cochlea. A stiff electrode holder encloses at least a portion of a cochlear implant electrode while allowing the electrode within to slide freely. A pointed distal tip of the electrode holder is adapted to pierce an electrode opening through an outer surface of the patient cochlea into the cochlea scala. The insertion support device prevents an apical tip of the enclosed electrode from contacting tissues around the electrode opening during the insertion surgery.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
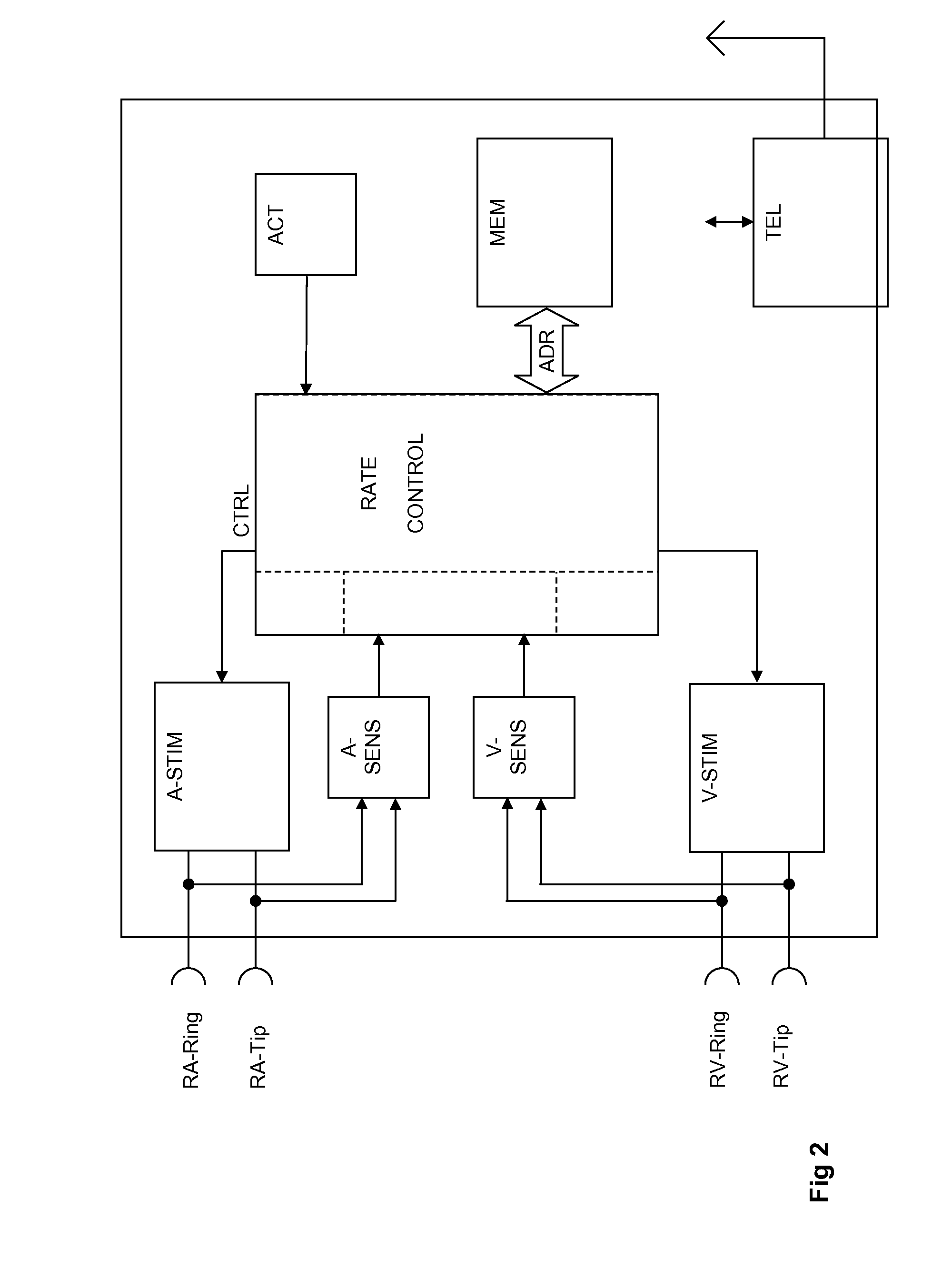
Heart stimulator
Heart stimulator that stimulates at least a heart's right atrium and ventricle in an atrium asynchronous stimulation mode with an overdrive stimulation rate. Interposes one resynchronization cycle after a sensed atrial event to regain AV synchrony during otherwise asynchronous stimulation mode. Allows for pacing mode that can pace the atrium with an overdrive stimulation rate in dual-chamber asynchronous mode while maintaining the AV synchrony and is called DDI(R)+. In DDI(R)+, pacemaker performs an atrial asynchronous (V synchronous) pacing mode such as DDI or DDI(R). The overdrive stimulation rate (OSR) is either a fixed rate (programmed by the external device) that is thought to be above the underlying intrinsic atrial rate, or is dynamically adjusted according to the measured atrial cycle length to be slightly above intrinsic atrial rate. The overdrive stimulation rate may be based on an intrinsic atrial rate or on hemodynamic need. DDI(R)+ timing may be ventricle-based.
