Patents
Literature
57 results about "Biostatistics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biostatistics are the development and application of statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experiments and the interpretation of the results.
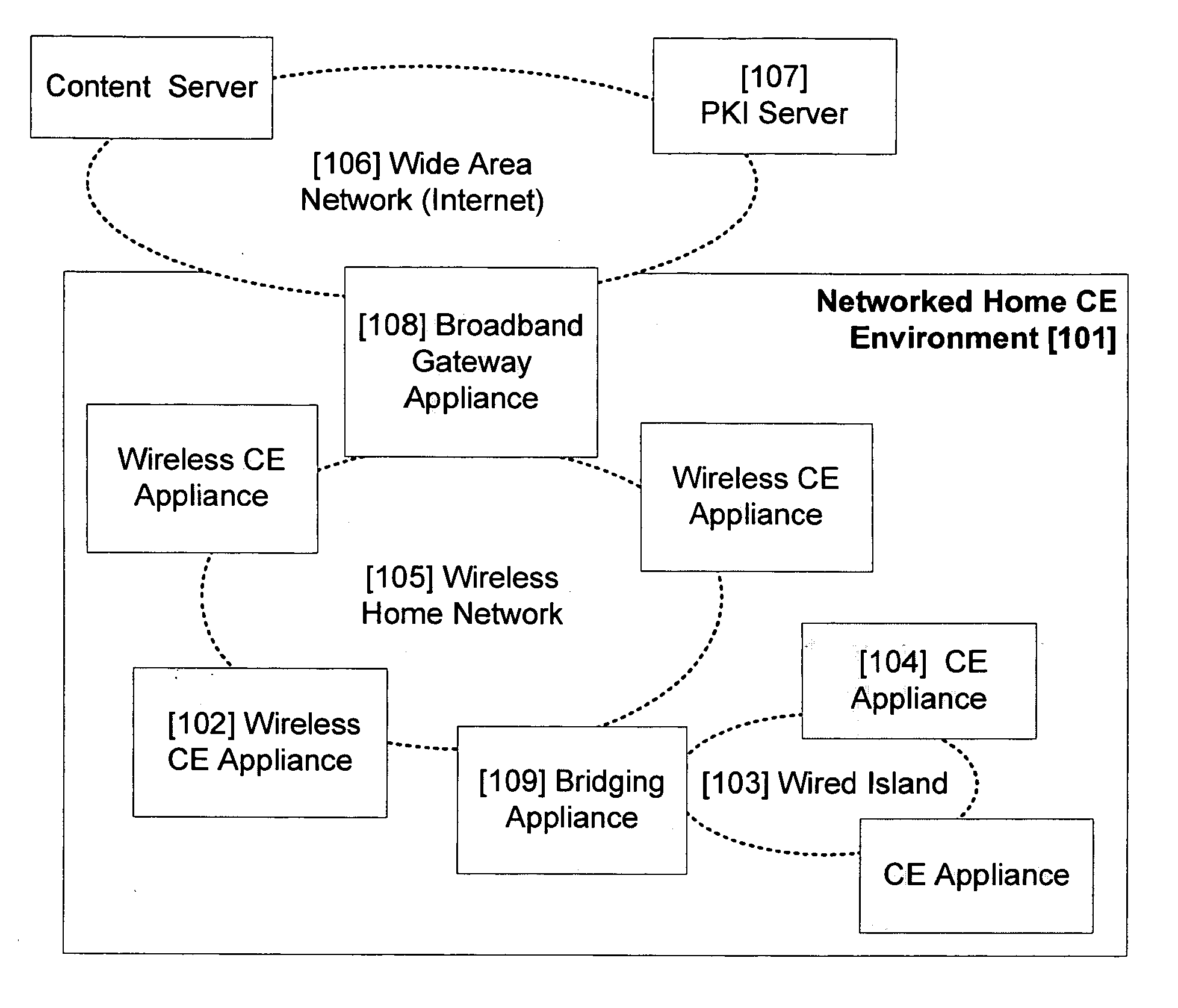
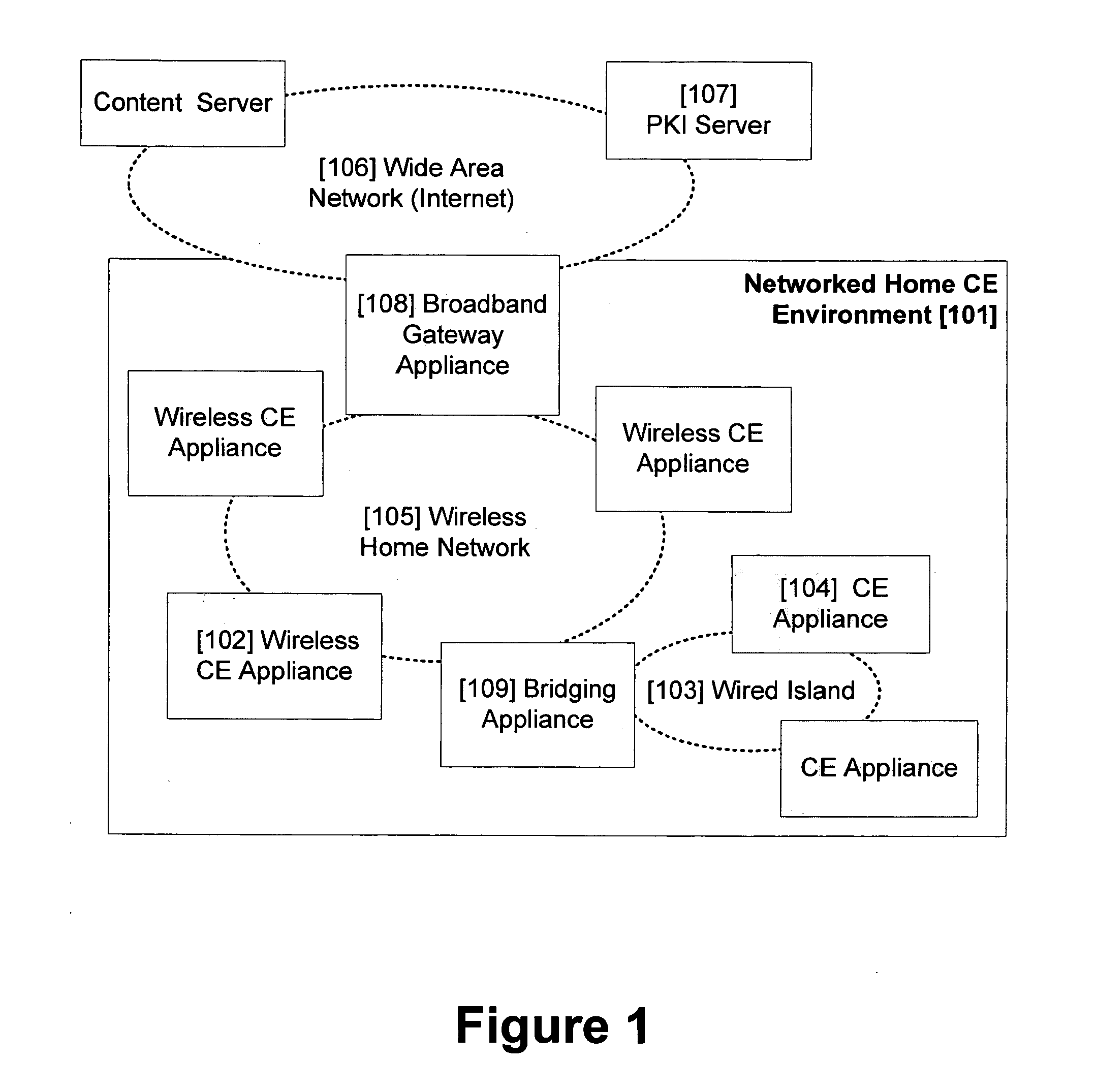
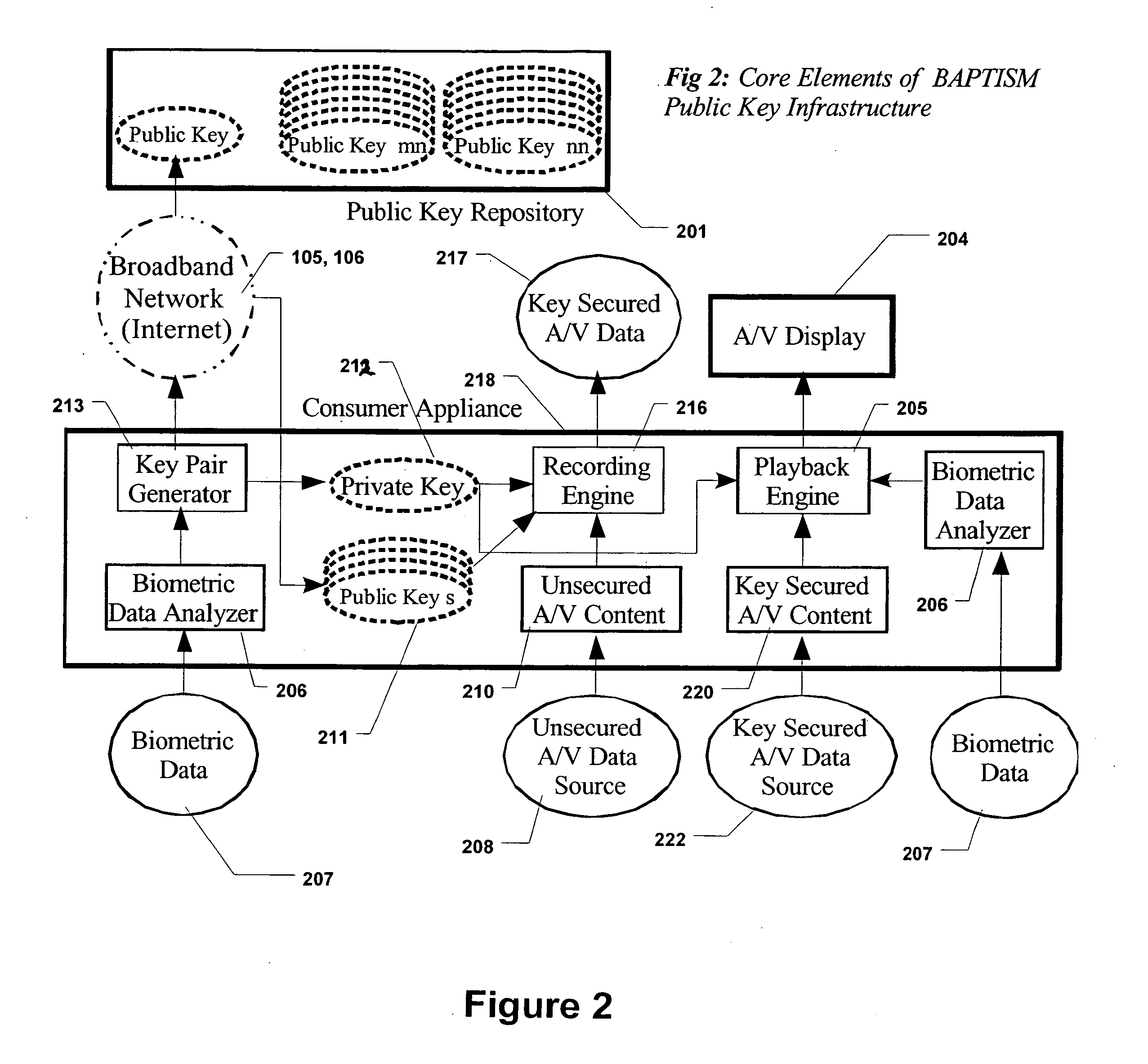
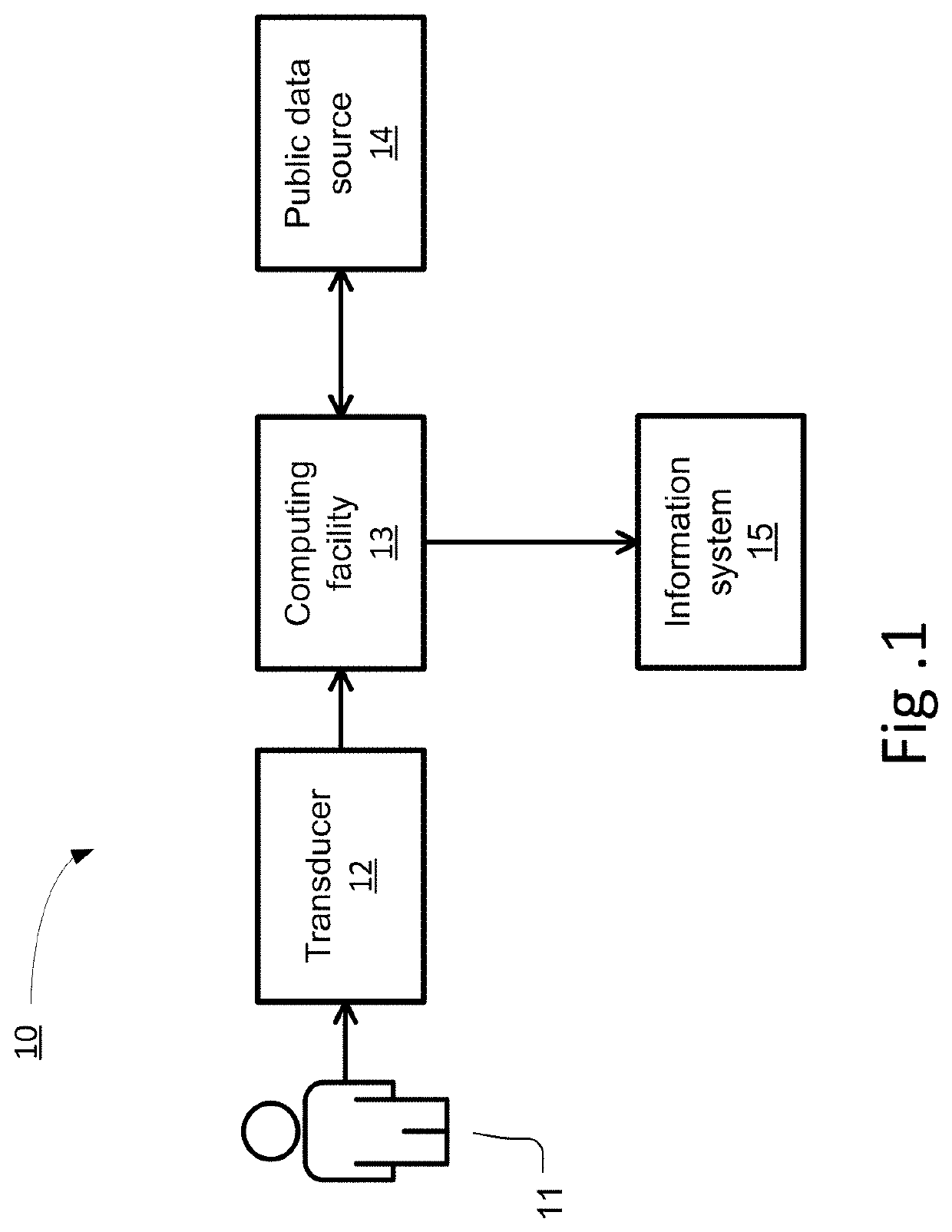
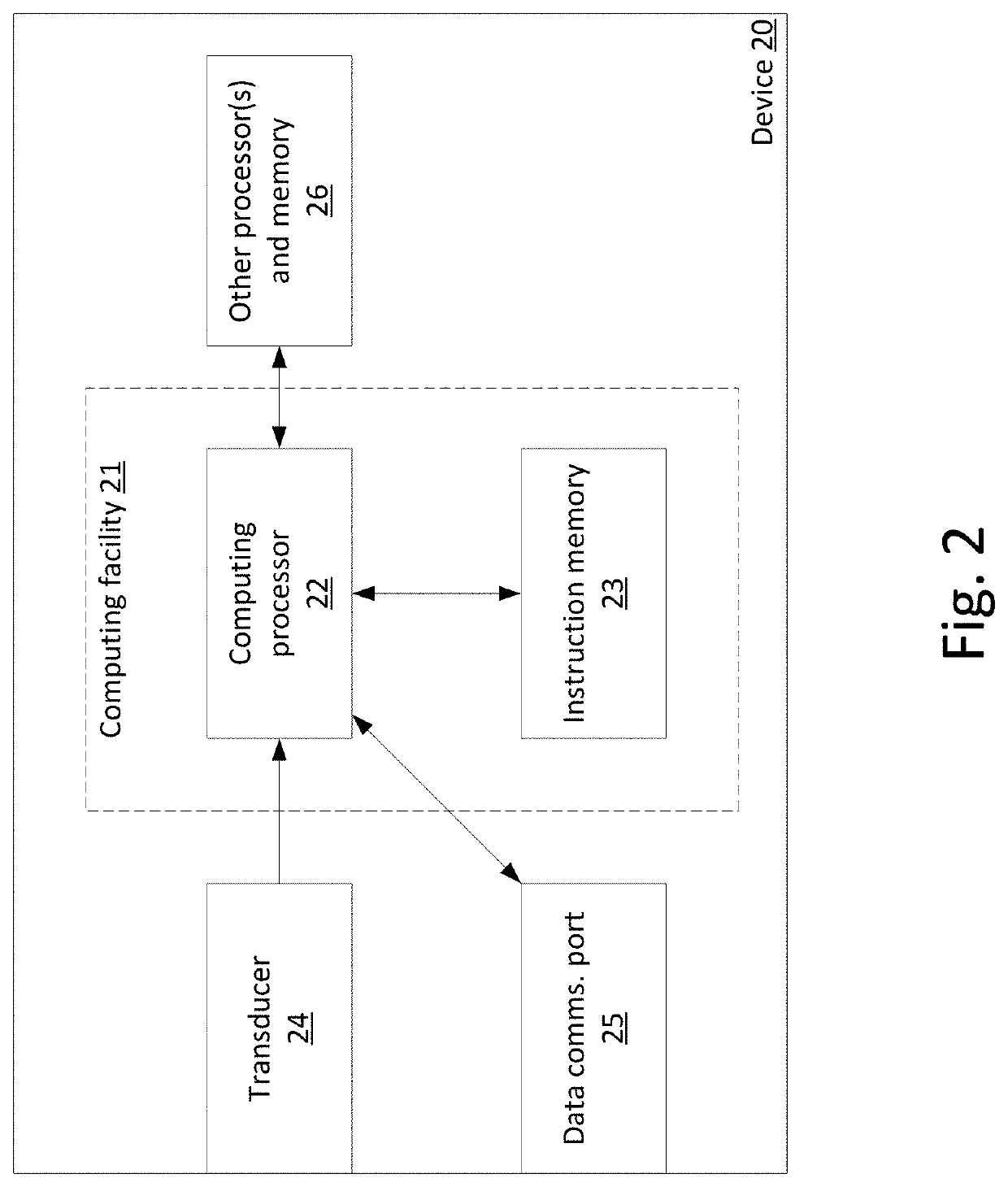
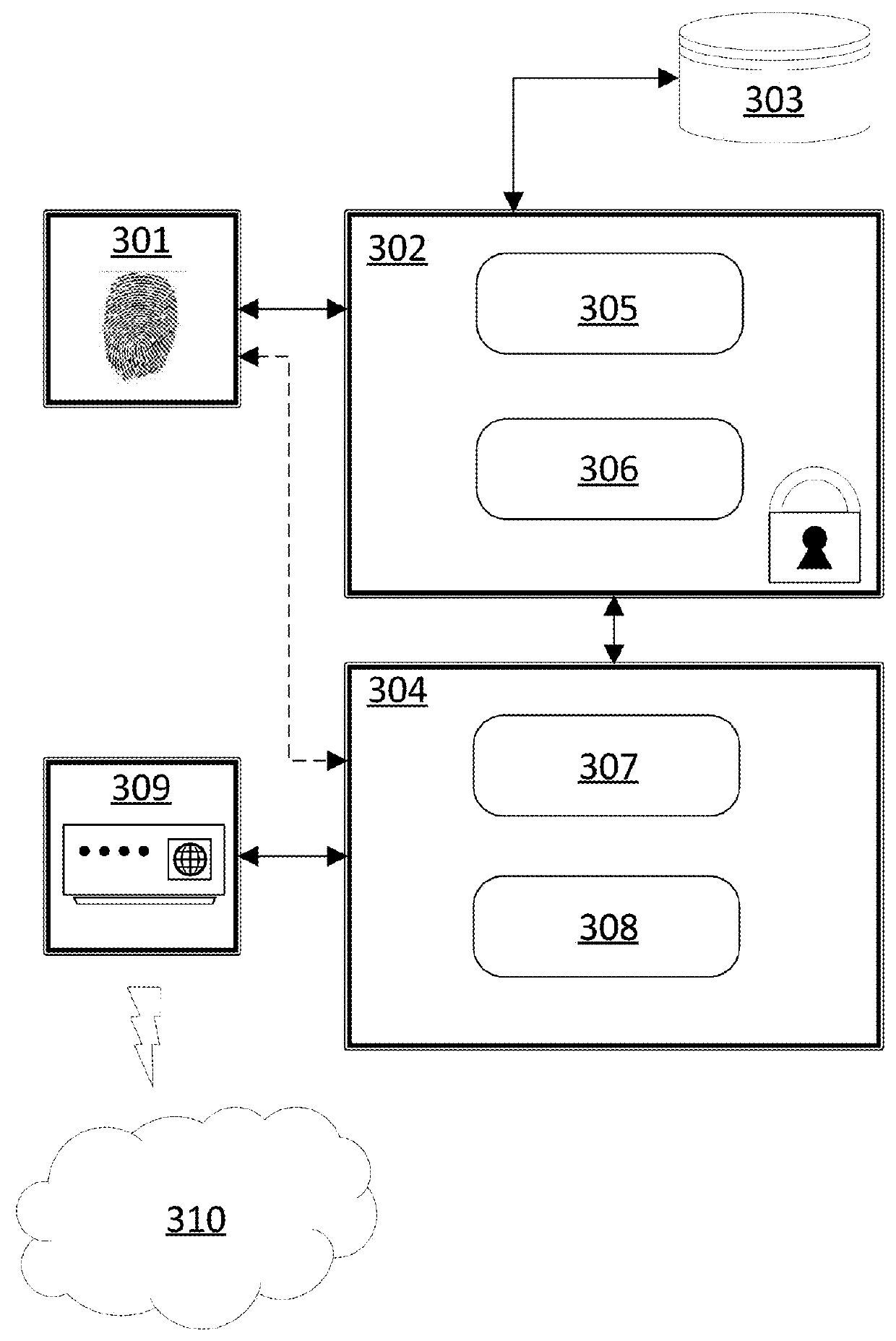
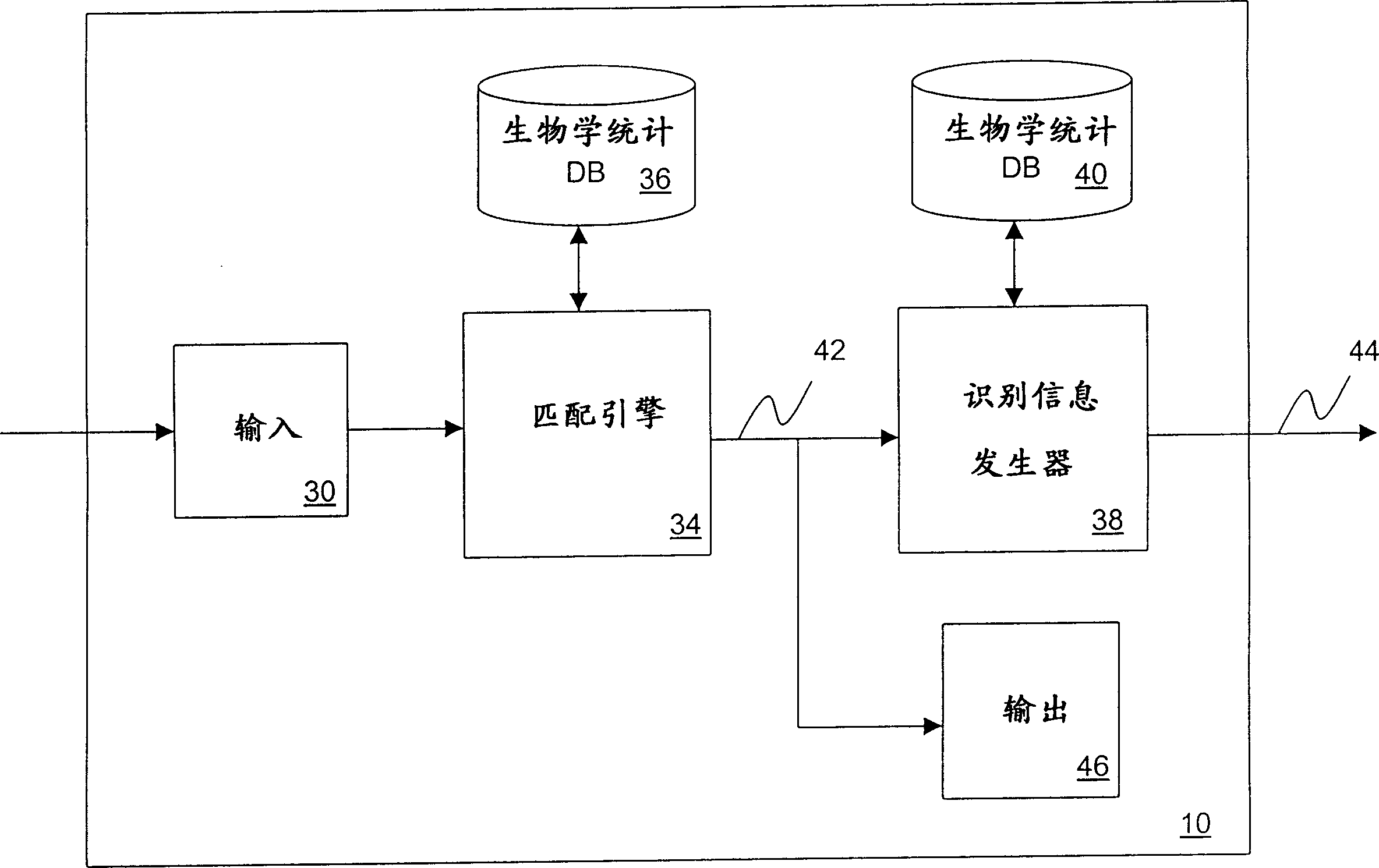
Secure digital content reproduction using biometrically derived hybrid encryption techniques
InactiveUS20050246763A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsDigital contentNumber content
A secure digital content reproduction method includes generating a private-public cryptographic key pair from a biometric signature. The public key is provided to one or more sources of digital content. A CE appliance receives the digital content secured with the public key. By applying the corresponding private key, rendering of the secured digital content is permitted.
