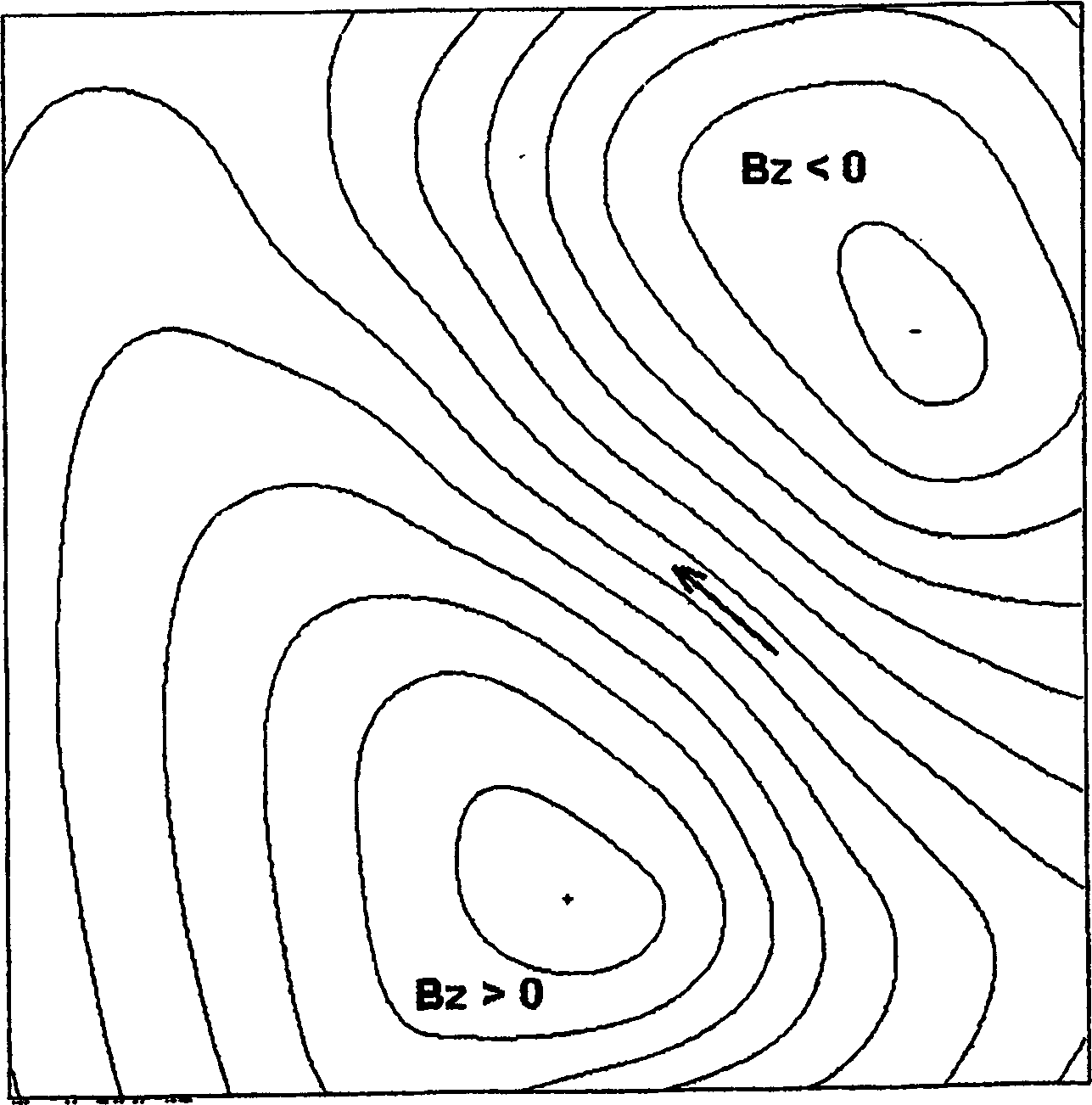
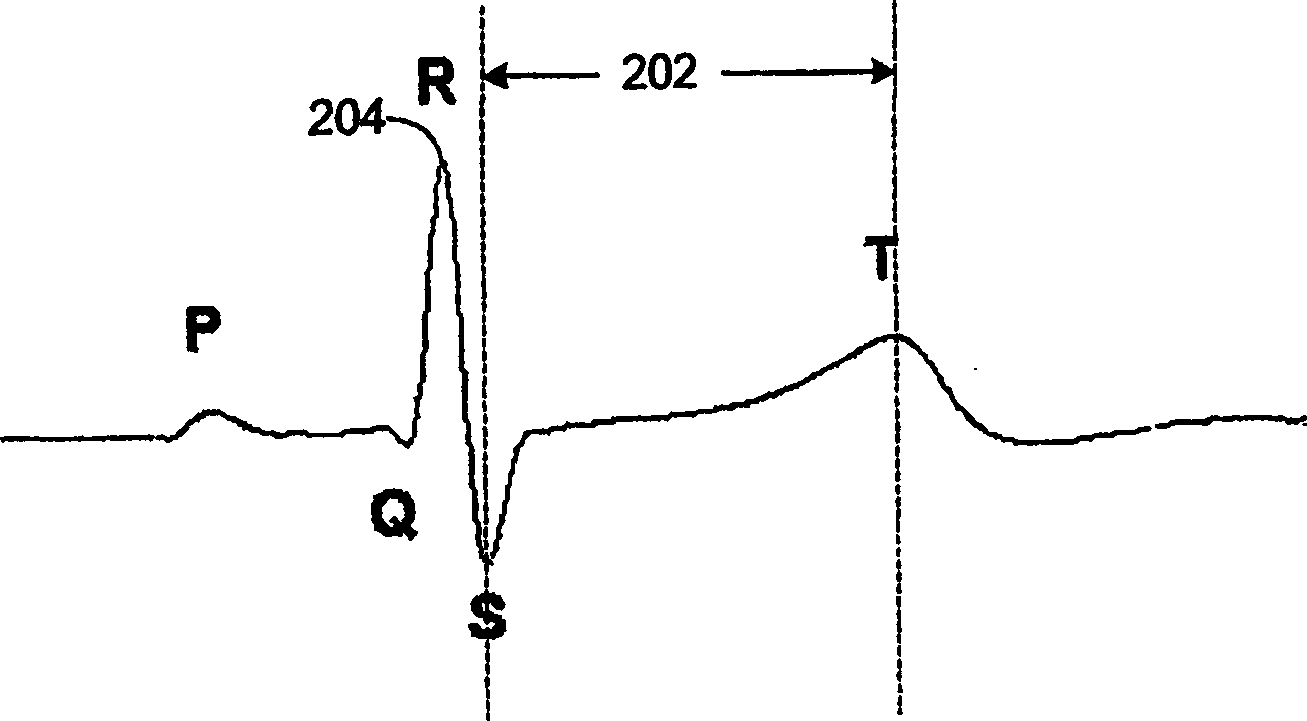
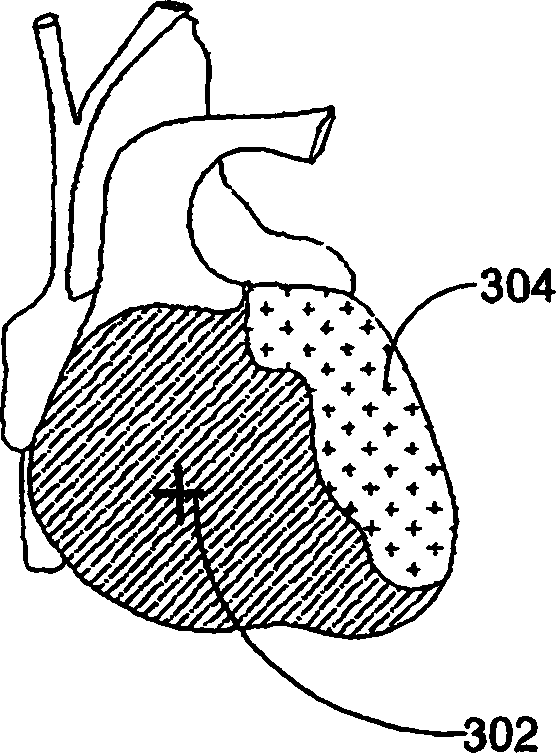
Ischemia identification, quantification and partial localization in MCG
An ischemia, cardiac technology, applied in the fields of adjusting magnetic variables, magnetic resonance measurement, image analysis, etc., can solve the problems of incapable ischemic heart disease severity, inability to fully achieve, spatial positioning damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] Although the invention has been described in terms of preferred embodiments, it can be realized in many different configurations, forms and materials. A preferred embodiment of the present invention as shown in the accompanying drawings will be specifically described below to explain the content of the present invention. It is an example of the principle of the present invention and its functional structural features, and is not intended to limit the present invention to the present invention. The example shown. Those skilled in the art will be able to implement many other possible variations within the scope of the invention. The term "identification" used in the specification refers to the identification of ischemic cardiac tissue, and it should be understood that a medical professional (such as a cardiologist) makes an effective decision based on the information provided by the MCG used in conjunction with the system and method of the present invention. No final det...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com