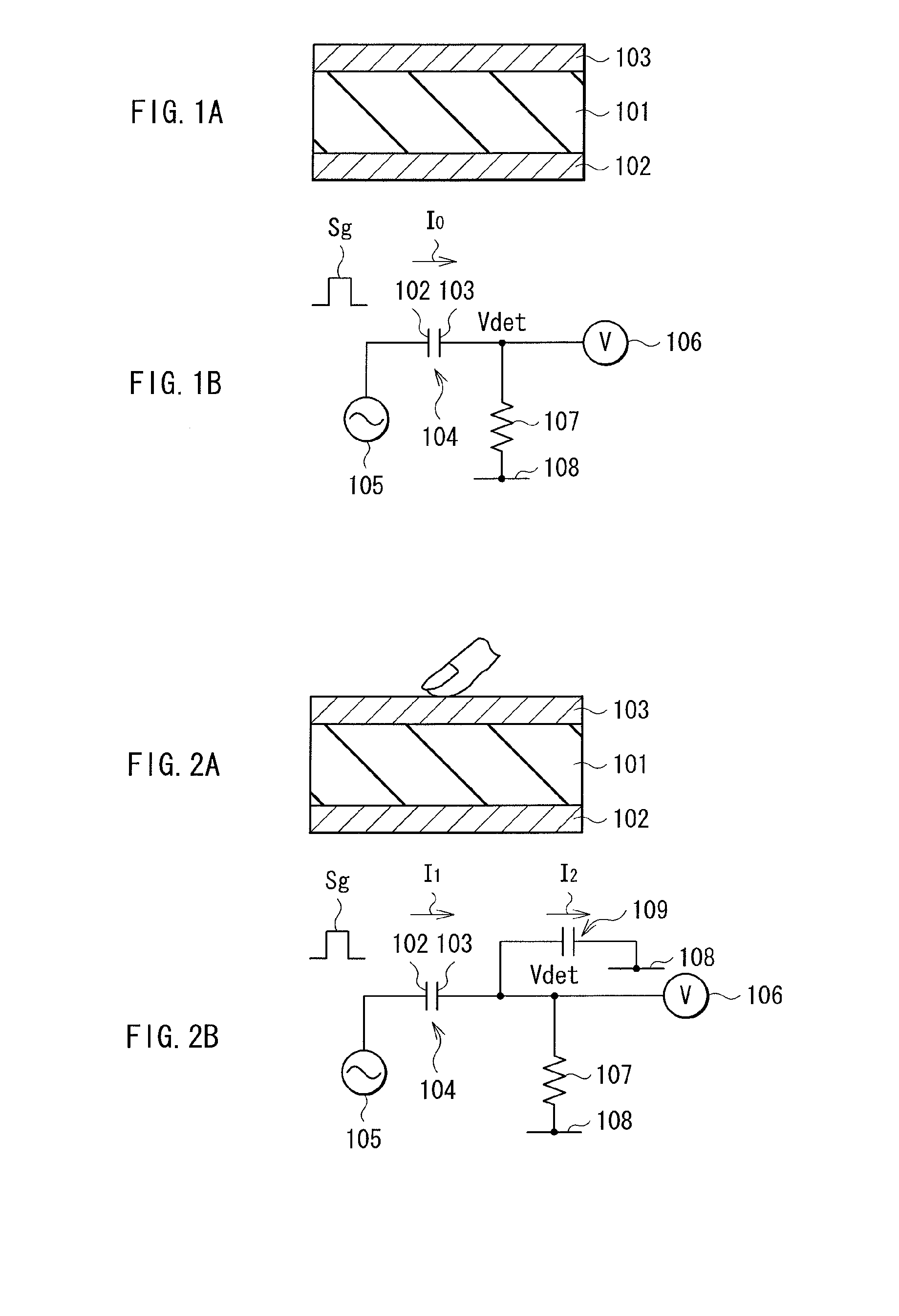
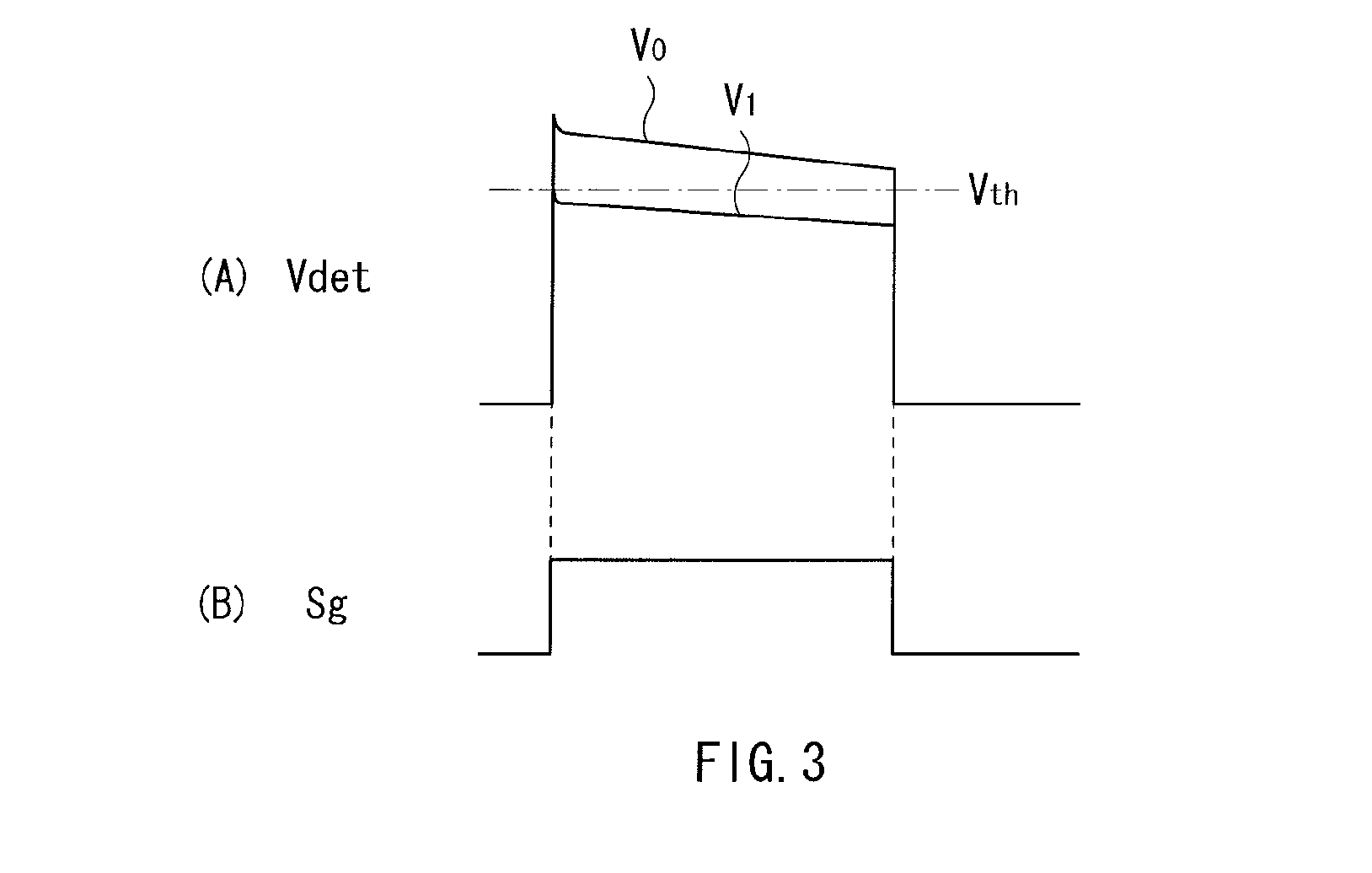
Patents
Literature
104 results about "Selective pulse" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
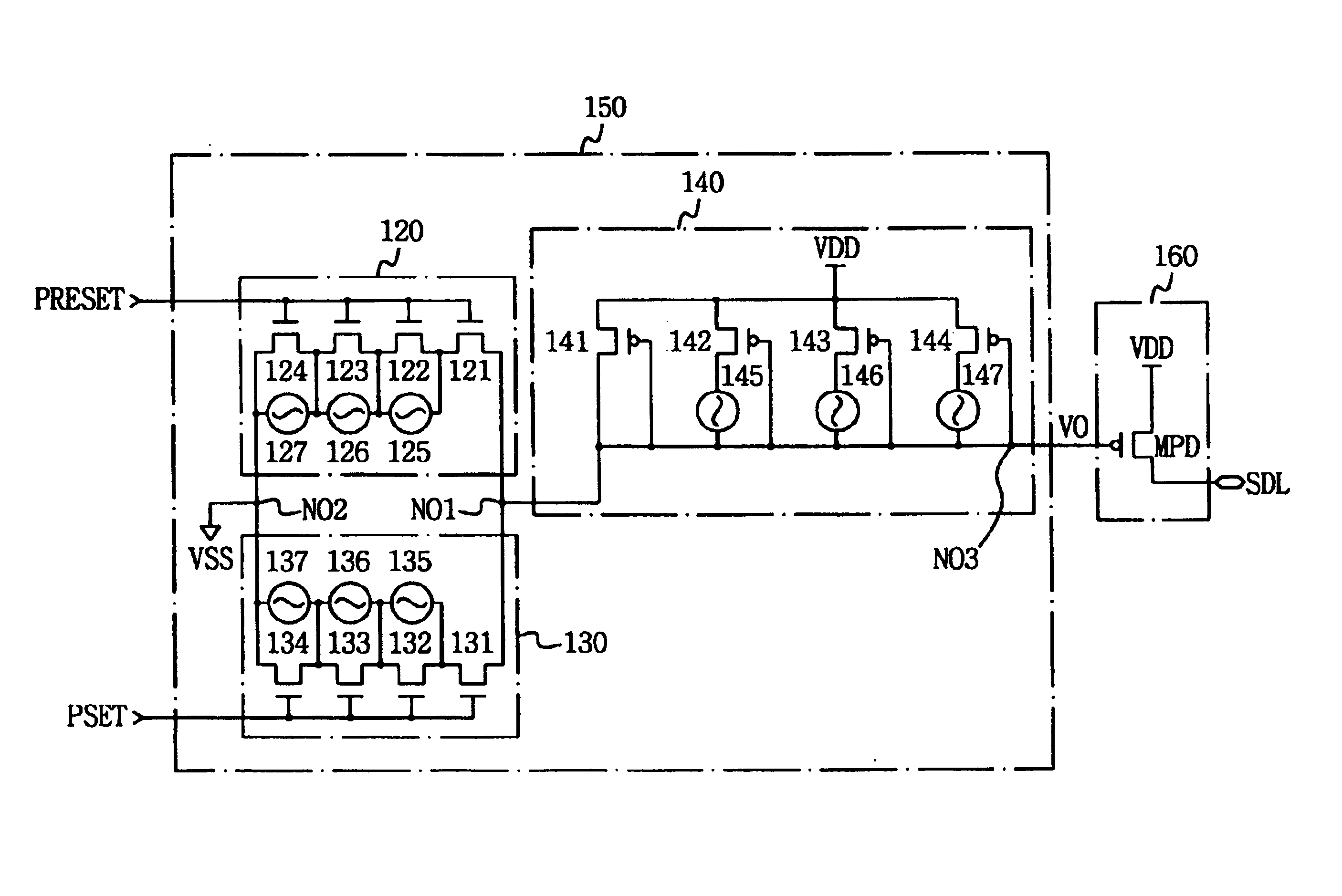
Write driver circuit in phase change memory device and method for applying write current
ActiveUS6928022B2Maximize reliabilityReduce the voltage levelSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDriver circuitPhase-change memory
A write driver circuit including a plurality of programmable fuses for a phase change memory device in which a write operation is correctly performed even in the case where a current output shift in a write current generation circuit; or in the case where a phase change memory cell having a phase change property shift due to an external factor or due a process change. The write driver circuit includes a write current control unit for outputting a first or second level of voltage selected, by selecting one of a first or second programmable current path, based on whether a first or second selection pulse signal is applied; and a current driving unit for generating a write current controlled by the output voltage of the write current control unit. Each of the first and second programmable current paths includes fuses that can be programmed to adjust their resistance to adjust the respective selected output voltage to compensate for the current output shift in the write current generation circuit or for the phase change memory cell having the phase change property shift.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
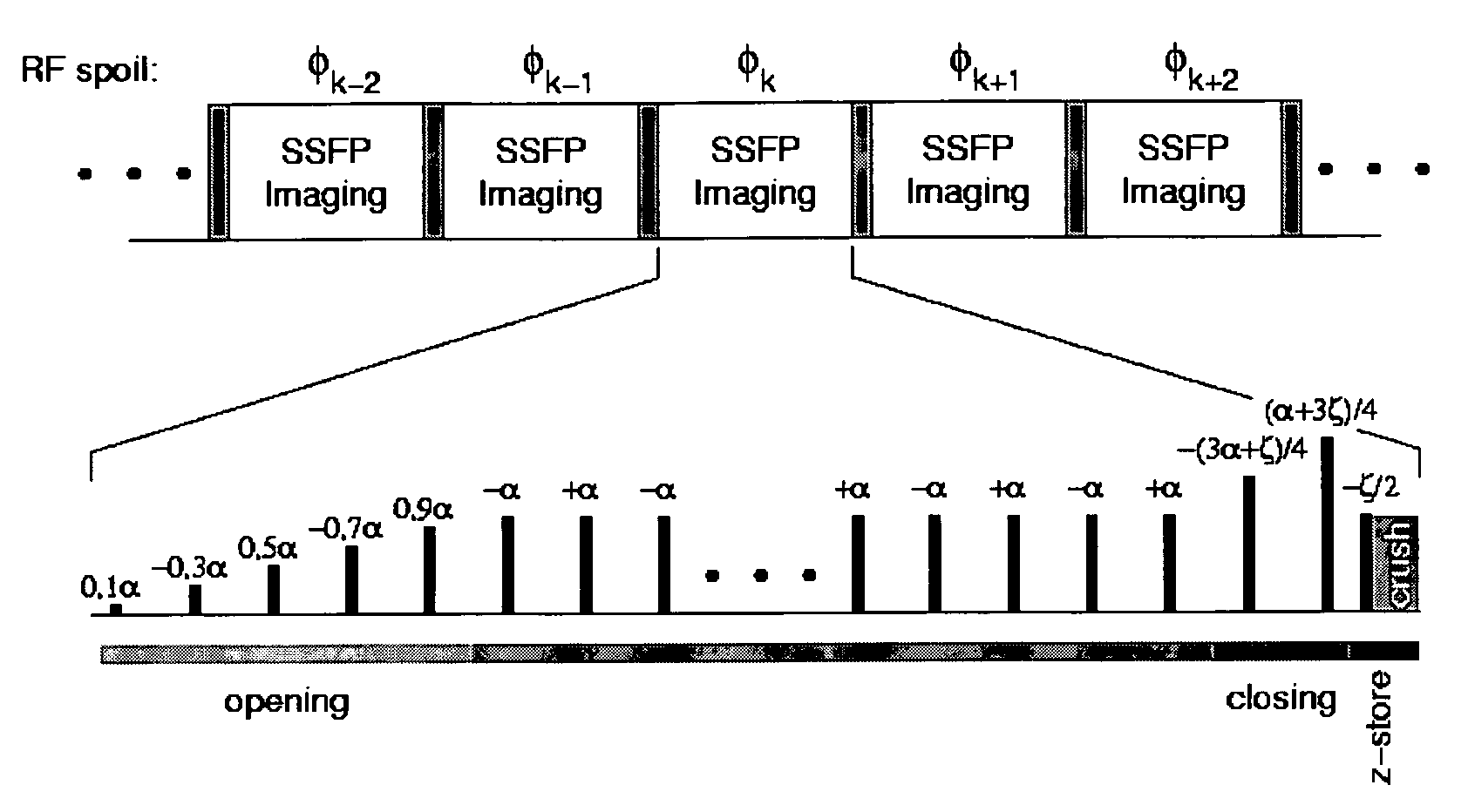
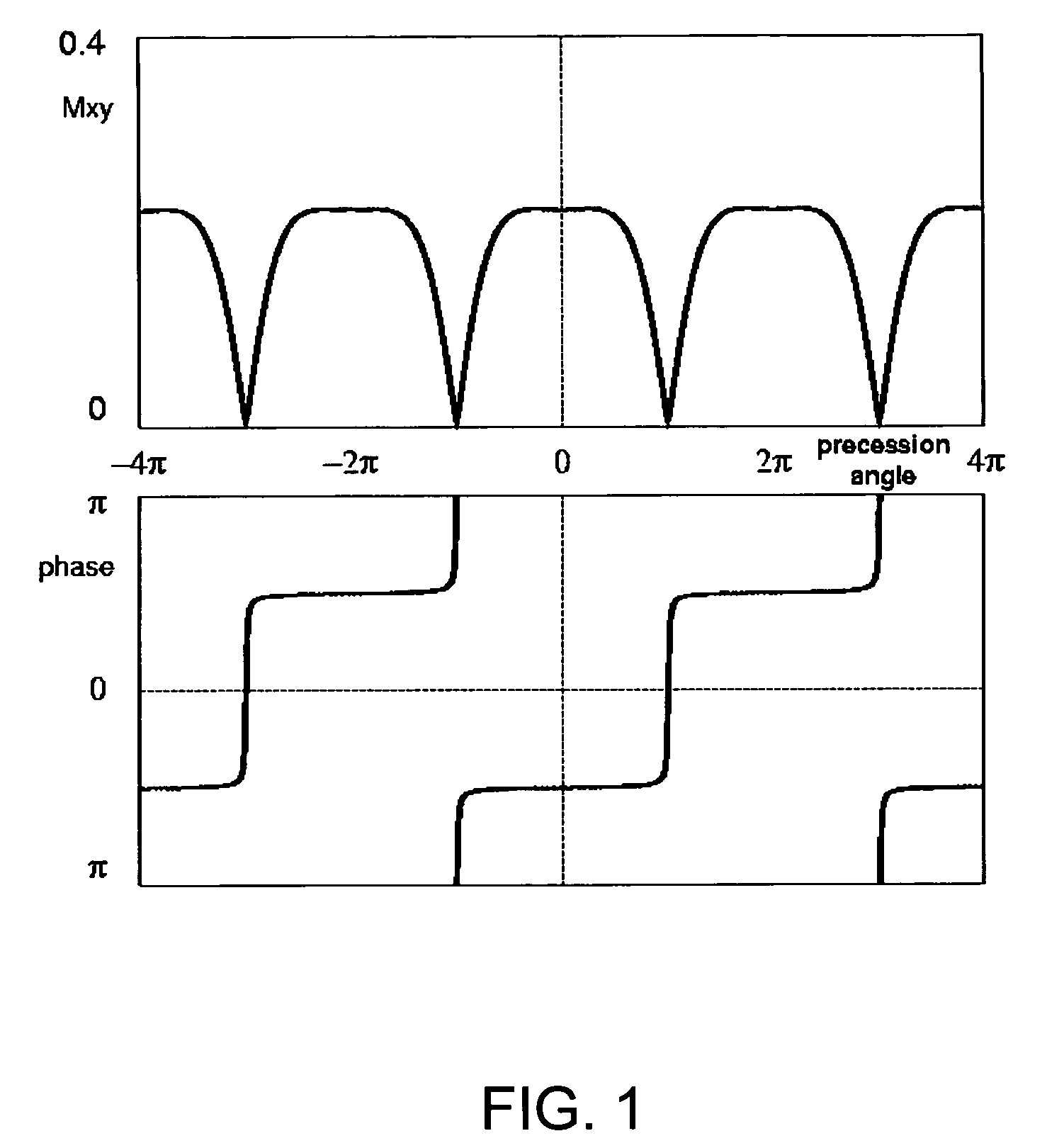
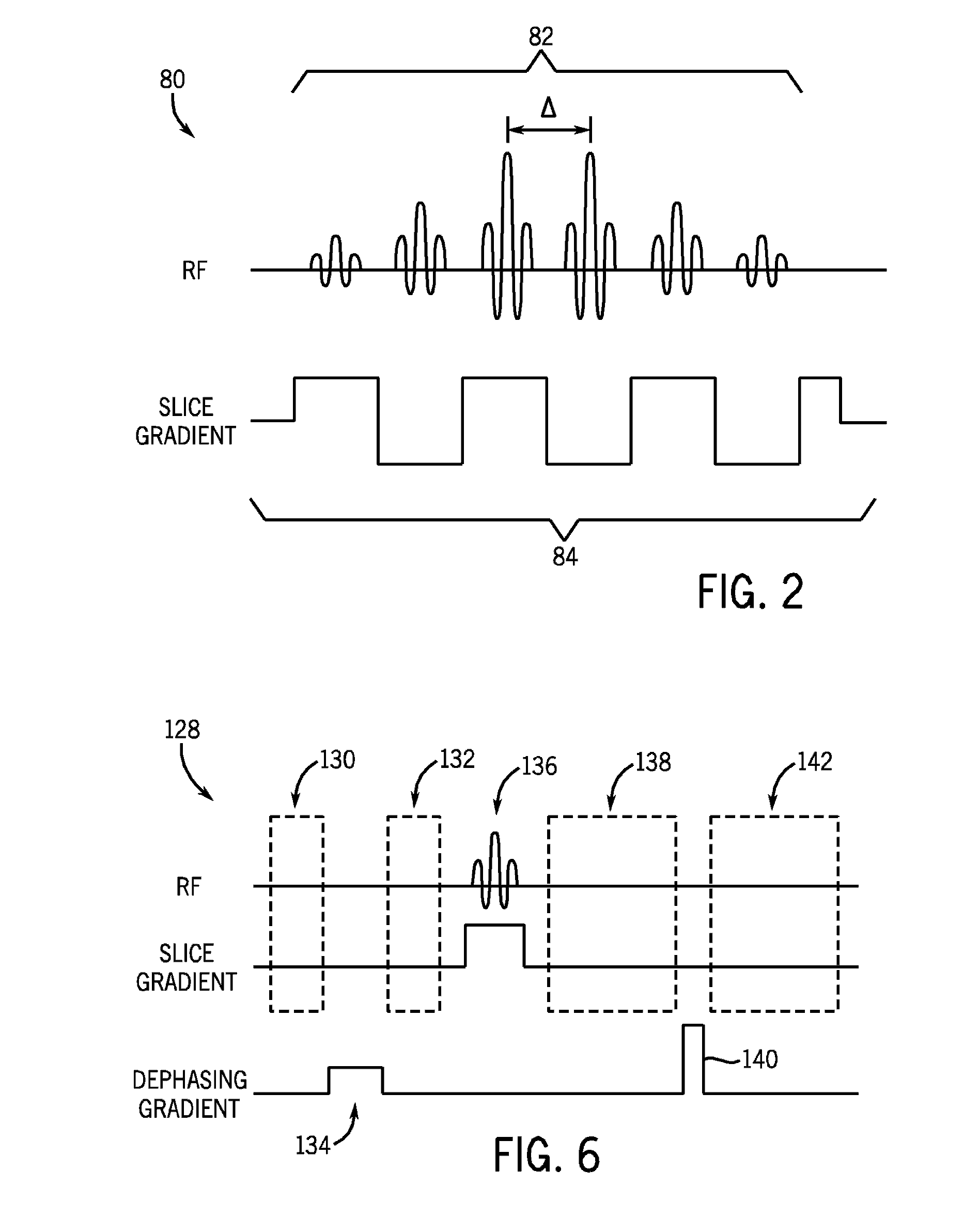
Spectrally selective suppression with steady-state free precession
ActiveUS7253620B1Little disturbanceEnhanced inhibitory effectMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTransverse magnetizationCine imaging
A method that exploits the intrinsic selectivity of steady-state free precession (SSFP) to perform spectral suppression is disclosed. Such a method avoids the need to incorporate additional spectrally selective pulse sequence elements. The scheme is based on breaking the FISP imaging sequence into short trains having, for example, 8–64 RF pulses. At the moment of echo formation (i.e., TE=TR / 2) after the last full RF pulse of the train, water signal is z-stored. Residual transverse magnetization, which include isochromats phase-opposed to the on-resonance water, is gradient crushed and RF spoiled. The stored magnetization is subsequently re-excited with little disturbance to the on-resonance steady-state water signal. The additional time required to perform the steady-state interruption is typically as little as a single TR, minimally affecting the efficiency of the imaging process. The sequence can be employed repetitively, greatly reducing the amplitude of fat signals throughout a real-time or cine imaging process.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
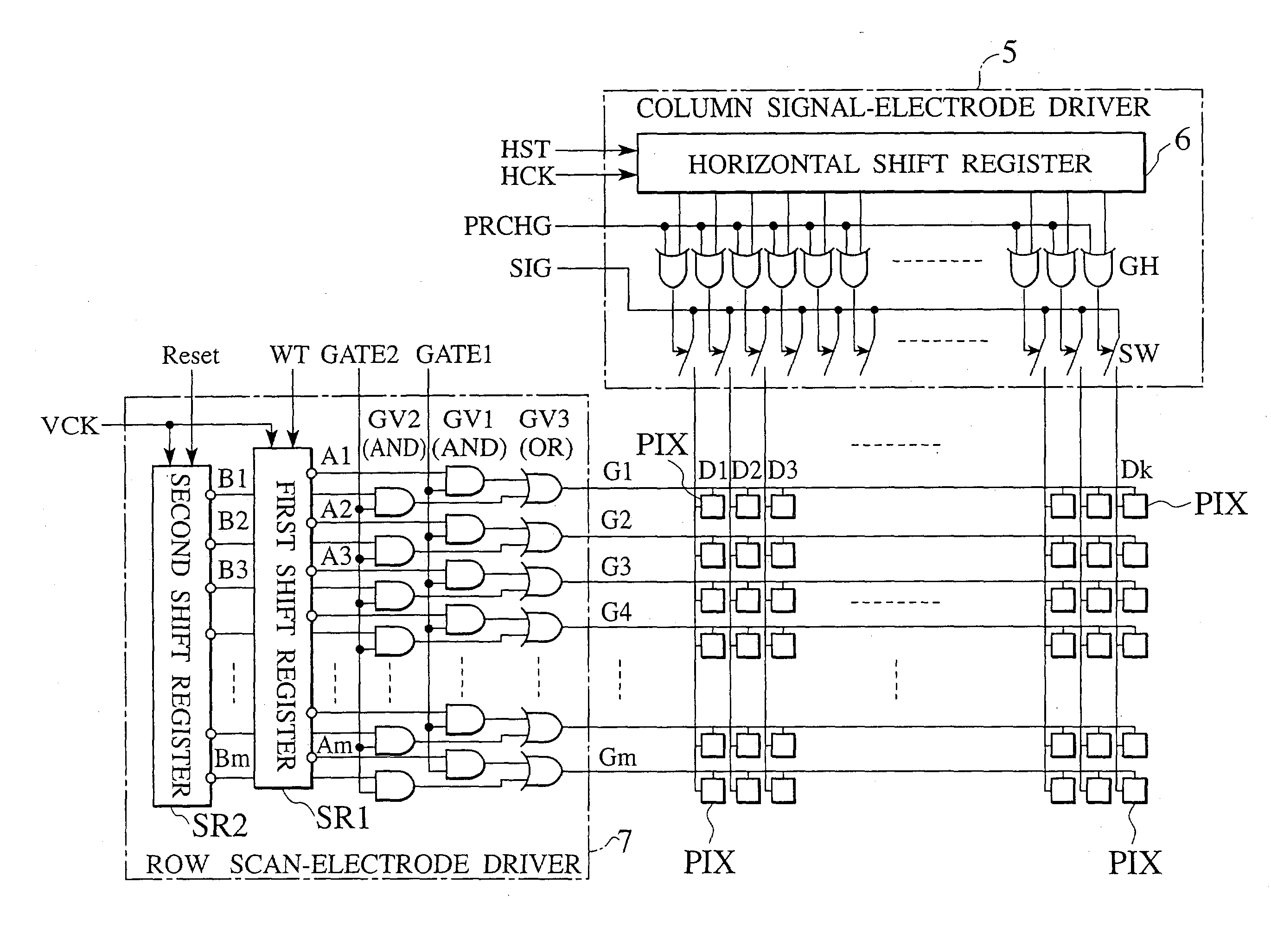
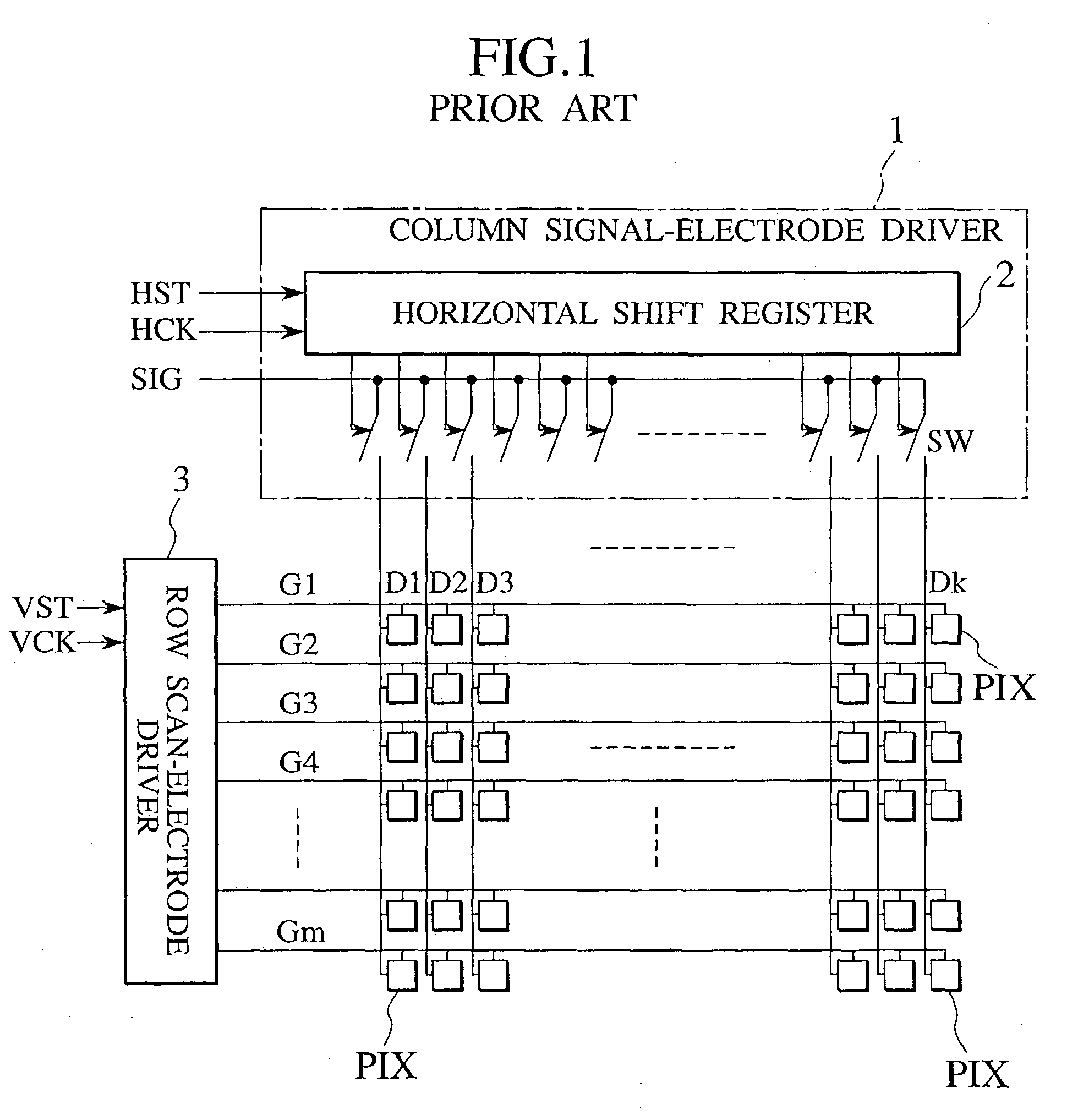
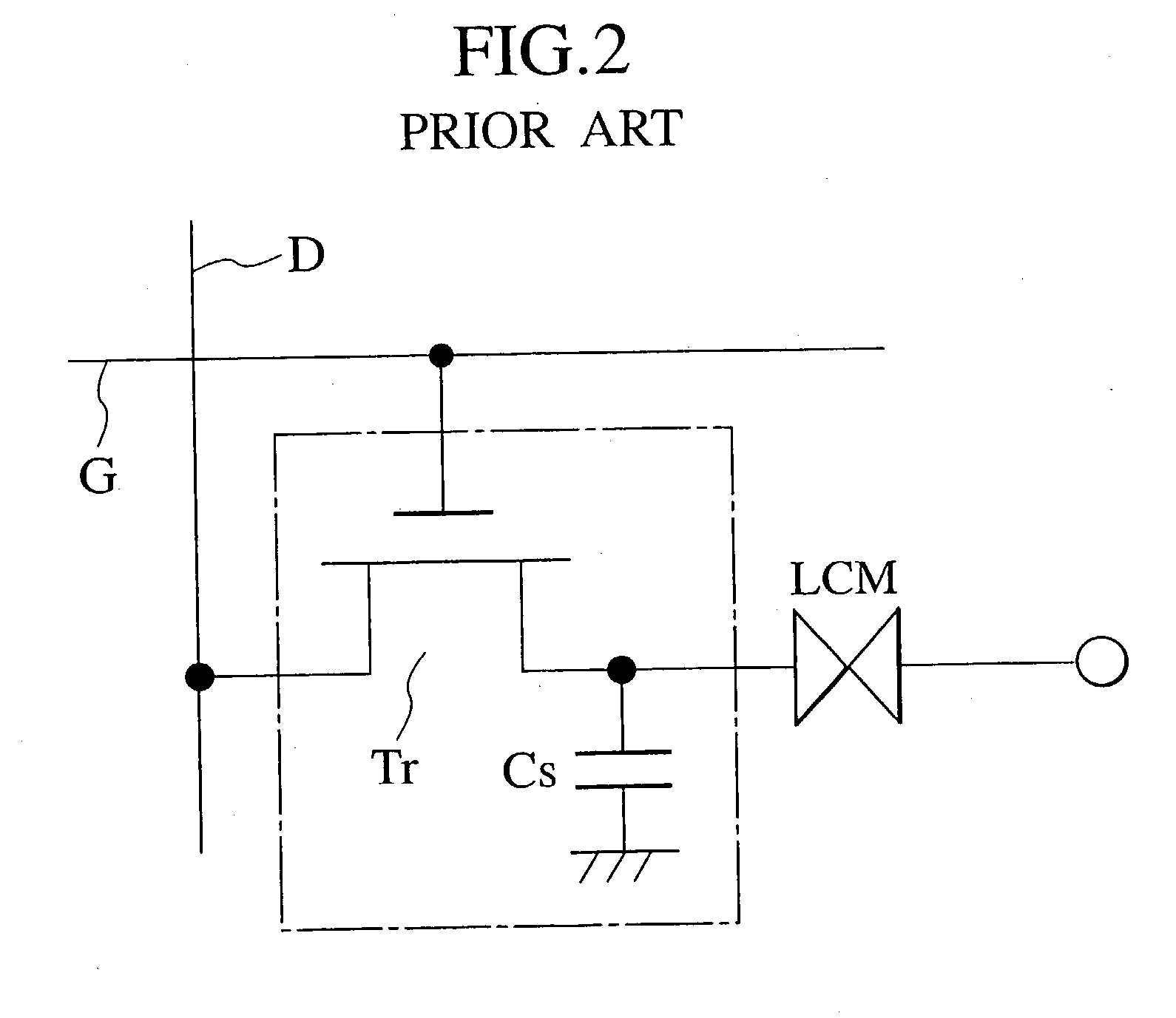
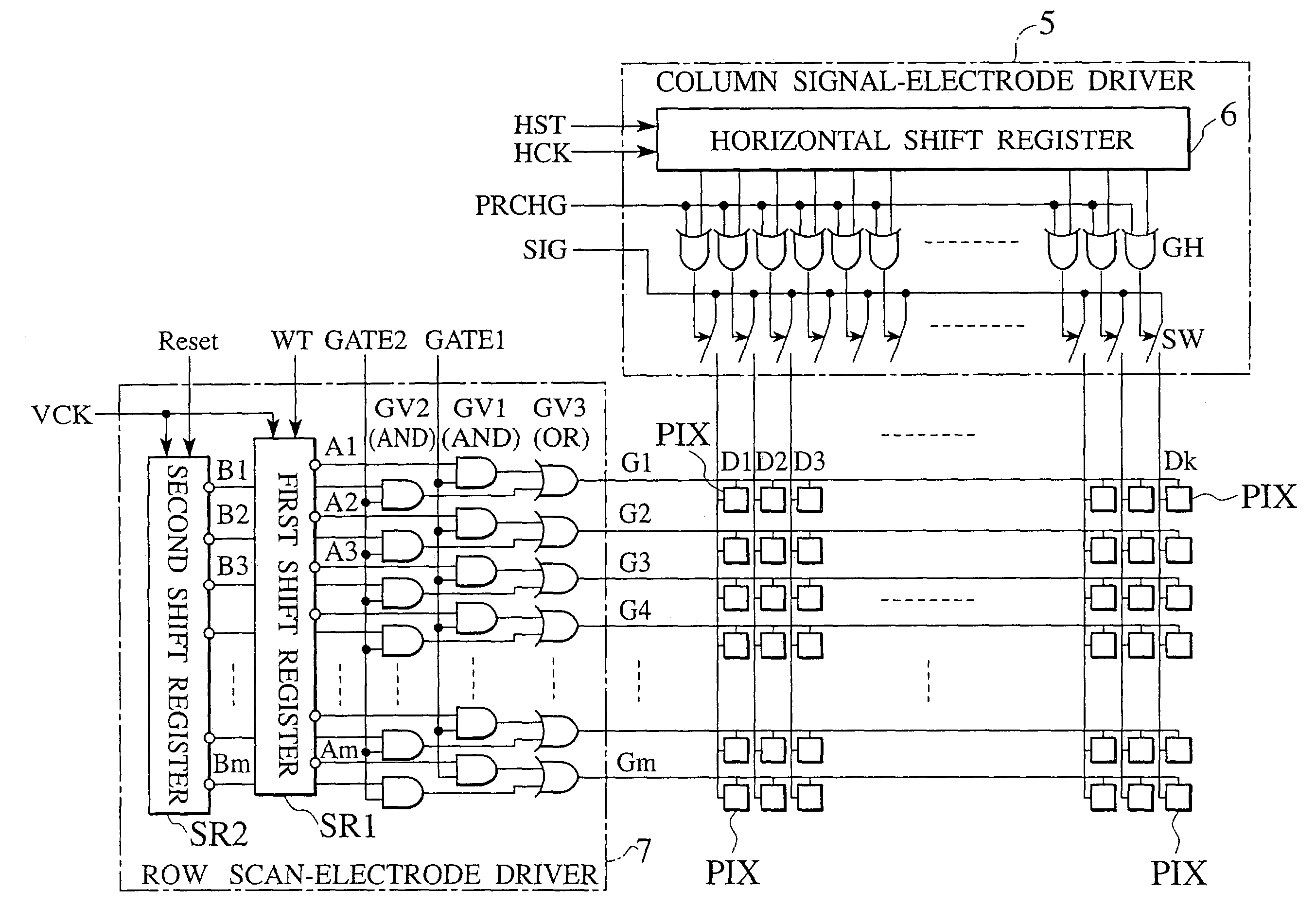
