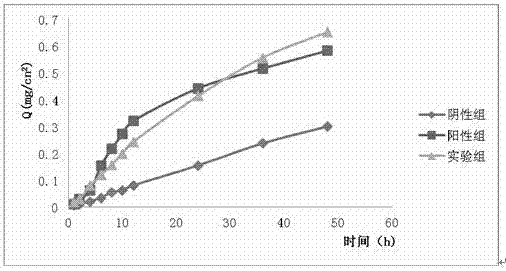
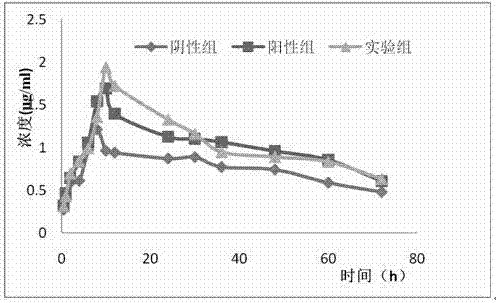
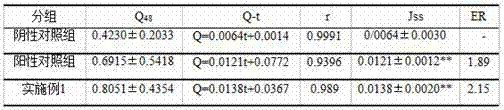
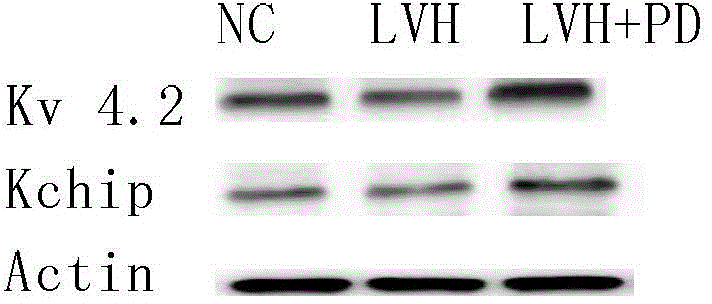
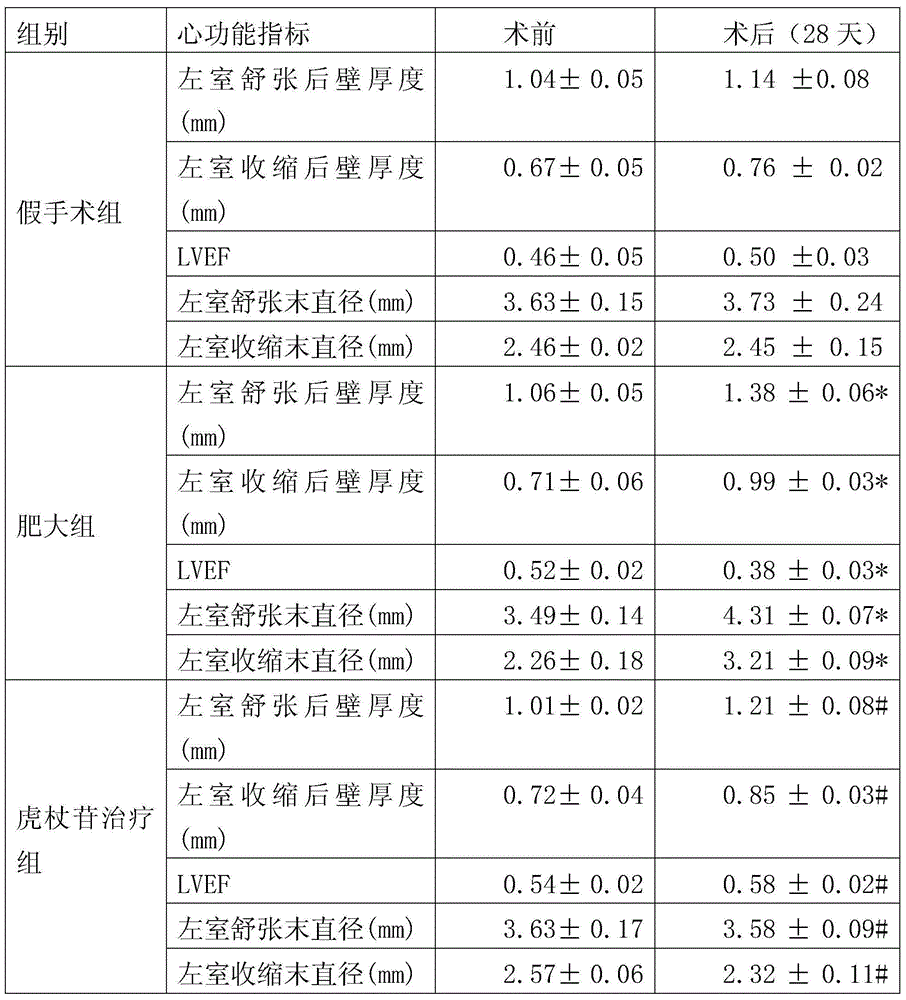
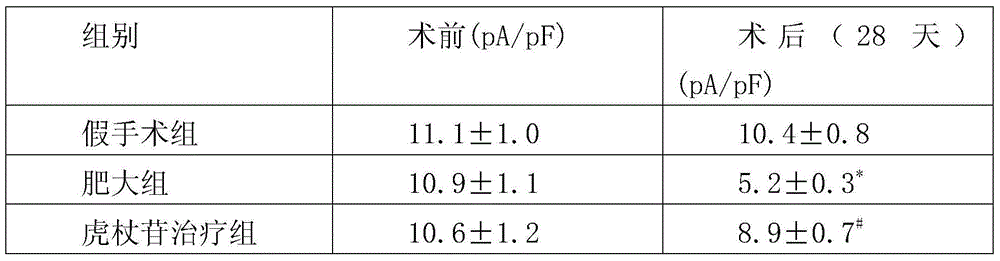
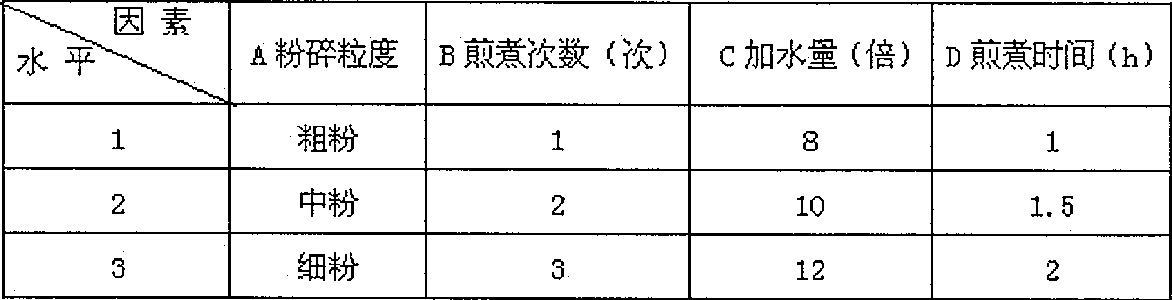
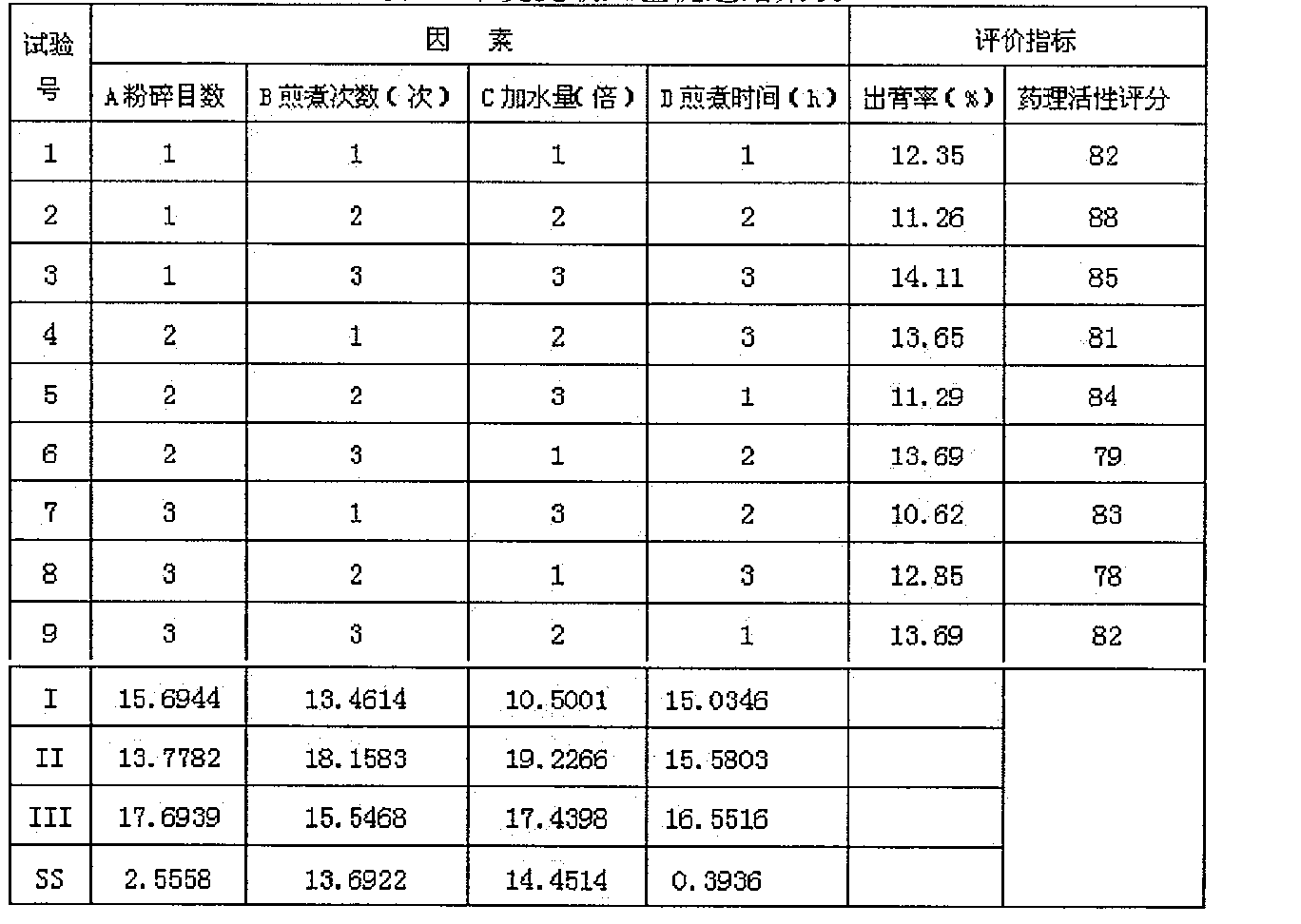
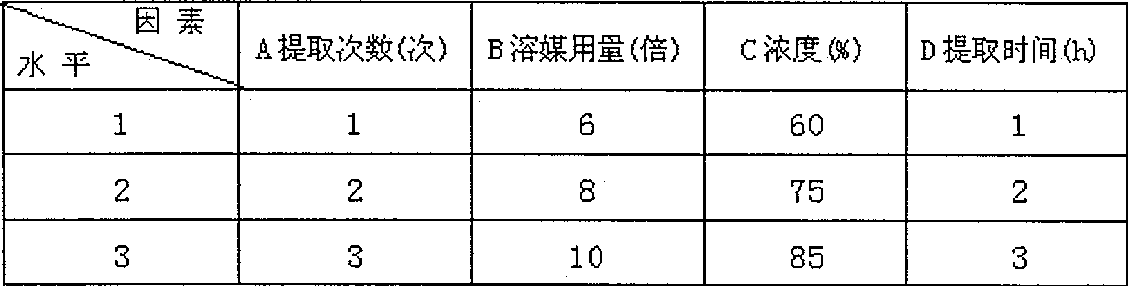
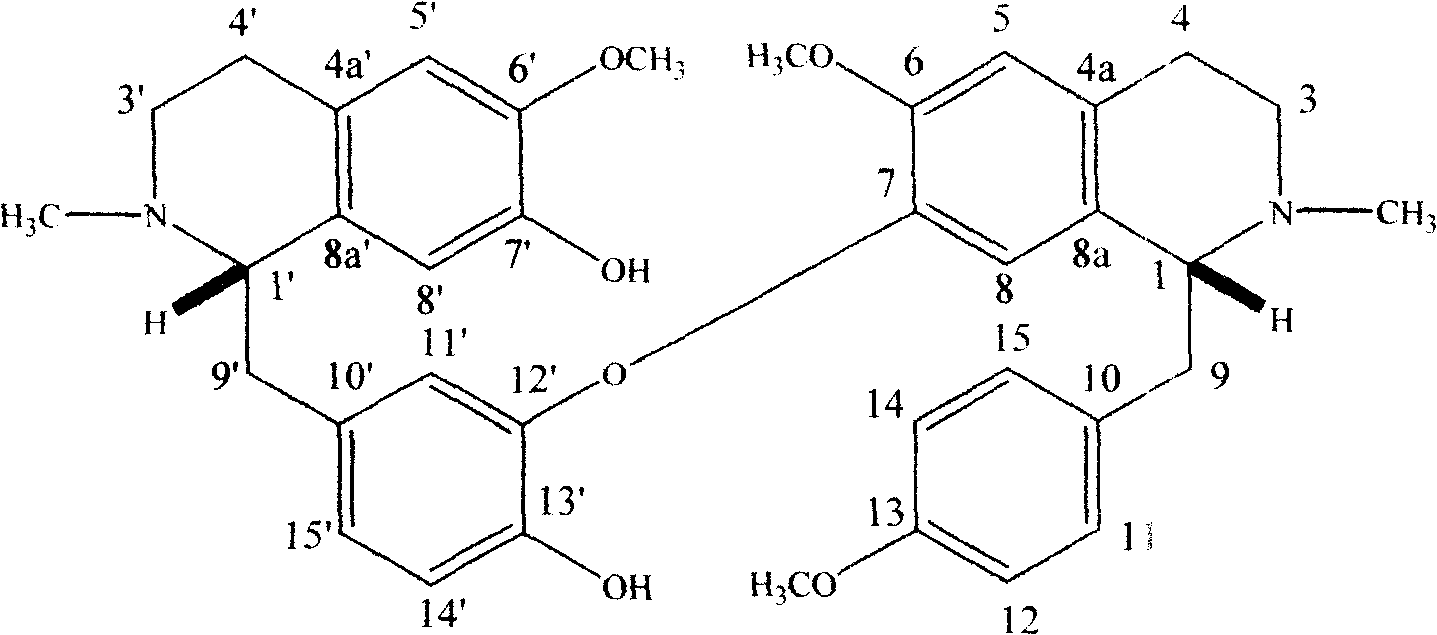
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Antiarrhythmic effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antiarrhythmic drugs can cause a range of side effects. Possible effects include allergic reaction, cough, appetite loss, constipation or diarrhea, blurred vision, shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, abnormally fast or slow heartbeat and swelling of the legs or feet.
