Patents
Literature
451 results about "Process changes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
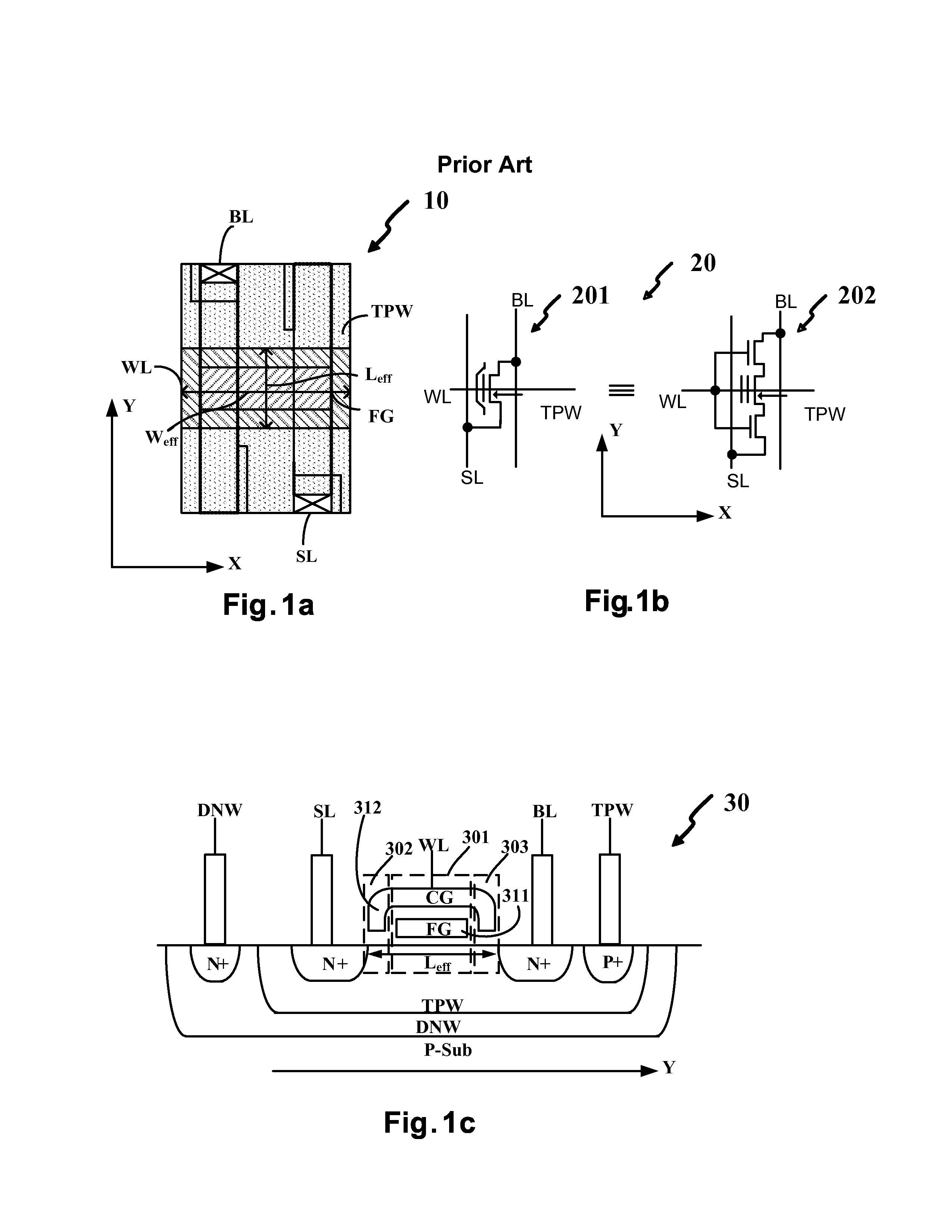
Process Change. Corporate processes refer to steps and procedures that top leadership puts into place to ensure effectiveness in operating activities and prevent losses resulting from fraud, technological malfunction or error. Department chiefs and segment leaders change existing processes to improve them, follow industry practices...
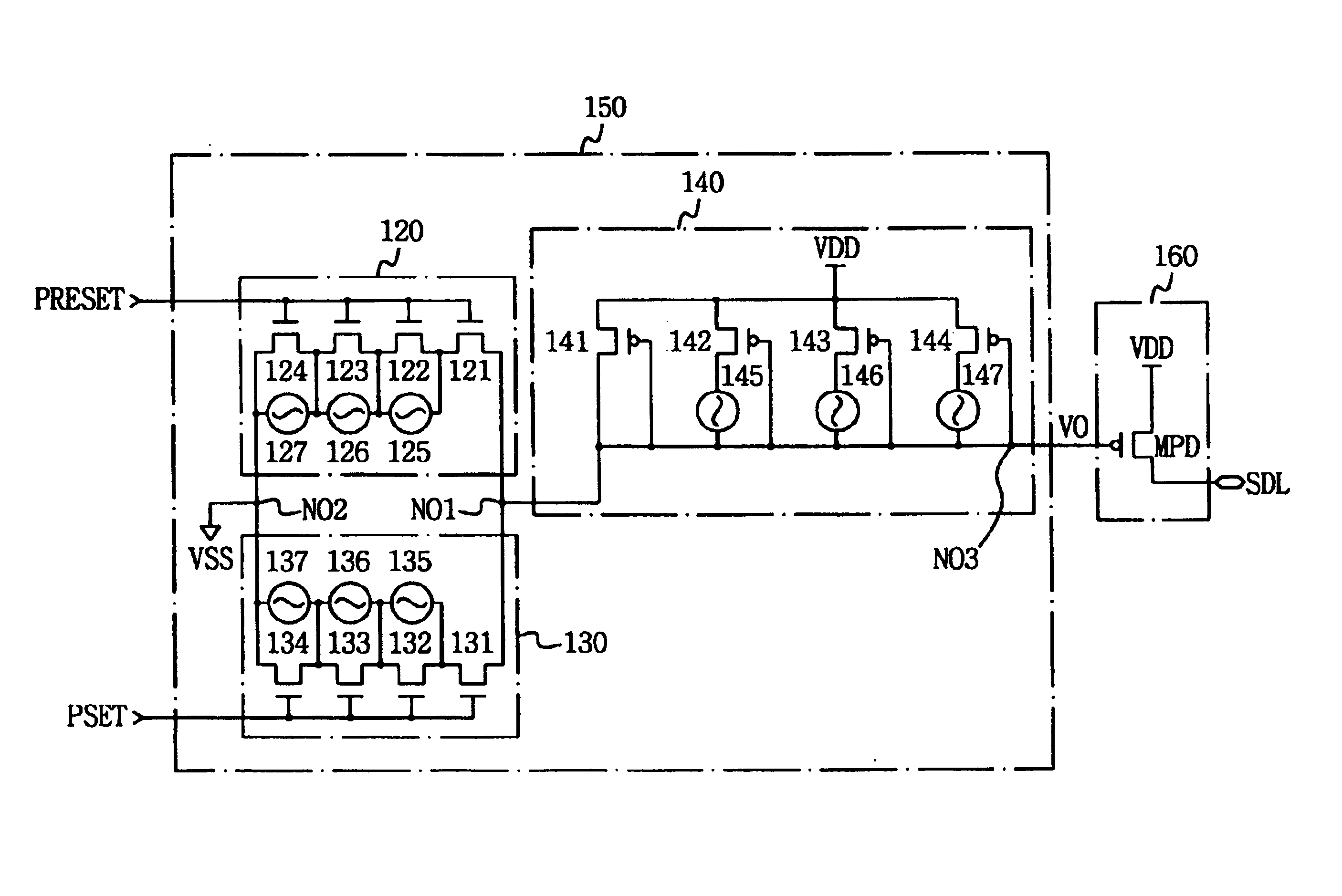
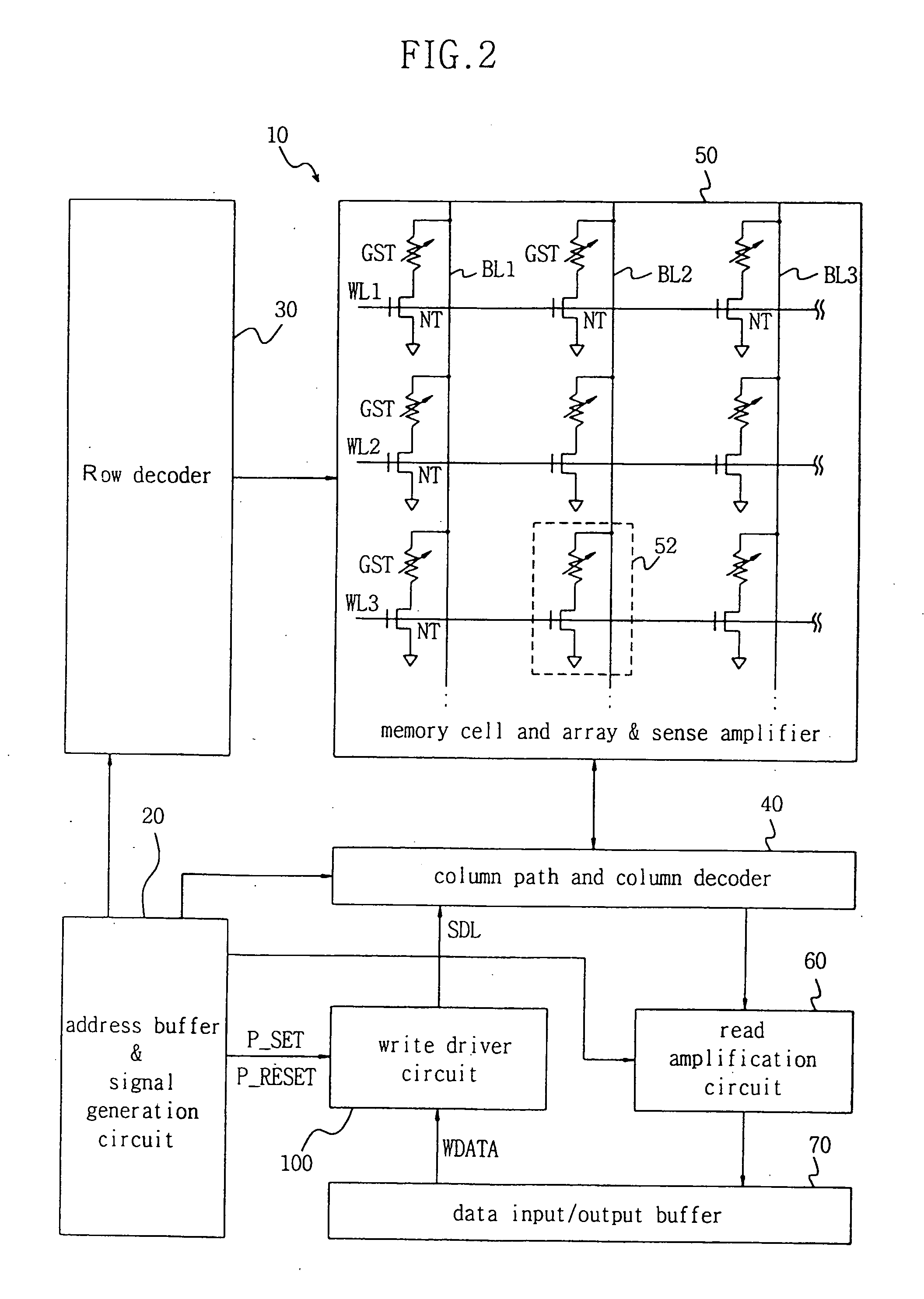
Write driver circuit in phase change memory device and method for applying write current
ActiveUS6928022B2Maximize reliabilityReduce the voltage levelSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDriver circuitPhase-change memory
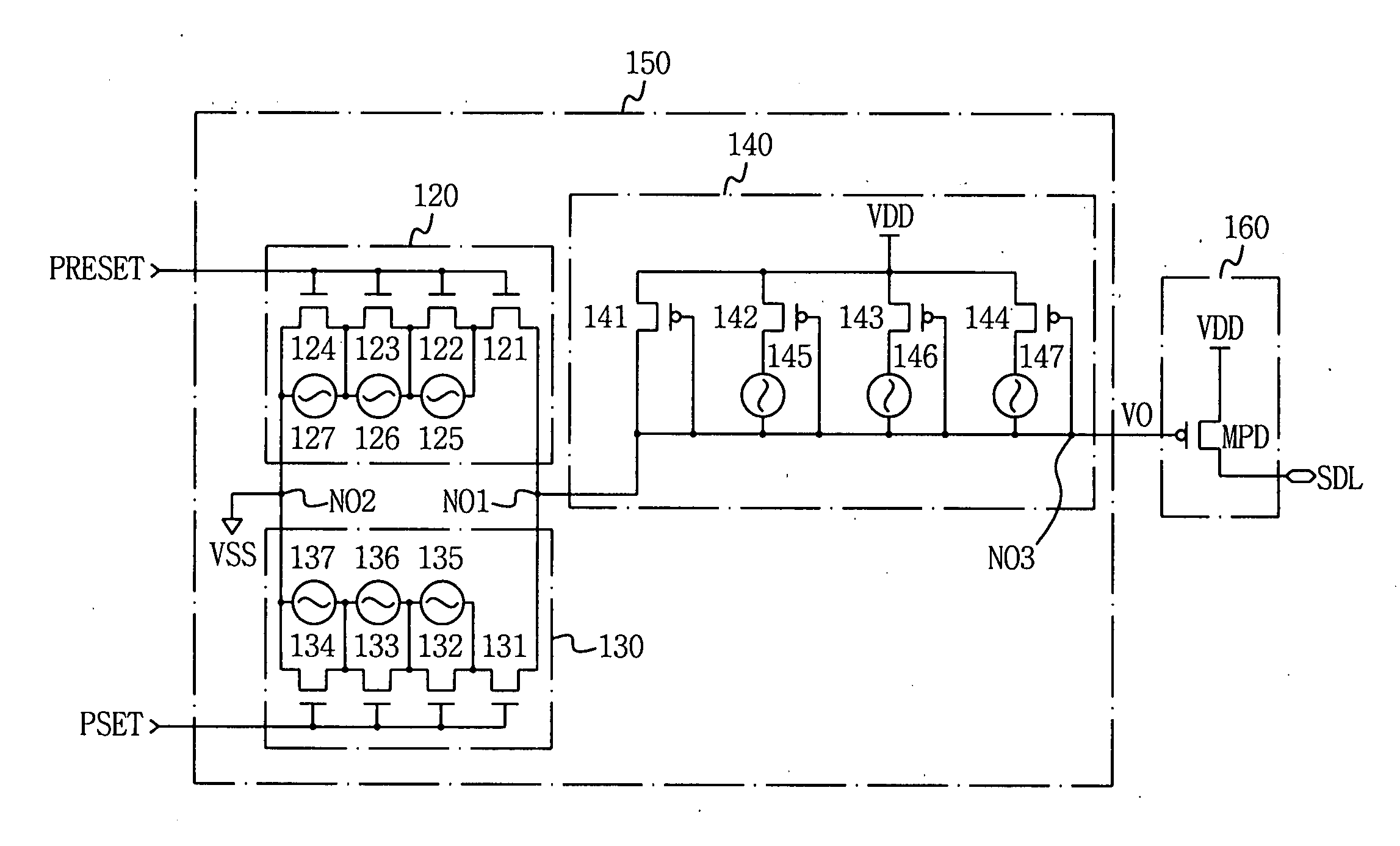
A write driver circuit including a plurality of programmable fuses for a phase change memory device in which a write operation is correctly performed even in the case where a current output shift in a write current generation circuit; or in the case where a phase change memory cell having a phase change property shift due to an external factor or due a process change. The write driver circuit includes a write current control unit for outputting a first or second level of voltage selected, by selecting one of a first or second programmable current path, based on whether a first or second selection pulse signal is applied; and a current driving unit for generating a write current controlled by the output voltage of the write current control unit. Each of the first and second programmable current paths includes fuses that can be programmed to adjust their resistance to adjust the respective selected output voltage to compensate for the current output shift in the write current generation circuit or for the phase change memory cell having the phase change property shift.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
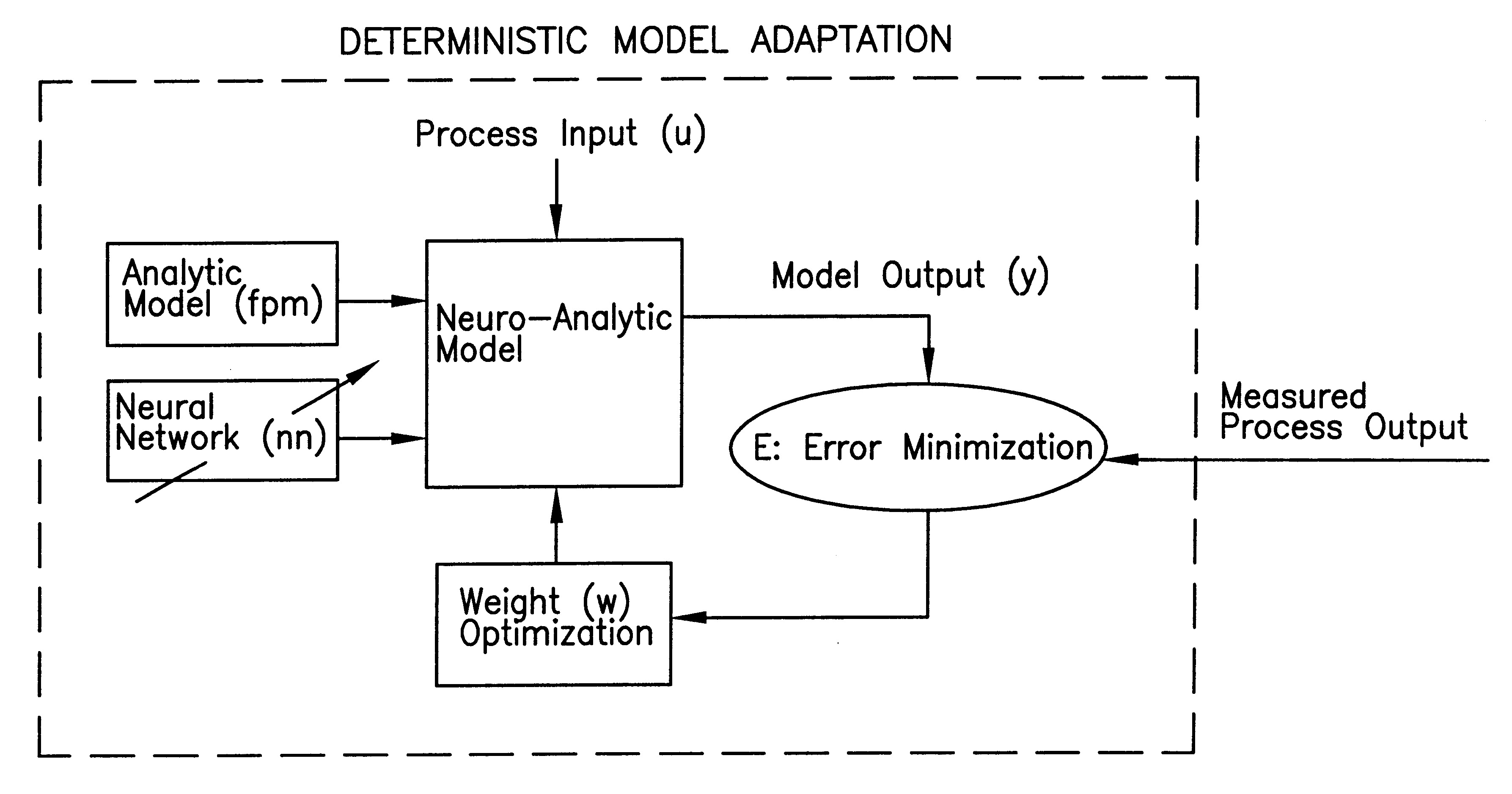
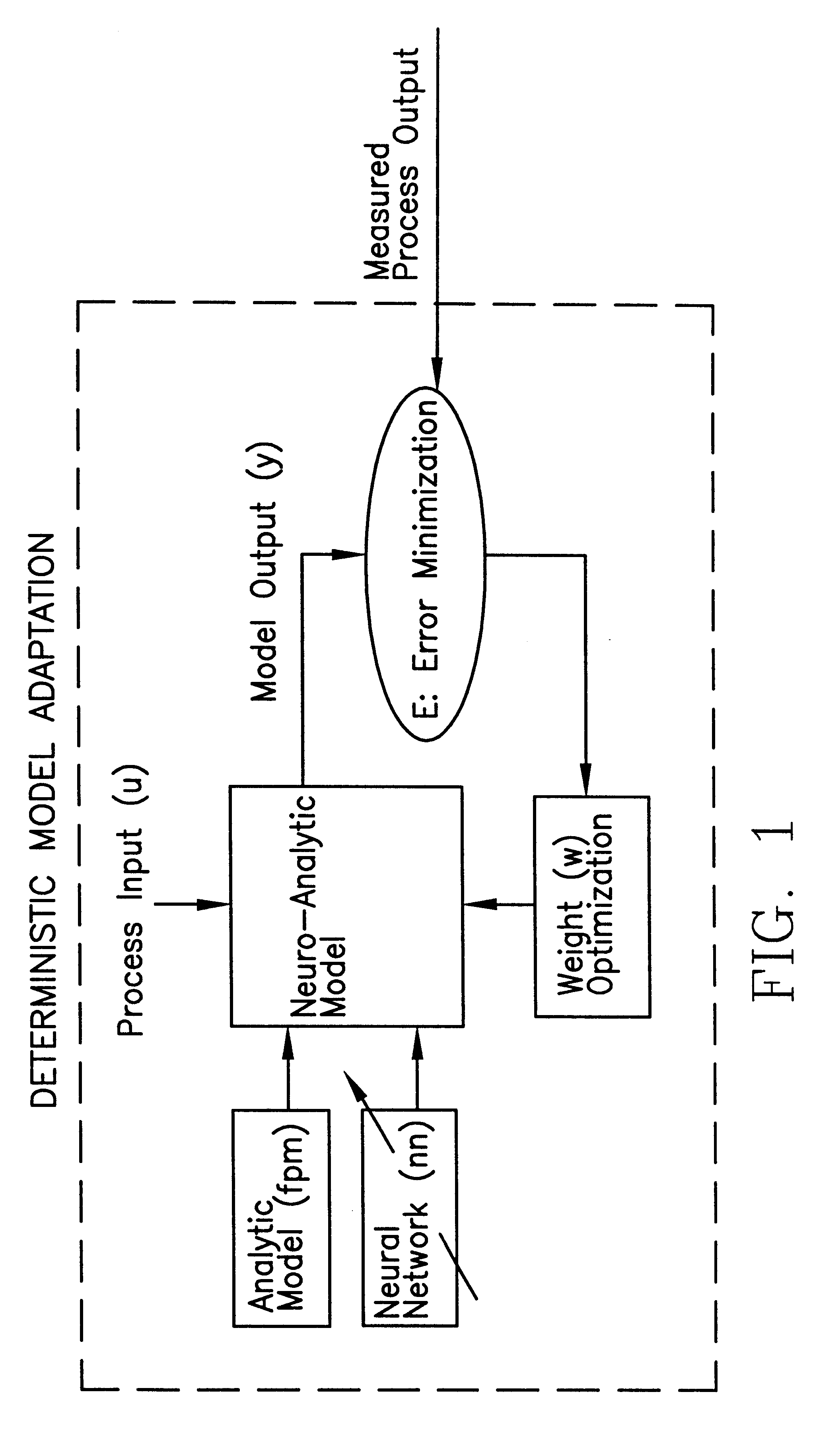
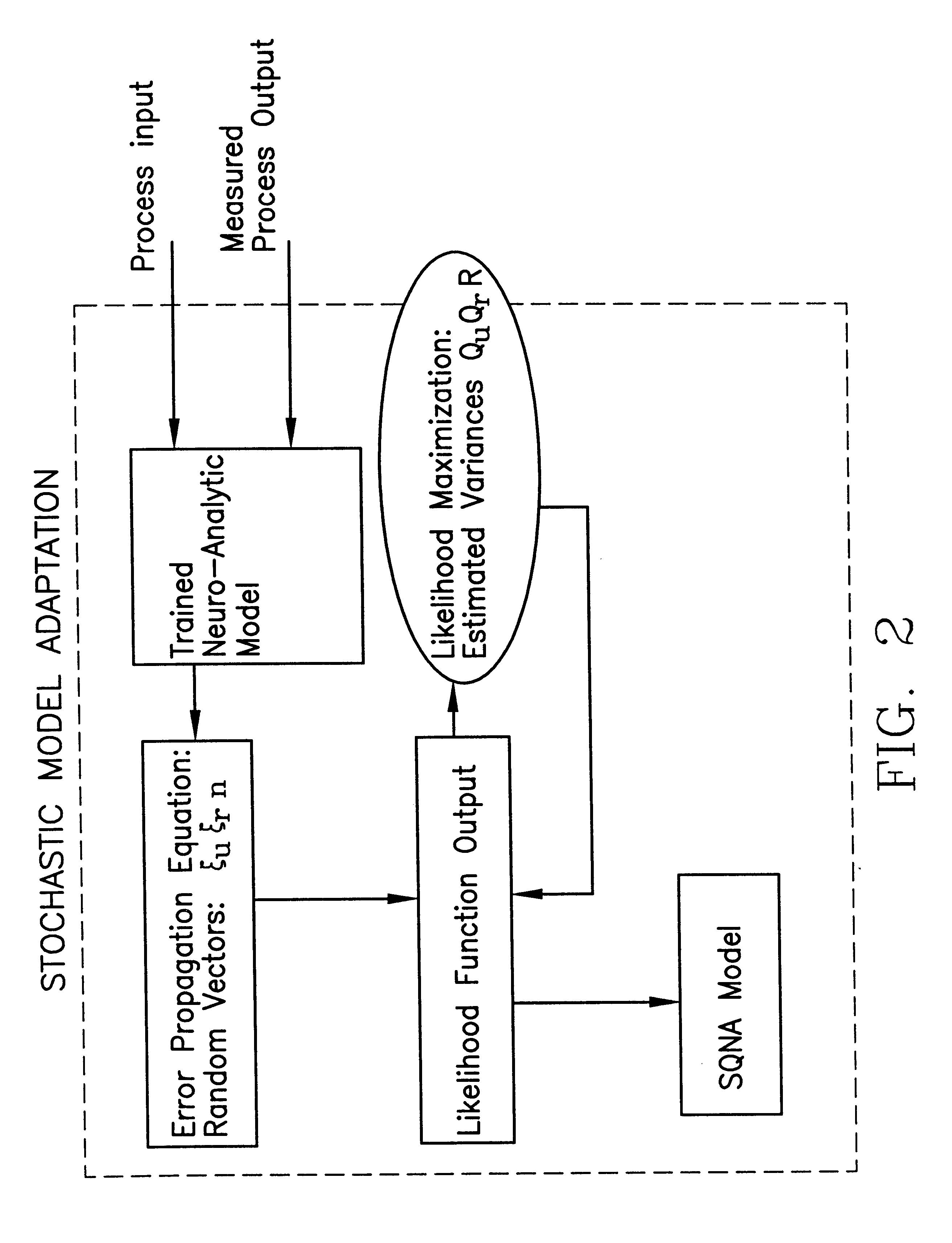
Statistically qualified neuro-analytic failure detection method and system
InactiveUS6353815B1Accurate and reliable on-lineImprove the level ofSimulator controlDigital computer detailsPeristaltic pumpAnalytic model
