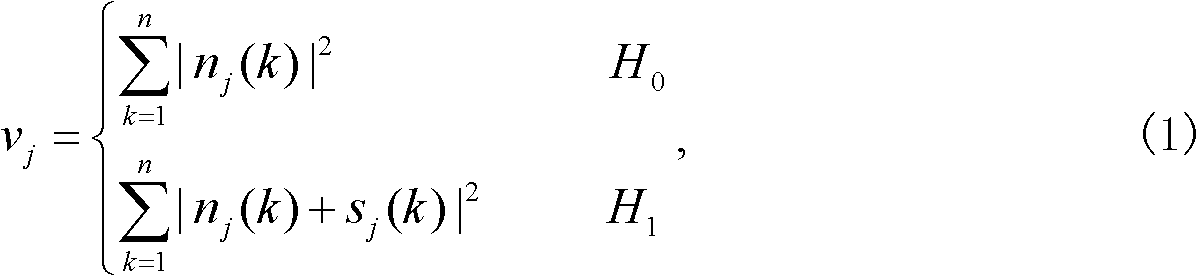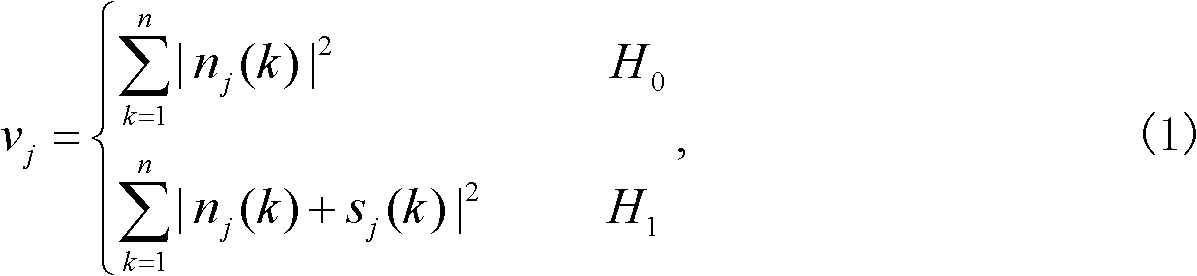Patents
Literature
46 results about "Sequential probability ratio test" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) is a specific sequential hypothesis test, developed by Abraham Wald and later proven to be optimal by Wald and Jacob Wolfowitz. Neyman and Pearson's 1933 result inspired Wald to reformulate it as a sequential analysis problem. The Neyman-Pearson lemma, by contrast, offers a rule of thumb for when all the data is collected (and its likelihood ratio known).
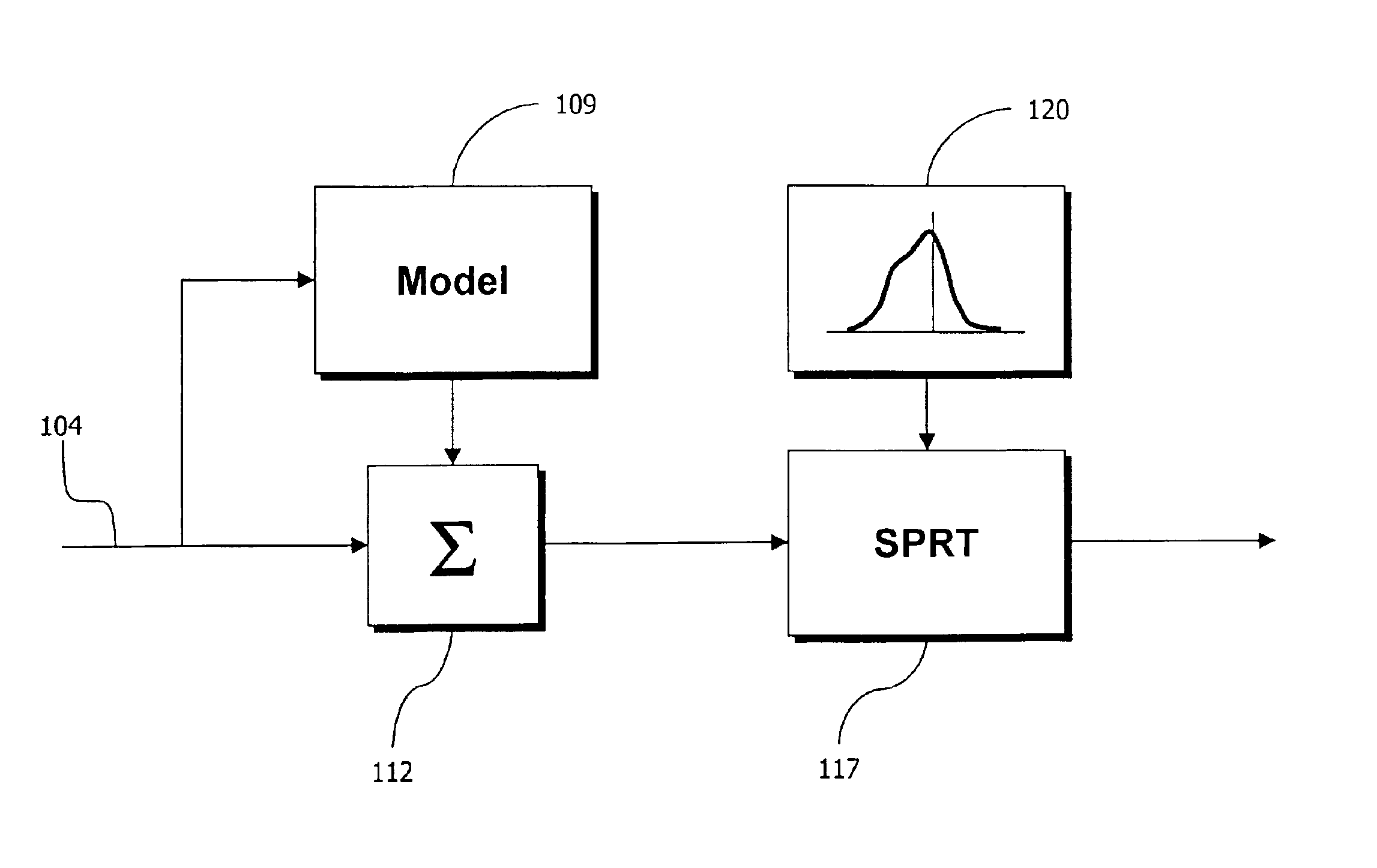
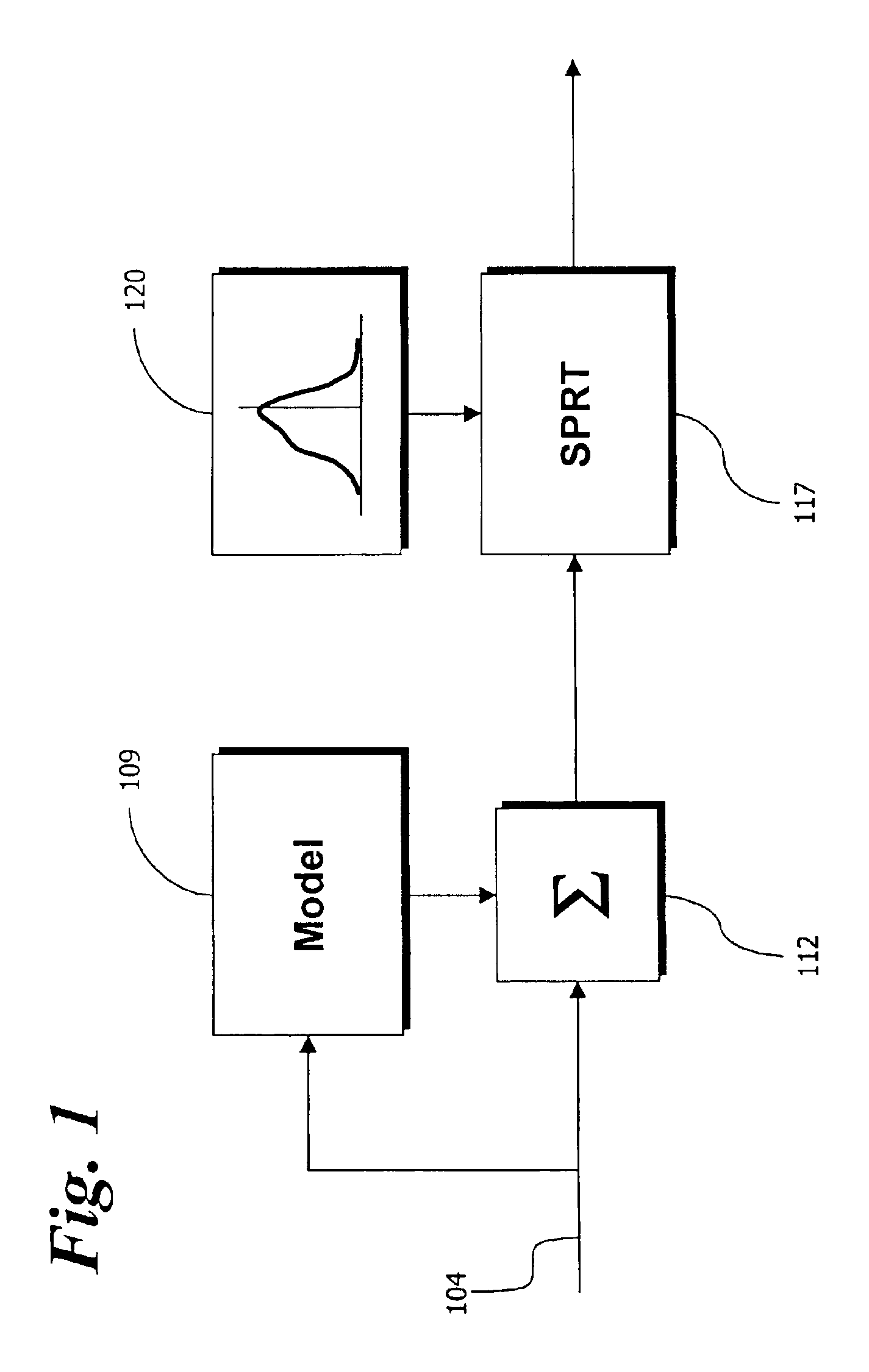
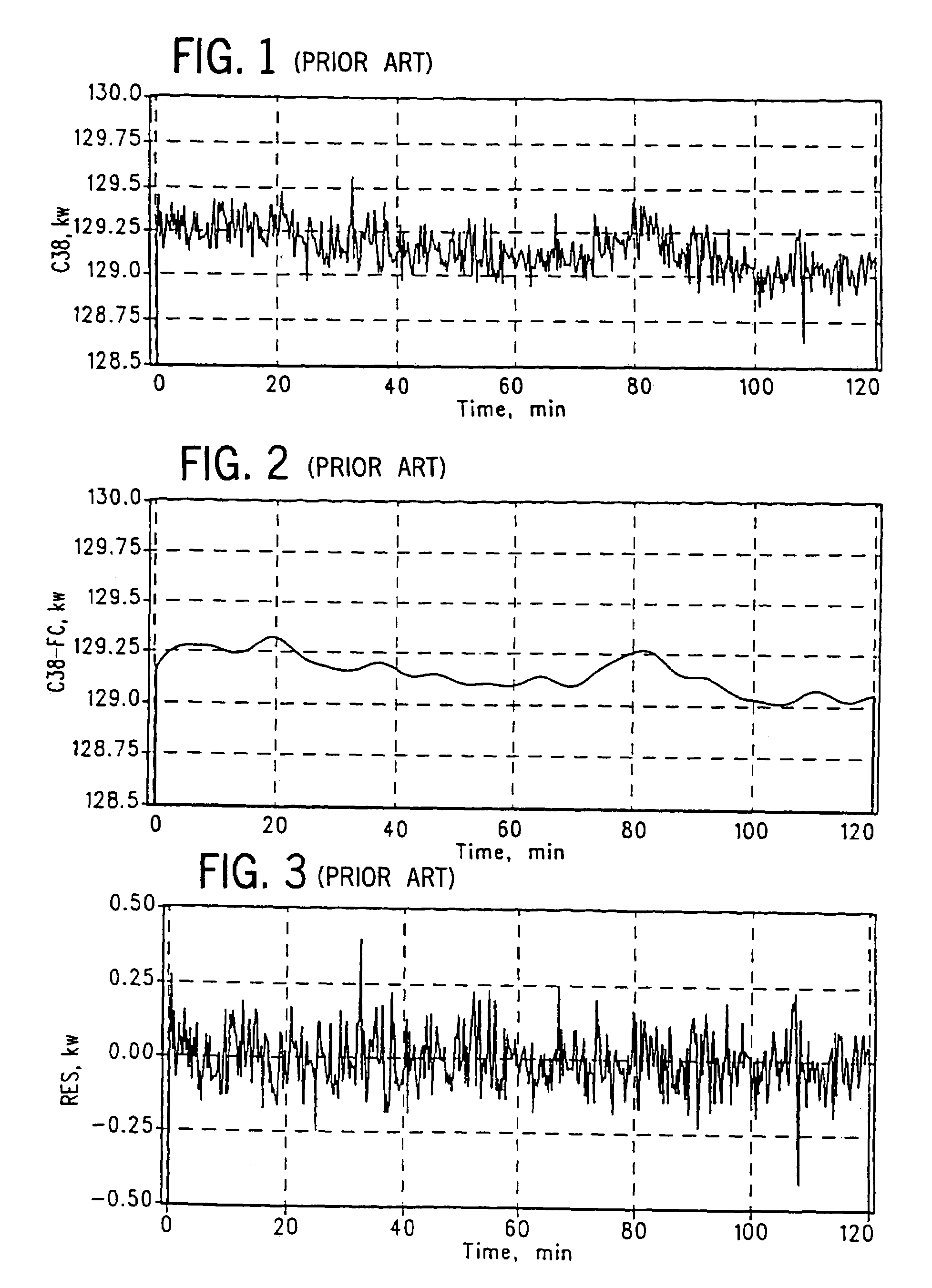
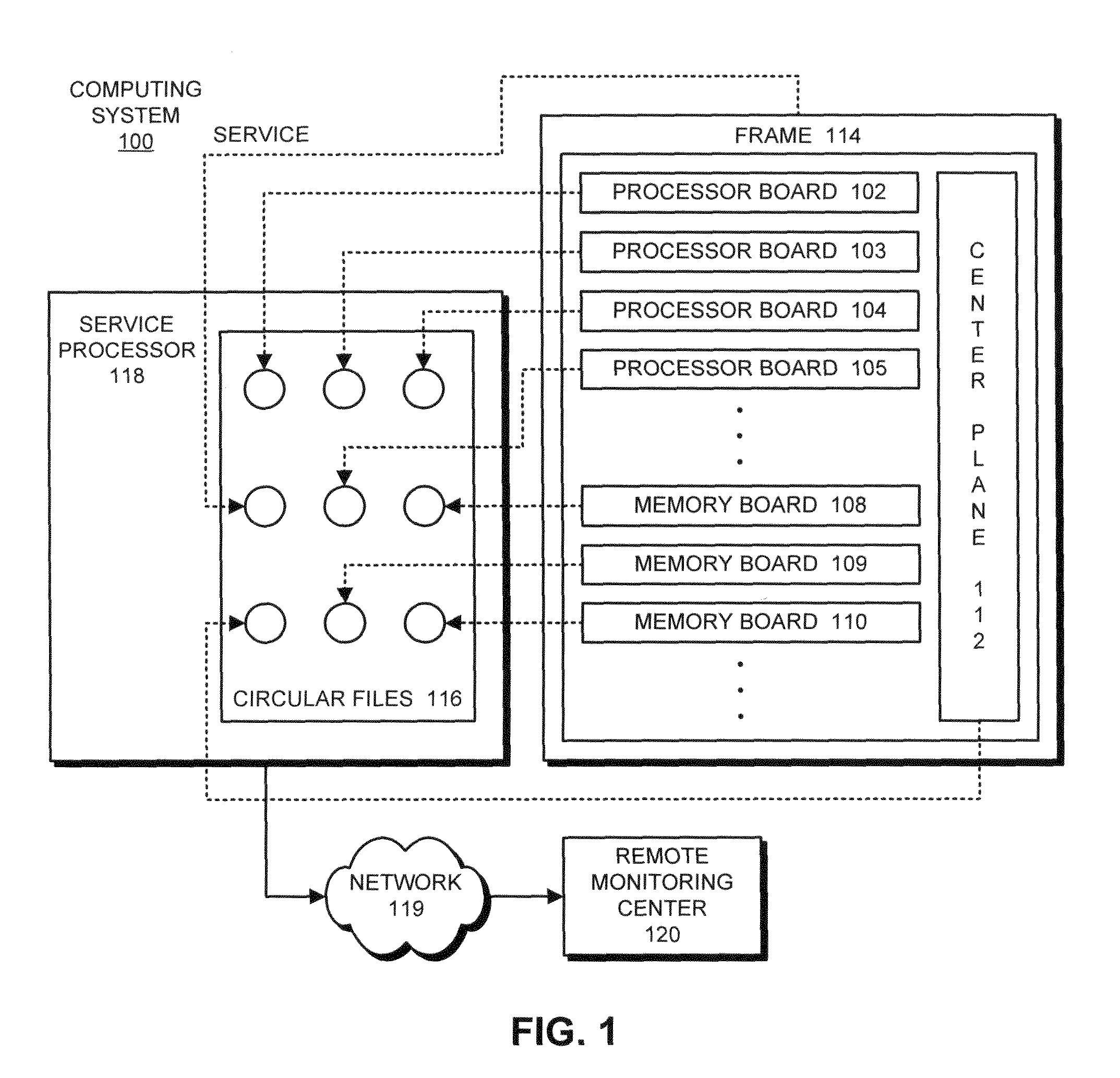
Residual signal alert generation for condition monitoring using approximated SPRT distribution
InactiveUS6975962B2Registering/indicating working of machinesDigital computer detailsProcess deviationsMonitoring system
A system and method for monitoring a condition of a monitored system. Estimates of monitored parameters from a model of the system provide residual values that can be analyzed using a sequential probability ratio test (“SPRT”). The invention employs empirically derived distributions in the SPRT to provide more accurate and sensitive alerts of impending faults, breakdowns and process deviations. The distributions can be generated from piecewise continuous approximation or spline functions based on the actual distribution of residual data to provide improved computational performance. The distributions can be provided before monitoring, or can be updated and determined during monitoring in an adaptive fashion.
Owner:SMARTSIGNAL CORP
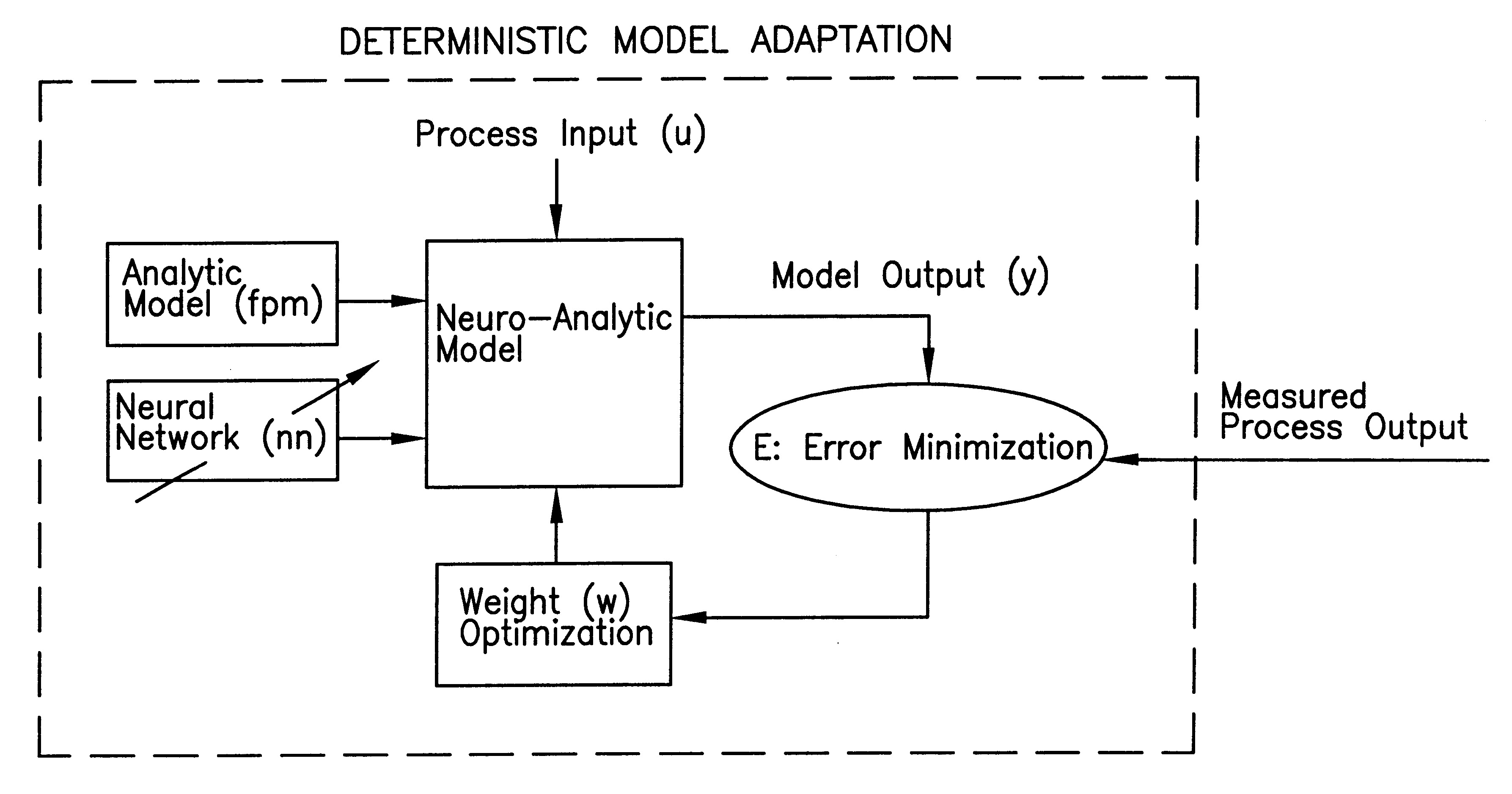
Statistically qualified neuro-analytic failure detection method and system
InactiveUS6353815B1Accurate and reliable on-lineImprove the level ofSimulator controlDigital computer detailsPeristaltic pumpAnalytic model
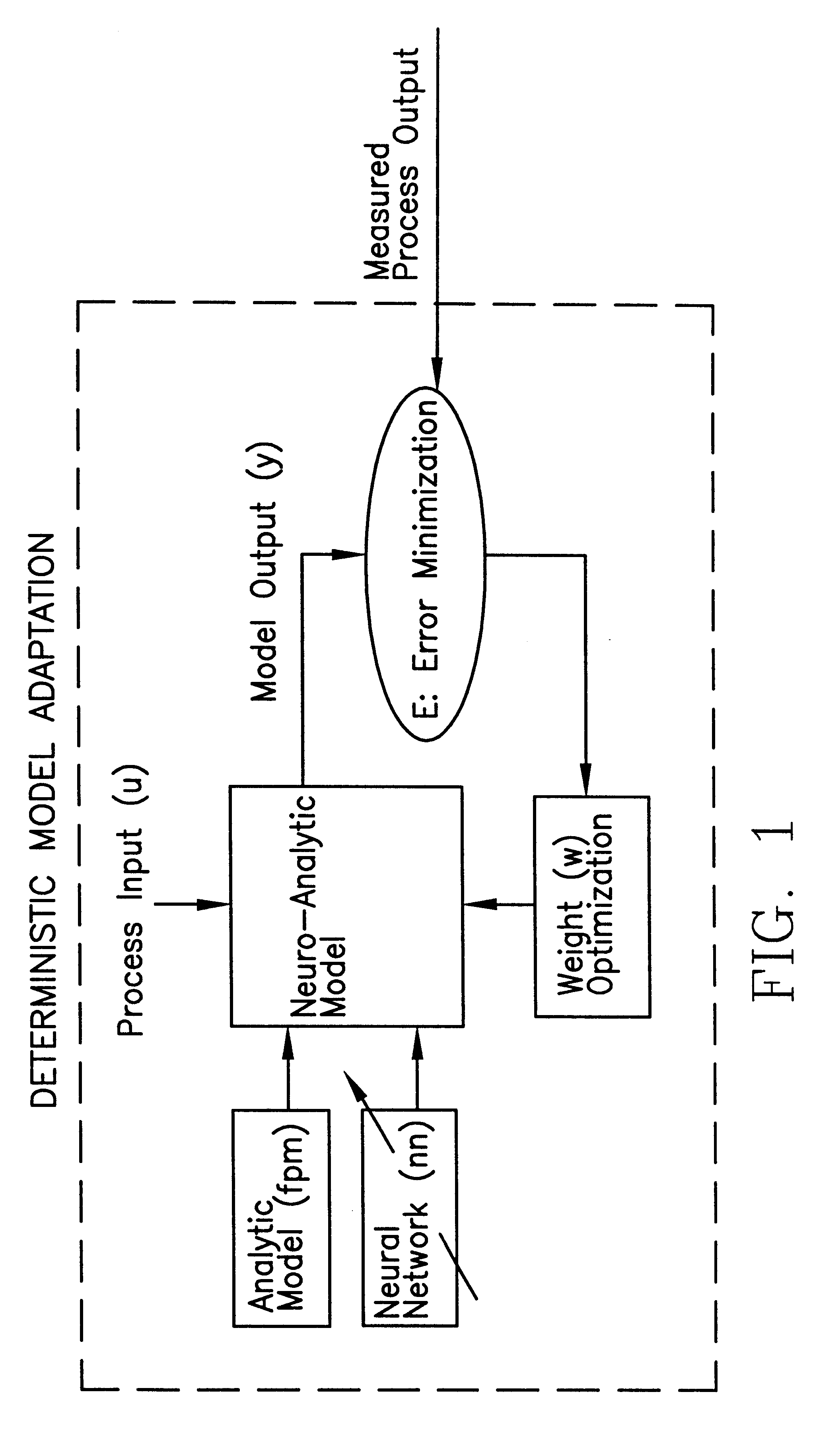
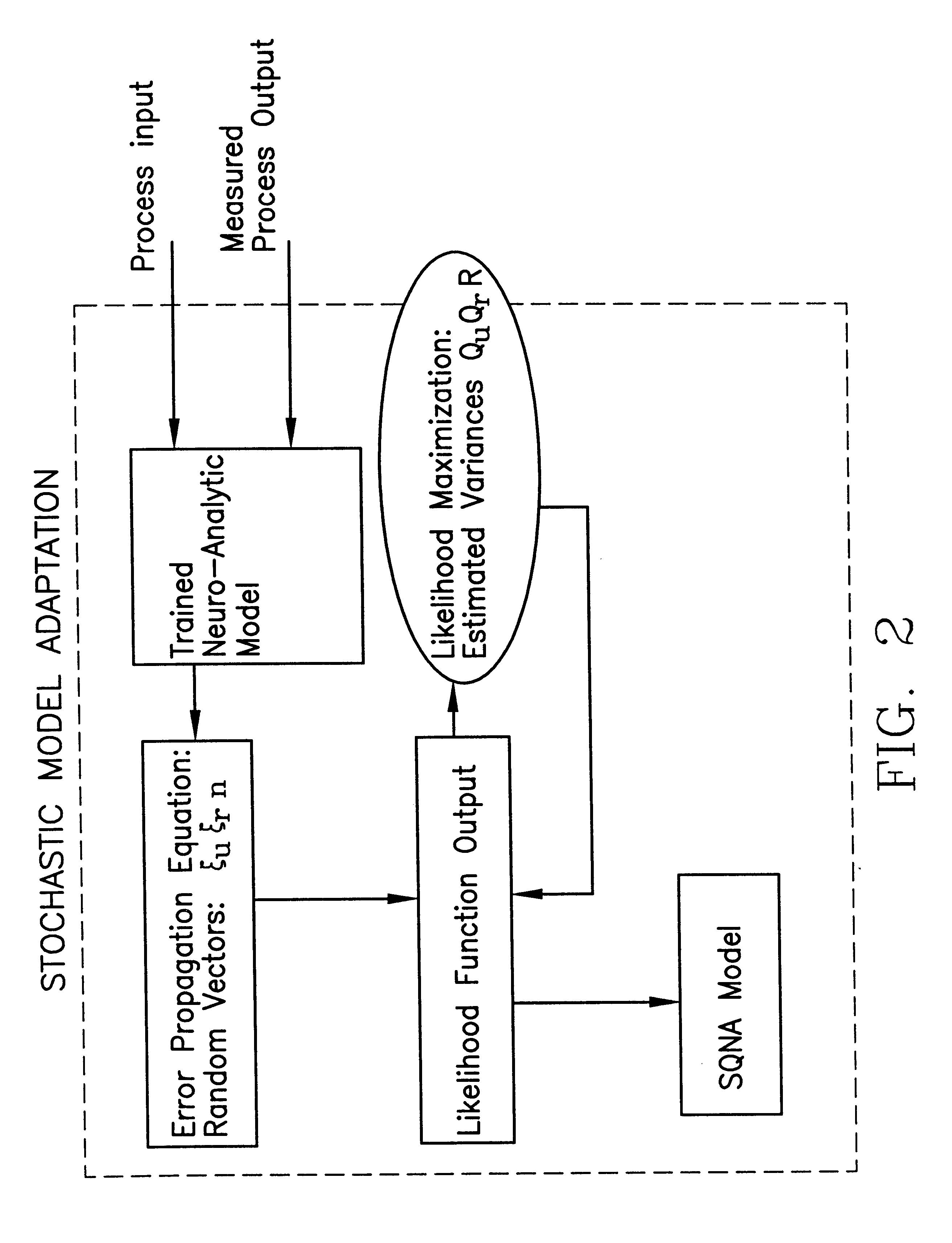
An apparatus and method for monitoring a process involve development and application of a statistically qualified neuro-analytic (SQNA) model to accurately and reliably identify process change. The development of the SQNA model is accomplished in two stages: deterministic model adaption and stochastic model modification of the deterministic model adaptation. Deterministic model adaption involves formulating an analytic model of the process representing known process characteristics, augmenting the analytic model with a neural network that captures unknown process characteristics, and training the resulting neuro-analytic model by adjusting the neural network weights according to a unique scaled equation error minimization technique. Stochastic model modification involves qualifying any remaining uncertainty in the trained neuro-analytic model by formulating a likelihood function, given an error propagation equation, for computing the probability that the neuro-analytic model generates measured process output. Preferably, the developed SQNA model is validated using known sequential probability ratio tests and applied to the process as an on-line monitoring system. Illustrative of the method and apparatus, the method is applied to a peristaltic pump system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
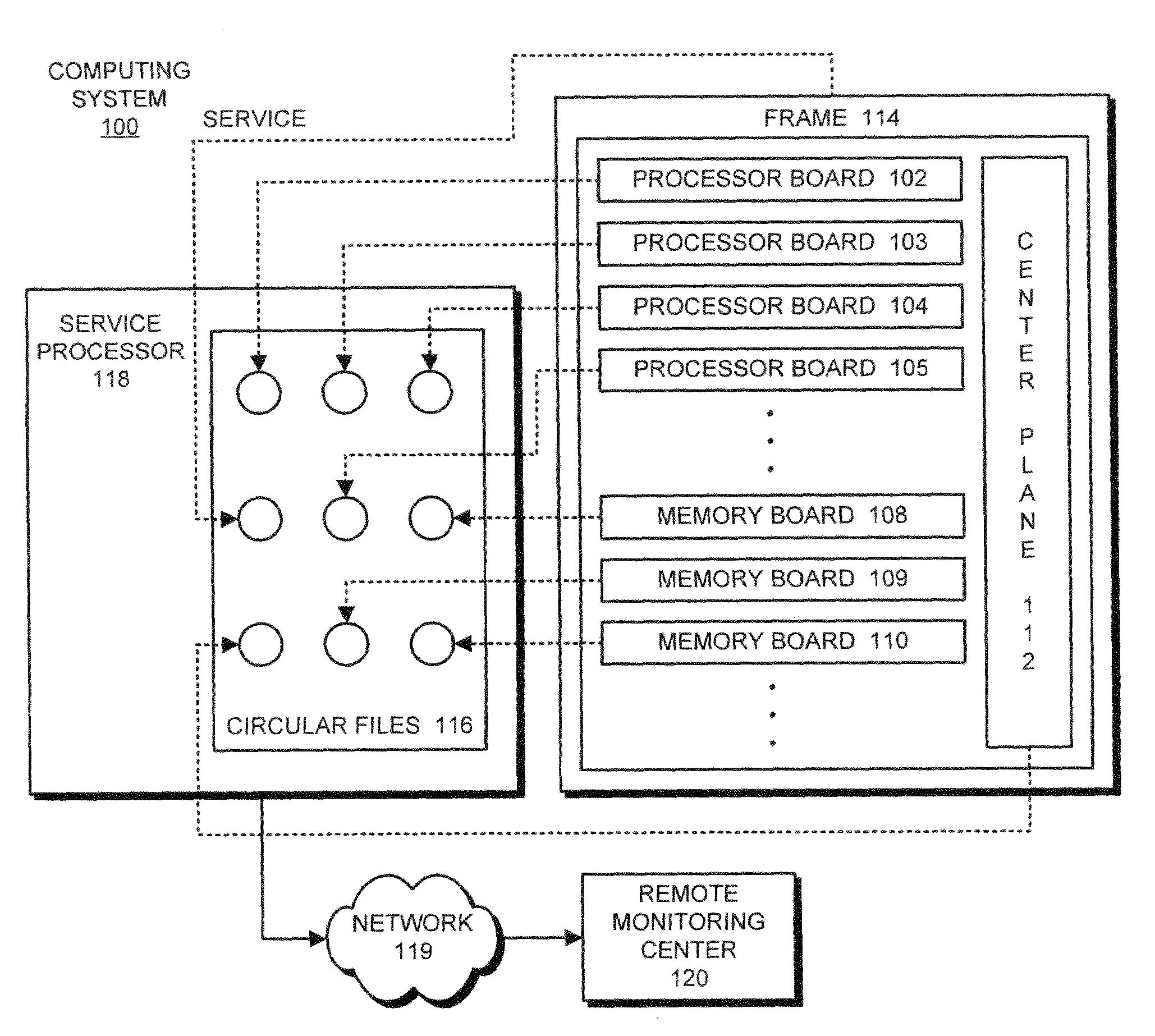
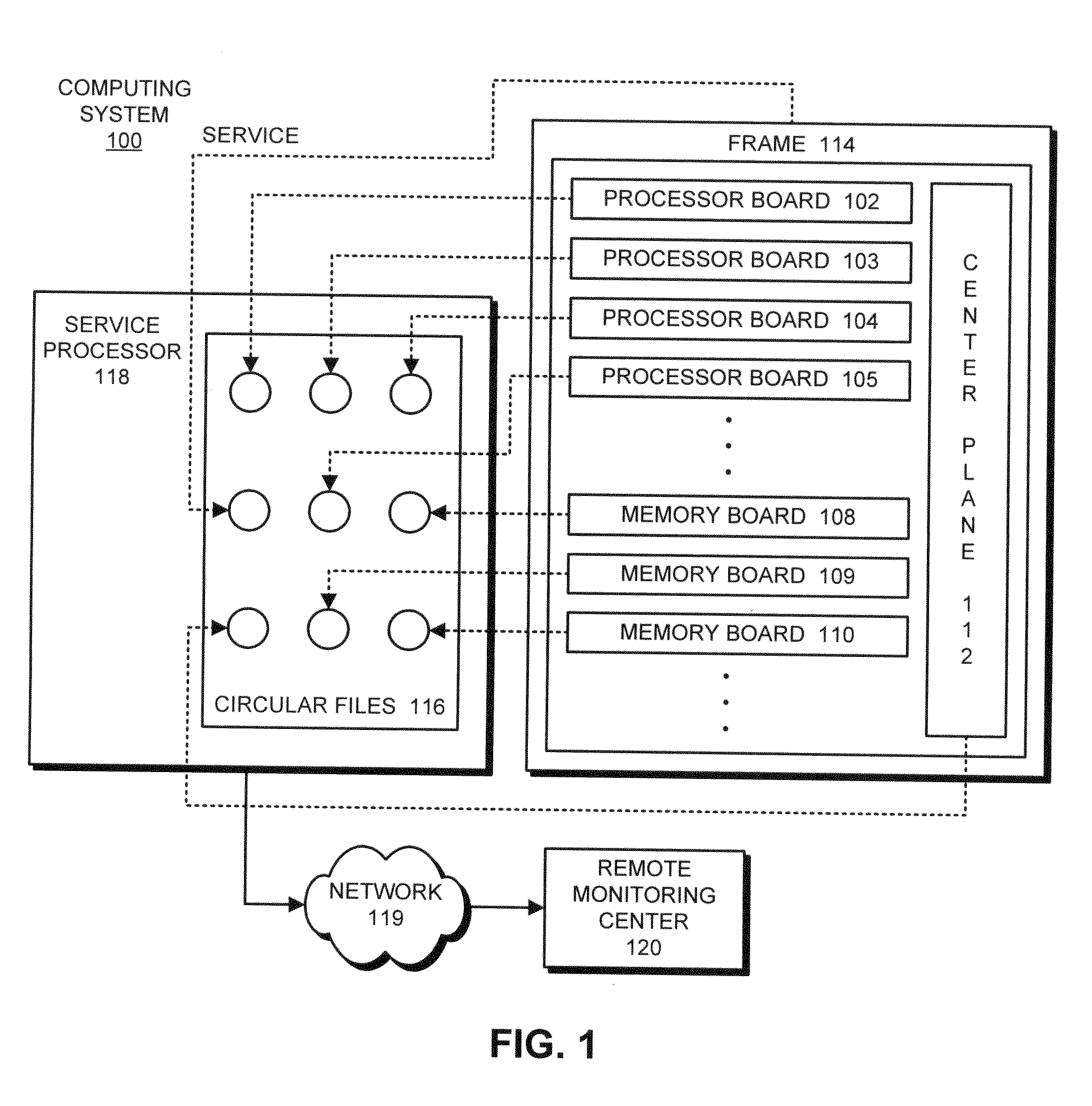
High-efficiency time-series archival system for telemetry signals
ActiveUS20070226554A1High-efficiency time-series archivingElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionSequential probability ratio testTest algorithm
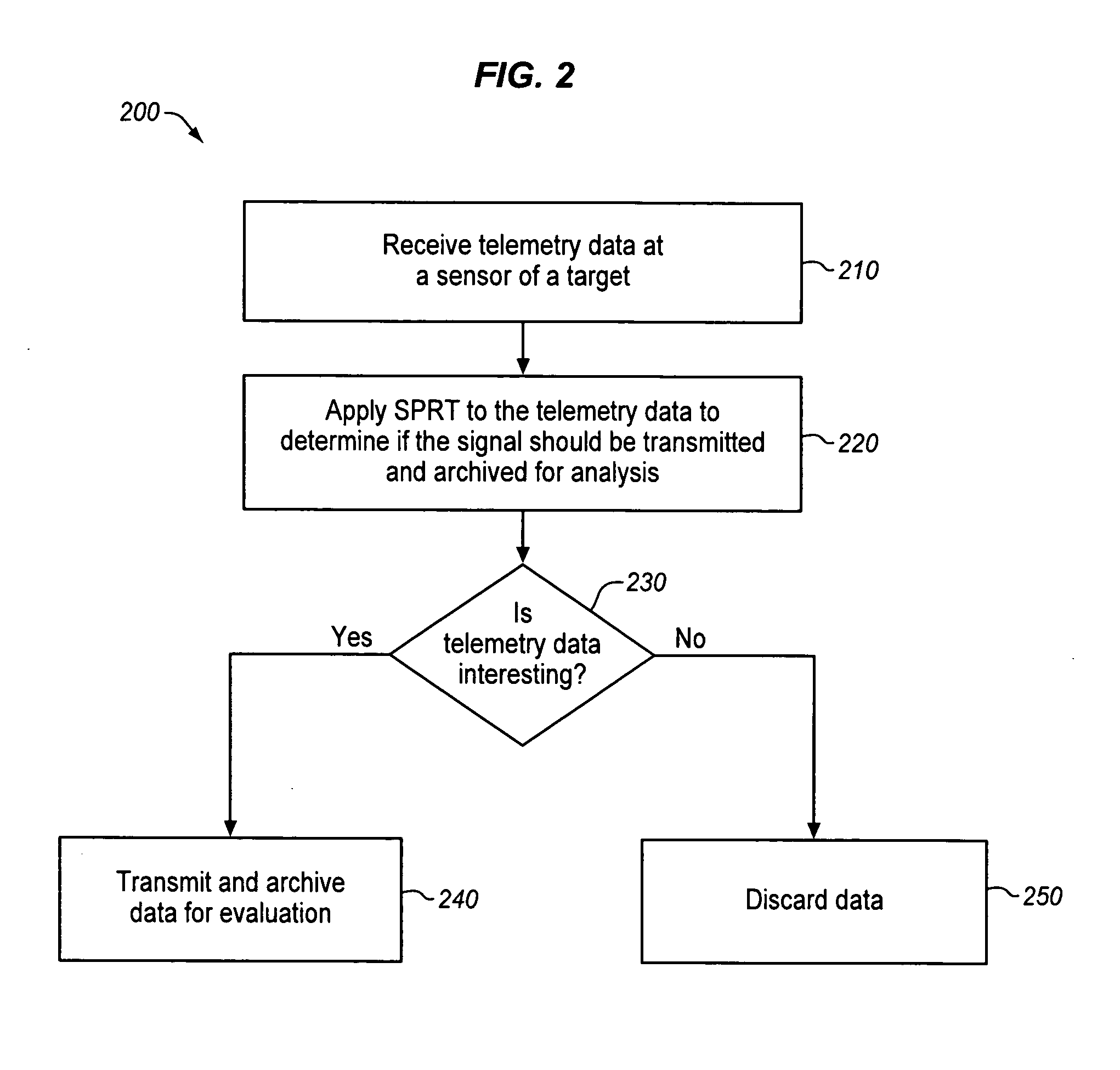
In one embodiment, a method and apparatus for high-efficiency time-series archiving for computer server telemetry signals is disclosed. The method includes selecting one or more telemetry signals of a plurality of telemetry signals by a sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) algorithm, the SPRT algorithm identifying the one or more telemetry signals as not consistent with normal behavior of the plurality of telemetry signals, injecting synthetic samples around the selected one or more telemetry signals to create a continuous time series telemetry sample, and analyzing the continuous time series telemetry sample to identify leading indicators of faults in the target. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
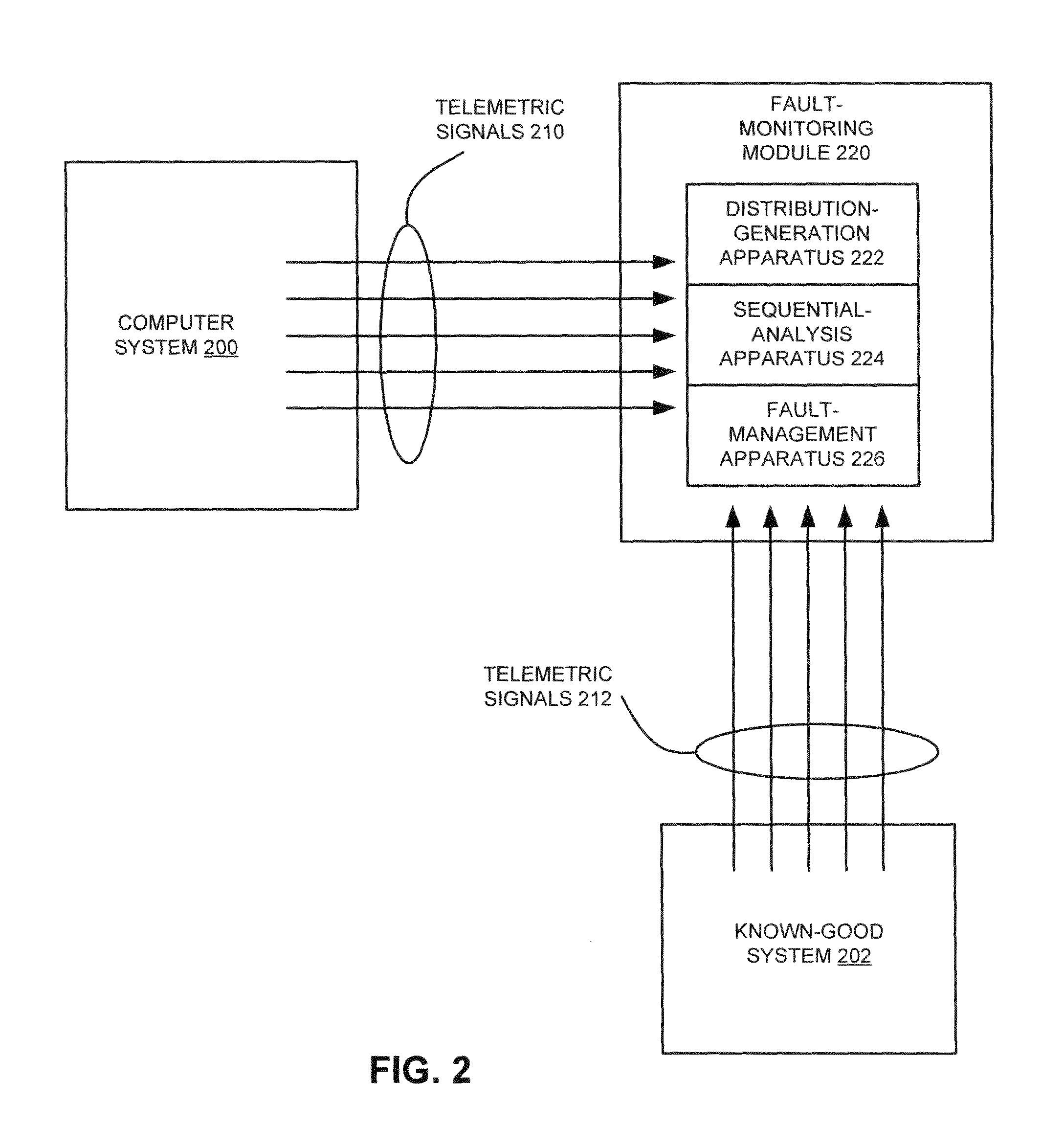
Telemetry data analysis using multivariate sequential probability ratio test
ActiveUS20100292959A1Digital computer detailsNuclear monitoringMultidimensional scalingMonitoring system