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
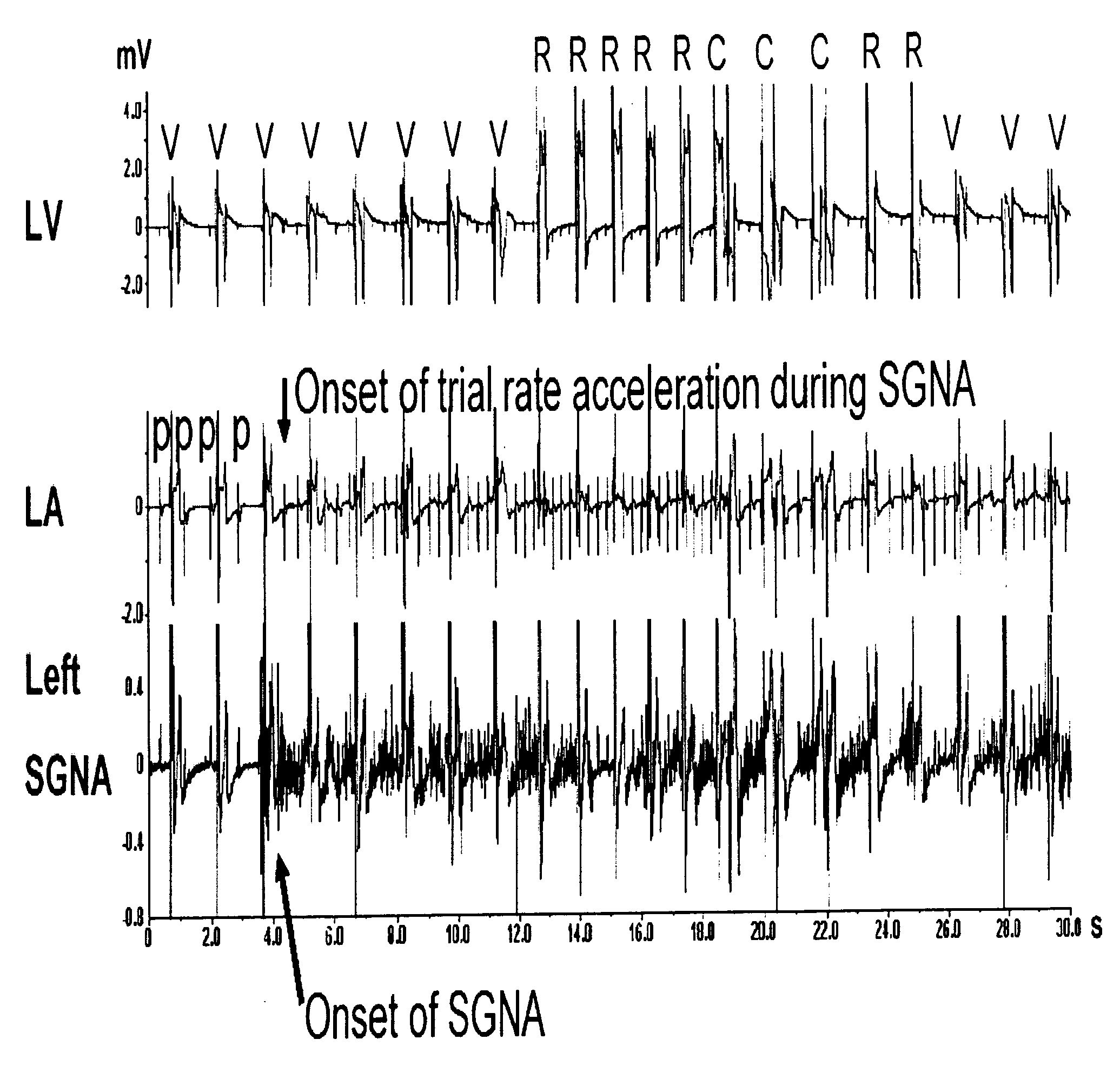
InactiveUS20060074451A1Raise the possibilityIncrease heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAntiarrhythmic effect
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Use of autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters inhibition and atrial parasympathetic fibers ablation for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to preserve drug effects
InactiveUSRE42961E1Increased occurrence of initiation of atrial flutterShorten the construction periodDiagnosticsHeart defibrillatorsNervous systemRight atrium
Atrial arrhythmias, a major contributor to cardiovascular morbidity, are believed to be influenced by autonomic nervous system tone. The main purpose of this invention was to highlight new findings that have emerged in the study of effects of autonomic nervous system tone on atrial arrhythmias, and its interaction with class III antiarrhythmic drug effects. This invention evaluates the significance of sympathetic and parasympathetic activation by determining the effects of autonomic nervous system using a vagal and stellar ganglions stimulation, and by using autonomic nervous system neurotransmitters infusion (norepinephrine, acetylcholine). This invention evaluates the autonomic nervous system effects on the atrial effective refractory period duration and dispersion, atrial conduction velocity, atrial wavelength duration, excitable gap duration during a stable circuit (such atrial flutter circuit around an anatomical obstacle), and on the susceptibility of occurrence (initiation, maintenance and termination) of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias in canine. This invention also evaluates whether autonomic nervous system activation effects via a local neurotransimitters infusion into the right atria can alter those of class III antiarrhythmic drug, sotalol, during a sustained right atrial flutter. This invention represents an emergent need to set-up and develop a new class of anti-cholinergic drug therapy for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias and to combine this new anti-cholinergic class to antiarrhythmic drugs. Furthermore, this invention also highlights the importance of a local application of parasympathetic neurotransmitters / blockers and a catheter ablation of the area of right atrium with the highest density of parasympathetic fibers innervation. This may significantly reduce the occurrence of atrial arrhythmias and may preserve the antiarrhythmic effects of any drugs used for the treatment of atrial re-entrant arrhythmias.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Composition with anti-tumor effect and application thereof in preparing medicament for treating tumor
InactiveCN101822832AImprove anti-tumor effectReduce cardiotoxicityAmphibian material medical ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsAntiarrhythmic effectToad Venom
The invention provides a composition with anti-tumor effect and application thereof. The composition consists of 0.01 to 10 weight parts of pure bufadienolide compound, extract rich in bufadienolide compound, raw toad venom or toad skin and 0.01 to 99.9 weight parts of medicament with anti-arrhythmic effect. The composition with the anti-tumor effect has the advantage that the match among the components is scientific and reasonable; multiple in vitro tumor cytotoxicity and in vivo tumor inhibiting experiments show that the composition provided by the invention has good anti-tumor effect and plays a role in synergy after combination; and cardiotoxic experiments show that the cardiotoxicity of the composition provided by the invention is obviously reduced, and the composition can reduce the cardiotoxicity caused by primary single use of the bufadienolide compound, the toad venom or the toad skin and plays a role in detoxifying. Therefore, the composition is safer and more effective to use, and is expected to develop a new generation anti-cancer medicament.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
InactiveUS20060004414A1Raise the possibilityIncrease heart rateCatheterHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAntiarrhythmic effect
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Application of Chinese medicine composition in preparing medicament for adjusting cardiac muscle cell potassium ion channel
ActiveCN101234169ARectified Potassium Current DelayProlonged action potential durationPowder deliveryAnthropod material medical ingredientsPotassium ionsPotassium current
The invention provides an application of a Chinese traditional medicine composition in regulation of potassium ion channel in myocardial cells. The Chinese traditional medicine composition inhibits an inward rectifier potassium current, a transient outward potassium current and delays an outward rectifier potassium current in a voltage dependent mode, which prolong the action potential duration (APD) to play a role of anti-arrhythmic effect through lowering the excitability of myocardial cells and inhibiting the repolarization process of the action potential (AP) of the myocardial cells.
