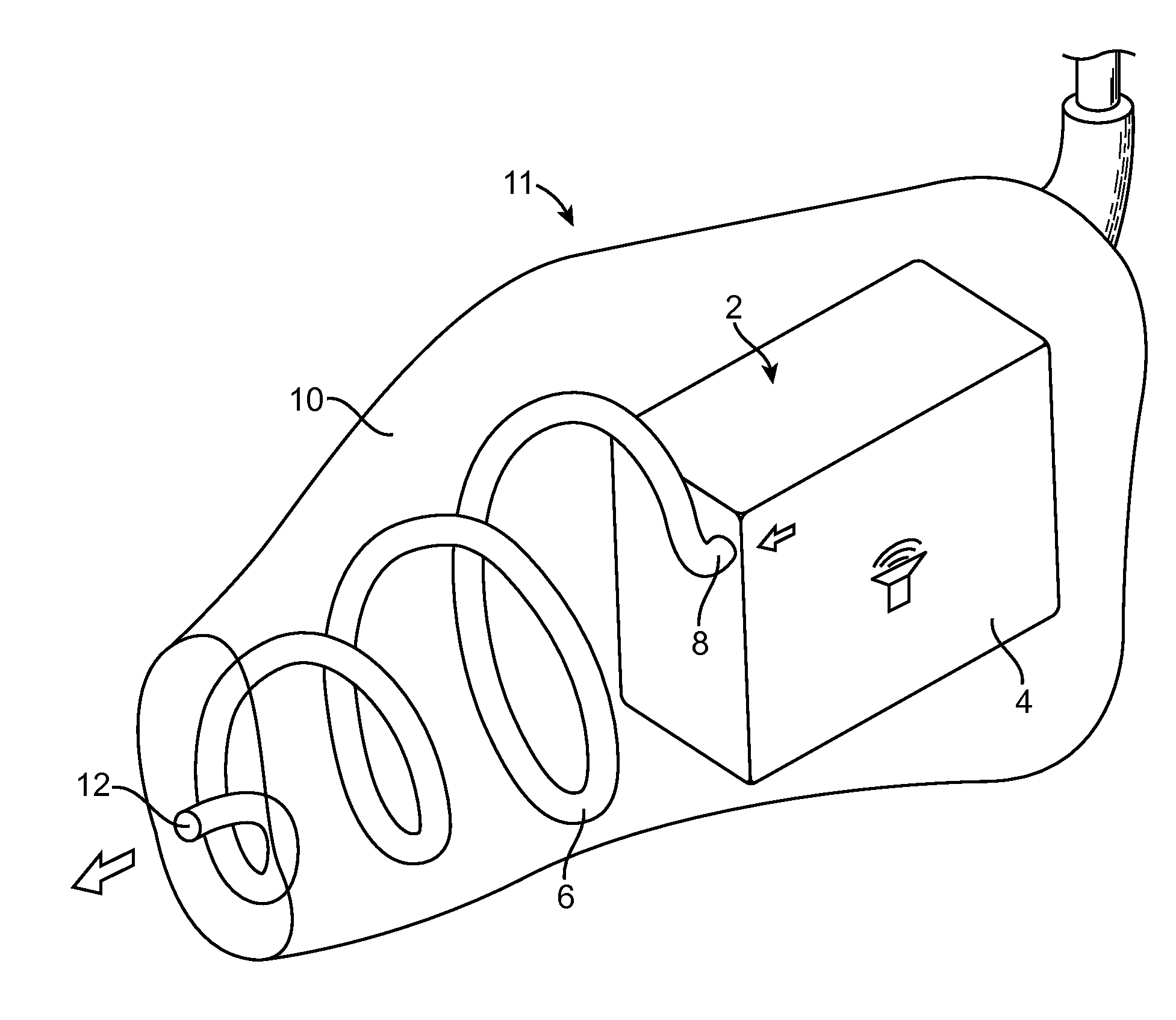
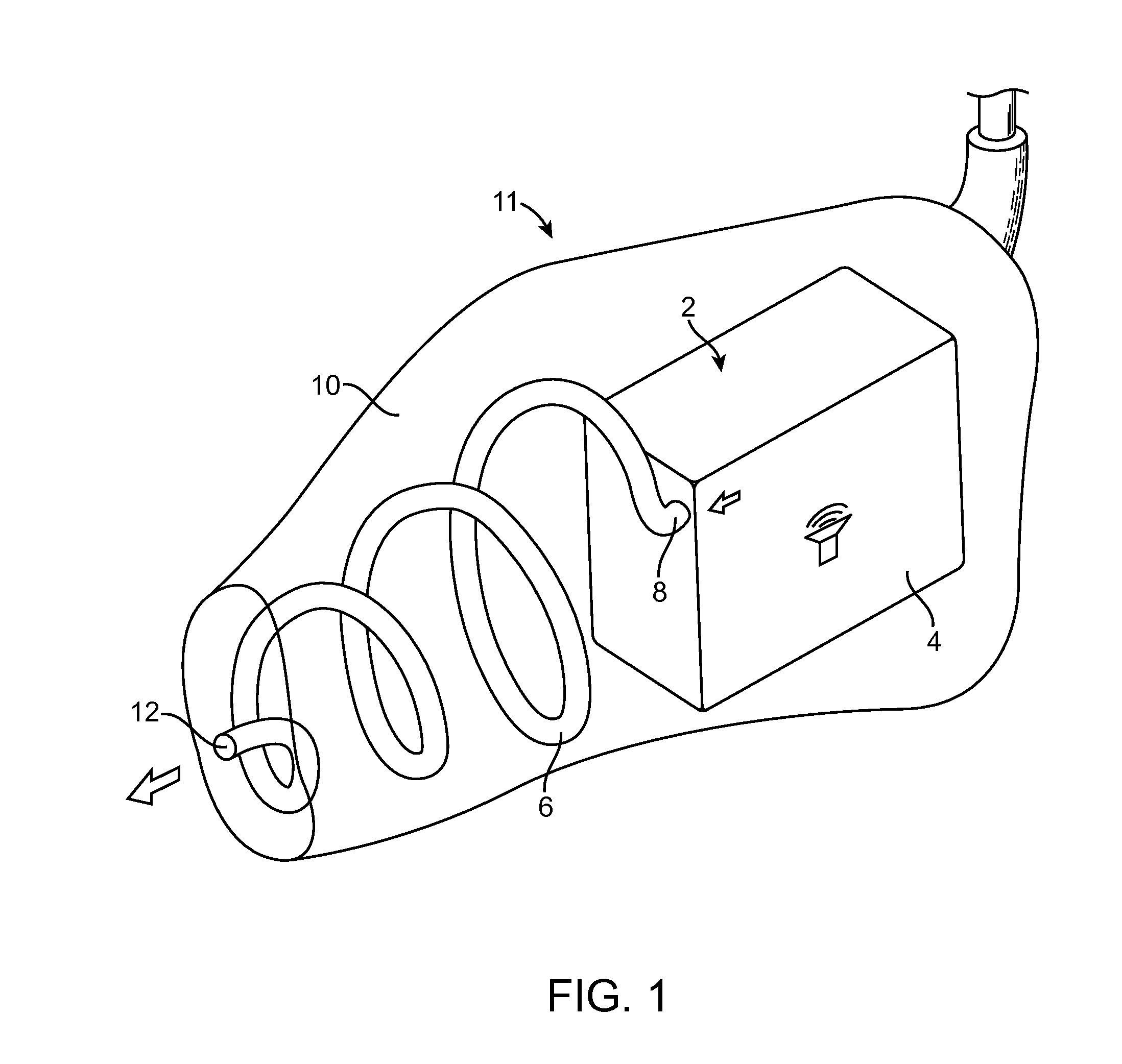
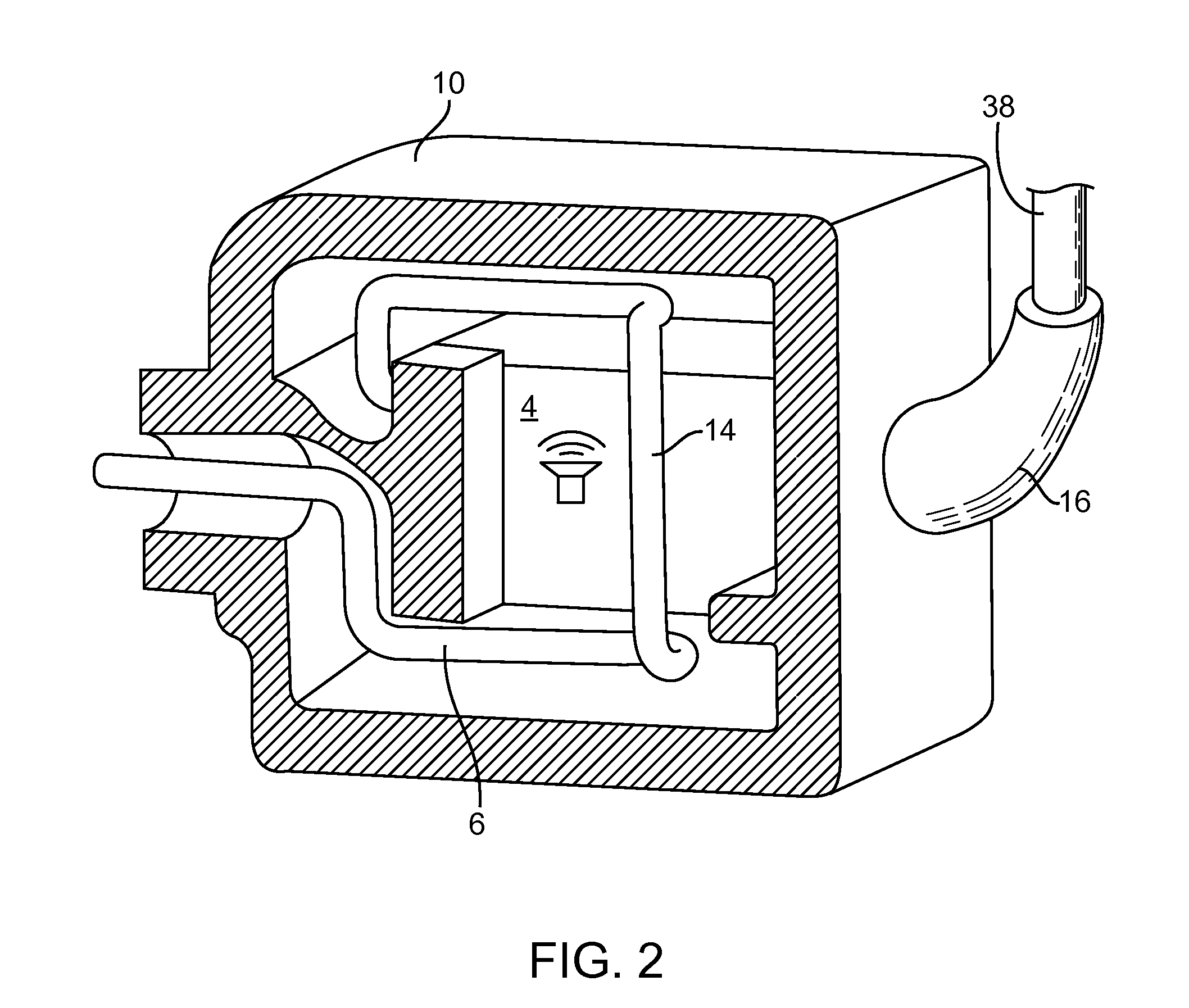
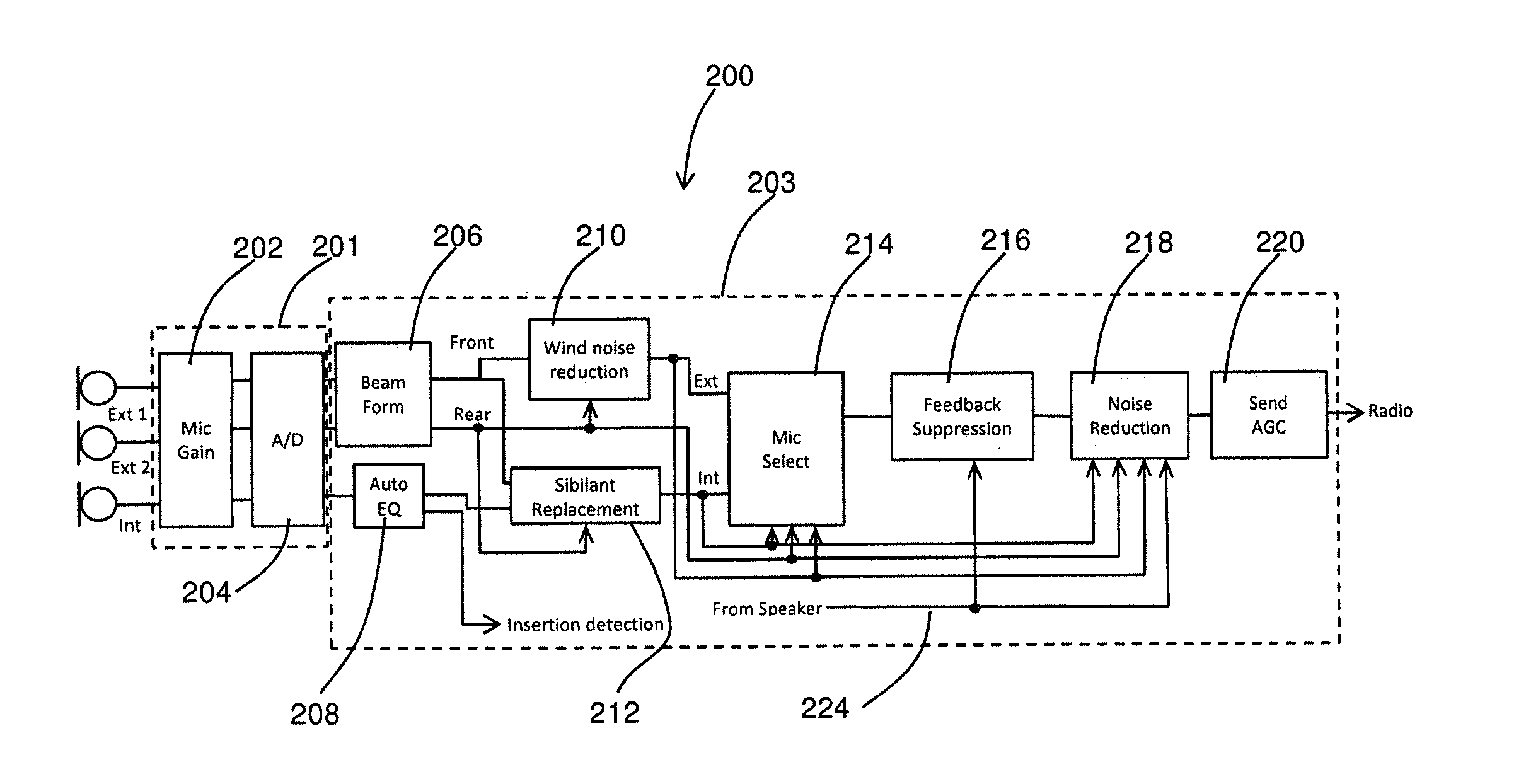
Patents
Literature
179results about "Details for specific frequency response" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
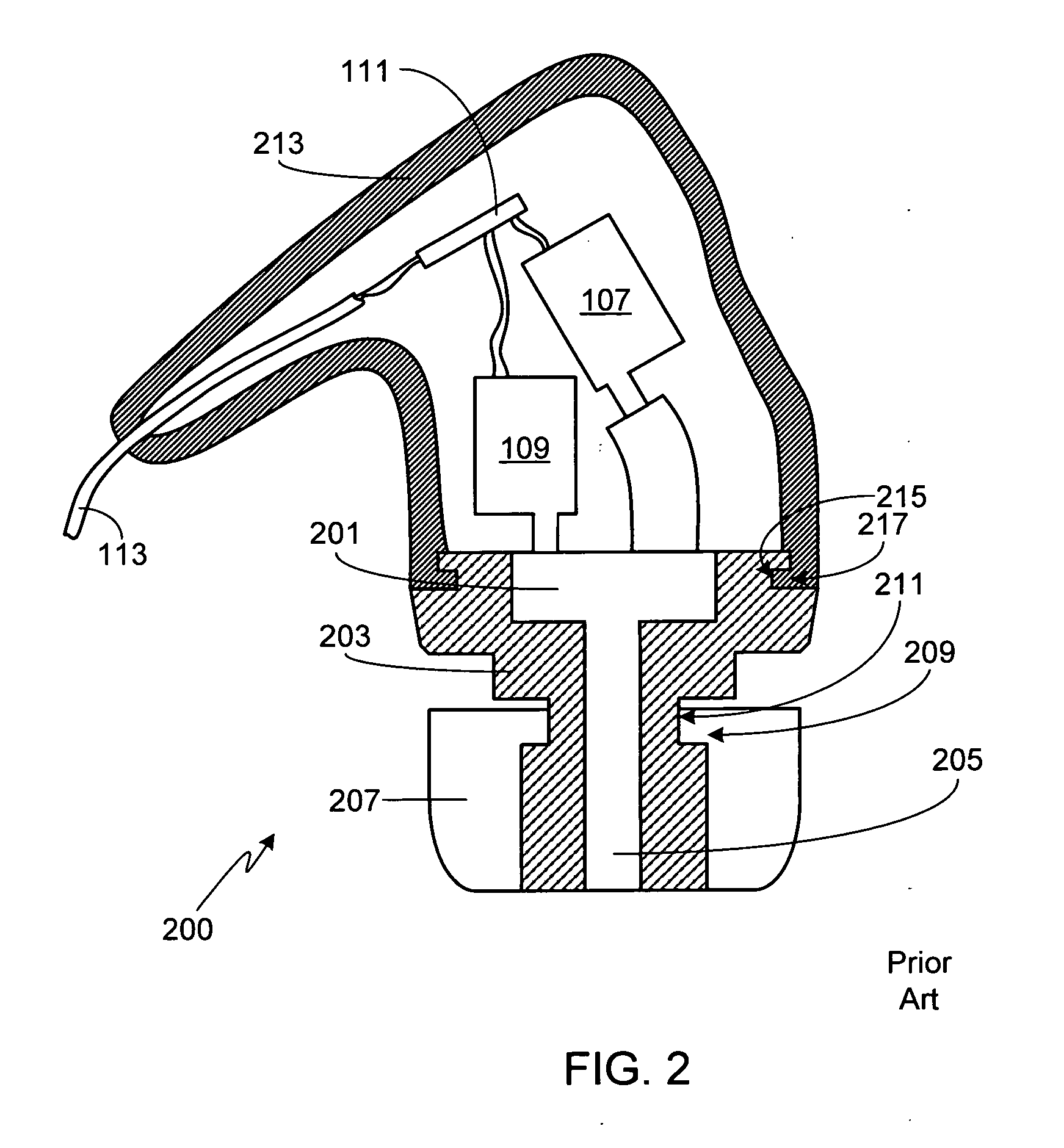
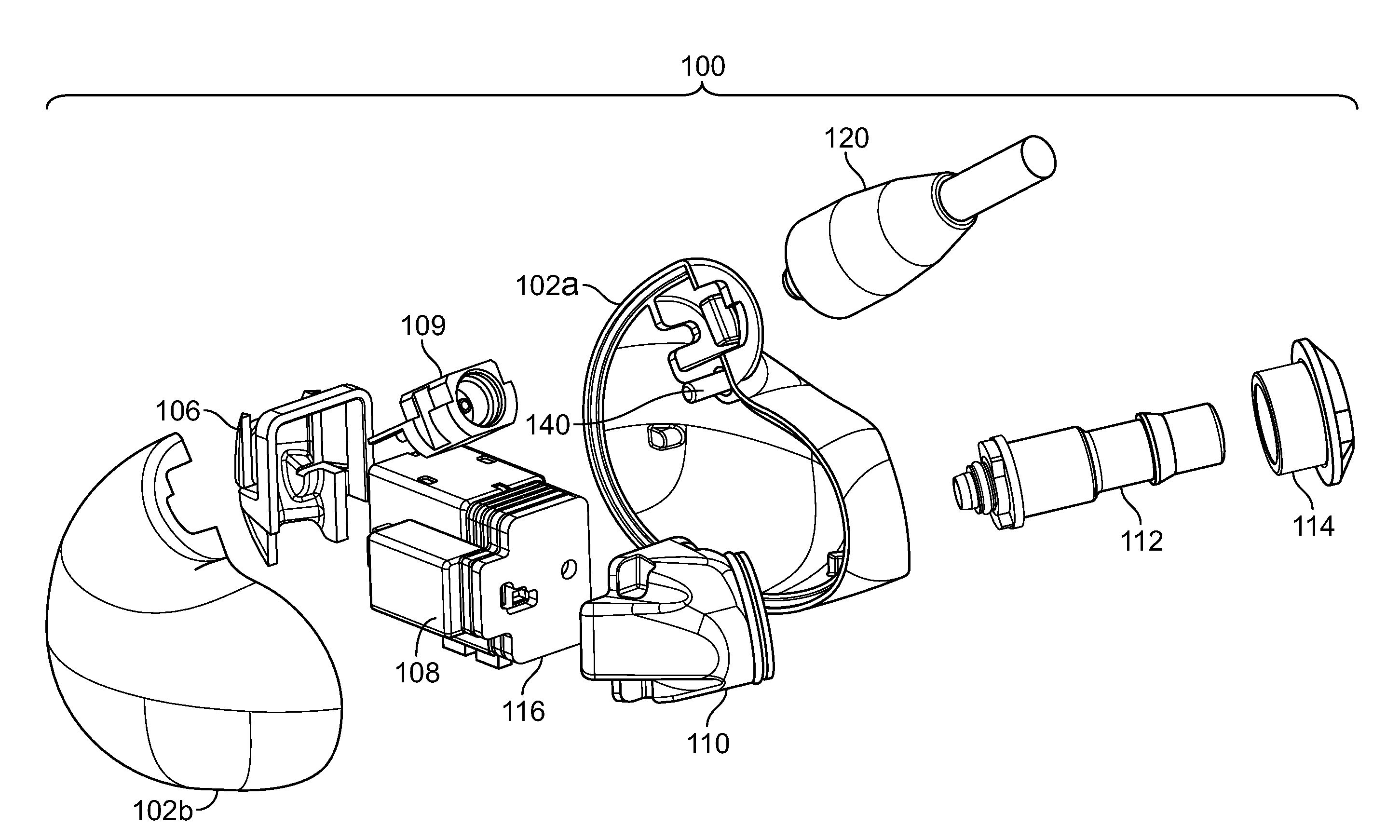
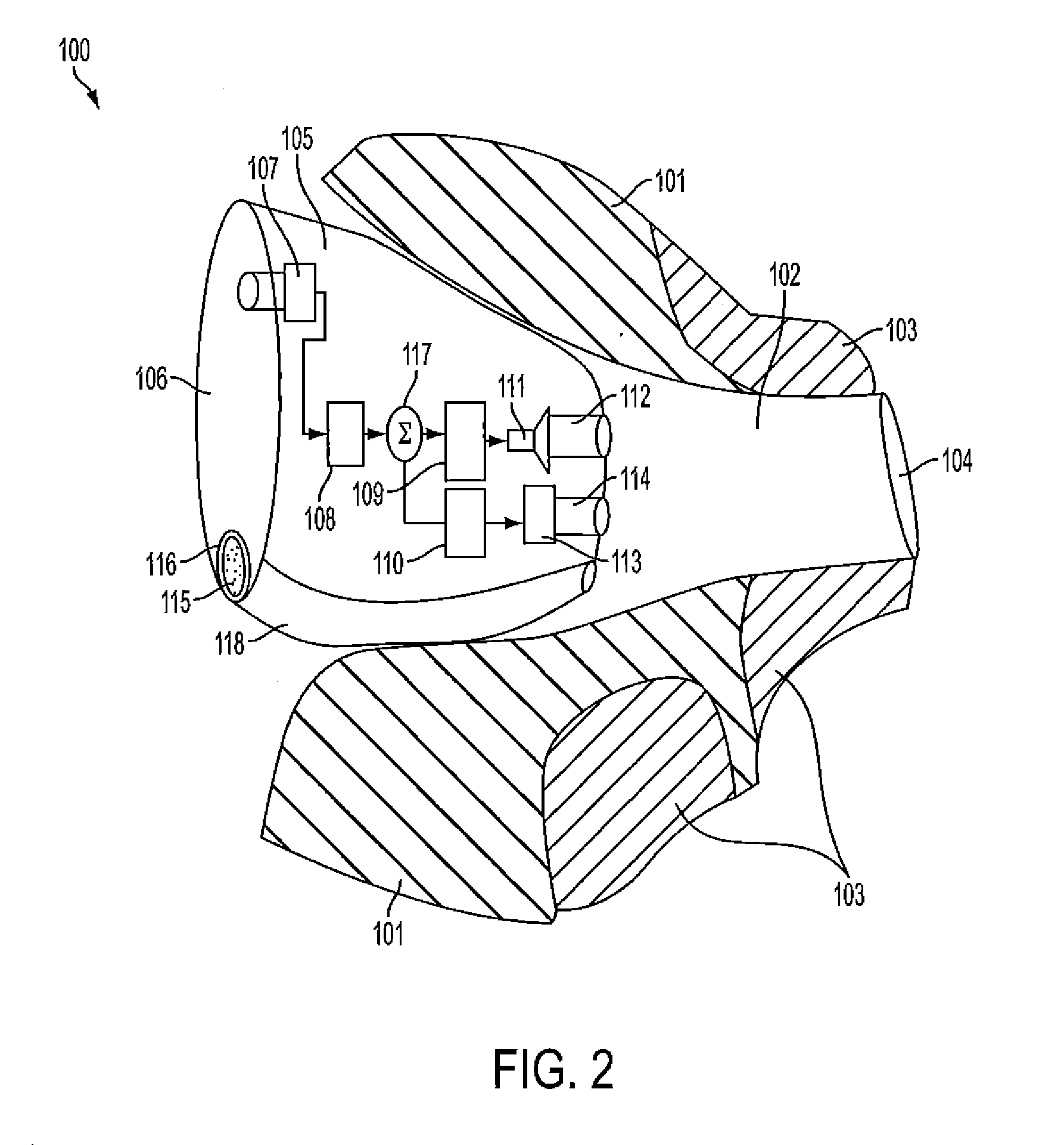
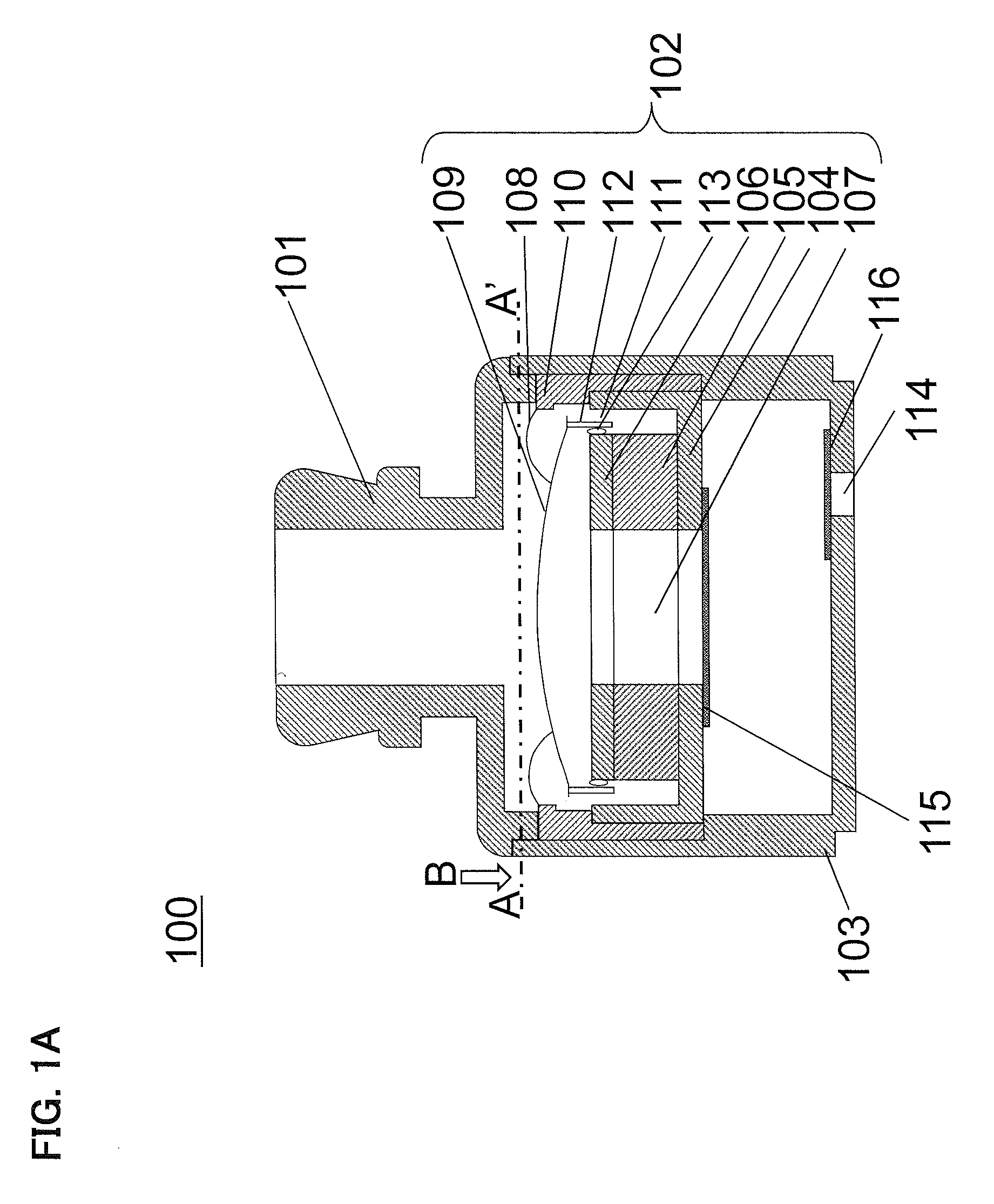
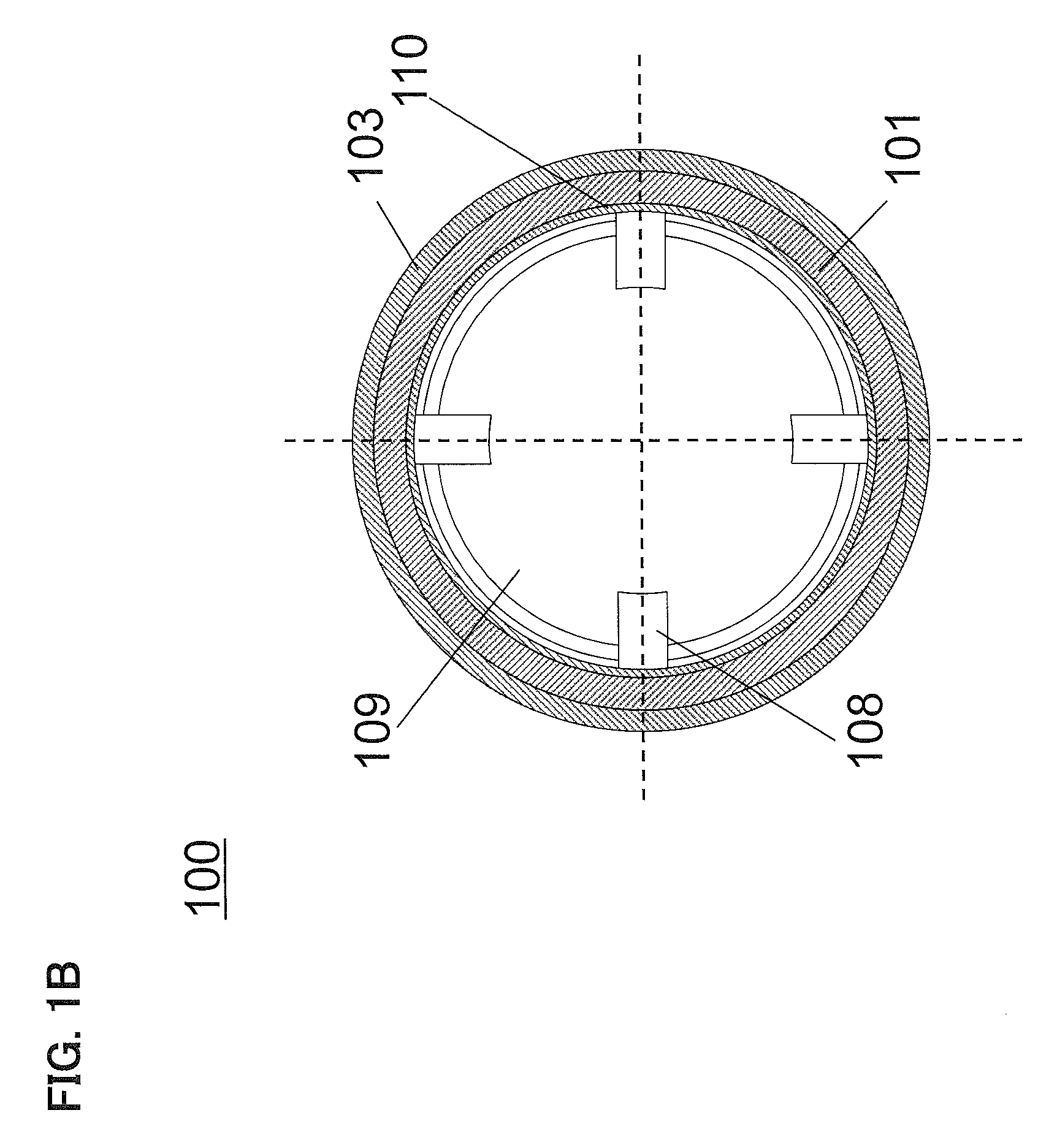
Silicon-based transducer for use in hearing instruments and listening devices
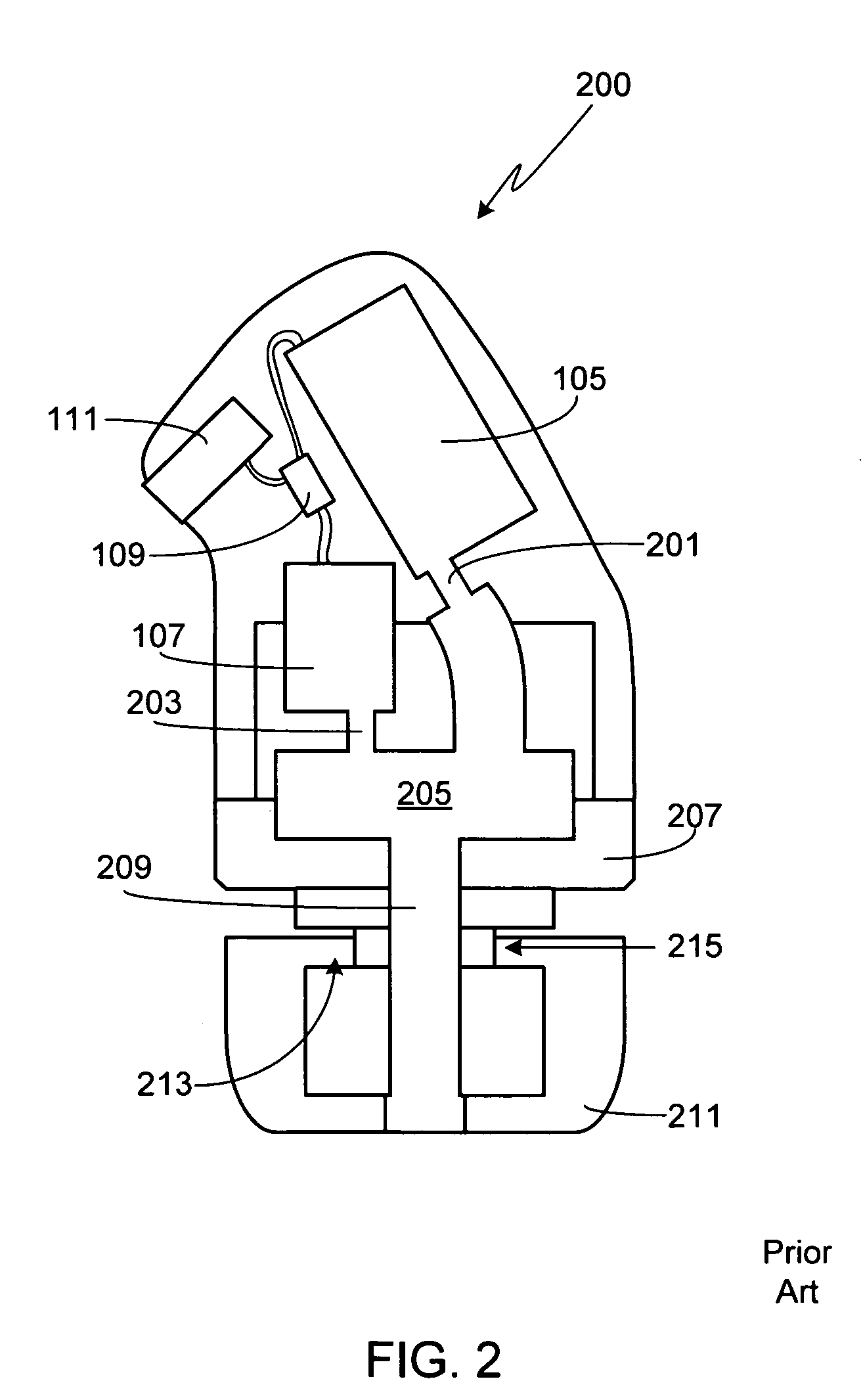
InactiveUS7142682B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor electrostatic transducersConvertersAudio power amplifier
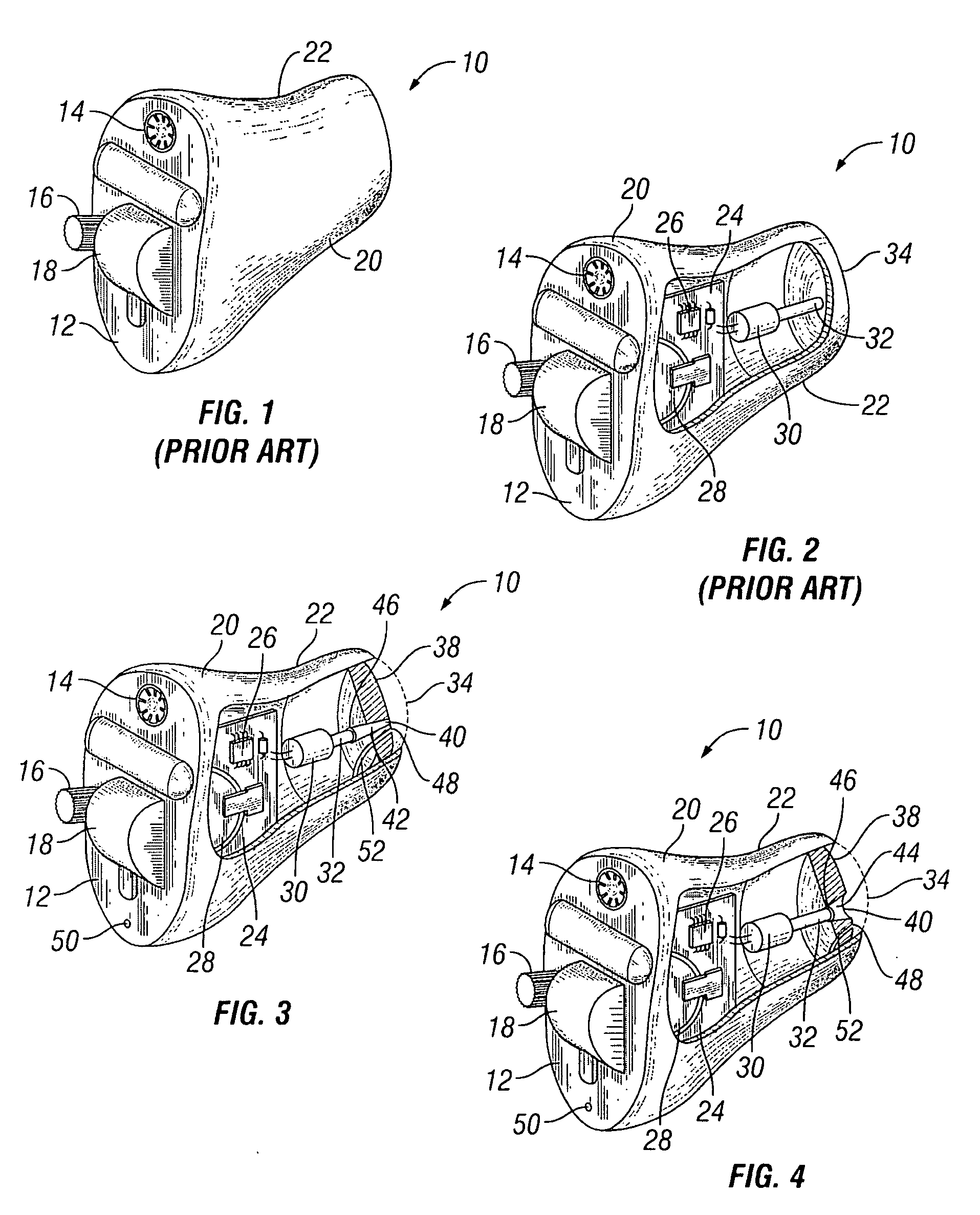
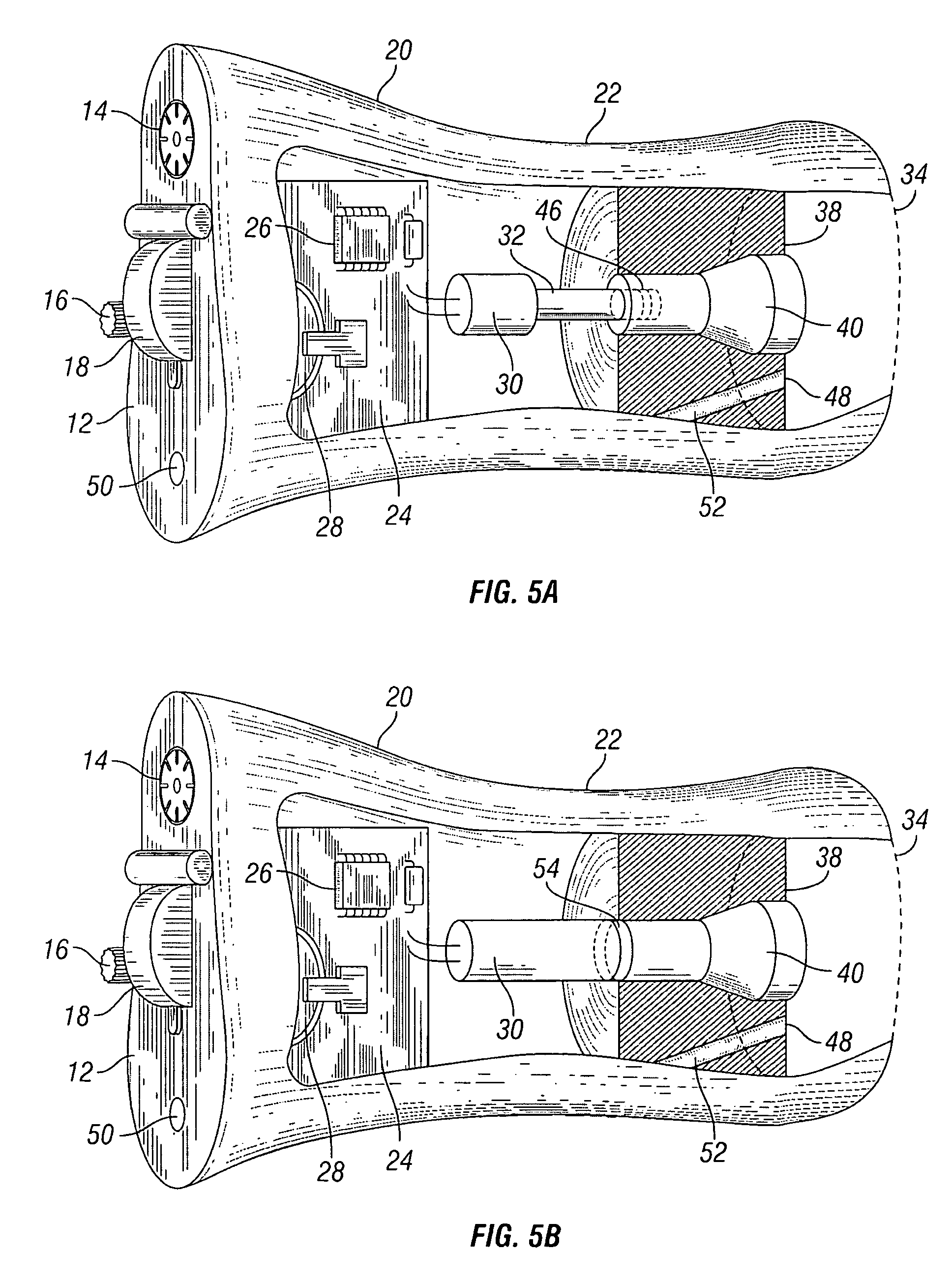
A silicon-based transducer assembly coupled to a movable structure in a hearing instrument. The transducer assembly includes at least one microphone chip and an ASIC having multiple integrated components such as any combination of a DSP, an A / D converter, an amplifier, a filter, or a wireless interface. The movable structure may be a battery access door, a volume dial, a switch, or a touch pad. A protection strip can be disposed across the battery access door to prevent debris from clogging the silicon-based transducer assembly. The transducer assembly may also include an