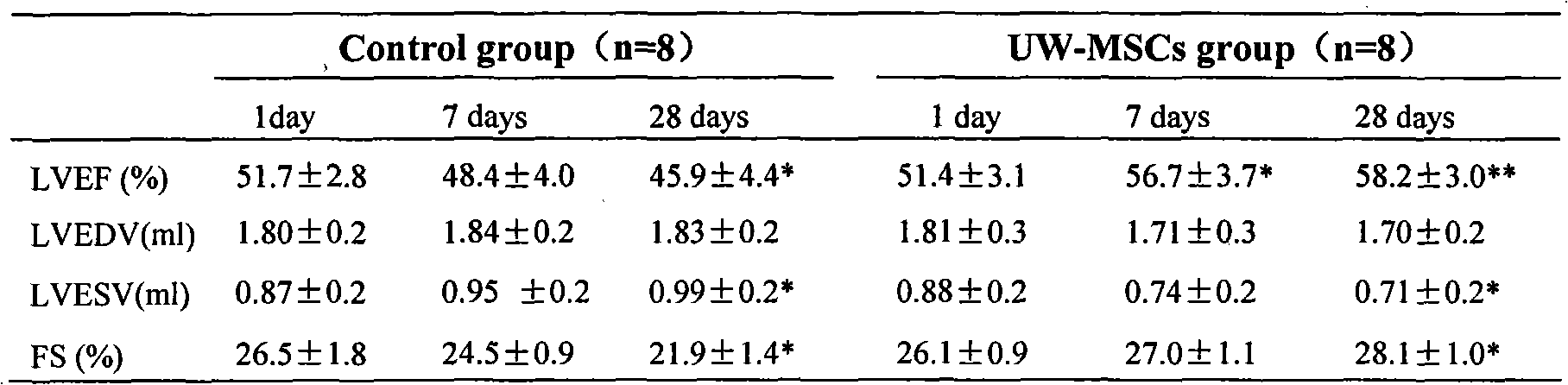Patents
Literature
117 results about "ST segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
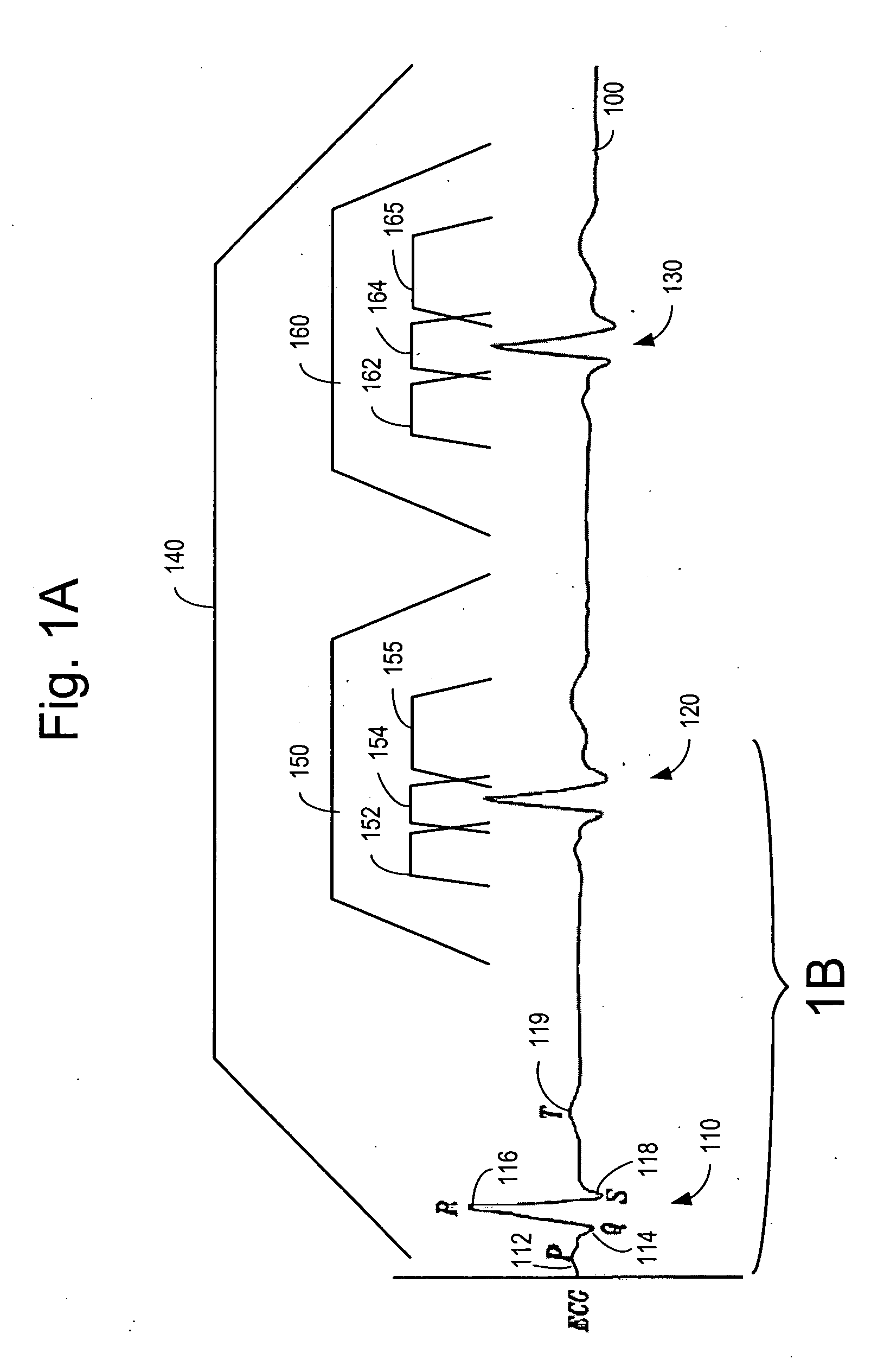
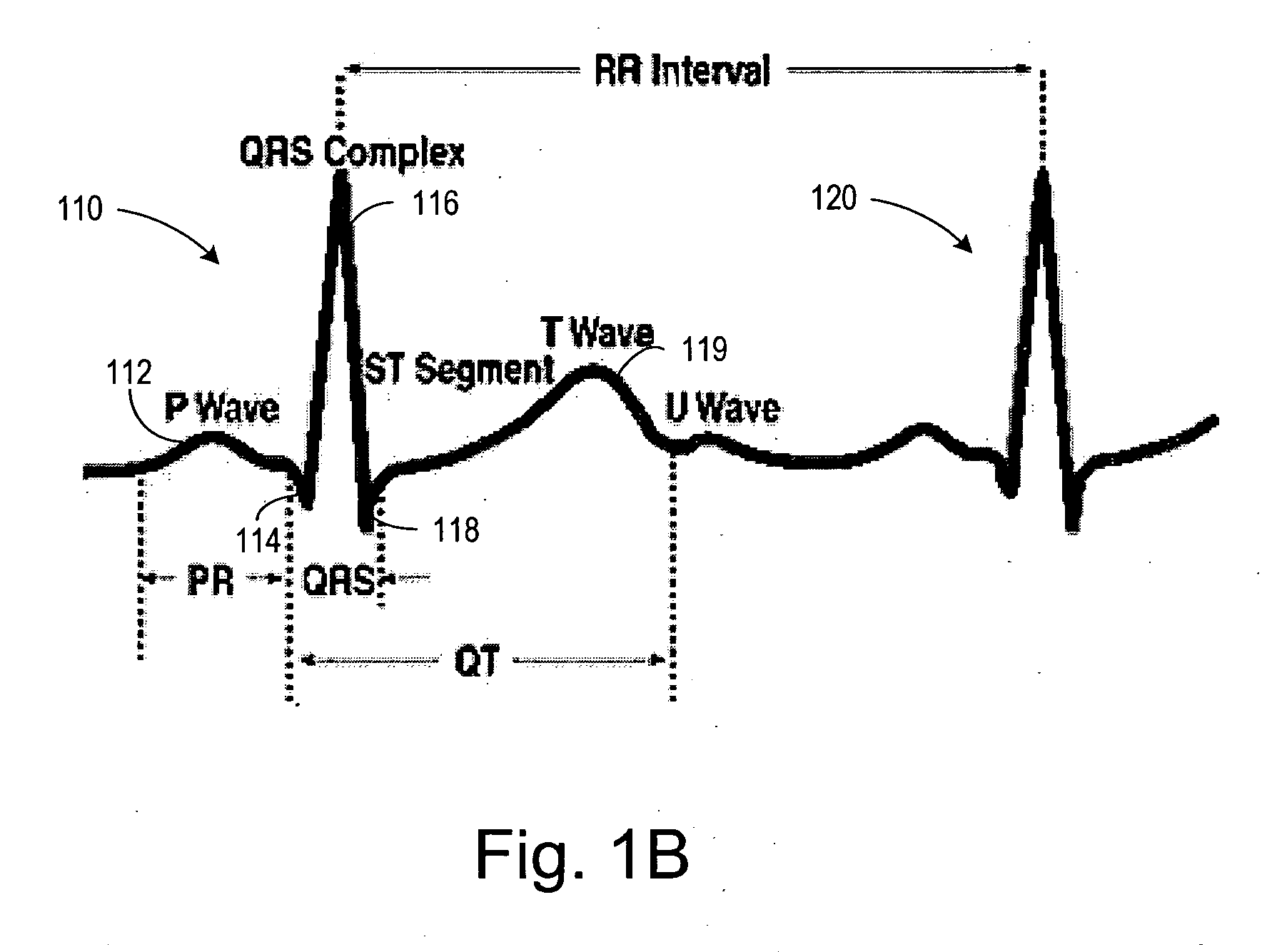
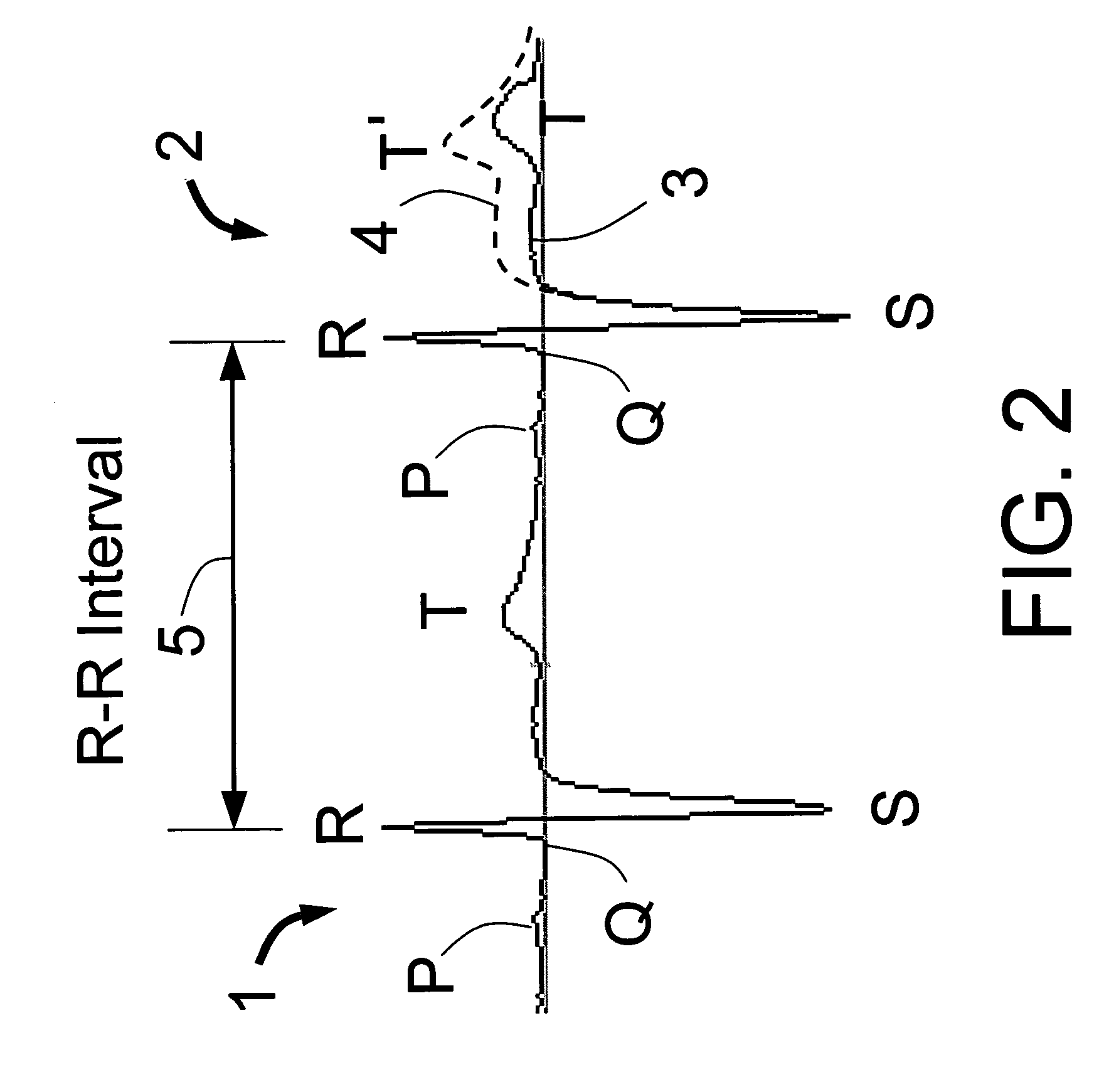
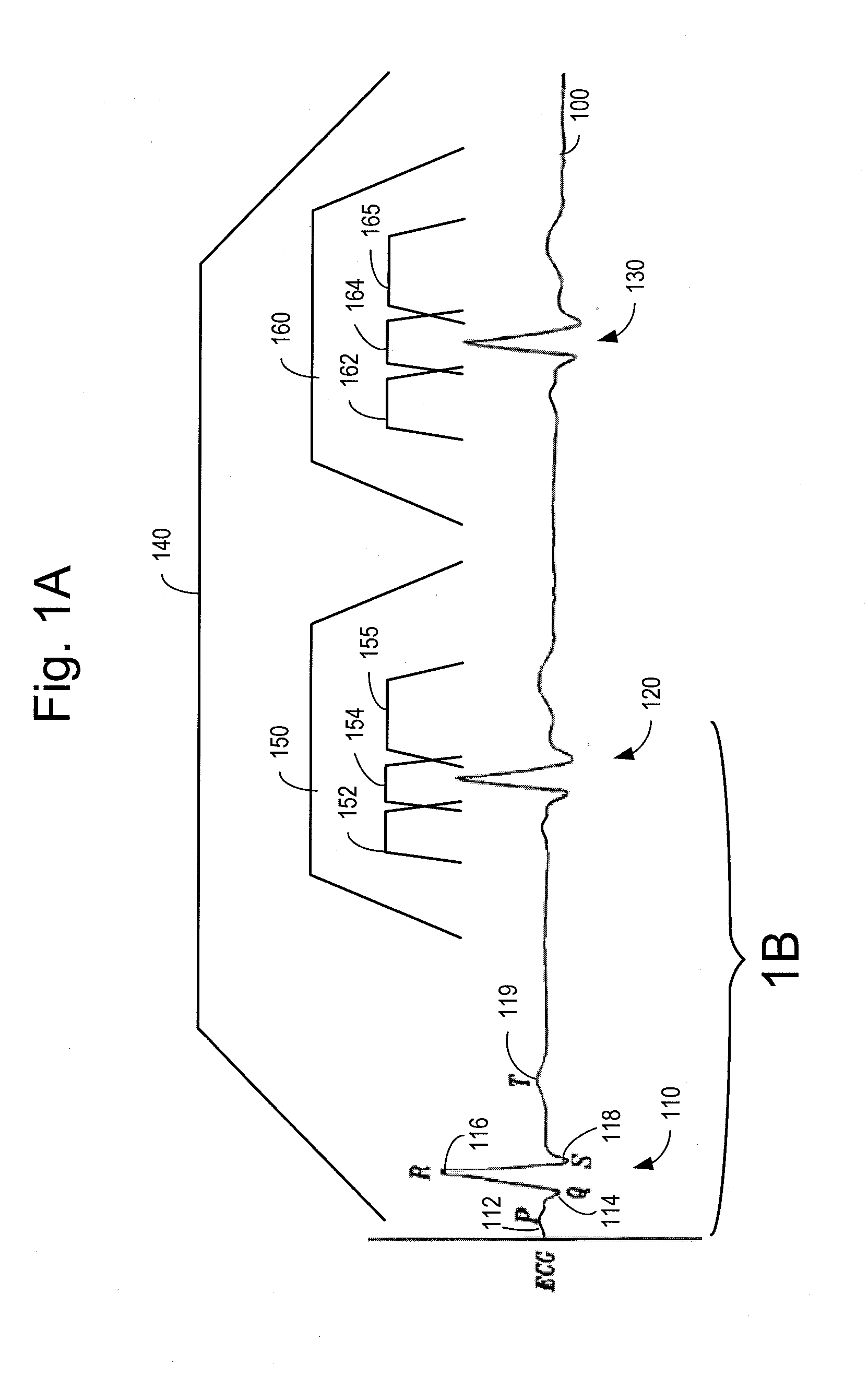
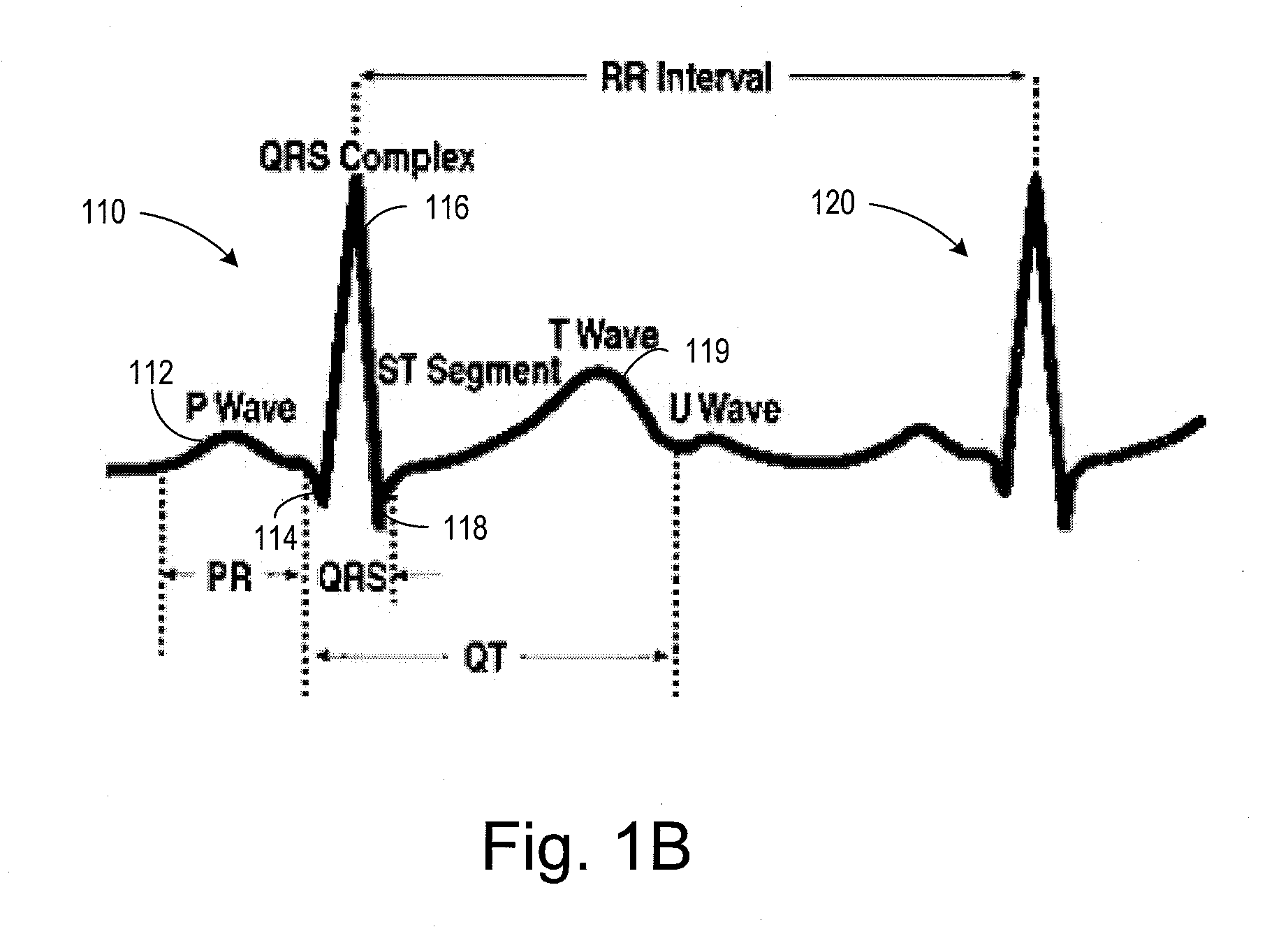
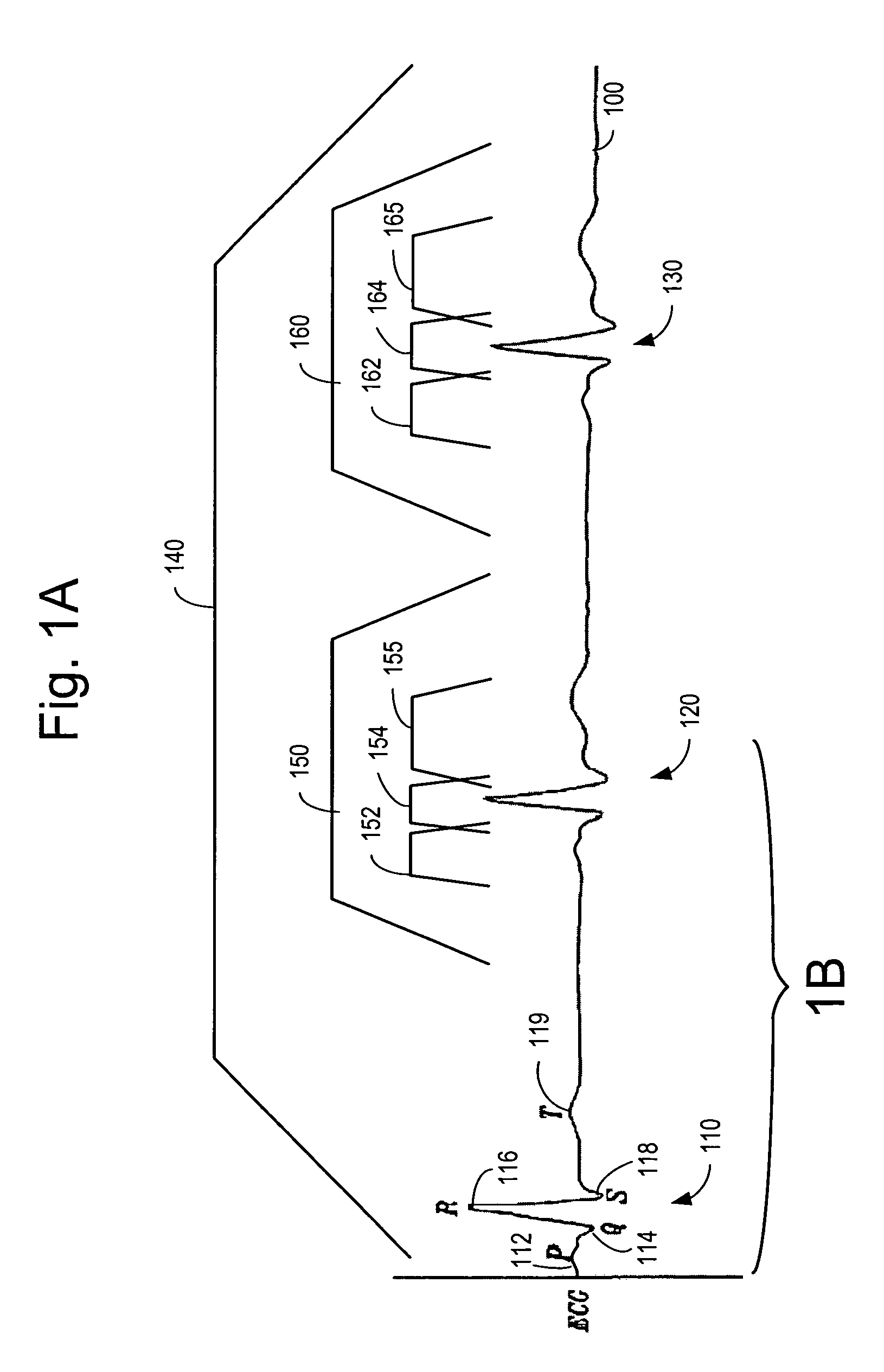
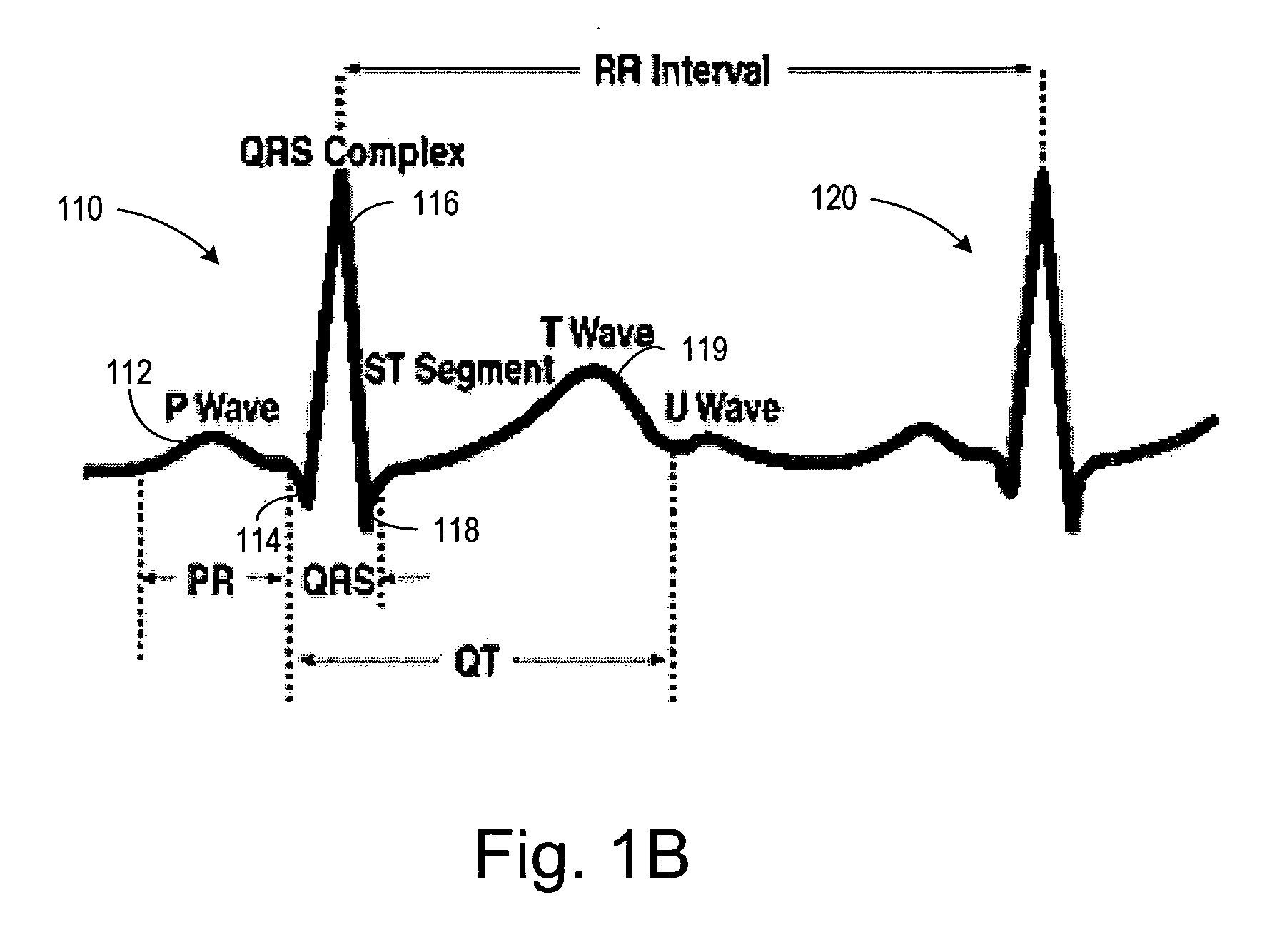
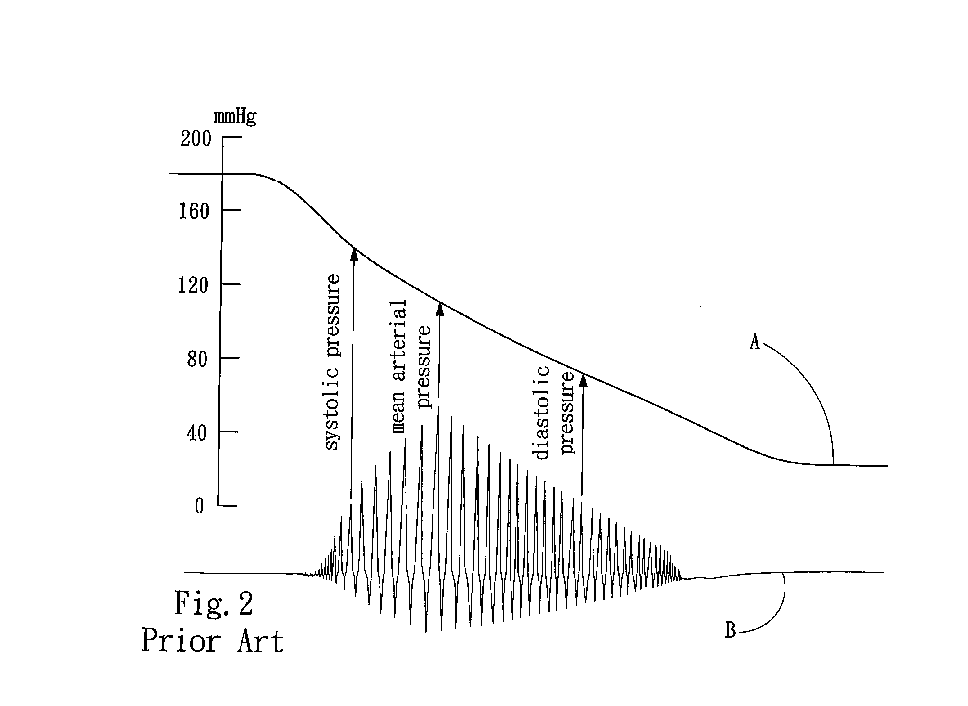
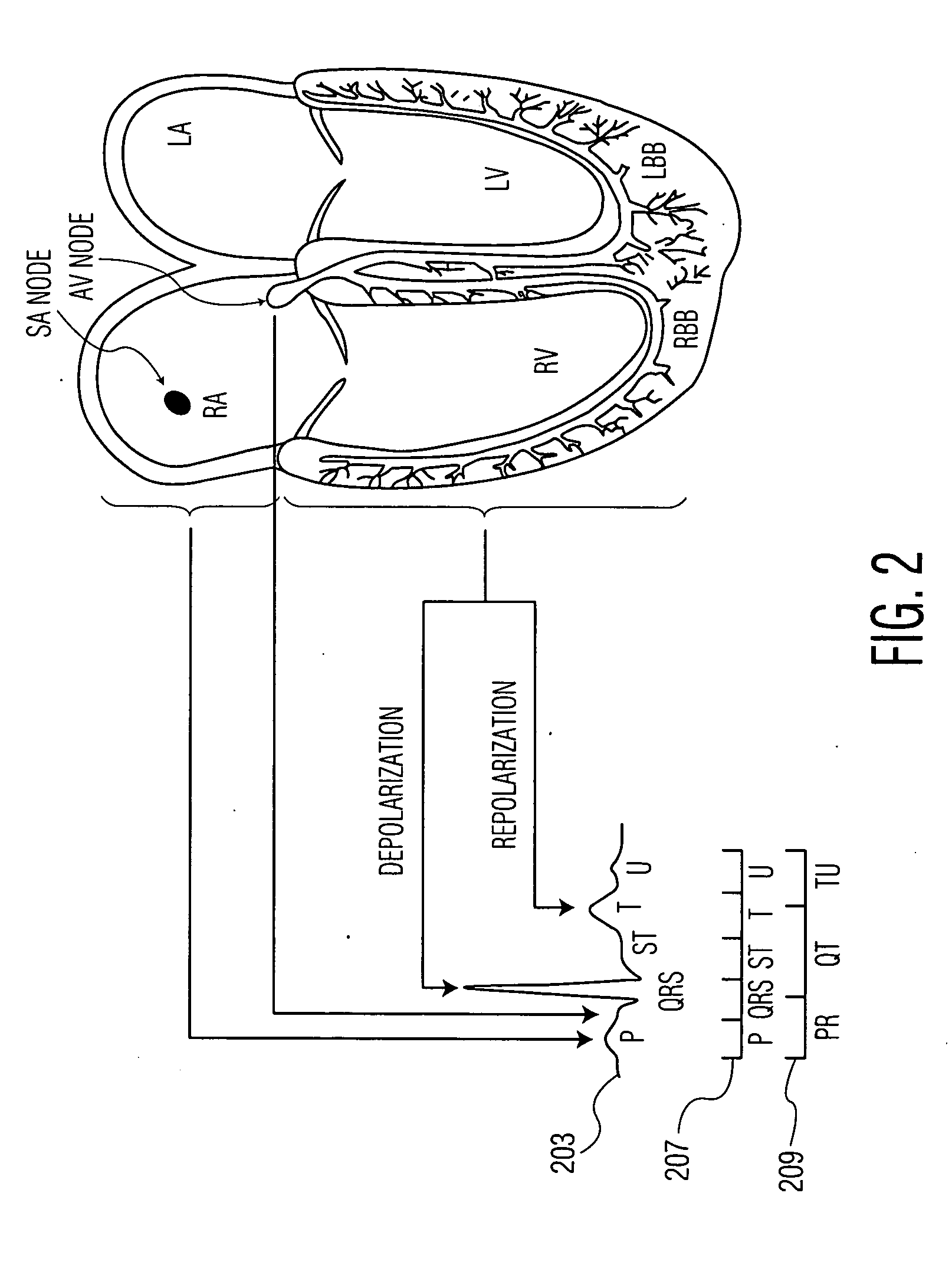
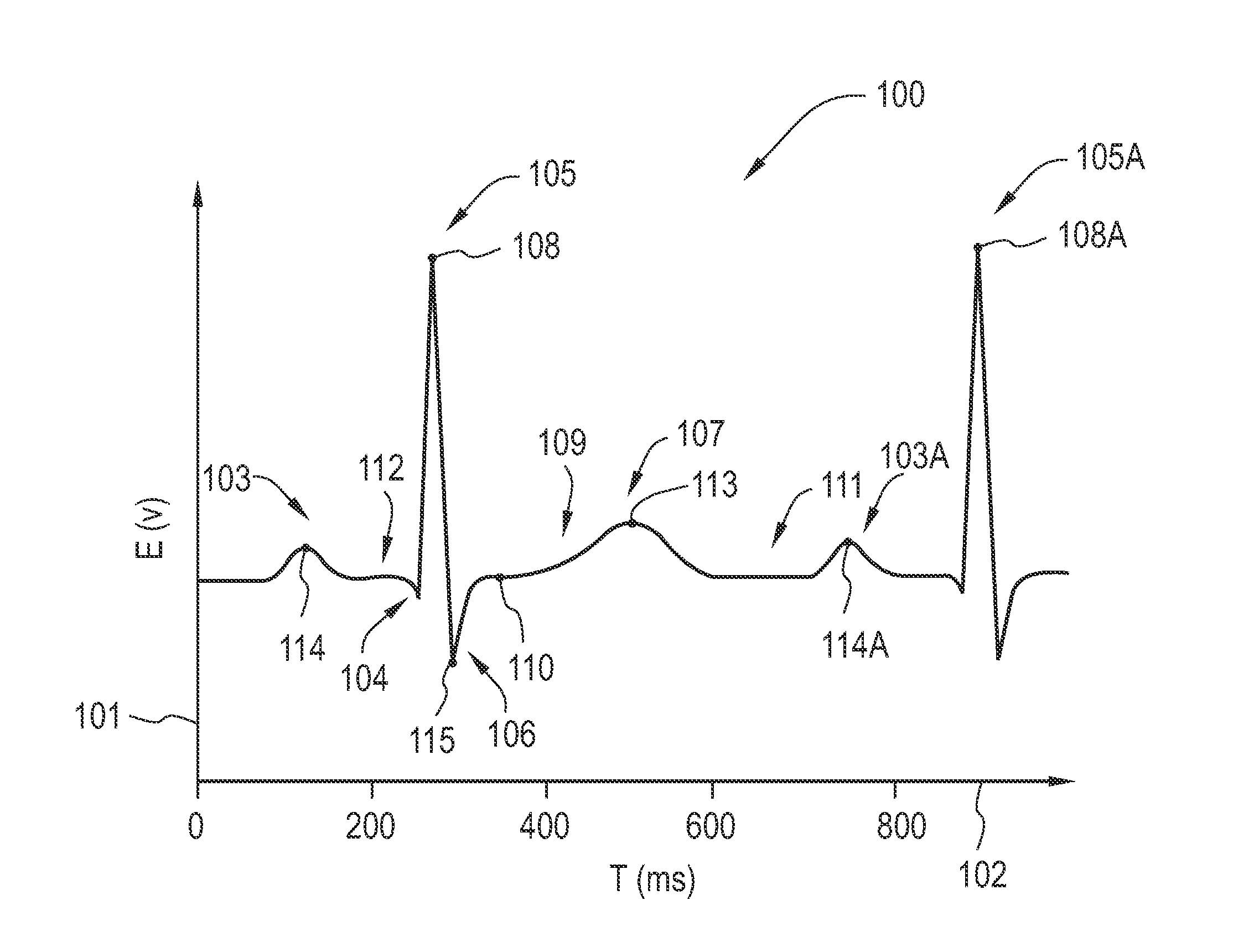
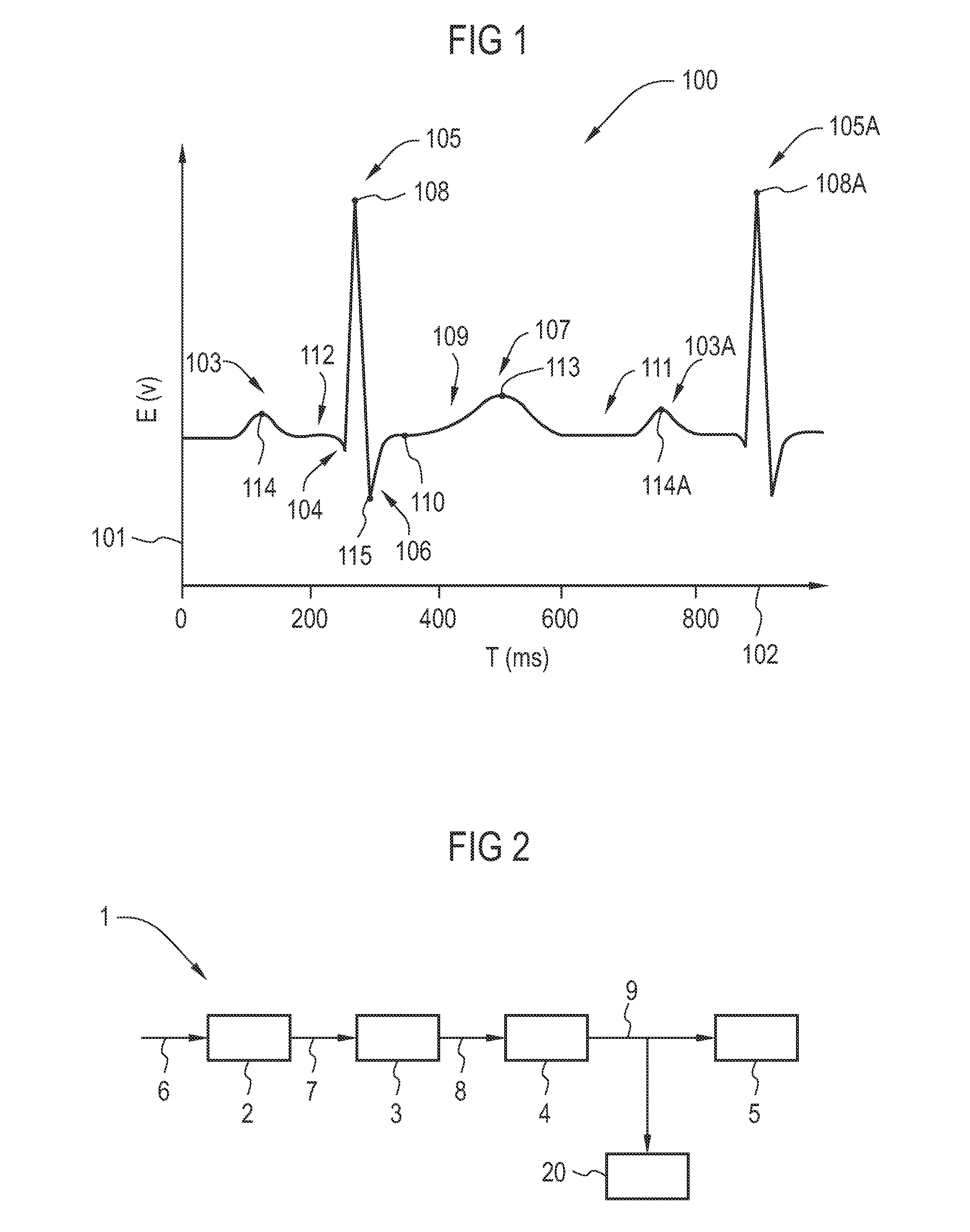
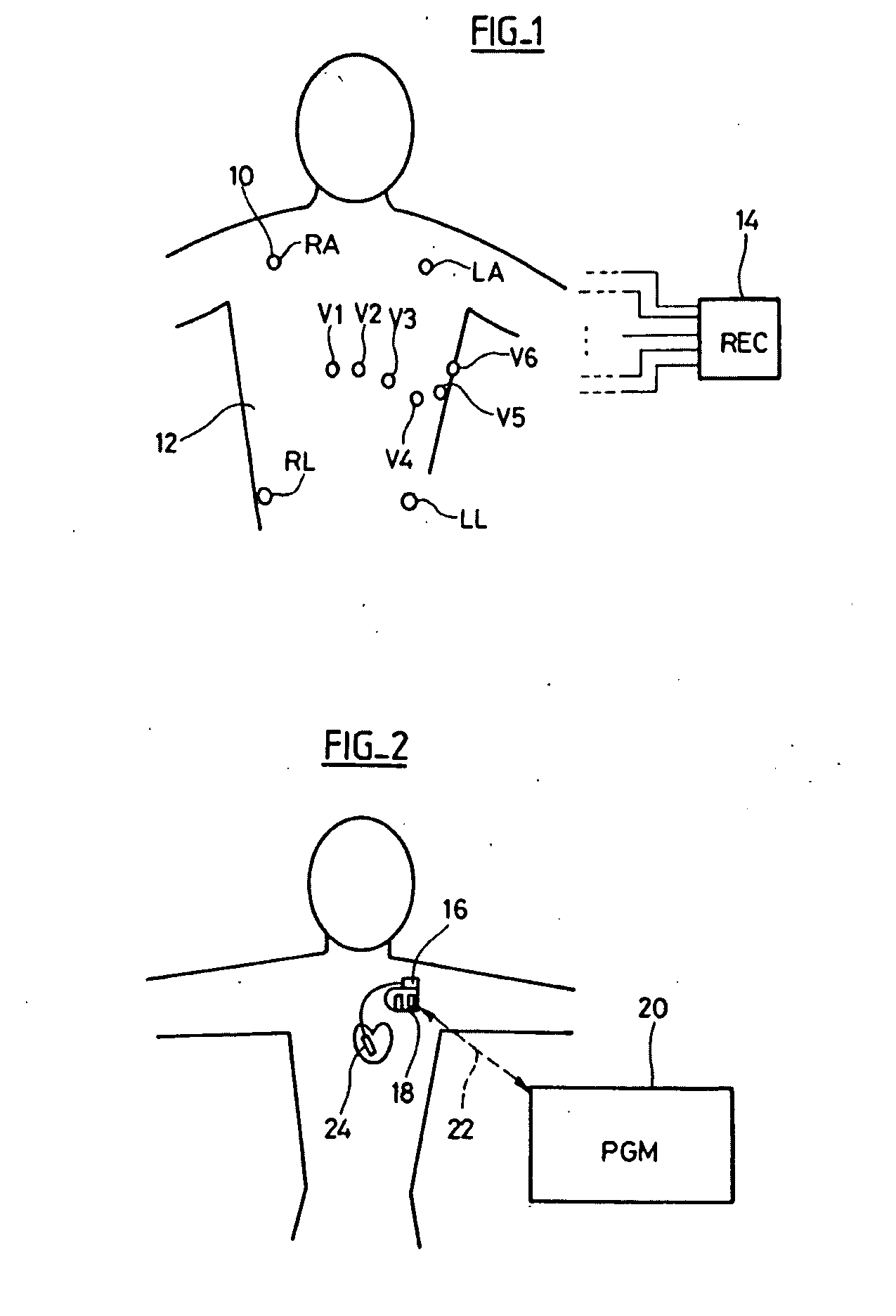
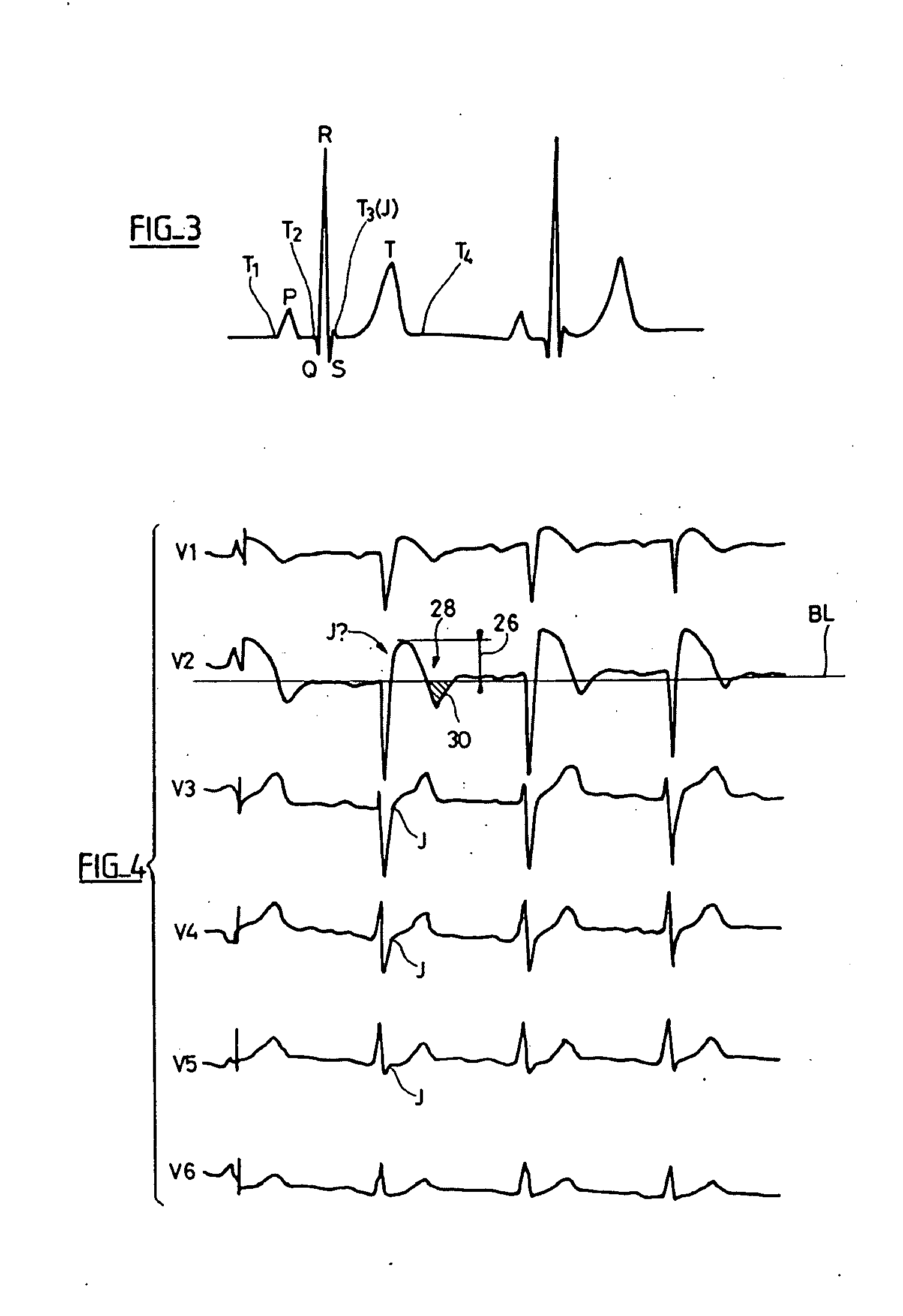
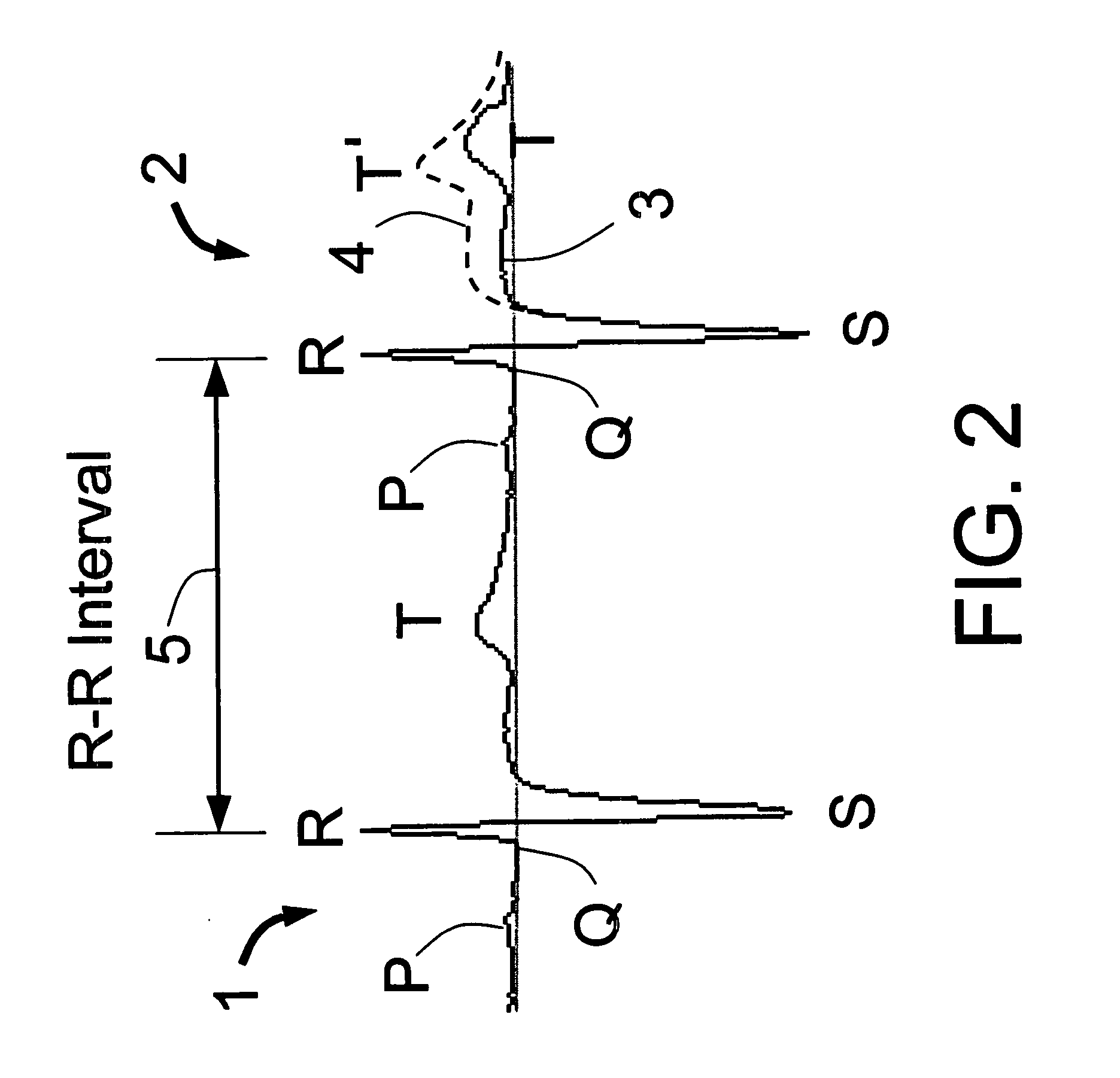