Owner:HEBEI YILING MEDICINE INST
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias
InactiveUS20060004413A1Raise the possibilityHeart stimulatorsSensorsAntiarrhythmic effectValproic Acid
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the left stellate ganglion, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering anti-arrhythmic therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of anti-arrhythmic therapy include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenyloin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
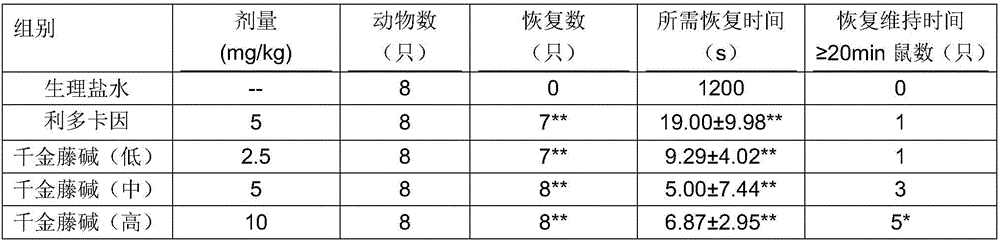
Stephanine and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt and application of solvate for preparing antiarrhythmic medicine
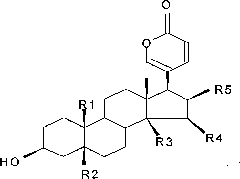
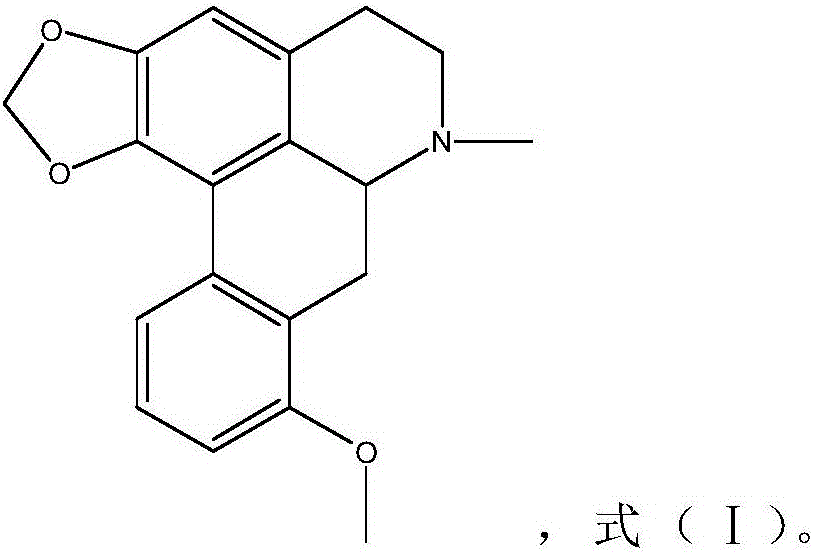
InactiveCN106466317AHas antiarrhythmic effectNo adverse reactionOrganic active ingredientsDispersion deliveryAntiarrhythmic effectStructural formula
The invention relates to stephanine and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt and an application of a solvate for preparing an antiarrhythmic medicine, which belongs to the technical field of medicine. A structural formula of stephanine is shown as a formula (I); the researches on chloroform-induced mice arrhythmia show that stephanine can resist chloroform-induced ventricular fibrillation, preliminary determination is confirmed that the stephanine has antiarrhythmic effect; then barium chloride-induced rat ventricular rhythm test, aconitine intravenous injection-induced rat cardiac rhythm test and rat myocardial ischemia and ischemia reperfusion arrhythmia test are carried out, so that stephanine has good antiarrhythmic effect, and provides a good base for preparing various antiarrhythmic medicines next time.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
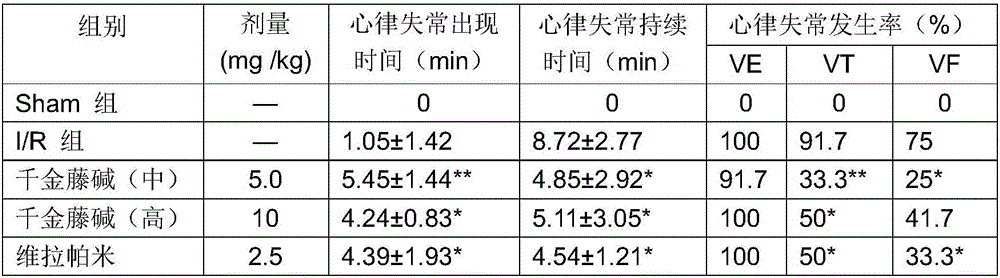
Novel application of Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicine
InactiveCN103156842ASmall contraction forceHeart rate slowing effectOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderSide effectAntiarrhythmic effect
The invention discloses a novel application of a traditional Chinese medicine extract product-Arctigenin in preparation of anti-arrhythmia medicines. A research found that the Arctigenin has bidirectional anti-arrhythmia effect and can adjust arrhythmia caused by aconitine and ouabain. Arctigenin has an effect for reducing ventricular muscle contraction force. A pharmacological effect of the Arctigenin is bidirectional adjusted cardiac muscle cell inner calcium current, the cardiac muscle cell inner potassium current is increased, and the sodium current is inhibited. The invention shows that the Arctigenin has anti-arrhythmia effect, and especially has bidirectional adjusting on arrhythmia, the side-effect is smaller, the Arctigenin has application prospect for treating toxic arrhythmia and ischemic-reperfusion arrhythmia in aconitine and ouabain; and the Arctigenin with myocardial contractility reduction effect can be taken as an auxiliary treatment measurement for hypertensive disease.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV +1
Application for preparing therapy antiarrhythmic medicament of Zacopride
InactiveCN101199521ADecreased antiarrhythmic effectGood effectOrganic active ingredientsSolution deliveryAntiarrhythmic effectReperfusion arrhythmias
The invention relates to the medicine field, particularly relating to a drug for treating arrhythmia, in particular to an application of Zacopride in preparing a drug for treating the arrhythmia. The invention aims at solving the problems that the present antiarrhythmic drugs have the effect of causing arrhythmia, and IK1 selective agonist has not been discovered at home and abroad so far. The Zacopride is an IK1 selective agonist which is discovered at present for the first time and is used on an antiarrhythmic drug. Used as a drug for treating ischemia-reperfusion arrhythmia, the Zacopride has the similar effect to that of lidocaine, takes effect stably and does not obviously affect the rhythm with wide safety range. In the experiments of arrhythmia induced by ischemia-reperfusion, lidocaine can make the rhythm slower, while the Zacopride has no obvious effect; and when the dosage of the lidocaine is increased by one-third, the antiarrhythmic effect is obviously weakened, while such phenomenon occurs when the Zacopride reaches one hundred times of effective concentration.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
Crebanine transdermal patch and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107019683ASmall molecular weightFat solubleOrganic active ingredientsOil/fats/waxes non-active ingredientsTransdermal patchAntiarrhythmic effect
The invention relates to a crebanine transdermal patch and a preparation method thereof. The crebanine transdermal patch is formed by sequentially overlapping a back lining layer, a medicine-containing adhesive layer and a protective layer, wherein the medicine-containing adhesive layer is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 0.03 to 0.135 part of crebanine or crebanine hydrochloride, 0.03 to 0.09 part of cross-linking agent, 0.3 to 0.9 part of pressure sensitive adhesive, 0.19 to 0.63 part of plasticizer, 0.1 to 0.3 part of moisturizer, and 0.007 to 0.206 part of percutaneous penetration enhancer. The crebanine transdermal patch has relatively good percutaneous absorption, is more lasting in action time than that of an oral preparation, is more convenient to use than an injection preparation, is good in compliance of patients, and has the characteristics of security, effectiveness, convenience in using, and no irritation and toxicity. Crebanine in the transdermal patch disclosed by the invention is relatively high in cumulative infiltration capacity and can maintain effective blood drug concentration for a longer time, has obvious and lasting antiarrhythmic effect, and overcomes the phenomena that the lasting time of arrhythmia caused by intravenous injection or gastric infusion administration is relatively short and relapse easily occurs.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Sea anemone neurotoxin gene Sr1 and application thereof
