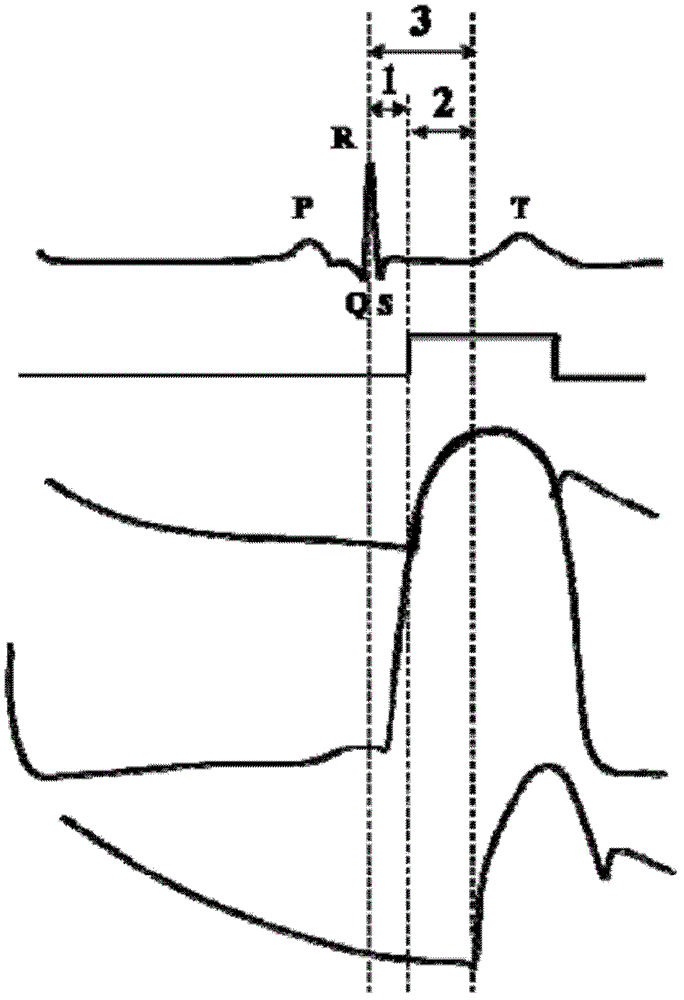
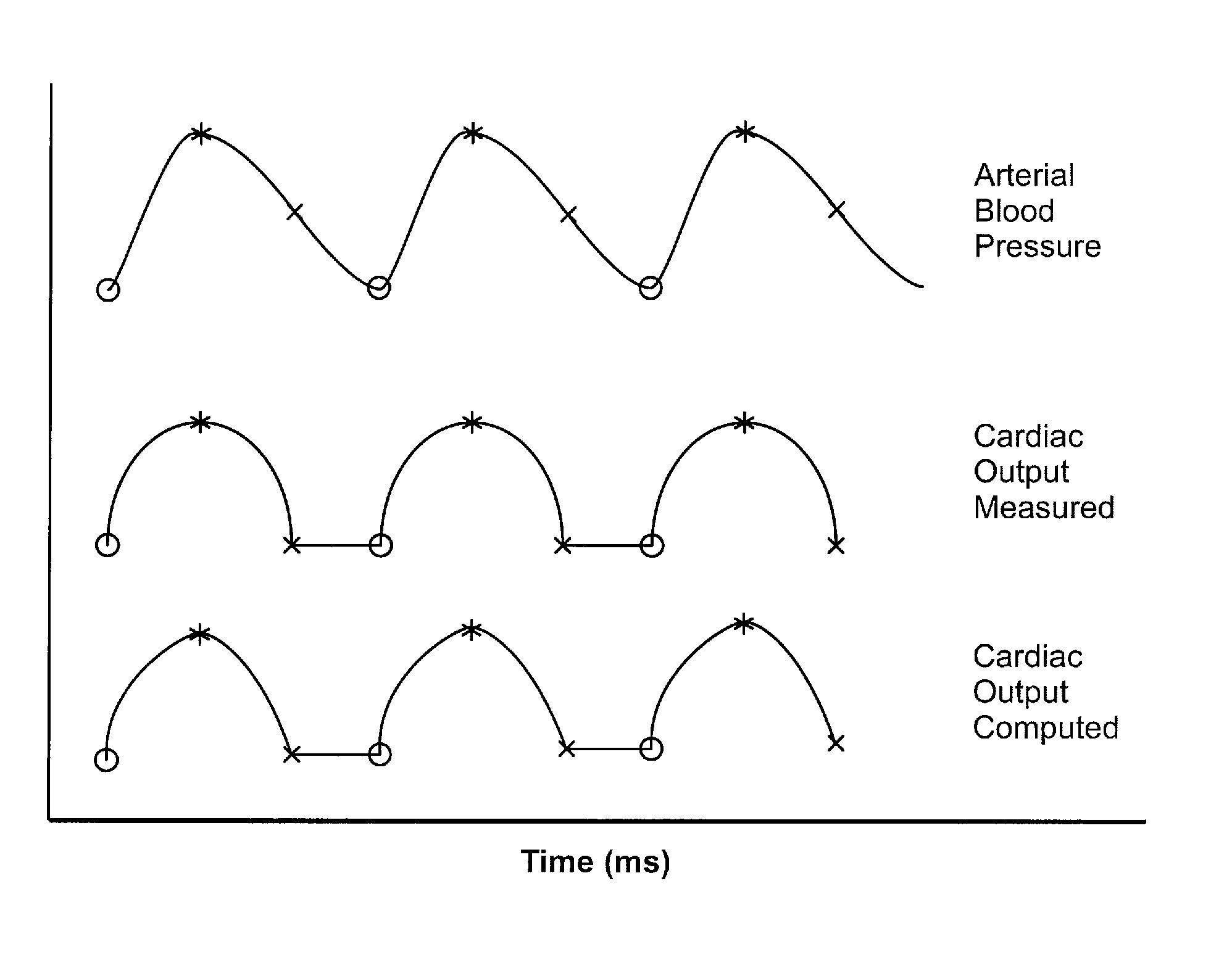
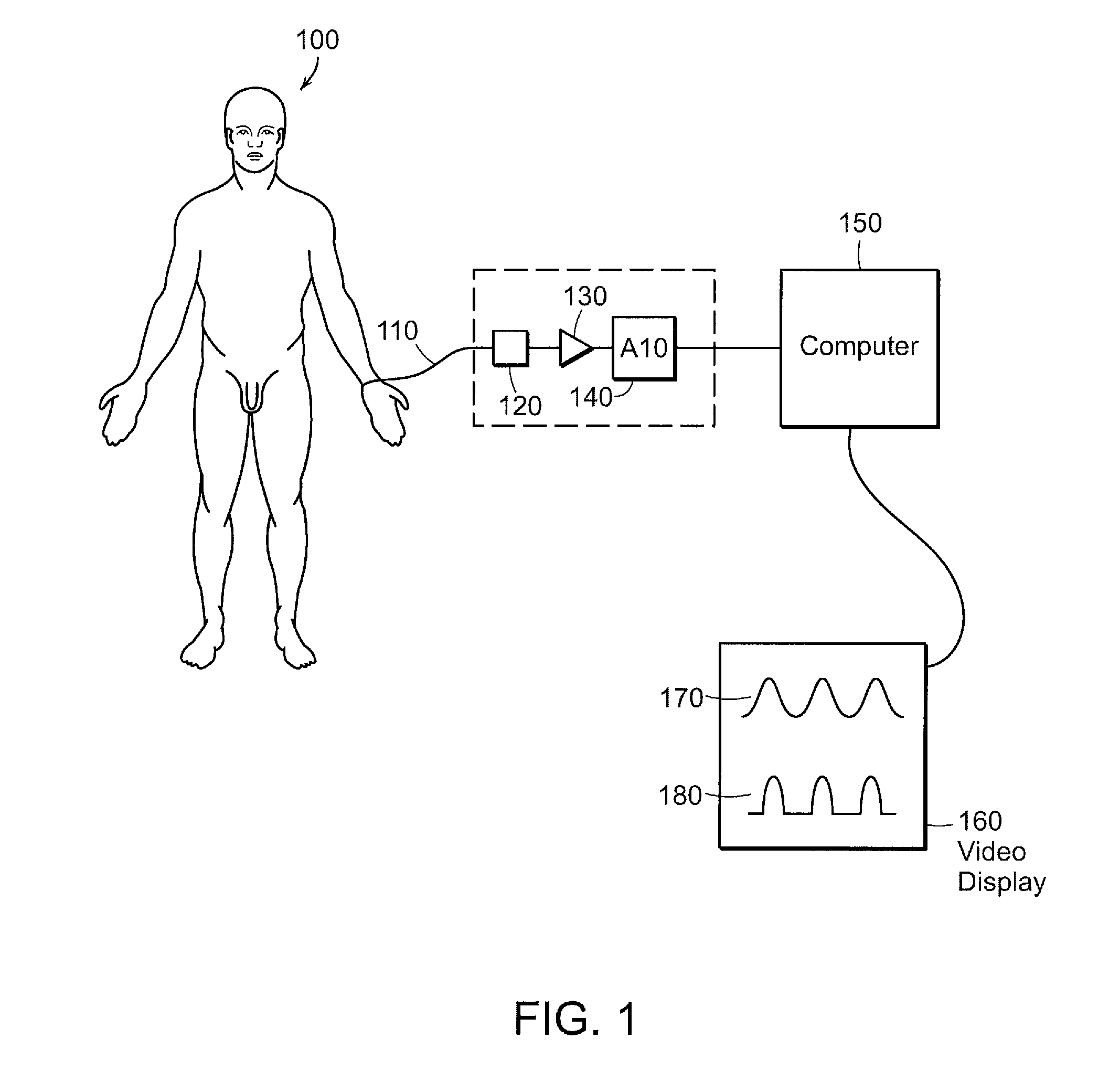
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Heart output" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cardiac output (CO) the volume of blood expelled by the ventricles of the heart with each beat (the stroke volume) multiplied by the heart rate. Cardiac output is commonly measured by the thermodilution technique. A normal, resting adult has a cardiac output of 4 to 8 L per minute.
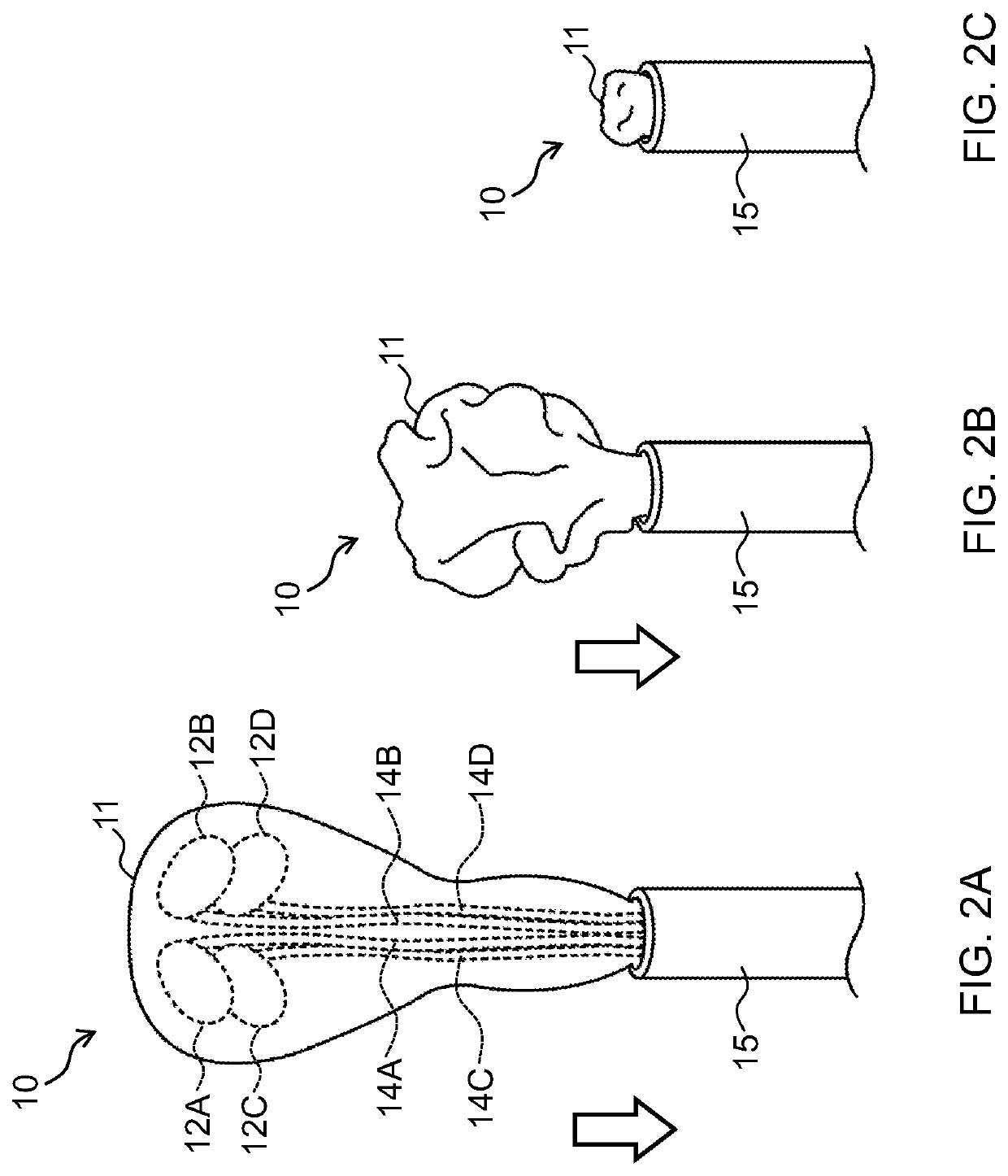
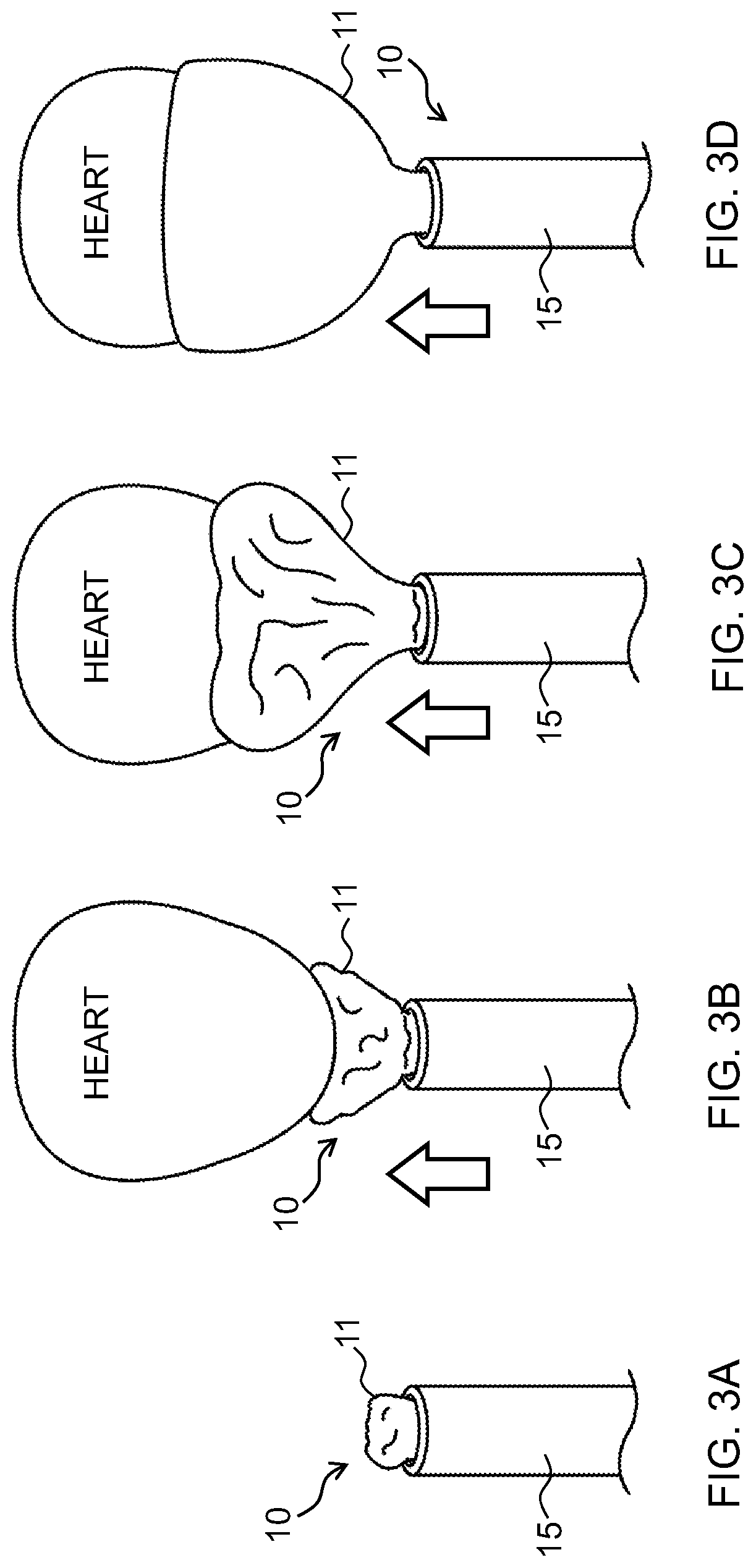
Device to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
InactiveUS6019722ALess effectEliminate needSurgical pincettesProsthesisLess invasive surgeryCardiac retractor
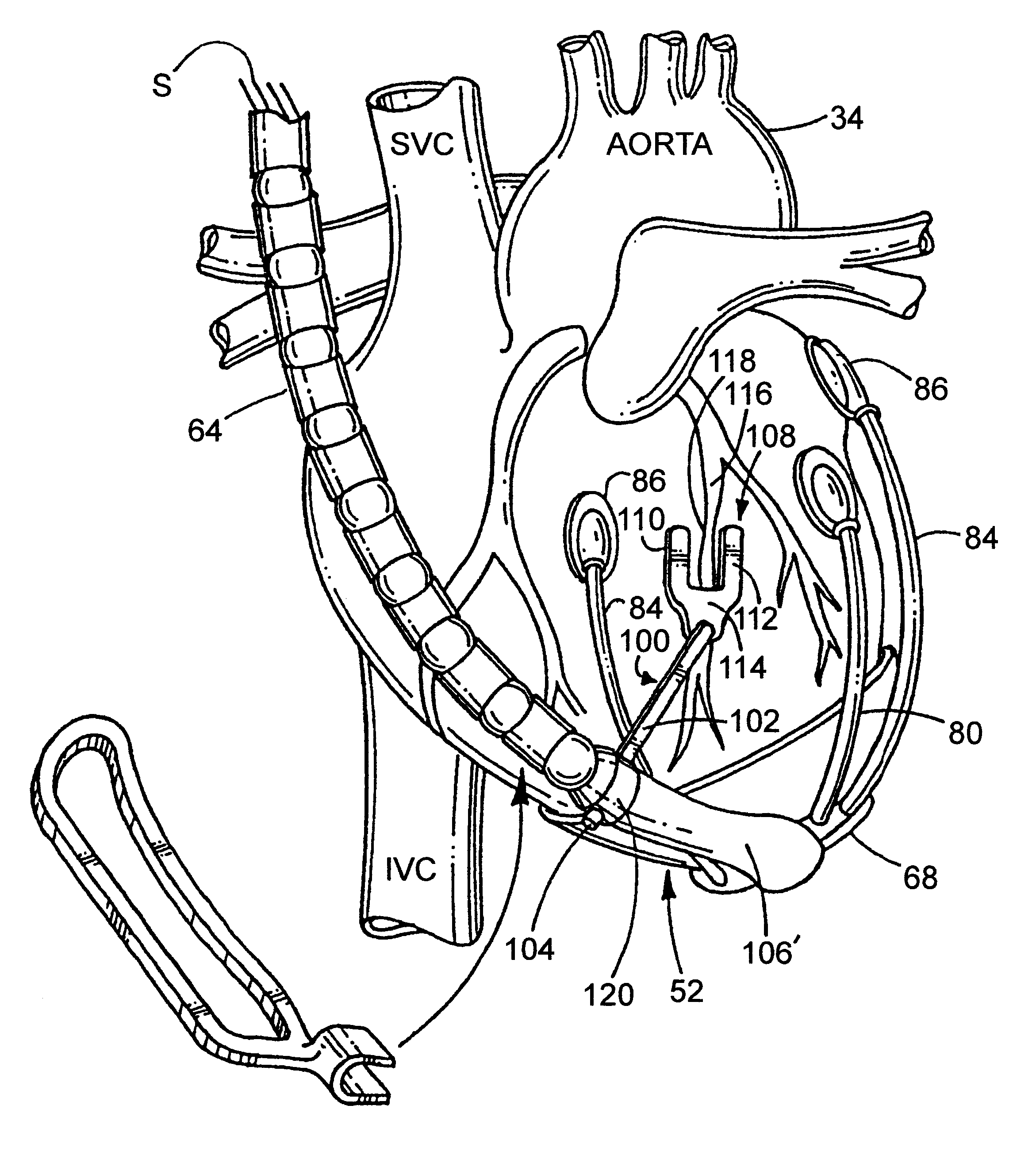
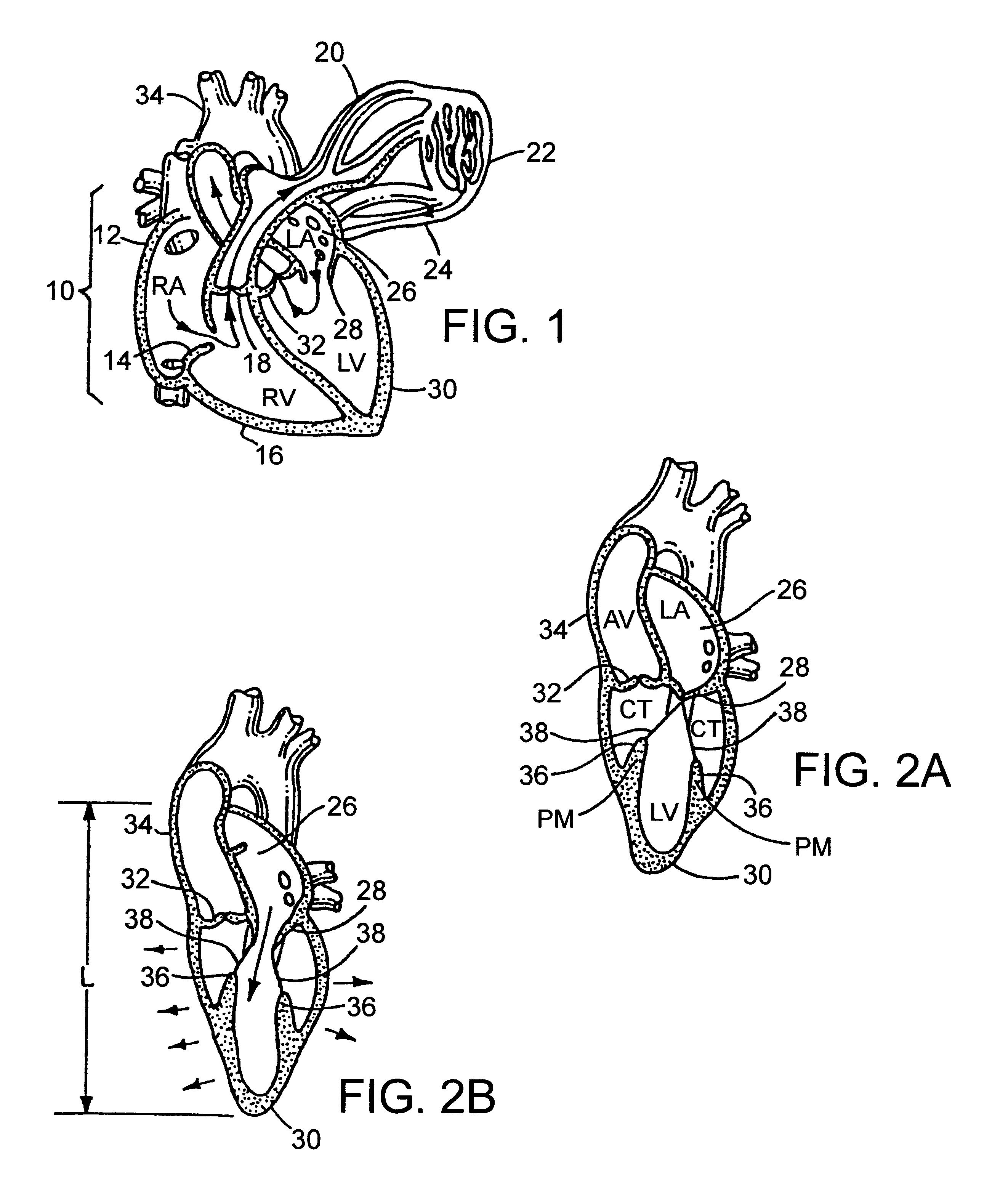
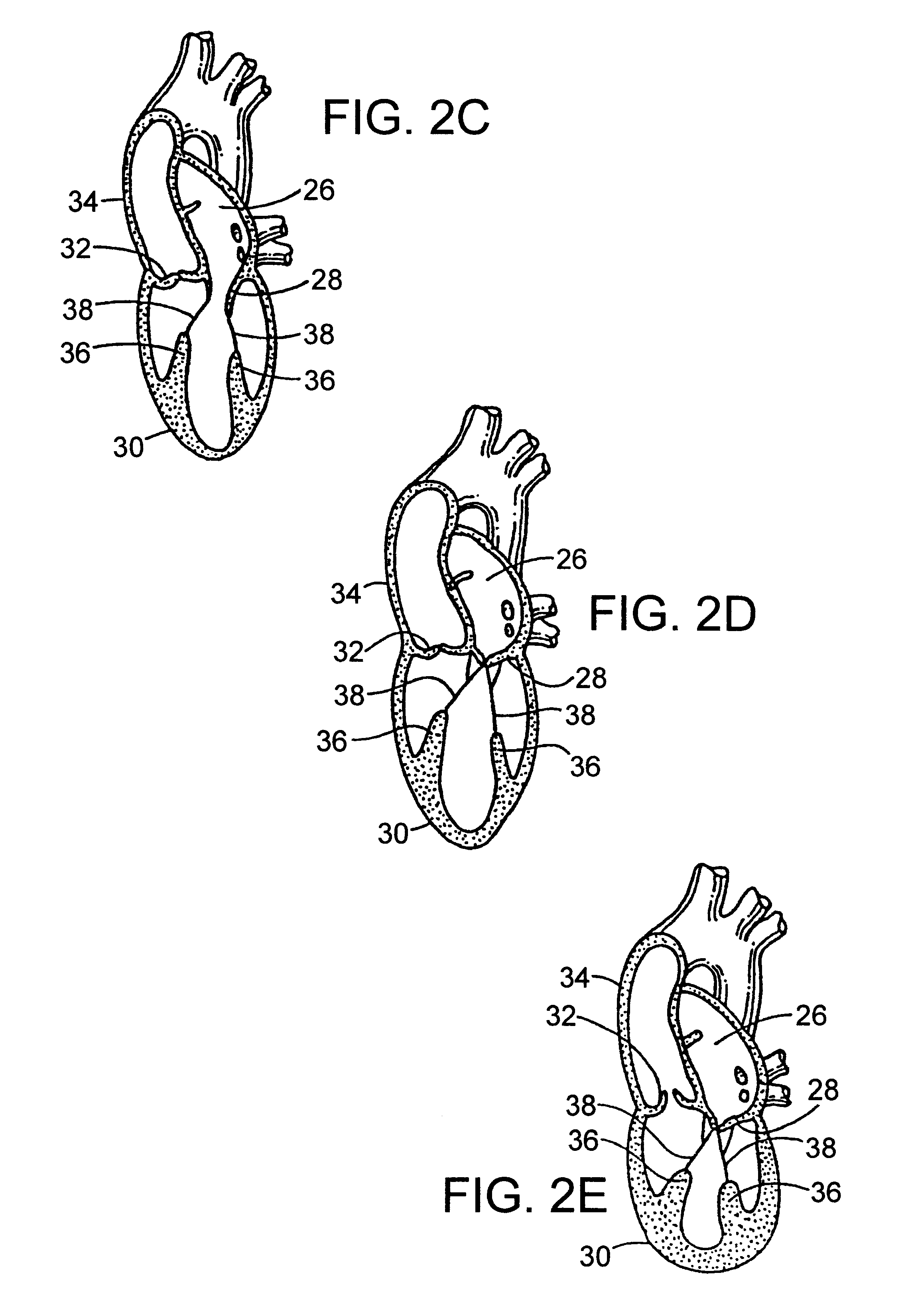
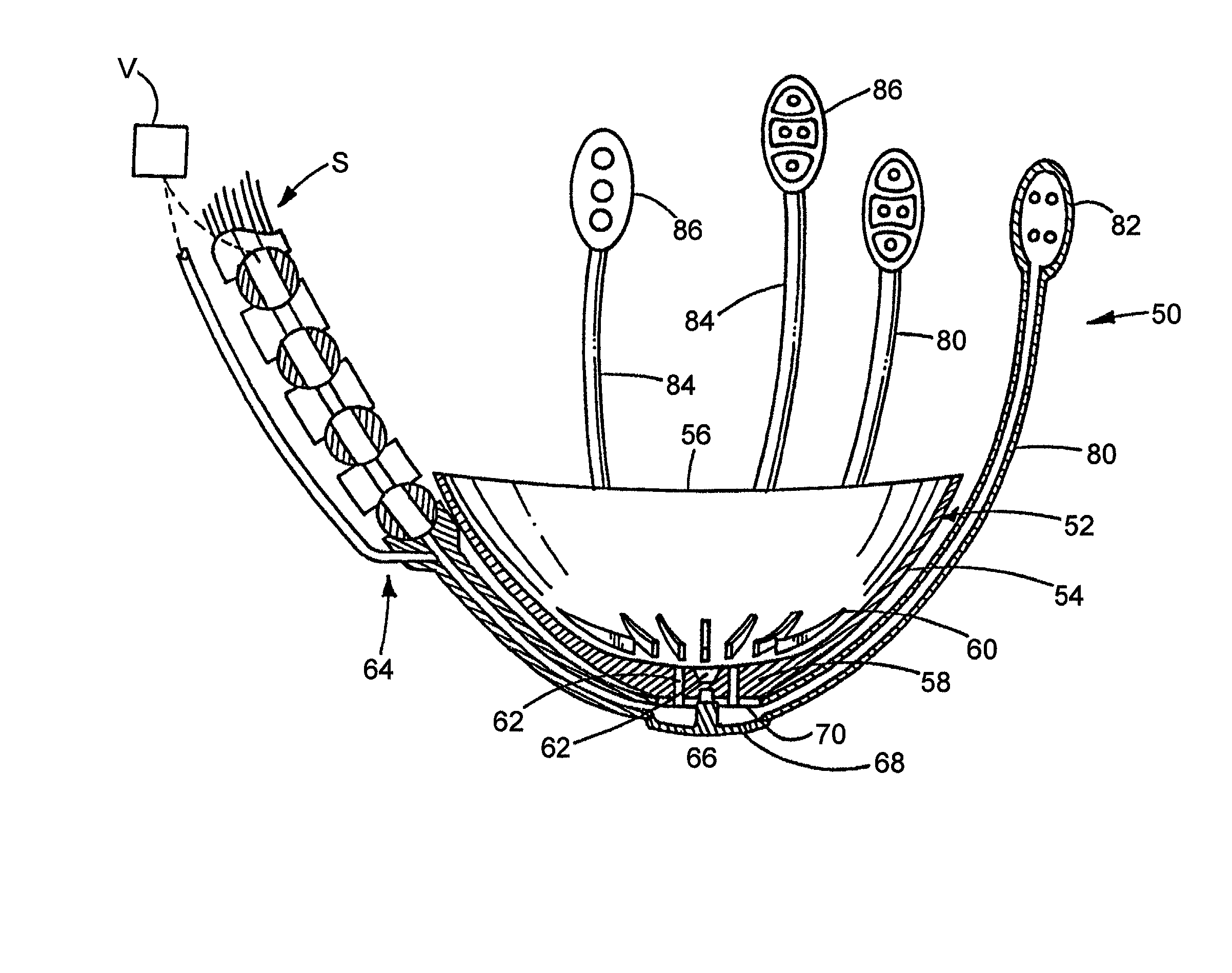
A heart retractor links lifting of the heart and regional immobilization which stops one part of the heart from moving to allow expeditious suturing while permitting other parts of the heart to continue to function whereby coronary surgery can be performed on a beating heart while maintaining cardiac output unabated and uninterrupted. Circumflex coronary artery surgery can be performed using the heart retractor of the present invention. The retractor includes a plurality of flexible arms and a plurality of rigid arms as well as a surgery target immobilizing element. One form of the retractor can be used in minimally invasive surgery, while other forms of the retractor can accommodate variations in heart size and paracardial spacing.