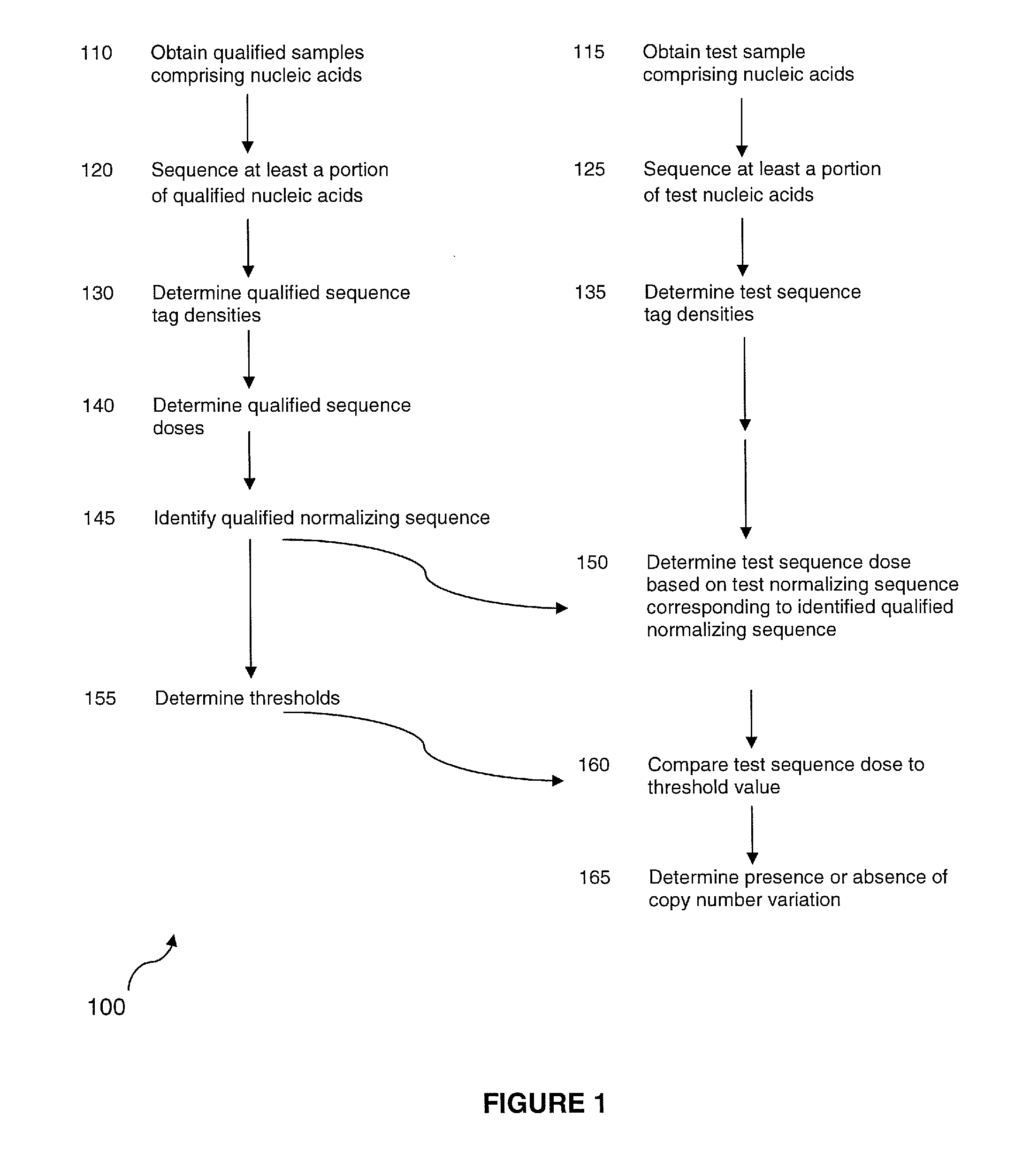
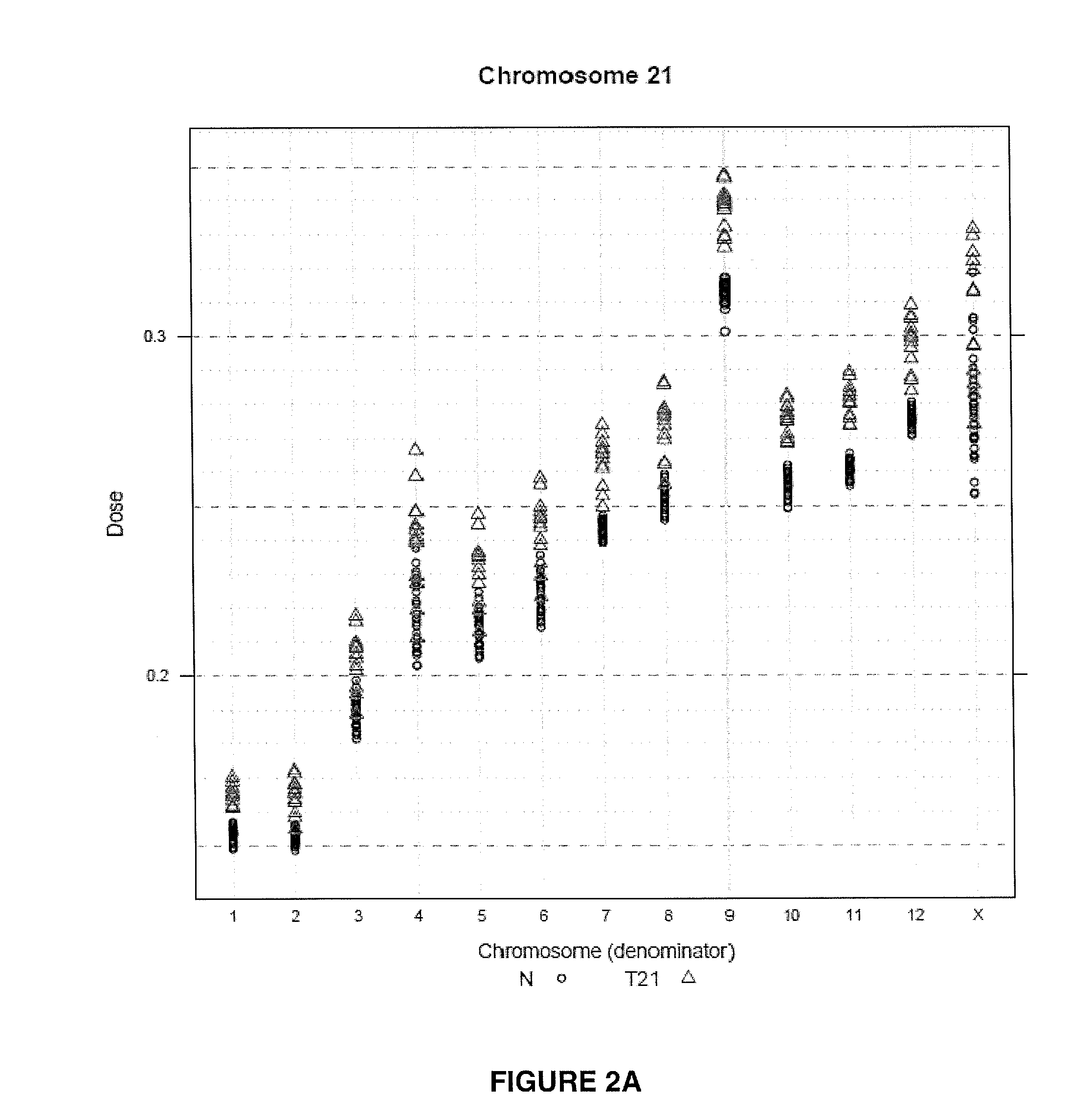
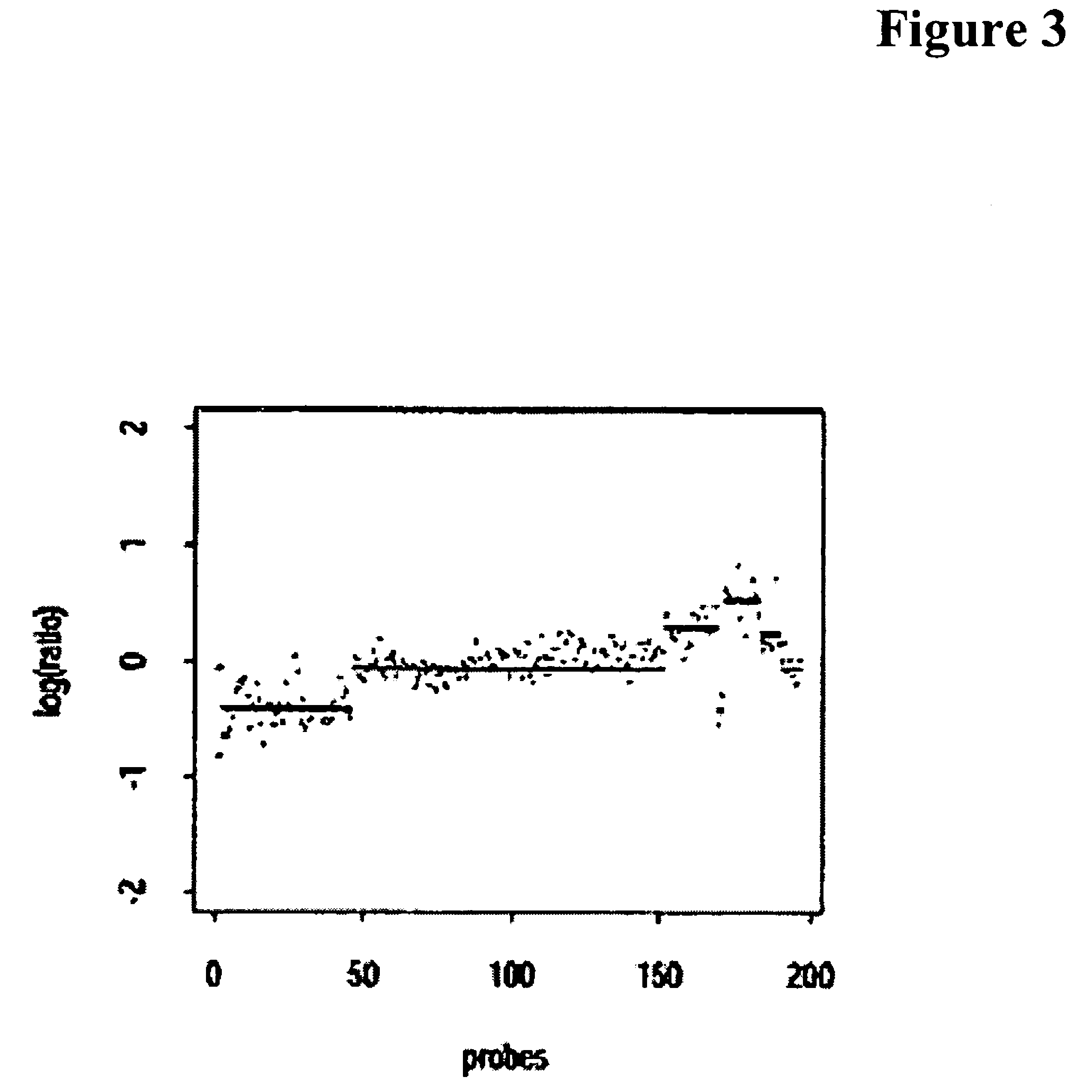
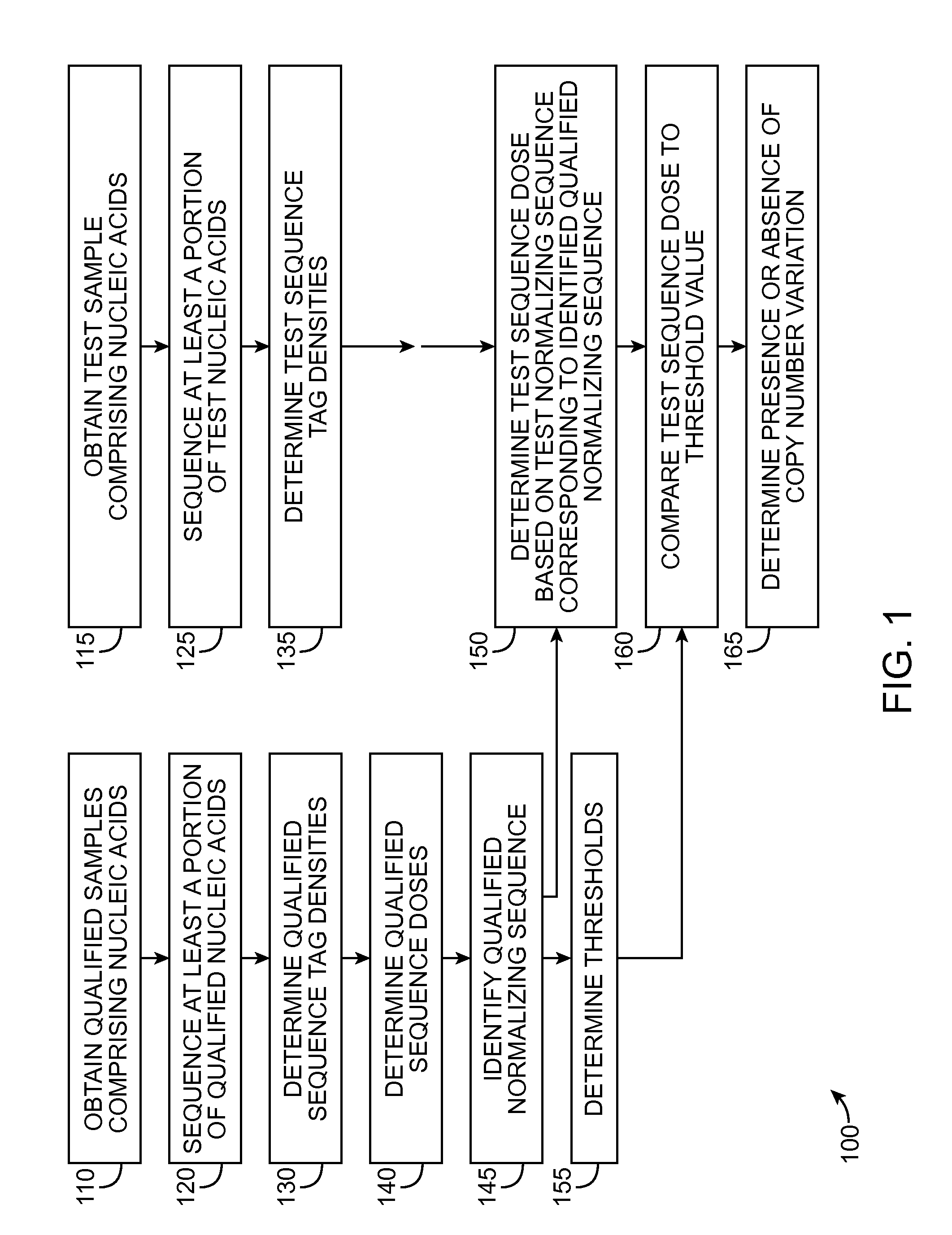
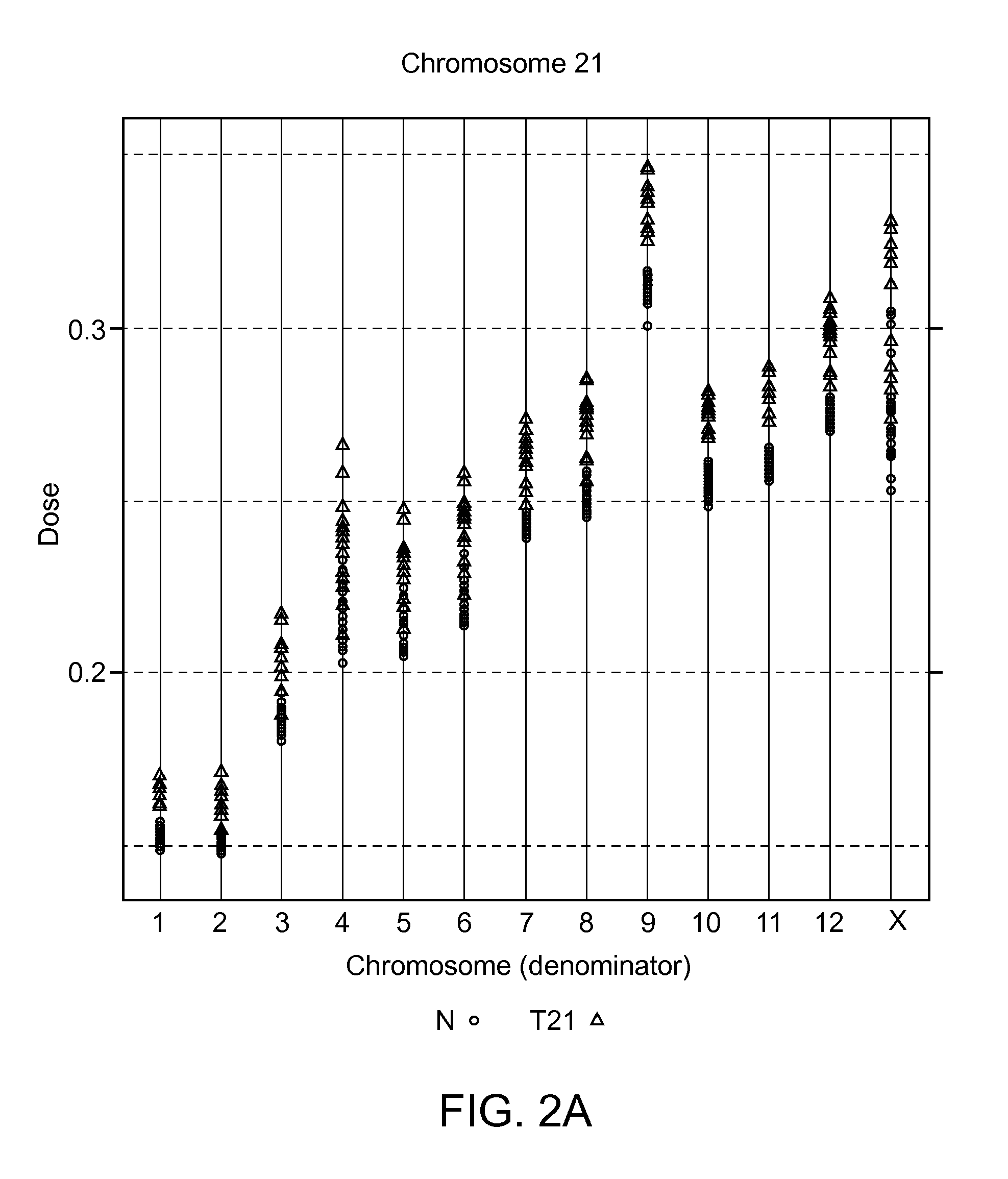
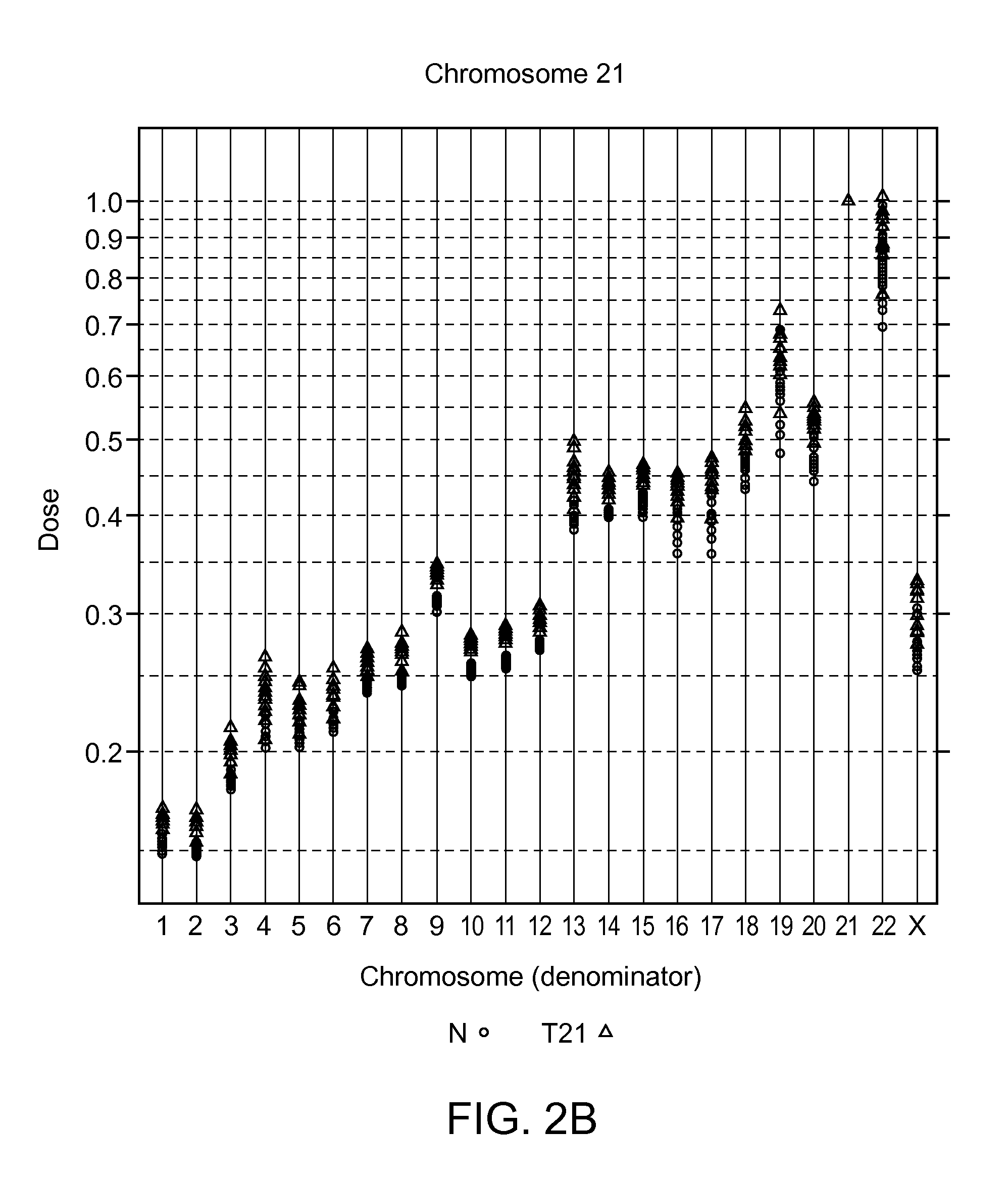
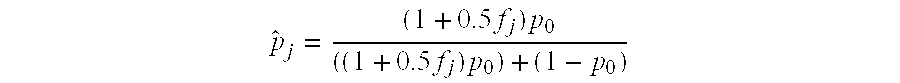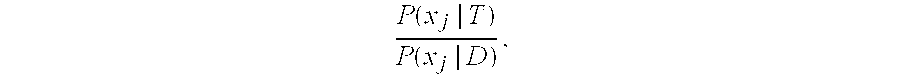Patents
Literature
507 results about "Copy-number variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
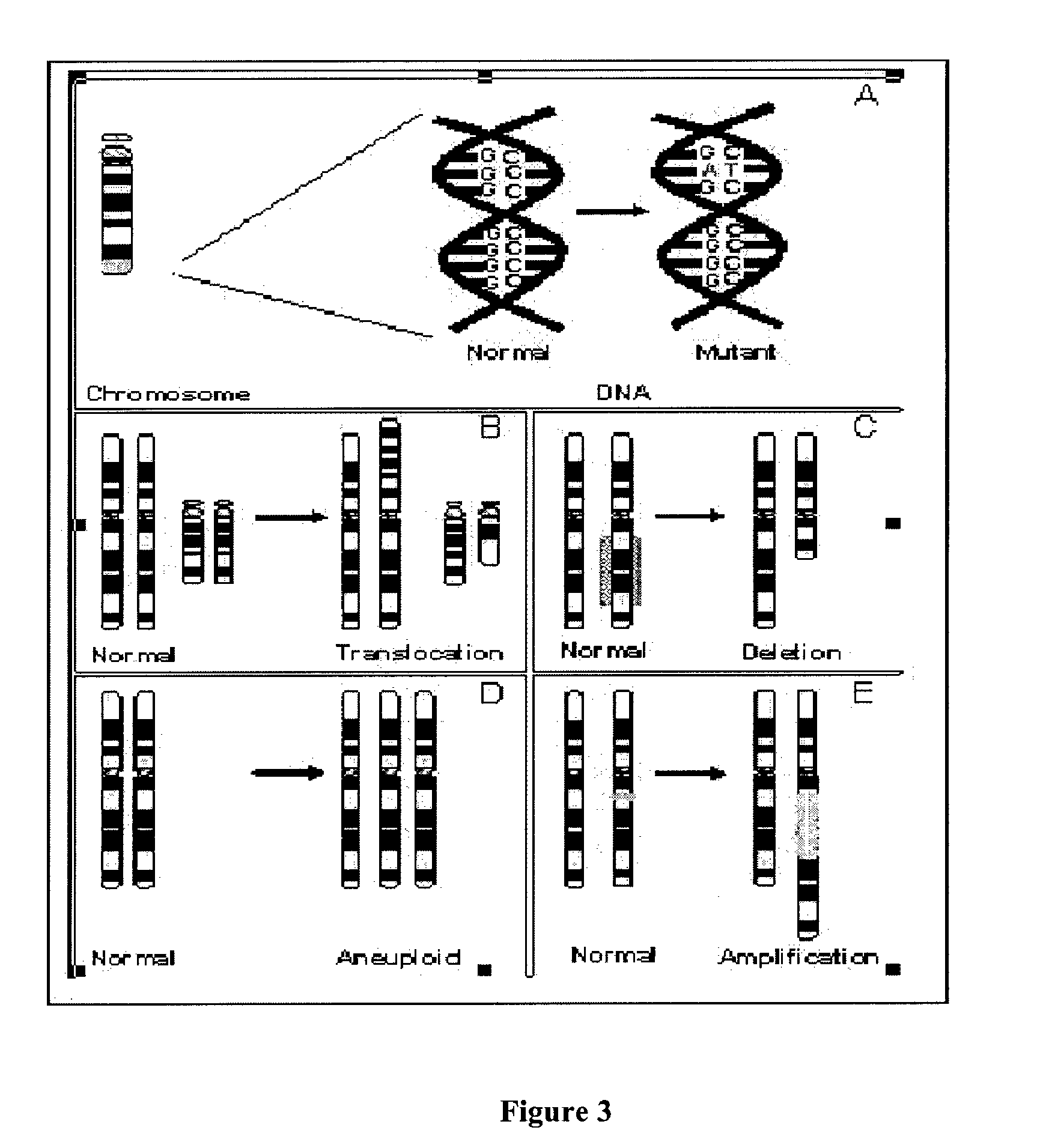
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals in the human population. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. However, note that although modern genomics research is mostly focused on human genomes, copy number variations also occur in a variety of other organisms including E. coli and S. cerevisiae. Recent research indicates that approximately two thirds of the entire human genome is composed of repeats and 4.8–9.5% of the human genome can be classified as copy number variations. In mammals, copy number variations play an important role in generating necessary variation in the population as well as disease phenotype.
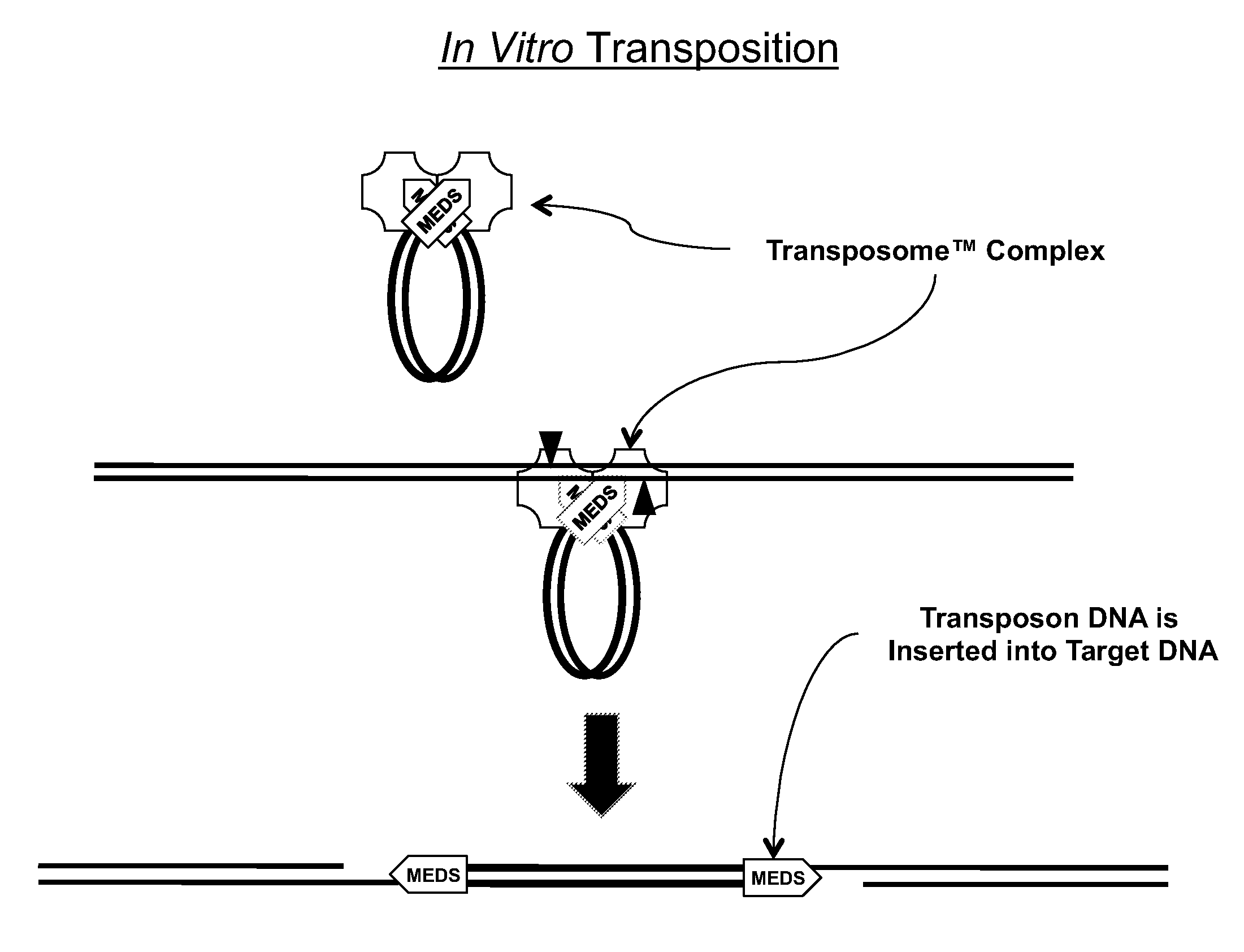
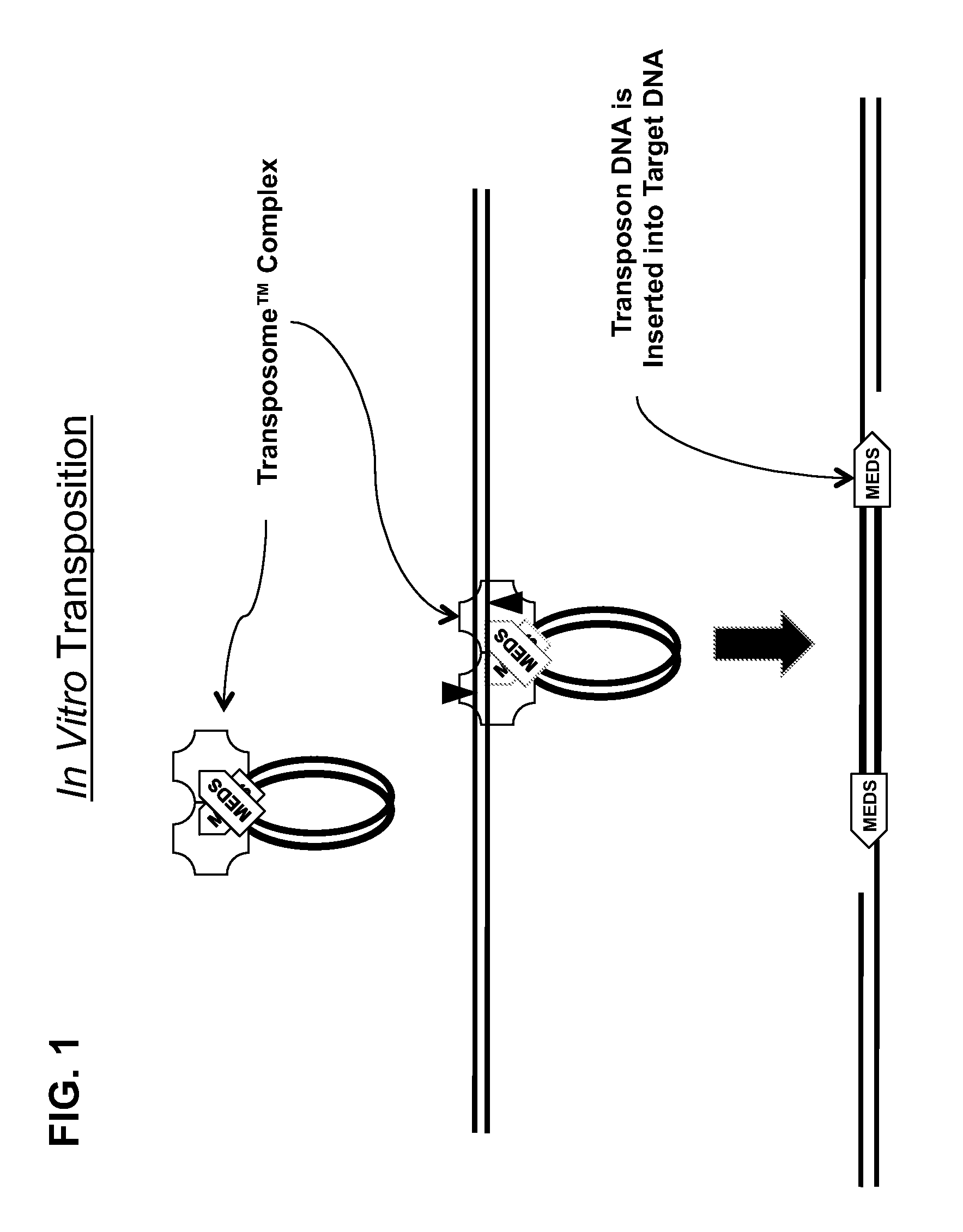
