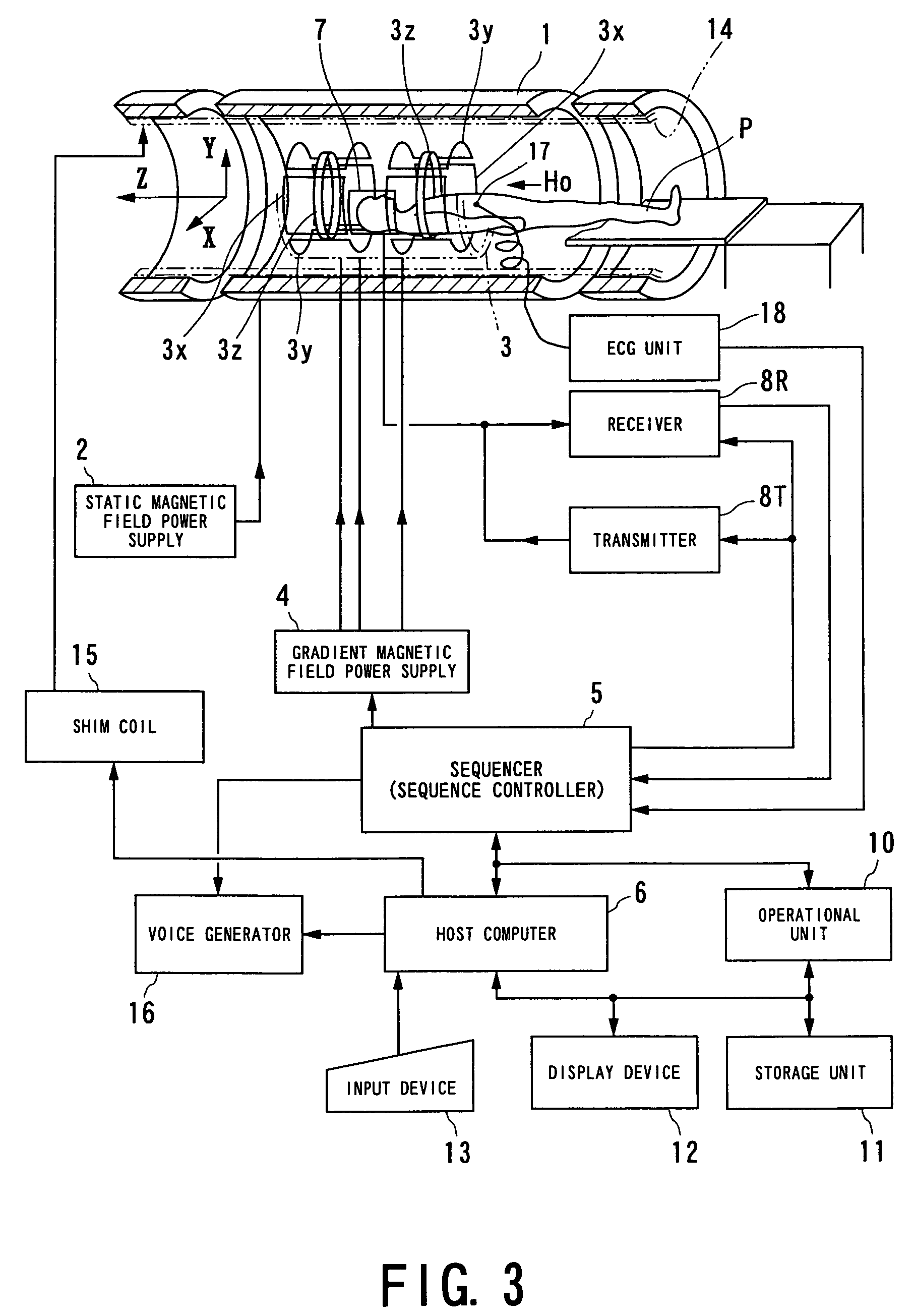
Patents
Literature
42 results about "Arterial spin labeling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
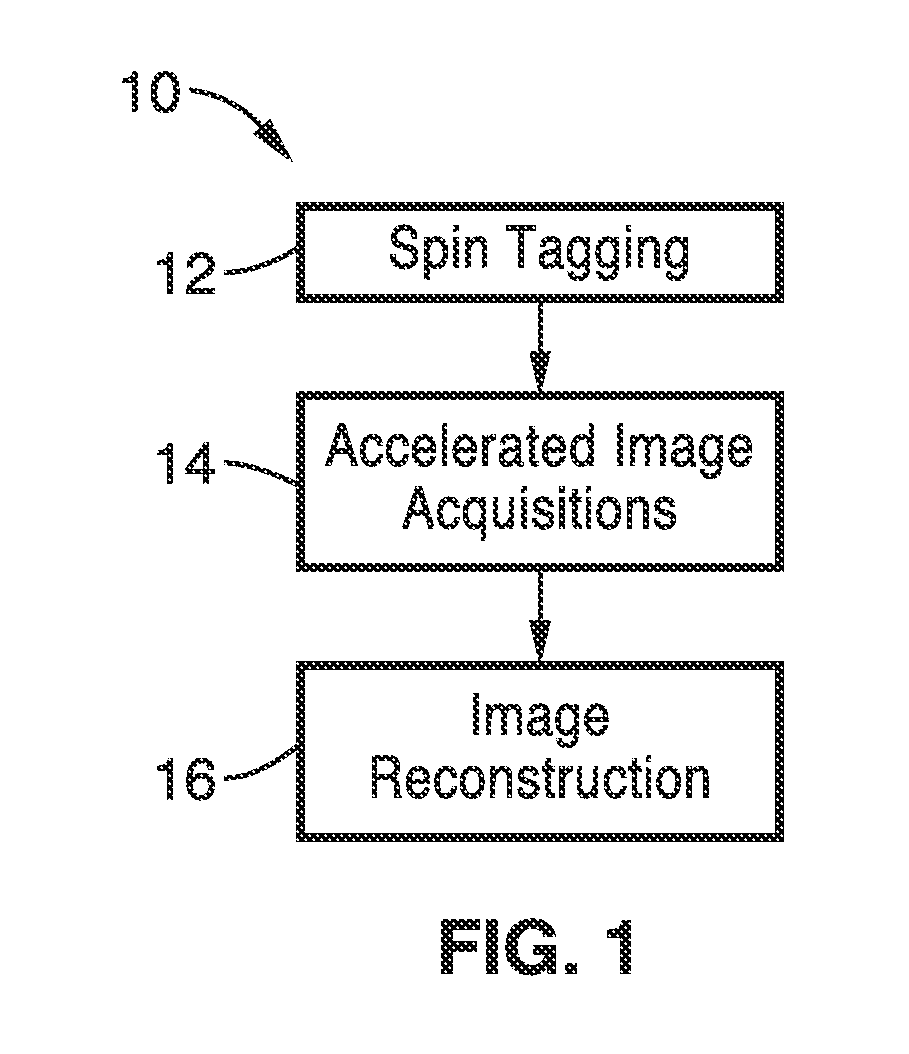
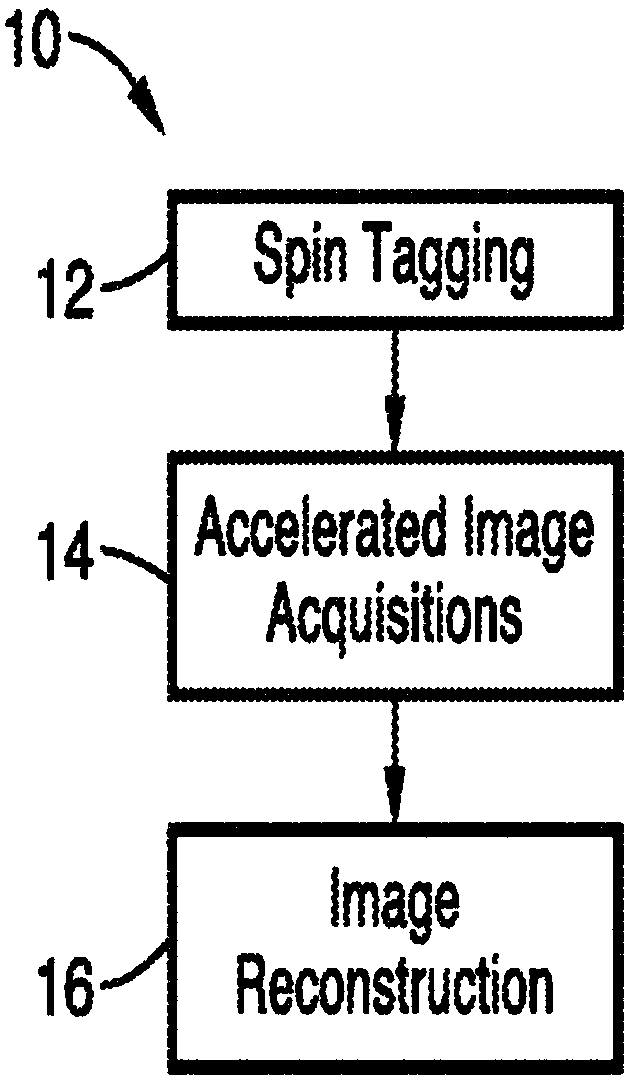
Arterial spin labeling (ASL), also known as arterial spin tagging, is a magnetic resonance imaging technique used to quantify cerebral blood perfusion by labelling blood water as it flows throughout the brain. ASL specifically refers to magnetic labeling of arterial blood below the imaging slab, without the need of gadolinium contrast, which is the first of its kind in terms of perfusion imaging.
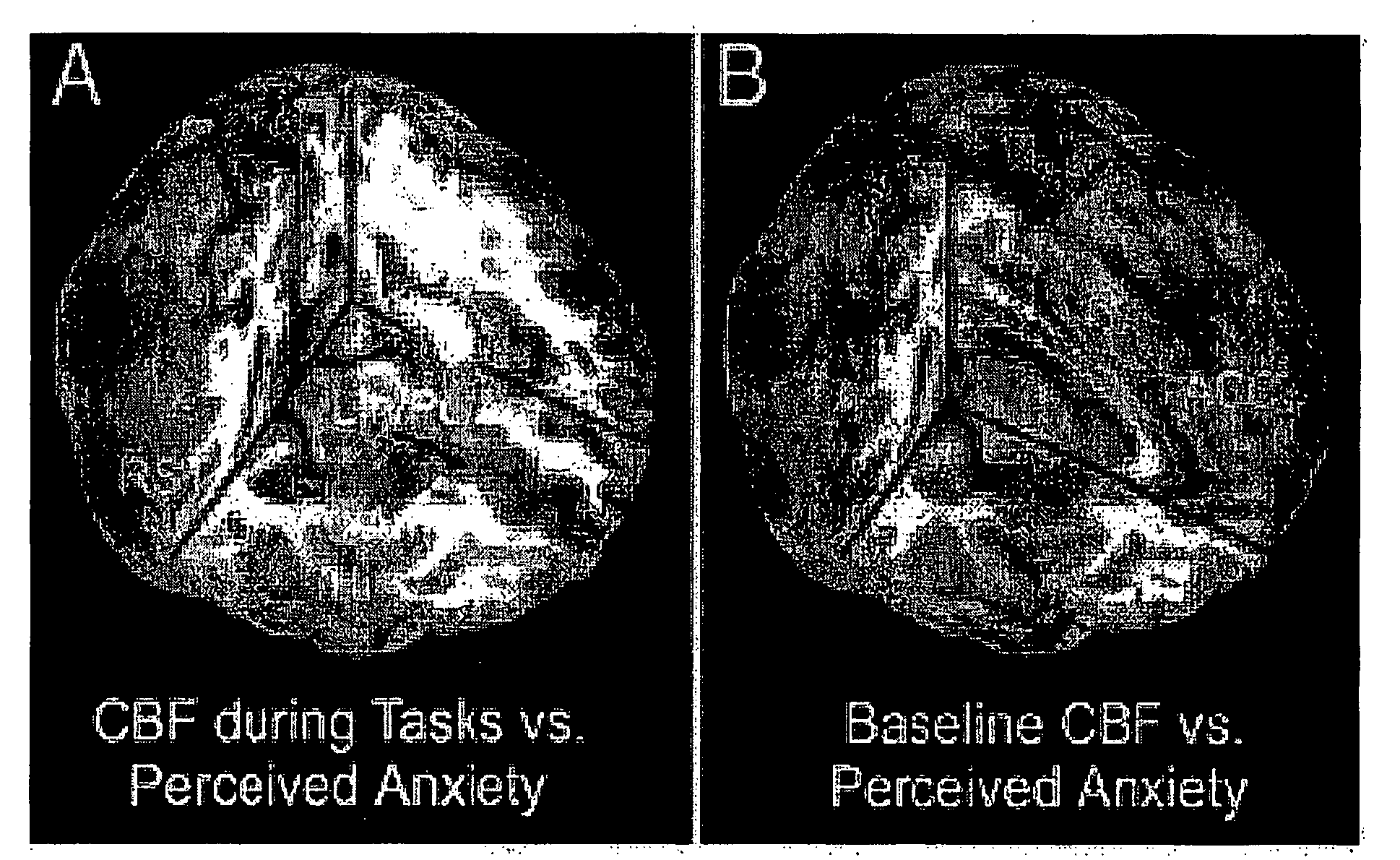
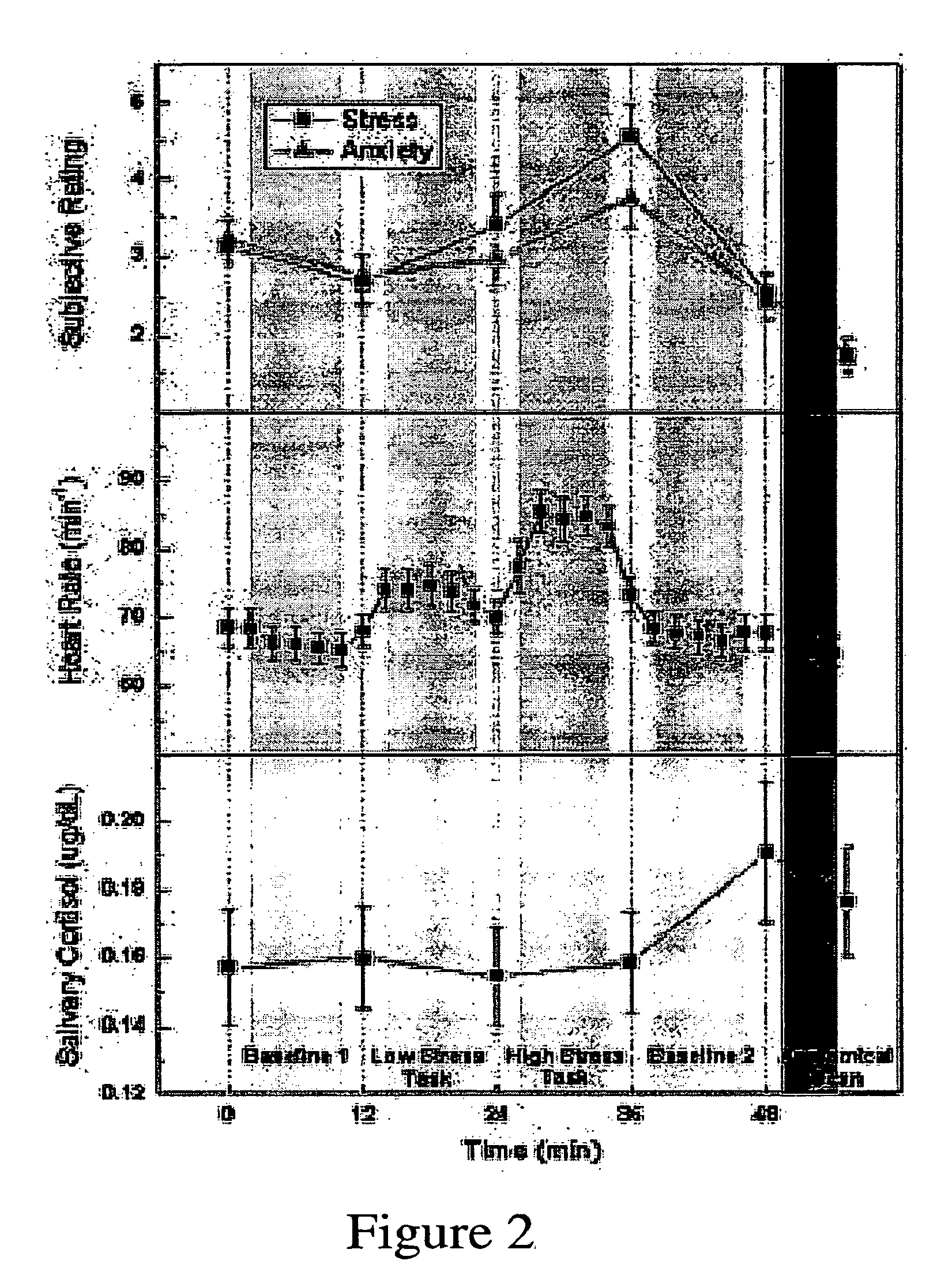
Assessing subject's reactivity to psychological stress using fmri
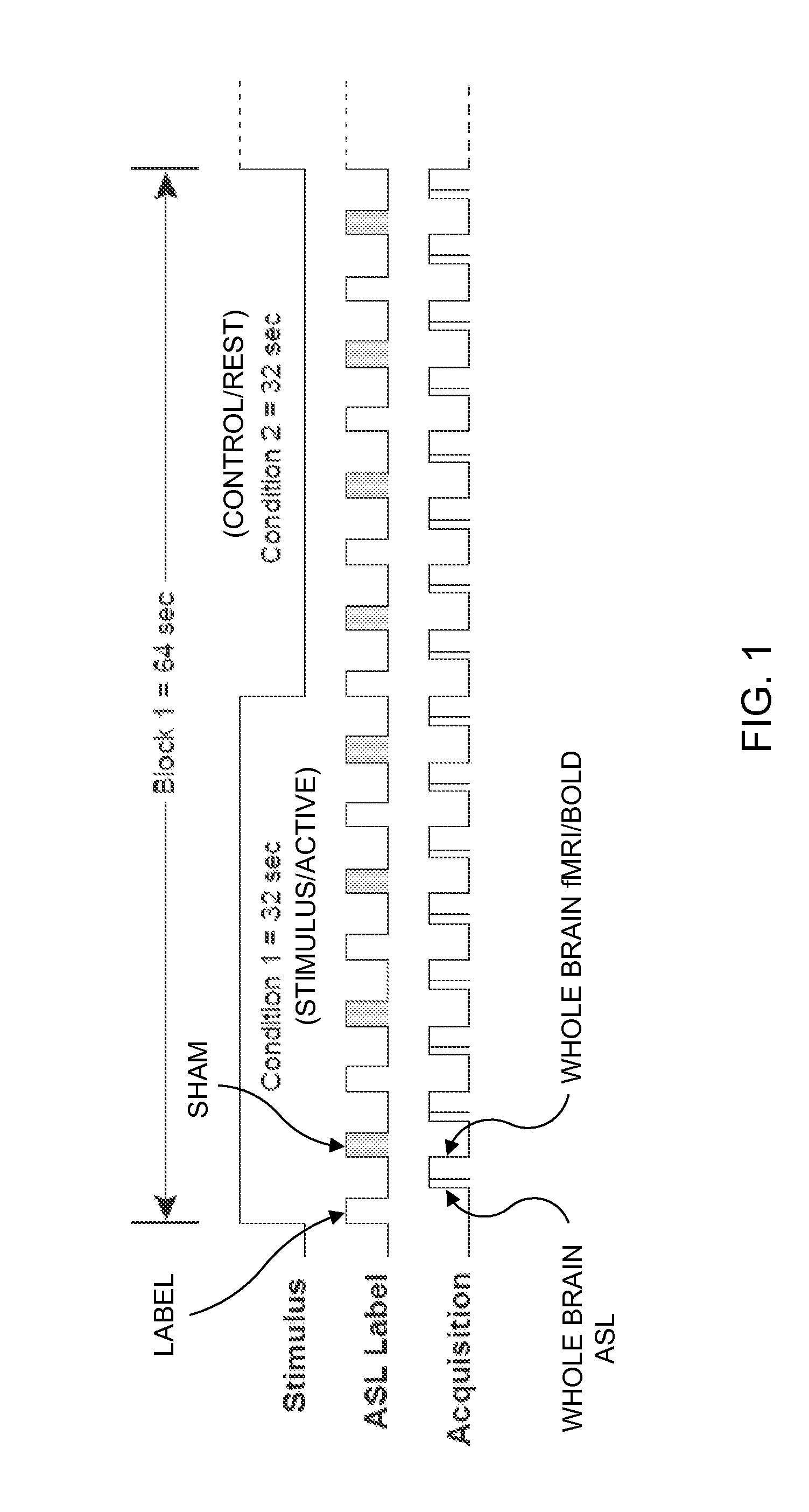
This invention relates to the use of a quantitative functional MRI (fMRI)—arterial spin-labeling perfusion MRI or absolute T2 mapping MRI or a combination thereof in the non-invasive neuroimaging of a subject's brain in response to stress-inducing psychological stimuli, which can be utilized to predict individual stress reactivity as well as to be used as a human model for testing or optimizing psychopharmacological agents.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
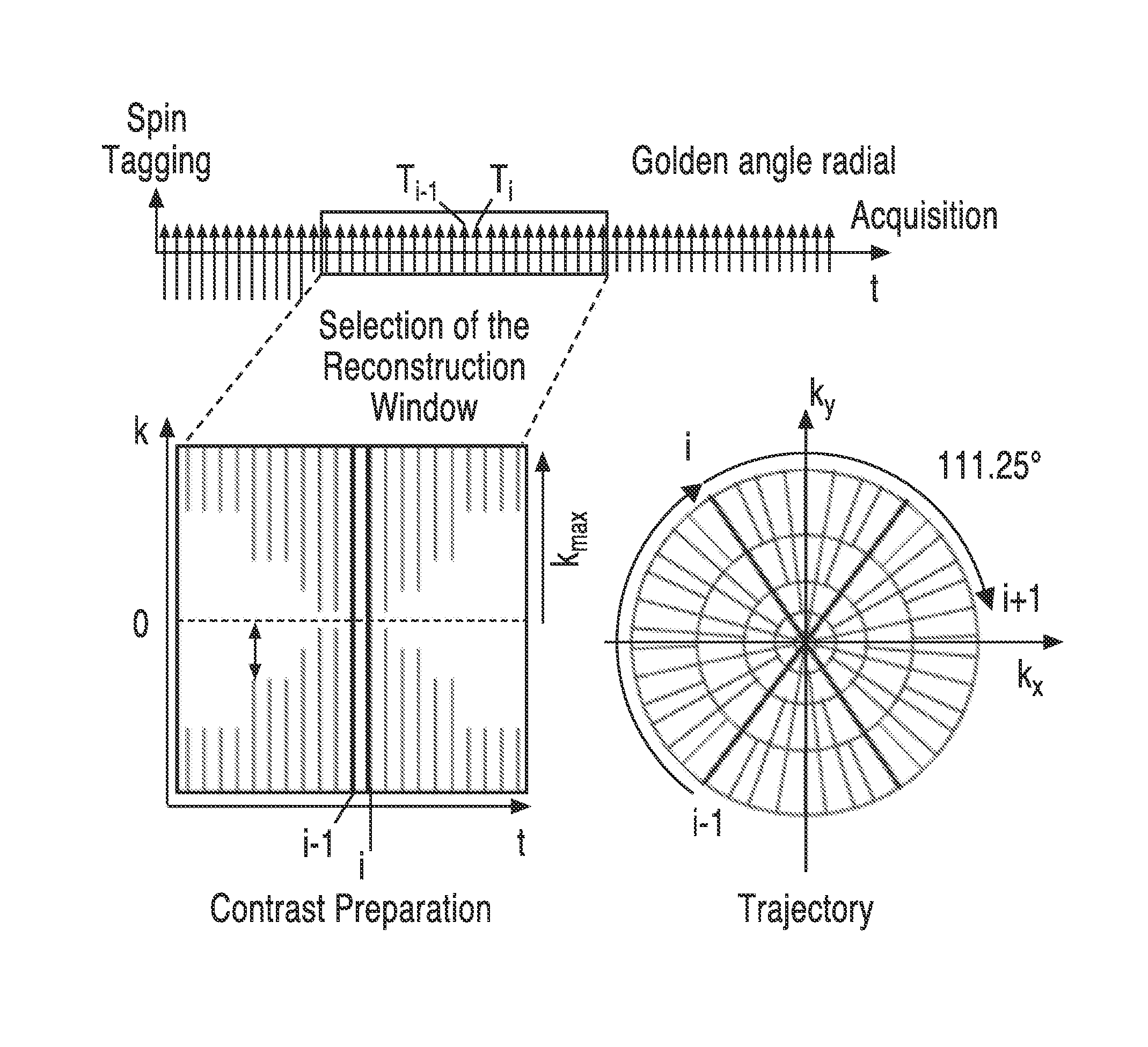
Noninvasive 4-d time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography
ActiveUS20150327783A1High degree of efficiencyIncrease flexibilityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsSystoleCardiac cycle
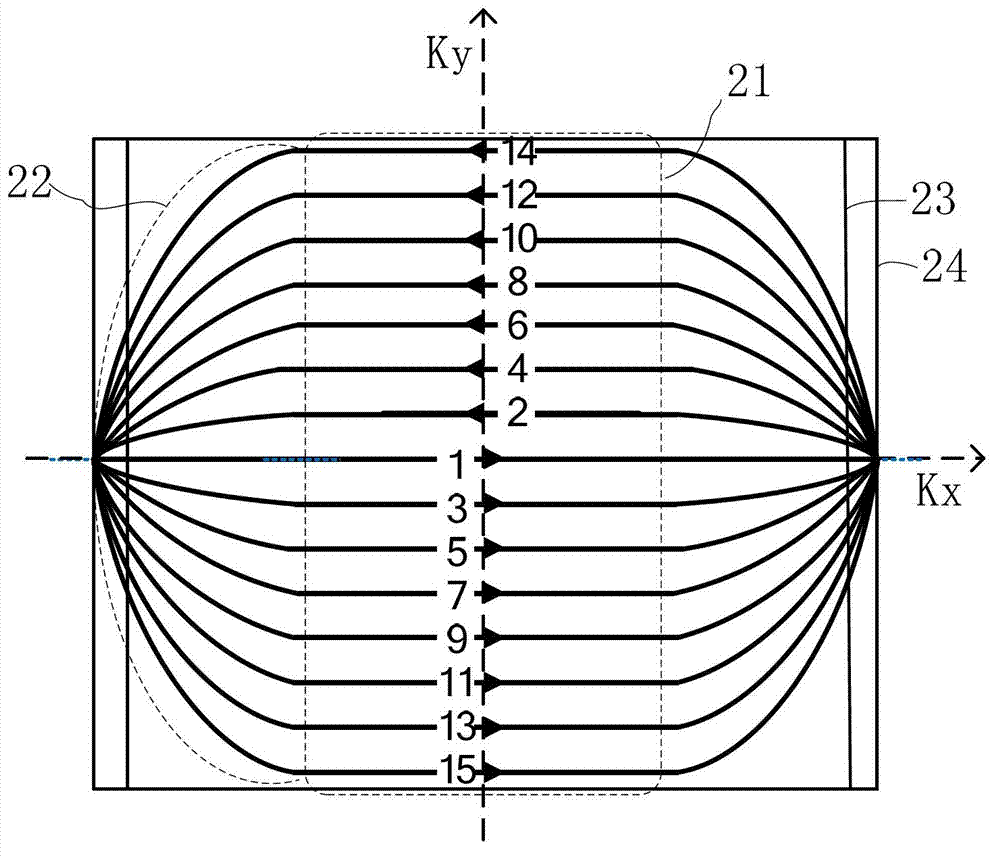
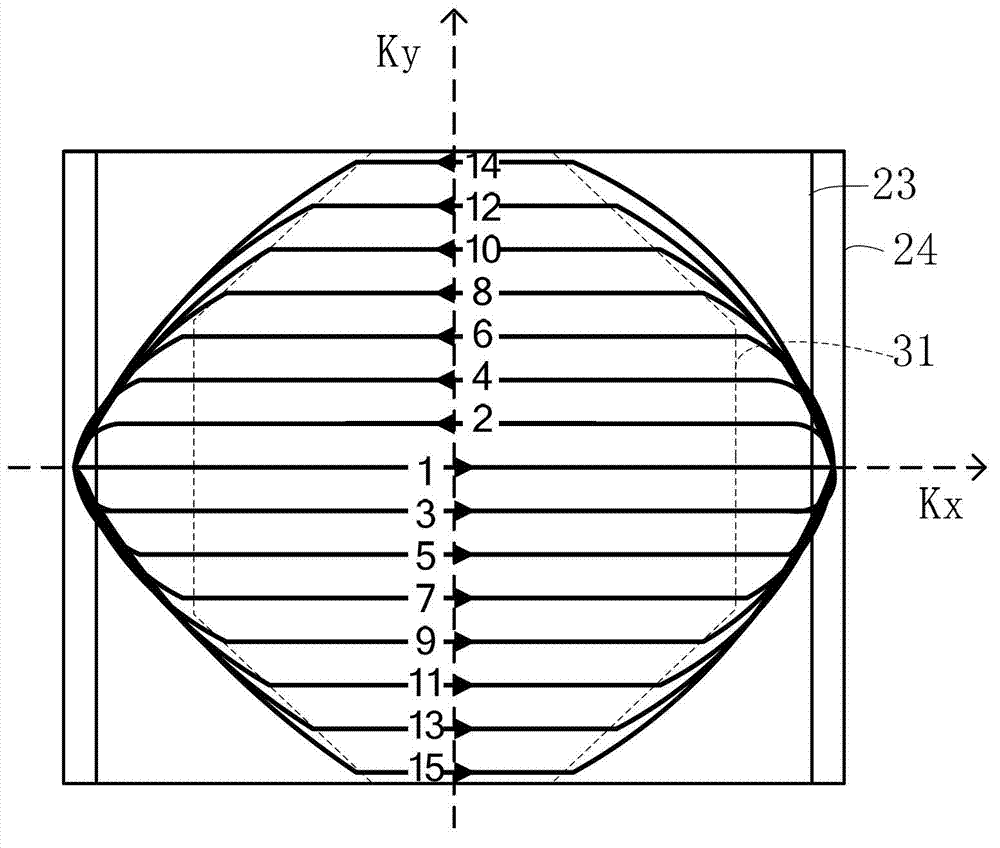
A method for non-contrast enhanced 4D time resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography using arterial spin labeling of blood water as an endogenous tracer and a multiphase balanced steady state free precession readout is presented. Imaging can be accelerated with dynamic golden angle radial acquisitions and k-space weighted imaging contrast (KWIC) image reconstruction and it can be used with parallel imaging techniques. Quantitative tracer kinetic models can be formed allowing cerebral blood volume, cerebral blood flow and mean transit time to be estimated. Vascular compliance can also be assessed using 4D dMRA by synchronizing dMRA acquisitions with the systolic and diastolic phases of the cardiac cycle.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
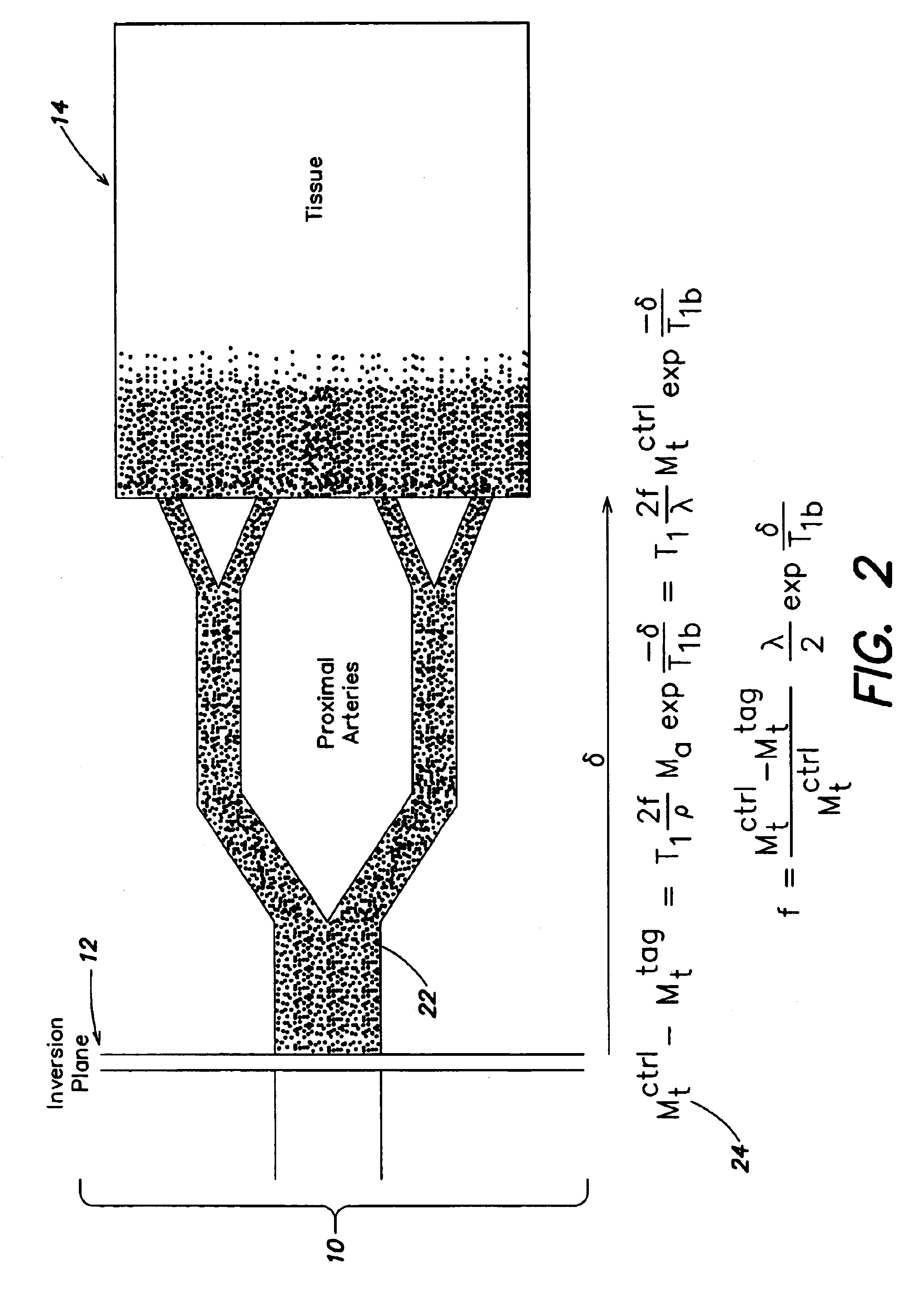
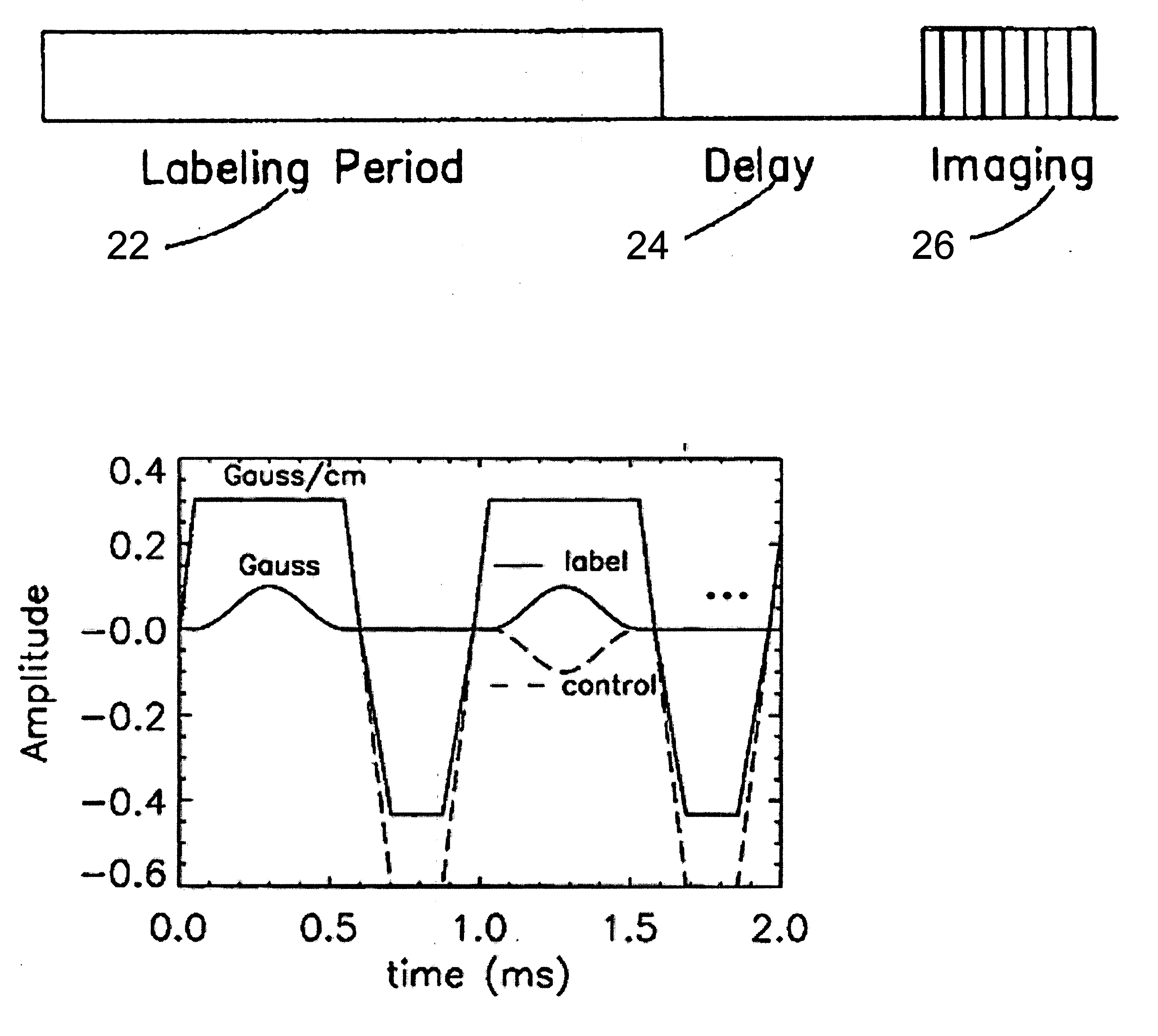
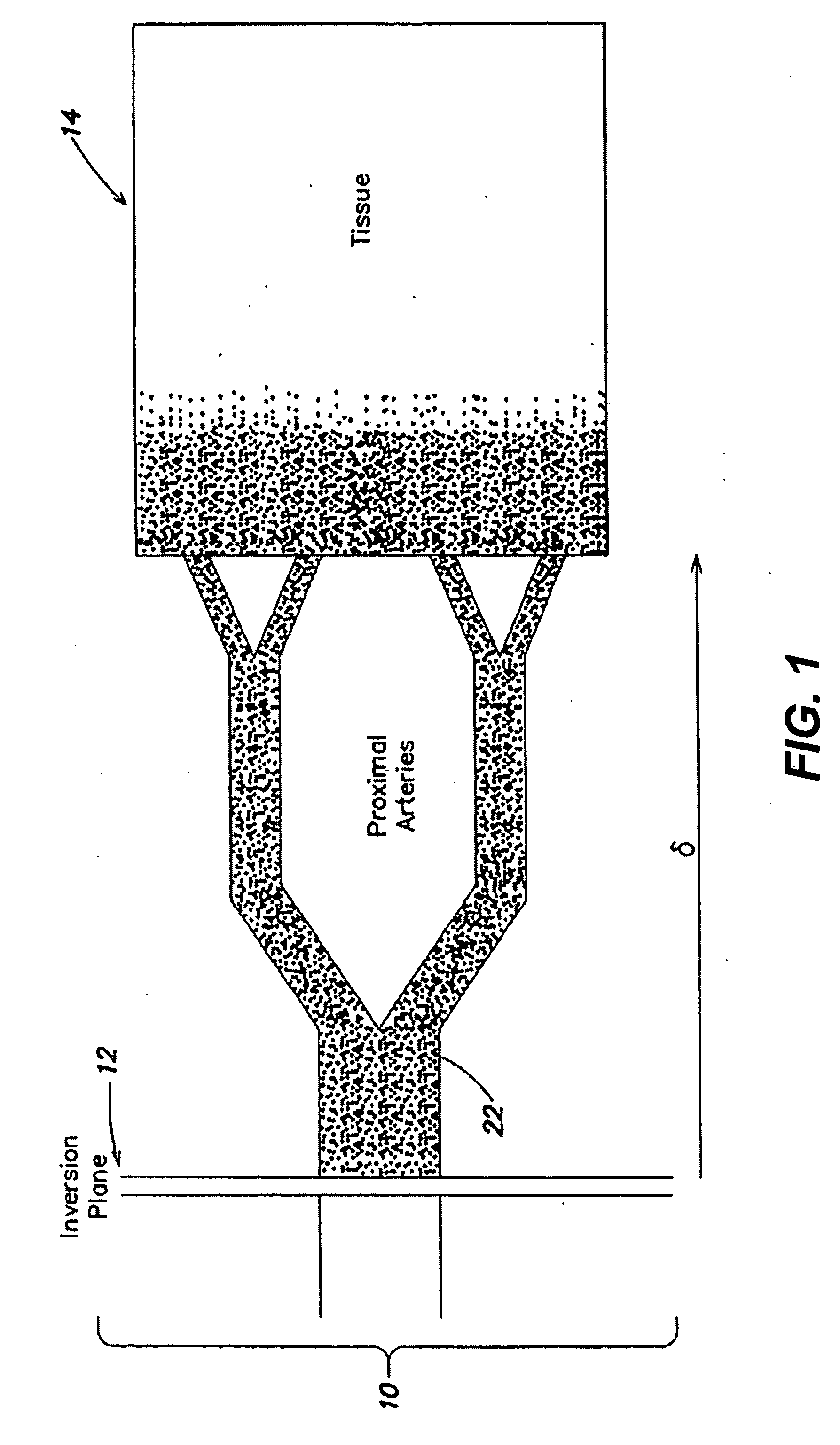
Arterial spin labeling using time varying gradients
InactiveUS6717405B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientResonance
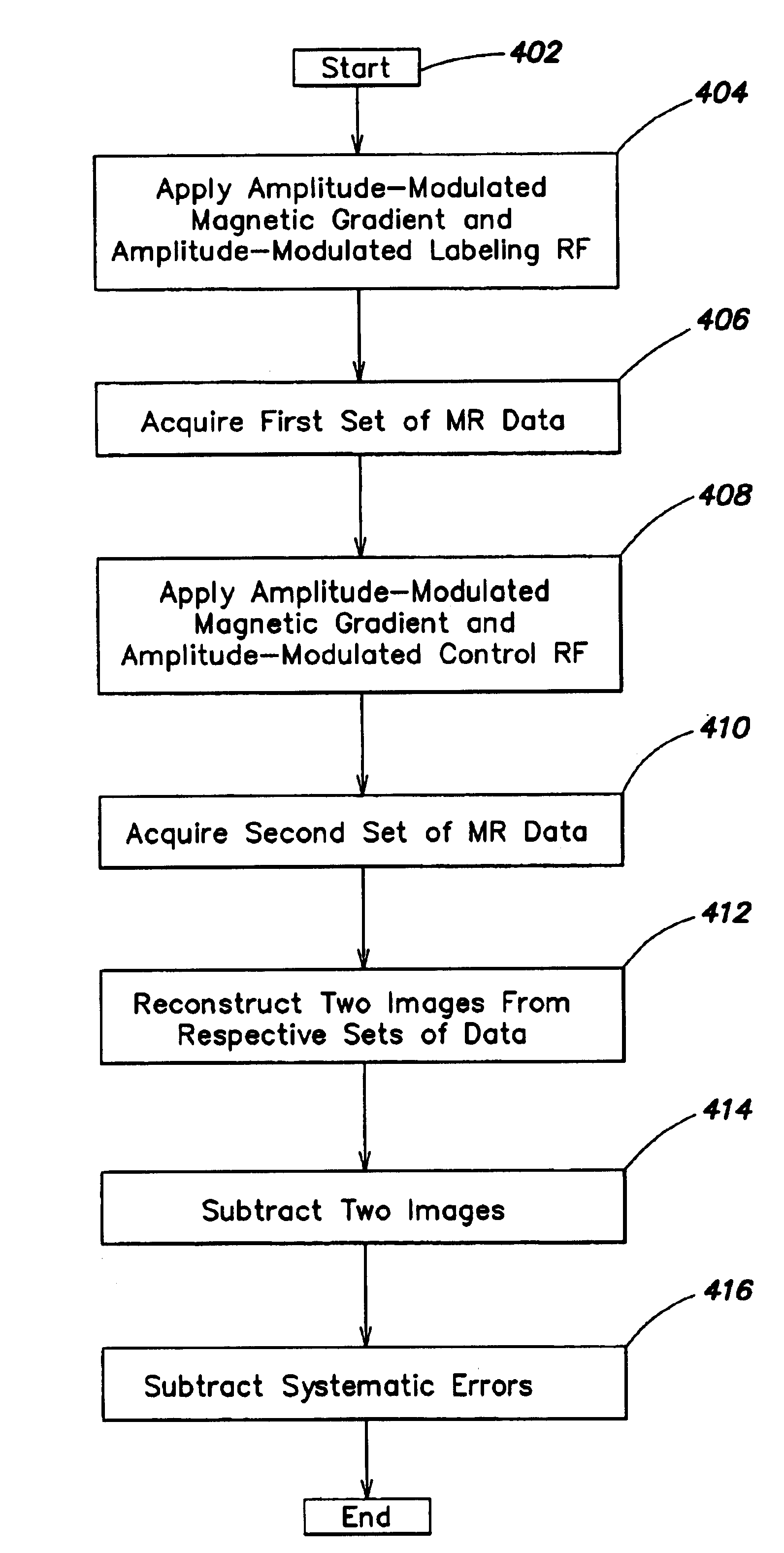
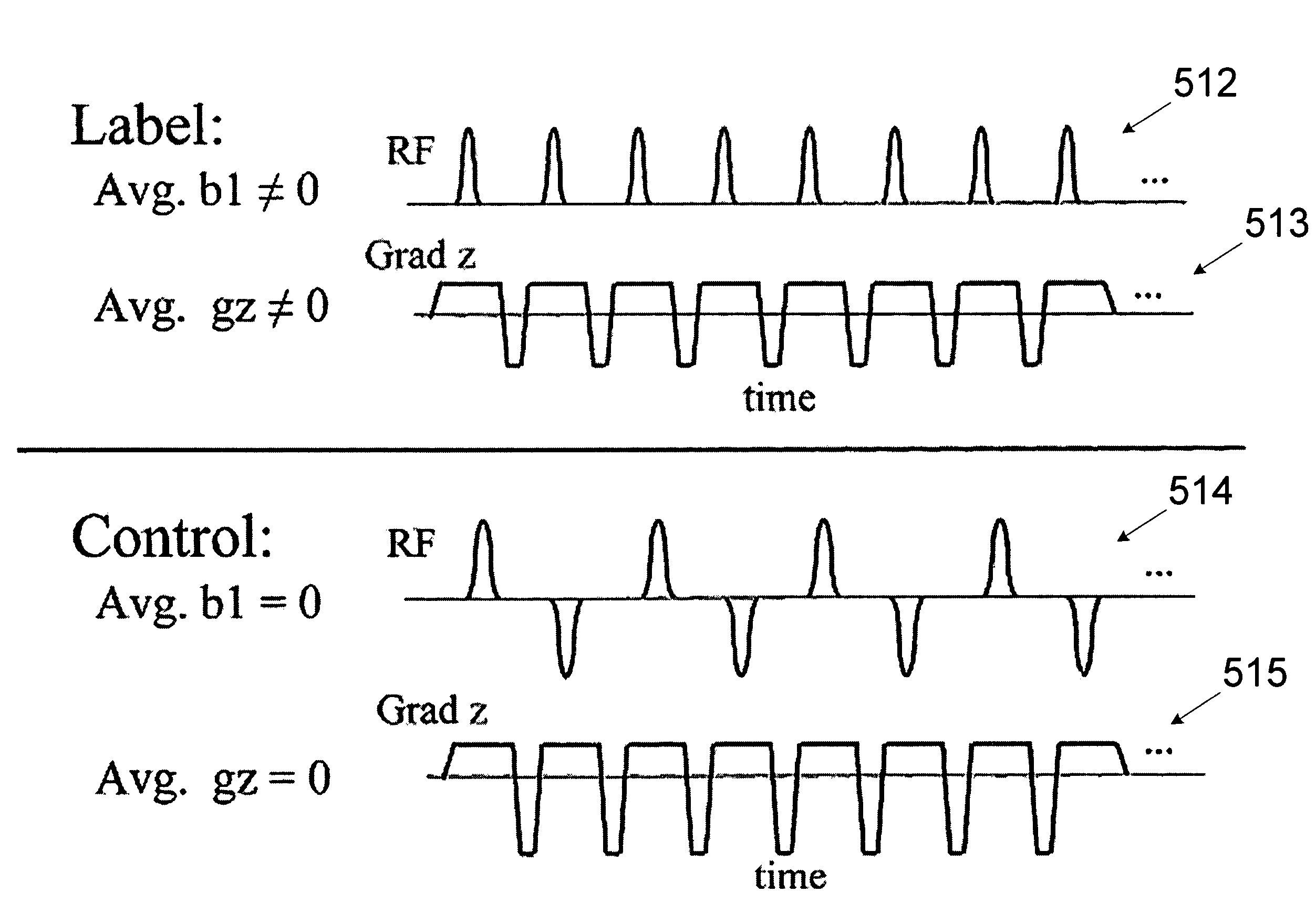
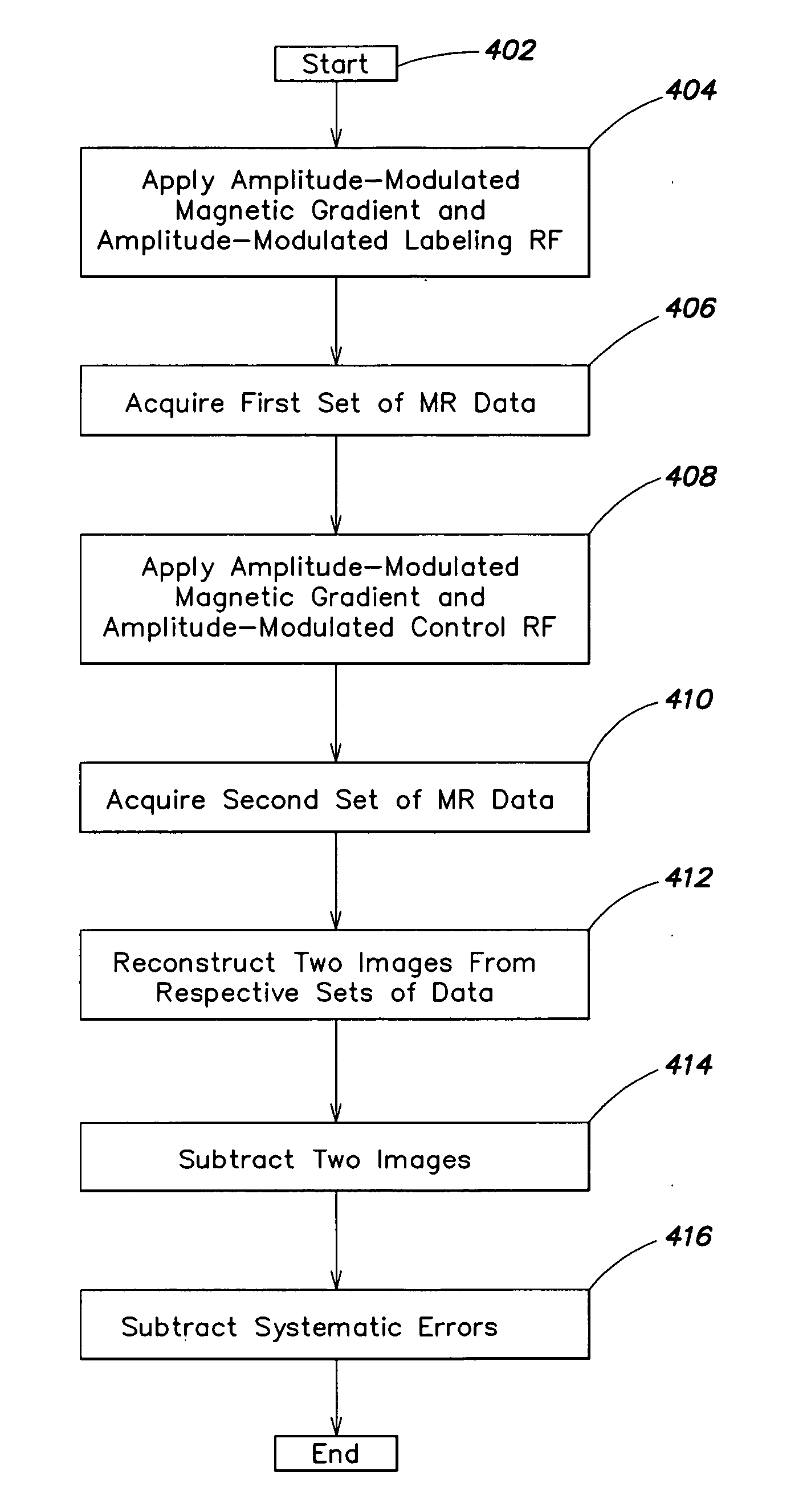