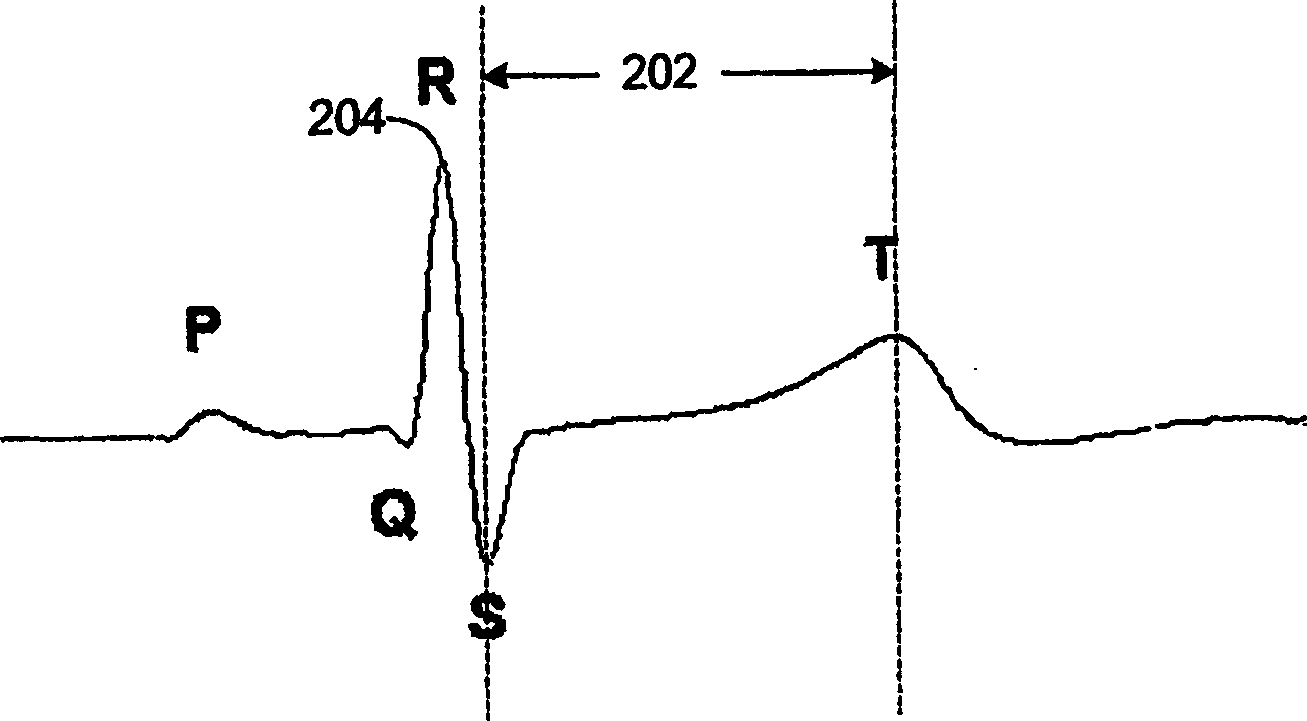
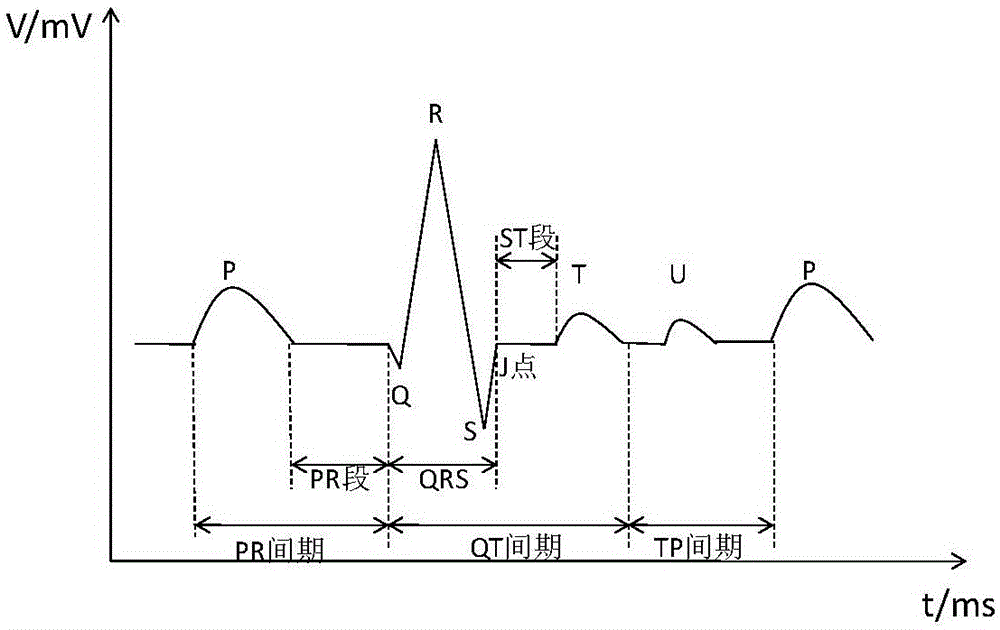
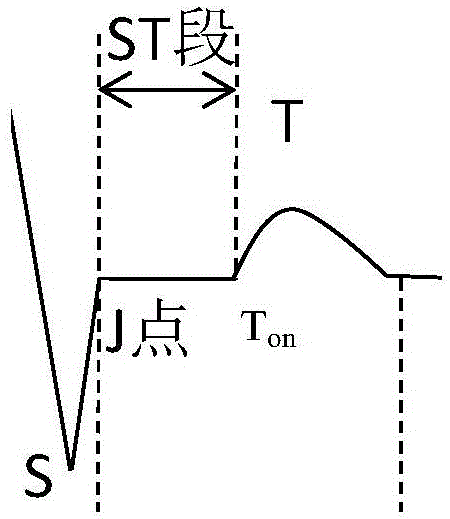
In electrocardiography, the ST segment connects the QRS complex and the T wave and has a duration of 0.005 to 0.150 sec (5 to 150 ms). It starts at the J point (junction between the QRS complex and ST segment) and ends at the beginning of the T wave. However, since it is usually difficult to determine exactly where the ST segment ends and the T wave begins, the relationship between the ST segment and T wave should be examined together. The typical ST segment duration is usually around 0.08 sec (80 ms). It should be essentially level with the PR and TP segments.