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Non-invasive method and apparatus for determining a physiological parameter
InactiveUS20050192488A1Accurate resultAccurately measureElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyLinear algorithmNon invasive
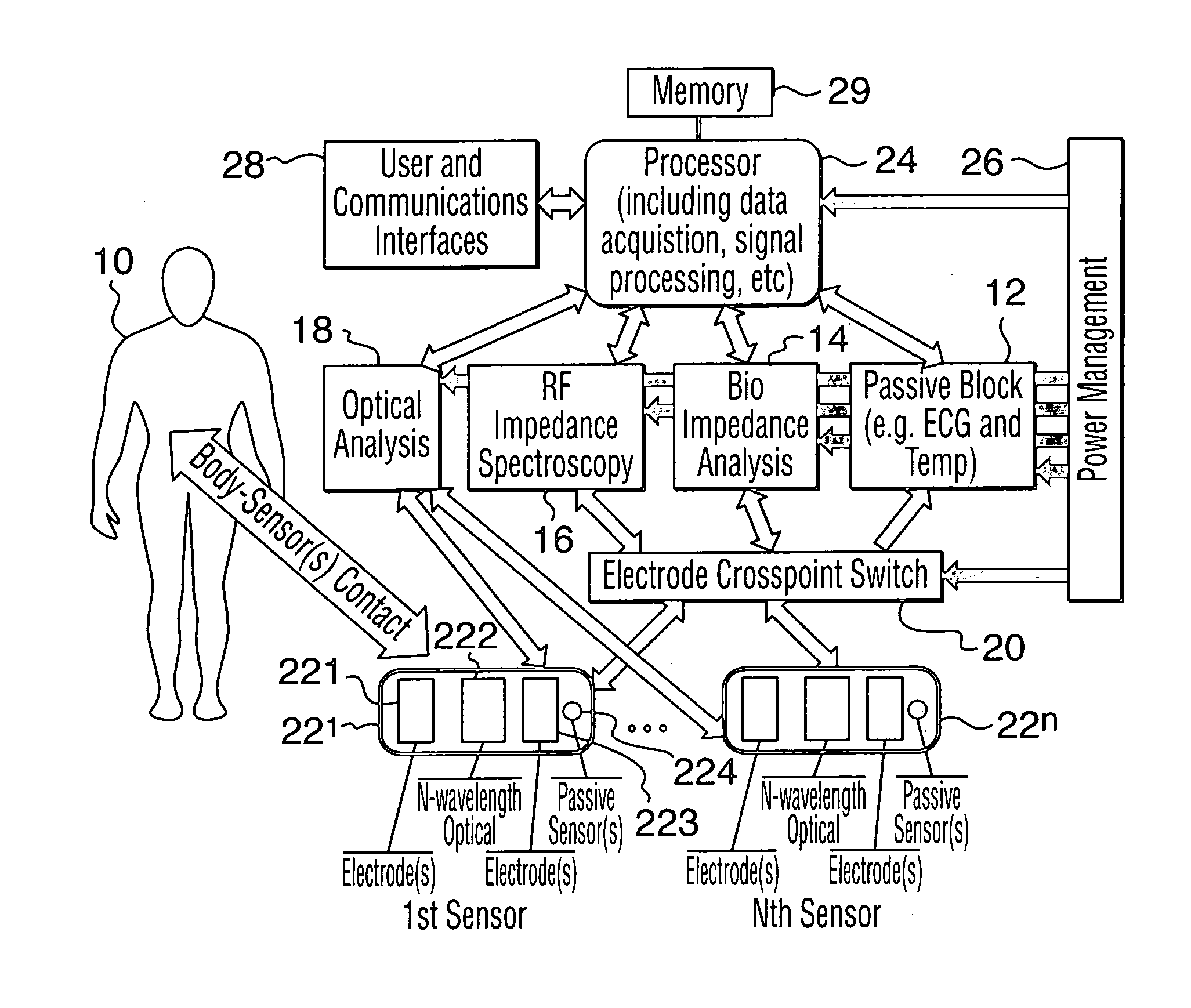
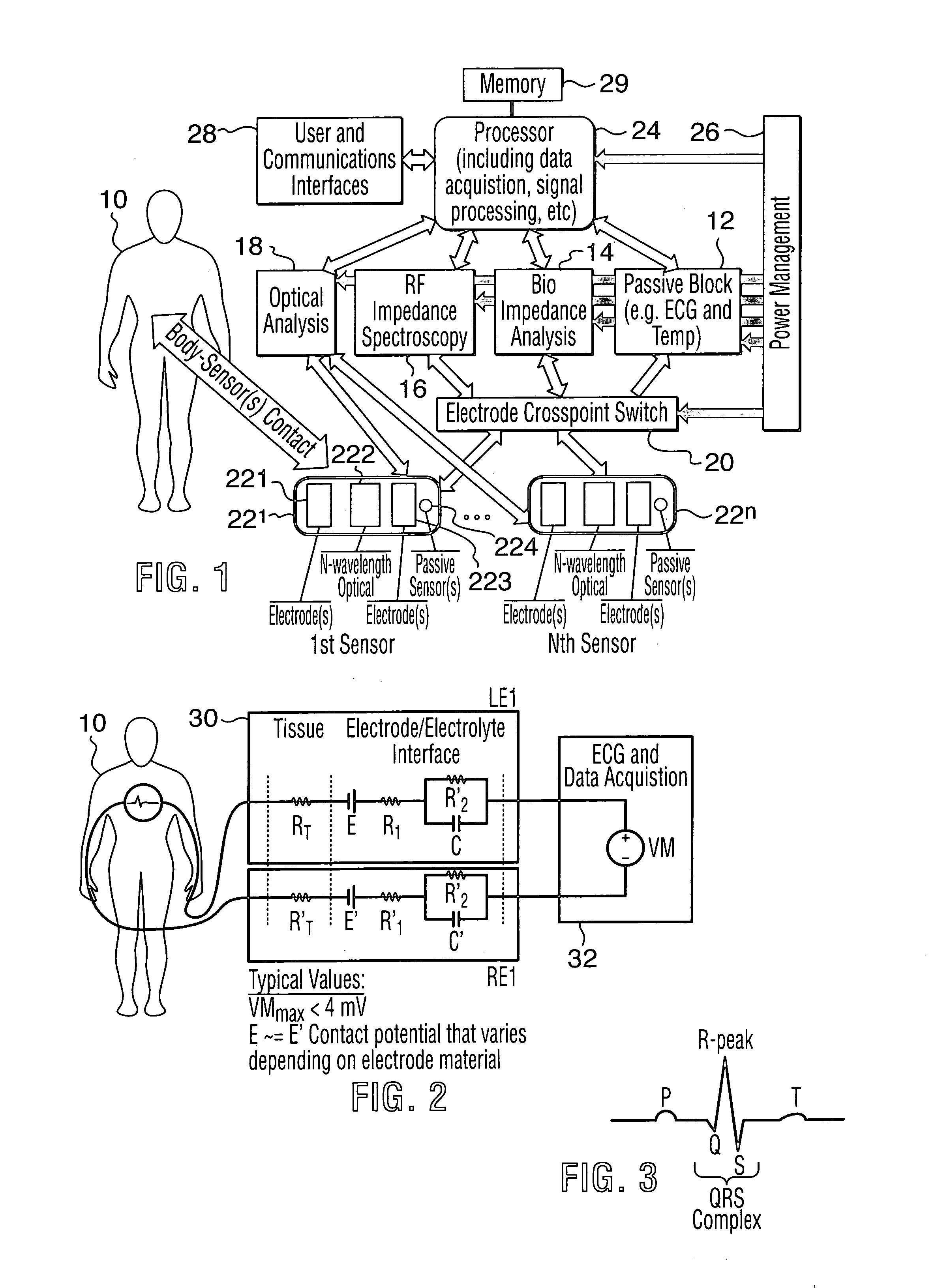
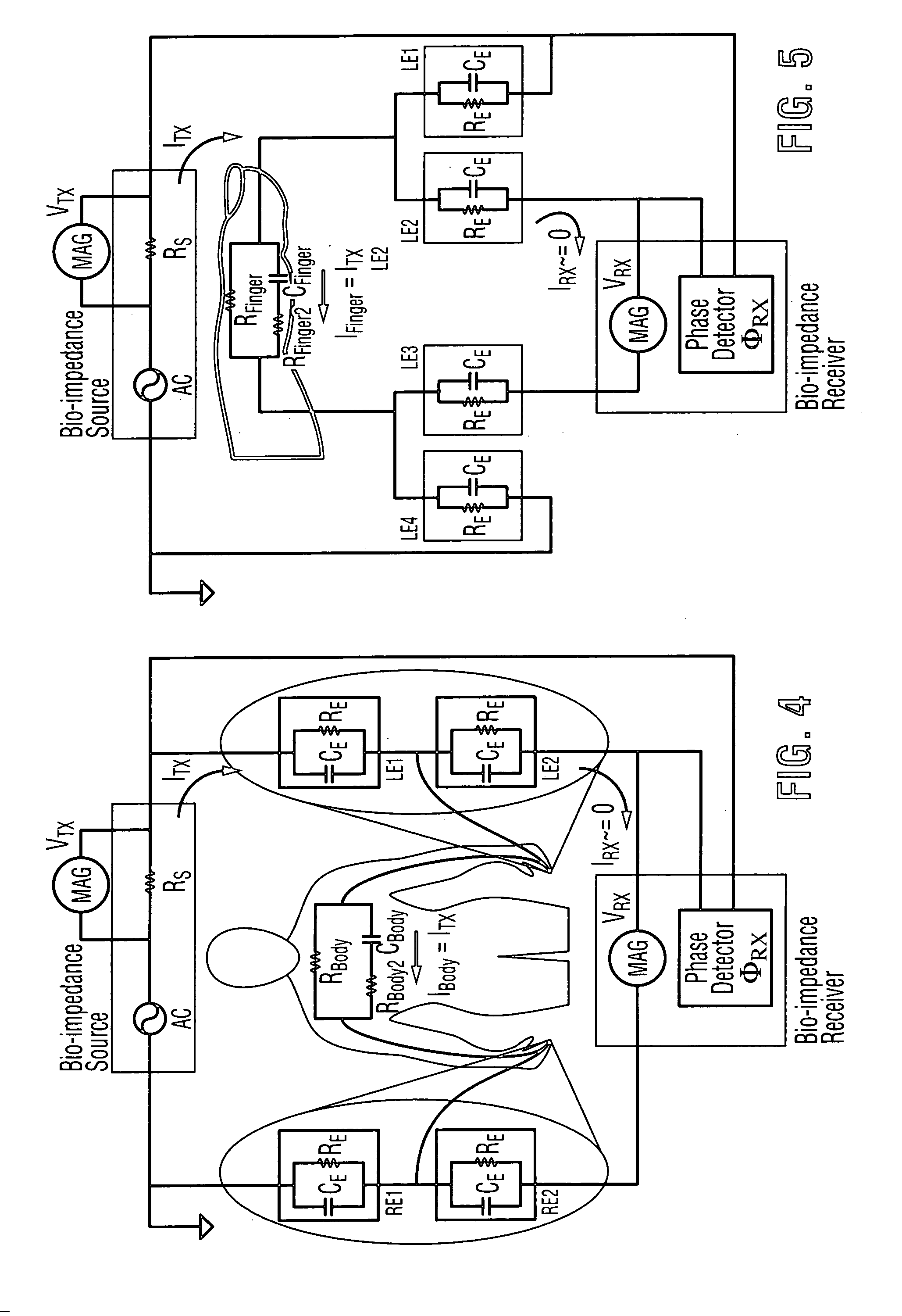
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for the non-invasive analysis of physiological attributes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, cardiac output, respiratory response, body composition, and blood chemistry analytes including glucose, lactate, hemoglobin, and oxygen saturation. Using a combination of multi-functioning disparate sensors, such as optical and electrical, improvements are made over existing physiological measurement devices and techniques. The special configuration of one or more multi-functional sensors is used to non-invasively measure multi-wavelength optical plus one or more of ECG, Bio-impedance, and RF-impedance spectroscopic data. This information is used to develop self-consistent, non-linear algorithm in order to derive the physiological attributes while compensating for various forms of interfering effects including motion artifacts, sensor attachment variability, device component variability, subject physical and physiology variability, and various interfering physiological attributes.
