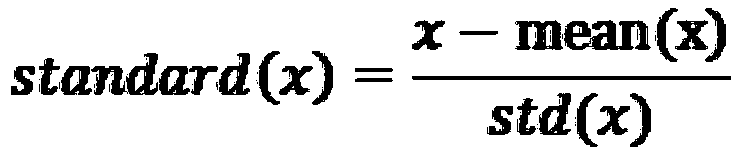Patents
Literature
58 results about "Normal heart" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
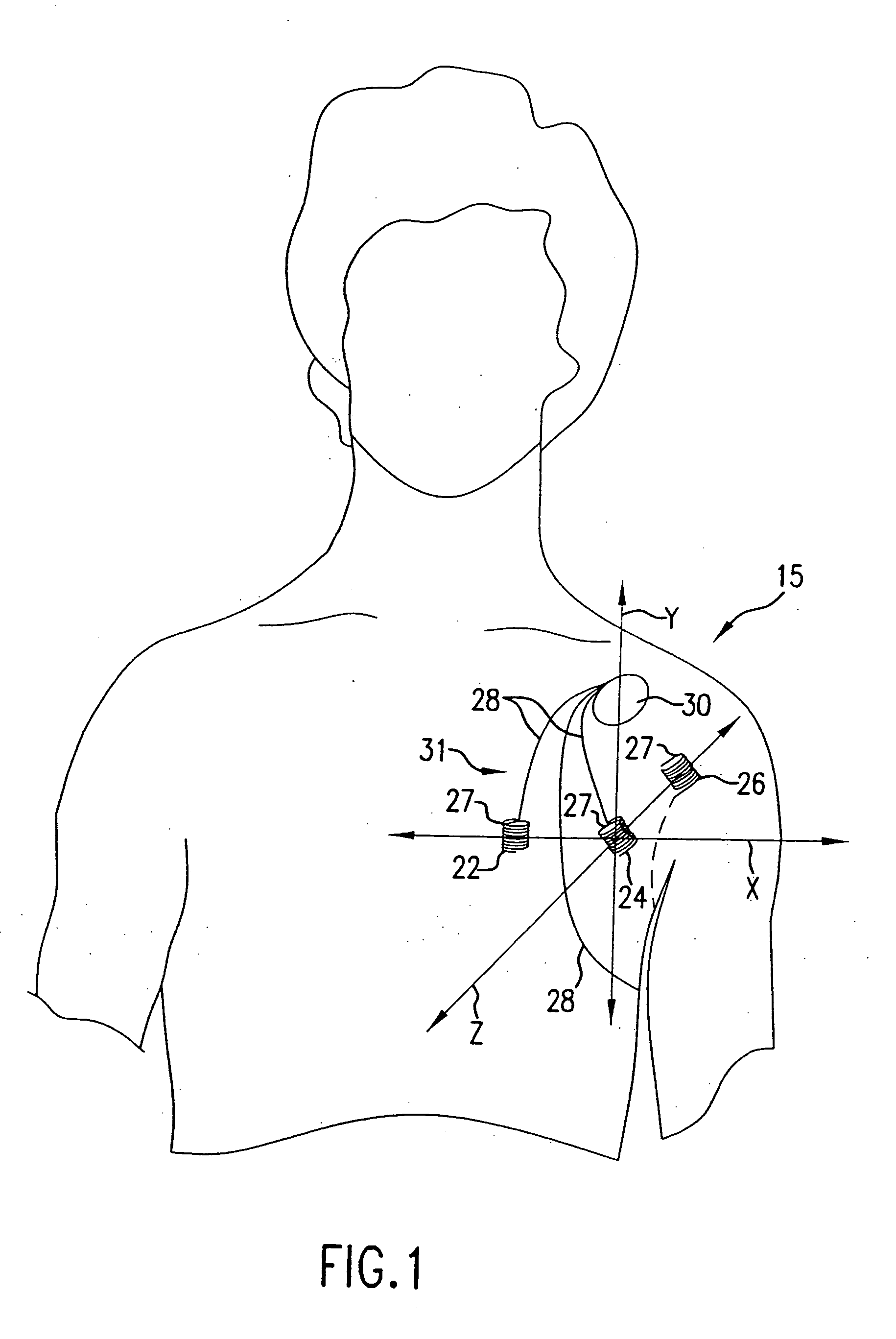
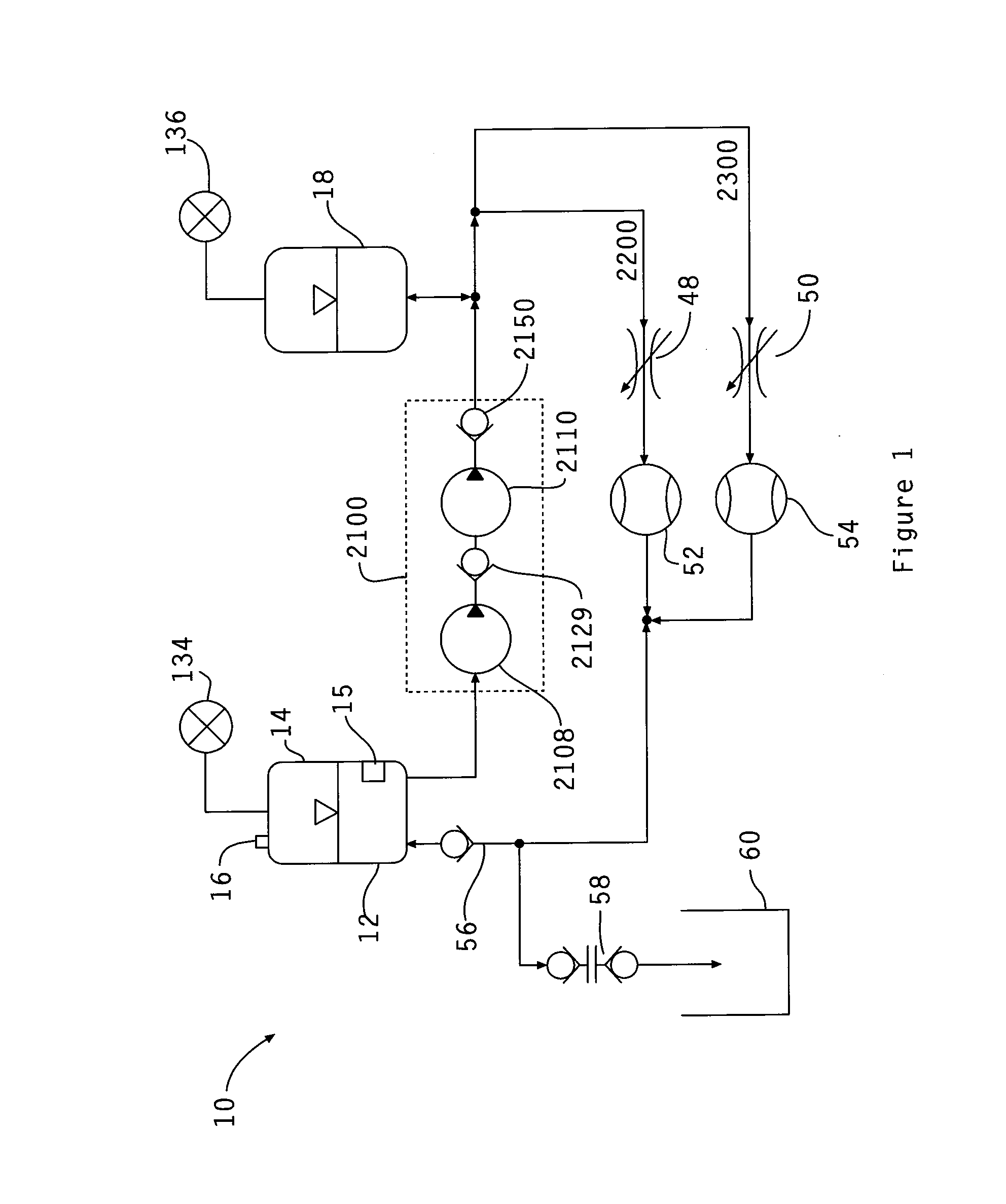
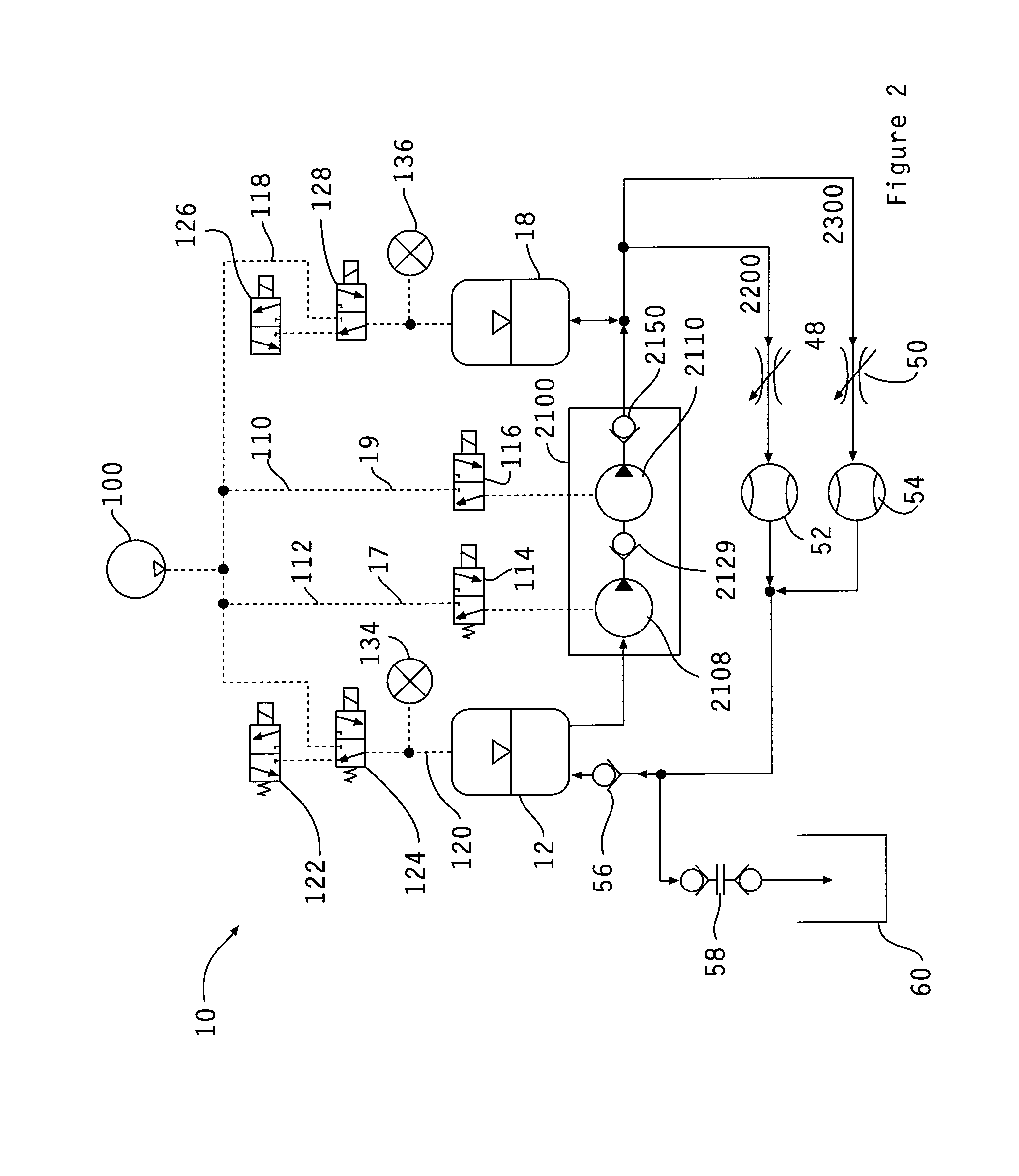
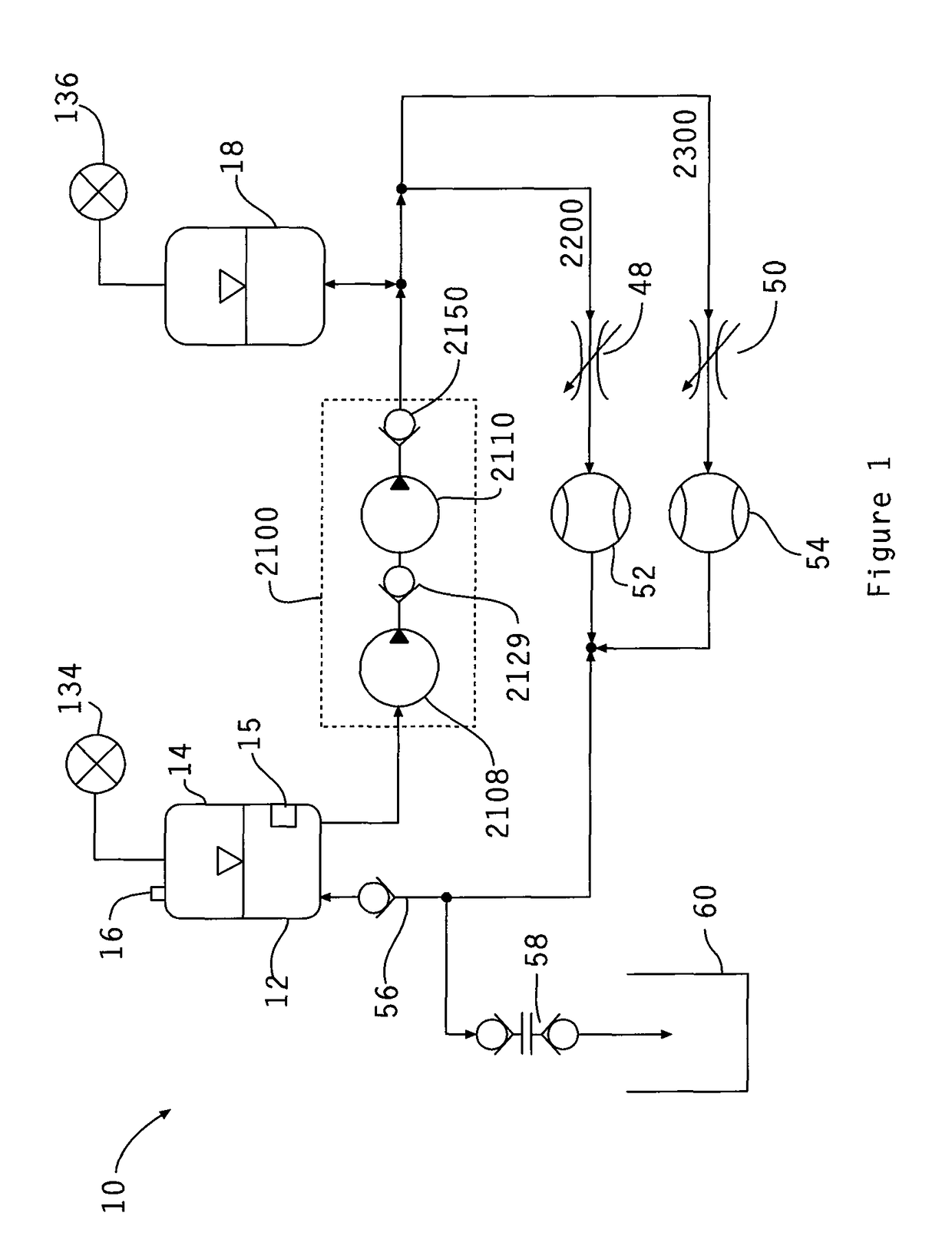
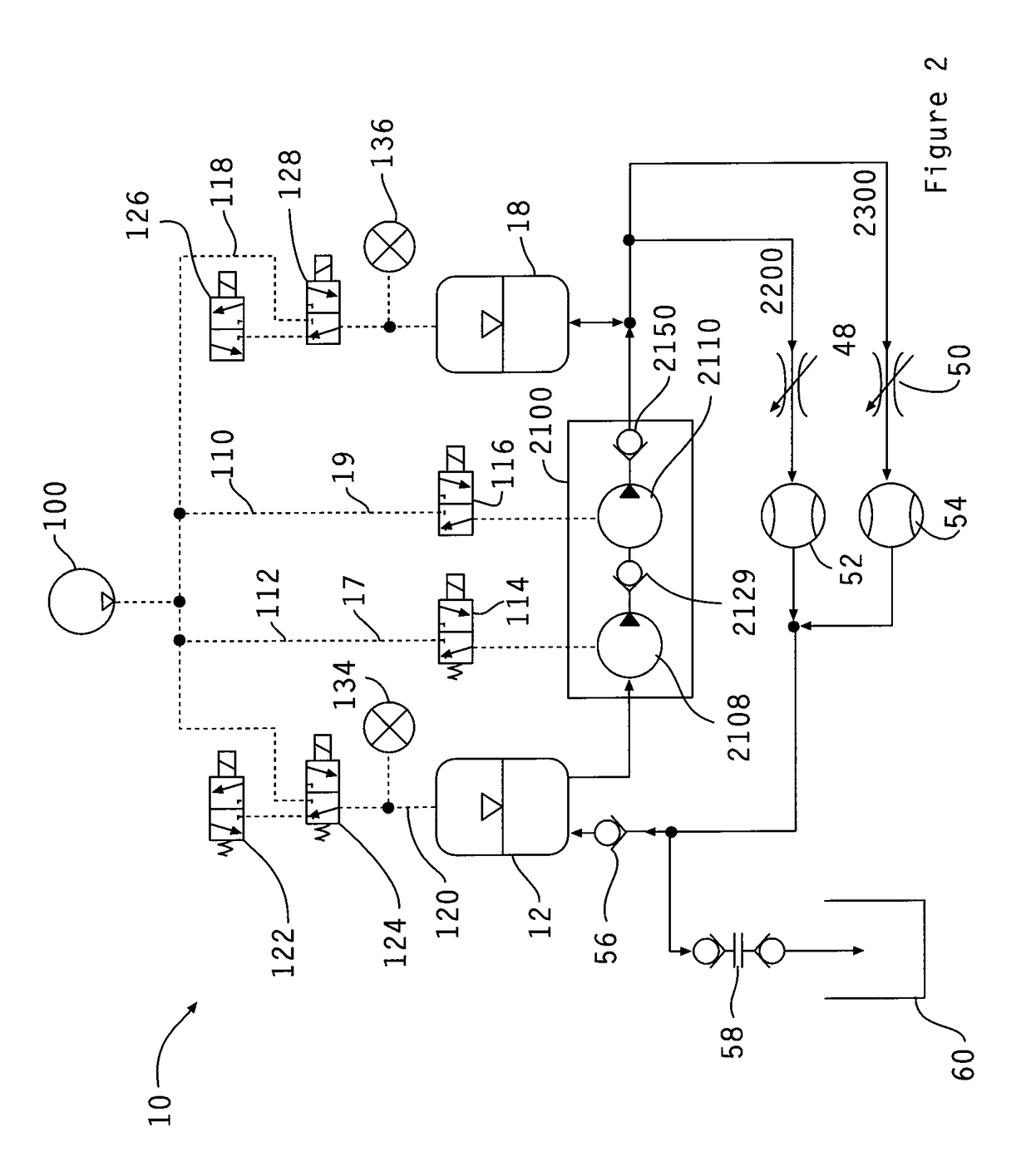
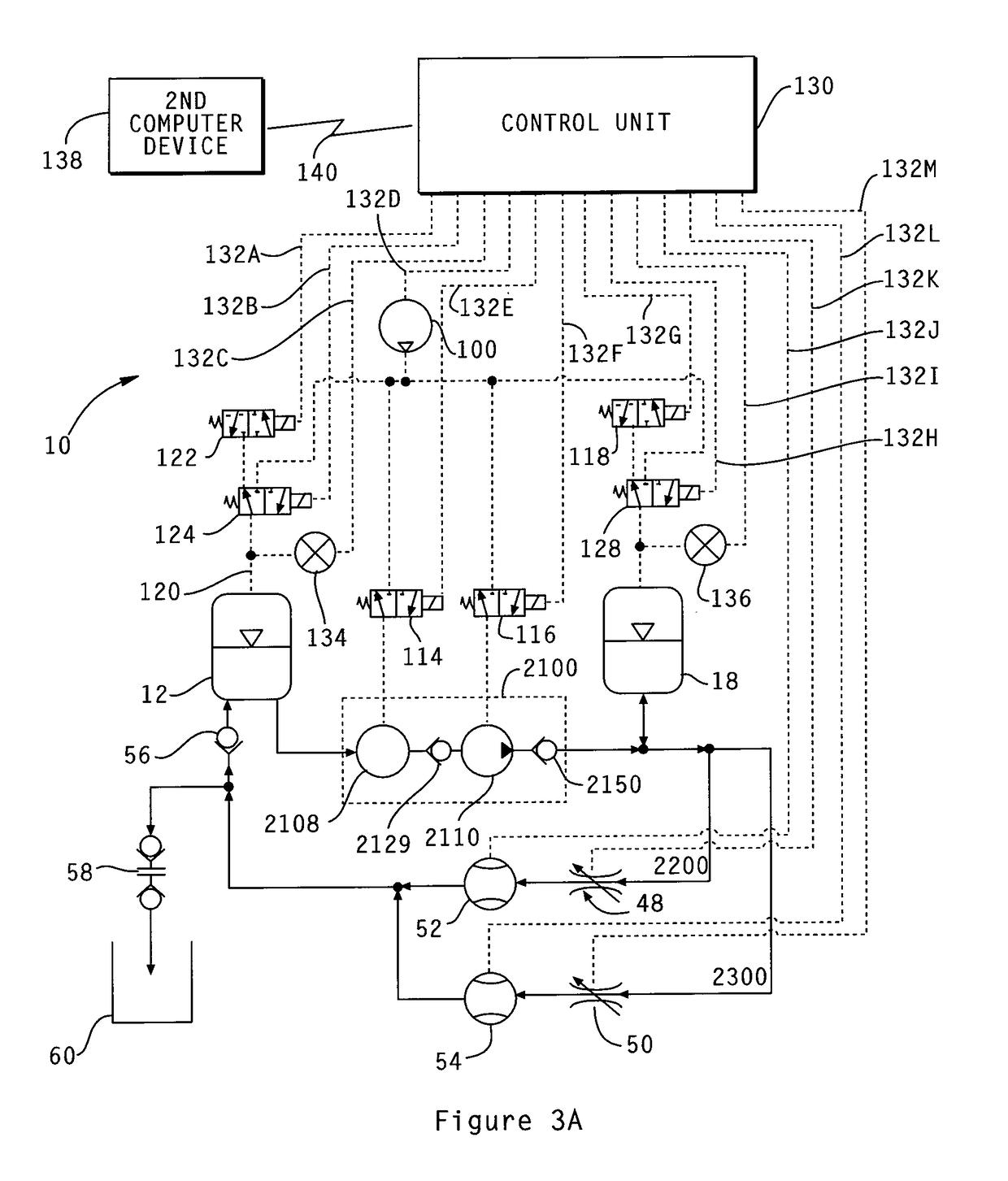
Determining the volume of a normal heart and its pathological and treated variants by using dimension sensors
InactiveUS20040106871A1Improve accuracyReduce in quantityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterVentricular volumeCardiac surface
A method and system measure the instantaneous volume of blood contained within a chamber of a heart, irrespective of its shape, whereby stroke volume and cardiac output volume can be continuously monitored and feedback to a non-blood contacting cardiac assist device. In a preferred form the device uses the distances between the sensors which are implanted in a biomaterial that integrates with a heart surface to determine changes in heart volume. Sonomicrometry crystal measurements are disclosed as a preferred mode of obtaining distance readings. A computer readable medium carries instructions to convert data from dimension sensors into sensor positions within a predetermined coordinate system. Ventricular volume is based on the sensor positions.
Owner:HEART ASSIST TECH PTY LTD
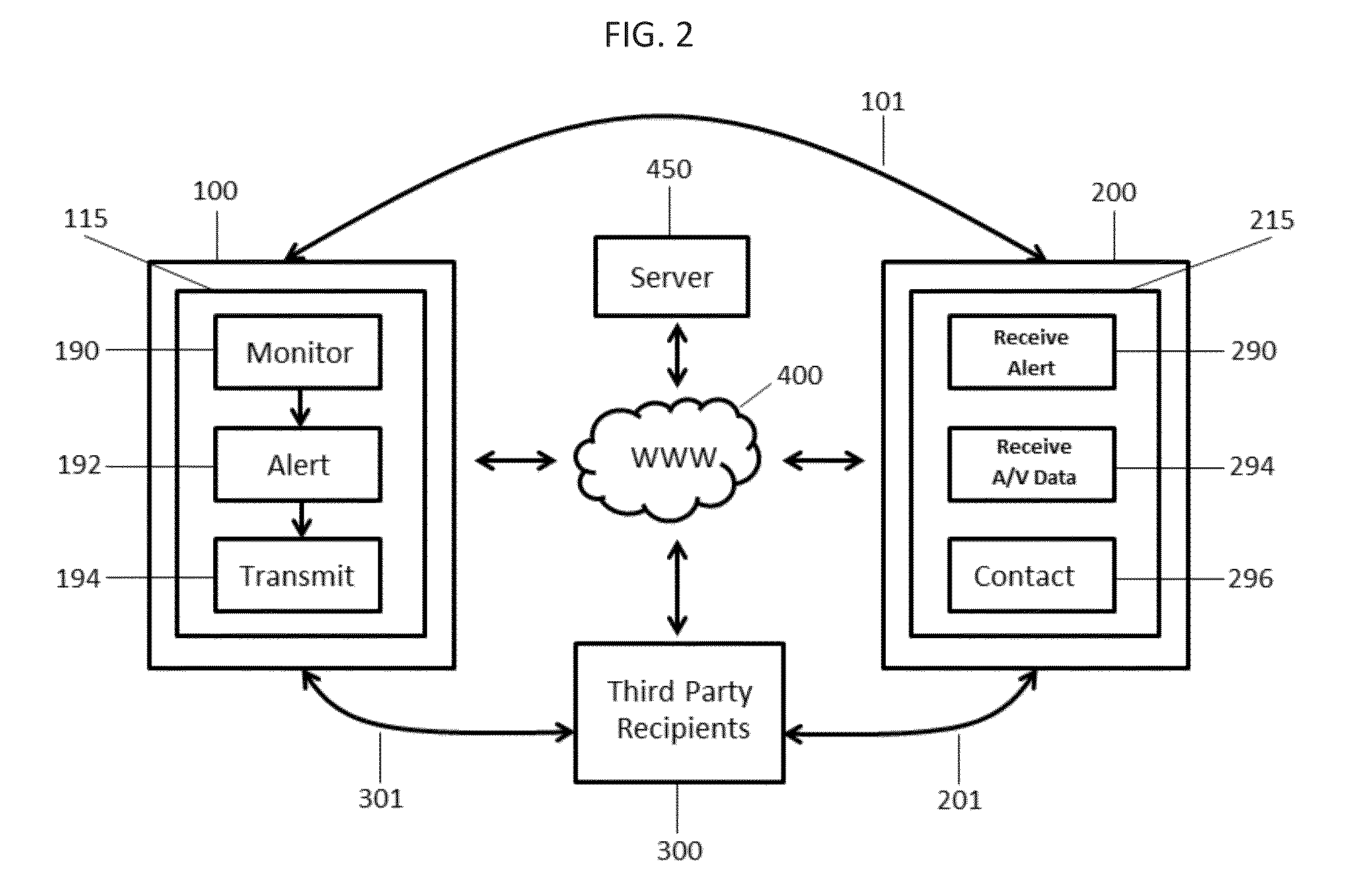
Cardiac arrest monitor and alarm system
InactiveUS20050065445A1Reduce materialImprove survivalElectrocardiographySensorsNormal heartTelecommunications link
A cardiac arrest monitor and alarm system including an implantable medical device having at least three electrodes, preferably but not necessarily subcutaneous, positioned with respect to a heart organ and forming an orthogonal lead configuration to continuously monitor an electrocardiographic signal of the heart organ. A microdevice, preferably but not necessarily operatively connected to the medical device, detects a deviation from a normal heart electrical activity and emits a signal to an external receiver. Upon verification of the signal from the microdevice, the external receiver activates a programmed annunciator circuit to alert bystanders to deploy an AED and / or activate a communication link automatically transmitting an alarm and the electrocardiographic signal to a remote transceiver.
