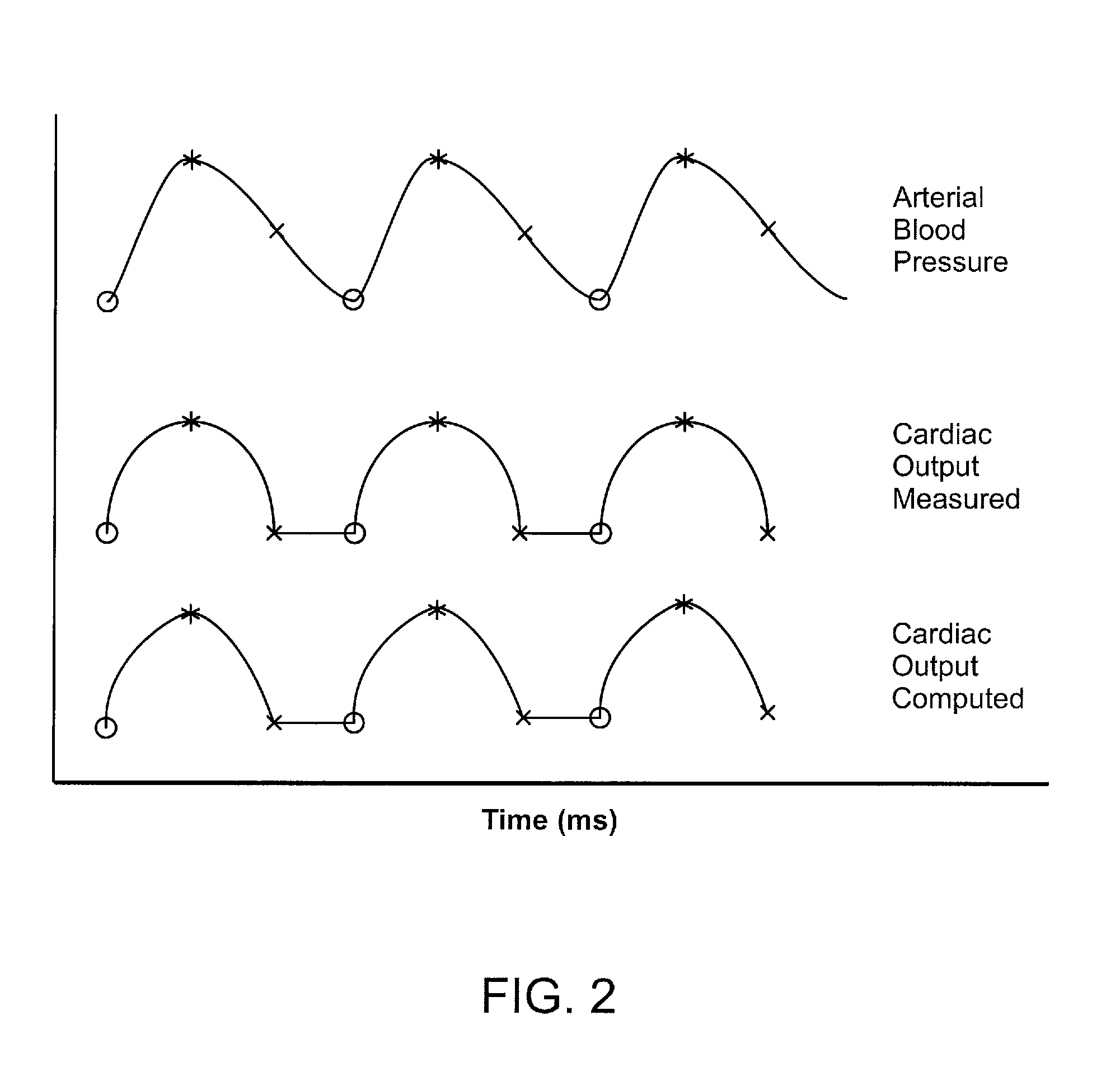
Patents
Literature
64 results about "Cardiac status" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
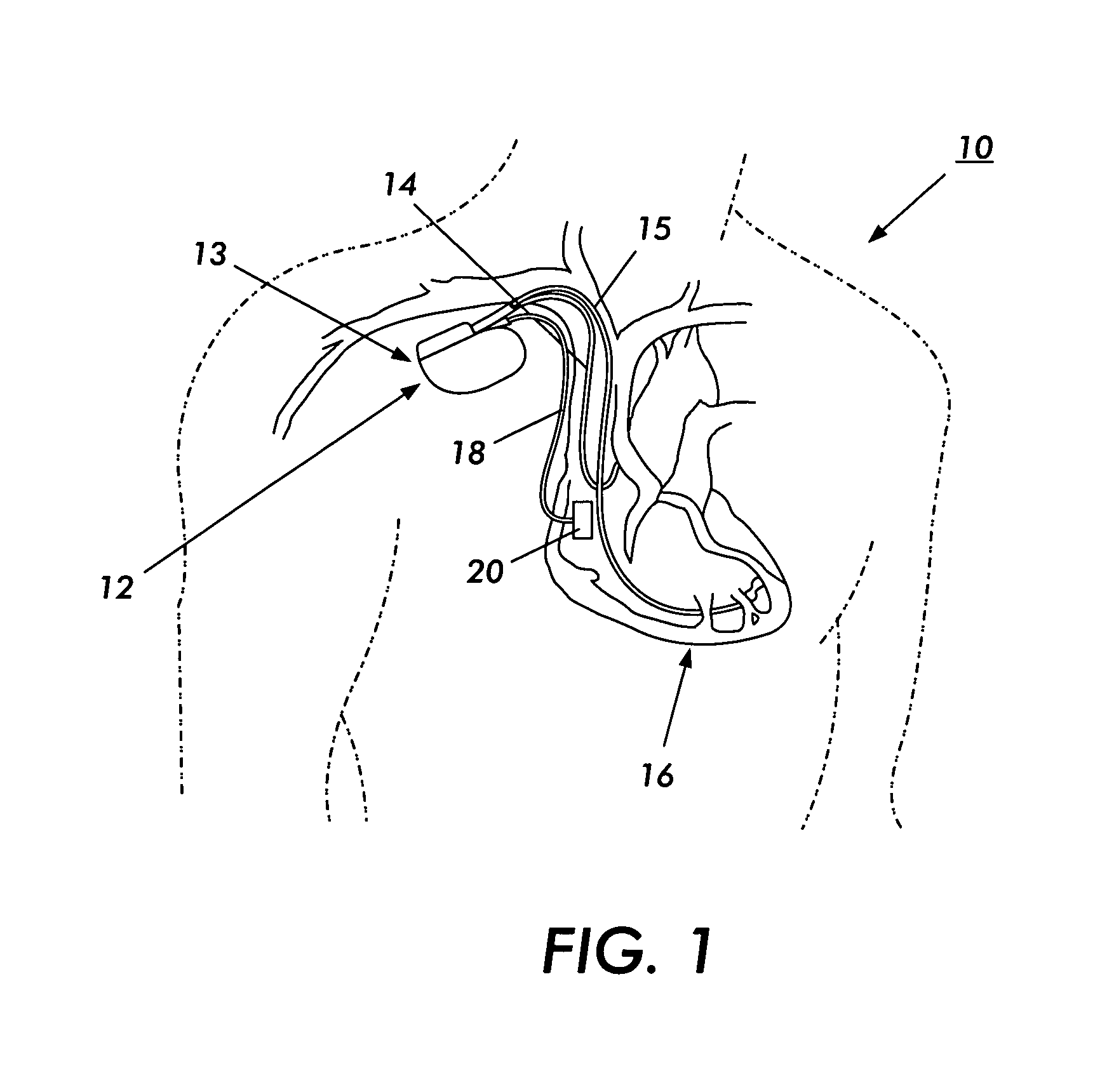
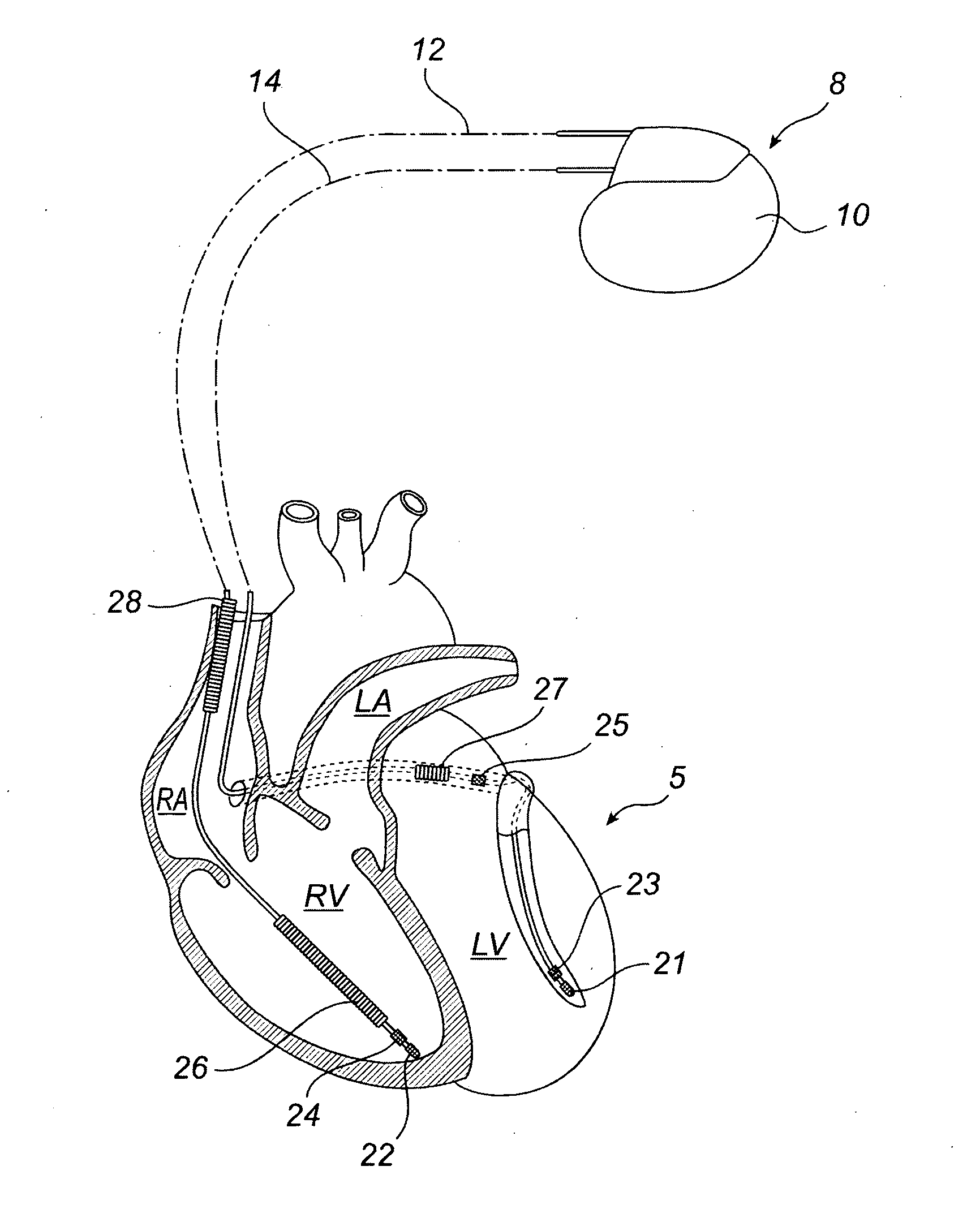
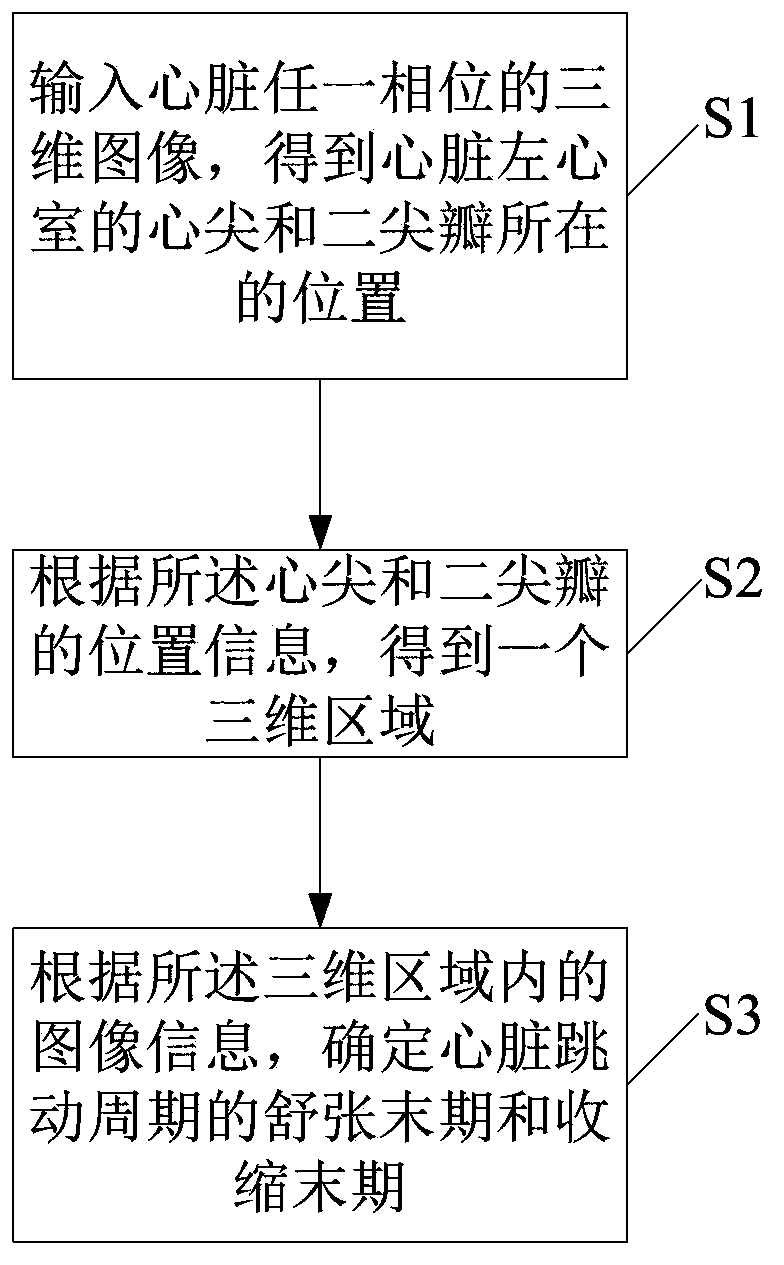
Method and system for image processing and assessment of a state of a heart
One embodiment discloses a computerized method of facilitating cardiac intervention. The method may include inputting patient data and creating a computerized interactive model of a heart based on the patient data. The model may include features. The model may simulate at least one proposed cardiac intervention by adding or deleting features to the model, and determining the effects of the proposed cardiac simulation upon the entire model. Simulations may be repeated to allow the user to determine an optimal cardiac intervention. A template and / or patient specific instrument may be created from the model to use as a guide during the cardiac intervention.
Owner:CAPITAL SOUTHWEST
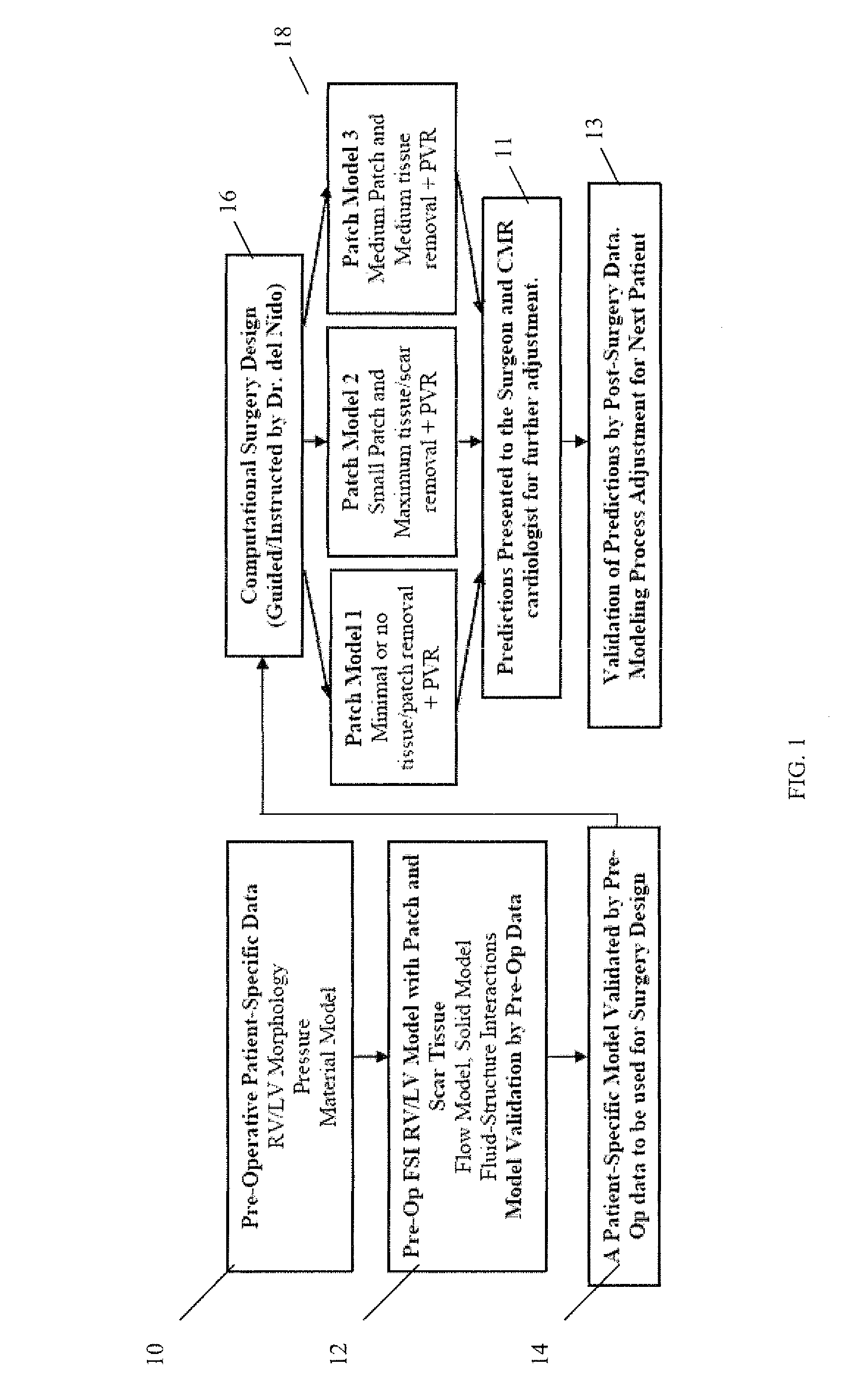
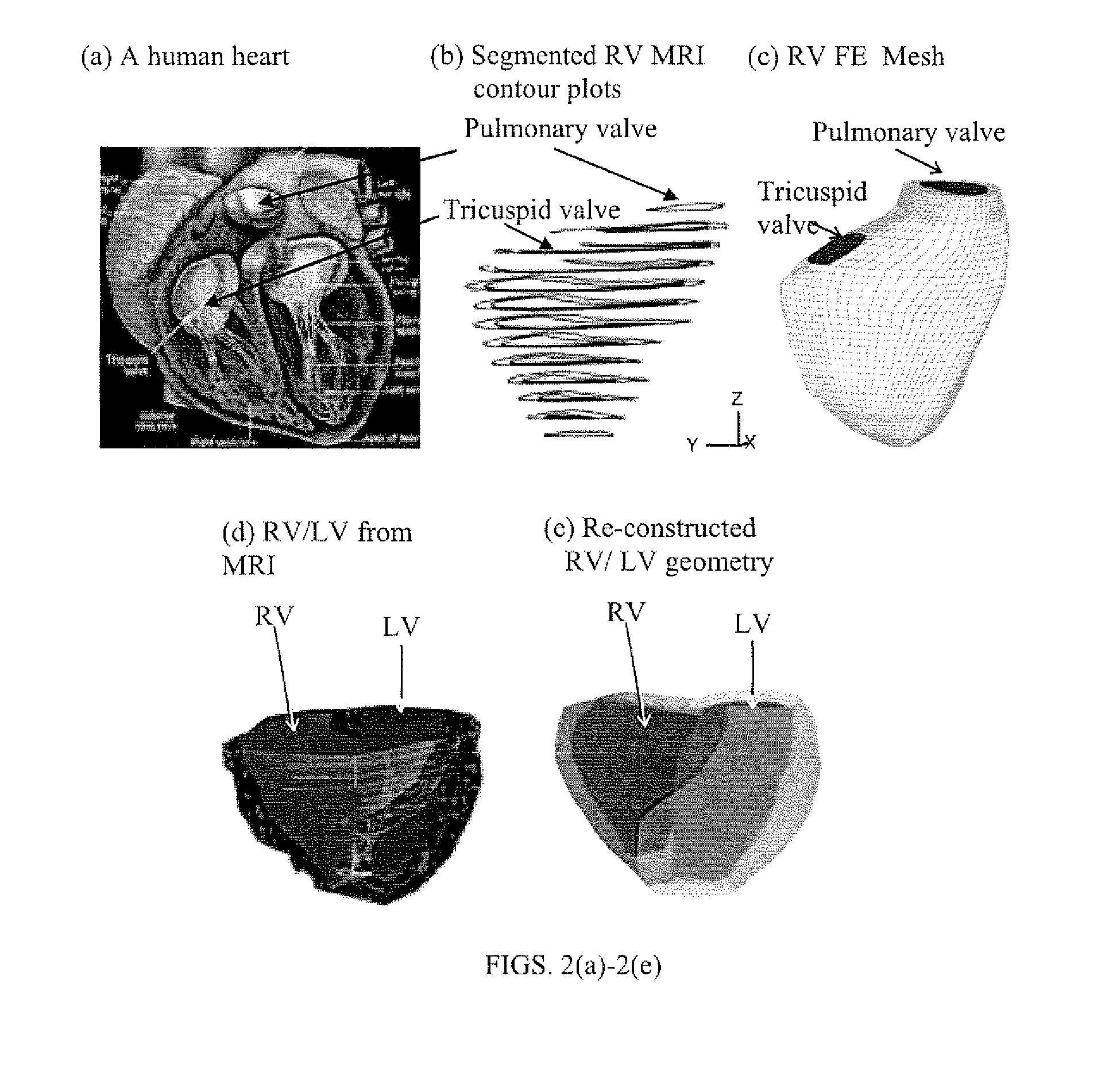
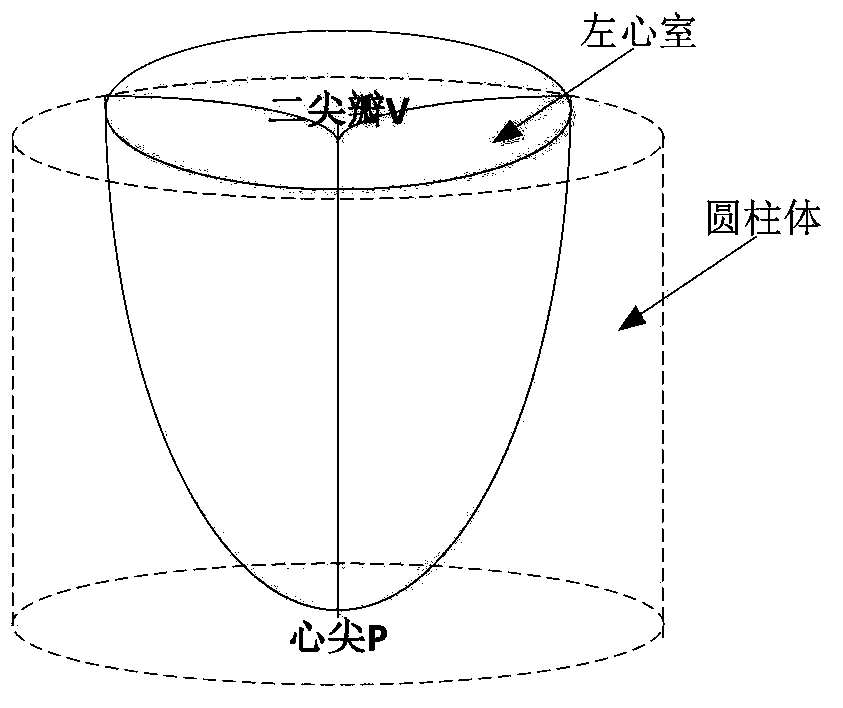
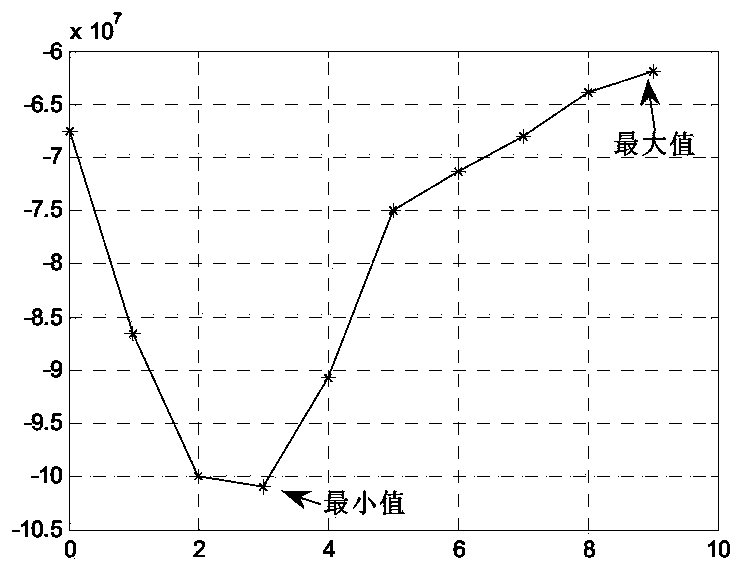
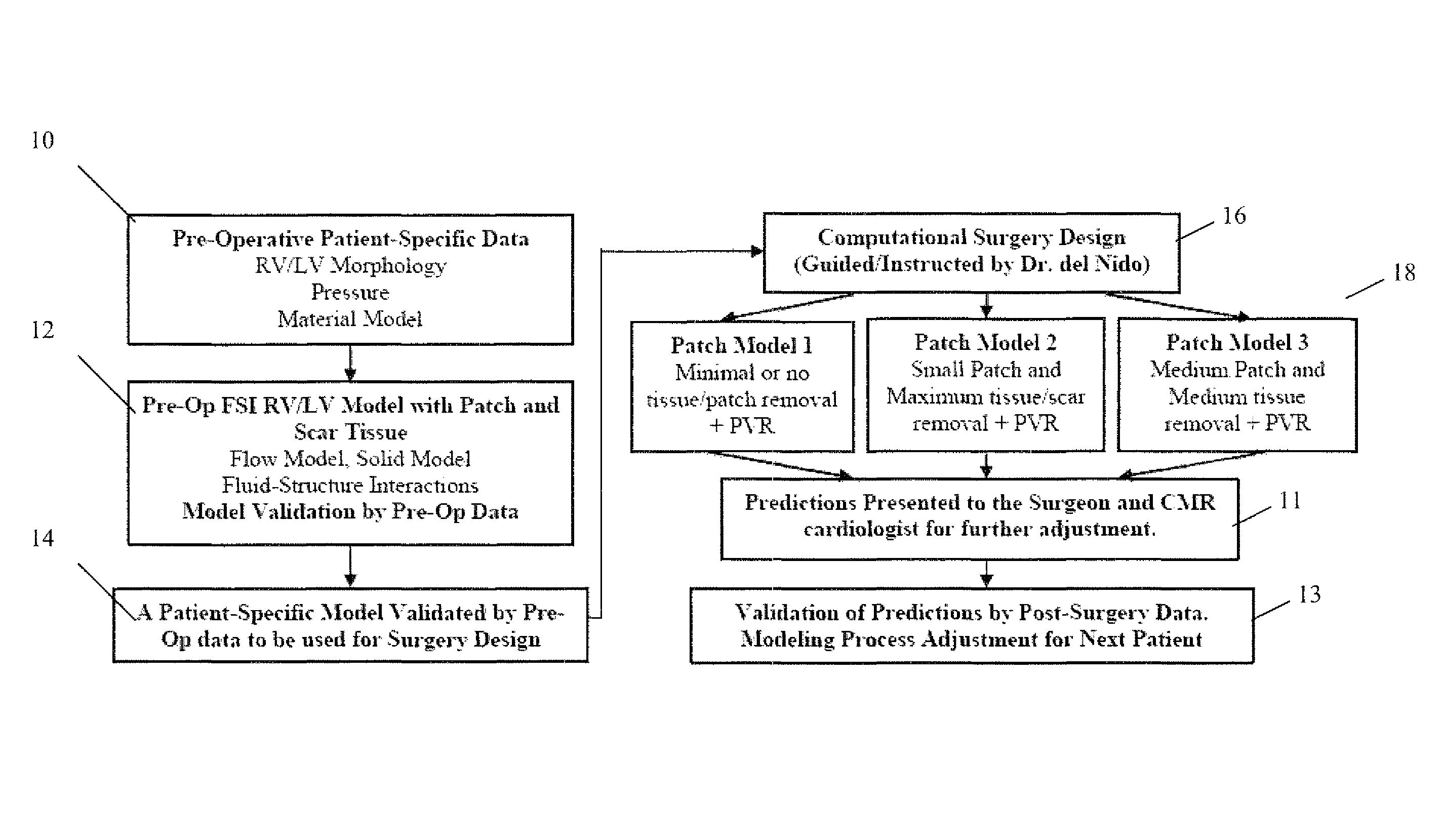
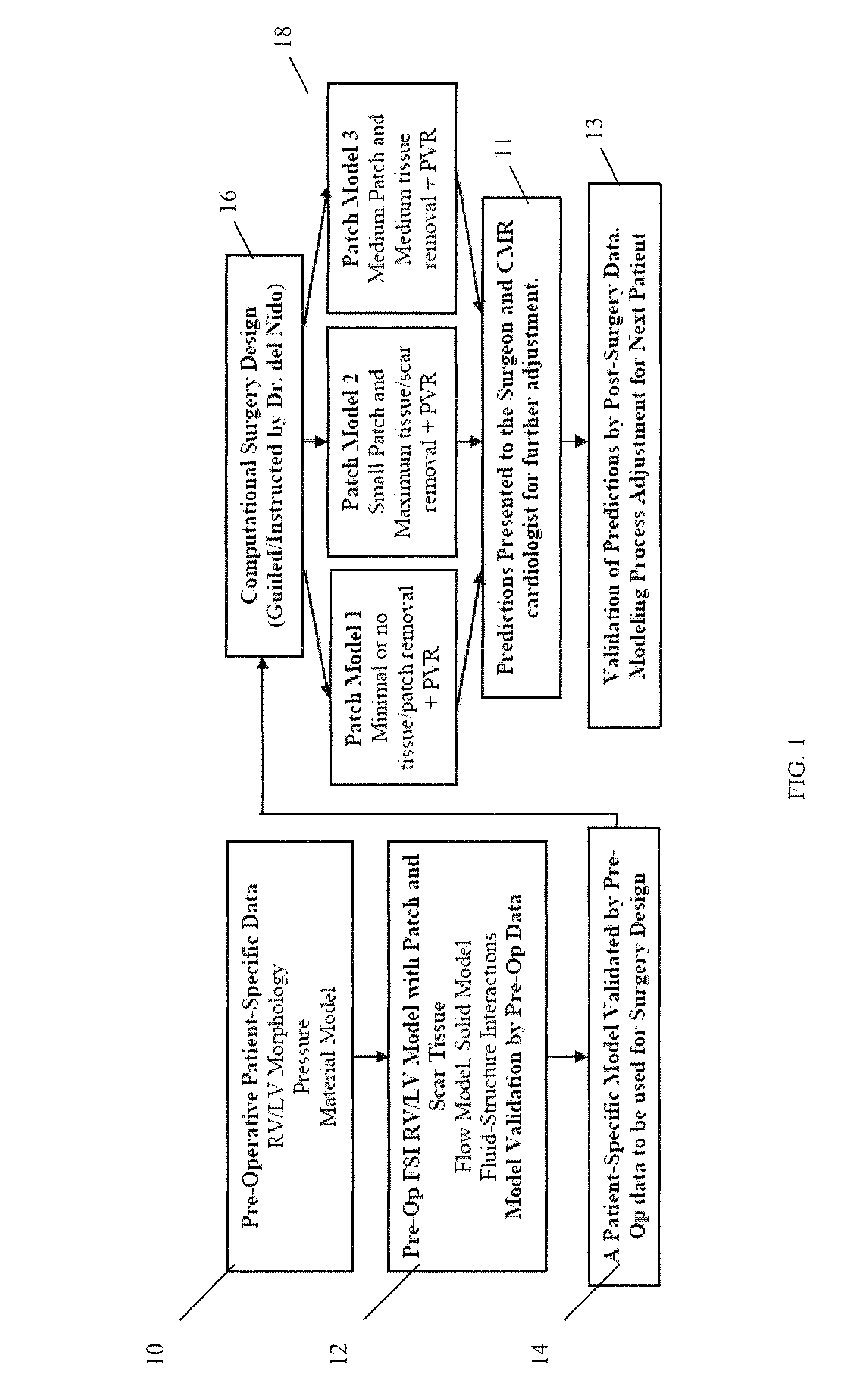
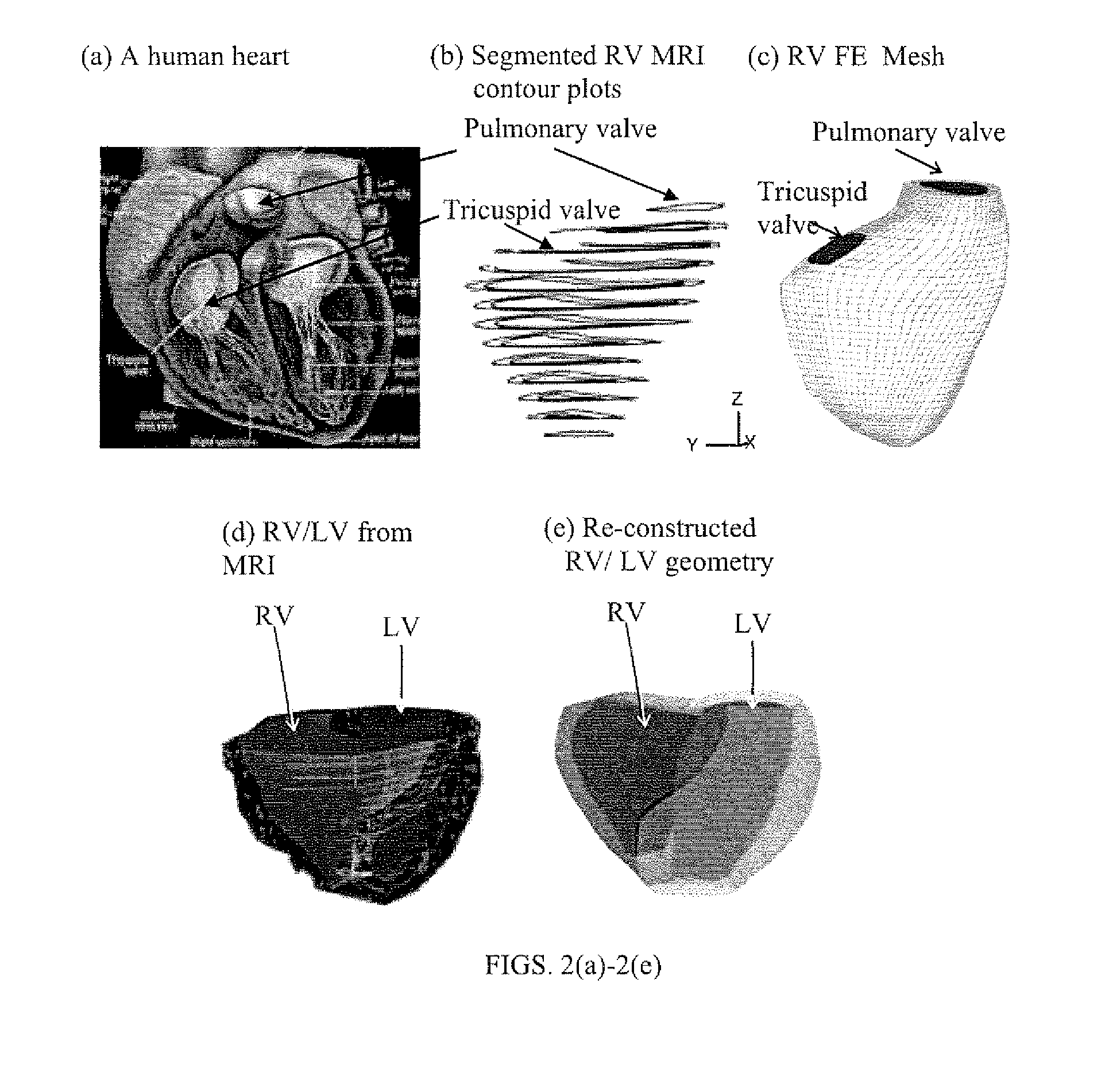
Patient-specific image-based computational modeling and techniques for human heart surgery optimization
A method for determining cardiac status comprises for a given patient, constructing a patient-specific, three-dimensional, computational model of the patient's heart; and executing the constructed computational model, said executing generating a quantitative analysis of cardiac function. A method of performing cardiac surgeries comprises: a) assessing surgical options based on a patient-specific, three-dimensional, computational model of a patient's heart; and b) performing surgery based on one or more of the surgical options. A computer system comprises: a) a data source containing data of a patient's heart; b) a modeler coupled to receive data from the data source, the modeler generating a patient-specific, three-dimensional, computational model of the heart based on the heart data; and c) a processor routine for computationally providing information about a certain cardiac function using the three-dimensional heart model and for applying computational, quantitative analysis of the cardiac function, wherein the quantitative analysis of the cardiac function provides an assessment for surgical options, optimizing surgical techniques, or predicting outcomes.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