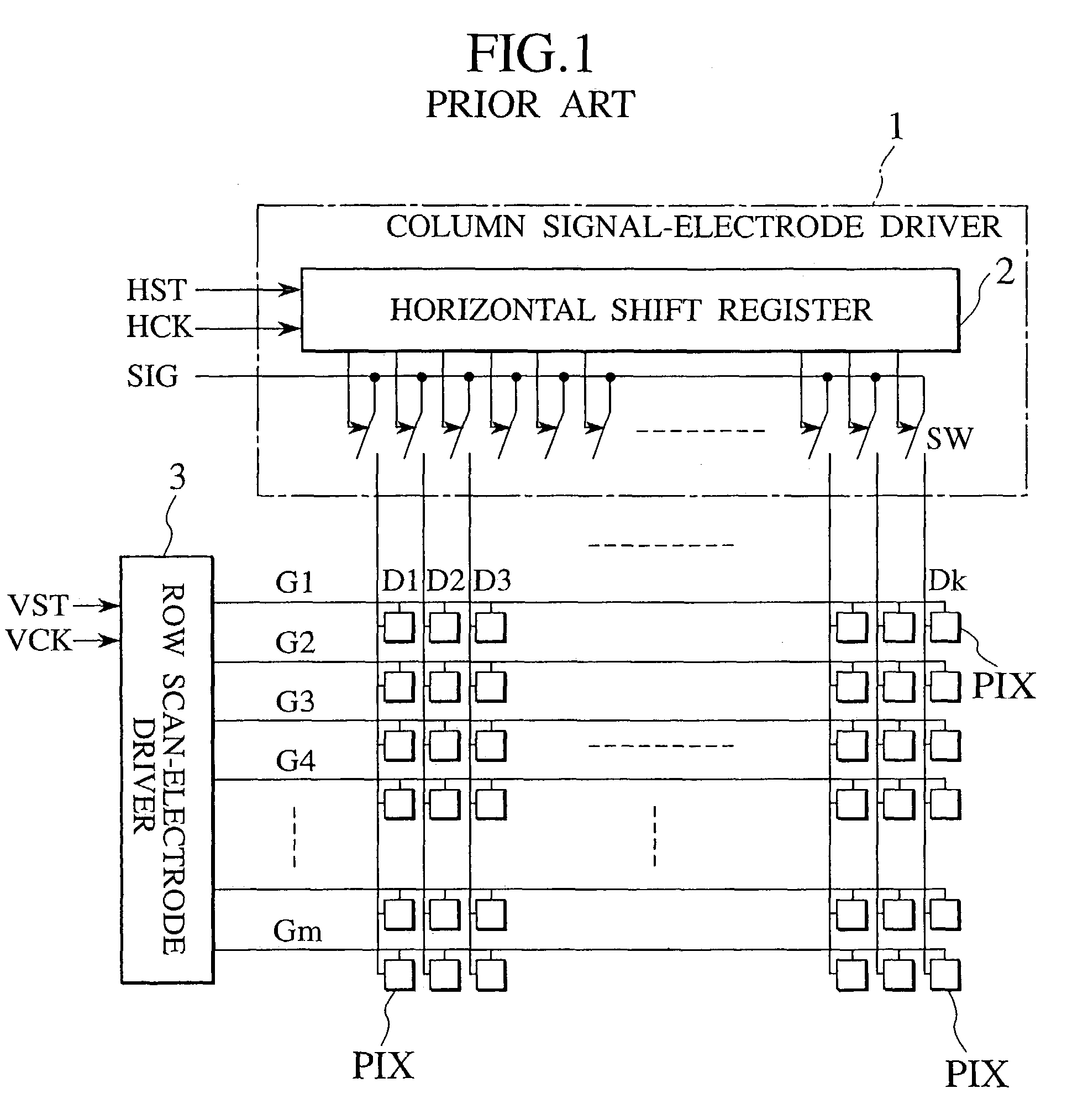
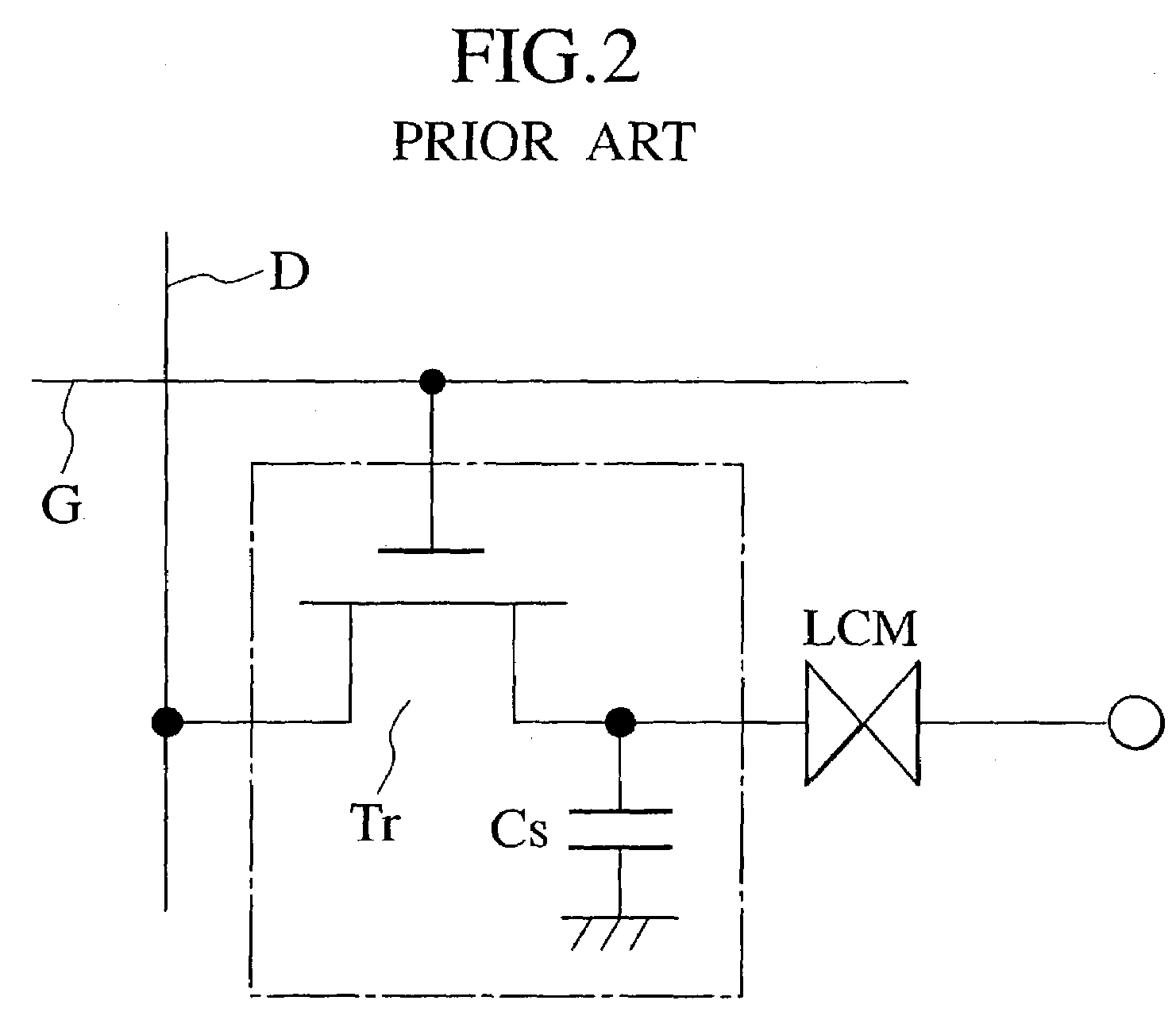
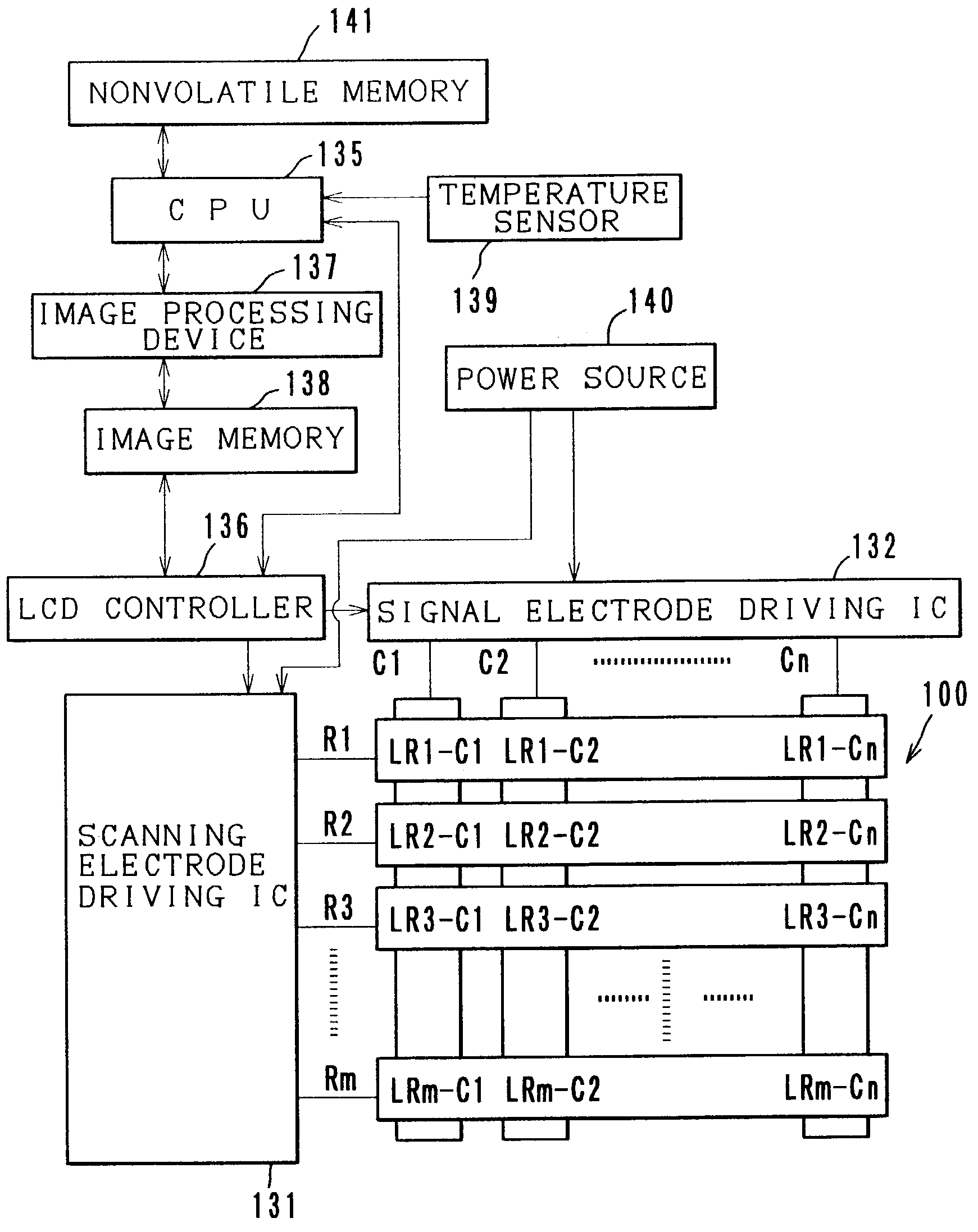
Active matrix liquid crystal display
An active matrix LCD defines a display signal period and a reset period in each vertical scan period. The display signal period is a period to write and hold display signals in pixels in response to a row select pulse generated from an output pulse of a first shift register (SR1). The reset period is a period to write and hold a reset voltage in the pixels in response to a row select pulse generated from an output pulse of a second shift register (SR2). The ratio of the display signal period to the reset period is adjustable in units of horizontal scan time by changing the number "n" of horizontal scan periods to be passed between the time when the first shift register receives a scan start signal (WT) and the time when the second shift register receives a scan start signal (Reset).
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP A CORP OF JAPAN
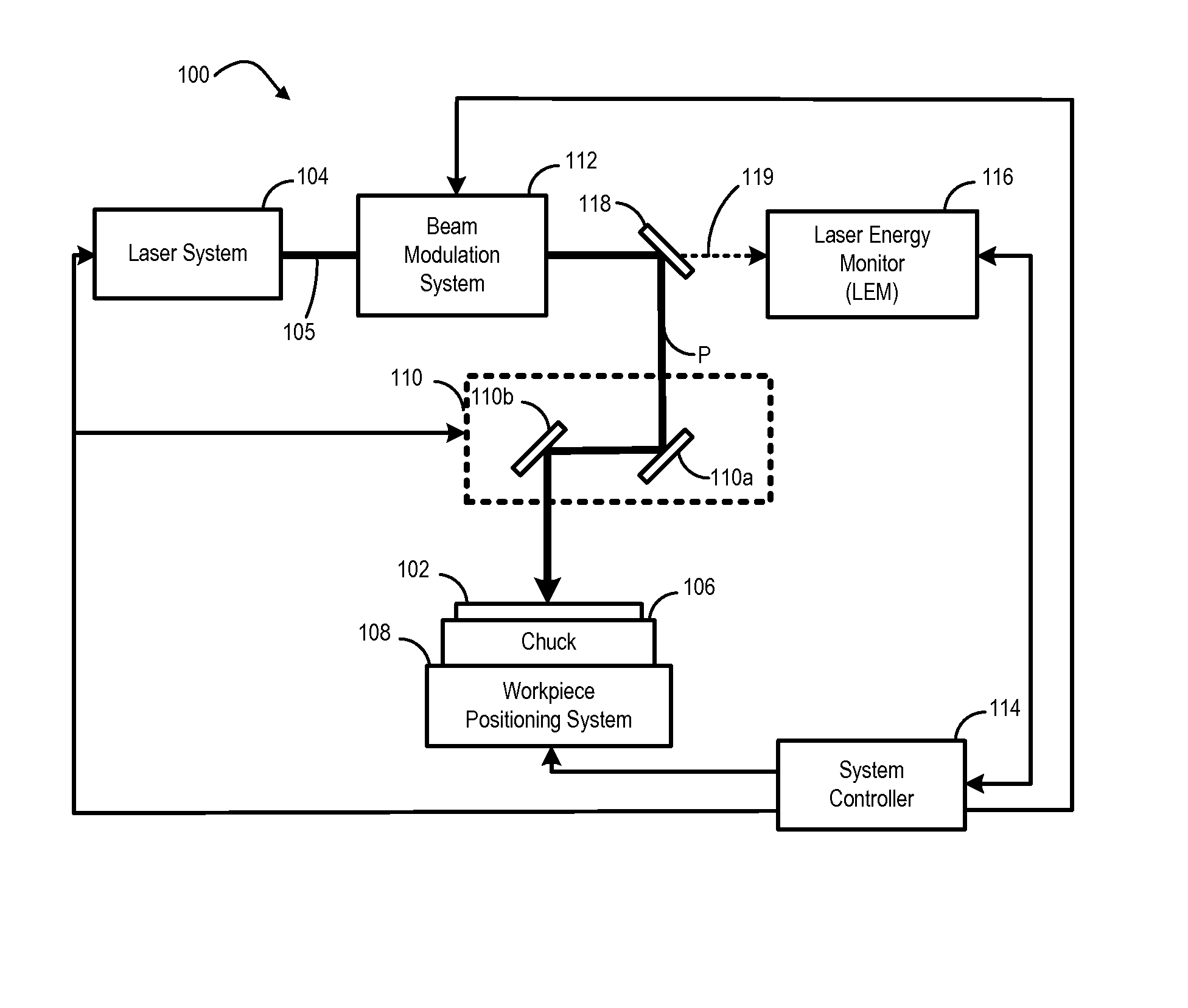
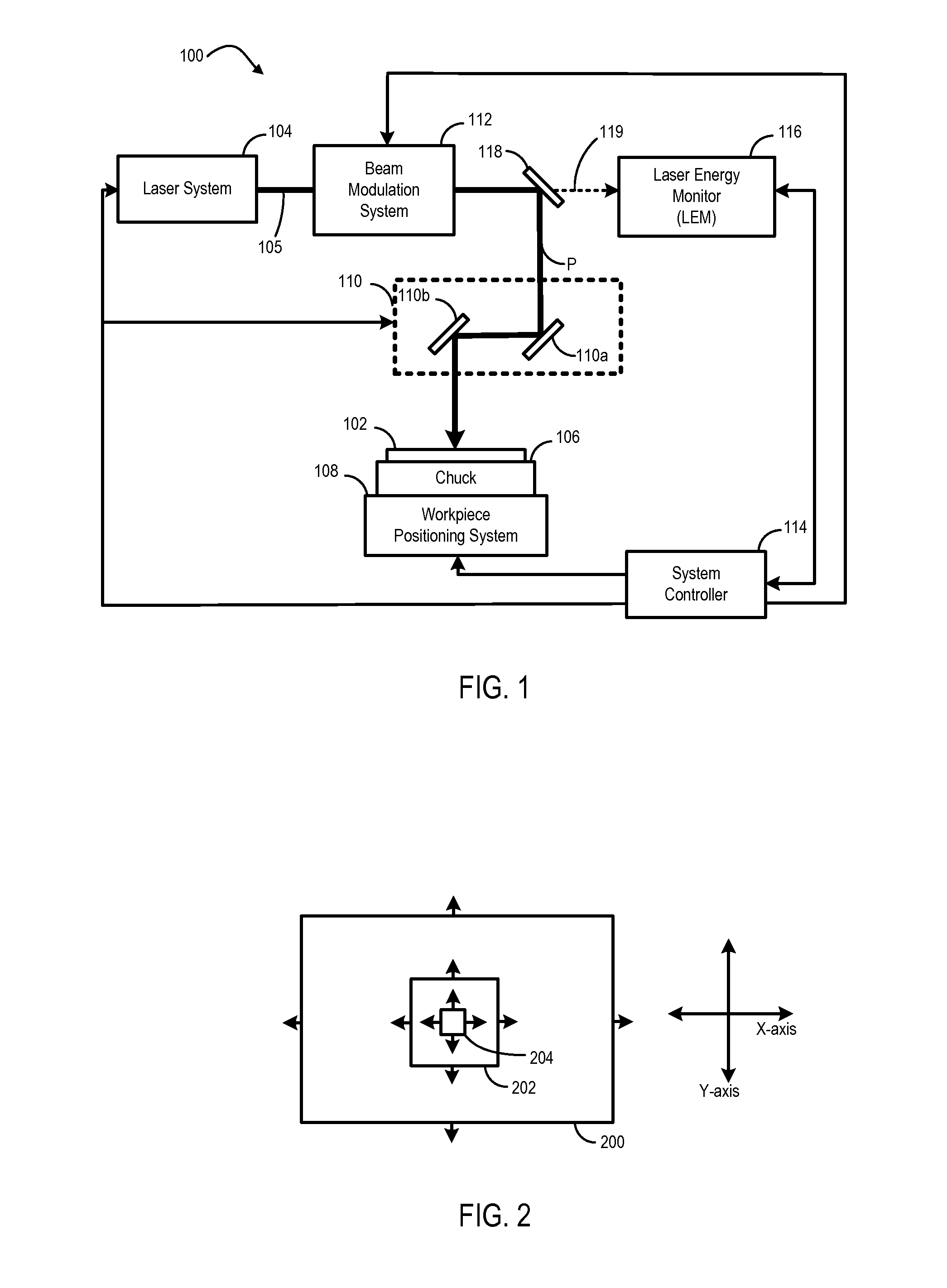
Laser pulse energy control systems and methods
Systems and methods provide laser pulse energy control and / or monitoring. An example laser processing apparatus includes a laser system to generate a beam of laser pulses and a pulse energy control system to adjust the pulse energy of each laser pulse in the beam on a pulse-by-pulse basis. The pulse energy control system includes an open loop feedforward control path that selects a pulse energy transmission value for each laser pulse based on a calibrated transmission curve that maps laser pulse energy as a function of pulse repetition frequency. A laser energy monitor measures the laser pulse energy of each laser pulse in the beam of laser pulses. A power control loop may further adjust the pulse energy of one or more laser pulses in the beam of laser pulses based on feedback from the laser energy monitor.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
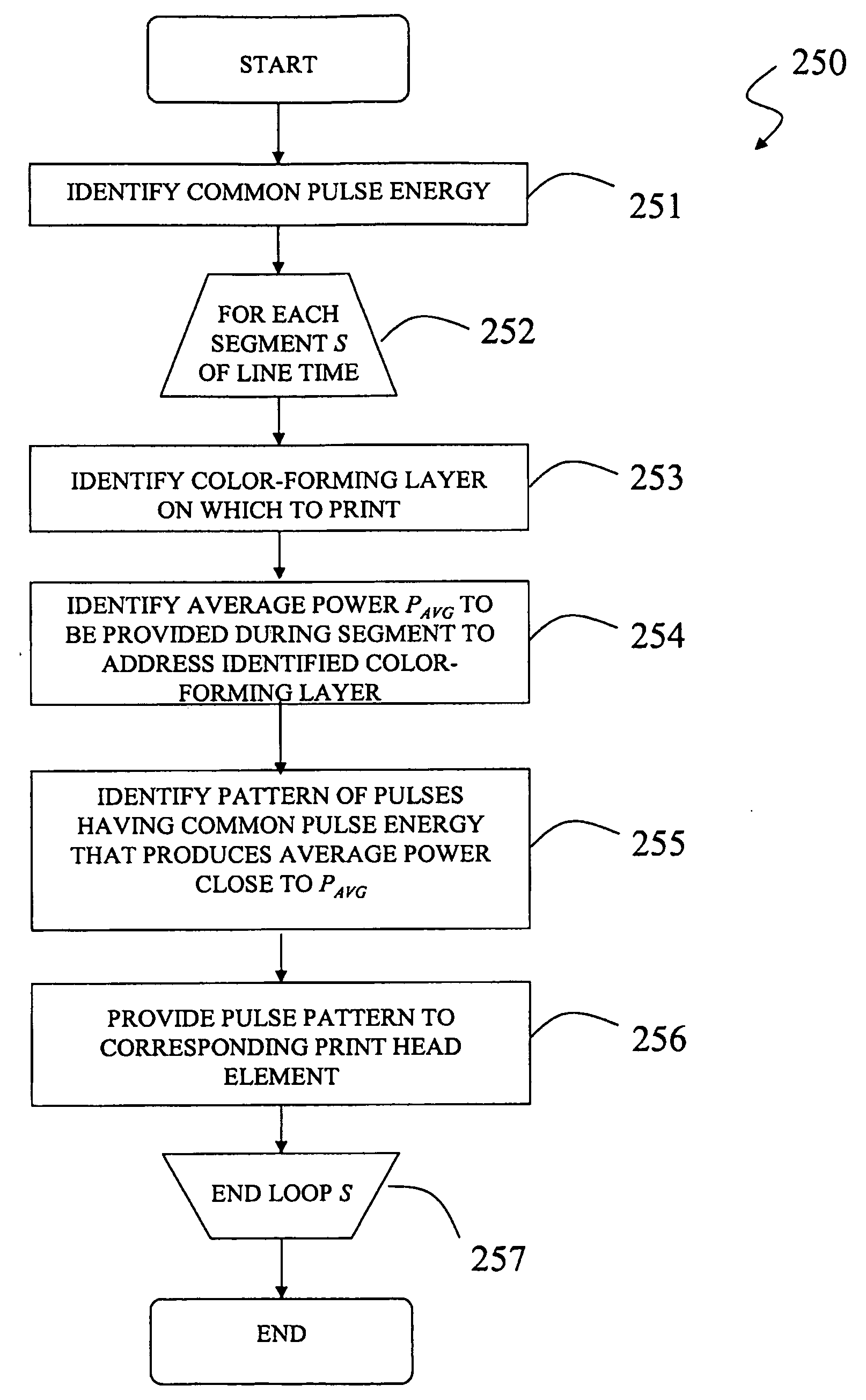
Print head pulsing techniques for multicolor printers
InactiveUS20080238967A1Reduce coincidenceReduce peak power requirementsRecording apparatusOther printing apparatusEngineeringPulse pattern
In one aspect of the invention there is disclosed a multicolor thermal imaging system wherein different heating elements on a thermal print head can print on different color-forming layers of a multicolor thermal imaging member in a single pass. The line-printing time is divided into segments, each of which is divided into a plurality of subintervals. All of the pulses within the segments have the same energy. In one embodiment, every pulse has the same amplitude and duration. Different colors are selected for printing during the different segments by varying the fraction of subintervals that contain pulses. This technique allows multiple colors to be printed using a thermal print head with a single strobe signal line. Pulsing patterns may be chosen to reduce the coincidence of pulses provided to multiple print head elements, thereby reducing the peak power requirements of the print head.
