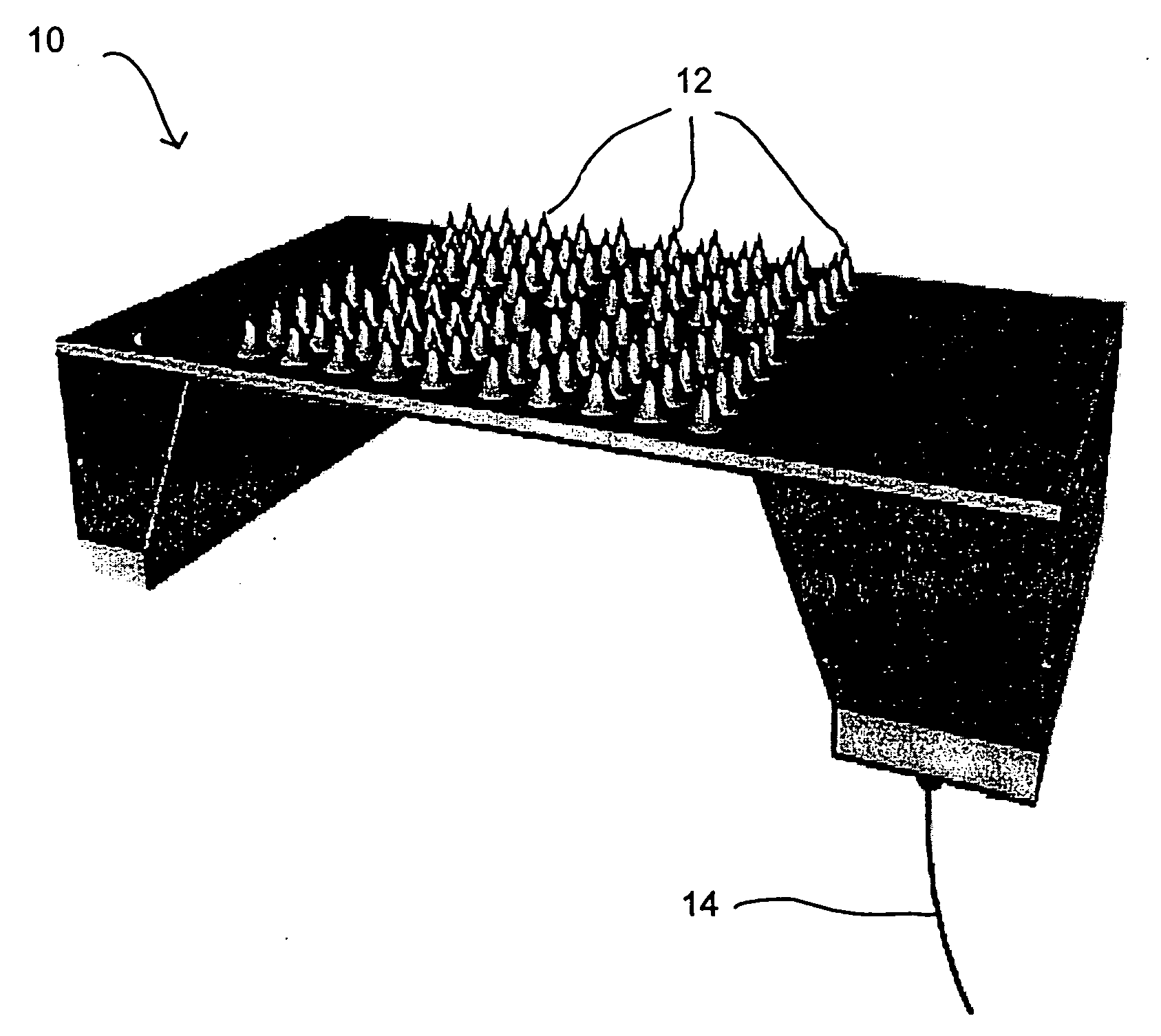
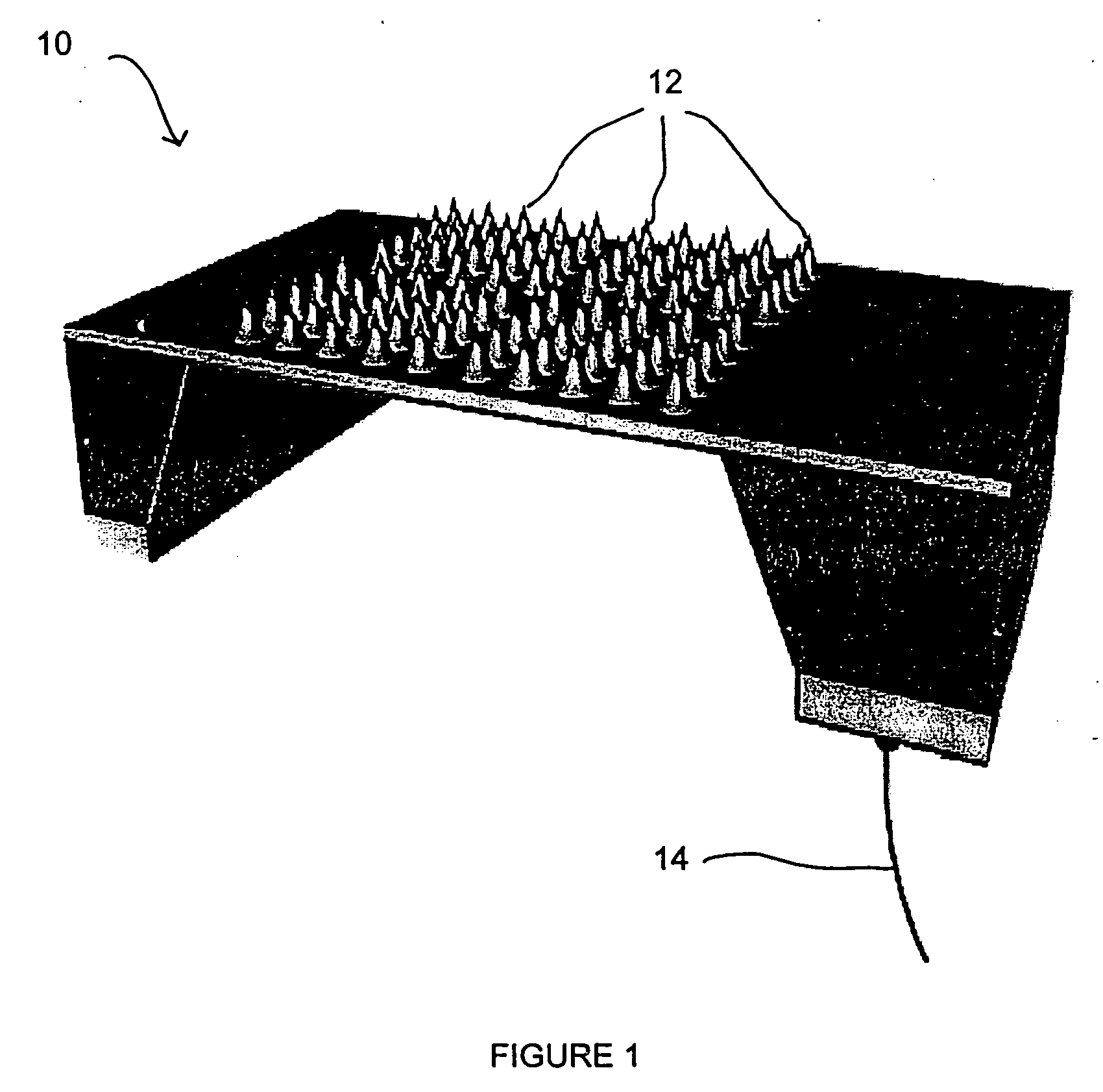
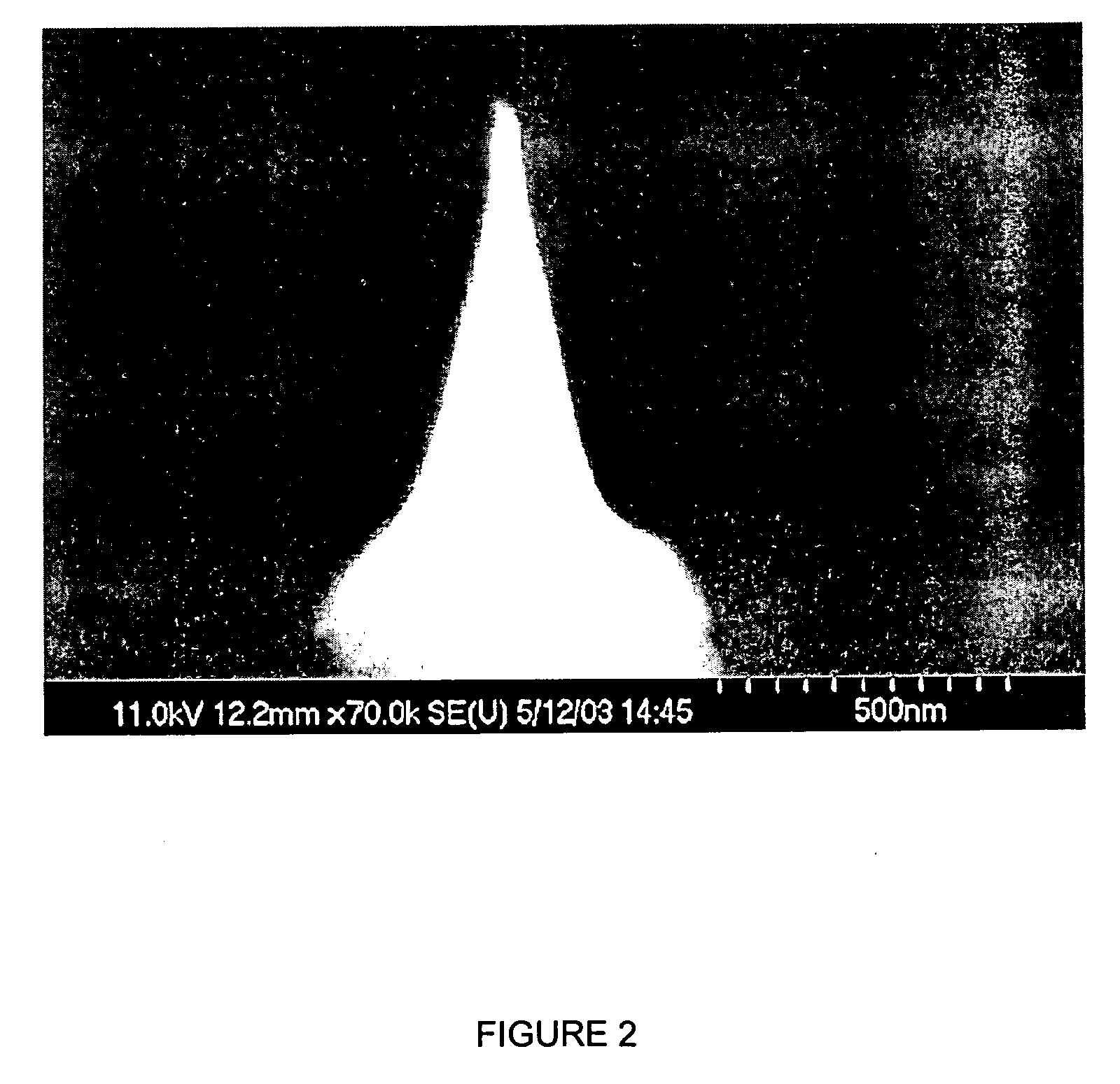
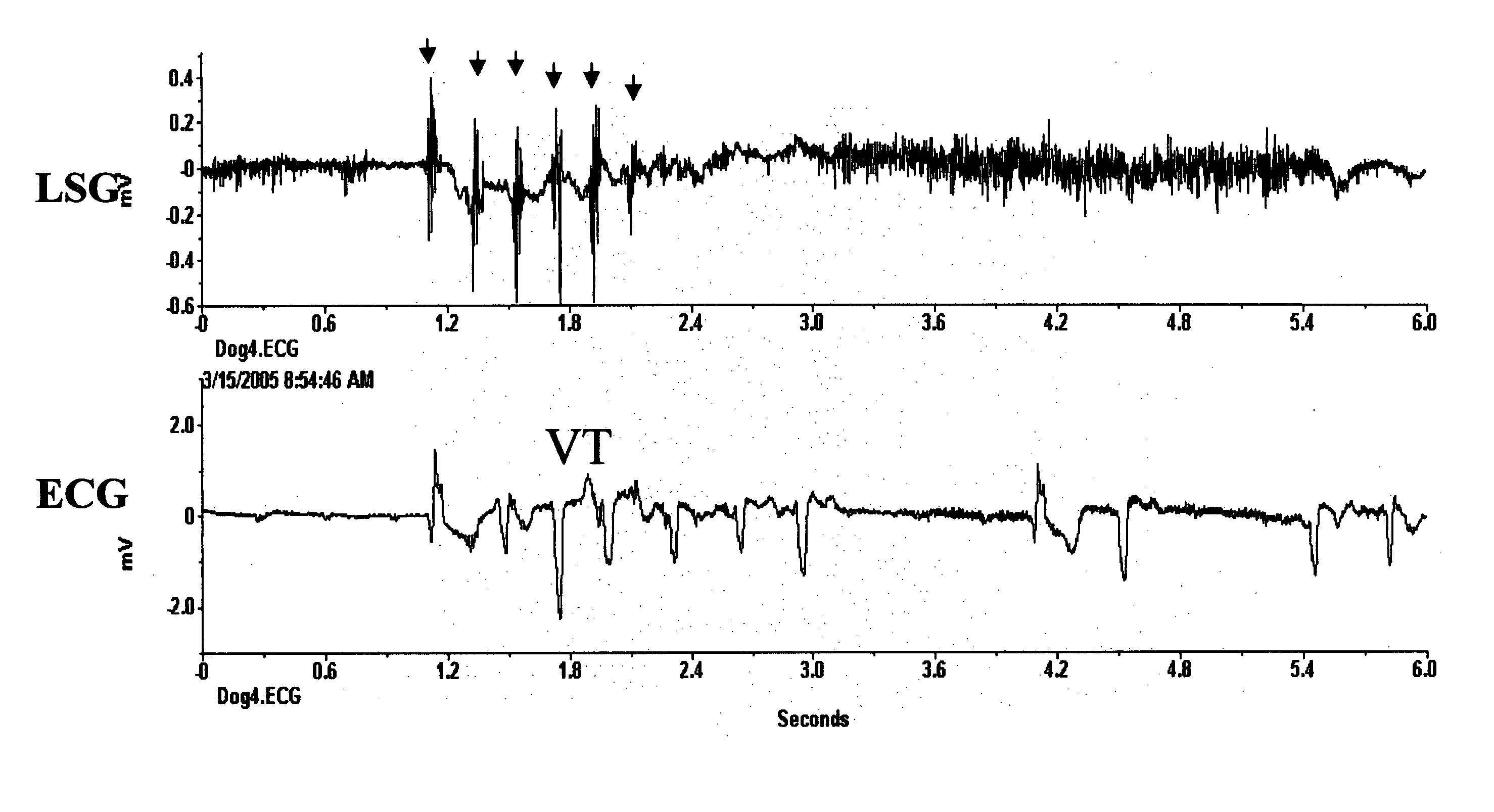
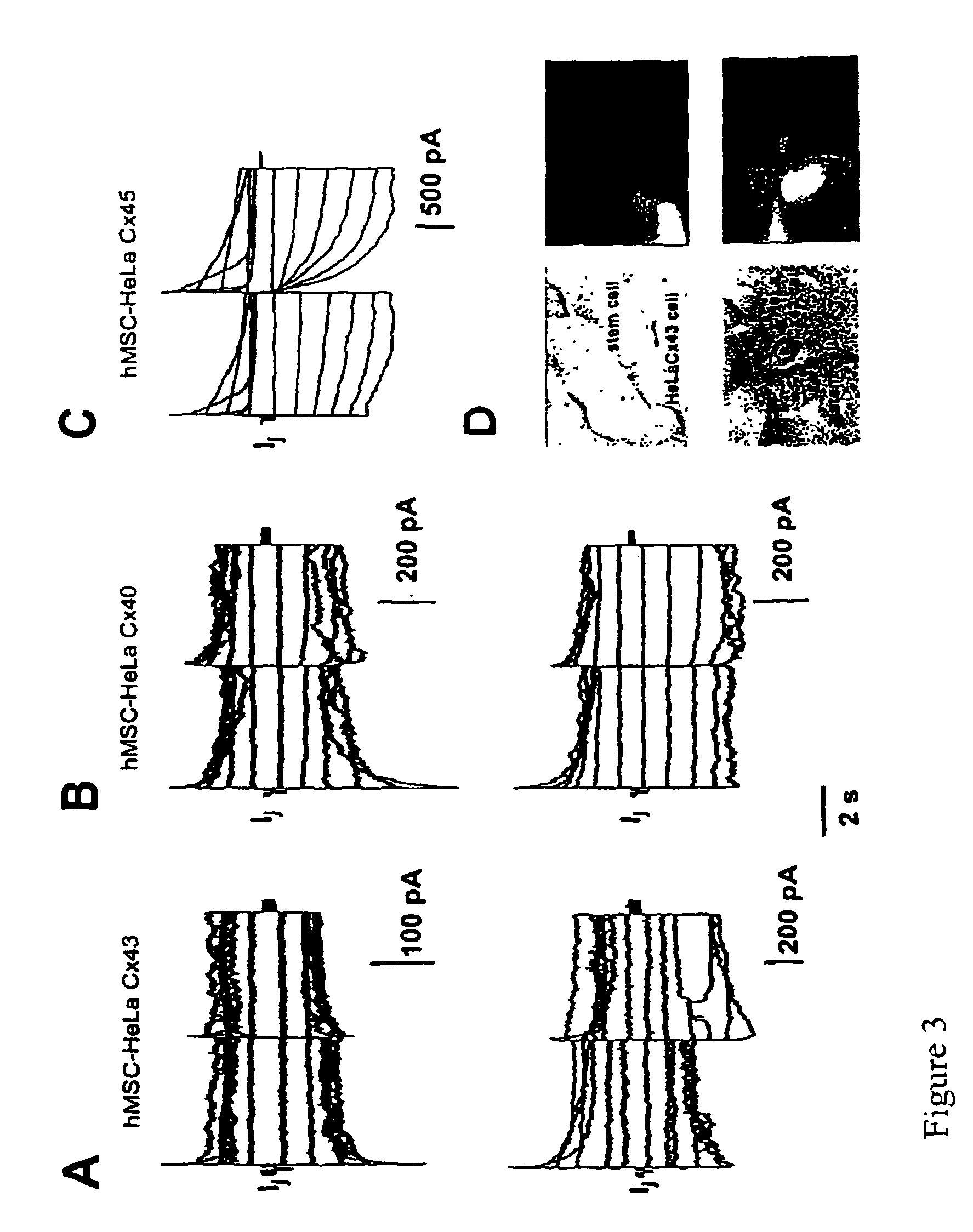
Patents
Literature
32 results about "Sinoatrial node" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
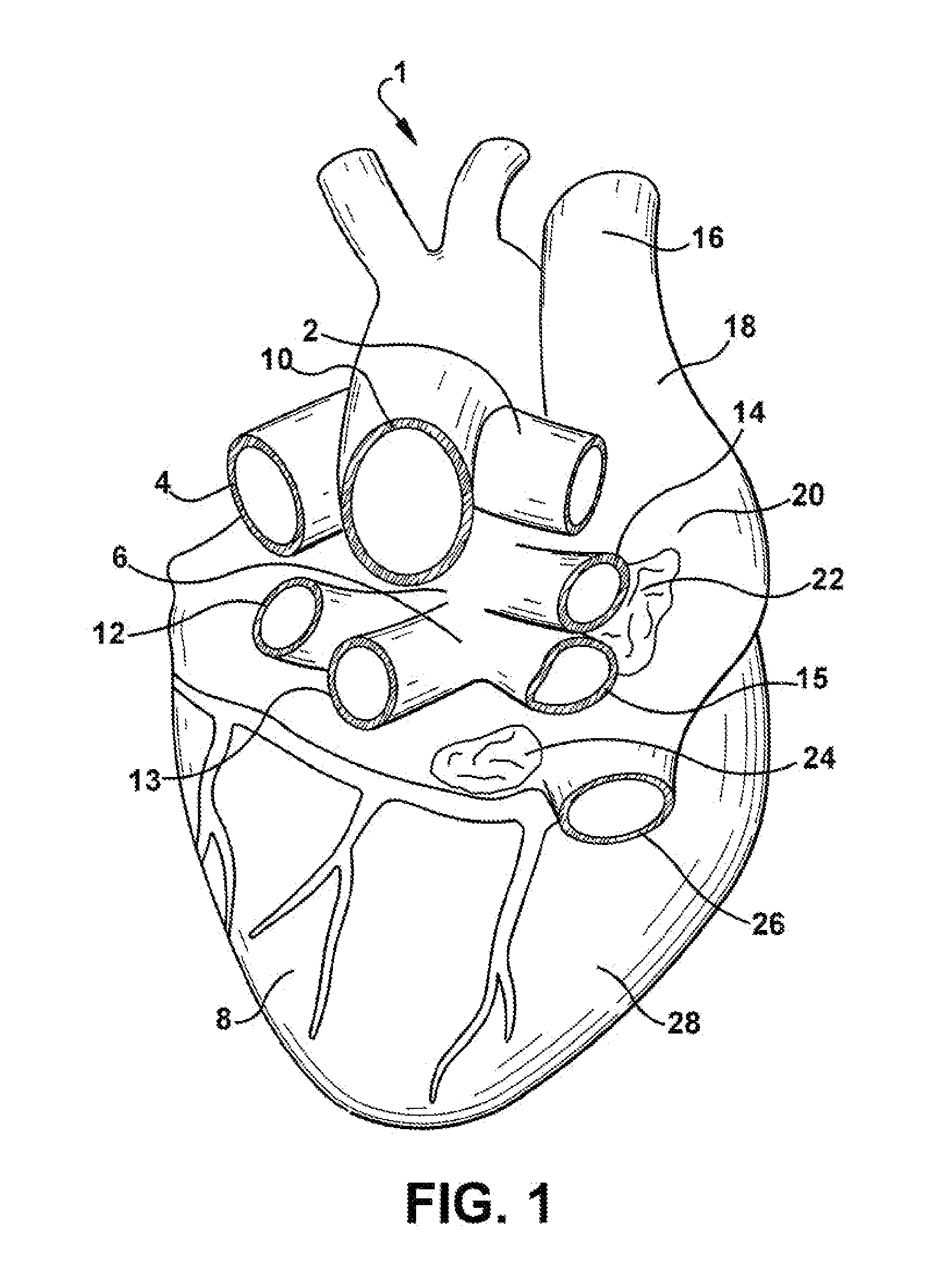
The sinoatrial node (also known as the SA node or the sinus node) is a group of cells located in the wall of the right atrium of the heart. These cells have the ability to spontaneously produce an electrical impulse (action potential; see below for more details), that travels through the heart via the electrical conduction system (see figure 1) causing it to contract. In a healthy heart, the SA node continuously produces action potential, setting the rhythm of the heart and so is known as the heart's natural pacemaker. The rate of action potential production (and therefore the heart rate) is influenced by nerves that supply it.