Owner:NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF IRELAND
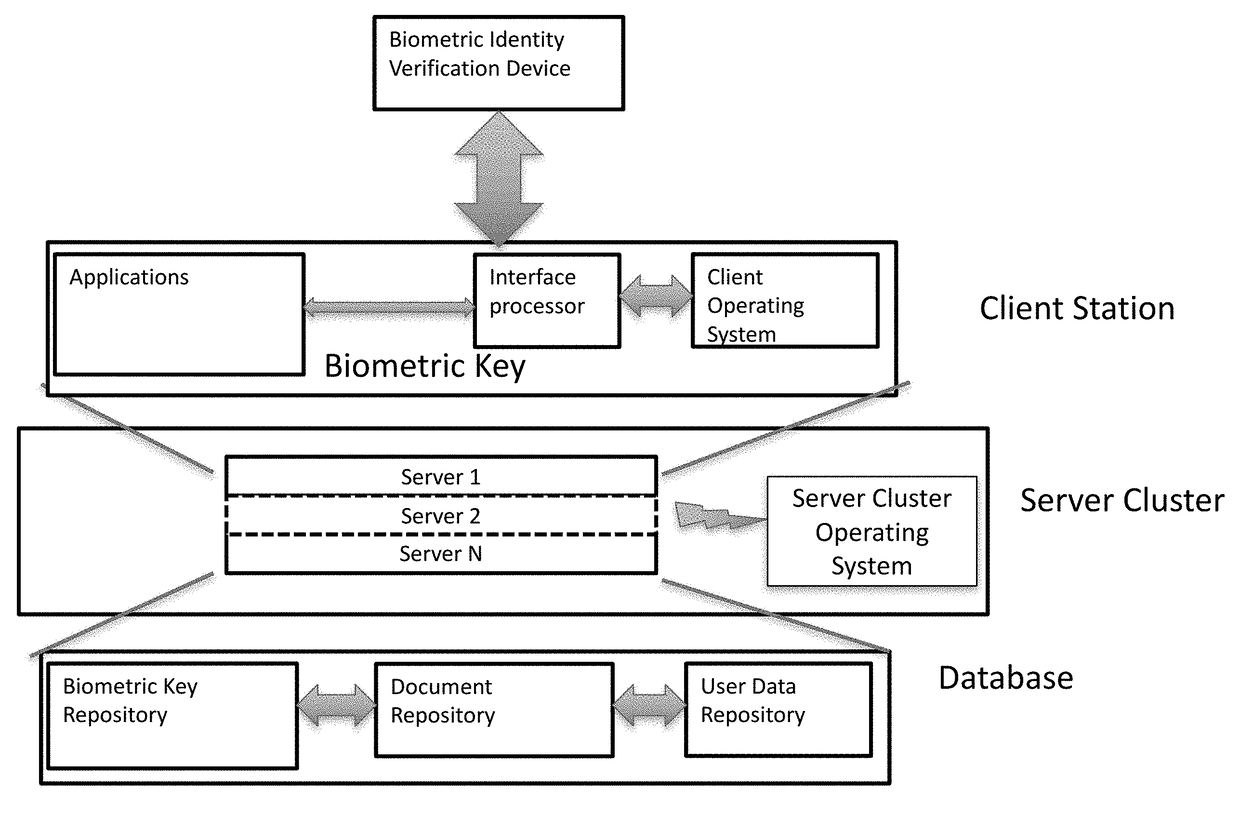
System and Method For Digitally Signing Documents Using Biometric Data in a Blockchain or PKI
ActiveUS20180152297A1Data processing applicationsMultiple keys/algorithms usageDigital signatureCard reader
A system and method executed in one or more servers that interface with a Database Management System (DBMS) for signing and exchanging documents electronically with or without a PIV. If a PIV card is used, a card reader reads embedded private biometric key stored on the card and sends the private key to a node that has the corresponding public key on the X.509 certificate. The public key is derived from the private biometric key embedded in the PIV card as described above. Information contained in X.509 certificate is used to authenticate a user for example using the SSH protocol. If a PIV card is not used, the biometric data represents captured biometric data blocks, which are used to generate a biometric hash at a subscriber node. The subscriber node sends the biometric hash to a plurality of observer nodes that validate the hash by sending validation responses based on hash ledgers states at each observer node. If most of the observer nodes validate the biometric hash, the subscriber is authenticated for signing documents under any role a subscriber may have in an organization.
Owner:NETCOMM INC
Systems and methods for assessing the risk of a financial transaction using biometric information
ActiveUS7398925B2Accurate descriptionAccurate transactionFinancePayment architectureConfidence metricCheque
Owner:FIRST DATA
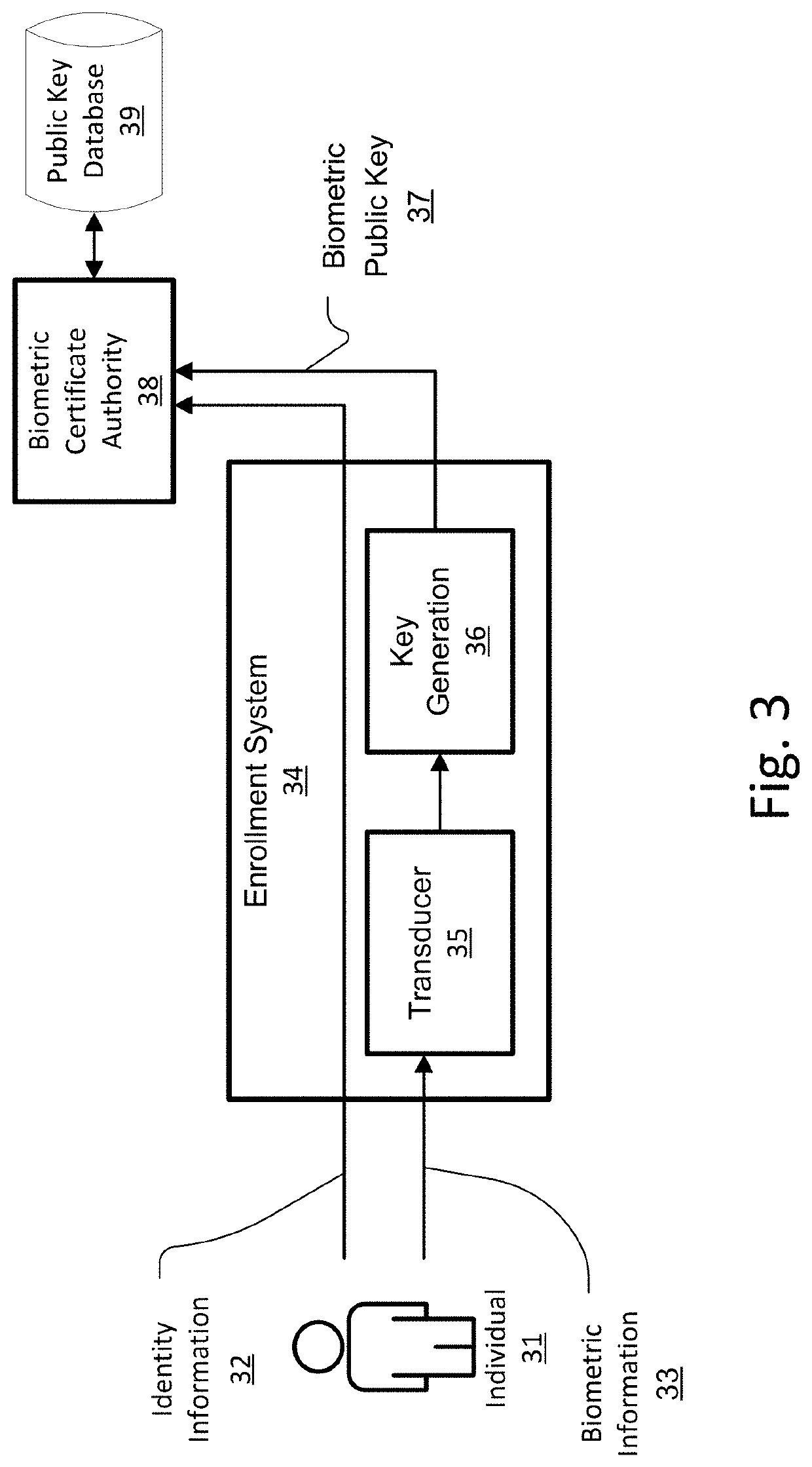
System and Method for Securing Personal Information Via Biometric Public Key
ActiveUS20190356491A1Avoid the needEasy authenticationKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesSecure communicationBiometric data
A device, method, and computer readable storage medium generate a biometric public key for an individual based on both the individual's biometric data and a secret, in a manner that verifiably characterizes both while tending to prevent recovery of either by anyone other than the individual. The biometric public key may be later used to authenticate a subject purporting to be the individual, using a computing facility that need not rely on a hardware root of trust. Such biometric public keys may be distributed without compromising the individual's biometric data, and may be used to provide authentication in addition to, or in lieu of, passwords or cryptographic tokens. Various use cases are disclosed, including: enrollment, authentication, establishing and using a secure communications channel, and cryptographically signing a message.