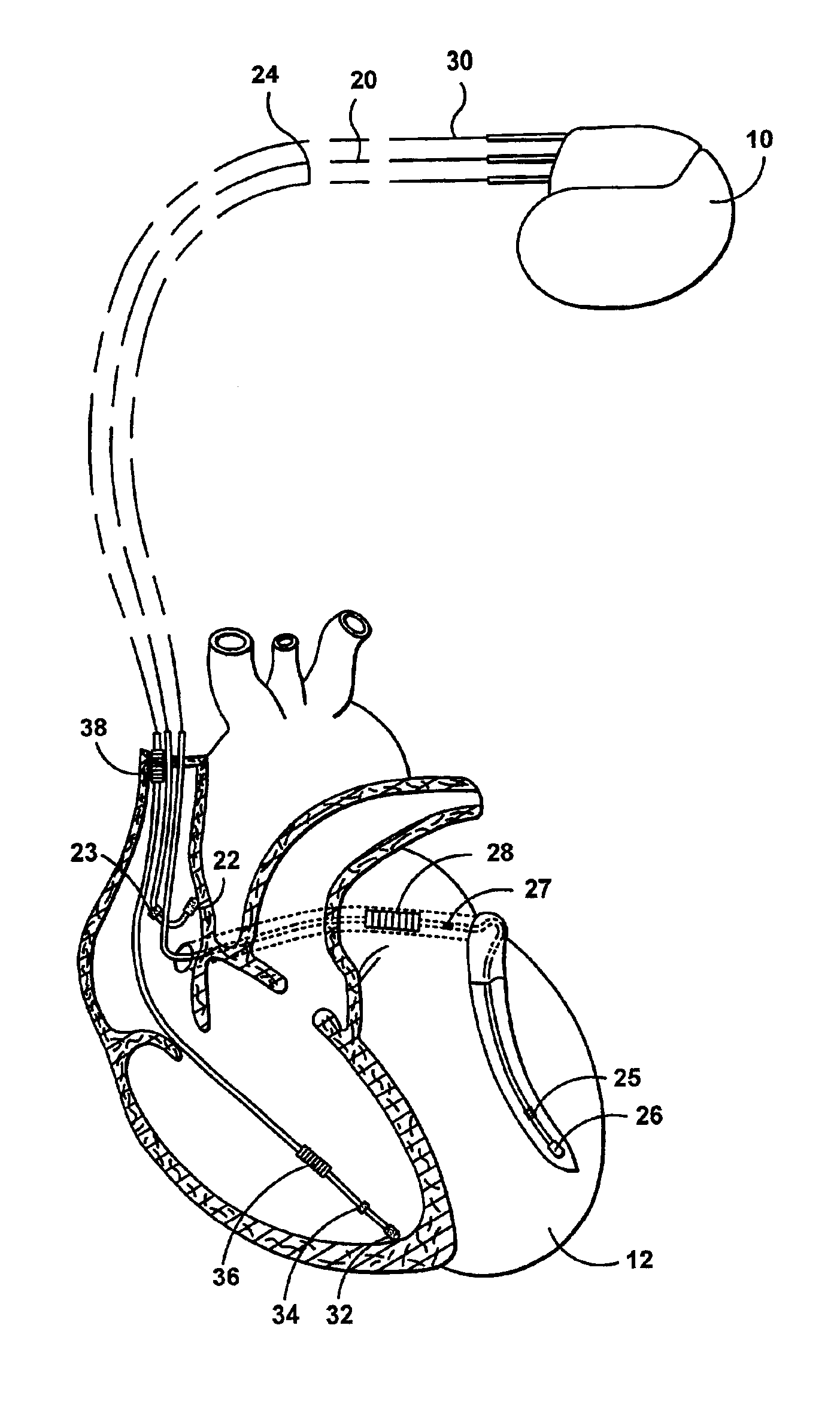
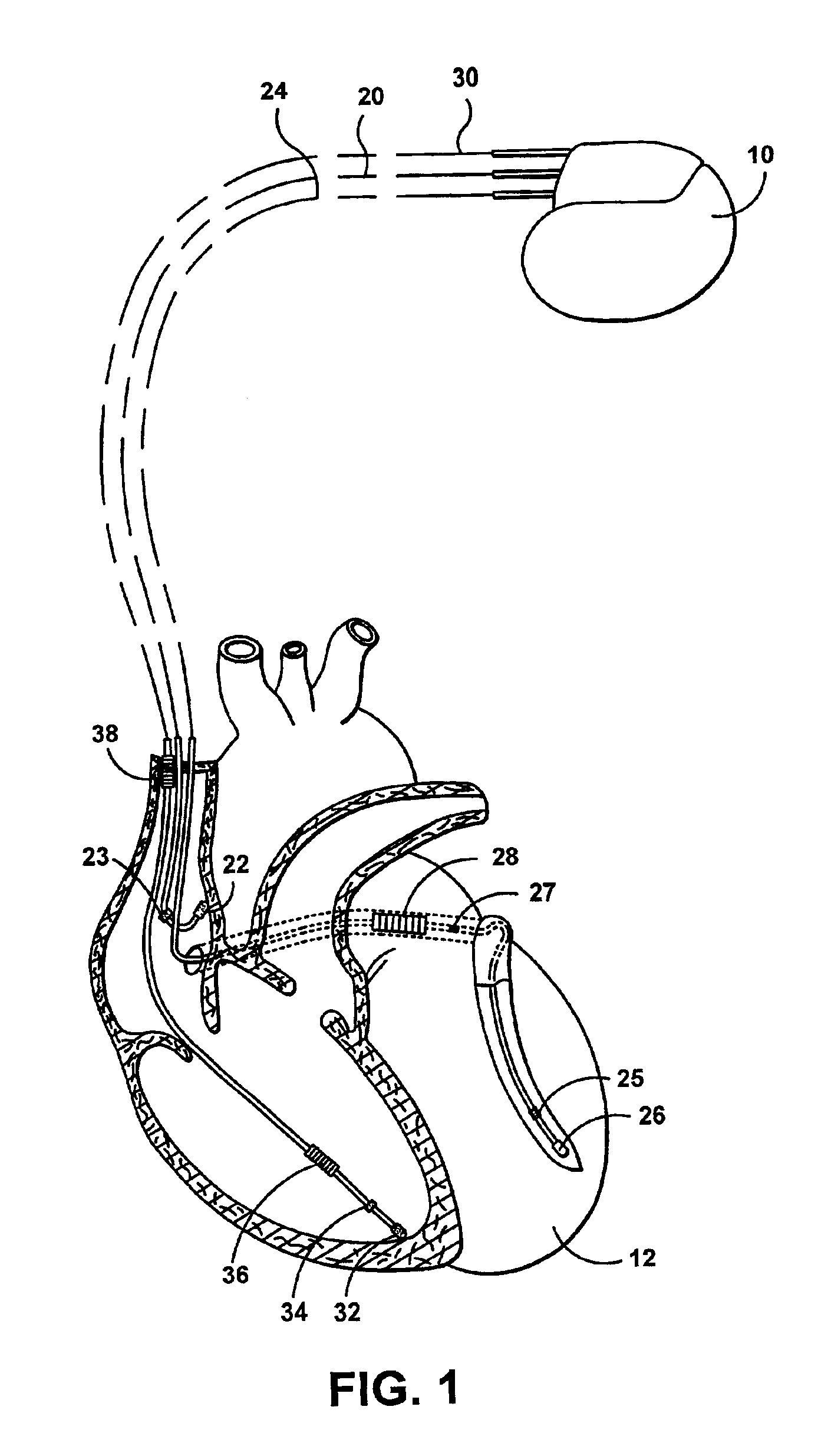
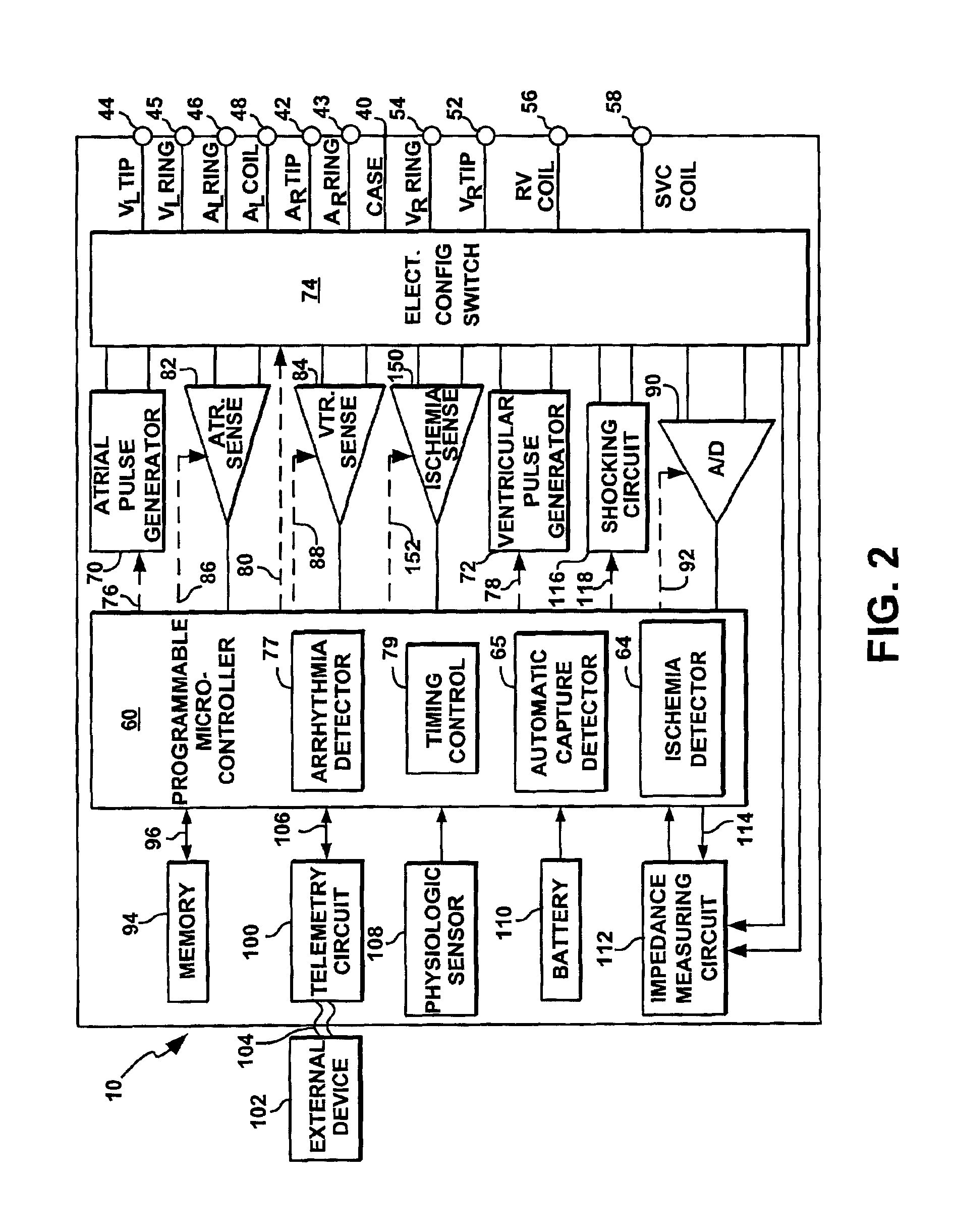
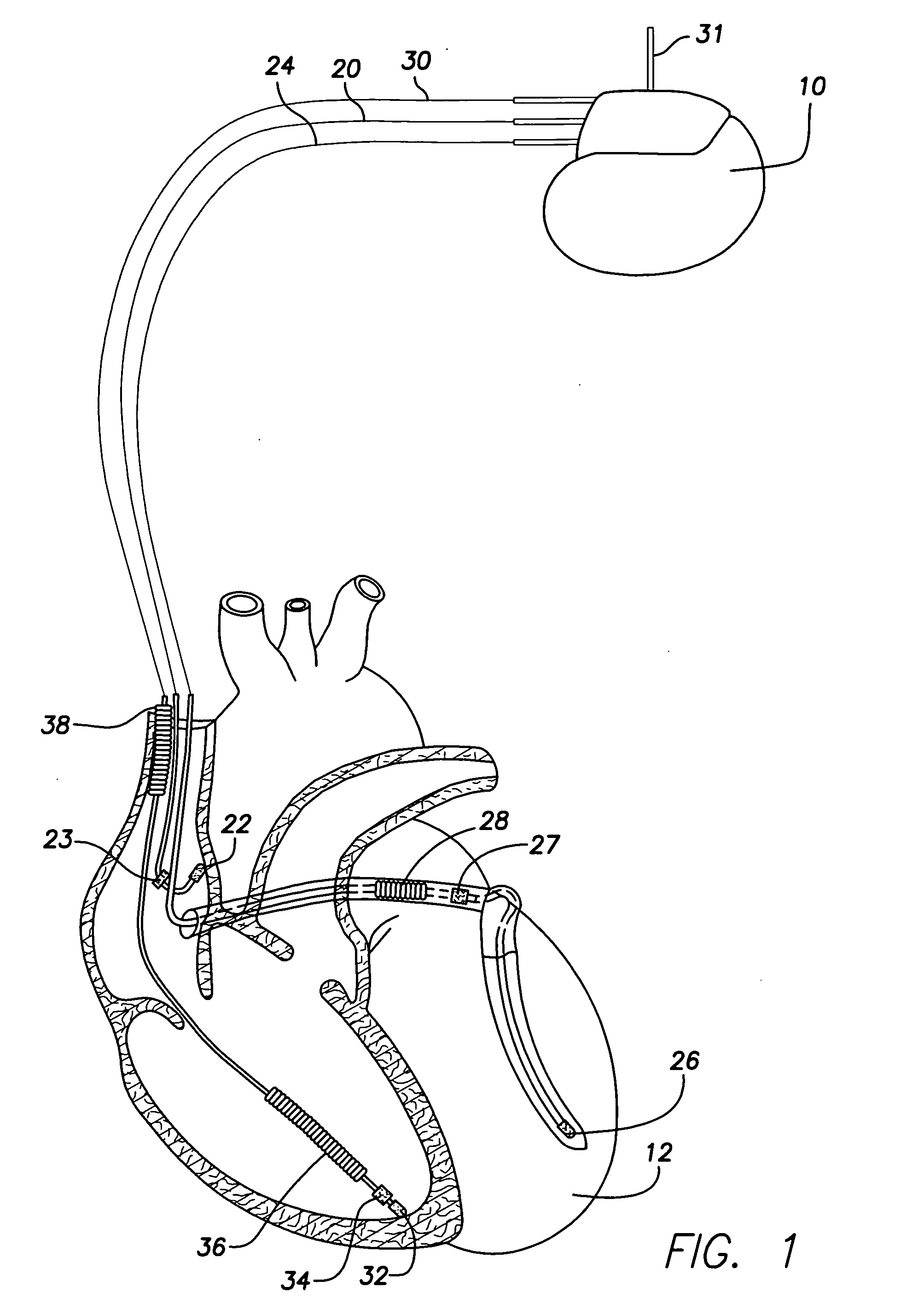
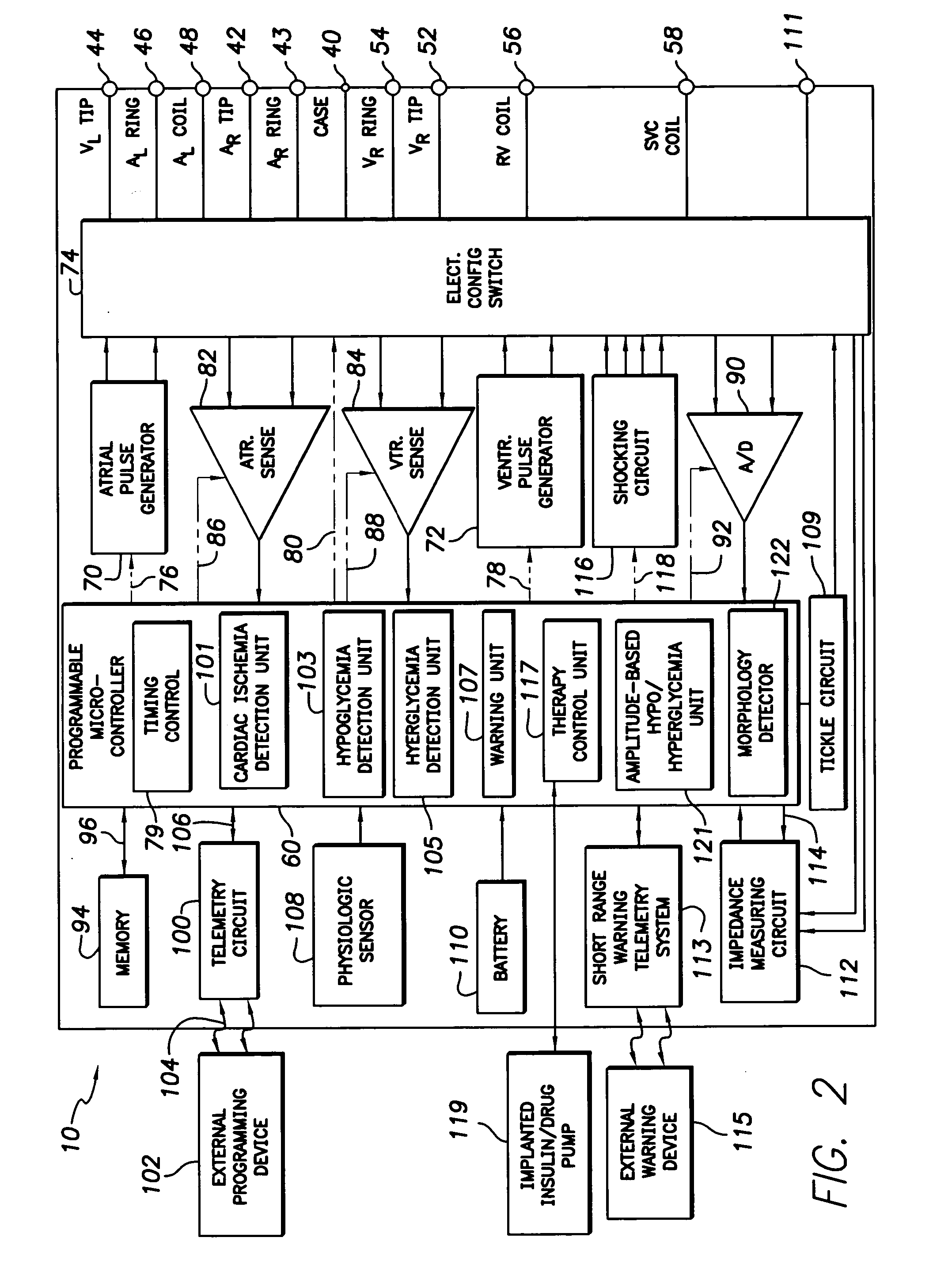
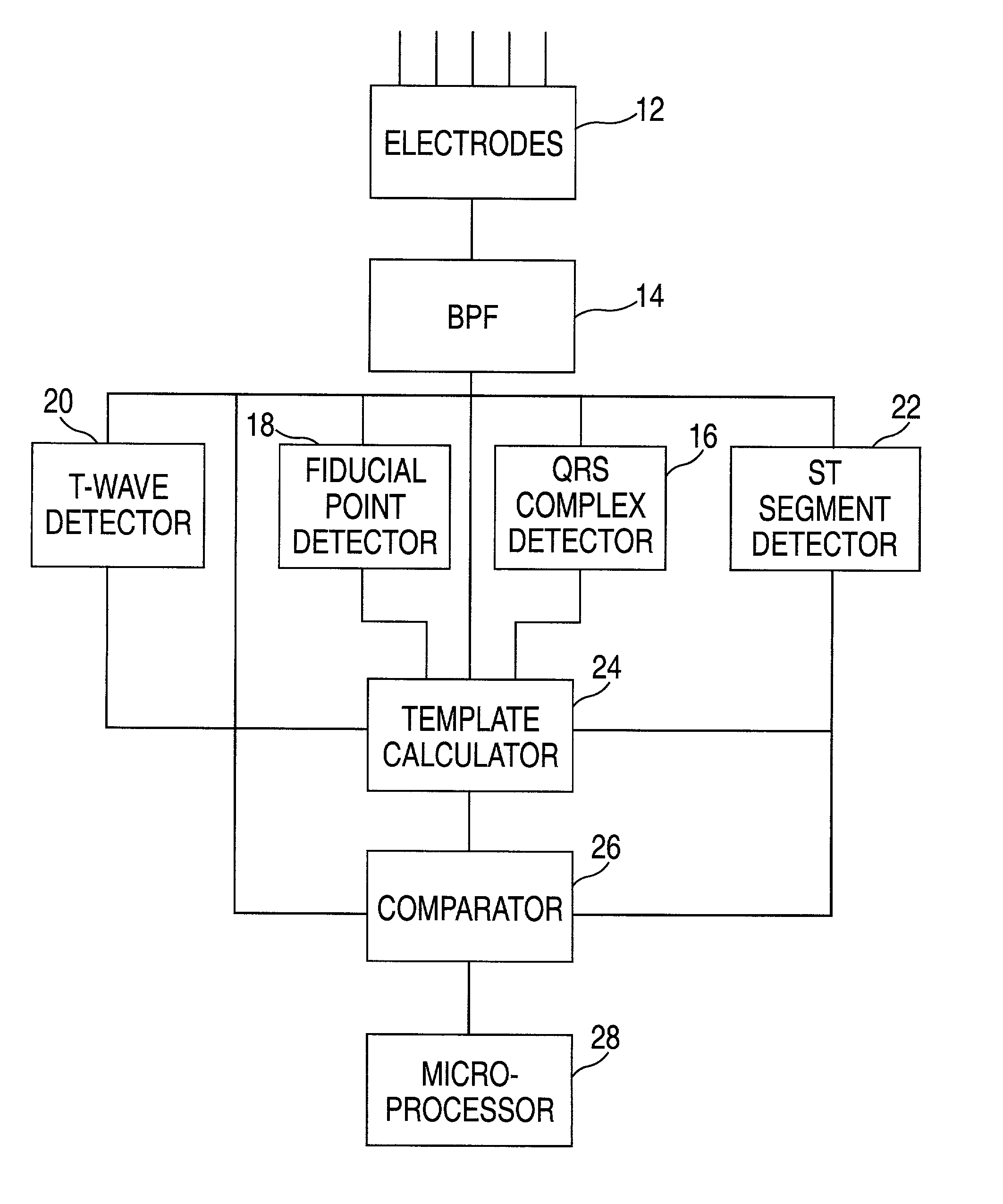
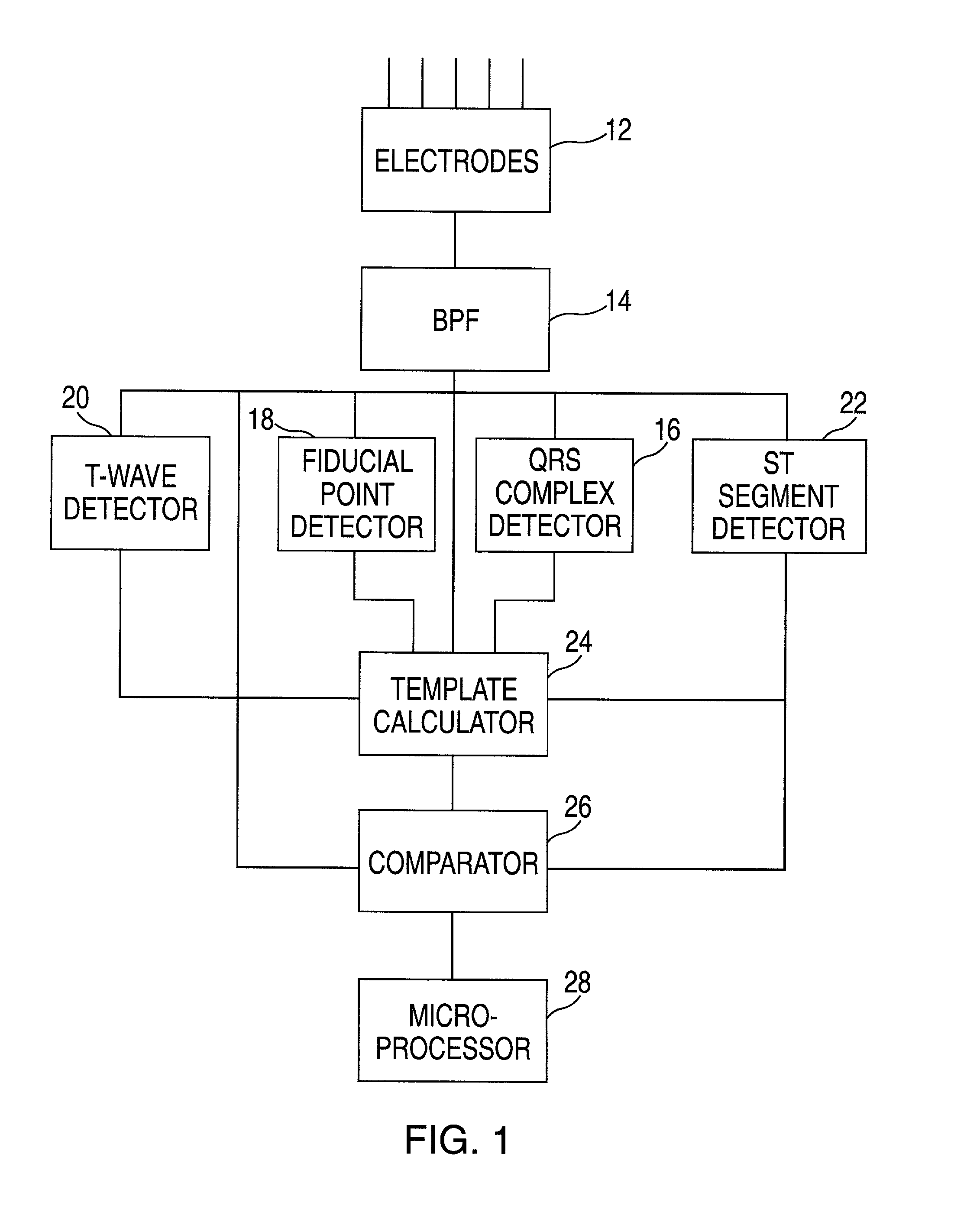
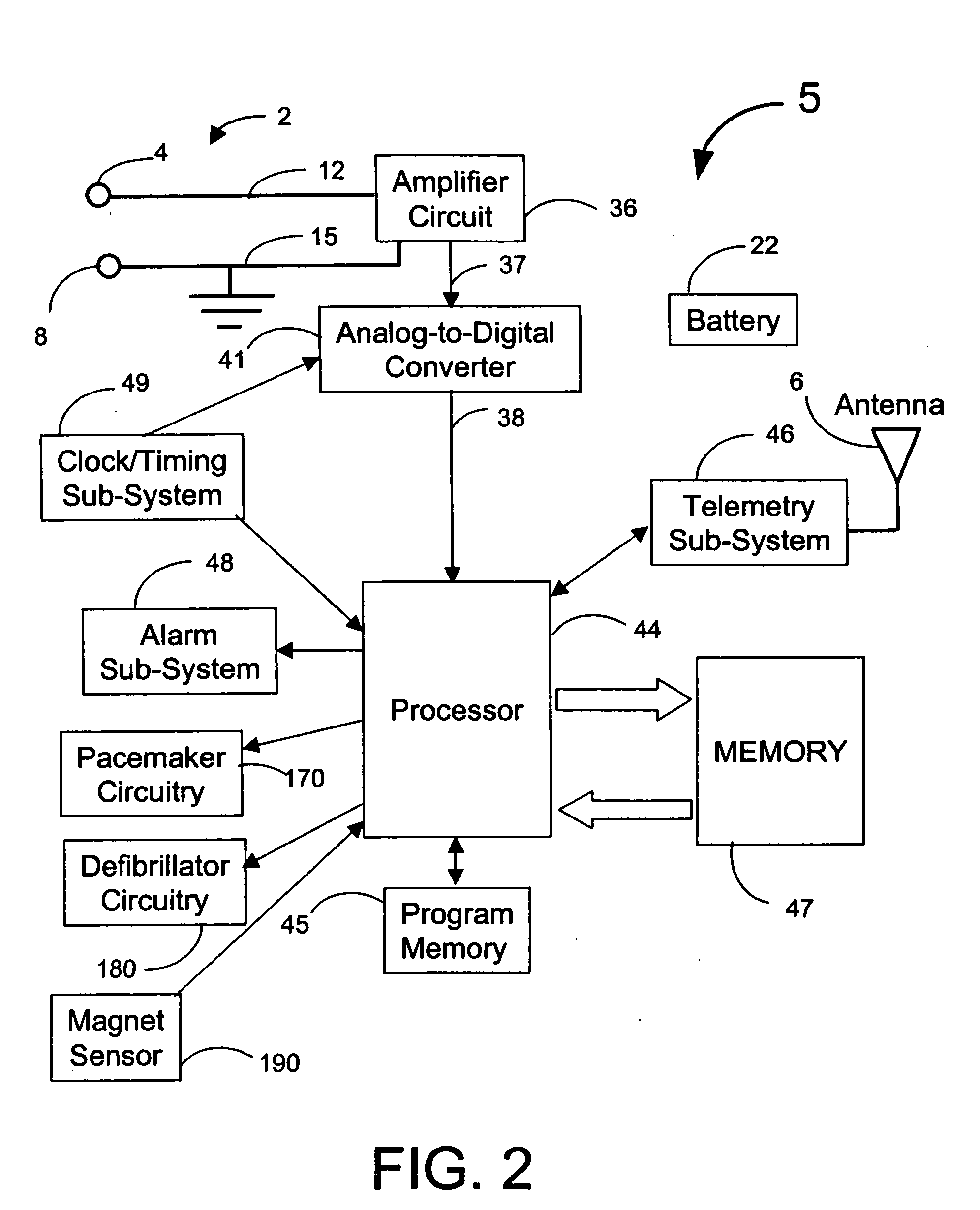
Cardiac stimulation device for optimizing cardiac output with myocardial ischemia protection
InactiveUS6865420B1Reduce demandReduce detectionHeart stimulatorsCardiac muscleIntracardiac Electrogram
A cardiac stimulation device and method detect myocardial ischemia and provide a response for alleviating the ischemia. Myocardial ischemia is detected by identifying changes in the ST-segment of the intracardiac electrogram (EGM) sensed using large sensing electrode surfaces created by electrically coupling one or more cardiac electrodes or by using larger surface area shocking coils. Myocardial ischemia monitoring is performed when stimulation parameters are adjusted for increasing cardiac output, causing an increased metabolic demand to be placed on the myocardium itself. When myocardial ischemia is detected, stimulation parameters are re-adjusted to reduce the demand placed on the myocardium and thereby alleviate the ischemia.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Cardiac activation sequence monitoring for ischemia detection
InactiveUS20060116593A1Convenient wireless communicationElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsImplantable ElectrodesCardiac cycle
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed to detect, monitor, track and / or trend ischemia using cardiac activation sequence information. Ischemia detection may involve sensing composite cardiac signals using implantable electrodes, and performing a signal separation that produces one or more cardiac activation signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences. A change in the signal vector may be detected using subsequent separations. The change may be an elevation or depression of the ST segment of a cardiac cycle or other change indicative of myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, or other pathological change. The change may be used to predict, quantify, and / or qualify an event such as an arrhythmia, a myocardial infarction, or other pathologic change. Information associated with the vectors may be stored and used to track the vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
System and methods for detecting ischemia with a limited extracardiac lead set
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions from a reduced number of extracardiac leads. A right side lead measures the electrical signal between the middle superior chest region over the heart and inferior right torso position. A left side lead measures the electrical signal between the left precordial chest region and an inferior left lateral or posterior torso position. The lead montage is preferably chosen so that, regardless of patient position (e.g. supine, upright), negative ST segments and / or T waves are used to detect right coronary or left circumflex ischemia. Also, in these positions, reduced slope of the final deflection in the QRS can be used to detect these types of ischemia. To detect transmural ischemia, the system examines changes in QRS slopes, ST segment, T wave and the difference between the J point and the PQ potentials. In addition, for transmural ischemia associated with the left anterior descending artery, a proxy for the propagation time across the front of the heart is examined by comparing QRS features of the right side lead with QRS features of the left side lead. Histogram profiles, trends, and statistical summaries, especially running averages, of all of the above mentioned features, corrected for heart rate, are maintained.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
System and methods for sliding-scale cardiac event detection
A system for the detection of cardiac events occurring in a human patient is provided. At least two electrodes are included in the system for obtaining an electrical signal from a patient's heart. An electrical signal processor is electrically coupled to the electrodes for processing the electrical signal. The system determines the presence of a cardiovascular condition by applying a sliding scale rule to heart signal feature values. When the cardiovascular condition is ischemia, the ST segment may be analyzed. A sliding scale is applied to ST segment shifts such that when the magnitudes of ST segment shifts are relatively small, a larger number of beats is required to detect ischemia compared to the case when the magnitudes of ST shifts are large.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
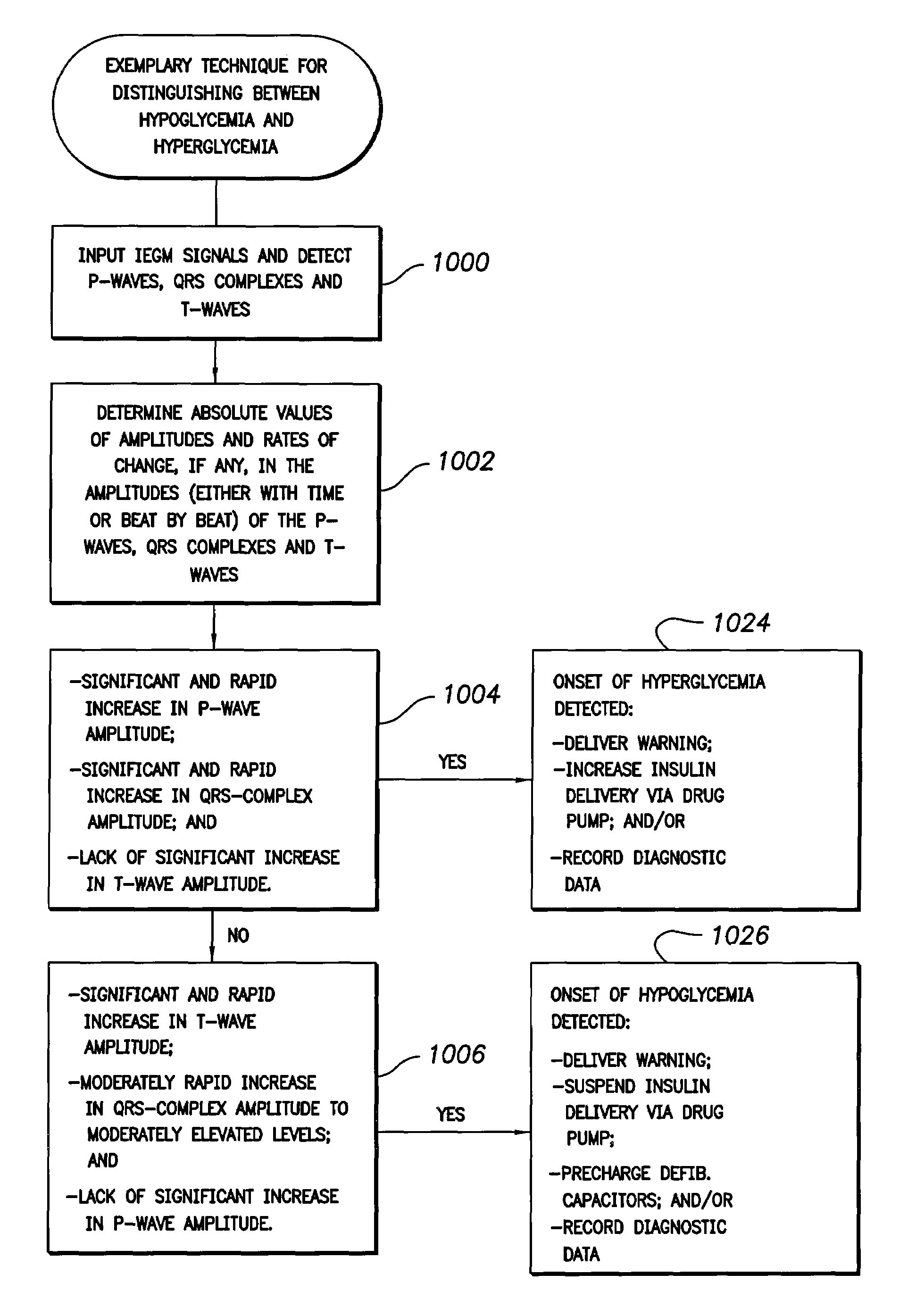
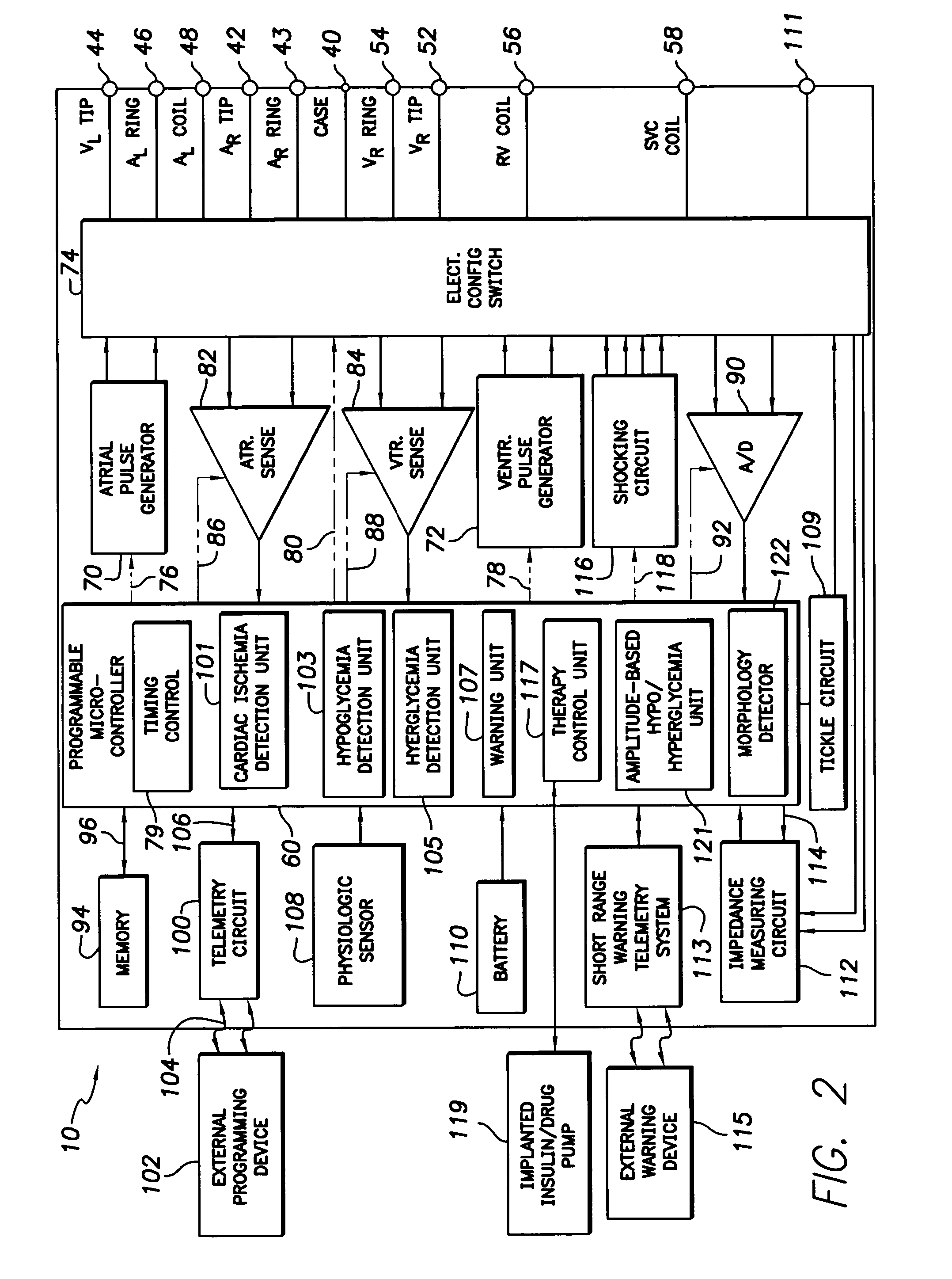
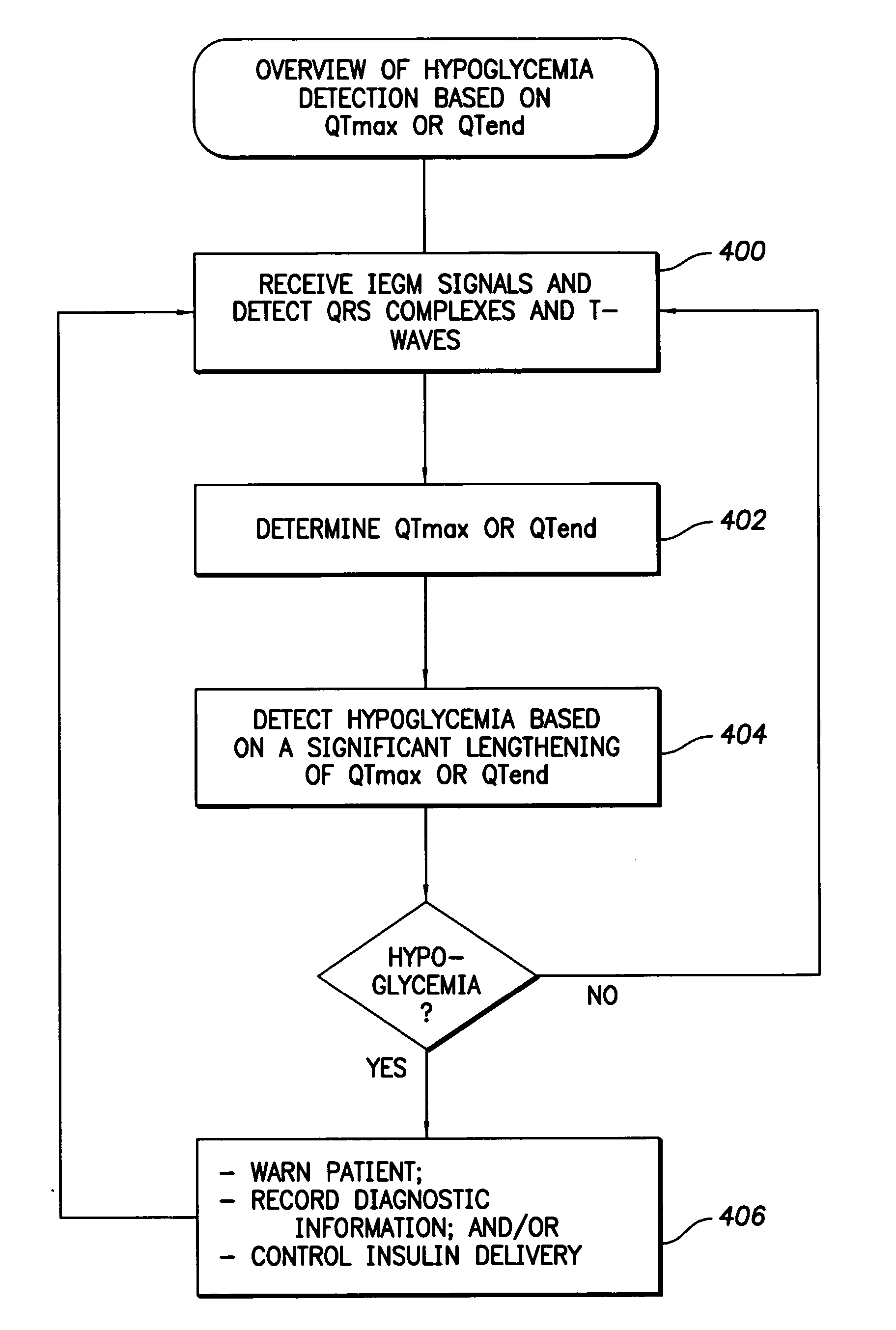
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS7524287B2Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
