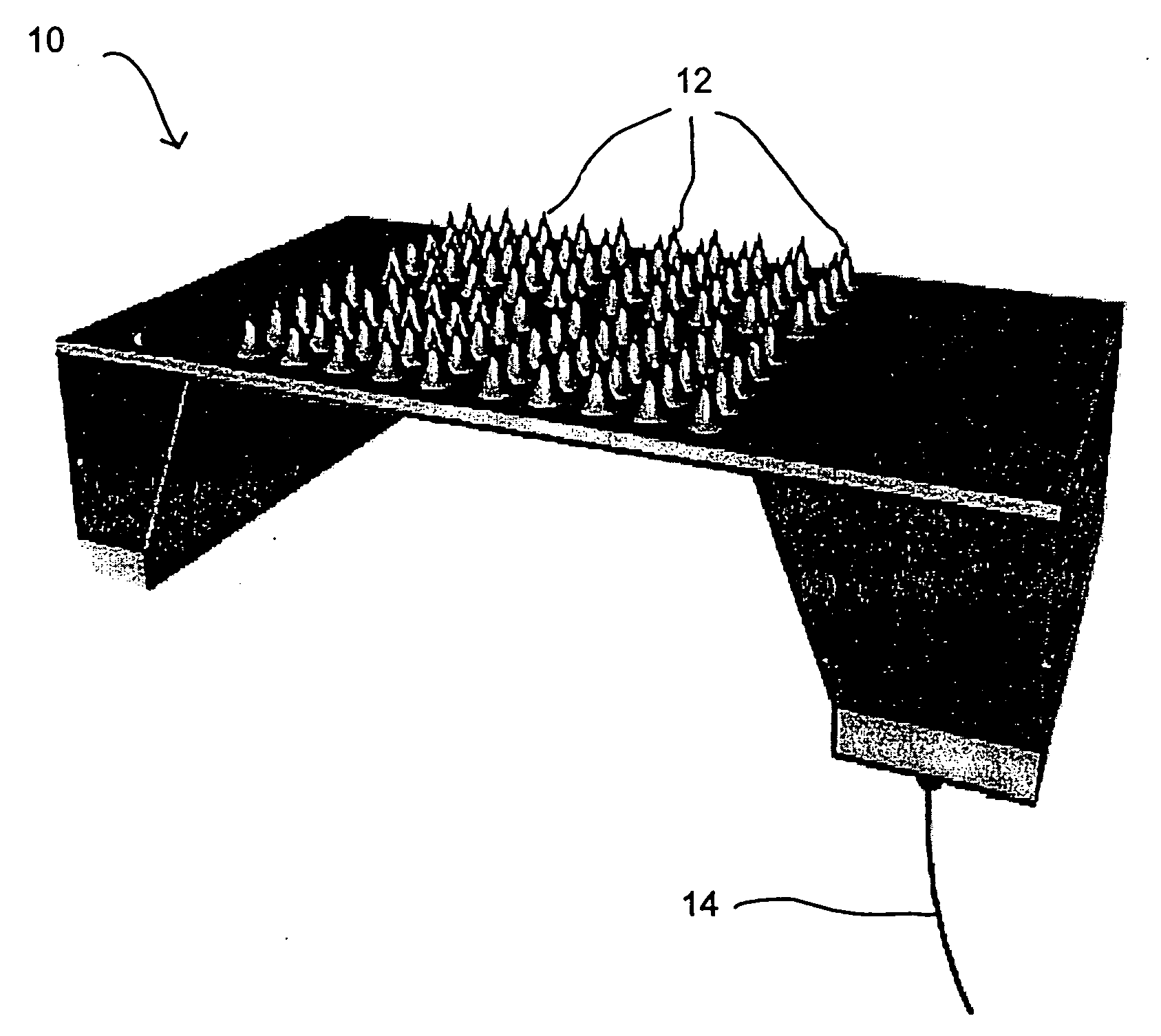
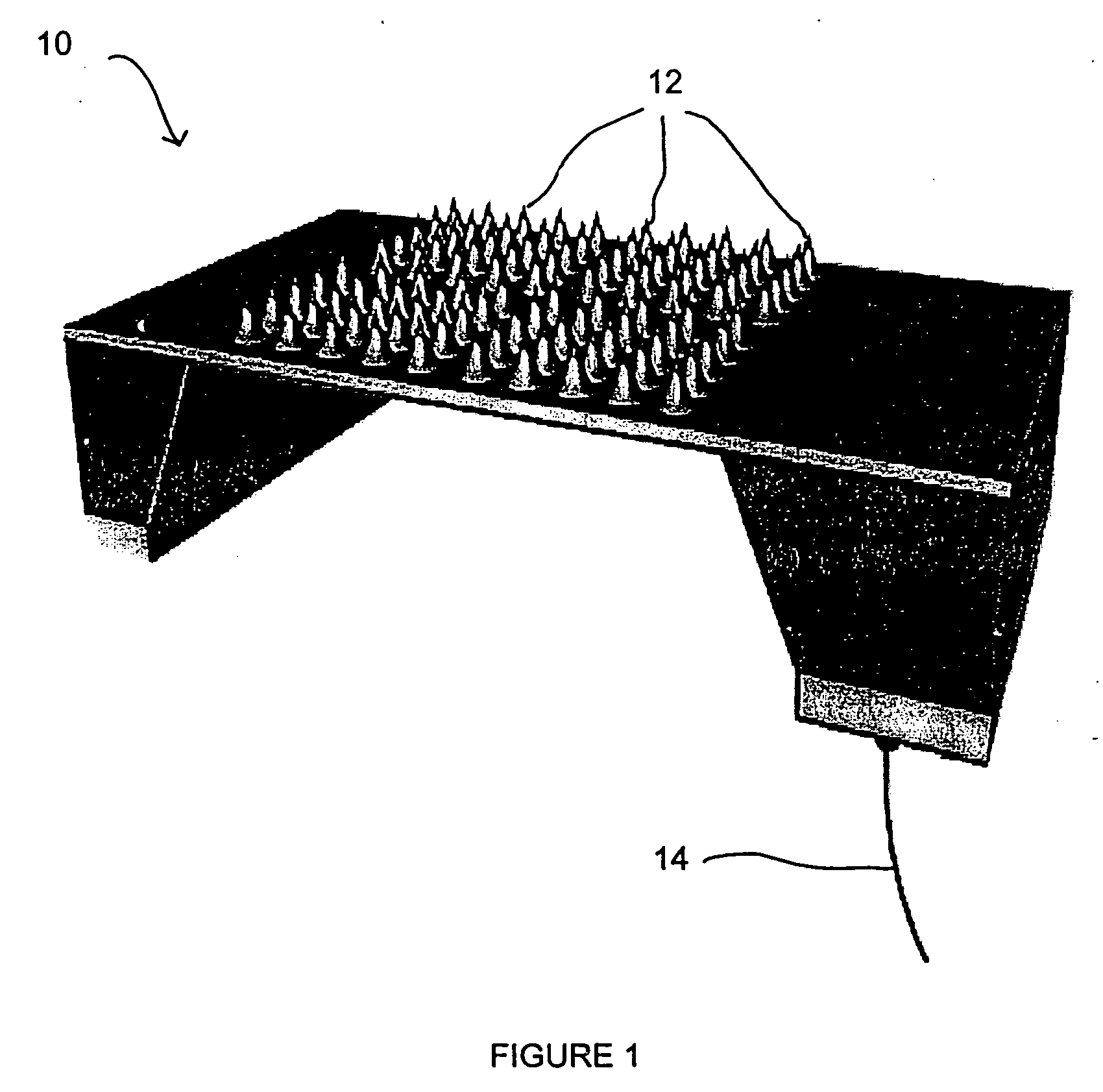
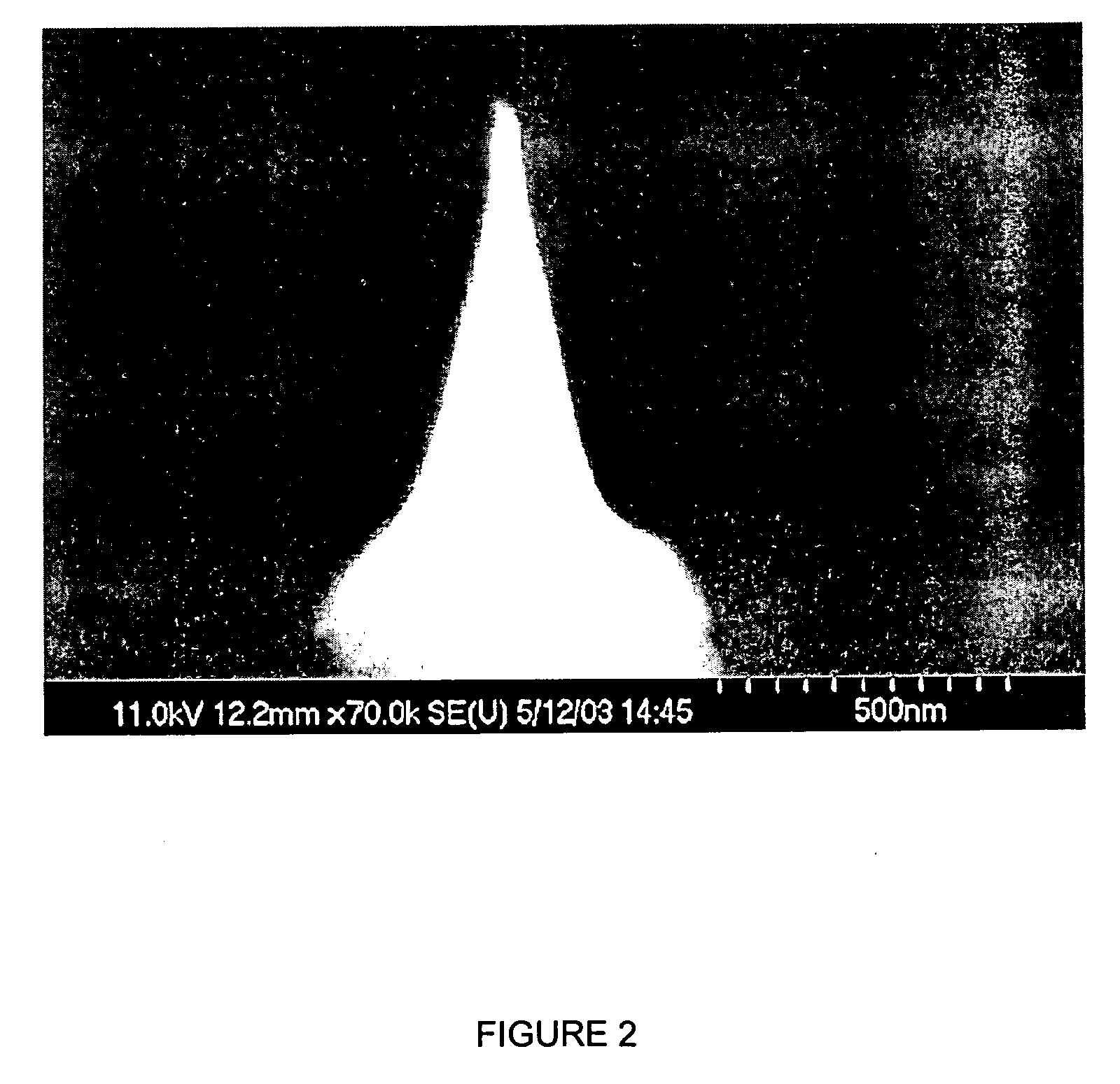
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias
a cardiac arrhythmia and system technology, applied in the field of methods and systems for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, can solve the problem of little time to protect the individual from death, and achieve the effect of increasing the likelihood of the occurrence of cardiac arrhythmias
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Rabbit Renal Sympathetic Nerve Recordings
[0050] A standard wire electrode and a nanoelectrode array was implanted on the renal sympathetic nerve of a New Zealand white rabbit. Simultaneous recordings of the ECG and renal sympathetic neural discharges were obtained. The renal sympathetic neural discharges was recorded with both a standard wire electrode and a nanoelectrode array and amplifier. The signals were digitized with a band pass filter of 30 to 500 Hz and a digitization rate of 1 K / sec.