The present invention relates to a method and system for conducting a magnetic resonance fluid flow study by conducting a labeling procedure and a control procedure and combining datasets from those procedures to create a dataset for the fluid flow study. An amplitude modulated magnetic field gradient and amplitude modulated RF irradiation may be applied during a labeling procedure. Likewise, amplitude modulated RF irradiation may be applied during a control procedure. An amplitude modulated magnetic field gradient may also be applied during the control procedure.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Arterial spin labeling with pulsed radio frequency sequences
In one aspect, a method for imaging fluid flow and / or perfusion using spin labeling is provided. The method comprises applying a first magnetic gradient sequence at least to a labeling region, applying a first pulsed radio frequency (RF) sequence to the labeling region to label the fluid, the first pulsed RF sequence comprising a first plurality of pulses wherein an amplitude envelope is non-zero, the first plurality of pulses each separated by a respective first plurality of intervals wherein the amplitude envelope is substantially zero, and acquiring at least one first signal emitted from an imaging region a predetermined delay after applying the first pulsed RF sequence.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
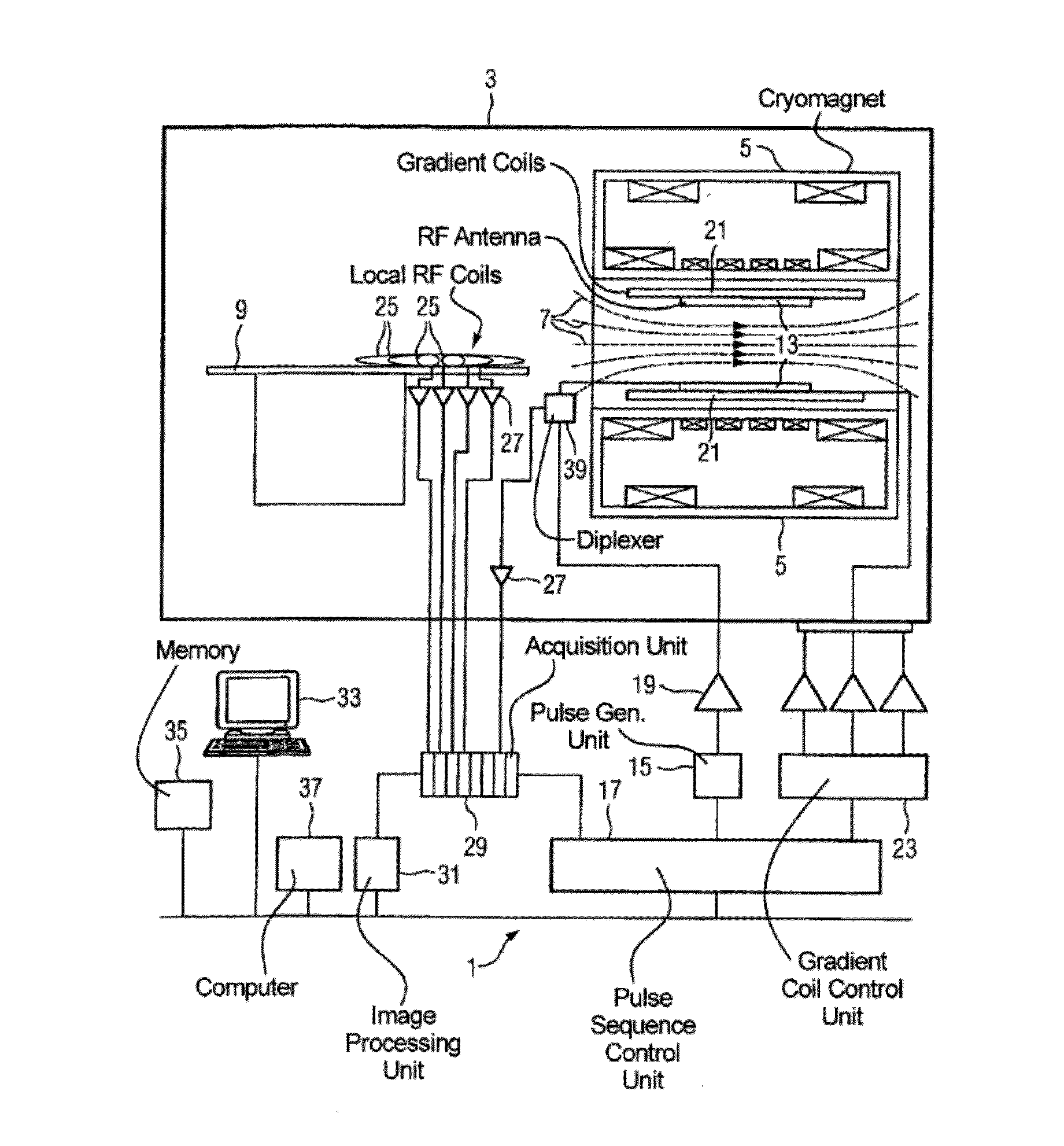
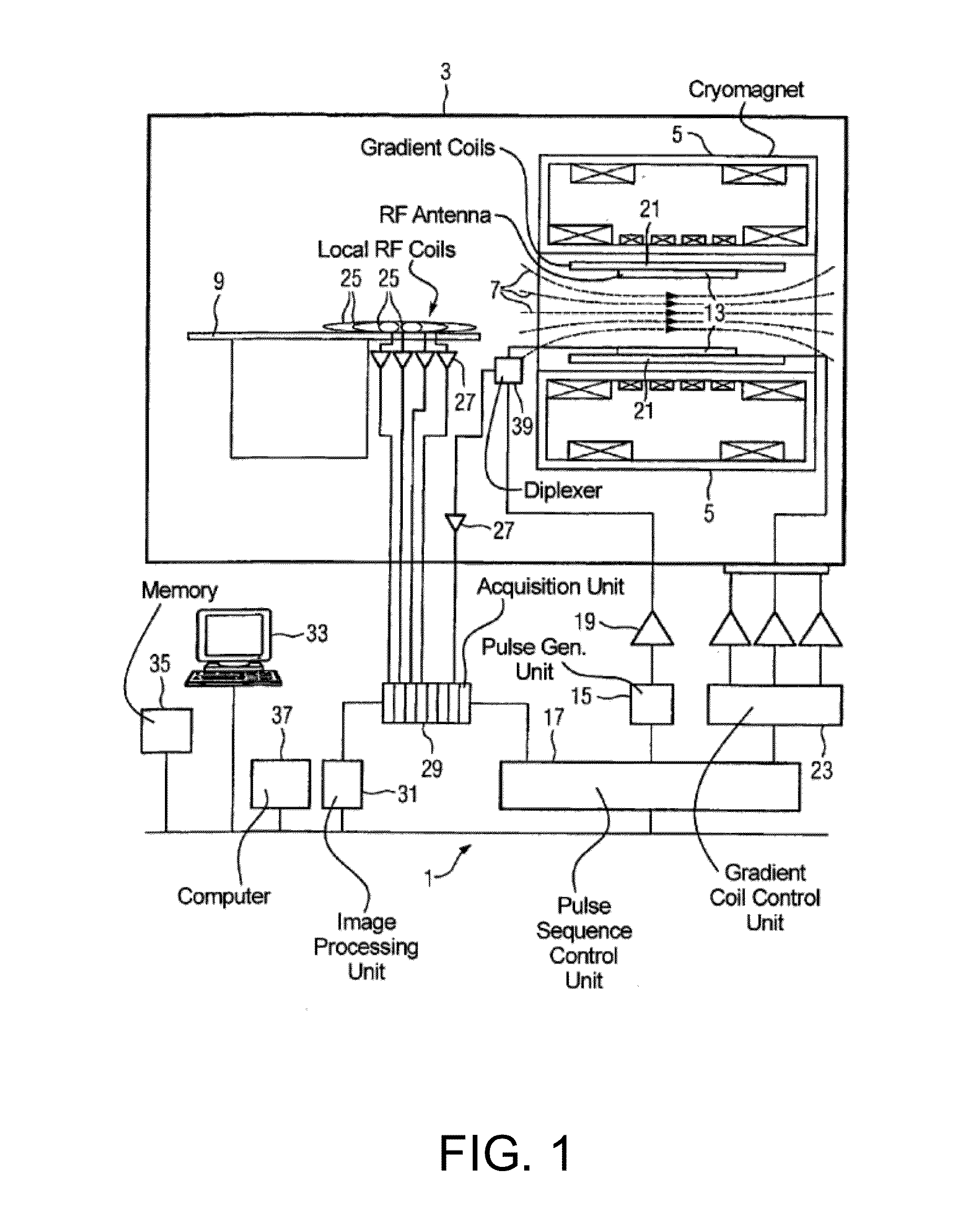
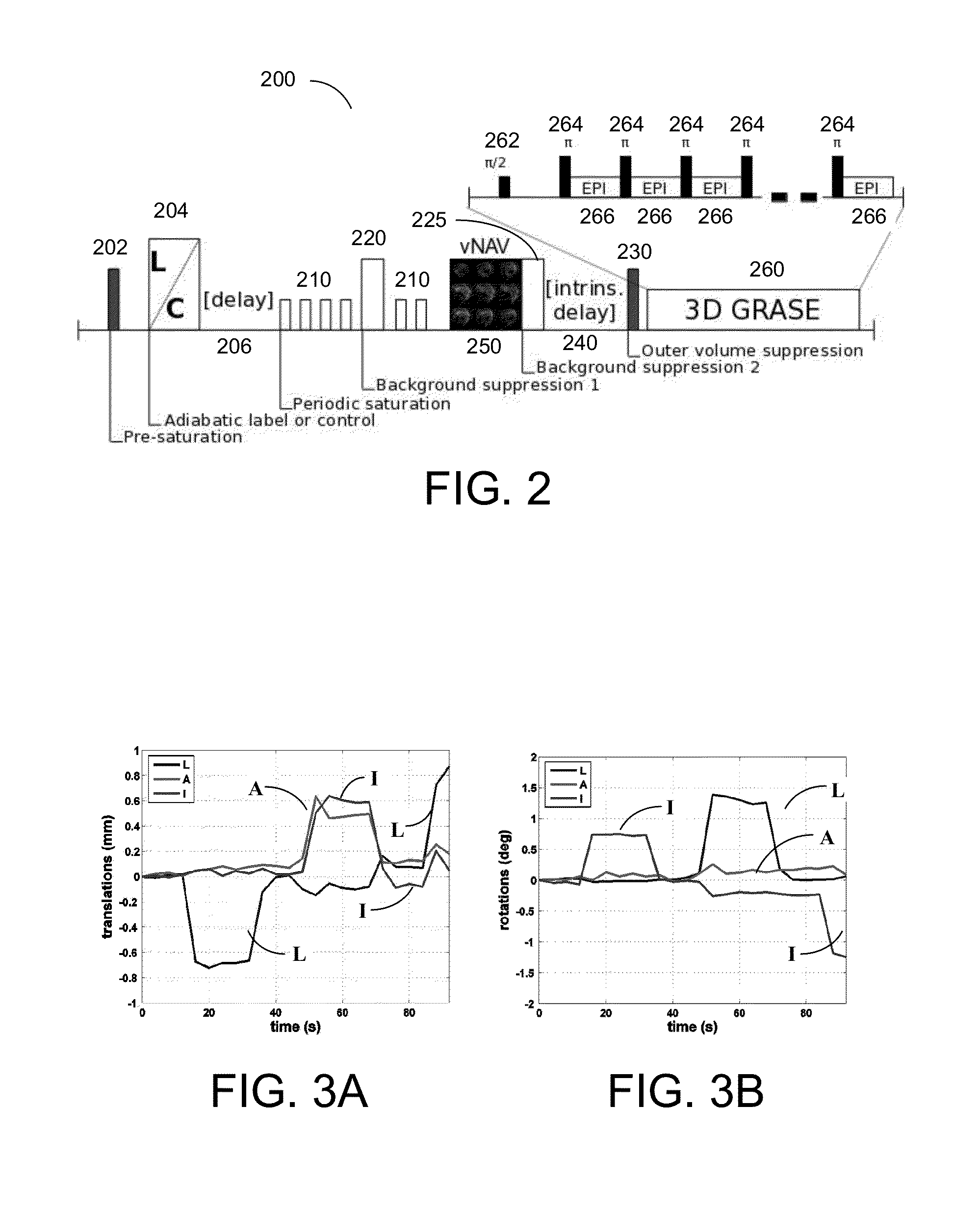
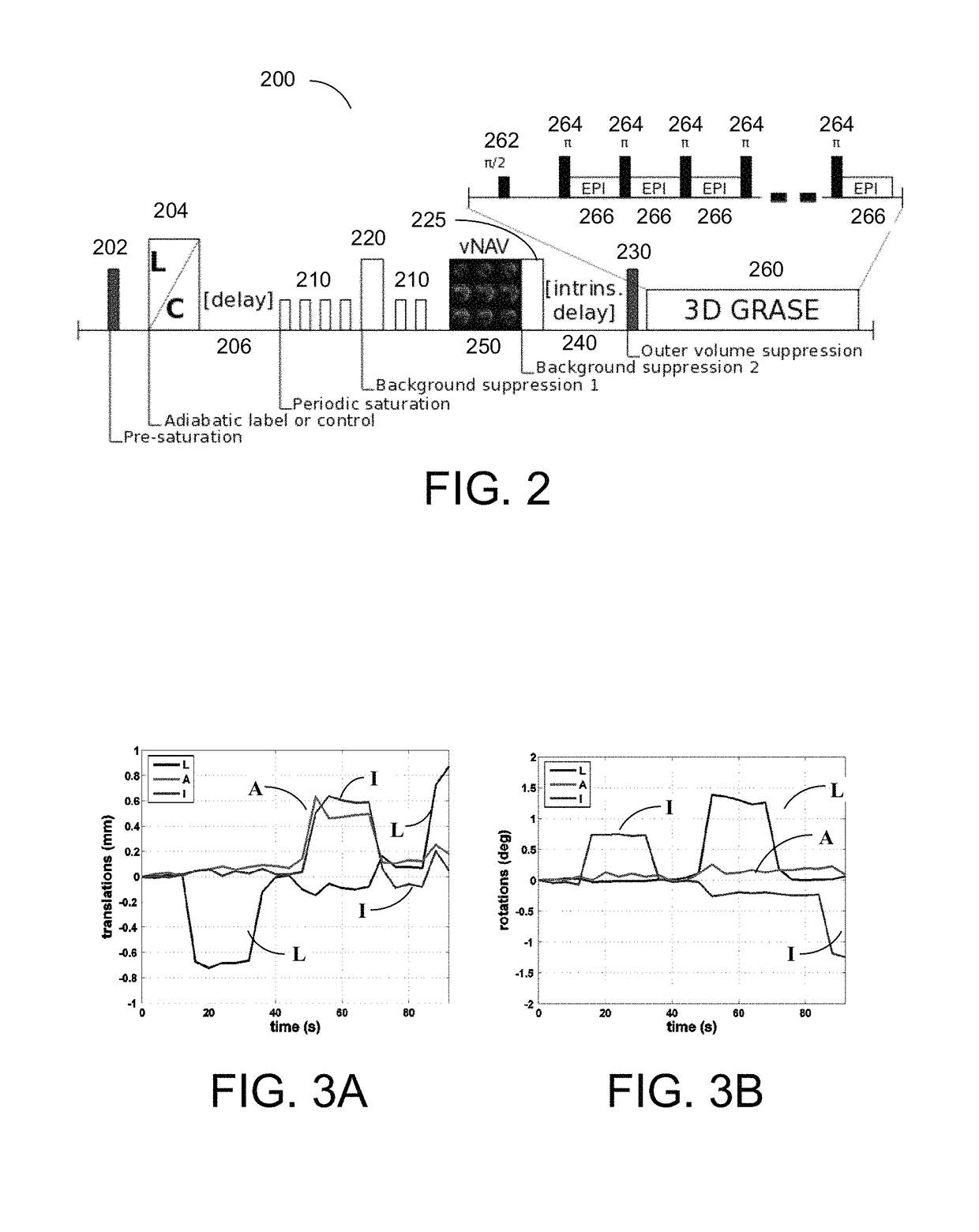
MR Imaging Apparatus And Method For Generating A Perfusion Image With Motion Correction
ActiveUS20150272453A1Maximum efficacyIncrease volumeMagnetic measurementsSensorsAcquisition timeResonance
A magnetic resonance method and system are provided for generating real-time motion-corrected perfusion images based on pulsed arterial spin labeling (PASL) with a readout sequence such as a 3D gradient and spin echo (GRASE) image data acquisition block. The real-time motion correction is achieved by using a volumetric 3D EPI navigator that is provided during an intrinsic delay in the PASL sequence, which corrects for motion prospectively and does not extend the image data acquisition time as compared to a similar non-motion-corrected imaging procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
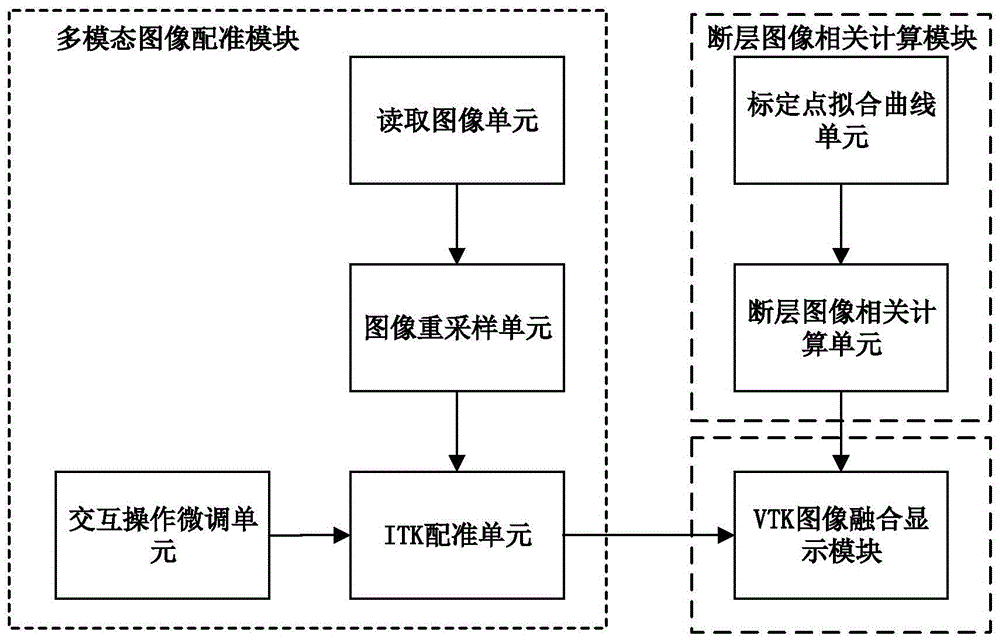
Brain ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling), SPECT (Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) image registration and fusion conjoint analysis method and system
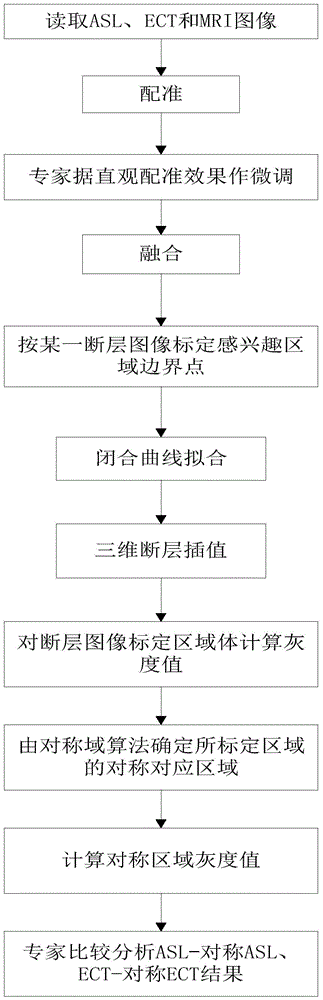
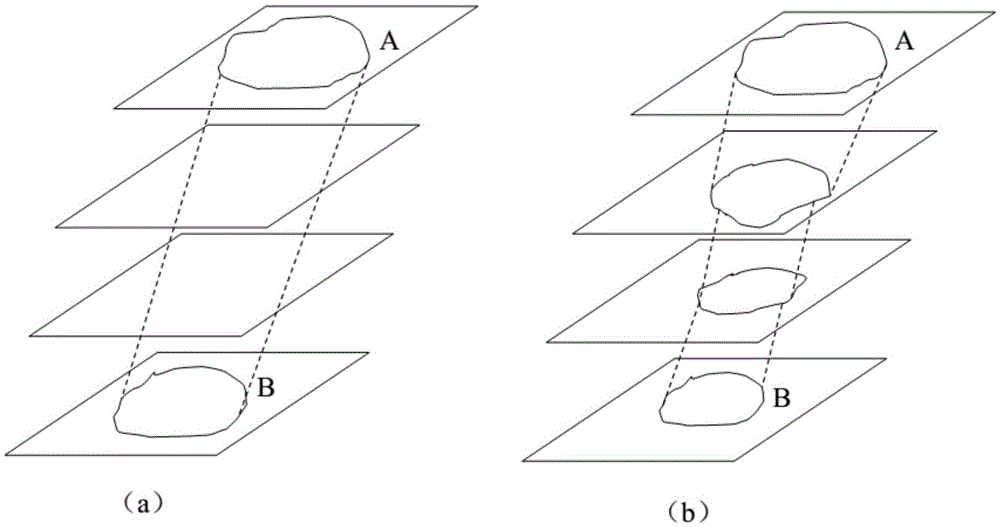
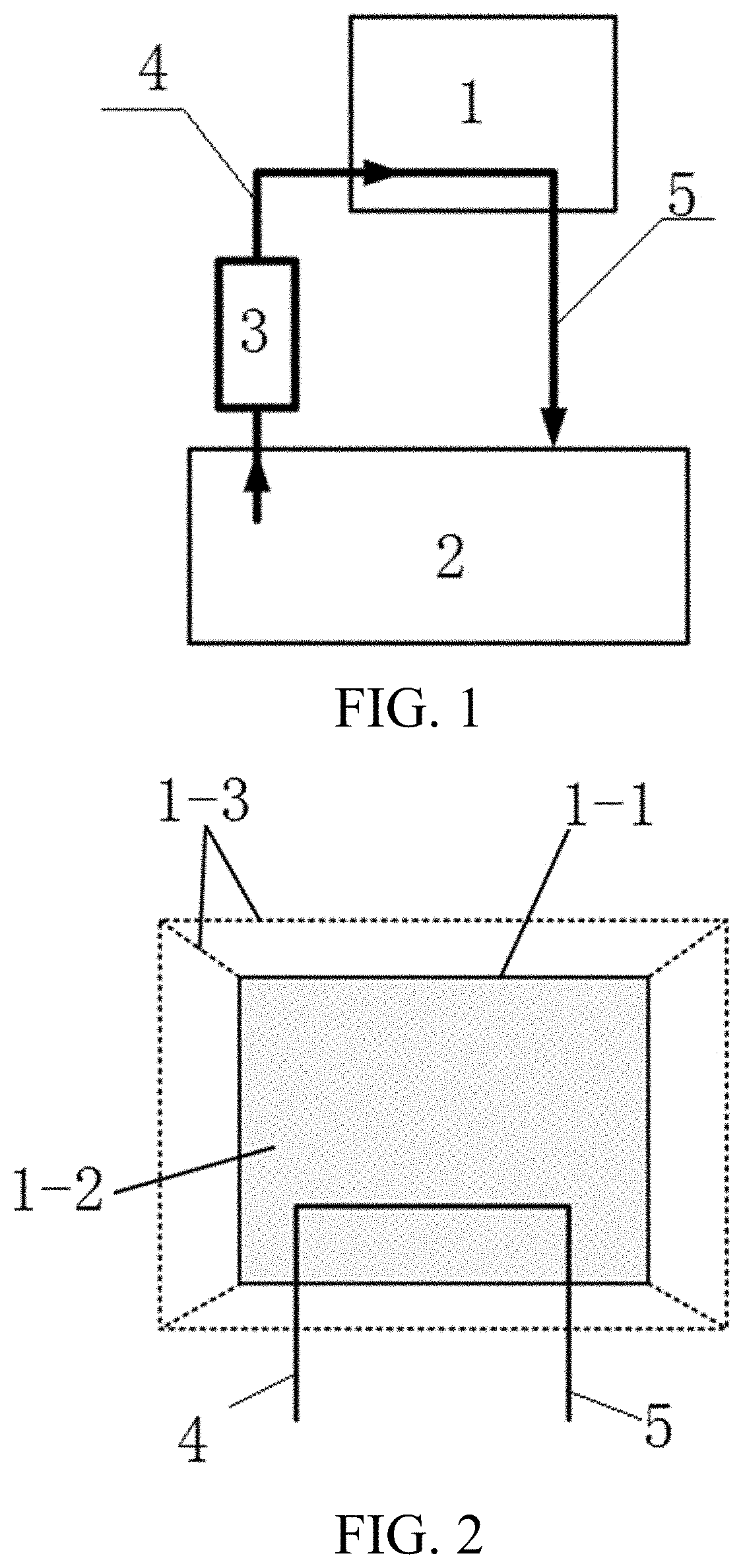
The invention discloses a brain ASL, SPECT and MRI image registration and fusion conjoint analysis method and system. Registration is respectively carried out to an ASL image and an MRI image by taking the MRI image as a standard; the ASL image and an SPECT image are fused according to different transparencies; a region to be computed is marked in the faultage of the SPECT image; a closed curve is obtained through carrying out a cubic spline interpolation to the ASL image; the volume and the gray value corresponding to the region to be computed and the gray value of an interesting region body through a circular truncated cone approach mode. According to