Owner:BIOPEAK CORP
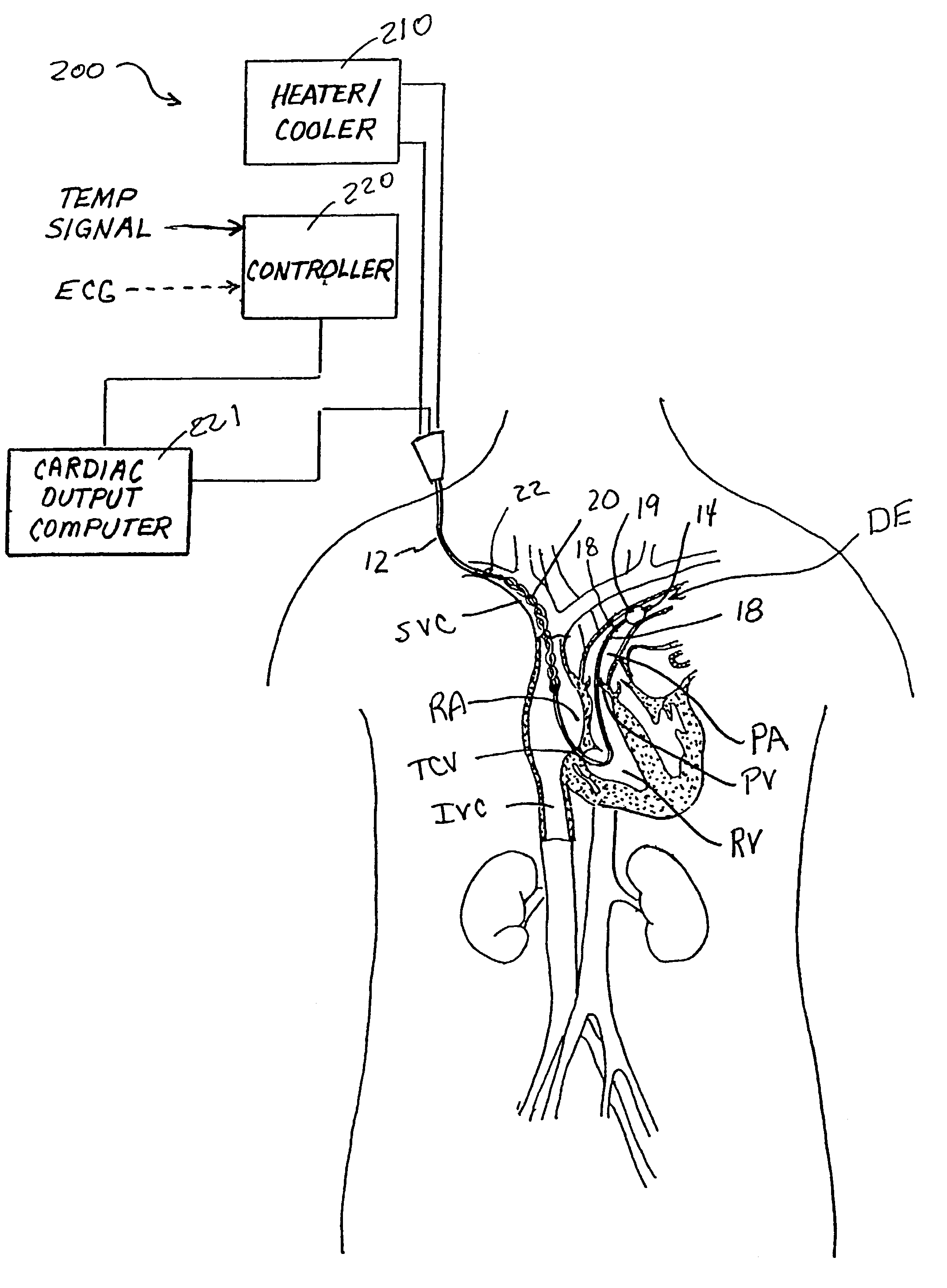
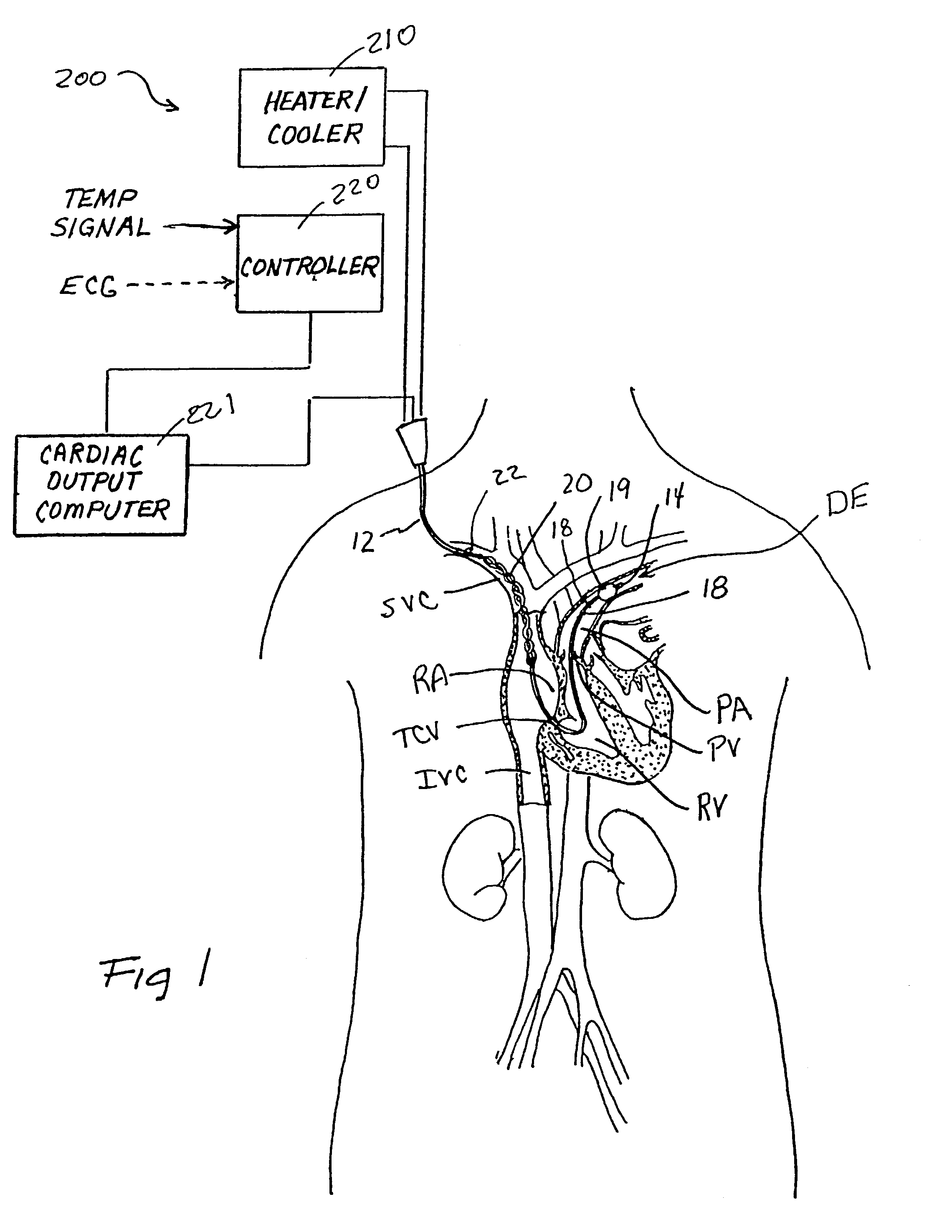
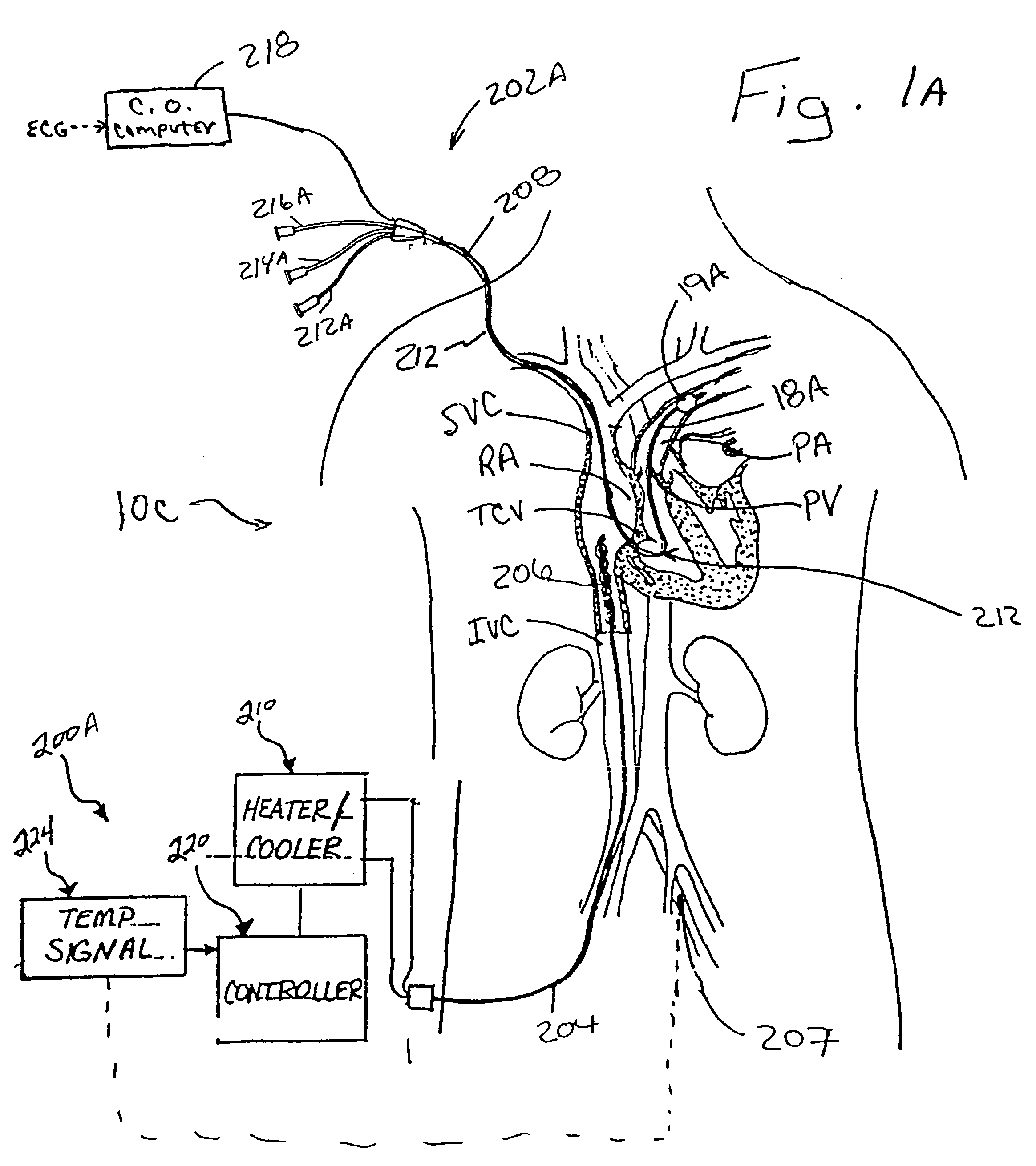
Devices and methods for measuring blood flow rate or cardiac output and for heating or cooling the body
Heat exchanger-equipped catheters and related methods that are useable for changing or maintaining at least a portion of the body of a human or veterinary patient at a desired temperature and for the measurement of cardiac output or blood flow rate within a blood vessel, without the need for introduction of saline solution or any other foreign substance into the patient's blood.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Determining the volume of a normal heart and its pathological and treated variants by using dimension sensors
InactiveUS20040106871A1Improve accuracyReduce in quantityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterVentricular volumeCardiac surface
A method and system measure the instantaneous volume of blood contained within a chamber of a heart, irrespective of its shape, whereby stroke volume and cardiac output volume can be continuously monitored and feedback to a non-blood contacting cardiac assist device. In a preferred form the device uses the distances between the sensors which are implanted in a biomaterial that integrates with a heart surface to determine changes in heart volume. Sonomicrometry crystal measurements are disclosed as a preferred mode of obtaining distance readings. A computer readable medium carries instructions to convert data from dimension sensors into sensor positions within a predetermined coordinate system. Ventricular volume is based on the sensor positions.
Owner:HEART ASSIST TECH PTY LTD
Device to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC +1
Optimal non-constant speed control method for miniature axial flow type blood pumps
InactiveCN1446592AIncrease speedReduce speedDiagnostic recording/measuringSpeed/accelaration controlOxygenHealth profile
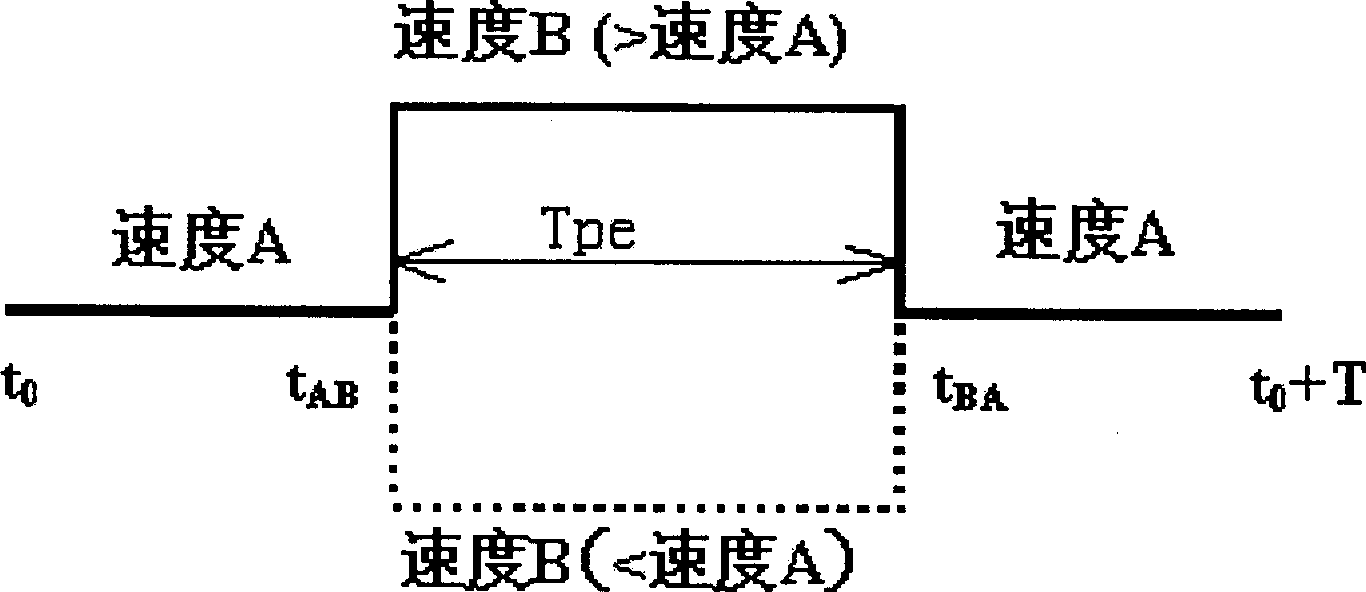
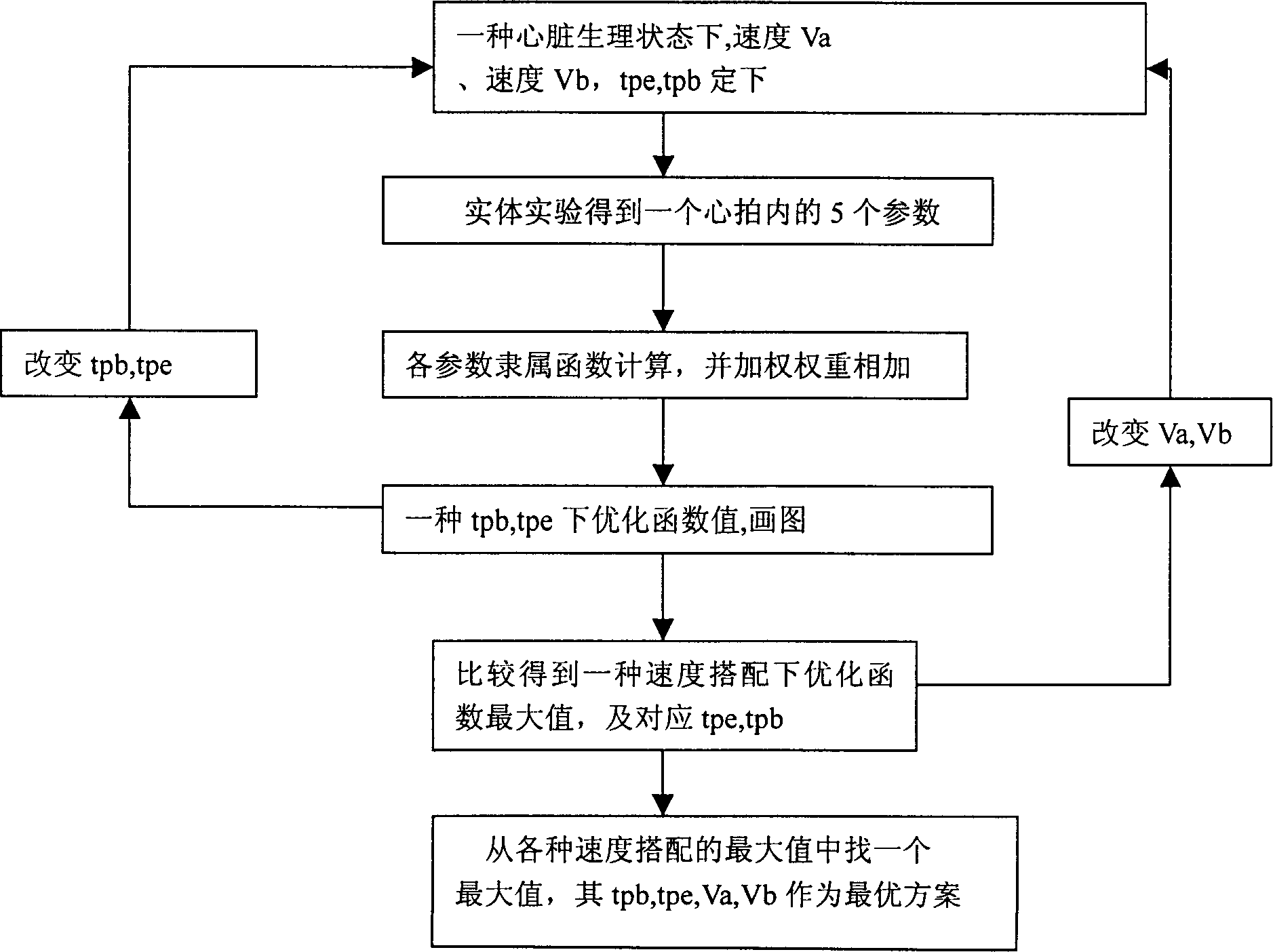
A method for optimizing the speed control of miniature axial-flow blood pump includes calculating the heart output, the ratio of supplied oxygen to consumed oxygen of cardiac muscle, and the highest systolic pressure and the lowest diastolic pressure of aorta, calculating average rotation speed according to 7 speeds and their running periods, calculating membership function, weighing it to obtaintarget function, and comparing the different schemes for various speeds to obtain optical scheme. Its advantages are high adaptability and safety, and low energy consumption.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
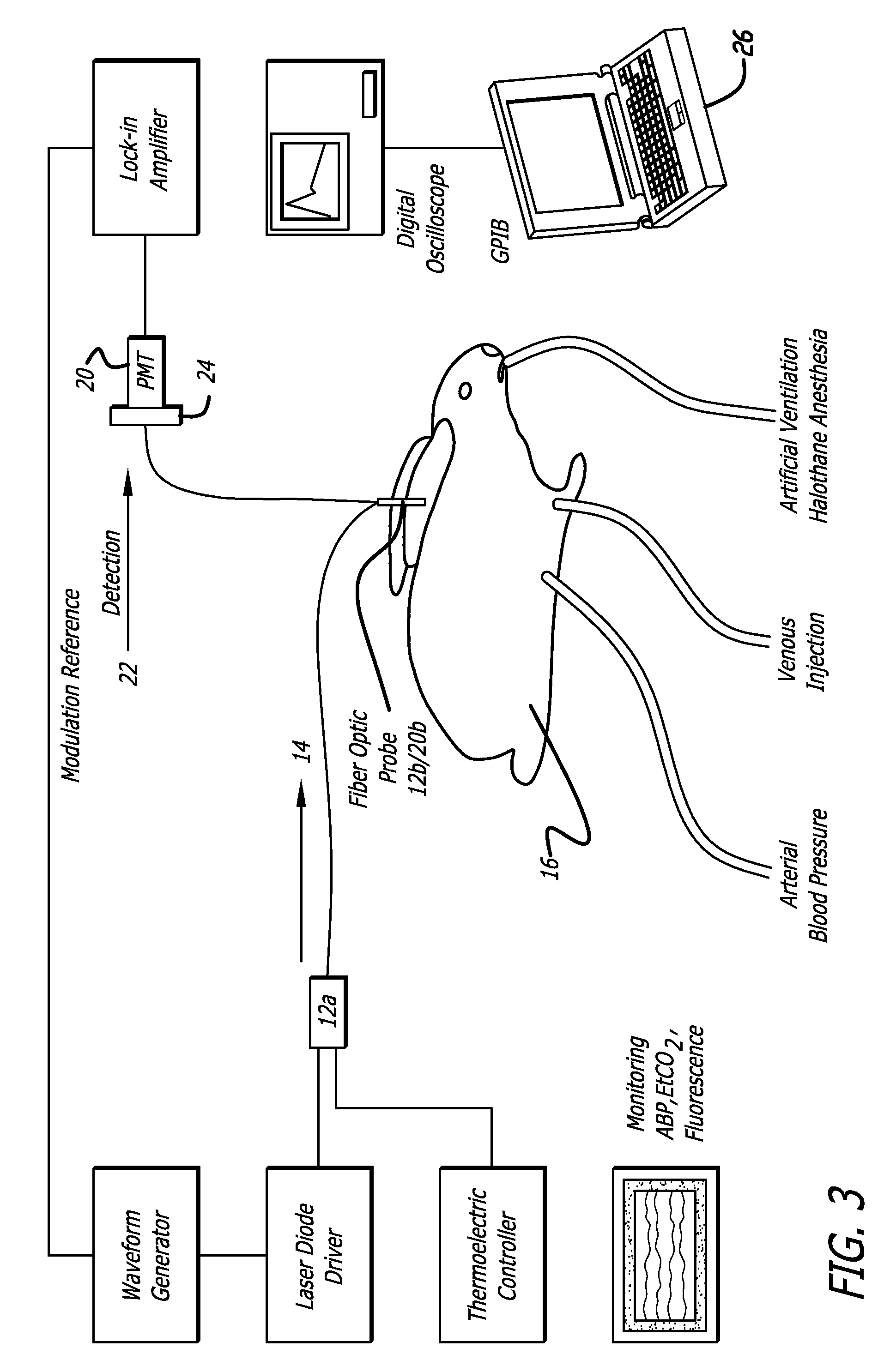
Method for dye injection for the transcutaneous measurement of cardiac output
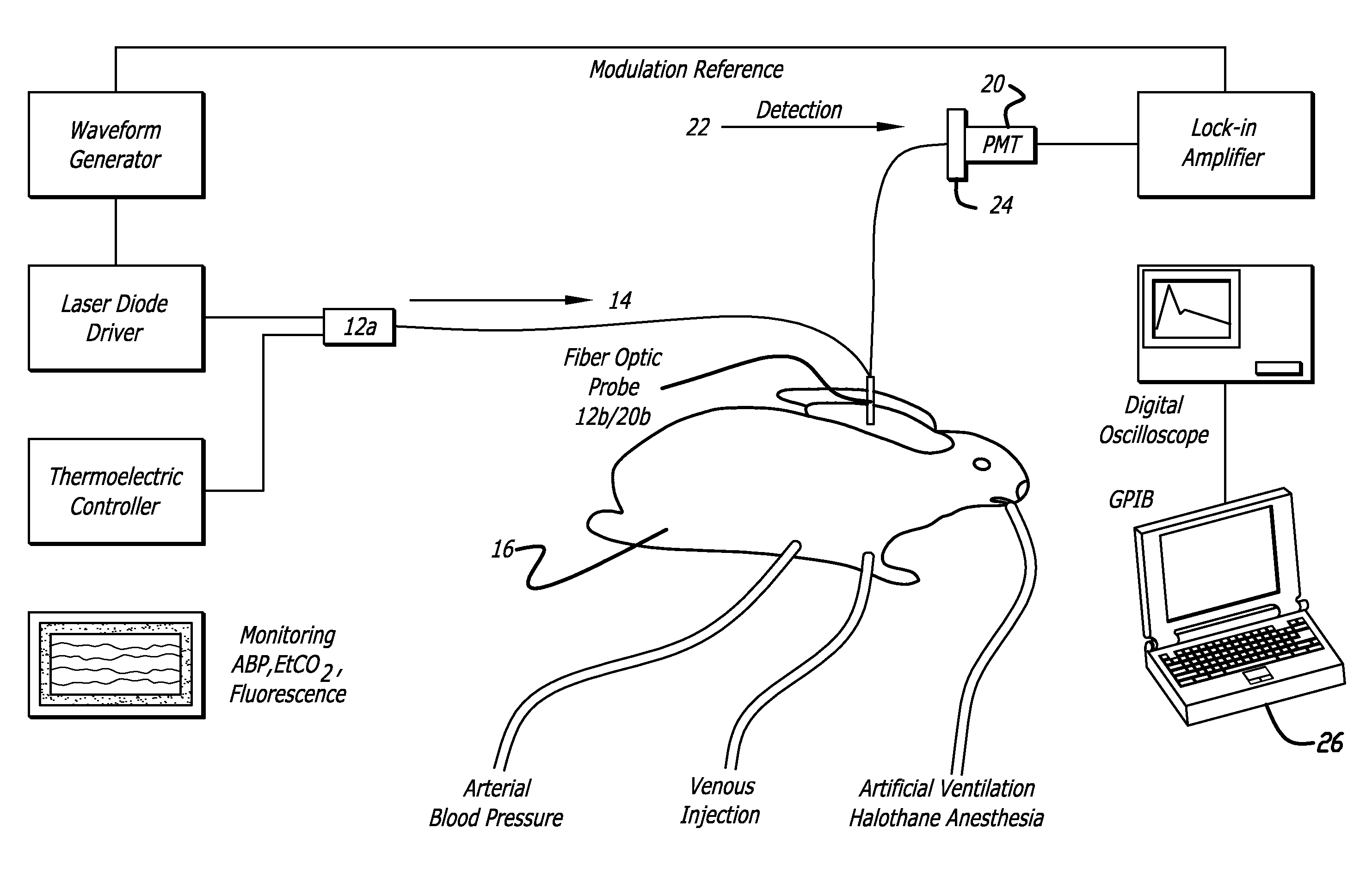
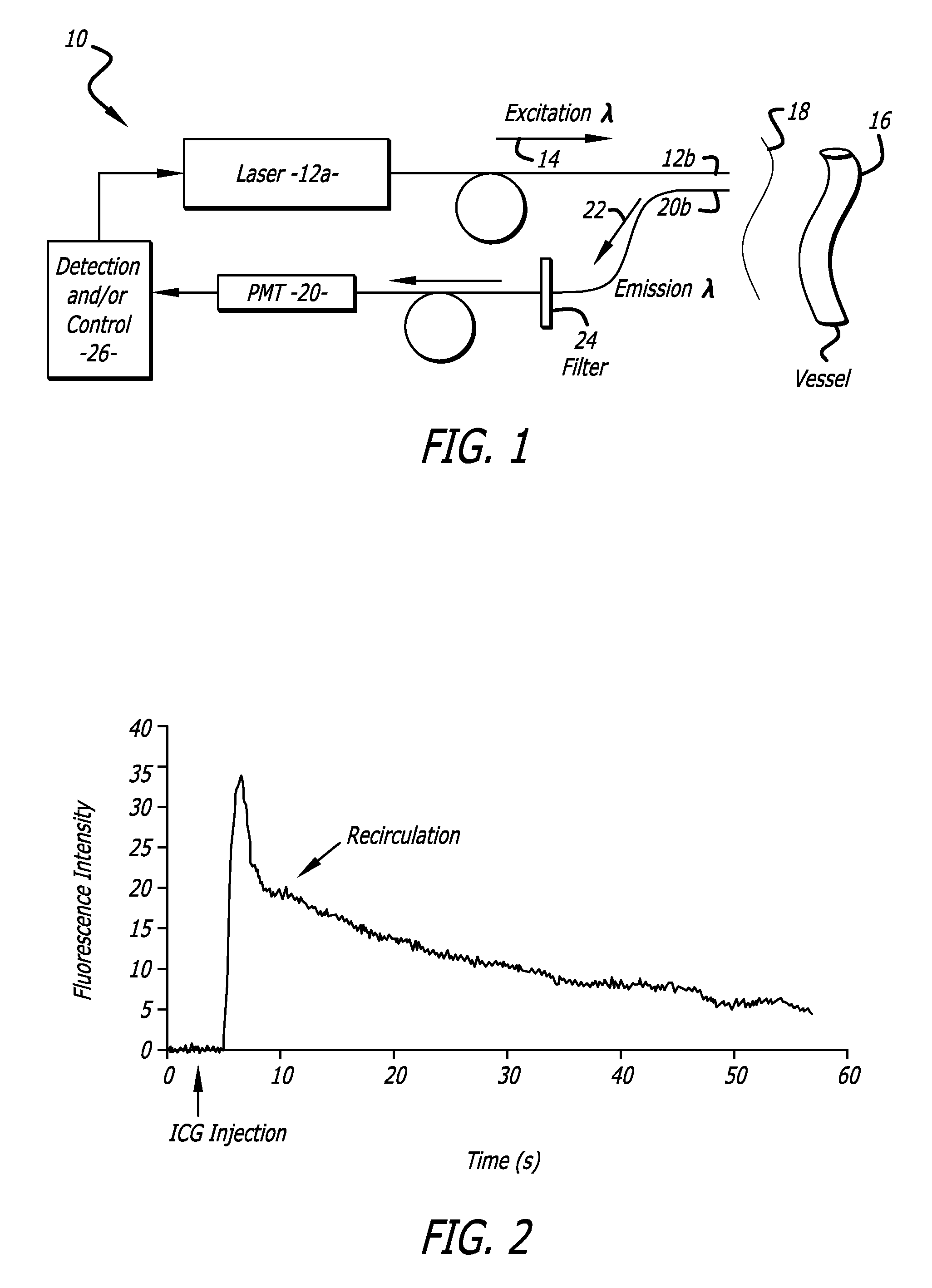
InactiveUS7474906B2Reduce complicationsReduction procedureDiagnostics using lightMaterial analysis by optical meansIndicator dilutionDye injection
A system for evaluating the cardiovascular system parameters using indicator dilution and non-invasive or minimally invasive detection and calibration methods are disclosed. Intravascular indicators are stimulated, and emissions patterns detected for computation of cardiac output, cardiac index, blood volume and other indicators of cardiovascular health.