Owner:BADGE INC
Chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation detecting method and application thereof
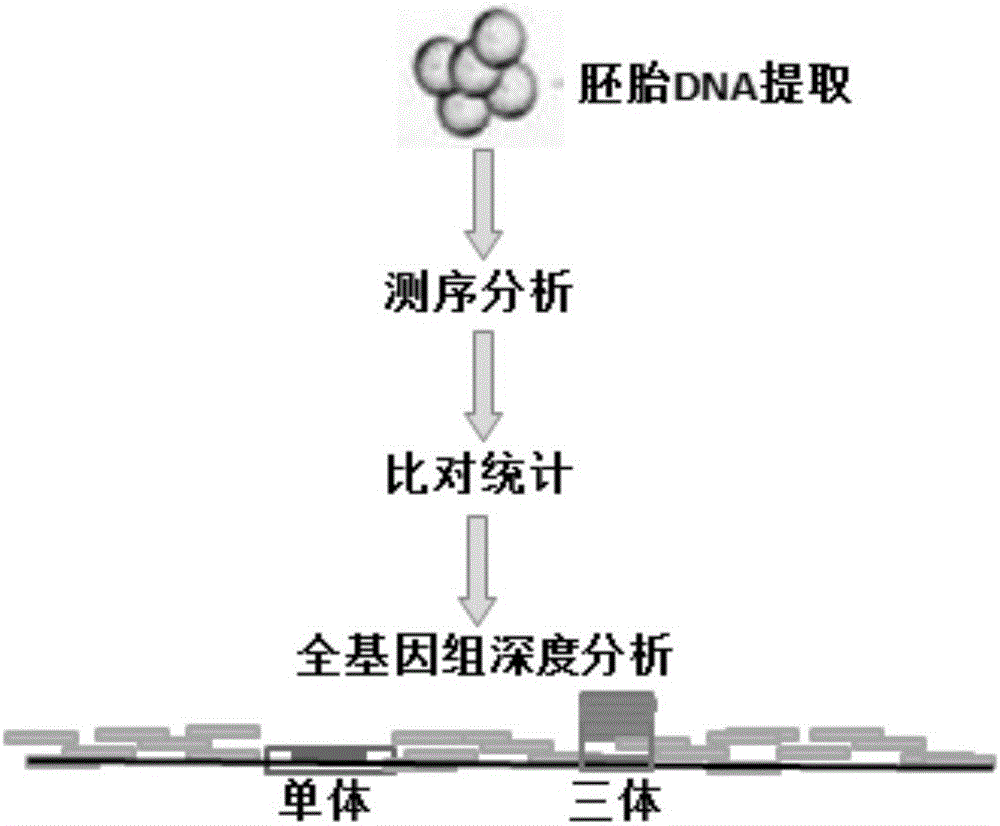
PendingCN106520940AShorten detection timeGuaranteed accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation analysisEmbryo
The invention provides a chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation detecting method and application thereof. Particularly, sequencing is performed on whole genomes of to-be-detected samples, and sequencing data of the samples are obtained. When a certain chromosome in an embryonic cell is a trisomy chromosome or haplochromosome, the copy rate of the chromosome is increased or decreased compared with that of a normal diploid chromosome, information analysis is performed through biostatistics, and aneuploids can be accurately detected. An experimental result shows that the chromosomal aneuploid and copy number variation can be simply, rapidly and accurately detected through the method.
Owner:BGI BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
System for combining geographic location information, database-derived affinity matches, and user control in order to permit individuals to rendezvous
InactiveCN1961588AVisible signalling systemsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsBiometricsData mining
A system combining features of affinity and / or preference matching, location services, wireless devices, and security to provide users with controllable ability to Rendezvous or track based upon user-defined interests or characteristics. Security features may include multiple levels of user-selected security and identification of users by a variety of means, including biometrics and image recognition.
Owner:克里斯托夫·S·韦弗 +1
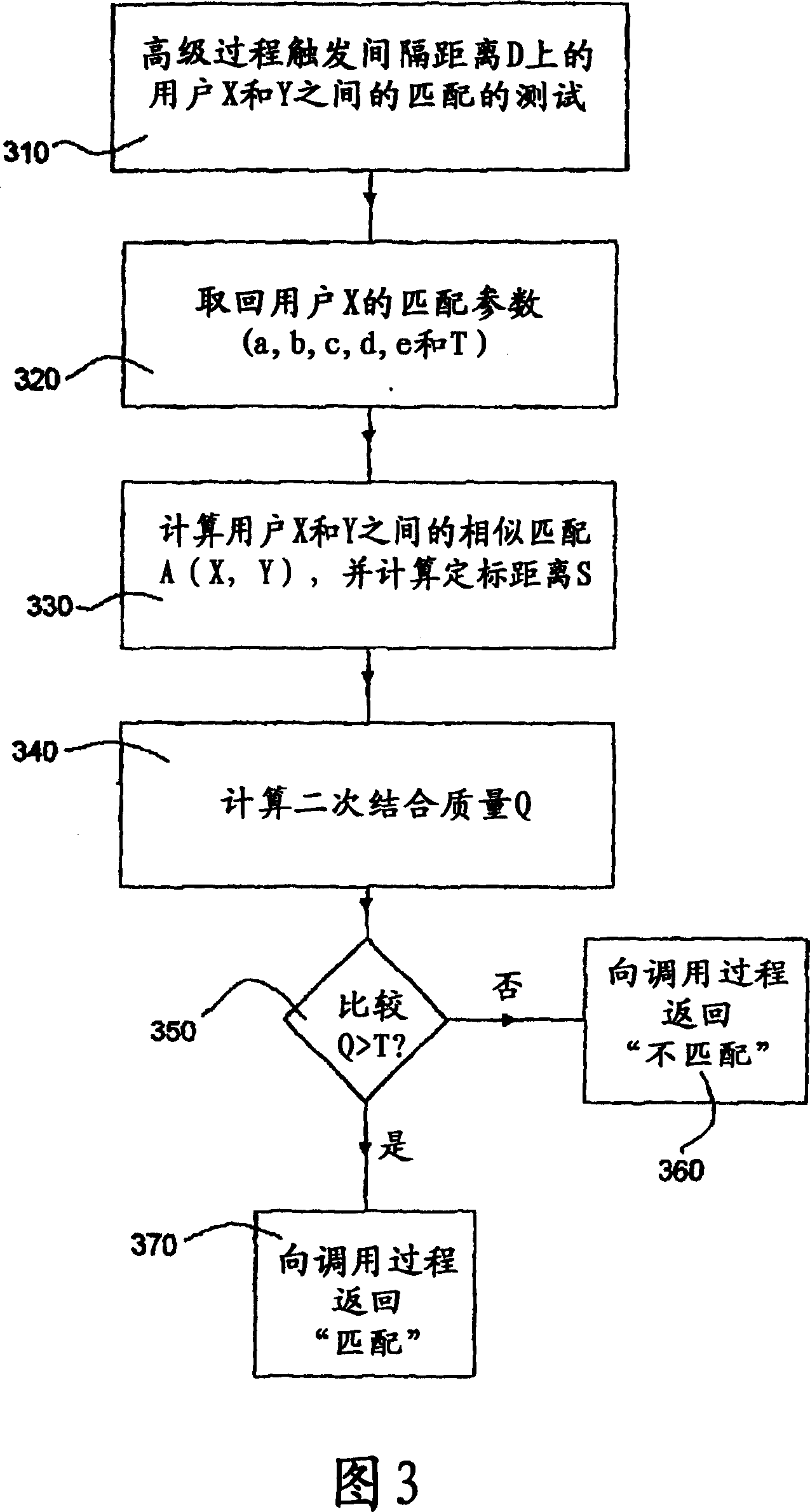
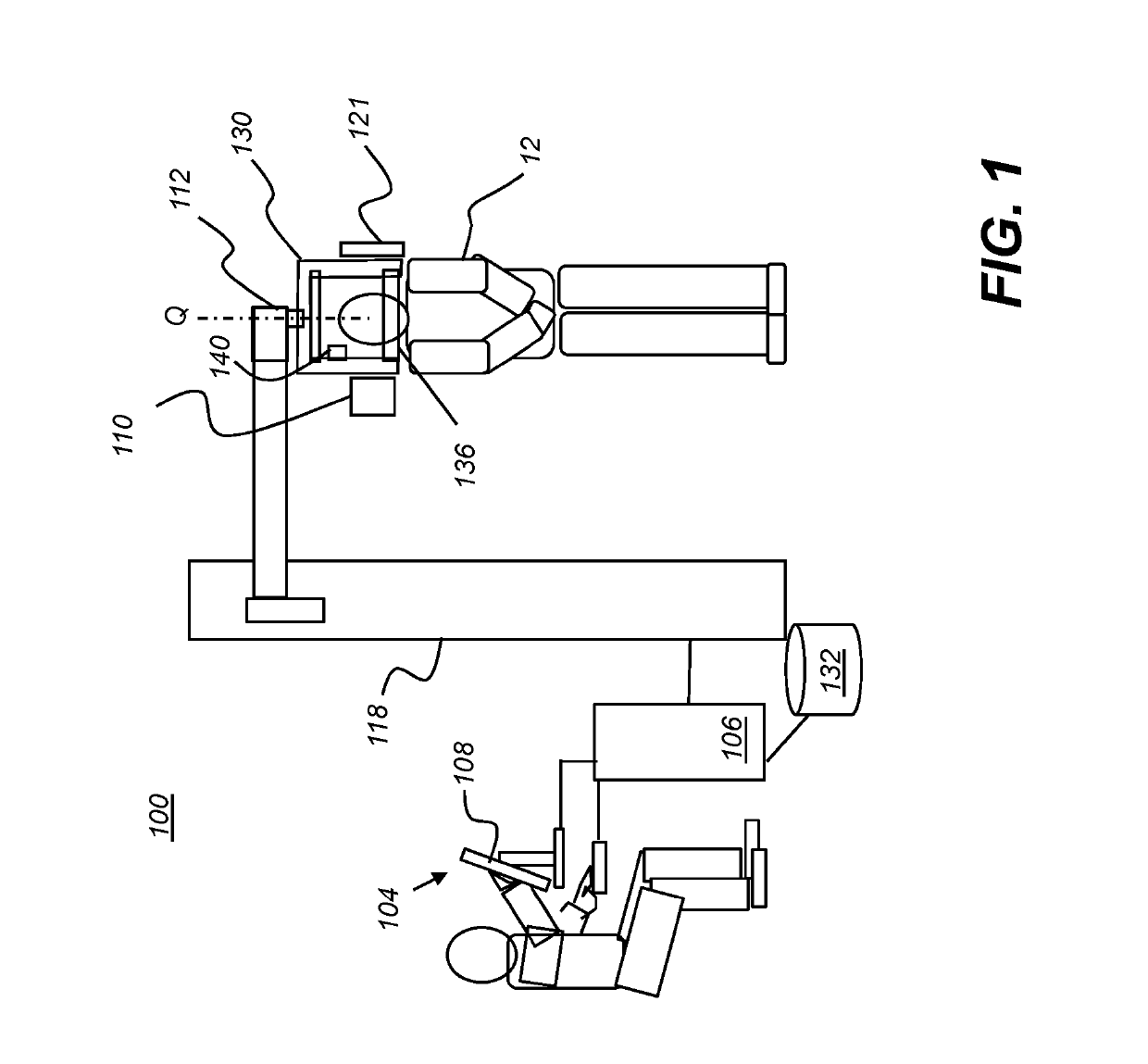
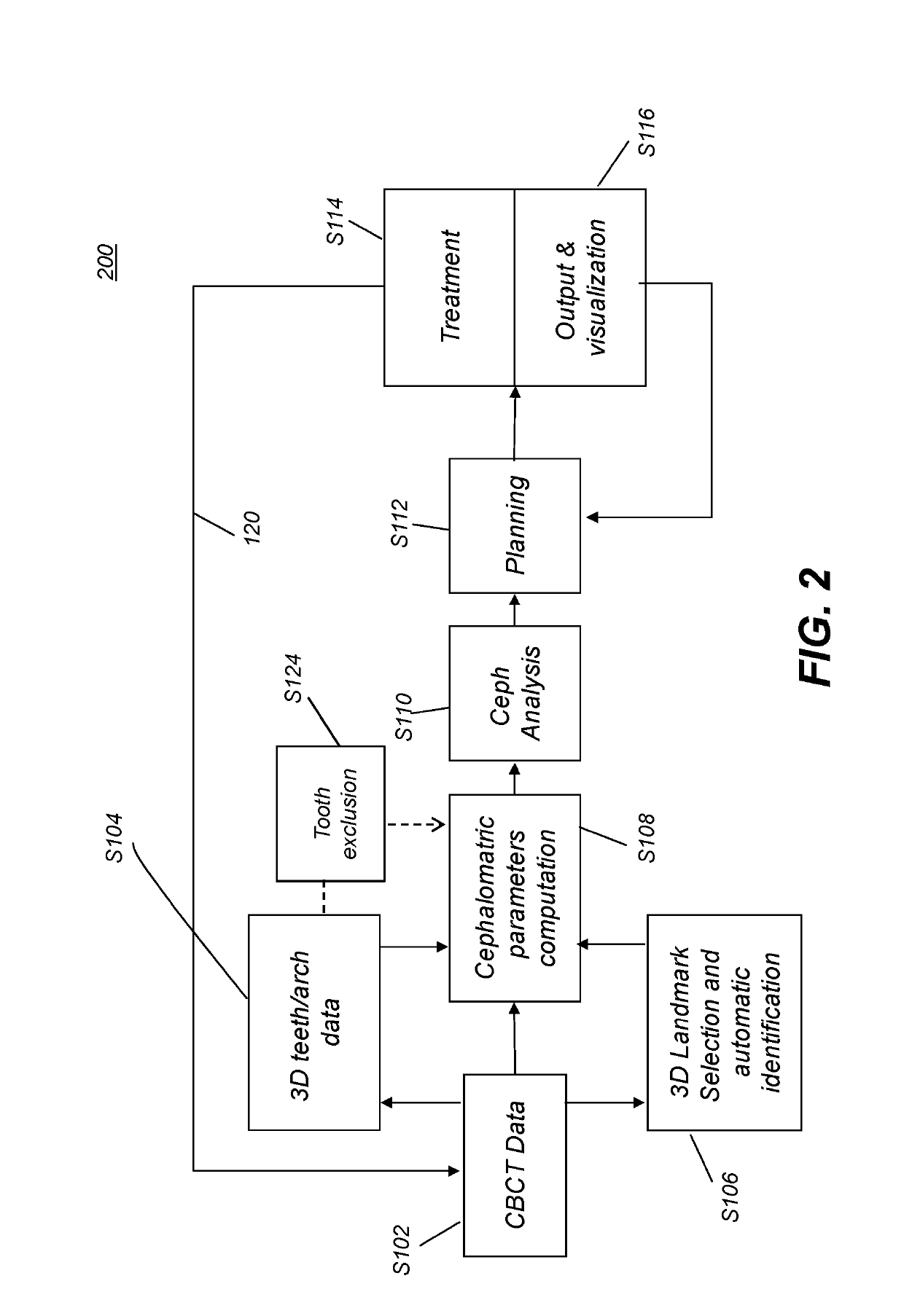
