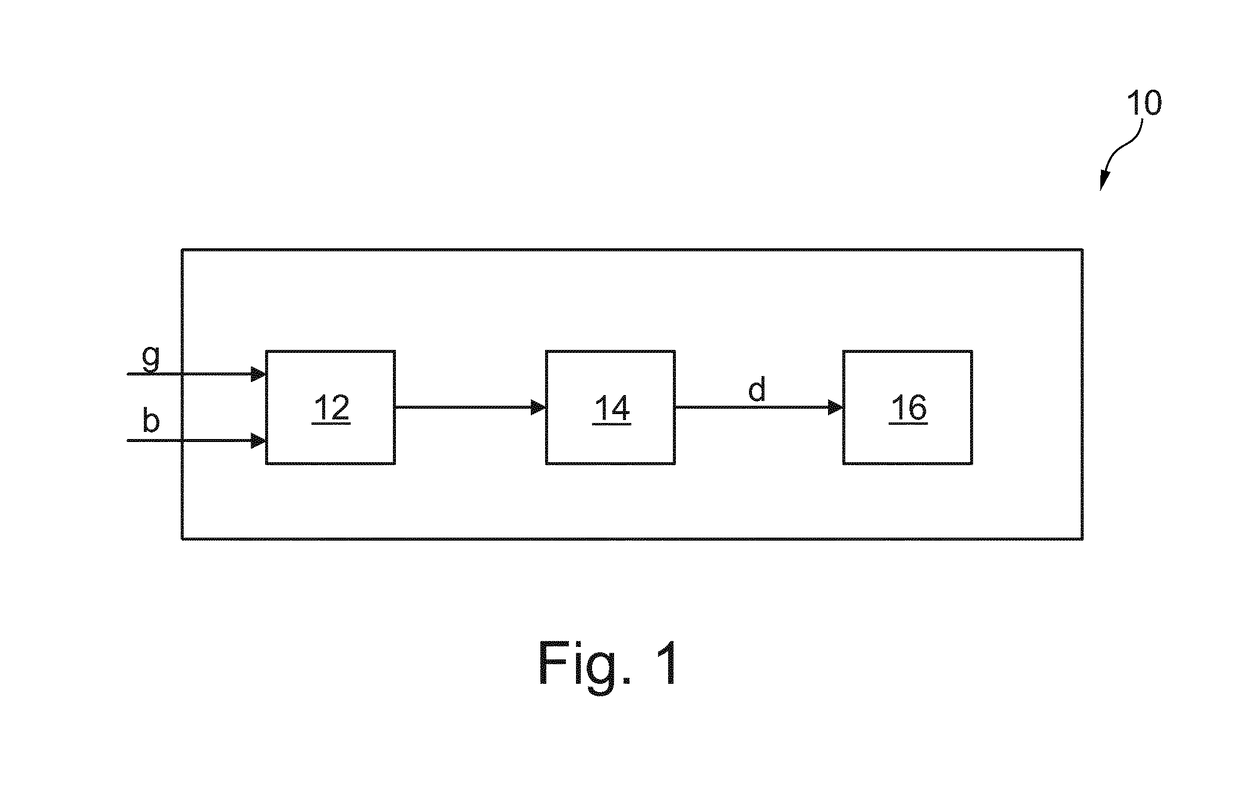
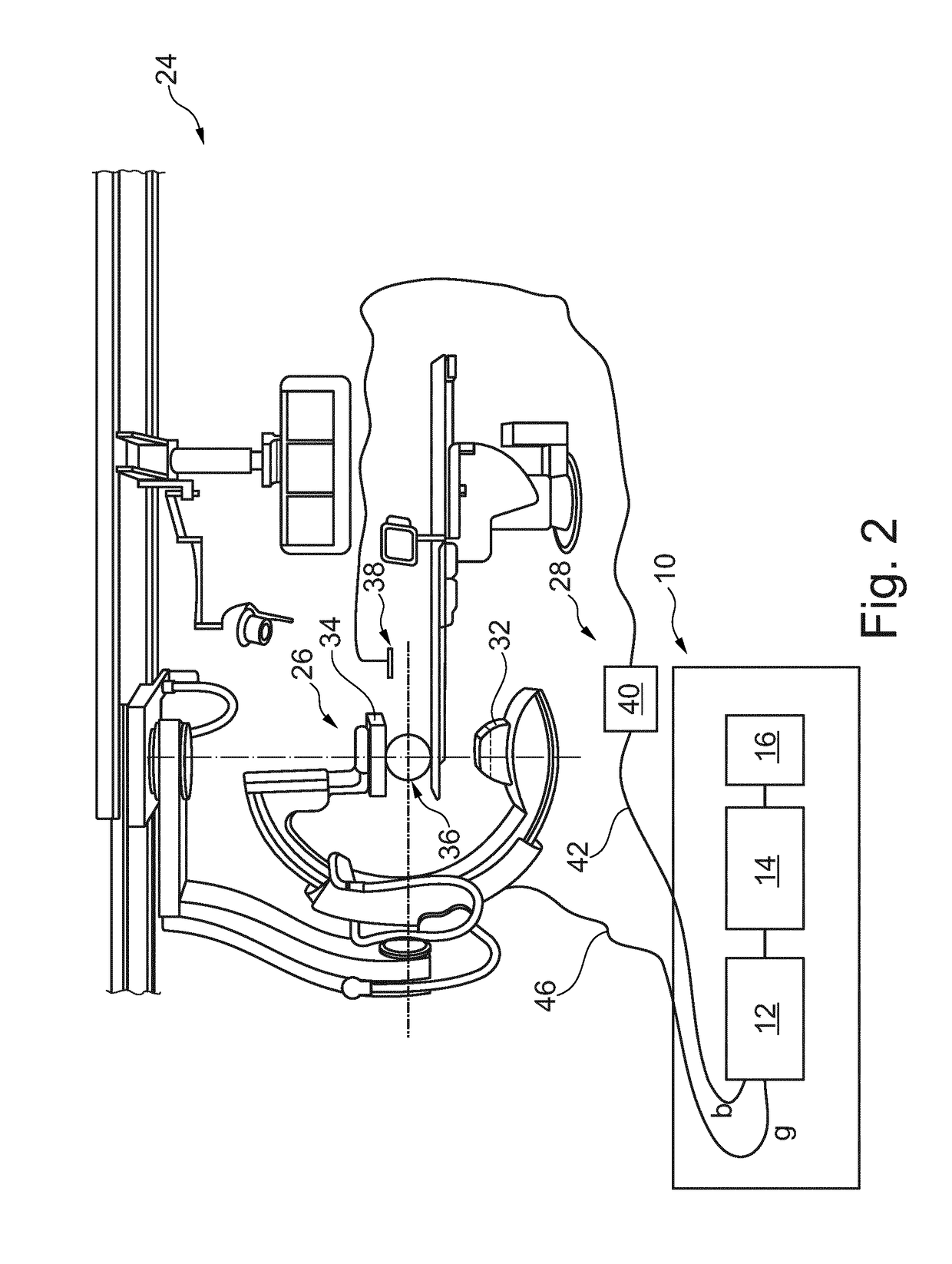
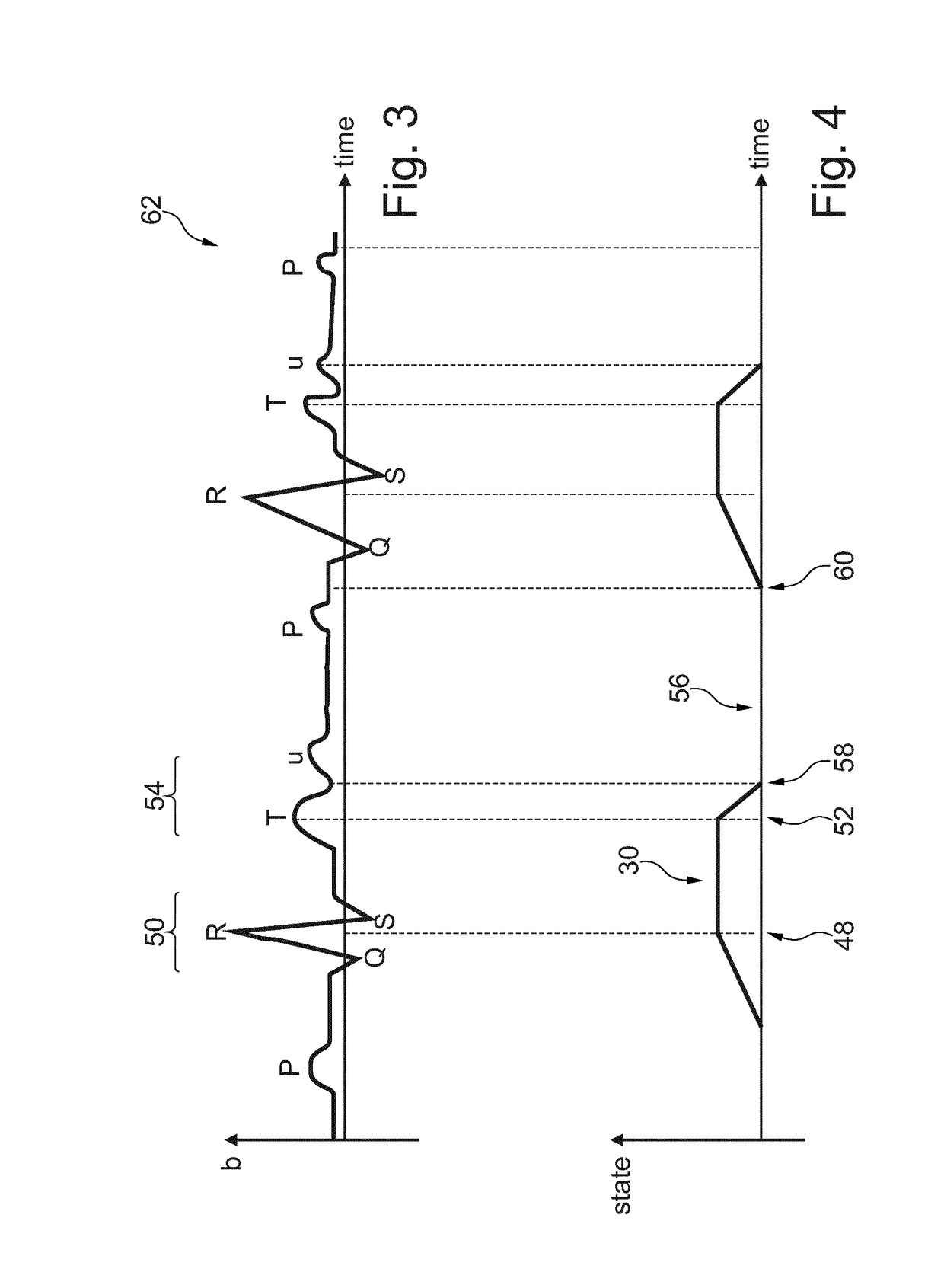
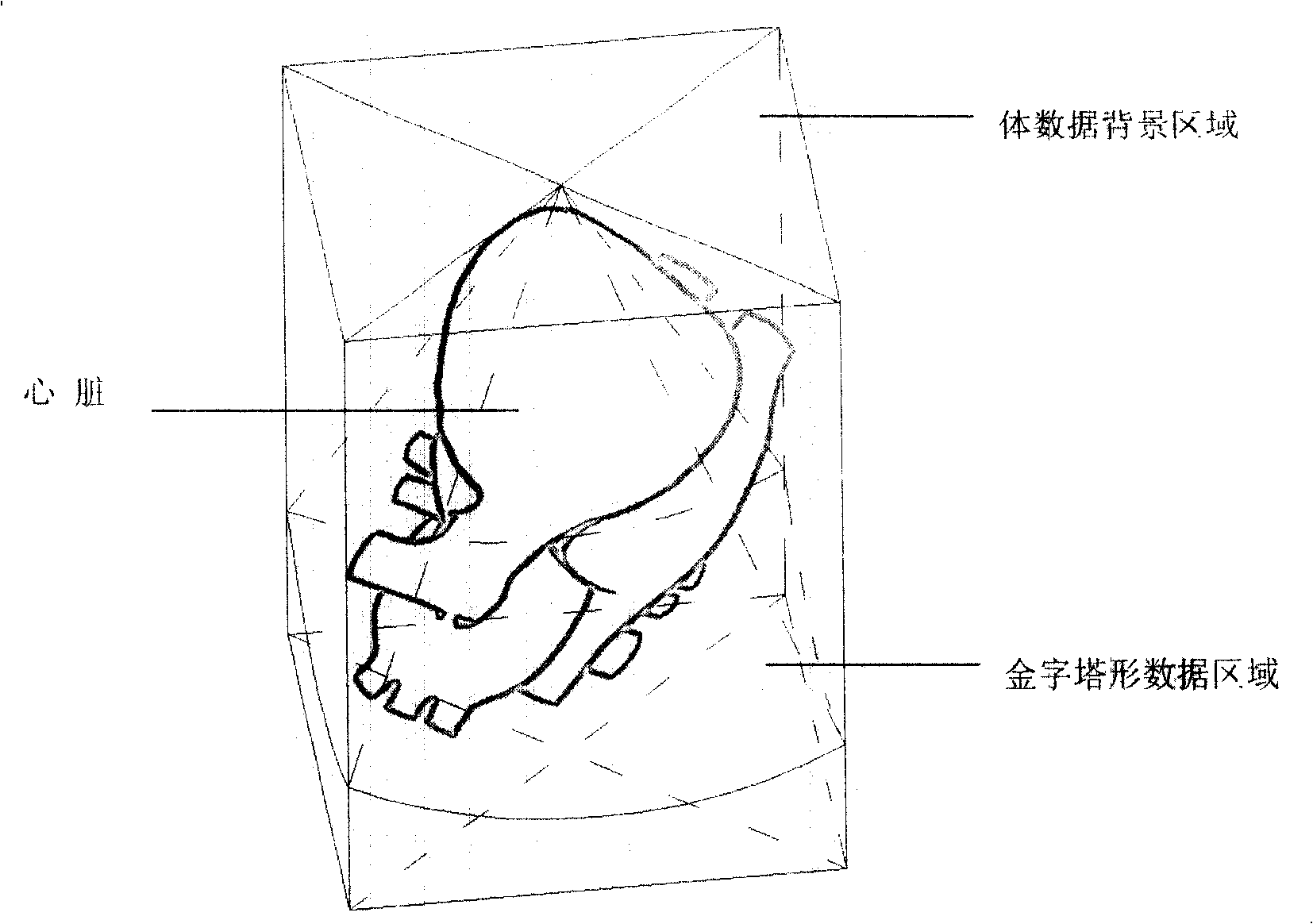
Patents
Literature
31 results about "Diastolic phase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
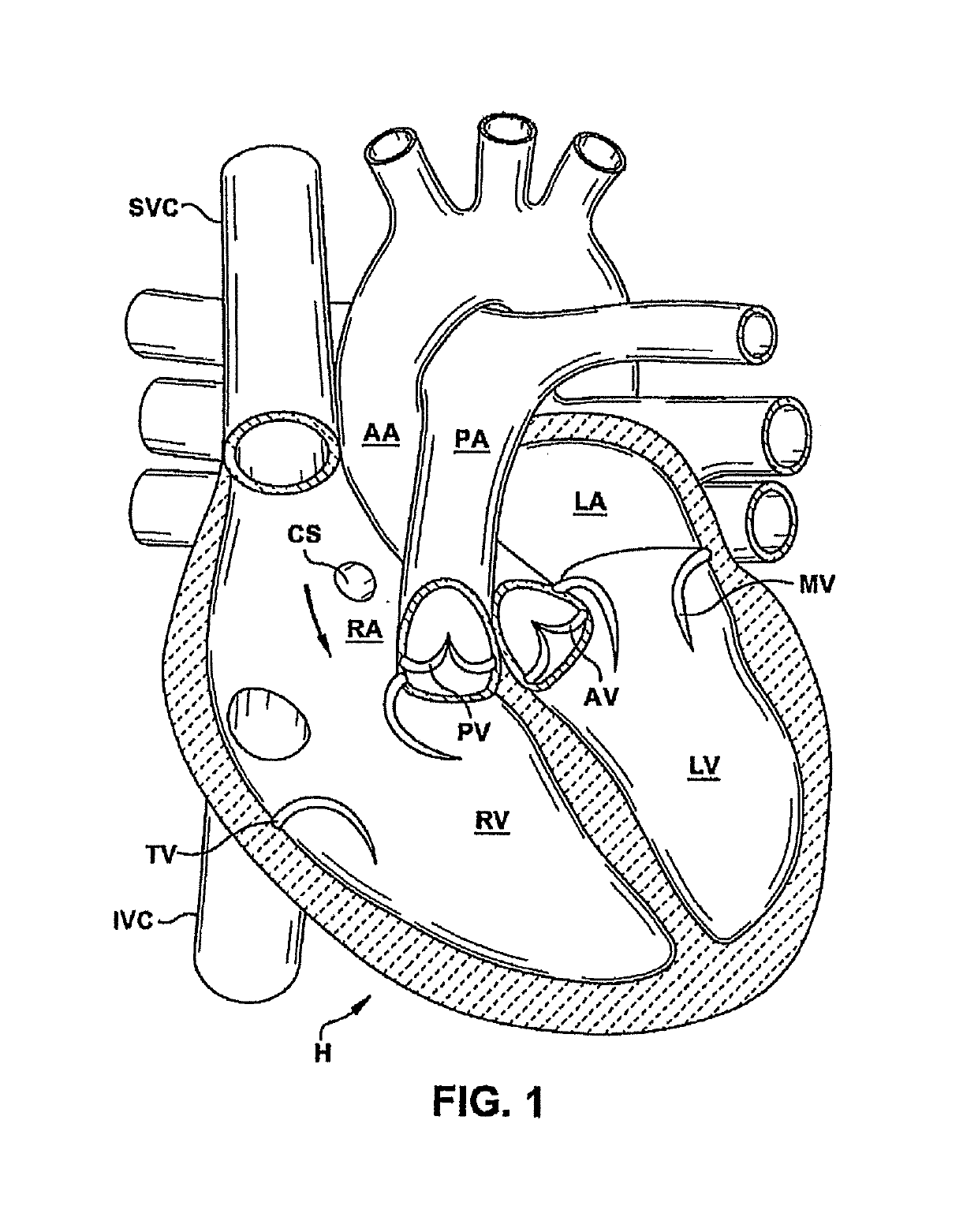
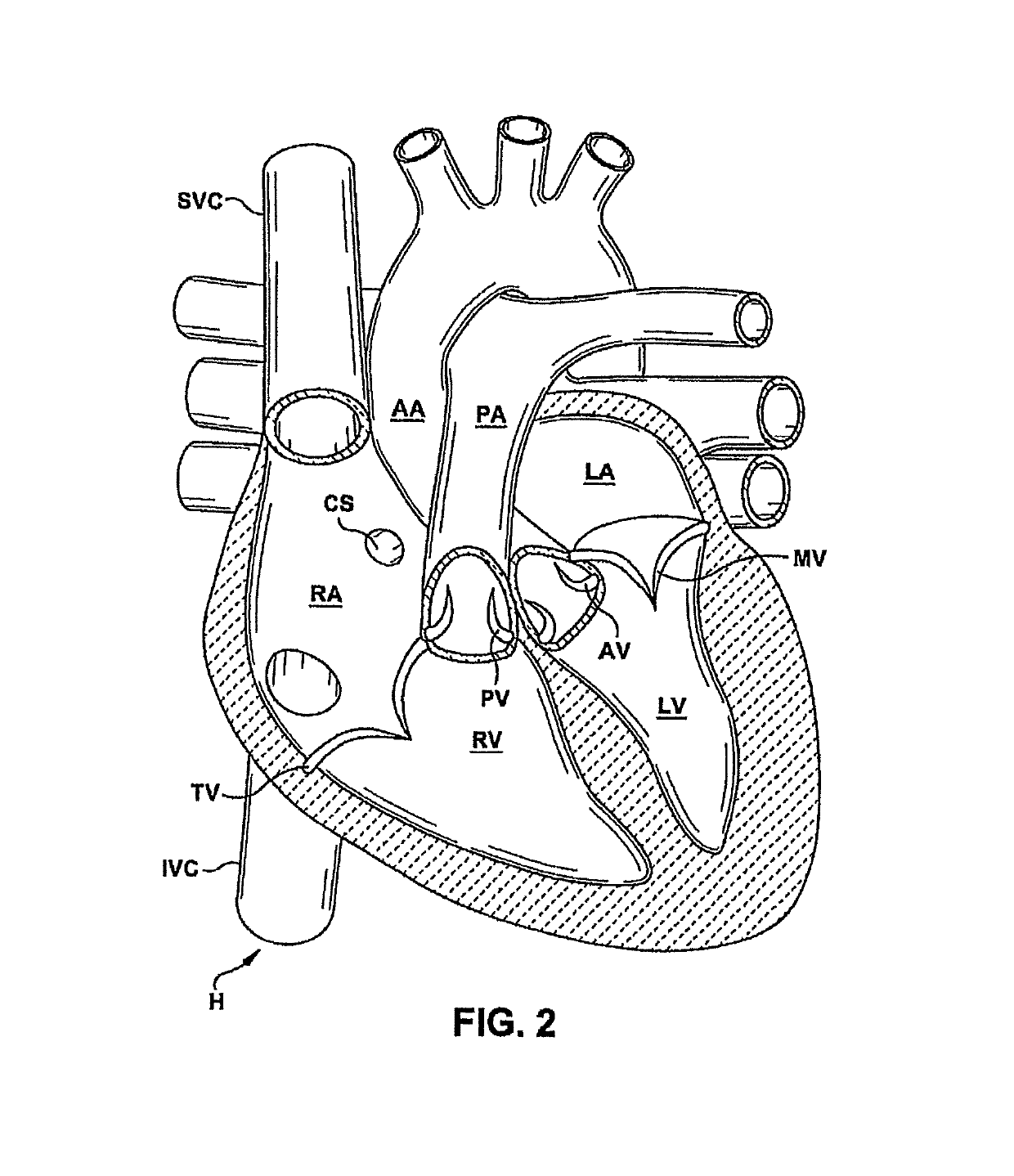
Diastole is divided into four phases and comprises 2/3 of the cardiac cycle. It begins when the aortic valve closes. This is the start of Isovolumic Relaxation (volume remains constant but the pressure in the ventricles fall). The next phase of diastole occurs when the mitral valve opens and allows for rapid ventricular filling.
