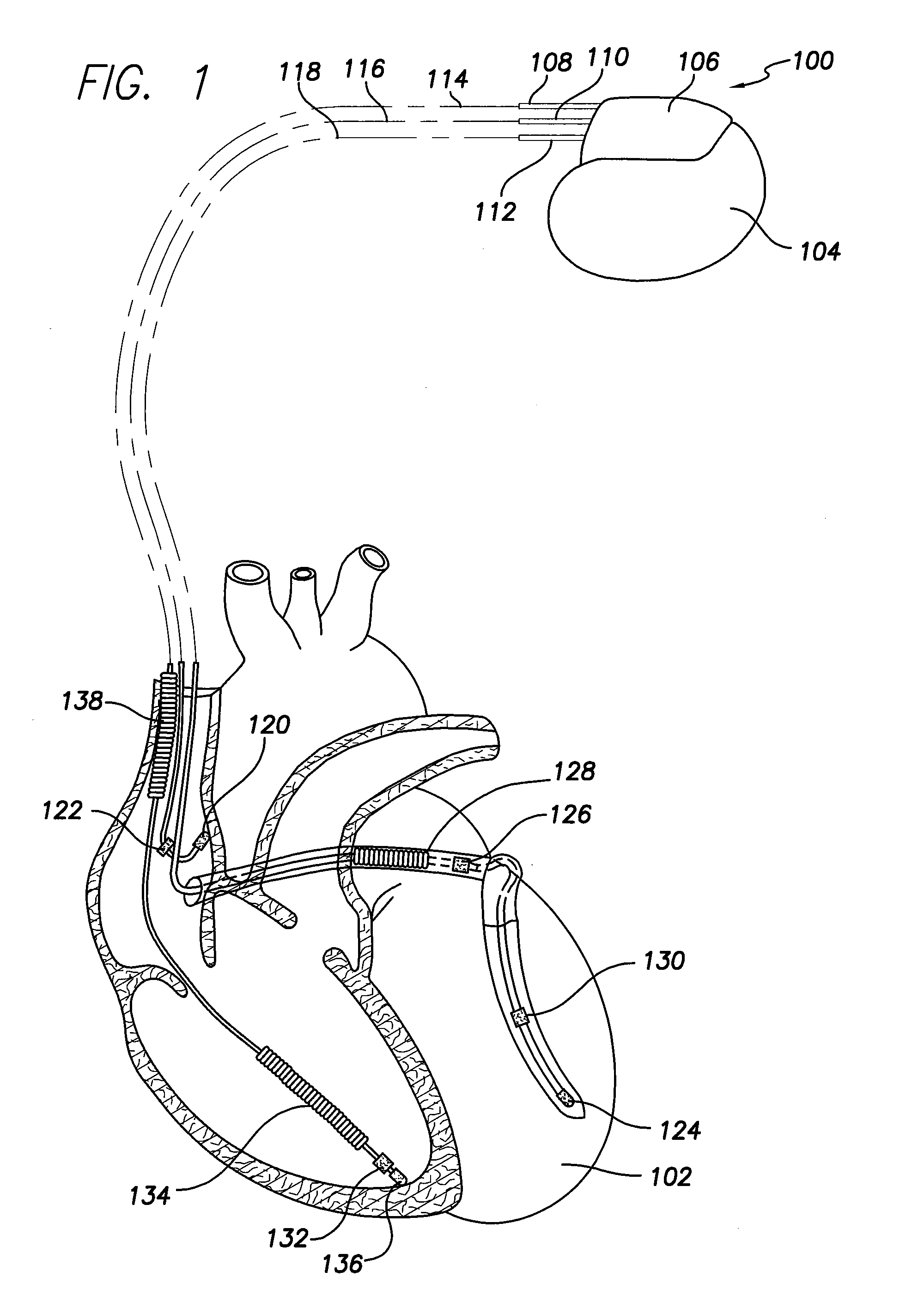
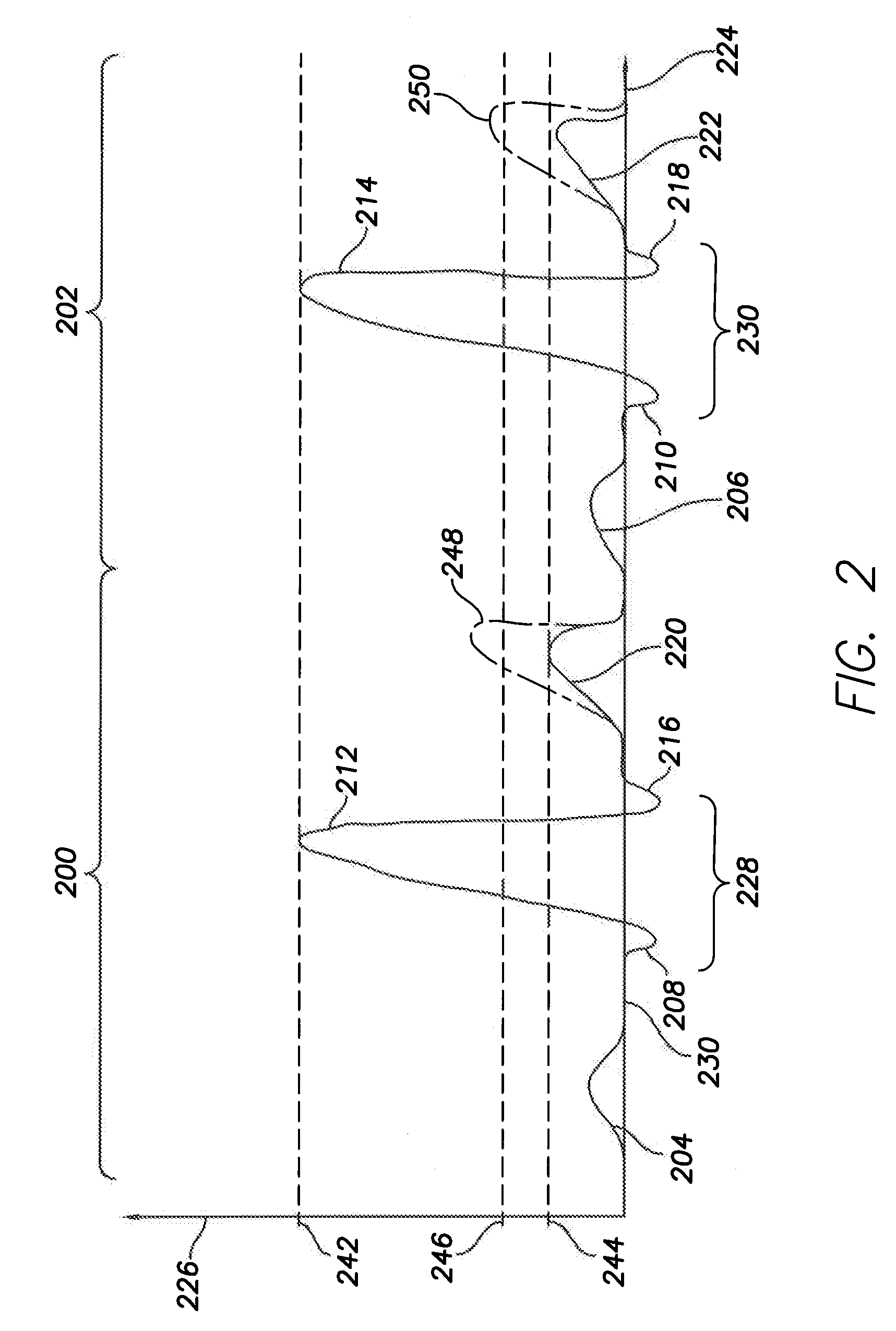
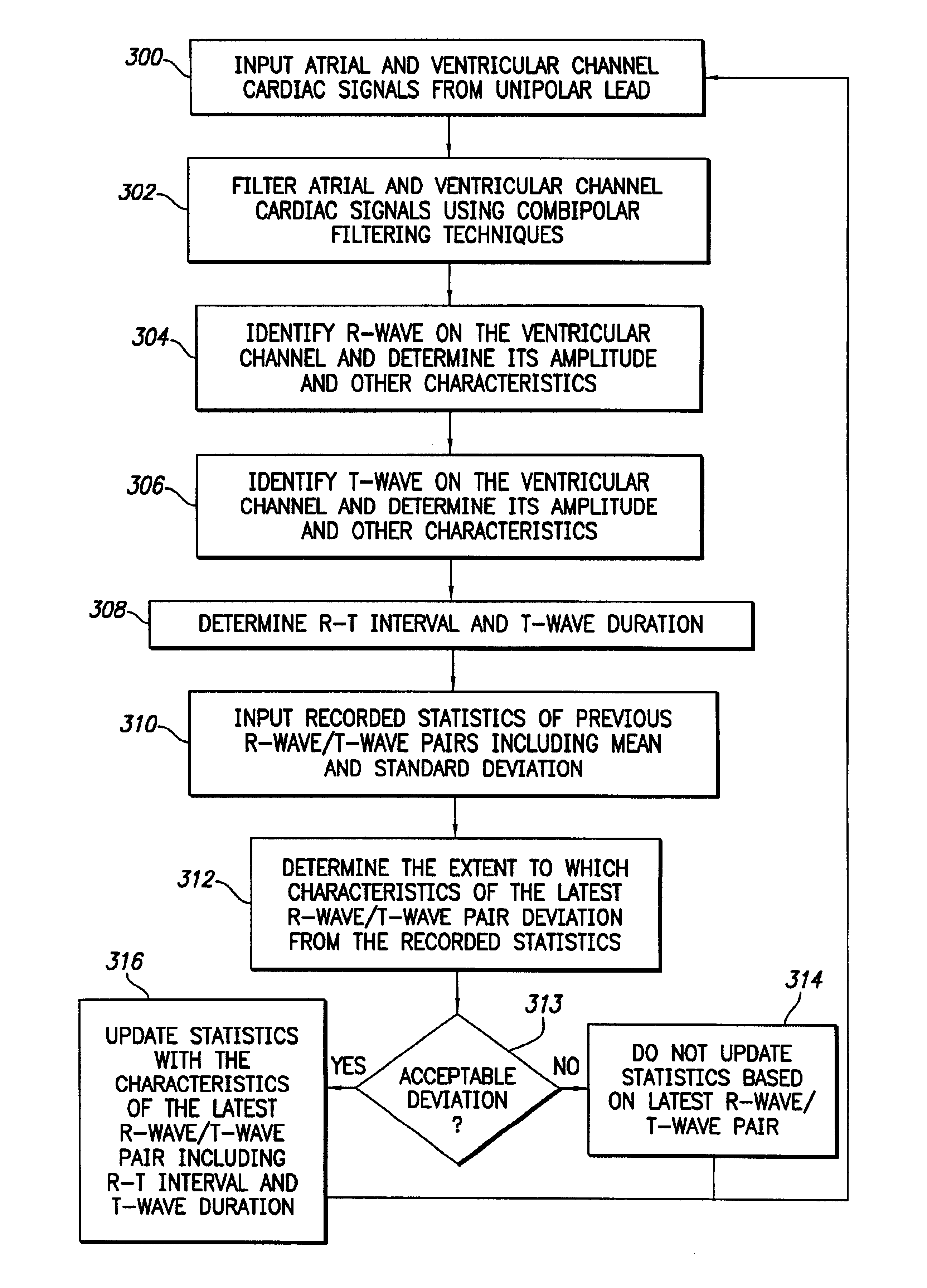
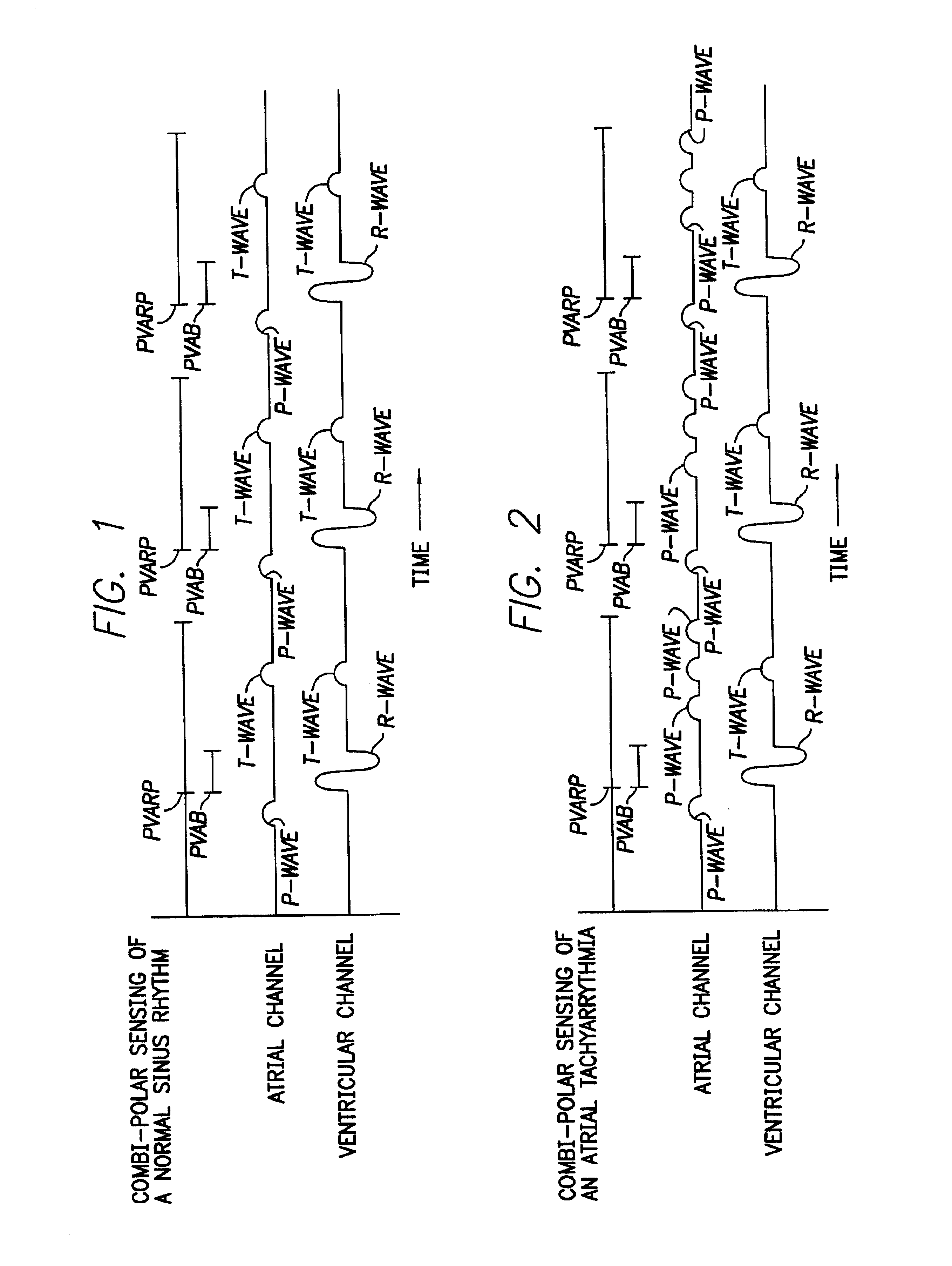
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Atrial rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The heart rate in atrial fibrillation may range from 100 to 175 beats a minute. The normal range for a heart rate is 60 to 100 beats a minute. Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles).
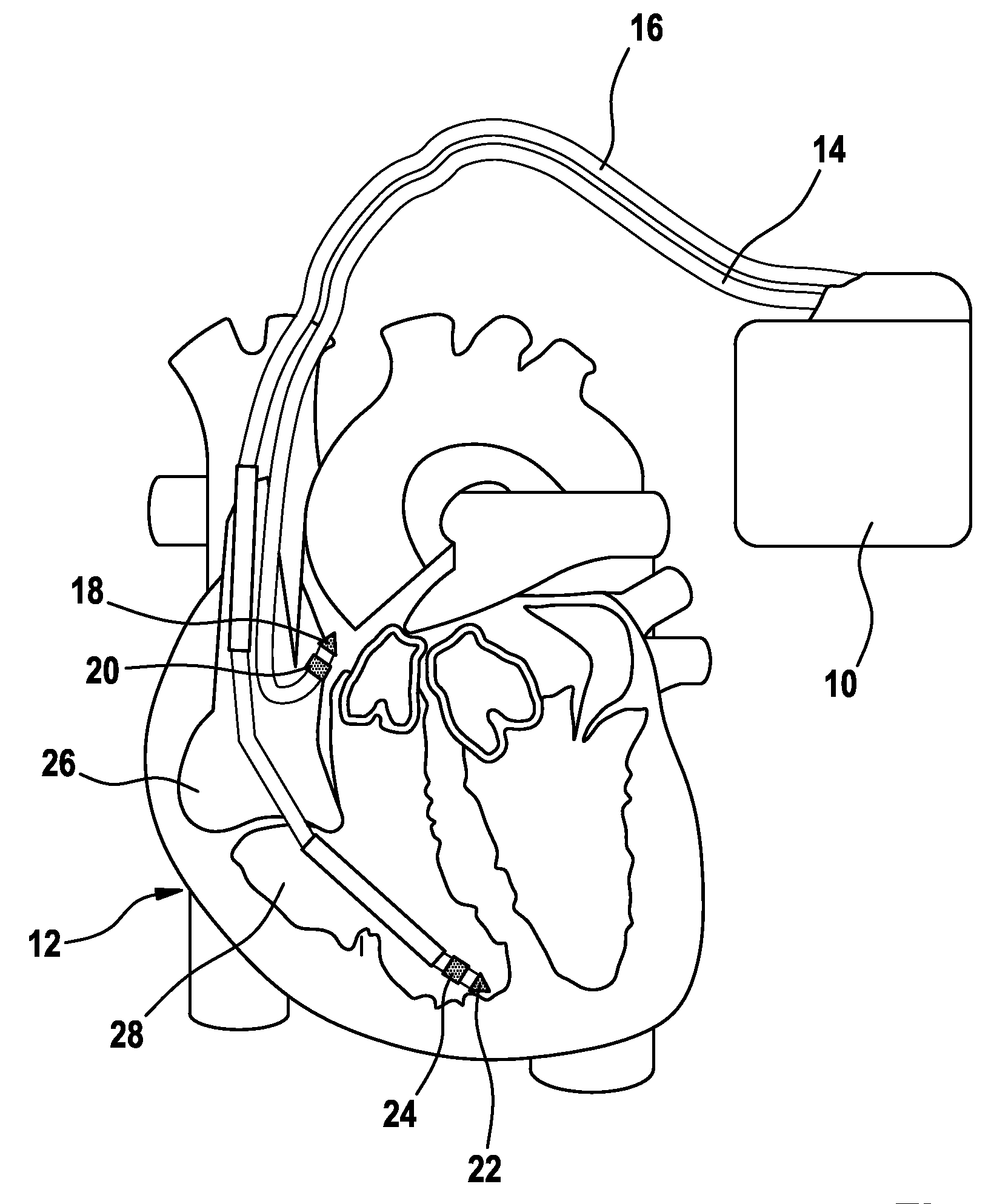
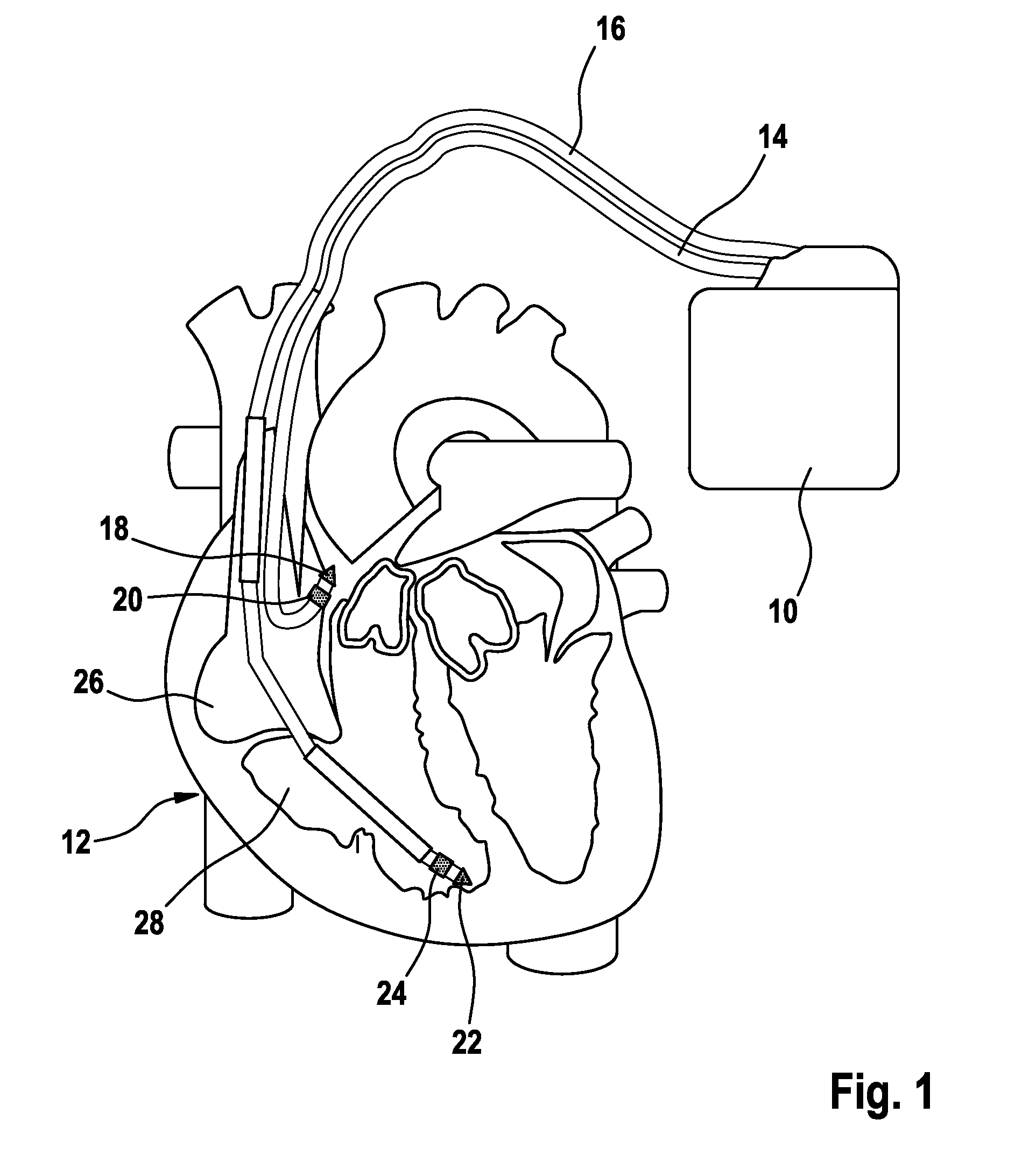
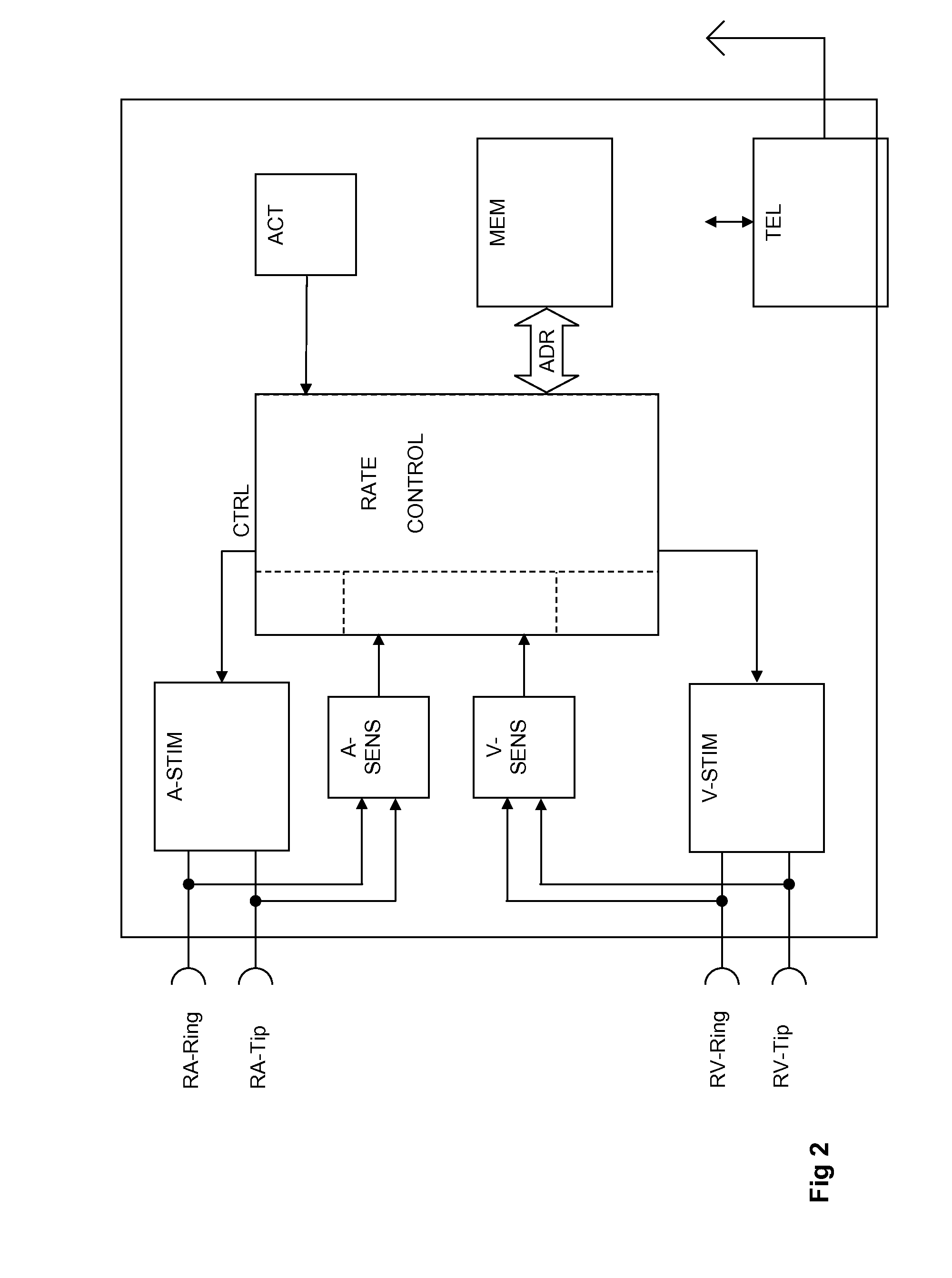
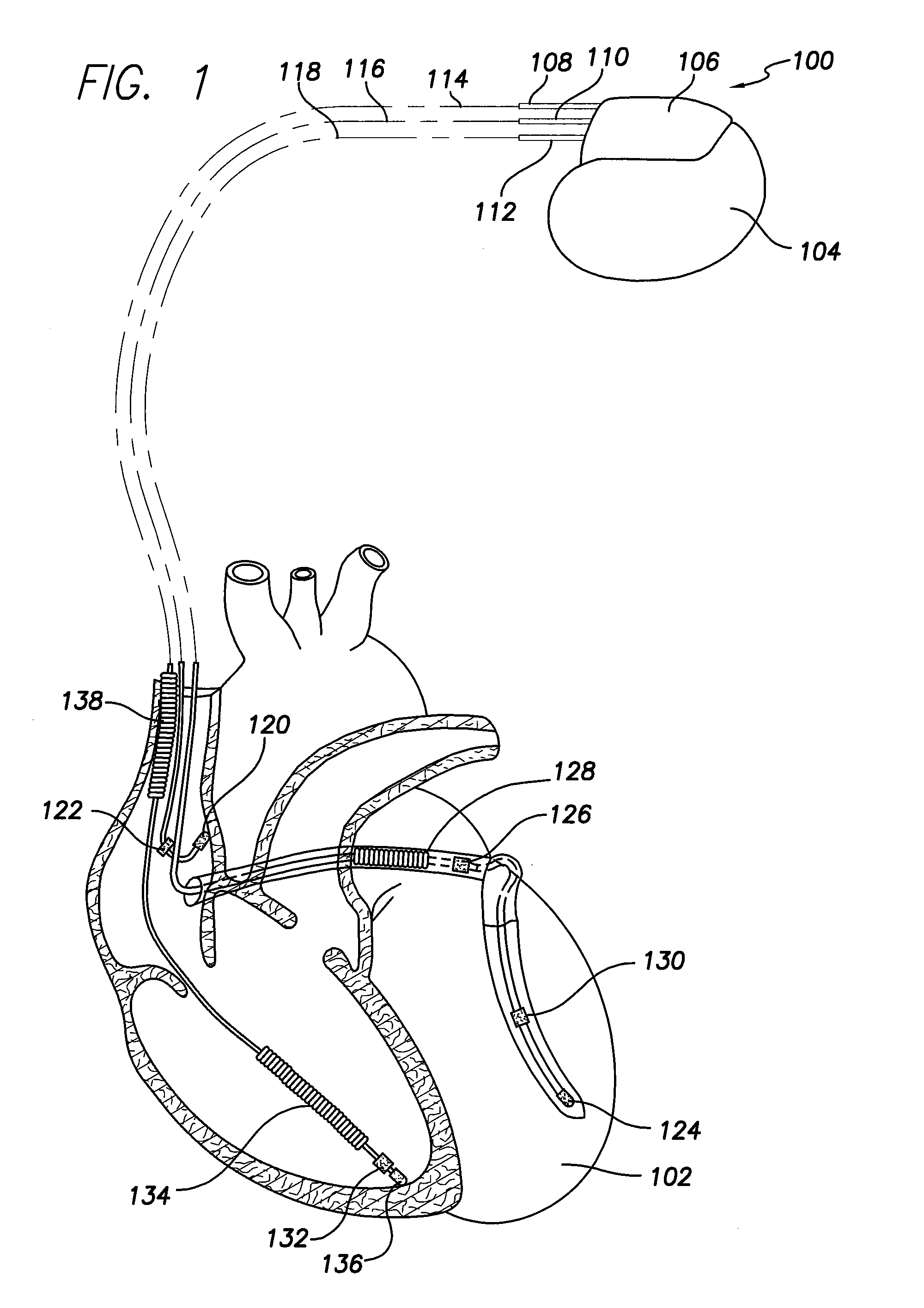
Cardiac rhythm management system promoting atrial pacing
InactiveUS6353759B1Promoting atrial pacingReduce the possibilityHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsVentricular dysrhythmiaInfinite impulse response
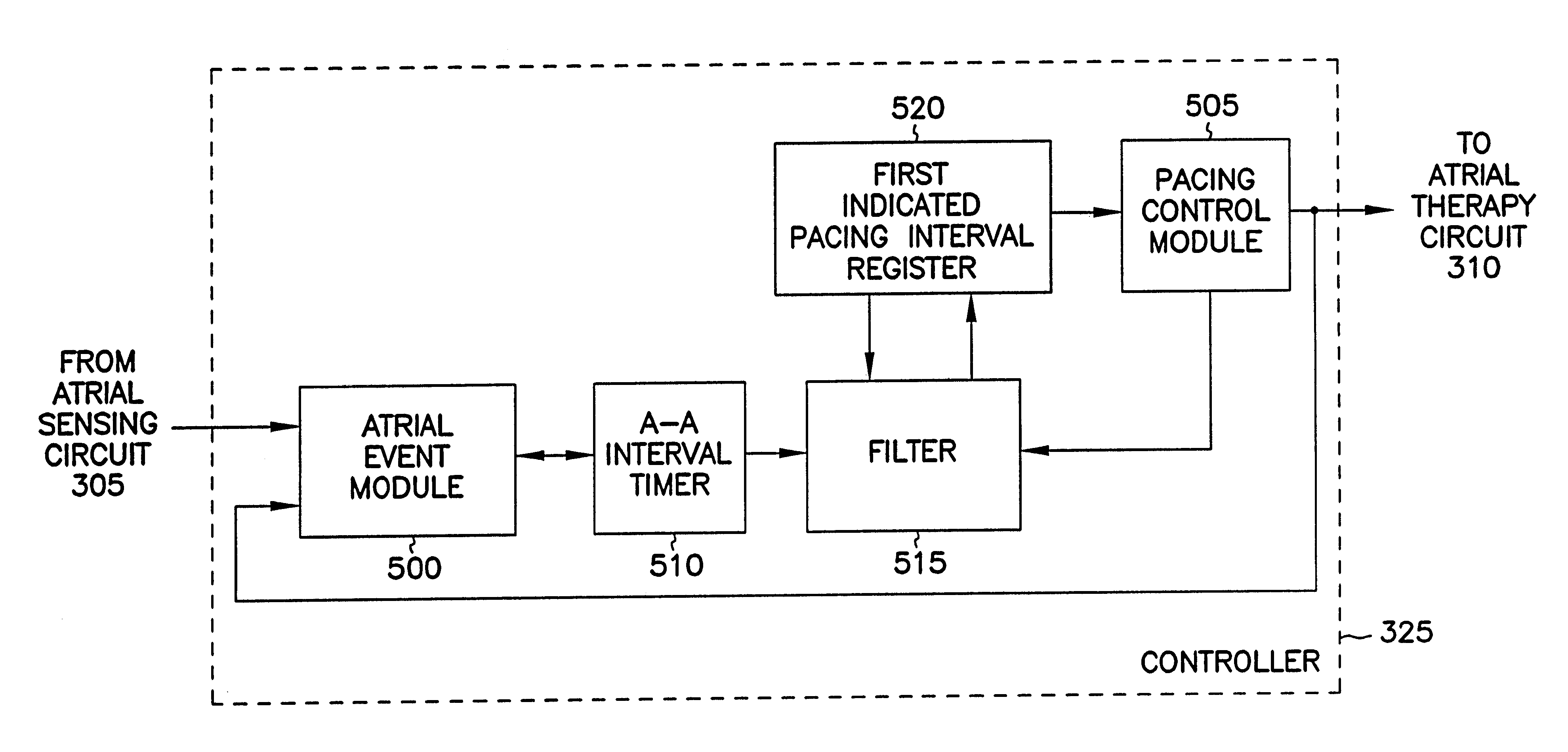
A cardiac rhythm management system includes an atrial pacing preference (APP) filter for promoting atrial pacing. The APP filter includes an infinite impulse response (IIR) or other filter that controls the timing of delivery of atrial pacing pulses. The atrial pacing pulses are delivered at an APP-indicated pacing rate that is typically at a small amount above the intrinsic atrial heart rate. For sensed beats, the APP indicated rate is increased until it becomes slightly faster than the intrinsic atrial heart rate. The APP-indicated pacing rate is then gradually decreased to search for the underlying intrinsic atrial heart rate. Then, after a sensed atrial beat, the APP filter again increases the pacing rate until it becomes faster than the intrinsic atrial rate by a small amount. As a result, most atrial heart beats are paced, rather than sensed. This decreases the likelihood of the occurrence of an atrial tachyarrhythima, such as atrial fibrillation. The decreased likelihood of atrial tachyarrhythmia, in turn, decreases the likelihood of inducing a ventricular arrhythmia, either as a result of the atrial tachyarrhythmia, or as the result of delivering a defibrillation shock to treat the atrial tachyarrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
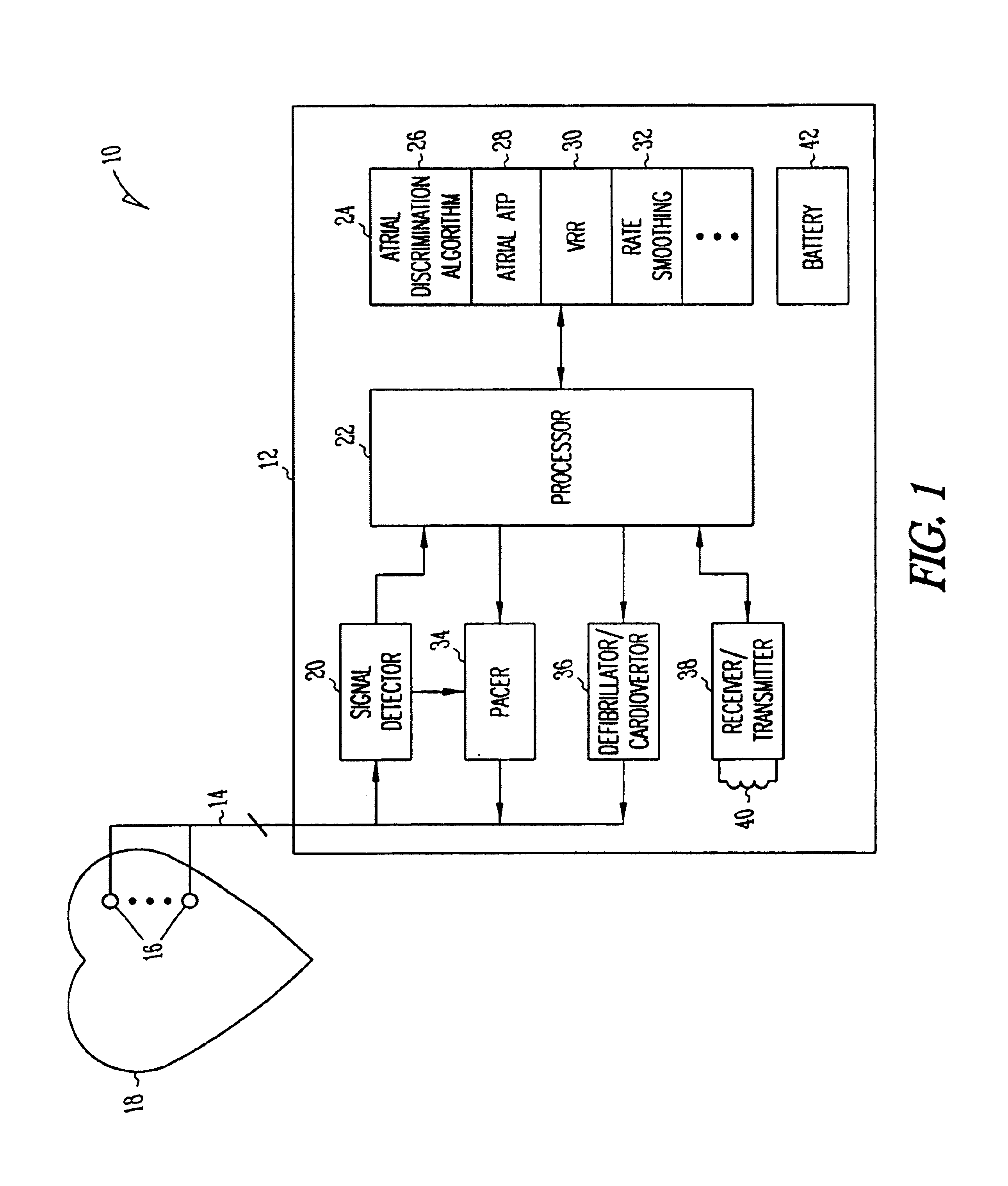
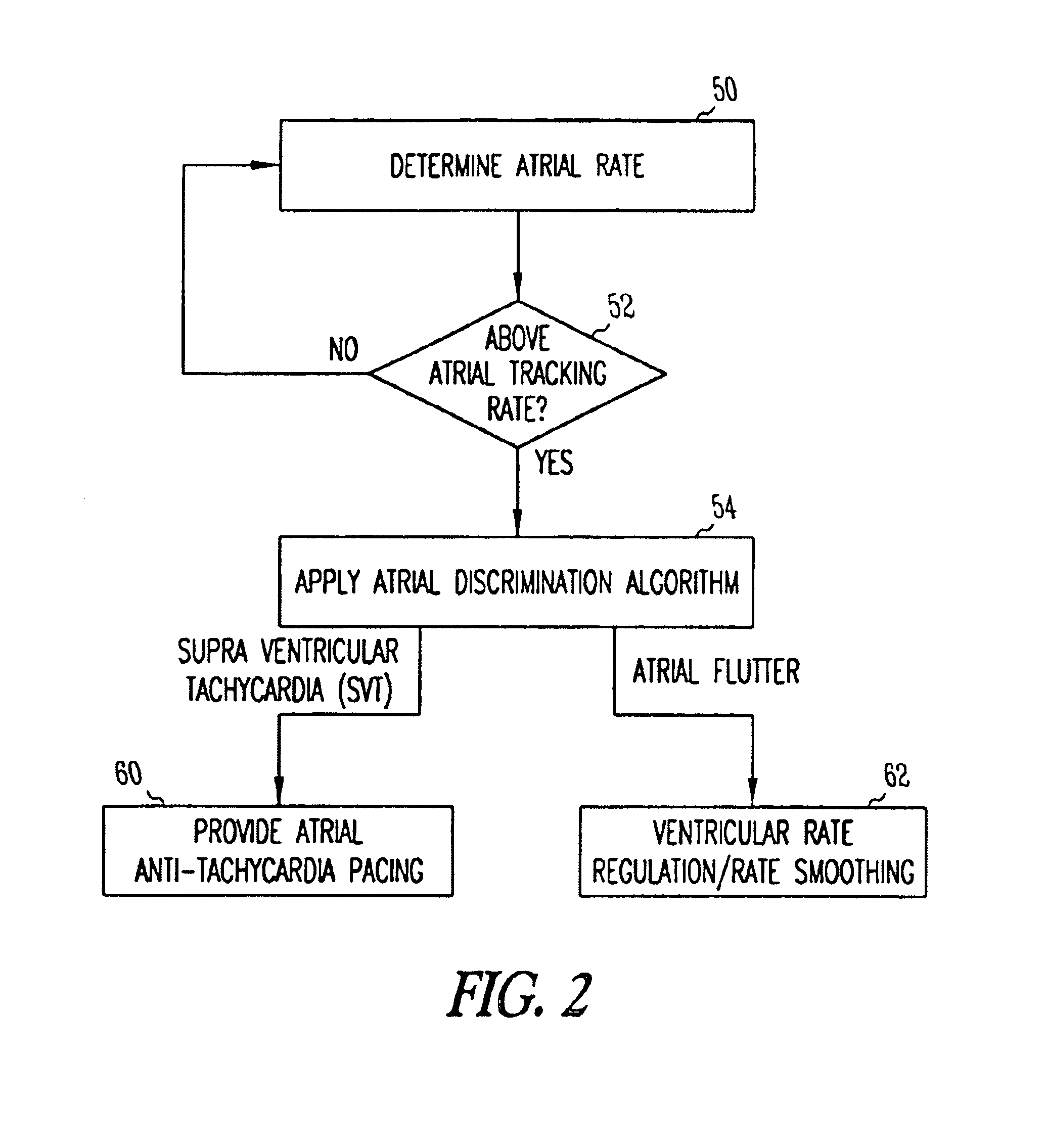
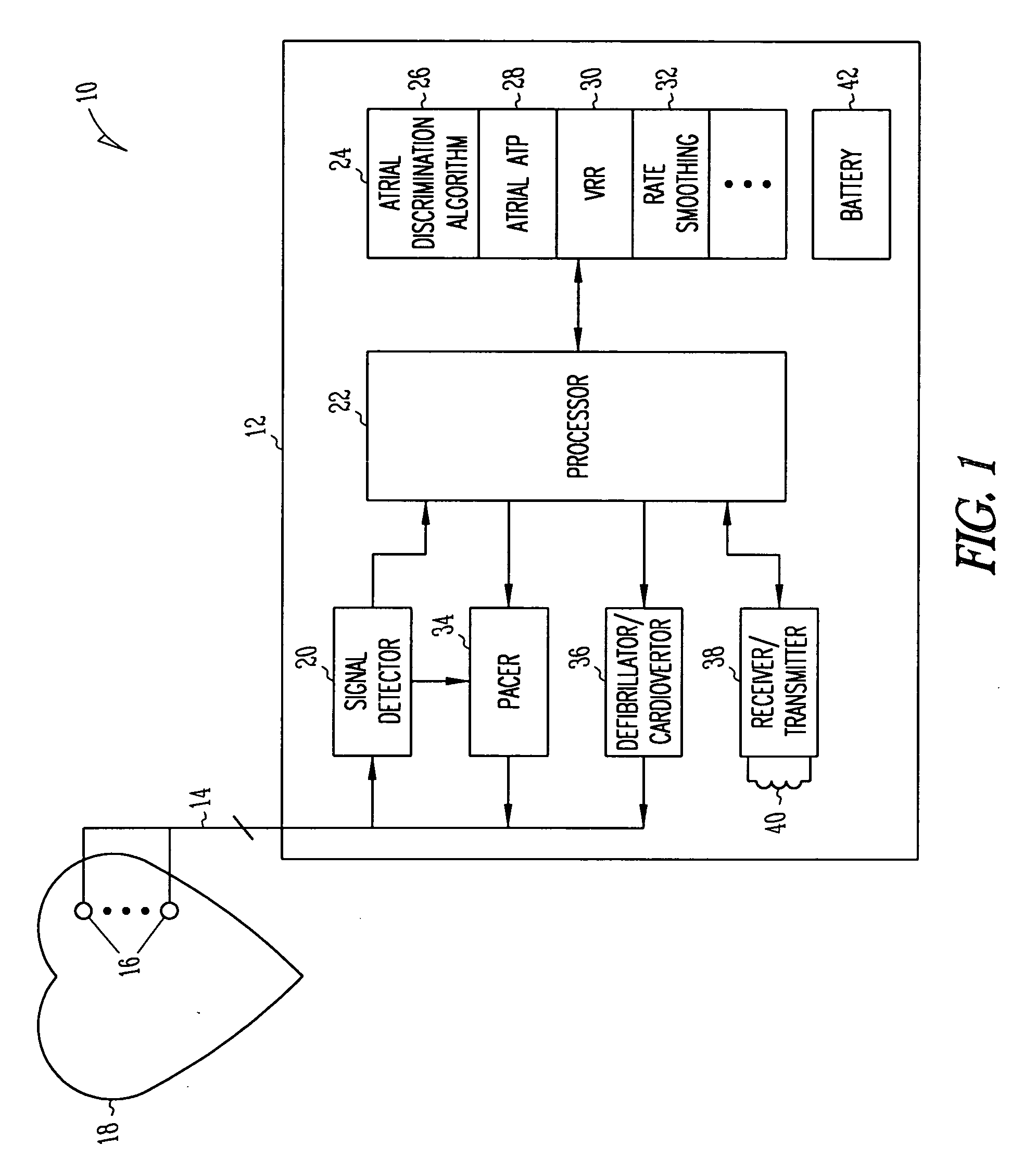
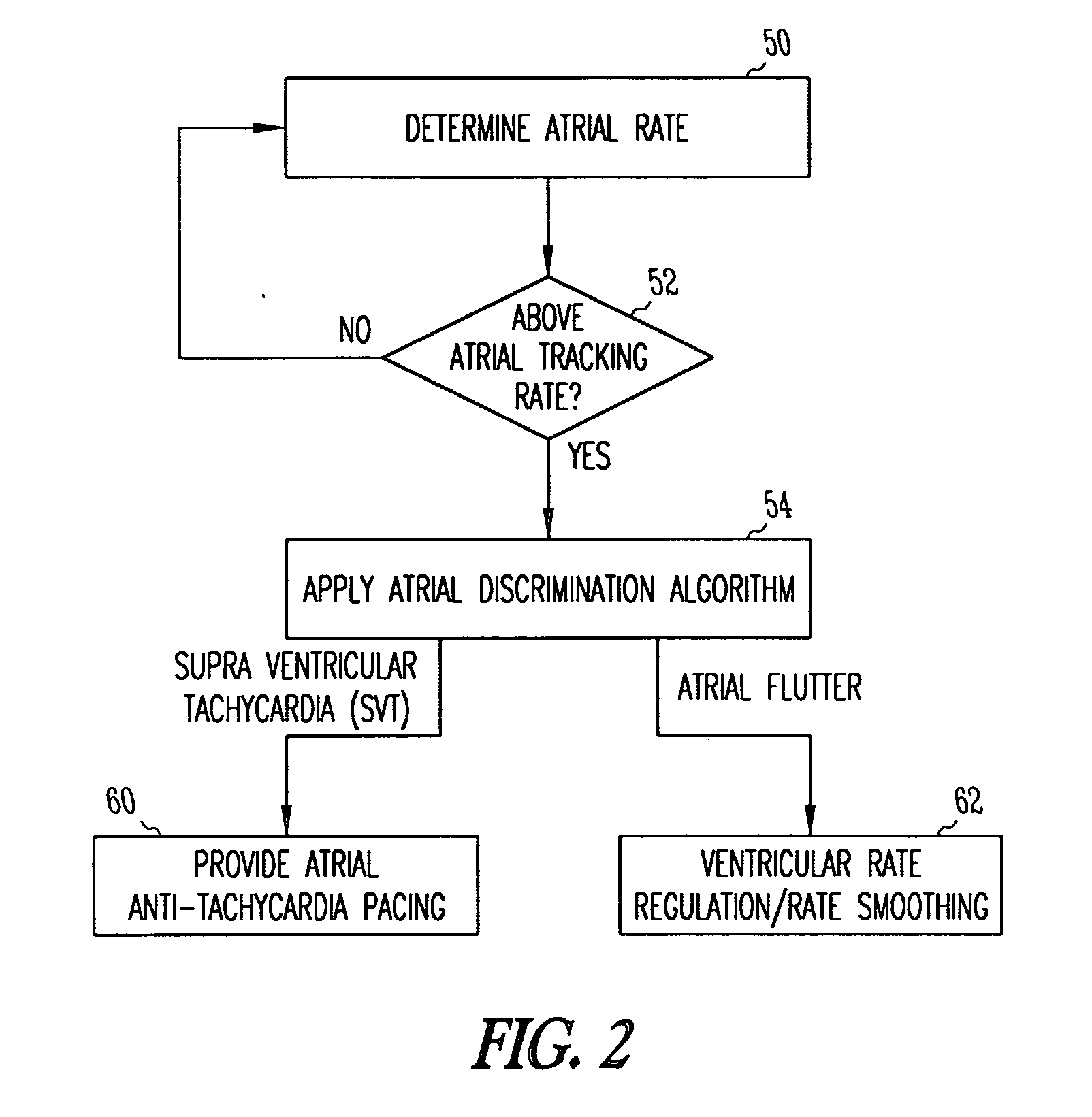
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. The invention may be implemented in a bradycardia pacemaker or other implantable cardiac device. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The discrimination criteria may be, for example, rate-based or morphology based. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. For example, antitachycardia pacing may be provided to the heart in response to the detection of a relatively lower rate supraventricular tachycardia / other atrial flutter, whereas another pacing control, e.g., ventricular pacing, such as ventricular rate regulation or Rate Smoothing, may be applied if a more rapid rate supraventricular tachycardia / fast atrial flutter is identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
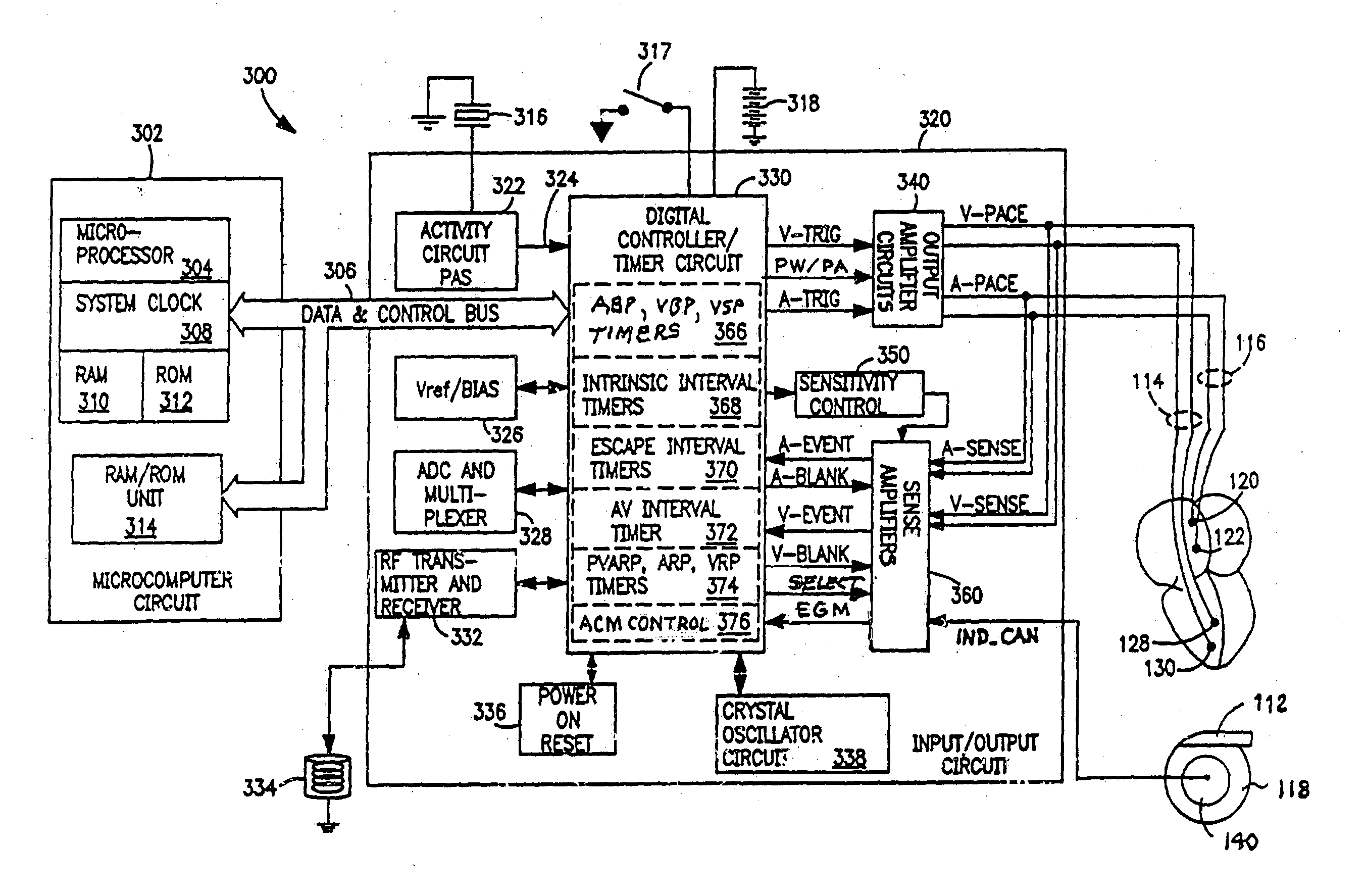
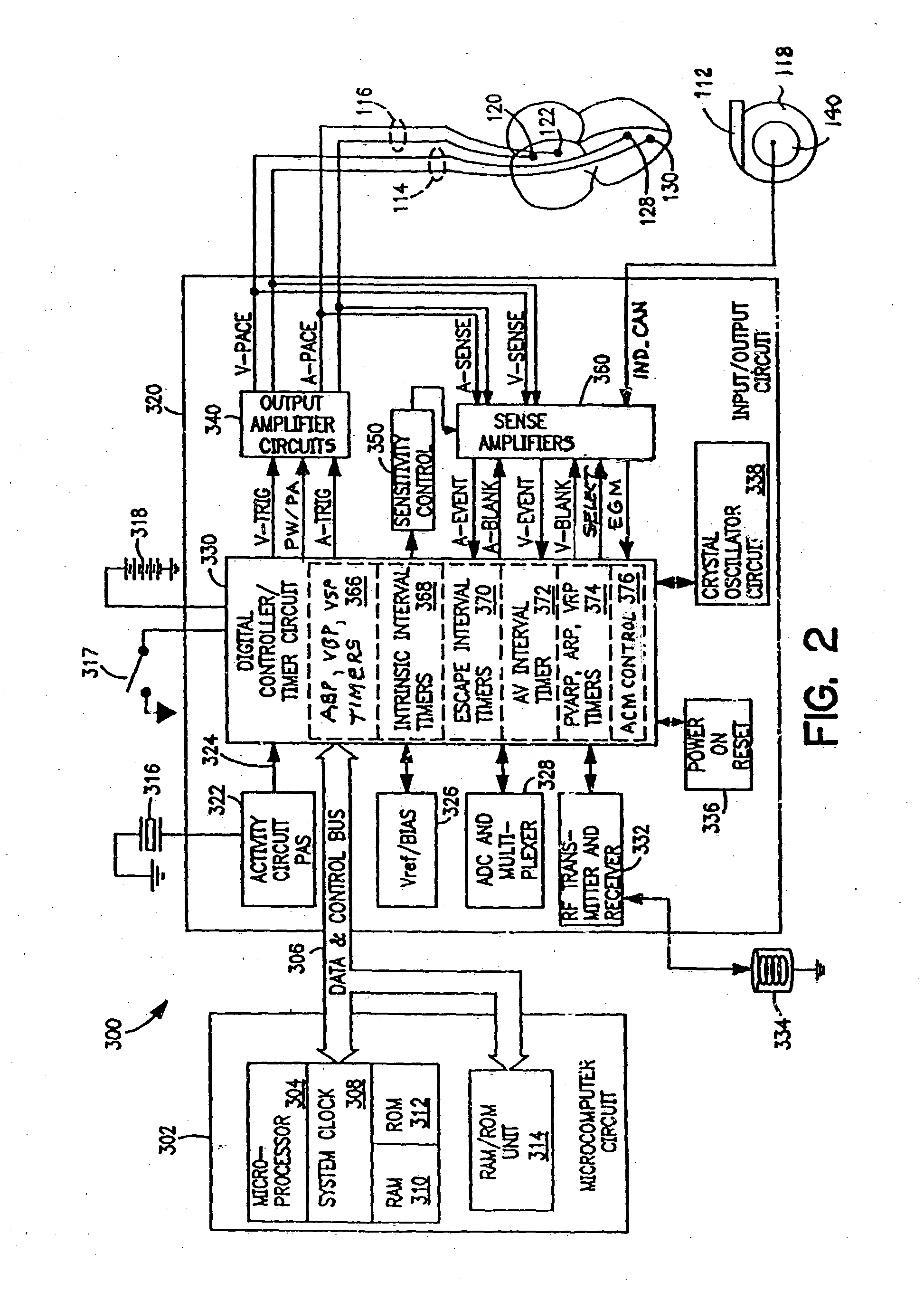
Atrial capture management during atrial and ventricular pacing
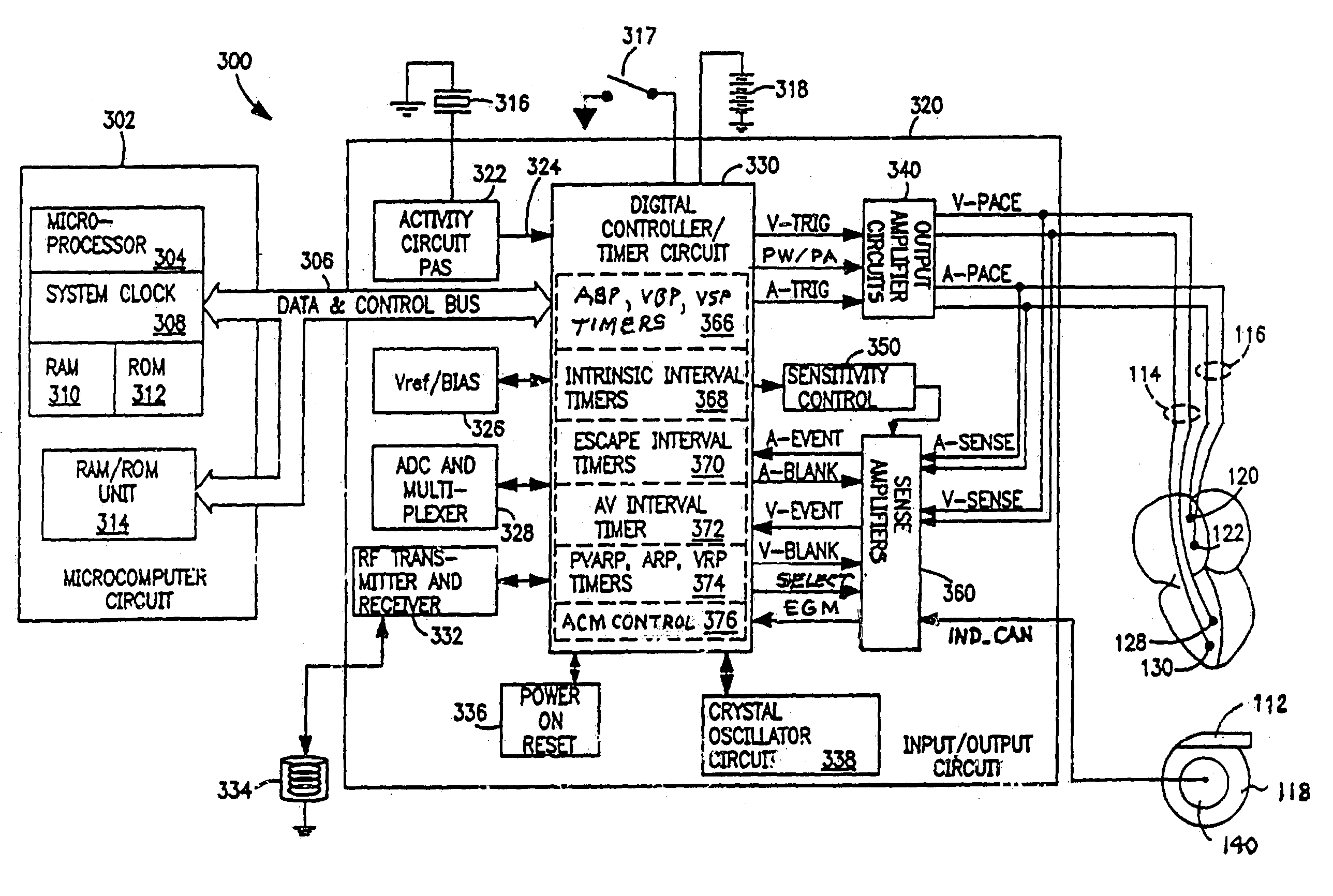
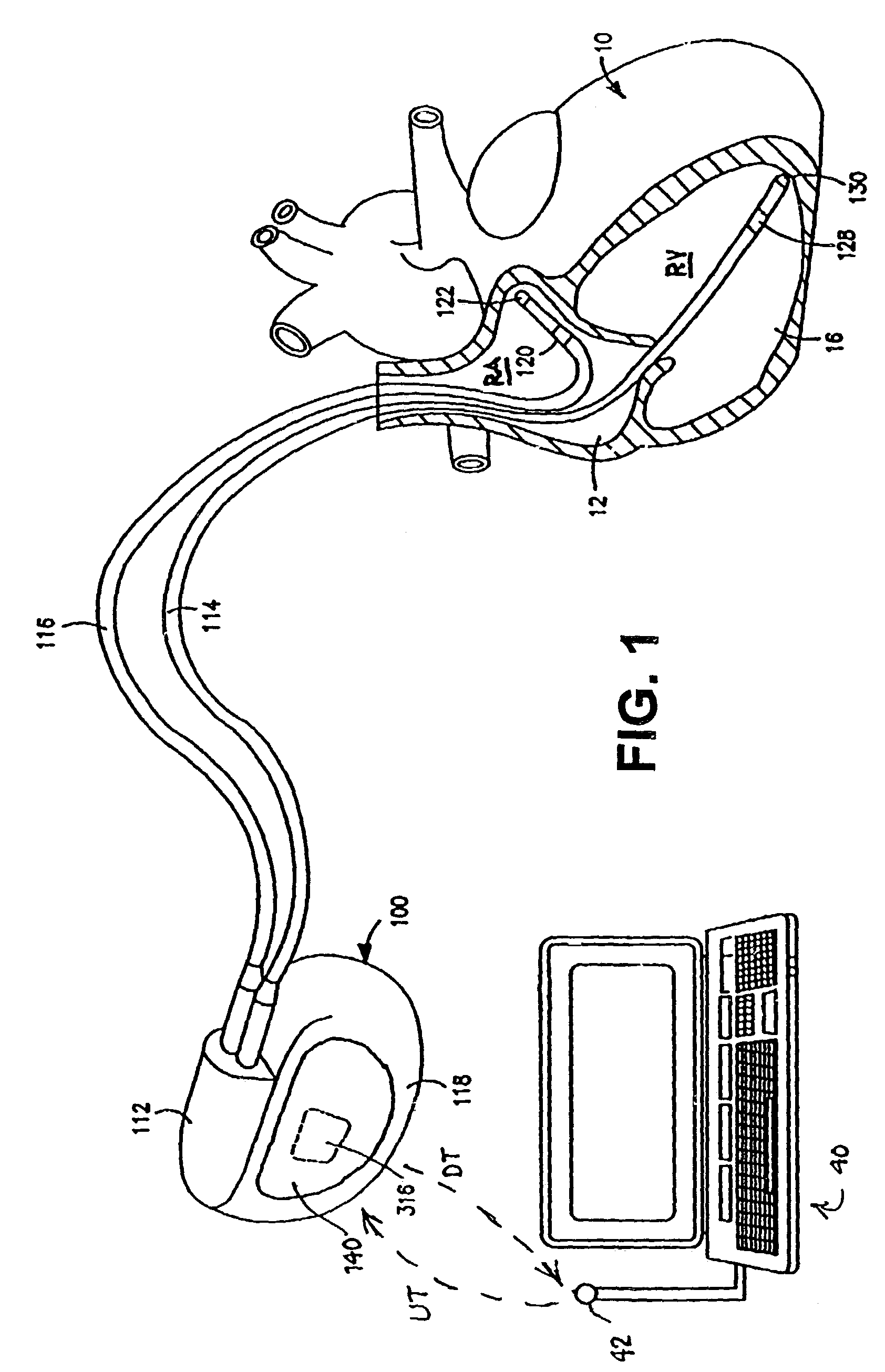
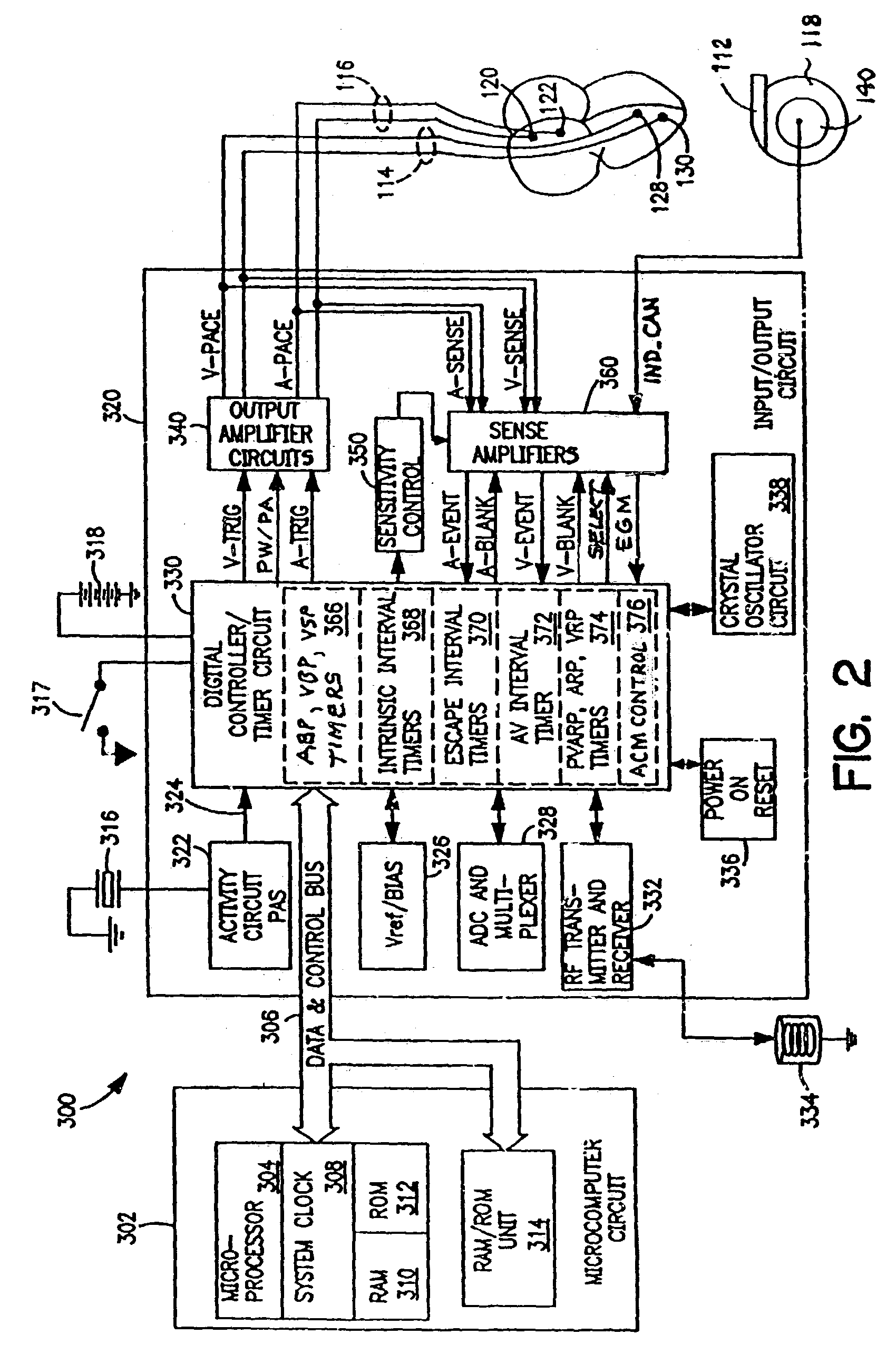
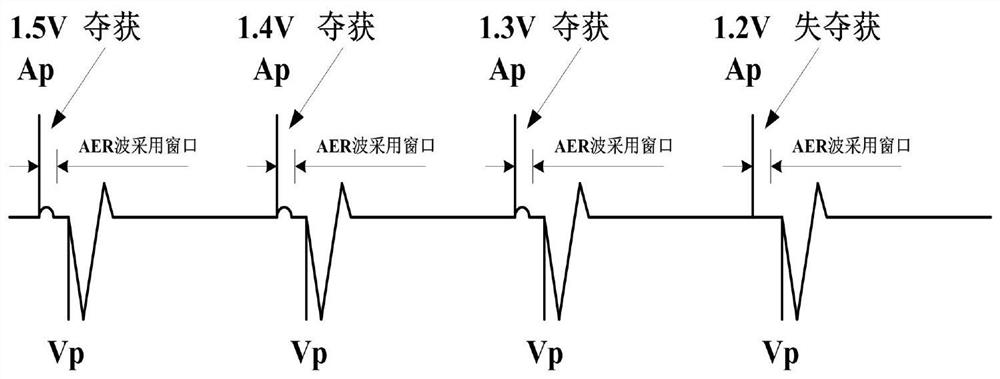