Owner:ZINK IMAGING
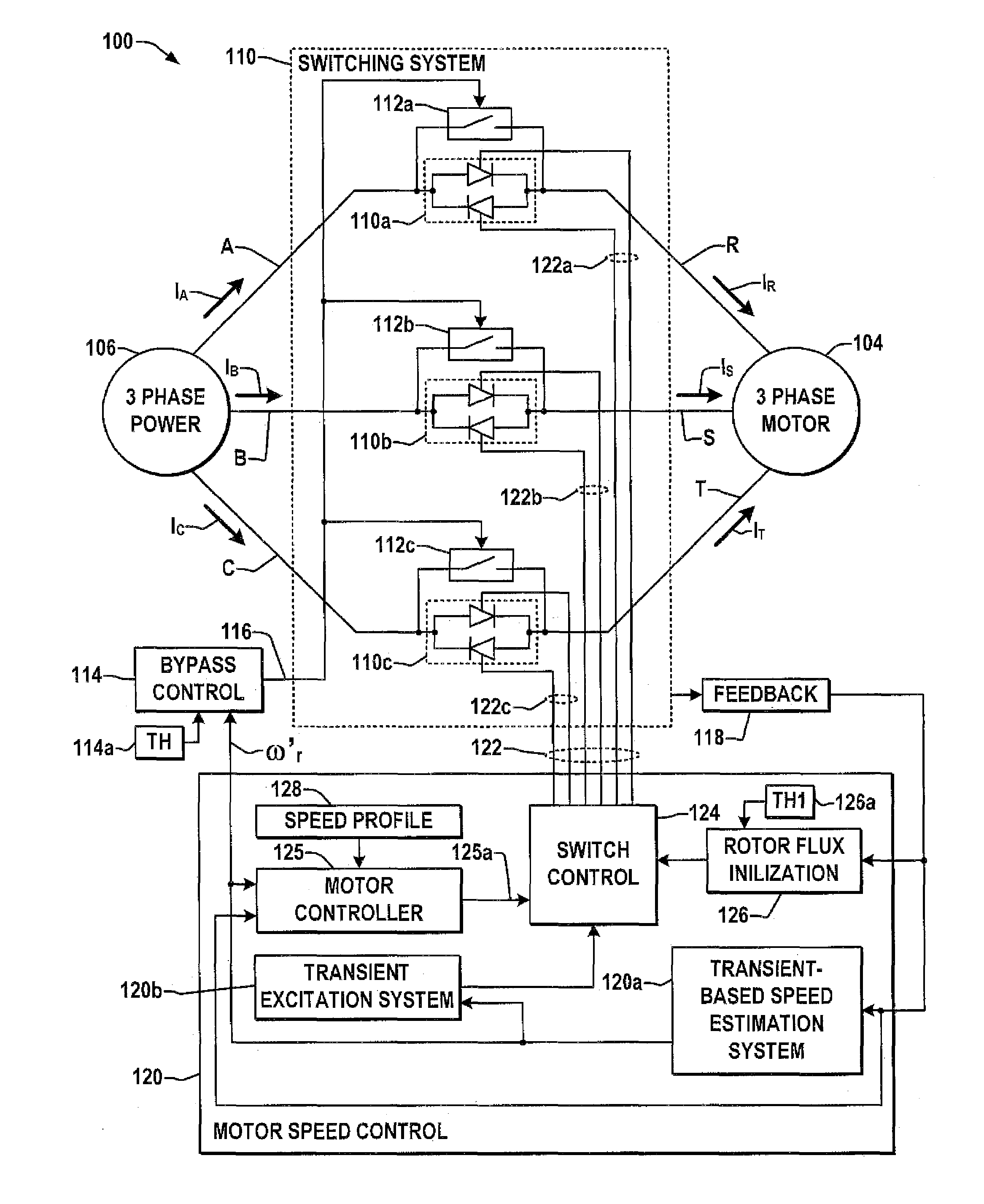
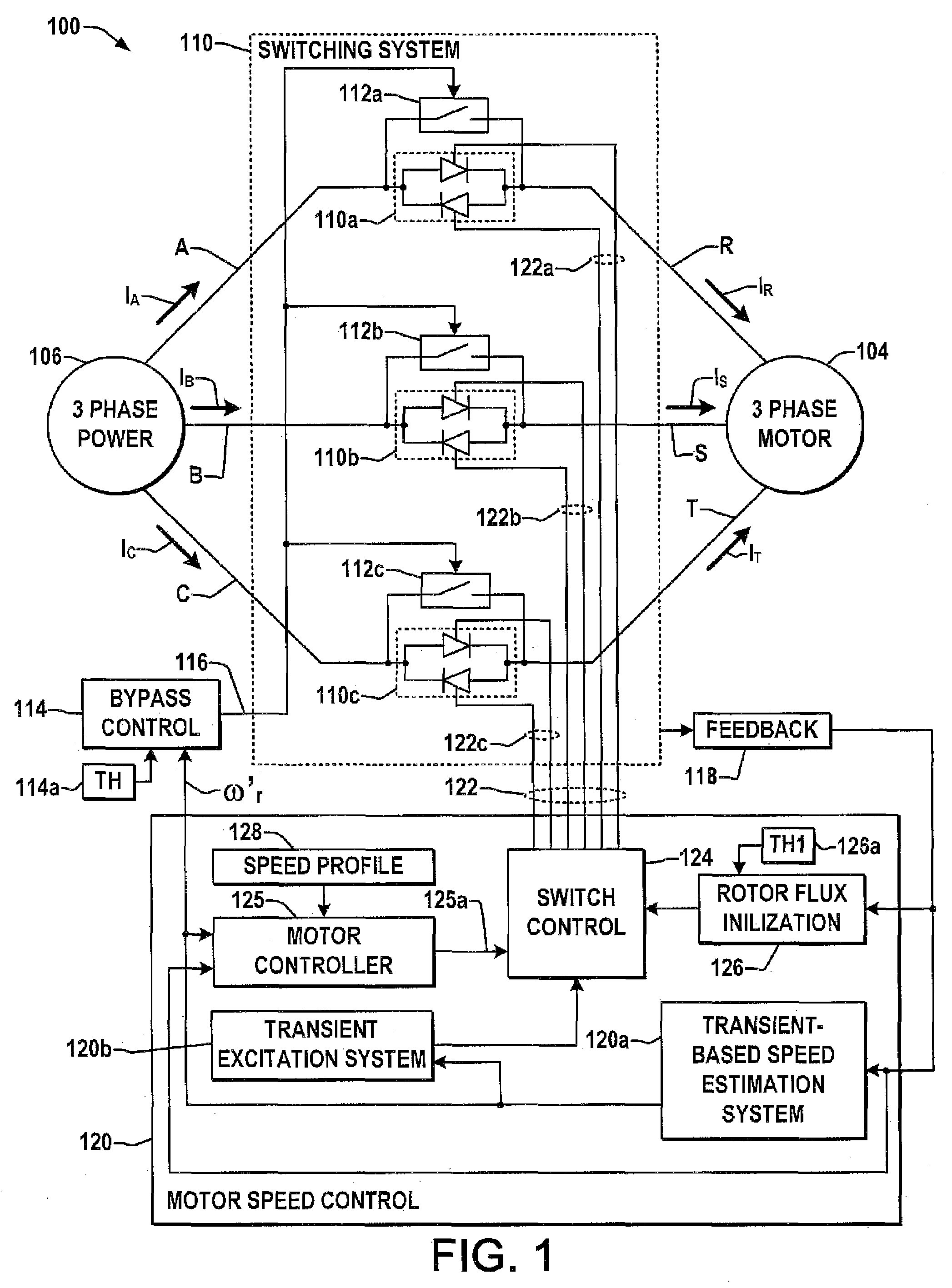
System and method for transient-based motor speed estimation with transient excitation
ActiveUS7227326B1Reduce sensitivityEasy to understandElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersMotor speedPulse stream
AC motor control systems and speed controllers are presented, including a transient-based speed estimation system that provides a rotor speed estimate based on a measured speed-related motor transient signal, and a transient excitation system which selectively modifies at least one switch control signal to excite the measured motor transient. The measured speed-related transient may include a phase error signal, a phase lag signal, a peak current signal, a voltage integral signal, a motor winding voltage signal, a switching device voltage, and a voltage zero crossing signal, and the switching signal modification can comprise removal of select pulse(s) from a switching control pulse stream or selective modification of spacings between pulses to re-excite the motor transient.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
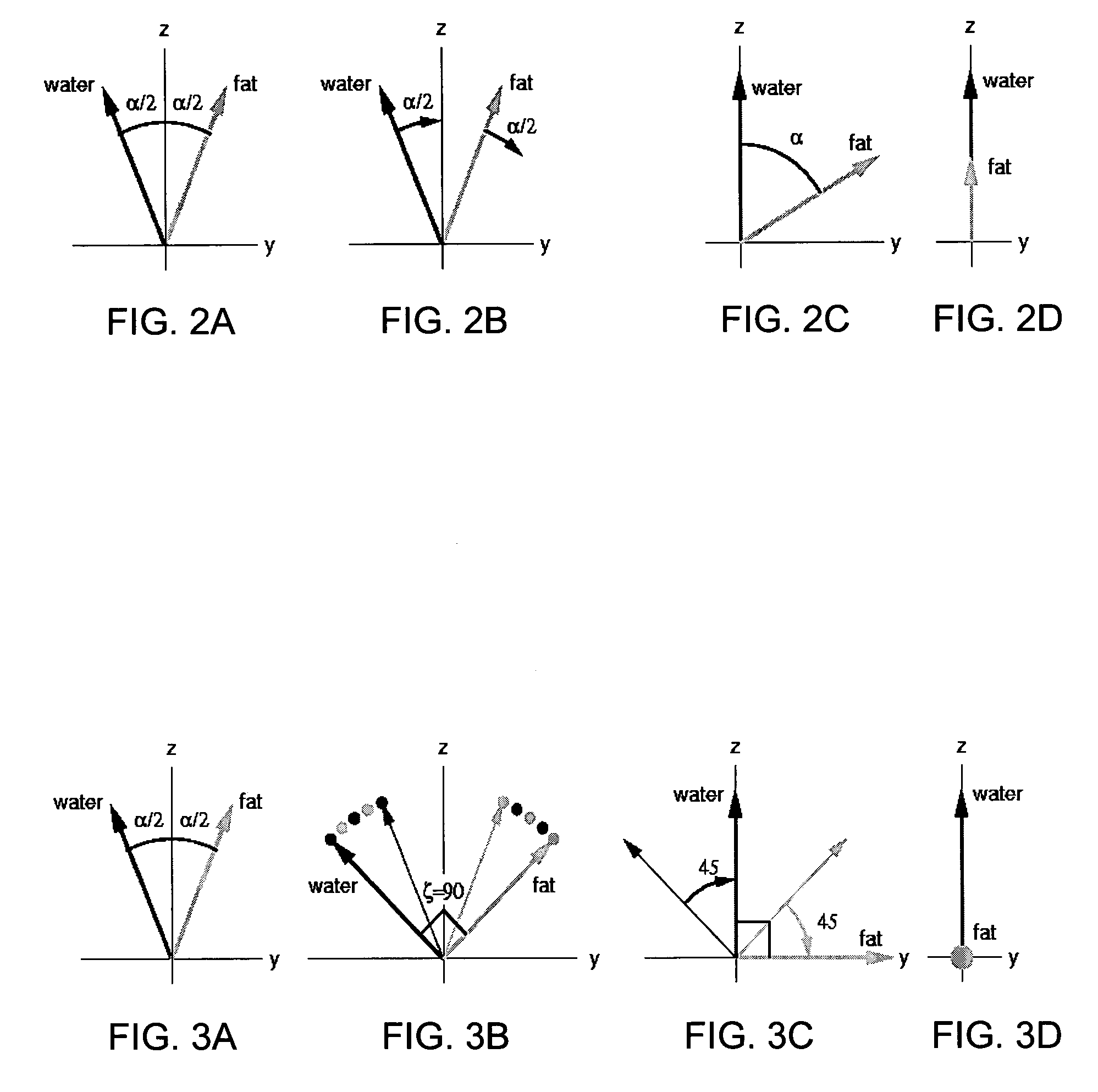
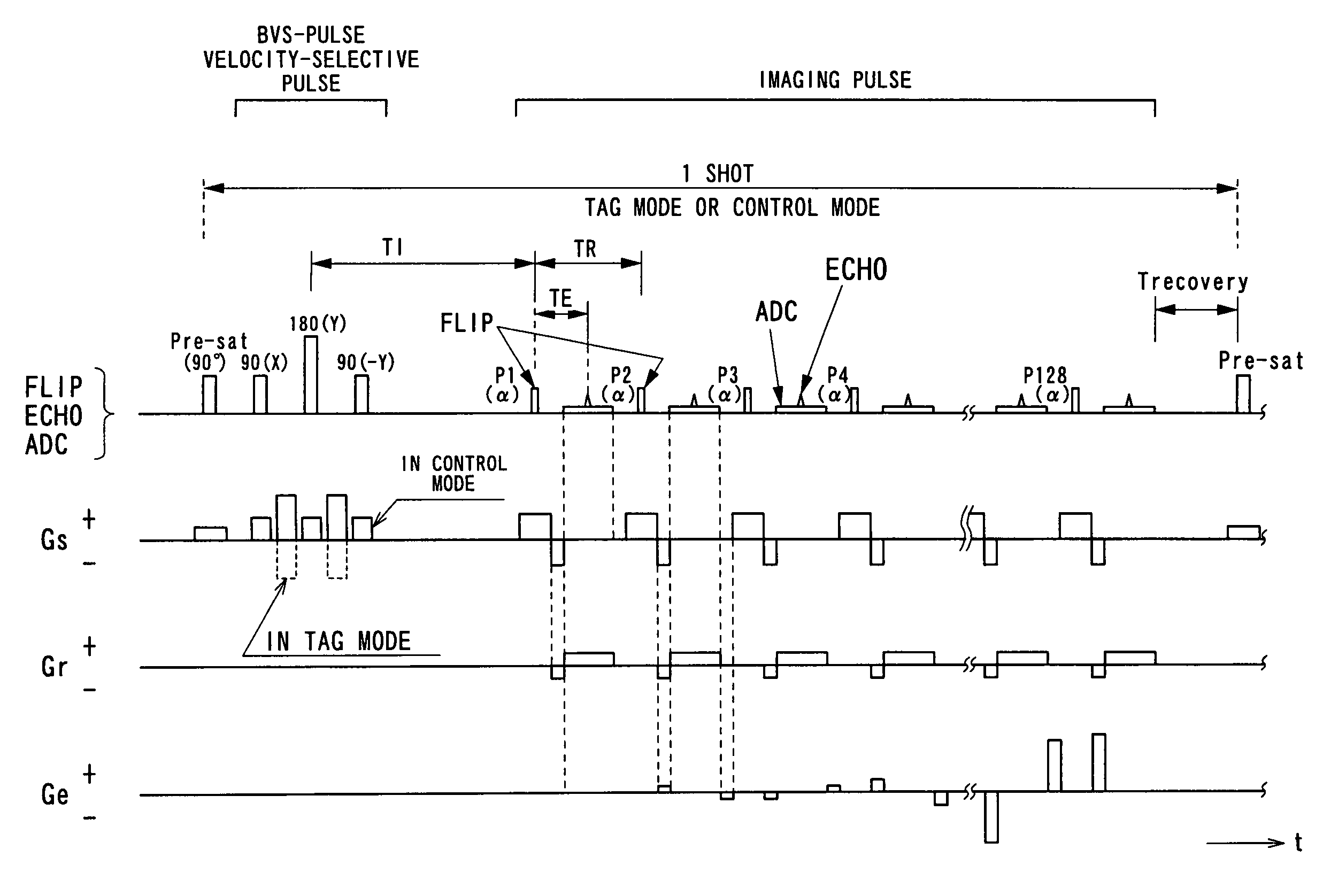
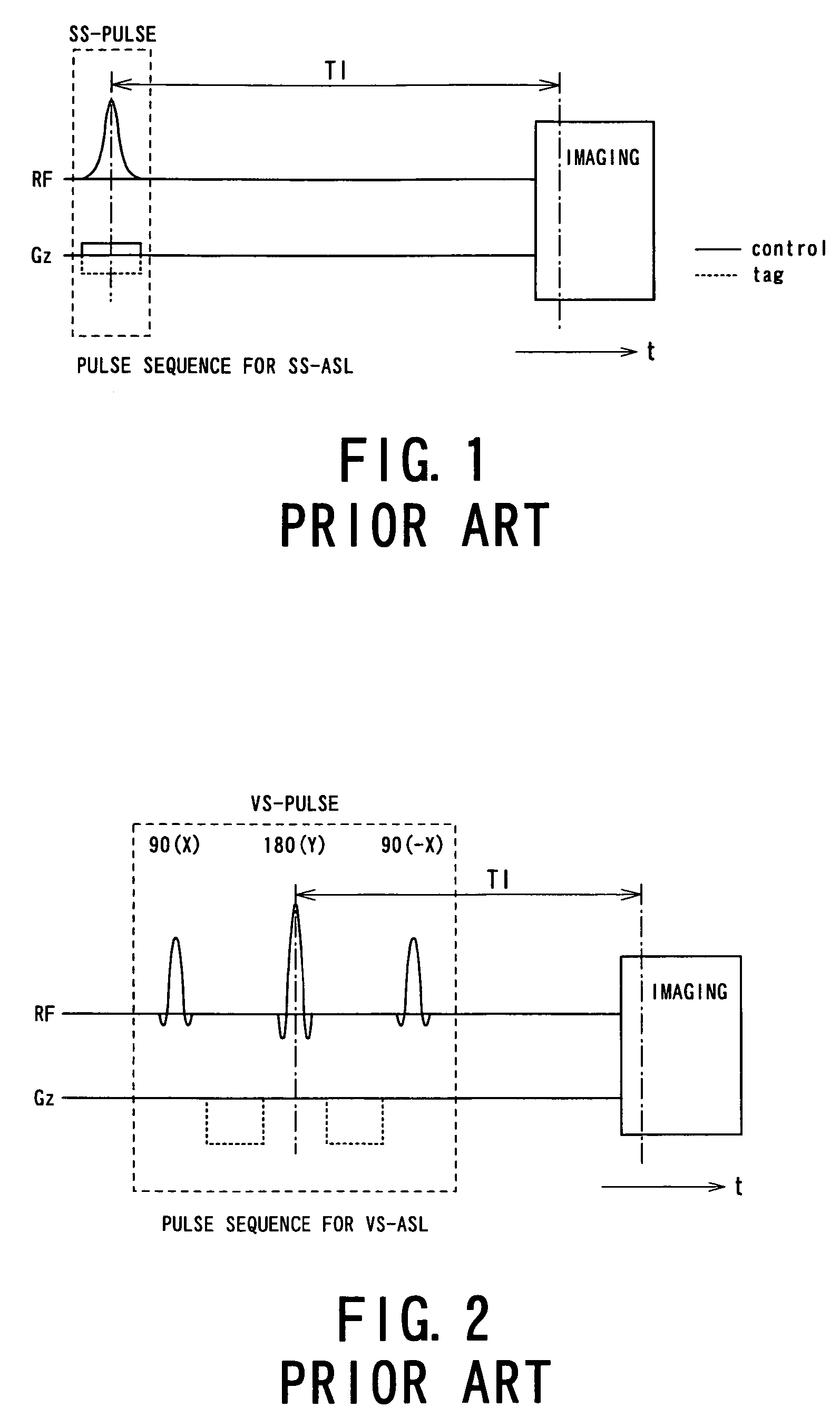
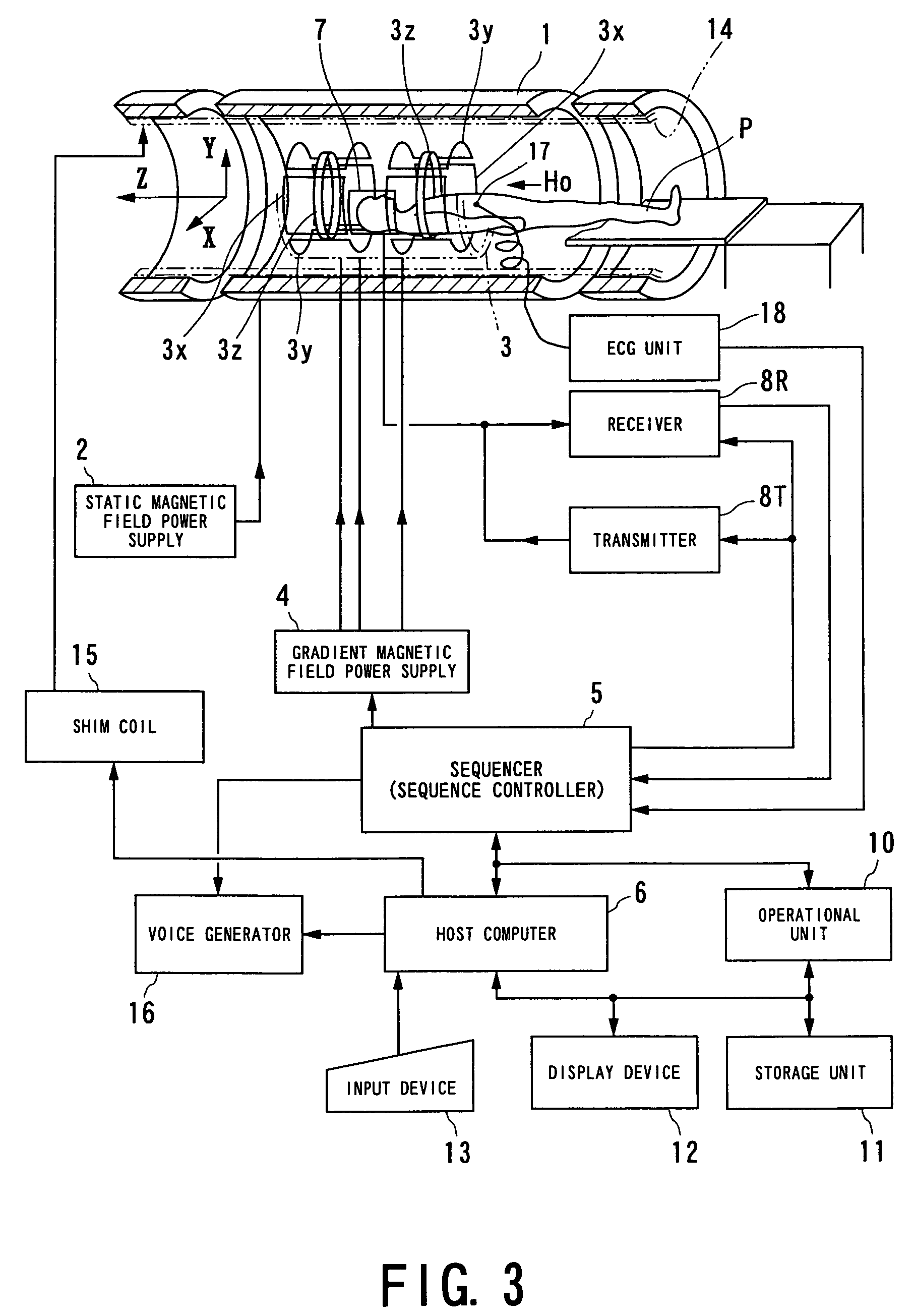
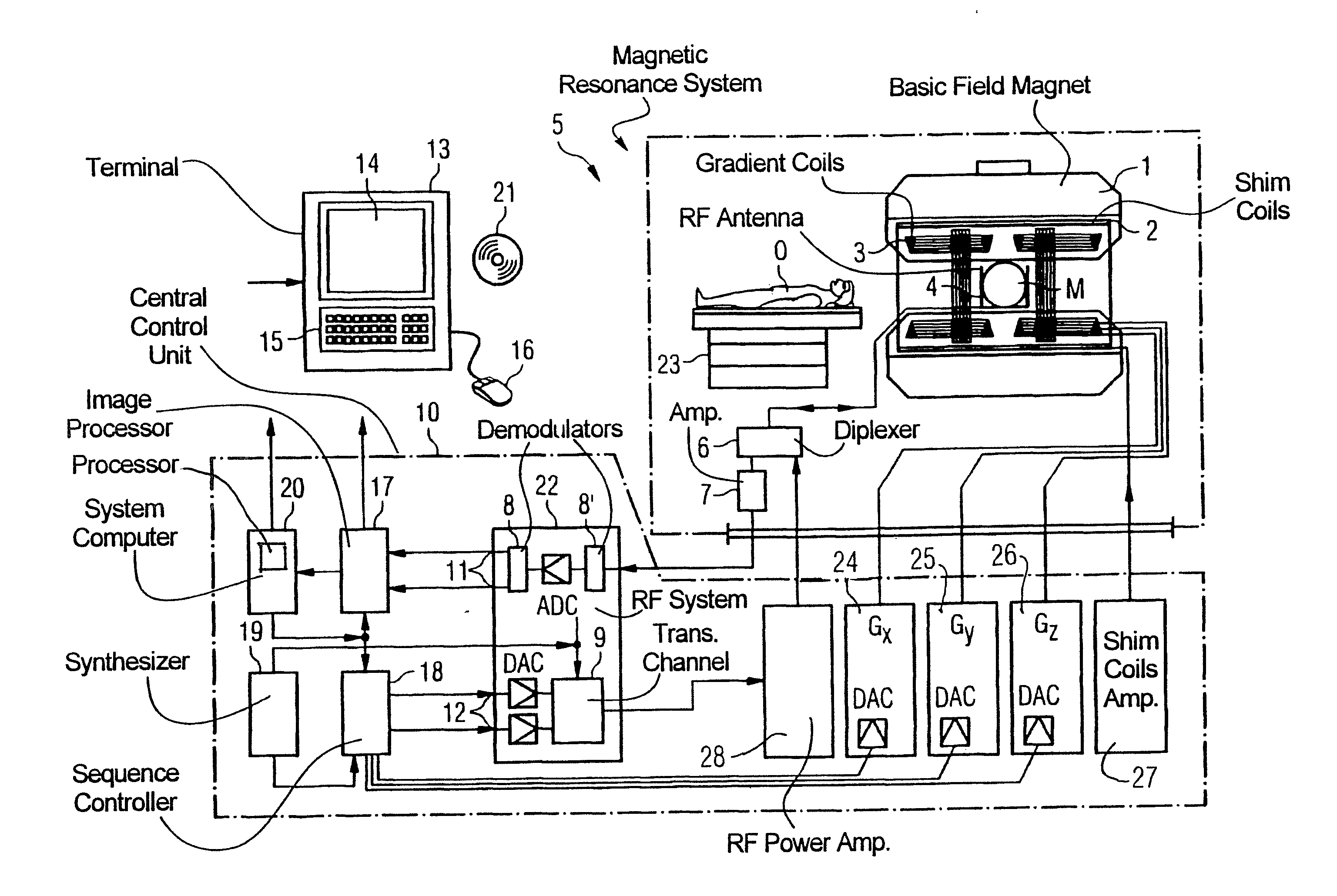
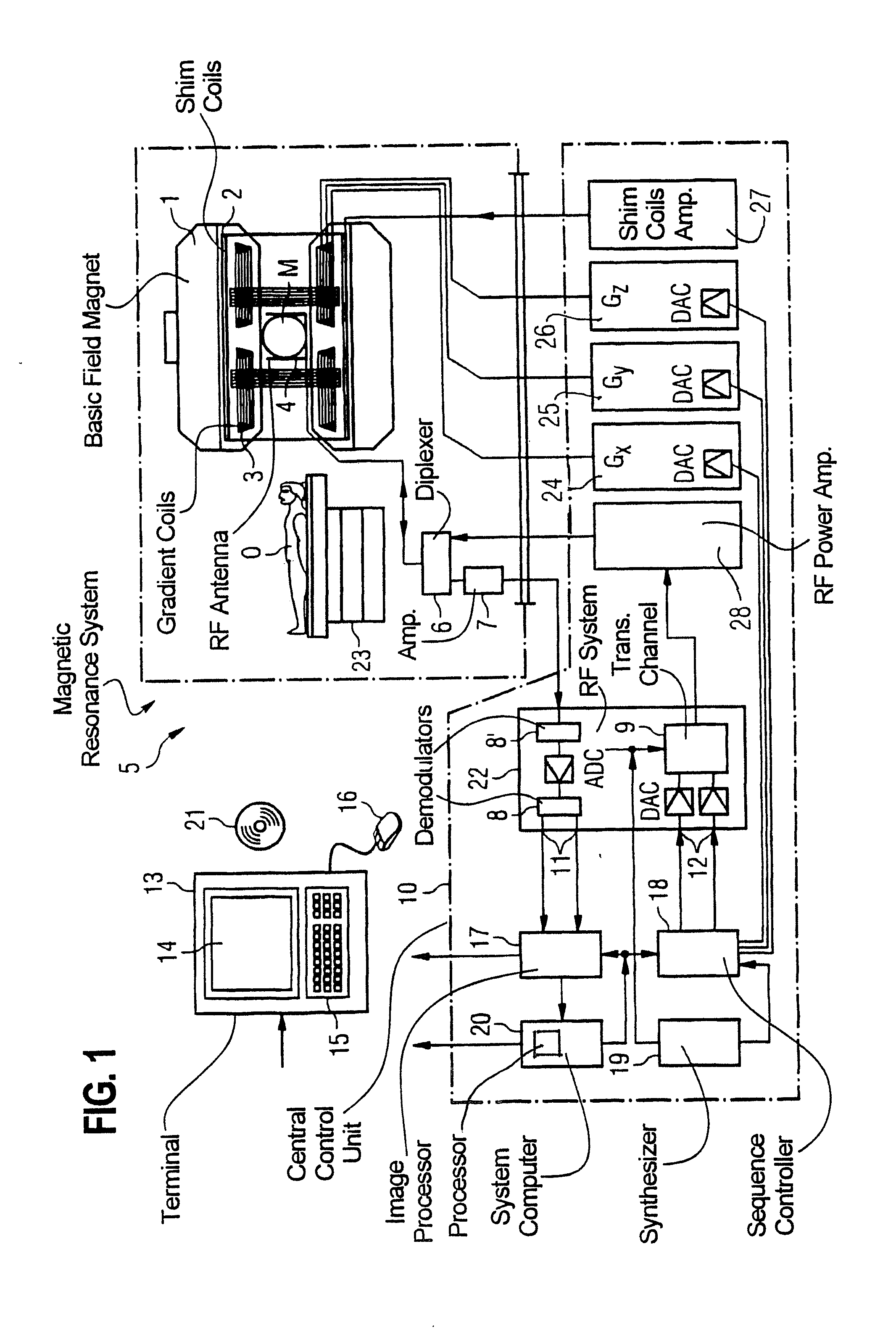
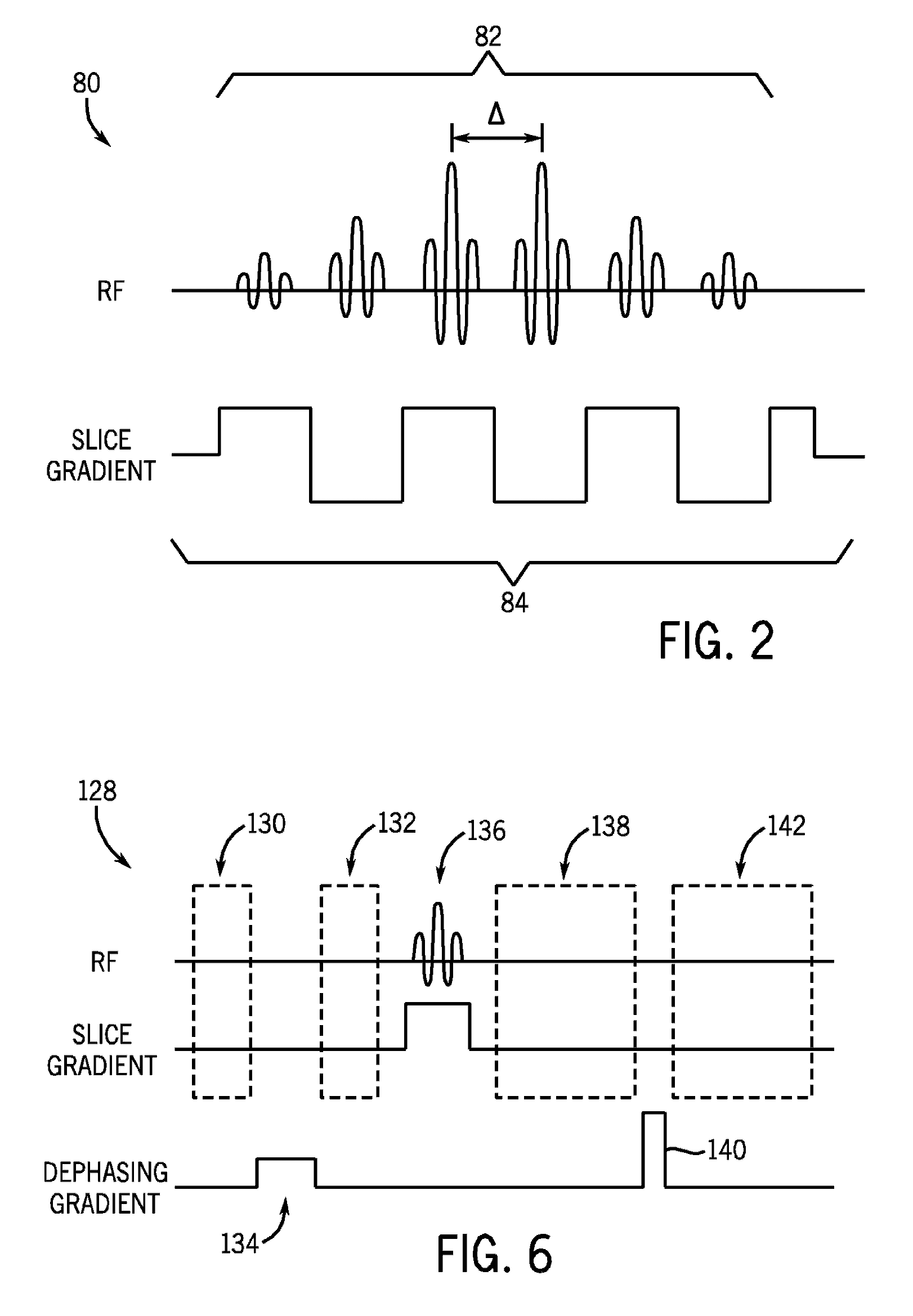
MRI apparatus and ASL imaging technique
ActiveUS7545141B2Reducing Td time-induced errorHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase shiftedSelective excitation
An MRI apparatus obtains an ASL (Arterial Spin Labeling) image of a region to be imaged in a subject by performing a scan to the region to be imaged independently in a control mode and in a tag mode according to a pulse sequence based on an ASL technique. The pulse sequence includes a velocity-selective pulse, BVS (Band-limited Velocity-Selective)-pulse, that selectively excites magnetization spins in a blood flow passing through the region to be imaged and having a constant velocity range for the spins to undergo transition to transverse magnetization, and then performs excitation to cause the transverse magnetization to flip back to longitudinal magnetization. The velocity-selective pulse is formed in such a manner that the transverse magnetization excited in each of the control mode and the tag mode gives rise to a phase shift in an opposite polarity upon velocity-selective excitation.