InactiveCN1594573ABiologically activeCardiotonicPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationAntiarrhythmic effectToxin protein
The invention relates to actinocongestin gene Sr1 and its coded protein, and also the uses of the said protein in preparation of drugs for cardiovascular disease. The invention employs RT-PCR method, extracts sequence 1 from total RNA of tentacles of sagartia rosea ( sequence 1 indicates) the protein coded by the gene( sequence 2 indicate) Recombinant actinocongestin protein in the invention has cardiac and anti-arrhythmia action, can prepare the cardiovascular disease drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating arrhythmia
InactiveCN105535852AImprove clinical symptomsImprove the number of contractionsInanimate material medical ingredientsAlkali/alkaline-earth metal chloride active ingredientsAntiarrhythmic effectCoronary heart disease
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine preparation for treating arrhythmia. The traditional Chinese medicine preparation consists of the following traditional Chinese medicine raw materials: codonopsis pilosula, valerian, amber powder, panax notoginseng powder, angelica sinensis, fried date kernels, curcuma rcenyujin, ophiopogon japonicas, alisma plantago-aquatica, kudzuvine roots, honey-fried licorice roots, fructus forsythia, cassia twigs, amethyst, acorus calamus, white sandalwood and eupatorium. The medicines are well matched and reasonable in formula, can take the effects of nourishing spleen and tonifying qi, conditioning viscera, clearing heat and removing fire as well as supplementing qi and restoring pulse together, not only is the antiarrhythmic function achieved, but also the function tendency of increasing coronary blood-flow volume, reducing myocardial oxygen consumption and increasing oxygen utilization rate can be achieved, coronary thrombus can be prevented, and the traditional Chinese medicine preparation is an ideal medicine for reducing myocardial ischemia and treating arrhythmia and is worthy of clinical popularization and application.
Owner:李宪秋
Purposes of polydatin in preparing anti-arrhythmic products
ActiveCN104688750ALow priceExert antiarrhythmic effectOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderAntiarrhythmic effectDeath sudden cardiac
The invention relates to purposes of polygonum cuspidatum extract, namely polydatin. Myocardial hypertrophy is the most important reason for triggering congestive heart failure. Ventricular hypertrophy usually involves ventricular structure change, namely ventricular remodeling. The ventricular remodeling is a complication of multiple cardiovascular diseases and a vital and decisive element in the development process of the congestive heart failure. The arrhythmia occurrence rate after the myocardial remodeling is increased by 28%, and cardiac sudden deaths caused in the end are increased by over five times. It is indicated that through in vitro study tests, the polydatin remarkably restrains heart ion channels caused by ischemia indury of mice from remodeling and has a great protective effect for arrhythmia, and therefore the polydatin can be used for preparing products resisting against arrhythmia caused by myocardial hypertrophy and / or ventricular hypertrophy. According to the method, the polydatin plays the anti-arrhythmic role by increasing the electric current density of transient outward potassium current (Ito), shortening the action potential duration (APD) of cardiac muscle cells and restraining the QT inter-phase from being prolonged.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Pinellia tuber extract and its preparation process, medicine composition and use
InactiveCN100531765CGood secretion effectGood against rat pyloric ligation ulcerDigestive systemRespiratory disorderRefluxBile Juice
The present invention discloses one kind of pinellia tuber extract and its preparation process, medicine composition and use. The pinellia tuber extract is prepared with fresh pinellia tuber, and through air dying, crushing to operate pinellia tuber meal, heat reflux or percolating with organic solvent and / or water for 2-4 times to obtain the extracted liquid, concentrating and drying the extract liquid. The pinellia tuber extract has excellent effects of relieving cough, eliminating phlegm, stopping vomiting, diminishing inflammation, etc. and may be used in treating pneumosilicosis, cough, gastric ulcer, arrhythmia, tumor and other diseases.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sulfonation technique for isoliensinine, arrhythmia resistant function of products produced thereby
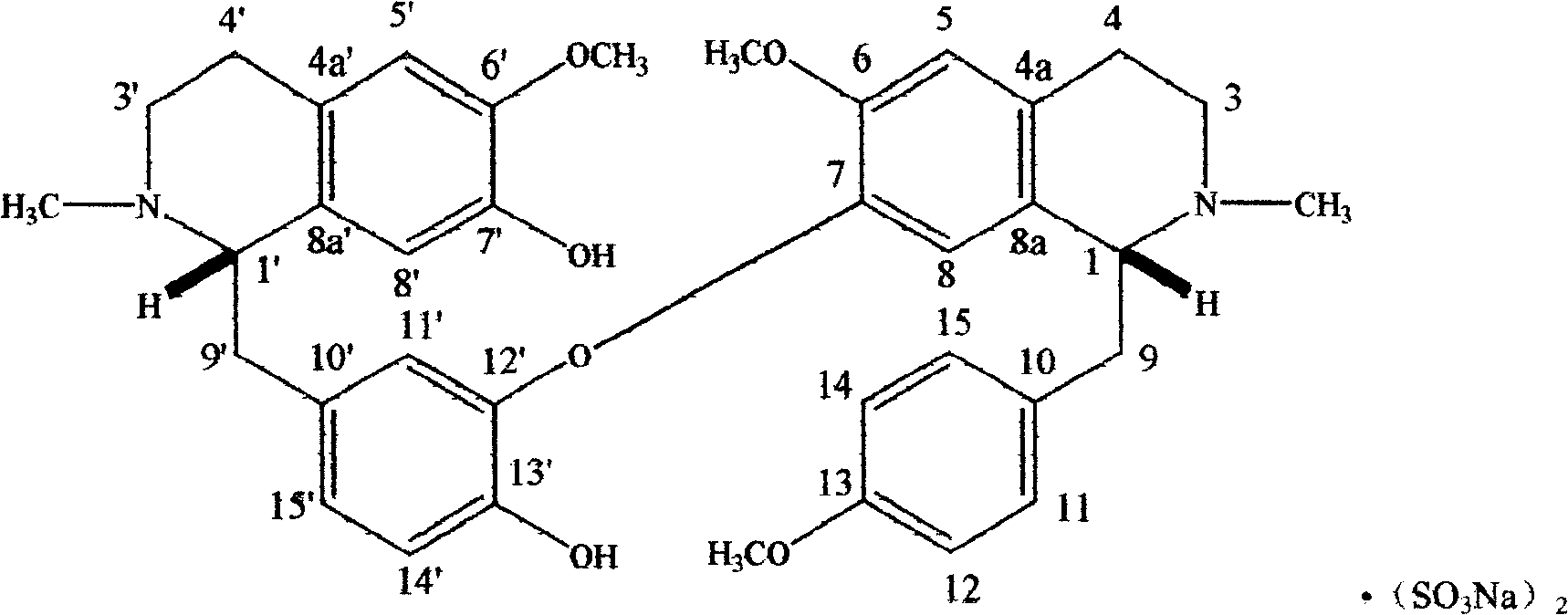
The present invention relates to di-benzyl isoquinoline monoether-key alkaloid, isoliensinine, which is extracted from lotus seeds. The present invention also discloses a preparation process of sulfonation. Isoliensinine sodium sulfonate that is prepared through the sulfonation, which not only improves the stability of the phenol alkaloid of isoliensinine, but also improves the water solubility and bioavailability of the isoliensinine. The content of the isoliensinine sodium sulfonate prepared in the method is above 97 percent. Based on the pharmacodynamic results, the method further discloses the anti-arrhythmic security and effectiveness of the isoliensinine sodium sulfonate and preparations thereof.