One embodiment provides a system that analyzes telemetry data from a monitored system. During operation, the system periodically obtains the telemetry data as a set of telemetry variables from the monitored system and updates a multidimensional real-time distribution of the telemetry data using the obtained telemetry variables. Next, the system analyzes a statistical deviation of the multidimensional real-time distribution from a multidimensional reference distribution for the monitored system using a multivariate sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) and assesses the integrity of the monitored system based on the statistical deviation of the multidimensional real-time distribution. If the assessed integrity falls below a threshold, the system determines a fault in the monitored system corresponding to a source of the statistical deviation.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
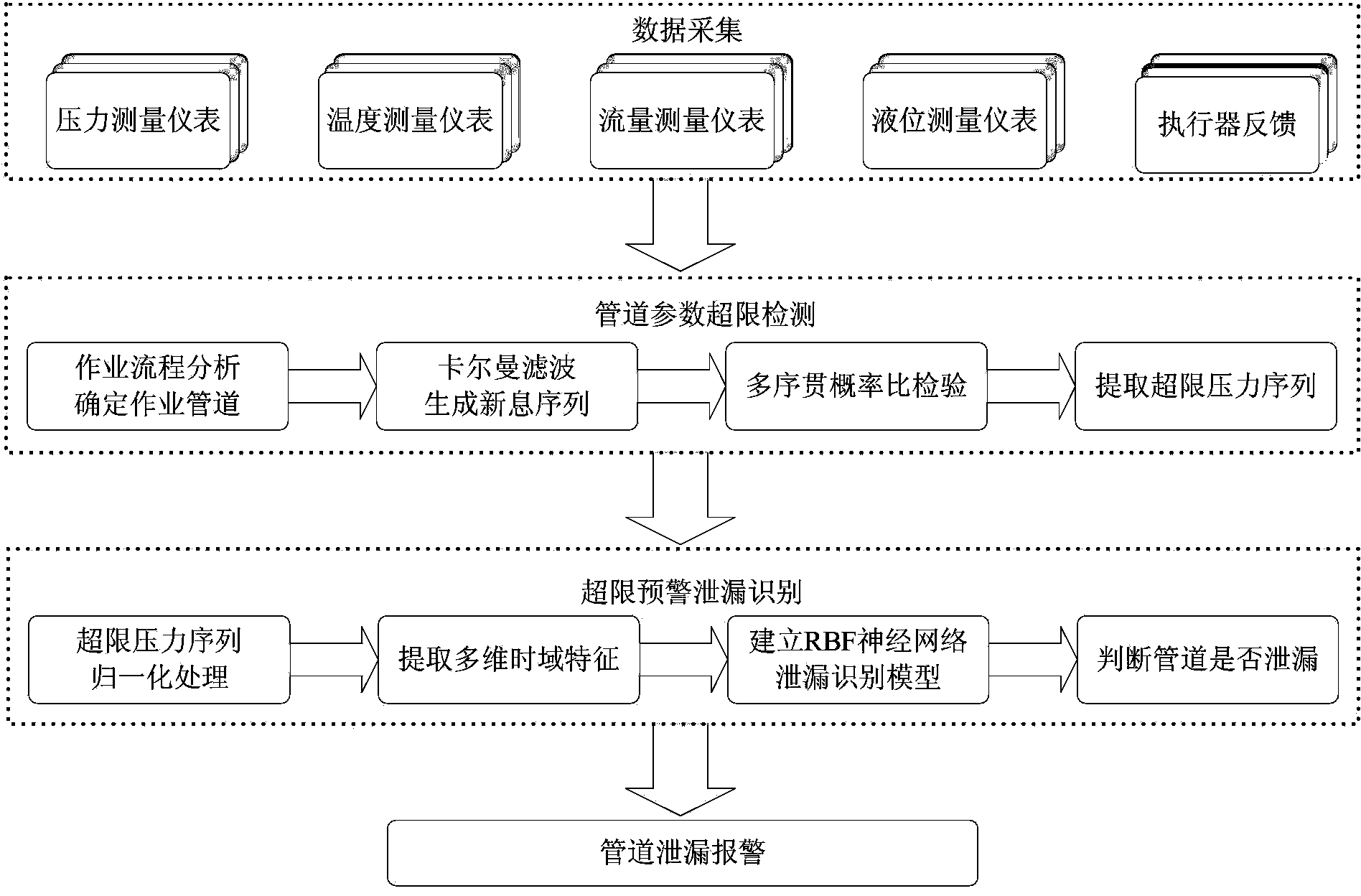
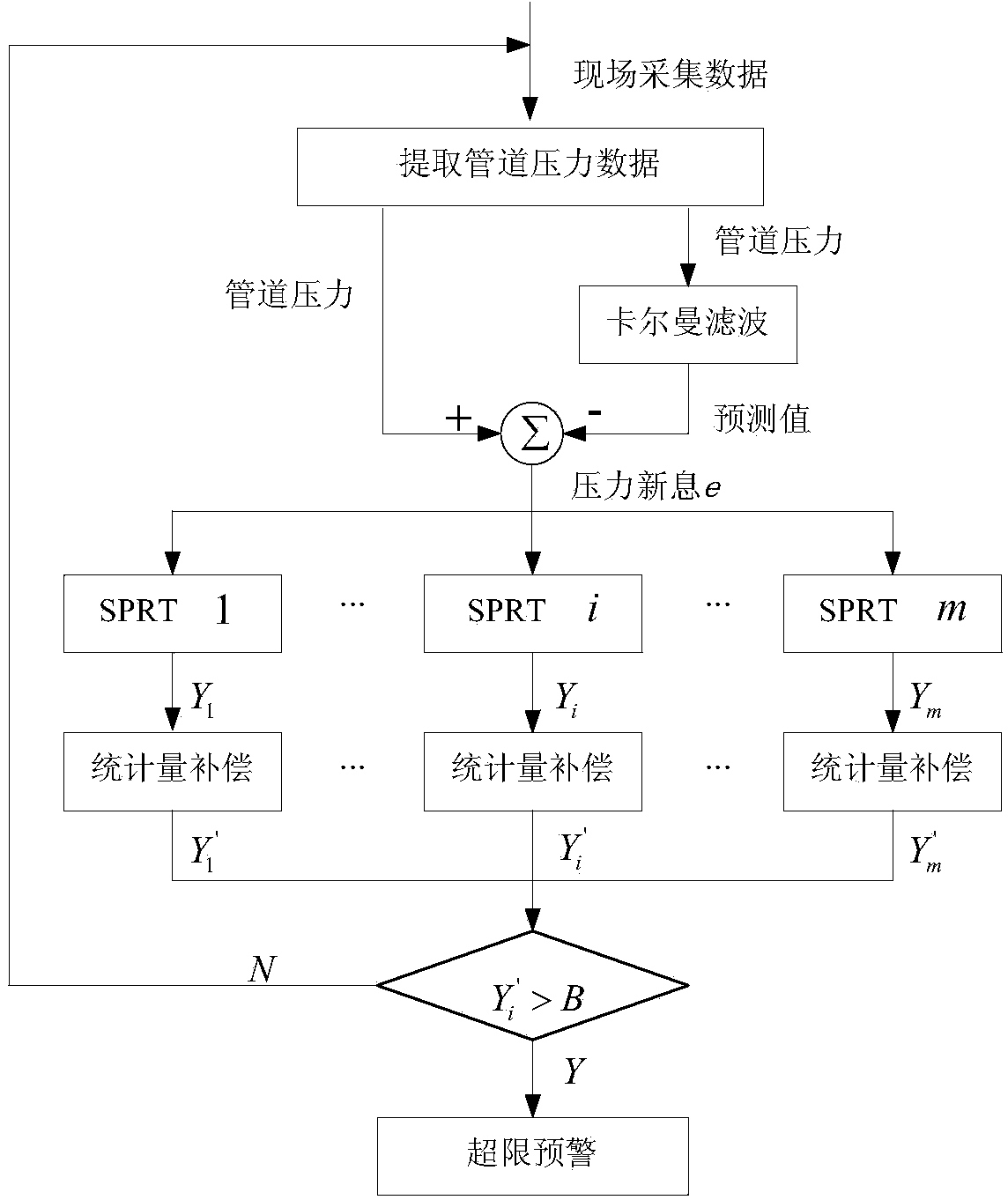
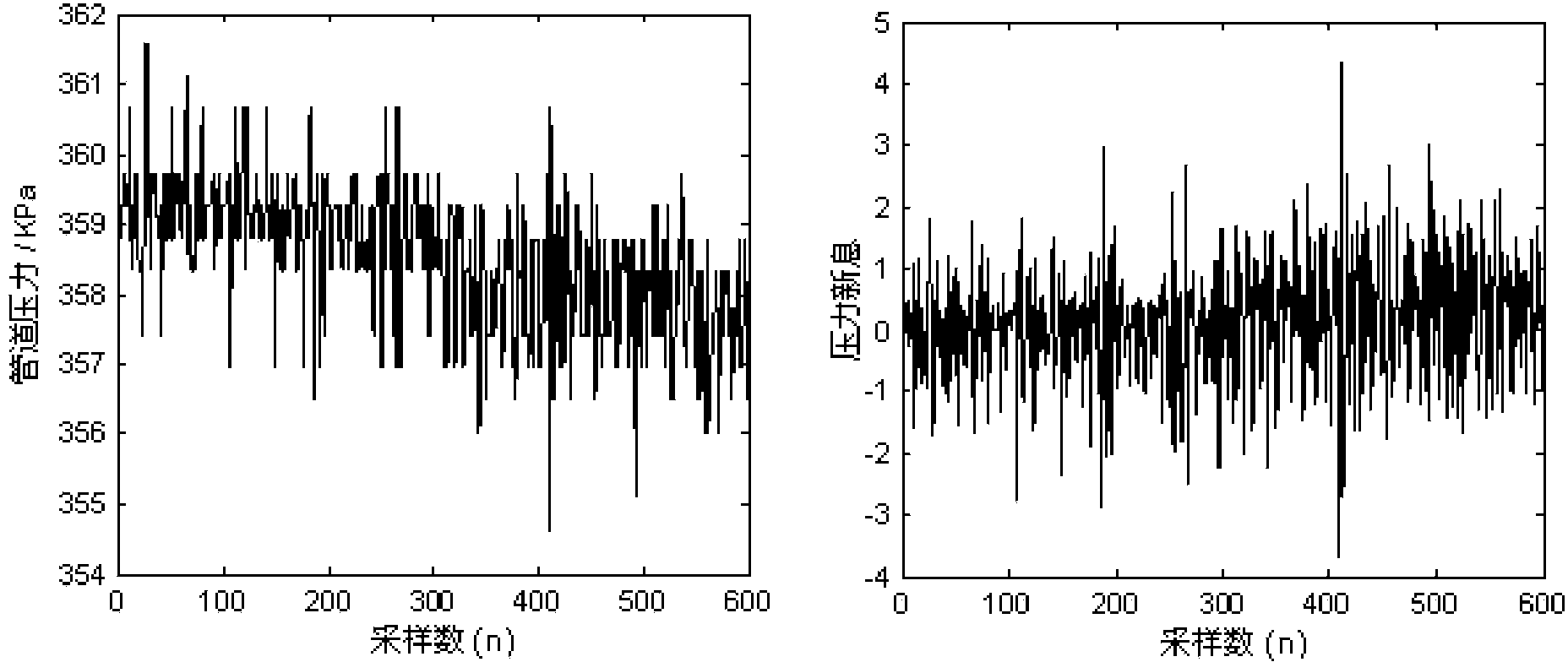
Method for detecting leakage of pipeline of tank farm
InactiveCN103968256AImprove the ability to adapt to changing working conditionsReduce false alarm ratePipeline systemsTime domainMonitoring system
The invention discloses a method for detecting leakage of a pipeline of a tank farm by combining the statistical hypothesis testing technology and the pattern recognition technology. The method comprises the steps that measuring meter data and actuator state feedback information of a working site are acquired through a tank farm monitoring system, an oil transportation path is determined, and Kalman filtering is carried out on pressure measuring meter data to generate pressure information; whether the pressure of the pipeline exceeds a limit is detected according to the multi-sequential probability ratio test, and if yes, an over-limit pressure sequence and the multidimensional time domain features of the over-limit pressure sequence are extracted; recognition of leakage of the pipeline and adjustment of working conditions are carried out based on an established neural network leakage recognition model. By means of the method, a small change of the pressure of the pipeline can be detected in the least time within a regulated false alarm rate and a regulated alarm failure rate, and then whether leakage of the pipeline occurs can be determined.
Owner:税爱社
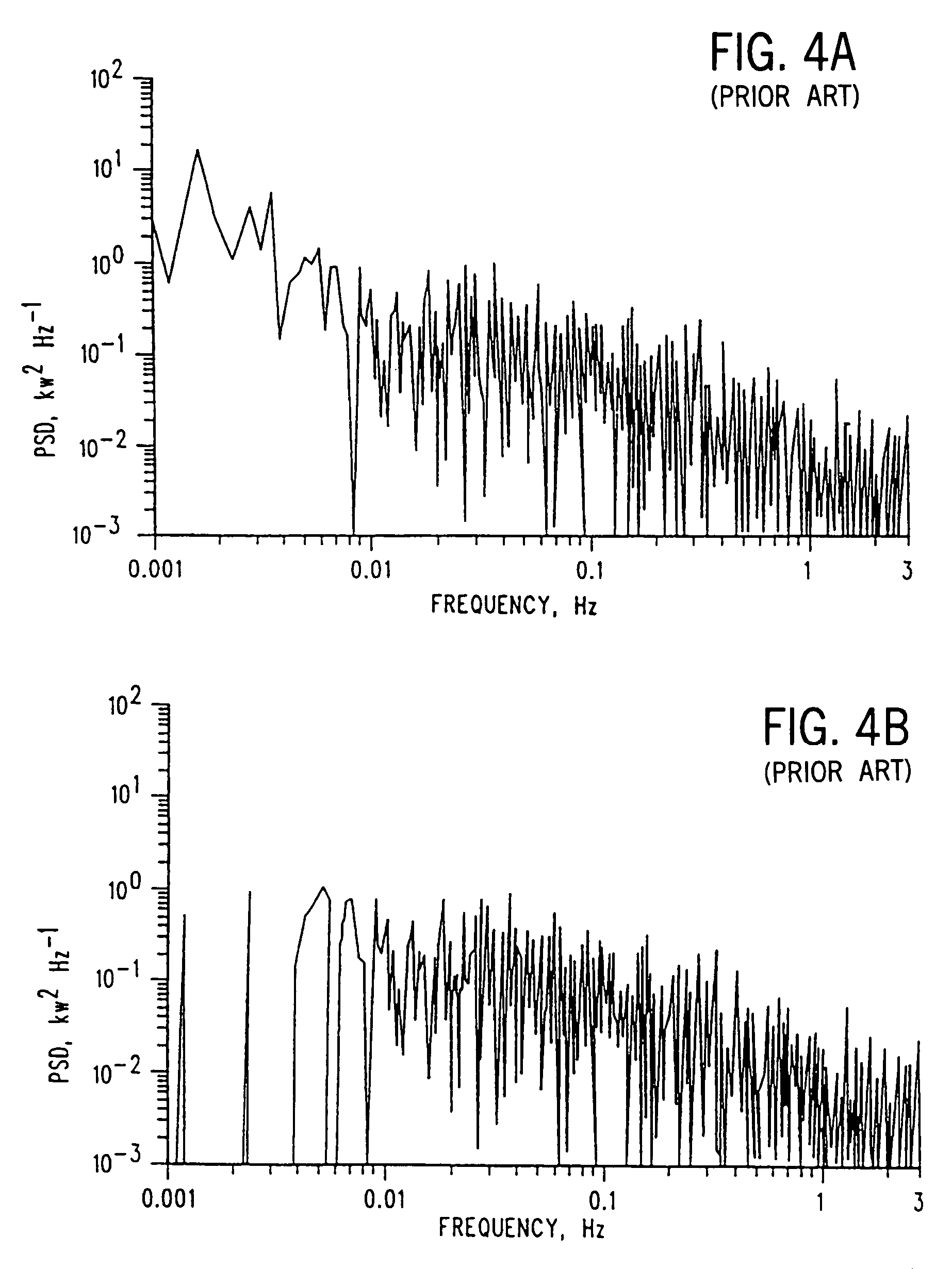
System for surveillance of spectral signals
InactiveUS6999899B2Spectral/fourier analysisAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTime domainFrequency spectrum
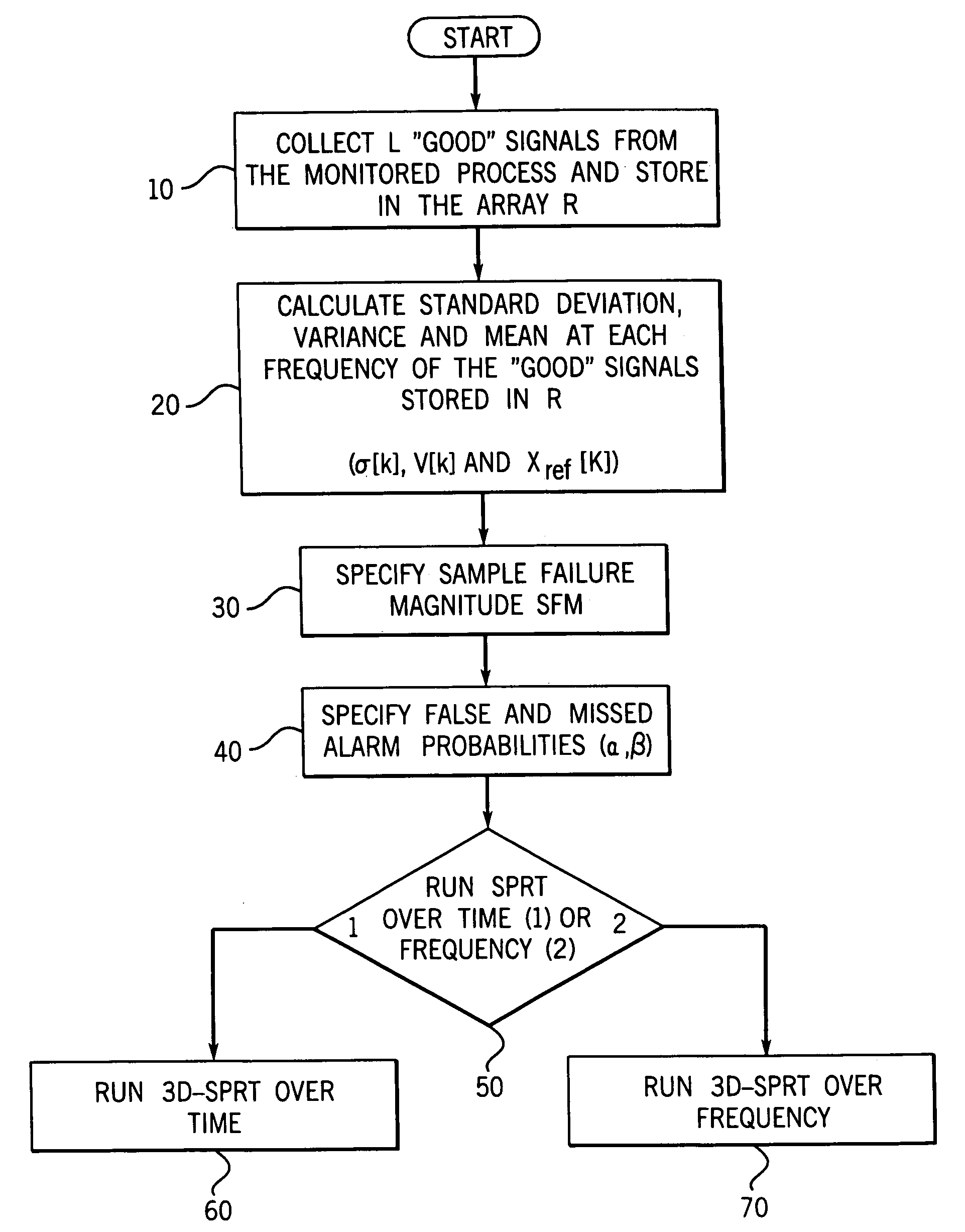
A method and system for monitoring at least one of a system, a process and a data source. A method and system have been developed for carrying out surveillance, testing and modification of an ongoing process or other source of data, such as a spectroscopic examination. A signal from the system under surveillance is collected and compared with a reference signal, a frequency domain transformation carried out for the system signal and reference signal, a frequency domain difference function established. The process is then repeated until a full range of data is accumulated over the time domain and a Sequential Probability Ratio Test (“SPRT”) methodology applied to determine a three-dimensional surface plot characteristic of the operating state of the system under surveillance.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
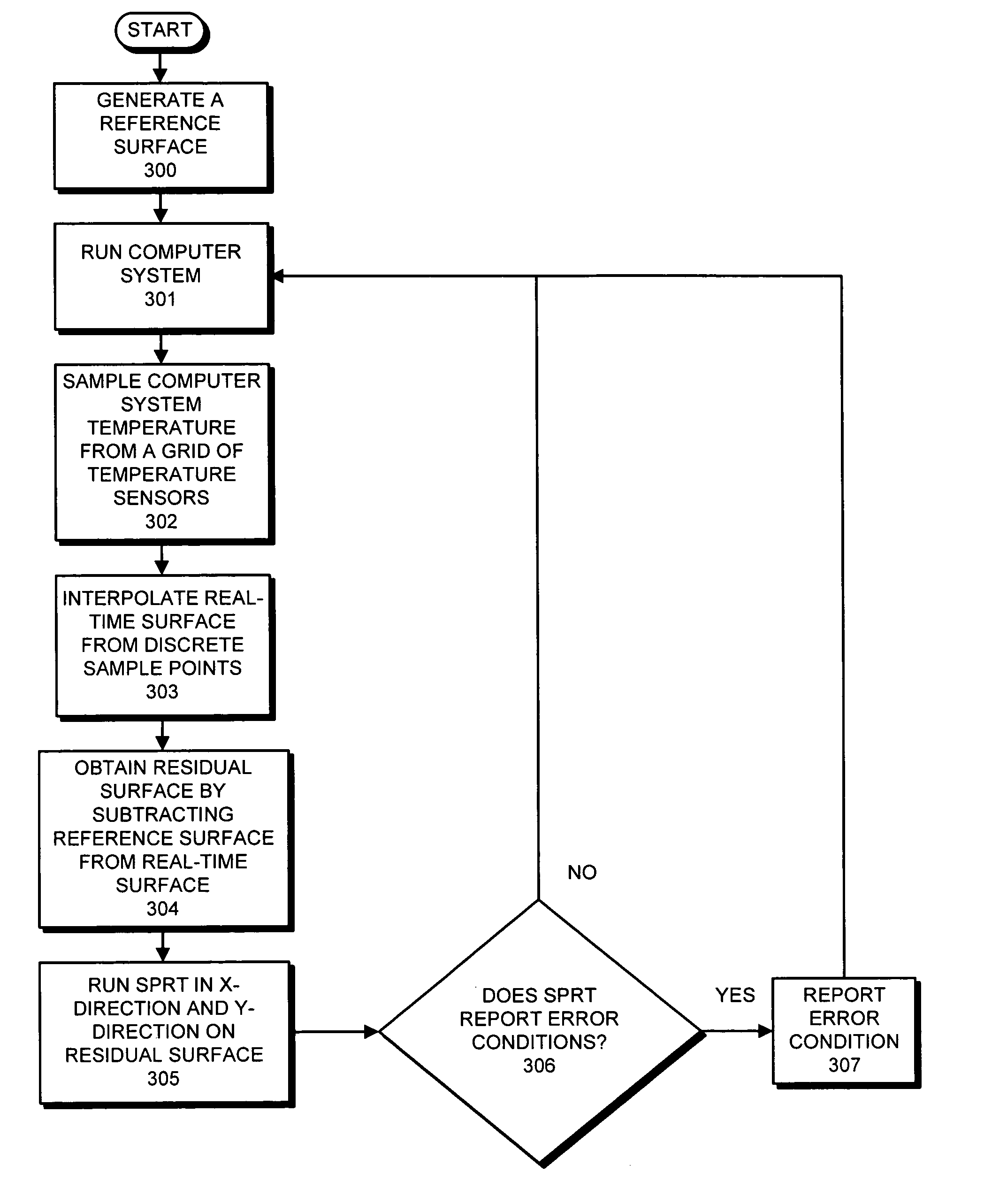
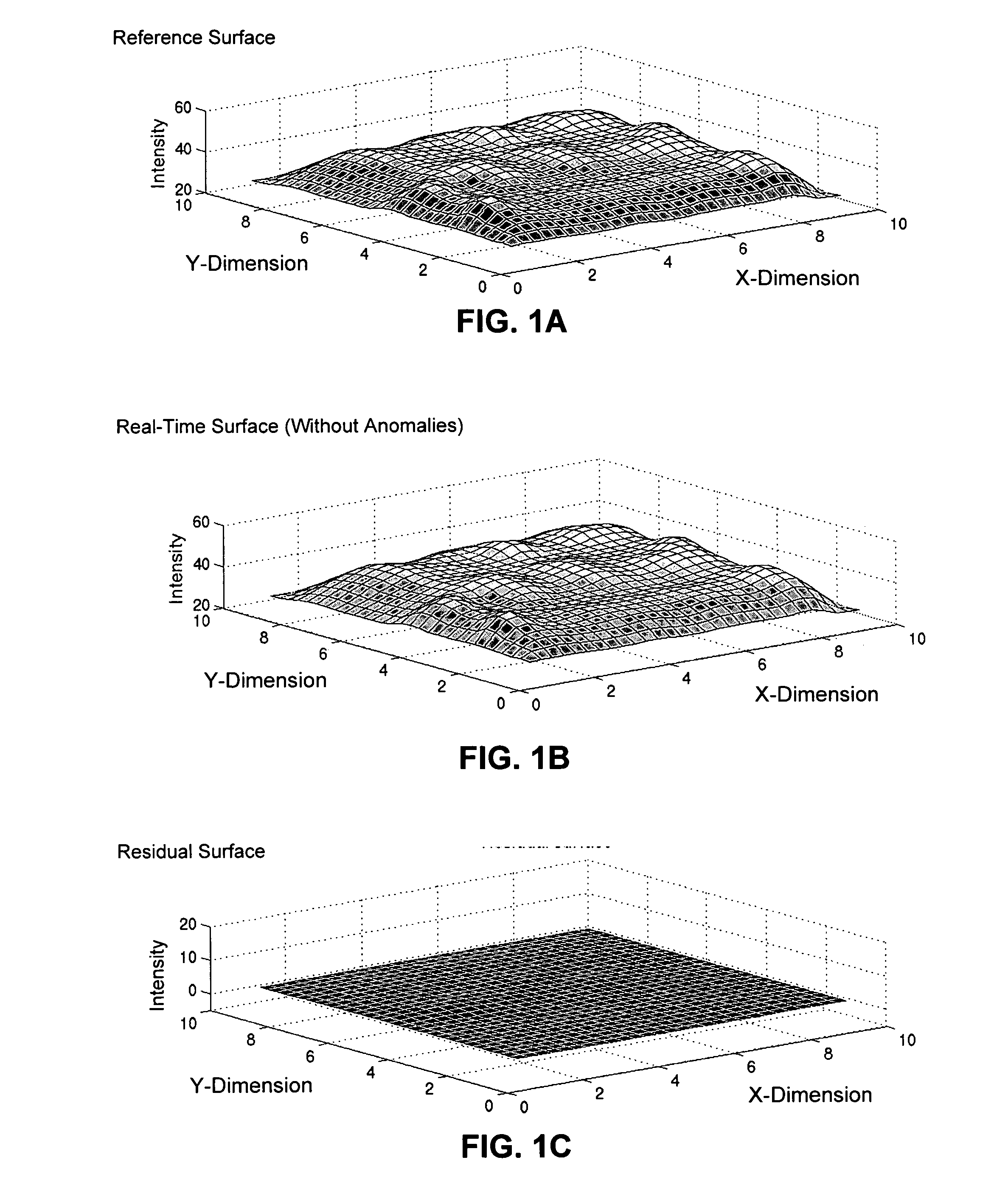
Multi-dimensional sequential probability ratio test for detecting failure conditions in computer systems
ActiveUS7191096B1High sensitivityHigh false positive rateDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringComputerized systemMonitoring system
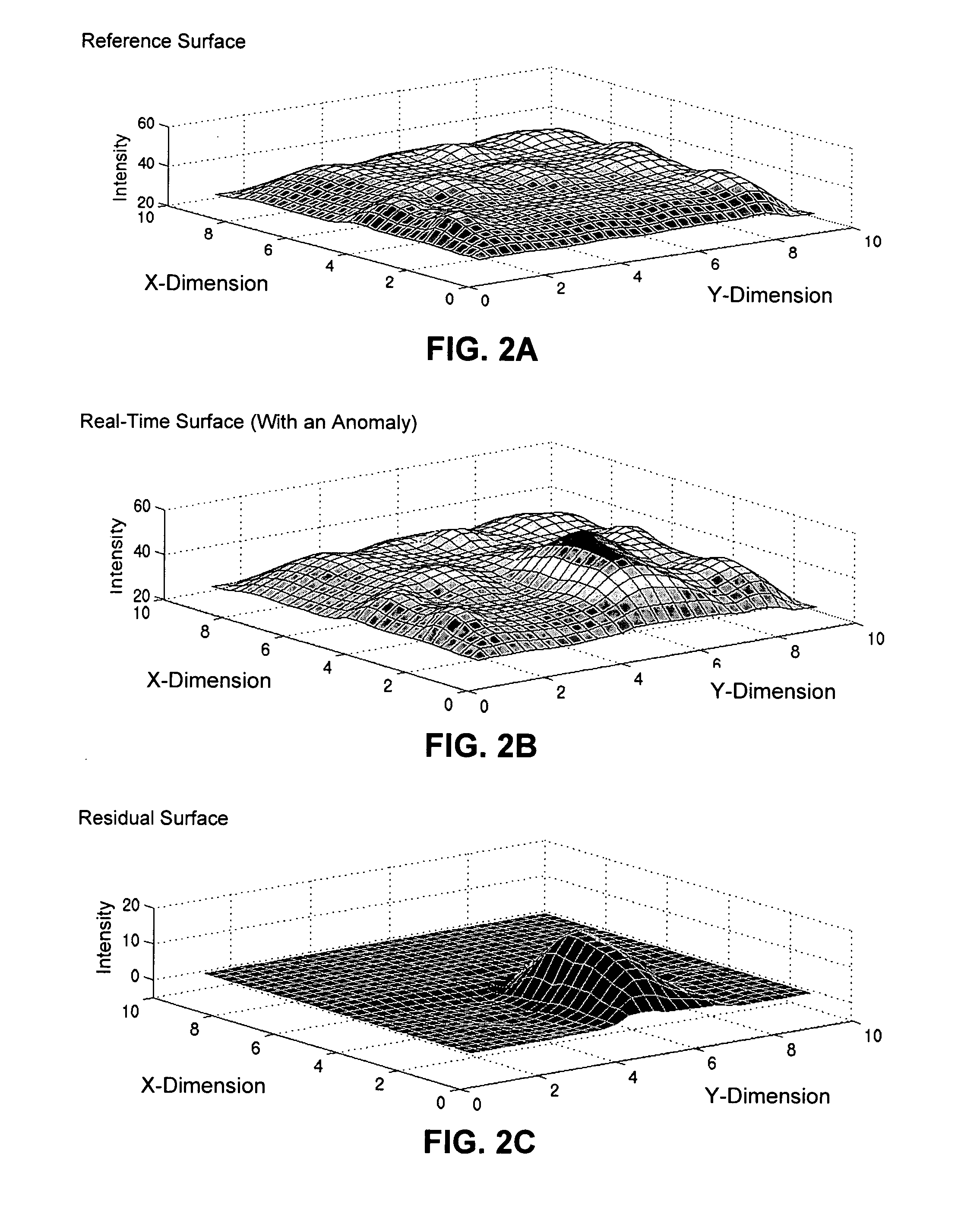
One embodiment of the present invention provides a monitoring system that detects anomalies in data gathered from sensors in a computer system. During operation, the monitoring system samples data from a plurality of sensors located at various sampling points throughout the computer system. Next, the monitoring system interpolates the data from the sampling points to produce a real-time digitized surface. The monitoring system then subtracts a reference digitized surface from the real-time digitized surface to produce a residual digitized surface. Finally, the monitoring system applies a multi-dimensional sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) to the residual digitized surface to detect anomalies in the residual digitized surface which indicate an impending failure of the computer system.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Device and method for infrasonic monitoring and pipe leakage positioning