An apparatus and method for monitoring a process involve development and application of a statistically qualified neuro-analytic (SQNA) model to accurately and reliably identify process change. The development of the SQNA model is accomplished in two stages: deterministic model adaption and stochastic model modification of the deterministic model adaptation. Deterministic model adaption involves formulating an analytic model of the process representing known process characteristics, augmenting the analytic model with a neural network that captures unknown process characteristics, and training the resulting neuro-analytic model by adjusting the neural network weights according to a unique scaled equation error minimization technique. Stochastic model modification involves qualifying any remaining uncertainty in the trained neuro-analytic model by formulating a likelihood function, given an error propagation equation, for computing the probability that the neuro-analytic model generates measured process output. Preferably, the developed SQNA model is validated using known sequential probability ratio tests and applied to the process as an on-line monitoring system. Illustrative of the method and apparatus, the method is applied to a peristaltic pump system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
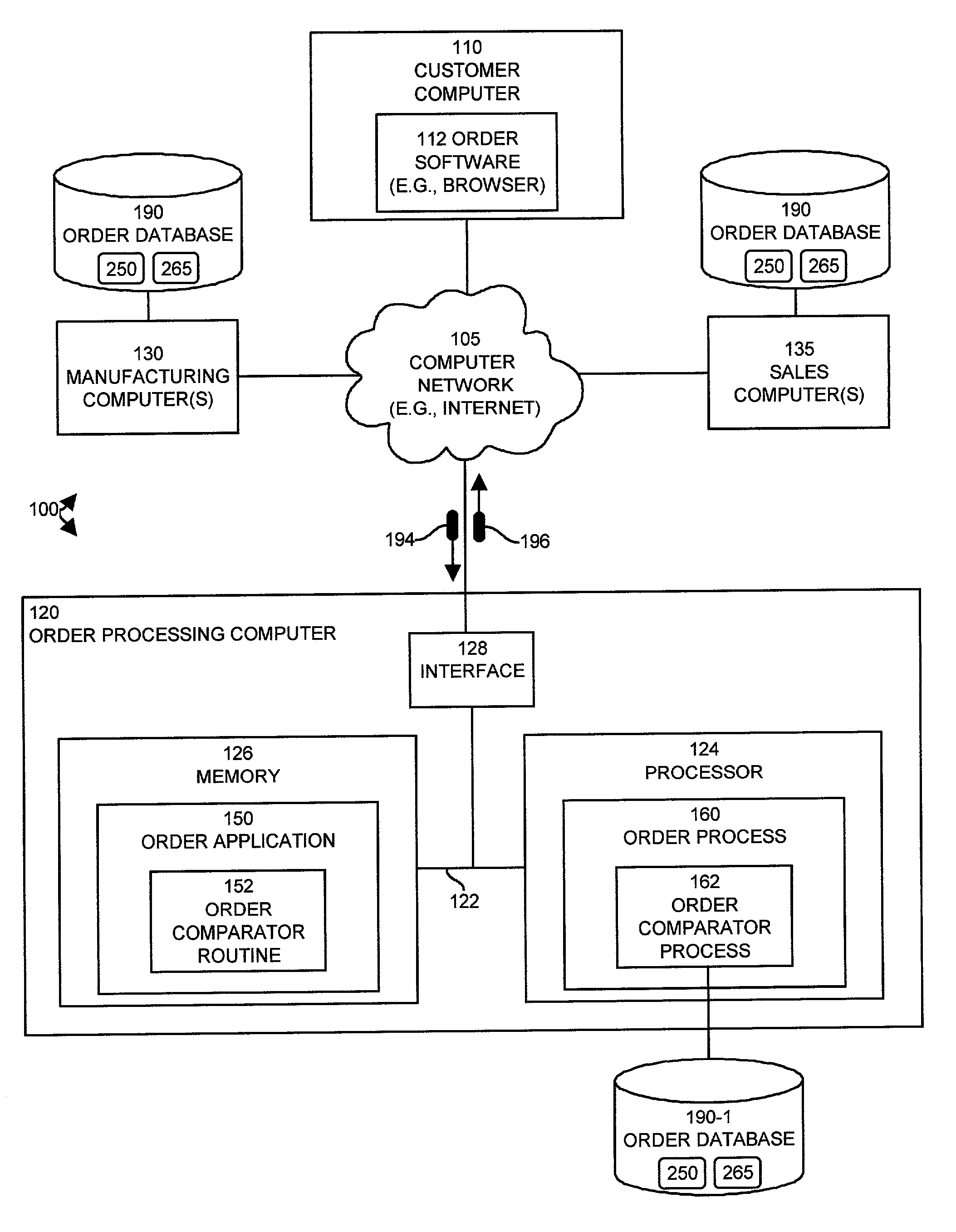
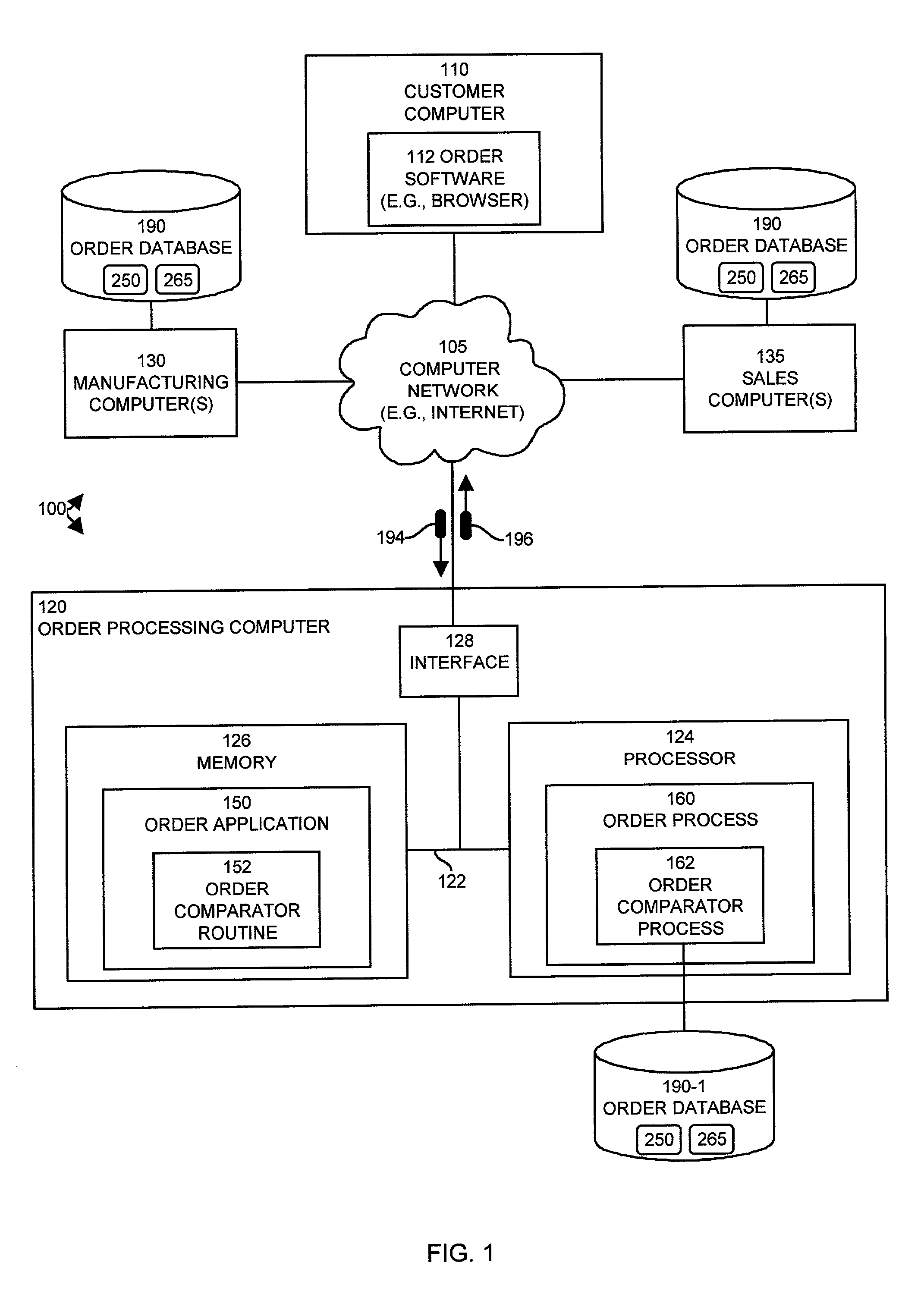
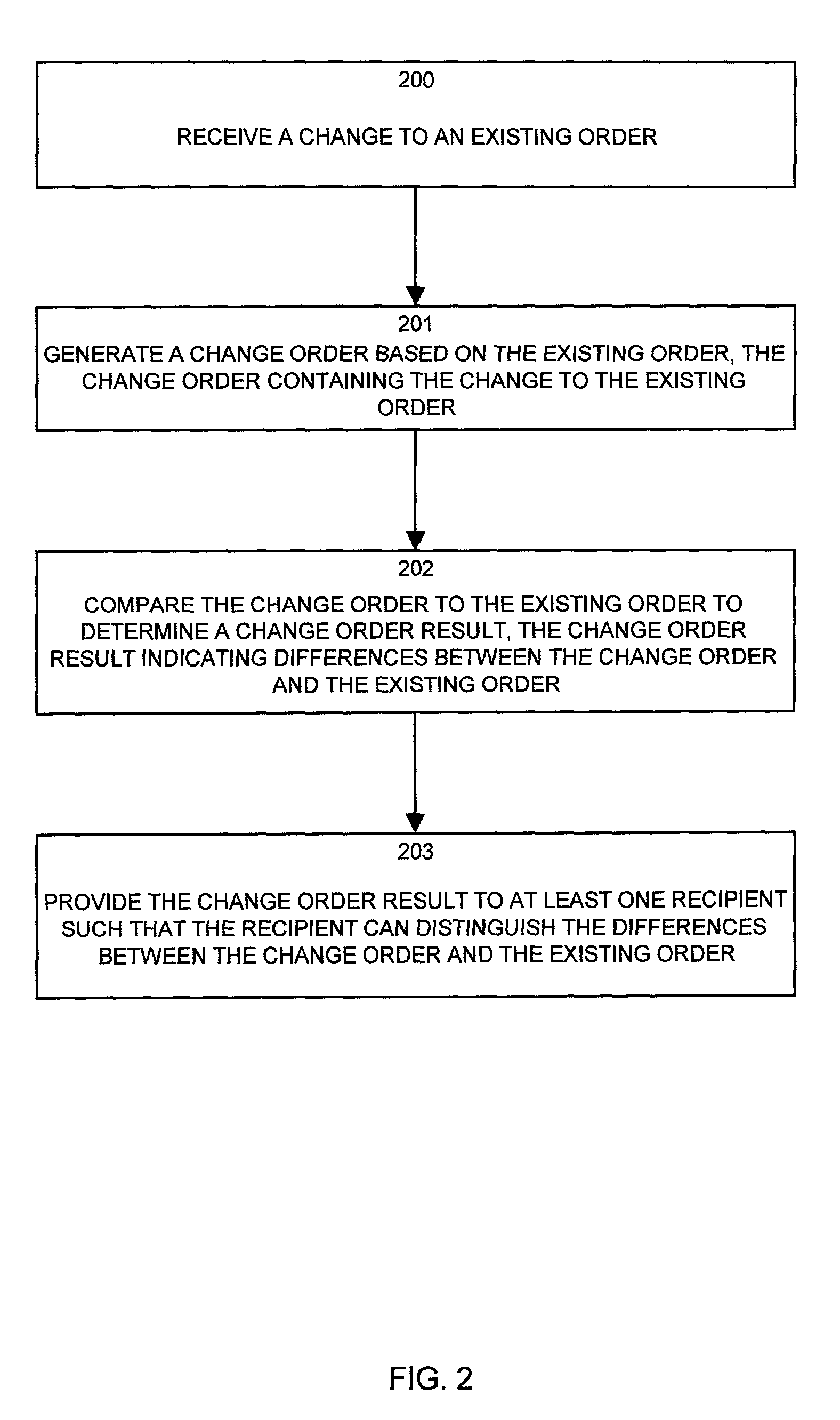
Methods and system for processing changes to existing purchase orders in an object-oriented order processing system
In an order processing system, mechanisms and techniques receive a change to an existing order in the order processing system and generate a change order based on the existing order. The change order includes the change to the existing order. The system can then compare the change order to the existing order to generate change order result that indicates differences between a change order in the existing order. The system then provides the change order result to at least one recipient such that the recipient may distinguish the differences between a change order in the existing order. Since a change to an existing order can result in changes other than those specifically specified in the received change, the system of the invention allows a person making the change to be presented with the change order results that convey all of the changes that result to the existing order.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
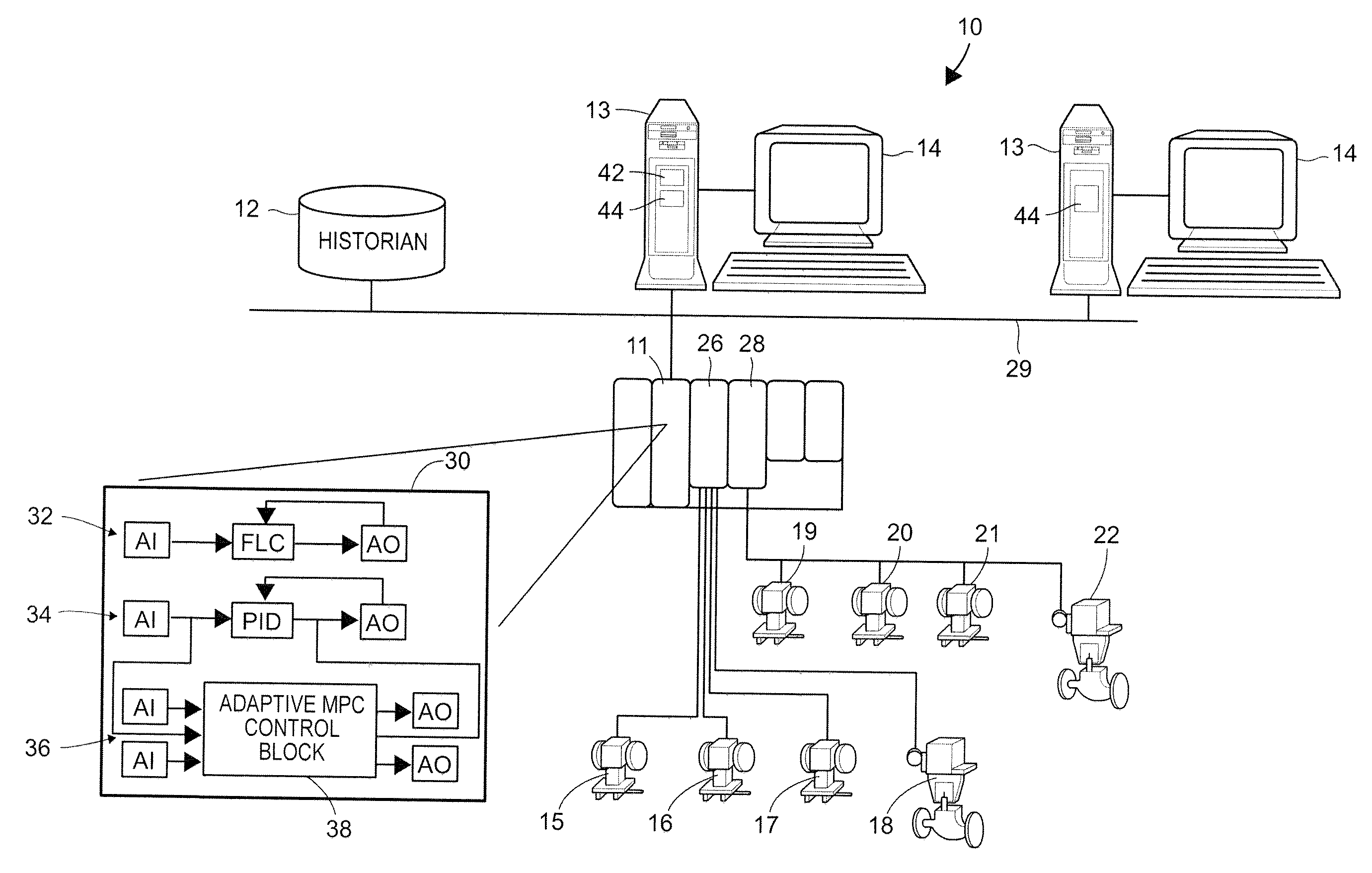
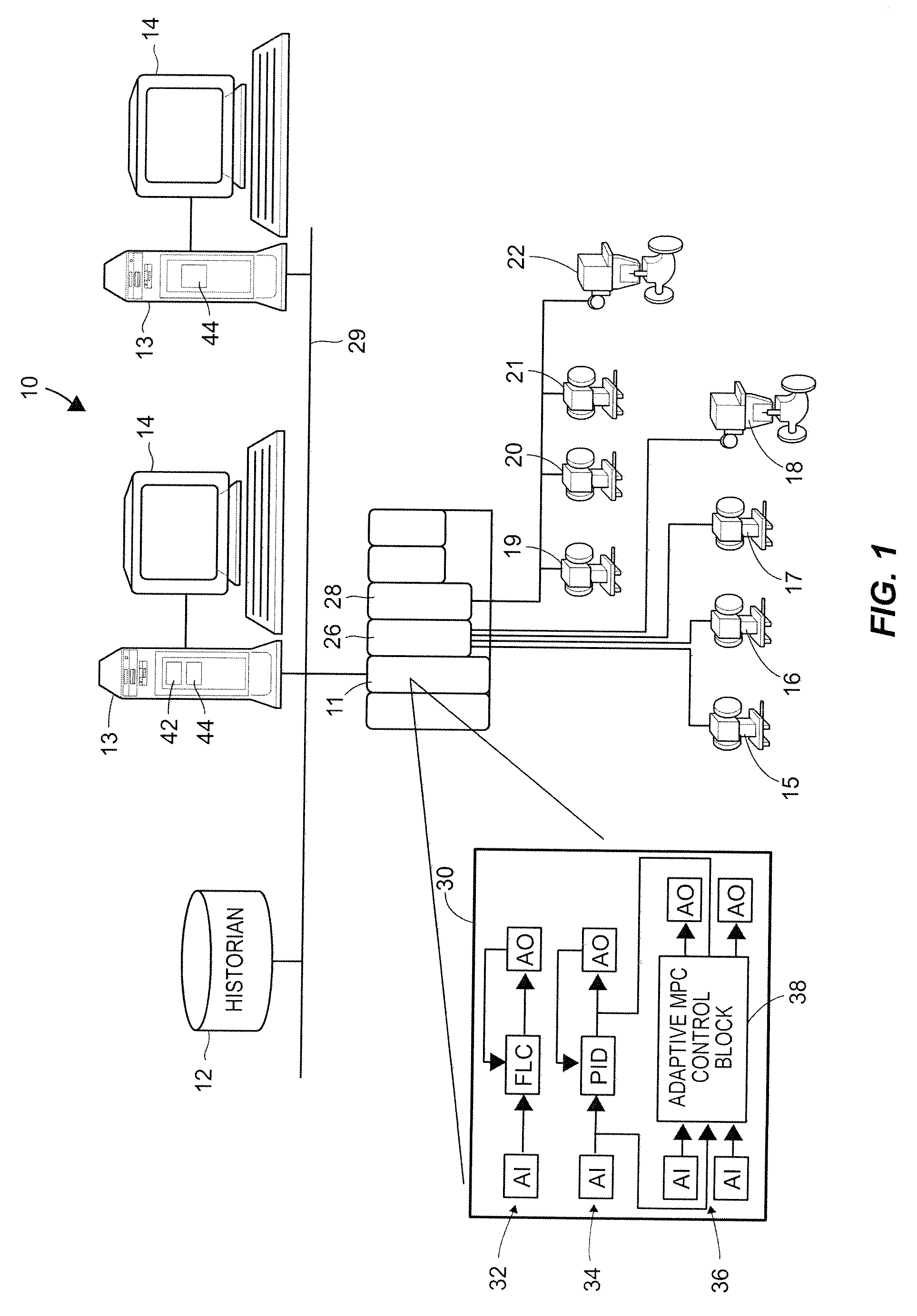
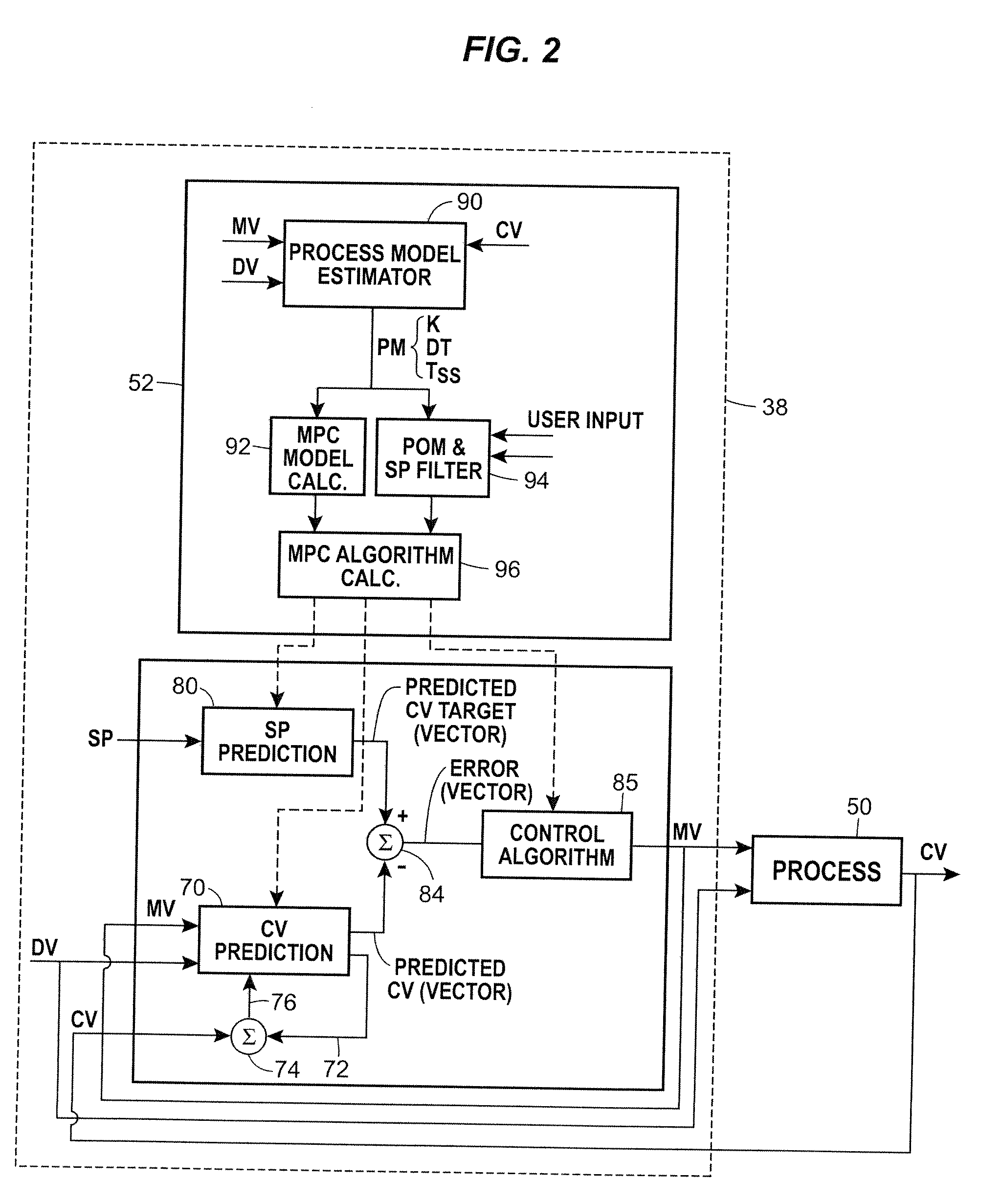
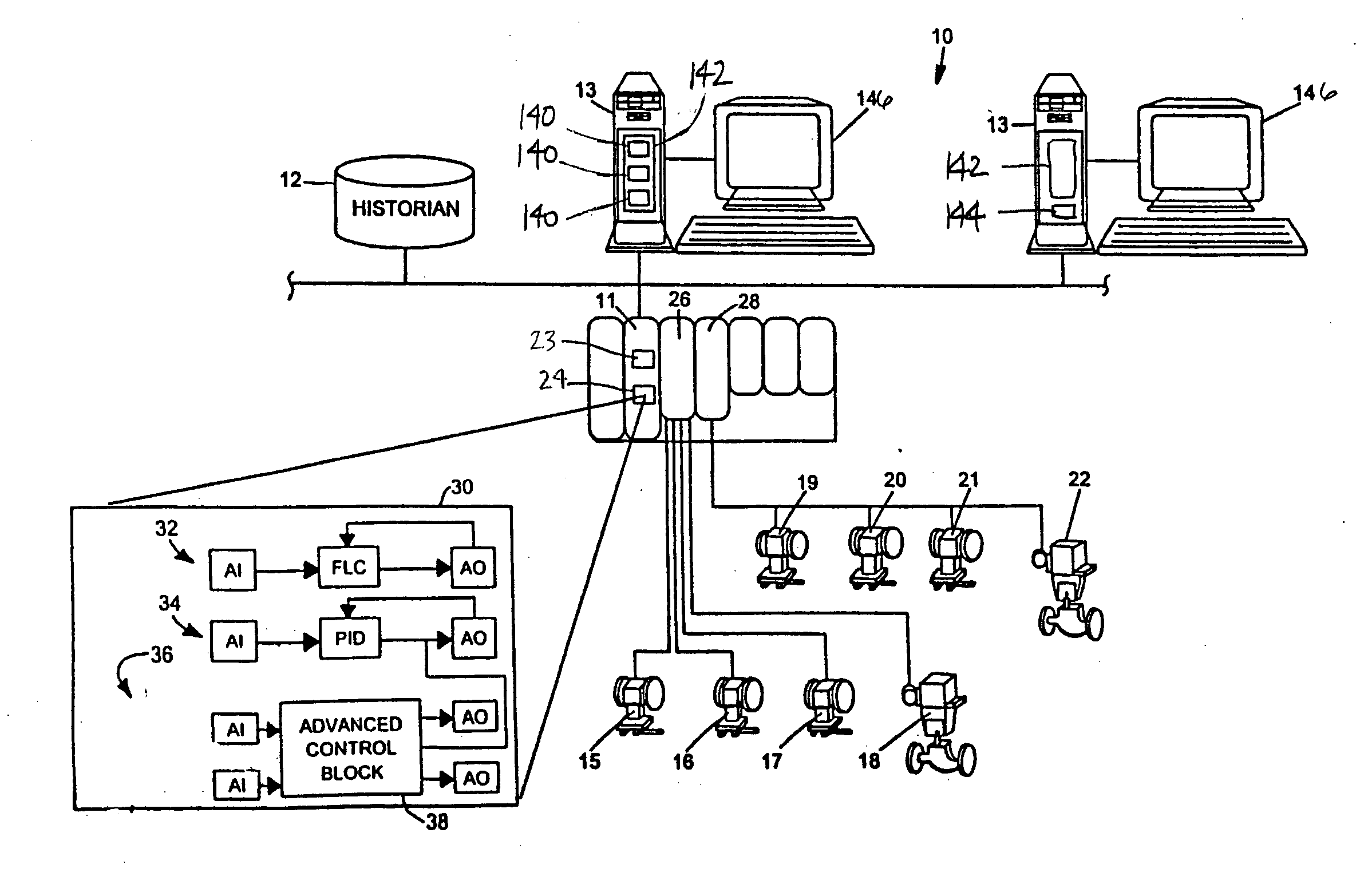
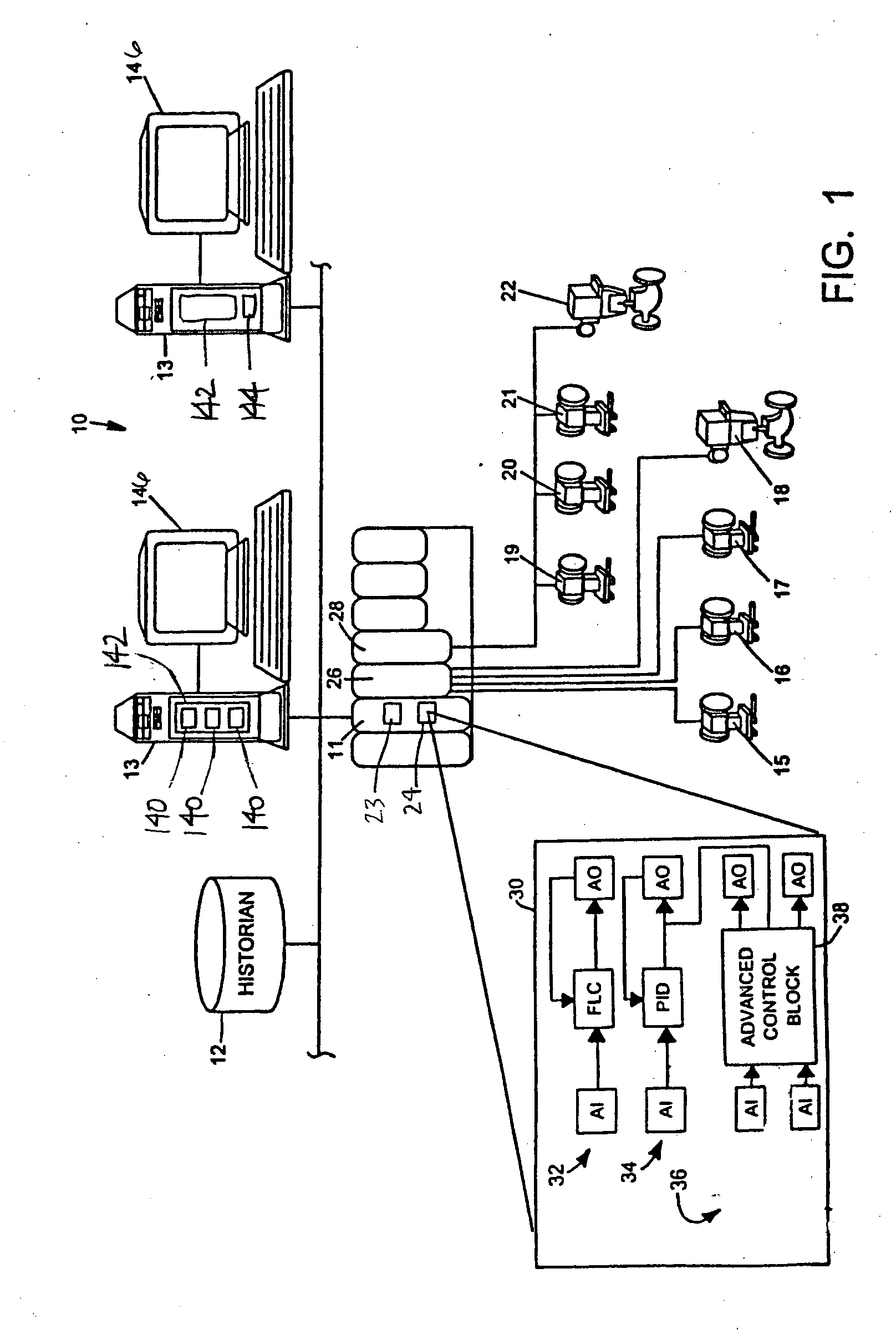
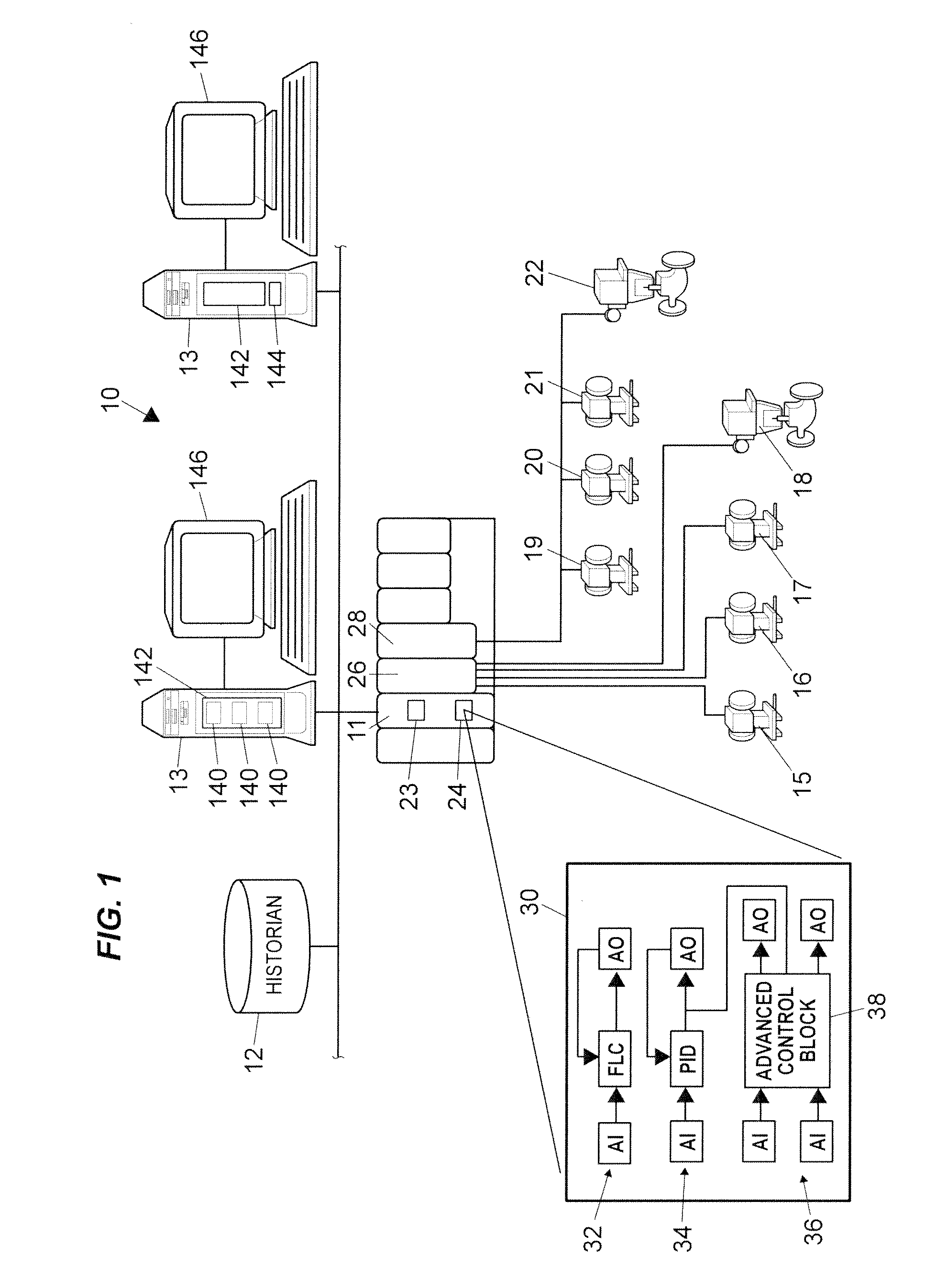
On-line adaptive model predictive control in a process control system
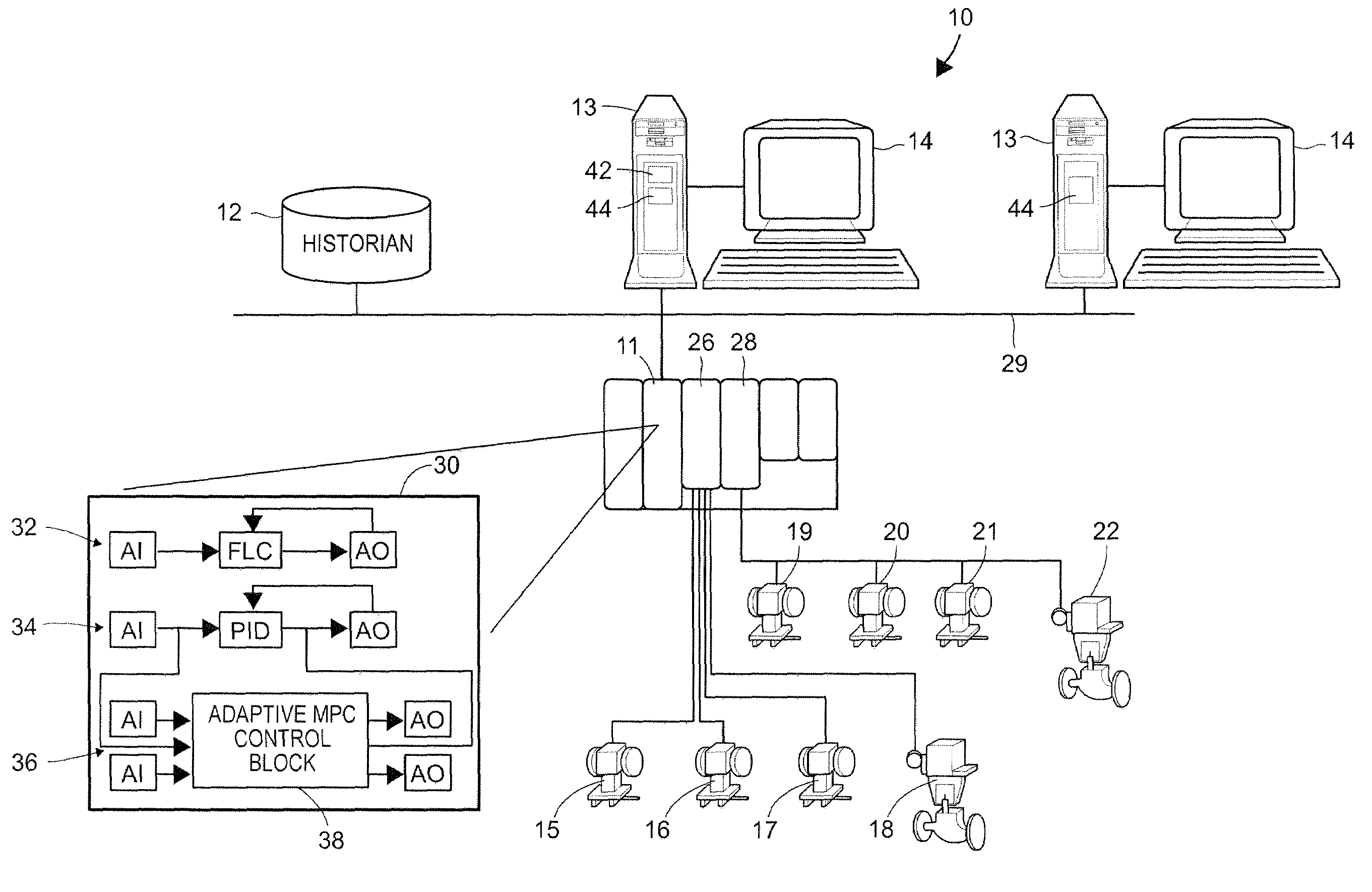
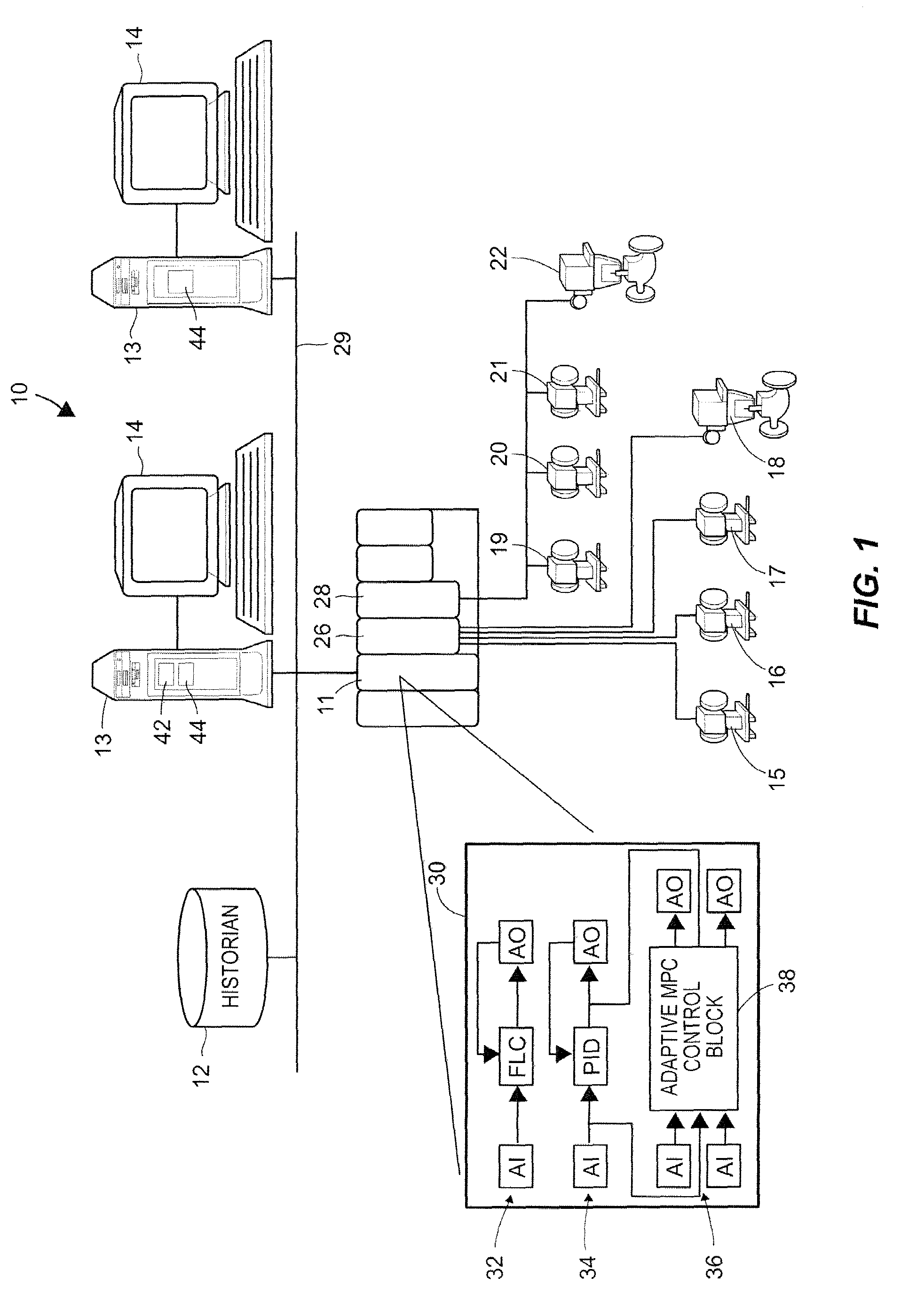
