Patents
Literature
643 results about "Electrophysiology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
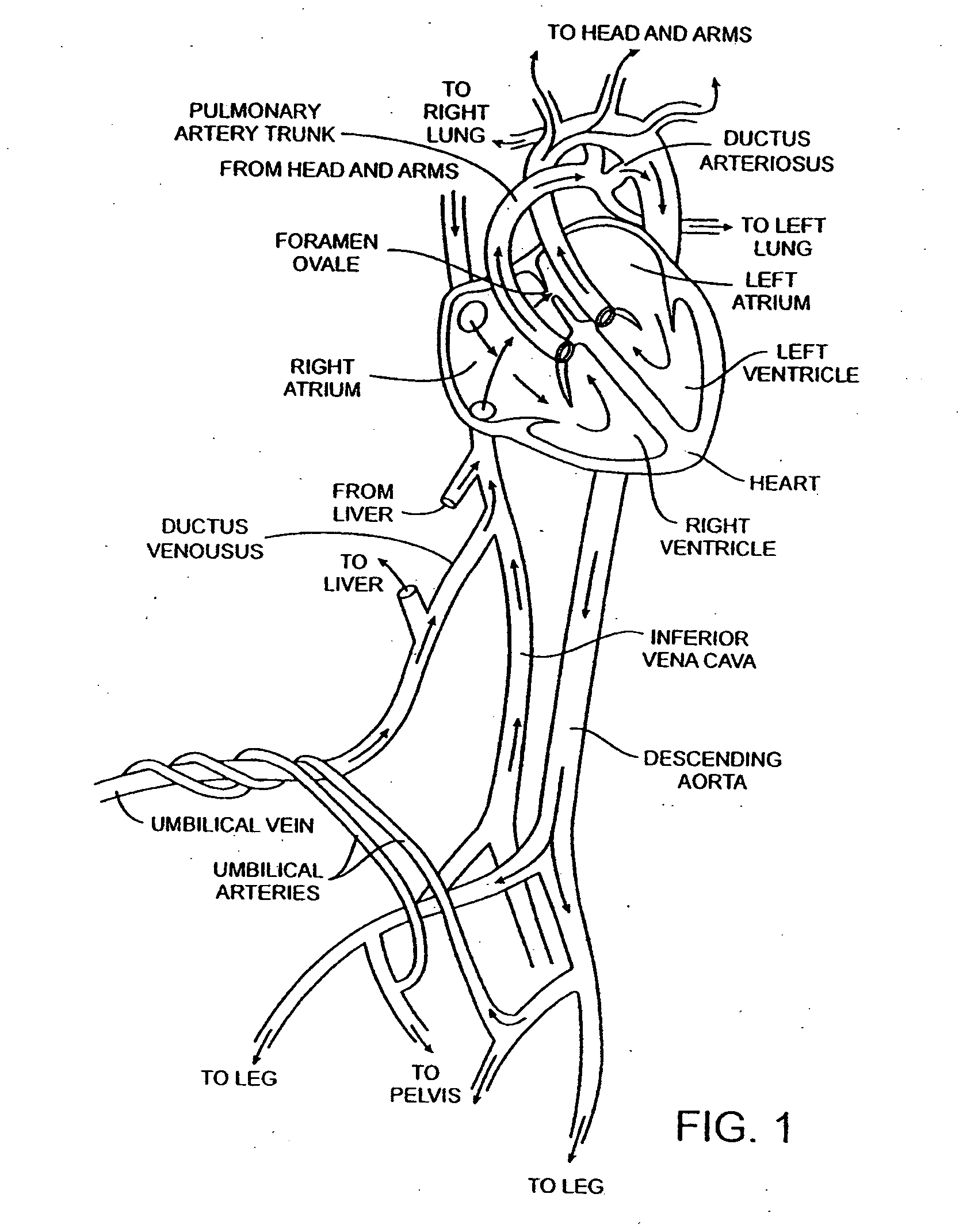
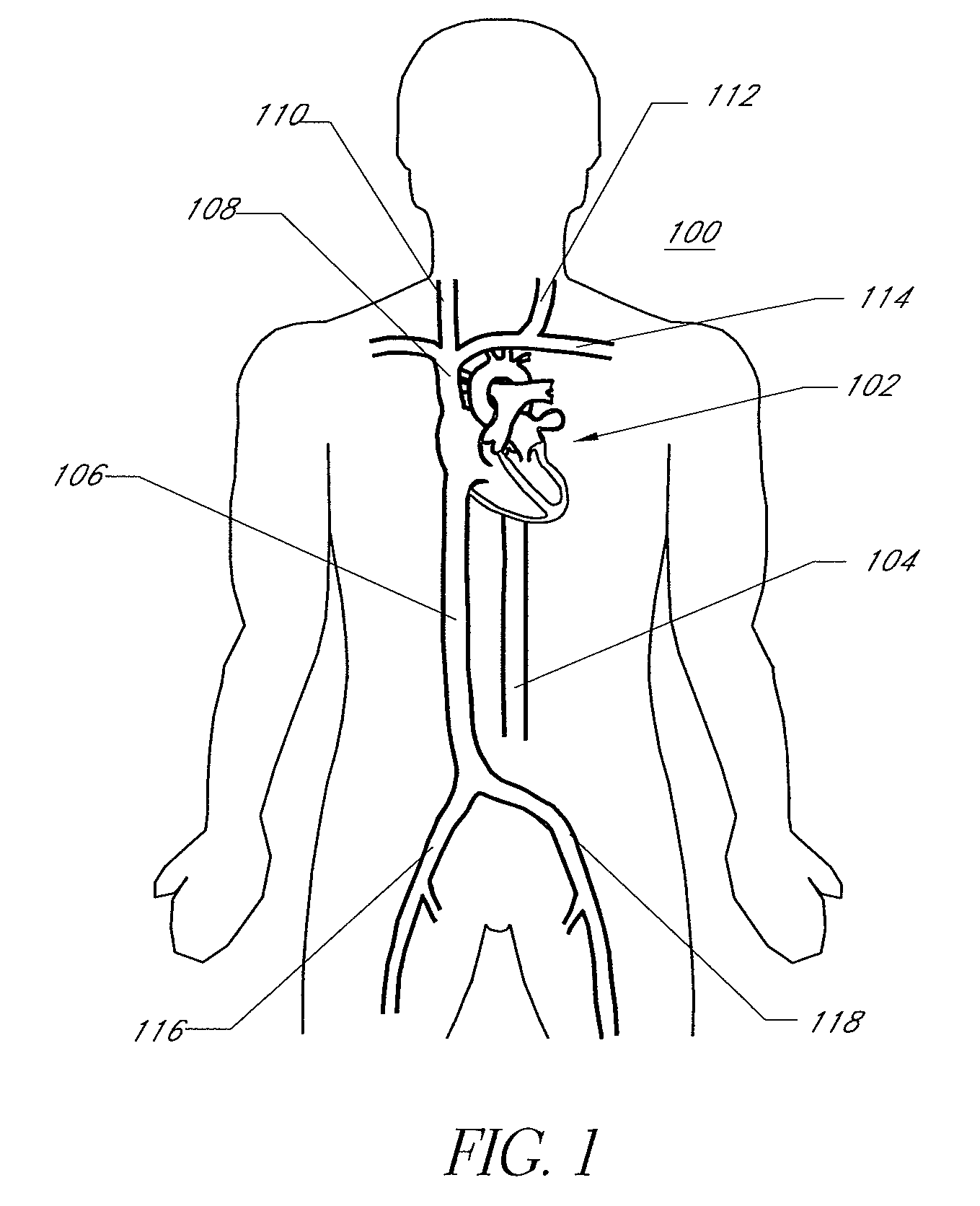
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, "amber" [see the etymology of "electron"]; φύσις, physis, "nature, origin"; and -λογία, -logia) is the branch of physiology that studies the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage changes or electric current or manipulations on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and, in particular, action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system, such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings. They are useful for electrodiagnosis and monitoring.
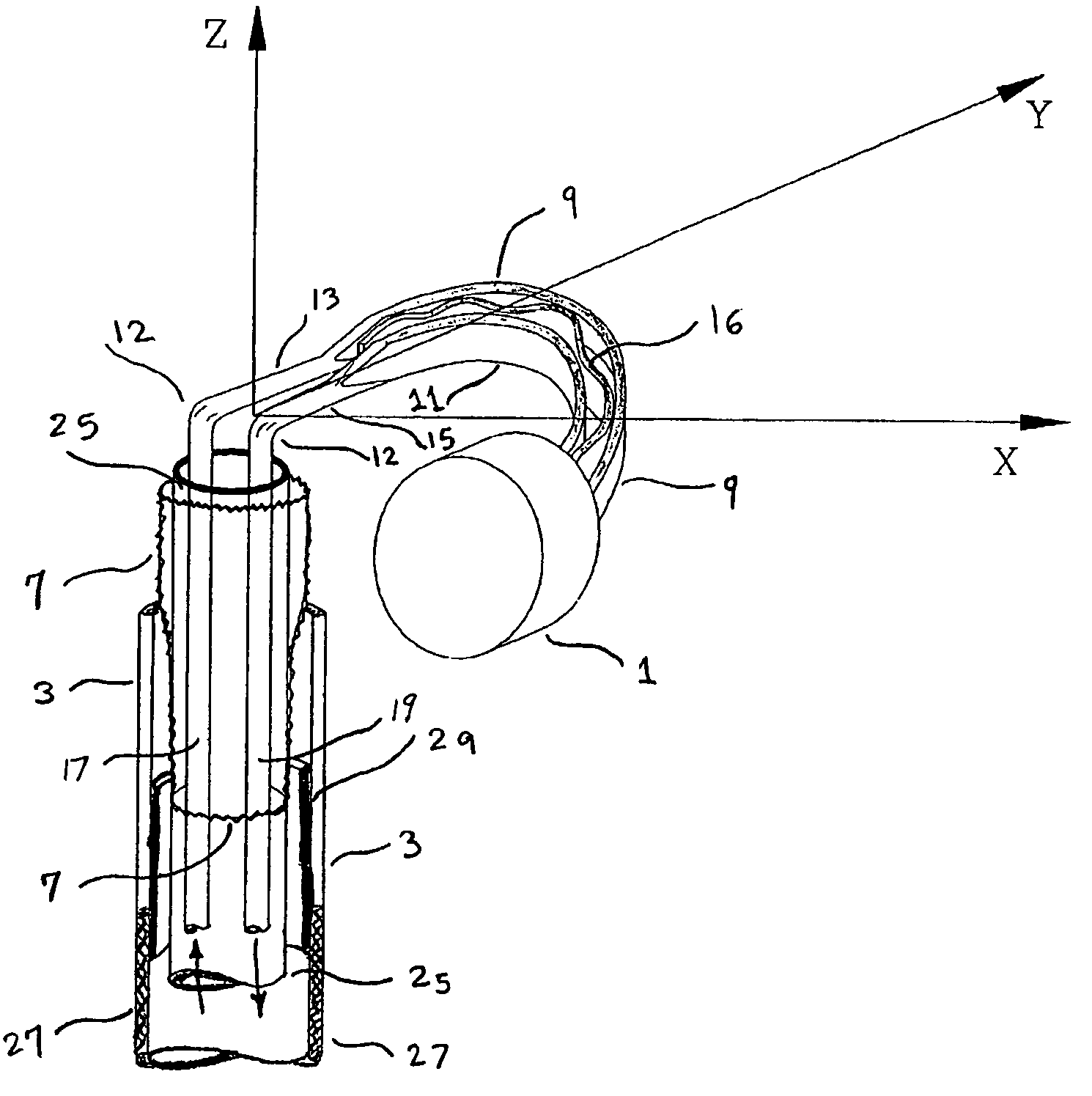
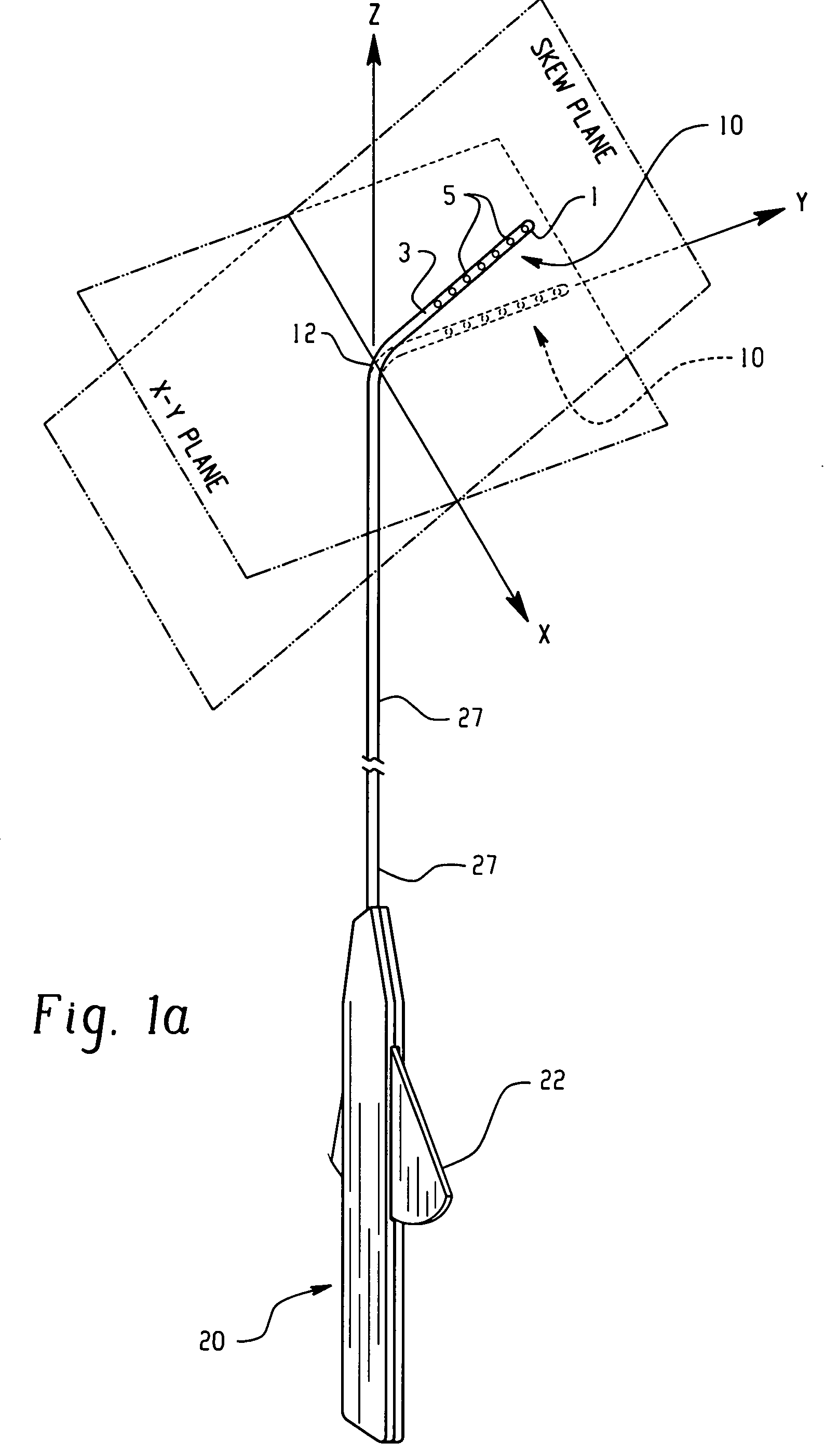
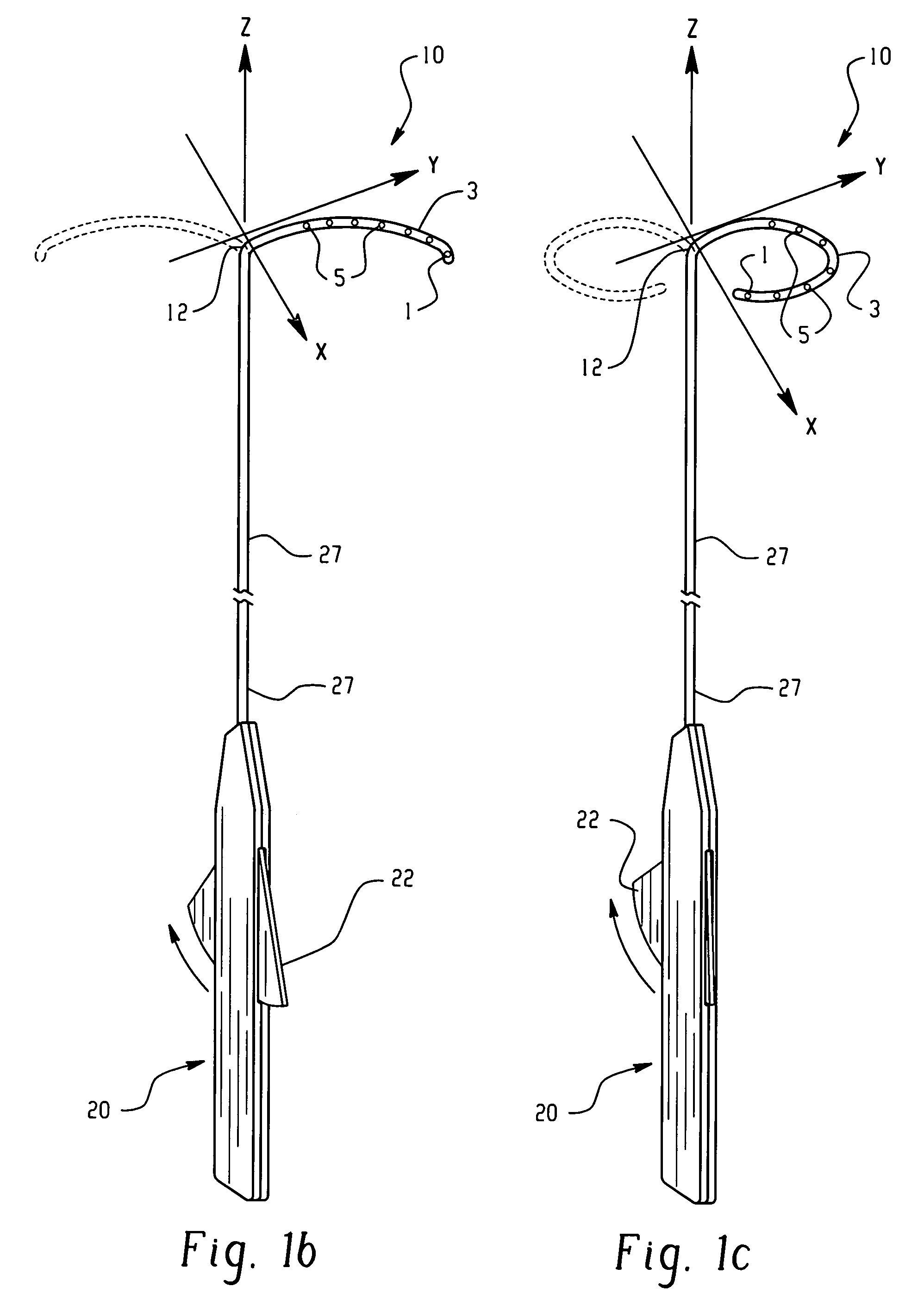
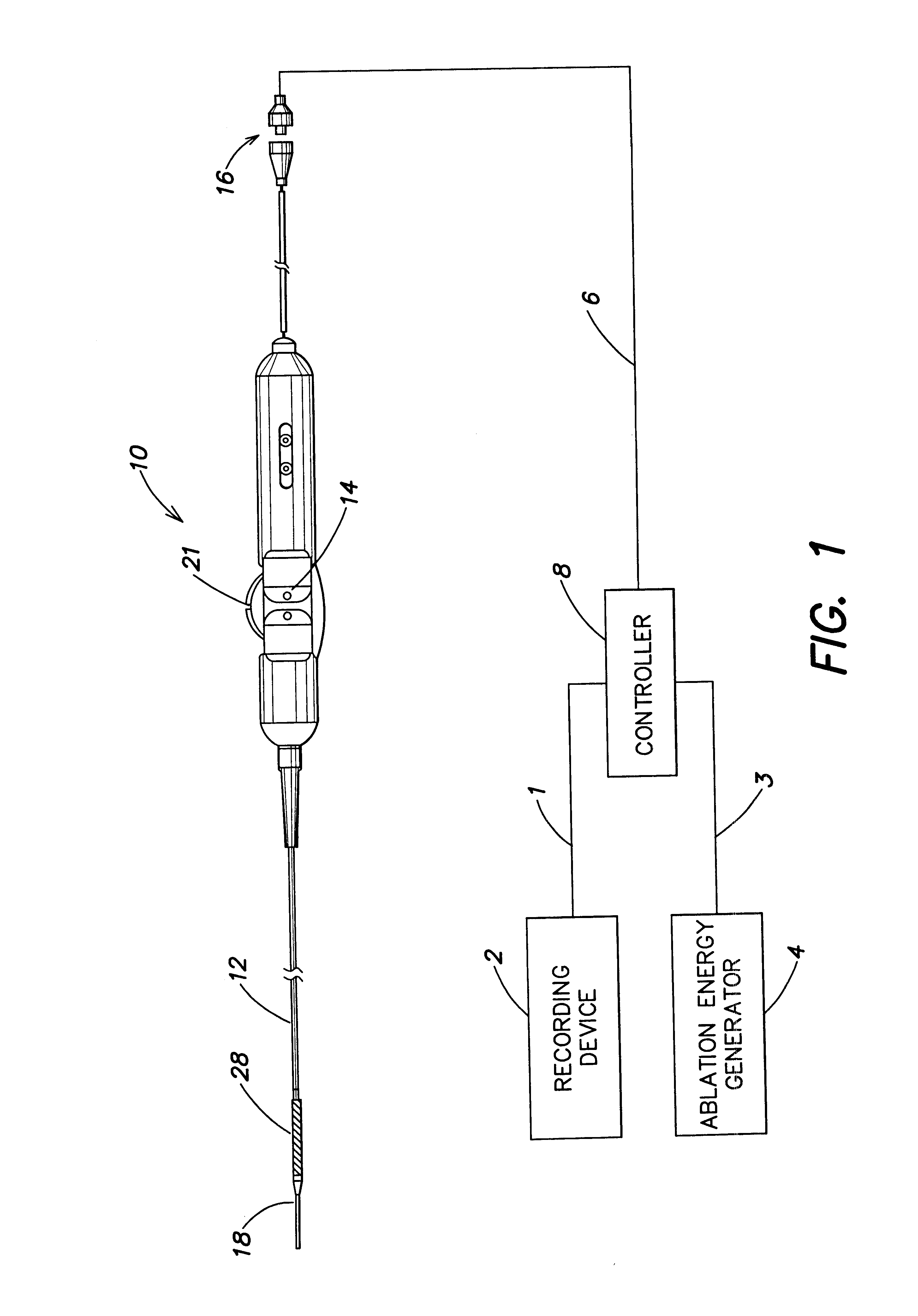
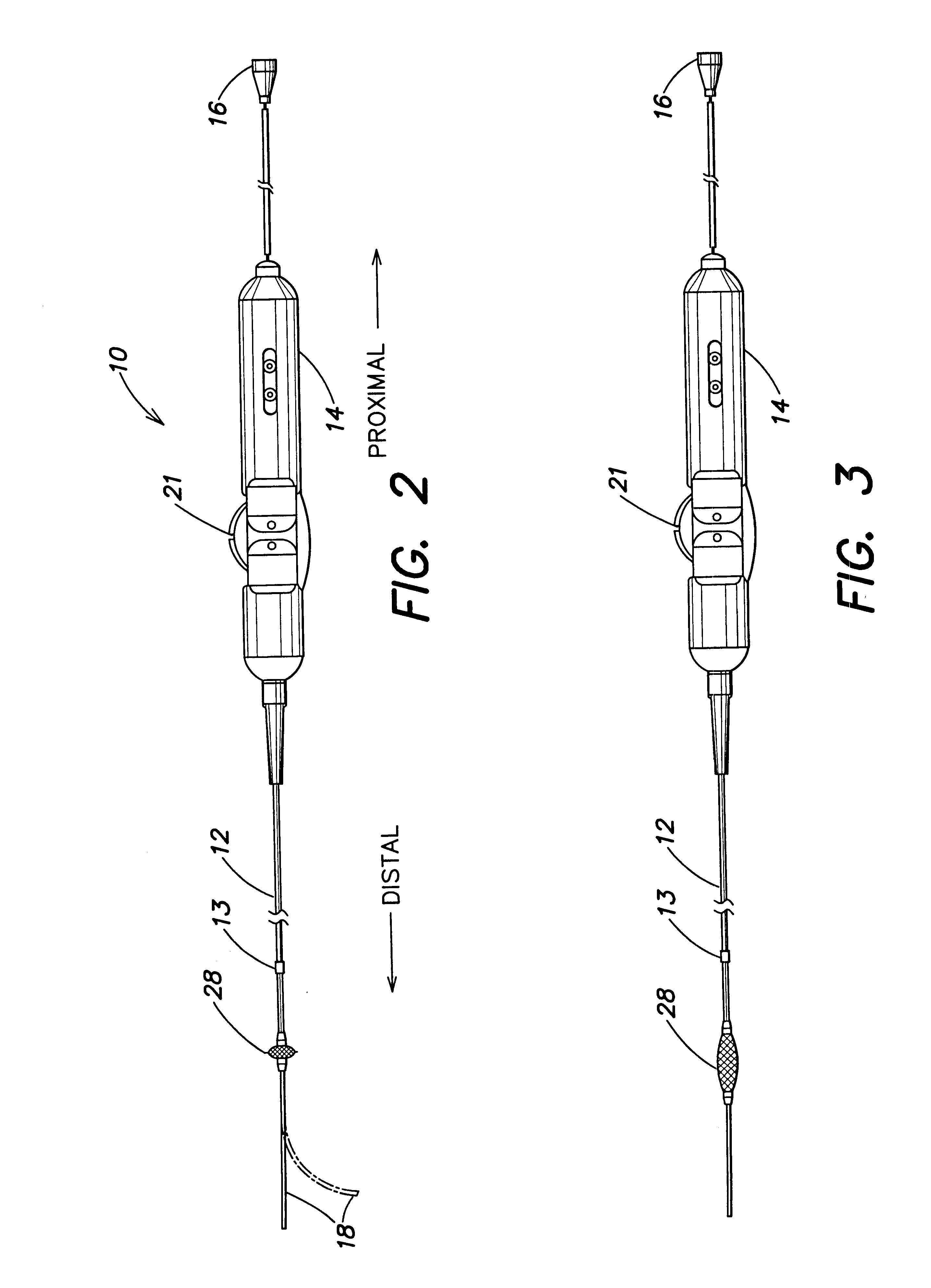
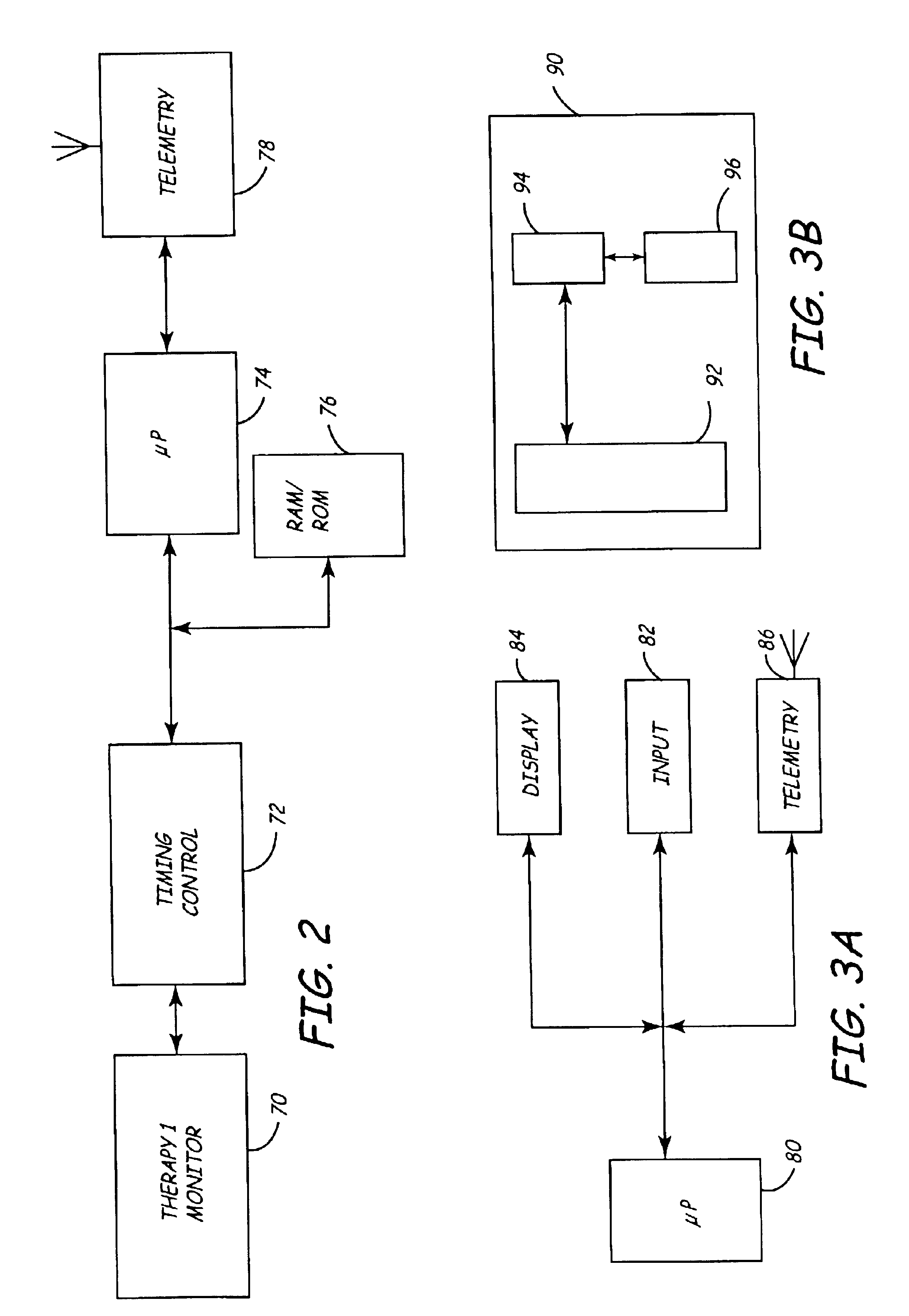
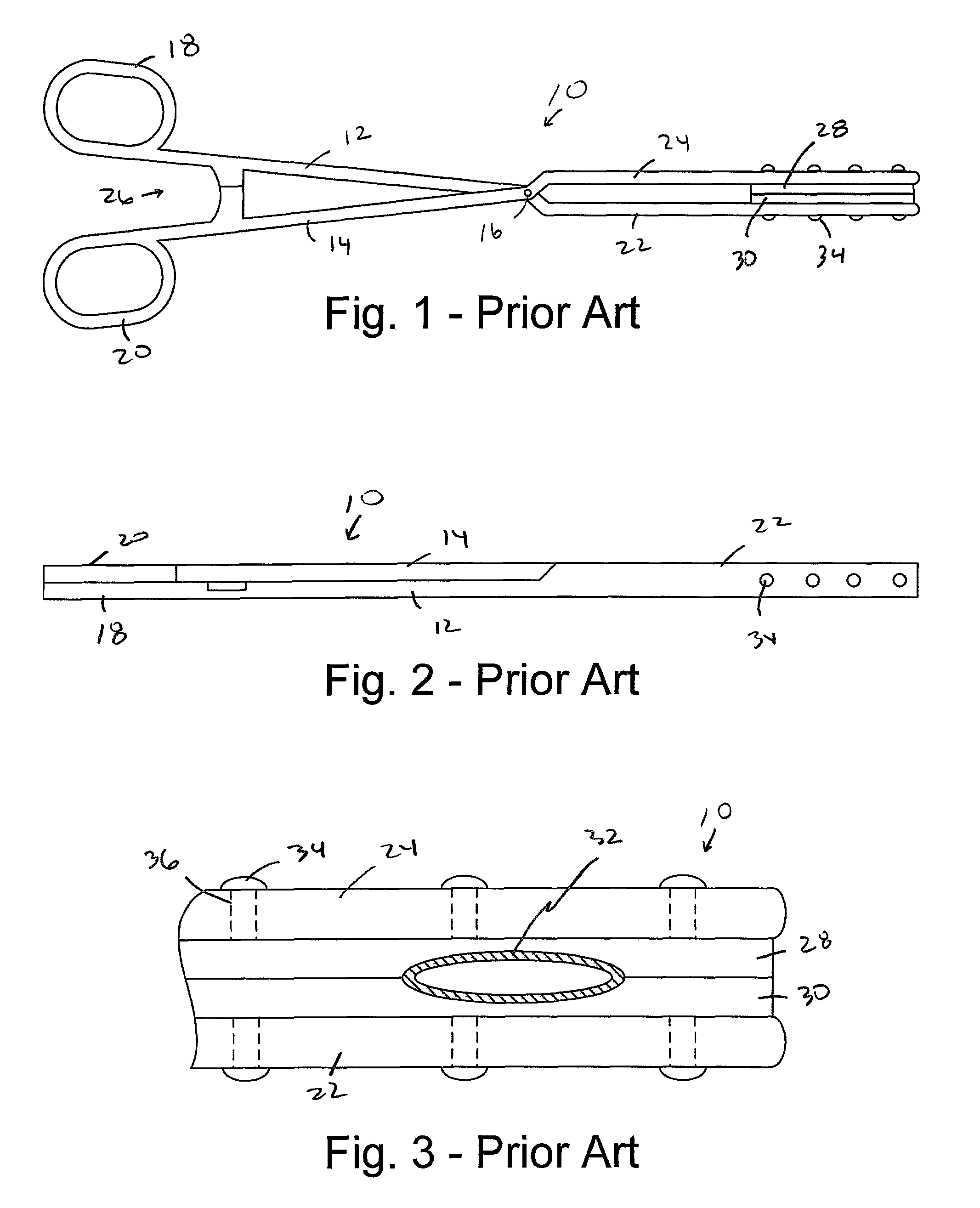
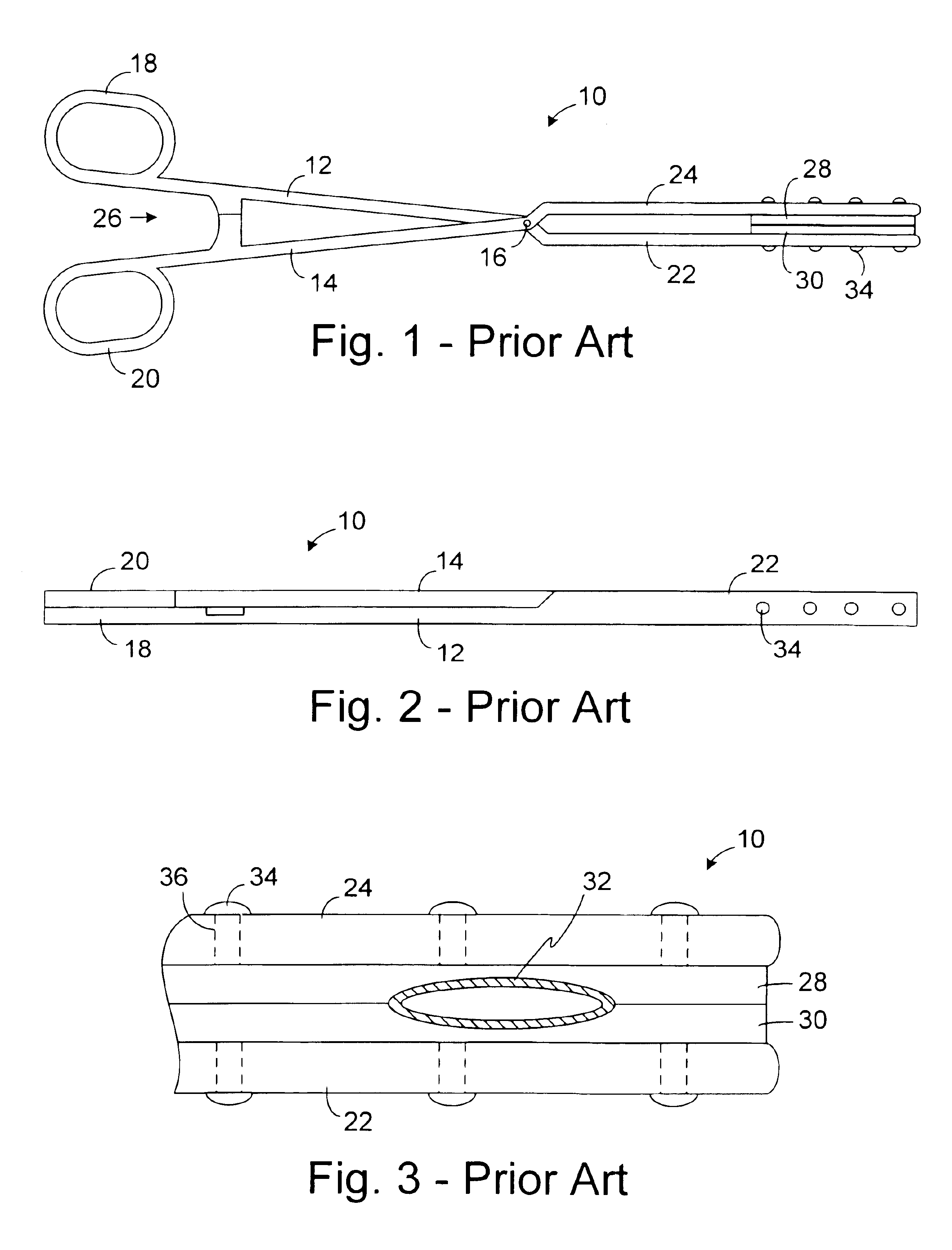
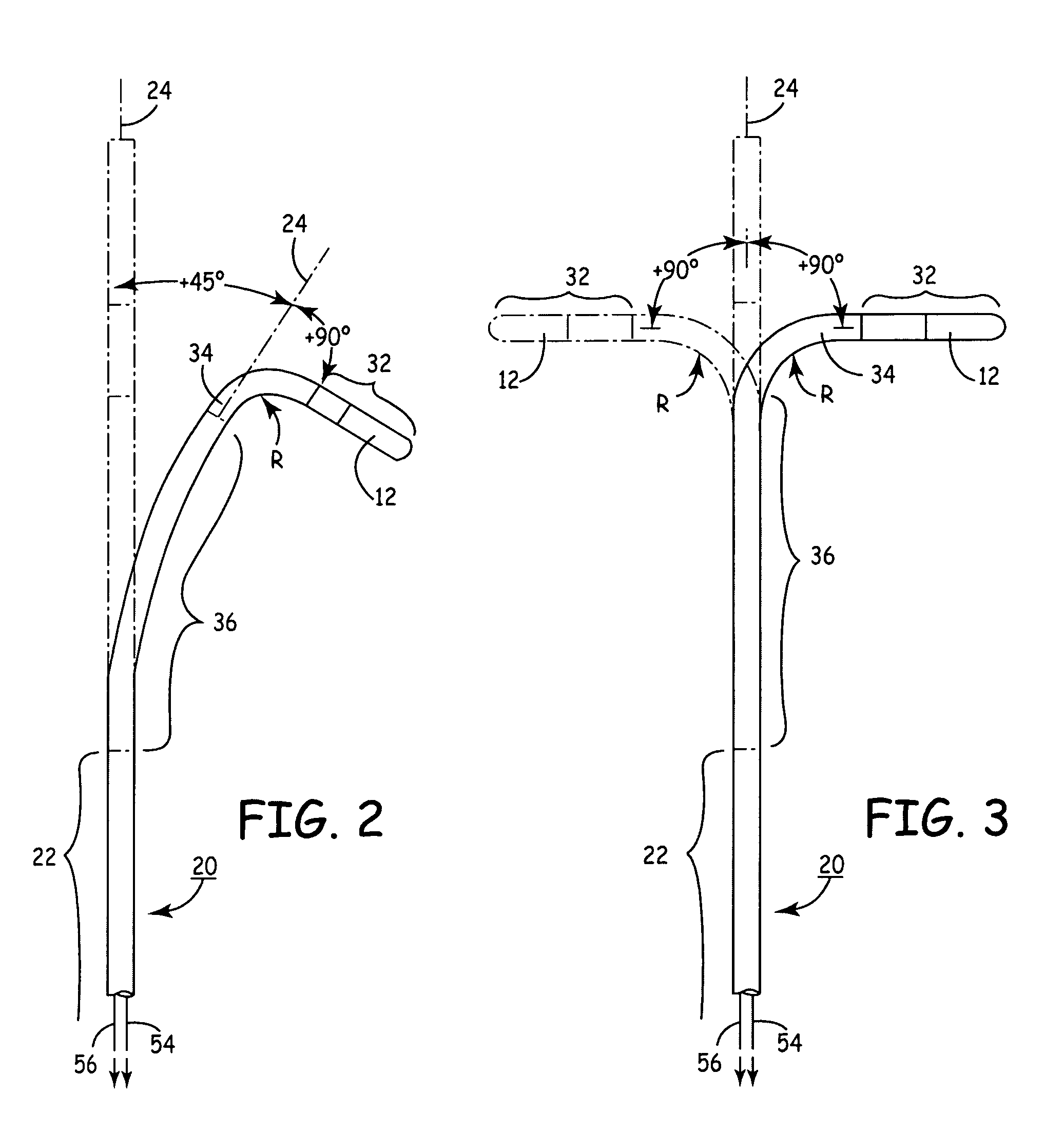
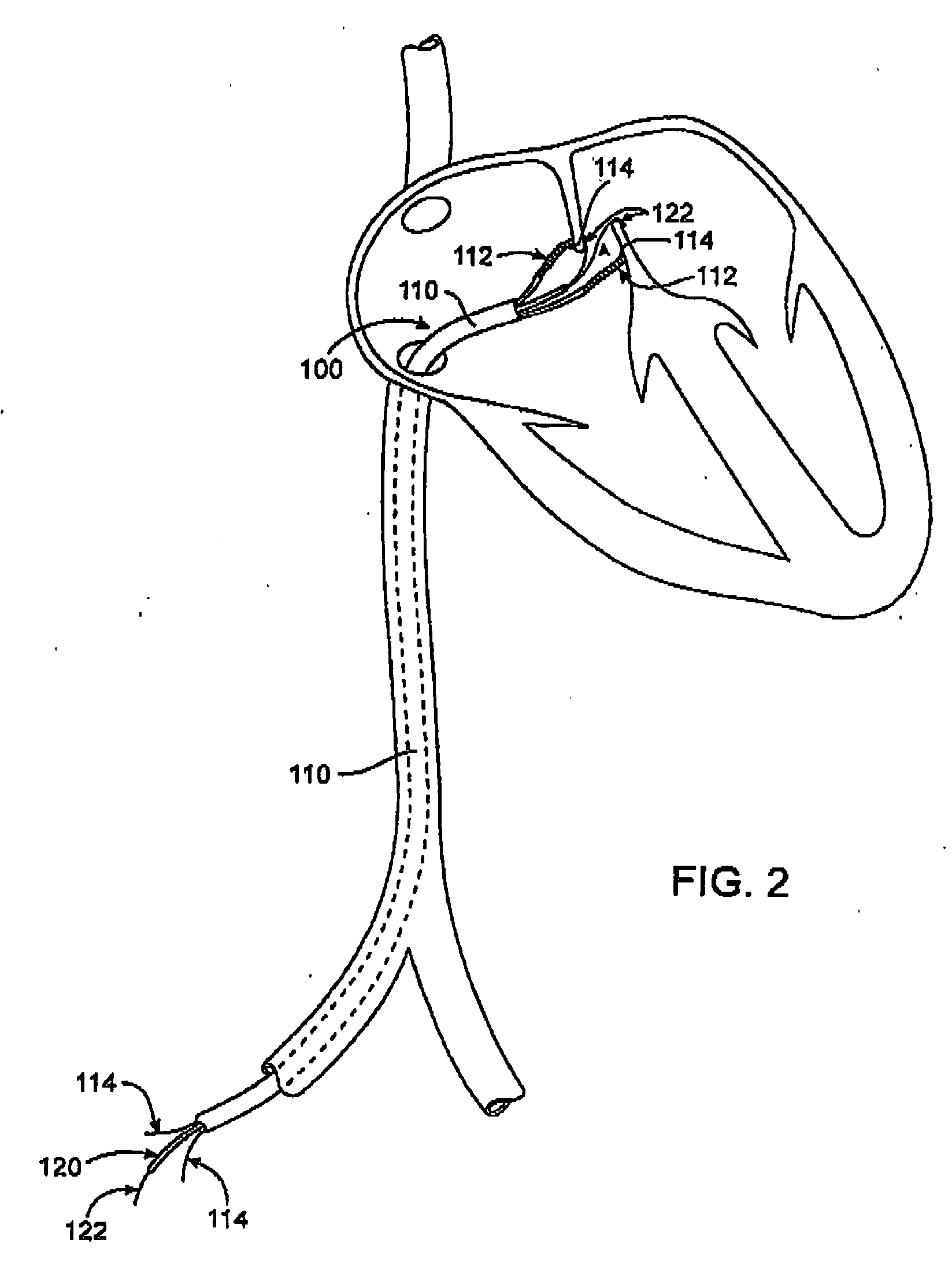
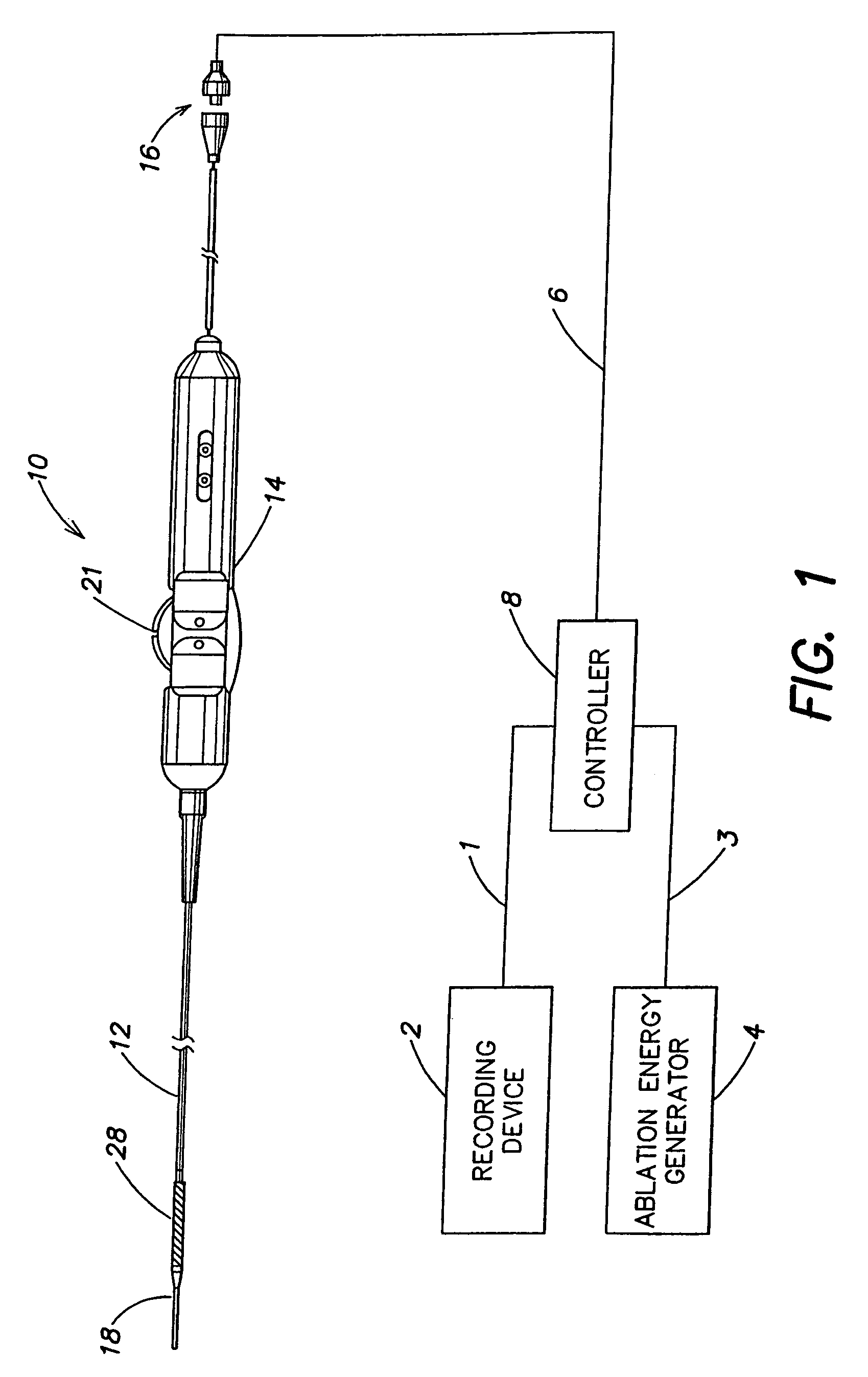
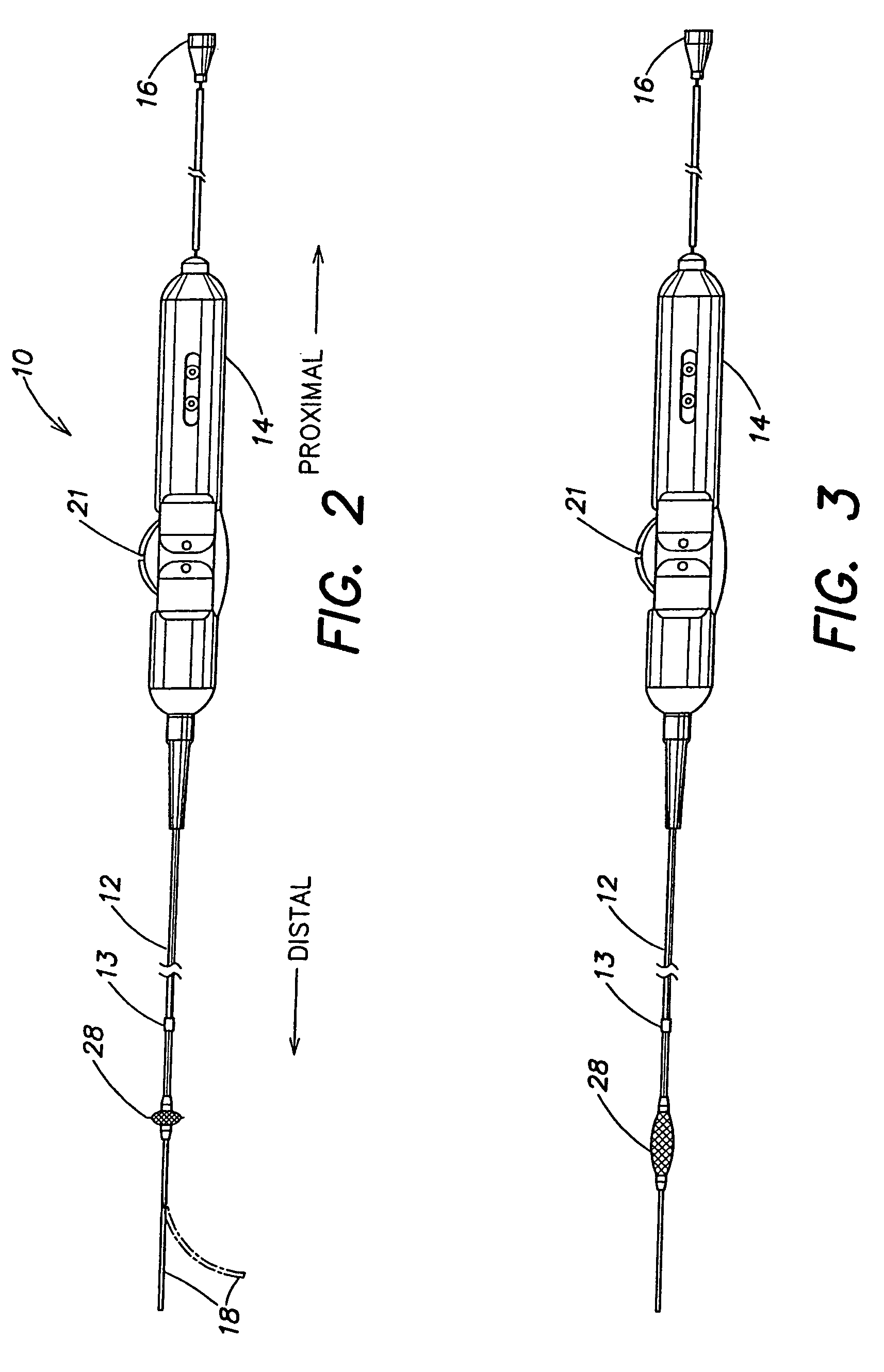
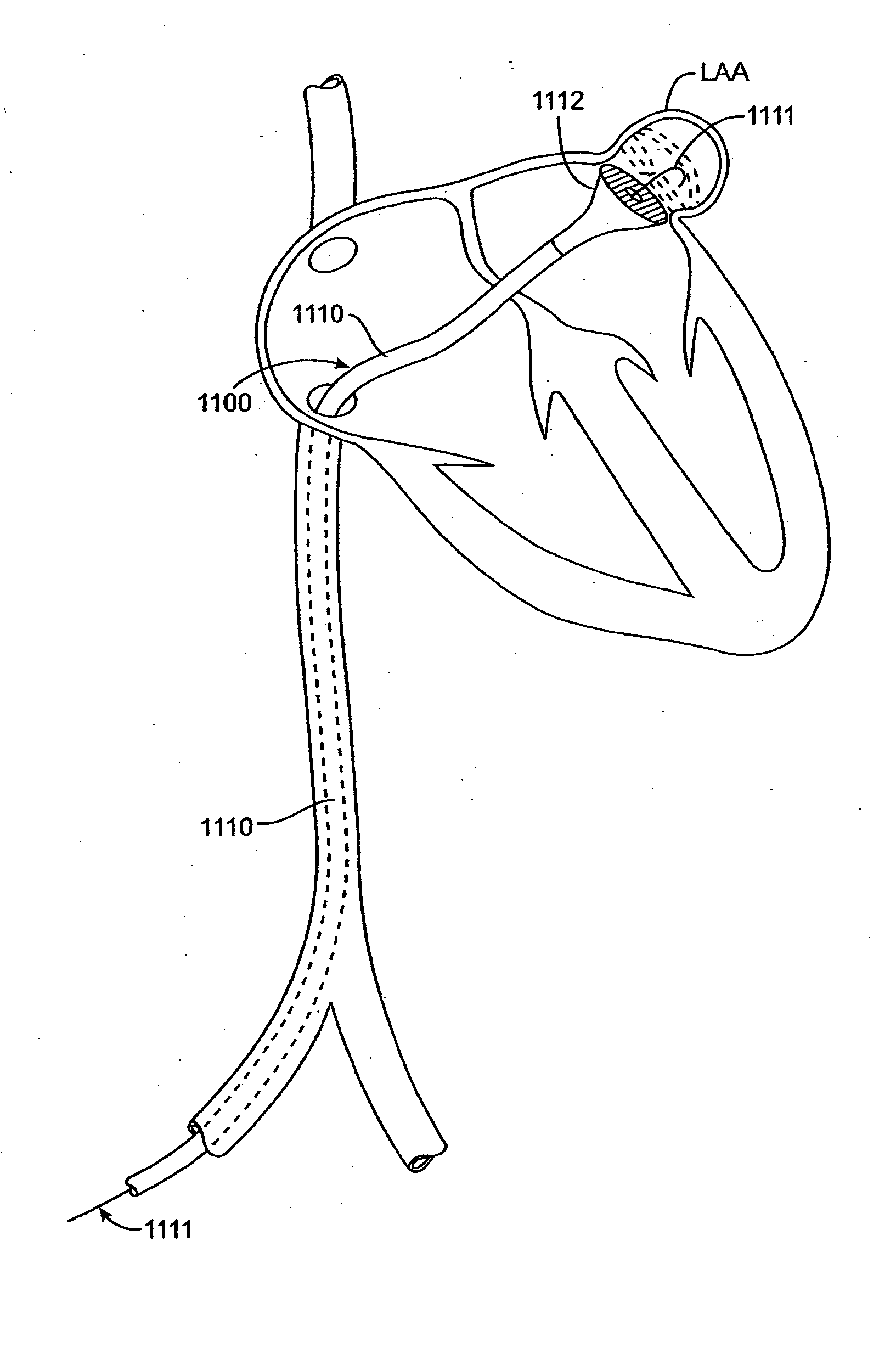
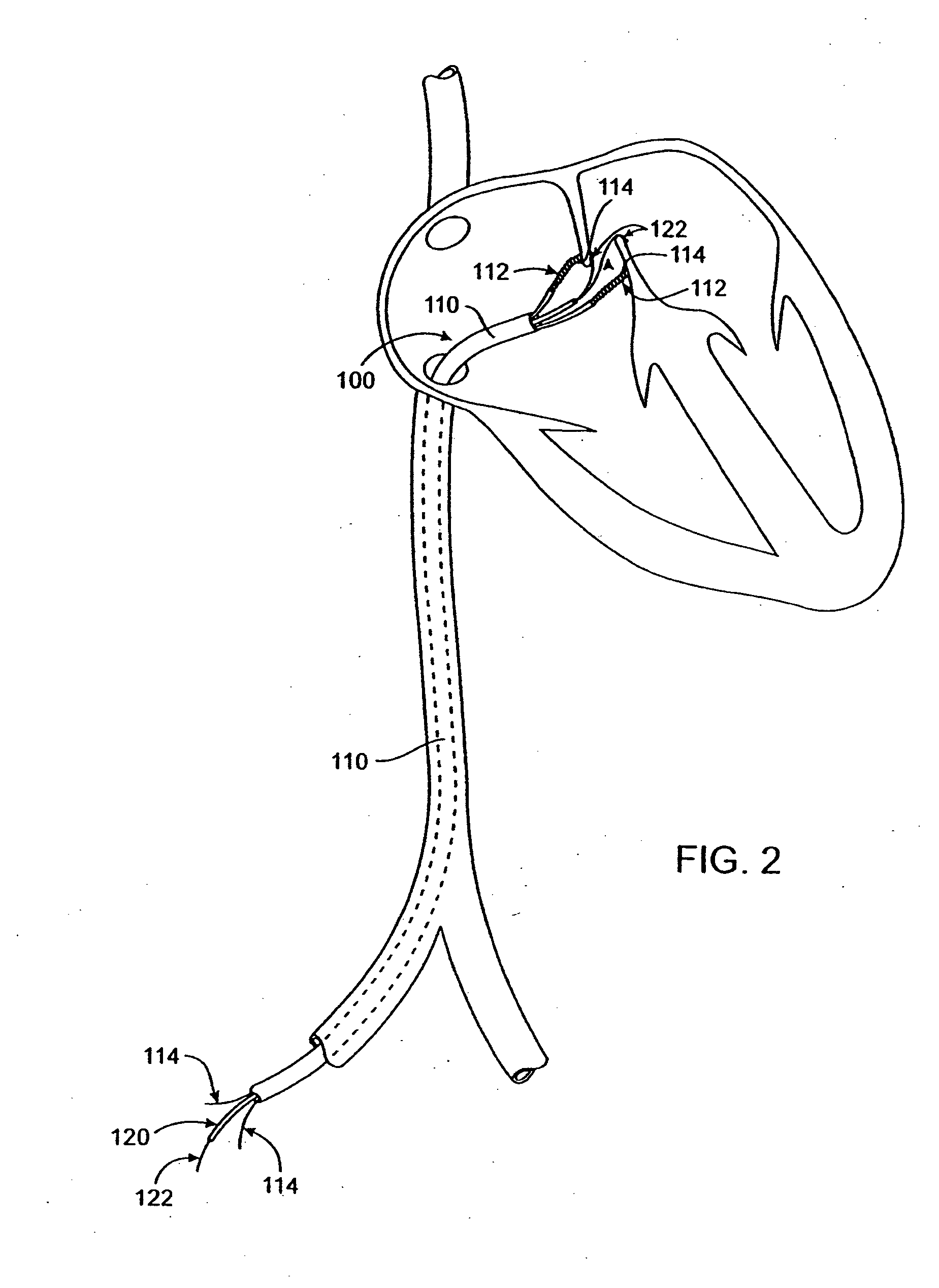
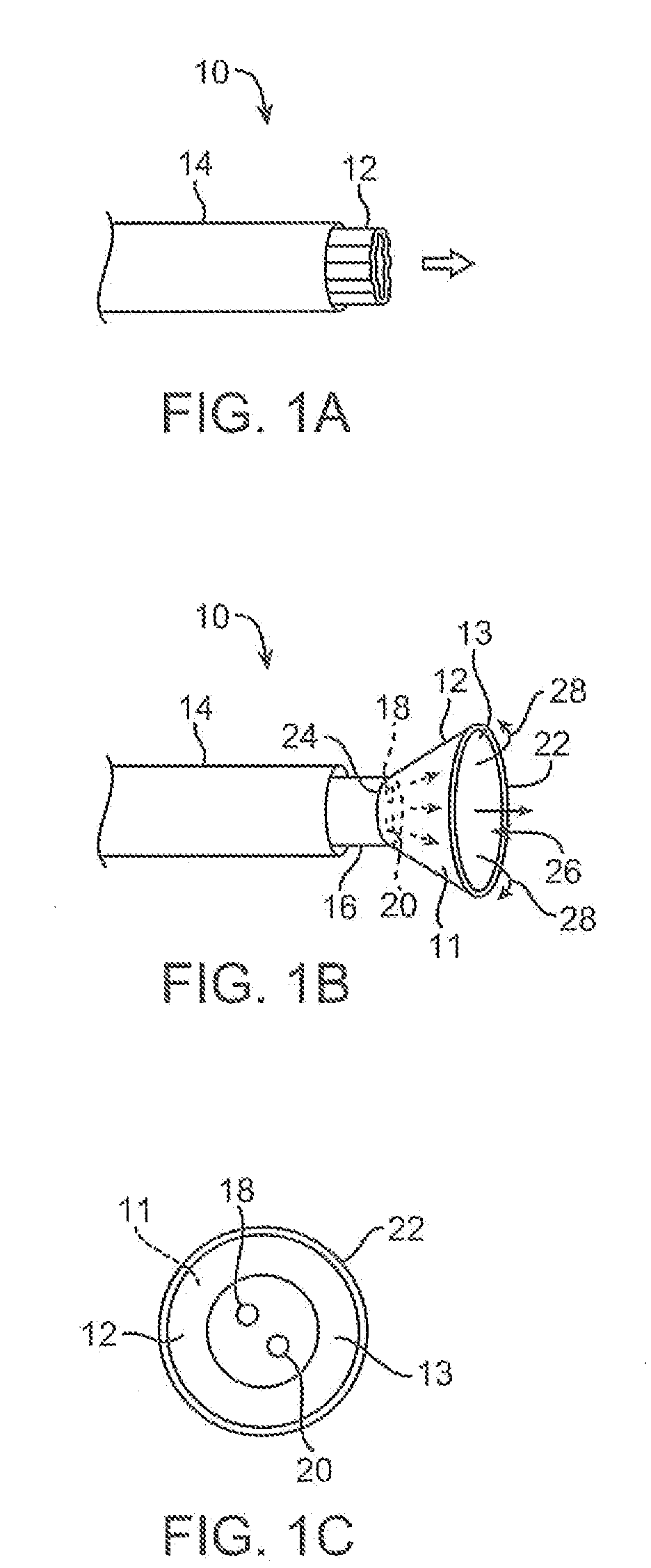
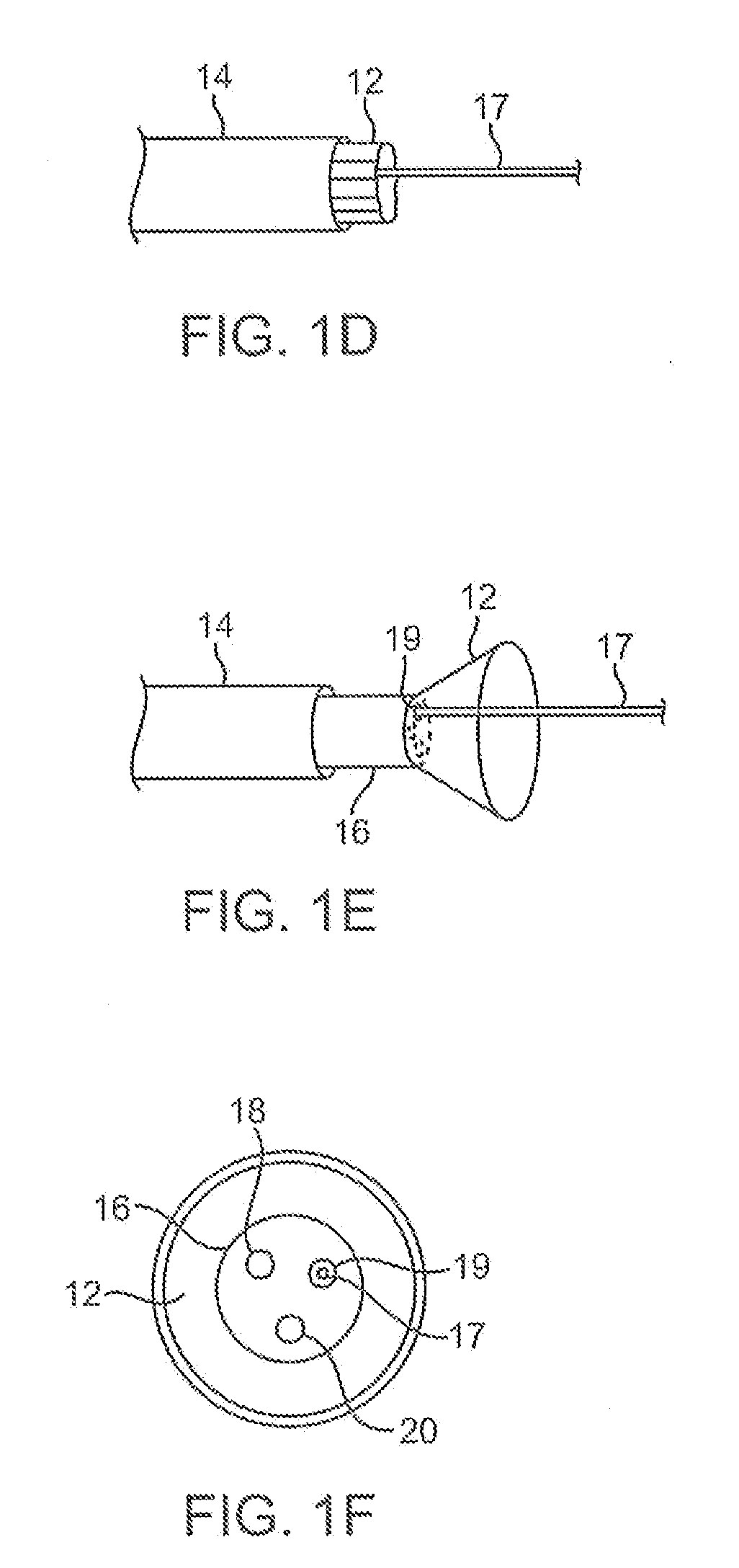
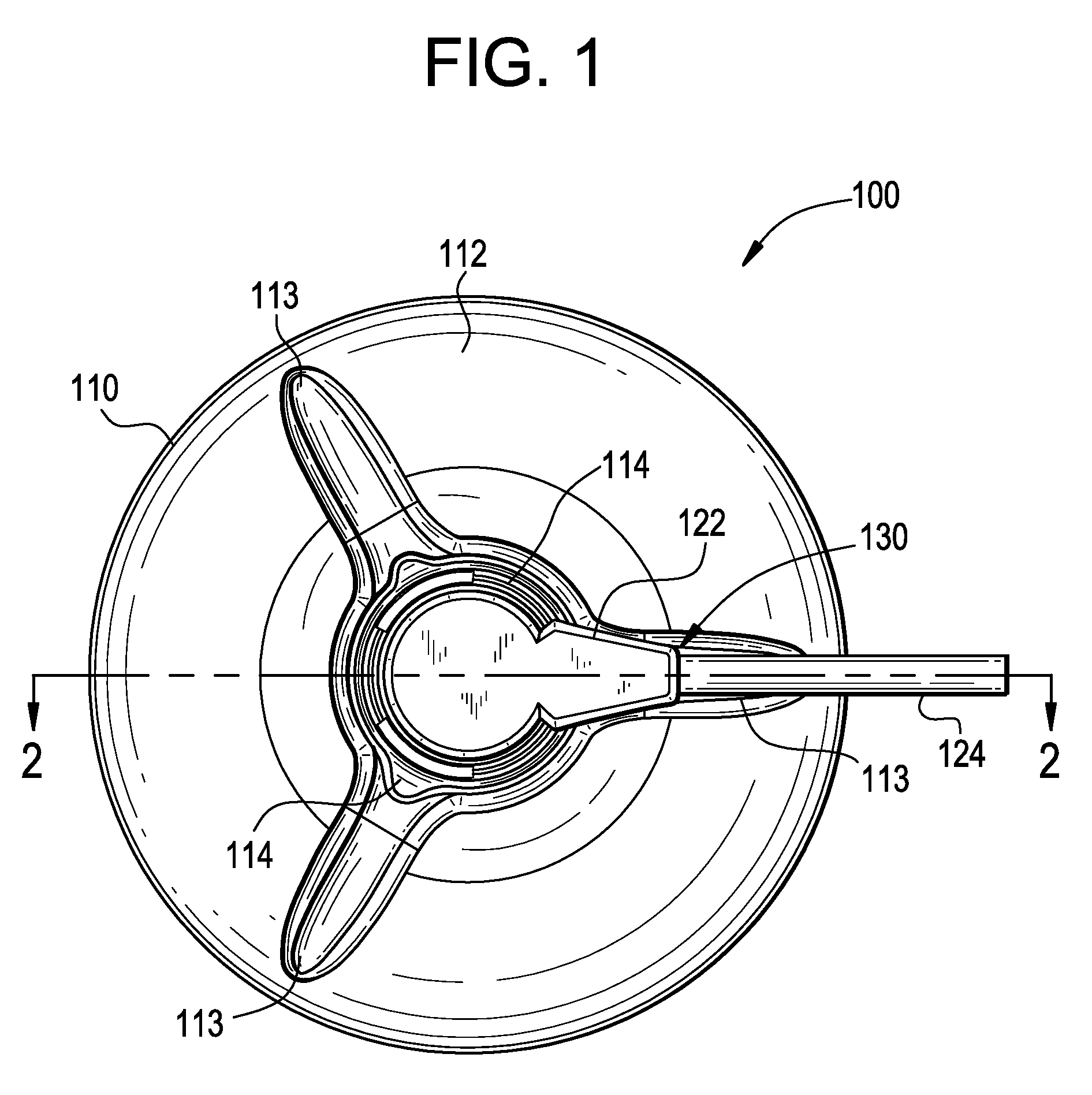
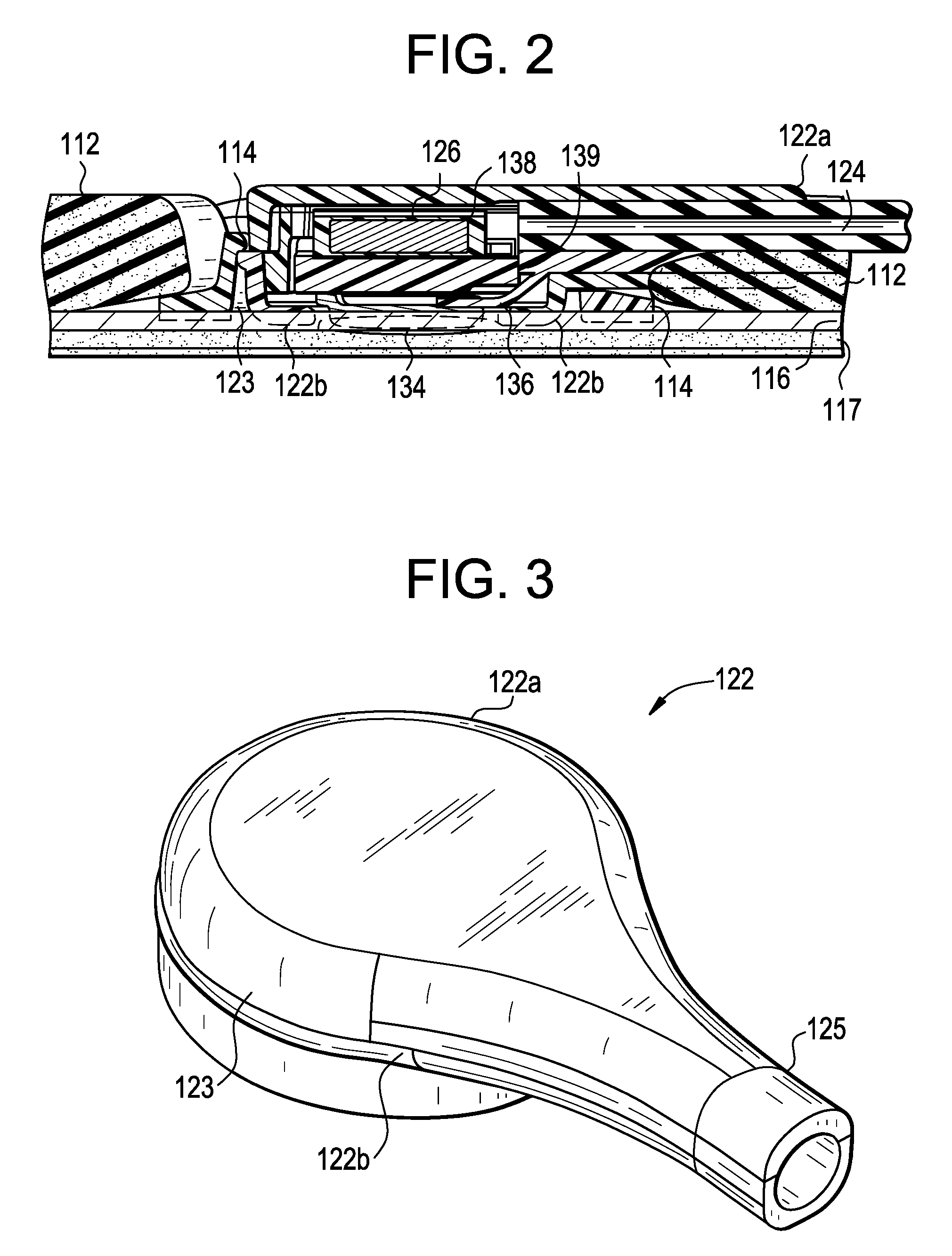
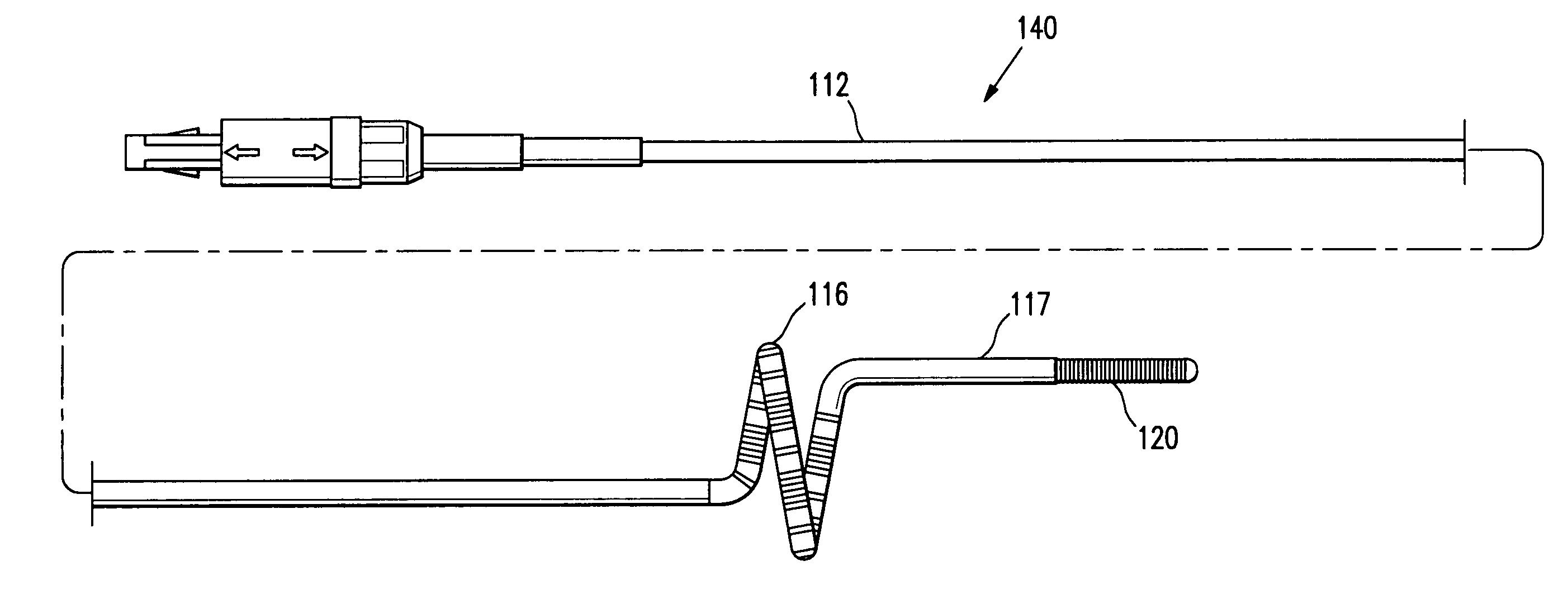
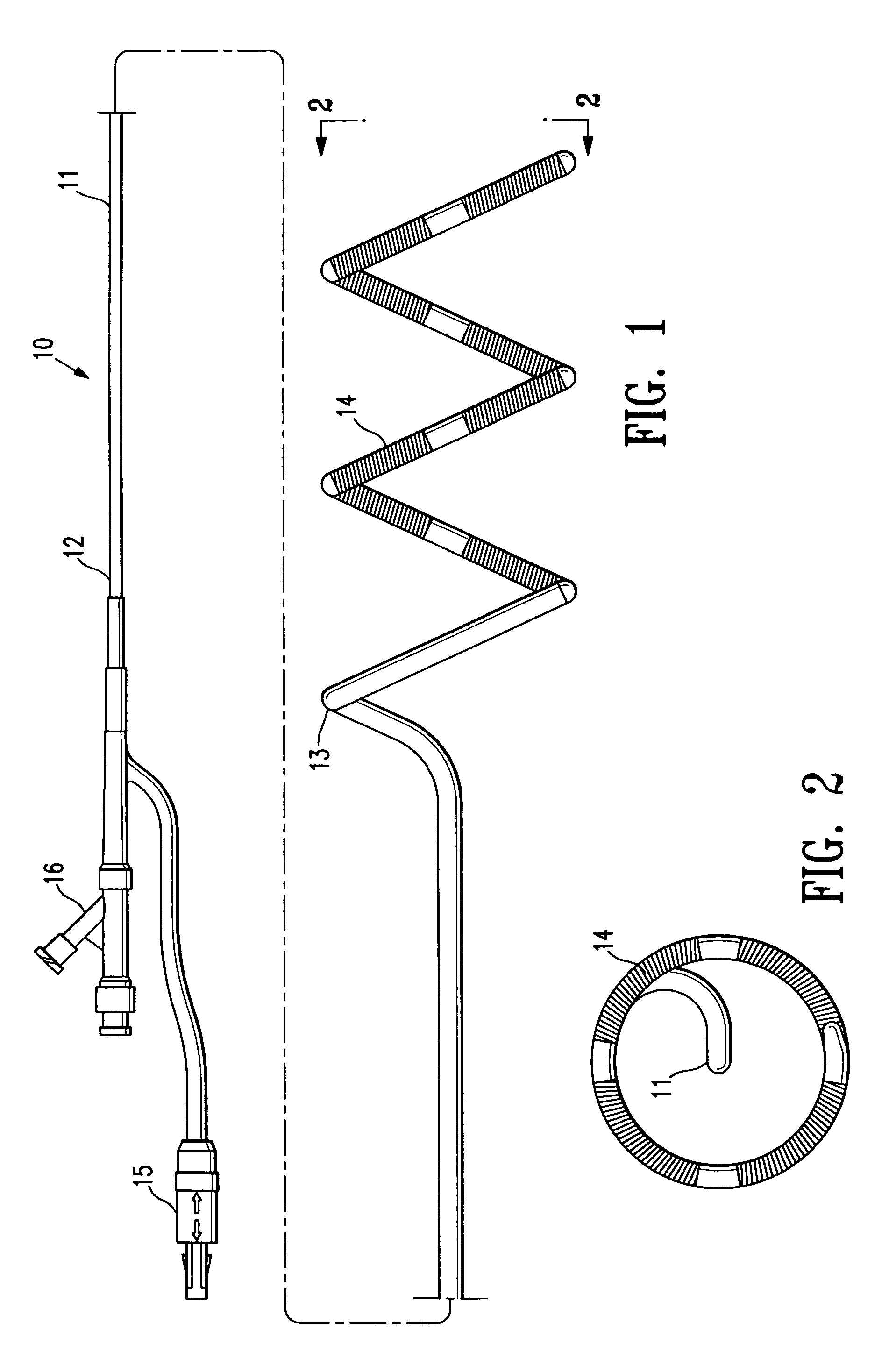
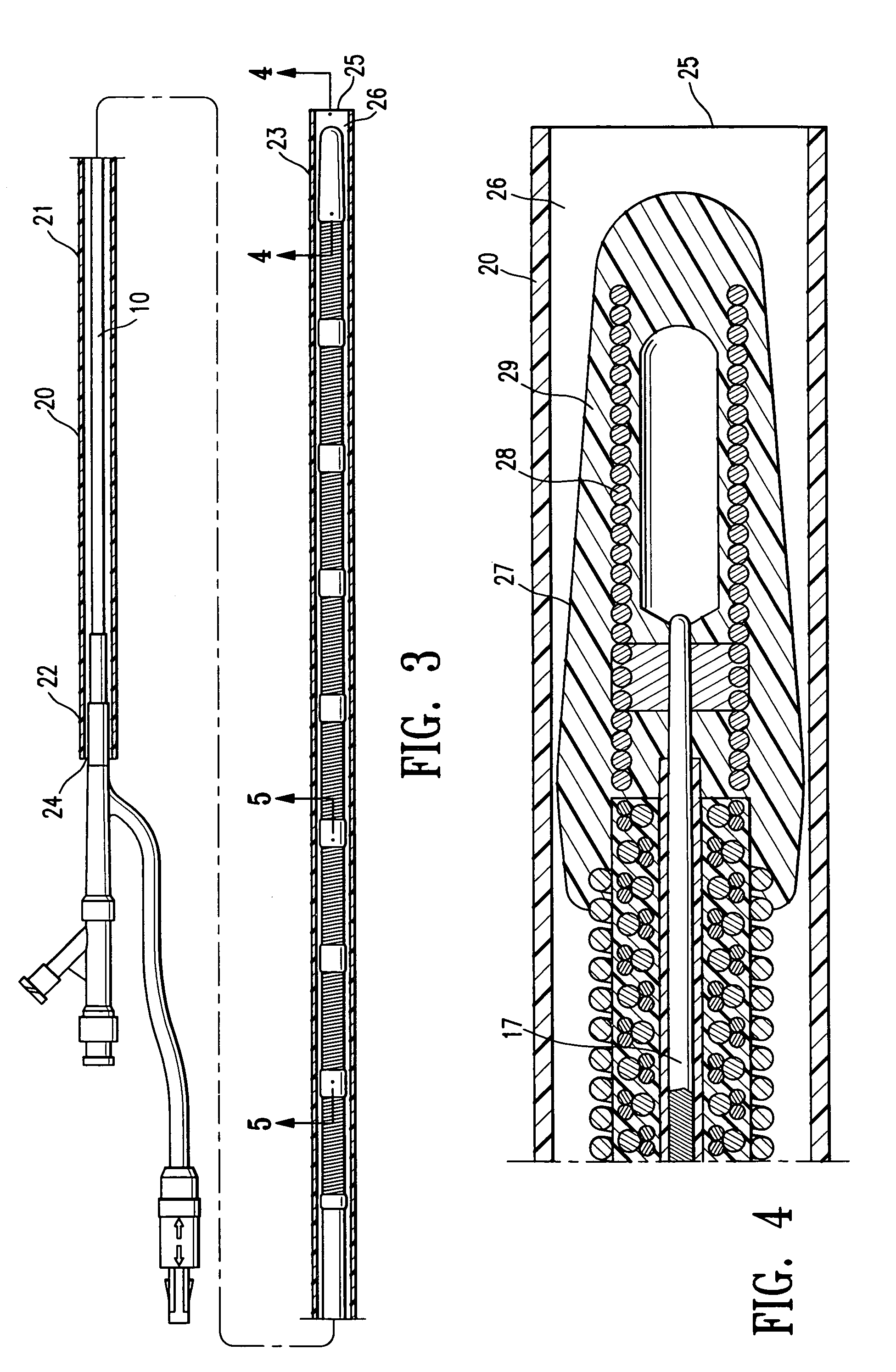
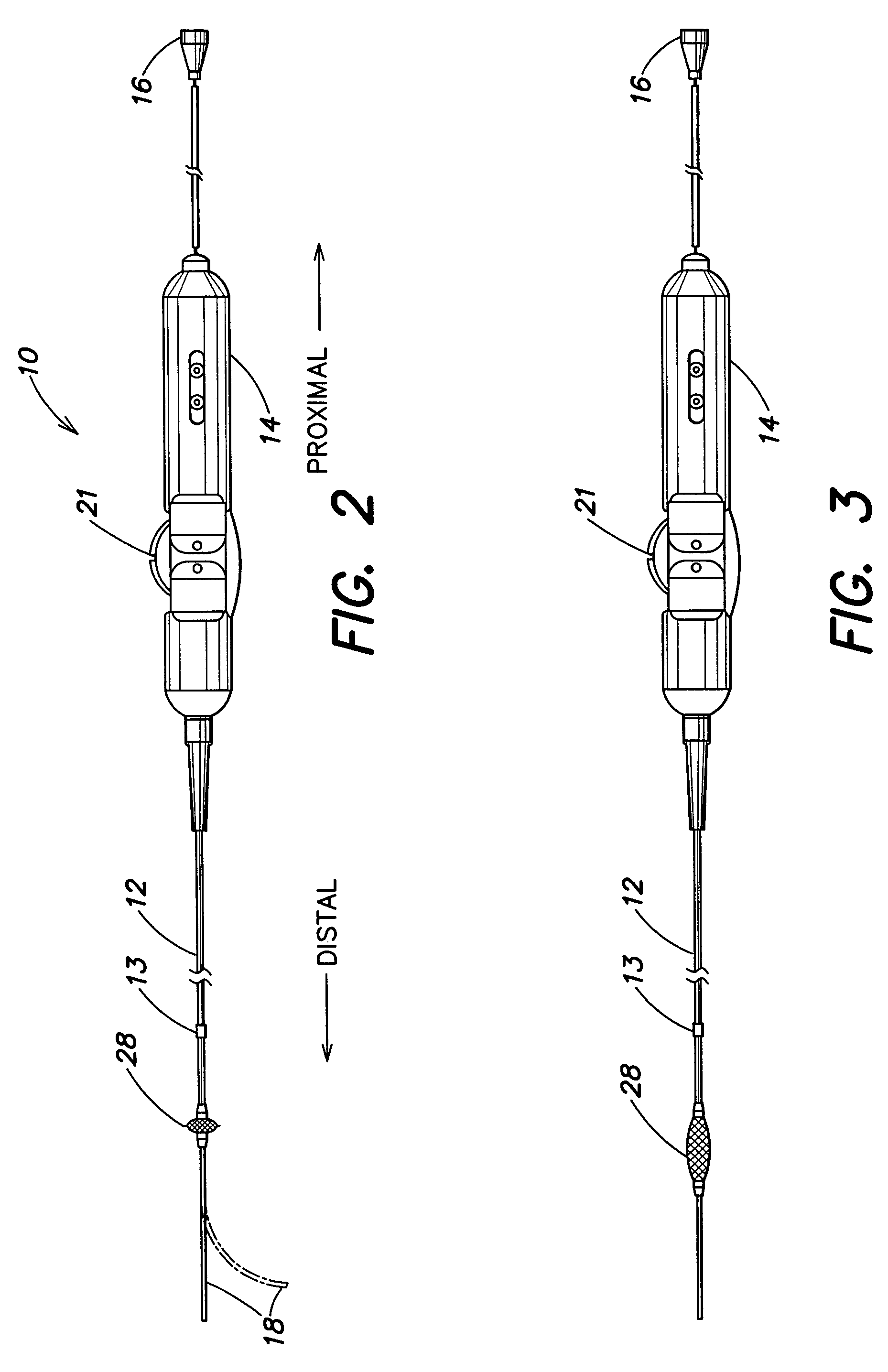
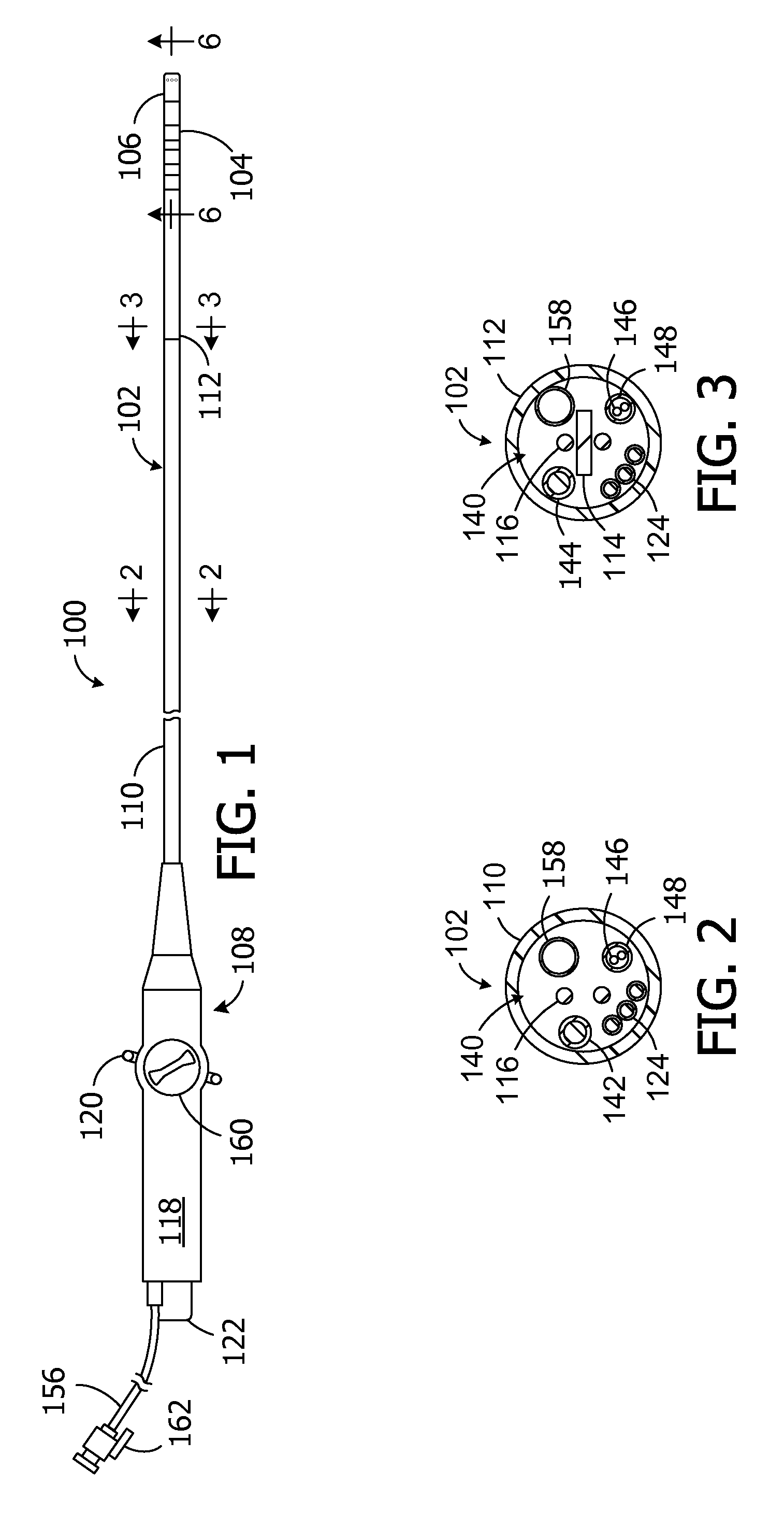
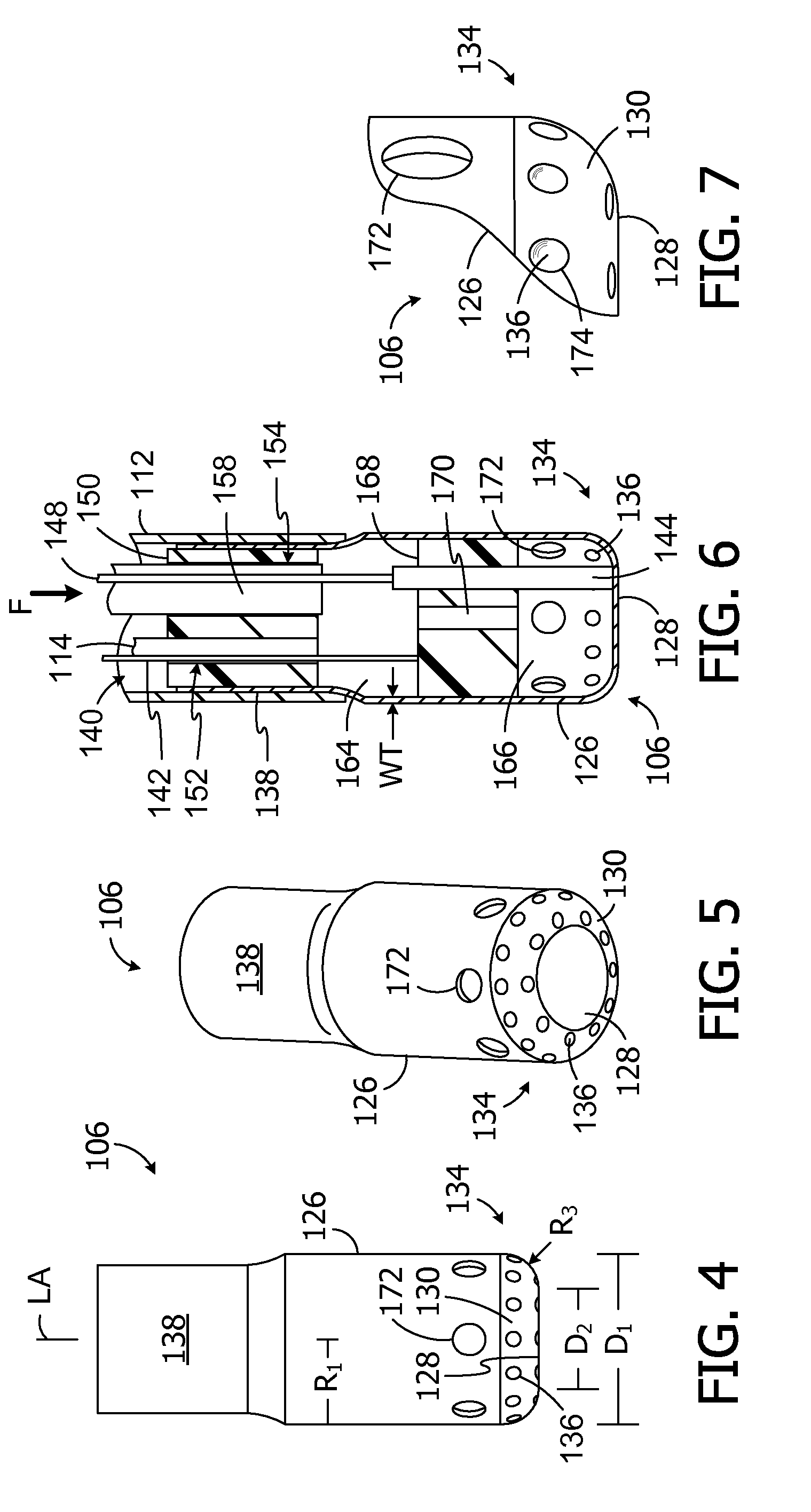
Electrophysiology/ablation catheter having lariat configuration of variable radius