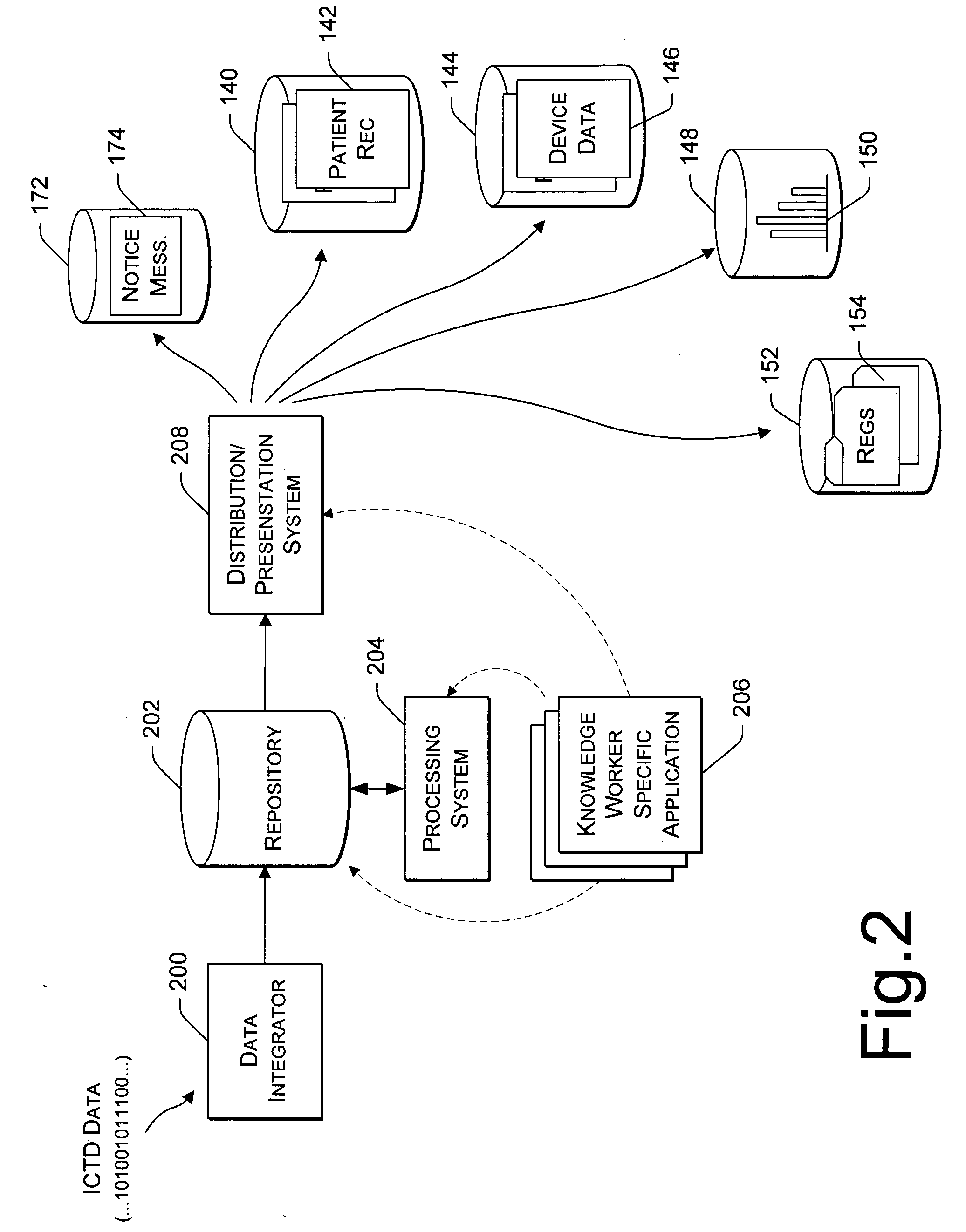
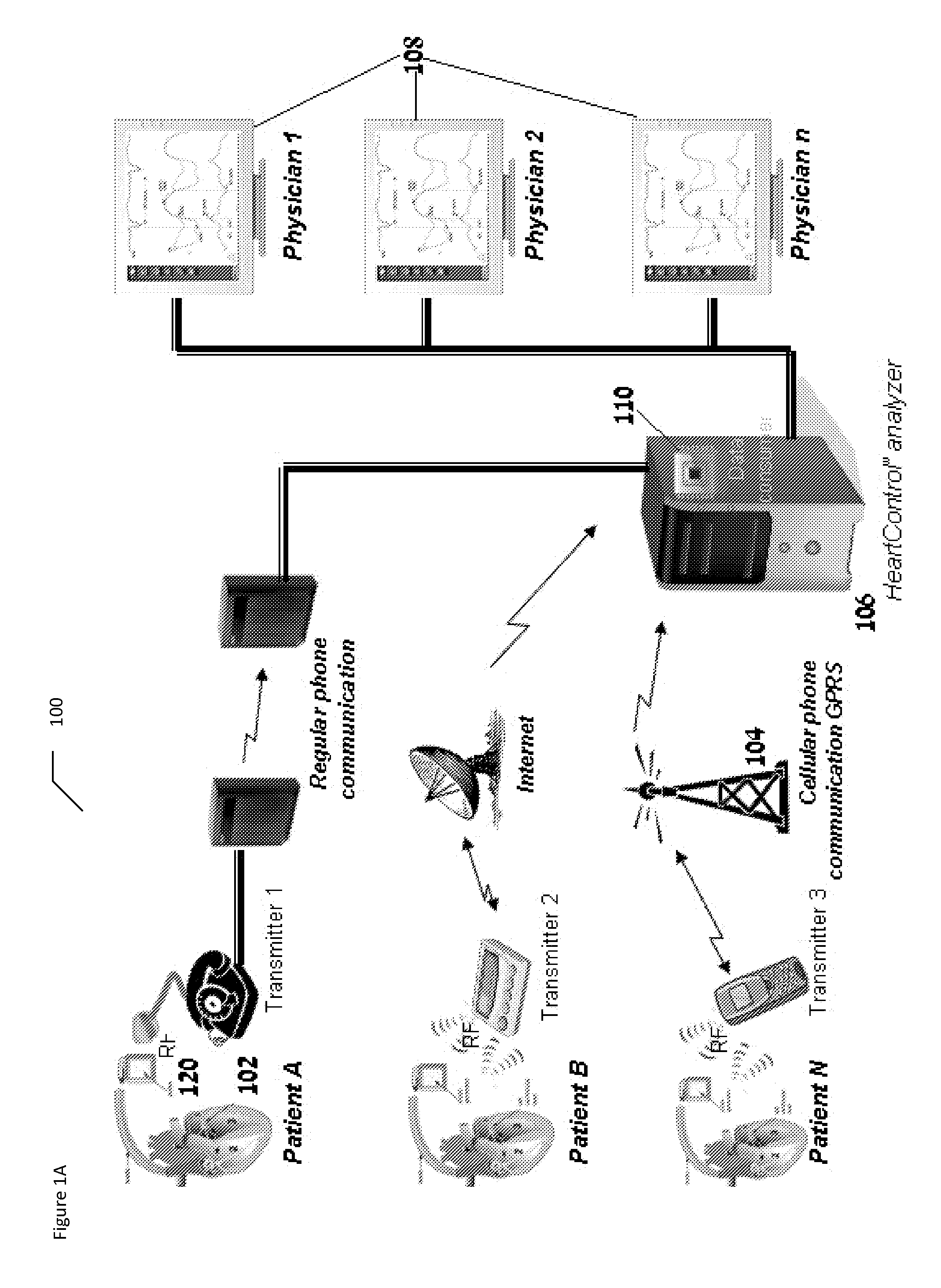
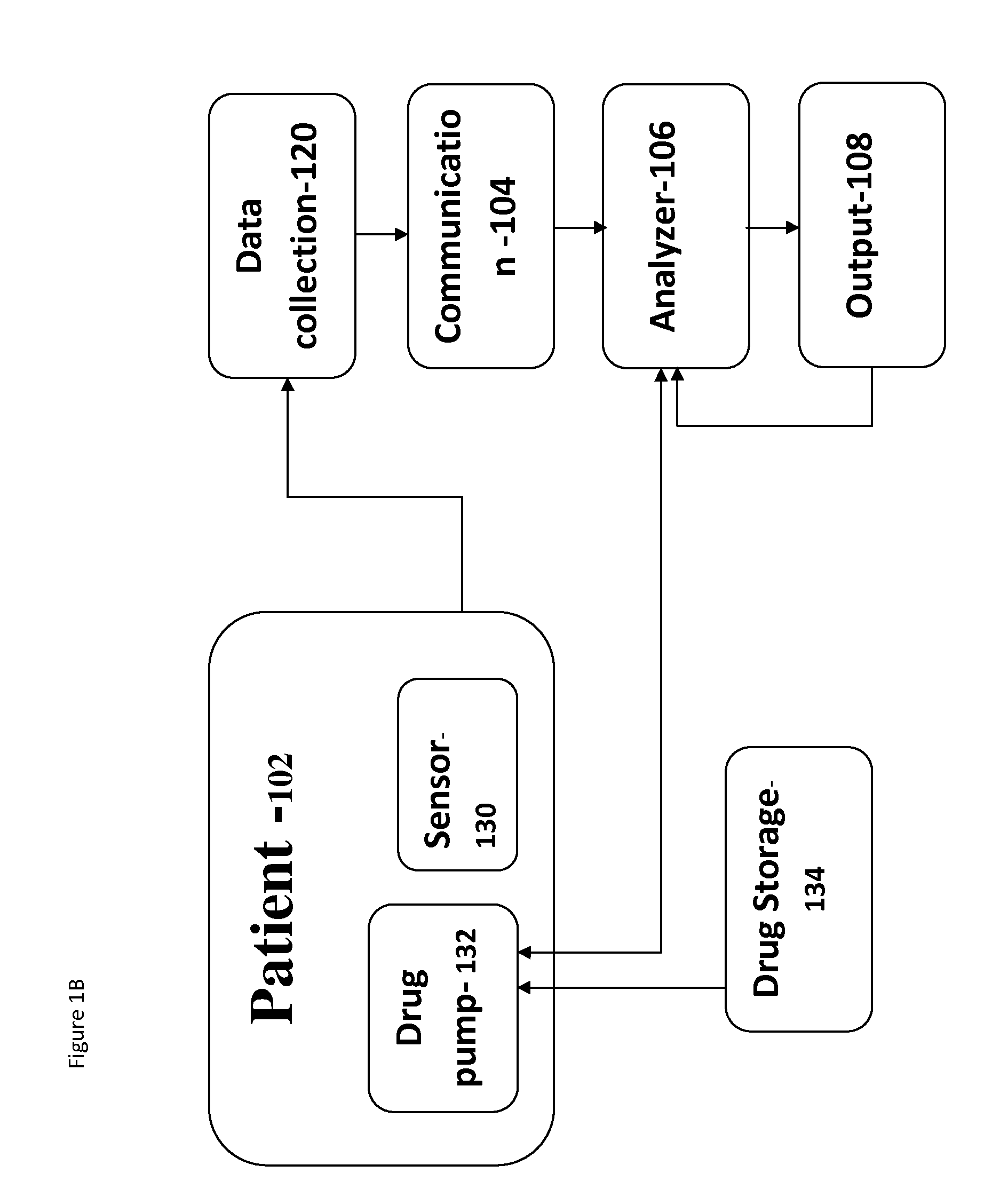
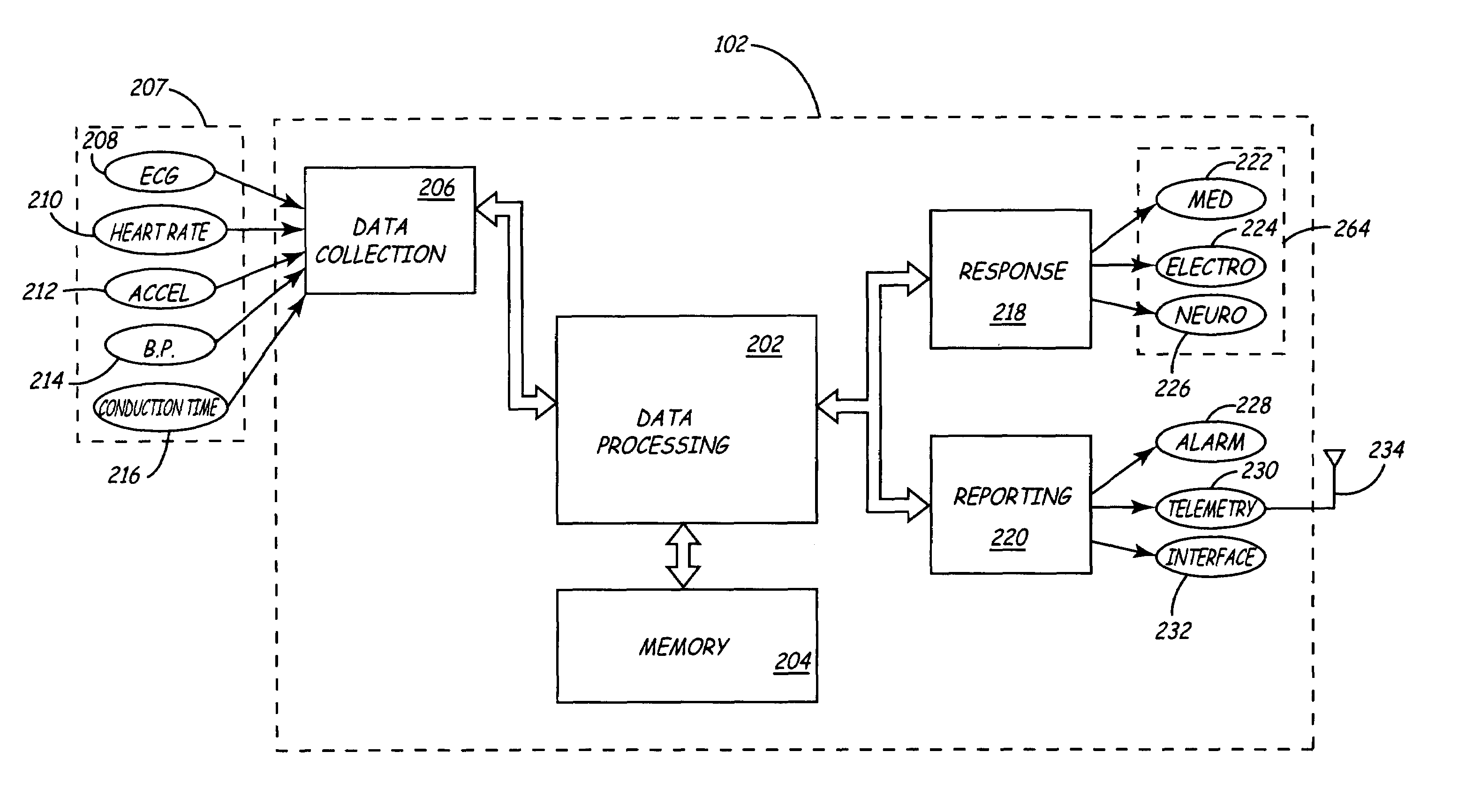
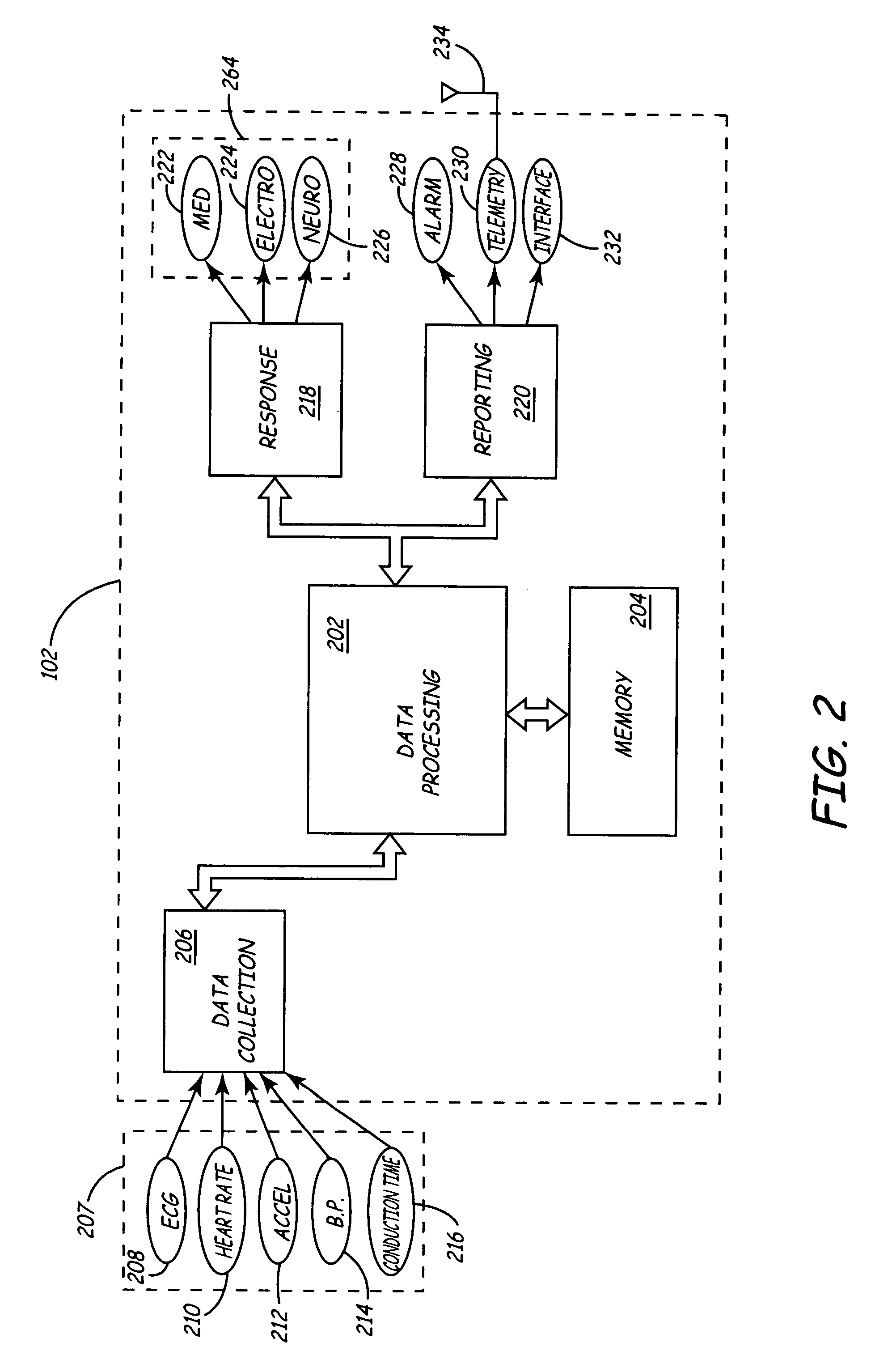
Data Feedback loop for medical therapy adjustment
InactiveUS20050033369A1Telephonic communicationData switching by path configurationCardiac statusData field
An implementation of a technology, described herein, for implantable medical therapy devices and techniques related to gathering and processing data field-collected by such implantable medical therapy devices. With an ICTD system and a central database, at least one embodiment of the invention, described herein, collects and analyzes data—which includes historical cardiac-status-and-treatment information—for a specific patient and adjusts a patient's therapy accordingly. With an ICTD system and a central database, at least one embodiment of the invention, described herein, collects and analyzes data—which includes historical cardiac-status-and-treatment information—for a patient population and adjusts a patient's therapy accordingly. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
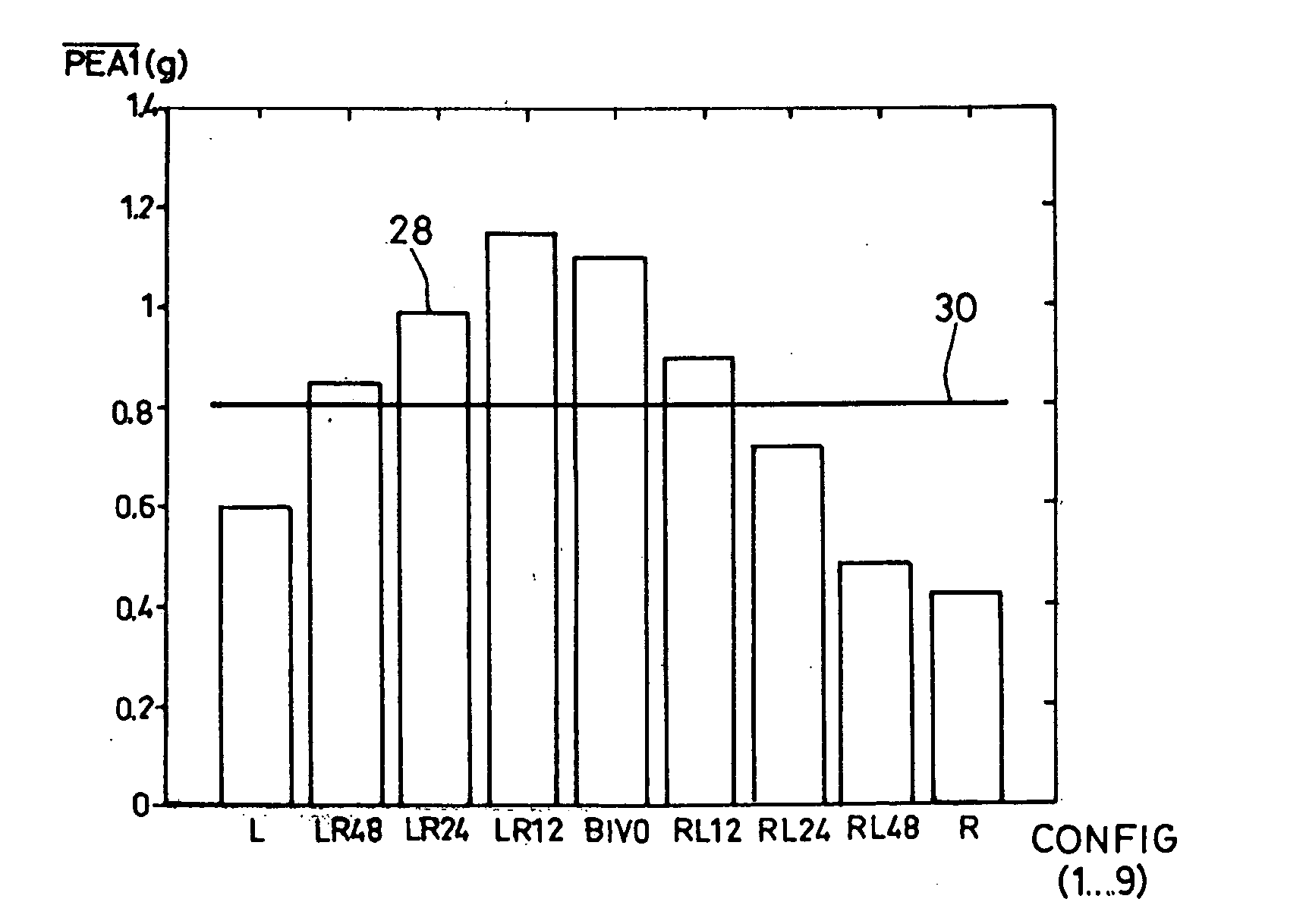
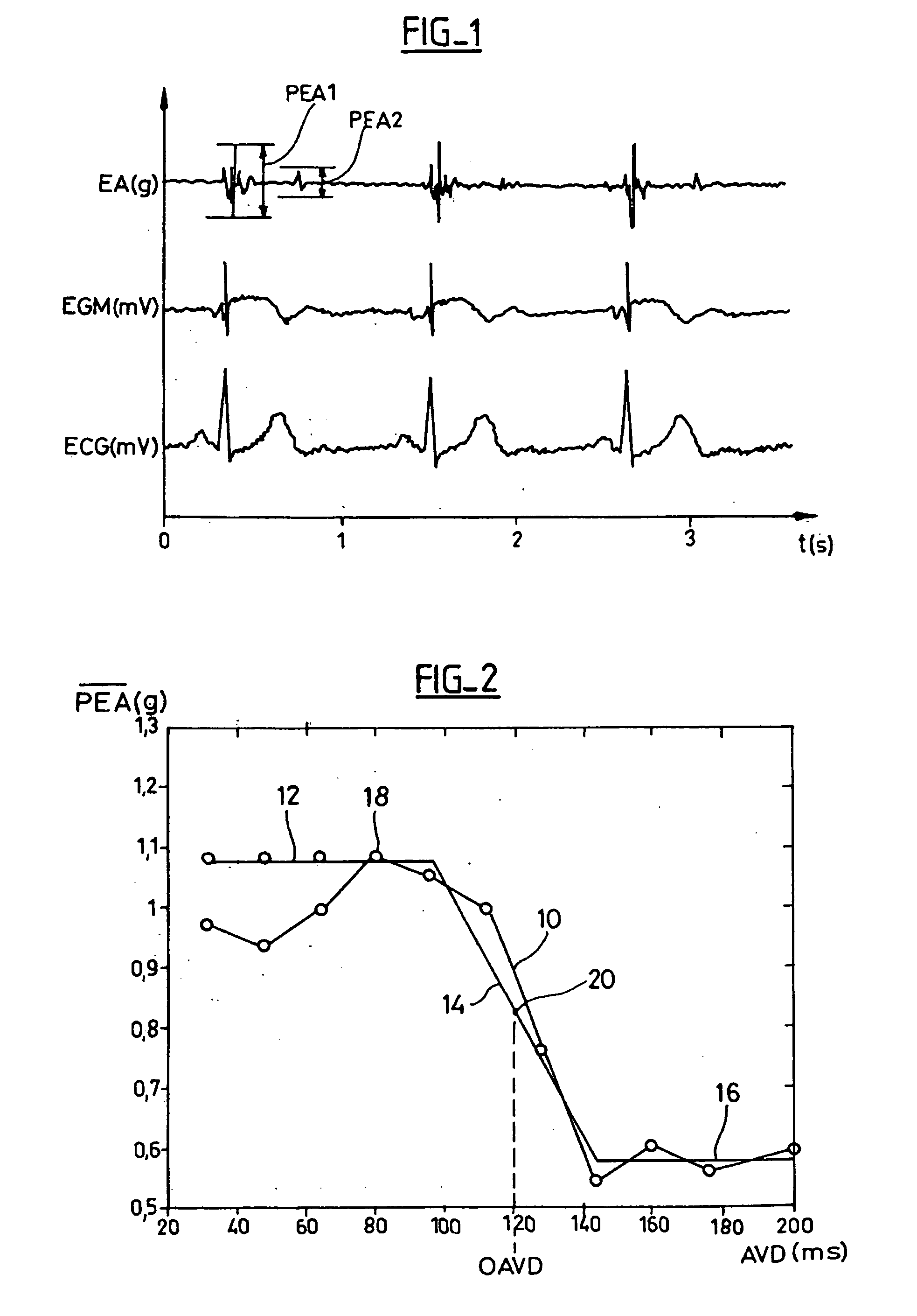
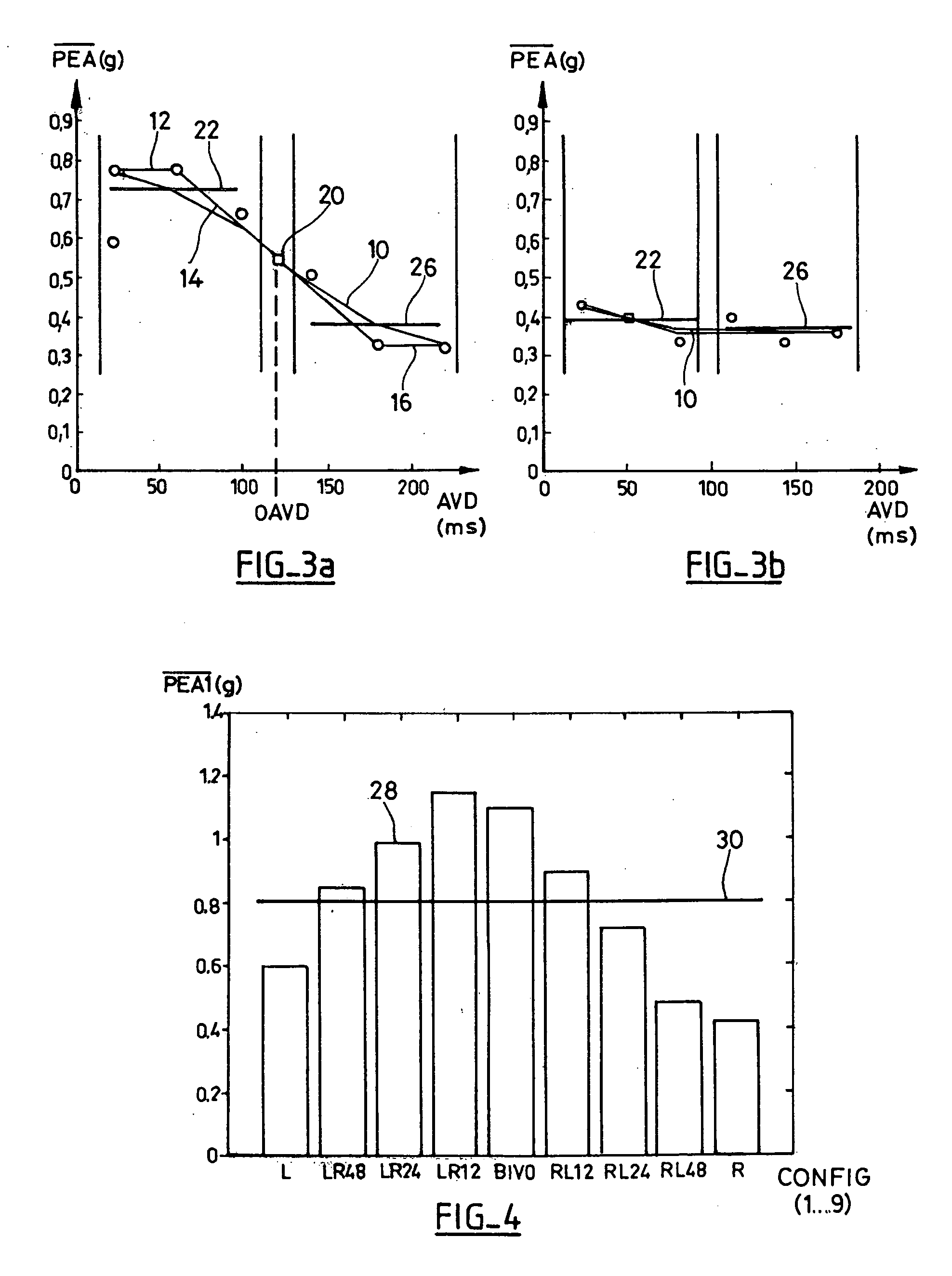
Device For Characterizing the Cardiac Status Of A Patient Equipped With A Biventricular Pacing Active Implant
A medical device for characterizing the cardiac status of a patient equipped with a bi-ventricular pacing active implant device. The implant collects an endocardiac acceleration signal and searches for an optimal pacing configuration. This latter tests a plurality of different pacing configurations and delivers for each tested configuration parameters derived from the endocardiac acceleration peak (PEA). The device derives a patient clinical status from those parameters, the indication being representative of the patient's response to the cardiac resynchronization therapy. Those parameters include: the possibility to automatically get or not a valid optimal AV Delay among all the biventricular pacing configurations; a factor indicating the character sigmoid of the PEA / AVD characteristic; the average value of the PEA for the various configurations; and the PEA signal / noise ratio. The active implantable medical device includes control software and processes for executing the characterizing functionality described.