Owner:BIOTRONIX CRM PATENT AG
Atrial overdrive pacing in non-atrial tracking mode while maintaining AV synchrony
Owner:BIOTRONIX CRM PATENT AG
Heart Stimulator
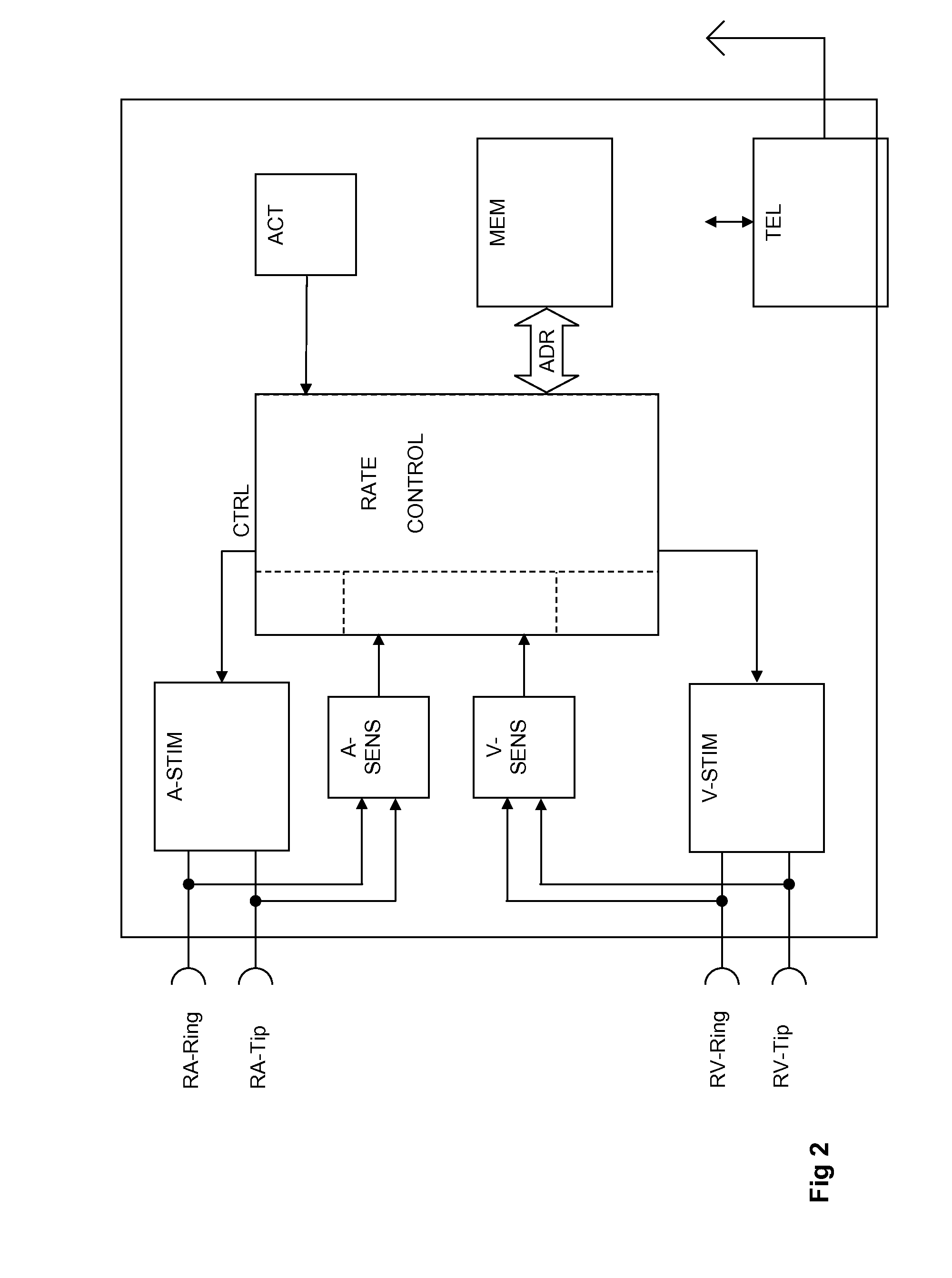
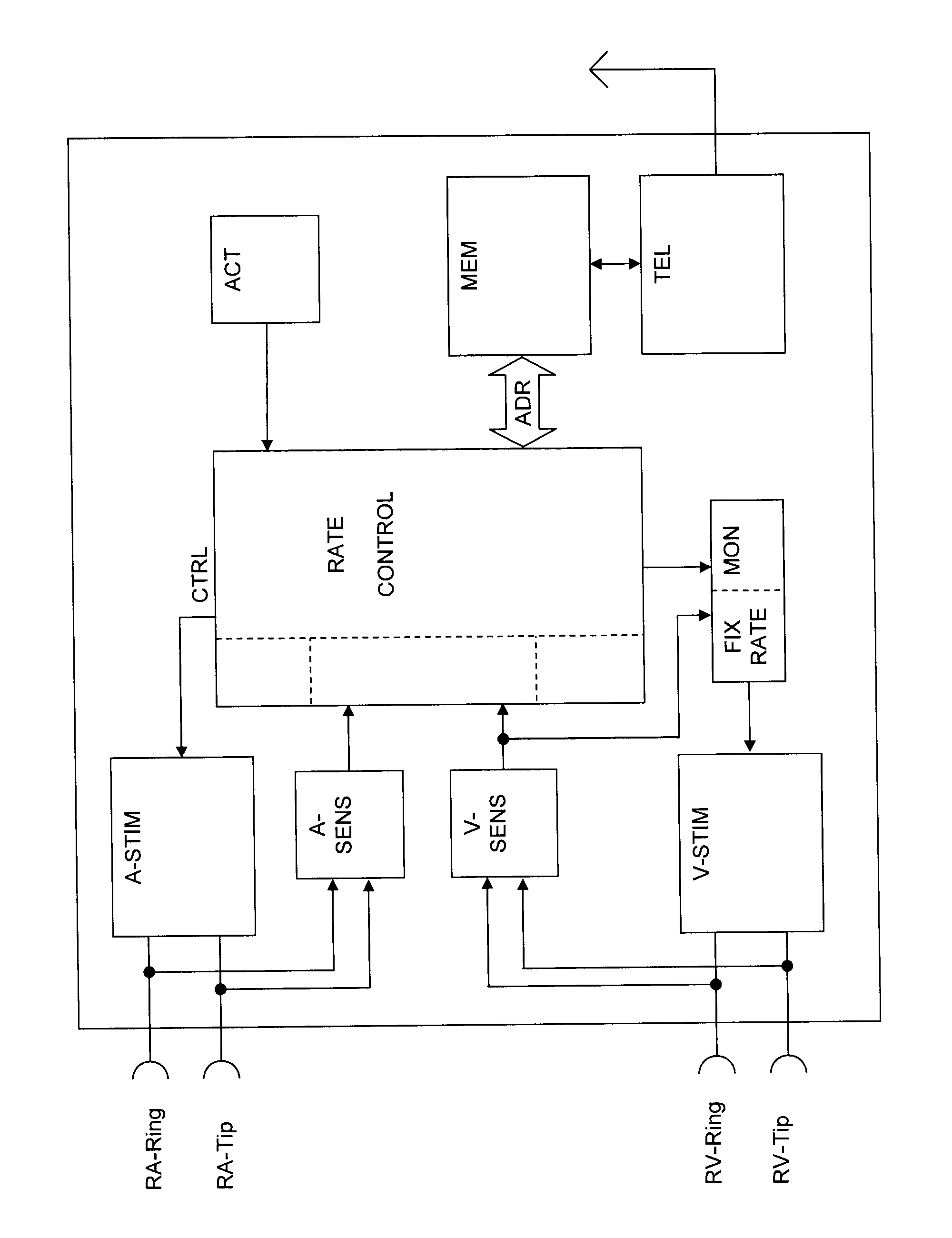
InactiveUS20080125823A1Reduce probabilityShort maintenance periodHeart stimulatorsElectricityHeart chamber
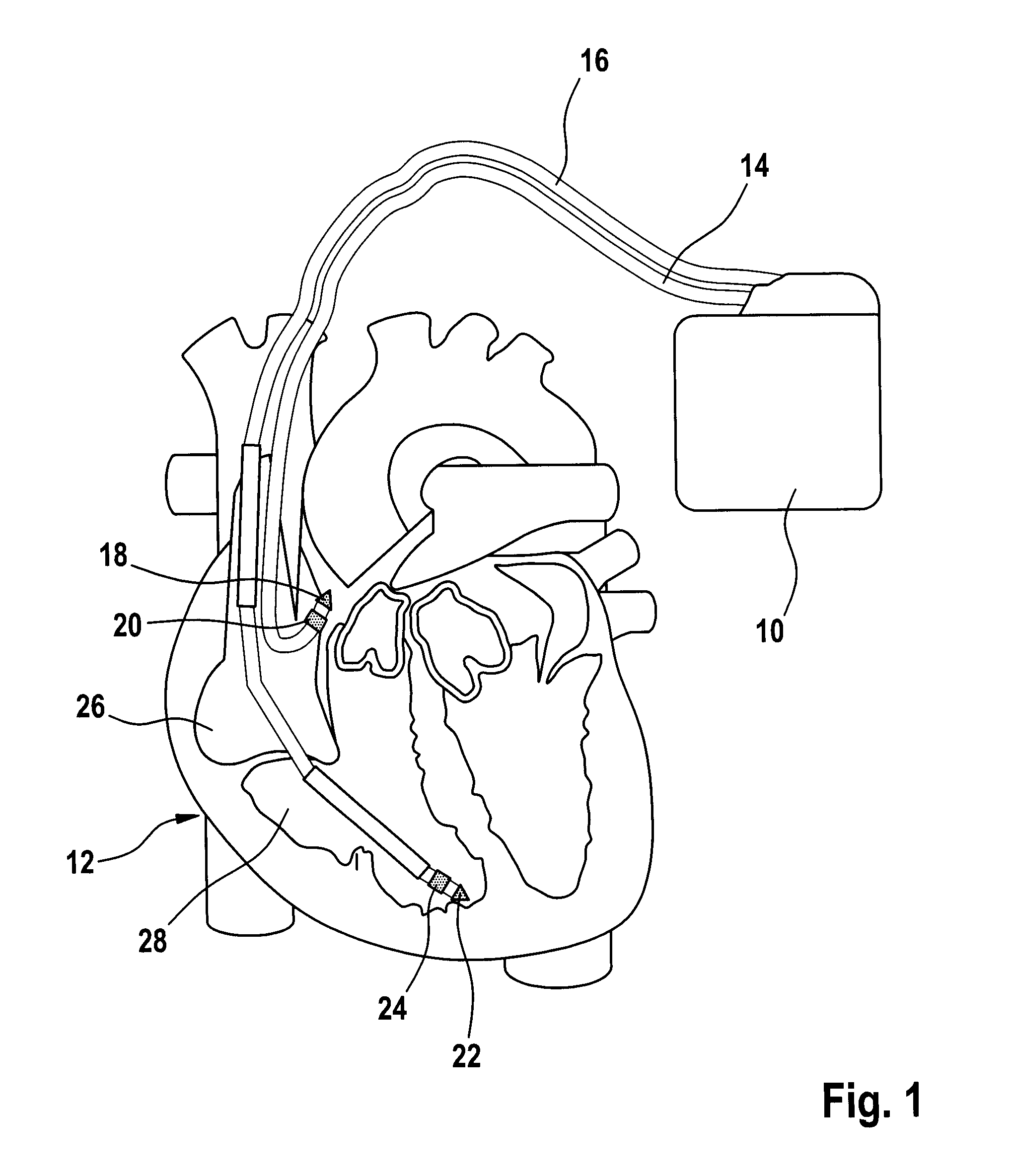
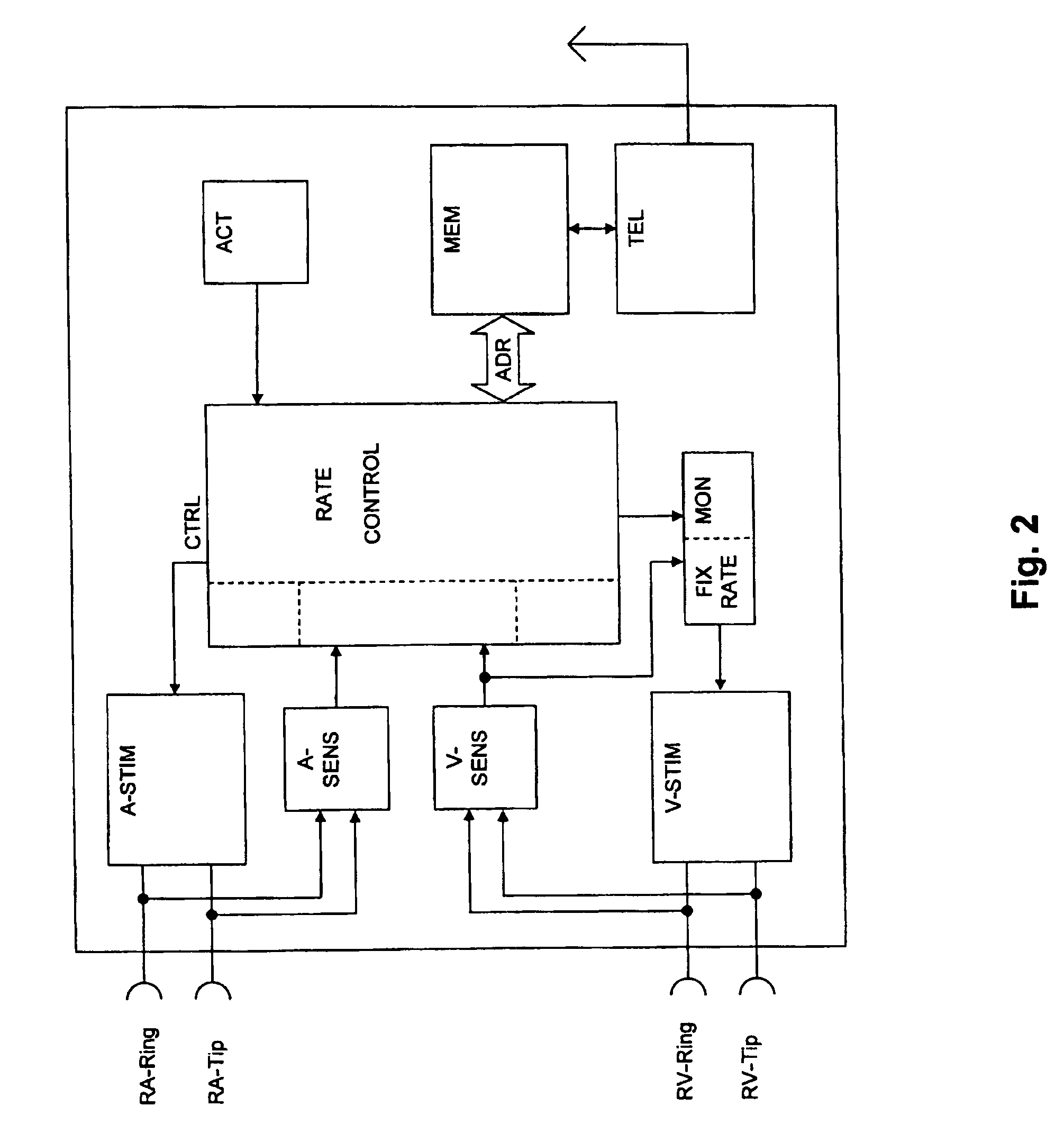
A heart stimulator for stimulating a chamber of a heart by way of electrical stimulation pulses, said pacemaker comprises a sensing stage connected or being