InactiveCN106704834AImprove accuracyHigh positioning accuracyPipeline systemsGradient operatorsSequential probability ratio test
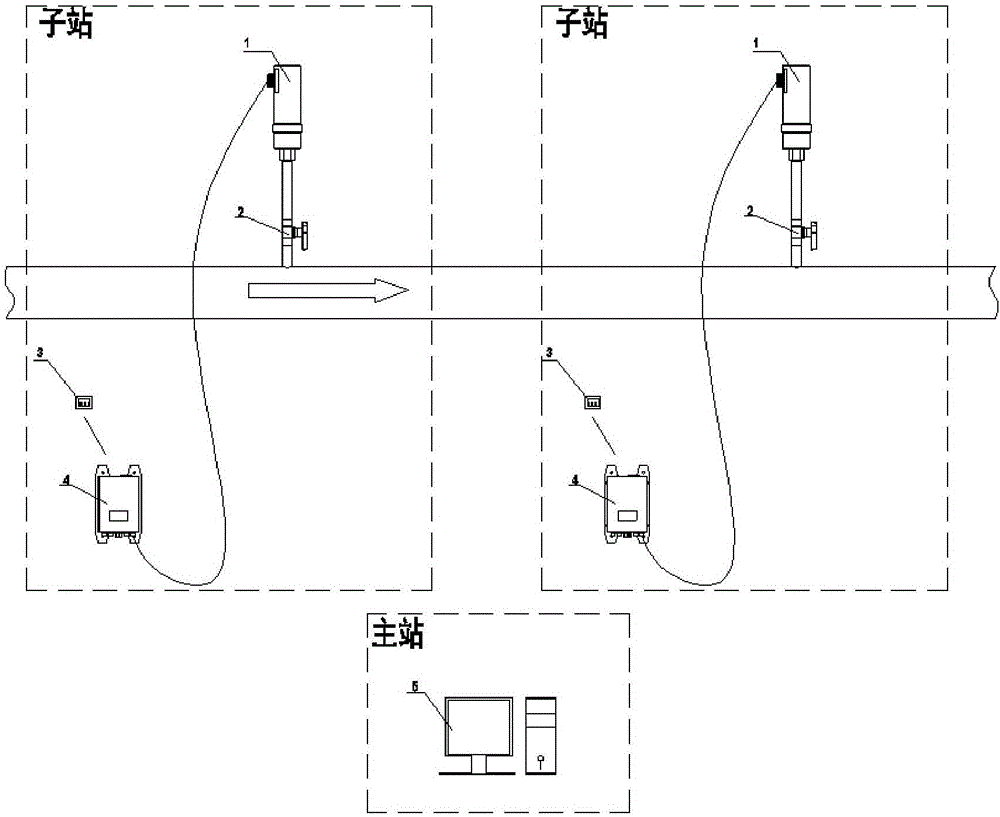
The invention discloses a full-automatic online monitoring and positioning system and a method for leakage of fluids in pipes. The system comprises one set of main station systems and two or more sets of sub station systems, wherein each set of sub station systems include high-precision infrasonic sensors, valves, external power supplies and digital instruments. The method is combined with such algorithms as Kalman filtering, wavelet transform, gradient operator and region segmentation and a sequential probability ratio test method, and is combined with weak signals provided by the high-precision infrasonic sensors for multiple times of cross-correlation calculations so as to greatly improve the warning accuracy.
Owner:JILIN PROVINCE BAIRUISHENG SCI & TECH DEV
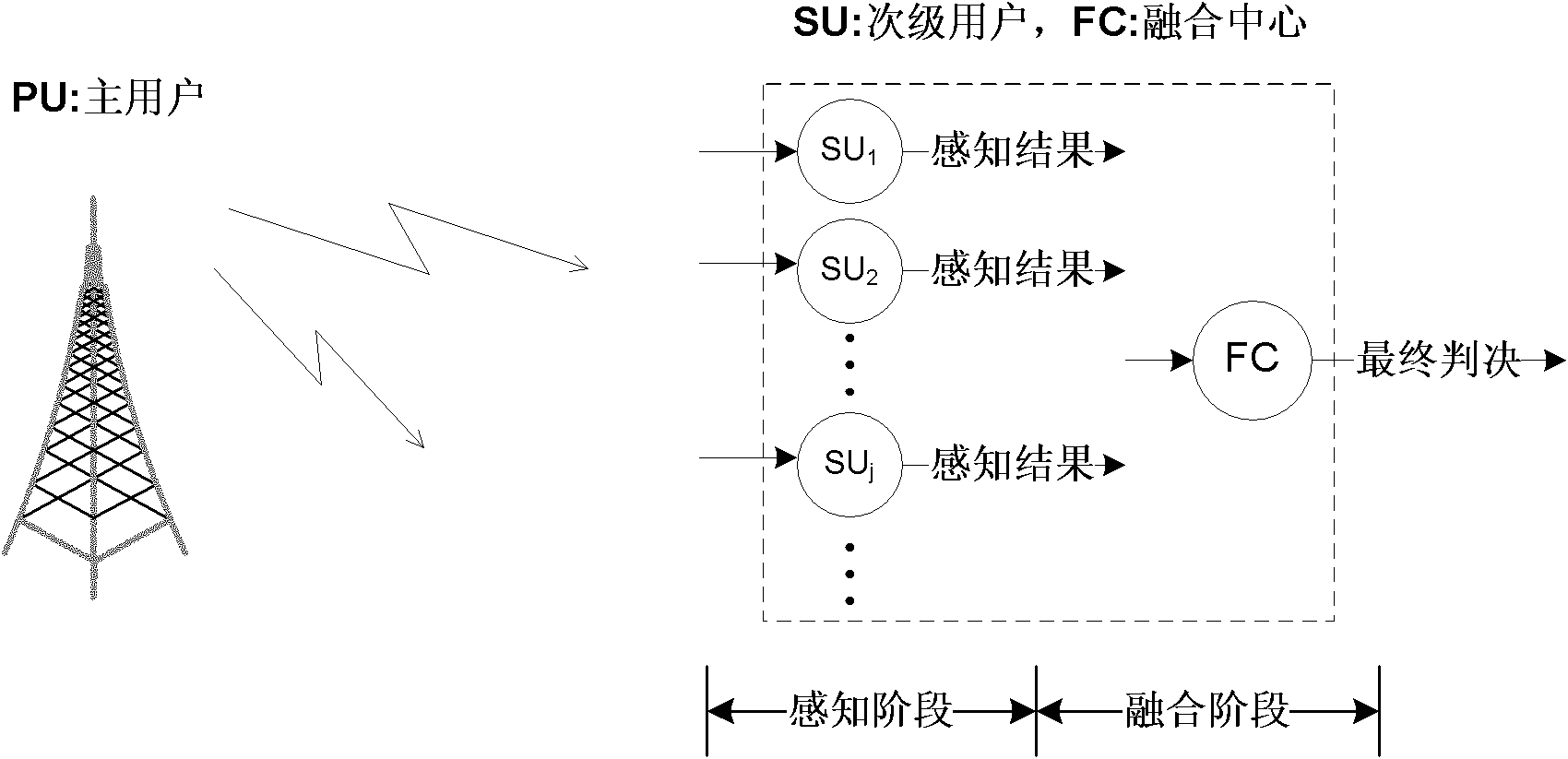
Adaptive sequential cooperative spectrum detection method
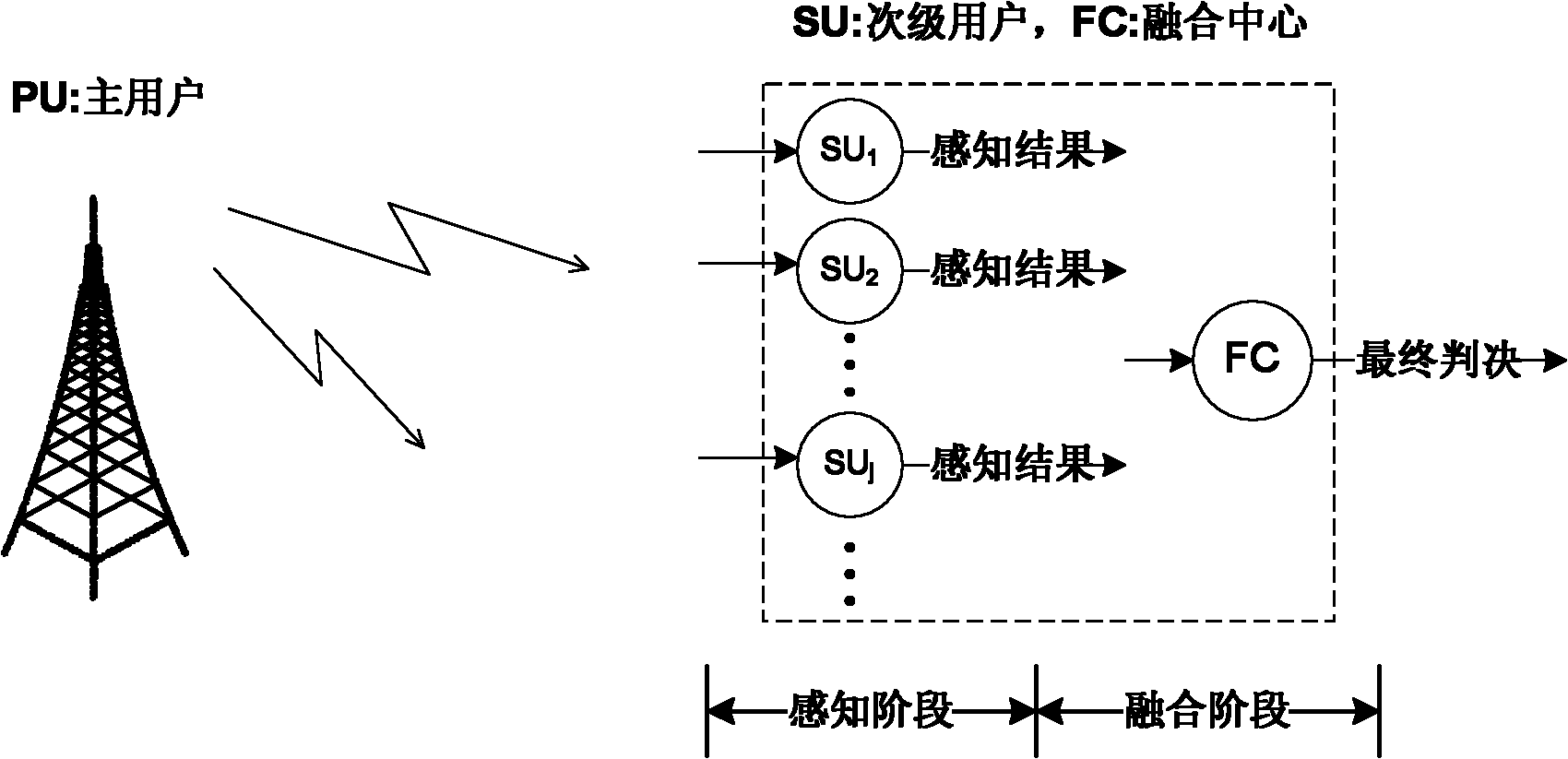
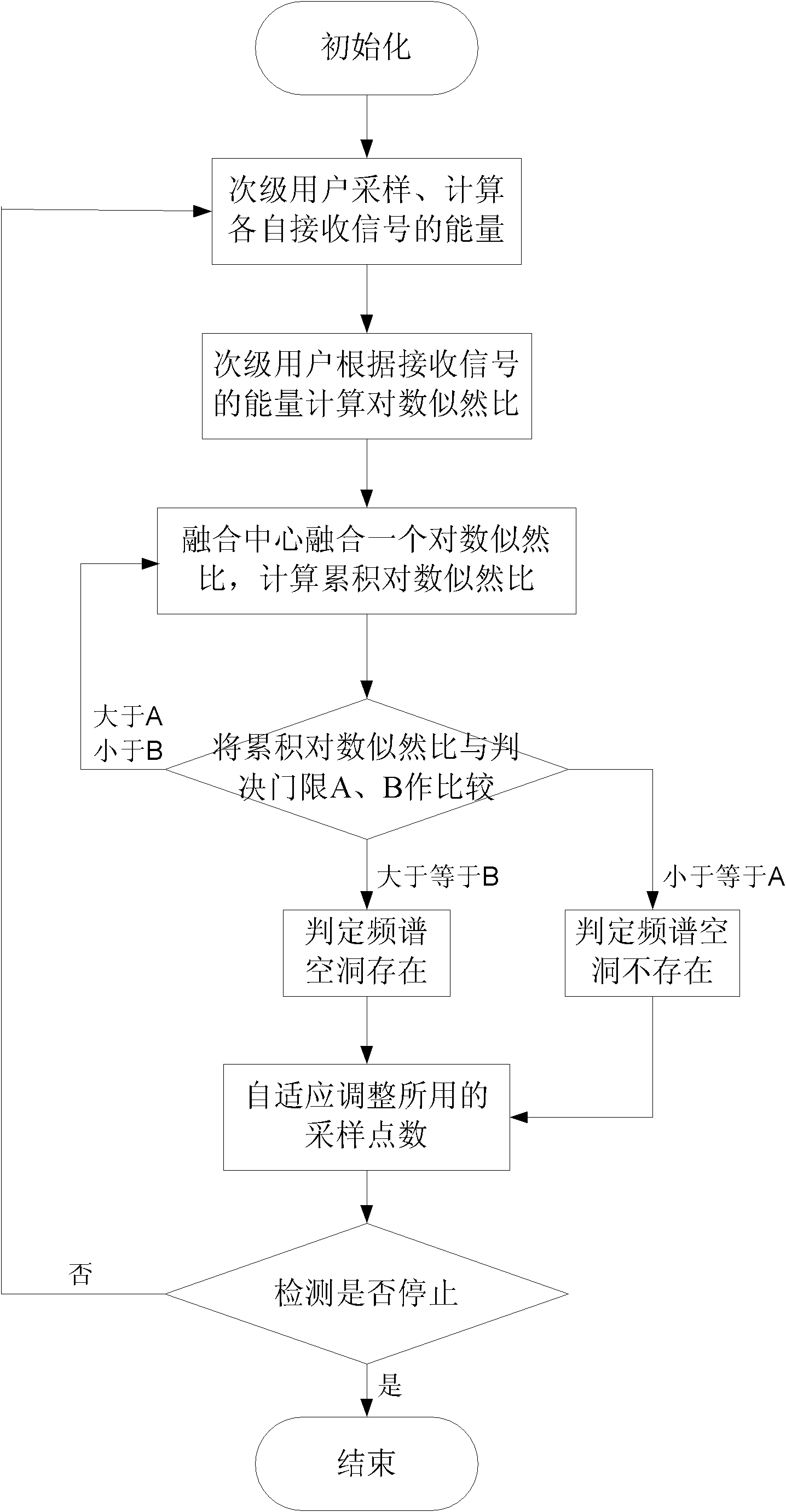
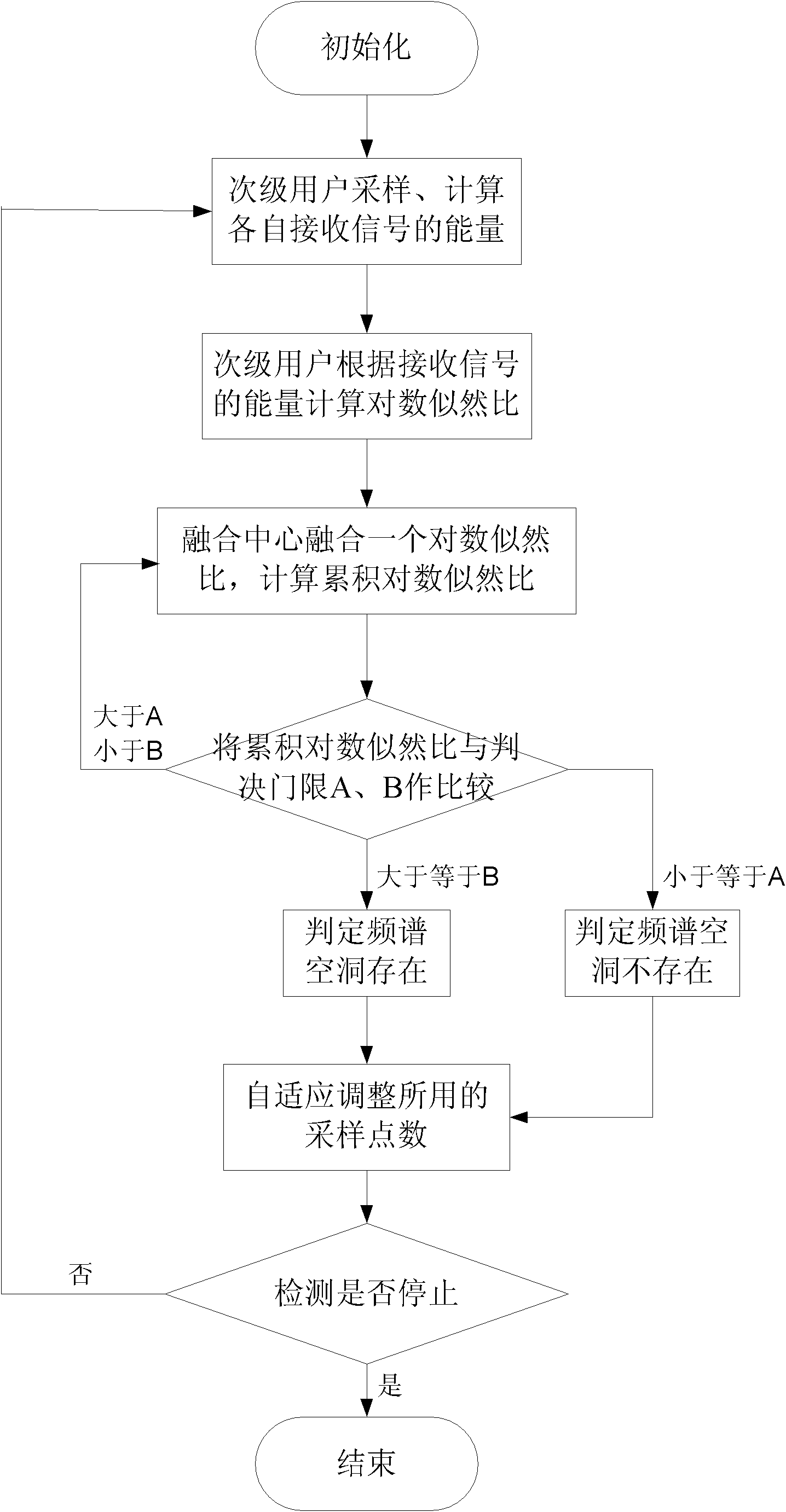
InactiveCN102006609AEasy to implementShorten detection timeTransmission monitoringWireless communicationFusion centerFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a method for cooperatively detecting spectrum holes by a plurality of subprime users in the field of cognitive radio in communication technology. The method is characterized by making a decision on the basis of sequential probability ratio test in a fusion stage and adaptively adjusting sampling points used in a perceptive stage. By the characteristics, the method can ensure the needed detection precision and minimize the detection time. The method comprises the following steps of: a. carrying out parallel sampling and obtaining a perception result according to the sampling points by all subprime users; b. fusing one perception result of the subprime users by a fusion center; c. if the fused perception result is enough, making the decision; or else, returning backto the step b to continue to fuse the perception result of the subprime users; and d. adaptively adjusting the sampling points, if the detection is not stopped, returning back to the step a to carry out next detection.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
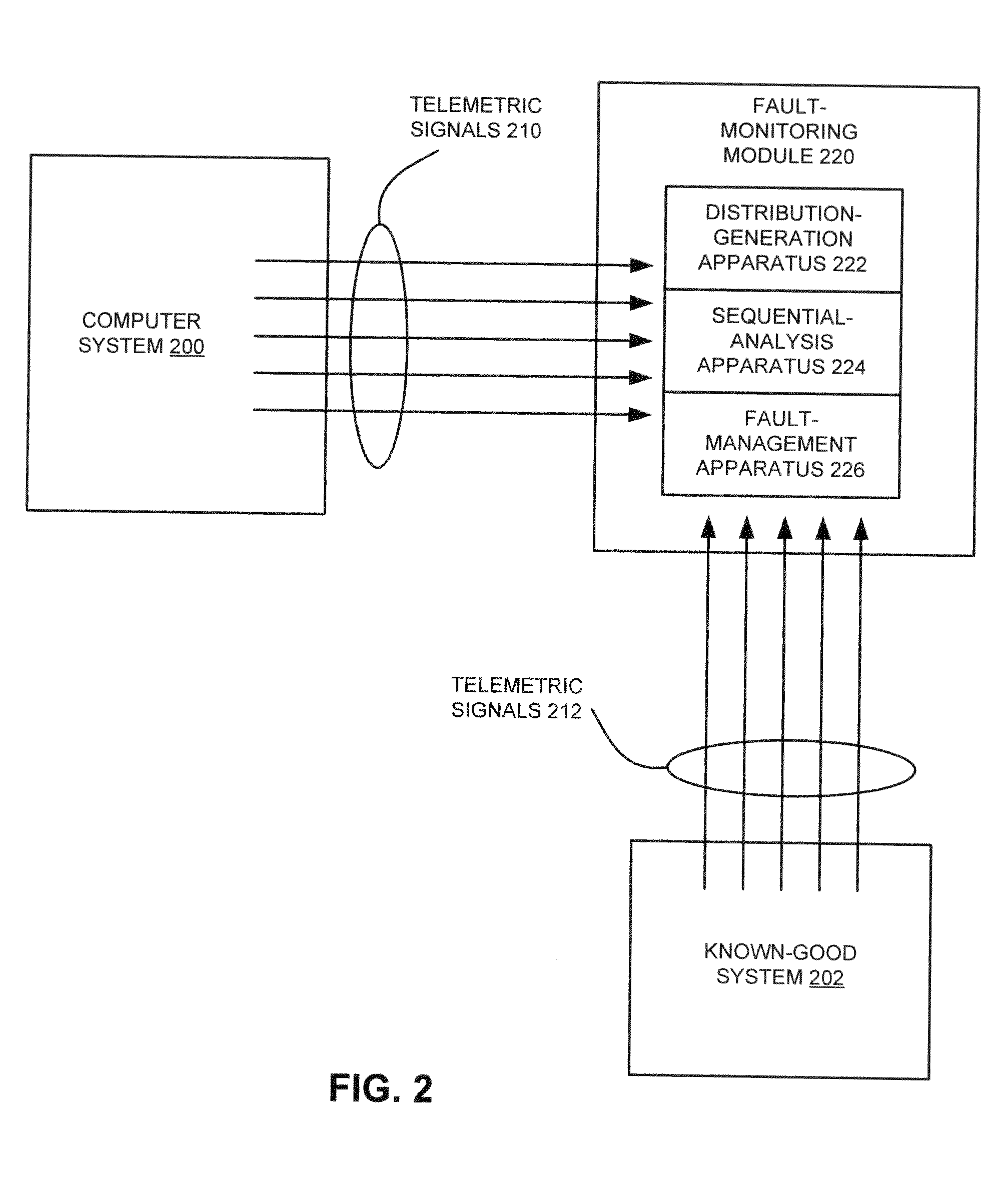
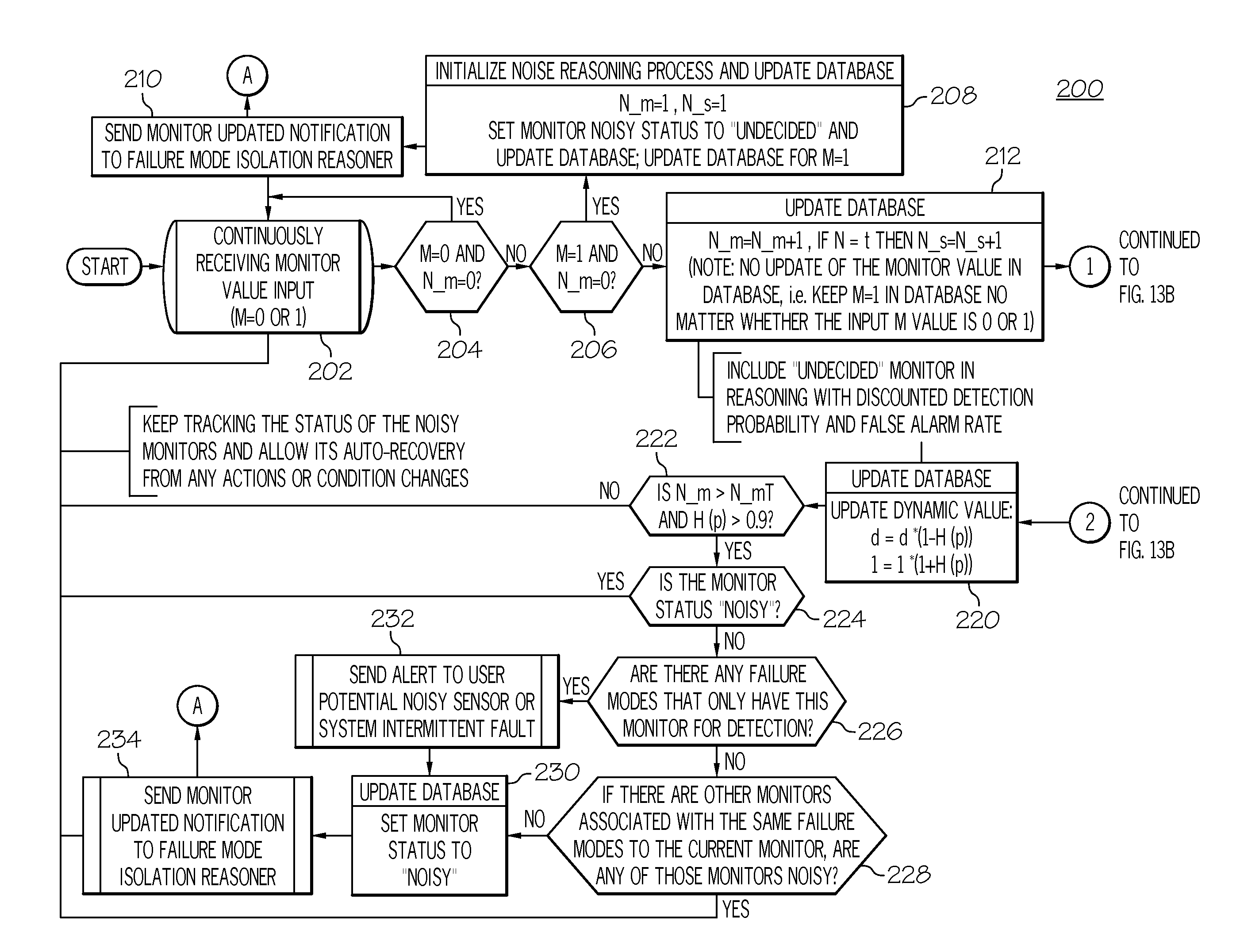
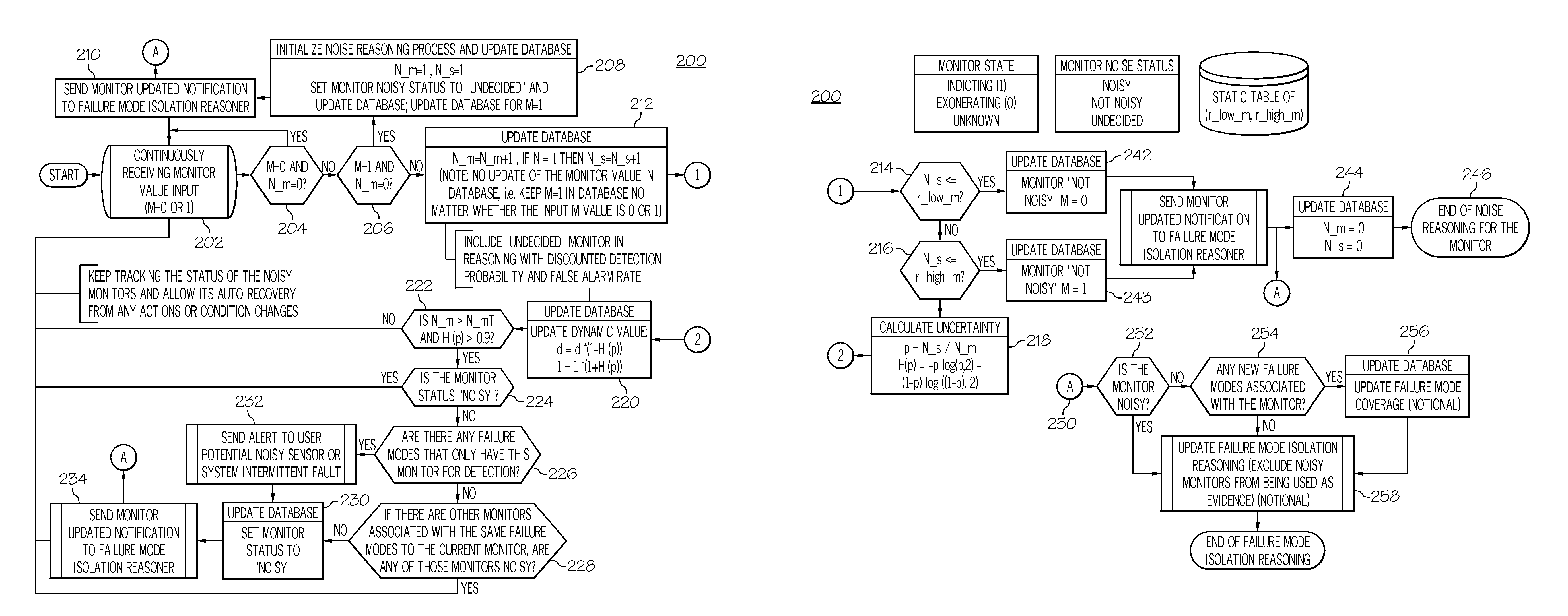
Noisy monitor detection and intermittent fault isolation
InactiveUS20110191635A1Digital data processing detailsNon-redundant fault processingSequential probability ratio testIntermittent fault
A method of detecting and diagnosing system faults, includes detecting the noisy status of a monitor during operations and incorporating a quantified monitor uncertainty level to support fault isolation reasoning. A sequential probability ratio test is used to statistically test the noisy status of a monitor and Shannon's entropy theory is used to quantify the uncertainty levels of the monitor to support the use of the monitor values in fault isolation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method and apparatus for quantitatively determining severity of degradation in a signal
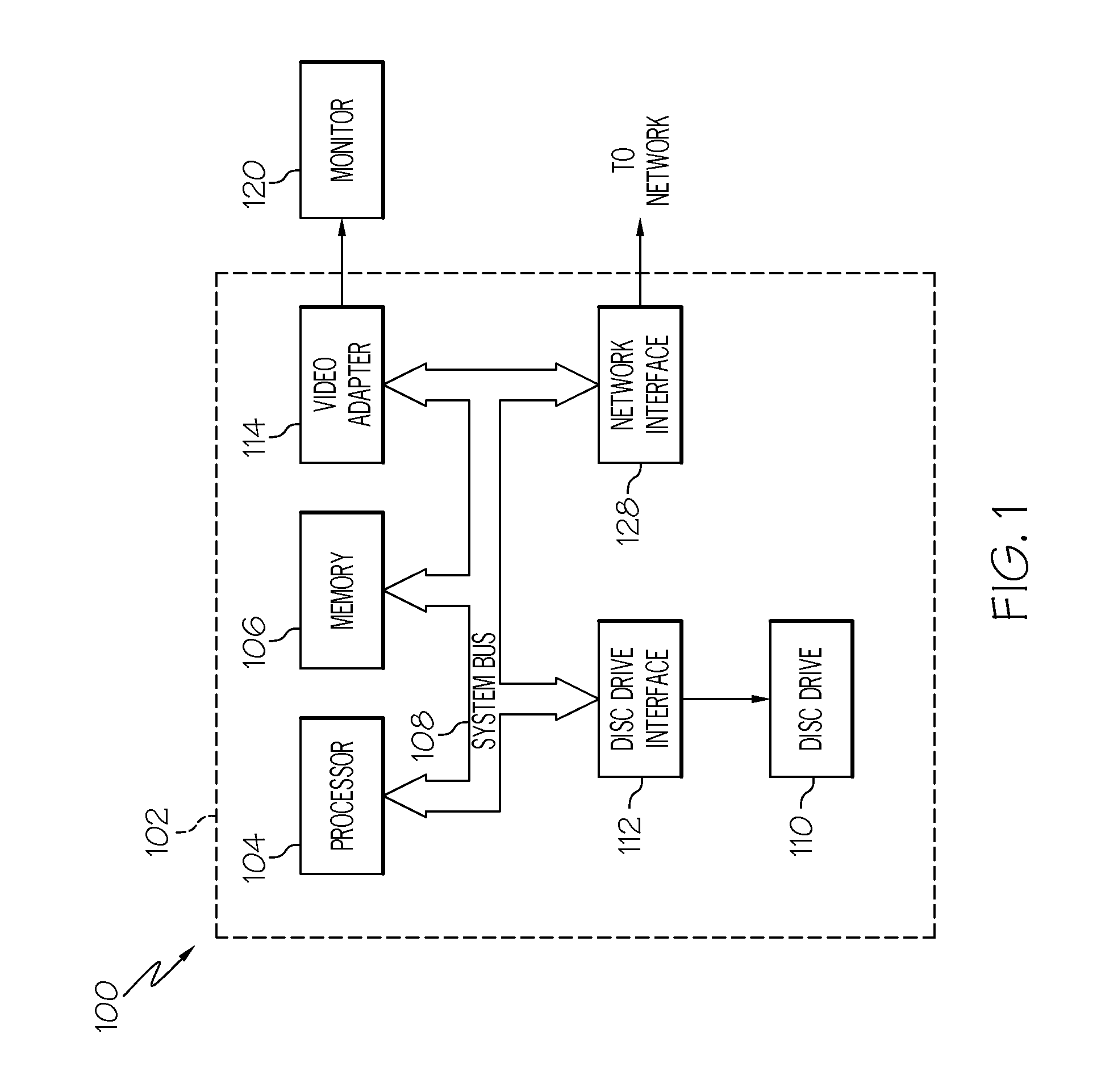
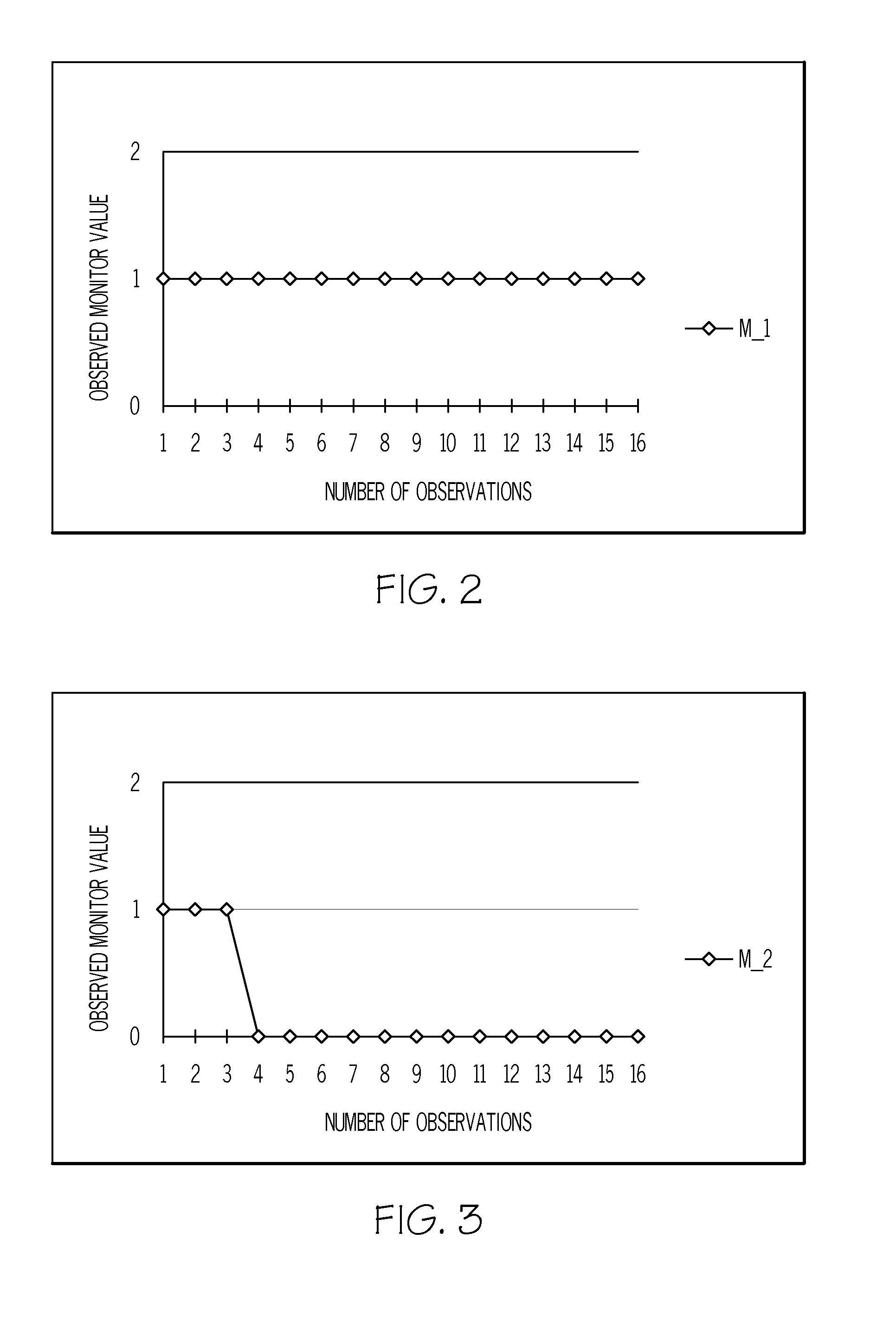
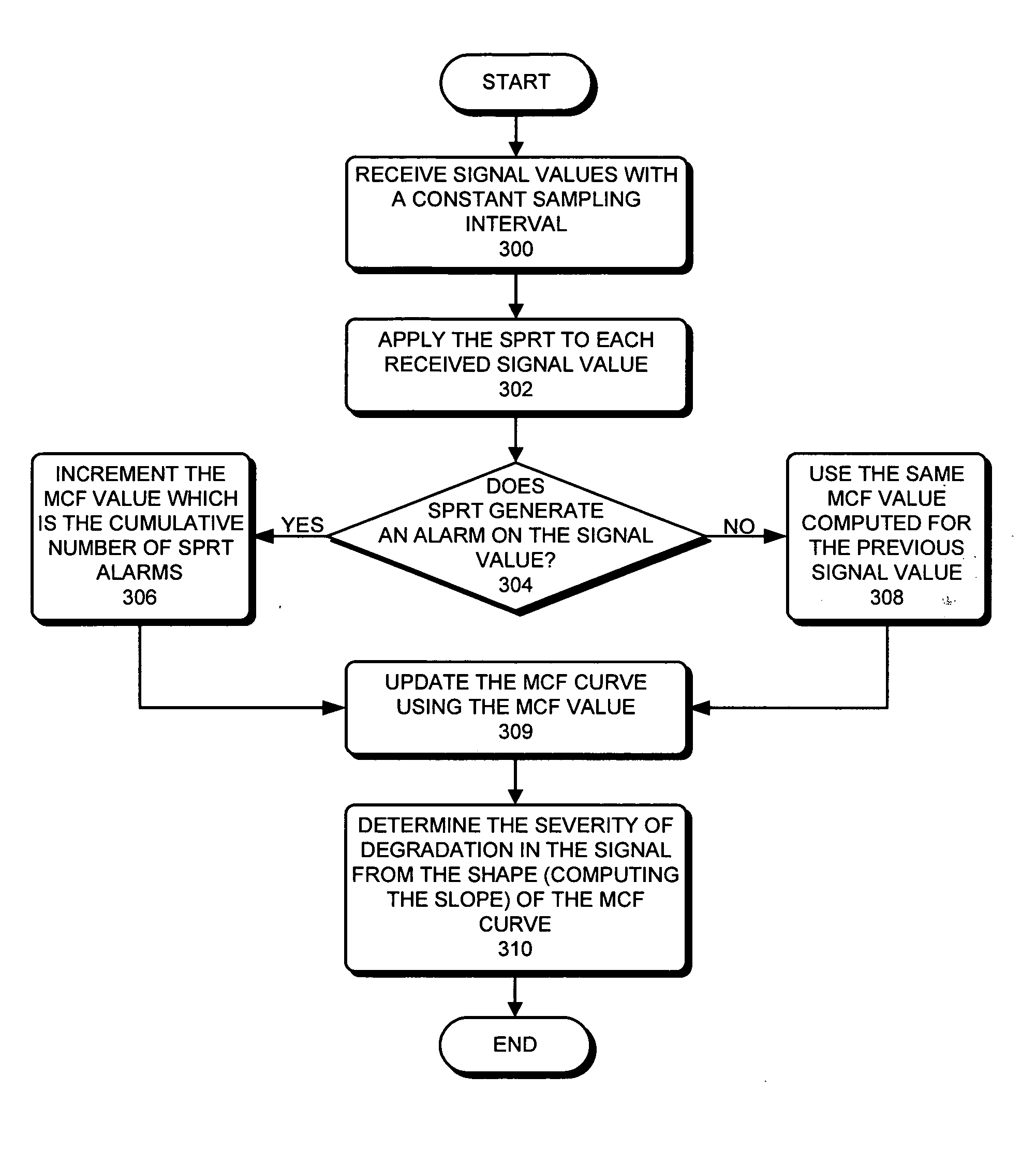
ActiveUS20070225926A1Noise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementNuclear monitoringEngineeringSequential probability ratio test
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that determines a severity of degradation in a signal. During operation, the system receives signal values for the signal, wherein the signal values are received with a constant sampling interval. Next, for each received signal value, the system applies a Sequential Probability Ratio Test (SPRT) to the signal value. If the SPRT generates an alarm on the signal value, the system increments a cumulative counter which records a running total number of the SPRT alarms. Upon receiving each signal value, the system updates a cumulative function using a value in the cumulative counter. Next, the system determines the severity of degradation in the signal from the shape of the cumulative function.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Bivariate optimization technique for tuning sprt parameters to facilitate prognostic surveillance of sensor data from power plants
ActiveUS20190163719A1Structural/machines measurementComplex mathematical operationsPower stationEngineering