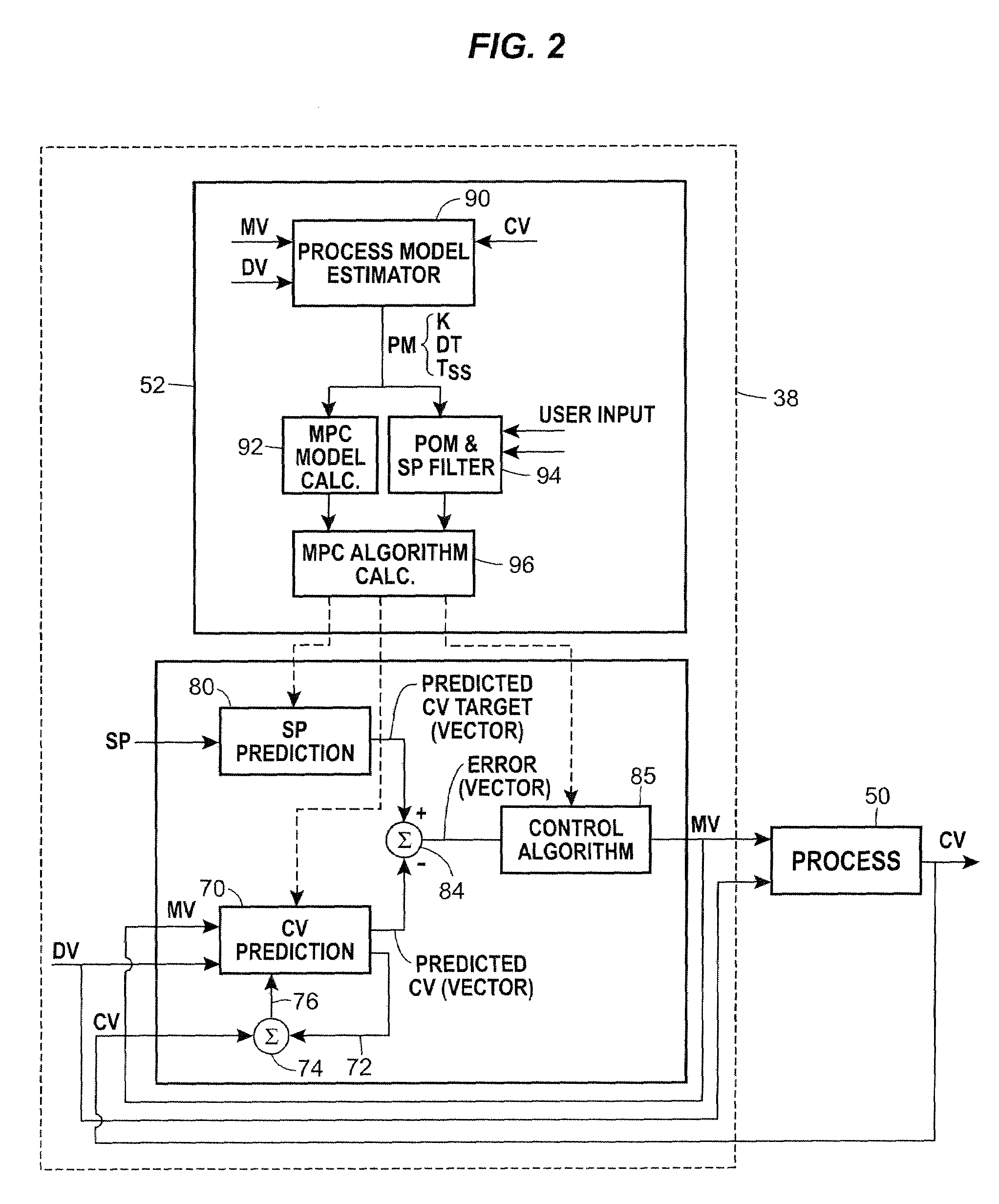
A method of creating and using an adaptive DMC type or other MPC controller includes using a model switching technique to periodically determine a process model, such as a parameterized process model, for a process loop on-line during operation of the process. The method then uses the process model to generate an MPC control model and creates and downloads an MPC controller algorithm to an MPC controller based on the new control model while the MPC controller is operating on-line. This technique, which is generally applicable to single-loop MPC controllers and is particularly useful in MPC controllers with a control horizon of one or two, enables an MPC controller to be adapted during the normal operation of the process, so as to change the process model on which the MPC controller is based to thereby account for process changes. The adaptive MPC controller is not computationally expensive and can therefore be easily implemented within a distributed controller of a process control system, while providing the same or in some cases better control than a PID controller, especially in dead time dominant process loops, and in process loops that are subject to process model mismatch within the process time to steady state.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
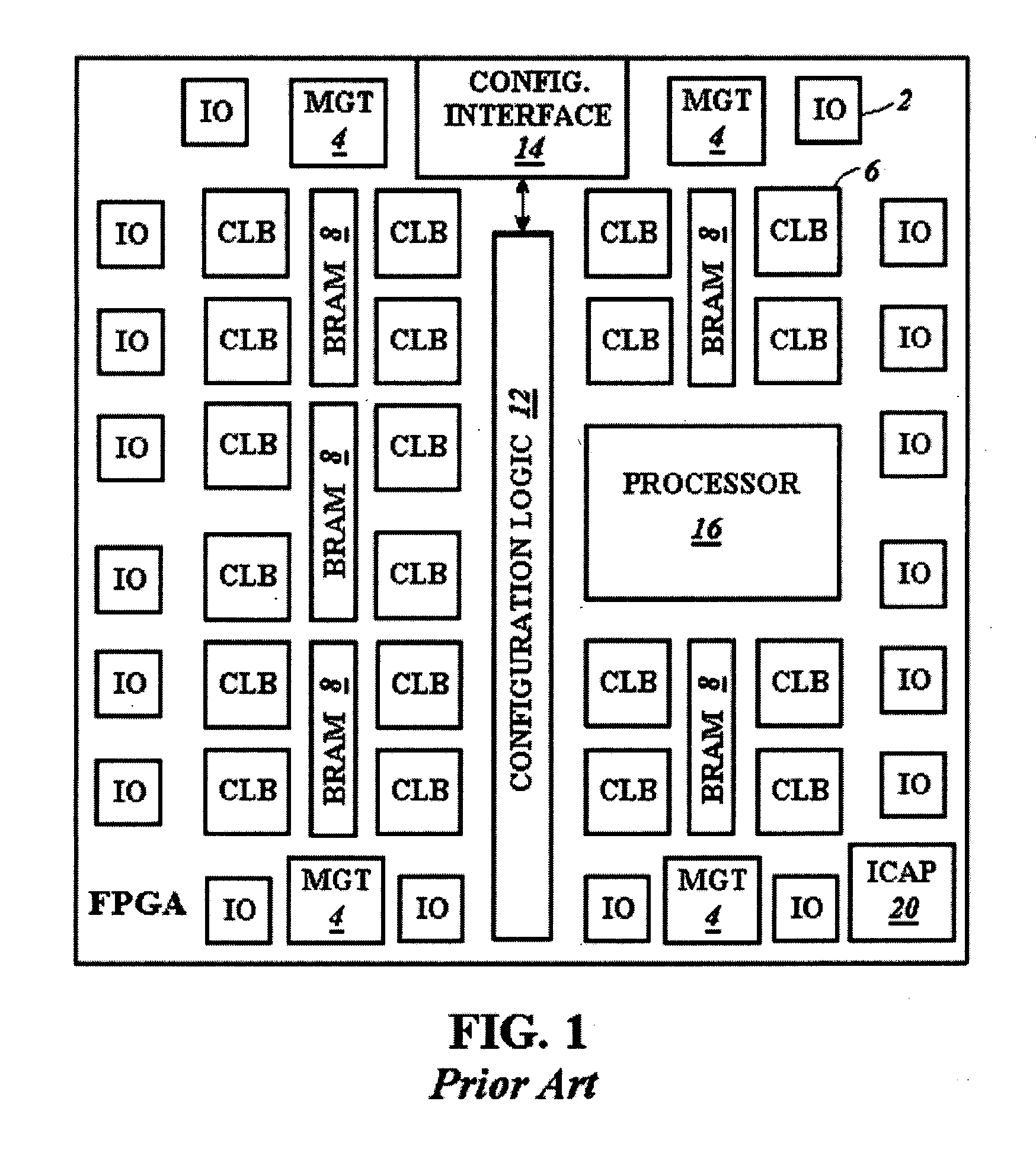
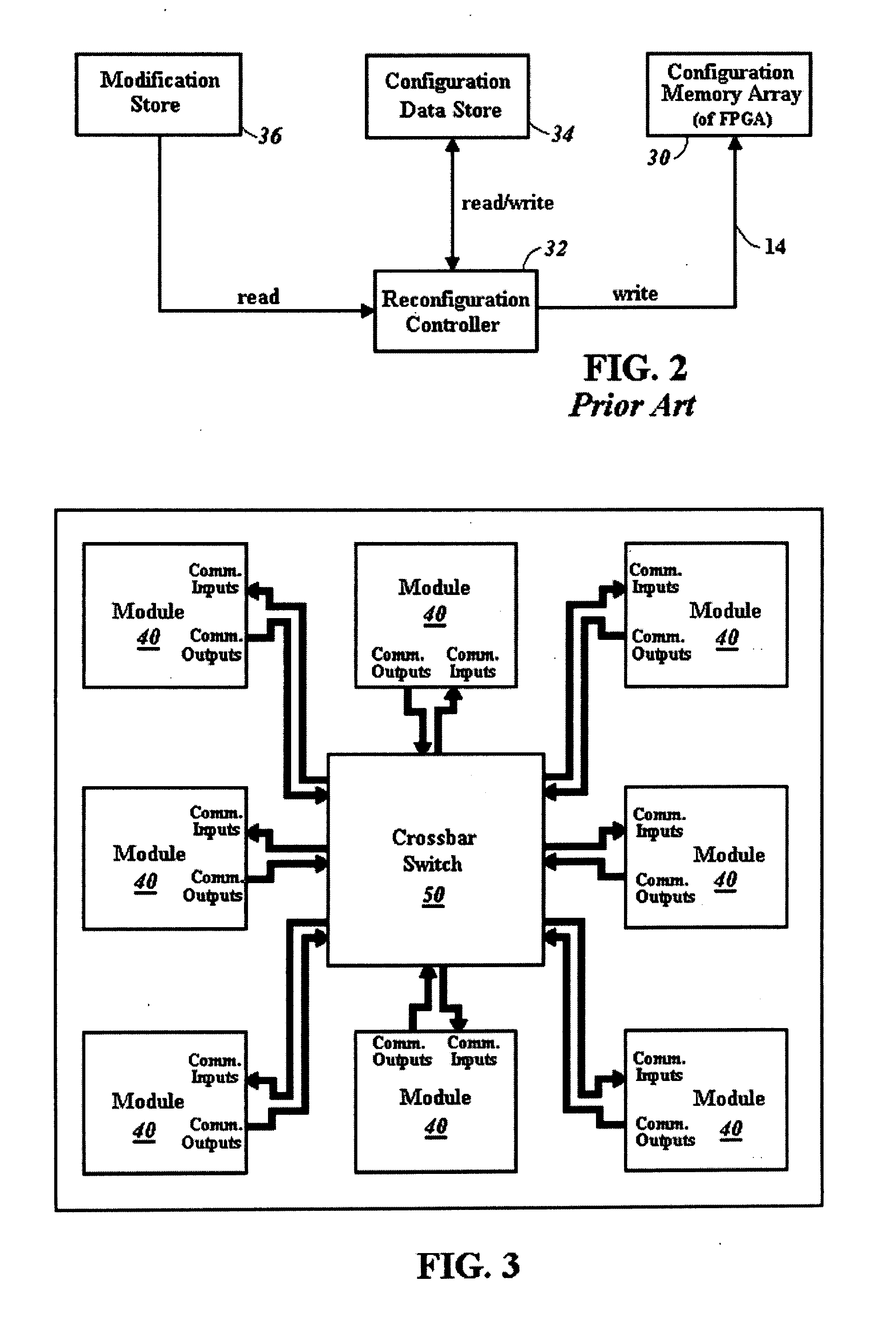
High bandwidth reconfigurable on-chip network for reconfigurable systems
ActiveUS7224184B1Quickly reconfiguredReduce necessarySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsCrossbar switchAsynchronous communication
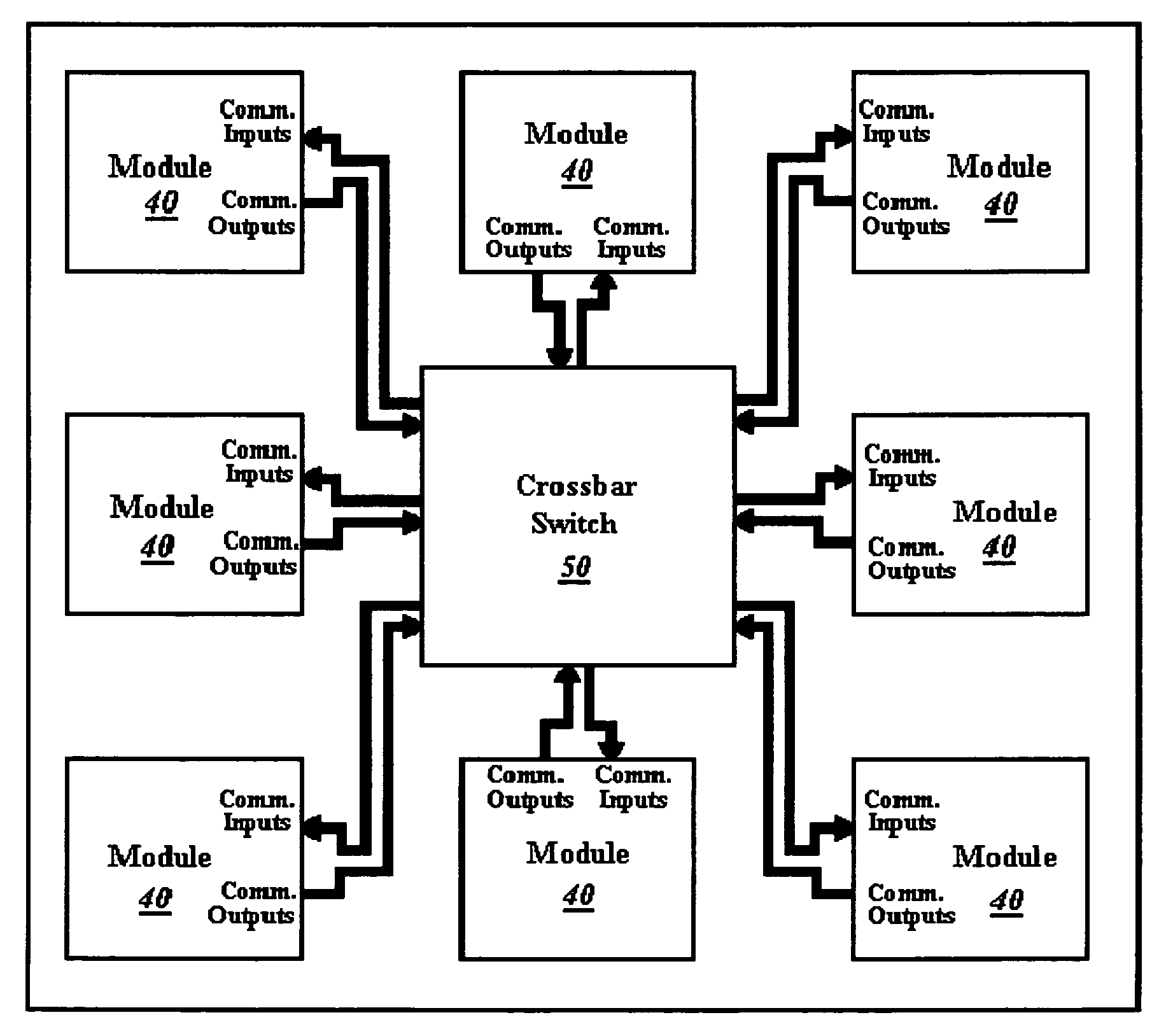
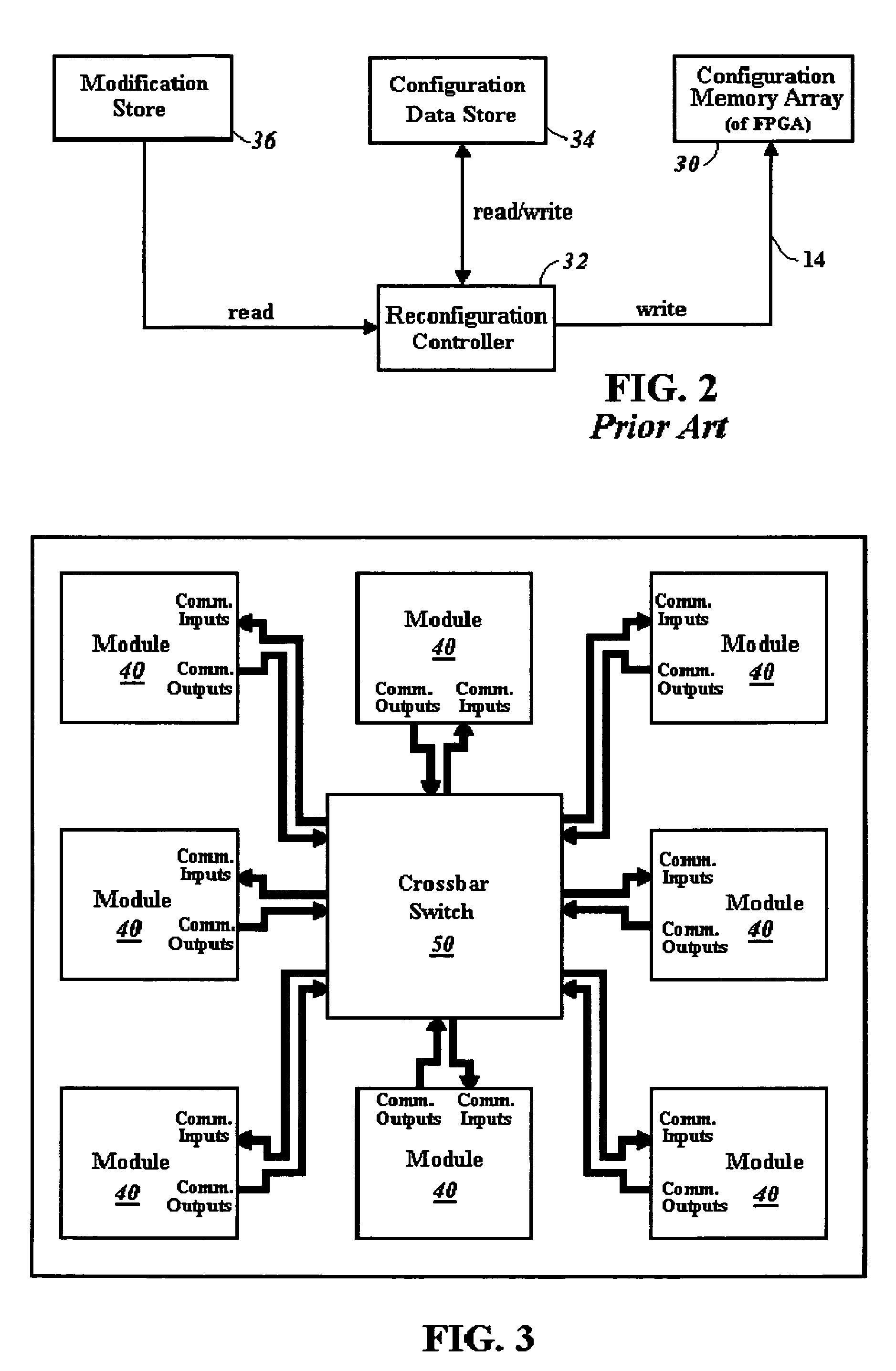
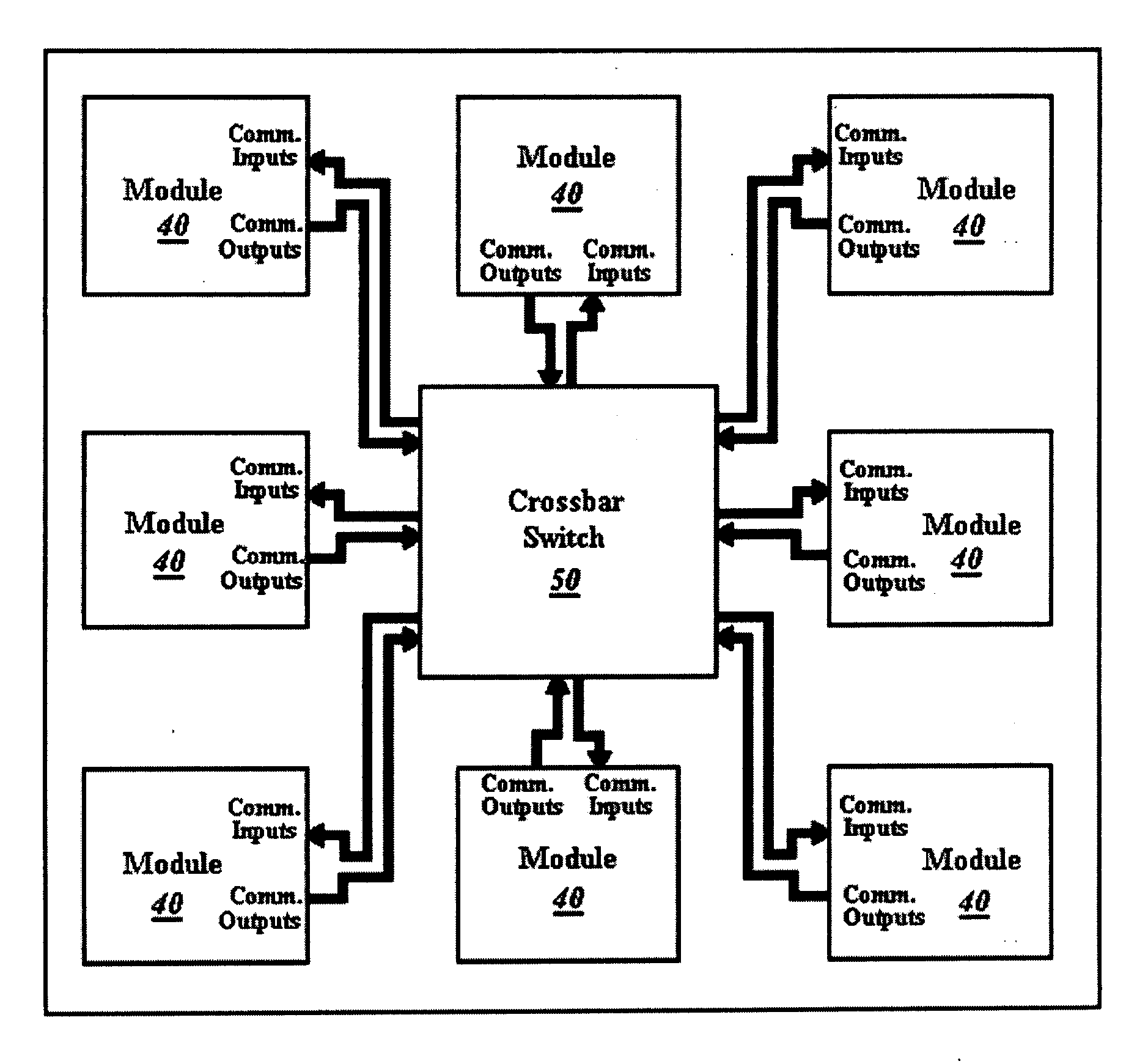
A crossbar switch (50) is implemented in a reconfigurable circuit, such as a FPGA, instantiated with a number of modules (40), the crossbar switch (50) providing communication links between the modules (40). The modules (40) and crossbar switch (50) can be easily updated in a partial reconfiguration process changing only portions of modules (40) and the crossbar switch (50) while other portions remain active. The crossbar switch (50) uses individual wiring to independently connect module outputs and inputs so that asynchronous communications can be used. The crossbar switch (50) can be implemented in different embodiments including a Clos crossbar switch, and a crossbar switch connecting each module output only to a corresponding module input, allowing for a reduction in the amount of FPGA resources required to create the crossbar switches.