Owner:潘阳
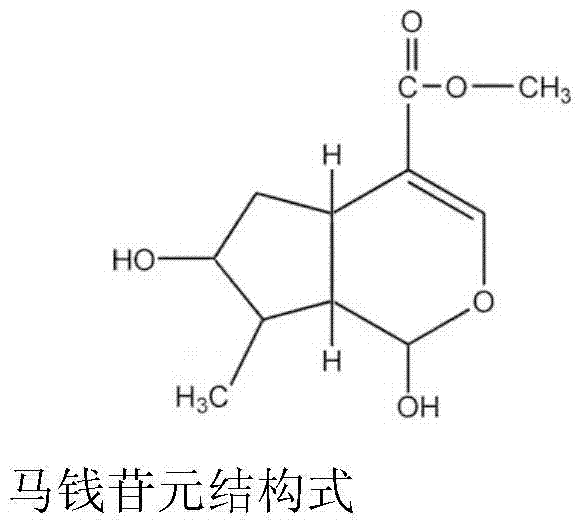
Applications of loganetin in preparation of drugs for prevention or treatment of arrhythmia
ActiveCN106943390AGood treatment effectExtended appearance timeOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderAntiarrhythmic effectSide effect
The present invention relates to uses of loganetin in preparation of drugs for prevention or treatment of arrhythmia, and belongs to the field of medicine. According to the present invention, the loganetin is the tradition Chinese medicine monomer extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine; the animal test results show that the loganetin can significantly prevent and treat arrhythmia, can significantly delay the occurrence of premature ventricualr contraction, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation of arrhythmia rats due to aconitine, can significantly reduce the animal mortality, and can significantly inhibit the ventricular fibrillation incidence rate of chloroform-induced arrhythmia mice; and the loganetin has advantages of exact arrhythmia treatment effect, low side effect, and broad medical application prospect.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Sea anemone neurotoxin gene Sr6 and application thereof
InactiveCN1594575ABiologically activeCardiotonicPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationAntiarrhythmic effectProtein C
The invention relates to actinocongestin gene Sr6 and its coded protein, and also the uses of the said protein in preparation of drugs for cardiovascular disease. The invention employs RT-PCR method, extracts sequence 1 from total RNA of tentacles of sagartia rosea ( sequence 1 indicates) the protein coded by the gene( sequence 2 indicates) Recombinant actinocongestin protein in the invention has cardiac and anti-arrhythmia action, can prepare the cardiovascular disease drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Sea anemone neurotoxin gene Sr5 and application thereof
The invention relates to actinocongestin gene Sr5 and its coded protein, and also the uses of the said protein in preparation of drugs for cardiovascular disease. The invention employs RT-PCR method, extracts sequence 1 from total RNA of tentacles of sagartia rosea ( sequence 1 indicates) the protein coded by the gene( sequence 2 indicates) Recombinant actinocongestin protein in the invention has cardiac and anti-arrhythmia action, can prepare the cardiovascular disease drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Low-toxicity antiarrhythmic medicine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN113149906AOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistry methodsAntiarrhythmic effectChemical compound
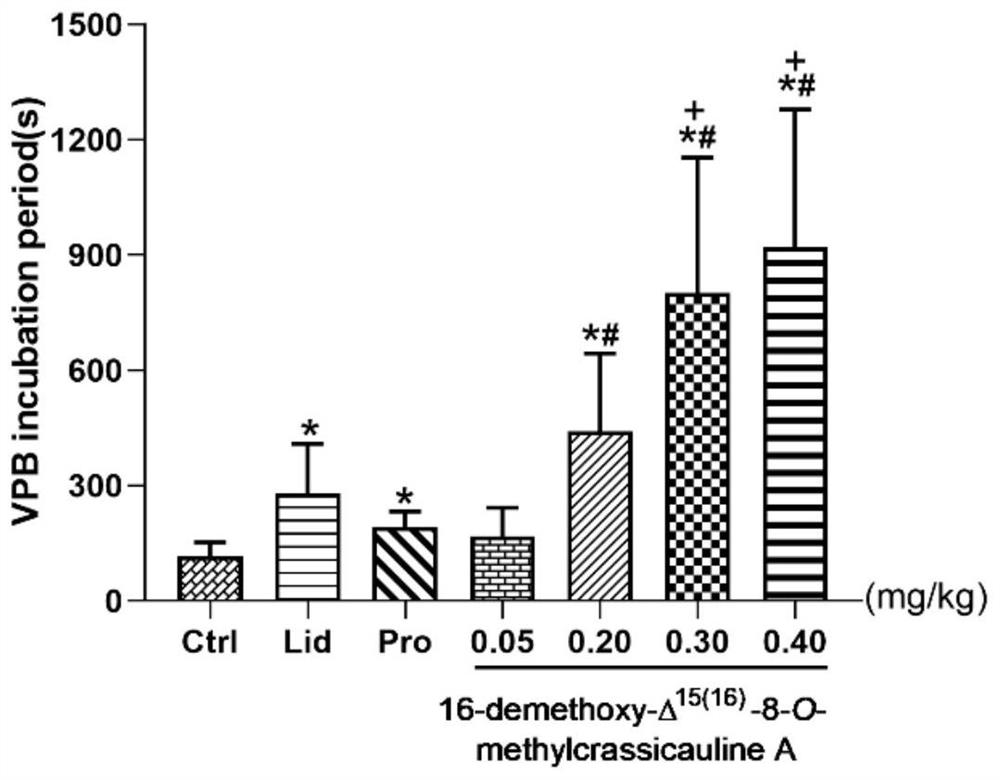
The invention provides a low-toxicity anti-arrhythmia medicine and a preparation method thereof. The structure of the compound is shown as a formula I in the specification. Experimental results show that the compound provided by the invention has excellent anti-arrhythmia activity, can delay the VPB latency period of aconitine induced arrhythmia rats and effectively prevent further development of VPB, and the anti-arrhythmia effect of the compound is even superior to that of a positive drug lidocaine under the dosage of 0.30 mg / kg and 0.40 mg / kg. More importantly, compared with bulleyaconitine A, the cardiotoxicity of the compound disclosed by the invention is obviously reduced; compared with the known sand-fried product delta 15, 16-16-demethoxyindinacitine, the compound disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the acute toxicity is obviously lower, and the safety is higher. The invention provides a new choice for preparing a low-toxicity anti-arrhythmia medicine, and provides a new method for controlling the quality of the sand-fried Aconitum bulleyanum or sand-fried Aconitum crassicaule.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