Owner:AJ MEDICAL DEVICES
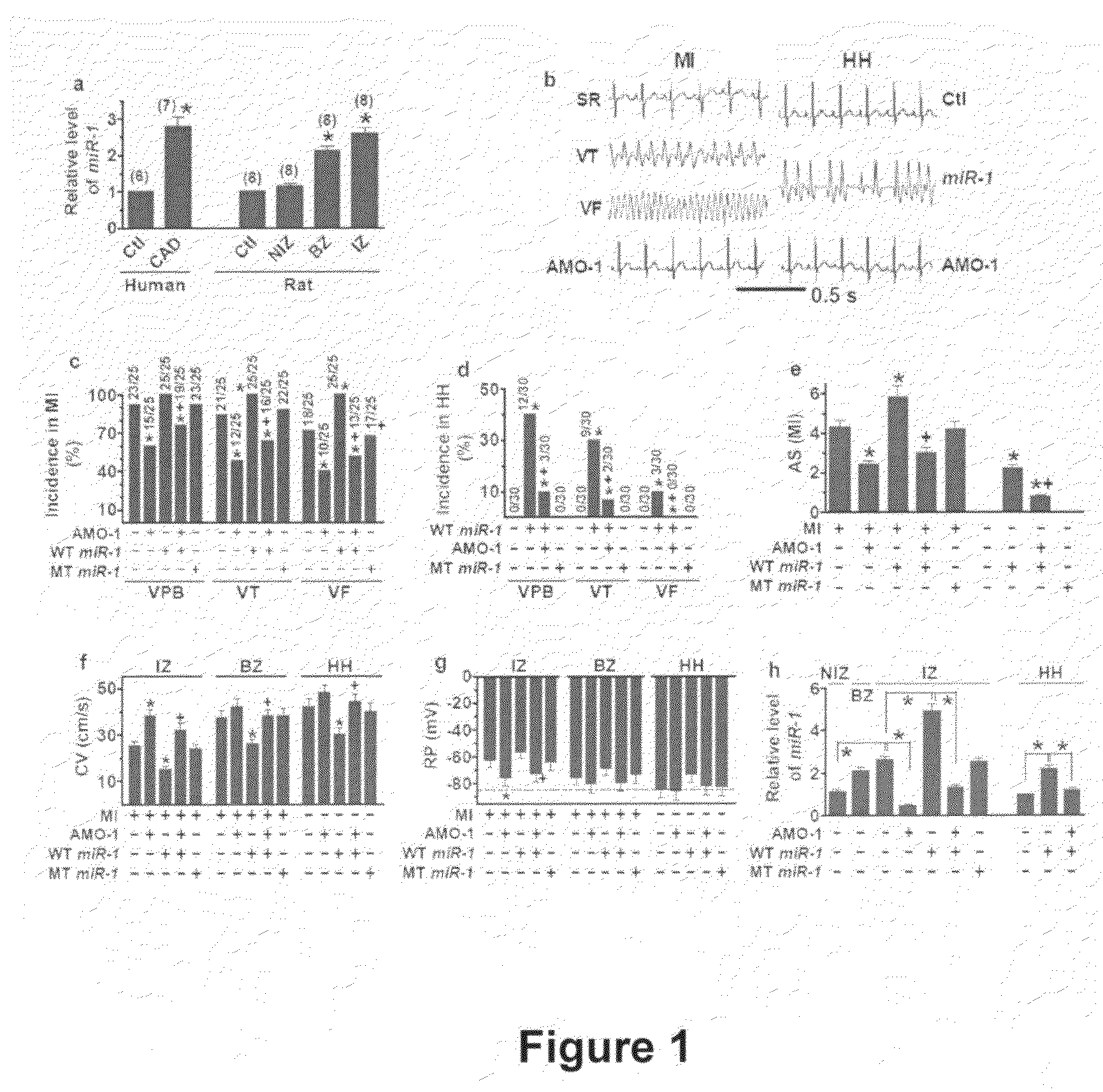
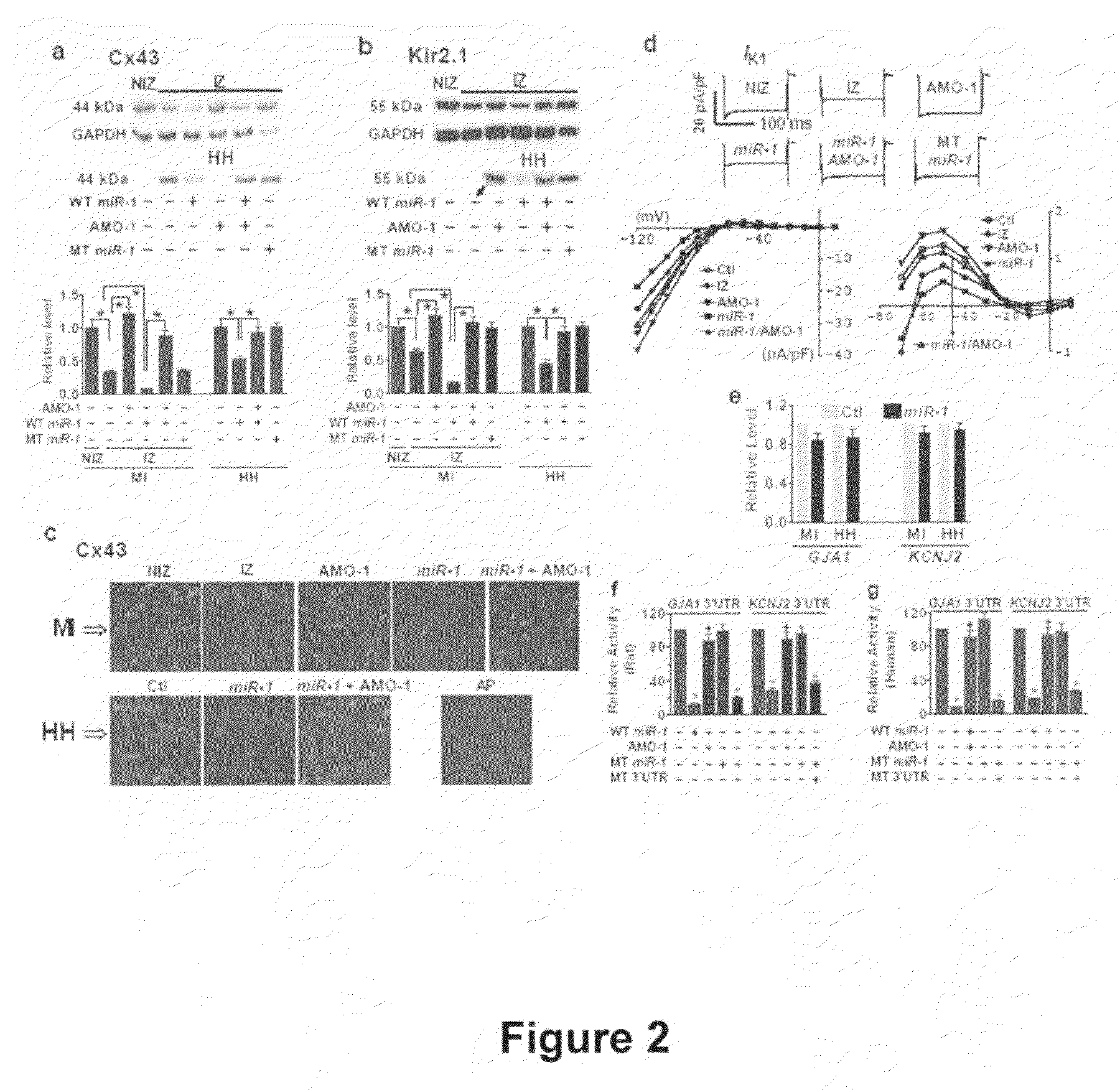
Use of the microRNA miR-1 for the treatment, prevention, and diagnosis of cardiac conditions
InactiveUS20090005336A1High expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseCoronary artery disease
Among >300 miRNAs known to date, miR-1 is considered muscle-specific. Here we show that that miR-1 overexpressed in individuals with coronary artery disease, and when overexpressed, it exacerbated arrhythmogenesis in both infarcted and normal hearts of rats whereas elimination of miR-1 by its antisense inhibitor relieved it. MiR-1 rendered slowed conduction and depolarized membrane by post-transcriptionally repressing KCNJ2 and GJA1 genes, likely accounting for its arrhythmogenic potential. Thus, miR-1 may have important pathophysiological functions in heart, being a novel antiarrhythmic target useful in the treatment and prevention of various cardiac pathologies.
Owner:WANG ZHIGUO
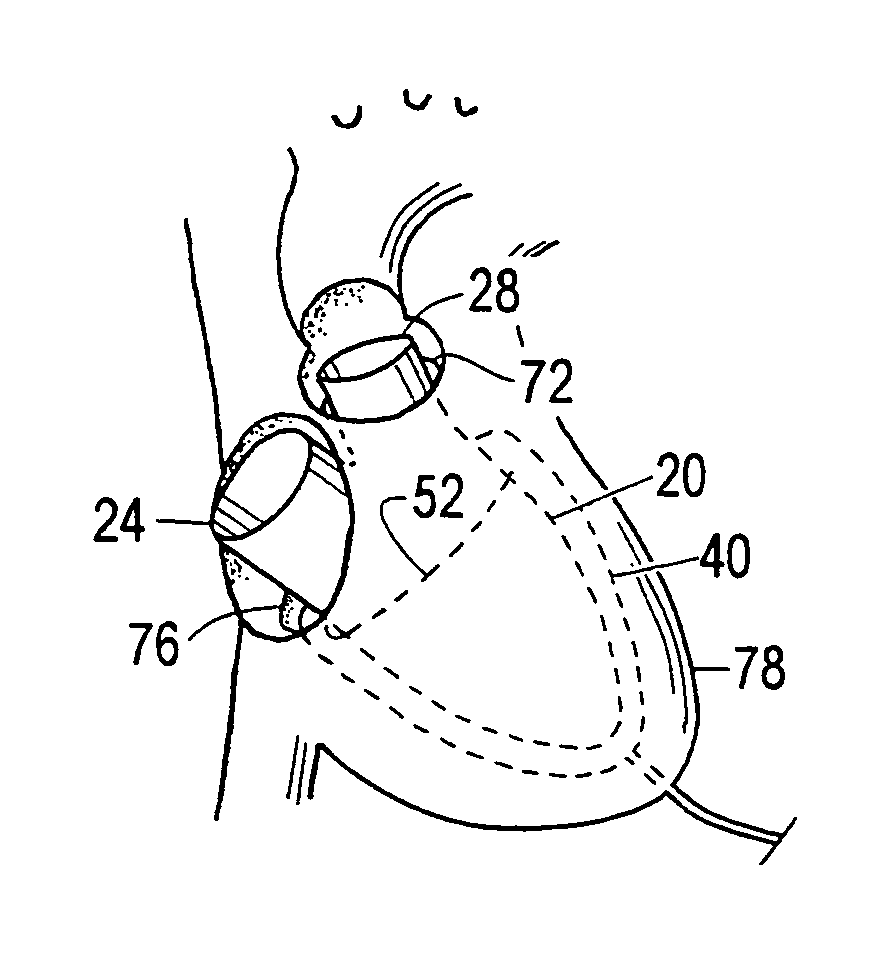
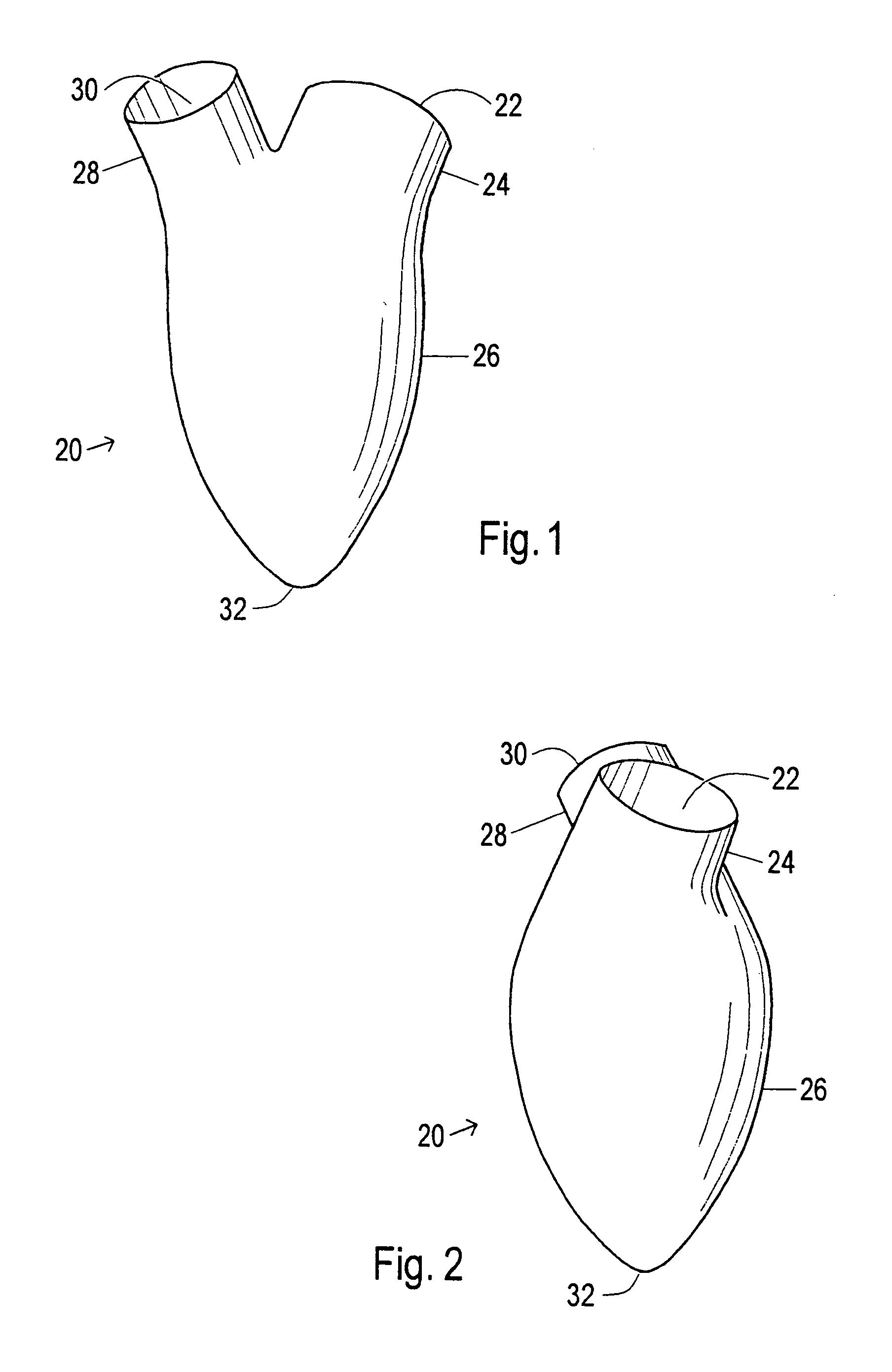
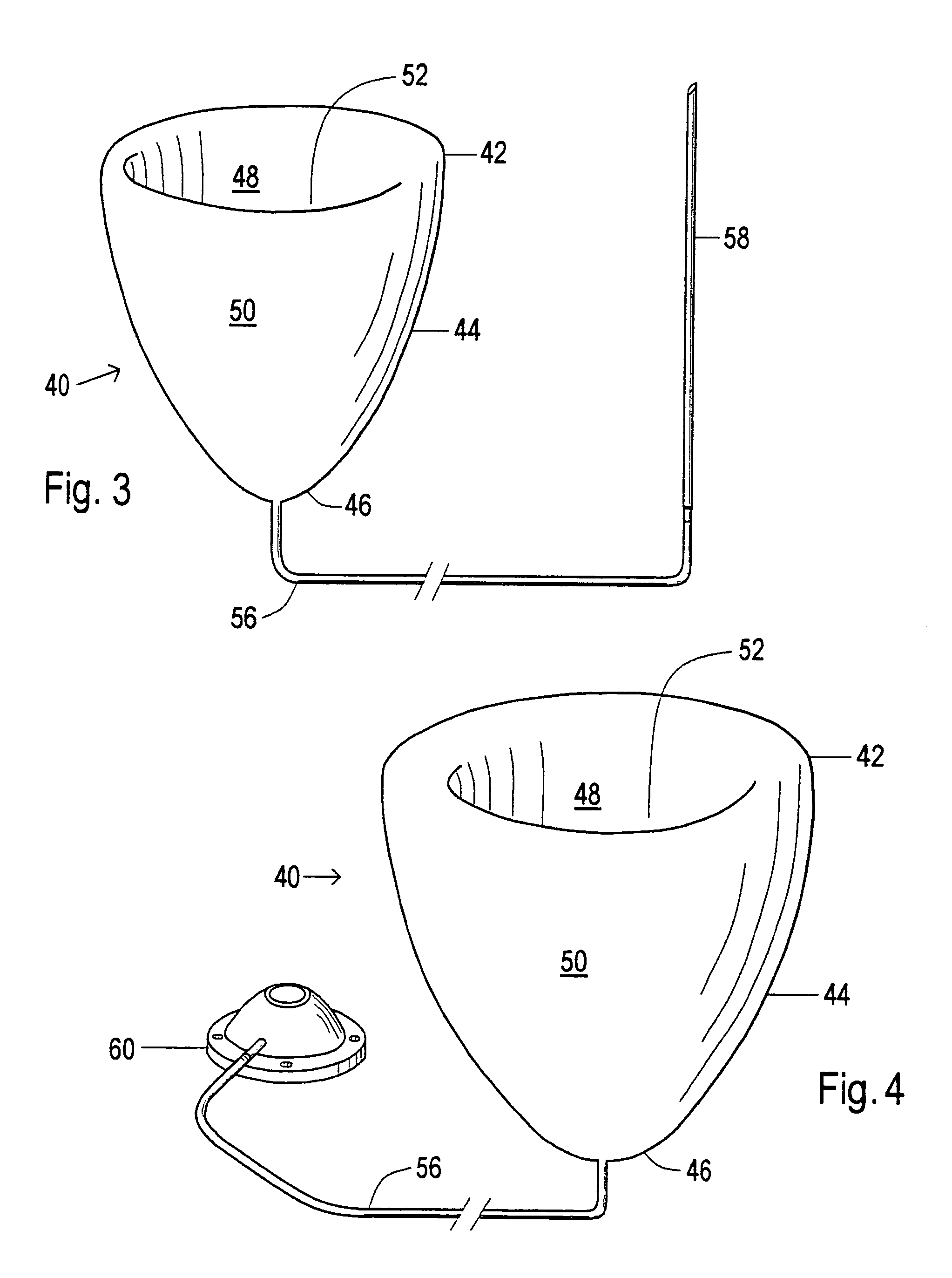
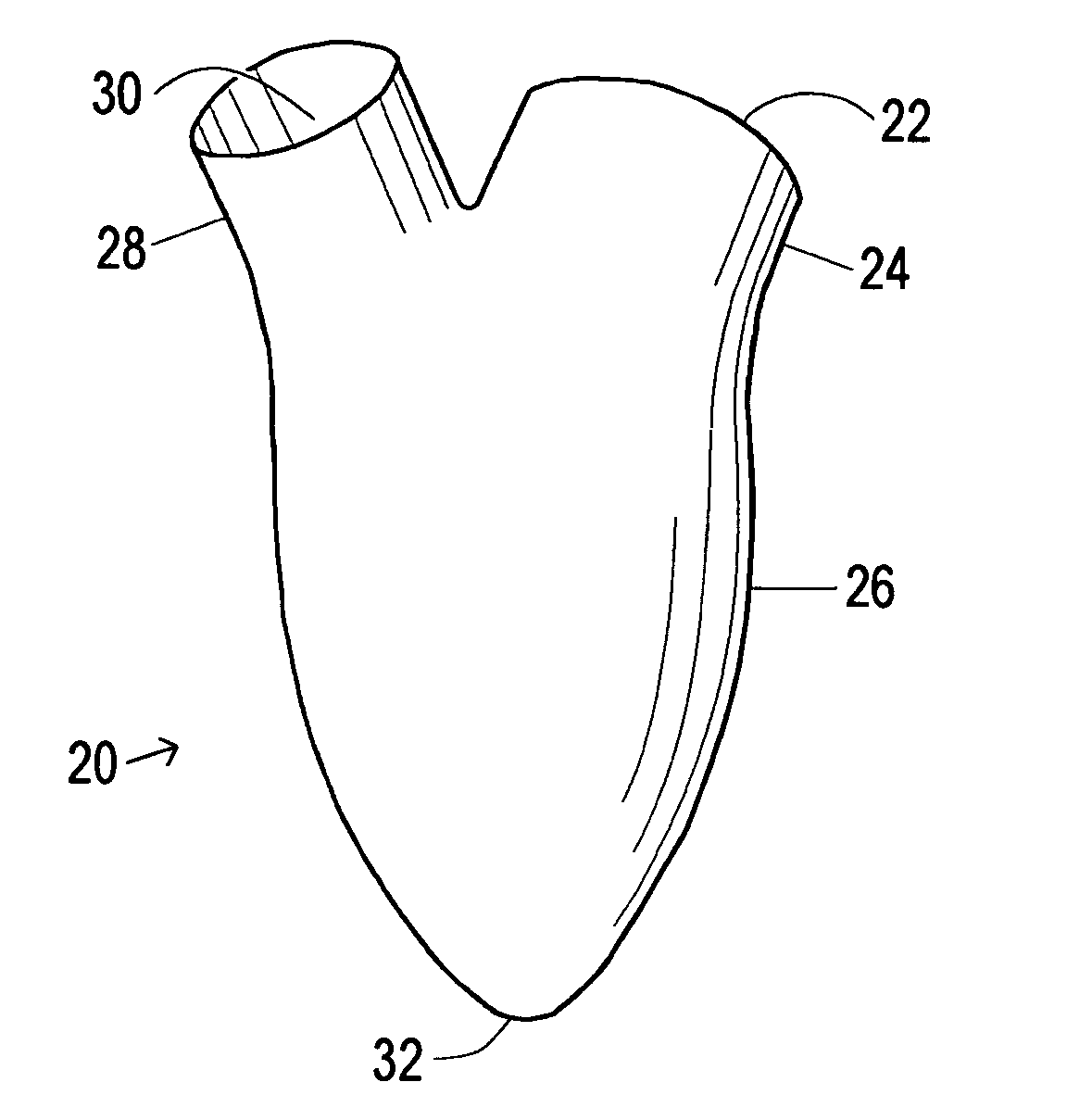
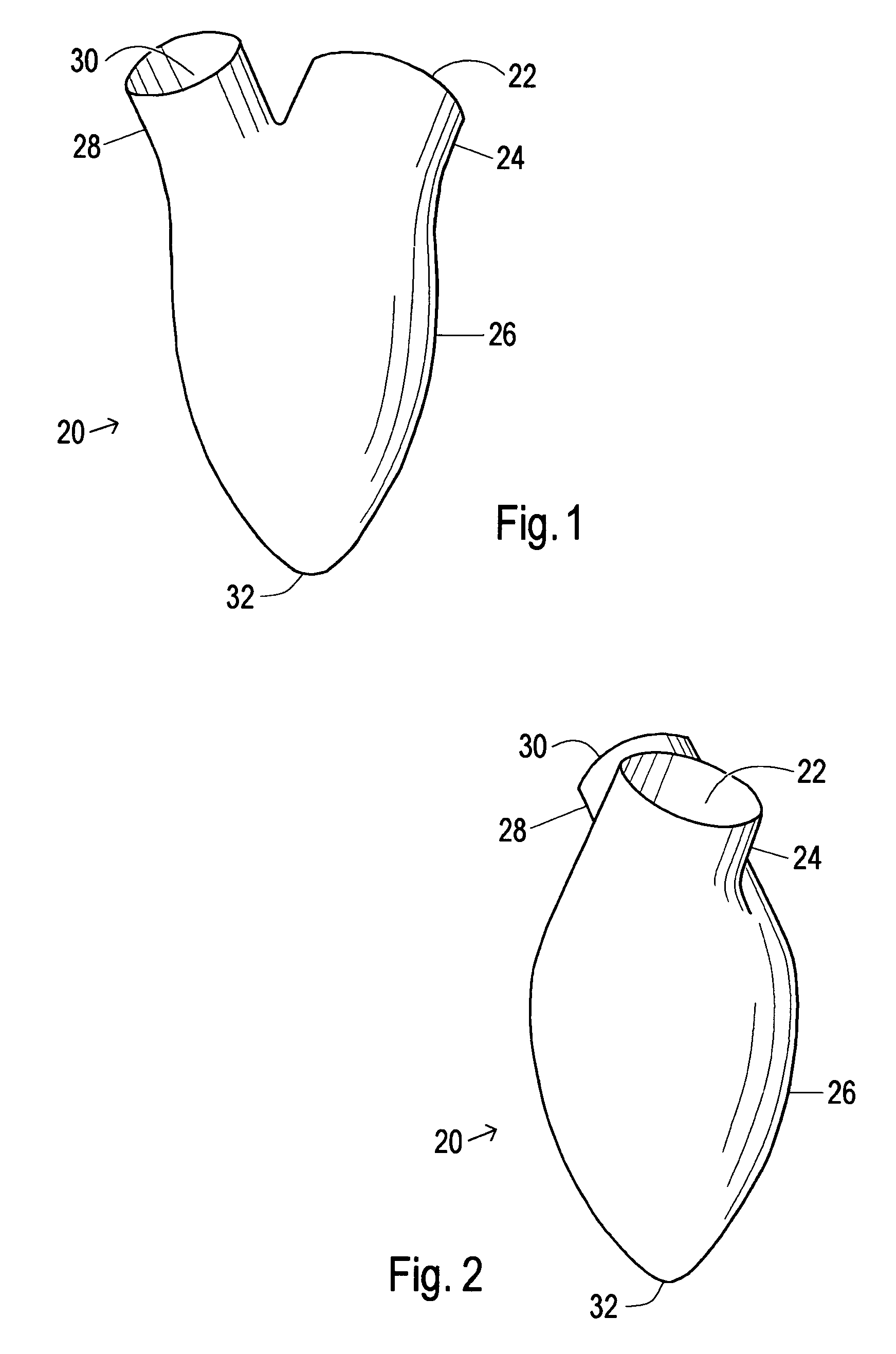
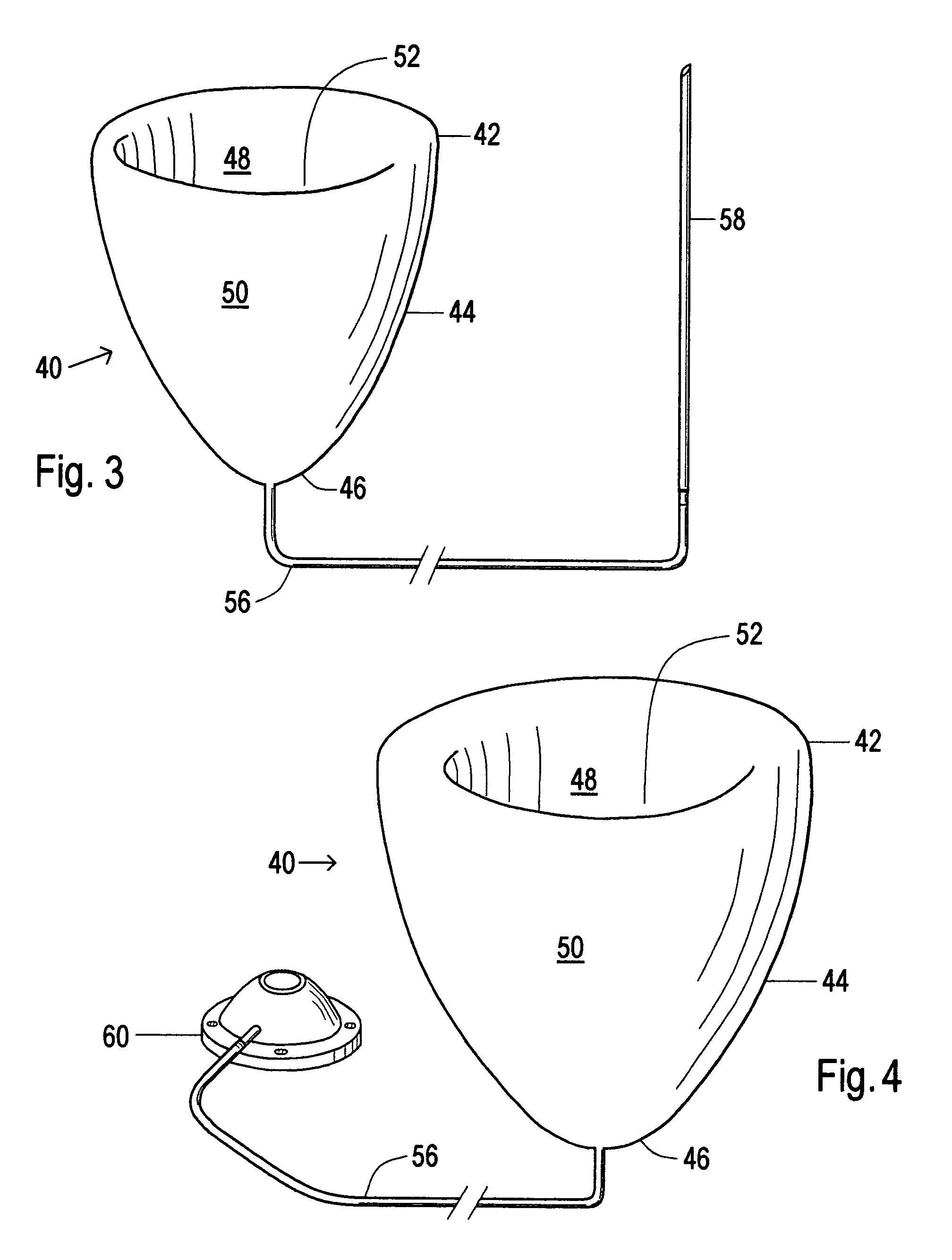
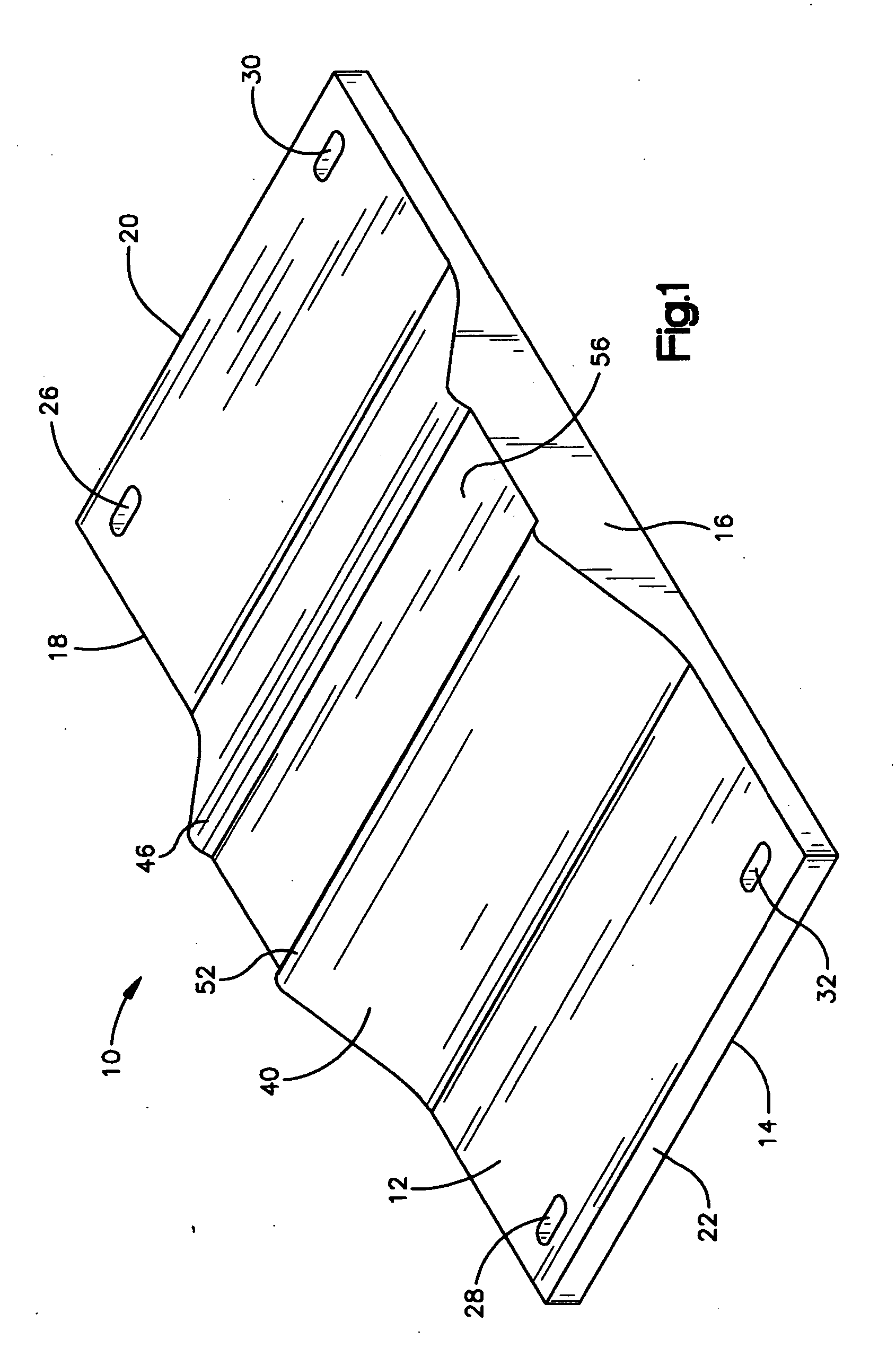
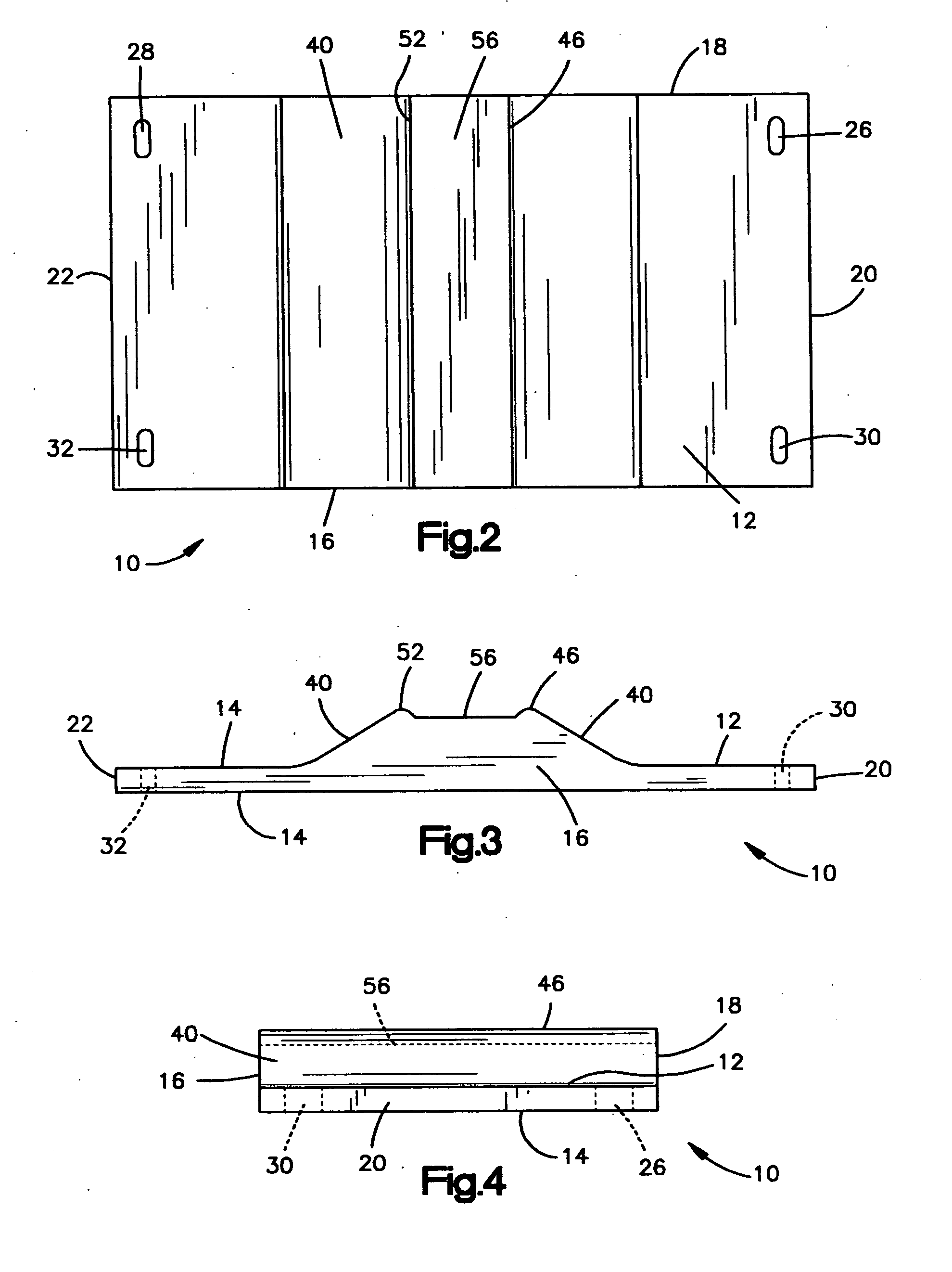
Device and method to control volume of a ventricle