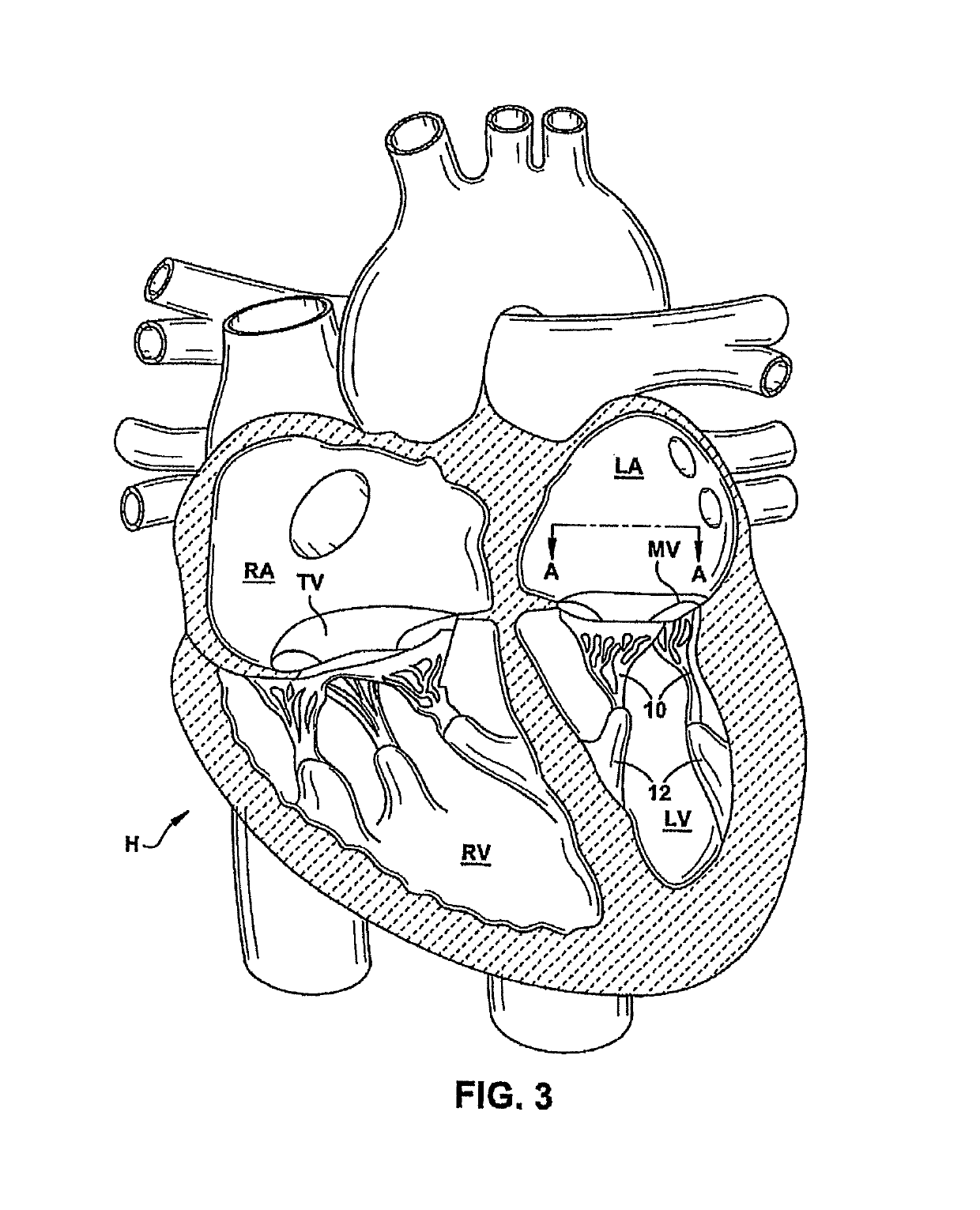
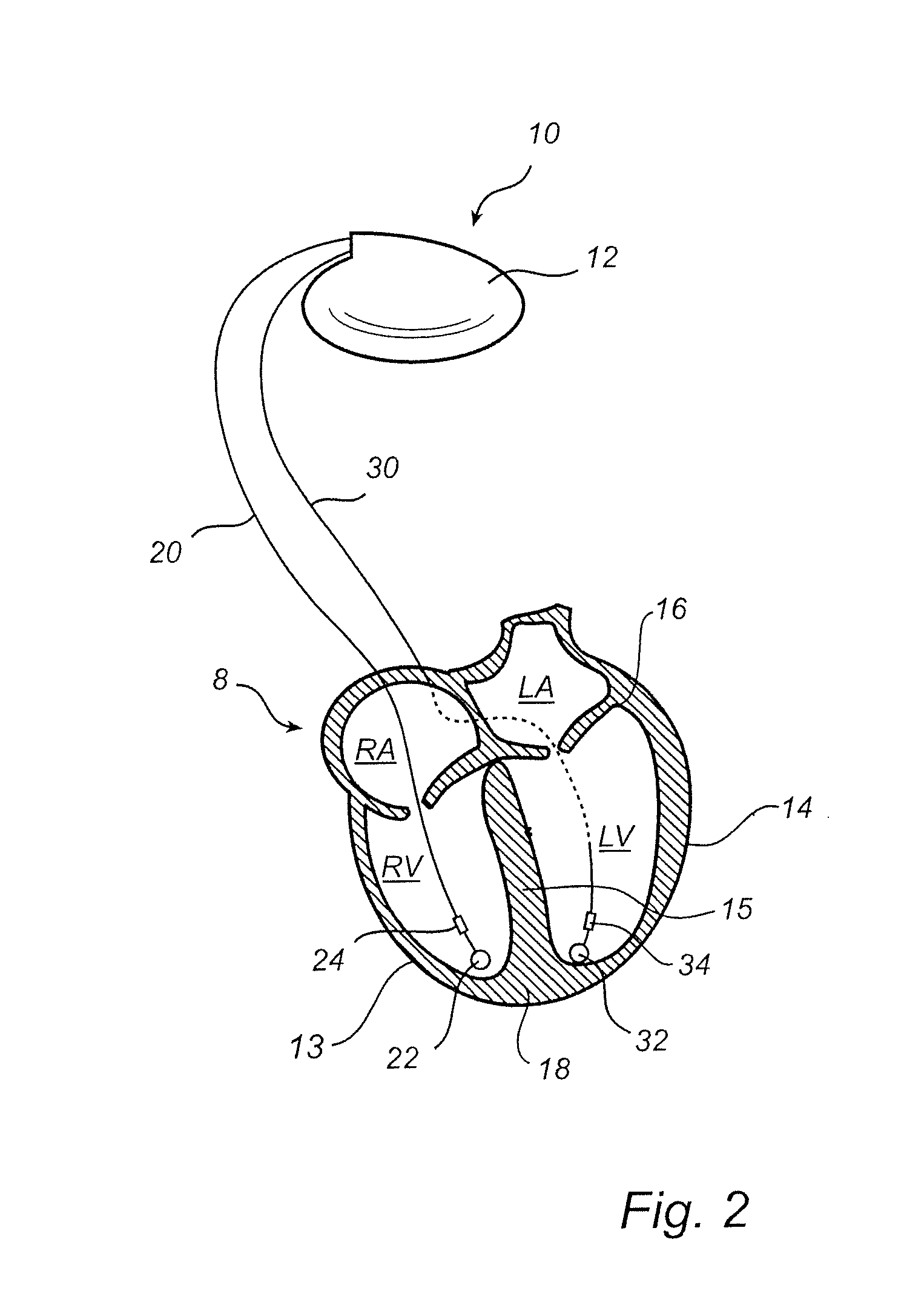
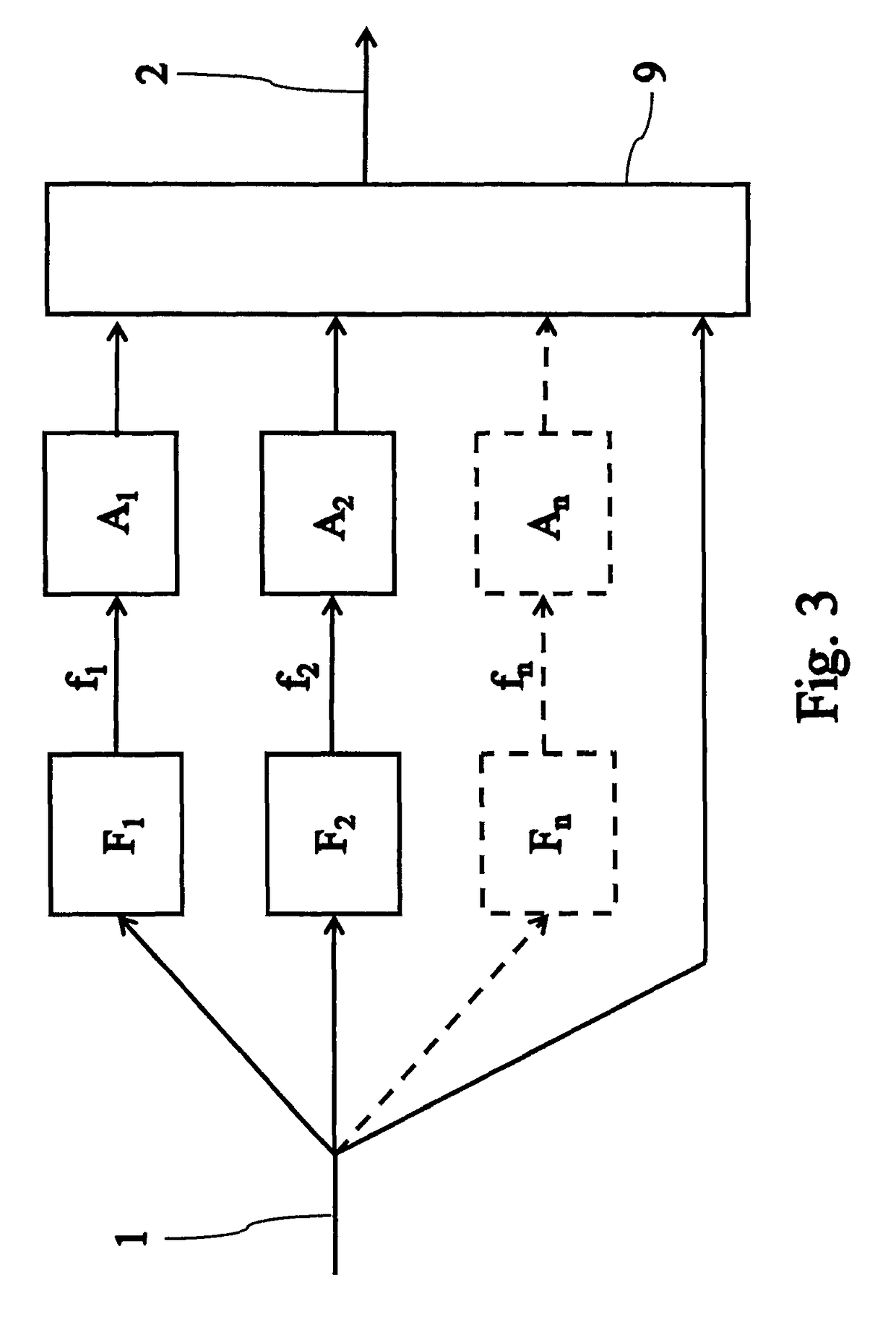
Methods and apparatus for mitral valve repair
InactiveUS20080039935A1Inhibiting and preventing prolapseSlide freelyAnnuloplasty ringsPosterior leafletSystole
Methods and apparatus for mitral valve repair are disclosed herein where the posterior mitral leaflet is supported or buttressed in a frozen or immobile position to facilitate the proper coaptation of the leaflets. An implantable apparatus may be advanced and positioned intravascularly beneath the posterior leaflet of the mitral valve. The apparatus may include one or more individual balloon members, each of which may be optionally configured with supporting integrated structures. A magnet chain catheter may be positioned within the coronary sinus and adjacent to the mitral valve to magnetically secure the apparatus in position beneath the posterior mitral leaflet. Alternatively, a split-ring device may be placed about the chordae tendineae supporting the mitral valve such that the ring slides along the chordae tendineae alternately against the mitral leaflet and towards the papillary muscles during systole and diastole.
Owner:BUCH WALLY +1
Aortic annuloplasty ring
ActiveUS20060015179A1Preserve and restore normal aortic rootPreserve and restore and valve leafletAnnuloplasty ringsBlood vesselsCardiac cycleAnnuloplasty rings
An annuloplasty ring to resize a dilated aortic root during valve sparing surgery includes a scalloped space frame having three trough sections connected to define three crest sections. The annuloplasty ring is mounted outside the aortic root, and extends in height between a base plane and a spaced apart commissure plane of the aortic root. At least two adjacent trough sections are coupled by an annulus-restraining member or tether that limits the maximum deflection of the base of the annuloplasty ring. In use, the tether is preferably located in proximity to the base plane of the aortic root. The annuloplasty ring is movable between a first, substantially conical configuration occurring during a diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle, and a second, substantially cylindrical configuration occurring during a systolic phase of the cardiac cycle. The attachment of the annuloplasty ring in proximity to the cardiac valve annulus allows the ring to regulate the dimensions of a dynamic aortic root during the different phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:CORONEO
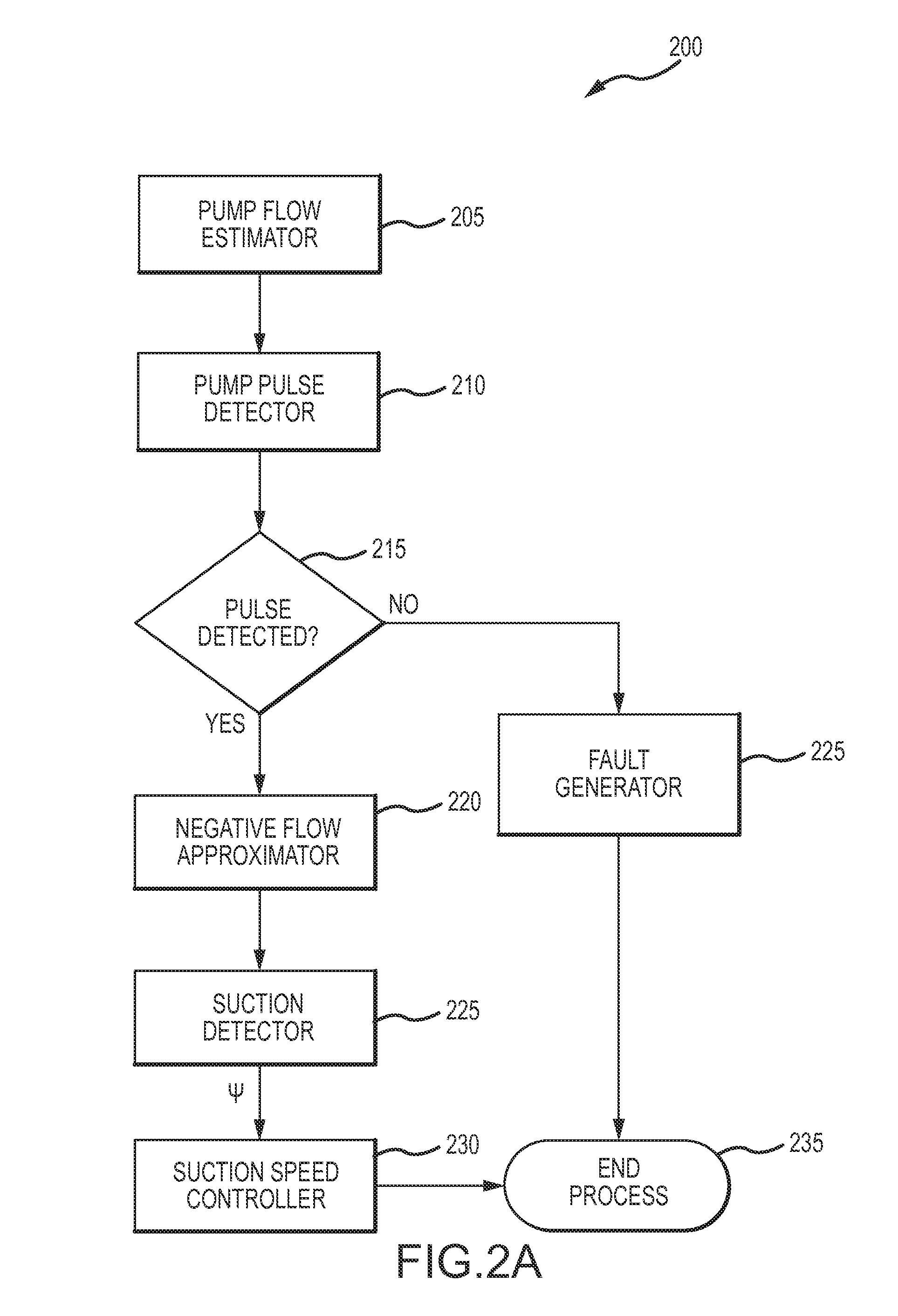
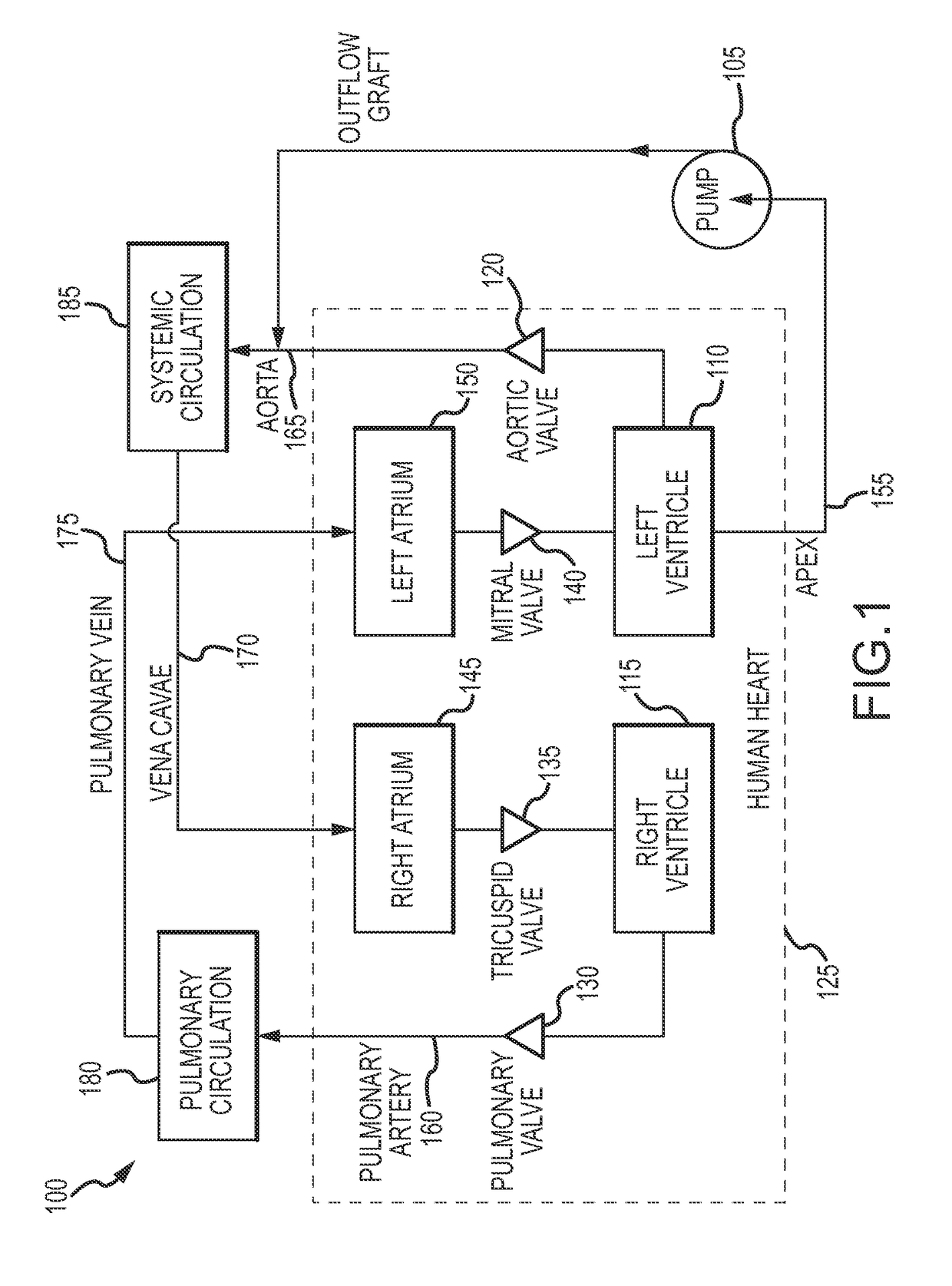
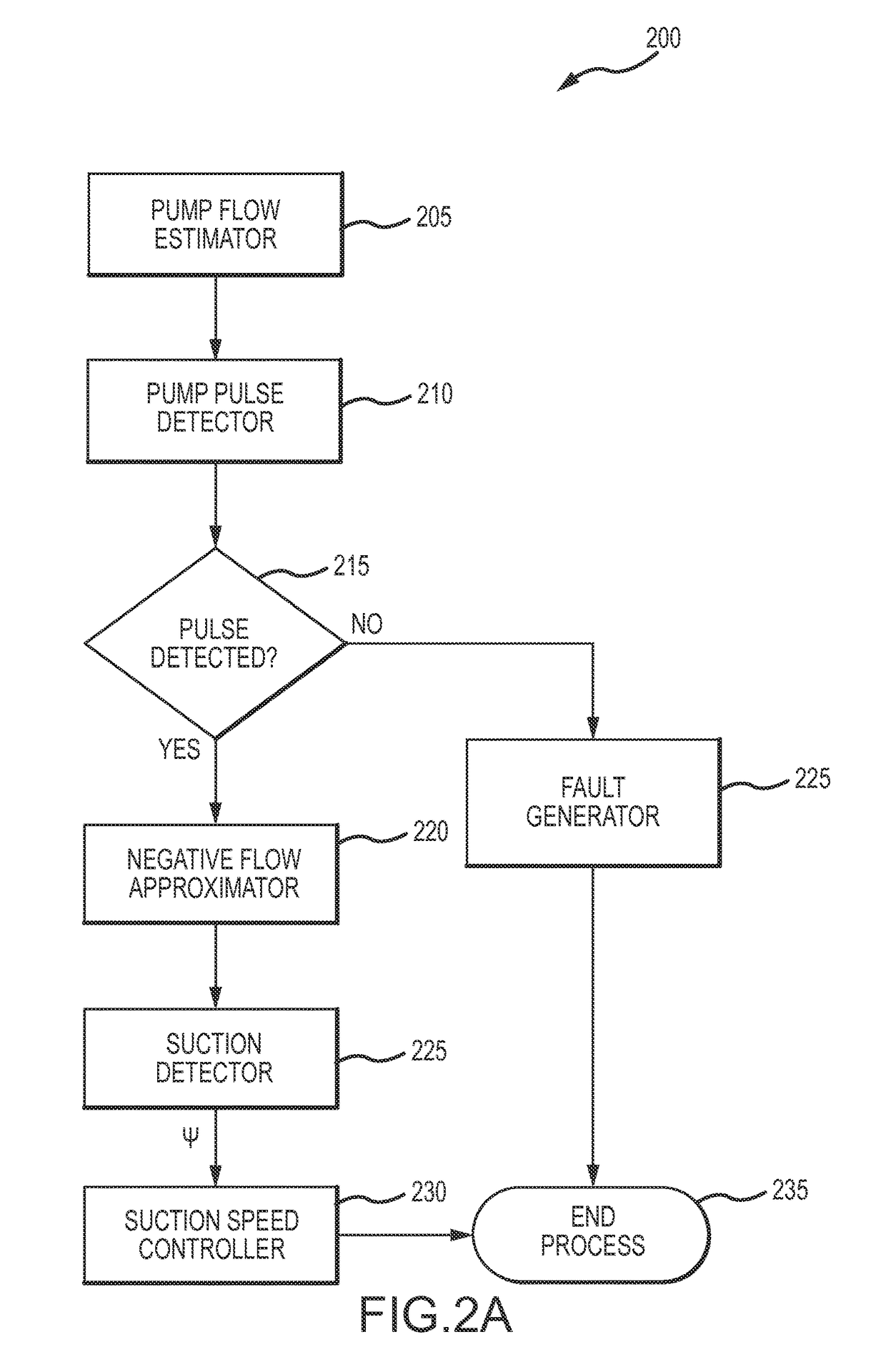
Blood pump and method of suction detection
A system and method for detecting and mitigating a suction condition are disclosed. The method may include estimating a flow waveform of the pump, identifying pulses in the flow waveform, determining a negative flow based on a valid identification of a pulse, and evaluating a characteristic of the pulse for an existence of a suction condition. In various embodiments, a suction marker is located based on a minimum in a diastolic phase, and the suction marker location is used to identify a probability of a suction condition. A speed of the pump may be adjusted to mitigate the suction condition. A system and method for estimating flow is further disclosed. The method may include interpolating data sets defining pump power to flow for various pump speed values.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Cardiac pump with speed adapted for ventricle unloading
ActiveUS20140323796A1Readily contractedReduce resistanceControl devicesBlood pumpsImpellerPump chamber
A blood pump system is implantable in a patient for ventricular support. A pumping chamber has an inlet for receiving blood from a ventricle of the patient. An impeller is received in the pumping chamber. A motor is coupled to the impeller for driving rotation of the impeller. A motor controller is provided for tracking systolic and diastolic phases of a cardiac cycle of the patient and supplying a variable voltage signal to the motor in a variable speed mode to produce a variable impeller speed linked to the cardiac cycle. The impeller speed comprises a ramping up to an elevated speed during the diastolic phase in order to reduce a load on the ventricle at the beginning of the systolic phase.
Owner:TC1 LLC
Cardiac pump with speed adapted for ventricle unloading
A blood pump system is implantable in a patient for ventricular support. A pumping chamber has an inlet for receiving blood from a ventricle of the patient. An impeller is received in the pumping chamber. A motor is coupled to the impeller for driving rotation of the impeller. A motor controller is provided for tracking systolic and diastolic phases of a cardiac cycle of the patient and supplying a variable voltage signal to the motor in a variable speed mode to produce a variable impeller speed linked to the cardiac cycle. The impeller speed comprises a ramping up to an elevated speed during the diastolic phase in order to reduce a load on the ventricle at the beginning of the systolic phase.