Owner:XILINX INC
System, Method, and Program Product for Targeting and Optimal Driving Force Distribution in Energy Recovery Systems
ActiveUS20080015839A1Efficient designGuaranteed uptimeLevel controlTemperatue controlEnergy recoveryTrade offs
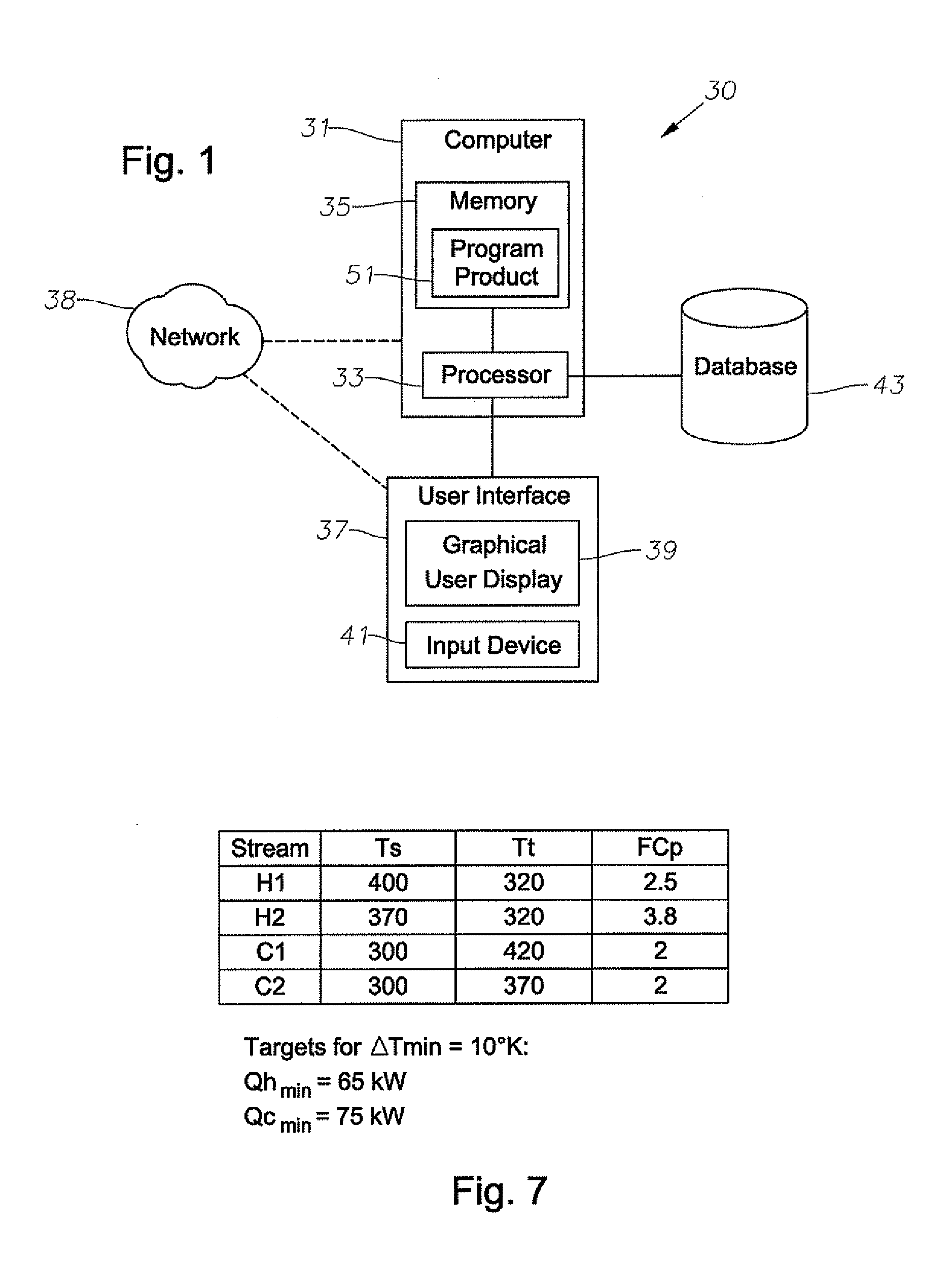
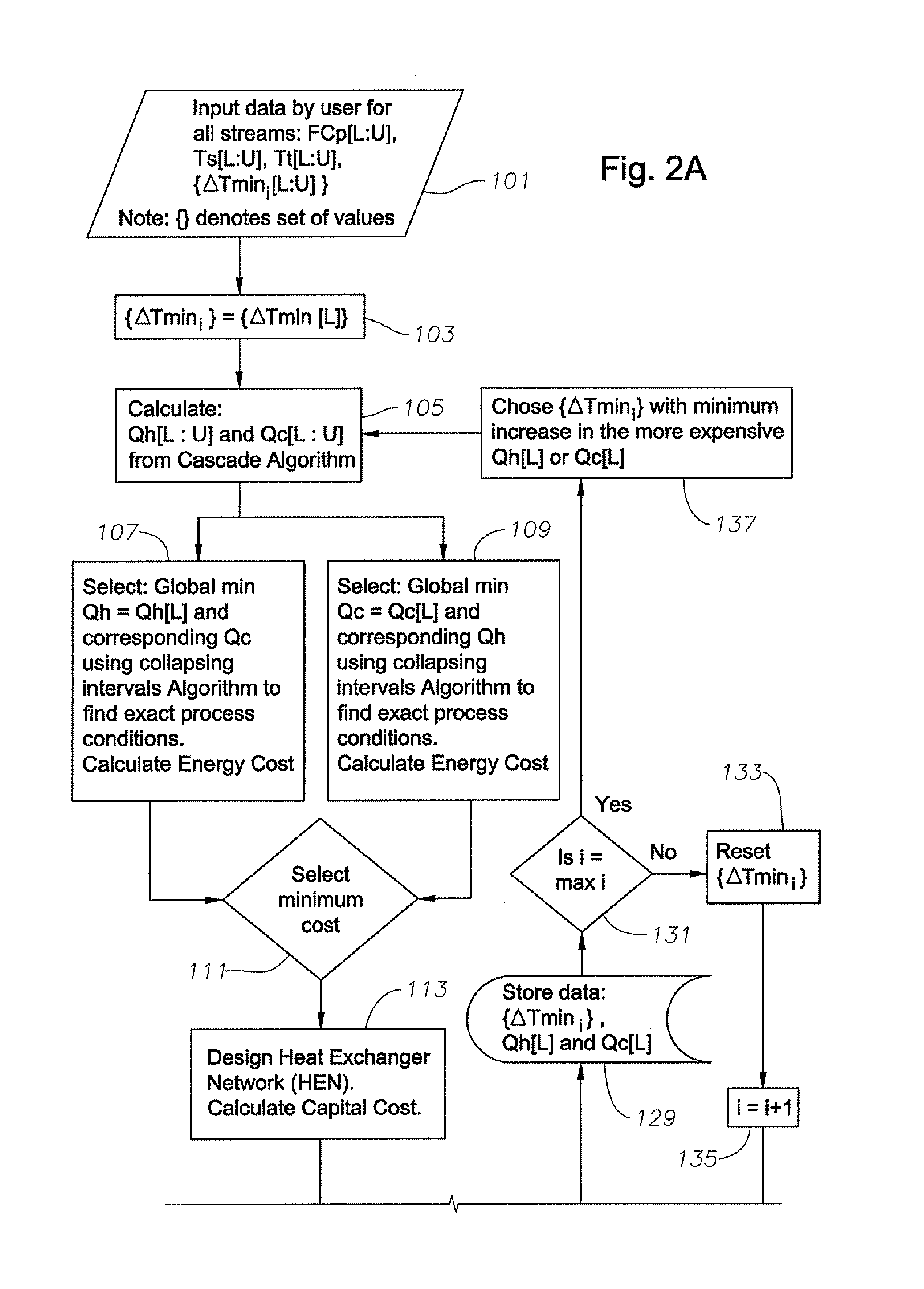
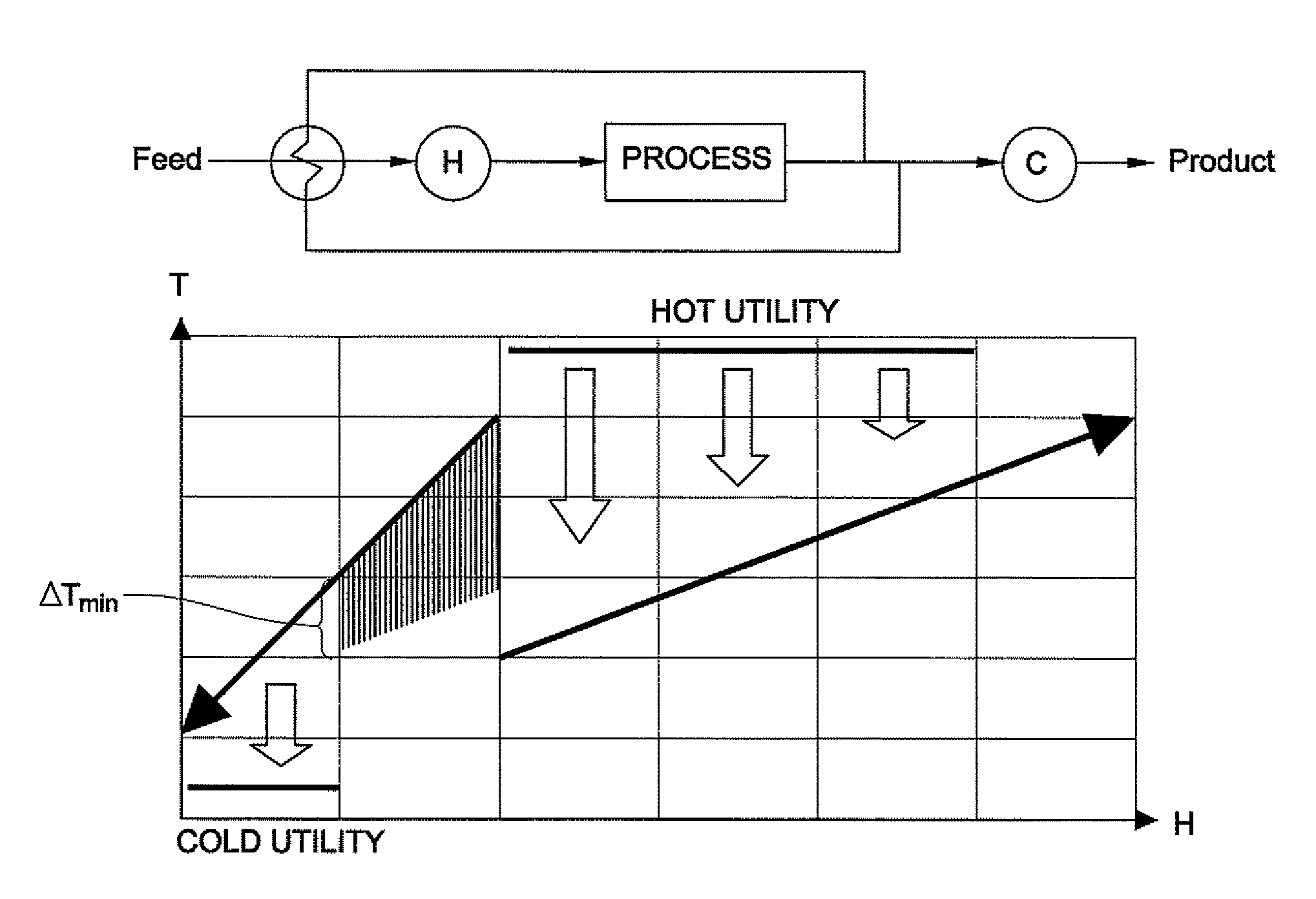
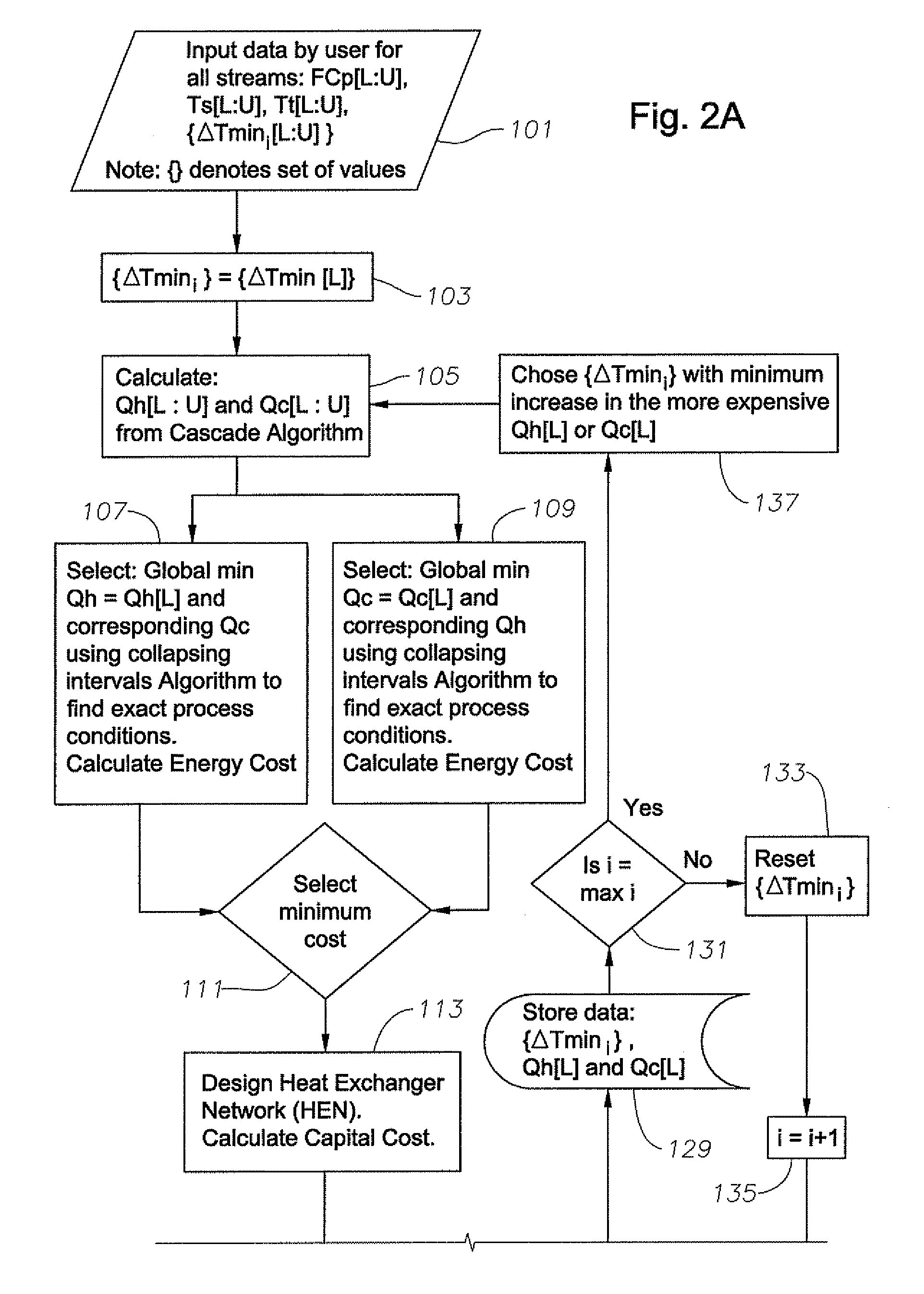
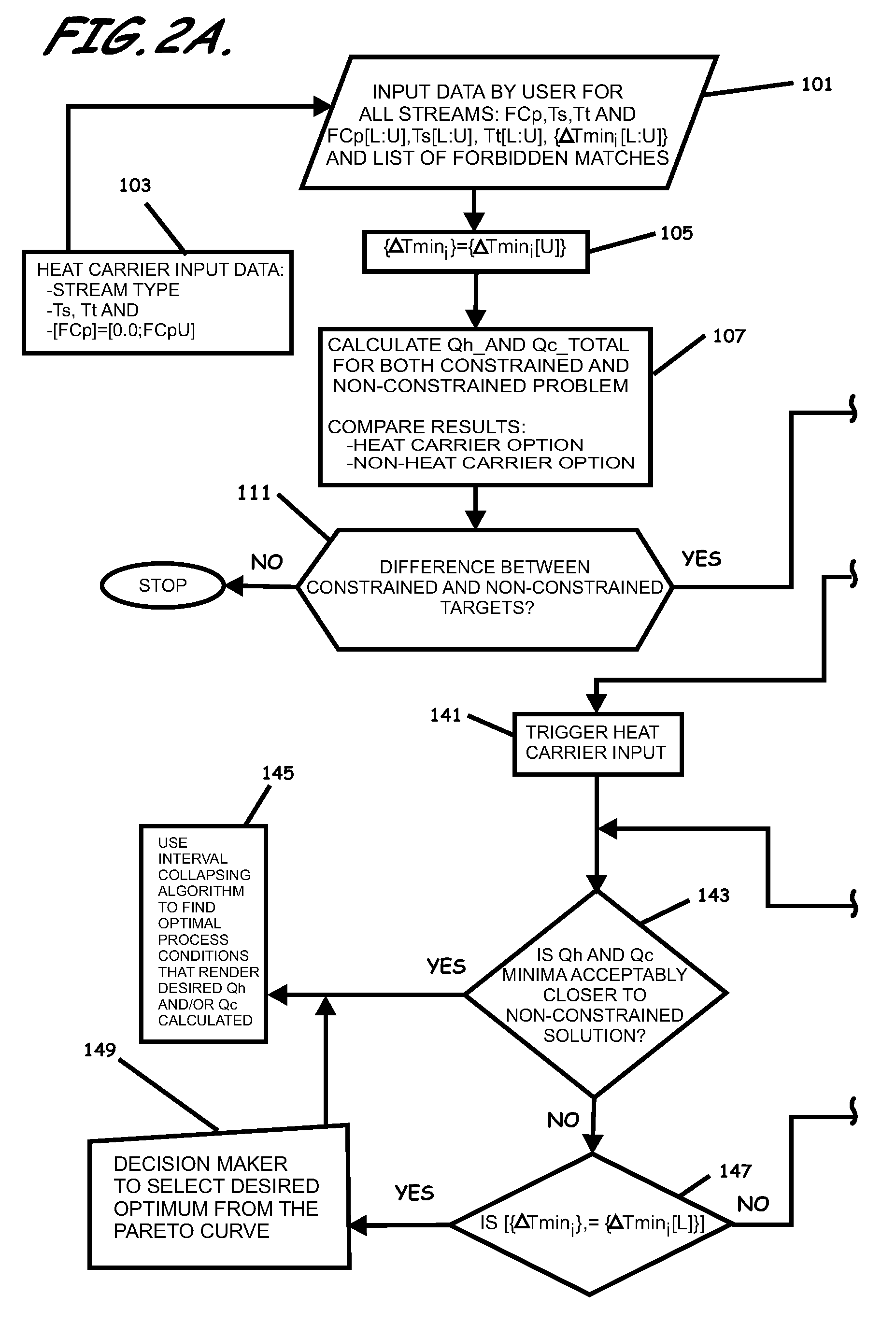
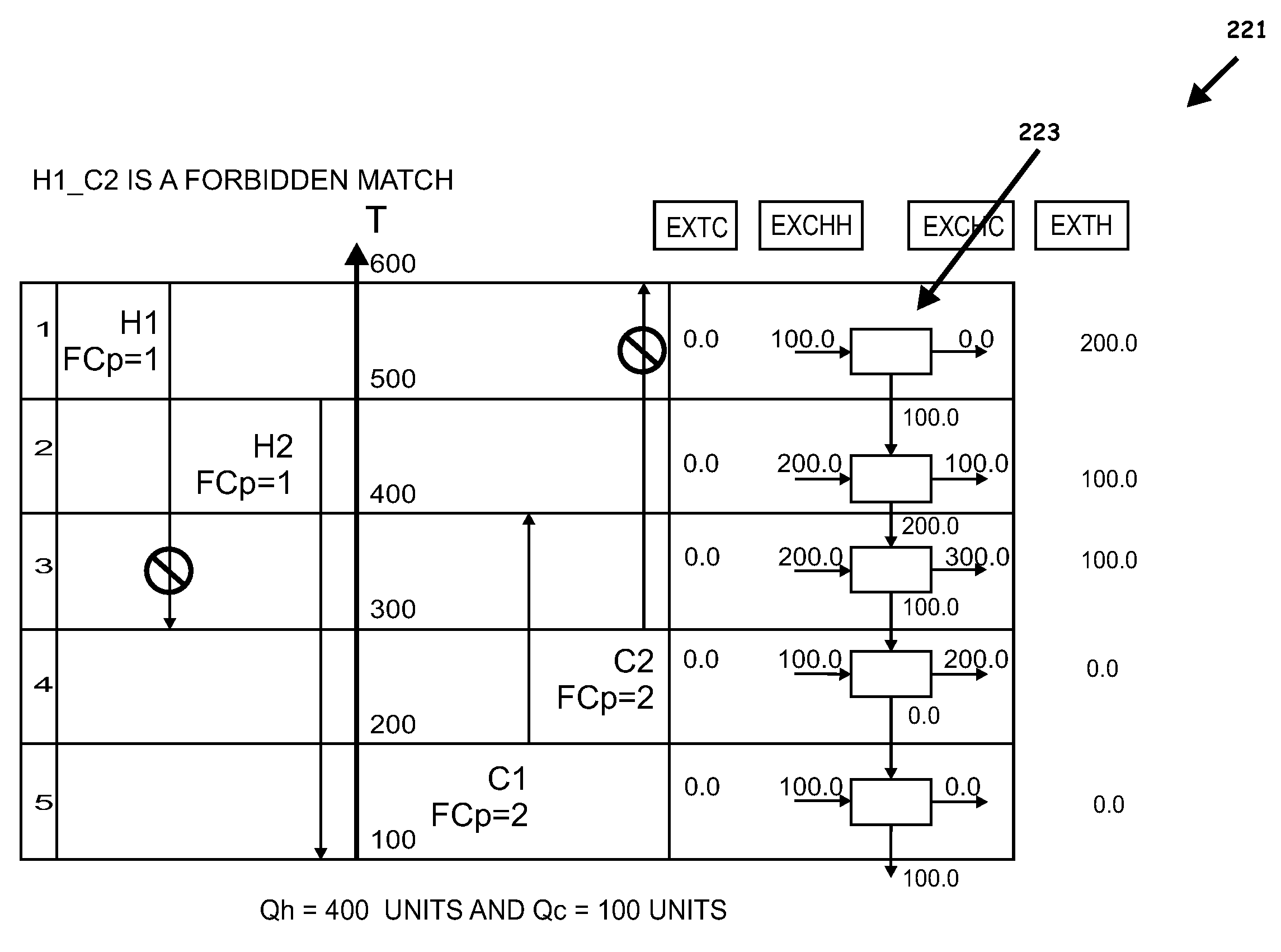
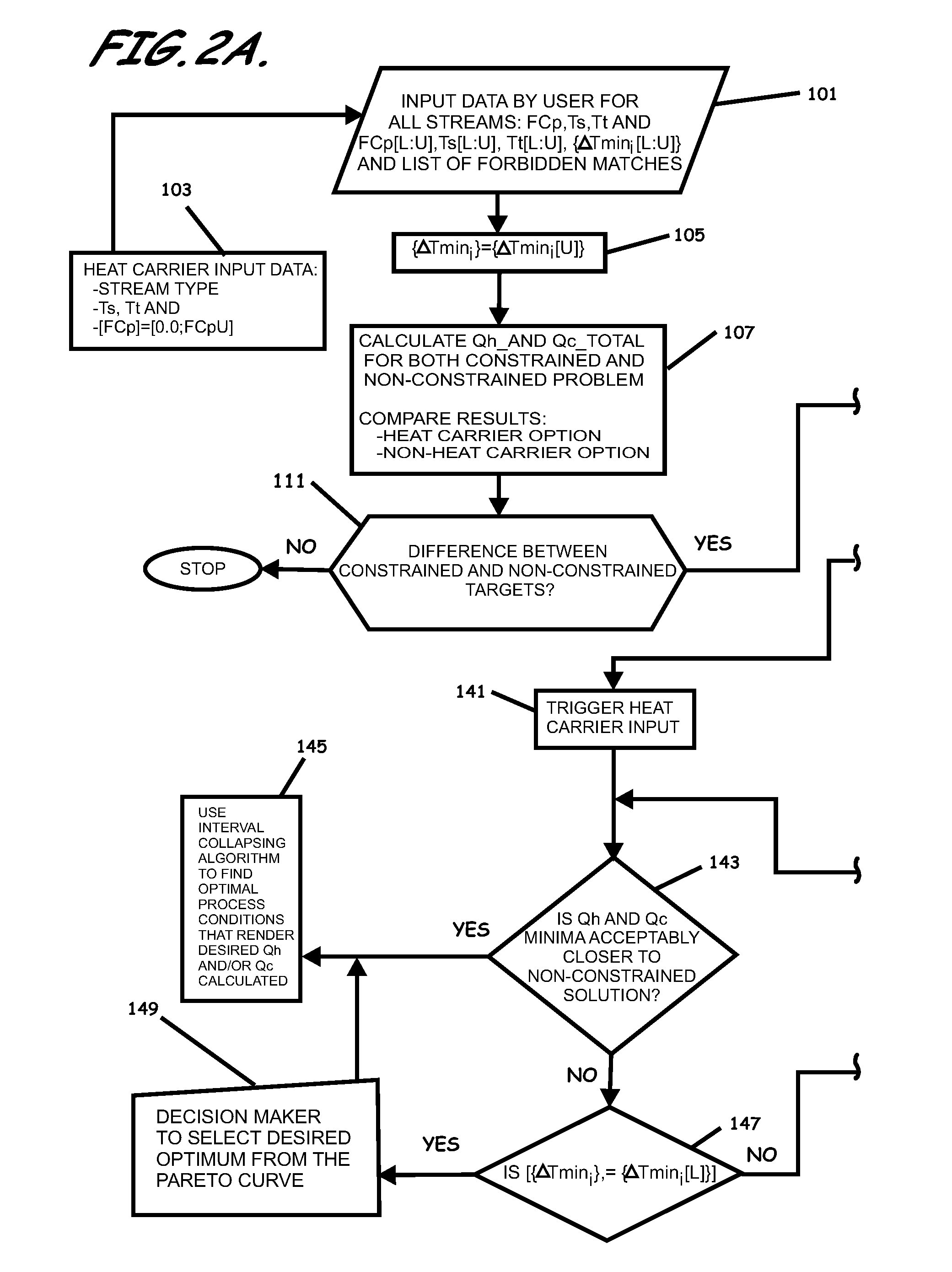
A system, methods, and user-friendly program product to calculate global energy utility targets and define optimal driving force distribution for a process or cluster of processes under all possible process changes and streams specific minimum temperature approach values, simultaneously, and without enumeration, are provided. The program product can utilize stream-specific minimum temperature approach values ΔTmini, where the superscript i represents the specific hot stream, as the optimization parameters instead of the single global ΔTmin currently used, in addition to identifying the optimal operating conditions. The program product can define optimal process conditions and an optimal driving force distribution in heat recovery systems, and can produce an optimal Pareto-curve that shows the rigorous trade off between energy cost and capital cost for any energy recovery system.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Write driver circuit in phase change memory device and method for applying write current
ActiveUS20050117388A1Easy to implementMaximize reliabilitySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDriver circuitPhase-change memory
A write driver circuit including a plurality of programmable fuses for a phase change memory device in which a write operation is correctly performed even in the case where a current output shift in a write current generation circuit; or in the case where a phase change memory cell has a phase change property shift due to an external factor or due a process change. The write driver circuit includes; a write current control unit for outputting a first or second level of voltage selected, by selecting one of a first or second programmable current path, based on whether a first or second selection pulse signal is applied; and a current driving unit for generating a write current controlled by the output voltage of the write current control unit. Each of the first and second programmable current paths includes fuses that can be programmed to adjusted their resistance to adjust the respective selected output voltage to compensate for a current output shift in a write current generation circuit or for a phase change memory cell has a phase change property shift.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
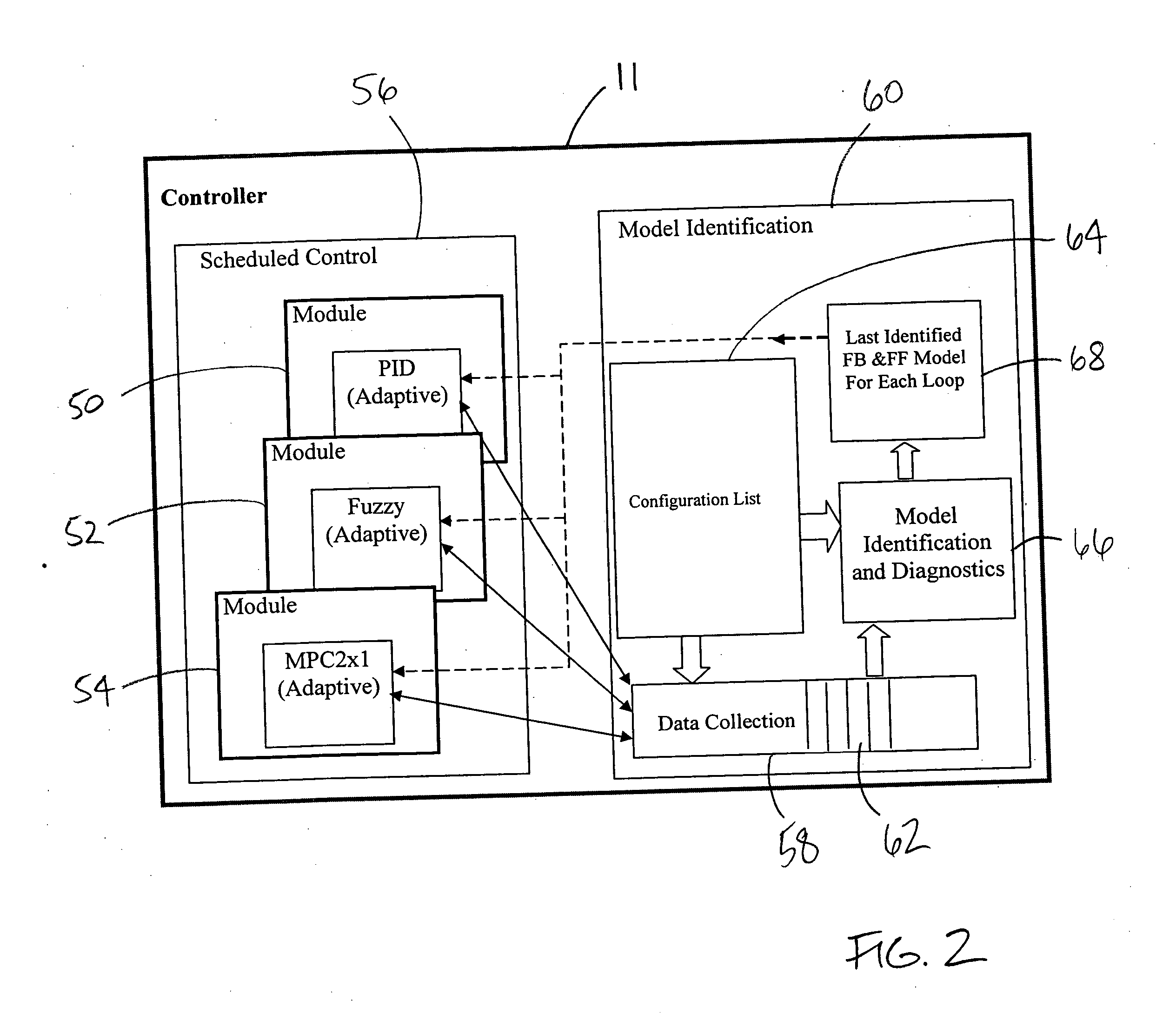
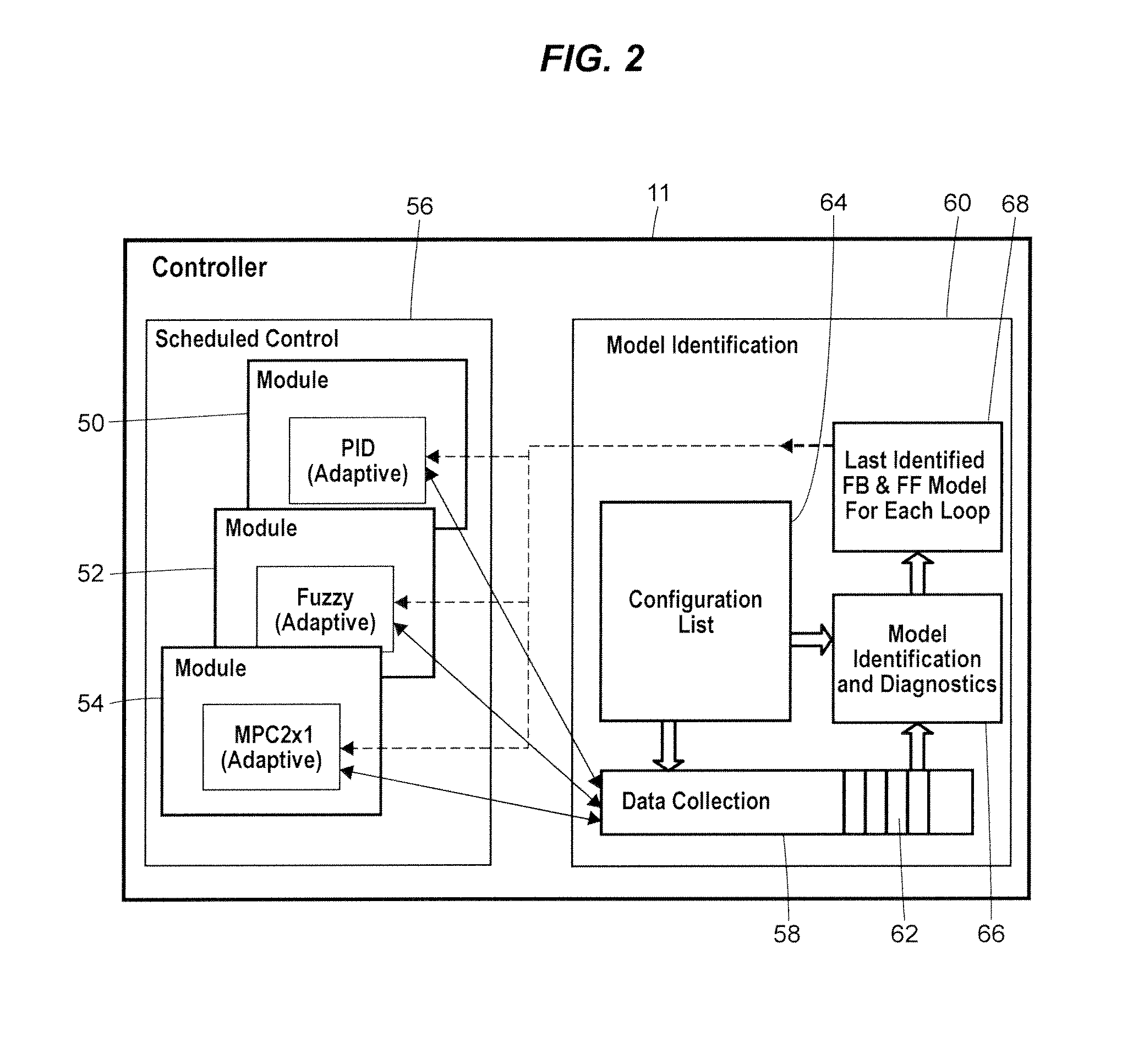
Process model identification in a process control system
ActiveUS20070078533A1Programme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsControl systemOperant conditioning