In an atrial pacing system, the A-PACE pulse energy, defined by the pulse width and pulse amplitude, sufficient to reliably capture the atrium without being wasteful of battery energy is periodically determined in accordance with atrial capture management (ACM) algorithms. The ACM algorithms allow a slow intrinsic atrial heart rate that is suppressed by delivered A-PACE pulses resulting in A-CAPTURE and that occurs when delivered test A-PACE pulses result in ALOC to be detected. ALOC is declared if an A-EVENT of the slow intrinsic atrial heart rate is detected either during an ACM test window timed from the last delivered test A-PACE pulse or during delivery of a sequence of test A-PACE pulses delivered within or defining the ACM test window correlated to the slow intrinsic atrial heart rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Apparatus and method for treating ventricular tachyarrhythmias
InactiveUS20050149135A1Heart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsAtrial cavityVentricular Tachyarrhythmias
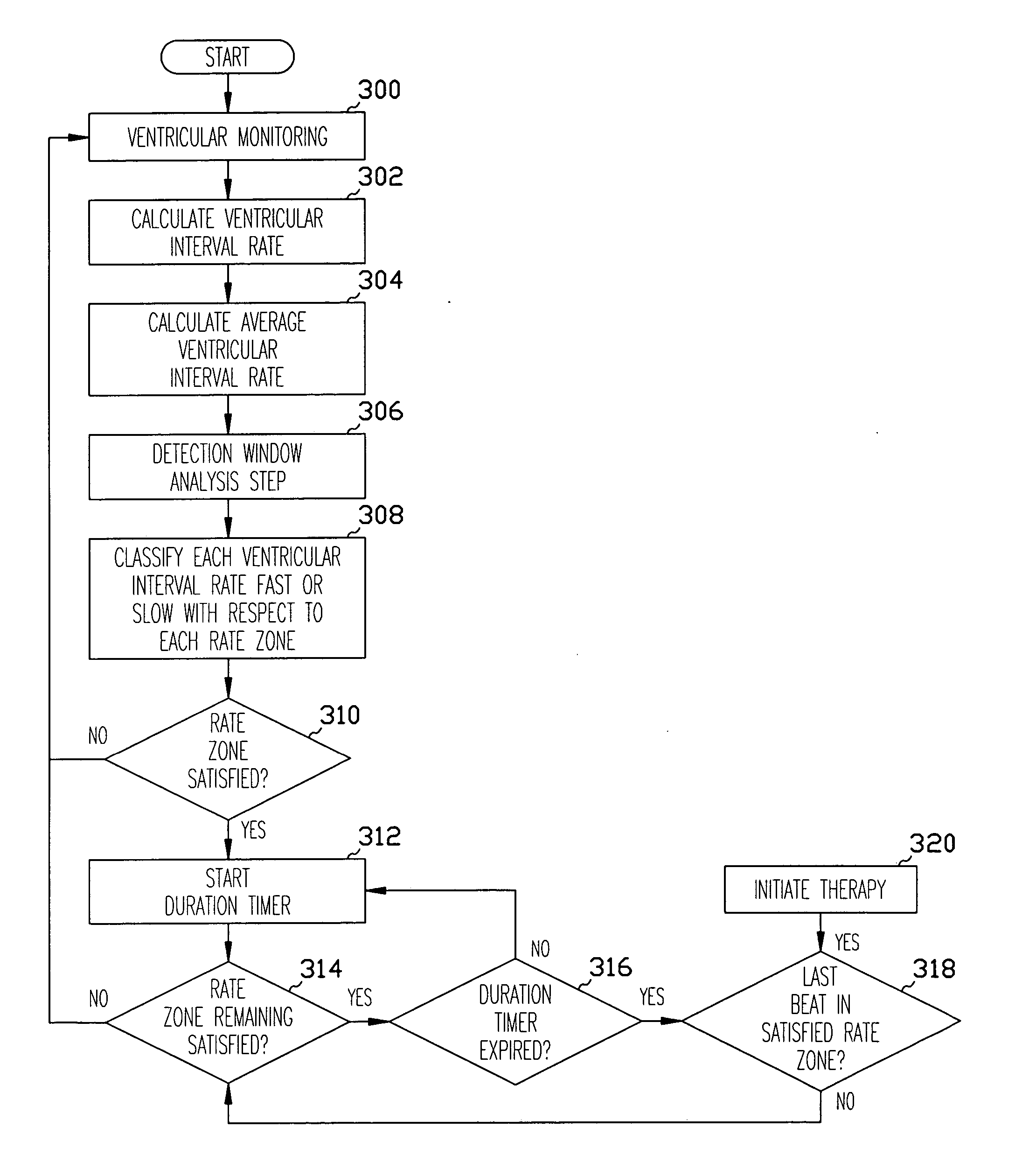
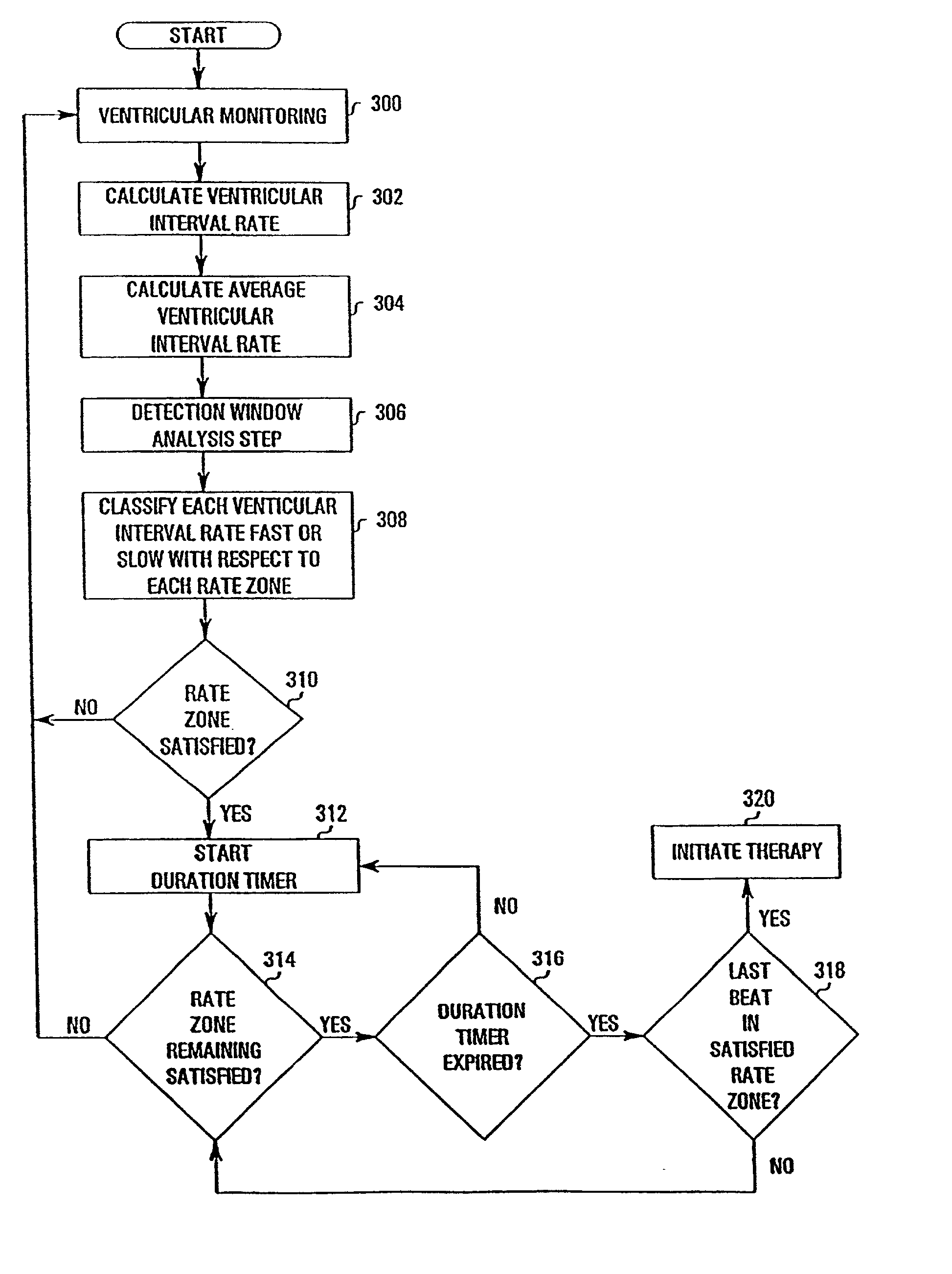
A system and method for selectively treating a ventricular tachycardia based on sensed atrial and ventricular intervals from the patient's heart. A detection window of the ten most recent atrial and ventricular intervals are analyzed for the occurrence of either tachycardia or fibrillation. When a majority of the sensed intervals are satisfied, the apparatus starts a duration time interval. Ventricular intervals and atrial intervals are compare, ventricular interval greater than the atrial interval by a bias factor the system delivers tachycardia therapy to the heart. Alternatively, the method withholds tachycardia therapy to the heart when the atrial rate is classified as atrial fibrillation and the ventricular response is unstable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Atrial capture management during atrial and ventricular pacing
In an atrial pacing system, the A-PACE pulse energy, defined by the pulse width and pulse amplitude, sufficient to reliably capture the atrium without being wasteful of battery energy is periodically determined in accordance with atrial capture management (ACM) algorithms. The ACM algorithms allow a slow intrinsic atrial heart rate that is suppressed by delivered A-PACE pulses resulting in A-CAPTURE and that occurs when delivered test A-PACE pulses result in ALOC to be detected. ALOC is declared if an A-EVENT of the slow intrinsic atrial heart rate is detected either during an ACM test window timed from the last delivered test A-PACE pulse or during delivery of a sequence of test A-PACE pulses delivered within or defining the ACM test window correlated to the slow intrinsic atrial heart rate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
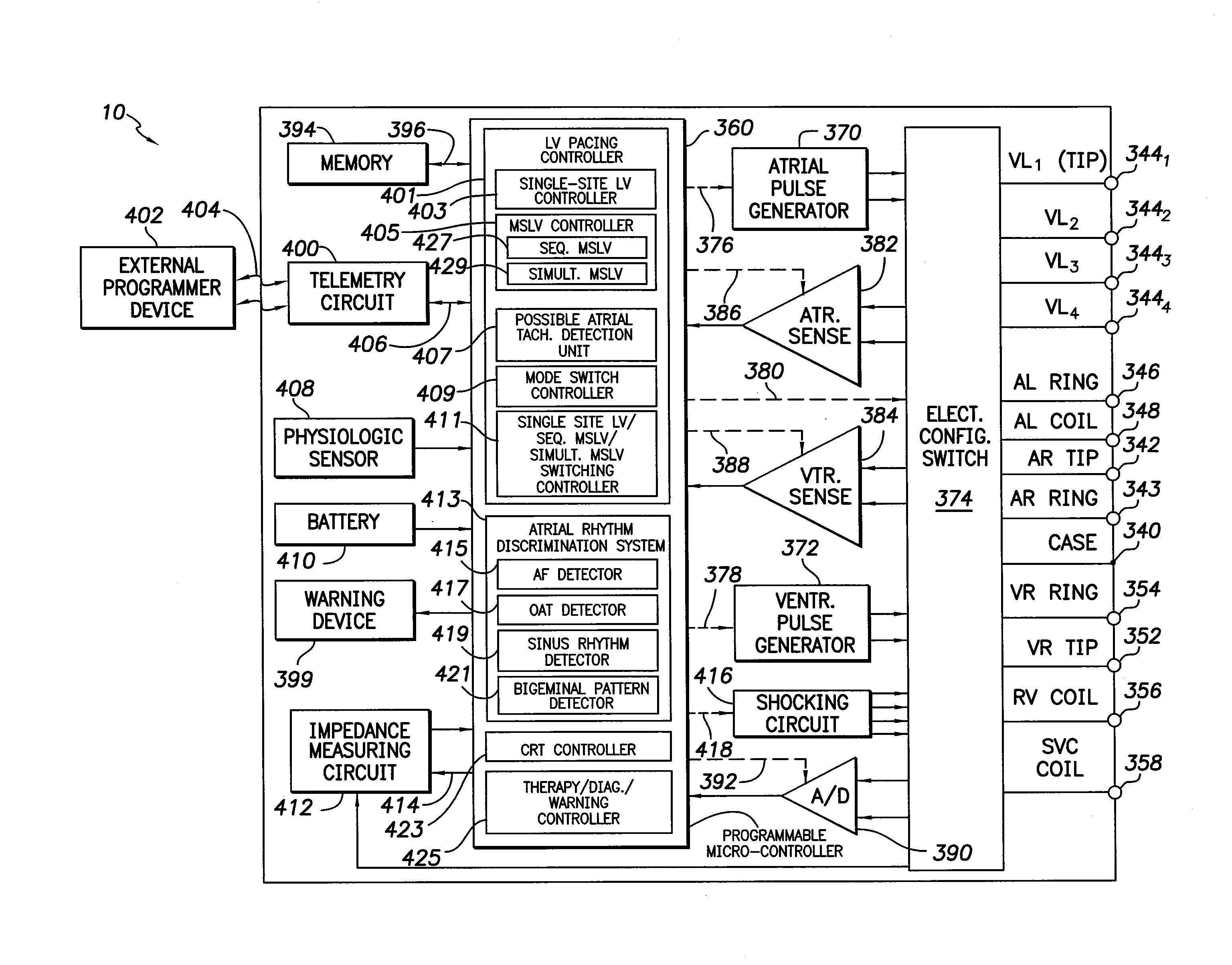
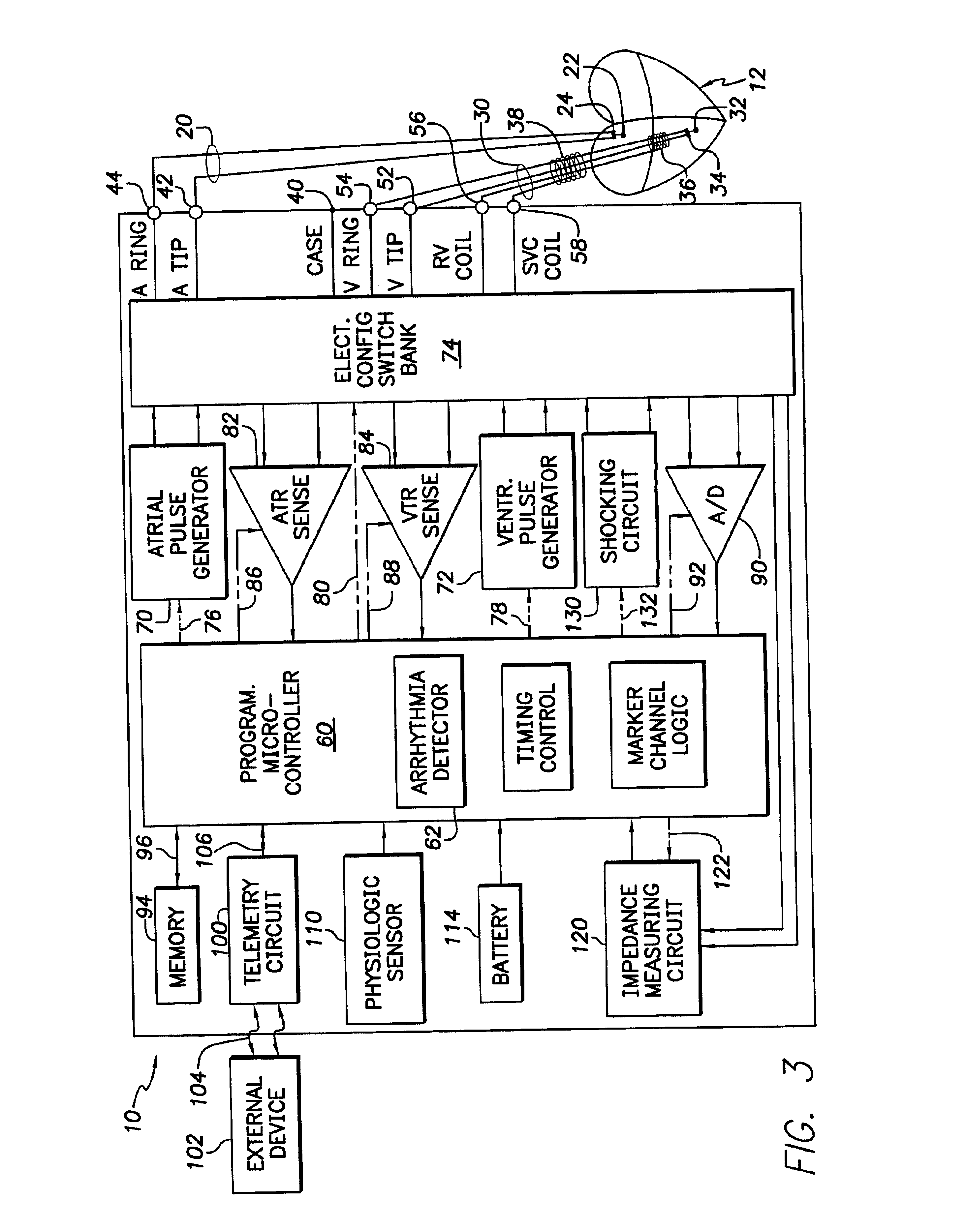
Systems and methods for use by an implantable medical device for controlling multi-site CRT pacing in the presence of atrial tachycardia
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for providing improved specificity for automatic mode switching within an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7062328B1Avoiding inappropriate mode switchingStrong specificityHeart stimulatorsPacemaker mediated tachycardiaCombined use