Owner:TC1 LLC
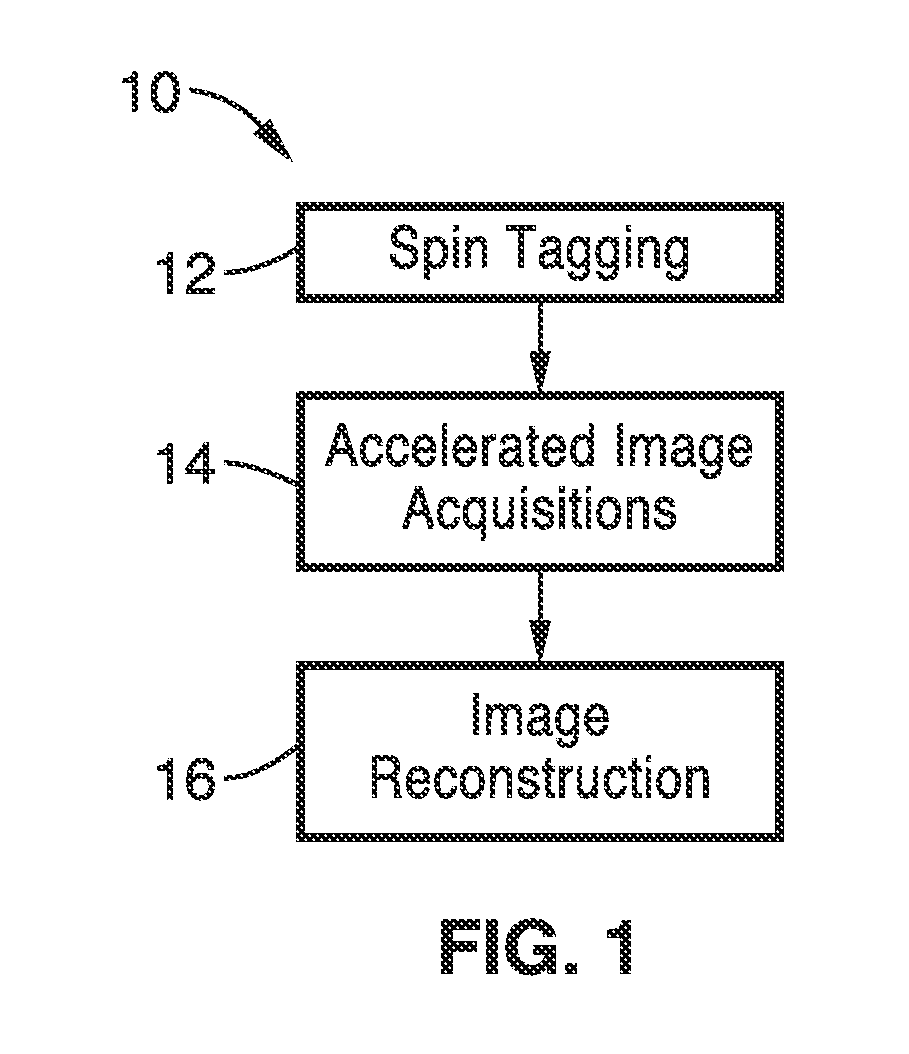
Noninvasive 4-d time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography
ActiveUS20150327783A1High degree of efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsSystoleCardiac cycle
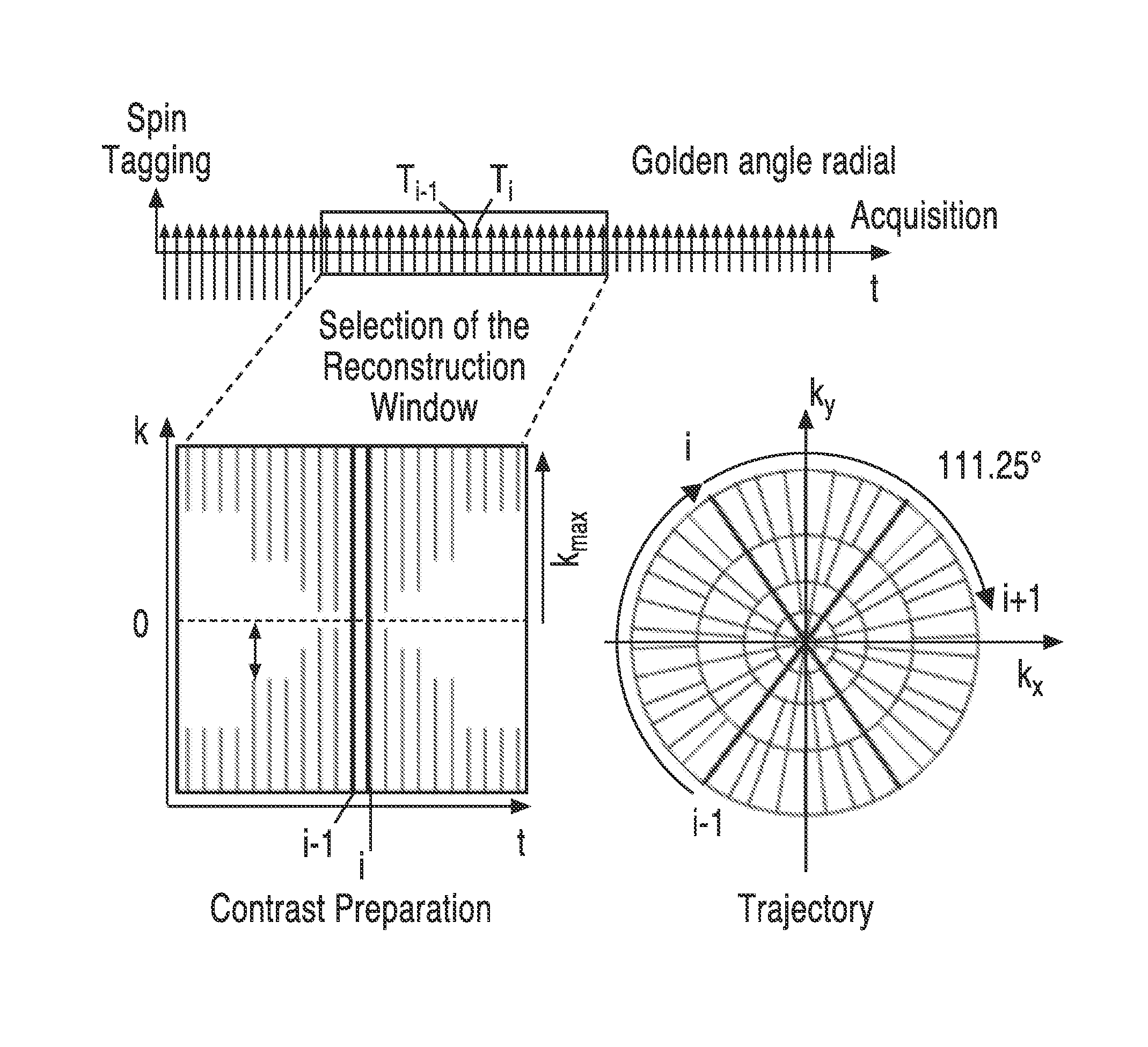
A method for non-contrast enhanced 4D time resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography using arterial spin labeling of blood water as an endogenous tracer and a multiphase balanced steady state free precession readout is presented. Imaging can be accelerated with dynamic golden angle radial acquisitions and k-space weighted imaging contrast (KWIC) image reconstruction and it can be used with parallel imaging techniques. Quantitative tracer kinetic models can be formed allowing cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow and mean transit time to be estimated. Vascular compliance can also be assessed using 4D dMRA by synchronizing dMRA acquisitions with the systolic and diastolic phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Three-dimensional ultrasound cardiogram four-cavity section image automatic detection method
InactiveCN101011266AFacilitate diagnostic workHeavy calculationImage enhancementOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationImage database
The invention relates to a method for realizing the three-dimension ultrasonic cardiogram four-chamber section image automatic check, which comprises that 1, extracting one three-dimension data from the end-diastolic phase of heart from the heart full-volume data; 2, extracting 180 section images from the three-dimension data to build an image database; 3, calculating out the similarity between each image of database and the template image, to be selected and using wavelet system statistic character to check out the image with highest similarity in the left image, to record the position in the data as the four-chamber watch position. The invention realizes the automatic search function of four-chamber section; therefore, medical staff can use real-time three-dimension ultrasonic technique to diagnose the patient.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Blood pump and method of suction detection
A system and method for detecting and mitigating a suction condition are disclosed. The method may include estimating a flow waveform of the pump, identifying pulses in the flow waveform, determining a negative flow based on a valid identification of a pulse, and evaluating a characteristic of the pulse for an existence of a suction condition. In various embodiments, a suction marker is located based on a minimum in a diastolic phase, and the suction marker location is used to identify a probability of a suction condition. A speed of the pump may be adjusted to mitigate the suction condition. A system and method for estimating flow is further disclosed. The method may include interpolating data sets defining pump power to flow for various pump speed values.
Owner:TC1 LLC
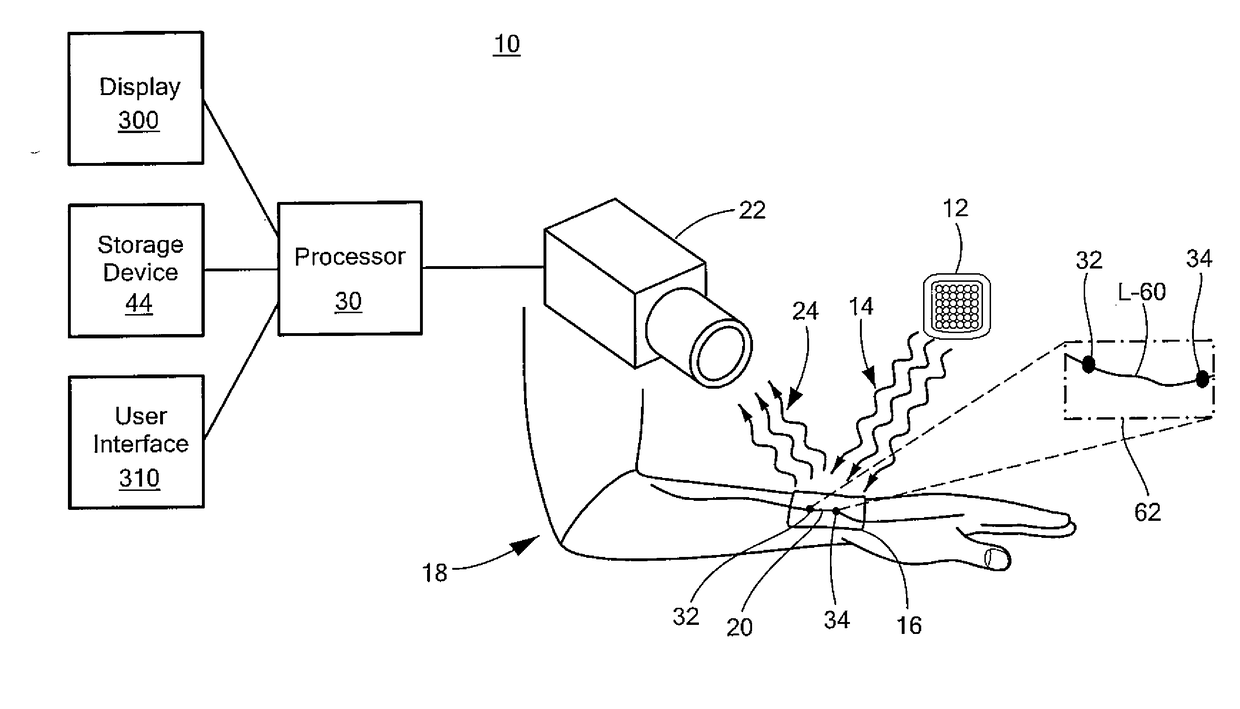
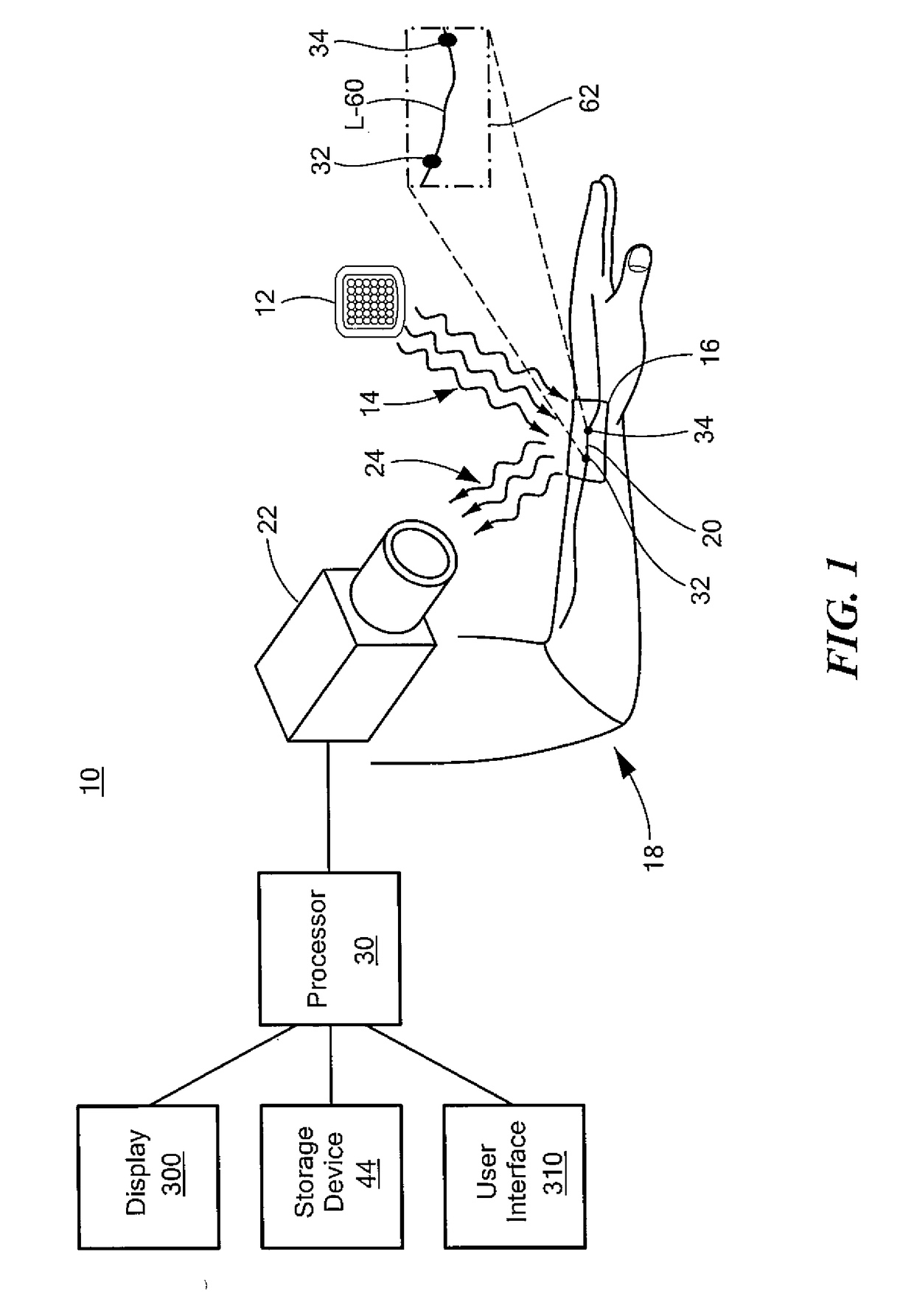
Contactless System and Method For Measuring and Continuously Monitoring Arterial Blood Pressure
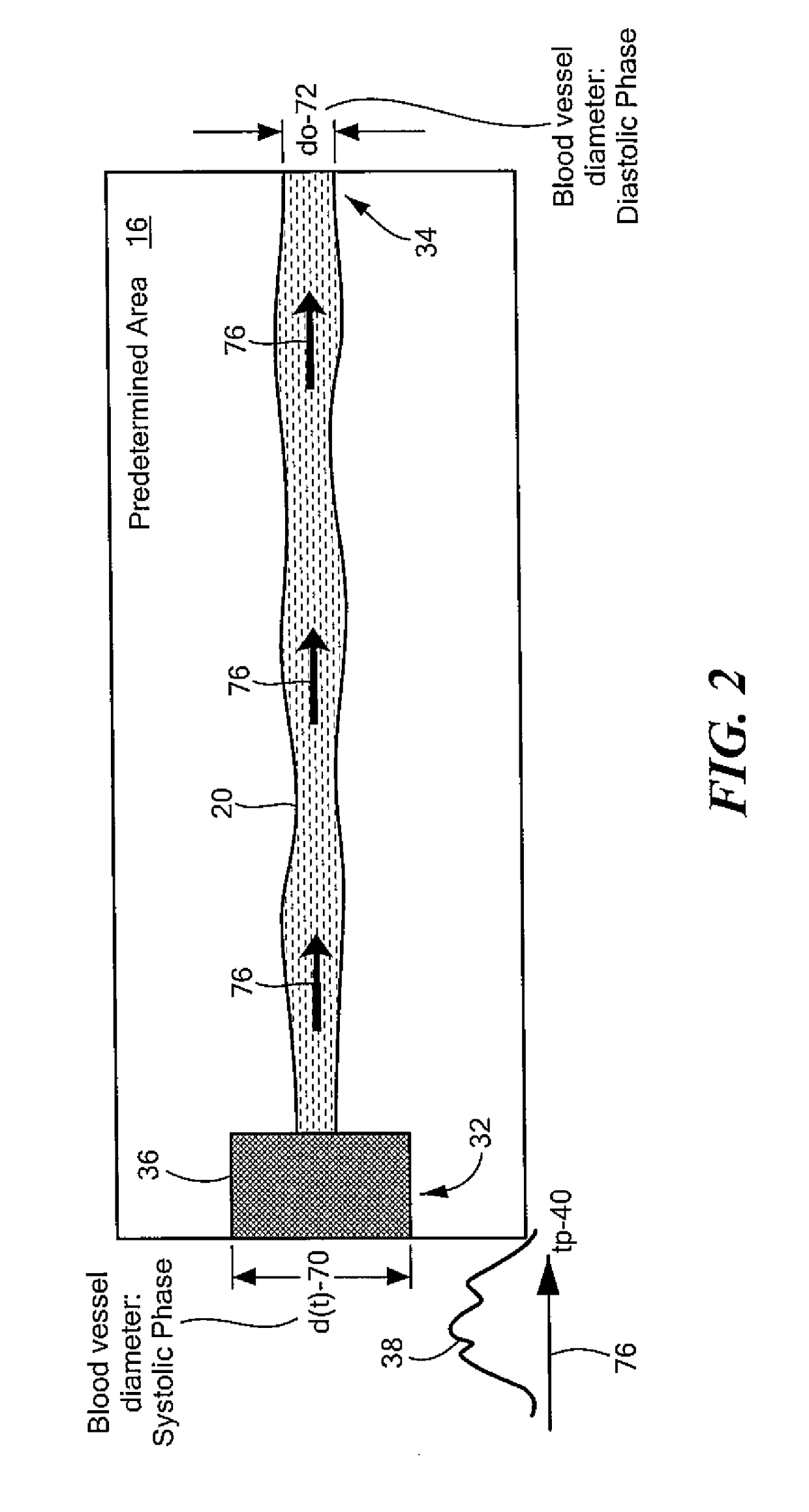
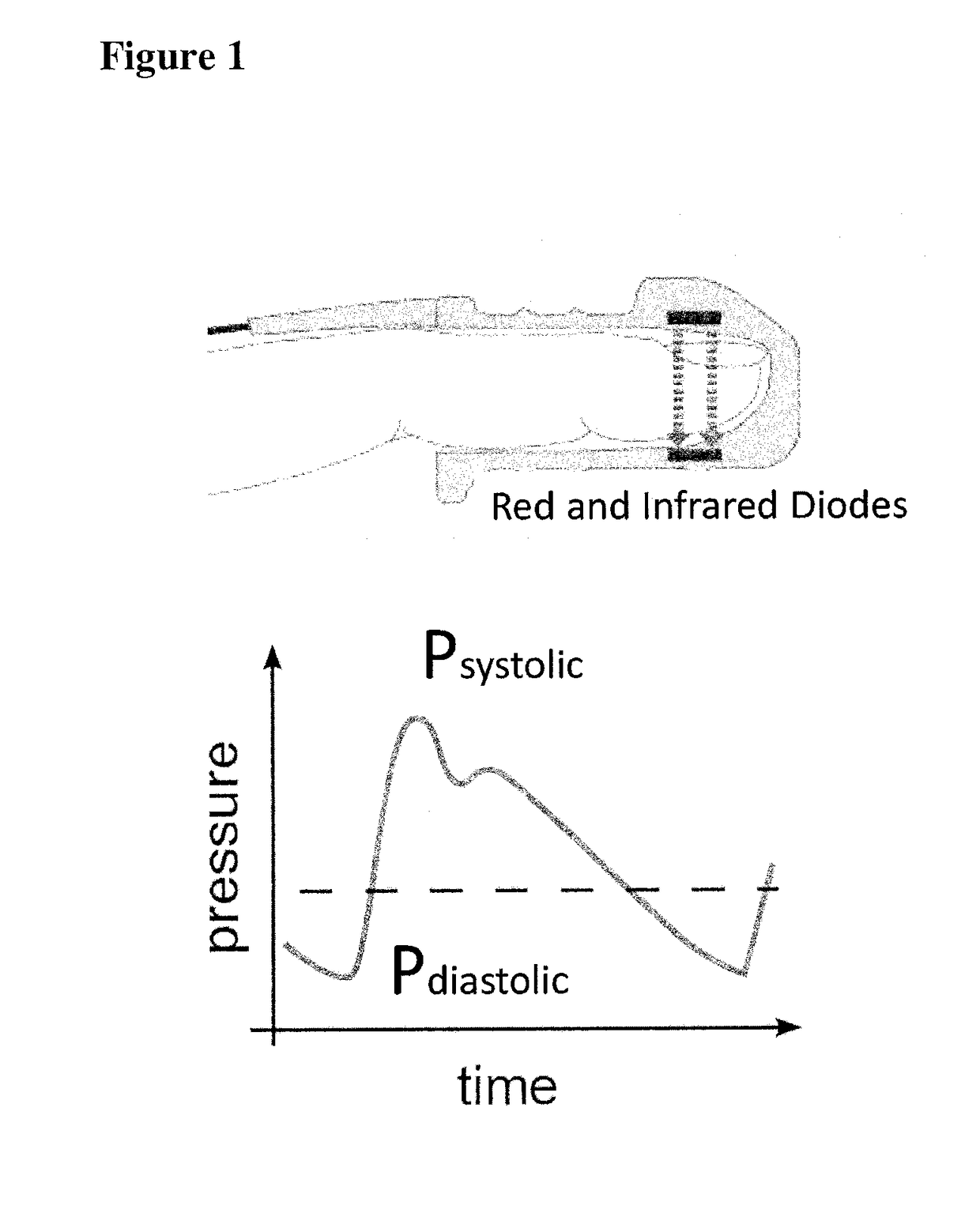
A contactless system for measuring and continuously monitoring arterial blood pressure includes a light source configured to illuminate light having at least one predetermined wavelength at a predetermined area of a human subject having an artery therein. A detector responsive to reflected light from the predetermined area is configured to continuously acquire images of the artery in the predetermined area. A processor is configured to process the images and determine: when an image at a proximal location of the predetermined area is darker indicating transition of a pulse wave into the artery at the proximal location and at a proximal time and when an image at a distal location of the predetermined area is darker indicating transition of the pulse wave into the artery at a distal location at a distal time, determine the difference in time between the distal time and the proximal time to calculate a pulse transit time (PTT), determine a length between the proximal location and the distal location, determine a diameter of the artery during a systolic phase of a cardiac pulse, determine a diameter of the artery during a diastolic phase of a cardiac pulse, calculate a pulse wave velocity of the pulse wave, calculate pulse pressure (ΔP), calculate an elastic modulus (E) of the artery, and contactlessly and continuously calculate the arterial blood pressure for each cardiac cycle of the human subject.