array of microphone chips to achieve adaptive beam steering or directionality. When equipped with a wireless interface, the hearing instrument wirelessly communicates with another hearing instrument or with a network.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
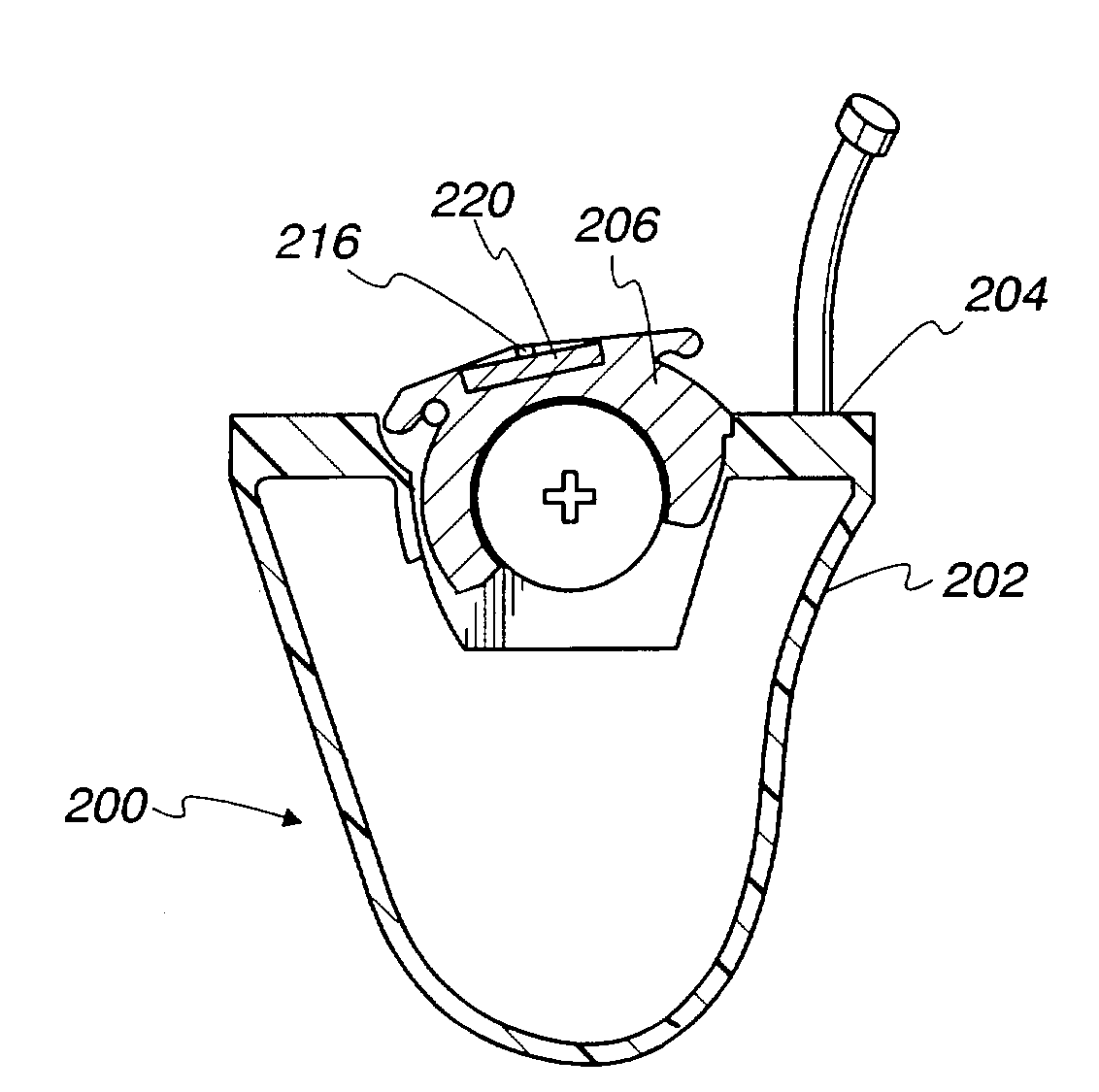
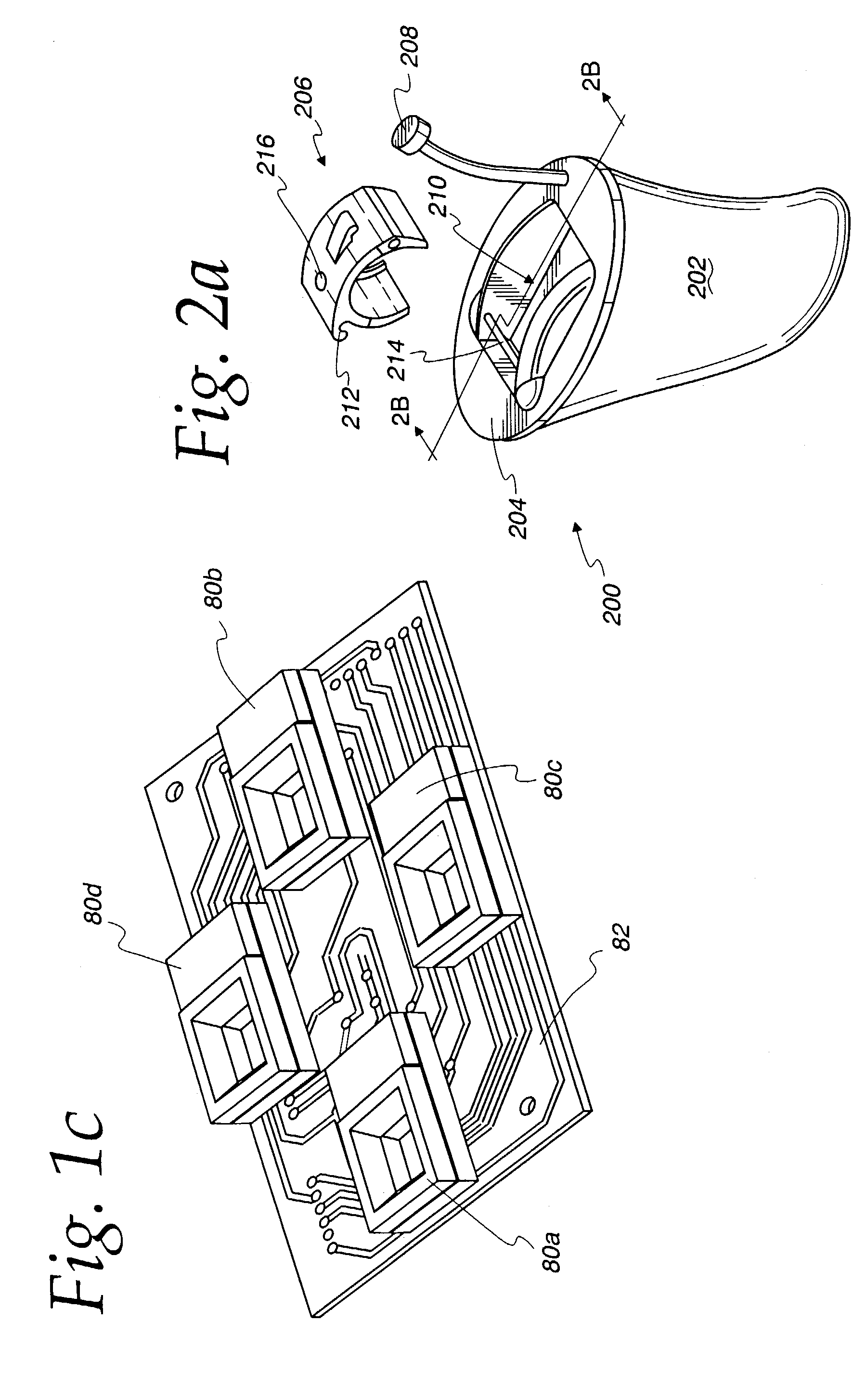
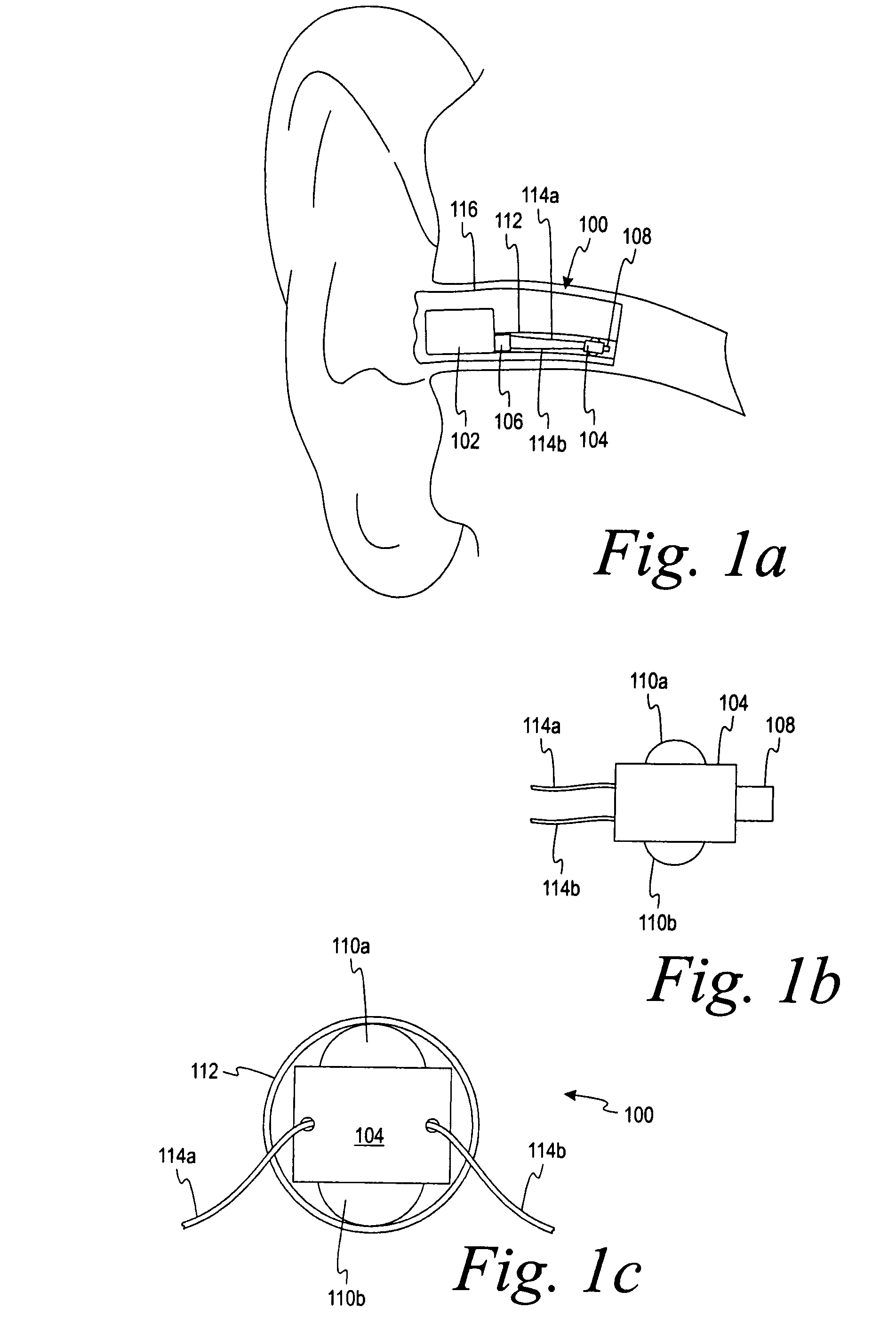
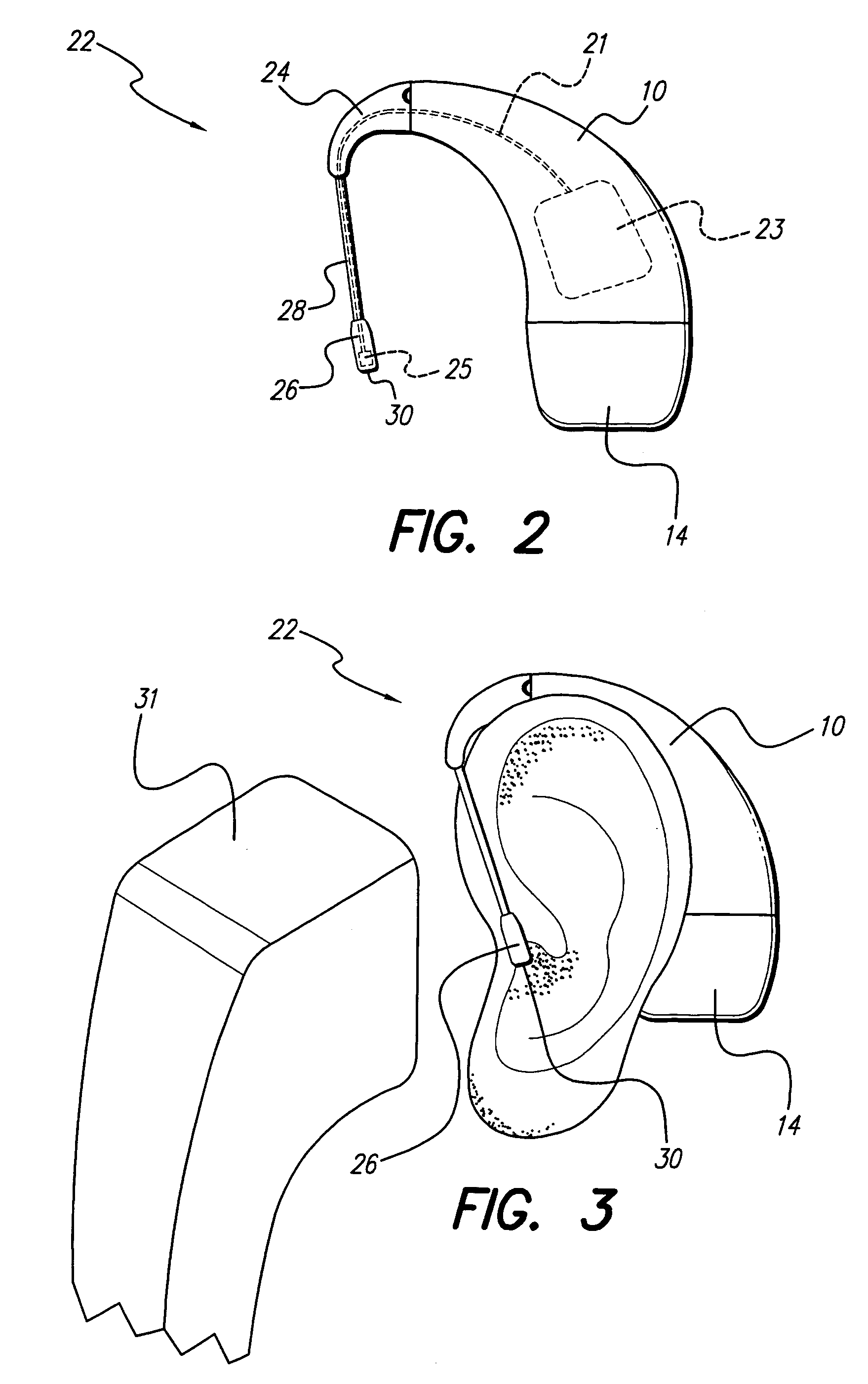
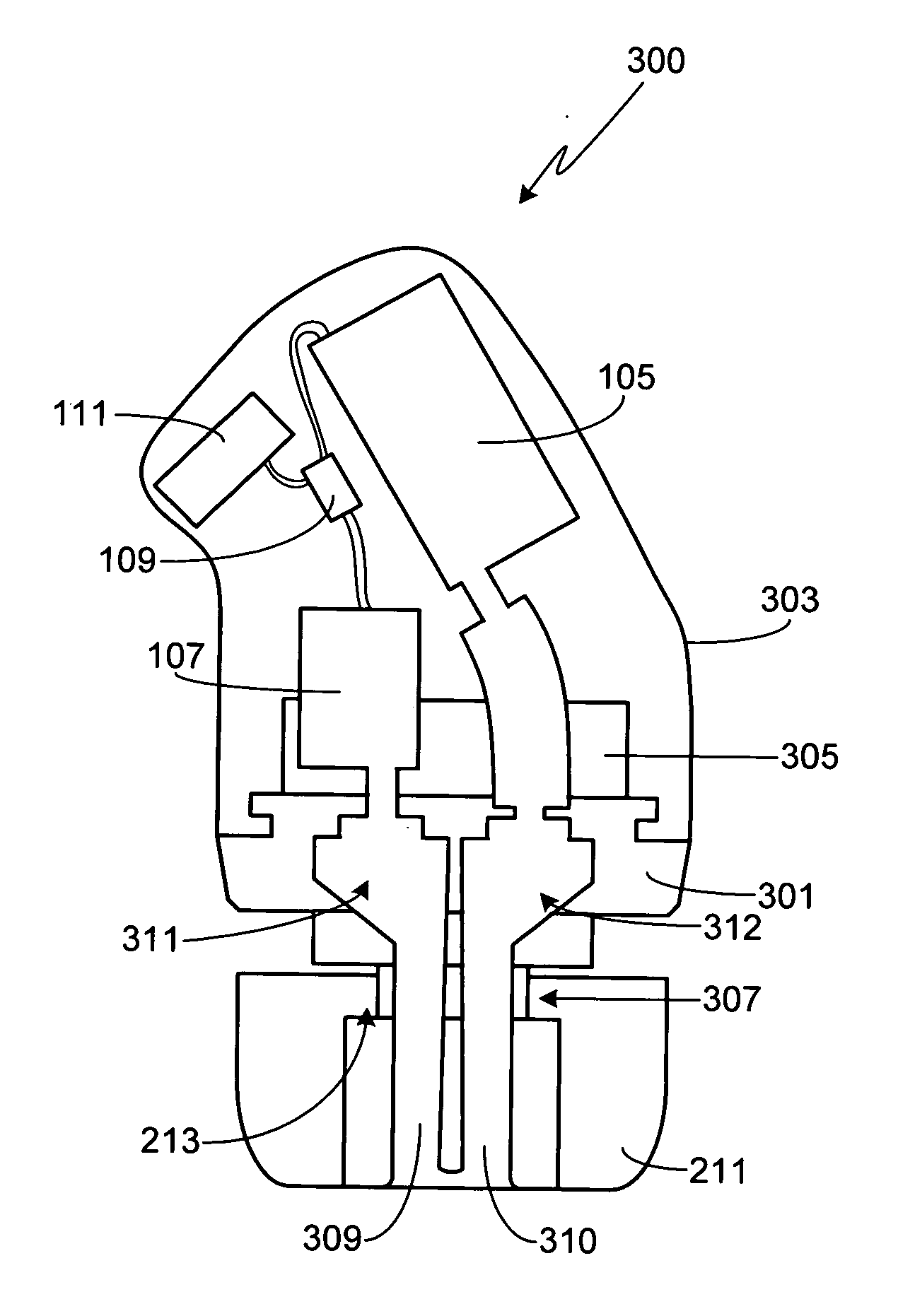
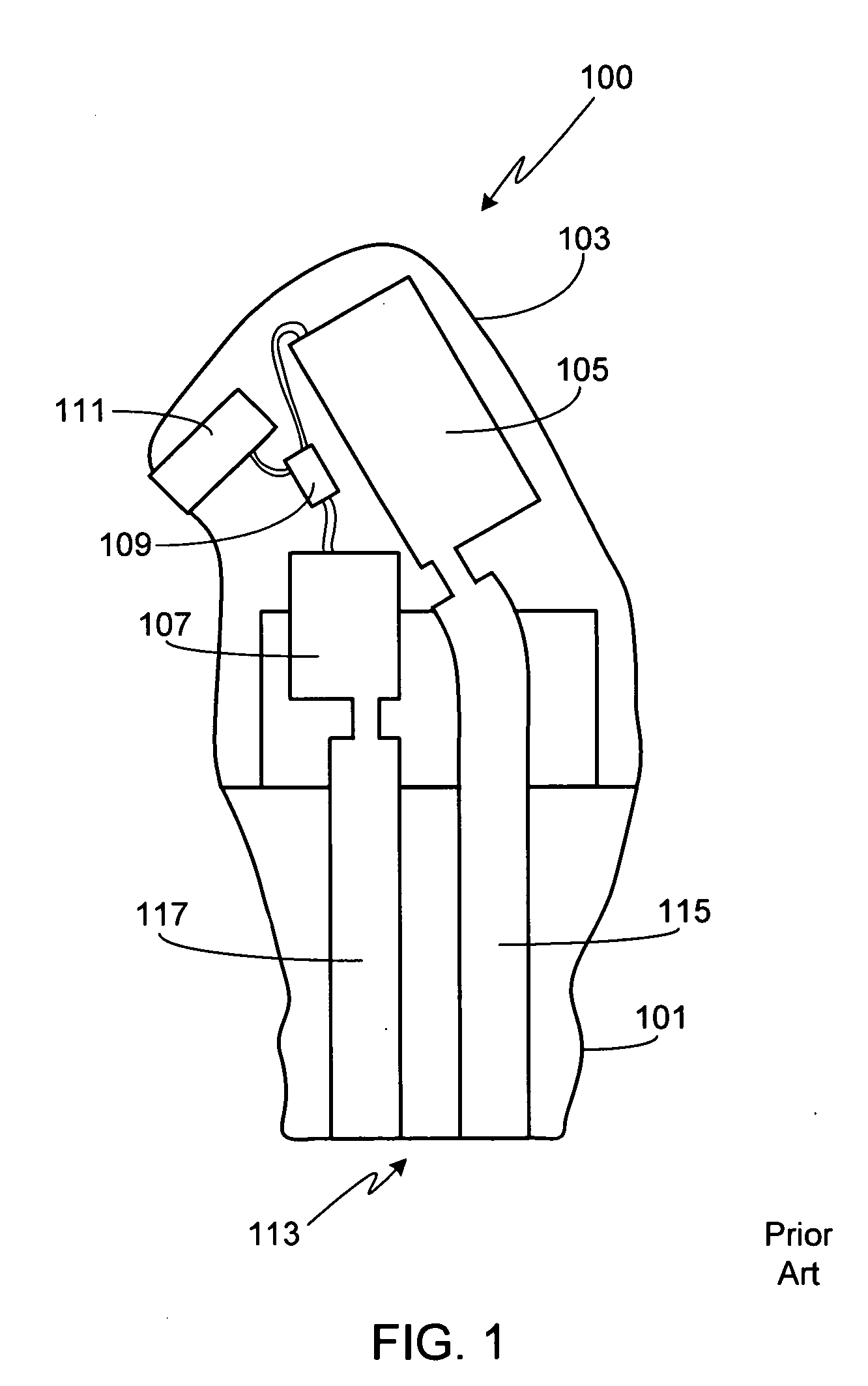
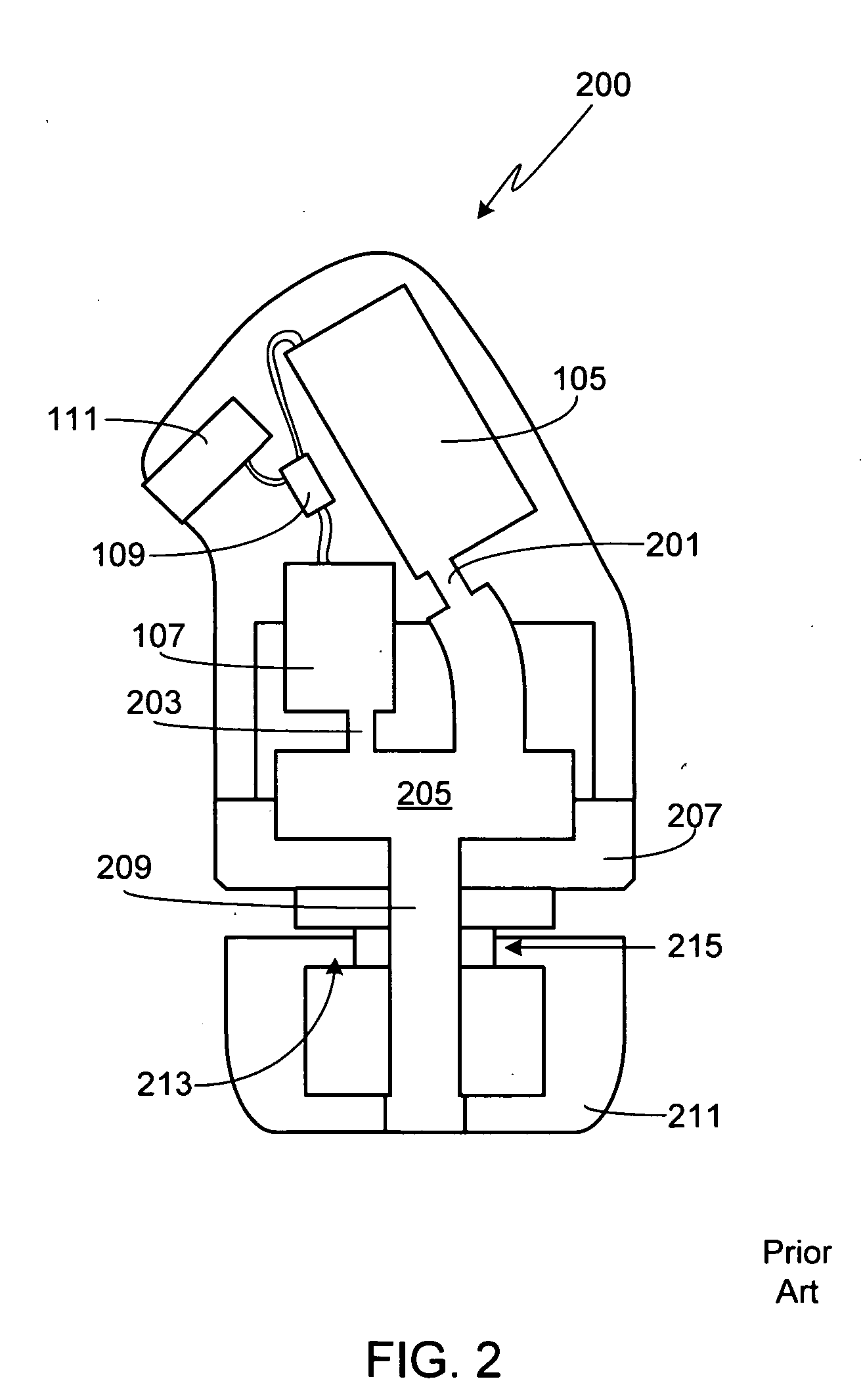
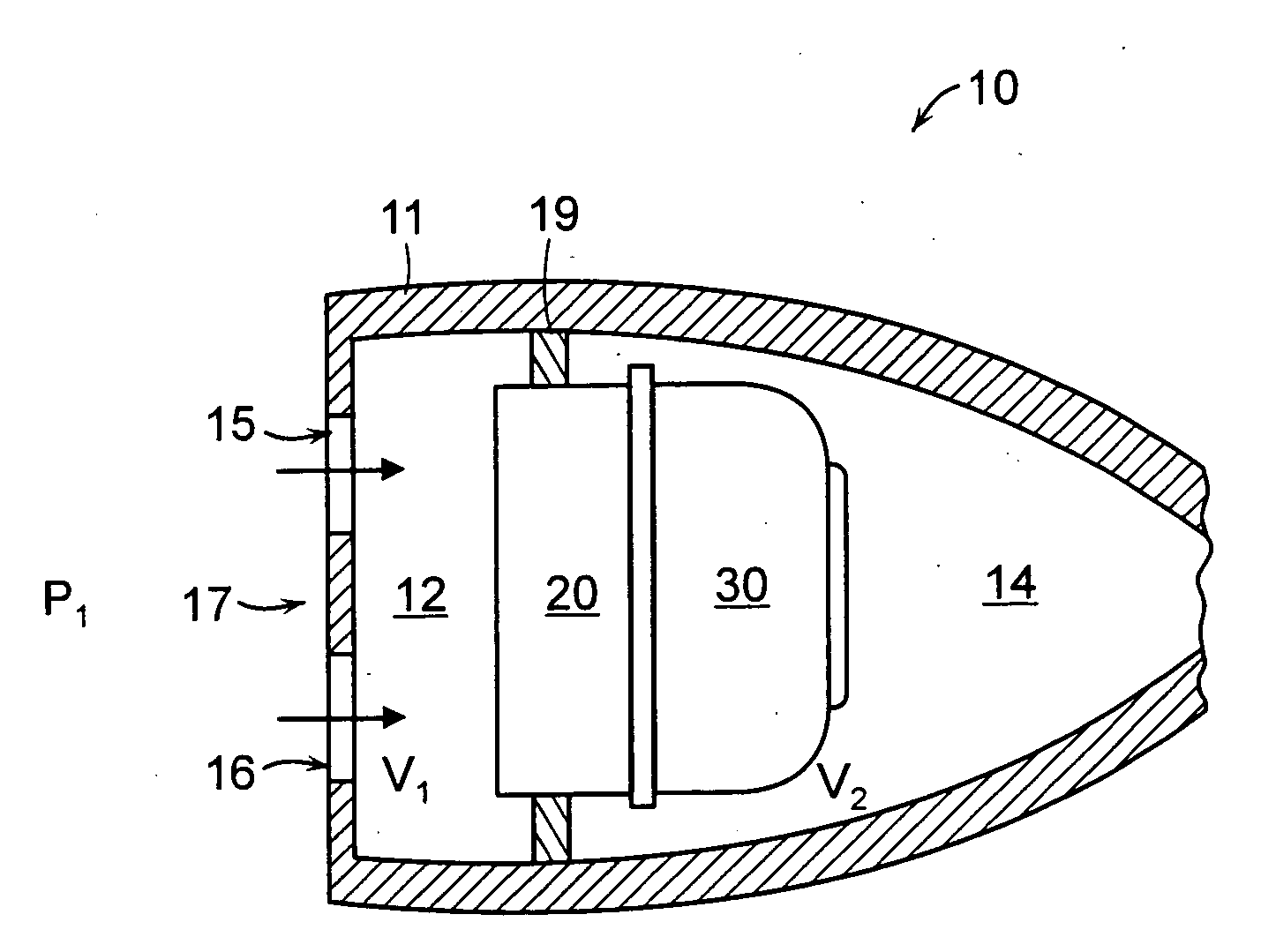
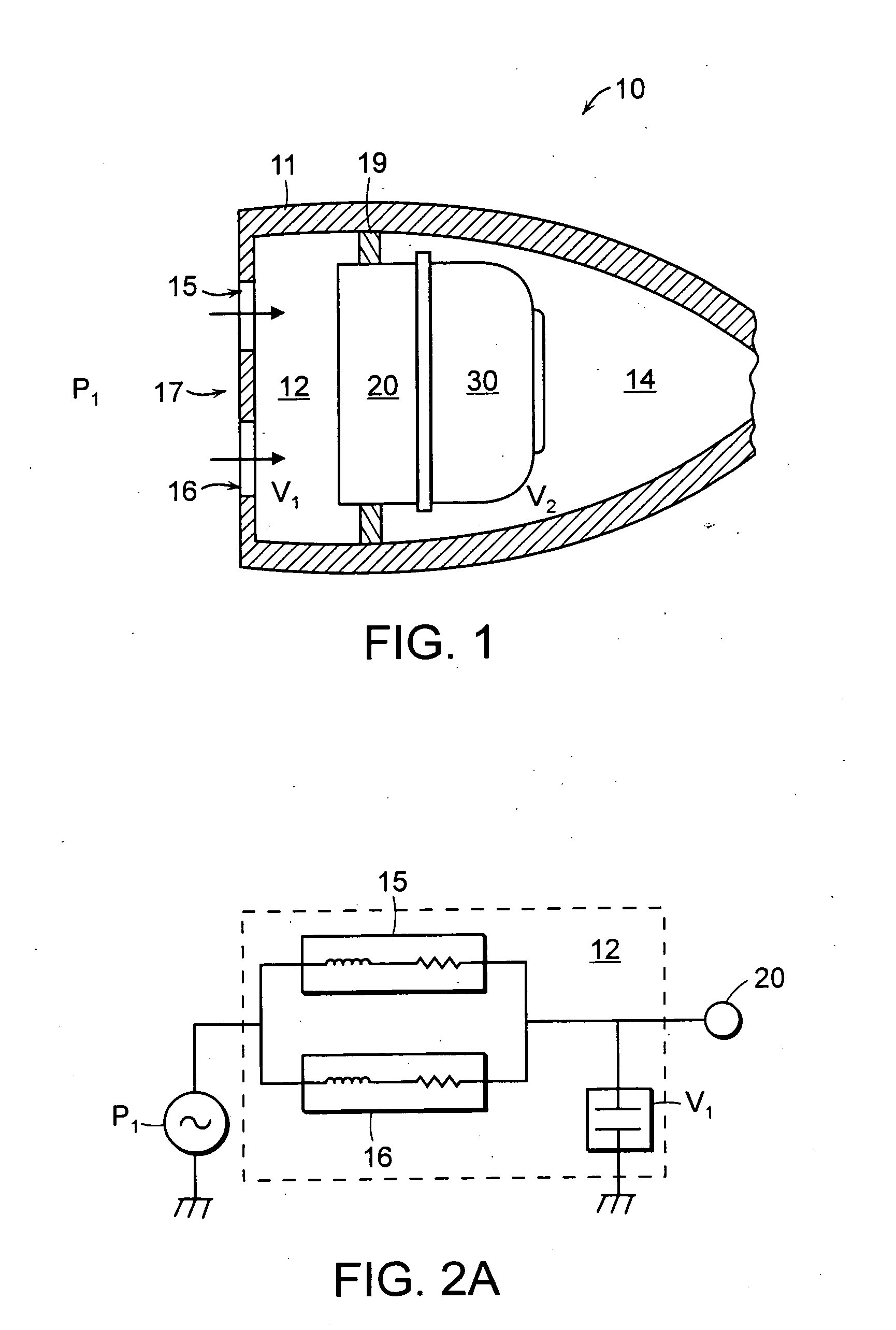
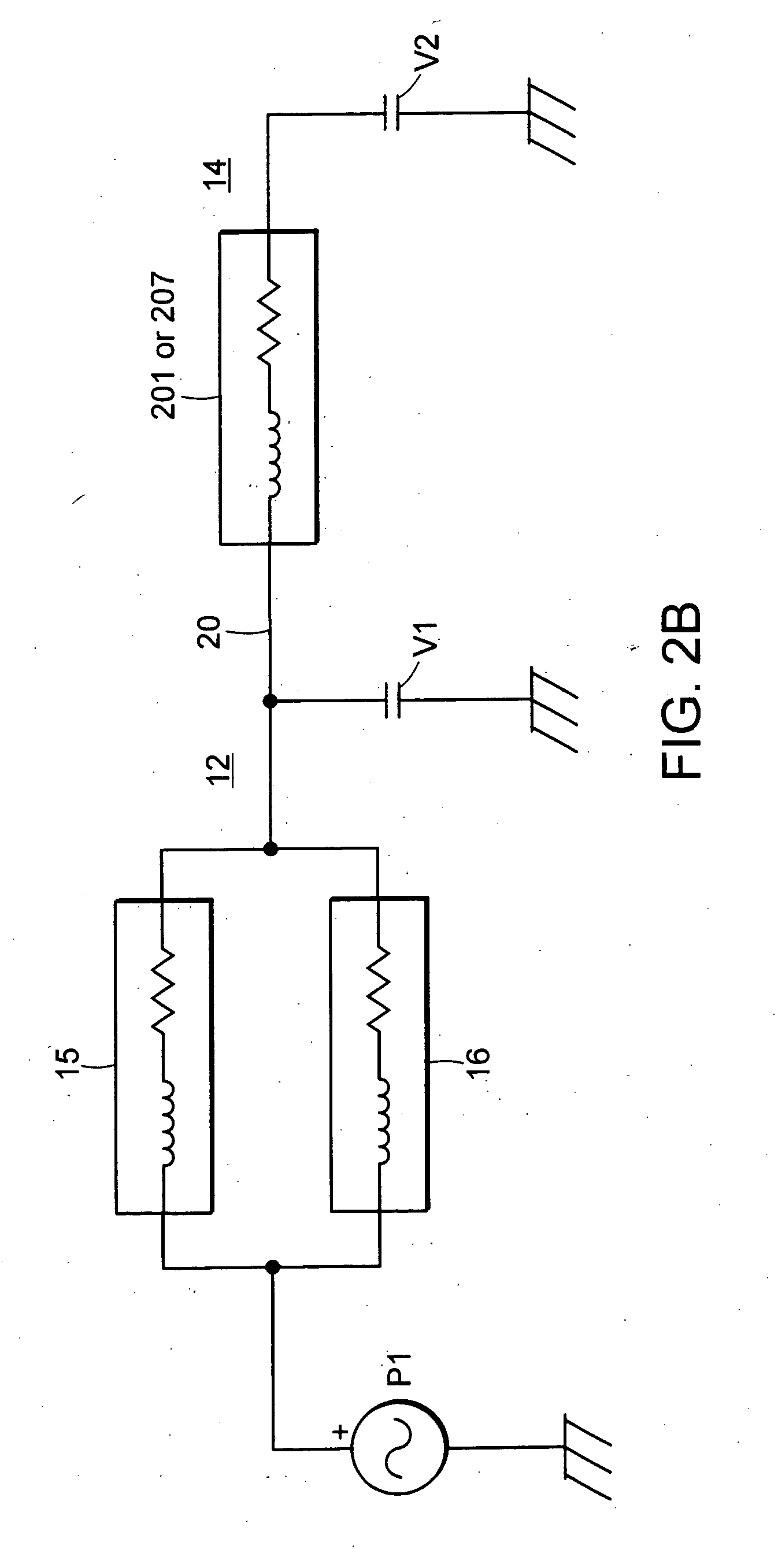
Hearing instrument
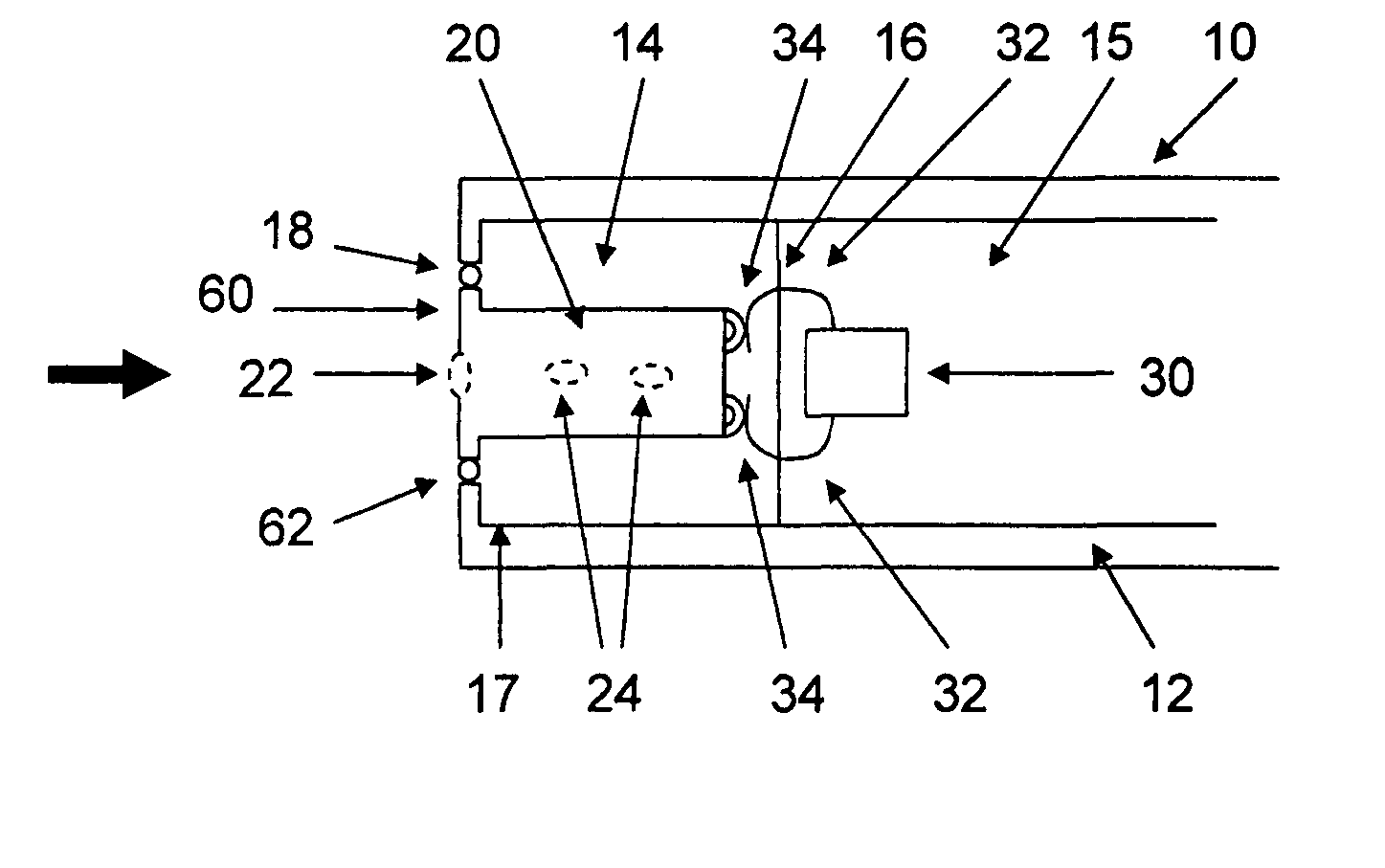
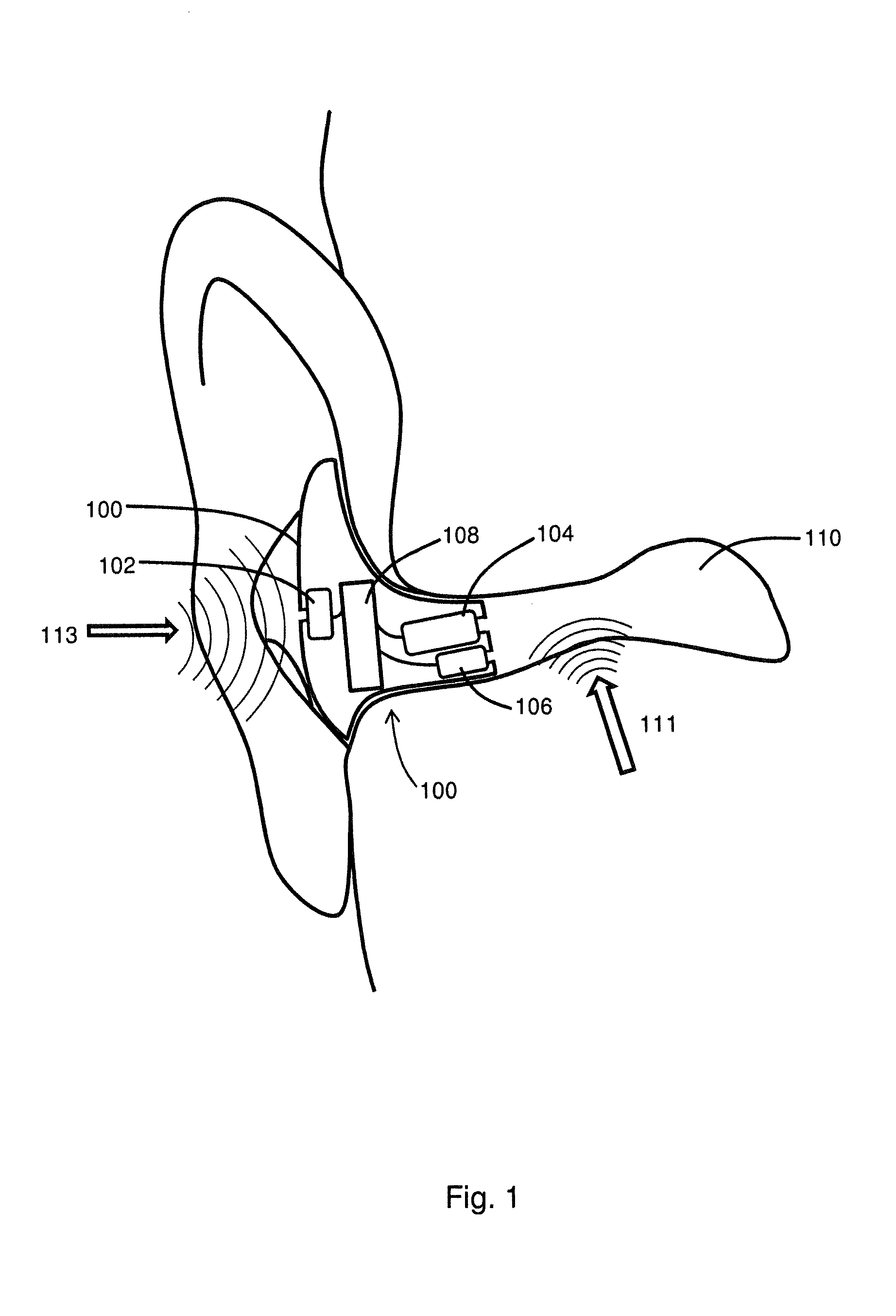
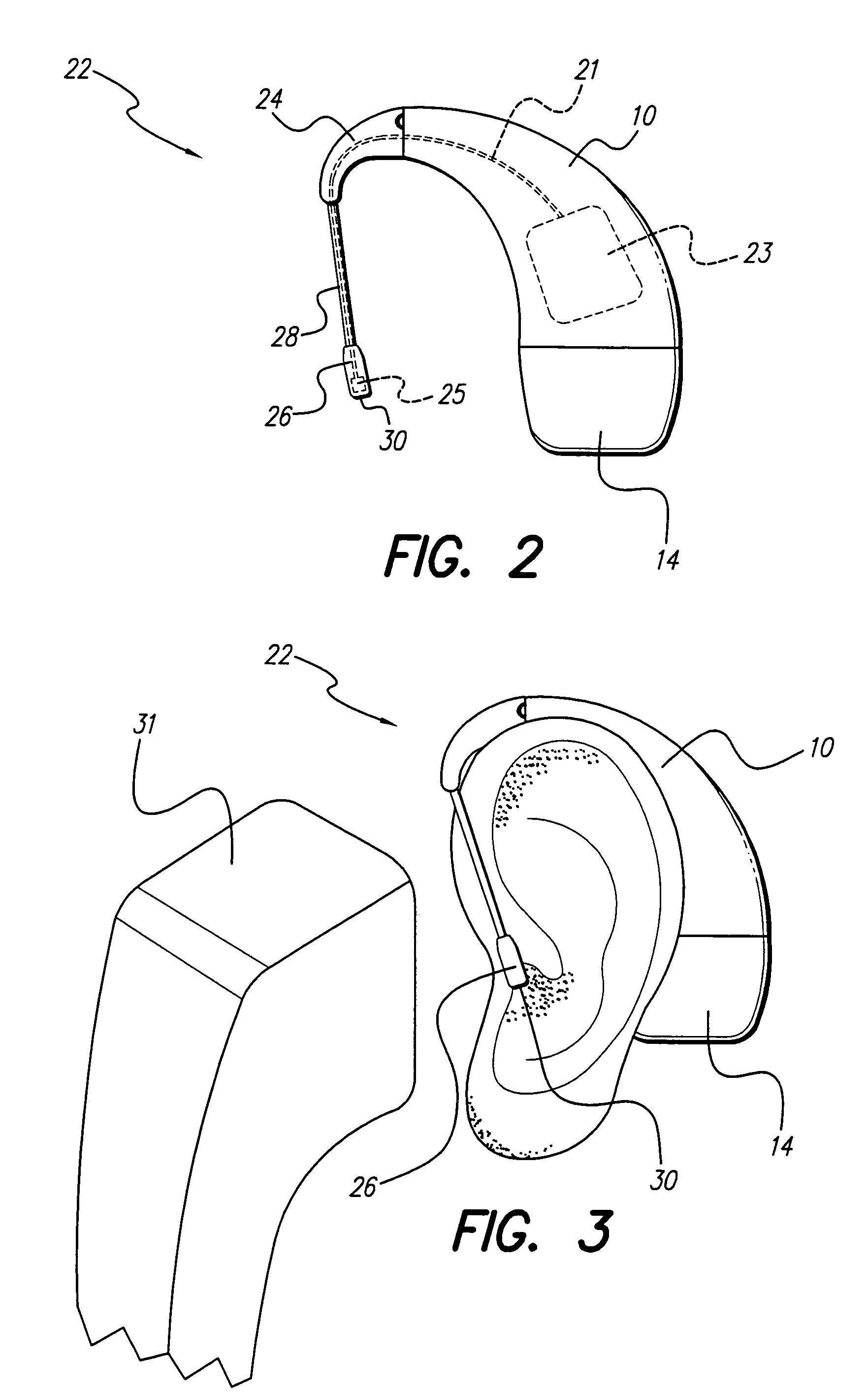
InactiveUS20060159298A1Improve sound qualityIncrease rangeAdditive manufacturing apparatusHearing aid ventsHearing perceptionComputer science
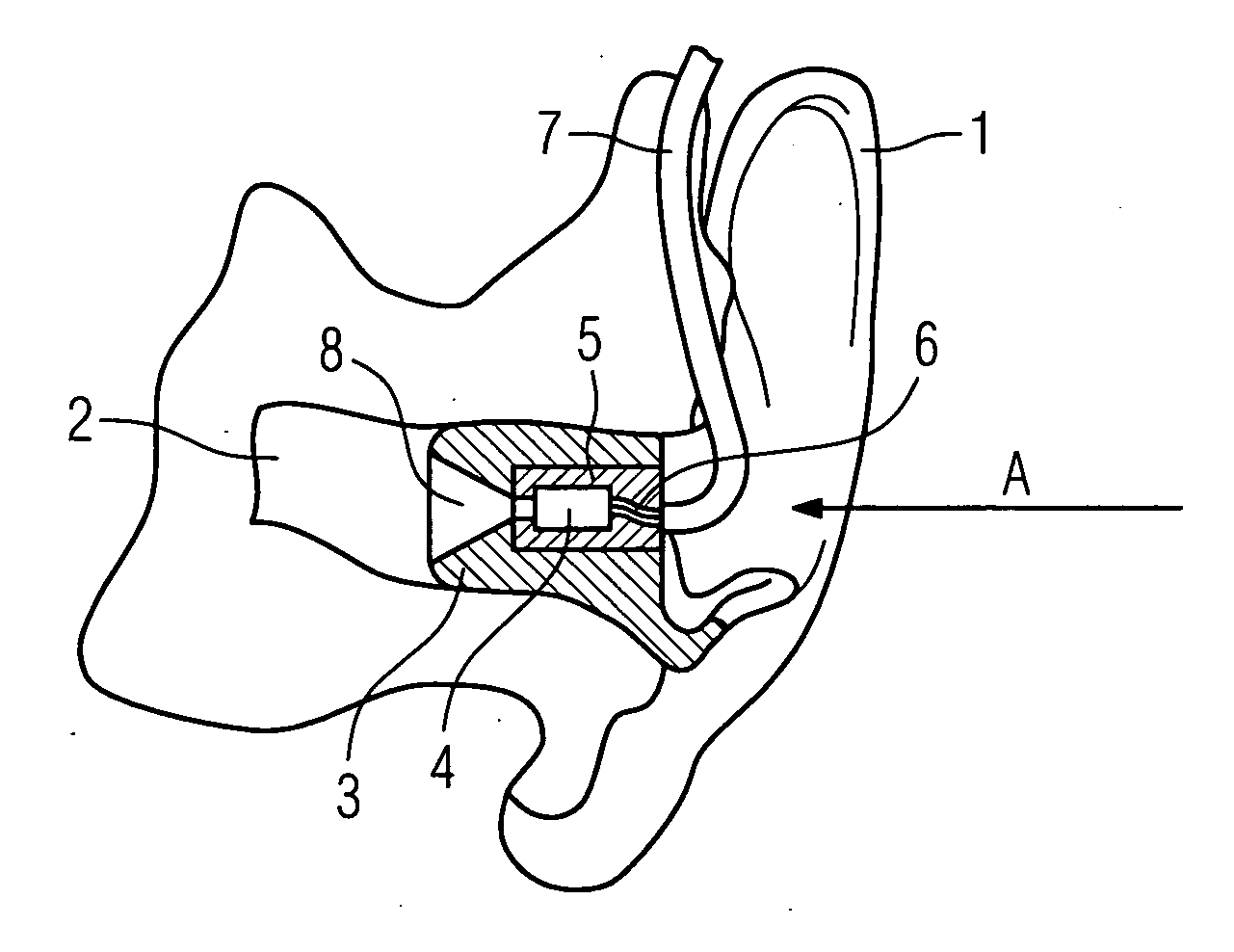
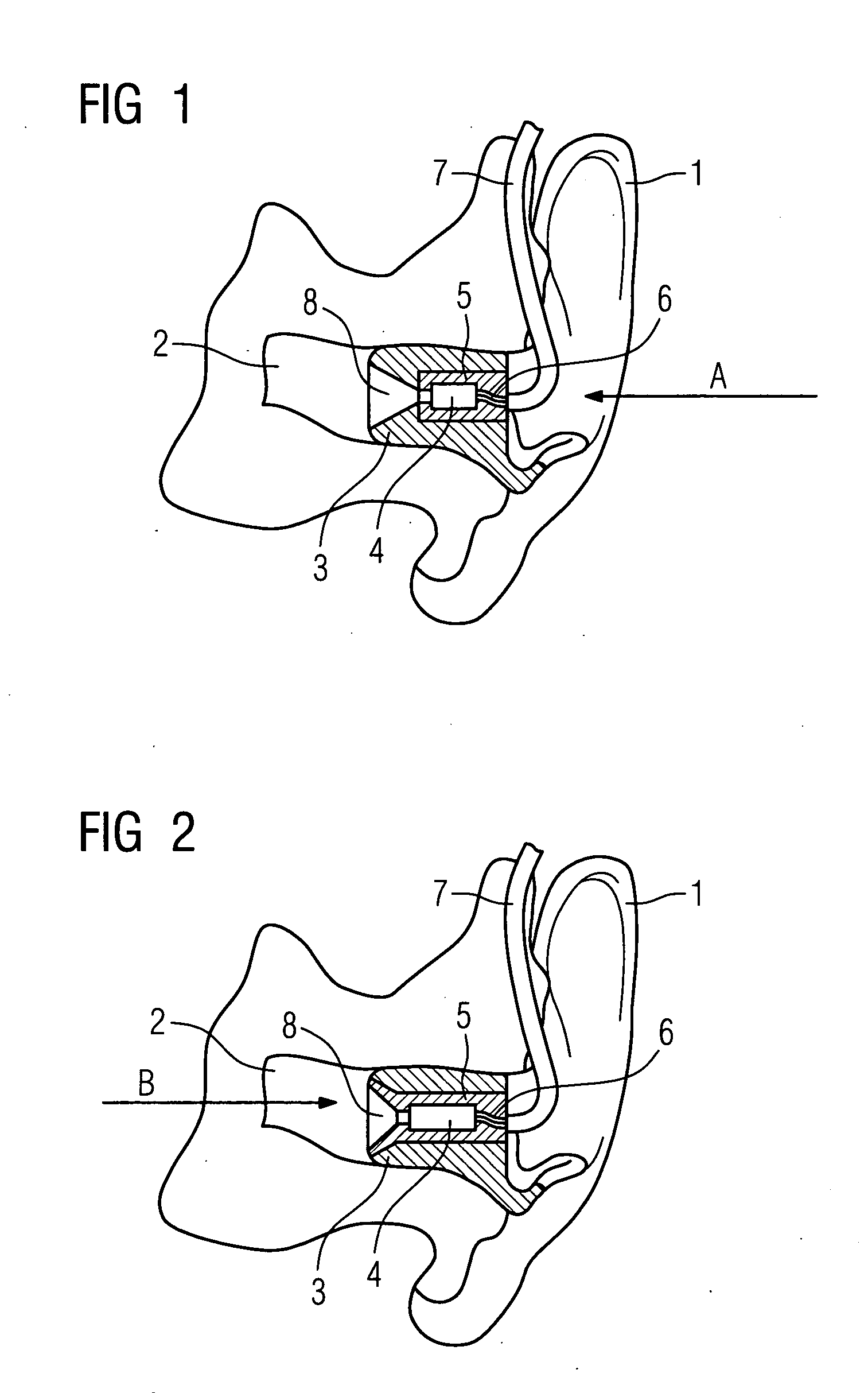
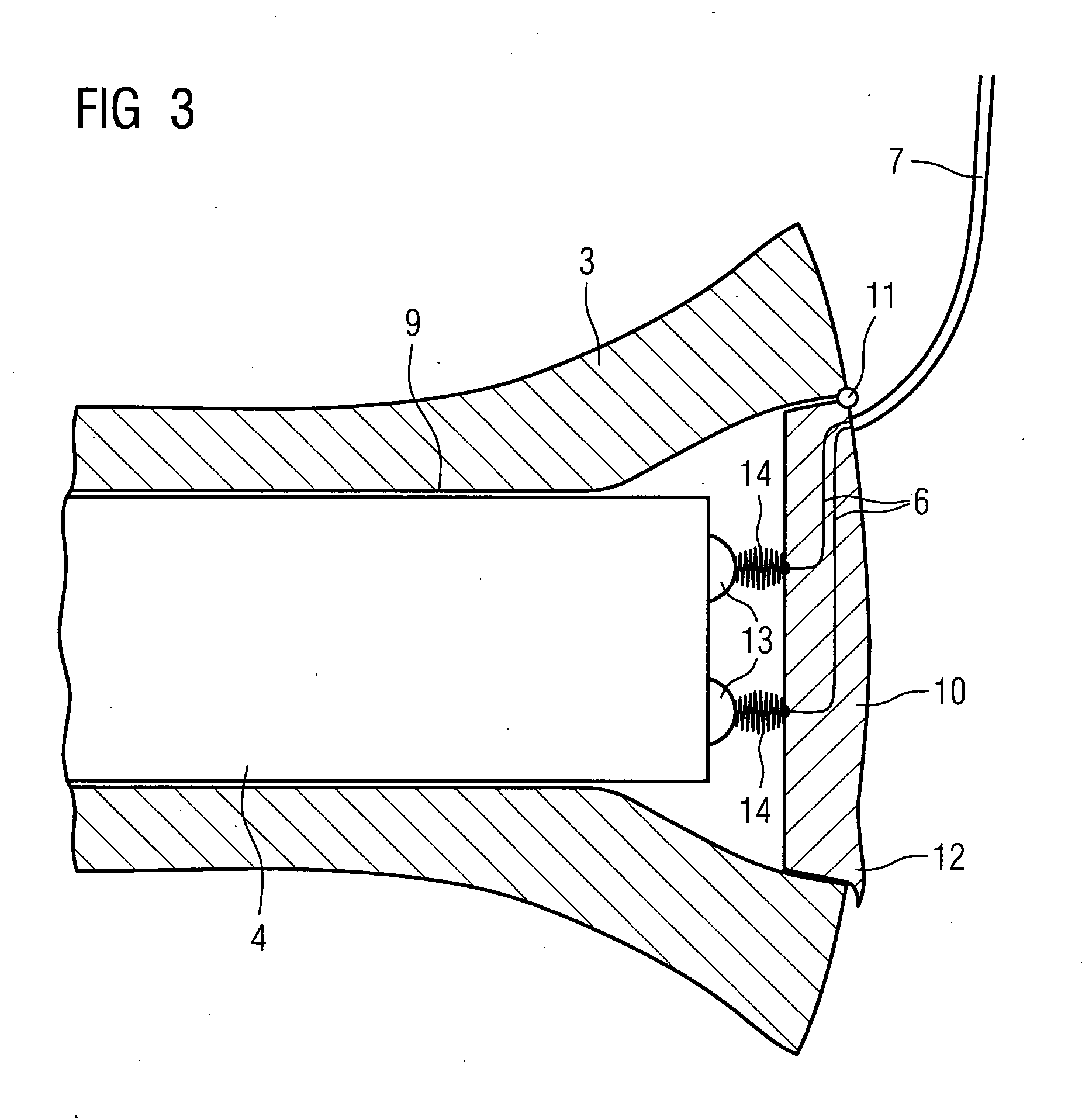
According to the first aspect of the invention, a hearing instrument with at least one microphone and signal processing comprises at least two receivers having a different frequency response. At least a first one of the receivers is placed outside the ear canal, for example in a behind-the-ear component. According to the second aspect of the invention, a hearing instrument comprising a behind-the-ear component and an external component for being placed in the user's ear canal or in the user's ear as well as a connection link between the behind-the-ear component and the external component is provided, where the connection link is reversibly pluggable to the behind-the-ear component and / or the in-the-ear-canal component and has a length that is reversibly adjustable. The hearing instrument also comprises fixation means for reversibly fixing the adjusted length of the connection link. A hearing instrument according to the third aspect comprises a fixation means separate from the in-the-ear-canal component. The fixation means may be positioned in the ear canal and rest therein. The in-the-ear-canal component may be connected to the fixation means and detached therefrom when the same is already in the ear canal. A hearing instrument according to the fourth aspect of the invention comprises an in-the-ear-canal component to be placed in a user's ear canal and fixation means for fixing it in the ear canal. The fixation means comprise an outer shell which is shaped to fit (i.e. custom shaped to fit the specific user's ear geometry) in the user's ear canal and a mounting structure for holding the in-the-ear-canal component. The outer shell is preferably resilient, i.e. has an elasticity allowing temporal deformation.