connectable to an electrode lead comprising an electrode for picking up electric potentials inside a heart chamber, said sensing stage being adapted to sense an excitation of a heart chamber by way of picked up electric potentials, a stimulation pulse generator adapted to generate electric stimulation pulses and being connected or being connectable to an electrode lead comprising a stimulation electrode for delivering electric stimulation pulses to said chamber of a heart, and a control unit being connected to said sensing stage and to said stimulation pulse generator and being adapted to trigger stimulation pulses to be generated by the stimulation pulse generator and to be delivered via said electrode lead, said stimulation pulses being triggered with a controlled stimulation rate controlled by the control unit. For preventing too high a stimulation rate for too long a period of time a monitoring stage is provided that connected to the control unit and being adapted to monitor said controlled stimulation rate and override the controlled stimulation rate by a fixed stimulation rate for a predetermined period of time if the average controlled stimulation rate exceeds a predetermined maximum rate.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Implantable heart stimulating device with stimulation rate optimization
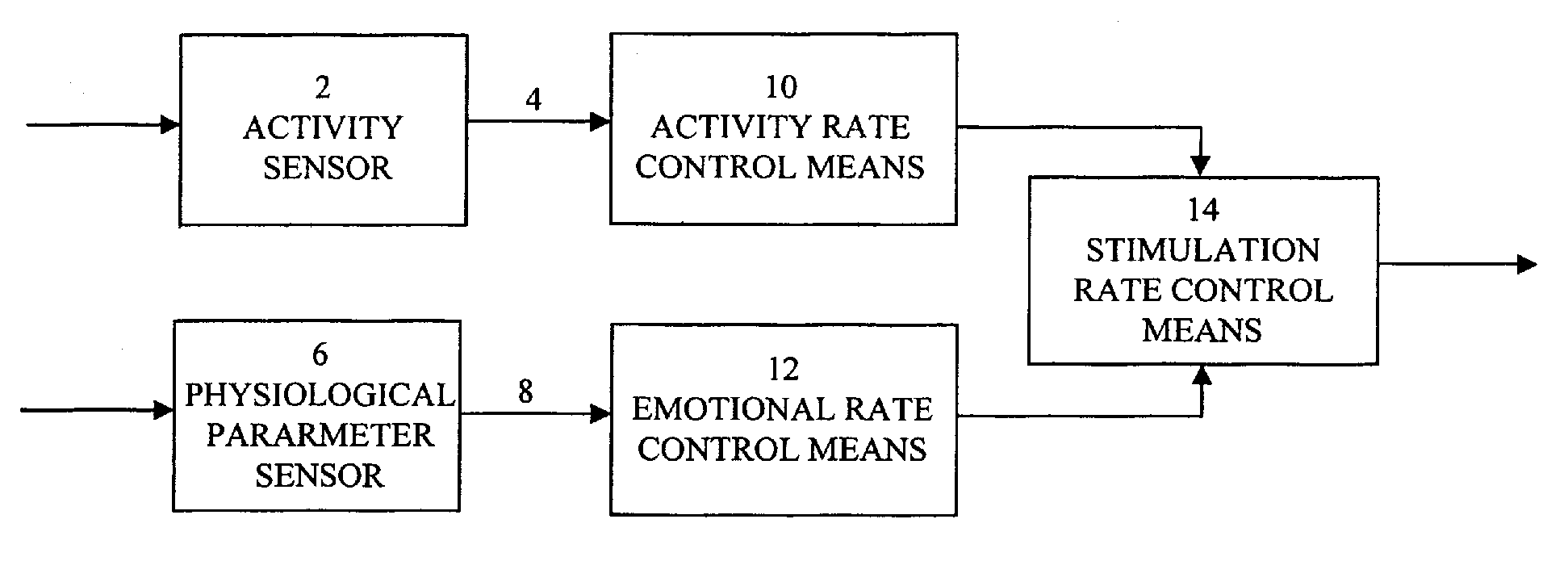
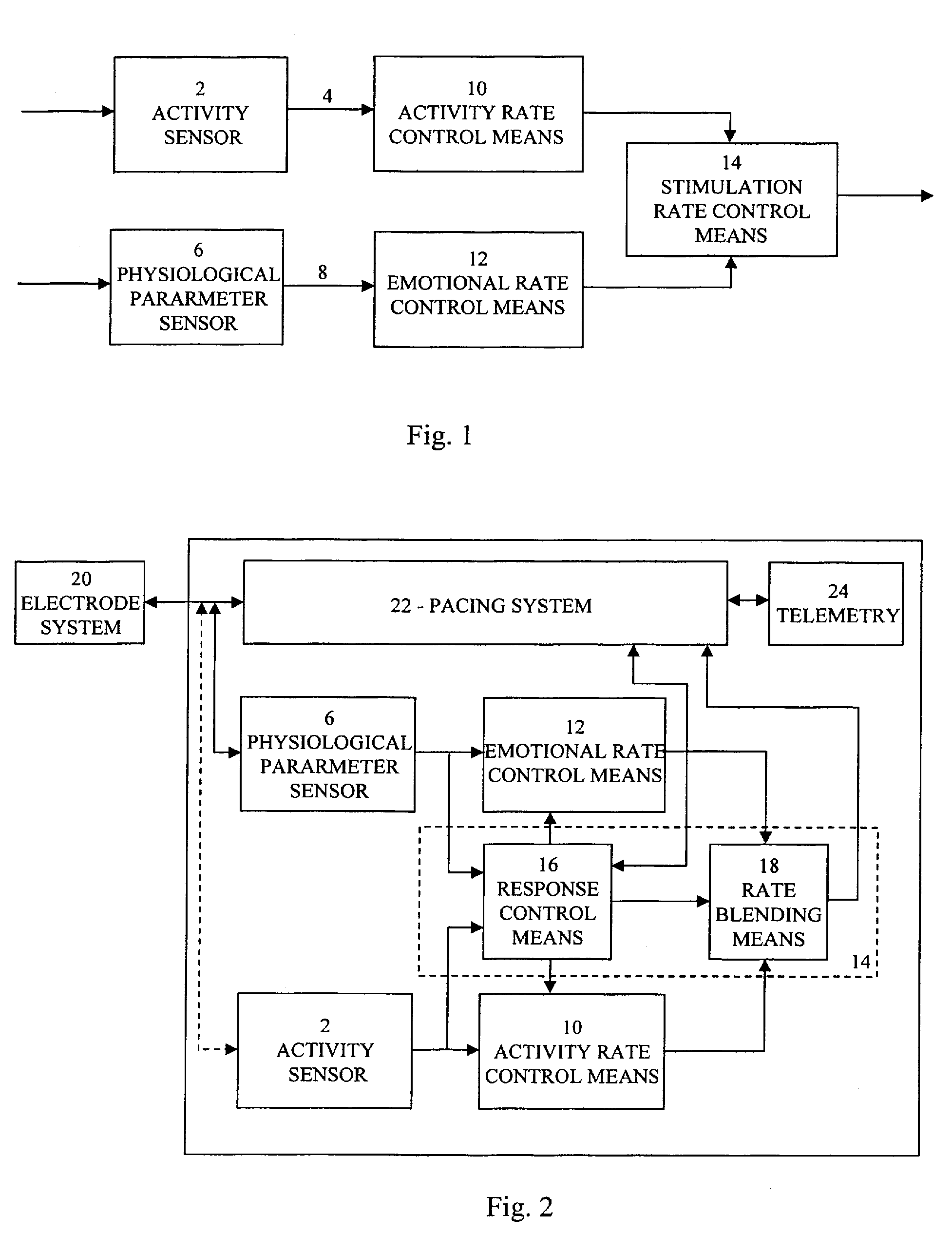
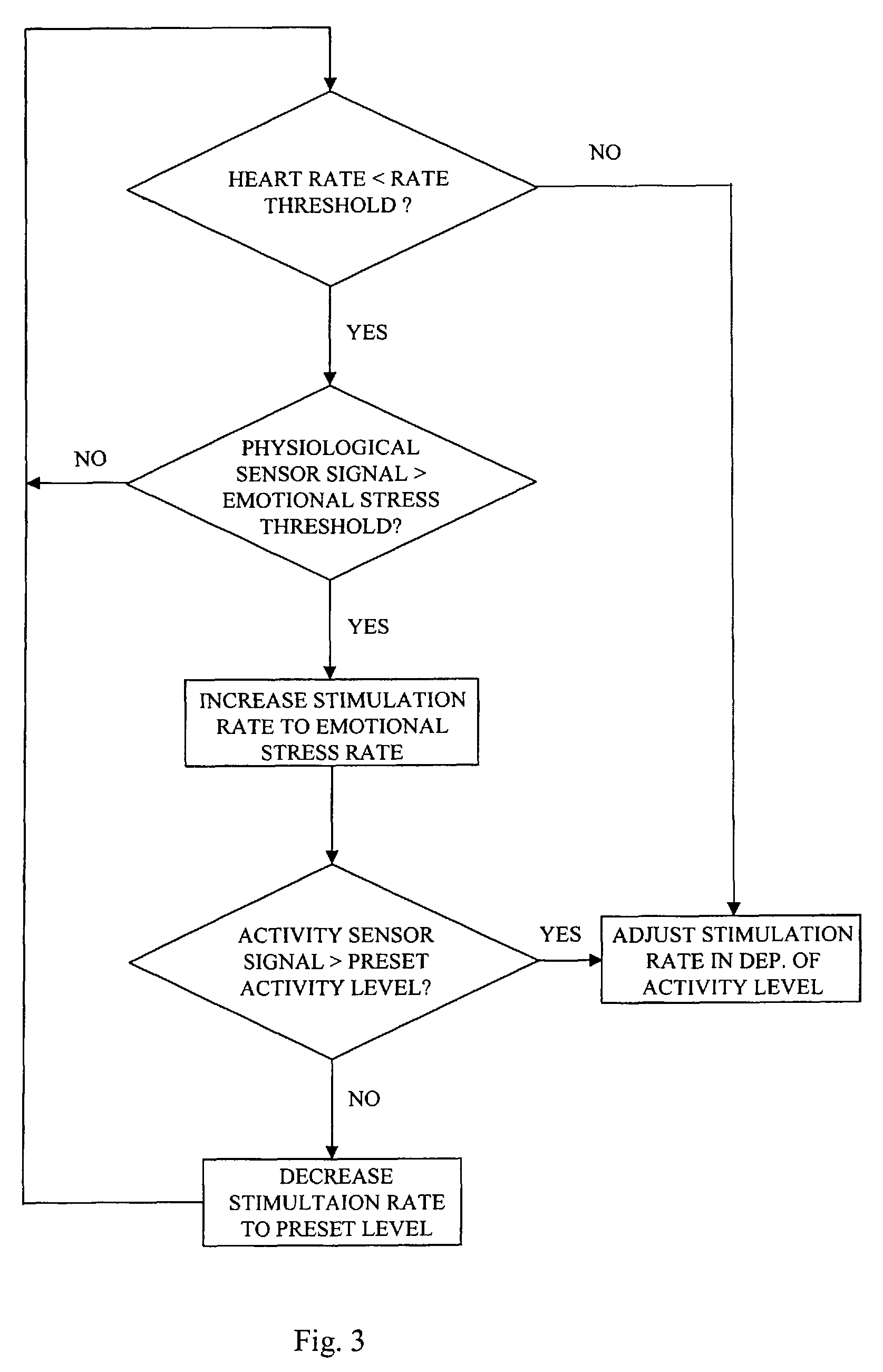
An implantable heart stimulating device has a stimulation pulse generator that emits stimulation pulses at an adjustable stimulation rate, an activity sensor that emits an activity signal in response to detected activity of the patient, and a physiological parameter sensor that generates a physiological sensor