Owner:SORIN CRM
State machine interface system
InactiveUS20100030094A1Easy diagnosisEasy assessment processMedical simulationInertial sensorsGraphicsGraphical user interface
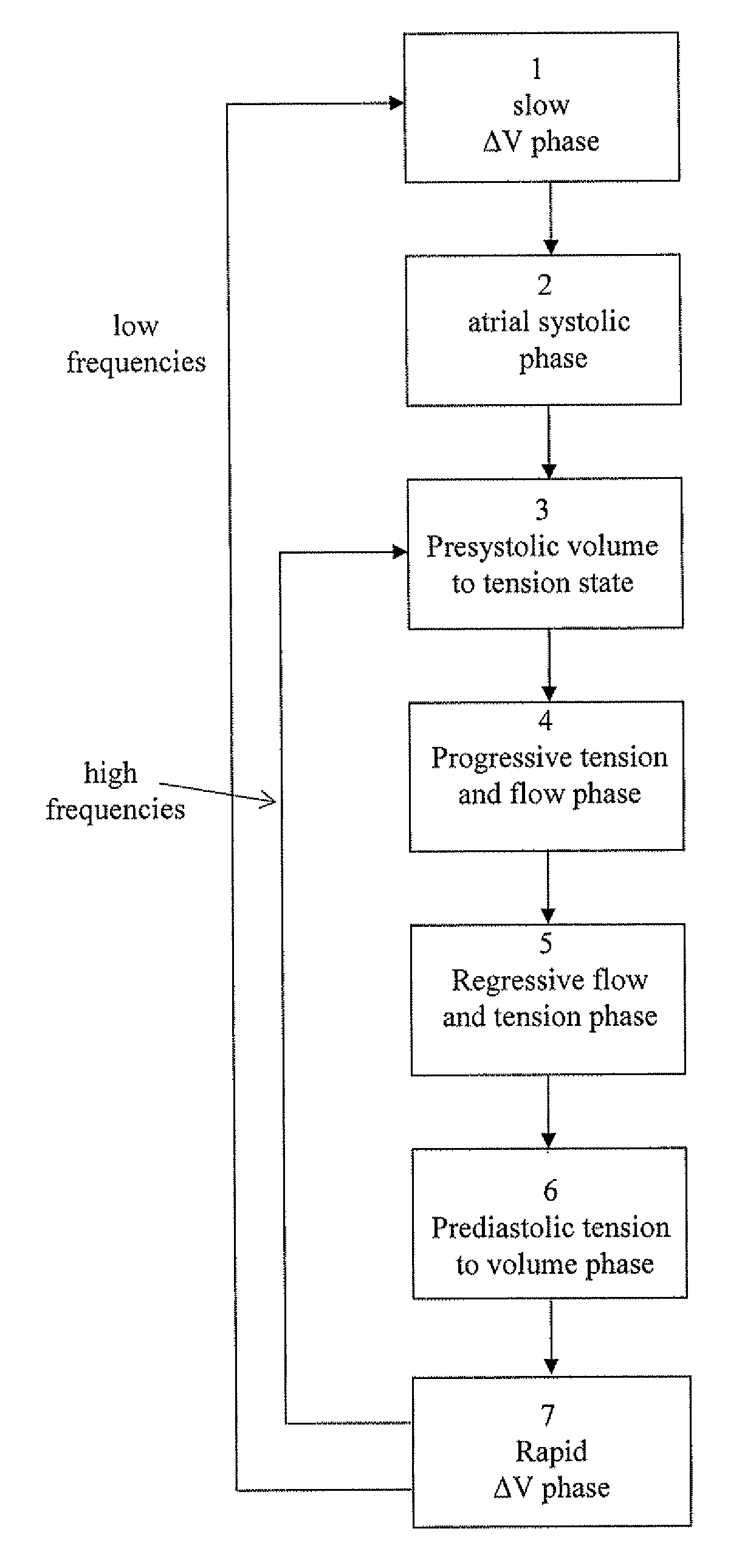
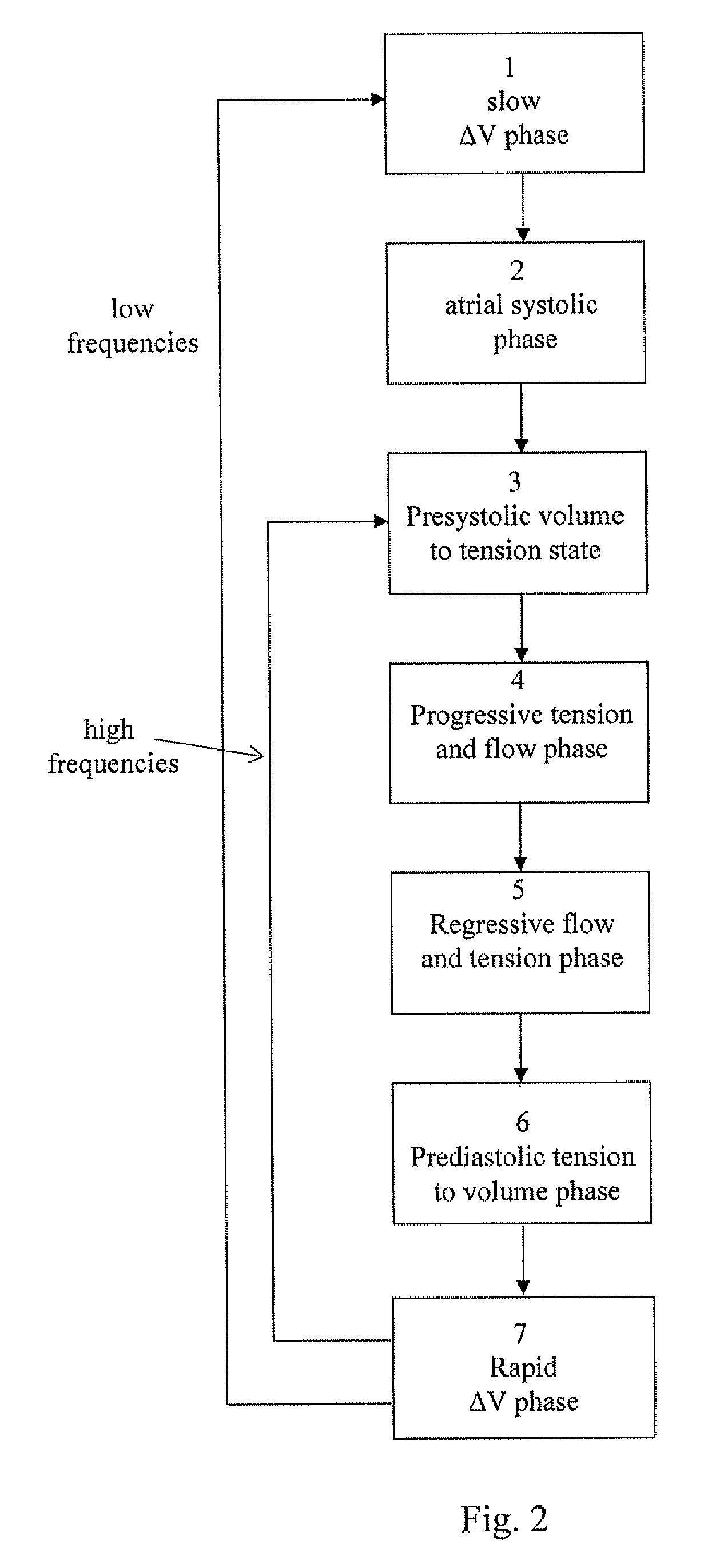
State machine interface system, heart state machine analyzer and / or stimulator, comprising state machine algorithms and a graphical user interface, adapted to receive signals from a sensor device that are related to physiological activities of the heart and / or the circulatory system of a living being and the state machine algorithms determine states of heart cycles based upon the signals. The determined heart cycle states are graphically presented at the graphical user interface such that the temporal relation between the different states are illustrated. The graphical user interface may be circular diagrams or bar graphs including parts representing the temporal relation between the different states.
Owner:GRIPPING HEART
Fibrillation/tachycardia monitoring and preventive system and methodology
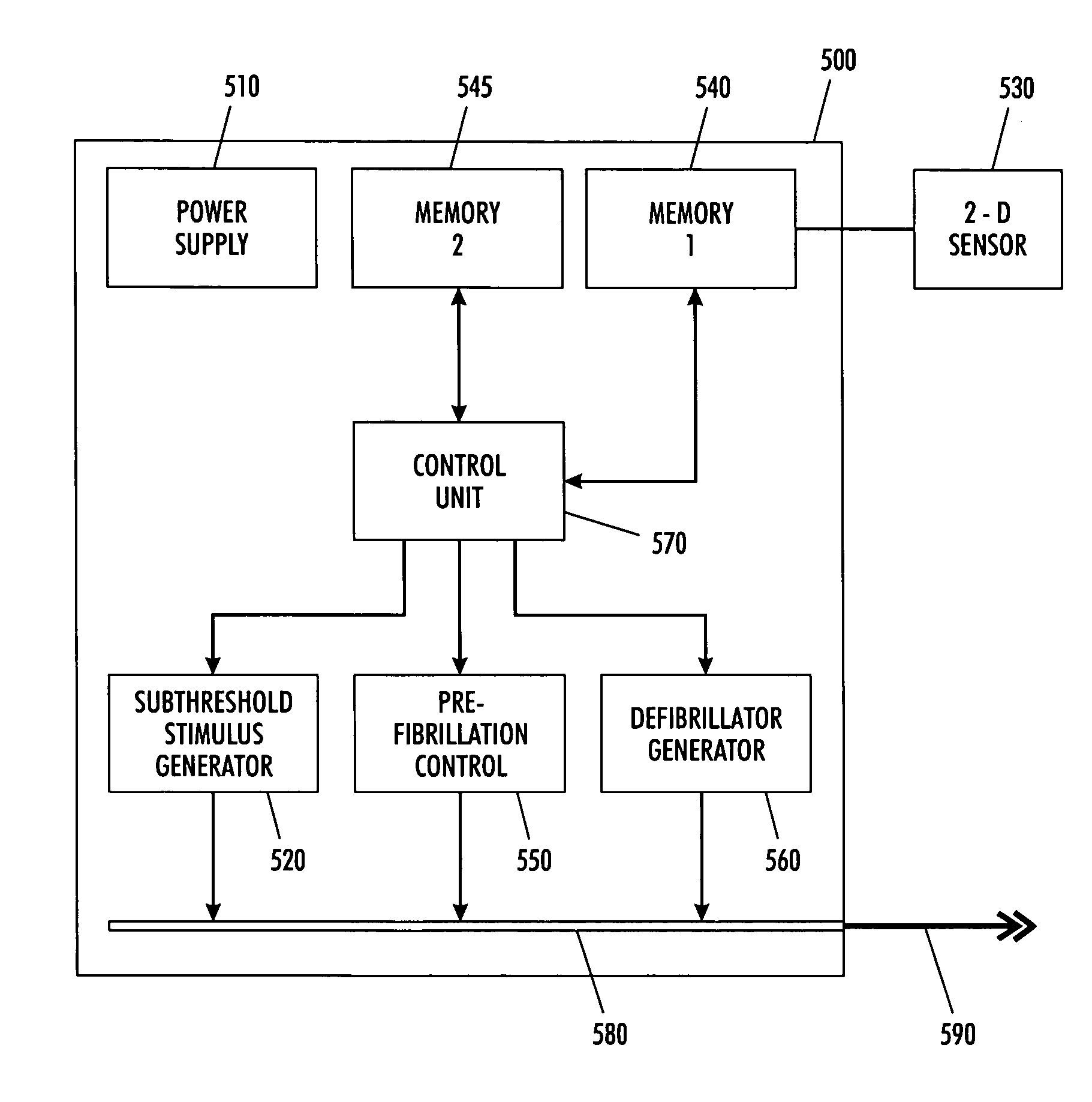
A cardiac assist device senses conditions of a heart and controls the generation of various electrical stimuli in response to sense conditions of the heart. The cardiac assist device generates a electrical pulse so as to defibrillate a fibrillated heart when the cardiac assist device determines from the sensed conditions a state of fibrillation. The cardiac assist device generates a chaos control electrical signal so as to bring a pre-fibrillated heart condition back into a normal beating condition when the cardiac assist device determines from the sensed conditions a pre-state of fibrillation. Lastly, the cardiac assist device generates an electrical enhancement signal that causes a threshold of pacing cells in the heart to be exceeded in response to a subthreshold stimulus when the cardiac assist device determines from the sensed conditions a subthreshold pacing signal.
Owner:ELECTROHEALING HLDG
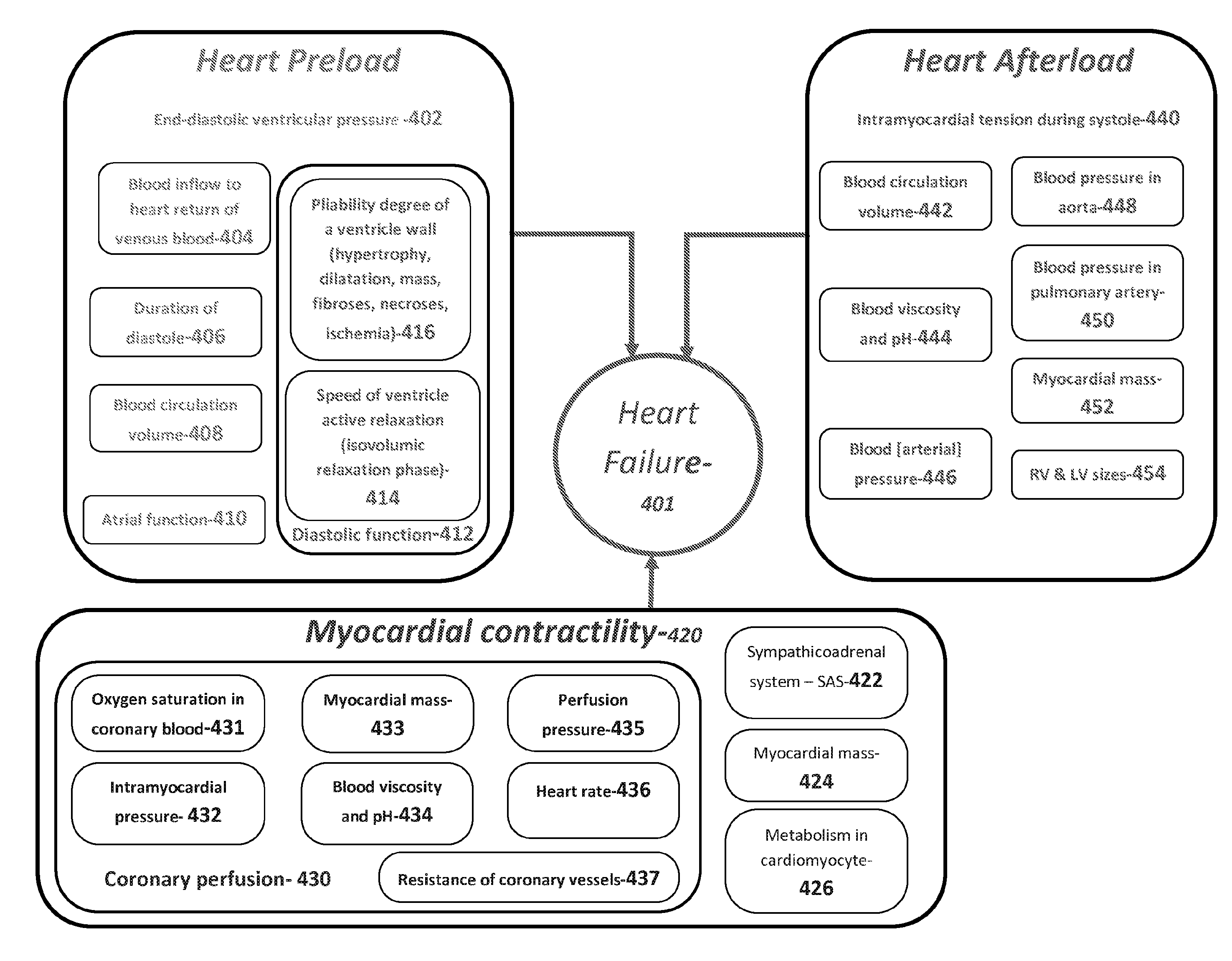
System and method for dynamic cardiac analysis, detection, prediction, and response using cardio-physiological mathematical modeling
A system and a method for evaluating the cardiac status of a heart by evaluating a plurality of cardio-physiological parameters, and in particular, to such a system and method in which a plurality of cardio-physiological mathematical models are evaluated to produce a user specific cardiac model.