ActiveUS7530998B1Small sizePrevent further enlargement of a diseased heartHeart valvesHeart stimulatorsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
Cardiac simulation device
ActiveUS20160027345A1Accurate gradientAccurate volume fractionEducational modelsDiseaseAutomatic control
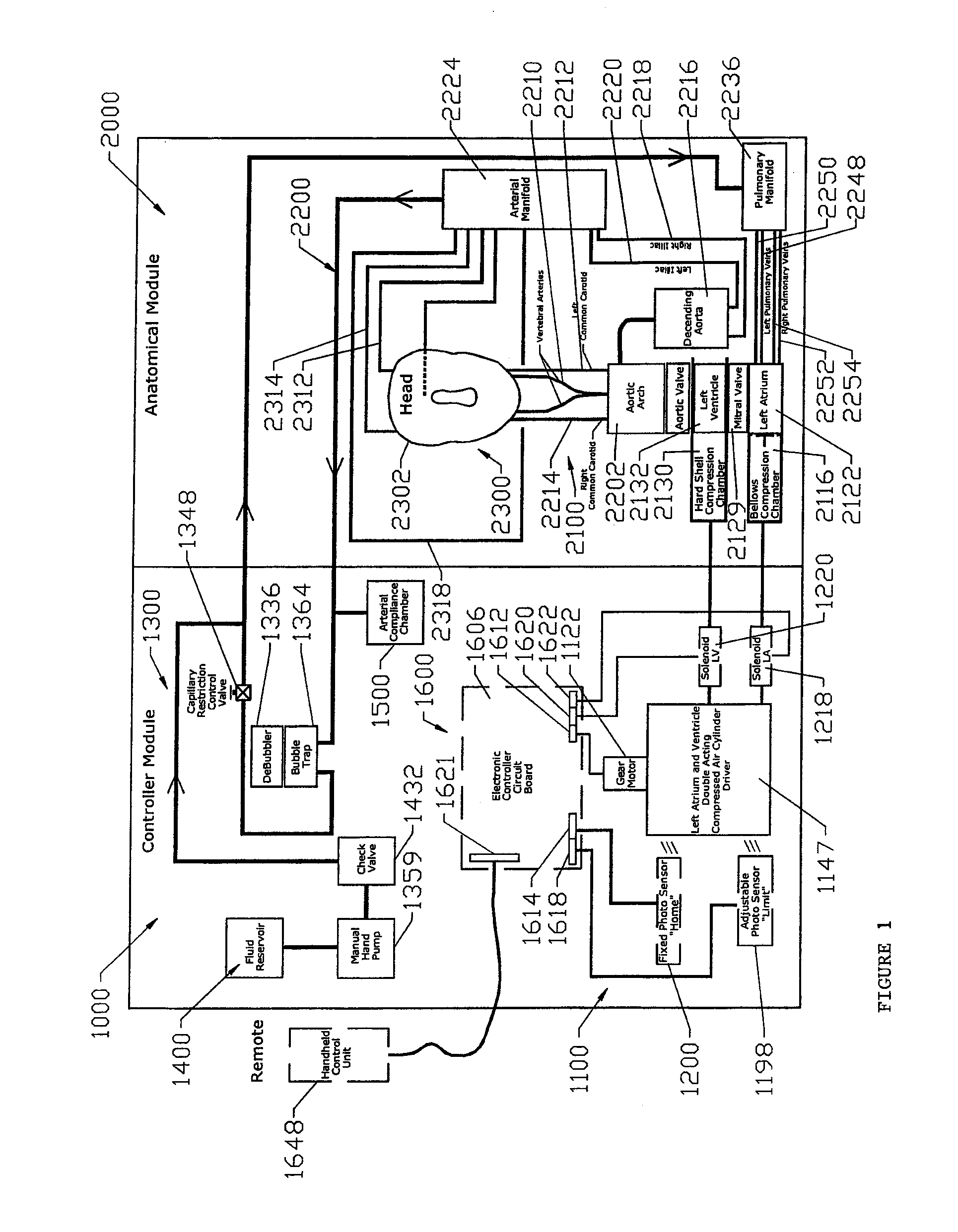
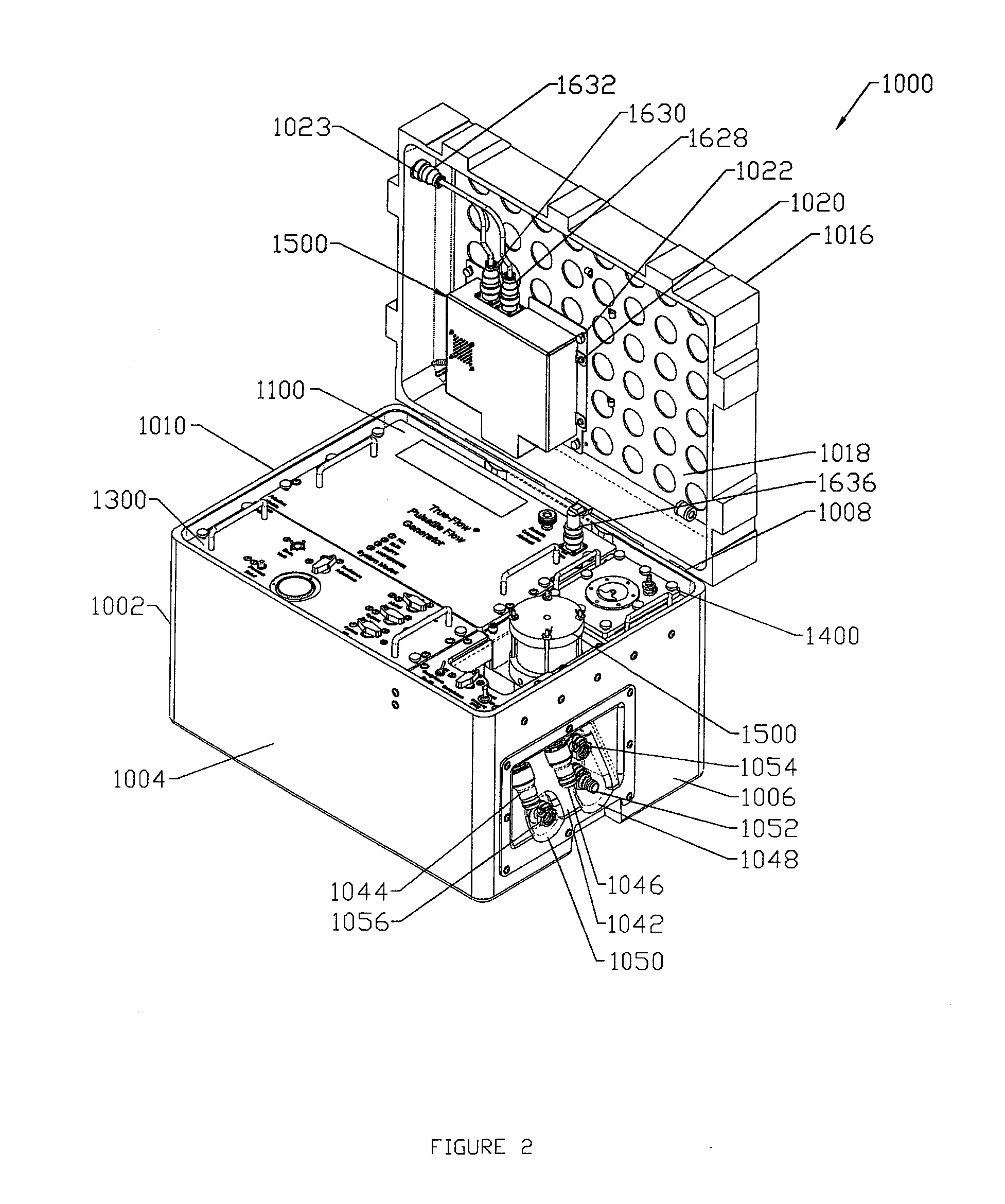
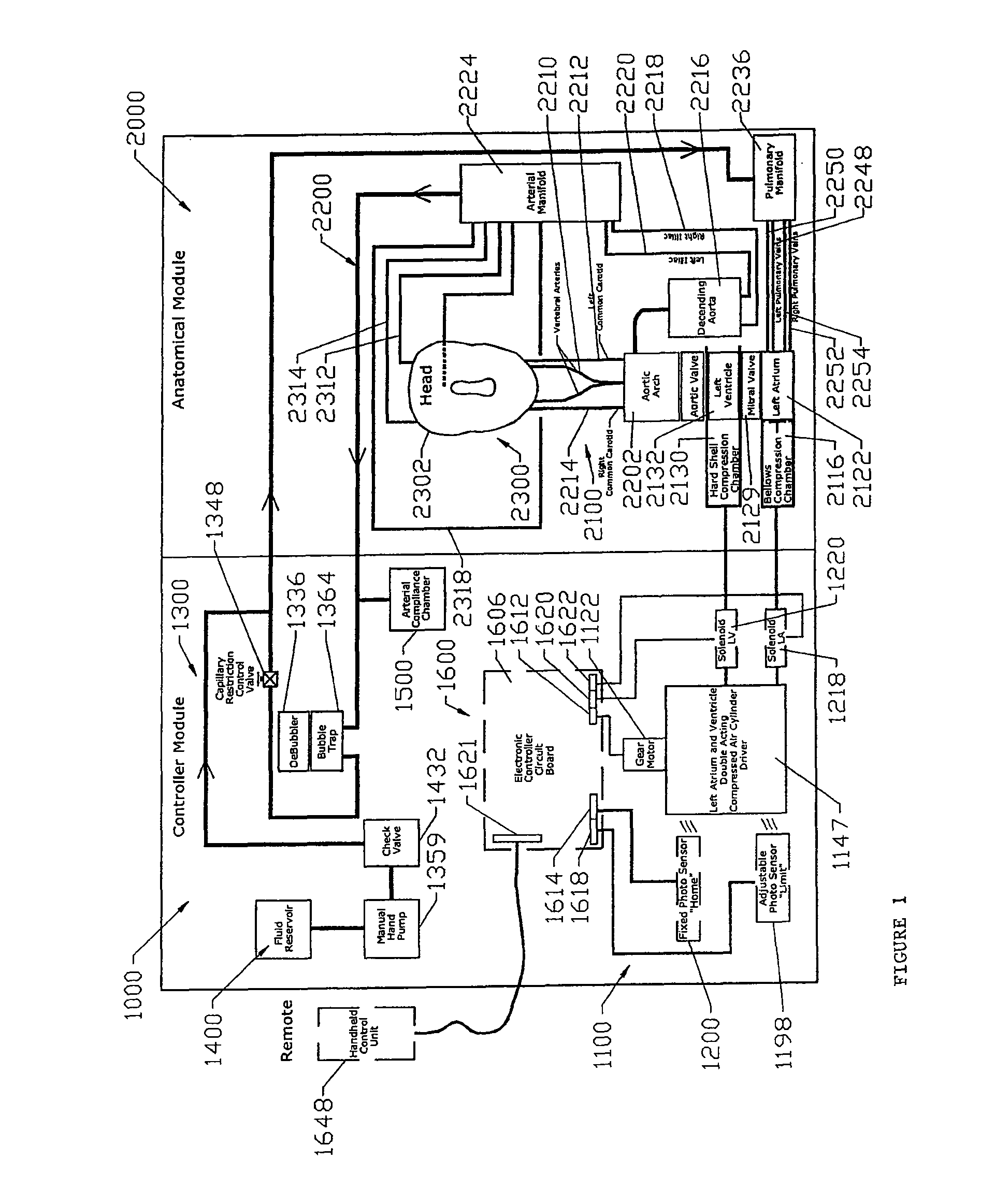
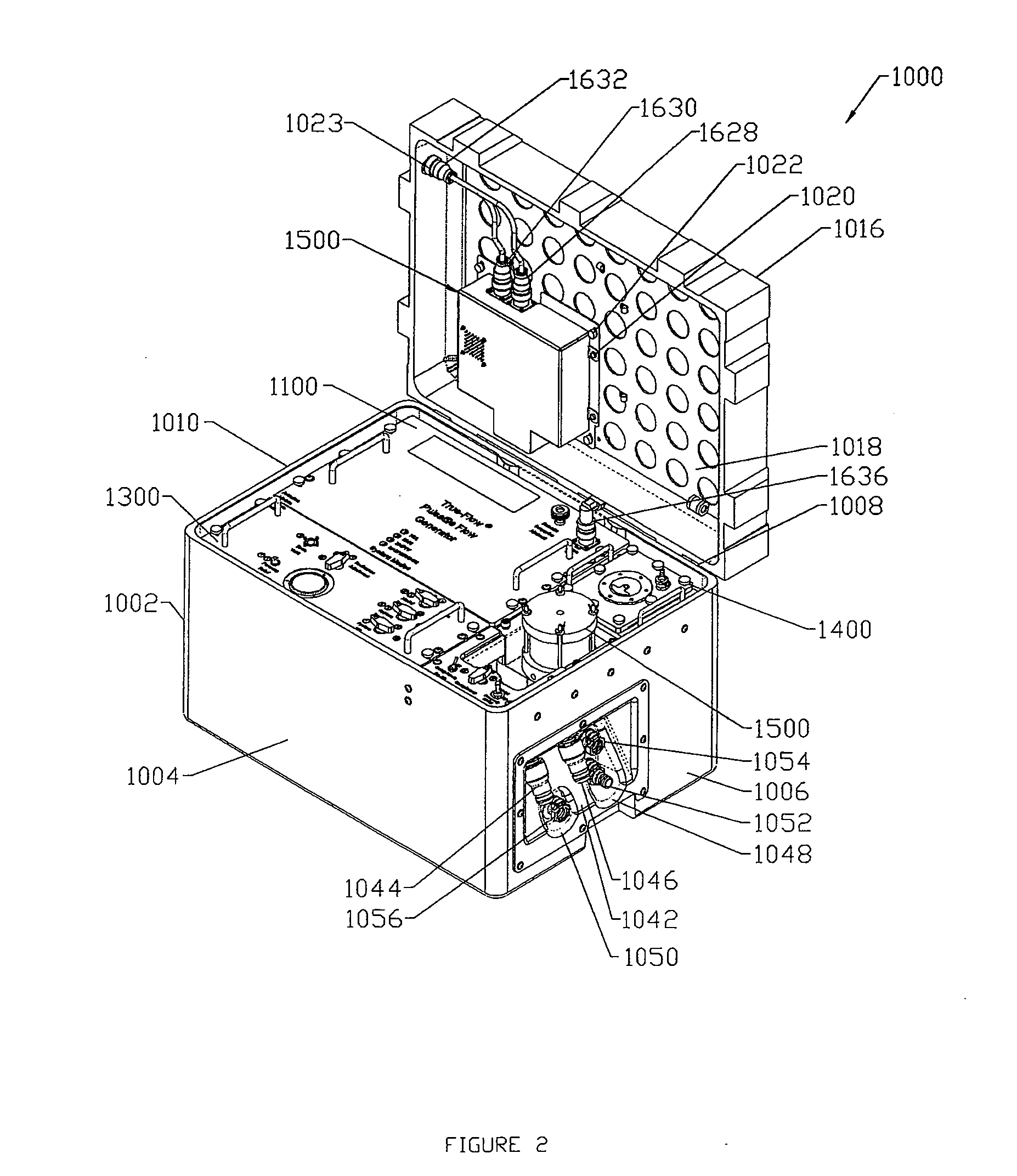
The present invention describes a device and system for simulating normal and disease state cardiovascular functioning, including an anatomically accurate left cardiac simulator for training and medical device testing. The system and device uses pneumatically pressurized chambers to generate ventricle and atrium contractions. In conjunction with the interaction of synthetic valves which simulate mitral and aortic valves, the system is designed to generate pumping action that produces accurate volume fractions and pressure gradients of pulsatile flow, duplicating that of a human heart. Through the use of a control unit and sensors, one or more parameters such as flow rates, fluidic pressure, and heart rate may be automatically controlled, using feedback loop mechanisms to adjust parameters of the hydraulic system simulate a wide variety of cardiovascular conditions including normal heart function, severely diseased or injured heart conditions, and compressed vasculature, such as hardening of the arteries.