Techniques for improving the specificity of automatic mode switching (AMS) are provided to prevent inappropriate mode switching and to ensure that mode switching is performed when needed. In one example, improved techniques for calculating a filtered rate interval (FARI) are provided, which help avoid inappropriate mode switching within devices that employ FARI in connection with the determination of the atrial rate. Also, techniques are provided for detecting atrial tachycardia and for distinguishing between a true tachycardia and a false tachycardia (such as pacemaker mediated tachycardia). The techniques described herein for detecting atrial tachycardia and for distinguishing between true and false tachycardia are advantageously employed in connection with AMS but may be used in other circumstances as well. Techniques employed in conjunction with dynamic atrial overdrive (DAO) pacing are also discussed.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Multi-site cardiac stimulation device and method for detecting retrograde conduction
InactiveUS6862477B1Prevent inappropriate arrhythmia detectionImprove responseHeart stimulatorsMulti siteCardiac pacemaker electrode
An implantable cardiac stimulation device, such as a pacemaker, defibrillator and / or cardioverter, and an associated method that provide cardiac stimulation to at least two ventricular stimulation sites, within a single ventricle or across two ventricles. A high intrinsic atrial rate triggers a retrograde conduction detection routine when a high ventricular stimulation rate is sustained for a predetermined number of cycles during an atrial sensing mode. This routine interrupts concurrent stimulation, and alternates the stimulation output to the different ventricular sites.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Apparatus and method for treating ventricular tachyarrhythmias
A system and method for selectively treating a ventricular tachycardia based on sensed atrial and ventricular intervals from the patient's heart. A detection window of the ten most recent atrial and ventricular intervals are analyzed for the occurrence of either tachycardia or fibrillation. When a majority of the sensed intervals are satisfied, the apparatus starts a duration time interval. Ventricular intervals and atrial intervals are compare, ventricular interval greater than the atrial interval by a bias factor the system delivers tachycardia therapy to the heart. Alternatively, the method withholds tachycardia therapy to the heart when the atrial rate is classified as atrial fibrillation and the ventricular response is unstable.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and apparatus for using atrial discrimination algorithms to determine optimal pacing therapy and therapy timing
A system and method which employs atrial discrimination algorithms to distinguish between different atrial arrhythmias occurring in a patient for selecting an optimal pacing therapy corresponding to the type of arrhythmia identified. In response to the detection of an atrial rate above the atrial tracking rate, discrimination criteria are applied to a detected atrial activity signal to distinguish between different types of supraventricular tachycardia, such as fast atrial flutter and other atrial flutter at a relatively slower rate, which may be occurring in the patient. The pacer is controlled to provide pacing therapy to a heart in a manner corresponding to the type of supraventricular tachycardia identified. The output of an atrial discrimination algorithm may be tracked and the trend thereof used to improve therapy timing. Various embodiments are disclosed herein.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