InactiveUS7081114B2Easy to curlReduced radiusElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringDistal portionElectrophysiology
A remotely deflectable electrophysiology / ablation catheter of the type intended for placing into an interior passage of the heart is disclosed. The distal end of this elongated tubular catheter has a pair of tension / compression members each with a flattened end portion connected to the distal electrode and extending through the catheter casing and attached to a user moveable actuator for effecting the tension / compression thereon for remotely curling the distal end of the catheter. Spaced ring electrodes are provided adjacent the distal electrode. A permanent bend is pre-formed in the casing and tension / compression members adjacent the ring electrodes about an axis perpendicular to the elongated tension / compression members. Movement of the remote actuator causes the distal portion of the catheter to curl into a lariat in a plane perpendicular to the axis along the elongated catheter casing, thus permitting electrical mapping or ablation with the distal and / or ring electrodes about the inner surface of the heart passage into which the lariat is formed and situated. The lariat can achieve a curvature greater than 360 degrees and at a significantly reduced radius to allow insertion of the catheter distal end into passages of reduced dimension.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Apparatus and methods for mapping and ablation in electrophysiology procedures
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
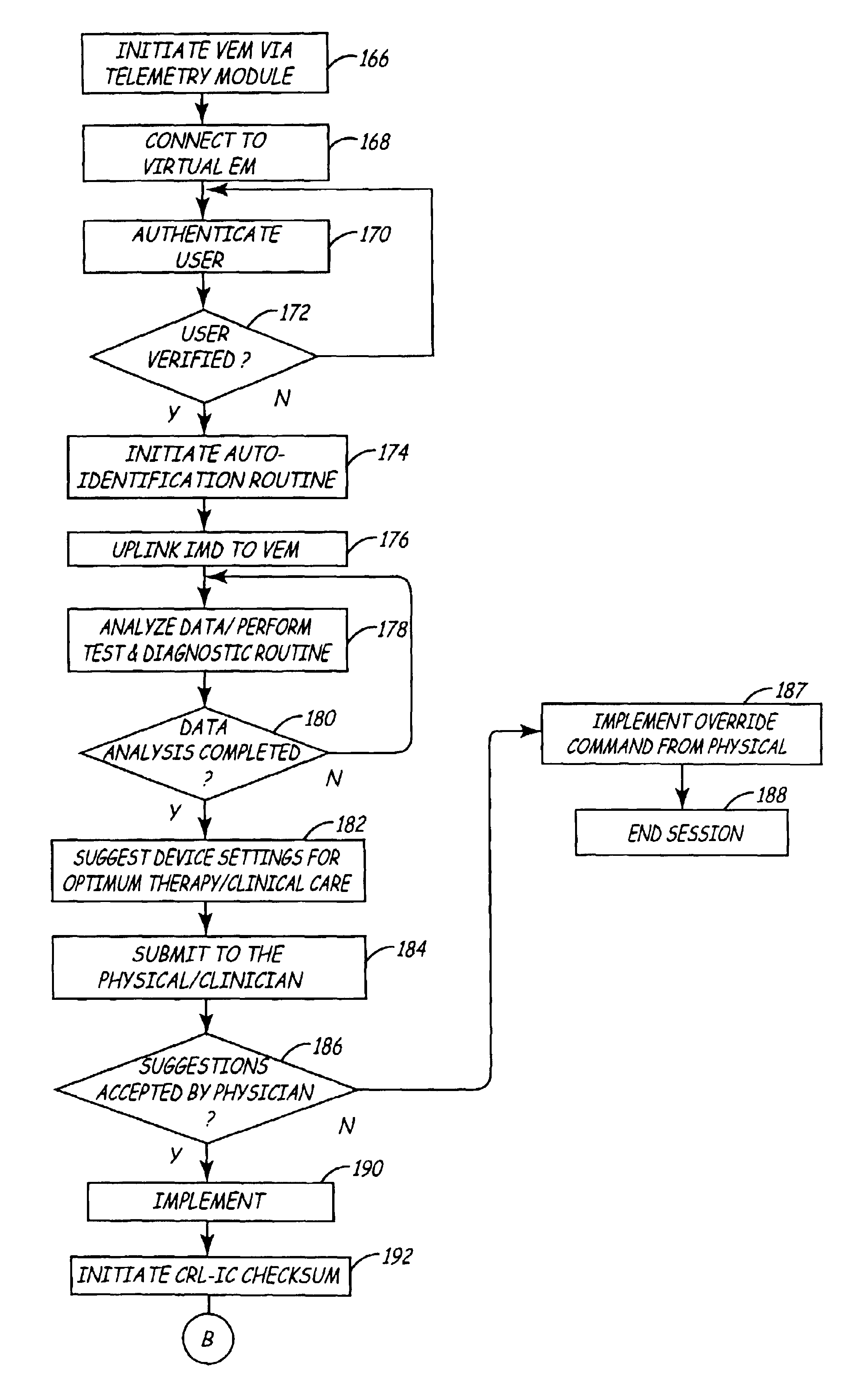
Virtual remote monitor, alert, diagnostics and programming for implantable medical device systems