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Display device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS7538753B2Increase consumptionIncrease valueElectronic switchingCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
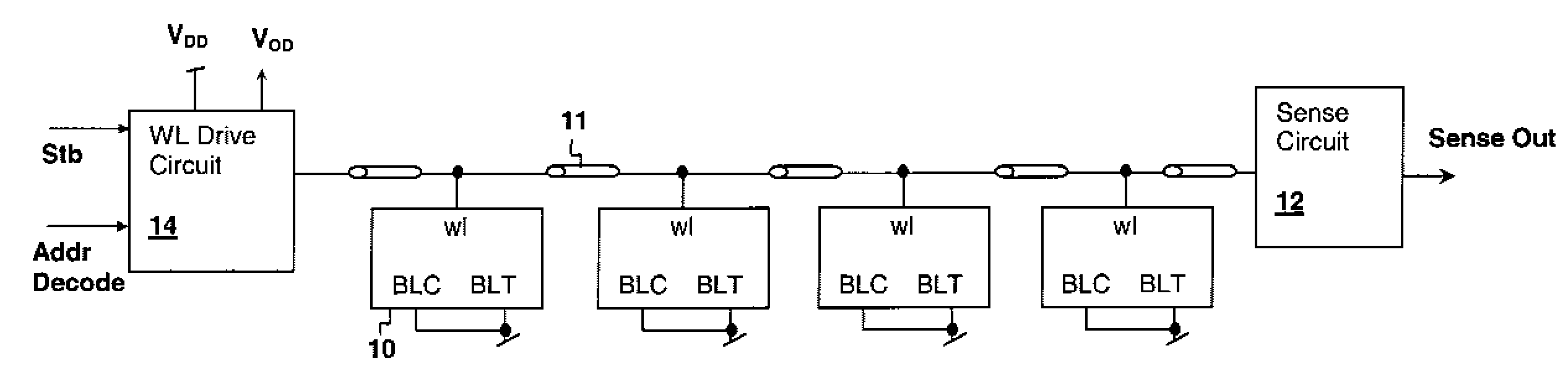
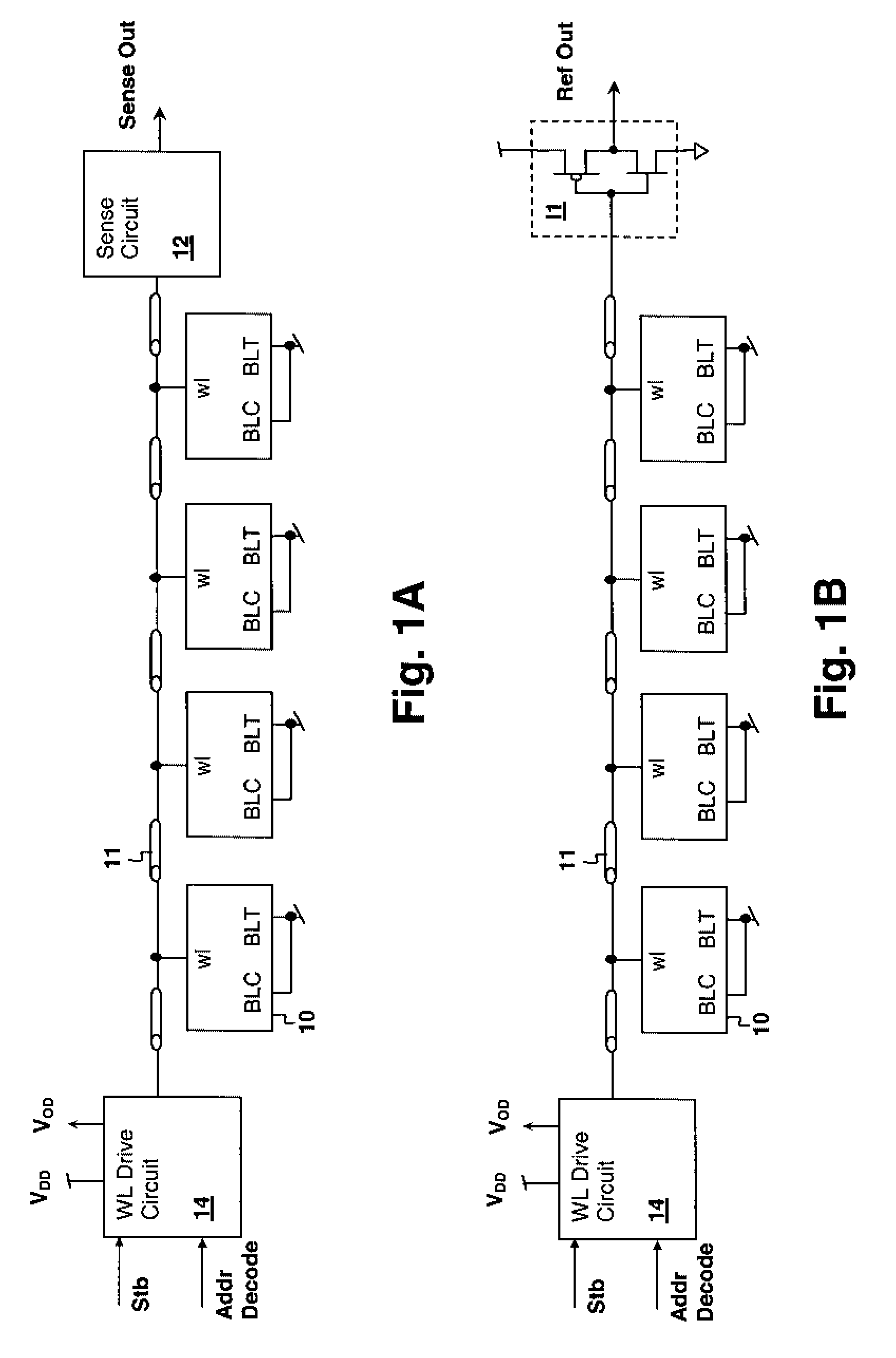
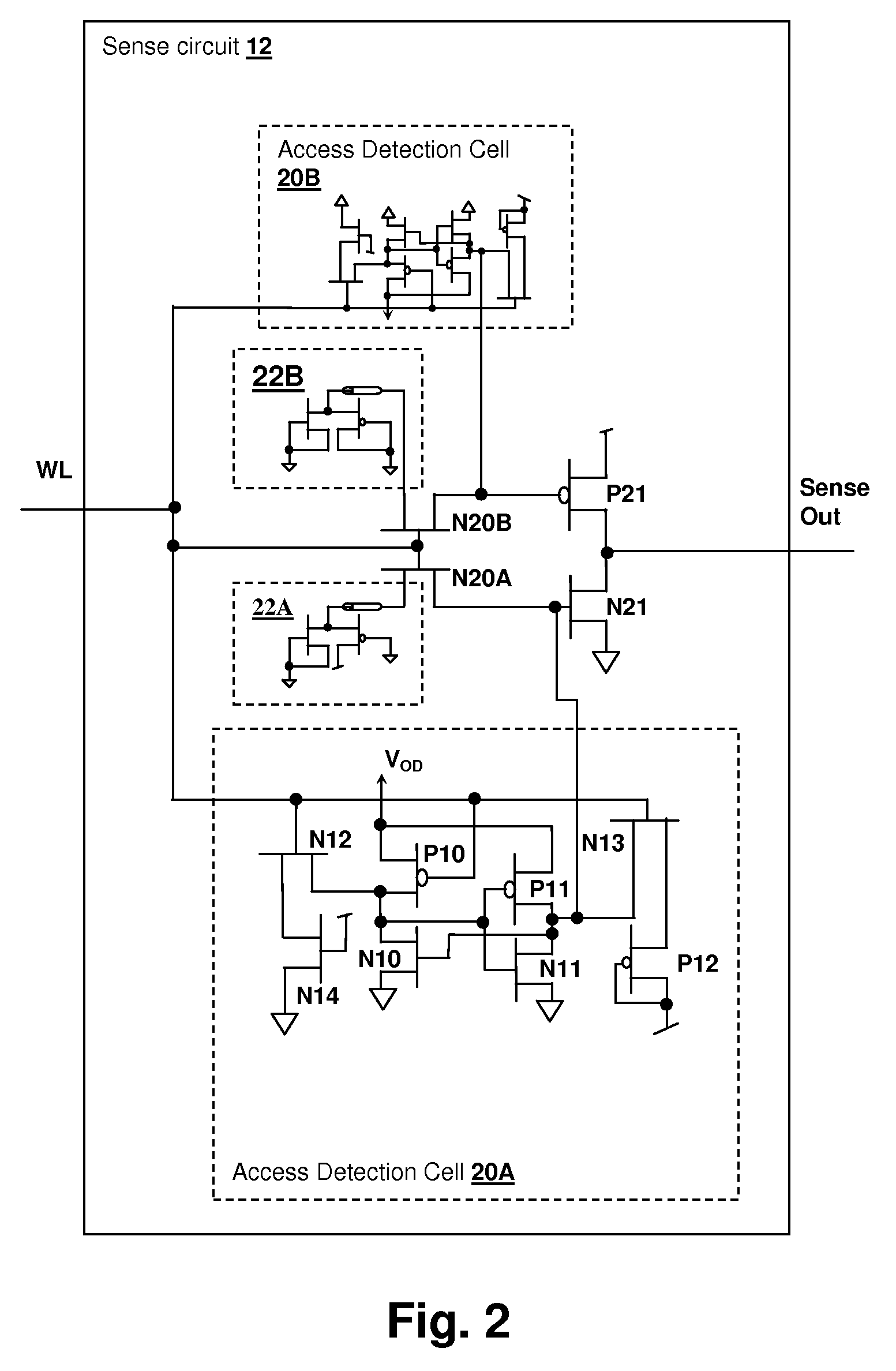
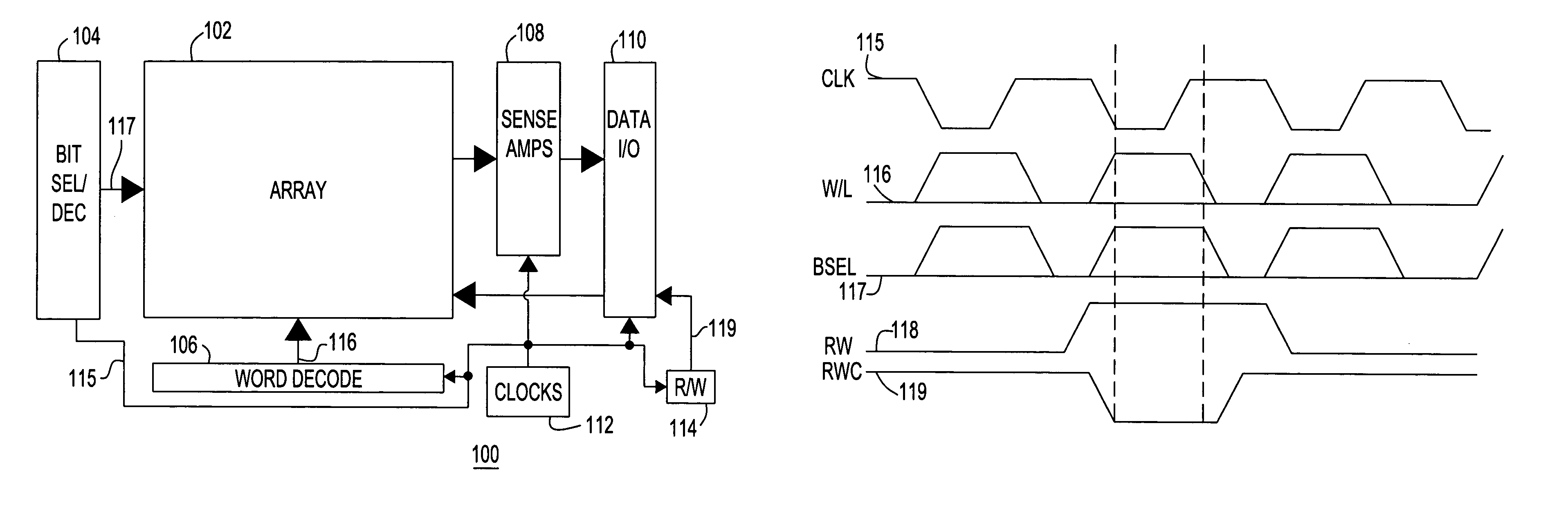
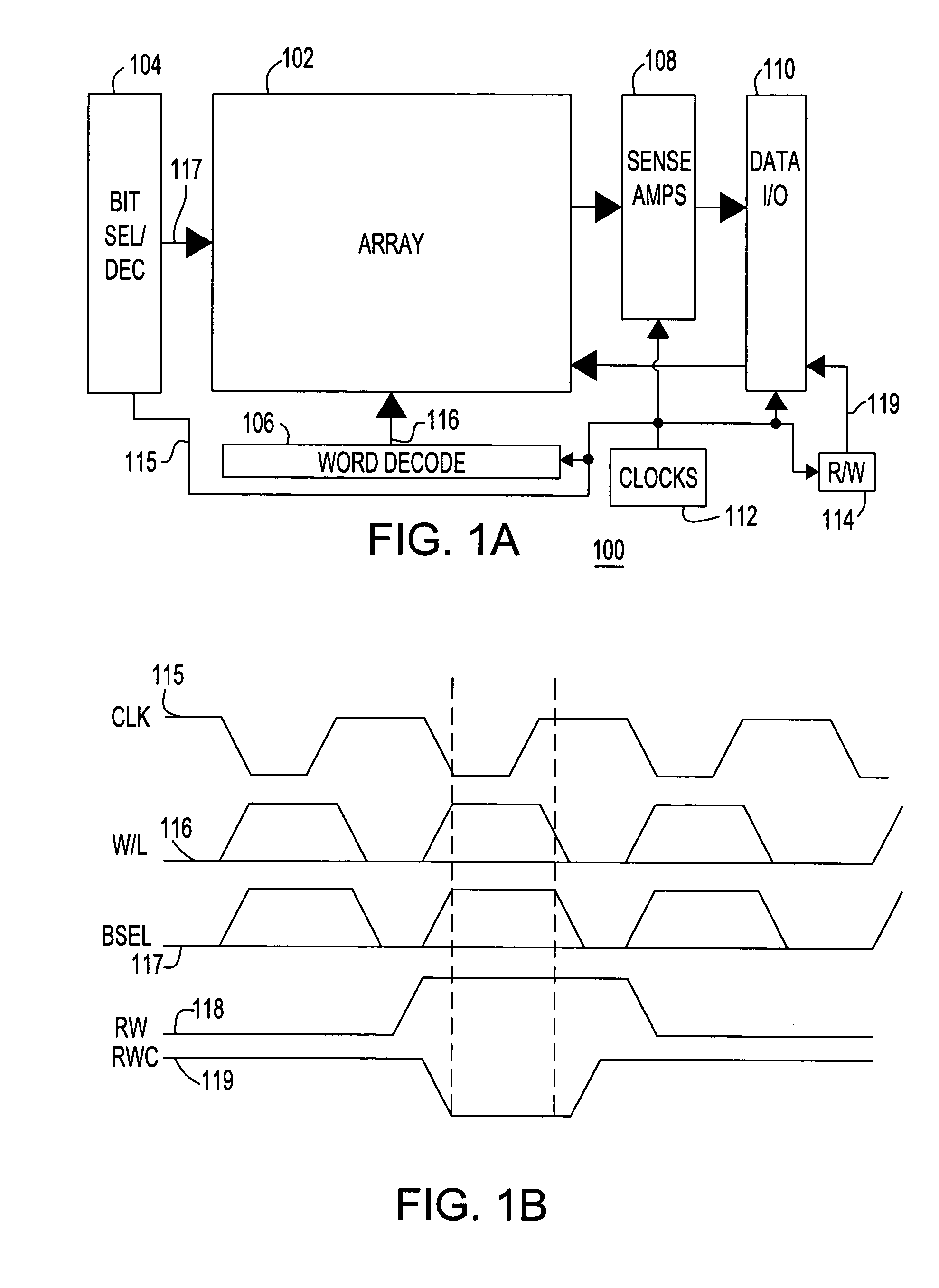
Method for evaluating storage cell design using a wordline timing and cell access detection circuit
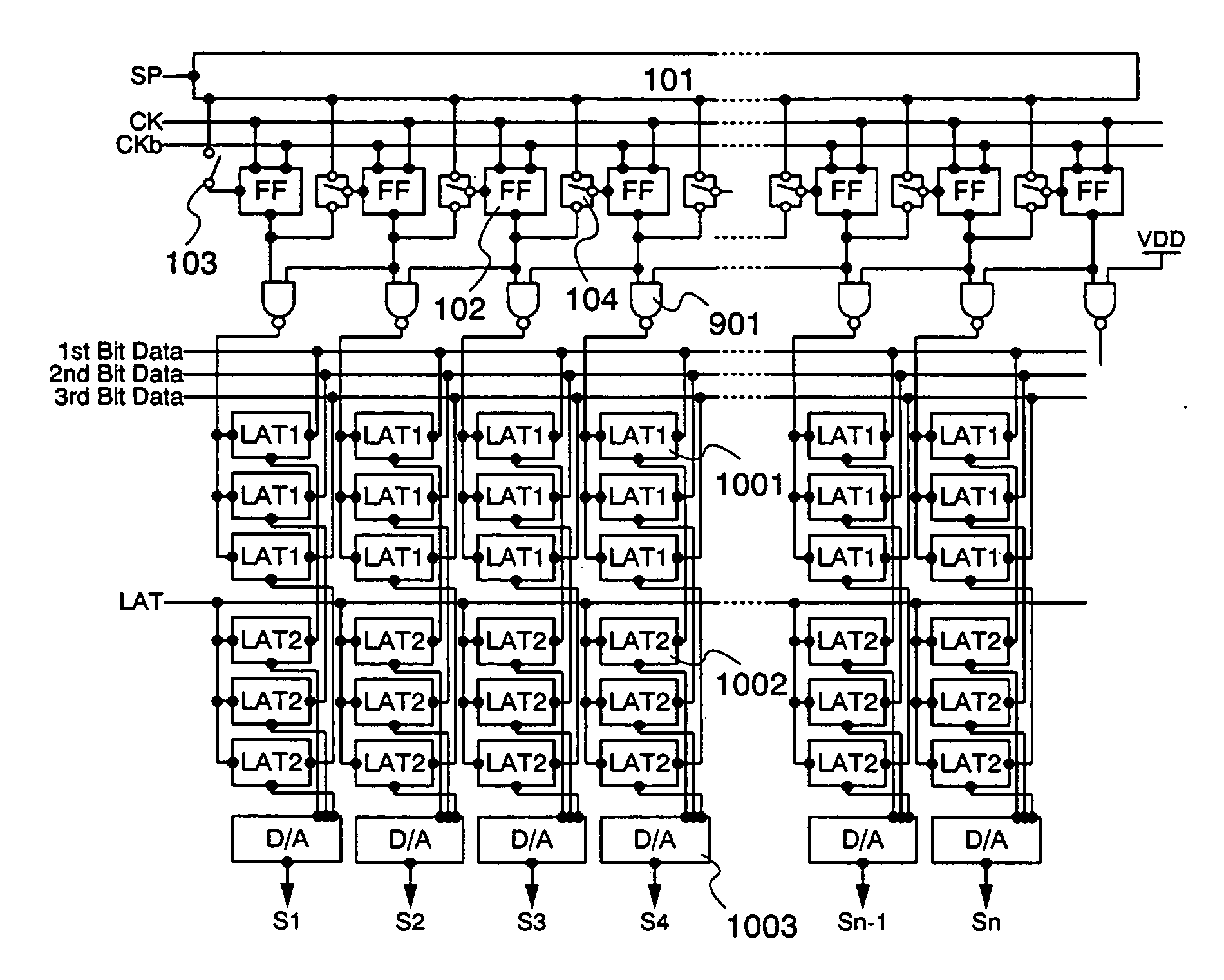
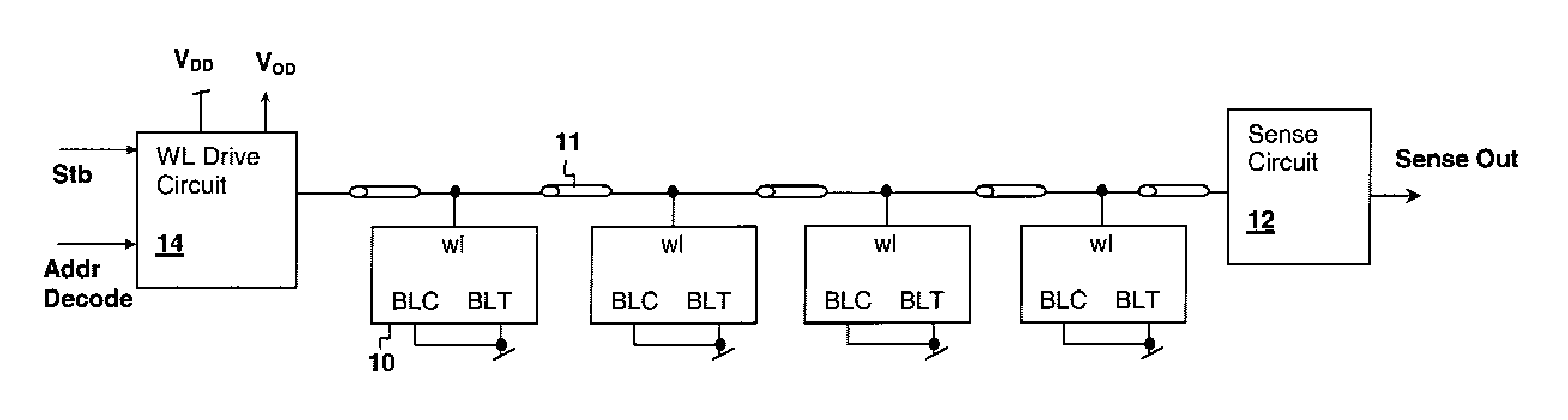
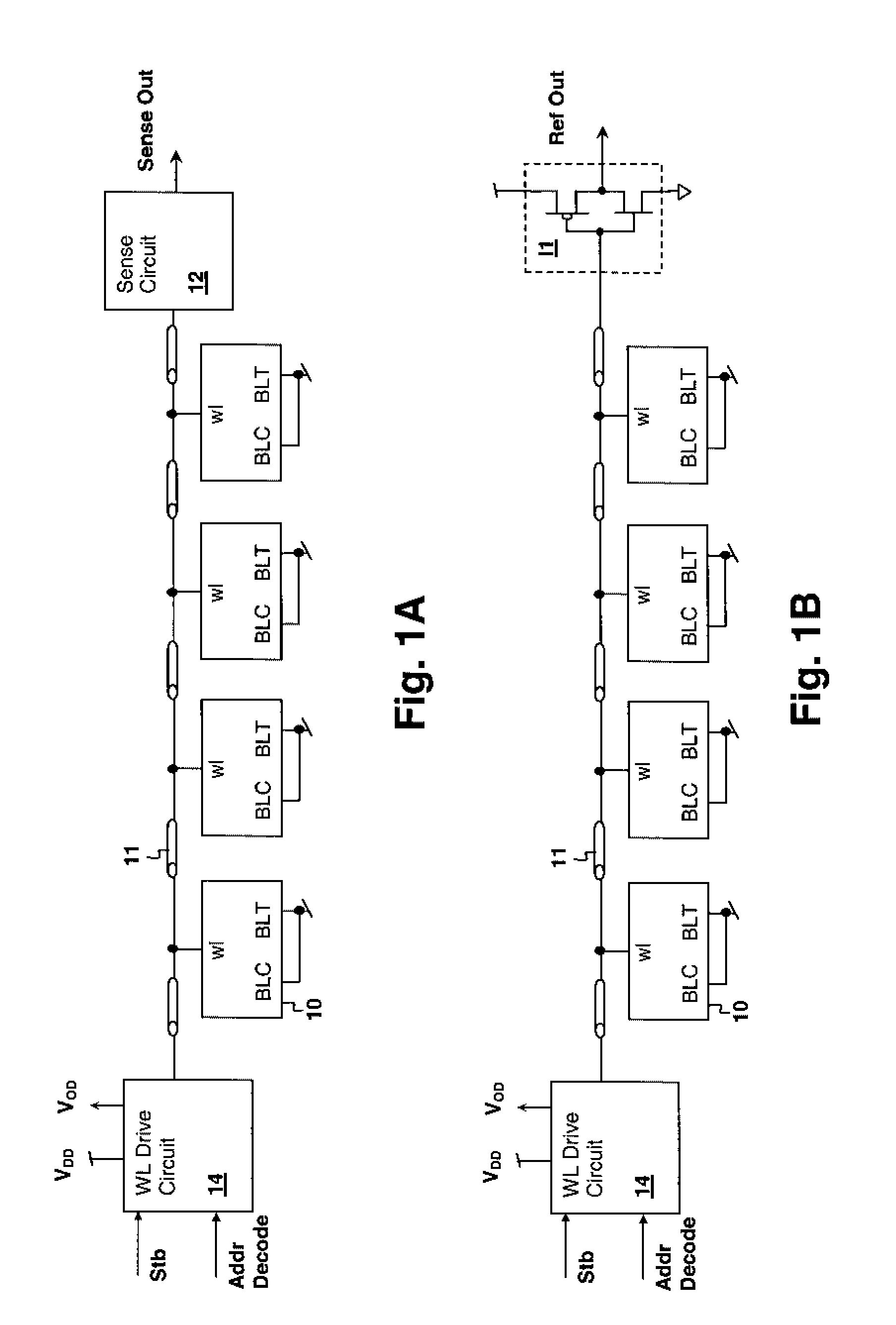
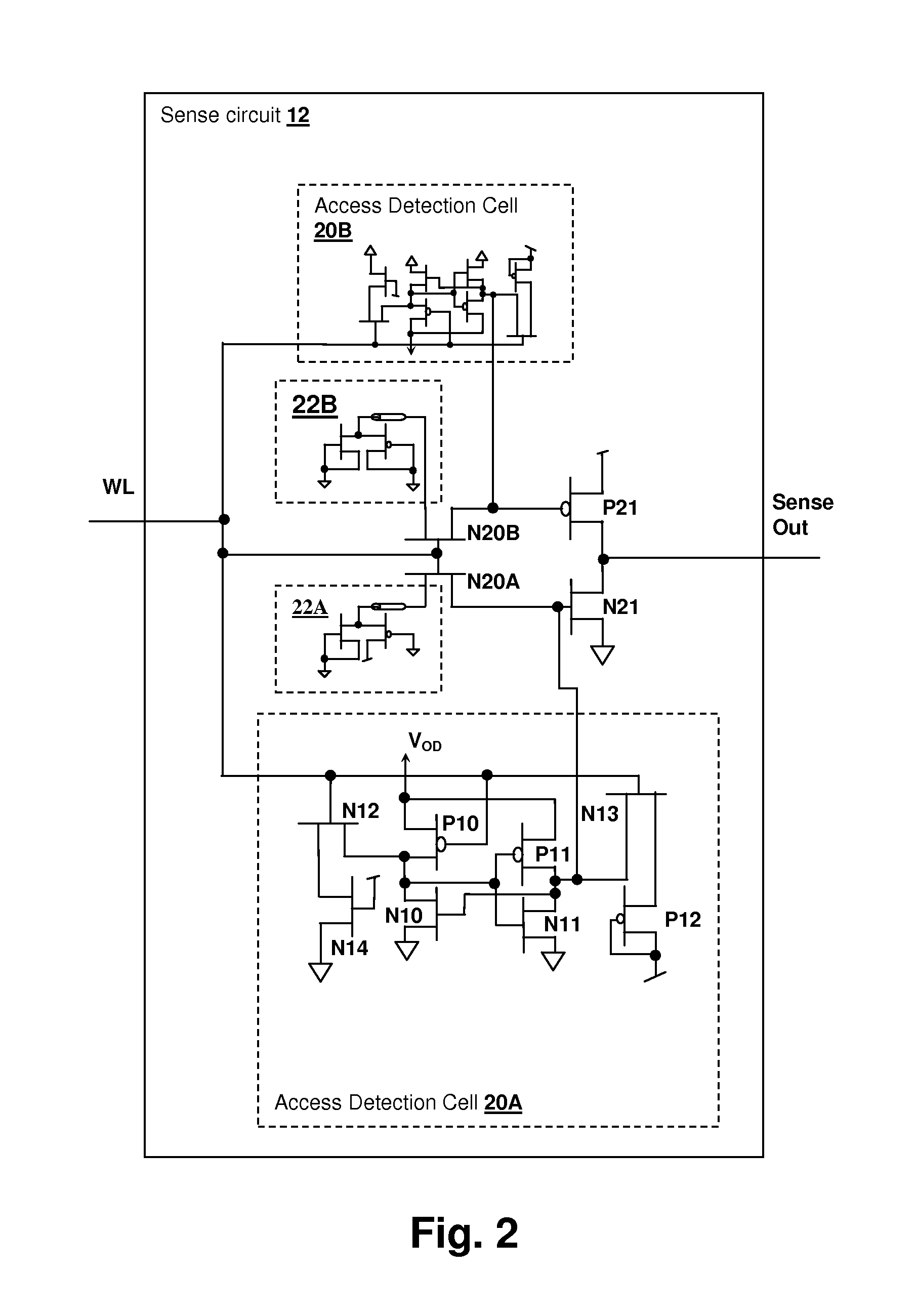
InactiveUS7414904B2Accurately determining wordline timingDigital storageDriver circuitImage resolution
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Active matrix liquid crystal display
ActiveUS7193601B2Secure image resolutionStatic indicating devicesActive-matrix liquid-crystal displayShift register
Owner:JVC KENWOOD CORP
Print head pulsing techniques for multicolor printers
ActiveUS20060290769A1Reduce coincidenceReduce peak power requirementsRecording apparatusPrintingEngineeringHeat sensitive
In one aspect of the invention there is disclosed a multicolor thermal imaging system wherein different heating elements on a thermal print head can print on different color-forming layers of a multicolor thermal imaging member in a single pass. The line-printing time is divided into portions, each of which is divided into a plurality of subintervals. All of the pulses within the portions have the same energy. In one embodiment, every pulse has the same amplitude and duration. Different colors are selected for printing during the different portions by varying the fraction of subintervals that contain pulses. This technique allows multiple colors to be printed using a thermal print head with a single strobe signal line. Pulsing patterns may be chosen to reduce the coincidence of pulses provided to multiple print head elements, thereby reducing the peak power requirements of the print head.