System and method for distinguishing between hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia using an implantable medical device
ActiveUS20060167365A1Improve blood sugar controlReduce deliveryElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyAcute hyperglycaemiaT wave
Techniques are described for detecting and distinguishing among ischemia, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia based on intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals. In one technique, these conditions are detected and distinguished based on an analysis of: the interval between the QRS complex and the peak of a T-wave (QTmax), the interval between the QRS complex and the end of a T-wave (QTend), alone or in combination with a change in ST segment elevation. By exploiting QTmax and QTend in combination with ST segment elevation, changes in ST segment elevation caused by hypo / hyperglycemia can be properly distinguished from changes caused by cardiac ischemia. In another technique, hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia are predicted, detected and / or distinguished from one another based on an analysis of the amplitudes of P-waves, QRS-complexes and T-waves within the IEGM. Appropriate warning signals are delivered and therapy is automatically adjusted.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Means and method for the detection of cardiac events
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Cardiac Activation Sequence Monitoring for Ischemia Detection
InactiveUS20100298729A1Convenient wireless communicationElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsImplantable ElectrodesCardiac cycle
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed to detect, monitor, track and / or trend ischemia using cardiac activation sequence information. Ischemia detection may involve sensing composite cardiac signals using implantable electrodes, and performing a signal separation that produces one or more cardiac activation signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences. A change in the signal vector may be detected using subsequent separations. The change may be an elevation or depression of the ST segment of a cardiac cycle or other change indicative of myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, or other pathological change. The change may be used to predict, quantify, and / or qualify an event such as an arrhythmia, a myocardial infarction, or other pathologic change. Information associated with the vectors may be stored and used to track the vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Integrated physiological signal assessing device
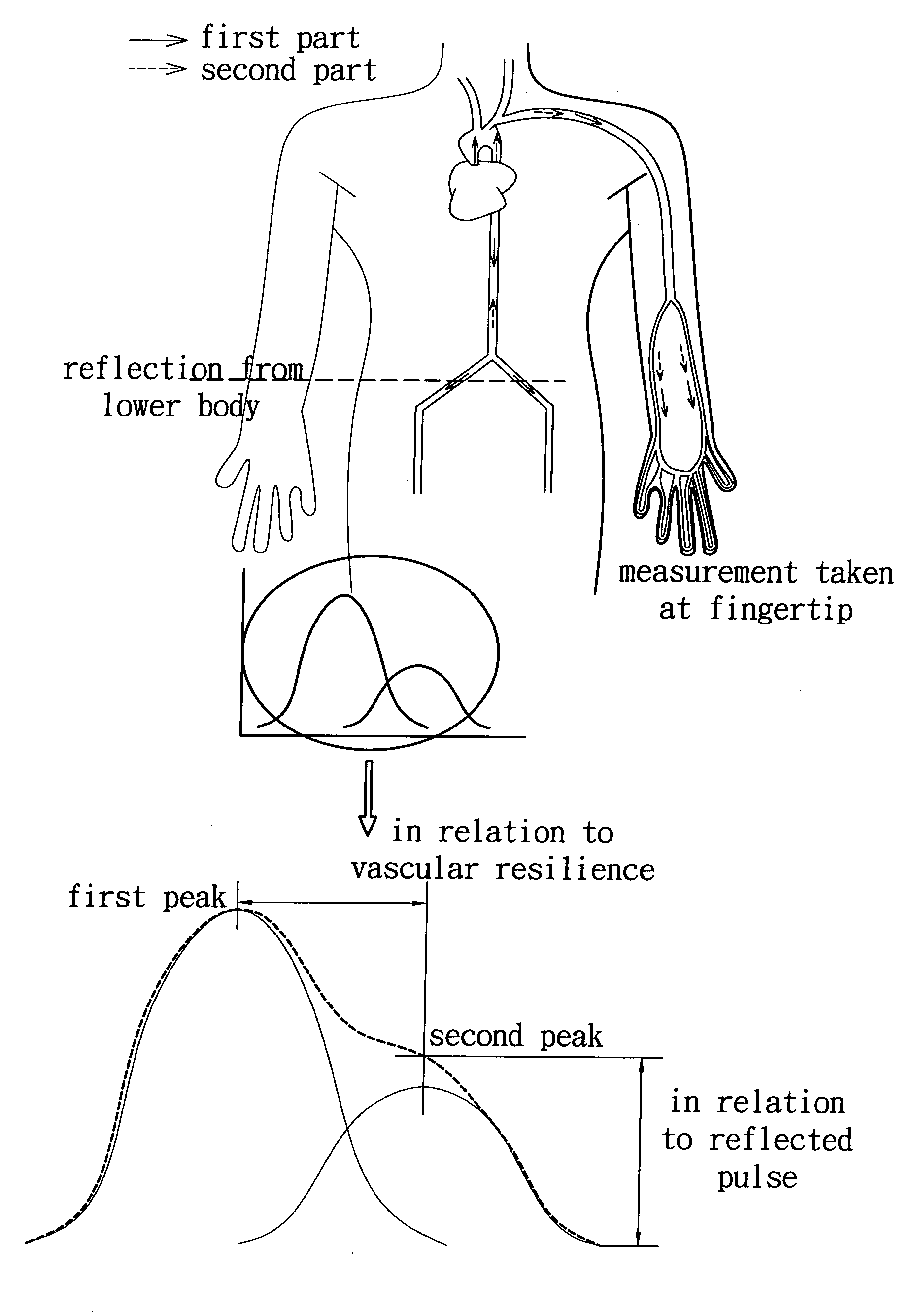
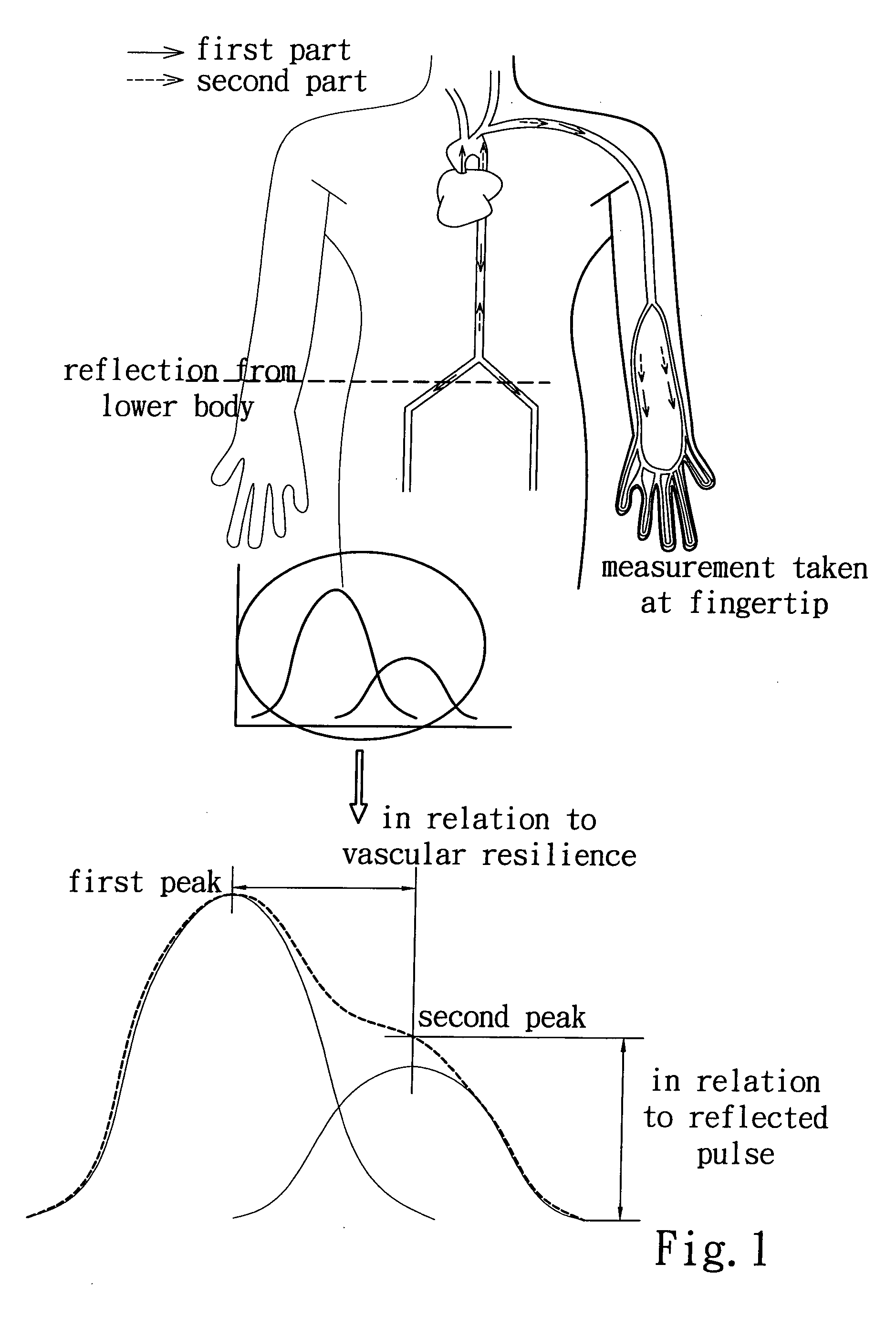
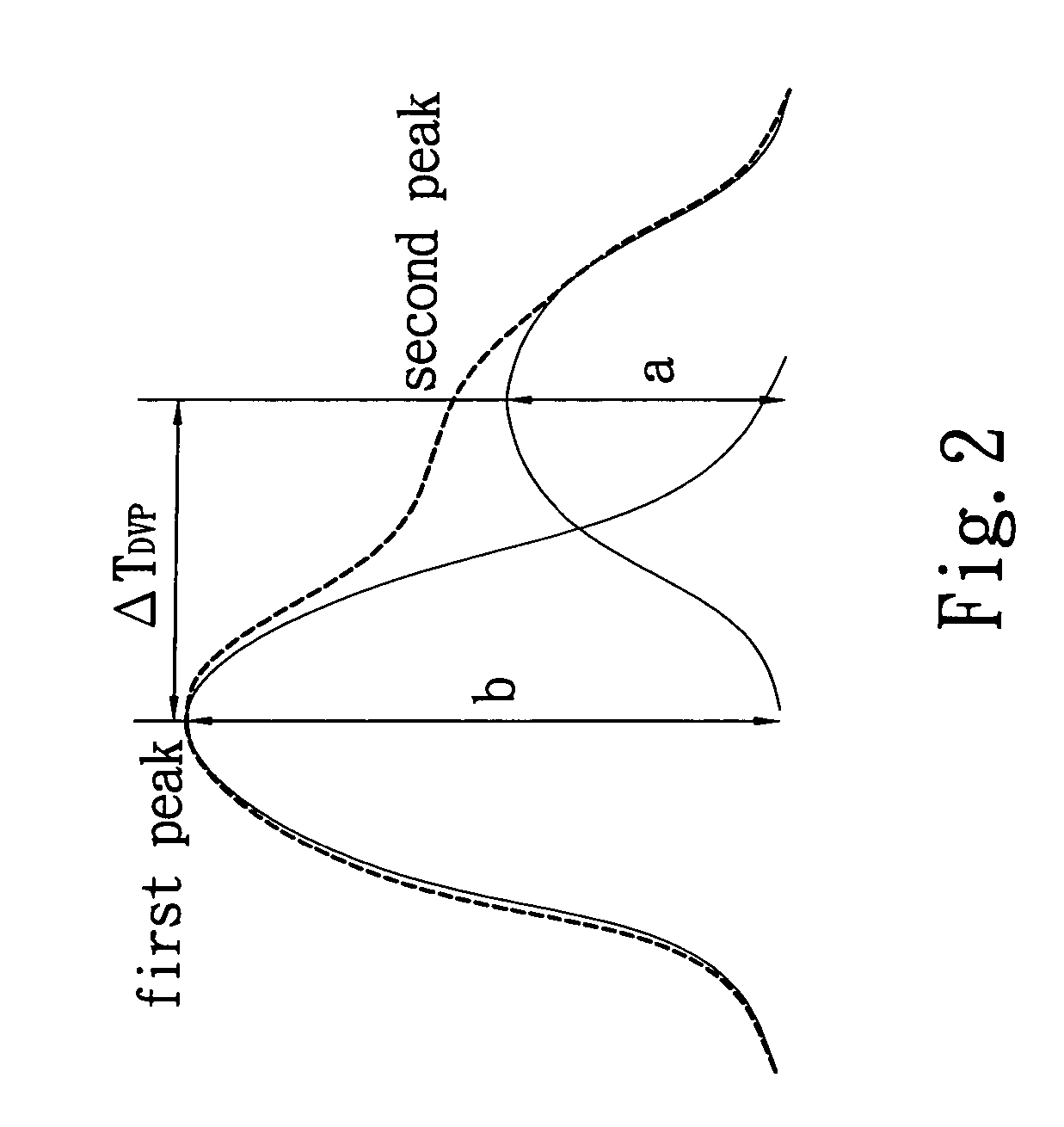
An integrated physiological signal assessing device integrates electrical signal detecting technology and optical detecting technology to design a sensing interface module for simultaneously measuring ECG signals and PPG signals, and utilizes multiple algorithm processing methods to obtain ECG parameters, such as rhythm of a heart, ST segment, and QRS interval, as well as vascular parameters, such as vascular stiffness index (SI), vascular reflection index (RI), pulse wave velocity (PWV), and pulse oxygen saturation (SpO2), so as to simplify the conventional vascular functions measuring devices, easily understand physiological conditions of a subject, and helpfully apply on diagnosis and prevention of cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:DAILYCARE BIOMEDICAL
Cardiac activation sequence monitoring for ischemia detection
InactiveUS7797036B2Convenient wireless communicationElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsImplantable ElectrodesCardiac cycle
Cardiac monitoring and / or stimulation methods and systems that provide one or more of monitoring, diagnosing, defibrillation, and pacing. Cardiac signal separation is employed to detect, monitor, track and / or trend ischemia using cardiac activation sequence information. Ischemia detection may involve sensing composite cardiac signals using implantable electrodes, and performing a signal separation that produces one or more cardiac activation signal vectors associated with one or more cardiac activation sequences. A change in the signal vector may be detected using subsequent separations. The change may be an elevation or depression of the ST segment of a cardiac cycle or other change indicative of myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction, or other pathological change. The change may be used to predict, quantify, and / or qualify an event such as an arrhythmia, a myocardial infarction, or other pathologic change. Information associated with the vectors may be stored and used to track the vectors.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Apparatus for evaluating cardiovascular functions
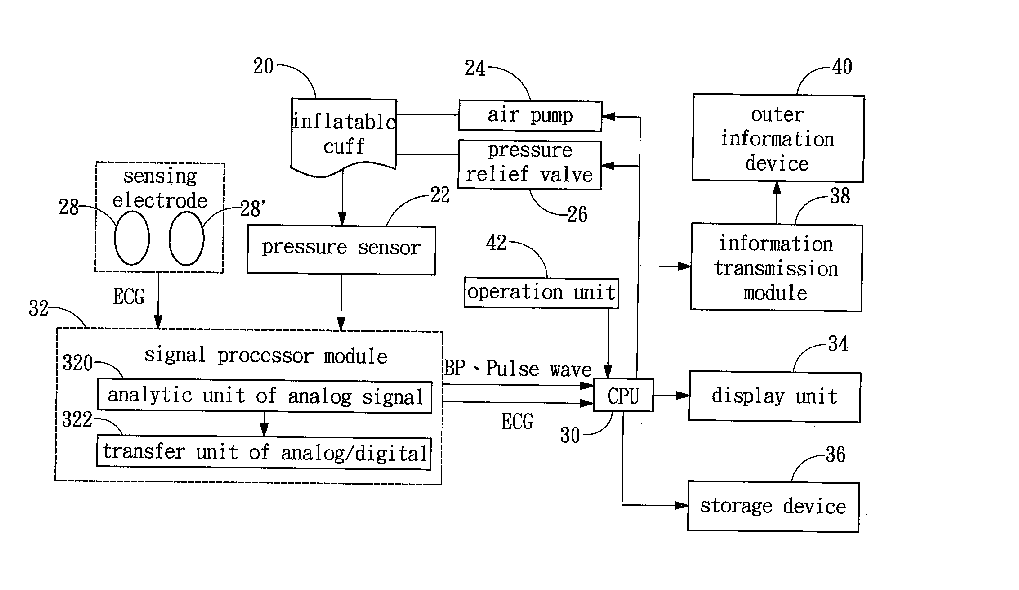