InactiveUS6878112B2Promote the patient's well beingSignificant compatibilityPhysical therapies and activitiesElectrotherapyClinical settingsData center
A plurality of co-operative and complementary software programs are implemented in a web-enabled high speed computer system to remotely monitor, manage and modify the operational and functional parameters of a plurality of implanted medical devices (IMDs). The system utilizes virtual electrophysiologist module (VEM), chronic monitoring module (CMM) and prescription program module (PPM) programs to effect specific therapeutic and diagnostic methods for managing the IMDs, remotely on a conditions and real-time basis. The modules enable remote and continuous monitoring, management and maintenance of the IMDs by identifying critical medical events, determining optimal clinical settings and upgrading performance parameters based on prescriptive data. The modules are implemented in a data center having high-speed computers operating in a web-enabled environment. The modules and the IMDs communicate through wireless communications system via a programmer or an interface medical unit (IMD).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Expandable trans-septal sheath
InactiveUS20060135962A1Inhibit bindingAvoid interferenceGuide needlesEar treatmentAccess routeDilator
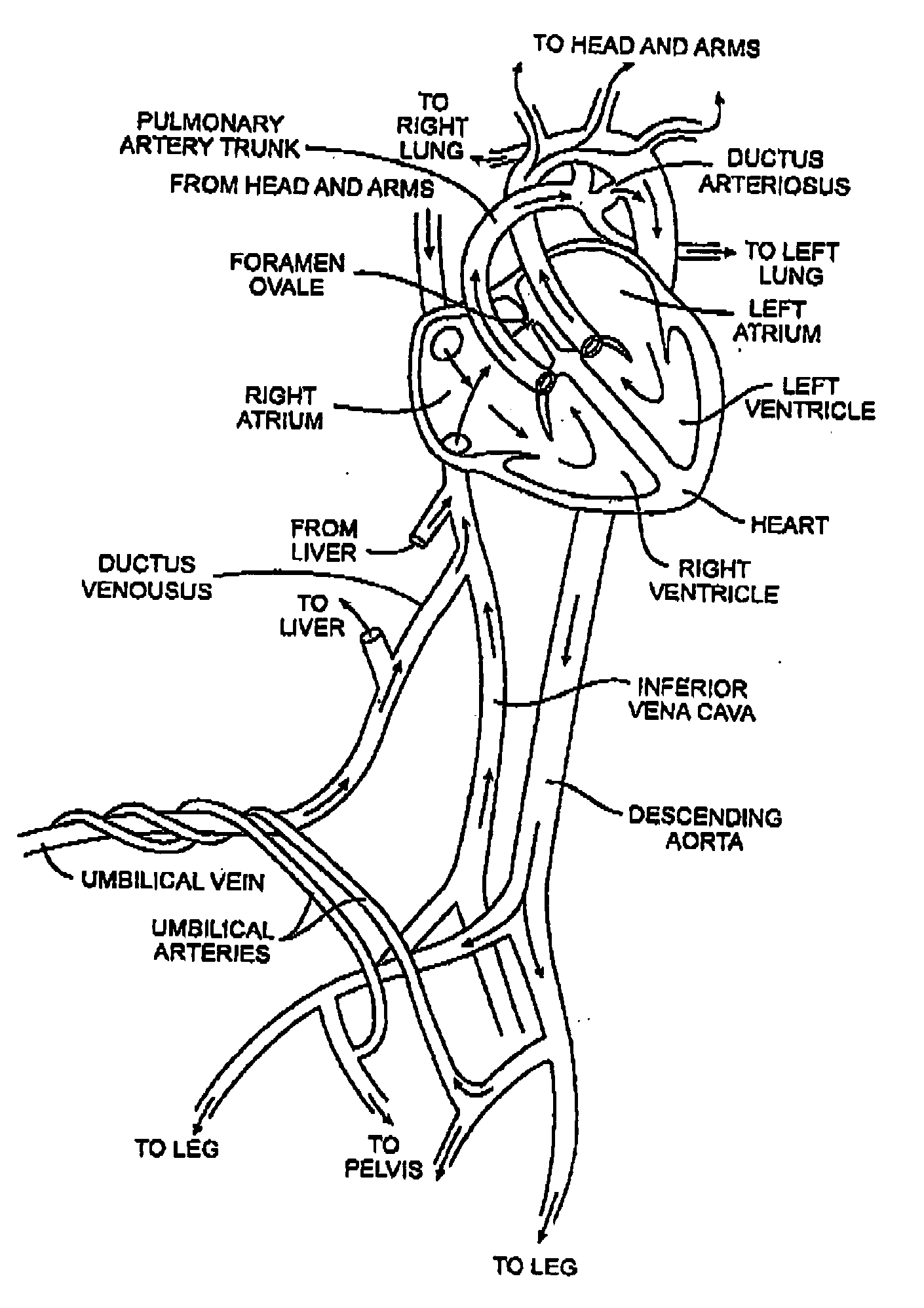
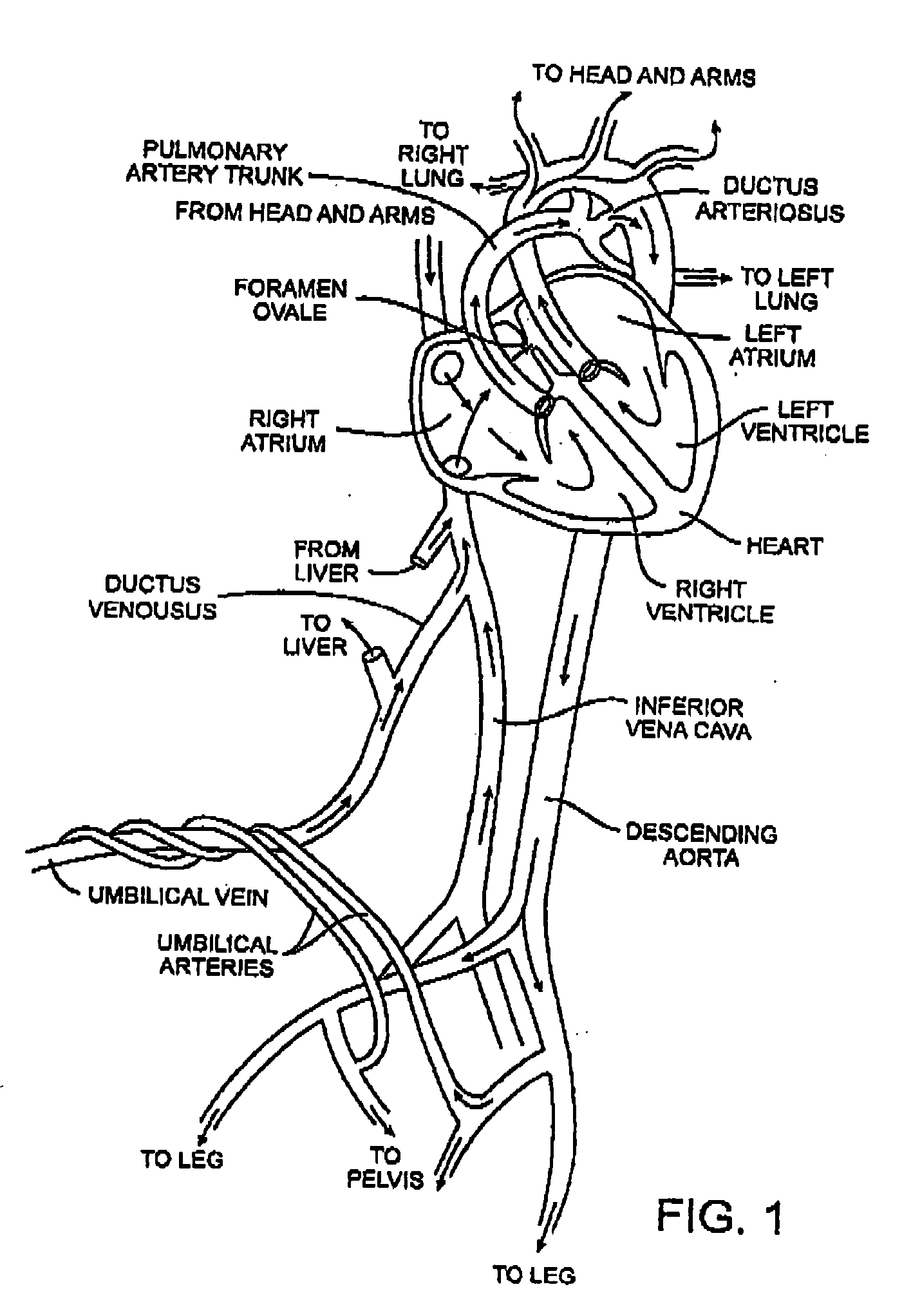
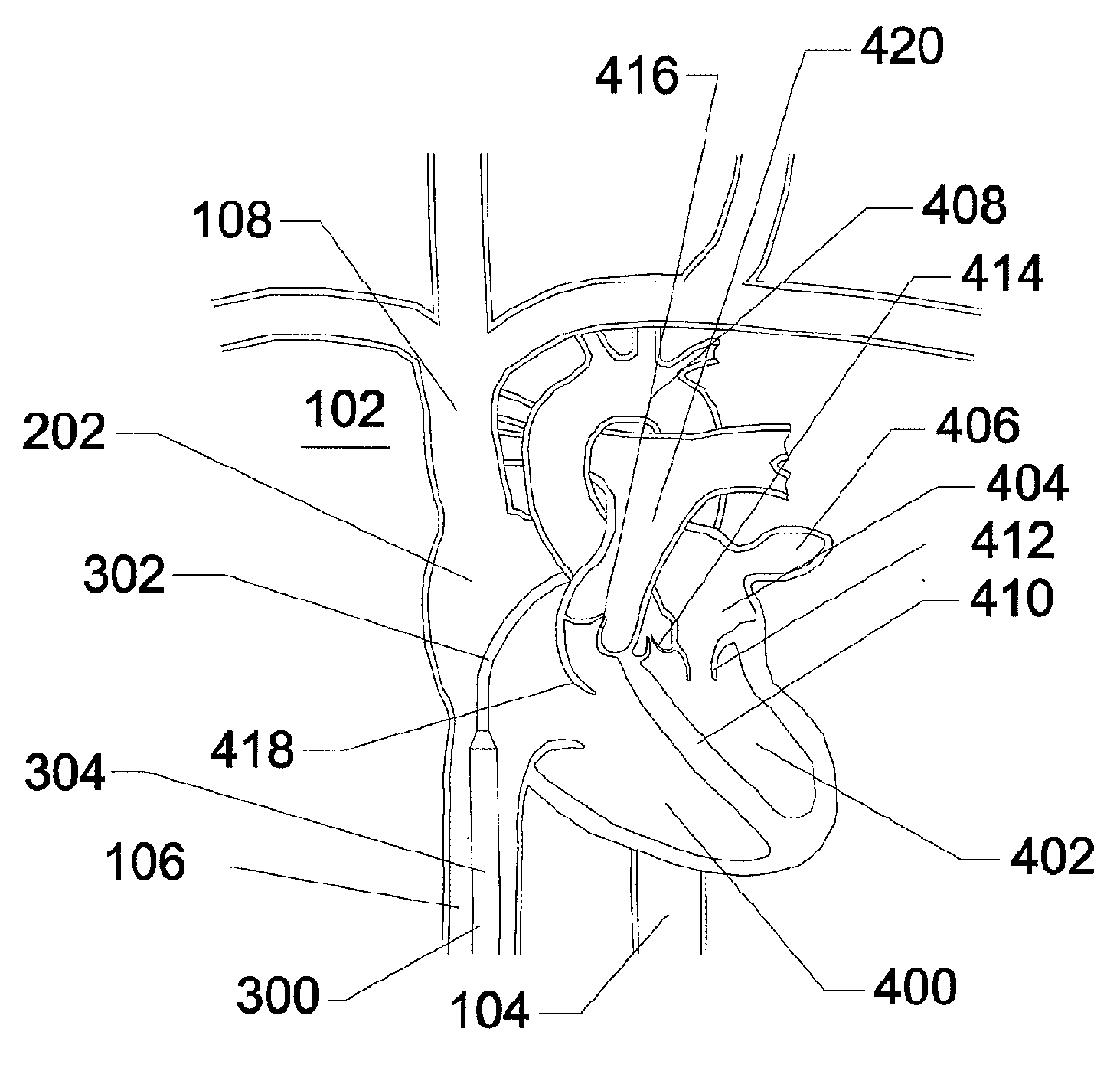
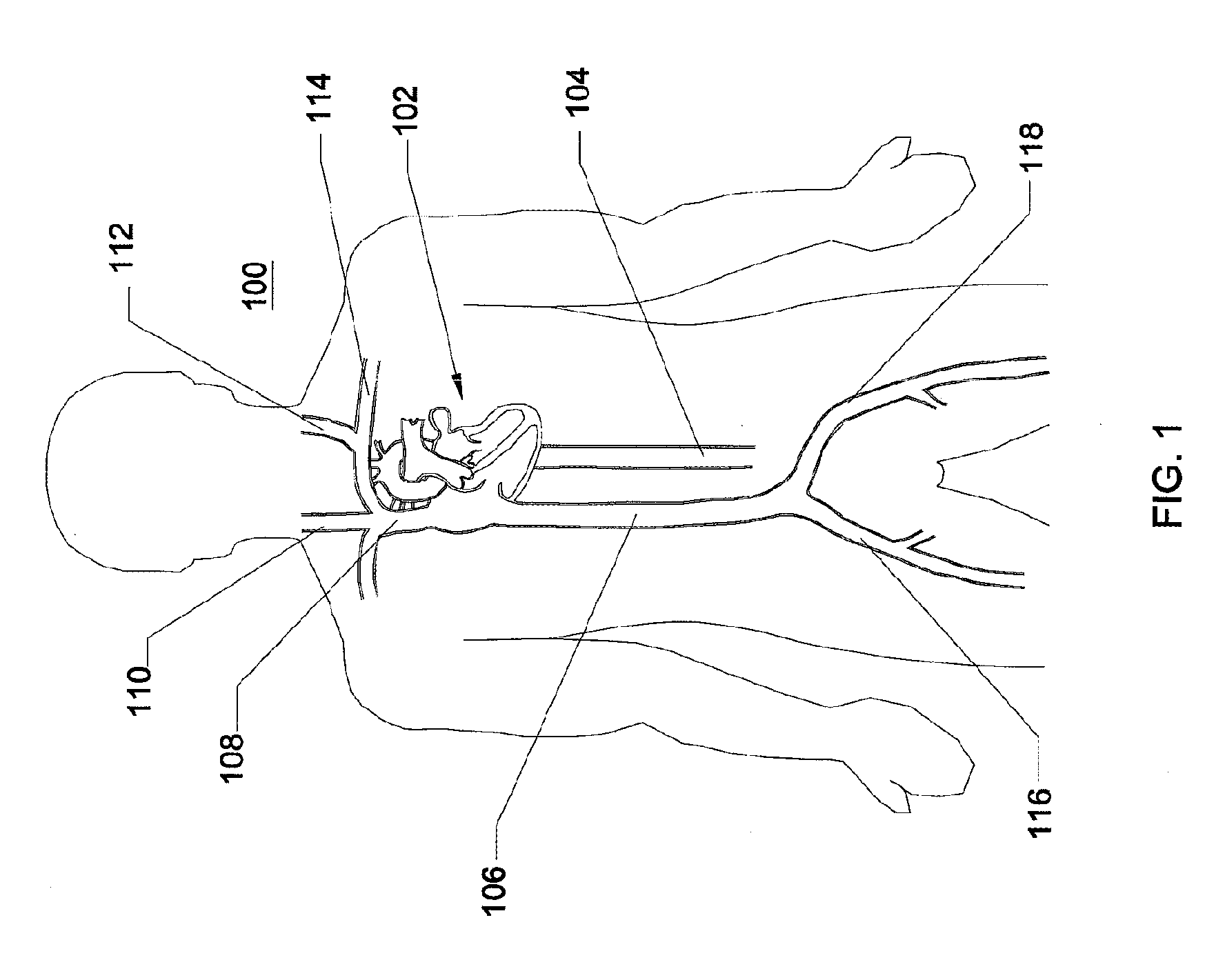
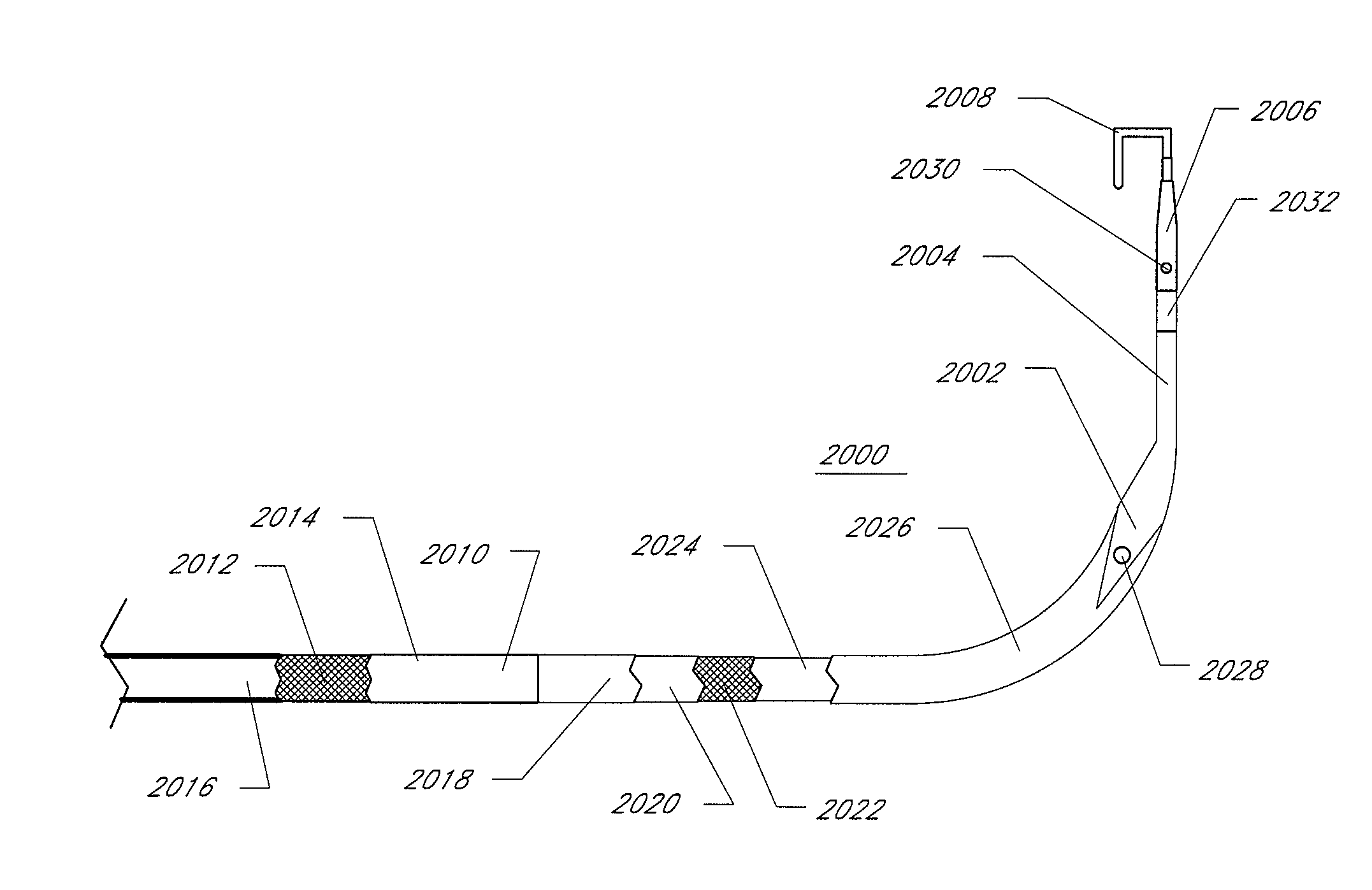
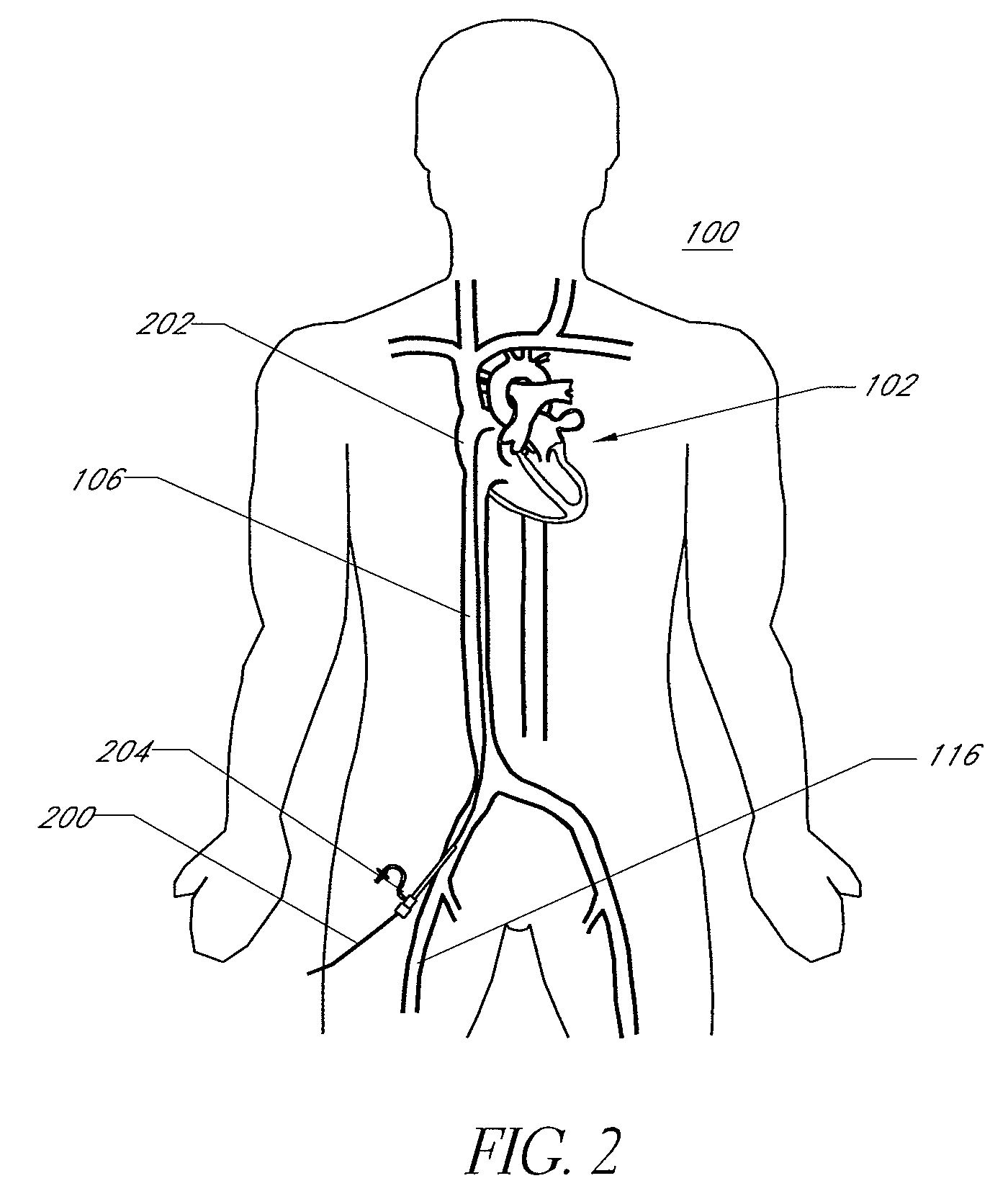