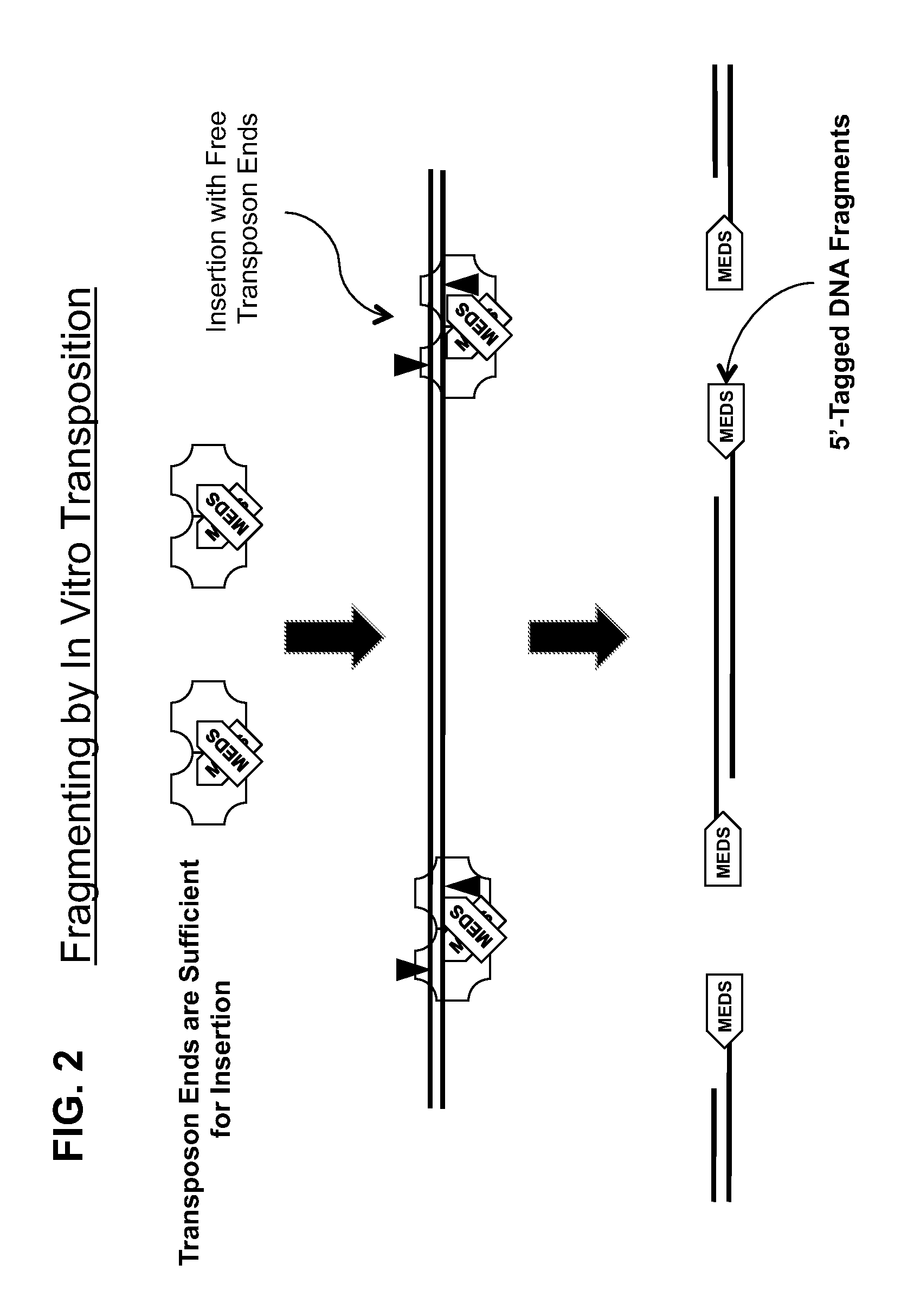
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
ActiveUS20100120098A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic sequencingPolymerase L
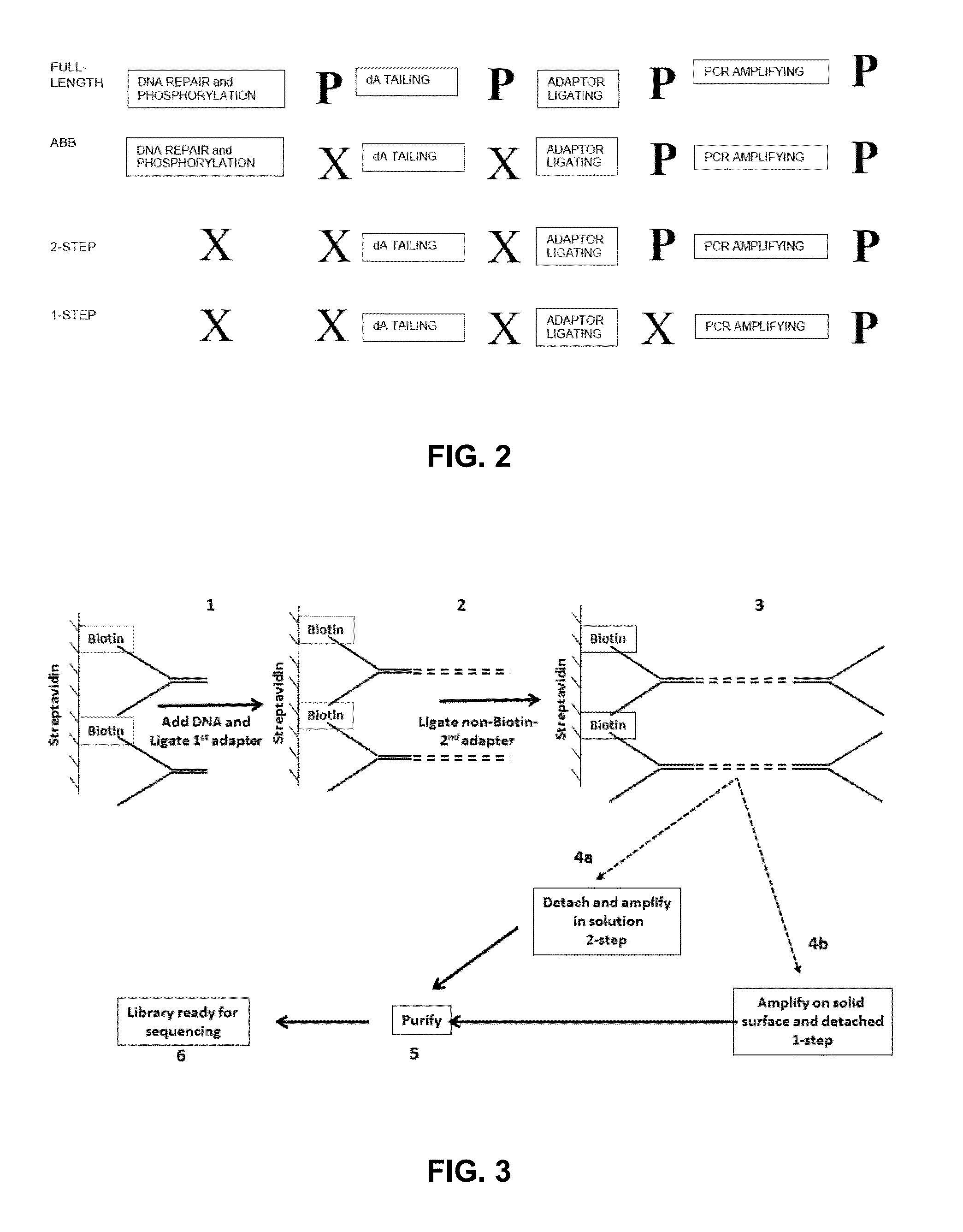
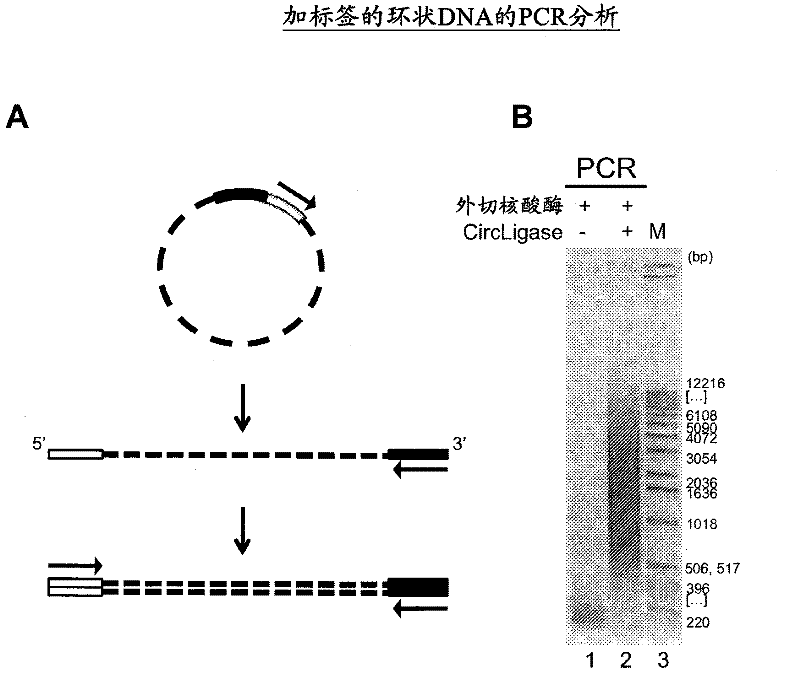
The present invention provides methods, compositions and kits for using a transposase and a transposon end for generating extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, then using a DNA polymerase for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged single-stranded DNA fragments without performing a PCR amplification reaction, wherein the first tag on the 5′-ends exhibits the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally, an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second tag on the 3′-ends exhibits a different sequence from the sequence exhibited by the first tag. The method is useful for generating 5′- and 3′-tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes, including processes for metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and comparative genomic sequencing (CGS), including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called “next-generation sequencing.)