Owner:ZINK IMAGING
Display device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20040130542A1Electronic switchingCathode-ray tube indicatorsDisplay deviceBackground image
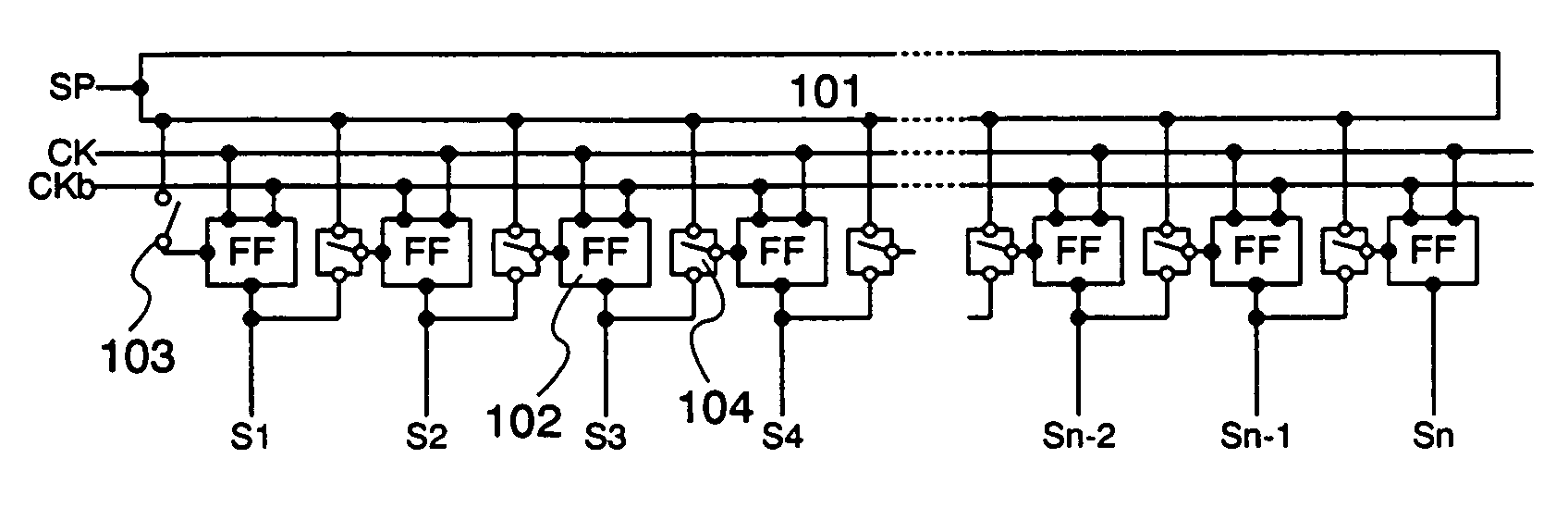
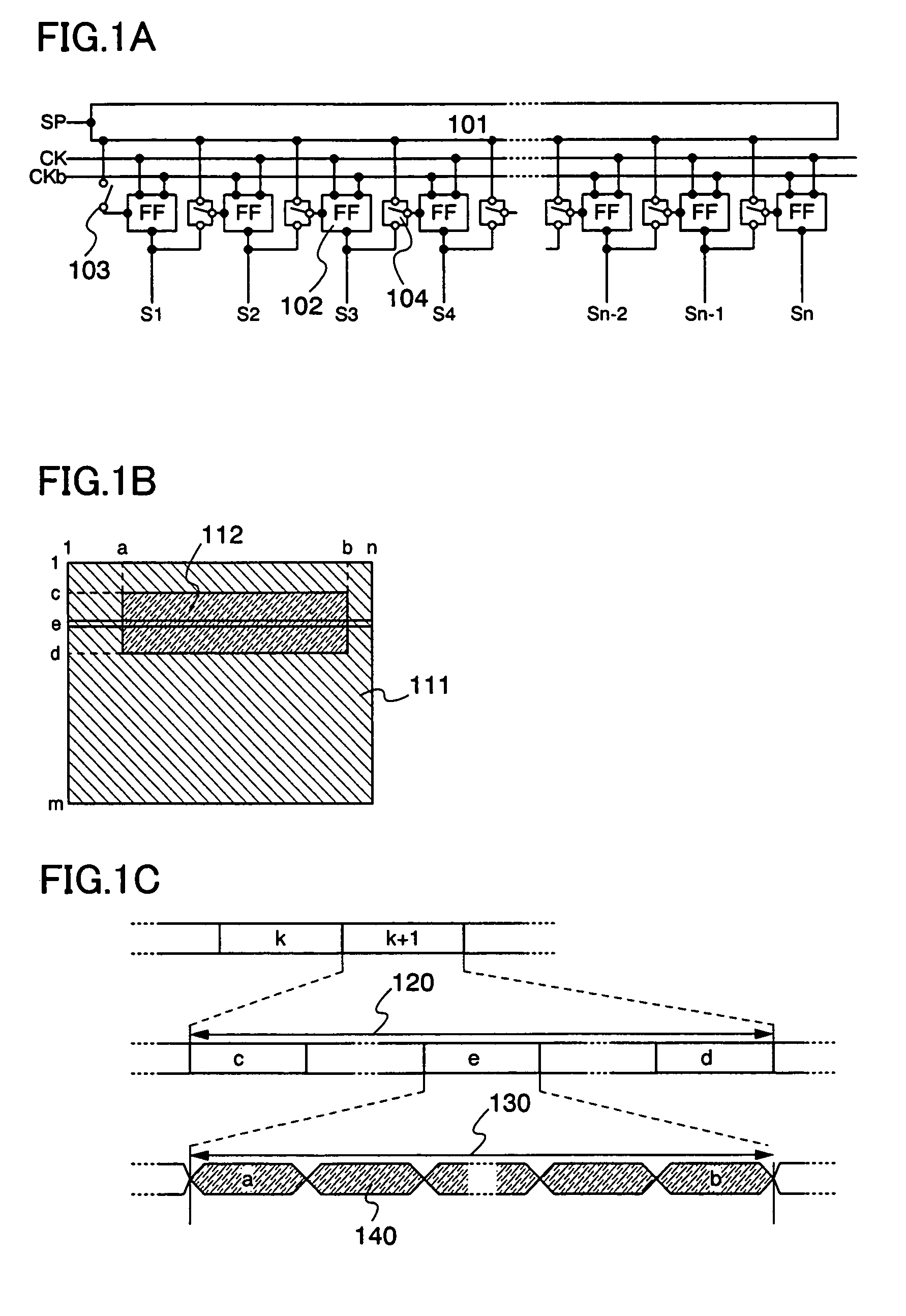
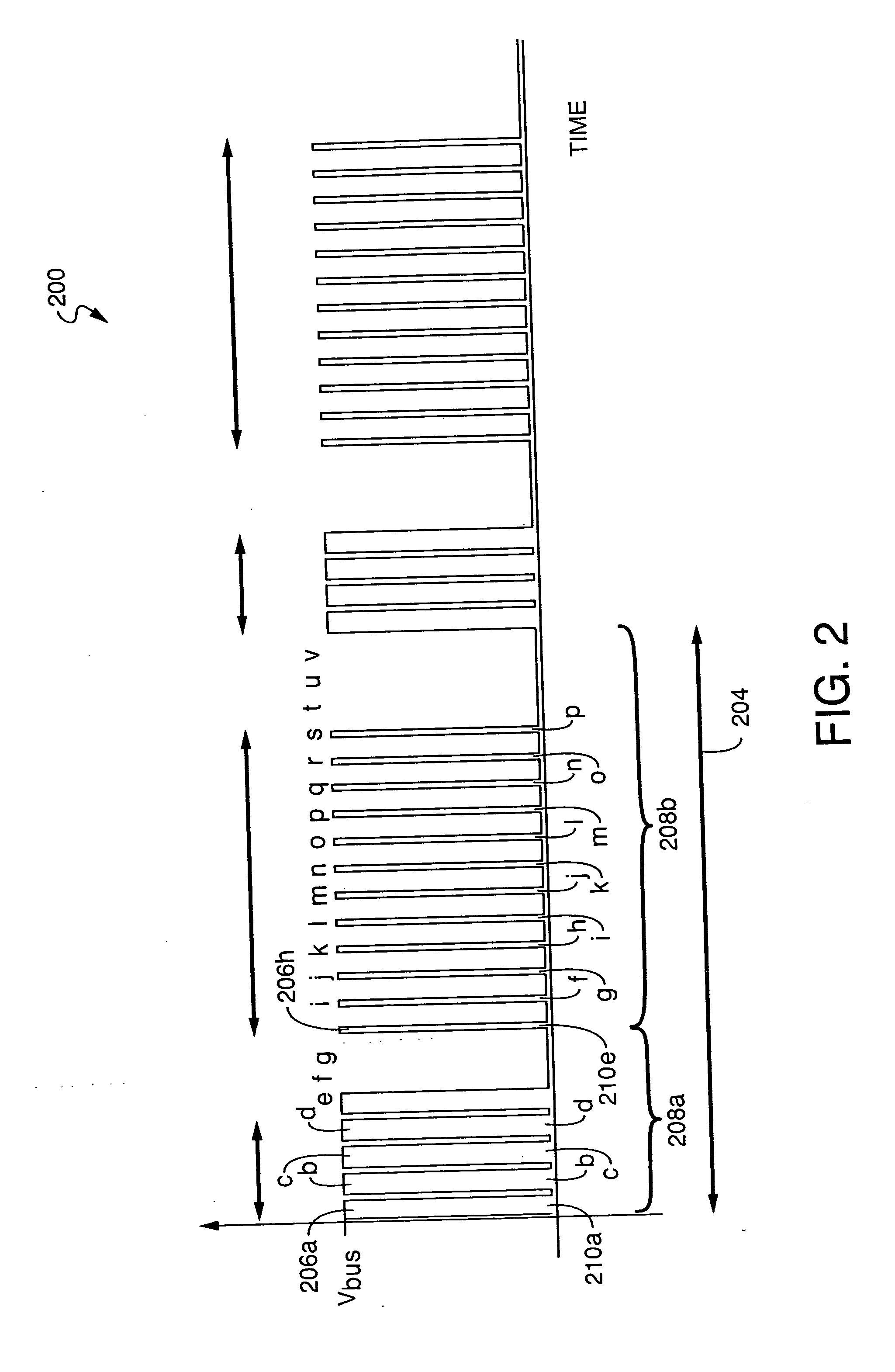
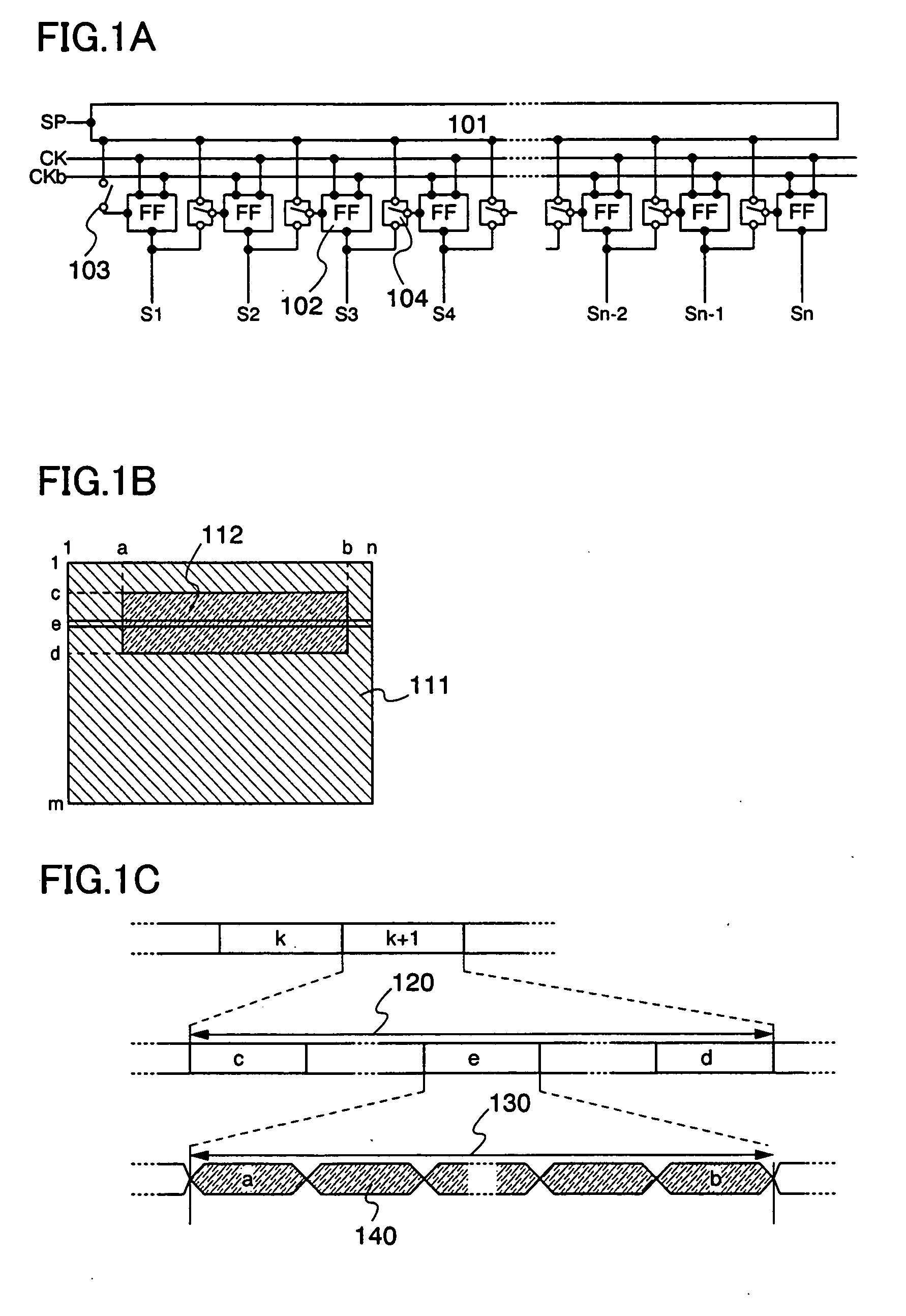
A display device enabling a superimpose display in which an image is superimposed on a background image with low power consumption is provided. By providing a switch at an input terminal of each stage of a scanning circuit which has a plurality of stages for outputting a sampling pulse or a row selection pulse, and by selecting whether or not to permit an input of a start pulse or each output pulse of a prior stage by the switch, it becomes possible to input a start pulse to an arbitrary mid-stage and output a sampling pulse or a row selection pulse from the stage. Accordingly, the pulse is outputted only to a region where a video signal needs to be updated in a display screen, and a row and a column are selected, thus a new video signal is written thereto.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Analysis of trains of pulses
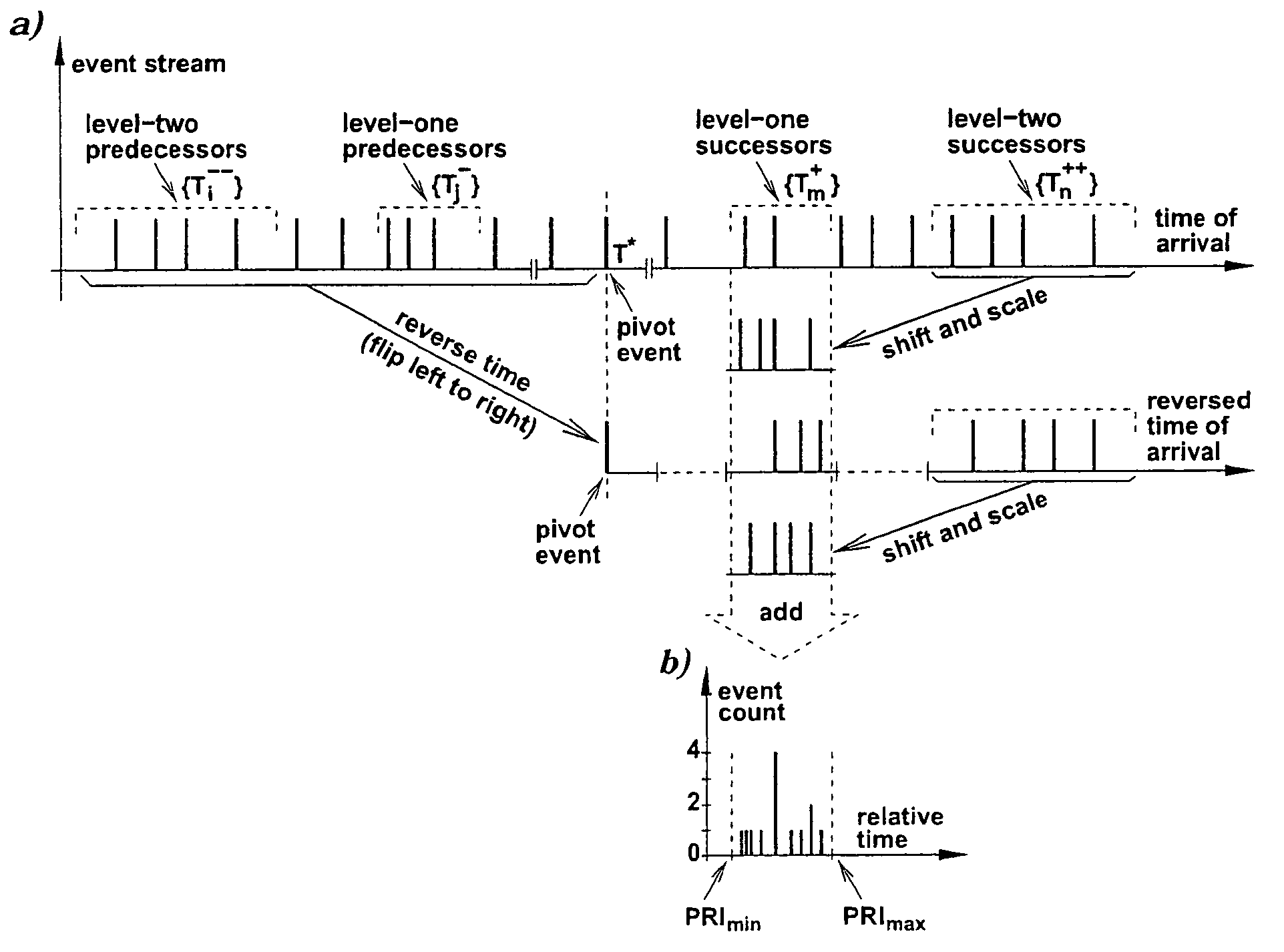
InactiveUS20080192864A1The result is accurateWave based measurement systemsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPulse sequenceTime of arrival
Candidate moments within a pulse train are selected. For each such moment, it is determined whether pulses occur at uniform intervals both before and after the moment; if so, the relevant pulses are classified as belonging to a particular group. An accurate calculation of interpulse interval is carried out by working out the repetition interval from the times of arrival of the pulses relative to the candidate moment, and then taking a weighted angular average.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Touch panel, display panel, and display unit
ActiveUS20150235607A1Eliminate false detectionsHigh sensitivityStatic indicating devicesAlternating current plasma display panelsEngineeringFringing capacitance
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Translocation control for sensing by a nanopore
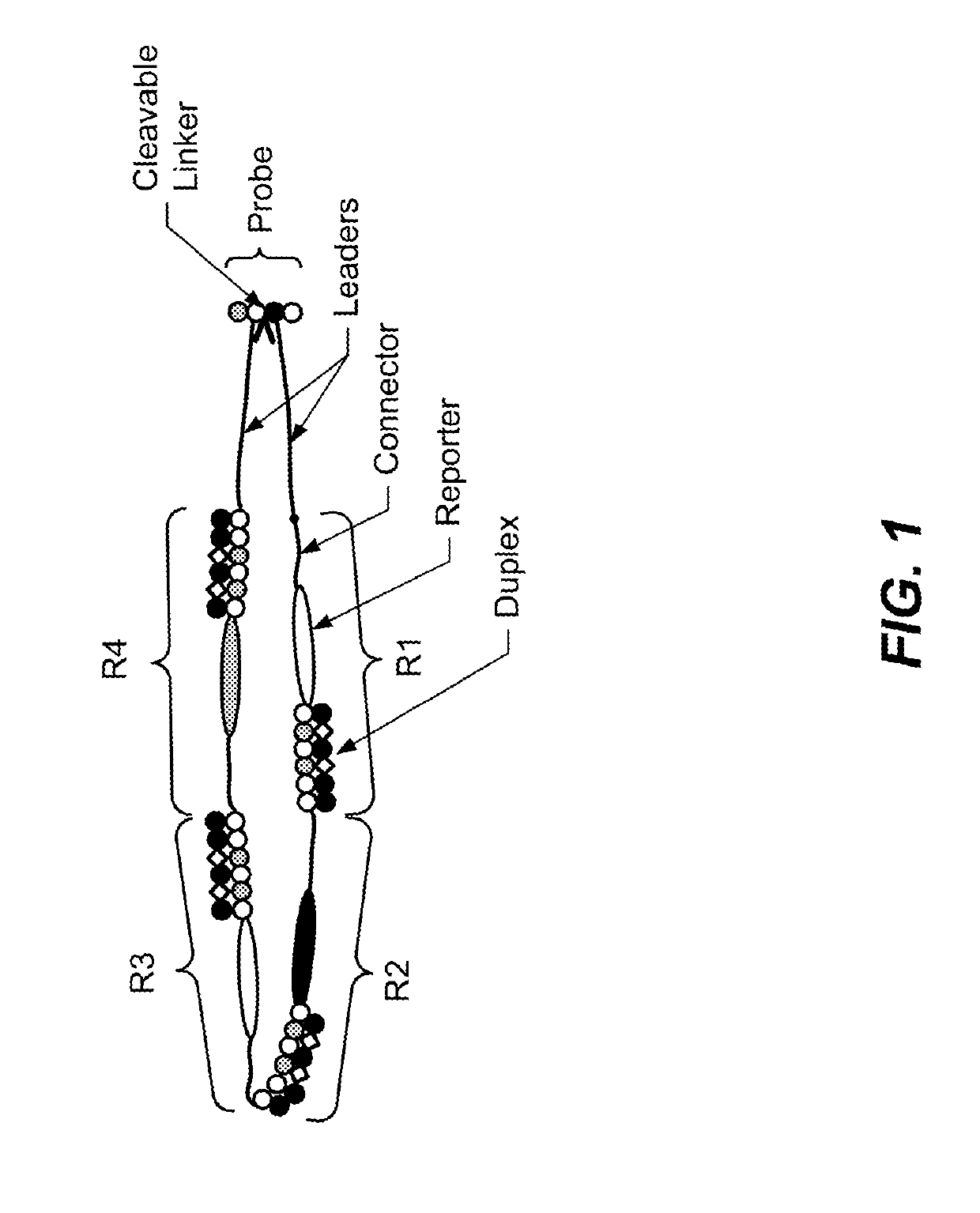
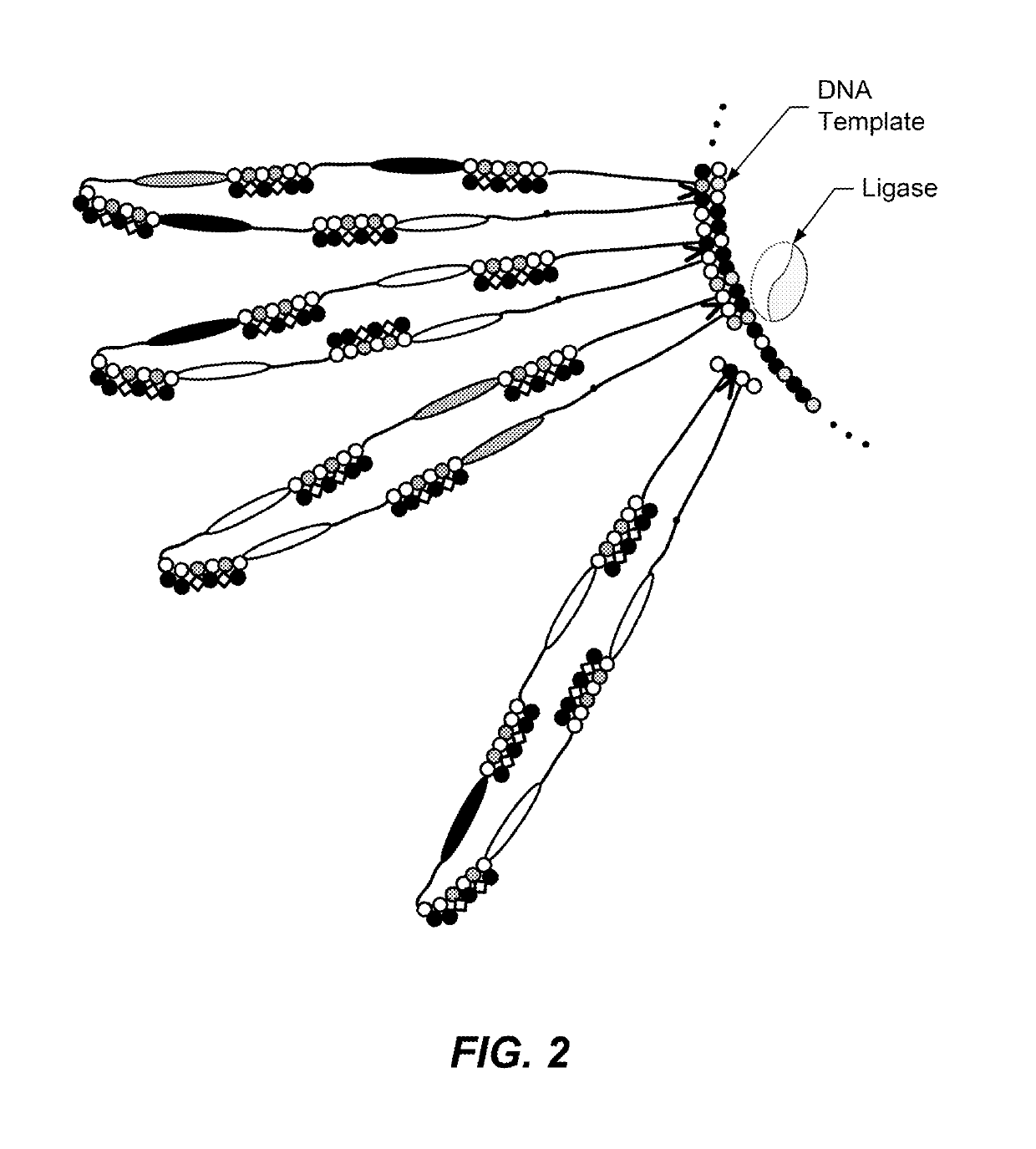
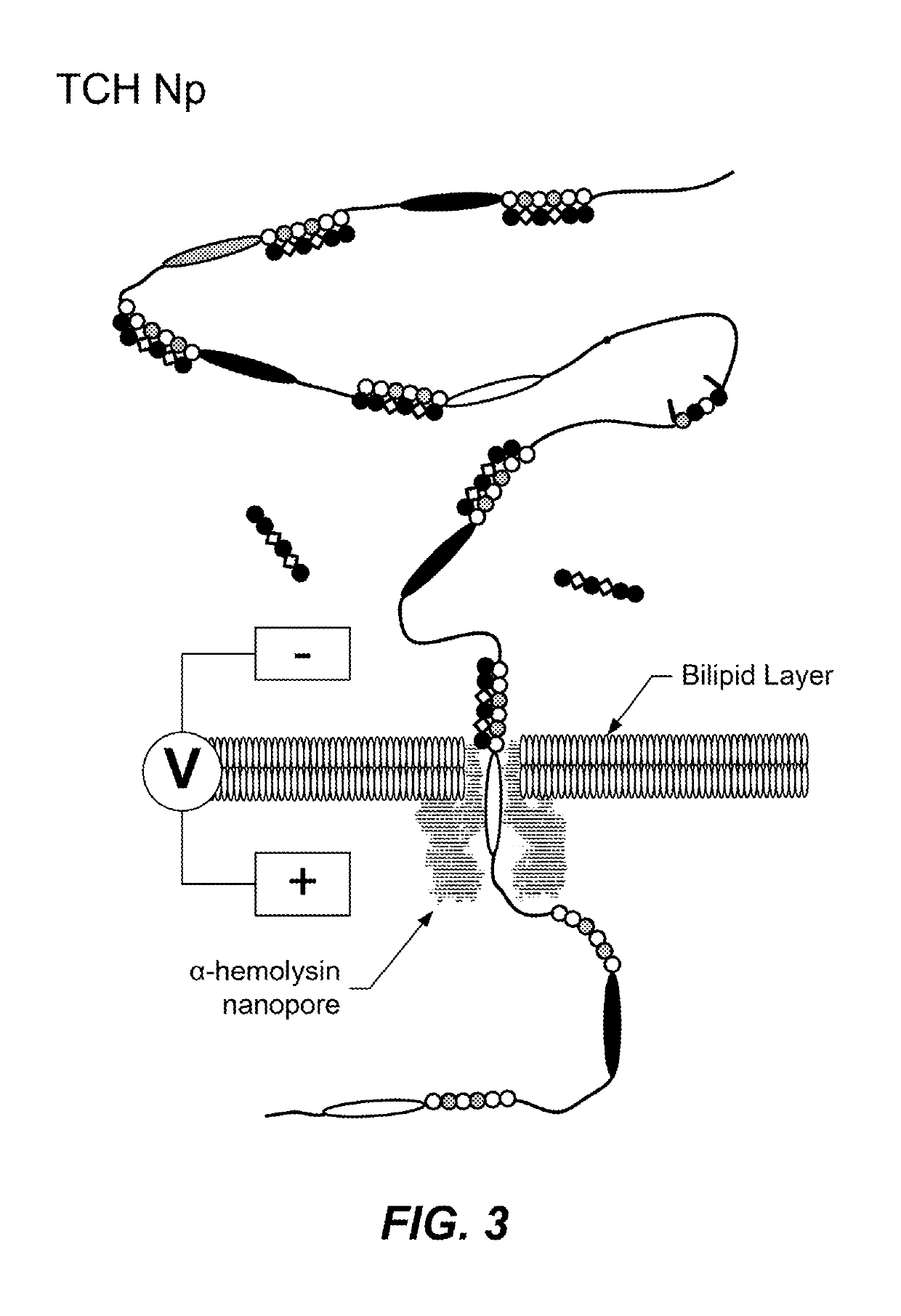
ActiveUS10457979B2Prevent rapid dissociationImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFill rateProtein translocation
Translocation control for sensing by a nanopore, as well as methods and products related to the same, are provided. Such methods optimize duplex stability to provide high fill rate (of the hybridization sites) but do not prevent rapid dissociation required for high read rates, as well as controlling the translocation of a target molecule for sensing by a nanopore by use of a selective pulsed voltage. Products related to the same include a reporter construct comprising two or more phosphoramidites.