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the vascular system. The access route is through the inferior vena cava to the right atrium, where a trans-septal puncture, followed by advancement of the catheter is completed. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement through the atrial septum into the left atrium. The distal end of the sheath is expanded using a radial dilator. In one application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure such as electrophysiological mapping of the heart, radio-frequency ablation of left atrial tissue, placement of atrial implants, valve repair, or the like.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Method of Forming a Lesion in Heart Tissue
InactiveUS7100614B2Facilitate responsive and precise positionabilitySuture equipmentsElectrotherapyDefect repairPatch type
Owner:HEARTPORT
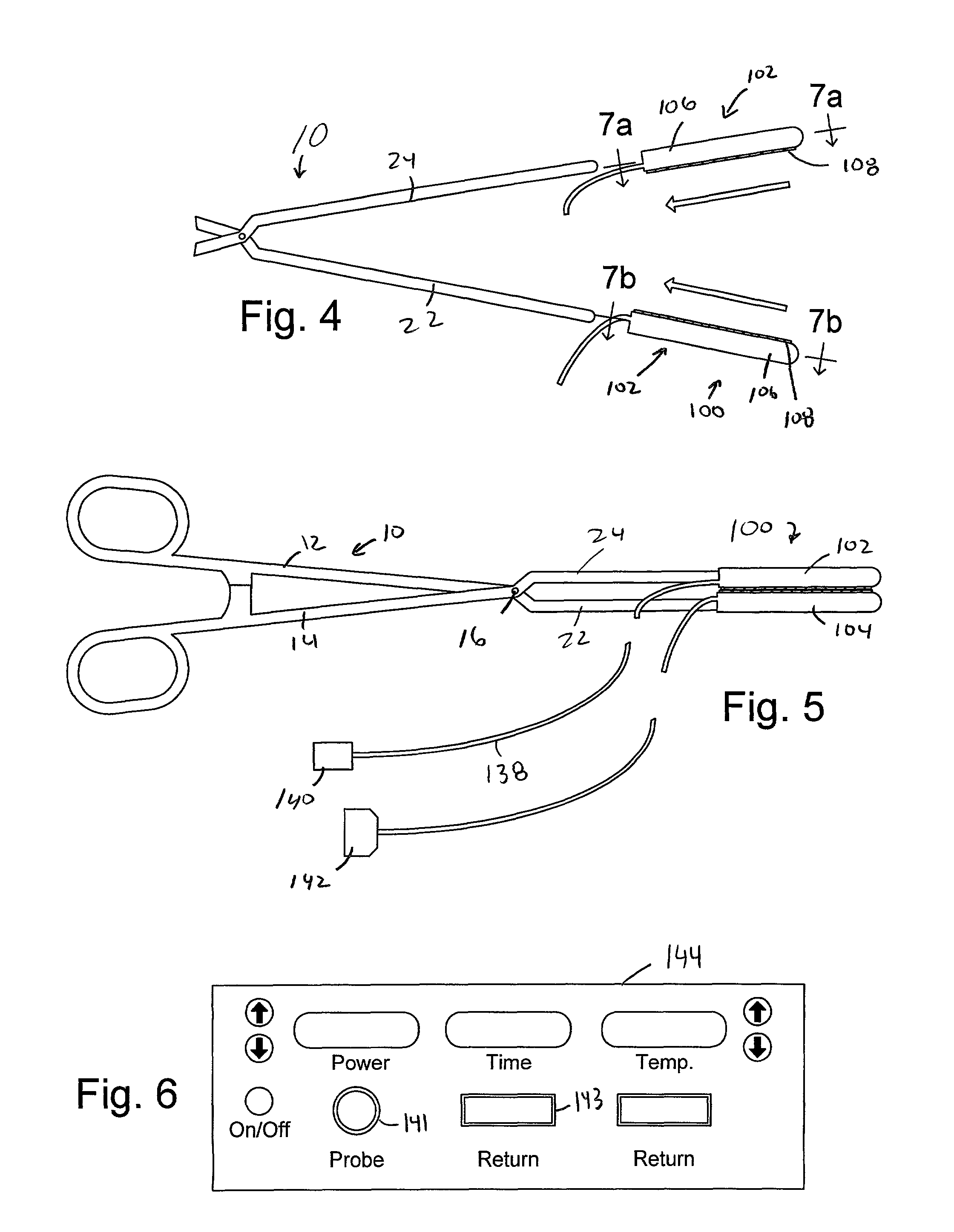
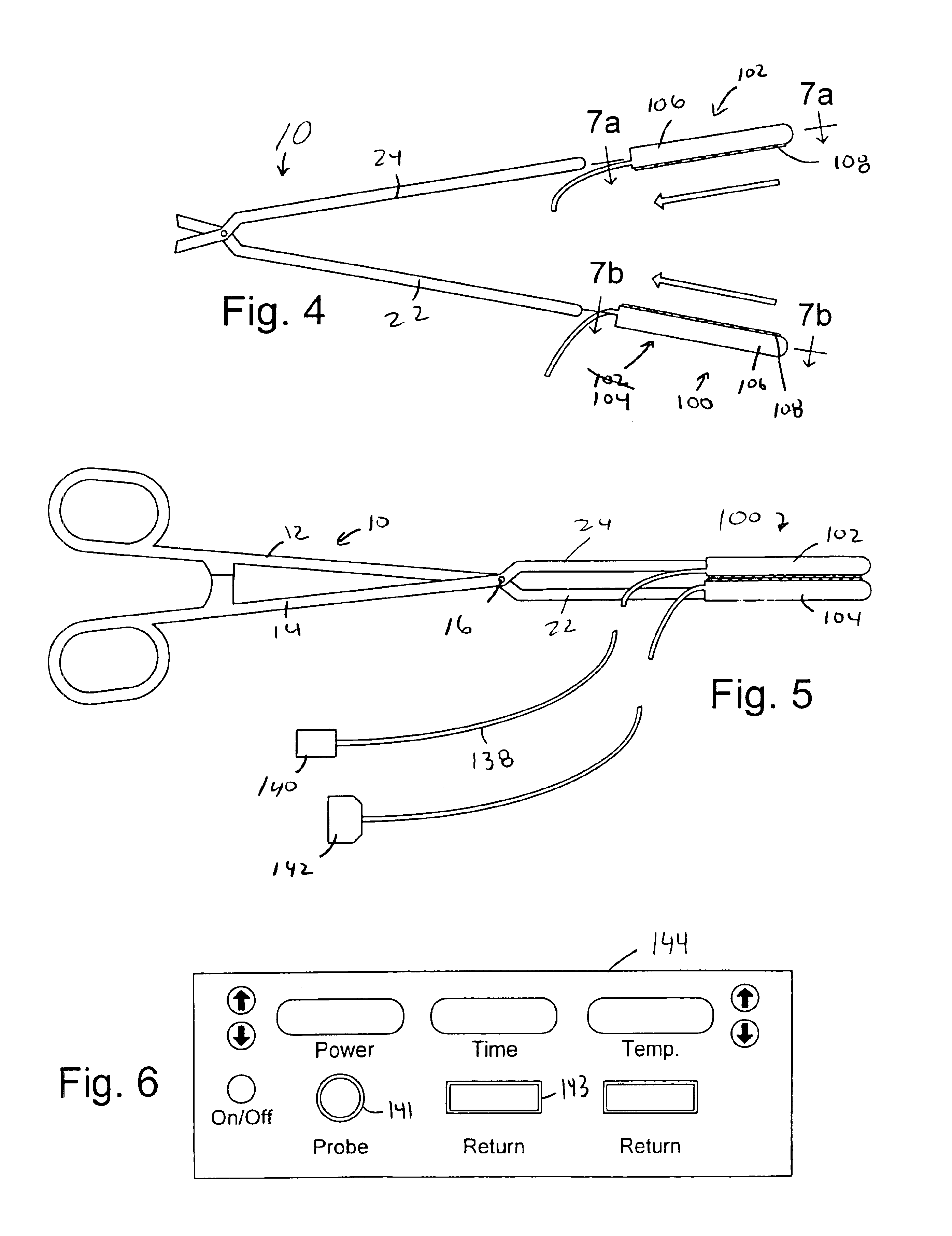
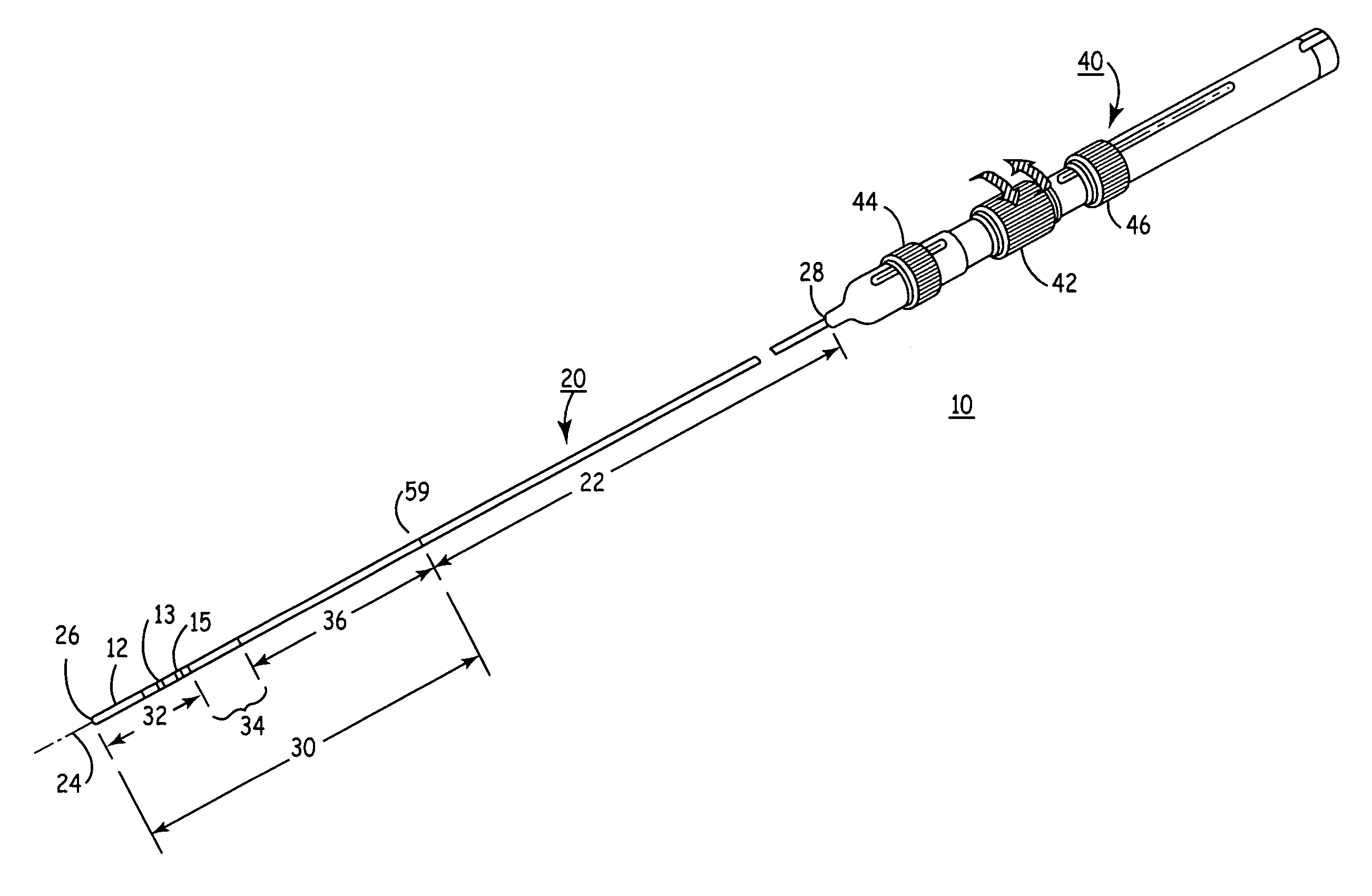
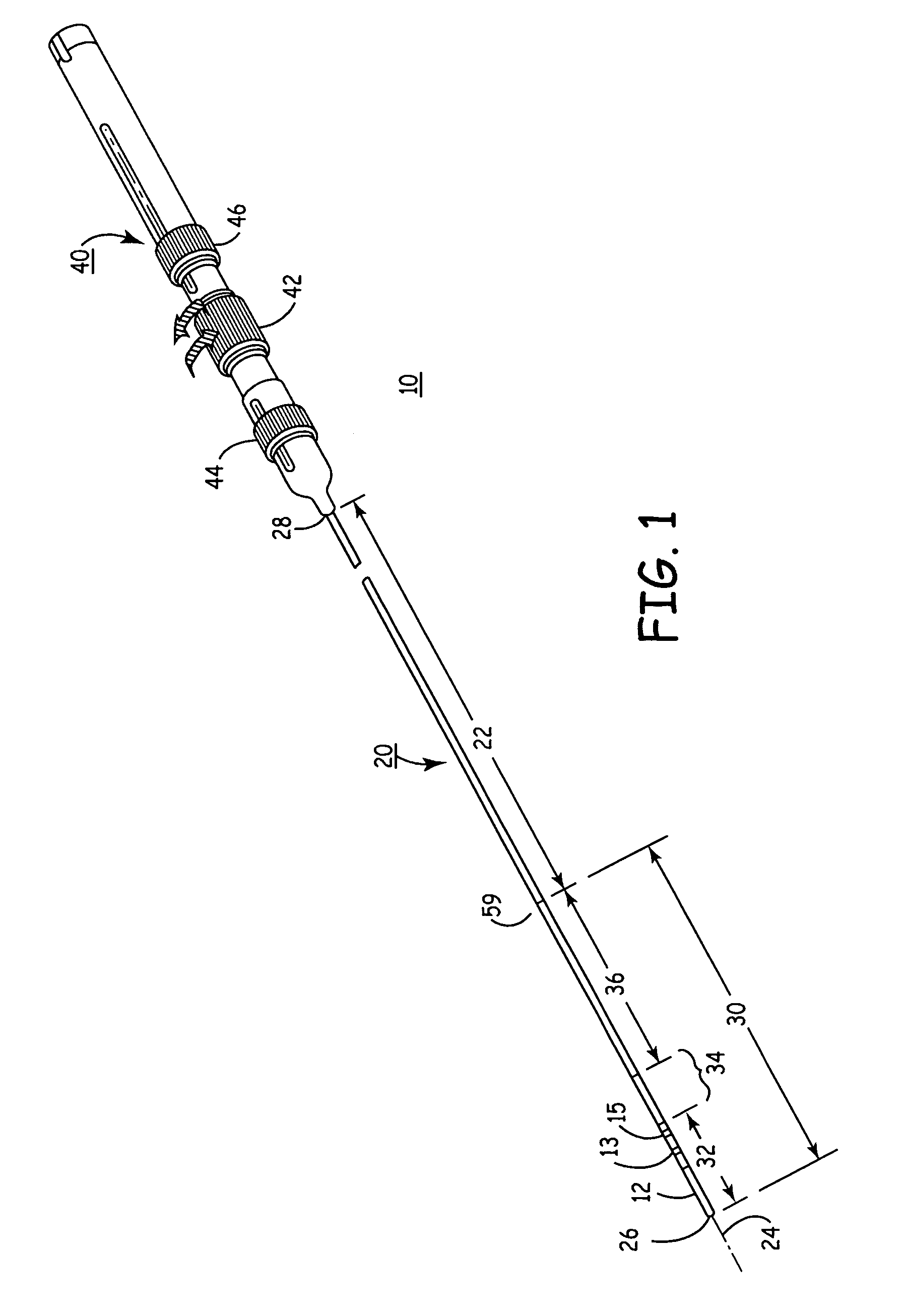
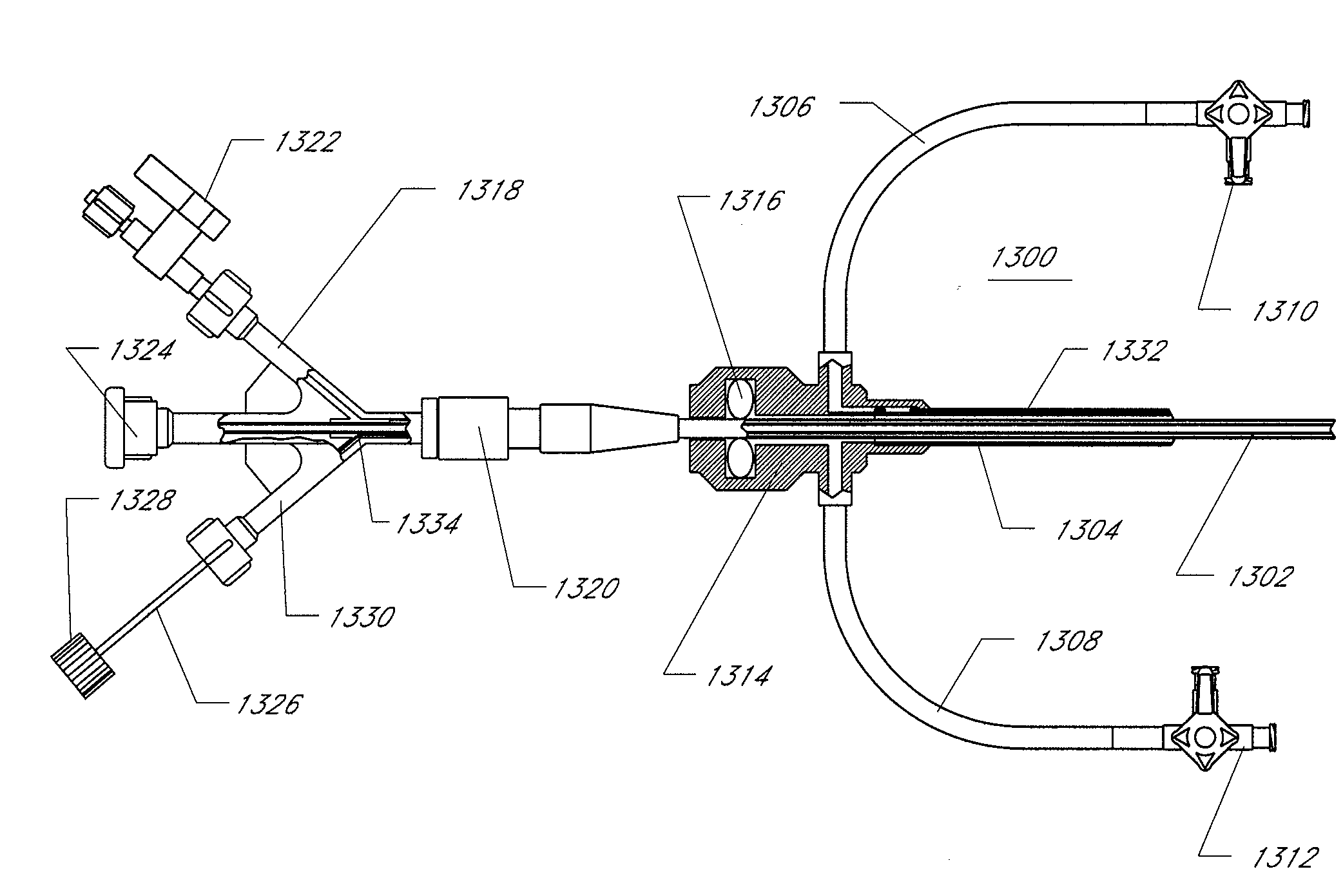
Apparatus for securing an electrophysiology probe to a clamp
InactiveUS7753908B2Quick conversionLow costDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEngineeringElectrophysiology
An apparatus for use with a clamp including a base member configured to be secured to the clamp and at least one energy transmission device carried by the base member. An apparatus for use with a clamp and a probe that carries at least one energy transmission device including a base member configured to be secured to the clamp and an engagement device associated with the base member and configured to engage the probe. A clamp including first and second clamp members, at least one of which is malleable, and a movement apparatus that moves at least one of the first and second clamp members relative to the other. A surgical system including a clamp with first and second clamp members and a device that removably mounts at least one electrode on at least one of the first and second clamp members.