Owner:ALFRED E MANN INST FOR BIOMEDICAL ENG AT THE UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
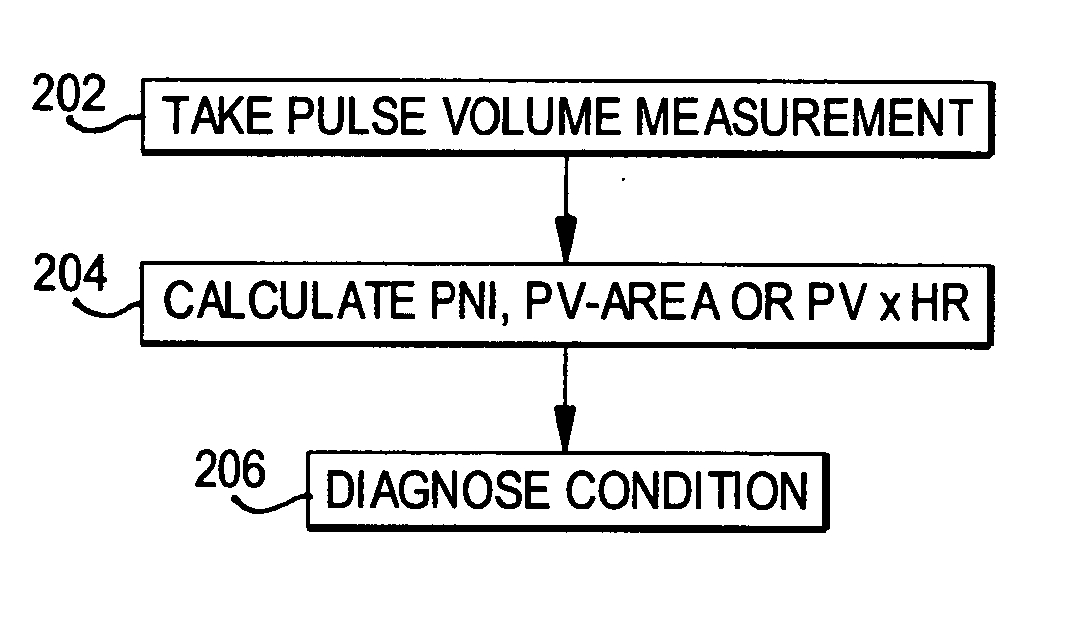
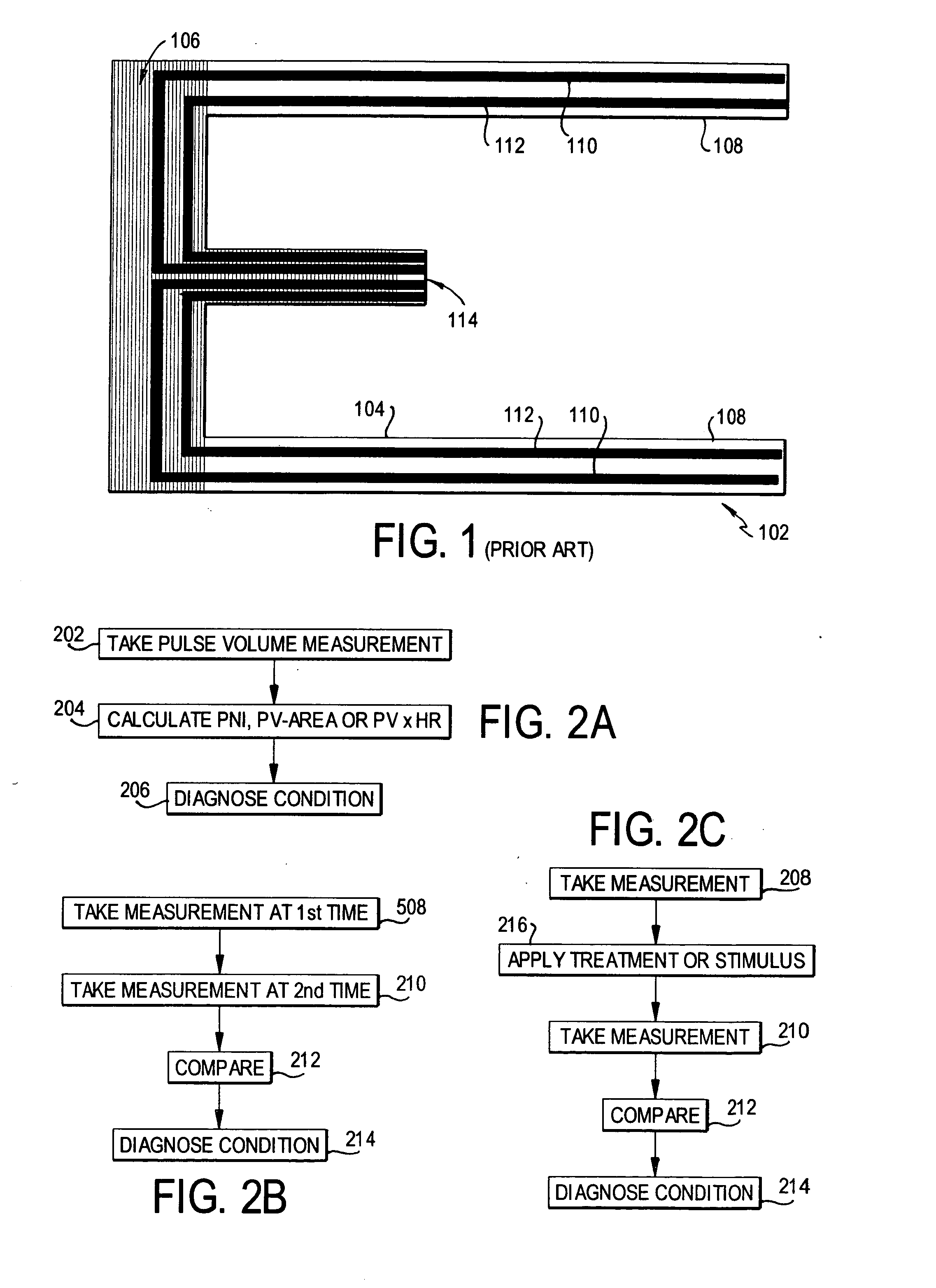
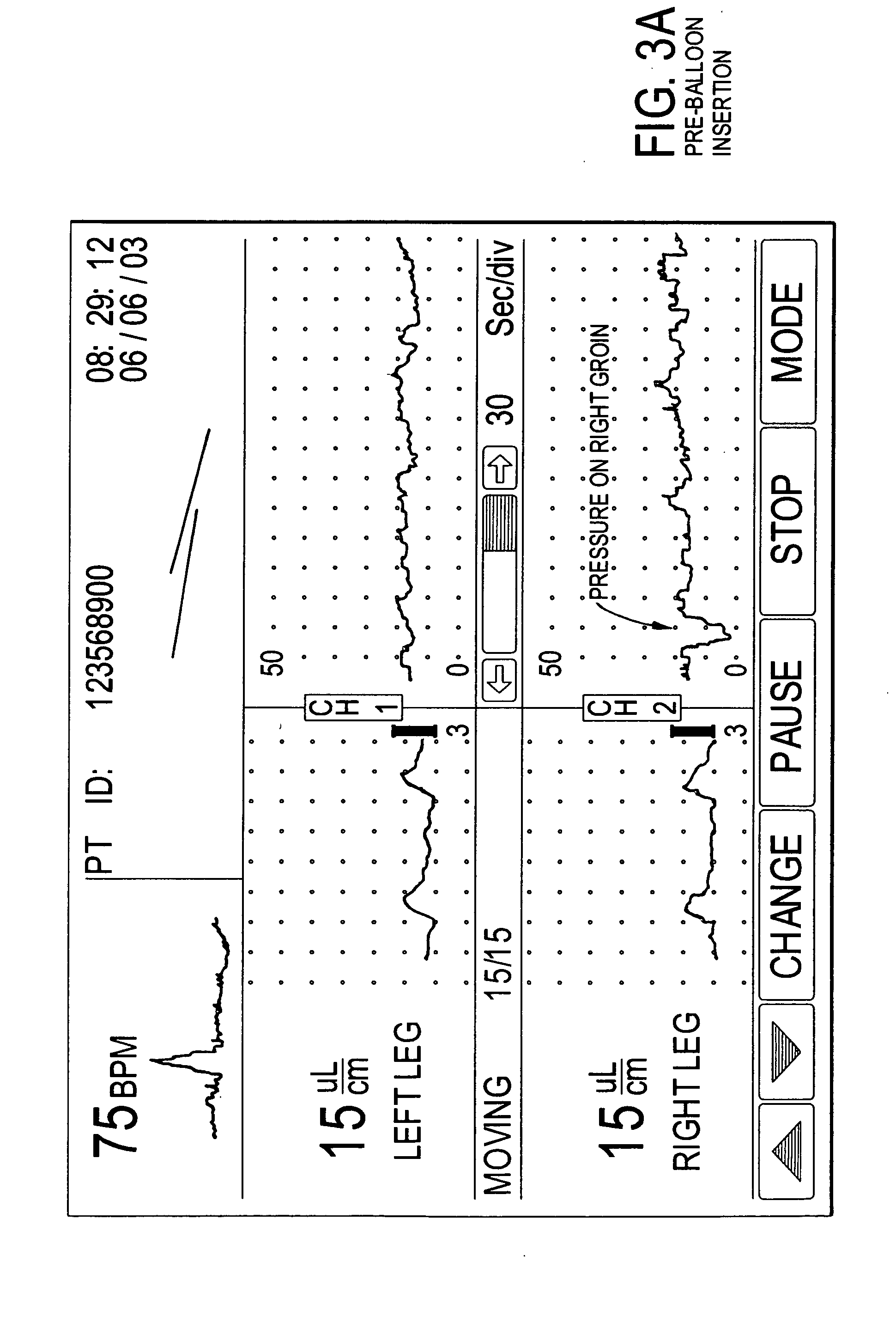
Methods of diagnosis using pulse volume measurement
ActiveUS20050070807A1Increase usageMore and more conditionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringCongestive heart failure chfIntra-aortic balloon pump
The utility of pulse volume measurement is expanded to detection of many conditions which have previously not been detected or have been detected using more complicated techniques. Such conditions include blood loss, septic shock, cardiogenic shock, neonatal sepsis, patent ductus arteriosus, limb ischemia, intra-aortic balloon pump performance, peripheral vascular disease, congestive heart failure, the effectiveness of vasoactive medications, syncope, dehydration, pre-eclampsia, deep vein thrombosis, thermal injuries, vascular instability due to renal dialysis, compromising of circulation to the hand caused by radial artery harvesting, changes in cardiac output, and hypertension. According to the present invention, such diagnoses can be performed by taking one measurement, by taking measurements over time to detect a change or by taking measurements before and after application of a treatment or stimulus.
Owner:SMITHMARKS INC
Device to permit offpump beating heart coronary bypass surgery
A heart retractor links lifting of the heart and regional immobilization which stops one part of the heart from moving to allow expeditious suturing while permitting other parts of the heart to continue to function whereby coronary surgery can be performed on a beating heart while maintaining cardiac output unabated and uninterrupted. Circumflex coronary artery surgery can be performed using the heart retractor of the present invention. The retractor includes a plurality of flexible arms and a plurality of rigid arms as well as a surgery target immobilizing element. One form of the retractor can be used in minimally invasive surgery, while other forms of the retractor can accommodate variations in heart size and paracardial spacing.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC +1
Non-invasive determination of conditions in the circulatory system of a subject
InactiveUS7070569B2Improve accuracyNon-invasivelyCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationVeinVenous blood
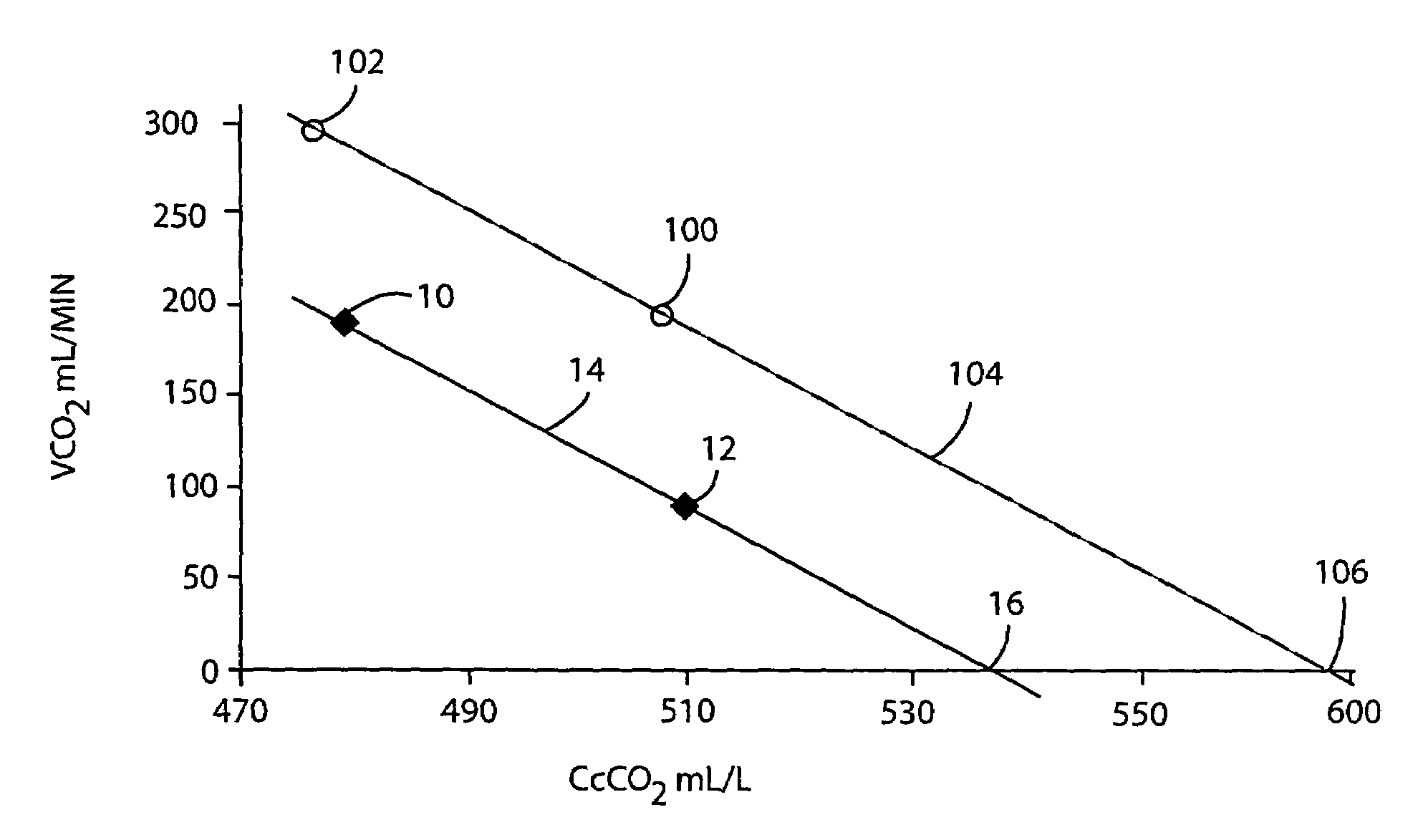
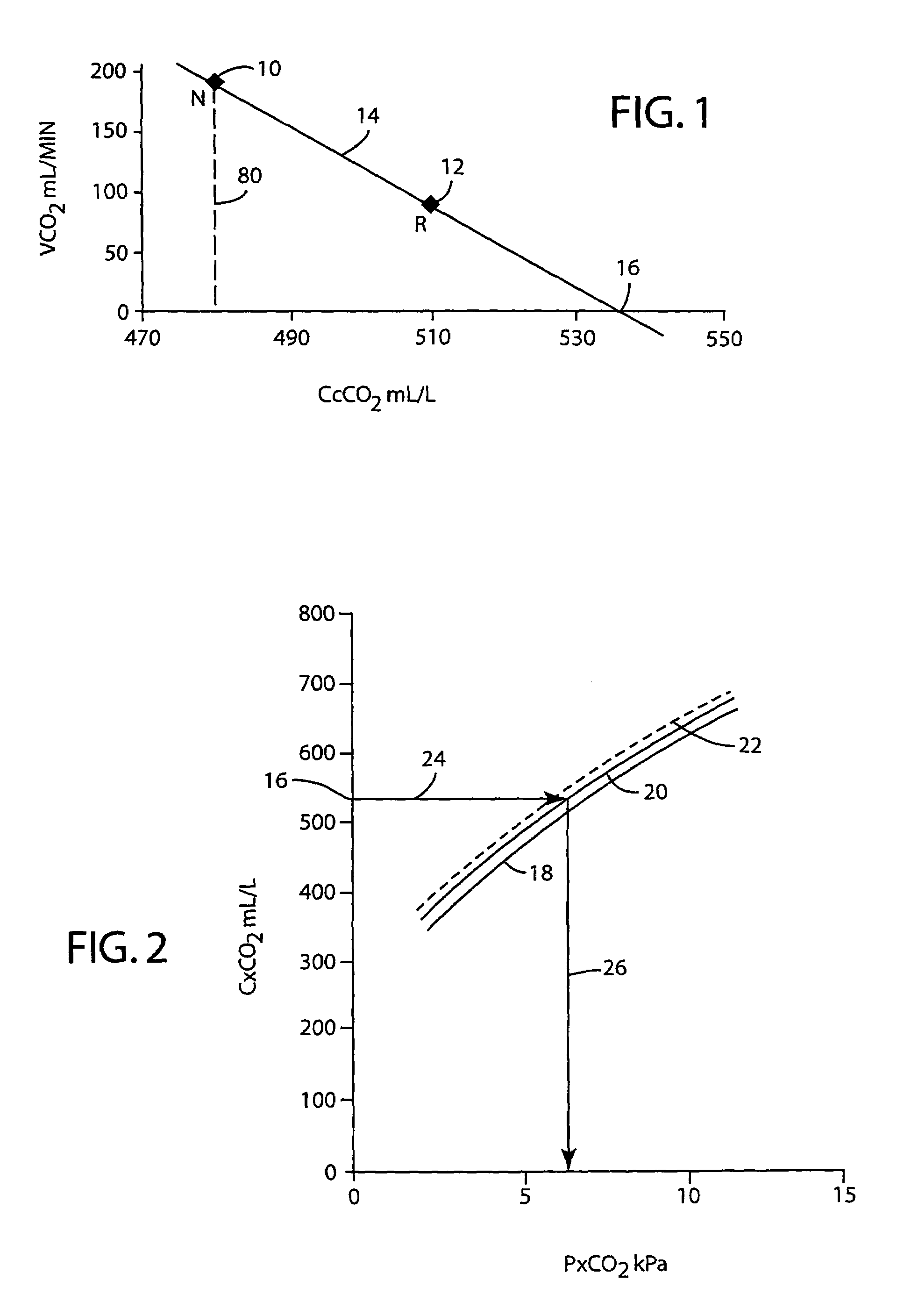
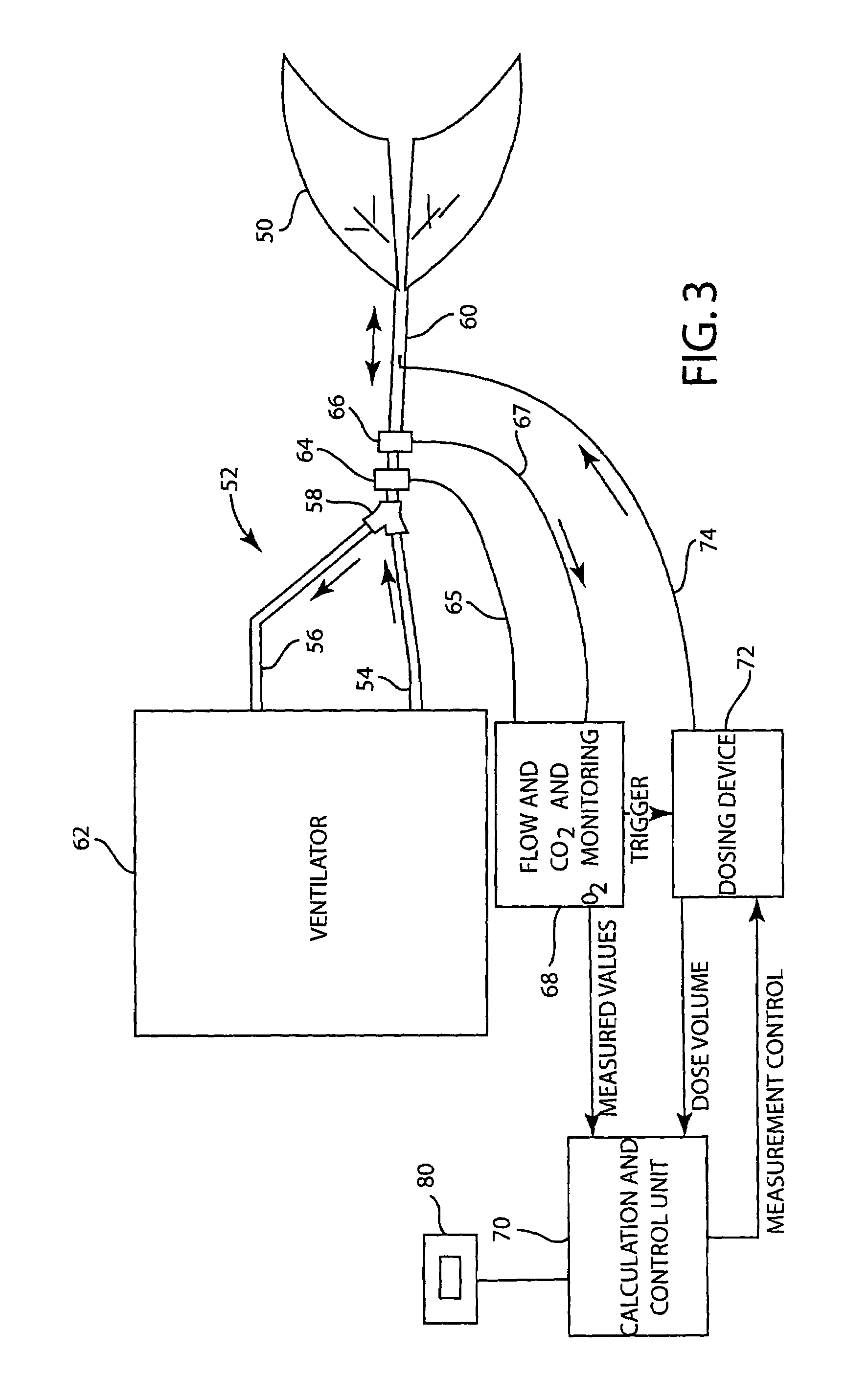
A method for non-invasively determining functional cardiac output (FCO) and / or venous blood CO2 partial pressure (PvCO2). The amount of CO2 (VCO2N) released from the blood and end capillary blood CO2 content (CcCO2N) are determined from measurements from exhaled breathing gases. The CO2 content of the breathing gases inhaled by the subject is increased and values for VCO2R and CcCO2R are obtained. A regression analysis is performed using the obtained VCO2N, VO2R, CcCO2N, and CcCO2R values. The regression line is extrapolated to obtain a value for CcCO2 when (VCO2) is zero so that CvCO2 becomes known. The CvCO2 thus determined can be inserted in a non-differential form in the Fick equation, along with VCO2 and CcCO2 values from normal breathing, to determine FCO. To determine PvCO2, CvCO2 is altered in accordance with the amount of oxygen in the venous blood, to correctly indicate PvCO2. The continuing validity of the FCO measurement can be examined on a breath-by-breath basis by noting changes in an indicator variable, such as VCO2 or end tidal CO2 amounts.