Owner:ADIROVICH LEV
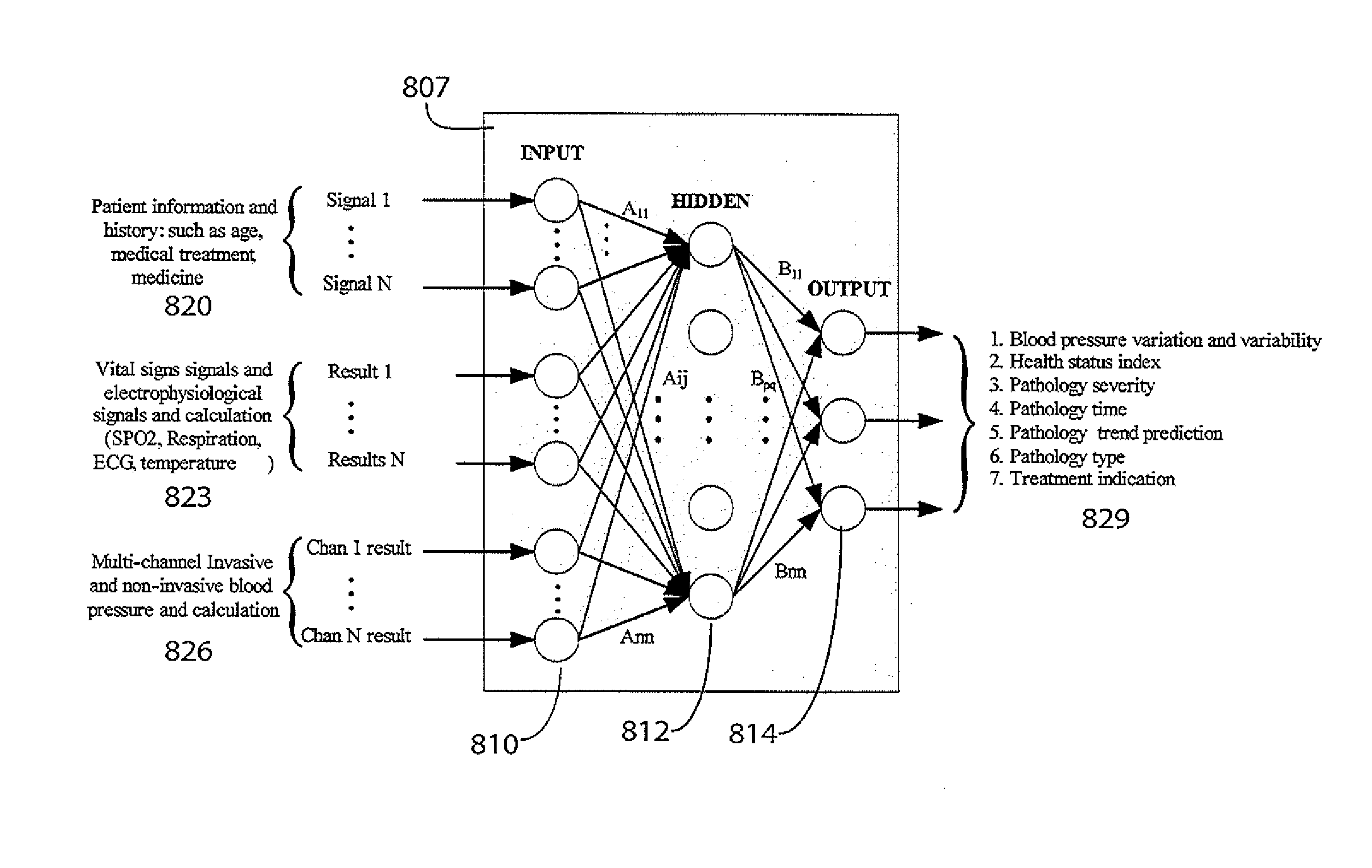
System for Cardiac Status Determination
InactiveUS20110190643A1Health-index calculationEvaluation of blood vesselsCardiac disordersCardiac status
A system improves detection and diagnosis of blood pressure based cardiac function and tissue activities by analyzing and characterizing cardiac blood pressure signals (including non-invasive and invasive blood pressure, discrete values and continuous waveforms) using pressure signal variation and variability calculation and evaluation. The system combines blood pressure analysis with multi clinical related factors and parameters to detect and quantify cardiac health status and arrhythmia severity. The system determines an accurate time, location and severity of cardiac pathology and events by calculating blood pressure variability and statistical variation. The accurately and reliably identifies cardiac disorders, differentiates cardiac arrhythmias, characterizes pathological severity, predicts the life-threatening events, and supports evaluation of drug delivery effects.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and apparatus for gauging cardiac status using post premature heart rate turbulence
A hemodynamic status of a patient is determined in an implanted medical device (IMD) by observing a perturbation of the patient's heart, measuring heart rate turbulence resulting from the perturbation, and quantifying the heart rate turbulence to determine the hemodynamic status. The perturbation may be naturally-occurring, or may be generated by the implantable medical device. The patient's response to heart rate turbulence may also be used to provide a response to the patient, such as providing an alarm and / or administering a therapy. Heart rate turbulence may also be used to tune and / or optimize a device parameter such as A-V or V—V pacing intervals.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Dynamic characteristic analysis method of real-time tendency of heart state
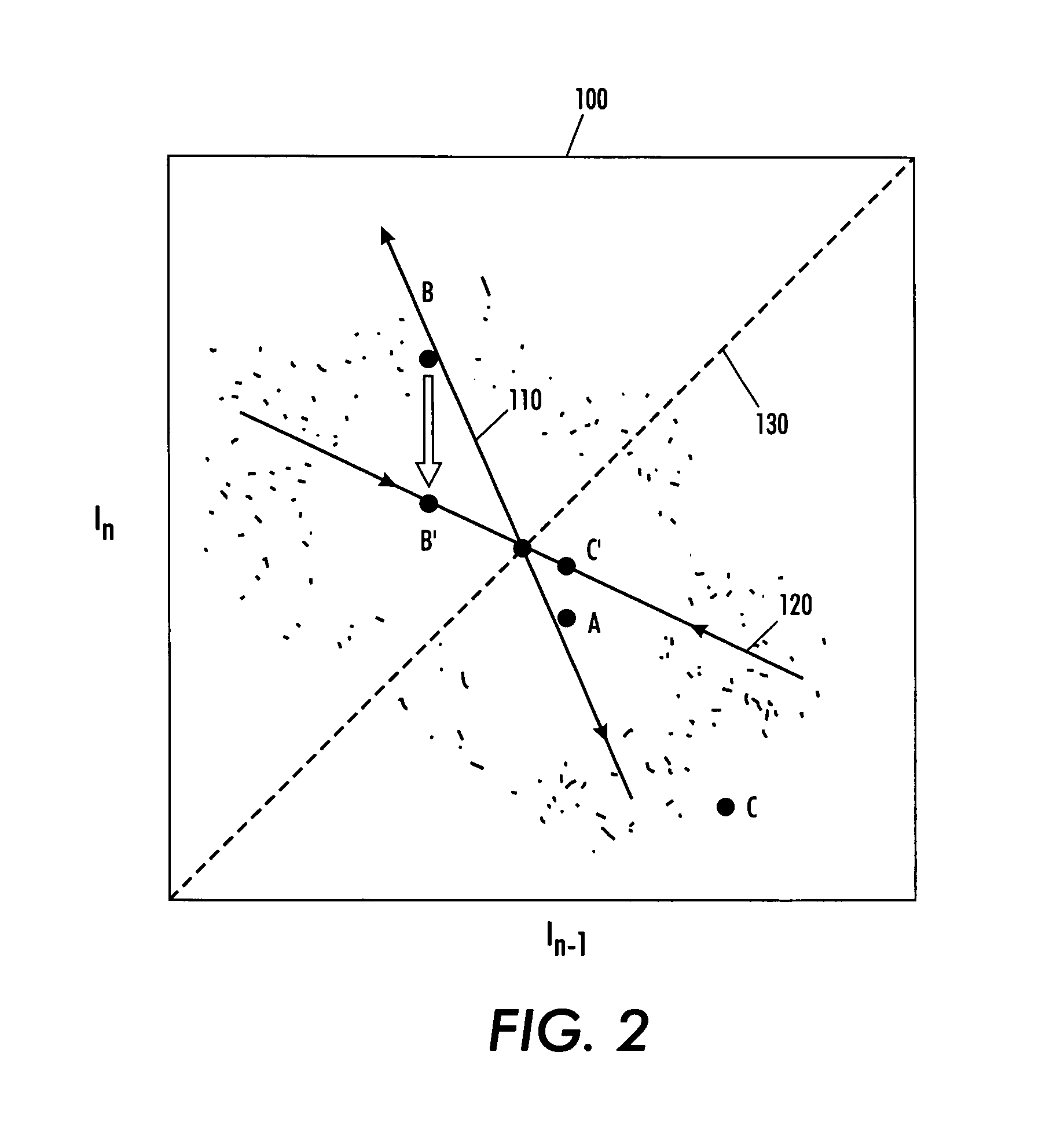
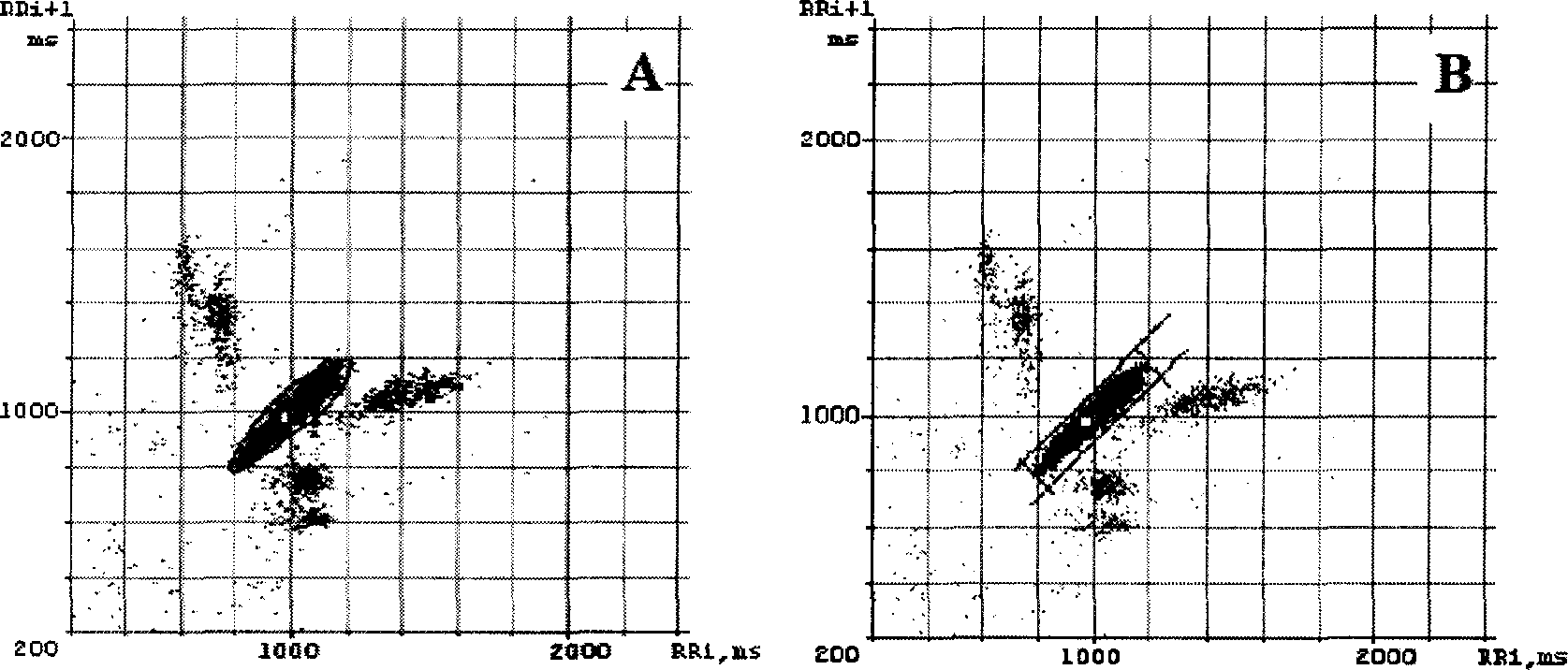
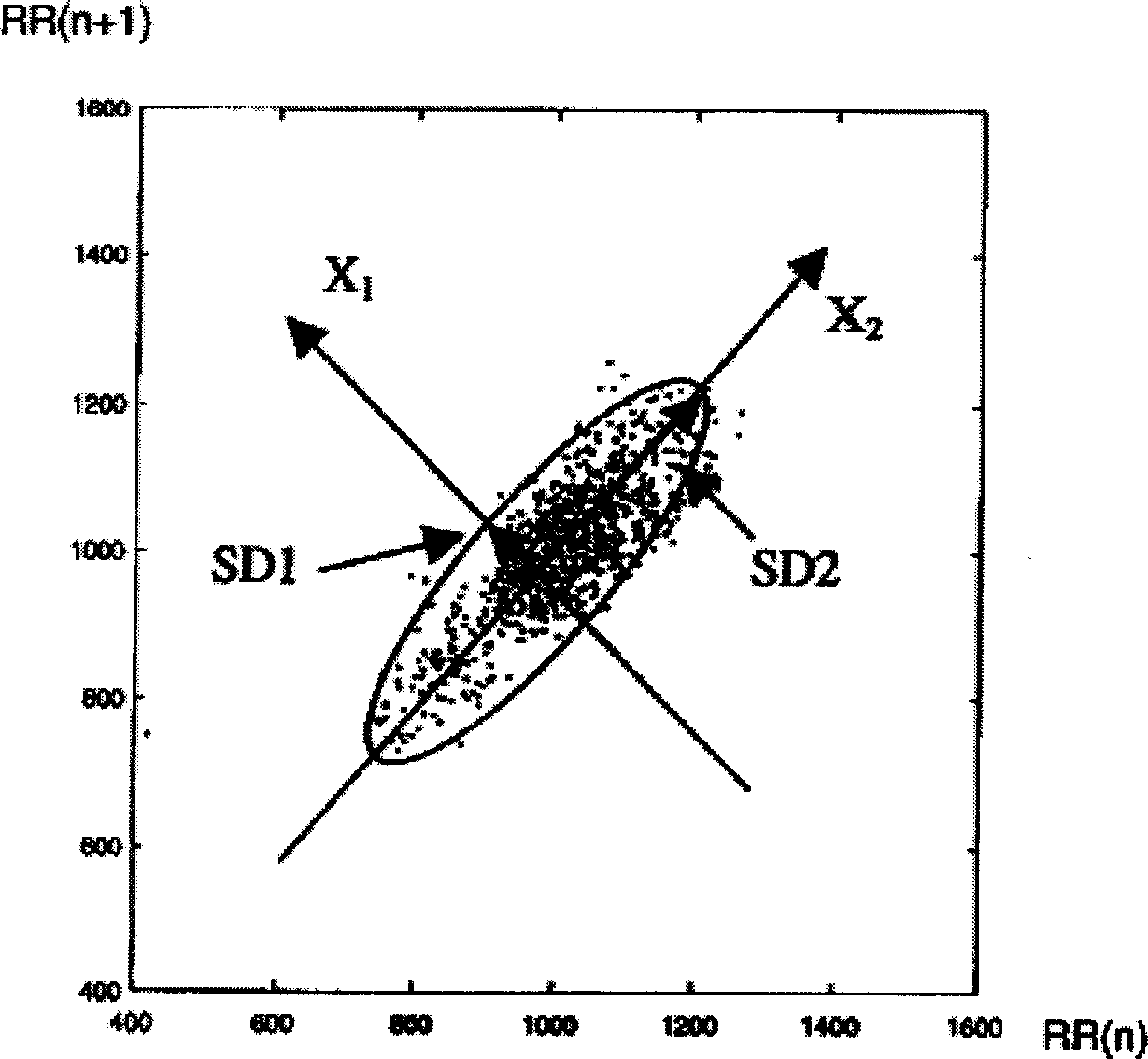
InactiveCN1887223AHigh input impedanceHigh Common Mode Rejection RatioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFeature parameterFive-dimensional space
The dynamic characteristic analysis method of real-time tendency of heart state includes: obtaining electorcardiac waveform with multipath electorcardiac amplifier and 12-bit A / D converter; forming time sequence related heart rate variation scatter diagram by means of space-time correlation technology and scatter diagram technology; extracting time sequence related characteristic parameters, short time-real time characteristic conversion illustration parameter and quantized space-time parameter indexes of characteristic illustration via automatic and manual interaction; classifying the illustration and quantized space-time parameters in artificial neural network; and describing dynamic characteristics and relevant invariance characteristics of heart rate variation in a nine-dimensional and a five-dimensional space with two independent curve surfaces and their boundary to represent the heart function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
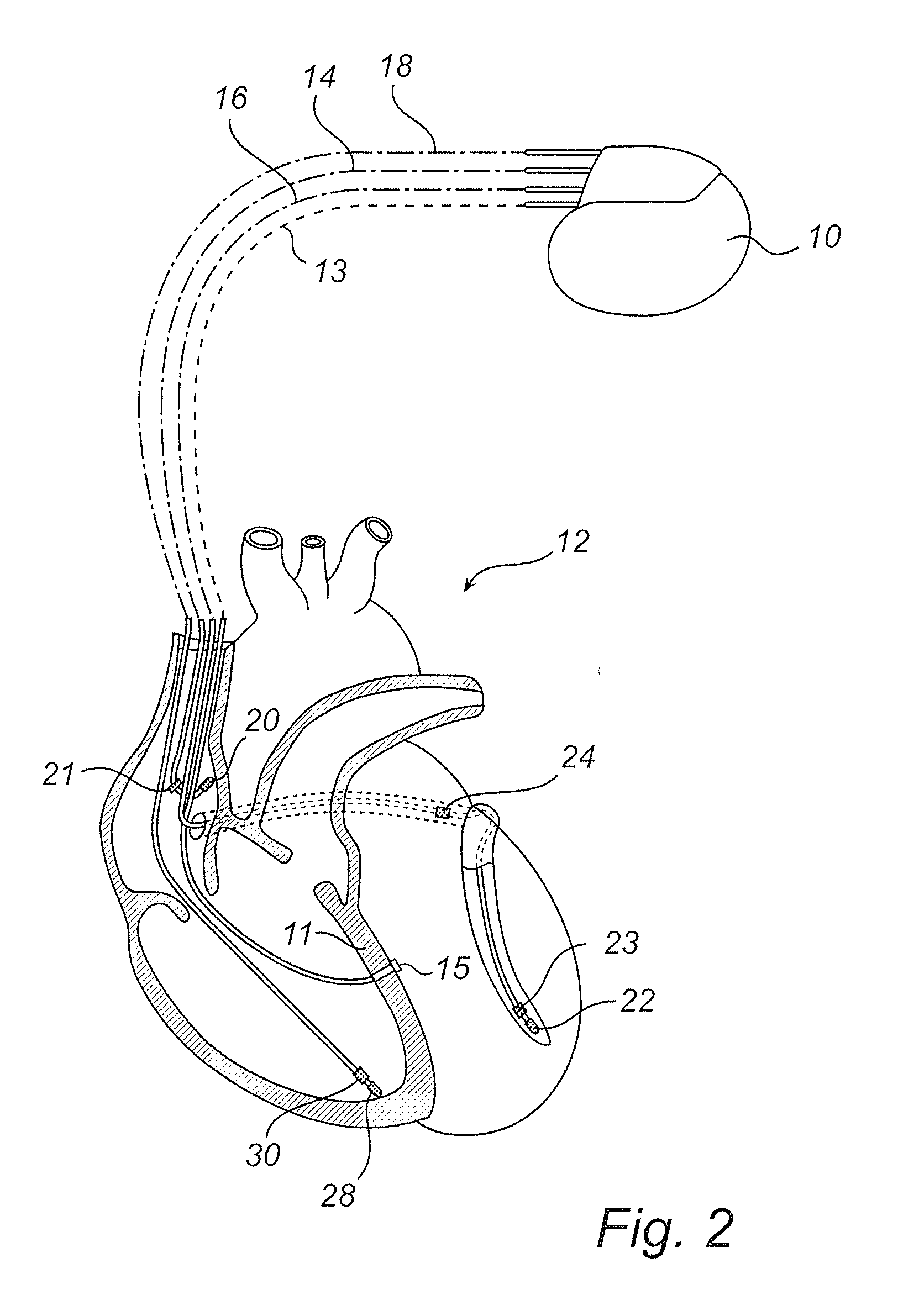
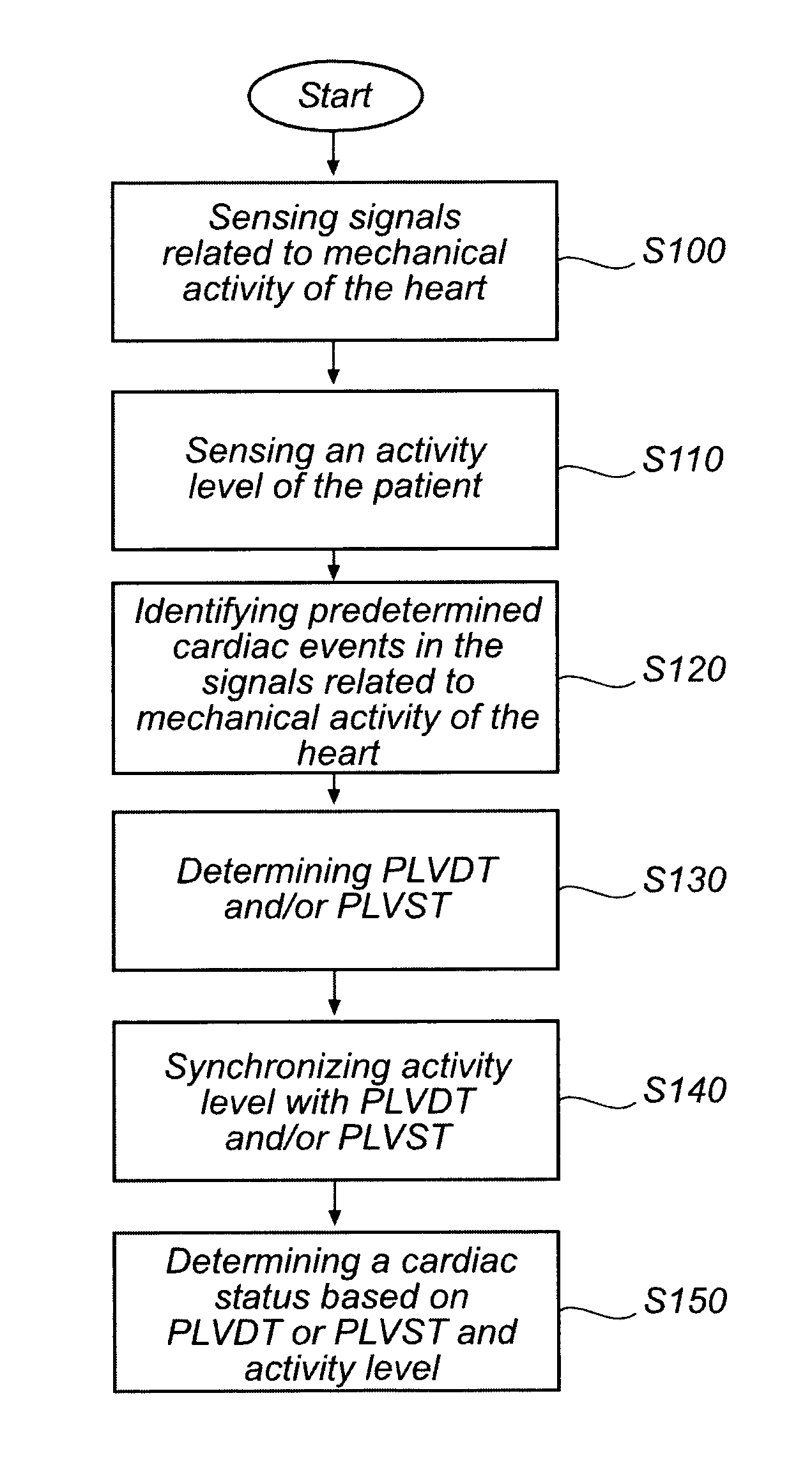
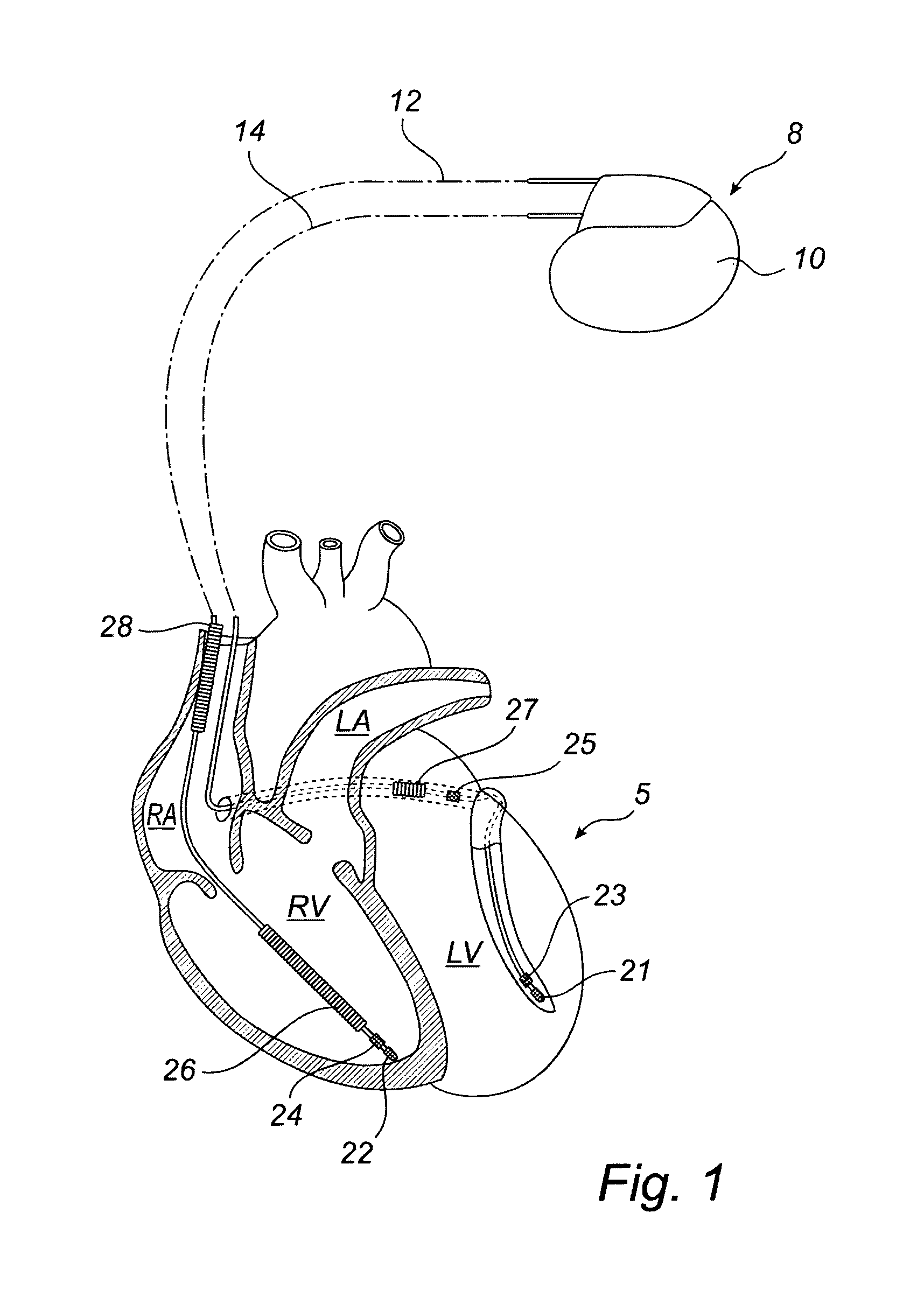
Devices and method for determining and monitoring a cardiac status of a patient by using plvdt or plvst parameters