Owner:MENTICE
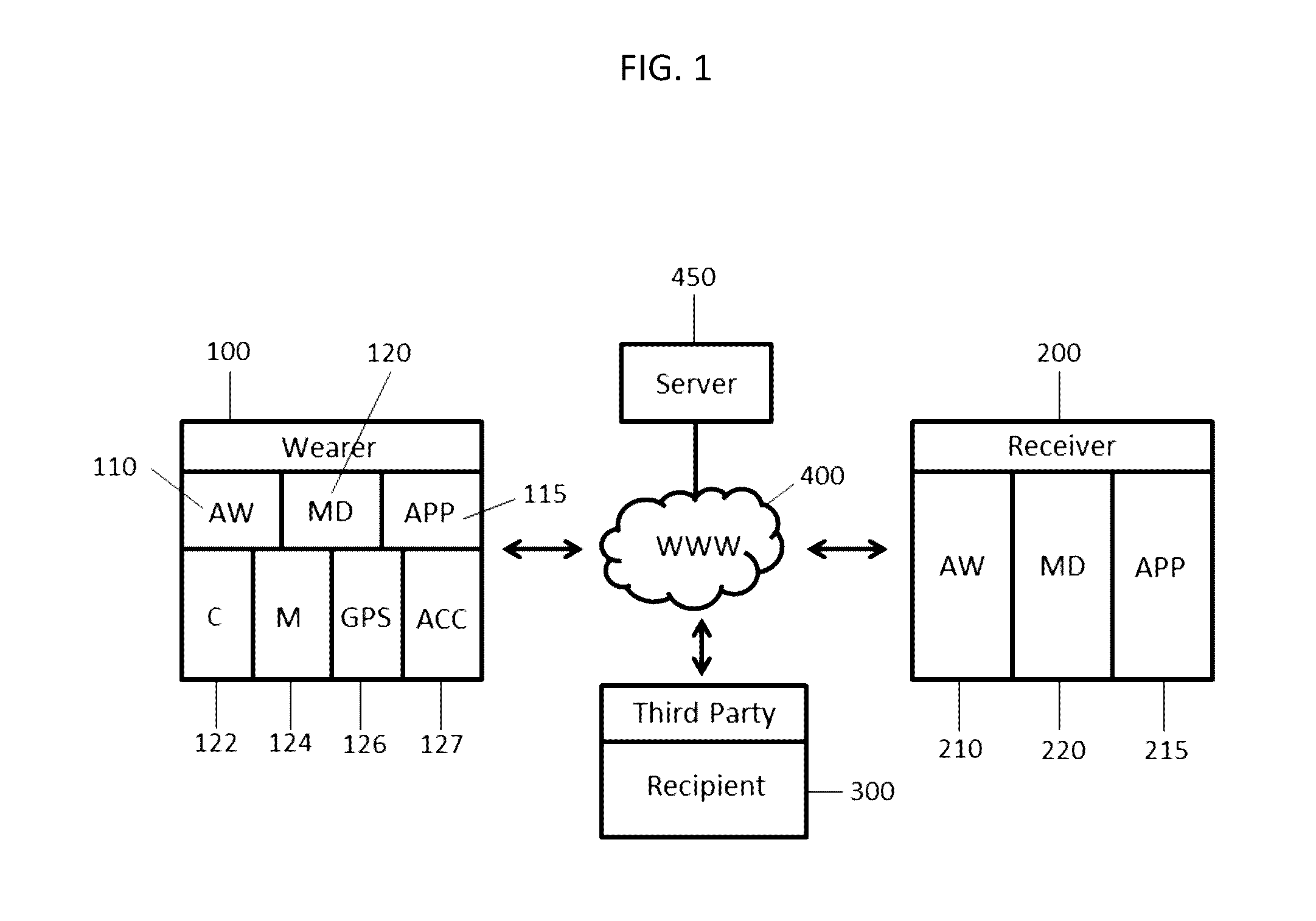
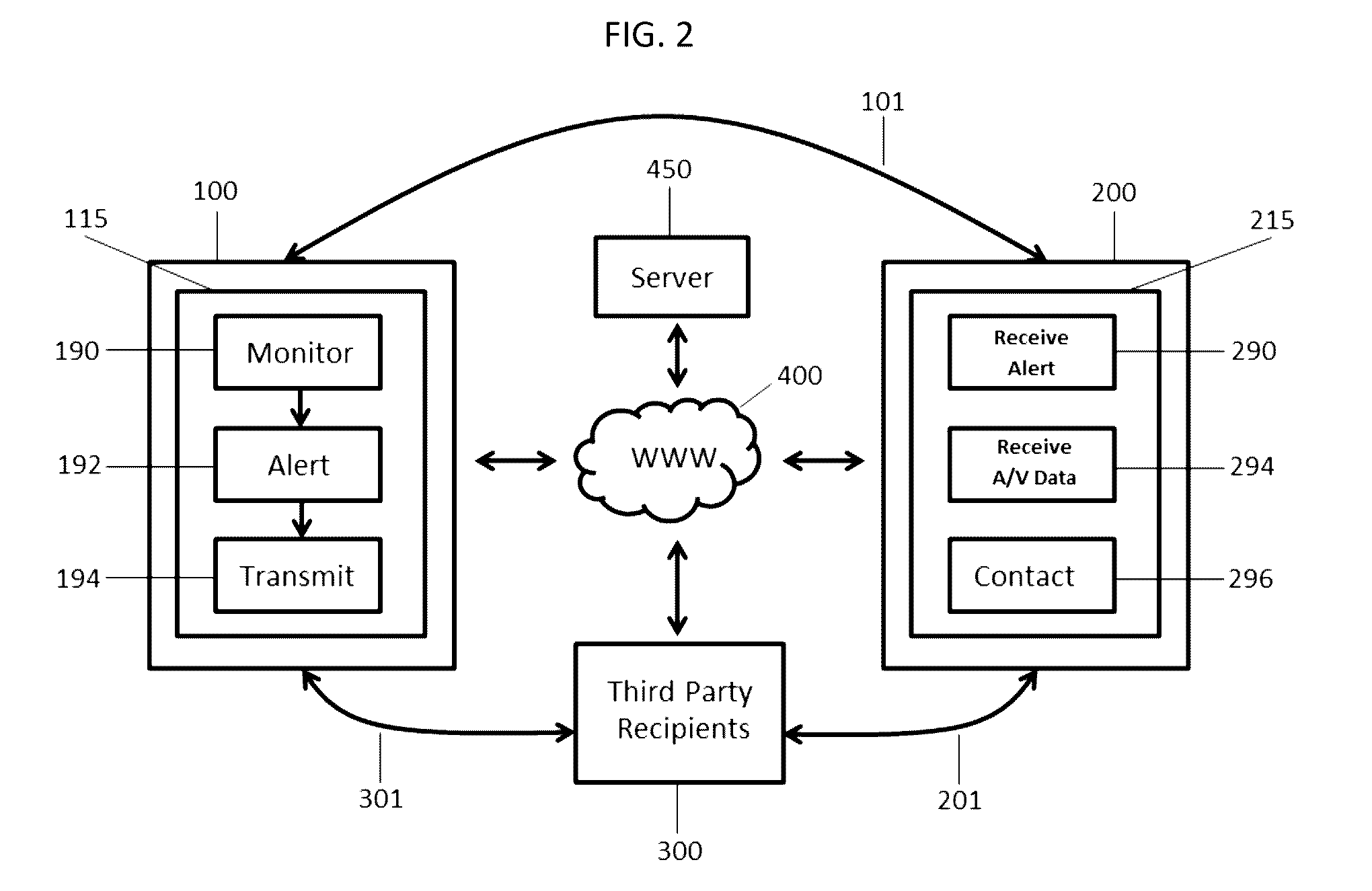
Personal Safety and Security Mobile Application Responsive to Changes in Heart Rate
A software app for a mobile device is disclosed for alerting a custodian of a person to be protected of an emergency situation involving the person to be protected. The app includes software instructions for carrying out a method including: establishing a range of normal heart rates for the person using a heart rate monitor; detecting a heart rate for the person that is outside of the established range; activating at least one of a camera, a microphone, an accelerometer, and a location indicator on the mobile device carried by the person; establishing a wireless data connection between the mobile device and a communication network; and transmitting data to the custodian from the activated camera, microphone, accelerometer, or location indicator via the communication network. The app can notify a custodian of a medical or safety emergency as it is happening, giving that custodian the ability to immediately notify emergency personnel.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
System and method for personalized cardiac arrhythmia risk assessment by simulating arrhythmia inducibility
ActiveUS20140122048A1Physical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationData processing systemNormal cardiac rhythm
A method of determining a likelihood of an occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia in a patient includes receiving three-dimensional imaging data of said patient's heart, constructing a whole-heart model for simulating at least one of electrophysiological activity or electromechanical activity of the patient's heart using the three-dimensional imaging data, simulating a response of the patient's heart to each of a plurality of stimulations to a corresponding plurality of different locations within the patient's heart using the whole-heart model, classifying each simulation outcome for each stimulation as one of a normal heart rhythm or a cardiac arrhythmia, calculating a likelihood index based on results of the classifying, and determining the likelihood of the occurrence of the cardiac arrhythmia in the patient based on the likelihood index. Software and data processing systems that implement the above methods are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Monitoring a property of the cardiovascular system of a subject
ActiveUS20130023776A1Overcome limitationsElectrocardiographyMedical devicesCalcificationEctopic beat
A device is configured to monitor a cardiovascular property of a subject. The device obtains measurement data from a primary pressure wave sensor arranged to detect pressure waves in an extracorporeal fluid circuit in fluid communication with the cardiovascular system of the subject. The device has a signal processor configured to generate a time-dependent monitoring signal based on the measurement data, such that the monitoring signal comprises a sequence of heart pulses, wherein each heart pulse represents a pressure wave originating from a heart beat in the subject; determine beat classification data for each heart pulse in the monitoring signal; and calculate, based at least partly on the beat classification data, a parameter value indicative of the cardiovascular property. The beat classification data may distinguish between heart pulses originating from normal heart beats and heart pulses originating from ectopic heart beats. The cardiovascular property may be an arterial status of the cardiovascular system, a degree of calcification in the cardiovascular system, a status of a blood vessel access used for connecting the extracorporeal fluid circuit to the cardiovascular system, a heart rate variability, a heart rate, a heart rate turbulence, an ectopic beat count, or an origin of ectopic beats. The device may be attached to or part of a dialysis machine.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Device and method to limit filling of the heart
ActiveUS7341584B1Small sizeLimiting volume of bloodHeart valvesSurgical instrument detailsCardiac cycleReverse remodeling
A device used to treat heart disease by decreasing the size of a diseased heart, or to prevent further enlargement of a diseased heart. The device works by limiting the volume of blood entering the heart during each cardiac cycle. The device partitions blood within the heart, and protects the heart from excessive volume and pressure of blood. The device is placed within the interior of the heart, particularly within a ventricular cavity. The device is a hollow sac, with two openings, which simulates the shape and size of the interior lining of a ventricle of a normal heart. It allows the ventricle to fill through one opening juxtaposed to the annulus of the inflow valve to a predetermined, normal volume, and limits filling of the heart beyond that volume. It then allows blood to be easily ejected through the second opening through the outflow valve. By limiting the amount of blood entering the ventricle, the ventricle is not subjected to the harmful effect of excessive volume and pressure of blood during diastole, the period of the cardiac cycle when the heart is at rest. This allows the heart to decrease in size, or to reverse remodel, and to recover lost function. In some applications, a second device may be simultaneously placed inside the heart to take up excessive space between the heart and the primary device.
Owner:STARKEY THOMAS DAVID
Electrophysiologic Testing Simulation For Medical Condition Determination
InactiveUS20110224962A1Medical simulationPhysical therapies and activitiesCardiac functioningElectrical stimulations
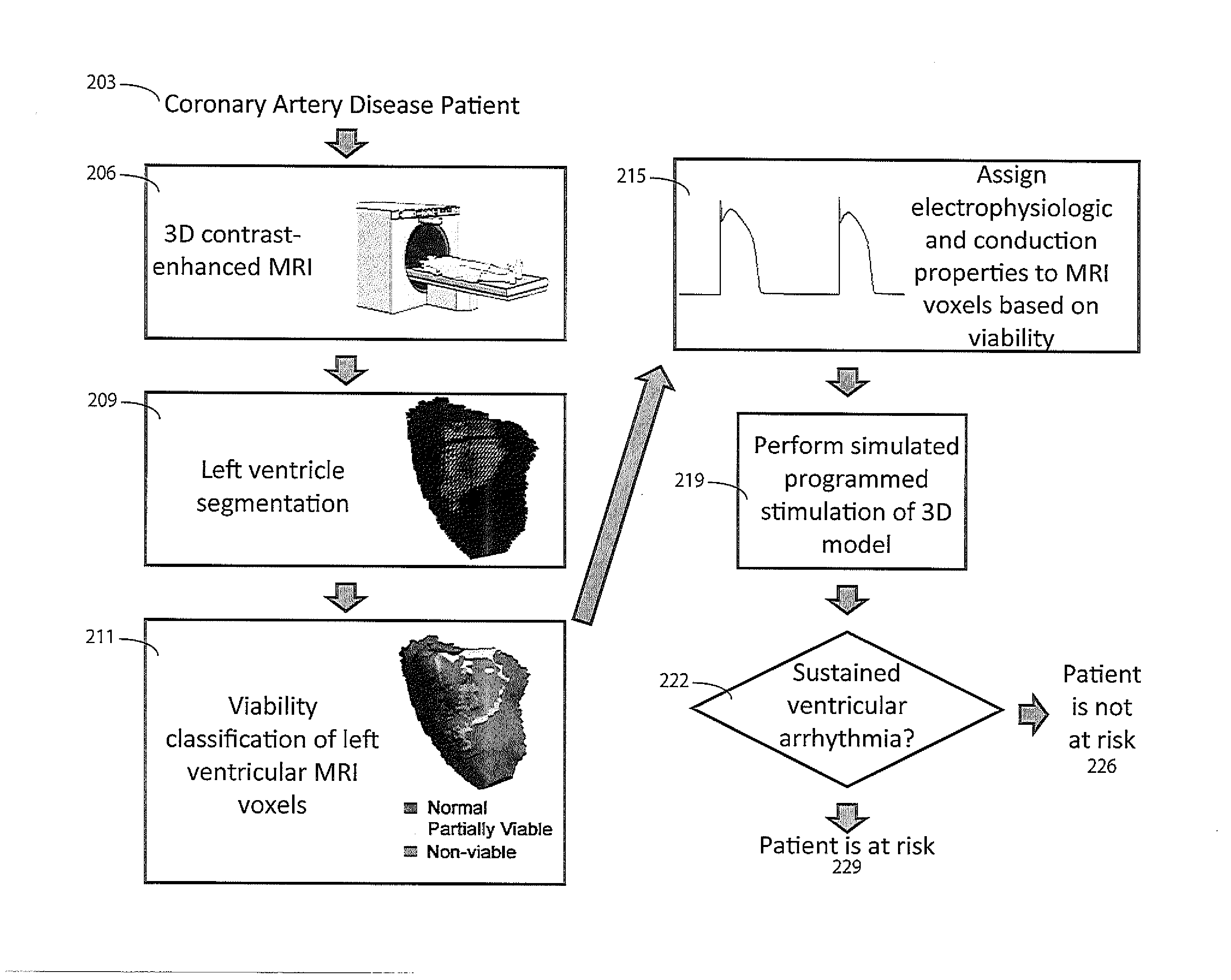
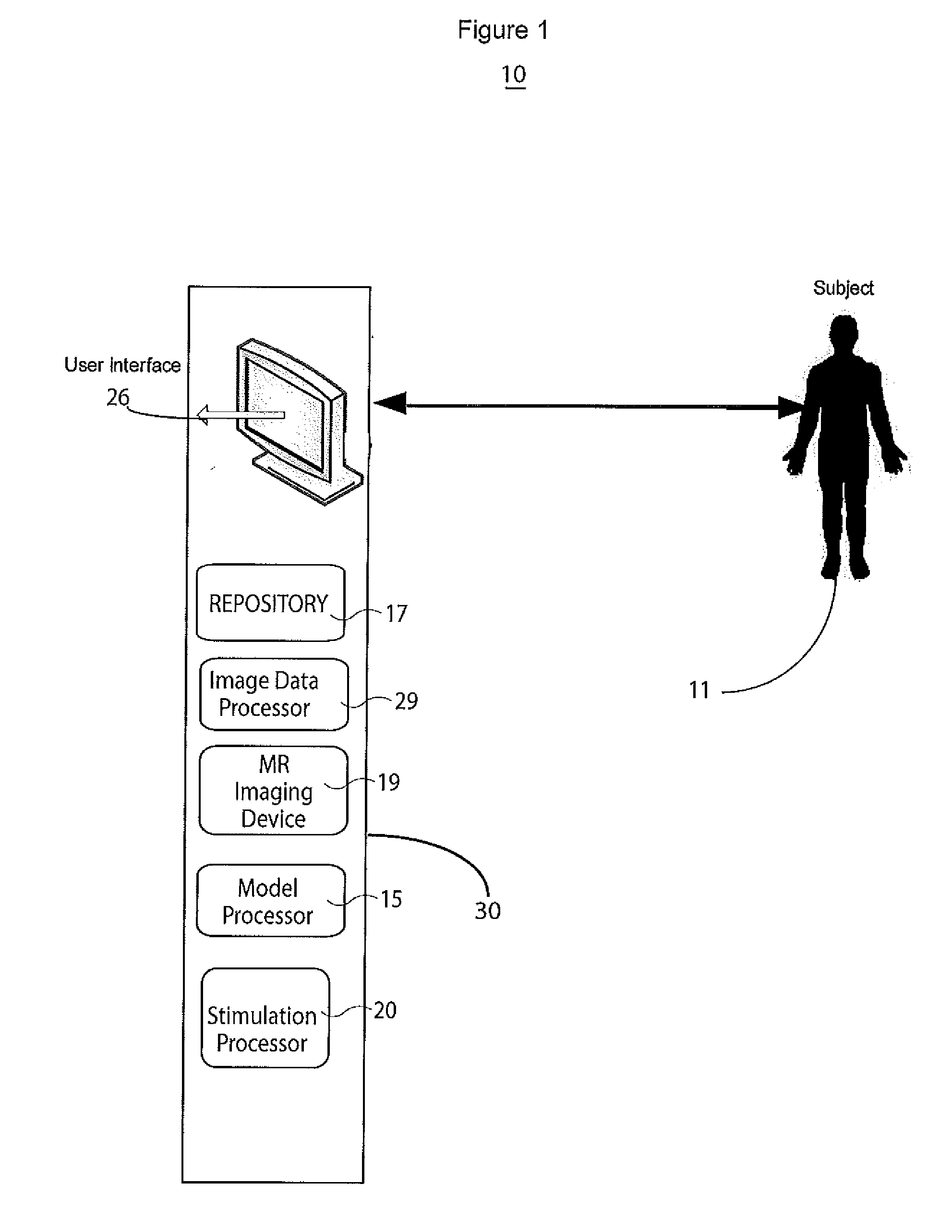
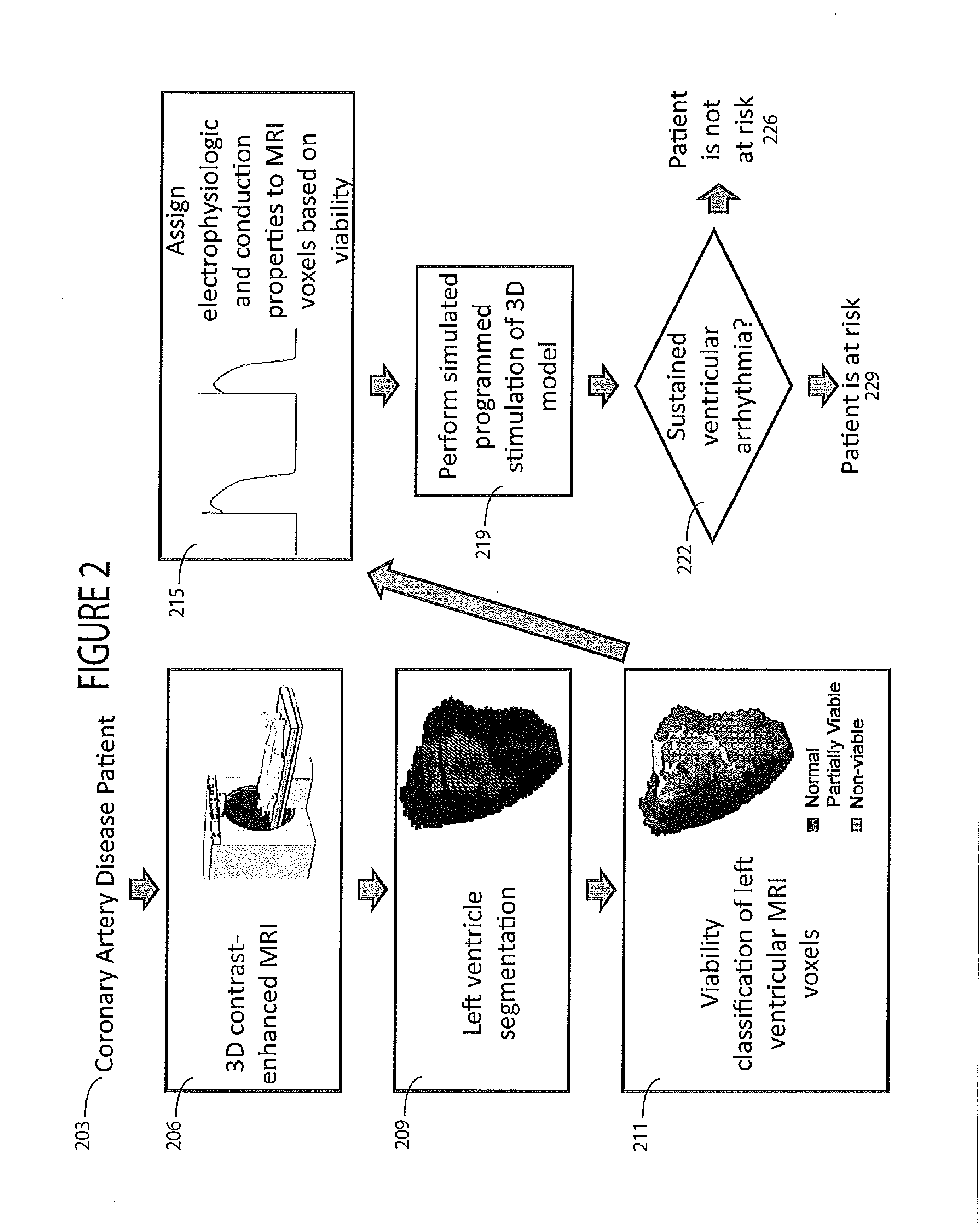
A system simulates stimulation of scar tissue identified as hyper-enhanced areas in a medical image with variable luminance thresholds and categorizes partially-viable myocardium as distinct from non-viable scar tissue. A cardiac function analysis system includes a repository of imaging data representing a 3D volume comprising a patient heart. A model processor provides a model of the patient heart using the imaging data said model being for use in allocating electrical properties to model parameters determining electrical conductivity associated with image data classified as, (a) scar tissue, (b) impaired tissue and (c) normal heart tissue. The electrical properties allocated to scar tissue are different to electrical properties allocated to normal tissue. A stimulation processor simulates electrical stimulation of the patient heart using the model to identify risk of heart impairment.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Cardiac Simulation Device
ActiveUS20130196301A1Reduced collateral damageEliminate riskEducational modelsDiseaseElectronic controller
The present invention describes a device and system for simulating normal and disease state cardiac functioning, including an anatomically accurate left cardiac simulator for training and medical device testing. The system and device uses pneumatically pressurized chambers to generate ventricle and atrium contractions. In conjunction with the interaction of synthetic mitral and aortic valves, the system is designed to generate pumping action that produces accurate volume fractions and pressure gradients of pulsatile flow, duplicating that of a human heart. Through the use of a remote handheld electronic controller and manual adjustments from a main control panel, the air pressure level, fluidic pressure, and heart rate is controlled to induce contractions that simulate a wide variety of heart conditions ranging from normal heart function to severely diseased or injured heart conditions.