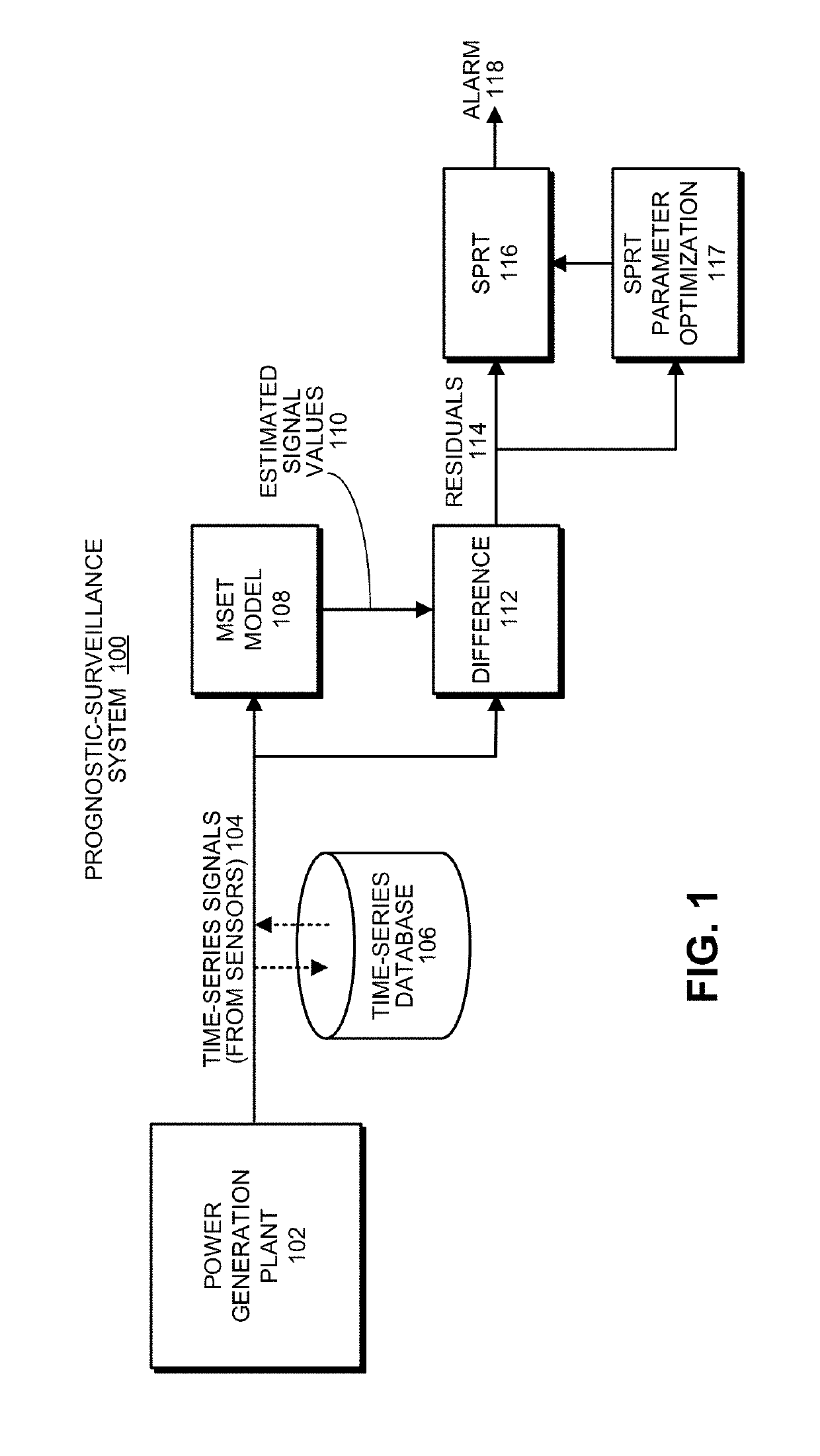
We present a system that performs prognostic surveillance operations based on sensor signals from a power plant and critical assets in the transmission and distribution grid. The system obtains signals comprising time-series data obtained from sensors during operation of the power plant and associated transmission grid. The system uses an inferential model trained on previously received signals to generate estimated values for the signals. The system then performs a pairwise differencing operation between actual values and the estimated values for the signals to produce residuals. The system subsequently performs a sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) on the residuals to detect incipient anomalies that arise during operation of the power plant and associated transmission grid. While performing the SPRT, the system dynamically updates SPRT parameters to compensate for non-Gaussian artifacts that arise in the sensor data due to changing operating conditions. When an anomaly is detected, the system generates a notification.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
A method and apparatus for evaluating semiconductor reliability
PendingCN109145460AEnsure trusted settingsReliability is quickly measuredSpecial data processing applicationsSequential probability ratio testDependability
The invention provides a method and apparatus for rapid reliability evaluation of semiconductor, including an efficient and reliable reliability reference (BL) management system and a test scheme baseon sequential probability ratio test (SPRT). In order to ensure the credibility of the SPRT test scheme, the Bayesian approach is used to update the BL database continuously. This is the first time that the SPRT has been applied to reliability risk assessment with two unknown parameters. By using the method and the device provided by the invention, the reliability of the semiconductor can be quickly measured, and the sample size and the test time can be reduced.
Owner:洪启集成电路(珠海) 有限公司
Prognostic-surveillance technique that dynamically adapts to evolving characteristics of a monitored asset
PendingUS20210158202A1Reduce contributionFacilitates tracing an evolutional history of MSET models associatedRelational databasesProbabilistic networksMonitoring systemSequential probability ratio test
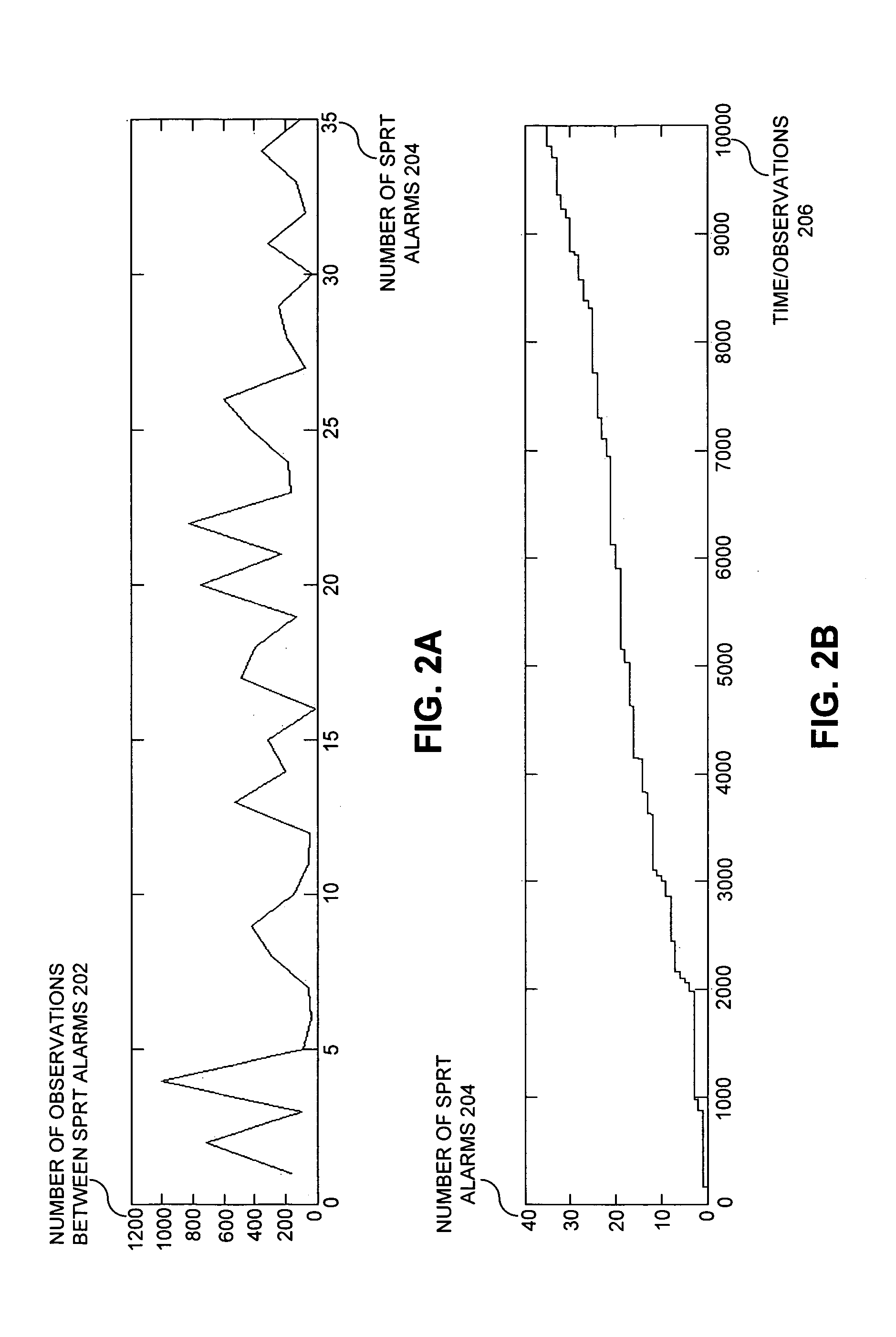
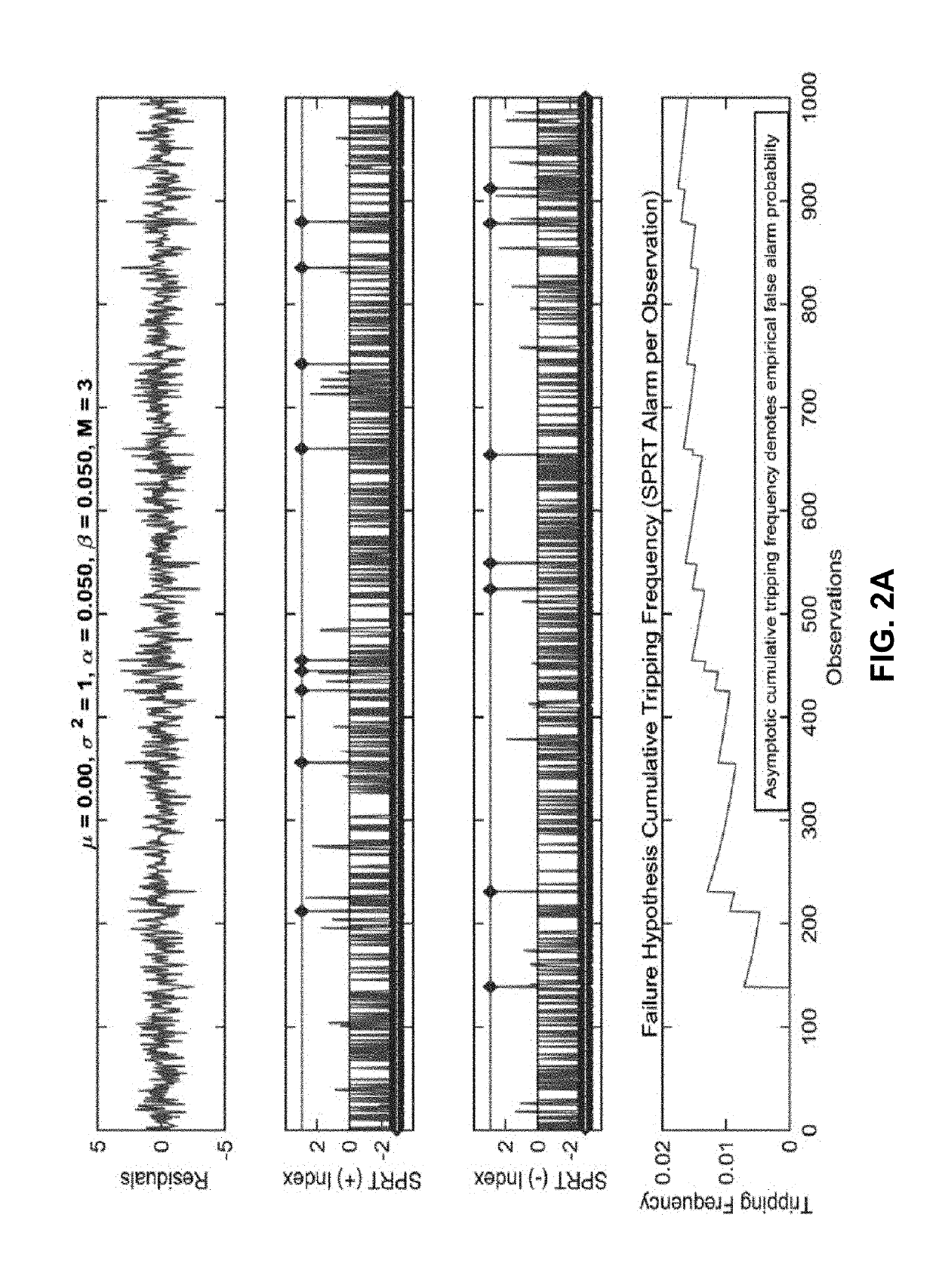
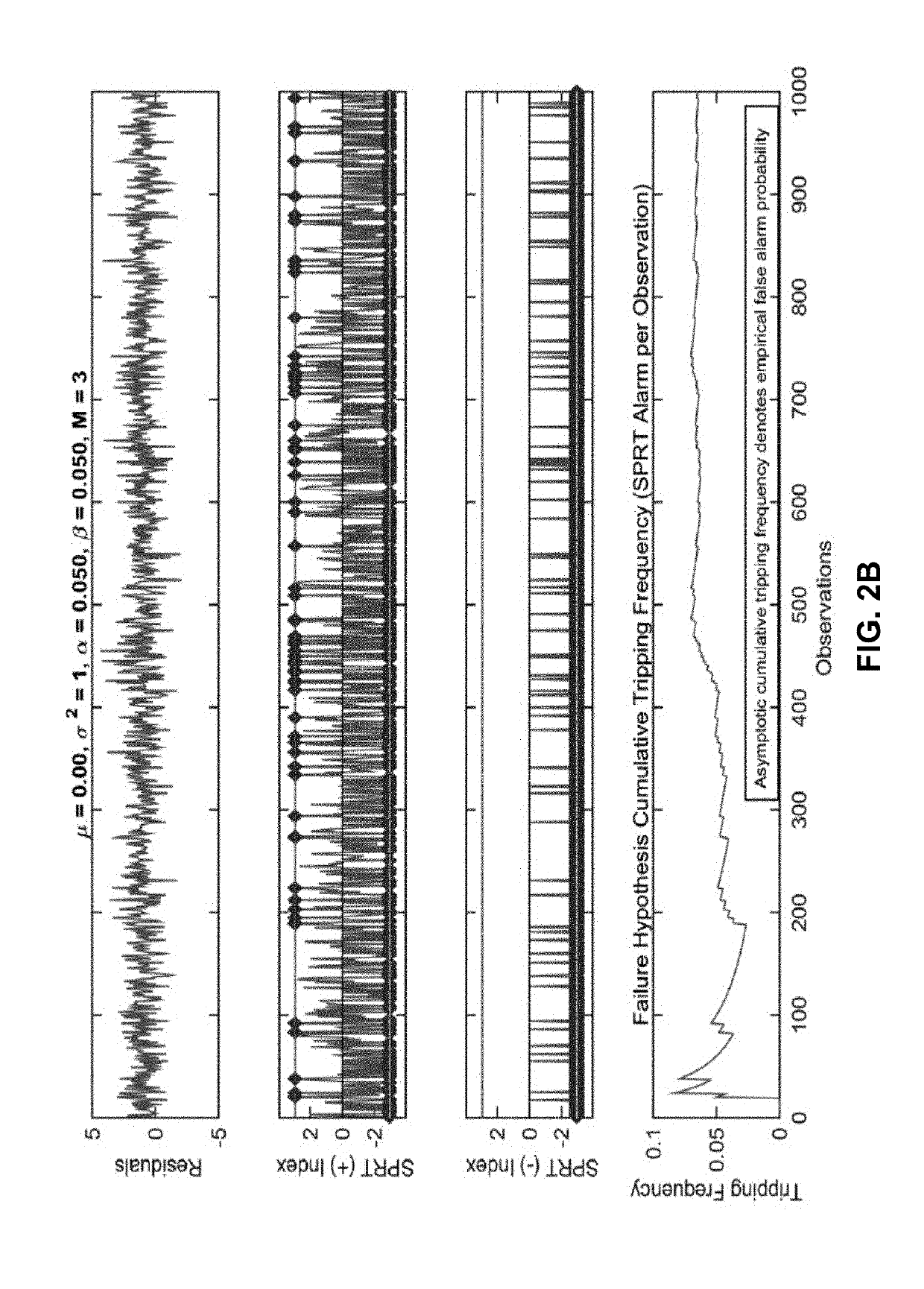
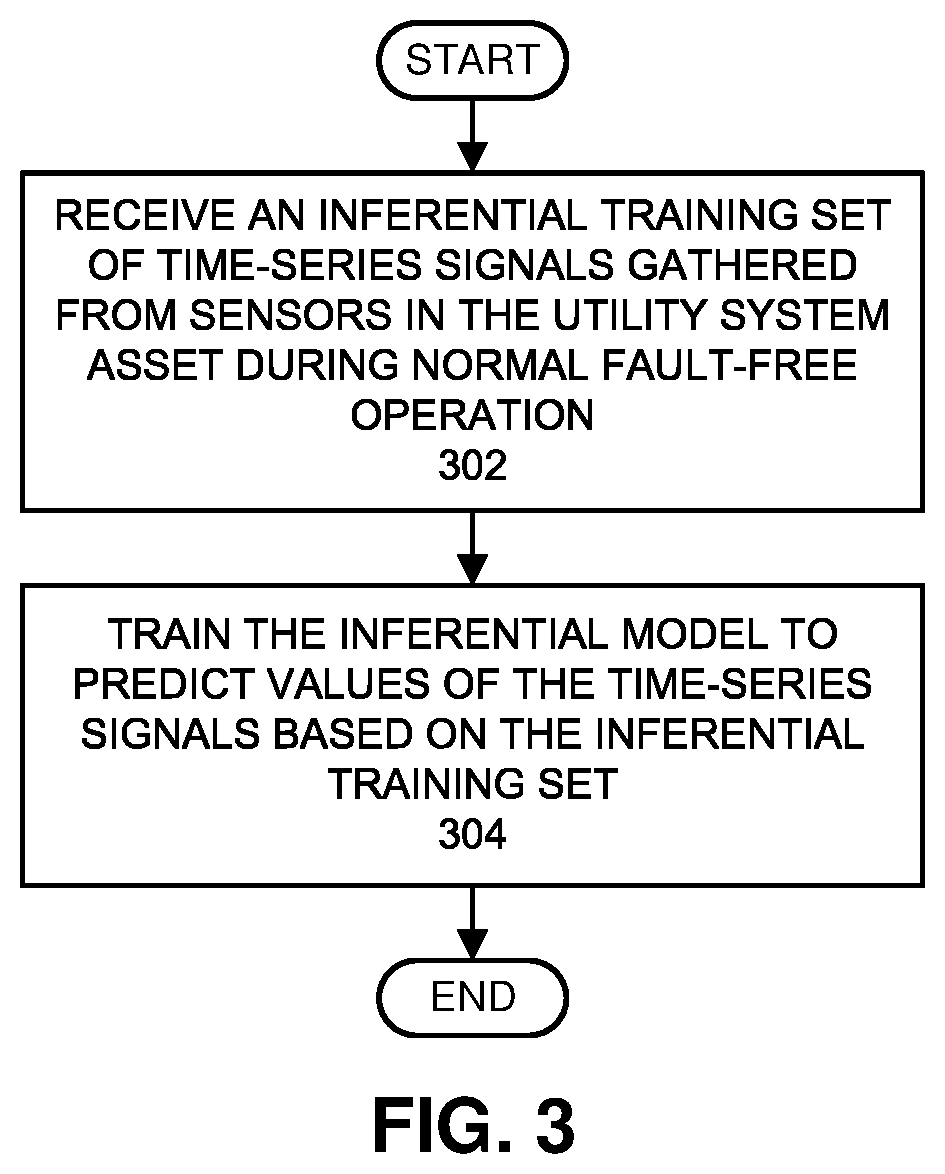
We describe a system that performs prognostic-surveillance operations based on an inferential model that dynamically adapts to evolving operational characteristics of a monitored asset. During a surveillance mode, the system receives a set of time-series signals gathered from sensors in the monitored asset. Next, the system uses an inferential model to generate estimated values for the set of time-series signals, and then performs a pairwise differencing operation between actual values and the estimated values for the set of time-series signals to produce residuals. Next, the system performs a sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) on the residuals to produce SPRT alarms. When a tripping frequency of the SPRT alarms exceeds a threshold value, which is indicative of an incipient anomaly in the monitored asset, the system triggers an alert. While the prognostic-surveillance system is operating in the surveillance mode, the system incrementally updates the inferential model based on the time-series signals.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
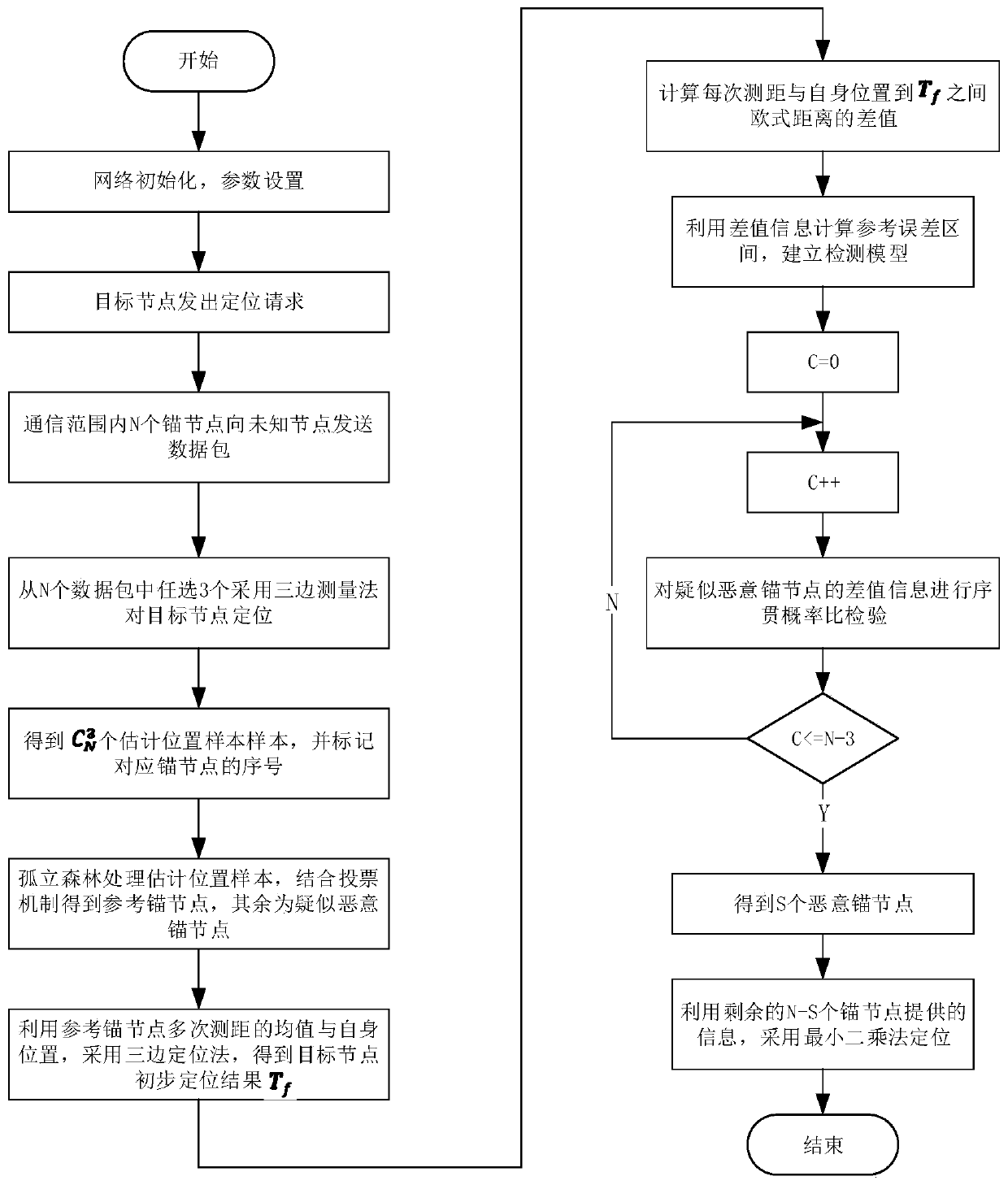
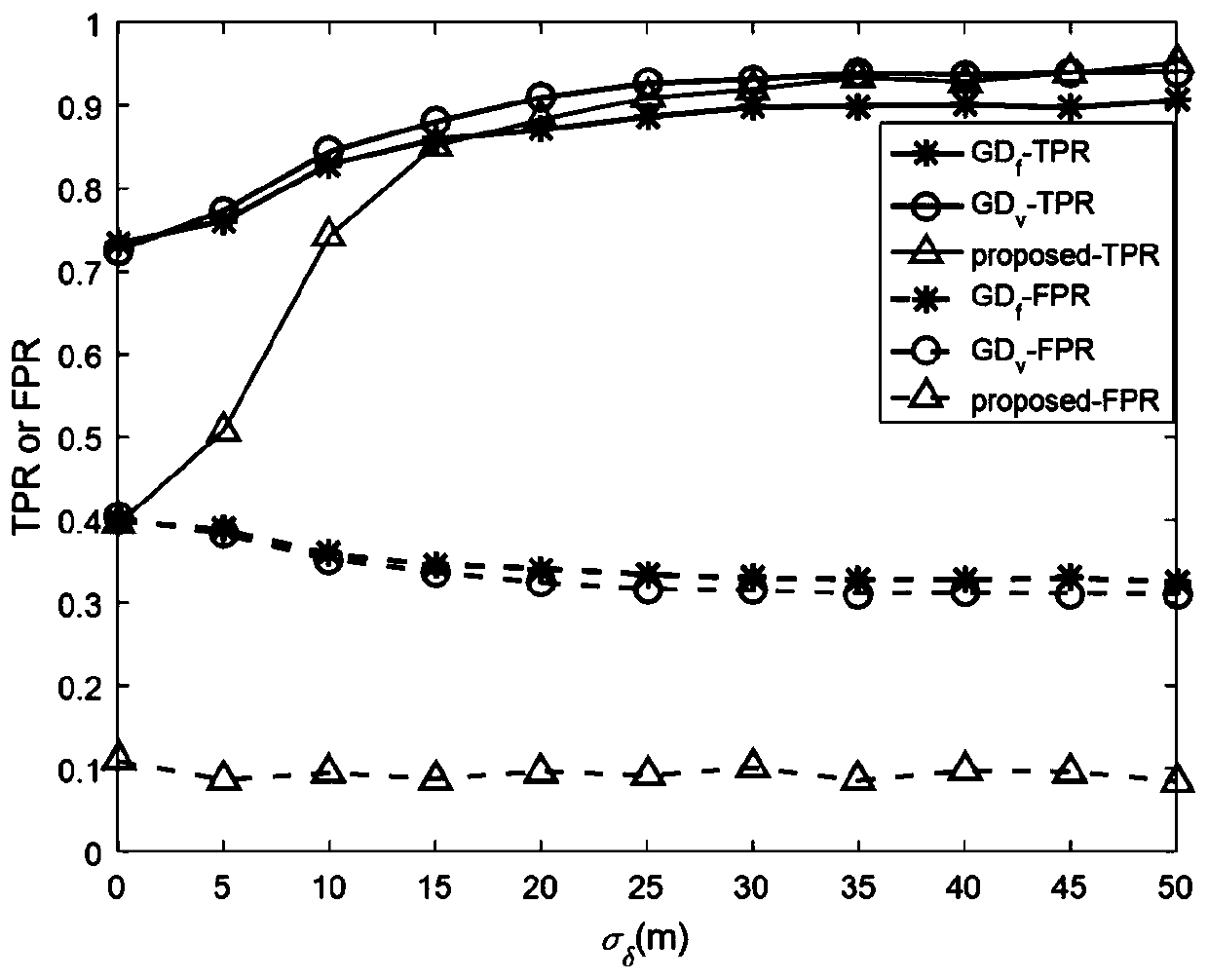
Malicious anchor node detection method based on isolated forest and sequential probability ratio test
ActiveCN110475246AGuaranteed uniformityDetect True and AccurateLocation information based serviceSecurity arrangementNODALSequential probability ratio test
The invention discloses a malicious anchor node detection method based on an isolated forest and a sequential probability ratio test. The malicious anchor node detection method combines an isolated forest algorithm and a voting mechanism to obtain reliable information in anchor nodes, and builds a detection model through the reliable information. According to the malicious anchor node detection method, only a single ranging algorithm is needed for ranging, and multiple ranging algorithms do not need to be used for ranging, and meanwhile, the assumption that one of multiple ranging methods is not attacked completely is avoided, so that the malicious anchor node detection method is more suitable for being used in a real field, that