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Method and apparatus for determining copy number variation using digital PCR
ActiveUS20090239308A1Easy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsConfidence intervalStatistical Confidence
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
Evaluating Genetic Disorders
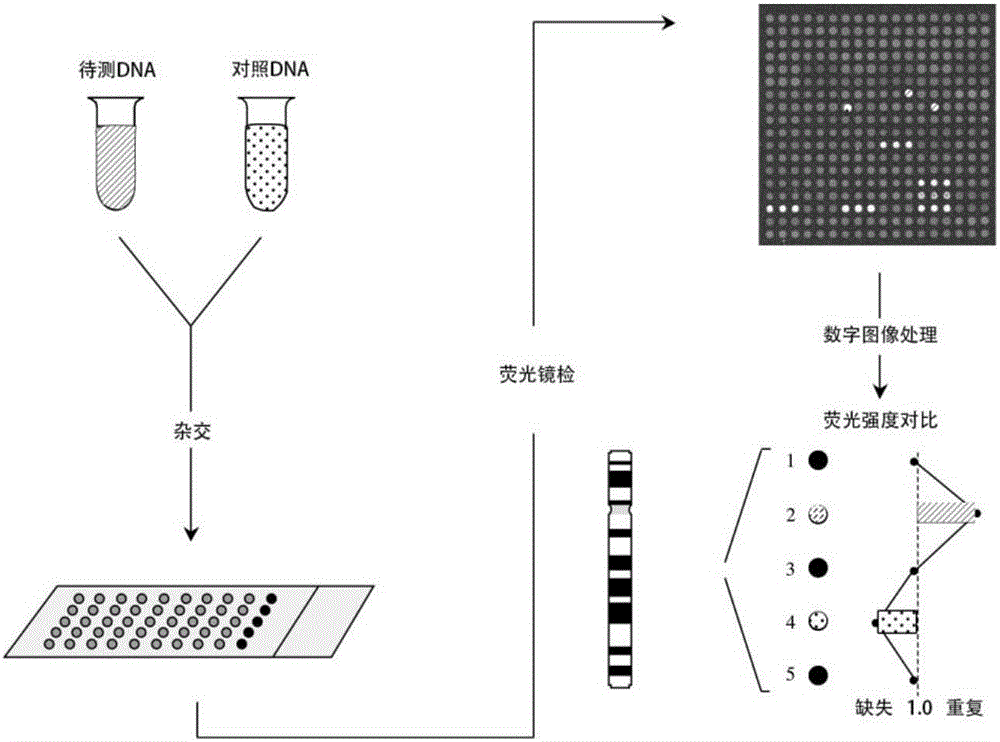
ActiveUS20070259351A1Microbiological testing/measurementProteomicsGeneticsArray-Based Comparative Genomic Hybridization
The present invention relates to genetic analysis and evaluation utilizing copy-number variants or polymorphisms. The methods utilize array comparative genomic hybridization and PCR assays to identify the significance of copy number variations in a subject or subject group.
Owner:POPULATION BIO INC
Ligation-based detection of genetic variants
InactiveUS20120034603A1Eliminate needElimination contentMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsOligonucleotide
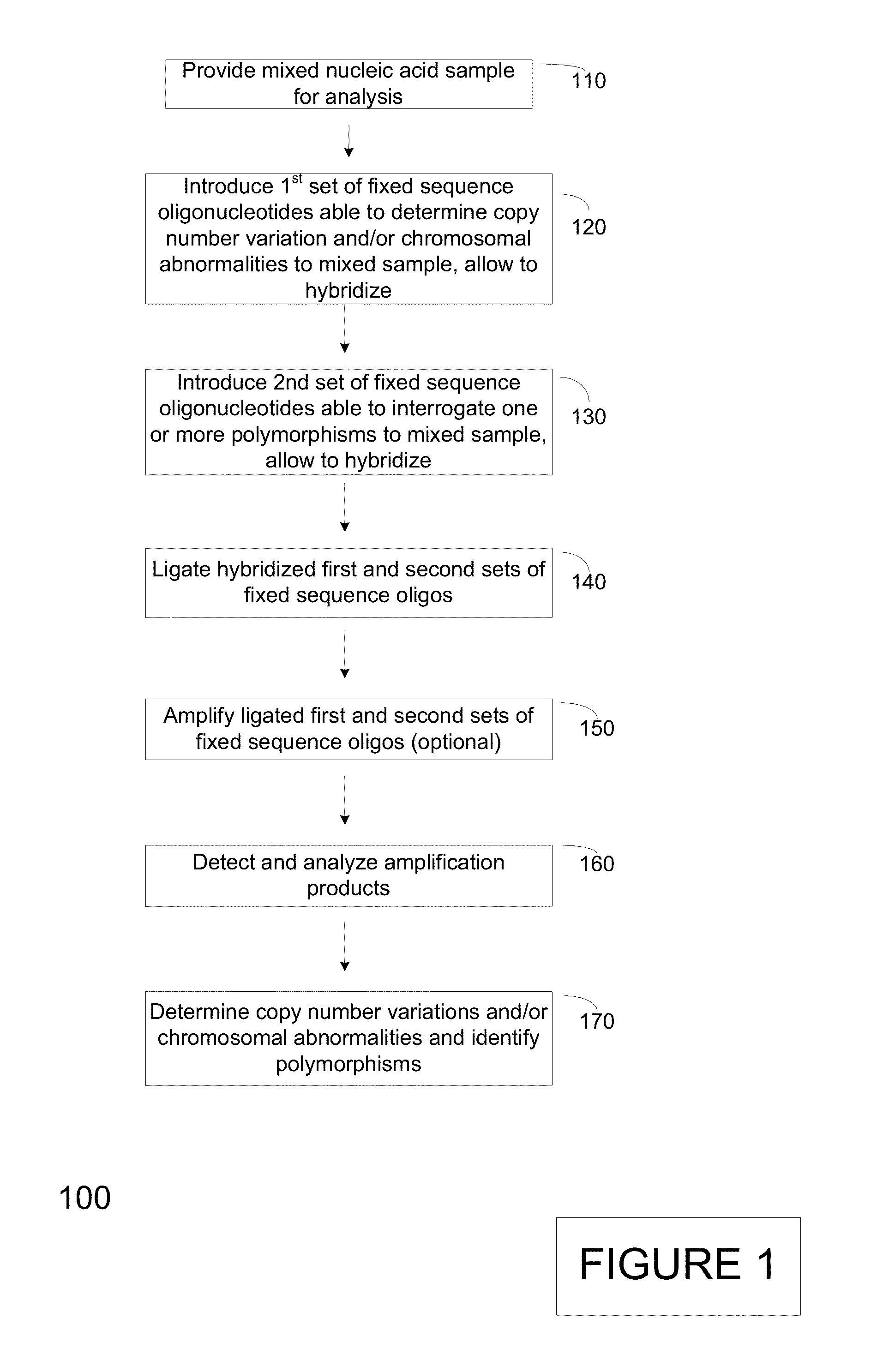
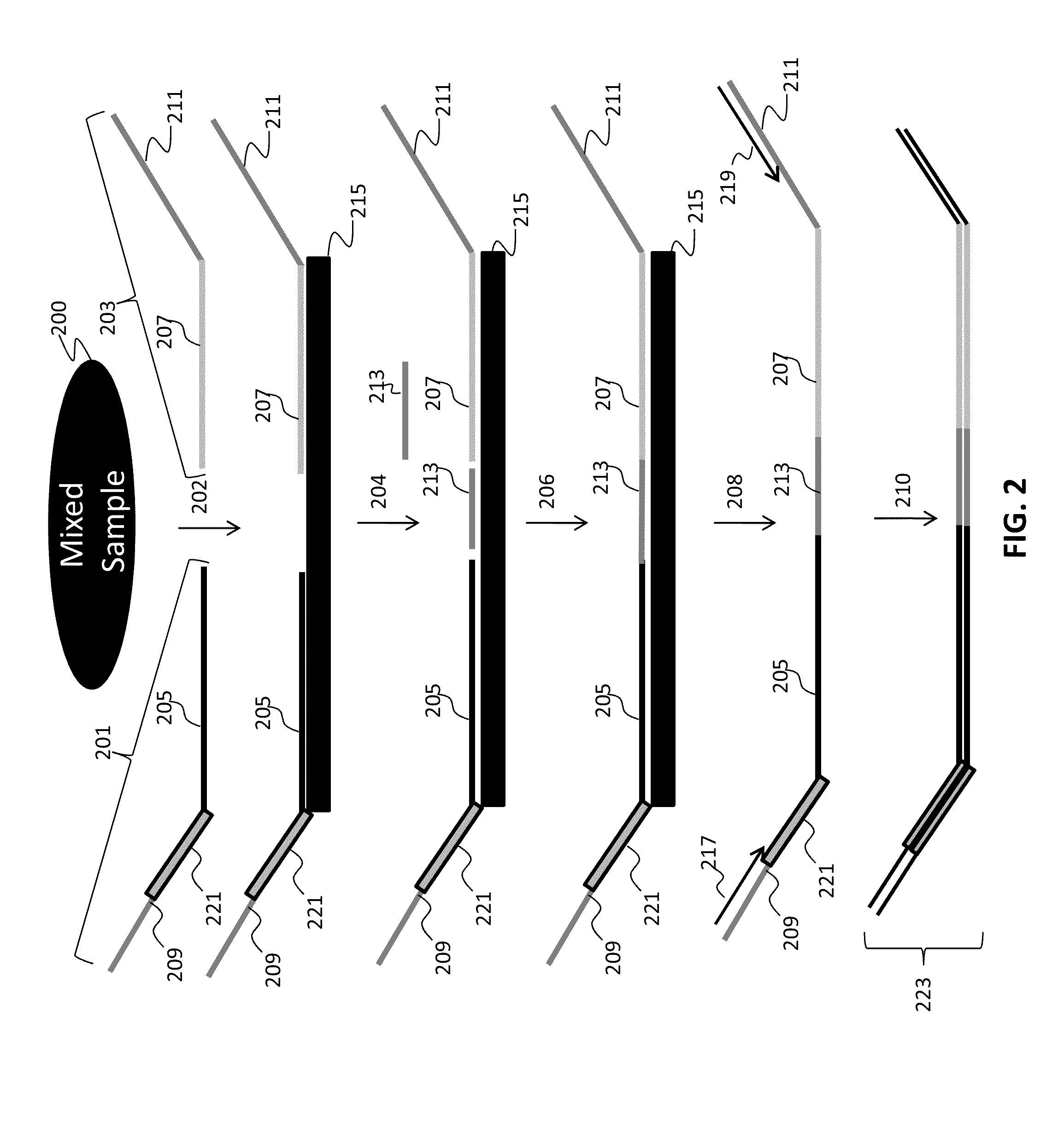
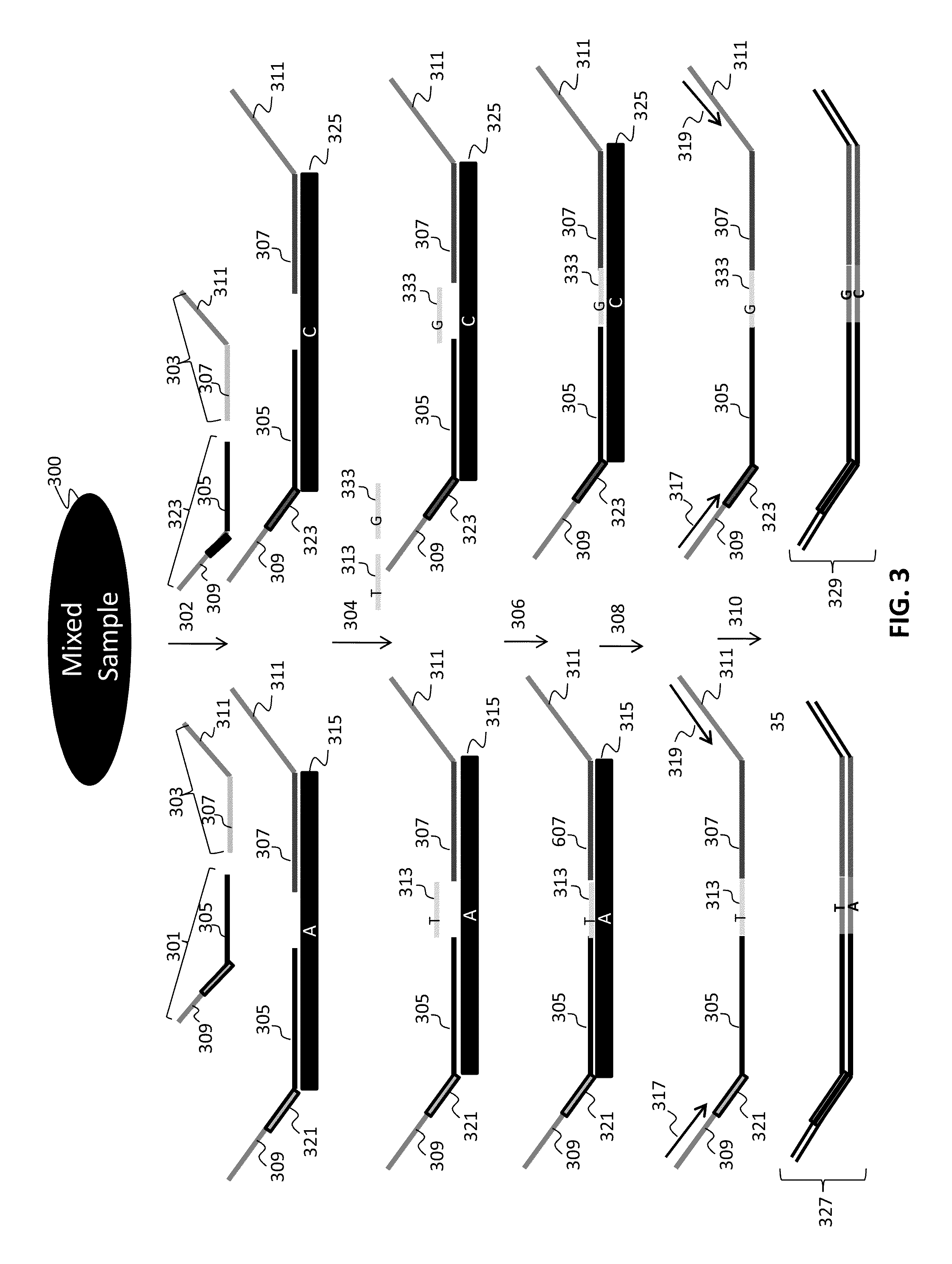
The present invention provides assays systems and methods for detection of genetic variants in a sample, including copy number variation and single nucleotide polymorphisms. The invention preferably employs the technique of tandem ligation, i.e. the ligation of two or more fixed sequence oligonucleotides and one or more bridging oligonucleotides complementary to a region between the fixed sequence oligonucleotides.