Disclosed is a method of controlling and managing a process control system having a plurality of control loops. The method includes implementing a plurality of control routines to control operation of the plurality of control loops, respectively. The plurality of control routines may include at least one non-adaptive control routine. Operating condition data is then collected in connection with the operation of each control loop of the plurality of control loops, and a respective process model is identified for each control loop of the plurality of control loops from the respective operating condition data collected for each control loop of the plurality of control loops. In some embodiments, the identification of the respective process models may be automatic as a result of a detected process change or be on-demand as a result of an injected parameter change.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
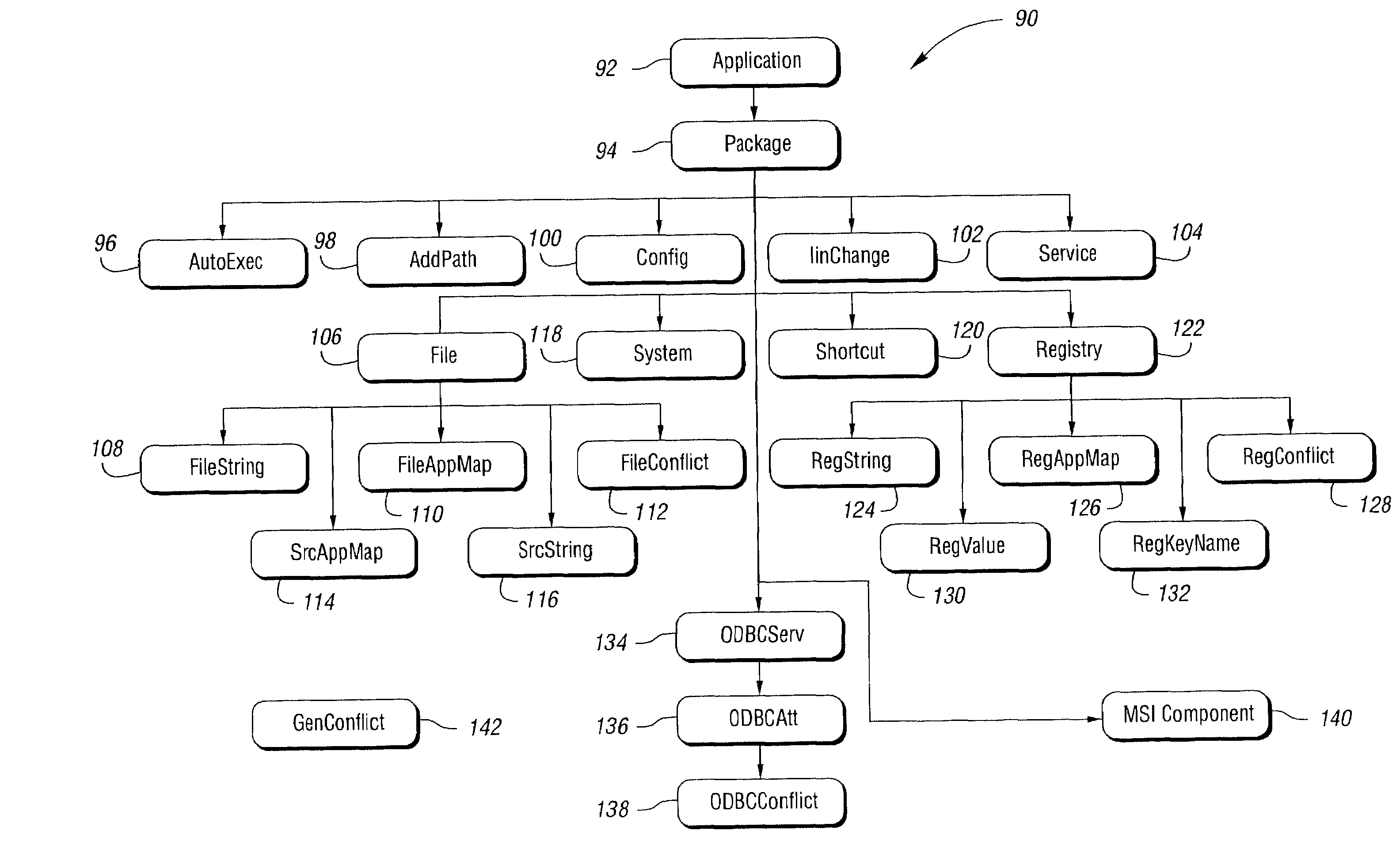
Method and system of managing software conflicts in computer system that receive, processing change information to determine which files and shared resources conflict with one another
InactiveUS7028019B2Improve productivitySaves an organization valuable support staff timeData processing applicationsDigital computer detailsComputerized systemApplication software
Owner:CA TECH INC
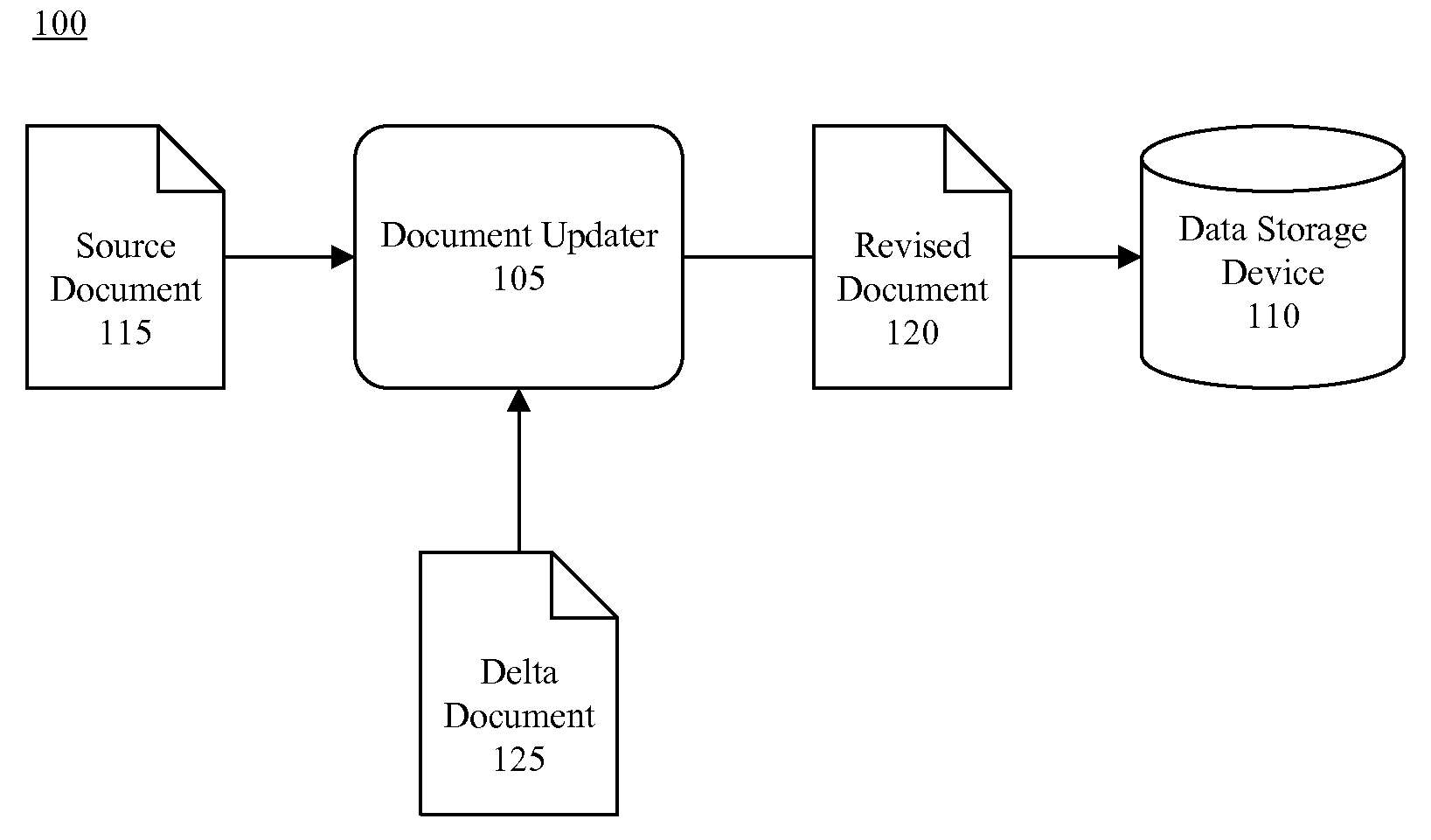
Capturing and Processing Change Information in a Web-Type Environment
ActiveUS20080077848A1Natural language data processingSpecial data processing applicationsDocument preparationDocumentation
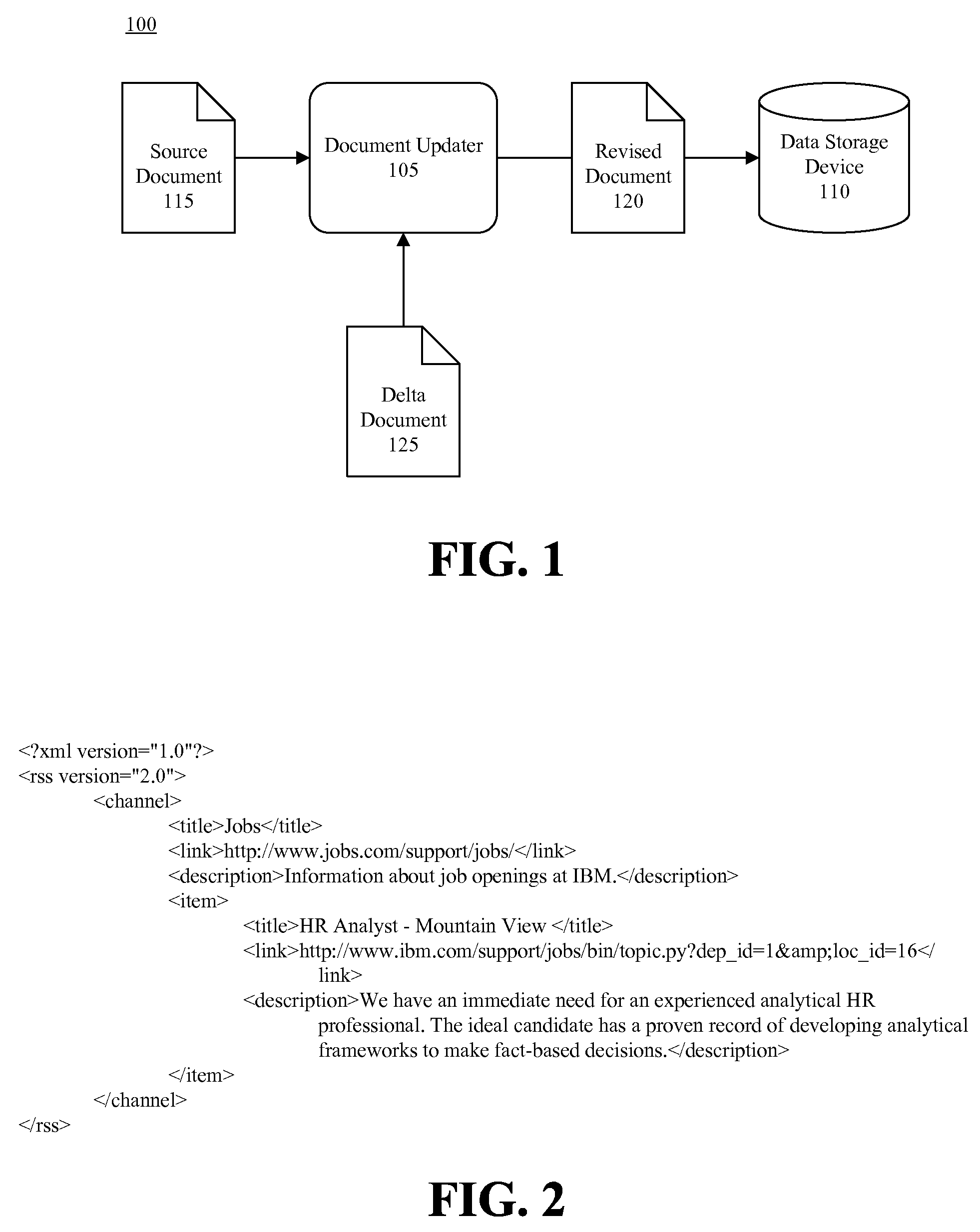
A source markup language document and a modification to the source markup language document can be identified. One or more delta documents specifying the modification to the source markup language document can be created. The delta document can be independent of the source markup language document and can be coded in a different language than the source markup language document. The source markup language document and the delta document can be stored within a data storage device.
Owner:IBM CORP
Interactive scaling feature having scalability in three dimensional space
InactiveUS20060293847A1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlGraphicsGraphical user interface
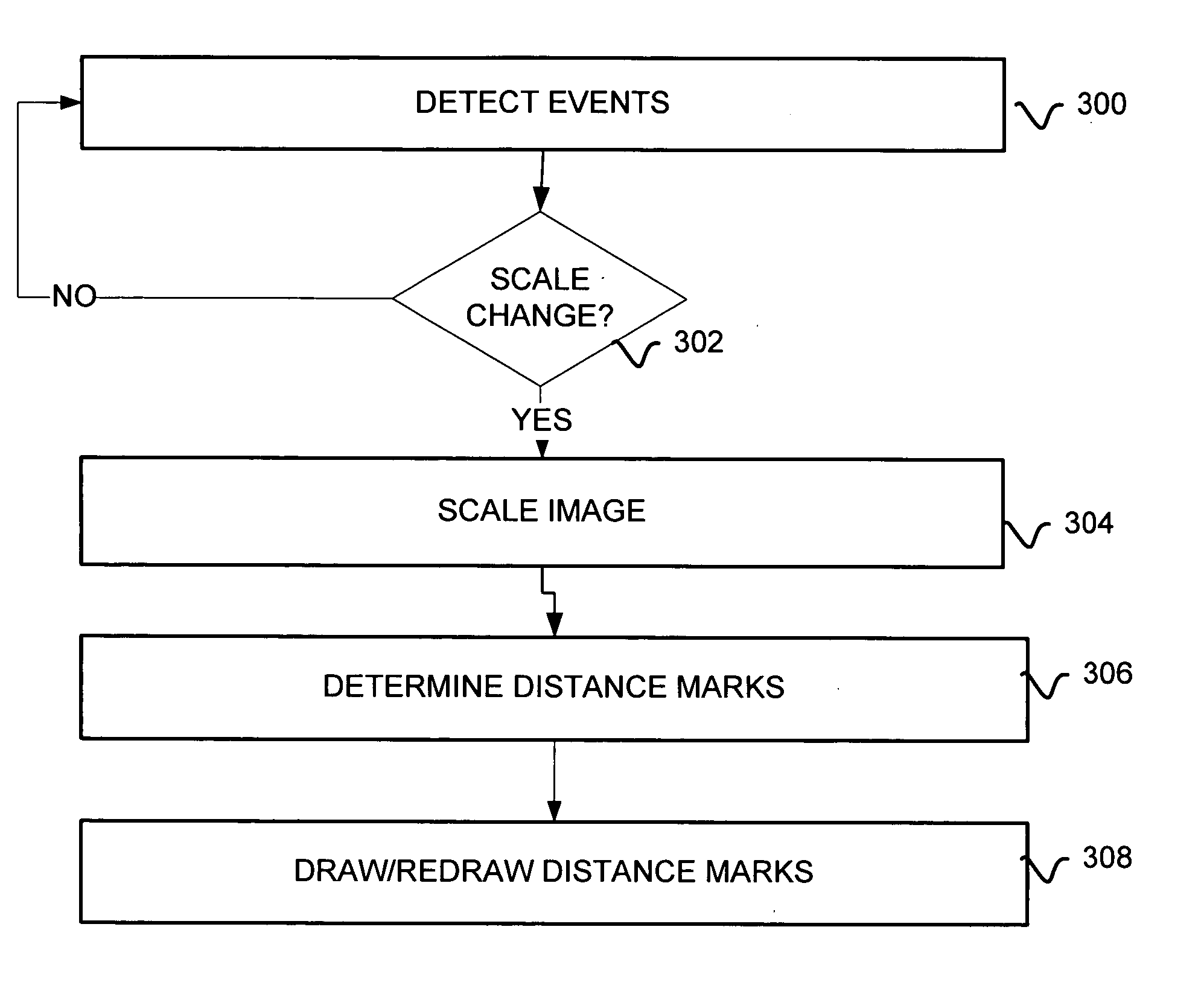
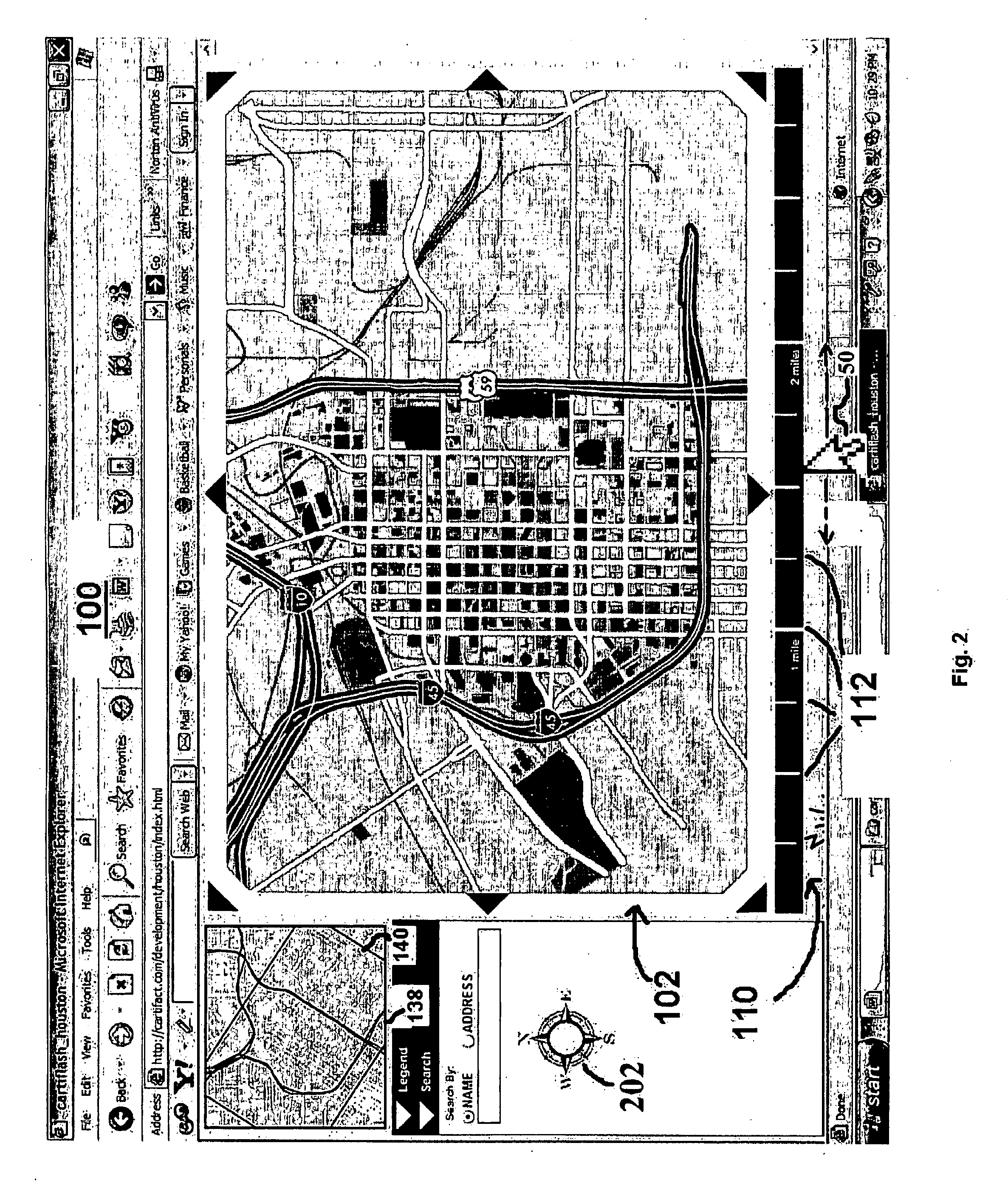
A system and method for controlling the scale of an image is disclosed, which comprises an image object in a graphical user interface. A ruler object provides a ruler display for distance measurement in the image. A button object comprising the ruler detects a cursor event that is sent to the image object for processing changes in the scale of the image responsive to the cursor event. Further disclosed is a system and method to provide directional orientation in an electronic map. Data is stored that indicates local perceptions of north, south, east and west for regions on the map. When each region is displayed, the system provides a toggle for switching between displaying the region with true north at an angle of 0 degrees orientation, or displaying the region at an angle with the local perception of north at an angle of 0 degrees orientation.