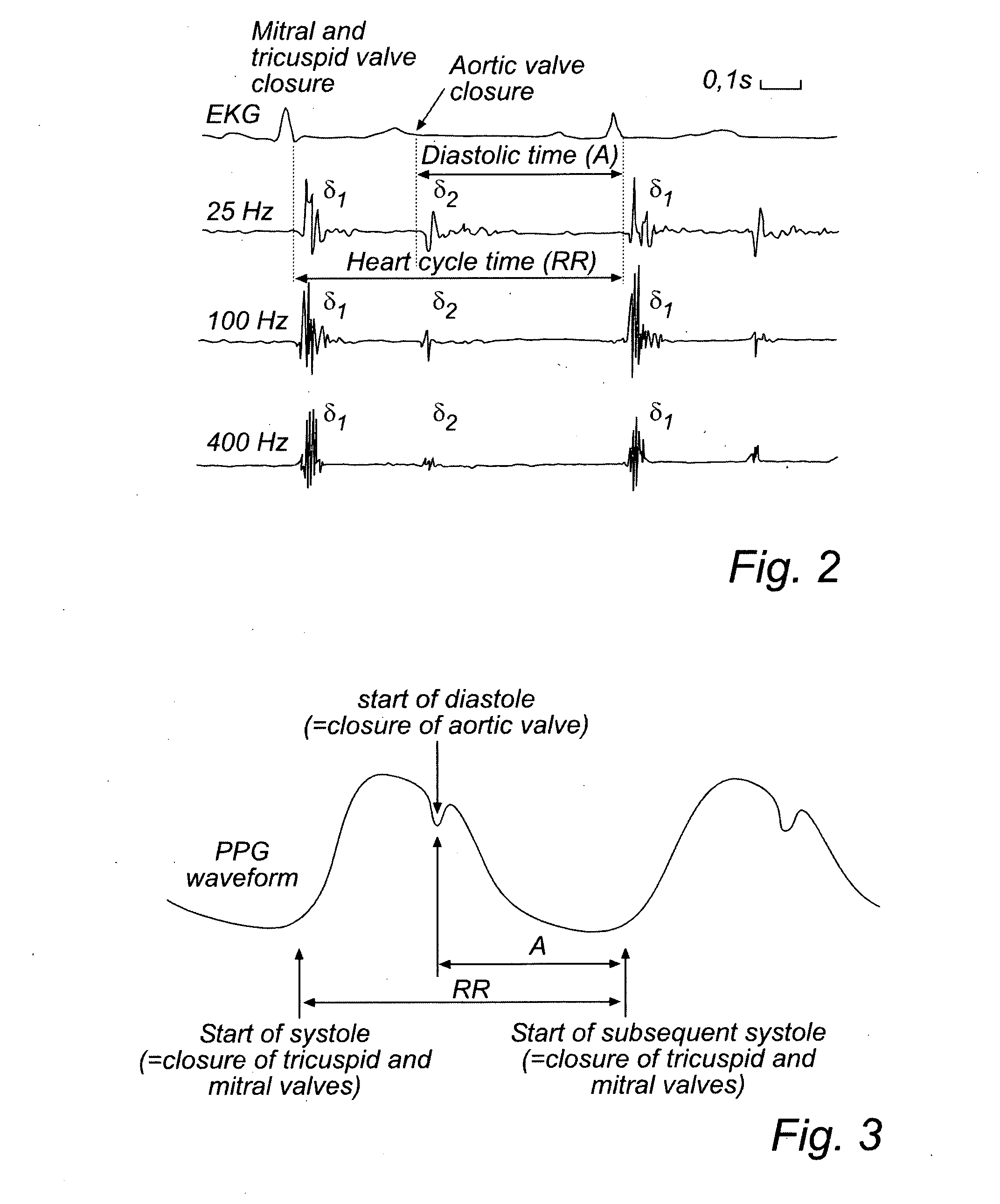
ActiveUS20120157861A1Accurately and reliably determiningStrong specificityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCardiac cycleLeft ventricular size
The present invention relates to an improved medical device and method for accurately and reliably determining a cardiac status of a patient. An implantable medical device, IMD, comprises a sensor arrangement adapted to sense signals related to mechanical activity of the heart and an activity level sensor arrangement adapted to sense an activity level of the patient. Further, the IMD calculates a percentage of left ventricular diastolic time (PLVDT) for a cardiac cycle corresponding to a relation between a diastolic time interval and a cardiac cycle time interval using the determined systolic and diastolic time intervals or a percentage of left ventricular systolic time (PLVST) for a cardiac cycle corresponding to a relation between a systolic interval time interval and a cardiac cycle time interval. A cardiac status is determined based on the calculated PLVDT (or PLVST) and on an activity level of the patient.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
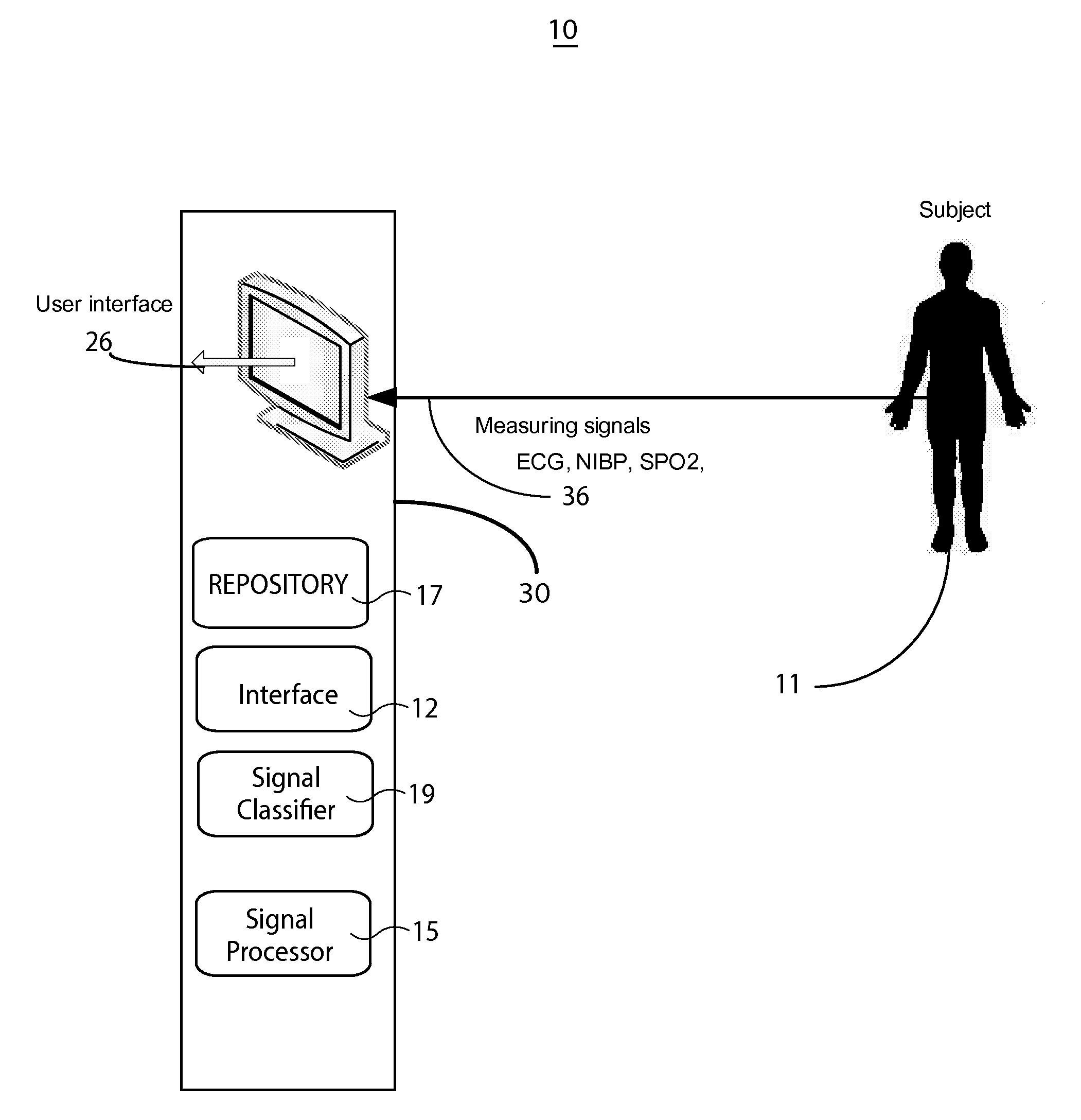
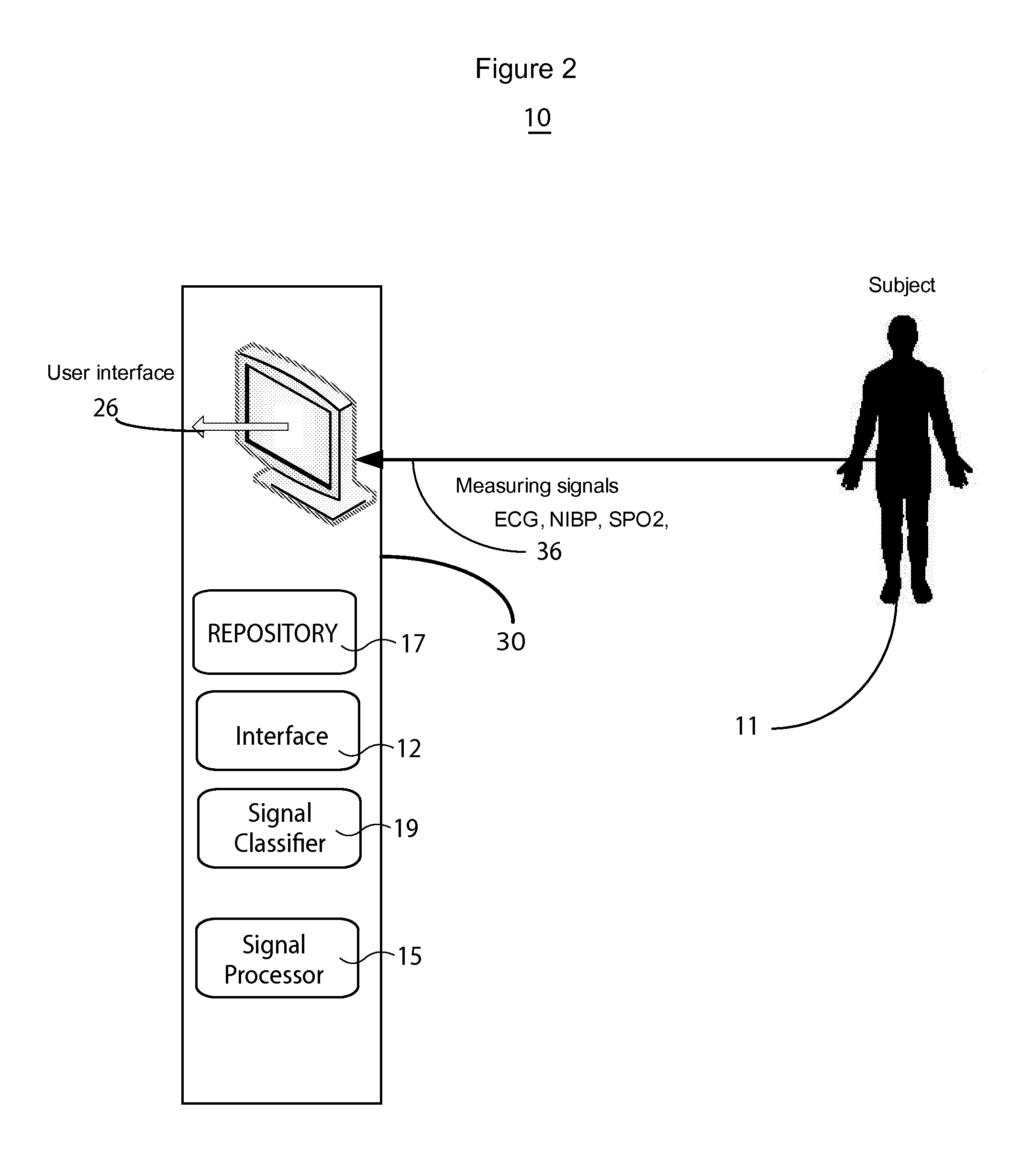
Automated Cardiac Status Determination System
InactiveUS20100286543A1ElectrocardiographyMedical automated diagnosisElectricitySignal classification
A system fits a curve to a filtered ECG signal, processes the fitted curve (e.g., by applying transforms such as a KL Transform) and derives parameters for use in classifying heart cycle signal portions (such as an ST segment portion) into particular heart cycle signal portion categories associated with particular segment morphology. A system for heart signal classification includes an interface for receiving an electrical signal waveform comprising an R-wave and including an ST segment portion associated with heart electrical activity of a patient over a heart beat cycle. A signal processor processes data representing the electrical signal waveform by fitting a curve to the ST segment and applying a transform to the fitted curve to derive variance data indicating variance in the fitted curve. A signal classifier classifies the ST segment into one of multiple predetermined categories associated with the fitted ST segment curve geometry in response to the derived variance data.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC +1
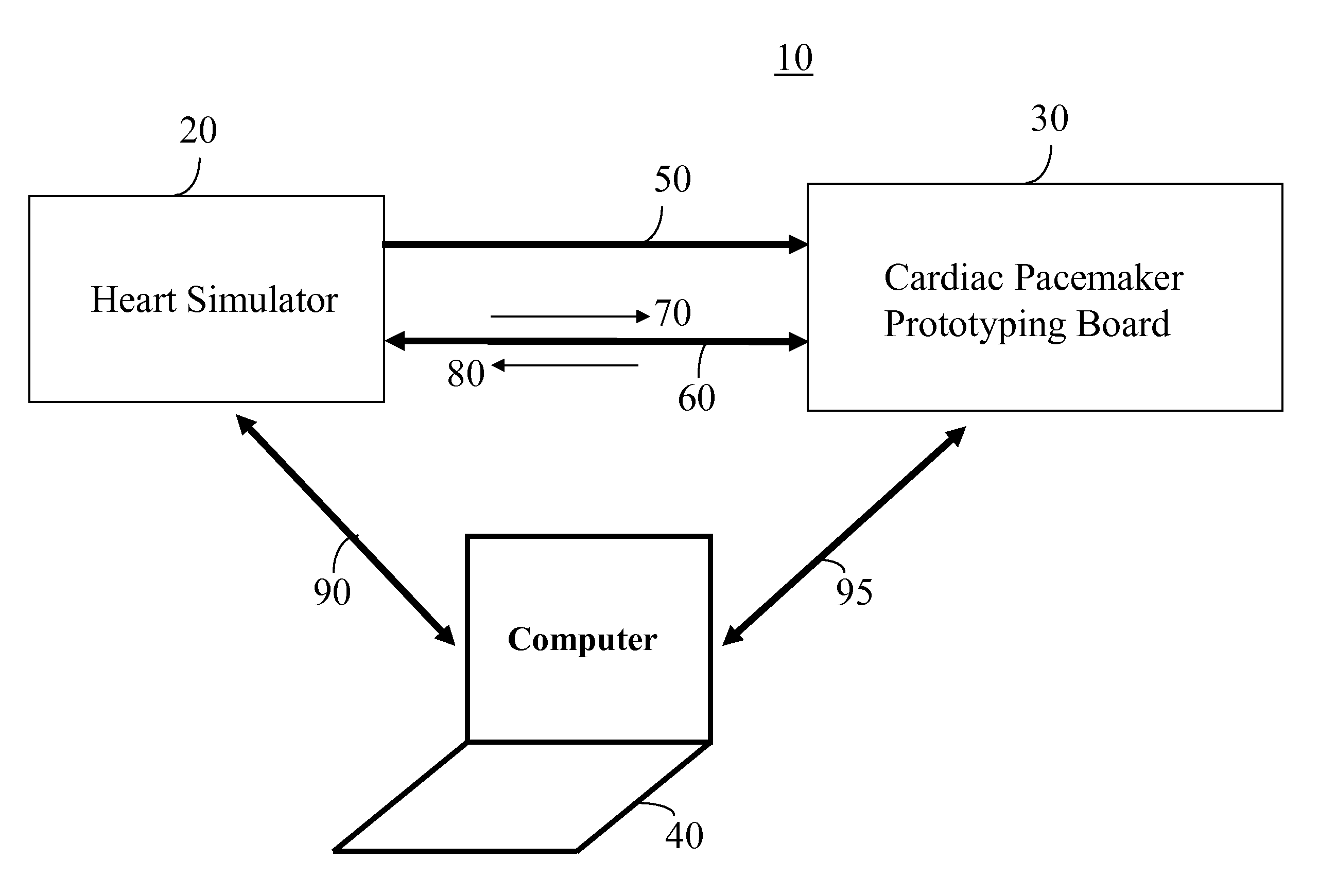
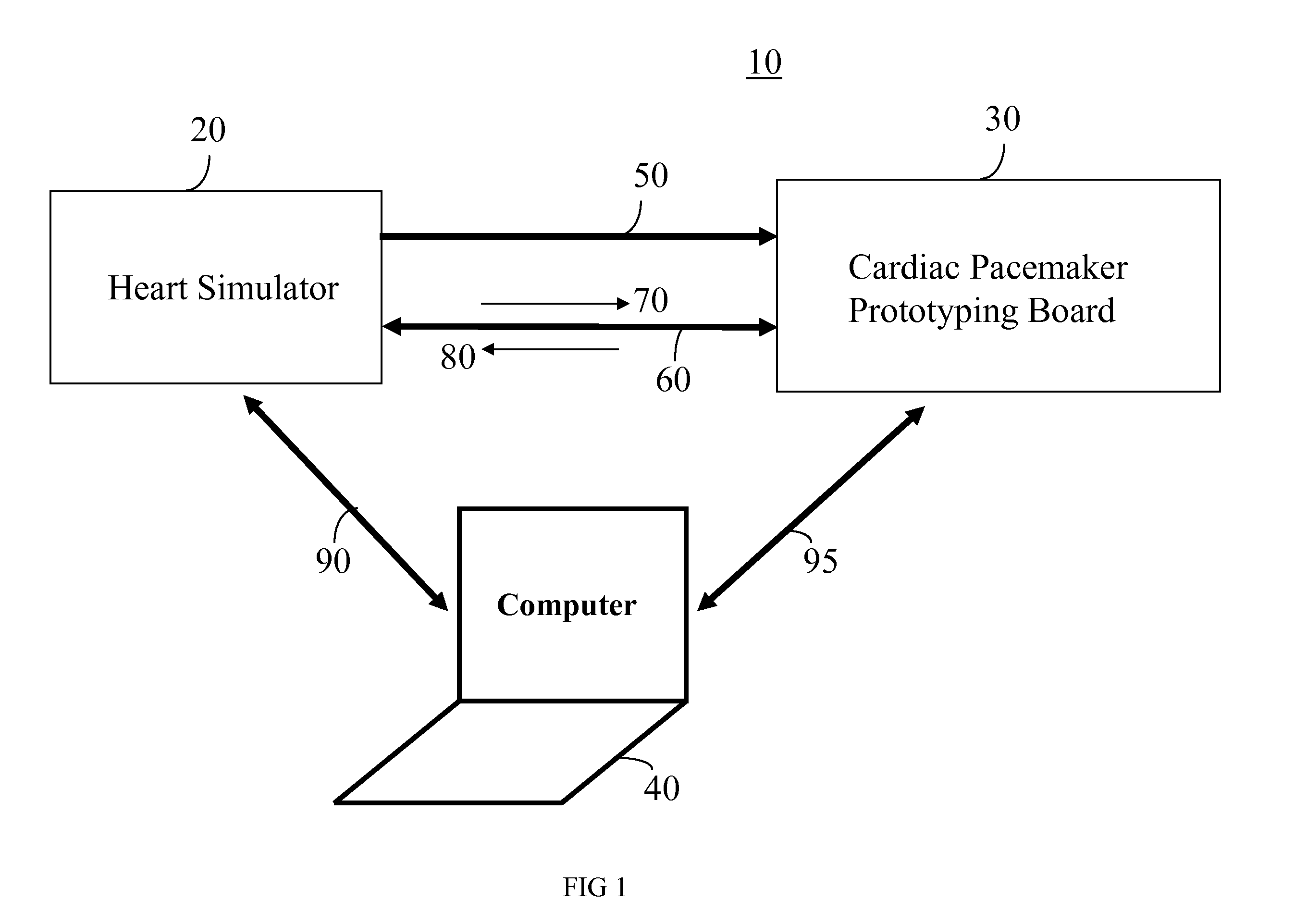
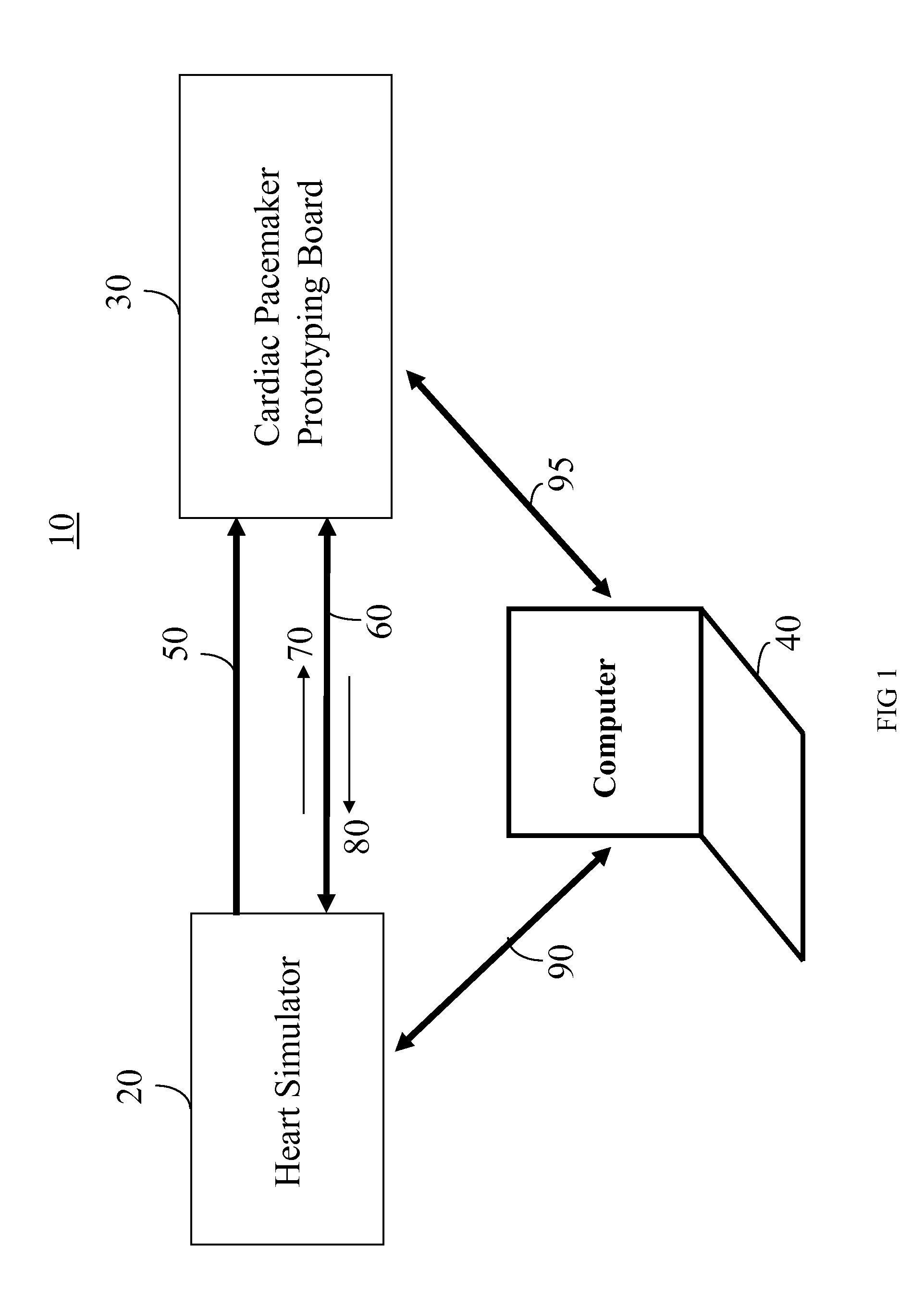
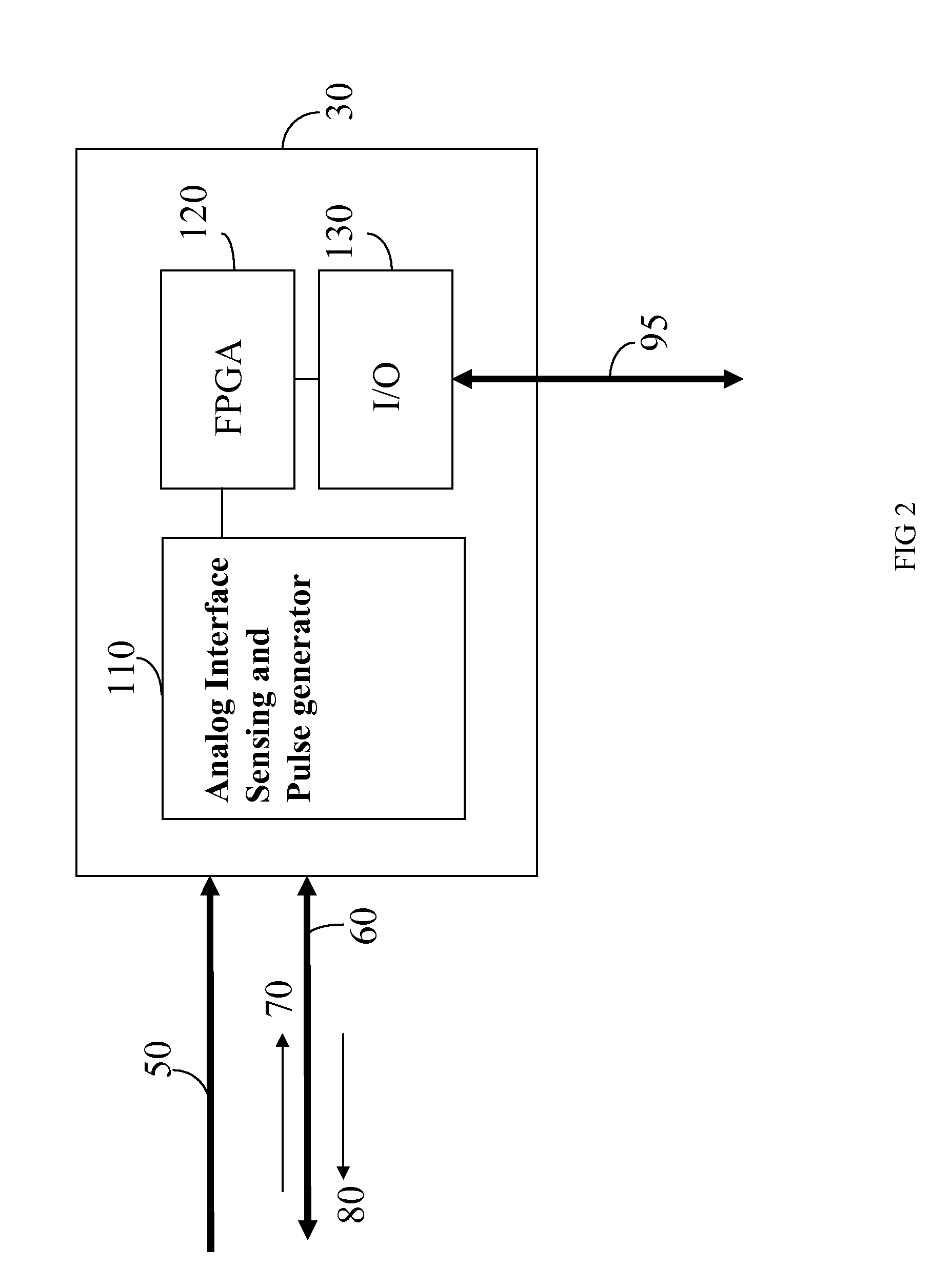
Heart Simulator
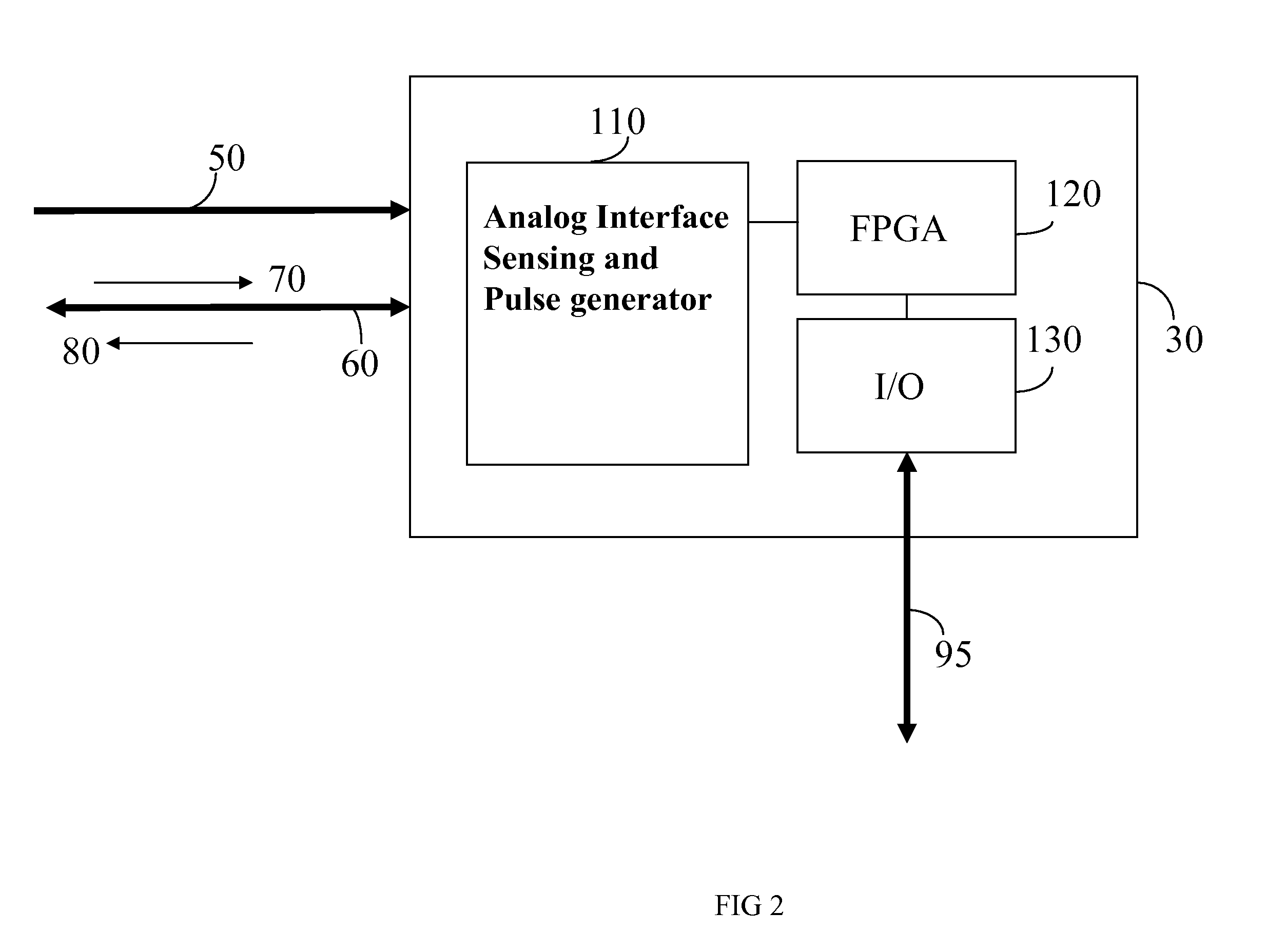
InactiveUS20080103744A1Overcome disadvantagesMedical simulationElectrotherapyCardiac statusControl system
A development system for a cardiac pacemaker control system, the development system comprising: a cardiac pacemaker prototype including an adaptive control system; and a heart simulator in communication with the cardiac pacemaker prototype comprising: a means for receiving pacing stimulations output from the cardiac pacemaker prototype; and a hemodynamic sensor model responsive to the received pacing stimulations, the hemodynamic sensor model being operable to output a signal simulating a hemodynamic sensor in a plurality of heart states, the hemodynamic sensor model being further operative to output the signal simulating the hemodynamic sensor in the plurality of heart states in a plurality of heart conditions.