Owner:ROCHE SEQUENCING SOLUTIONS INC
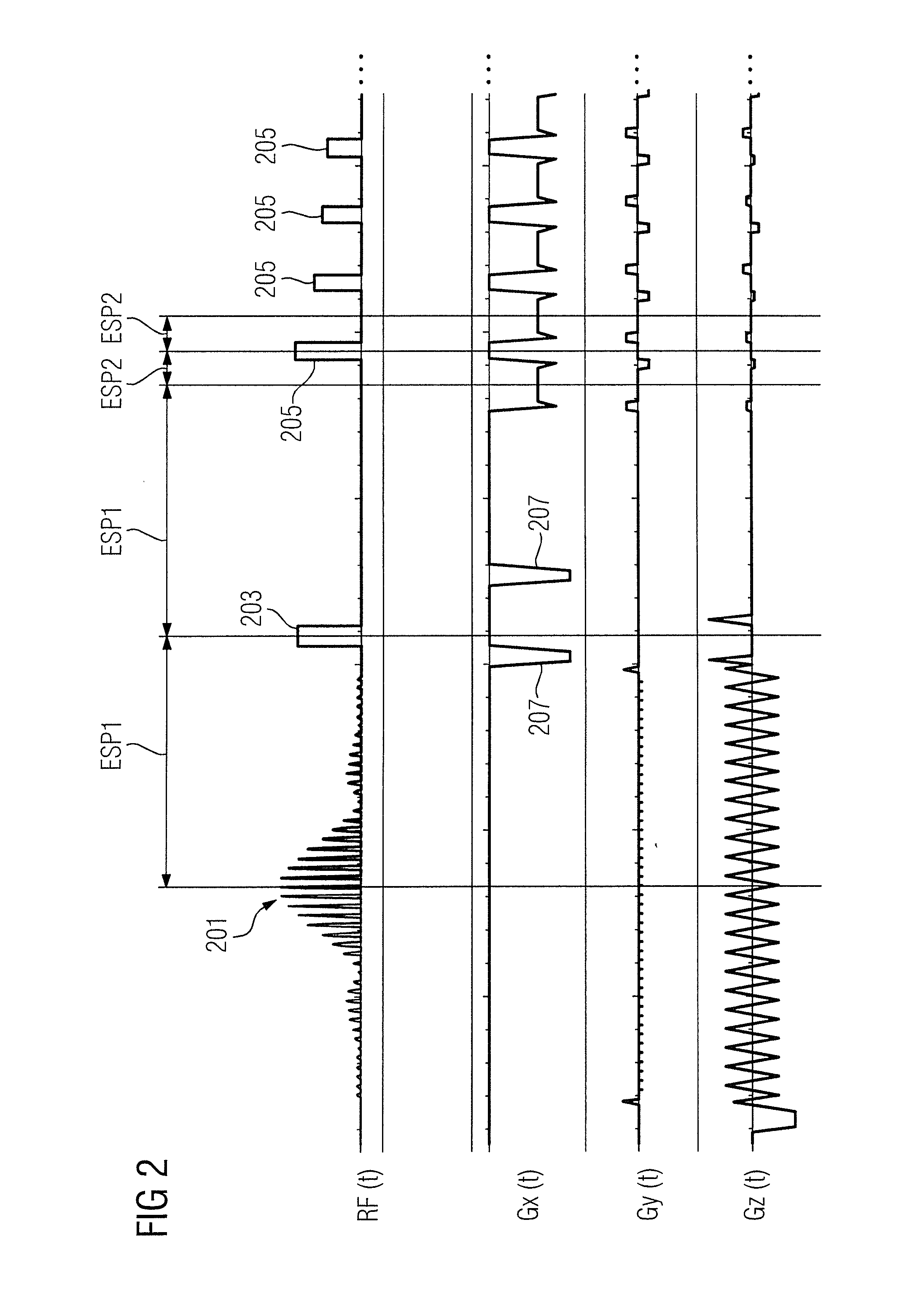
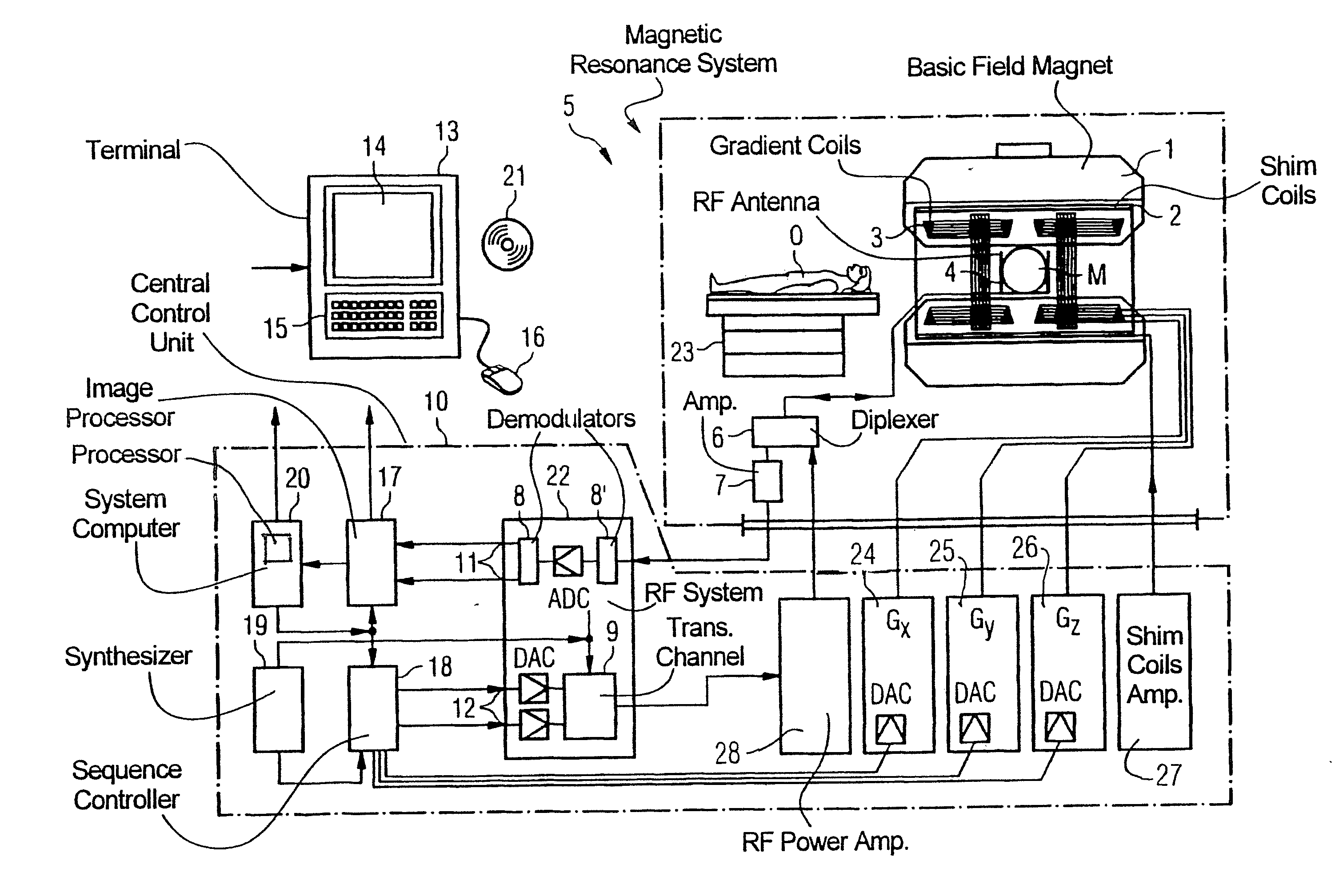
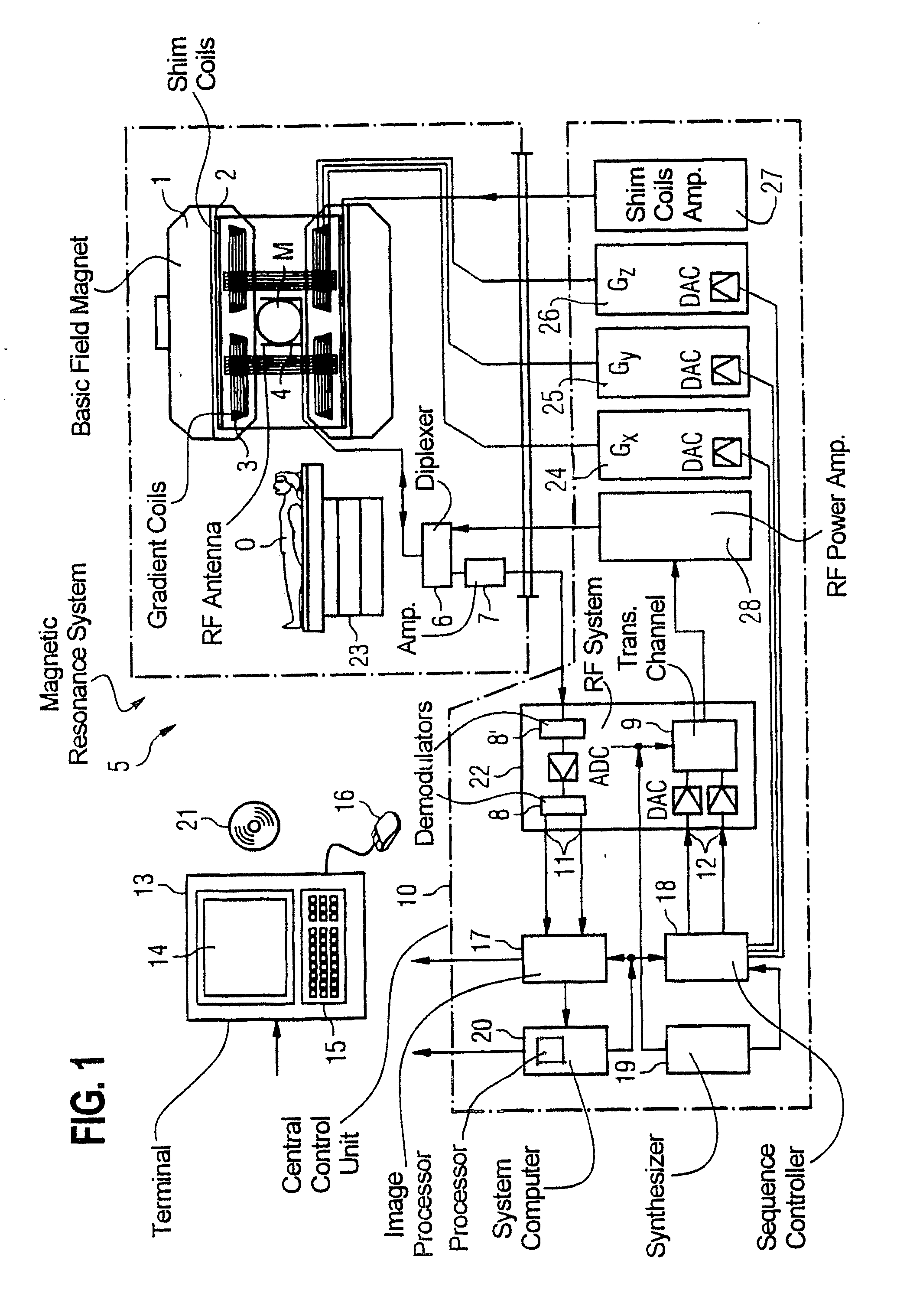
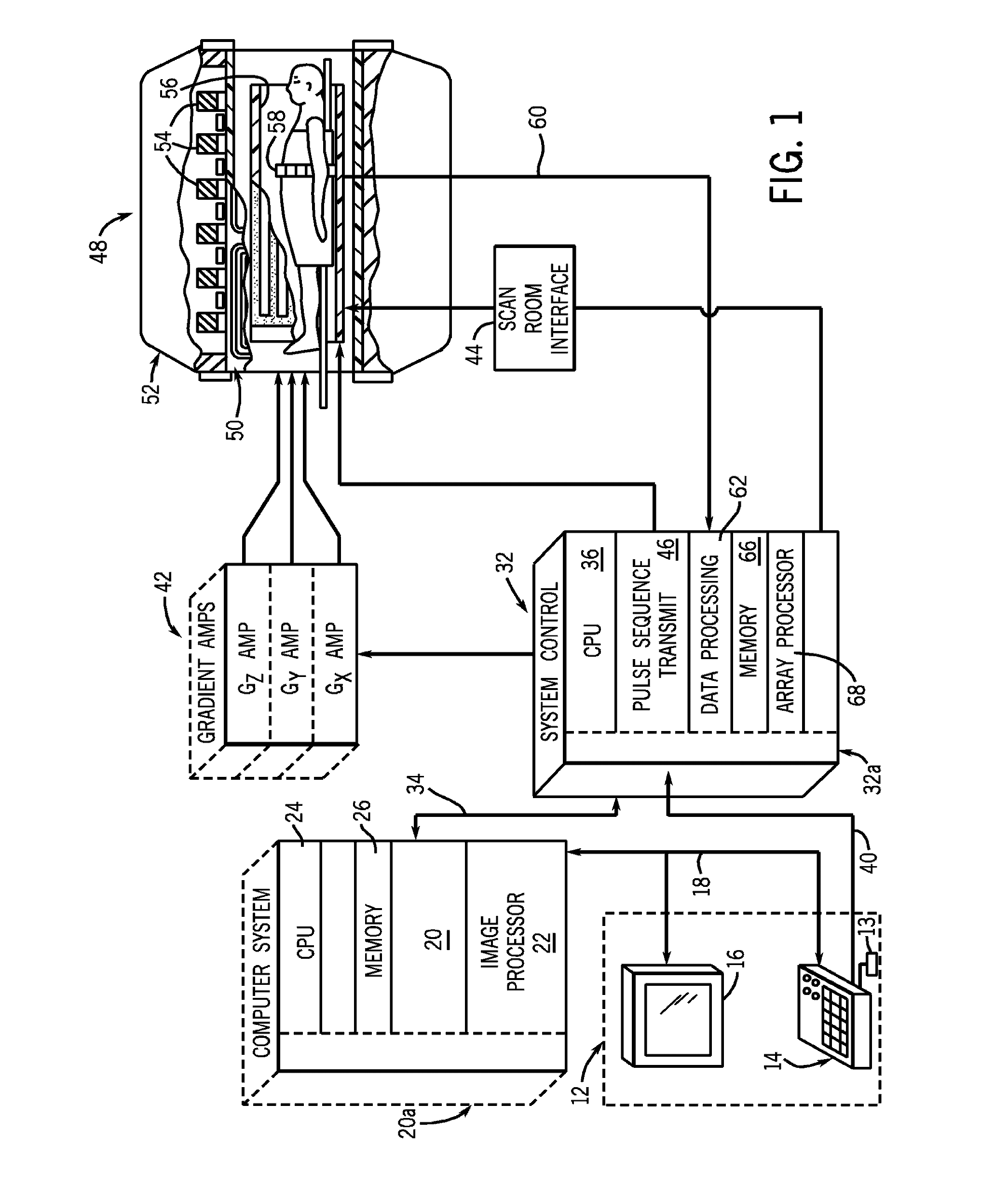
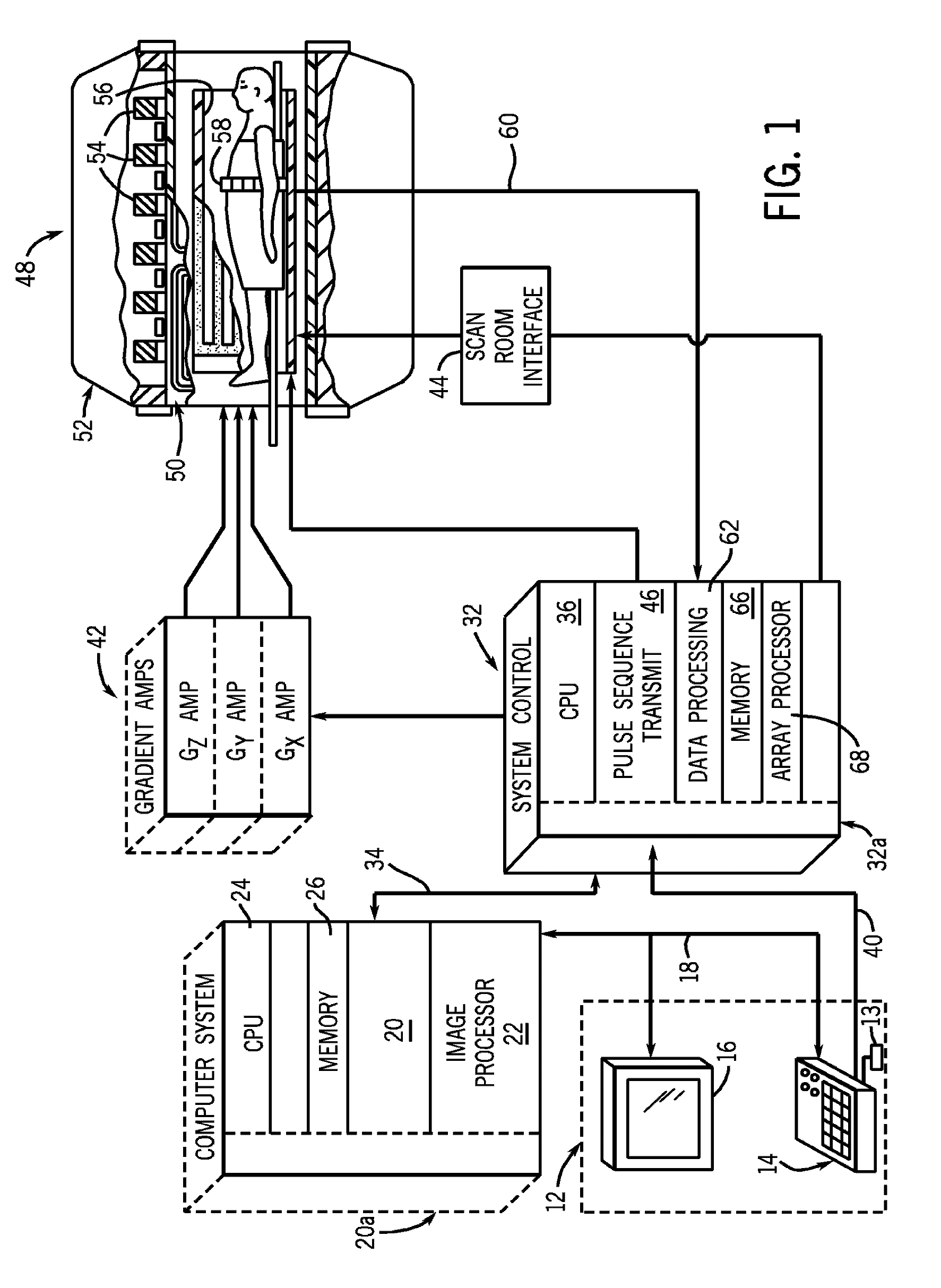
Method and apparatus to acquire magnetic resonance data
ActiveUS20140028313A1Reduced measurement timeAvoid artifactsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSelective excitationResonance
In a method and apparatus to acquire magnetic resonance data in a selected region of an examination subject without aliasing artifacts and with a reduced acquisition time, a spatially selective excitation pulse is radiated into the examination subject to excite nuclear spins in at least the selected region, and after radiating the excitation pulse, a series of at least two refocusing pulses is radiated into the examination subject, which generate variable flip angles adapted to a predetermined signal curve. At least the second refocusing pulse, and possibly every additional one of the refocusing pulses of this series, is a non-selective pulse. The spin echo signals generated by the refocusing pulses are acquired as magnetic resonance data. Gradients for spatial coding are activated before and after the spatially selective excitation pulse, the refocusing pulses and during the data acquisition. The acquired magnetic resonance data are stored and / or converted into image data for display.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Plasma display panel and method of driving the same
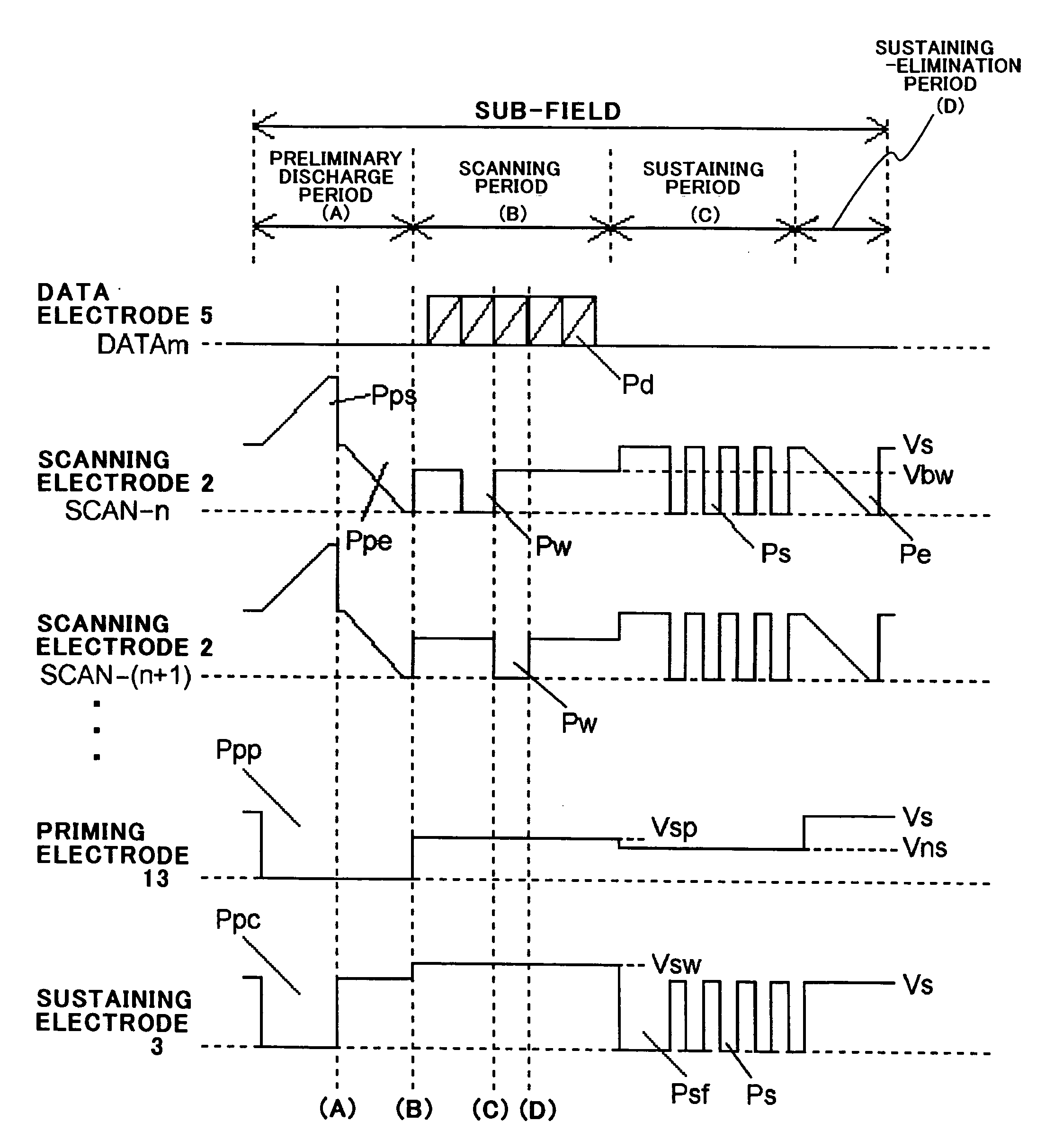
InactiveUS20050128166A1Shorten the overall cycleReduction ratio of generationAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesEngineeringPlasma display
A plasma display panel includes (a) first and second substrates facing each other, (b) a plurality of first electrodes formed on the first substrate and extending in parallel with one another, (c) a plurality of second electrodes formed on the second substrate and extending in parallel with one another perpendicularly to the first electrodes, and (d) a plurality of display cells arranged at intersections of the first electrodes with the second electrodes, wherein a first selection pulse is input into the first electrodes and a second selection pulse is input selectively into one or more of the second electrodes to thereby control whether light is to be emitted in each of the display cells, and at least one of the display cells has a third electrode formed on the first substrate and being electrically connected to a first electrode other than a first electrode belonging to a display cell to which the third electrode belongs.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
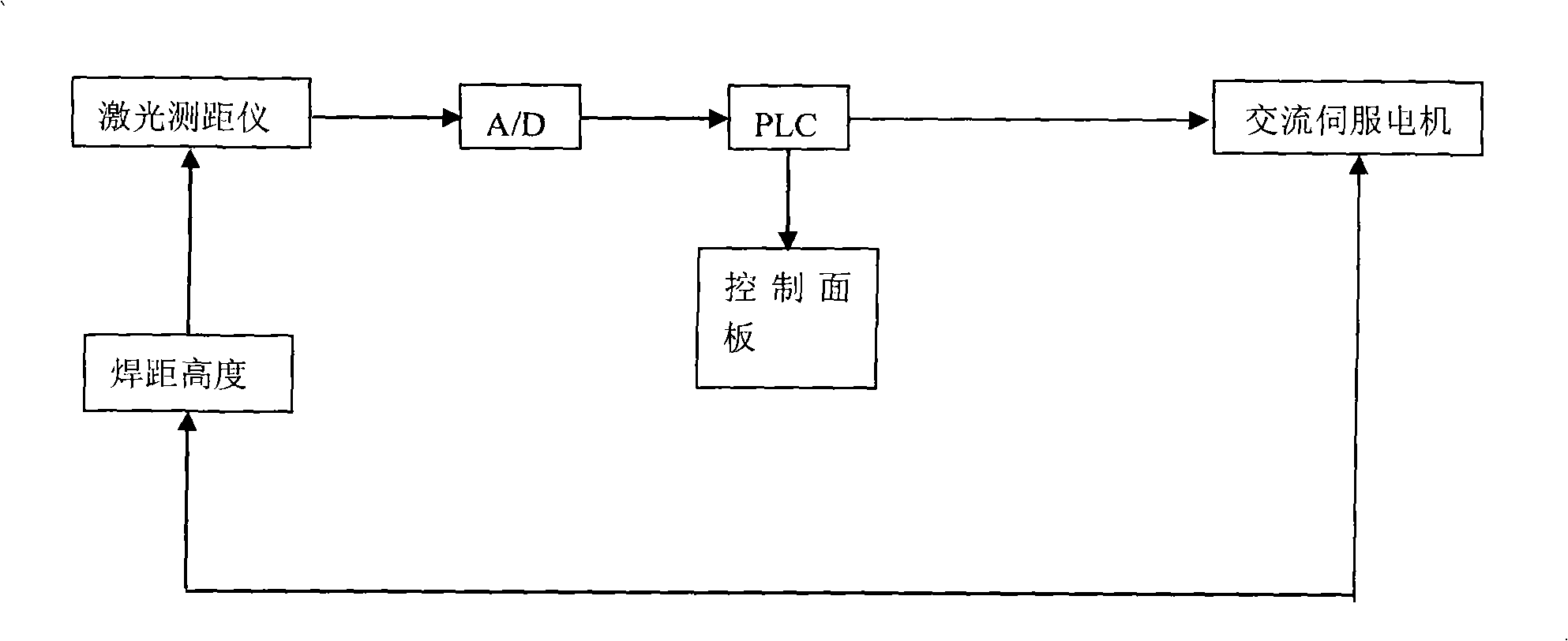
Device and method for controlling length of electric arc
InactiveCN101406980ASimple structureHigh control precisionArc welding apparatusLaser sensorLaser rangefinder
The invention discloses a welding-distance height control device and a welding-distance height control method. The device can accurately control the distance between a nozzle of a welding torch and a workpiece, namely the welding-distance height, and belongs to the technical field of welding. The method directly measures the distance between a laser sensor and the workpiece through a laser ranging device. The actual distance is transferred into a PLC control unit after the AD conversion; and after the processing of the PLC, the PLC can automatically select pulse frequency according to the preset speed and the difference between the welding-distance height and the preset height at the moment and output a pulse signal and a rotating direction signal to an alternating motor for servo. The alternating current motor can drive the welding torch to move back and forth, and the distance between the welding torch and the workpiece is adjusted to ensure that the distance is consistent with the preset distance. The proposal is applicable to the piercing welding, has higher control accuracy, a simple structure, and steady effect, and is superior to the prior arc voltage feedback to control the length of an electric arc.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and apparatus for acquisition of magnetic resonance data while avoiding signal inhomogeneities
InactiveUS20140028314A1Avoid unevennessIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceCenter frequency
In a method and apparatus for the acquisition of magnetic resonance data while avoiding signal inhomogeneities, an excitation pulse is radiated into the examination subject, and following a first time period thereafter, a first refocusing pulse is radiated into the examination subject. After a second time period after the radiation of the first refocusing pulse, a series of at least two additional refocusing pulses is radiated that generate variable flip angles adapted to a predetermined signal curve and that are non-selective pulses. Spin echo signals generated by the radiated pulses are acquired as magnetic resonance data. Gradients are activated for spatial coding. The center frequency of at least one of the radiated refocusing pulses is adjusted such that it is between the resonance frequency of fat molecules and the resonance frequency of water molecules in the examination subject in the magnetic resonance system.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
