Audio processing method and system implantted cochlea
A sound and excitation pulse technology, applied in electrotherapy, ear support, ear therapy, etc., can solve problems such as inability to distinguish complex sound tones
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
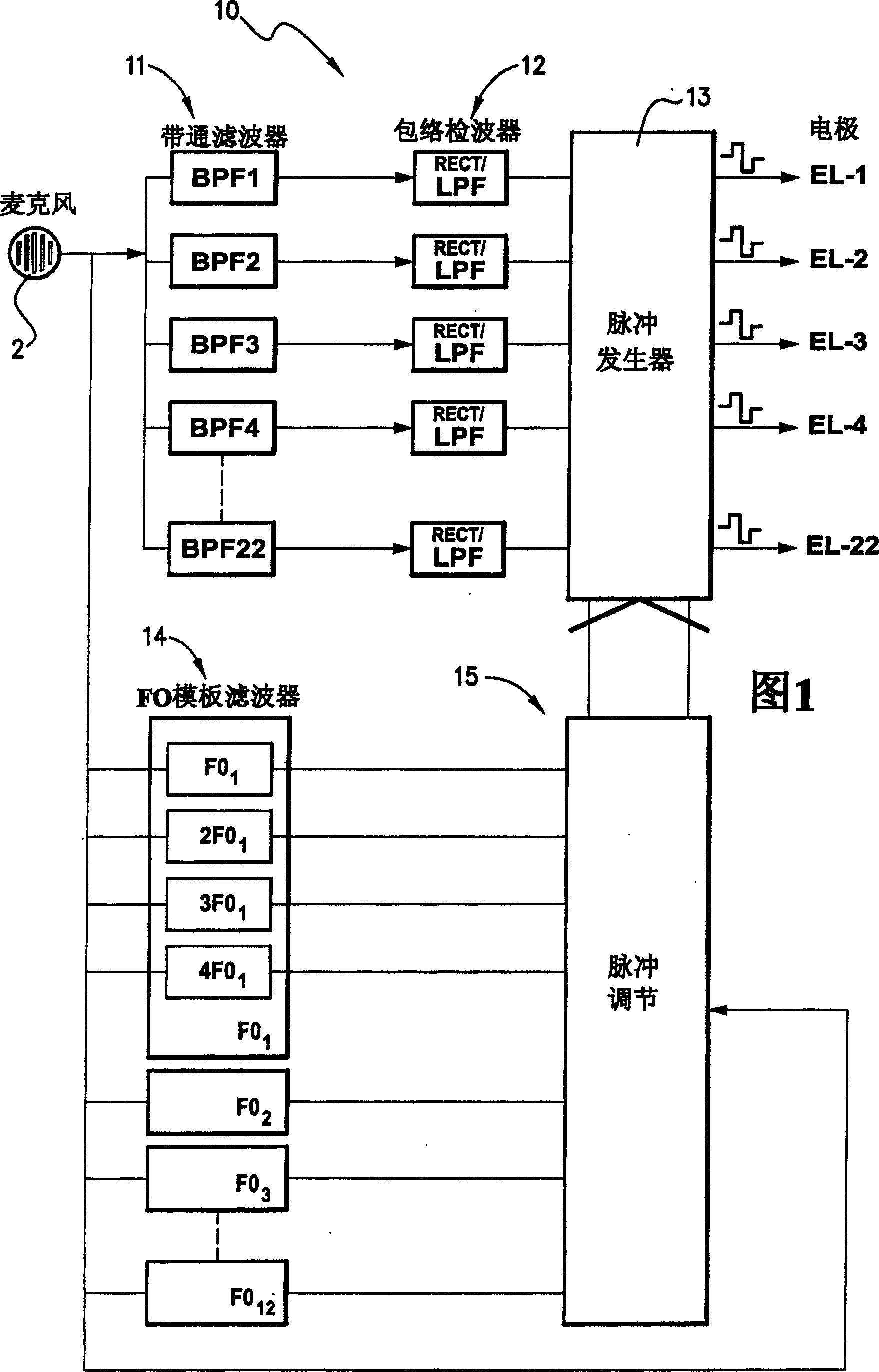
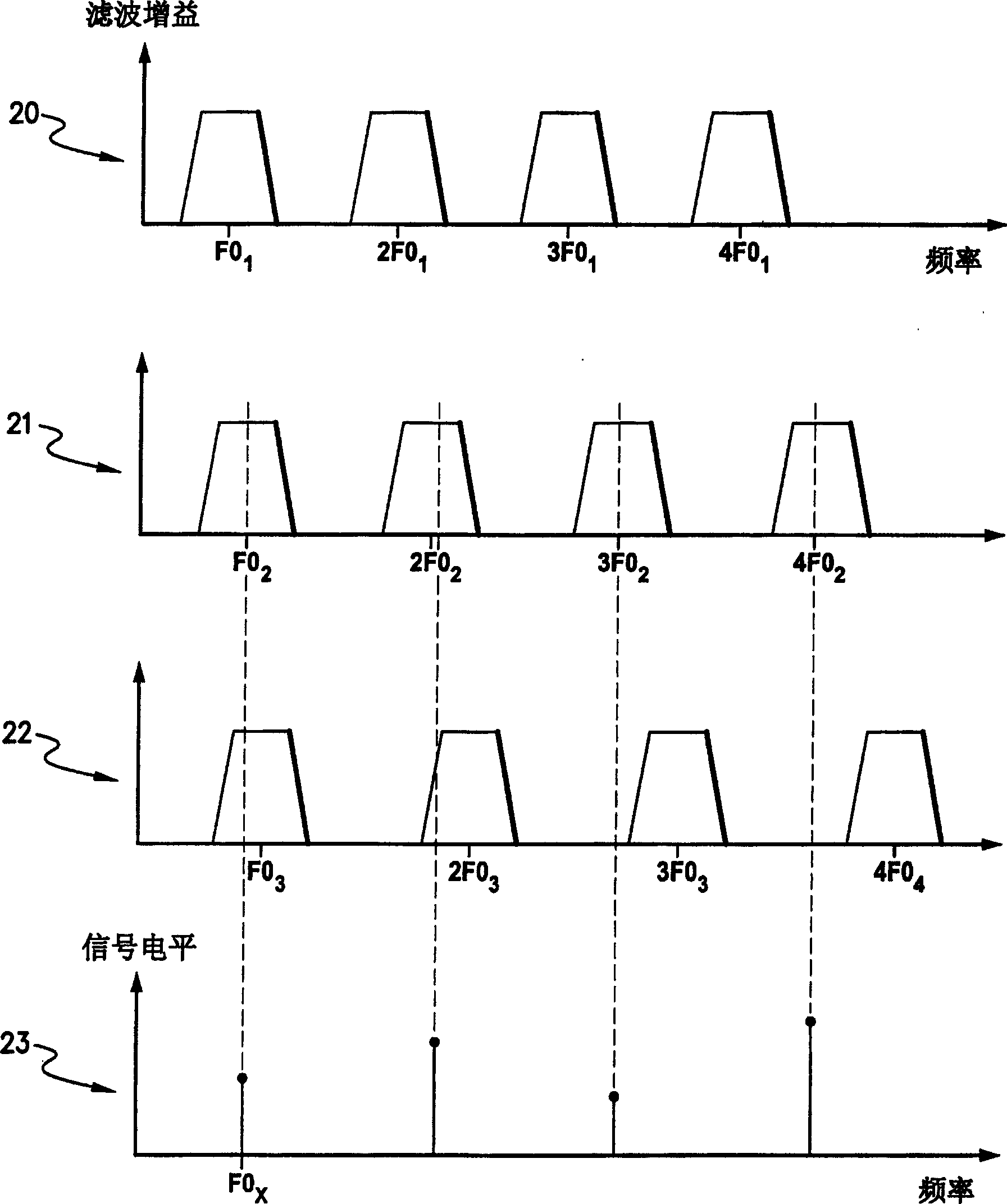
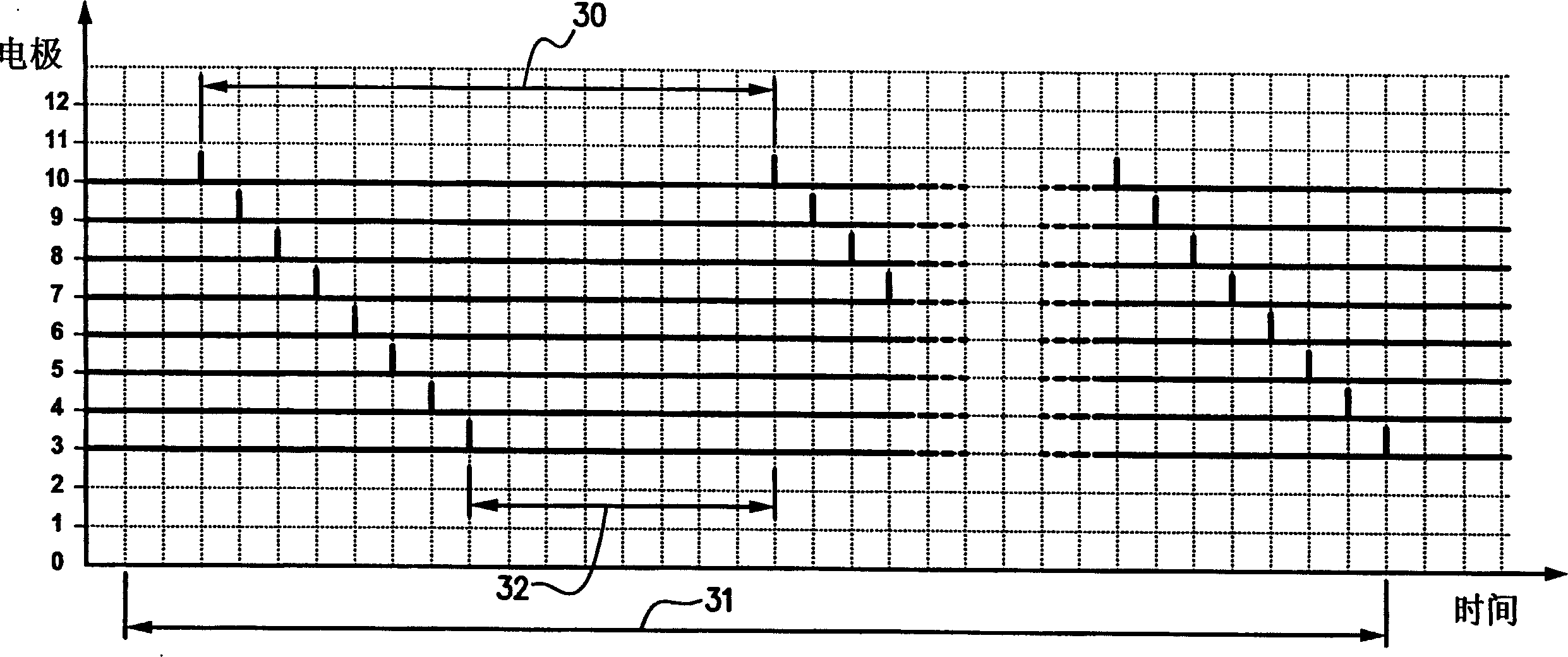
[0047] Existing hearing aid devices include: a microphone that converts sound into electrical signals; a sound processor that responds to the electrical signals output by the microphone and selectively generates excitation pulses that are applied to the electrodes in the electrode array. In a multichannel cochlear implant, an electrode array is inserted into the cochlea so that different auditory nerve fibers can be stimulated at different locations within the cochlea. Typically, the electrode array includes 22 electrodes. Pulses generated by the sound processor excite different electrodes in the electrode array, depending on the frequency of the electrical signal received from the microphone. Electrodes near the base of the cochlea are excited with electrical pulses from high-frequency sound information, and electrodes near the top are stimulated with electrical pulses from low-frequency sound information. The role of the sound processor is to decompose the input signal into...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com