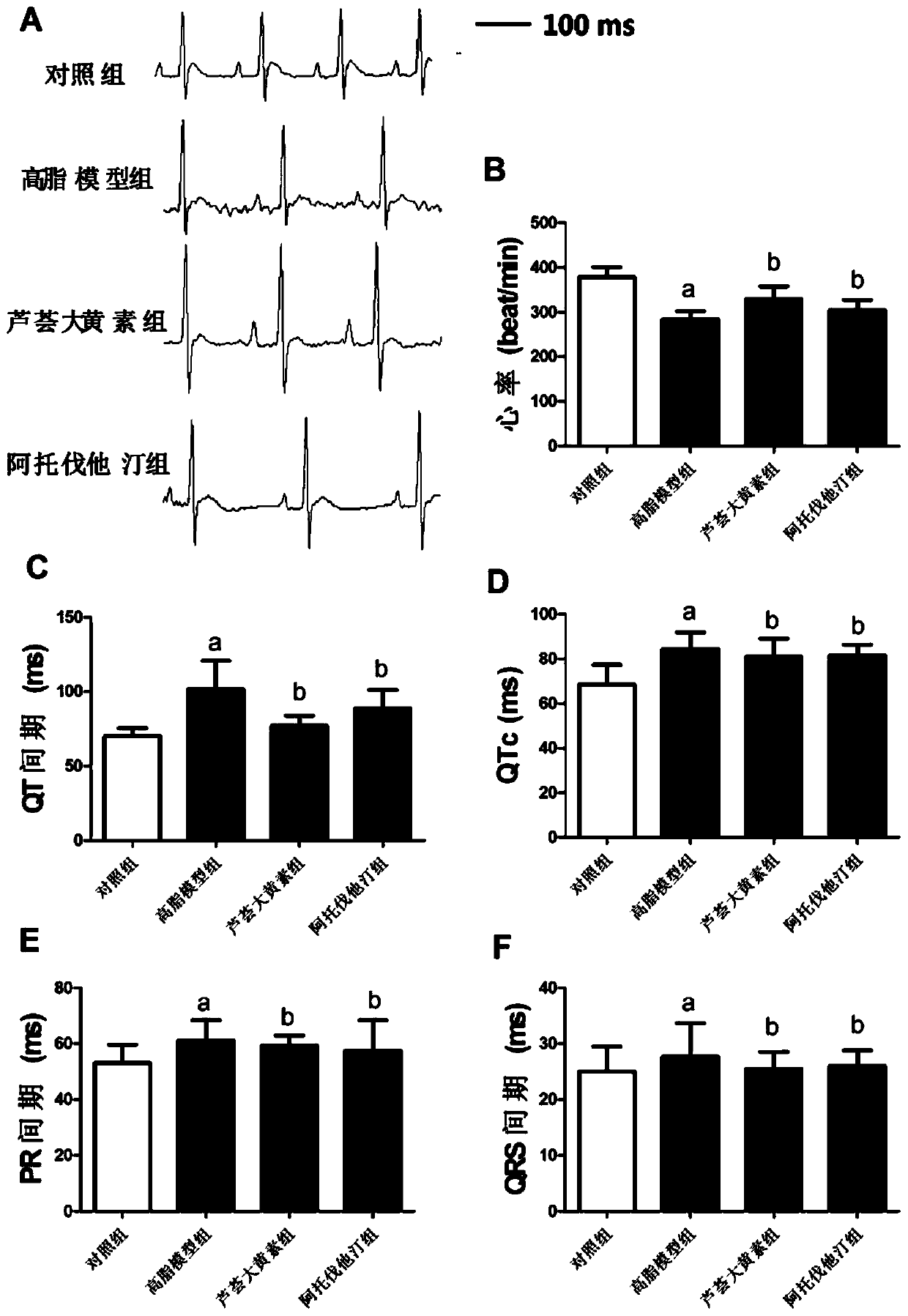
Use of aloe-emodin in the preparation of drugs for the prevention and treatment of myocardial ischemia and arrhythmia
ActiveCN107157970BImprove protectionImprove heart functionOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderAntiarrhythmic effectAcute myocardial ischaemia
The invention discloses use of aloeemodin in preparing of medicament for preventing and treating myocardial ischemia and arrhythmia, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. Pharmacodynamic experiments of the aloeemodin show that the aloeemodin can significantly improve left ventricular ejection fraction and shortening fraction of an animal model of acute myocardial ischemia, and has obvious protective effect against myocardial ischemia; at the same time, the aloeemodin can also reverse heart QT interval prolongation caused by an animal model of hyperlipidemia, and has potential antiarrhythmic effect. The invention discloses the use of the aloeemodin in prevention and treatment of the myocardial ischemia and the arrhythmia, and the aloeemodin has the advantages of obvious myocardial protection effects, low toxicity, low price, and convenient production, transportation, storage and use, and has broad application prospects as a myocardial protection drug.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Bromocarbanine compound and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN106380472BLow acute toxicityAntagonize ventricular fibrillationOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAntiarrhythmic effectAcute toxicity testing
The invention relates to a brominated crebanine compound and preparation method and an application thereof, which belongs to the technical field of medicine. The invention firstly discloses the synthesis of 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine, through research on effect of chloroform for inducing mice arrhythmia, the research shows that the 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine can antagonize the chloroform-induced ventricular fibrillation, so that the 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine have anti-arrhythmia effect through preliminary determination; the barium chloride-induced rat ventricular rhythm tests confirm that the 3-brominated crebanine and 10, 11-brominated crebanine have good anti-arrhythmia effect, acute toxicity of two brominated crebanine compounds is lower than that of crebanine, LD50 is 65.15+ / -1.132 mg / kg of 3-brominated crebanine and 59.62+ / -2.610 mg / kg of 10,11-brominated crebanine respectively, and a good base can be established for further deep researches.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Sea anemone neurotoxin gene Sr3 and application thereof
InactiveCN1594578ABiologically activeCardiotonicPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationAntiarrhythmic effectProtein C