Owner:CARTIFACT
Method and apparatus for moving processes between isolation environments
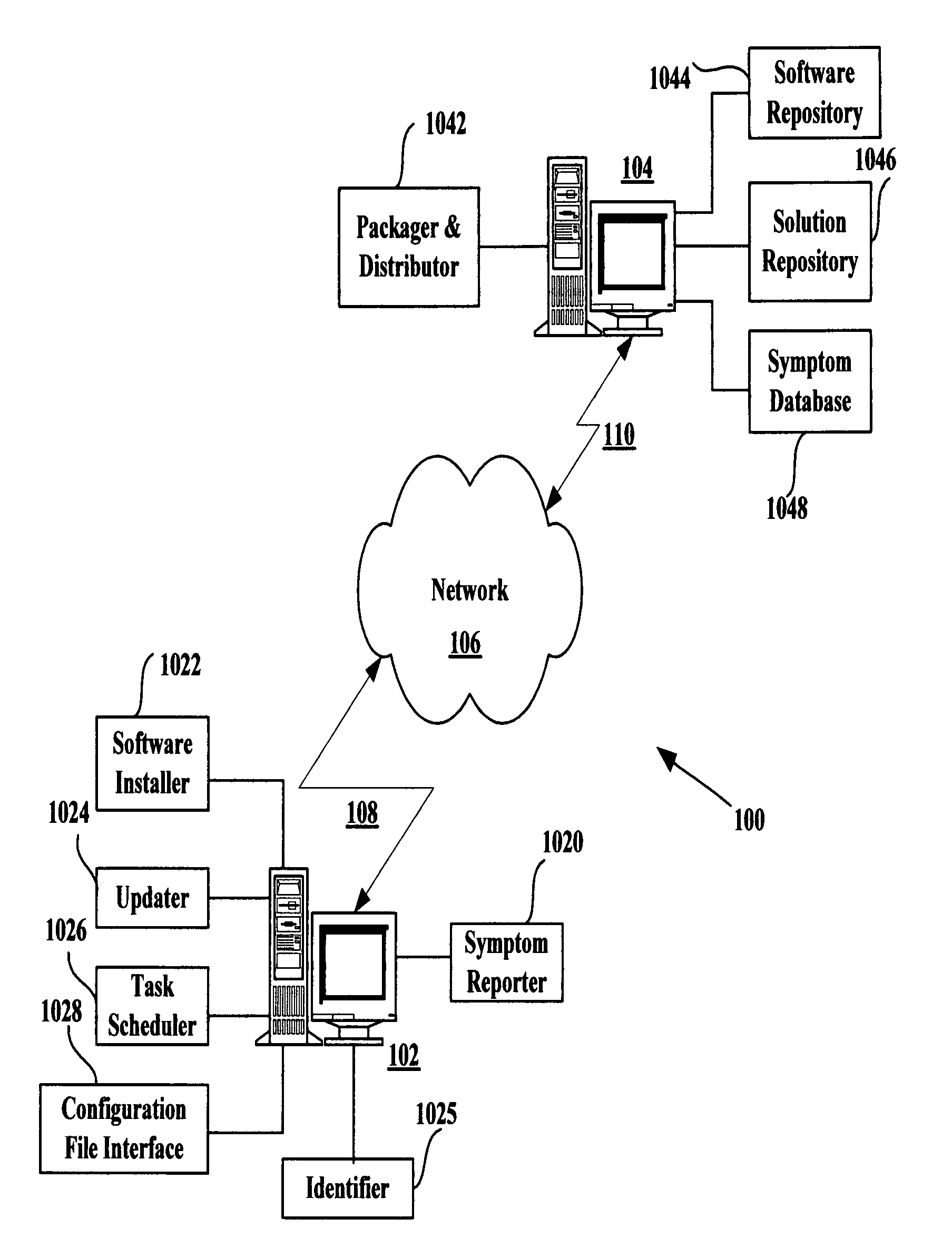
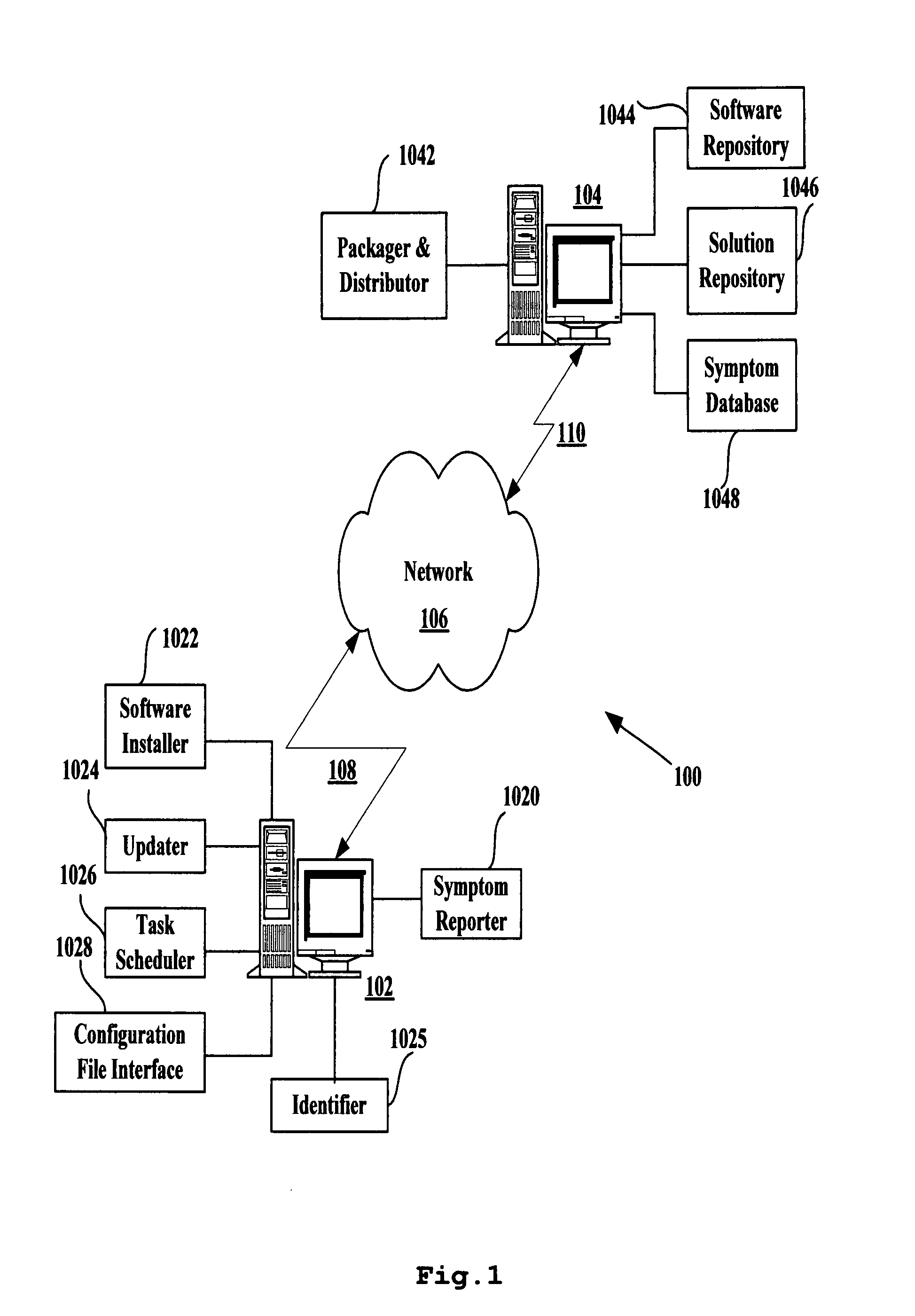
ActiveUS20060085789A1Specific access rightsData processing applicationsComputer scienceProcess changes
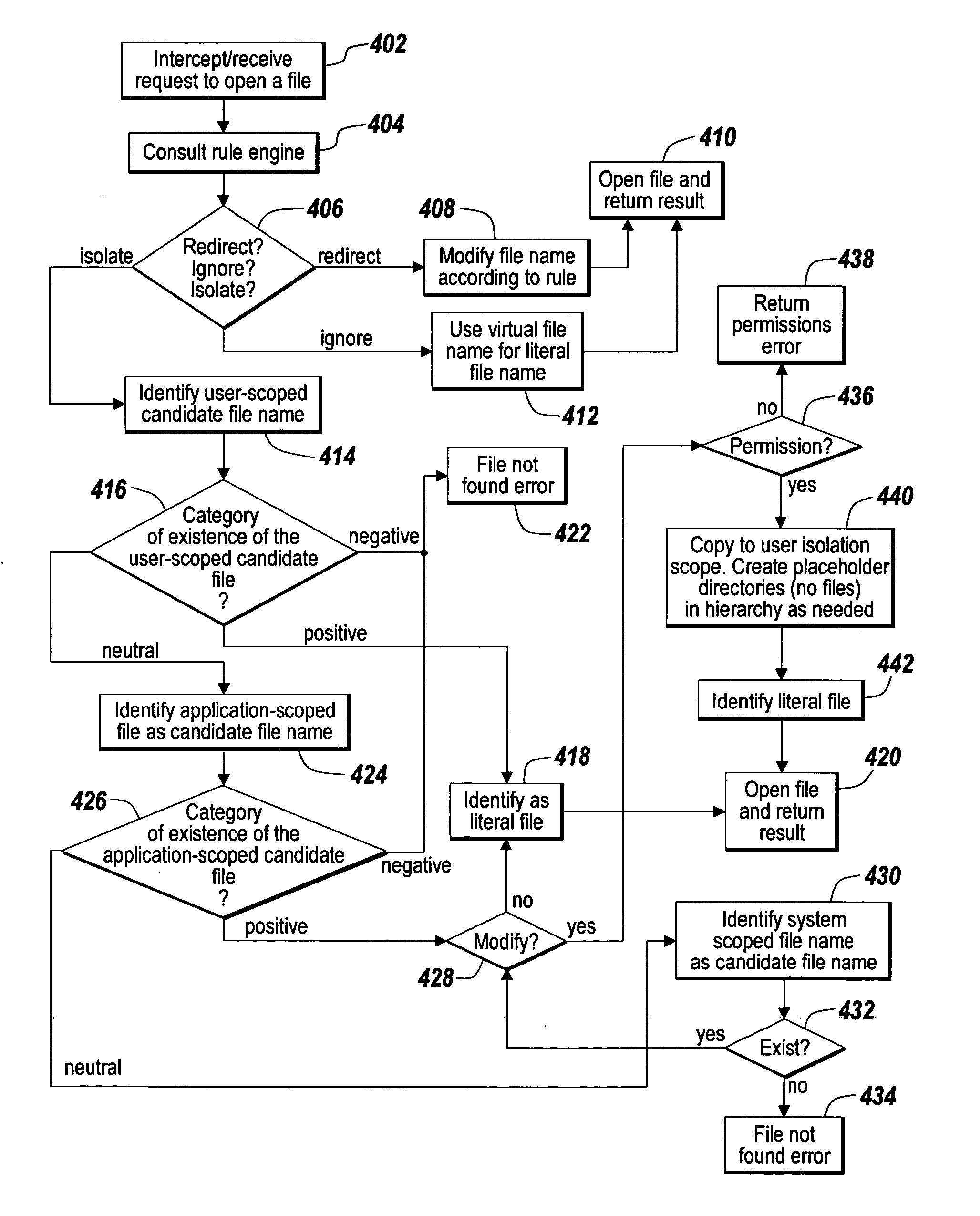
A method for moving an executing process from a source isolation scope to a target isolation scope includes the step of determining that the process is in a state suitable for moving. The association of the process changes from a source isolation scope to a target isolation scope. A rule loads in association with the target isolation scope.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
System, method, and program product for targeting and optimal driving force distribution in energy recovery systems
ActiveUS7698022B2Facilitate energy recoveryEasy to calculateLevel controlTemperatue controlEnergy recoveryTrade offs
A system, methods, and user-friendly program product to calculate global energy utility targets and define optimal driving force distribution for a process or cluster of processes under all possible process changes and streams specific minimum temperature approach values, simultaneously, and without enumeration, are provided. The program product can utilize stream-specific minimum temperature approach values ΔTmini, where the superscript i represents the specific hot stream, as the optimization parameters instead of the single global ΔTmin currently used, in addition to identifying the optimal operating conditions. The program product can define optimal process conditions and an optimal driving force distribution in heat recovery systems, and can produce an optimal Pareto-curve that shows the rigorous trade off between energy cost and capital cost for any energy recovery system.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
On-line adaptive model predictive control in a process control system
A method of creating and using an adaptive DMC type or other MPC controller includes using a model switching technique to periodically determine a process model, such as a parameterized process model, for a process loop on-line during operation of the process. The method then uses the process model to generate an MPC control model and creates and downloads an MPC controller algorithm to an MPC controller based on the new control model while the MPC controller is operating on-line. This technique, which is generally applicable to single-loop MPC controllers and is particularly useful in MPC controllers with a control horizon of one or two, enables an MPC controller to be adapted during the normal operation of the process, so as to change the process model on which the MPC controller is based to thereby account for process changes. The adaptive MPC controller is not computationally expensive and can therefore be easily implemented within a distributed controller of a process control system, while providing the same or in some cases better control than a PID controller, especially in dead time dominant process loops, and in process loops that are subject to process model mismatch within the process time to steady state.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
System and method for facilitating installing software
A system and method for facilitating installing software includes steps and means for identifying whether the phase of a software installing process changes and, responsive to the identifying a change in the phase of the software installing process, executing an additional task of the current phase of the software installing process.
Owner:IBM CORP
Process model identification in a process control system
ActiveUS7444191B2Programme controlTesting/monitoring control systemsControl systemOperant conditioning
Disclosed is a method of controlling and managing a process control system having a plurality of control loops. The method includes implementing a plurality of control routines to control operation of the plurality of control loops, respectively. The plurality of control routines may include at least one non-adaptive control routine. Operating condition data is then collected in connection with the operation of each control loop of the plurality of control loops, and a respective process model is identified for each control loop of the plurality of control loops from the respective operating condition data collected for each control loop of the plurality of control loops. In some embodiments, the identification of the respective process models may be automatic as a result of a detected process change or be on-demand as a result of an injected parameter change.
Owner:FISHER-ROSEMOUNT SYST INC
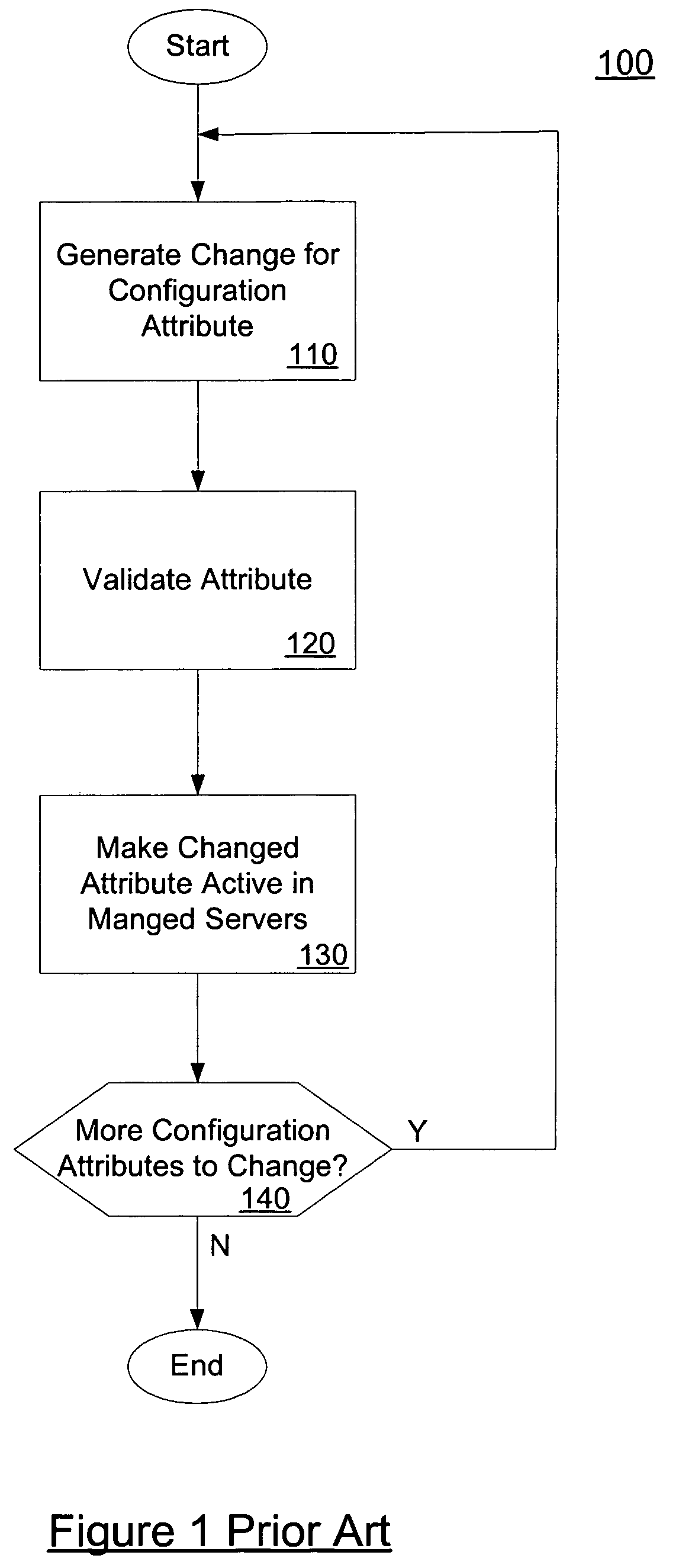
System and method for performing batch configuration changes
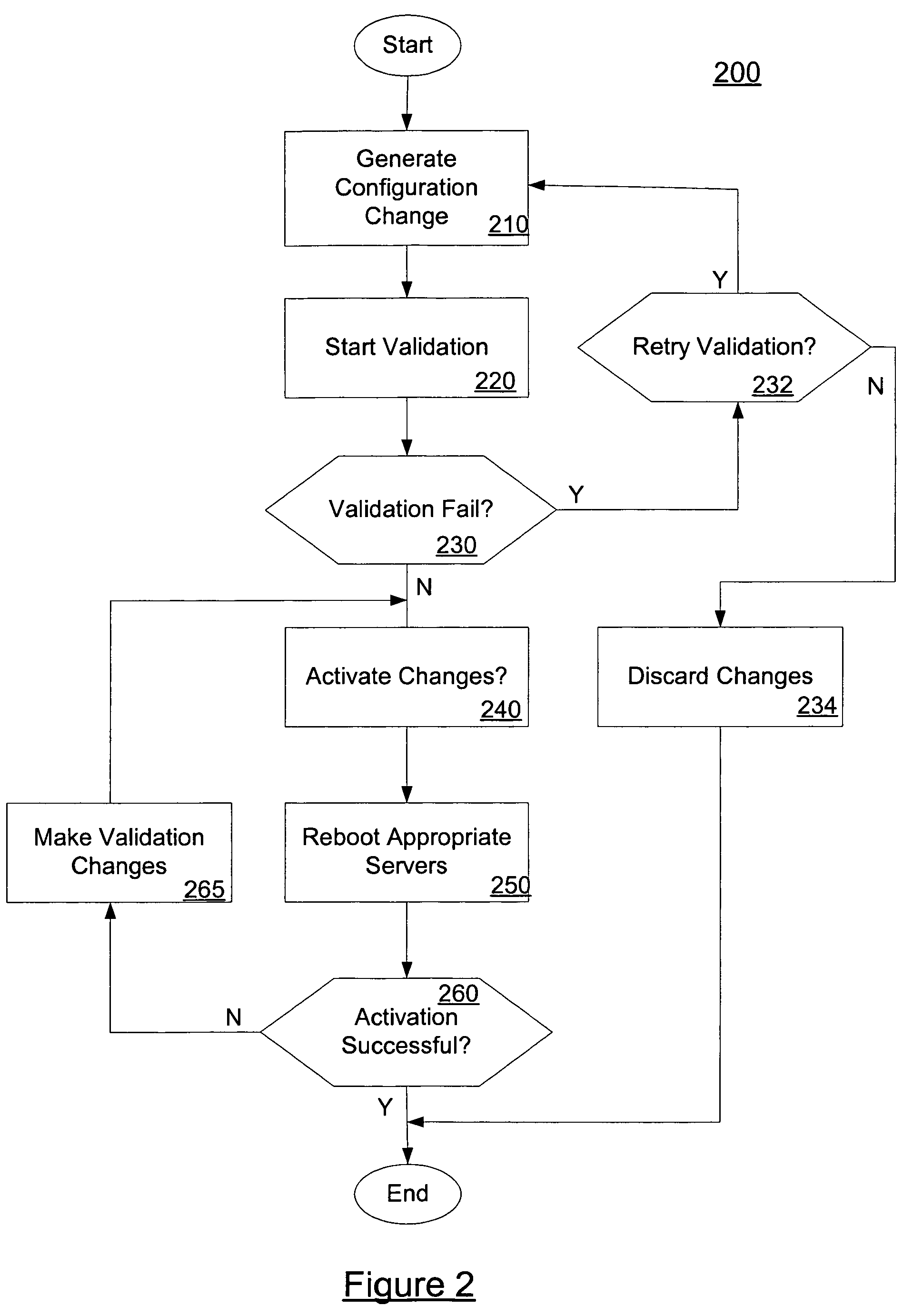
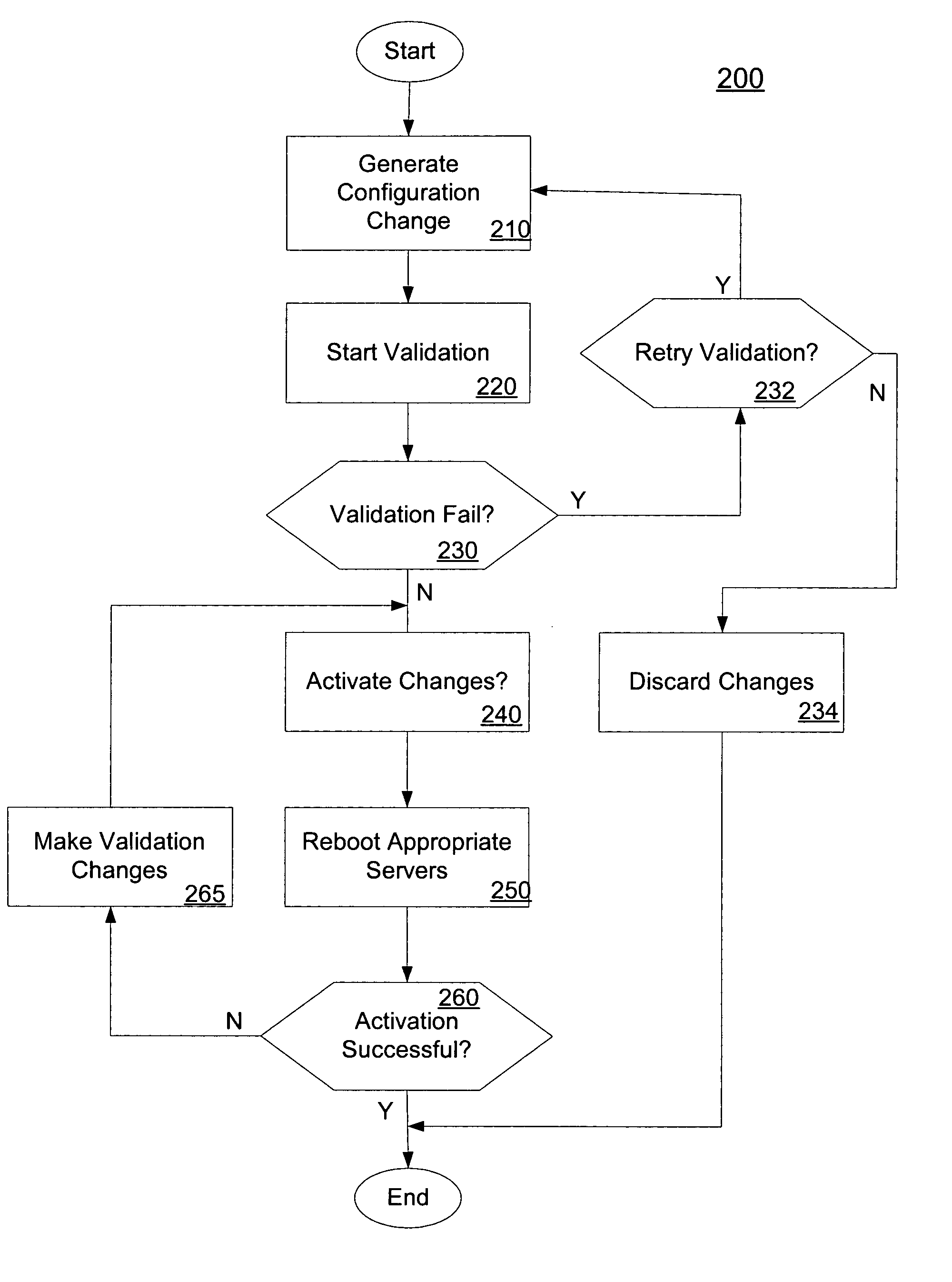
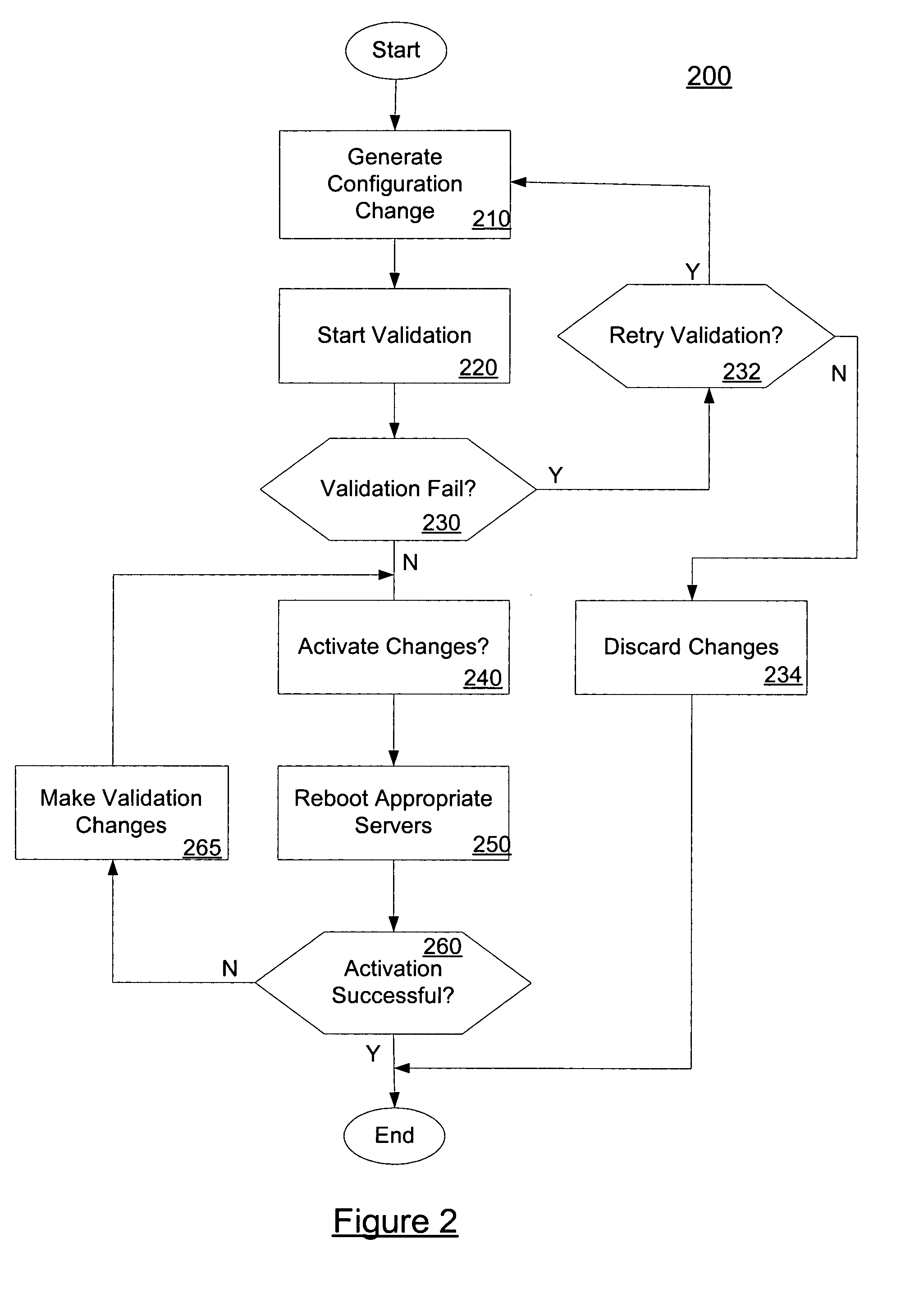
ActiveUS7660824B2Digital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsDistributed computingProcess changes
In embodiments, the present invention provides mechanisms and methods for making a plurality of configuration changes to a set of servers comprised of an administration server and one or more managed servers. These mechanisms and methods can enable a number of changes to be made to the configuration at once, i.e., in a batch. The ability of an administrator to make a number of changes to the configuration, validate the changes and then persist the changes to the servers is termed a “transaction based” change process. In such transaction based processing, embodiments process changes in batches, which enables embodiments to avoid failures in configuration changes that result in the machines being in a non-recoverable or unknown configuration state.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Systems and methods for processing changing data
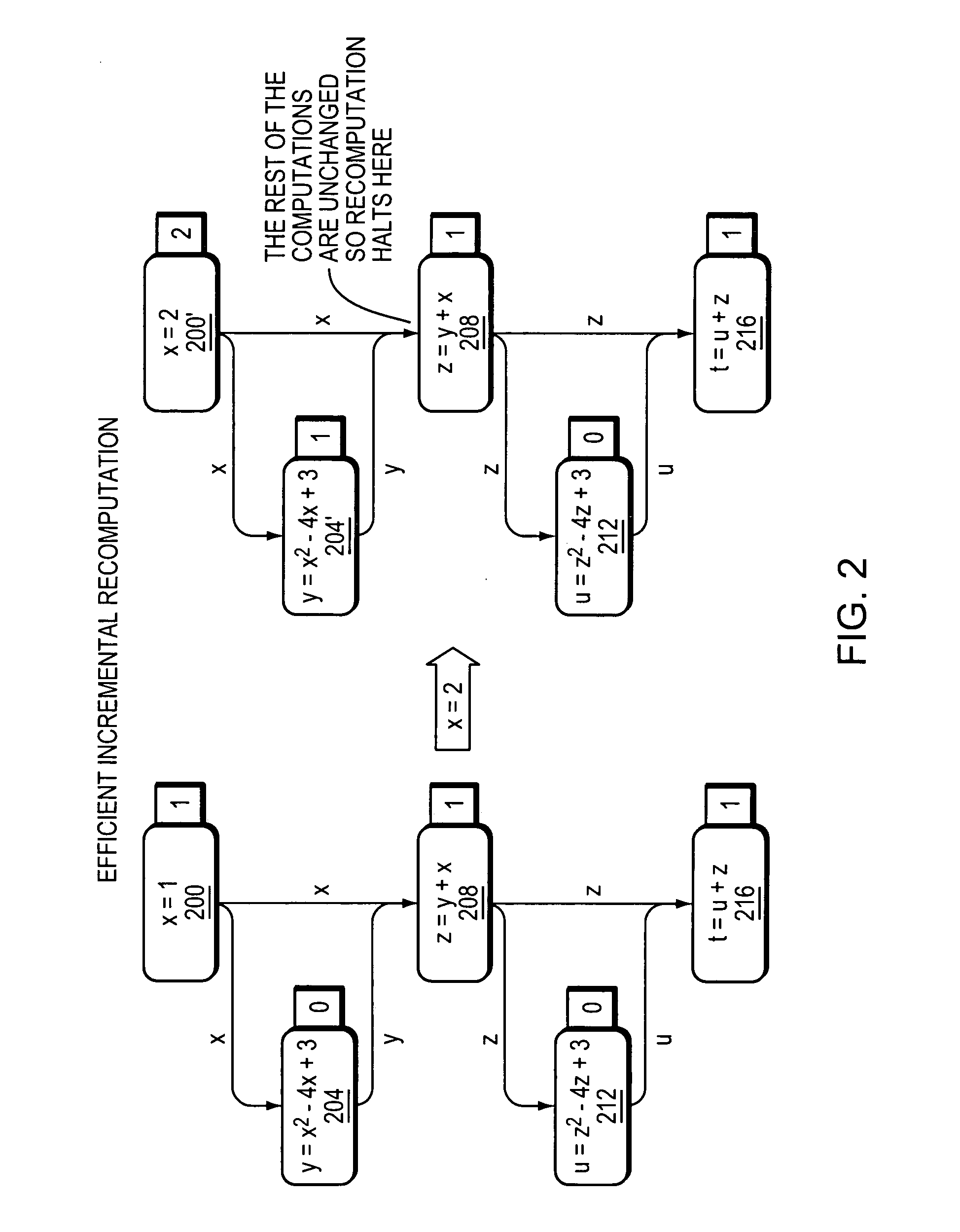
InactiveUS20060282474A1Digital data information retrievalProgram synchronisationData systemIncremental computing
Systems and methods for data processing using incremental algorithms. Embodiments of the invention decompose complex or monolithic data processing problems into one or more incremental computations called flows. These flows may be distributed across a networked cluster of commodity computers, facilitating the easy scaling of the system and robust recovery functionality. Once a request is submitted to the system, its solution may be maintained from that point in time forward, such that whenever changes are made to a problem's data the solution is efficiently recomputed.