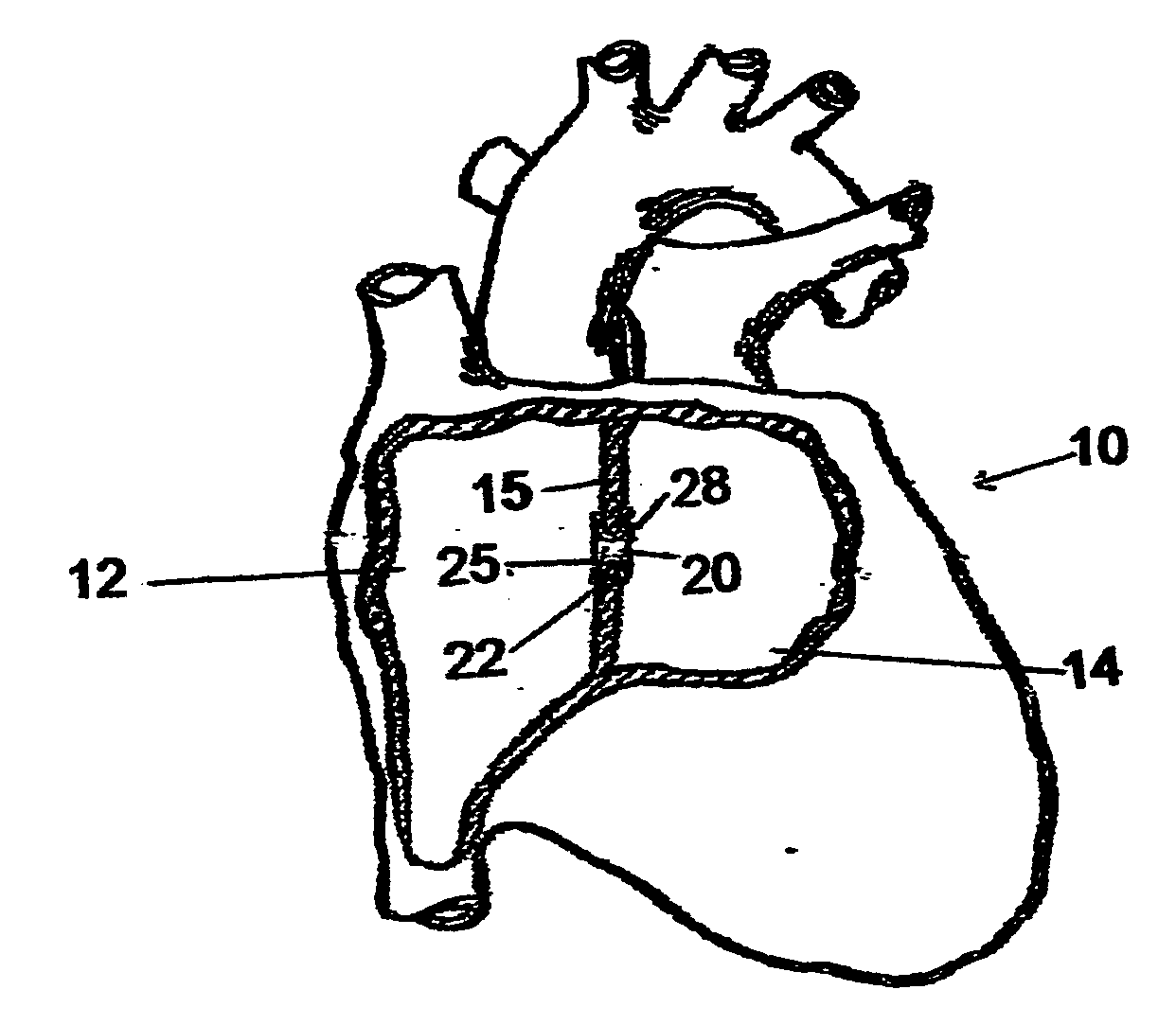
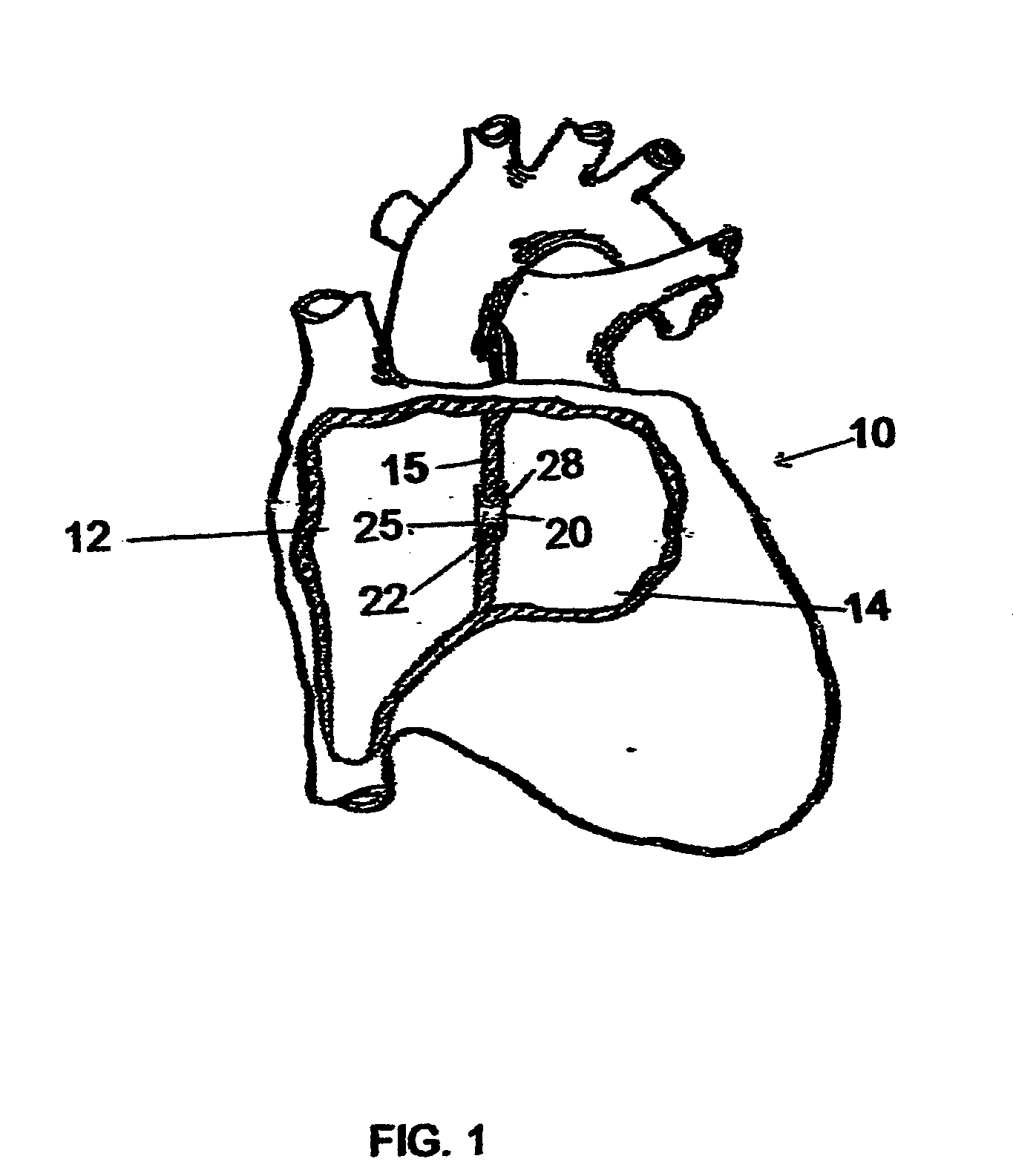
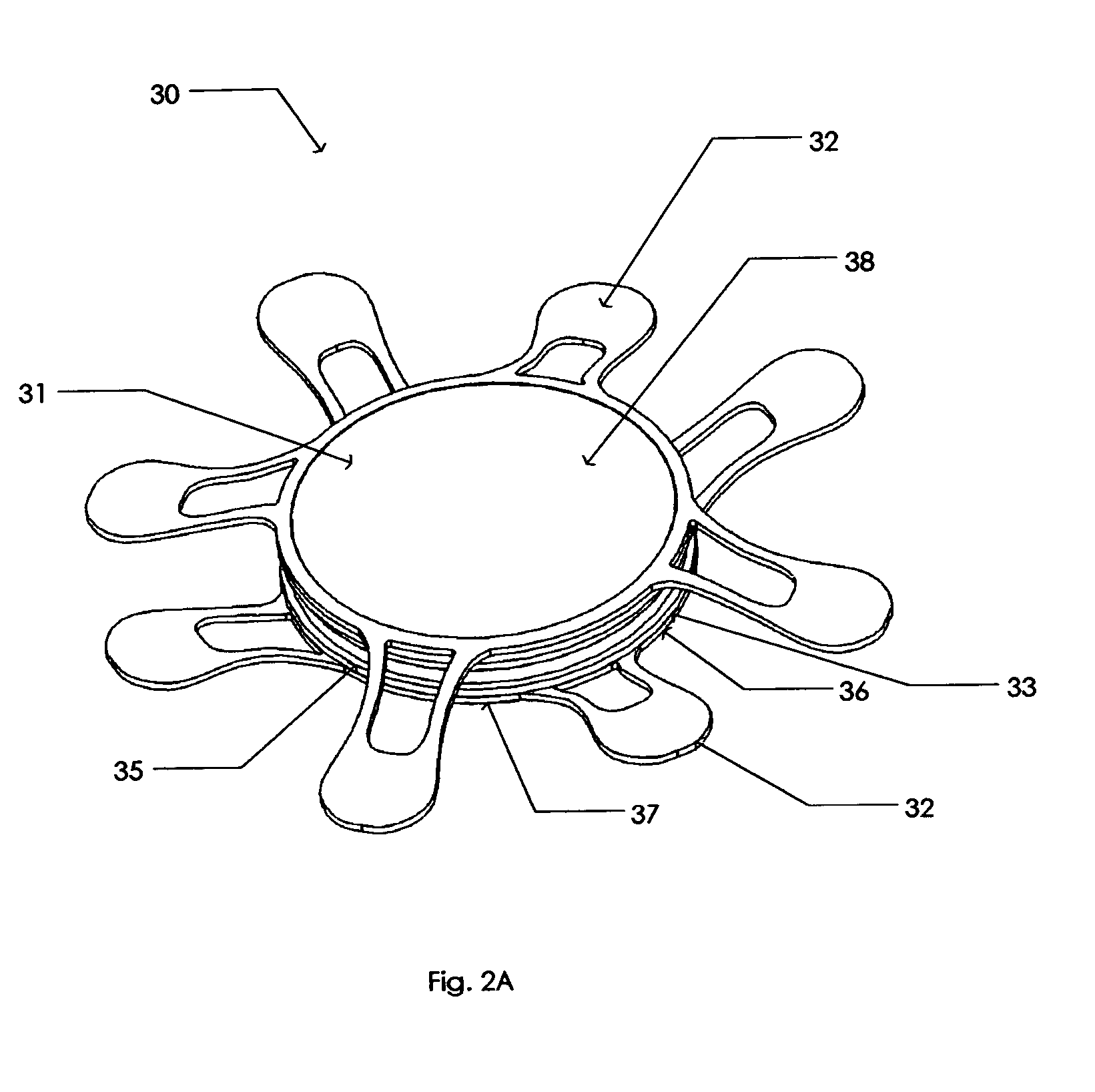
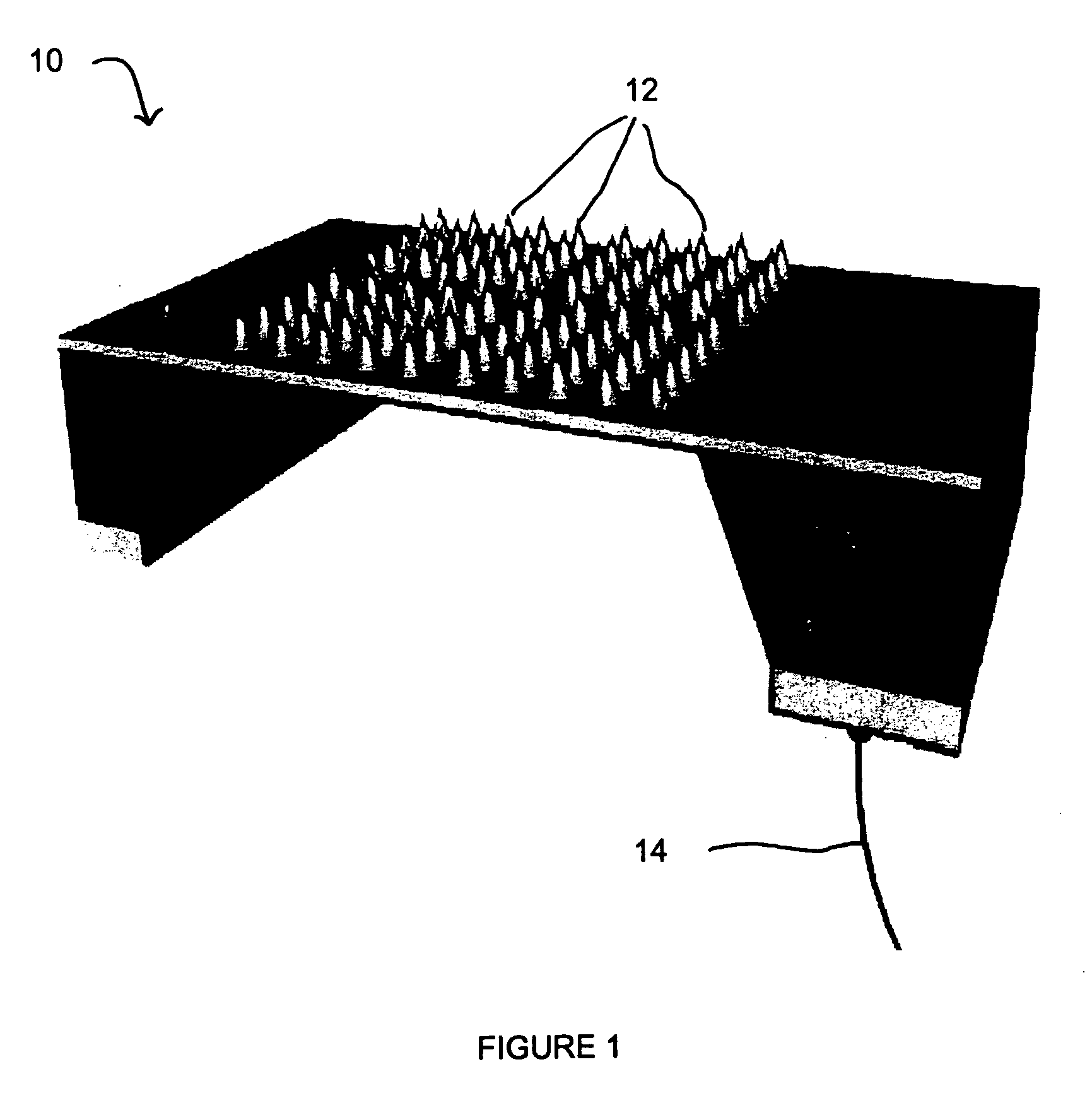
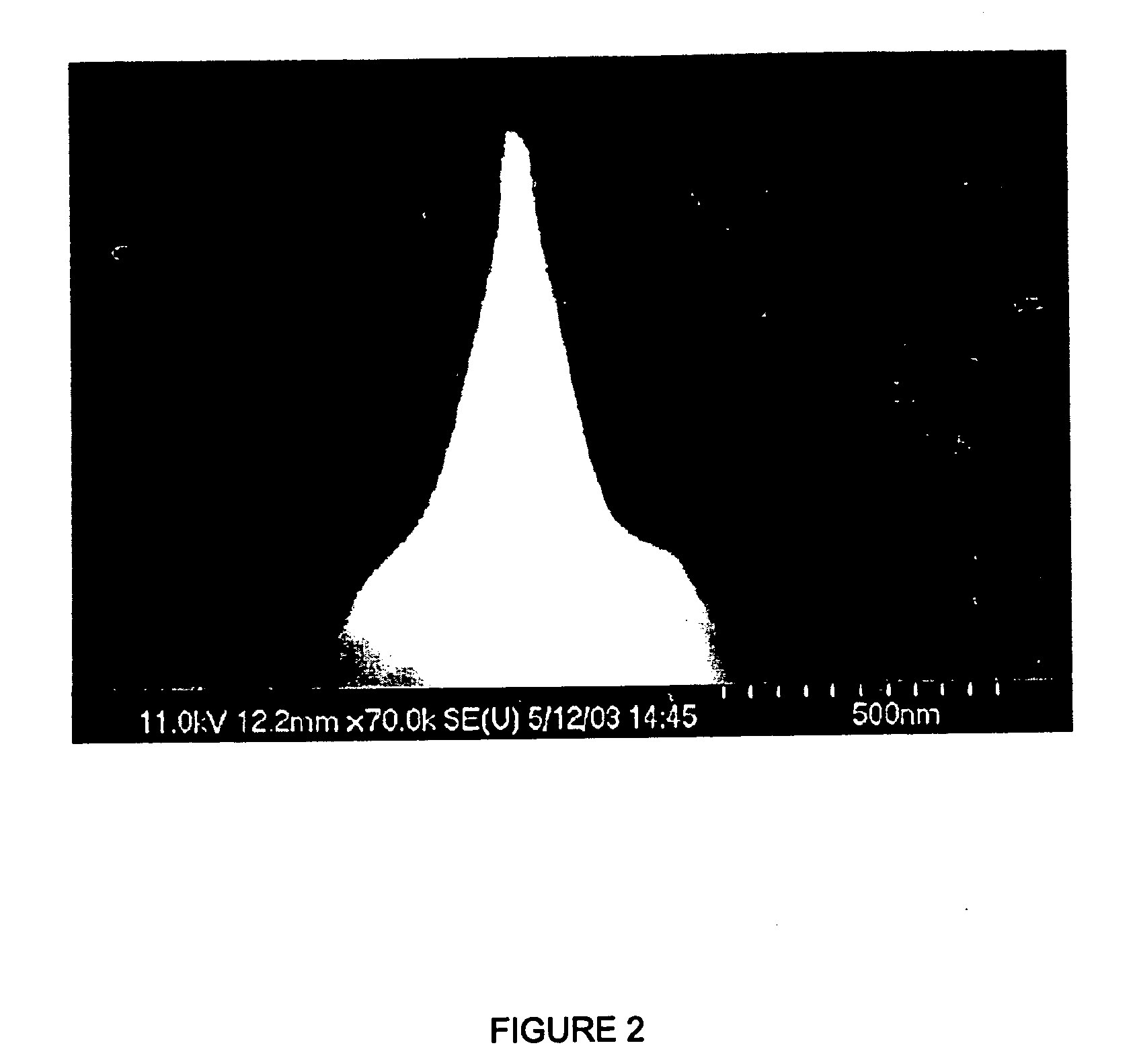
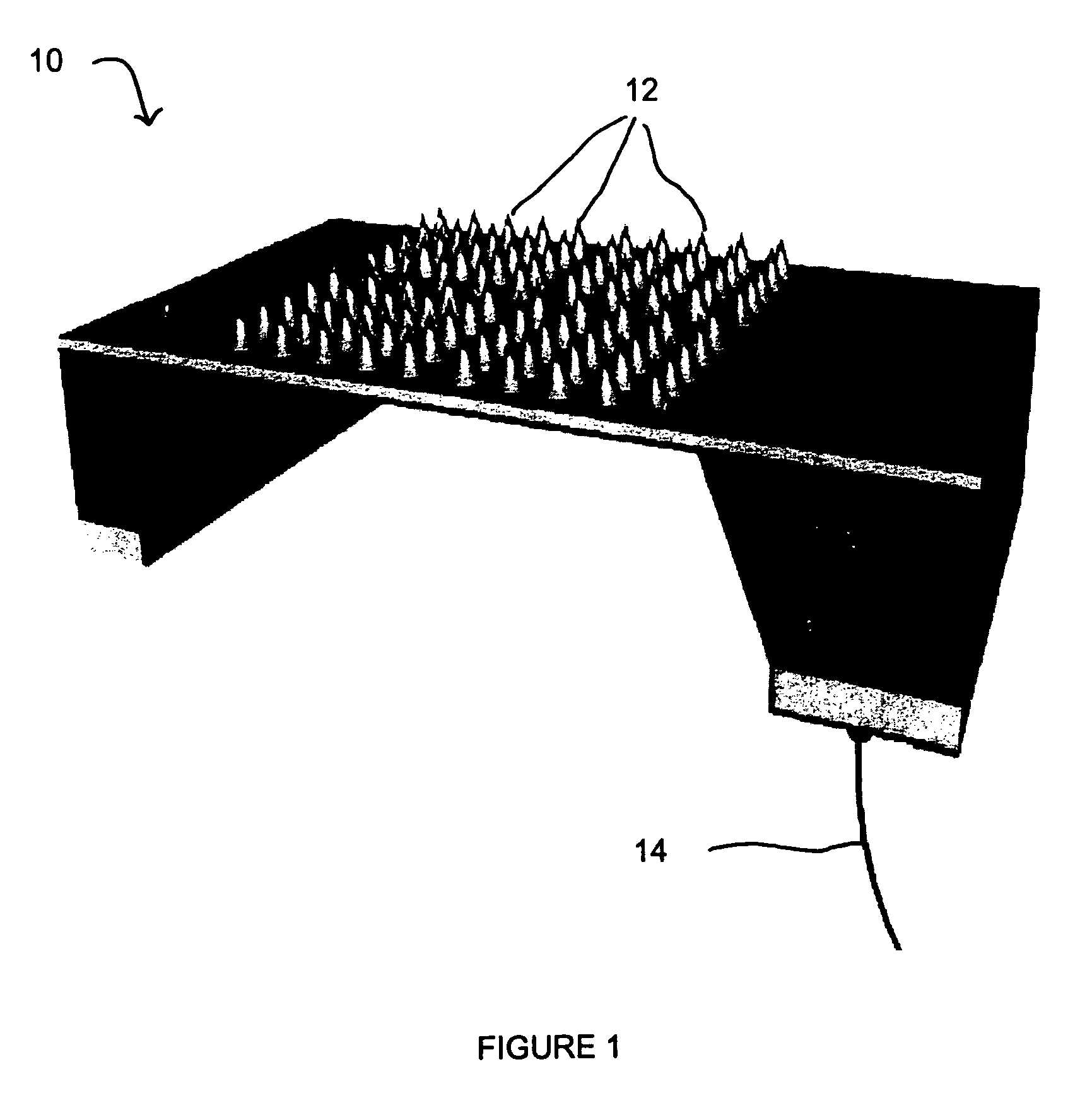
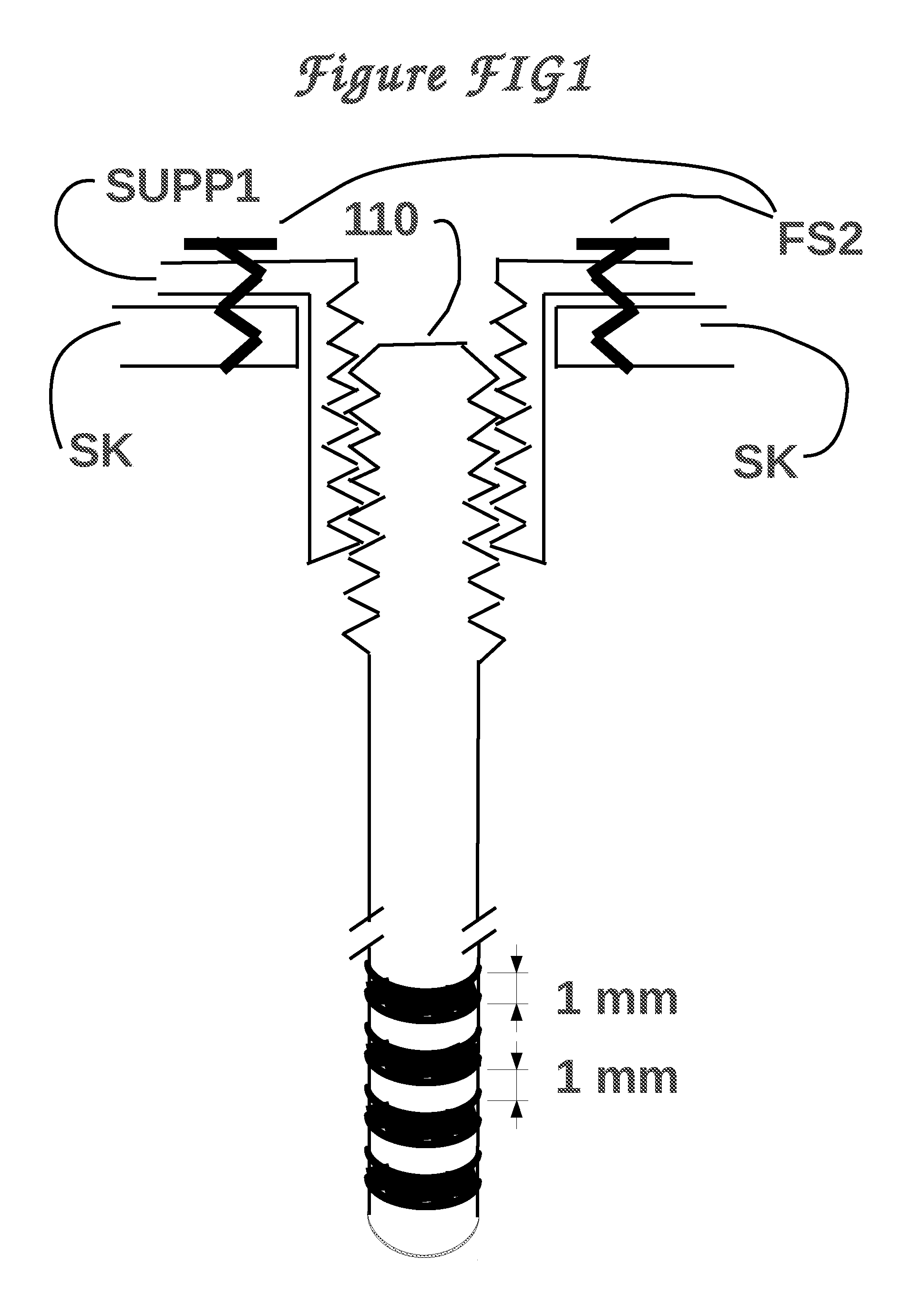
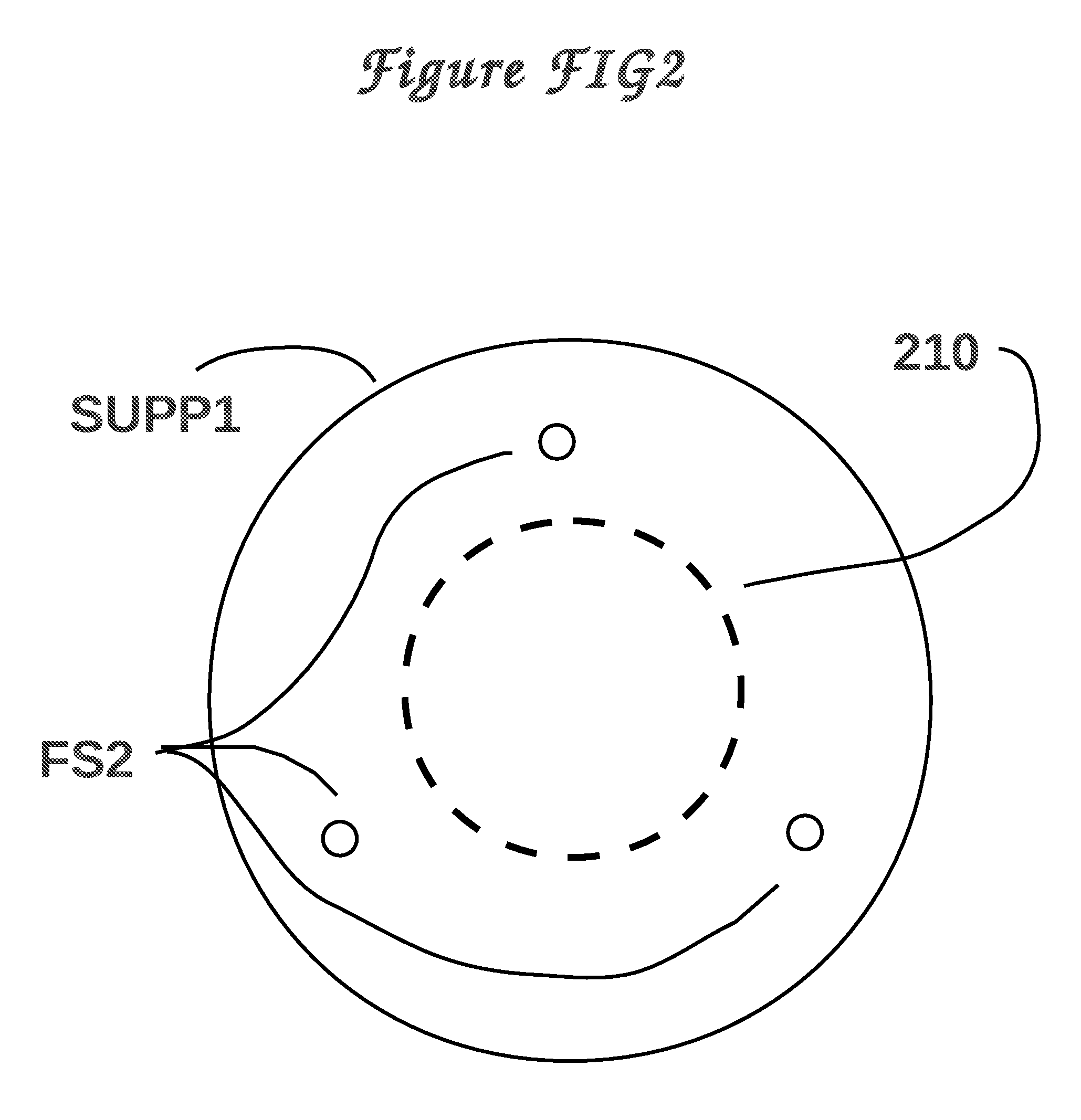
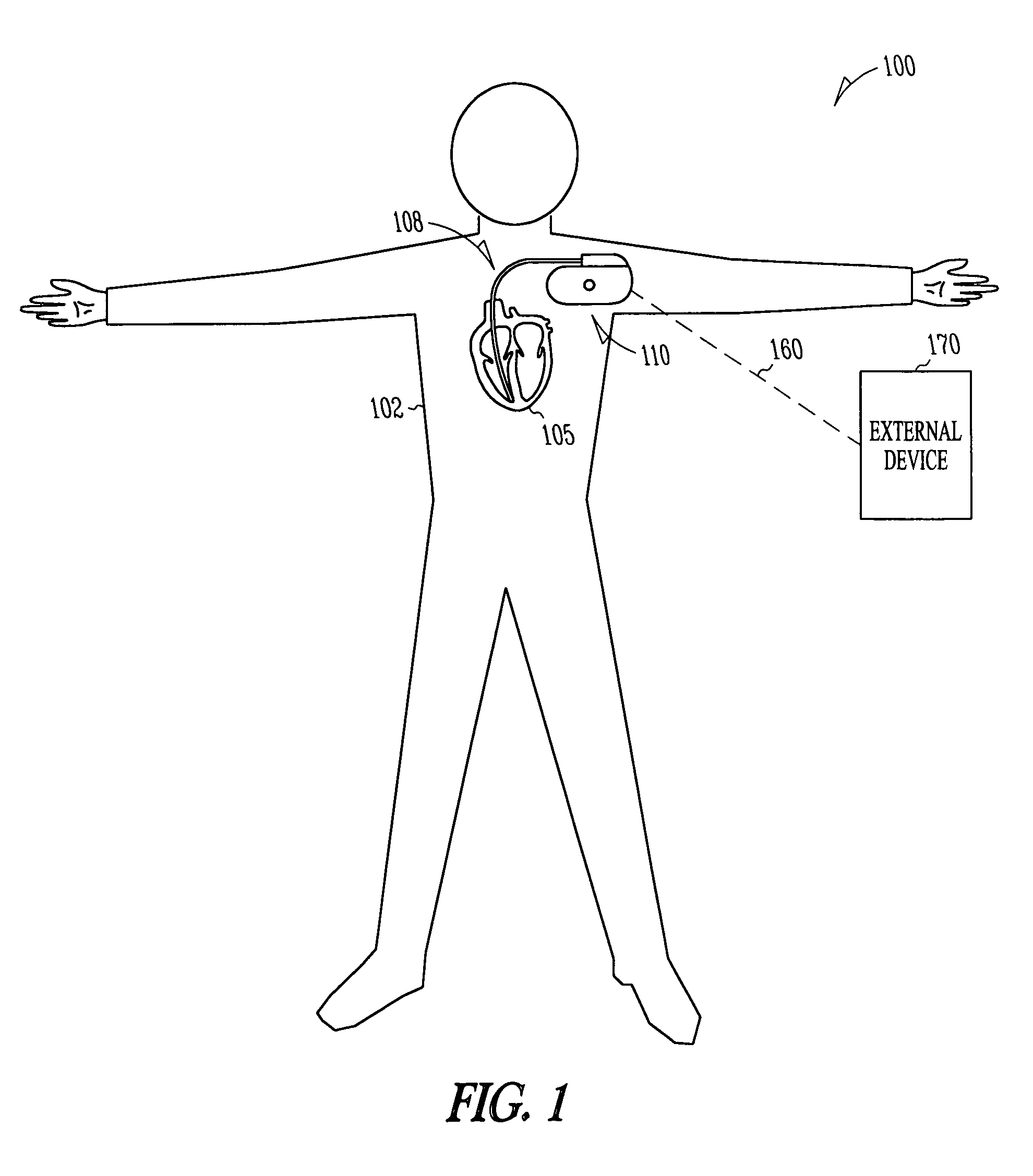
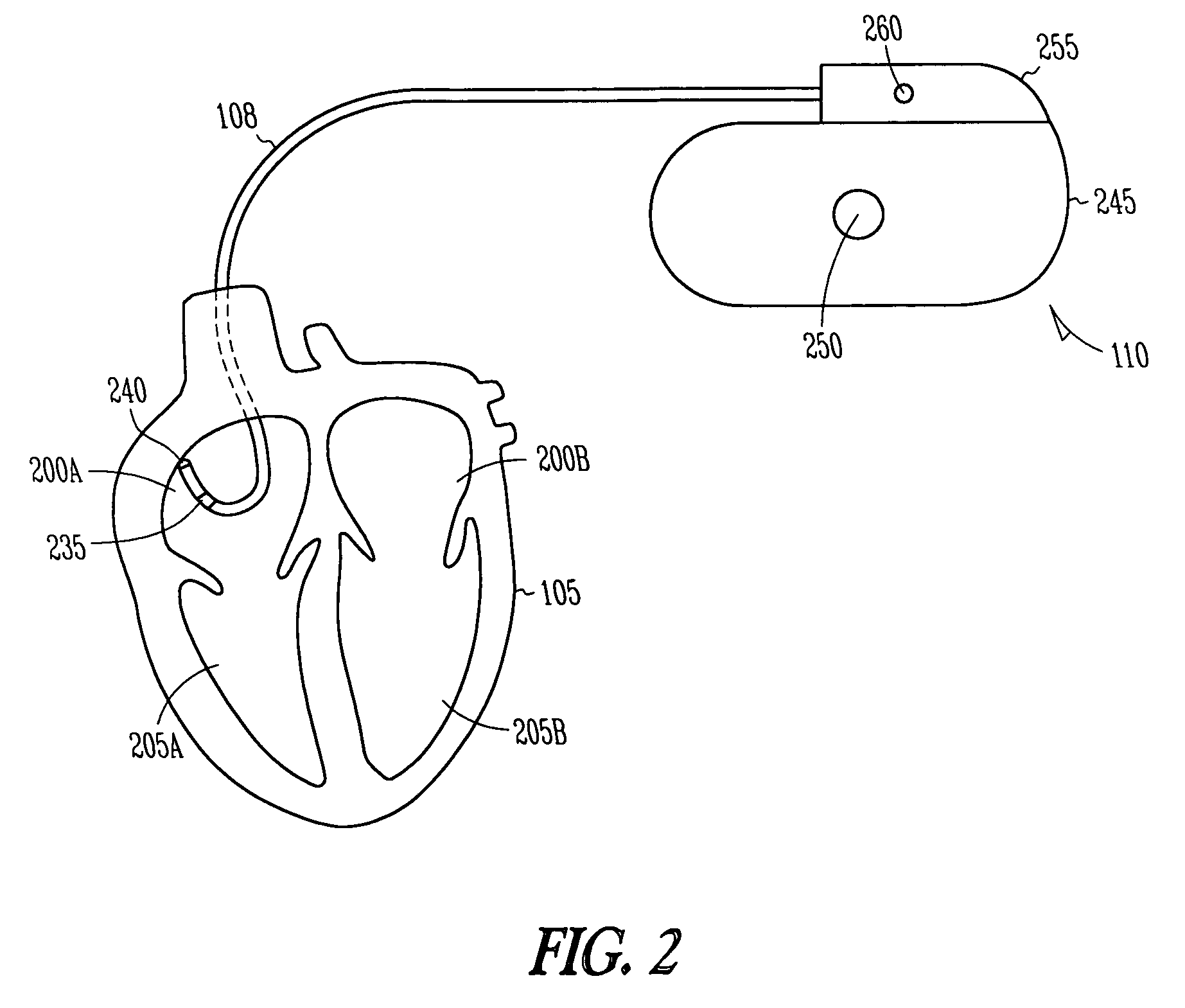
Implantable chamber for biological induction or enhancement of muscle contraction
InactiveUS20050283218A1Improve conductivityAvoid overgrowthTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseSinoatrial node
A percutaneously implantable chamber for the treatment of a cardiac condition is disclosed herein, the chamber capable of delivery and maintenance of viable cells comprising a pacemaker gene or other genes intended to impart a specific function via a host cell. An artificial sinoatrial node and artificial atrial ventricular node for the restoration of the pacemaker function of the heart of a subject comprises a chamber comprising cells expressing a pacemaker gene. Further, a chamber may be used for the implantation and maintenance of viable, responsive, immunoisolated cells to induce or enhance muscle contraction of a subject for the treatment of a disorder.