the invention, the advantages of the ASL image reflected brain blood perfusion, the SPECT image reflected brain blood perfusion and the MRI provided brain structure change are combined; an interesting region is segmented and analyzed through providing interactive calibration operation a doctor and a medical expert; the judgement accuracy of a brain ischemic disease is improved; and iconography instructions are provided for a clinician to formulate a rational therapeutic schedule.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
MRI apparatus and ASL imaging technique
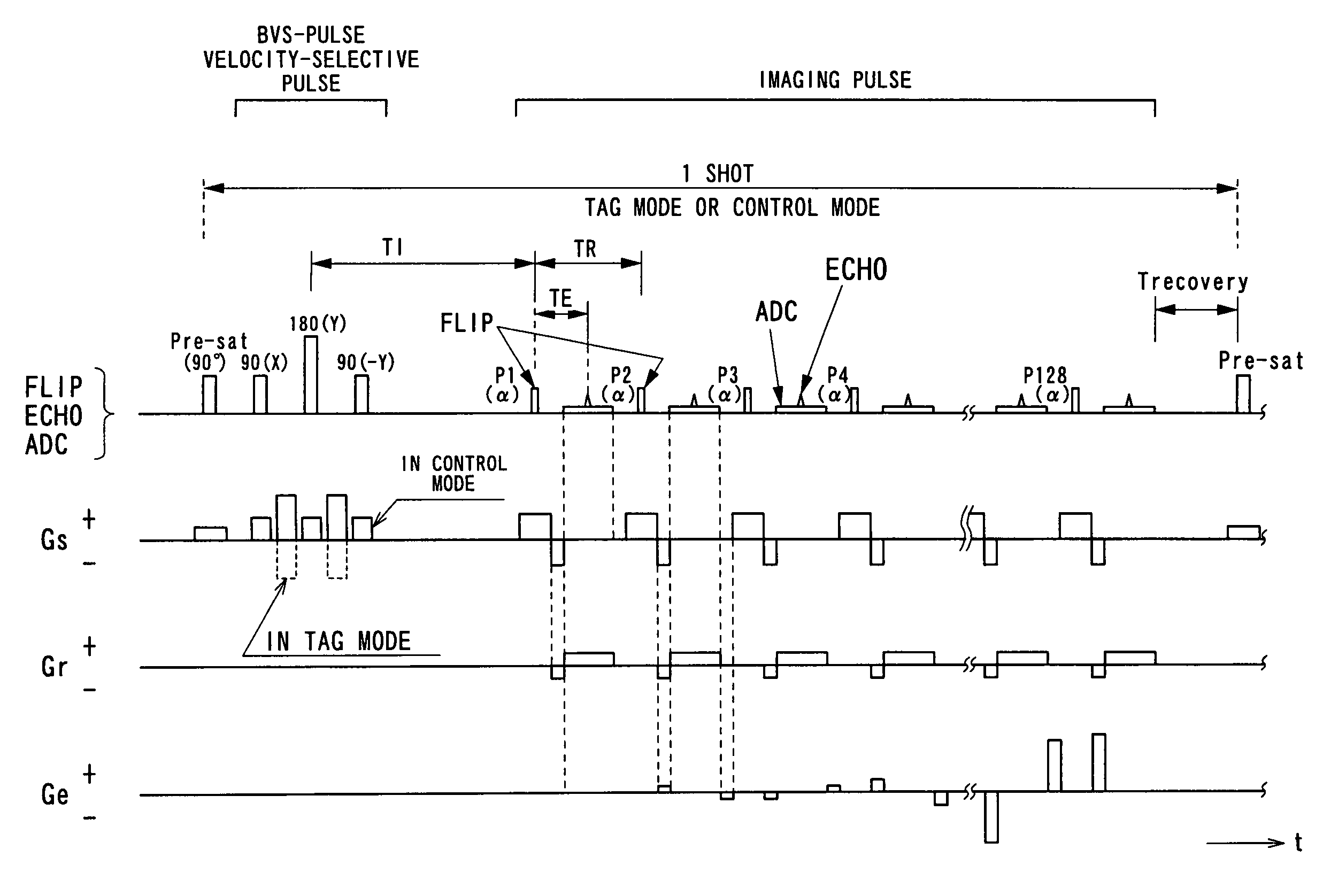
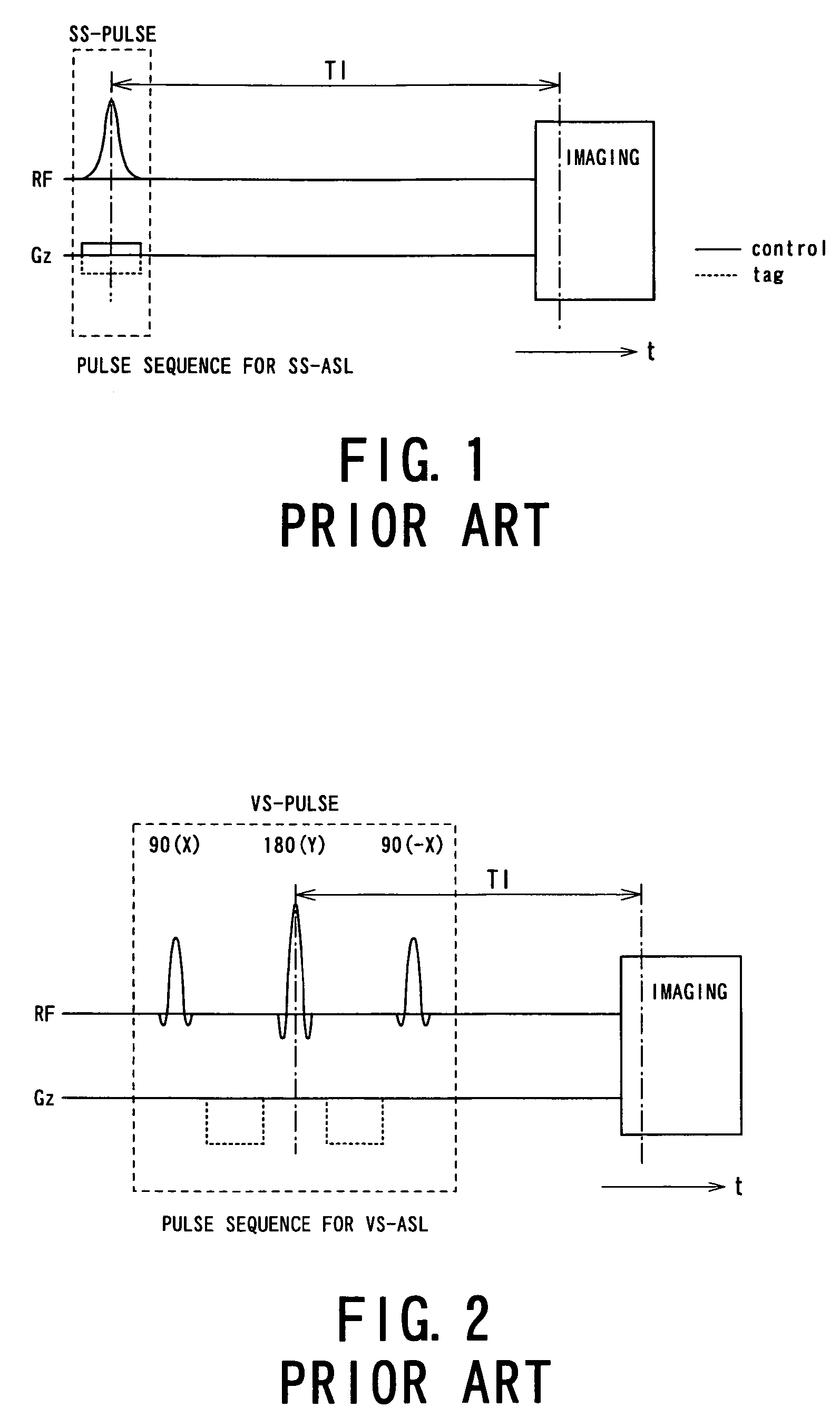
ActiveUS7545141B2Reducing Td time-induced errorHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase shiftedSelective excitation
An MRI apparatus obtains an ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling) image of a region to be imaged in a subject by performing a scan to the region to be imaged independently in a control mode and in a tag mode according to a pulse sequence based on an ASL technique. The pulse sequence includes a velocity-selective pulse, BVS (Band-limited Velocity-Selective)-pulse, that selectively excites magnetization spins in a blood flow passing through the region to be imaged and having a constant velocity range for the spins to undergo transition to transverse magnetization, and then performs excitation to cause the transverse magnetization to flip back to longitudinal magnetization. The velocity-selective pulse is formed in such a manner that the transverse magnetization excited in each of the control mode and the tag mode gives rise to a phase shift in an opposite polarity upon velocity-selective excitation.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Arterial spin labeling with pulsed radio frequency sequences
In one aspect, a method for imaging fluid flow and / or perfusion using spin labeling is provided. The method comprises applying a first magnetic gradient sequence at least to a labeling region, applying a first pulsed radio frequency (RF) sequence to the labeling region to label the fluid, the first pulsed RF sequence comprising a first plurality of pulses wherein an amplitude envelope is non-zero, the first plurality of pulses each separated by a respective first plurality of intervals wherein the amplitude envelope is substantially zero, and acquiring at least one first signal emitted from an imaging region a predetermined delay after applying the first pulsed RF sequence.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Medical image display processing method, device, and program
ActiveUS20120195485A1Easily and reliably extractedReduce the burden onImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingParenchyma
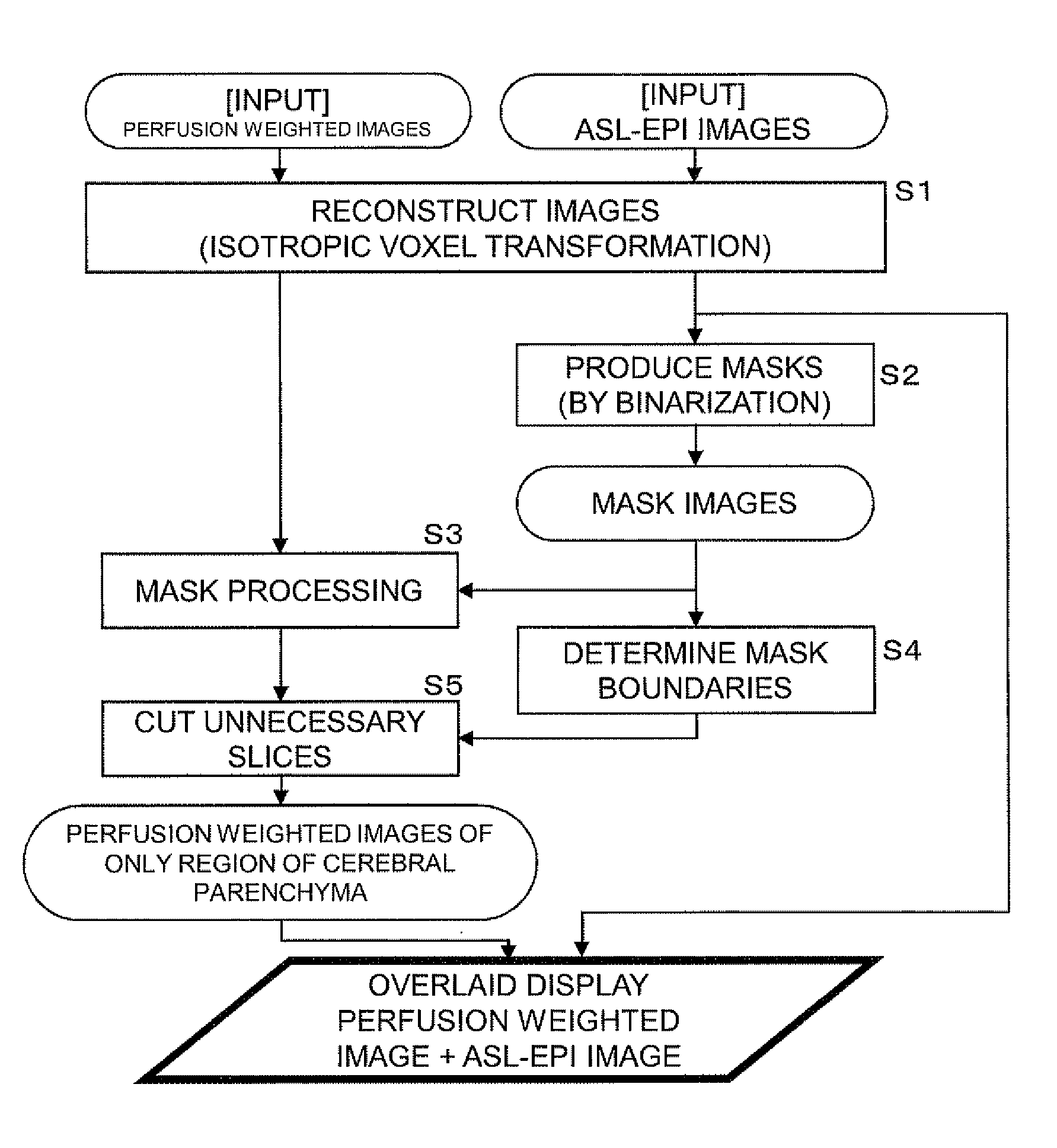
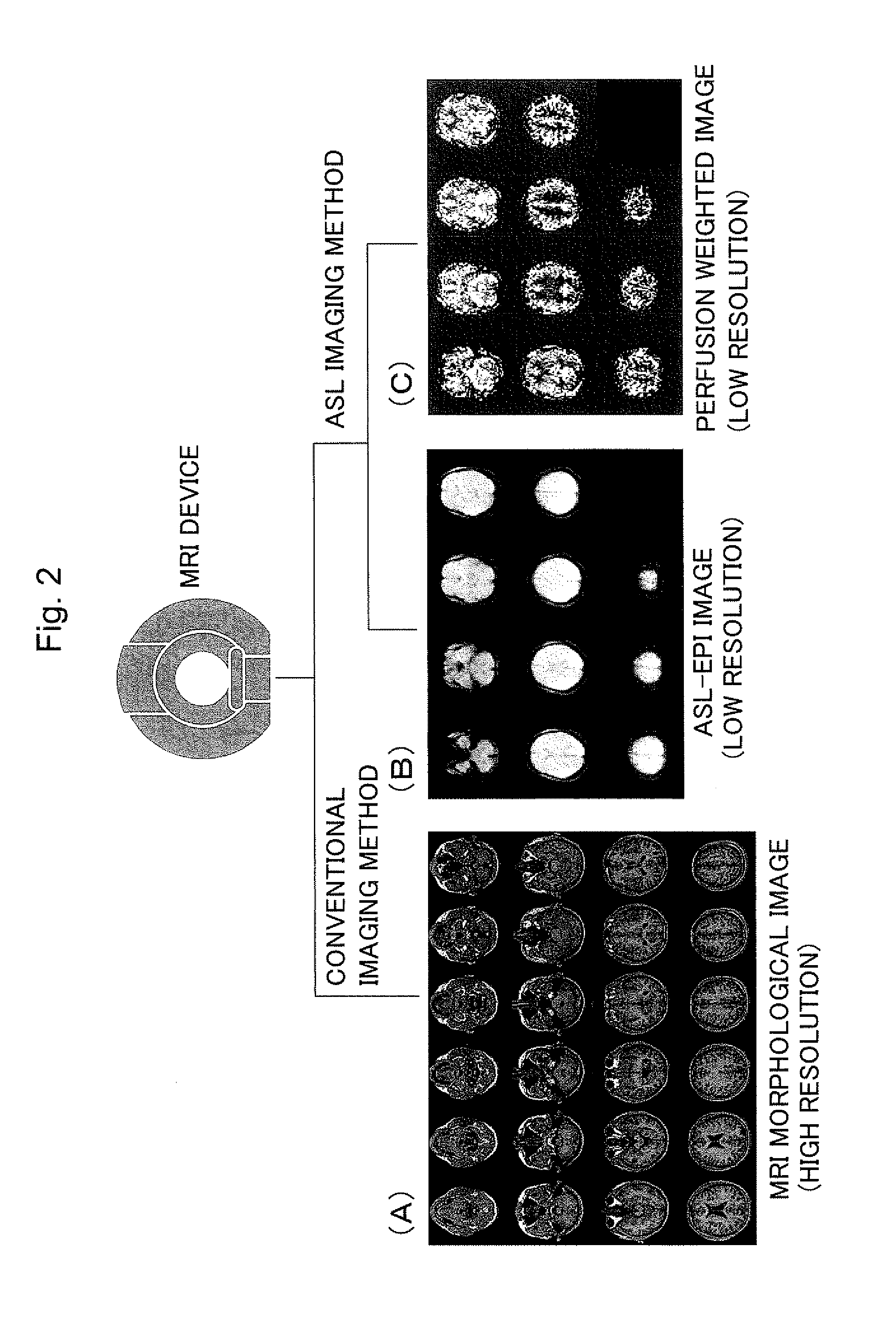
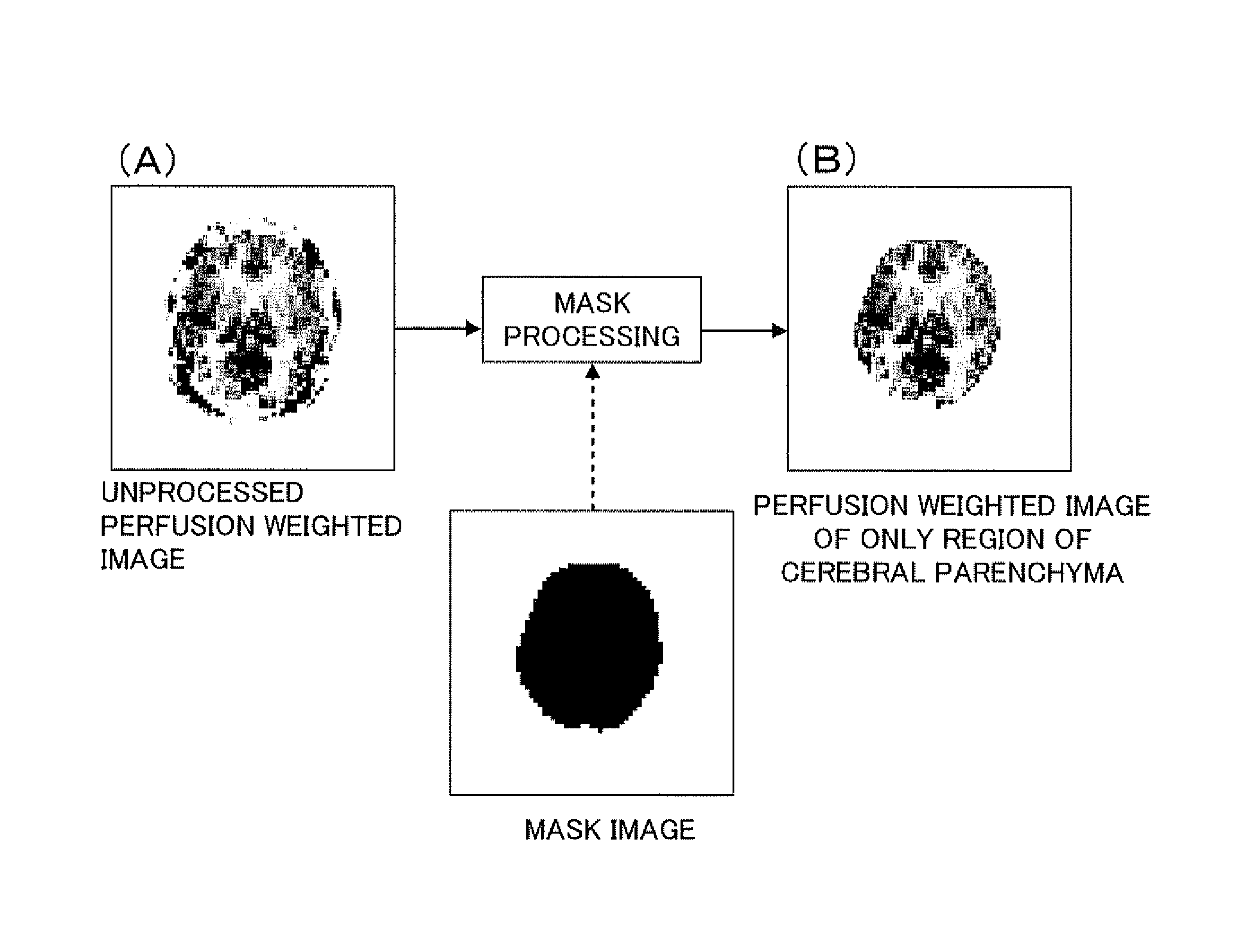