is, it does not need to assume that the malicious anchor node detection method is not attacked completely. Normal samples are screened by utilizing an isolated forest, and reference anchor nodes in the normal samples are screened by utilizing a voting mechanism to realize multiple selection, and the reliability of the reference anchor nodes is ensured, so that the subsequent process of obtaining malicious anchor nodes according to the reference anchor nodes is indirectly ensured; and the difference value information is used for sequential probability ratio inspection, so that the detection of malicious anchor nodes is further improved, and the detection accuracy of the anchor nodes is improved, and the final positioning accuracy of subsequent target nodes is also improved.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
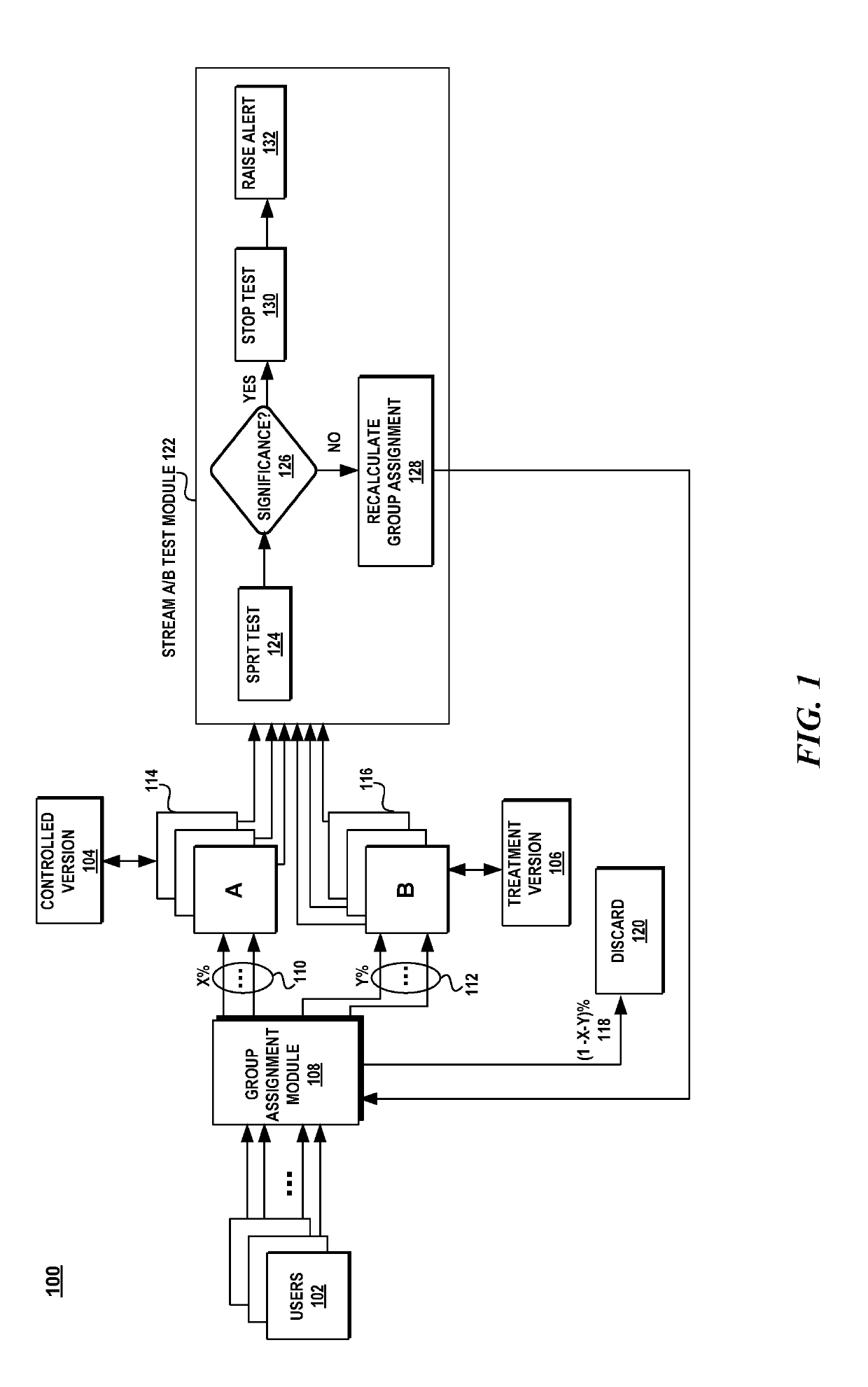
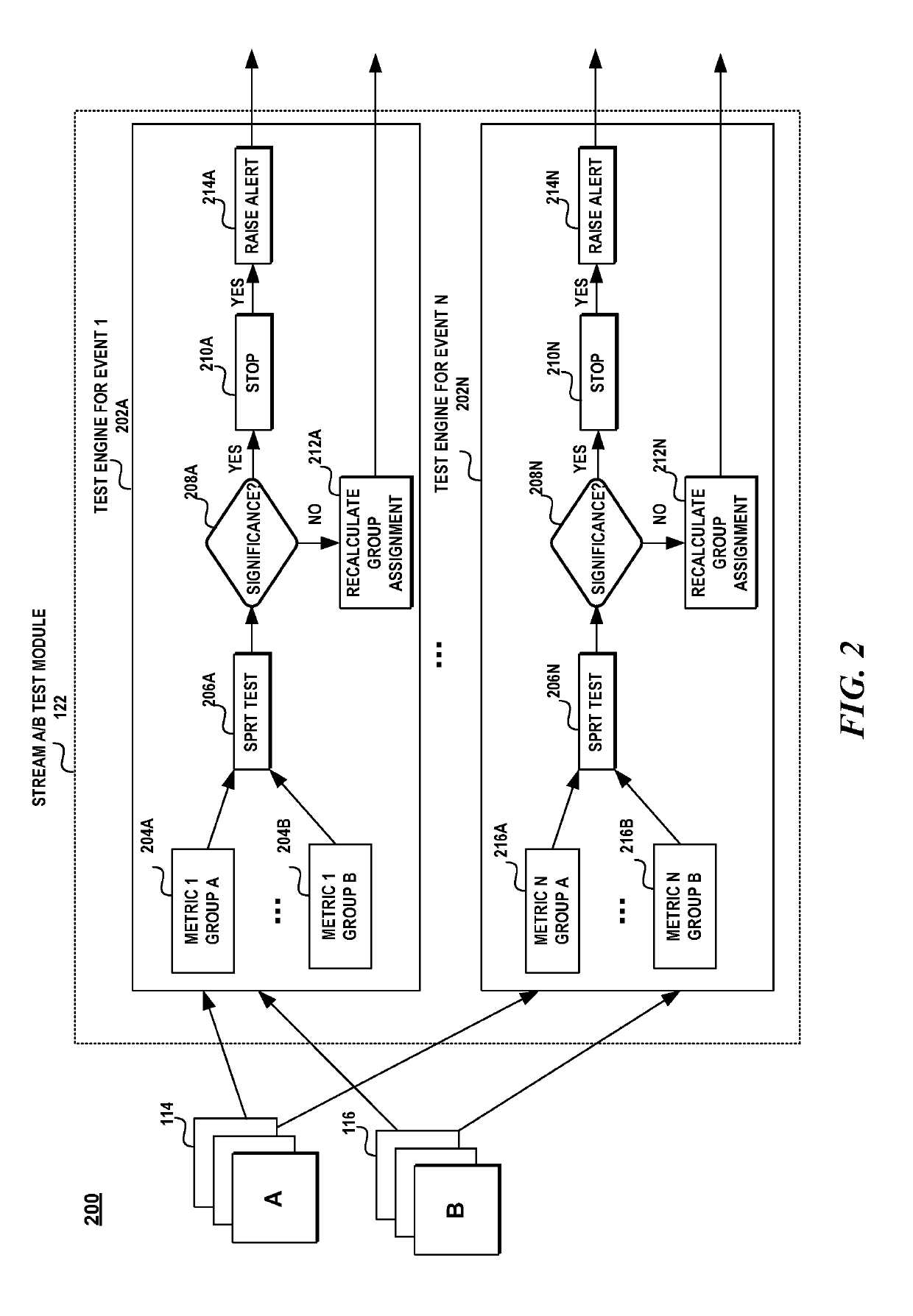
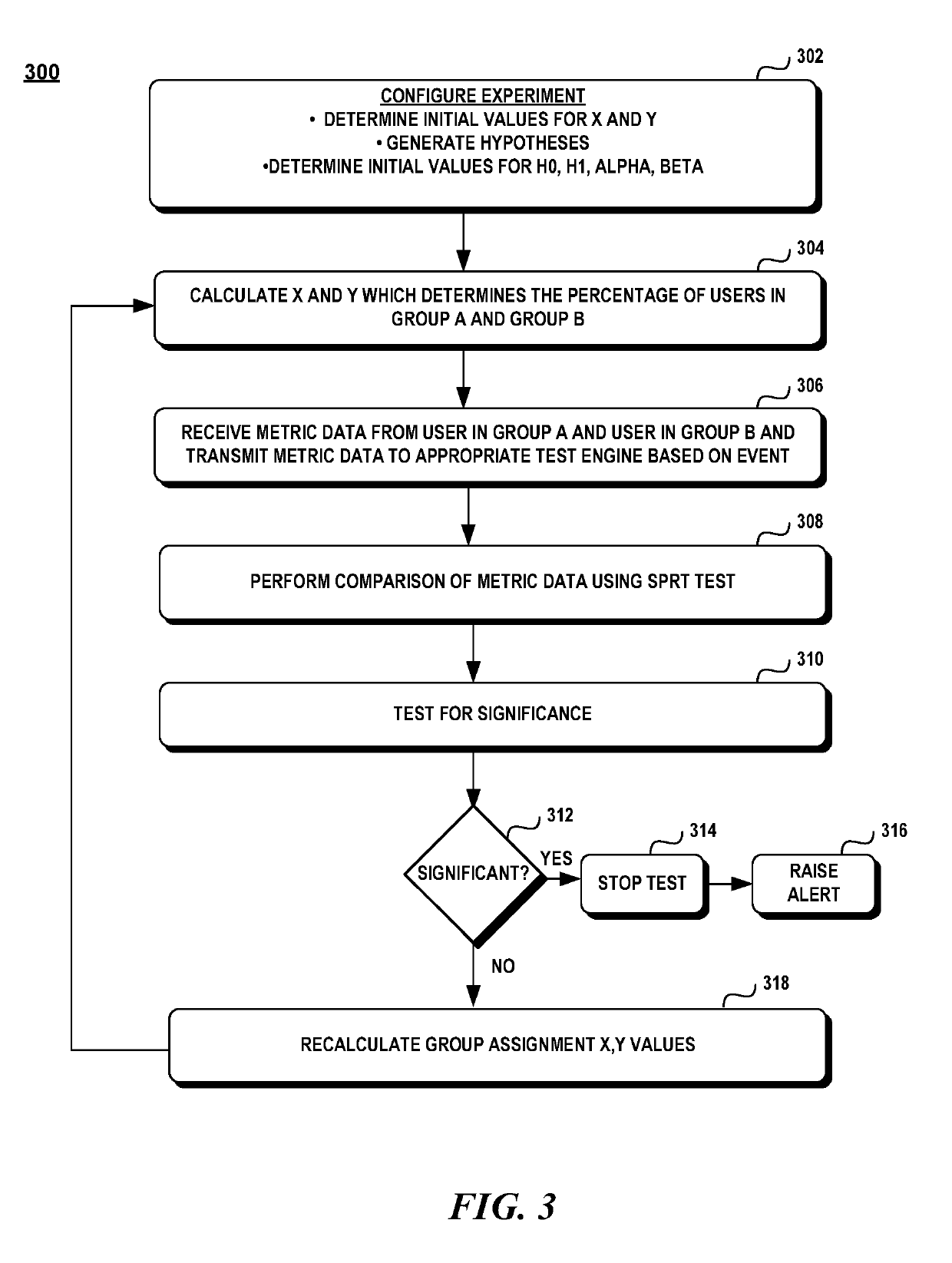
Dynamic experimentation evaluation system
A dynamic experimentation evaluation system provides a framework in which a continuous stream of metric data is monitored to establish a causal relationship between changes in a software program and the effect of user-observable behavior. In one aspect, an A / B test is performed continuously on a stream of metric data representing the usage of a control version of software product and the usage of a treatment version of the software product. A sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) is used as the test statistic to determine when to terminate the test and produce results within a specific confidence interval and controlled error rate.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
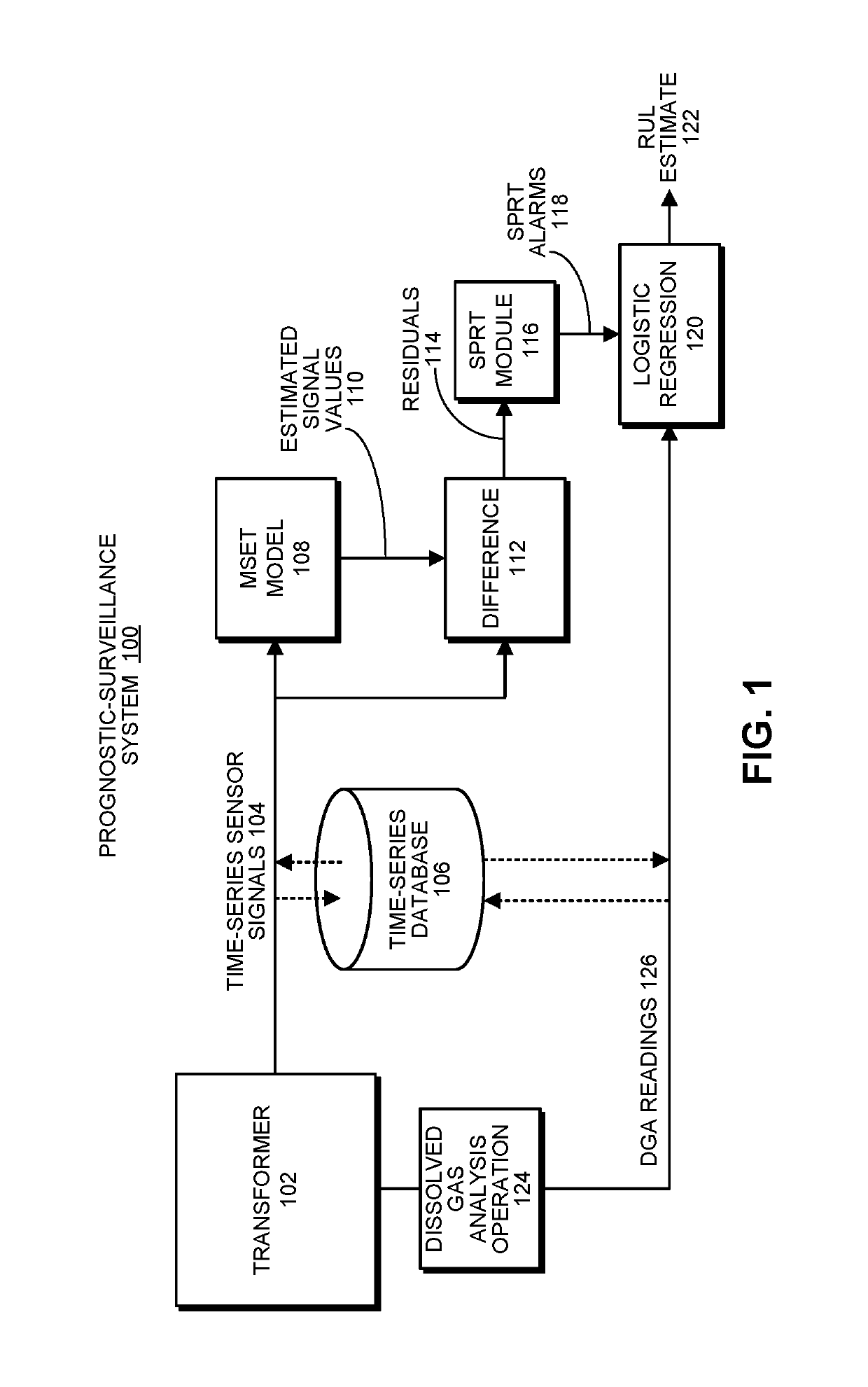
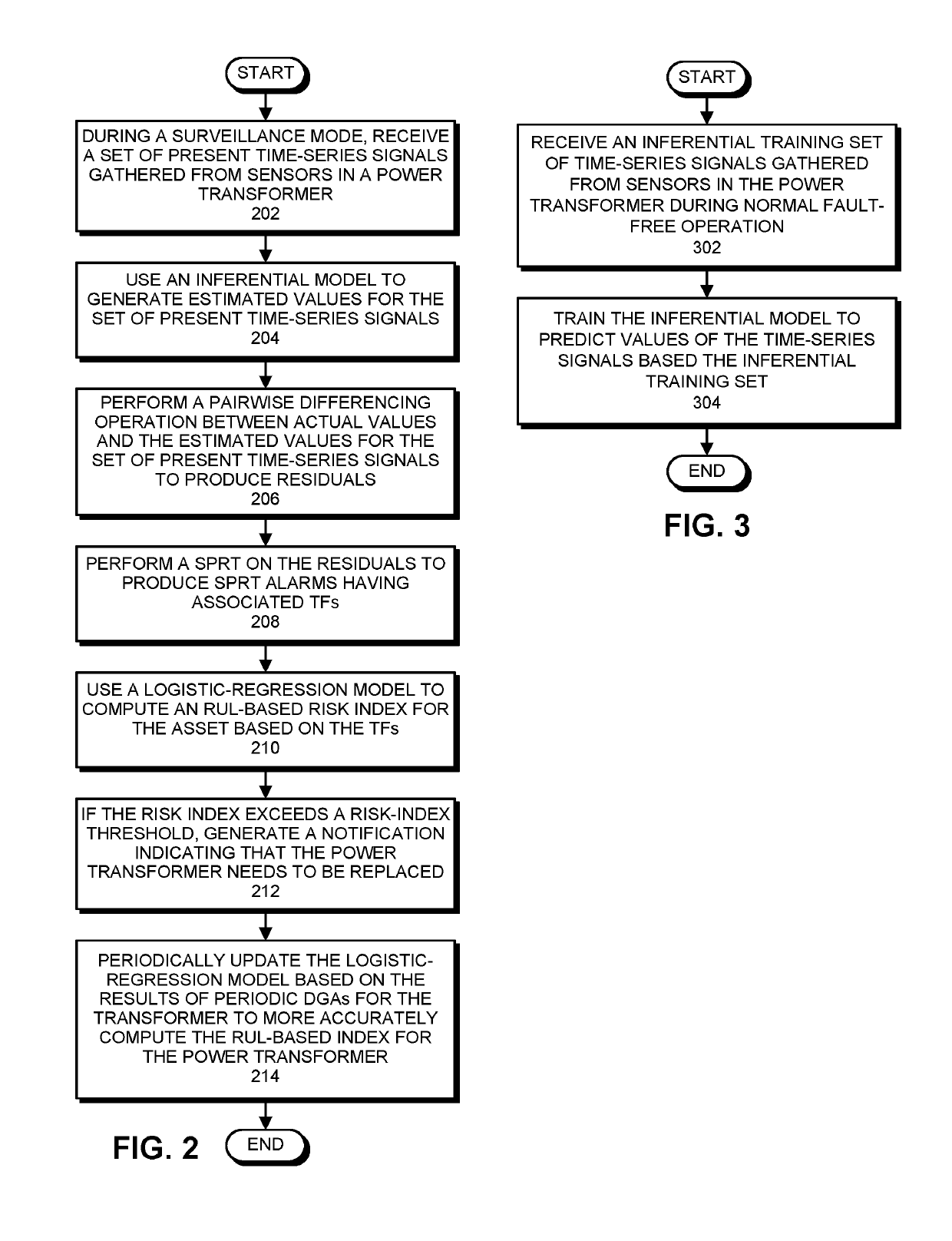
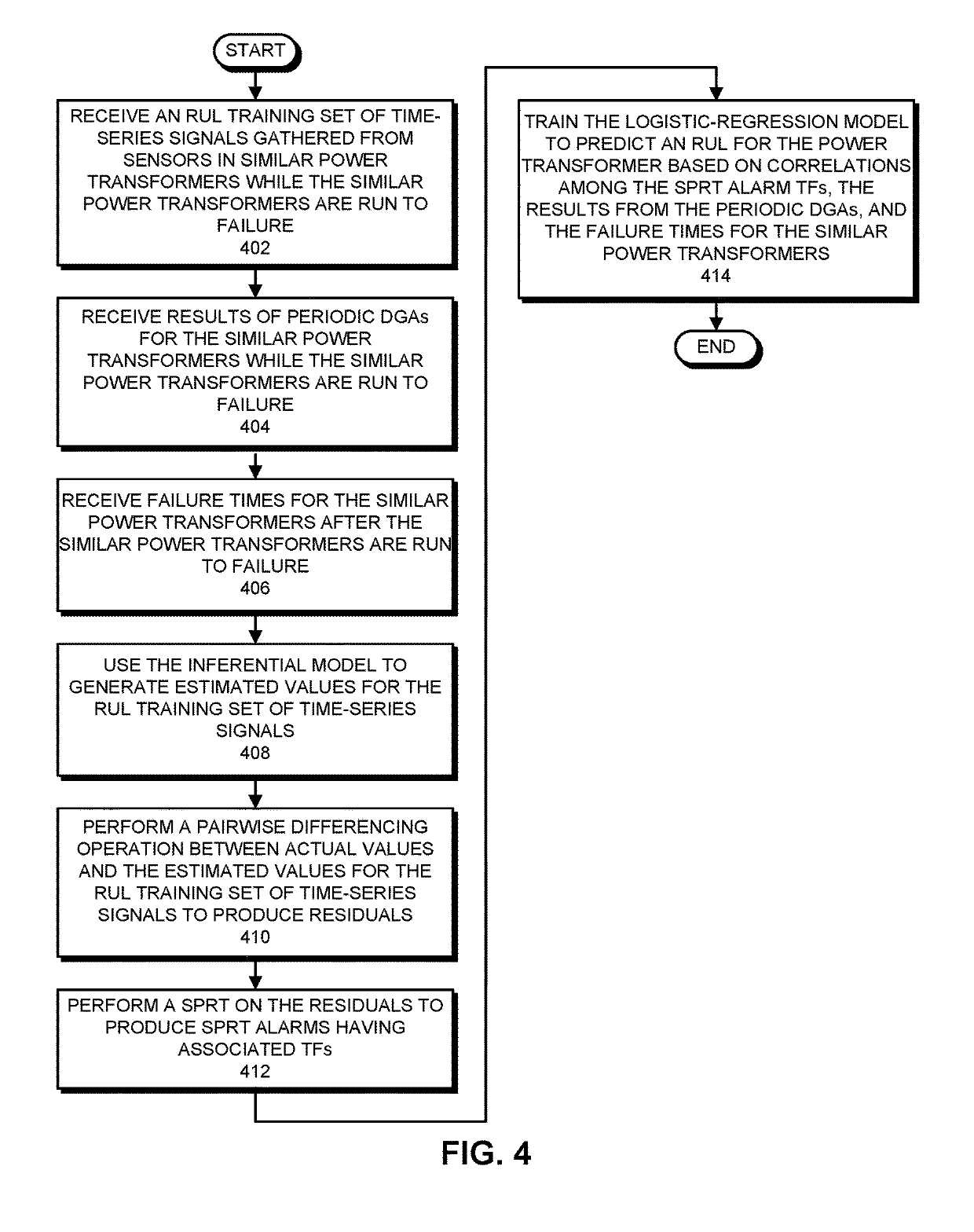
Estimating the remaining useful life of a power transformer based on real-time sensor data and periodic dissolved gas analyses
ActiveUS20190293697A1Accurate calculationTransformers testingMachine learningBlood gas analysisTransformer
During a surveillance mode, the system receives present time-series signals gathered from sensors in the power transformer. Next, the system uses an inferential model to generate estimated values for the present time-series signals, and performs a pairwise differencing operation between actual values and the estimated values for the present time-series signals to produce residuals. The system then performs a sequential probability ratio test on the residuals to produce alarms having associated tripping frequencies (TFs). Next, the system uses a logistic-regression model to compute a risk index for the power transformer based on the TFs. If the risk index exceeds a threshold, the system generates a notification that the power transformer needs to be replaced. The system also periodically updates the logistic-regression model based on the results of periodic dissolved gas analyses for the transformer to more accurately compute the index for the power transformer.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Telemetry data analysis using multivariate sequential probability ratio test
ActiveUS9152530B2Hardware monitoringRedundant operation error correctionMultidimensional scalingMonitoring system
One embodiment provides a system that analyzes telemetry data from a monitored system. During operation, the system periodically obtains the telemetry data as a set of telemetry variables from the monitored system and updates a multidimensional real-time distribution of the telemetry data using the obtained telemetry variables. Next, the system analyzes a statistical deviation of the multidimensional real-time distribution from a multidimensional reference distribution for the monitored system using a multivariate sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) and assesses the integrity of the monitored system based on the statistical deviation of the multidimensional real-time distribution. If the assessed integrity falls below a threshold, the system determines a fault in the monitored system corresponding to a source of the statistical deviation.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
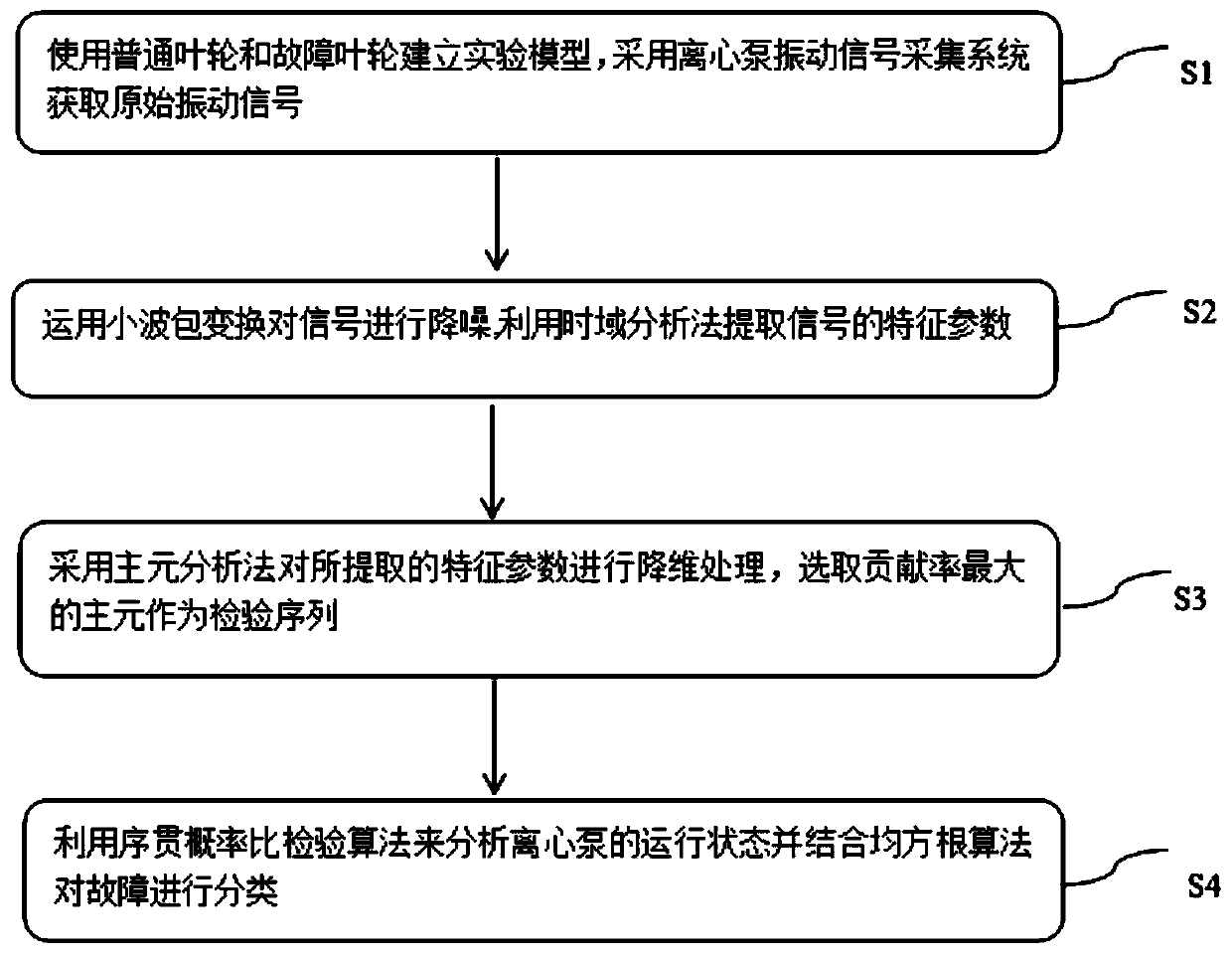
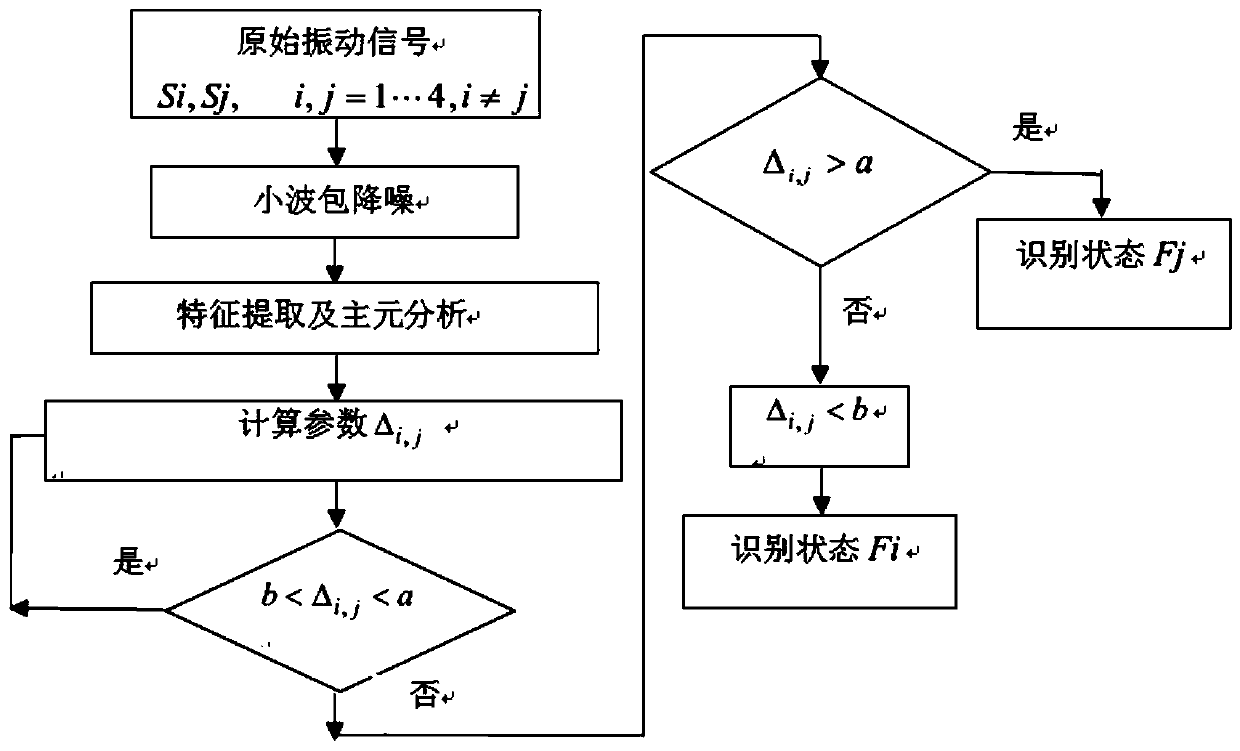
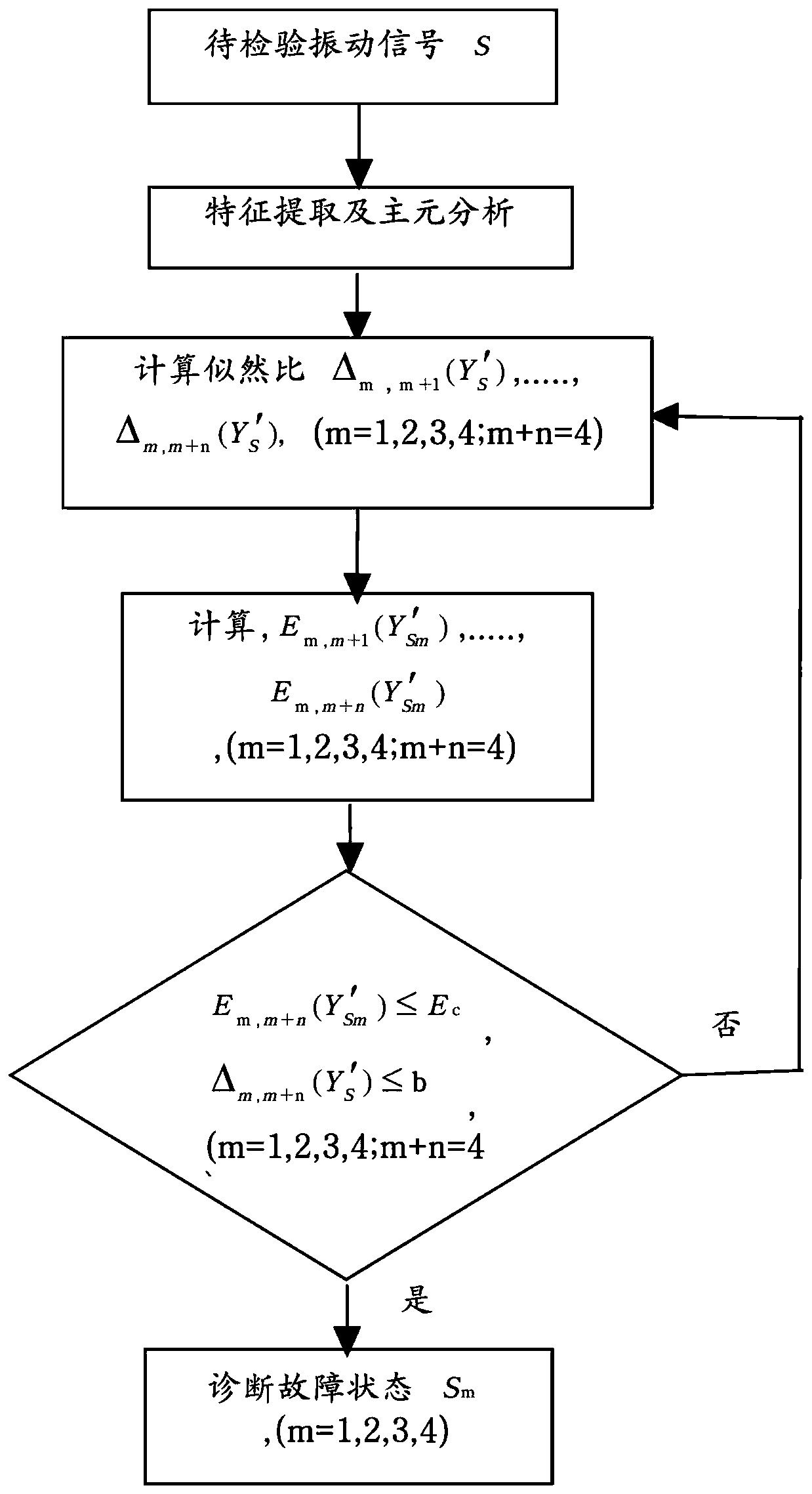
Principal component analysis and sequential probability ratio test-based centrifugal pump fault diagnosis method
InactiveCN110159554AReduce dimensionalitySimplify complexityEngine fuctionsPump controlPrincipal component analysisEngineering