Owner:VIVONICS
System and method for crossing a native heart valve with a guidewire
A system for crossing a heart valve with a guidewire includes an advancement motor and a controller. The controller controls when the advancement motor advances and retracts the guidewire. The controller is coupled to an electrocardiogram device and determines the systolic and diastolic phase of the heart from information / data from the electrocardiogram device. The guidewire advances or retracts based on the controller's determination of the systolic or diastolic phase corresponding with the heart valve being in an open configuration. The system may include a catheter including a lumen through which the guidewire is disposed. The system may further include a sensor. The sensor is in communication with the controller, and the controller will stop advancement of the guidewire if the controller determines the guidewire has not advanced between open leaflets of the heart valve based upon information / data from the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Heart valve sealing devices and delivery devices therefor
A valve repair device for repairing a native heart valve of a patient includes a pair of clasps, where each clasp is configured to attach to native valve leaflet. The ends of the pair of clasps can move away from one another to a partially open position when the native valve leaflets open during a diastolic phase of a cardiac cycle, and the ends of the pair of clasps can move toward one another when the native valve leaflets close during a systolic phase of a cardiac cycle.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Quantification of absolute blood flow in tissue using fluorescence-mediated photoplethysmography
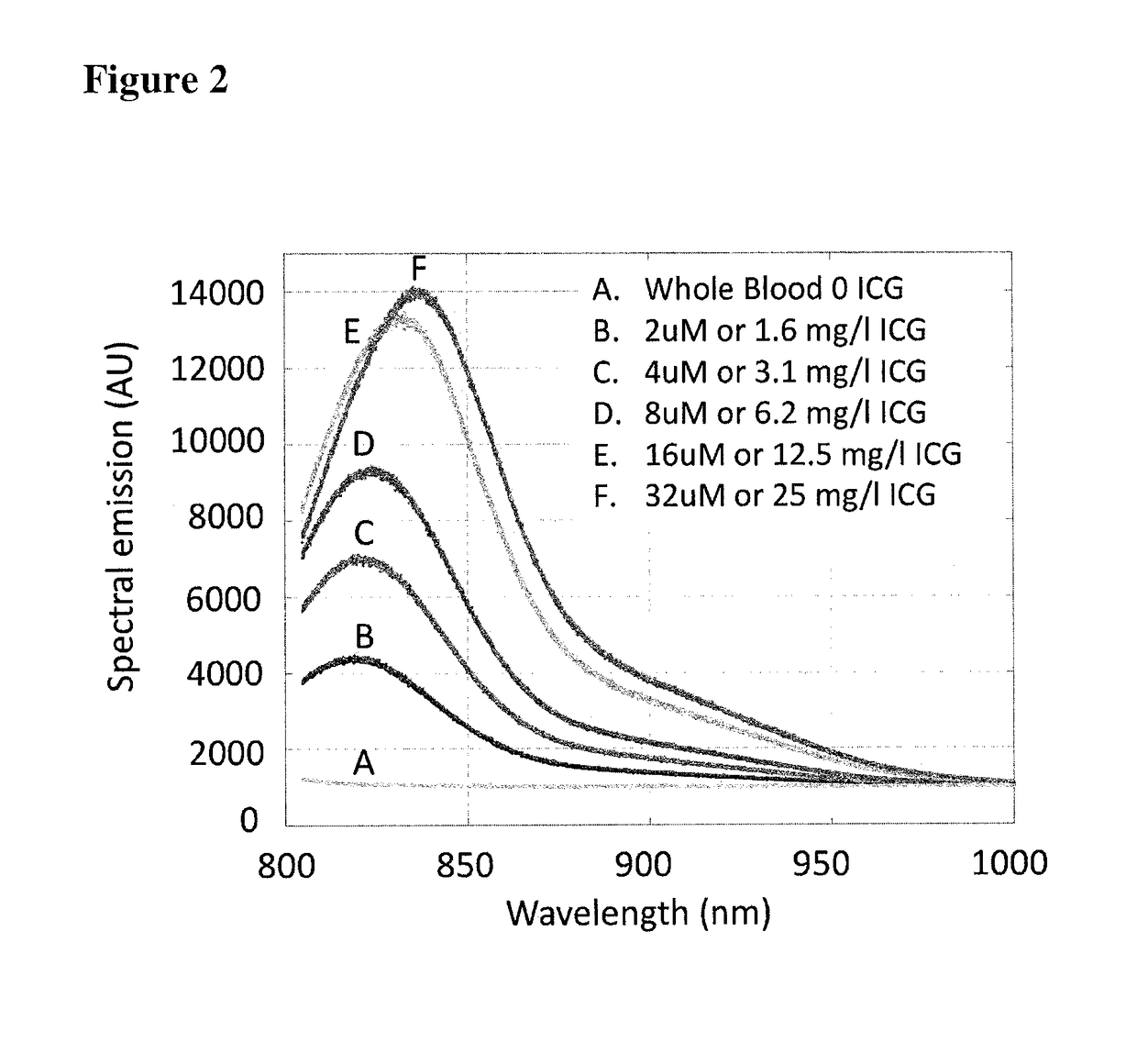
A method, an apparatus, and a kit including the apparatus and a fluorescence agent are provided for measuring a time-varying change in an amount of blood in a tissue volume, and include exciting a fluorescence agent in the blood, acquiring a time-varying light intensity signal during a pulsatile flow of the blood through the tissue volume, the pulsatile flow having a systolic and a diastolic phase resembling a conventional photoplethysmogram, and processing the acquired signal by applying a modified Beer-Lambert law to obtain a measurement of the time-varying change in the amount of blood in the tissue volume. The instantaneous molar concentration of the fluorescence agent is determined by utilizing a concentration-mediated change in a fluorescence emission spectrum of the fluorescence agent. There is further provided a fluorescence agent for use in the method.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
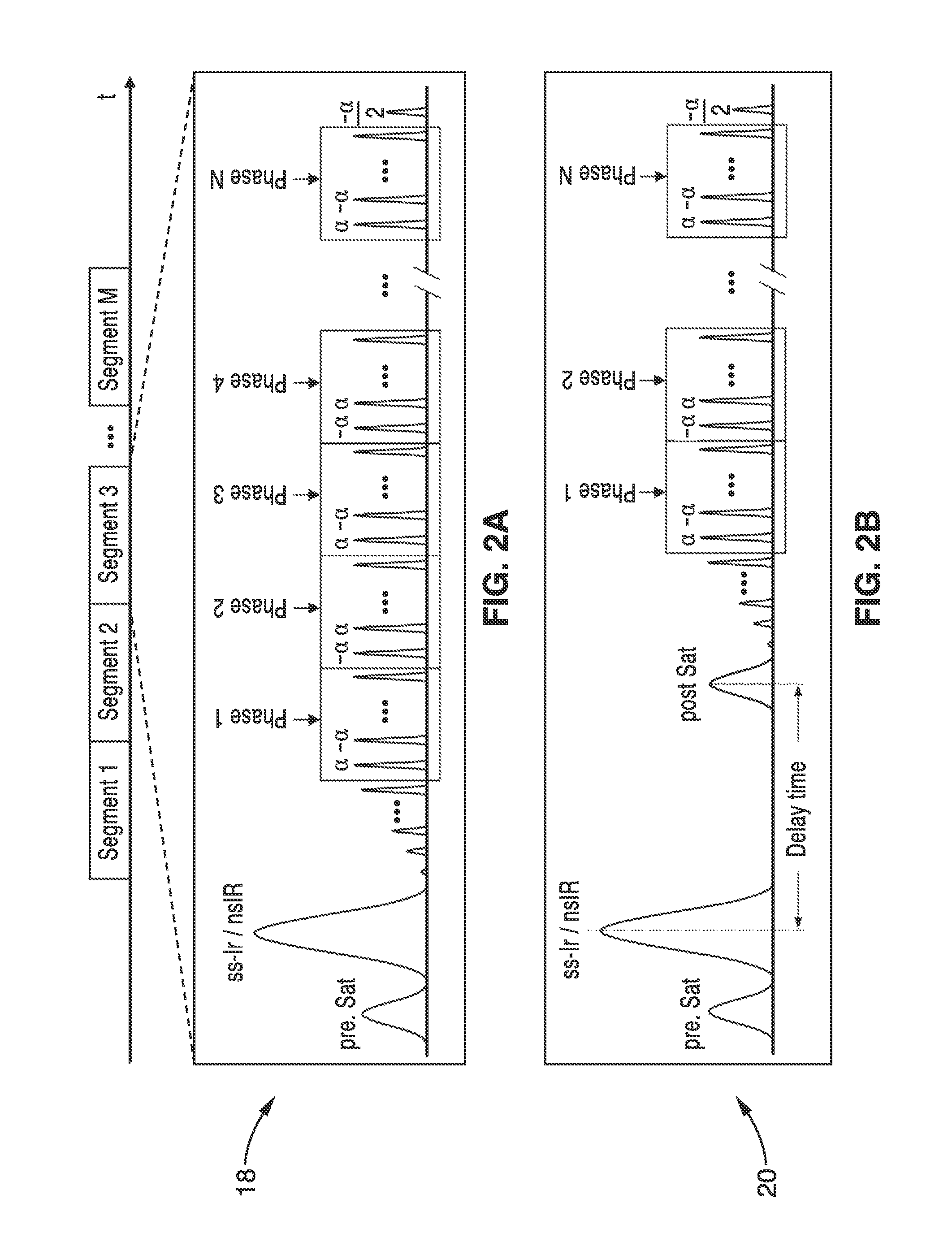
Mr imaging with b1 mapping
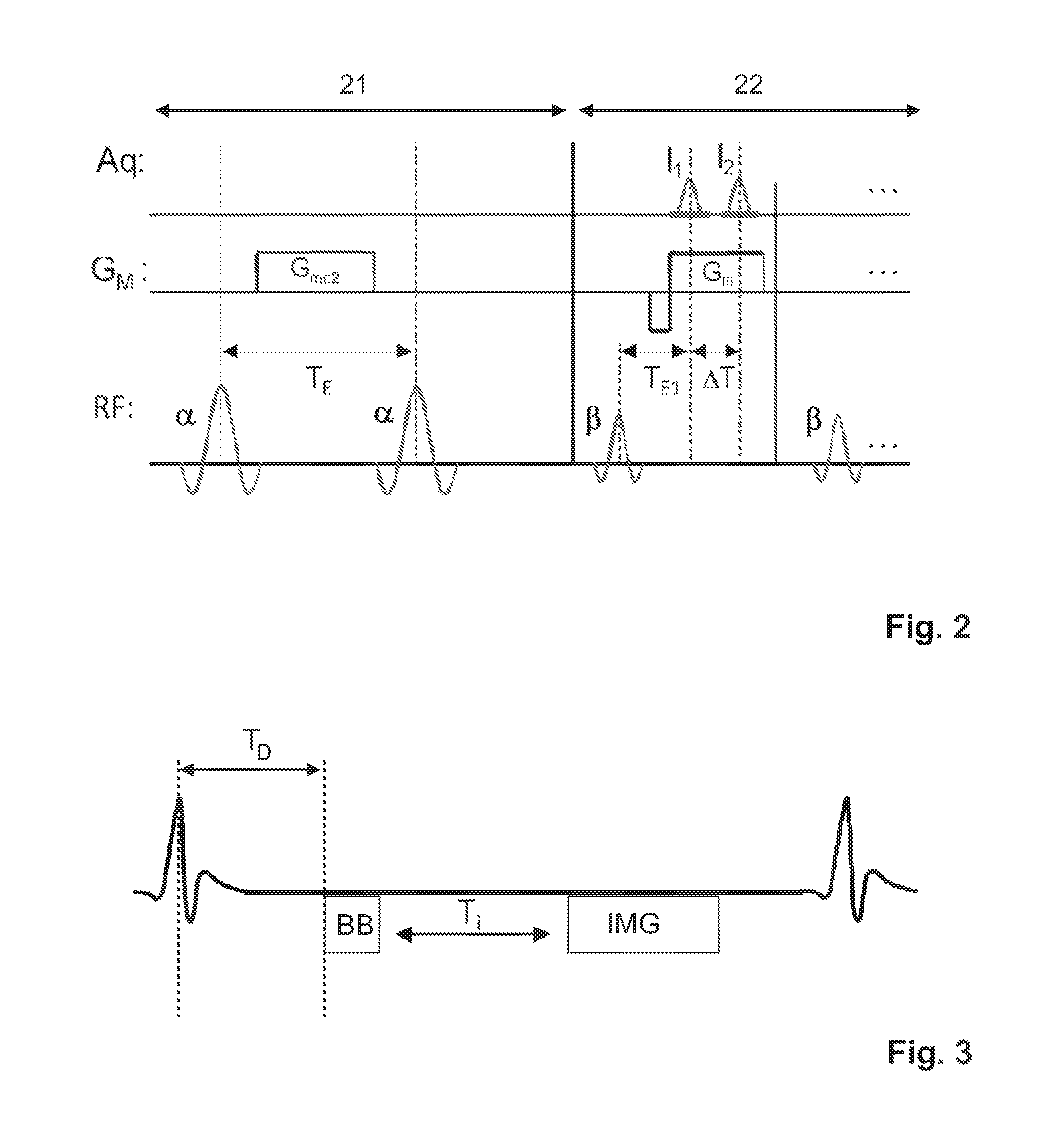
ActiveUS20150042335A1Avoid artifactsFast readoutSensorsBlood flow measurementMagnetic field gradientStimulated echo
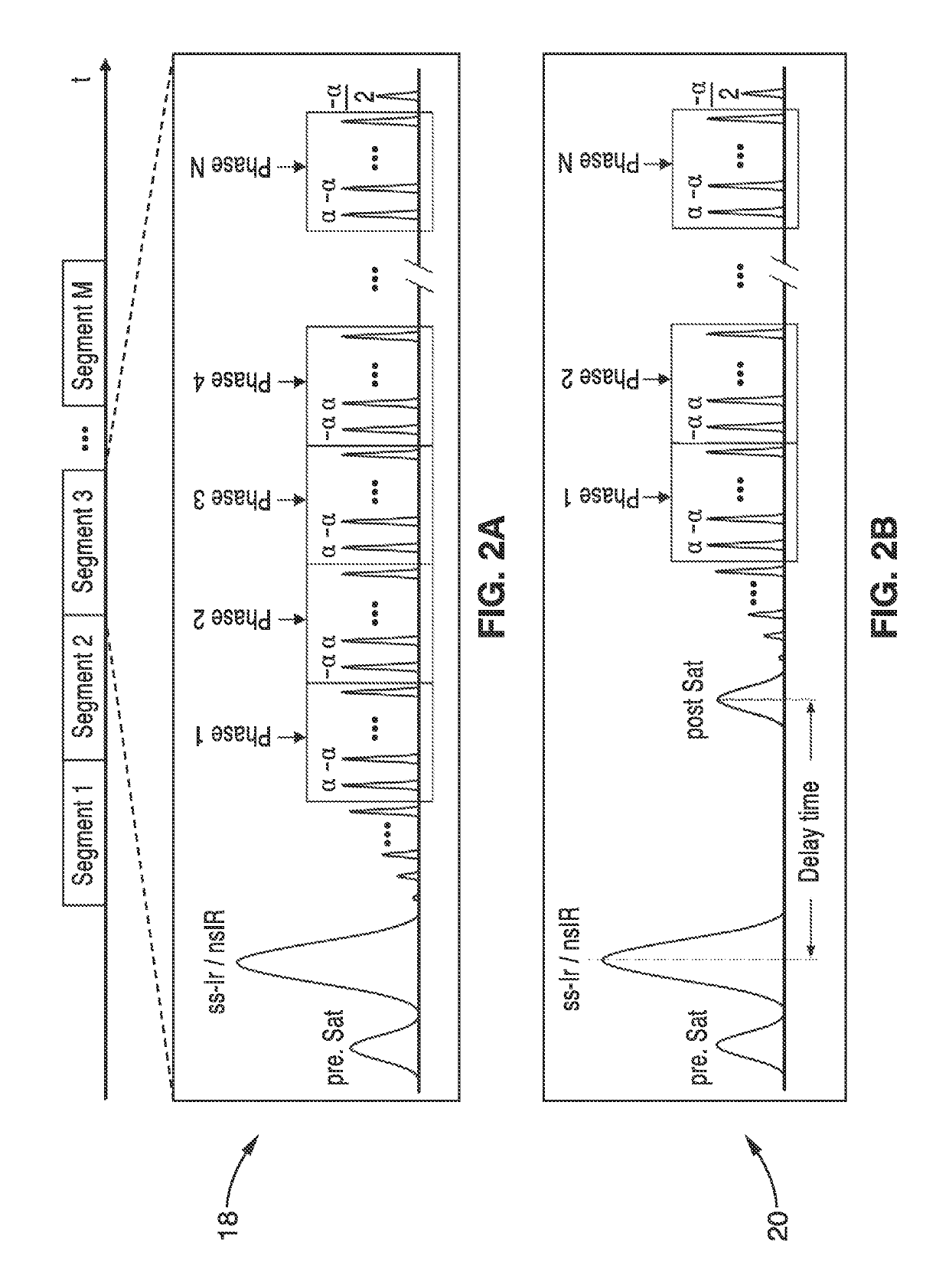
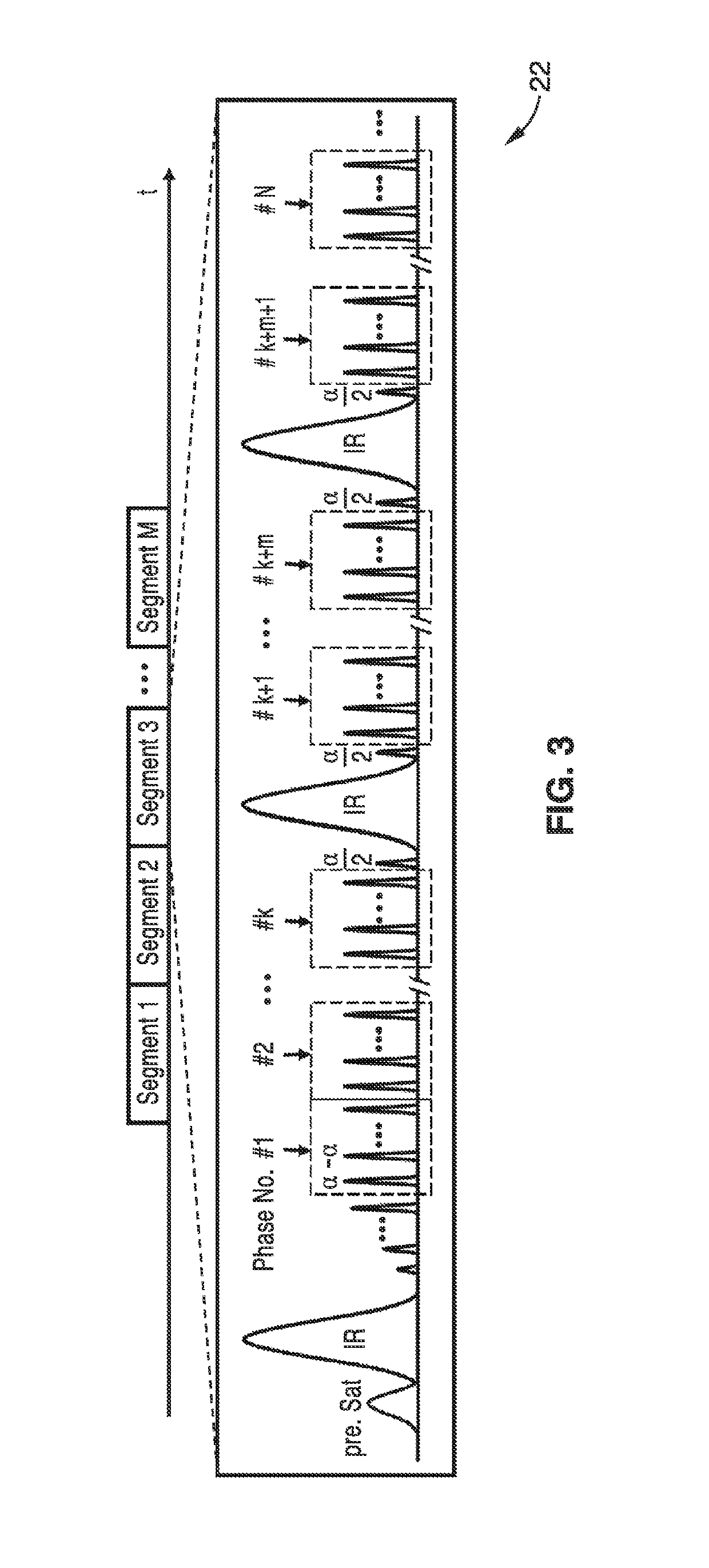
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging, wherein a portion of a body (10) placed in the examination volume of a MR device (1) is subjected to an imaging sequence (IMG) of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients. The imaging sequence (IMG) is a stimulated echo sequence including i) at least two preparation RF pulses (α) radiated toward the portion of the body (10) during a preparation period (21), and ii) one or more reading RF pulses (β) radiated toward the portion of the body (10) during an acquisition period (22) temporally subsequent to the preparation period (21). One or more FID signals (I1) and one or more stimulated echo signals (I2) are acquired during the acquisition