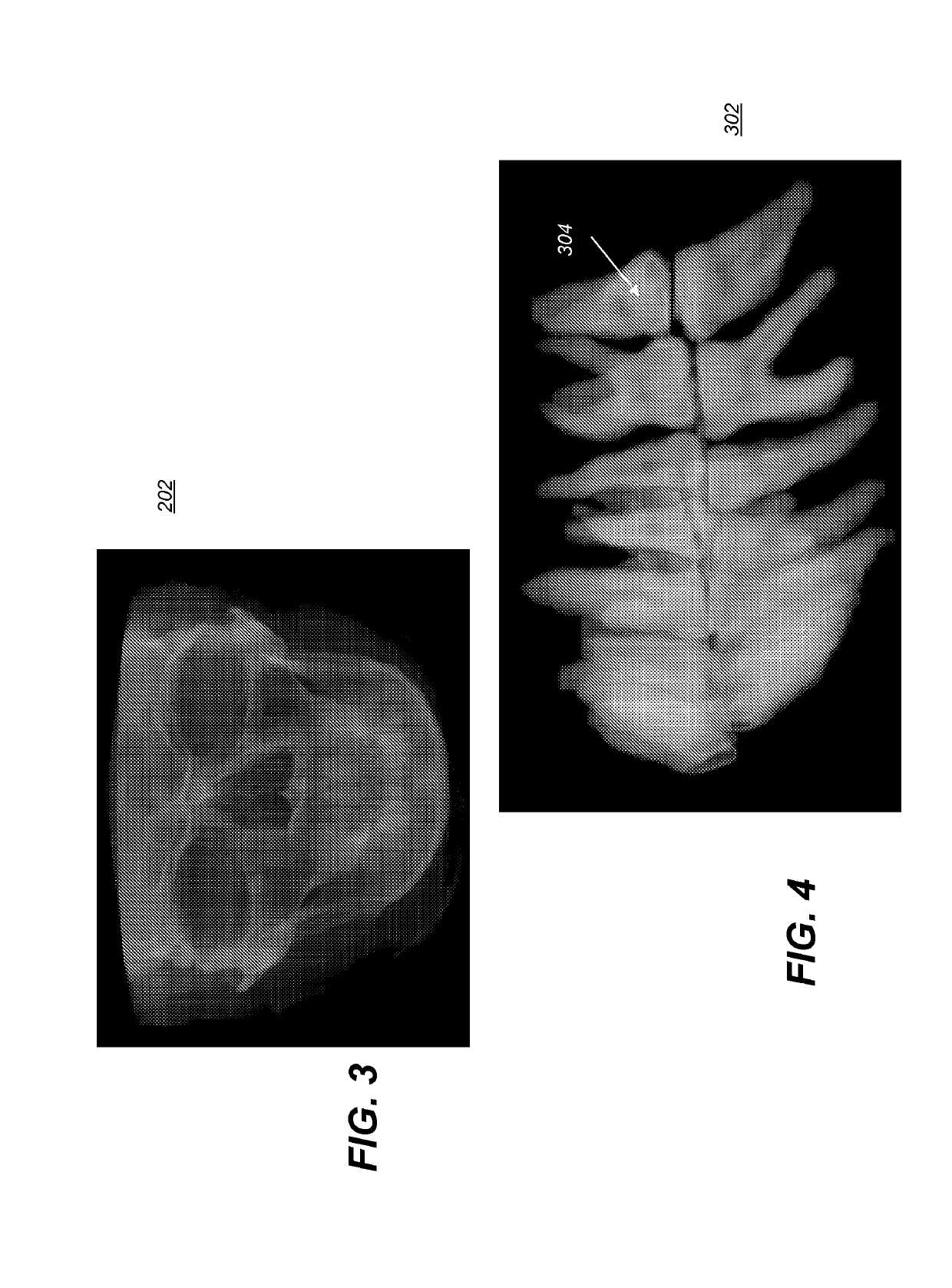
Reconstruction of a virtual computed-tomography volume to track orthodontics treatment evolution
ActiveUS20190328489A1Speed of computationCorrection capabilityMedical simulationImage enhancementCephalometric filmCephalometric analysis
Method and / or apparatus embodiments for 3-D cephalometric analysis of a patient according to the application can display reconstructed volume image data from a computed tomographic scan of a patient's head including segmented dentition elements having an initial arrangement from one or more 2D / 3D views; can compute and display a plurality of cephalometric parameters for the patient according to the reconstructed volume image data; then use the patient specific cephalometric parameters and population biometry data, to identify one or more maxillofacial / dental abnormalities; and compose patient specific treatment plans to correct selected dentition abnormalities using maxillofacial / dental structure, which can be composed in a final tooth arrangement in a final virtual CT volume. One or more aligners can be generated to incrementally move dentition from the initial arrangement to the final tooth arrangement.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Personal healthcare device
ActiveUS20180353137A1Physical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationBiometric dataComputer science
A method and system for measuring personal health, the method comprising detecting a photoplethysmograph (PPG) wave, the PPG wave generated based on a combination of infra-red and red lights, transmitting the PPG wave to a server, the server processing the PPG wave to infer biometric statistics based on machine learned correlations generated from a training set of PPG waves and biometric data, receiving the biometric statistics from the server, and generating display data based on the biometric statistics.