The invention relates to actinocongestin gene Sr3 and its coded protein, and also the uses of the said protein in preparation of drugs for cardiovascular disease. The invention employs RT-PCR method, extracts sequence 1 from total RNA of tentacles of sagartia rosea ( sequence 1 indicates) the protein coded by the gene( sequence 2 indicates) Recombinant actinocongestin protein in the invention has cardiac and anti-arrhythmia action, can prepare the cardiovascular disease drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Application of loganin in preparation of drugs for preventing or treating arrhythmia
ActiveCN106943390BGood treatment effectExtended appearance timeOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderAntiarrhythmic effectSide effect
The present invention relates to uses of loganetin in preparation of drugs for prevention or treatment of arrhythmia, and belongs to the field of medicine. According to the present invention, the loganetin is the tradition Chinese medicine monomer extracted from the traditional Chinese medicine; the animal test results show that the loganetin can significantly prevent and treat arrhythmia, can significantly delay the occurrence of premature ventricualr contraction, ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation of arrhythmia rats due to aconitine, can significantly reduce the animal mortality, and can significantly inhibit the ventricular fibrillation incidence rate of chloroform-induced arrhythmia mice; and the loganetin has advantages of exact arrhythmia treatment effect, low side effect, and broad medical application prospect.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Sea anemone neurotoxin gene Sr4 and application thereof
The invention relates to actinocongestin gene Sr4 and its coded protein, and also the uses of the said protein in preparation of drugs for cardiovascular disease. The invention employs RT-PCR method, extracts sequence 1 from total RNA of tentacles of sagartia rosea ( sequence 1 indicates) the protein coded by the gene( sequence 2 indicates) Recombinant actinocongestin protein in the invention has cardiac and anti-arrhythmia action, can prepare the cardiovascular disease drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Sea anemone neurotoxin gene Sr3 and application thereof
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Sea anemone neurotoxin gene Sr7 and application thereof
InactiveCN1594572ABiologically activeCardiotonicPeptide/protein ingredientsFermentationAntiarrhythmic effectToxin protein
The invention relates to actinocongestin gene Sr7 and its coded protein, and also the uses of the said protein in preparation of drugs for cardiovascular disease. The invention employs RT-PCR method, extracts sequence 1 from total RNA of tentacles of sagartia rosea ( sequence 1 indicates), the protein coded by the gene( sequence 2 indicate). Recombinant actinocongestin protein in the invention has cardiac and anti-arrhythmia action, can prepare the cardiovascular disease drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
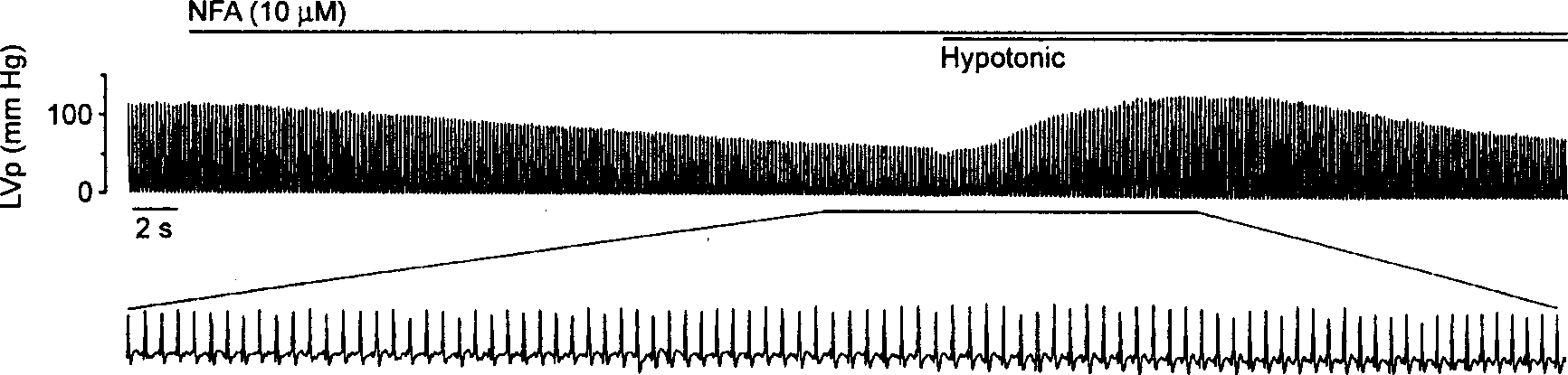
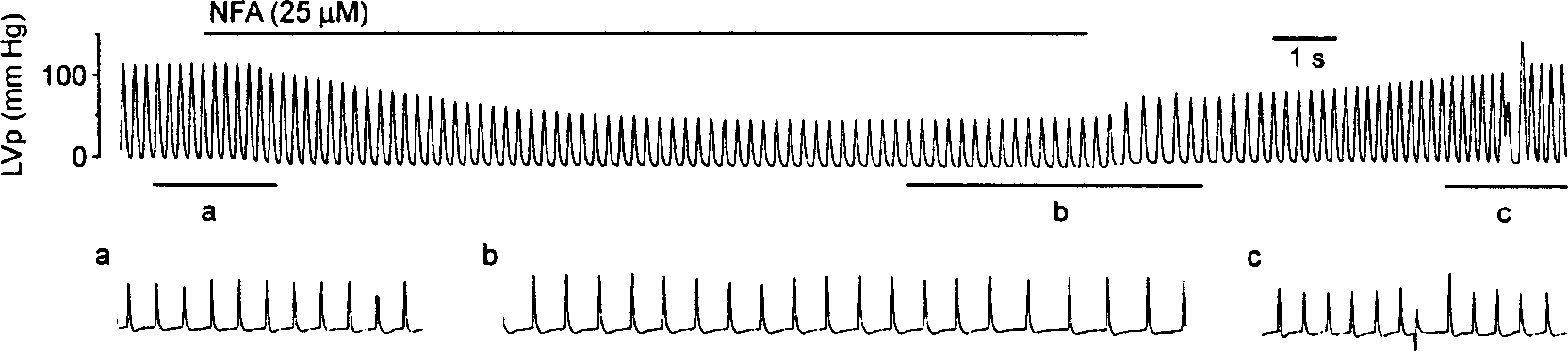
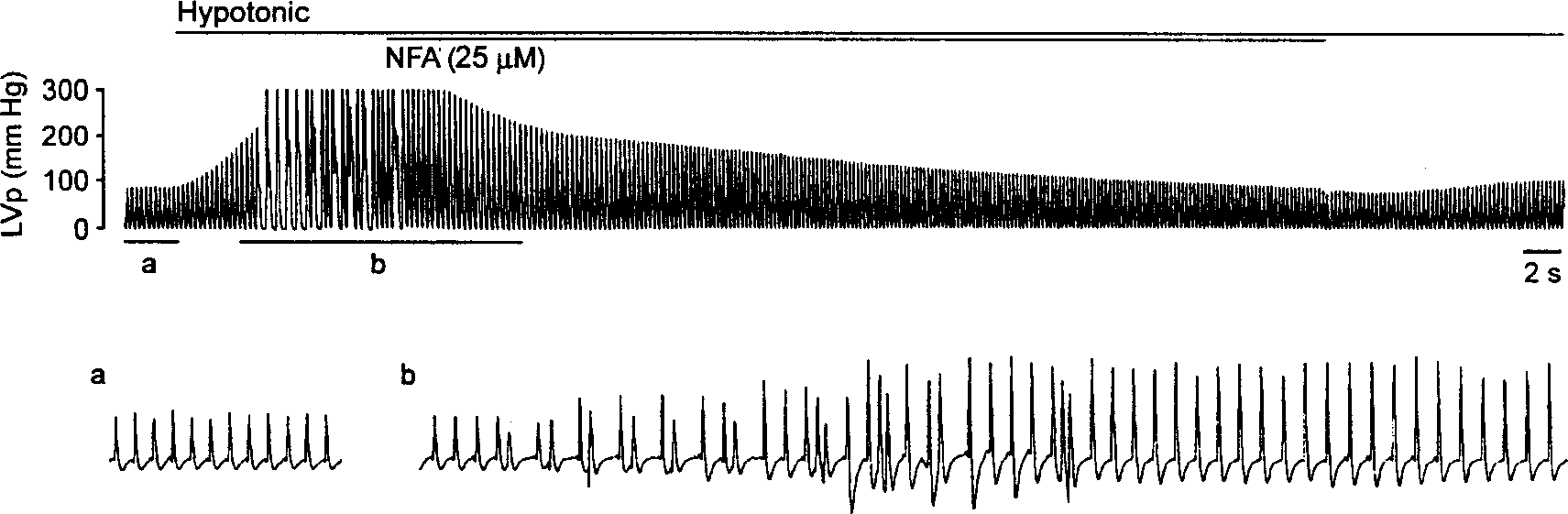
Application of niflumic acid in preventing and treating arrhythmia
InactiveCN1386502ASlow down heart rateAntinoxious agentsCardiovascular disorderAntiarrhythmic effectDecreased Oncotic Pressure
A novel application of niflumic acid (NFA) in treating arrhythmia is disclosed. It can block the chlorine ion channel to treat the arrhythmia caused by low osmotic pressure and aconitine. It can be also used for auxiliary therapy of hypertension.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com