Owner:SYNECOR LLC
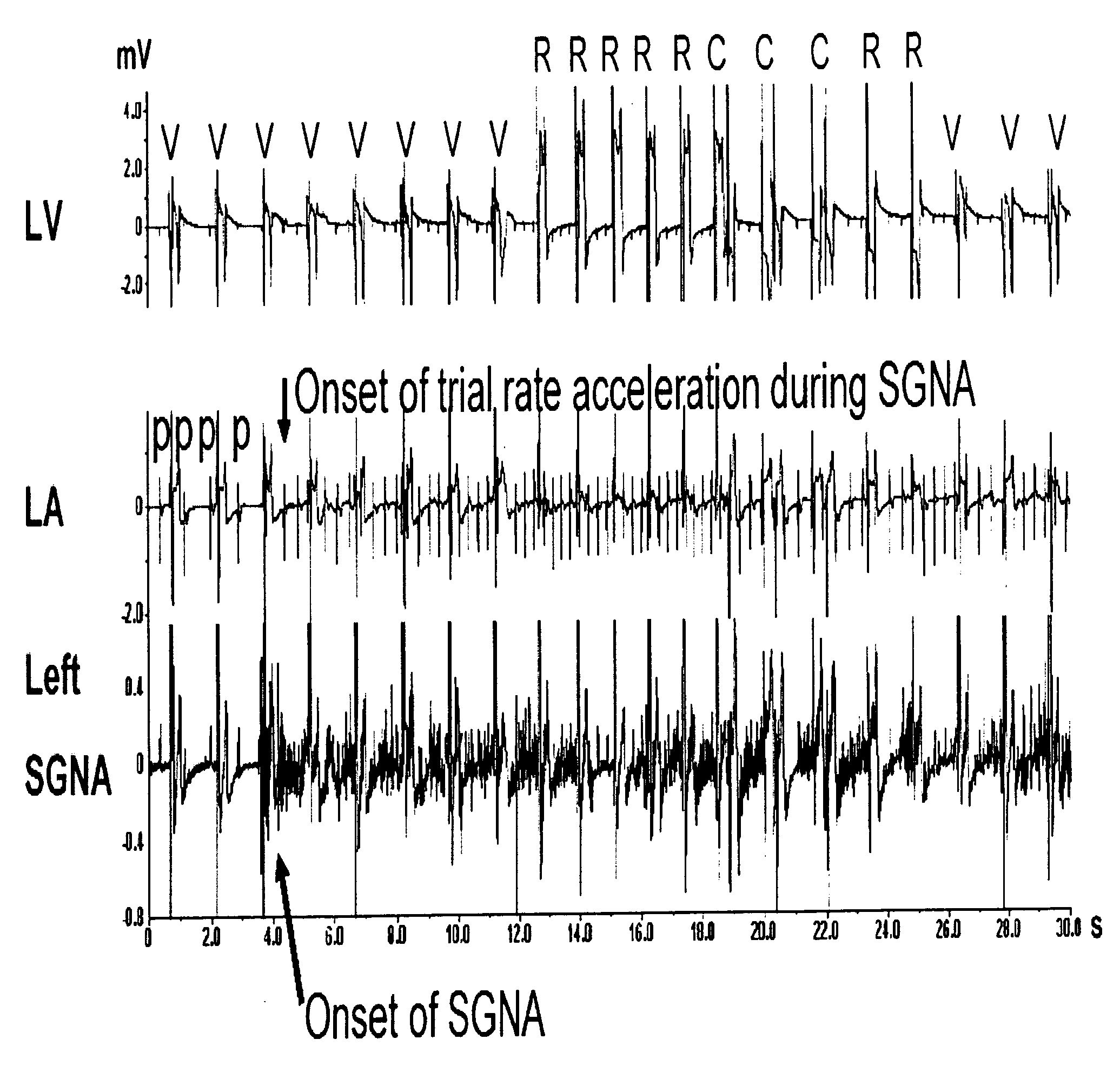
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
InactiveUS20060074451A1Raise the possibilityIncrease heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAntiarrhythmic effect
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
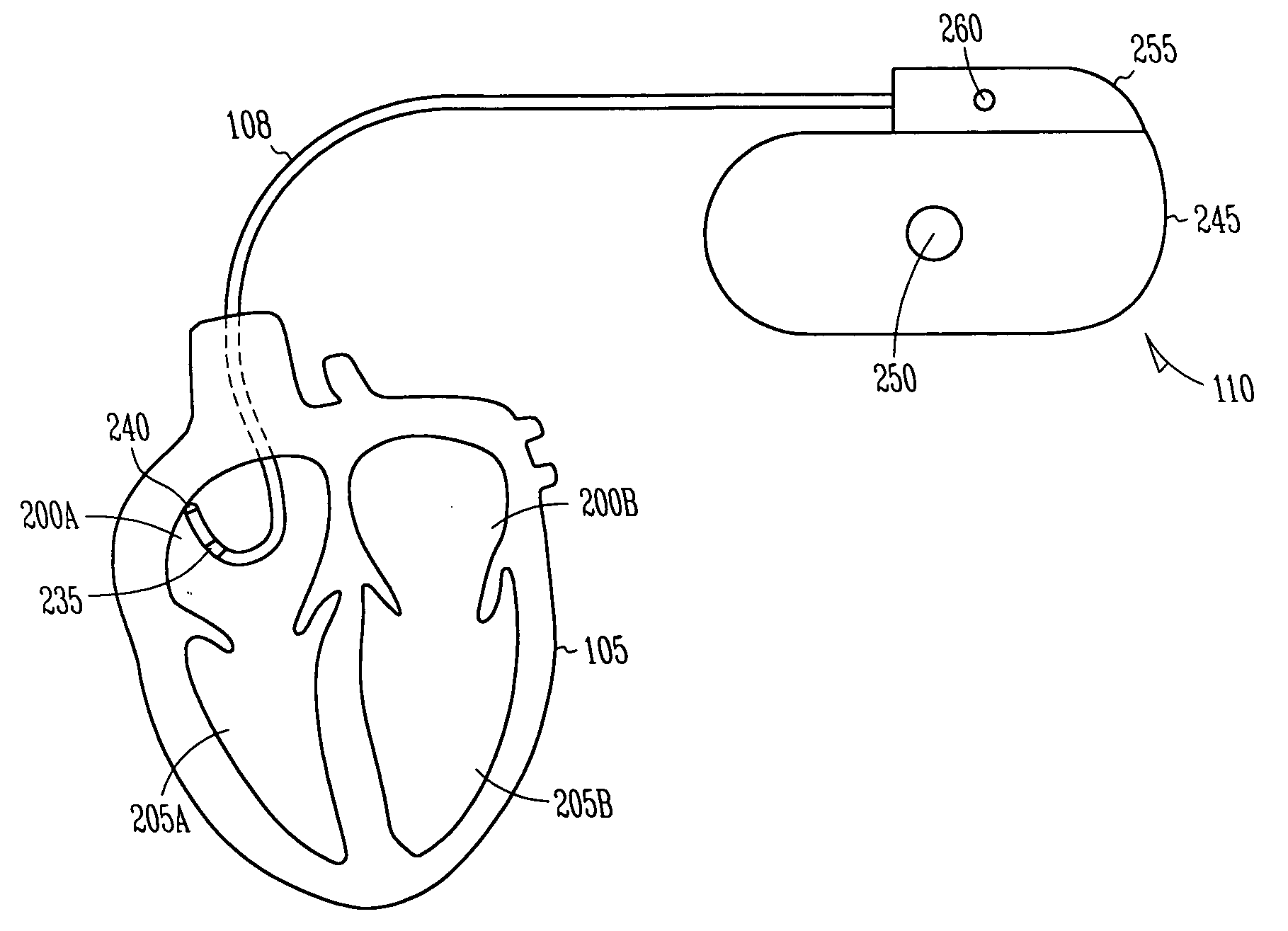
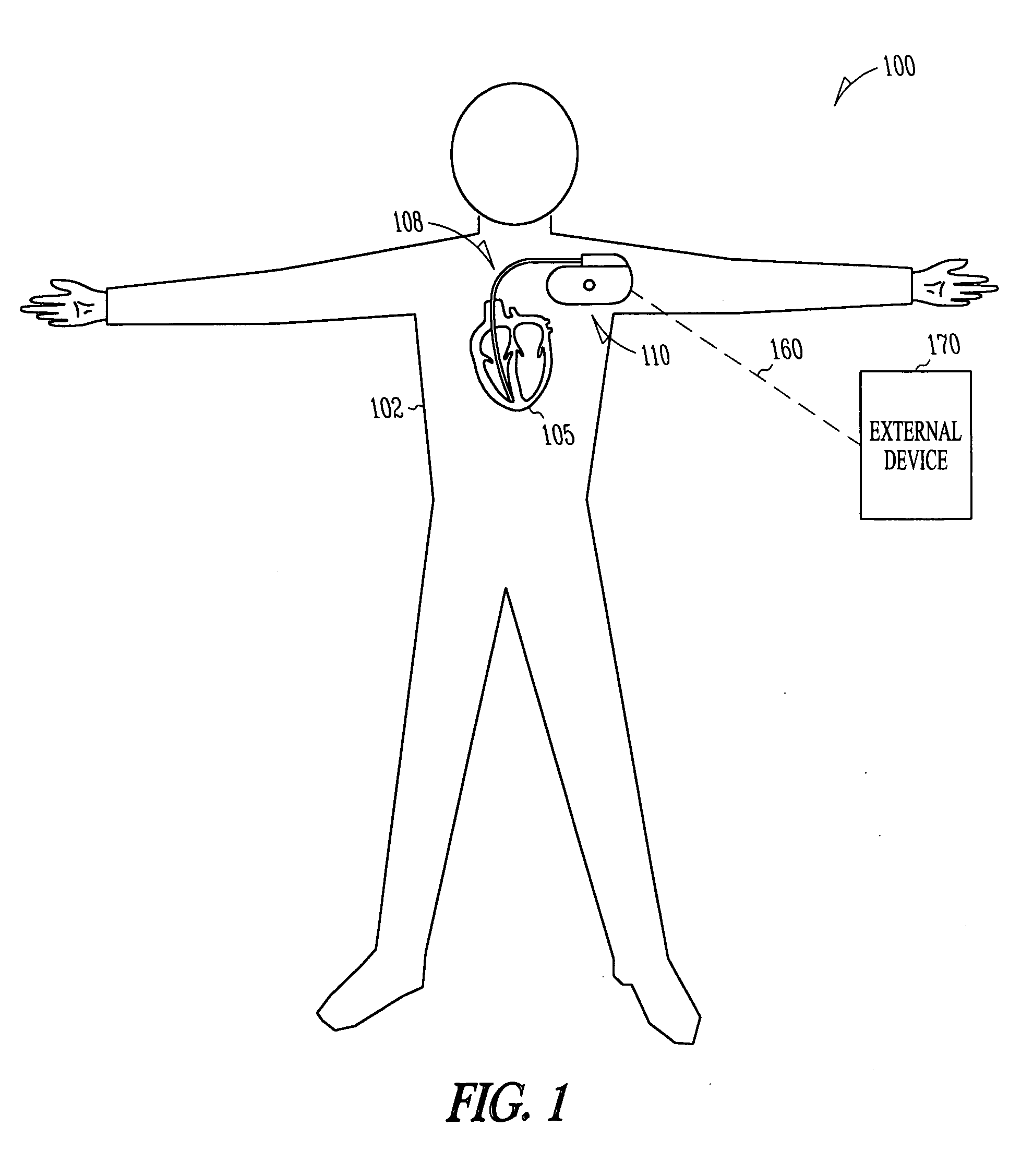
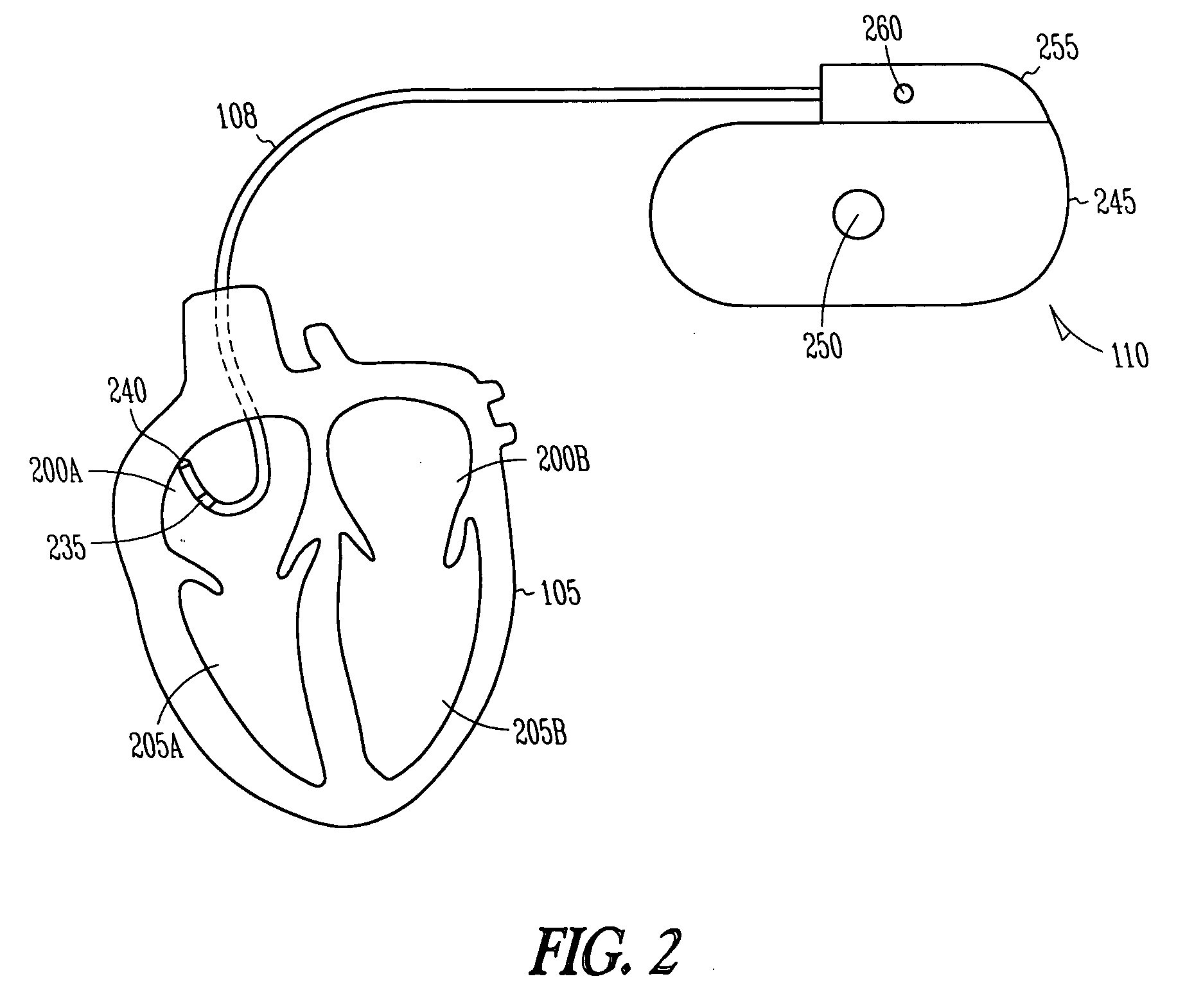
Cardiac stimulation device for sinus rate modulation
ActiveUS20080147138A1Reduce probabilityEpicardial electrodesExternal electrodesEcg signalSinoatrial node
A system comprising an implantable electrical cardiac signal sensing circuit, an implantable sinoatrial cardiac action potential detector circuit, and an implantable electrical stimulation circuit in electrical communication with the electrical cardiac signal sensing circuit and the sinoatrial cardiac action potential detector circuit. The electrical cardiac signal sensing circuit is configured to receive one or more intrinsic heart signals from one or more respective electrodes configured for placement in a vicinity of a sinoatrial node of a subject. The implantable electrical stimulation circuit is configured to initiate delivery of at least one inhibitory electrical stimulation pulse in a vicinity of the sinoatrial node in a timed relationship to a sensed sinoatrial cardiac action potential. Other systems and methods are disclosed.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Method for orienting inducing and differentiating heart pacemaker cell by embryo source pluripotent stem cell
Cell transplantation for constructing biological heart pacemaker is used embryo source dry / ancestral cell and adult mesogalia dry cell as cell sources. The process is carried out by oriented differentiation inducing for heart pacemaker cell by embryo source multifunctional dry cell, bone marrow adhering to obtain primary culture cell, clone culturing to obtain purifying system by diluting, applying paracrine factor endothelin-1 or nervous adjusting protein-1, extracellular matrix laminated adherent protein and fiber connecting protein etc. substrate glue, trans-dyeing pacemaker gene HCN4, and in-vitro inducing embryo source multifunctional dry cell. It is various and non-immunogenicity. It can be used to treat sick sinus syndrome.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
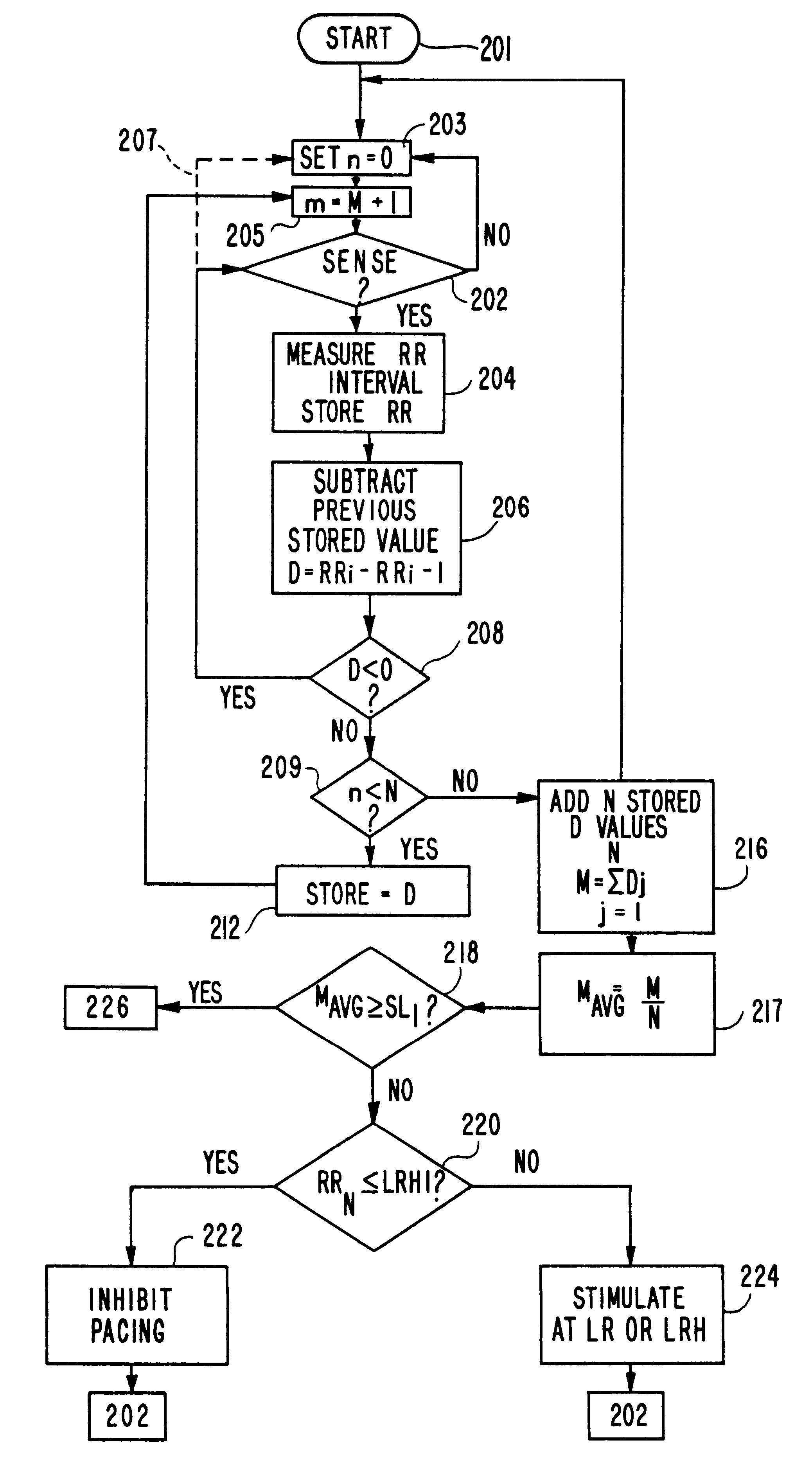
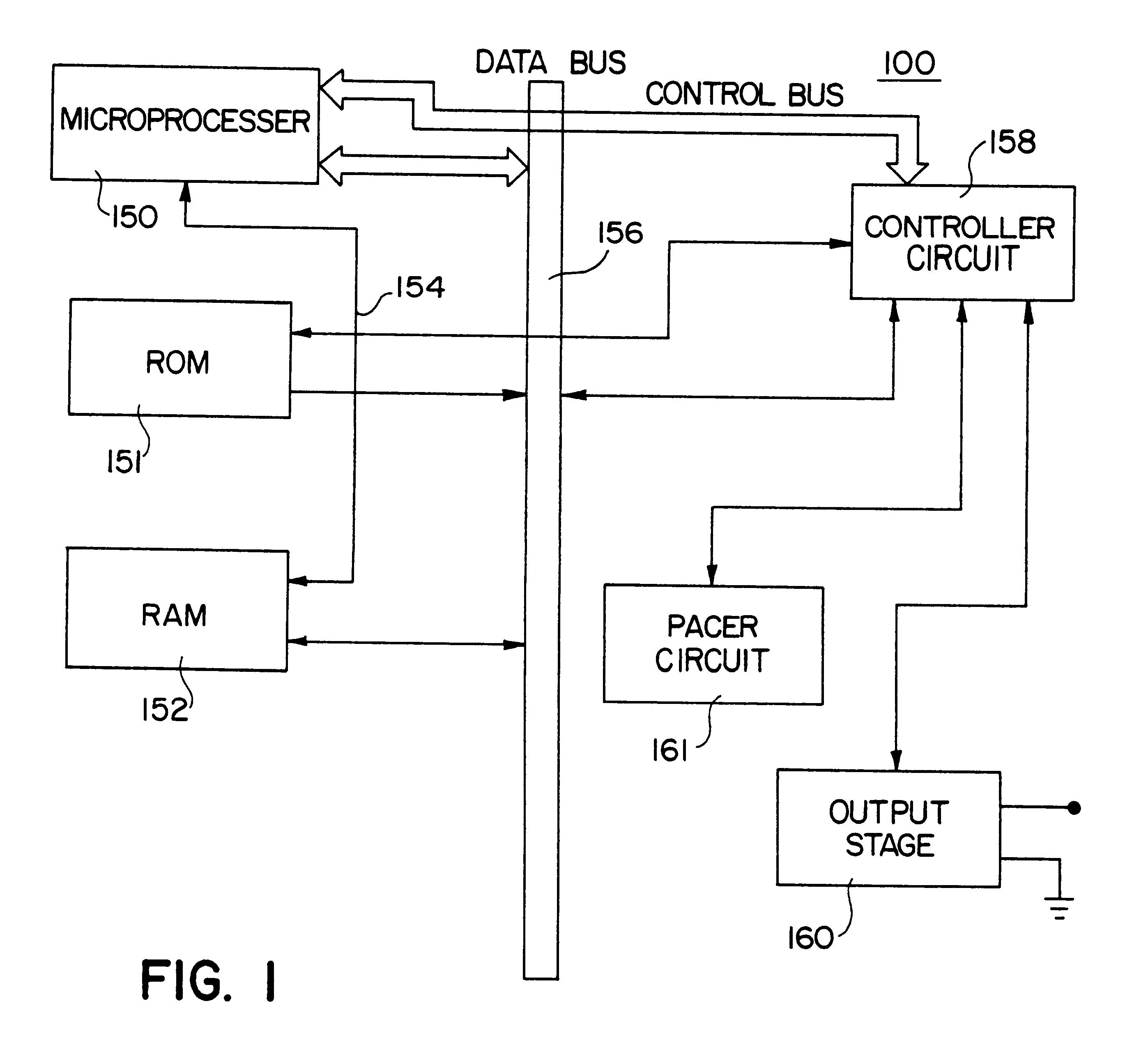
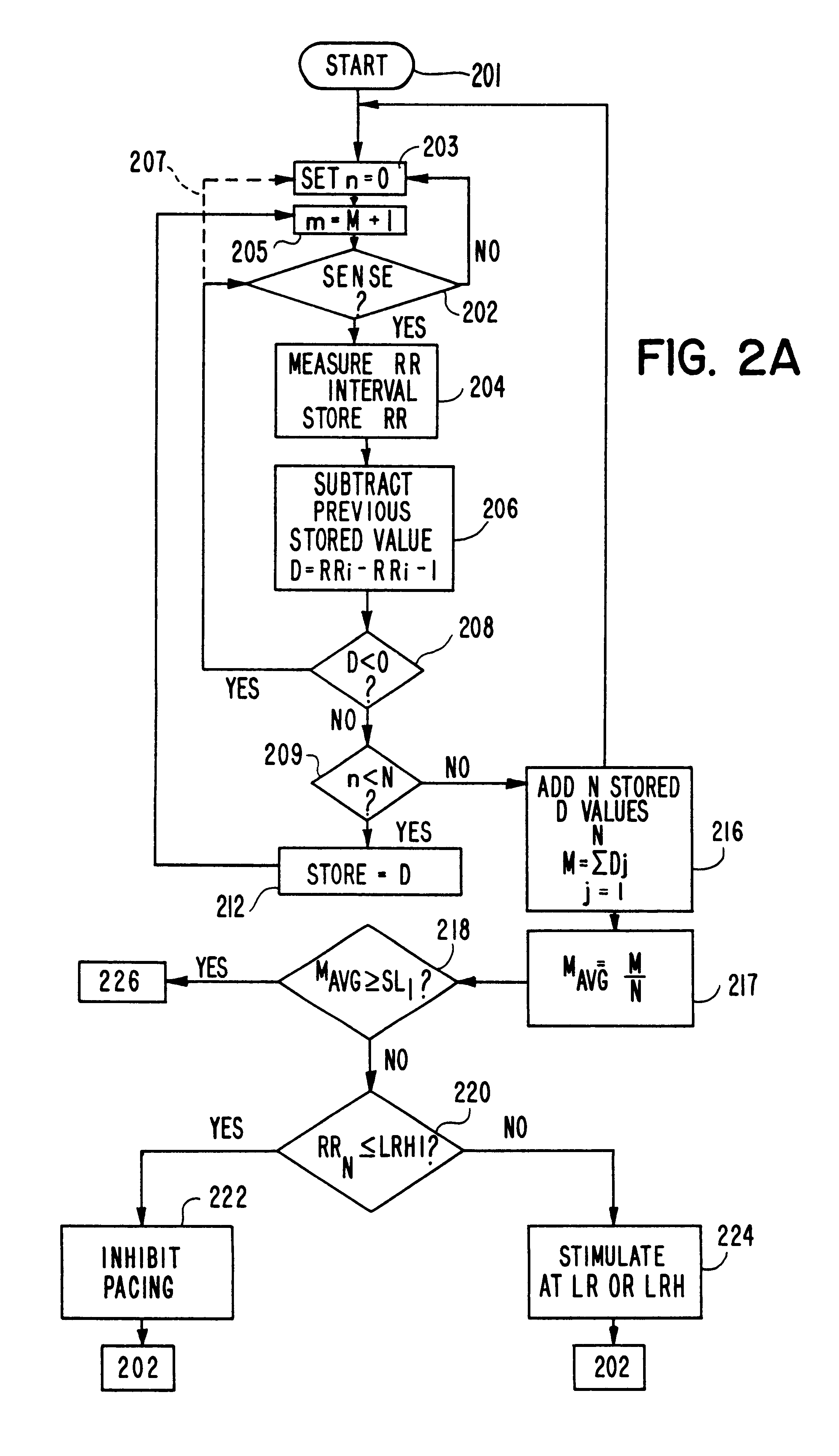
Cardiac pacemaker with hystersis behavior
A pacemaker having a hysteresis feature which permits intrinsic heart activity, controlled by the sinus node to resume optimally after pacing. The pacemaker has a programmable lower rate and upper rate, a programmable lower hysteresis rate (LRH) corresponding to a lower rate hysteresis interval (LRHI), and a programmable rate (IR) intermediate an upper pacing rate (UR) and a lower pacing rate (LR). A microprocessor measures the average rate of change MAVG in the intervals between consecutive ventricular depolarizations, and compares the last intrinsic escape interval RRN to the lower rate hysteresis interval (LRHI).If the last intrinsic escape interval RRN is longer than the lower rate hysteresis interval (LRHI), and if the value of MAVG is greater than a first preselected value SL1 but less than a second preselected value SL2, the pacemaker stimulates at the lower rate hysteresis (LRH) and thereafter gradually increases the pacing rate up to the intermediate rate (IR). A time counter maintains a continuous pacing at the intermediate rate (IR) for a predefined period of time, and the pacing rate is gradually decreased toward the lower pacing rate (LR).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
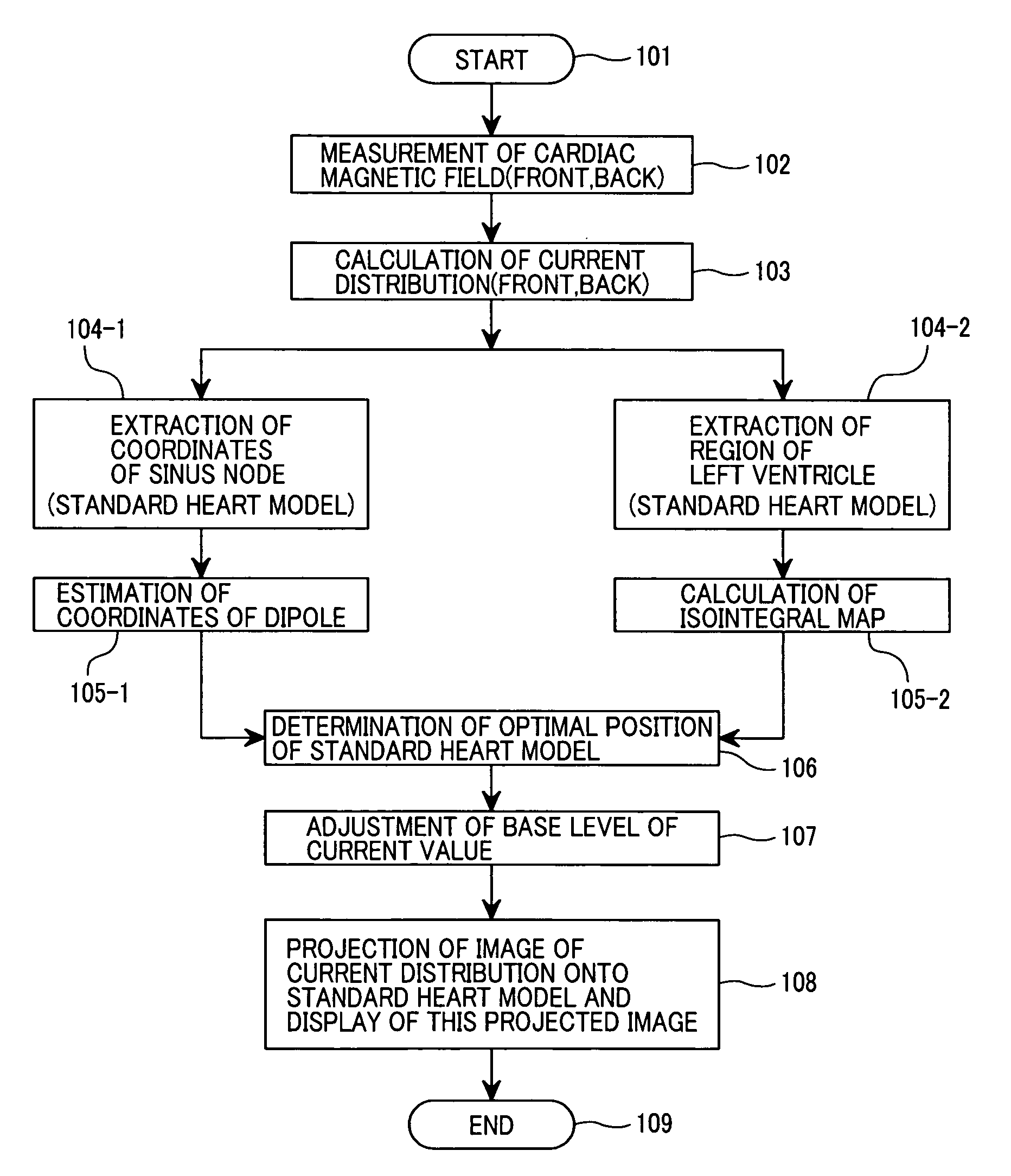
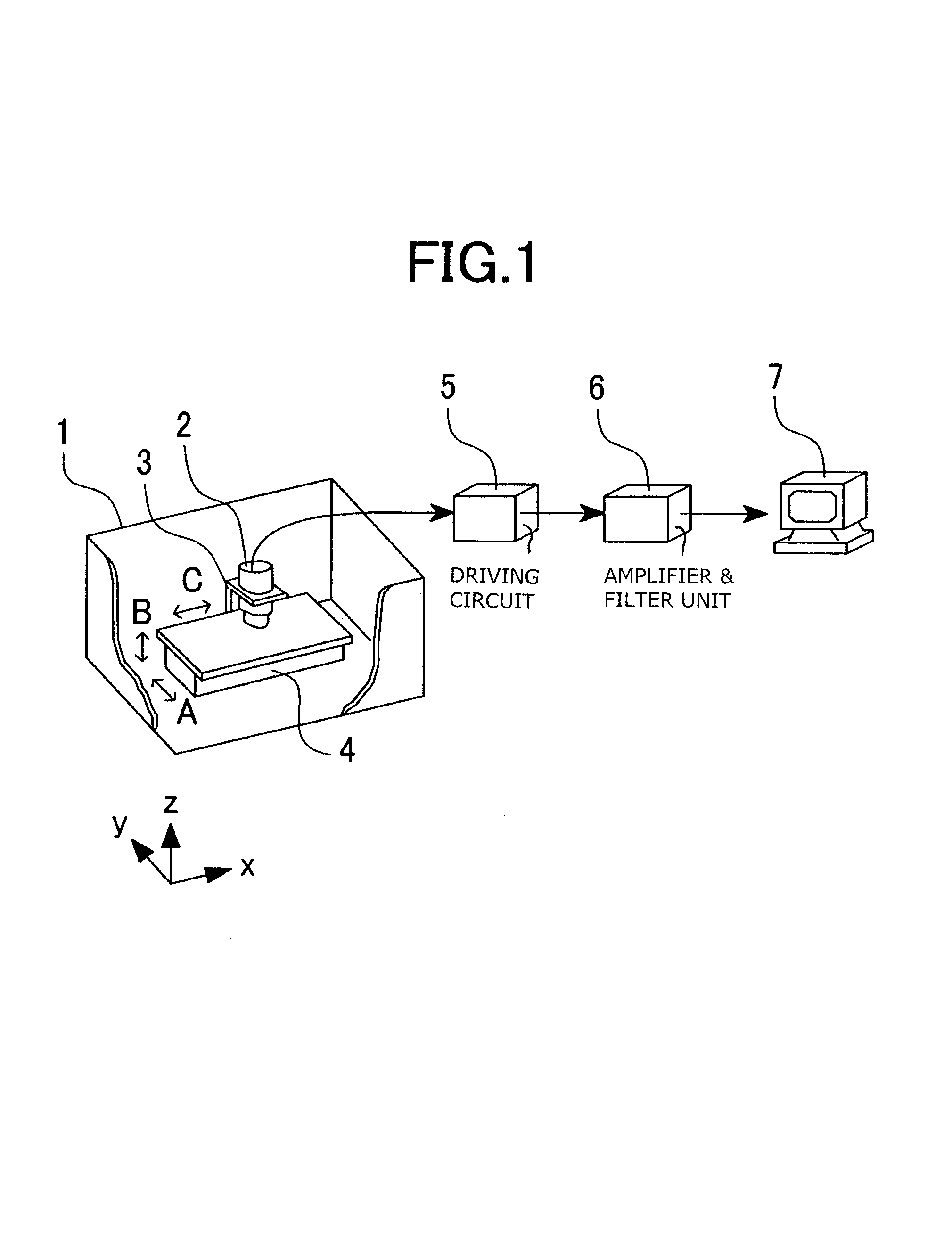
Biomagnetic measurement apparatus
ActiveUS7363070B2Minimize the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsSinoatrial nodePower flow
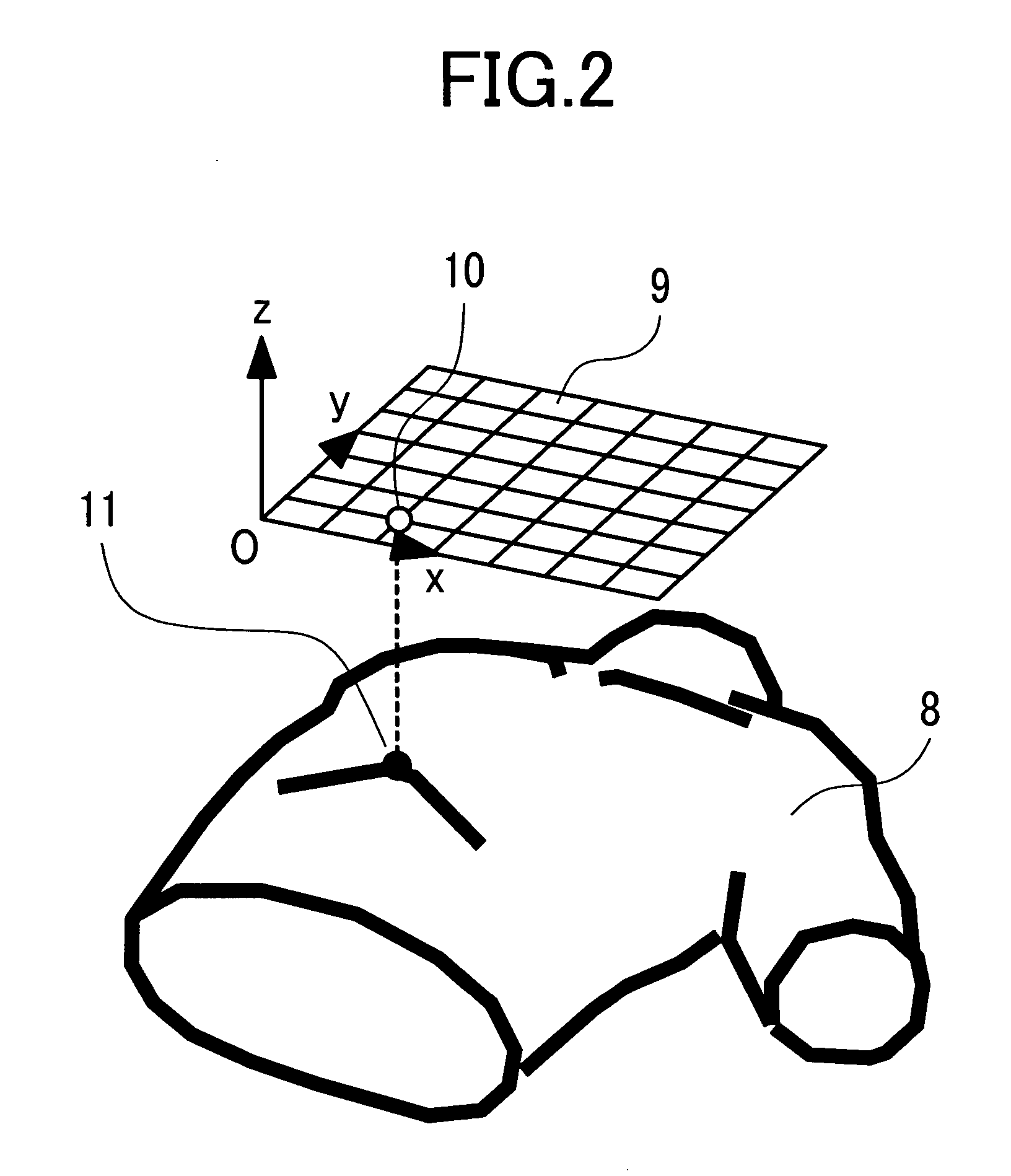