Owner:ATRICURE
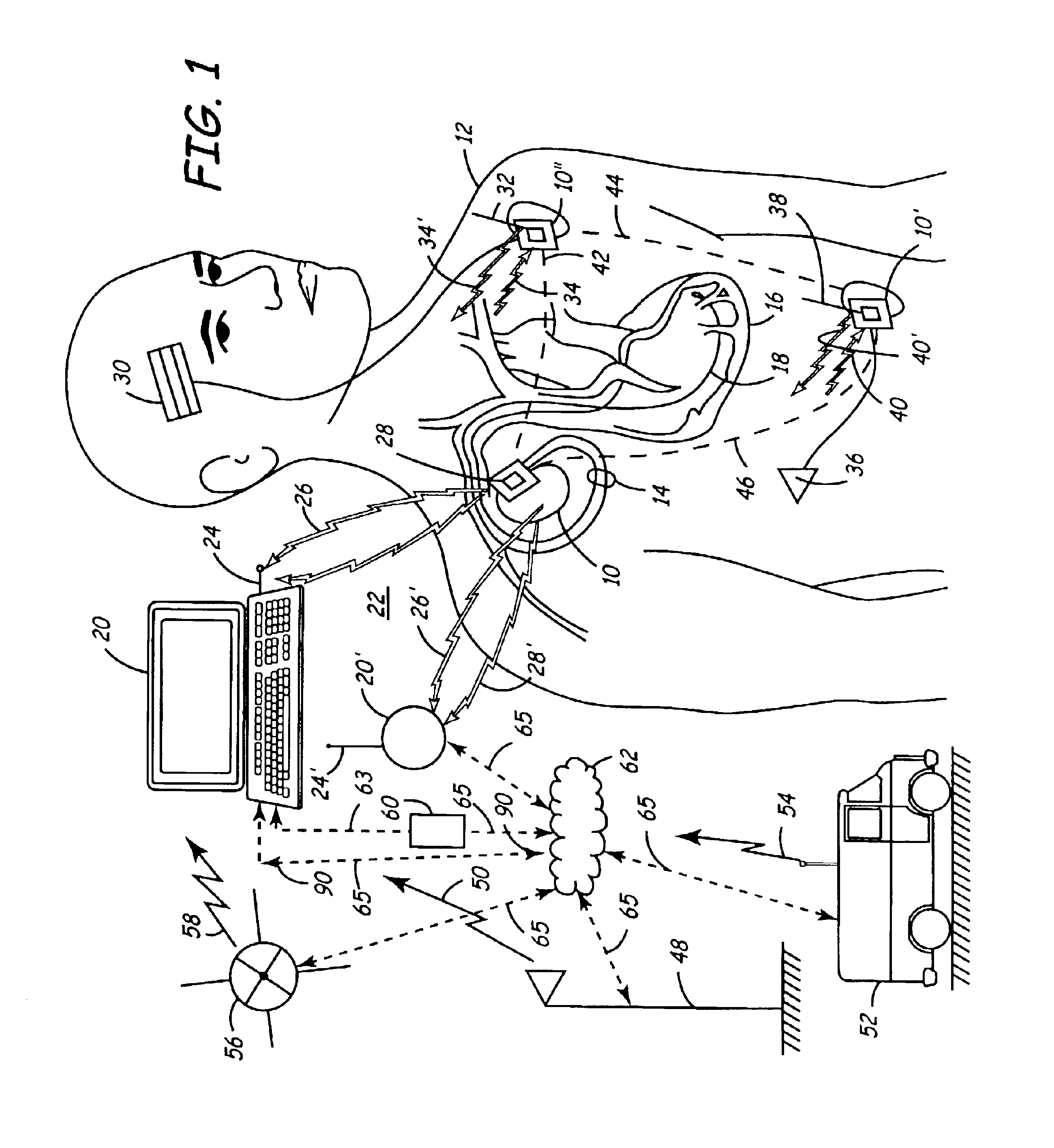
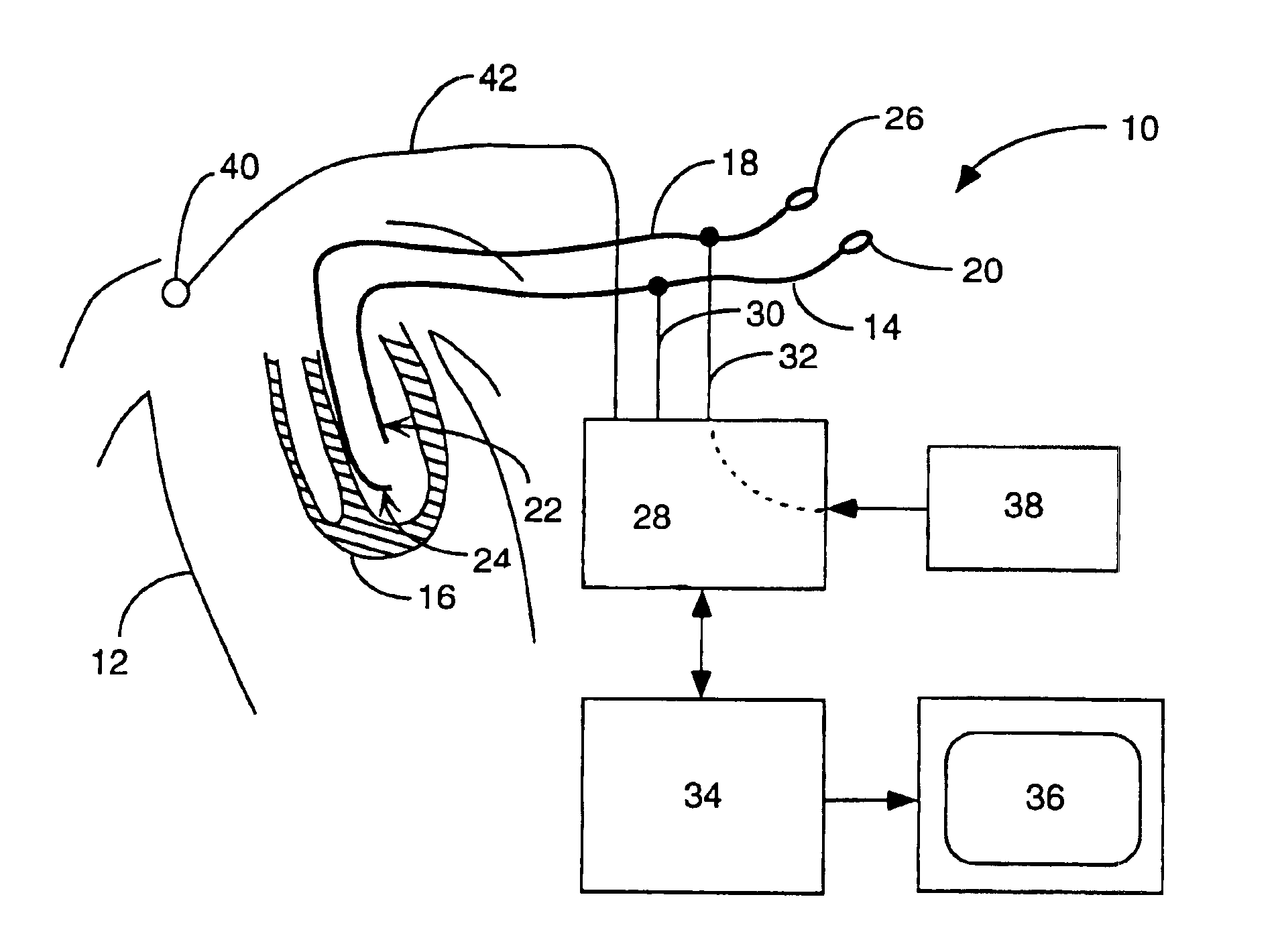
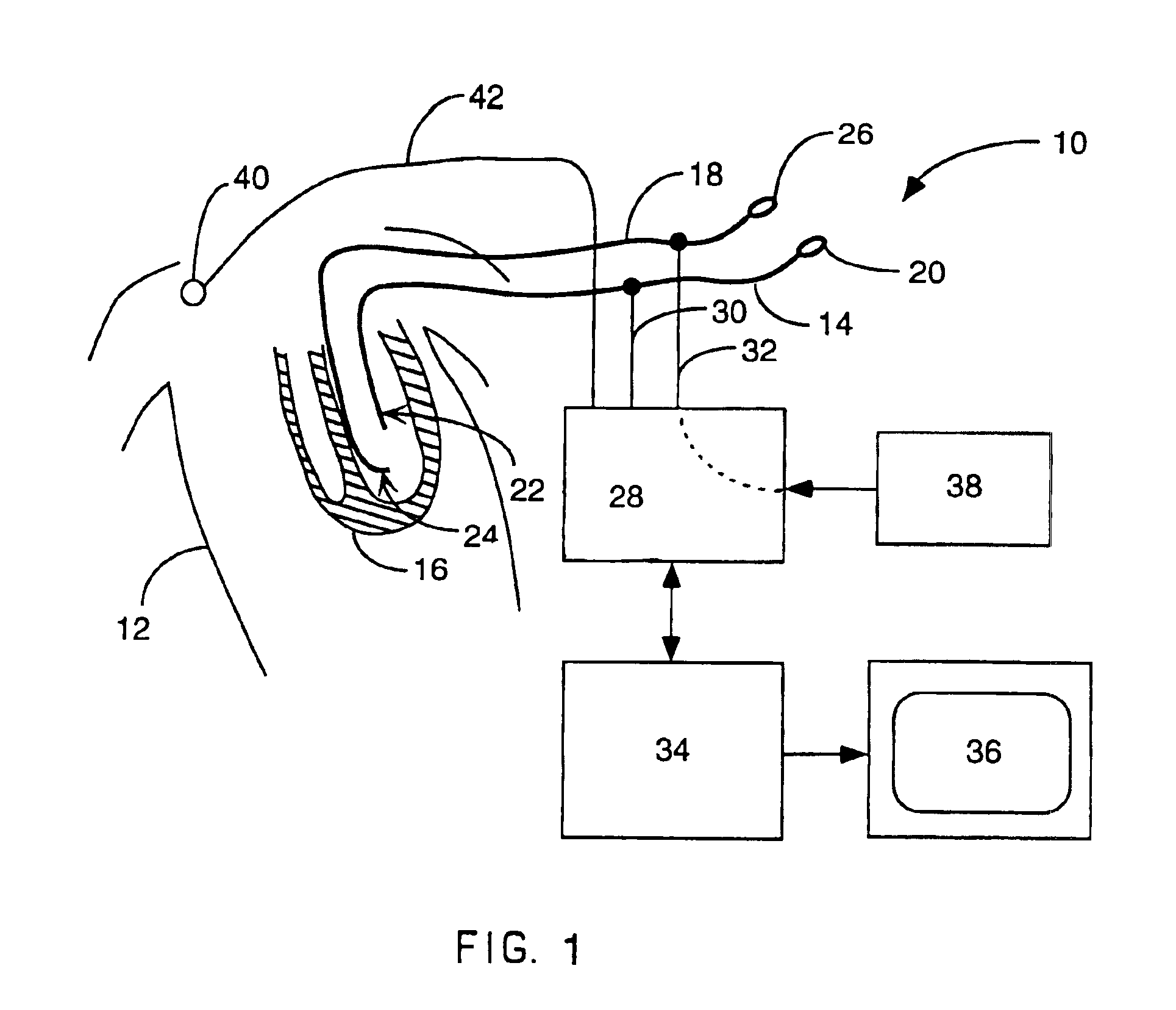
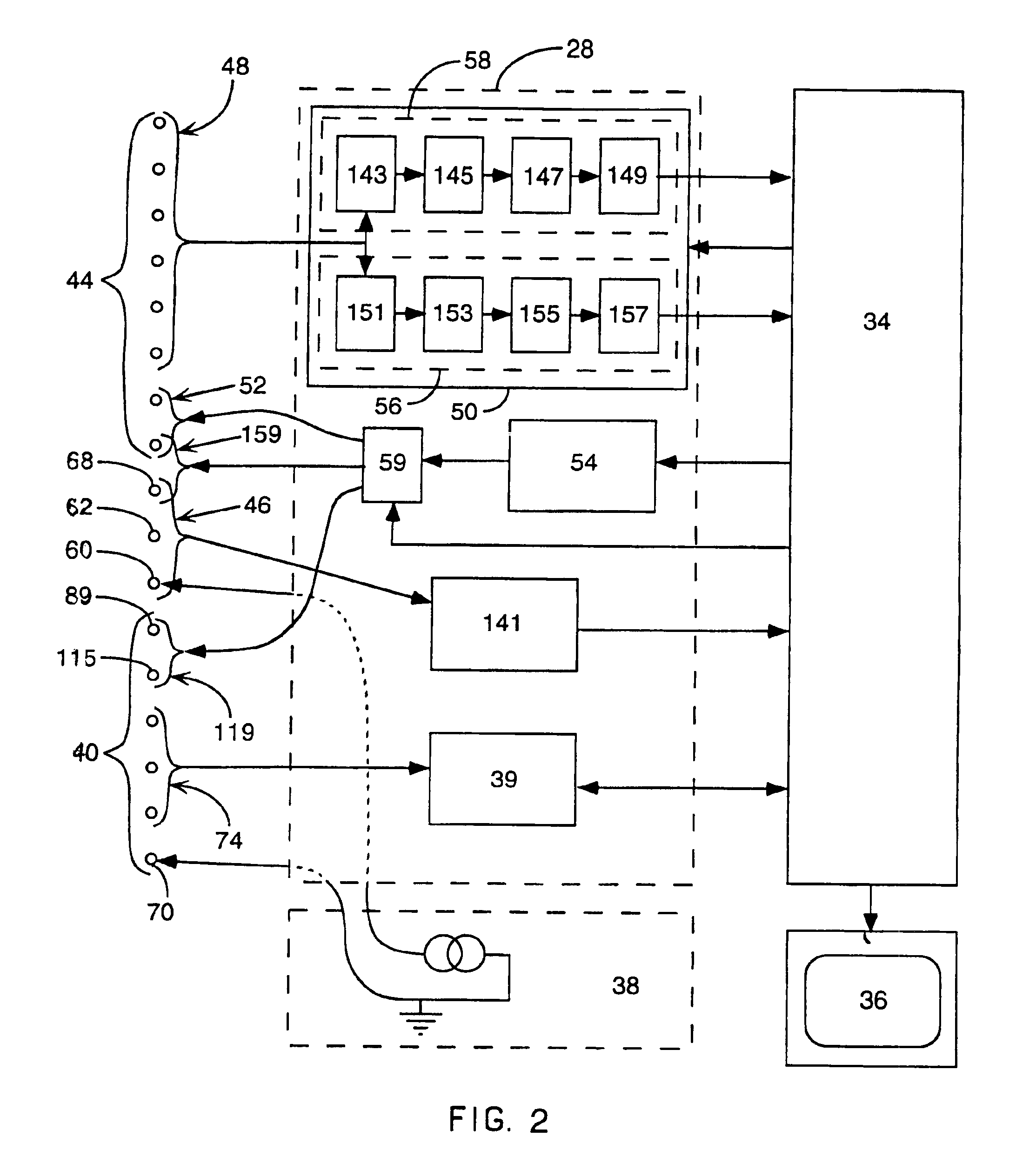
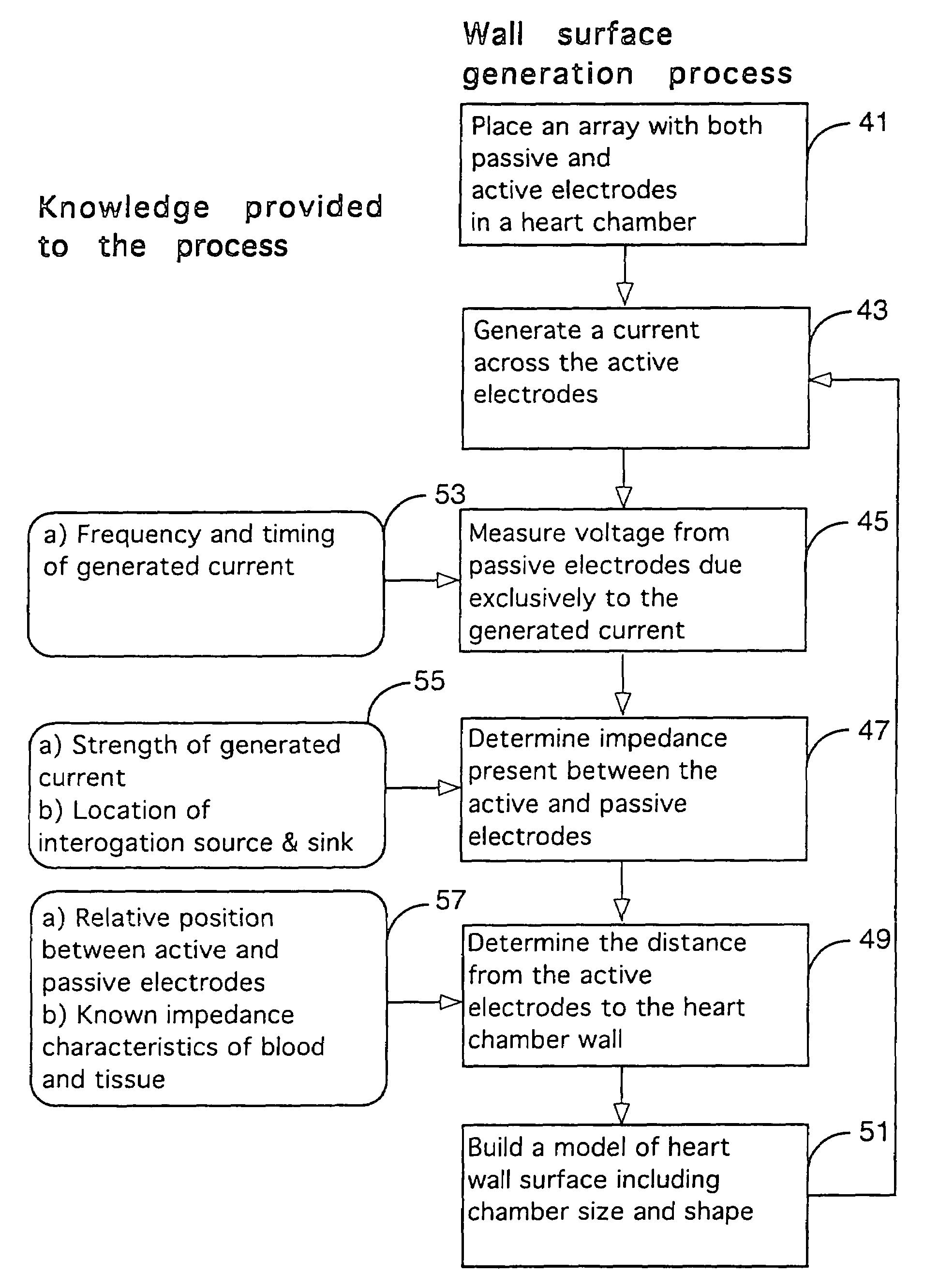
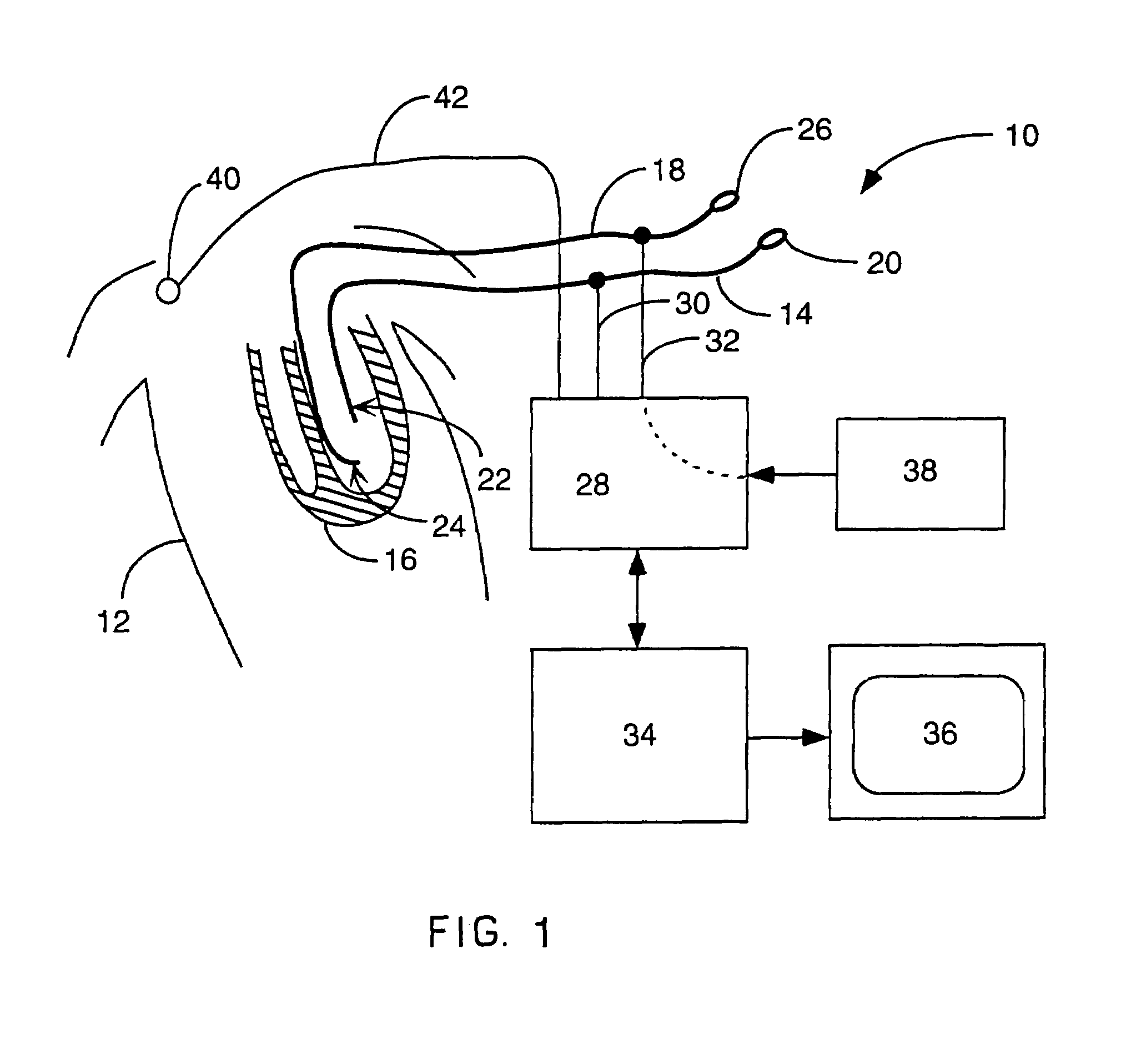
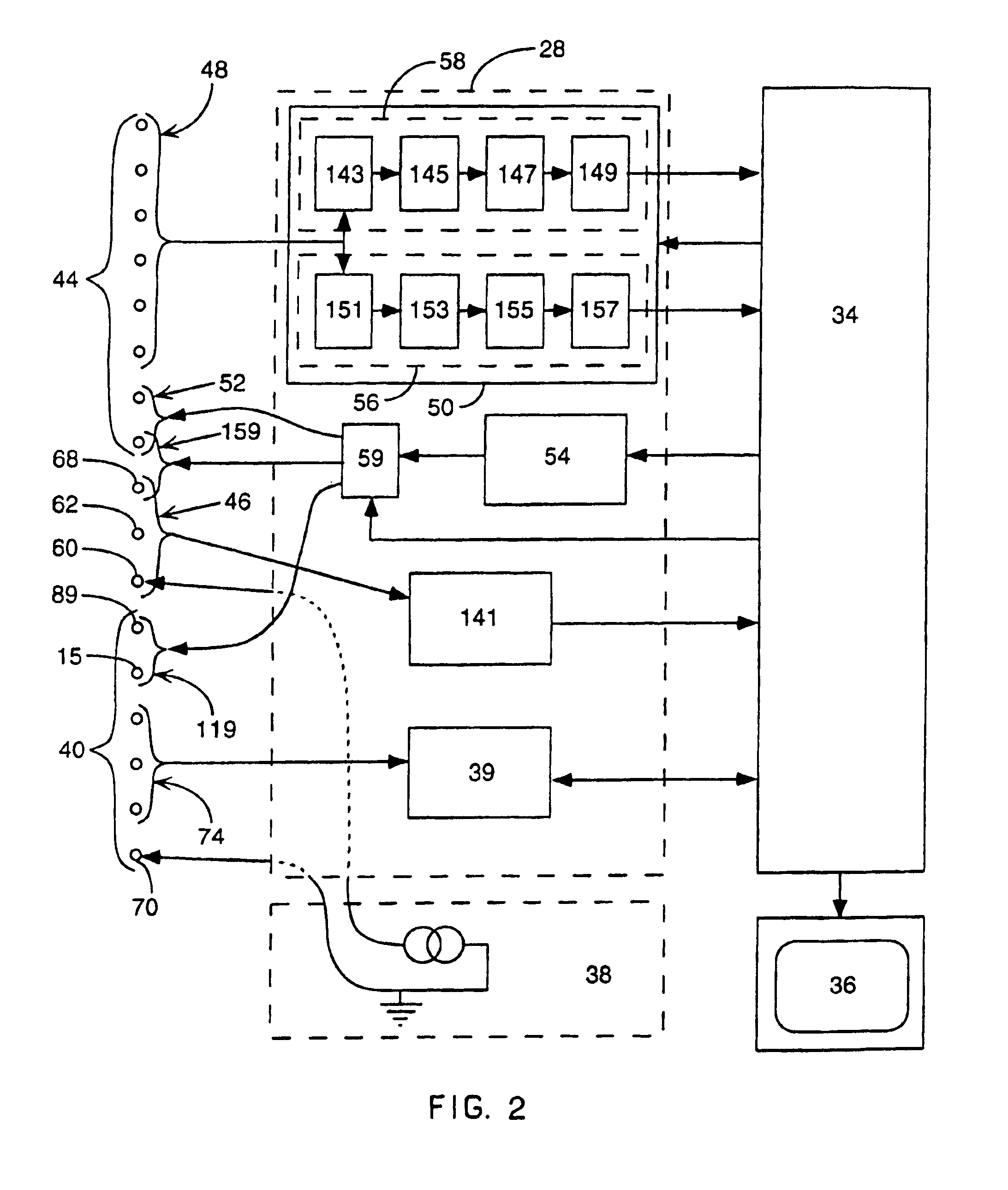
Interface system for endocardial mapping catheter
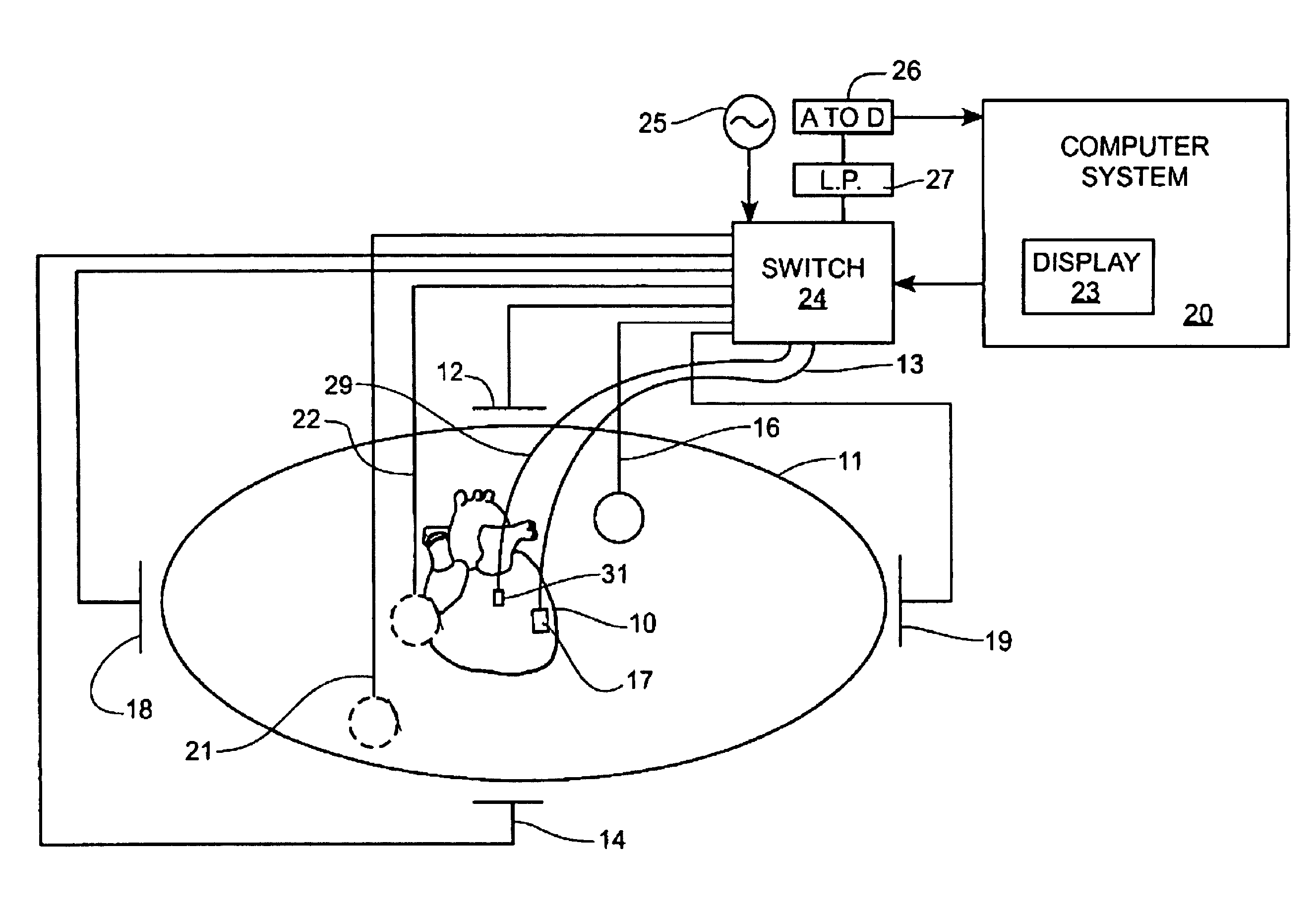
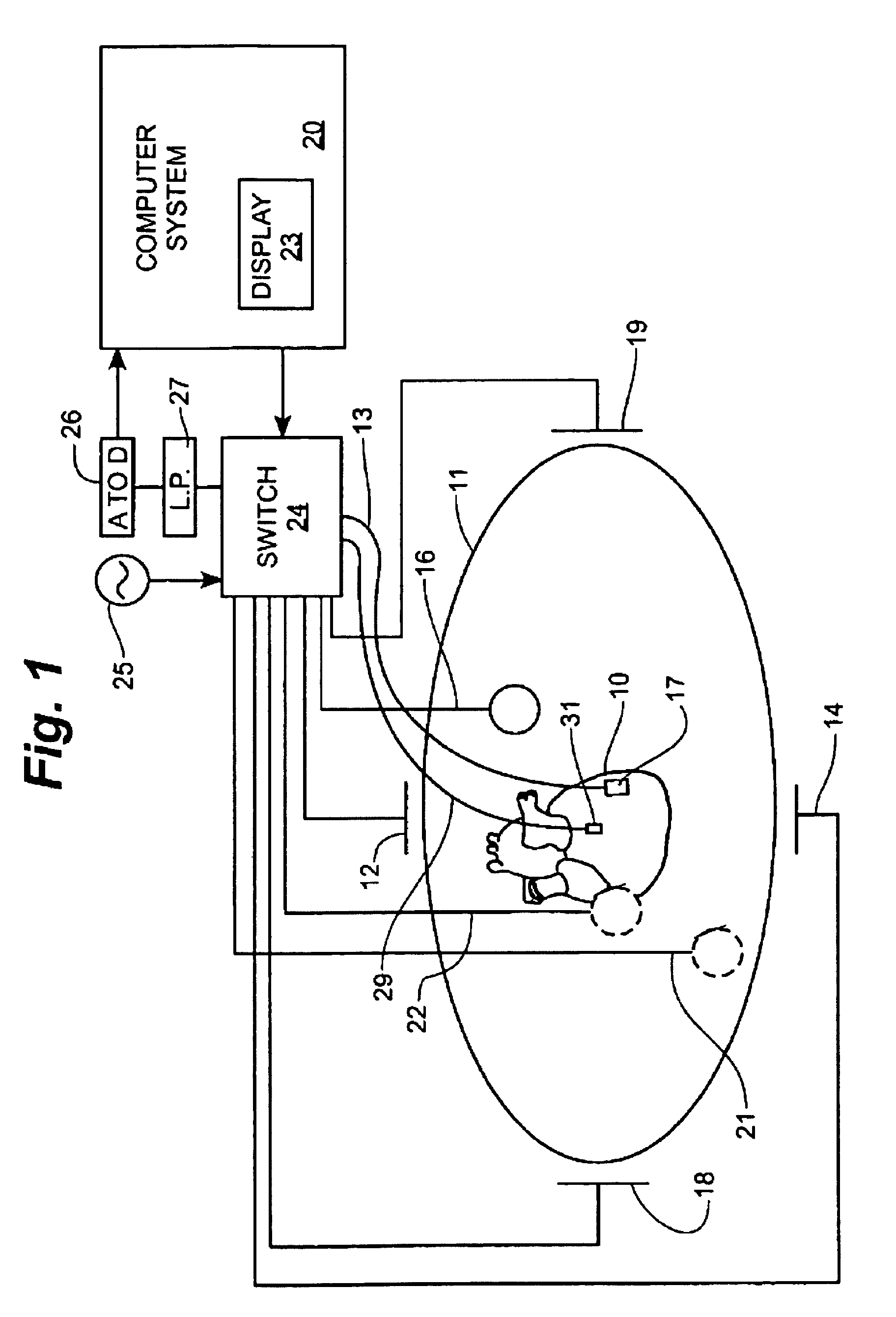
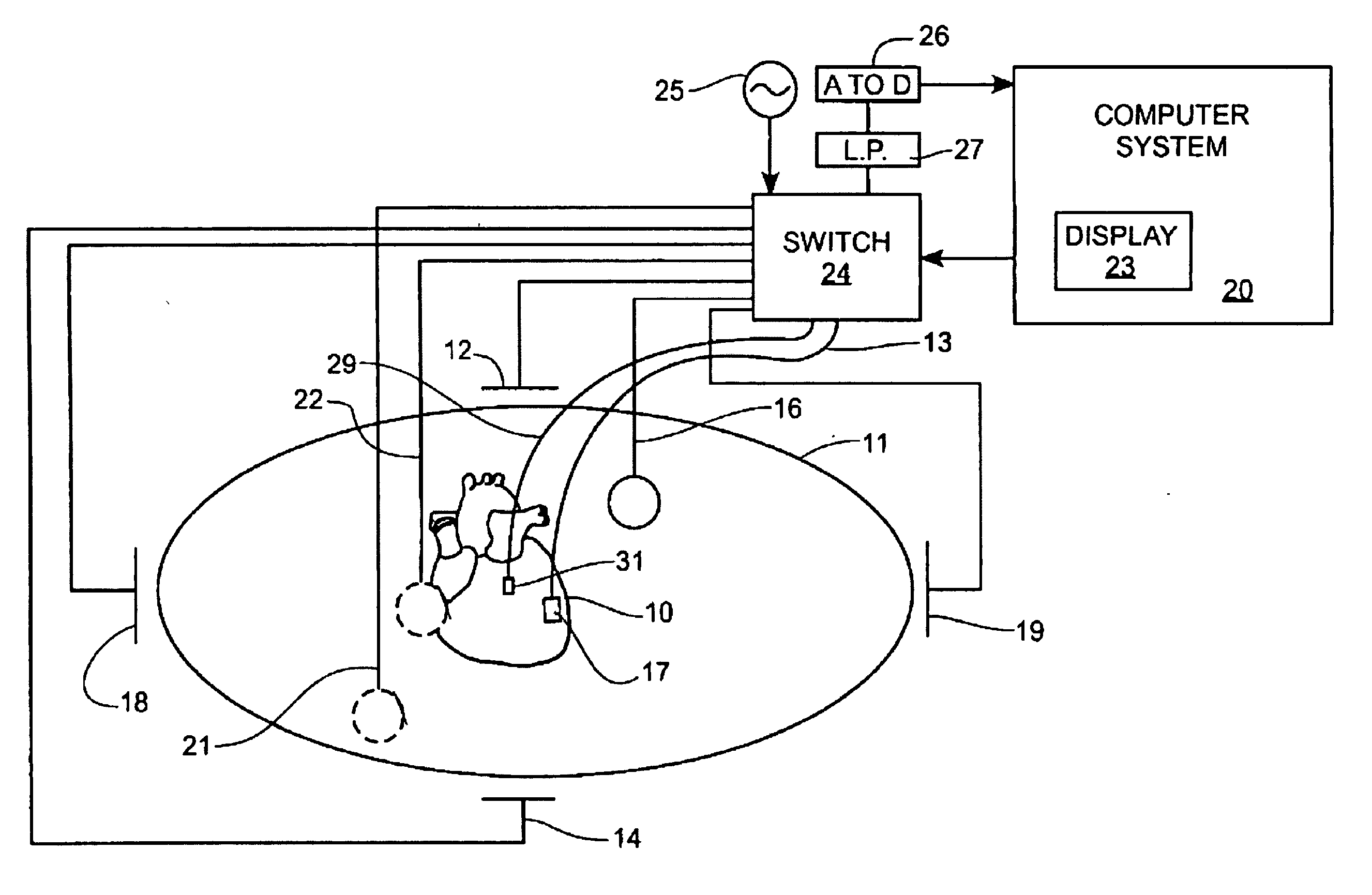
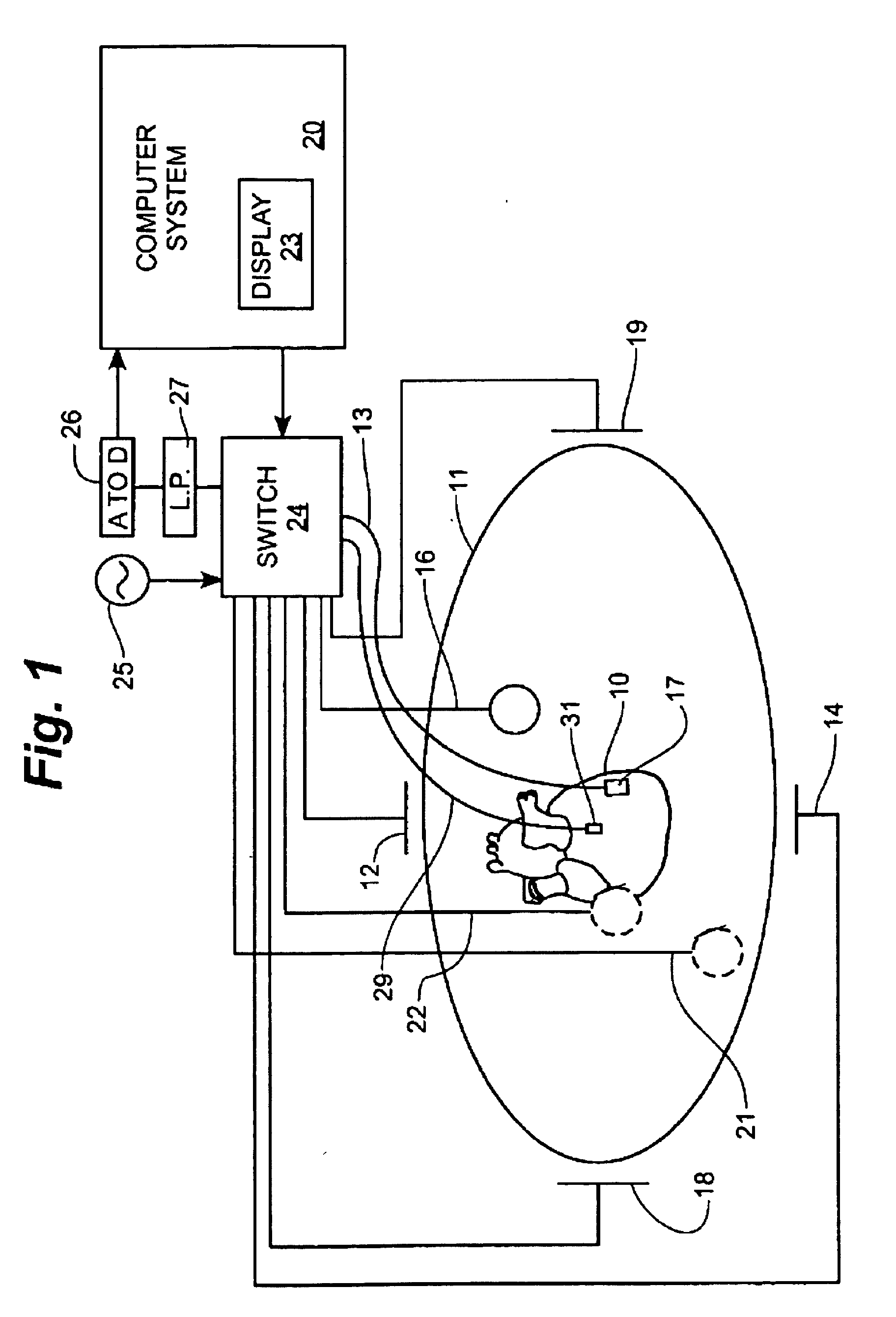
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method for measuring heart electrophysiology
A mapping catheter is positioned in a heart chamber, and active electrode sites are activated to impose an electric field within the chamber. The blood volume and wall motion modulates the electric field, which is detected by passive electrode sites on the preferred catheter. Electrophysiology measurements, as well as geometry measurements, are taken from the passive electrodes and used to display a map of intrinsic heart activity.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
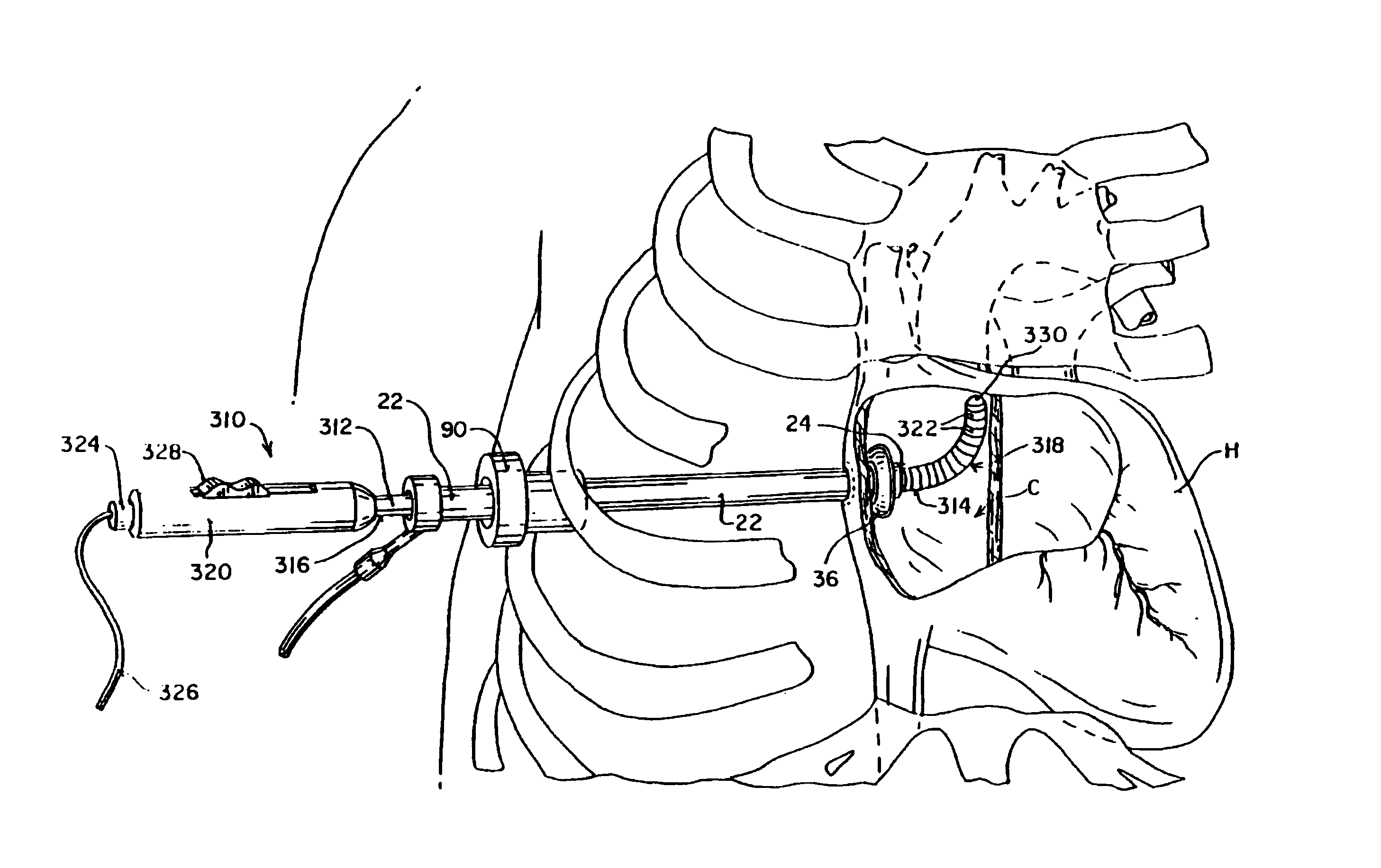
Method and apparatus for thoracoscopic intracardiac procedures
InactiveUS6955175B2Facilitate responsive and precise positionabilitySuture equipmentsElectrotherapyDefect repairThoracic cavity
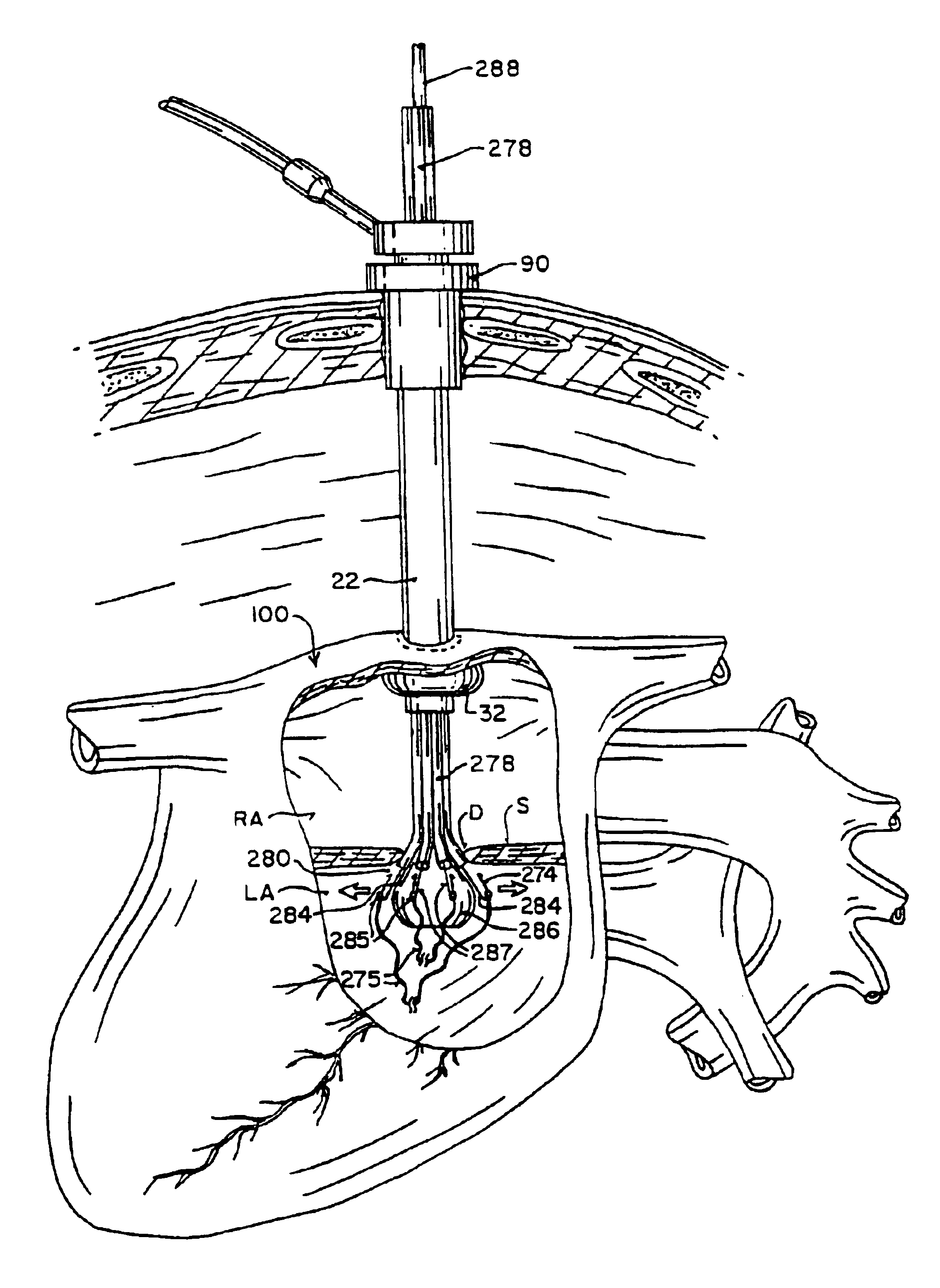
Devices, systems, and methods are provided for accessing the interior of the heart and performing procedures therein while the heart is beating. In one embodiment, a tubular access device having an inner lumen is provided for positioning through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, the access device having a means for sealing within the penetration to inhibit leakage of blood through the penetration. The sealing means may comprise a balloon or flange on the access device, or a suture placed in the heart wall to gather the heart tissue against the access device. An obturator is removably positionable in the inner lumen of the access device, the obturator having a cutting means at its distal end for penetrating the muscular wall of the heart. The access device is preferably positioned through an intercostal space and through the muscular wall of the heart. Elongated instruments may be introduced through the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart to perform procedures such as septal defect repair and electrophysiological mapping and ablation. A method of septal defect repair includes positioning a tubular access device percutaneously through an intercostal space and through a penetration in a muscular wall of the heart, passing one or more instruments through an inner lumen of the tubular access device into an interior chamber of the heart, and using the instruments to close the septal defect. Devices and methods for closing the septal defect with either sutures or with patch-type devices are disclosed.
Owner:STEVENS JOHN H +4
Apparatus for converting a clamp into an electrophysiology device
InactiveUS6932816B2Quick conversionLow costSurgical instruments for heatingCoatingsEngineeringElectrophysiology
An apparatus for use with a clamp including a base member configured to be secured to the clamp and at least one energy transmission device carried by the base member. An apparatus for use with a clamp and a probe that carries at least one energy transmission device including a base member configured to be secured to the clamp and an engagement device associated with the base member and configured to engage the probe. A clamp including first and second clamp members, at least one of which is malleable, and a movement apparatus that moves at least one of the first and second clamp members relative to the other. A surgical system including a clamp with first and second clamp members and a device that removably mounts at least one electrode on at least one of the first and second clamp members.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Heart wall ablation/mapping catheter and method
InactiveUS6926669B1Wide angleSmall knuckle curveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChiropractic devicesCardiac wallAngular orientation