Owner:TANDEM DIAGNOSTICS
Systems and methods to detect copy number variation
InactiveUS20120046877A1Correction biasMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsData fileWorkstation
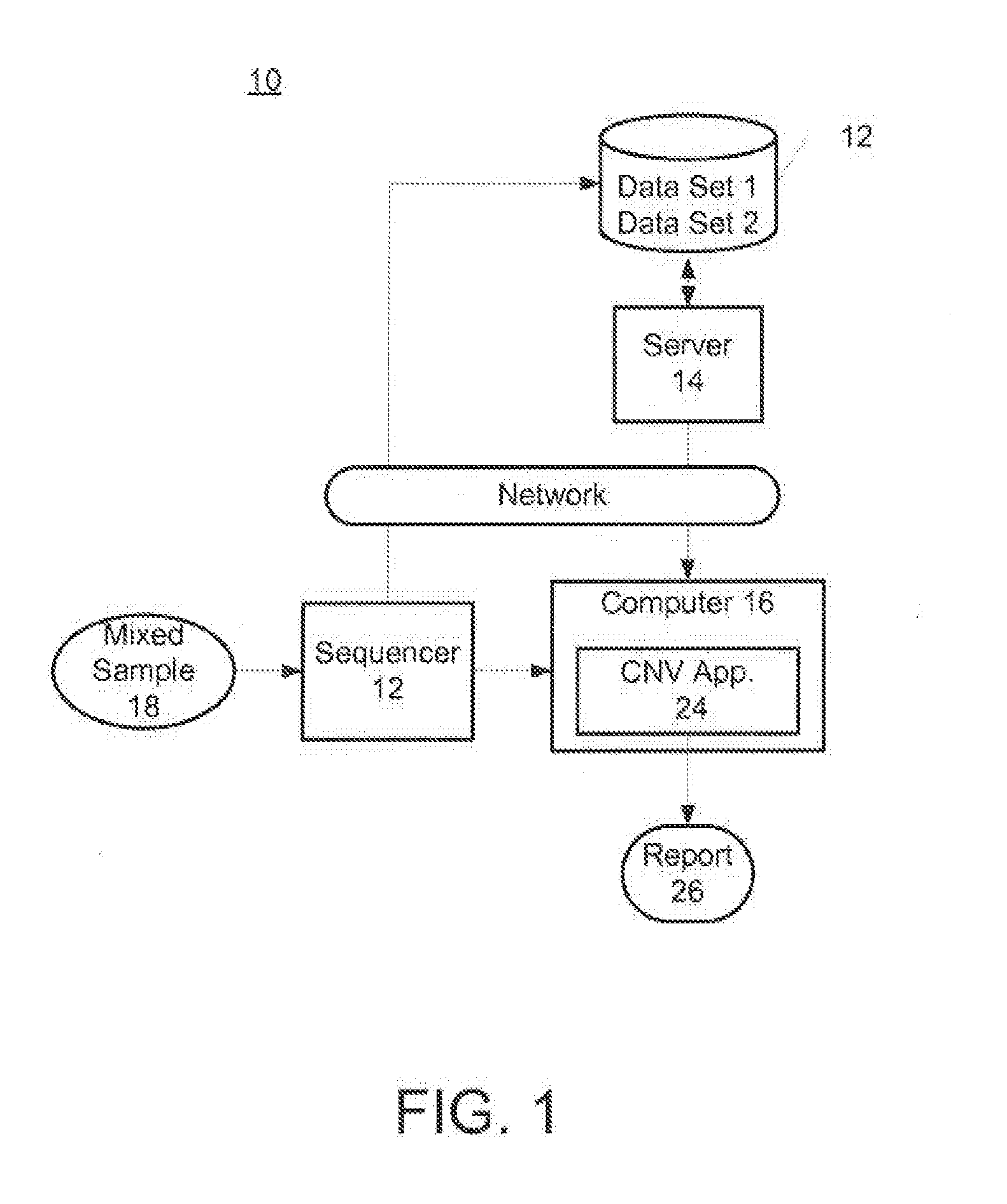
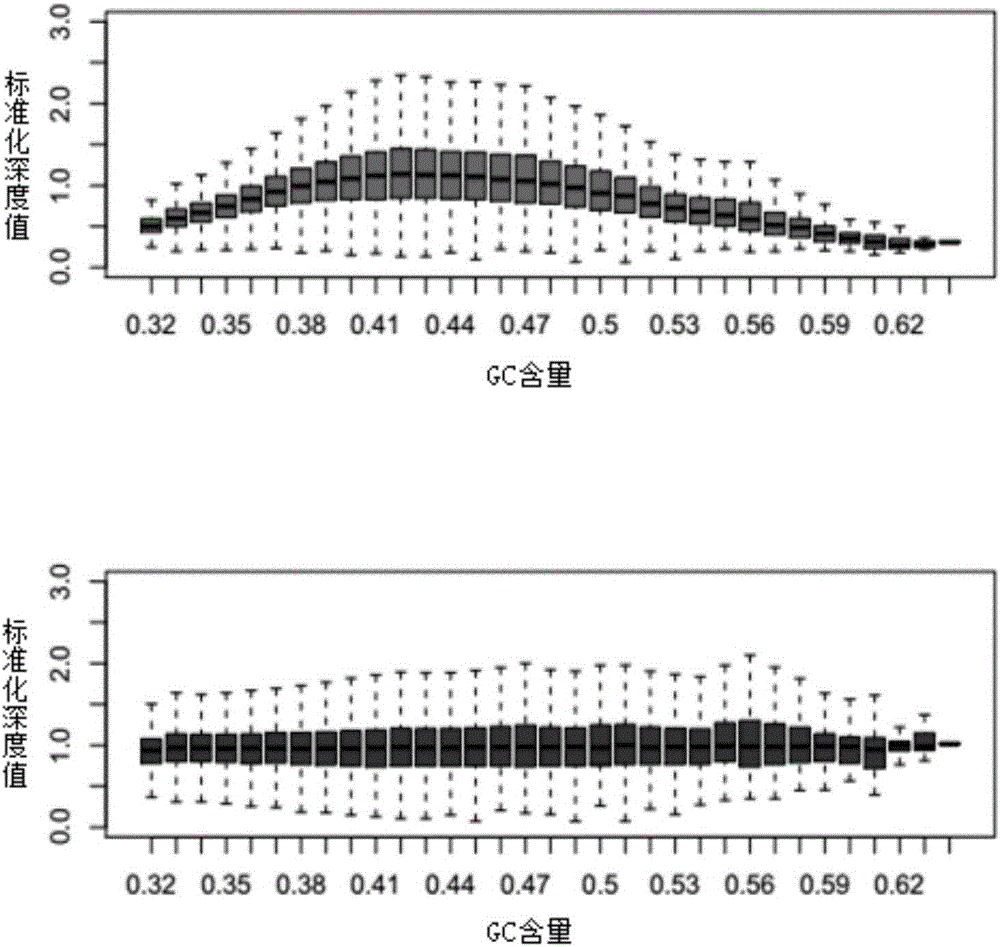
In one aspect, a system for implementing a copy number variation analysis method, is disclosed. The system can include a nucleic acid sequencer and a computing device in communications with the nucleic acid sequencer. The nucleic acid sequencer can be configured to interrogate a sample to produce a nucleic acid sequence data file containing a plurality of nucleic acid sequence reads. In various embodiments, the computing device can be a workstation, mainframe computer, personal computer, mobile device, etc.The computing device can comprise a sequencing mapping engine, a coverage normalization engine, a segmentation engine and a copy number variation identification engine. The sequence mapping engine can be configured to align the plurality of nucleic acid sequence reads to a reference sequence, wherein the aligned nucleic acid sequence reads merge to form a plurality of chromosomal regions. The coverage normalization engine can be configured to divide each chromosomal region into one or more non-overlapping window regions, determine nucleic acid sequence read coverage for each window region and normalize the nucleic acid sequence read coverage determined for each window region to correct for bias. The segmentation engine can be configured to convert the normalized nucleic acid sequence read coverage for each window region to discrete copy number states. The copy number variation identification engine can be configured to identify copy number variation in the chromosomal regions by utilizing the copy number states of each window region.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Probe set and kit for detecting whole exons of extended genetic diseases and application of probe set
InactiveCN110499364AComprehensive diagnostic extended whole exome testingIncrease positive rateMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationFresh TissueExon
The invention discloses a probe set for detecting whole exons of extended genetic diseases. The probe set for detecting the whole exons of the extended genetic diseases comprises a standard whole exonprobe set, a whole genome copy number variation probe, and a mitochondrial loop full-length probe, and the genetic diseases comprise 6161 genetic diseases; the standard whole exon probe set can detect the genetic diseases caused by whole exon mutation, the genetic diseases comprise nervous system diseases, metabolic system diseases, endocrine system diseases, digestive system diseases, skeletal system diseases, urinary system diseases, immune system diseases, cardiovascular system diseases, blood system diseases, integument system diseases, ophthalmic system diseases, ear system diseases, respiratory system diseases, and genital system diseases; and the density of the mitochondrial probe is 6X; test samples comprise blood, fresh tissue, FFPE samples, and saliva. The invention discloses using method and kit and application of the probe set for detecting the whole exons of the extended genetic diseases.
Owner:北京凯昂医学诊断技术有限公司
Method for determining copy number variations
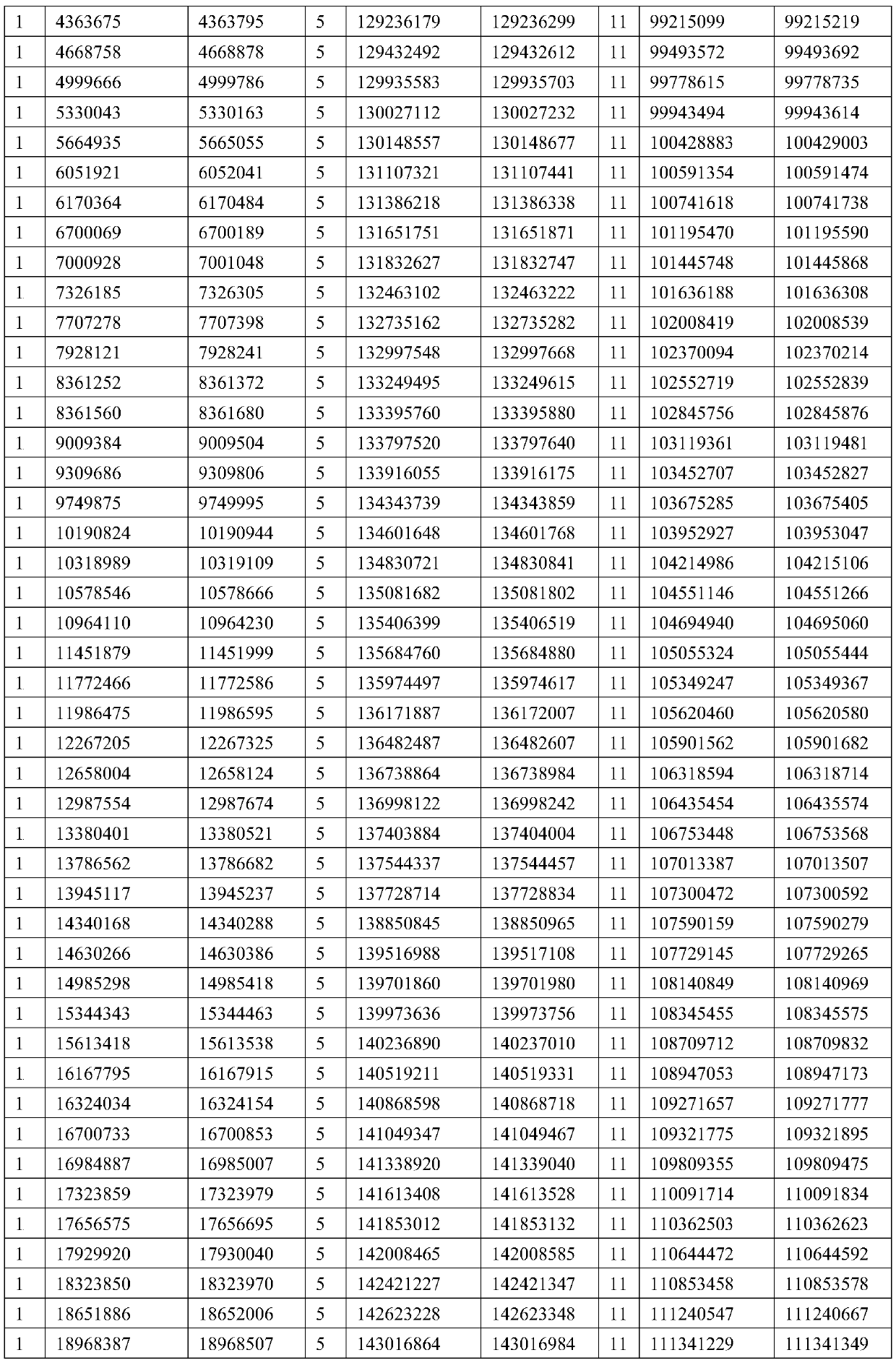
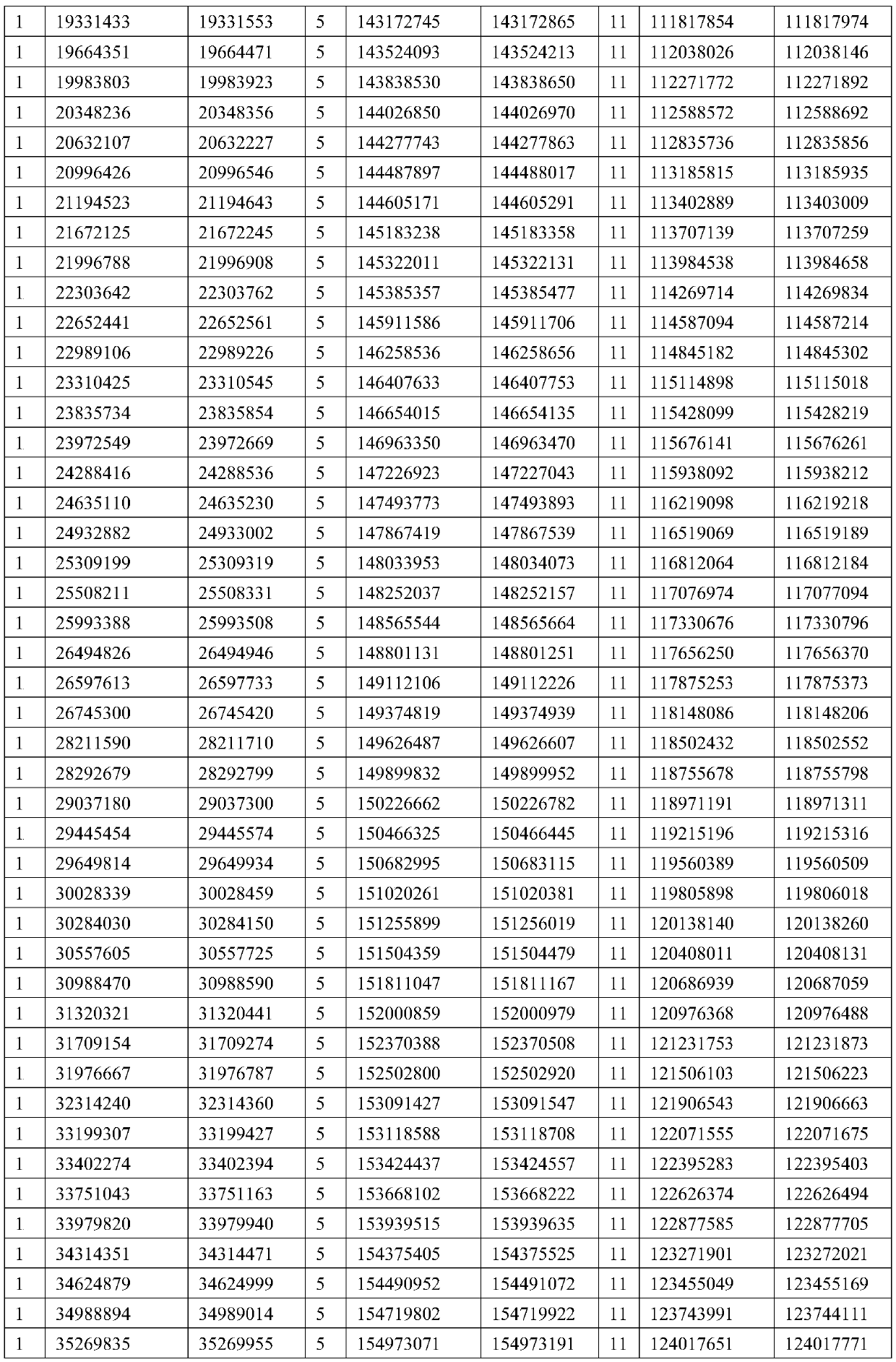
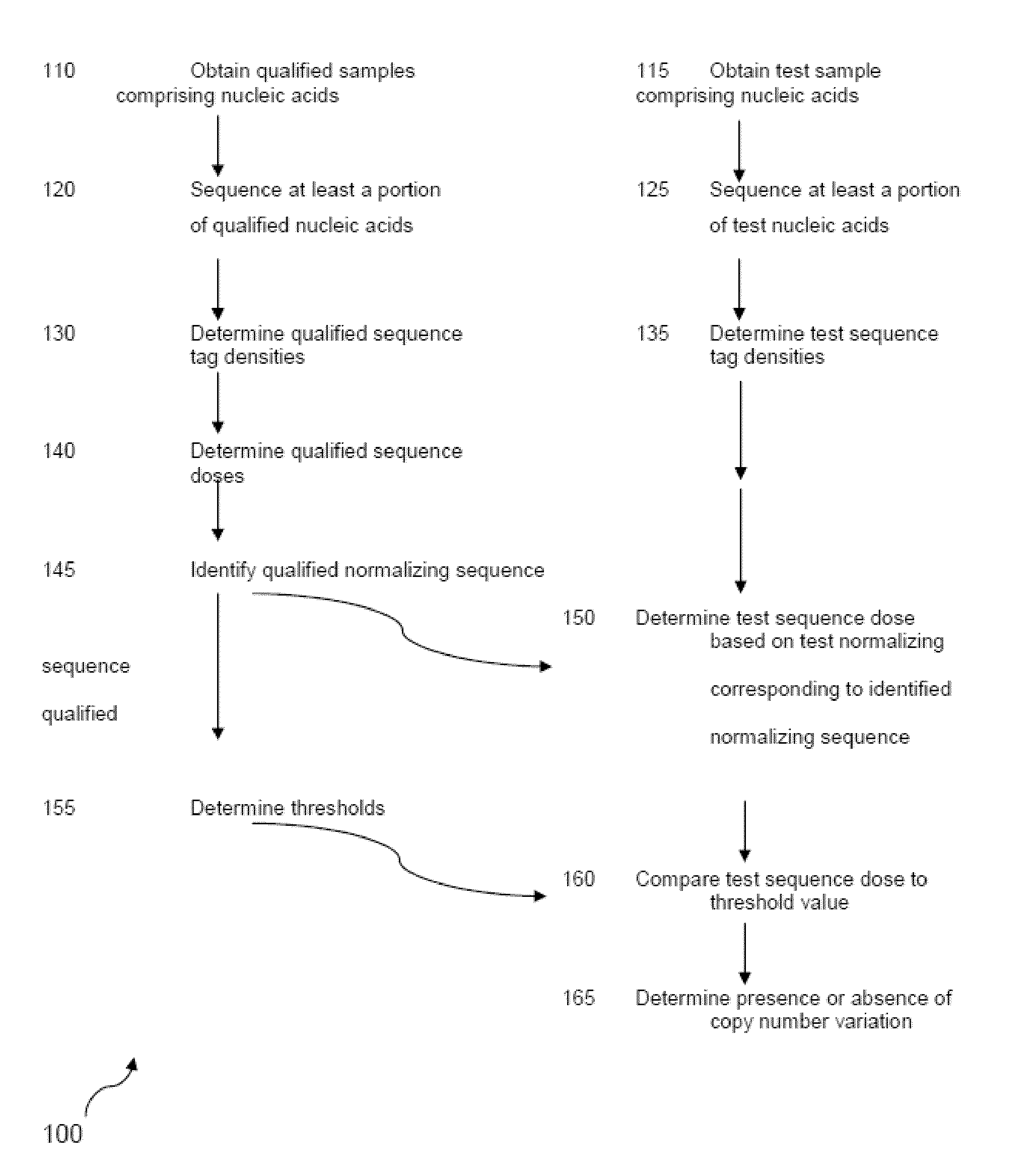
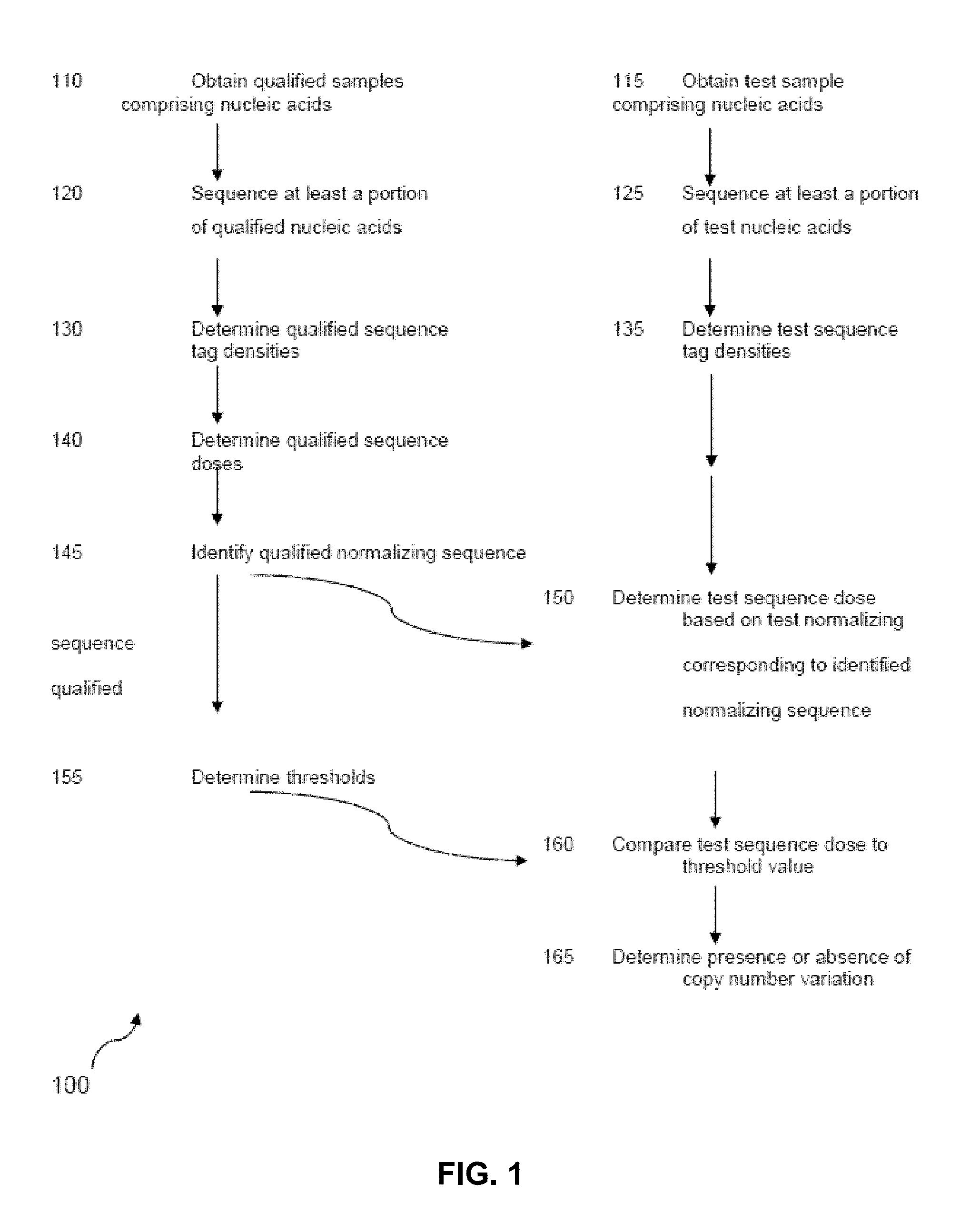
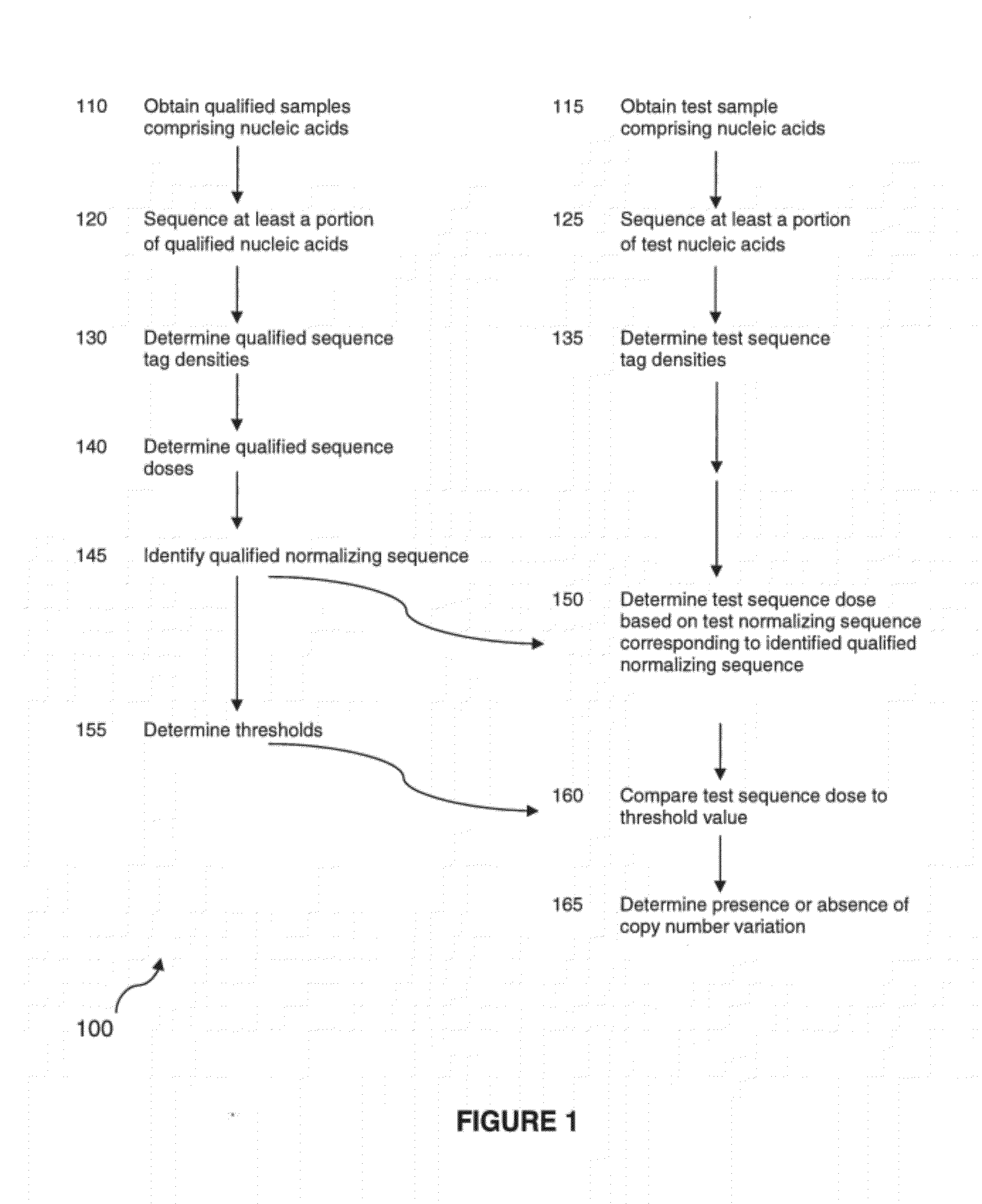
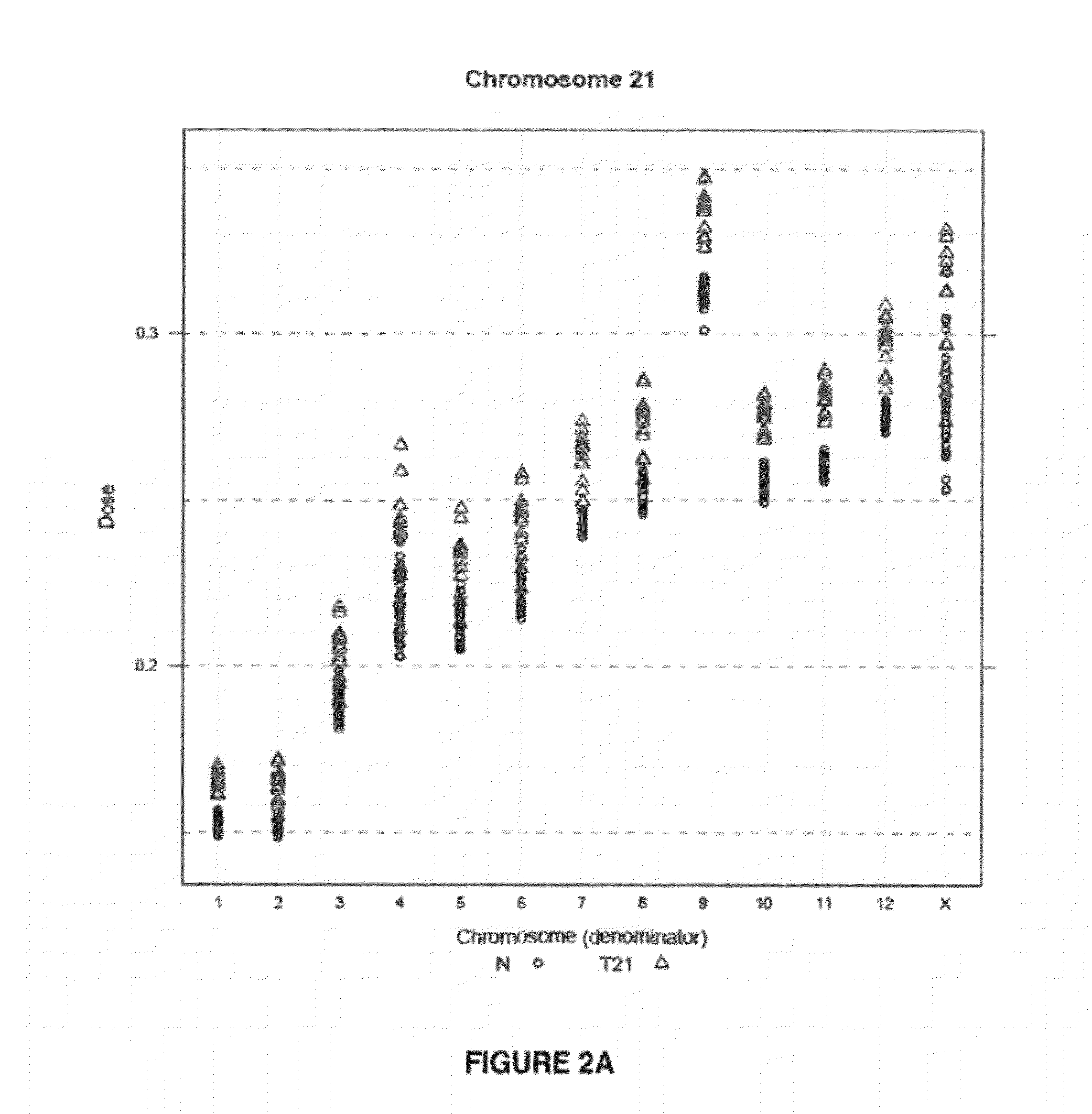
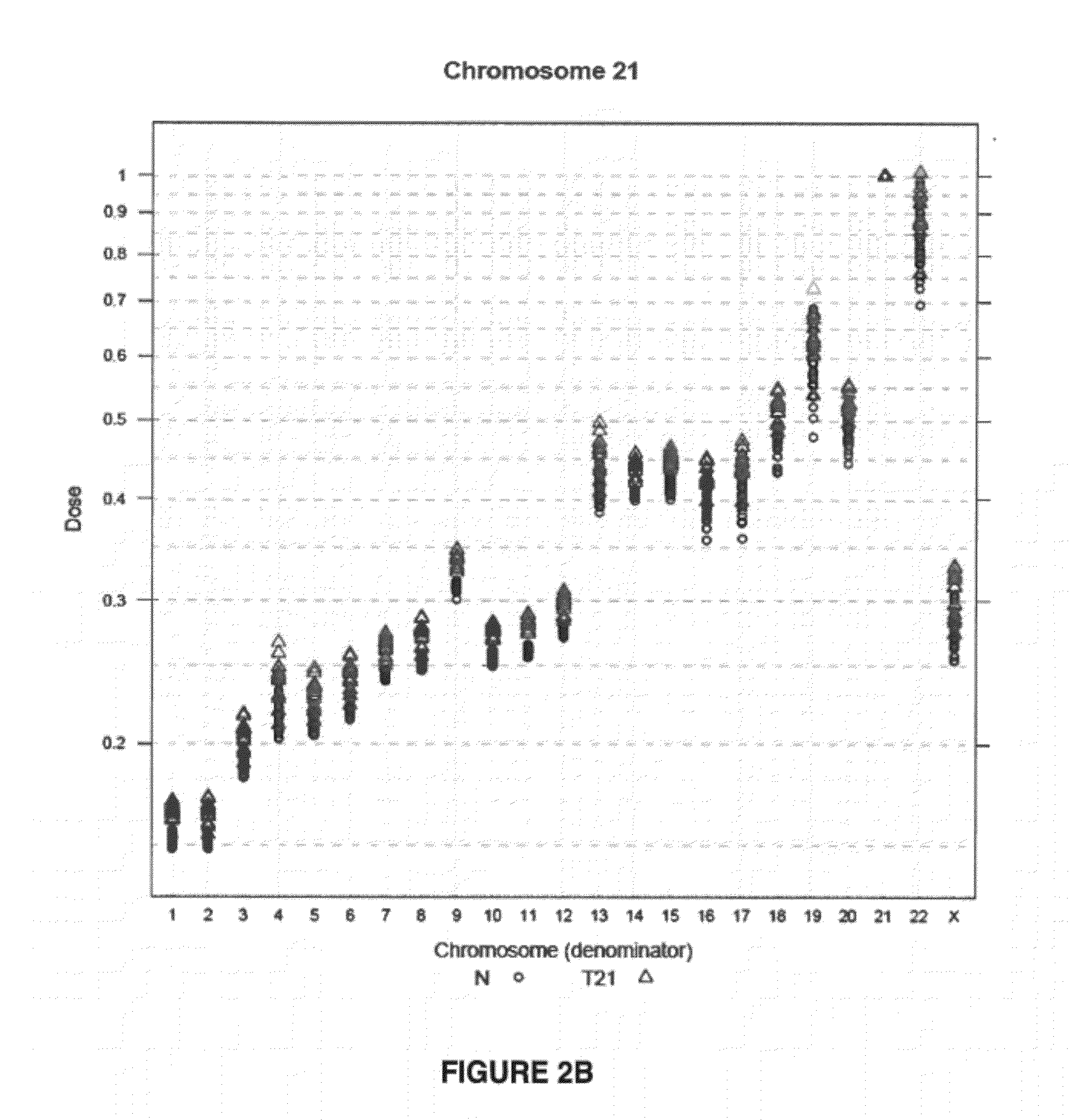
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the present method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample. Any aneuploidy can be determined from sequencing information that is obtained by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Pluripotent cell lines and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20100167286A1Microbiological testing/measurementDrug screeningSequence variationBioinformatics