Disclosed herein is a biomagnetic measurement apparatus capable of visualizing cardiac electrical current distributions with information on the cardiac morphology of a subject. A magnetic field component in the z direction, vertical to the chest surface of a subject, is measured from two directions, front and back of the chest, and then to calculate the current distributions in the two directions and the distributions of the amplitudes of those current distributions. A three-dimensional standard heart model is created from average data on the cardiac morphology obtained from plural healthy subjects. An optimal position of the model is determined using the coordinates of the sinus node and the coordinates of the left ventricle. Then, a weight coefficient is obtained by front and back current distributions and front and back the distributions of the amplitudes of those current distributions on a set boundary of the model.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
InactiveUS20060004414A1Raise the possibilityIncrease heart rateCatheterHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAntiarrhythmic effect
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
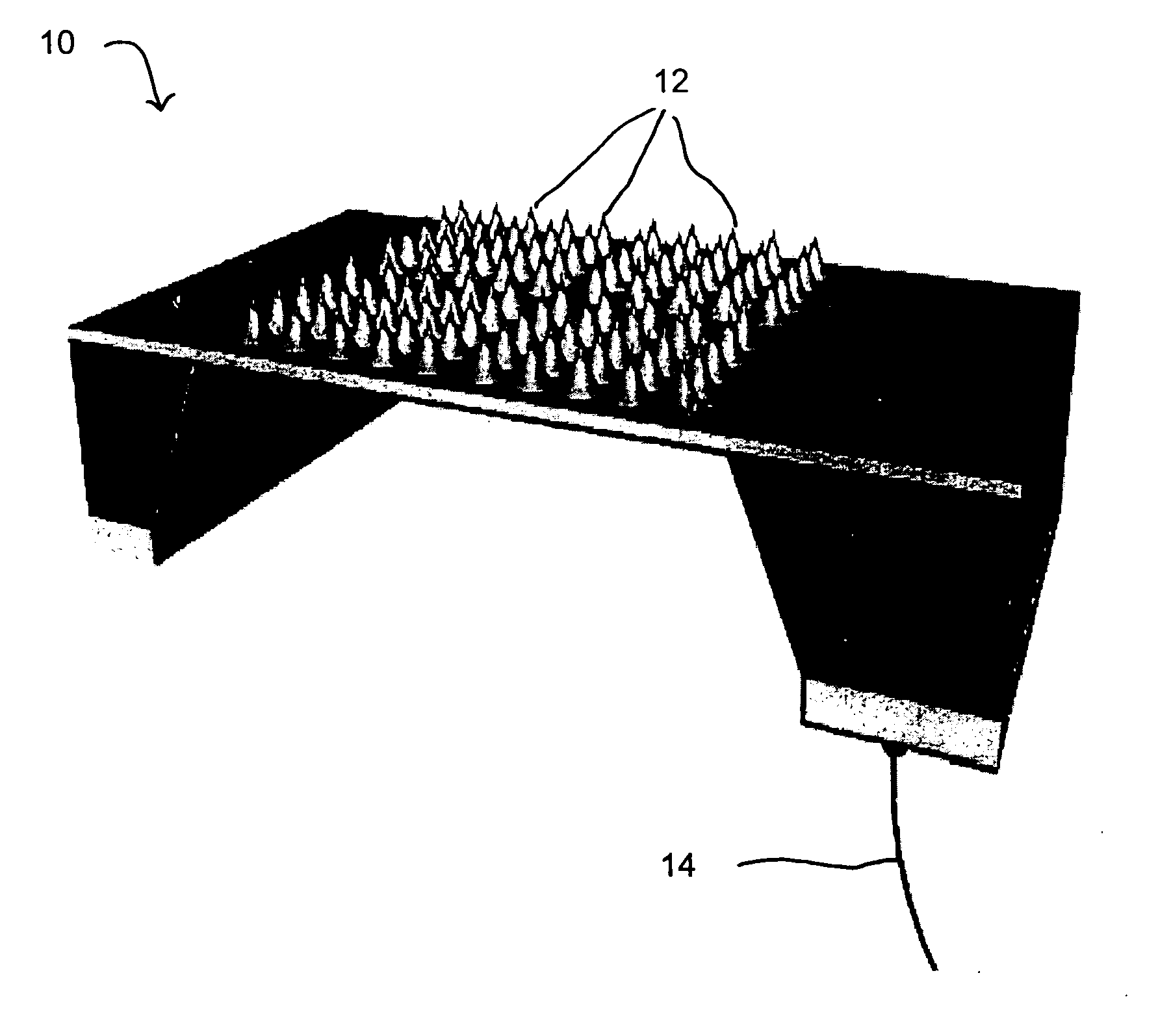
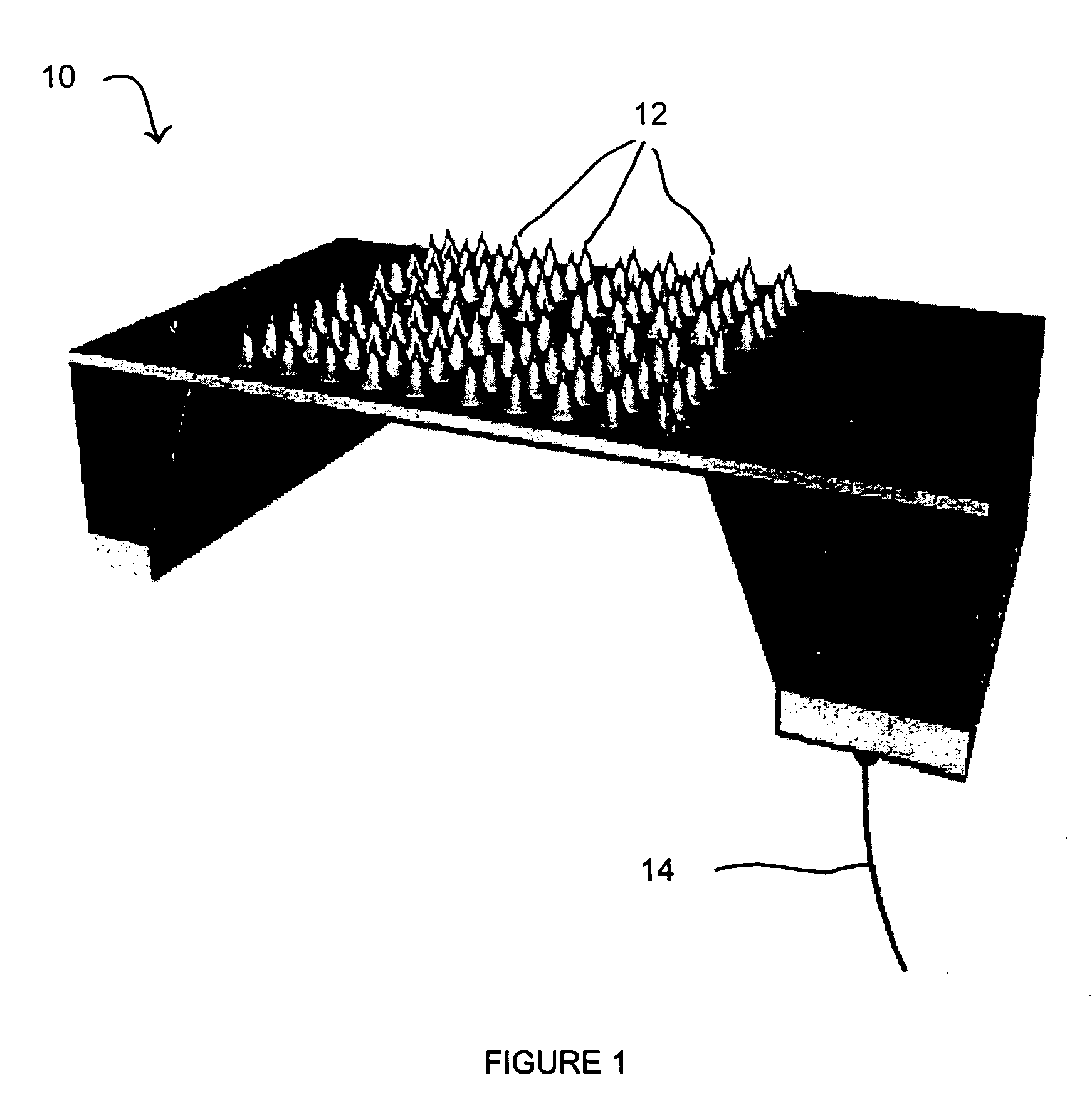
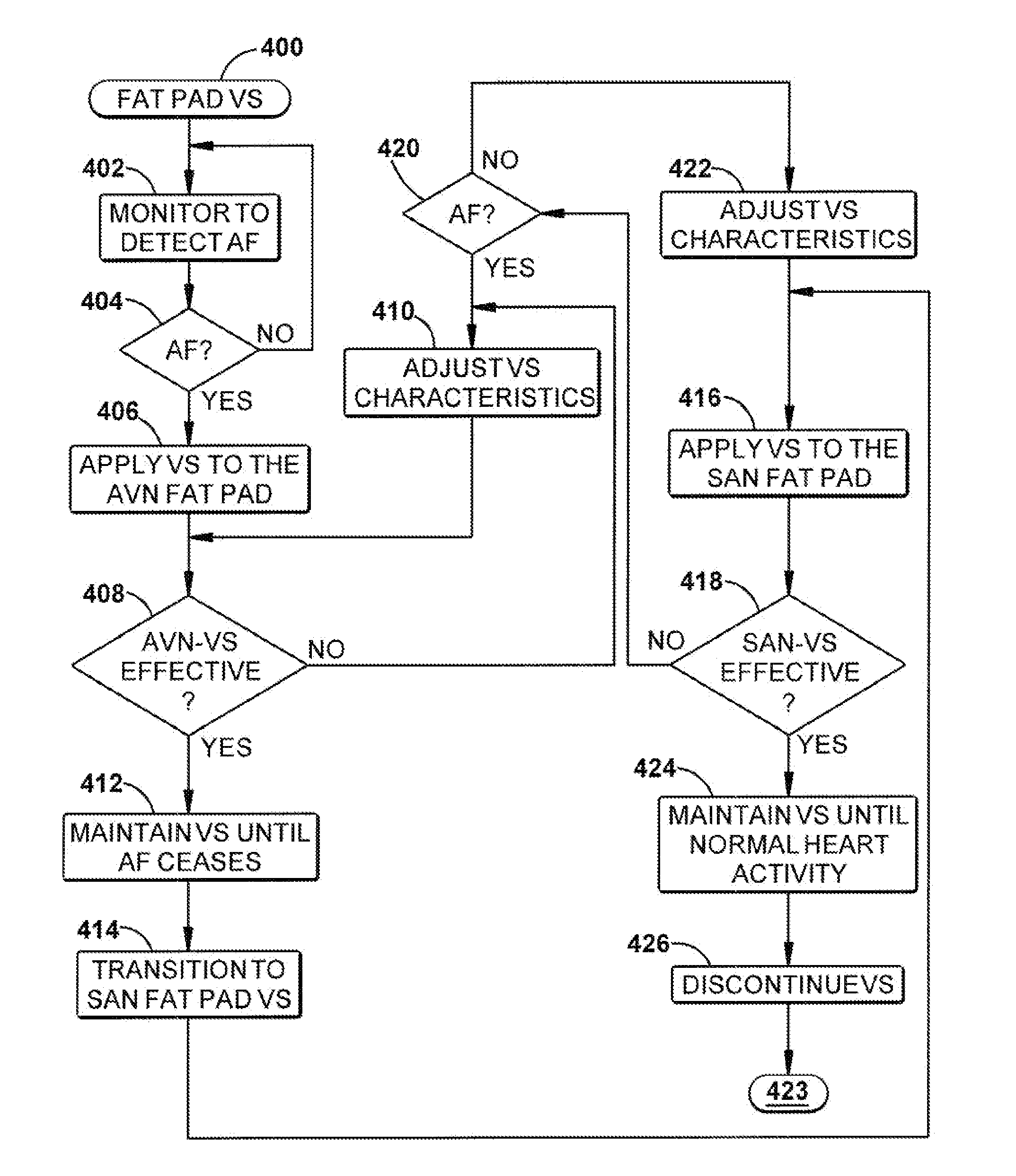
Control of cardiac arrhythmia by vagal stimulation at the atrioventricular and sinoatrial nodal fat pads of the heart
Vagal stimulation applied to the atrioventricular nodal (“AVN”) fat pad and the sinoatrial nodal (“SAN”) fat pad via epicardial leads is useful for controlling cardiac arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation (‘AF”). In the case of AF, for example, vagal stimulation may be applied initially to the AVN fat pad to reduce ventricular rate, and vagal stimulation may be applied to the SAN fat pad after restoration of sinus rhythm to control atrial rate. The technique is applicable to control acute AF and chronic AF. The vagal stimulation may be optimized for exciting ganglia in the fat pads to produce dromotropic and chronotropic effects in the atrioventricular node and the sinoatrial node, respectively. In addition, the SAN fat lead can also be used to pace the atrium in case of sinus bradycardia.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Biomagnetic measurement apparatus
ActiveUS20050148844A1Minimize the differenceCharacter and pattern recognitionComputerised tomographsLeft VentriclesSinoatrial node
Disclosed herein is a biomagnetic measurement apparatus capable of visualizing cardiac electrical current distributions with information on the cardiac morphology of a subject. A magnetic field component in the z direction, vertical to the chest surface of a subject, is measured from two directions, front and back of the chest, and then to calculate the current distributions in the two directions and the distributions of the amplitudes of those current distributions. A three-dimensional standard heart model is created from average data on the cardiac morphology obtained from plural healthy subjects. An optimal position of the model is determined using the coordinates of the sinus node and the coordinates of the left ventricle. Then, a weight coefficient is obtained by front and back current distributions and front and back the distributions of the amplitudes of those current distributions on a set boundary of the model.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias
InactiveUS20060004413A1Raise the possibilityHeart stimulatorsSensorsAntiarrhythmic effectValproic Acid
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the left stellate ganglion, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering anti-arrhythmic therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of anti-arrhythmic therapy include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenyloin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
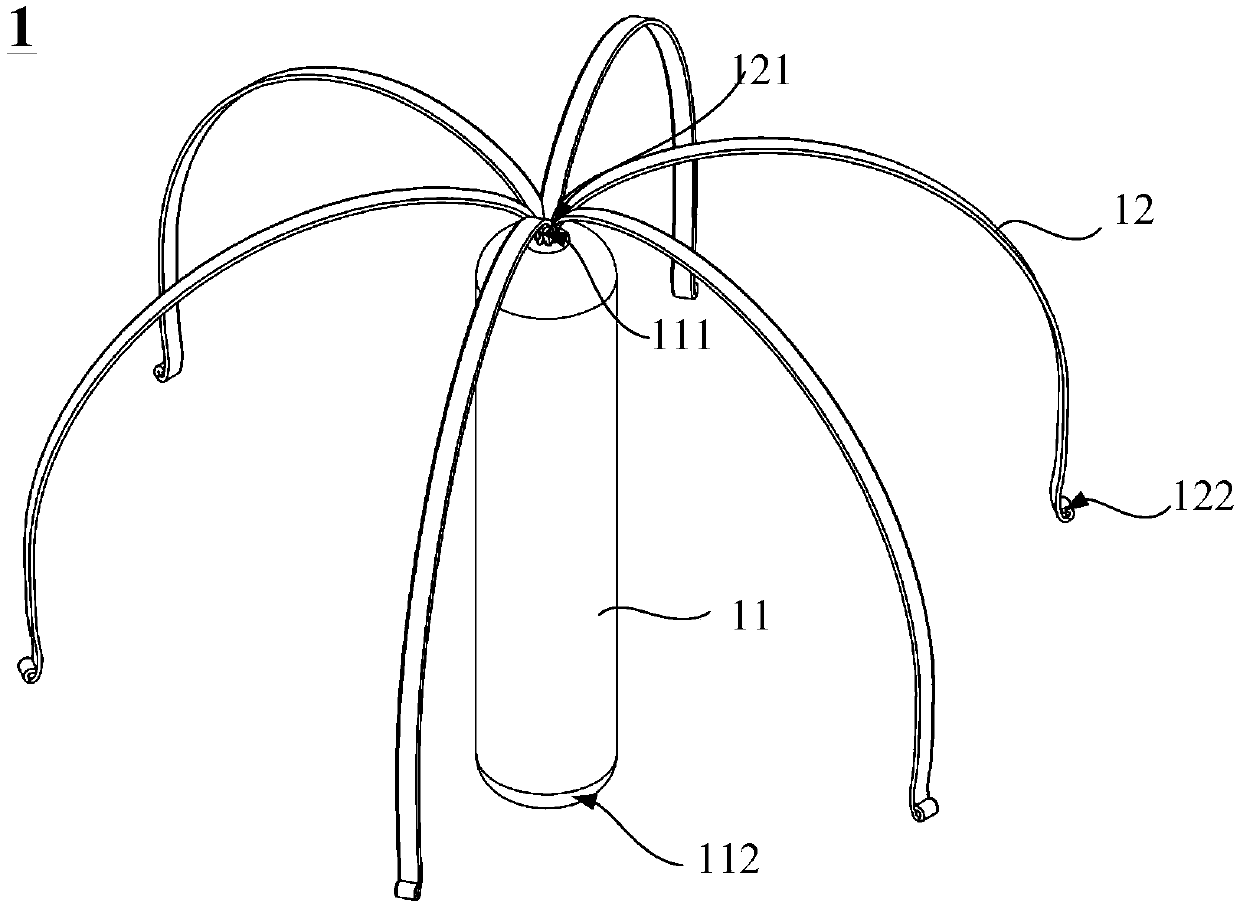
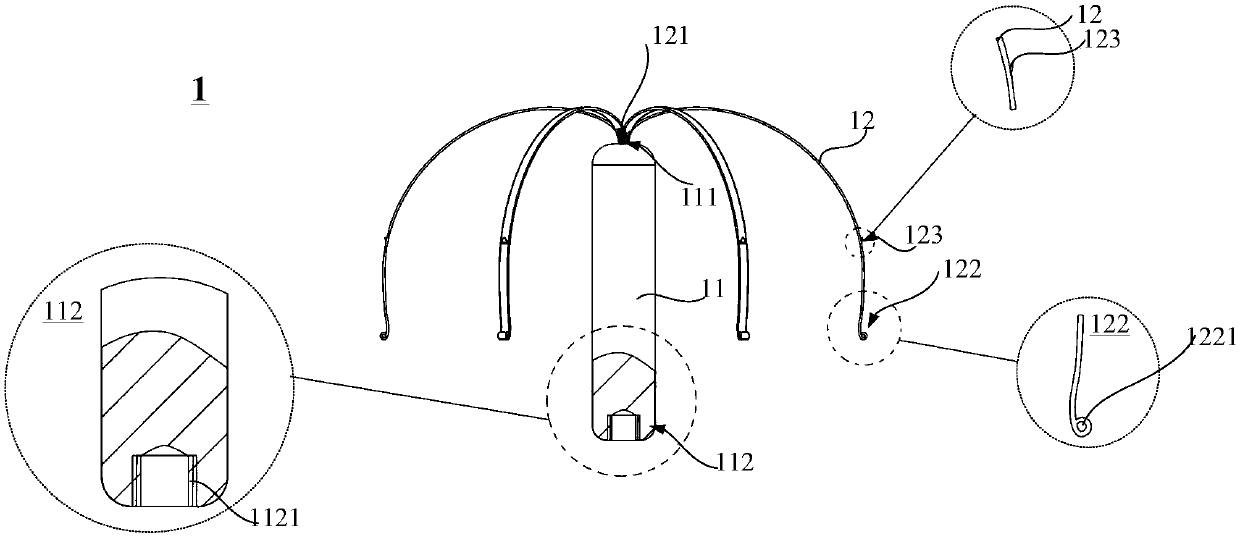
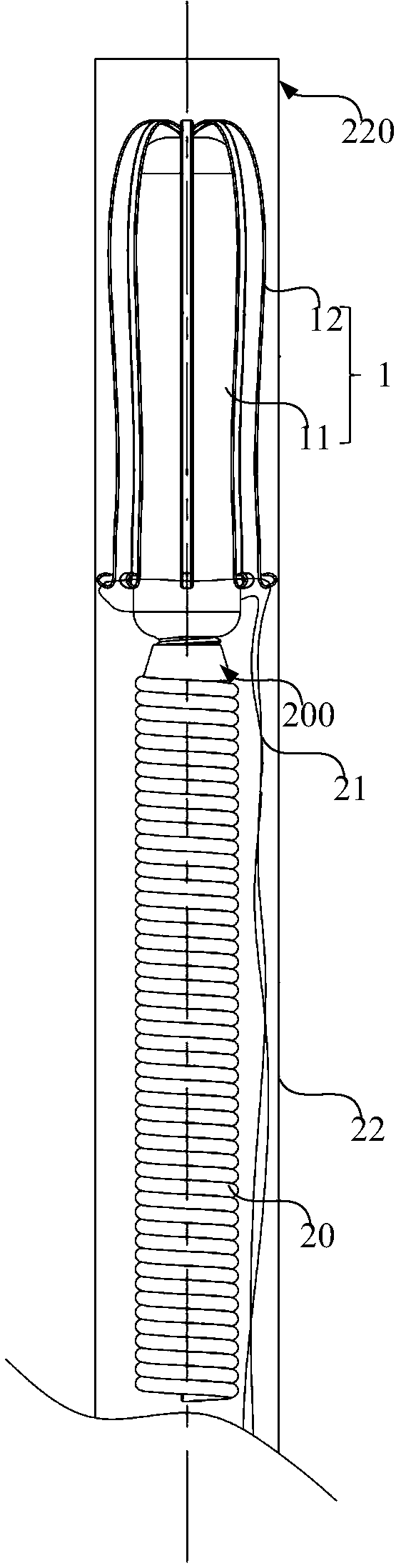
Conducting-wire-free pacemaker and conducting-wire-free pacing system
ActiveCN109568793AEliminate side effectsPacing PhysiologyTransvascular endocardial electrodesHeart stimulatorsSinoatrial nodeSide effect