Owner:SORIN CRM
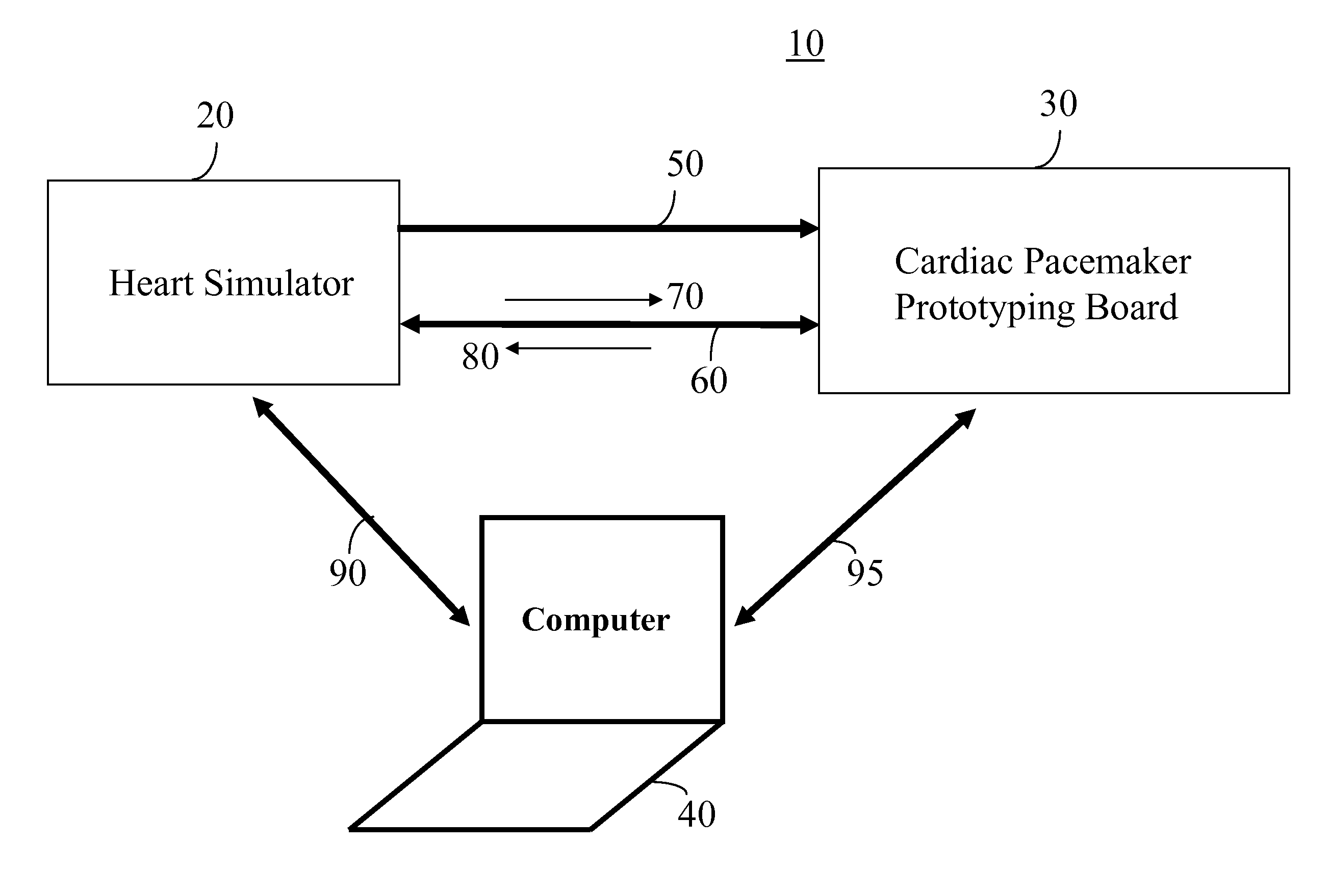
Heart simulator
InactiveUS7963924B2Overcome disadvantagesMedical simulationElectrotherapyControl systemCardiac status
A development system for a cardiac pacemaker control system, the development system comprising: a cardiac pacemaker prototype including an adaptive control system; and a heart simulator in communication with the cardiac pacemaker prototype comprising: a means for receiving pacing stimulations output from the cardiac pacemaker prototype; and a hemodynamic sensor model responsive to the received pacing stimulations, the hemodynamic sensor model being operable to output a signal simulating a hemodynamic sensor in a plurality of heart states, the hemodynamic sensor model being further operative to output the signal simulating the hemodynamic sensor in the plurality of heart states in a plurality of heart conditions.
Owner:SORIN CRM
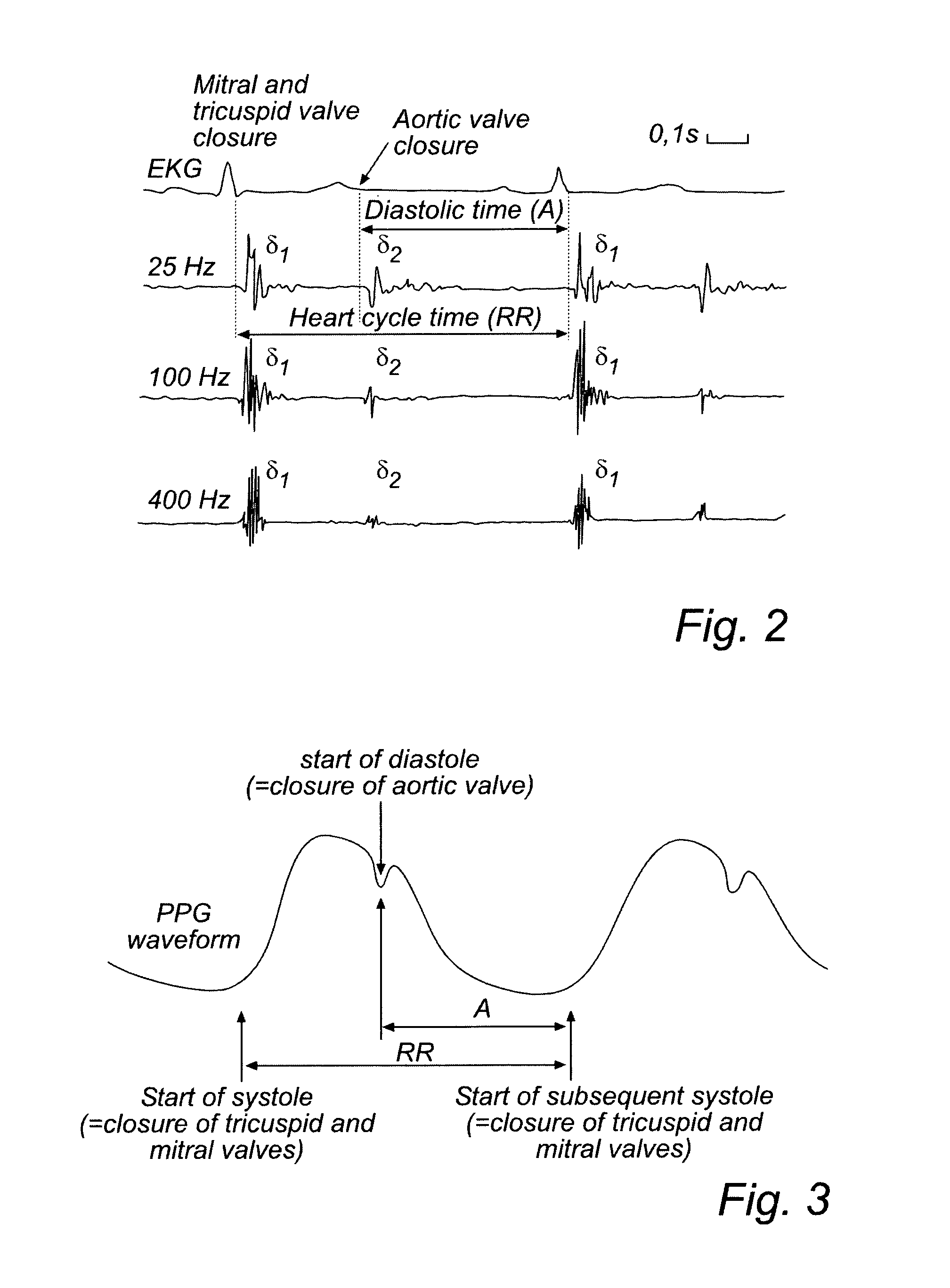
Household cardiac monitoring system based on electrocardio and cardiac sound analysis
InactiveCN108324266ATimely medical treatmentStethoscopeDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac statusT wave
Provided is a household cardiac monitoring system based on electrocardio and cardiac sound analysis. The system comprises a portable electrocardio and cardiac sound meter and its disposable application; the disposable application comprises a paster with a viscose layer; the paster is provided with a cardiac sound probe and multiple electrocardio electrodes; the cardiac sound probe and the electrocardio electrodes are exposed from the viscose layer; electrocardiogram and phonocardiogram are input to the electrocardio and cardiac sound meter; a same timeline is used for the real-time synchronously acquired electrocardiogram and phonocardiogram and the user's heart rate is obtained from the electrocardiogram; identifying electrocardio characteristics in the electrocardiogram and locating phonocardiogram using the electrocardio characteristics and finding cardiac sound characteristics; when R wave and first cardiac sound S1 do not appear correspondingly , or T wave and second cardiac soundS2 do not appear correspondingly, or the first cardiac sound S1 is abnormal or the second cardiac sound S2 is abnormal, then outputting cardiac abnormality alarm. The invention has the advantages ofbeing able to simultaneously monitor the electrocardio and the cardiac sound signals, and locating the cardiac sound characteristics by the electrocardiographic characteristics, thereby facilitating the user to monitor the heart state at home.
Owner:河南善仁医疗科技有限公司
System for cardiac status determination
A system improves detection and diagnosis of blood pressure based cardiac function and tissue activities by analyzing and characterizing cardiac blood pressure signals (including non-invasive and invasive blood pressure, discrete values and continuous waveforms) using pressure signal variation and variability calculation and evaluation. The system combines blood pressure analysis with multi clinical related factors and parameters to detect and quantify cardiac health status and arrhythmia severity. The system determines an accurate time, location and severity of cardiac pathology and events by calculating blood pressure variability and statistical variation. The accurately and reliably identifies cardiac disorders, differentiates cardiac arrhythmias, characterizes pathological severity, predicts the life-threatening events, and supports evaluation of drug delivery effects.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
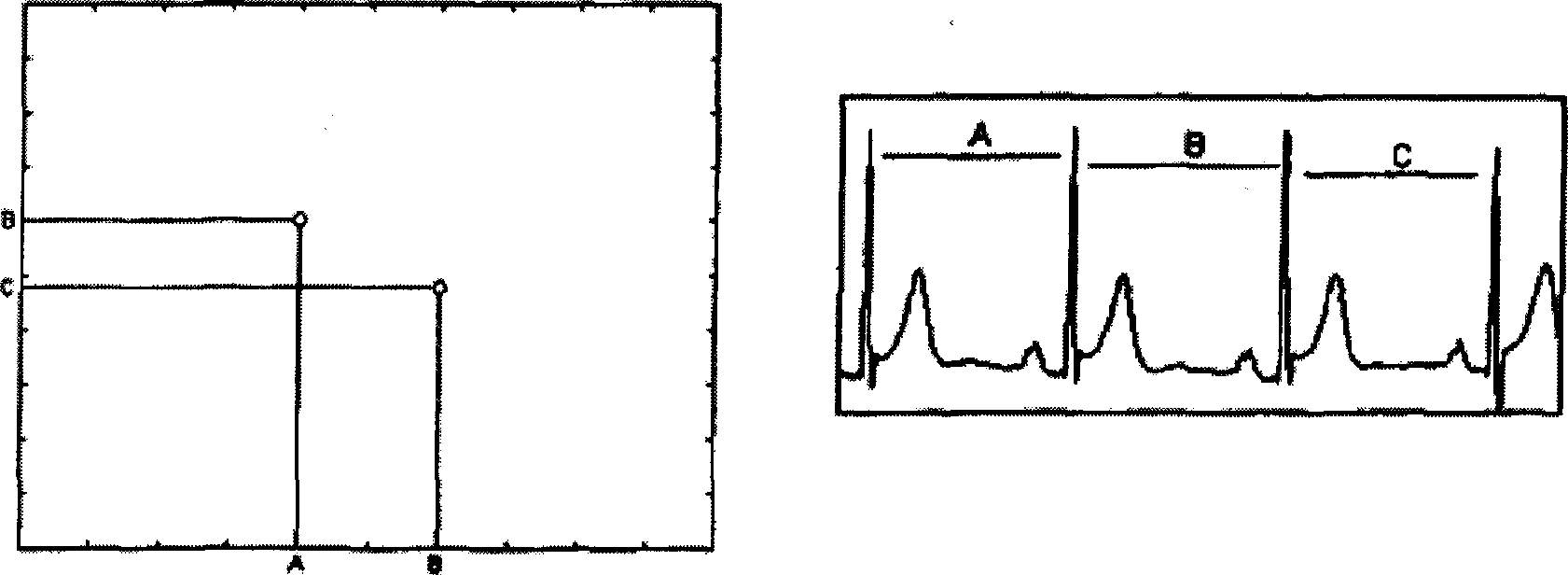
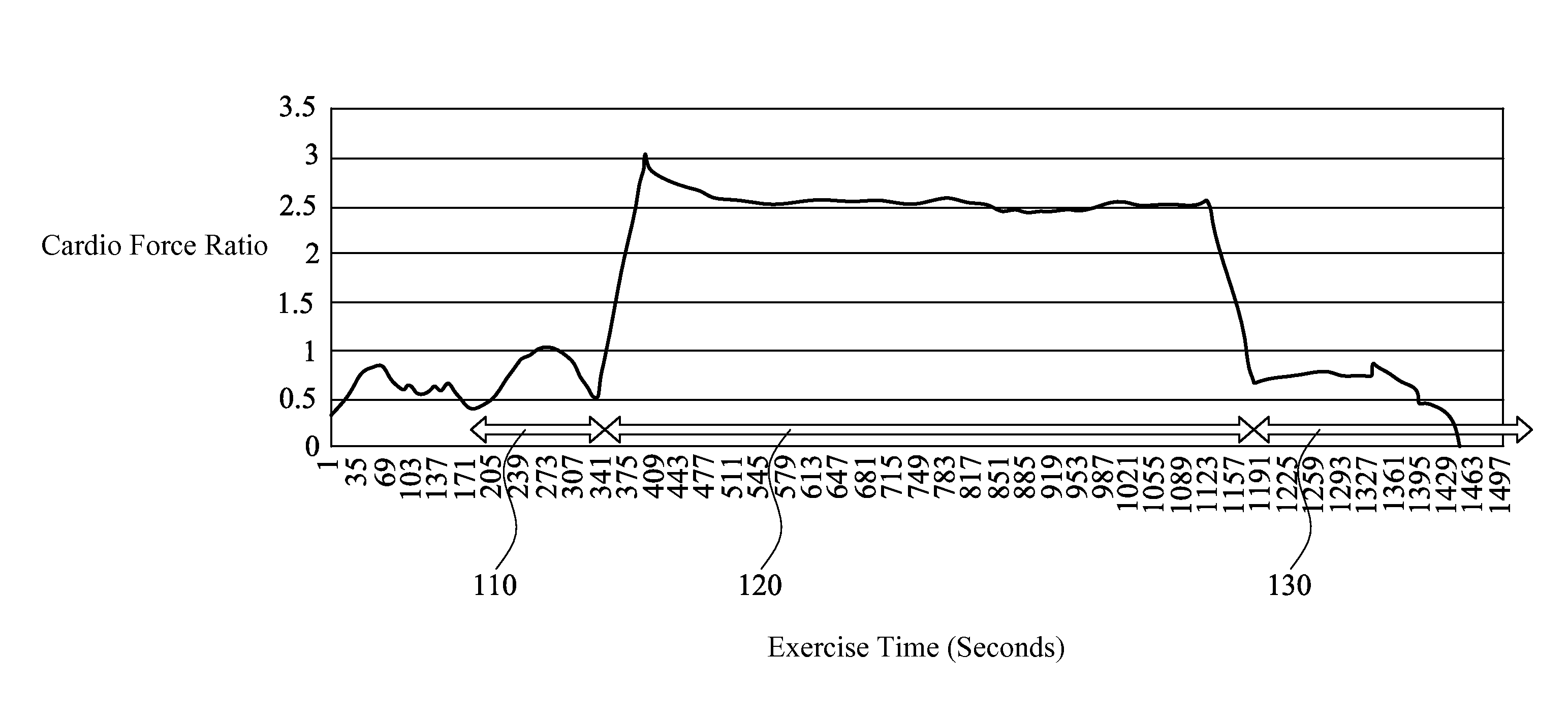
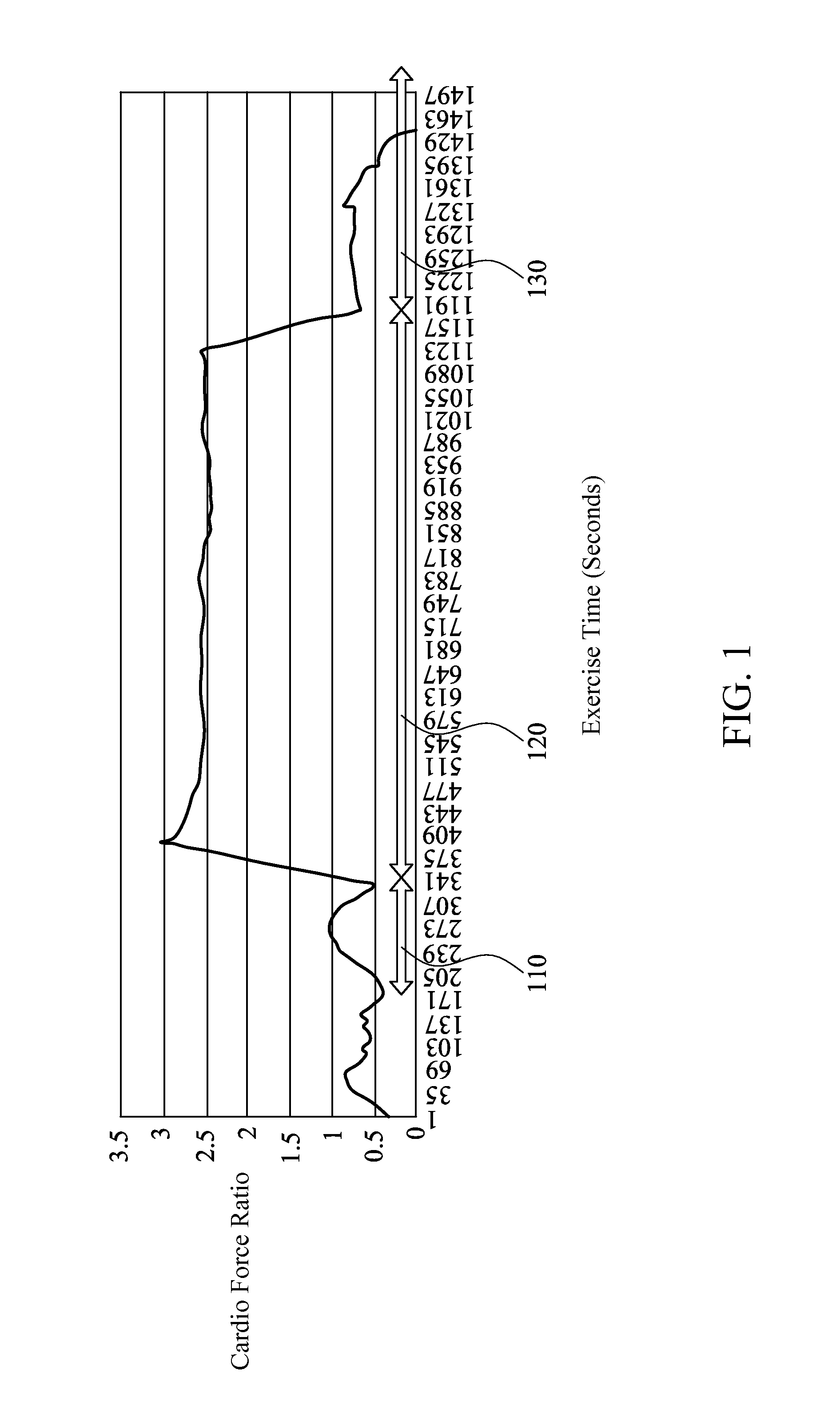
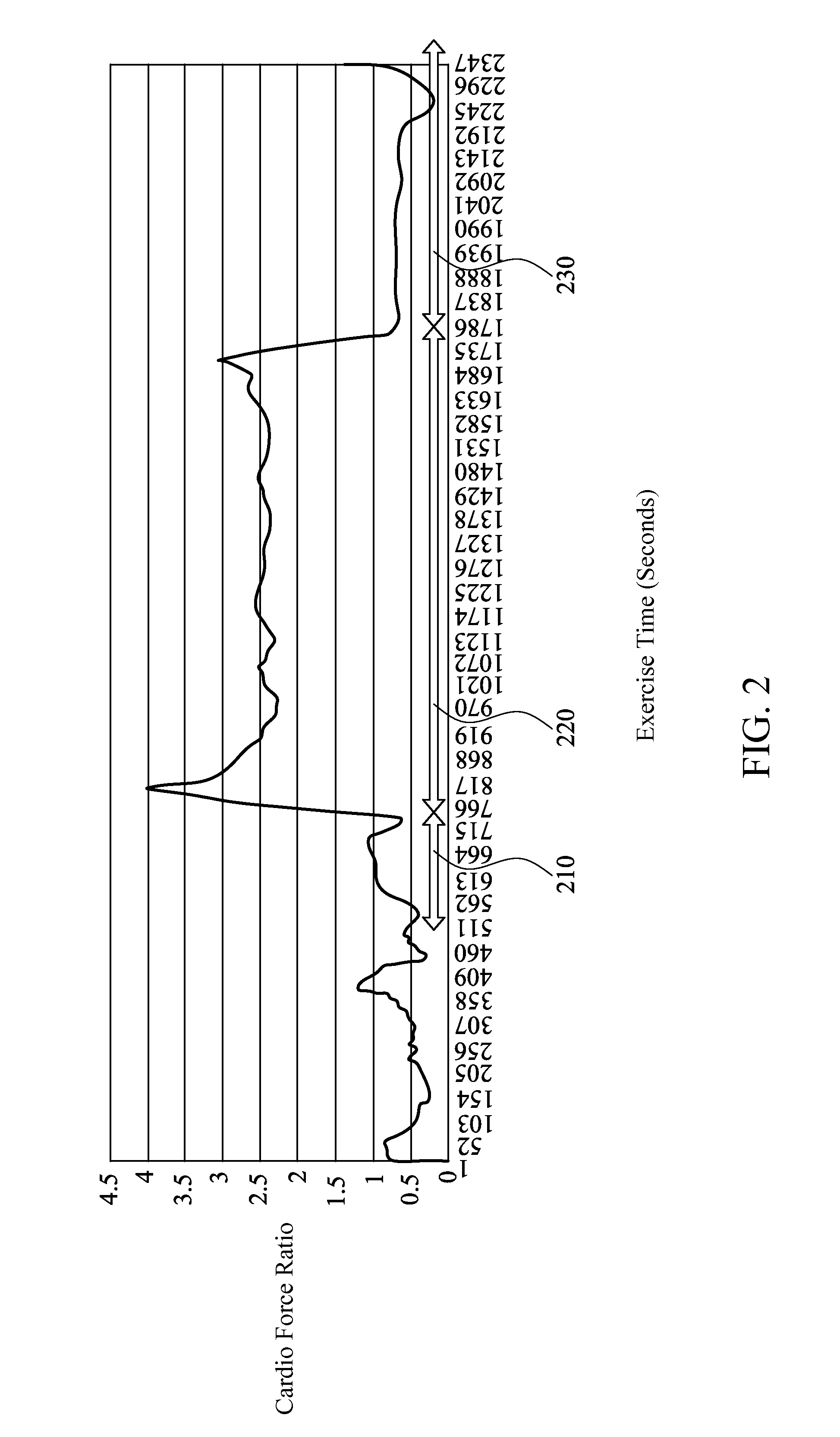
Method for detecting cardiac status, method for monitoring cardiac status during exercise, and apparatus for monitoring cardiac status
A method for detecting cardiac status is provided. A user's heart rate is measured by a heart rate detection unit, and the user's acceleration or activity level is measured by an acceleration detection unit, which the activity level is calculated by the acceleration detection unit. A cardio force index is obtained by a calculating unit based on the heart rate, and the acceleration, or the weight as the following formula (Ia) or (Ib):CFI=(Weight×) Acceleration / Heart Rate (Ia)CFI=(Weight×) Activity Level / Heart Rate (Ib)The cardio force ratio is a ratio of the user as the following formula (II):Cardio Force Ratio=CFI of Exercise / CFI of Walking (II)A method for monitoring cardiac status during exercise and an apparatus for monitoring cardiac status are also provided.