Owner:EVERYPOINT
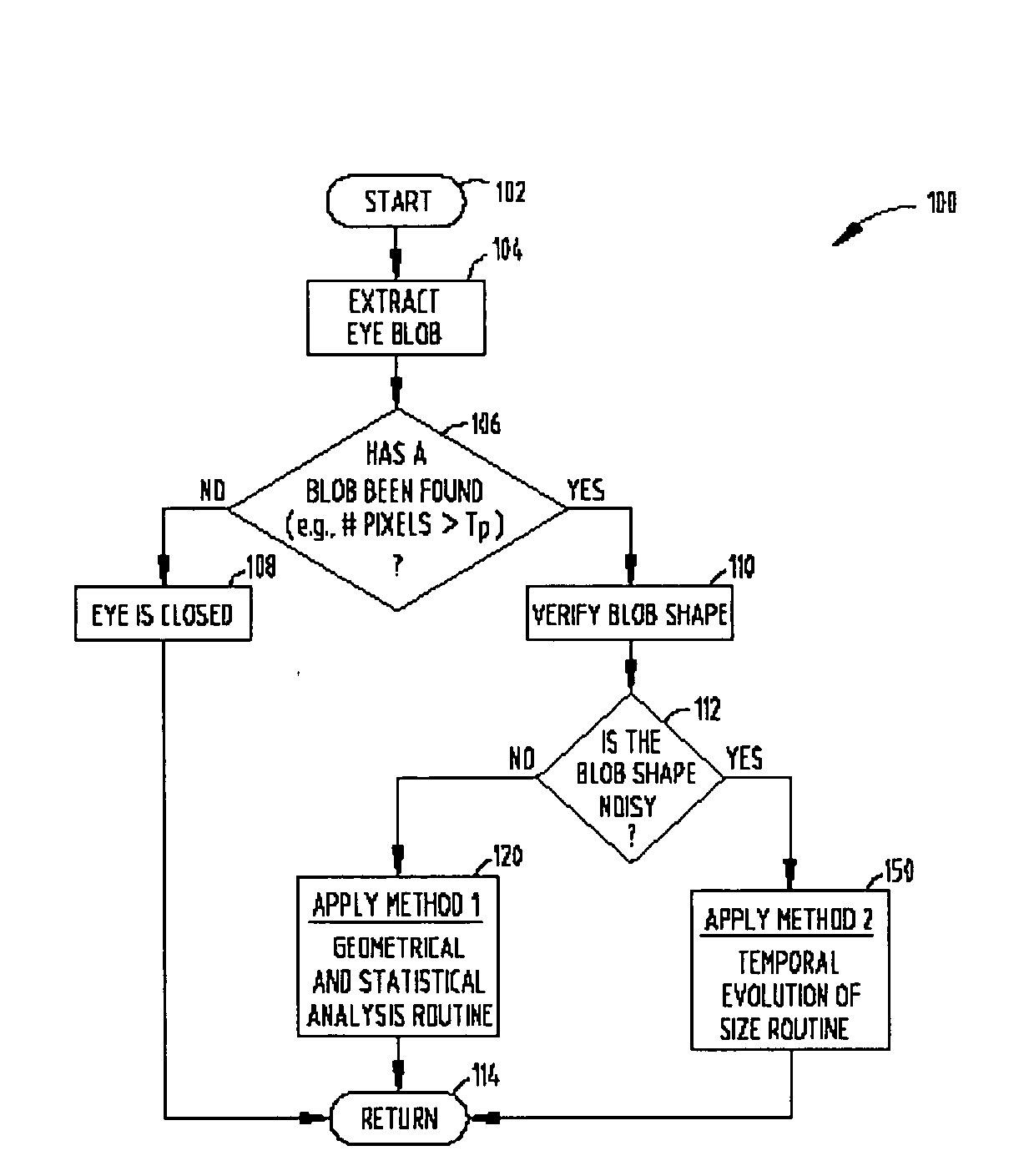
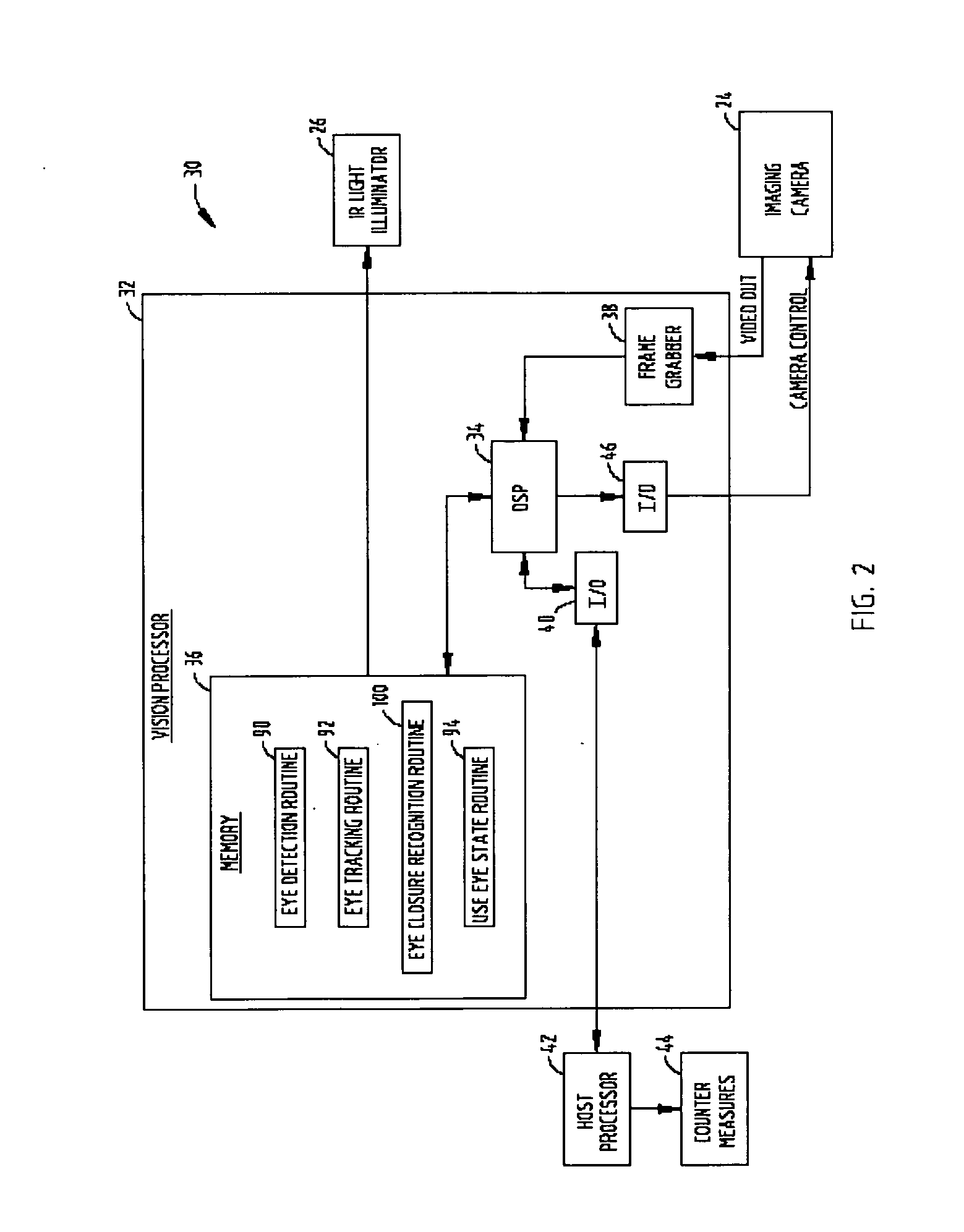
Eye closure recognition system and method
ActiveUS20080101659A1Efficiently determinedOvercomes drawbackCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsVideo processingEye closure
A system and method are provided for determining eye closure state of the eye of a subject. The system includes a video imaging camera oriented to generate images of an eye of a subject and a video processor for processing the images generated with the video imaging camera. The video processor is configured to detect an eye in the video images' and determine whether the images of the eye are noisy. The video processor processes geometrical and statistical shape of the eye in the images if the eye is not noisy, and processes changes in the size of the eye over time if the images are noisy. The processor further determines eye closure state based on a ratio of horizontal to vertical dimensions.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
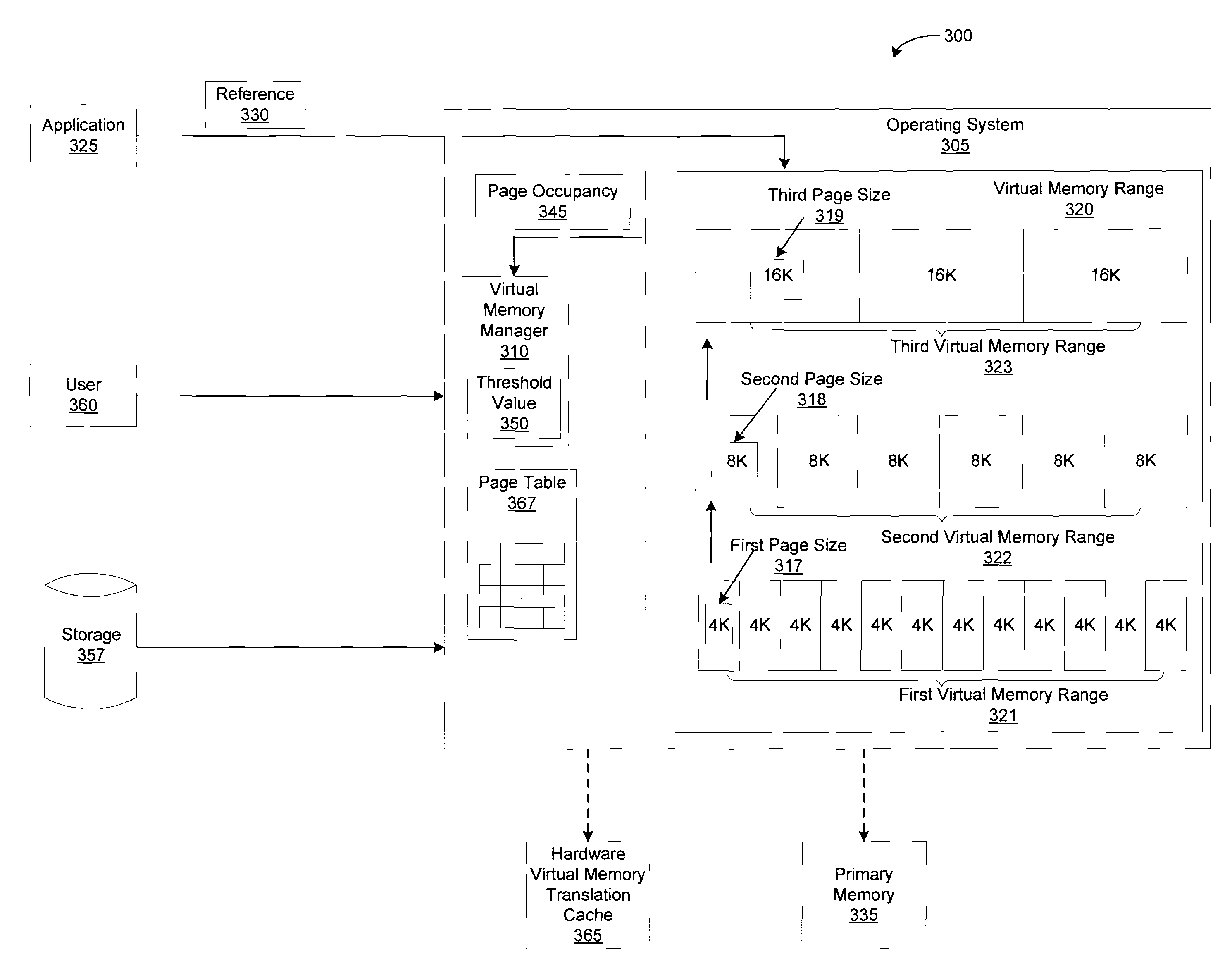
Method and apparatus for dynamically adjusting page size in a virtual memory range
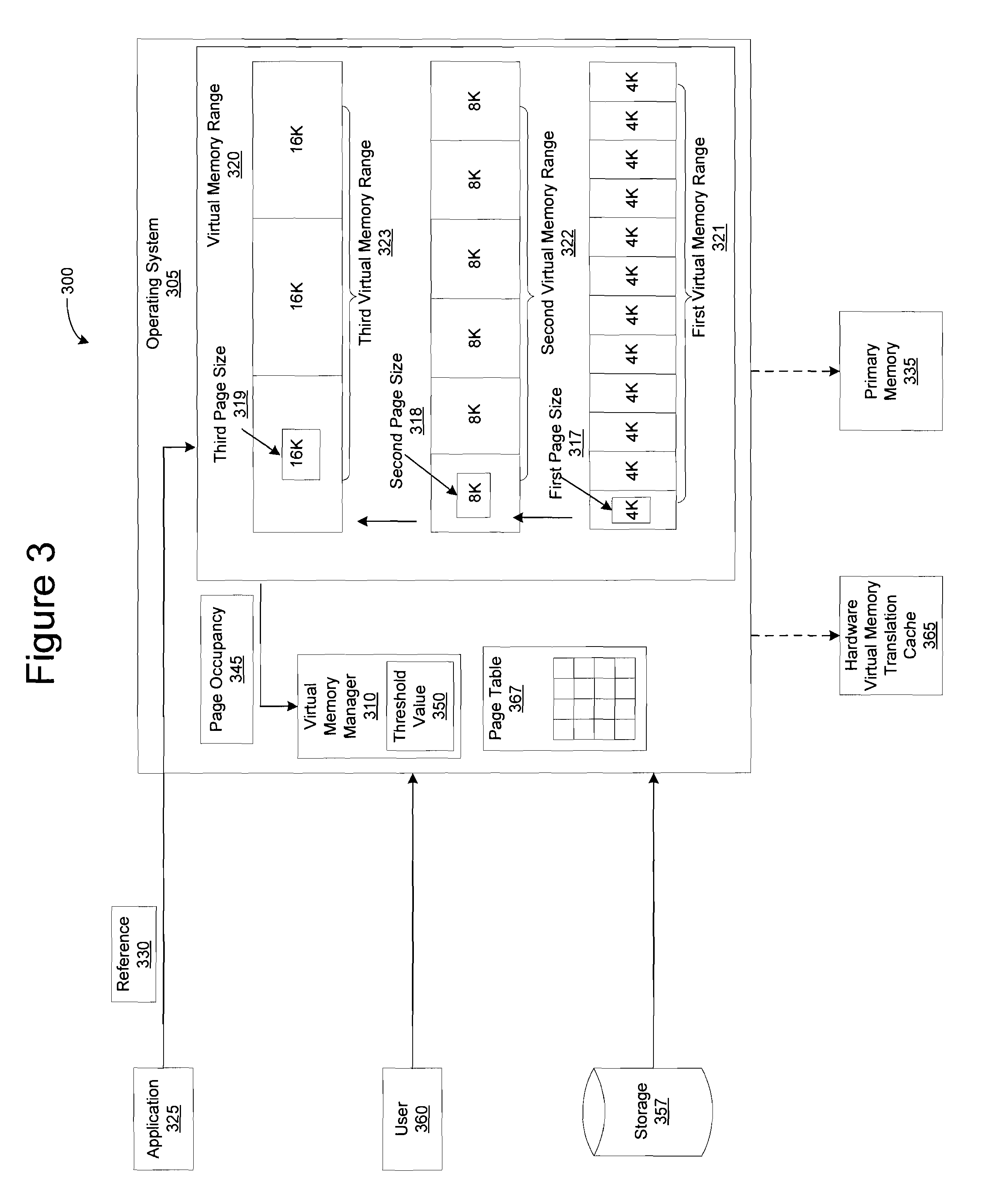
InactiveUS20080288742A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProcess changesVirtual memory
The illustrative embodiments described herein provide a computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer program product for adjusting a page size for a virtual memory range. The process identifies a set of pages in the virtual memory range that reside on a primary memory to form a page occupancy. Each of the set of pages has a first page size. The process changes the first page size to a second page size in response to a comparison of the page occupancy to a threshold value indicating that the first page size should be adjusted.
Owner:IBM CORP
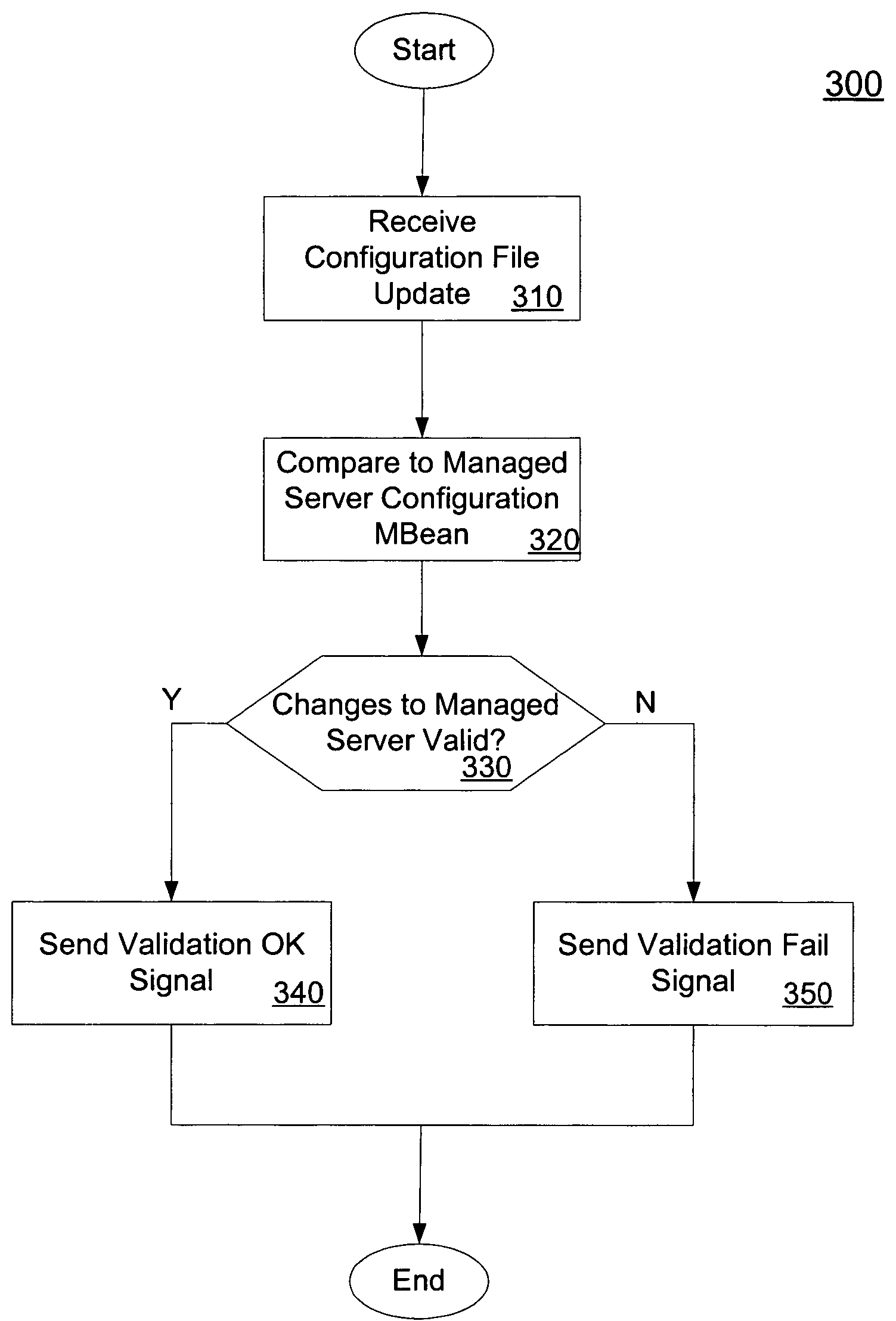
System and method for performing validation of a configuration
ActiveUS20050262225A1Digital computer detailsProgram loading/initiatingProgramming languageProcess changes
In embodiments, the present invention provides mechanisms and methods for making a set of configuration changes to a set of servers comprised of an administration server and one or more managed servers. These mechanisms and methods can enable a number of changes to be made to the configuration at once, e.g., in a batch. In such transaction based processing, embodiments process changes in batches, which enables embodiments to avoid failures in configuration changes that result in the machines being in a non-recoverable or unknown configuration state.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for specifying an order for changing an operational state of software application components
ActiveUS20090077090A1Special data processing applicationsSpecific program execution arrangementsSoftware engineeringApplication software
A computer implemented method, apparatus, and computer usable program product for managing a distributed software application. The process identifies metadata describing a set of dependencies of a set of software components in the distributed software application from data associated with the set of software components. The process then identifies a sequence for changing an operational state of the set of software components of the distributed software application from the metadata to form an identified sequence. Thereafter, the process changes the operational state of the set of software components using the identified sequence.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thermal pre-treatment process for soda lime glass substrate for thin film photovoltaic materials
InactiveUS20110020980A1Easy to implementHigh efficiency photovoltaic absorber layerFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterials scienceSoda-lime glass
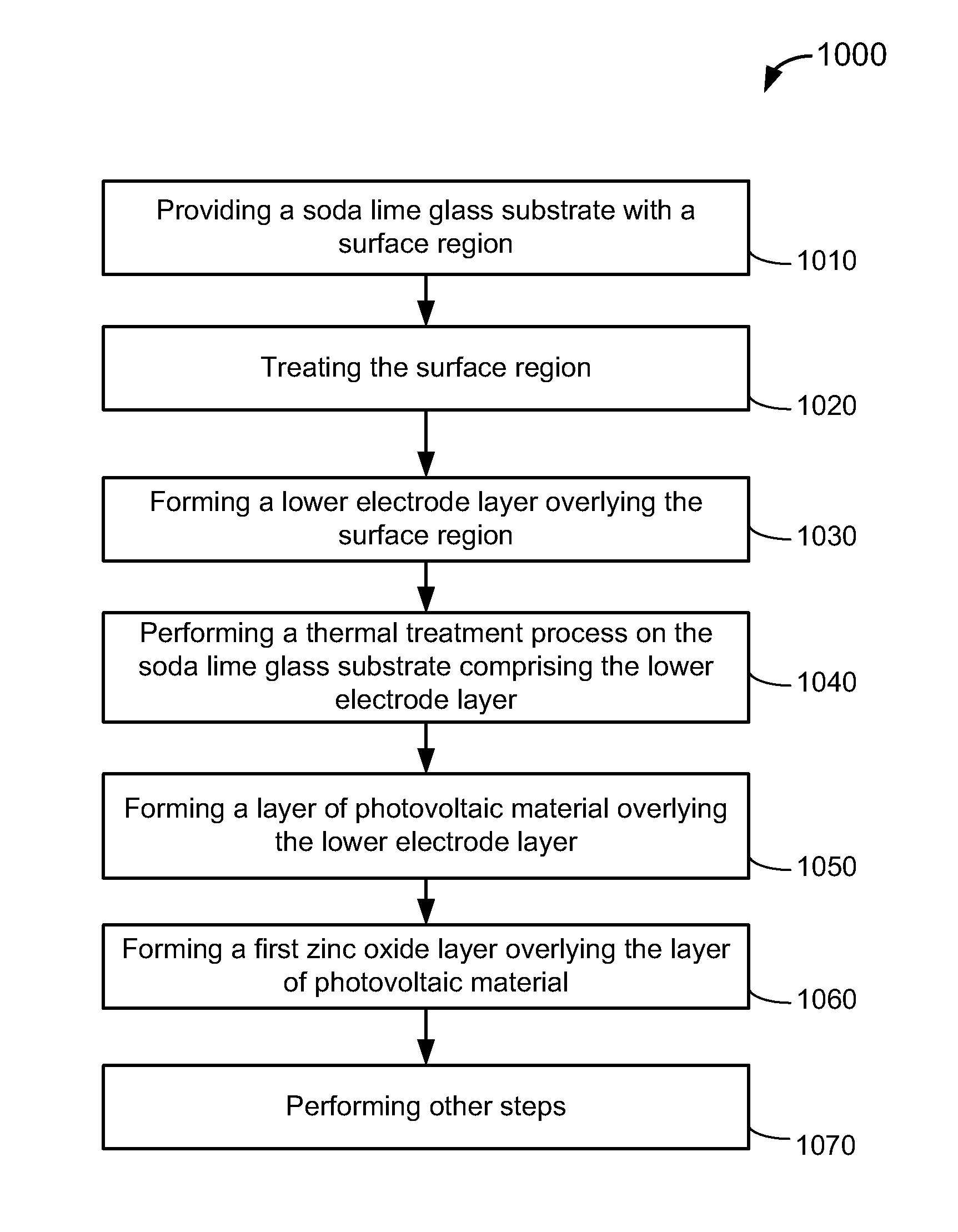
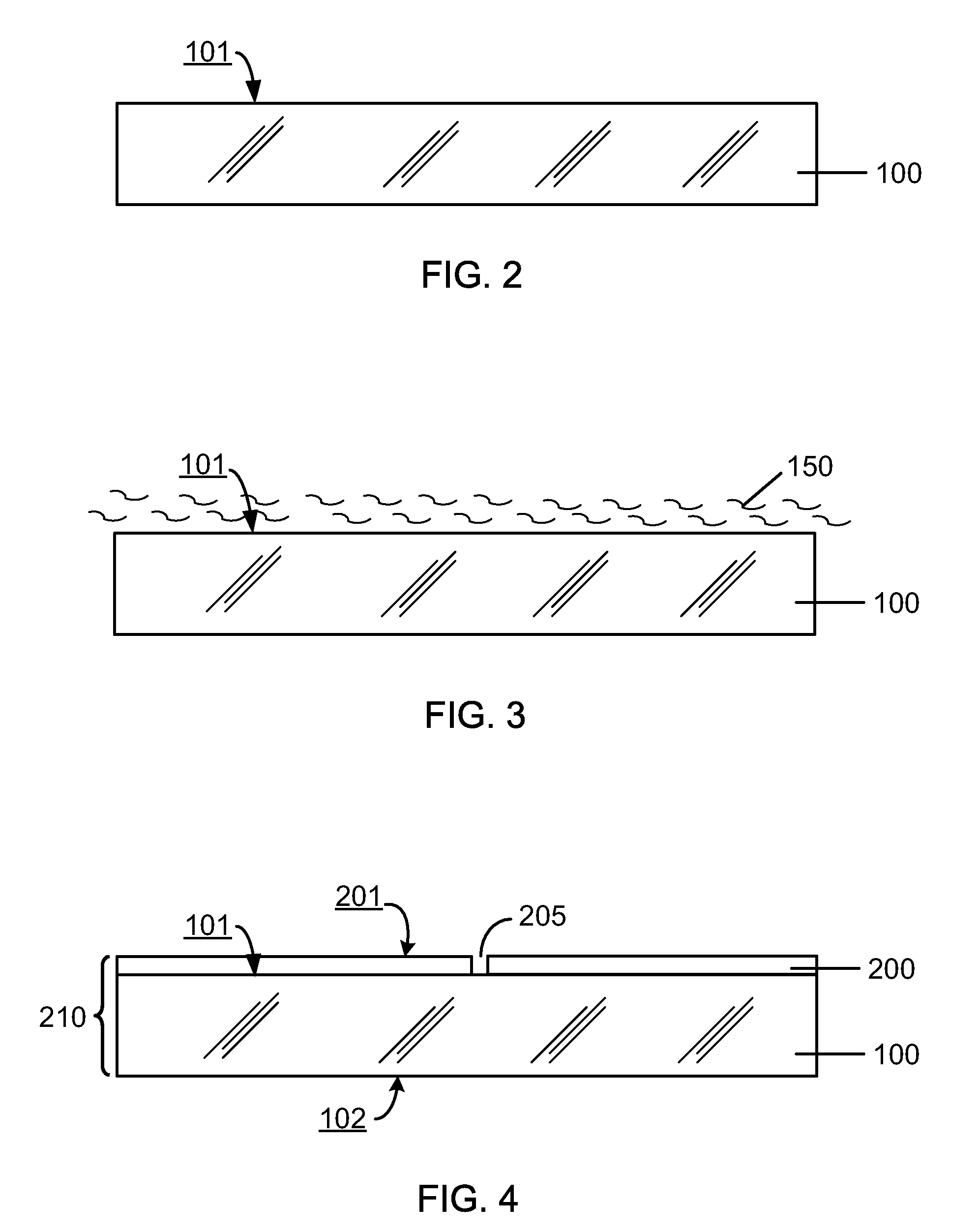
A method for fabricating a thin film solar cell includes providing a soda lime glass substrate comprising a surface region, treating the surface region with one or more cleaning process including an aqueous solution to remove one or more contaminants and / or particulates, and forming a lower electrode layer overlying the surface region. The method also includes performing a thermal treatment process to remove any residual water species to substantially less than a monolayer of water species from the lower electrode layer and soda lime glass substrate. The thermal treatment process changes a temperature of the soda lime glass substrate from a first temperature to a second temperature to pre-heat the soda lime glass substrate. Additionally, the method includes transferring the soda lime glass substrate, which has been preheated, to a deposition chamber and forming a layer of photovoltaic material overlying the lower electrode layer within the deposition chamber.
Owner:CM MFG
High bandwidth reconfigurable on-chip network for reconfigurable systems
ActiveUS20070200594A1Reduce necessaryExtension of timeSolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsCrossbar switchTelecommunications link
A crossbar switch is implemented in a reconfigurable circuit, such as a FPGA, instantiated with a number of modules, the crossbar switch providing communication links between the modules. The modules and crossbar switch can be easily updated in a partial reconfiguration process changing only portions of modules and the crossbar switch while other portions remain active. The crossbar switch uses individual wiring to independently connect module outputs and inputs so that asynchronous communications can be used. The crossbar switch can be implemented in different embodiments including a Clos crossbar switch, and a crossbar switch connecting each module output only to a corresponding module input, allowing for a reduction in the amount of FPGA resources required to create the crossbar switches.