Methods of generating cell lines with a sequence variation or copy number variation of a gene of interest, methods of use thereof, and cell lines with a sequence variation or copy number variation of a gene of interest are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Detecting and classifying copy number variation
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
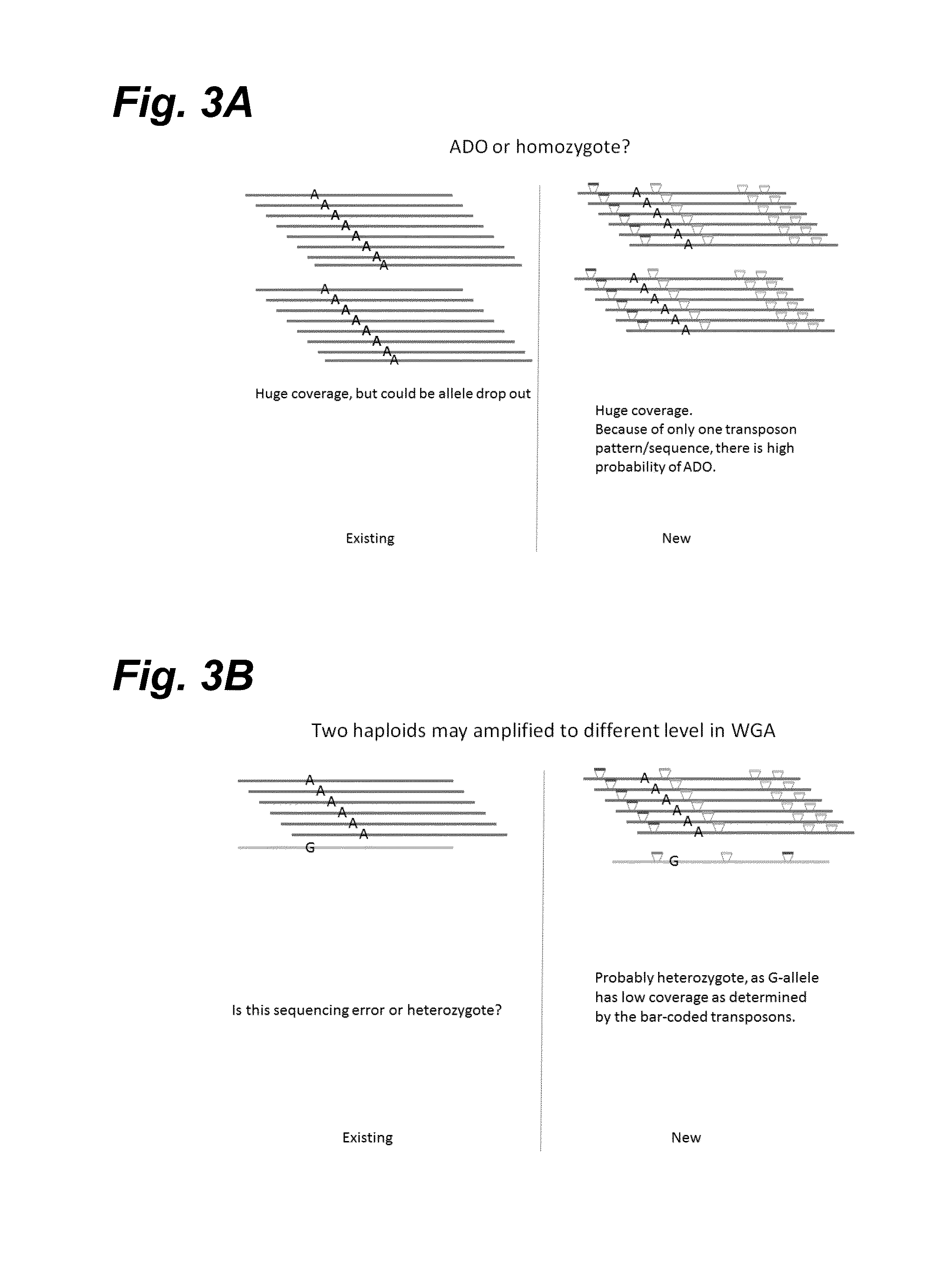
Haploidome determination by digitized transposons
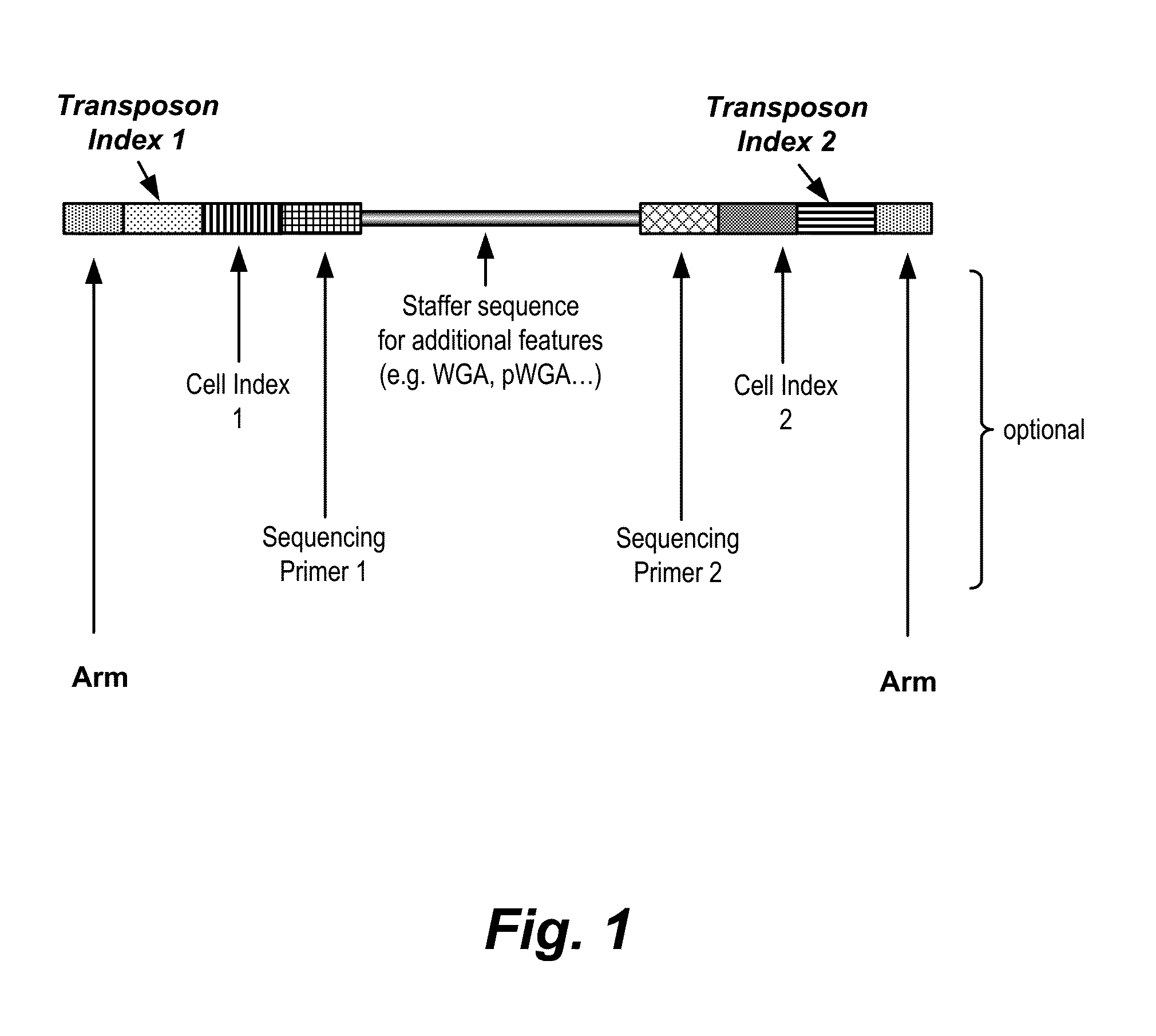
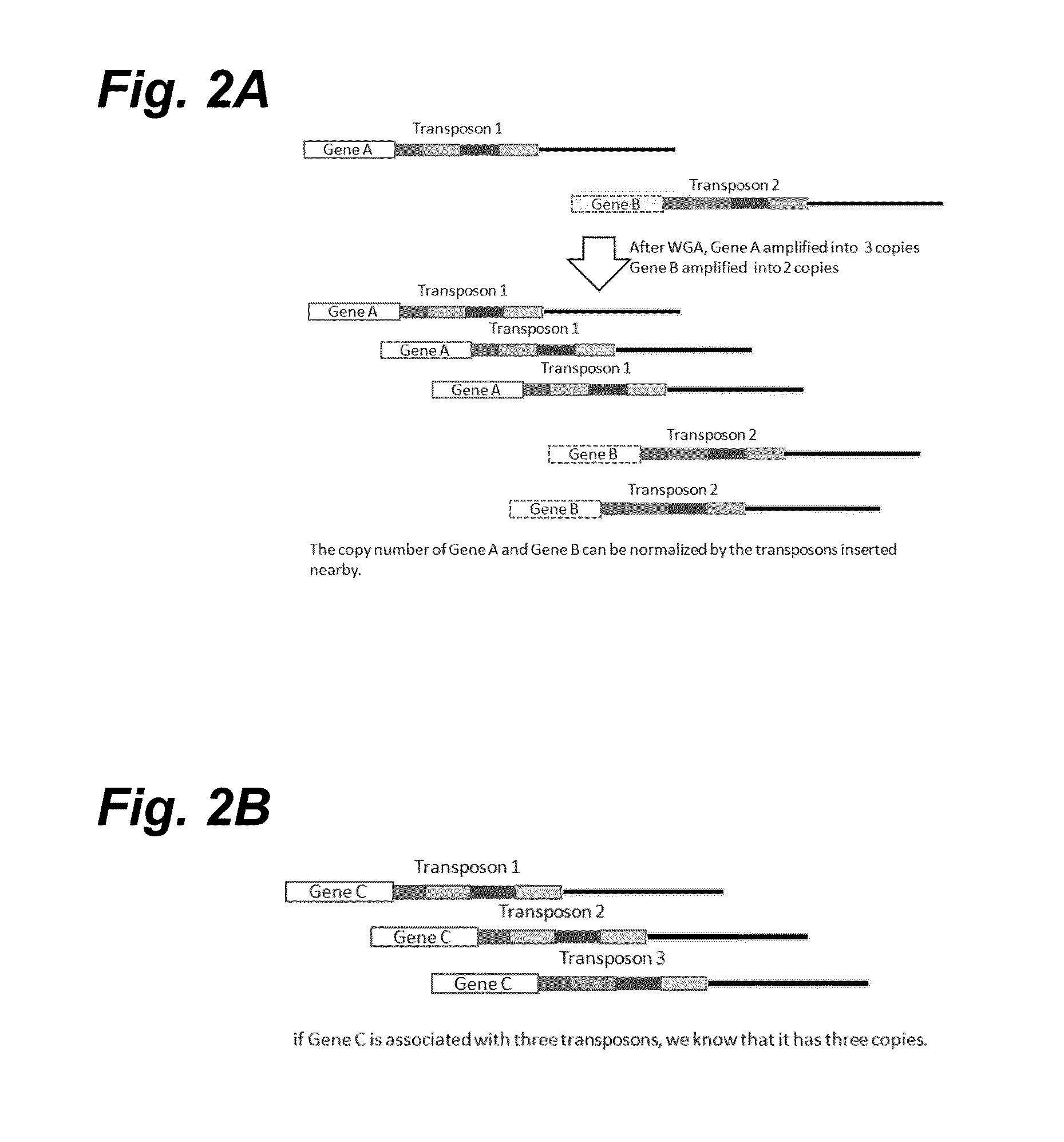
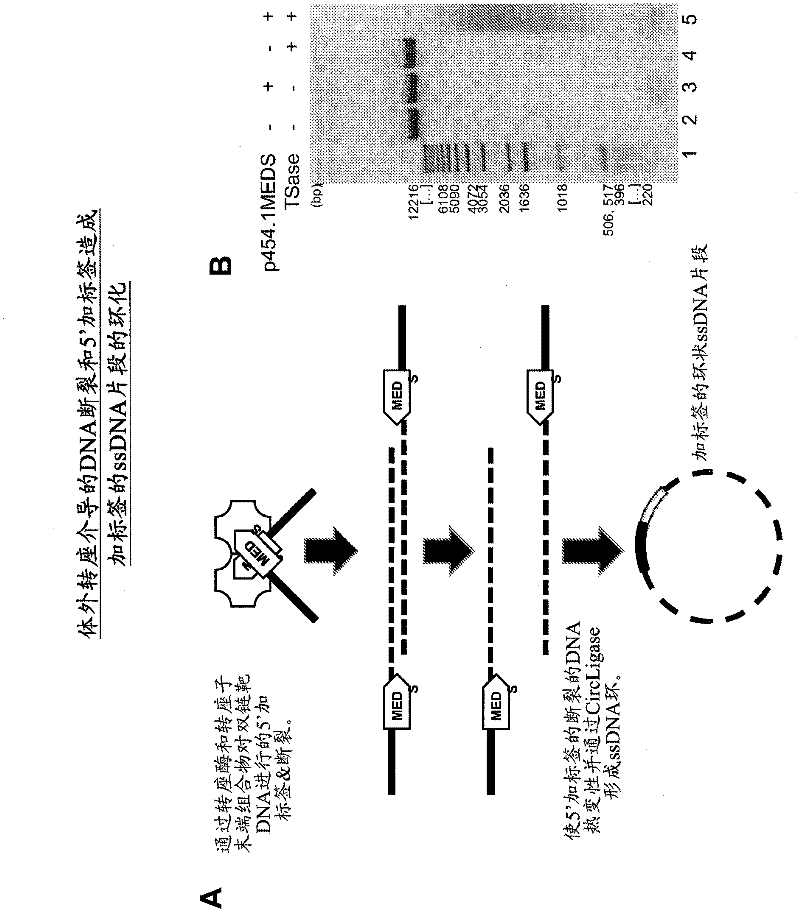
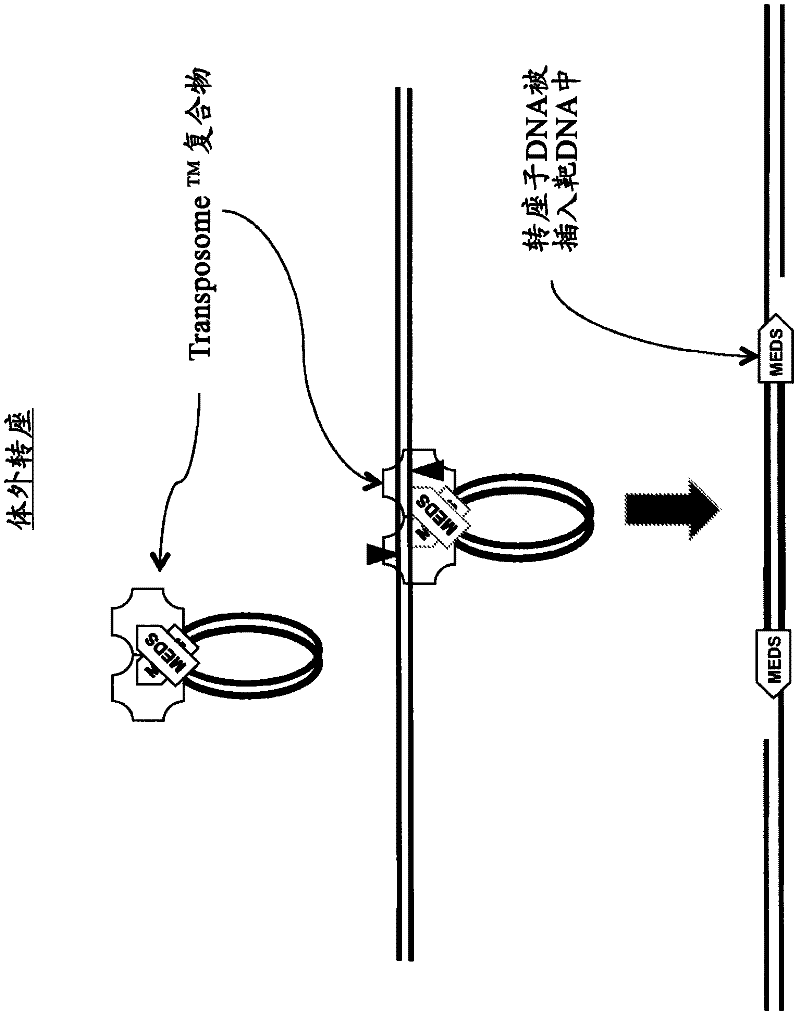
In certain embodiments, the present invention provides a way of “digitally” marking different the alleles of different chromosomes by using a transposase to insert differently barcoded transposons into genomic DNA before further analysis. According to this method, each allele becomes marked with a unique pattern of transposon barcodes. Because each unique pattern of transposon barcodes identifies a particular allele, the method facilitates determinations of ploidy and copy number variation, improves the ability to discriminate among homozygotes, heterozygotes, and patterns arising from sequencing errors, and allows loci separated by uninformative stretches of DNA to be identified as linked loci, thereby facilitating haplotype determinations. Also provided is a novel artificial transposon end that includes a barcode sequence in two or more positions that are not essential for transposition.
Owner:DIGENOMIX CORP
Assay systems for genetic analysis
InactiveUS20130040375A1Improve throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayPolymorphism Detection
The present invention provides assay systems and methods for detection of copy number variation at one or more loci and polymorphism detection at one or more loci in a mixed sample from an individual.
Owner:TANDEM DIAGNOSTICS
Assay systems for determination of fetal copy number variation
The present invention provides processes for determining accurate risk probabilities for chromosome dosage abnormalities. Specifically, the invention provides non-invasive evaluation of genomic variations through chromosome-selective sequencing and non-host fraction data analysis of maternal samples.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Induced malignant stem cells
InactiveUS20140137274A1High and low degree of methylationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrosatelliteSomatic cell
PROBLEMThere are provided induced malignant stem cells capable of in vitro proliferation that are useful in cancer research and drug discovery for cancer therapy, as well as processes for production thereof, cancer cells derived from these cells, and applications of these cells.MEANS FOR SOLVINGAn induced malignant stem cell capable of in vitro proliferation are characterized by satisfying the following two requirements:(1) having at least one aberration selected from among (a) an aberration of methylation (high or low degree of methylation) in a tumor suppressor gene or a cancer-related genetic region in endogenous genomic DNA, (b) a somatic mutation of a tumor suppressor gene or a somatic mutation of an endogenous cancer-related gene in endogenous genomic DNA, (c) abnormal expression (increased or reduced / lost expression) of an endogenous oncogene or an endogenous tumor suppressor gene, (d) abnormal expression (increased or reduced / lost expression) of a noncoding RNA such as an endogenous cancer-related microRNA, (e) abnormal expression of an endogenous cancer-related protein, (f) an aberration of endogenous cancer-related metabolism (hypermetabolism or hypometabolism), (g) an aberration of endogenous cancer-related sugar chain, (h) an aberration of copy number variations in endogenous genomic DNA, and (i) instability of microsatellites in endogenous genomic DNA in an induced malignant stem cell; and(2) expressing genes including POU5F1 gene, NANOG gene, SOX2 gene, and ZFP42 gene.