When brain images are inputted through MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and subjected to image processing to assist the diagnosis of brain diseases, functional and morphological images in an ASL coordinate system are inputted from the head of a subject by an ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling) imaging method using an MRI device. The inputted functional images are subjected to mask processing to extract only the region of cerebral parenchyma, and functional images of only the extracted region of the cerebral parenchyma are thereby produced and displayed to be overlaid on the morphological images. In this manner, a functional image such as a perfusion weighted image of only the region of the cerebral parenchyma can be extracted and displayed overlaid on a morphological image.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time
InactiveCN102890255AShortened echo timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Arterial spin labeling
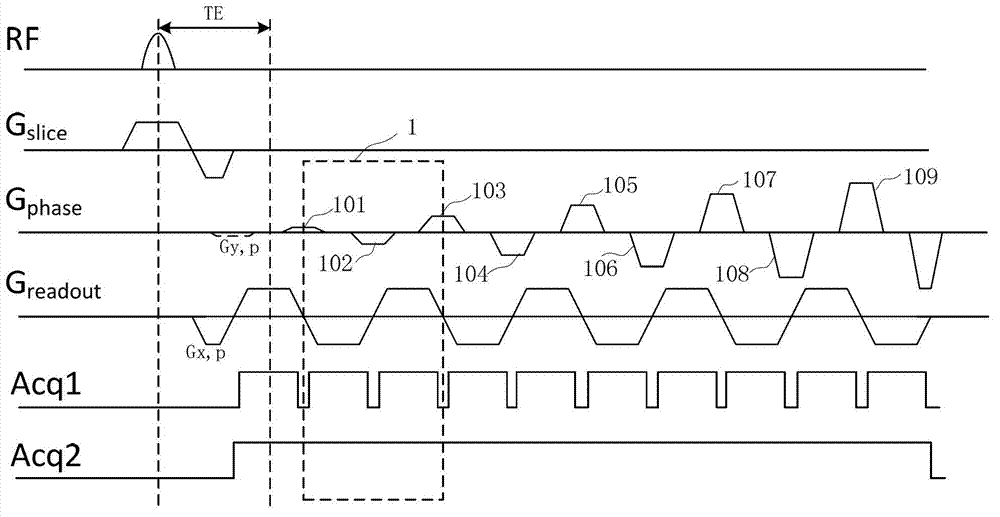
The invention discloses an inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time. The method is characterized in that: a k-space trajectory extends to the outer side of a phase encoding direction from the center, wherein a gradient for generating the trajectory is composed of reading-out gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and phase encoding gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and gradually increases from zero. The method further comprises a step that: in order to accommodate the phase encoding gradients of which the area increases gradually without adding an echo spacing, the phase encoding gradient and a data collecting window are permitted to be overlapped. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an effective echo time in a sequence is located in the center of a first echo, the echo time is shortened greatly, and the signal to noise ratio is increased; since the contrast ratio of an image depends on signals of a k-space centre, and data of the k-space center are from an initial echo, T2 or T2* weighing of the obtained image is very small; and in diffusion imaging and arterial spin labeling imaging, the decreasing of the T2 or the T2* weighing is beneficial to improving the quality of the image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
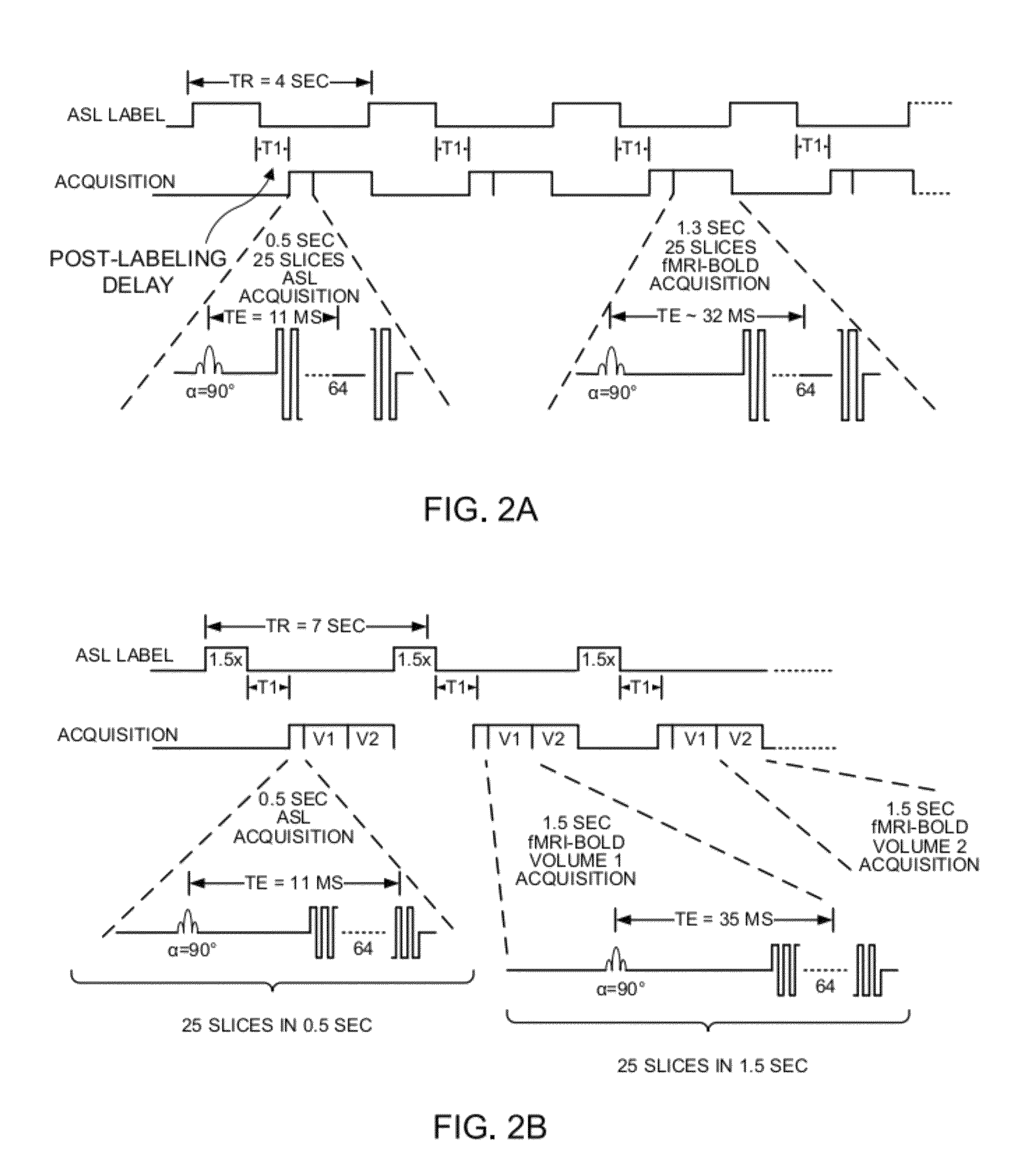
Simultaneous asl/bold functional MRI
InactiveUS20120139537A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionArterial spin labelingOxygen level
This disclosure is generally drawn to methods, systems, appliances and / or apparati related to obtaining magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images. More specifically, the disclosure relates to obtaining MRI images using arterial spin labeling (ASL) and blood-oxygen-level dependence functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD-fMRI) techniques. In some examples, a method of obtaining magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) image(s) is provided. An example method may include providing arterial spin labeling (ASL) labeling, obtaining at least one ASL acquisition after ASL labeling, and obtaining at least one blood-oxygen-level dependence functional magnetic resonance imaging (BOLD-fMRI) acquisition after ASL labeling.