Owner:HELO CORP
Combined individual authentication system
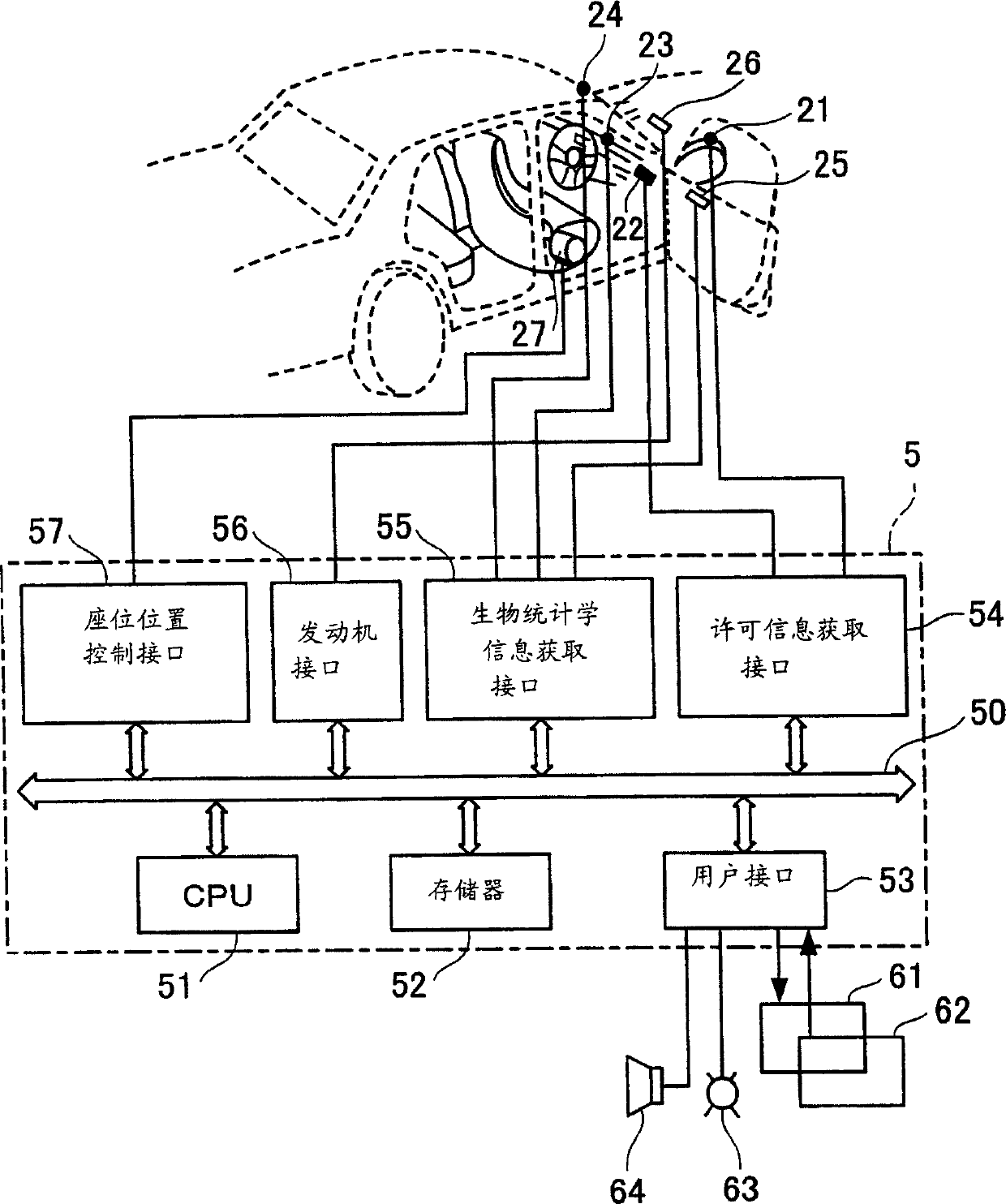
InactiveCN1664290AImprove securityVehicle locksAnti-theft devicesAuthentication systemVerification system
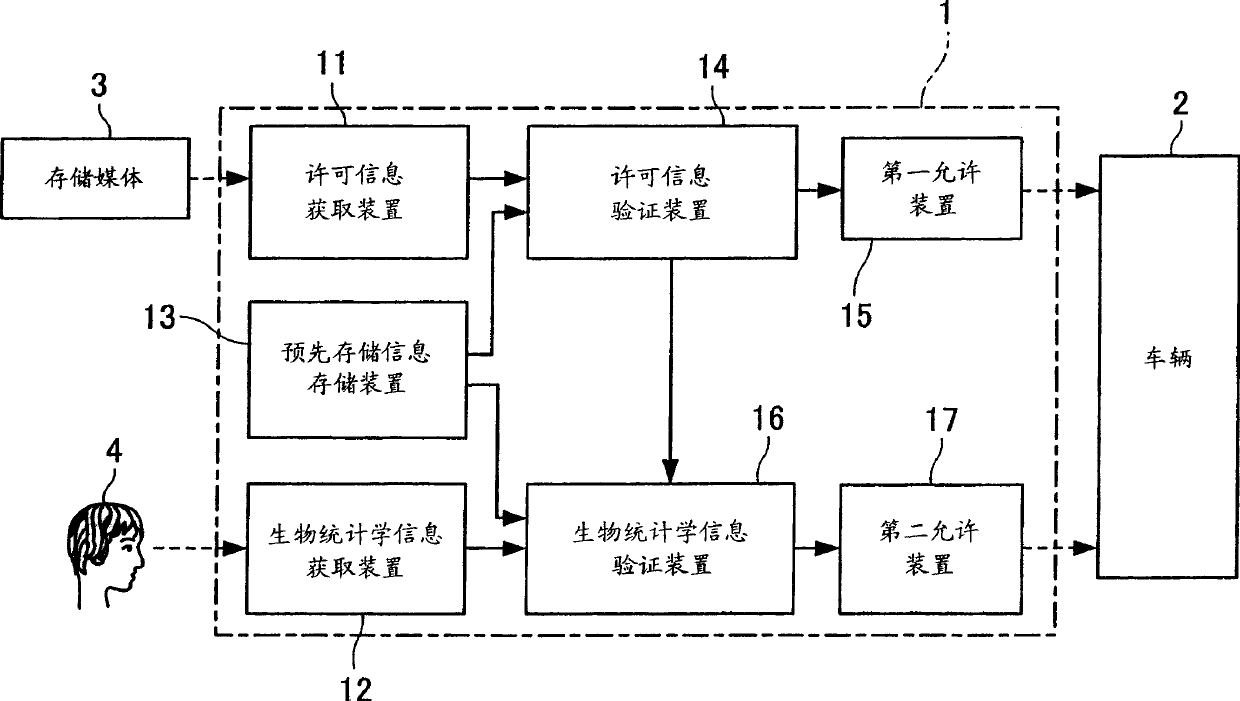
A combined individual authentication system 1 comprises a license information acquiring means 11 for acquiring license information from a storage media 3 which a driver 4 carries before or after a vehicle 2 runs, a biometric information acquiring means 12 for acquiring biometric information of the driver 4, a pre-stored information storing means 13 for storing pre-stored license and biometric information of the driver 4, a license information authenticating means 14 for authenticating the driver 4 based on the pre-stored license information, a first permitting means 15 for permitting at least one of functions which the vehicle 2 equipped, when the license information authenticating means 14 authenticates the driver 4 as an authenticated driver, a biometric information authenticating means 16 for authenticating the driver 4 based on the pre-stored biometric information, when the license information authenticating means 14 authenticates the driver 4 as an authenticated driver, and a second permitting means 17 for permitting at least one of functions which the vehicle 2 equipped.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Machine learned biometric token