The invention provides a conducting-wire-free pacemaker and a conducting-wire-free pacing system. The conducting-wire-free pacemaker uses an umbrella-shaped structural design, and comprises a conducting-wire-free pacing device positioned on the umbrella handle and a support device positioned on the umbrella surface; the support device can fix the conducting-wire-free pacing device onto a specifiedposition; side effects caused by a conventional electrode conducting wire are eliminated. Meanwhile, compared with other conducting-wire-free pacemakers used for the ventriculus dexter (particularlyright ventricular apex), the conducting-wire-free pacemaker has the advantages that the umbrella-shaped structure is used, so that the contact area with the heart tissue is greater; the fixation stability is higher, so that the conducting-wire-free pacemaker can be used in a position of auricula dextra near the sinoatrial node, the pacing sequence better conforming to the physiologic performance can be provided, and the harm to the heart is reduced accordingly. The conducting-wire-free pacing system provided by the invention uses the conducting-wire-free pacemaker; a special conveyor and a guide device are configured for the conducting-wire-free pacemaker, so that the implementation of the conducting-wire-free pacemaker becomes more convenient and more precise.
Owner:MICROPORT SORIN CRMSHANGHAICO LTD
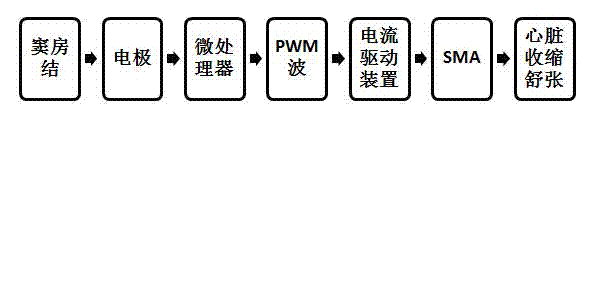
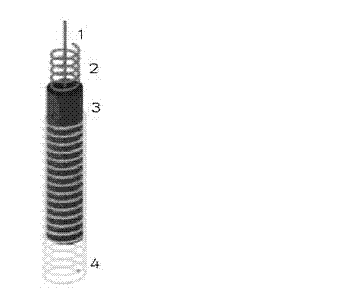
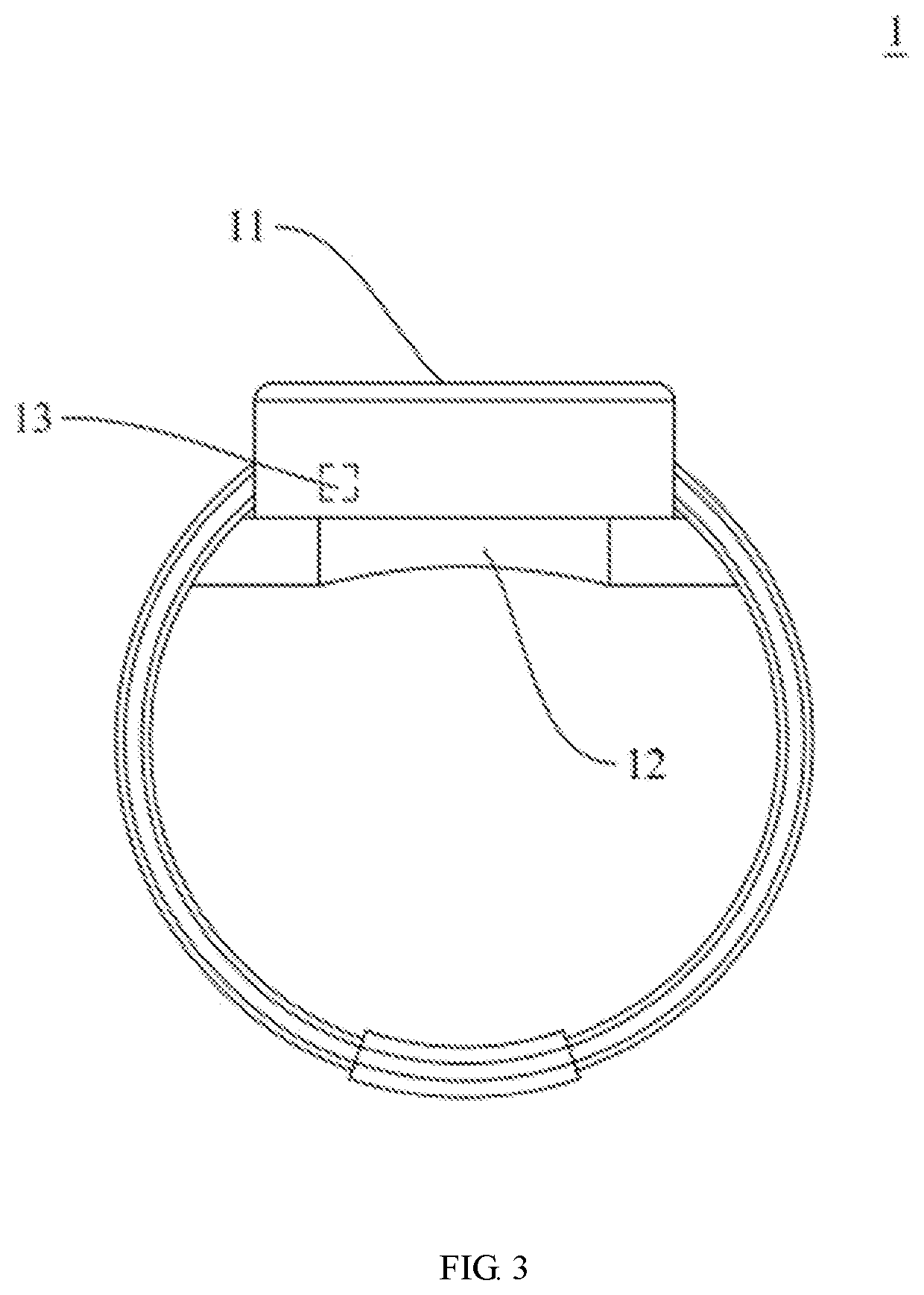
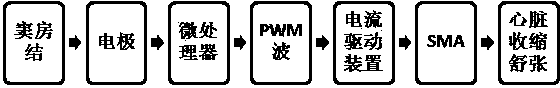
Direct heart-assist device based on artificial muscle network
InactiveCN102499872ARefactoring prevents or reversesOptimize geometryElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSinoatrial nodeShape-memory alloy
The invention relates to a direct heart-assist device based on an artificial muscle network, wherein the artificial muscle network consists of artificial muscle units and is provided with an extractor of atrionector heart rhythm, a contraction and diastole process controller and a current drive device. Each artificial muscle unit is formed by combining a shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring and a heat-conducting wire, wherein each heat-conducting wire is arranged at the center of the corresponding shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring, a layer of thin film is arranged outside each shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring and is used for preventing double-layer springs from mutually locking in a clamping manner, the outmost layer is a pressure spring with the certain K value and a sealed shell, and the two ends of each shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring are connected with an inner shape memory alloy wire, thus the shape memory alloy wires are stretched at a normal state and the artificial muscle units are linked to form a network covering outside a heart so as to form the direct heat-assist device based on the artificial muscle network. The current drive device outputs to the shape memory alloy wires of the artificial muscle units.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method and means to adjust the positioning of stimulating neural and muscular electrode
ActiveUS20120029590A1Eliminate side effectsHead electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesElectrical stimulationsCurrent source
A device for electrical stimulation of the brain, heart, and other neurons and muscles, capable of modifying the electrical activity of its environment in ways that are desirable for a better life style of a patient with brain, heart, or other problems. When used for brain stimulation, the device is able to superimpose an electrical current on the natural current that happens to occur, when the natural currents cause some undesirable effect, as in Parkinson's disease. When used for heart stimulation, the device is able to superimpose an electrical current on the natural current that happens to occur, originating at the sino-atrial node, which causes a healthy heart to pump blood to the lungs and to the body. The device offers an improvement over prior art of being capable of adjusting the position of the stimulating electrodes.