period (22). A B1 map indicating the spatial distribution of the RF field of the RF pulses within the portion of the body (10) is derived from the acquired FID (I1) and stimulated echo (I2) signals. It is an object of the invention to provide an improved B1 mapping method which can be applied in magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and, in particular, in cardiac imaging, where the acquisition of a complete B1 map needs to be performed within the diastolic phase of the heartbeat. The invention proposes that the portion of the body (10) is subjected to a suppression sequence (BB) for suppression of MR signals emanating from blood prior to the imaging sequence (IMG). Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program for a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Ventricular assist device and related computer program product
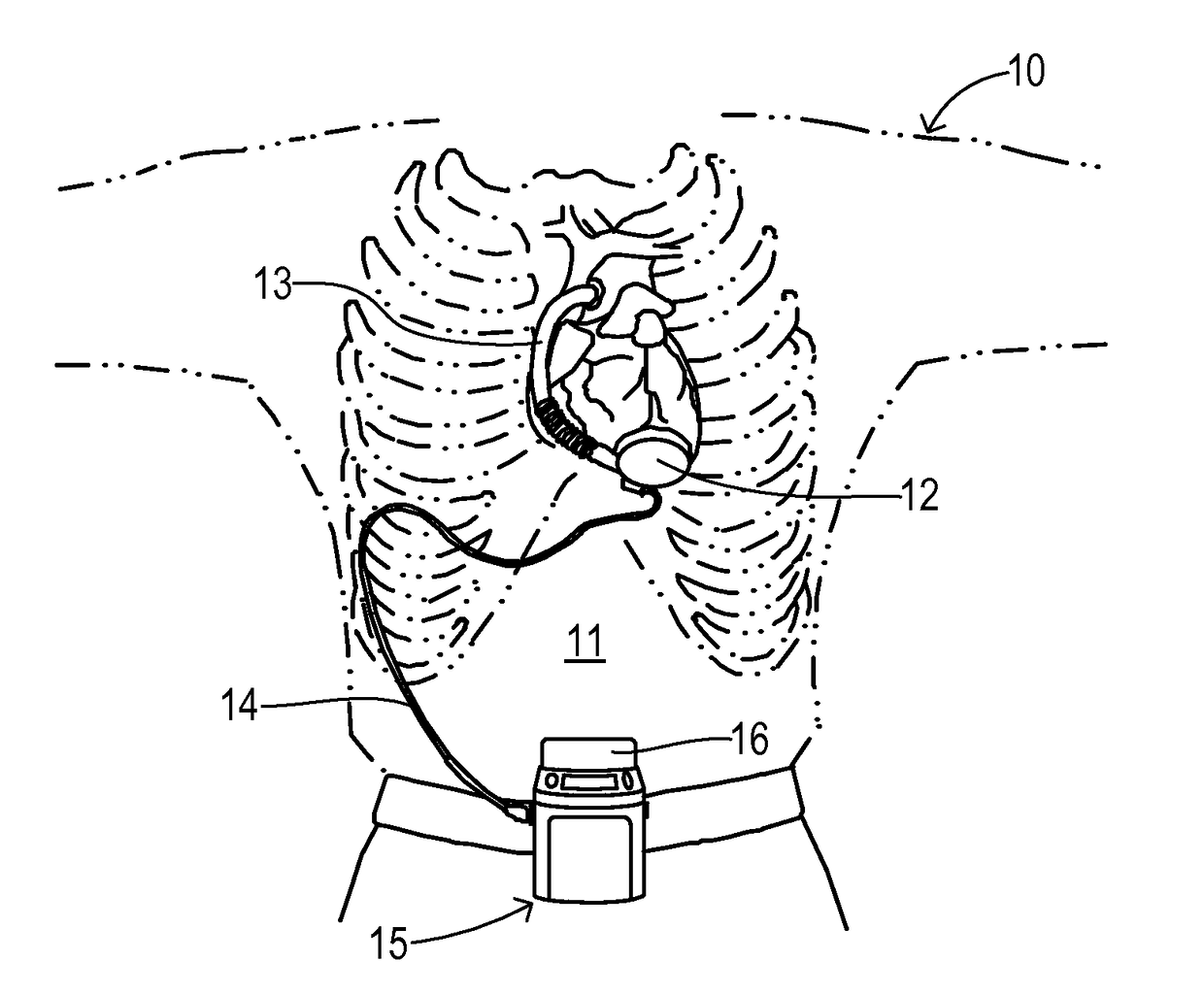
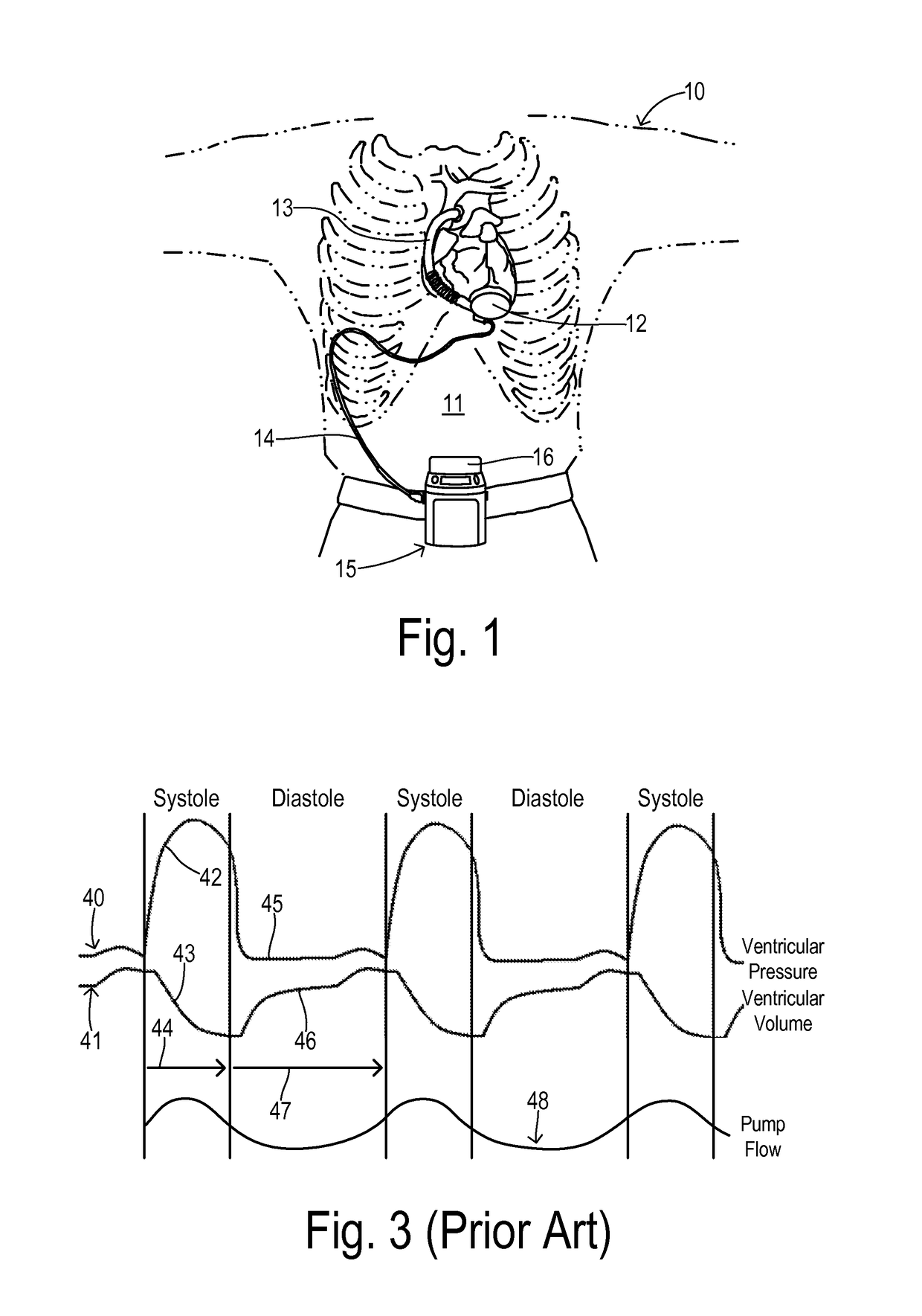
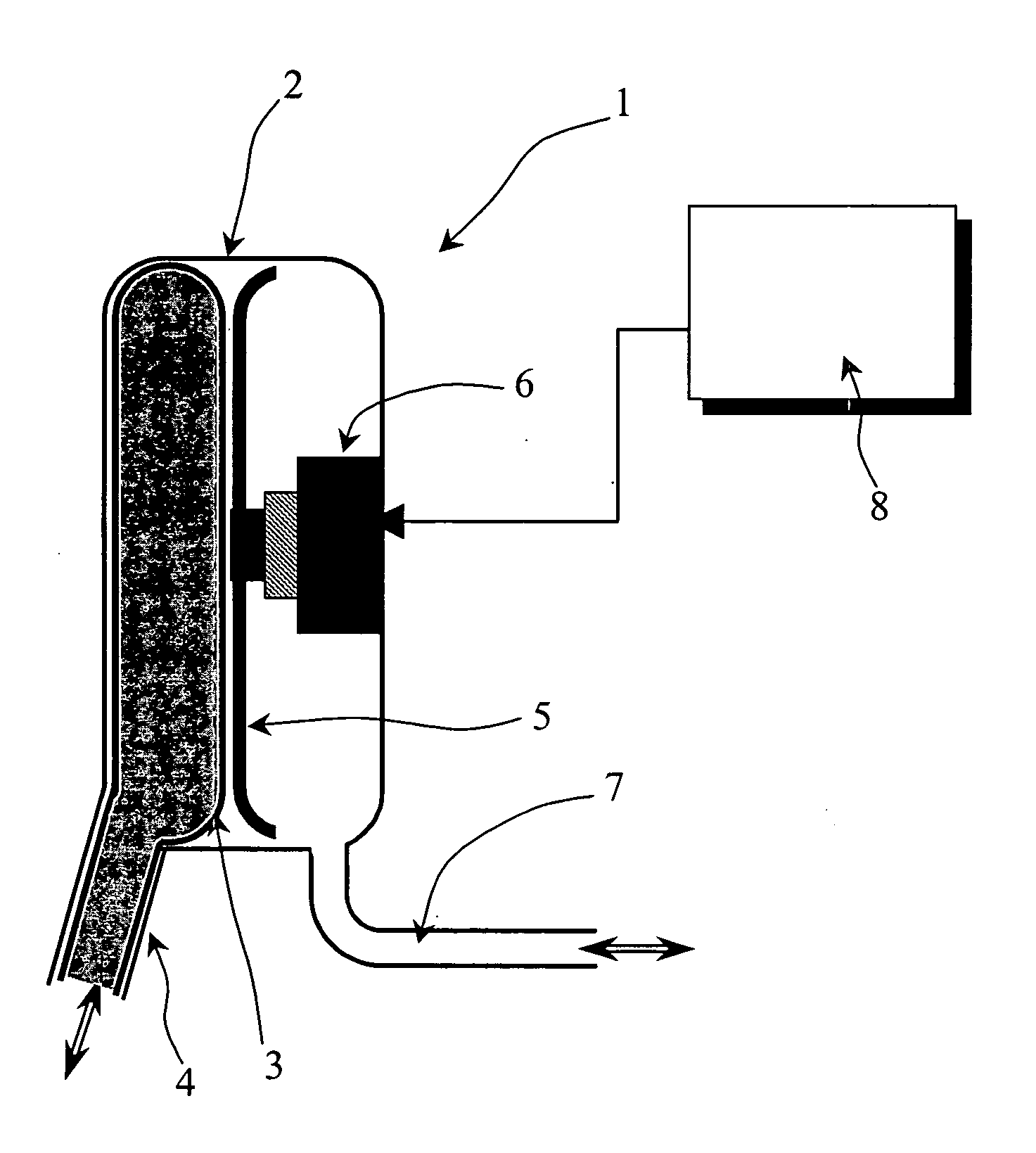
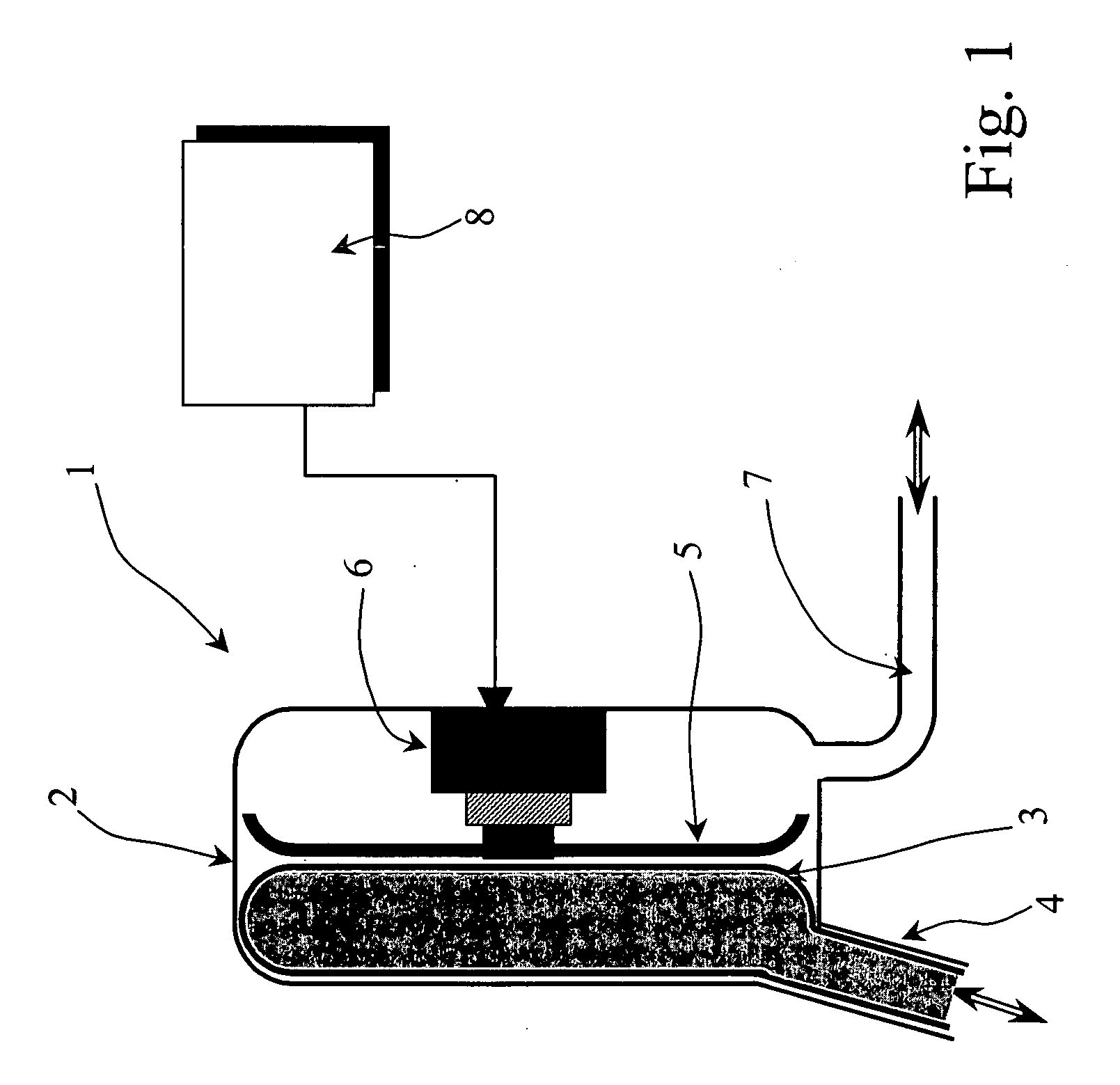
InactiveUS20080045779A1Easily repairableEasily replaceableControl devicesFlexible member pumpsVentricular assistanceDiastolic phase
Owner:NEWCORTEC
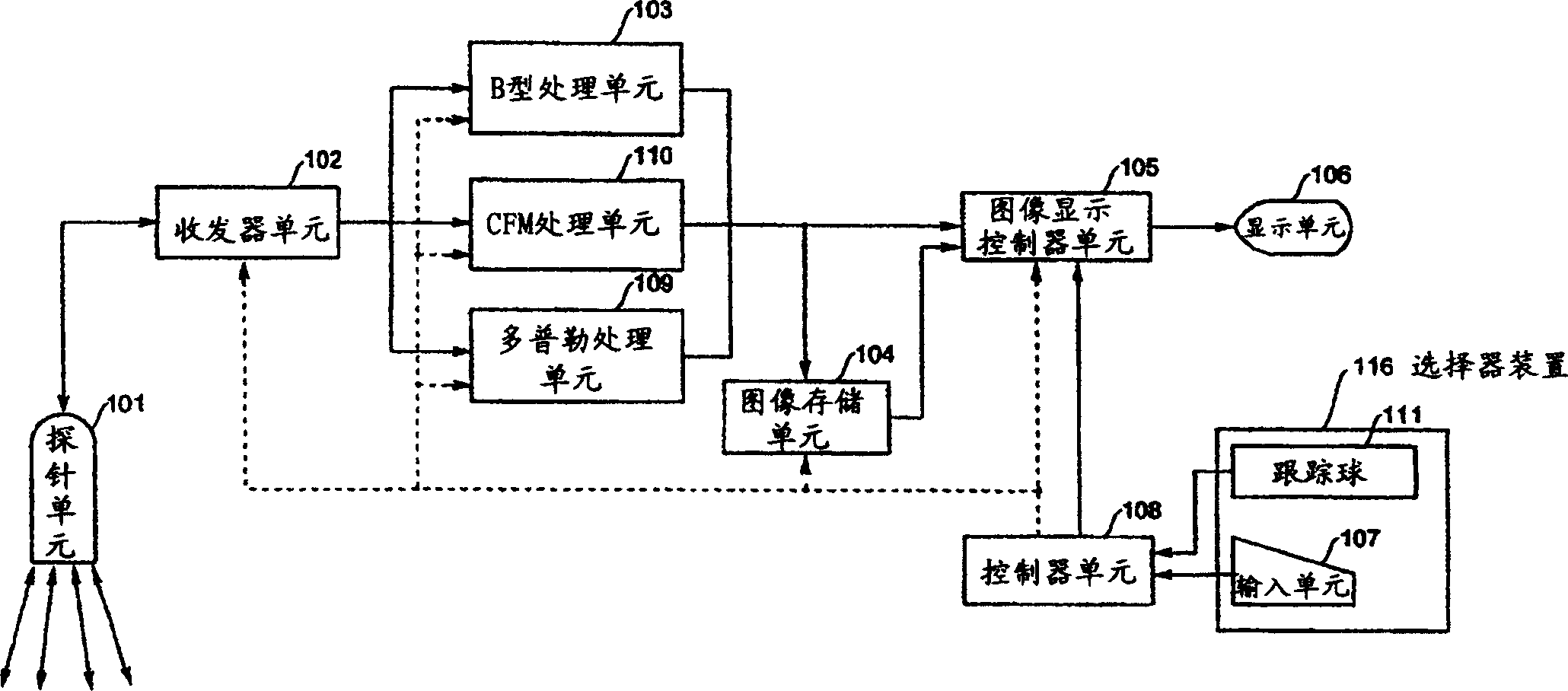
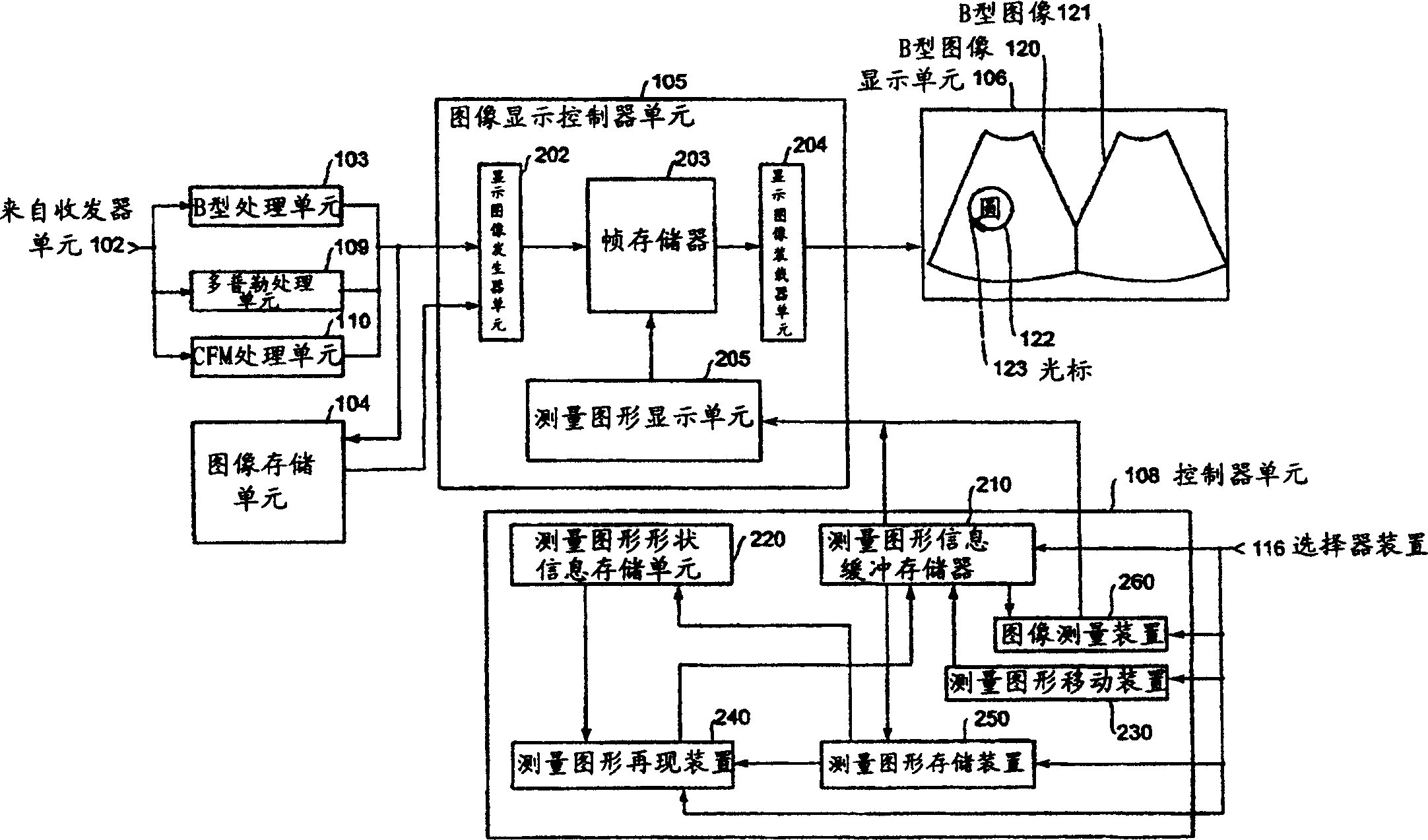
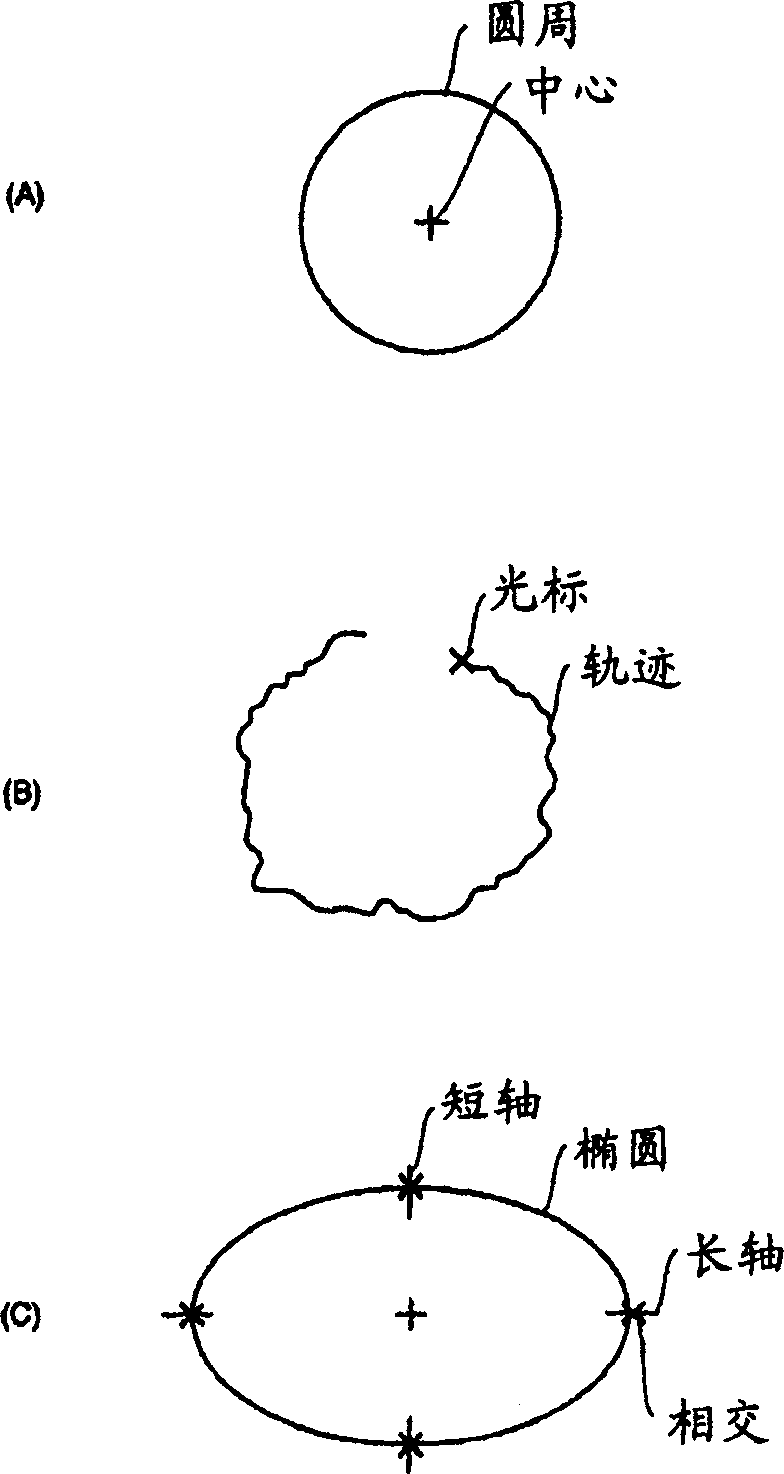
Ultrasonic imaging apparatus
InactiveCN1785124AProper inspectionRelatively intuitive and reliableWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesGraphicsMeasurement device
The present invention provides an ultrasound imaging device which allows to carry out a morphological comparison of measurement patterns set within a plurality of ultrasound images in a reliable and easier manner. The measurement pattern storage device (250) stores the circle indicating the size of the inner wall of the left ventricle, and is designated in the B-mode image of the diastolic period of the left ventricle, and the measurement pattern reproduction device (240) reproduces the circle indicating the systole period of the left ventricle in the B-mode image, so that A morphological comparison of the left ventricular inner wall in systole and diastole can be done in an easier and very reliable manner with the Numerical data are obtained together in order to provide an appropriate determination of the numerical data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
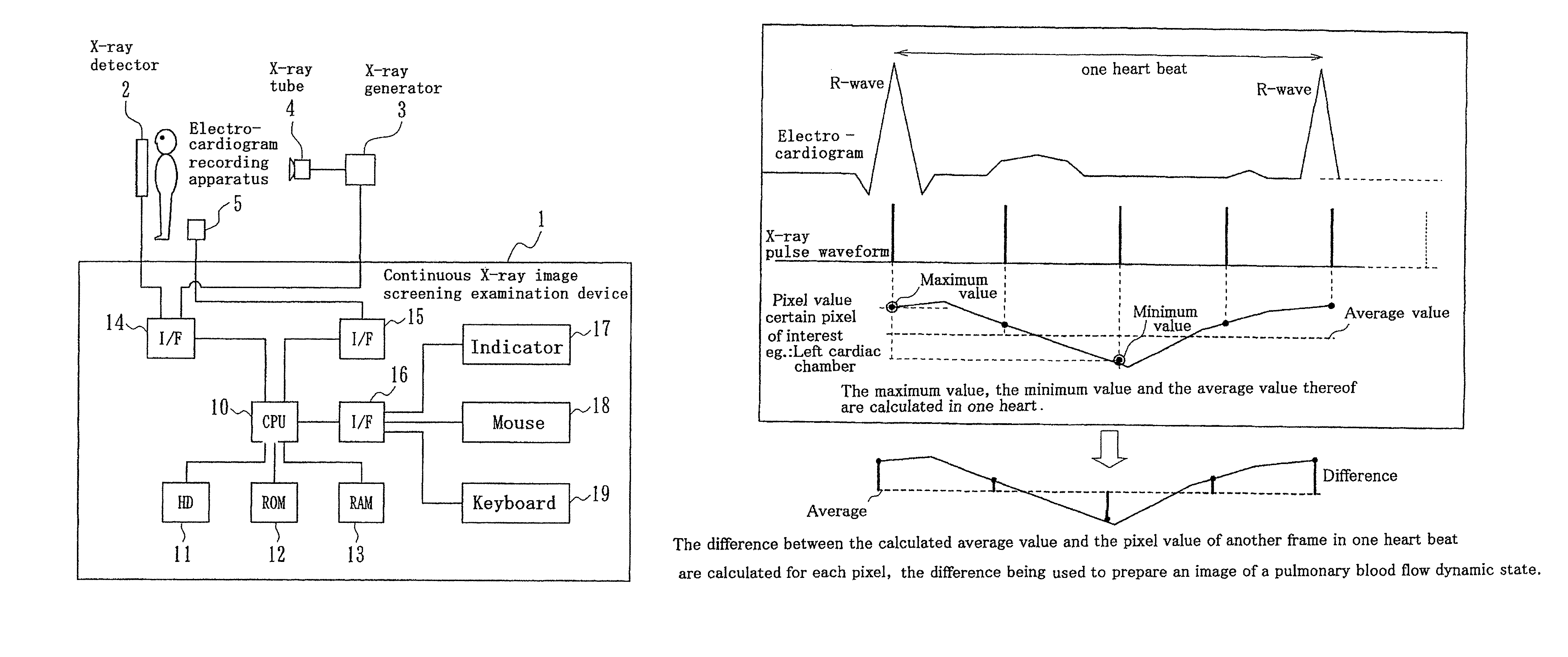
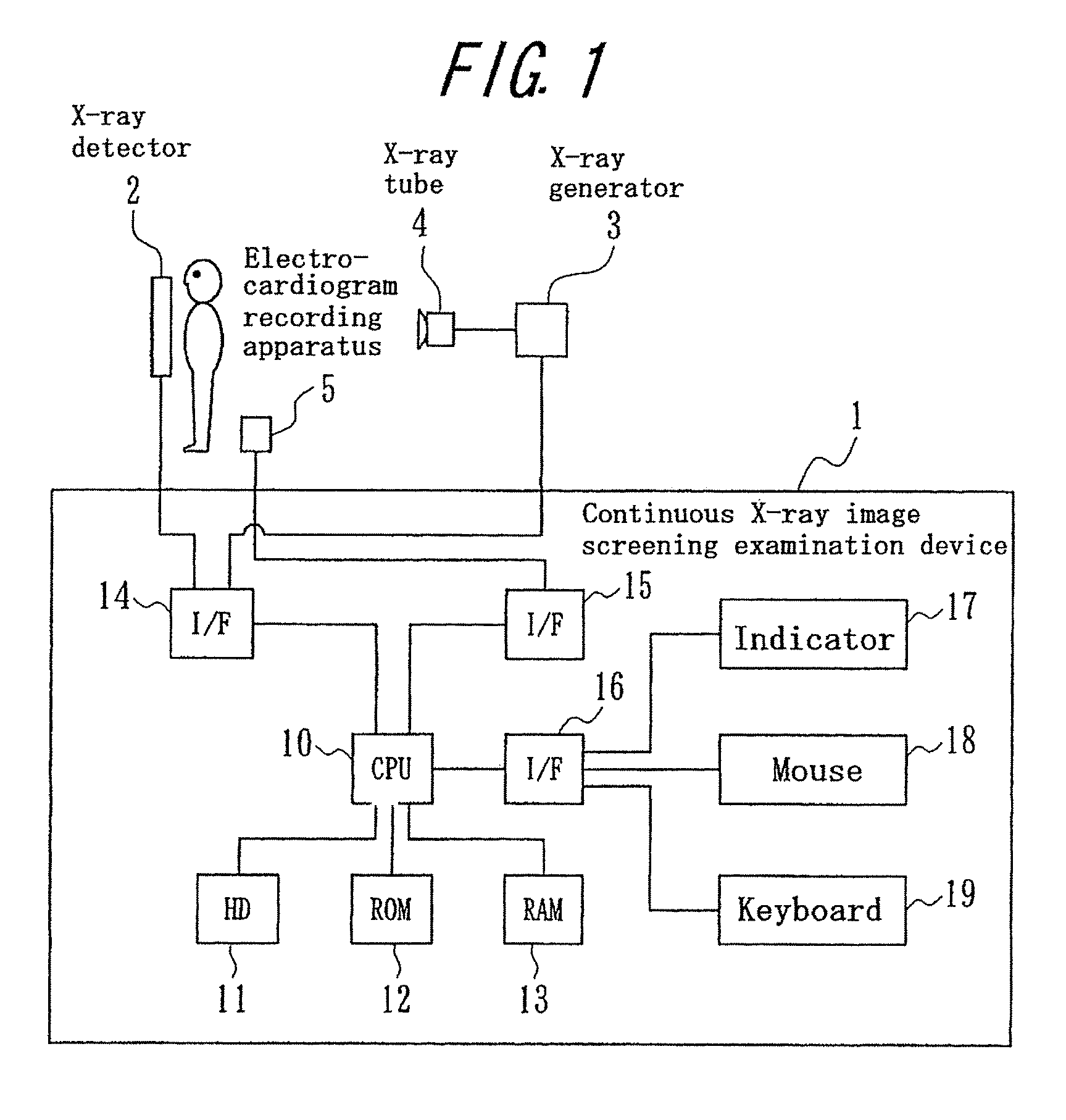
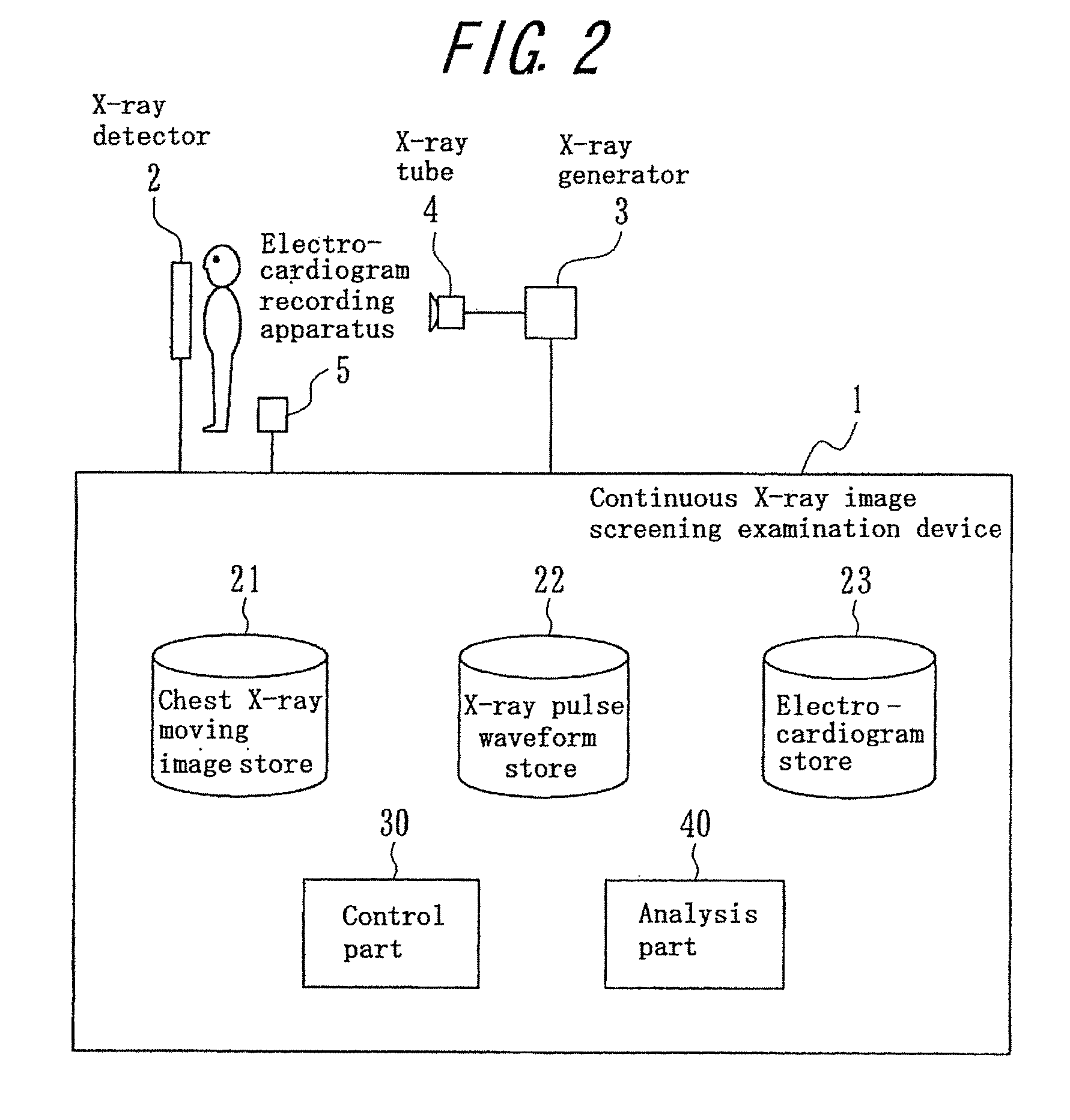
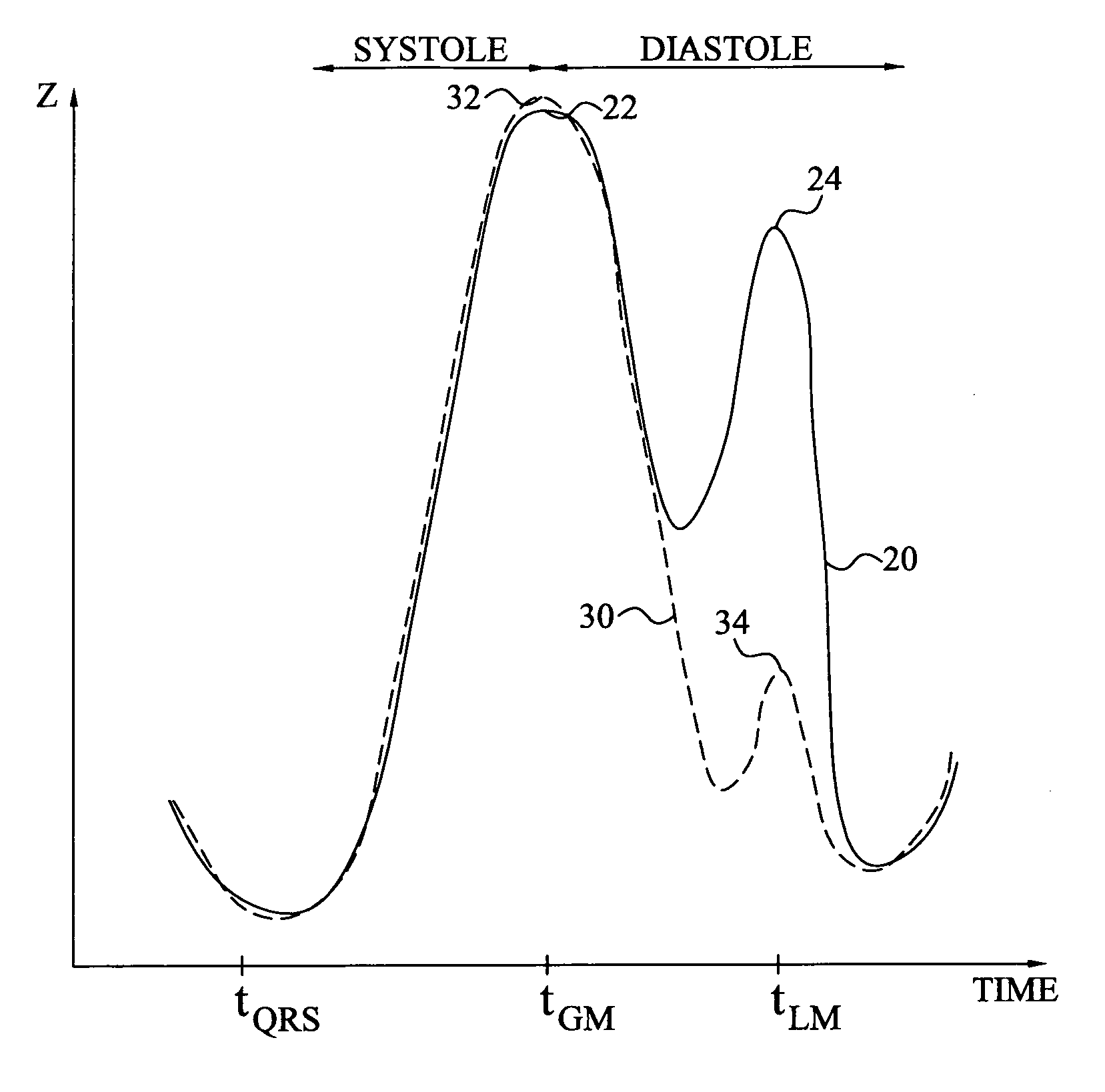
Continuous X-ray image screening examination device, program, and recording medium
InactiveUS8300912B2Simple and convenient generationEffectively utilizableImage enhancementElectrocardiographyX-rayScreening Examination
Using nature that a pixel value in a lung of a chest X-ray moving image varies due to heart beat, the variation information on the pixel value is effectively used for diagnosis such as of a lung embolism or a heart disease, considering the variation information as lung blood flow information. A continuous X-ray image screening examination device receives a chest X-ray moving image from an X-ray detector and receives an electrocardiogram to become original information on a heart beat variation from an electrocardiogram recording apparatus. From the dynamic state of the heart wall measured by the electrocardiograph or the chest X-ray moving image, the heart dynamic state during the cardiac chamber systolic and diastolic phases is grasped, and information such as the variation of the pixel value of the chest X-ray moving image due to increase (lung blood flow increase) of the blood flow from the heart to the lung during the cardiac chamber systolic phase is generated.