Owner:CINNCINATI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT
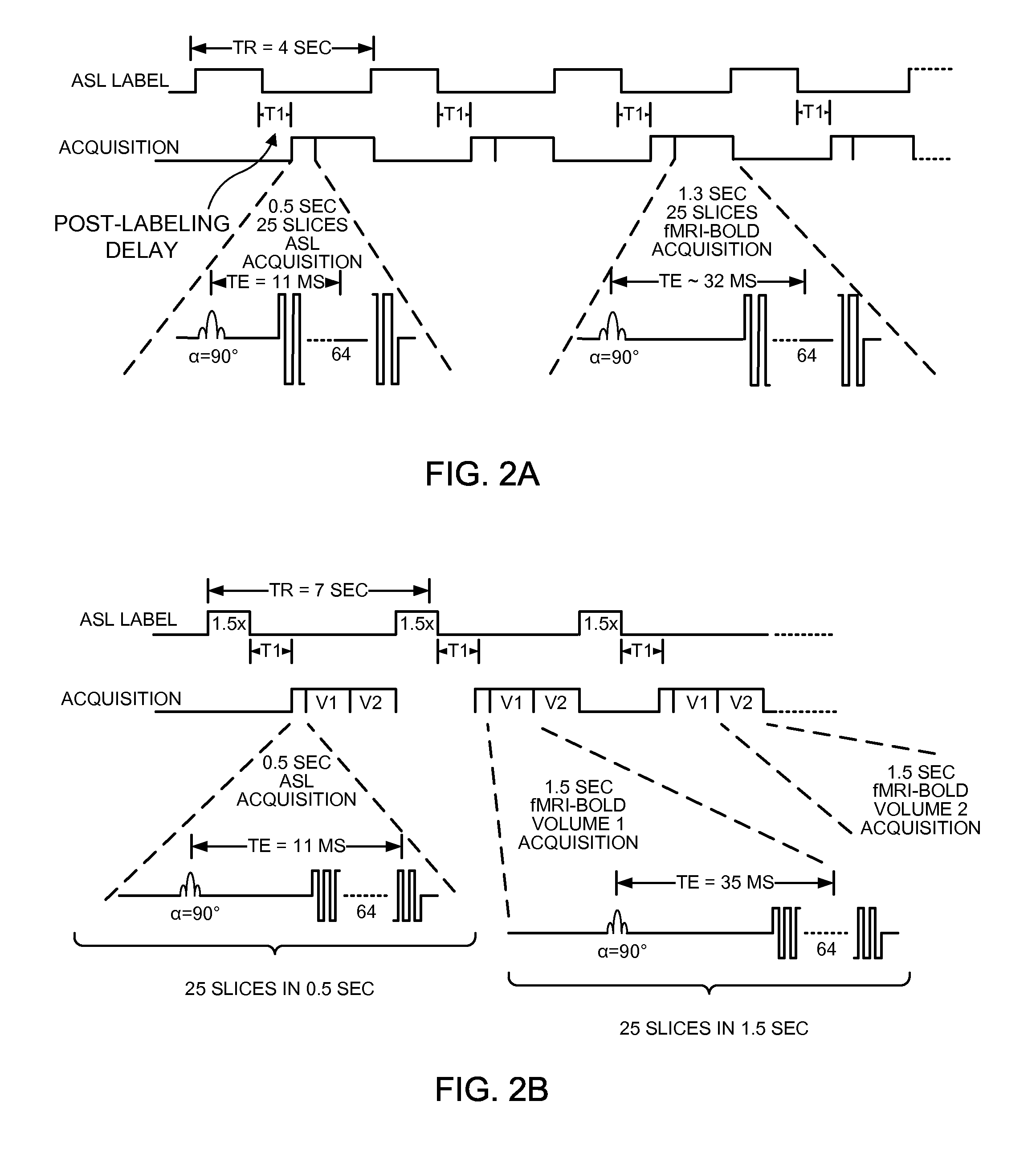
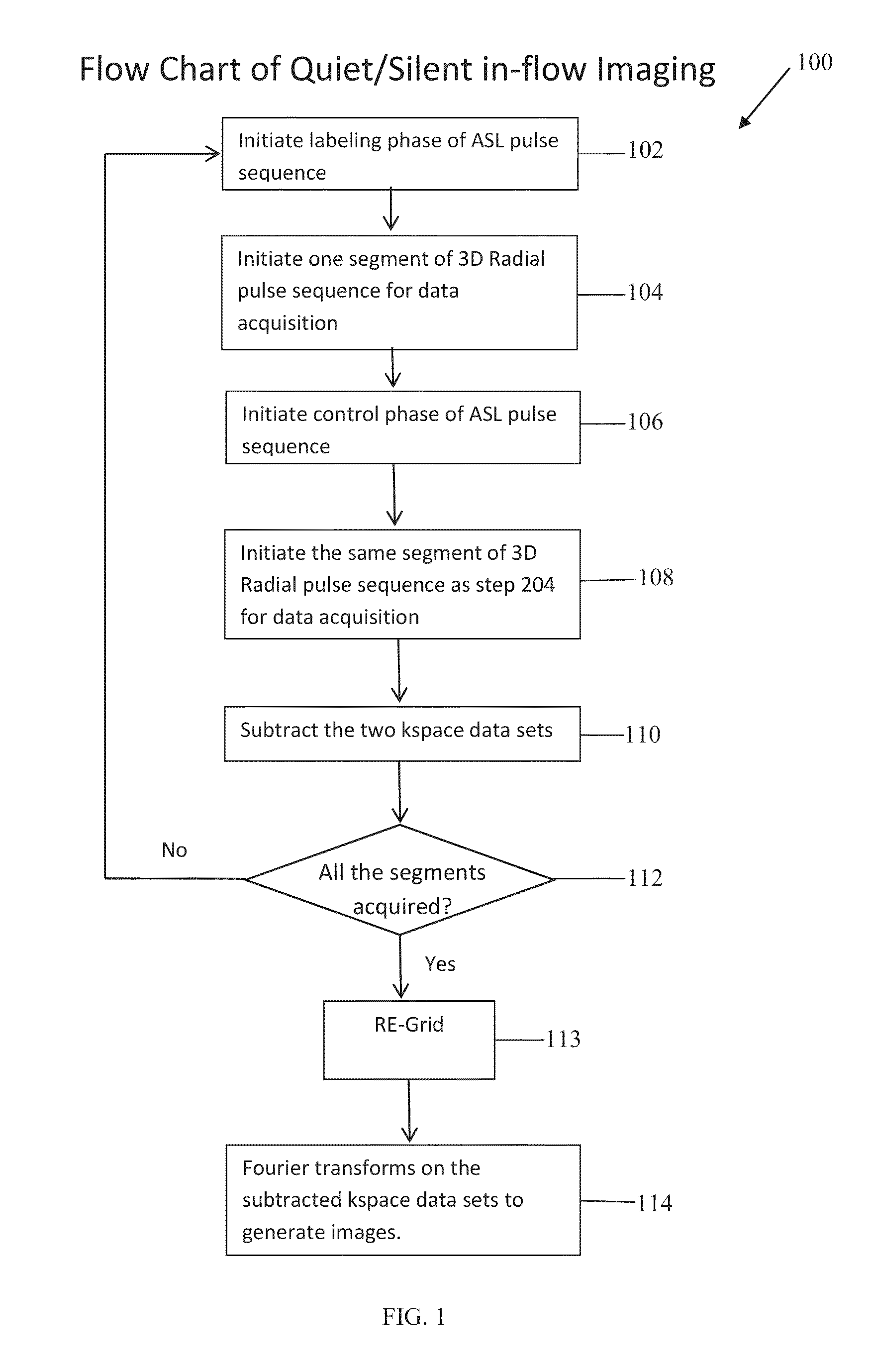
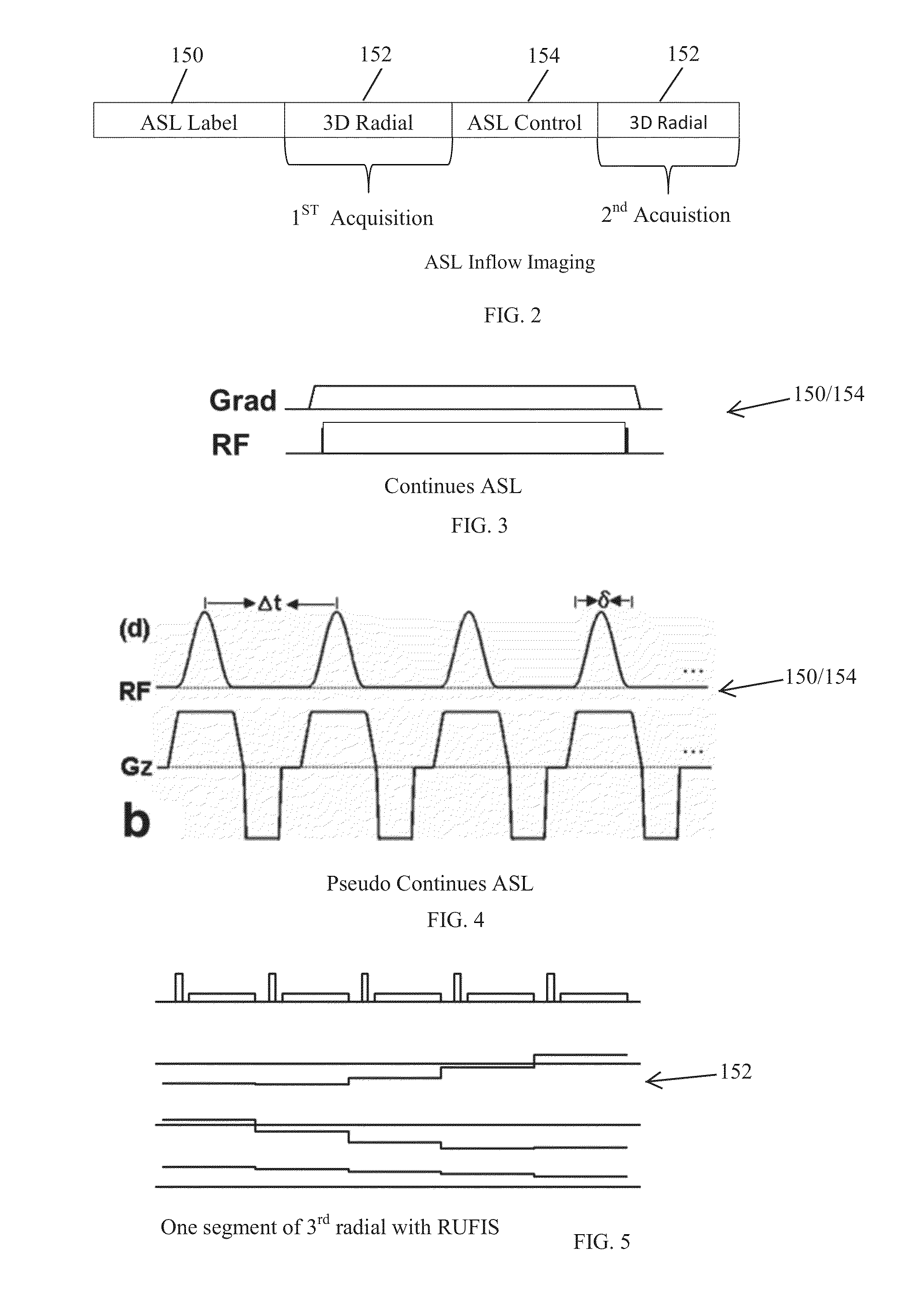
Systems and methods for reducing magnetic resonance (MR) imaging acoustic noise in mr inflow imaging
ActiveUS20140347048A1Reduce noiseMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionRadial pulseResonance
Systems and methods for reducing acoustic noise in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) are provided. One method includes applying a labeling phase of an arterial spin labeling (ASL) pulse sequence to a region of interest, applying a three-dimensional (3D) radial pulse sequence to the region of interest to generate a tag image, applying a control phase of the ASL pulse sequence to the region of interest, and applying the 3D radial pulse sequence to the region of interest to generate a control image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cerebral perfusion weighted imaging method based on arterial spin labeling and variable delay time
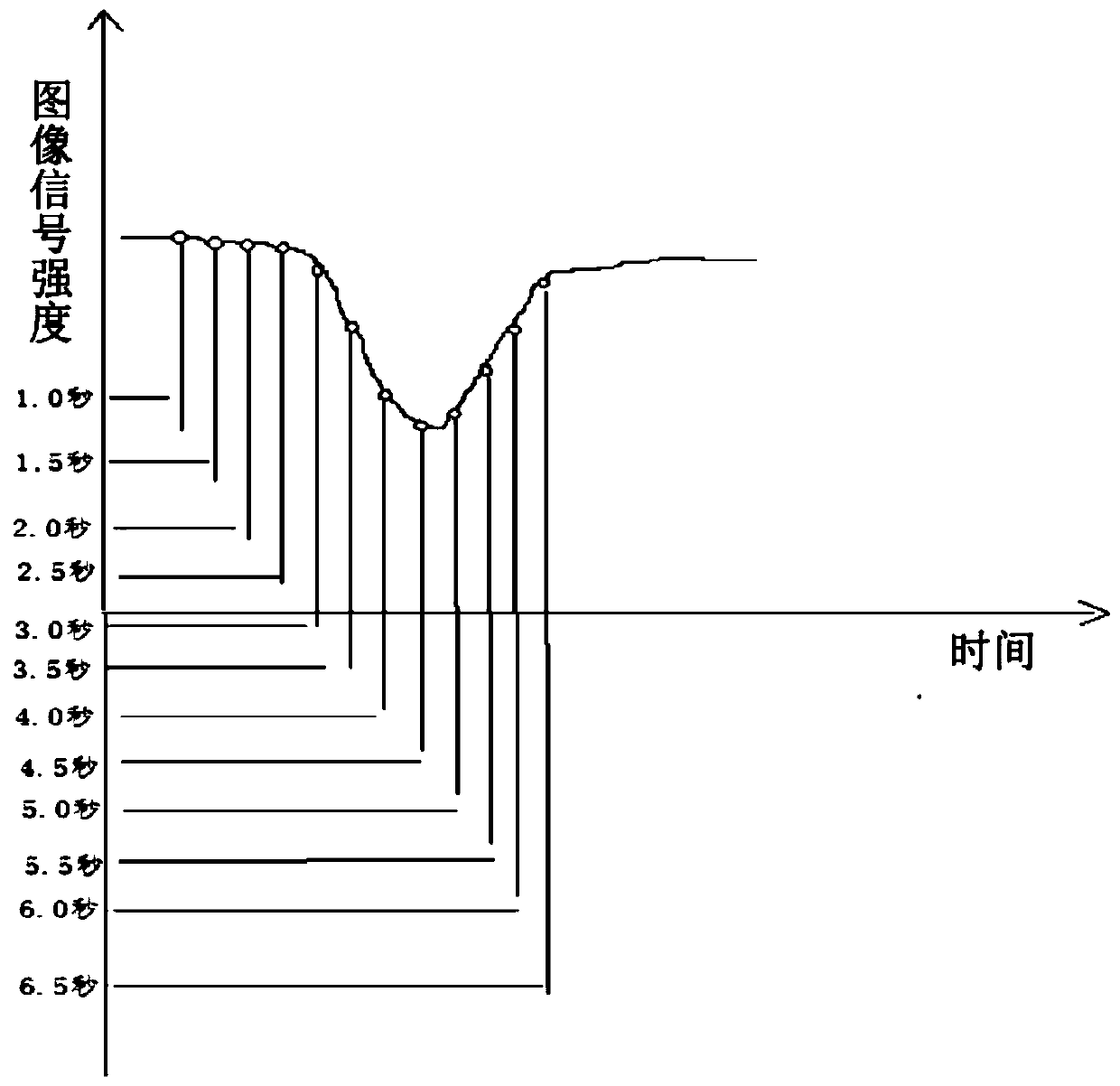
ActiveCN111543973AReduce sensitivityRF energy deposition is smallDiagnostic signal processingSensorsRadio frequency energySignal on
The invention discloses a cerebral perfusion weighted imaging method based on artery spin labeling and variable delay time, wherein the method comprises the steps: applying 180-degree pulses to a marked area, and acquiring signals on an imaging layer by adopting a rapid sequence after t time to obtain an image signal scanned for the first time; applying 180-degree pulses to the marked area, aftert+(n-1)*m time, collecting signals on the imaging layer in a rapid sequence mode, and thus obtaining image signals scanned for the n time, wherein n is greater than or equal to 3; constructing animage signal intensity-time curve according to the n scanned image signals; and calculating the image signal intensity-time curve to obtain cerebral perfusion parameters. According to the method, twice scanning of marking and unmarking is not needed, so that the sensitivity to motion is reduced; the radio frequency energy deposition is small; brain perfusion parameters such as blood volume, bloodflow, average transfer time and arrival time can be generated.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
Simultaneous ASL/bold functional MRI
InactiveUS8791699B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionArterial spin labelingBold fmri
Owner:CINNCINATI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT
Noninvasive 4D time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography method
The invention discloses a non-invasive 4D time-resolved dynamic magnetic resonance angiography method. Arterial spin labeling was used to label water molecules as endogenous markers, and multiphase equalization was used to preferentially read pulses to form a dataset. Quantitative tracer kinetic model was established by estimating blood volume, blood flow and mean transit time. The acquired data were used to reconstruct images to provide a set of MR images. The invention can display the blood vessel structure from the viewpoint of improving the spatial resolution, furthermore, the establishment of blood flow model can be optimized from the viewpoint of improving time resolution, and the examination and diagnosis of cerebrovascular diseases by magnetic resonance angiography can be improvedfrom two aspects, and the harmful effects caused by injecting contrast medium and ionizing radiation exposure can be reduced or even eliminated by conventional methods.
Owner:安影科技(北京)有限公司
Medical image display processing method, device, and program
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
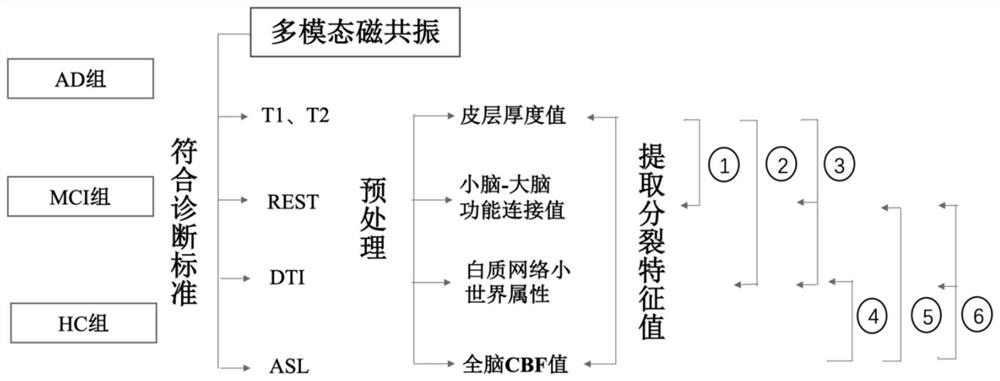
Alzheimer's disease early-stage prediction model based on cerebellar function connection characteristics
ActiveCN113571195AHigh benefitImprove evaluation efficiencyMedical simulationMulti modal dataMR - Magnetic resonance
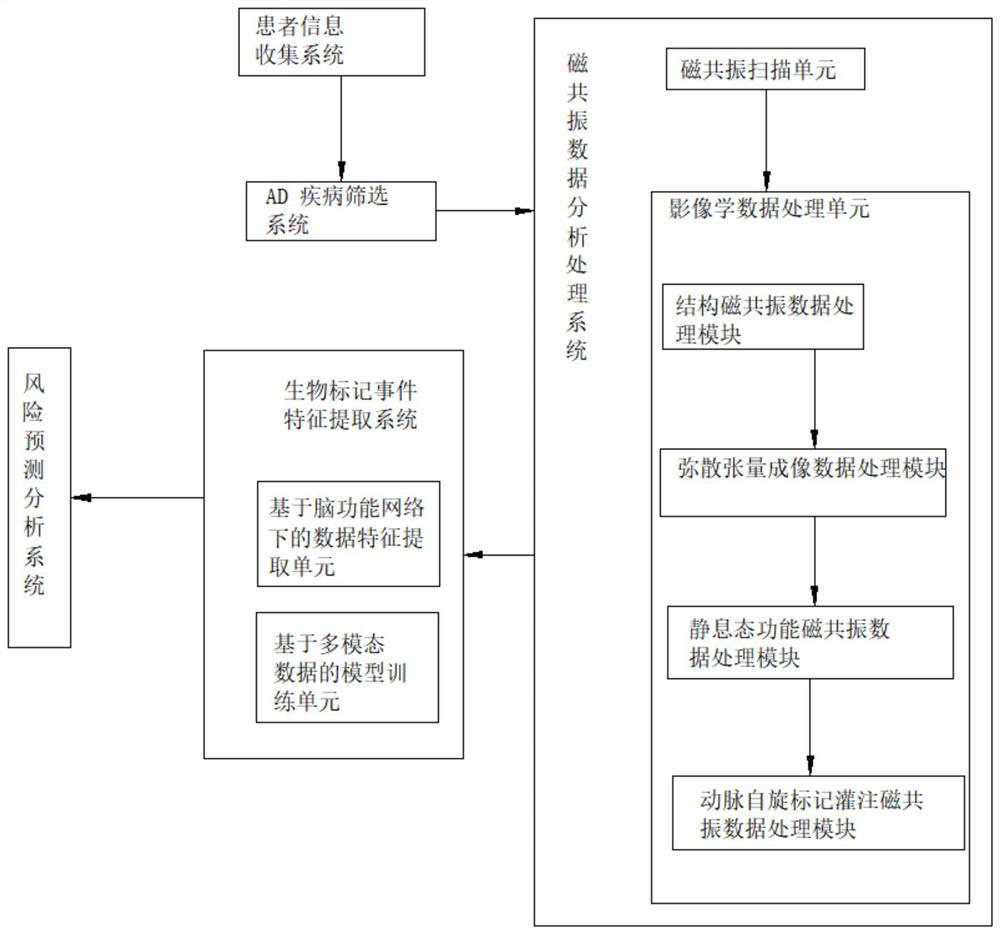
The invention discloses an Alzheimer's disease early-stage prediction model based on cerebellar function connection characteristics. The prediction model comprises a patient information collection system, an AD disease screening system, a magnetic resonance data analysis and processing system, a biomarker event feature extraction system and a risk prediction and analysis system. On the basis of magnetic resonance data, multi-modal data of structural phase magnetic resonance, resting state functional magnetic resonance and arterial spin labeling perfusion magnetic resonance are combined, and outcome and prognosis conditions of patients with different cognitive function states are predicted by using a feature classification method. And clinical doctors can select more effective treatment means. The magnetic resonance detection method combination can play a synergistic role, the evaluation efficiency of a single detection method is improved, and outcome and prognosis of a patient with cognitive impairment are effectively predicted. Compared with an existing method, the optimized combination of the method is more efficient, and the limitation that the existing method is high in cost, long in time and large in wound is reduced.
Owner:NANJING BRAIN HOSPITAL
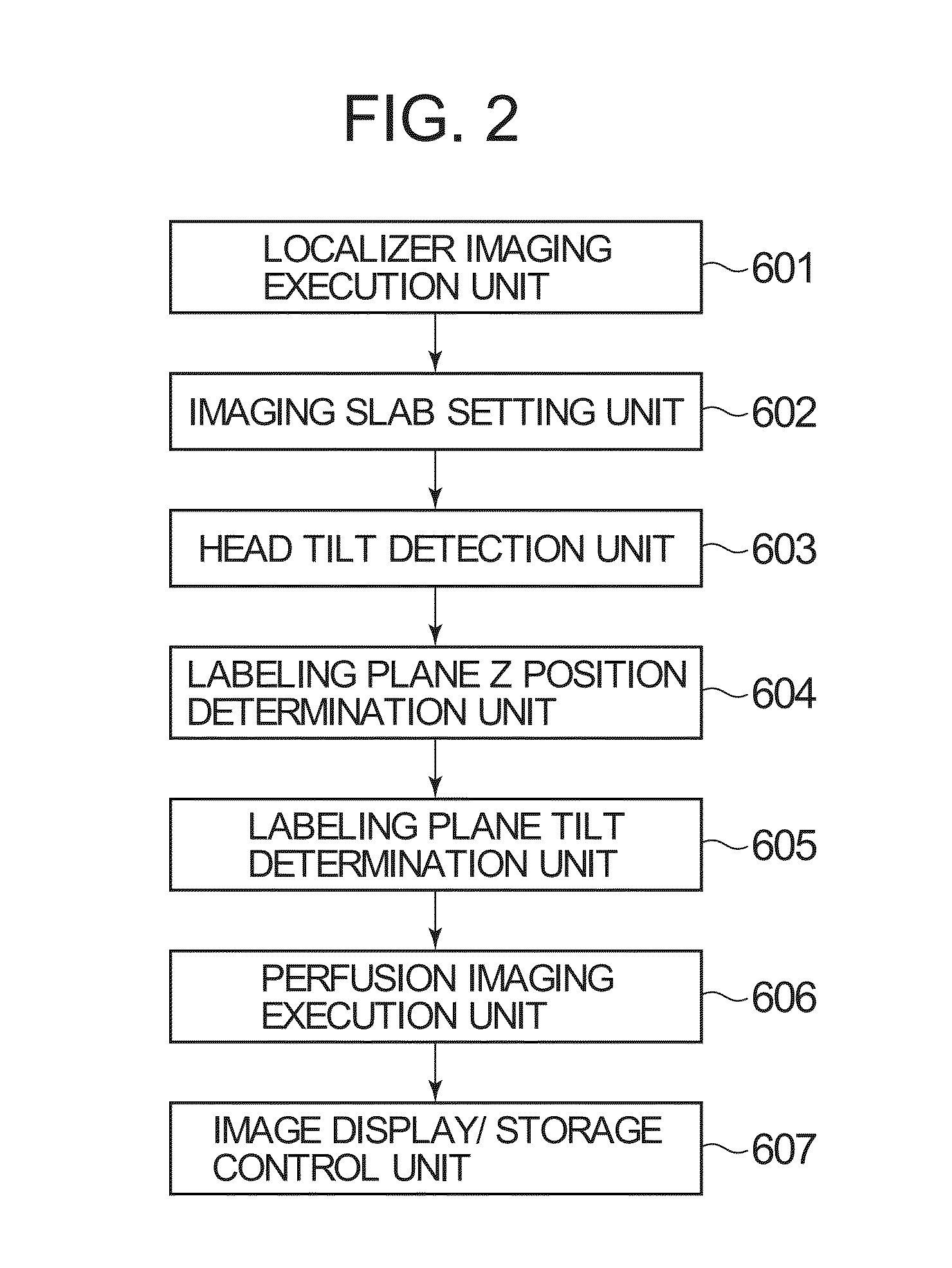
Labeling area determining apparatus, magnetic resonance apparatus and method for determining tilt of labeling area
A labeling area determining apparatus is provided. The labeling area determining apparatus includes a detecting device configured to detect a tilt of a head relative to a body axial direction of a subject to be imaged by an arterial spin labeling method, and a determining device configured to determine a tilt of a labeling area of spins relative to the body axial direction of the subject, based on the tilt of the head detected by the detecting device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Arterial spin labeling using time varying gradients