An apparatus is provided for evaluating cardiovascular functions. The apparatus combines the principles of measuring pressure and pulse signals, and monitors blood pressure, pulse wave velocity and electrocardiogram (ECG) signals simultaneously. An inflatable cuff measures blood pressure and pulse wave velocity. The apparatus also calculates systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, mean arterial pressure and other parameters related to blood pressure. The apparatus not only calculates vascular Stiffness Index (SI), vascular Reflection Index (RI) and other arterial related parameters but also Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV), heartbeat, QRS interval, ST segment, and other ECG parameters.
Owner:DAILYCARE BIOMEDICAL
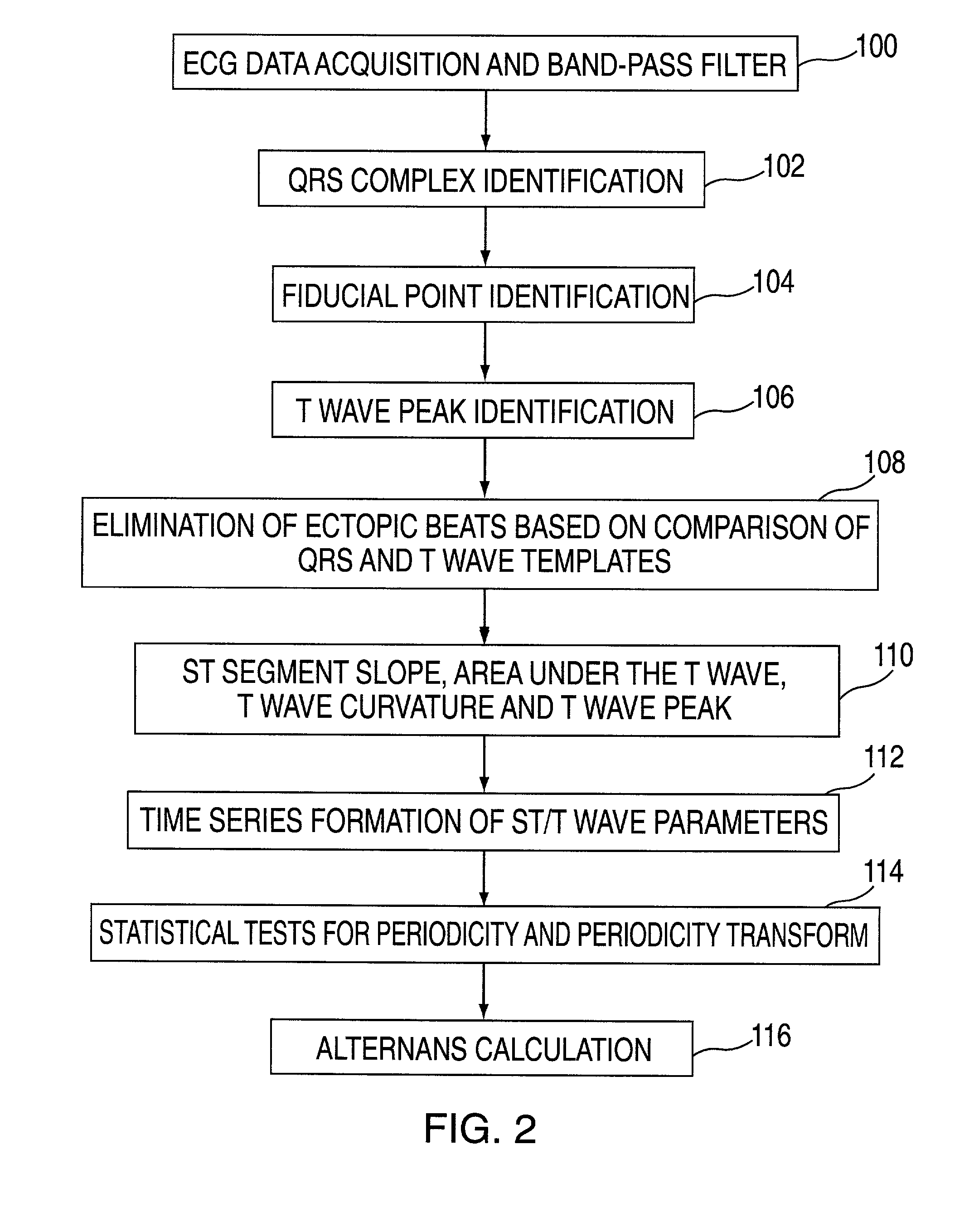
Method and apparatus for monitoring cardiac patients for T-wave alternans
InactiveUS6983183B2Eliminate the effects ofReliable measurementElectrocardiographySensorsEcg signalArray data structure
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
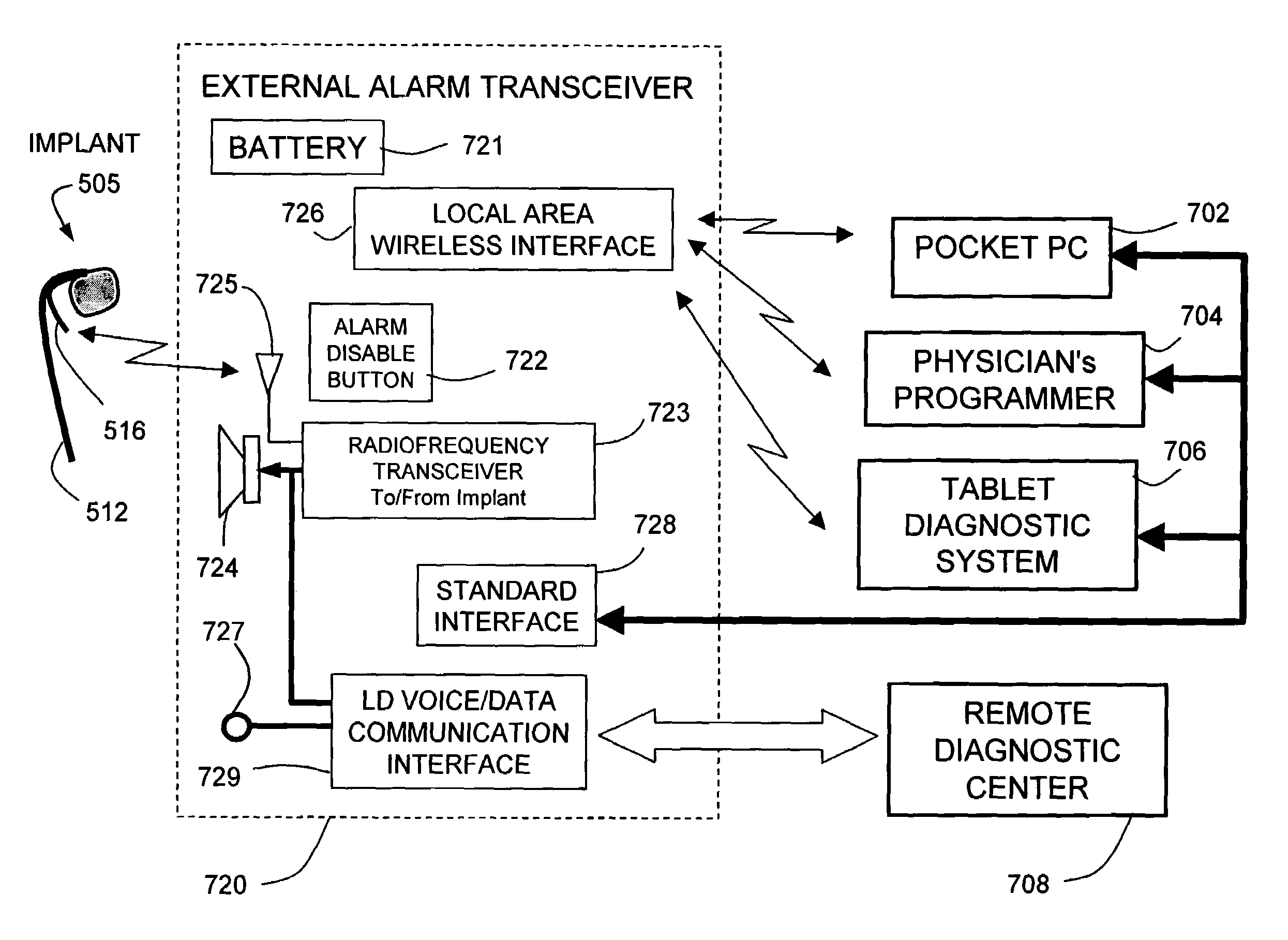
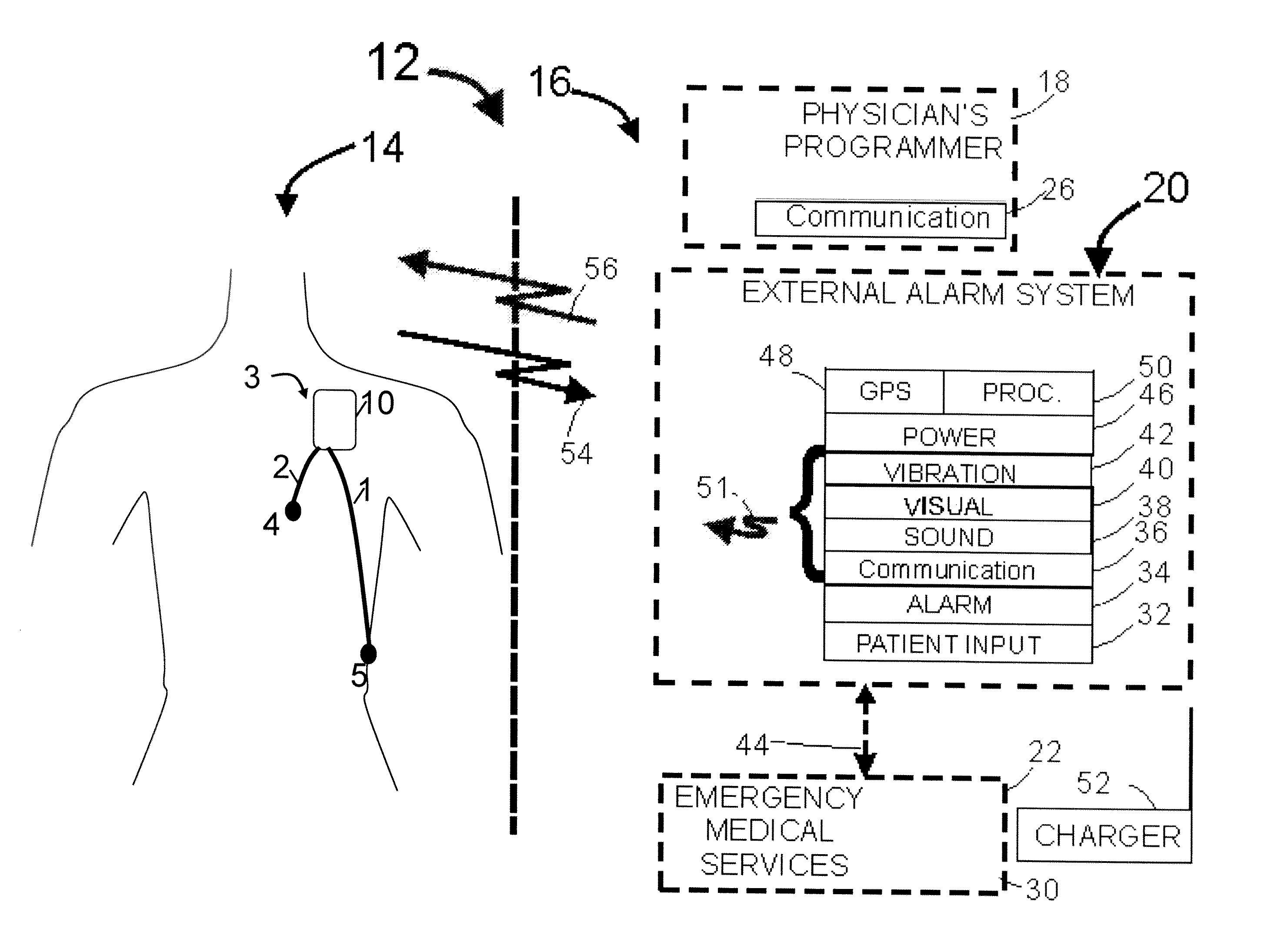
Emergency room triage system
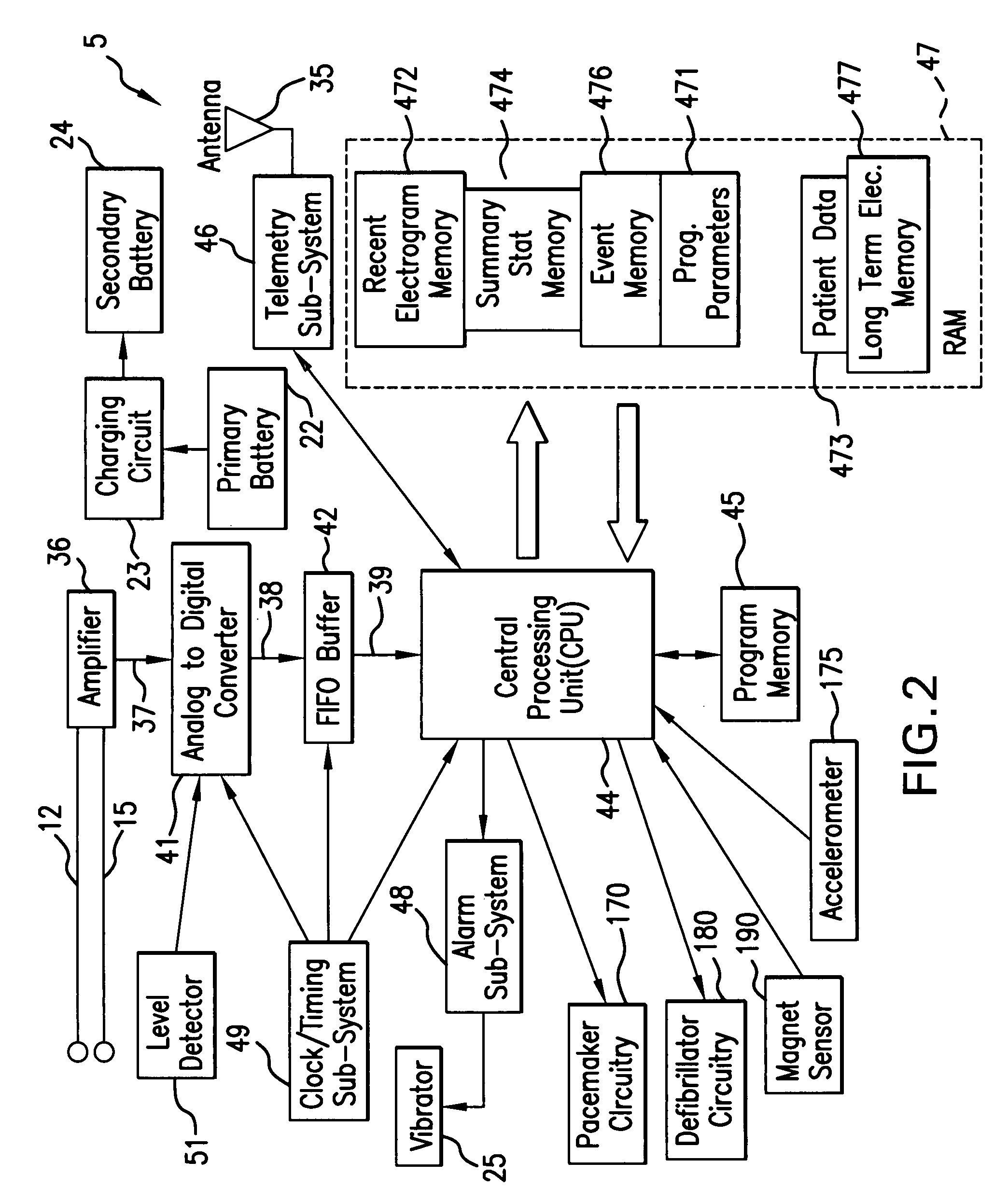
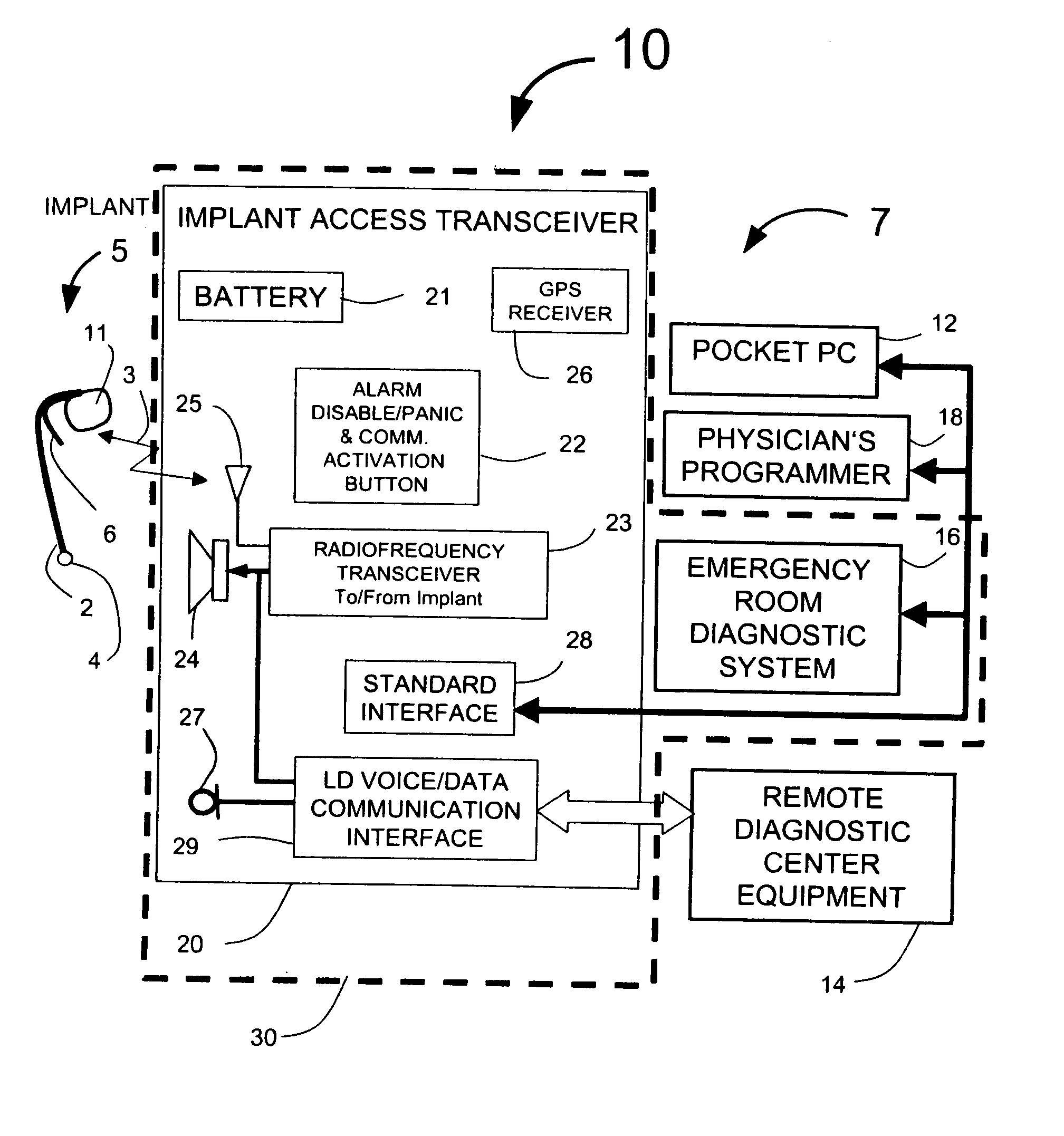
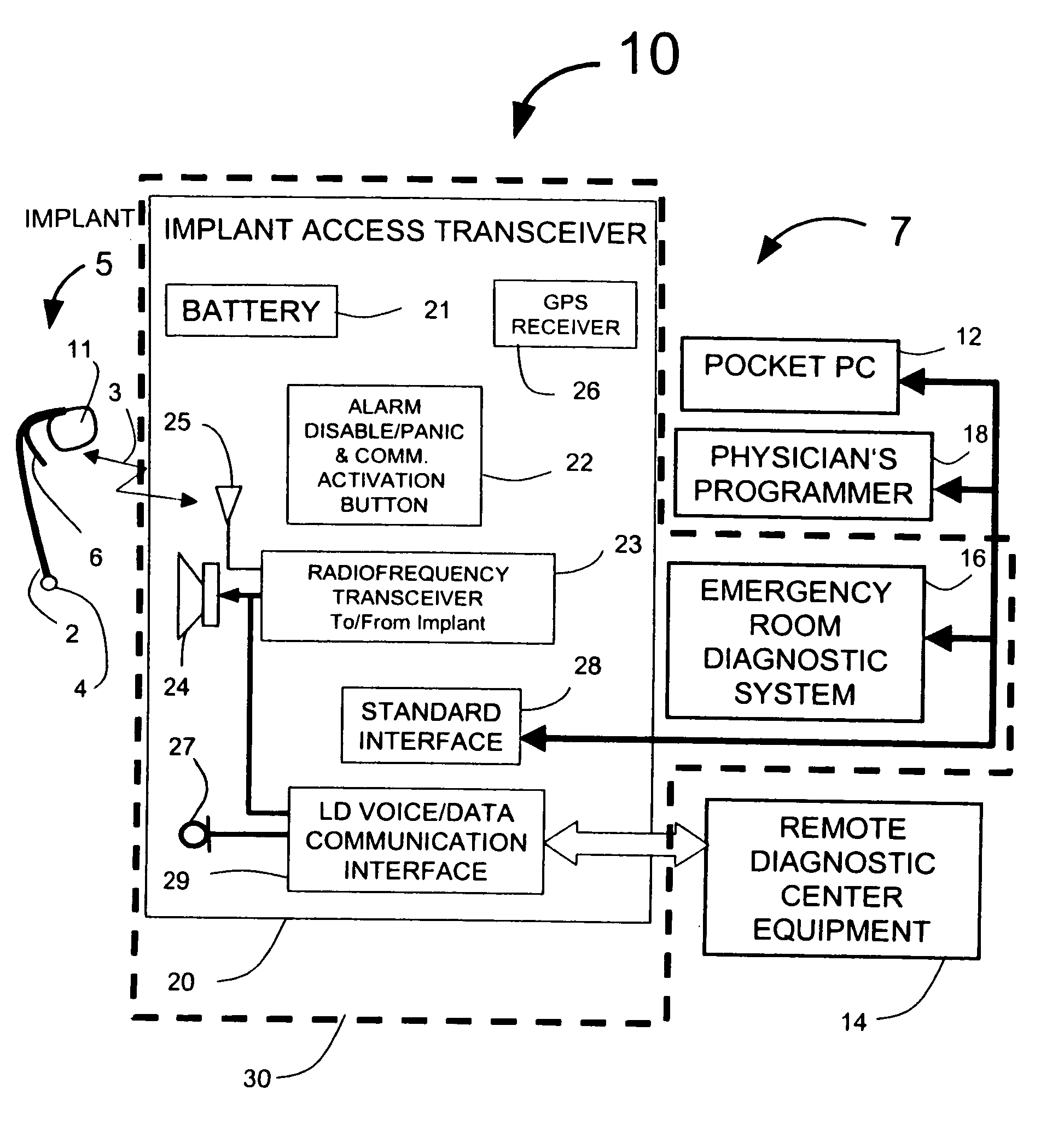
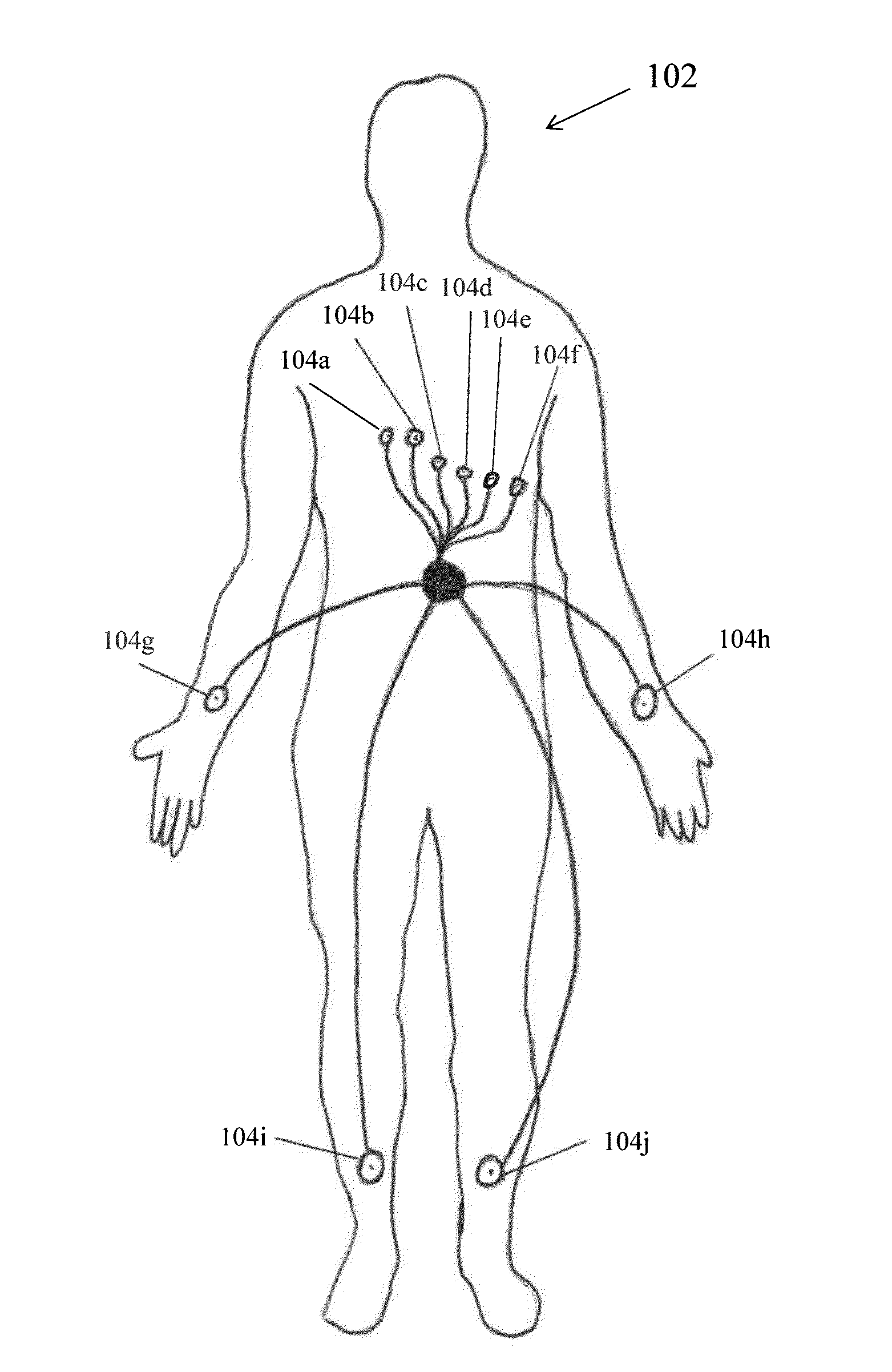
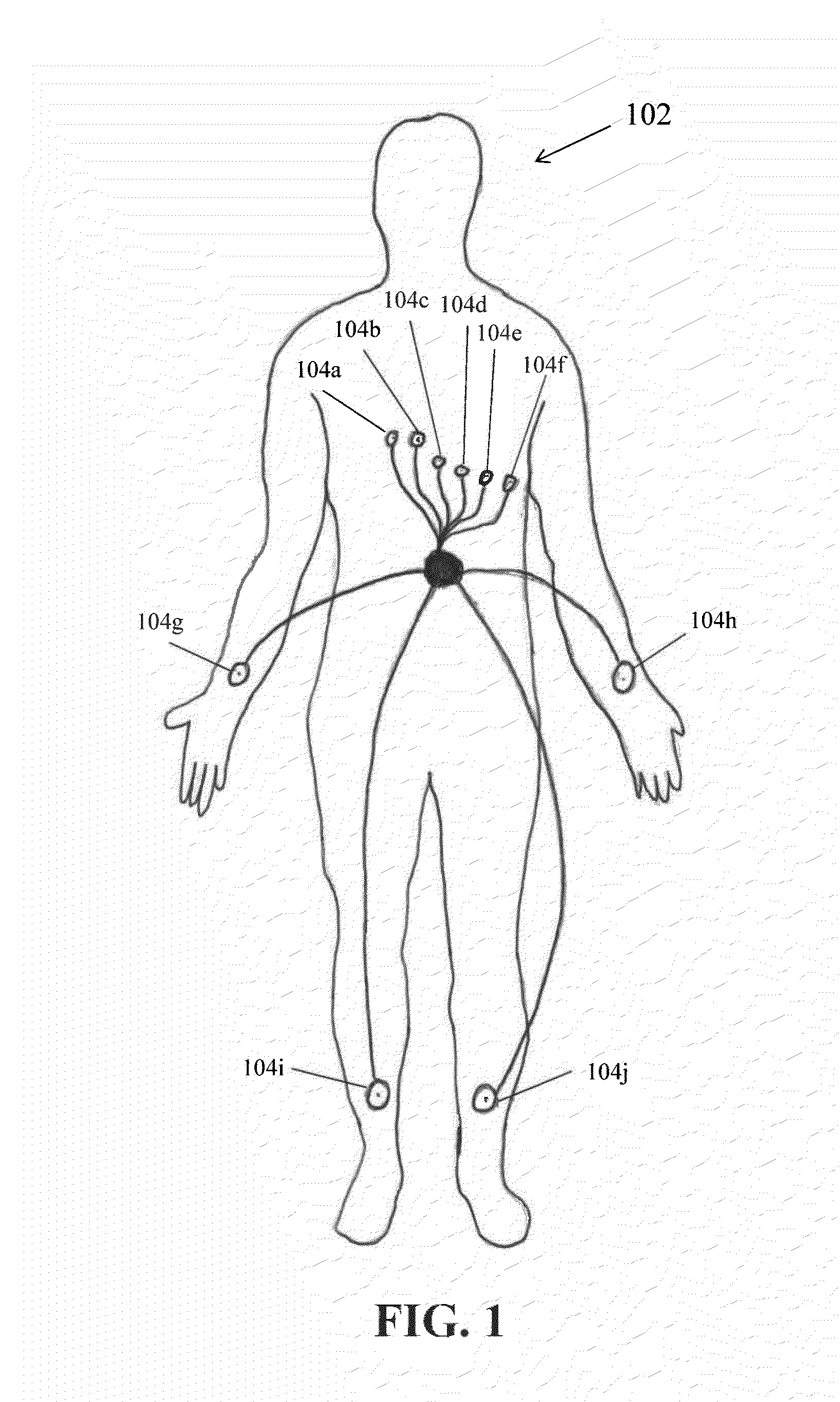
InactiveUS20050256417A1Extend battery lifeShorten treatment timeMedical communicationElectrocardiographyTriage CodeCardiac pacemaker electrode
A patient diagnostic emergency room triage system includes an implanted cardiac device which may be a cardiosaver, pacemaker or cardiac defibrillator for recording electrogram data associated with the detection of a cardiac event. A communication mechanism receives electrogram data from the implanted cardiac device and a visual display displays the electrogram data recorded by the implanted cardiac device. The visual display permits displaying electrogram data associated with an ST segment related cardiac event.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
System for Heart Performance Characterization and Abnormality Detection
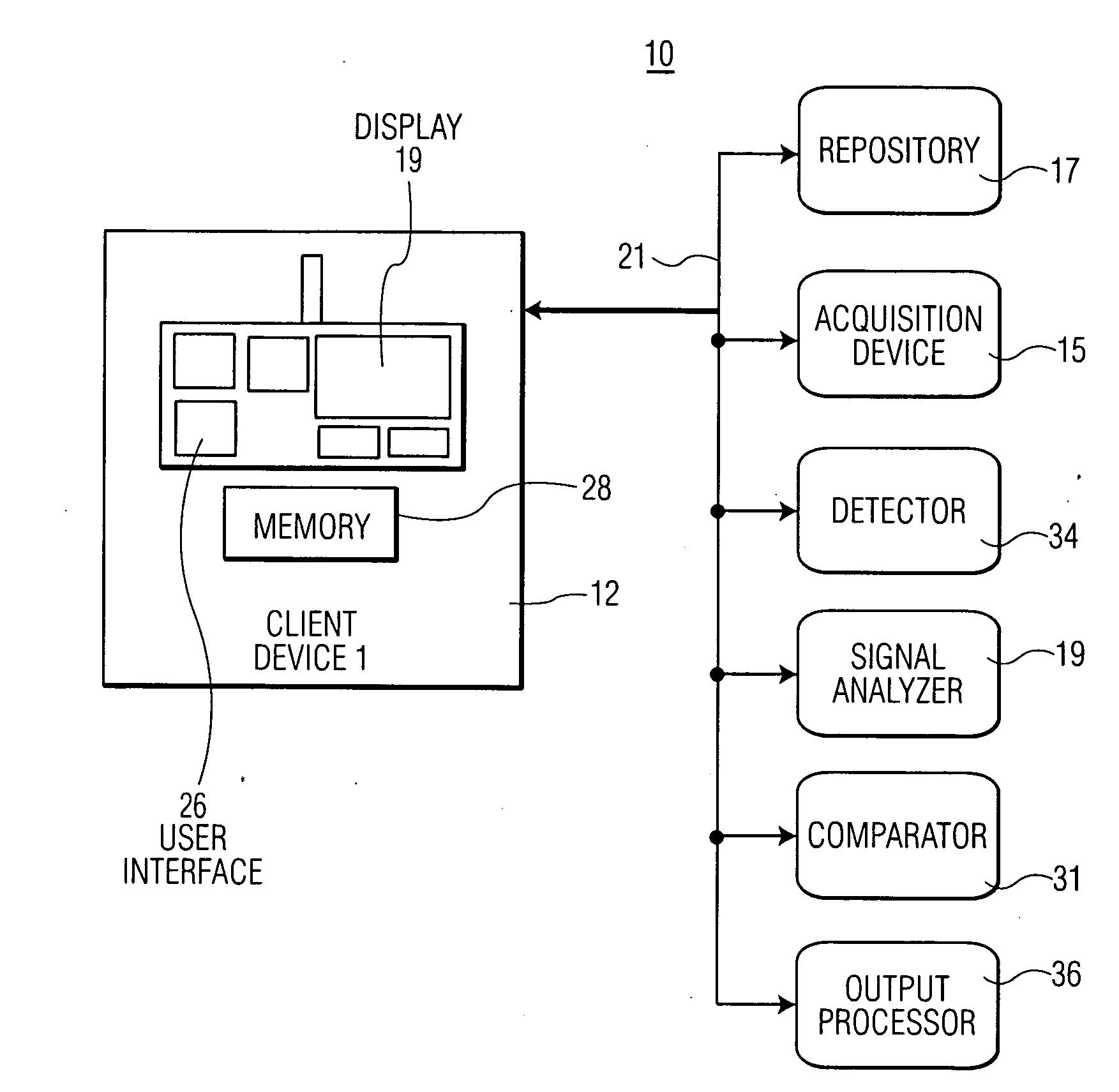
ActiveUS20090281441A1Improve precisionImprove reliabilityElectrocardiographyMedical devicesT wavePeak value
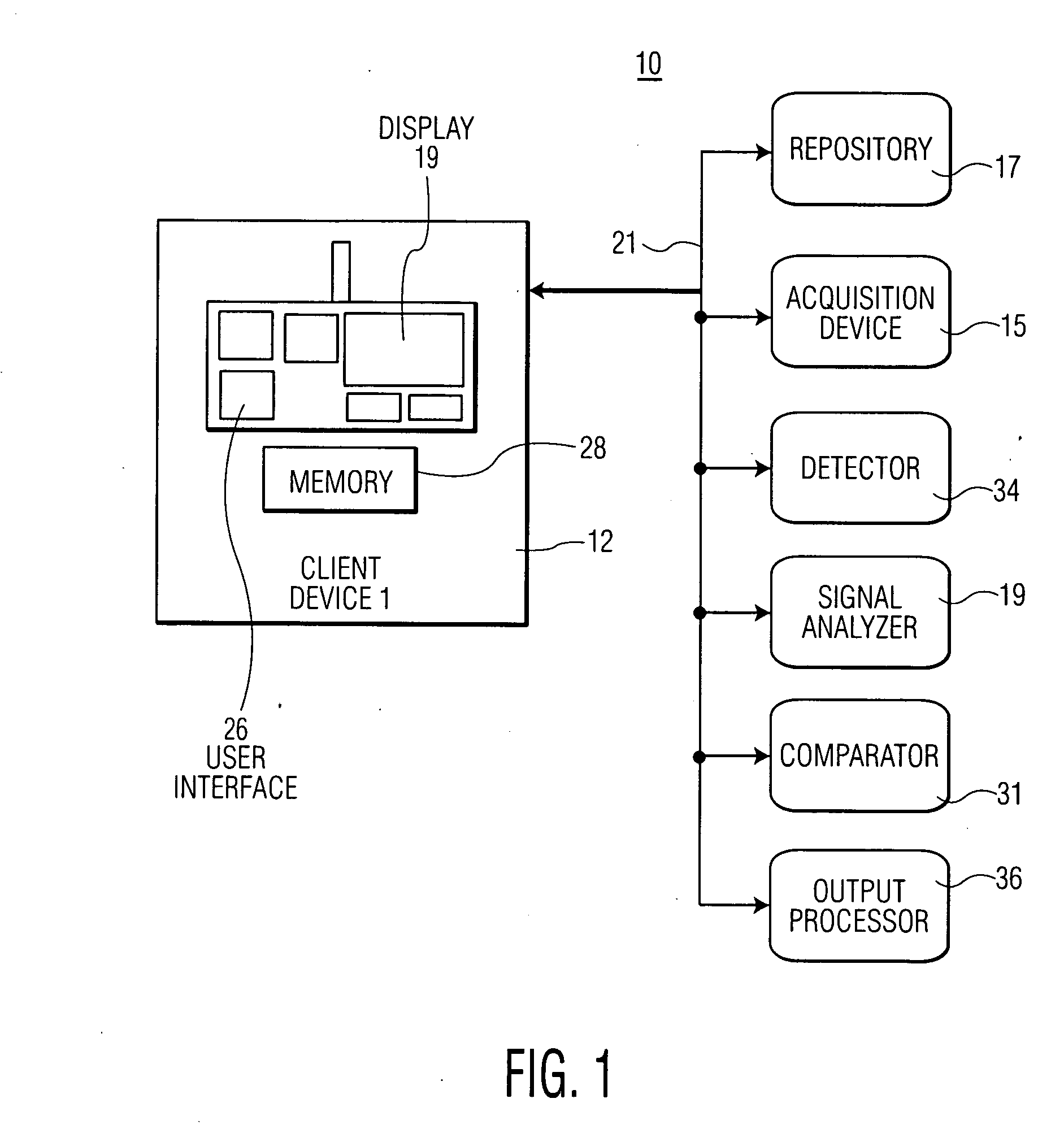
A system for heart performance characterization and abnormality detection includes an acquisition device for acquiring an electrophysiological signal representing heart beat cycles of a patient heart. A detector detects one or more parameters of the electrophysiological signal of parameter type comprising at least one of, (a) amplitude, (b) time duration, (c) peak frequency and (d) frequency bandwidth, of multiple different portions of a single heart beat cycle of the heart beat cycles selected in response to first predetermined data. The multiple different portions of the single heart beat cycle being selected from, a P wave portion, a QRS complex portion, an ST segment portion and a T wave portion in response to second predetermined data. A signal analyzer calculates a ratio of detected parameters of a single parameter type of the multiple different portions of the single heart beat cycle. An output processor generates data representing an alert message in response to a calculated ratio exceeding a predetermined threshold.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
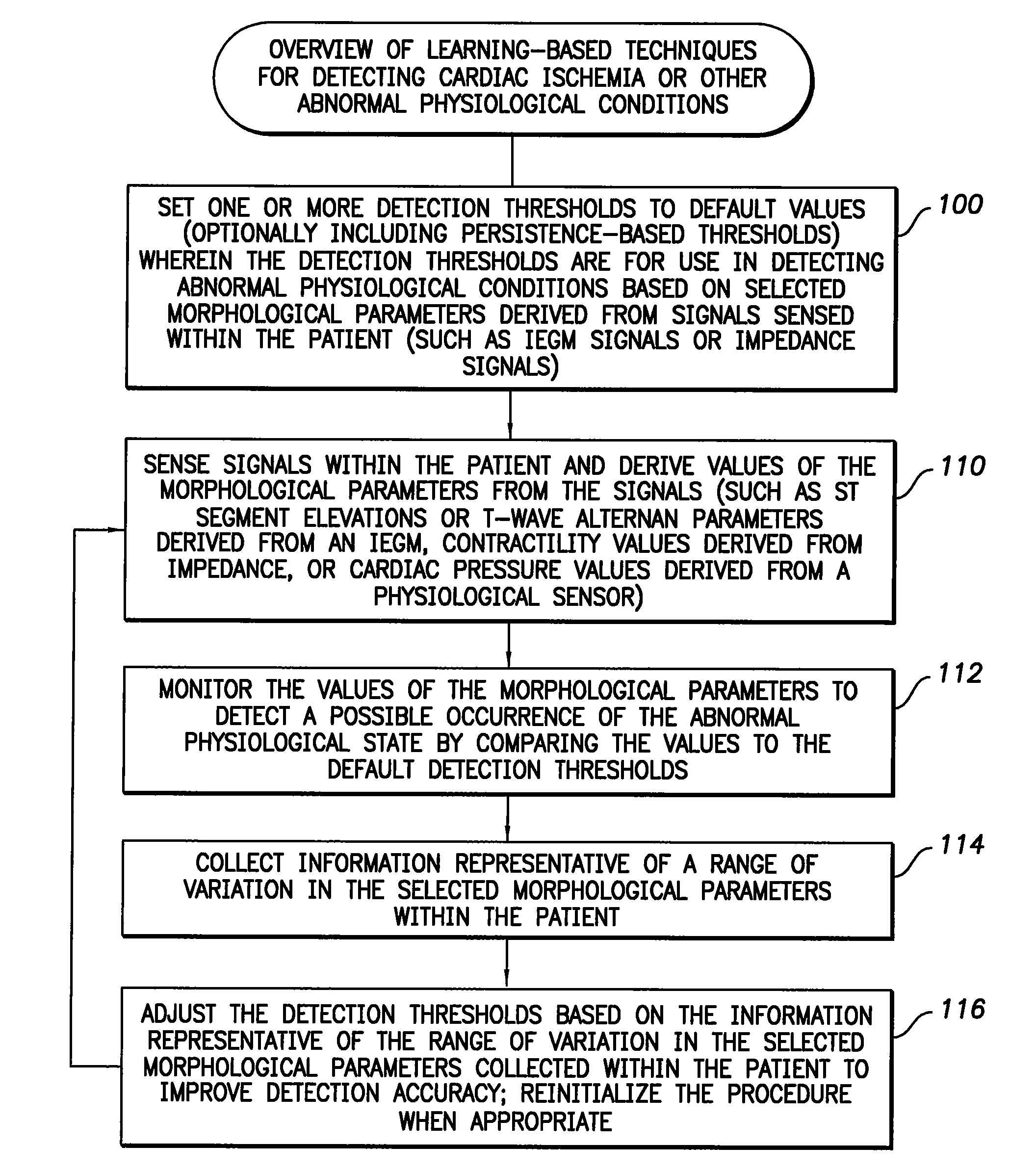
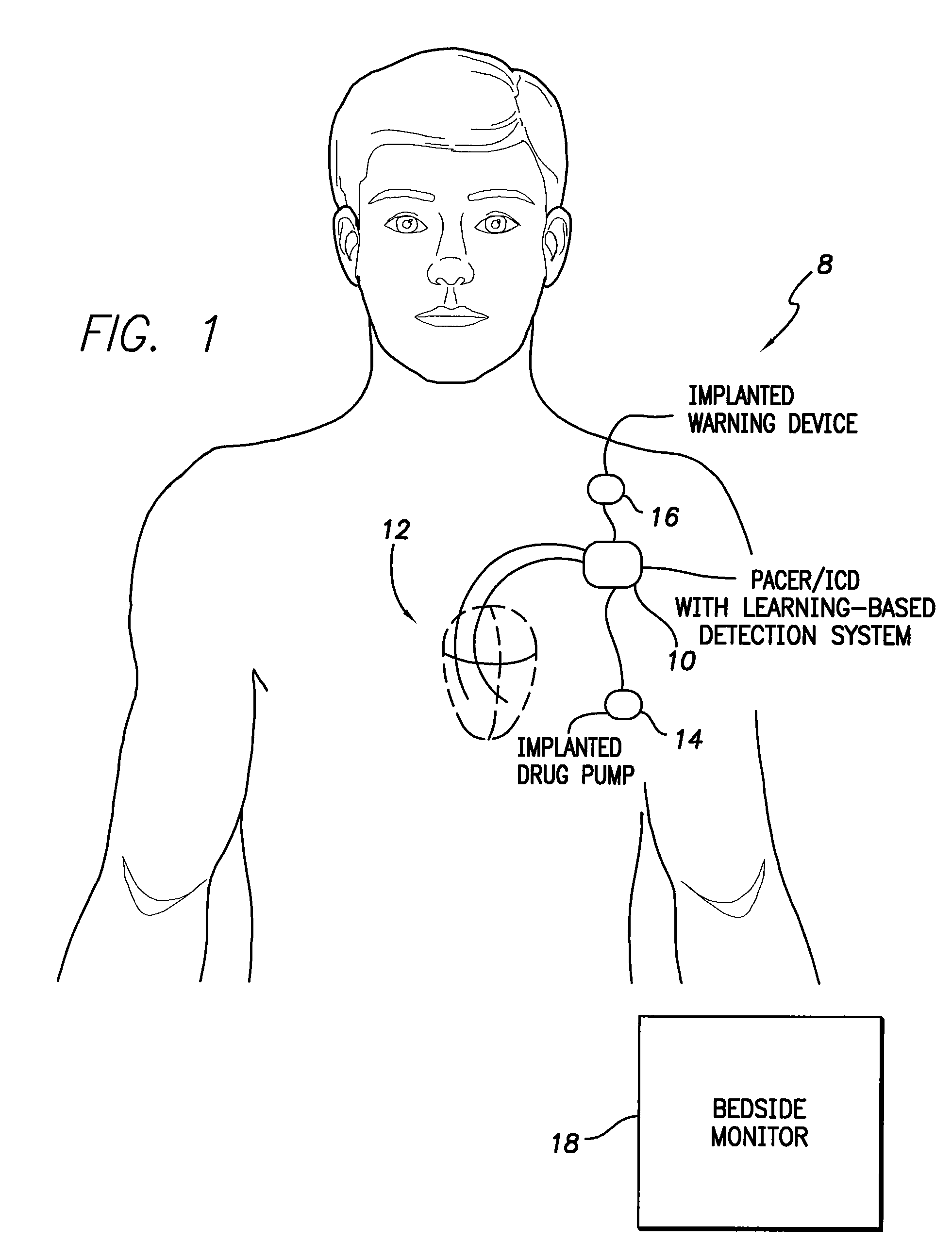
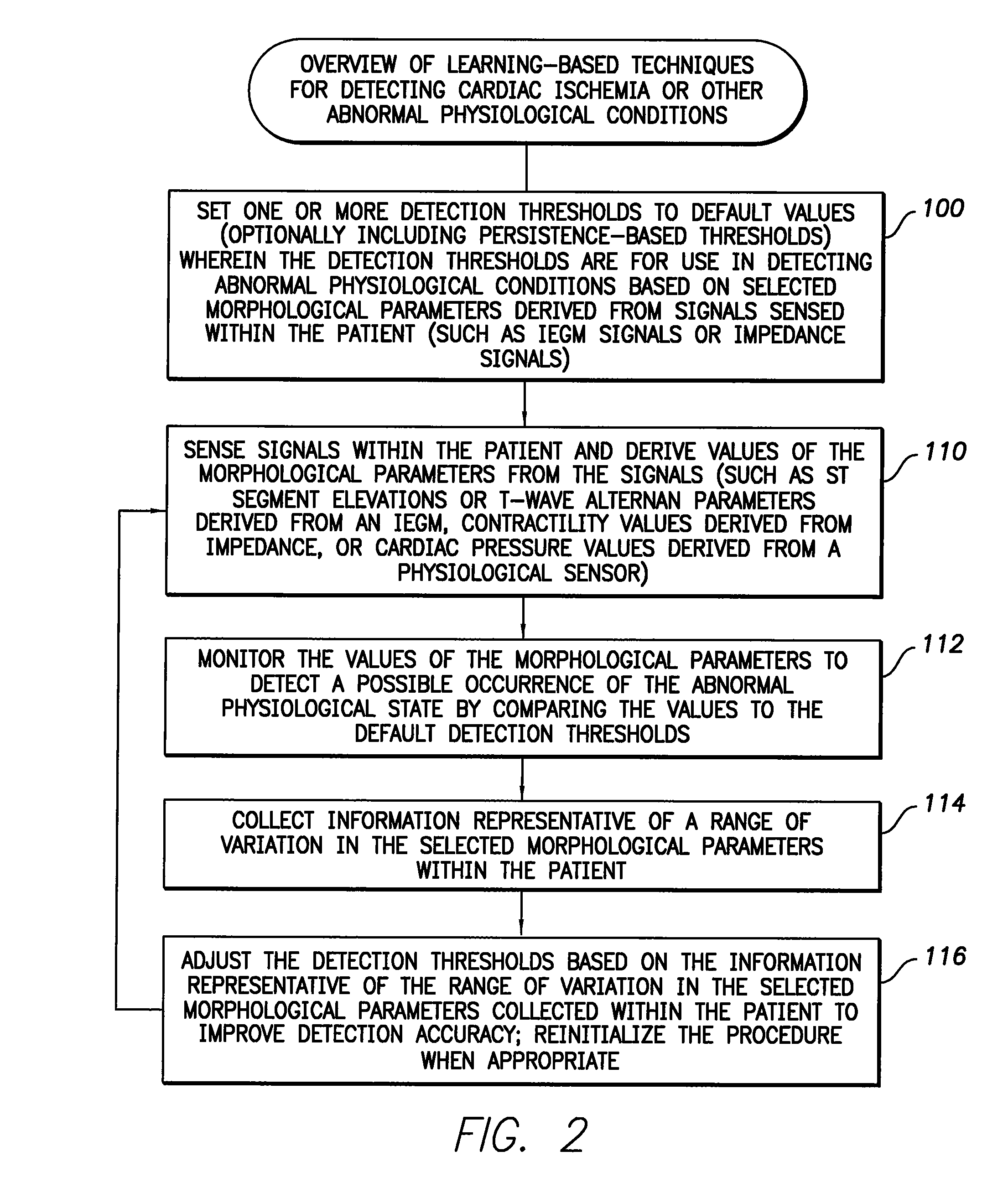
System and method for adaptively adjusting cardiac ischemia detection thresholds and other detection thresholds used by an implantable medical device
InactiveUS7769436B1Simple technologyFacilitate warningElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyCardiac pacemaker electrodeSelf adaptive
Techniques are described for adaptively adjusting detection thresholds for use in detecting cardiac ischemia and other abnormal physiological conditions based on morphological parameters derived from intracardiac electrogram (IEGM) signals, impedance measurements, or other signals. In one example, where ST segment elevation is used to detect cardiac ischemia, default detection thresholds are determined in advance from an examination of variations in ST segment elevations occurring within a population of patients. Thereafter, an individual pacemaker or other implantable medical device uses the default thresholds during an initial learning period to detect ischemia within the patient in which the device is implanted. During the initial learning period, the pacemaker also collects data representative of the range of variation in ST segment elevations occurring within the patient. The pacemaker then adaptively adjusts the thresholds based on the range of variation so as to improve detection specificity within the patient.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Waveform feature value averaging system and methods for the detection of cardiac events