Owner:KANAZAWA UNIV
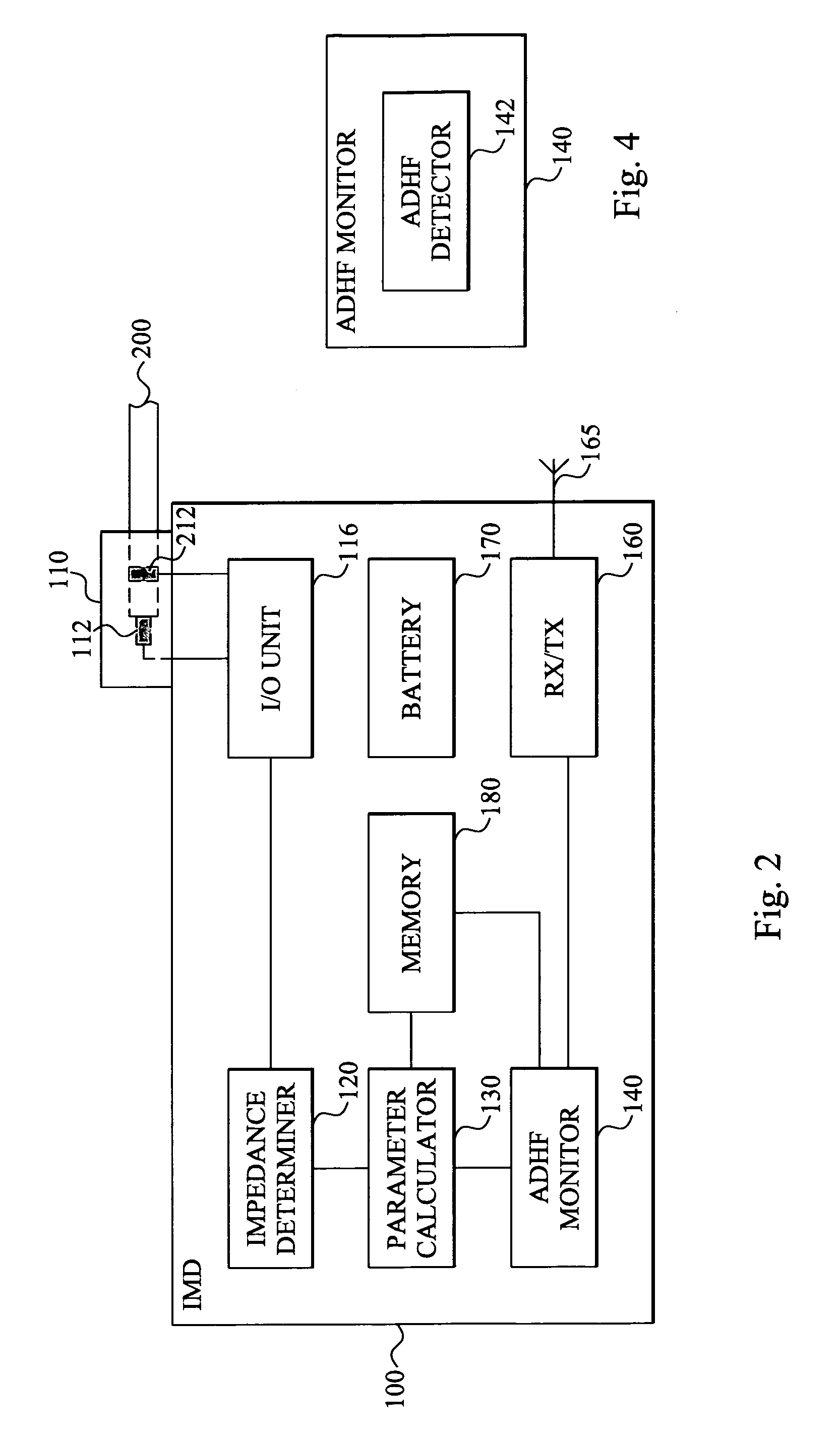
Method and device for monitoring acute decompensated heart failure
InactiveUS8565866B2Detection is simple and fastElectrocardiographyCatheterCardiac cycleAcute decompensated heart failure
An implantable medical device has an impedance determiner for determining a cardiogenic impedance signal based on electric signals sensed by connected electrodes. A parameter calculator processes the impedance signal to calculate an impedance parameter representative of the cardiogenic impedance in connection with the diastolic phase of a heart cycle. This parameter is then employed by the device for monitoring acute decompensated heart failure status of a subject.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
Method and Apparatus for Measuring Blood Pressure
ActiveUS20140316288A1Easy to adjustMinimize complexityEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterPeripheral pulsesDiastolic phase
Embodiments of the present invention provide an improved transformation method whereby the peripheral pulse waveform is filtered to separate different phases which make up the waveform. The separate phases are transformed before being re-combined to provide an estimated intra-arterial transfer function. For example, in one embodiment the peripheral pulse waveform is filtered by a first high pass filter, and a copy of the peripheral pulse waveform filtered by a second high pass filter, having a different cut-off frequency. The two filtered waveforms may then be further processed, for example by being added back to original wave-form, and are then multiplexed together in a time division manner to provide a final waveform. For example, the part of the first filtered waveform corresponding to the systolic phase may be combined with the part of the second filtered waveform corresponding to the diastolic phase to produce the final waveform, and the respective filter cut-off frequencies may be chosen to extract characteristics of the respective phases of the heart.
Owner:SUNTECH MEDICAL
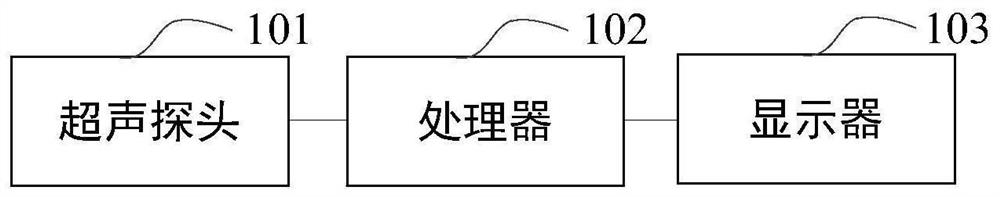
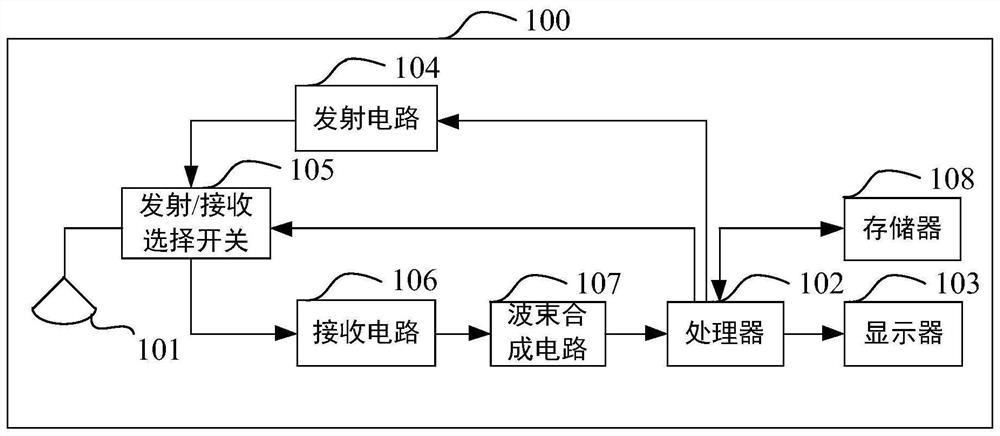
Ultrasonic equipment, ultrasonic image processing method and storage medium
ActiveCN112656445AOrgan movement/changes detectionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic dianostic techniquesVentricular volumeCardiac cycle
The invention discloses ultrasonic equipment, an ultrasonic image processing method and a storage medium, which are used for automatically measuring heart state parameters and improving the measurement accuracy. The equipment comprises a processor and a display. The processor obtains an image sequence composed of ultrasonic images from the continuously collected ultrasonic image information of the heart; the ventricular volume corresponding to each frame of ultrasonic image in the image sequence is determined to obtain a ventricular volume sequence; the end-diastolic volume corresponding to the central ventricular end diastolic phase of at least one cardiac cycle and the end-systolic volume corresponding to the ventricular end-systolic phase is determined according to the change trend of the central ventricular volume of the ventricular volume sequence; and heart state parameters can be determined according to the end-diastolic volume and the end-systolic volume. The ventricular volume is determined according to the ultrasonic images in the acquired image sequence, so that the ventricular volume is determined quickly and accurately; the heart state parameters are determined according to the determined end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume, so that the accuracy of the heart state parameters is improved.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MEDICAL EQUIP
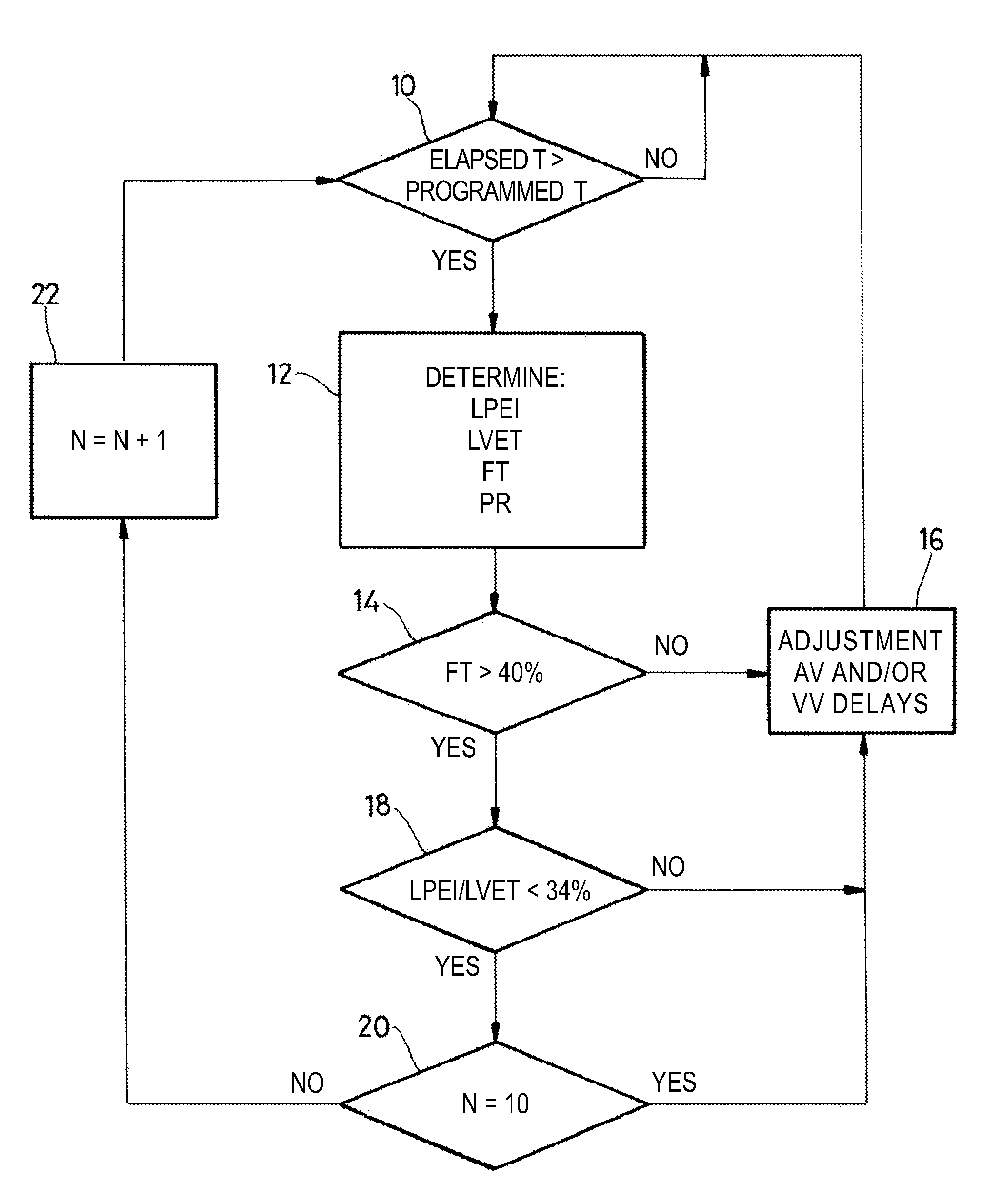
Treatment of heart failure by controlled adjustment of the atrioventricular and interventricular delays in an active implantable medical device
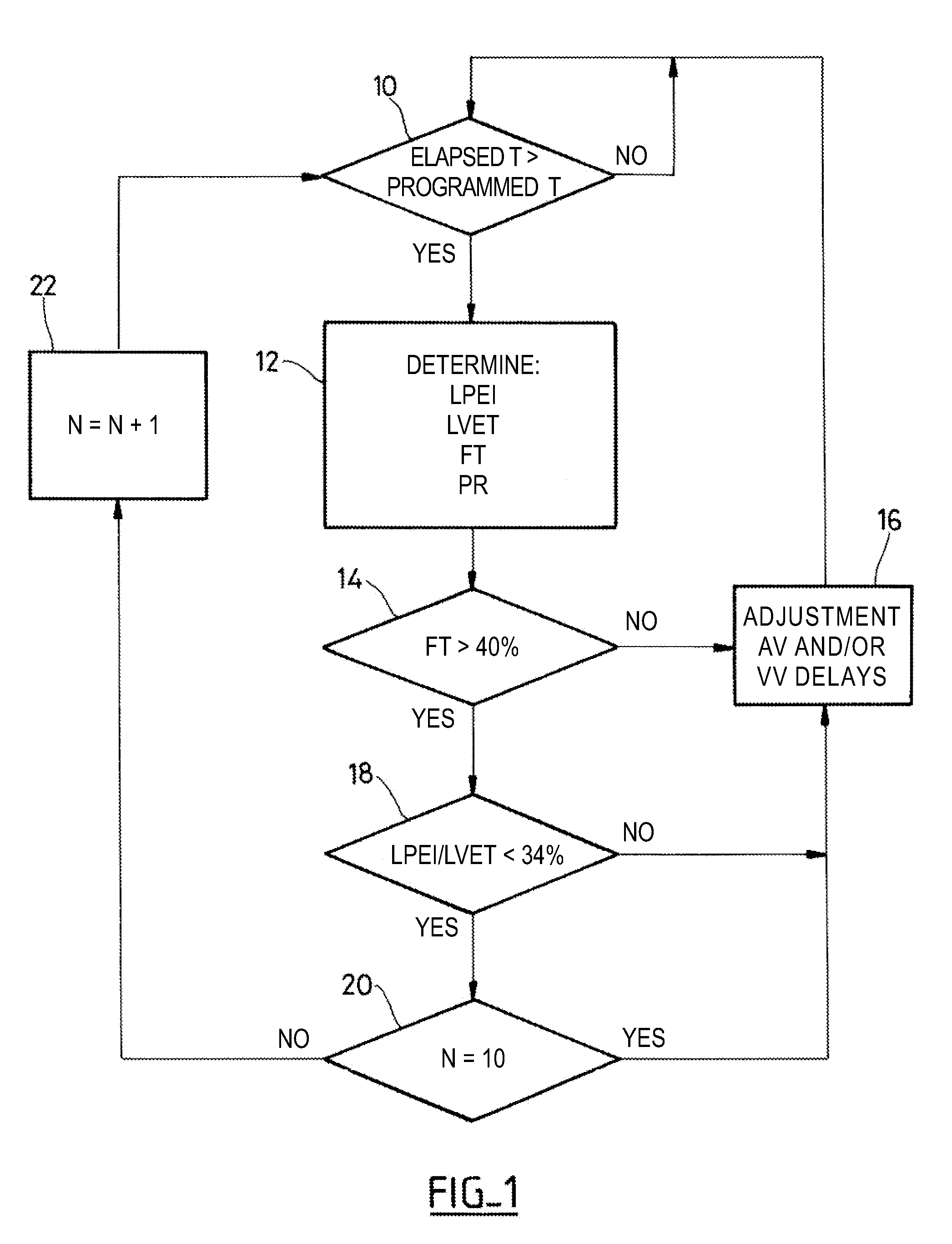
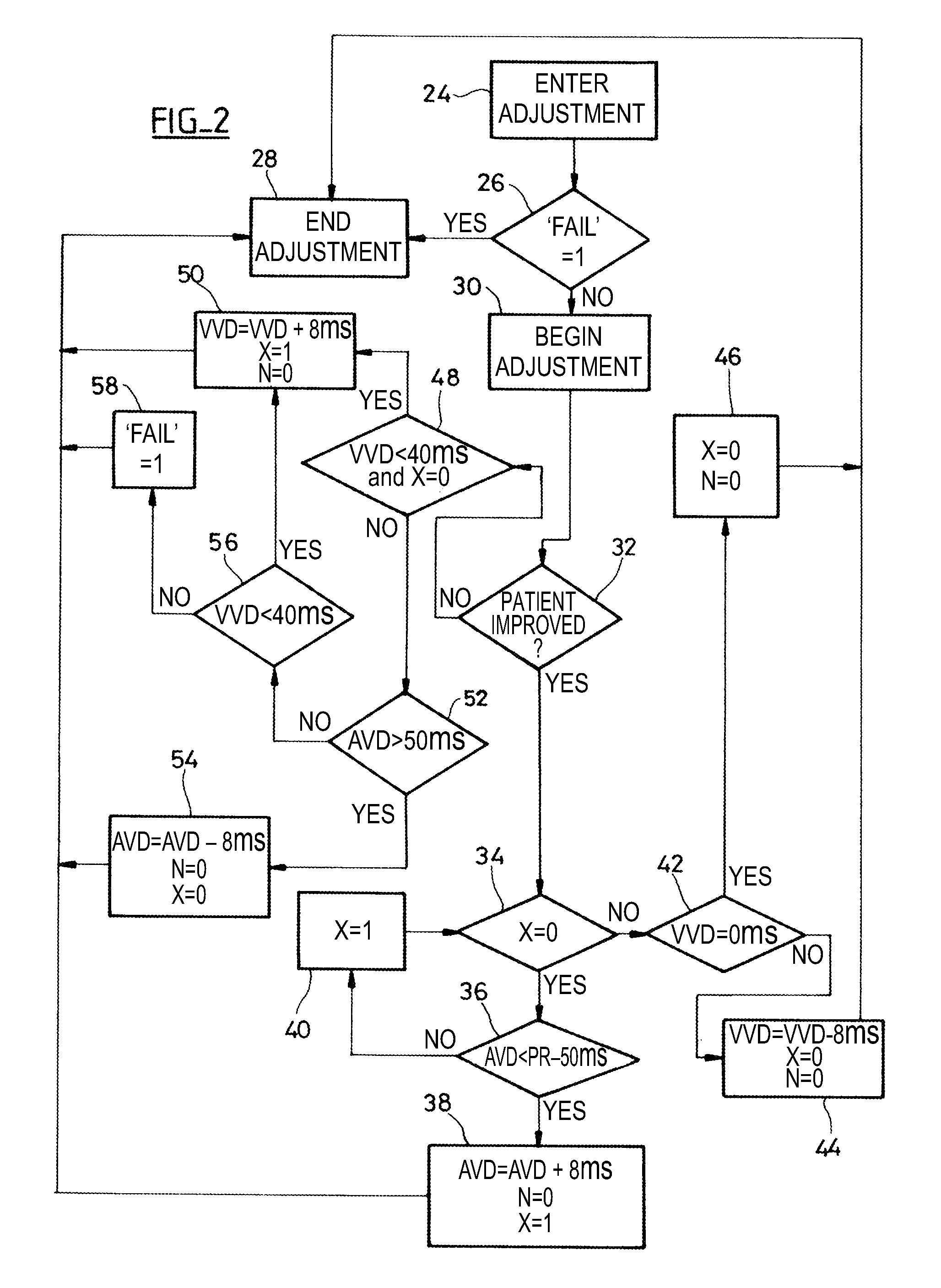
An active implantable medical device such as a cardiac prosthesis for the treatment of a heart failure by controlled adjustment of the atrioventricular and interventricular delays. The device provides atrioventricular and / or biventricular stimulation, a sensor delivering at least one hemodynamic parameter correlated with time intervals representative of the succession of the systolic and diastolic phases, and circuits to adjust the AV delay and / or VV delay. The device determines (12) during one cardiac cycle several parameters such as the left ventricular pre-ejection interval LPEI, the left ventricular ejection time LVET, the diastolic filling time FT and the conduction time PR. The device compares (14, 18) these parameters with at least one predetermined criterion. If a condition is met, the device readjusts (16) the AV delay and / or VV delay to maximize the ventricular filling and ejection.