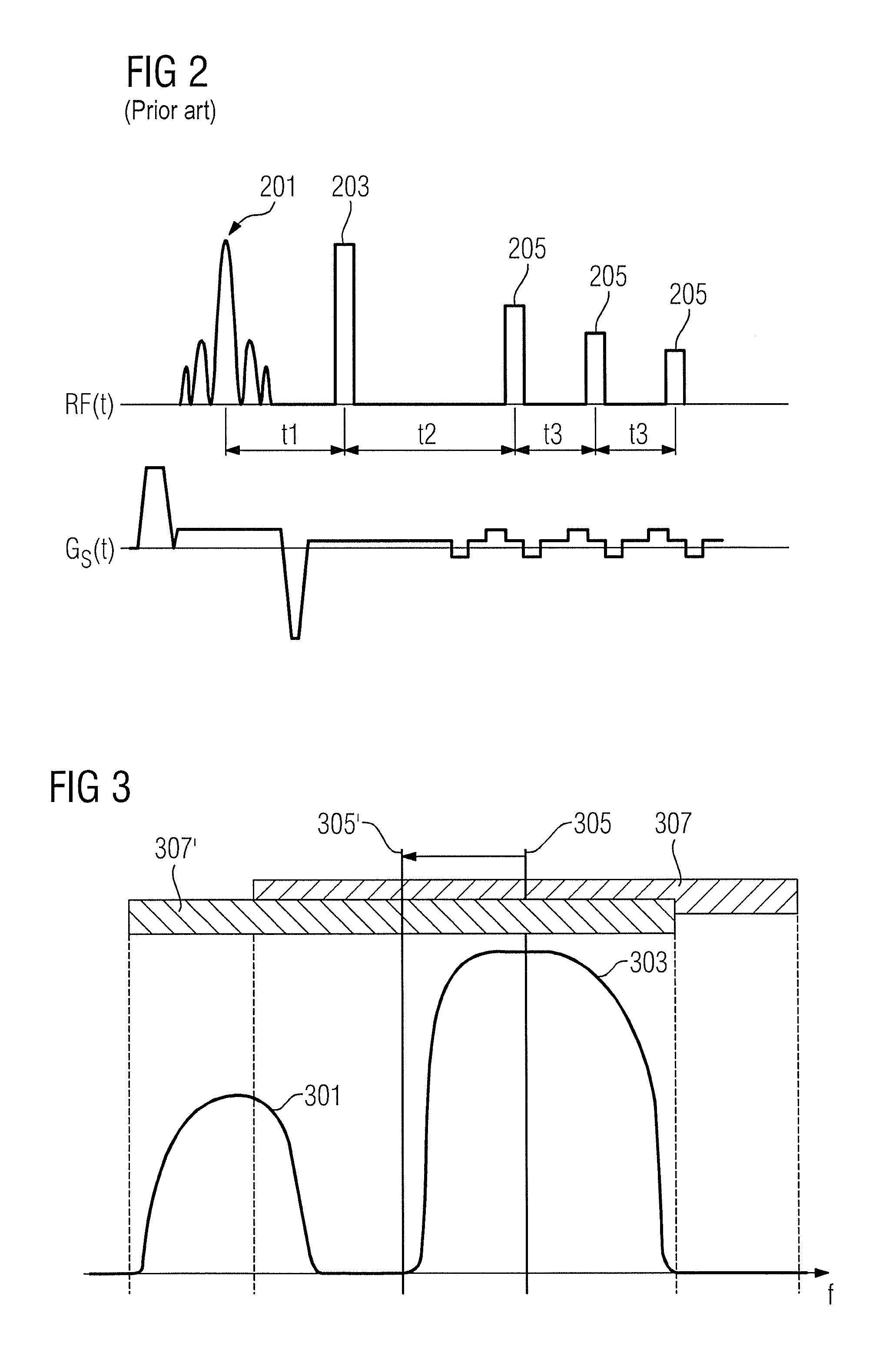
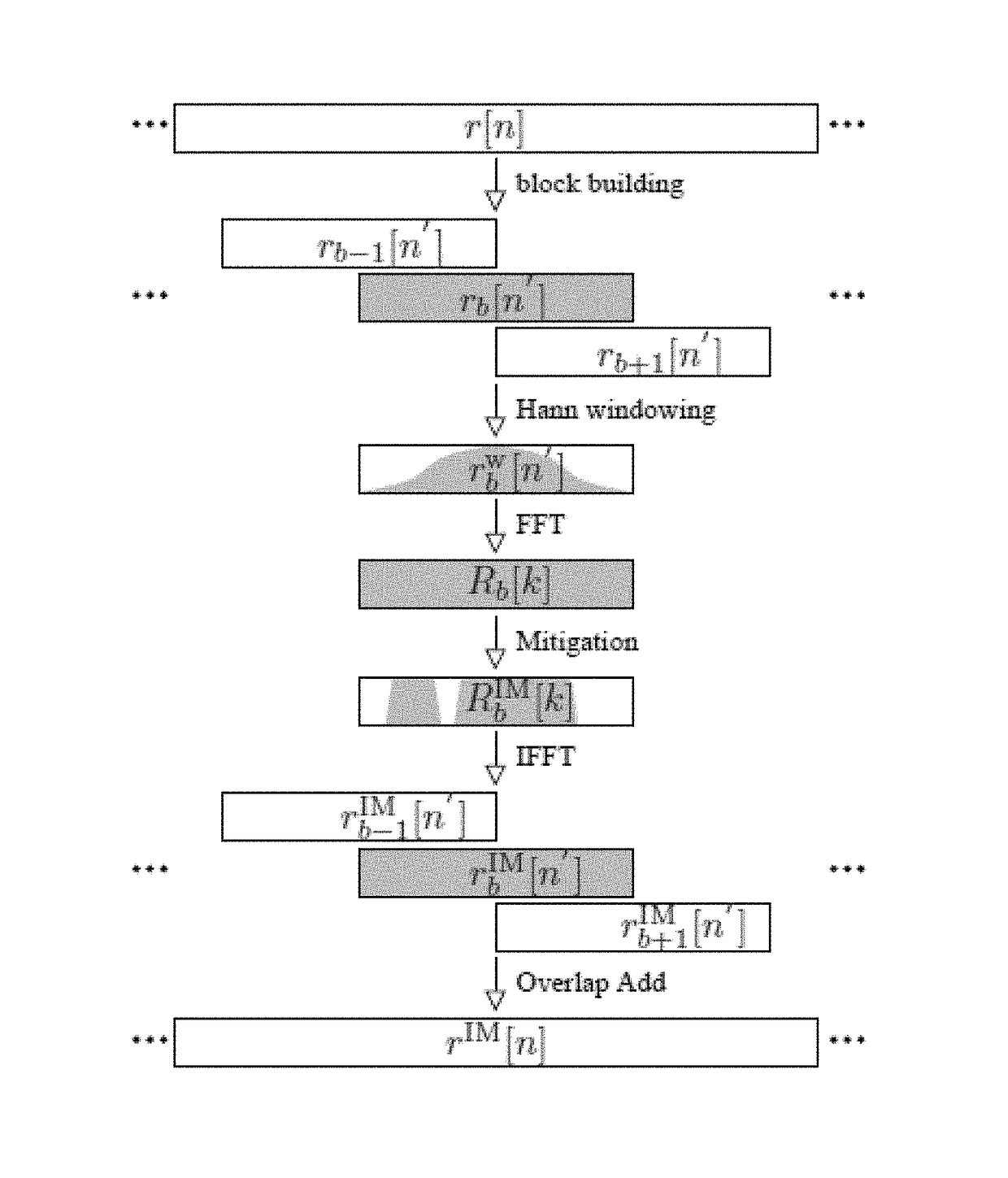
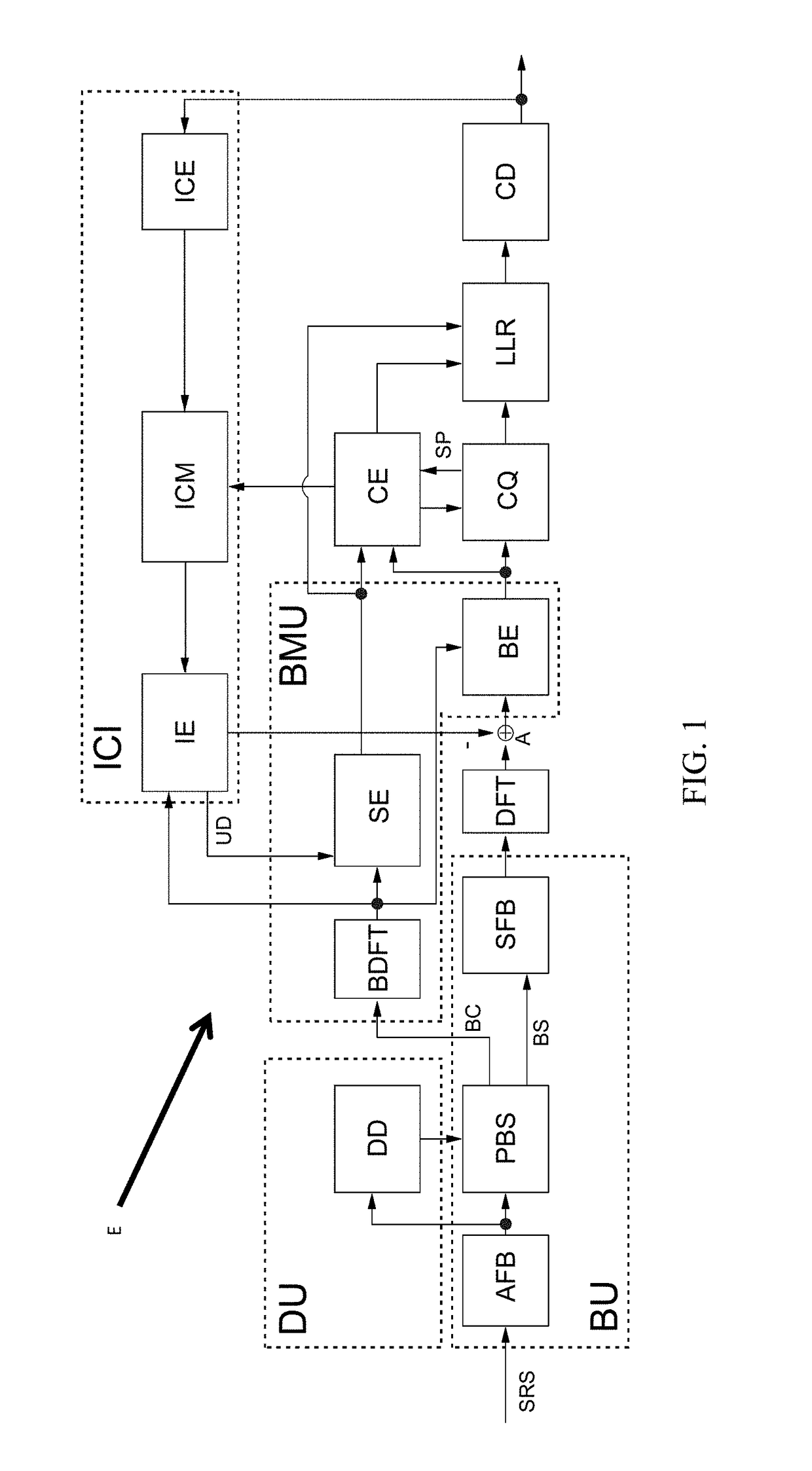
Method for frequency- and time-selective interference suppression for a communication system based on ofdm, and receiver therefor
ActiveUS20180019774A1Frequency easyTime facilitatedChannel estimationMulti-frequency code systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Communications system
A method for frequency- and time-selective interference suppression for a communication system based on OFDM, and a receiver therefor. To achieve a much lower bit error rate at the output of the receiver or to permit greater interference or a lower signal-to-noise ratio (in a prior art L-DACS1 receiver, at least 45 nautical miles) for the same transmission power, the invention provides: a filter bank pulse blanking method FBPB in which the sampled received signal is applied to a blanking unit for frequency-selective pulse blanking, which blanking unit consists of an analysis filter bank having M sub-bands; a module for frequency-selective pulse blanking of the sub-band signals; and a synthesis filter bank, which reassembles the signal. The analysis filter bank, which breaks down the received signal into multiple sub-bands on a frequency-selective basis, is used before OFDM windowing, such that the sub-band breakdown applies pulse blanking on a sub-band-selective basis.
Owner:IAD GESELLSCHAFT FUER INFORMATIK AUTOMATISIERUNG & DATENVERARBEITUNG MBH
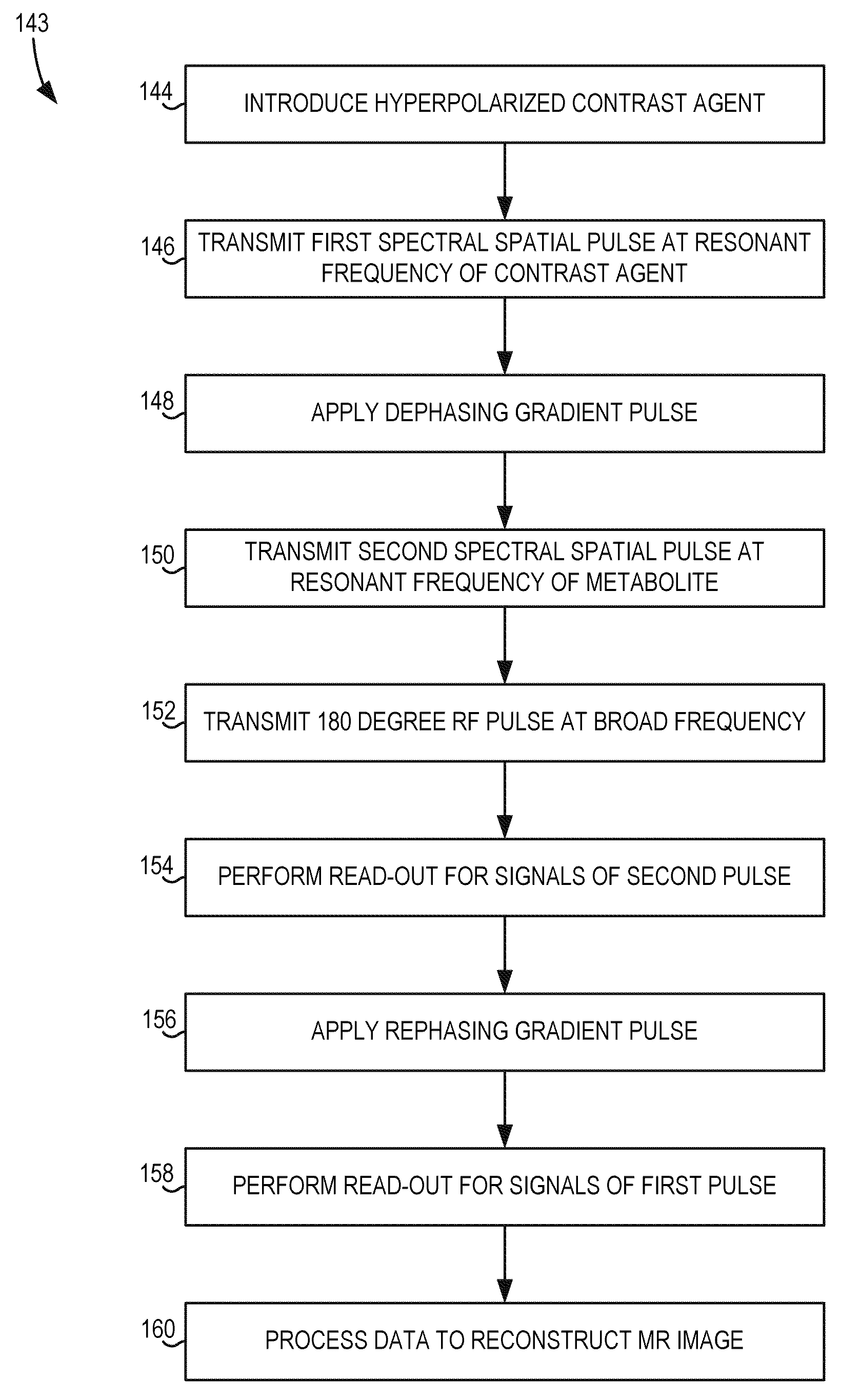
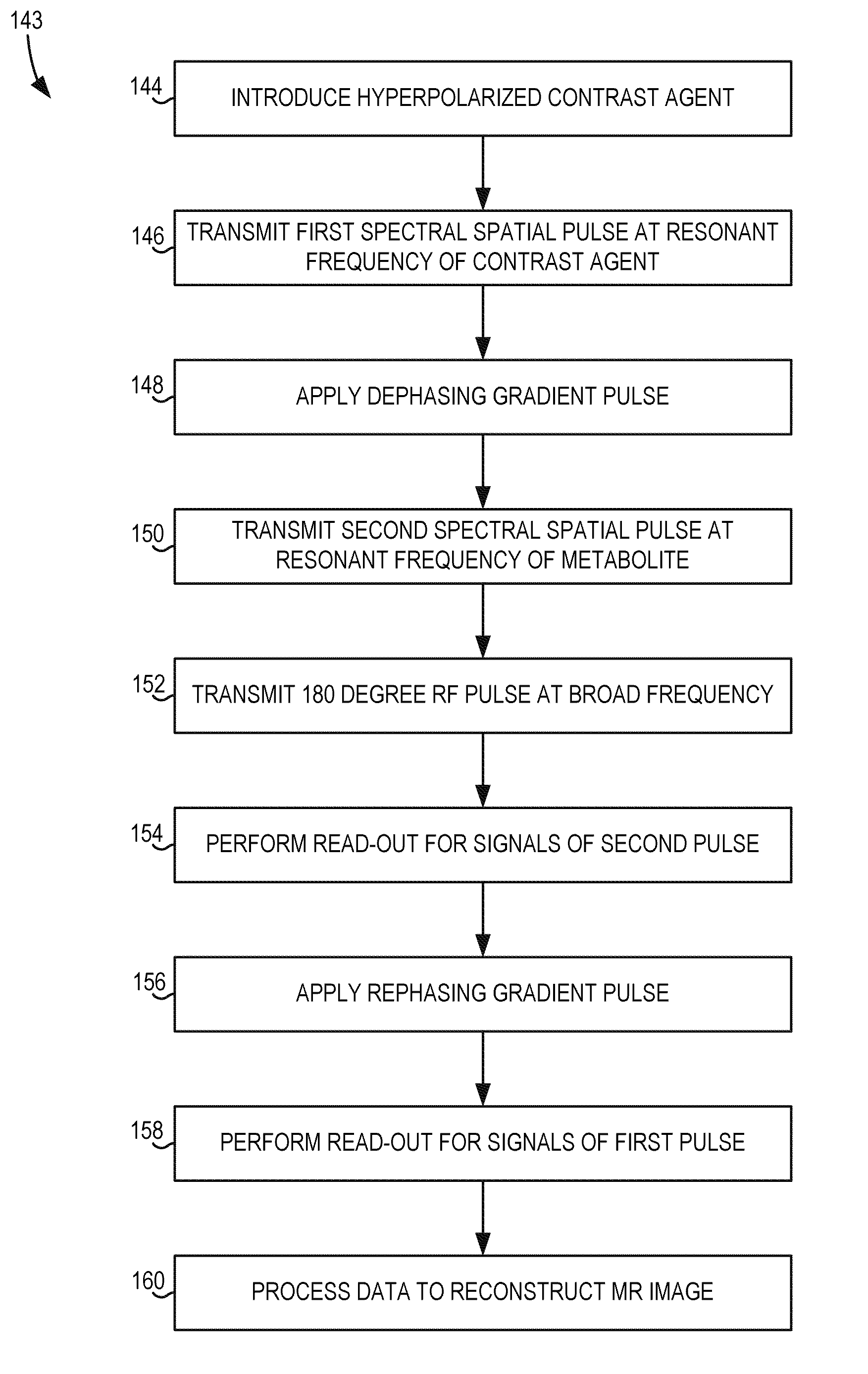
System and method for fast mr imaging of metabolites at selective excitation frequencies
InactiveUS20080116893A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMetaboliteSelective excitation
A system and method are provided for imaging multiple substances, such as contrast agents and metabolites in vivo, with selective excitation frequencies. A first substance is excited with a frequency selective pulse, then a second substance is excited with another frequency selective pulse. The signals resulting from these pulses are acquired in an order reversed from the order in which the pulses were applied. In some embodiments, more than two substances may be imaged. The system and method thus provide for quick and efficient utilization of the magnetization of multiple substances for spectral-spatial imaging.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Liquid crystal display device and method for driving a liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20010048414A1Reduce consumptionConsume moreLiquid crystal compositionsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
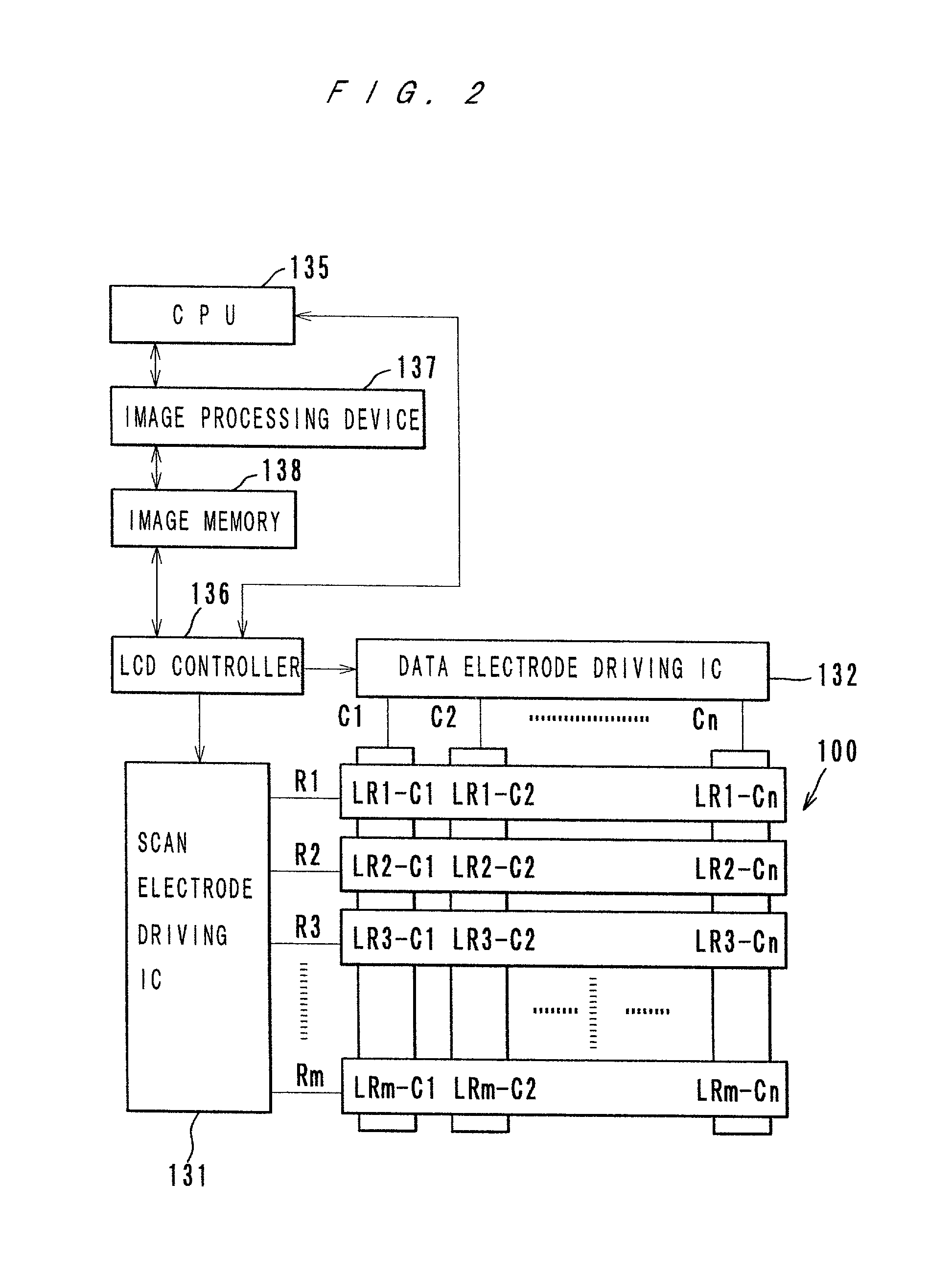
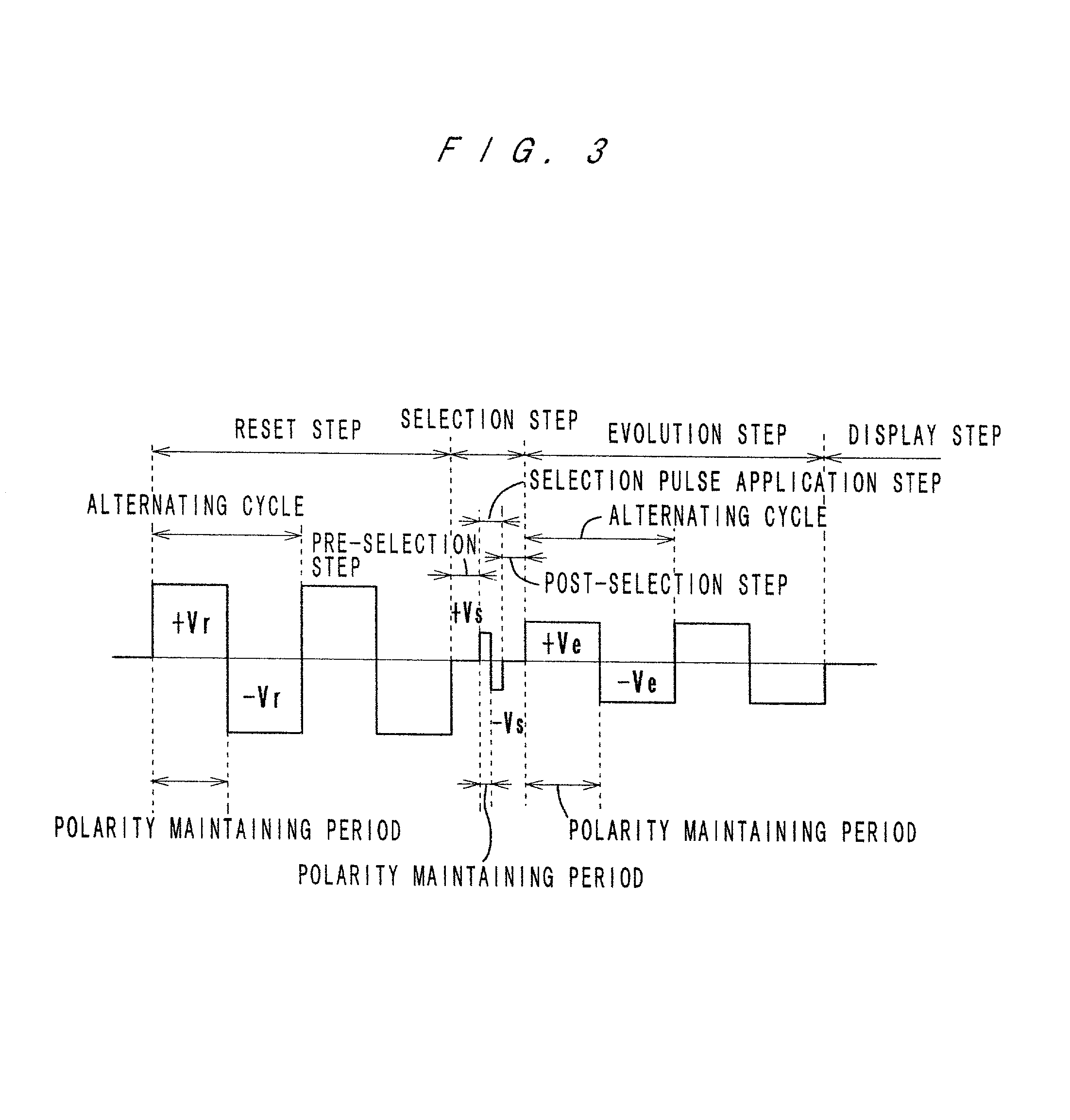
A liquid crystal display device which carries out matrix driving of a liquid crystal layer by applying AC pulses to the liquid crystal layer through a plurality of scan electrodes and a plurality of data electrodes which face and cross each other. A method of driving such a liquid crystal display comprises a reset step of applying a reset pulse to liquid crystal to reset the liquid crystal to an initial state, a selection step of applying a selection pulse to the liquid crystal to select a final state of the liquid crystal, an evolution step of applying an evolution pulse to the liquid crystal to cause the liquid crystal to evolve to the selected final state. The reset pulse and the evolution pulse have alternating cycles which are longer than that of the selection pulse, and the adjustment of the alternating cycles of the reset pulse and of the evolution pulse are made by changing the pulse waveform applied to each of the scan electrodes.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
System and method for fast MR imaging of metabolites at selective excitation frequencies
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and a device for driving a liquid crystal display, and a liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS7038648B2Reduce power consumptionPermit useStatic indicating devicesLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
Disclosed herewith is a matrix driving method of liquid crystal which exhibits a cholesteric phase. In the method, there is a selection pulse application step of applying pulses to select the final state of the liquid crystal, and between the selection pulse application step of a scanning line and the selection pulse application step of the next scanned scanning line, a delay step is inserted. During the delay step, a signal pulse is of 0V or of a pulse voltage for a display of a specified density.