Owner:SONOVA AG
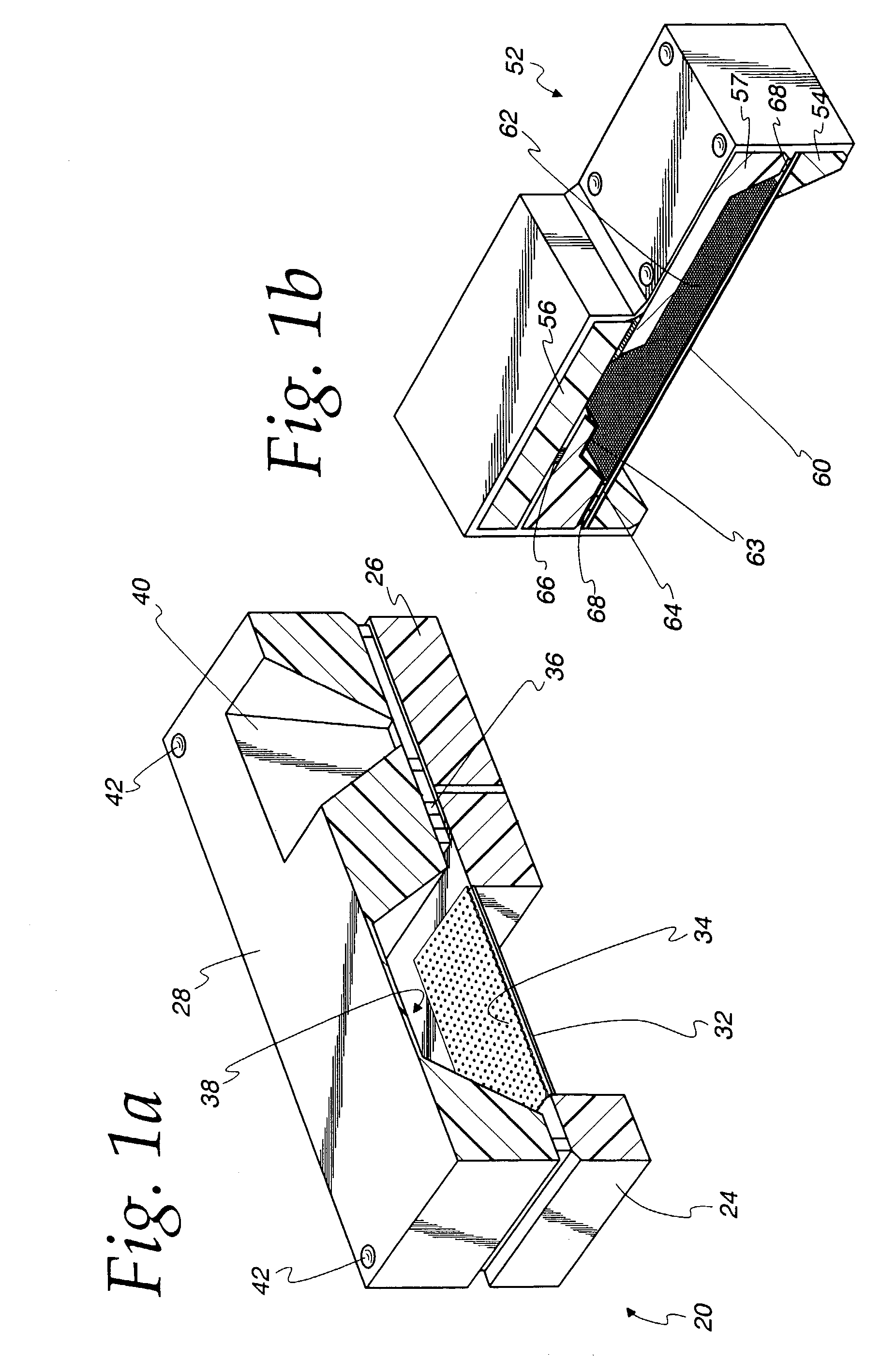
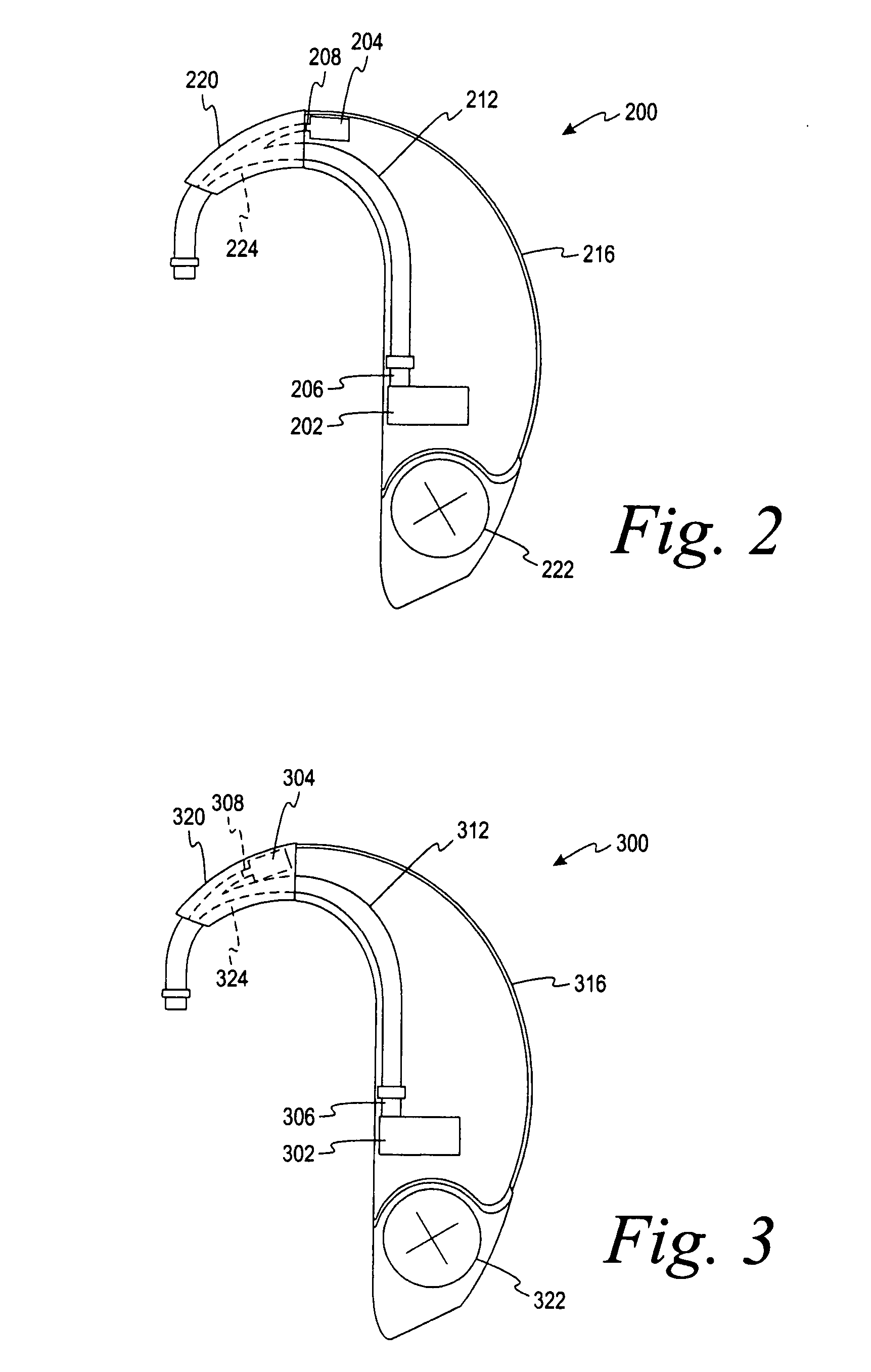
Sound tube tuned multi-driver earpiece
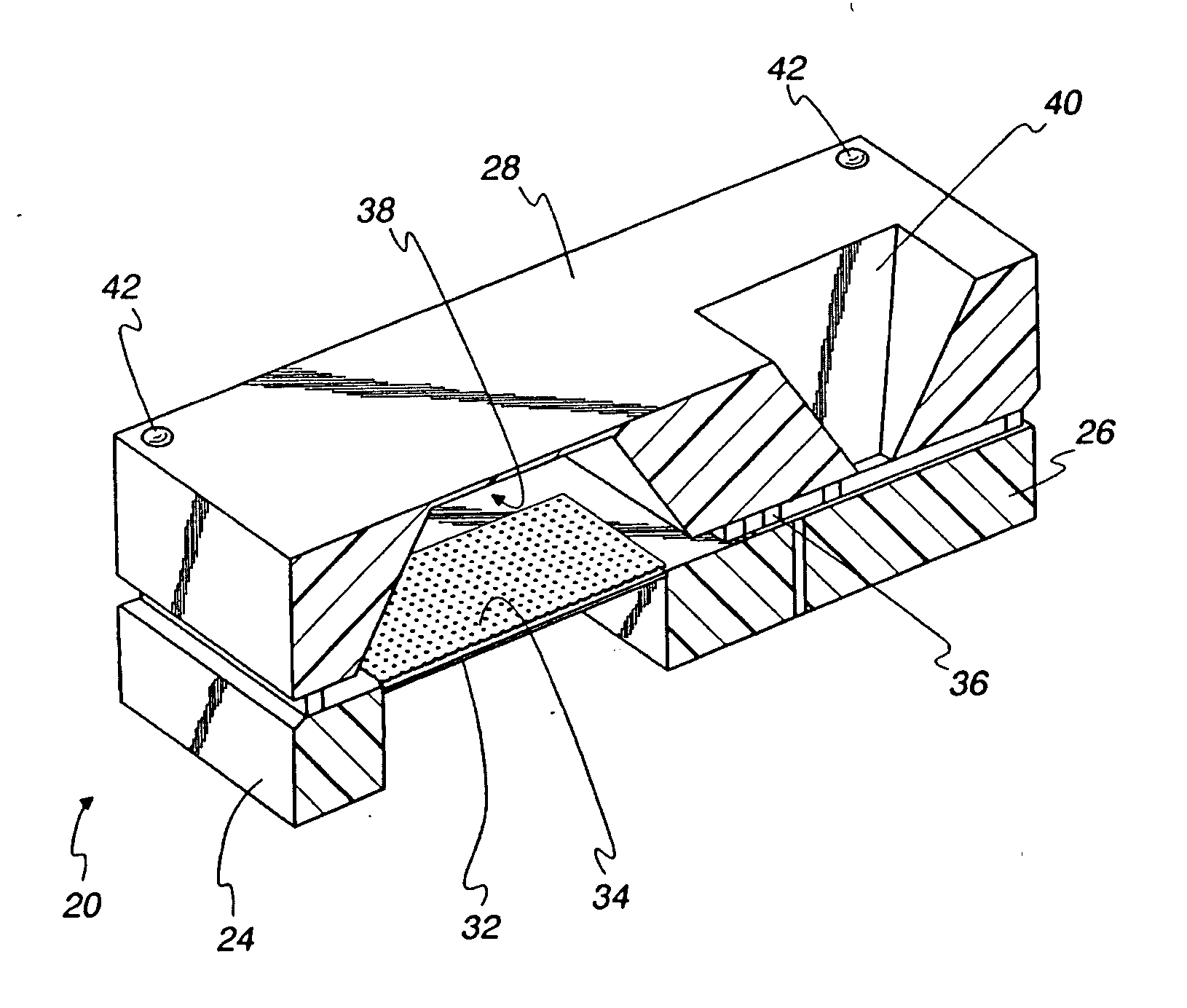
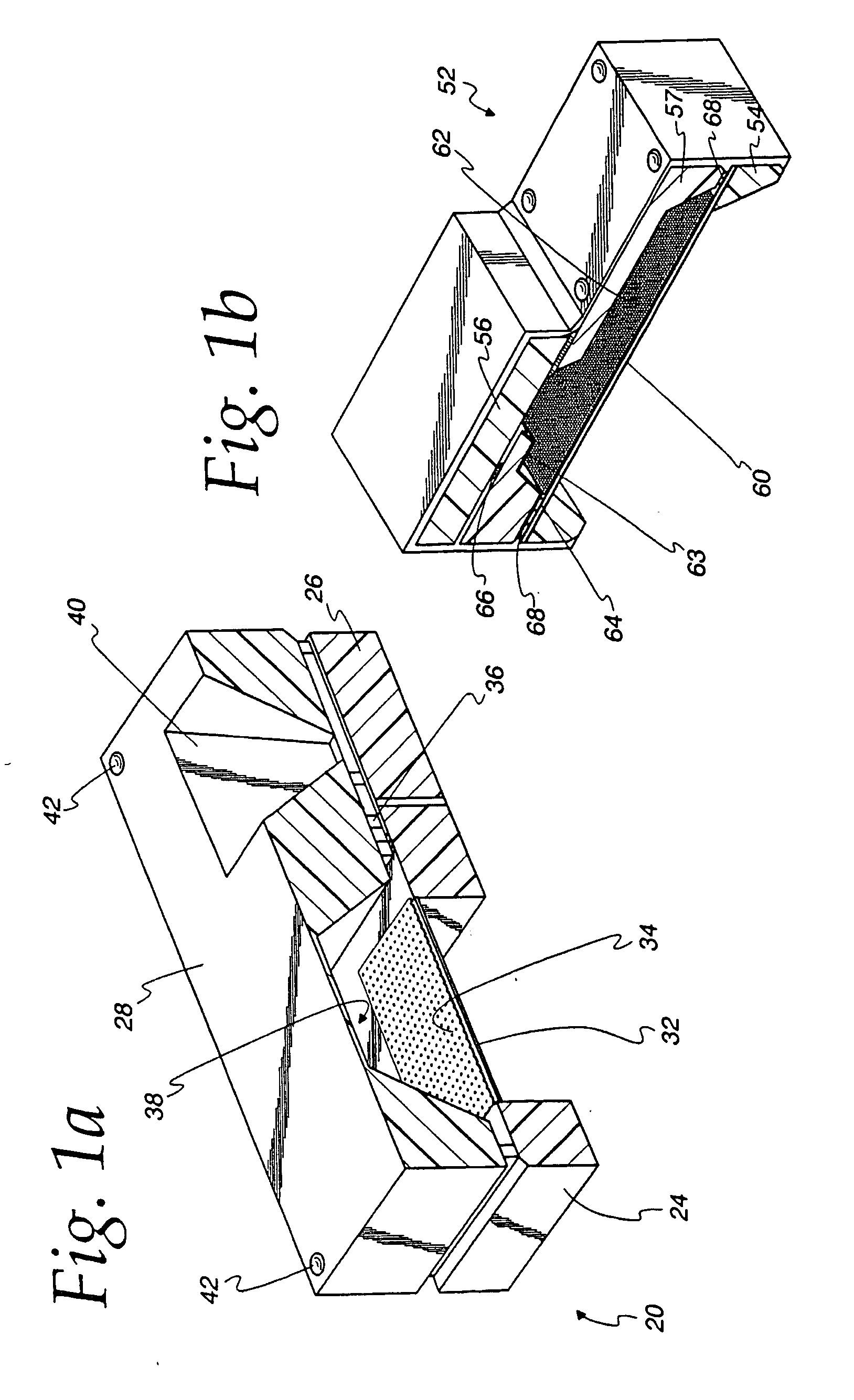
ActiveUS20060133636A1Good audioDetails for specific frequency responseIntra aural earpiecesAcoustic transmissionPhase shifted
A method of optimizing the audio performance of an earpiece and the resultant device are provided. The disclosed earpiece combines at least two drivers within a single earpiece. If a pair of drivers is used, each driver has a discrete sound delivery tube. If more than two drivers are used, preferably the outputs from the two lower frequency drivers are merged into a single sound delivery tube while the output from the third driver is maintained in a separate, discrete sound tube. To compensate for the inherent phase shift of the earpiece the lengths of the sound delivery tubes, and thus driver offset, are regulated. Further audio performance optimization can be achieved through an iterative process of measuring the performance of the earpiece and making further, minor adjustments to the sound delivery tube lengths. The sound delivery tubes can include transition regions. The earpiece is configured to use removable / replaceable eartips. Acoustic filters can be interposed between one or both driver outputs and the earpiece output.
Owner:LOGITECH INT
Hearing aid with Anti-occlusion effect techniques and ultra-low frequency response
InactiveUS20090310805A1Improve sound outputAvoid performance degradationOcclusion effect electronic compensationBone conduction transducer hearing devicesControl signalEngineering
An occluding hearing aid having anti-occlusion effect techniques combined with at least one improvement which, in the preferred embodiment, includes enhancement of acoustic output in the lower-midrange and bass frequency regions, typically between substantially 40 and 500 Hz, which regions are crucial for natural reproduction of multimedia sound and music but are not optimally processed, and generally not provided at all, in prior art hearing aids in order to avoid exacerbation of the occlusion effect. In specific embodiments, the hearing aid of the present invention includes primary or first microphone exposed to external sound plus a secondary or second microphone exposed to sound within an ear canal, in which a signal produced by the secondary microphone is applied as negative feedback to an input of a non-gain controlling signal process and amplifier driving a hearing aid receiver (transducer), whereby, it has been determined by the present inventor, the occlusion effect may be substantially canceled. The hearing aid further comprises at least one of ten combinational improvements each providing substantial performance benefits over known techniques and devices.
Owner:PETROFF MICHAEL
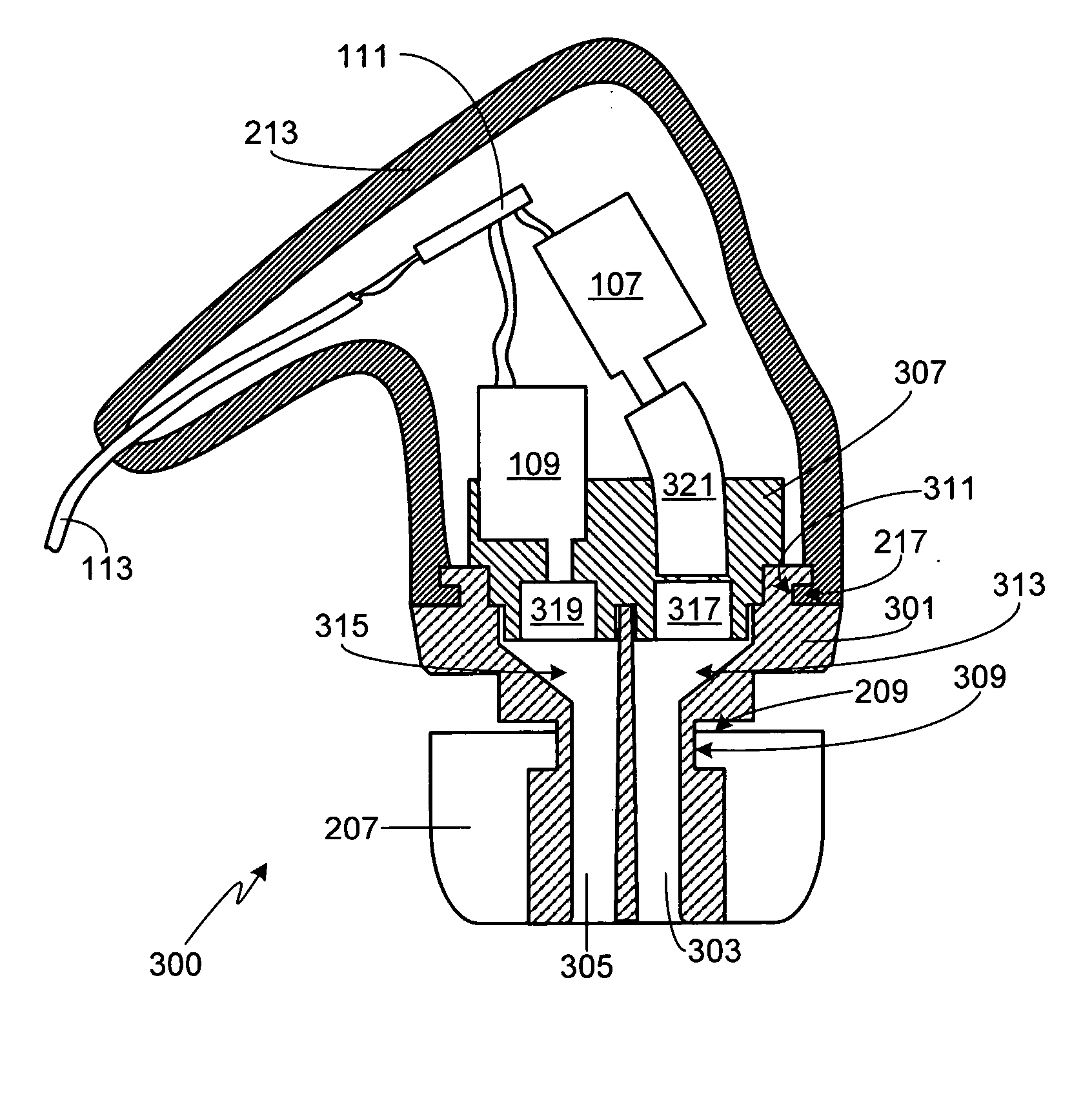
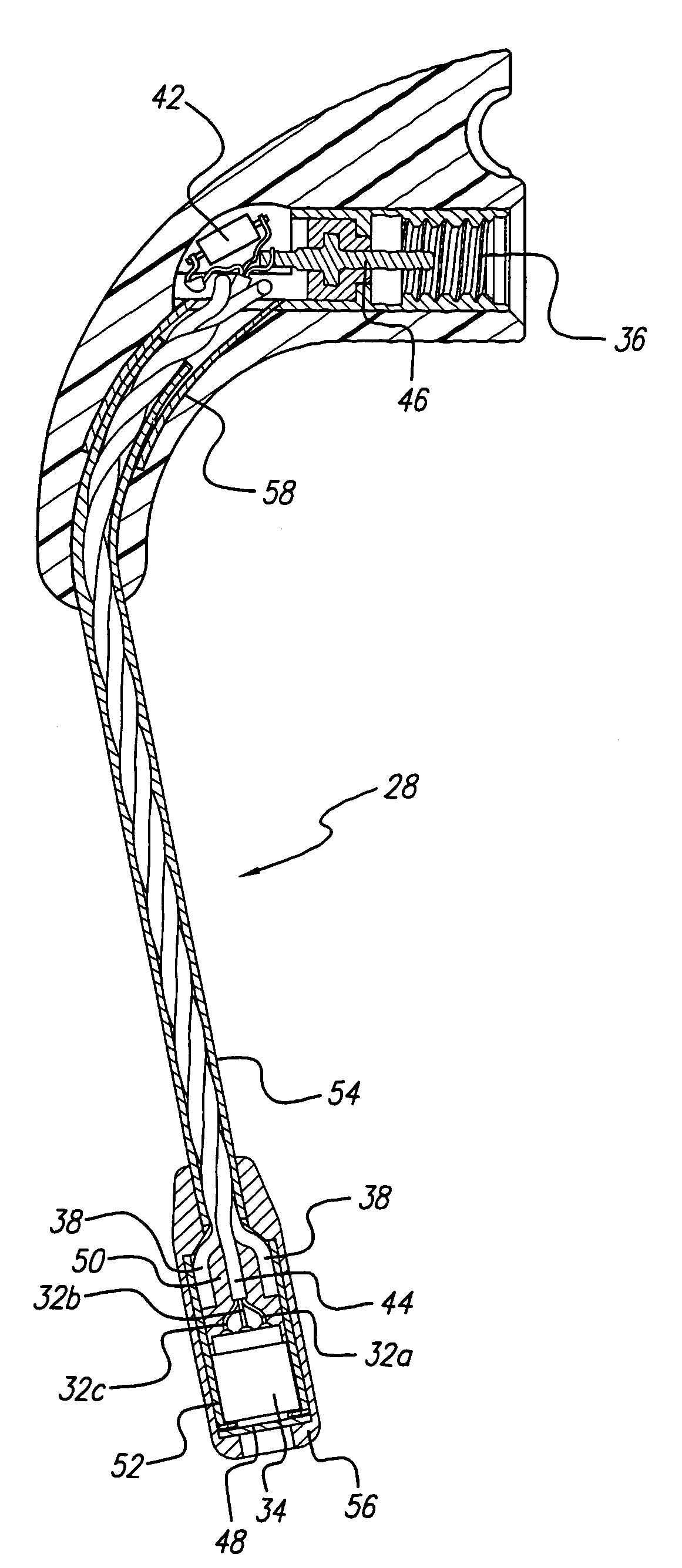
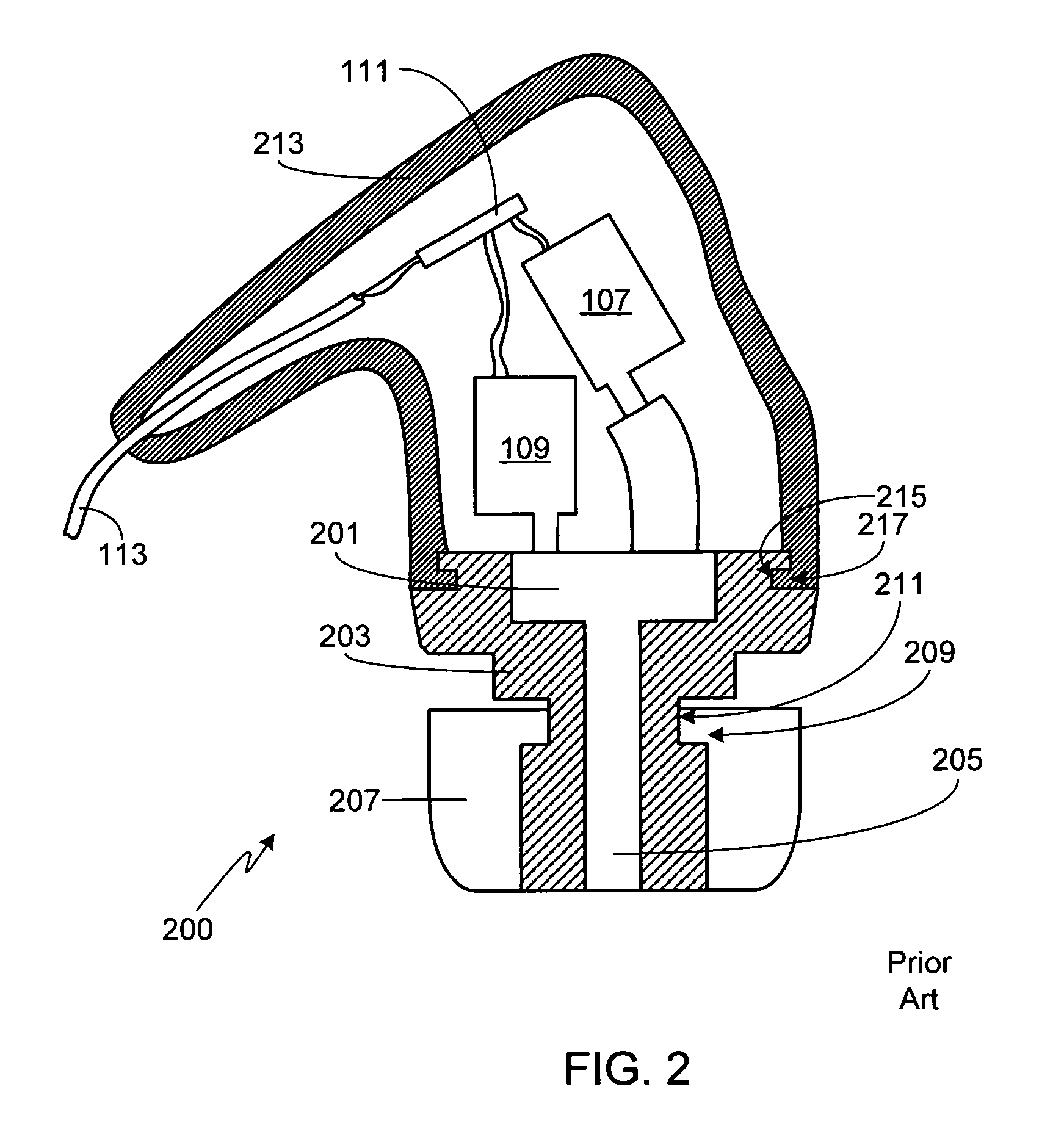
Electroacoustic transducer mounting in shells of hearing prostheses
InactiveUS7822218B2To offer comfortAdditive manufacturing apparatusElectrical transducersTransducerElectrical connection
Owner:SONION NEDERLAND
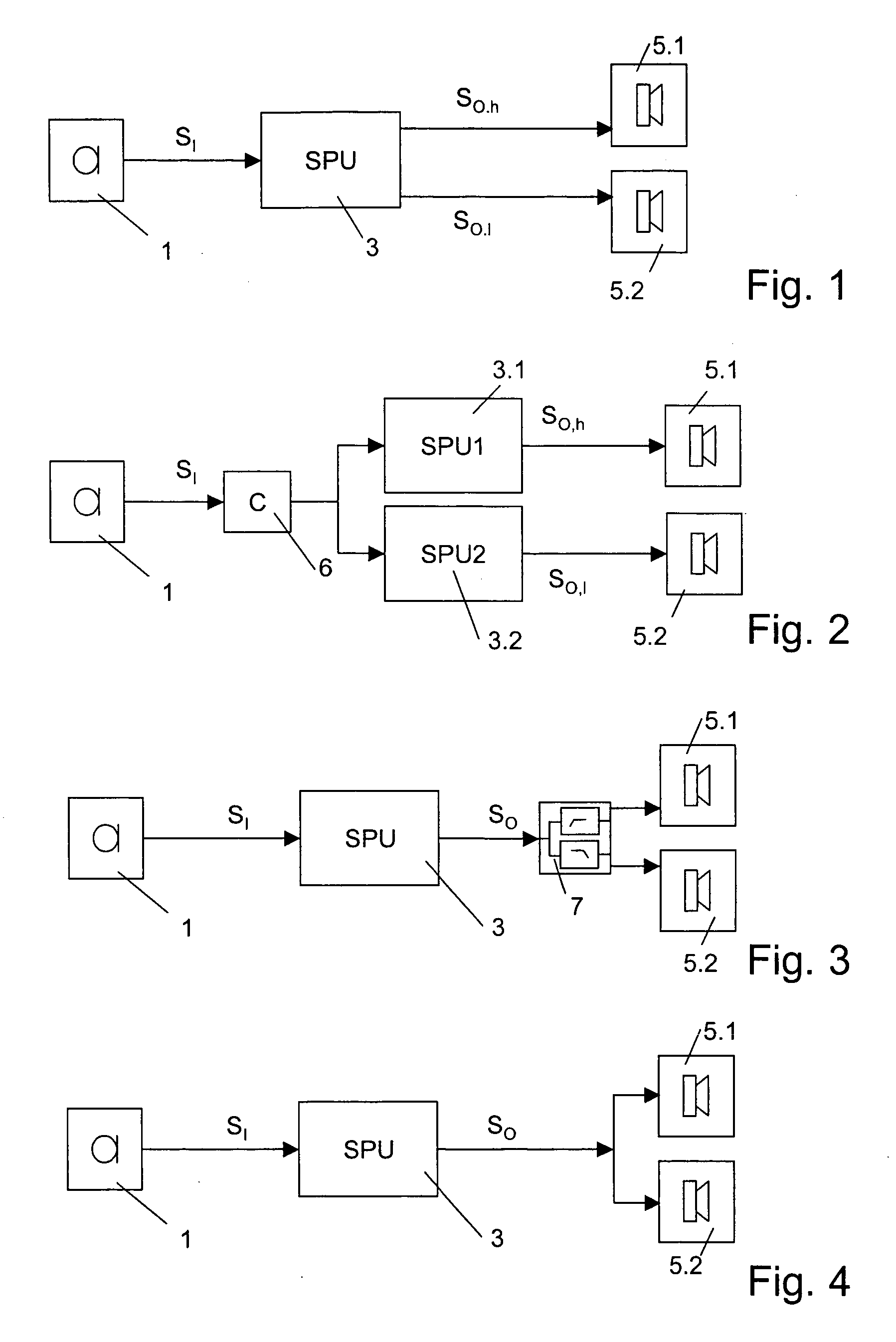
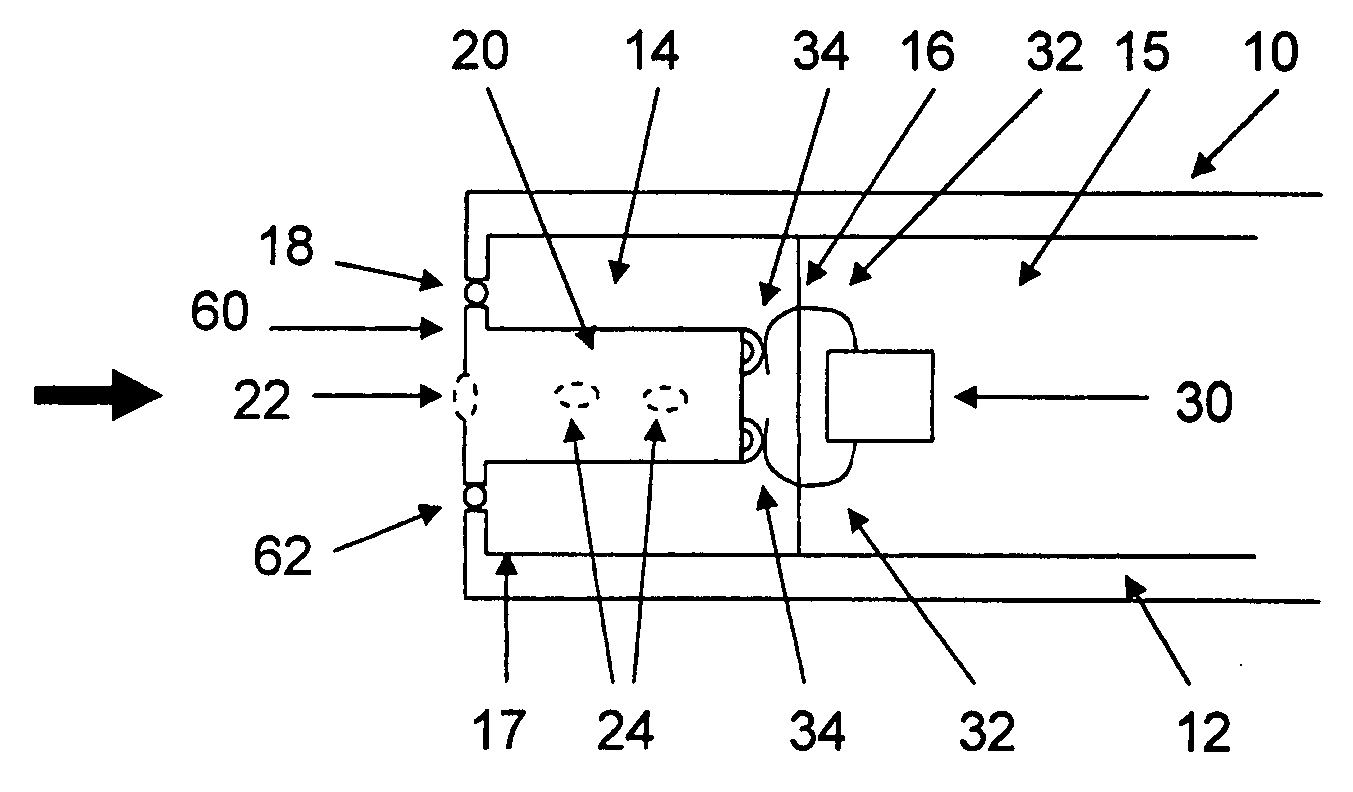
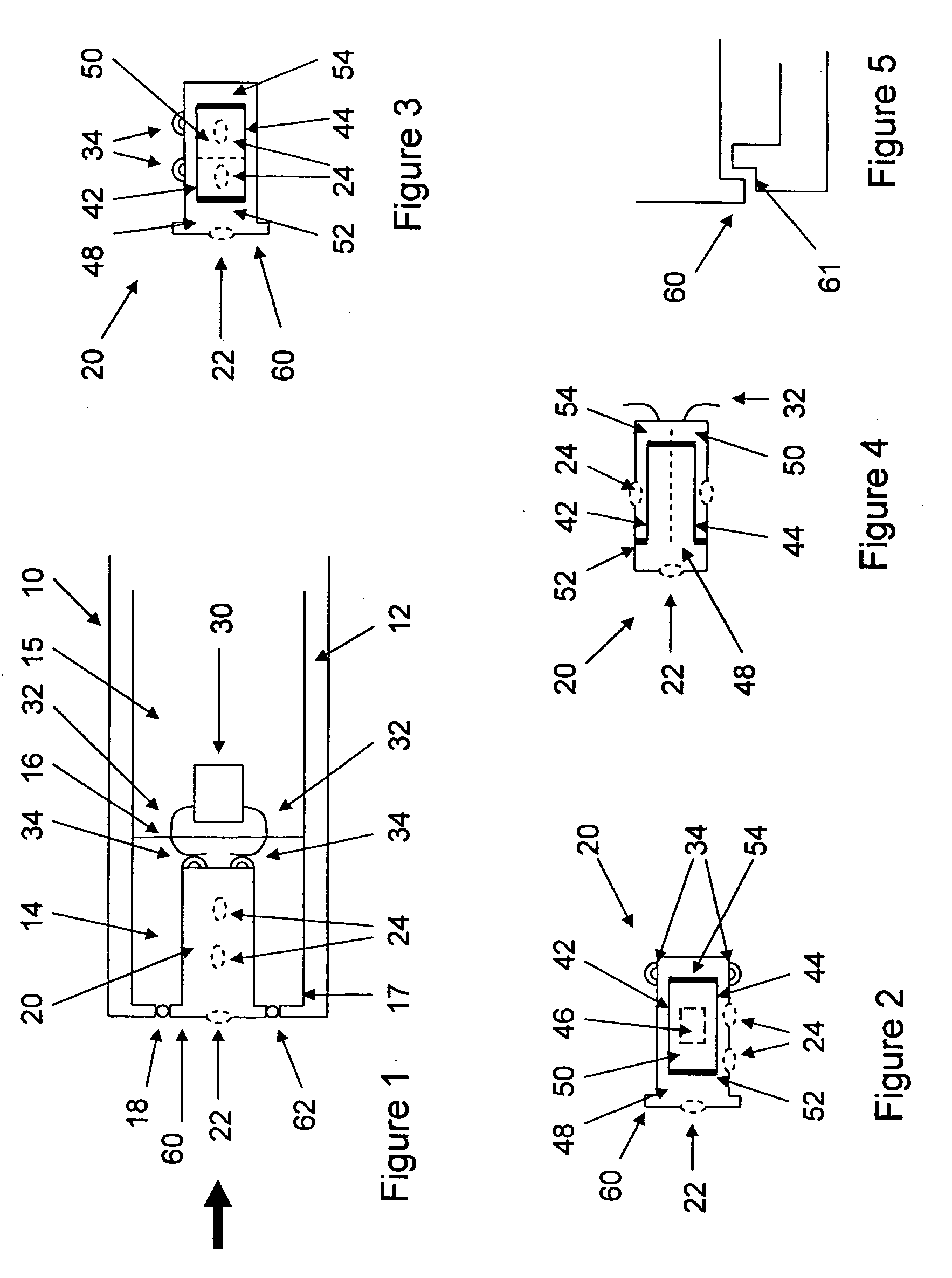
Hearing aid having two receivers each amplifying a different frequency range
A hearing aid having two physically separate receivers, one for outputting low frequency (LF) acoustic sounds and another for outputting high frequency (HF) acoustic sounds. The LF receiver's output port is connected to a tube in which the HF receiver is inserted. The LF acoustic sounds either flow around the HF receiver, which include standoffs to space the HF receiver away from the inner tube wall, or through a channel in the HF receiver. At the output of the HF receiver, the LF and HF acoustic sounds are combined to form an acoustic signal that is transmitted to the ear canal. The LF receiver can be optimized for compliance, distortion, resonance frequency, and output. Its orientation is selected for reducing the overall size of the hearing aid. The HF receiver is smaller and placed far away from any microphone(s), reducing feedback effects, and may have a cylindrical or rectangular shape.