Owner:SORIN CRM
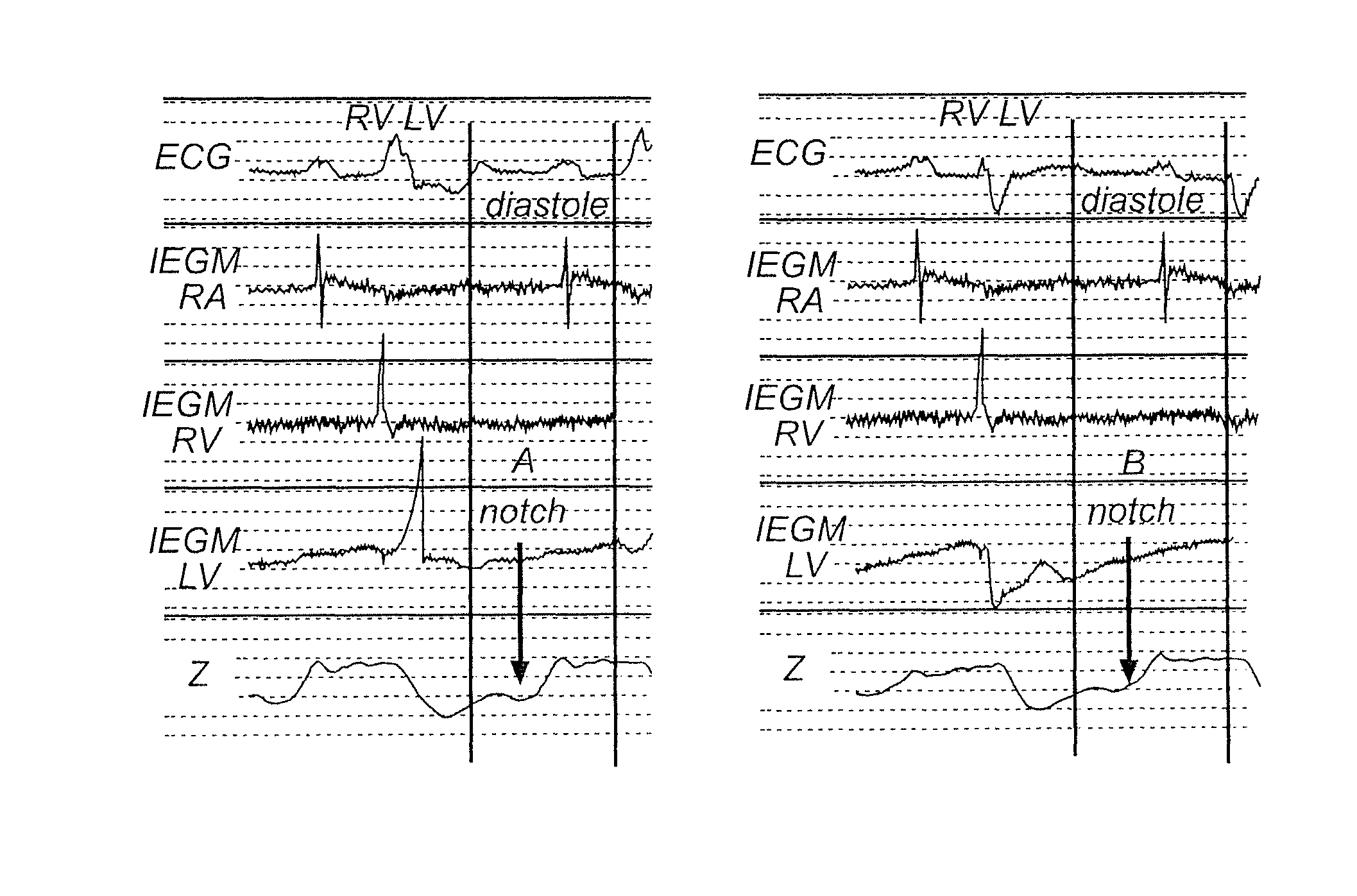
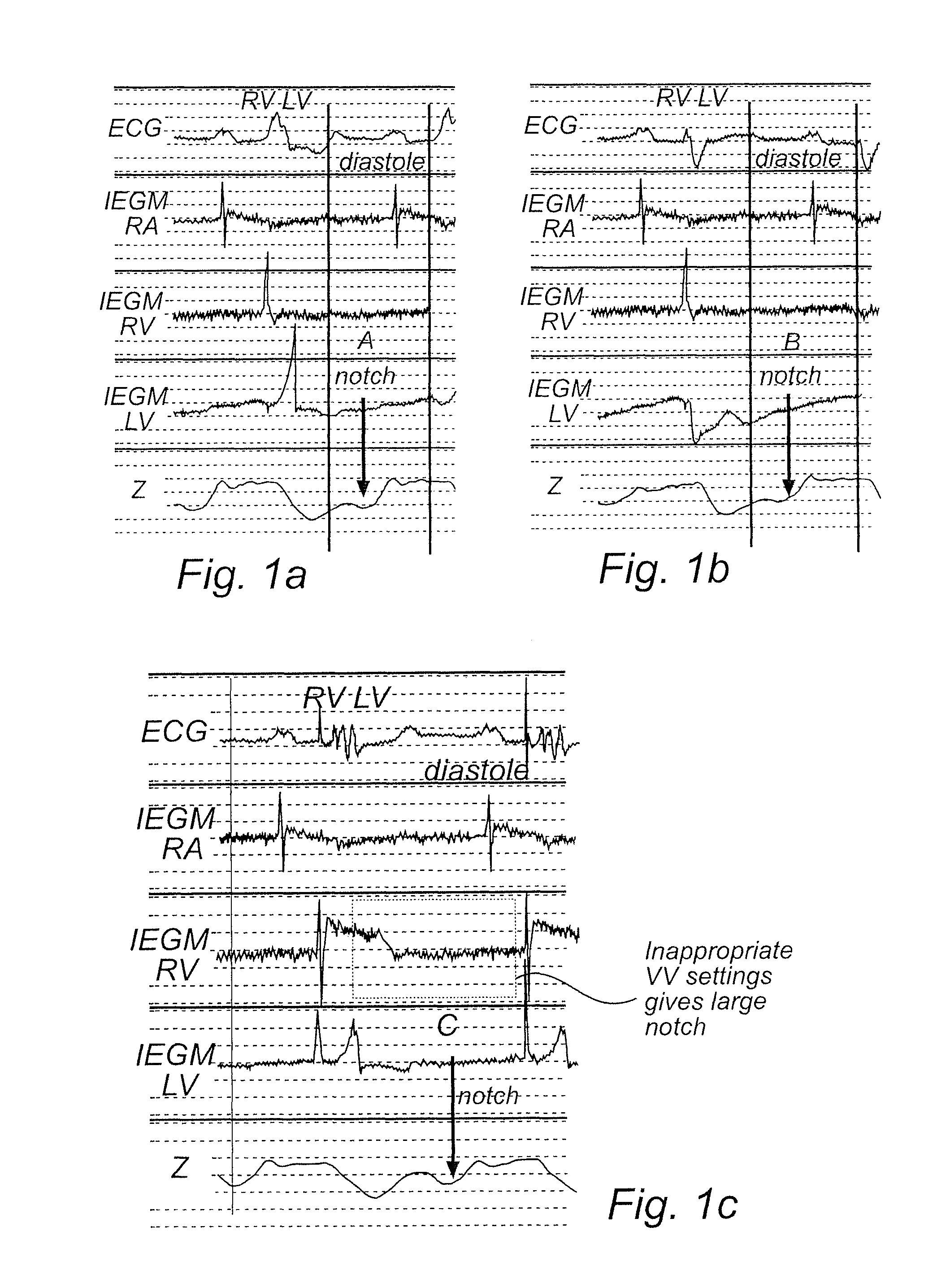
Implantable medical device and method for monitoring synchronicity of the ventricles of a heart
ActiveUS8498702B2Increase pressureMinimize notchHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringCardiac cycleMedical device
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL
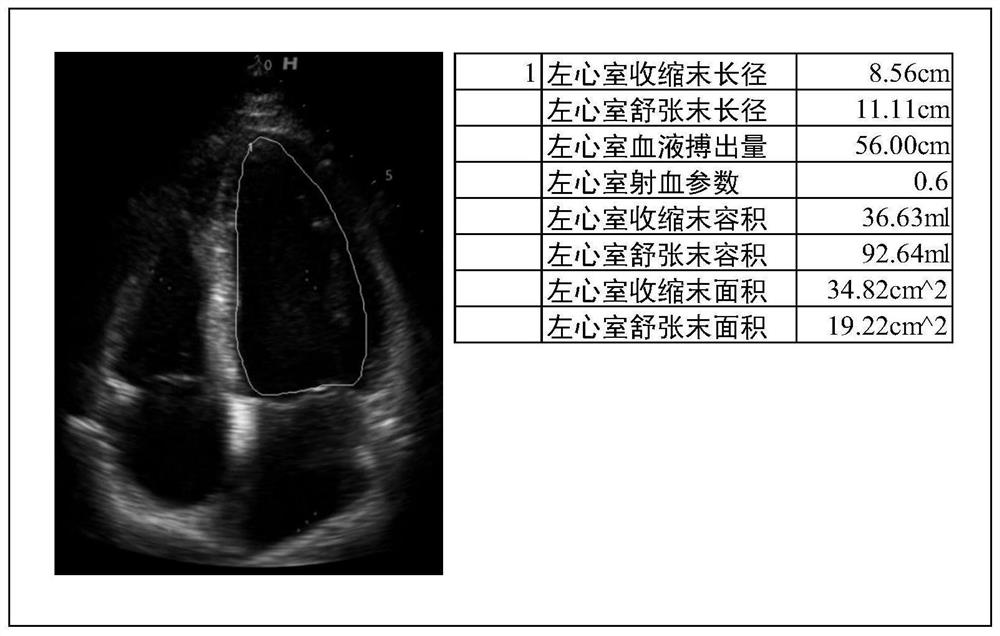
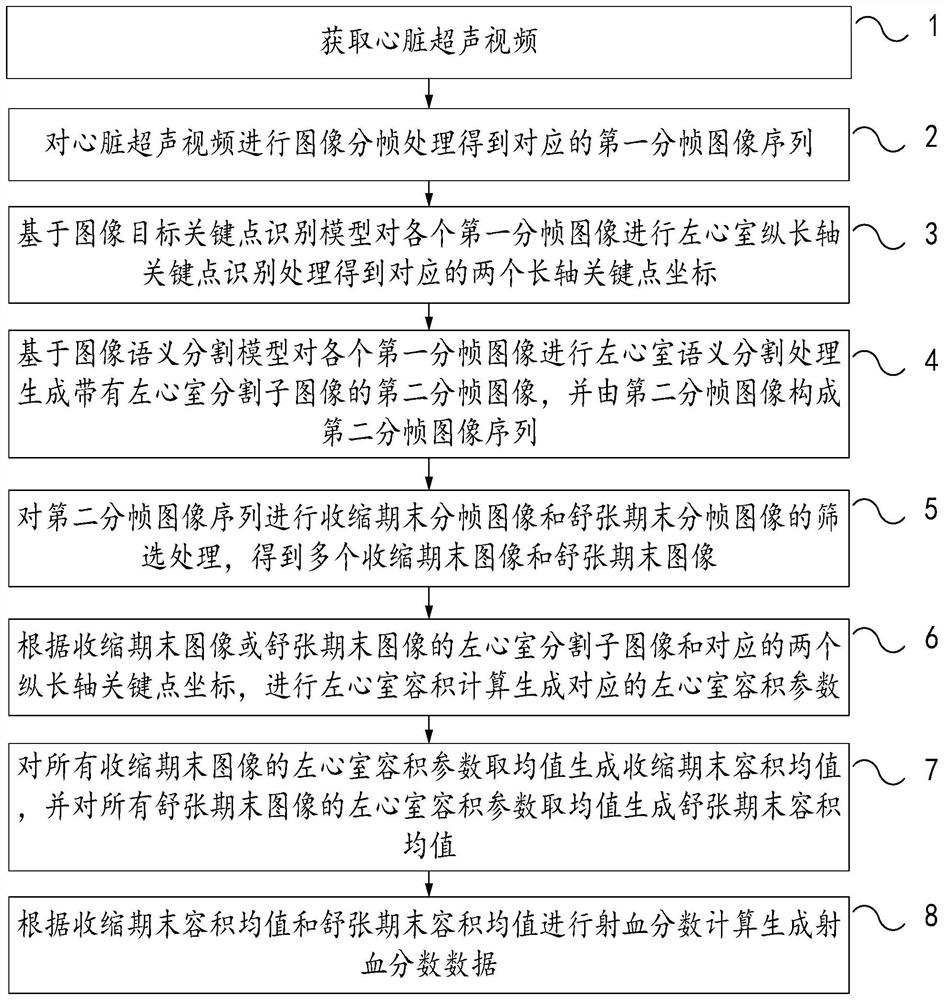
Ejecting fraction data processing method and device based on cardiac ultrasound video
PendingCN114419499AHigh marking accuracyImprove recognition accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisVentricular volumeSystole
The embodiment of the invention relates to an ejection fraction data processing method and device based on a cardiac ultrasound video. The method comprises the steps that the cardiac ultrasound video is acquired; performing image framing to obtain a first framed image sequence; performing left ventricle lengthwise axis key point identification on each first sub-frame image based on an image target key point identification model; performing left ventricle semantic segmentation processing on each first framing image based on an image semantic segmentation model to generate a second framing image with a left ventricle segmented sub-image; screening processing of framing images at the end of a systolic period and at the end of a diastolic period is carried out on the second framing image sequence; performing left ventricular volume calculation to generate corresponding left ventricular volume parameters; generating a systolic end volume mean value and a diastolic end volume mean value; and ejection fraction data is calculated and generated according to the volume mean value of the end of the systolic period and the end of the diastolic period. By means of the method, the manual intervention link in a traditional method can be eliminated, and the ejection fraction calculation precision and accuracy can be improved.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
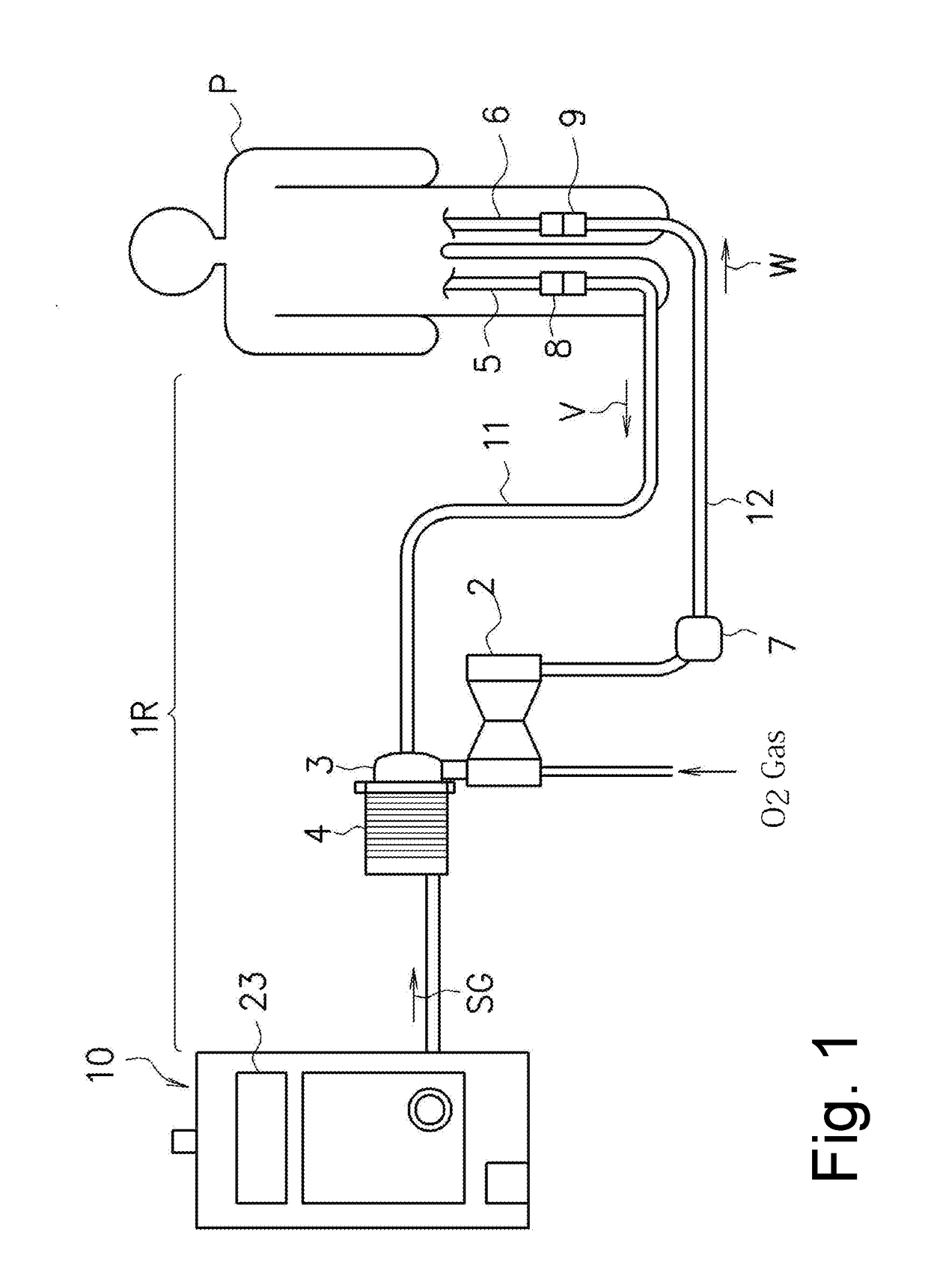
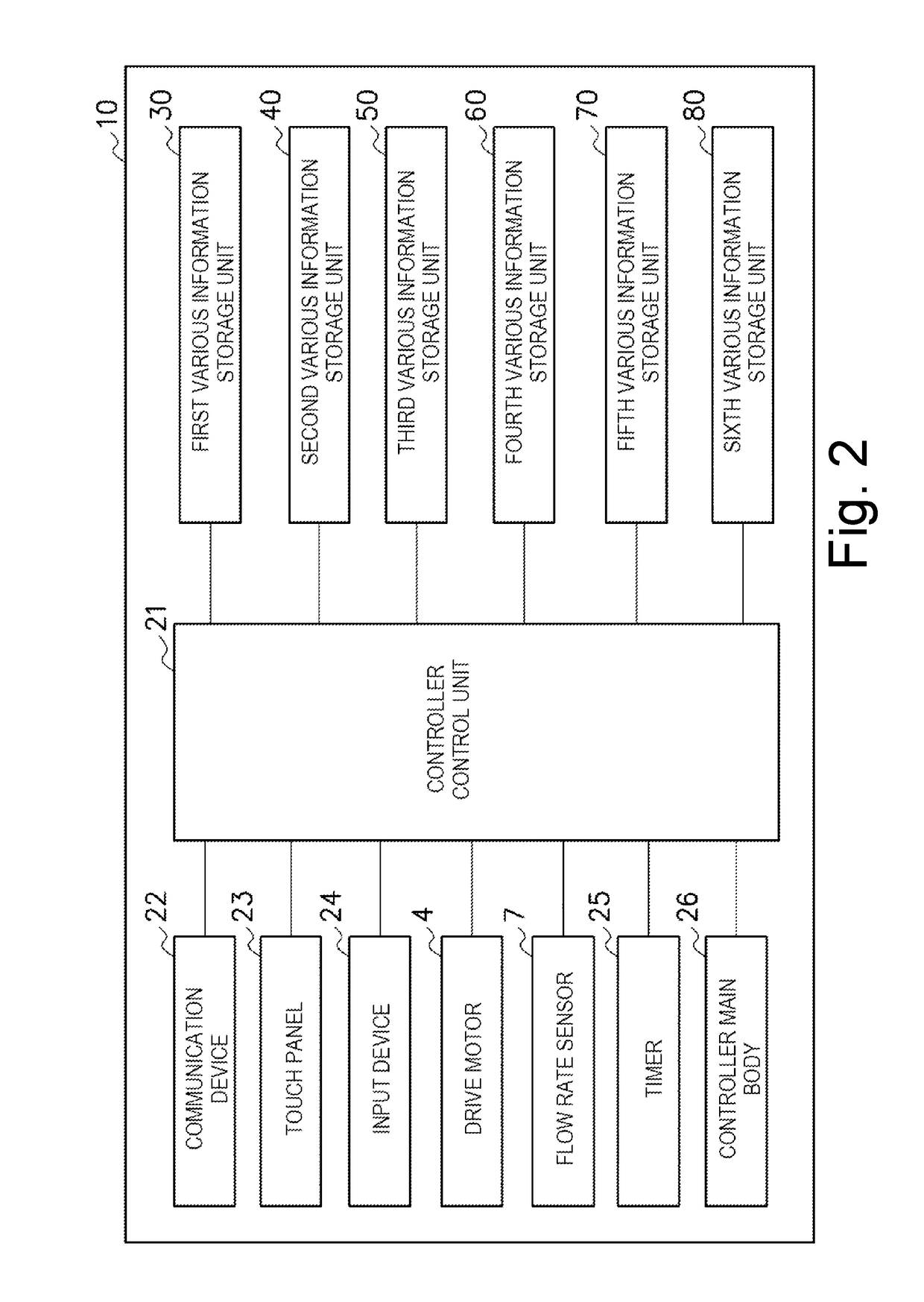
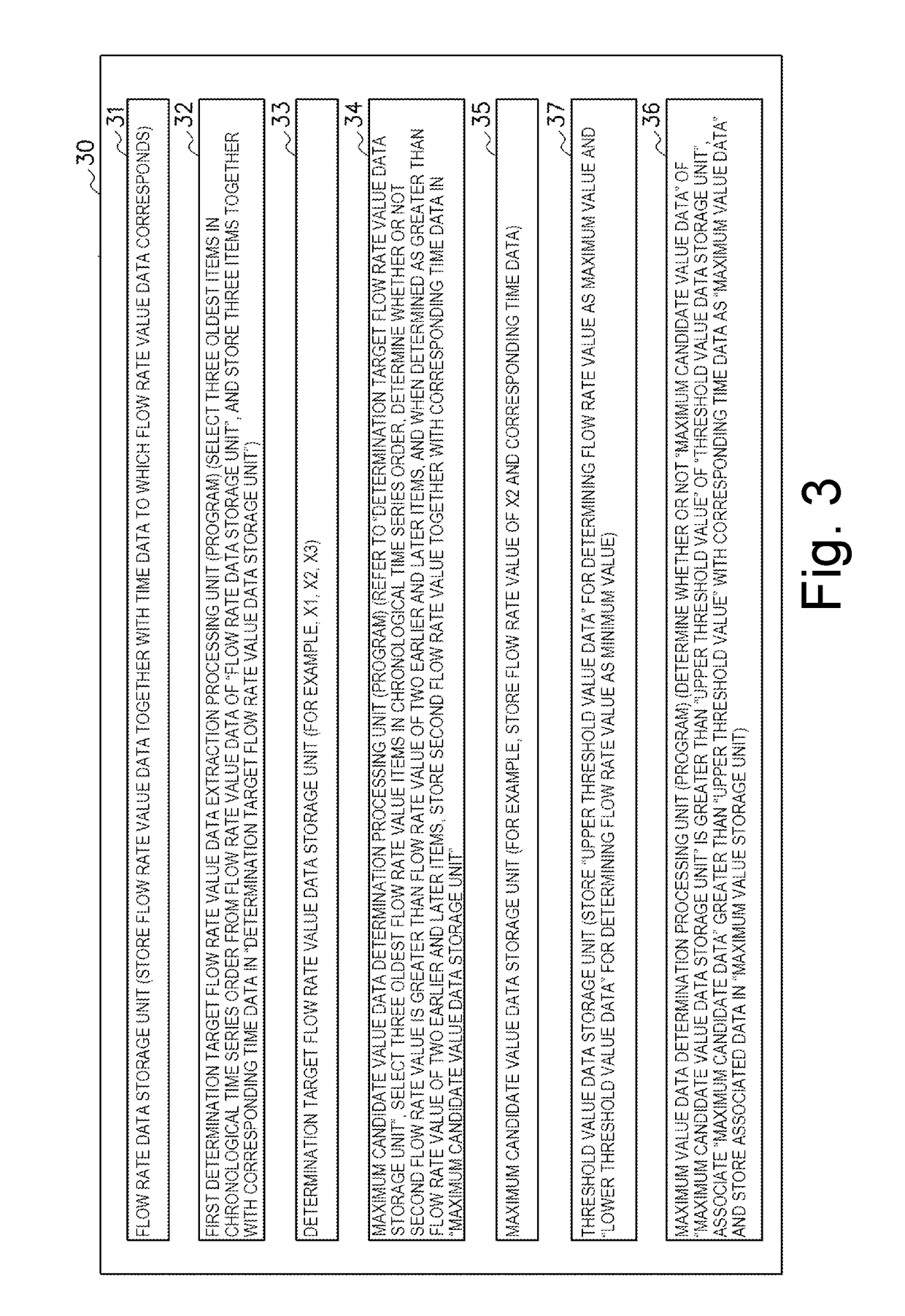
Extracorporeal circulation management device with heartbeat synchronizaton
ActiveUS20180369465A1Without causing damage to the bloodElectrocardiographyOther blood circulation devicesExtracorporeal circulationDiastolic phase
An extracorporeal circulation management device pumps blood in synchronization with heartbeats of a patient based on measurements of blood flow. Maximum and minimum blood flow measurement samples are compared with upper and lower threshold values to identify candidate timing for a systolic phase and diastolic phase of the heartbeat. During pulsatile pumping of the blood using the candidate timing, differences in the pulsatile flow measurements are determined. Based on the size of the difference, a final correction may be made to identification of the systolic and diastolic phases, and the corrected phase information is used to start and stop the motor unit.