Owner:MINOLTA CO LTD
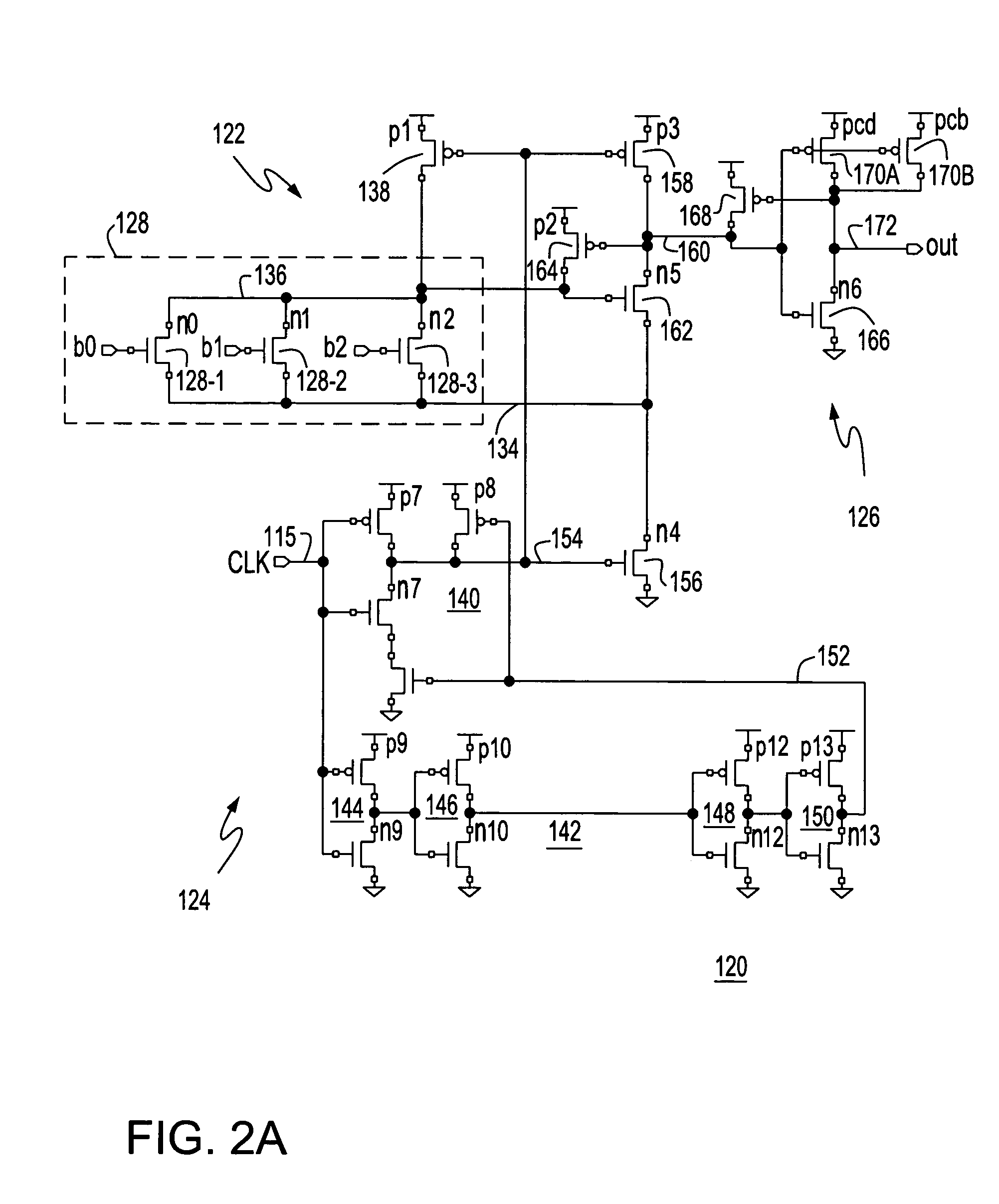
Self timed bit and read/write pulse stretchers
ActiveUS7006403B2High data reliabilityMinimize timeDigital storageRandom access memoryPulse stretcher
Bit and write decode / drivers, a random access memory (RAM) including the decode / drivers and an IC with a static RAM (SRAM) including the decode / drivers. The decode / drivers are clocked by a local clock and each produce access pulses wider than corresponding clock pulses. The bit decode / driver produces bit select pulses that are wider than a word select pulse and the write decode / driver produces write pulses that are wider than the bit select pulses for stable self timed RAM write accesses.
Owner:TWITTER INC
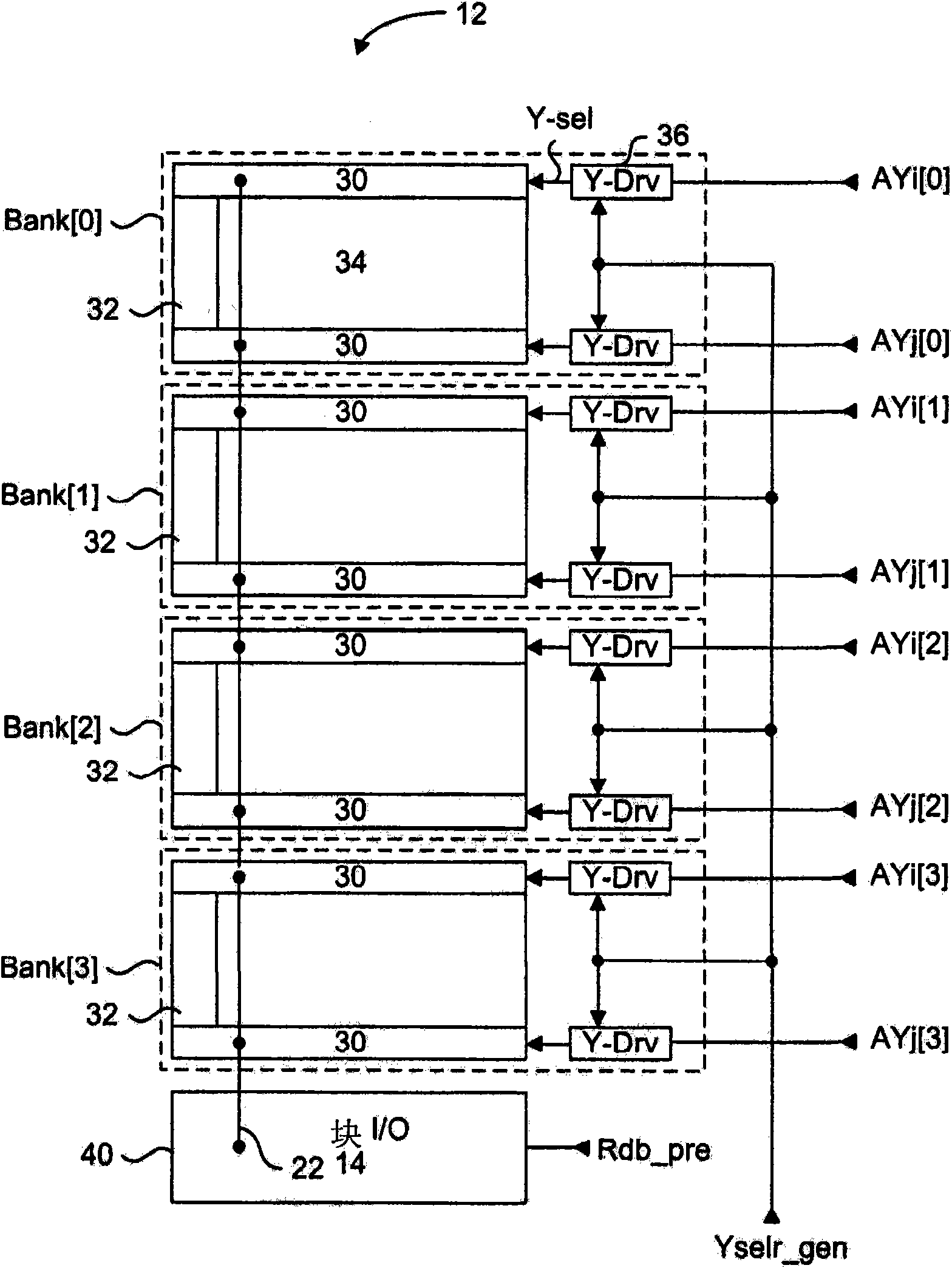
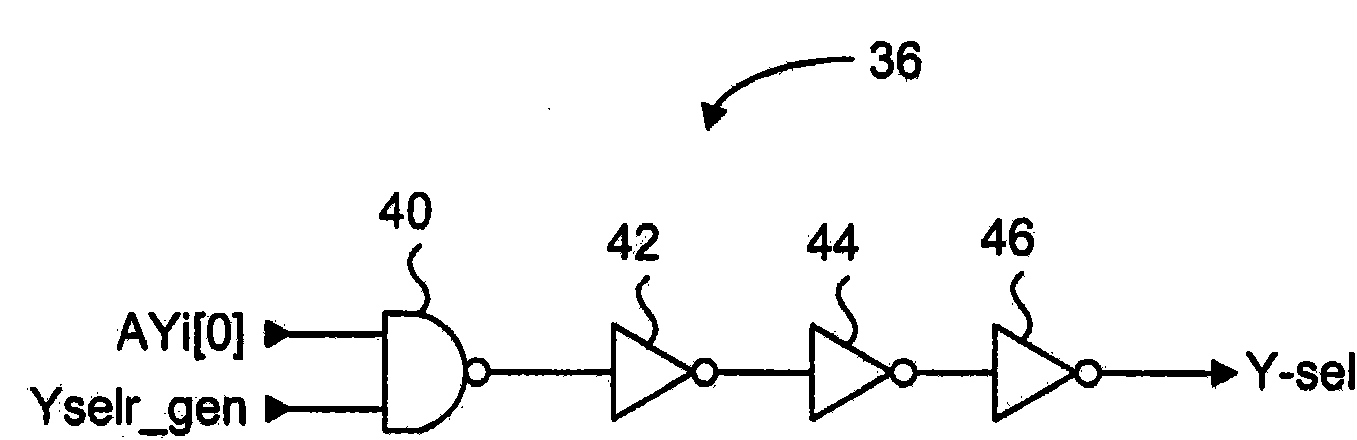
Interlock of read column select and read databus precharge control signals
A column select and databus precharge signal interlock scheme for a DRAM memory. The signal interlock system includes column read enable circuits associated with each bank of a DRAM memory for generating column select signals for coupling data to a common read databus, and a read databus precharge disable signal for disabling read databus precharge devices. Each column read enable circuit includes pulse generator circuits with tunable components for generating at least one column select signal pulse and the read databus precharge disable pulse in a read operation. The pulse generator circuits ensure that the column select pulse is always nested with respect to the read databus precharge disable pulse. Therefore, there is no overlap between active column select devices and active read databus precharge devices.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
ATM vibration detection alerter
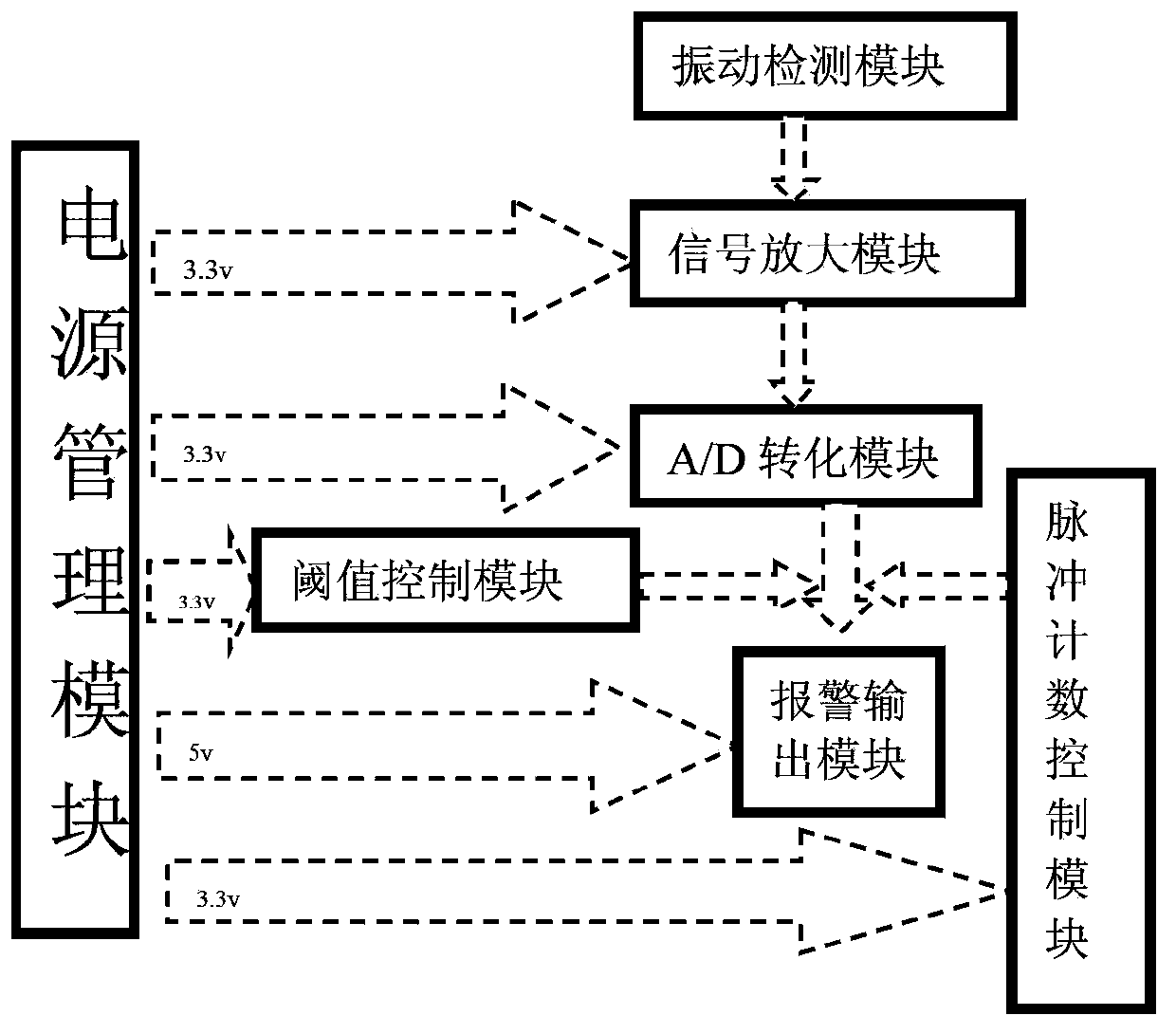
InactiveCN104183070AImprove adaptabilitySimple structureBurglar alarm mechanical actuationBurglar alarm electric actuationSupply managementCounting Number
The invention provides an ATM vibration detection alerter which mainly comprises a power supply management module, a vibration detection module which is used for detecting a vibration signal, a signal amplification module which is used for amplifying the signal, an A / D conversion module, a threshold control module which is used for setting alarm difficulty, a pulse number control module which is used for selecting the counting number of pulse number, and an alarm output module. The ATM vibration detection alerter is small in size and easy to use, and can be directly adhered on an object requiring protection. When the object requiring protection is intruded and vibrates, cables are damaged, the ATM vibration detection alerter is disassembled or an alarm terminal falls off, an alarm signal can be transmitted to an alarm host by the ATM vibration detection alerter. Besides, the ATM vibration detection alerter is high in detection sensitivity and quite high in security and reliability.
Owner:北京国通创安报警网络技术有限公司
Photoelectric conversion cell and array, reading method therefor, and circuit thereof
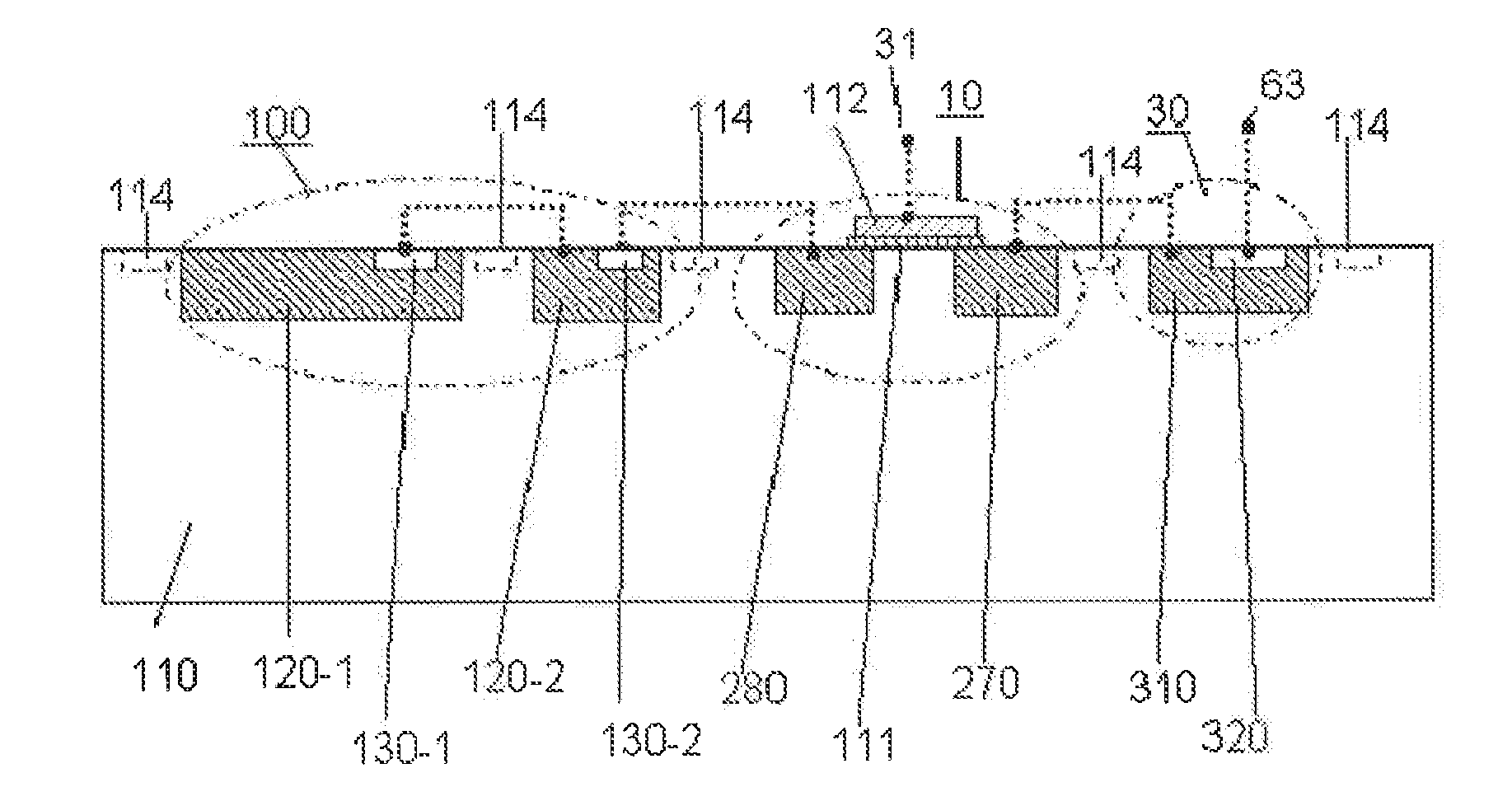
InactiveUS20130119240A1Increase of reading delayInhibition effectTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesHemt circuitsEngineering
In order to achieve a photovoltaic cell and an array of high sensitivity and high dynamic range, there is a need for a photovoltaic cell and an array which are combined so that an amplified photovoltaic element and a selection element are resistant to external noise, and so that the combination is resistant to effects from address selection pulse noise at array readout time. In the present invention, in order to solve the problem, a photovoltaic cell has been configured with a combination of an amplified photovoltaic element (100) and a selection element (10 and the like) which are resistant to external noise, and various means of solution of the combination are provided which are resistant to the effects of address selection pulse noise at array readout time. As a result, a dynamic range of 6 to 7 orders of magnitude for light detection has become possible.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
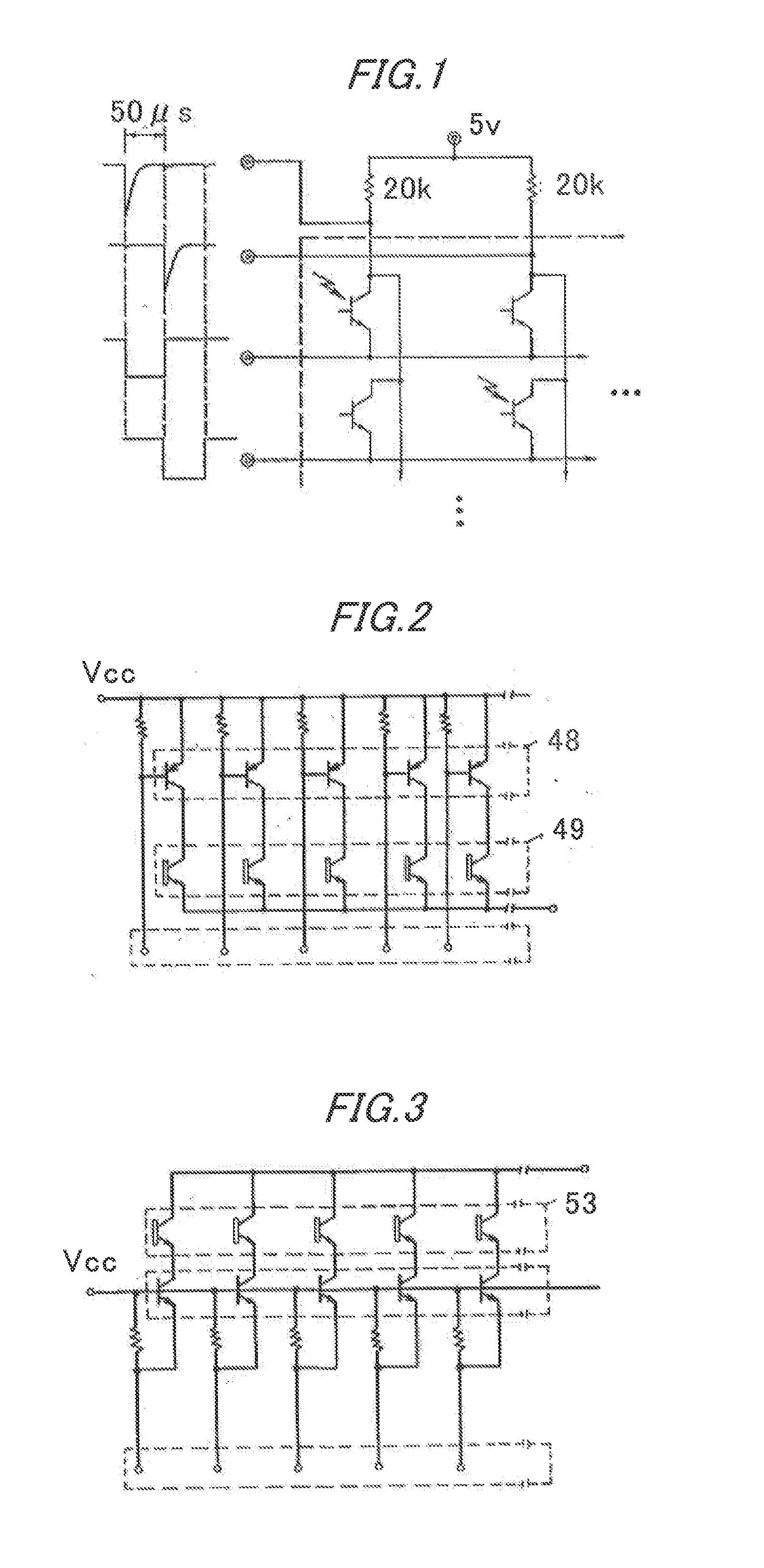
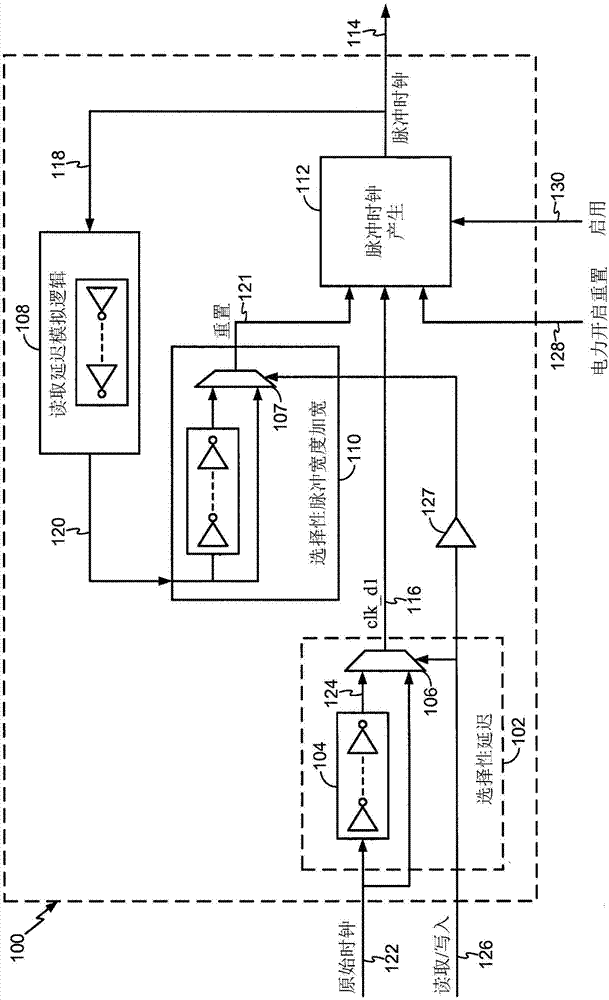
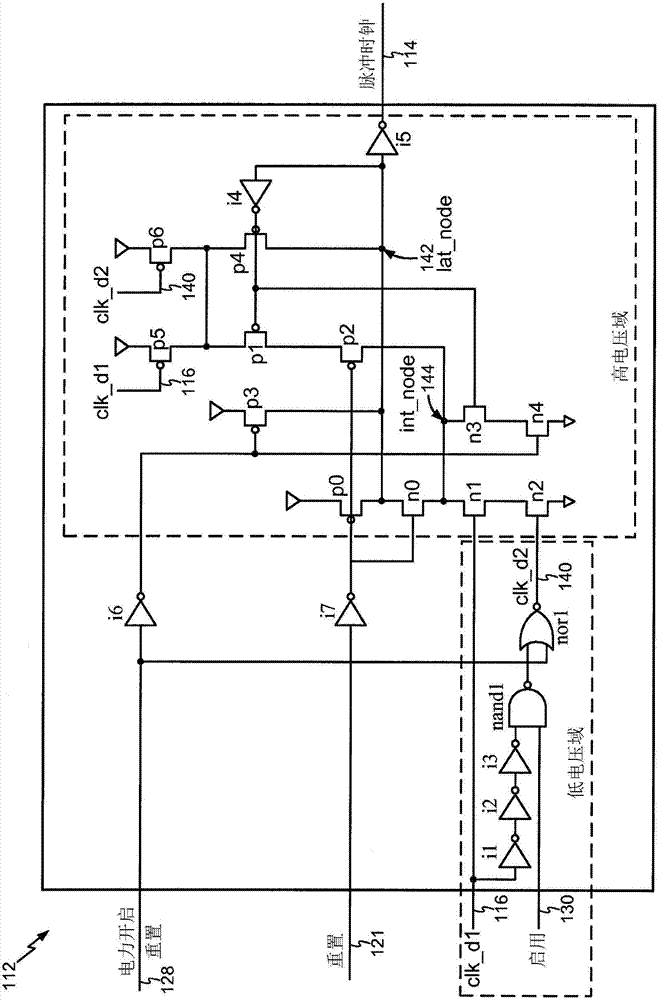
A pulse clock generation logic with built-in level shifter and programmable rising edge and pulse width
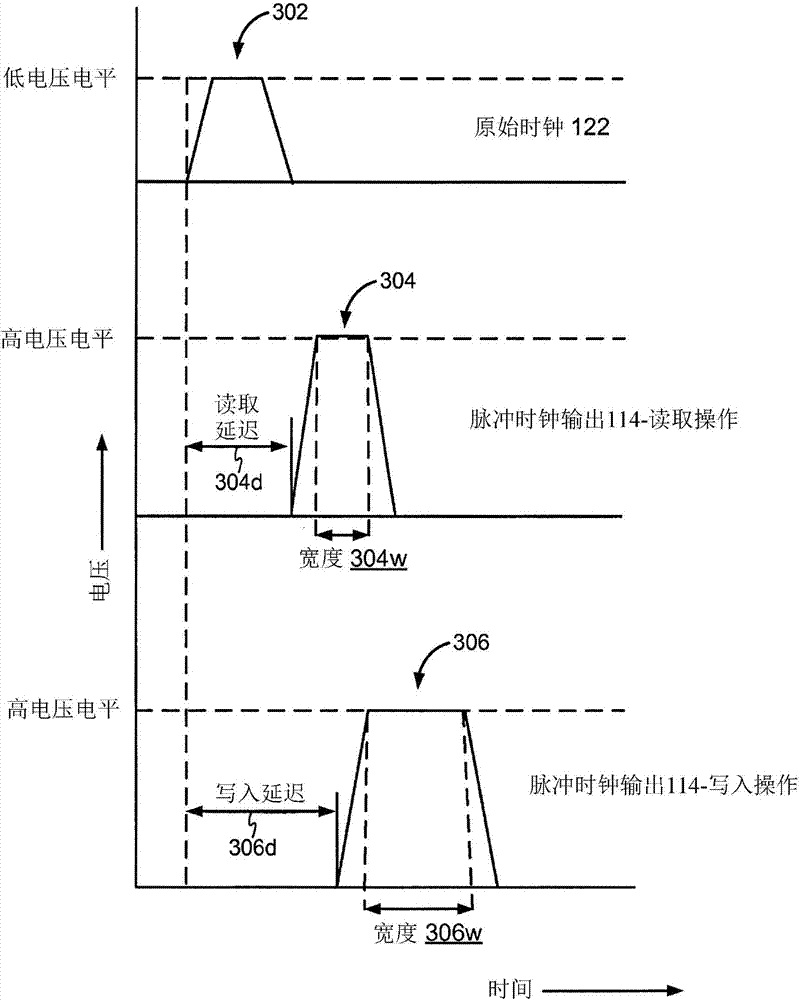
Systems and methods for generating pulse clocks with programmable edges and pulse widths configured for varying requirements of different memory access operations. A pulse clock generation circuit includes a selective delay logic to provide a programmable rising edge delay of the pulse clock, a selective pulse width widening logic to provide a programmable pulse width of the pulse clock, and a built-in level shifter for shifting a voltage level of the pulse clock. A rising edge delay for a read operation is programmed to correspond to an expected read array access delay, and the pulse width for a write operation is programmed to be wider than the pulse width for a read operation.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Storage Cell Design Evaluation Circuit Including a Wordline Timing and Cell Access Detection Circuit
InactiveUS20080137455A1Accurately determining wordline timingDigital storageDriver circuitImage resolution
A method for storage cell design evaluation provides accurate information about state changes in static storage cells. A wordline select pulse is propagated along the wordline select path of the test row to an output driver circuit, in order to test the clock and / or address timing of the row, so that variation of access timing, read stability and writeability with wordline strength / access voltage can be determined. An access detection cell holds the input of the output driver circuit until a simulated access operation activated by the wordline select pulse is complete. Multiple test rows may be cascaded among columns to provide a long delay line or ring oscillator for improved measurement resolution.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com