Owner:INSTRUMENTARIUM CORP
Heart parameter measuring method and device
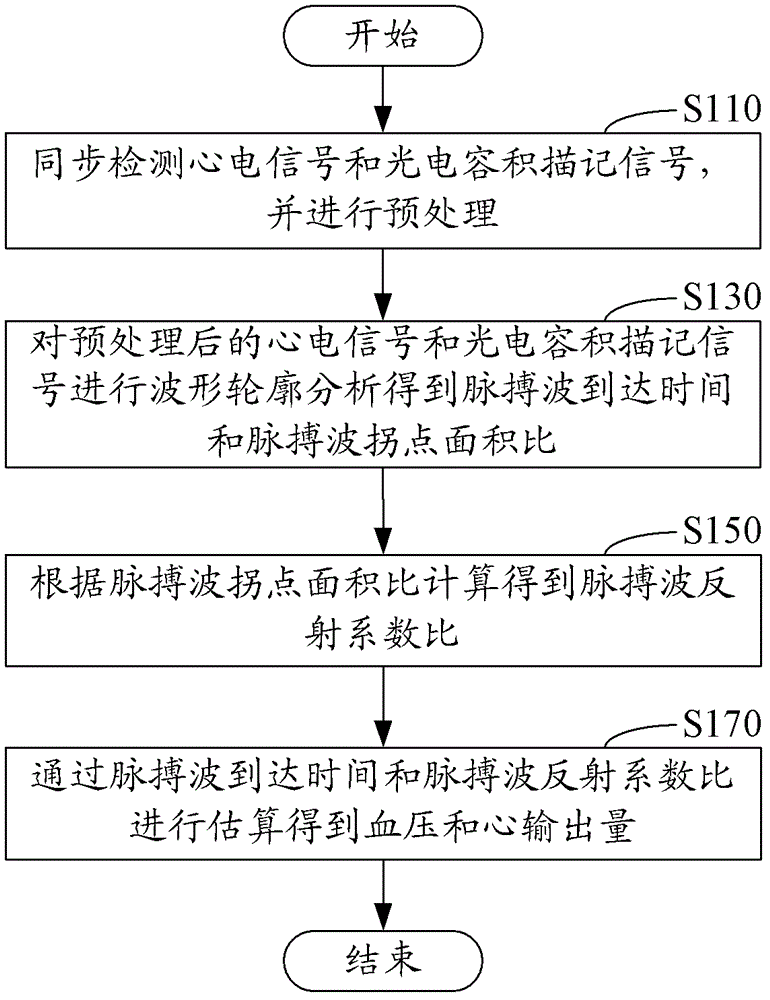
ActiveCN102499669AGuaranteed accuracyImprove operational convenienceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalBlood pressure
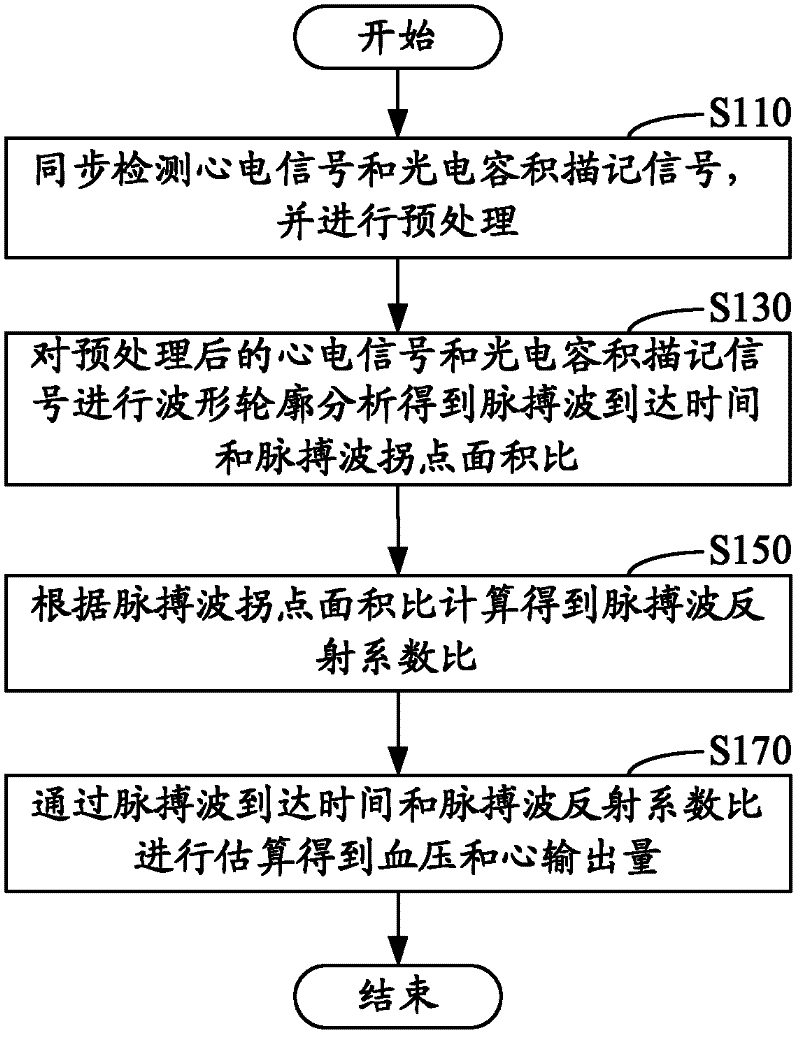
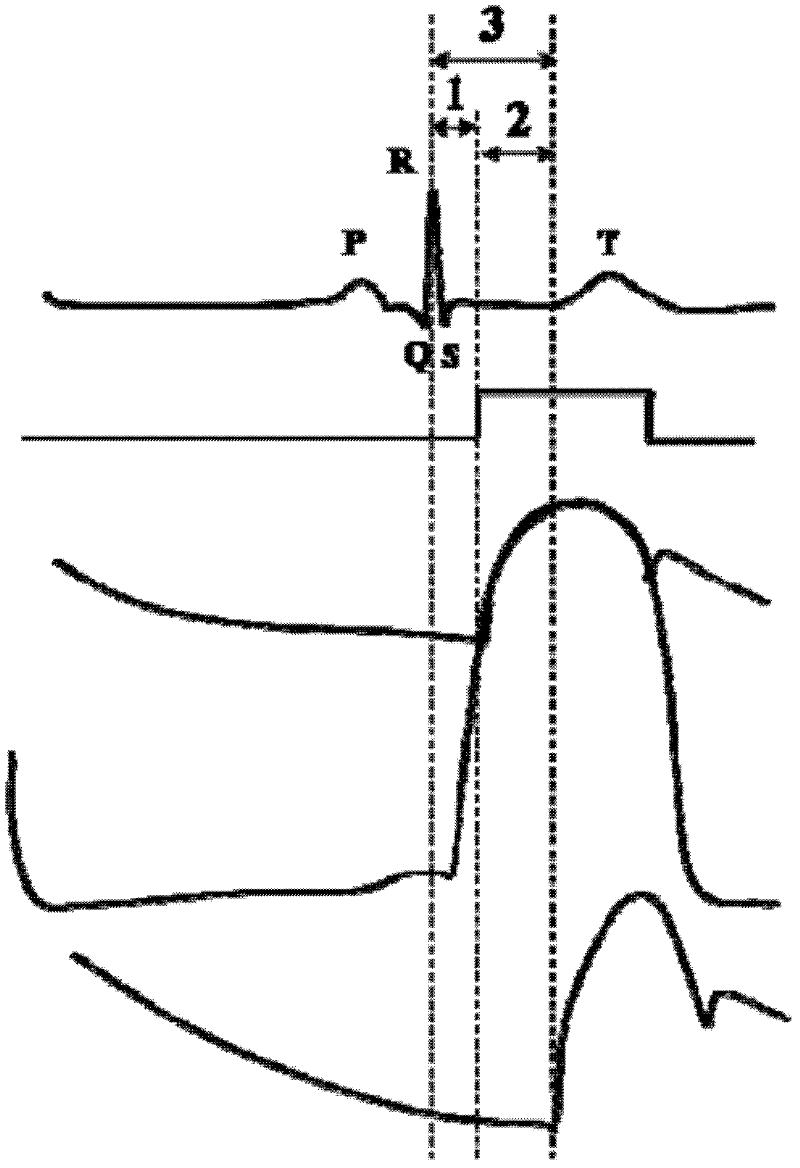
A heart parameter measuring method comprises following steps: synchronously detecting electrocardiosignals and photoplethysmography signals and carrying out preprocessing; carrying out waveform contour analysis for the electrocardiosignals and the photoplethysmography signals which are preprocessed to obtain pulse wave arrival time and pulse wave inflection point area ratios; calculating a pulse wave reflection coefficient ratio according to the pulse wave inflection point area ratios; and estimating the pulse wave arrival time and the pulse wave inflection point area ratios to obtain blood pressure and heart output. By means of calculating the pulse wave inflection point area ratios obtained from the electrocardiosignals and the photoplethysmography signals, the pulse wave reflection coefficient ratio is obtained, then the pulse wave reflection coefficient ratio and the pulse wave arrival time are estimated so as to obtain the blood pressure and the heart output, the blood pressure and the heart output are synchronously measured, accuracy is guaranteed, invasive-method measurement is omitted, and operation convenience under a movement state is greatly improved.
Owner:珠海中科先进科技产业有限公司
System Non-invasive Cardiac Output Determination
InactiveUS20120150003A1Decreased blood flowSensorsBlood flow measurementNormal blood volumeHematological test
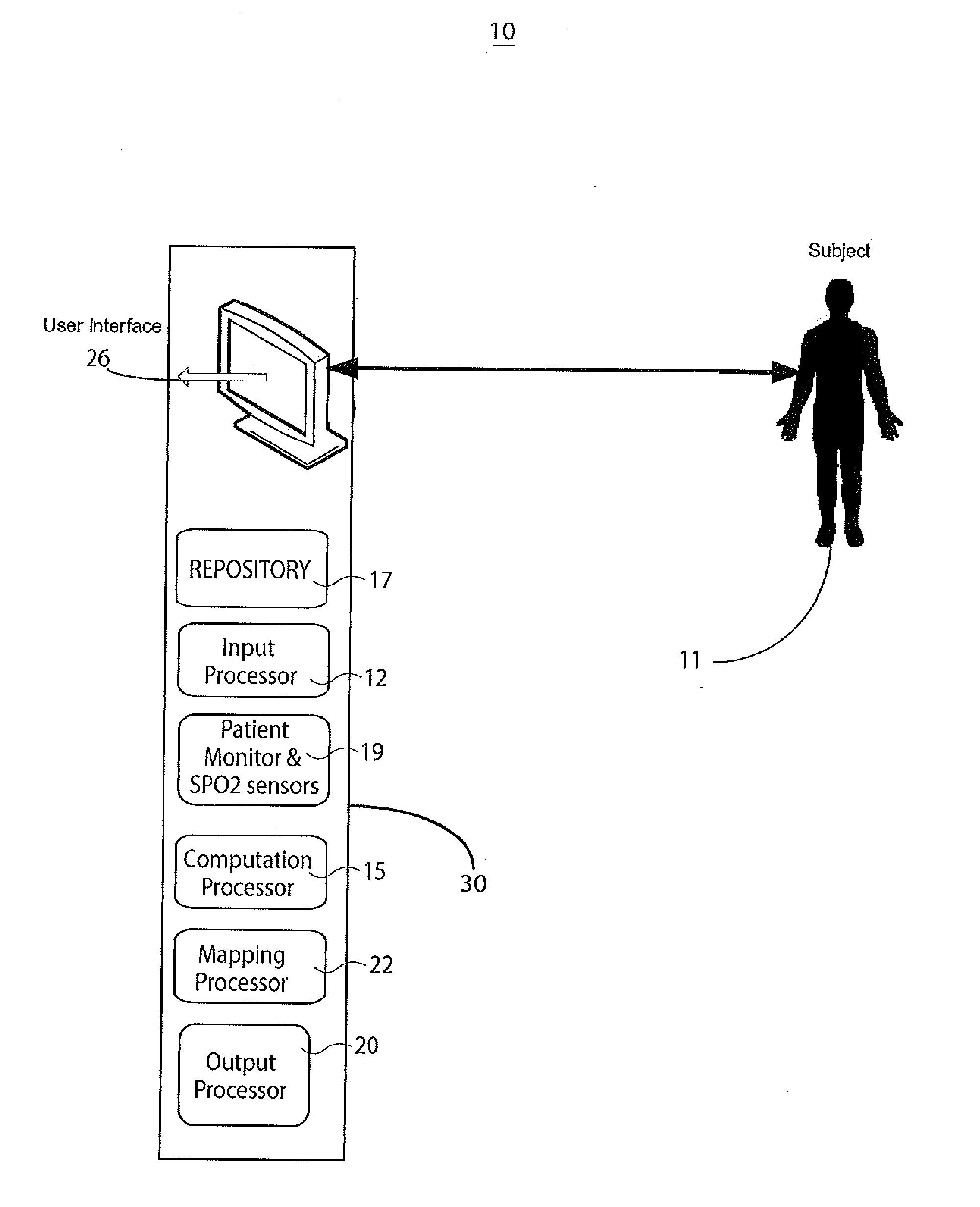
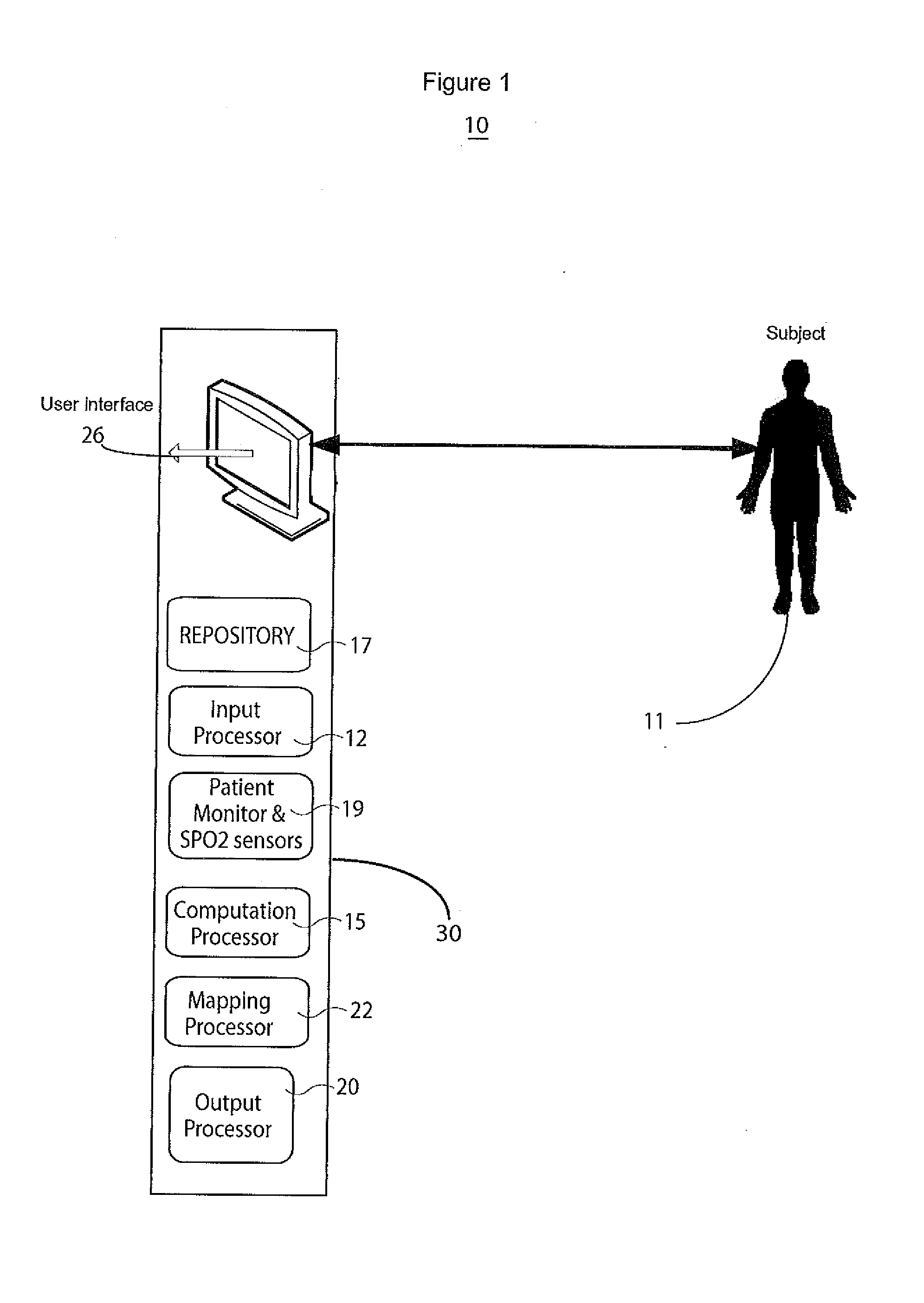
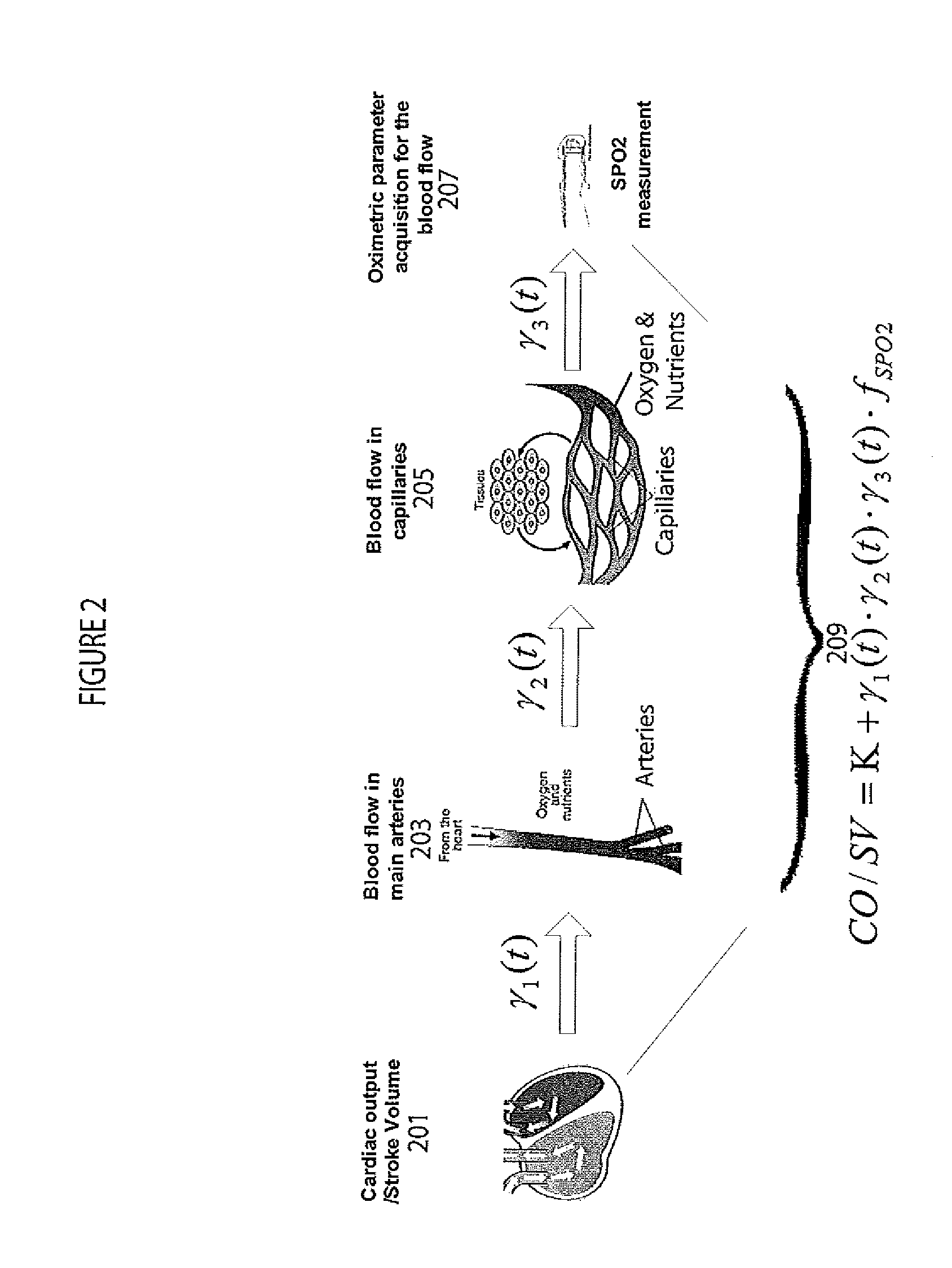
A system determines cardiac output and stroke volume by using non-invasive oximetric signals, such as SPO2 data and waveform, to determine blood flow quantitatively. A non-invasive system determines cardiac output or stroke volume. The system includes an input processor for receiving signal data representing oxygen content of blood of a patient at a particular anatomical location. A computation processor uses the received signal data in calculating a heart stroke volume of the patient comprising volume of blood transferred through the blood vessel in a heart cycle, in response to, a blood volume derived in response to oxygen content of patient blood and at least one factor representing reduction in blood flow volume from a patient heart to the particular anatomical location. An output processor provides data representing the calculated heart stroke volume to a destination device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
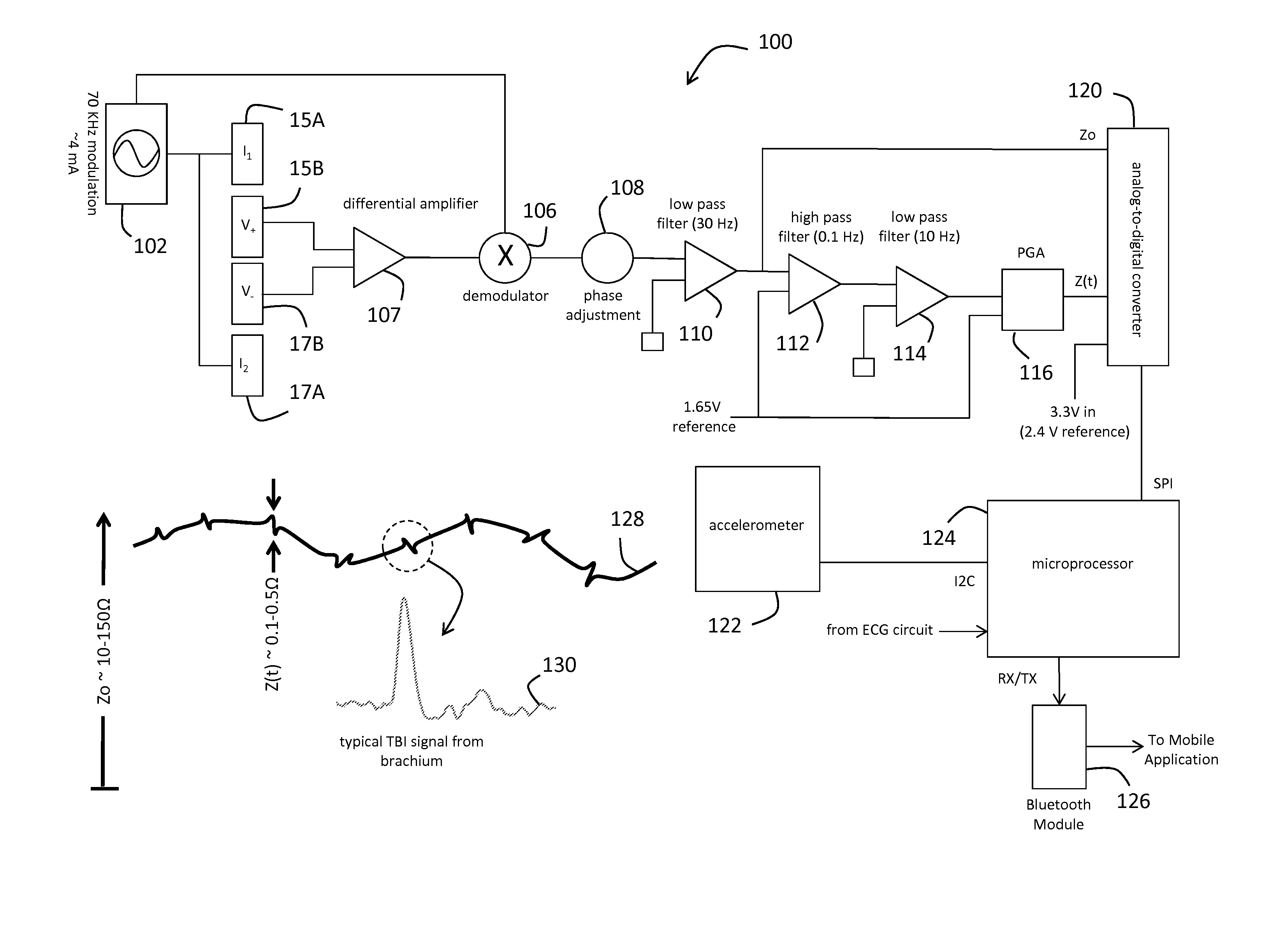
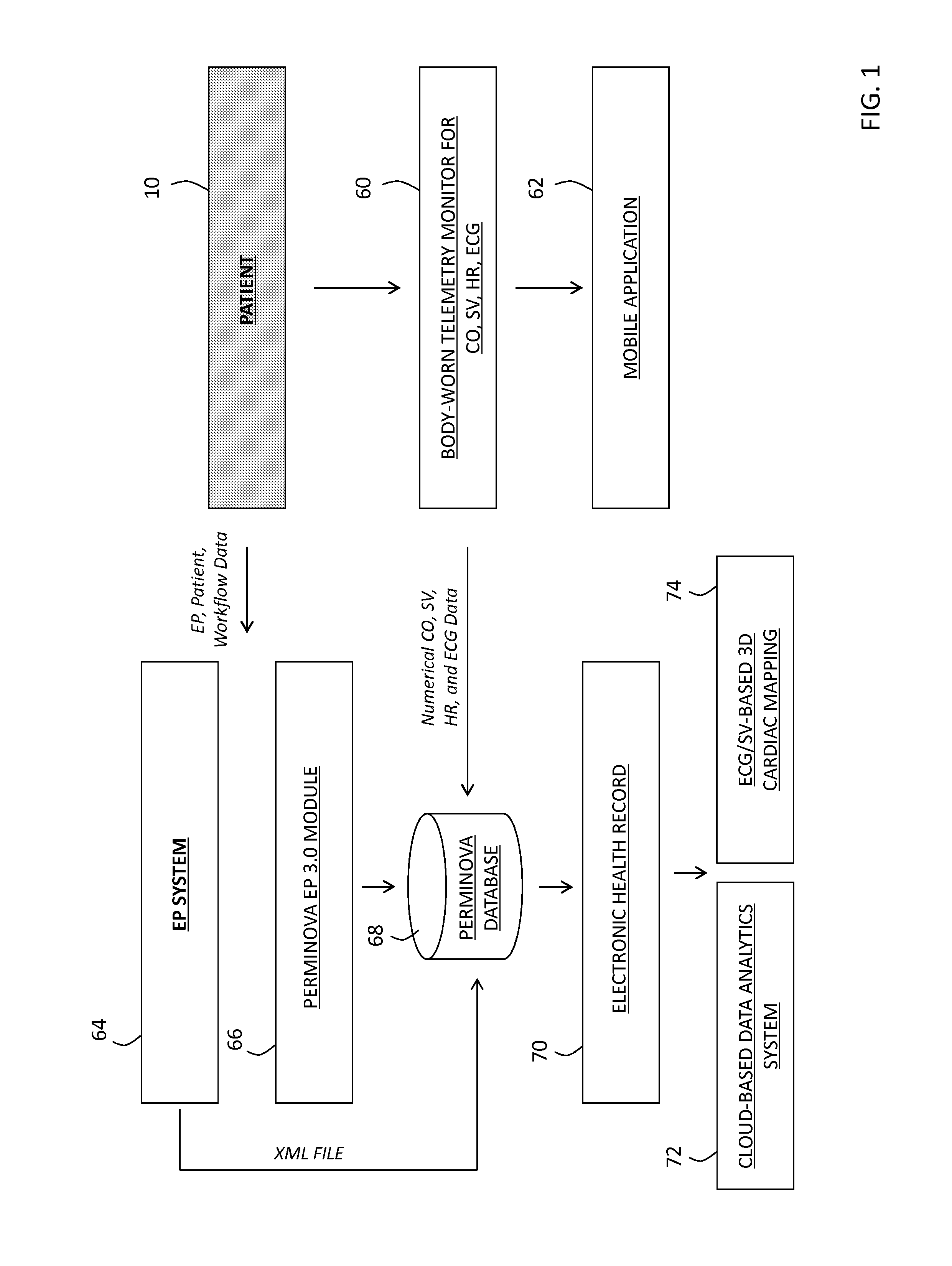
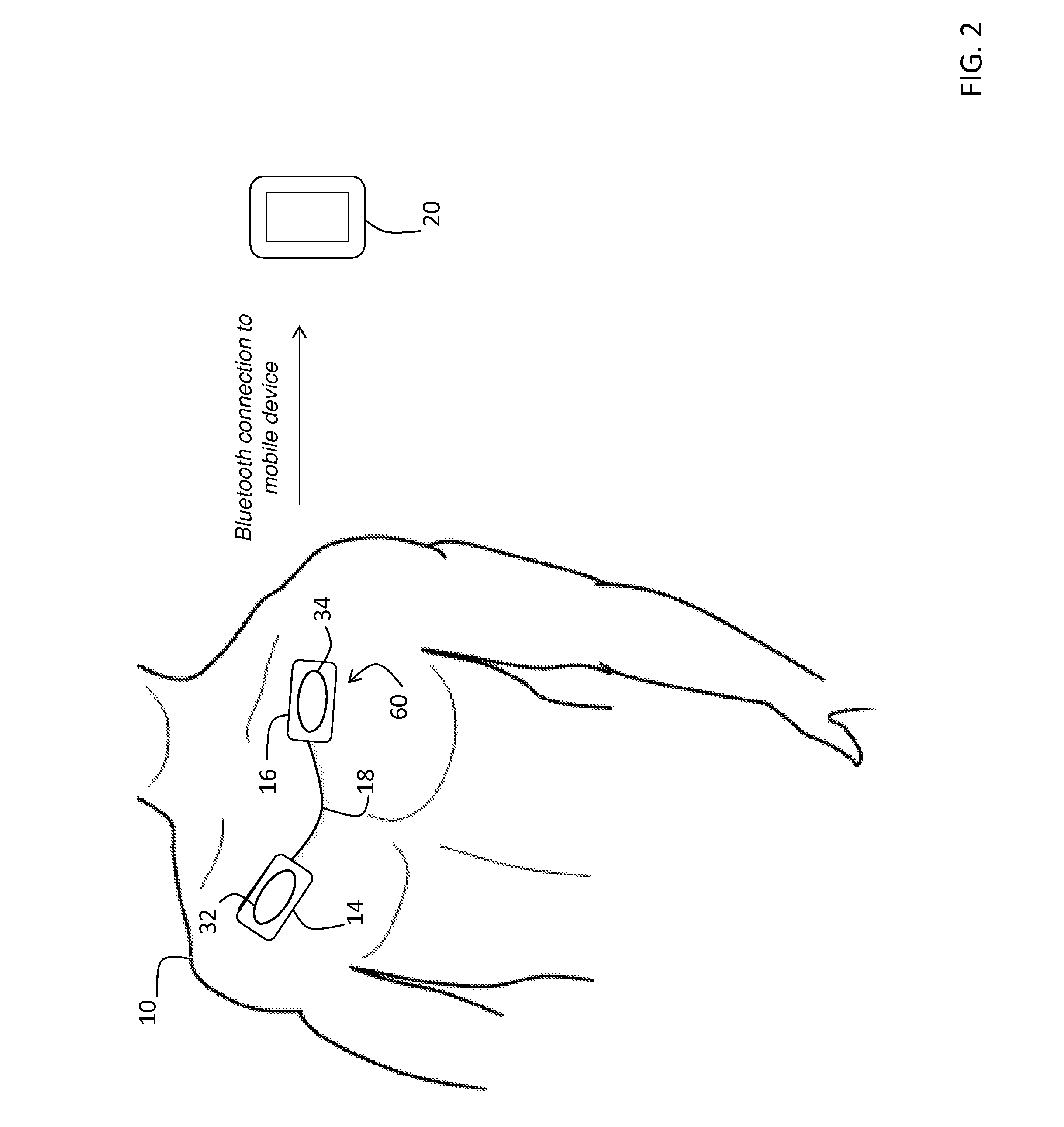
System for electrophysiology that includes software module and body-worn monitor
InactiveUS20140128715A1Performed quickly and efficientlySignificant financial and time investmentElectrocardiographySurgical instrument detailsData setSoftware system