Disclosed is a system for detecting pathophysiological cardiac conditions. The system comprises a diagnostic device that contains electronic circuitry that can detect a cardiac event such as an acute ischemia. The cardiac diagnostic device receives electrical signals from subcutaneous or body surface sensors. The cardiac diagnostic device includes a processor that computes QRS onset and offset points and fiducial points associated with T and U waves. The processor than baseline corrects the original signal / waveform by fitting a polynomial function to QRS offset points, and subtracting this function from the original waveform. Based on the baseline adjusted signal and / or the above mentioned fiducial points, the processor then computes averages of various waveform feature values, including a QRS measure sensitive to QRS curvature, T wave timing measures, ST segment deviation (difference between signal amplitudes at QRS offset and onset and / or minimum amplitude between QRS offset and peak T wave); and T / U wave amplitudes. These averages are computed by exponential averaging. From the exponential averages, the processor computes an average of the change in the averages over time. Based on the averages and the change in the averages, the processor applies an ischemia test to determine a likelihood of ischemia.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
System and method for analyzing an electrocardiogram signal
A system for analyzing an ECG signal is provided. The system comprises an interface that receives an ECG waveform associated with heart beat cycle of a patient. The system includes signal processor that determines a first isoelectric portion lying between a T-wave of a first heart beat cycle and a P-wave of a successive heart beat cycle, and a second isoelectric portion lying between a P-wave and a QRS complex of the first heart beat cycle. The signal processor determines a stability measure for each of said first and second portions and adaptively selects the first or the second portion as a baseline for the first heart beat cycle based on the stability measures. The signal processor determines a point of reference on an ST segment associated with the first heart beat cycle and evaluates a deviation of the point of reference on the ST segment from the selected baseline.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Electrocardiologic device for assisted diagnosis for the diagnostic of brugada syndrome or early repolarization syndrome
InactiveUS20090137916A1Minimizes interpretationHigh sensitivityElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyEcg signalEARLY REPOLARIZATION SYNDROME
Electrocardiologic device for assisted diagnosis, preferably for the diagnosis of Brugada syndrome or Early Repolarization syndrome. This device allows characterizing the ventricular repolarization wave of an ECG signal collected from a patient. Extracting out of the ECG signal, for each heart beat, an ST segment is constituted of a successsion of samples of the ventricular repolarization wave, taken within a time window ([QON+80 ms, QON+140 ms]) of a predetermined duration spreading from a moment of window onset defined by a time offset applied to a predetermined temporal origin given by the moment (QON) of appearance of the QRS complex, whose time position is determined on the ECG signal for each heart beat. Quantizing computes an elevation index compared to a predetermined reference level (BL), and analyzing over a succession of heart beats the persistence and / or variation of this elevation index.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Emergency room triage system
InactiveUS20060212085A1Extend battery lifeShorten treatment timeElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsTriage CodeCardiac pacemaker electrode
A patient diagnostic emergency room triage system includes an implanted cardiac device which may be a cardiosaver, pacemaker or cardiac defibrillator for recording electrogram data associated with the detection of a cardiac event. A communication mechanism receives electrogram data from the implanted cardiac device and a visual display displays the electrogram data recorded by the implanted cardiac device. The visual display permits displaying electrogram data associated with an ST segment related cardiac event.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Threshold adjustment schemes for acute ischemia detection
A heart monitor is disclosed. The monitor computes ST segment deviations and stores the results in heart rate based histograms. Periodically, the monitor analyzes the histogram data to determine heart rate dependent acute ischemia detection thresholds. If the statistical distribution associated with a heart rate range is insufficient, the threshold for that heart rate range is set as a function of the threshold for a neighboring heart rate range. Thresholds are also increased for heart rate ranges associated with statistical distributions that are sufficient but that have a relatively small number of entries.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
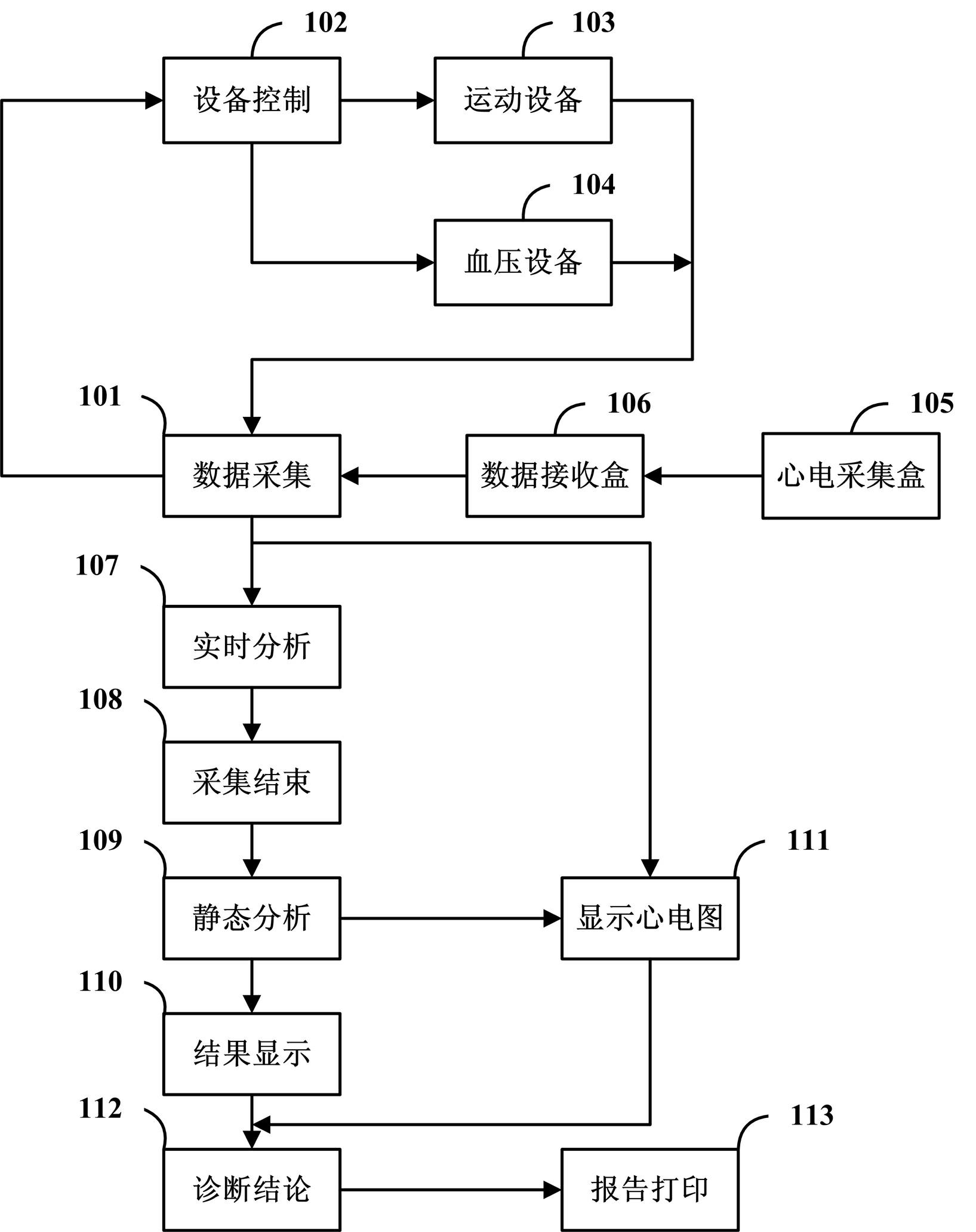
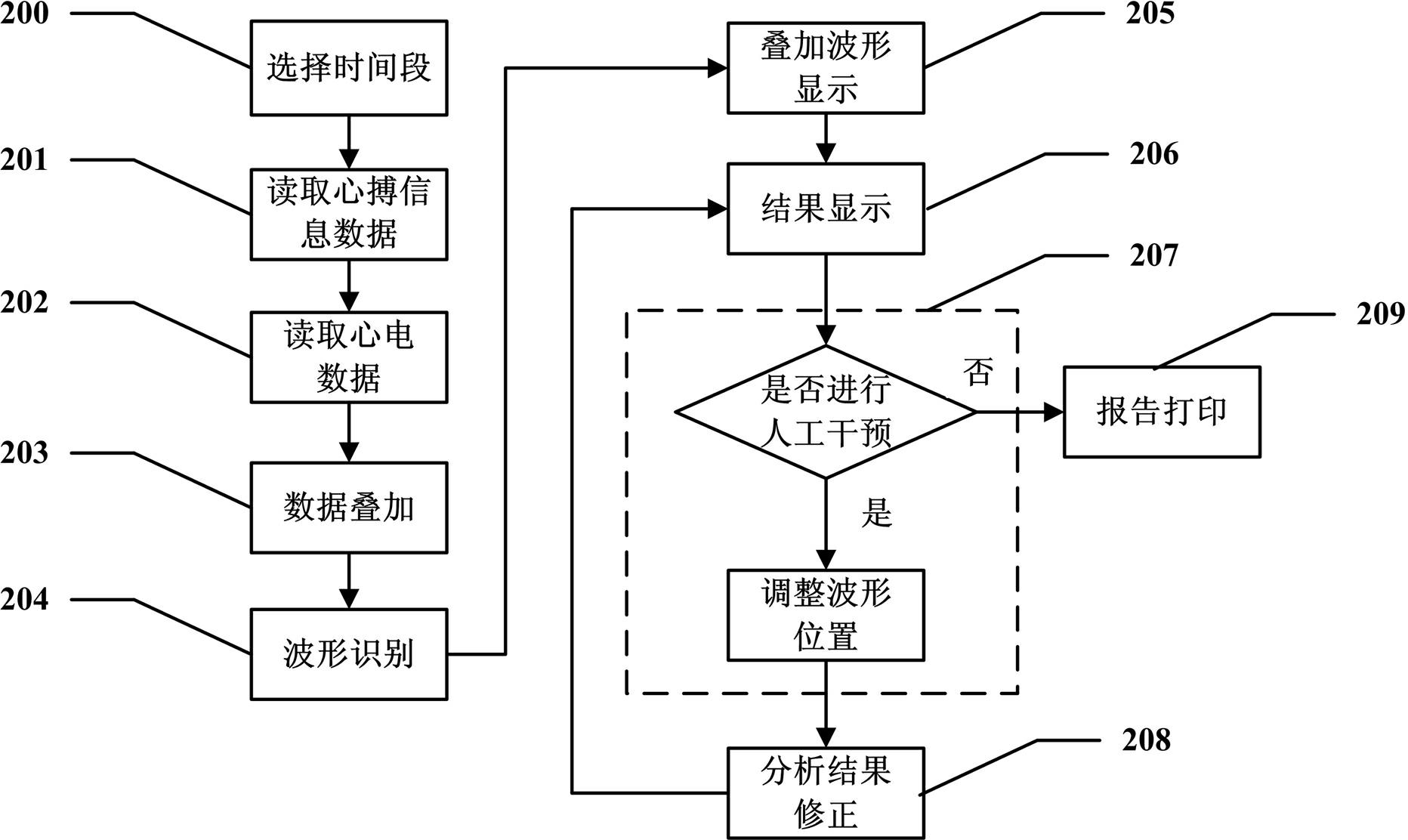