Owner:DANESHVAR KHOSROW +3
Application of Isl1 gene or protein in sinoatrial node abnormality related diseases
The invention provides an application of Isl1 gene or protein in sinoatrial node abnormality related diseases, concretely provides a use of an LIM homodomain transcription factor (Isl1) gene or its protein in the preparation of a reagent or kit for detecting or predicting the sinoatrial node (SAN) abnormality related diseases, and also provides a method for detecting or predicting the sinoatrial node abnormality related diseases. The Isl1 gene or protein can be used in prenatal screening and diagnosis of various kinds of congenital heart diseases with arrhythmia as the main symptoms, so it is in favor of realizing prenatal and postnatal care.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL EAST HOSPITAL TONGJI UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
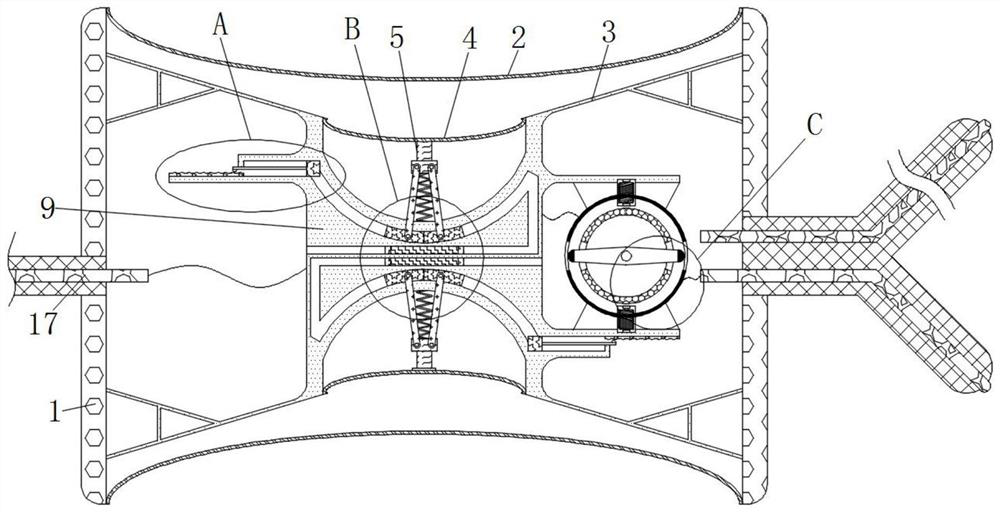
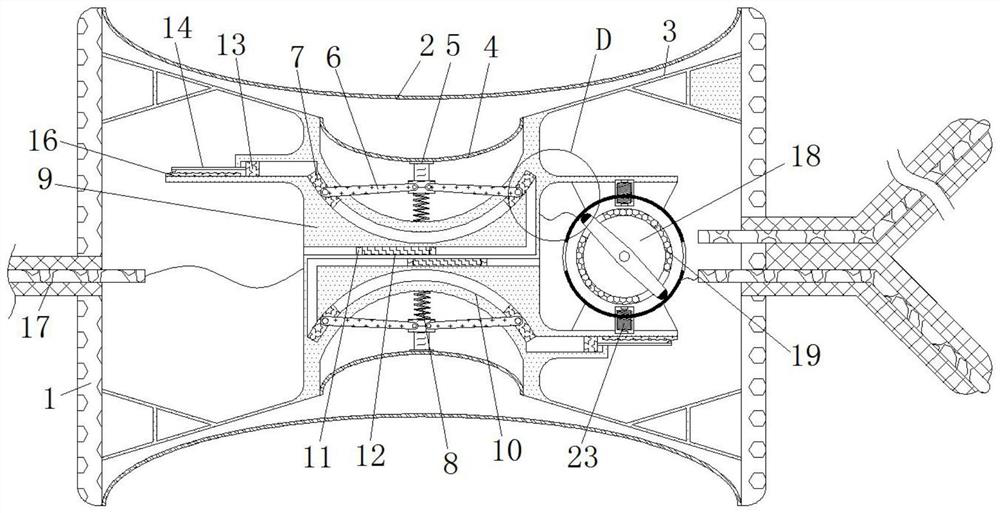
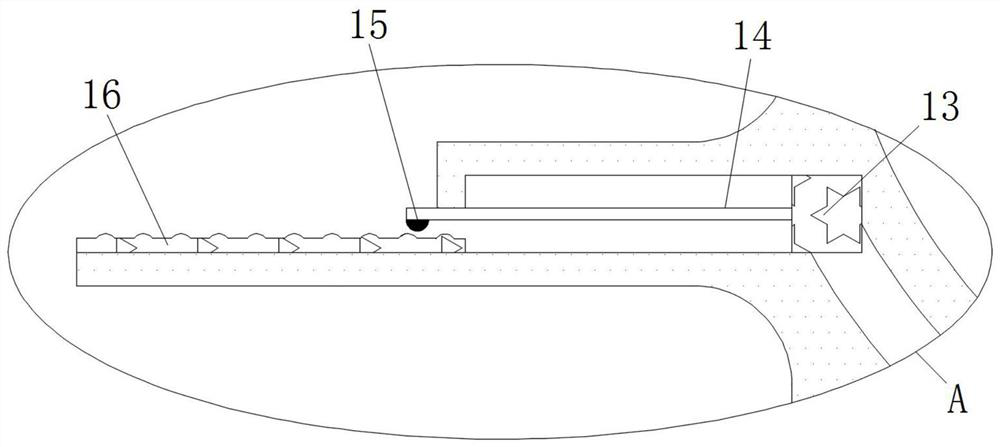
Cardiology department nursing heart pace-making monitoring device
ActiveCN112657060APrevent pacing-dependent phenomenaReduce the facing areaHeart stimulatorsSinoatrial nodeBlood pressure
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, and discloses a cardiology department nursing heart pace-making monitoring device, which comprises a shell, outer membranes are fixedly connected to the upper end and the lower end of the shell, tripods are fixedly connected to the inner walls of the upper side and the lower side of the shell, and inner membranes are fixedly connected to the middles of the tripods; and a movable block is fixedly connected to the side, close to the center of the shell, of the inner film. According to the cardiology department nursing heart pace-making monitoring device, when the blood pressure in the atrium rises, the outer membrane is compressed and amplified through the inner membrane to change the position of the movable block to enable the pressurizing block to move, the first plug bodies get away from each other to increase the discharging frequency of the capacitor plate, and meanwhile the second plug bodies move to increase the intensity of pulse current to prevent excessive hydrops in the atrium; adn then current generated autonomously through sinus node and pulse current of the pacemaker enter the upper side electromagnet and the lower side electromagnet respectively; therefore, the second contact is disconnected when the magnetic field is balanced, the pacemaker stops working and the phenomenon of pacing dependence of a patient is prevented.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cardiology Nursing Cardiac Pacing Monitoring Device
ActiveCN112657060BReduce the facing areaLower resistanceHeart stimulatorsSinoatrial nodeBlood pressure
The invention relates to the technical field of medical devices, and discloses a cardiac pacing monitoring device for cardiology nursing, which includes a casing, the upper and lower ends of the casing are fixedly connected with outer membranes, and the inner walls of the upper and lower sides of the casing are fixed A tripod is connected, the middle part of the tripod is fixedly connected with an inner membrane, and the side of the inner membrane close to the center of the housing is fixedly connected with a movable block. When the blood pressure in the atrium rises, the epicardium compresses the inner membrane and changes the position of the movable block to move the pressurized block. The plug body 1 moves away from each other to increase the discharge frequency of the capacitor plate, and the plug body 2 moves at the same time. Increase the intensity of the pulse current to prevent excessive fluid accumulation in the atrium. The current generated independently through the sinoatrial node and the pulse current of the pacemaker enter the upper and lower electromagnets respectively. When the magnetic field is balanced, the second contact is disconnected and the pacemaker is no longer connected. Work to prevent the phenomenon of pacing dependence in patients.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Zero blood flow sensitive heart stimulator
A zero flow responsive heart stimulator contains a zero flow sensors, which generate signals at the moment of the termination of blood inflow in the right atrium and the right ventricle, sensing this the most precisely in the places, where the sinoatrial node and atrioventricular node reside, for the right atrium and the right ventricle, respectively. The stimulator is based on our discovery, that the two nodes are the same sensors in the biological systems, based on the fact that until the filling of the said two chambers continues, the venous blood flow sucks on Bernoulli's principle the Ca and Na cations from the two nodes interstices, preventing the inward currant in their cells, thus delaying the completion of the 0-phase of their depolarization and the action potential, until the blood flow stops. Our discovery proves that the alternating flow / no flow of the blood in the orifice of superior vena cava and the entrance of the right ventricle is the real pacemaker that fires the both nodes, but not the inverse, as generally assumed, approximating the natural pacemaker to a clock mechanism. This, together with the discovered by us arteriovenous, arteriolymphatic and capillary pumps, closes the loop of the autonomous automatic functioning of the cardiovascular system, even completely denervated and in the absence of muscle contractions. It is the first devise, which activates the atrial and the ventricular contractions in a function of the zero-flow of the filling them venous blood, which is the exact imitation of the sinoatrial and atrioventricular firing.
Owner:PANCHEVA ADELINA +2
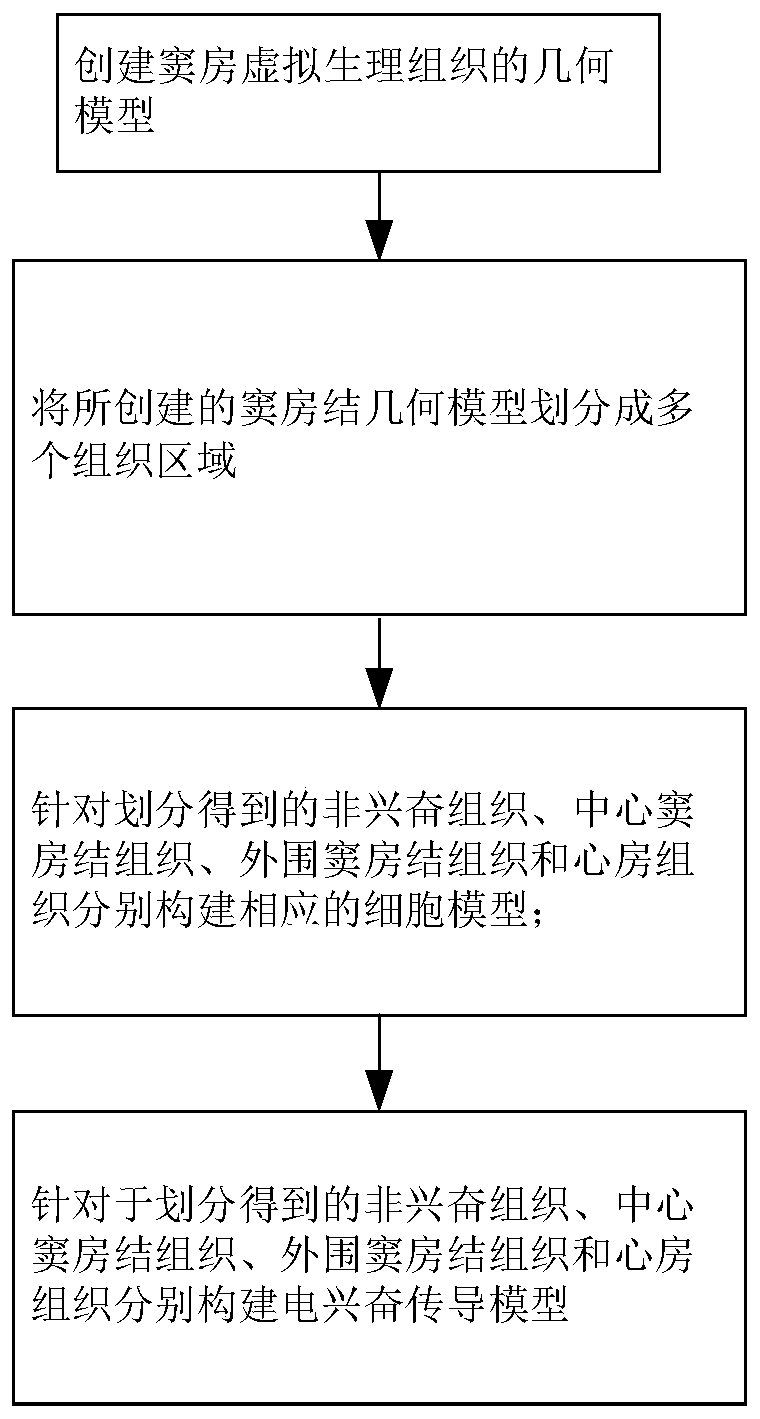
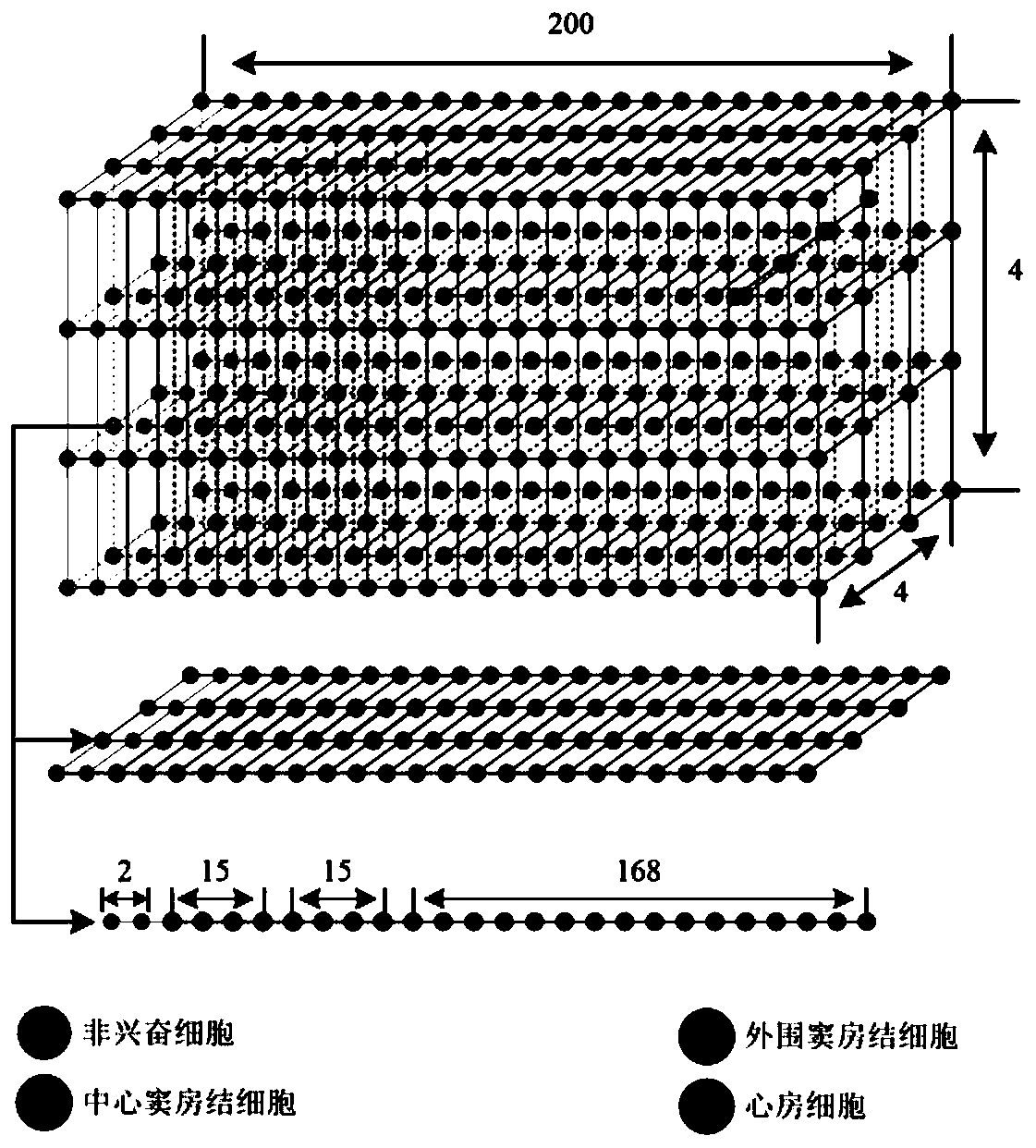
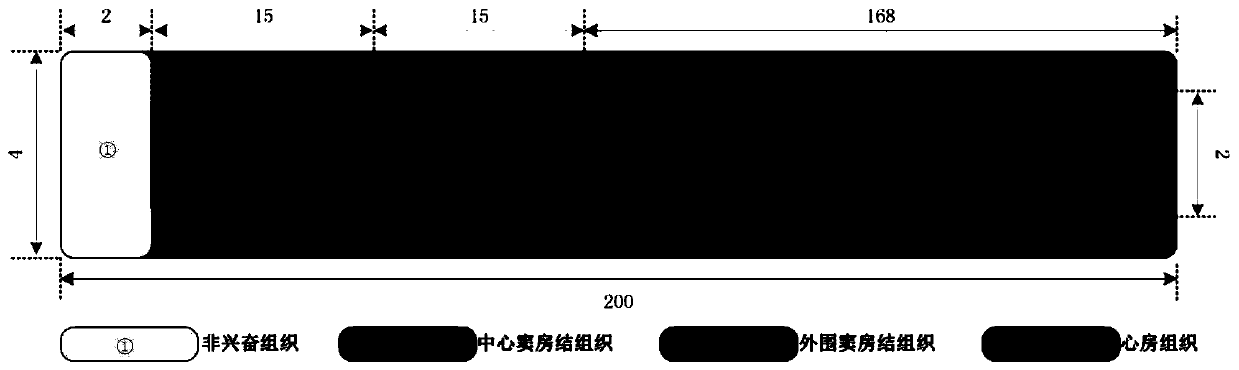
Method for constructing virtual physiological tissues of sinus node, storage medium and computing device
ActiveCN110310744AShorten the timeConvenient researchMedical simulationSinoatrial nodeElectrophysiology
The invention discloses a method for constructing virtual physiological tissues of a sinus node, a storage medium and a computing device. The method comprises the following steps: creating a geometricmodel for the virtual physiological tissues of a sinus; dividing the geometric model into a plurality of areas including a non-excited tissue area, a central sinus node tissue area, a peripheral sinus node tissue area and an atrium tissue area; respectively constructing corresponding cell models for the non-excited tissues, the central sinus node tissues, the peripheral sinus node tissues and theatrium tissues; and respectively constructing electrical excitation conduction models for the non-excited tissues, the central sinus node tissues, the peripheral sinus node tissues and the atrium tissues obtained after the division. The virtual physiological tissues constructed by the method of the invention construct a bridge for changing from microscopic molecules to macroscopic organ, recurring sinus node pace-making and electrical conduction processes are in line with the electrophysiology of the human sinus node, the time and money cost of animal experiments is reduced, and the pace-making mechanism of the sinus node can be fast, well and safely studied.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Creation of a biological atrioventricular bypass to compensate for atrioventricular block
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
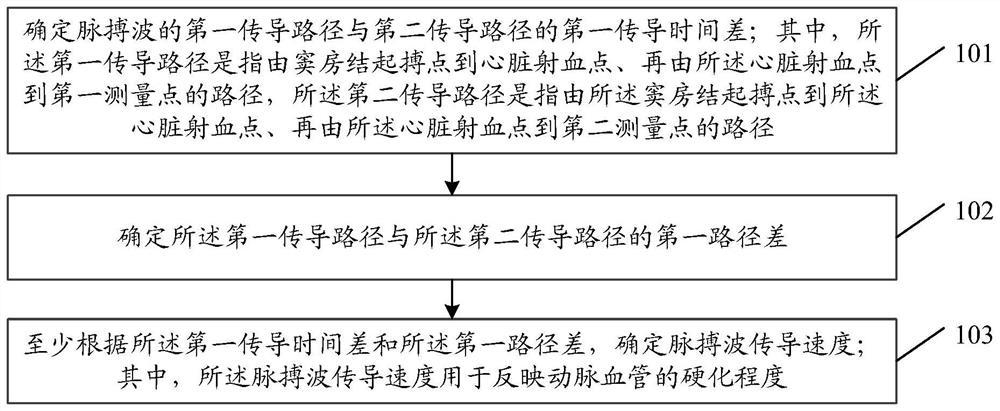
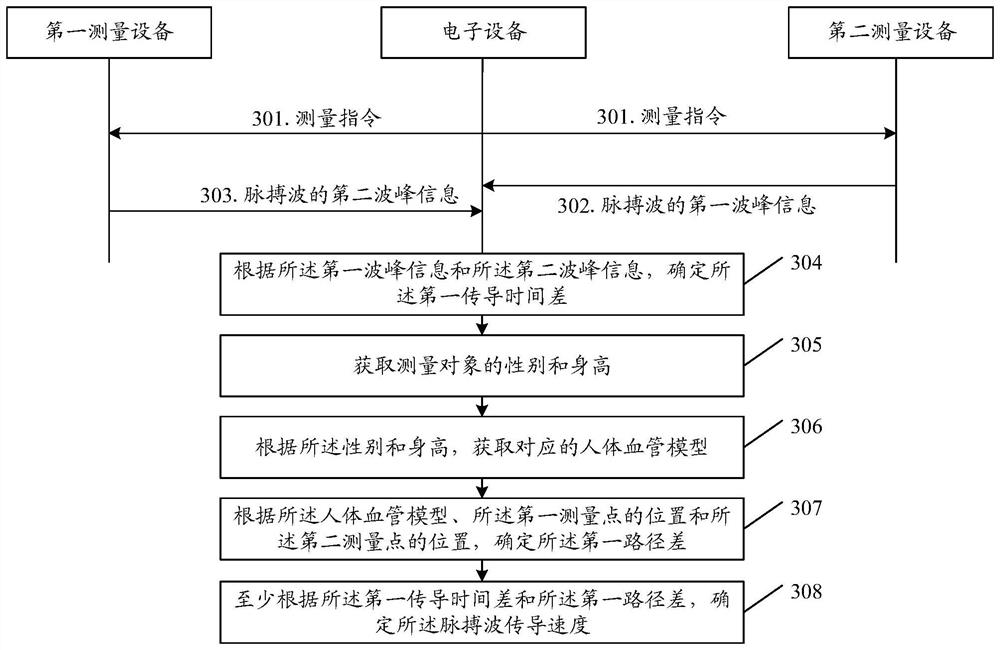
Artery hardness monitoring method and device
The invention provides an artery hardness monitoring method and device. The method comprises the following steps: determining a first conduction time difference between a first conduction path and a second conduction path of a pulse wave; wherein the first conduction path refers to a path from a sinus node pace-making point to a heart ejection point and then from the heart ejection point to a first measurement point, and the second conduction path refers to a path from the sinus node pace-making point to the heart ejection point and then from the heart ejection point to a second measurement point; determining a first path difference between the first conduction path and the second conduction path; determining a pulse wave conduction velocity at least according to the first conduction time difference and the first path difference; wherein the pulse wave conduction velocity is used for reflecting the arterial blood vessel hardening degree.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