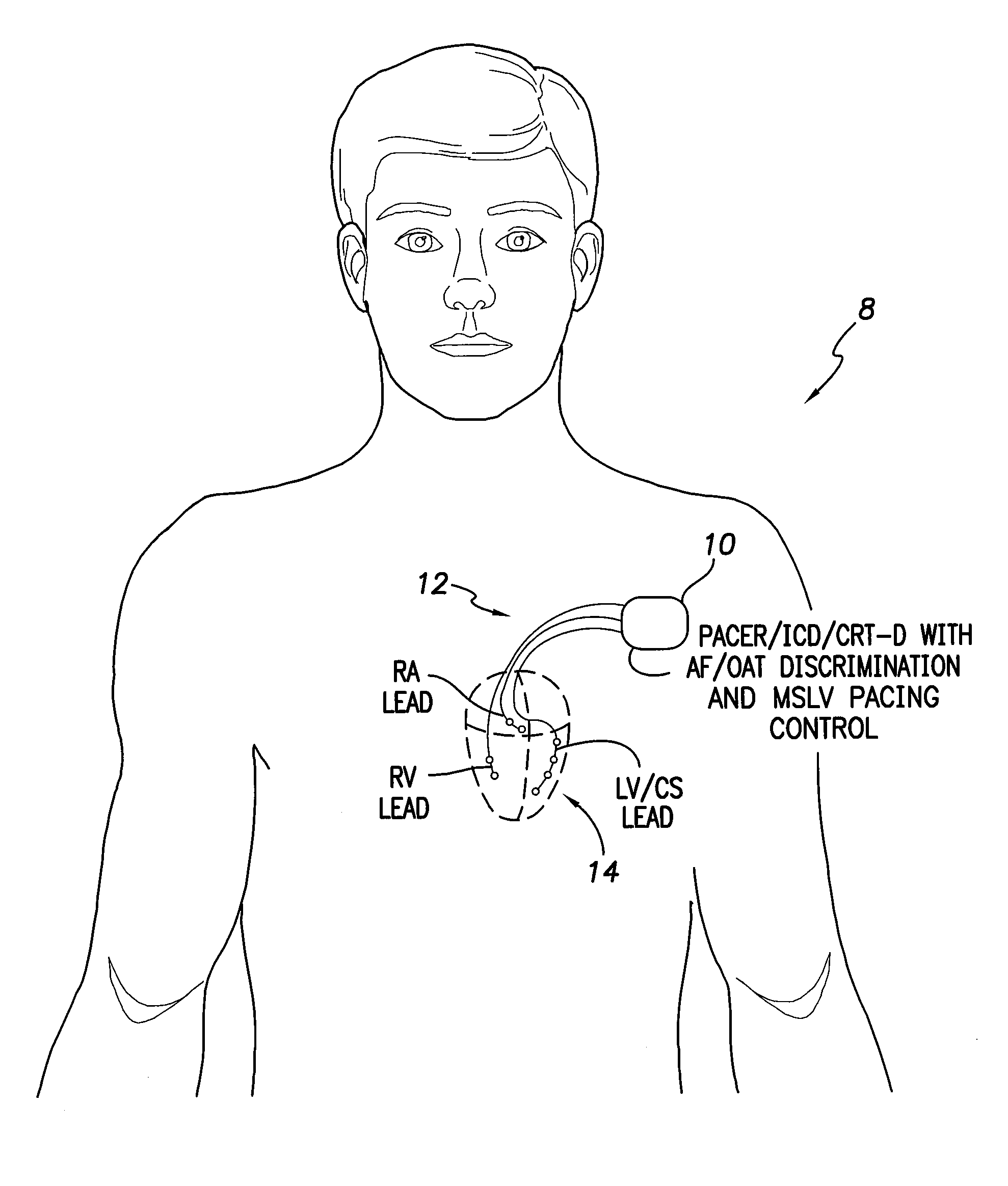
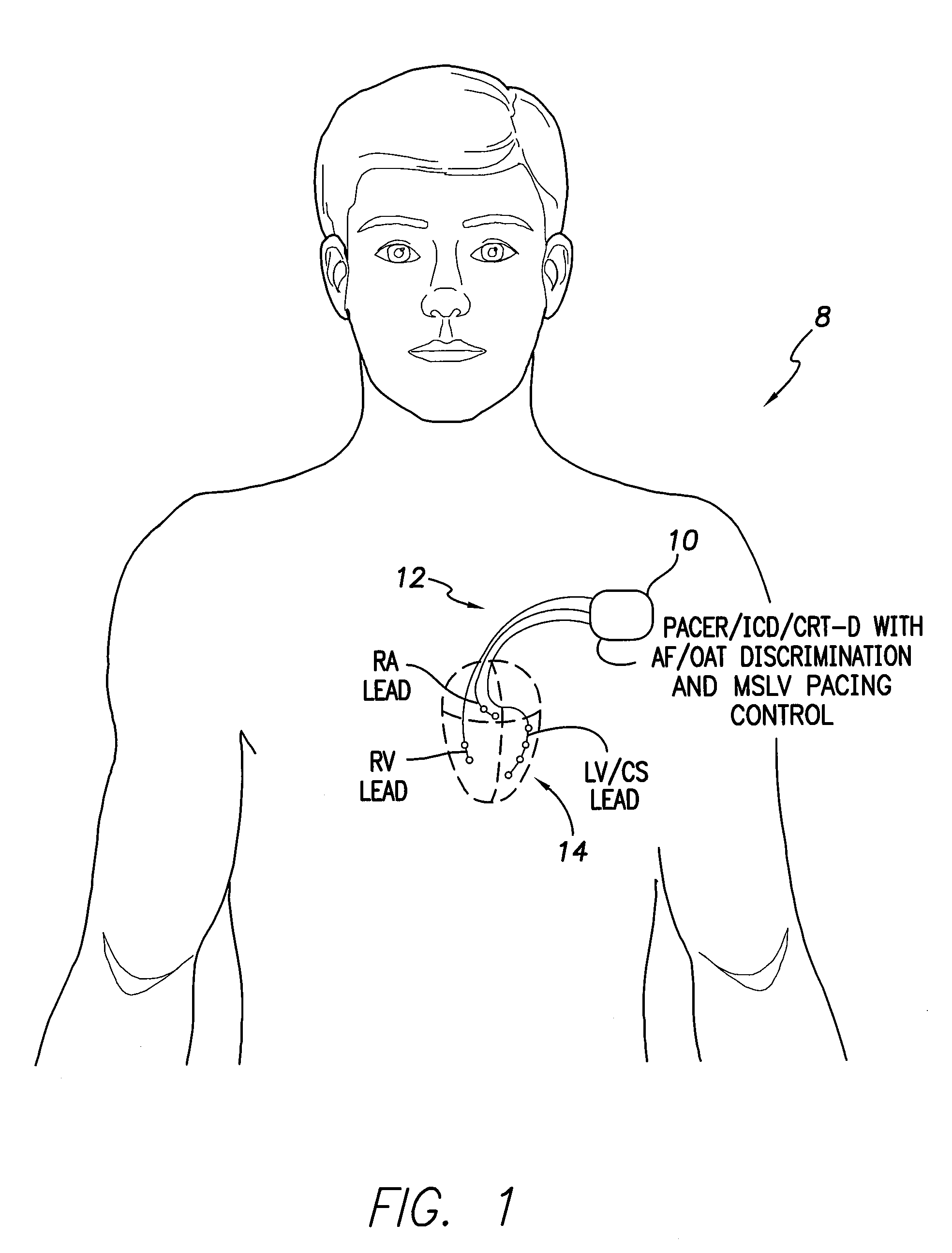
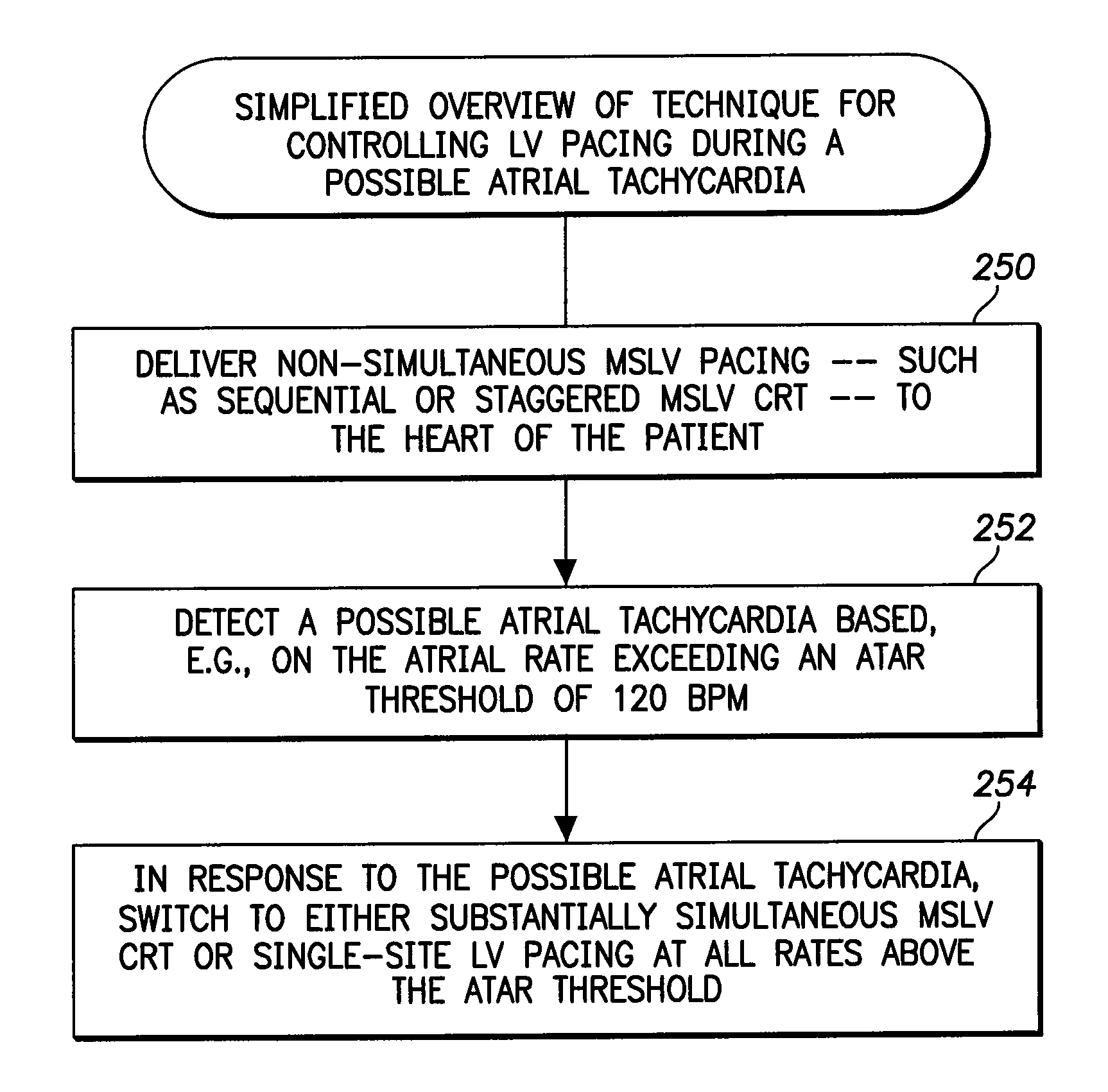
Systems and Methods for Use by an Implantable Medical Device for Controlling Multi-Site CRT Pacing in the Presence of Atrial Tachycardia
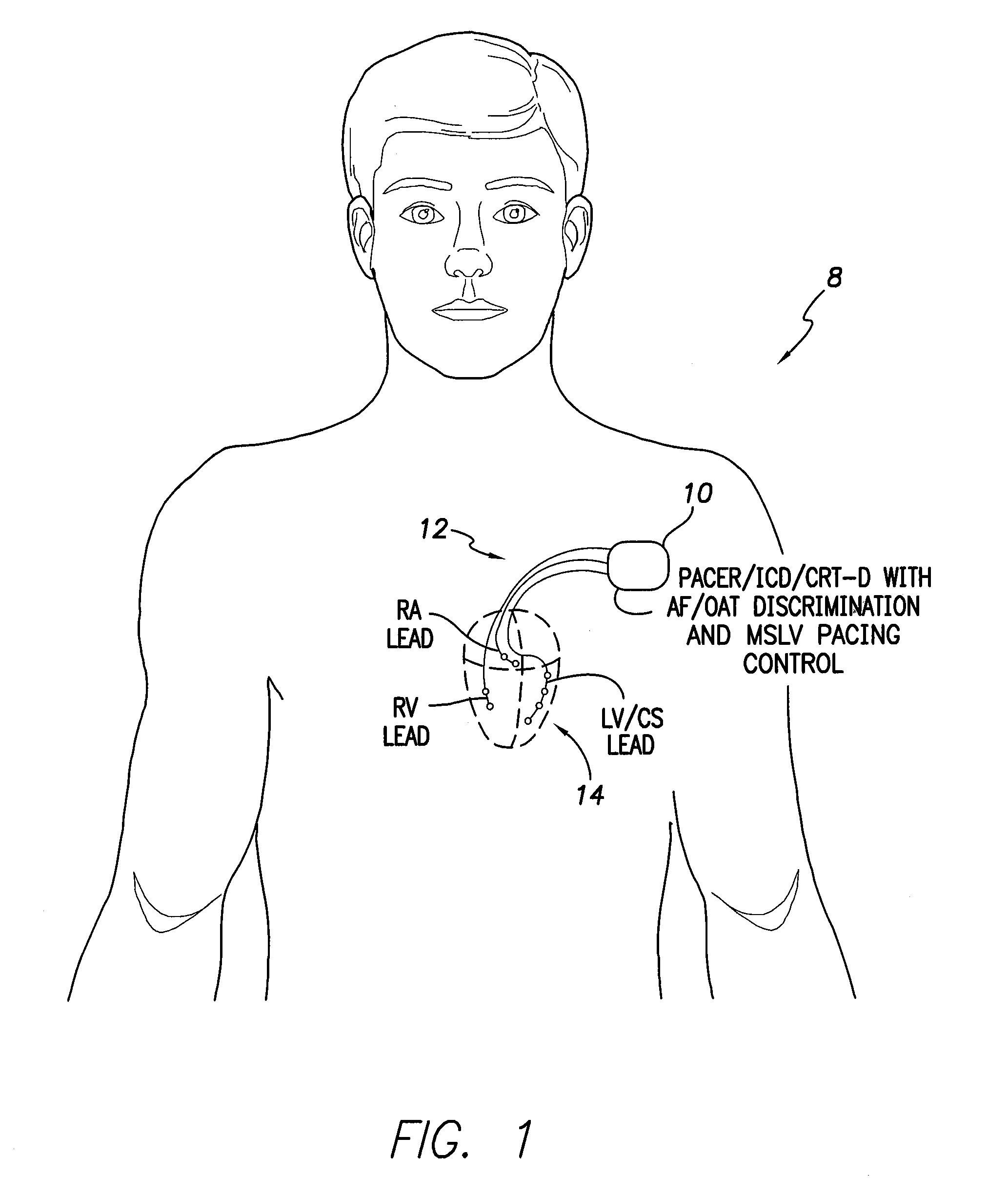
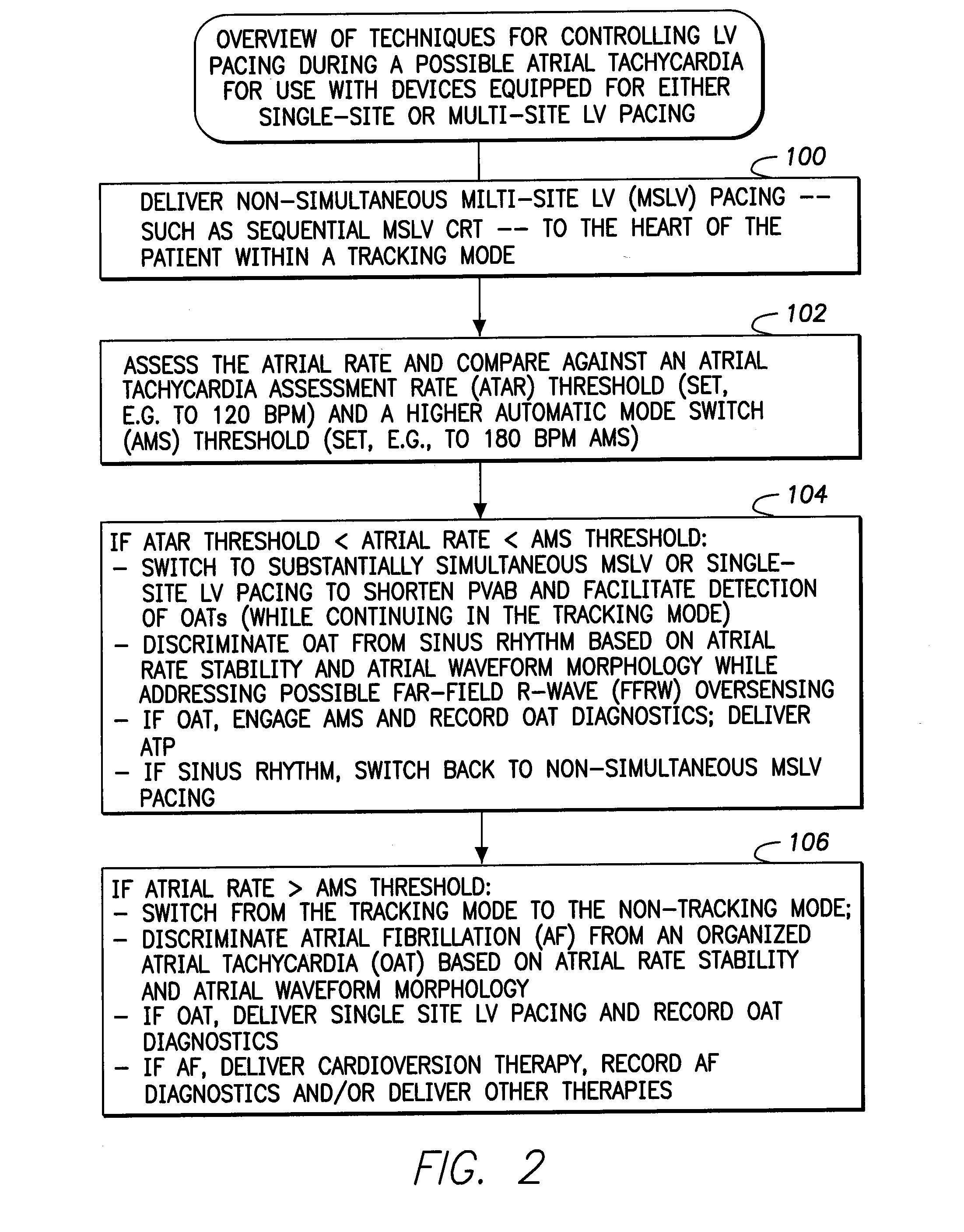
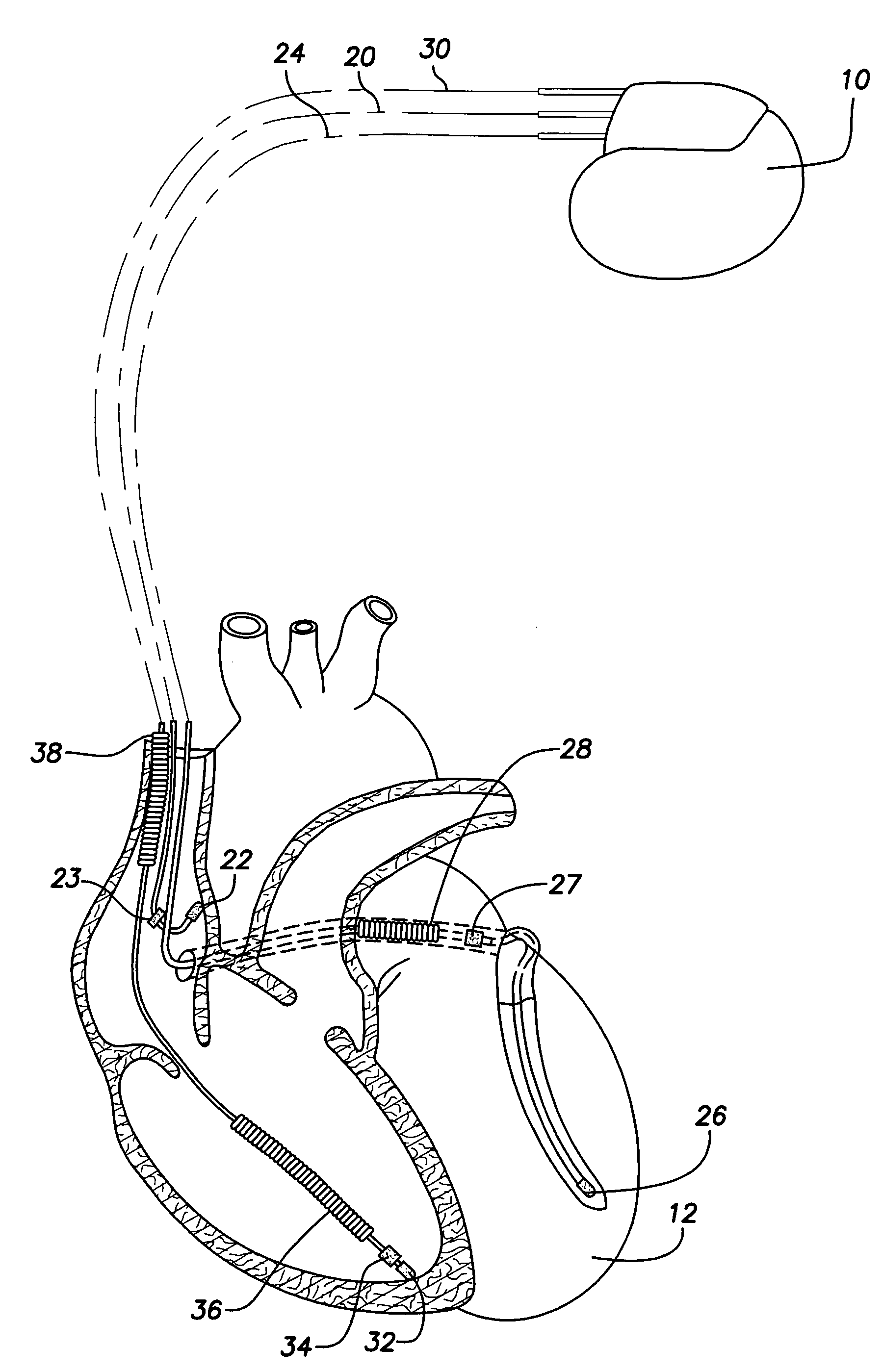
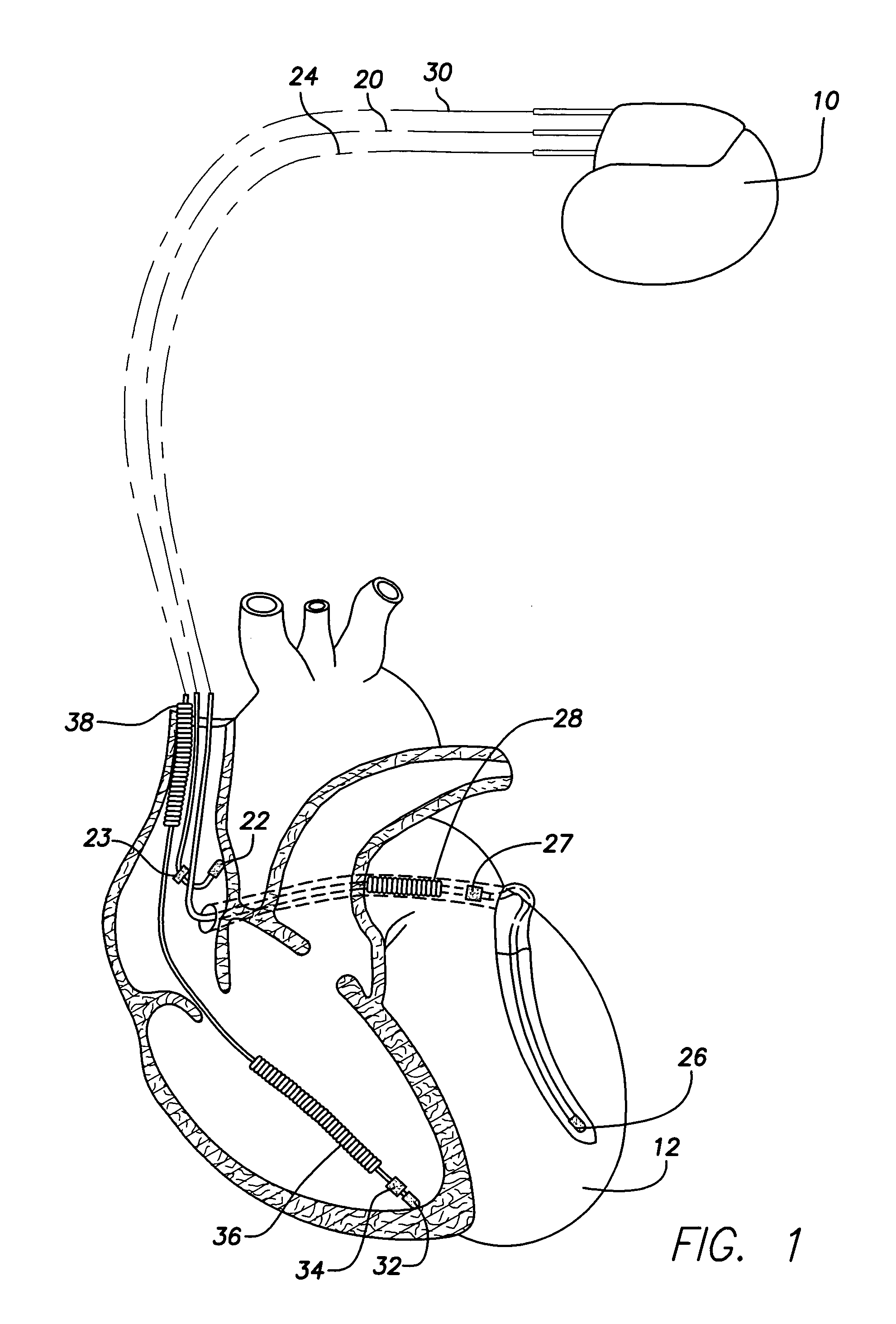
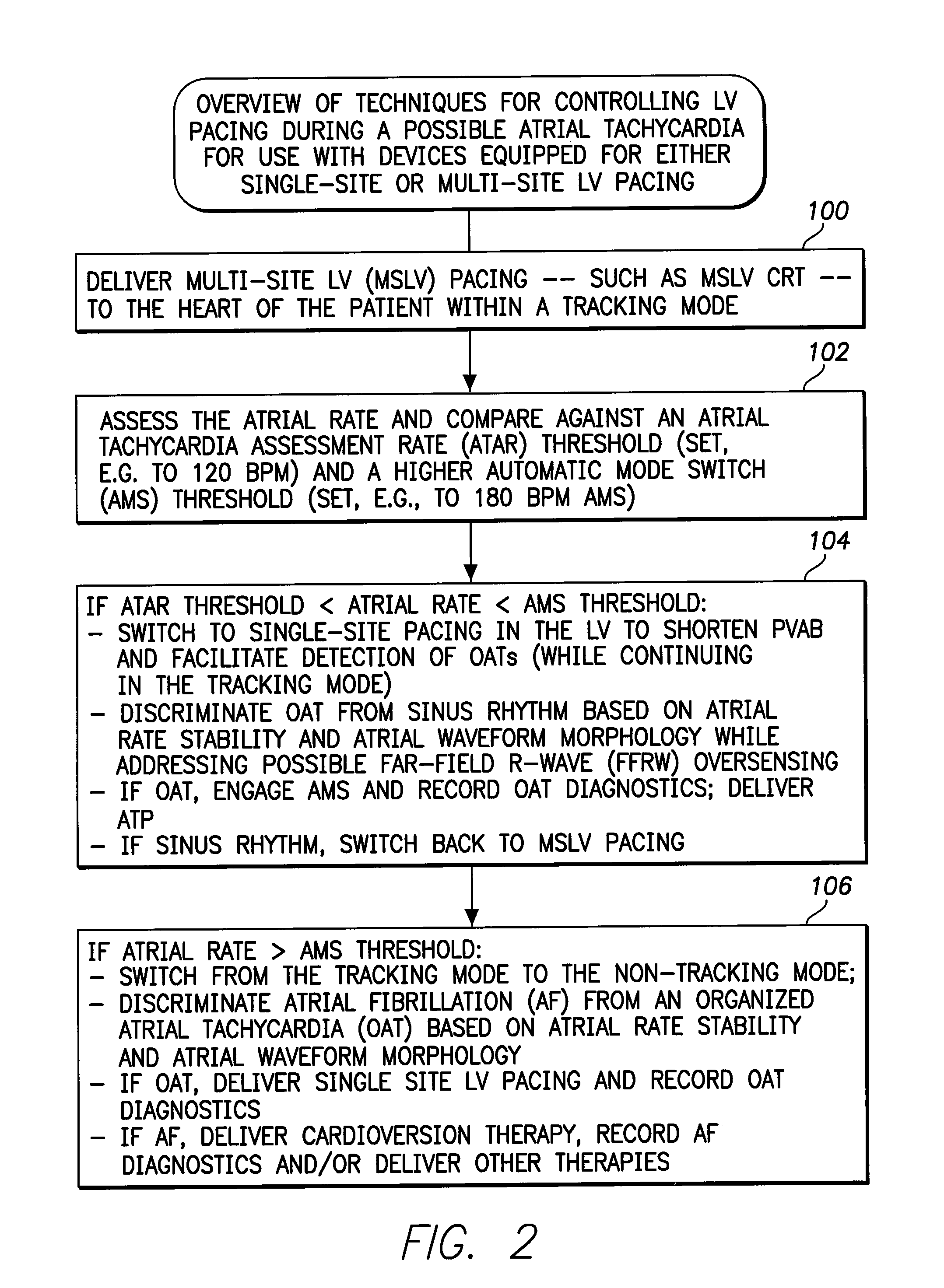
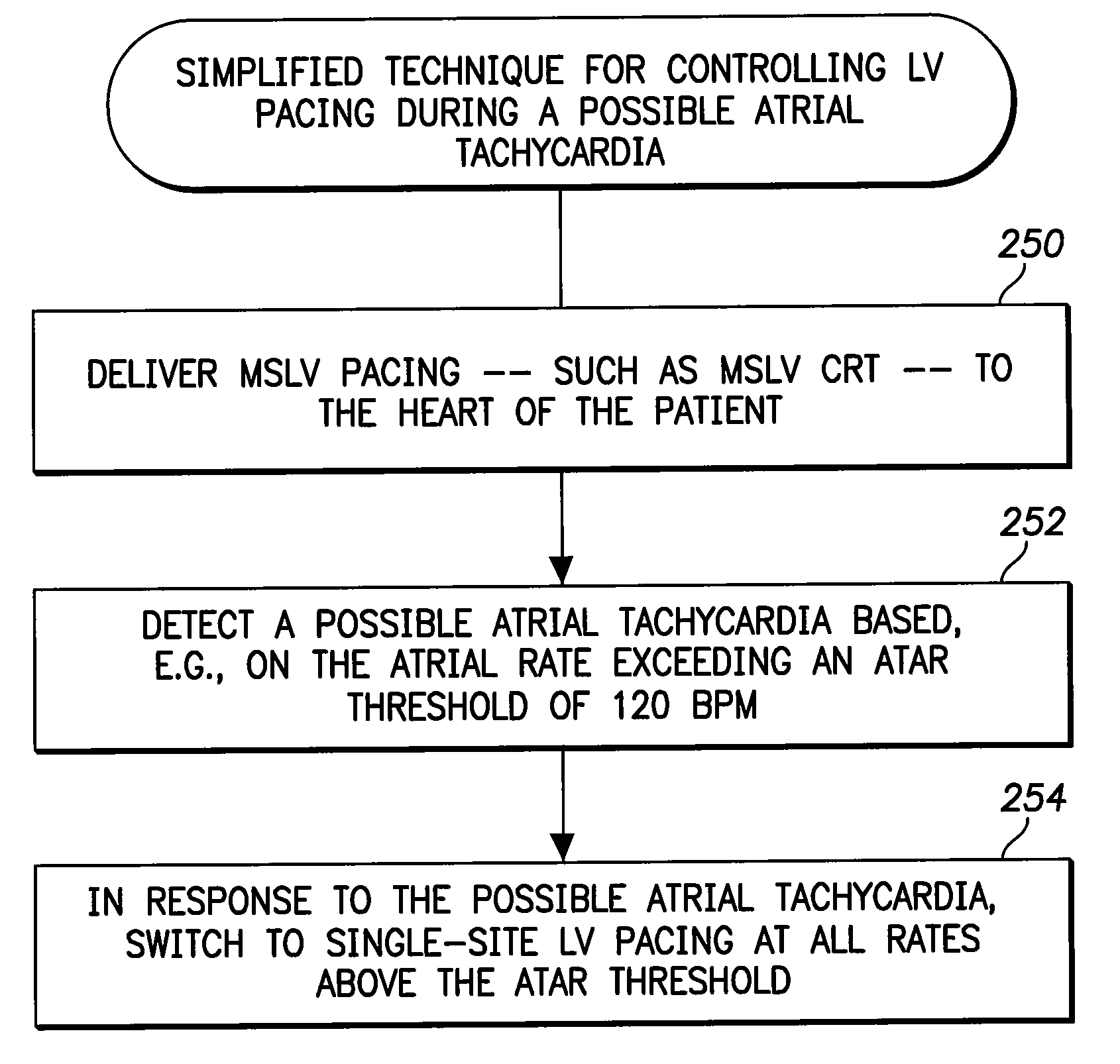
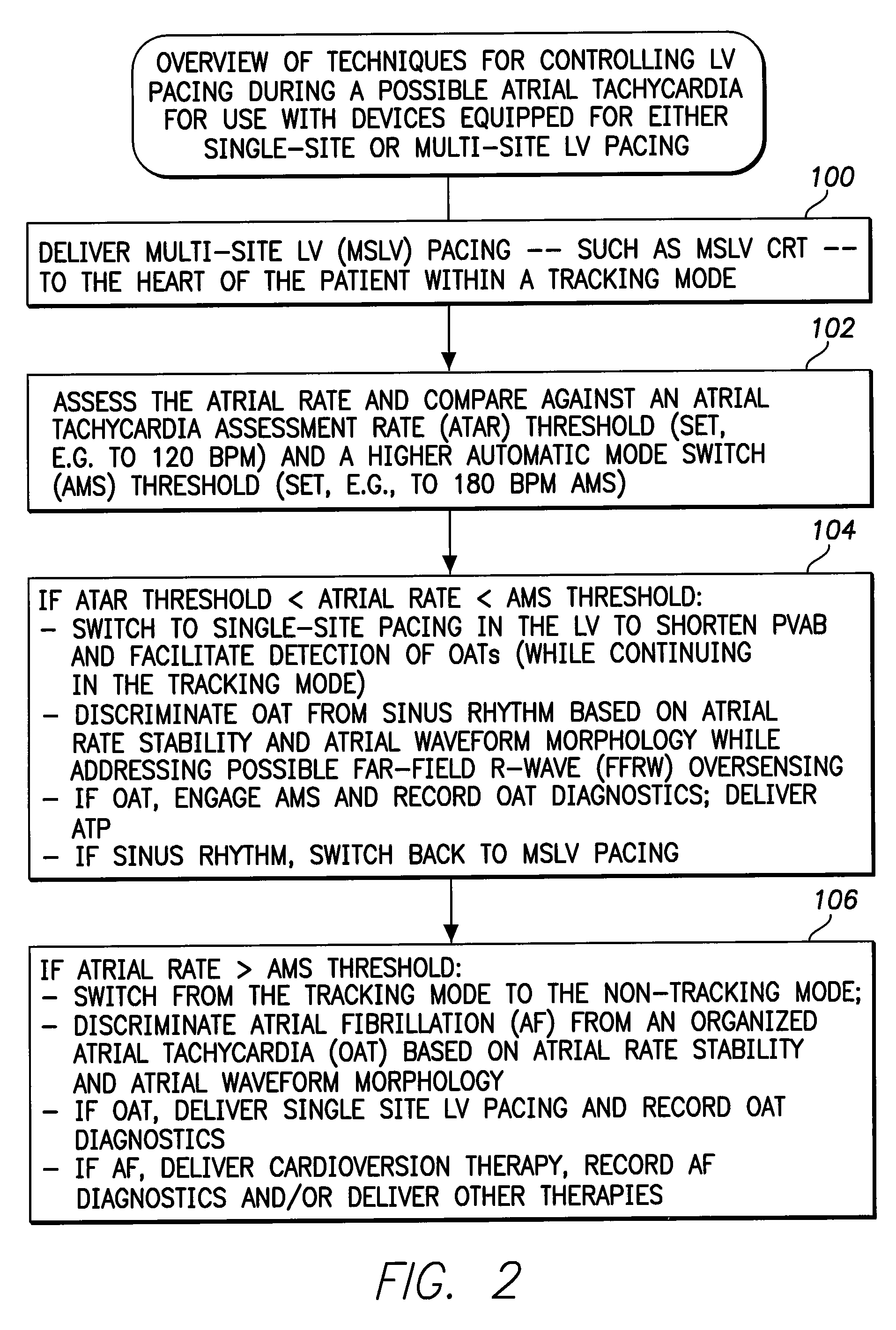
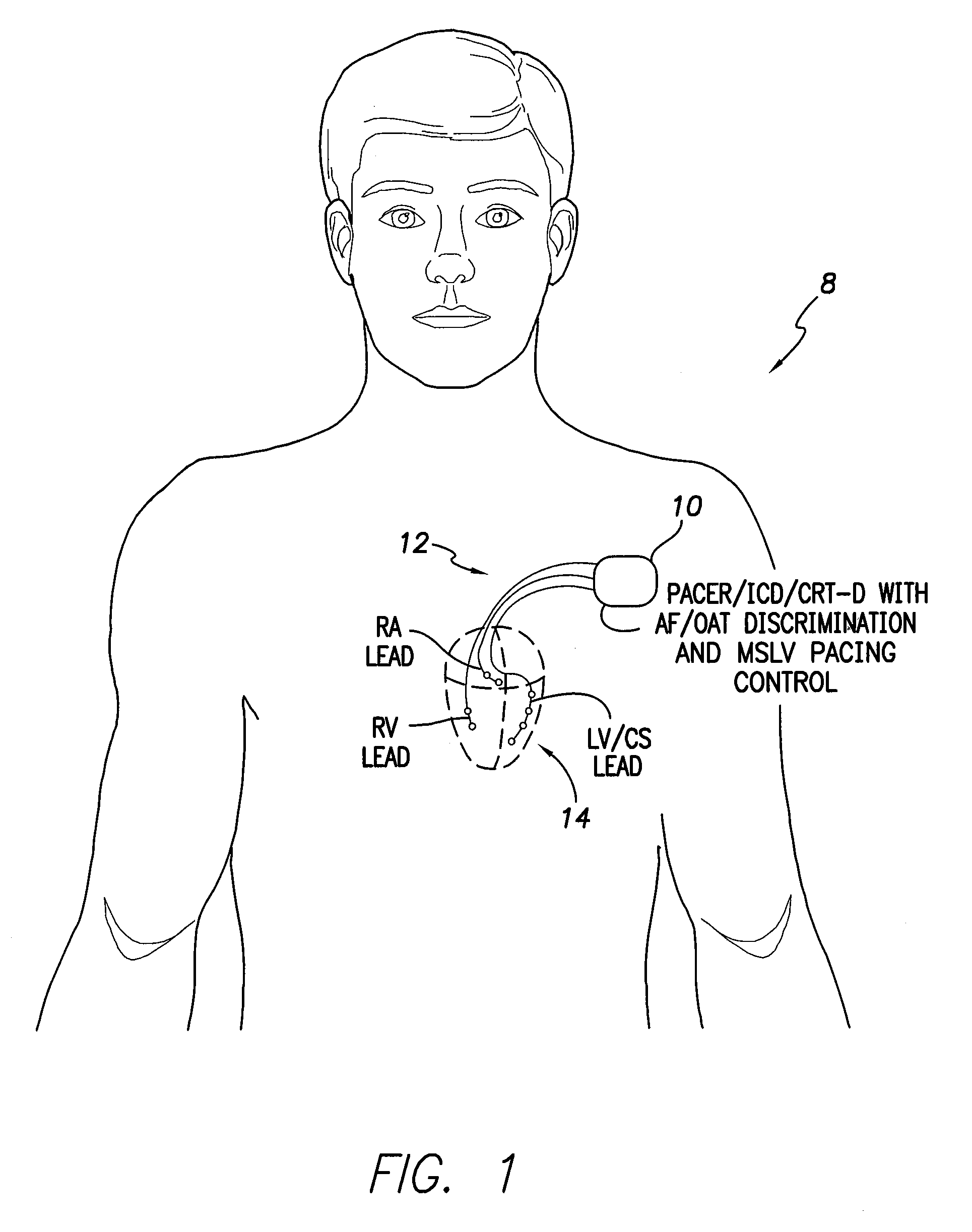
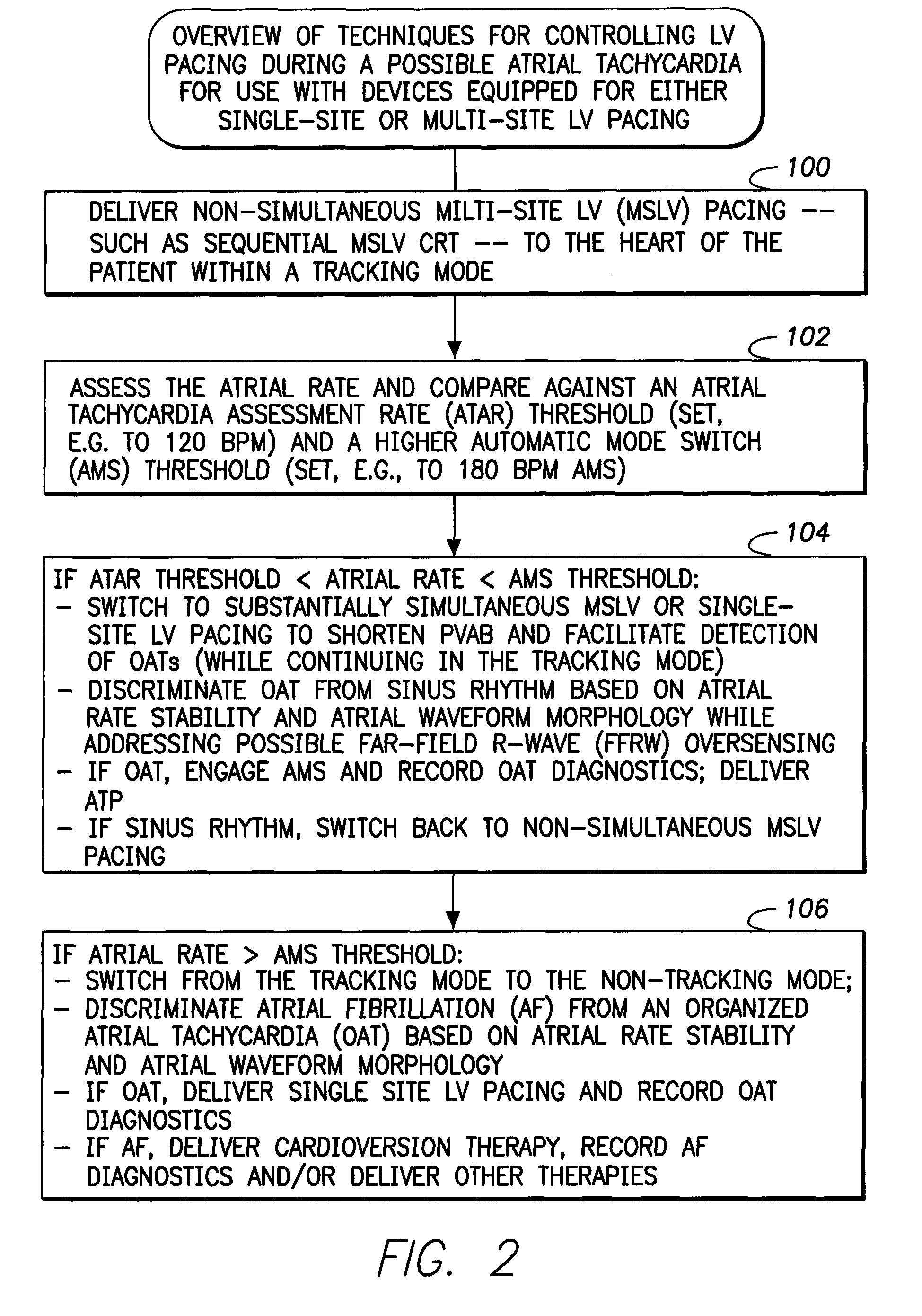
Systems and methods are provided for use by implantable medical devices equipped to deliver multi-site left ventricular (MSLV) pacing. MSLV is associated with a relatively long post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) period that might limit the detection of pathologic rapid organized atrial tachycardias (OAT). In one example, MSLV cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing is delivered within a tracking mode. A possible atrial tachycardia is detected based on the atrial rate exceeding an atrial tachycardia assessment rate (ATAR) threshold. The device then switches to single-site LV pacing, thereby effectively shortening the PVAB to detect additional atrial events that might otherwise be obscured, and thereby permitting the device to more reliably distinguish organized atrial tachycardias (such as atrial flutter) from sinus tachycardia. The device may also employ an automatic mode switch (AMS) threshold that is set higher than the ATAR threshold for use in switching from tracking modes to nontracking modes.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
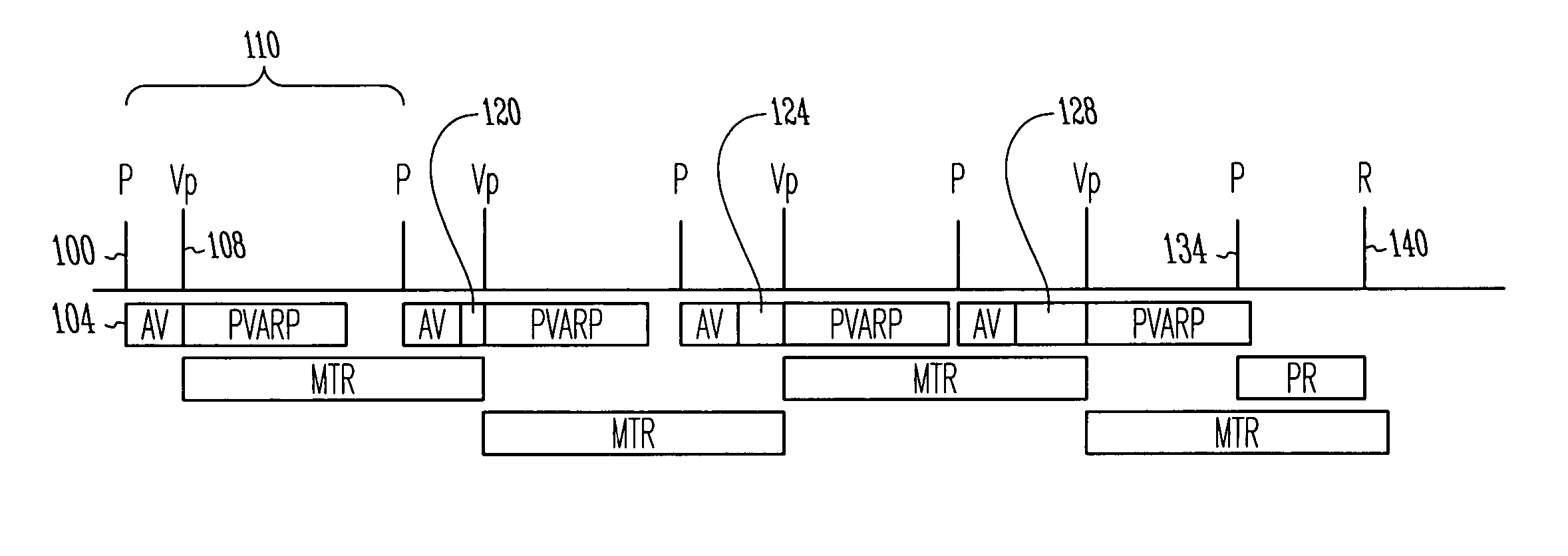
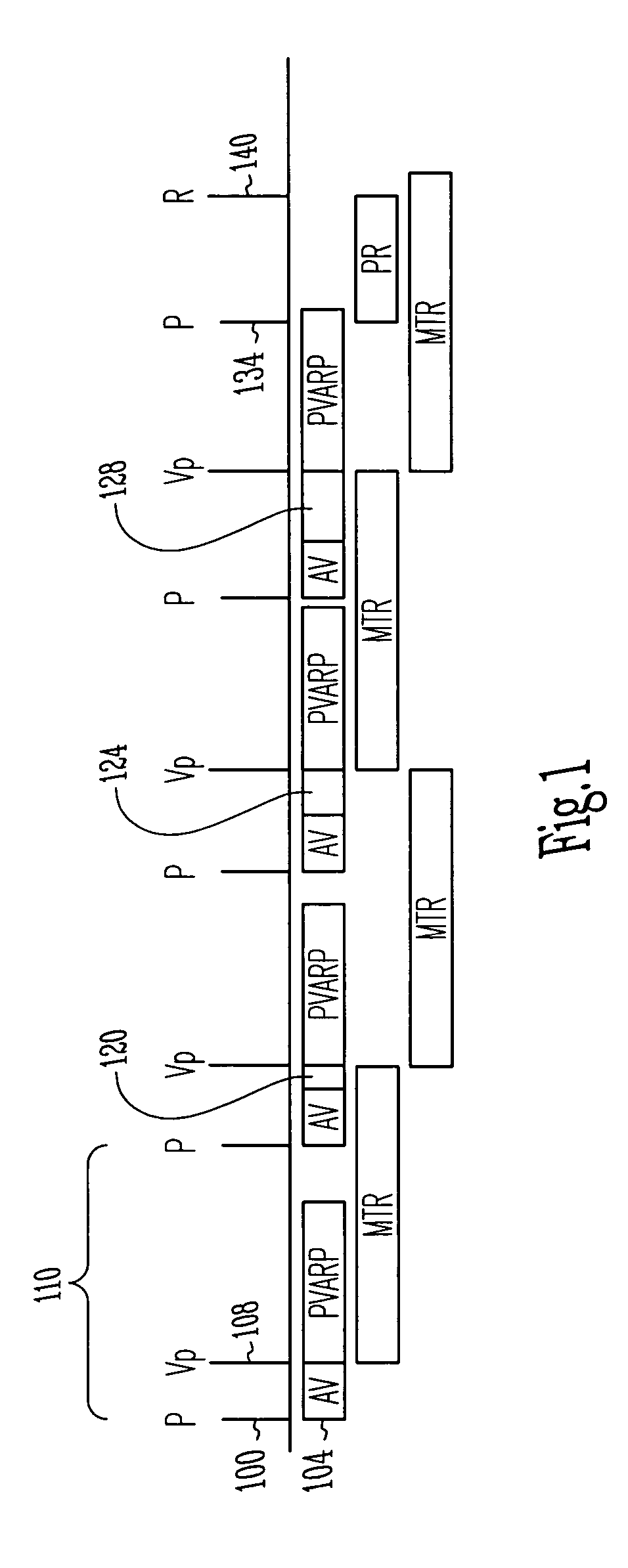
Cardiac rhythm management system with maximum tracking rate (MTR) hysteresis
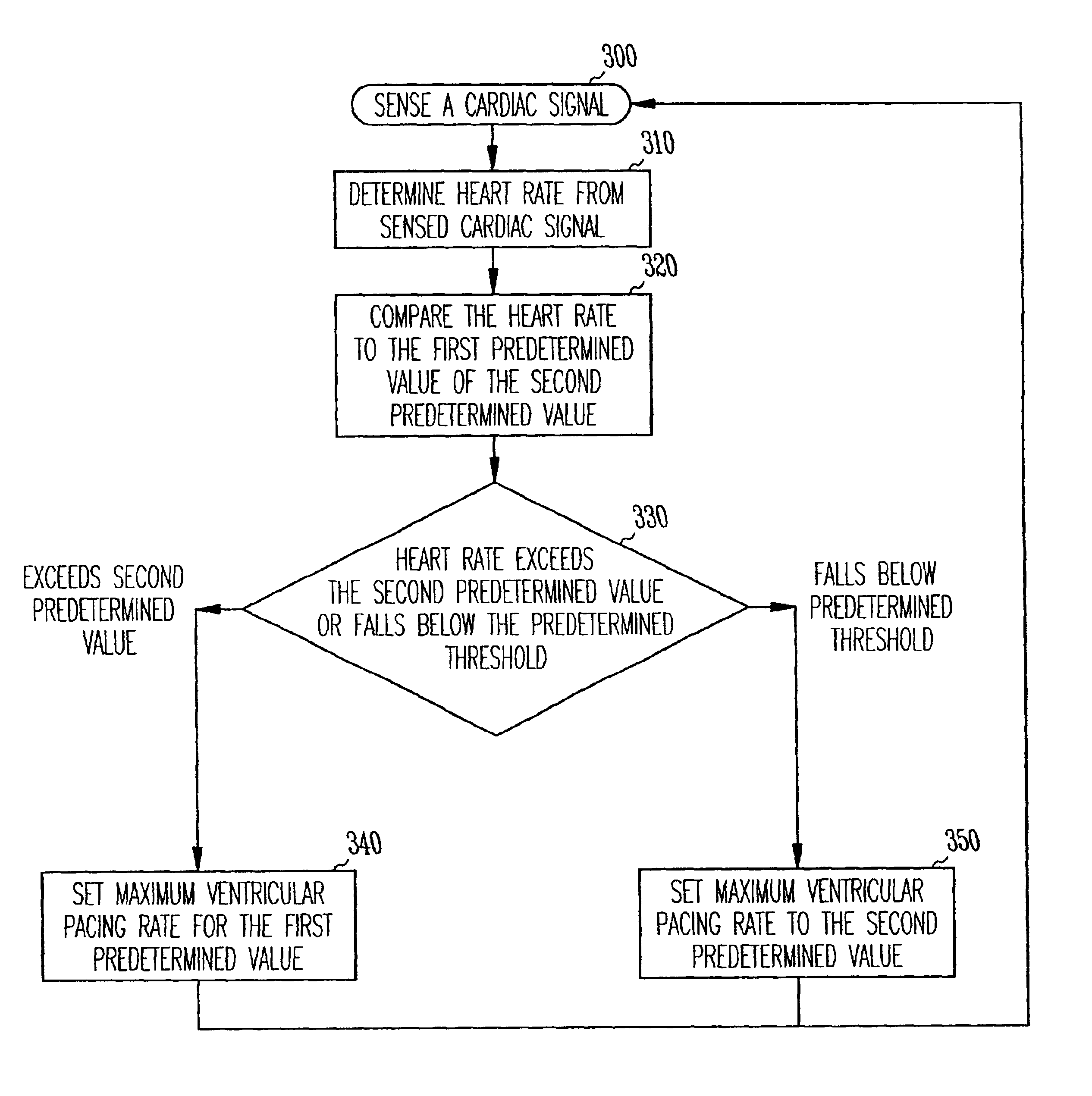
A cardiac rhythm management system provides both a safe maximum pacing rate limit and a physiological maximum pacing rate limit. The present subject matter provides a solution to problems associated with the use of a single maximum tracking rate (MTR). In one embodiment, the present subject matter utilizes two MTRs, where the first is a normal MTR and the second is a hysteresis MTR. In one embodiment, the hysteresis MTR is set higher than the normal MTR. The hysteresis MTR functions as a maximum pacing rate limit while tracking an atrial rate until the atrial rate exceeds the hysteresis MTR limit. When the atrial rate exceeds the hysteresis MTR limit, the maximum pacing rate limit is set to the normal MTR. Once the atrial rate falls below a predetermined threshold, the maximum pacing rate limit is set to the hysteresis MTR. The predetermined threshold may be set to the normal MTR, the hysteresis MTR, or other rates. In one embodiment, changing the maximum pacing rate limit in this fashion allows for uninterrupted pacing treatment for patients, such as congestive heart failure (CHF) patients, who may display fast but physiologically normal heart rates and need cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) at such fast heart rates. Such a pacing treatment provides for a more rapid and natural maximum pacing rate limit for the patient, while still protecting the patient from being paced at abnormally high rates.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Control of cardiac arrhythmia by vagal stimulation at the atrioventricular and sinoatrial nodal fat pads of the heart