The invention also provides an integrated system that combines an ablation system used in the electrophysiology (EP) lab with a novel, body-worn monitor and data-management software system. The body-worn monitor differs from conventional monitors in that it measures stroke volume (SV) and cardiac output (CO) in addition to heart rate (HR) and ECG waveforms. The combined system collects numerical and waveform data from patients before, during, and after an EP procedure, thereby providing a robust data set that can be used for a variety of analytics and reporting purposes. The body-worn monitor can be applied to the patient immediately after the EP procedure, e.g. while they are recovering in a hospital. Once applied, the body-worn monitor measures data in real-time, and transmits them to both an EMR and a software application running on a mobile device, such as a smartphone, tablet, or personal digital assistant.
Owner:TOSENSE
Korotkoff-sound-based blood pressure measurement method and blood pressure measurement and cardiovascular system evaluation system
PendingCN110840429ASimple structureReduce distractionsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyArterial velocity
The invention discloses a korotkoff-sound-based blood pressure measurement method and a blood pressure measurement and cardiovascular system evaluation system, aiming to solve the problems of inaccurate blood pressure measurement and large influences of individual differences on measurement results in the prior art. Through combination of information detection at radial arteries with intelligent pressurization and pressure relief techniques, signal sources are stable, accurate capture of korotkoff sounds is ensured, and accordingly, the stability and reliability of the measurement results areimproved. Cardiovascular parameters of a human body can be calculated according to basic information of the human body and the measurement results, information of the human body, such as age, height,gender, weight and arm length, is entered, and a series of measured cardiac function parameters such as PWV (pulse wave velocity), heartbeat, heart output and blood viscosity are acquired through algorithm processing, so that an examinee is assisted in evaluating the state of his / her cardiovascular system.
Owner:云鸿创新信息科技(武汉)有限公司
System, method and computer-accessible medium for utilizing cardiac output to improve measurement of tracer input function in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20120095328A1Image enhancementDiagnostic signal processingIndicator dilutionDynamic contrast
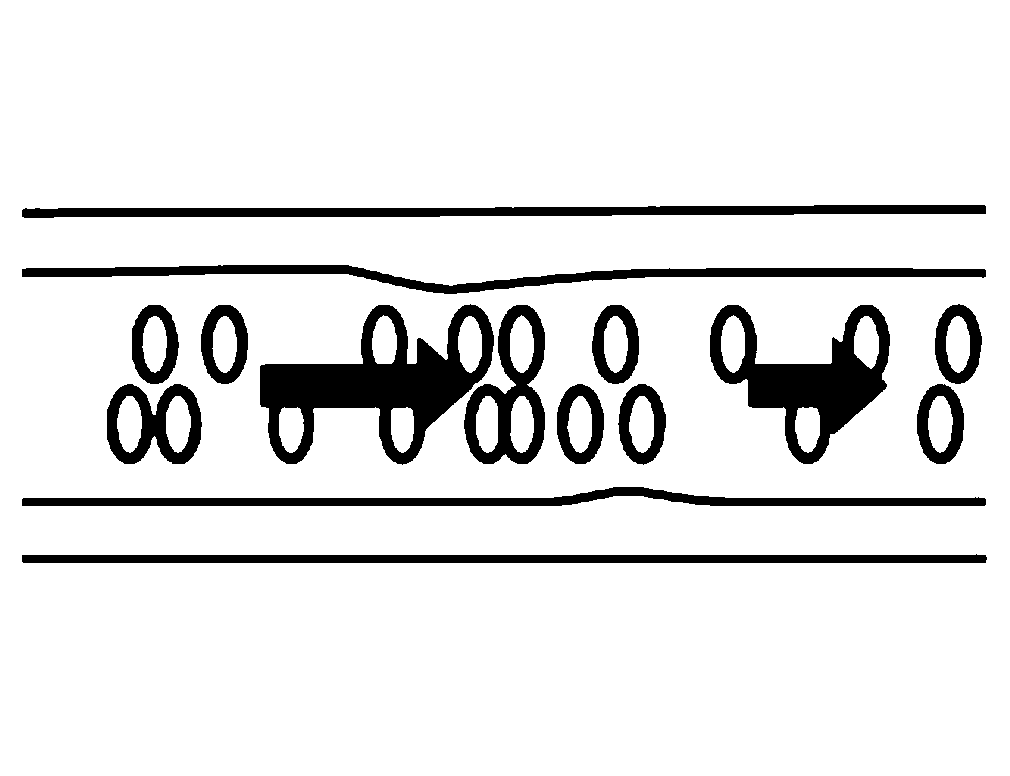
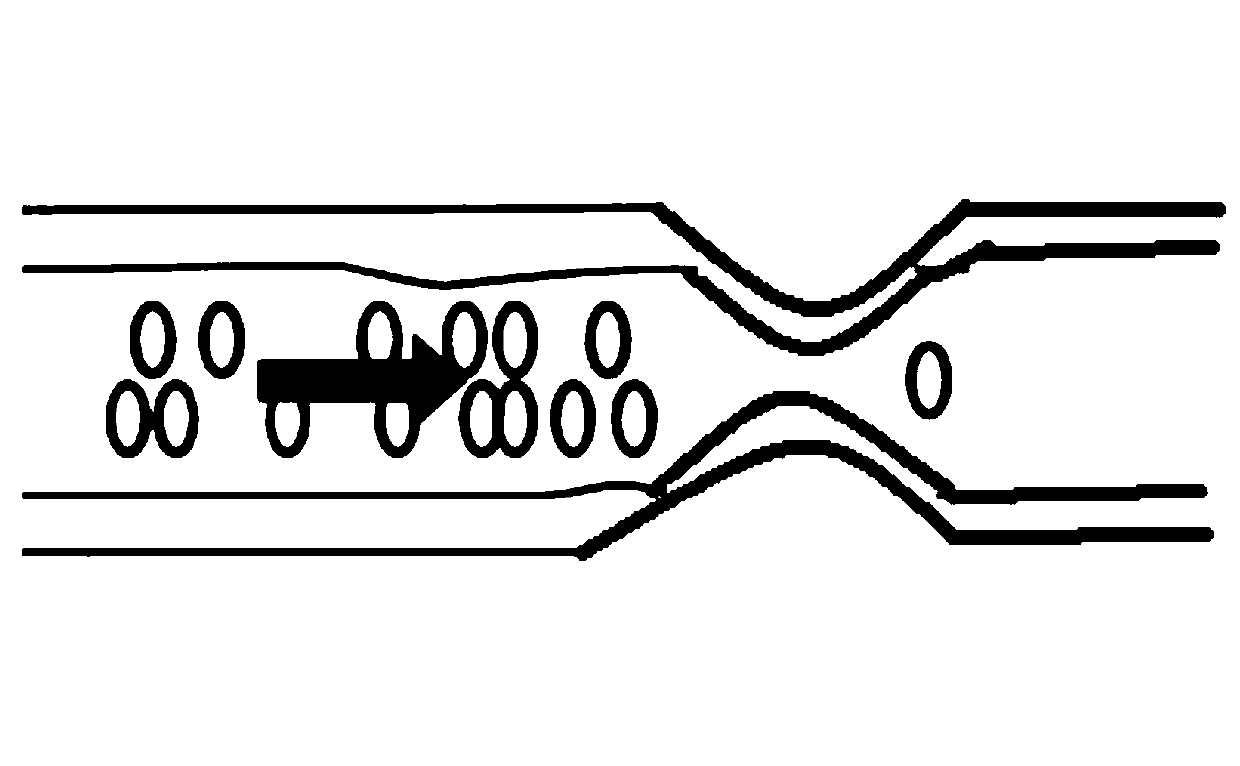
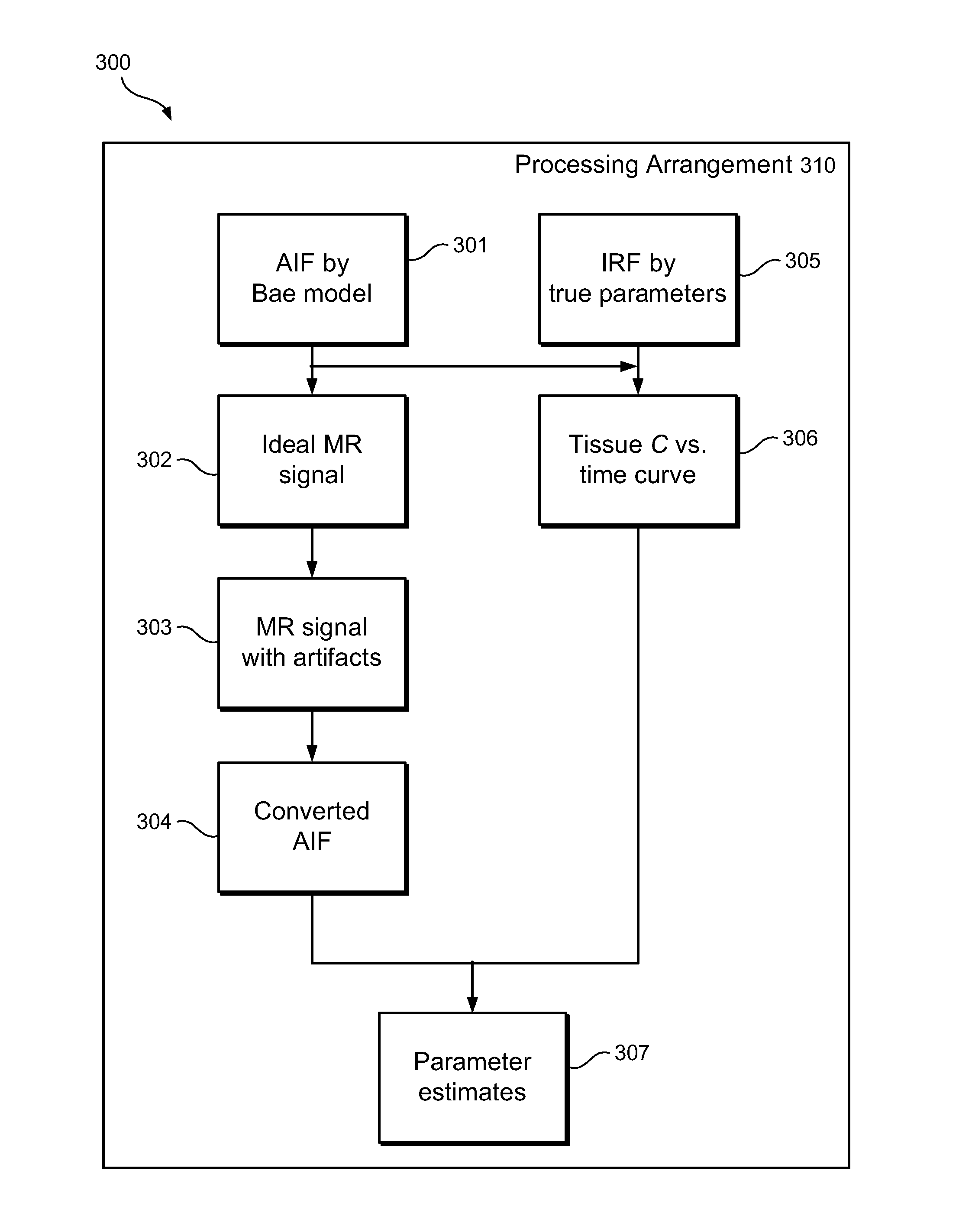
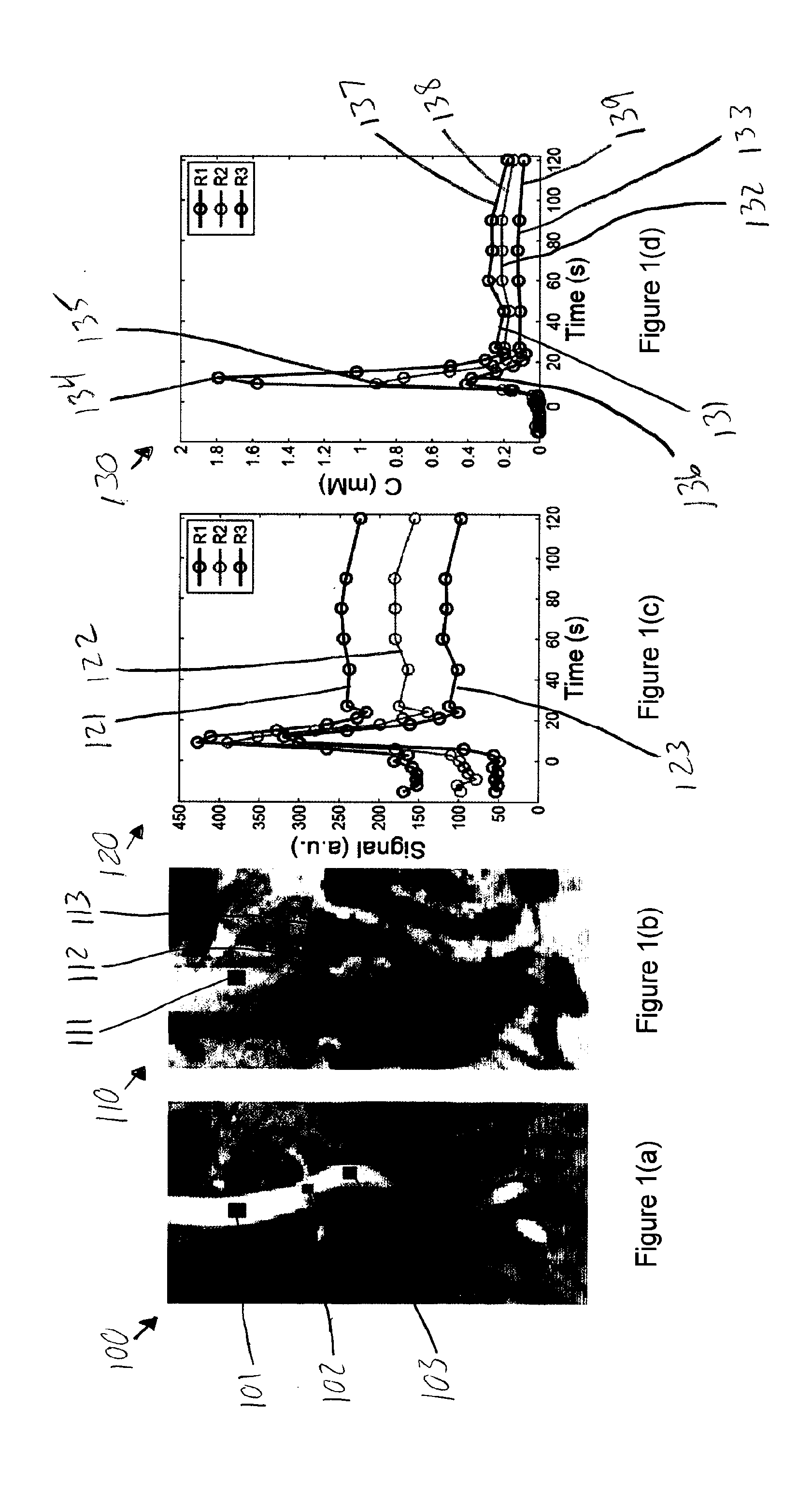
Exemplary embodiments of method, system and computer-accessible medium according to the present disclosure can be provided for converting magnetic resonance (MR) arterial signal intensity versus time curves to arterial input functions (AIF) with less susceptibility to artifacts such as flow-related enhancement. Exemplary methods, systems and computer-accessible medium can be used to constrain AIF to satisfies the indicator dilution principle, according to which the area under an initial pass component of AIF can be equal to the injected dose divided by the cardiac output. For example, Monte Carlo simulations of MR renography and tumor perfusion protocols can be performed for comparison with conventional methods.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Apparatus and methods for computing cardiac output of a living subject via applanation tonometry
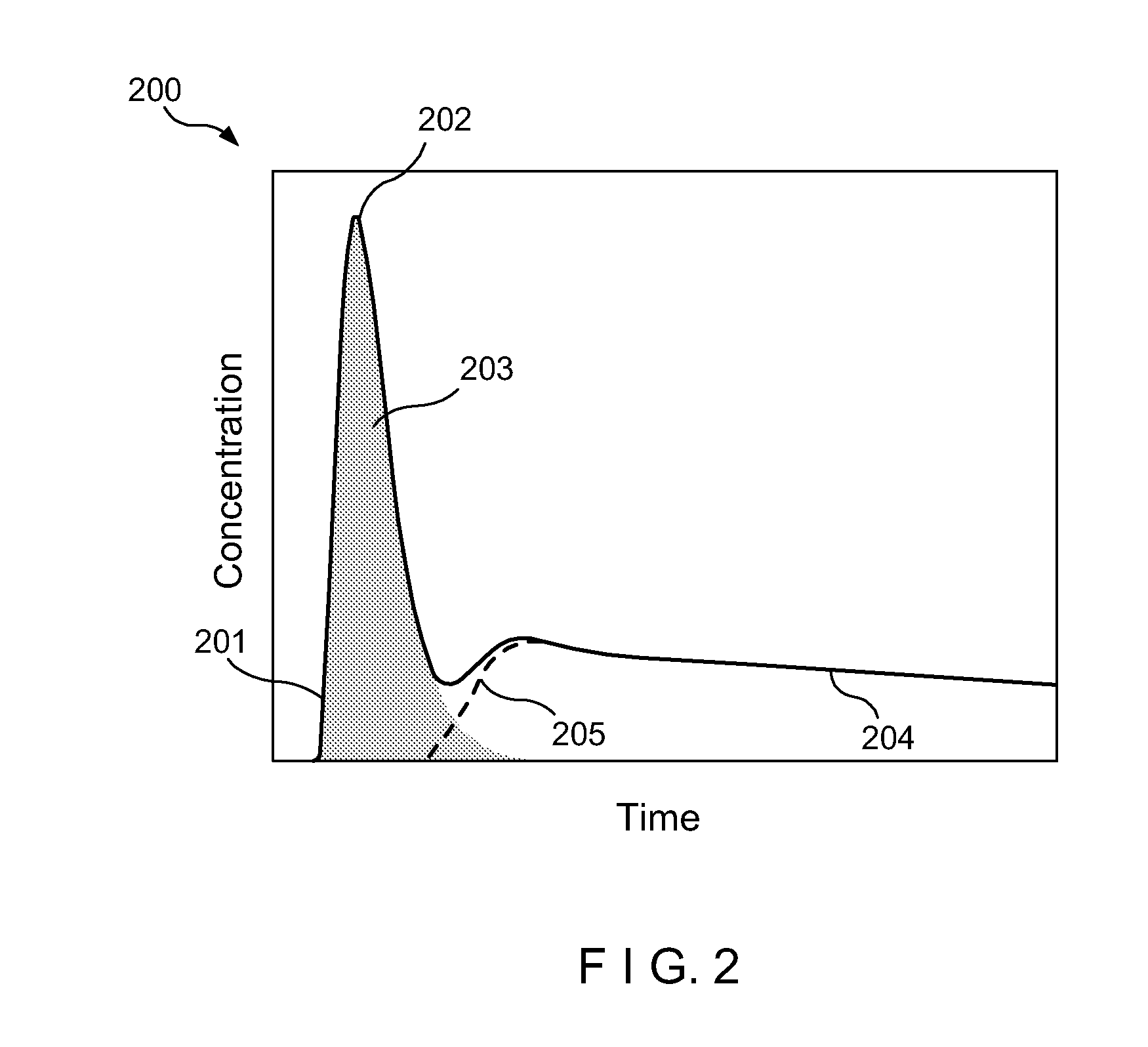