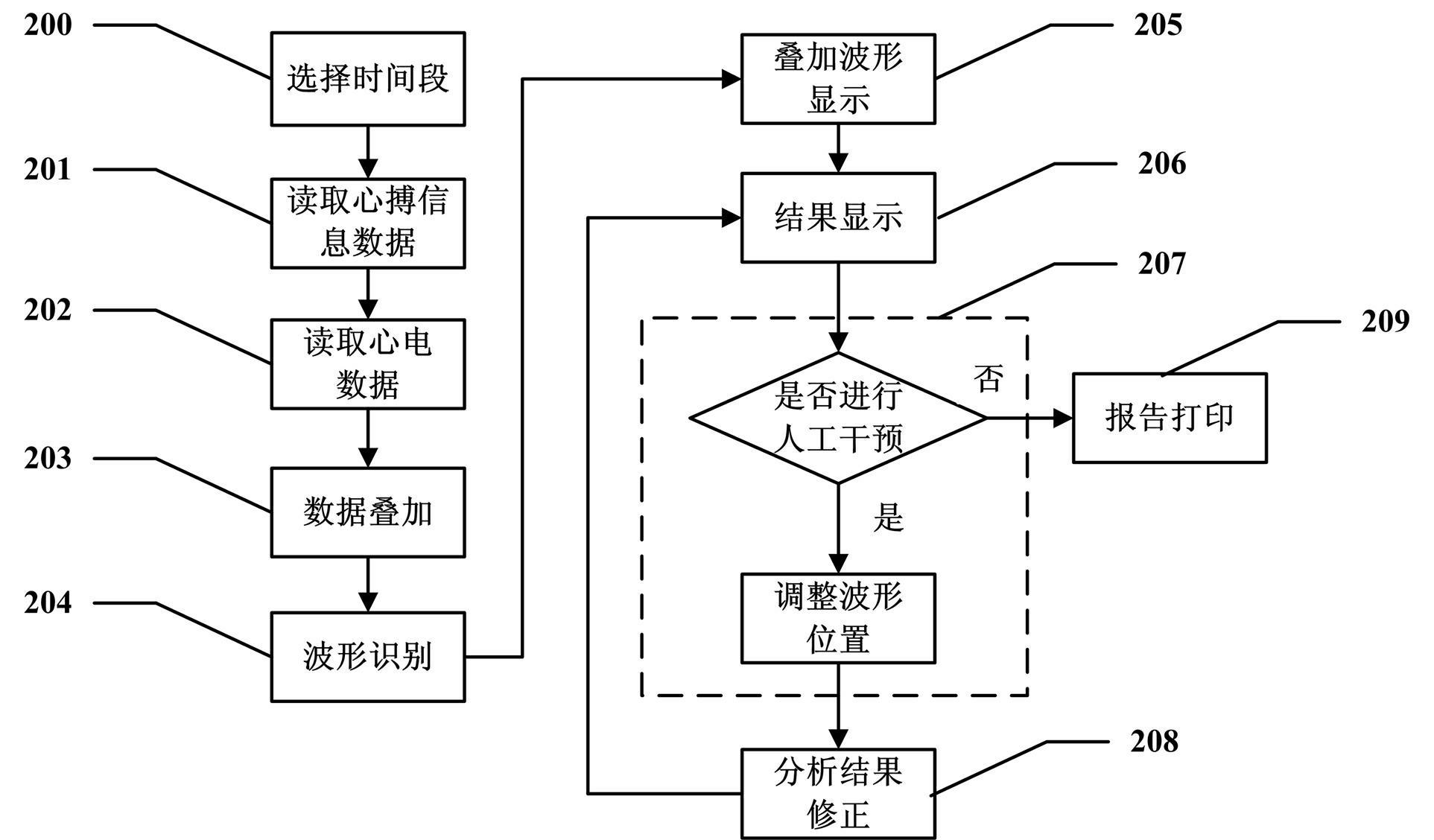
Method and system for performing superposition analysis on exercise load electrocardio waveforms
ActiveCN102397067AAccurate judgmentAccurate Waveform DataDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsT waveQT interval
The invention discloses a method for performing superposition analysis on electrocardio data of any time segment. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting any segment of representative waveforms from an electrocardiogram; reading electrocardio data and waveform information in the time period; superposing the waveform of each heart beat in the time period and analyzing the waveform type of the superposed waveforms, the forward voltage and the negative voltage of a P wave, the voltage of a Q wave, an R wave and an S wave, the average voltage of an ST segment, the forward voltage and the negative voltage of a T wave, the time limit of the P wave, the Q wave, the R wave, the S wave and the T wave, a QT interval and other data; and providing a human-computer interaction interface, displaying an analysis result obtained after waveforms are superposed, and allowing a user to perform manual intervention on the analysis result. The application scope of an exercise load test is broadened, the accuracy of the test result is improved, and the diagnostic report has higher reference value.
Owner:CONTEC MEDICAL SYST
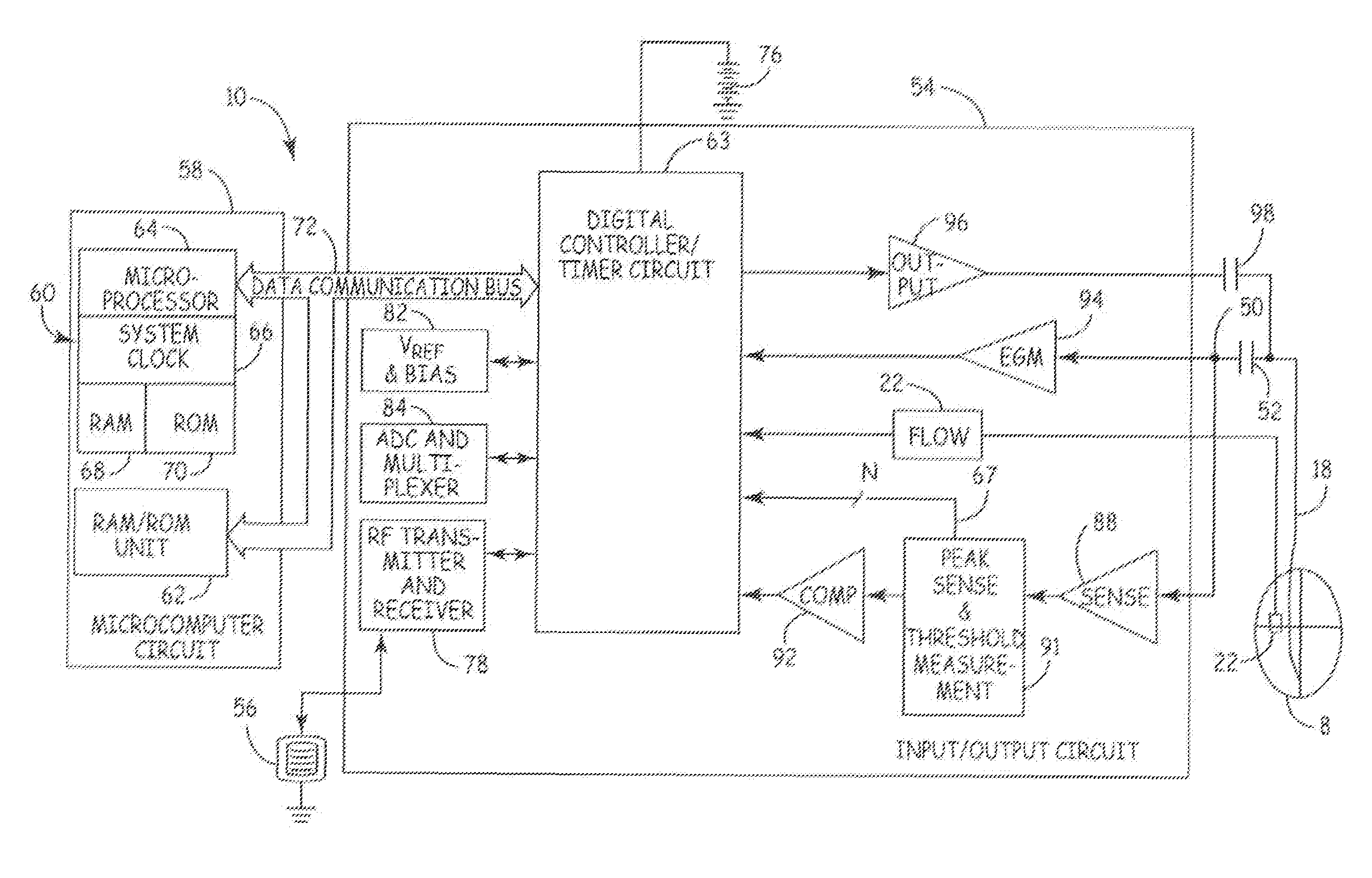
Ischemic heart disease detection
An implantable medical device system for detecting cardiac conditions such the long-term ischemic heart disease, an occlusion of a coronary artery by a thrombus or an impending as a myocardial infarction. The implantable medical device (IMD) system includes a sensor that outputs a blood flow rate signal representing a rate of blood flow through a coronary sinus of a patient's heart. An implantable medical device (IMD) includes a microcomputer circuit configured to analyze the blood flow rate signal and detect a cardiac condition as a function of the blood flow rate signal. The system can also includes an implantable lead that senses electrical activity from the patient's heart. The microcomputer circuit monitors an ST segment of the electrical activity signal and detects a cardiac condition as a function of blood flow rate signal in conjunction with the electrical activity signal.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
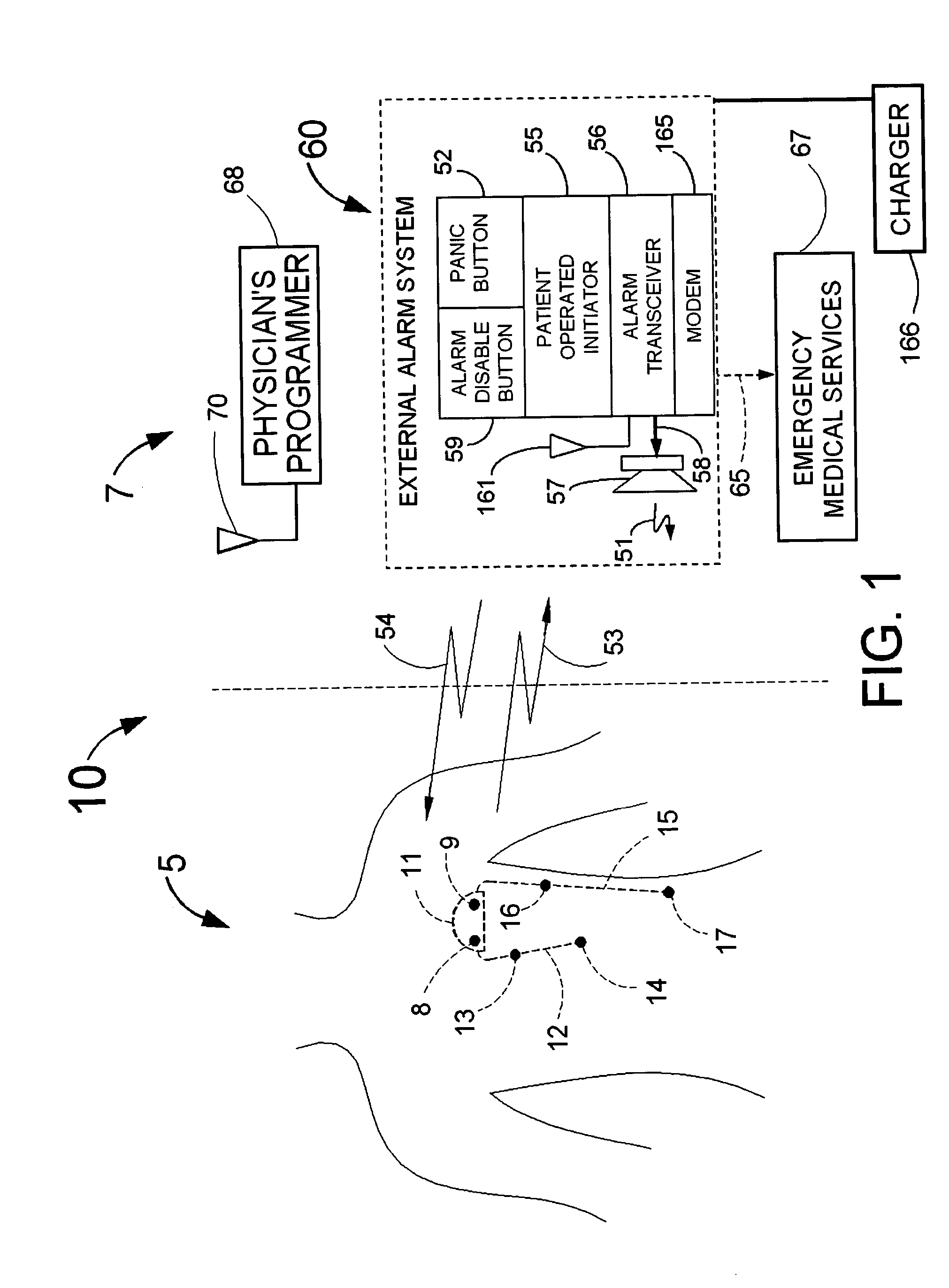
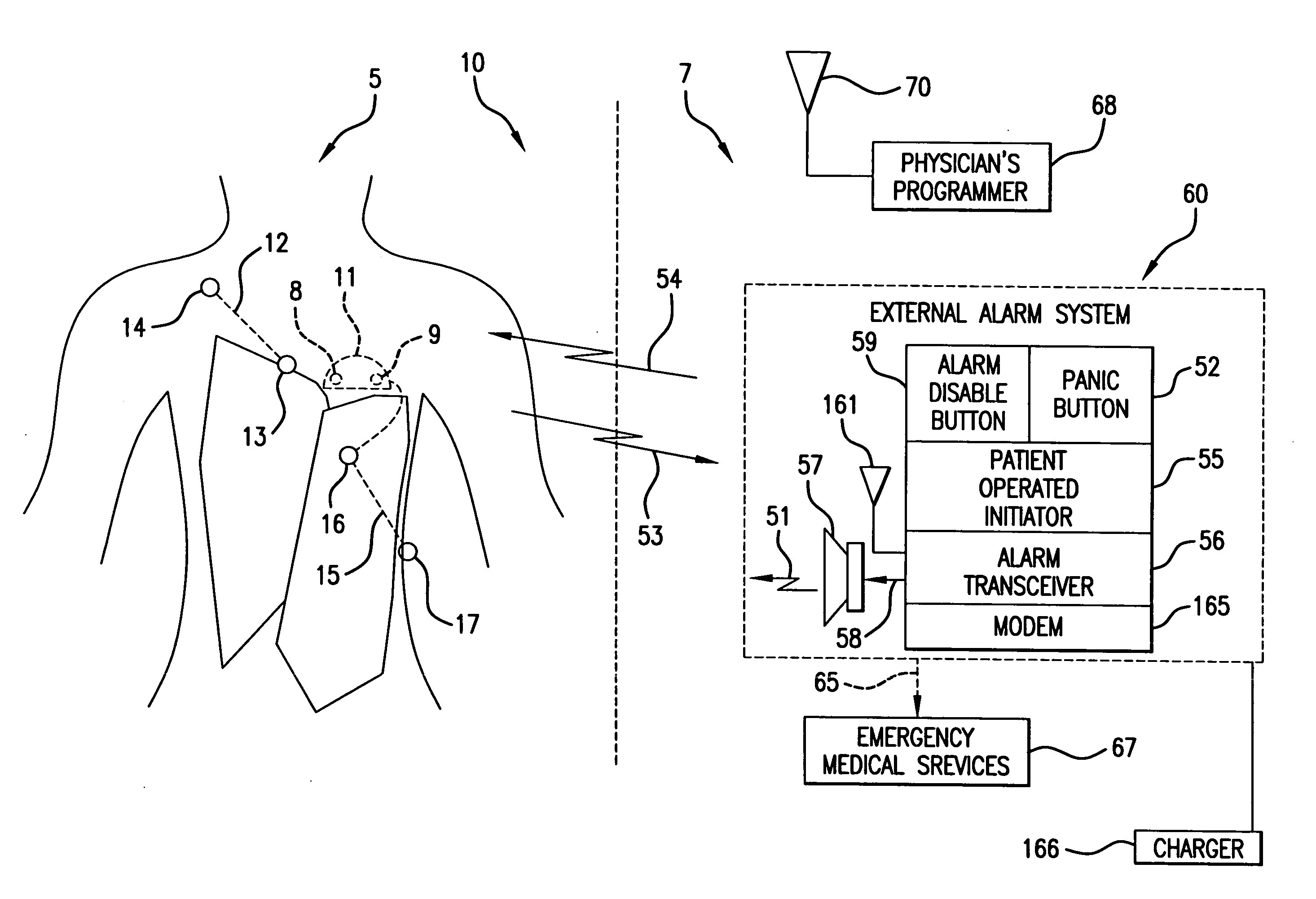
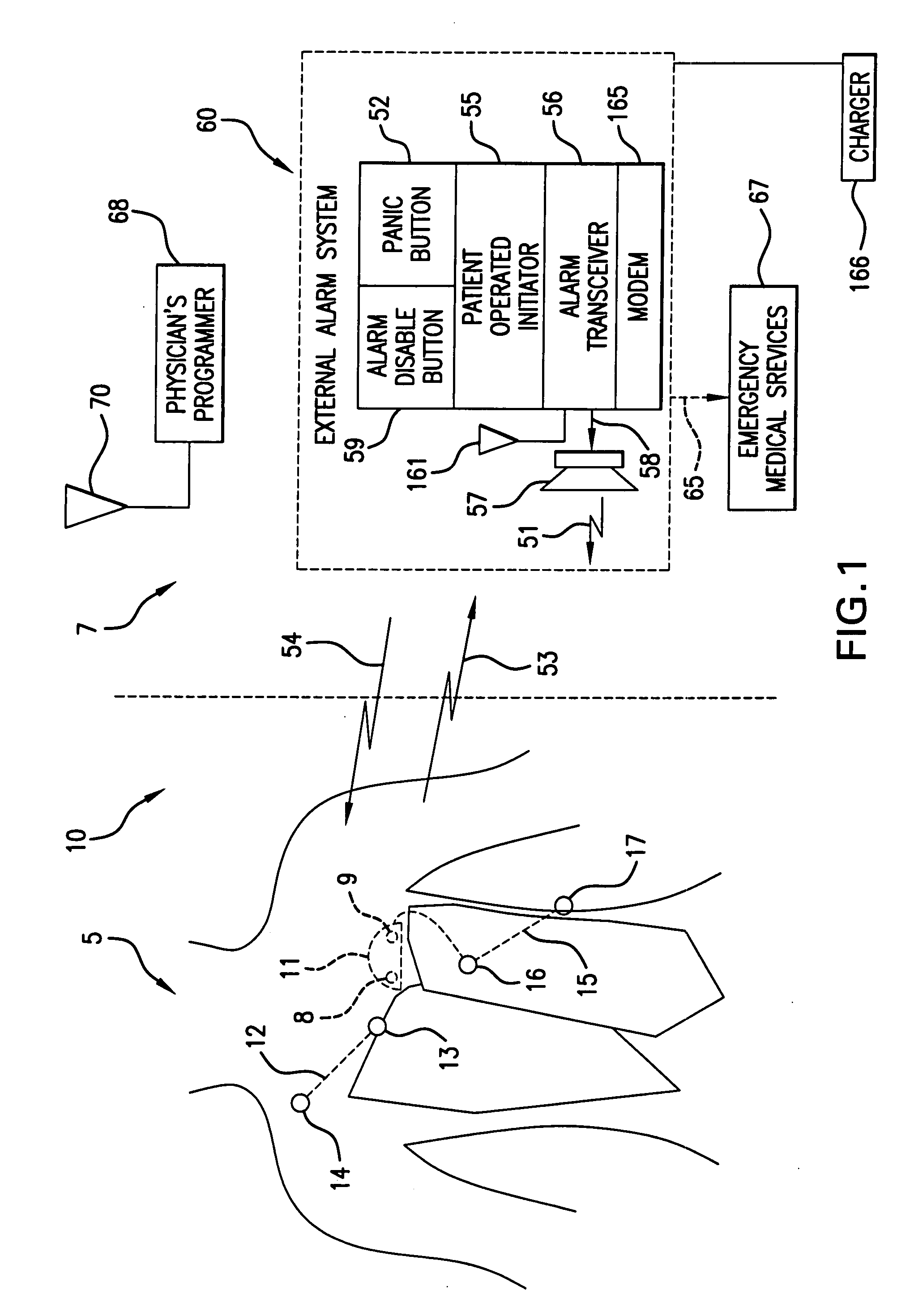
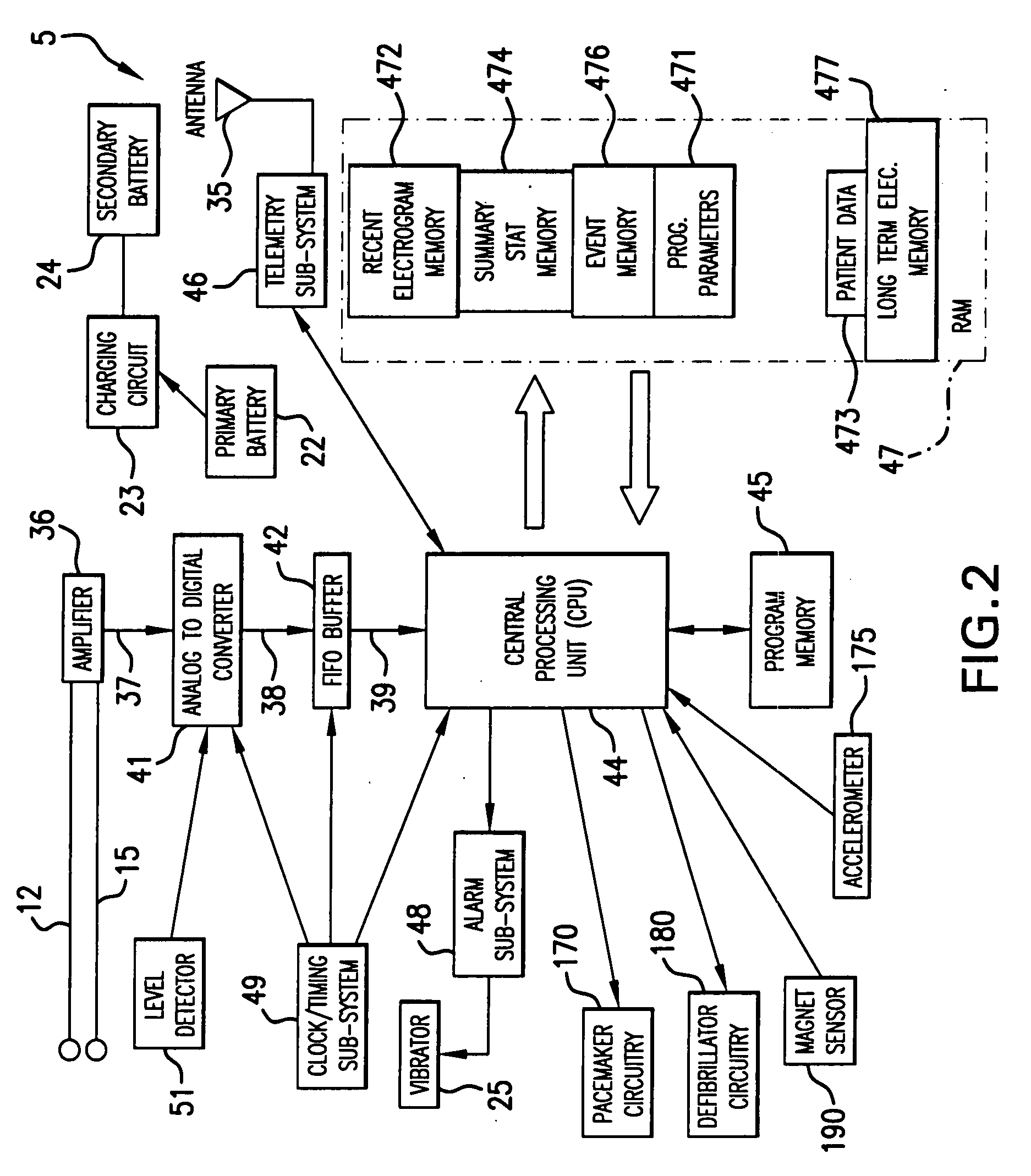
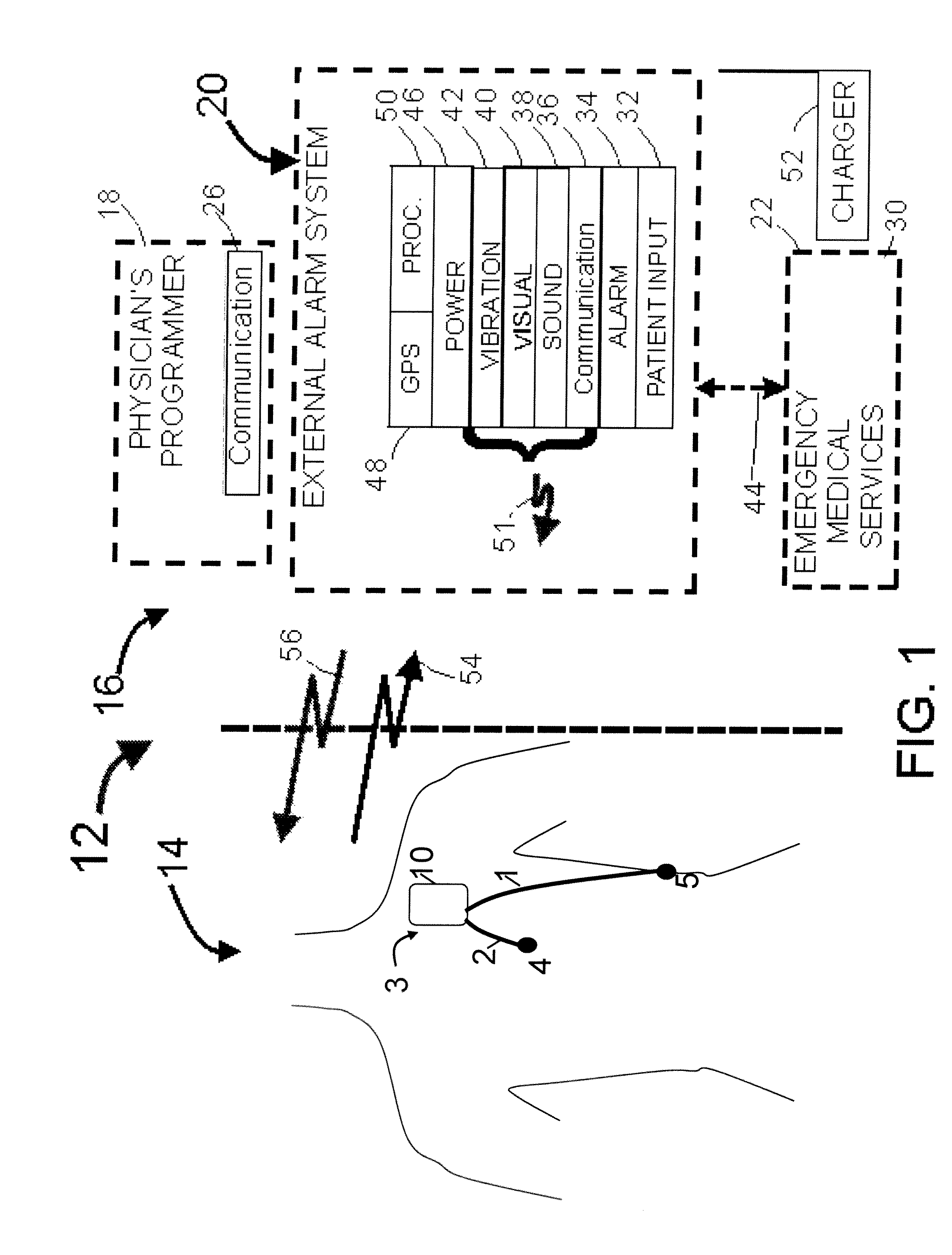
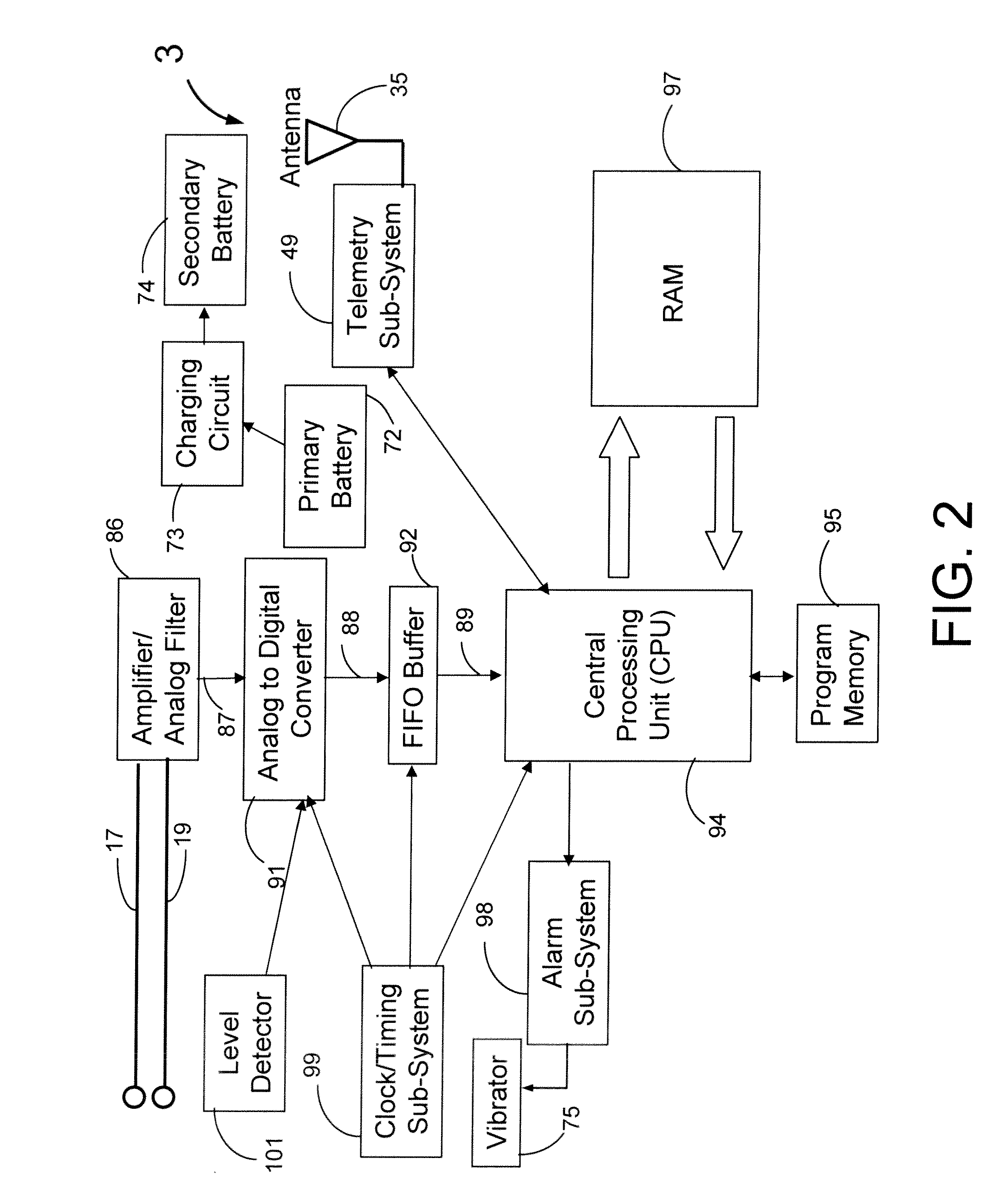
Means and method for the detection of cardiac events
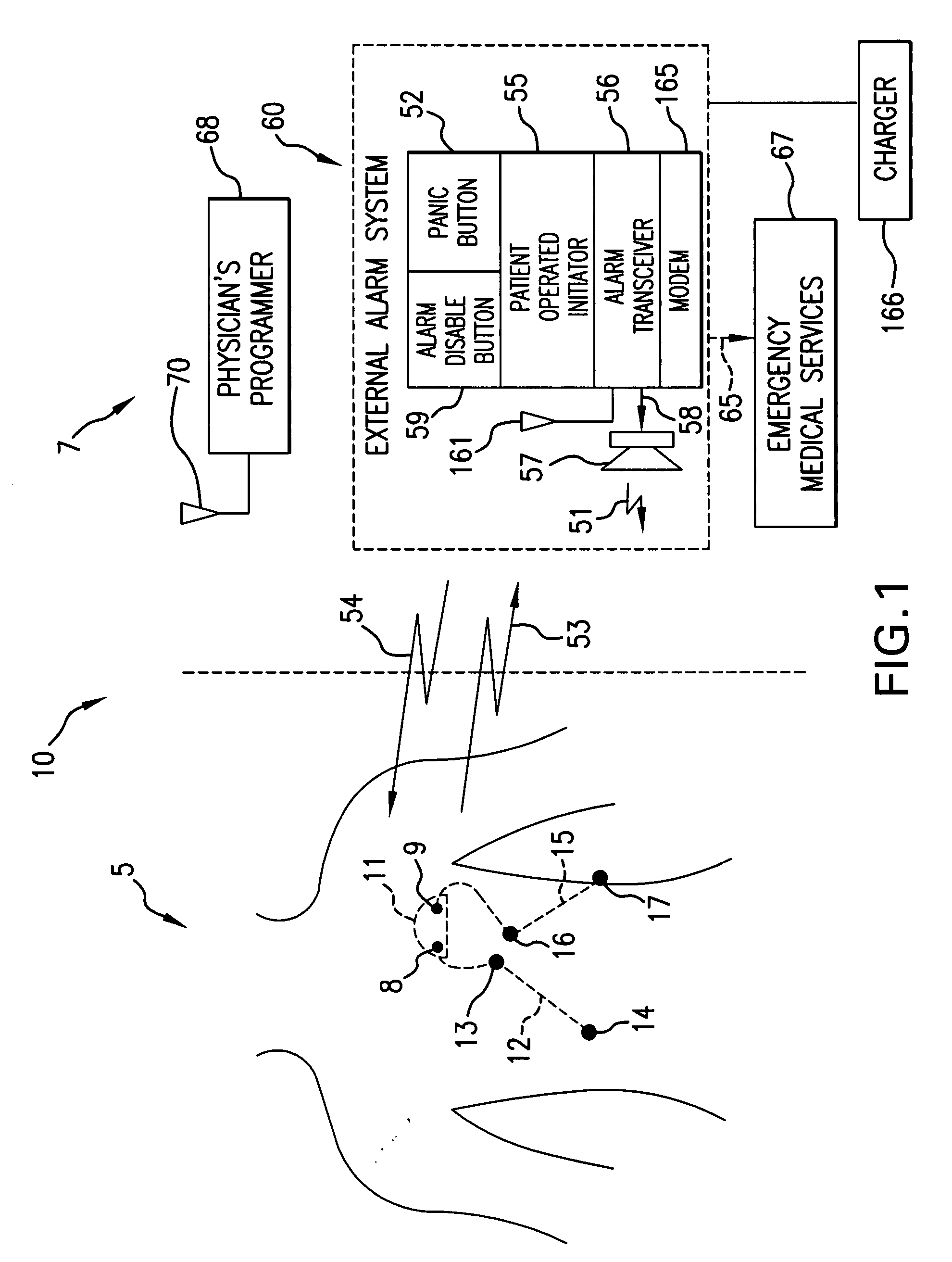
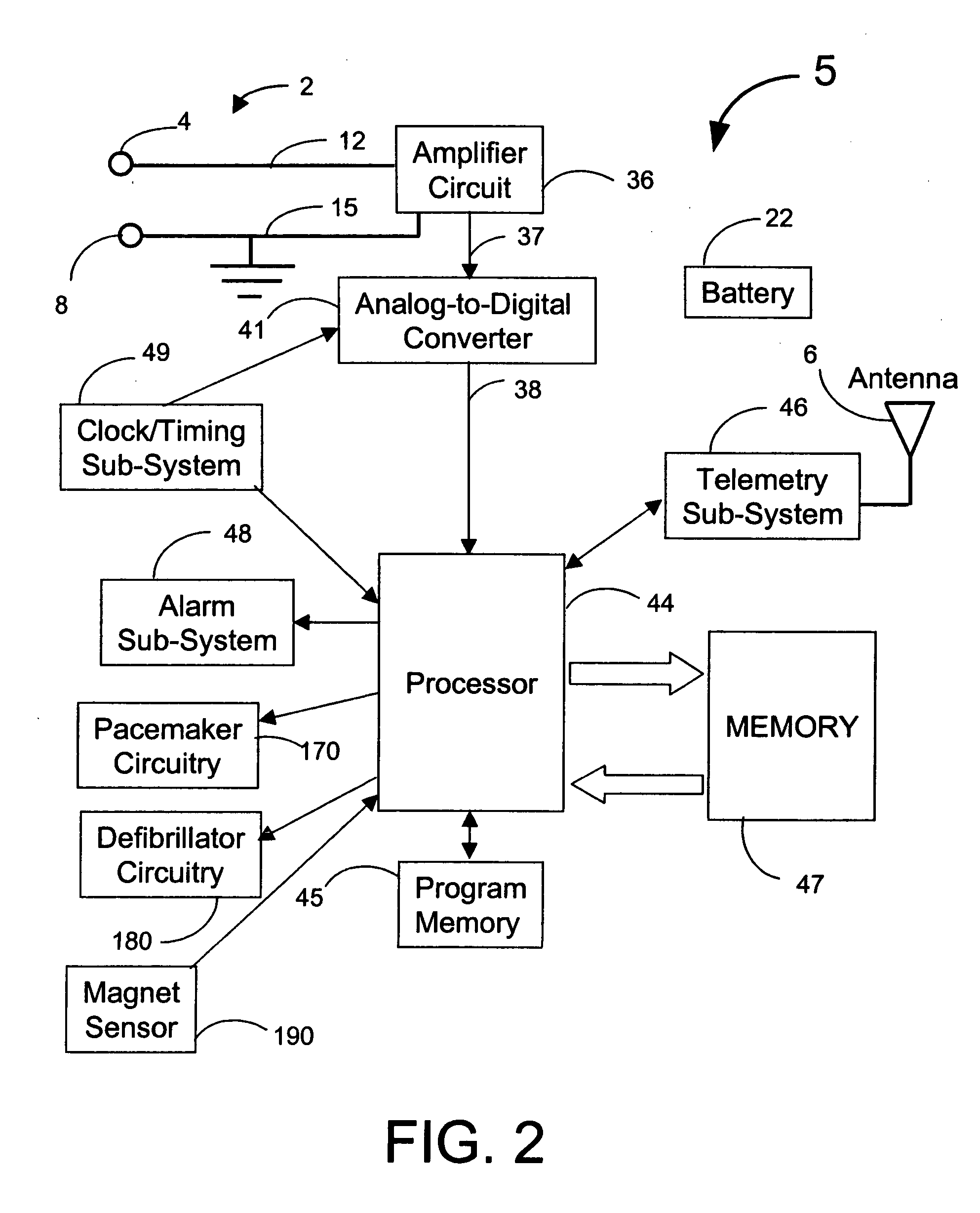
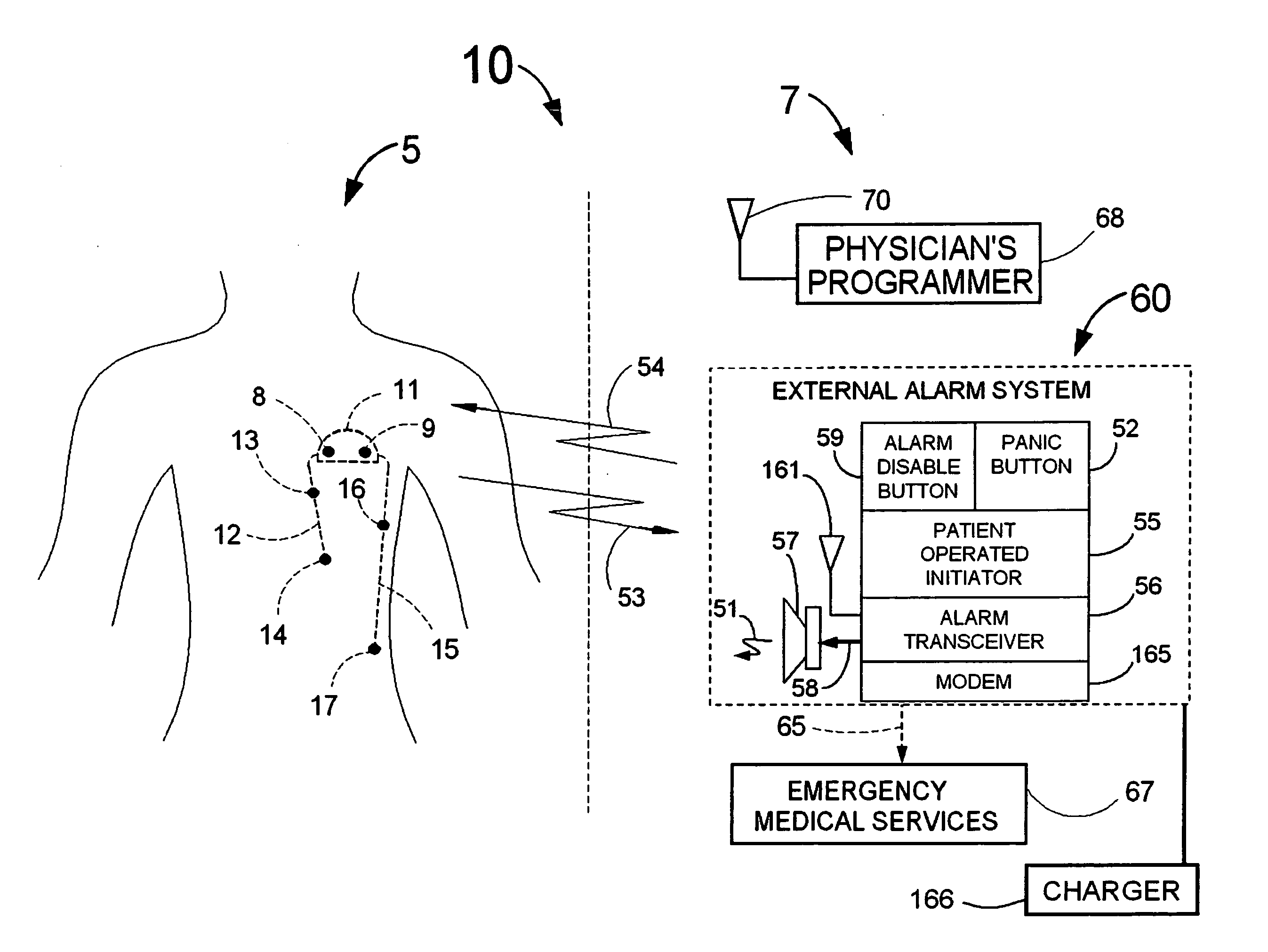
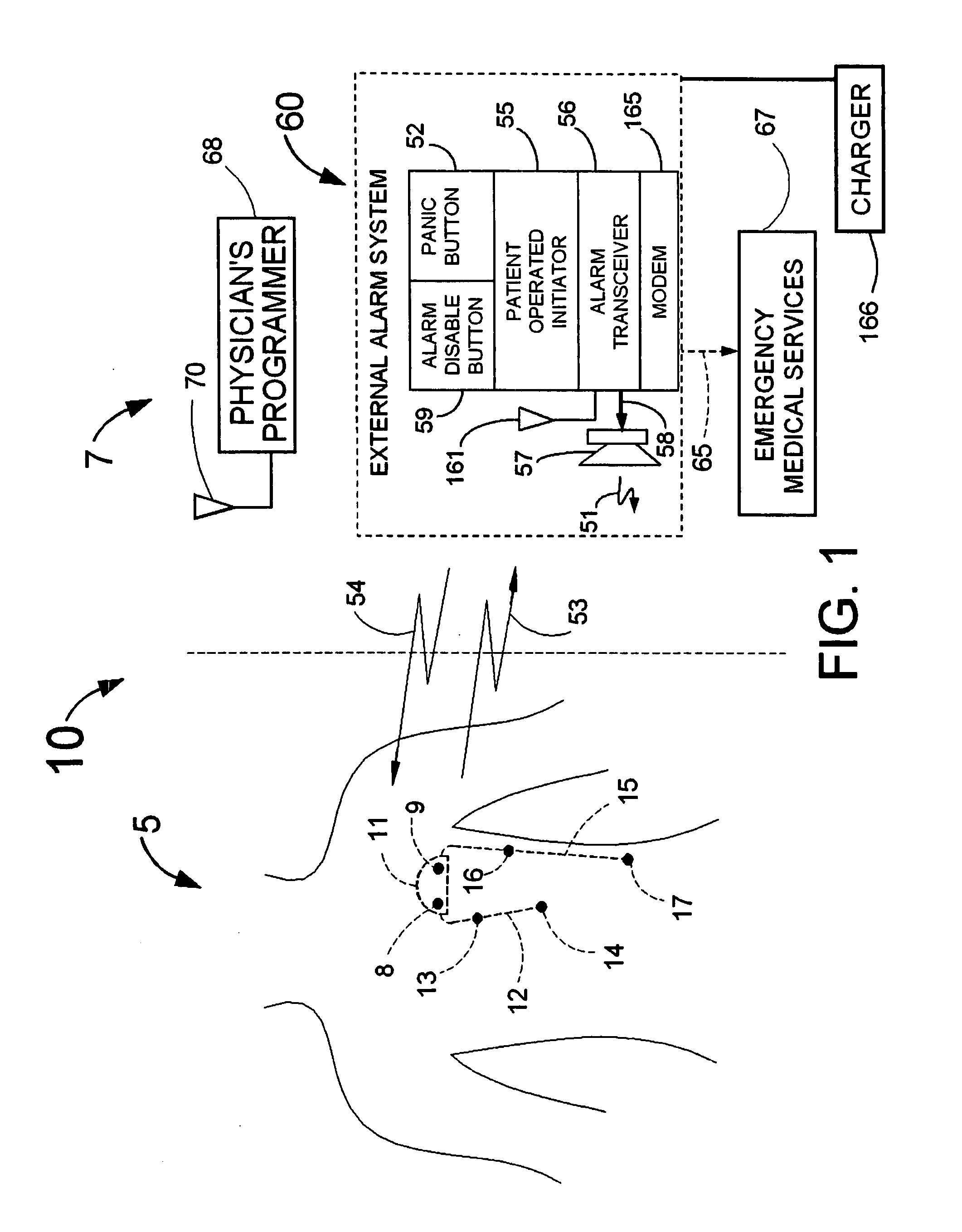
InactiveUS20070249944A1Shorten detection timeShort sleep timeElectrocardiographyHeart stimulatorsIncreased heart rateHeart arrhythmia
Disclosed is a system for the detection of cardiac events that includes an implanted device called a cardiosaver, a physician's programmer and an external alarm system. The system is designed to provide early detection of cardiac events such as acute myocardial infarction or exercise induced myocardial ischemia caused by an increased heart rate or exertion. The system can also alert the patient with a less urgent alarm if a heart arrhythmia is detected. Using different algorithms, the cardiosaver can detect a change in the patient's electrogram that is indicative of a cardiac event within five minutes after it occurs and then automatically warn the patient that the event is occurring. To provide this warning, the system includes an internal alarm sub-system (internal alarm means) within the cardiosaver and / or an external alarm system (external alarm means) which are activated after the ST segment of the electrogram exceeds a preset threshold.
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Application of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the acute myocardial infarction cell transplantation therapy
ActiveCN101642469AImproved prognosisImprove proliferative abilityMammal material medical ingredientsTissue cultureDiseaseCells transplantation
The invention discloses an application of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the acute myocardial infarction cell transplantation therapy; the application is suitable for ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction within one mouth or non ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction cases, a vascular remodeling is carried out to a patient who is attacked by the disease withinsix hours, after about four to six days, coronary perfusion is carried out to the patient; and the other patients who choose date to carry out vascular remodeling operation, the coronary perfusion iscarried out at the same time. The treating effect in the invention is superior to the bone mesenchymal stem cells transplantation.