Owner:NAT DEFENSE MEDICAL CENT
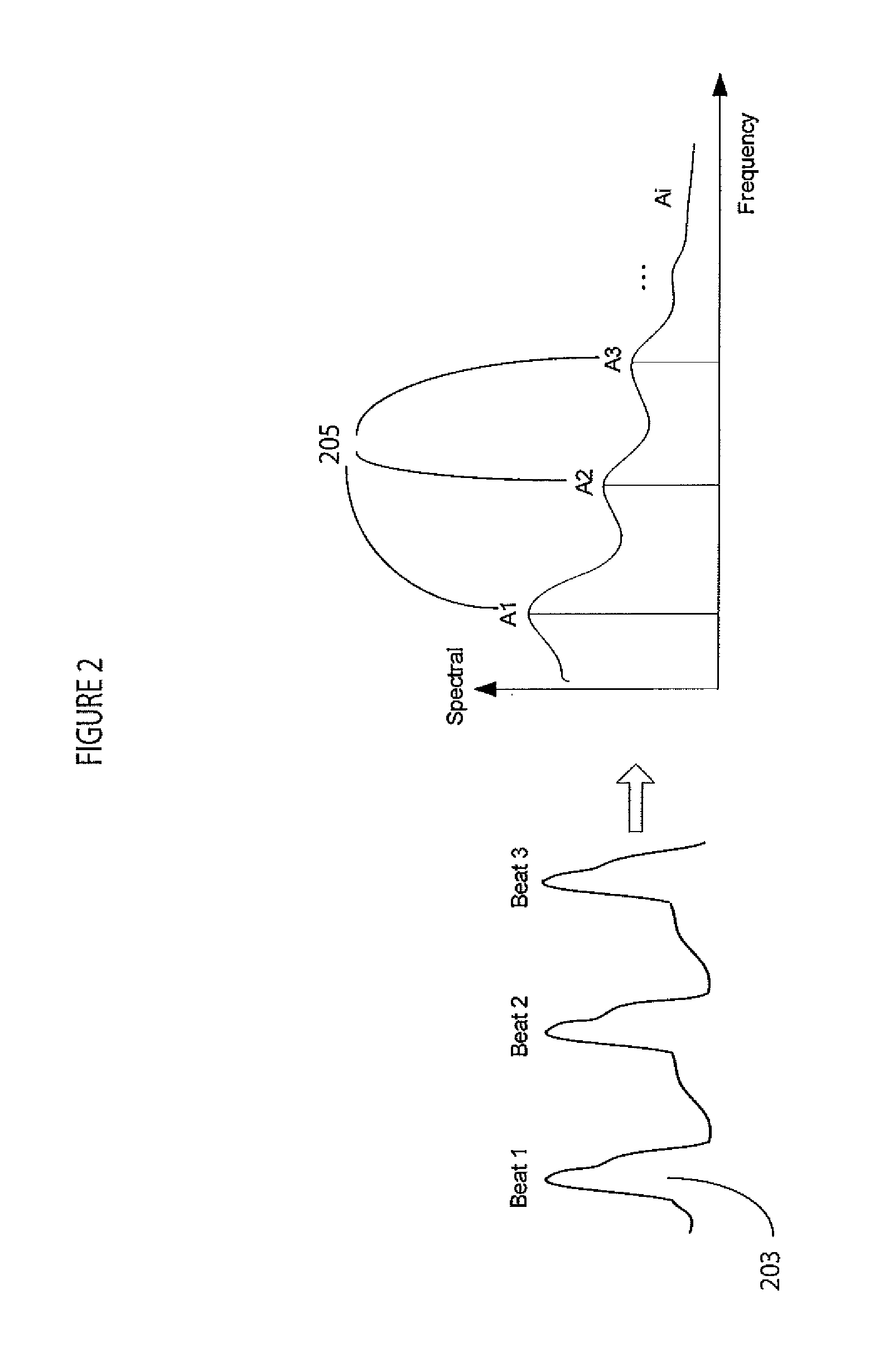
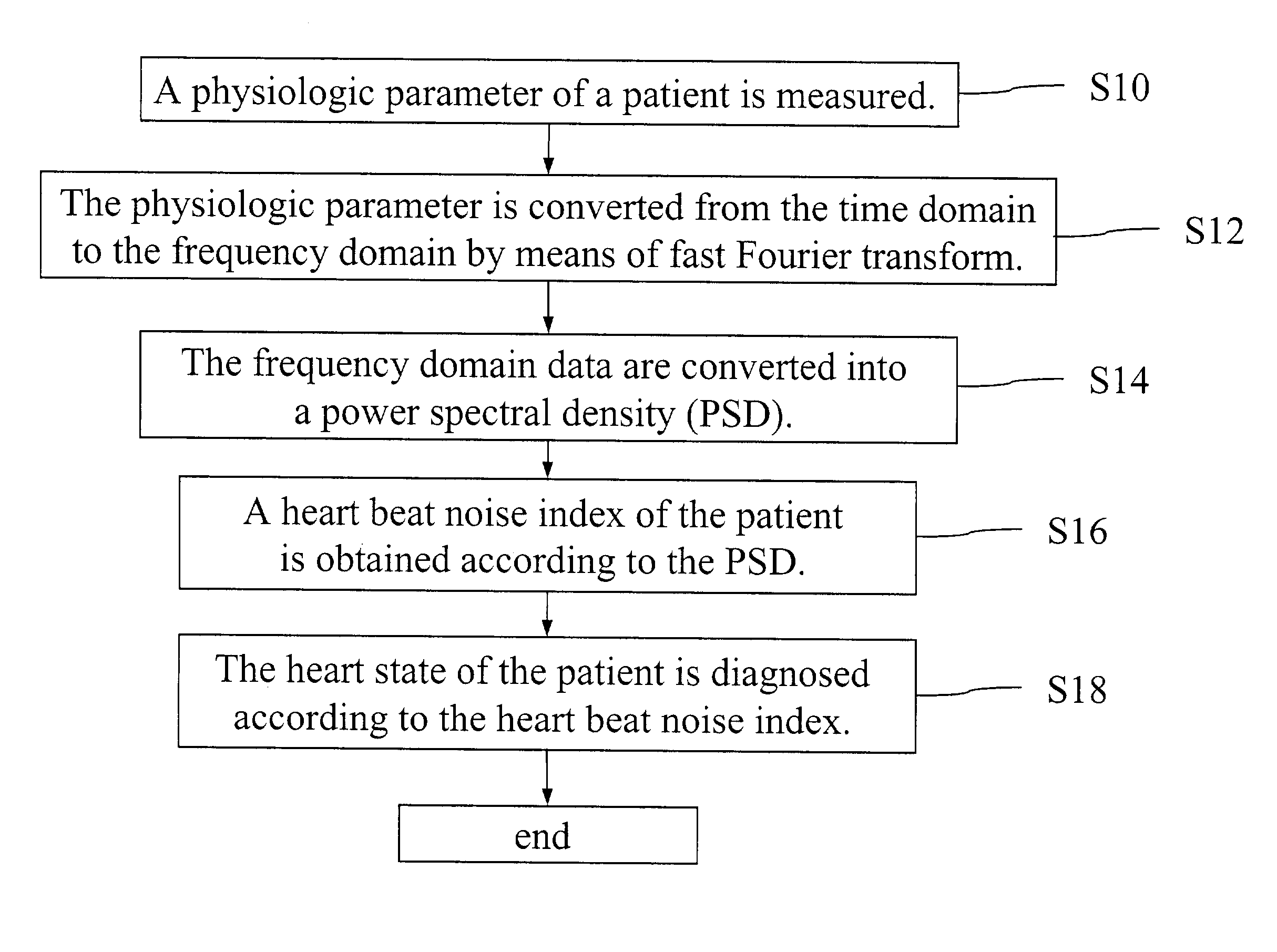
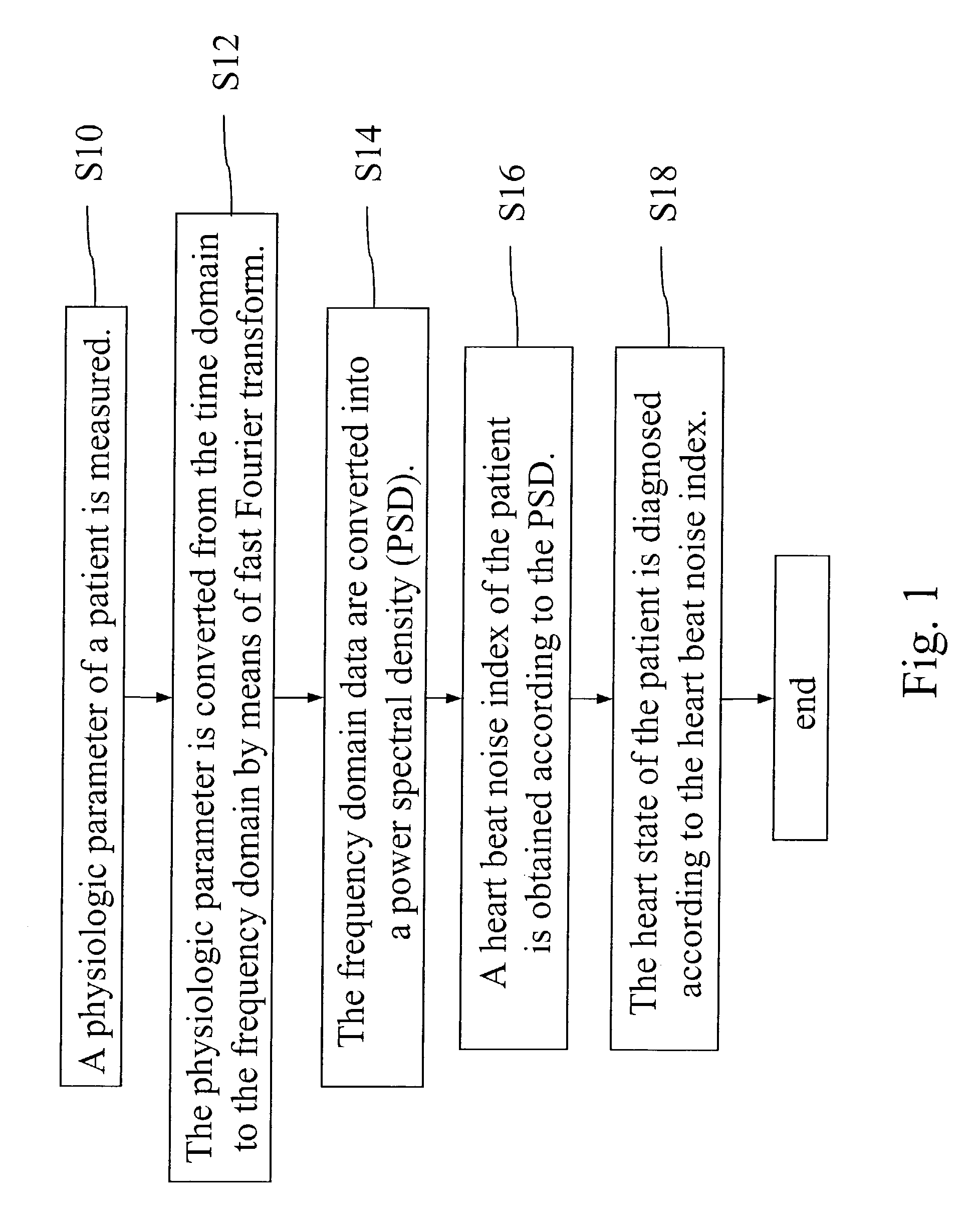
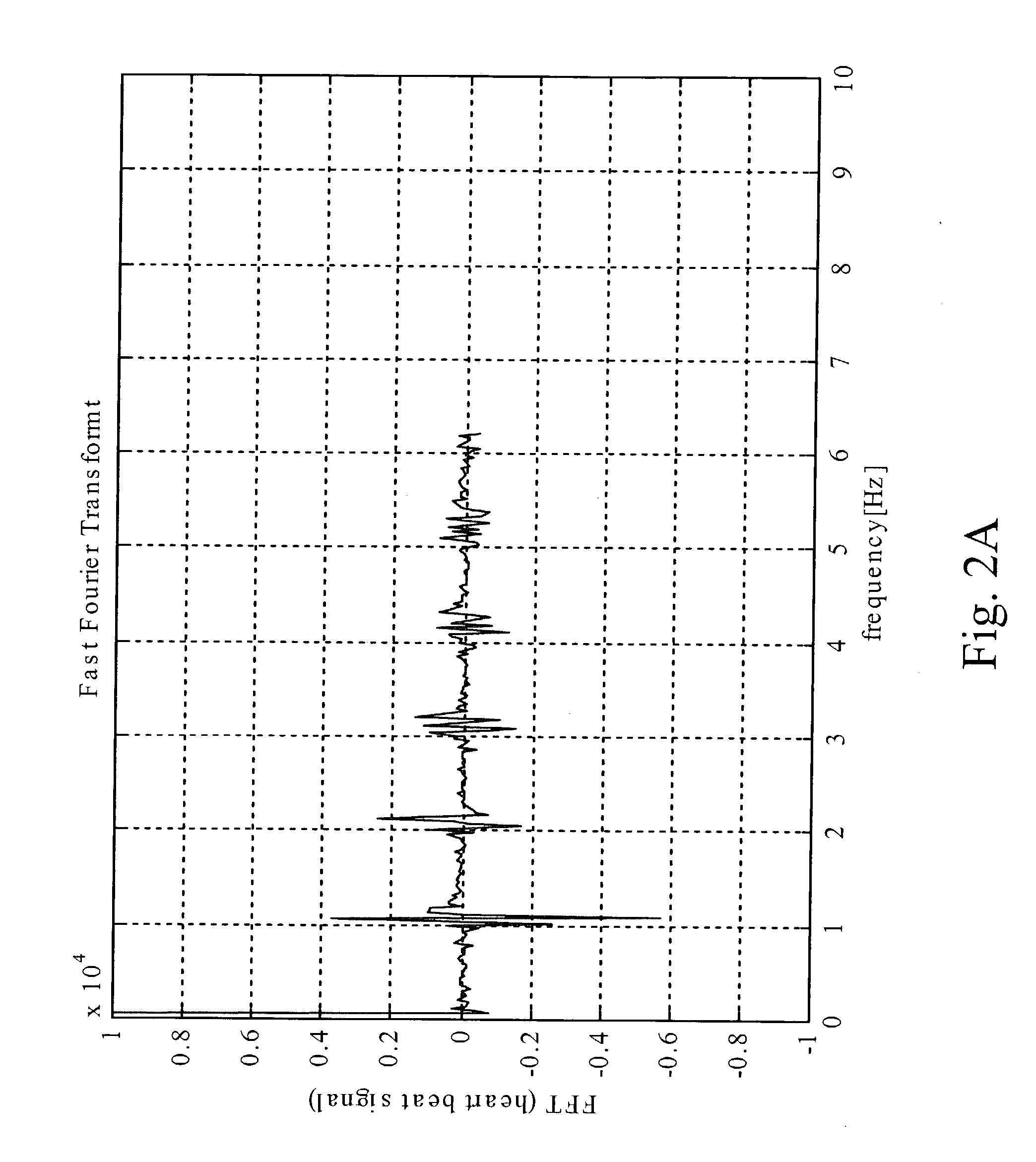
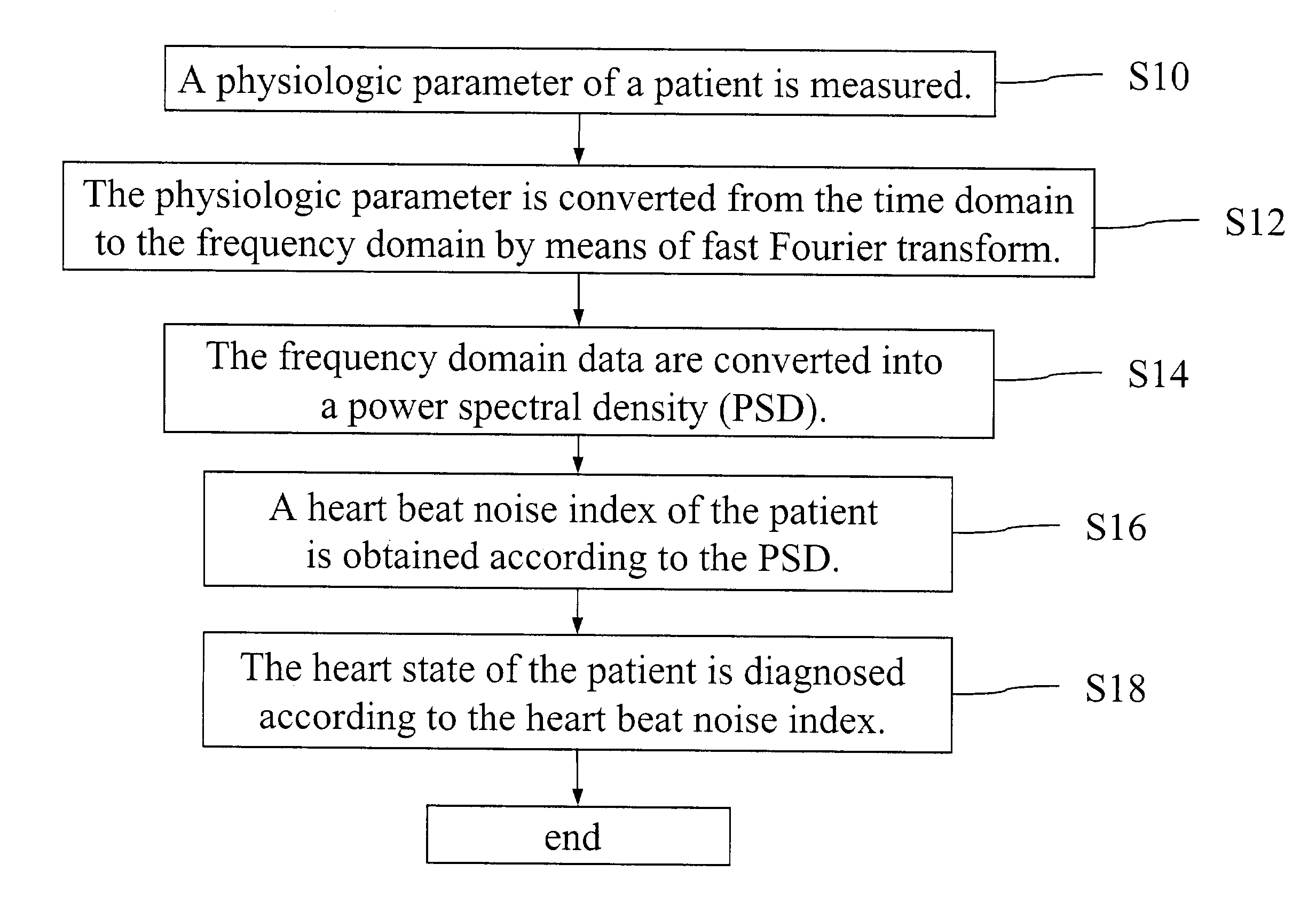
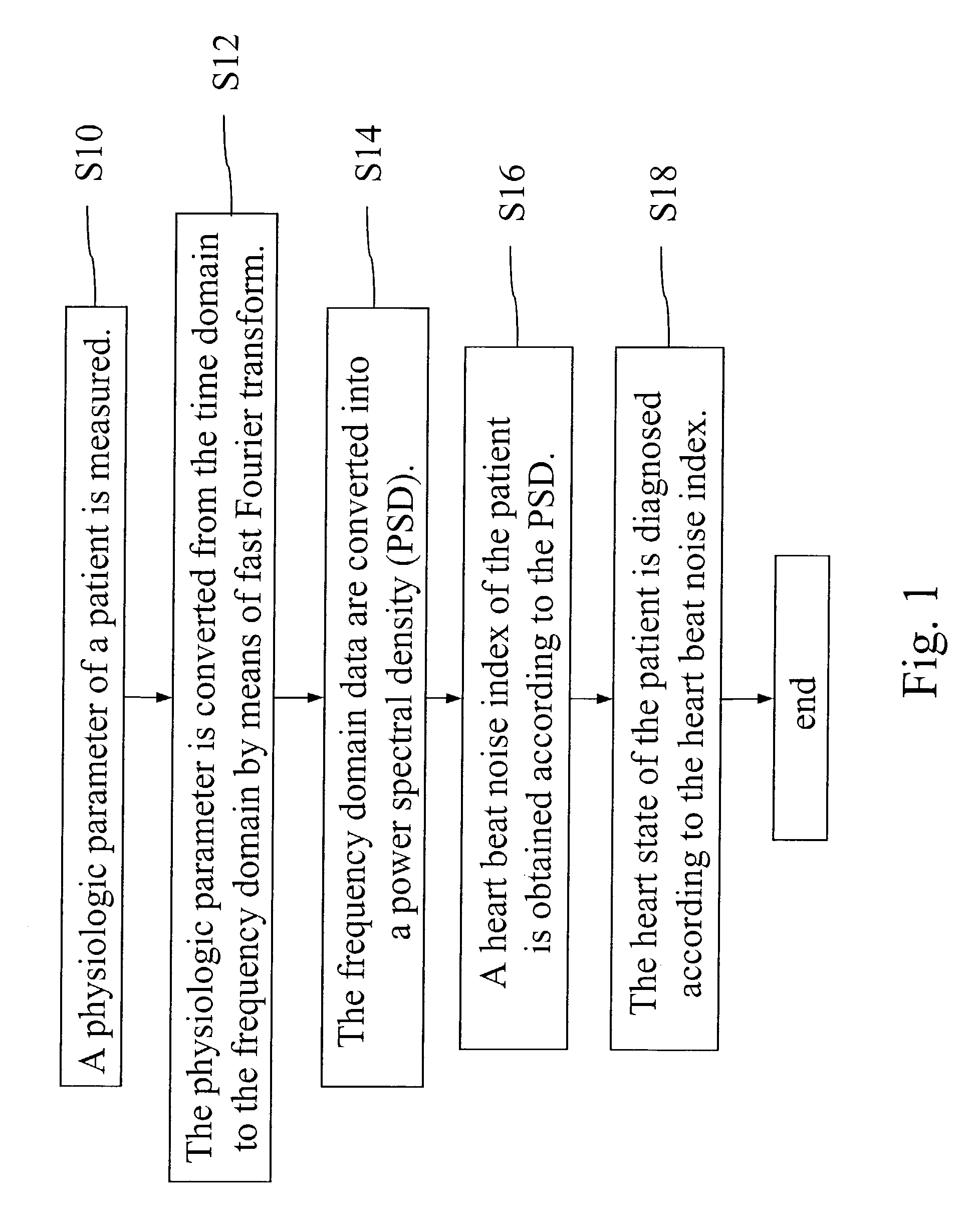
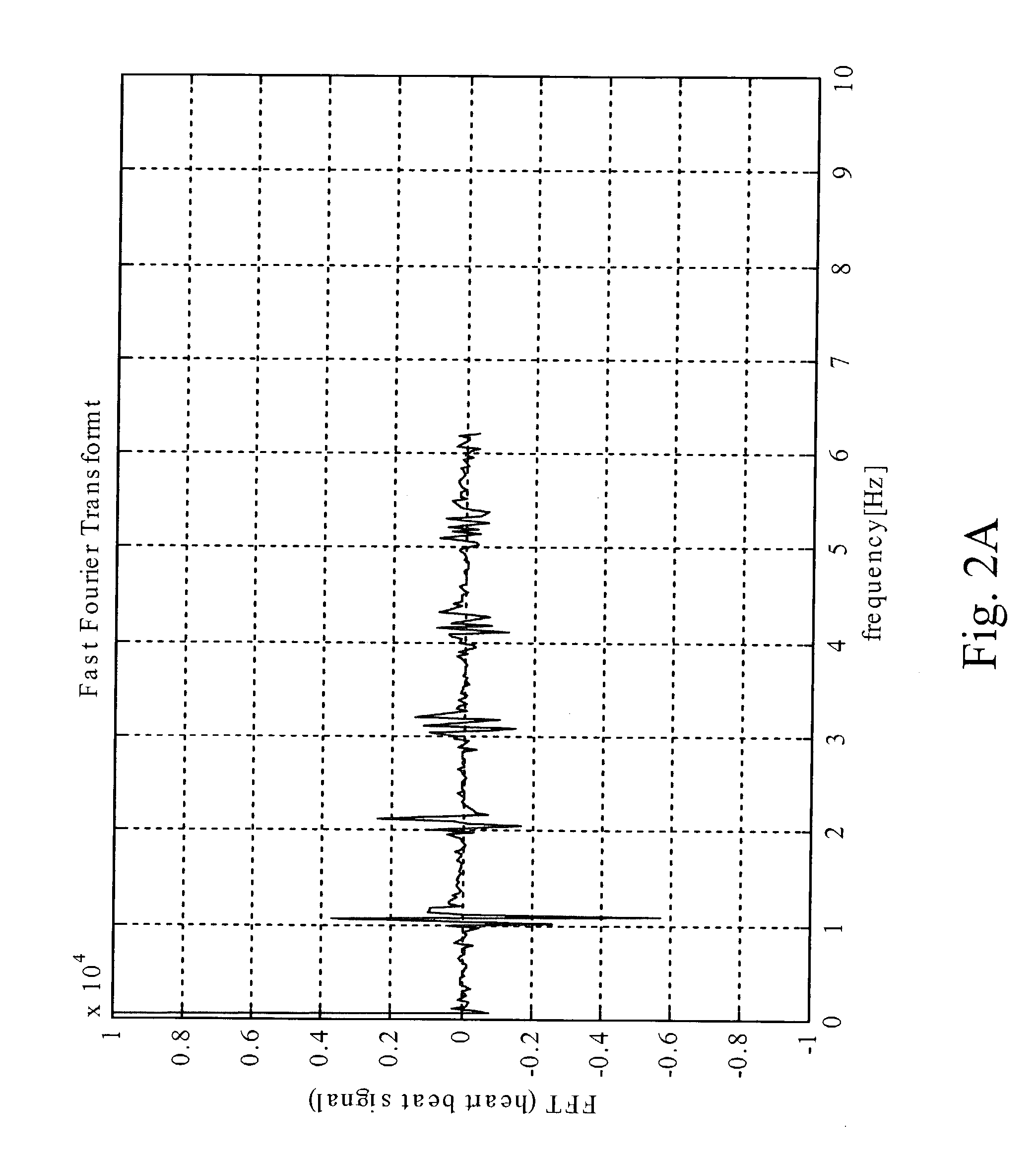
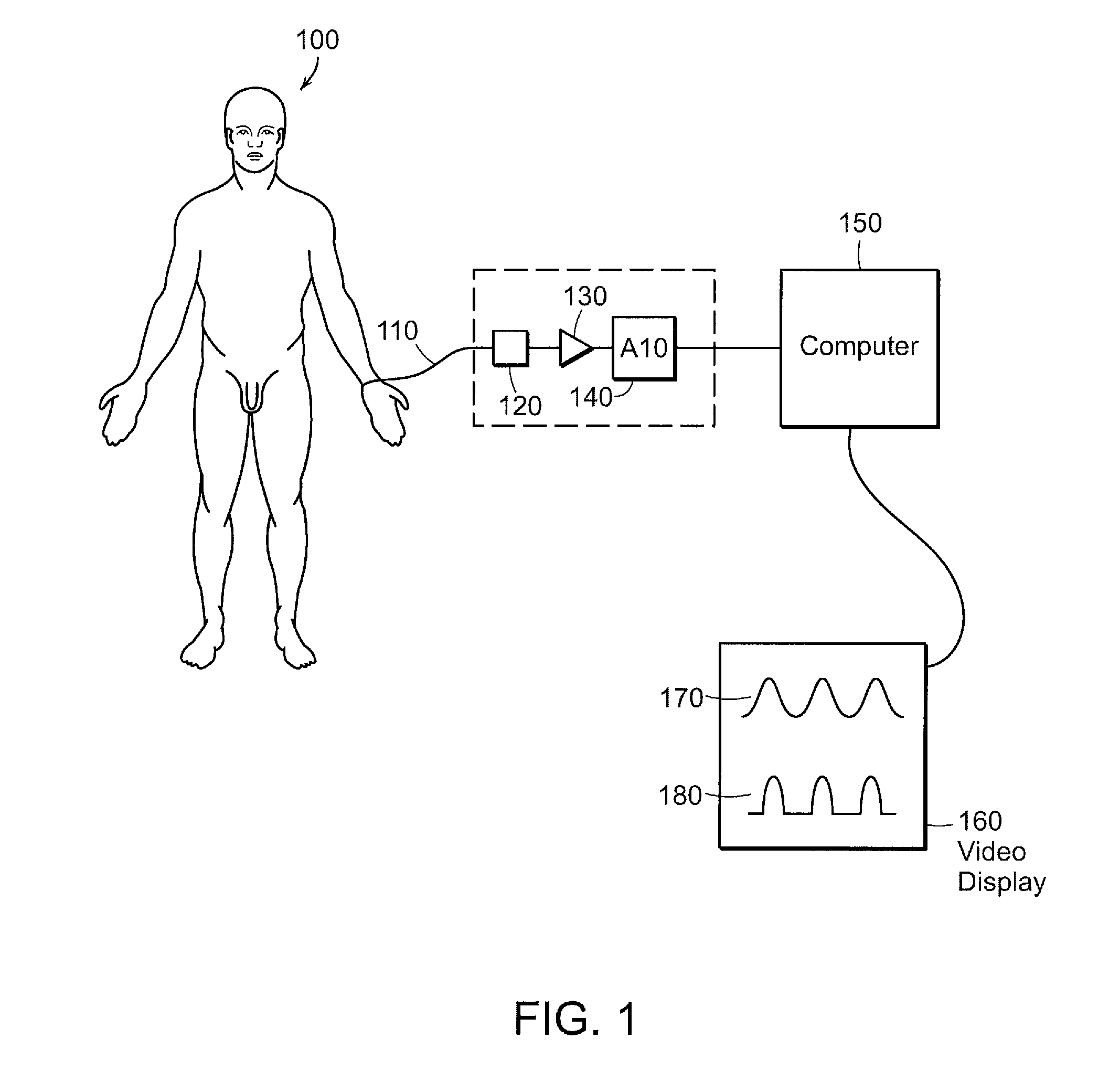
Heart state monitor method
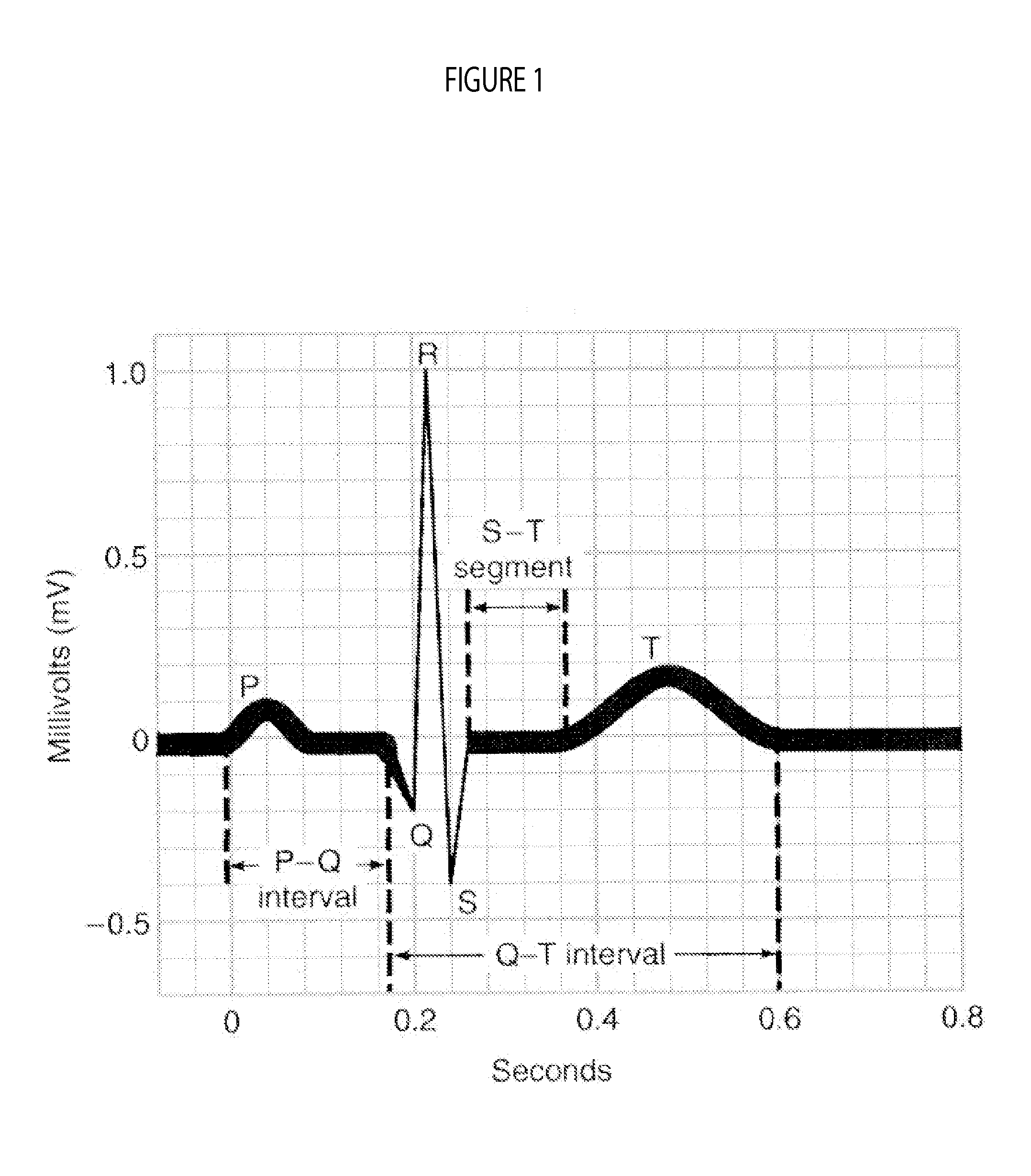
ActiveUS20040143192A1Accurately knowEasy to measureElectrocardiographySensorsTime domainCardiac status
A heart state monitor method is proposed. First, a physiologic parameter of a life body is measured. The physiologic parameter is then converted from the time domain to the frequency domain by means of Fourier transform. Next, the frequency domain data of the physiologic parameter are converted into a PSD. A heart beat noise index of the life body is then obtained according to the PSD. Finally, the heart state of the life body is diagnosed according to the heart beat noise index. Therefore, measurements of heart state can be performed for a life body. The heart beat noise index can be quickly discriminated to let the life body and medical staffs grasp the current heart state of the life body at any time.