The invention discloses a principal component analysis and sequential probability ratio test-based centrifugal pump fault diagnosis method. The method comprises the following steps of building a modelby using a common impeller and a fault impeller, and acquiring an original vibration signal by employing a centrifugal pump vibration signal acquisition system; then, performing noise reduction on the signal by applying wavelet packet transformation, and extracting a characteristic parameter of the signal by utilizing a time domain analysis method; then, performing dimension-reduced processing onthe extracted characteristic parameter by employing a principal component analysis method, and selecting a principal component of which the contribution ratio is maximum as a test sequence; and finally, analyzing the running status of a centrifugal pump by utilizing a sequential probability ratio test algorithm and performing classification on a fault by combining with a root-mean-square algorithm. According to the method disclosed by the invention, principal component analysis and sequential probability ratio test are mainly utilized to perform fault state diagnosis, and a classification criterion is established; and the method is higher in effectiveness and accuracy in the aspects of fault diagnosis and recognition of the centrifugal pump.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
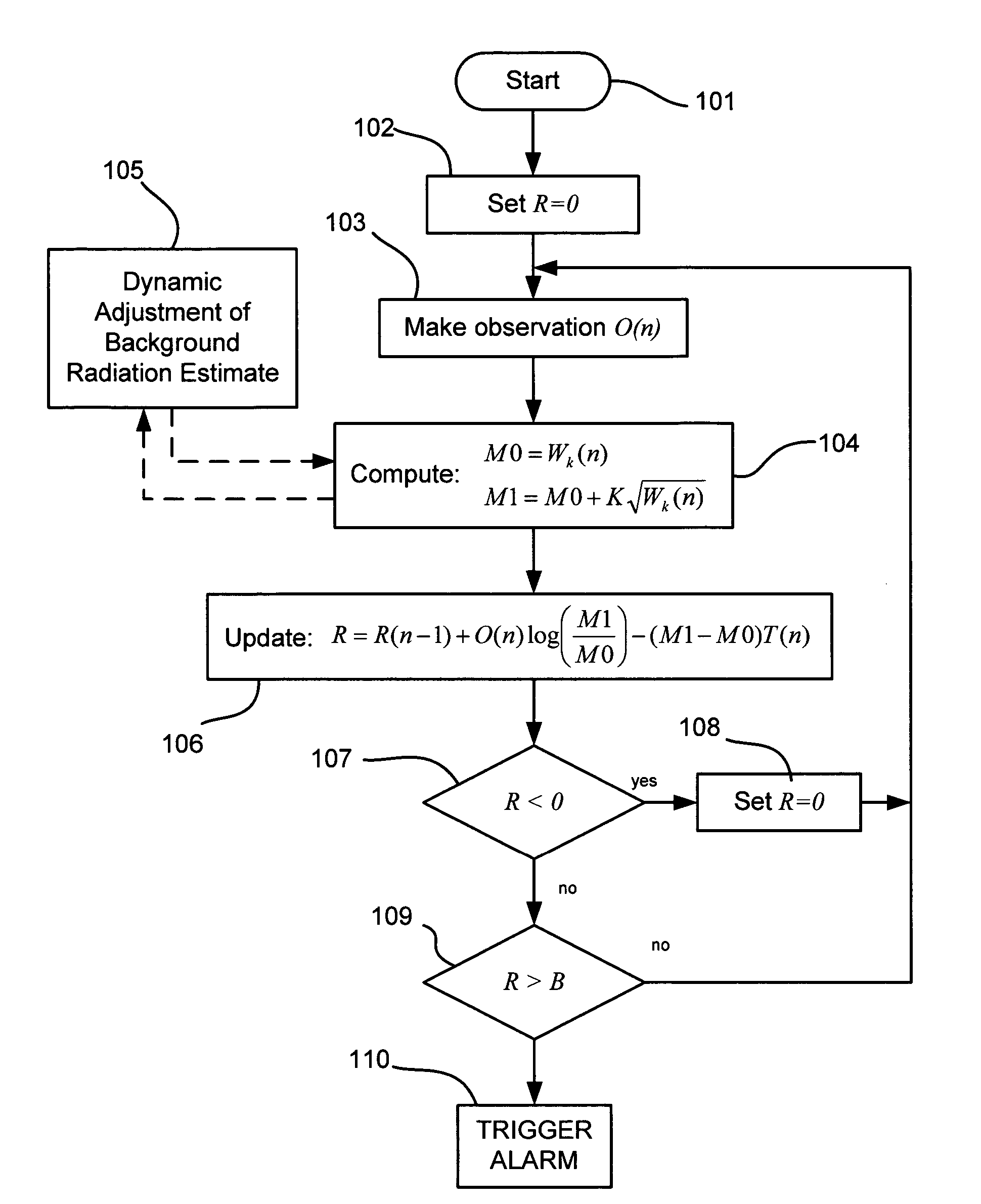
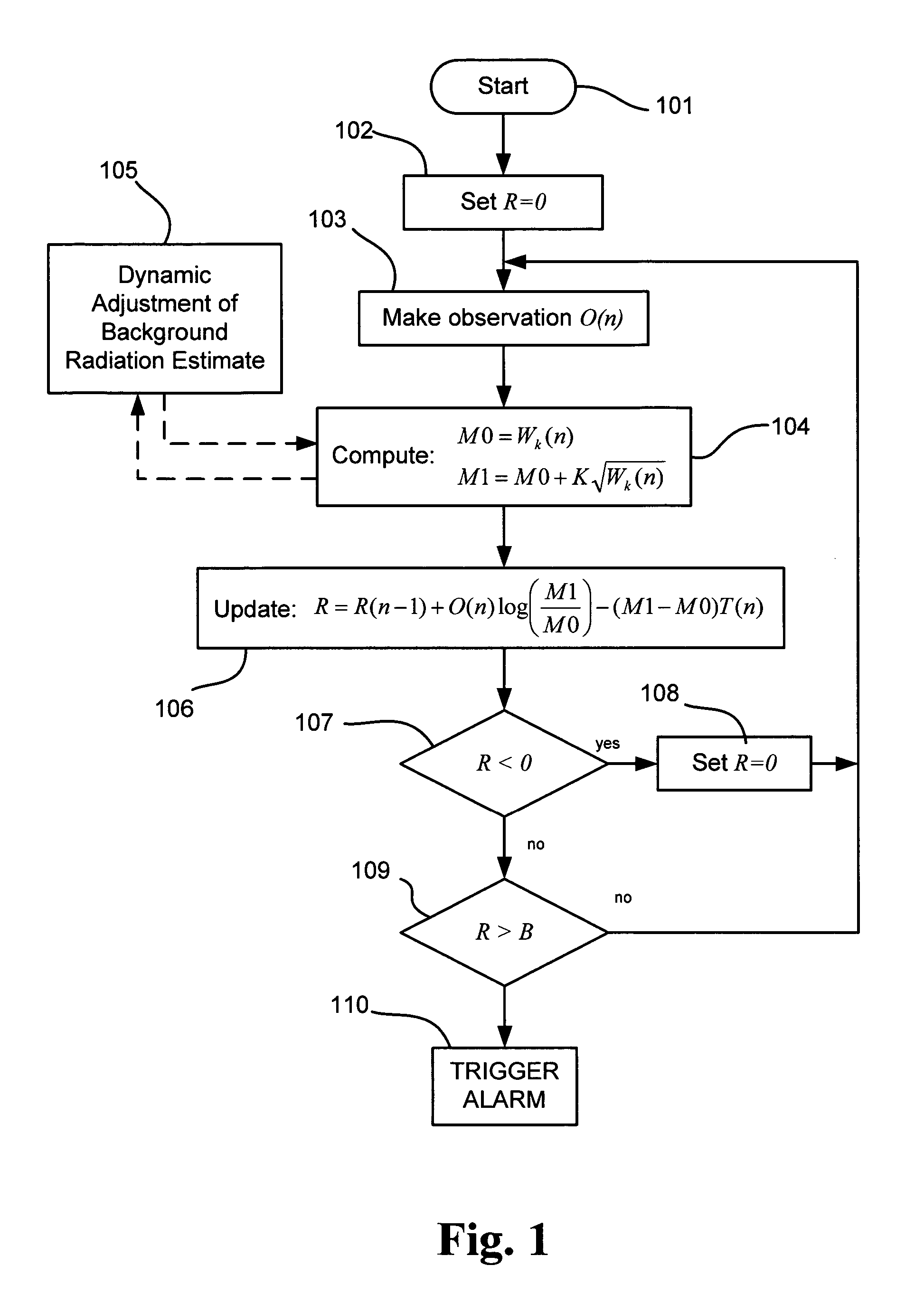
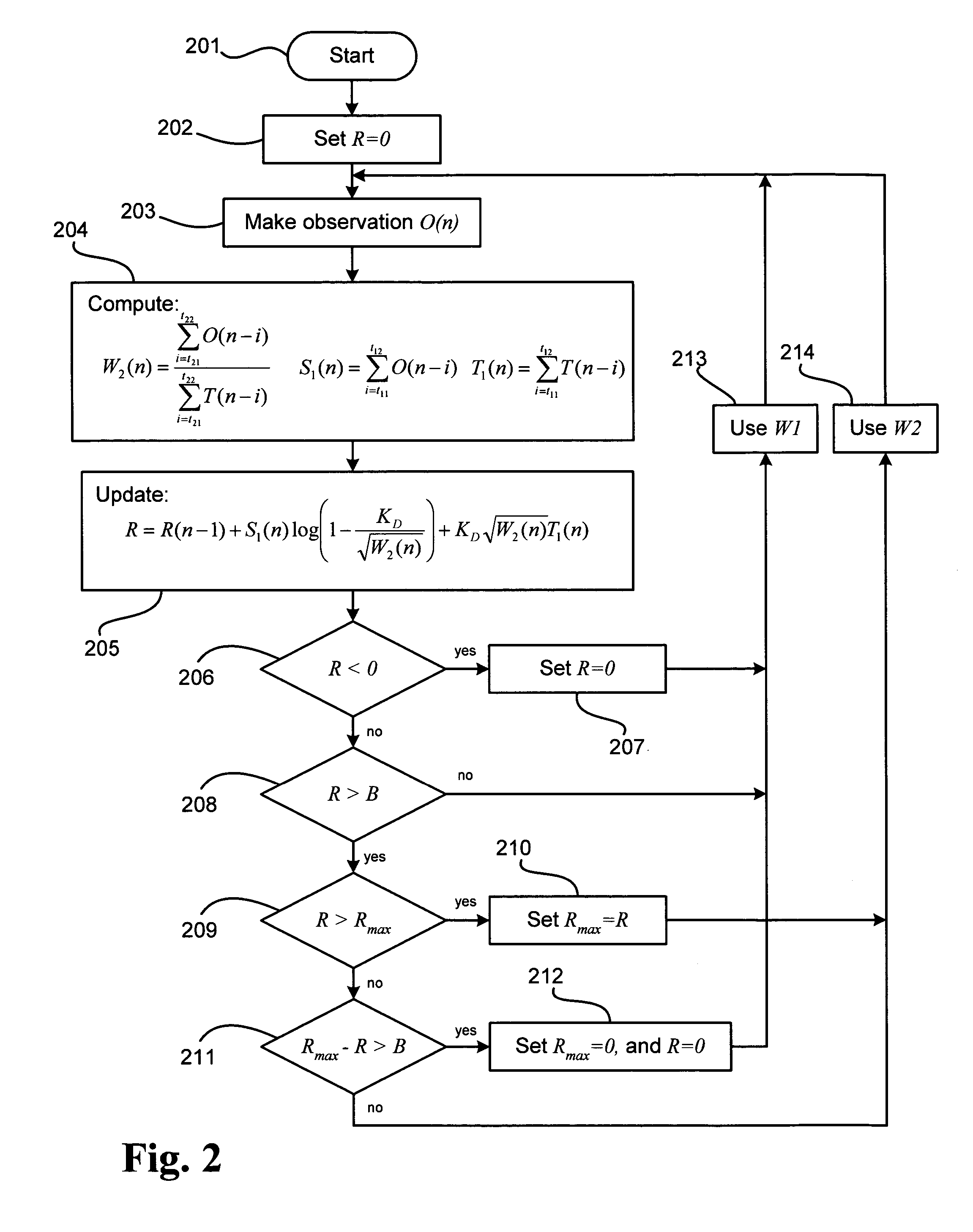
Radiation detection method and system using the sequential probability ratio test
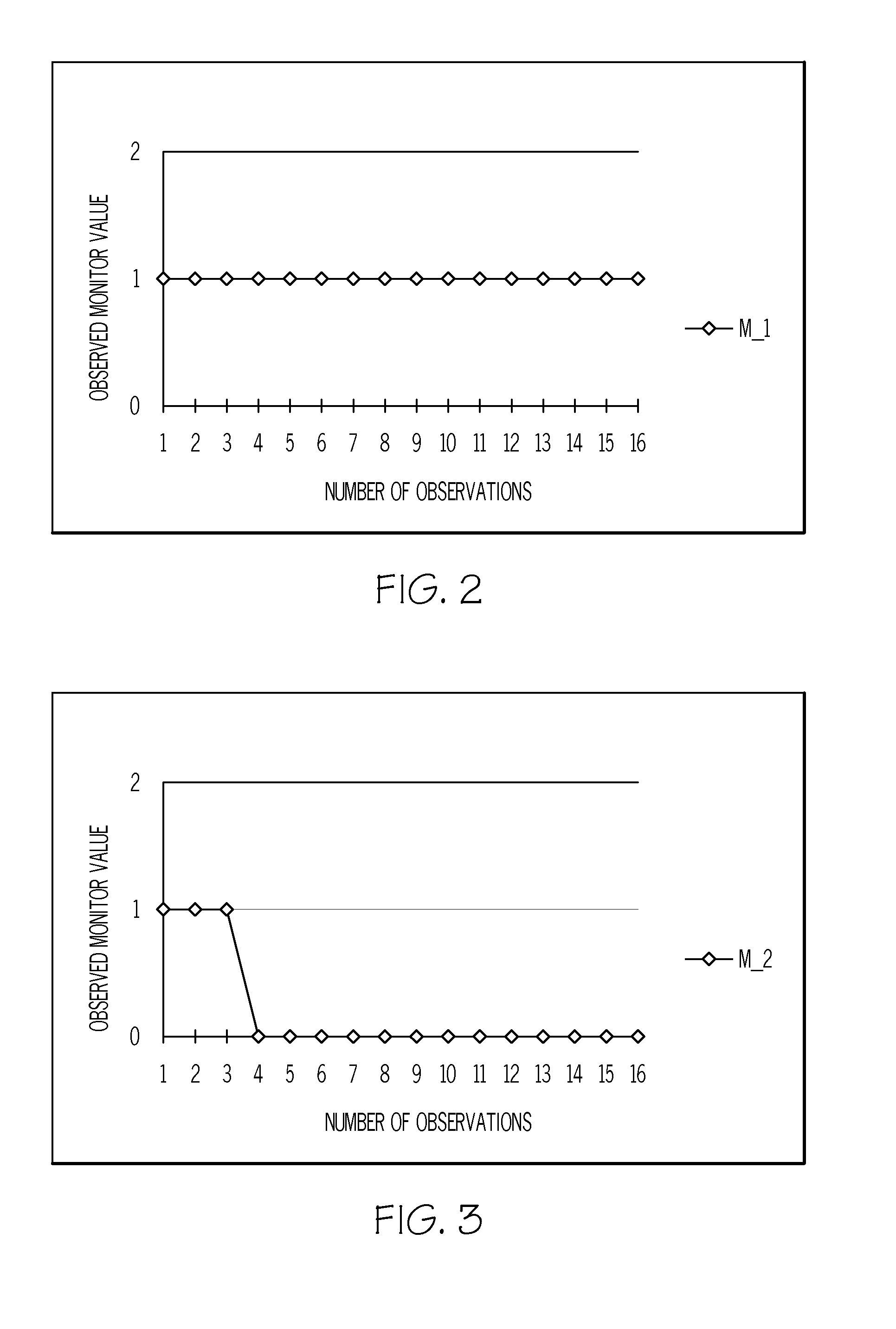
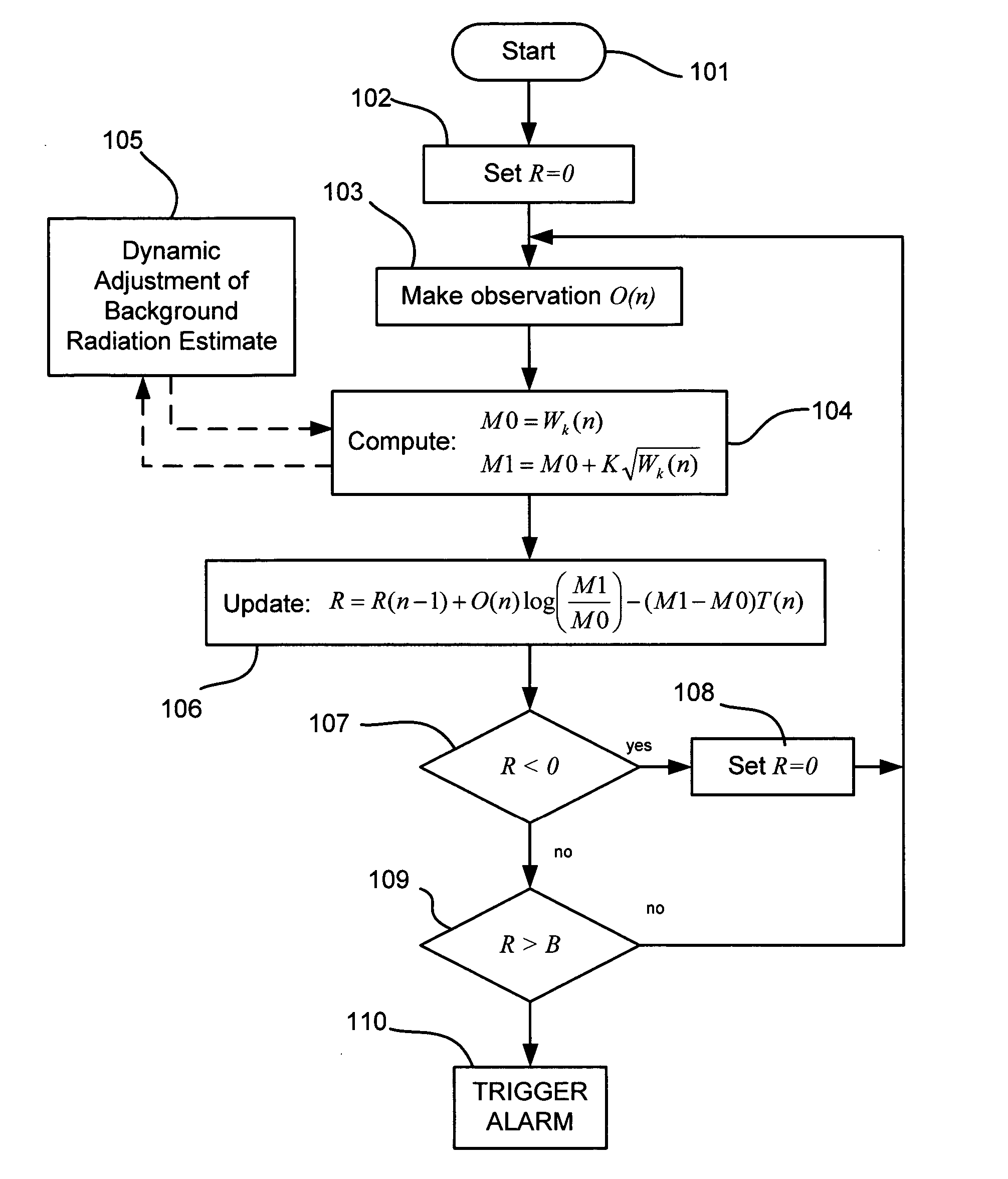
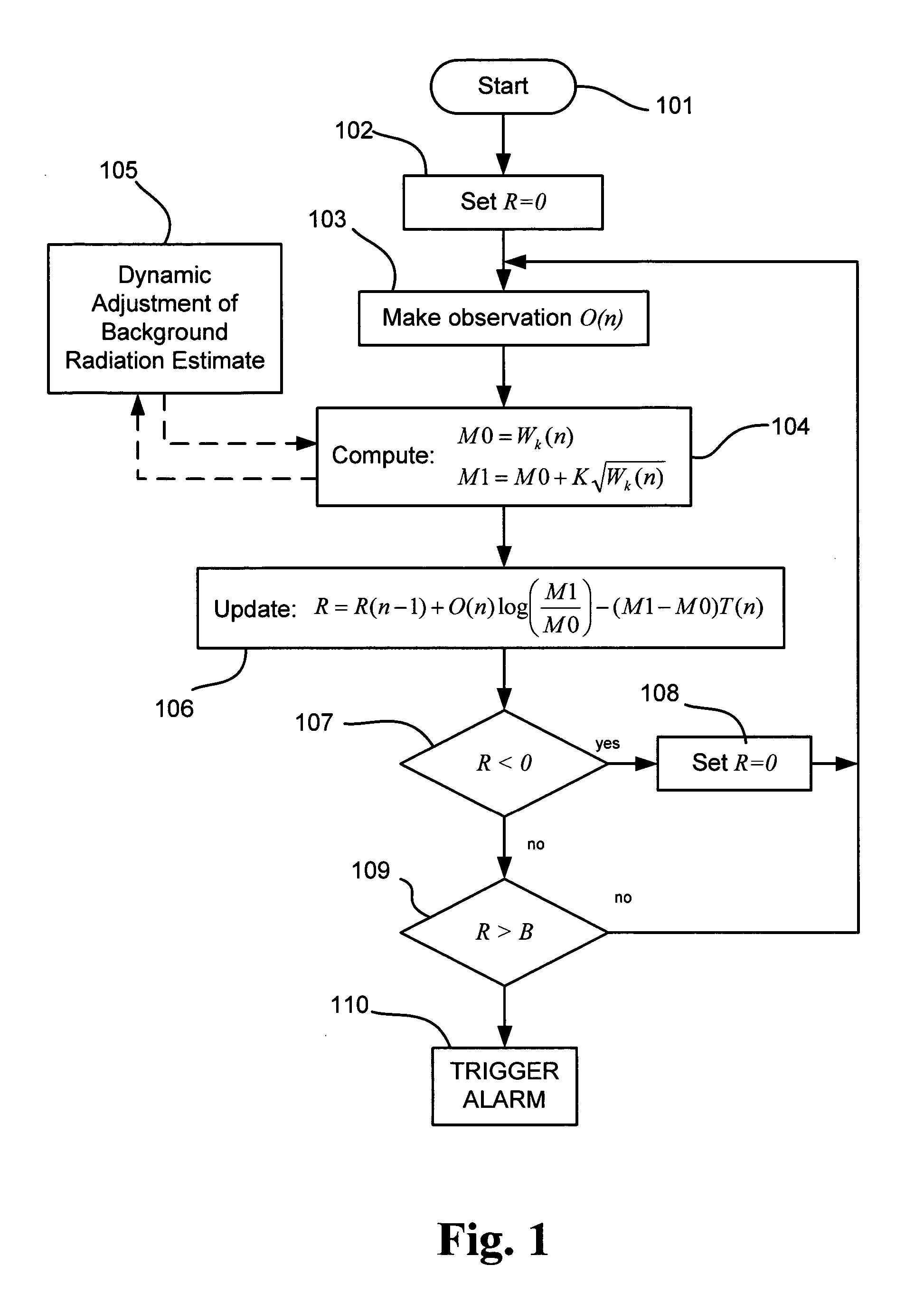
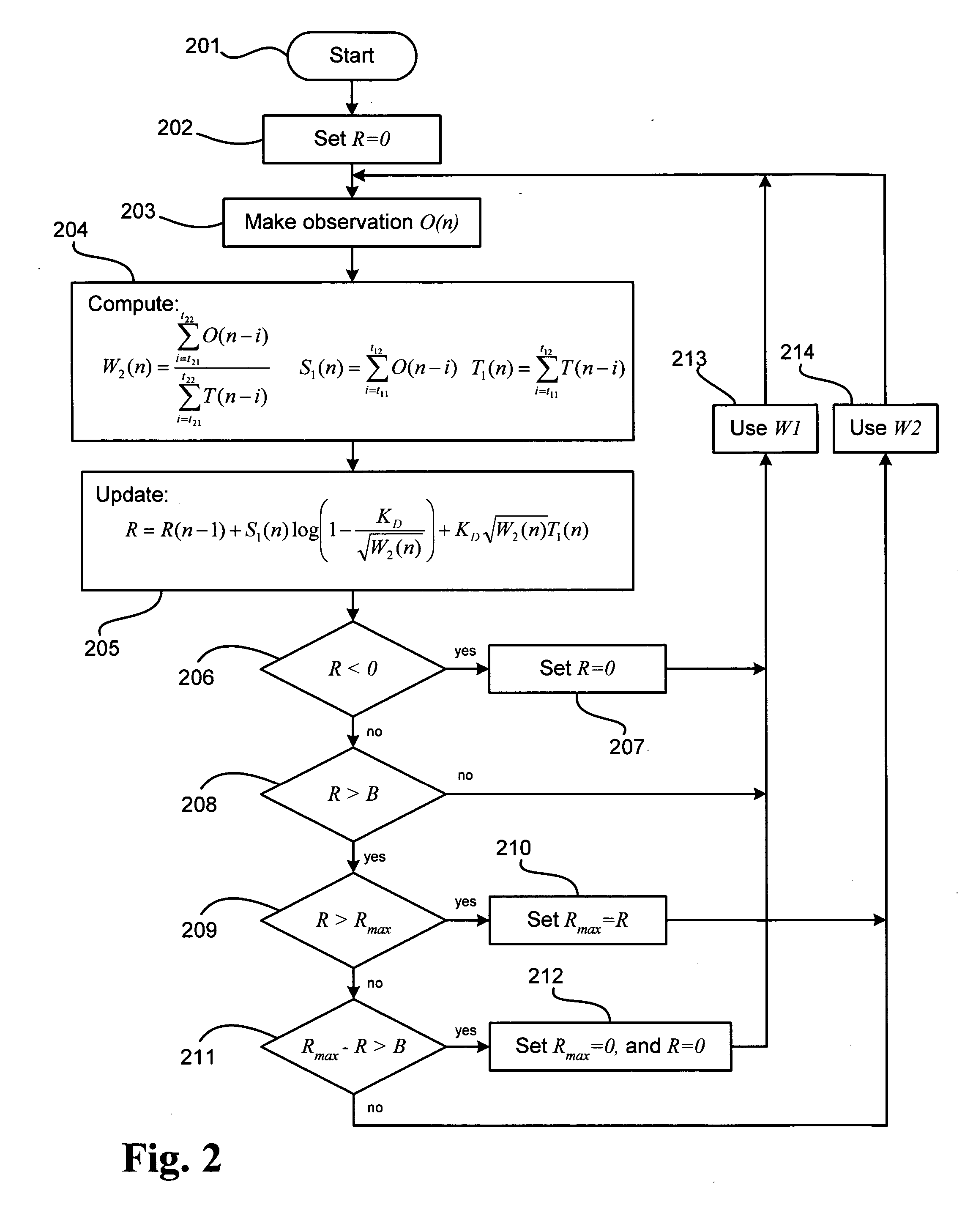
A method and system using the Sequential Probability Ratio Test to enhance the detection of an elevated level of radiation, by determining whether a set of observations are consistent with a specified model within a given bounds of statistical significance. In particular, the SPRT is used in the present invention to maximize the range of detection, by providing processing mechanisms for estimating the dynamic background radiation, adjusting the models to reflect the amount of background knowledge at the current point in time, analyzing the current sample using the models to determine statistical significance, and determining when the sample has returned to the expected background conditions.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Two-stage DDoS attack detection and defense method in software defined network
ActiveCN114513340AReduce loadImprove real-time detectionCharacter and pattern recognitionSecuring communicationAttackGradient boosting
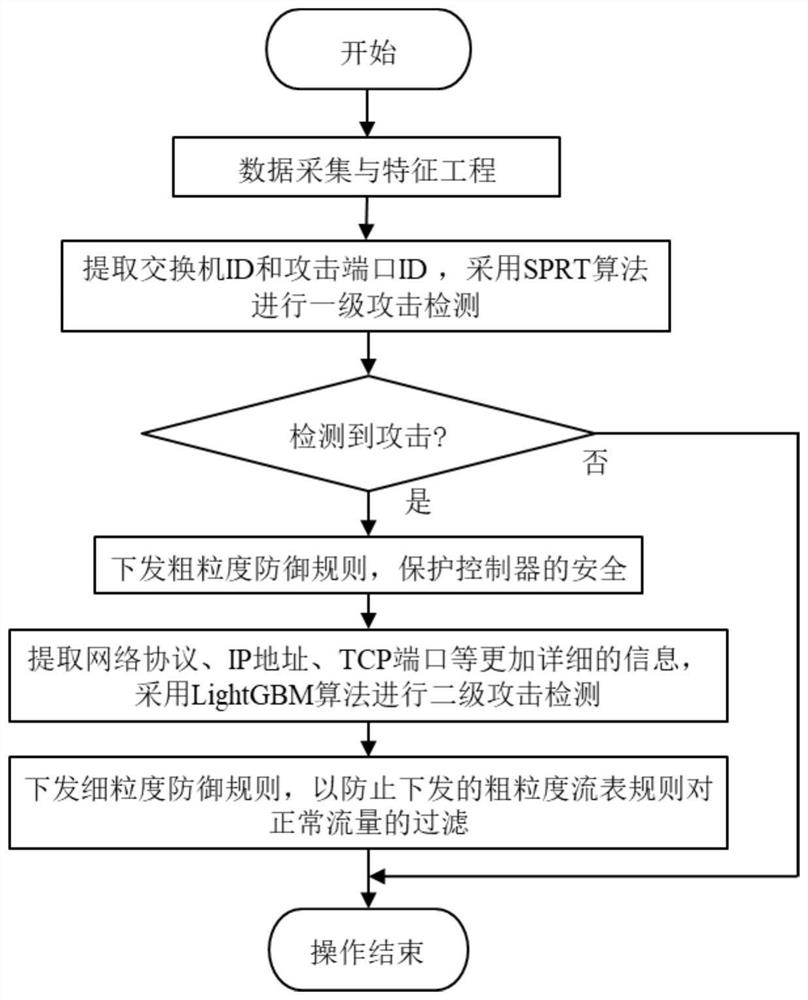
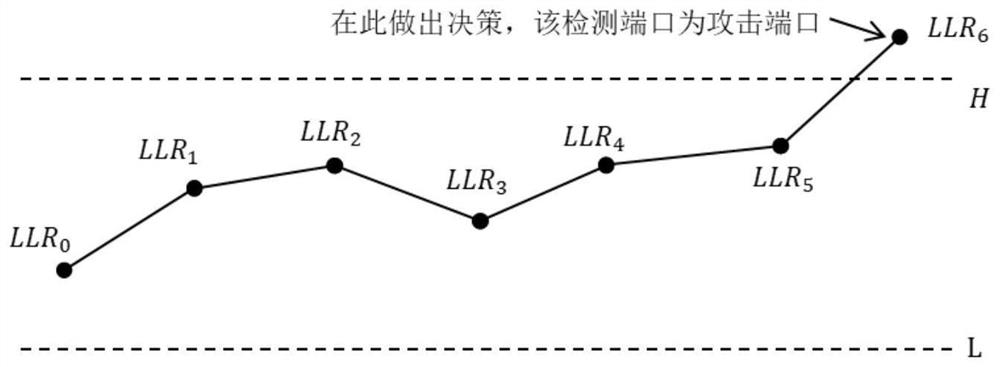
The invention discloses a two-stage DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack detection and defense method in a software defined network, which is characterized in that switch flow table data is acquired based on a northbound interface of a controller, direct features and derived features are extracted, a two-stage attack detection algorithm is designed by adopting an SPRT (Sequential Probability Ratio Test) and a Light Gradient Boosting Machine (Lightweight GBM) for attack detection, and the two-stage DDoS attack detection and defense method is applied to the software defined network. The SPRT first-level attack detection algorithm is used for quickly positioning an attack port in the early stage of an attack, the LightGBM second-level attack detection algorithm is used for specifically classifying the attack, attack defense filters attack traffic in real time by issuing a flow table rule, and a coarse-grained rule is used for quickly responding to the attack, so that the safety of a controller is protected; and the fine-grained rule is used for defending against a specific type of attack to prevent filtering of normal communication traffic, so that the security of the SDN network can be effectively protected when the DDoS attack occurs.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
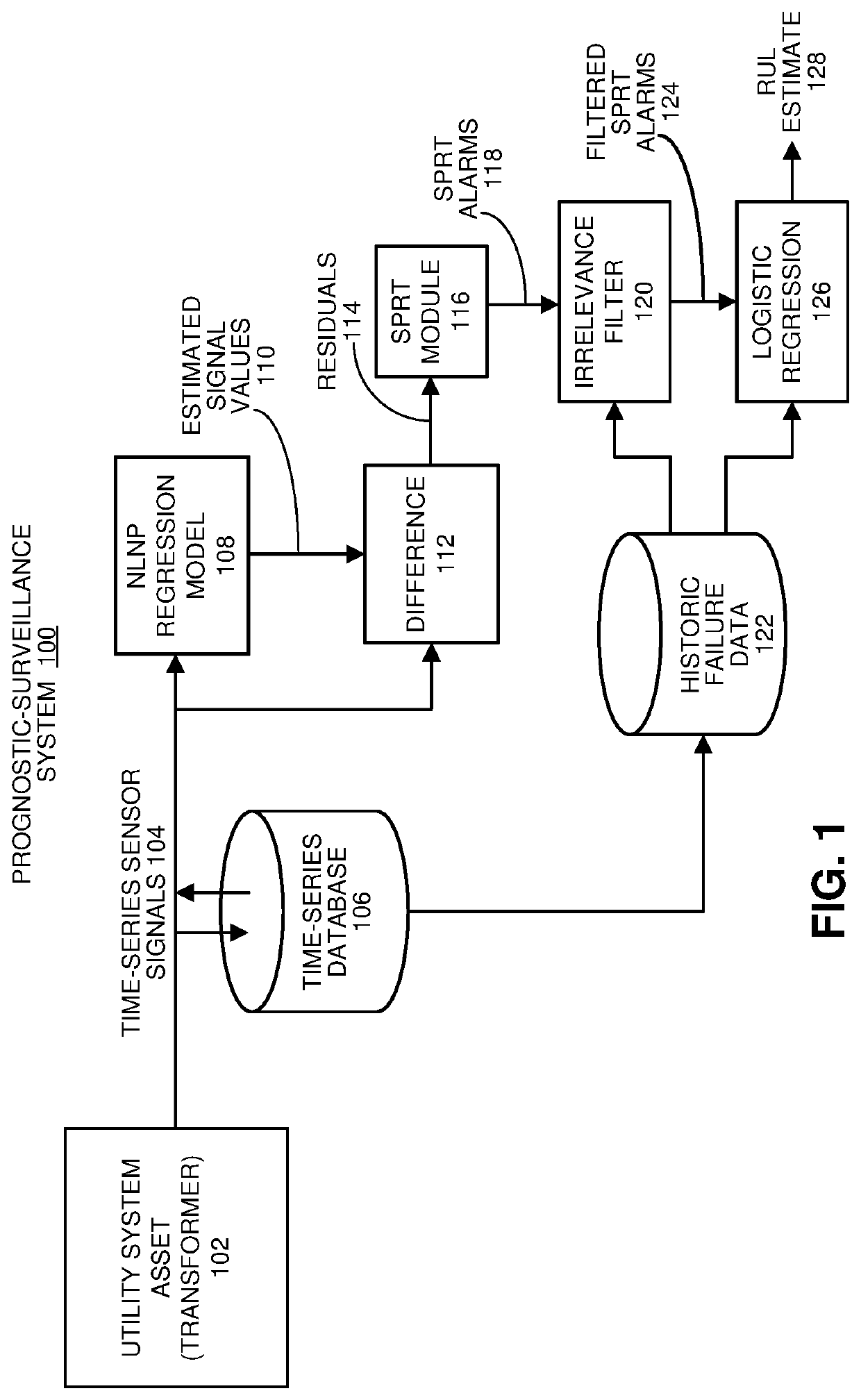
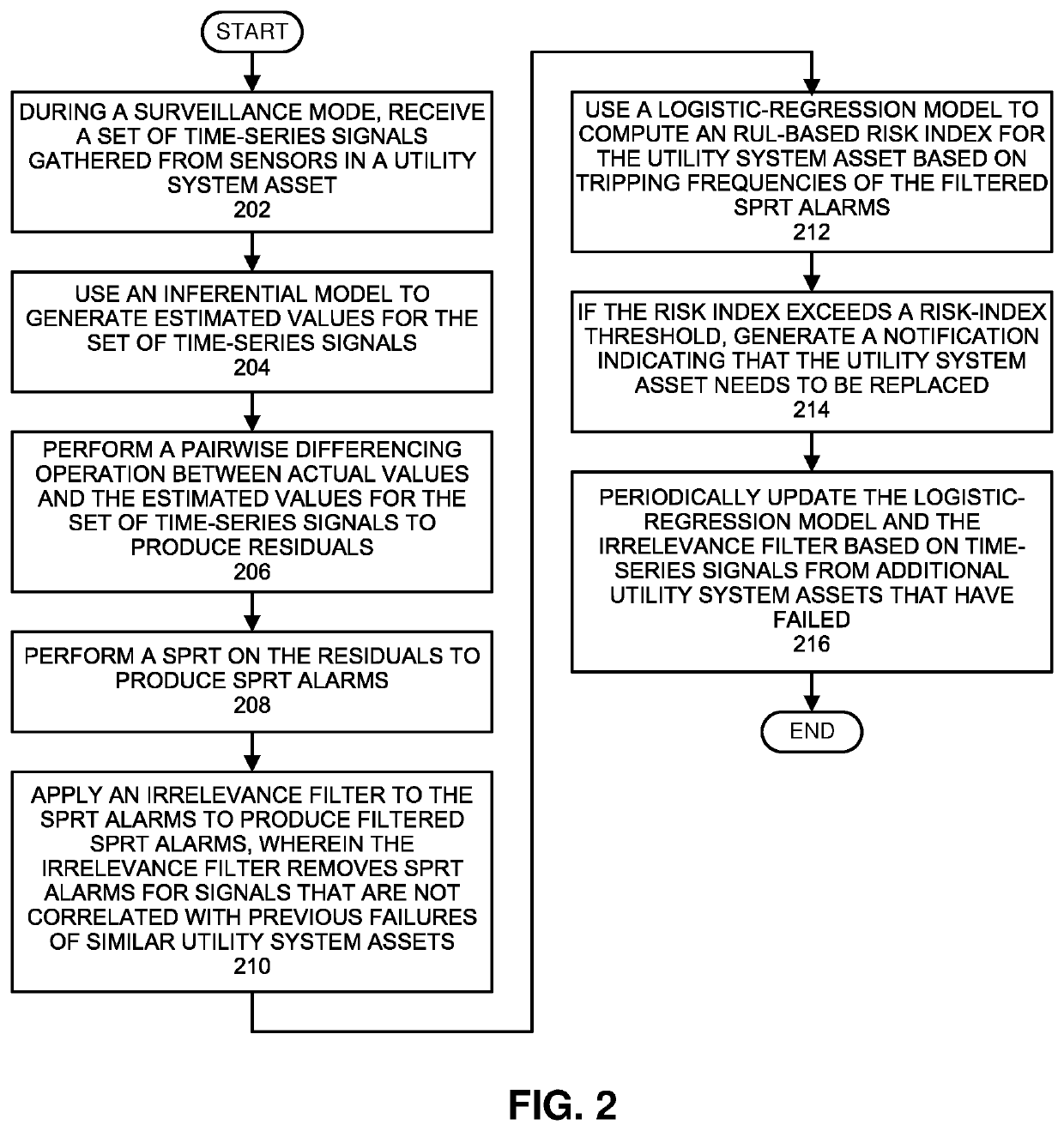
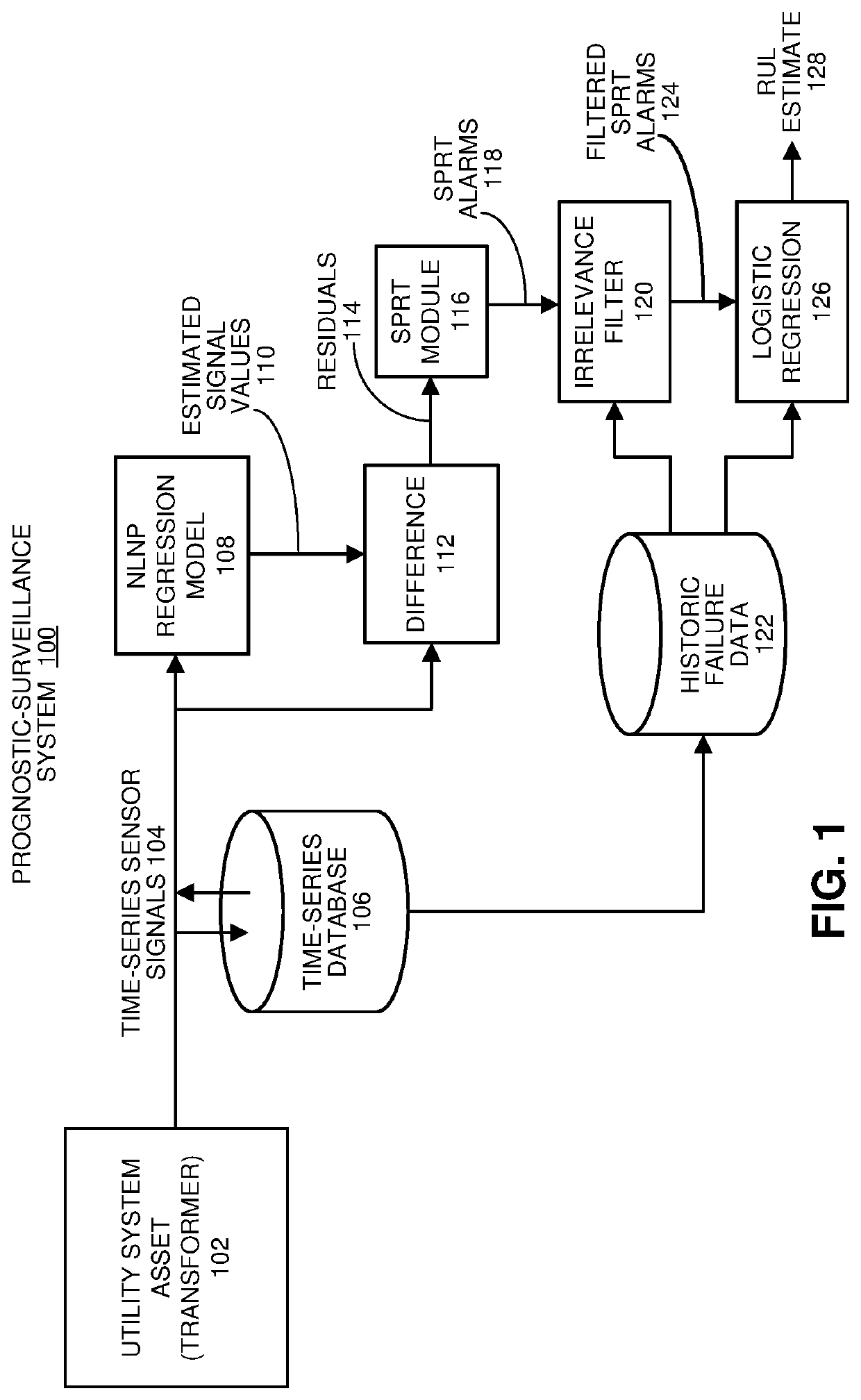
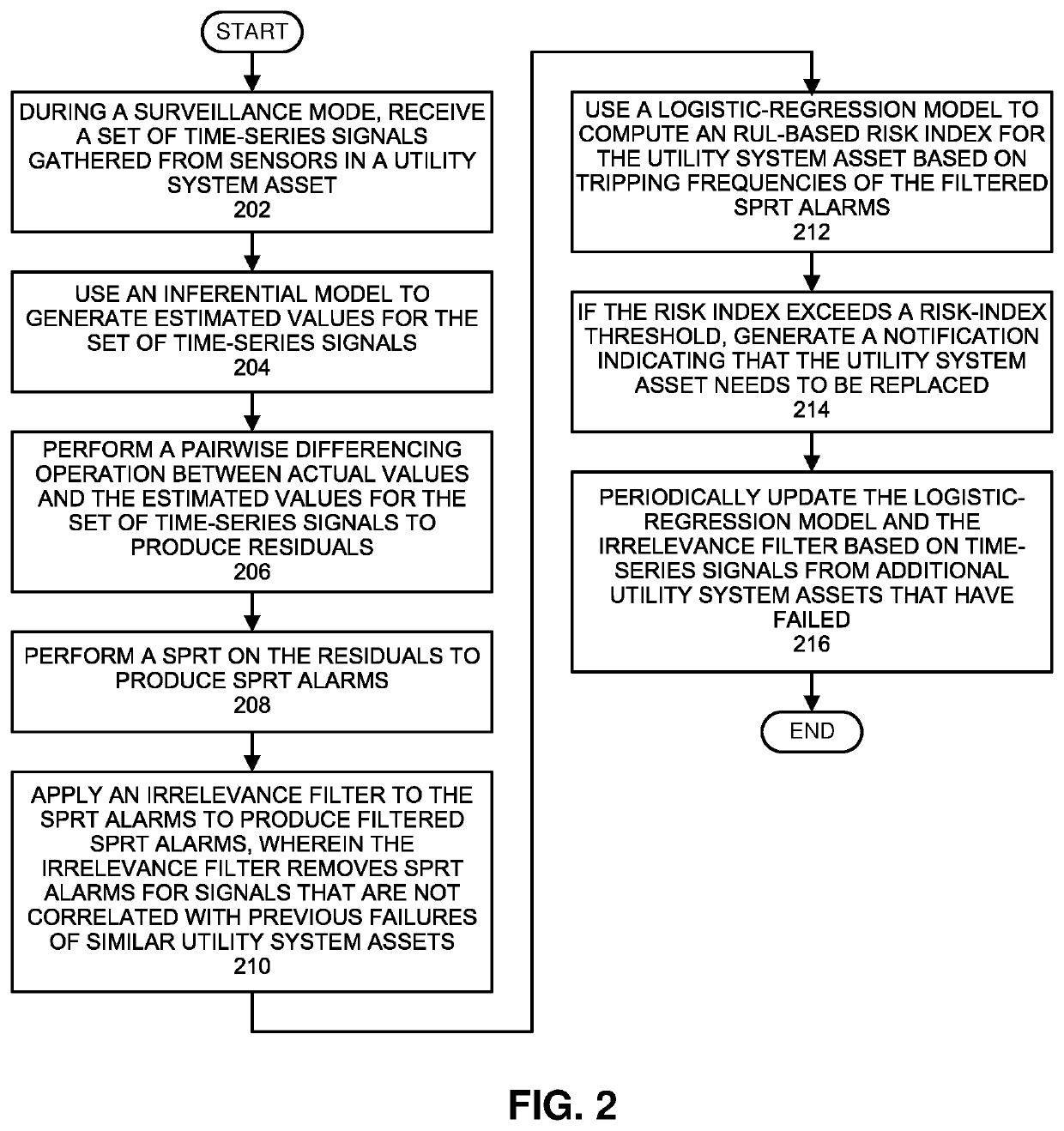
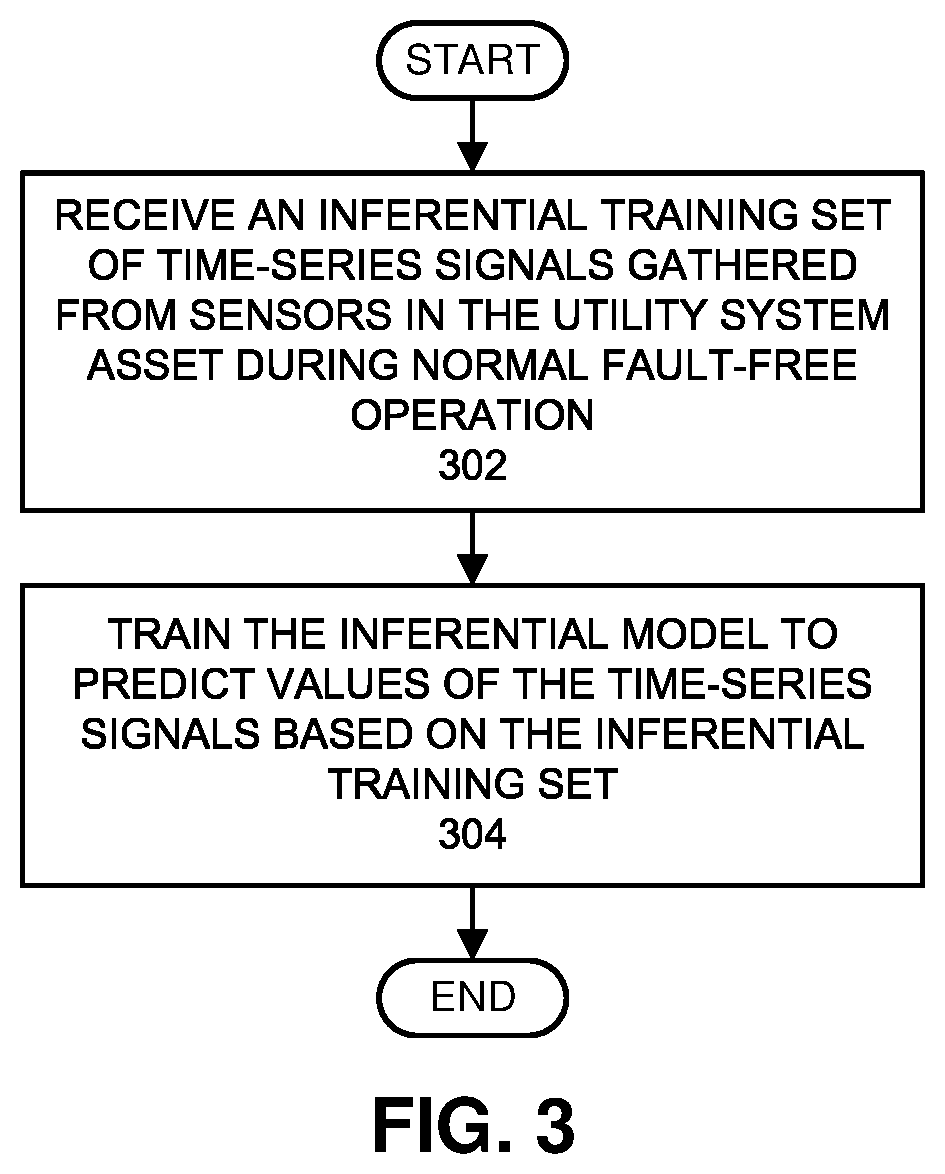
Using an irrelevance filter to facilitate efficient rul analyses for utility system assets