The present invention relates to a method and system for conducting a magnetic resonance fluid flow study by conducting a labeling procedure and a control procedure and combining datasets from those procedures to create a dataset for the fluid flow study. An amplitude modulated magnetic field gradient and amplitude modulated RF irradiation may be applied during a labeling procedure. Likewise, amplitude modulated RF irradiation may be applied during a control procedure. An amplitude modulated magnetic field gradient may also be applied during the control procedure.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
System and method for velocity selective pulses with arbitrary shape using MRI
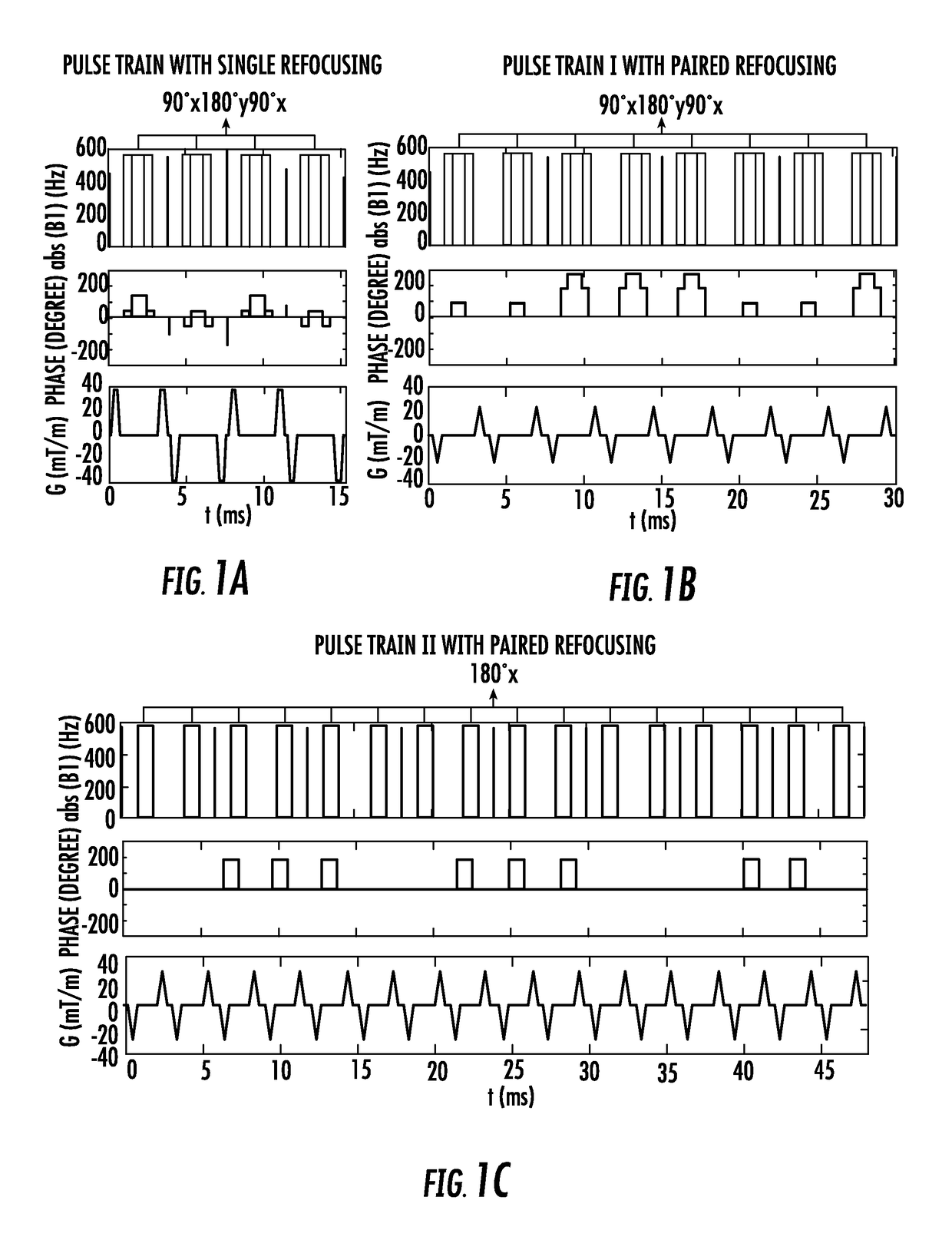
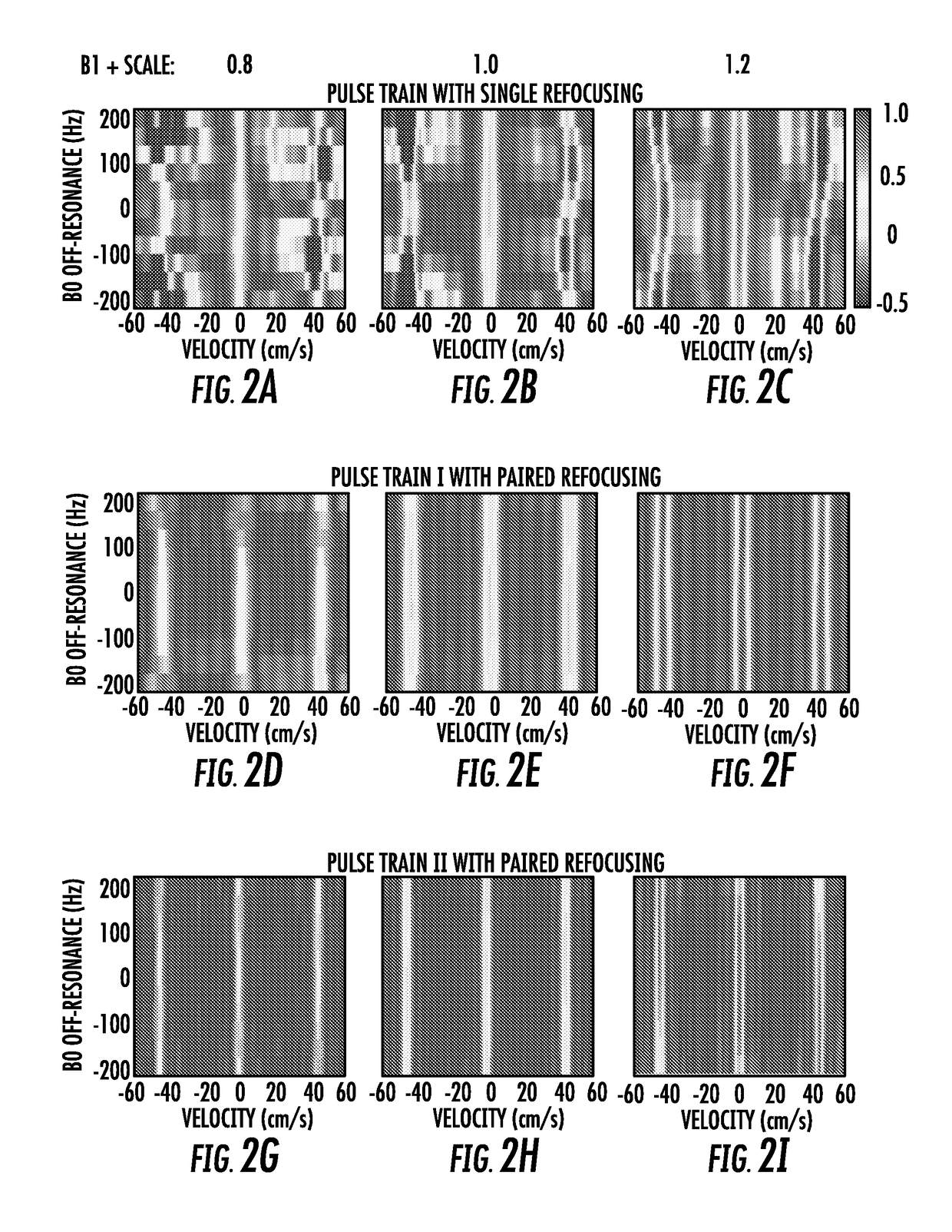
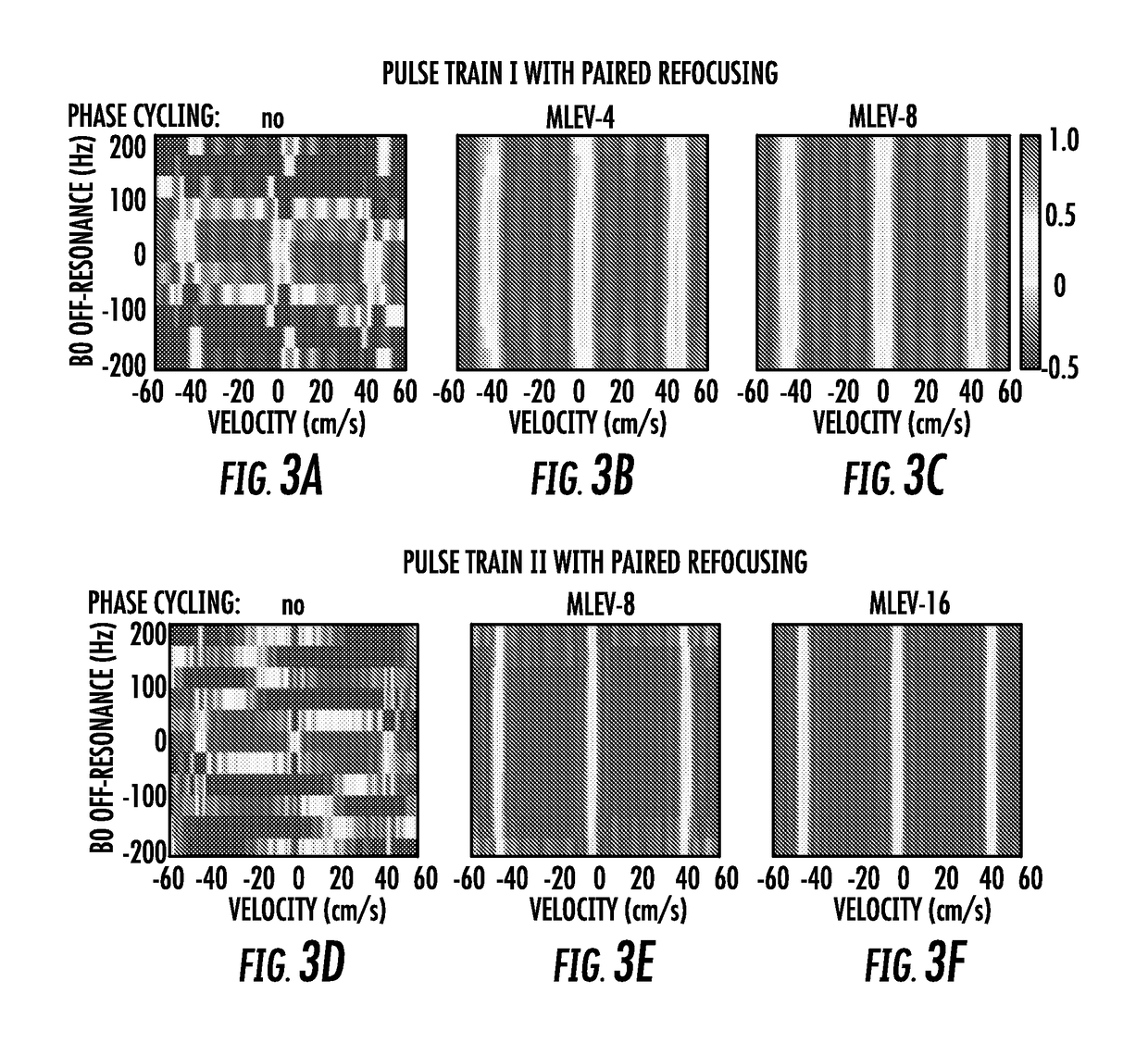
The present invention is directed to a system and method for magnetic resonance imaging including an extended Fourier transform-based velocity-selective pulse train design with a pair of refocusing pulses within each velocity encoding step and accompanying phase cycling between different velocity encoding steps. The present invention is robust to B0 / B1 field inhomogen-city and eddy current effects. The utility of this technique, through a velocity-selective inversion pulse, is demonstrated in a 2D velo-city-selective arterials spin labeling study, which shows a reasonable agreement in CBF quantification with the standard PCASL method.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
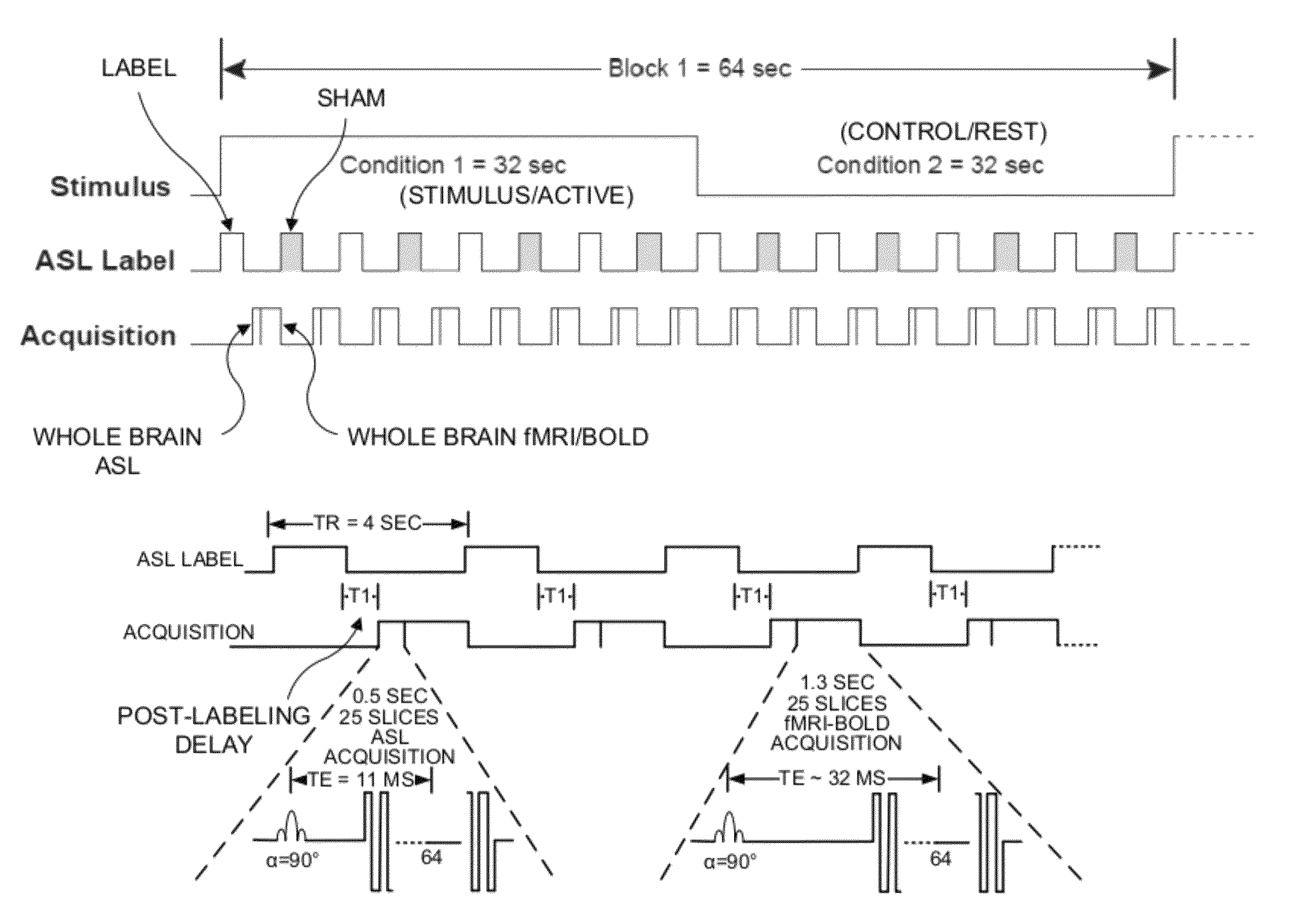
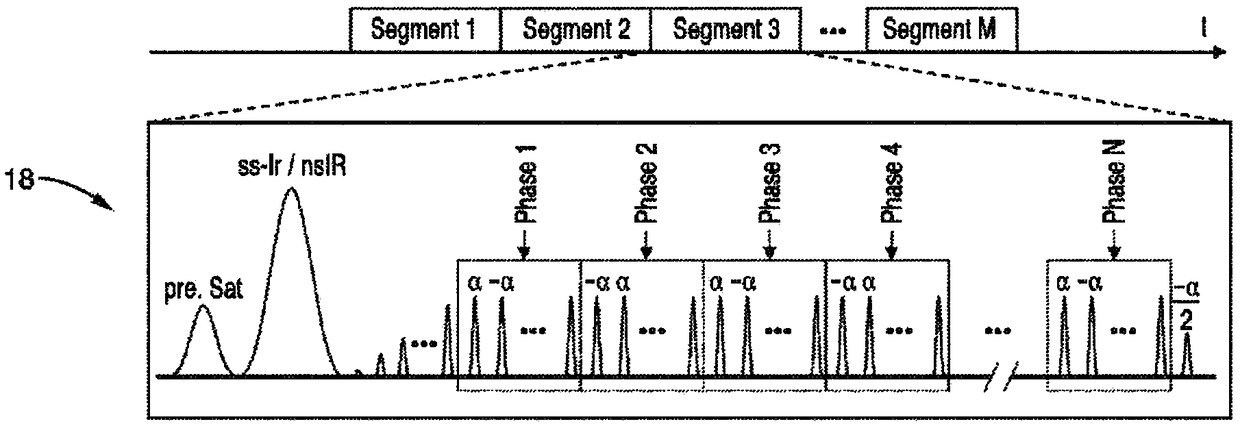
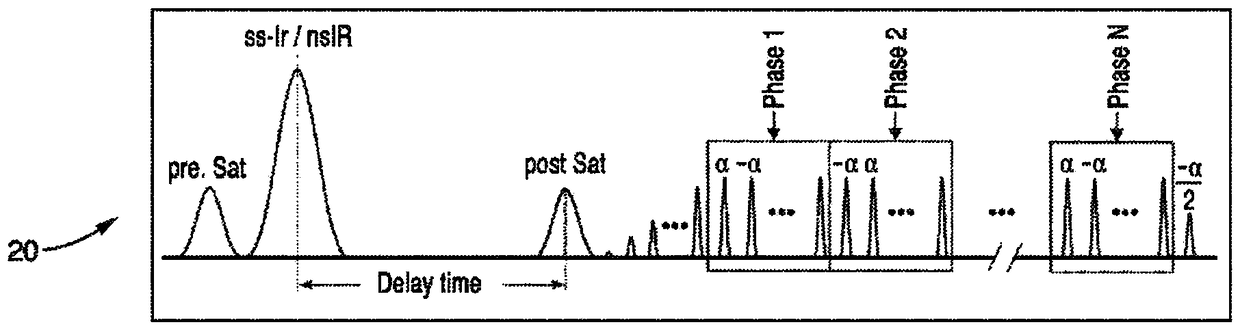
Combined arterial spin labeling and magnetic resonance fingerprinting
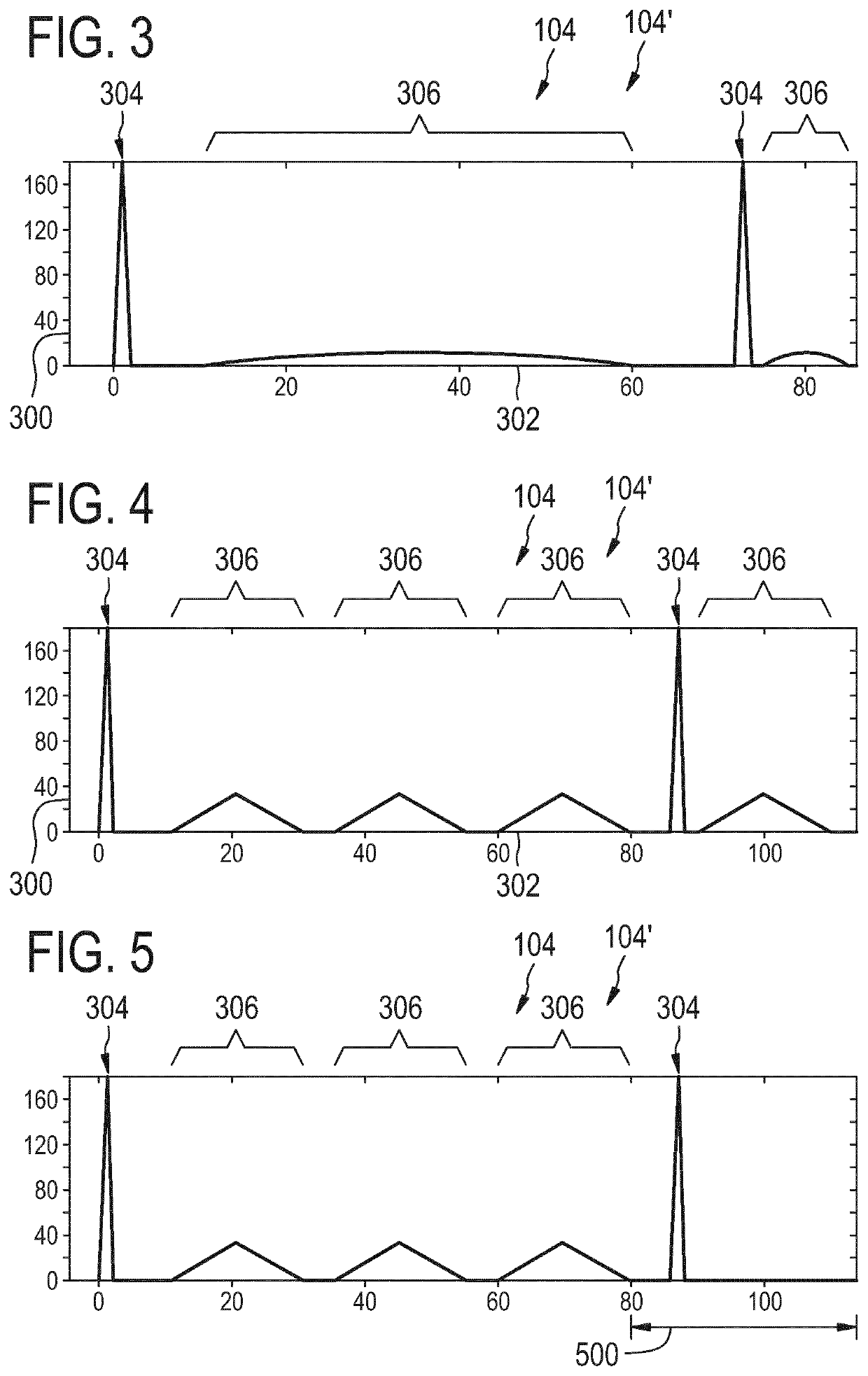
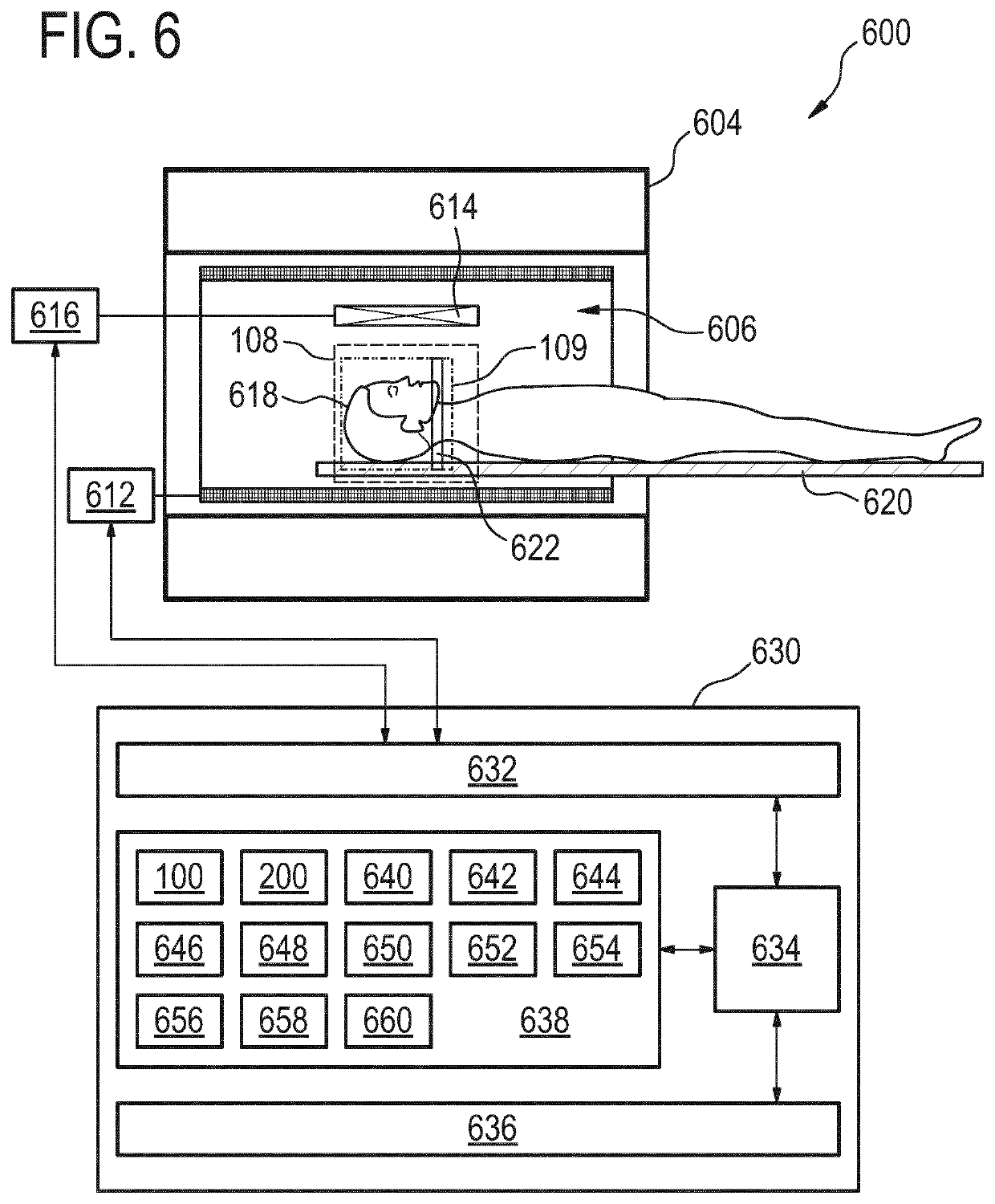
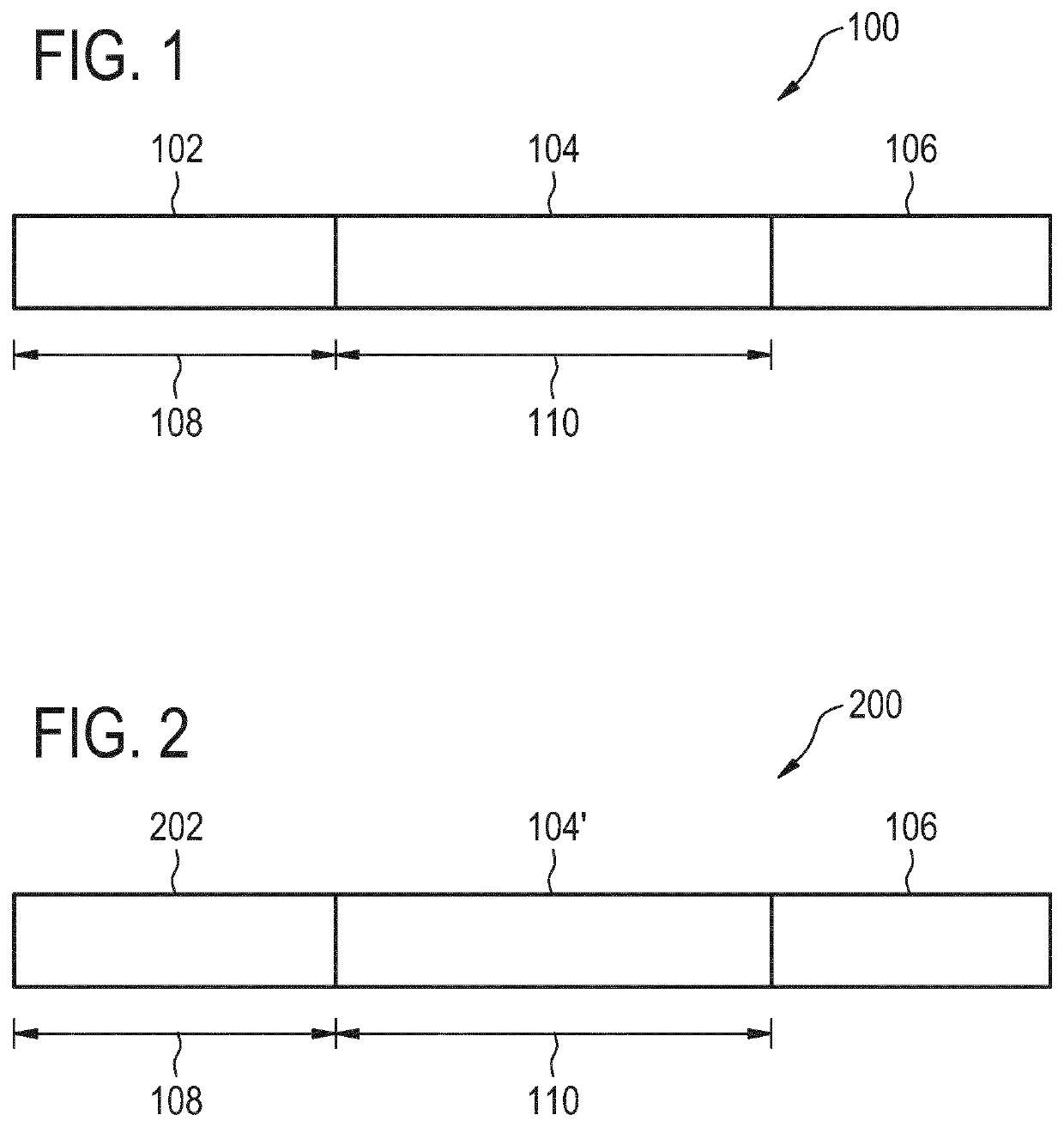
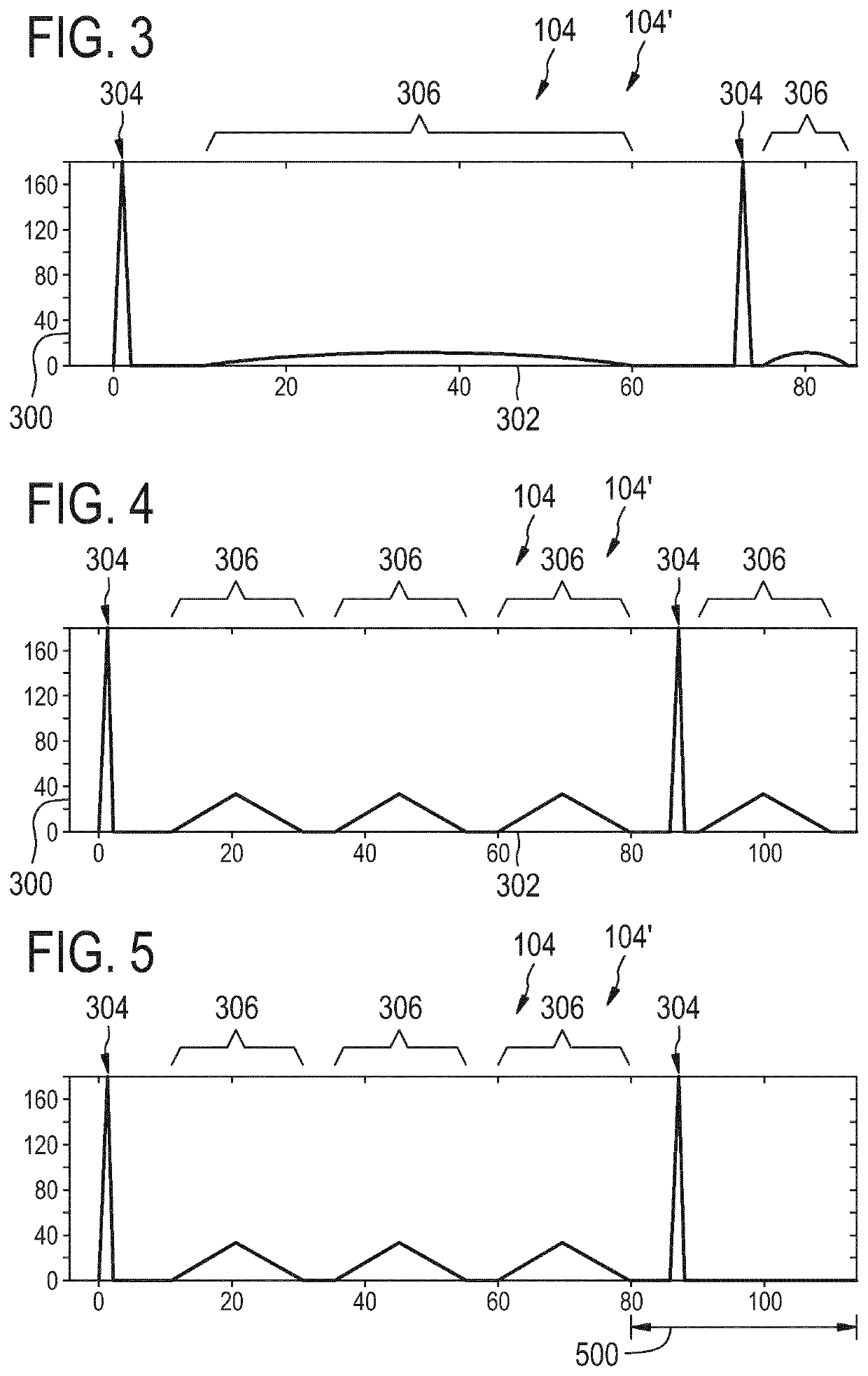
ActiveUS20200050819A1Reduction in noise artifactReduce artifactsImage enhancementImage analysisPulse sequenceBackground suppression
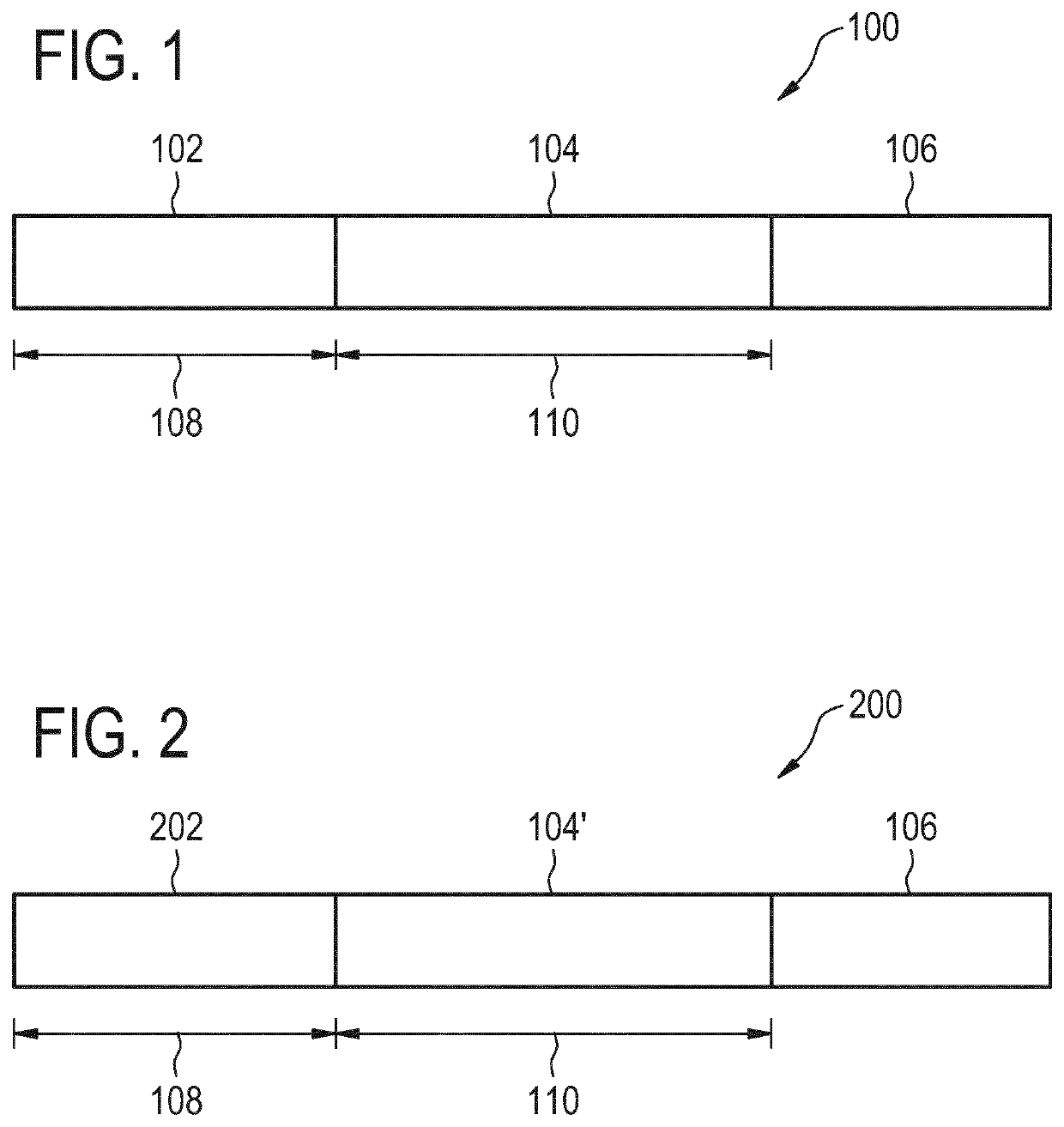
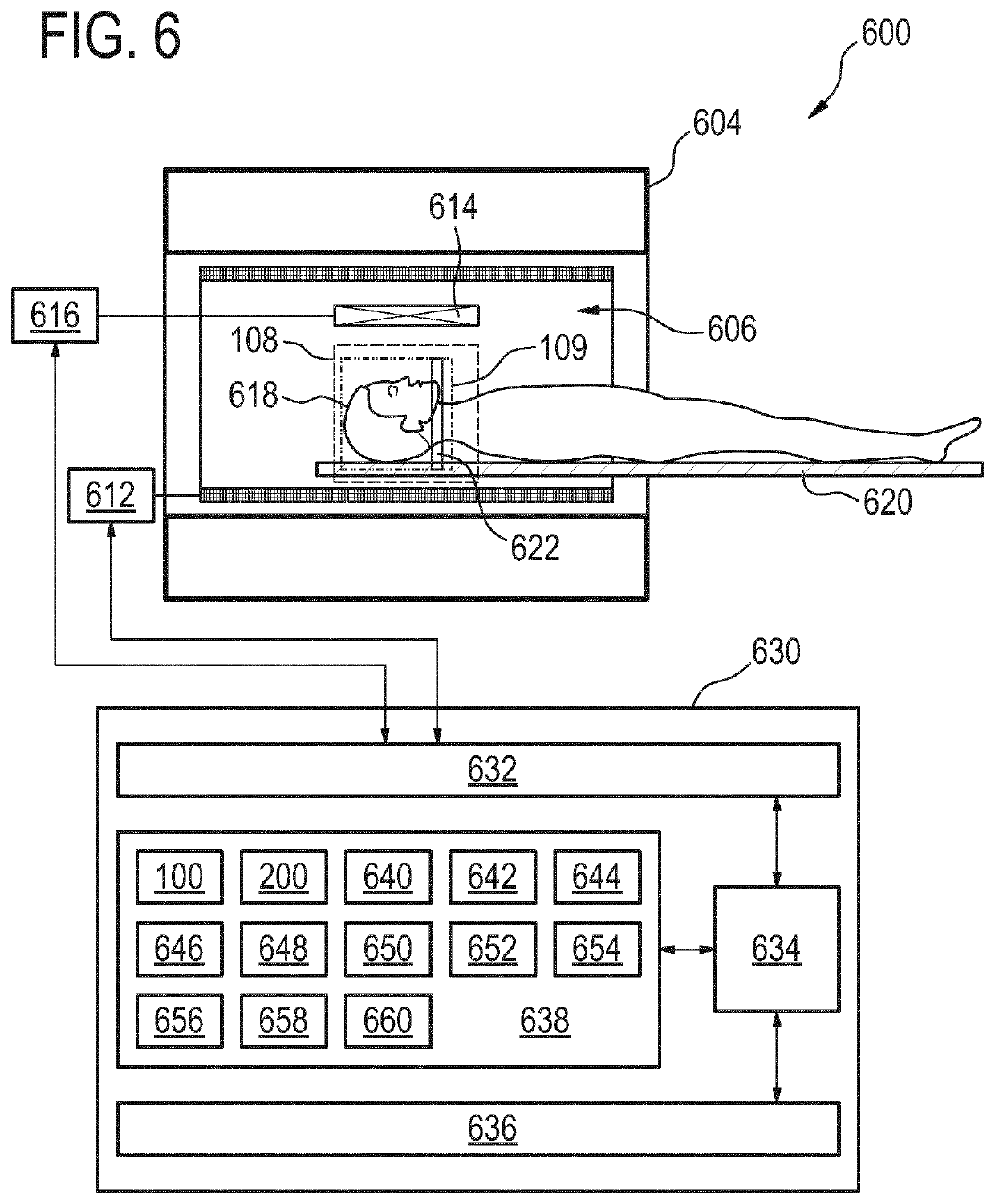
The invention provides for a method of operating a magnetic resonance imaging system for imaging a subject. The method comprises acquiring (700) tagged magnetic resonance data (642) and a first portion (644) of fingerprinting magnetic resonance data by controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system with tagging pulse sequence commands (100). The tagging pulse sequence commands comprise a tagging inversion pulse portion (102) for spin labeling a tagging location within the subject. The tagging pulse sequence commands comprise a background suppression portion (104). The background suppression portion comprises MRF pulse sequence commands for acquiring fingerprinting magnetic resonance data according to a magnetic resonance fingerprinting protocol. The tagging pulse sequence commands comprise an image acquisition portion (106). The method comprises acquiring (702) control magnetic resonance data (646) and a second portion (648) of the fingerprinting magnetic resonance data by controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system with control pulse sequence commands. The control pulse sequence commands comprise a control inversion pulse portion (202). The control pulse sequence commands comprise the background suppression portion (104′). The control pulse sequence commands comprise the image acquisition portion (106). The method comprises reconstructing (704) tagged magnitude images (650) using the tagged magnetic resonance data. The method comprises reconstructing (706) a control magnitude images (652) using the control magnetic resonance data. The method comprises constructing (708) an ASL image by subtracting the control magnitude images and the tagged magnitude images from each other. The method comprises reconstructing (710) a series of magnetic resonance fingerprinting images (656) using the first portion of the fingerprinting magnetic resonance data and / or the second portion of the fingerprinting magnetic resonance data. The method comprises generating (712) at least one magnetic resonance parametric map (658) by comparing the series of magnetic resonance fingerprinting images with a magnetic resonance fingerprinting dictionary.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
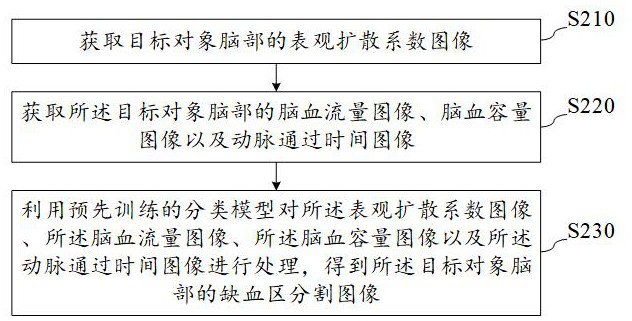
Ischemic region segmentation method, device and equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN114820602AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingRadiology
The invention relates to the technical field of image processing, in particular to an ischemic region segmentation method and device, equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an apparent diffusion coefficient image of the brain of a target object; acquiring a cerebral blood flow image, a cerebral blood volume image and an artery passing time image of the brain of the target object; and processing the apparent diffusion coefficient image, the cerebral blood flow image, the cerebral blood volume image and the artery passing time image by using a pre-trained classification model to obtain an ischemic region segmentation image of the brain of the target object. According to the ischemic region segmentation method, the ischemic region is segmented by combining the diffusion weighted image information and the delayed artery spin marking perfusion image information after marking, mutual information among various images is fully utilized, and the accuracy and robustness of ischemic region segmentation are improved.
Owner:脑玺(苏州)智能科技有限公司
Planning support for selective arterial spin labeling mr imaging methods