Owner:PLA NAVY GENERAL HOSIPTAL
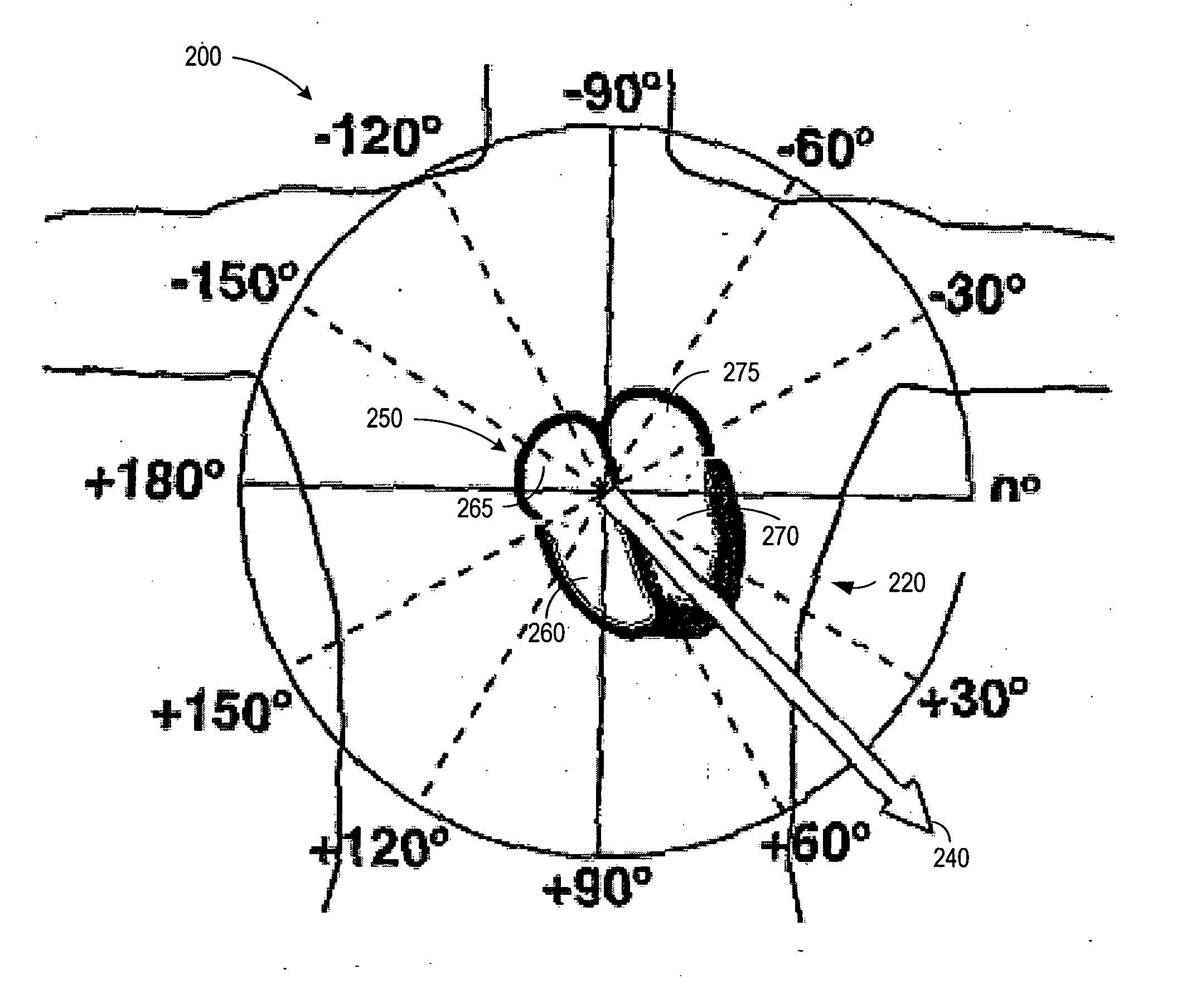
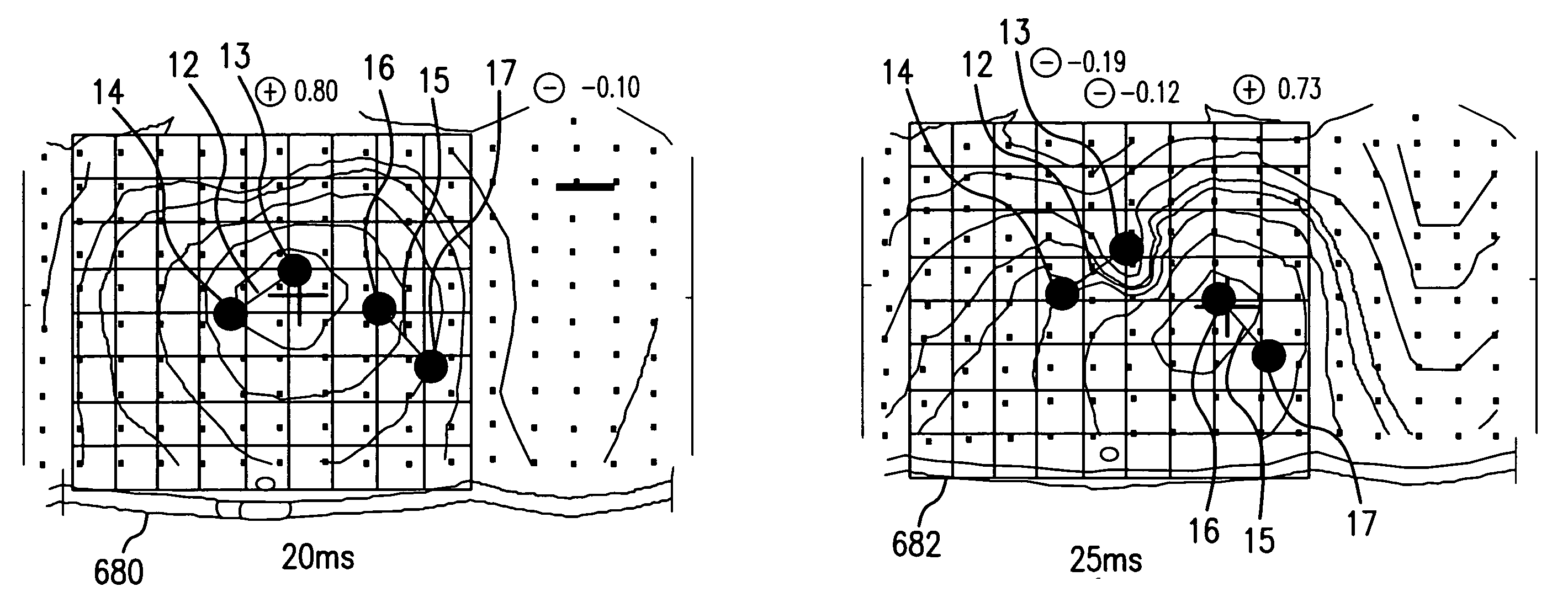
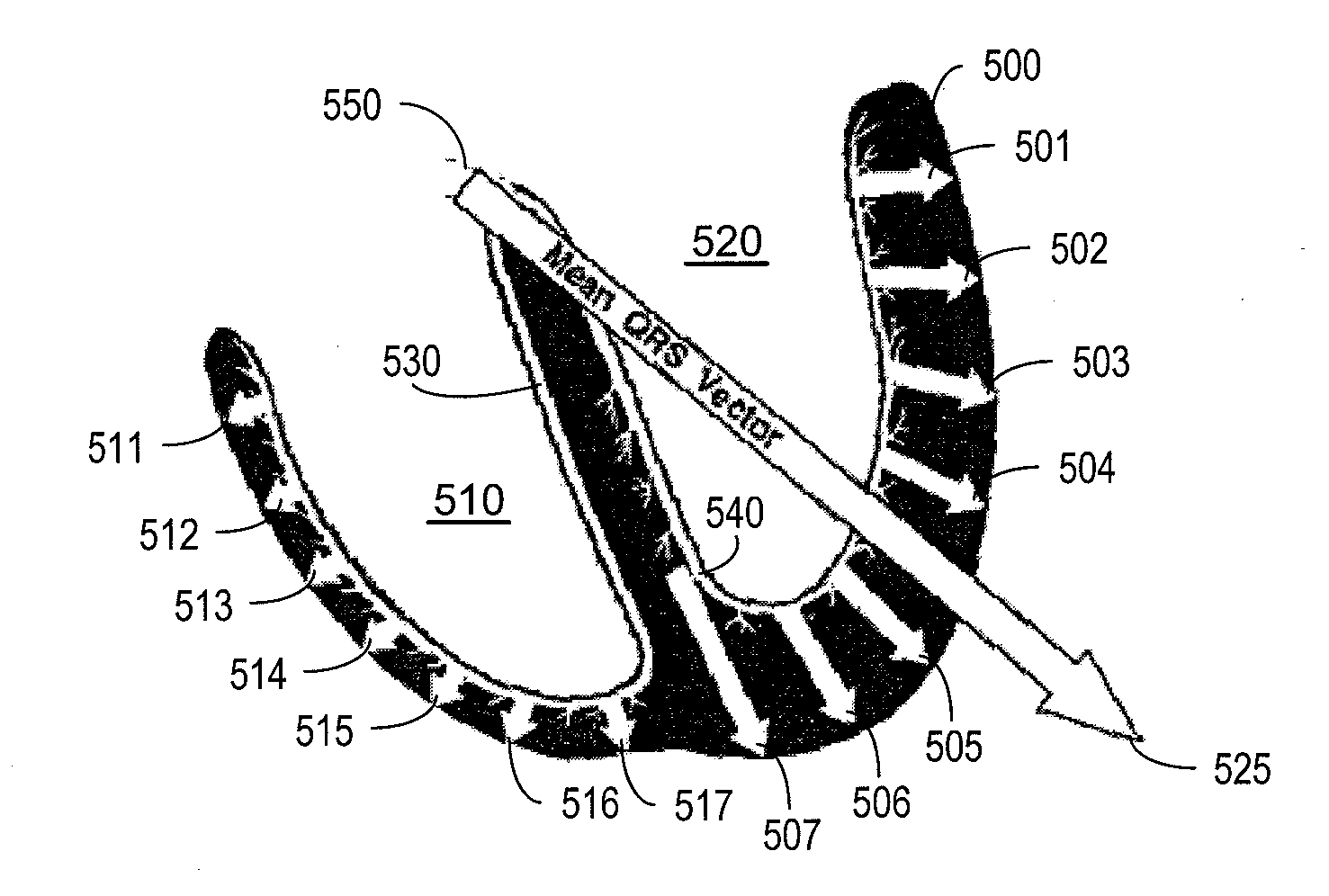
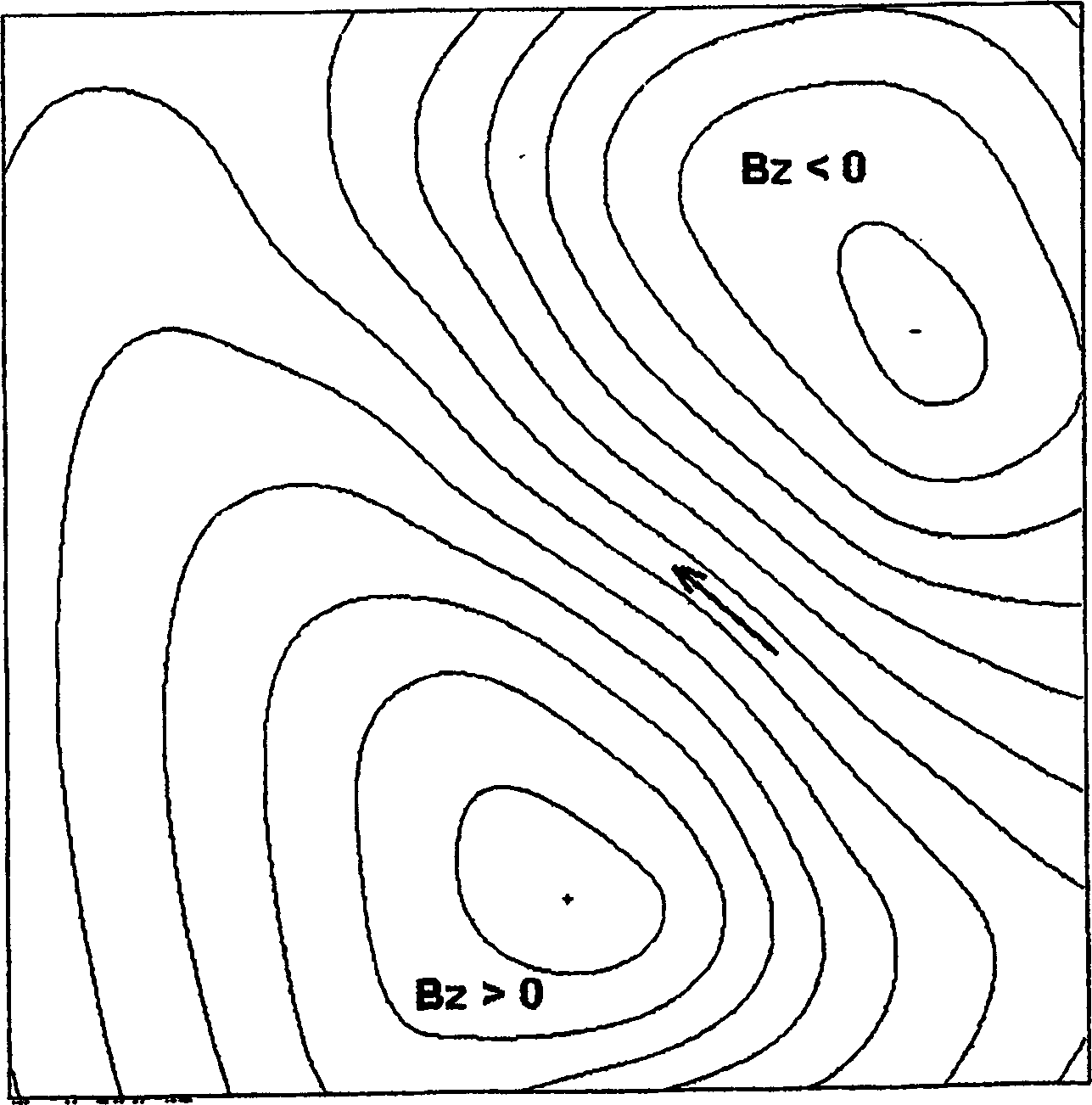
Ischemia identification, quantification and partial localization in MCG
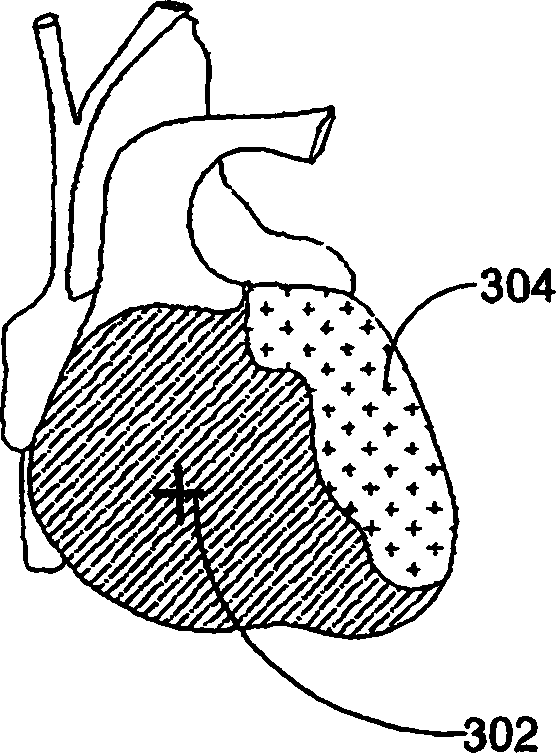
A magnetic dipole model based on MCG data of the heart is used to localize cardiac tissue afflicted with ischemia. The direction of diaplacement of the dipole during the ST segment, superimposed on the heart's general outline, indicates a rough location of the ischemic cardiac tissue. Furthermore, the extent of ischemia is quantified based upon the how much displacement occurs in the ST segment. For example, if significant dipole's displacement occurs in the first quarter of the ST segment, then it is identified as a first-degree ischemia. Similarly, if diaplacement occurs in 1 / 2, 3 / 4, or 1 full ST segment, then the level of ischemia is identified as second degree, third degree, or fourth degree ischemia (fourth degree being the worst kind of ischemia where the dipole's position is dynamic all through the ST segment).
Owner:CARDIOMAG IMAGING
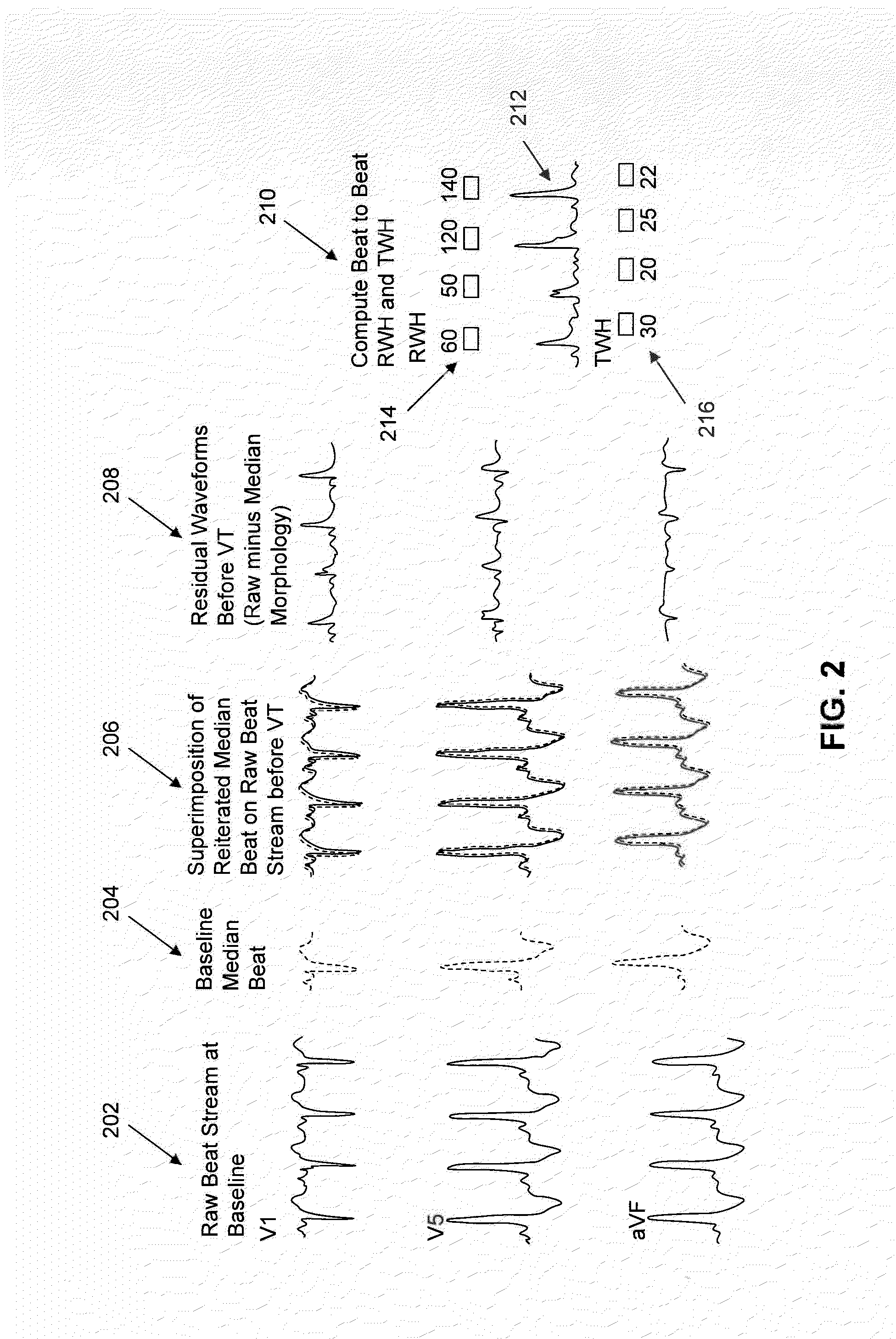
Multilead ECG template-derived residua for arrhythmia risk assessment
A method and system for predicting the onset of heart arrhythmias more accurately observes trends in abnormal or pathologic morphology of the electrocardiogram (ECG). A first set of ECG signals is monitored from a patient. A baseline measurement is generated from the monitored first set of ECG signals to contain nonpathologic ECG morphologies in each lead. A second set of ECG signals is monitored from the patient and the baseline measurement is subtracted from the second set of ECG signals on a beat-to-beat basis. Afterwards, a residuum signal is generated for each lead based on the subtraction. R-wave heterogeneity, T-wave heterogeneity, P-wave heterogeneity, or ST-segment heterogeneity or other indicators of arrhythmia risk or myocardial ischemia are quantified based on the generated residuum signals.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
System and methods for sliding-scale cardiac event detection
Owner:ANGEL MEDICAL SYST
Method for the prediction of vascular events and the diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome
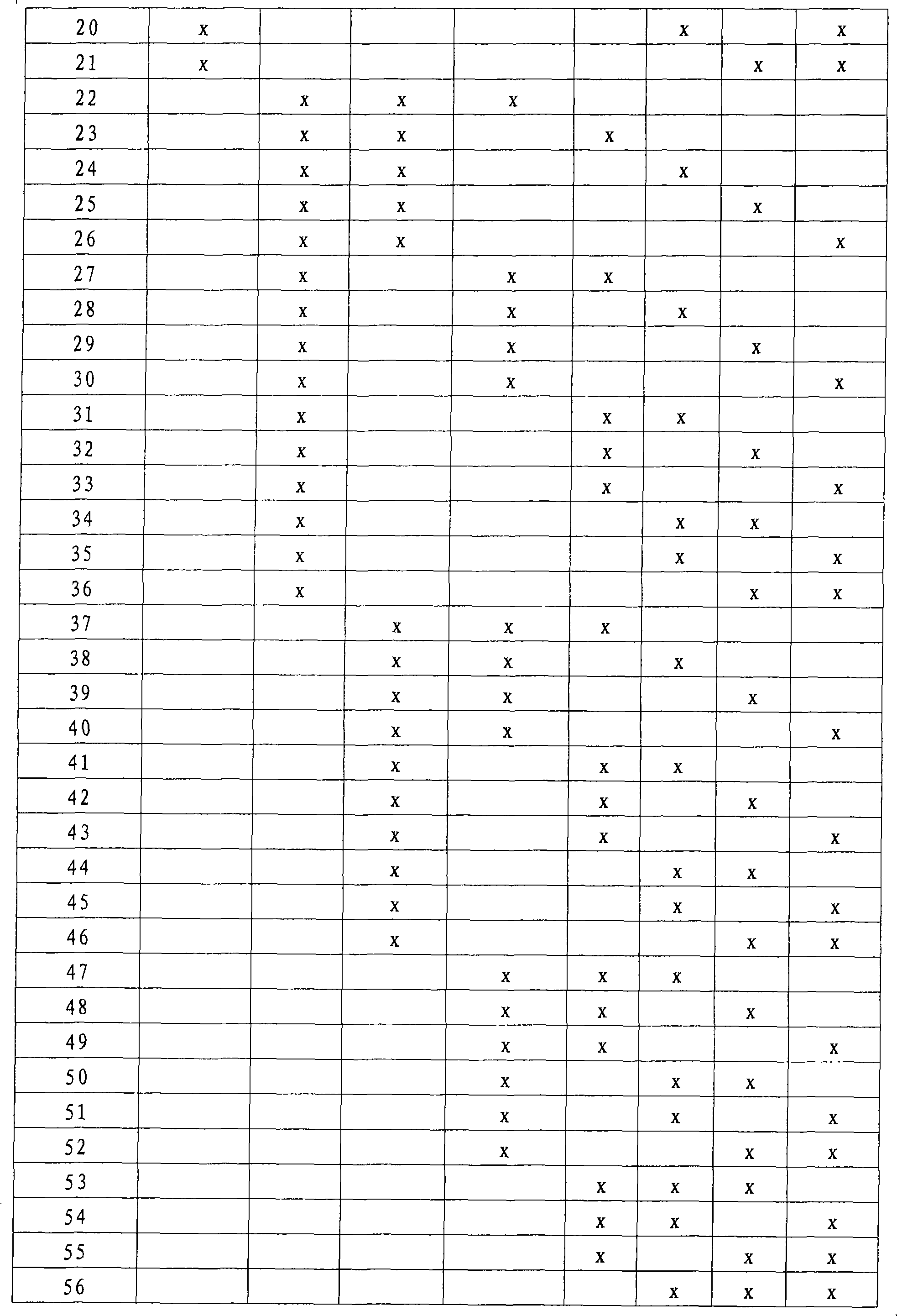
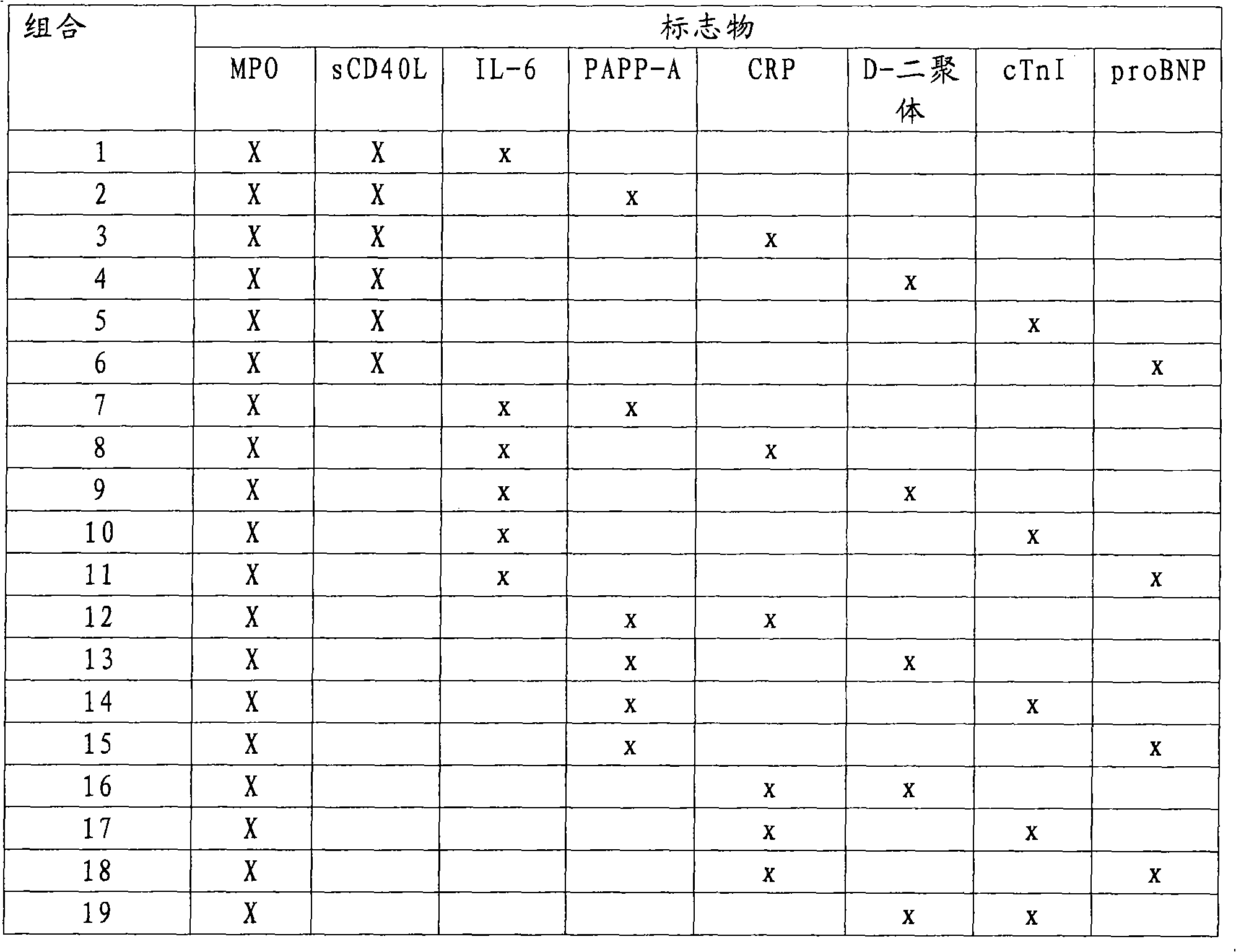
The present invention relates to a method for the prognosis of a vascular event in a patient suspected of being at risk for a vascular event, said patient presenting: - no elevation of the ST segment as seen on an electrocardiogram, and / or - a normal level of at least one myocardial necrosis marker, wherein the presence and / or levels of at least two different biochemical markers are measured in a biological sample of said patient, whereby the probability that the patient will experience a vascular event is deduced from the measured presence and / or levels of the biochemical markers such as MPO, sCD40L, IL-6, PaPP-A, CRP, D-dimer, troponin, and proBNP.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
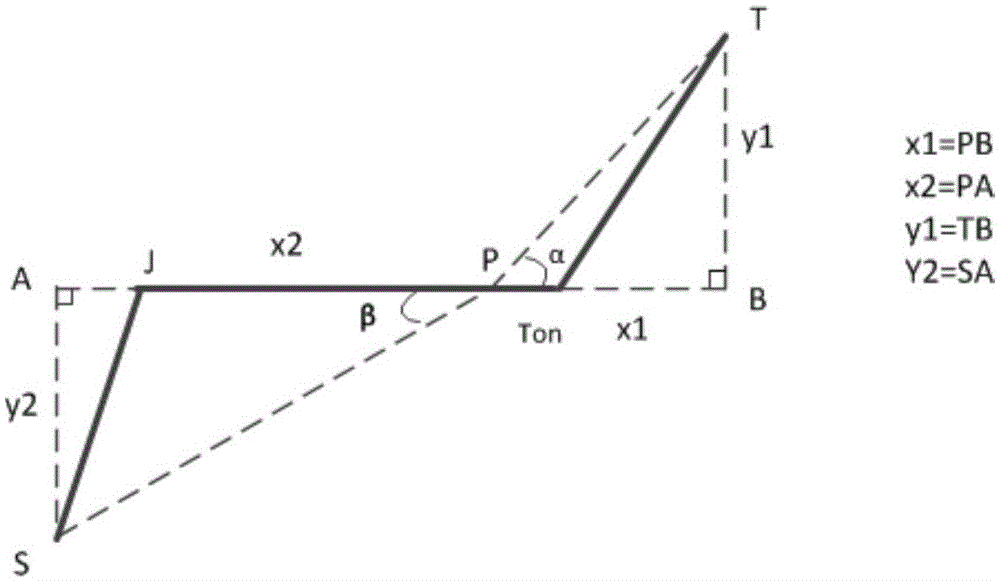
Method for recognizing ST segment of electrocardiosignal
ActiveCN105030233AAccurate identificationEfficient identificationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalSlope ratio
The invention discloses a method for recognizing the ST segment of an electrocardiosignal. According to the method, a wave S and a wave T are accurately located through a slope ratio extremum method based on a peak R for the filtered electrocardiosignal, and finally the displacement, slope and length characteristics of the ST segment are accurately recognized. The method is simple in calculation, easy to implement and high in accuracy rate, and a new way is provided for fast and effective recognition of the electrocardiosignal.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
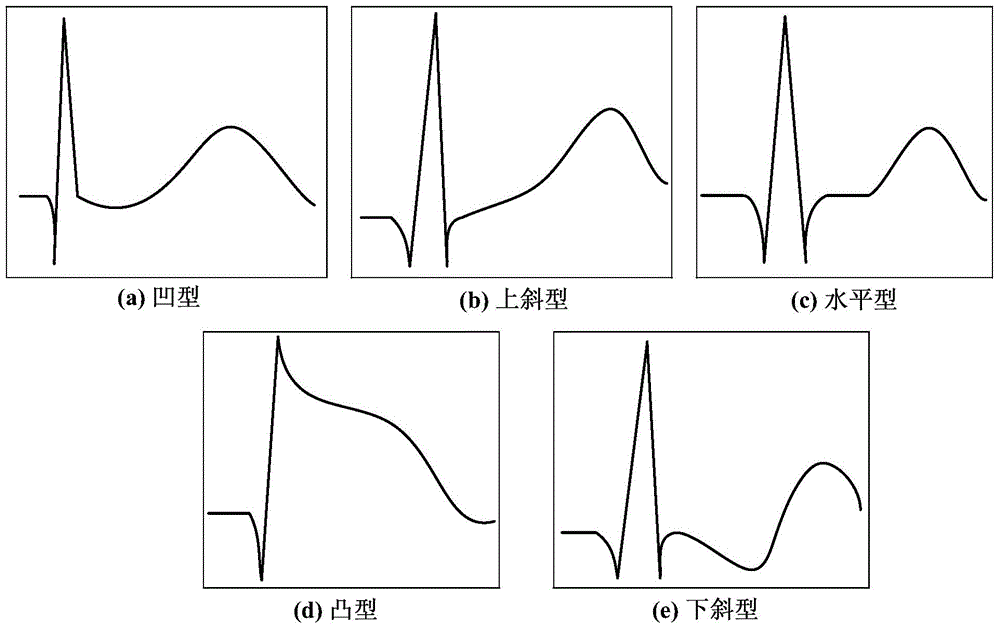
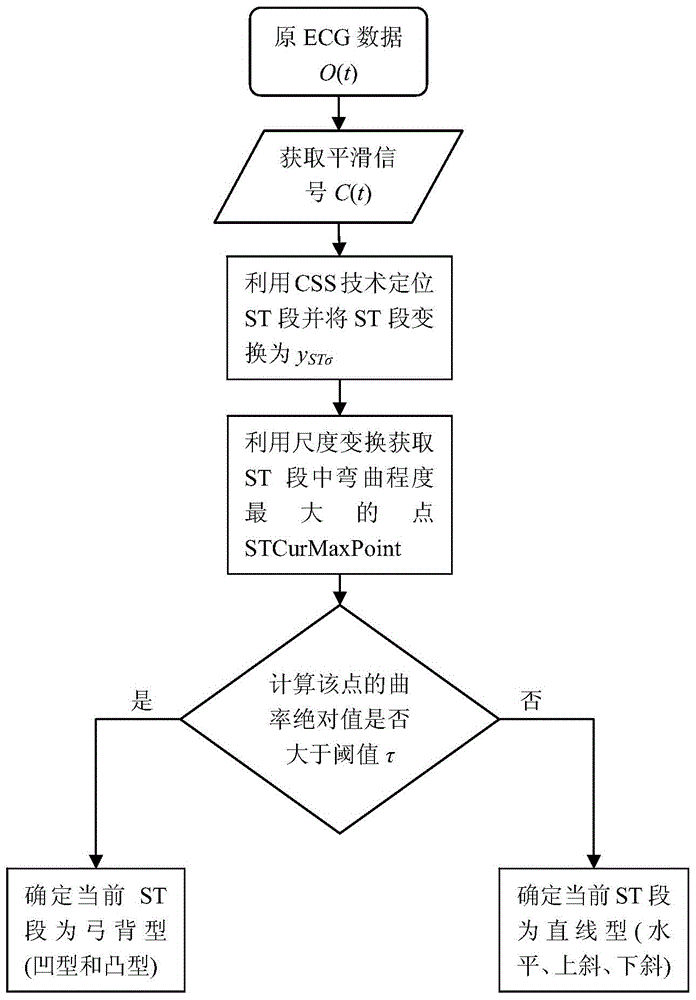
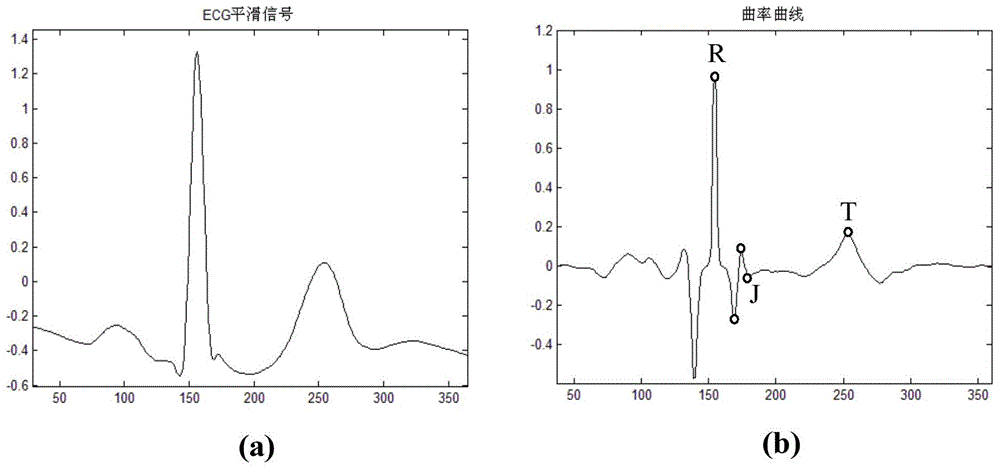
Automatic classification method for ST-segment evaluation patterns in electrocardiograph signals
ActiveCN104680186AGuaranteed real-timeAvoid noise disturbanceCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringEcg signalHuman body
The invention provides an automatic classification method for ST-segment evaluation patterns in electrocardiograph (ECG) signals. The automatic classification method is characterized by comprising the following steps: collecting the lead ECG signals of a human body; classifying the ST-segment evaluation patterns in the ECG signals into horizontal type, upper inclined type, lower inclined type, concave type and convex type; utilizing the multi-scale analysis method of curvature scale space technology to position ST-segment and obtain the point corresponding to the maximum value of the absolute value of the curvature in the ST-segment, namely the maximum point of the bending degree of the ST-segment; according to the characteristic of the curvature, utilizing the maximum point of the bending degree in the ST-segment to judge the ST-segment evaluation patterns. By introduction of the curvature scale space method, the influence of noise is effectively reduced, the ST-segment evaluation patterns can be accurately identified, and the method has an important use value for early warning of myocardial ischemia.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com