Owner:SONION NEDERLAND
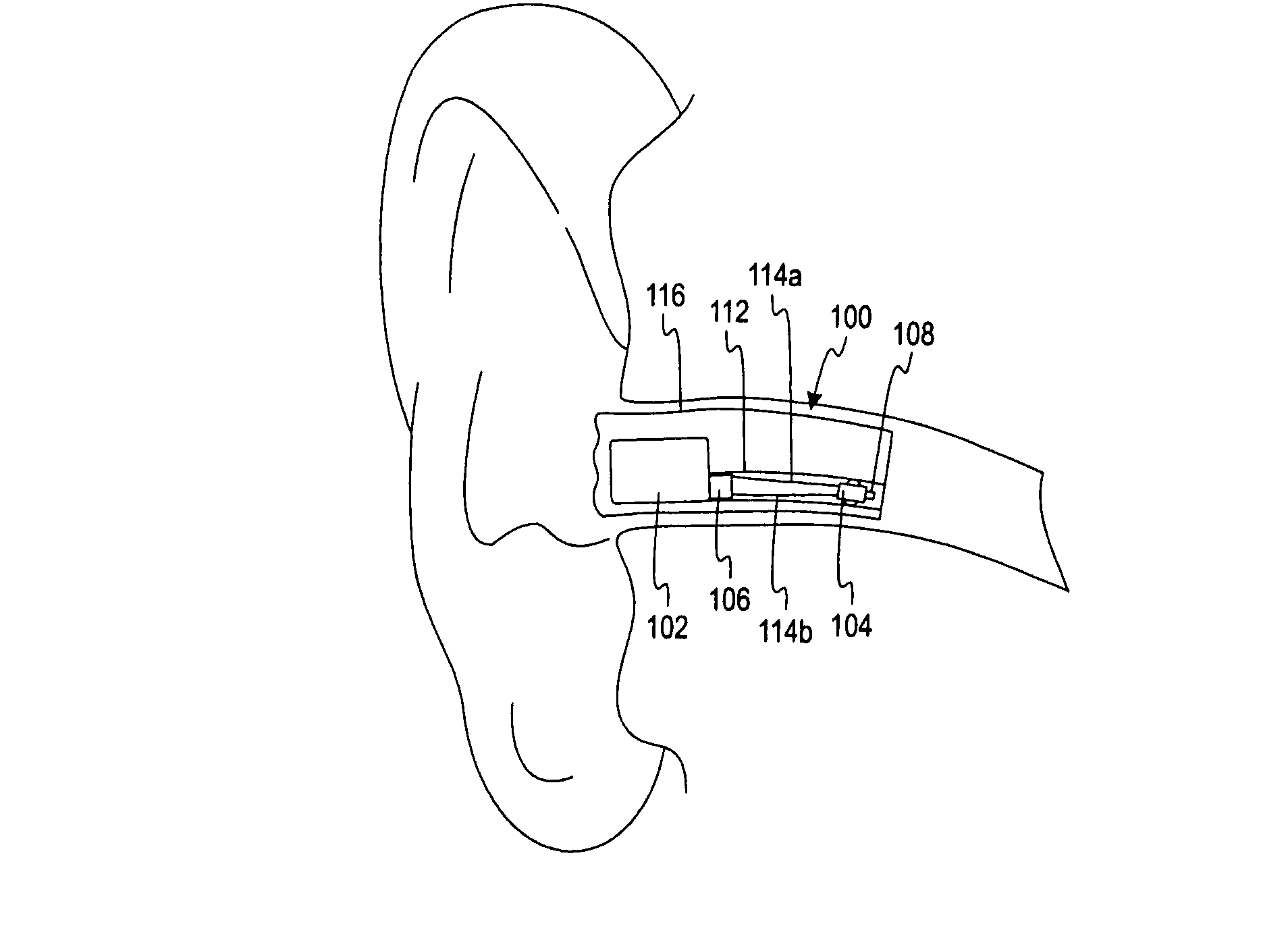
In the ear auxiliary microphone for behind the ear hearing prosthetic
InactiveUS7106873B1Improve responseEnhanced couplingElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsCouplingEngineering
An In The Ear (ITE) microphone improves the acoustic response of a Behind The Ear (BTE) Implantable Cochlear Stimulation (ICS) system during telephone use. An acoustic seal provided by holding a telephone earpiece against the ear provides improved coupling of low frequency (up to about 1 KHz) sound waves, sufficient to overcome losses due to the near field acoustic characteristics common to telephones. In a preferred embodiment, the ITE microphone is connected to a removable ear hook of the BTE ICS system by a short bendable stalk.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Electroacoustic transducer mounting in shells of hearing prostheses
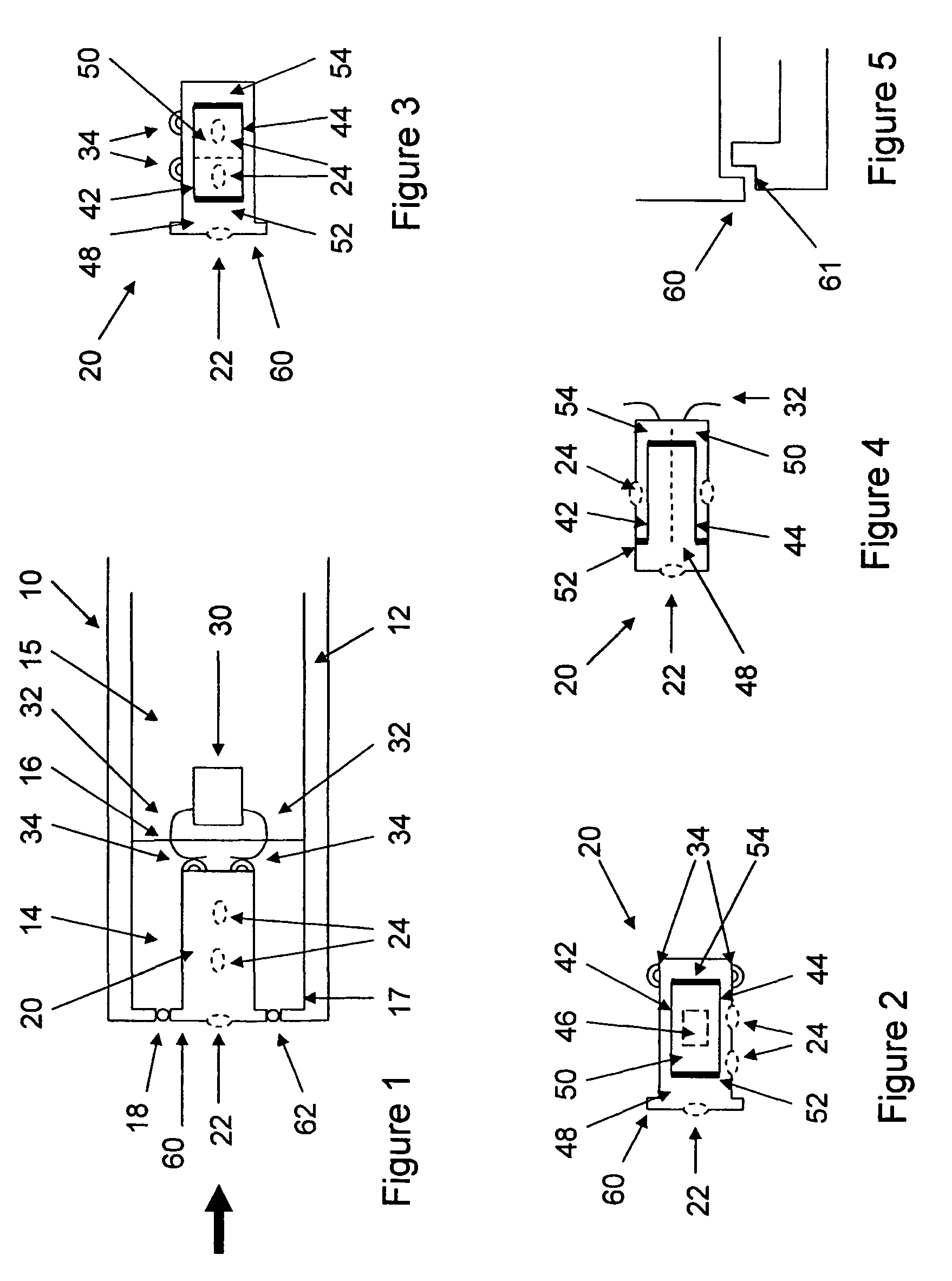
InactiveUS20060153418A1The process is simple and fastAvoid enteringAdditive manufacturing apparatusTransducer detailsTransducerElectrical connection
A hearing aid and a receiver for use therein, the receiver being tip-mountable in a chamber of a housing. The back chamber of the receiver is acoustically connected to the chamber of the housing. The receiver is a dual-diaphragm receiver providing no or very little vibrations, whereby the receiver is fixedly but removably mounted to the housing. Electrical connections are provided between the receiver and housing using solderless, biasing electrical contacts, whereby removal of the receiver is facilitated.
Owner:SONION NEDERLAND
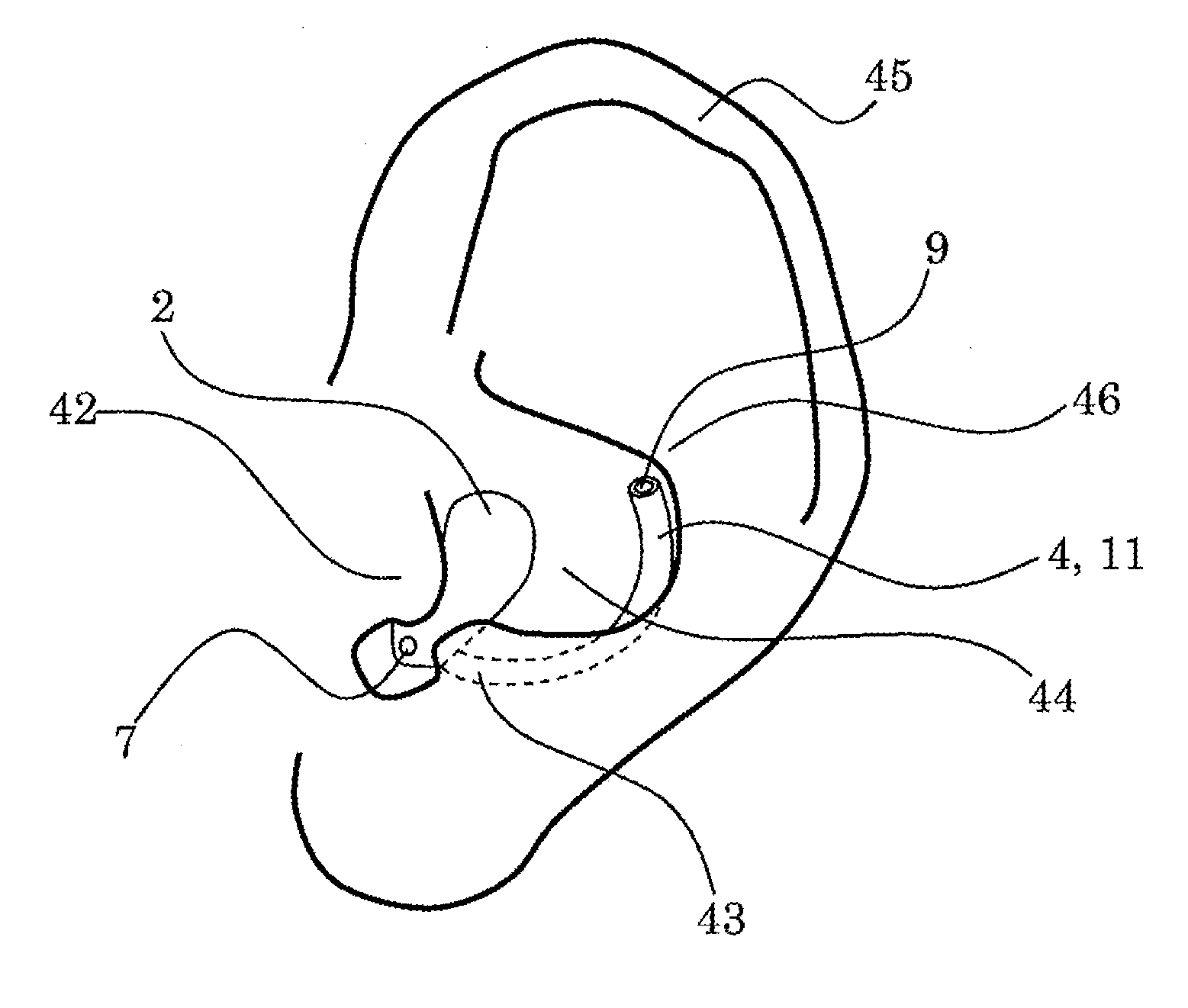
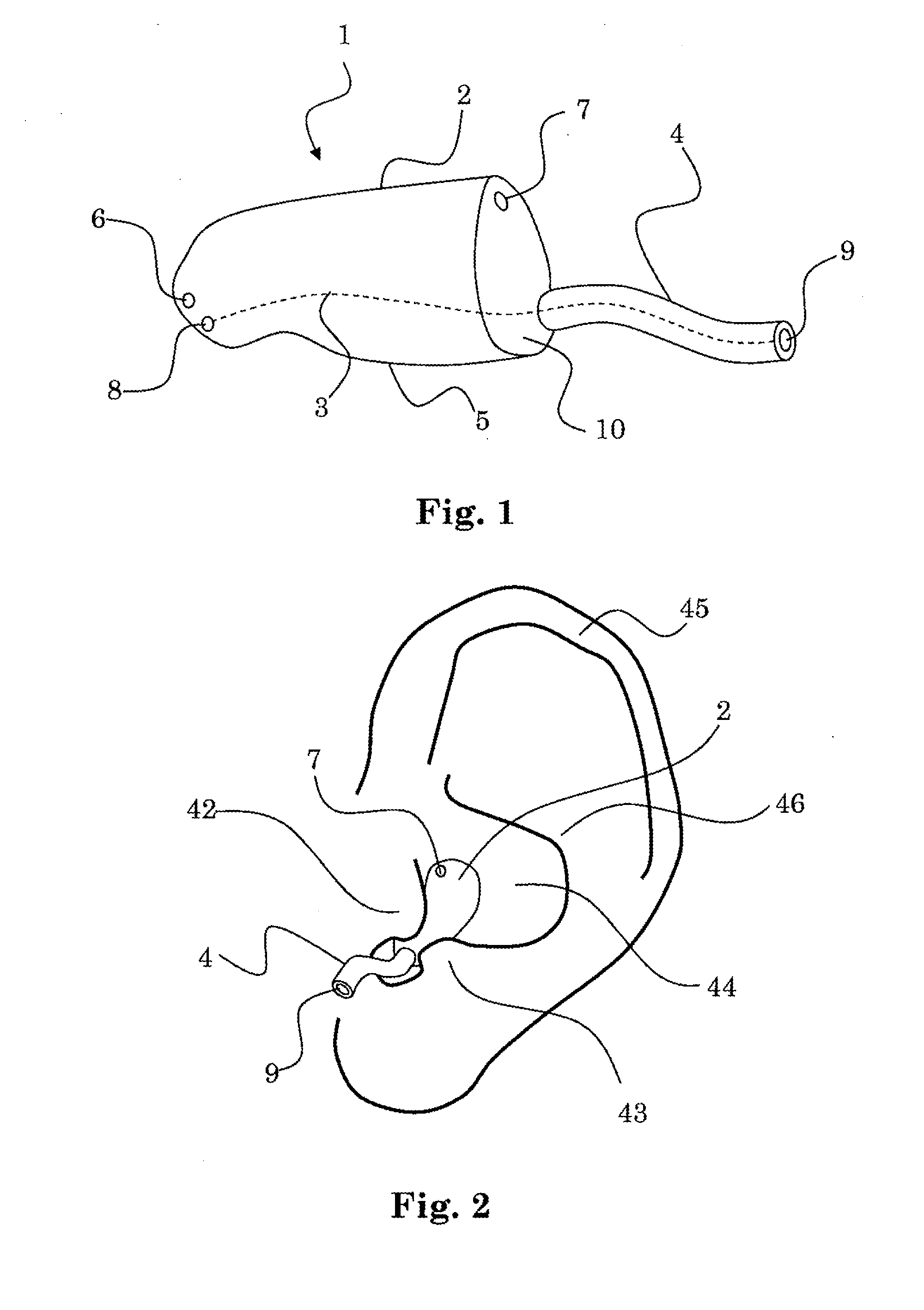
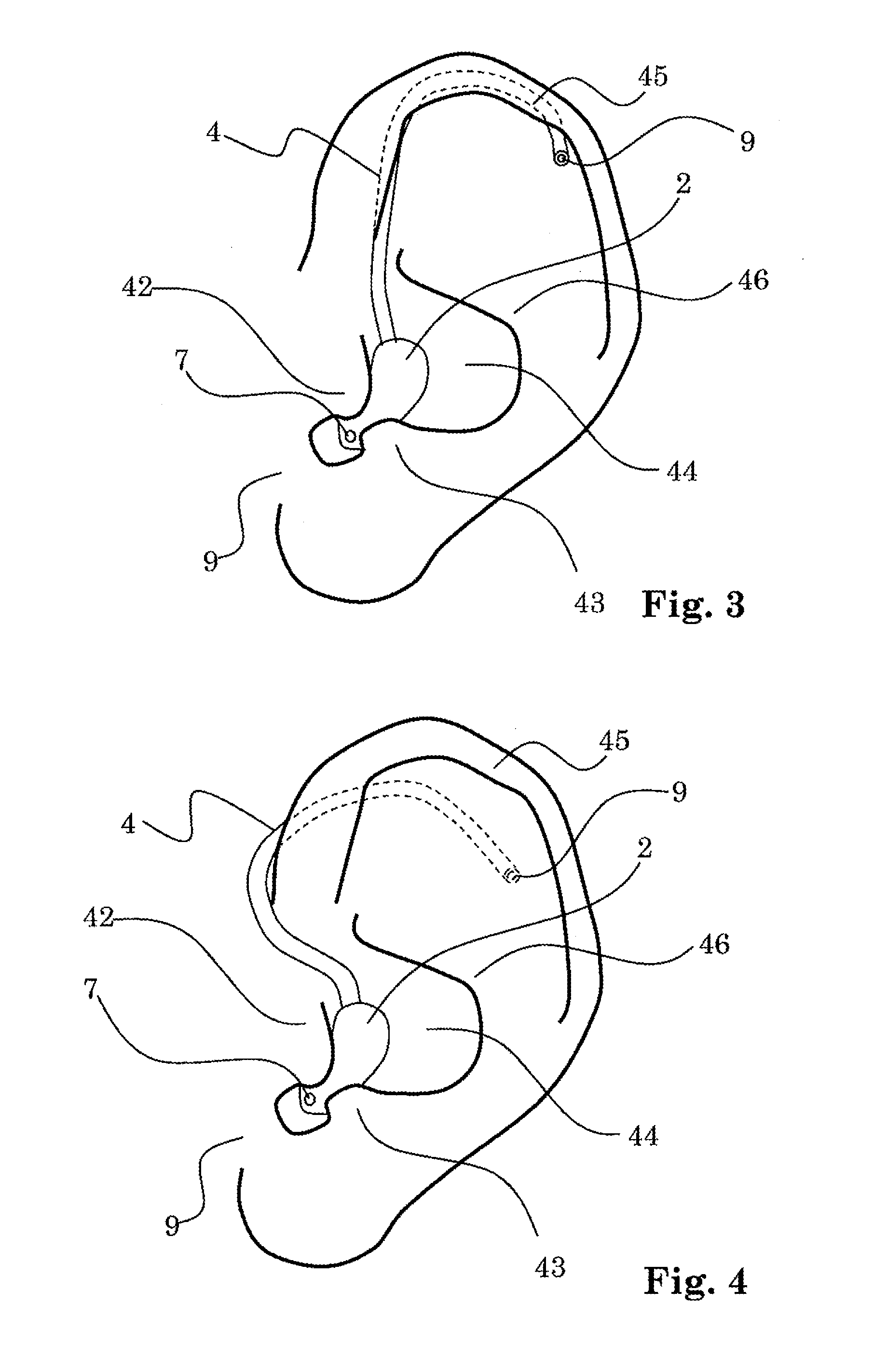
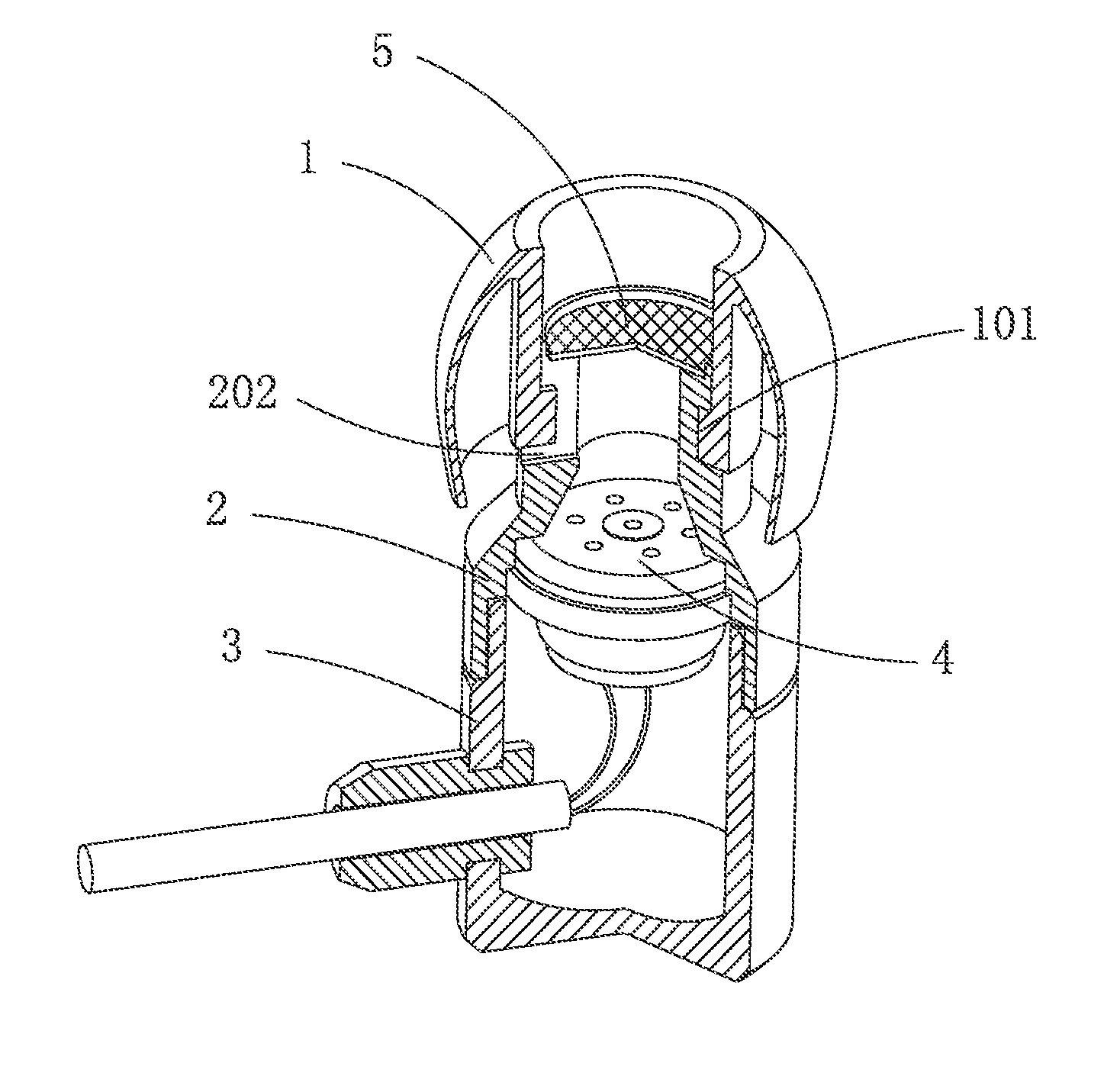
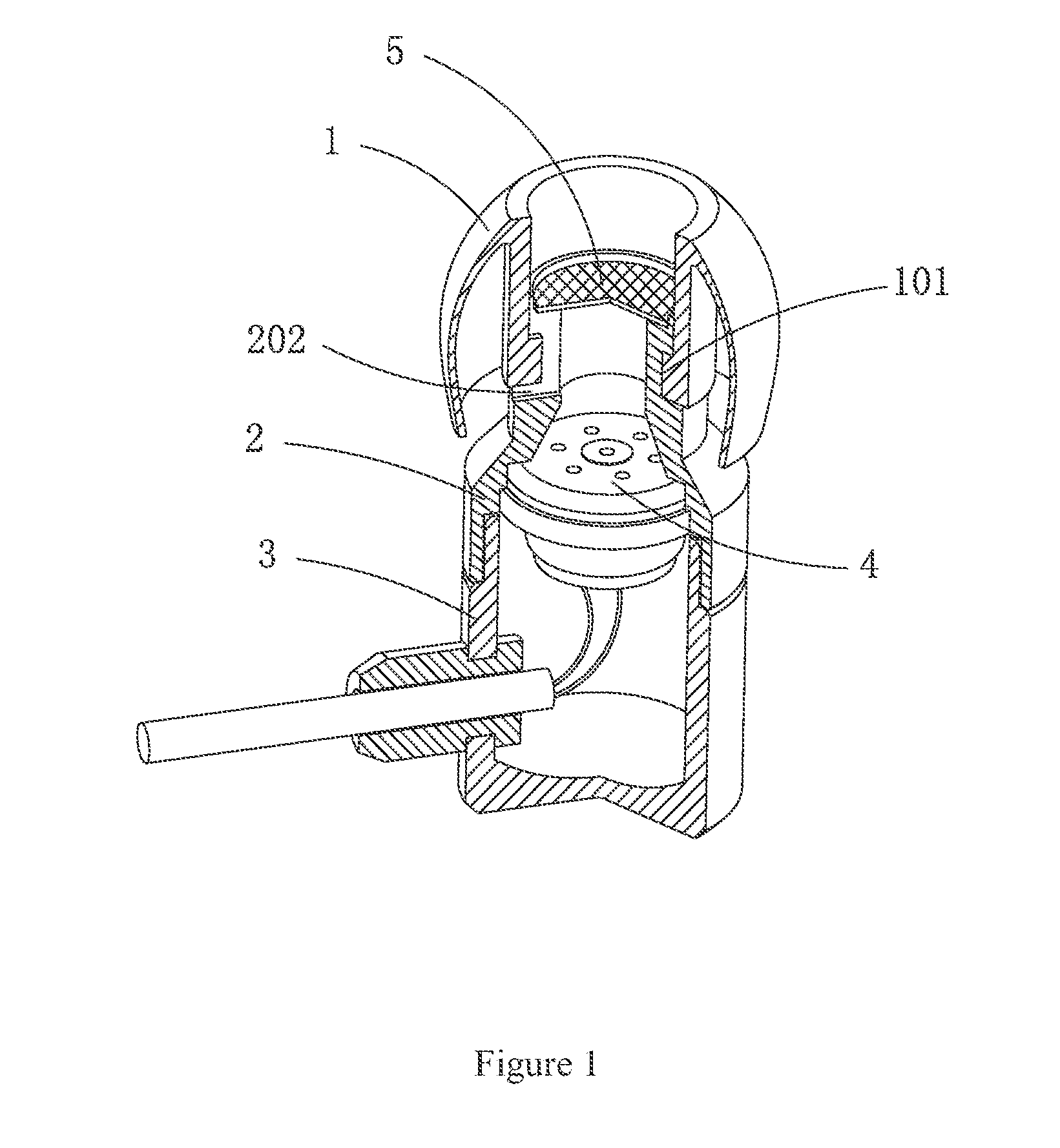
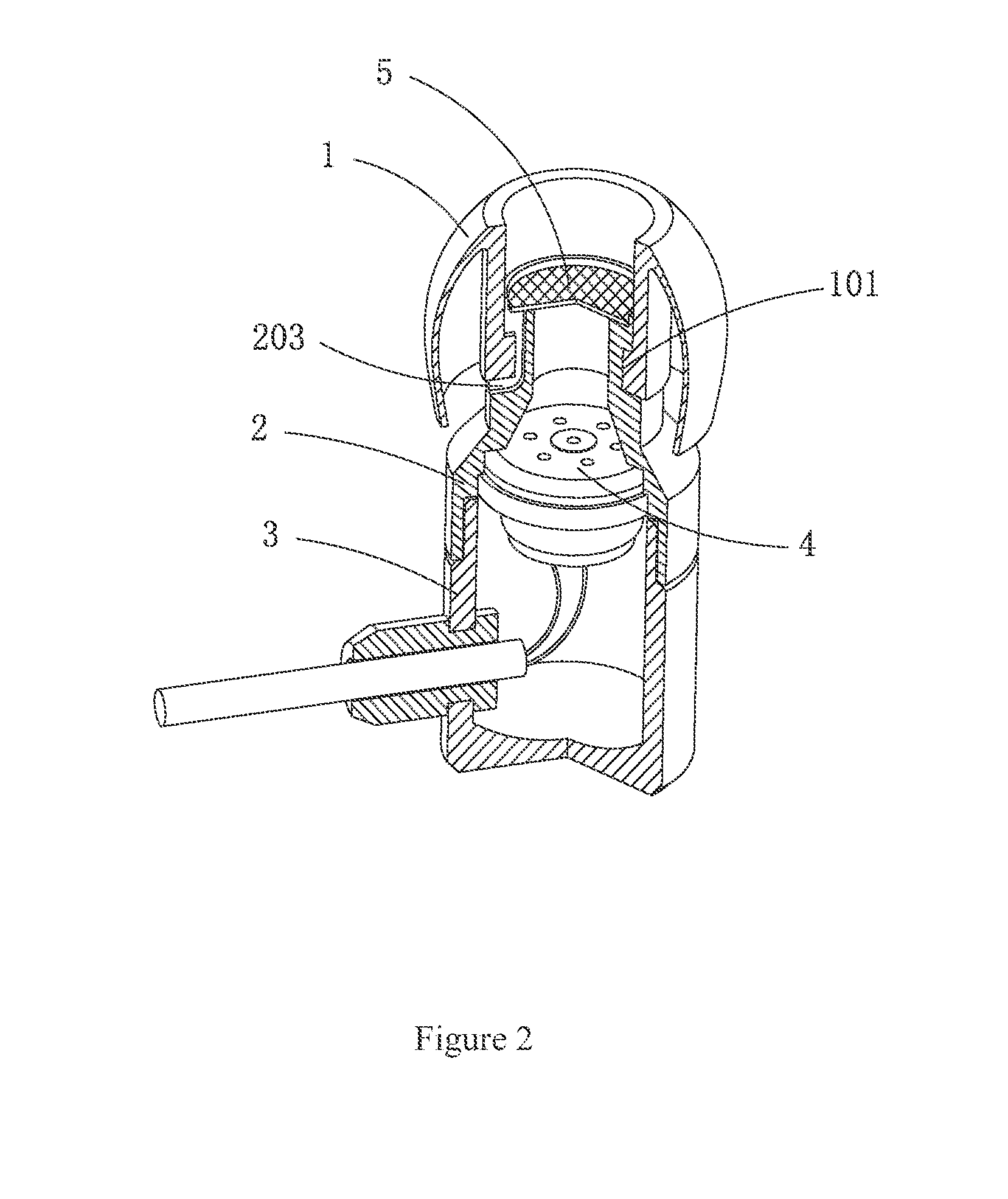
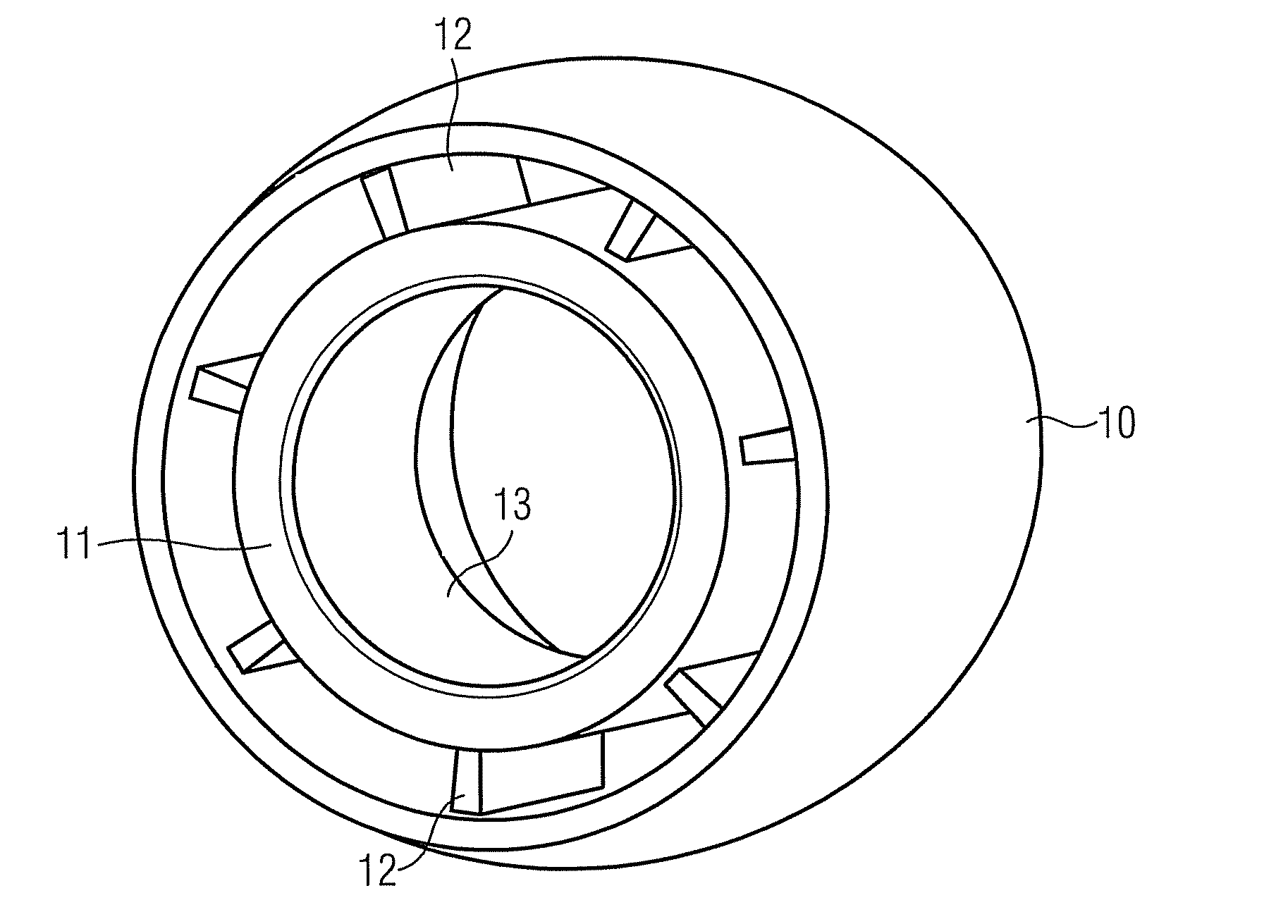
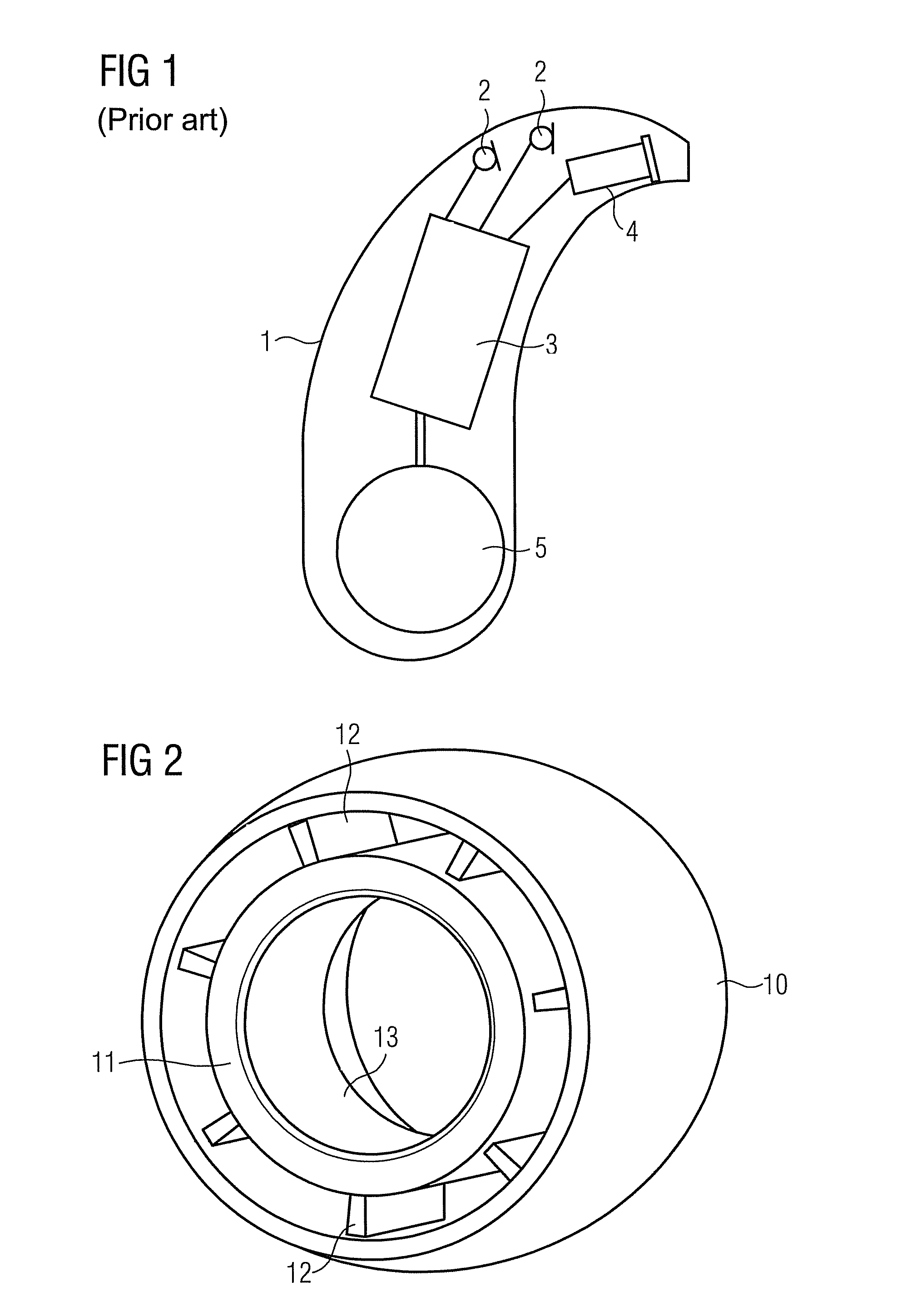
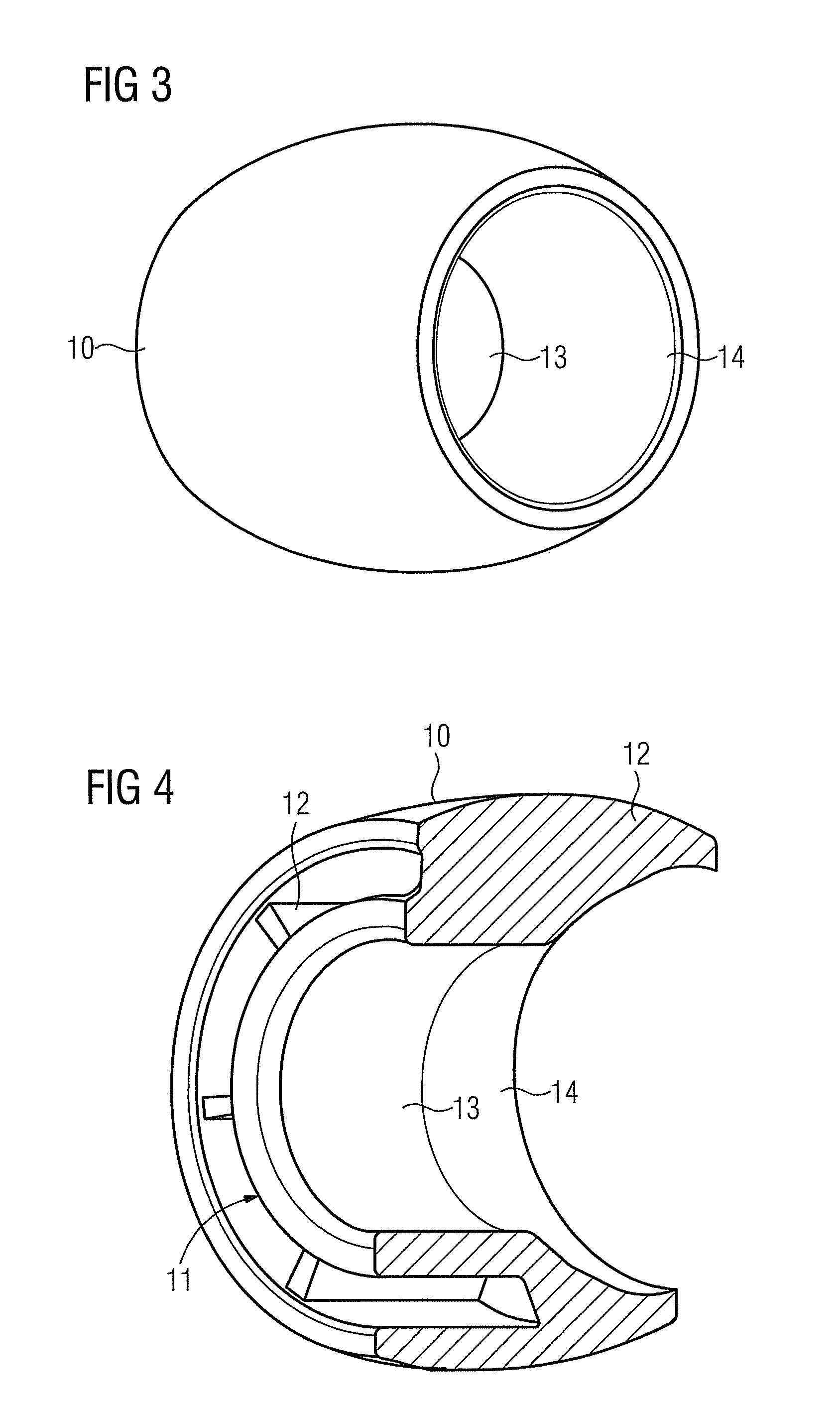
Hearing device with a vent extension and method for manufacturing such a hearing device
InactiveUS20120140967A1Equally distributedConvenient ArrangementElectrical transducersRecord carriersEngineeringHearing perception
The hearing device comprises an ear-piece (1) which is designed to be worn at least partially in an ear canal of a user of the hearing device. The ear-piece (1) comprises a vent passage (3) connecting the ear canal with the atmosphere. The vent passage (3) has an inner opening (8) towards the ear-canal and an outer opening (9) towards the atmosphere. The ear-piece (1) further comprises a vent extension (4). The vent extension (4) is a protrusion extending the vent passage (3) beyond the body (2) of the ear-piece (1). The vent extension (4) is adapted for abutting on a surface of the body of the user and is thereby inconspicuous and / or contributes thereby to retention. A method for manufacturing such a hearing device is also disclosed.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Earphone assembly
ActiveUS20130315431A1Details for specific frequency responseIntra aural earpiecesPath lengthAcoustic wave
An earphone assembly for an in-ear listening device and method for filtering a portion of an audible sound output are disclosed. An earphone comprises a housing configured to receive a nozzle, a plurality of drivers each having an acoustical output disposed within the housing, and an elongated passageway disposed within the housing configured to filter at least an audible portion of a sound wave output from at least one of the plurality of drivers. The method comprises providing an elongated passageway to provide an increased path length and connecting an output of the at least one driver to the elongated passageway to configure the sound output to be received within the elongated passageway to acoustically filter a portion of the sound output from the at least one driver.