Owner:CHANG KUO YUAN +1
Method and system for adapting pacing settings of a cardiac stimulator
InactiveUS20120221071A1Possible to checkHeart stimulatorsIncreased physical activityCardiac pacemaker electrode
In an implantable medical device, such as a cardiac stimulator such as a pacemaker, and method for predicting patient responses to physical exertion, the patient response is monitored over time to evaluate disease progression and pacing therapies of cardiac stimulators are adapted based on the predicted patient response. A current cardiac status indicator for the patient is created indicating a response of the patient to an increased physical activity as a primarily heart rate response or as a primarily a stroke volume response. The pacing parameters of the cardiac stimulator can thereafter be adapted depending on the current cardiac status indicator, wherein the adapted pacing parameters include a first pacing setting if the current cardiac status indicator indicates a primarily heart rate response or a second pacing setting if the current cardiac status indicator indicates a primarily stroke volume response.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Devices and method for determining and monitoring a cardiac status of a patient by using PLVDT or PLVST parameters
ActiveUS8998820B2Accurately and reliably determiningStrong specificityElectrocardiographyStethoscopeLeft ventricular sizeCardiac status
The present invention relates to an improved medical device and method for accurately and reliably determining a cardiac status of a patient. An implantable medical device, IMD, comprises a sensor arrangement adapted to sense signals related to mechanical activity of the heart and an activity level sensor arrangement adapted to sense an activity level of the patient. Further, the IMD calculates a percentage of left ventricular diastolic time (PLVDT) for a cardiac cycle corresponding to a relation between a diastolic time interval and a cardiac cycle time interval using the determined systolic and diastolic time intervals or a percentage of left ventricular systolic time (PLVST) for a cardiac cycle corresponding to a relation between a systolic interval time interval and a cardiac cycle time interval. A cardiac status is determined based on the calculated PLVDT (or PLVST) and on an activity level of the patient.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Multipath heart sound based heart sound sensor position error-correcting method
ActiveCN108378843AReduce dependenceSuitable for home monitoring of heart statusStethoscopeDiagnostic recording/measuringBase heartMedicine
The invention discloses a multipath heart sound based heart sound sensor position error-correcting method. The multipath heart sound based heart sound sensor position error-correcting method comprisesthe following steps of: synchronously collecting and synchronously recording an electrocardiograph and multipath phonocardiogram, wherein each phonocardiogram corresponds to a respective an auscultatory area to separately distinguish electrocardiographic characteristics of each cardiac cycle, correspondingly searches heart-sound characteristics of each phonocardiogram according to the electrocardiographic characteristics, and distinguish whether a heart sound sensor is within a correct auscultatory area or not. The multipath heart sound based heart sound sensor position error-correcting method has the advantages of being capable of distinguishing whether each heat sound sensor is within the correct auscultatory area or not and being suitable for monitoring a heart state in a household mode.
Owner:河南善仁医疗科技有限公司
Method for identifying heart status time phase
ActiveCN103908279ARecognition is stable and accurateSurgeryComputerised tomographsLeft ventricular sizeCardiac status
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Patient-specific image-based computational modeling and techniques for human heart surgery optimization
A method for determining cardiac status comprises for a given patient, constructing a patient-specific, three-dimensional, computational model of the patient's heart; and executing the constructed computational model, said executing generating a quantitative analysis of cardiac function. A method of performing cardiac surgeries comprises: a) assessing surgical options based on a patient-specific, three-dimensional, computational model of a patient's heart; and b) performing surgery based on one or more of the surgical options. A computer system comprises: a) a data source containing data of a patient's heart; b) a modeler coupled to receive data from the data source, the modeler generating a patient-specific, three-dimensional, computational model of the heart based on the heart data; and c) a processor routine for computationally providing information about a certain cardiac function using the three-dimensional heart model and for applying computational, quantitative analysis of the cardiac function, wherein the quantitative analysis of the cardiac function provides an assessment for surgical options, optimizing surgical techniques, or predicting outcomes.
Owner:WORCESTER POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE
Image analysis device, imaging system, and non-transitory recording medium
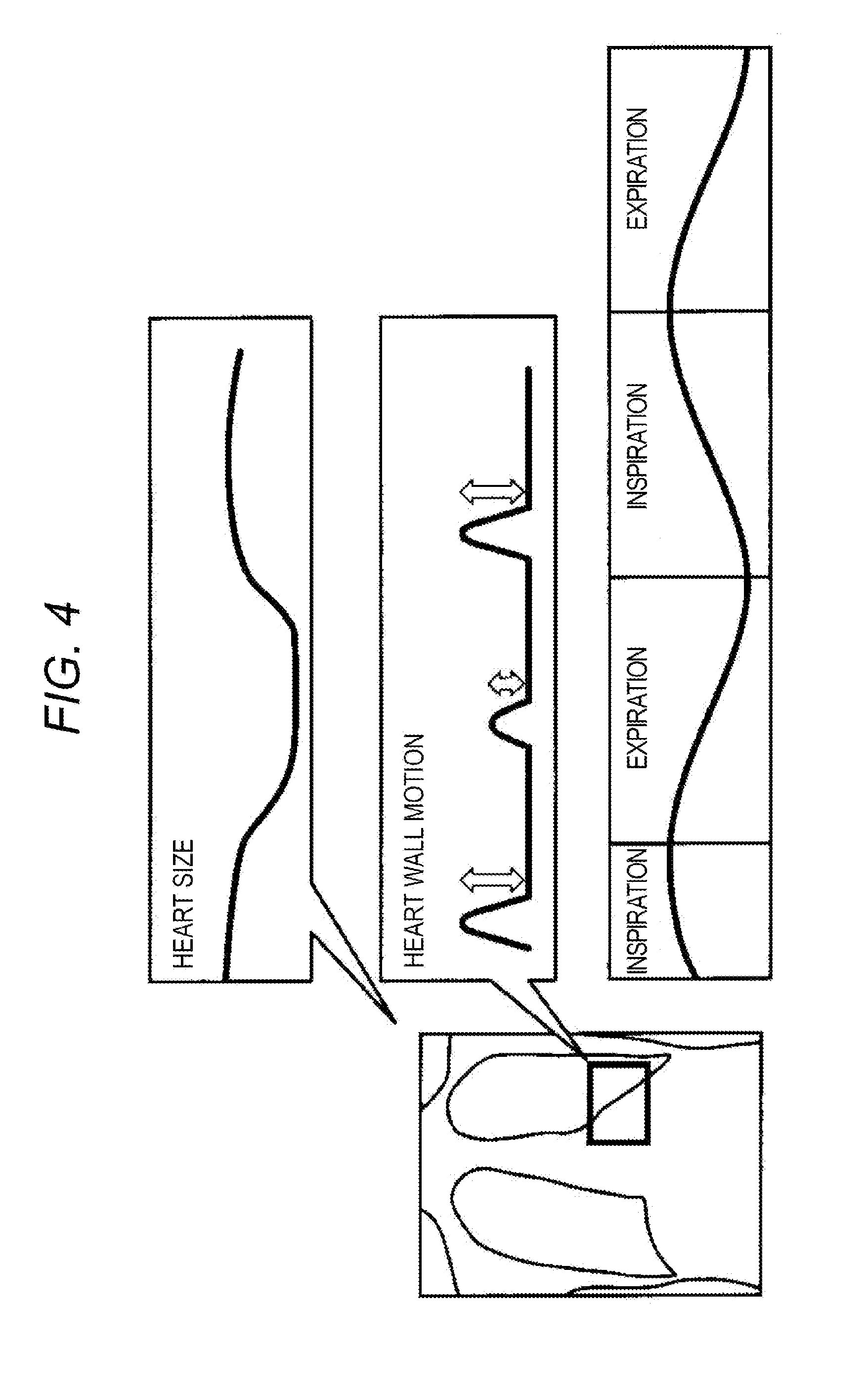
ActiveUS20150269726A1Good reproducibilityWithout imposing a heavy strain on the person being testedImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac statusImaging analysis
An image analysis device includes: an acquiring unit configured to acquire a moving image showing a variation of a respiratory status, the moving image being formed with frame images including an image of a heart; an image analyzing unit configured to generate a first index indicating a cardiac status with respect to each of the frame images; and an index analyzing unit configured to derive a second index indicating lung function from a change caused in the first indexes by the respiratory status.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
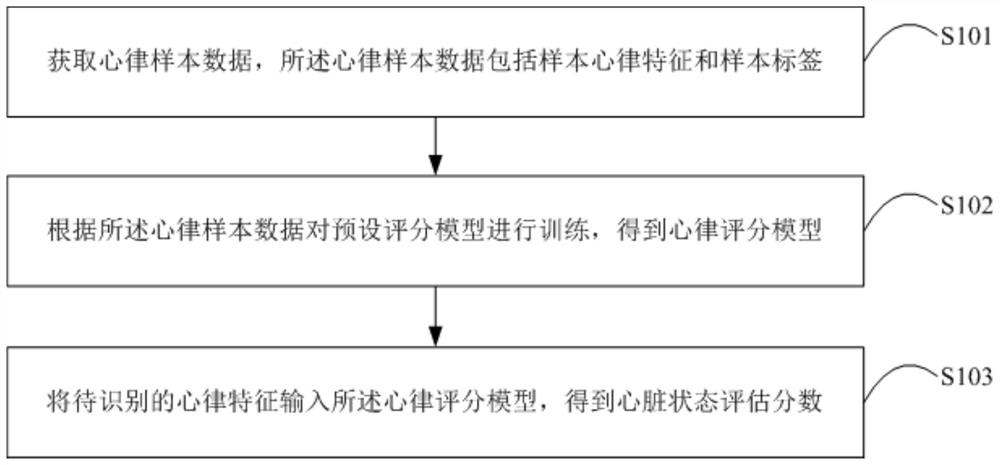
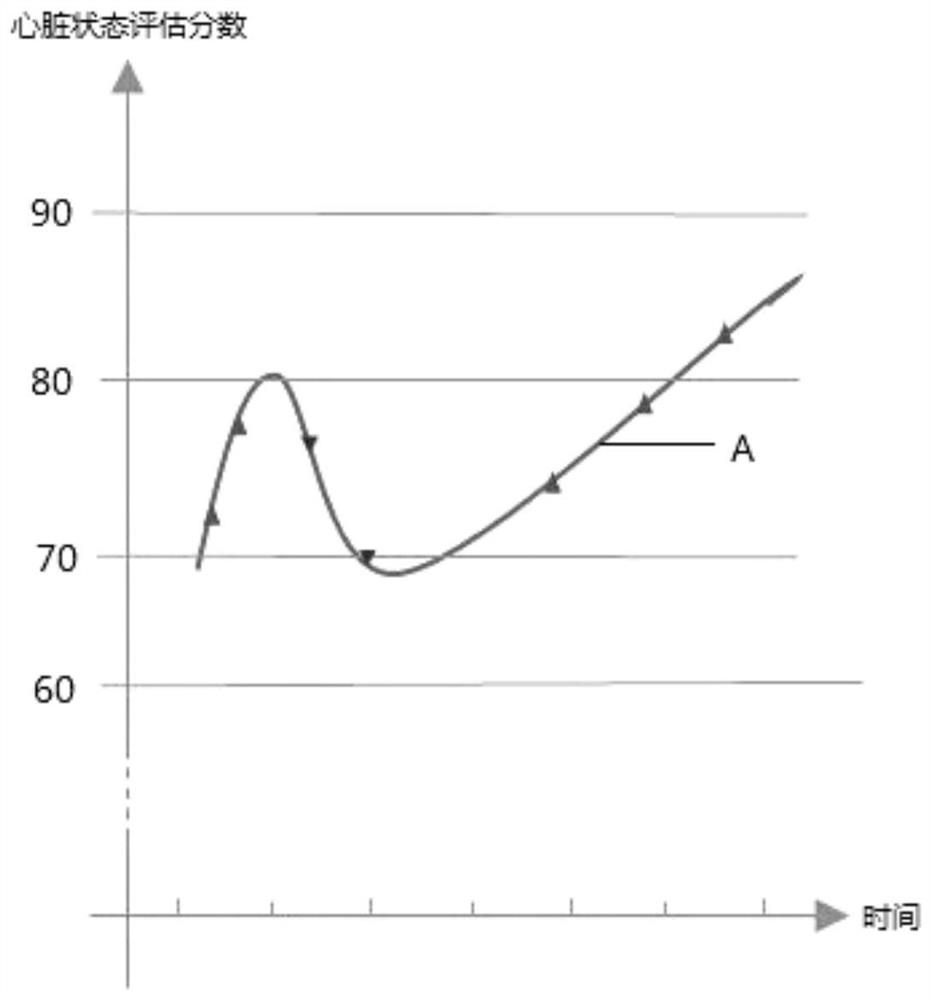
Heart state evaluation method and device, terminal equipment and storage medium
PendingCN112826479ASolve the problem of difficult recognition of heart healthLearn about heart healthSensorsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateData packCardiac status
The invention is suitable for the technical field of data processing, and provides a heart state evaluation method and a device thereof, terminal equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining heart rhythm sample data which comprises a sample heart rhythm feature and a sample label; training a preset scoring model according to the heart rhythm sample data to obtain a heart rhythm scoring model; and inputting the heart rhythm features to be recognized into the heart rhythm scoring model to obtain a heart state evaluation score. The problems that an existing heart health prompting scheme is not visual, the assessment granularity is coarse, and a user is difficult to know the heart health degree can be solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Image analysis device, imaging system, and image analysis method
InactiveCN104921741AIncrease the burdenImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac statusImaging analysis
An image analysis device includes: an acquiring unit configured to acquire a moving image showing a variation of a respiratory status, the moving image being formed with frame images including an image of a heart; an image analyzing unit configured to generate a first index indicating a cardiac status with respect to each of the frame images; and an index analyzing unit configured to derive a second index indicating lung function from a change caused in the first indexes by the respiratory status.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Heart state monitor method
A heart state monitor method is proposed. The physiologic parameter of a life body is measured and then preformed by Fourier transform analysis. Next, the frequency domain data of the physiologic parameter are converted into a power spectral density (PSD). A heart beat noise index of the life body is then obtained according to the PSD. Finally, the heart state of the life body is diagnosed according to the heart beat noise index. The heart beat noise index may be quickly discriminated to let the life body and medical staffs grasp the current heart state of the life body at any time.
Owner:CHANG KUO YUAN +1
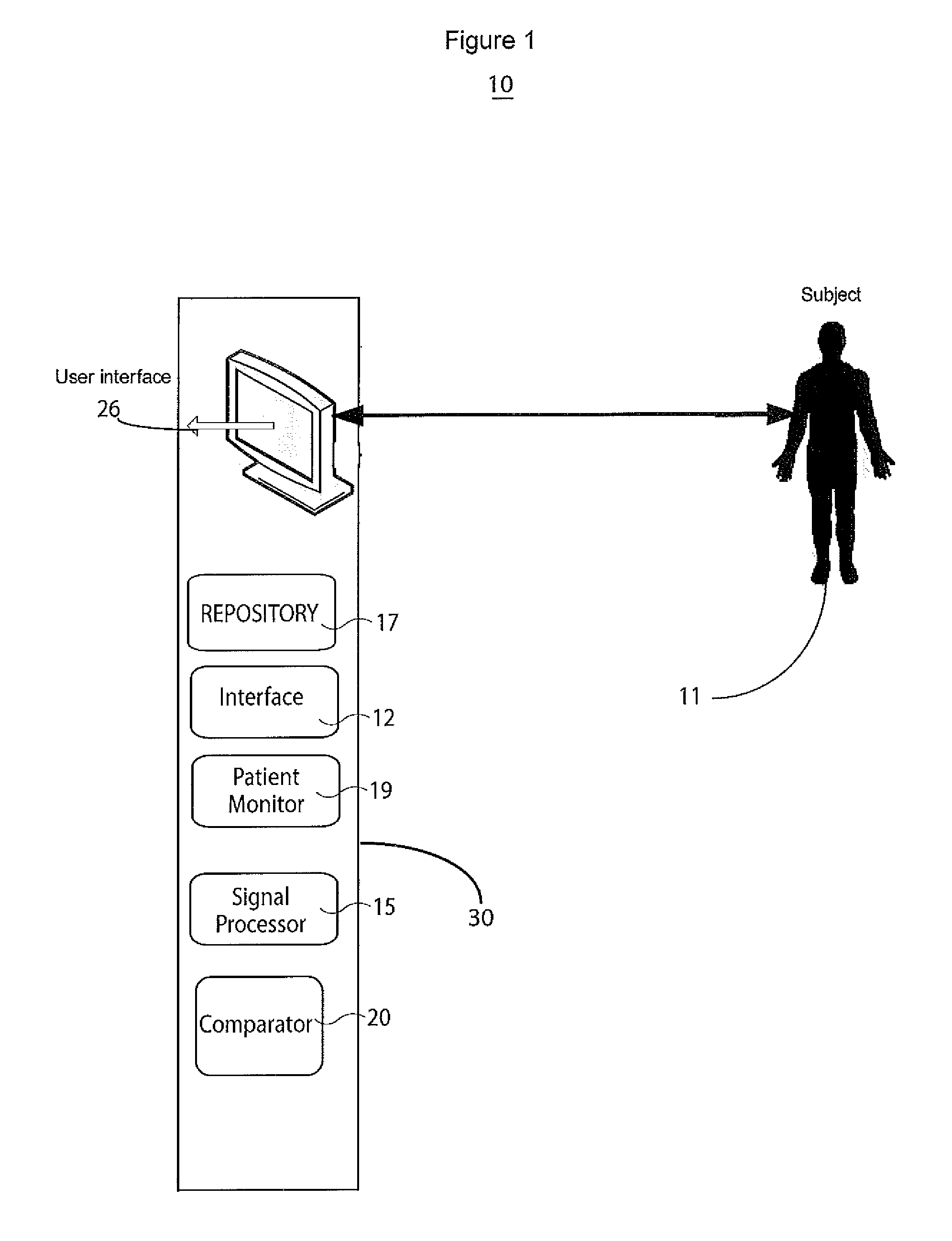
Methods and apparatus for visually representing a cardiac status of a patient
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
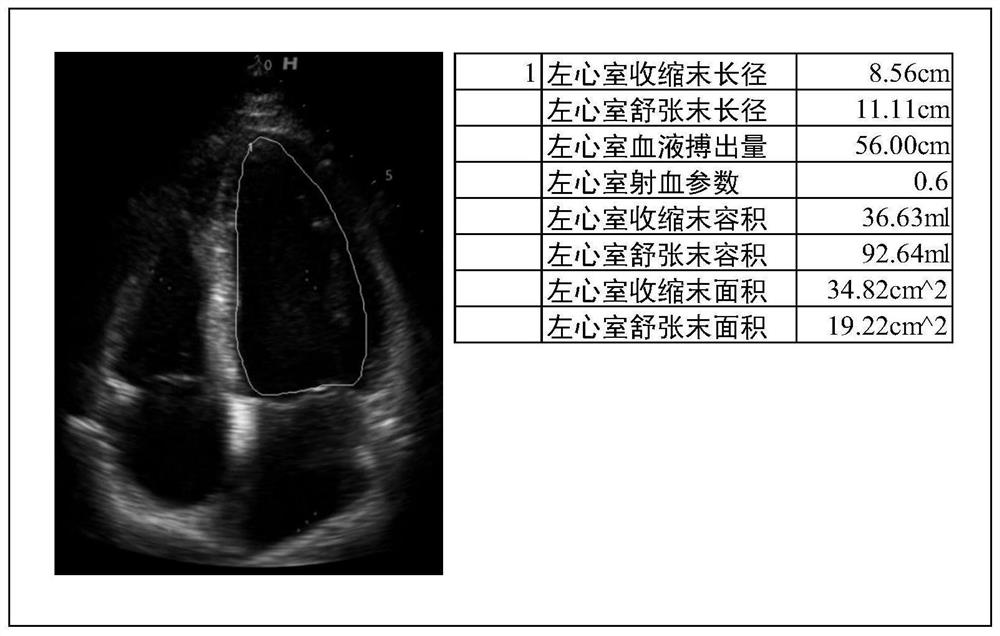
Ultrasonic equipment, ultrasonic image processing method and storage medium
ActiveCN112656445AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
The invention discloses ultrasonic equipment, an ultrasonic image processing method and a storage medium, which are used for automatically measuring heart state parameters and improving the measurement accuracy. The equipment comprises a processor and a display. The processor obtains an image sequence composed of ultrasonic images from the continuously collected ultrasonic image information of the heart; the ventricular volume corresponding to each frame of ultrasonic image in the image sequence is determined to obtain a ventricular volume sequence; the end-diastolic volume corresponding to the central ventricular end diastolic phase of at least one cardiac cycle and the end-systolic volume corresponding to the ventricular end-systolic phase is determined according to the change trend of the central ventricular volume of the ventricular volume sequence; and heart state parameters can be determined according to the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. The ventricular volume is determined according to the ultrasonic images in the acquired image sequence, so that the ventricular volume is determined quickly and accurately; the heart state parameters are determined according to the determined end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume, so that the accuracy of the heart state parameters is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MEDICAL EQUIP
Non-contact BCG signal processing system and method based on optical fiber sensing
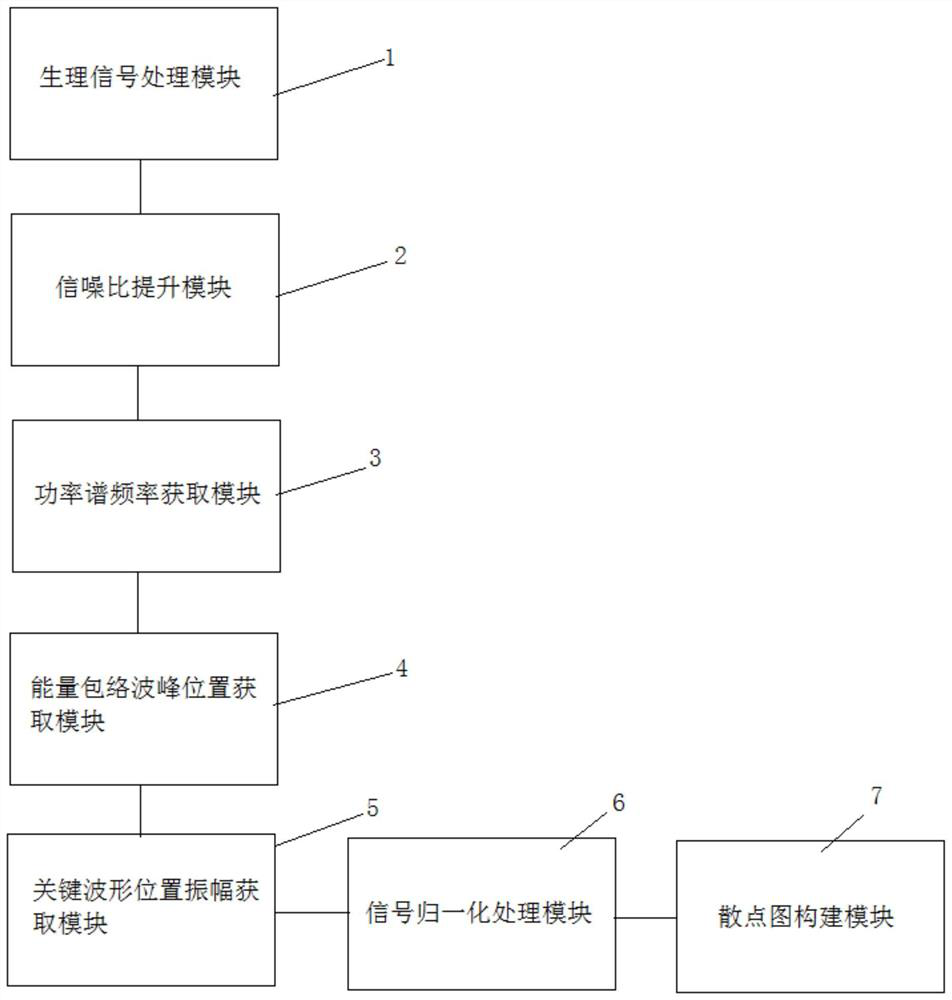
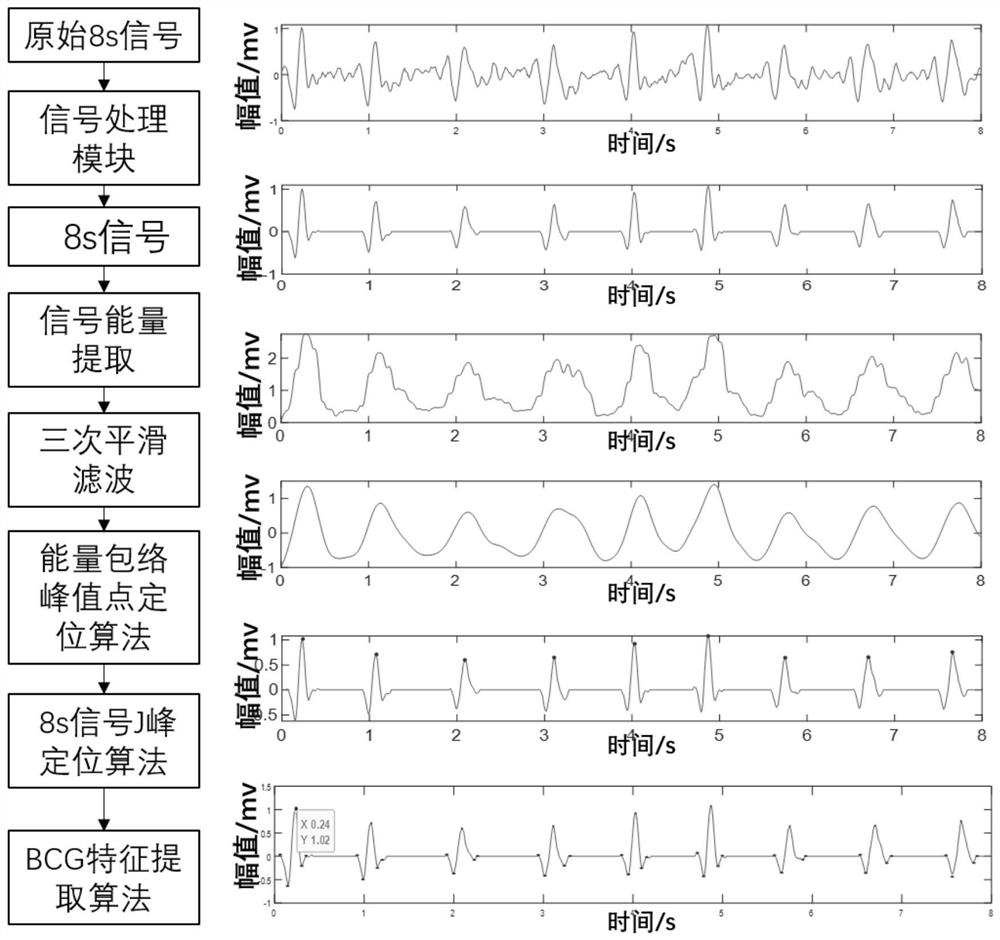
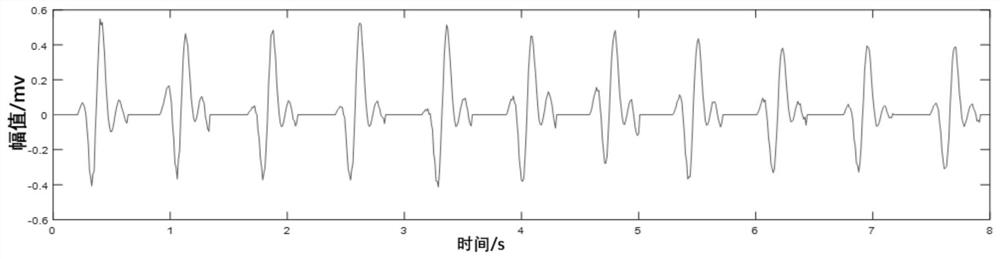
ActiveCN113499059AMulti-cardiac status assessment dataAccurate explanationDiagnostic signal processingSensorsCardiac statusEngineering
The invention discloses a non-contact BCG signal processing system based on optical fiber sensing. The non-contact BCG signal processing system comprises a physiological signal processing module, a signal-to-noise ratio increasing module, a power spectrum frequency obtaining module, an energy envelope wave crest position obtaining module, a key waveform position amplitude obtaining module, a signal normalization processing module and a scatter diagram construction module. According to the invention, after the signal is denoised, the signal is corrected to compensate the influence of the respiratory wave on the BCG signal acquisition process, so that the BCG signal provides more heart state evaluation data.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com