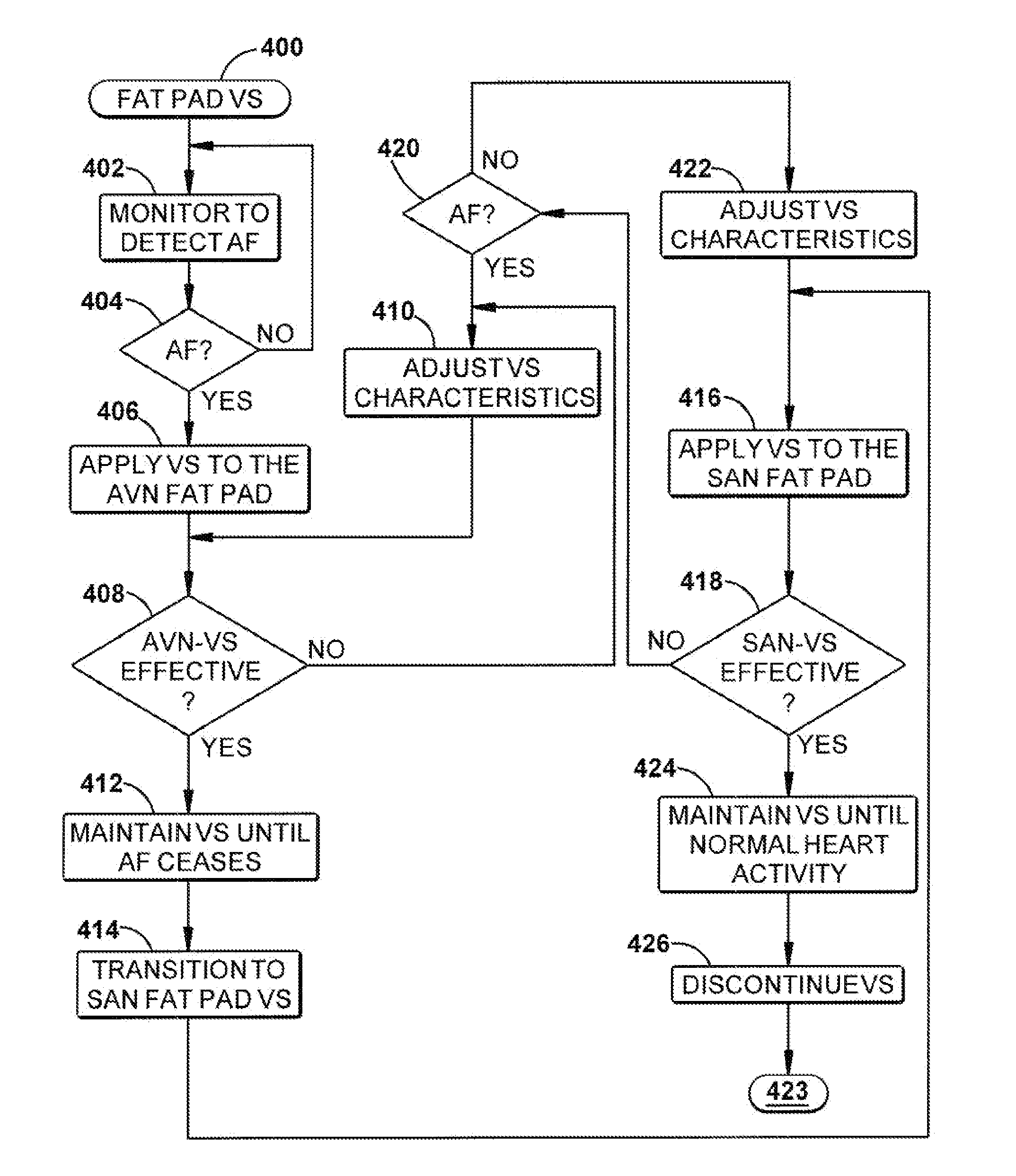
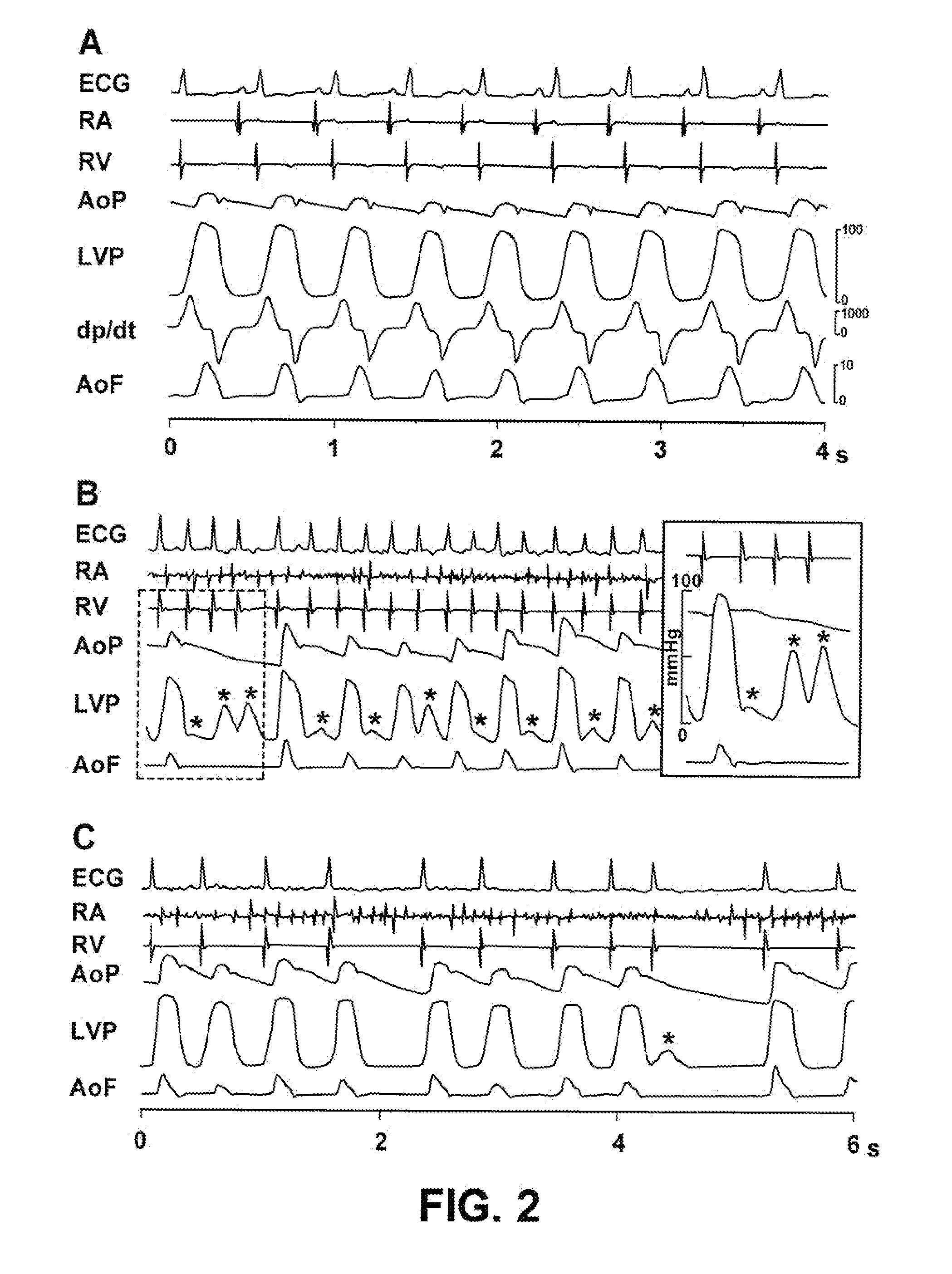
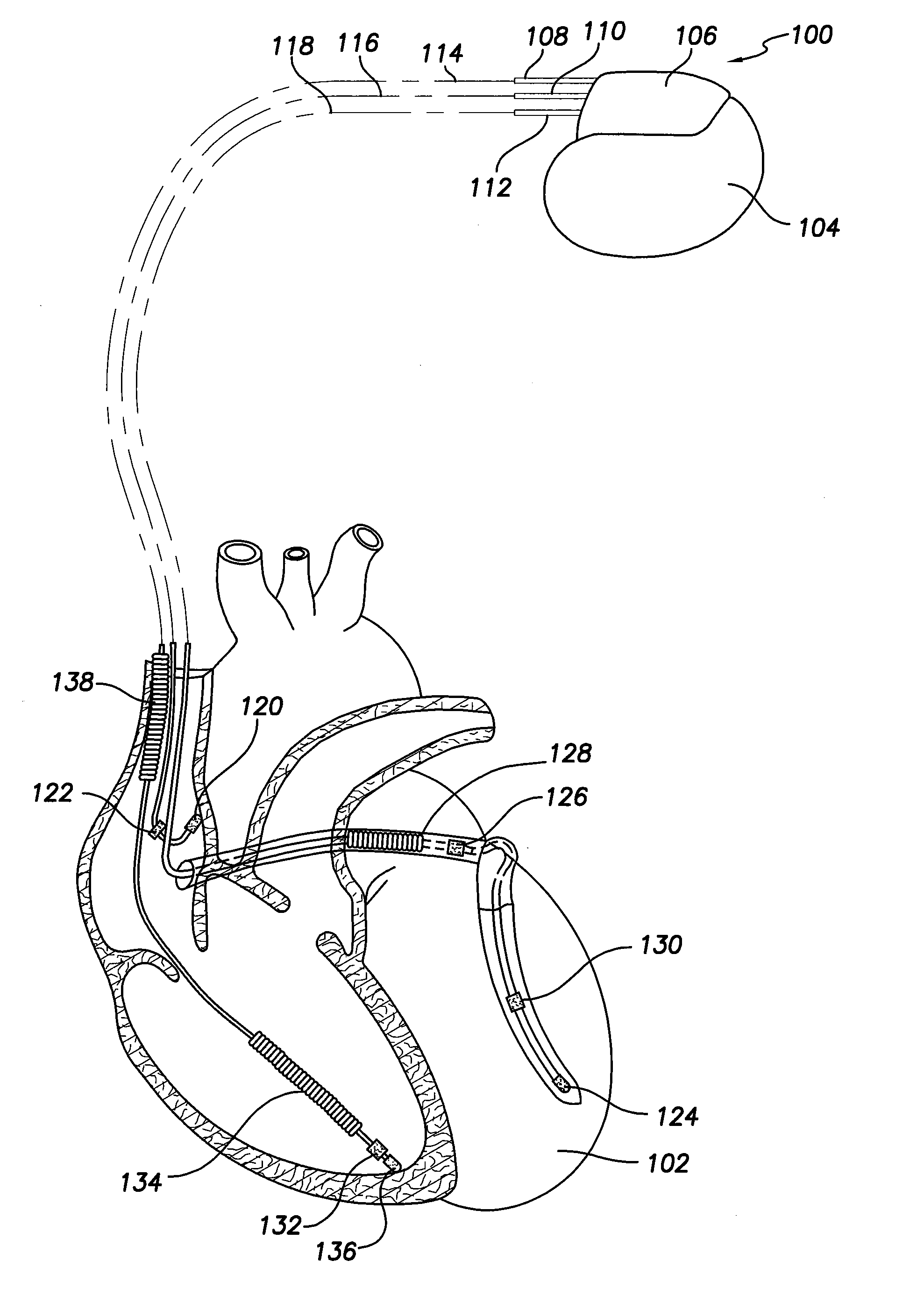
Vagal stimulation applied to the atrioventricular nodal (“AVN”) fat pad and the sinoatrial nodal (“SAN”) fat pad via epicardial leads is useful for controlling cardiac arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation (‘AF”). In the case of AF, for example, vagal stimulation may be applied initially to the AVN fat pad to reduce ventricular rate, and vagal stimulation may be applied to the SAN fat pad after restoration of sinus rhythm to control atrial rate. The technique is applicable to control acute AF and chronic AF. The vagal stimulation may be optimized for exciting ganglia in the fat pads to produce dromotropic and chronotropic effects in the atrioventricular node and the sinoatrial node, respectively. In addition, the SAN fat lead can also be used to pace the atrium in case of sinus bradycardia.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
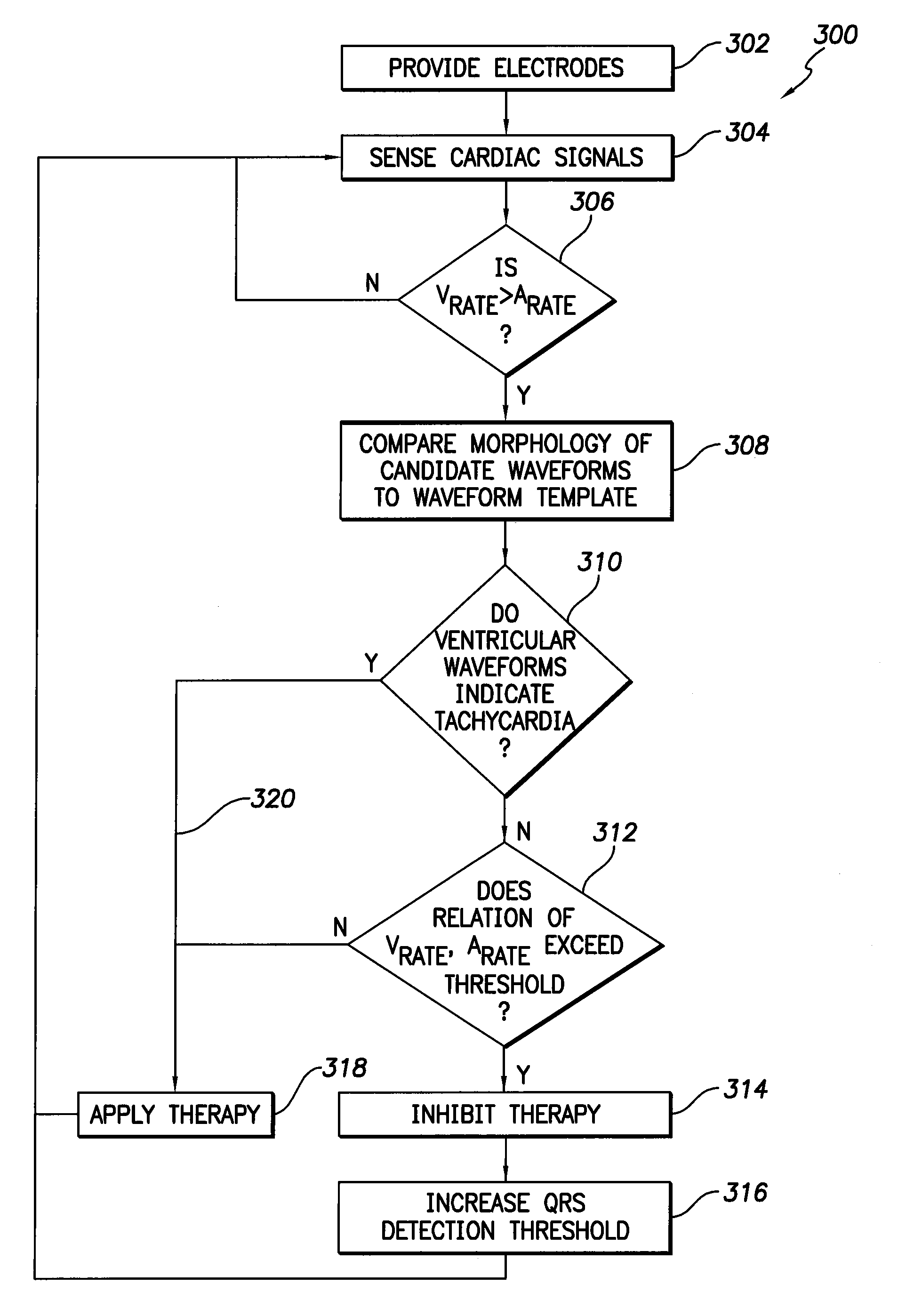
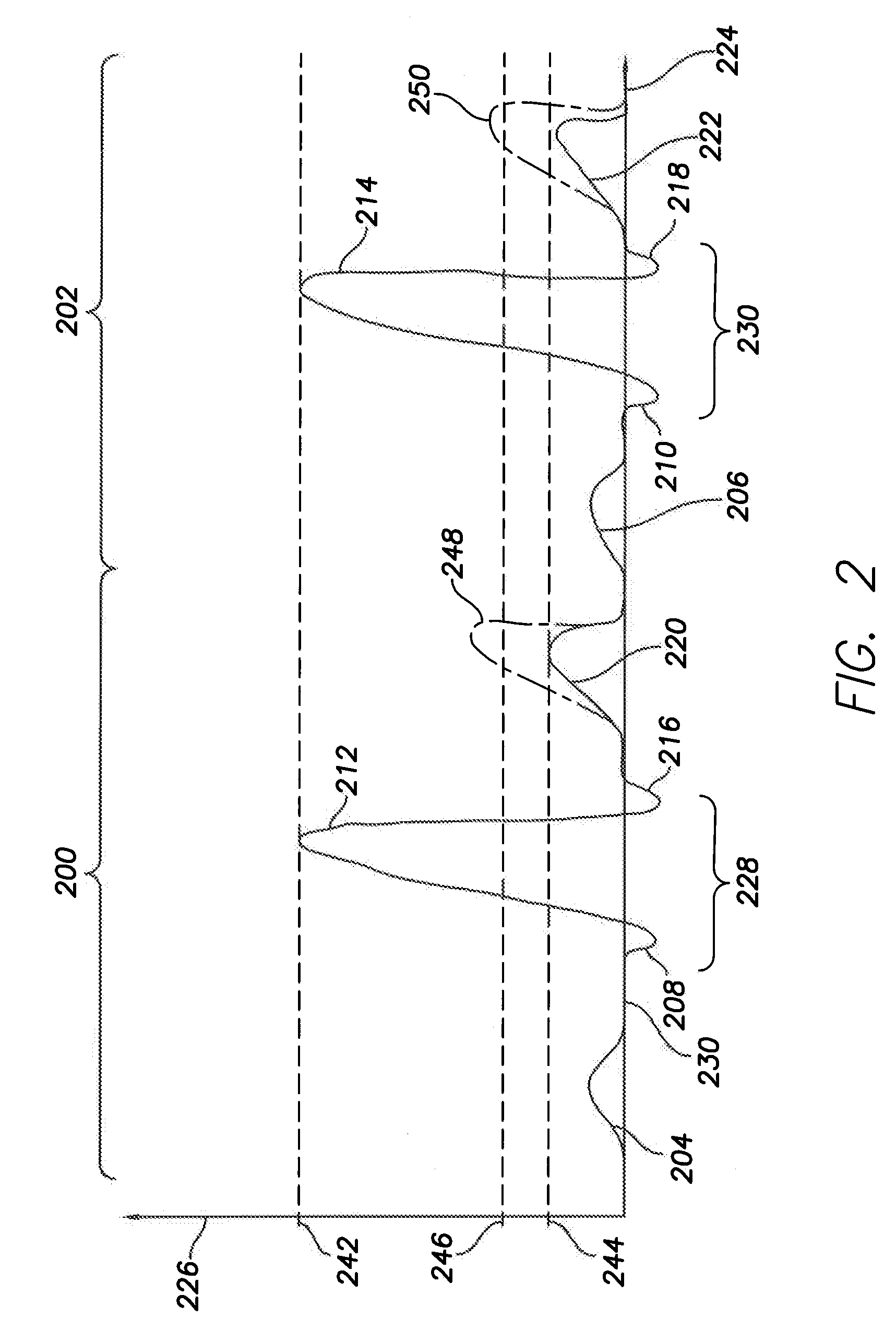
Methods and Systems for Discriminating Between Ventricular Waveforms When Ventricular Rate Exceeds Atrial Rate
A ventricular rate based on first candidate waveforms and second candidate waveforms within sensed ventricular waveforms is compared to an atrial rate. If the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate, the first candidate waveforms and second candidate waveforms are compared to a ventricular polarization complex template to obtain a first morphology indicator and a second morphology indicator. If a morphology match inconsistency is present, the amount by which the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate is compared to a threshold. If the threshold is exceeded, high-ventricular-rate therapy to the heart is inhibited. The ventricular polarization complex template may be a QRS-complex template, in which case a match inconsistency is present if each of the first candidate waveforms and the second candidate waveforms do not match the QRS-complex template. Alternatively, the ventricular polarization complex template may be a T-wave template, in which case a match inconsistency is present if either of the first candidate waveforms and the second candidate waveforms matches the T-wave template.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Method and apparatus for blanking T-waves from combipolar atrial cardiac signals based on expected T-wave locations
The stimulation device blanks T-waves from the atrial channel of an electrical cardiac signal by employing a T-wave blanking interval localized to the expected location and duration of the T-wave. To this end, the stimulation device determines the average interval between an R-wave and a T-wave in the patient in which the device is implanted and also determines the average duration of a T-waves within the patient. A T-wave blanking interval is initiated following the average R-T interval subsequent to detection of an R-wave and lasts for a period of time equal to the average T-wave duration. In this manner, highly localized T-wave blanking is achieved permitting P-waves or other atrial signals to be detected during remaining non-blanked portions of the atrial channel of the cardiac signal at least for the purposes of atrial rate detection. The relatively short T-wave blanking interval of the invention is particularly well suited for use in combipolar sensing systems. Method and apparatus implementations are described.