Owner:ISHIKAWA
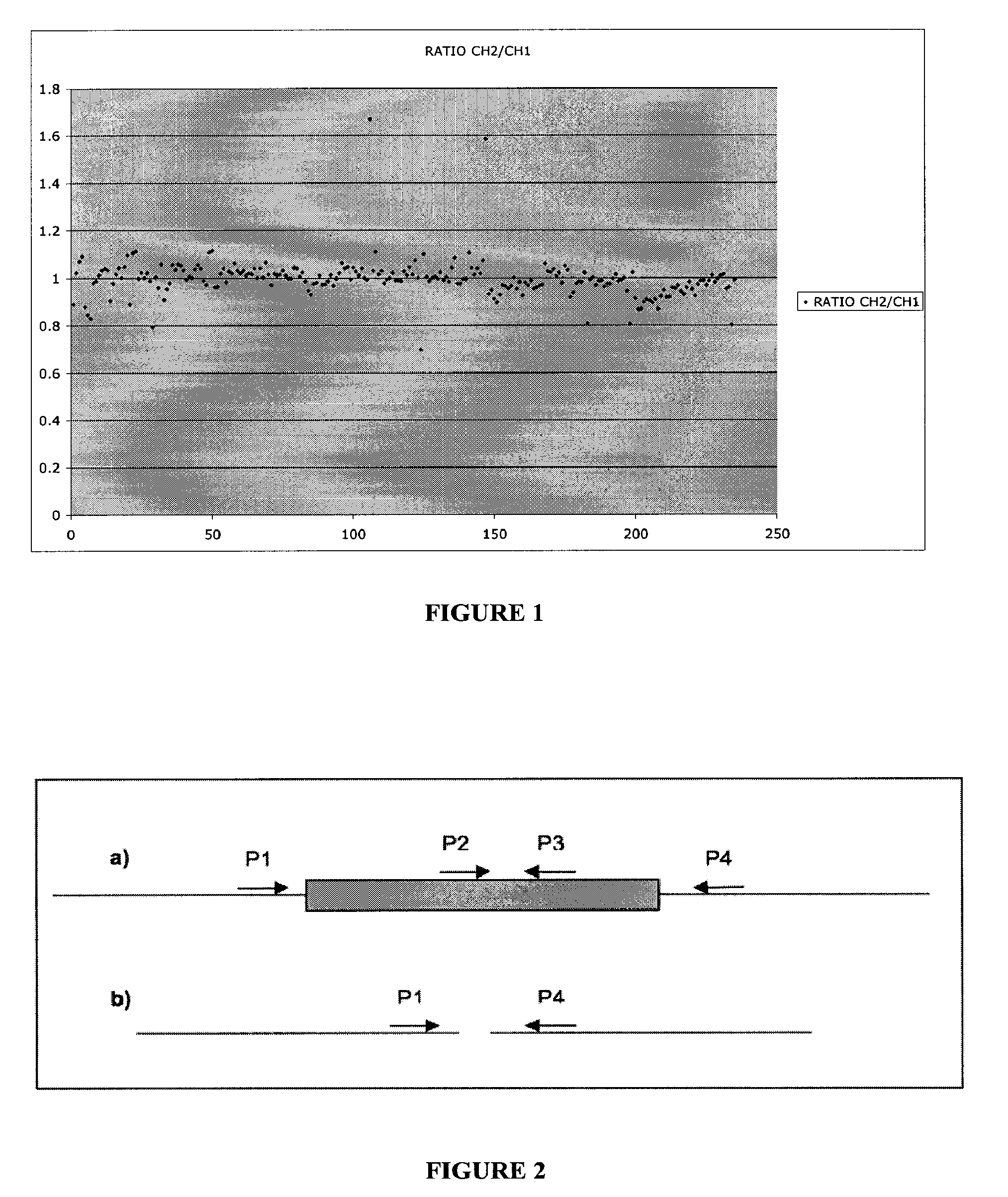
Systems, methods and software arrangements for detection of genome copy number variation
The present invention relates to systems, methods and software arrangements for the detection of variations in the copy number of a gene in a genome. These systems, methods and software arrangements are based on a simple prior model that uses a first process generating amplifications and deletions in the genome, and a second process modifying the signal obtained to account for the corrupting noise inherent in the technical methodology used to scan the genome. A Bayesian approach according to the present invention determines, e.g., the most plausible hypothesis of regional changes in the genome and their associated copy number. The systems, methods, and software arrangements can be are framed as optimization problems, in which a score function is minimized. The system, methods and software arrangements may be useful to assist the scientific study, diagnosis and / or treatment of any disease which has a genetic component, including but not limited to cancers and inherited diseases.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for determining copy number variations
The invention provides a method for determining copy number variations (CNV) of a sequence of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of nucleic acids that are known or are suspected to differ in the amount of one or more sequence of interest. The method comprises a statistical approach that accounts for accrued variability stemming from process-related, interchromosomal and inter-sequencing variability. The method is applicable to determining CNV of any fetal aneuploidy, and CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. CNV that can be determined according to the method include trisomies and monosomies of any one or more of chromosomes 1-22, X and Y, other chromosomal polysomies, and deletions and / or duplications of segments of any one or more of the chromosomes, which can be detected by sequencing only once the nucleic acids of a test sample.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Methods for assessing disease risk
InactiveUS20120220478A1High copy numberNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease riskAutoimmune disease
The invention relates to methods and biomarkers for assessing a subject's risk for a disease, such as cancer, an autoimmune disease or a neurological disease. In particular, the invention provides methods and biomarkers for creating exon copy number variation (ECNV) profiles, and determining disease risk according to the subject's ECNV profiles.
Owner:BAR HARBOR BIOTECH
Transposon end compositions and methods for modifying nucleic acids
The present invention provides the use of transposases and transposon ends to generate extensive fragmentation and 5′-tagging of double-stranded target DNA in vitro, followed by the use of DNA polymerases to generate 5′- and 3′-tagged single DNA without PCR amplification reactions. Methods, compositions and kits for stranded DNA fragments, wherein the first label on the 5' end shows the sequence of the transferred transposon end and optionally an additional arbitrary sequence, and the second label on the 3' end shows the same The first tab shows a sequence different from the sequence. The method can be used to generate 5' and 3' tagged DNA fragments for use in a variety of processes including metagenomic analysis of DNA in environmental samples, copy number variation (CNV) analysis of DNA, and including massively parallel DNA sequencing (so-called "next generation sequencing") involves the process of comparative genome sequencing (CGS).