Owner:MENTICE
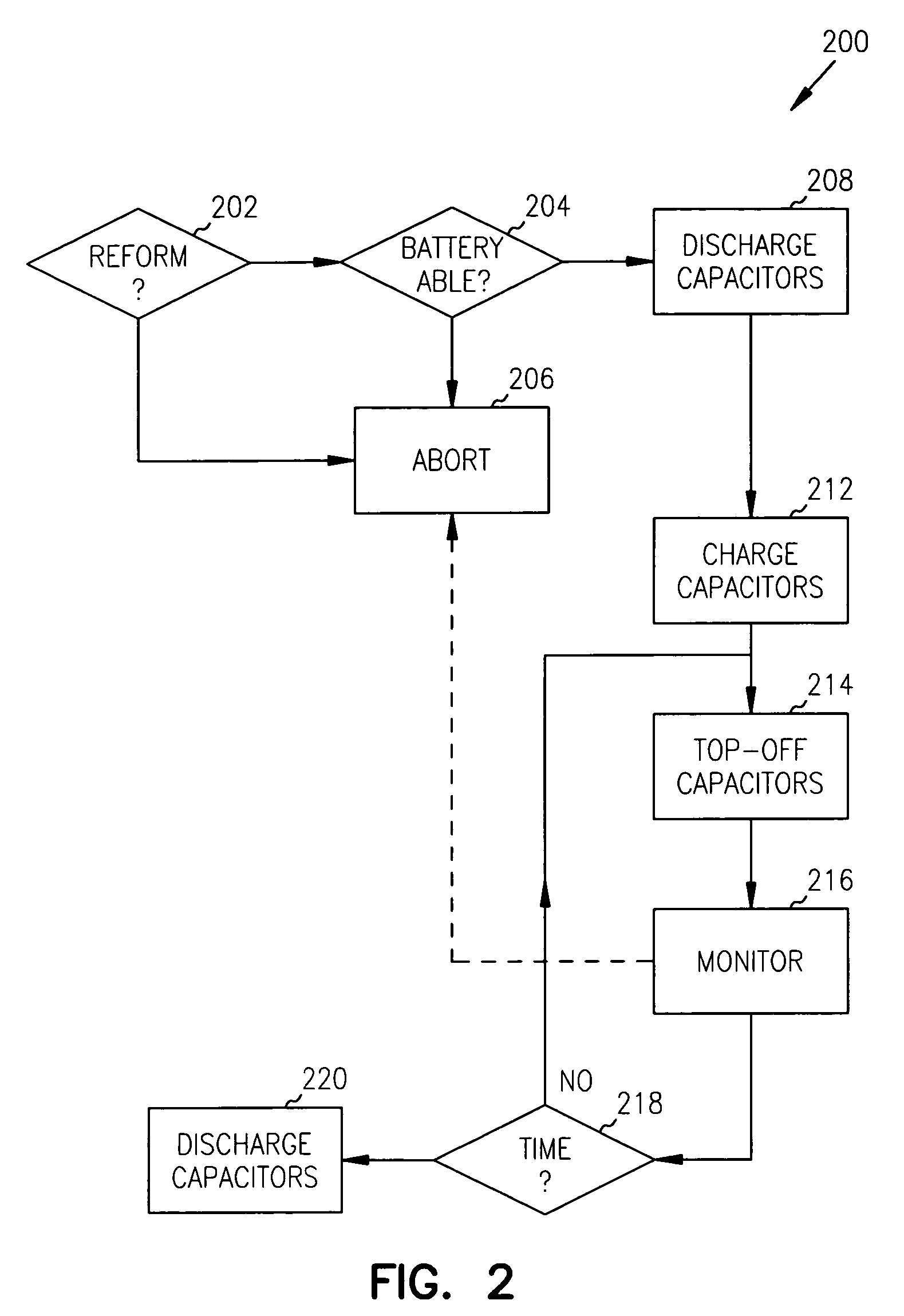
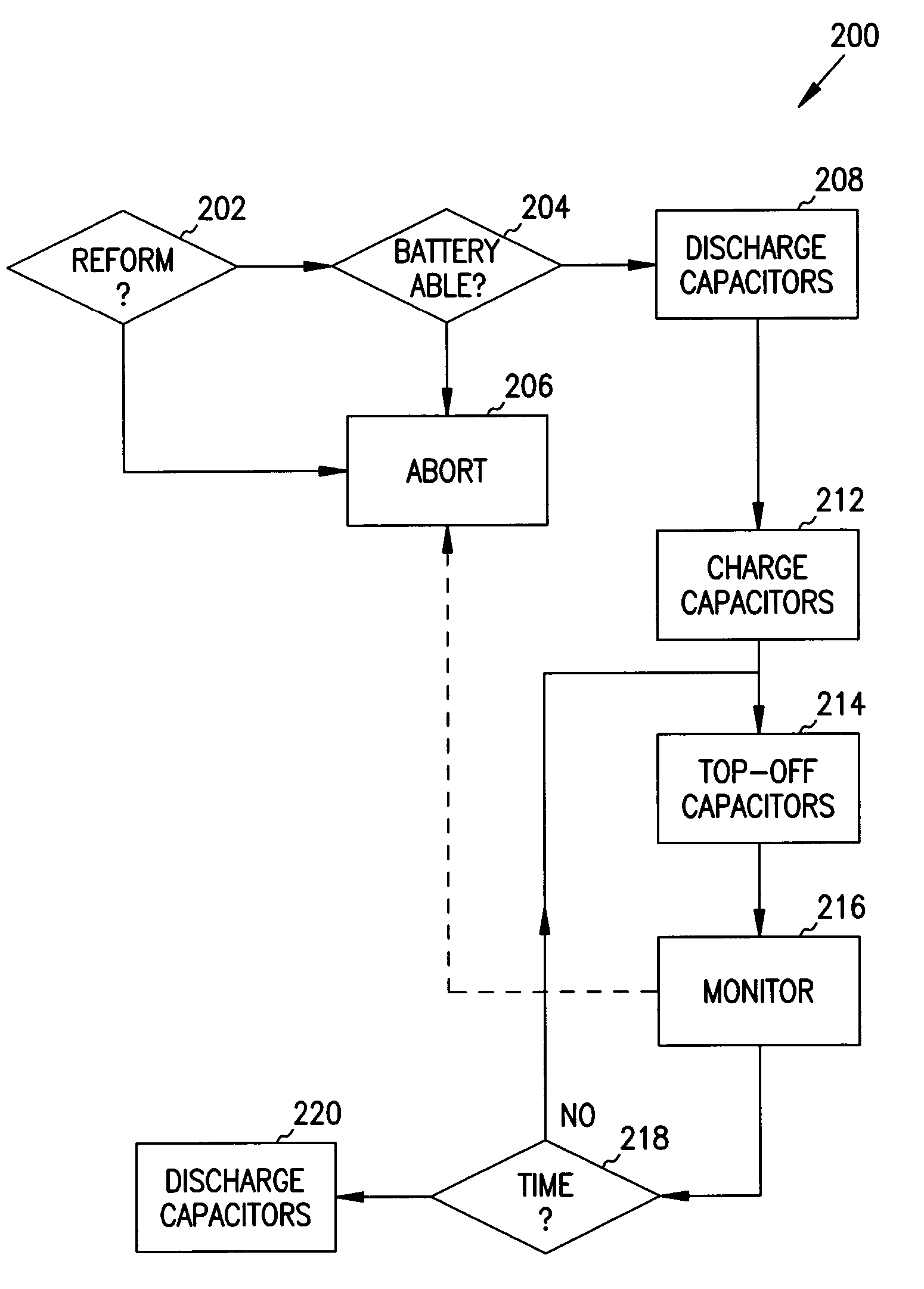
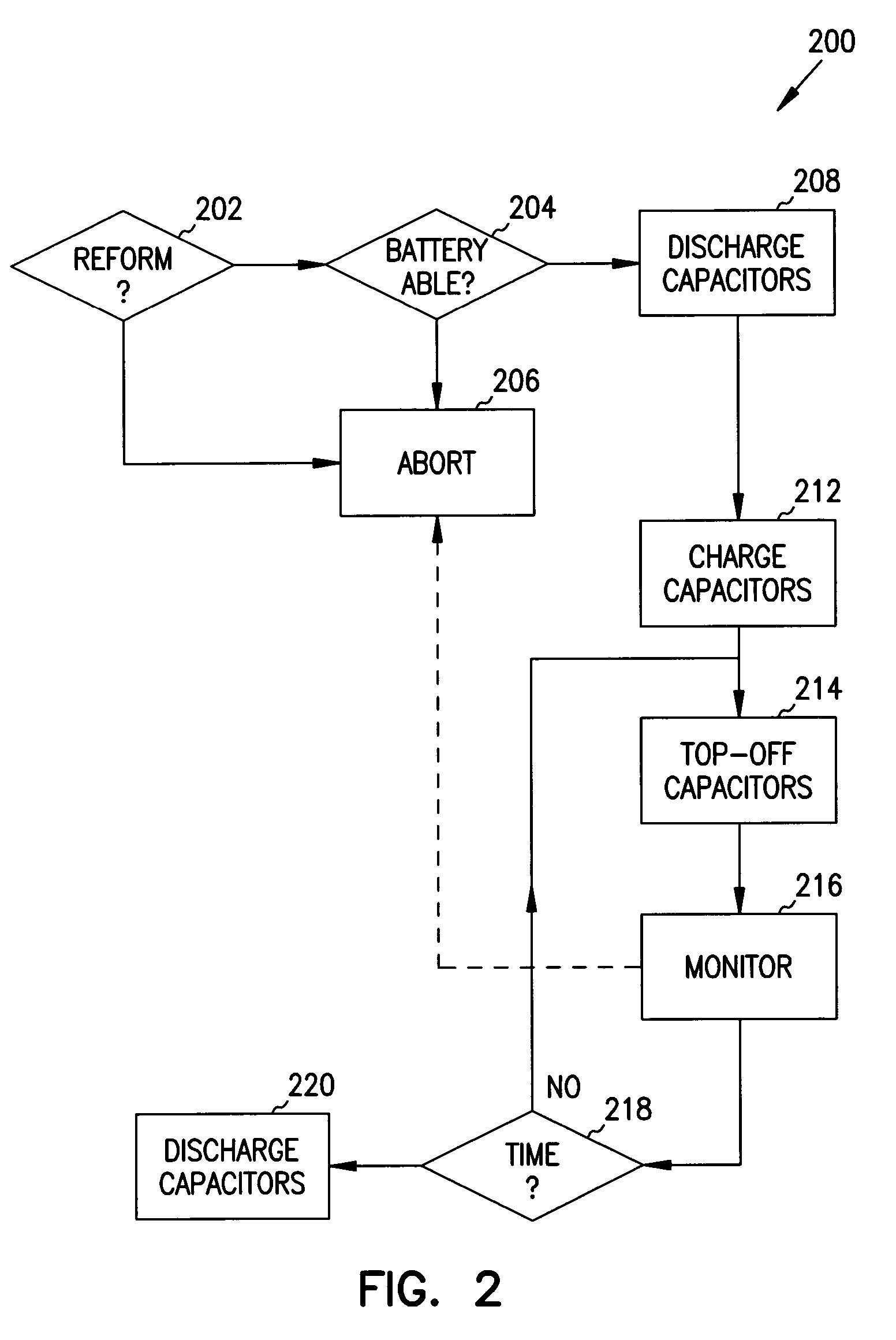
Reforming wet-tantalum capacitors in implantable medical devices
InactiveUS7131988B2Efficient chargingElectrolytic capacitorsHeart defibrillatorsElectrolysisEngineering
Miniature defibrillators and cardioverters detect abnormal heart rhythms and automatically apply electrical therapy to restore normal heart function. Critical to this function, aluminum-electrolytic capacitors store and deliver life-saving bursts of electric charge to the heart. This type of capacitor requires regular “reform” to preserve its charging efficiency over time. Because reform expends valuable battery energy, manufacturers developed wet-tantalum capacitors, which are generally understood not to require reform. Yet, the present inventors discovered through extensive study that wet-tantalum capacitors exhibit progressively worse charging efficiency over time. Accordingly, to address this problem, the inventors devised unique reform techniques for wet-tantalum capacitors. One exemplary technique entails charging wet-tantalum capacitors to a voltage equal to about 90% of their rated voltage and allowing the charge to dissipate through system leakage for a period of time, before discharging through a non-therapeutic load.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
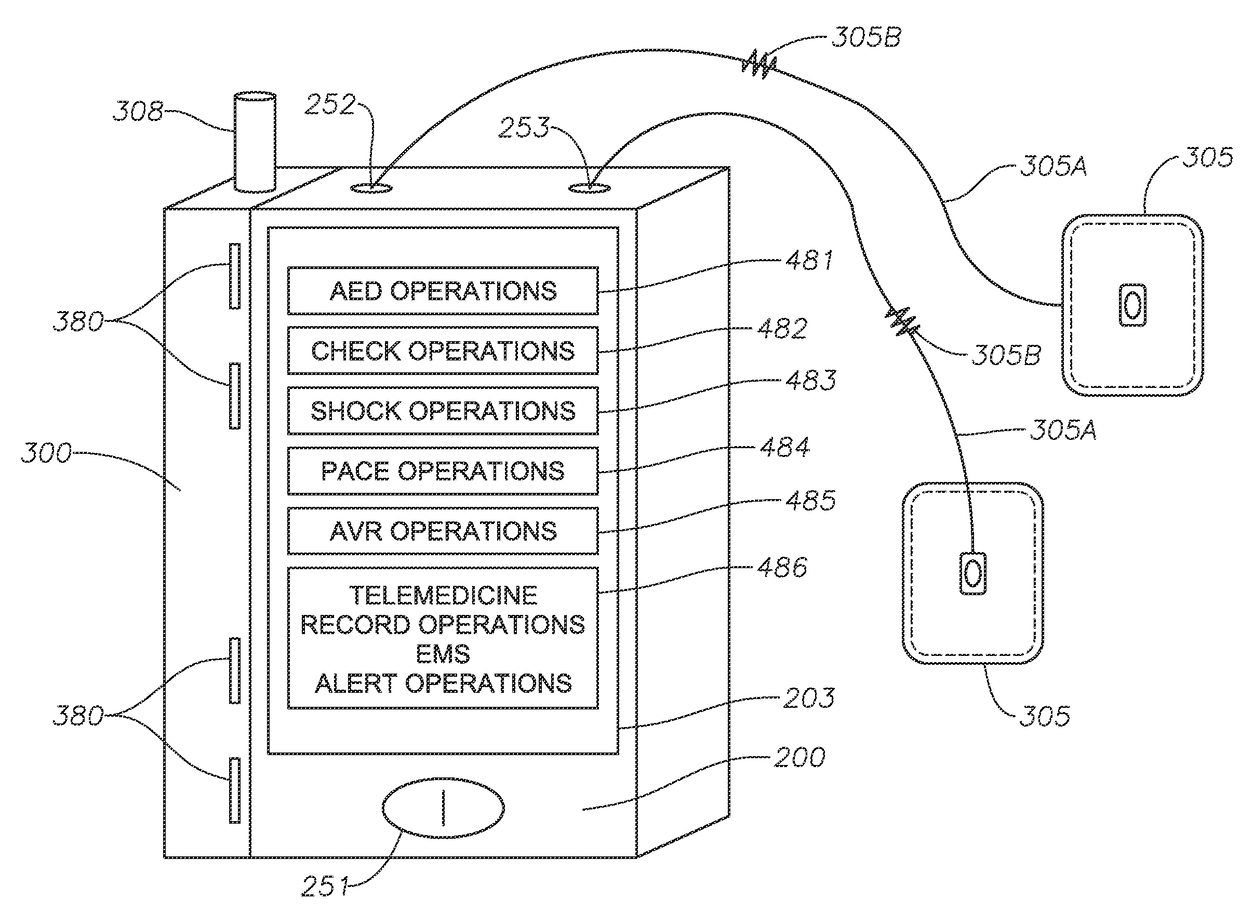
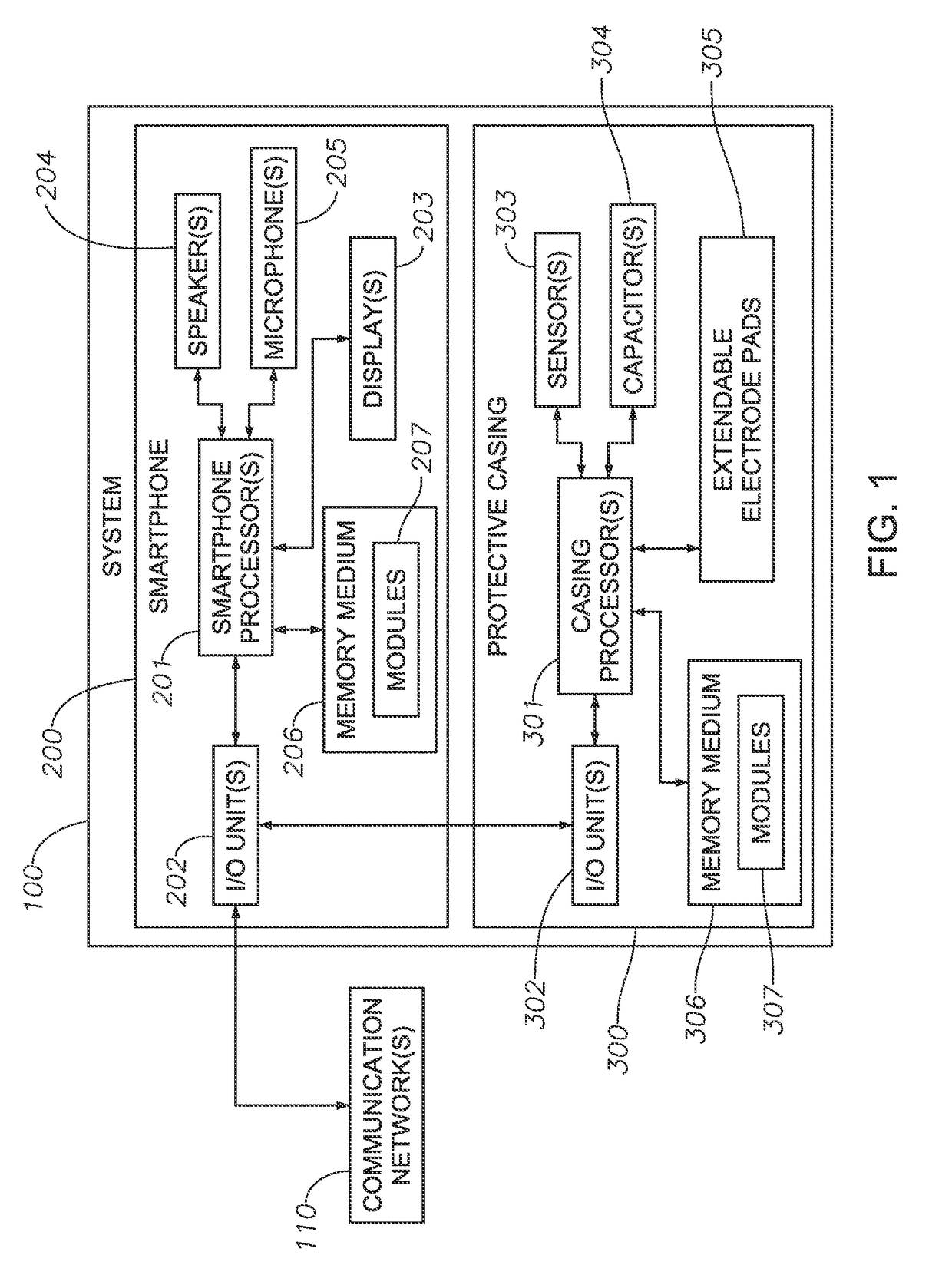
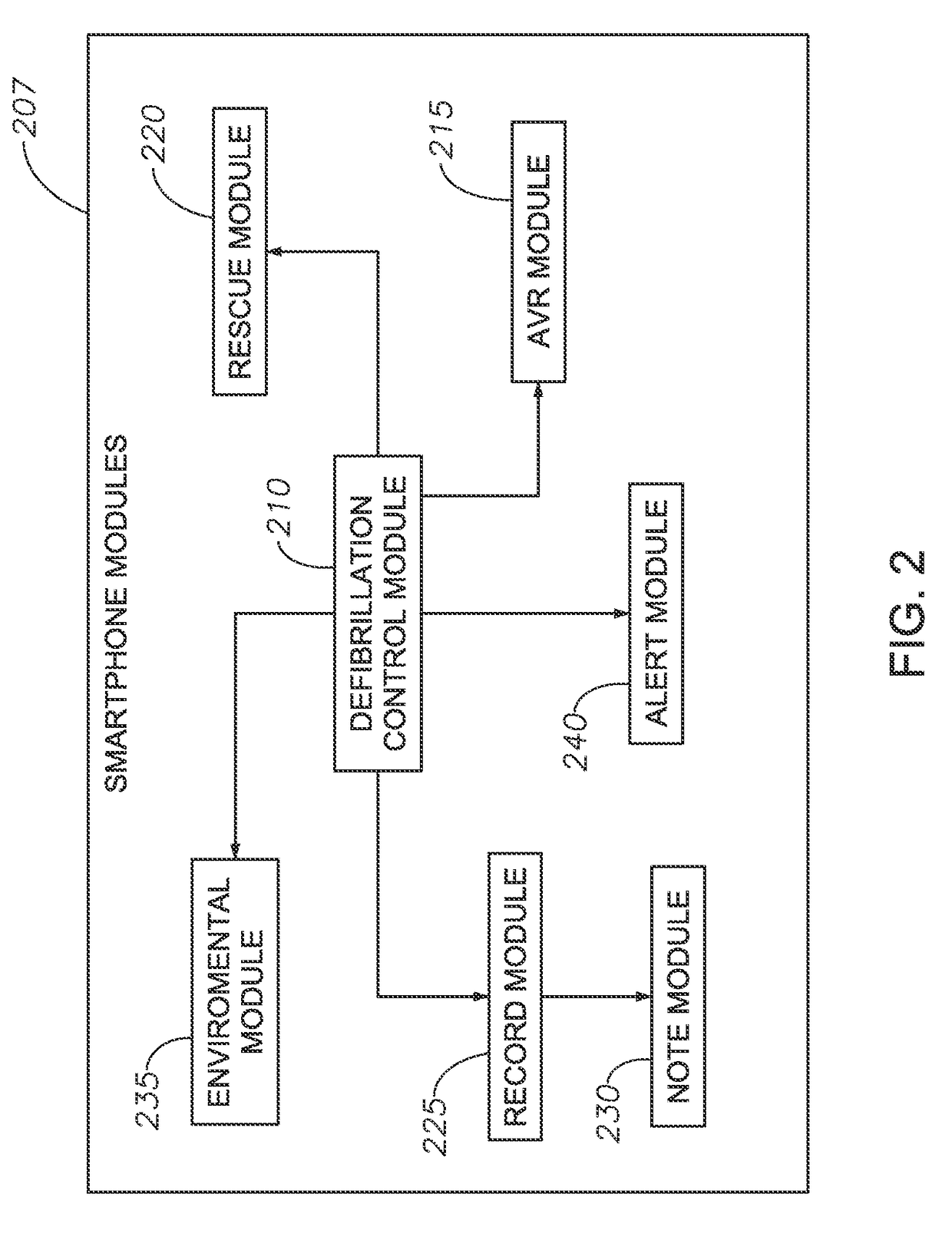
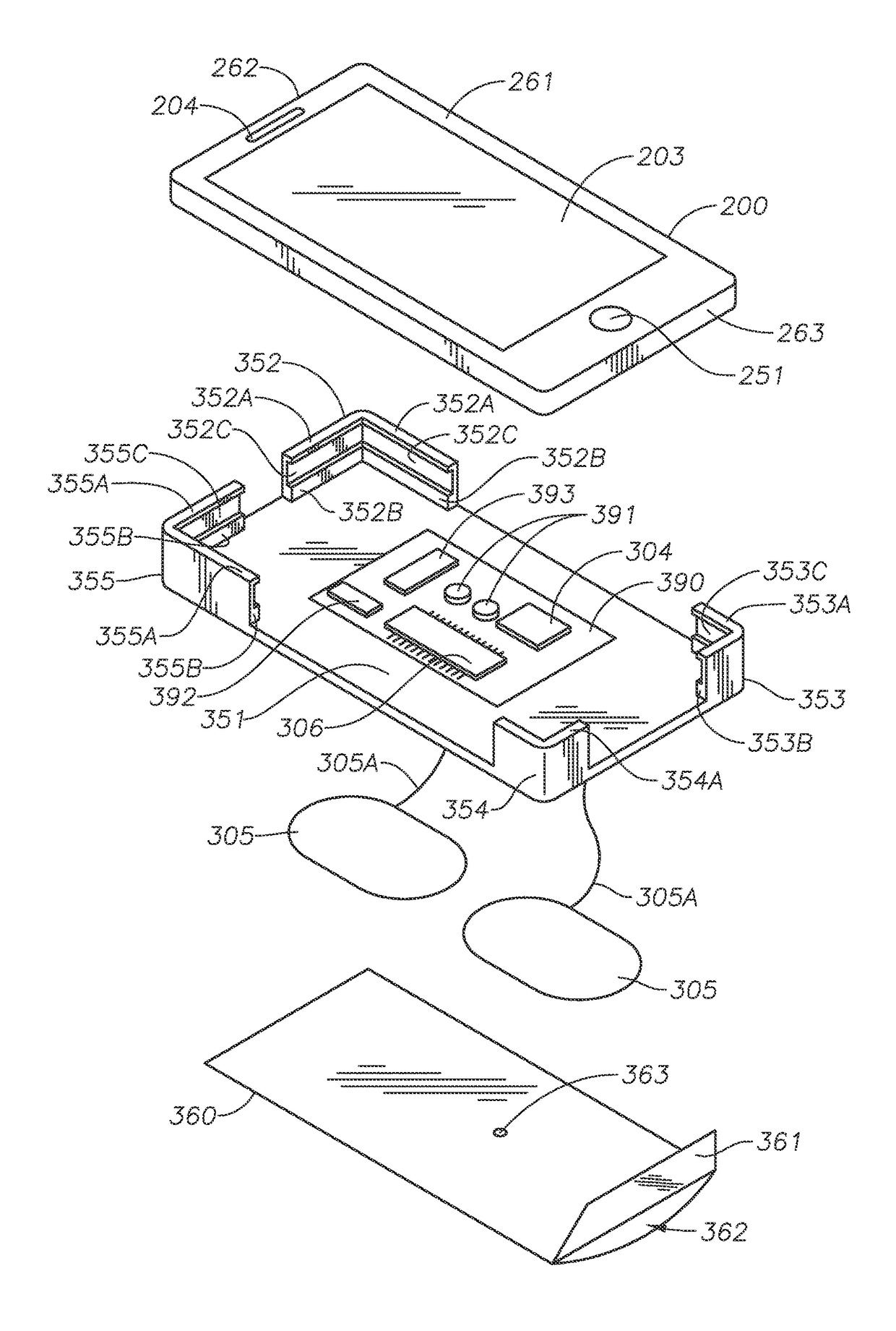
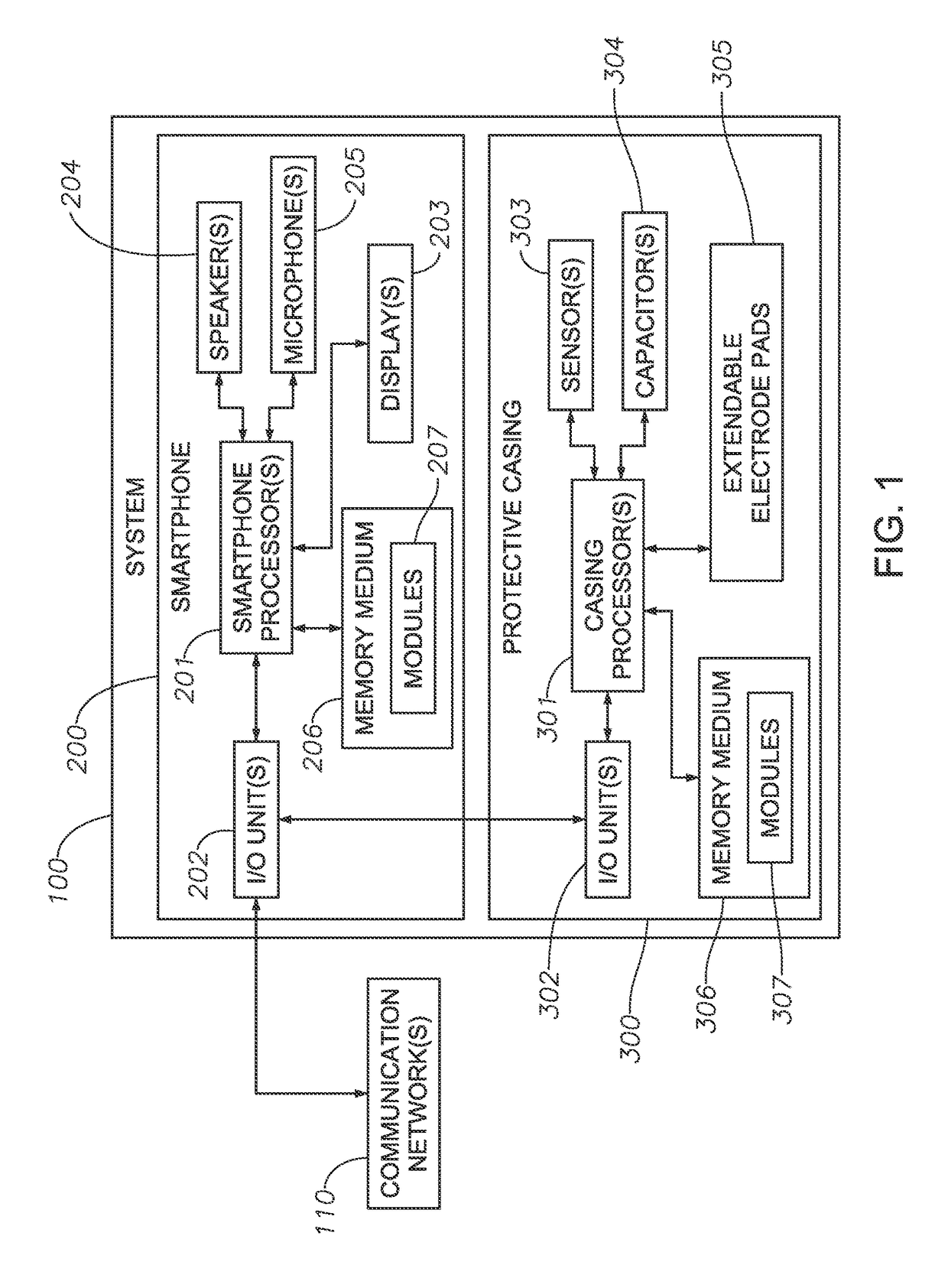
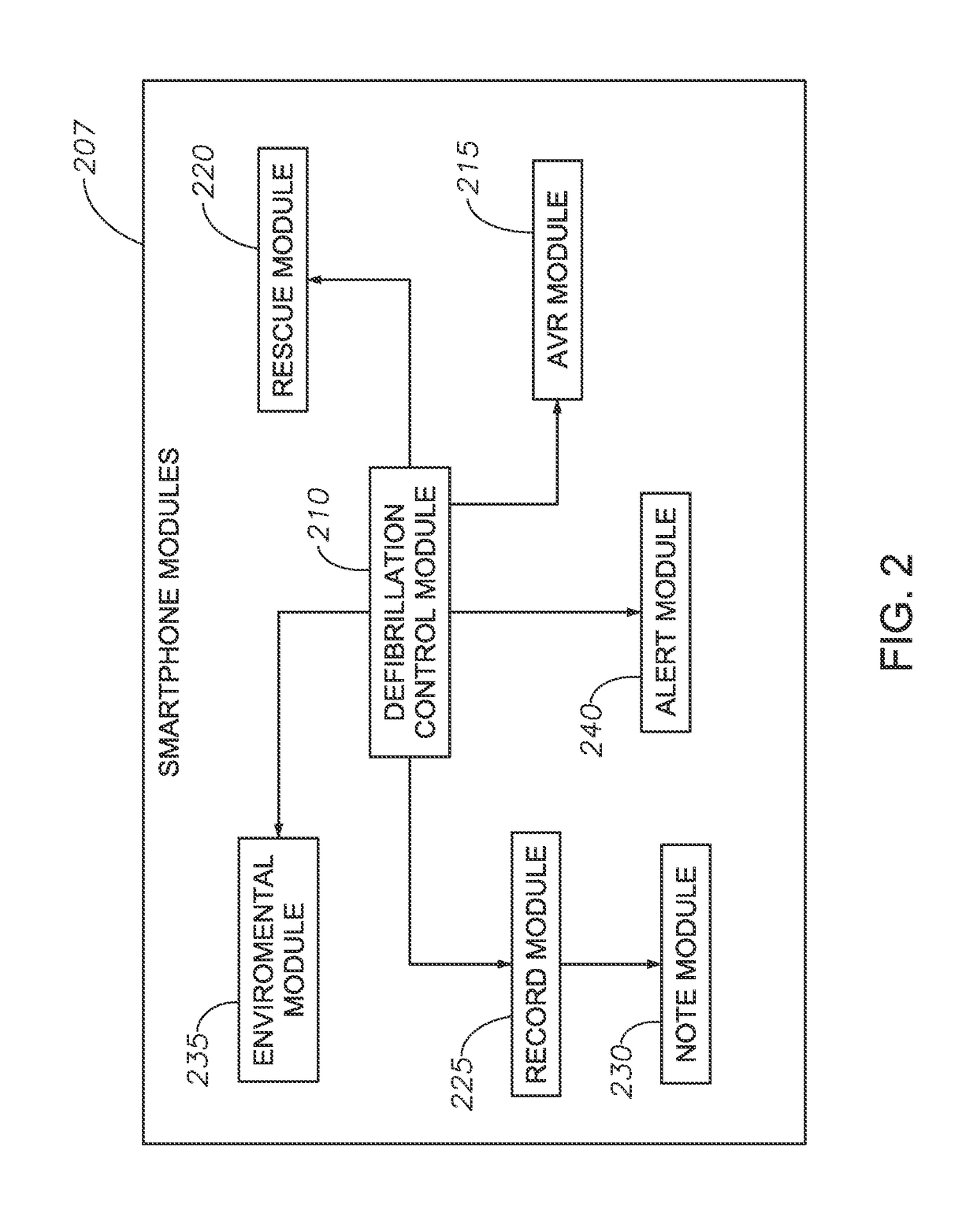
Systems, Protective Casings For Smartphones, And Associated Methods To Enhance Use Of An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Device
ActiveUS20170157415A1Improve usabilityIncreased riskPhysical therapies and activitiesHeart defibrillatorsEngineeringAutomated external defibrillator
Embodiments of the invention include systems, protective casings for smartphones, and associated methods to enhance use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) device before arrival of emergency medical personnel. A system can include a smartphone and a protective casing abuttingly contacting one or more side portions of the smartphone and retaining the smartphone positioned therein. The smartphone can include a defibrillation control module to control defibrillation of a victim of sudden cardiac arrest. The protective casing can include sensors, capacitors, and extendable electrode pads. The protective casing further can include a check module to determine whether the victim's heart rhythm requires an electrical shock to reestablish a normal heart rhythm, a space module to measure presence and amount of preselected materials relatively near the system, and a shock module to activate the one or more capacitors and generate an electrical current to deliver an electrical shock to the victim's chest.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Reforming wet-tantalum capacitors in implantable defibrillators and other medical devices
Miniature defibrillators and cardioverters detect abnormal heart rhythms and automatically apply electrical therapy to restore normal heart function. Critical components in these devices are aluminum electrolytic capacitors, which store and deliver one or more life-saving bursts of electric charge to a heart of a patient. This type of capacitor requires regular “reform” to preserve its charging efficiency over time. Because reform expends valuable battery life, manufacturers developed wet-tantalum capacitors, which are generally understood not to require reform. Yet, the present inventors discovered through extensive study that wet-tantalum capacitors exhibit progressively worse charging efficiency over time. Accordingly, to address this problem, the inventors devised unique reform techniques for wet-tantalum capacitors. One exemplary technique entails charging wet-tantalum capacitors to a voltage equal to about 90% of their rated voltage and maintaining this voltage for about five minutes before discharging them.
Owner:WILSON GREATBATCH LTD
Personal safety and security mobile application responsive to changes in heart rate