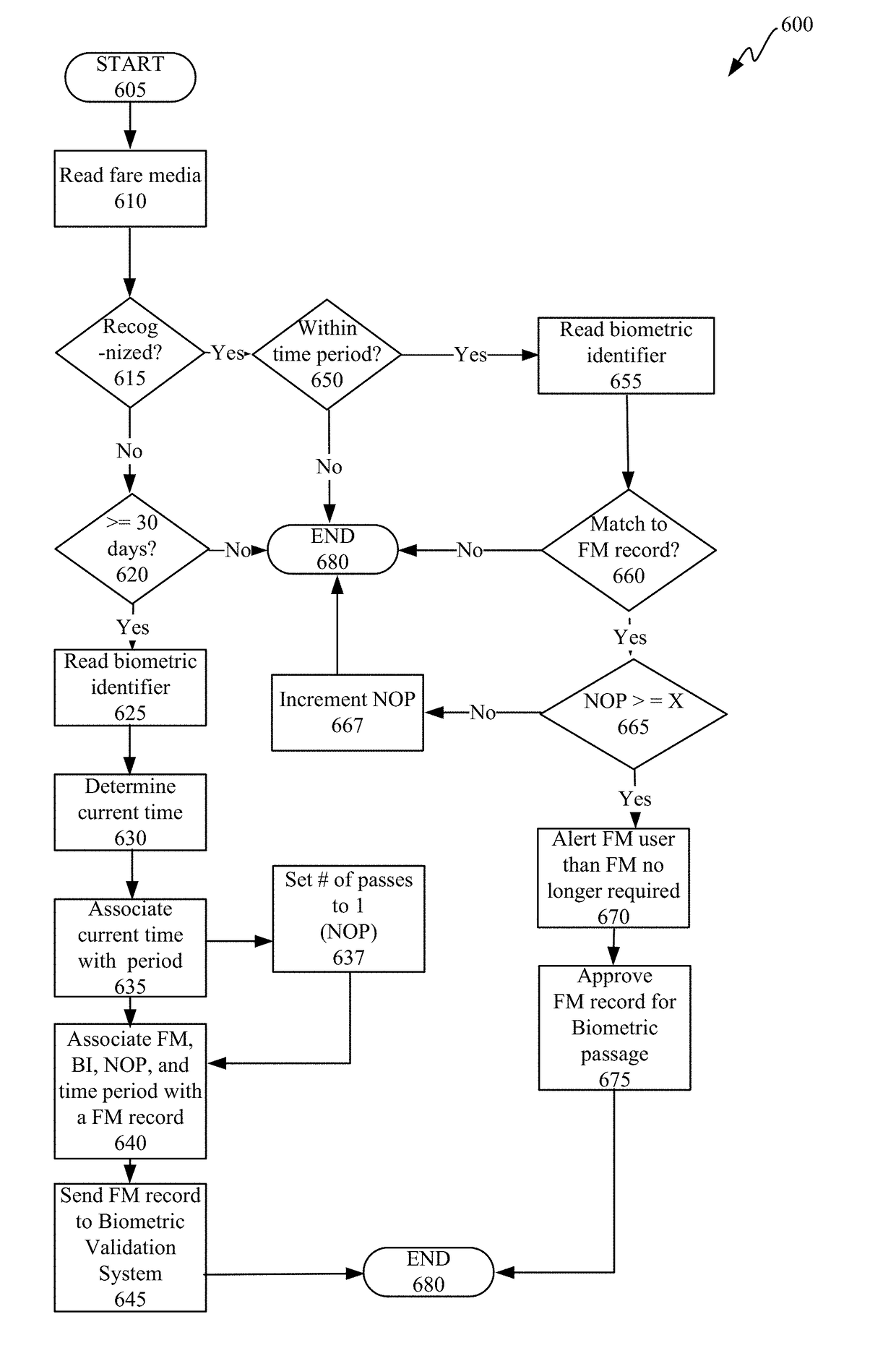
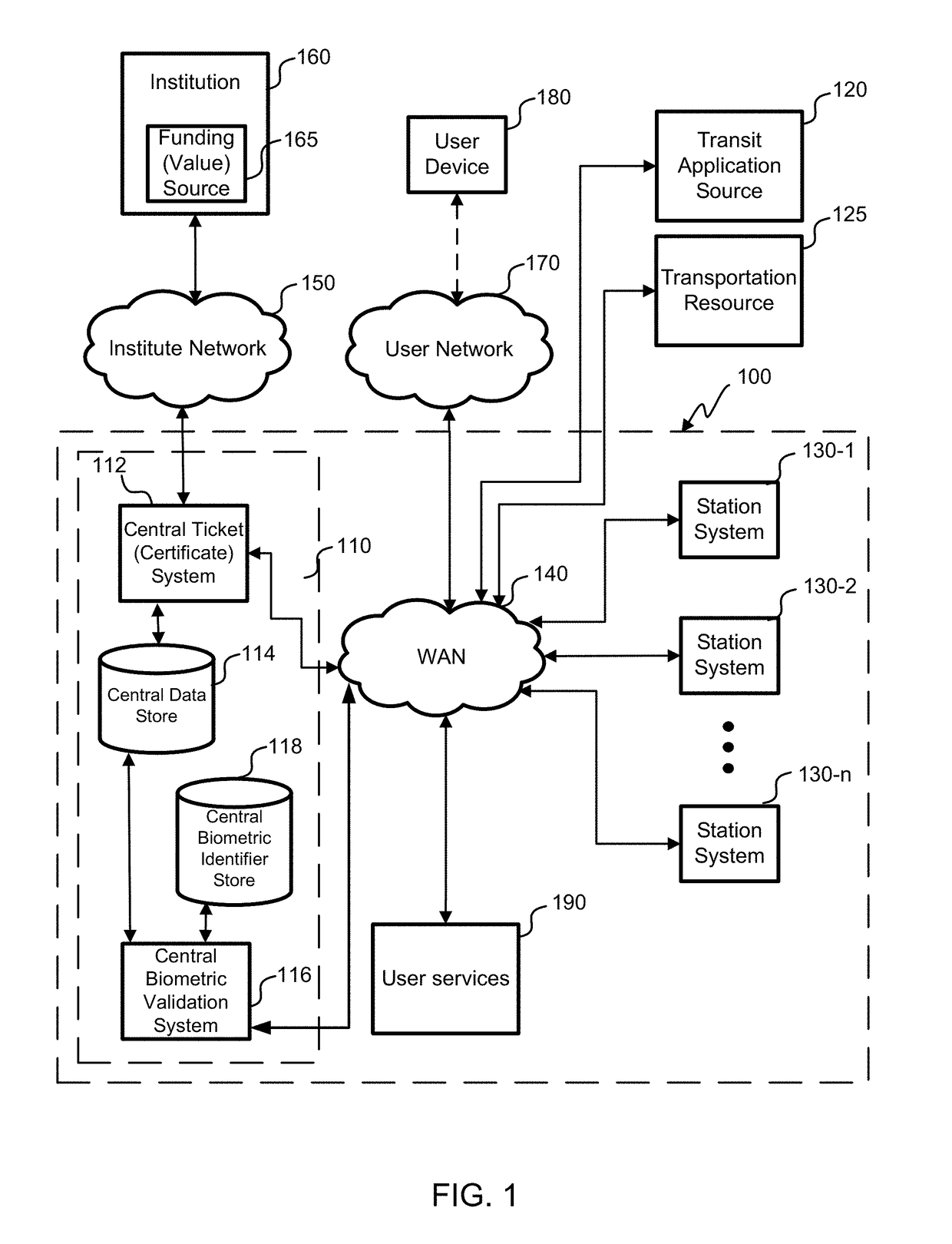
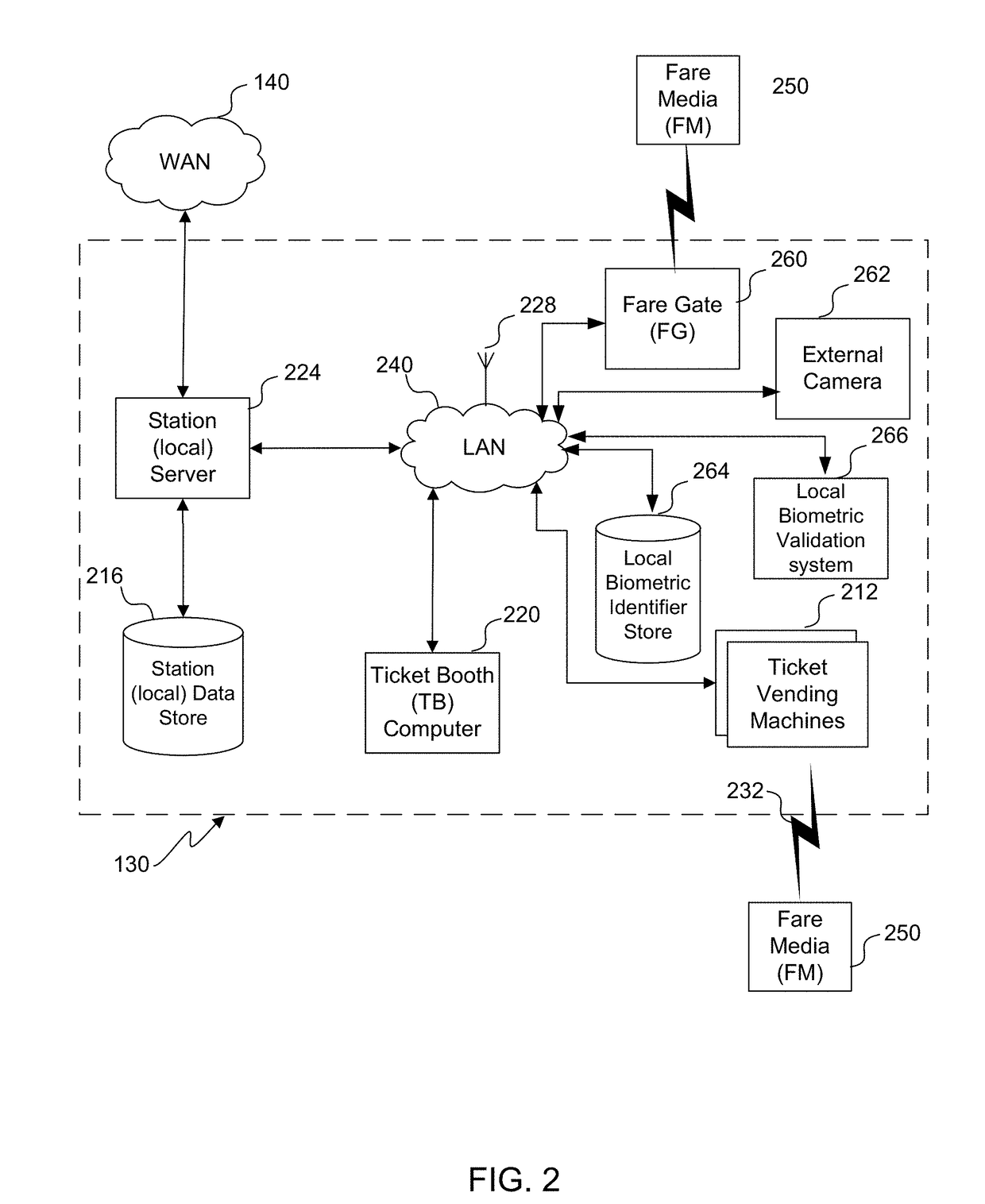
Embodiments of the invention(s) described herein enable a system that may rely on a biometric identifier entry validation system. The validation system “learns” the use pattern of a user. The validation system uses biometric methods such as facial recognition, palm veins, and thumb prints as an entry or passage token. When enough data has been collected, the validation system sends the user's biometric identifier to the use location within a bounded time frame when it expects a regular user to arrive at that location and within that time frame. In this manner the biometric identifier becomes a biometric token that replaces the need to use a form of fare media. Thus, the validation system becomes more efficient and recognizes a user faster after collecting data of a user for a short time. The validations system can record and interpret historic data. With this data, the validation system knows, on average, when to expect that passenger to arrive and where.
Owner:CUBIC CORPORATION
Method for identification
ActiveCN1860724AUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationDependabilityIris recognition
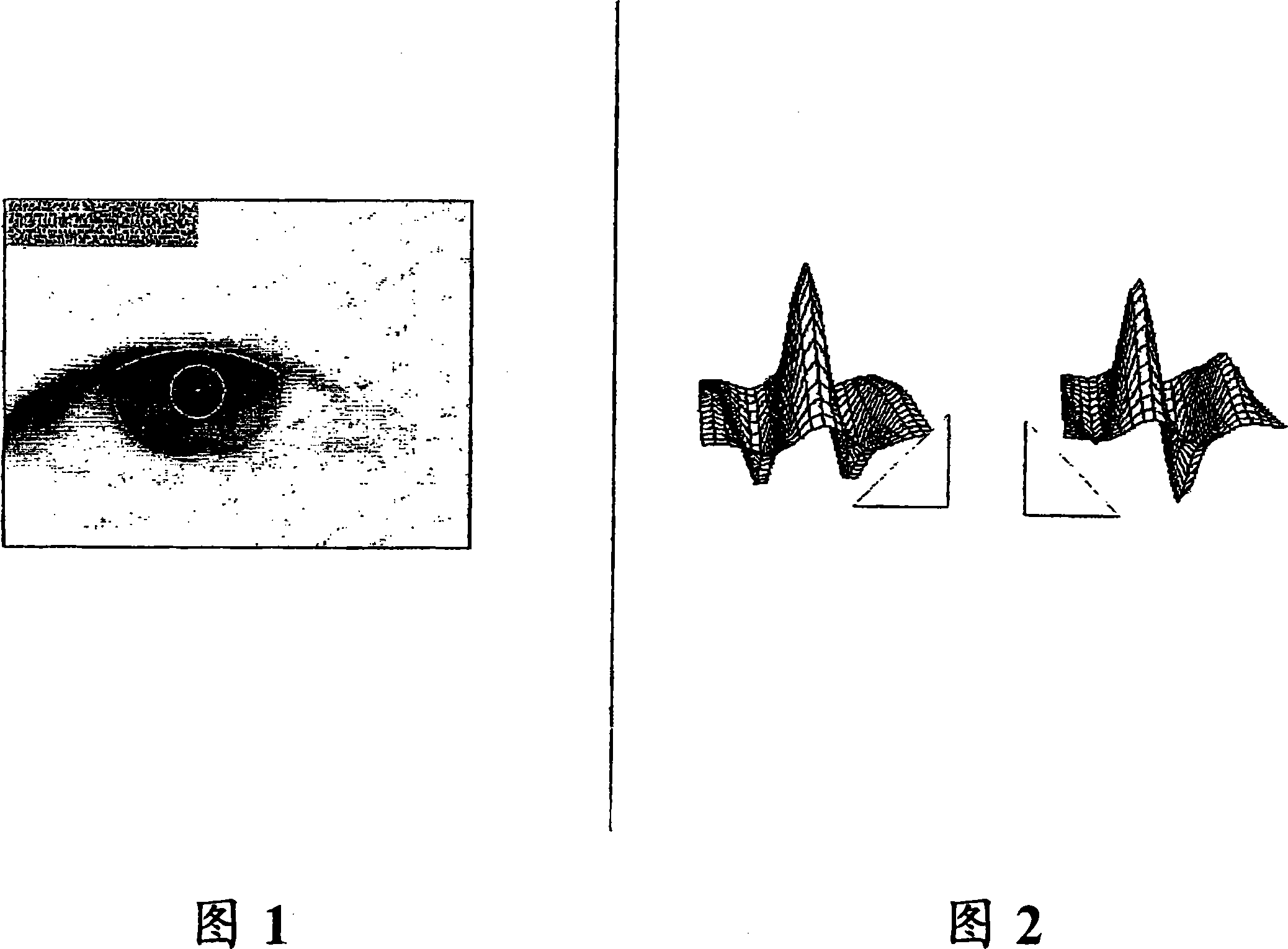
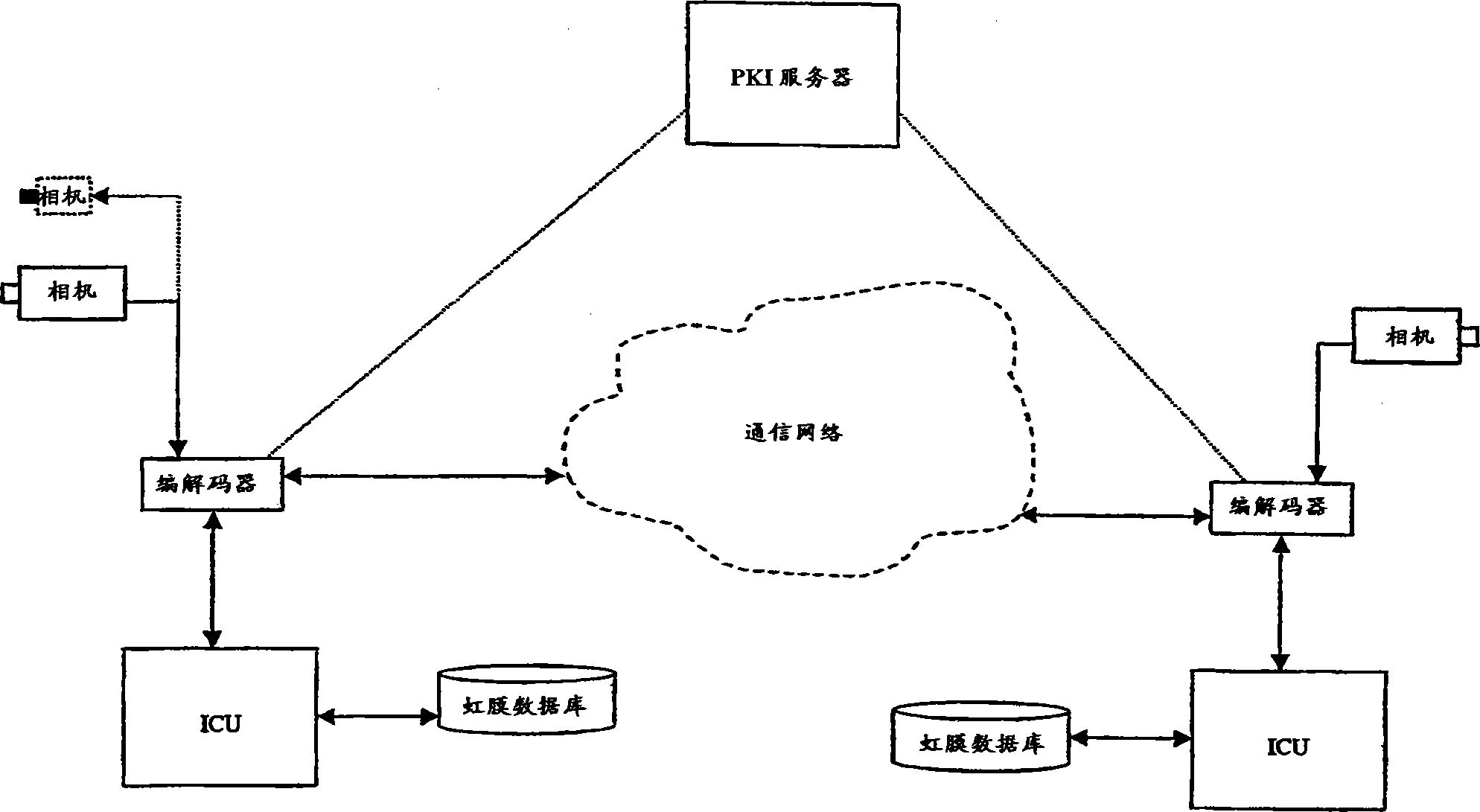