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for use by an implantable medical device for controlling multi-site CRT pacing in the presence of atrial tachycardia
Systems and methods are provided for use by implantable medical devices equipped to deliver multi-site left ventricular (MSLV) pacing. MSLV is associated with a relatively long post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) period that might limit the detection of pathologic rapid organized atrial tachycardias (OAT). In one example, MSLV cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) pacing is delivered within a tracking mode. A possible atrial tachycardia is detected based on the atrial rate exceeding an atrial tachycardia assessment rate (ATAR) threshold. The device then switches to single-site LV pacing, thereby effectively shortening the PVAB to detect additional atrial events that might otherwise be obscured, and thereby permitting the device to more reliably distinguish organized atrial tachycardias (such as atrial flutter) from sinus tachycardia. The device may also employ an automatic mode switch (AMS) threshold that is set higher than the ATAR threshold for use in switching from tracking modes to nontracking modes.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
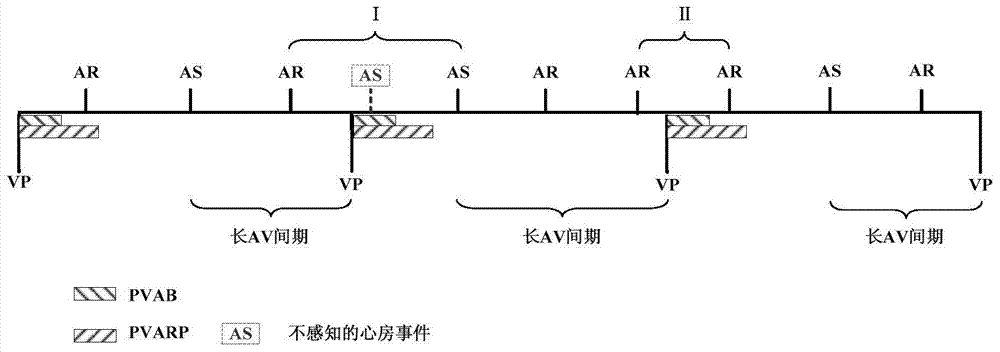
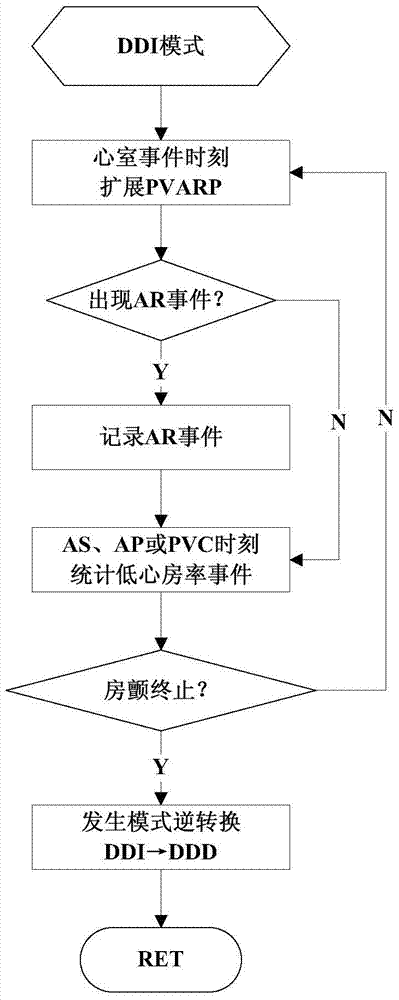
Low power consumption method for realization of mode inverse conversion of implantable pacemaker
ActiveCN105079964AReduce power consumptionReduce design difficultyHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleMedicine
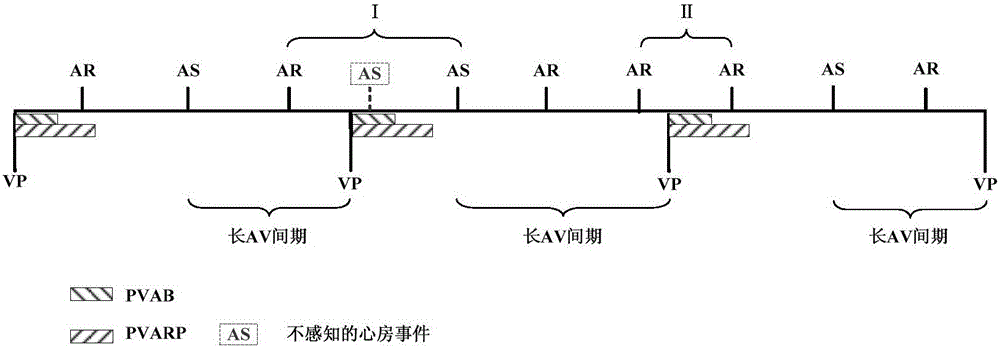
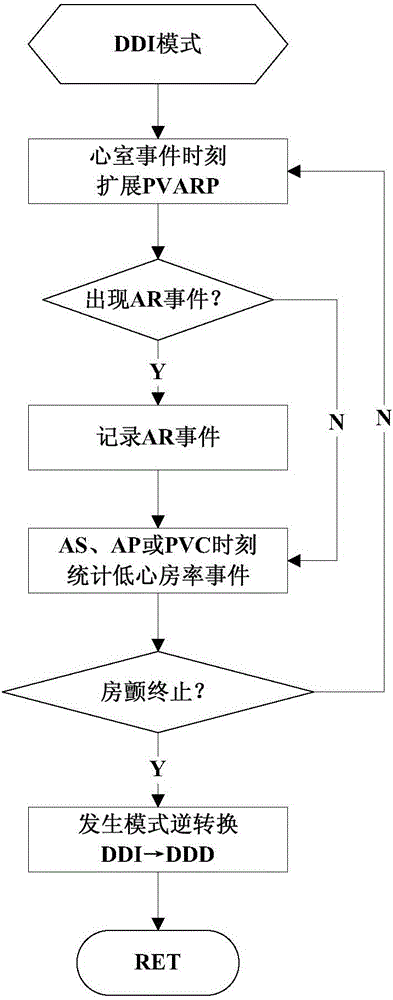
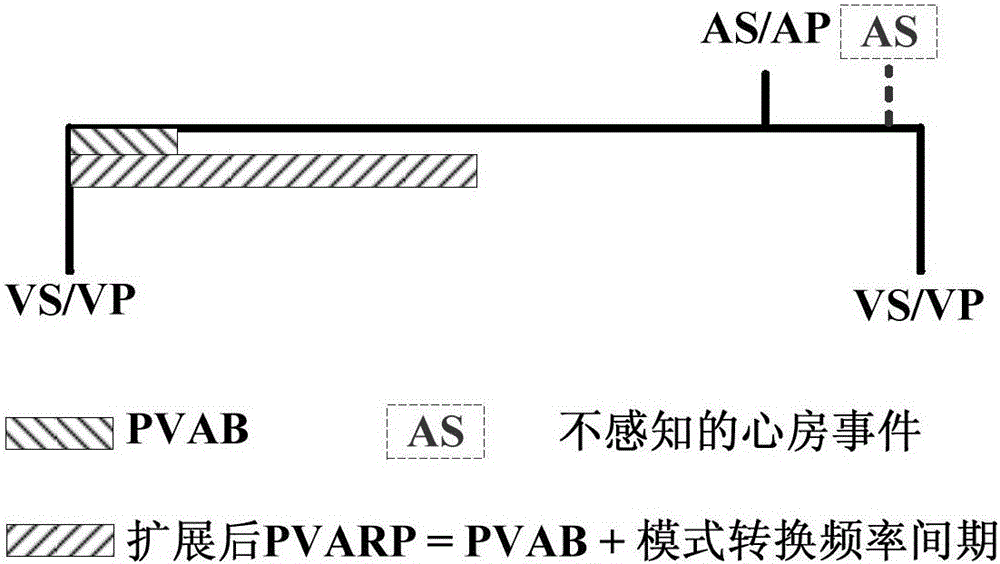
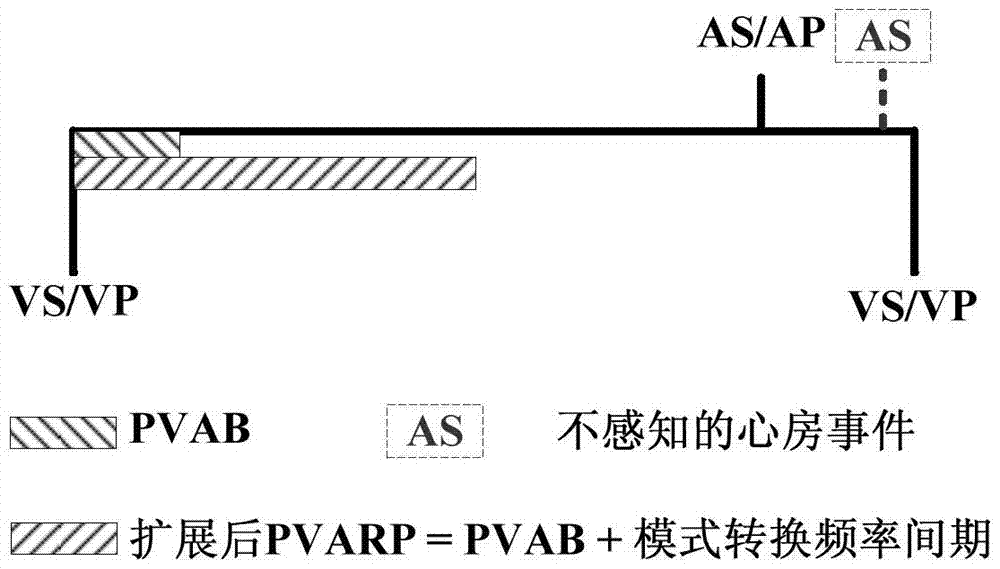
The present invention discloses a low power consumption method for realization of a mode inverse conversion of an implantable pacemaker. The low power consumption method provided by the invention comprises: when a patient has an atrial fibrillation symptom, the implantable pacemaker works in a DDI mode, an atrium perceptive function is opened in the VA interval, and the PVARP is extended at the moment of each ventricular event; in each VA interval of the cardiac cycle, the patient's AA interval values are acquired by the implantable pacemaker, and the acquired patient's AA interval values are compared with the mode inversion frequency intervals; when the AA interval values are larger than the mode inversion frequency intervals, the patient's atrial rate is lower than the preset atrial rate, and the event of the patient's atrial rate being lower than the preset atrial rate is recorded as a low atrial rate event; and when the number of the low atrial rate events is larger than or equal to the preset threshold values in a preset time, the atrial fibrillation stops, and the implantable pacemaker jumps back to the DDD mode followed by the atrium. According to the invention, the mode conversion of the implantable pacemaker from the DDI mode to the DDD mode is realized, and the service life is relatively long.