A software app for a mobile device is disclosed for alerting a custodian of a person to be protected of an emergency situation involving the person to be protected. The app includes software instructions for carrying out a method including: establishing a range of normal heart rates for the person using a heart rate monitor; detecting a heart rate for the person that is outside of the established range; activating at least one of a camera, a microphone, an accelerometer, and a location indicator on the mobile device carried by the person; establishing a wireless data connection between the mobile device and a communication network; and transmitting data to the custodian from the activated camera, microphone, accelerometer, or location indicator via the communication network. The app can notify a custodian of a medical or safety emergency as it is happening, giving that custodian the ability to immediately notify emergency personnel.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
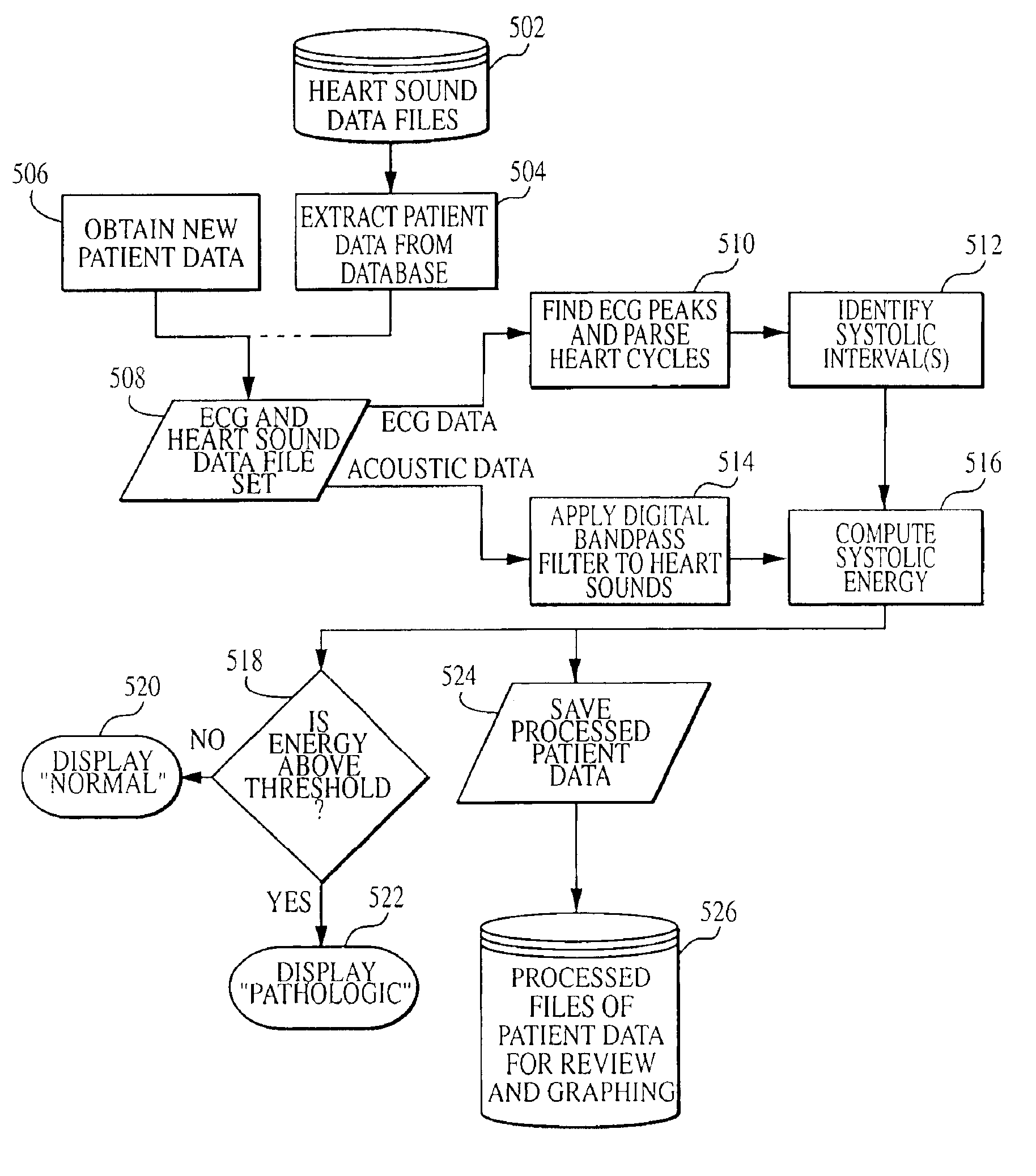
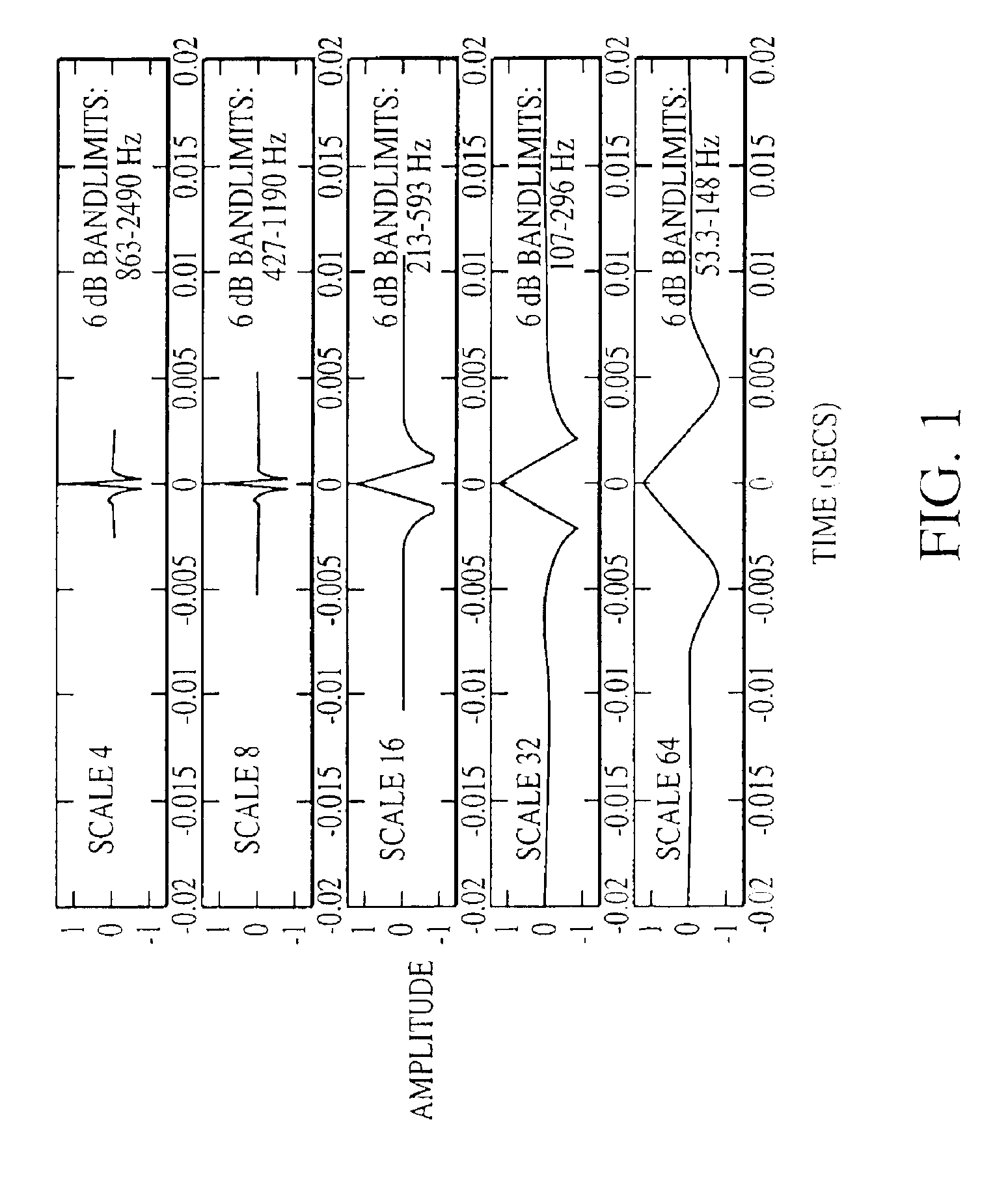
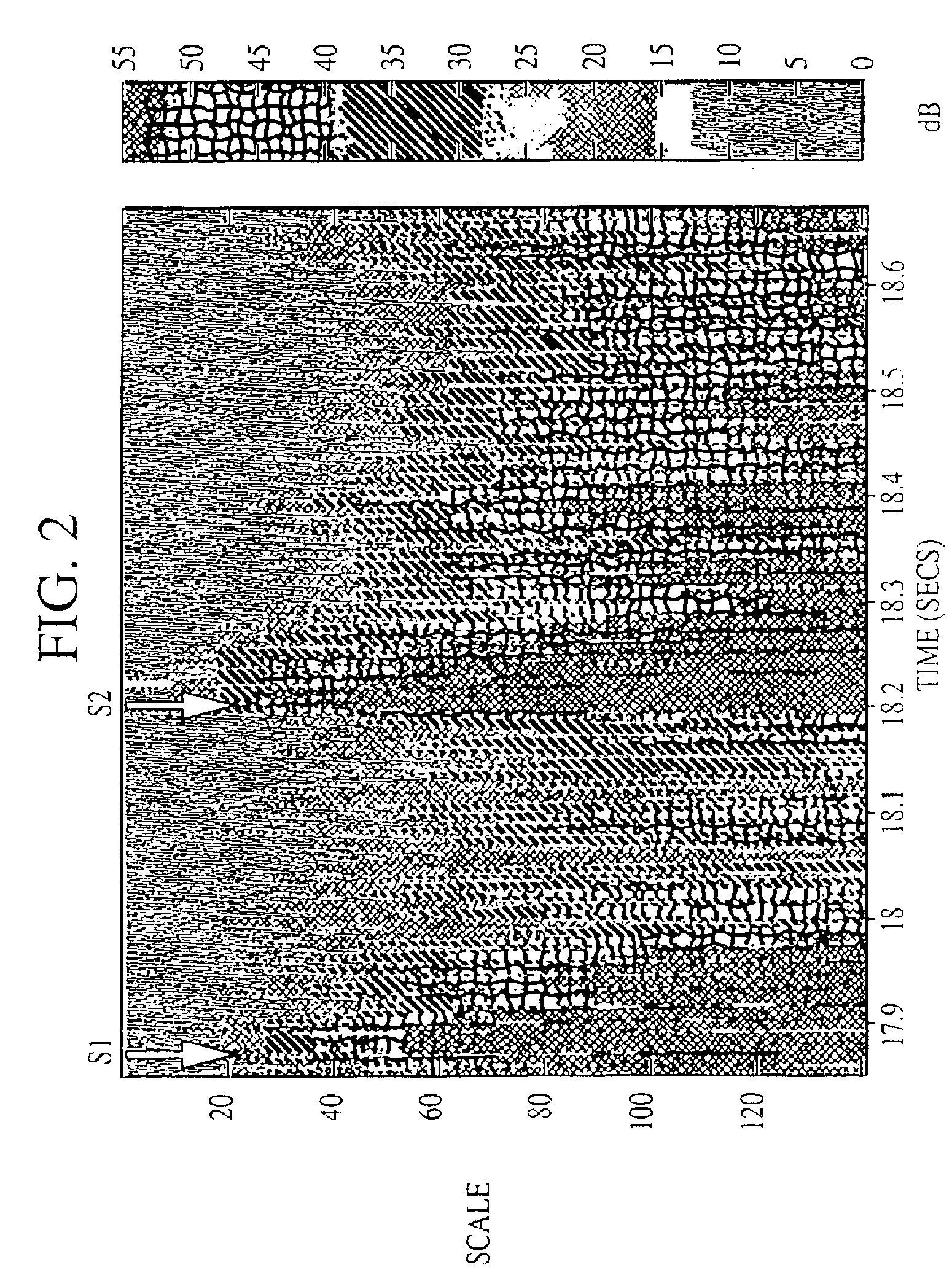
System and method for diagnosing pathologic heart conditions
A method of diagnosing pathologic heart conditions in which a time series of heart sounds is filtered and parsed into a sequence of individual heart cycles. A systolic interval as well as systolic sub-intervals are identified for each heart cycle. An energy value is computed for the systolic sub-interval of one or more heart cycles. The energy value computed is proportional to the energy level associated with the filtered series of heart sounds. A composite energy value is then computed for the systolic sub-intervals of one or more heart cycles and compared to a threshold level in order to distinguish between a normal heart and a pathologic heart. The system corresponding to the method is comprised of a portable computing device that manages data collection and stores data collected from new patients, and analyzes data.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Systems, protective casings for smartphones, and associated methods to enhance use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) device
ActiveUS9889311B2Increased riskSurvival ratePhysical therapies and activitiesHeart defibrillatorsEngineeringAutomated external defibrillator
Embodiments of the invention include systems, protective casings for smartphones, and associated methods to enhance use of an automated external defibrillator (AED) device before arrival of emergency medical personnel. A system can include a smartphone and a protective casing abuttingly contacting one or more side portions of the smartphone and retaining the smartphone positioned therein. The smartphone can include a defibrillation control module to control defibrillation of a victim of sudden cardiac arrest. The protective casing can include sensors, capacitors, and extendable electrode pads. The protective casing further can include a check module to determine whether the victim's heart rhythm requires an electrical shock to reestablish a normal heart rhythm, a space module to measure presence and amount of preselected materials relatively near the system, and a shock module to activate the one or more capacitors and generate an electrical current to deliver an electrical shock to the victim's chest.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Server fan redundancy control method and device
InactiveCN110990199AReduce energy consumptionReduce noiseProgramme control in sequence/logic controllersRedundant hardware error correctionProgrammable logic deviceHeartbeat
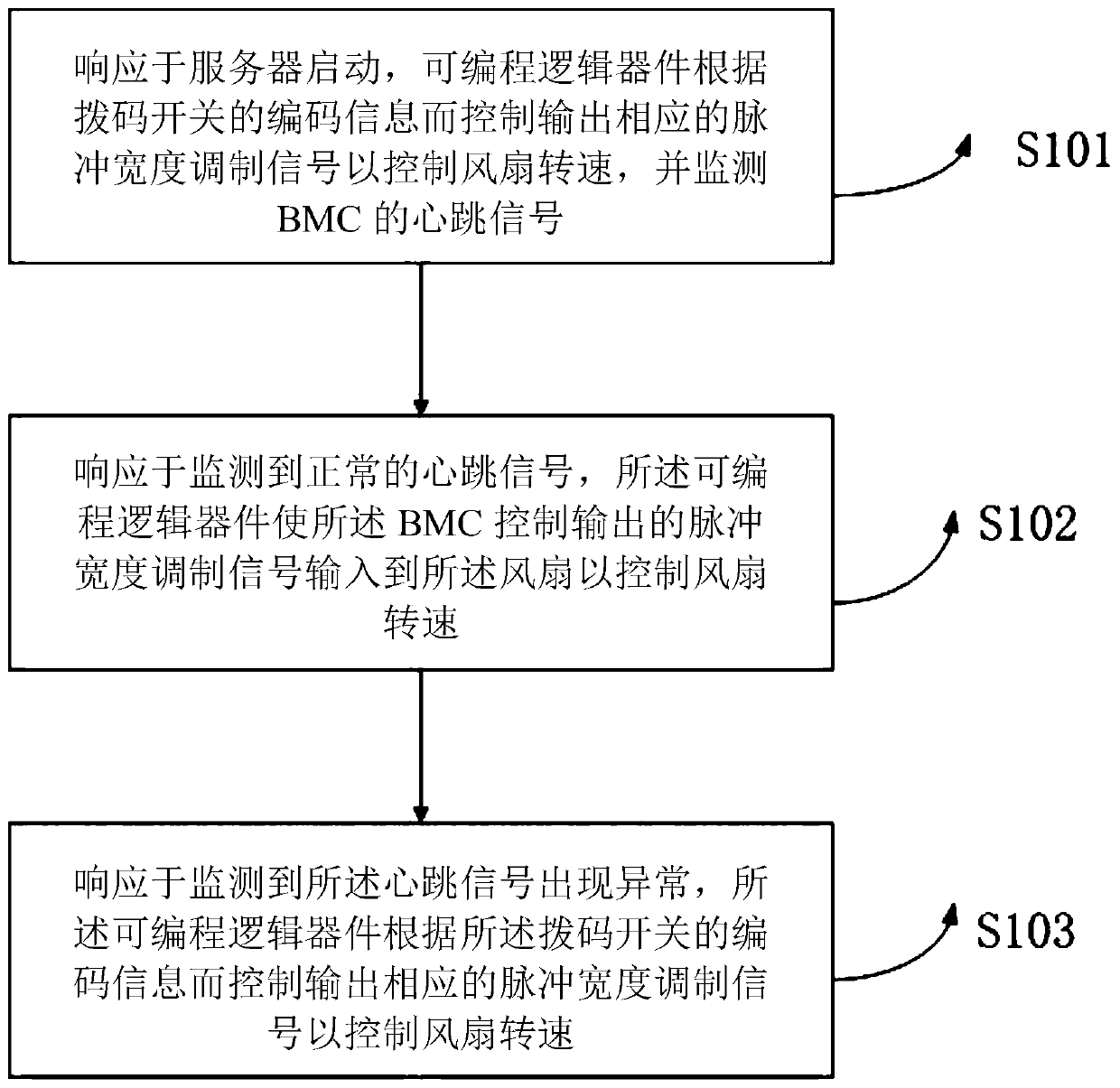
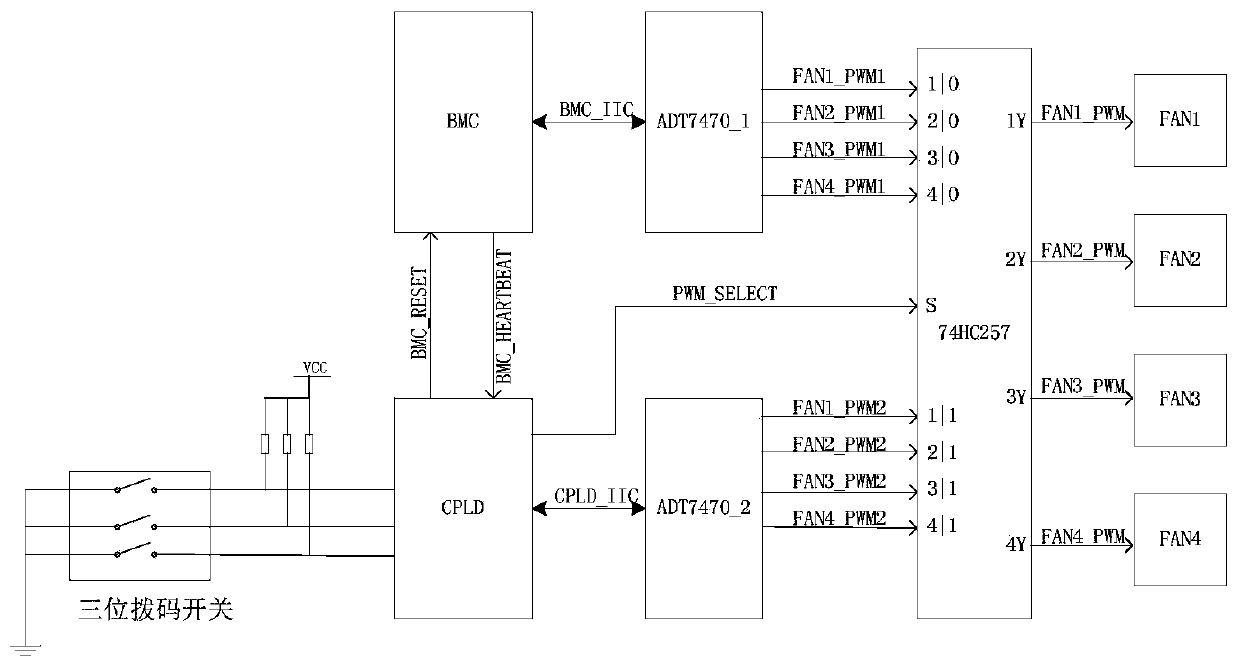
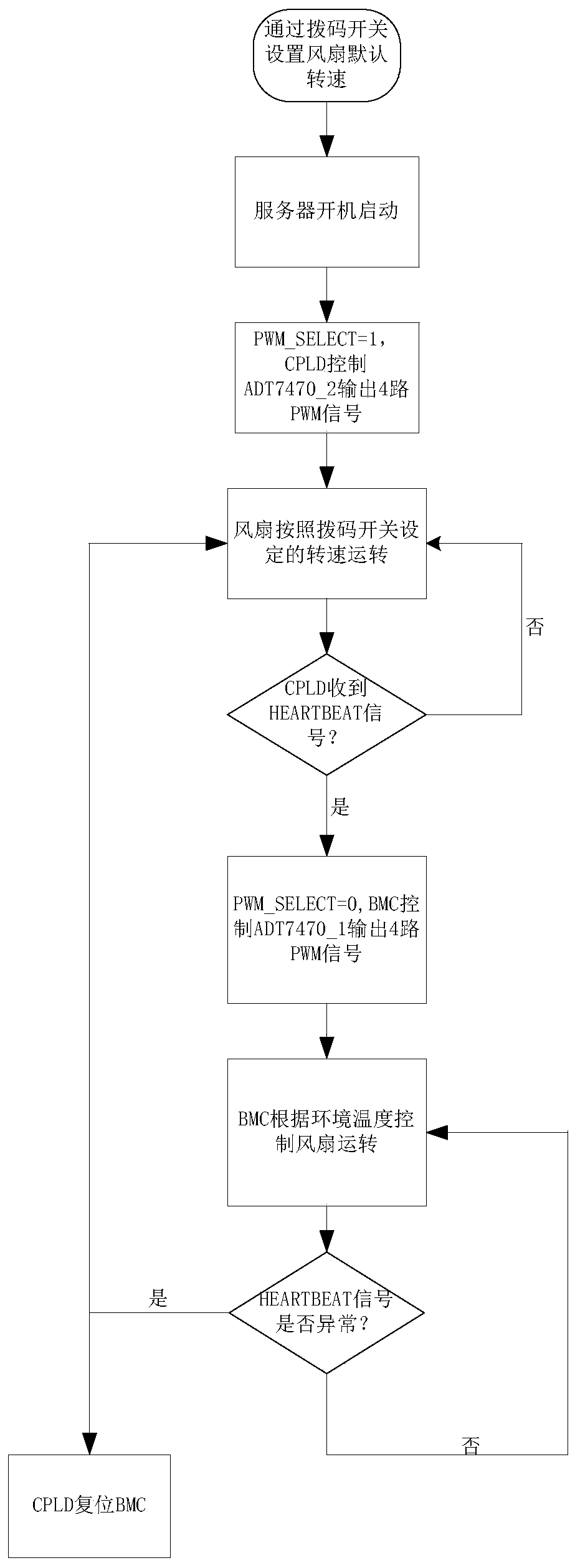
The invention provides a server fan redundancy control method, which comprises the following steps that: in response to the startup of a server, a programmable logic device controls to output a corresponding pulse width modulation signal according to the coding information of a dial switch so as to control the rotating speed of a fan, and monitors a heartbeat signal of a BMC (Baseboard ManagementController); in response to the monitored normal heartbeat signal, the programmable logic device enables a pulse width modulation signal controlled and output by the BMC to be input into the fan to control the rotating speed of the fan; and in response to monitoring that the heartbeat signal is abnormal, the programmable logic device controls to output a corresponding pulse width modulation signalaccording to the encoding information of the dial switch so as to control the rotating speed of the fan. According to the method, energy consumption and noise in the starting process of the server can be reduced, it can be ensured that the fan maintains a certain rotating speed under the condition that the BMC is hung up, and the reliability of the system is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Cardiopulmonary assist device