Steerable electrophysiology catheters for use in mapping and / or ablation of accessory pathways in myocardial tissue of the heart wall and methods of use thereof are disclosed. The catheter comprises a catheter body and handle, the catheter body having a proximal section and a distal section and manipulators that enable the deflection of a distal segment of the distal tip section with respect to the independently formed curvature of a proximal segment of the distal tip section through a bending or knuckle motion of an intermediate segment between the proximal and distal segments. A wide angular range of deflection within a very small curve or bend radius in the intermediate segment is obtained. At least one distal tip electrode is preferably confined to the distal segment which can have a straight axis extending distally from the intermediate segment. The curvature of the proximal segment and the bending angle of the intermediate segment are independently selectable. The axial alignment of the distal segment with respect to the nominal axis of the proximal shaft section of the catheter body can be varied between substantially axially aligned (0° curvature) in an abrupt knuckle bend through a range of about −90° to about +180° within a bending radius of between about 2.0 mm and 7.0 mm and preferably less than 5.0 mm. The proximal segment curve can be independently formed in a about +180° through about +270° with respect to the axis of the proximal shaft section to provide an optimum angular orientation of the distal electrode(s). The distal segment can comprise a highly flexible elongated distal segment body and electrode(s) that conform with the shape and curvature of the heart wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
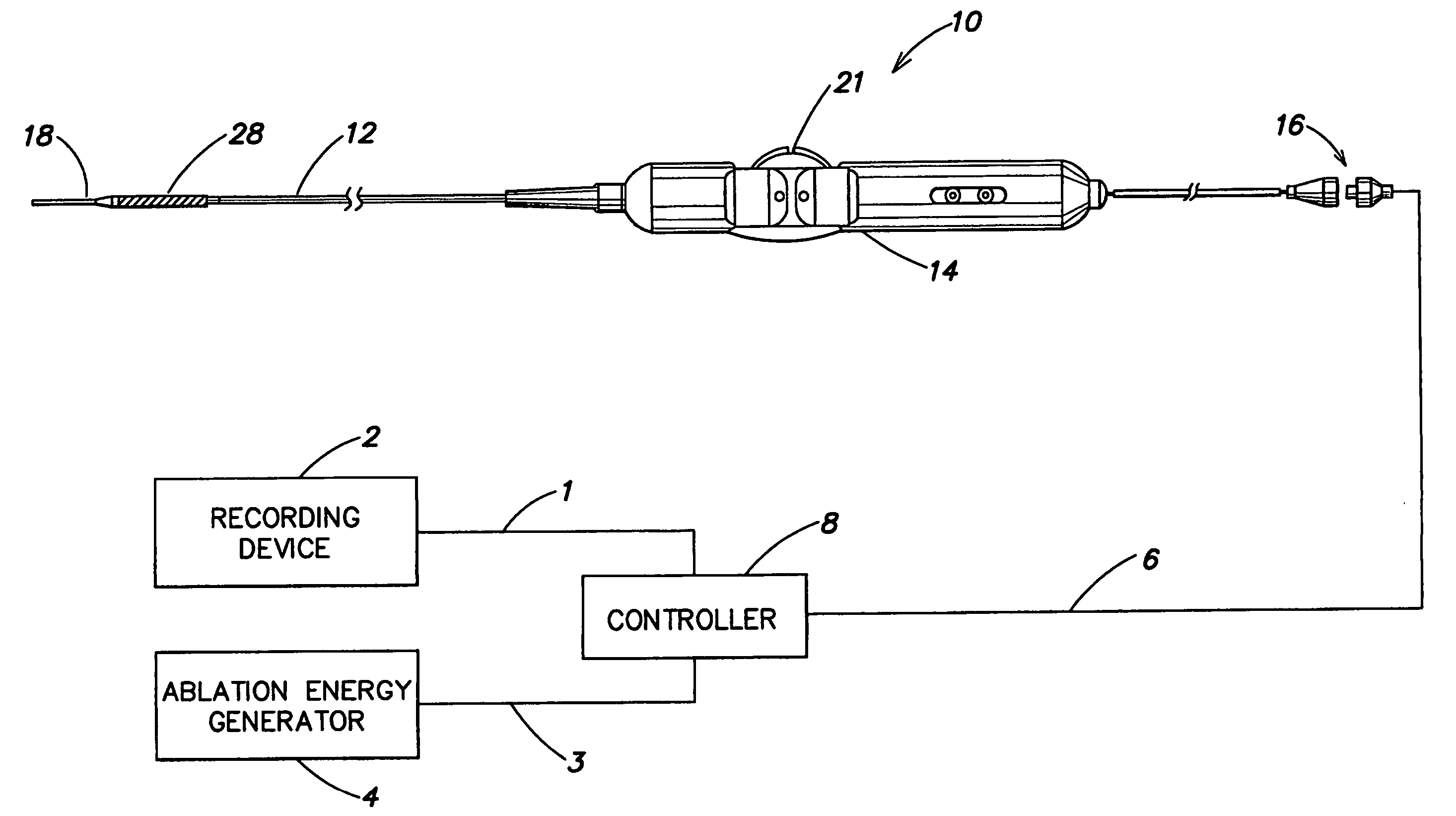
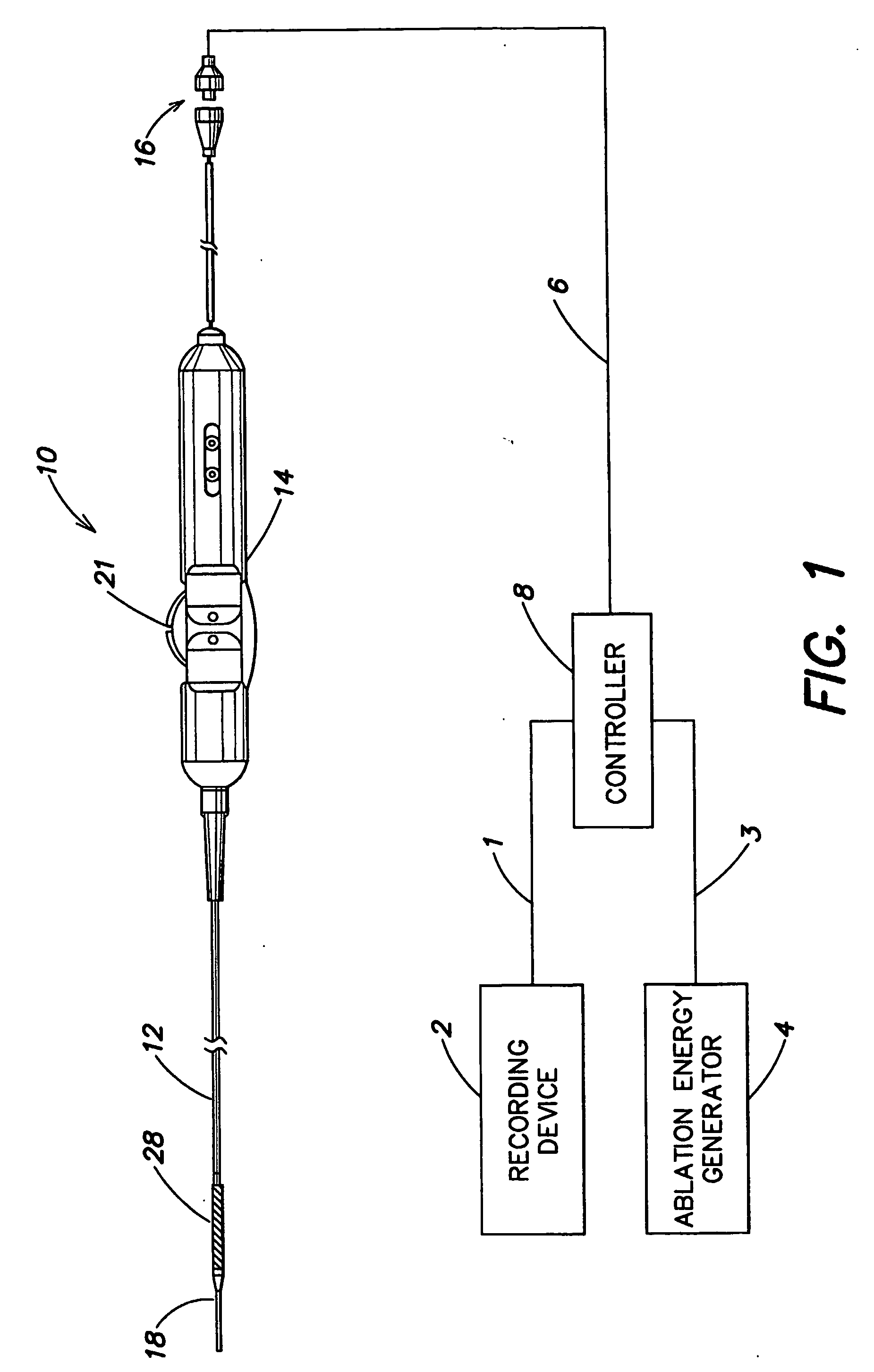
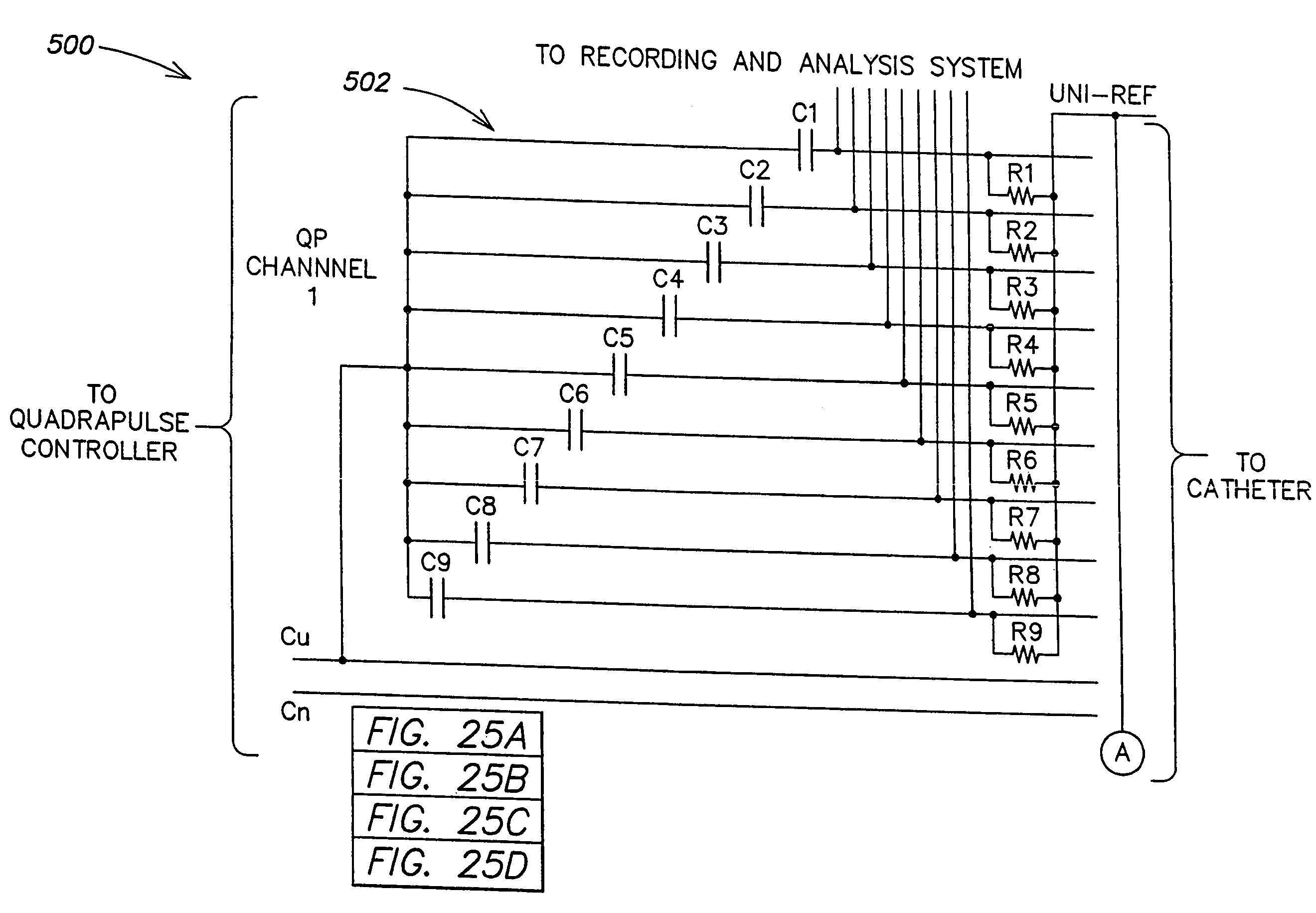
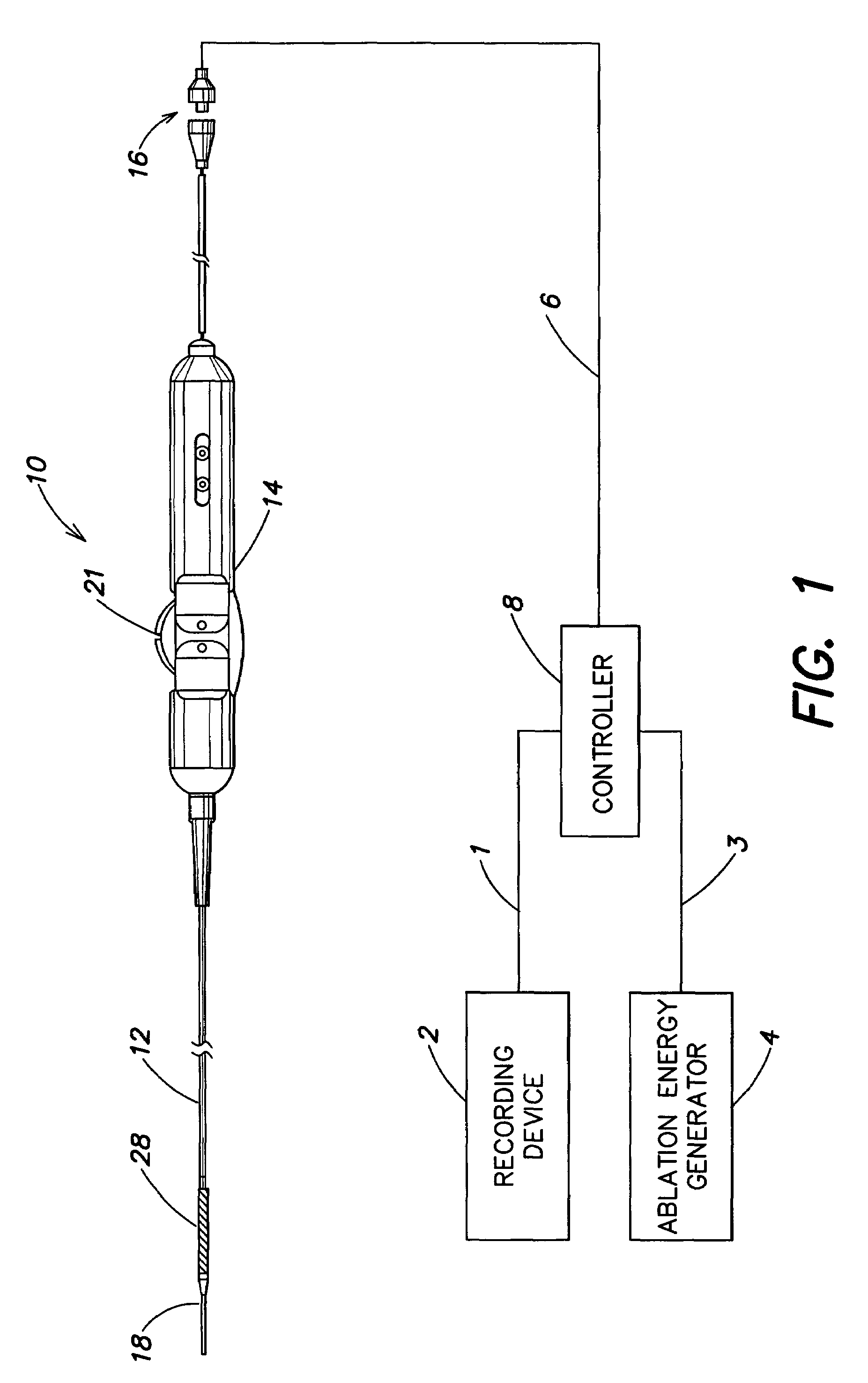
Method and apparatus for control of ablation energy and electrogram acquisition through multiple common electrodes in an electrophysiology catheter
Method and apparatus for control of ablation energy and electrogram acquisition through multiple common electrodes in an electrophysiology catheter. A device that routes ablation energy to and that routes mapping signals received from an electrophysiology catheter having a plurality of conductive filaments including circuitry that provides, for each conductive filament when ablation energy is being delivered, an electrical signal path that has a low impedance for ablation energy and a high impedance for mapping signals. The device also includes circuitry that provides, for each conductive filament, when mapping signals are being received, an electrical signal path that has a high impedance for ablation energy and low impedance for mapping signals. At least one switch is provided that selectively groups electrodes into sectors for delivery of ablation energy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
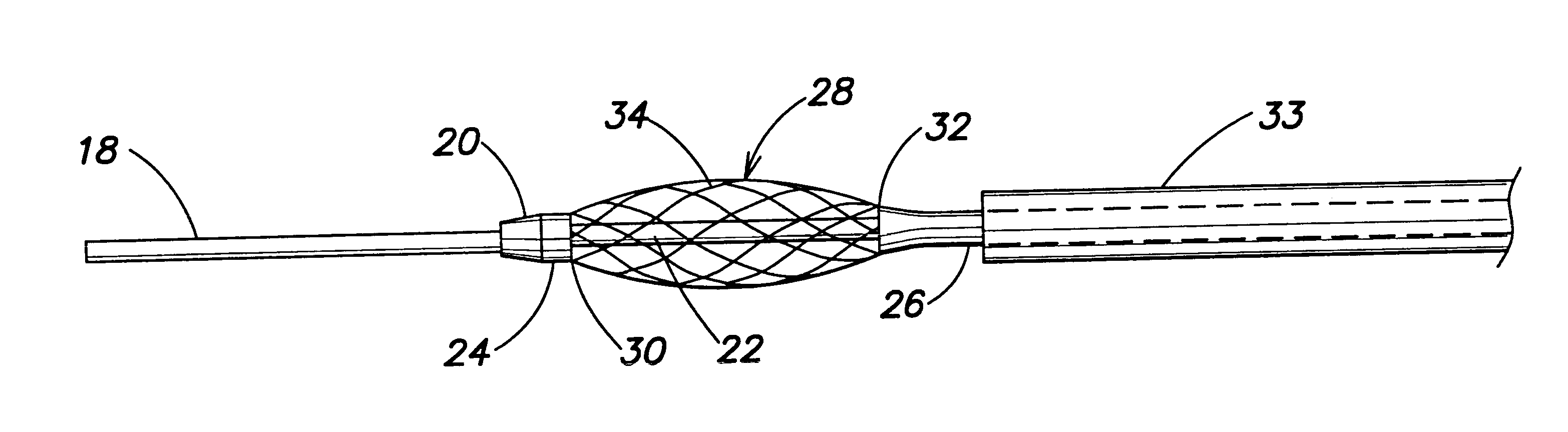
Energy based devices and methods for treatment of anatomic tissue defects
Methods and apparatus for treatment of anatomic defects in human tissues, such as patent foramen ovale (PFO), atrial or ventricular septal defects, left atrial appendage, patent ductus arteriosis, blood vessel wall defects and certain electrophysiological defects, involve positioning a distal end of an elongate catheter device at the site of the anatomic defect, engaging tissues at the site of the anatomic defect to bring the tissues together, and applying energy to the tissues with the catheter device to substantially close the anatomic defect acutely. Apparatus generally includes an elongate catheter having a proximal end and a distal end, a vacuum application member coupled with the distal end for engaging tissues at the site of the anatomic defect and applying vacuum to the tissues to bring them together, and at least one energy transmission member coupled with the vacuum application member for applying energy to tissues at the site of the anatomic defect to substantially close the defect acutely.