Owner:SHAANXI QINMING MEDICAL CO LTD
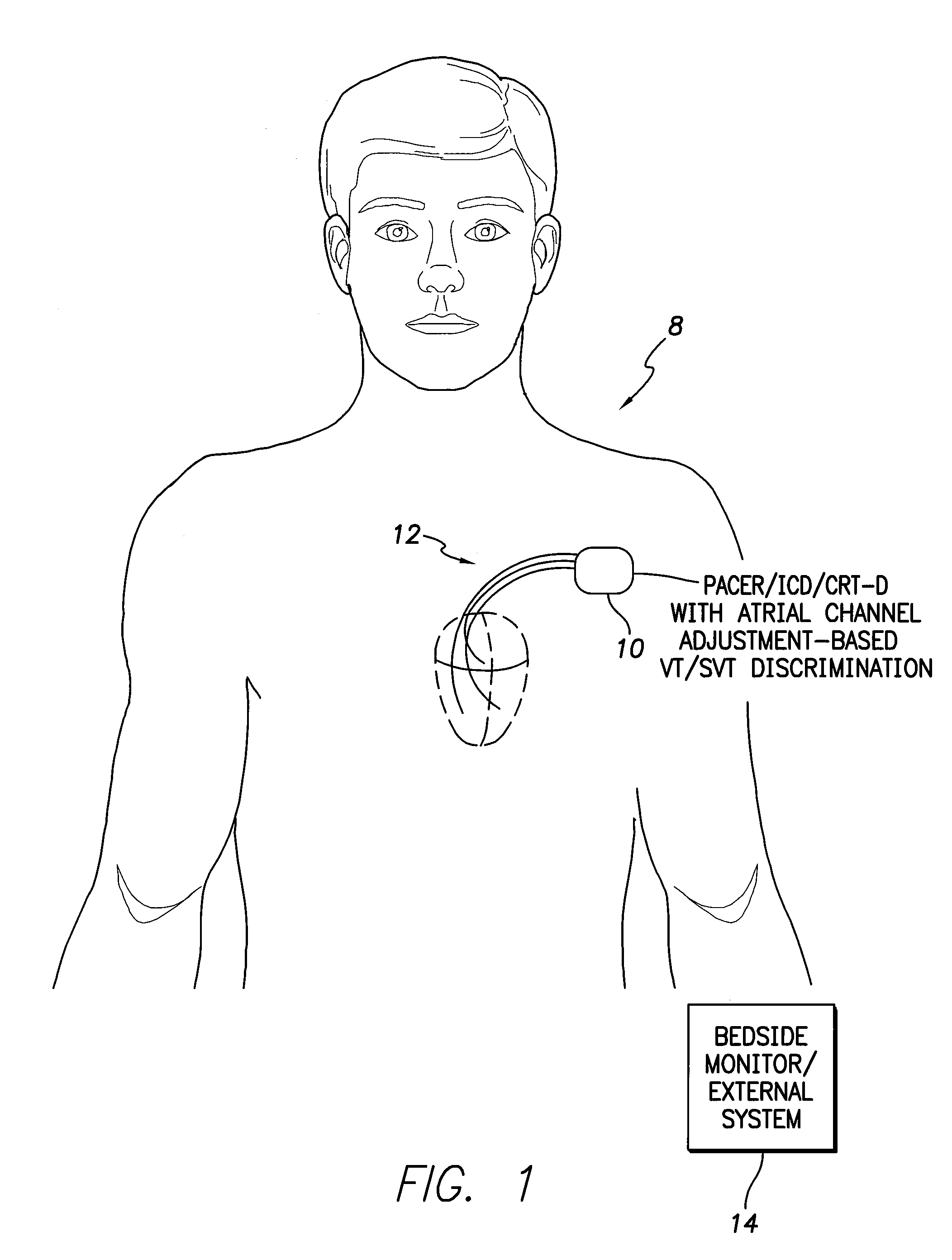
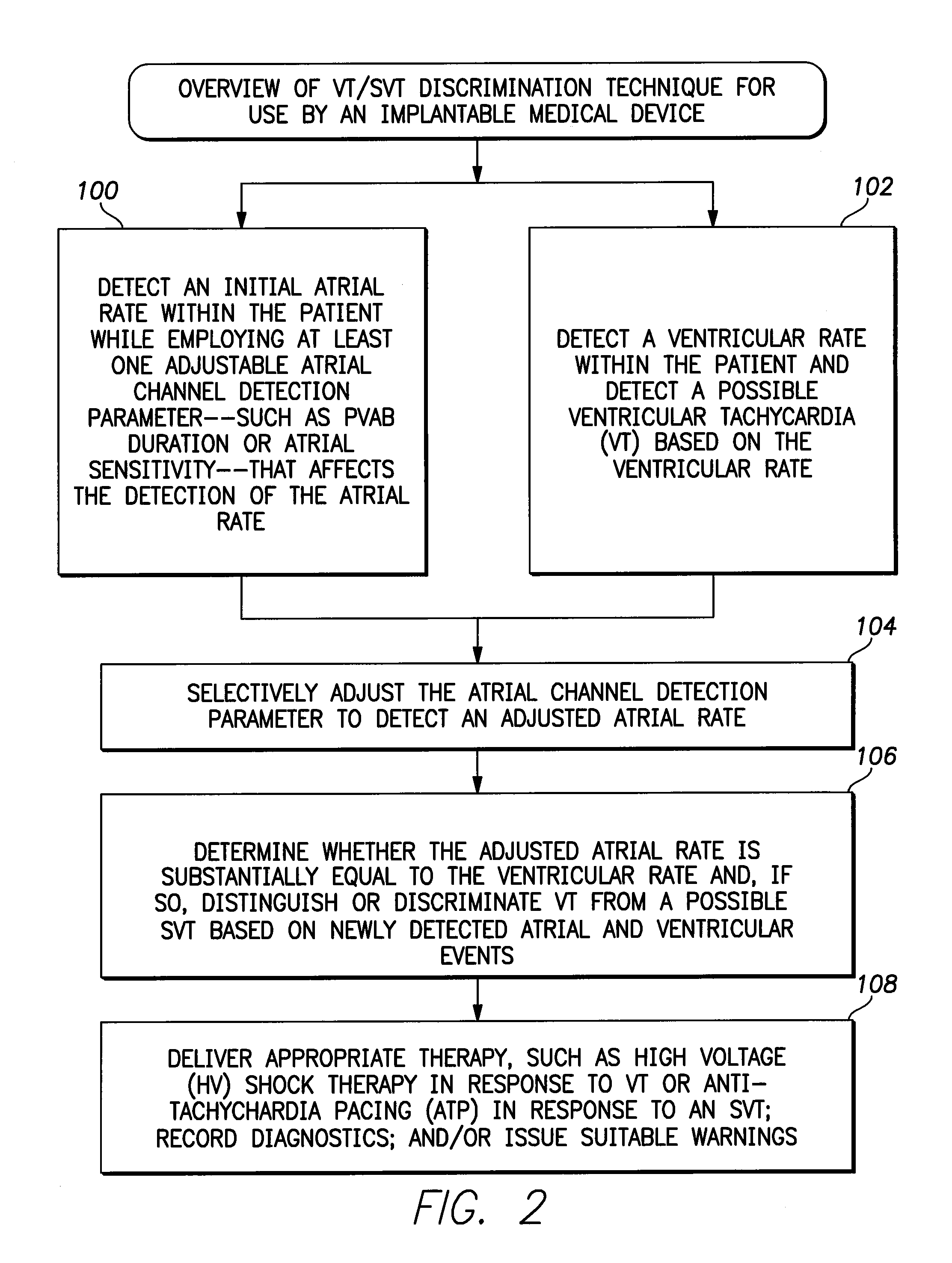
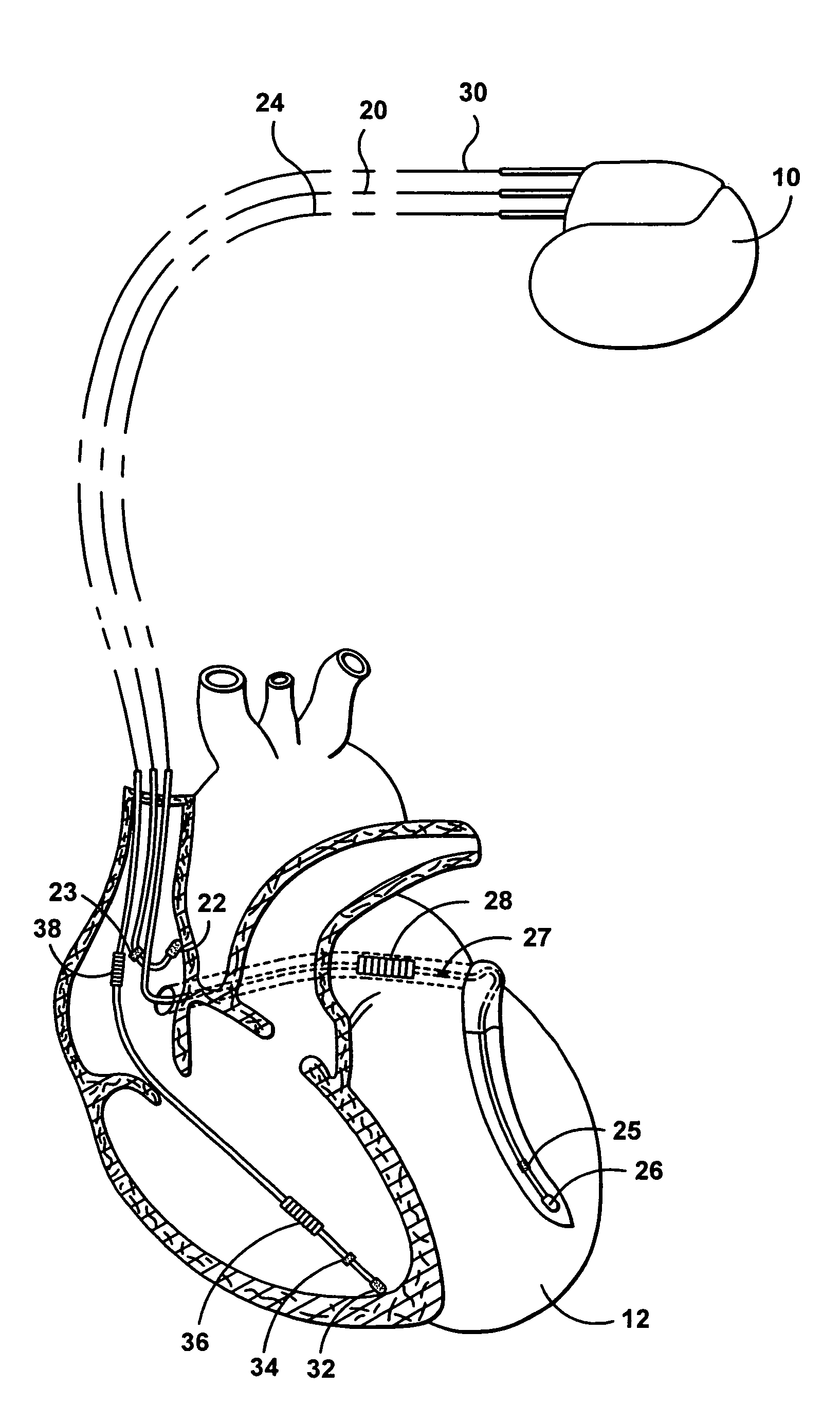
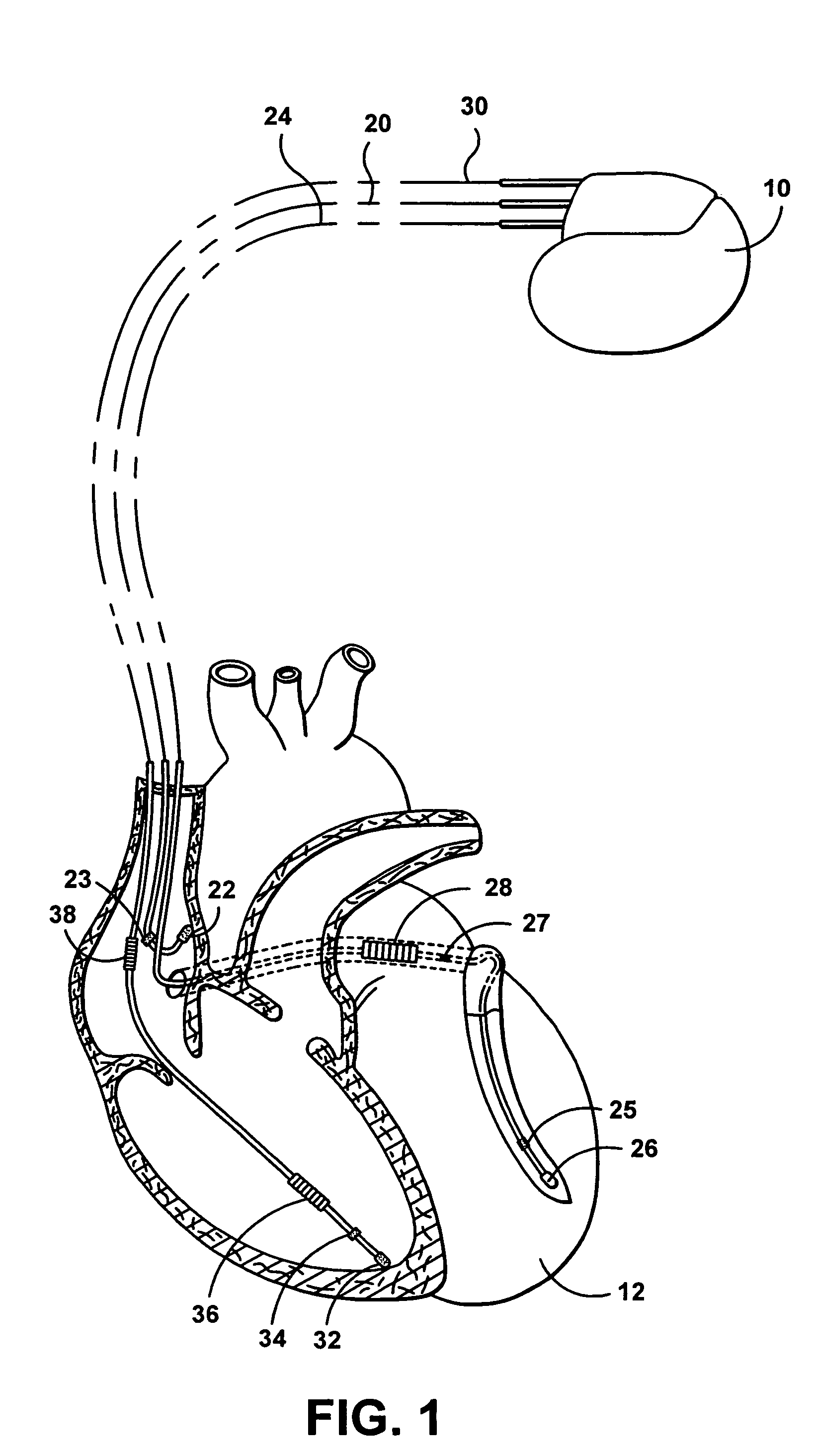
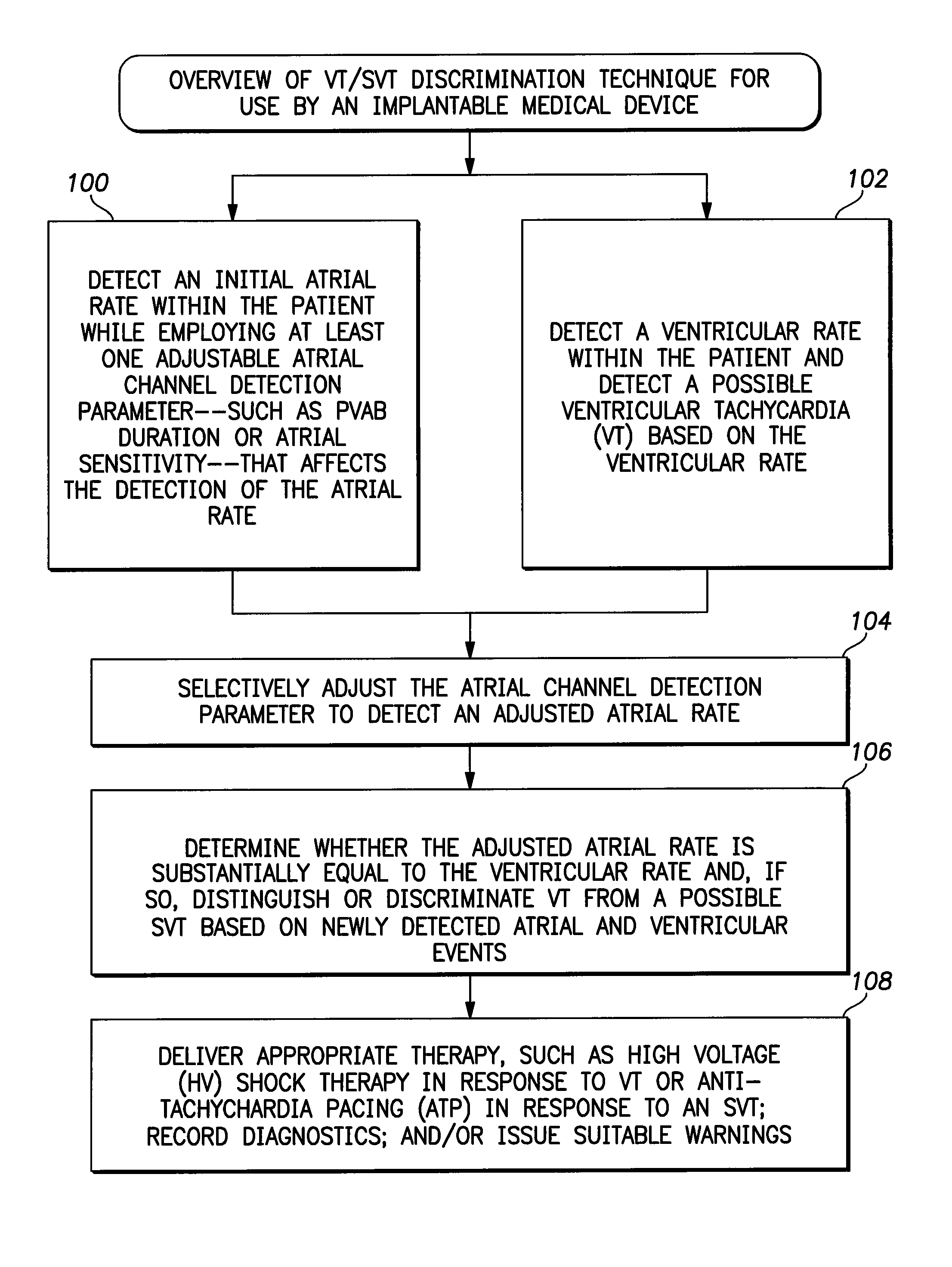
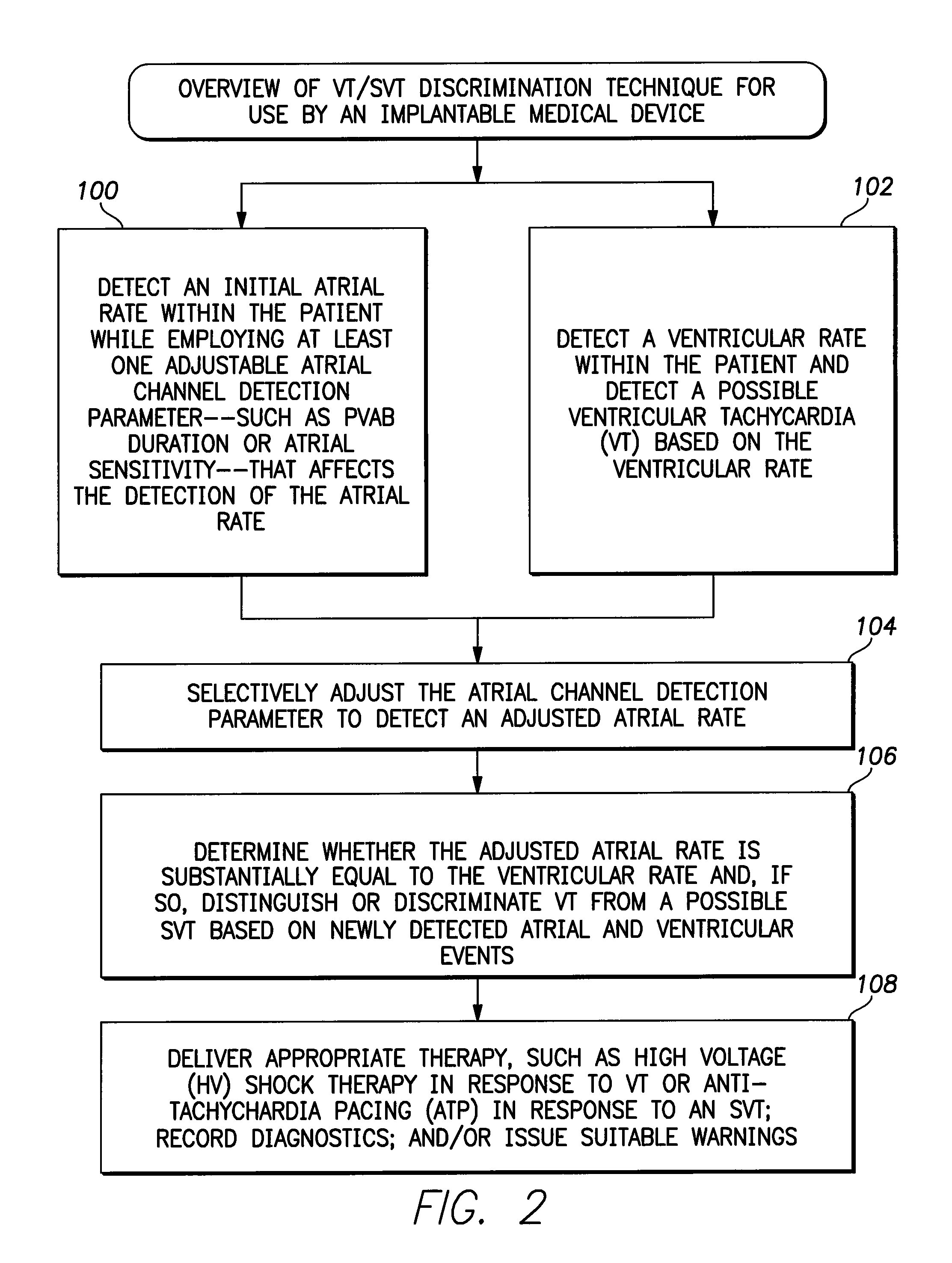
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating vt and svt be selectively adjusting atrial channel sensing parameters
ActiveUS20110282405A1Increase chanceAssessment of atrioventricular (AV) association stabilityElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsVentricular rateVentricular tachycardia
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in circumstances when the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate (i.e. V>A). In one example, an initial atrial rate is detected while employing adjustable atrial channel detection parameters that can affect the detection of the true atrial rate—such as a post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) interval or an atrial channel sensitivity level. If the ventricular rate exceeds a VT rate zone threshold with V>A, the device does not immediately deliver high voltage shock therapy as done in other devices. Rather, the device instead selectively adjusts the atrial channel detection parameter(s) to determine if the true atrial rate is equal to the ventricular rate. If so, then such is an indication that the arrhythmia might be SVT rather than VT and various discrimination procedures are employed to distinguish SVT from VT before therapy is delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Multi-site cardiac stimulation device and method for detecting retrograde conduction
InactiveUS7146215B1Prevent inappropriate arrhythmia detectionImprove responseHeart stimulatorsMulti siteCardiac pacemaker electrode
An implantable cardiac stimulation device, such as a pacemaker, defibrillator and / or cardioverter, and an associated method that provide cardiac stimulation to at least two ventricular stimulation sites, within a single ventricle or across two ventricles. A high intrinsic atrial rate triggers a retrograde conduction detection routine when a high ventricular stimulation rate is sustained for a predetermined number of cycles during an atrial sensing mode. This routine interrupts concurrent stimulation, and alternates the stimulation output to the different ventricular sites.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Heart stimulator
Heart stimulator that stimulates at least a heart's right atrium and ventricle in an atrium asynchronous stimulation mode with an overdrive stimulation rate. Interposes one resynchronization cycle after a sensed atrial event to regain AV synchrony during otherwise asynchronous stimulation mode. Allows for pacing mode that can pace the atrium with an overdrive stimulation rate in dual-chamber asynchronous mode while maintaining the AV synchrony and is called DDI(R)+. In DDI(R)+, pacemaker performs an atrial asynchronous (V synchronous) pacing mode such as DDI or DDI(R). The overdrive stimulation rate (OSR) is either a fixed rate (programmed by the external device) that is thought to be above the underlying intrinsic atrial rate, or is dynamically adjusted according to the measured atrial cycle length to be slightly above intrinsic atrial rate. The overdrive stimulation rate may be based on an intrinsic atrial rate or on hemodynamic need. DDI(R)+ timing may be ventricle-based.
Owner:BIOTRONIX CRM PATENT AG
Atrial overdrive pacing in non-atrial tracking mode while maintaining AV synchrony
Owner:BIOTRONIX CRM PATENT AG
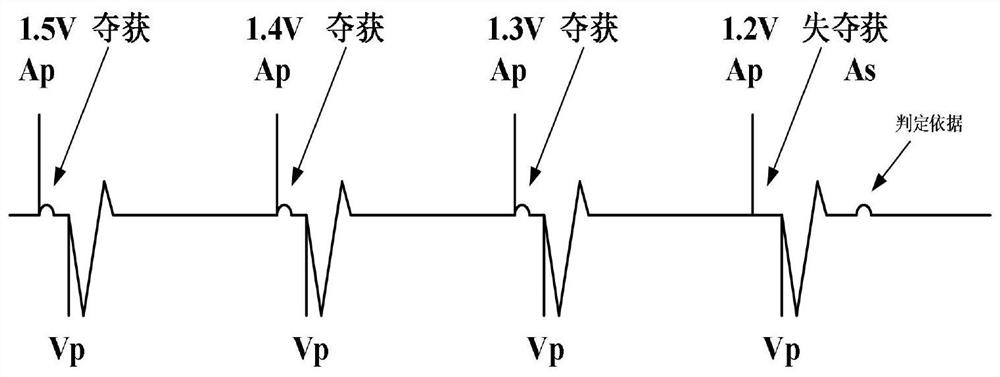
Automatic atrial pacing threshold searching method and circuit
The invention relates to an automatic atrial pacing threshold searching method and circuit, and the method comprises the steps: firstly obtaining the number of ventricular event occurrence times, the types of atrial events, a Vx-Ap interval average value and an Ax-Vx interval average value, and setting a proper adjustment self atrial searching margin value; comparing the acquired numerical value with a preset numerical value, judging an event type, and selecting to perform automatic atrial pacing threshold searching or encouraging an atrial event of a user, that is, the method can start or give up the automatic atrial pacing threshold searching without increasing the atrial pacing frequency after accurately identifying the heart rhythm, so that unnecessary atrial pace-making threshold searching is avoided, and automatic atrial pace-making threshold searching can be completed at a stable ventricular rate when necessary. The circuit comprises a basic heart rhythm detection unit and a self atrial rate searching unit, accurate recognition of heart rhythms is achieved through the circuit, and therefore automatic atrial pacing threshold searching is completed, or self atrial events are encouraged.
Owner:SHAANXI QINMING MEDICAL CO LTD
Cardiac rhythm management system with maximum tracking rate (MTR) hysteresis
A cardiac rhythm management system provides both a safe maximum pacing rate limit and a physiological maximum pacing rate limit. In one embodiment, a normal maximum tracking rate (MTR) and a hysteresis MTR are provided. The hysteresis MTR is set higher than the normal MTR and functions as a maximum pacing rate. When an atrial rate exceeds the hysteresis MTR limit, the maximum pacing rate limit is set to the normal MTR. Once the atrial rate falls below a predetermined threshold, the maximum pacing rate limit is set to the hysteresis MTR. This provides for a more rapid and natural maximum pacing rate limit for a patient, while still protecting the patient from being paced at abnormally high rates.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems and methods for use with an implantable medical device for discriminating VT and SVT be selectively adjusting atrial channel sensing parameters
ActiveUS8271081B2Increase chanceAssessment of atrioventricular (AV) association stabilityElectrocardiographyCatheterVentricular rateVentricular tachycardia
Techniques are described for discriminating ventricular tachycardia (VT) from supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) in circumstances when the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate (i.e. V>A). In one example, an initial atrial rate is detected while employing adjustable atrial channel detection parameters that can affect the detection of the true atrial rate—such as a post-ventricular atrial blanking (PVAB) interval or an atrial channel sensitivity level. If the ventricular rate exceeds a VT rate zone threshold with V>A, the device does not immediately deliver high voltage shock therapy as done in other devices. Rather, the device instead selectively adjusts the atrial channel detection parameter(s) to determine if the true atrial rate is equal to the ventricular rate. If so, then such is an indication that the arrhythmia might be SVT rather than VT and various discrimination procedures are employed to distinguish SVT from VT before therapy is delivered.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Systems and methods for use by an implantable medical device for controlling multi-site CRT pacing in the presence of atrial tachycardia
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Device for automatically measuring left ventricular pace-making threshold and control method thereof
PendingCN109771824ALeft Ventricular Pacing Threshold AcquisitionHeart stimulatorsLeft ventricular sizeRight atrium
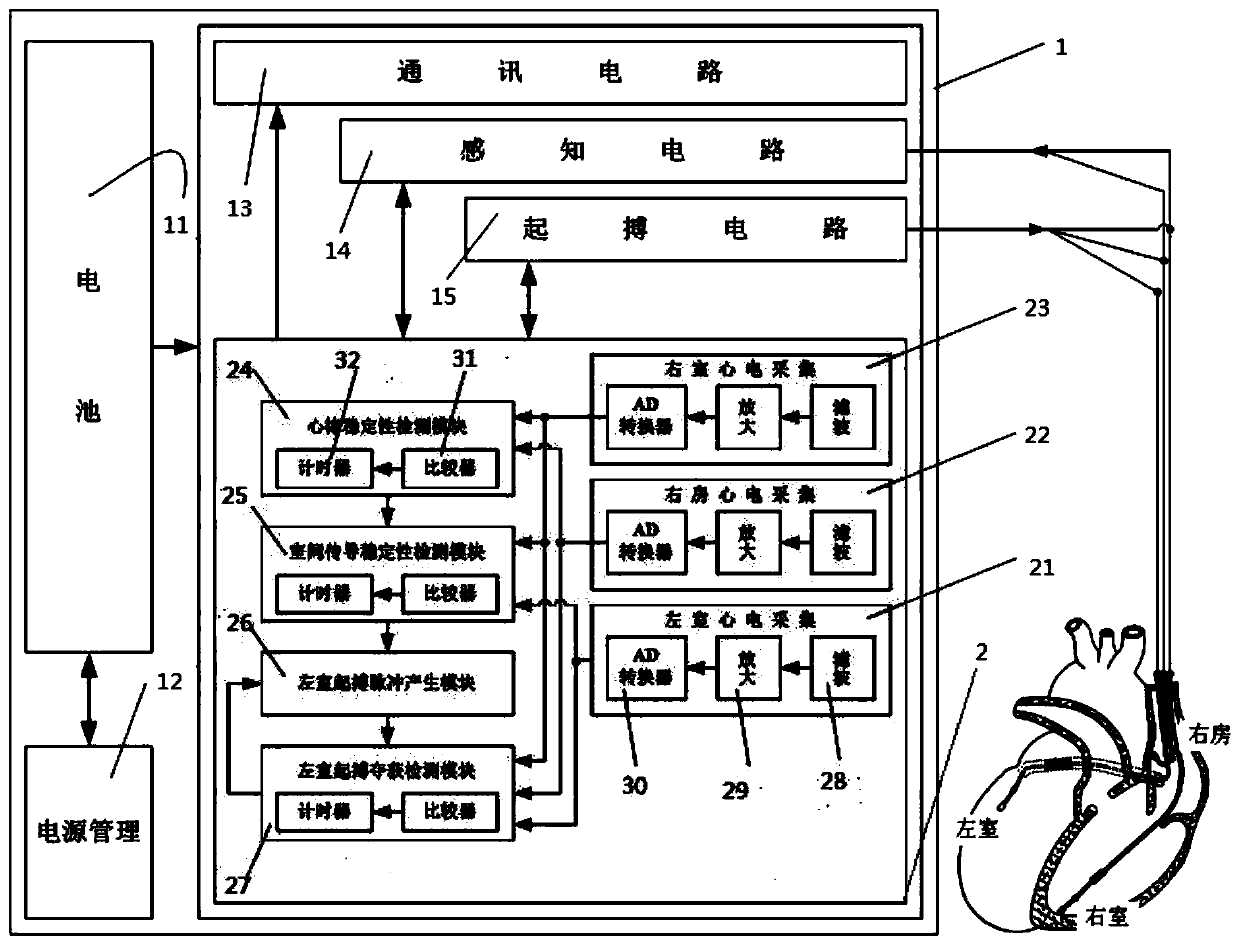
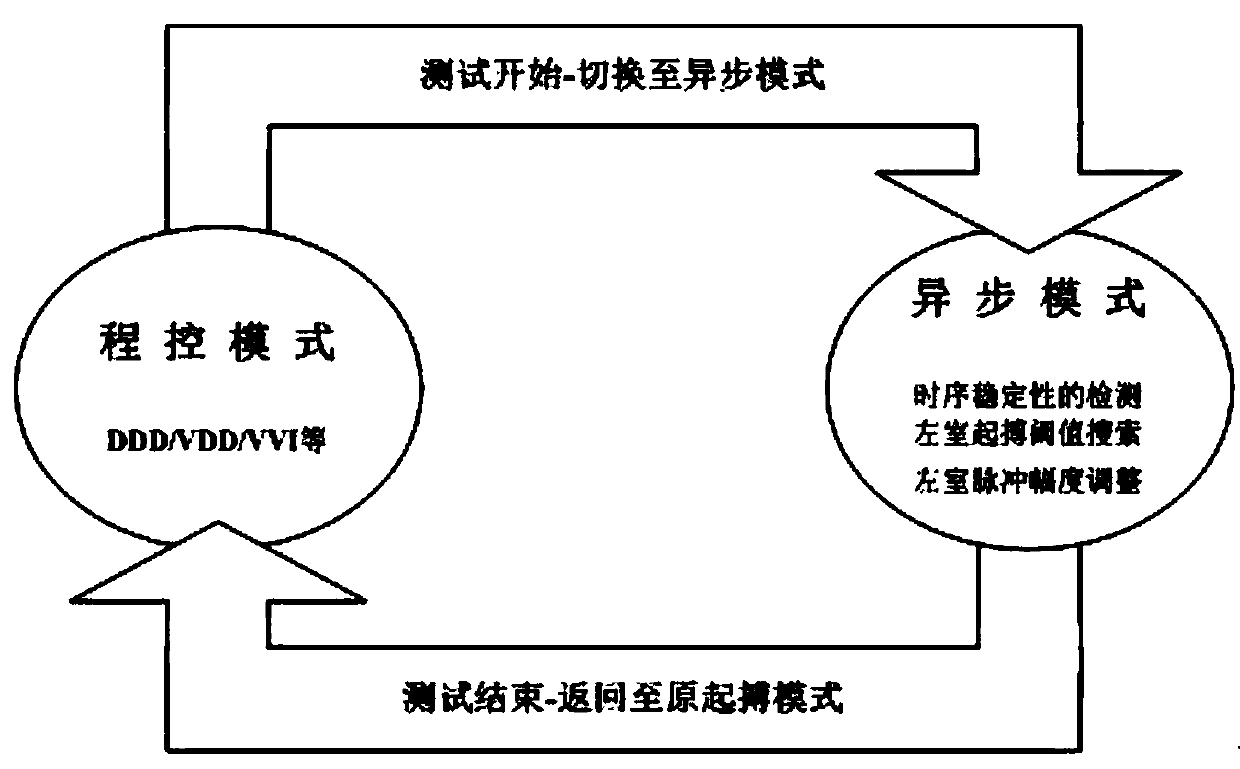
The invention provides a device for automatically measuring a left ventricular pace-making threshold and a control method thereof. The device comprises a right atrial electrocardio data acquisition module, a right ventricular electrocardio data acquisition module, a heart rhythm stability detection module, an interventricular conduction stability detection module, a left ventricular pacing capturedetection module and a left ventricular pacing pulse generation module. The control method comprises the following steps: 1, detecting heart rhythm stability, wherein if the atrial rate fluctuates around an average value, and the conduction from the right atrium to the right ventricle fluctuates around the average value, executing the step 2; 2, detecting interventricular conduction stability, wherein if the conduction from the left ventricle to the right ventricle fluctuates around an average value, executing the step 3; 3, setting a certain range near the conduction average value from the right atrium to the right ventricle as a capture loss window, setting a certain range near the conduction average value from the left ventricle to the right ventricle as a capture loss window, and if the two windows do not overlap, executing the step 4; 4, gradually decreasing the left ventricular pacing pulse amplitude, and determining the threshold by the capture and capture loss windows.