Owner:EPICENT TECH CORP
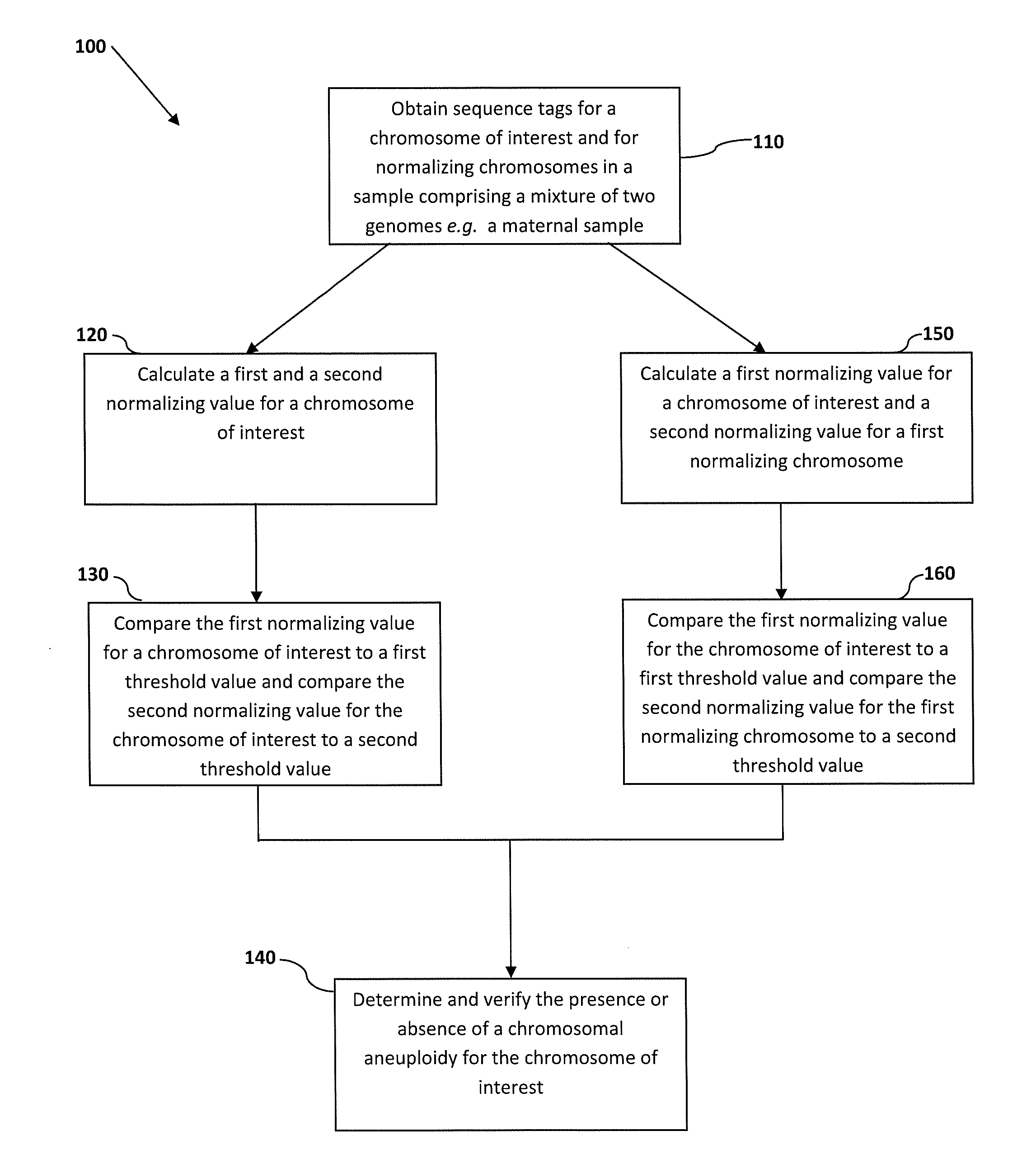
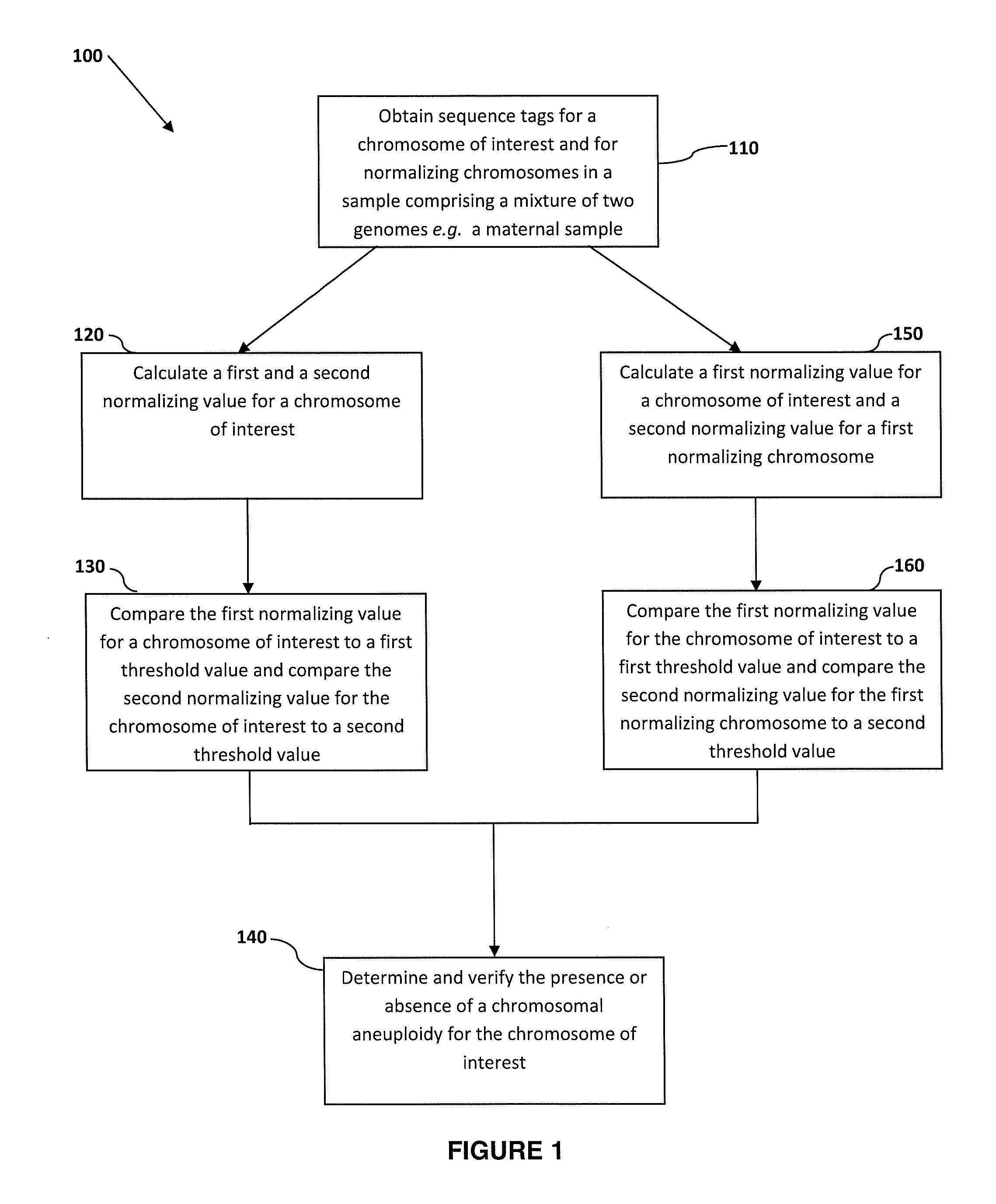
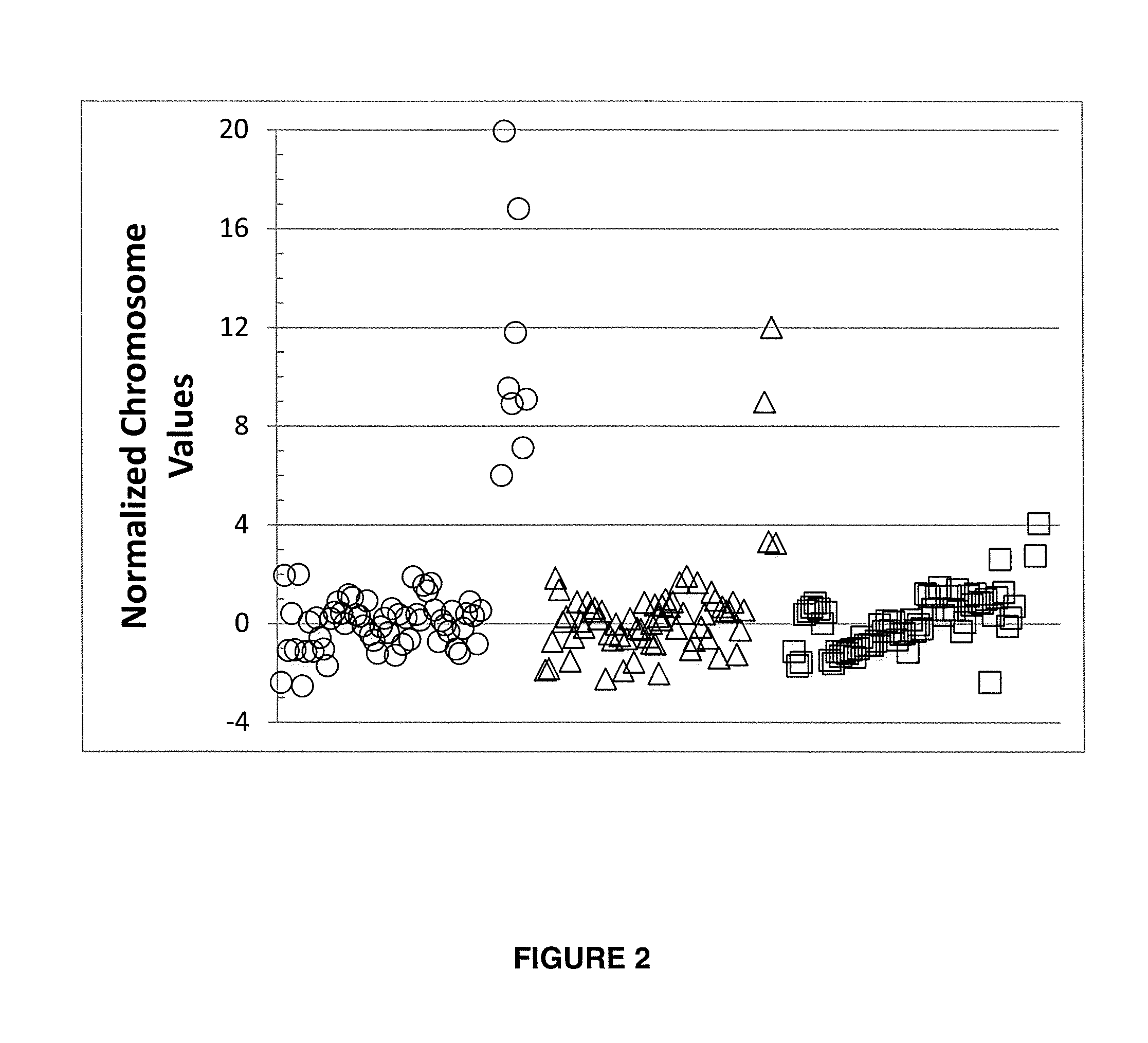
Normalizing chromosomes for the determination and verification of common and rare chromosomal aneuploidies
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Evaluating genetic disorders
ActiveUS7702468B2Digital data processing detailsMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr assayGenetics
Owner:POPULATION BIO INC
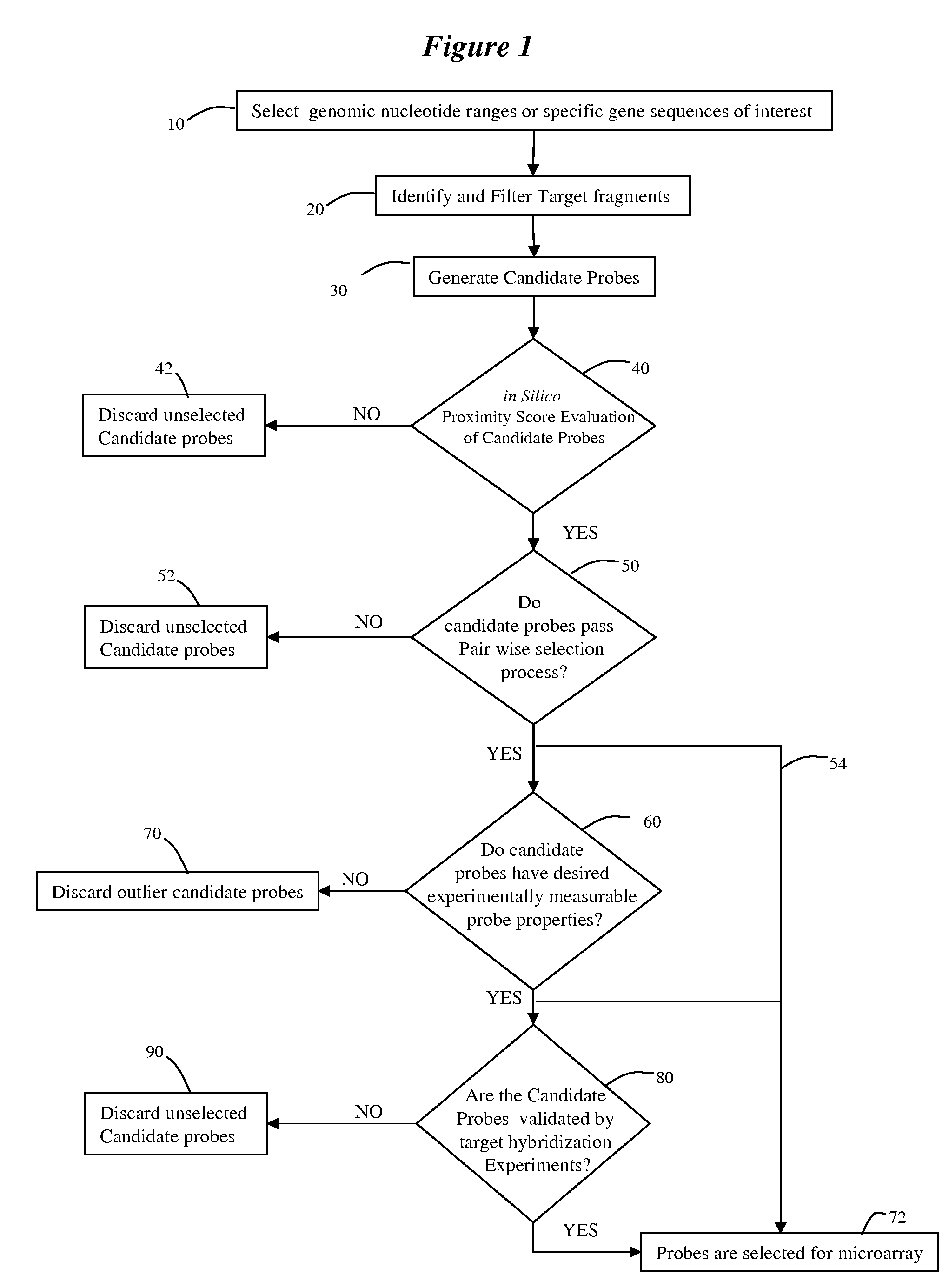
Methods and systems for evaluating CGH candidate probe nucleic acid sequences
ActiveUS7979215B2Digital data processing detailsAnalogue computers for chemical processesNucleic acid sequencingComputer programming
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Novel method of detecting genetic polymorphism
InactiveUS20080286783A1Easy to detectRealized gainSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPresent methodTyping
The present invention provides a novel polymorphism detecting method suitable for the detection and identification of copy number variation.Provided is a method of determining the genotype of a subject in a genomic region comprising an SNP site, comprising a step for performing typing of the SNP site by the invader assay with a DNA-containing sample comprising the genomic region from the subject as the template, wherein fluorescence is measured on a real time basis. The copy number ratio of both alleles is determined using the fluorescence intensity ratio of each allele at a time before saturation of fluorescence intensity. Preferably, the present method further comprises a step for amplifying the genomic region comprising an SNP site prior to the invader step. In this step of amplification, a plurality of regions comprising a plurality of SNP sites can be simultaneously amplified. Furthermore, the present method enables the determination of the copy number of each allele when combined with quantitative PCR.
Owner:RIKEN
Copy number variation detection method based on next generation sequencing
ActiveCN105760712ASolving Detection ErrorsAvoid detection errorsBiostatisticsSequence analysisComputation complexitySlide window
The invention discloses a copy number variation detection method based on next generation sequencing. The method comprises the following steps: pre-processing copy number variation data, constructing a sliding window, calculating of statistics, implementing a replacement policy, constructing zero distribution, and carrying out performance evaluation of an algorithm. The performance evaluation of the algorithm comprises the steps of judging whether a relatively high correct positive rate can be acquired by the algorithm under the condition that a false positive rate is controllable, evaluating whether the algorithm can relatively accurately estimate a p value or not, detecting a boundary detection capability of copy number variation, and analyzing the calculation complexity of the algorithm. With the adoption of the copy number variation detection method, the problem of copy number variation detection errors, caused by the fact that sequencing platforms and sequencing levels are different, is solved, and a result is relatively accurate; data is normalized by utilizing characteristics of a multi-peak frequency histogram, so that a normal region and a copy number variation region are accurately divided; and a new model is established by a comprehensive effect of relevance between a variation reads number and a variation site, so that the inconsistency problem is solved, and the remarkable level of copy number variation is objectively estimated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Systems and methods to detect copy number variation
InactiveUS20140051154A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsData filePersonal computer
In one aspect, a system for implementing a copy number variation analysis method, is disclosed. The system can include a nucleic acid sequencer and a computing device in communications with the nucleic acid sequencer. The nucleic acid sequencer can be configured to interrogate a sample to produce a nucleic acid sequence data file containing a plurality of nucleic acid sequence reads. In various embodiments, the computing device can be a workstation, mainframe computer, personal computer, mobile device, etc.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for predicating homologous recombination deficiency mechanism and method for predicating response of patients to cancer therapy
InactiveCN107287285AInnovativeOvercoming the pitfalls of inaccurate forecastsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisAbnormal tissue growthPolymerase L
The invention discloses a method for predicating a homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) mechanism and a method for predicating response of patients to cancer therapy and relates to the field of biological information predication. The method comprises the step of judging whether a tumor sample has homologous recombination deficiency or not according to one or more comprehensive values in a large-segment INDEL (Insertion / Deletion) fraction, a copy number variation fraction and a tumor mutation load fraction, wherein the comprehensive values can also comprise a loss of heterozygosity variation fraction. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, predication of a chromosome large-segment structure, a chromosome gene type number, a chromosome gene copy number, a chromosome variation interval and abnormal loss of heterozygosity and chromosome telomeric imbalance is realized, so that an evaluation range is more complete and HRD can be accurately predicated; the comprehensive values also can be used for determining whether the patients have response to a therapeutic regimen containing one or more of a PARP (Poly Adenosine Diphosphate Ribose Polymerase) inhibitor, an DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) injury inhibitor, a topoisomerase II / II+inhibitor, a topoisomerase I inhibitor and radiotherapy; the method is simple and has wide general applicability.