During operation, the system receives time-series signals gathered from sensors in a utility system asset. Next, the system uses an inferential model to generate estimated values for the time-series signals, and performs a pairwise differencing operation between actual values and the estimated values for the time-series signals to produce residuals. The system then performs a sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) on the residuals to produce SPRT alarms. Next, the system applies an irrelevance filter to the SPRT alarms to produce filtered SPRT alarms, wherein the irrelevance filter removes SPRT alarms for signals that are uncorrelated with previous failures of similar utility system assets. The system then uses a logistic-regression model to compute an RUL-based risk index for the utility system asset based on the filtered SPRT alarms. When the risk index exceeds a threshold, the system generates a notification indicating that the utility system asset needs to be replaced.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
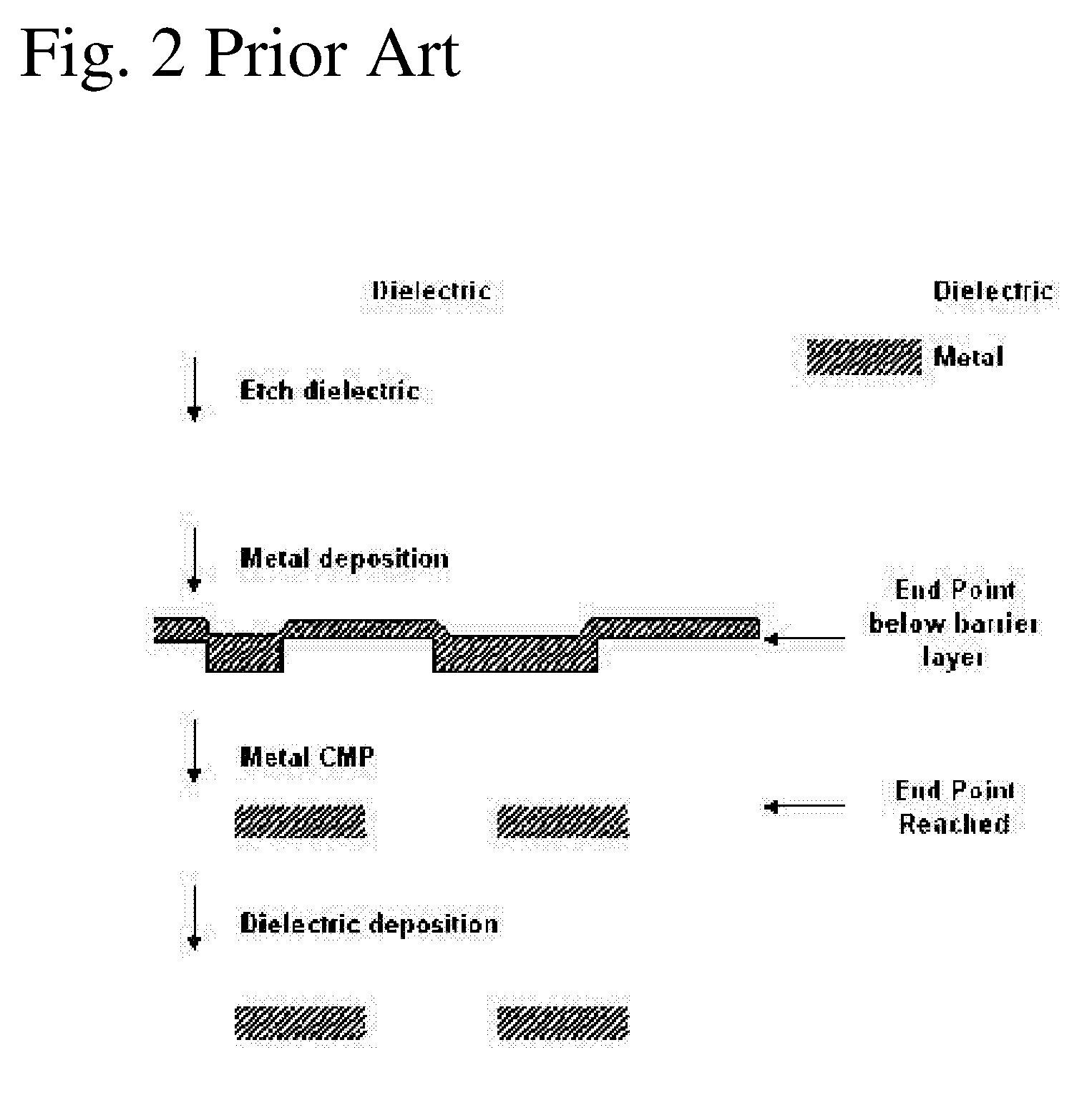
System and method for online end point detection for use in chemical mechanical planarization
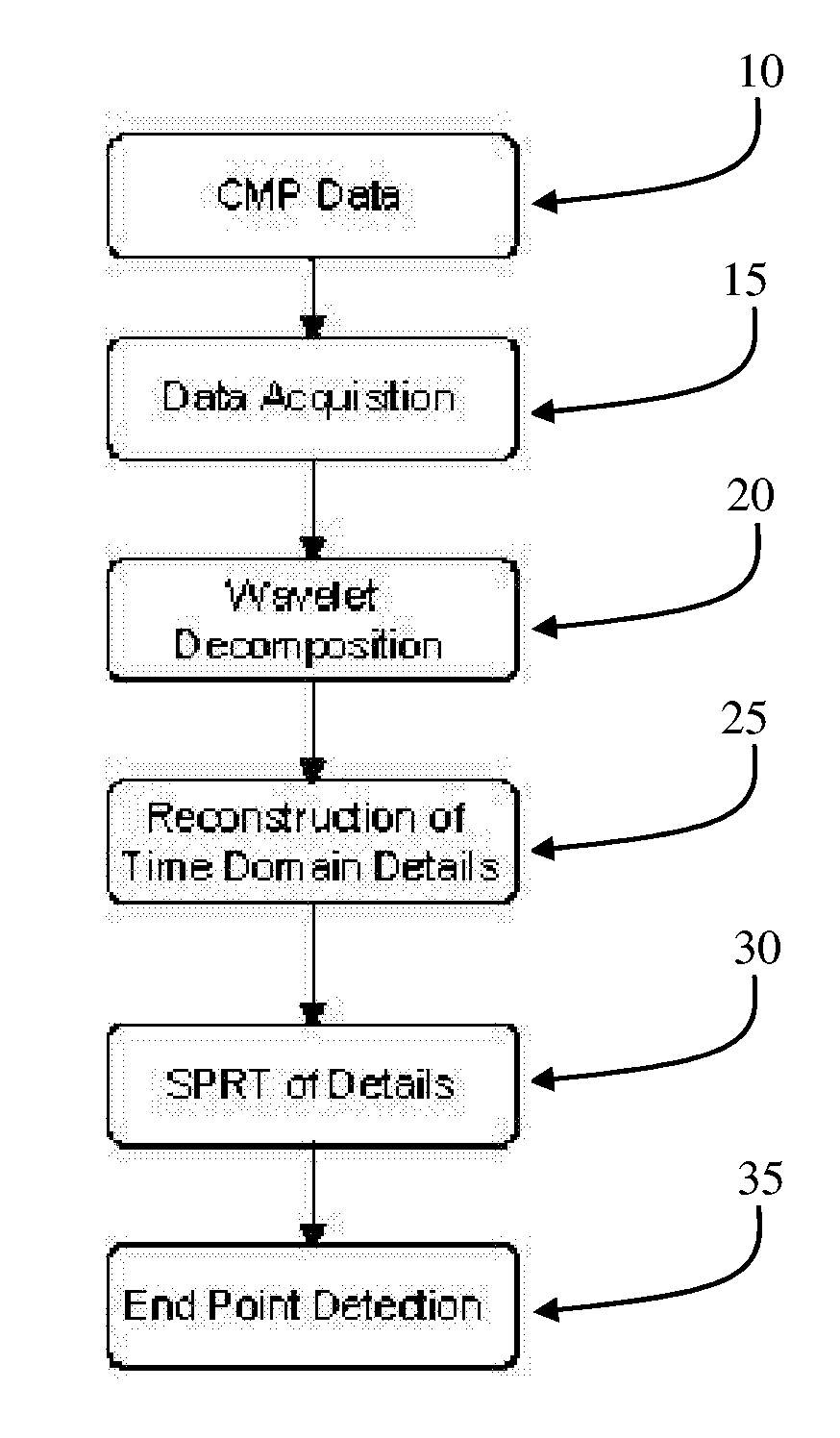
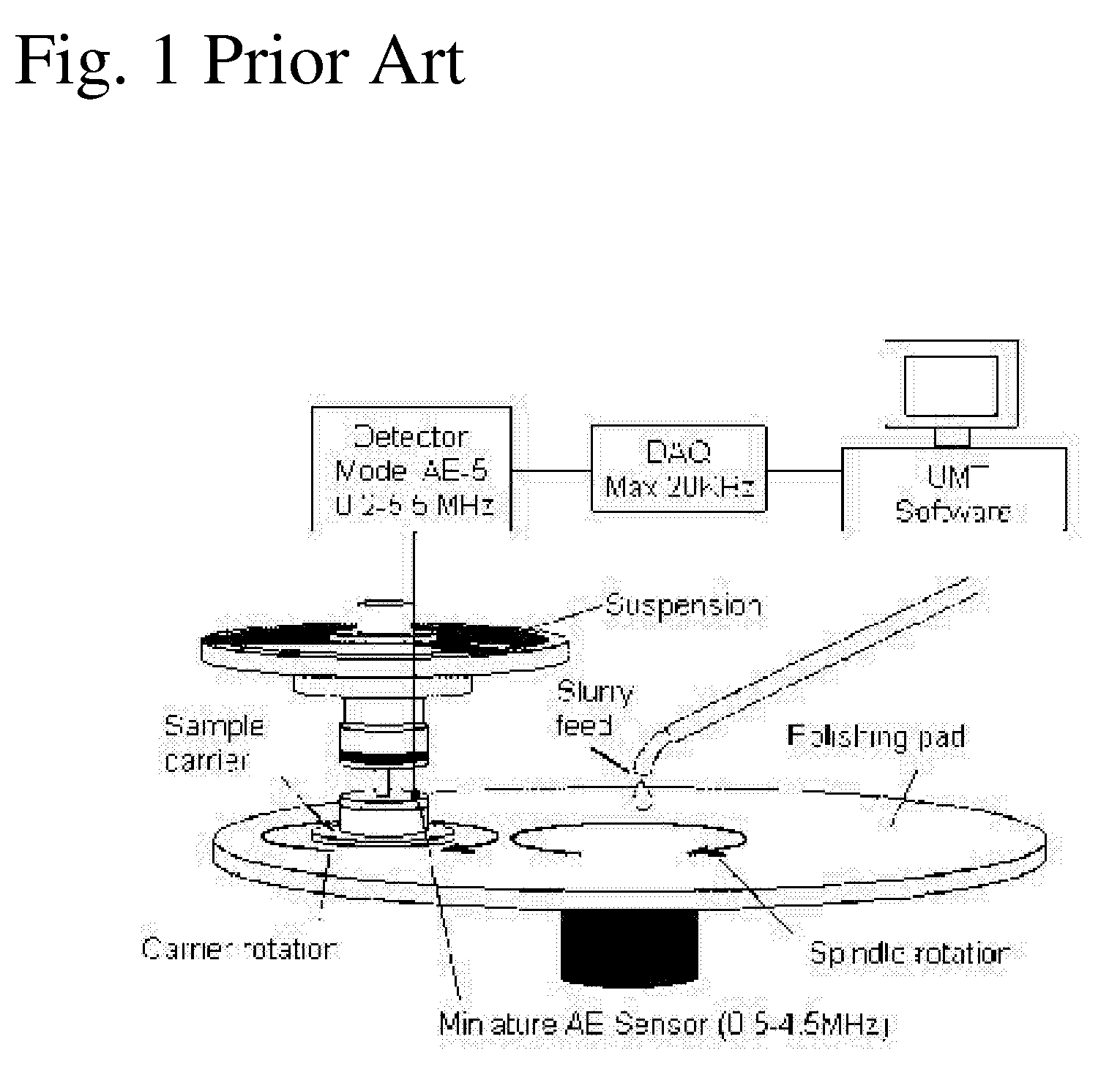
ActiveUS7406396B2Digital computer detailsLapping machinesMultiresolution analysisSequential probability ratio test
The present invention is an online methodology for end point detection for use in a chemical mechanical planarization process which is both robust and inexpensive while overcoming some of the drawbacks of the existing end point detection approaches currently known in the art. The present invention provides a system and method for identifying a significant event in a chemical mechanical planarization process including the steps of decomposing coefficient of friction data acquired from a chemical mechanical planarization process using wavelet-based multiresolution analysis, and applying a sequential probability ratio test for variance on the decomposed data to identify a significant event in the chemical mechanical planarization process.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
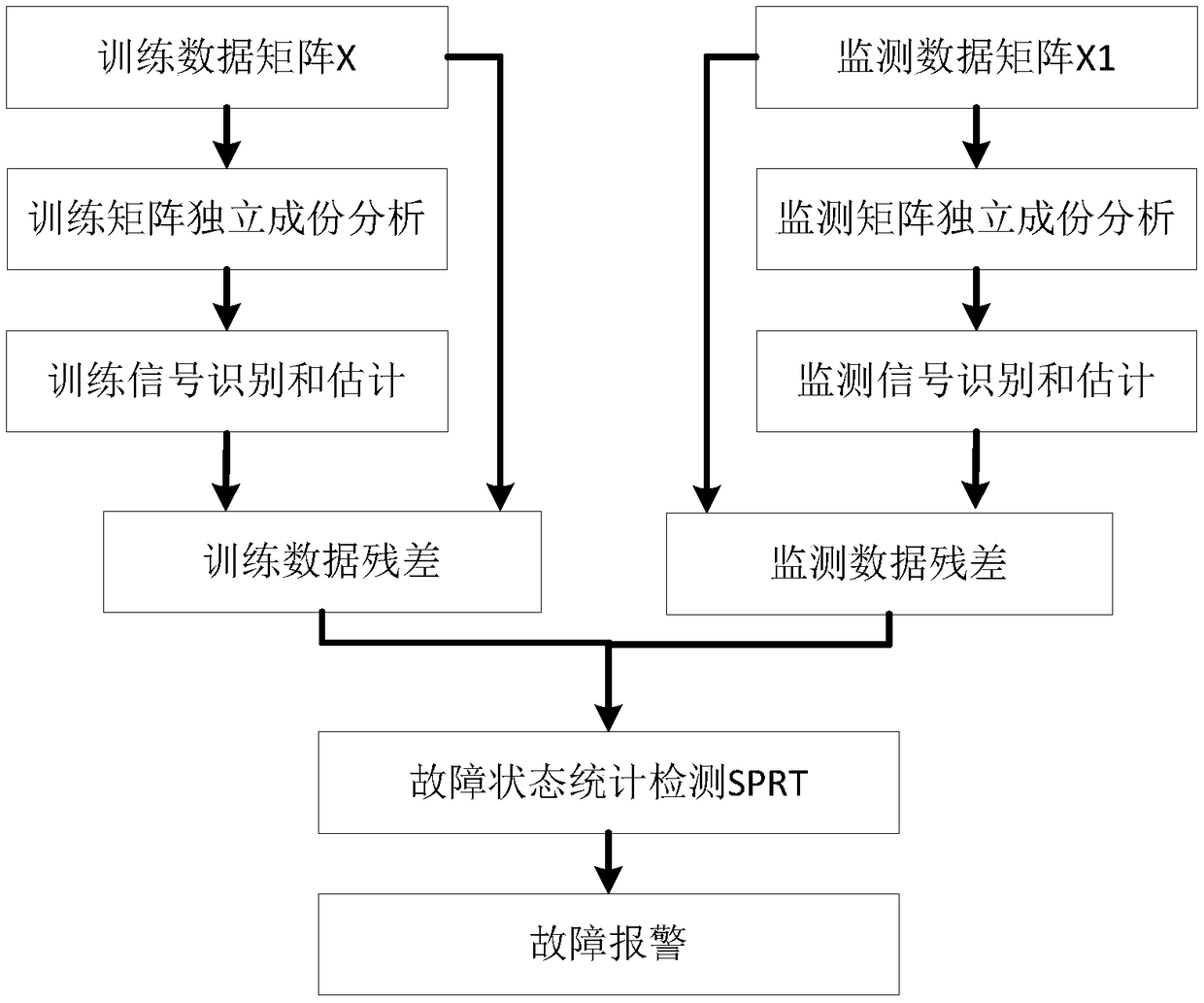
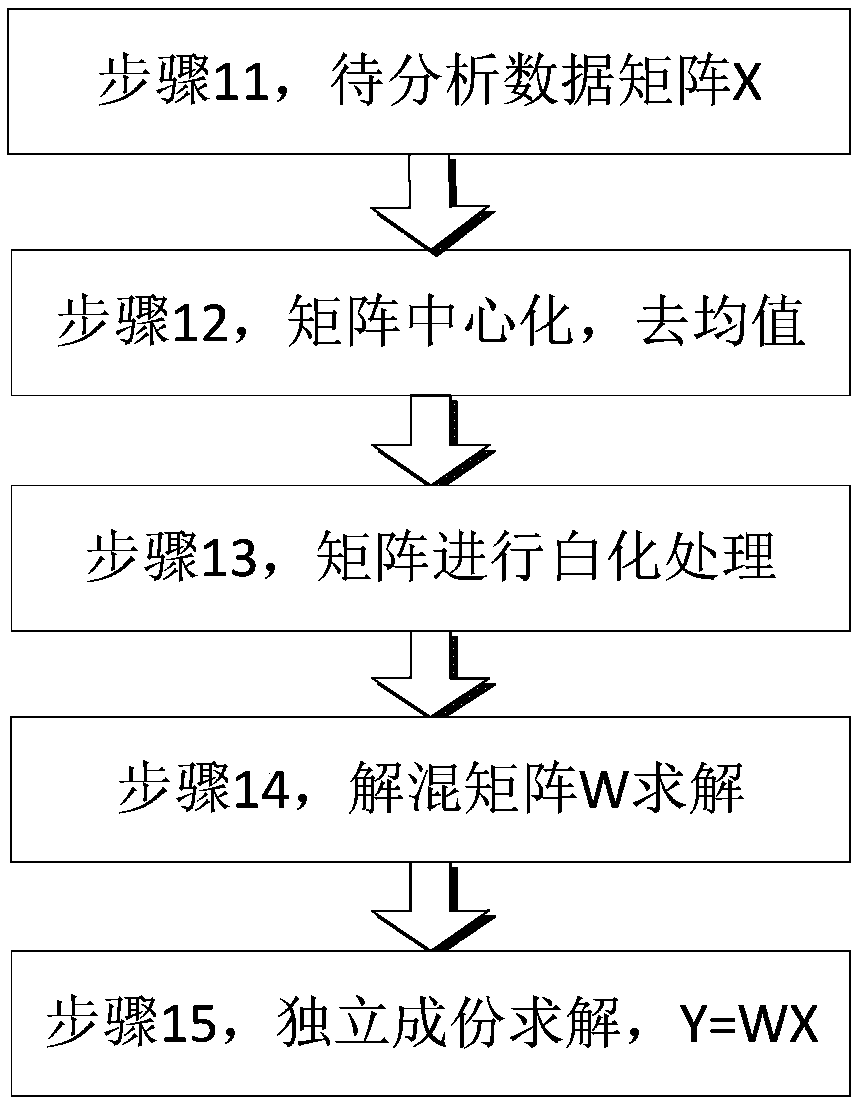
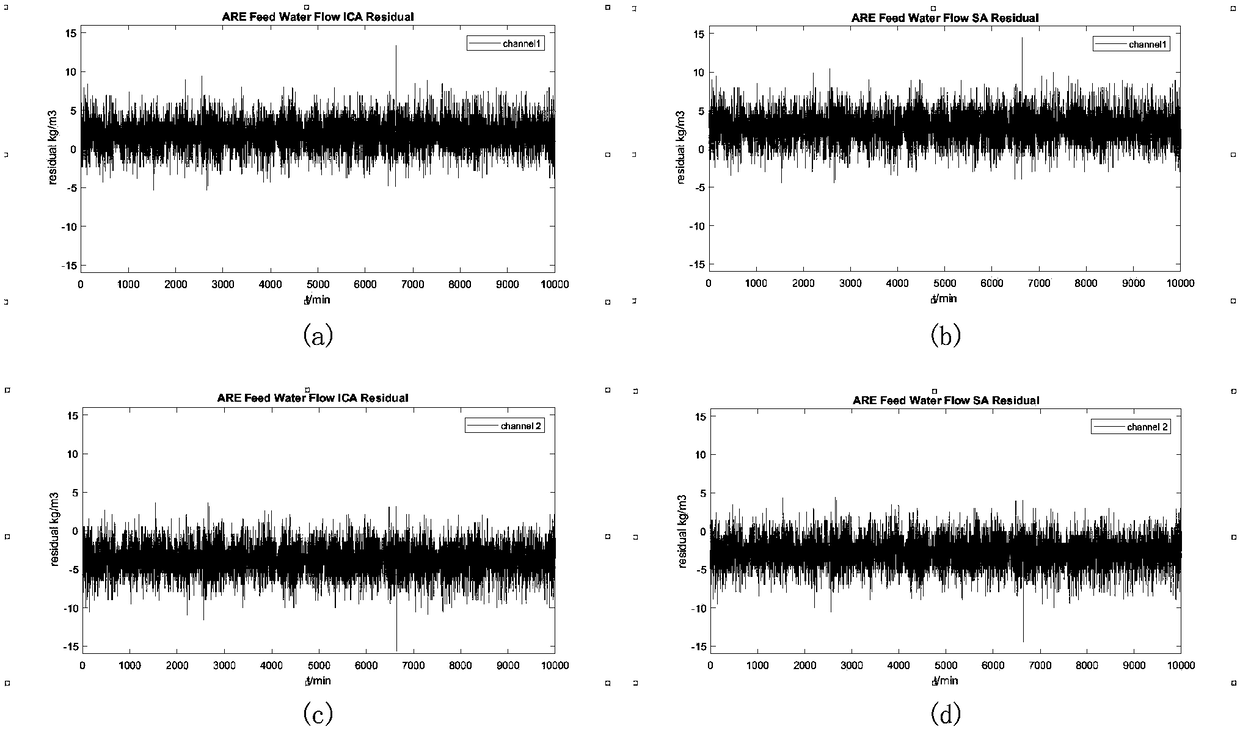
Fault detection method for redundant sensor based on ICA-SPRT (Independent Component Analysis-Sequential Probability Ratio Test)
ActiveCN108613695AEliminate System NoiseImprove detection accuracyTesting/calibration for volume flowComplex mathematical operationsIndependent component analysisSequential probability ratio test
The invention discloses a fault detection method for a redundant sensor based on an ICA-SPRT (Independent Component Analysis-Sequential Probability Ratio Test), which comprises an ICA-SPRT fault detection system, wherein the ICA-SPRT fault detection system comprises a signal independent component analysis module, a signal identification and estimation module and a fault state statistical detectionmodule; the signal independent component analysis module separates independent signals by adopting an ICA algorithm, and finds the independent signal corresponding to an original signal for restoration through the signal identification and estimation module; the fault state statistical detection module obtains fault judgment through an SPRT algorithm. The fault detection method provided by the invention for the redundant sensor based on the ICA-SPRT can effectively eliminate influences of system noise and channel noise, and still can realize accurate fault detection under the condition of lowredundancy.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
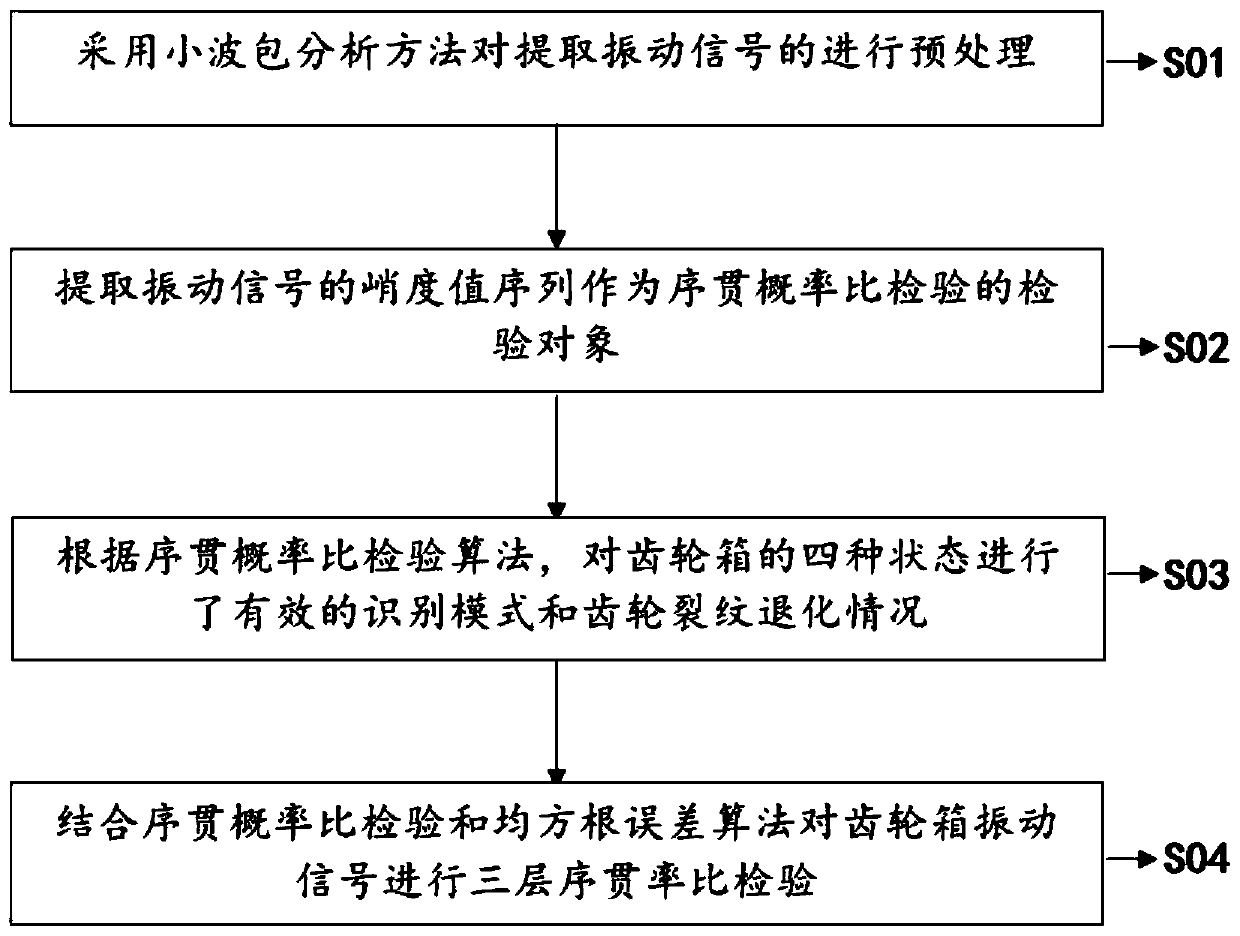
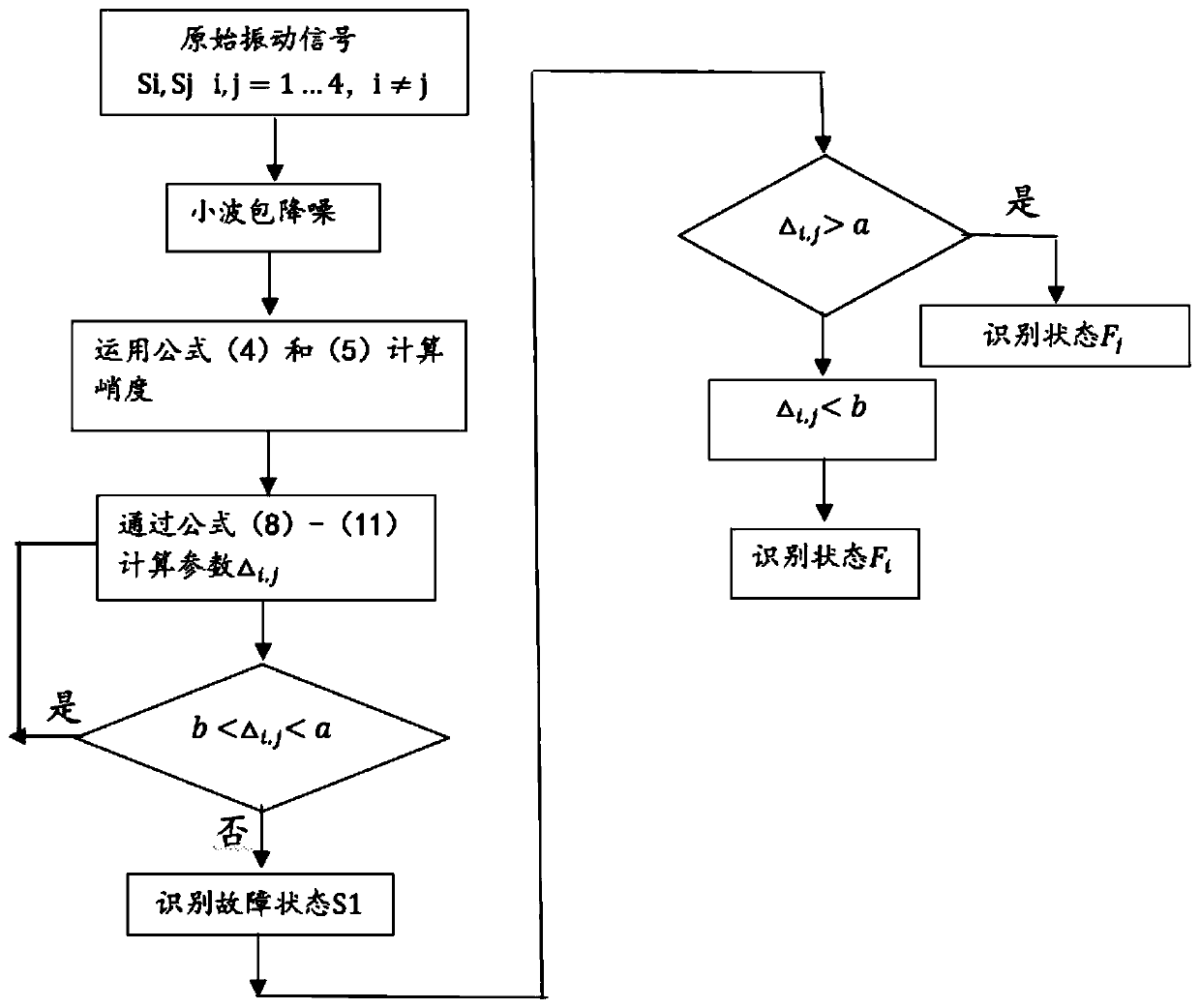
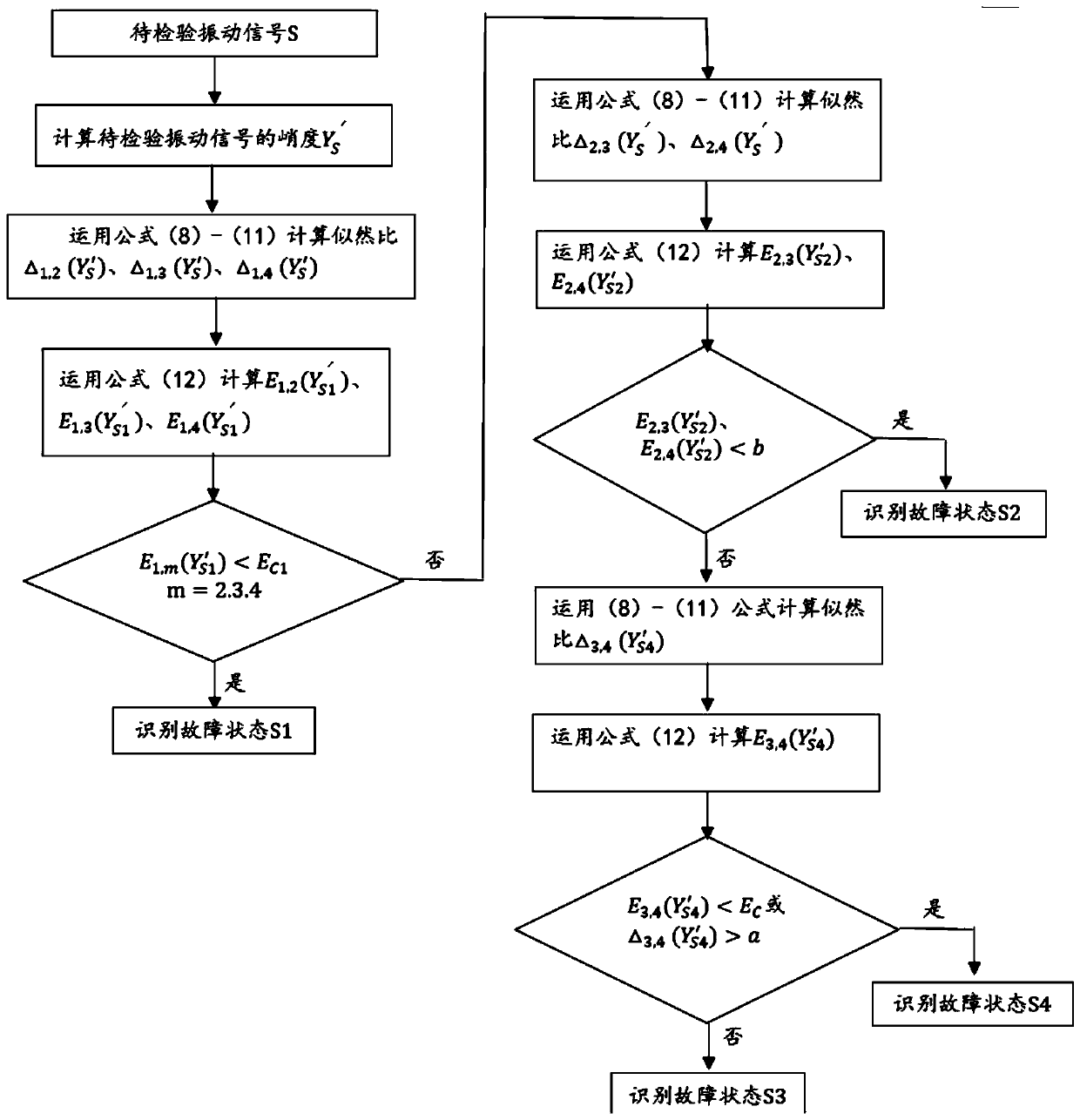
Gearbox malfunction identification method based on sequential hypothesis test
InactiveCN110160778ARealize intelligent diagnosisImprove detection efficiencyMachine part testingSequential probability ratio testTest object
The present invention discloses a gearbox malfunction identification method based on the sequential hypothesis test. The method is that an identification system carries out an adaptive intelligent query to a propagation channel with available data. Firstly, an extracted vibration signal is pretreated with the wavelet packet analysis method. Secondly, a sequence of kurtosis values of the extractedvibration signal is taken as a test object of the sequential probability ratio test. Then effective identification for the mode and gear crack degradation under four states of the gearbox is performedaccording to the sequential probability ratio test algorithm. Finally the gearbox vibration signal is subjected to the three-layer sequential ratio test by combining the sequential probability ratiotest and the root mean square error algorithm. The invention solves the problems of slow identification speed, inaccurate target identification and low identification efficiency in malfunction detection and multi-malfunction identification.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