Owner:SHAANXI QINMING MEDICAL CO LTD
Methods and devices for determination of heart arrhythmia type
ActiveUS20120265087A1Good curative effectQuick fixElectrocardiographyIntravenous devicesVentricular rateHeart arrhythmia
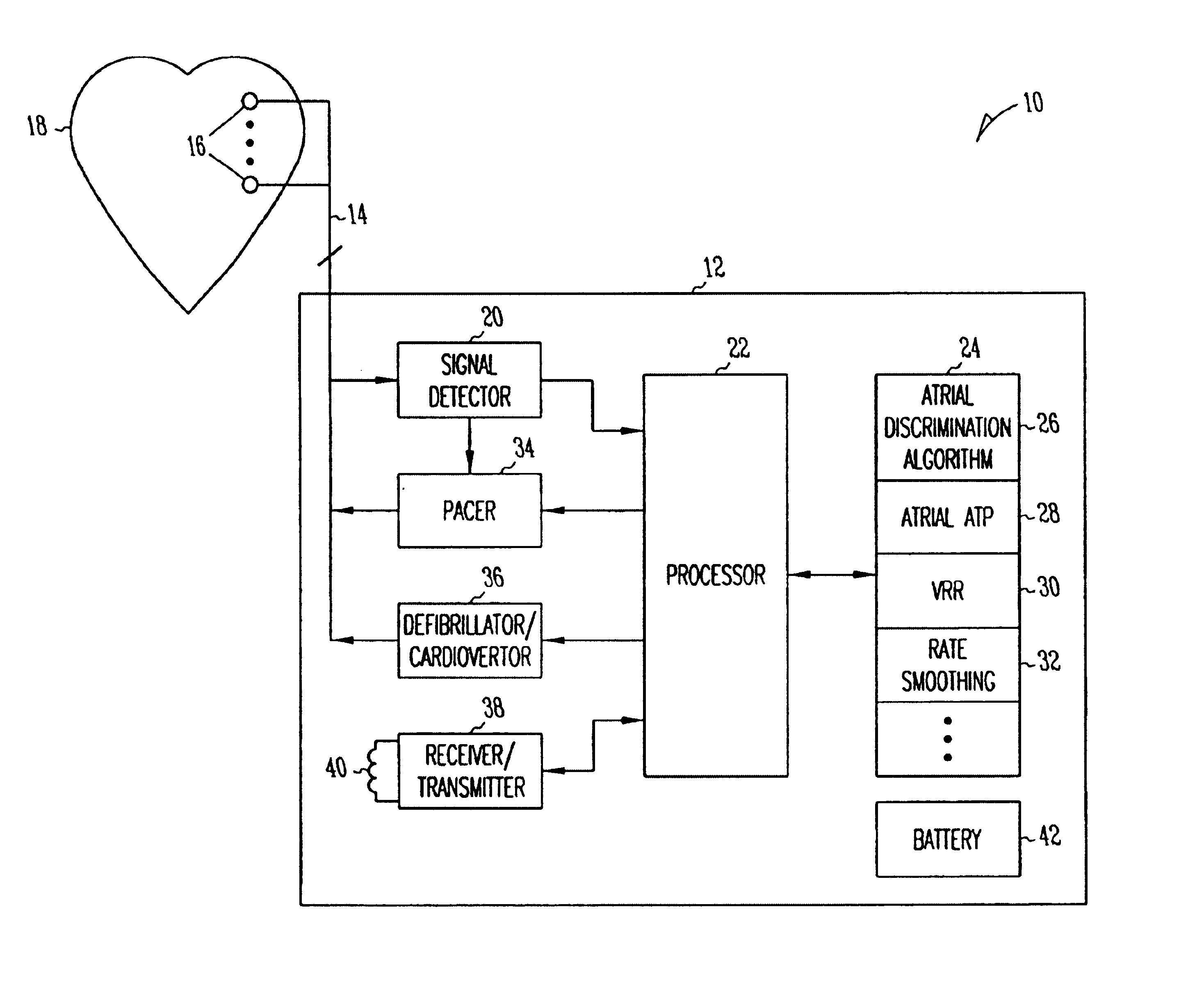
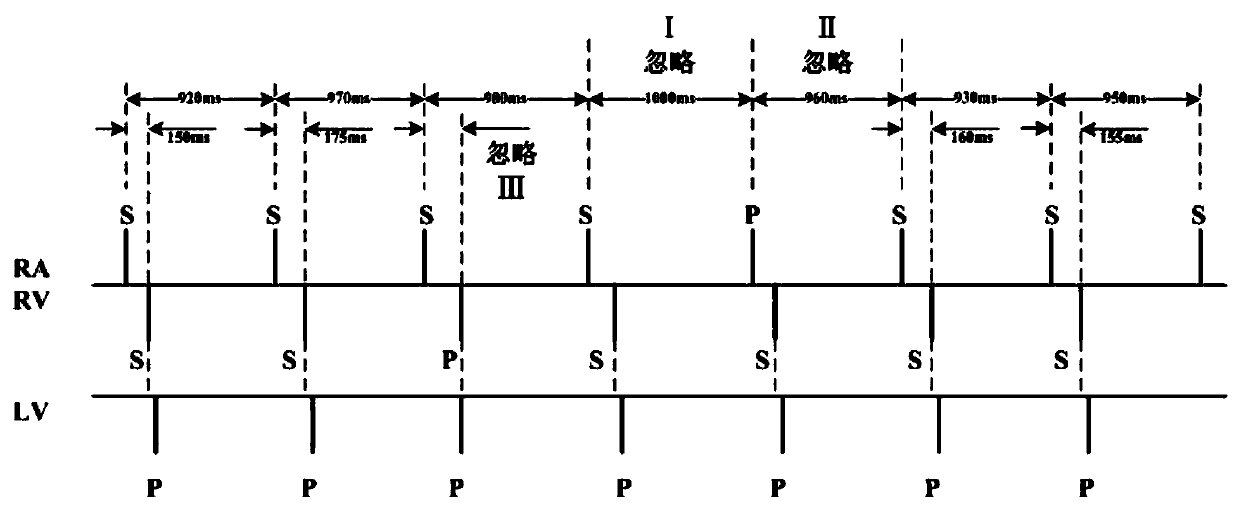
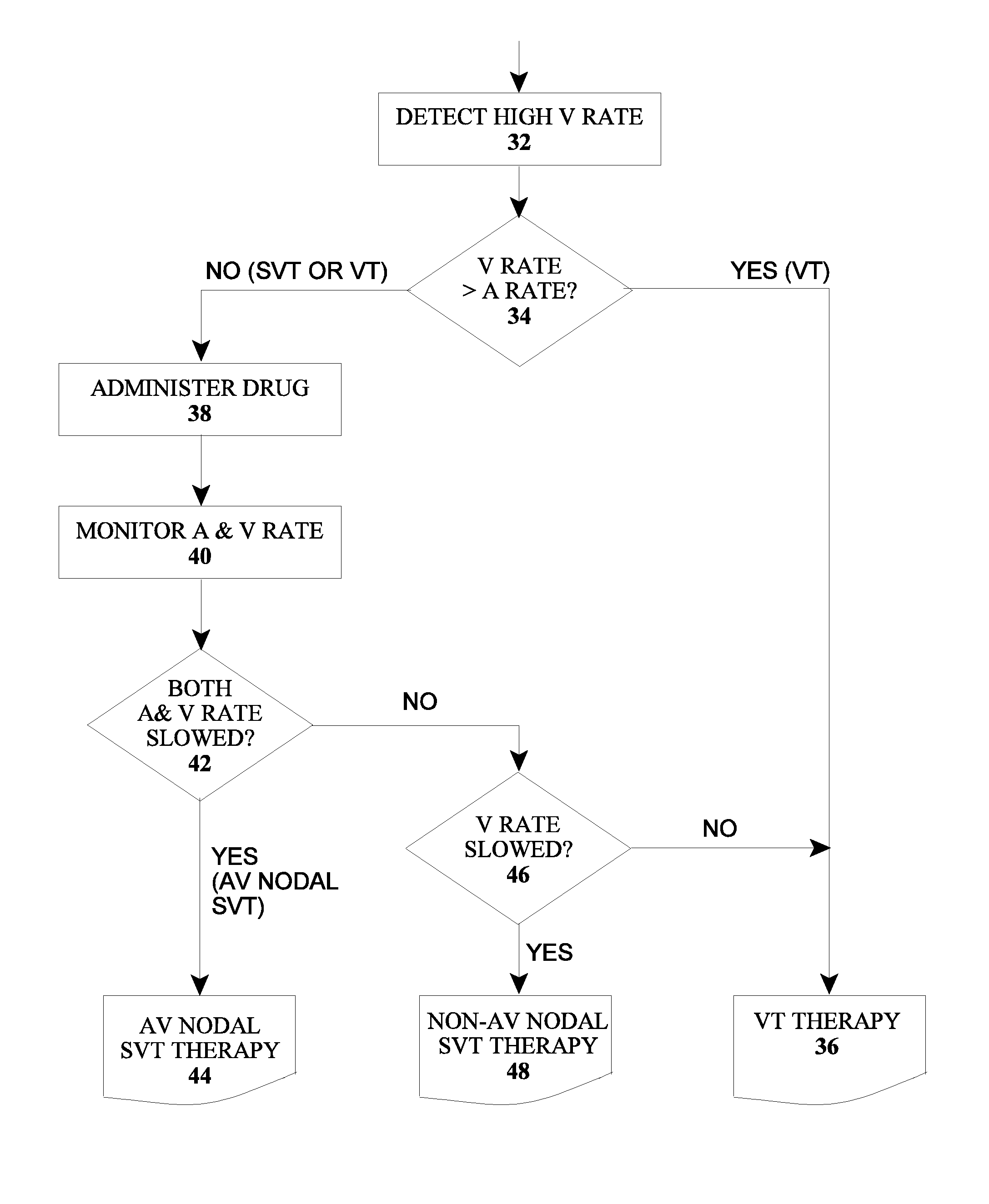
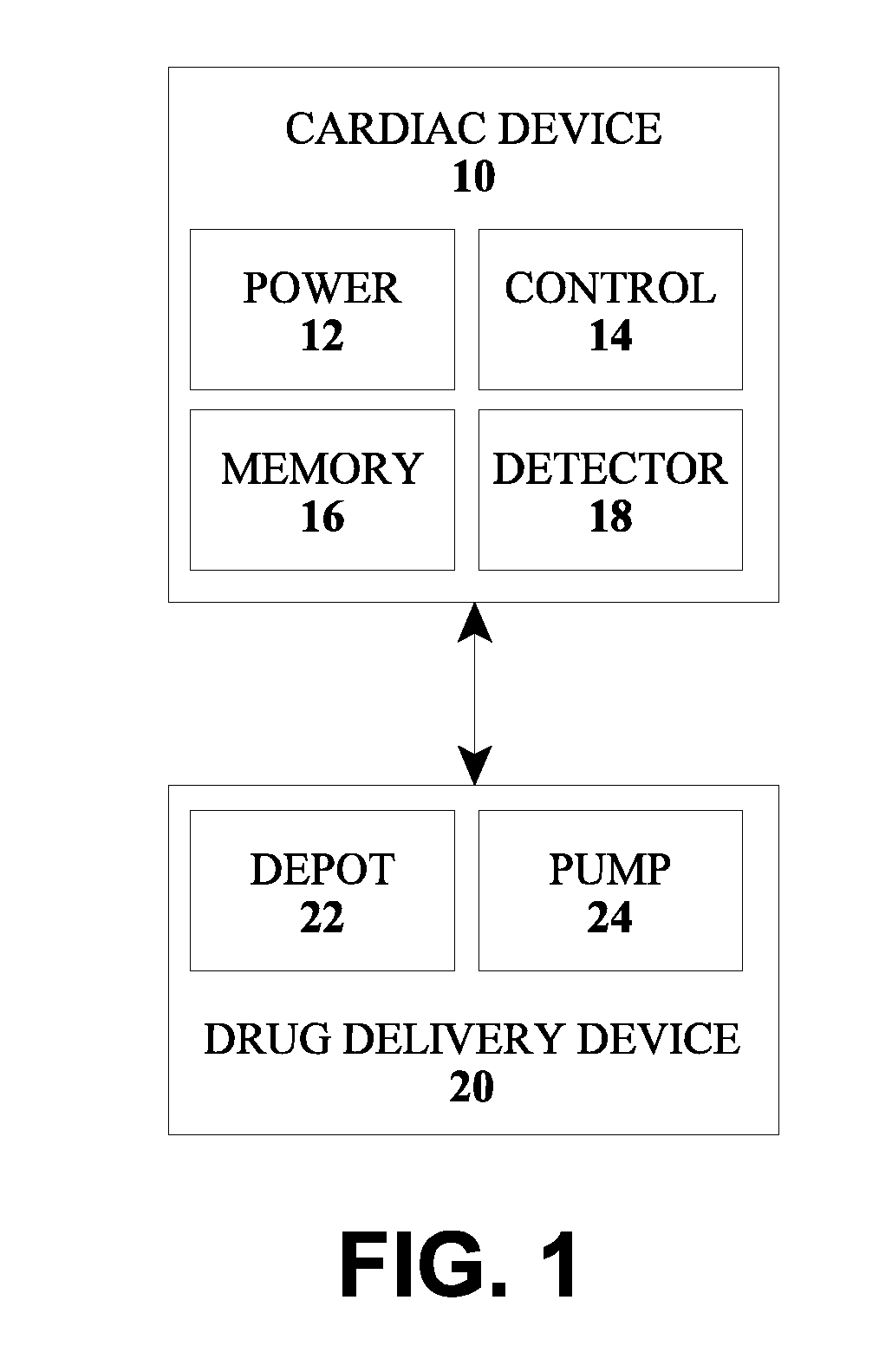
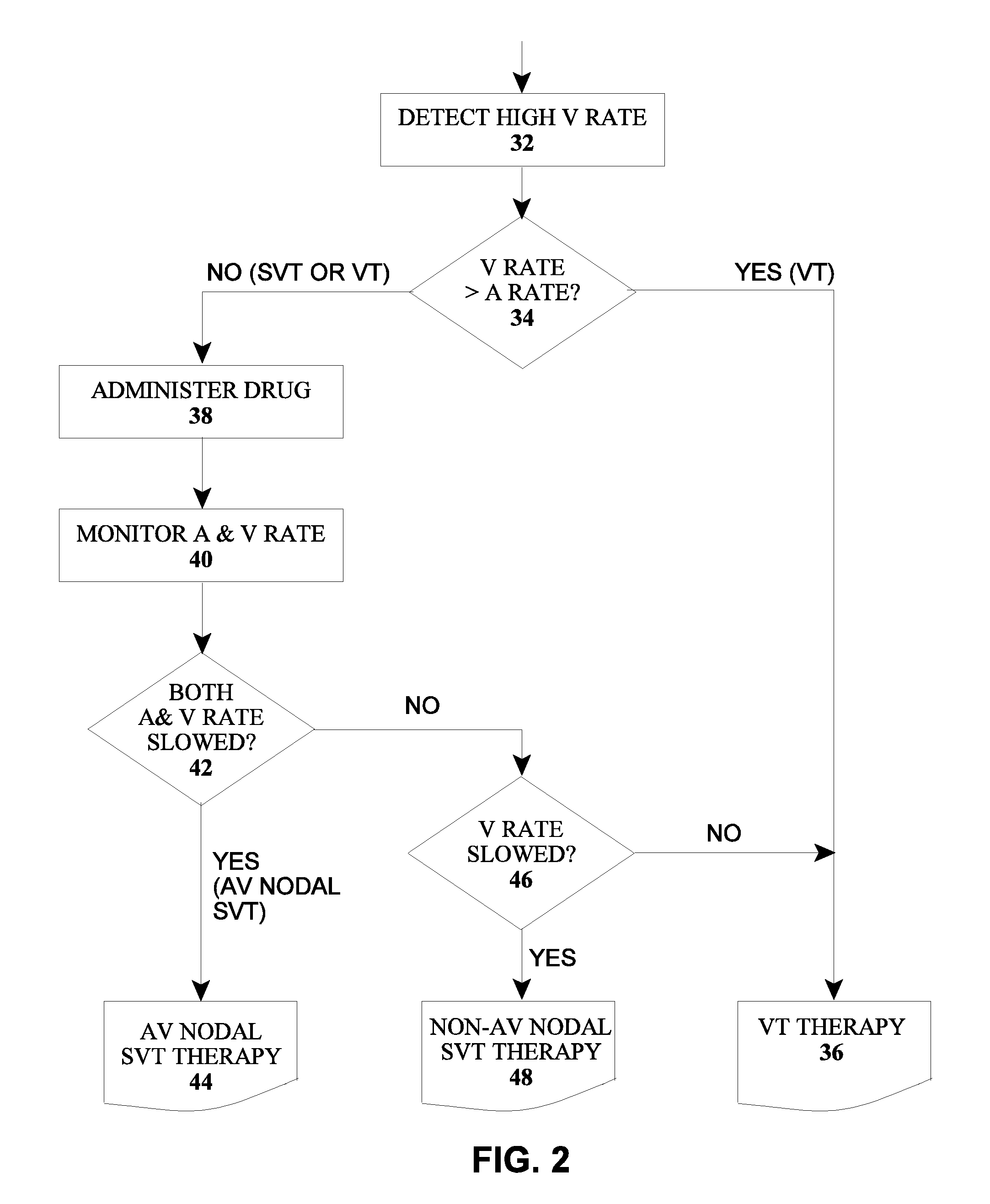
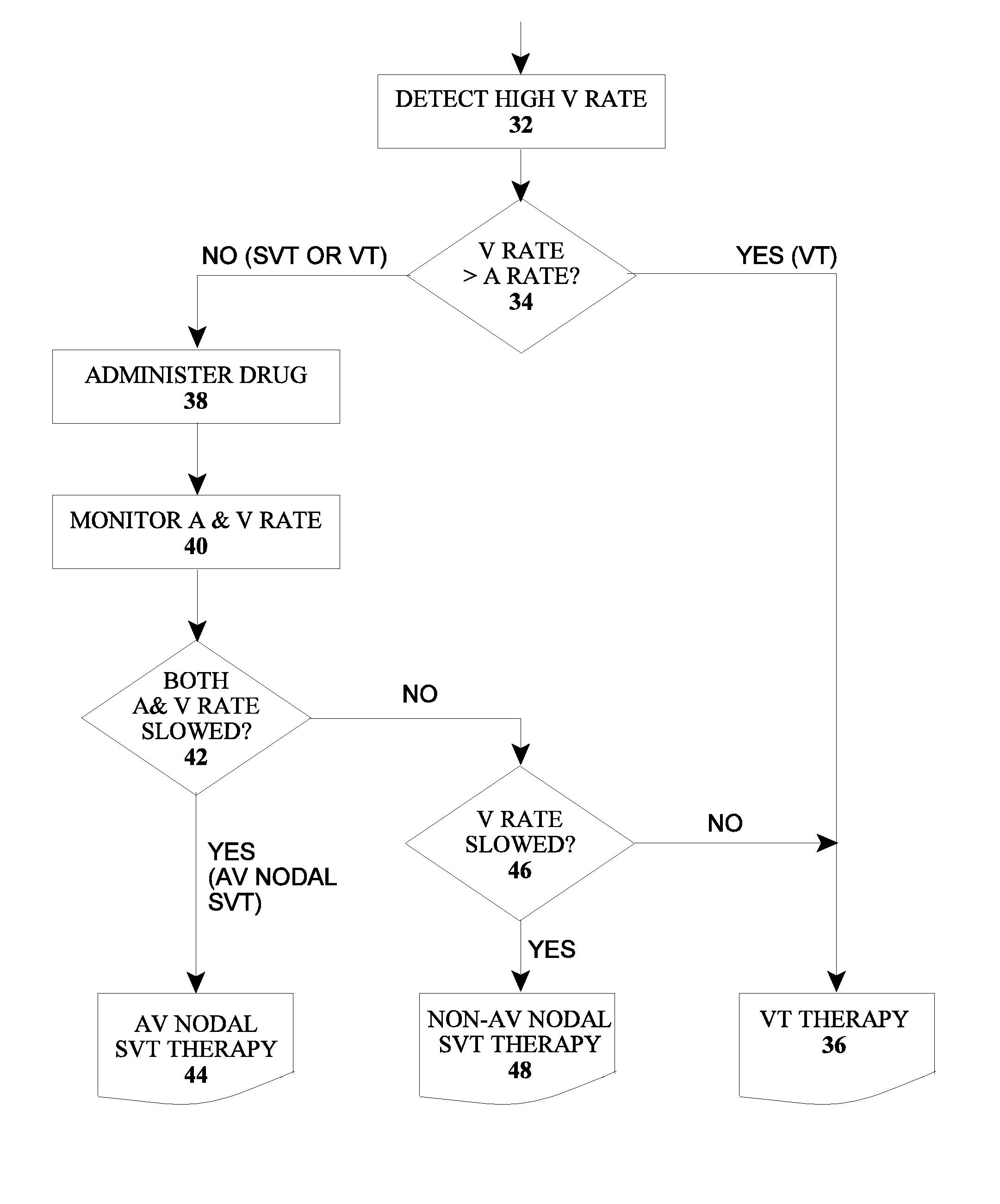
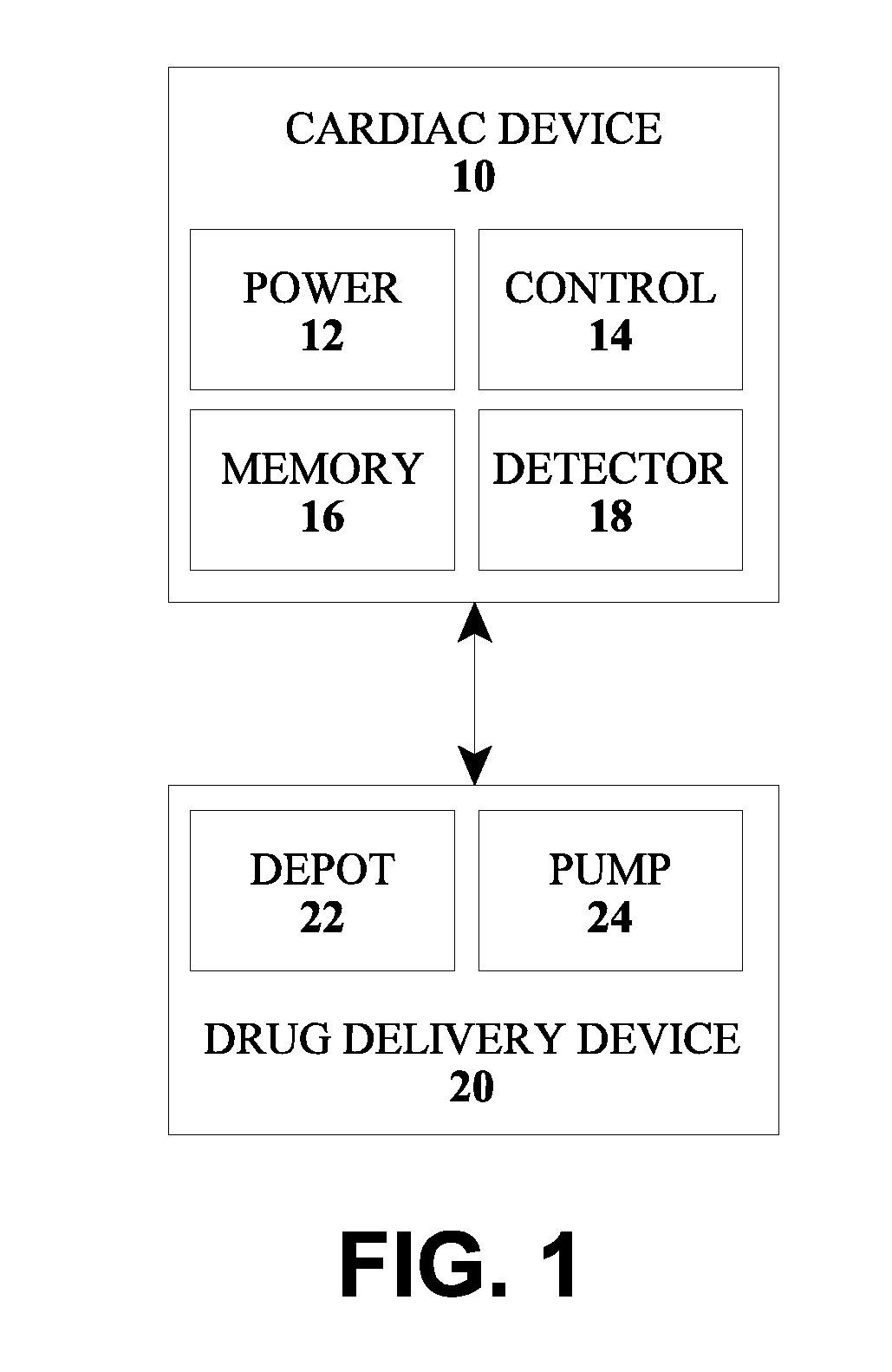
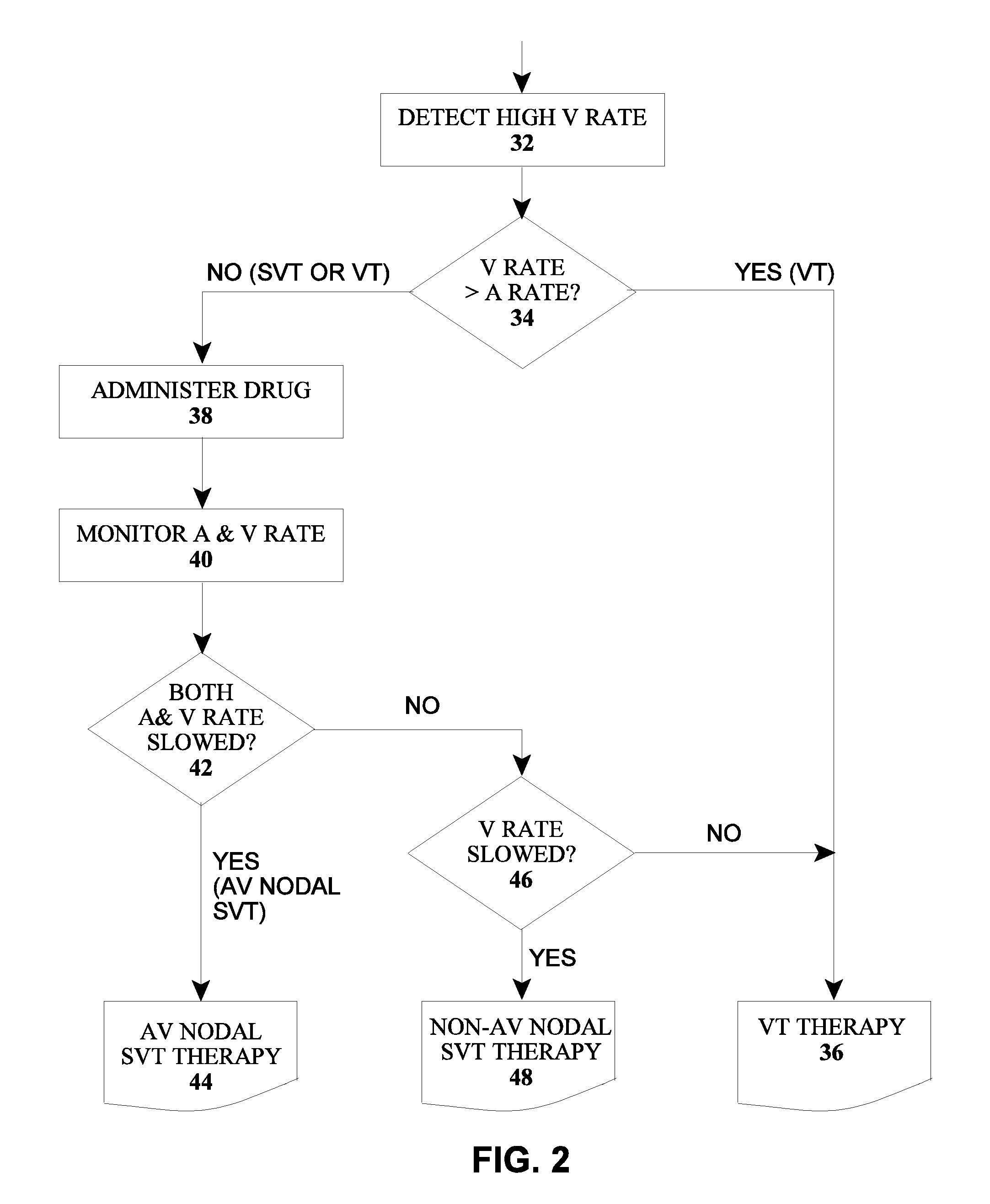
The type of arrhythmia in a patient's heart can be determined by monitoring the atrial and ventricular rate of the heart; detecting a pathological initial ventricular and / or atrial rate during a first time period; if a pathological initial rate is detected, then administering at least one antiarrhythmic cardioactive drug over a short second time period; detecting the heart's response to the administered drug(s), as by comparing the responsive ventricular and atrial rates with the initial ventricular and atrial rates, respectively, within a third time period; and determining the type of atrial or ventricular arrhythmia from the presence or absence of differences, and the type of differences, between the responsive atrial and ventricular rates compared with the initial atrial and ventricular rates. The invention further involves a related device which includes an implantable cardiac device (10) and a drug delivery device (20).
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Methods and devices for determination of heart arrhythmia type
ActiveUS8788026B2Increase influenceQuick fixElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyVentricular dysrhythmiaVentricular rate
The type of arrhythmia in a patient's heart can be determined by monitoring the atrial and ventricular rate of the heart; detecting a pathological initial ventricular and / or atrial rate during a first time period; if a pathological initial rate is detected, then administering at least one antiarrhythmic cardioactive drug over a short second time period; detecting the heart's response to the administered drug(s), as by comparing the responsive ventricular and atrial rates with the initial ventricular and atrial rates, respectively, within a third time period; and determining the type of atrial or ventricular arrhythmia from the presence or absence of differences, and the type of differences, between the responsive atrial and ventricular rates compared with the initial atrial and ventricular rates. The invention further involves a related device which includes an implantable cardiac device (10) and a drug delivery device (20).
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
Methods and systems for discriminating between ventricular waveforms when ventricular rate exceeds atrial rate
A ventricular rate based on first candidate waveforms and second candidate waveforms within sensed ventricular waveforms is compared to an atrial rate. If the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate, the first candidate waveforms and second candidate waveforms are compared to a ventricular polarization complex template to obtain a first morphology indicator and a second morphology indicator. If a morphology match inconsistency is present, the amount by which the ventricular rate exceeds the atrial rate is compared to a threshold. If the threshold is exceeded, high-ventricular-rate therapy to the heart is inhibited. The ventricular polarization complex template may be a QRS-complex template, in which case a match inconsistency is present if each of the first candidate waveforms and the second candidate waveforms do not match the QRS-complex template. Alternatively, the ventricular polarization complex template may be a T-wave template, in which case a match inconsistency is present if either of the first candidate waveforms and the second candidate waveforms matches the T-wave template.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
A Low-Power Method for Realizing Mode Inversion of Implantable Pacemaker
ActiveCN105079964BReduce power consumptionReduce design difficultyHeart stimulatorsMedicineCardiac cycle
The present invention discloses a low power consumption method for realization of a mode inverse conversion of an implantable pacemaker. The low power consumption method provided by the invention comprises: when a patient has an atrial fibrillation symptom, the implantable pacemaker works in a DDI mode, an atrium perceptive function is opened in the VA interval, and the PVARP is extended at the moment of each ventricular event; in each VA interval of the cardiac cycle, the patient's AA interval values are acquired by the implantable pacemaker, and the acquired patient's AA interval values are compared with the mode inversion frequency intervals; when the AA interval values are larger than the mode inversion frequency intervals, the patient's atrial rate is lower than the preset atrial rate, and the event of the patient's atrial rate being lower than the preset atrial rate is recorded as a low atrial rate event; and when the number of the low atrial rate events is larger than or equal to the preset threshold values in a preset time, the atrial fibrillation stops, and the implantable pacemaker jumps back to the DDD mode followed by the atrium. According to the invention, the mode conversion of the implantable pacemaker from the DDI mode to the DDD mode is realized, and the service life is relatively long.
Owner:SHAANXI QINMING MEDICAL CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com