Owner:SHURE ACQUISITION HLDG INC
Sound tube tuned multi-driver earpiece
ActiveUS7317806B2Details for specific frequency responseIntra aural earpiecesPhase shiftedEngineering
A method of optimizing the audio performance of an earpiece and the resultant device are provided. The disclosed earpiece combines at least two drivers within a single earpiece. If a pair of drivers is used, each driver has a discrete sound delivery tube. If more than two drivers are used, preferably the outputs from the two lower frequency drivers are merged into a single sound delivery tube while the output from the third driver is maintained in a separate, discrete sound tube. To compensate for the inherent phase shift of the earpiece the lengths of the sound delivery tubes, and thus driver offset, are regulated. Further audio performance optimization can be achieved through an iterative process of measuring the performance of the earpiece and making further, minor adjustments to the sound delivery tube lengths. The sound delivery tubes can include transition regions. The earpiece is configured to use removable / replaceable eartips. Acoustic filters can be interposed between one or both driver outputs and the earpiece output.
Owner:LOGITECH INT
Hearing Aid
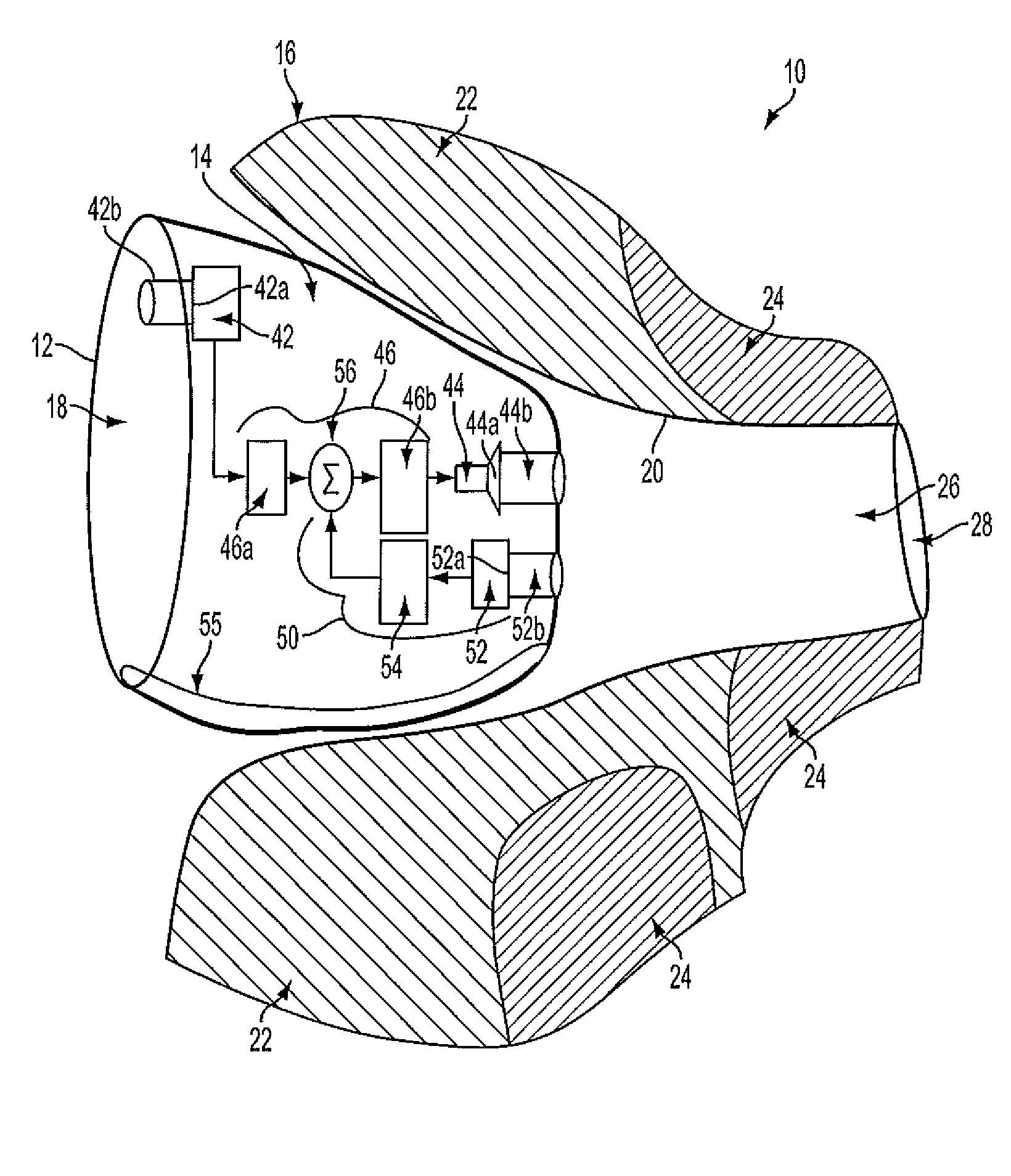
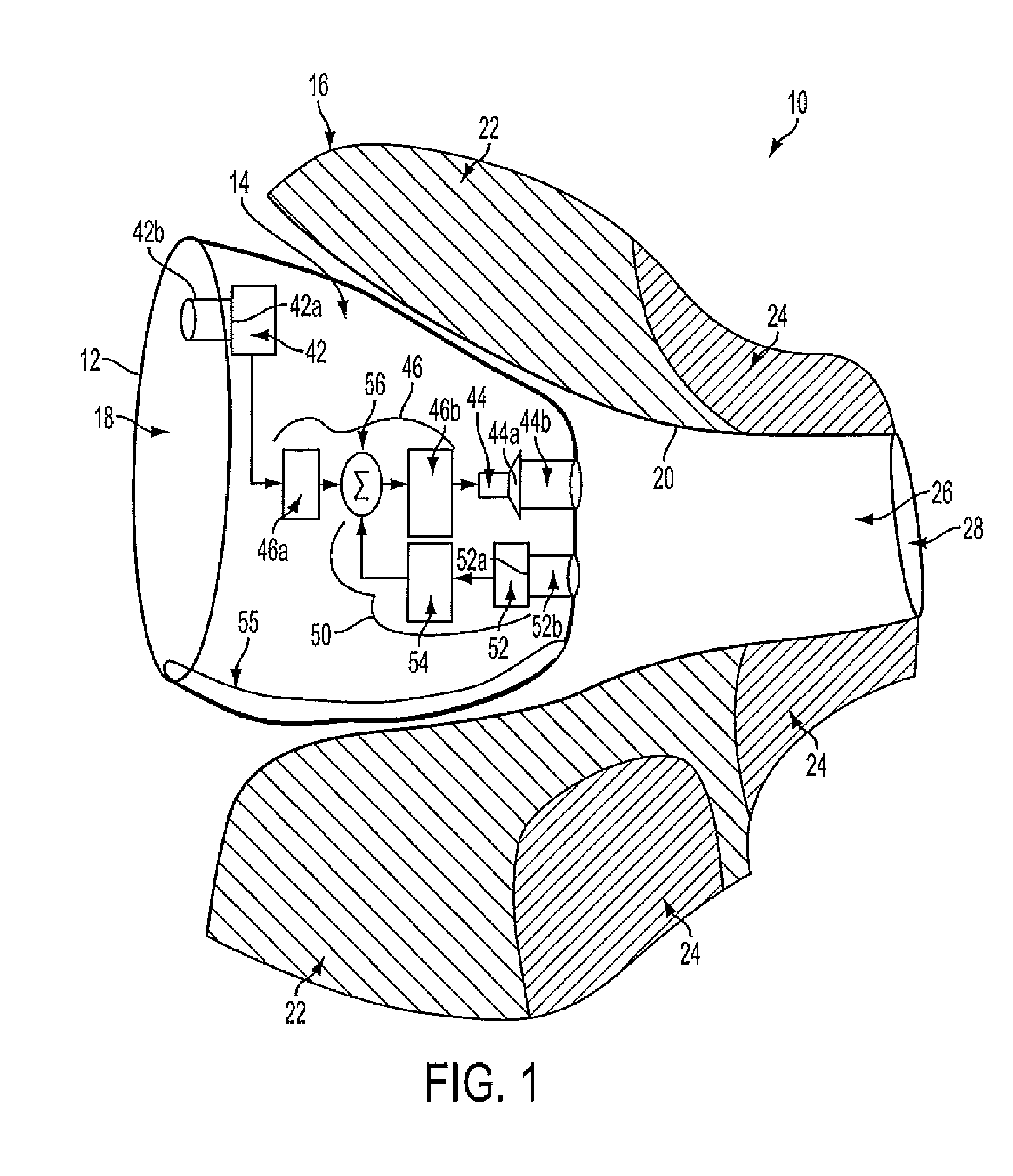
InactiveUS20110069852A1Wide rangeReduce decreaseOcclusion effect electronic compensationEar supported setsTransducerHeadphones
A hearing aid (10) having an active occlusion reduction system (50) that counteracts occluded sounds generated within the volume (24) of the ear canal (20) that is not blocked when the hearing aid (10), or an ear piece thereof, is inserted into the ear canal (20) and an AOR transducer (44, 52) that has a flattened frequency response for low frequency portions of the occlusion sounds to enable a wide range of frequency response by the active occlusion reduction system (50). The low frequency portions of the occlusion sounds may be in the range of 10-100 Hz.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
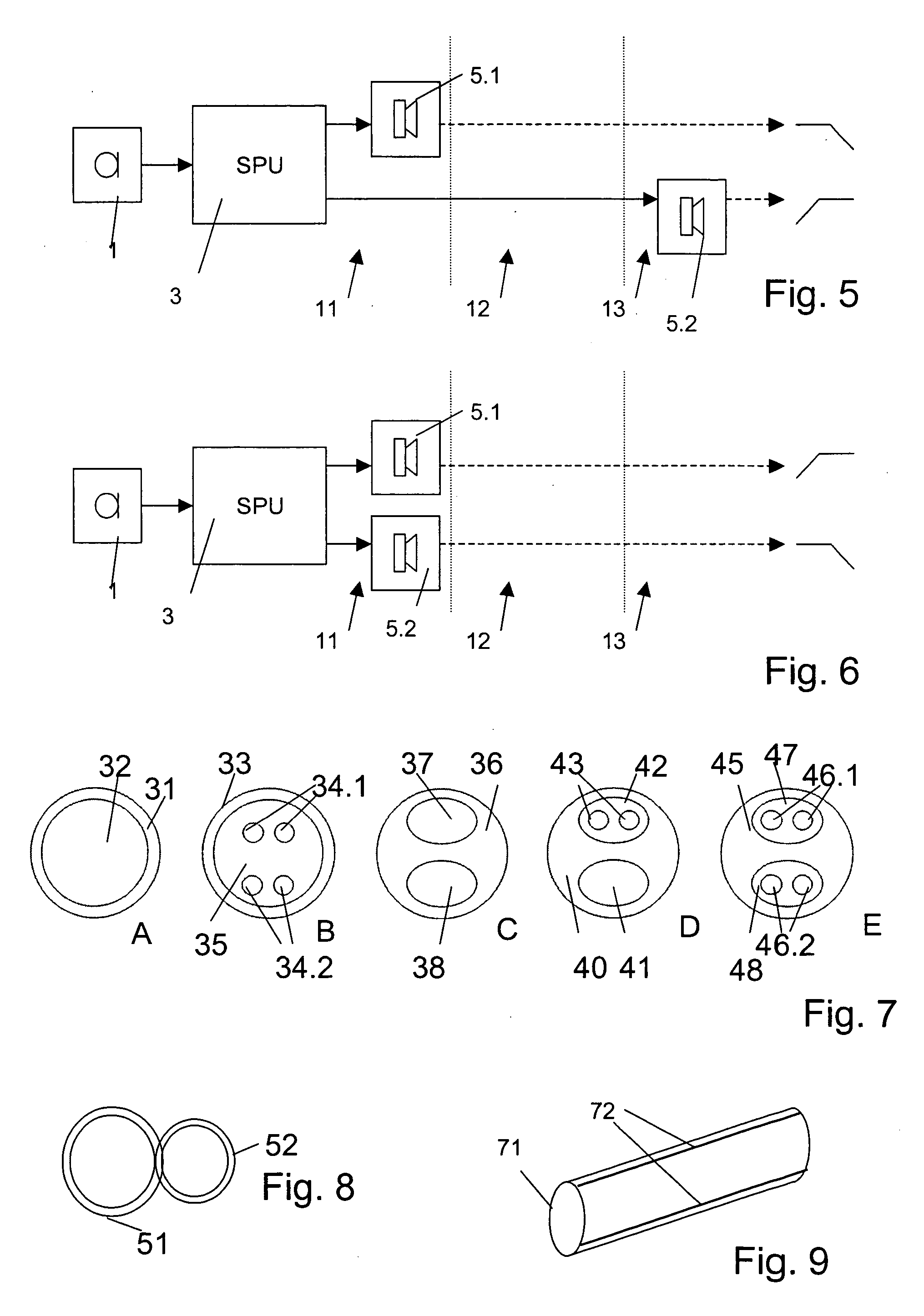
In-ear monitor with shaped dual bore
ActiveUS20060133631A1Easy to customizeDetails for specific frequency responseIntra aural earpiecesAcoustic transmissionEngineering
A multi-driver in-ear monitor for use with either a recorded or a live audio source is provided. If a pair of drivers is used, each driver has an individual sound delivery tube. If three drivers are used, the outputs from two of the drivers are merged into a single sound delivery tube while the output from the third driver is maintained in a separate, discrete sound tube. The sound delivery tubes remain separate throughout the end portion of the earpiece. The earpiece tip is configured to be fitted with any of a variety of sleeves (e.g., foam sleeves, flanged sleeves, etc.), thus allowing the in-ear monitor to be easily tailored to comfortably fit within any of a variety of ear canals. Due to the size constraints of such an earpiece, the sound delivery tubes include a transition region. Acoustic filters (i.e., dampers) can be interposed between one or both driver outputs and the earpiece output.