ActiveUS20190346524A1Easy to planImprove image qualityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPerfusion-Weighted MRImaging quality
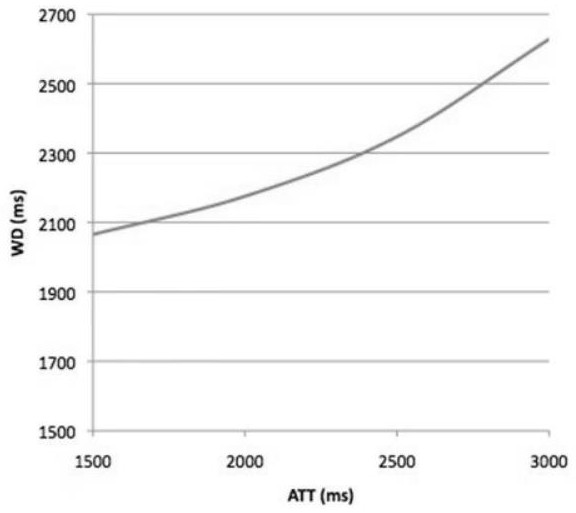
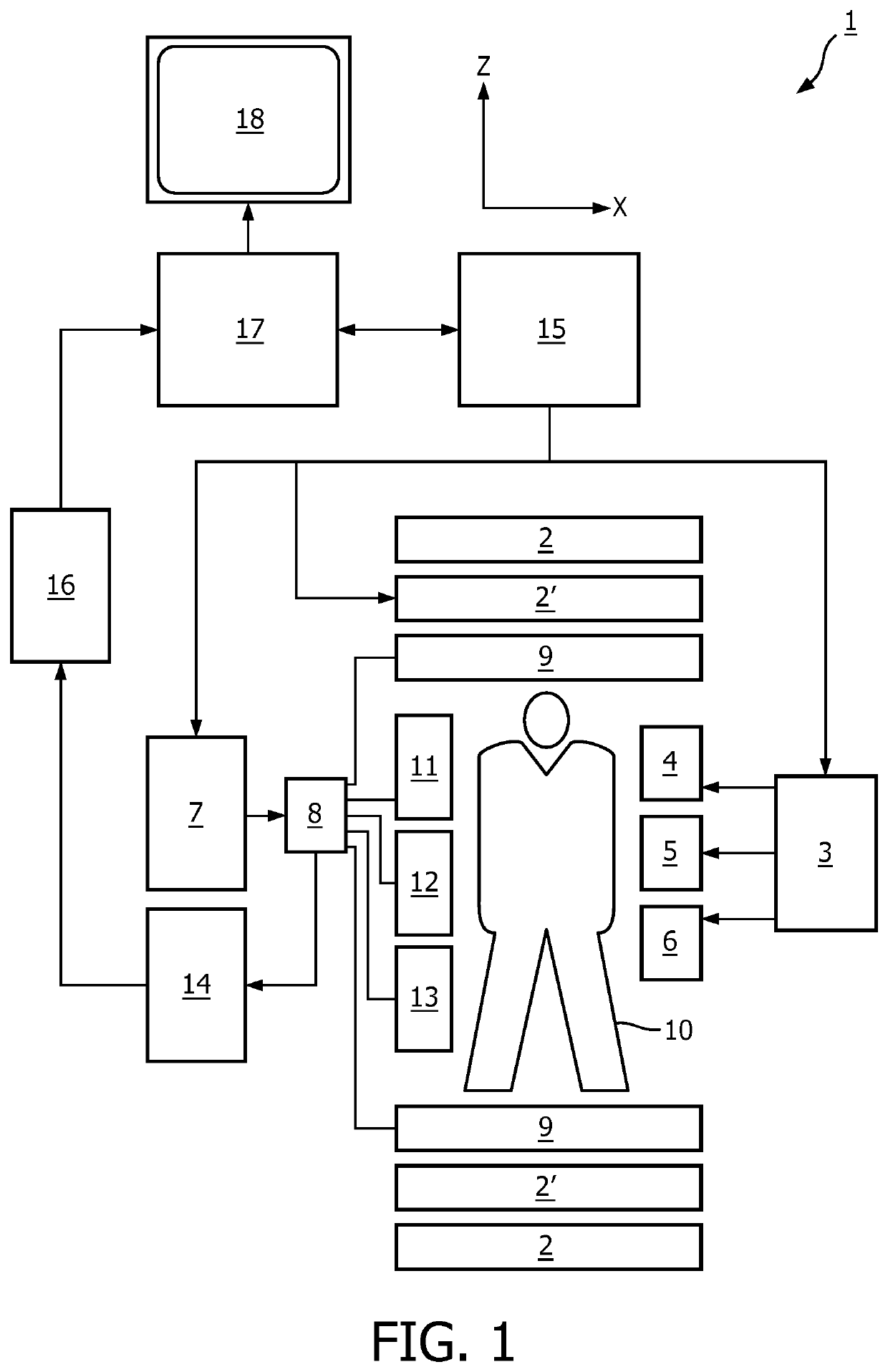
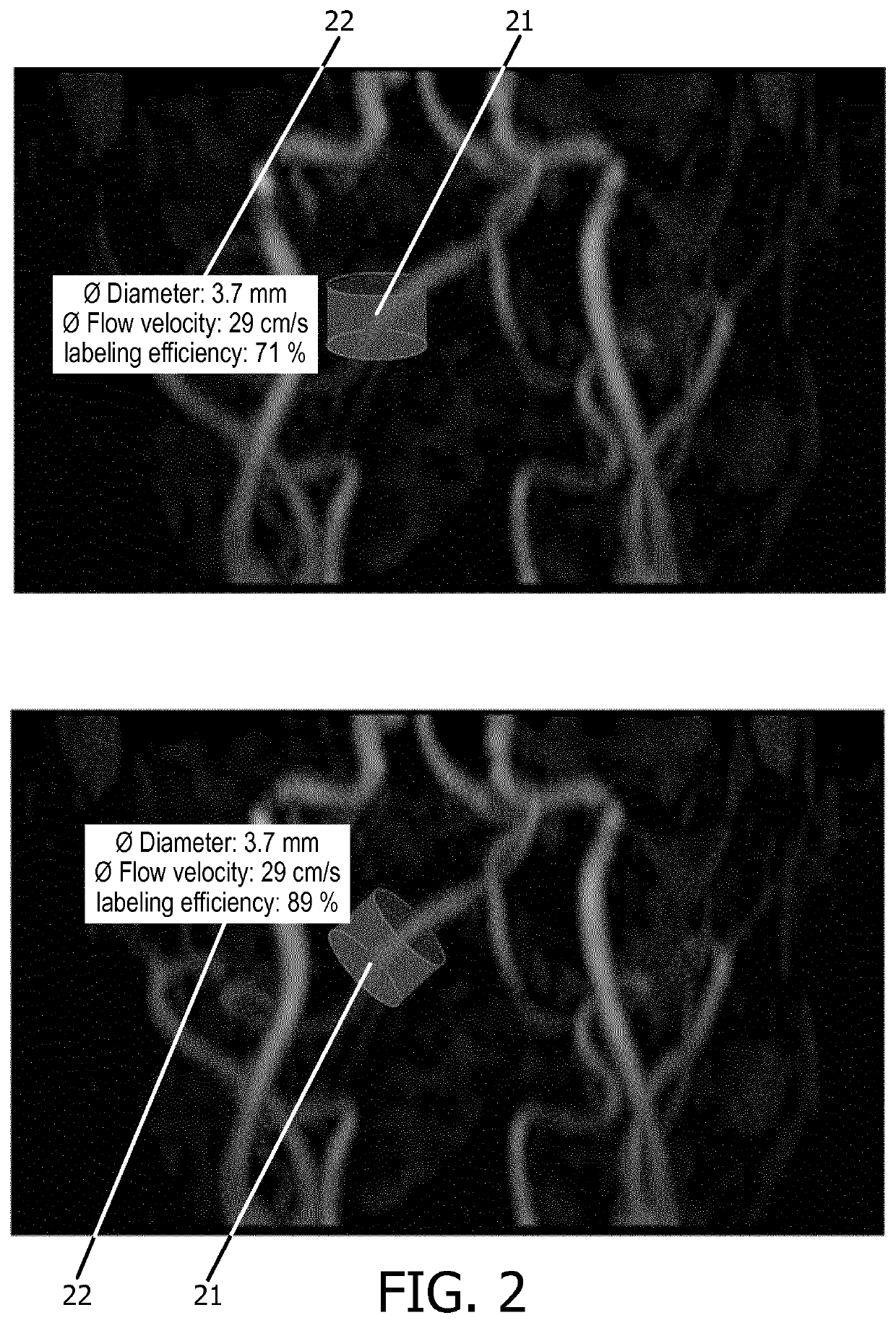
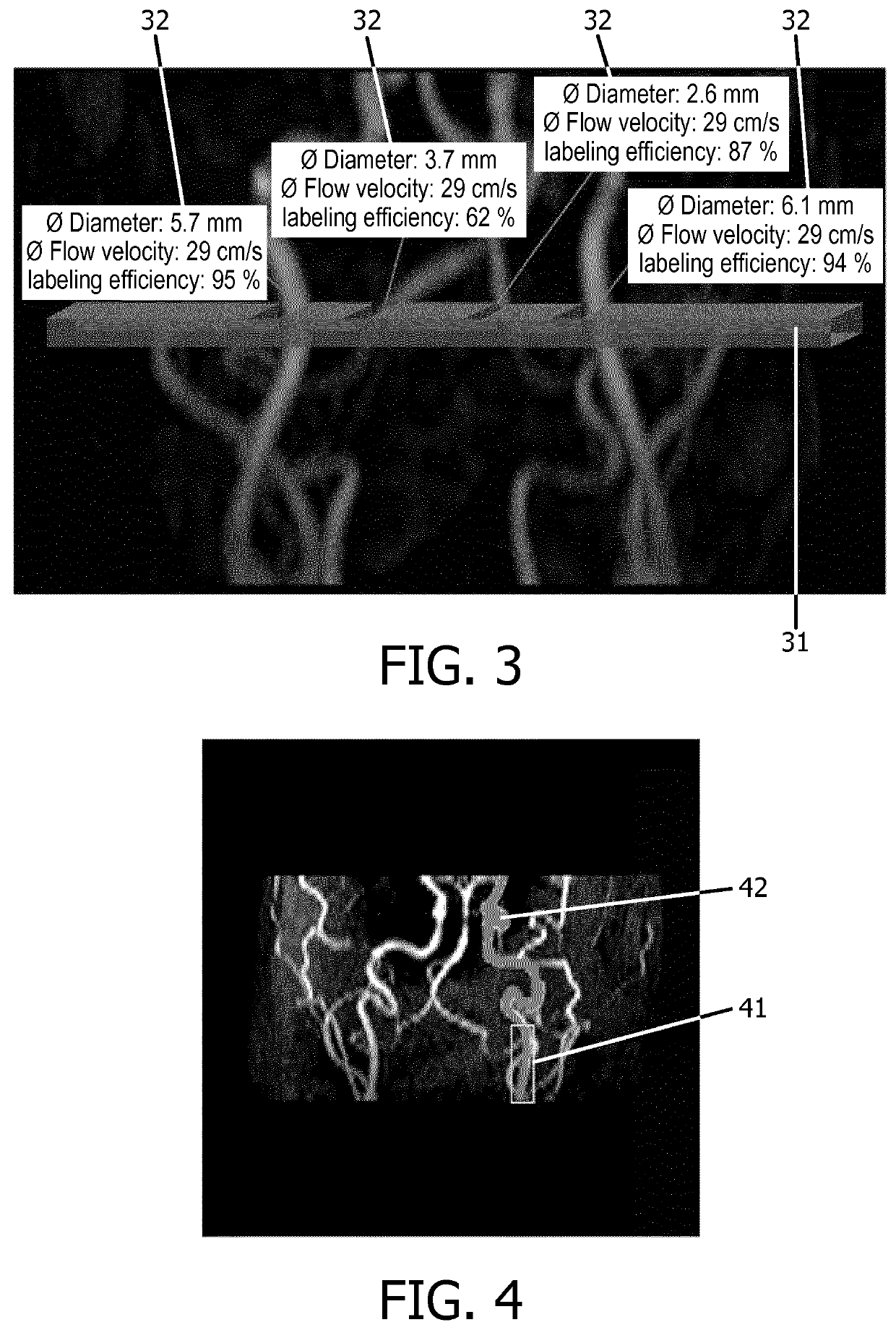
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of at least a portion of a body (10) placed in a main magnetic field within the examination volume of a MR device (1). It is an object of the invention to facilitate the planning of an arterial spin labeling (ASL) MR imaging session and to improve the image quality in perfusion weighted MR imaging. The method of the invention comprises the following steps: acquiring angiographic MR signal data by subjecting the portion of the examined body (10) to one or more MR angiography scans; deriving quantitative blood flow parameters from the angiographic MR signal data;—computing a labeling efficiency of an ASL sequence from the sequence parameters of the ASL sequence and from the quantitative blood flow parameters; optimizing the sequence parameters by maximizing the labeling efficiency; acquiring perfusion weighted MR signal data by subjecting the portion of the body to the ASL sequence; and—reconstructing a MR image from the perfusion weighted MR signal data. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program for a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
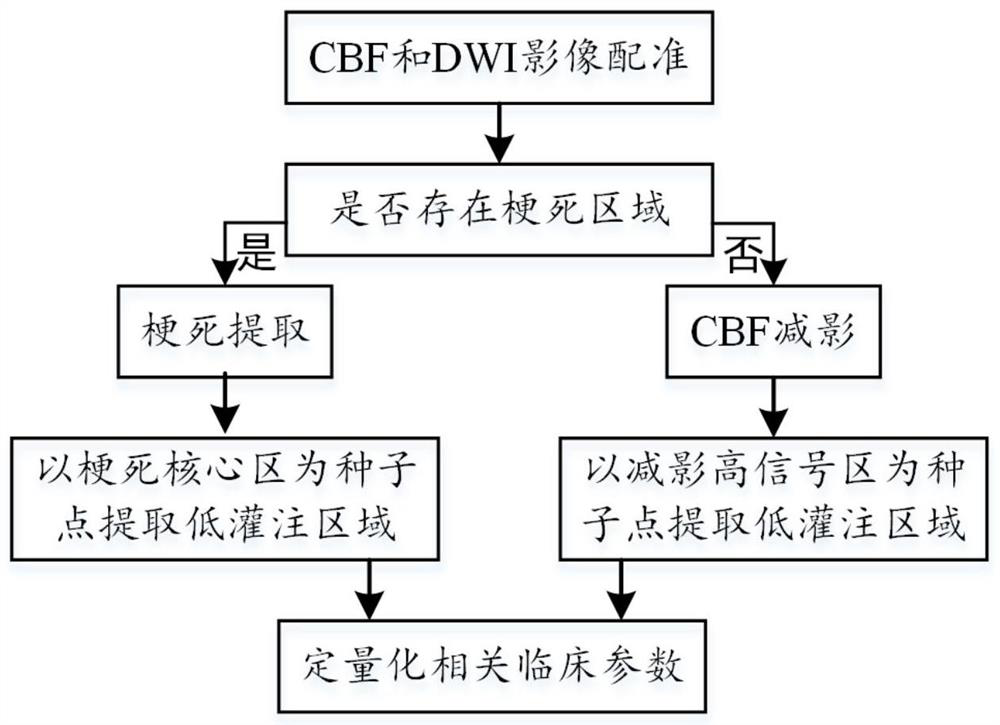
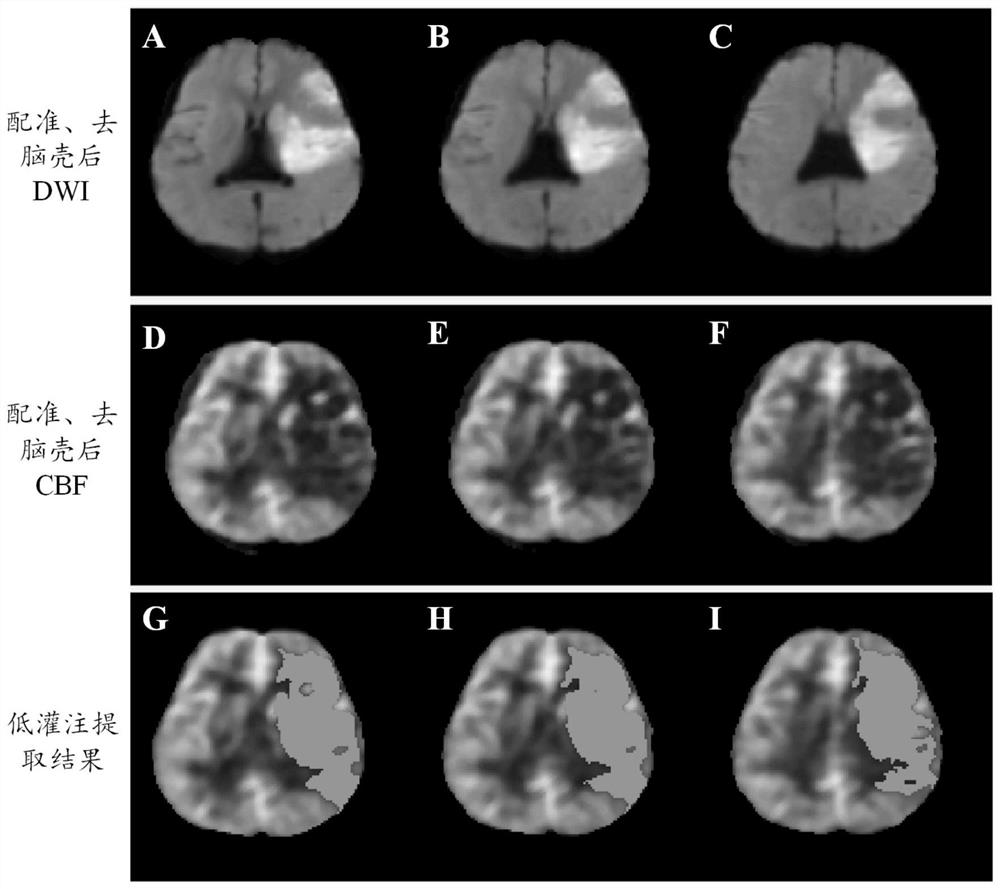
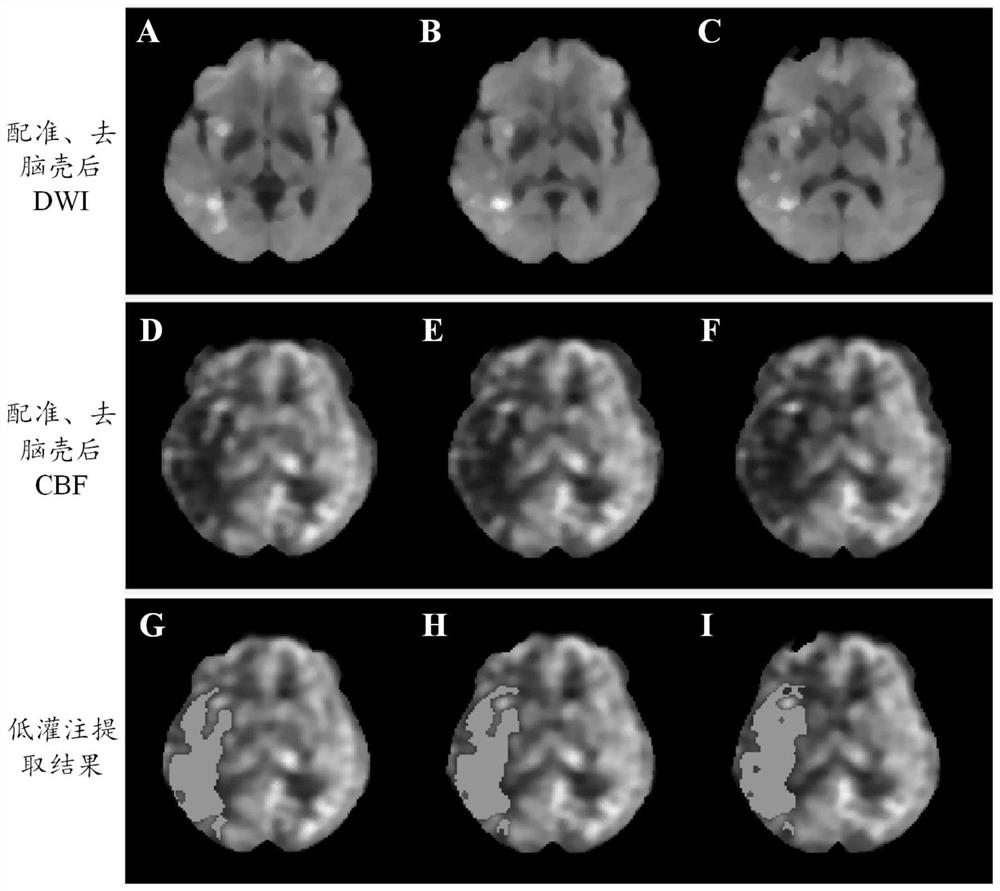
Arterial spin labeling-based cerebral hypoperfusion region accurate quantification method
ActiveCN112288705AConsistent spatial resolutionImage enhancementImage analysisAnatomical structuresCerebral hypoperfusion
The invention discloses an arterial spin labeling-based cerebral hypoperfusion region accurate quantification method, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, mapping a diffusion weighted image and a cerebral blood flow diagram of a stroke definite diagnosis patient on a spatial anatomical structure through a coarse-to-fine registration strategy; secondly, for the stroke definite diagnosispatient image with the infarction core area, taking the infarction core area extracted by the diffusion weighted image as a seed point, and extracting a hypoperfusion area on the cerebral blood flowdiagram corresponding to the spatial position; otherwise, extracting a hypoperfusion region by taking the high signal region extracted from the cerebral blood flow subtraction image as a seed point; and finally, quantitatively analyzing related parameters of the hypoperfusion area of the stroke definite diagnosis patient, such as the position, the size and the volume of the hypoperfusion area, mismatching of an infarction core / hypoperfusion area and the like. Accurate extraction and quantitative analysis of a hypoperfusion area of a stroke definite patient are helpful for evaluating a time window and a tissue window of a diagnosed patient.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR PRECISION MEASUREMENT SCI & TECH CAS +1
Imaging biomarkers based on ratio between diffusion and perfusion
ActiveUS20210255266A1Magnetic measurementsMedical automated diagnosisImaging biomarkerArterial spin labeling
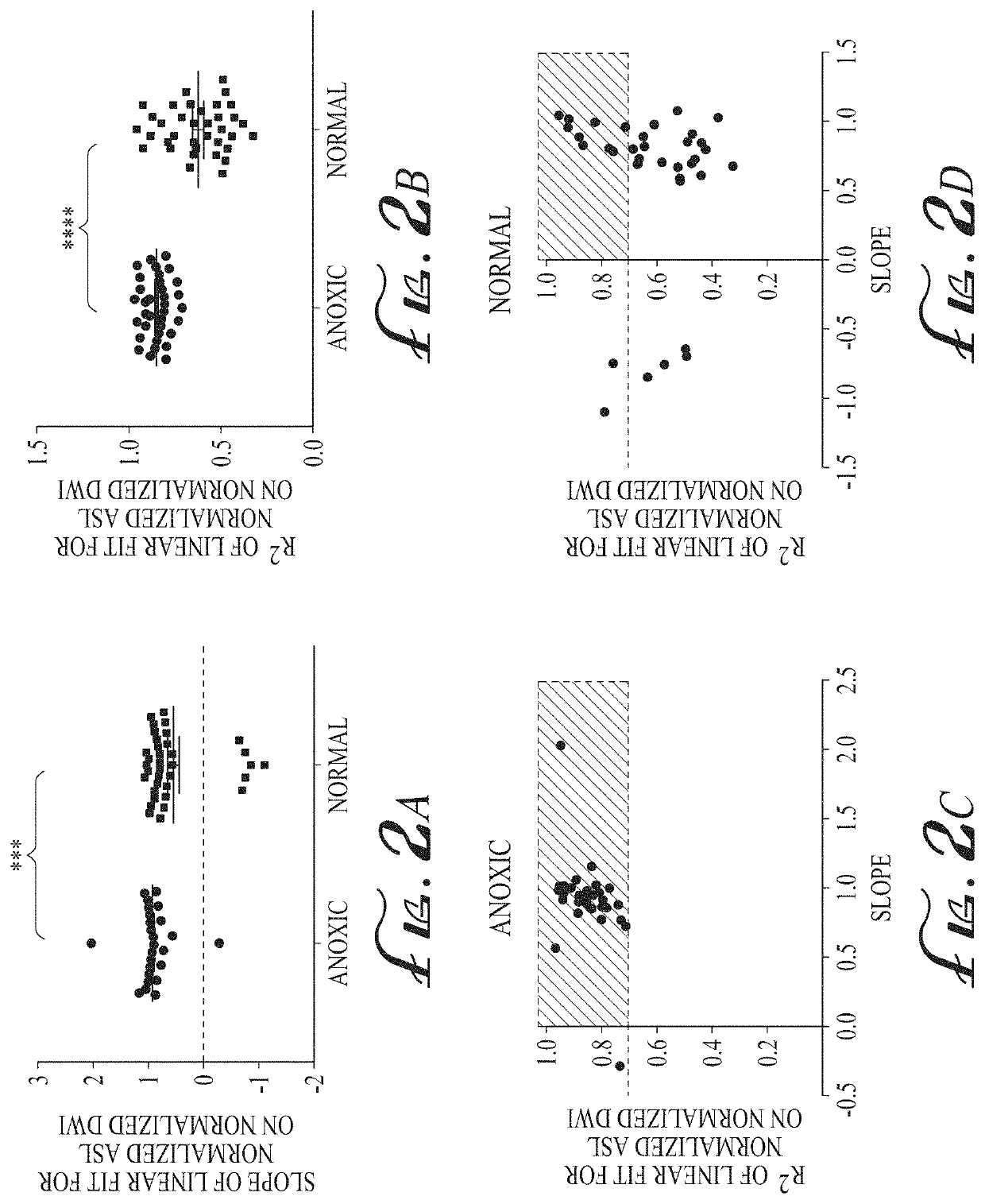
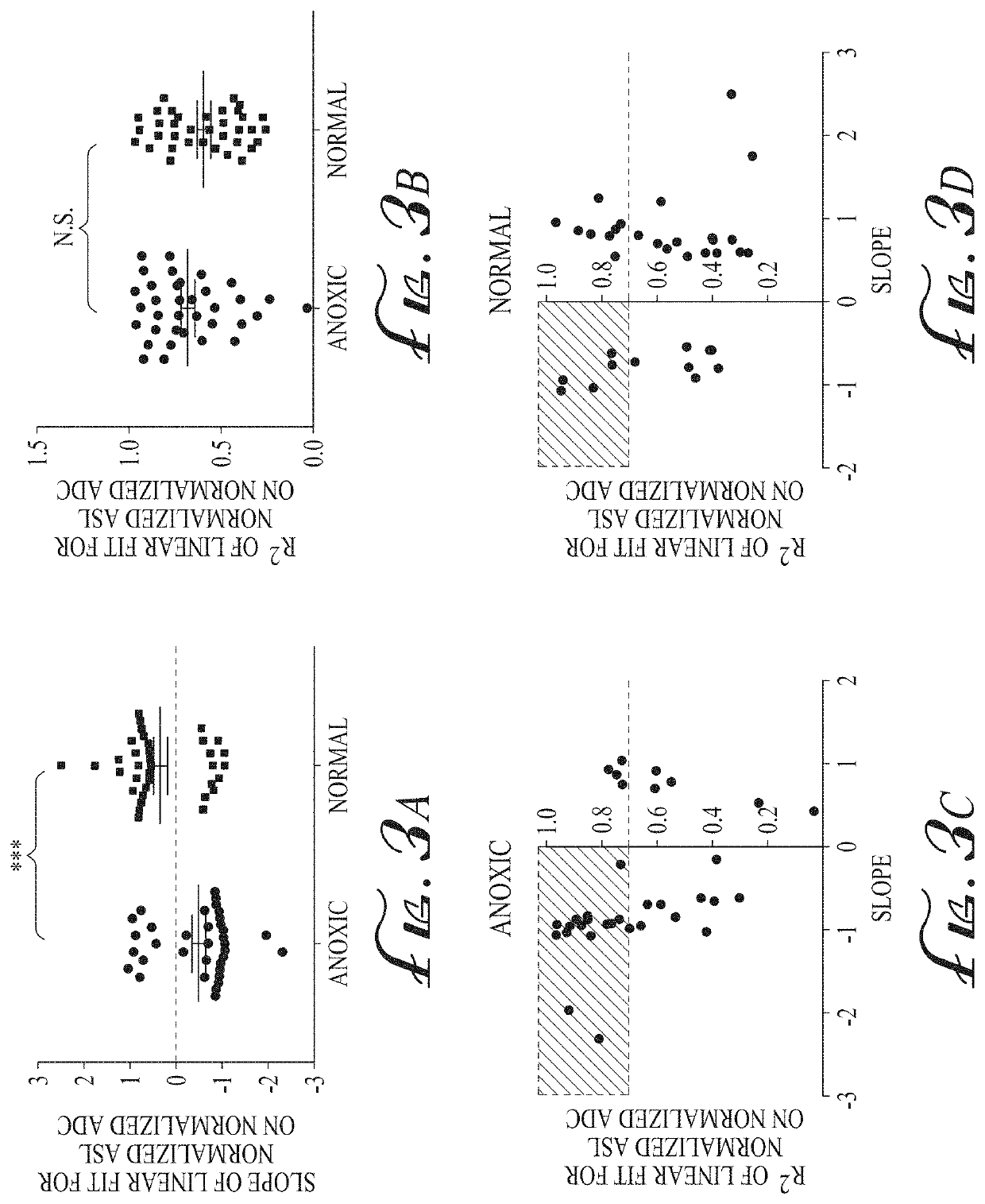
The ratio of arterial spin labeled (ASL) perfusion to diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) is generally homogeneous in the anoxic / hypoxic injury population. Conversely, the ratio is more heterogeneous in the non-anoxic / hypoxic population. By plotting these ratios in a graphical format in the form of an axial color map of the brain—referred to as a normalized diffusion to perfusion (NDP) ratio colormap—it may be determined whether a patient has suffered from an anoxic / hypoxic injury. Thus, the anoxic and non-anoxic injury patients will have, respectively, homogenous and heterogeneous color maps. Anoxic brain injury patients have a global homogeneously positive relationship between qualitative ASL perfusion and diffusion weighted signal such that areas of restricted diffusion show significantly increased ASL perfusion signal, which may be attributable to BBB integrity. The NDP ratio colormap provides an imaging biomarker to differentiate anoxic brain injury from normal controls and to potentially assess BBB integrity.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
MR imaging apparatus and method for generating a perfusion image with motion correction
ActiveUS10092199B2Maximum efficacyIncrease volumeMagnetic measurementsSensorsResonanceAcquisition time
A magnetic resonance method and system are provided for generating real-time motion-corrected perfusion images based on pulsed arterial spin labeling (PASL) with a readout sequence such as a 3D gradient and spin echo (GRASE) image data acquisition block. The real-time motion correction is achieved by using a volumetric 3D EPI navigator that is provided during an intrinsic delay in the PASL sequence, which corrects for motion prospectively and does not extend the image data acquisition time as compared to a similar non-motion-corrected imaging procedure.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
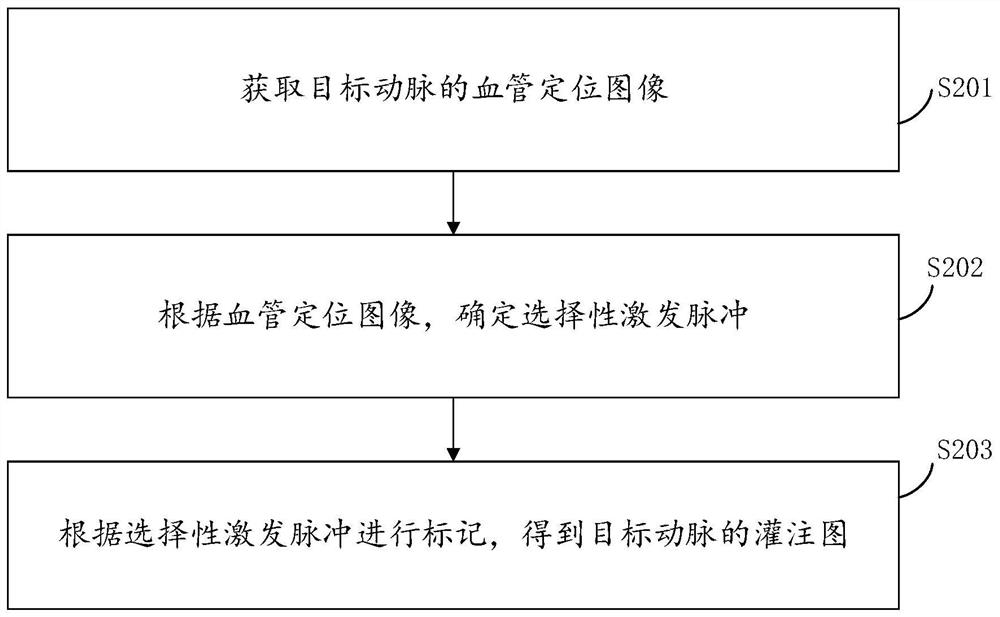
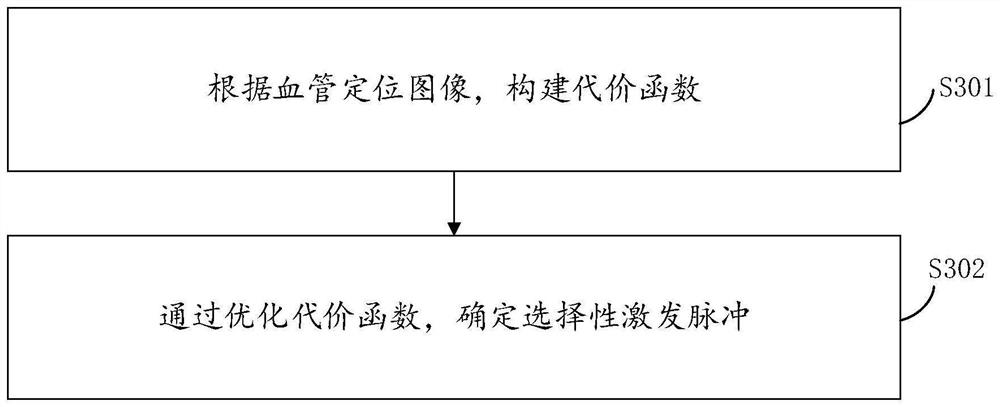
Target artery selective marking method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
PendingCN114596270AInhibition effectEliminate errors caused by uneven magnetic fieldImage enhancementImage analysisSelective excitationArterial spin labeling