Owner:TERUMO KK
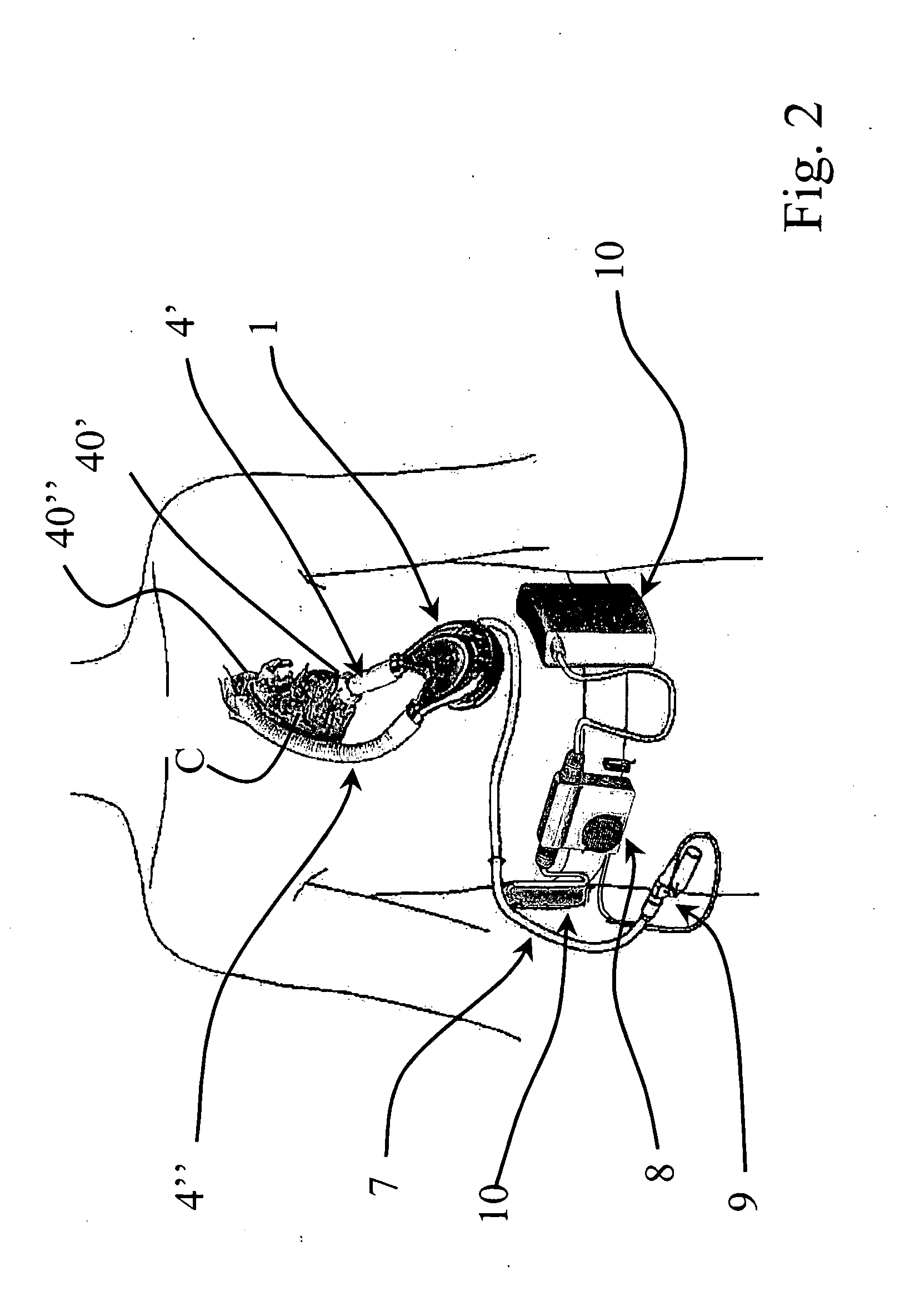
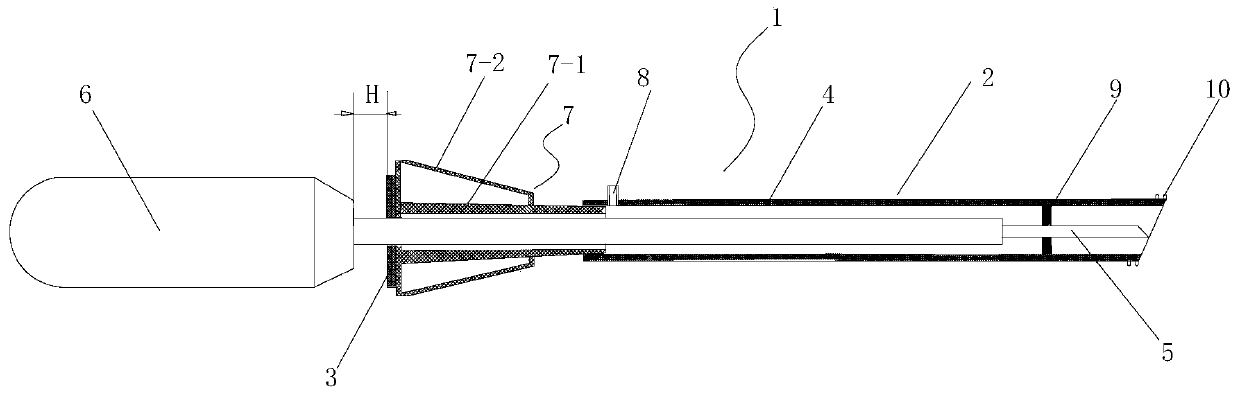
Minimally invasive path of extracorporeal blood pump aorta counterpulsation circulation auxiliary device and implantation method
ActiveCN110975113ARaise diastolic blood pressureReduce loadBalloon catheterEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a minimally invasive path of an extracorporeal blood pump aorta counterpulsation circulation auxiliary device and an implantation method. The implantation method of the extracorporeal blood pump aorta counterpulsation minimally invasive path is characterized in that: making a cutting mark in the center of sternum corresponding to a selected part on an aortic valve, drilling a circular hole, implanting and fixing a counterpulsation pump pipeline into an ascending aorta through minimally invasive surgery, and connecting the pipeline to an external counterpulsation pump balloon after exhausting. The method has the advantages that: the circular hole is drilled in the center of the sternum, a hose is implanted into the ascending aorta and fixed through minimally invasive surgery, and the hose is connected to the external counterpulsation pump balloon after exhausting. Through pressure or electrocardio waveforms, a controller achieves synchronous counterpulsation assistance through the diastolic period of the counterpulsation pump, and the purposes of assisting circulation and treating heart failure are achieved. The cure rate of acute heart failure can be greatly improved; after implantation, physical strength permitted, the patient is allowed to take food, urinate, defecate and move out of bed by himself / herself; the ICU residence time is shortened; and long-time assistance is achieved, and no obvious complications exist.
Owner:张杰民
Signaling of an aortic valve state
ActiveUS20190059839A1Improve visualizationAdd supportUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsEvaluation of blood vesselsRelevant informationCardiac phase
The invention relates to an apparatus configured to display an aortic valve image and an indicator when the aortic valve is in its open-state and / or when the valve is in its closed-state. The indicator is supposed to be in an overlay to the image of the aortic valve, such that a physician can see on the same display image the information needed to advance a guide wire or catheter through the aortic valve of a heart. This may prevent damaging ensures not to damage the aortic valve. The physician receives the relevant information, when the aortic valve is in its open-state and thus being in a state to be passed by the catheter. The information, whether the aortic valve is in its open-state or in its closed-state, corresponds to the systolic phase and the distal phase of the heart, respectively. The information, when the heart is in its systolic phase and when it is in the diastolic phase may be extracted from an ECG measurement. From the detection of these cardiac phases, the closed-state of the valve and / or the open-state of the valve can be estimated using general knowledge about flood flow during the cardiac cycle.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Three-dimensional ultrasound cardiogram four-cavity section image automatic detection method
InactiveCN100448409CFacilitate diagnostic workHeavy calculationImage enhancementOrgan movement/changes detectionSonificationDiastolic phase
The invention relates to a method for realizing the three-dimension ultrasonic cardiogram four-chamber section image automatic check, which comprises that 1, extracting one three-dimension data from the end-diastolic phase of heart from the heart full-volume data; 2, extracting 180 section images from the three-dimension data to build an image database; 3, calculating out the similarity between each image of database and the template image, to be selected and using wavelet system statistic character to check out the image with highest similarity in the left image, to record the position in the data as the four-chamber watch position. The invention realizes the automatic search function of four-chamber section; therefore, medical staff can use real-time three-dimension ultrasonic technique to diagnose the patient.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for measuring blood pressure
ActiveUS10159445B2Low skill levelSuitable for useEvaluation of blood vesselsSensorsPeripheral pulsesEngineering
Embodiments of the present invention provide an improved transformation method whereby the peripheral pulse waveform is filtered to separate different phases which make up the waveform. The separate phases are transformed before being re-combined to provide an estimated intra-arterial transfer function. For example, in one embodiment the peripheral pulse waveform is filtered by a first high pass filter, and a copy of the peripheral pulse waveform filtered by a second high pass filter, having a different cut-off frequency. The two filtered waveforms may then be further processed, for example by being added back to original wave-form, and are then multiplexed together in a time division manner to provide a final waveform. For example, the part of the first filtered waveform corresponding to the systolic phase may be combined with the part of the second filtered waveform corresponding to the diastolic phase to produce the final waveform, and the respective filter cut-off frequencies may be chosen to extract characteristics of the respective phases of the heart.
Owner:SUNTECH MEDICAL
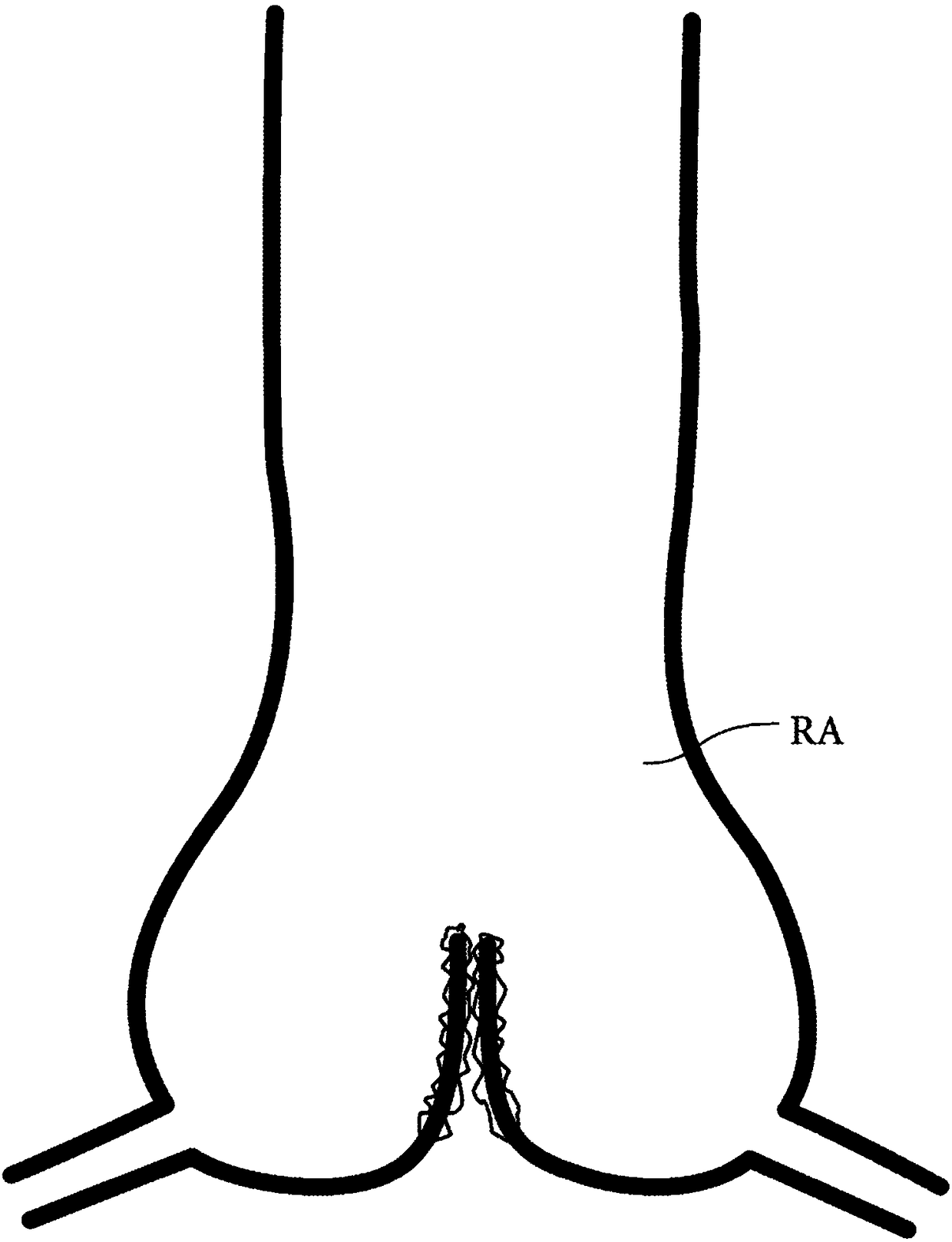
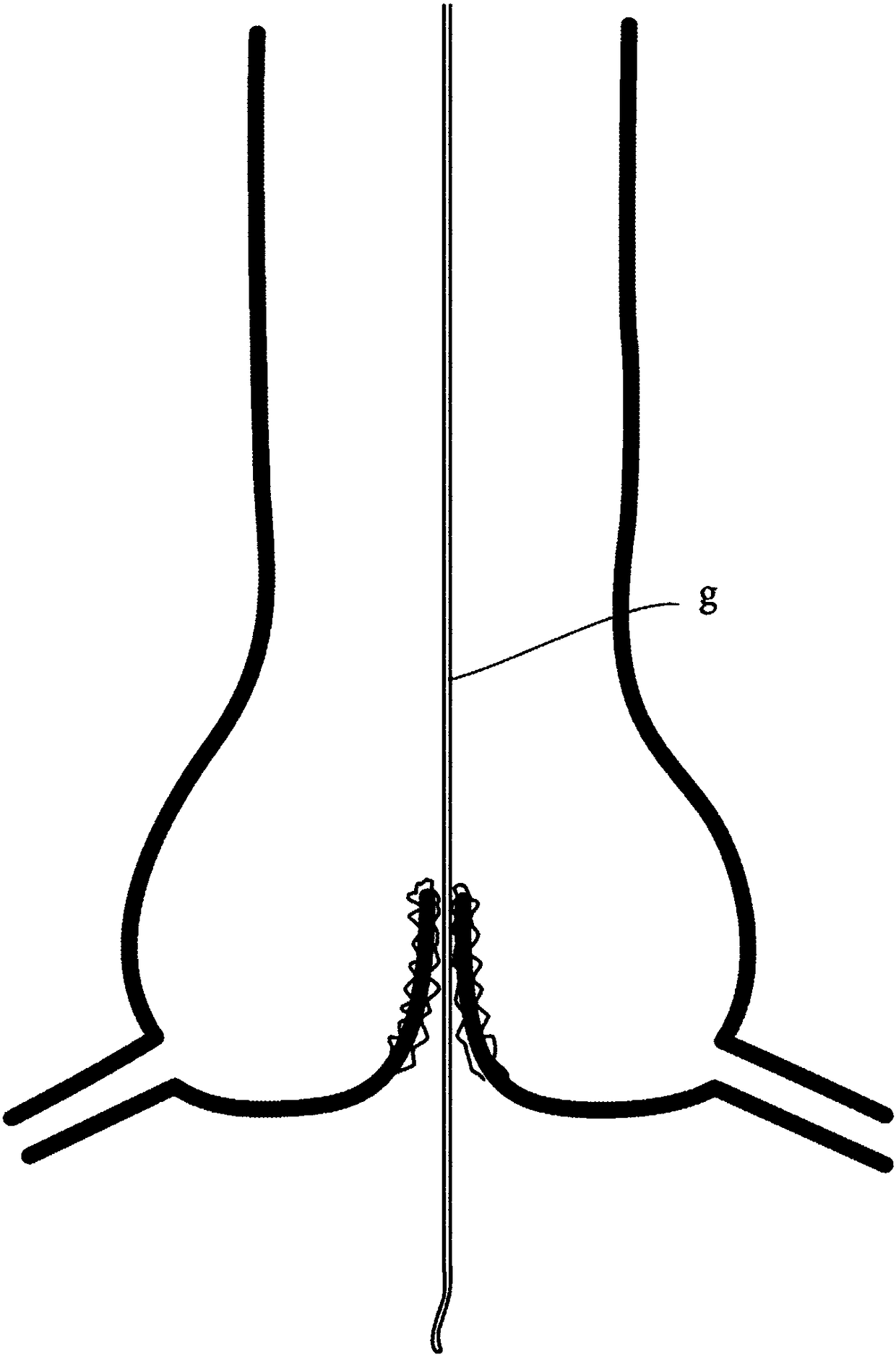
Device for transcatheter insertion into the aortic root at the sinotubular junction
A device for transcatheter insertion into the aortic root at the sinotubular junction by means of a guide wire and a catheter (1), the catheter (1) having means for protecting the surrounding tissue, characterized in that the device comprises An assembly (E) of an embolic filter mounted to slide in a guided manner into said catheter (1), said assembly (E) having a configuration capable of forming a safe lumen in the aortic root (RA) , the safety cavity performs valve function and protection function against accidental embolism, said structure includes a tubular body (2) fixed at one end thereof to be able to expand or retract outside the catheter (1) as required to a portion (2a) in the catheter (1) having a filtering configuration incorporating means capable of reproducing the function of a temporary valve corresponding to opening during systole and closing during diastole, to Any backflow of blood in the deployed position of the portion is prevented, thereby covering the native aortic valve with a seat secured in the aortic root at the sinus of Valsalva without obstructing blood flow.
Owner:圣艾蒂安大学中心医院 +1
Coronary Artery Segmentation Method Fused with Dual Source CT Data
ActiveCN109345498BAchieve integrationImprove output qualityImage enhancementImage analysisBlood vesselImage sequence
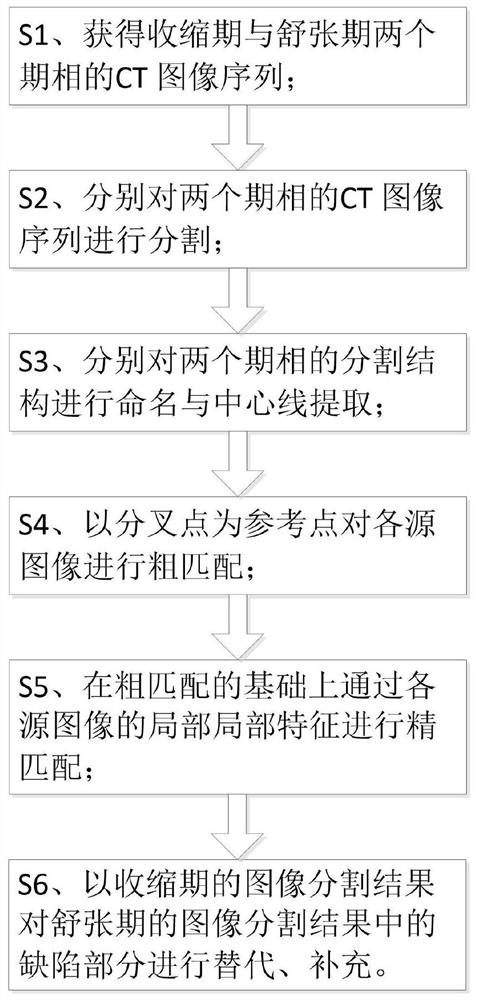
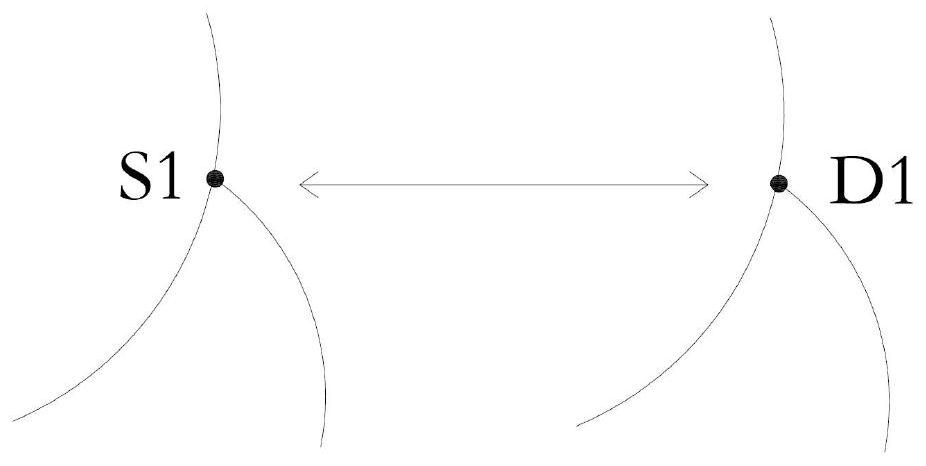
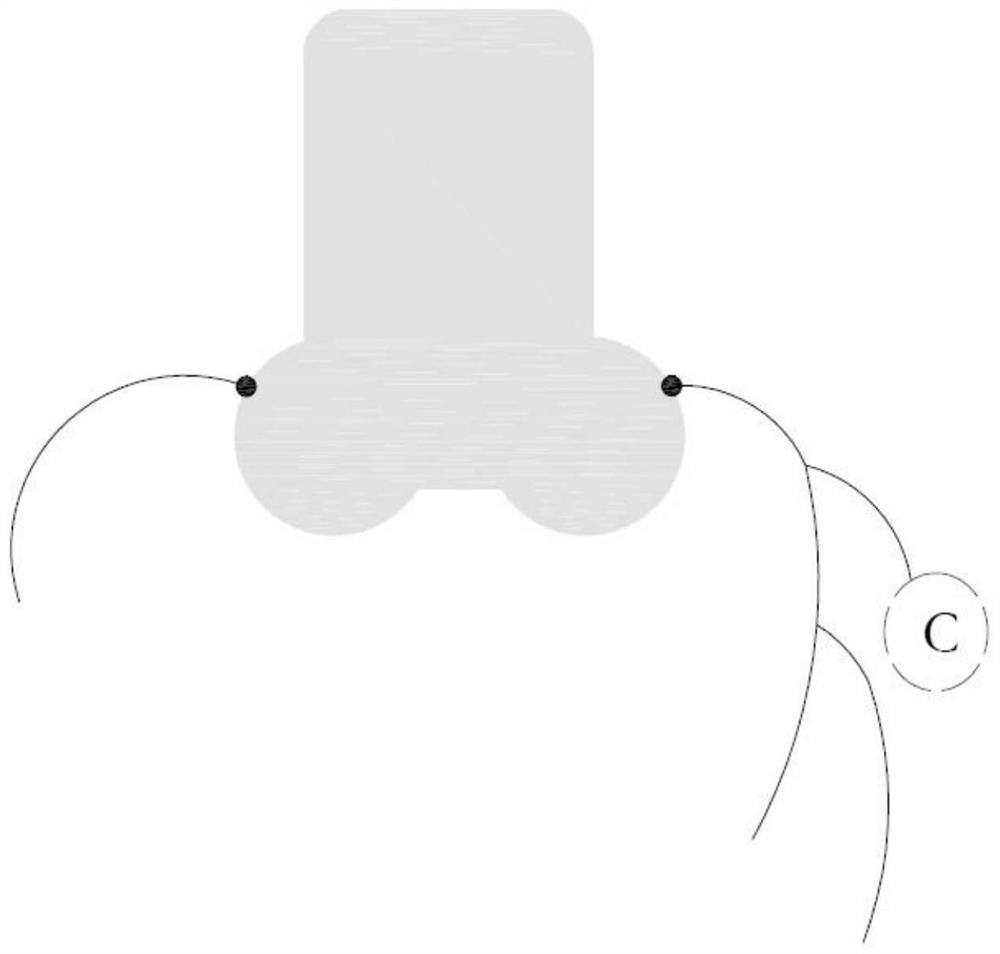
The invention discloses a method for coronary artery segmentation fused with dual-source CT data, comprising: S1, performing dual-source CT scans, respectively obtaining CT image sequences of the systolic phase and the diastolic phase; S2, respectively analyzing the CT images of the two phases sequence; S3, name each blood vessel in the segmentation results of the two phase CT image sequences and extract the centerline; S4, find the bifurcation point in each centerline, and use the bifurcation point as a reference point to Perform rough matching on the CT images of the two phases; S5, extract local matching features in the CT image sequences of the two phases through the neural network, perform fine matching on the basis of rough matching through the local matching features, and obtain two The mapping relationship of the CT image sequence of phase; S6, based on the CT image sequence and segmentation result of the diastolic period, select the corresponding part from the CT image of the systolic period and the segmentation result to splice or replace the defective part of the image, and output Fused CT image sequence and segmentation results.
Owner:数坤(上海)医疗科技有限公司
Noninvasive 4-D time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography
ActiveUS10470676B2High temporal resolution and spatial resolutionEnhanced/prolonged labeling bolusMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsCardiac cycleParallel imaging
A method for non-contrast enhanced 4D time resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography using arterial spin labeling of blood water as an endogenous tracer and a multiphase balanced steady state free precession readout is presented. Imaging can be accelerated with dynamic golden angle radial acquisitions and k-space weighted imaging contrast (KWIC) image reconstruction and it can be used with parallel imaging techniques. Quantitative tracer kinetic models can be formed allowing cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow and mean transit time to be estimated. Vascular compliance can also be assessed using 4D dMRA by synchronizing dMRA acquisitions with the systolic and diastolic phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com