Owner:TERUMO KK
Expandable trans-septal sheath
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
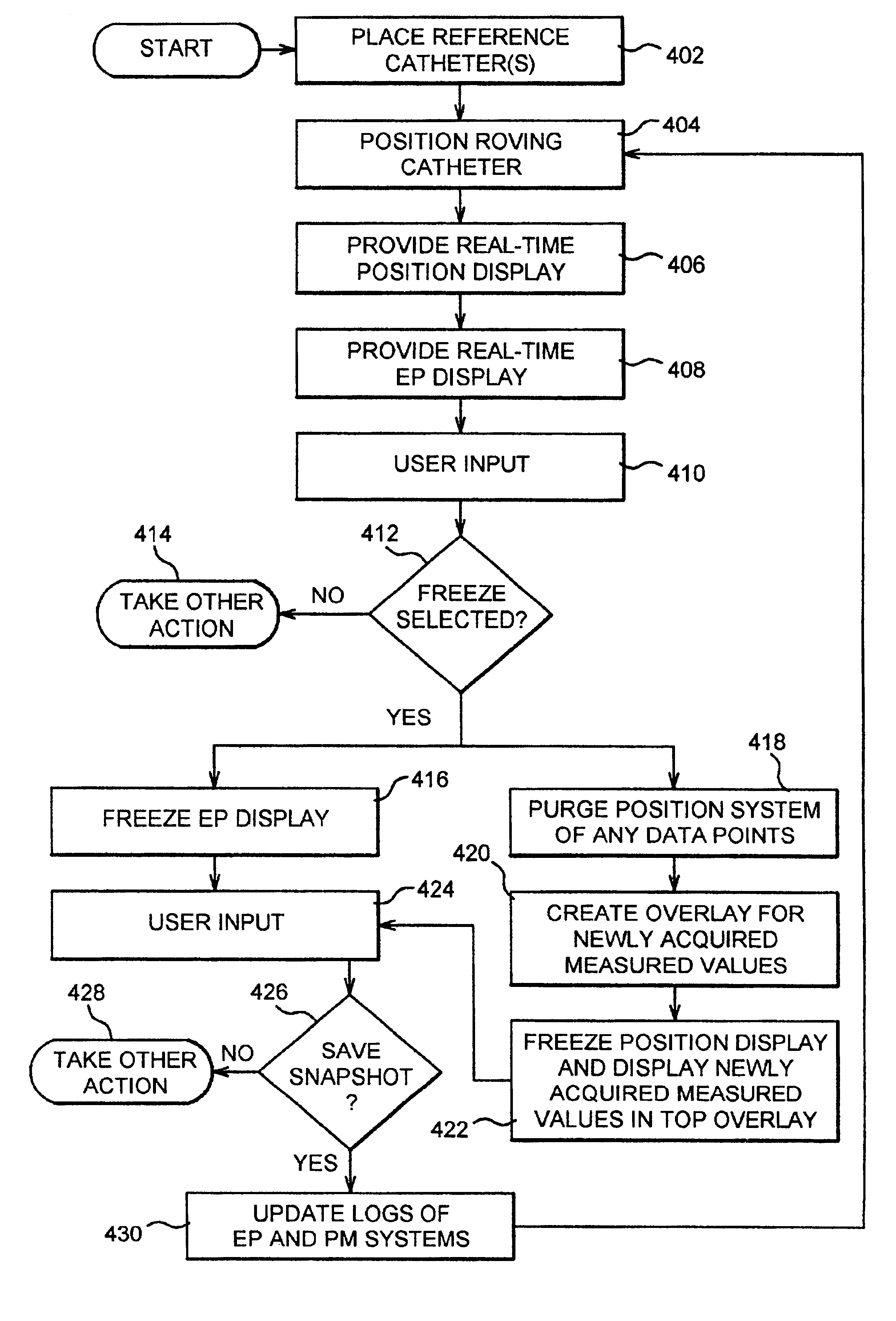
Rapid 3D mapping using multielectrode position data
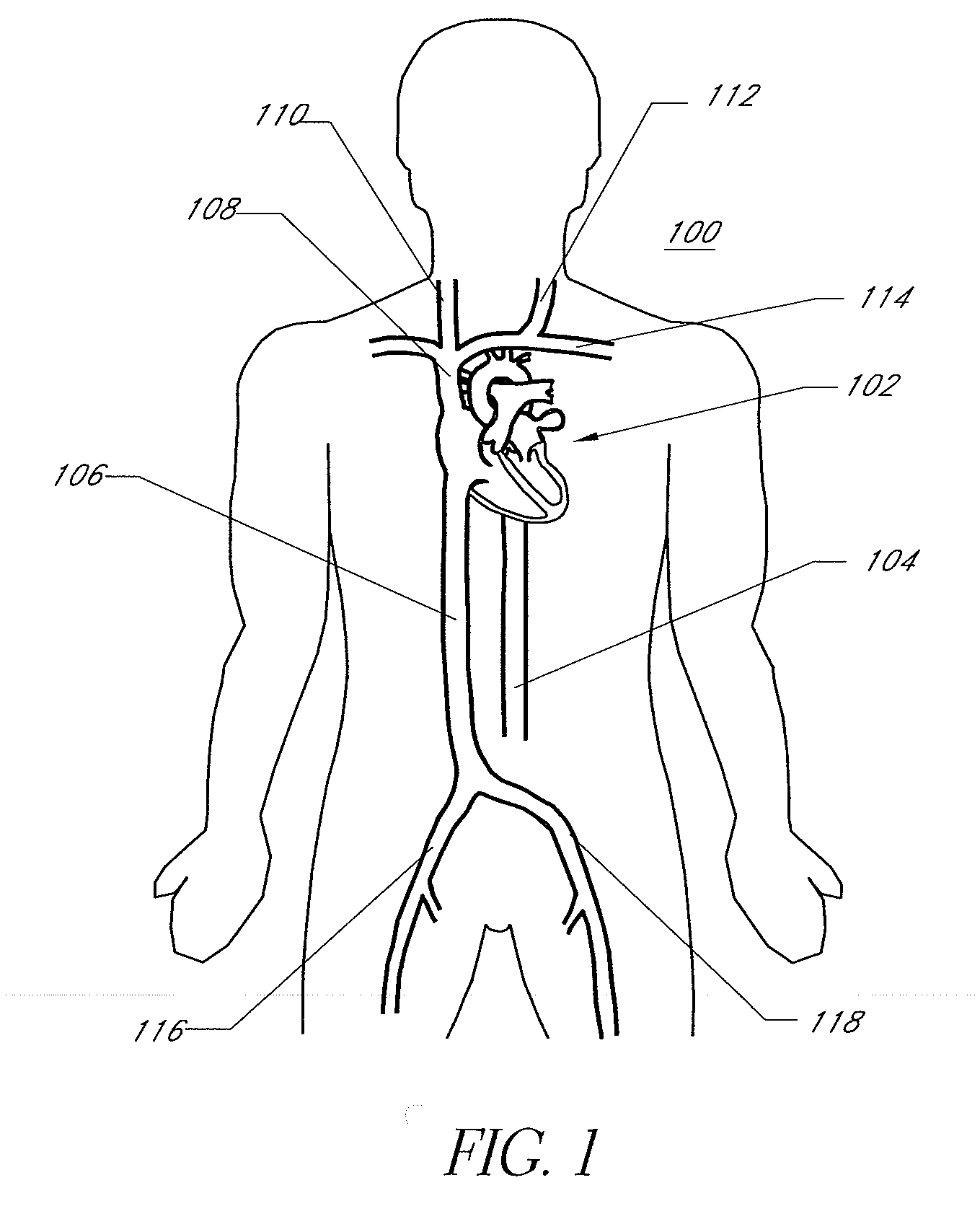
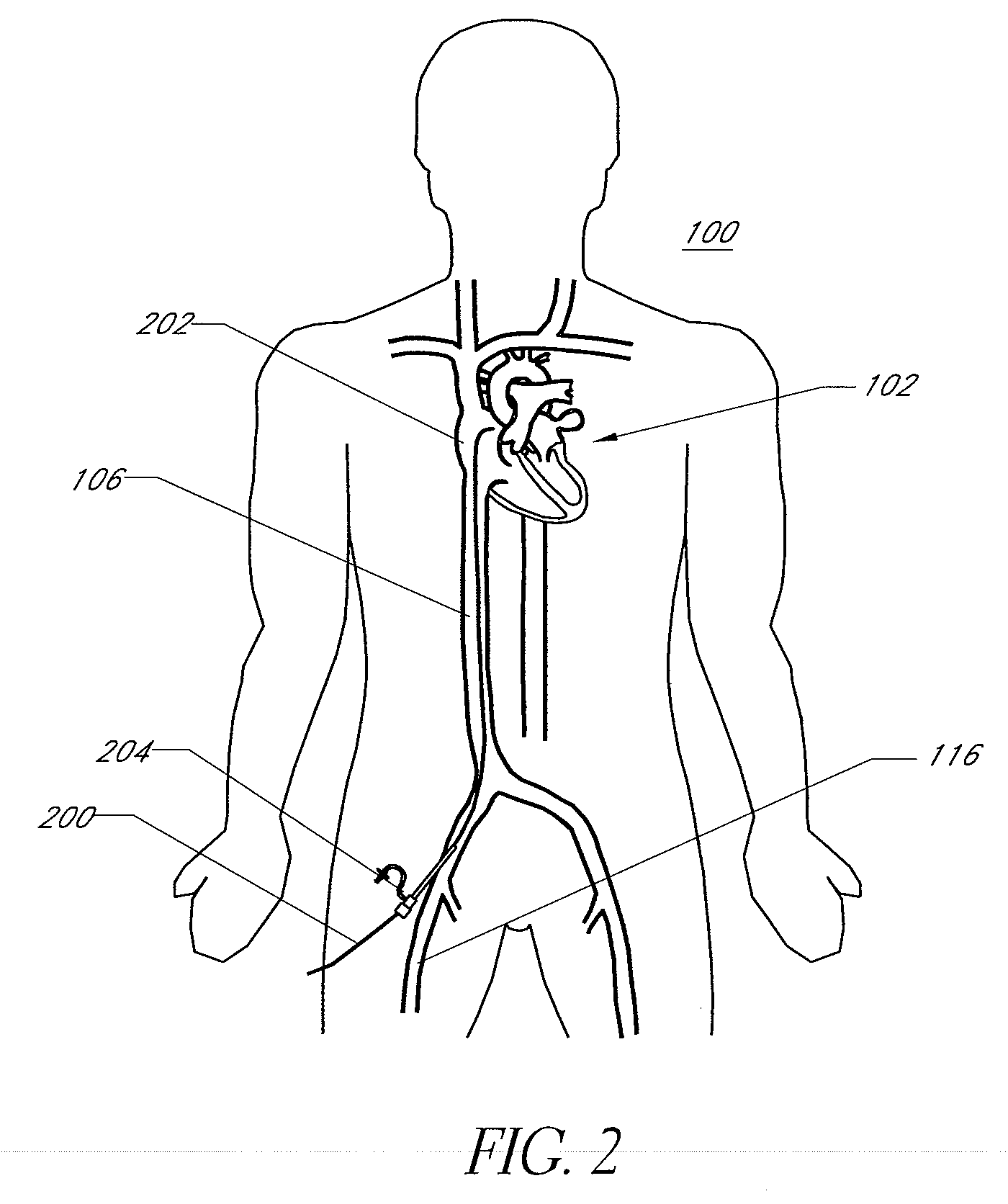
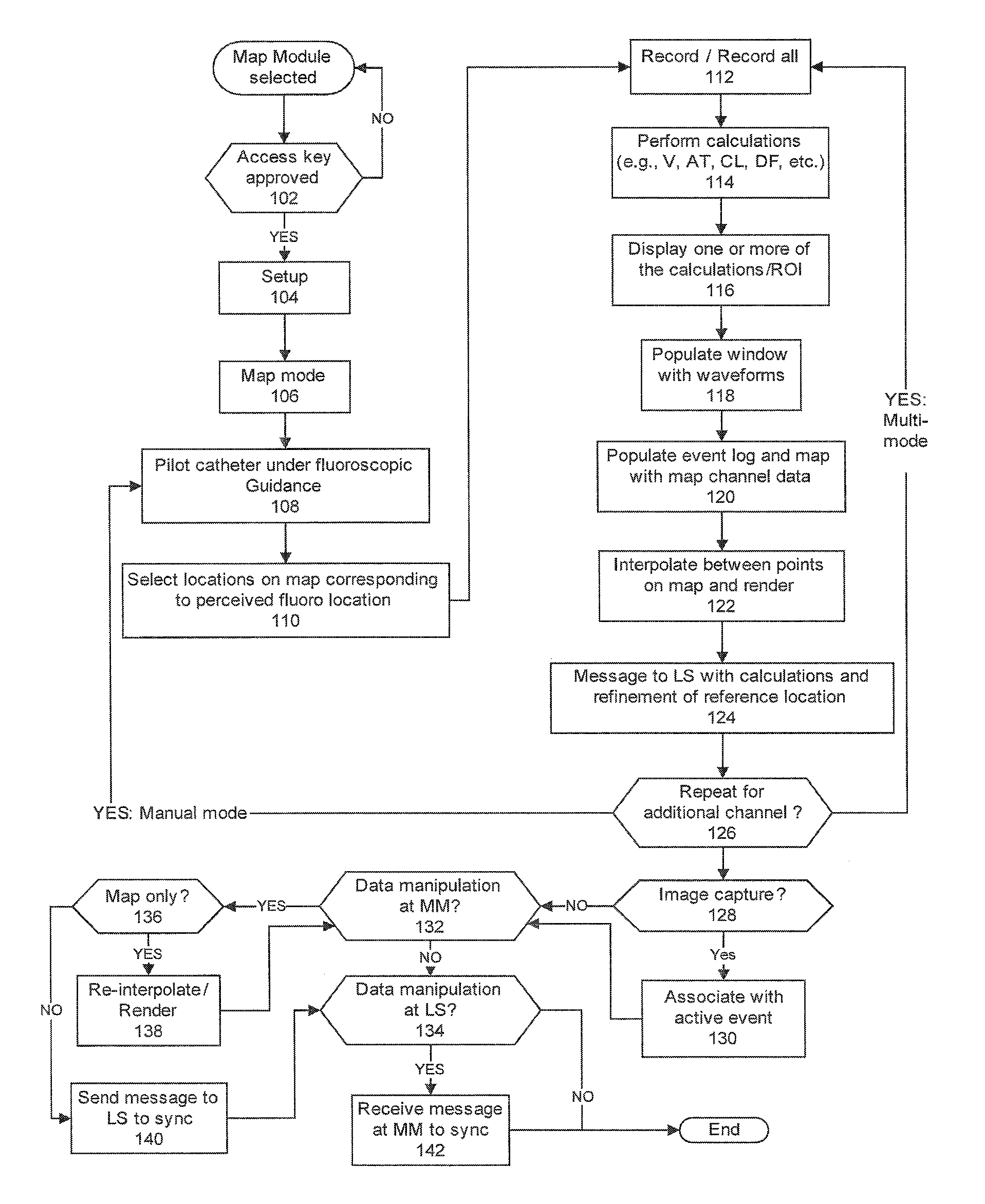
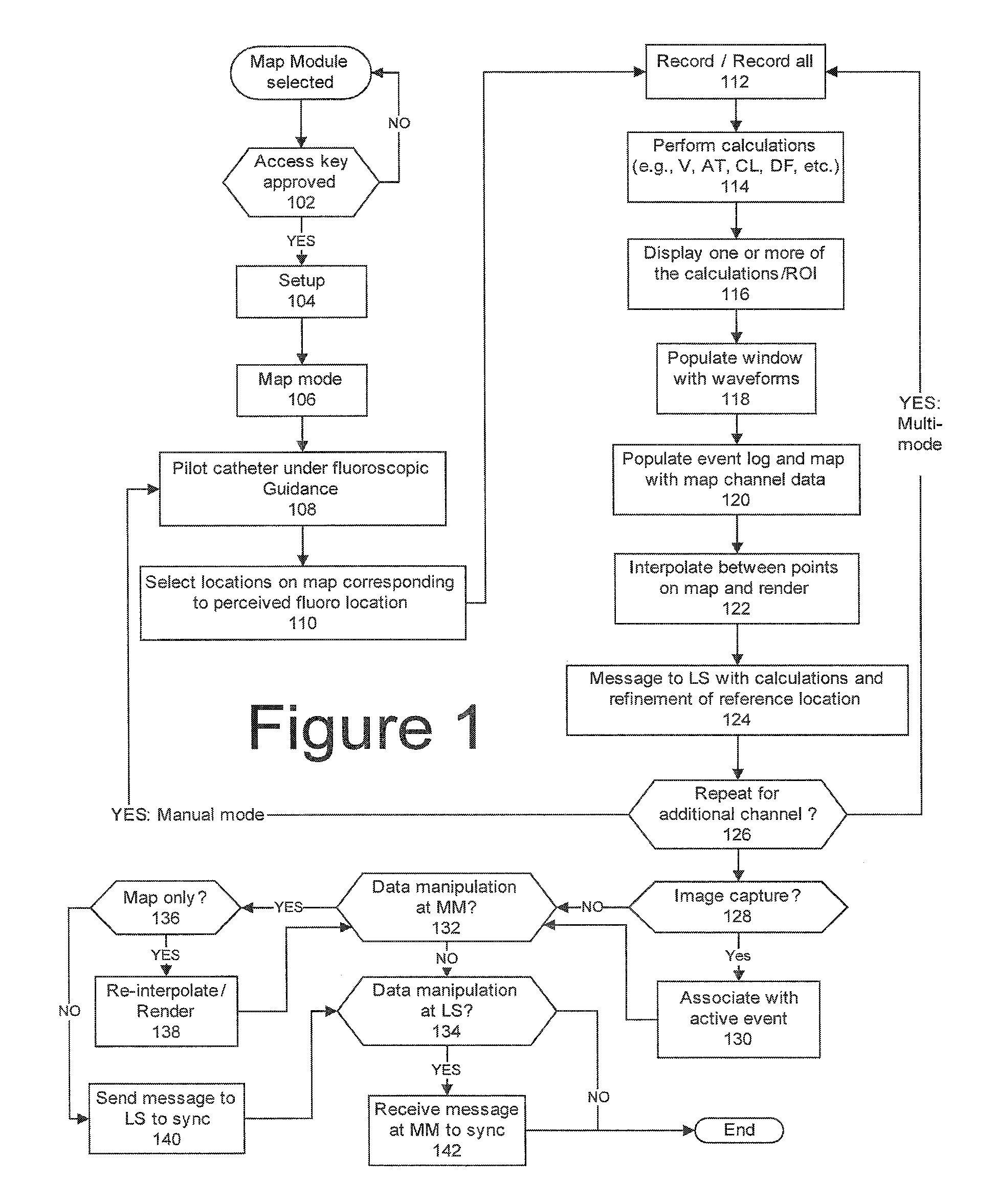
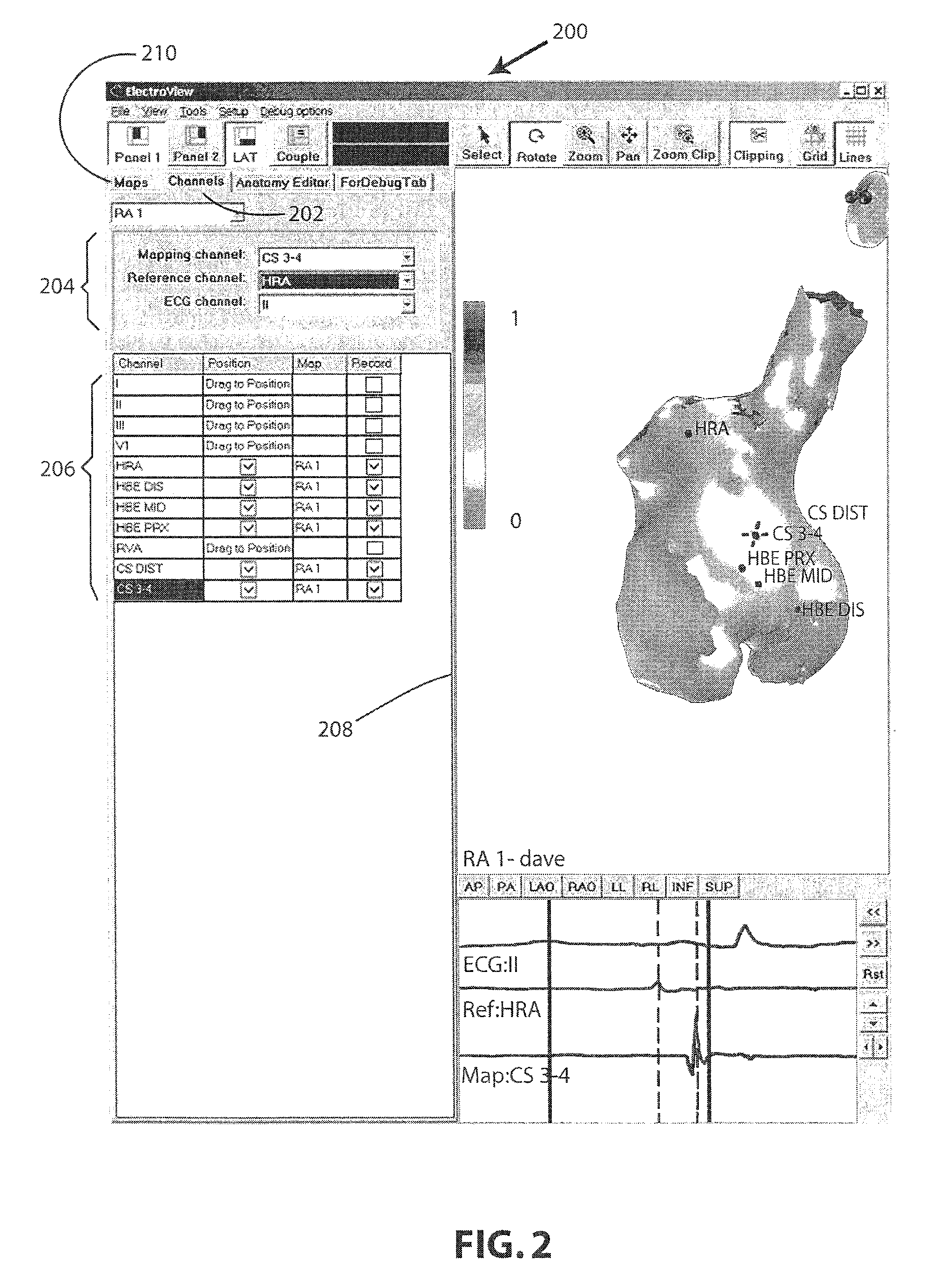
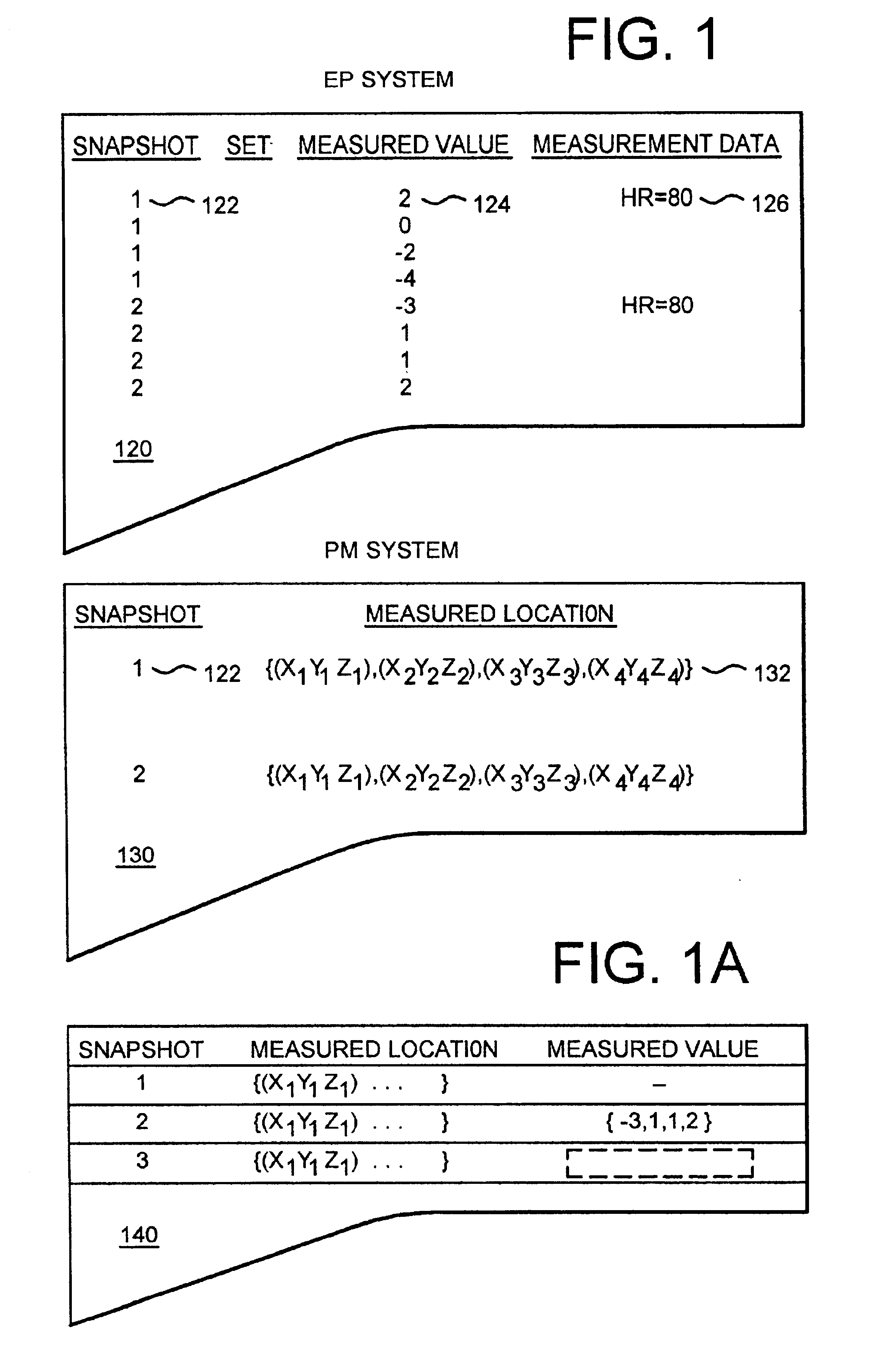
An electrophysiology (EP) system includes an interface for operator-interaction with the results of code executing therein. A template model can have channels positioned or repositioned thereupon by the user to define a set-up useful in rapid catheter positioning. Mapping operations can be performed without the requirement for precise catheter location determinations. A map module coordinates EP data associated with each selected channel and its associated position on the template model to provide this result, and can update the resulting map in the event that the channel or location is changed. Messaging and other dynamic features enable synchronized presentation of a myriad of EP data. Additional systems and methods are disclosed herein.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method of scaling navigation signals to account for impedance drift in tissue
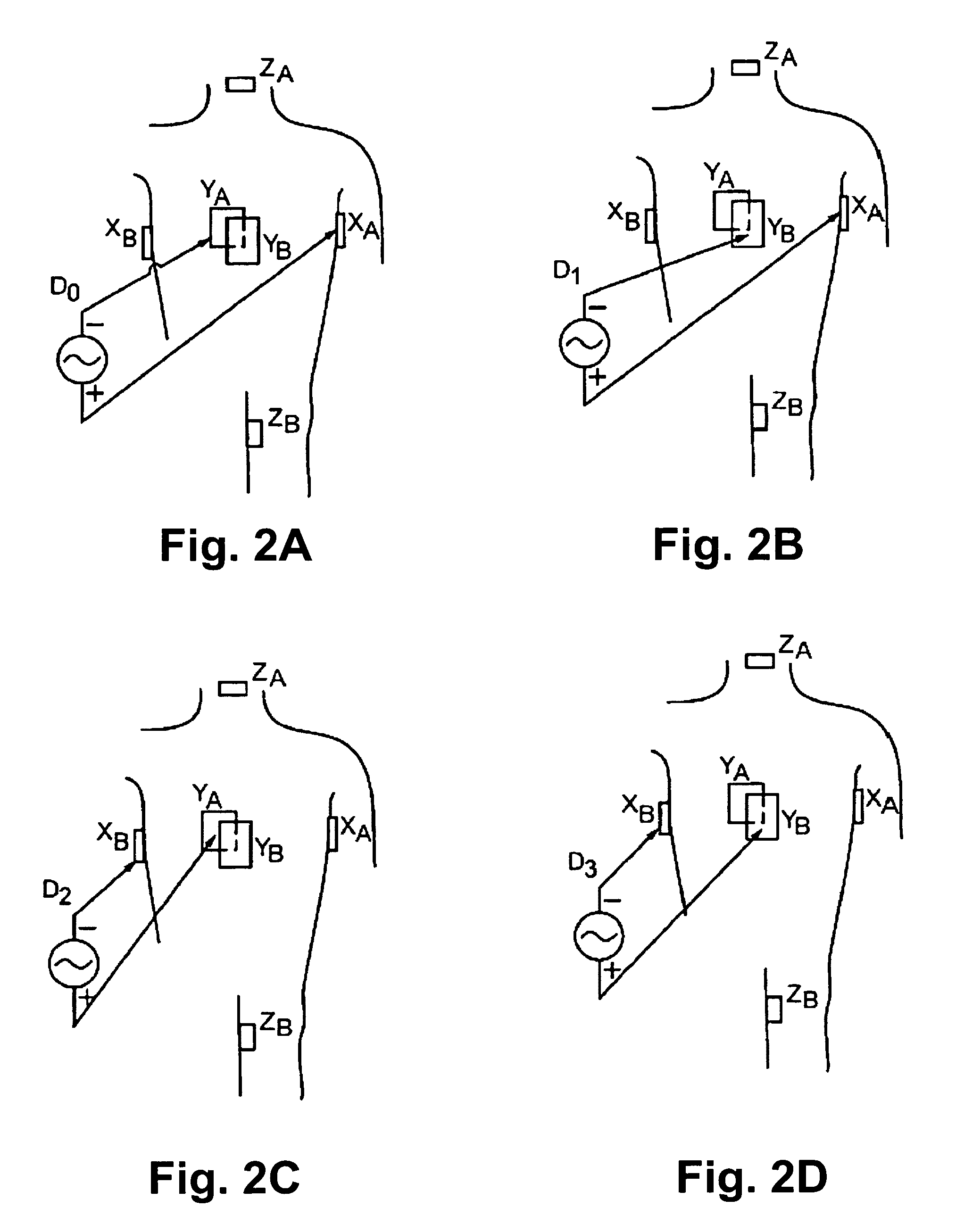
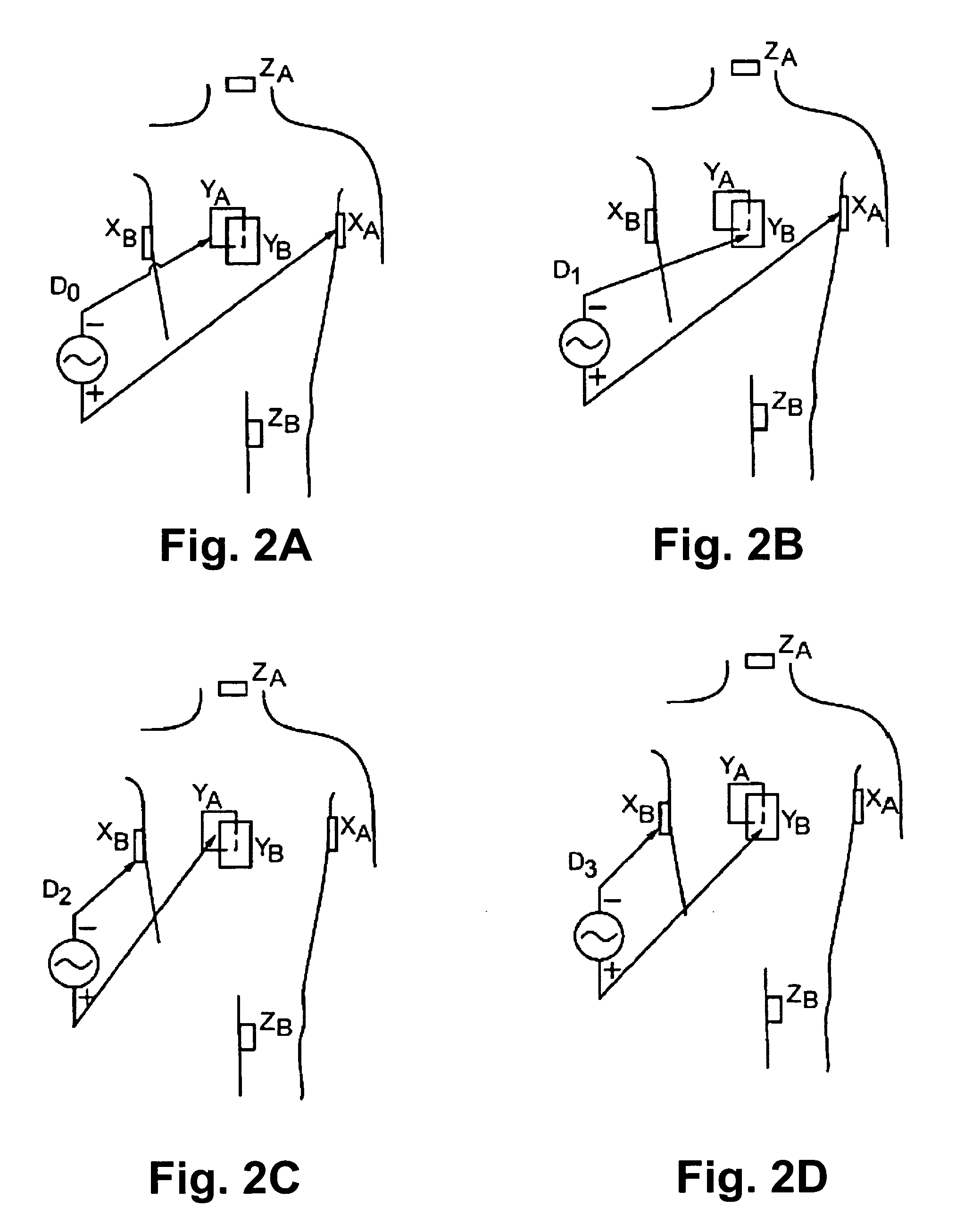
A method for scaling the impedance measured during the course of an electrophysiology study accounts for impedance drifts. By scaling the impedance there is greater assurance that previously recorded positional information can be used to accurately relocate an electrode at a prior visited position. The scale factor may be based upon a mean value across several sensing electrodes. Alternatively, the scale factor may be calculated specifically with respect to an orientation of a dipole pair of driven electrodes.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method of scaling navigation signals to account for impedance drift in tissue
ActiveUS20070060833A1Accurate positional readingDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrophysiology studyElectrophysiology
A method for scaling the impedance measured during the course of an electrophysiology study accounts for impedance drifts. By scaling the impedance there is greater assurance that previously recorded positional information can be used to accurately relocate an electrode at a prior visited position. The scale factor may be based upon a mean value across several sensing electrodes. Alternatively, the scale factor may be calculated specifically with respect to an orientation of a dipole pair of driven electrodes.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Method and apparatus for control of ablation energy and electrogram acquisition through multiple common electrodes in an electrophysiology catheter
Method and apparatus for control of ablation energy and electrogram acquisition through multiple common electrodes in an electrophysiology catheter. A device that routes ablation energy to and that routes mapping signals received from an electrophysiology catheter having a plurality of conductive filaments including circuitry that provides, for each conductive filament when ablation energy is being delivered, an electrical signal path that has a low impedance for ablation energy and a high impedance for mapping signals. The device also includes circuitry that provides, for each conductive filament, when mapping signals are being received, an electrical signal path that has a high impedance for ablation energy and low impedance for mapping signals. At least one switch is provided that selectively groups electrodes into sectors for delivery of ablation energy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Expandable trans-septal sheath
ActiveUS20080215008A1Lower potentialLess time-consumingCannulasInfusion syringesAccess routeRight atrium
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the vascular system and has utility in the performance of procedures in the left atrium. The access route is through the inferior vena cava to the right atrium, where a trans-septal puncture, followed by advancement of the catheter is completed. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement to the right atrium and through the atrial septum into the left atrium. The distal end of the sheath is subsequently expanded using a radial dilatation device. In an exemplary application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure such as electrophysiological mapping of the heart, radio-frequency ablation of left atrial tissue, placement of left atrial implants, mitral valve repair, or the like.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Head-mounted physiological signal monitoring system, devices and methods
ActiveUS9579060B1Superior signal collection siteReduce motion artifact noiseAcoustic sensorsInertial sensorsEngineeringElectrophysiology
Hat, helmet, and other headgear apparatus includes dry electrophysiological electrodes and, optionally, other physiological and / or environmental sensors to measure signals such as ECG from the head of a subject. Methods of use of such apparatus to provide fitness, health, or other measured or derived, estimated, or predicted metrics are also disclosed.