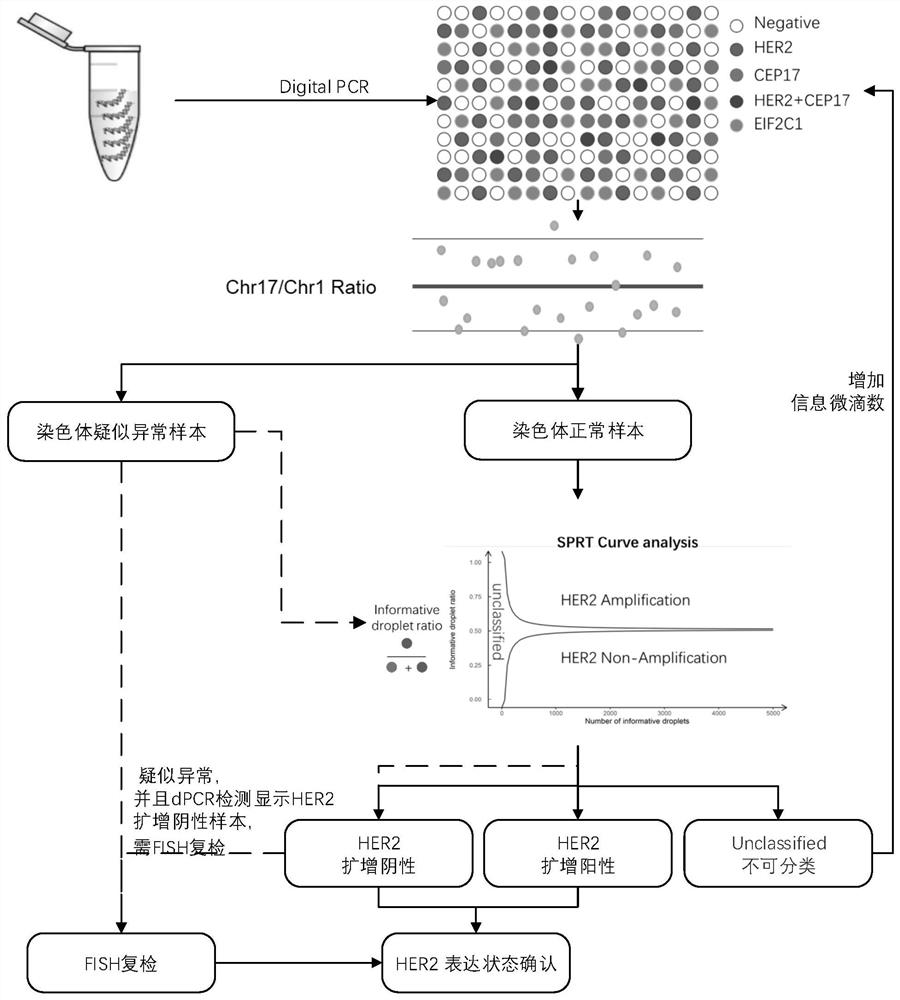
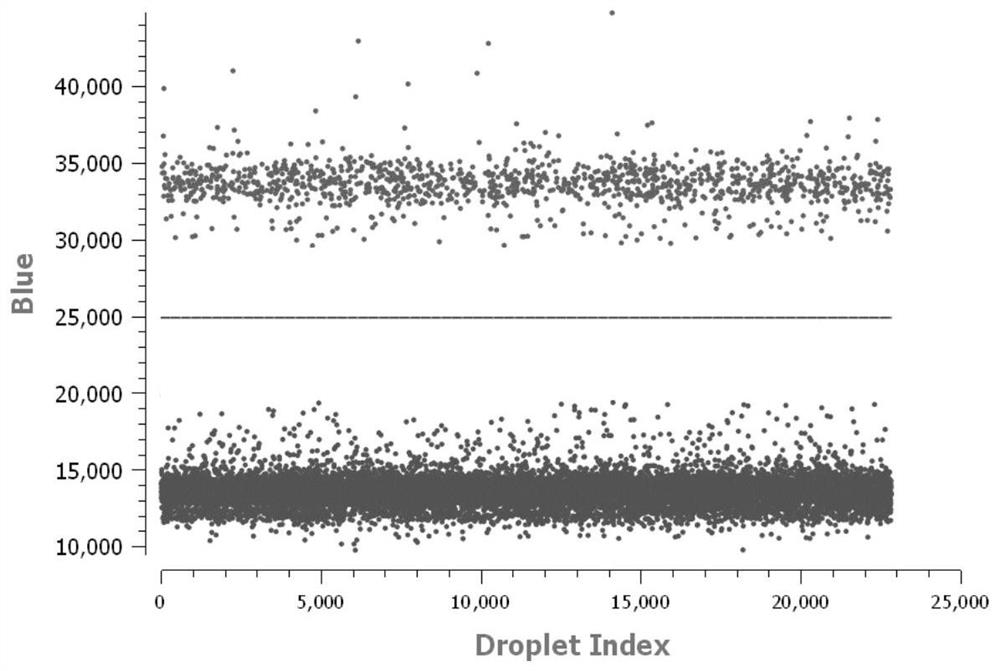
Kit for analyzing HER2 gene copy number variation by combining multiple internal references with sequential probability ratio test and use method
ActiveCN112048560AAvoid consistencyAvoid errorsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisReference genesFluorescein sodium salt
The invention relates to a kit and a method for analyzing HER2 gene copy number variation based on a digital PCR method and by combining multiple internal references with sequential probability ratiotest (SPRT). The kit comprises a digital PCR enzyme premixed solution, a primer probe mixed solution for detecting a target gene HER2 and internal reference CEP17 and EIF2C1, a fluorescein sodium saltsolution and ddH2O. By comparing the expression levels of the two reference genes, whether the 17 # chromosome where the HER2 gene is located has the conditions of polysome, monomer, centromere amplification and the like or not can be accurately and effectively judged. Besides, accurate interpretation of the HER2 gene copy number variation state can be completed through SPRT analysis, the accuracy of detection result judgment is remarkably improved, and the kit and the method can be used as a kit and a method for HER2 gene copy number variation primary detection and have the irreplaceable advantages of other methods.
Owner:北京爱普拜生物技术有限公司
Noisy monitor detection and intermittent fault isolation
InactiveUS8386849B2Digital data processing detailsNon-redundant fault processingSequential probability ratio testIntermittent fault
A method of detecting and diagnosing system faults, includes detecting the noisy status of a monitor during operations and incorporating a quantified monitor uncertainty level to support fault isolation reasoning. A sequential probability ratio test is used to statistically test the noisy status of a monitor and Shannon's entropy theory is used to quantify the uncertainty levels of the monitor to support the use of the monitor values in fault isolation.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Radiation detection method and system using the sequential probability ratio test
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Using an irrelevance filter to facilitate efficient RUL analyses for utility system assets
During operation, the system receives time-series signals gathered from sensors in a utility system asset. Next, the system uses an inferential model to generate estimated values for the time-series signals, and performs a pairwise differencing operation between actual values and the estimated values for the time-series signals to produce residuals. The system then performs a sequential probability ratio test (SPRT) on the residuals to produce SPRT alarms. Next, the system applies an irrelevance filter to the SPRT alarms to produce filtered SPRT alarms, wherein the irrelevance filter removes SPRT alarms for signals that are uncorrelated with previous failures of similar utility system assets. The system then uses a logistic-regression model to compute an RUL-based risk index for the utility system asset based on the filtered SPRT alarms. When the risk index exceeds a threshold, the system generates a notification indicating that the utility system asset needs to be replaced.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Adaptive sequential cooperative spectrum detection method
InactiveCN102006609BEasy to implementShorten detection timeTransmission monitoringWireless communicationFusion centerFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a method for cooperatively detecting spectrum holes by a plurality of subprime users in the field of cognitive radio in communication technology. The method is characterized by making a decision on the basis of sequential probability ratio test in a fusion stage and adaptively adjusting sampling points used in a perceptive stage. By the characteristics, the method can ensure the needed detection precision and minimize the detection time. The method comprises the following steps of: a. carrying out parallel sampling and obtaining a perception result according to the sampling points by all subprime users; b. fusing one perception result of the subprime users by a fusion center; c. if the fused perception result is enough, making the decision; or else, returning back to the step b to continue to fuse the perception result of the subprime users; and d. adaptively adjusting the sampling points, if the detection is not stopped, returning back to the step a to carry out next detection.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com