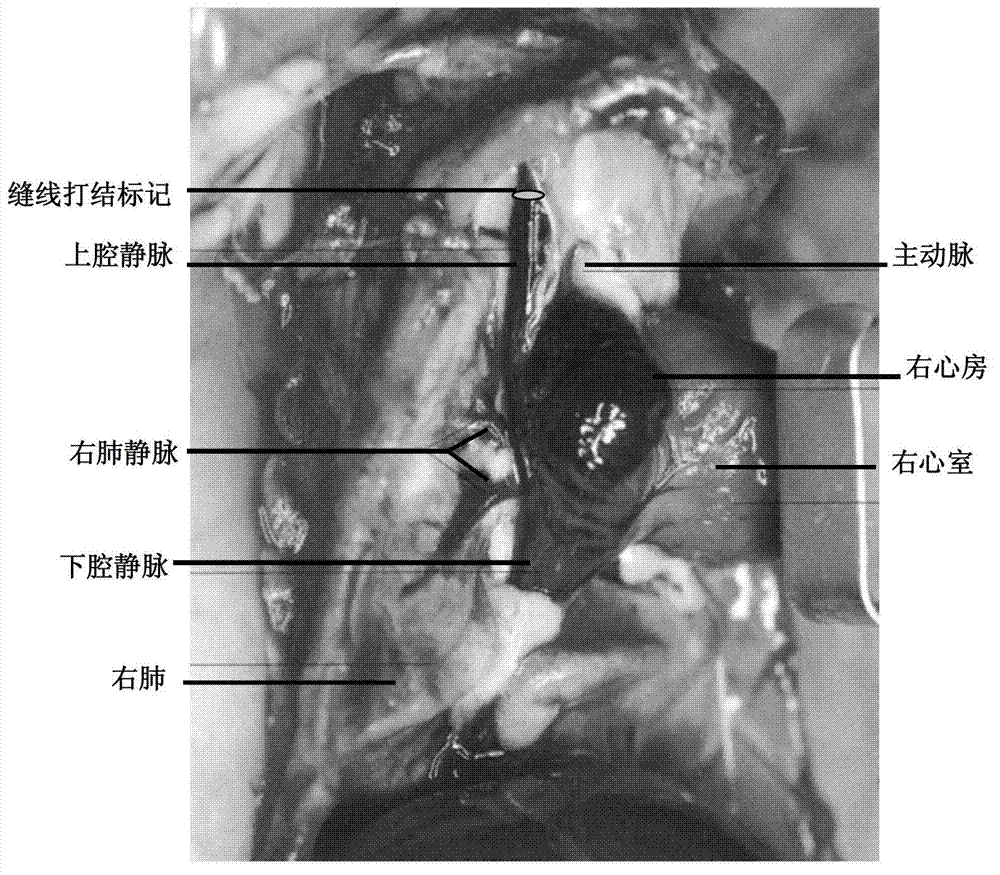
Precise positioning and material taking method of adult rat atrionector
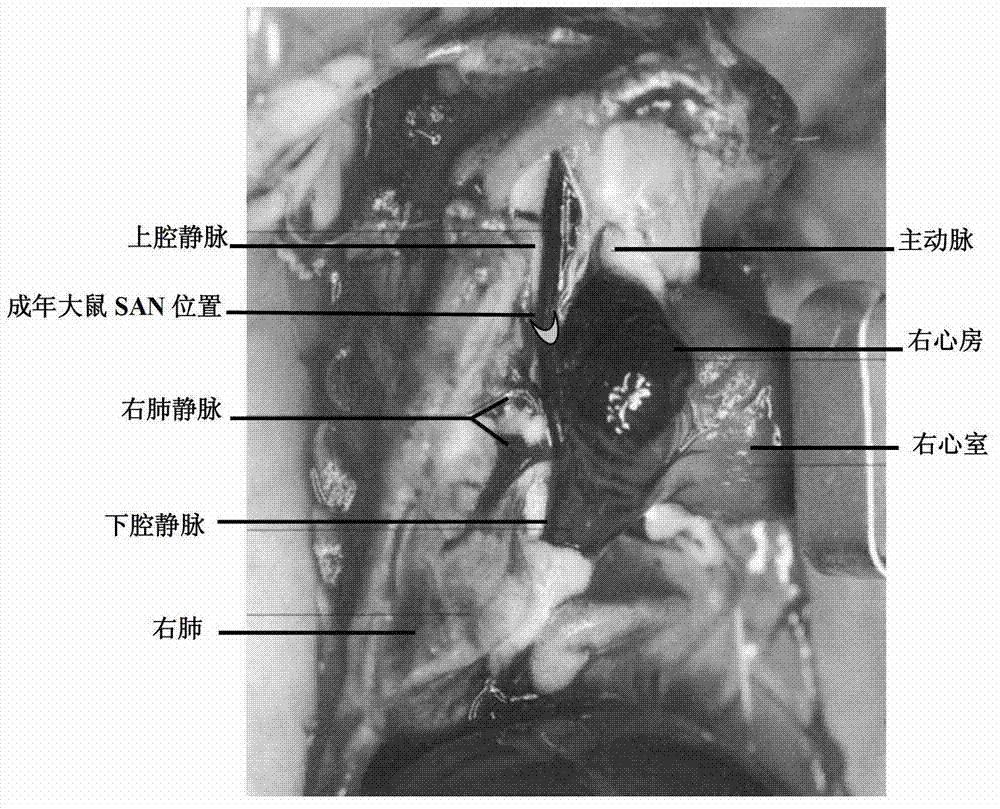
InactiveCN102961197AAccurate materialsAccurate and precise sampling methodSurgical needlesSurgical veterinaryVeinSinoatrial node
The invention relates to a precise positioning and material taking method of adult rat atrionector. According to the method, the rat atrionector is macroscopically positioned in the proximal part wall of the precava and extends into a junctional zone of the right atrium and the precava, and after the right precava is marked by a body suturing knotting method, the rat heart is taken down along the far end of the precava. The invention also relates to a naked eye precise positioning method of the serial section of the adult rat atrionector. The atrionector subjected to material taking is subjected to the serial section after the fixation, the position and the form of the atrionector on the precava wall is simultaneously observed in the section process through naked eyes, and the atrionector is precisely positioned.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
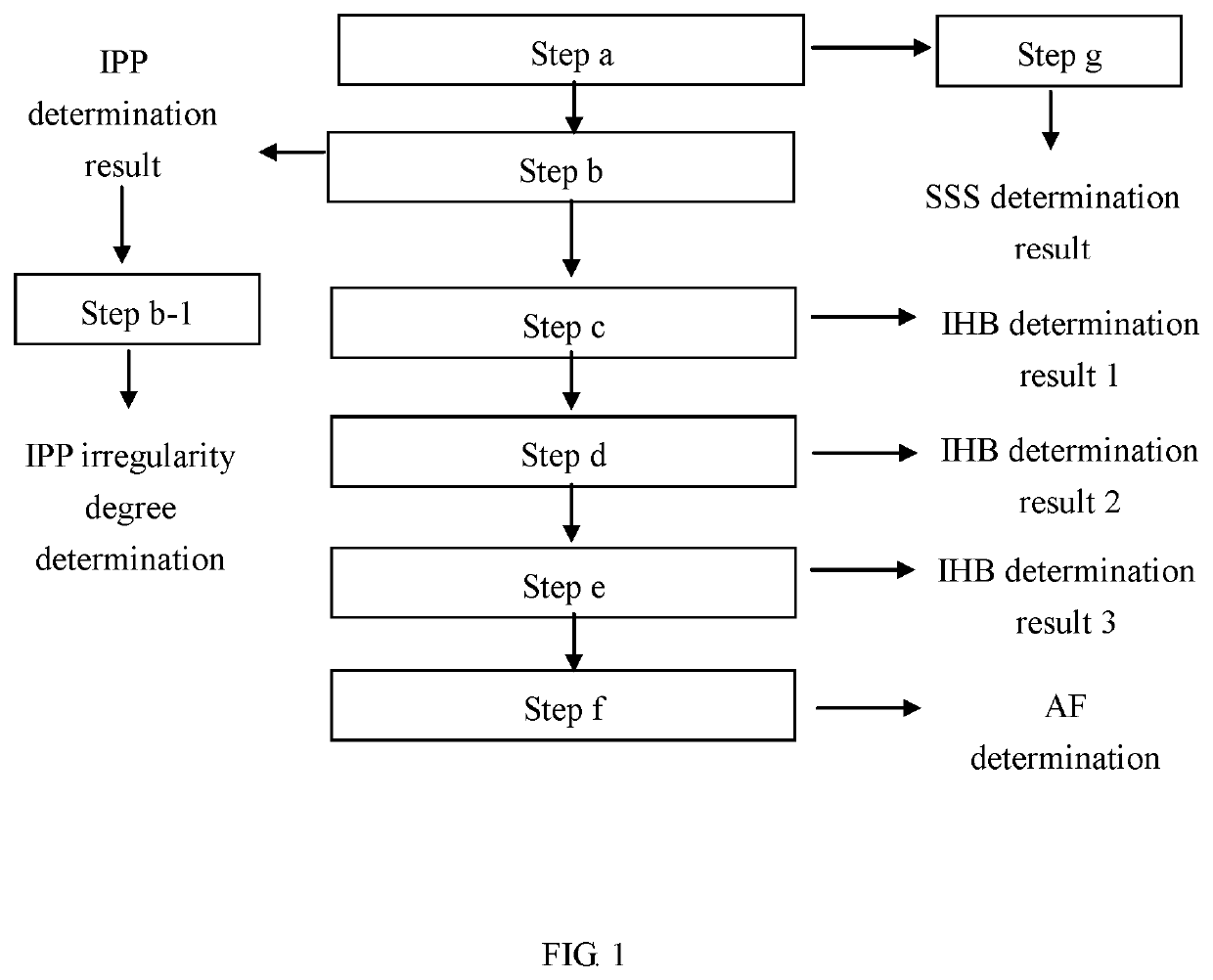
Method and device for detecting heart rhythm irregularities
InactiveUS20200060562A1Reduce errorsHigh utility valueElectrocardiographyPositive displacement pump componentsSphygmomanometerIrregular heart rhythm
A method for detecting heart rhythm irregularities, including the steps of: measuring pulse peaks continuously over a period of time to obtain pulse peak sequence and pulse peak time interval sequence corresponding to the pulse peak sequence; and calculating the absolute value of a difference between a single pulse peak time interval in the pulse peak time interval sequence and an average value of the pulse peak time interval sequence, and determining that an irregular pulse peak (IPP) has occurred if the absolute value is larger than or equal to 15% to 25% of the average value of the pulse peak time interval sequence. A detection device using the method is also provided. This uses a non-invasive approach to detect heart rhythm irregularities such as sick sinus syndrome, irregular pulse peaks, irregular heartbeat, and atrial fibrillation, and can be applied to a sphygmomanometer or a wearable device.
Owner:LIN SHIMING +1
Direct heart-assist device based on artificial muscle network
InactiveCN102499872BRefactoring prevents or reversesOptimize geometryElectrotherapyArtificial respirationSinoatrial nodeShape-memory alloy
The invention relates to a direct heart-assist device based on an artificial muscle network, wherein the artificial muscle network consists of artificial muscle units and is provided with an extractor of atrionector heart rhythm, a contraction and diastole process controller and a current drive device. Each artificial muscle unit is formed by combining a shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring and a heat-conducting wire, wherein each heat-conducting wire is arranged at the center of the corresponding shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring, a layer of thin film is arranged outside each shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring and is used for preventing double-layer springs from mutually locking in a clamping manner, the outmost layer is a pressure spring with the certain K value and a sealed shell, and the two ends of each shape memory alloy wire inner-layer spring are connected with an inner shape memory alloy wire, thus the shape memory alloy wires are stretched at a normal state and the artificial muscle units are linked to form a network covering outside a heart so as to form the direct heat-assist device based on the artificial muscle network. The current drive device outputs to the shape memory alloy wires of the artificial muscle units.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Cardiac stimulation device for sinus rate modulation
A system comprising an implantable electrical cardiac signal sensing circuit, an implantable sinoatrial cardiac action potential detector circuit, and an implantable electrical stimulation circuit in electrical communication with the electrical cardiac signal sensing circuit and the sinoatrial cardiac action potential detector circuit. The electrical cardiac signal sensing circuit is configured to receive one or more intrinsic heart signals from one or more respective electrodes configured for placement in a vicinity of a sinoatrial node of a subject. The implantable electrical stimulation circuit is configured to initiate delivery of at least one inhibitory electrical stimulation pulse in a vicinity of the sinoatrial node in a timed relationship to a sensed sinoatrial cardiac action potential. Other systems and methods are disclosed.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Creation of a Biological Atrioventricular Bypass to Compensate for Atrioventricular Block
InactiveUS20080247998A1Raise the possibilityPromote disseminationBiocideElectrotherapySinoatrial nodeMesenchymal stem cell
A method of creating an atrioventricular bypass tract for a heart comprises growing mesenchymal stem cells into a strip with two ends, attaching one end of the strip onto the atrium of the heart, and attaching the other end of the strip to the ventricle of the heart, to create a tract connecting the atrium to the ventricle to provide a path for electrical signals generated by the sinus node to propagate across the tract and excite the ventricle.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods and compounds for inhibition of inactivation of voltage-gated sodium channels
PendingUS20220125784A1Avoid inactivationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySick Sinus Node SyndromeSIDS - Sudden infant death syndrome
The current application relates to compounds that bind and inhibit the inactivation of Navi.5 voltage-gated sodium channel (VGSC). The compounds can be used for treating cardiovascular diseases such as Brugada syndrome, cardiac arrhythmia disorder, progressive cardiac conduction disorder (PCCD), sick sinus syndrome, progressive familial block, atrial fibrillation, sudden infant death syndrome, dilated cardiomyopathy, myocardial ischemia / infarction, or heart failure.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
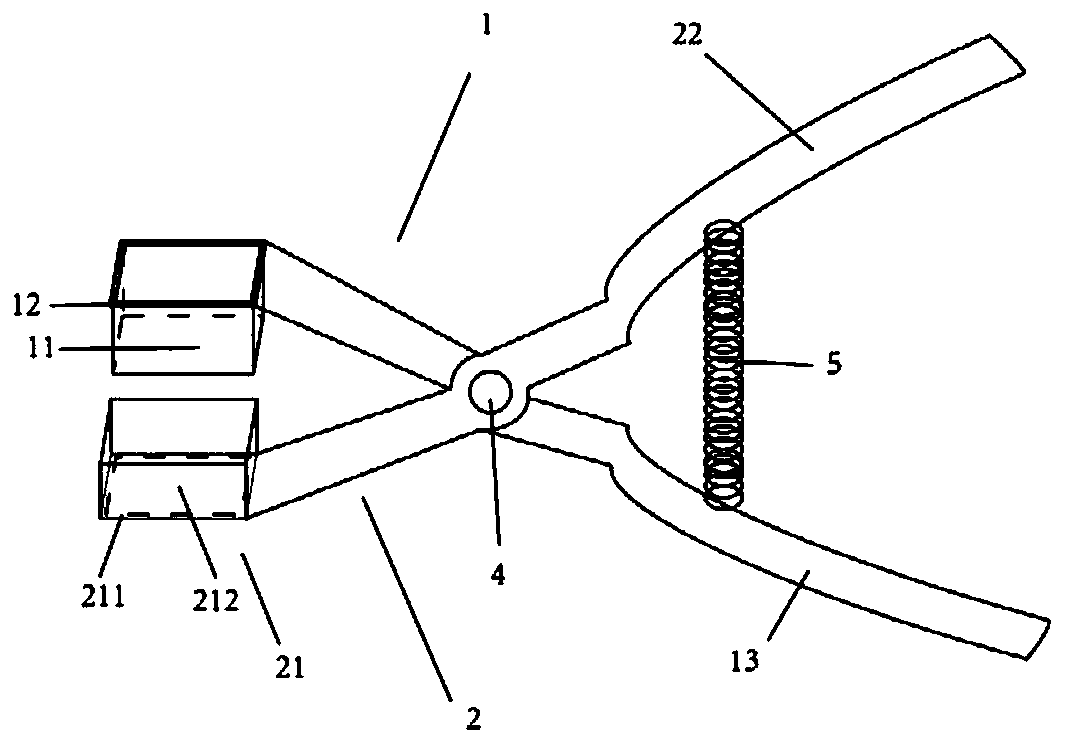
Pathological sampler of heart conduction system tissue and sampling method for sampling heart conduction system tissue
PendingCN110333096AFlexible installationFlexible replacementWithdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationSinoatrial nodeAtrioventricular node
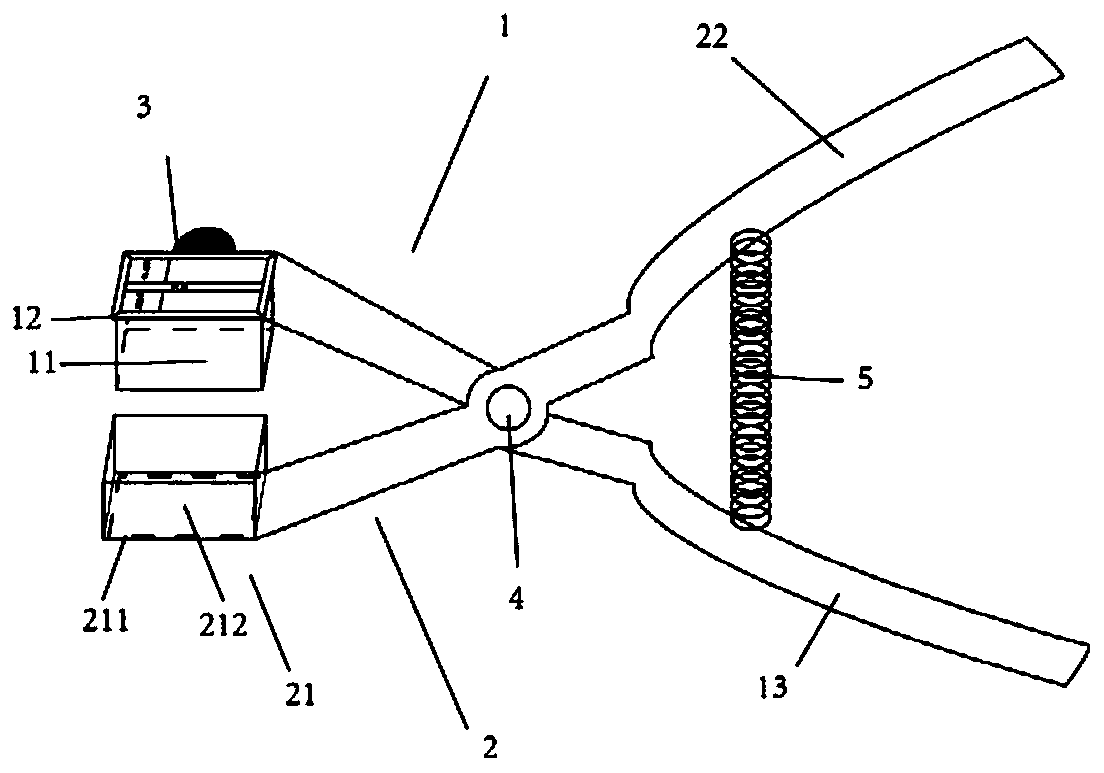
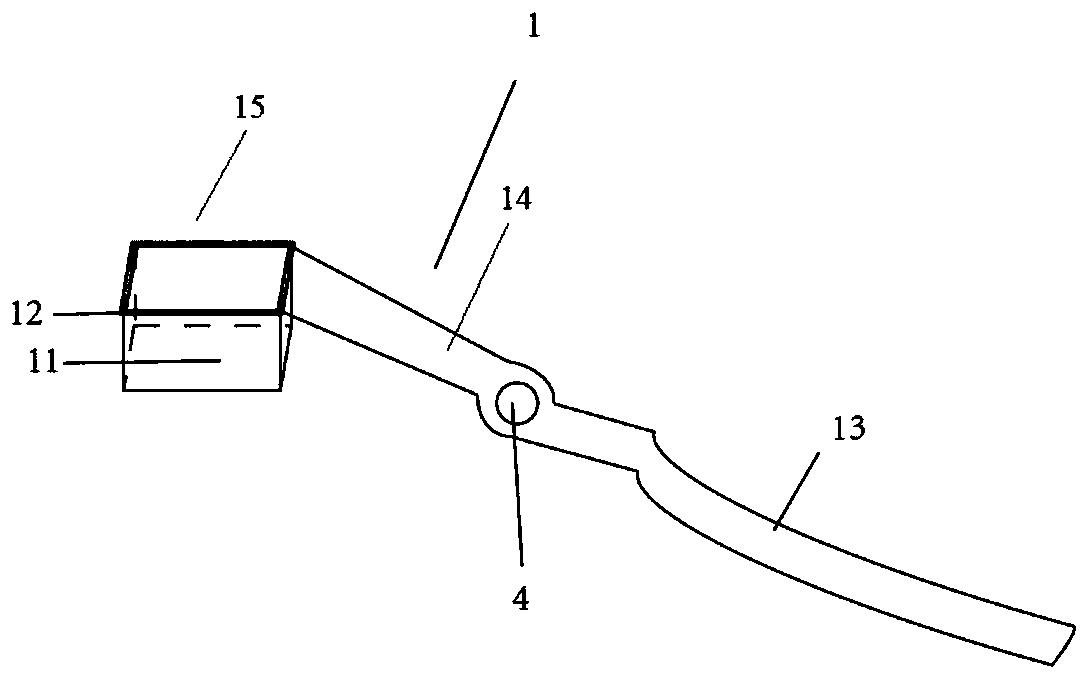
The invention discloses a pathological sampler of a heart conduction system tissue and a sampling method for sampling a heart conduction system tissue. The invention firstly provides a pathological sampler of a heart conduction system tissue. The pathological sampler includes locating and sampling scissors and a slicing groove. A rectangular cutting area can be formed by an observation and sampling component of the invention. When a sinoatrial node and an atrioventricular node are cut, a locating area is defined by six easily identified structures to realize simple and accurate identification.The rectangular area formed by the locating and sampling scissors and a holding component are meshed with each other, and a target tissue block can be cut off successfully at one time. A locating observation window insertion groove is arranged on the locating and sampling scissors to flexibly install and replace two transparent insertion sheets so that location and sampling in the two areas can be realized. A tissue slice with a uniform thickness can be obtained by the slicing groove. In addition, the invention provides a method for sampling a heart conduction system tissue. The method is simple and safe, is able to obtain a high-quality tissue specimen slice, and is of great value in application and popularization.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com