Owner:LOGITECH INT
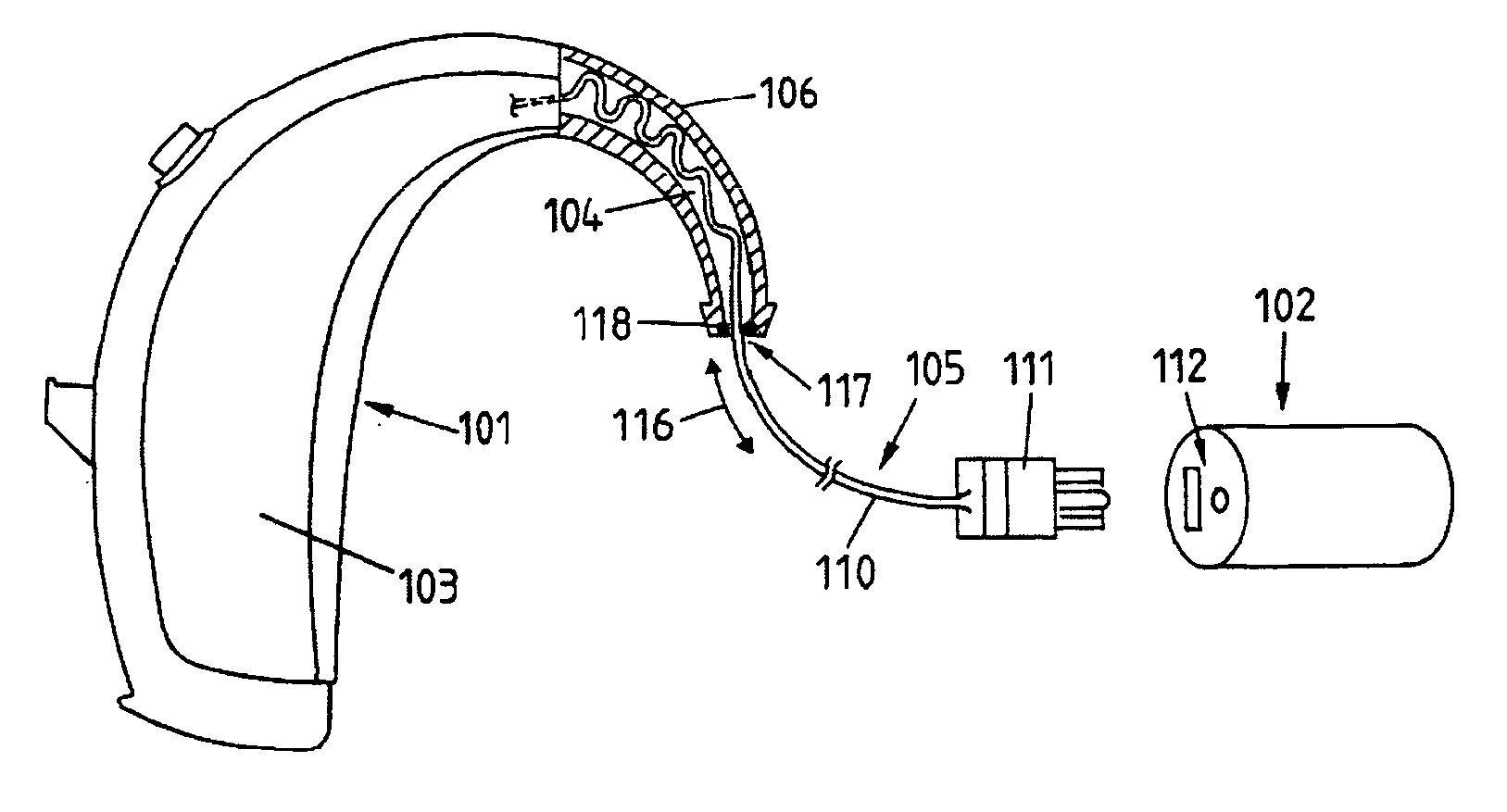
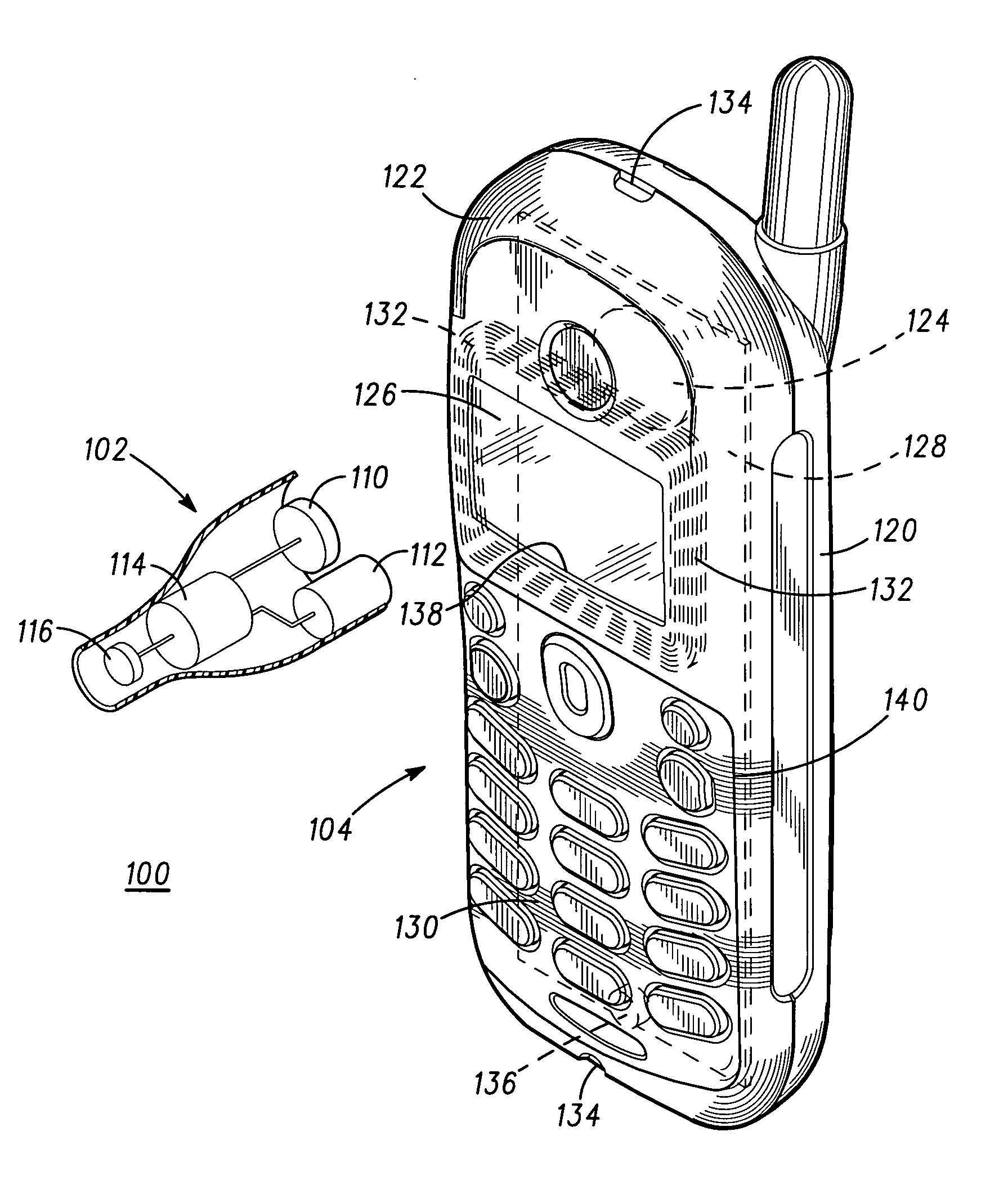
Hearing aid compatible device
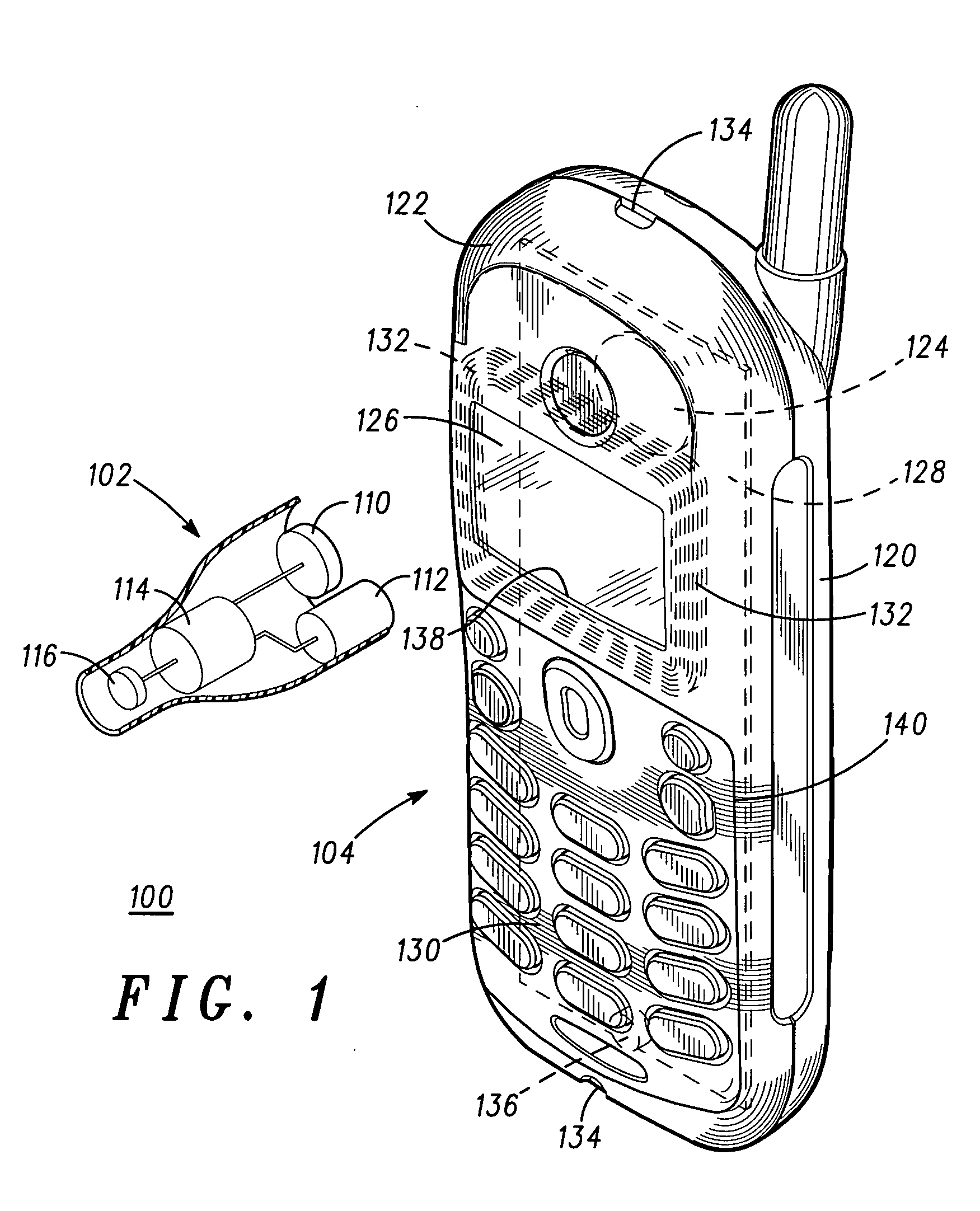
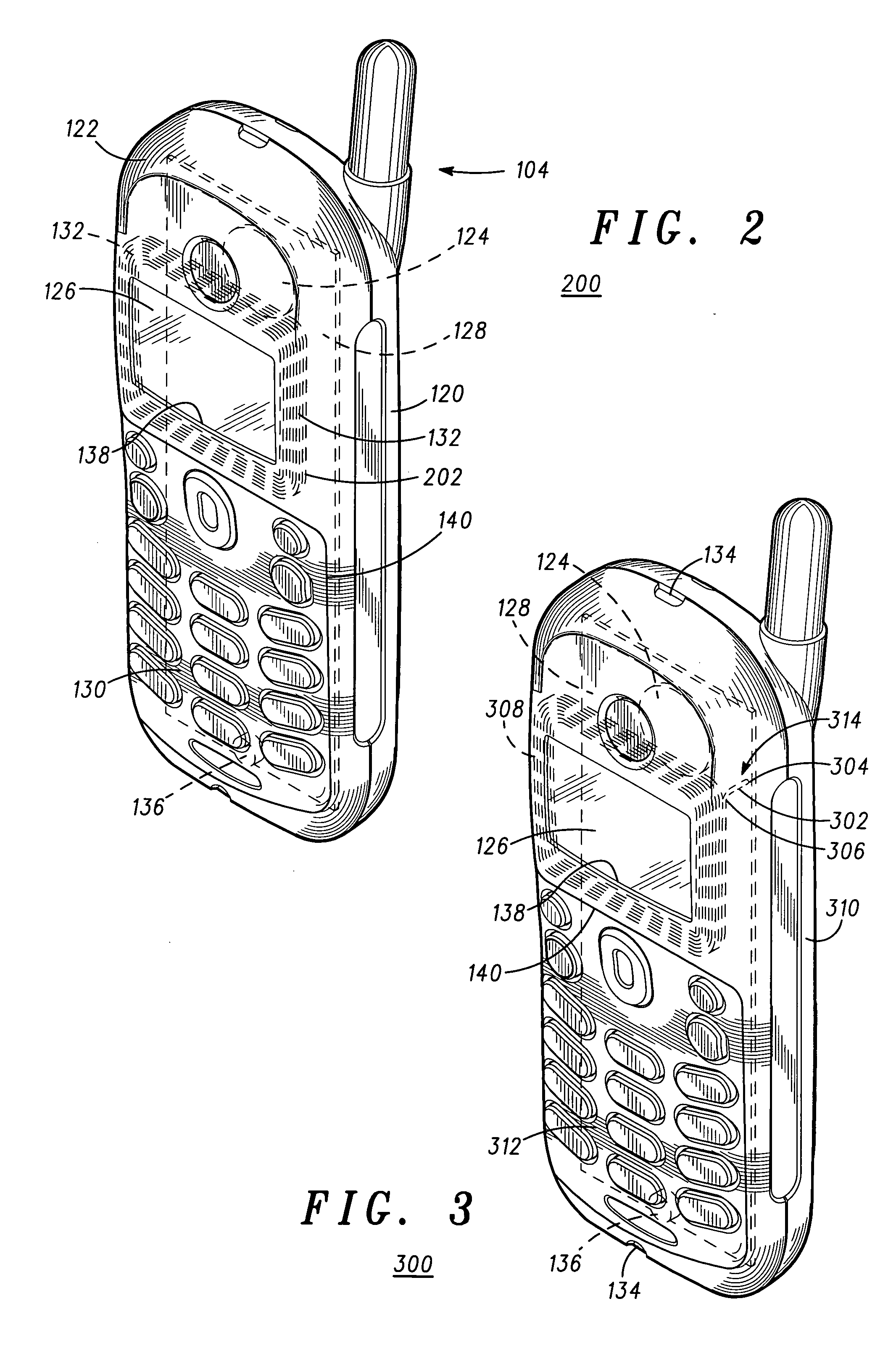
InactiveUS20050244022A1Interconnection arrangementsIn the ear hearing aidsTransducerElectrical connection
A removable bezel (122) for use with an audio device (120) to enhance operation with a hearing aid (102). The removable bezel (122) has an electromagnetic coil (132) that is coupled to the audio output (124, 304, 404, 406) of the audio device. The electromagnetic coil (132) is either inductively coupled to an acoustic transducer (124) within the audio device (120) or by a direct electrical connection (314). The electromagnetic coil (132) has multiple turns and provides an enhanced magnetic field to a “T-Coil” magnetic pick up (112) within most conventional hearing aids (102). A cellular phone (104) is an example of an audio device used with the present invention. A method for use of the removable bezel (122) is also provided.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Hearing aid with tuned microphone cavity
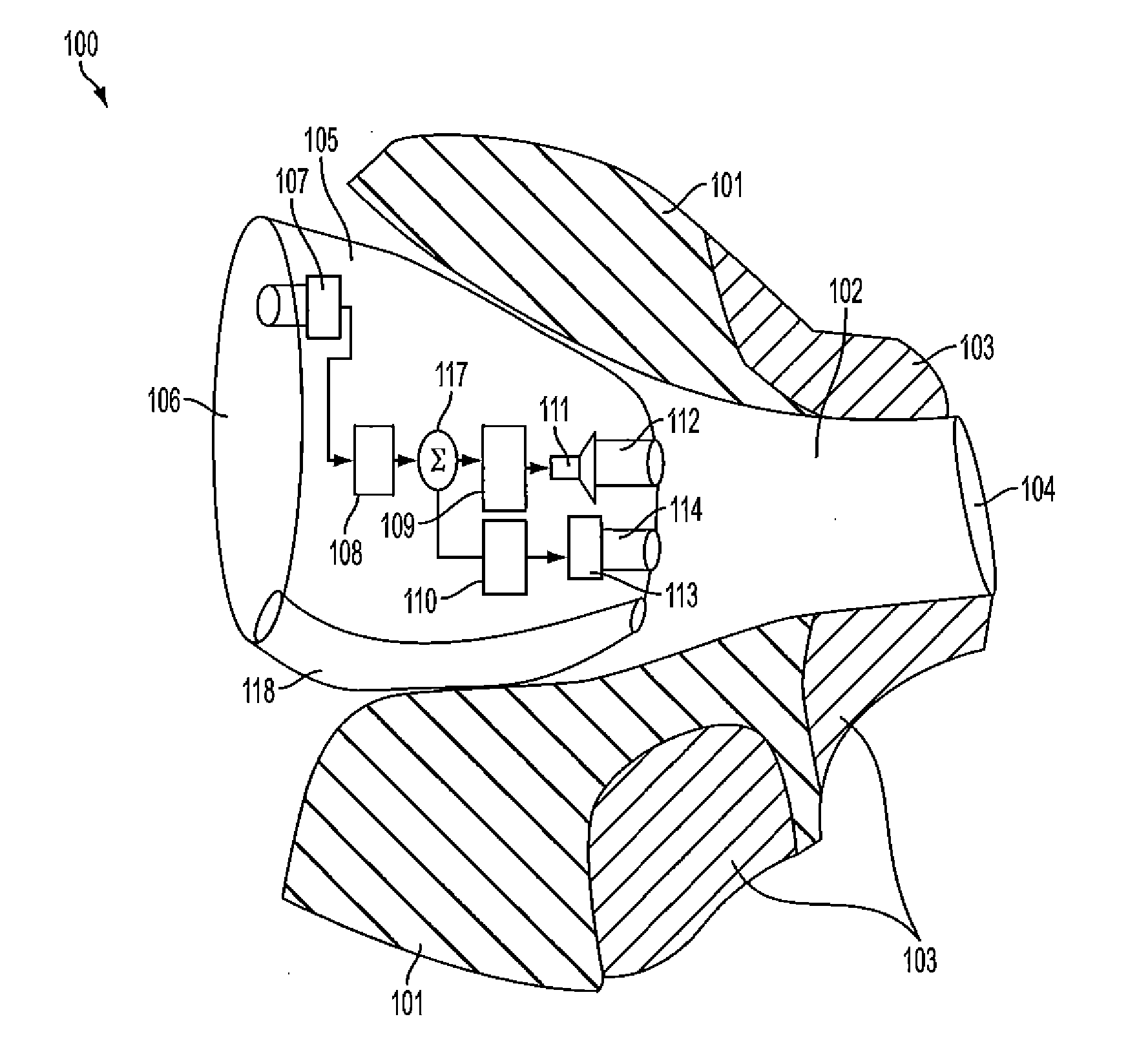
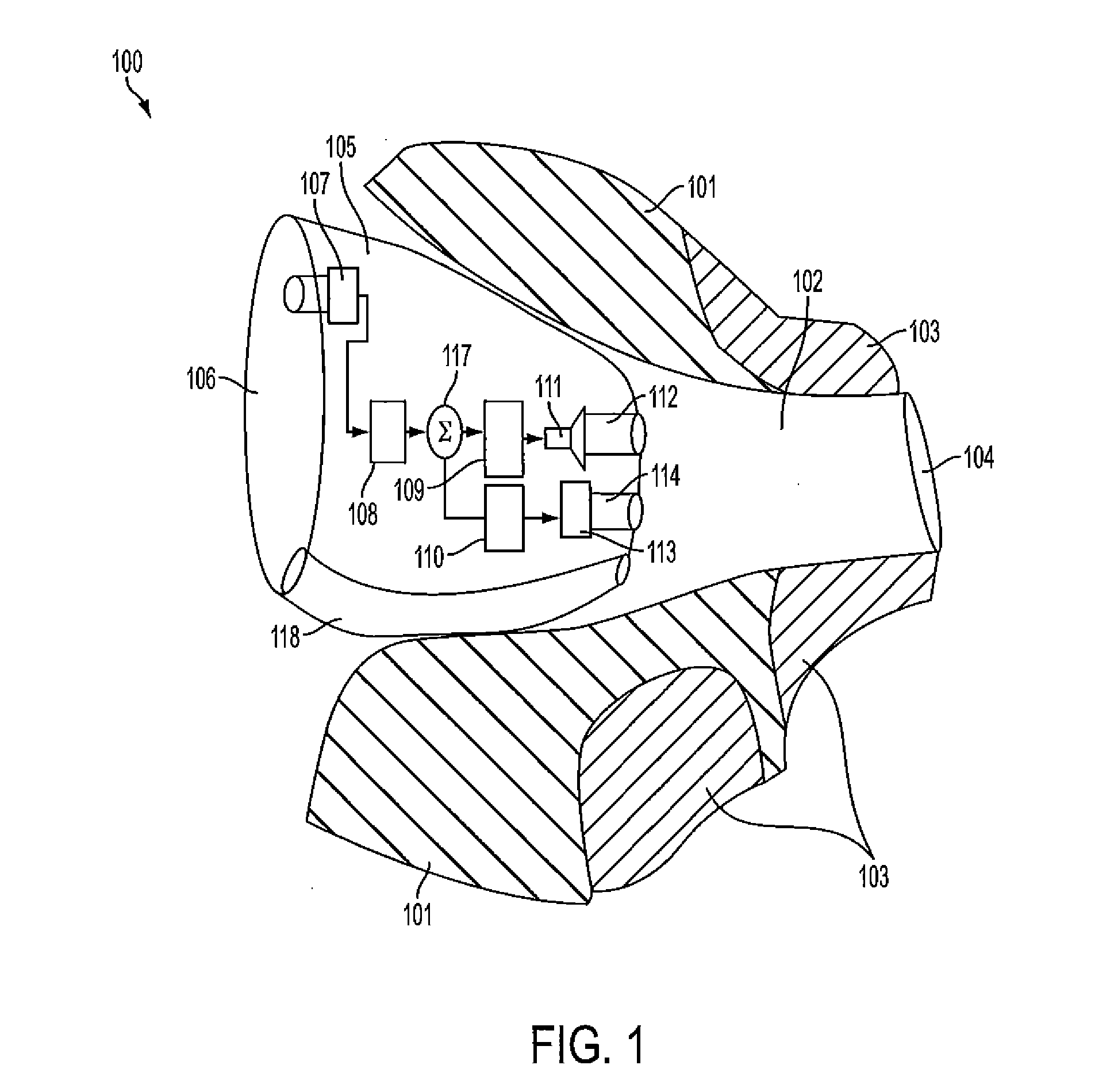
InactiveUS7756285B2Low costHigh gainDetails for specific frequency responseResonant cavitySound sources
A hearing aid comprises a microphone that receives incident sound waves from one or more sources external to the hearing aid, and converts the sound waves into electronic signals; a circuit that amplifies the electronic signals; a receiver that converts the amplified electronic signals into amplified sound waves; and a tuned resonant cavity between the microphone and the at least one external sound source. At least one parameter of the tuned resonant cavity is selected to modify the frequency response of the incident sound waves that are received by the microphone. In particular, the geometry of one or more openings through which sound waves enter the chamber, the geometry of the chamber itself, and / or the geometry of one or more openings through which sound waves exit the chamber, are selected to condition the incident sound waves by modifying the frequency response of the audio signal prior to the signal being received at the microphone.
Owner:HIMPP
Hearing instrument
InactiveUS7844065B2Improve sound qualityIncrease rangeAdditive manufacturing apparatusHearing aid ventsComputer scienceSignal processing
According to the first aspect of the invention, a hearing instrument with at least one microphone and signal processing comprises at least two receivers having a different frequency response. At least a first one of the receivers is placed outside the ear canal, for example in a behind-the-ear component. According to the second aspect of the invention, a hearing instrument comprising a behind-the-ear component and an external component for being placed in the user's ear canal or in the user's ear as well as a connection link between the behind-the-ear component and the external component is provided, where the connection link is reversibly pluggable to the behind-the-ear component and / or the in-the-ear-canal component and has a length that is reversibly adjustable. The hearing instrument also comprises fixation means for reversibly fixing the adjusted length of the connection link. A hearing instrument according to the third aspect comprises a fixation means separate from the in-the-ear-canal component. The fixation means may be positioned in the ear canal and rest therein. The in-the-ear-canal component may be connected to the fixation means and detached therefrom when the same is already in the ear canal.
Owner:SONOVA AG
Hearing aid
ActiveUS20110255723A1Easy to useCompletely in canal hearing aidsBehind the ear hearing aidsElectrical conductorEngineering
A hearing aid includes a receiver with a receiver housing, the receiver having a sound port opening, and being configured to be placed at least partly in an ear canal of a user, and a sound tube acoustically connected to the sound port opening of the receiver, the sound tube having a longitudinal extension in at least two directions, wherein the sound tube has a total length of at least 16 mm. A hearing aid includes a behind the ear (BTE) unit configured to process sound and generate an electrical signal, an earpiece, and a signal conductor configured to communicate the electrical signal to the earpiece, wherein the earpiece comprises a receiver that is configured to convert the electrical signal into a sound signal, and wherein the earpiece further comprises a sound tube that is coupled to a sound port opening at the receiver, the sound tube having a longitudinal extension in at least two directions.
Owner:GN HEARING AS
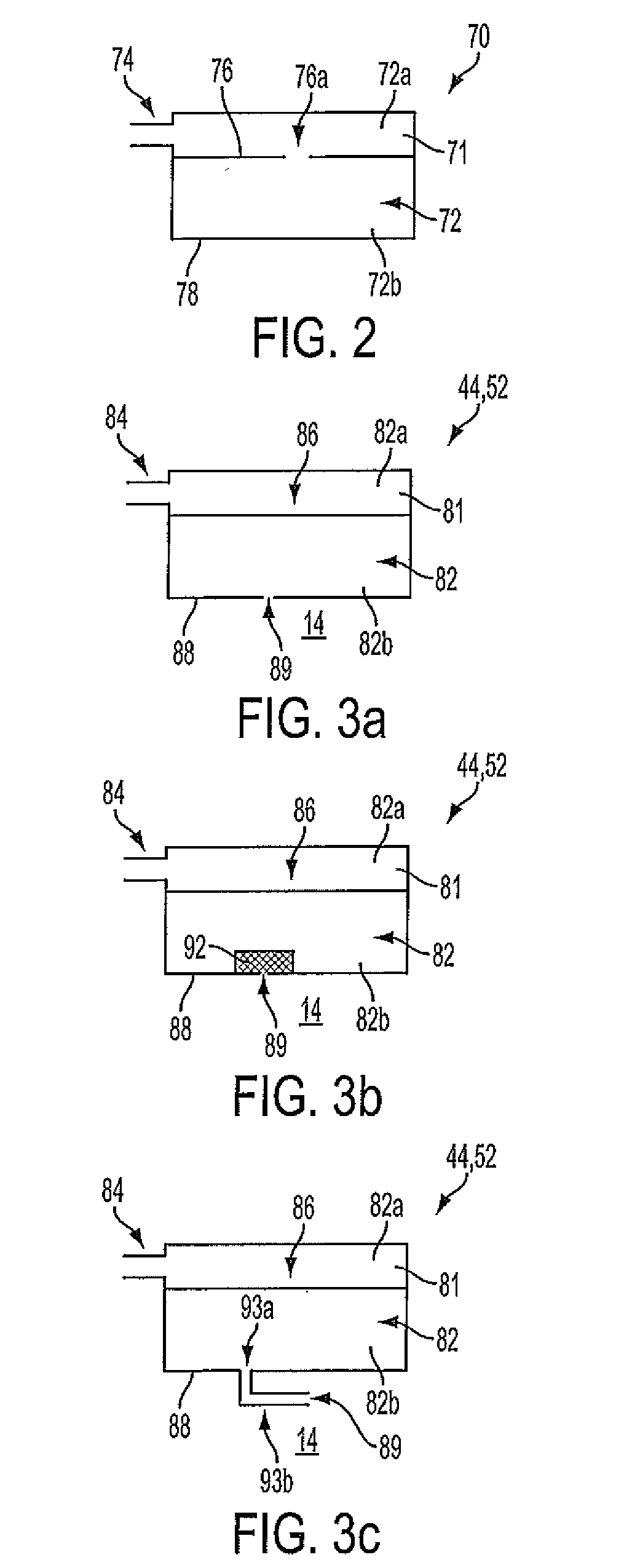
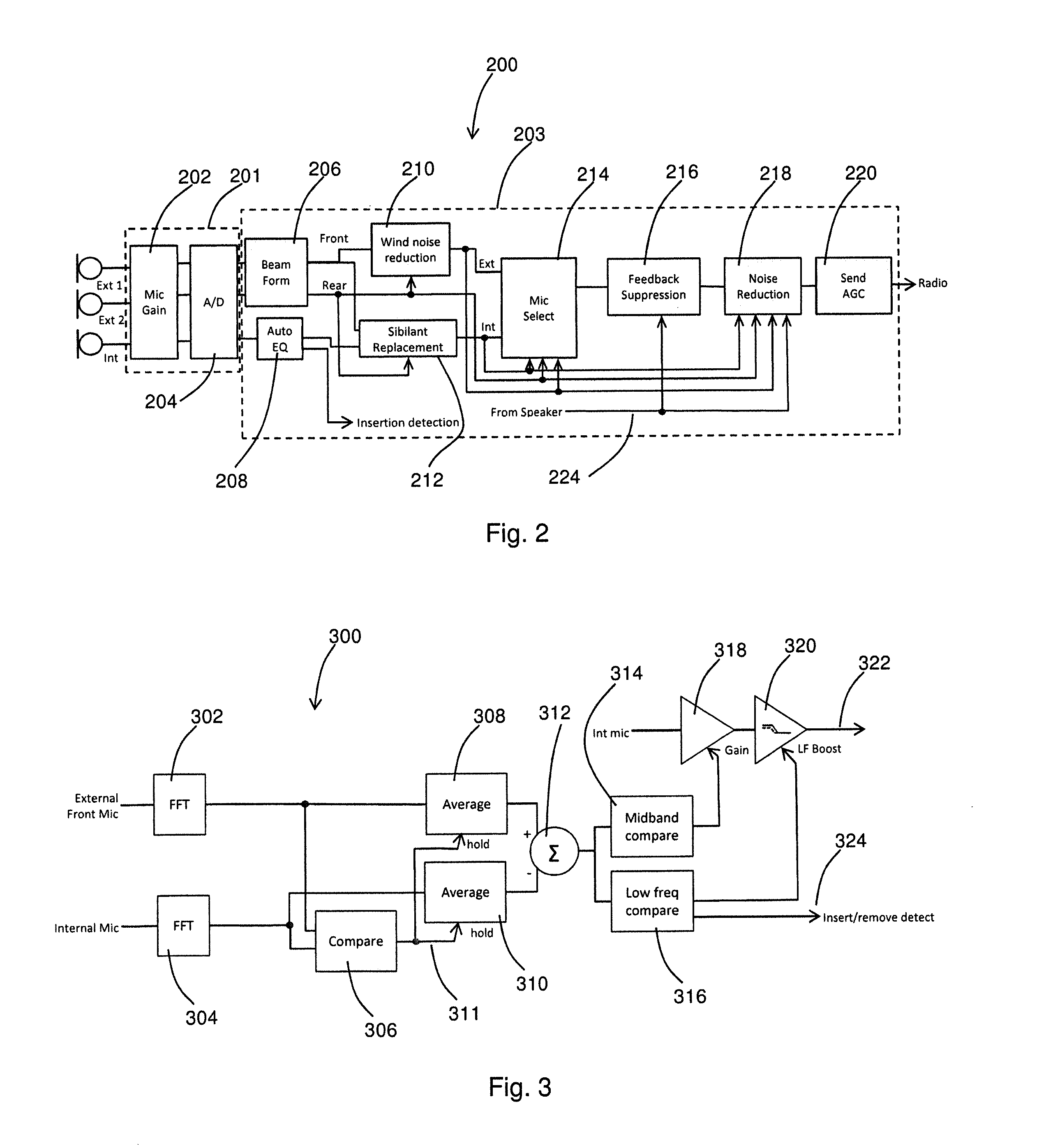
Apparatus and method for digital signal processing with microphones
At least a partial seal between a housing of a hearing instrument and an ear canal is provided. First signals are received from an internal microphone disposed in the ear canal. Second signals are received from an external microphone disposed outside of the ear canal. A condition of the at least a partial seal is determined, and when the condition of the at least a partial seal indicates a leak, one or more of the level and the spectrum of the first signals is adjusted to compensate for the leak and producing first adjusted signal. A first amount of the first adjusted signals is blended with a second amount of the second signals to produce a blended signal, the first amount and the second amount selected based upon a level of noise.
Owner:KNOWLES ELECTRONICS INC
In-ear monitor with shaped dual bore
ActiveUS7263195B2Easy to customizeDetails for specific frequency responseIntra aural earpiecesEngineeringHeadphones
A multi-driver in-ear monitor for use with either a recorded or a live audio source is provided. If a pair of drivers is used, each driver has an individual sound delivery tube. If three drivers are used, the outputs from two of the drivers are merged into a single sound delivery tube while the output from the third driver is maintained in a separate, discrete sound tube. The sound delivery tubes remain separate throughout the end portion of the earpiece. The earpiece tip is configured to be fitted with any of a variety of sleeves (e.g., foam sleeves, flanged sleeves, etc.), thus allowing the in-ear monitor to be easily tailored to comfortably fit within any of a variety of ear canals. Due to the size constraints of such an earpiece, the sound delivery tubes include a transition region. Acoustic filters (i.e., dampers) can be interposed between one or both driver outputs and the earpiece output.