Apparatus and methods for calculating cardiac output (CO) of a living subject using applanation tonometry measurements. In one embodiment, the apparatus and methods build a nonlinear mathematical model to correlate physiologic source data vectors to target CO values. The source data vectors include one or more measurable or derivable parameters such as: systolic and diastolic pressure, pulse pressure, beat-to-beat interval, mean arterial pressure, maximal slope of the pressure rise during systole, the area under systolic part of the pulse pressure wave, gender (male or female), age, height andweight. The target CO values are acquired using various methods, across a plurality of individuals. Multidimensional nonlinear optimization is then used to find a mathematical model which transformsthe source data to the target CO data. The model is then applied to an individual by acquiring physiologic data for the individual and applying the model to the collected data.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHANSHI BIOLOGICAL MEDICAL DEVICES (SHANGQIU) CO LTD
Parameter calibration method and parameter calibration system for continuously monitoring cardiac output
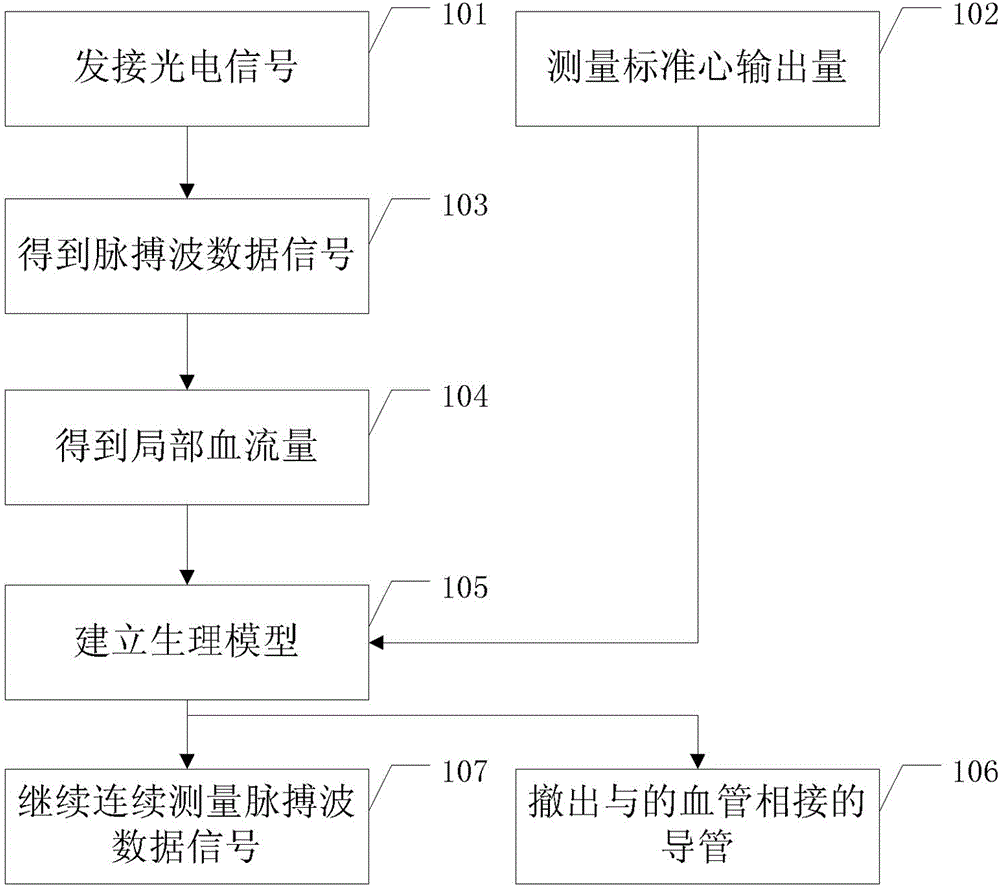
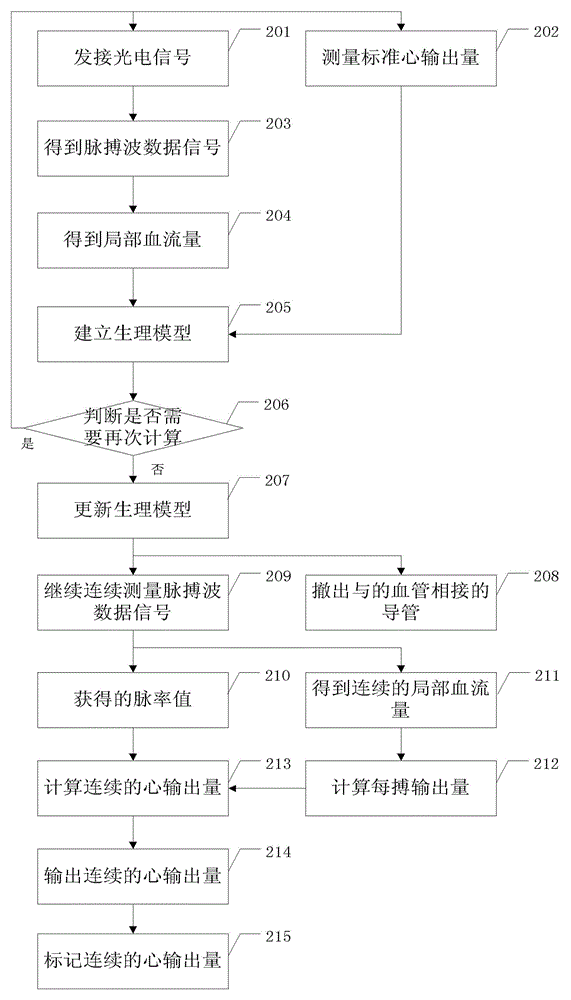
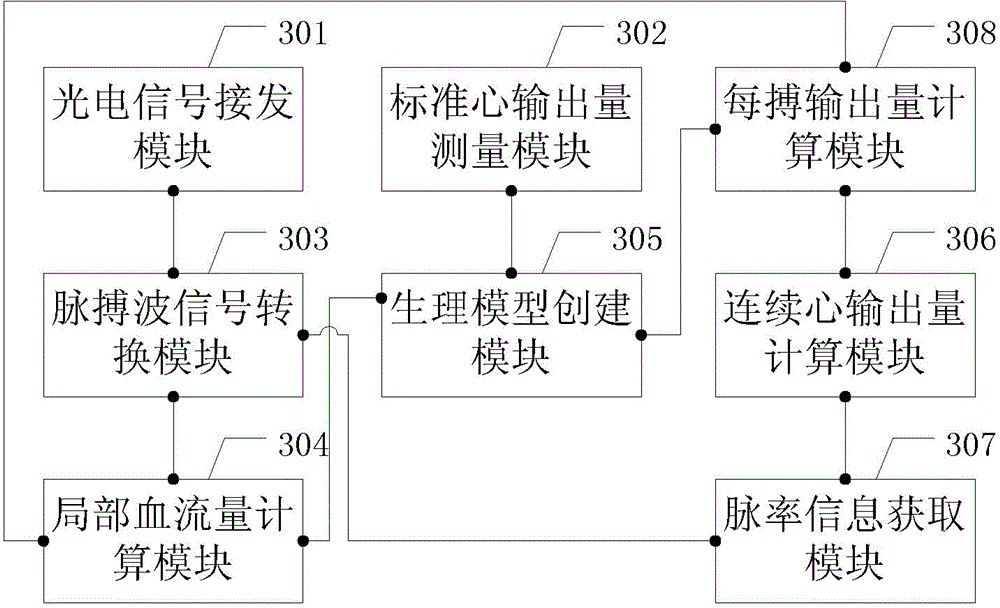
The invention relates to the technical field of medical detection, and particularly relates to a parameter calibration method and a parameter calibration system for continuously monitoring cardiac output. The method comprises the steps of measuring a pulse wave data signal through a luminescent device; simultaneously connecting a vessel of a target to be measured by a conduit, and measuring the standard cardiac output; calculating the pulse wave data signal to obtain local blood flow; establishing a physiological model according to the mapping relation; after the physiological model is established, withdrawing the conduit connected with the vessel of the target to be measured, and transmitting two paths of optical signals with different wavelength to the vessel of the target to be measured via the luminescent device till a continuous pulse wave data signal is obtained; and adjusting the continuous pulse wave data signal according to the physiological model. According to the invention, the conduit does not need to be retained in the body of the patient for a long time, thereby reducing the operation complexity of the medical personnel, and reducing the pain of the patient and potential harm to the patient.
Owner:EDAN INSTR
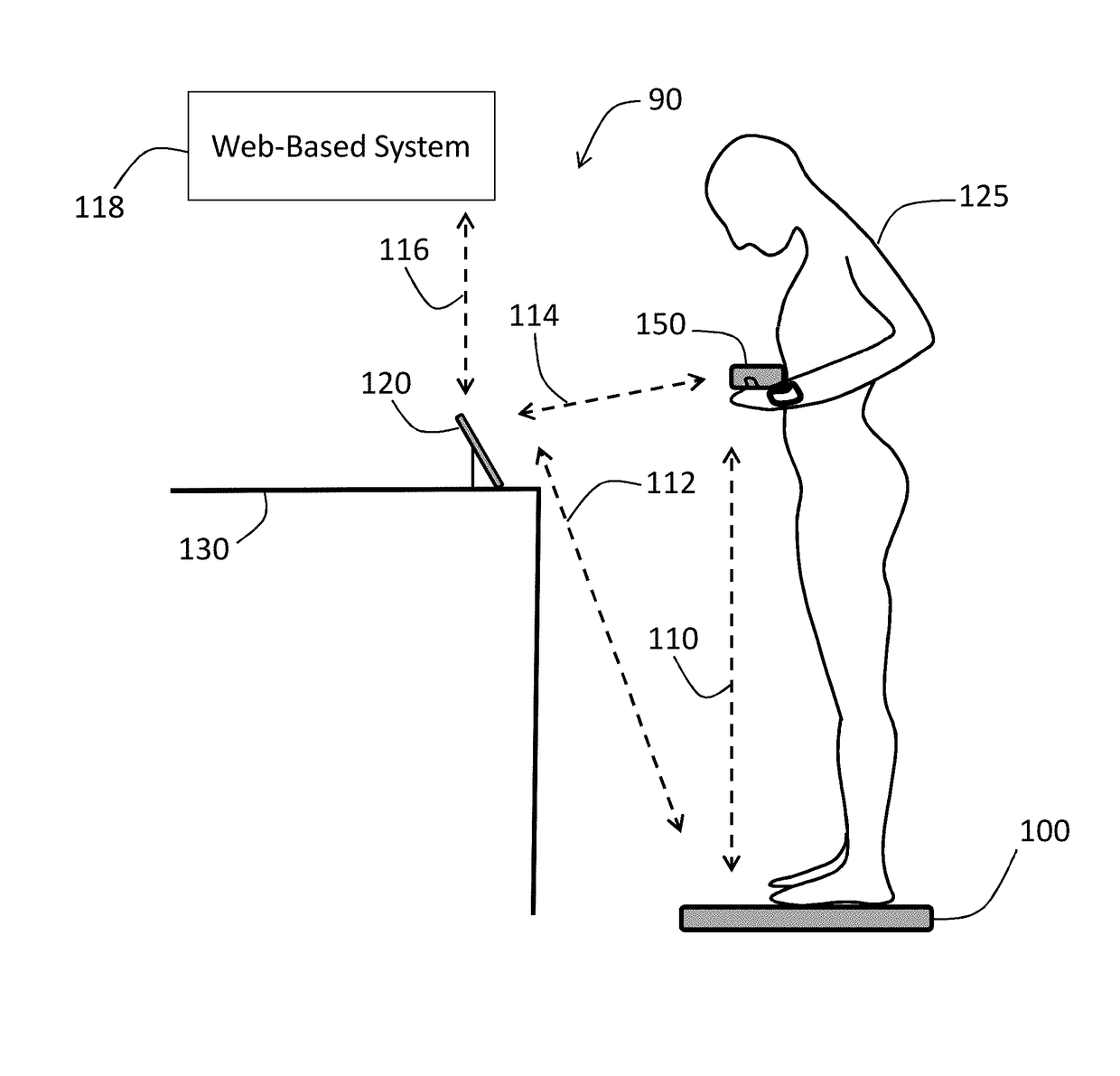
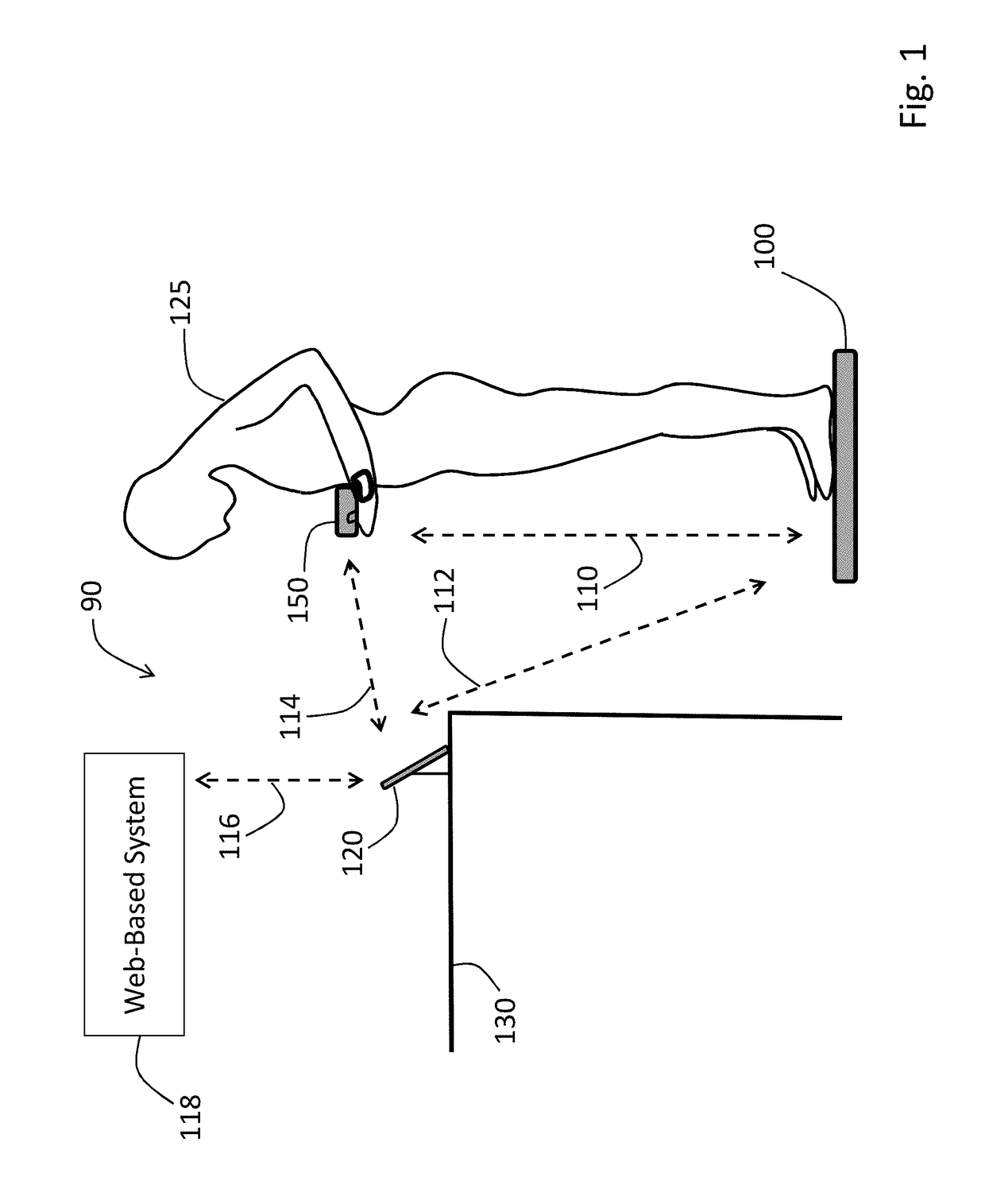
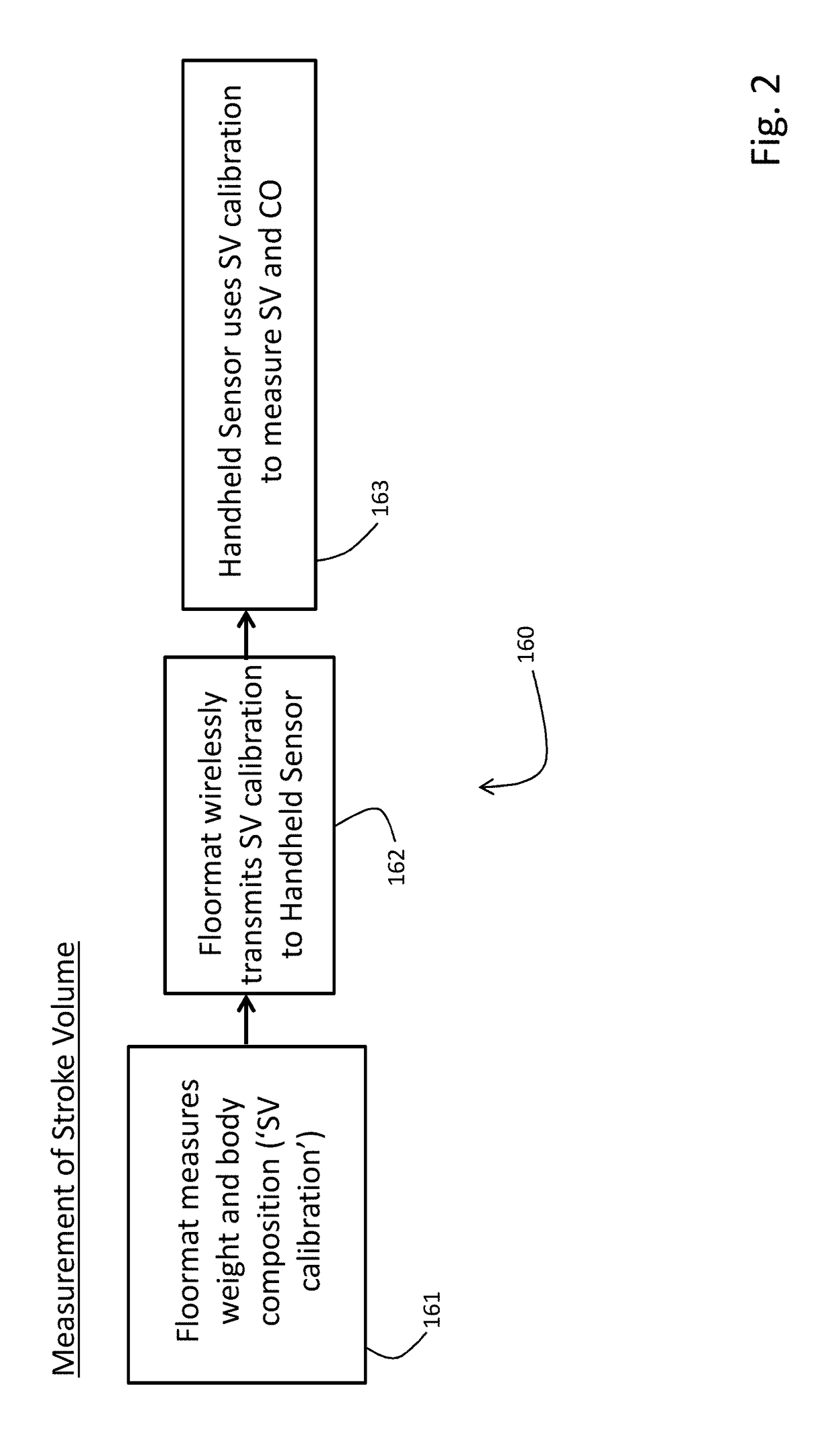
Physiological monitoring system featuring floormat and handheld sensor
InactiveUS20170188964A1Easy to measureEasy to useElectrocardiographySensorsPulse pressureMedical emergency
The invention described herein is a system that features a Floormat and Handheld Sensor that operate in concert with a user's mobile device. The Floormat resembles a conventional bathroom scale, but features an enhanced set of measurements that include pulse rate and / or heart rate, SpO2, respiratory rate, weight, body composition, and Fluids. The Handheld Sensor features an integrated form factor that fits in a user's hand, which measures parameters such as blood pressure (e.g. systolic, diastolic, mean and pulse pressures), stroke volume, and cardiac output. Measurements of stroke volume and cardiac output require information from the Floormat (e.g., weight and body composition) to be sent to and processed by the Handheld Sensor. The Handheld Sensor can also make redundant measurements of heart rate, SpO2, and respiratory rate. Both systems transmit information through a wireless interface to a web-based system, where a clinician can analyze it to help diagnose a user.