Owner:SHANGHAI ORIGIMED CO LTD
Method for determining copy number variations
InactiveUS20120149582A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationPresent methodTest sample
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation detecting method and application thereof
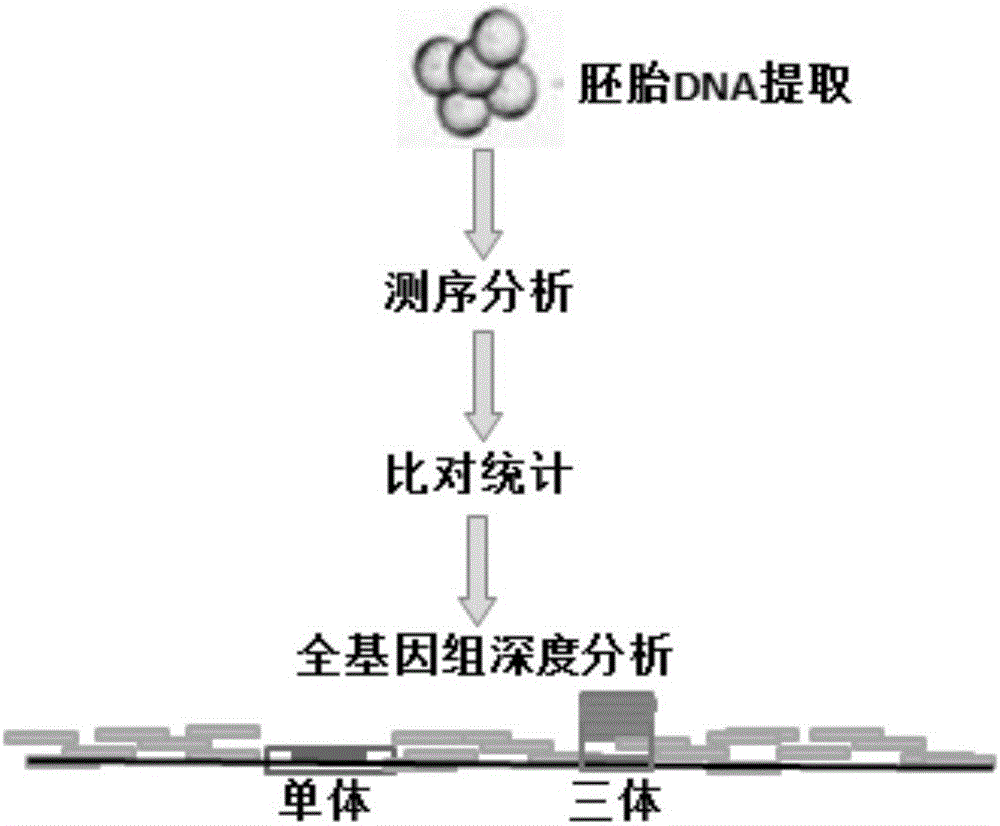
PendingCN106520940AShorten detection timeGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation analysisEmbryo
The invention provides a chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation detecting method and application thereof. Particularly, sequencing is performed on whole genomes of to-be-detected samples, and sequencing data of the samples are obtained. When a certain chromosome in an embryonic cell is a trisomy chromosome or haplochromosome, the copy rate of the chromosome is increased or decreased compared with that of a normal diploid chromosome, information analysis is performed through biostatistics, and aneuploids can be accurately detected. An experimental result shows that the chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation can be simply, rapidly and accurately detected through the method.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
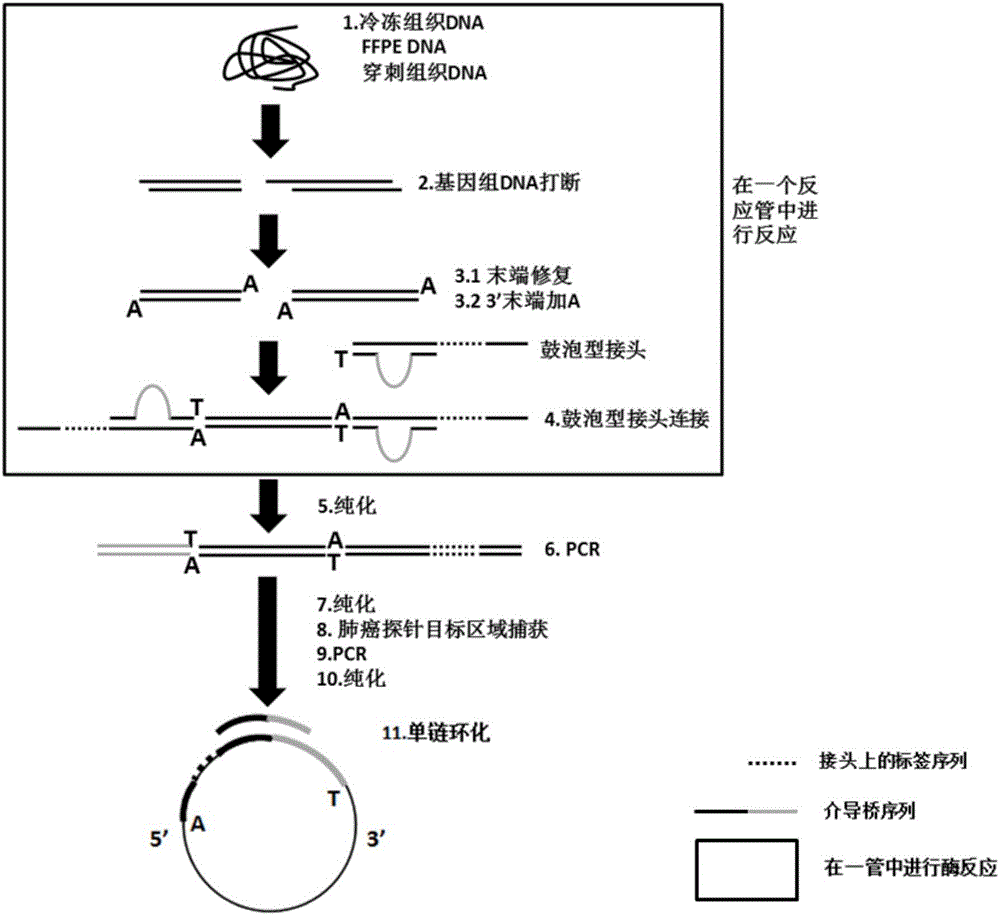
Building method of library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and kit
PendingCN106497920AImprove recycling efficiencyImprove utilization efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationGene targetingGene mutation
The invention discloses a building method of a library for detecting non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation and a kit. The method includes: using tubular reaction to complete genome DNA breaking and connector connection, performing hybrid capture on connection products after amplification and non-small cell lung cancer related gene target area probes, and performing BGISEQ-500 / 1000 platform sequencing and data analysis to obtain mutation conditions. The method has the advantages that the experiment flow is optimized greatly by the tubular reaction, operation complexity and time are reduced, and the requirements on clinical sample initial amount are lowered; multiple genes and multiple sites can be detected in one step, point mutation, insertion and deletion, structural variation and copy number variation are covered, the detecting result is accurate and overcomes the defect that a PCR capture method cannot detect the structural variation in one step, and the effectiveness of the high-throughput sequencing applied to the detection of the non-small cell lung cancer gene mutation; the method is wide in coverage, high in cost performance, capable of providing a reference basis for the diagnosing, treatment and drug use performed by doctors, and the method is suitable for being popularized and used in a large-scale manner.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
Probe and sequence combination for simultaneous detection of various mutation types
InactiveCN106480205ARealize multiple comprehensive detectionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHydrothoraxTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a probe and a sequence combination for simultaneous detection of various mutation types and particularly provides a kit, a method, a gene chip, a probe and a sequence combination which are high in sensitivity and specificity and used for simultaneous detection of point mutation, short segment insertion and deletion, copy number variation and fusion genes of 57 tumor driver genes listed in a detection list. The invention further discloses a sequence combination and probe associated gene chip and kit and a method for simultaneous detection of various mutation types. By detection of body fluid including blood, hydrothorax, abdominal dropsy and the like and tumor frozen tissues or paraffin sections, comprehensive tumor driver gene mutation information can be acquired, sensitivity and accuracy in tumor gene detection are improved, and accordingly clinicians can be assisted in making of individualized medication schemes to achieve best accurate treatment effects.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
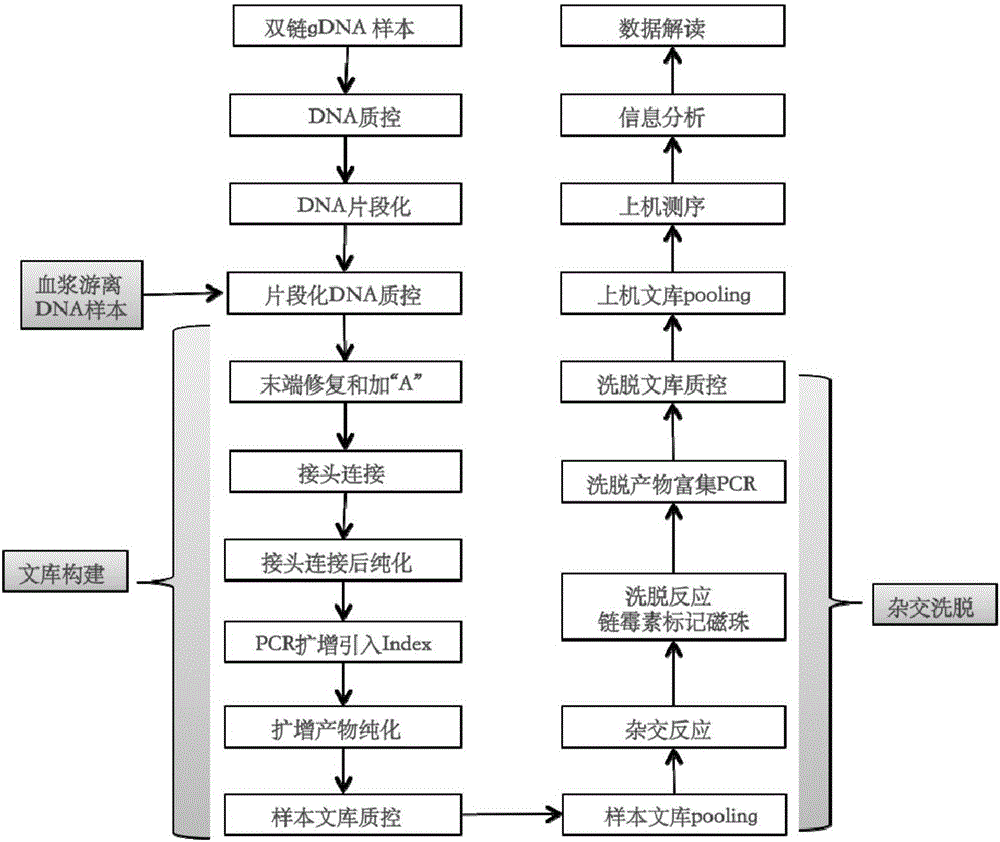
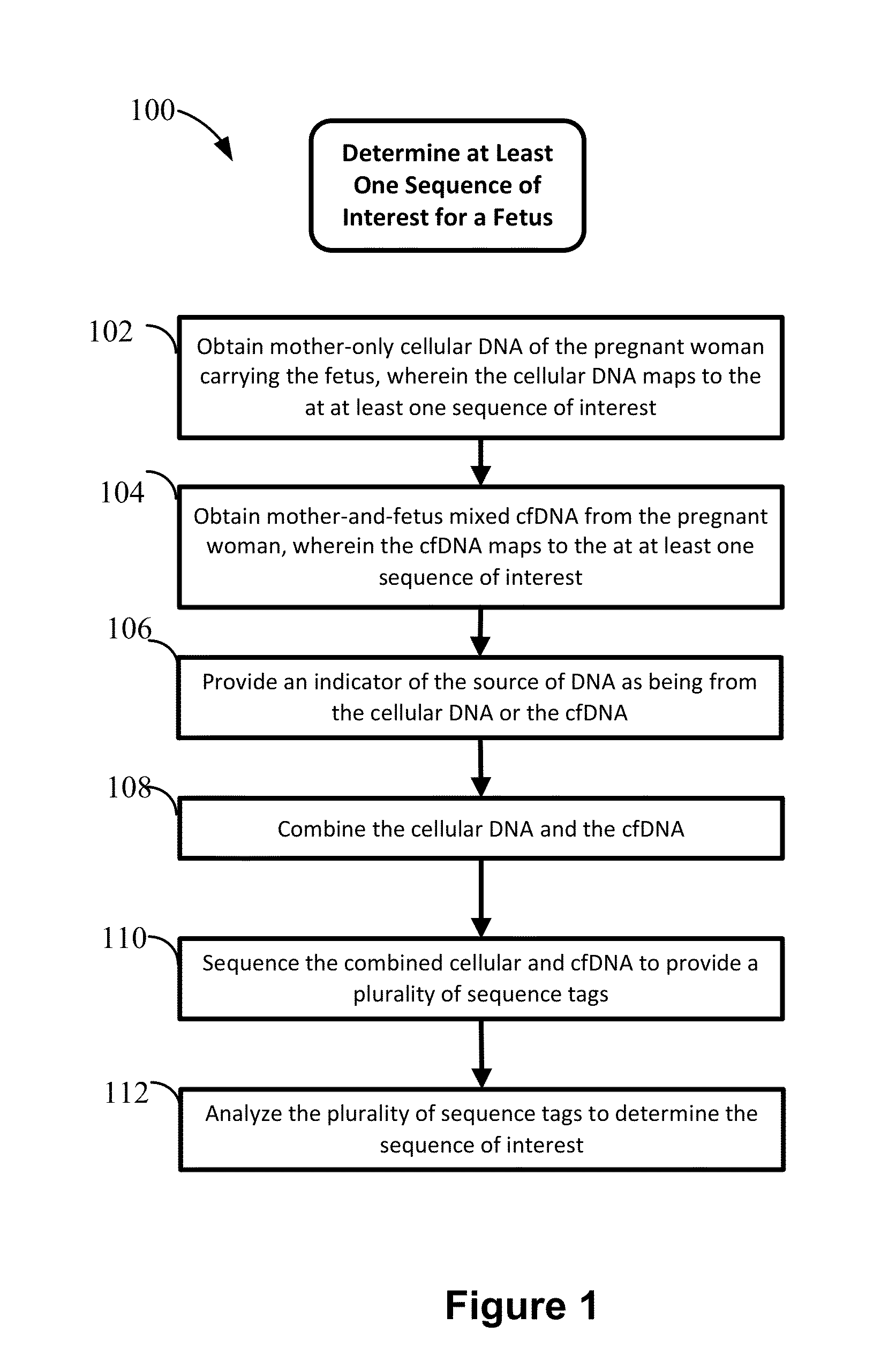
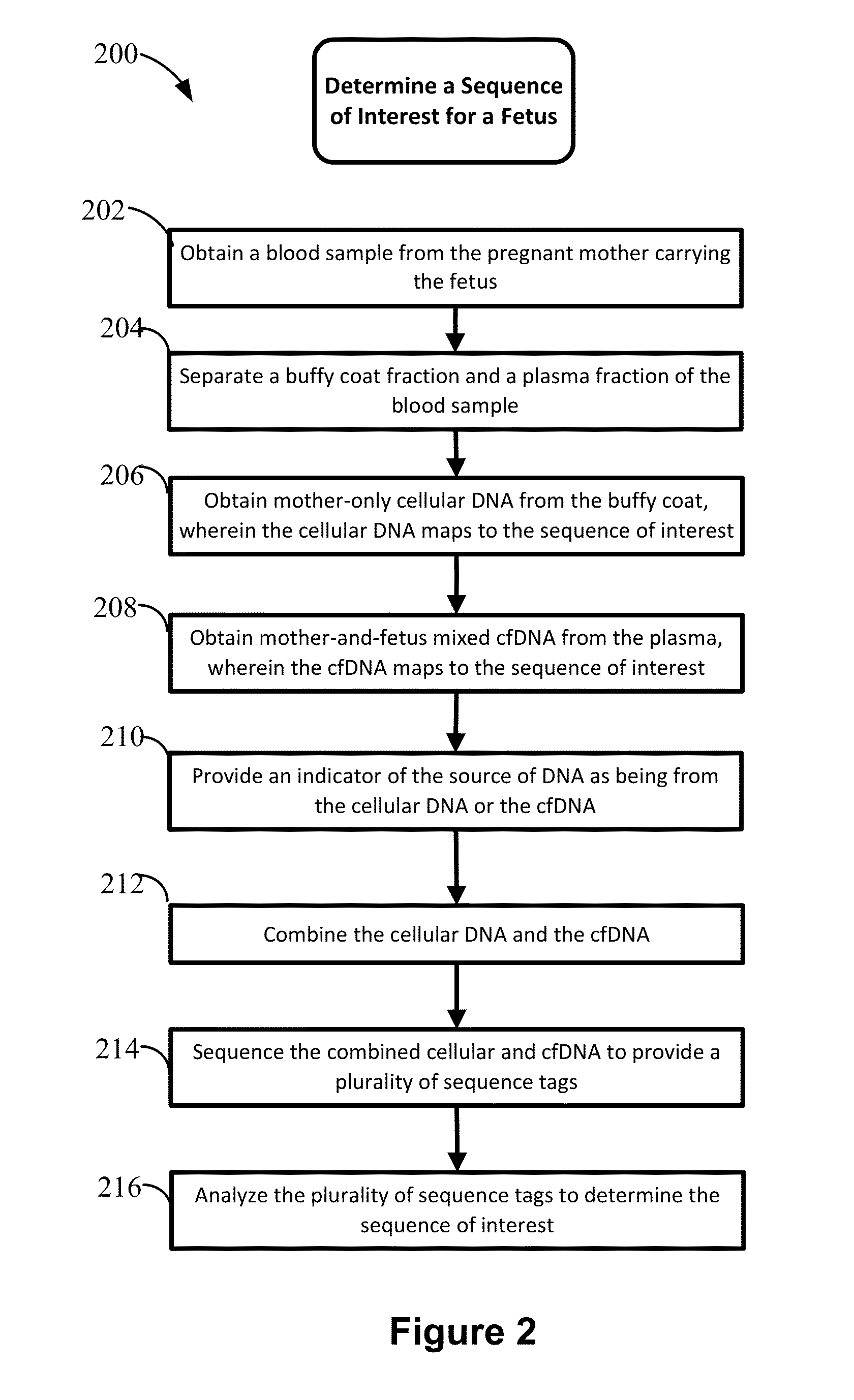
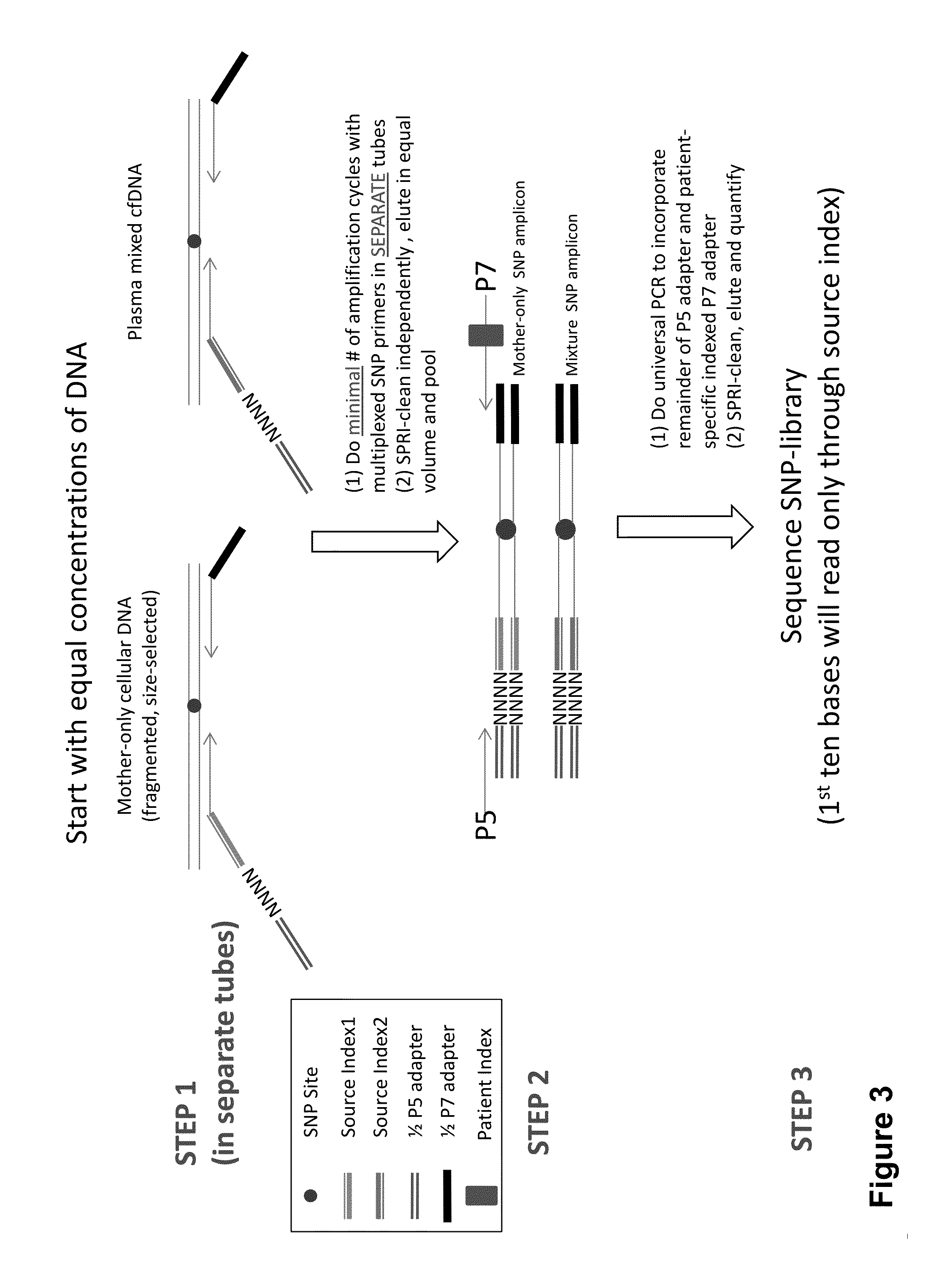
Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal genetic condition using cellular DNA and cell free DNA
Disclosed are methods for determining at least one sequence of interest of a fetus of a pregnant mother. In various embodiments, the method can determine one or more sequences of interest in a test sample that comprises a mixture of maternal cellular DNA and mother-and-fetus cfDNA. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining whether the fetus has a genetic disease. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining whether the fetus is homozygous in a disease causing allele when the mother is heterozygous of the same allele. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining whether the fetus has a copy number variation (CNV) or a non-CNV genetic sequence anomaly.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com