The invention relates to a target artery selective marking method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a blood vessel positioning image of a target artery; determining a selective excitation pulse according to the blood vessel positioning image; marking according to the selective excitation pulse to obtain a perfusion map of the target artery. According to the method, the selective excitation pulse taking the artery as the target is designed on line through the selected artery position needing to be marked and based on a single-channel or multi-channel parallel emission platform, and the selective excitation pulse is applied to the marking section in the artery spin marking sequence, so that the effects of selectively marking the specific artery and obtaining the specific arterial perfusion map are achieved.
Owner:UNITED IMAGING RES INST OF INNOVATIVE MEDICAL EQUIP
Quality control phantom and evaluation method for magnetic resonance arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging
PendingUS20220120836A1Quantitatively verifyQuantitatively evaluateMagnetic measurementsSensorsMedicineImaging quality
A quality control phantom and an evaluation method for magnetic resonance arterial spin labeling perfusion imaging includes: a phantom main body; a container, a circulating liquid being provided in the container; a tube, comprising a first tube and a second tube, one end of the first tube being in communication with the container, the other end being in communication with a liquid inlet of the phantom main body, one end of the second tube being in communication with the container, the other end being in communication with a liquid outlet of the phantom main body, and the first tube, the phantom main body, the second tube and the container jointly forming a closed loop; a pump, provided on the first tube and used to drive the circulating liquid to circulate along the closed loop to generate a perfusion signal in the phantom main body.
Owner:SHANDONG FIRST MEDICAL UNIV & SHANDONG ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Combined arterial spin labeling and magnetic resonance fingerprinting
ActiveUS11226389B2Reduce the amount of solutionIncrease typeImage enhancementImage analysisPulse sequenceBackground suppression
The invention provides for a method of operating a magnetic resonance imaging system for imaging a subject. The method comprises acquiring (700) tagged magnetic resonance data (642) and a first portion (644) of fingerprinting magnetic resonance data by controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system with tagging pulse sequence commands (100). The tagging pulse sequence commands comprise a tagging inversion pulse portion (102) for spin labeling a tagging location within the subject. The tagging pulse sequence commands comprise a background suppression portion (104). The background suppression portion comprises MRF pulse sequence commands for acquiring fingerprinting magnetic resonance data according to a magnetic resonance fingerprinting protocol. The tagging pulse sequence commands comprise an image acquisition portion (106). The method comprises acquiring (702) control magnetic resonance data (646) and a second portion (648) of the fingerprinting magnetic resonance data by controlling the magnetic resonance imaging system with control pulse sequence commands. The control pulse sequence commands comprise a control inversion pulse portion (202). The control pulse sequence commands comprise the background suppression portion (104′). The control pulse sequence commands comprise the image acquisition portion (106). The method comprises reconstructing (704) tagged magnitude images (650) using the tagged magnetic resonance data. The method comprises reconstructing (706) a control magnitude images (652) using the control magnetic resonance data. The method comprises constructing (708) an ASL image by subtracting the control magnitude images and the tagged magnitude images from each other. The method comprises reconstructing (710) a series of magnetic resonance fingerprinting images (656) using the first portion of the fingerprinting magnetic resonance data and / or the second portion of the fingerprinting magnetic resonance data. The method comprises generating (712) at least one magnetic resonance parametric map (658) by comparing the series of magnetic resonance fingerprinting images with a magnetic resonance fingerprinting dictionary.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
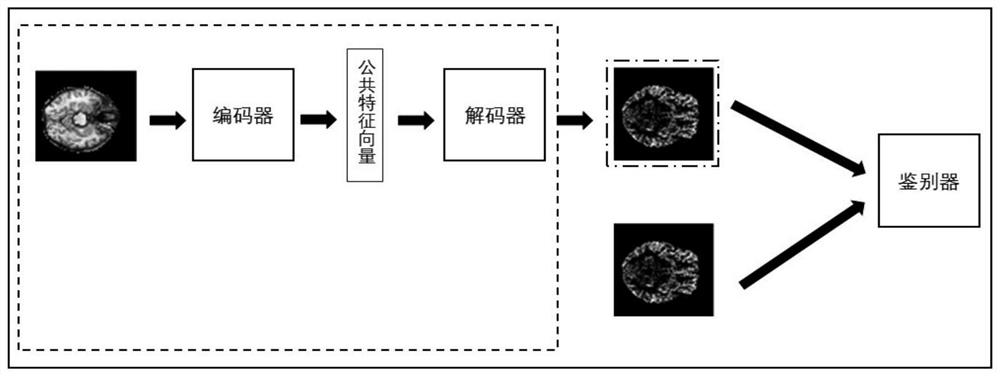
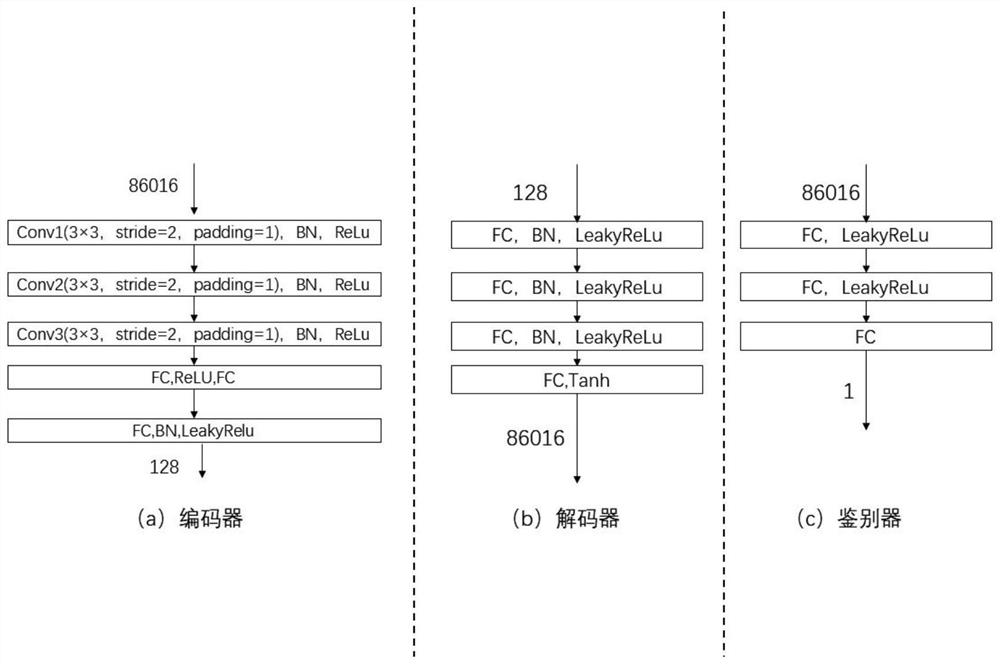
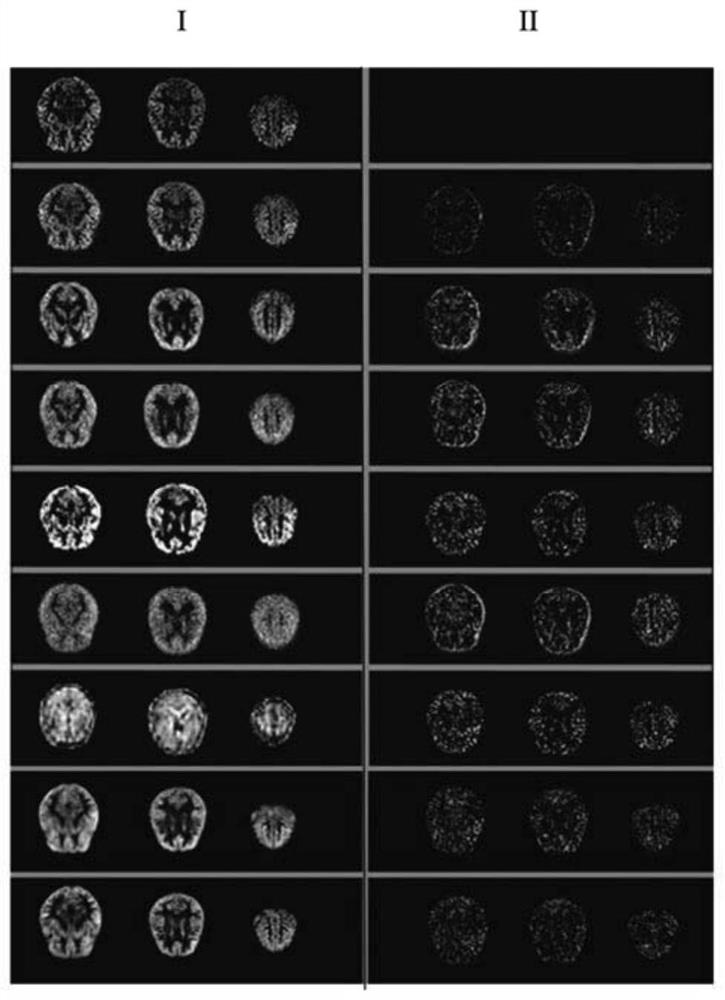
Arterial spin labeling image synthesis method based on generative adversarial hybrid model network
PendingCN114049429AImprove fitting abilityAvoid vanishing gradientsMedical automated diagnosisCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionArterial spin labeling
The invention discloses an arterial spin labeling image synthesis method based on a generative adversarial hybrid model network. The method comprises the following steps: 1, obtaining a structural magnetic resonance image and an arterial spin labeling image which are needed for generation, and executing a preprocessing operation; 2, inputting structural magnetic resonance data and arterial spin labeling data into an automatic coding machine for generation training; 3, inputting the corresponding arterial spin labeling image and an image synthesized by the automatic coding machine into a discriminator for training; 4, repeating the steps 2 and 3, and training a generative adversarial hybrid model network to obtain a trained generator; and 5, using the trained generator to iteratively generate predicted arterial spin labeling data by randomly inputting eight pieces of real structural magnetic resonance data. According to the invention, a synthesized arterial spin labeling image has clearer details and contours, the research of an arterial spin labeling technology in Alzheimer's disease can be promoted, and a high-quality supplementary data set is provided.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com