[0051]FIG. 3 shows the ECG and renal sympathetic neural discharge recordings obtained from the rabbit. The nanoelectrode recordings provided a lower baseline noise than the wire electrode and therefore a higher signal-to-noise ratio. FIG. 3A shows bursts of renal sympathetic neural discharges, which did not correlate with changes in the heart rate. FIG. 3B shows the suppression of renal sympathetic neural discharges by intravenous bolus dose of xylazine and ketamine.
example 2
Sympathetic Neural Discharges of the Left Stellate Ganglion and Heart Rate Control
[0052] The relationship between the sympathetic neural discharges of the left stellate ganglion and the heart rate was investigated in a normal canine subject. A normal canine subject was anesthetized with isoflurane and the chest was opened at the third intercostal space. The left stellate ganglion was identified and a nanoelectrode was implanted under the fibrous capsule. The fibrous capsule was then closed with a 4-0 silk suture and additional sutures were placed on the wire to secure the nanoelectrodes. The nanoelectrodes were then connected to a DSI transmitter (DSI TL 10M3-D70-EEE, Data Sciences, International) with a band pass filter of 0.05 to 100 Hz and a digitization rate of 1 K / sec. An additional bipolar pair of the DSI transmitter was used for ECG recordings between the right and left chest. All recordings shared a common ground.
[0053]FIG. 4 shows the relationship between the sympathetic ...
example 3
Effects of Anti-Convulsants on SNA
[0058] Anti-convulsant drugs may exert an anti-arrhythmic effect by suppressing the high frequency sympathetic nerve discharges from the left stellate ganglion. Phenyloin (Dilantin®) is one of the most commonly used anti-convulsants and has been shown to suppress the sympathetic neural discharges in ambulatory dogs within the therapeutic range of 10-20 mg / L.
[0059] After confirming the successful recording of sympathetic neural discharges from the canine subject, 400 mg (approximately 18 mg / kg) of phenyloin was administered intravenously to the canine subject. FIG. 9 shows the continuous tracings of heart rate and sympathetic neural discharges over a 24 hour period for a canine subject. Phenyloin was injected at 9:45 a.m. and the tracings following that time show the effects of phenyloin injection on the heart rate and the sympathetic neural discharges of the canine subject.
[0060] The serum concentration of the canine subject two hours after the i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com