Owner:XILINX INC
System, method, and program product for targeting and identification of optimal process variables in constrained energy recovery systems
ActiveUS7729809B2Superior in pointImprove the forceLevel controlTemperatue controlDegrees of freedomEnergy recovery
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
System, Method, and Program Product for Targeting and Identification of Optimal Process Variables in Constrained Energy Recovery Systems
ActiveUS20100070258A1Improve fidelitySuperior in pointLevel controlTemperatue controlEnergy recoveryEnergy expenditure
Systems, methods, and program product to calculate global energy utility targets and to model and determine an optimal solution for a non-thermodynamically constrained process or cluster of processes subject to non-thermodynamic constraints under all possible process changes and streams specific minimum temperature approaches, are provided. An exemplary system can utilize thermodynamic constraints exhibited in stream-specific minimum temperature approach values ΔTmini as optimization parameters, in addition to other process conditions degrees of freedom including the addition of new waste heat carrier streams to target for minimizing energy consumption of the non-thermodynamic constrained waste heat recovery problem and to identify the optimal operating conditions that result in desired minimum energy consumption subject to the non-thermodynamic constraints.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Universal multi-source heterogeneous large-scale data synchronizing system
ActiveCN107729366AReliable Synchronous Transaction Advance MechanismProgram controlSpecial data processing applicationsInformation processingData synchronization
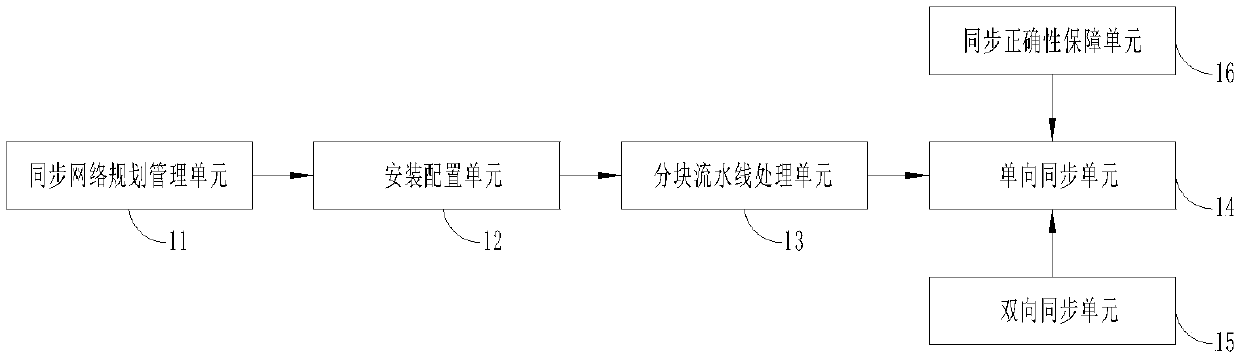
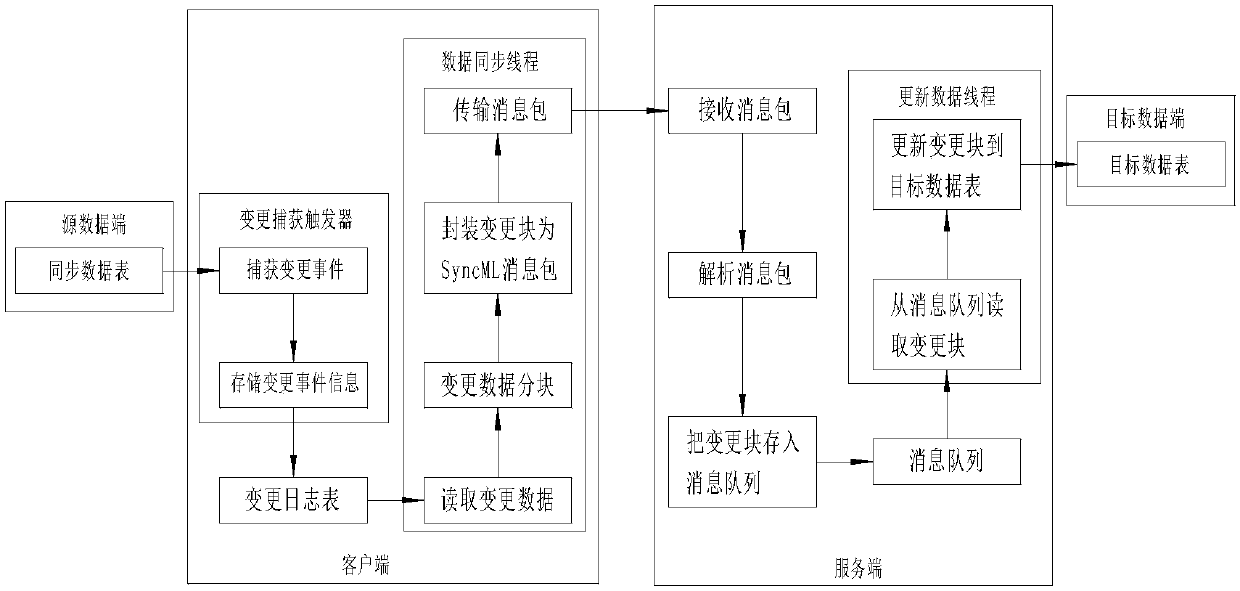
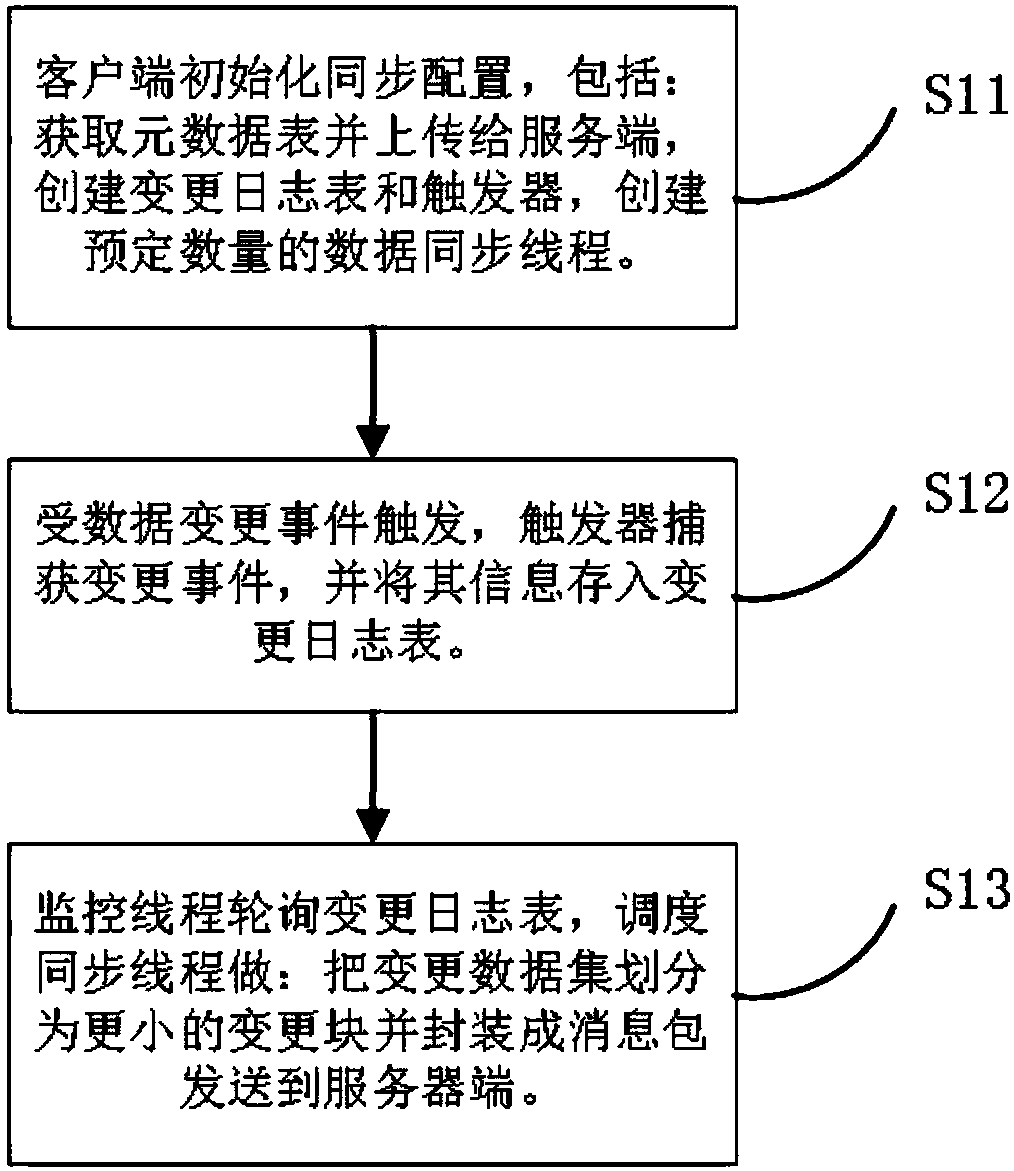
The invention provides a universal multi-source heterogeneous large-scale data system. The system comprises a synchronous network planning management unit, an installation configuration unit, a blockassembly line processing unit, a one-way synchronizing unit, a two-way synchronizing unit and a synchronous correctness guaranteeing unit. The system works on a node database layer and on a middle layer below an application logic layer. In the data synchronizing process, a client transmits captured local change information to a server according to a synchronizing task plan; the server receives thechange information and transmits the change information to an asynchronous parallel information processing mechanism to store the change information in a corresponding information queue; the server polls the local information queues to read the to-be-processed change information, and then carries out subsequent data change according to an heterogeneous data mapping rule so as to maintain the consistency of synchronous data of a source data copy and synchronous data of a target data copy. The system independently runs parallel to a synchronous node local application, and provides a relaxationaffair guarantee mechanism of internet distributed multi-source heterogeneous data synchronization by means of loose coupling coordination.
Owner:GUANGDONG CONSTR INFORMATION CENT
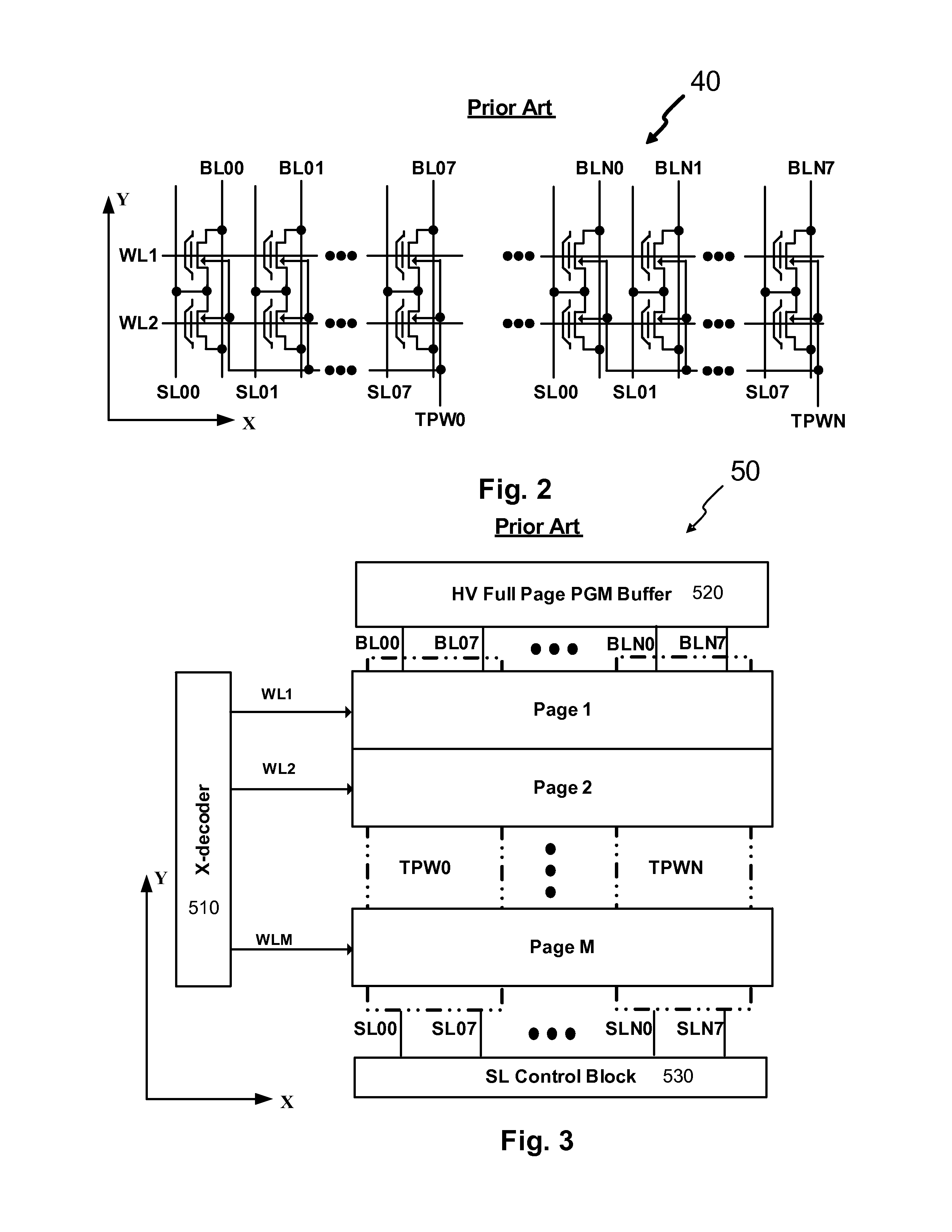
NEW 1T1b AND 2T2b FLASH-BASED, DATA-ORIENTED EEPROM DESIGN
InactiveUS20130182509A1Reducing effective cell sizeSmall cell sizeRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit linePre-charge
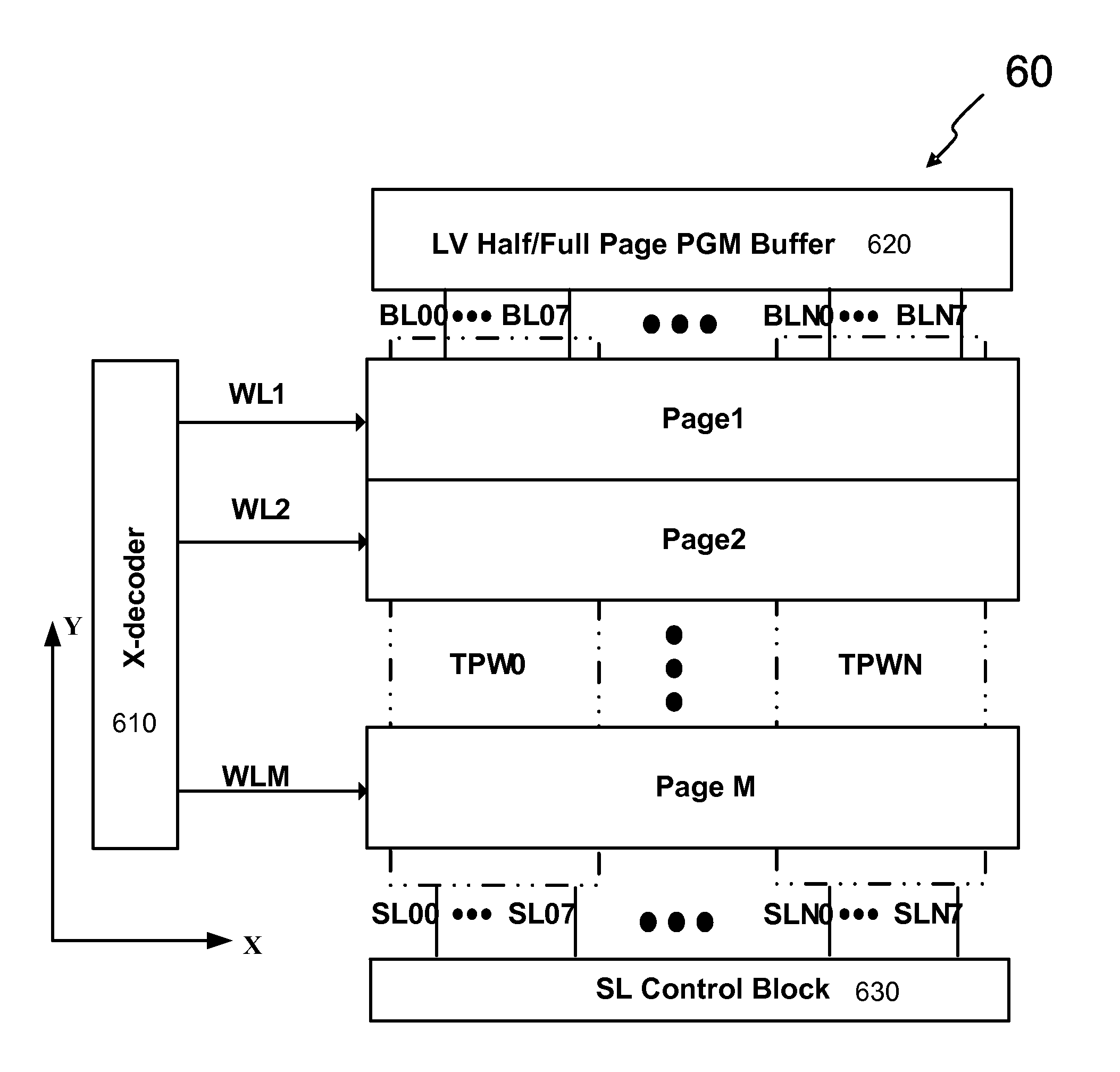
An one-transistor-one-bit (1T1b) Flash-based EEPROM cell is provided along with improved key operation schemes including applying a negative word line voltage and a reduced bit line voltage for perform erase operation, which drastically reduces the high voltage stress on each cell for enhancing the Program / Erase cycles while reducing cell size. An array made by the 1T1b Flash-based EEPROM cells can be operated with Half-page or Full-page divided programming and pre-charging period for each program cycle. Utilizing PGM buffer made of Vdd devices in the cell array further save silicon area. Additionally, a two-transistor-two-bit (2T2b) EEPROM cell derived from the 1T1b cell is disclosed with additional cell size reduction but with the operation of program and erase the same as that for the 1T1b cells with benefits of no process change but much enhanced storage density, superior Program / Erase endurance cycle, and capability for operating in high temperature environment.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Method for preparing volume expansion type granular profile control agent using oil production mud
ActiveCN1781860AHeat-resistant and salt-resistantGood expansion performanceSludge treatmentDrilling compositionCross-linkPolymer science
The present invention discloses process of synthesizing expanded granular profile control agent with oil production mud, and the synthesized profile control agent is used in the deep profile control of macroporous oil reservoir. The expanded granular profile control agent is prepared with ternary polymer system of acrylic acid, acrylamide and cross-linking agent and through adding oil production mud, oxidant and reductant in certain weight proportion to produce adiabatic free radical polymerization forming colloid block and subsequent palletizing, stoving and crushing to required granularity. The said process changes the oil production mud into useful resource and the prepared expanded granular profile control agent has the features of heat resistance, salt tolerance, high expanding performance, long stable period, etc.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
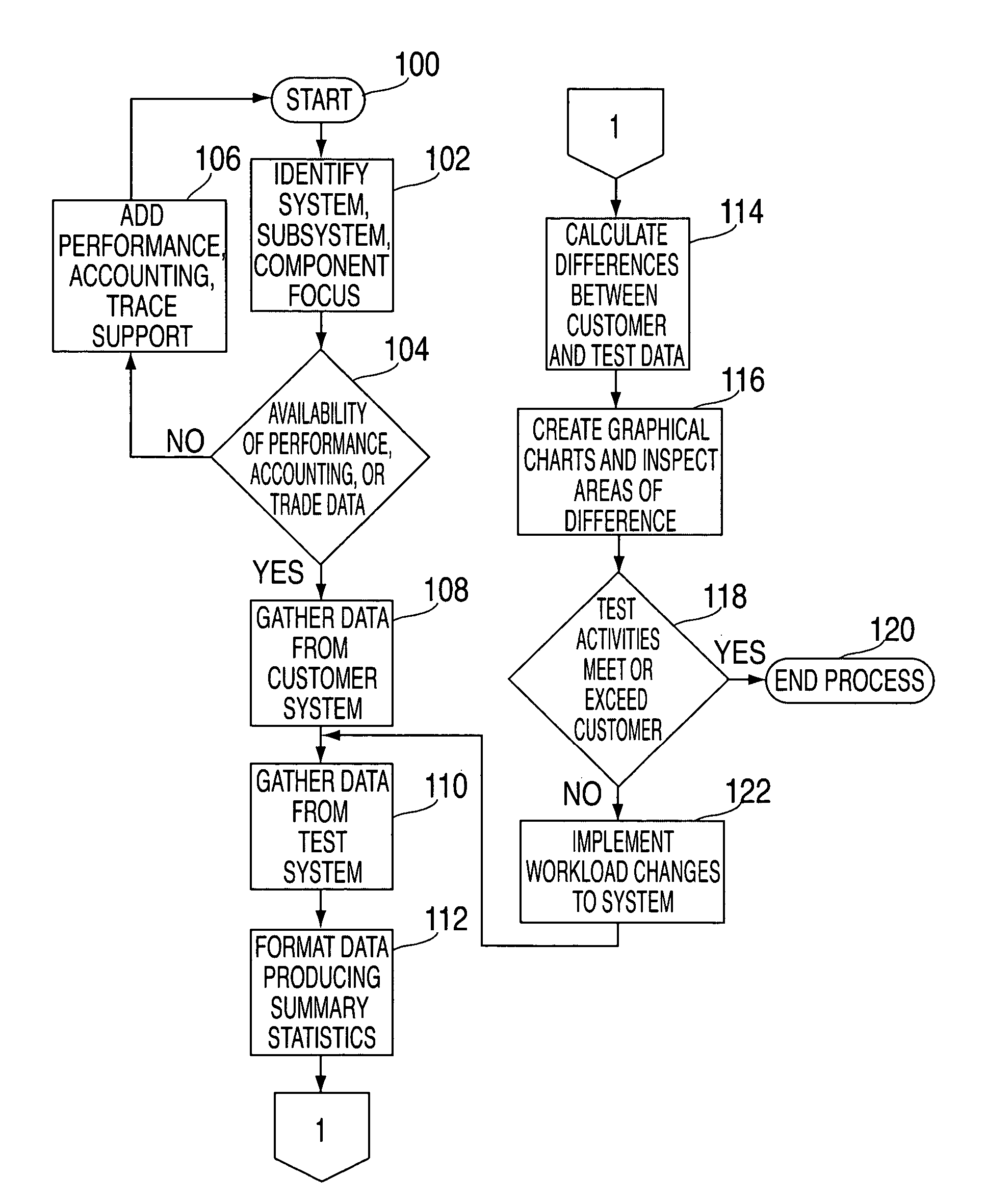
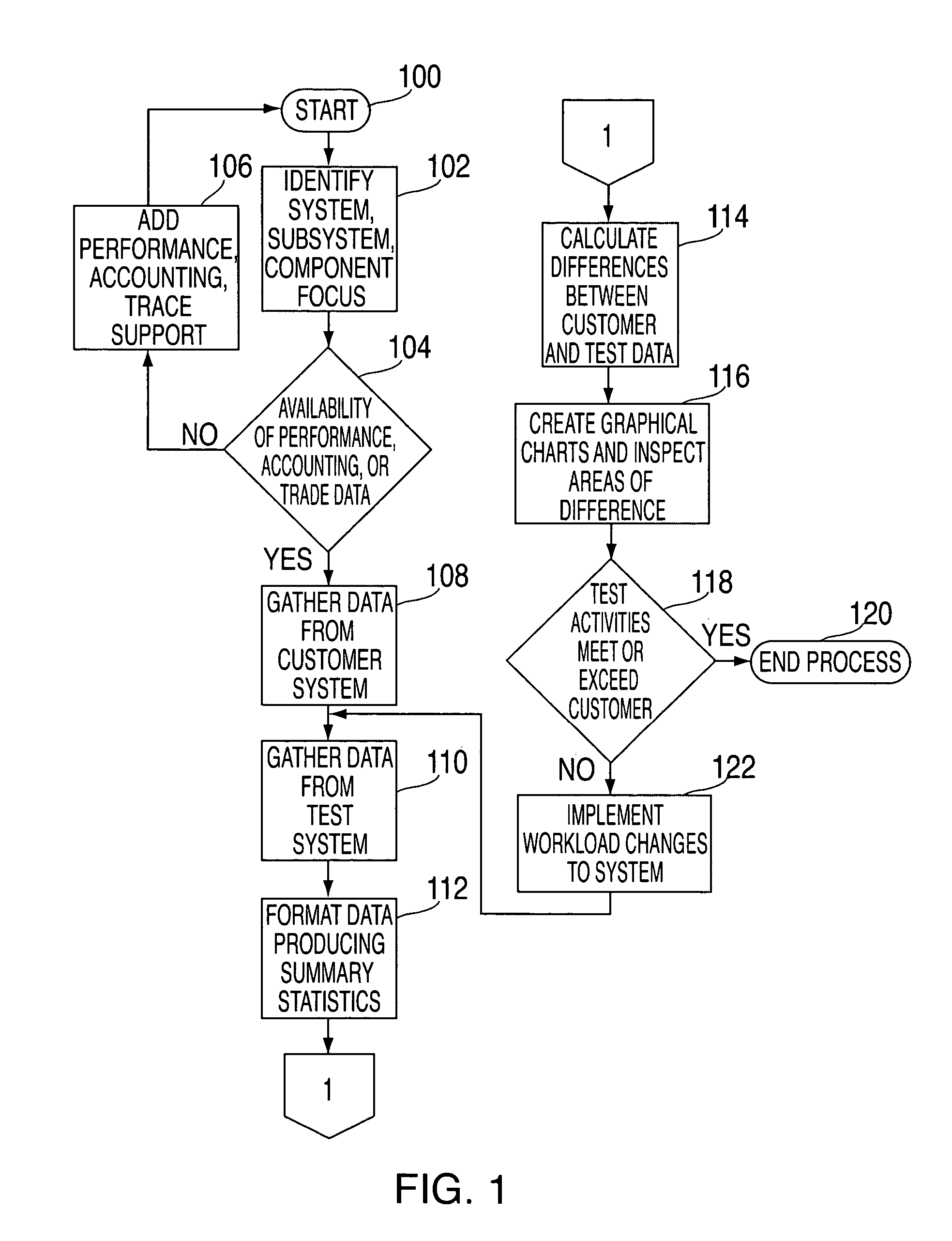
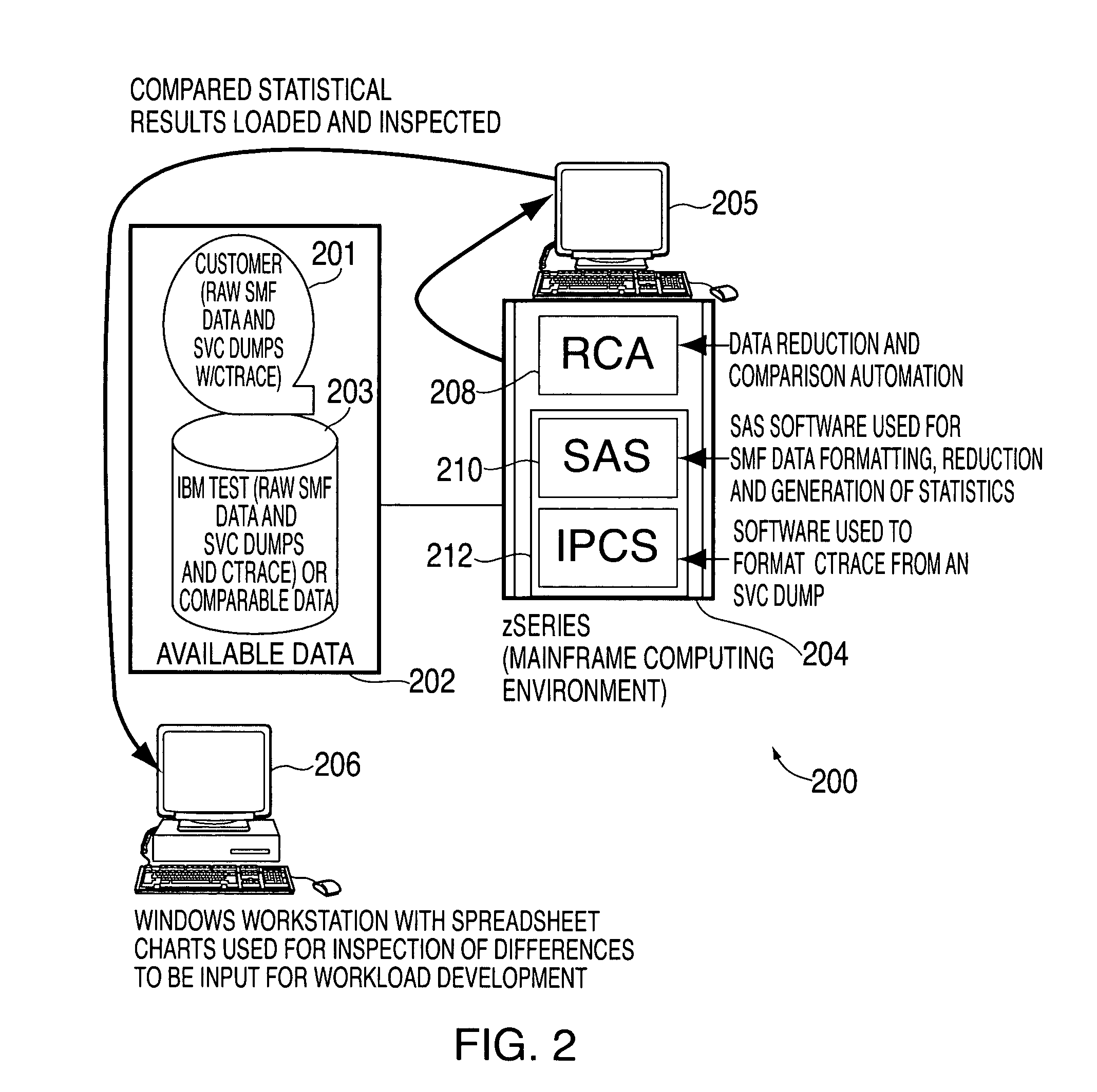
Method, system, and storage medium for using comparisons of empirical system data for testcase and workload profiling
InactiveUS20060095312A1Error detection/correctionSpecial data processing applicationsSpecific testWorkload profiling
Systems and methods for using comparisons of empirical system data, (e.g., performance, accounting, software module or function frequency), for testcase and workload profiling are provided. Instead of asking a customer what he does, simply asking for some set of empirical data that can be formatted, reduced, and analyzed. By gathering the same kind of data for the test systems that is used by the customer, testcases and workload profiling are improved by making comparisons between the customer data and the test data in an iterative process. The iterative processes change test data and compare not only customer data with test data but also compare data from prior iterations with current data. There is a feedback loop for providing a comparison of how close or distant the testcases and workload profiling are from customer-like data and workloads in a particular test.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com