Owner:ORBITAL RES
Electrophysiology mapping and visualization system
ActiveUS20090054803A1Suture equipmentsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBody fluidElectrophysiology
Electrophysiology mapping and visualization systems are described herein where such devices may be used to visualize tissue regions as well as map the electrophysiological activity of the tissue. Such a system may include a deployment catheter and an attached hood deployable into an expanded configuration. In use, the imaging hood is placed against or adjacent to a region of tissue to be imaged in a body lumen that is normally filled with an opaque bodily fluid such as blood. A translucent or transparent fluid, such as saline, can be pumped into the imaging hood until the fluid displaces any blood, thereby leaving a clear region of tissue to be imaged via an imaging element in the deployment catheter. A position of the catheter and / or hood may be tracked and the hood may also be used to detect the electrophysiological activity of the visualized tissue for mapping.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
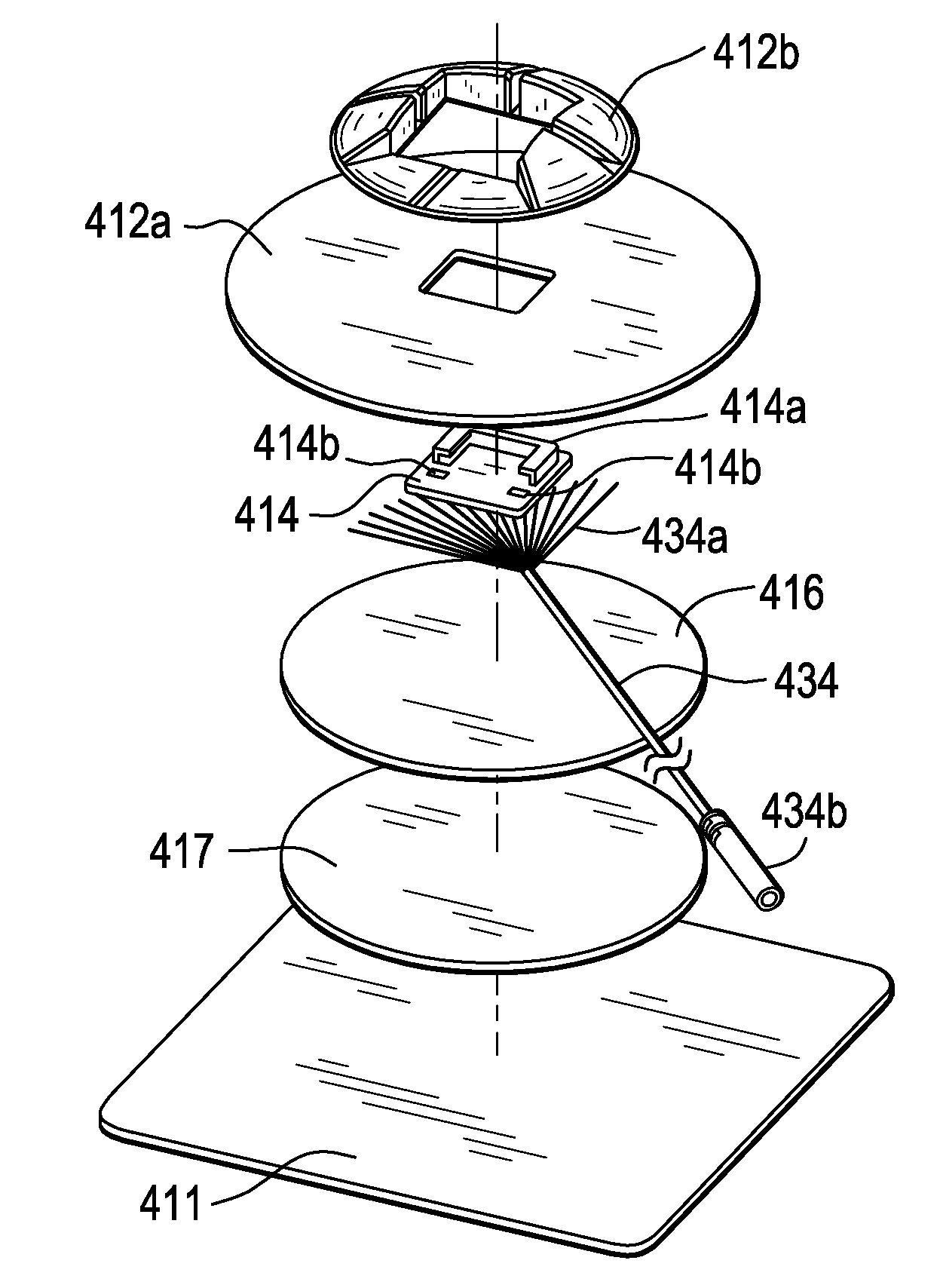
Disposable Patch and Reusable Sensor Assembly for Use in Medical Device Localization and Mapping Systems
ActiveUS20090318793A1Reduce mechanical strainDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic field sensorsAdhesiveElectrophysiology
An patch and sensor assembly for use in an EP mapping system has two portions: a reusable portion and a disposable portion. The reusable portion houses the biosensors used in magnetic based location and mapping systems and the electrical lead necessary to communicate between the biosensor and the mapping system. The reusable portion may also contain a portion of the electrode necessary to receive electrical signals from the body of the patient. The disposable portion of the patch and sensor assembly contains an adhesive covered flexible patch having at least a portion of the electrode used to receive electrical signals form the body of the patient and may contain the electrical lead necessary to communicate such an electrical signal to the mapping system. The disposable portion contains a receptacle adapted to receive and mechanically secure the reusable portion to the disposable portion of the assembly. Such a patch and sensor assembly is useful in hybrid magnetic and impedance based location and mapping systems such as those used in electrophysiology.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Expandable trans-septal sheath
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is configured for use in the vascular system and has utility in the performance of procedures in the left atrium. The access route is through the inferior vena cava to the right atrium, where a trans-septal puncture, followed by advancement of the catheter is completed. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration during advancement to the right atrium and through the atrial septum into the left atrium. The distal end of the sheath is subsequently expanded using a radial dilatation device. In an exemplary application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure such as electrophysiological mapping of the heart, radio-frequency ablation of left atrial tissue, placement of left atrial implants, mitral valve repair, or the like.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Helically shaped electrophysiology catheter
InactiveUS6972016B2Reduce configurationEasy to deployElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingElectrophysiologyBiomedical engineering
An electrophysiology (EP) device suitable for ablating tissue within a patient's body lumen. The EP device of the invention generally comprises an elongated shaft having a distal shaft section with a helical shape and at least one electrode on an exterior portion thereof. One aspect of the invention comprises a method of performing a medical procedure, such as treating a patient for atrial arrhythmia, by forming a lesion using an EP device embodying features of the invention.
Owner:SICHUAN JINJIANG ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Software controlled electrophysiology data management
Methods for conducting an electrophysiology procedure using a programmed machine are described, including methods for managing discrete data capture requests received throughout the course of an electrophysiology procedure and for discretizing the display of independent data capture events that occur during the course of the electrophysiology procedure. These methods enable an operator to review location maps of sites visited during the course of a procedure and to review data from discrete moments in the procedure and to play back data over a sequence of times throughout the procedure, one moment at a time. The invention further includes software constructs that enable data management.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Systems and methods for three-dimensional mapping of electrical activity
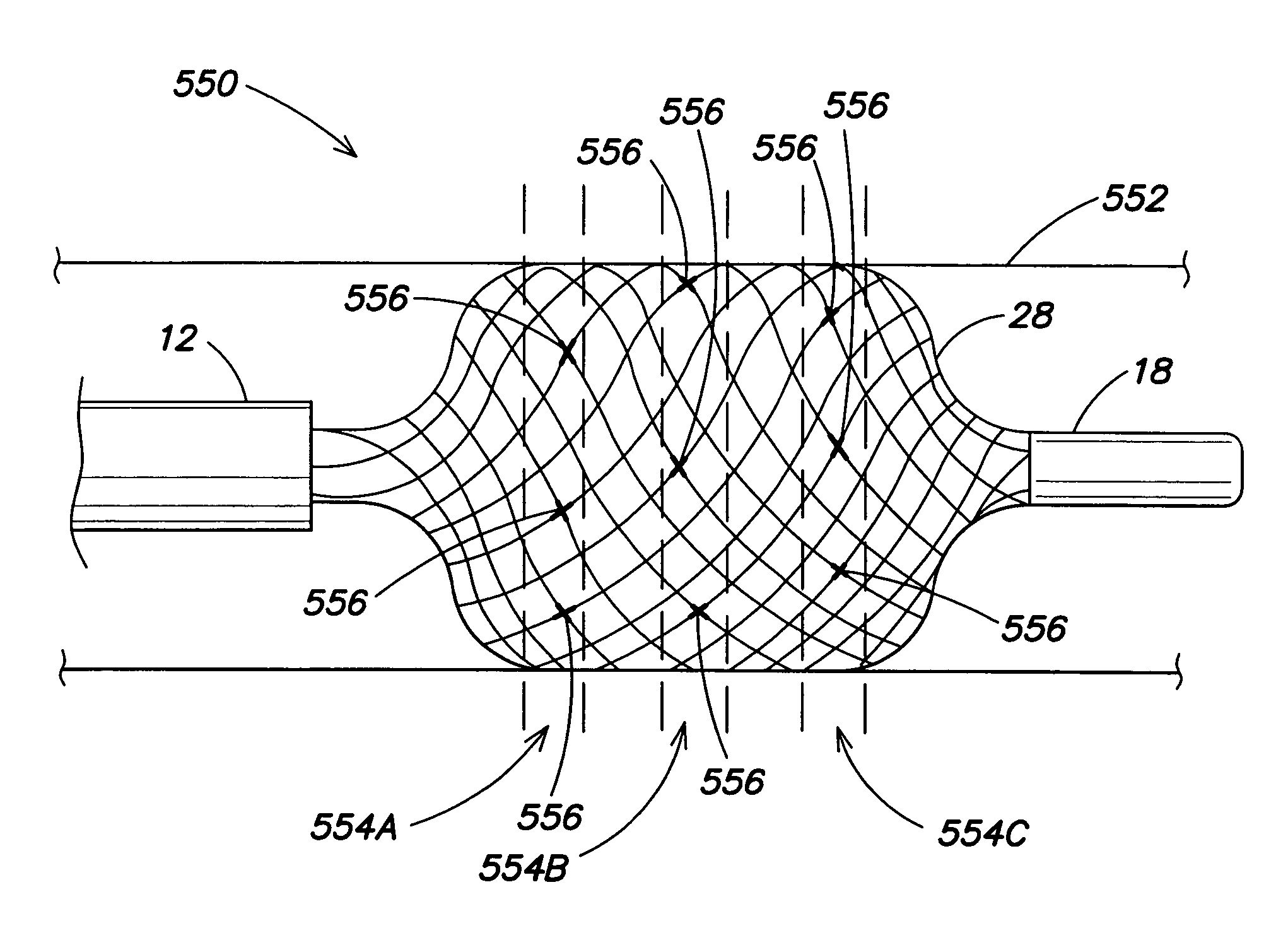
An electrophysiology catheter and method of use for mapping and ablation procedures. The catheter includes a braided conductive member at its distal end that can be radially expanded.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
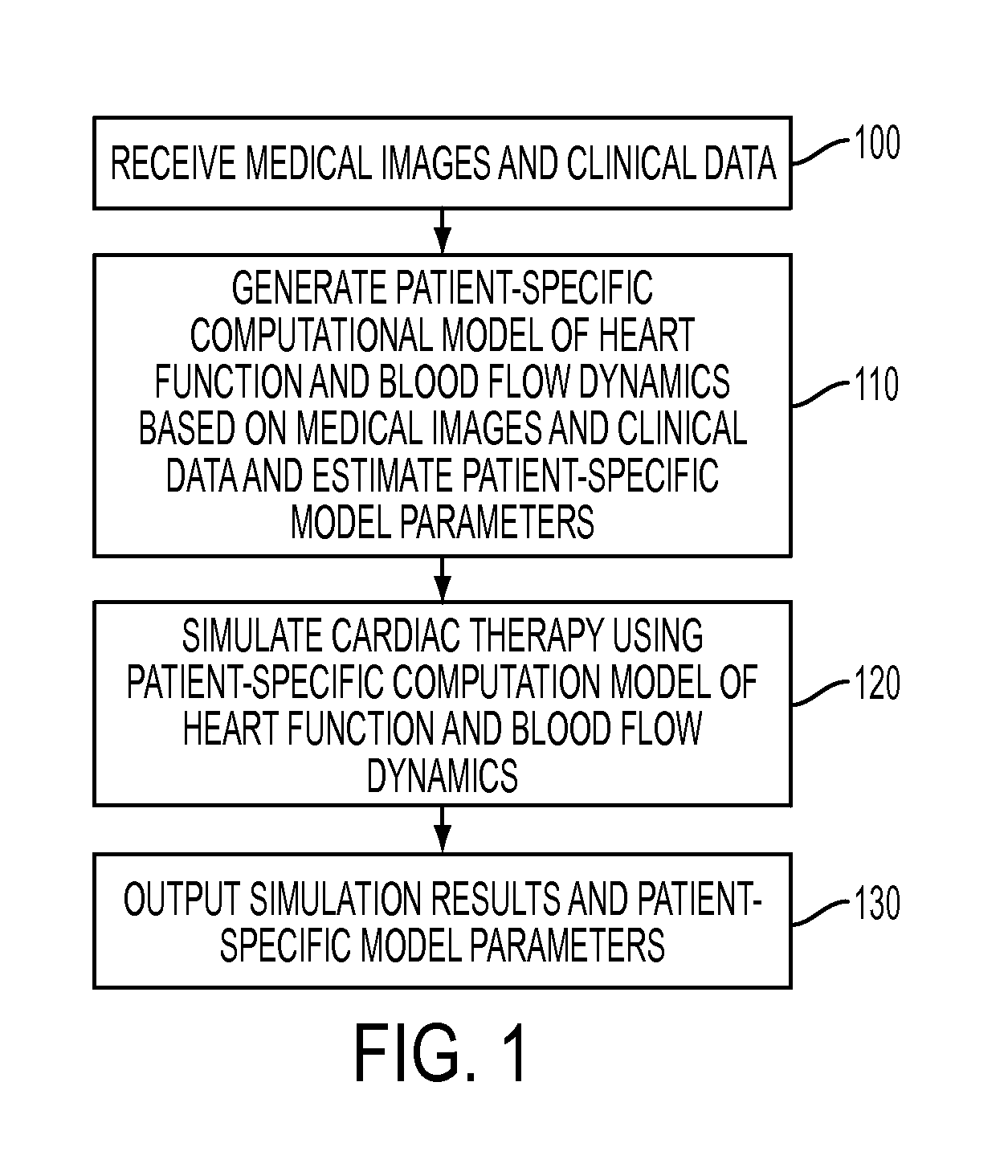
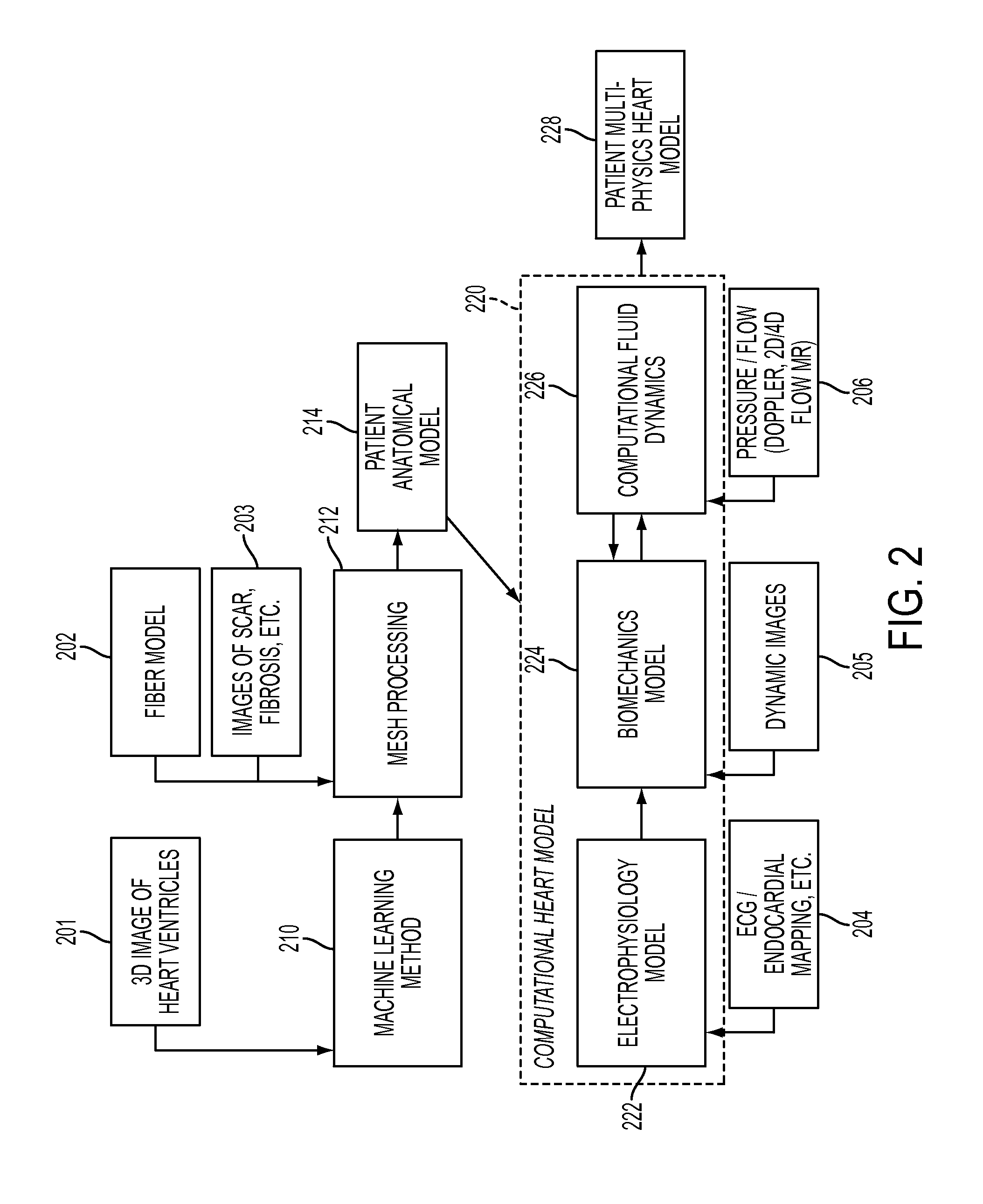
Method and System for Advanced Measurements Computation and Therapy Planning from Medical Data and Images Using a Multi-Physics Fluid-Solid Heart Model
ActiveUS20130197884A1Exact reproductionMedical simulationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComputational modelPatient data
Method and system for computation of advanced heart measurements from medical images and data; and therapy planning using a patient-specific multi-physics fluid-solid heart model is disclosed. A patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles is generated from medical image patient data. A patient-specific computational heart model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical model of the left and right ventricles and patient-specific clinical data. The computational model includes biomechanics, electrophysiology and hemodynamics. To generate the patient-specific computational heart model, initial patient-specific parameters of an electrophysiology model, initial patient-specific parameters of a biomechanics model, and initial patient-specific computational fluid dynamics (CFD) boundary conditions are marginally estimated. A coupled fluid-structure interaction (FSI) simulation is performed using the initial patient-specific parameters, and the initial patient-specific parameters are refined based on the coupled FSI simulation. The estimated model parameters then constitute new advanced measurements that can be used for decision making.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
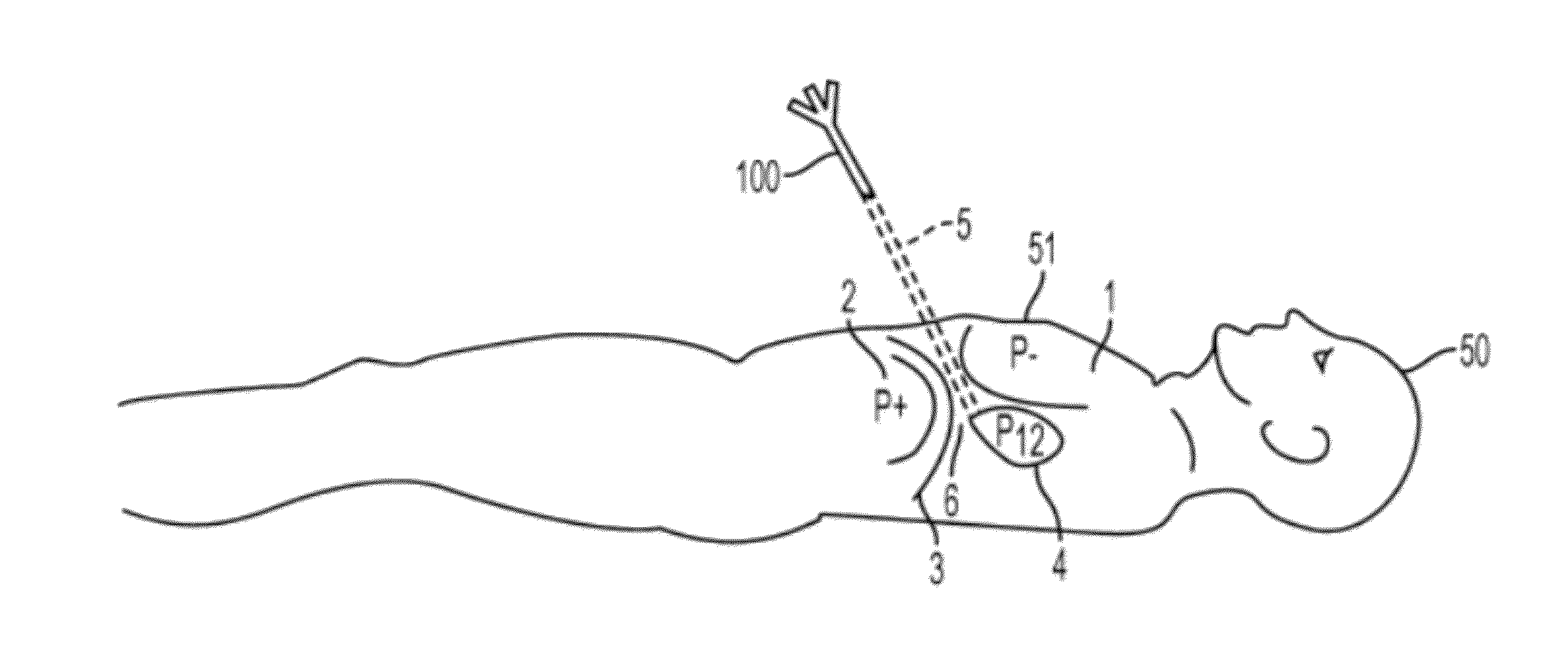
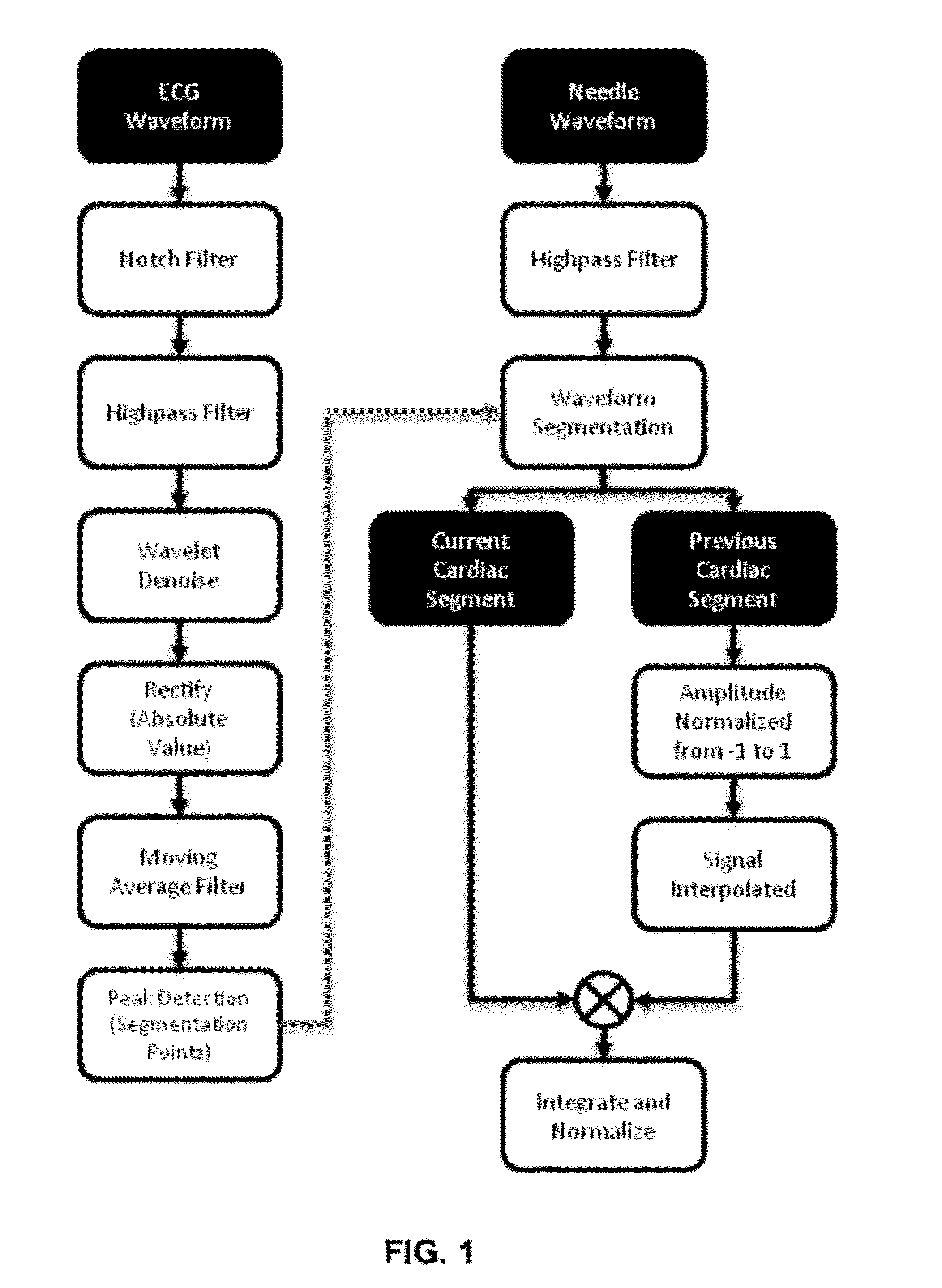
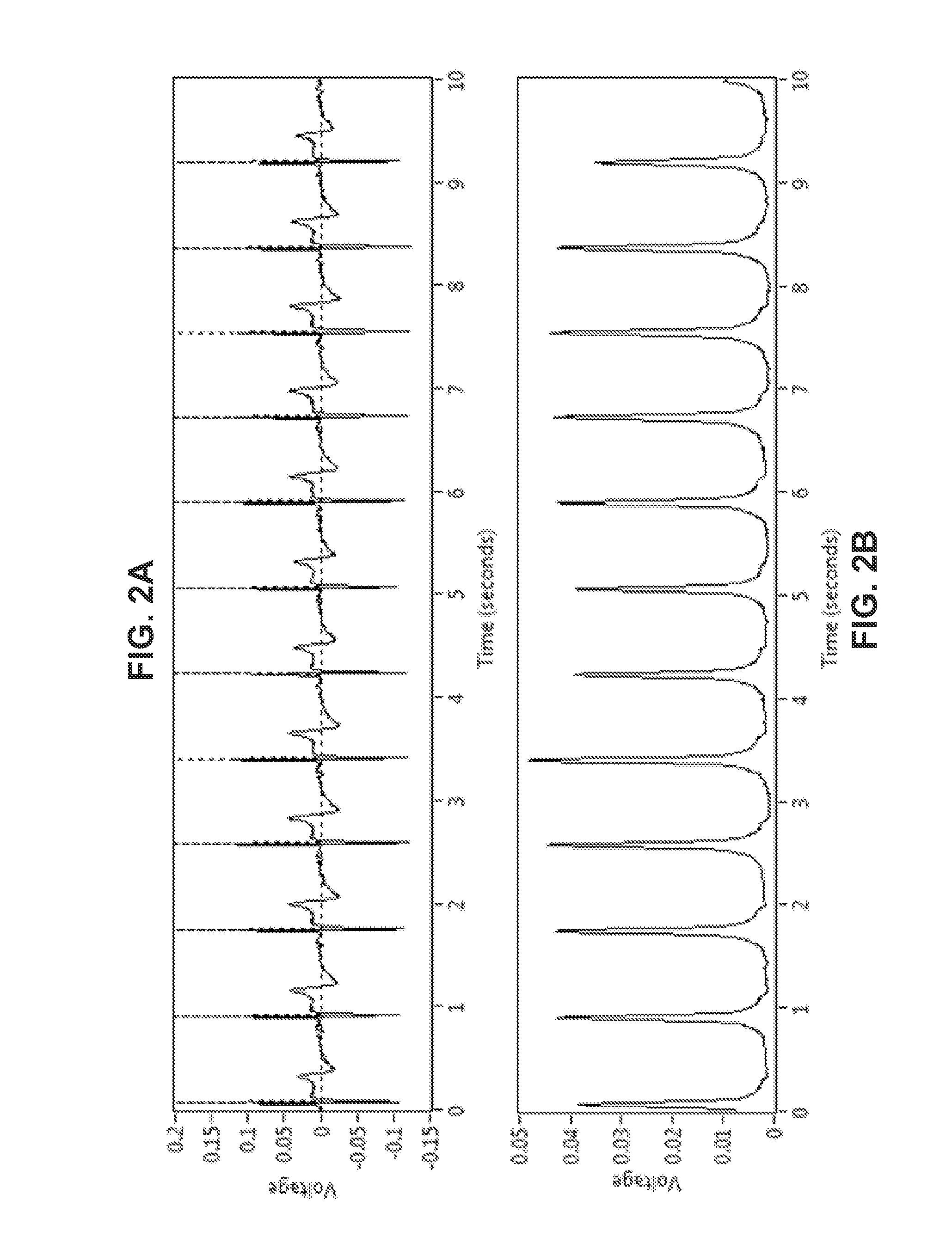
Systems and methods for determining location of an access needle in a subject
ActiveUS20120283582A1Reduce clinical riskImprove efficacyElectrocardiographyCatheterMedicineElectrophysiology
Systems and methods for epicardial electrophysiology and other procedures are provided in which the location of an access needle may be inferred according to the detection of different pressure frequencies in separate organs, or different locations, in the body of a subject. Methods may include inserting a needle including a first sensor into a body of a subject, and receiving pressure frequency information from the first sensor. A second sensor may be used to provide cardiac waveform information of the subject. A current location of the needle may be distinguished from another location based on an algorithm including the pressure frequency information and the cardiac waveform information.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Electrophysiology Electrodes and Apparatus Including the Same
InactiveUS20090093810A1High densityElectrotherapySurgical instruments for heatingElectrophysiologyBiomedical engineering
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com