The present invention deals with a simple device to aid in cardiac compression to assist in reestablishing normal heart rhythm. The design and size of the device is particularly useful in morbidly obese individuals that require cardiac compressions in order to optimize resuscitation efforts.
Owner:KORNAKER KATHLEEN M
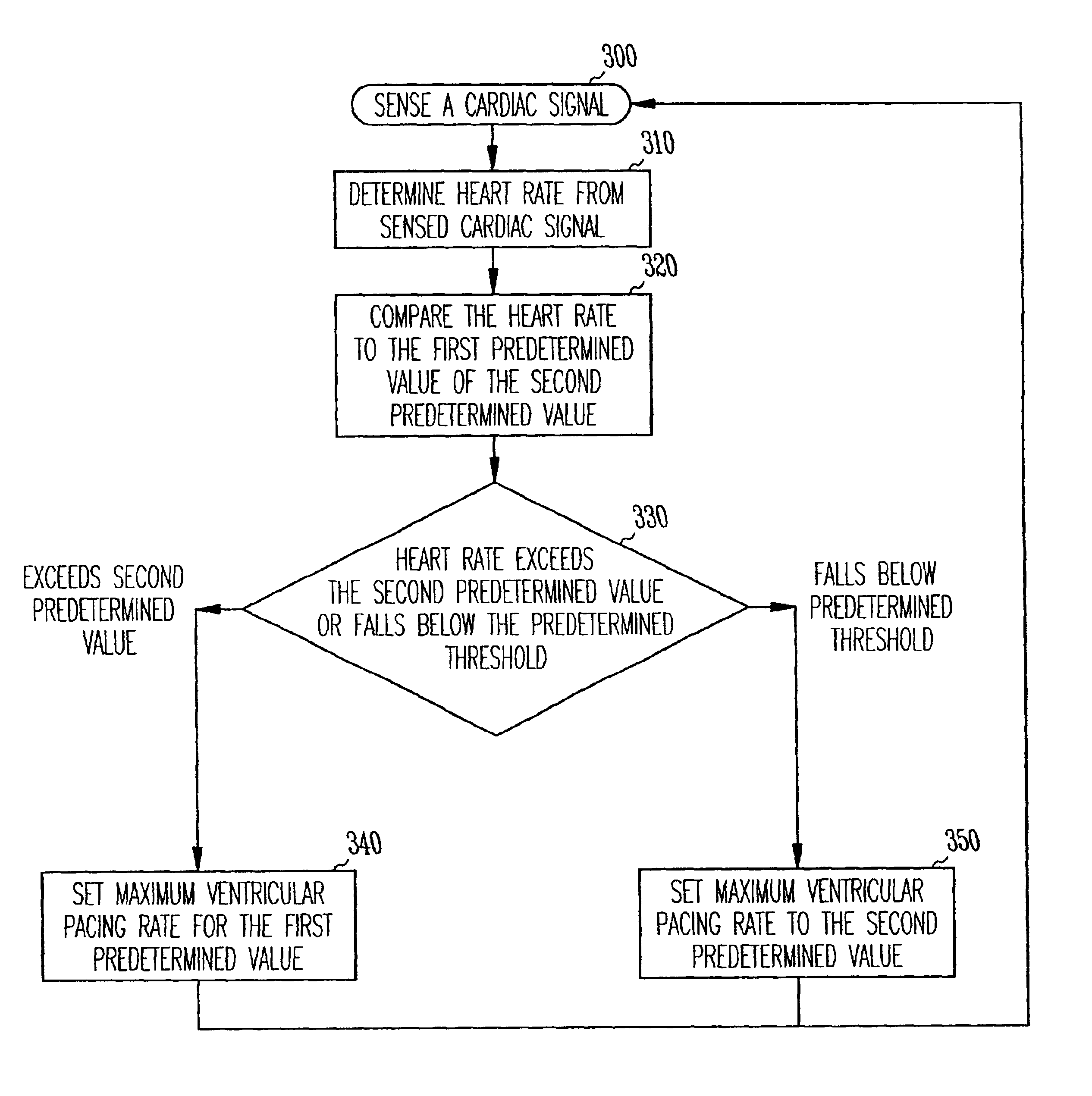
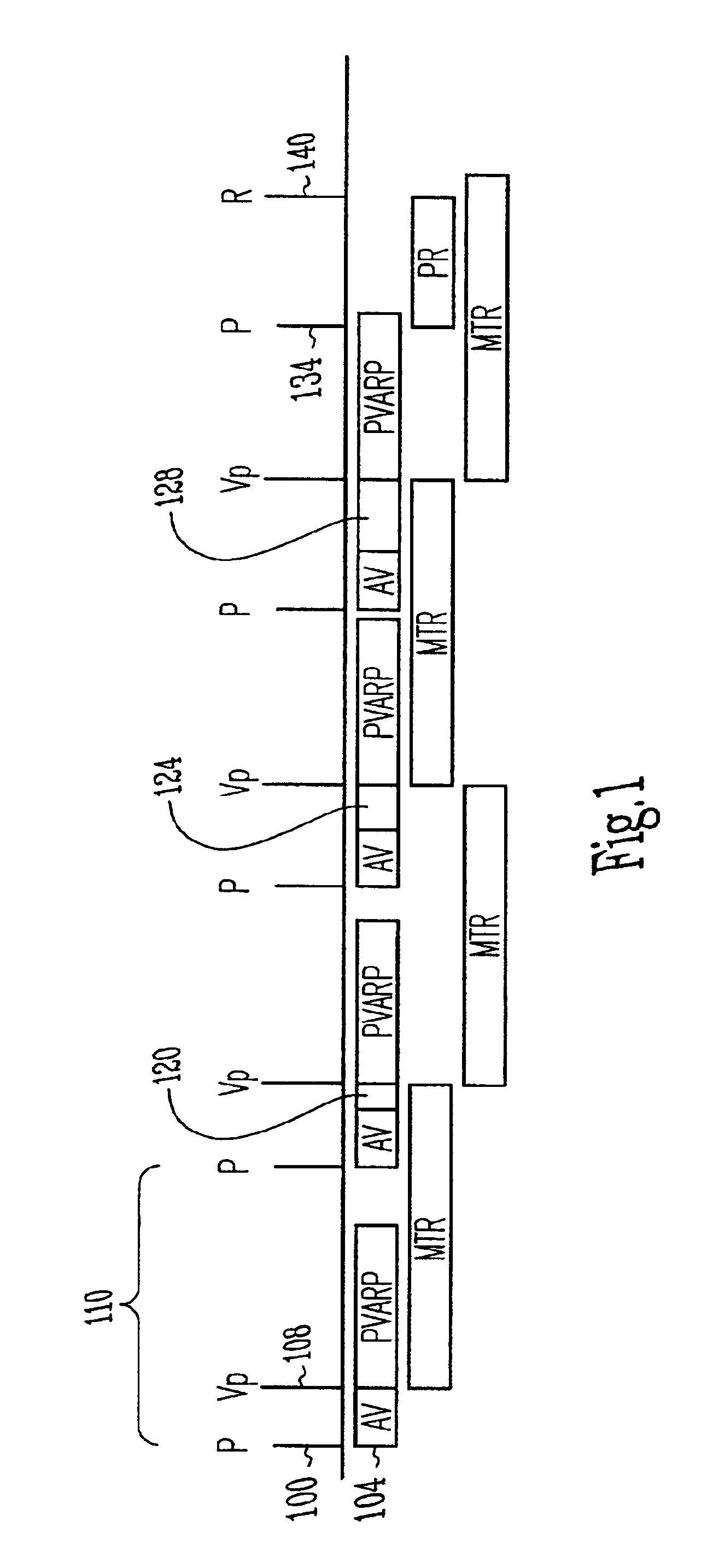
Cardiac rhythm management system with maximum tracking rate (MTR) hysteresis
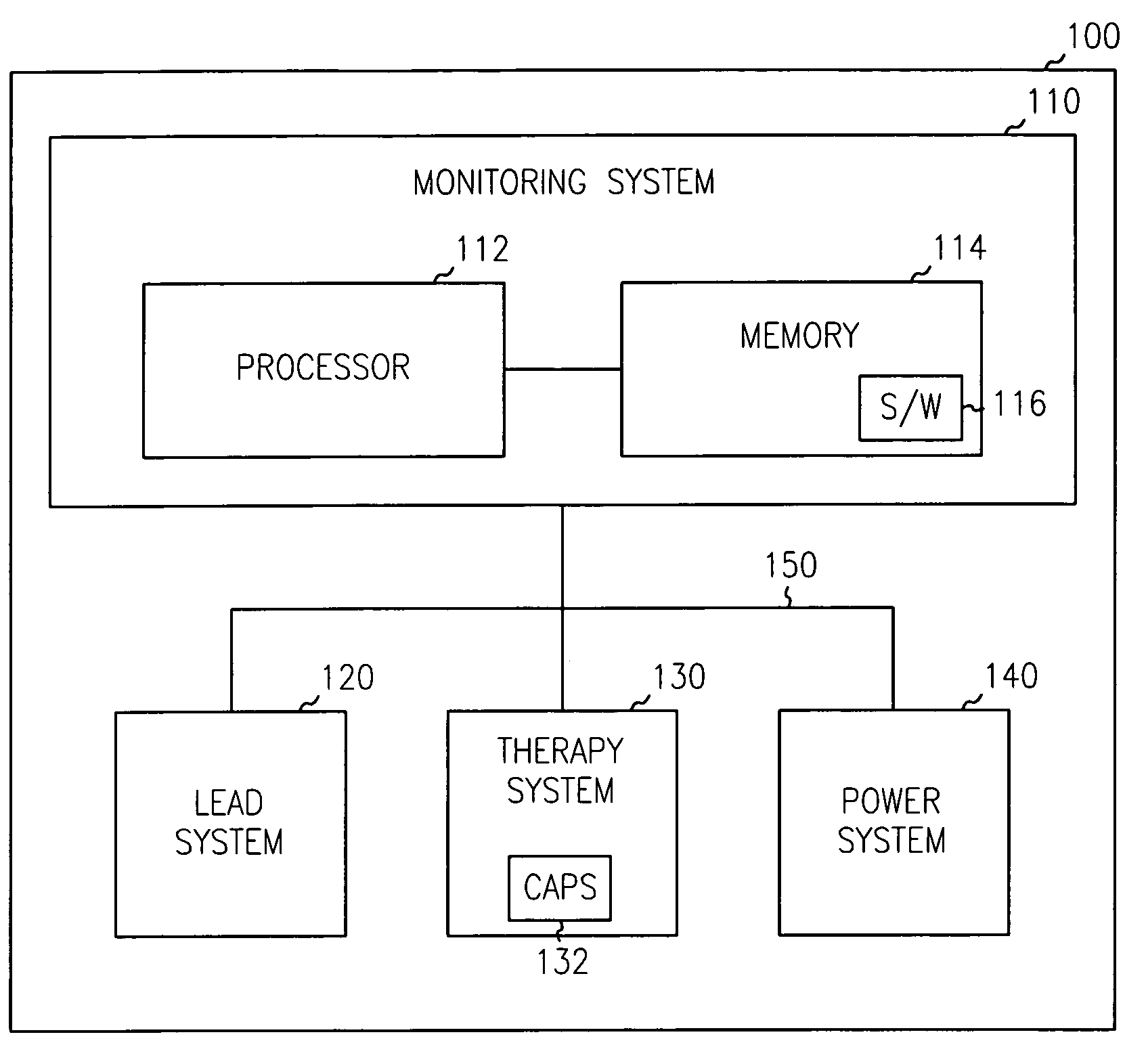
A cardiac rhythm management system provides both a safe maximum pacing rate limit and a physiological maximum pacing rate limit. The present subject matter provides a solution to problems associated with the use of a single maximum tracking rate (MTR). In one embodiment, the present subject matter utilizes two MTRs, where the first is a normal MTR and the second is a hysteresis MTR. In one embodiment, the hysteresis MTR is set higher than the normal MTR. The hysteresis MTR functions as a maximum pacing rate limit while tracking an atrial rate until the atrial rate exceeds the hysteresis MTR limit. When the atrial rate exceeds the hysteresis MTR limit, the maximum pacing rate limit is set to the normal MTR. Once the atrial rate falls below a predetermined threshold, the maximum pacing rate limit is set to the hysteresis MTR. The predetermined threshold may be set to the normal MTR, the hysteresis MTR, or other rates. In one embodiment, changing the maximum pacing rate limit in this fashion allows for uninterrupted pacing treatment for patients, such as congestive heart failure (CHF) patients, who may display fast but physiologically normal heart rates and need cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) at such fast heart rates. Such a pacing treatment provides for a more rapid and natural maximum pacing rate limit for the patient, while still protecting the patient from being paced at abnormally high rates.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
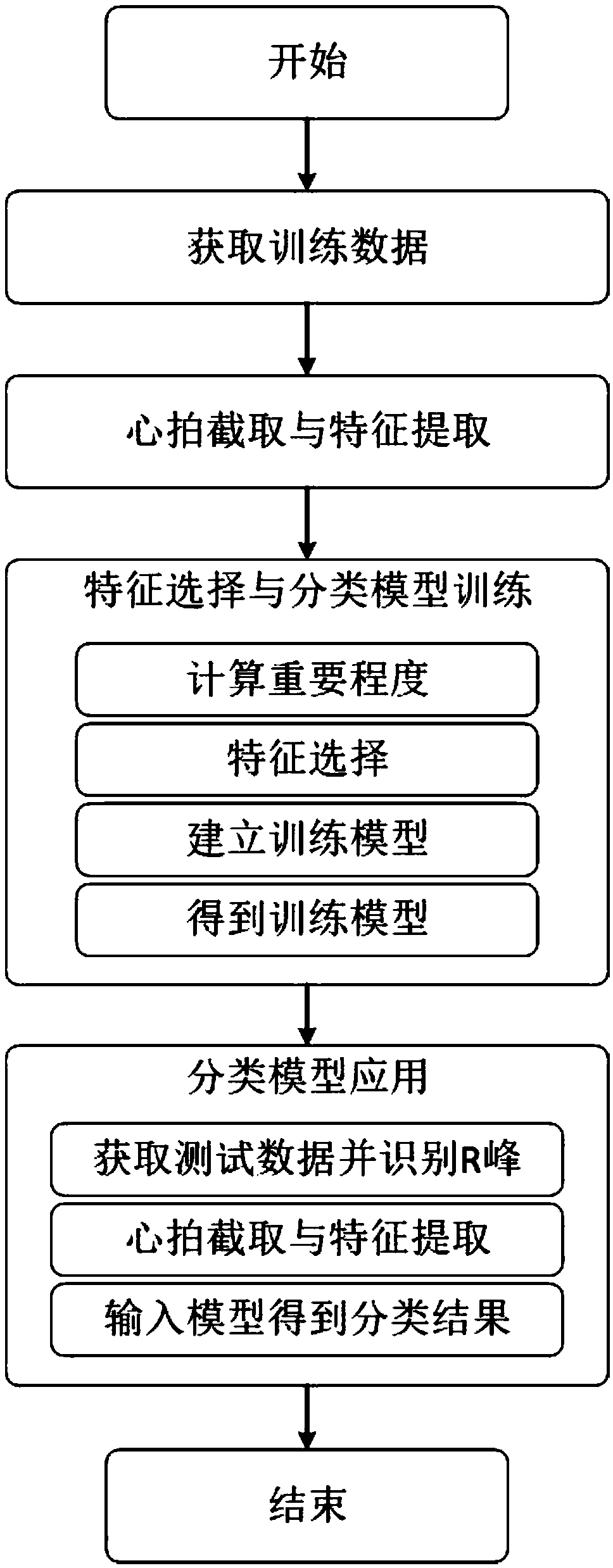
Dynamic electrocardiogram heart beat classification method based on gradient boosting decision tree
ActiveCN109303559AAccurate identificationAvoid the influence of abnormal heartbeatDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalSupraventricular Ectopic Beats
The invention relates to a dynamic electrocardiogram heart beat classification method based on a gradient boosting decision tree. The method comprises the steps that in actual dynamic electrocardiogram, classification is conducted on single heart beats in an electrocardiogram signal according to whether or not arrhythmia exists and the types of arrhythmia, specific classification categories comprise normal heart beats, supraventricular ectopic beat heart beats, ventricular ectopic beats, ventricular beat and normal beat fusion heart beats and pacemaker heart beats; the method comprises the following steps that 1, training data is obtained; 2, heart beat interception and feature extraction are conducted; 3, feature selection and classification model training are conducted; 4, classificationmodel application is conducted, wherein a tree-model-based feature selection method is adopted in step 3 to select features, and the classification model is trained through a gradient boosting decision tree classification method. The method is suitable for arrhythmia classification training of dynamic electrocardiogram and classification identification of different types of heart beats, and a doctor can be assisted in accurately reading and analyzing the electrocardiogram.
Owner:杭州质子科技有限公司
Cardiac simulation device
The present invention describes a device and system for simulating normal and disease state cardiac functioning, including an anatomically accurate left cardiac simulator for training and medical device testing. The system and device uses pneumatically pressurized chambers to generate ventricle and atrium contractions. In conjunction with the interaction of synthetic mitral and aortic valves, the system is designed to generate pumping action that produces accurate volume fractions and pressure gradients of pulsatile flow, duplicating that of a human heart. Through the use of a remote handheld electronic controller and manual adjustments from a main control panel, the air pressure level, fluidic pressure, and heart rate is controlled to induce contractions that simulate a wide variety of heart conditions ranging from normal heart function to severely diseased or injured heart conditions.