Owner:LOGITECH INT
Ear insert for hearing aids
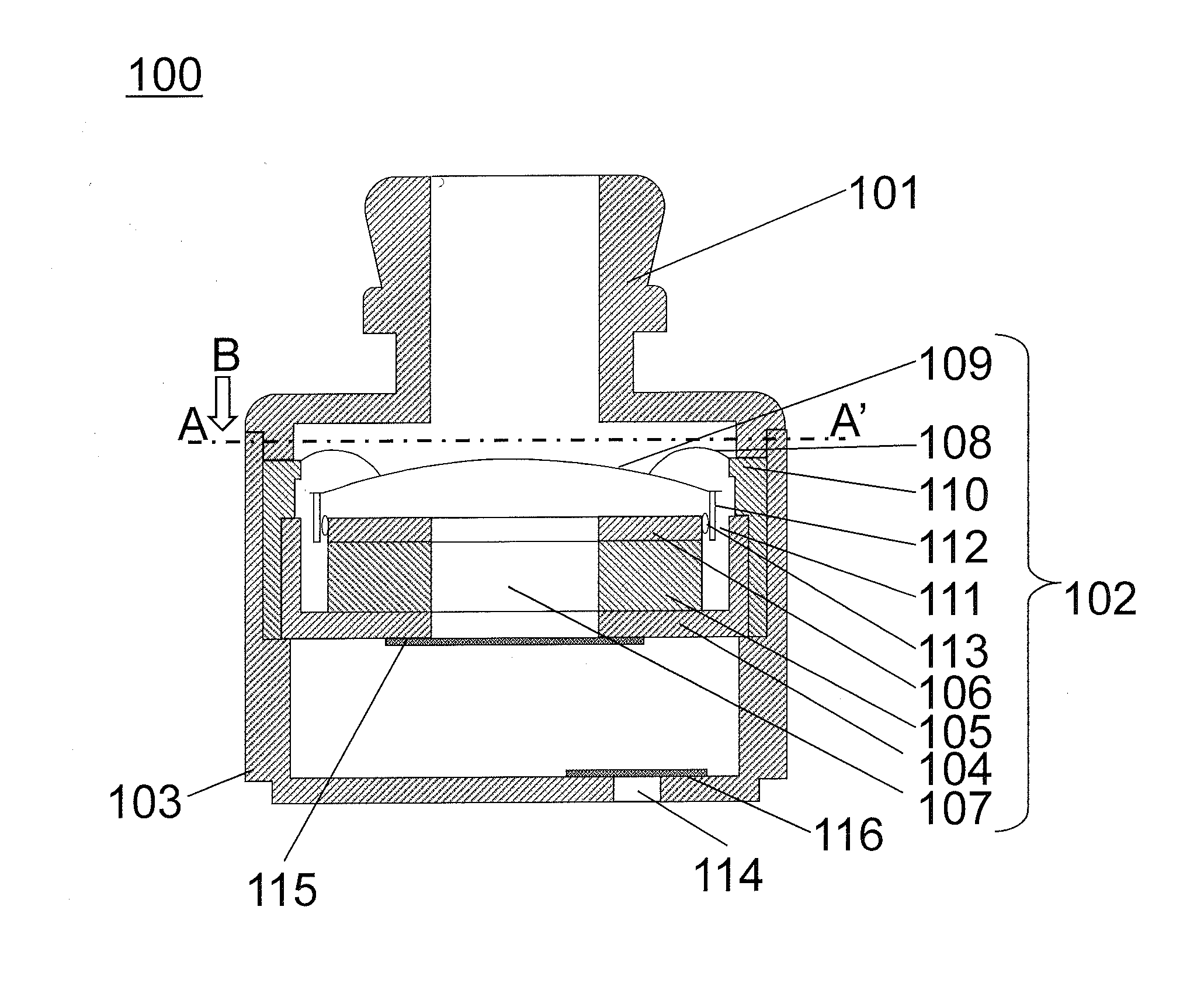
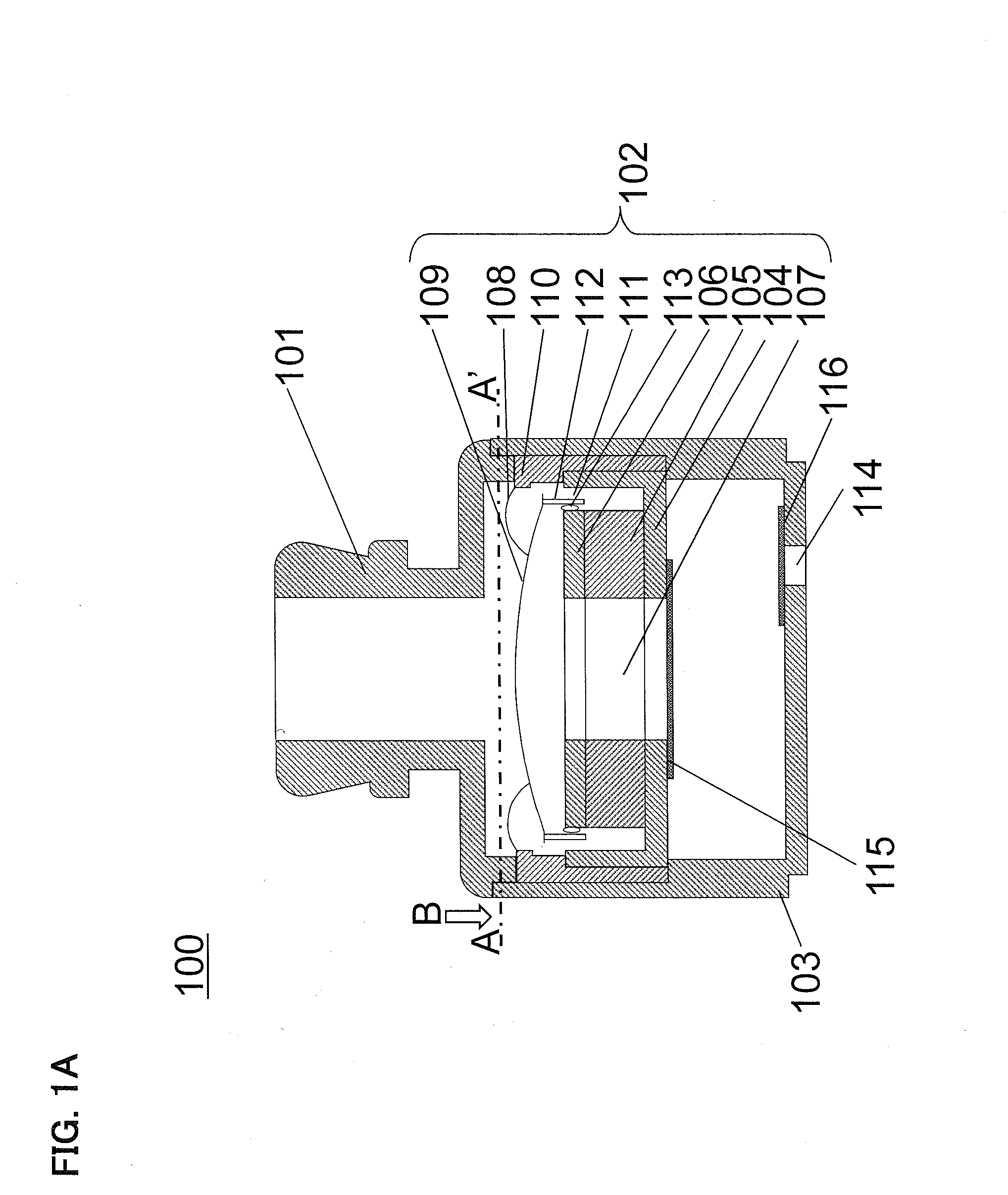
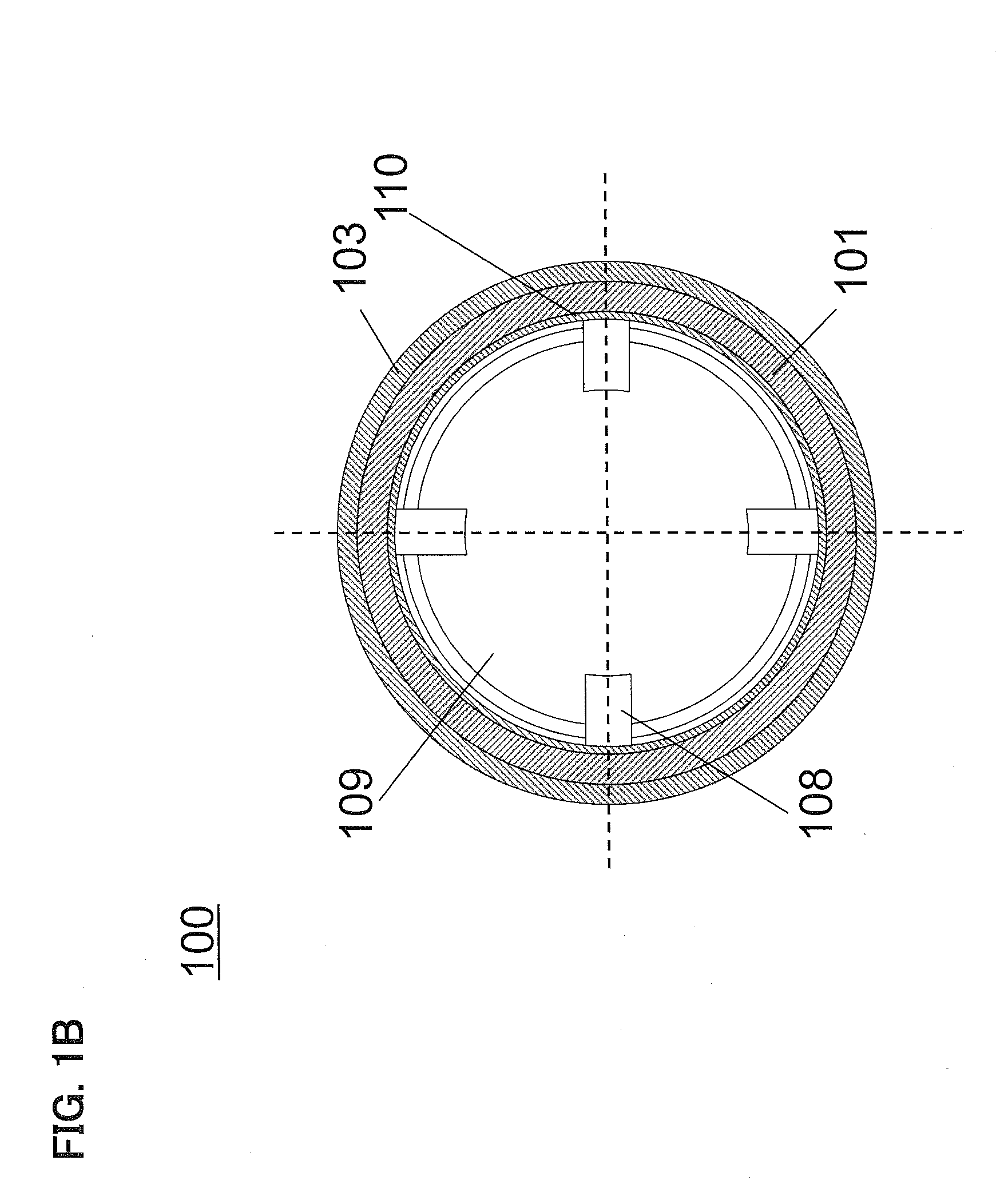
InactiveUS20050190940A1Improve acoustic propertiesReduce manufacturing costEar supported setsDetails for specific frequency responseEar AuricleEngineering
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Earphone
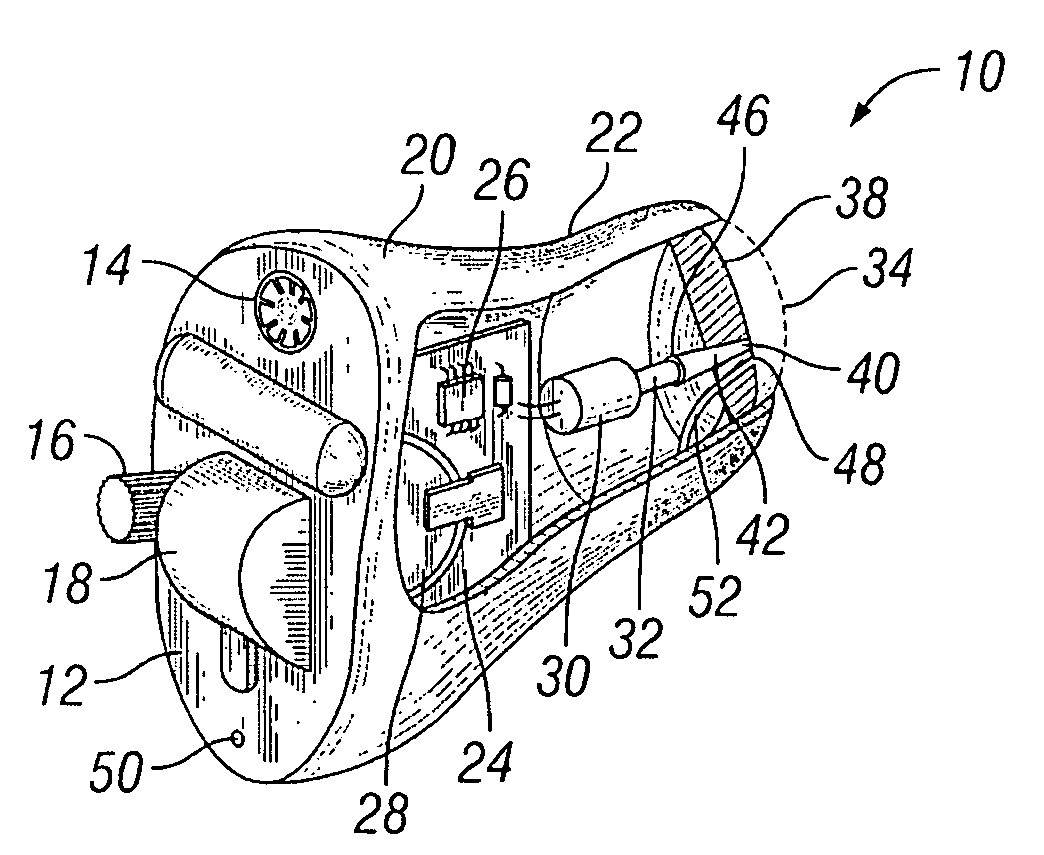
An earphone includes: a loudspeaker unit; a sound conductive tube which is connected to a front surface having a diaphragm included in the loudspeaker unit, and has a hole through which a sound generated from the loudspeaker unit is emitted; a housing which is connected to a back surface of the loudspeaker unit so that a space is formed between the housing and the back surface of the loudspeaker unit, and has a first air hole connecting the space to external air; a first braking part which closes a sound hole of the loudspeaker unit; and a second braking part which closes the first air hole.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
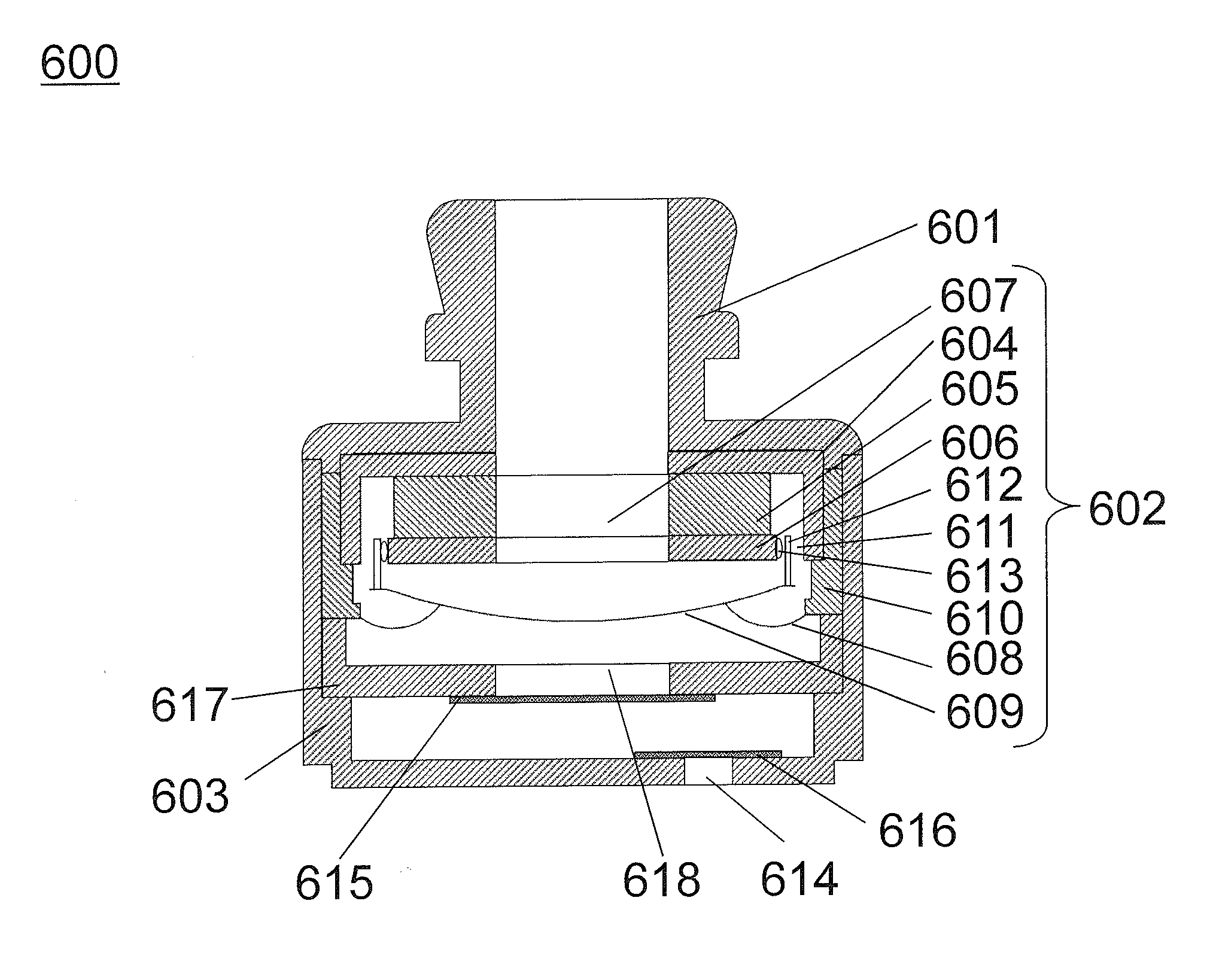
Acoustically tailored hearing aid and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20060115105A1Accurate compensationDetails for specific frequency responseEngineeringHearing aid
An apparatus and method for tailoring the audio frequency response of a hearing aid or other ear piece by altering the physical characteristics of the device to more accurately compensate for a user's specific hearing loss attributes. The device has a bore formed within its ear piece shell which provides a passage for the transmission of sound from the speaker or receiver of the device toward the user's eardrum. The bore has a custom-designed shape to emphasize desired sound frequencies and therefore produce a predetermined frequency response of sound in combination with any frequency response changes of the device's circuitry.
Owner:SYNYGIS
Method of constructing an in the ear auxiliary microphone for behind the ear hearing prosthetic
InactiveUS7003876B2Improve responseEnhanced couplingLine/current collector detailsElectrotherapyCouplingSound wave
An In The Ear (ITE) microphone improves the acoustic response of a Behind The Ear (BTE) Implantable Cochlear Stimulation (ICS) system during telephone use. An acoustic seal provided by holding a telephone earpiece against the ear provides improved coupling of low frequency (up to about 1 KHz) sound waves, sufficient to overcome losses due to the near field acoustic characteristics common to telephones. In a preferred embodiment, the ITE microphone is connected to a removable ear hook of the BTE ICS system by a short bendable stalk.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONICS AG
Headphone structure for adjusting audio frequencies
ActiveUS20150382099A1Promote resultsEasy to manufactureDetails for specific frequency responseIntra aural earpiecesEngineeringHeadphones
A headphone structure for adjusting audio frequencies is provided, which comprises a front housing, a rear housing, a sound-producing unit in the front housing and an elastic ear-contacting body sleeving the front housing. The front housing has at least one slot or recess, and the elastic ear-contacting body sleeves the front housing to form at least one gap. The headphone structure for adjusting audio frequencies of the present invention has better results for the adjustment of bass frequencies. In addition, the headphone structure of the present invention is not complicated and is easy to manufacture. The headphone structure of the present invention can be applied to various types of headphone, such as in-ear headphones and circumaural headphones.
Owner:HUIYANG DONGMEI AUDIO PRODS
Hearing aid with tuned microphone cavity
InactiveUS20070189563A1Low costHigh gainDetails for specific frequency responseResonant cavitySound sources
A hearing aid comprises a microphone that receives incident sound waves from one or more sources external to the hearing aid, and converts the sound waves into electronic signals; a circuit that amplifies the electronic signals; a receiver that converts the amplified electronic signals into amplified sound waves; and a tuned resonant cavity between the microphone and the at least one external sound source. At least one parameter of the tuned resonant cavity is selected to modify the frequency response of the incident sound waves that are received by the microphone. In particular, the geometry of one or more openings through which sound waves enter the chamber, the geometry of the chamber itself, and / or the geometry of one or more openings through which sound waves exit the chamber, are selected to condition the incident sound waves by modifying the frequency response of the audio signal prior to the signal being received at the microphone.
Owner:HIMPP
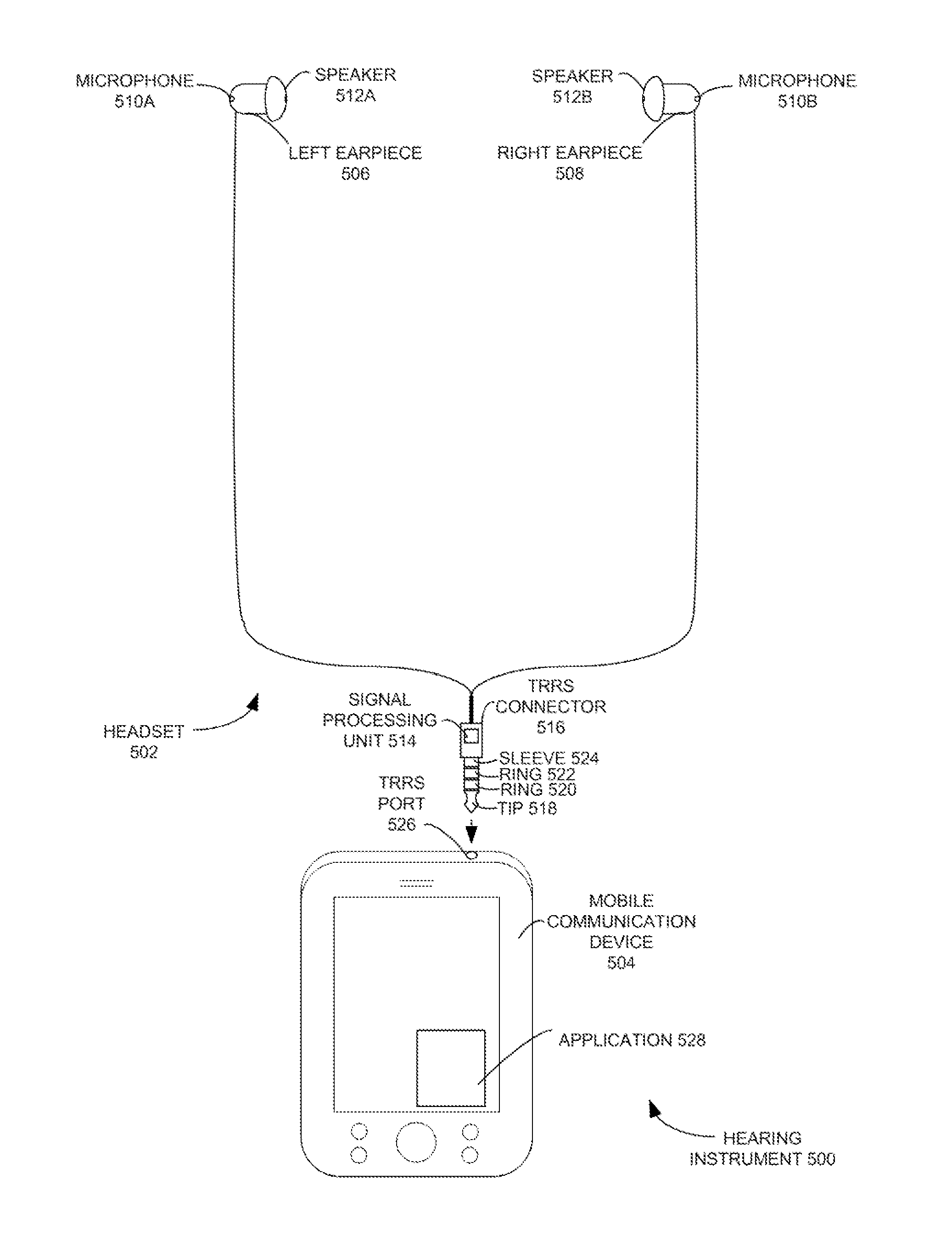
Hearing instrument
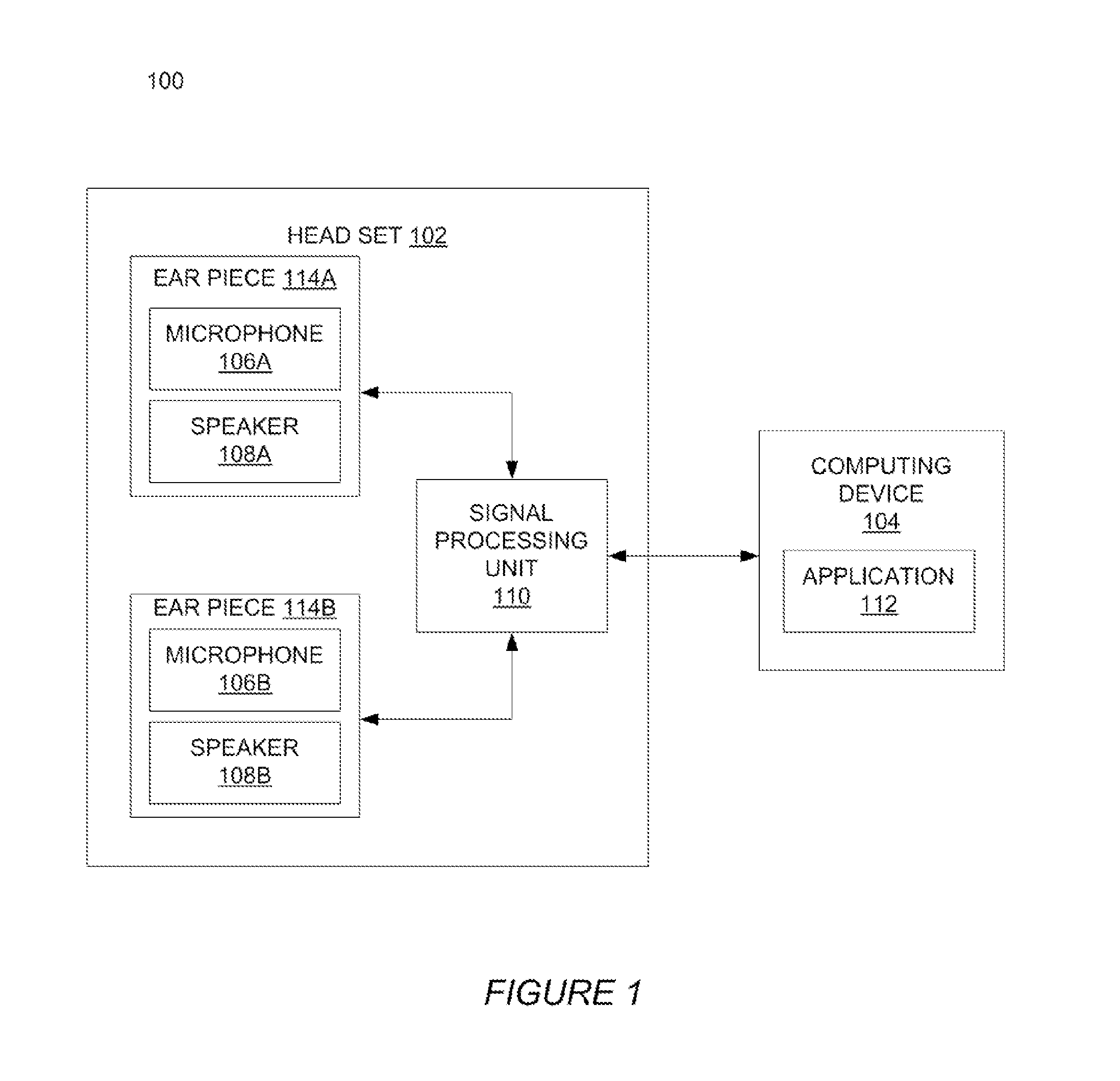
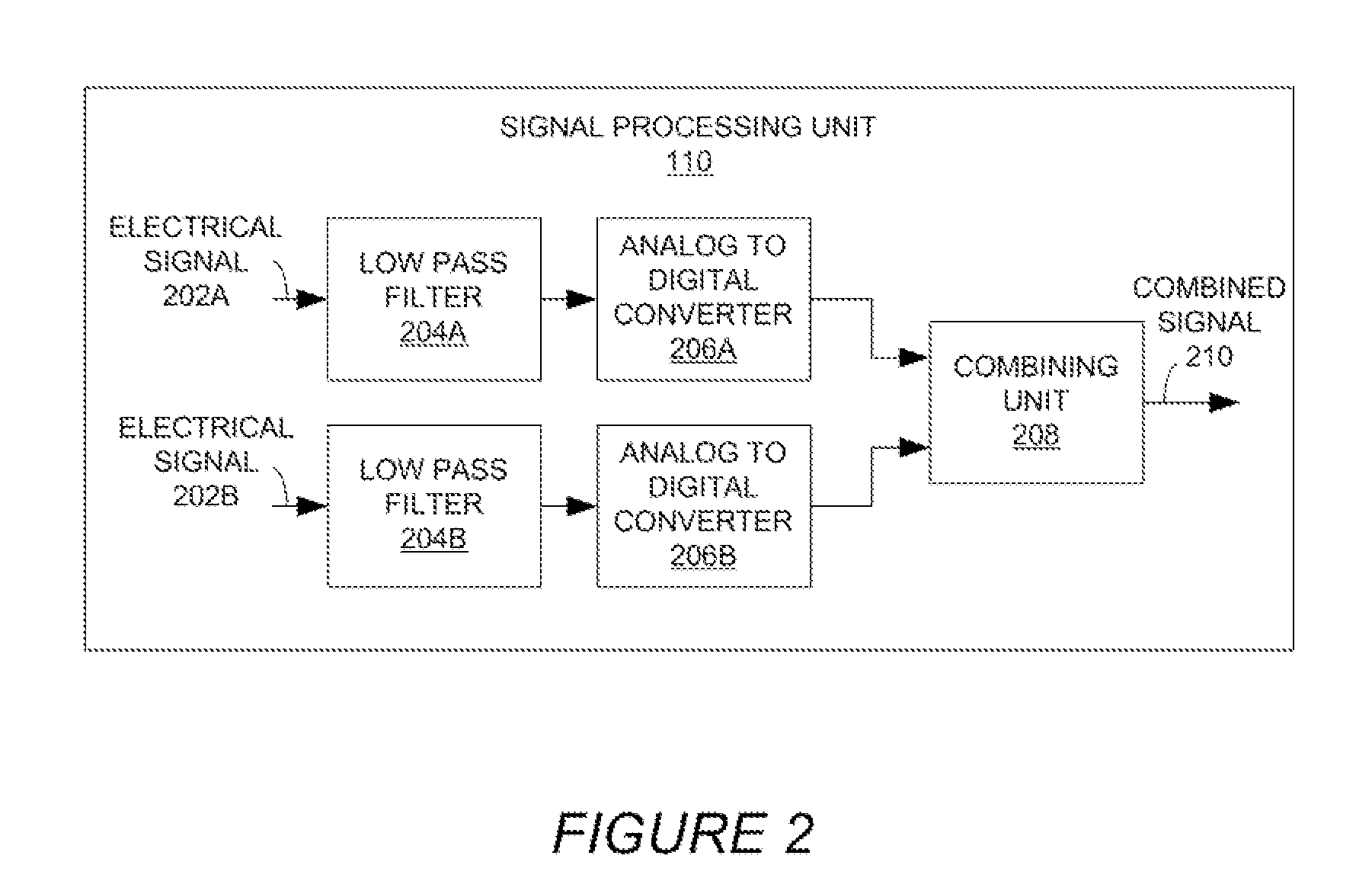
ActiveUS20140169601A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationSets with pocket amplifiersEngineeringHeadphones
An audio system includes a headset and a portable computing device. The headset includes a first speaker and a first microphone, a second speaker, a second microphone and a processing unit. The first microphone and the second microphone output a first signal and a second signal, respectively. The processing unit combines the first electrical signal and the second electrical signal into a third electrical signal, and communicates the third electrical signal to a portable computing device through an output channel. The portable computing device preferably includes an application that separates the third electrical signal into the first electrical signal and the second electrical signal. The application compensates the first electrical signal and the second electrical signal for a hearing loss of an individual.
Owner:OTICON
Hearing aid with occlusion reduction
ActiveUS20120008808A1Minimize distortionOcclusion effect electronic compensationIn the ear hearing aidsEngineeringHearing aid
A hearing aid having hearing loss-compensating components, active occlusion reduction components, a vent, a tuned piston, and a flexible surround. The piston and the surround combination are assembled on the faceplate and cover the outside end of the vent that is situated on the faceplate. The piston and the surround combination minimize the adverse effects of walk-induced head vibrations.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Earpiece with bars
ActiveUS8165332B2Suppress feedbackImprove convenienceHearing aid ventsDetails for specific frequency responsePliabilityHearing apparatus
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Silicon-based transducer for use in hearing instruments and listening devices
InactiveUS20070071260A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor electrostatic transducersTransducerEngineering
A silicon-based transducer assembly coupled to a movable structure in a hearing instrument. The transducer assembly includes at least one microphone chip and an ASIC having multiple integrated components such as any combination of a DSP, an A / D converter, an amplifier, a filter, or a wireless interface. The movable structure may be a battery access door, a volume dial, a switch, or a touch pad. A protection strip can be disposed across the battery access door to prevent debris from clogging the silicon-based transducer assembly. The transducer assembly may also include an array of microphone chips to achieve adaptive beam steering or directionality. When equipped with a wireless interface, the hearing instrument wirelessly communicates with another hearing instrument or with a network.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Earphone
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Popular searches
Hearing device specific tools Frequency/directions obtaining arrangements Earpiece/earphone manufacture/assembly Hearing aids mounting/interconnection Loudspeaker signals distribution Ear moulds/tips acoustic seals Artificial respiration Hearing aids housing Electronic input selection/mixing Telephone set constructions
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com