Owner:TOSENSE
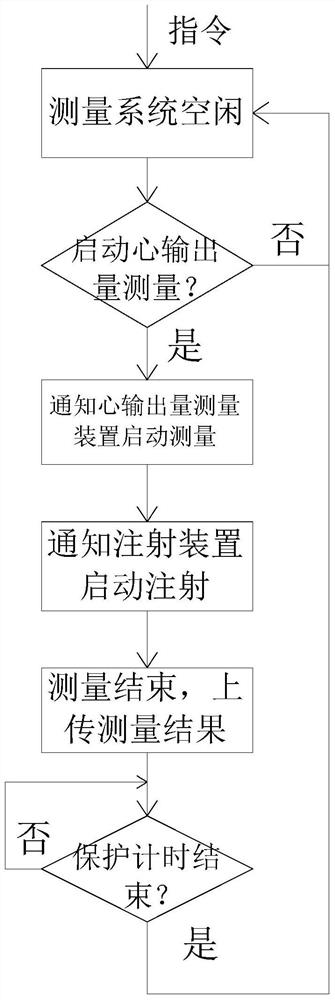
Cardiac output automatic measurement system
ActiveCN104739400BGuaranteed uniformityGuaranteed accuracyCatheterSensorsSwan Ganz CatheterIntensive care medicine
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Application of ester group-containing aromatic propionamide compound and metabolites thereof in preparation of drugs for treating heart failure
ActiveCN112007027AImprove LVSPDecreased cardiac outputOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderMetabolitePharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses an application of an ester group-containing aromatic propionamide compound and metabolites thereof in preparation of a drug for treating heart failure. The ester group-containing aromatic propionamide compound is C25H17F3N4O4. The invention has the outstanding effects that the ester group-containing aromatic propionamide compound can improve the ejection fraction, the shortaxis shortening rate and the cardiac output reduction of rats with chronic heart failure, and improve the LVSP of the rats with heart failure. The compound has a positive effect in the application ofpreparing the medicine for treating heart failure.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GENESCIENCE PHARM CO LTD
Non-invasive monitoring system for cardiac output
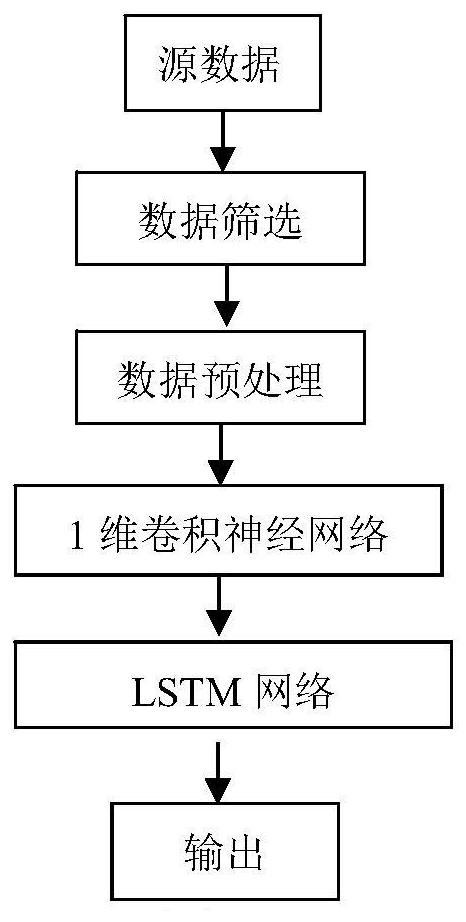
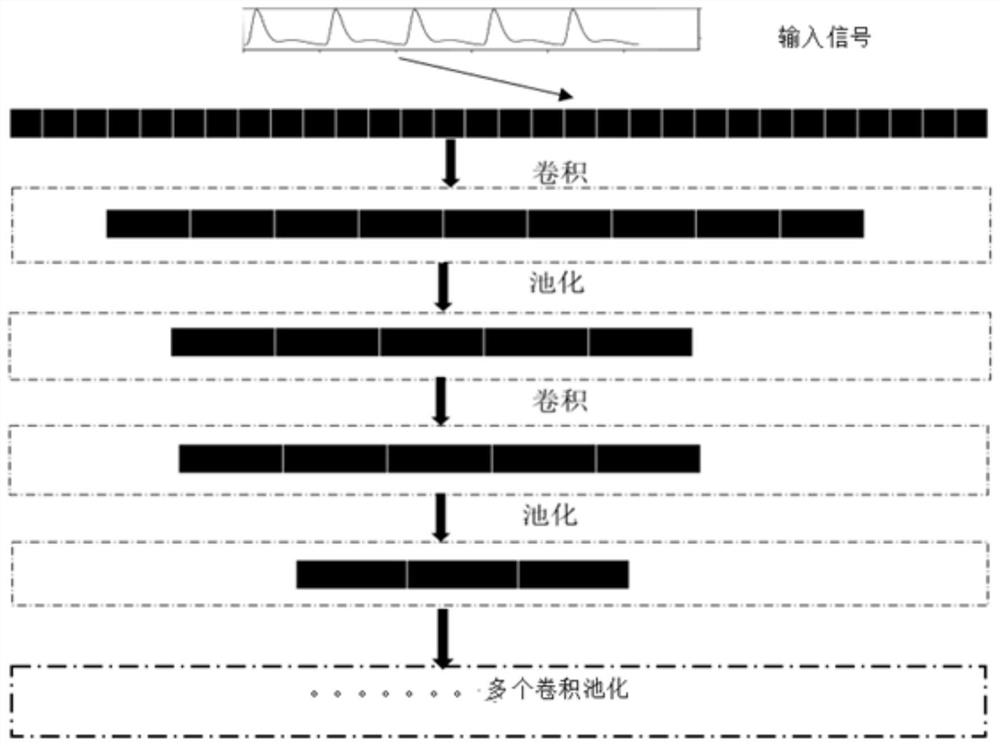
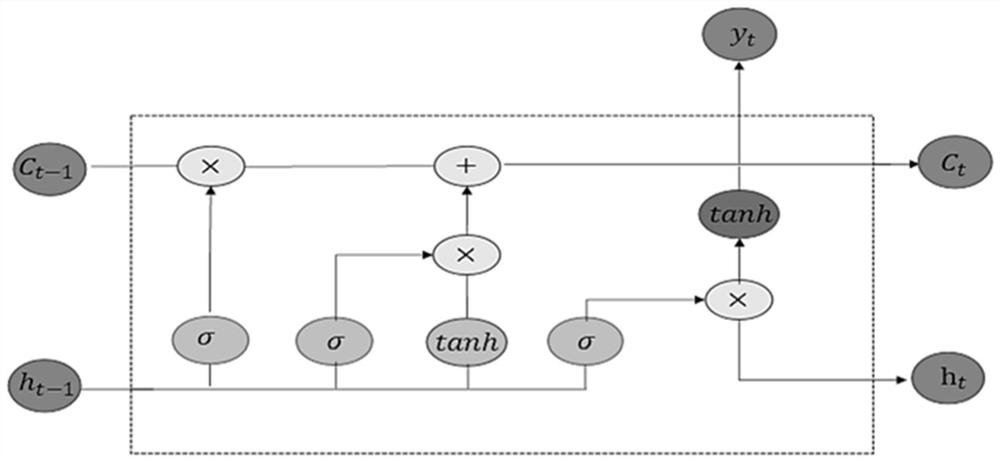
ActiveCN113057617AAvoid typingImprove performanceEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsData displayNerve network
The invention discloses a non-invasive monitoring system for cardiac output. The non-invasive monitoring system comprises a data acquisition control module, a non-invasive peripheral arterial blood pressure measurement module, a waveform screening module, a data preprocessing module, a cardiac output calculation module and a data display module; the data acquisition control module is used for controlling a data acquisition and data transmission process; the waveform screening module is used for classifying and screening peripheral arterial blood pressure waveforms to obtain A-type waveforms; the data preprocessing module is used for preprocessing A-type waveforms and sending the A-type waveforms to the cardiac output calculation module; the cardiac output calculation module comprises a neural network trained through a sample set, the trained neural network has the end-to-end recognition capability, namely, peripheral arterial blood pressure waveforms are input, corresponding cardiac output is output, and the cardiac output is sent to the data display module through the data acquisition control module. According to the invention, end-to-end identification is carried out, and the cardiac output can be continuously monitored in a non-invasive manner.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Heart parameter measuring method and device
ActiveCN102499669BGuaranteed accuracyImprove operational convenienceDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalBlood pressure
A heart parameter measuring method comprises following steps: synchronously detecting electrocardiosignals and photoplethysmography signals and carrying out preprocessing; carrying out waveform contour analysis for the electrocardiosignals and the photoplethysmography signals which are preprocessed to obtain pulse wave arrival time and pulse wave inflection point area ratios; calculating a pulse wave reflection coefficient ratio according to the pulse wave inflection point area ratios; and estimating the pulse wave arrival time and the pulse wave inflection point area ratios to obtain blood pressure and heart output. By means of calculating the pulse wave inflection point area ratios obtained from the electrocardiosignals and the photoplethysmography signals, the pulse wave reflection coefficient ratio is obtained, then the pulse wave reflection coefficient ratio and the pulse wave arrival time are estimated so as to obtain the blood pressure and the heart output, the blood pressure and the heart output are synchronously measured, accuracy is guaranteed, invasive-method measurement is omitted, and operation convenience under a movement state is greatly improved.
Owner:珠海中科先进科技产业有限公司
Methods and apparatus for visually representing a cardiac status of a patient
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for determining blood flow characteristics in small infants
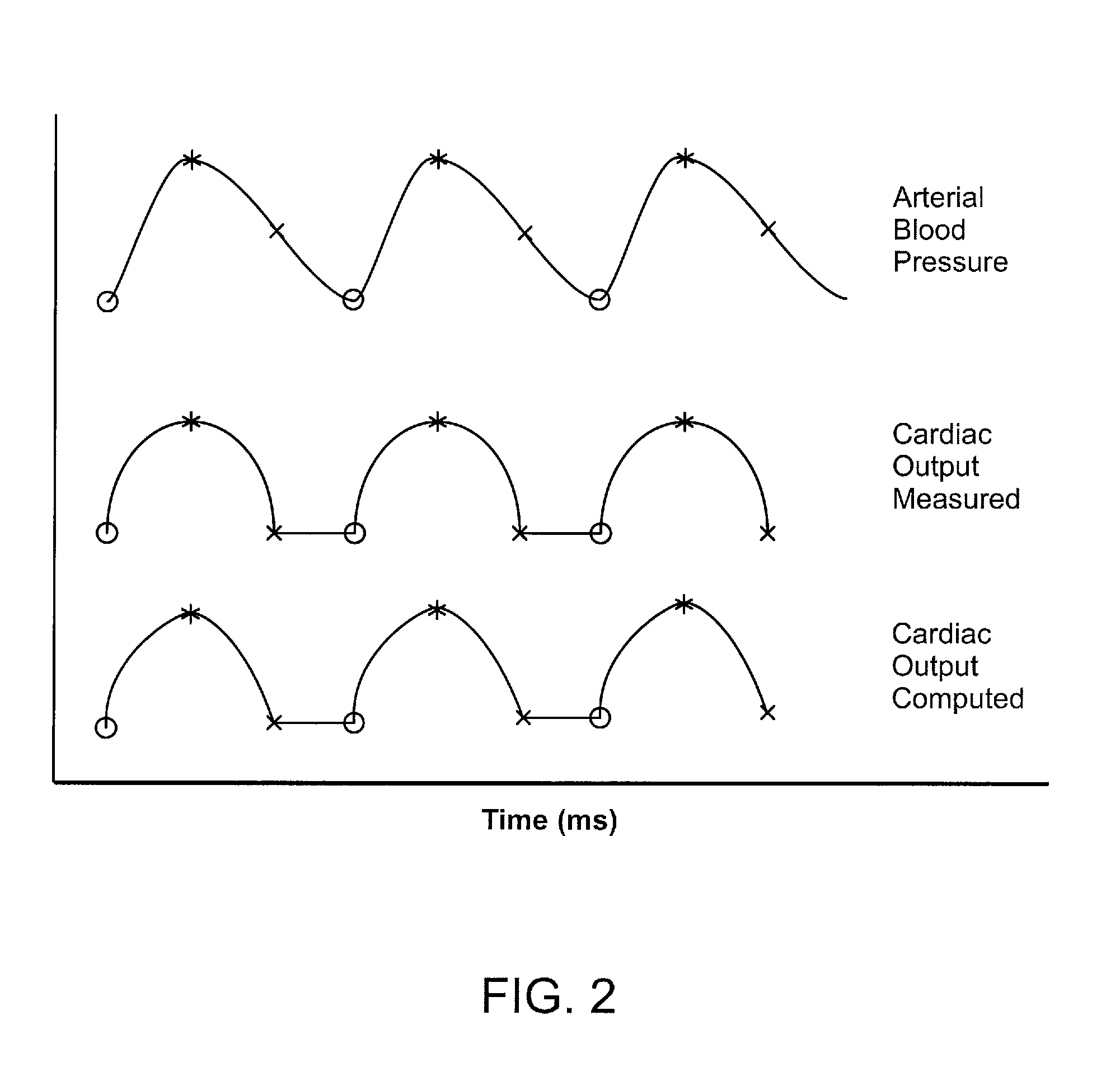
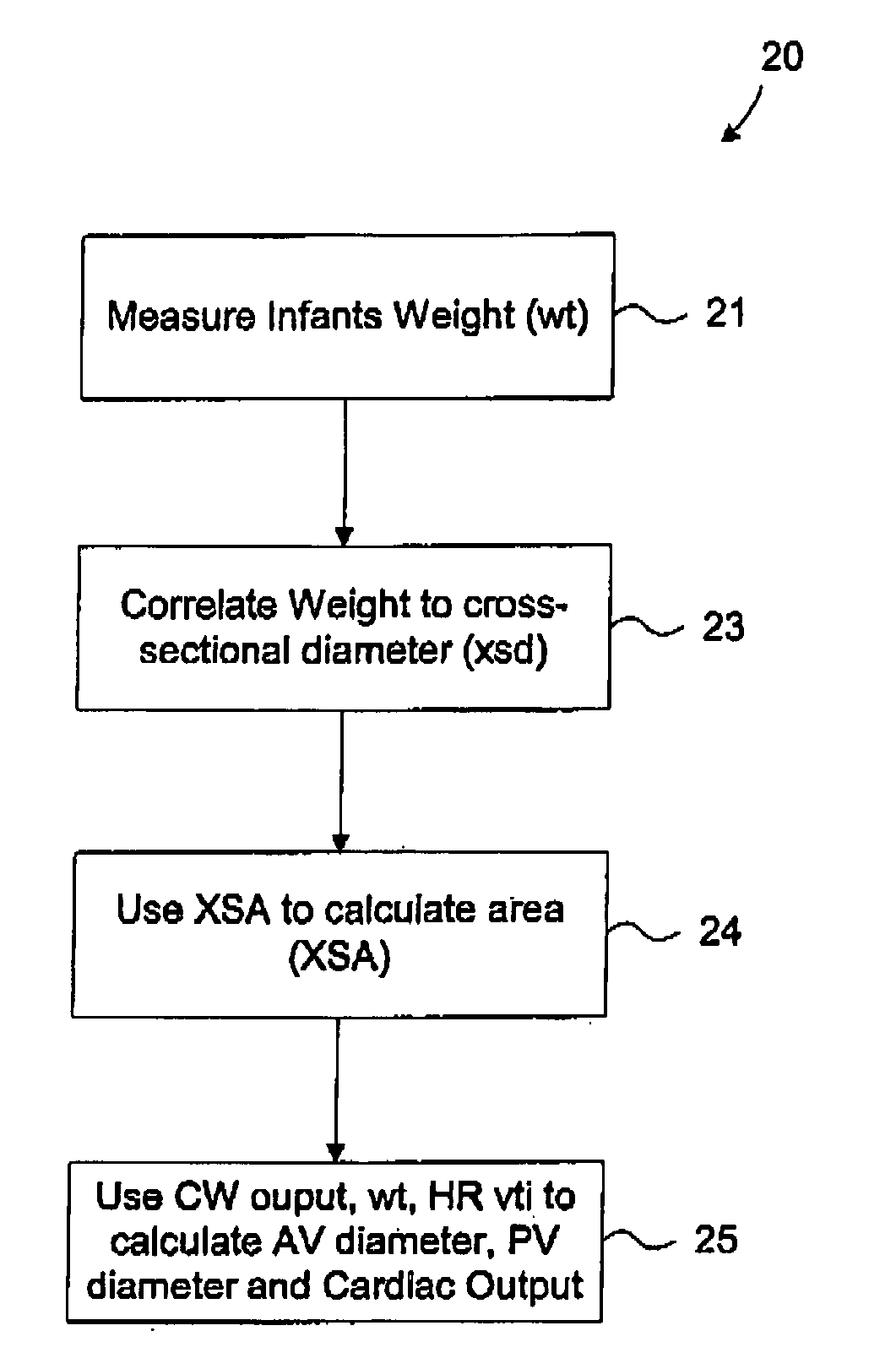
ActiveUS20050159664A1Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionVelocity time integralHematological test
A method of determining the cardiac output of an infant, the method comprising the steps of: (a) measuring the infant's weight; (b) measuring the velocity time integral and stroke distance of blood flowing from the heart of the patient; and (c) utilising the two measurement in step (a) and step (b) to determine the cardiac output of the infant.
Owner:USCOM
Heart recovery device suitable for severe exercise endpoint
PendingCN111728821AEasy to useSimple structureSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsLeg muscleHealth maintenance
The present invention discloses a heart recovery device suitable for a severe exercise endpoint. The heart recovery device suitable for a severe exercise endpoint comprises a base seat, a health maintenance platform and power-assisted bicycles, the health maintenance platform is arranged at a middle position at an upper side of the base seat and a plurality of the power-assisted bicycles are arranged symmetrically around the health maintenance platform on the base seat; and the power-assisted bicycles are driven by motors to rotate and main controllers for controlling the motors are arranged on inner sides of handrails of the power-assisted bicycles. The device is simple in structure, people who undergo severe exercise can use the device to perform passive exercise, a leg muscle exercise in a running state can be simulated, leg muscle stimulation is assisted to maintain returned blood volume level of the heart close to a running process and oxygen supply stimulation environment provided for the heart by skeletal muscle stretch reflection, and the device avoids a series of health problems caused by sudden reduction of cardiac output and rapid reduction of blood pressure.
Owner:NANJING FOREST POLICE COLLEGE
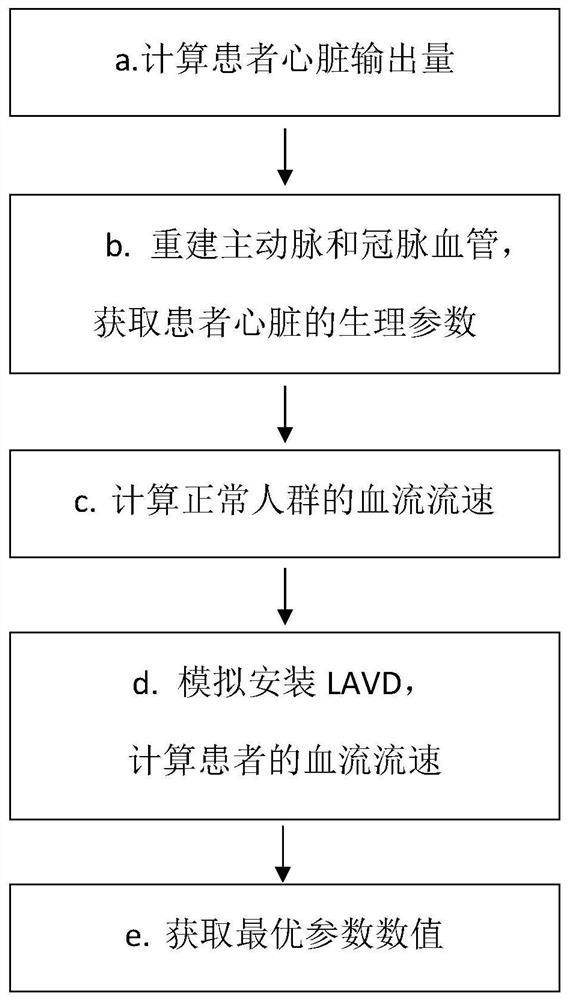
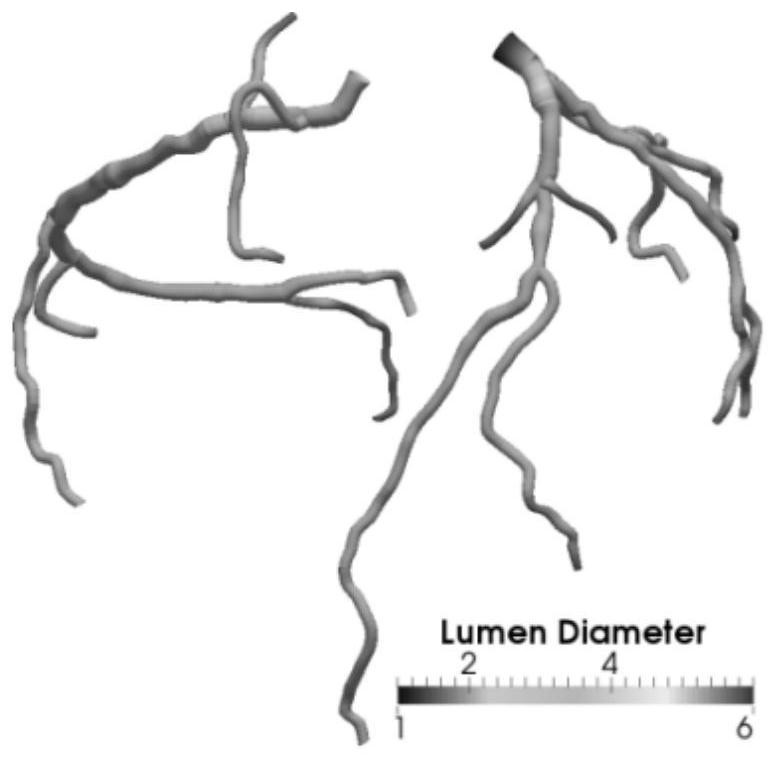
Left ventricle auxiliary device implantation method based on blood flow distribution optimization
ActiveCN114098692AReduce formationReduce the chance of formationMedical simulationBlood pumpsLeft ventricular sizeThrombus
The invention relates to a left ventricular assist device implantation method based on blood flow distribution optimization. The method comprises the steps that the heart output quantity of a patient is calculated; physiological parameters of the heart of the patient are obtained by reconstructing aorta and coronary vessels; calculating the blood flow velocity of the normal crowd by using the blood flow volume and resistance of the normal crowd; simulating installation of a left ventricular auxiliary device, importing physiological parameters of the heart of the patient, and calculating the blood flow velocity of the patient; and obtaining an optimal parameter value according to the error function. According to the method, after the optimal parameter values are obtained, implantation and use of the left ventricular assist device can be guided, and it is guaranteed that when the left ventricular assist device is actually implanted, parameters such as the included angle between the artificial blood vessel and the ascending aorta, the diameter of the artificial blood vessel and the motor rotating speed of the left ventricular assist device are optimal parameters; therefore, the blood supply condition of each blood vessel after the left ventricular auxiliary device is implanted is optimized, vortex formation is reduced, thrombus formation is reduced, and the probability of formation of complications such as pulmonary embolism and cerebral infarction is reduced.
Owner:北京心世纪医疗科技有限公司
Apparatus and method for a heating patch
PendingUS20220313480A1High outputInduce vasodilationTherapeutic coolingTherapeutic heatingElectrical conductorMedicine
A heating patch assembly adapted for use on a human. The preferred heating patch assembly includes a heating patch assembly lining and a heating patch assembly thermal conductor. The preferred heating patch assembly thermal conductor is disposed within the heating patch assembly lining. The preferred heating patch assembly is adapted to induce vasodilation and increase cardiac output in the human. A method for increasing cardiac output including applying the heating patch assembly to a human chest.
Owner:PARKER ALIA E
Cardiac output support apparatus
PendingUS20210338998A1Lessen the burden on the bodyControl devicesMedical devicesEngineeringEmergency medicine
A first drive unit, in a state where a top end of a tubular joint is interposed into a chest of a target person and is located at a lower heart part, pushes a diaphragm out from the top end of the tubular joint while pressing a gas into the diaphragm, and simultaneously causes the diaphragm to start flexing to cover and wrap the lower heart part, and then stops pressing the gas into the diaphragm at a time point where compression balloons are positioned at atriums and ventricles of a heart, respectively; and second drive units support a pumping function of the heart by alternately repeating an ejecting operation to fill each of the compression balloons with a fluid and cause each compression balloon to expand and an absorbing operation to cause each compression balloon to discharge the fluid and contract.
Owner:CYBERDYNE INC +1
Systems and methods for calibrating and correcting speckle contrast flowmeters
ActiveCN109314764BVolume/mass flow measurementScattering properties measurementsContrast levelPhotodetector
Owner:柯惠股份公司
Method and apparatus for determining blood flow characteristics in small infants
ActiveUS7235053B2Blood flow measurement devicesOrgan movement/changes detectionVelocity time integralHematological test
Owner:USCOM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com