Owner:MENTICE
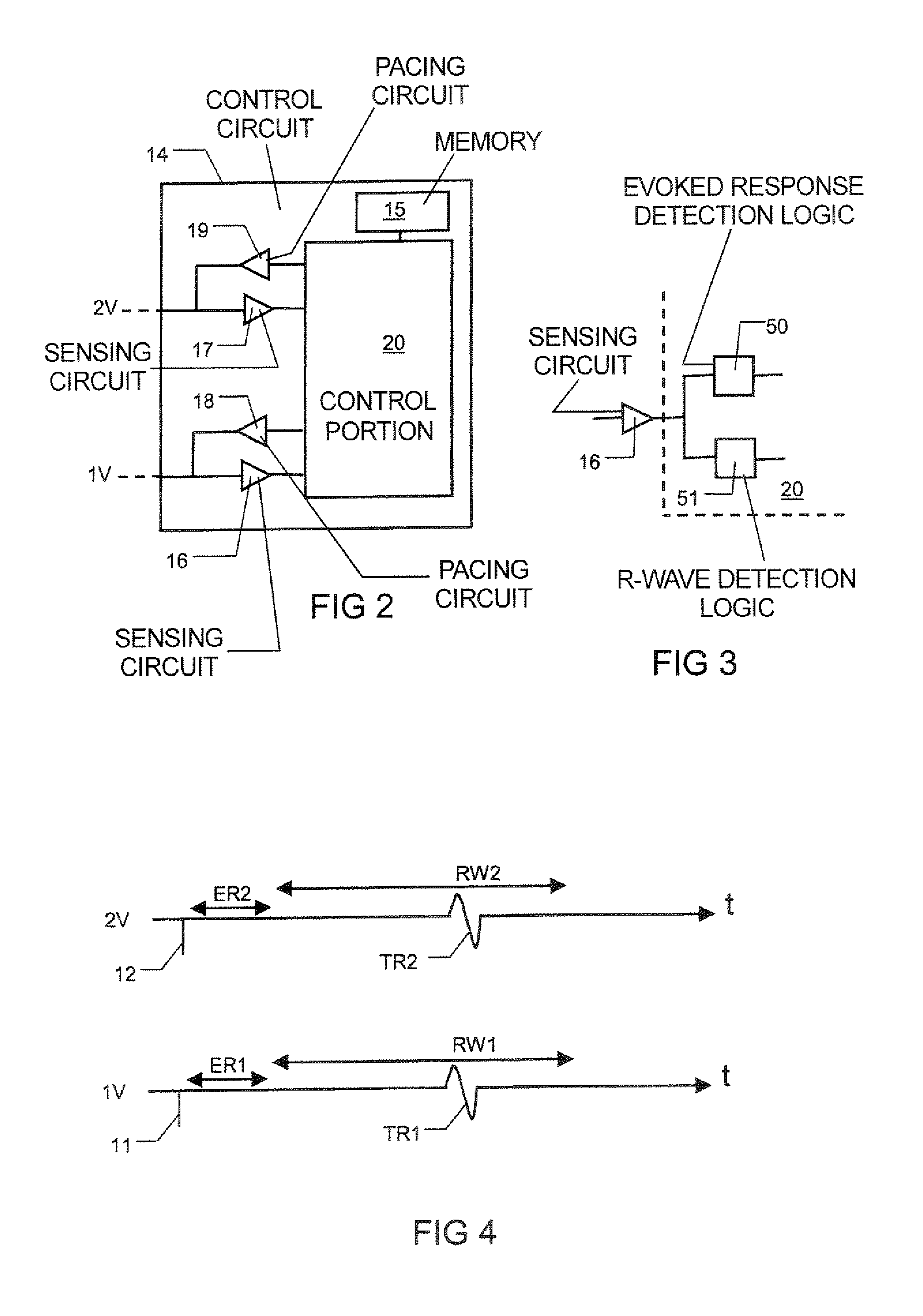
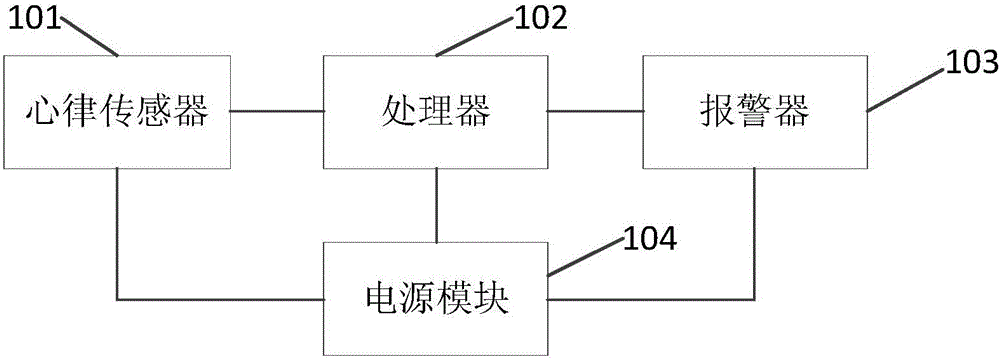
Bi-ventricular pacer, system and method
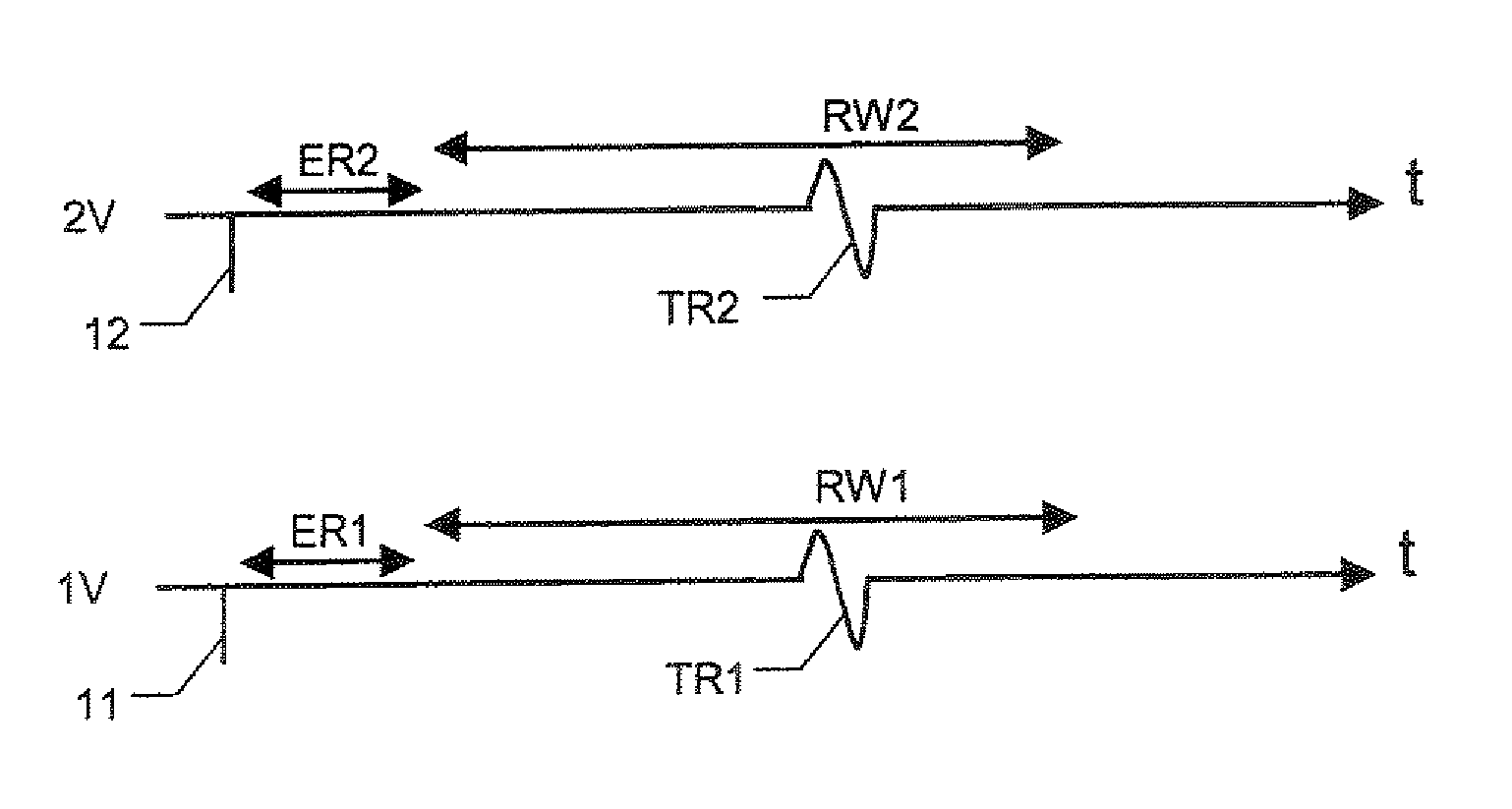
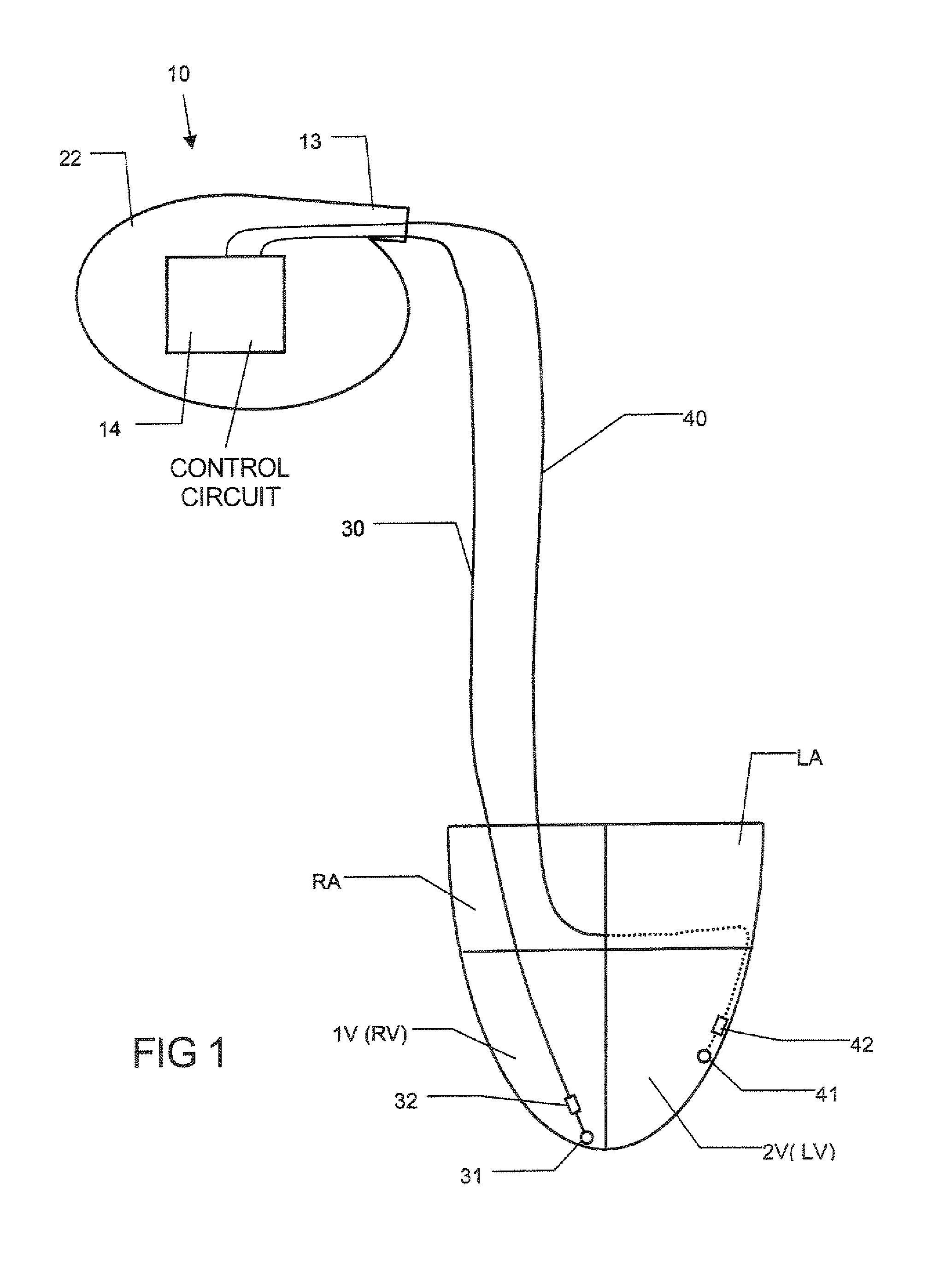
An implantable bi-ventricular heart stimulating device and system, suitable for treating congestive heart failure, have a control circuit with first and second pacing circuits and first and second sensing circuits. The device operates with time cycles corresponding to normal heart cycles. The control circuit determines: (a) whether a signal typical of an evoked response to a pacing pulse delivered by the first pacing circuit is sensed within a first time interval and (b) whether a signal typical for an R-wave transferred from the second ventricle, or from some other part of the heart, to the first ventricle is detected within a first time window. The operation of the device depends on whether the conditions (a) and (b) are fulfilled.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
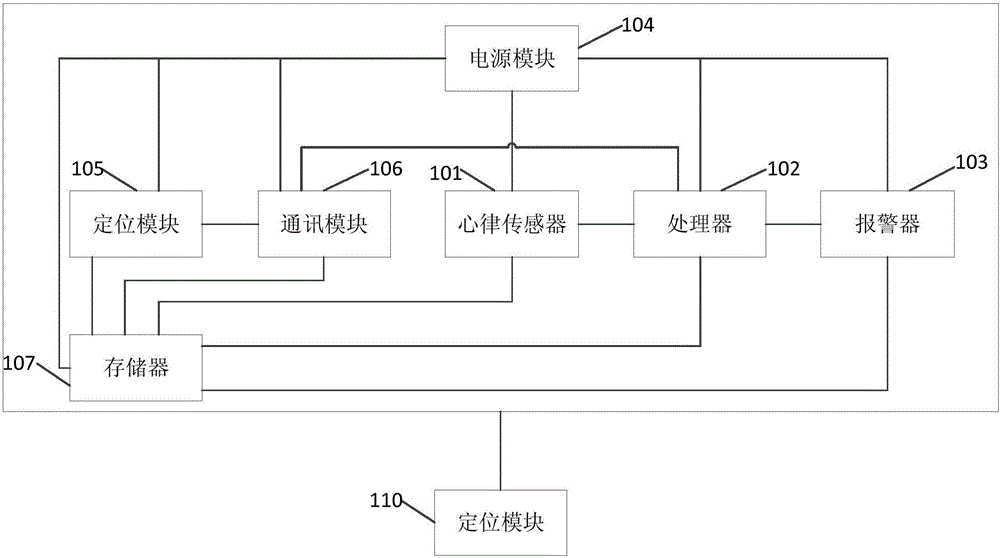
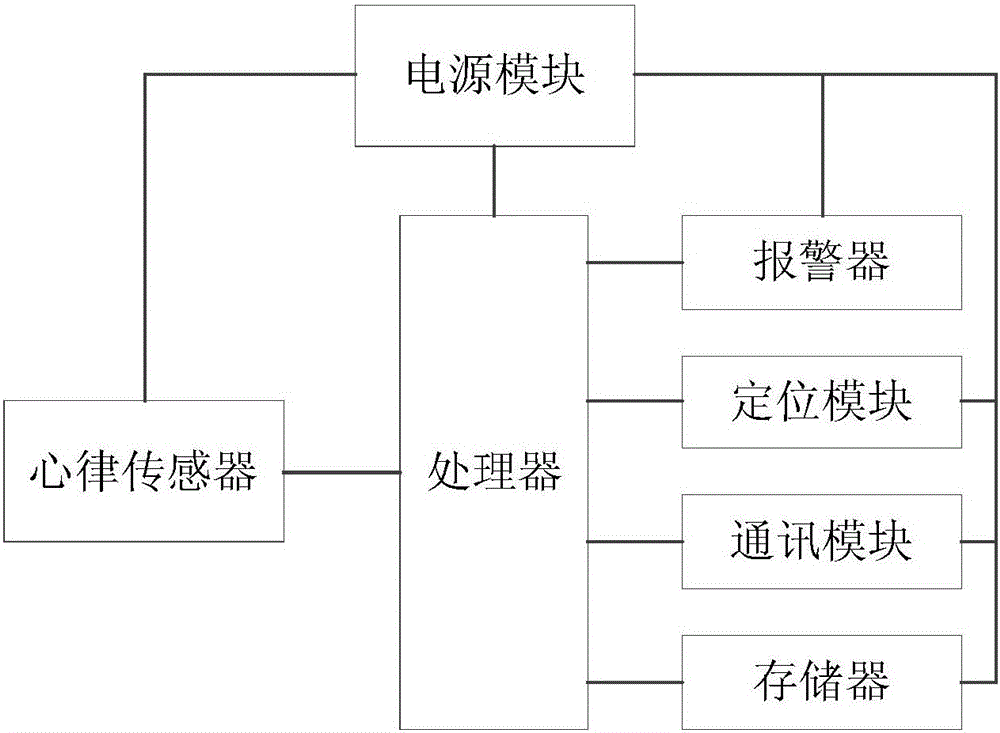
Heart rhythm monitoring device
PendingCN105852840ATimely rescueDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAlarm messageCardiac rhythm monitoring
An embodiment of the invention discloses a heart rhythm monitoring device. The heart rhythm monitoring device comprises a heart rhythm sensor, a processor, an alarm and a power module, wherein the heart rhythm sensor is used for acquiring heart rhythm information in real time and outputting the heart rhythm information; the processor is used for acquiring the heart rhythm information and sending alarm information after detecting that the heart rhythm information exceeds a normal heart rhythm threshold value; the alarm is used for giving out an alarm according to the alarm information; the power supply module is used for supplying power to the heart rhythm sensor, the processor and the alarm. The heart rhythm monitoring device is used for monitoring the heart state of a user in real time; the processor sends out the alarm information after determining that the heart of a patient has a hidden safety risk, so that the alarm can give out an alarm; the heart rhythm monitoring device can monitor the patient feeling uncomfortable in the heart in real time, can remind the patient when the heart of the patient has a hidden safety risk and can remind people around the patient to help the patient when an emergency occurs to the patient.
Owner:GREE ELECTRIC APPLIANCES INC
Treatment of cardiovascular disorders using the cell differentiation signaling protein Nell1
ActiveUS20090087415A1Avoid delayShorten the progressOrganic active ingredientsBiocideBlood vesselNormal heart
It has been identified in accordance with the present invention that Nell1 is essential for normal cardiovascular development by promoting proper formation of the heart and blood vessels. The present invention therefore provides therapeutic methods for treating cardiovascular disorders by employing a Nell1 protein or nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
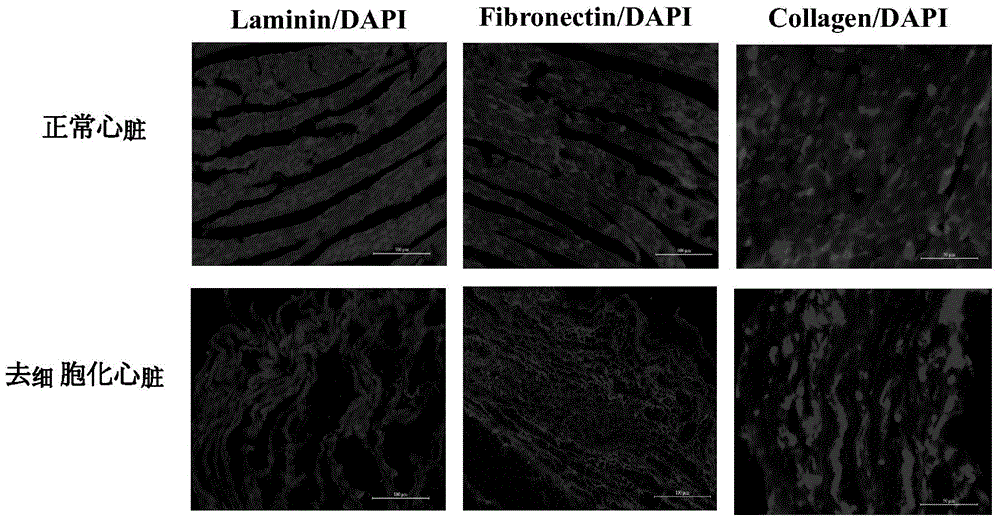
Human tissue-engineered cardiac muscle tissue
InactiveCN104940997ARealize individualized treatmentGood biocompatibilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsProsthesisInduced pluripotent stem cellCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical engineering, and relates to a human tissue-engineered cardiac muscle tissue and a preparation method thereof. The human tissue-engineered cardiac muscle tissue disclosed by the invention is prepared by inoculating all kinds of cell components of a normal heart differentiated from human induced multipotential stem cells by taking a natural decellularized heart substrate as the scaffold. The human tissue-engineered cardiac muscle tissue has cell components, extracellular matrixes and biological functions similar to that of a normal human cardiac muscle tissue; testing and screening of in-vitro drugs, initial in-vivo transplantation researches of clinical earlier-stage small animals and observation of treatment effects can be carried out; and helps can be finally offered for realizing individualized treatment of human cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Cardiac simulation device
ActiveUS10229615B2Accurate volume fraction and pressure gradientAccurate representationEducational modelsDiseaseAutomatic control
Owner:MENTICE
Cardiac simulation device
ActiveUS20200160753A1Eliminate riskReduced collateral damageMedical simulationHealth-index calculationControl cellNeoaortic valve
A device and system for simulating normal and disease state cardiovascular functioning, including an anatomically accurate cardiac simulator for training and medical device testing. The system and device uses pneumatically pressurized chambers to generate ventricle and atrium contractions. In conjunction with the interaction of synthetic valves, which simulate mitral and aortic valves, the system is designed to generate pumping action that produces accurate volume fractions and pressure gradients of pulsatile flow, duplicating that of a human heart. Through the use of a control unit and sensors, one or more parameters, such as flow rates, fluidic pressure, and heart rate, may be automatically controlled, using feedback loop mechanisms to adjust parameters of the hydraulic system to simulate a wide variety of cardiovascular conditions including normal heart function, severely diseased or injured heart conditions, and compressed vasculature, such as hardening of the arteries.
Owner:MENTICE
Cardiac simulation device
PendingUS20210043113A1Eliminate riskReduced collateral damageFlow control using electric meansEducational modelsControl cellEngineering
The present invention describes a device and system for simulating normal and disease state cardiovascular functioning, including an anatomically accurate left cardiac simulator for training and medical device testing. The system and device uses pneumatically pressurized chambers to generate ventricle and atrium contractions. In conjunction with the interaction of synthetic valves, which simulate mitral and aortic valves, the system is designed to generate pumping action that produces accurate volume fractions and pressure gradients of pulsatile flow, duplicating that of a human heart. Through the use of a control unit and sensors, one or more parameters, such as flow rates, fluidic pressure, and heart rate, may be automatically controlled, using feedback loop mechanisms to adjust parameters of the hydraulic system to simulate a wide variety of cardiovascular conditions including normal heart function, severely diseased or injured heart conditions, and compressed vasculature, such as hardening of the arteries.
Owner:MENTICE
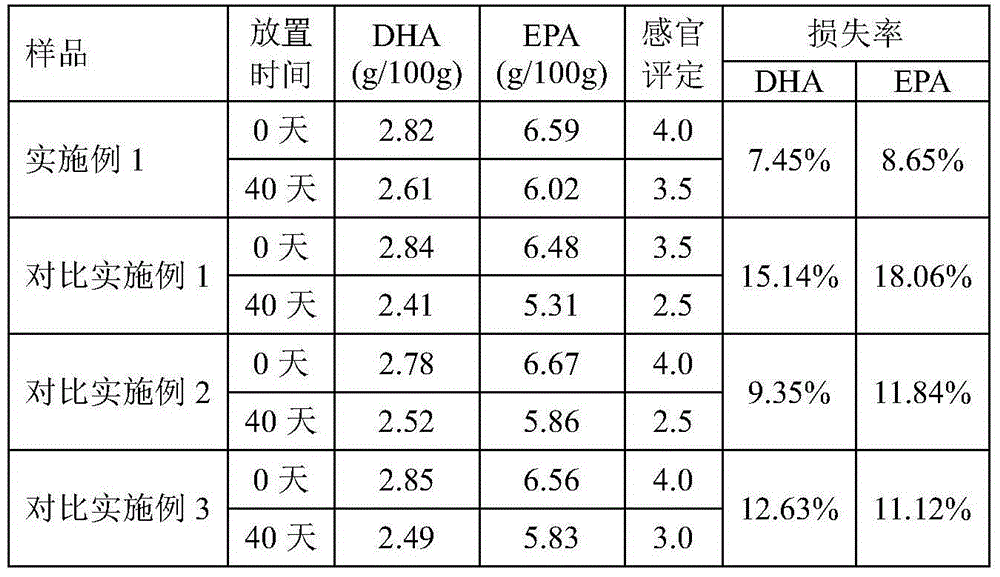
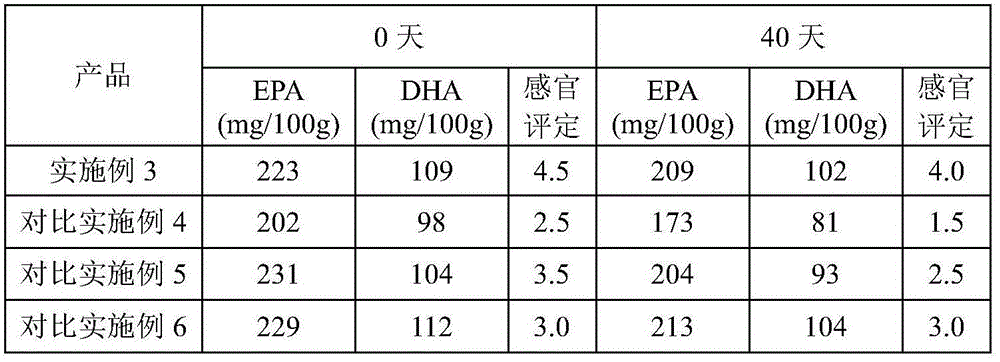
Fish oil composition, preparation method of fish oil composition and milk powder containing fish oil composition
The invention discloses a fish oil composition, a preparation method of the fish oil composition and milk powder containing the fish oil composition. The preparation method of the fish oil composition comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving sodium caseinate, vitamin E and lemon essence into water, and homogenizing and sterilizing to obtain an emulsion; (2) spraying the emulsion obtained in the step (1) onto fish oil powder, and meanwhile, drying to obtain the fish oil composition. According to the preparation method of the fish oil composition, the fishlike smell of the fish oil is covered successfully and the flavor of the product is improved; EPA and DHA in the milk powder have a good anti-oxidization effect and the stability of the quality of the milk powder is improved; the total content of the EPA and the DHA of the milk powder containing the fish oil is within the range of 100-350mg / 100g, and is equivalently 40%-140% of the daily intake (250mg) recommended and declared by European Commission so as to be beneficial to maintaining the normal heart functions.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com