signal in response to a detected physiological parameter. The activity and physiological sensor signals are supplied to a control arrangement that sets the stimulation rate for the stimulation pulse generator by executing a stimulation rate algorithm dependent on those signals. In the stimulation rate algorithm, if the physiological signal indicates an emotional stress on the part of the patient, the stimulation rate is increased to an adjustable emotional stress rate level, and if no increase in the activity signal occurs during a predetermined time period following the stimulation rate increase, the stimulation rate is decreased.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Heart stimulator with override for stimulation exceeding a maximum rate
A heart stimulator for electrical stimulation of a heart chamber includes a sensing stage sensing excitation of the heart chamber via an electrode lead having an electrode for picking up heart chamber electric potentials, a stimulation pulse generator generating electric stimulation pulses for delivery to the heart chamber via a stimulation electrode, and a control unit connected to the sensing stage and the stimulation pulse generator and being adapted to trigger the stimulation pulses at a controlled stimulation rate. A monitoring stage is provided for preventing too high of a stimulation rate for too long of a period of time, with the monitoring stage being connected to the control unit and being adapted to monitor the controlled stimulation rate, and to override the controlled stimulation rate by a fixed stimulation rate for a predetermined period of time if the average controlled stimulation rate exceeds a predetermined maximum rate.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com