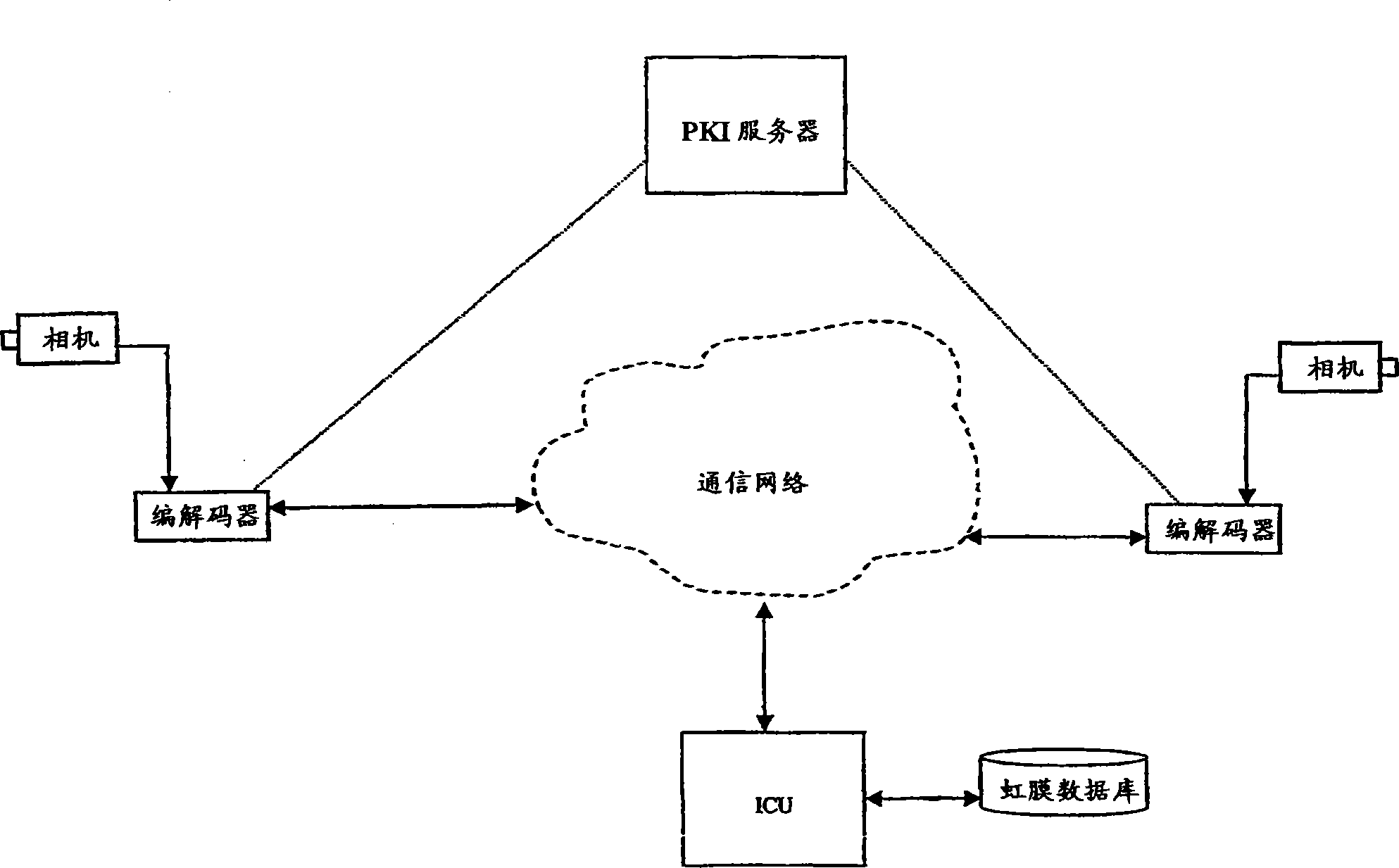
The present invention relates to conferencing and data recording, in particular to providing secured and verified transactions by means of biometrics. The uniqueness of biometrics is combined with the robustness and reliability of PKI for use in conference applications. The invention is about identifying an individual from a biometric pattern, like the iris of the individual's eye, by means of an iris recognition system. The recognition system then provides the identity of the individual, which is further used to provide secure and reliable digital actions or verifications like authentication, signing and encryption.
Owner:CISCO SYST INT R L
Assay for neuromuscular diseases
InactiveUS20060278532A1CellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesDiseaseNeuromuscular disease
The present invention is an assay for determining if a patient has a neuromuscular disease. The method comprises collecting a biological sample from a patient, separating the proteins present in the biological sample, quantitating a panel of proteins by proteomic techniques, analyzing the quantity of the protein panel using biostatistics, and determining whether or not the patient has a neuromuscular disease based on the statistical analysis of the results.
Owner:NEOGENOMICS INC
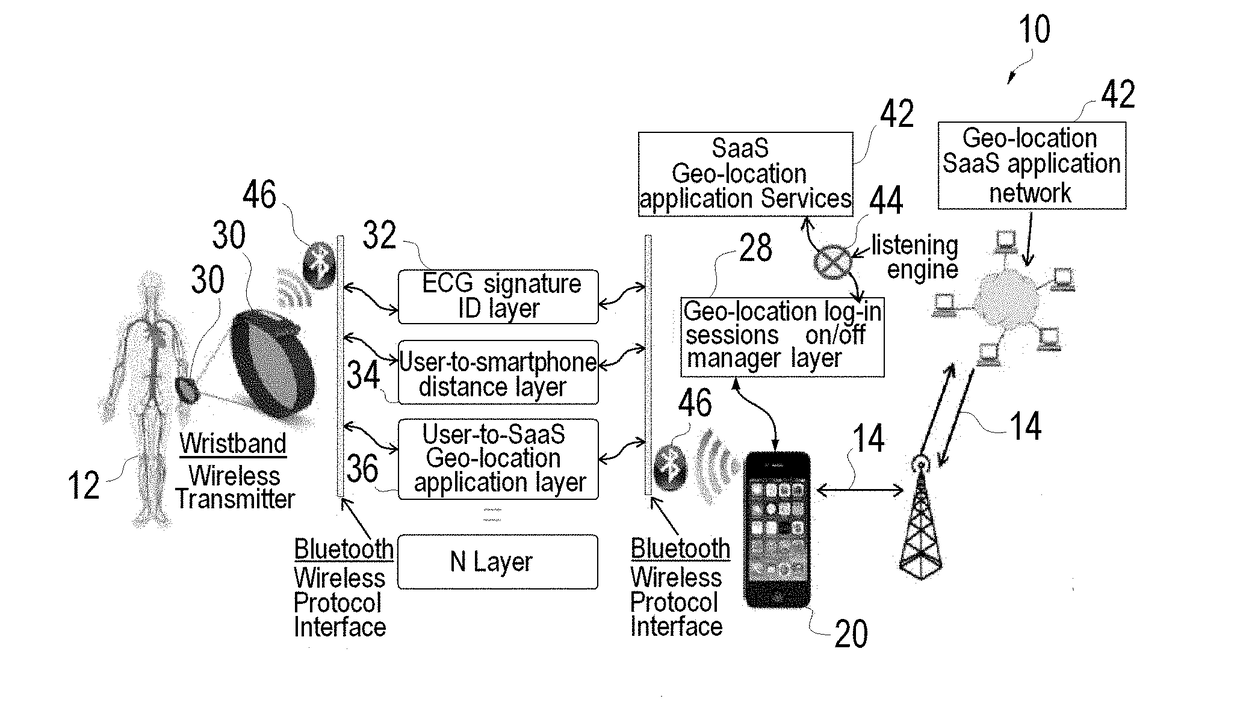
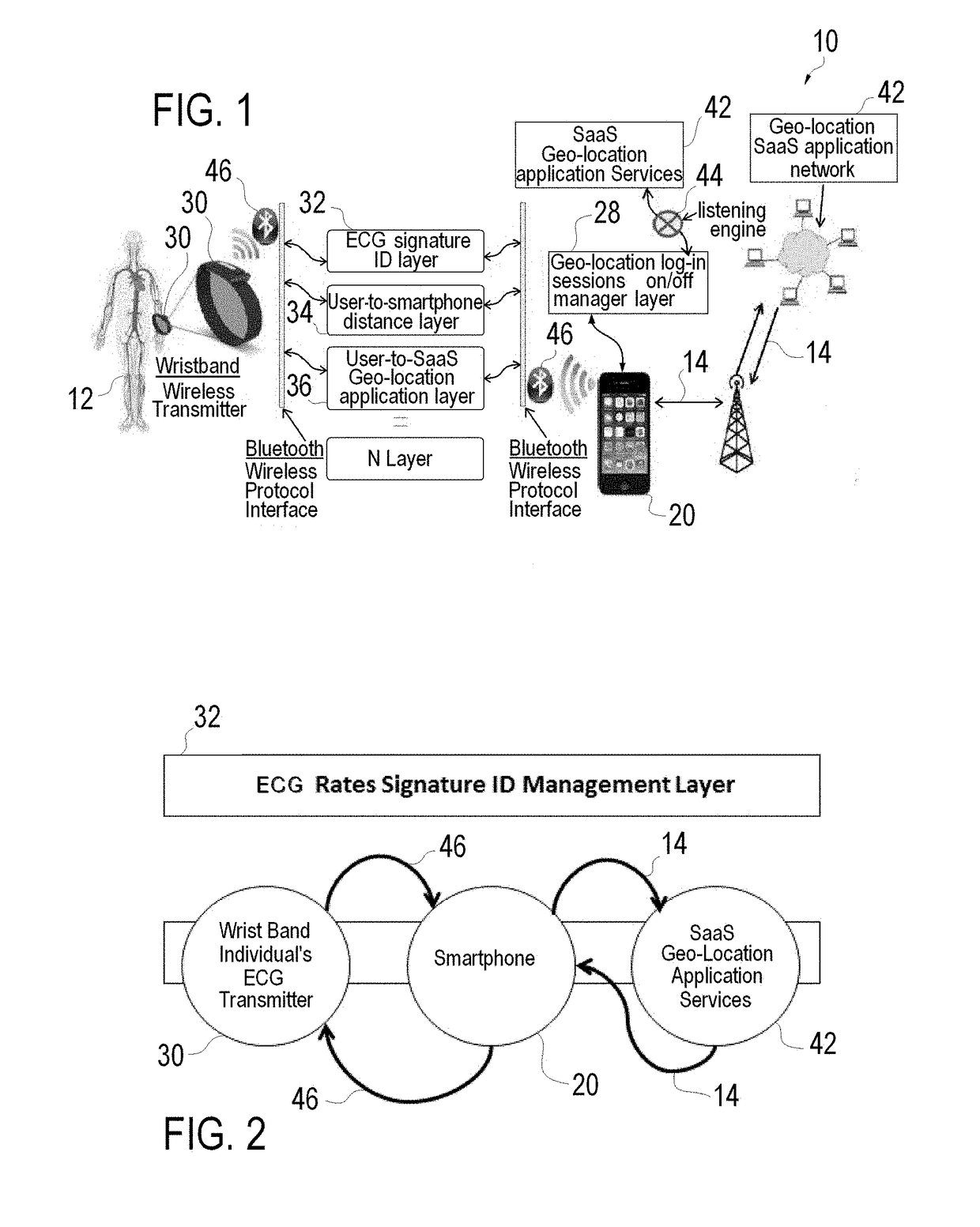
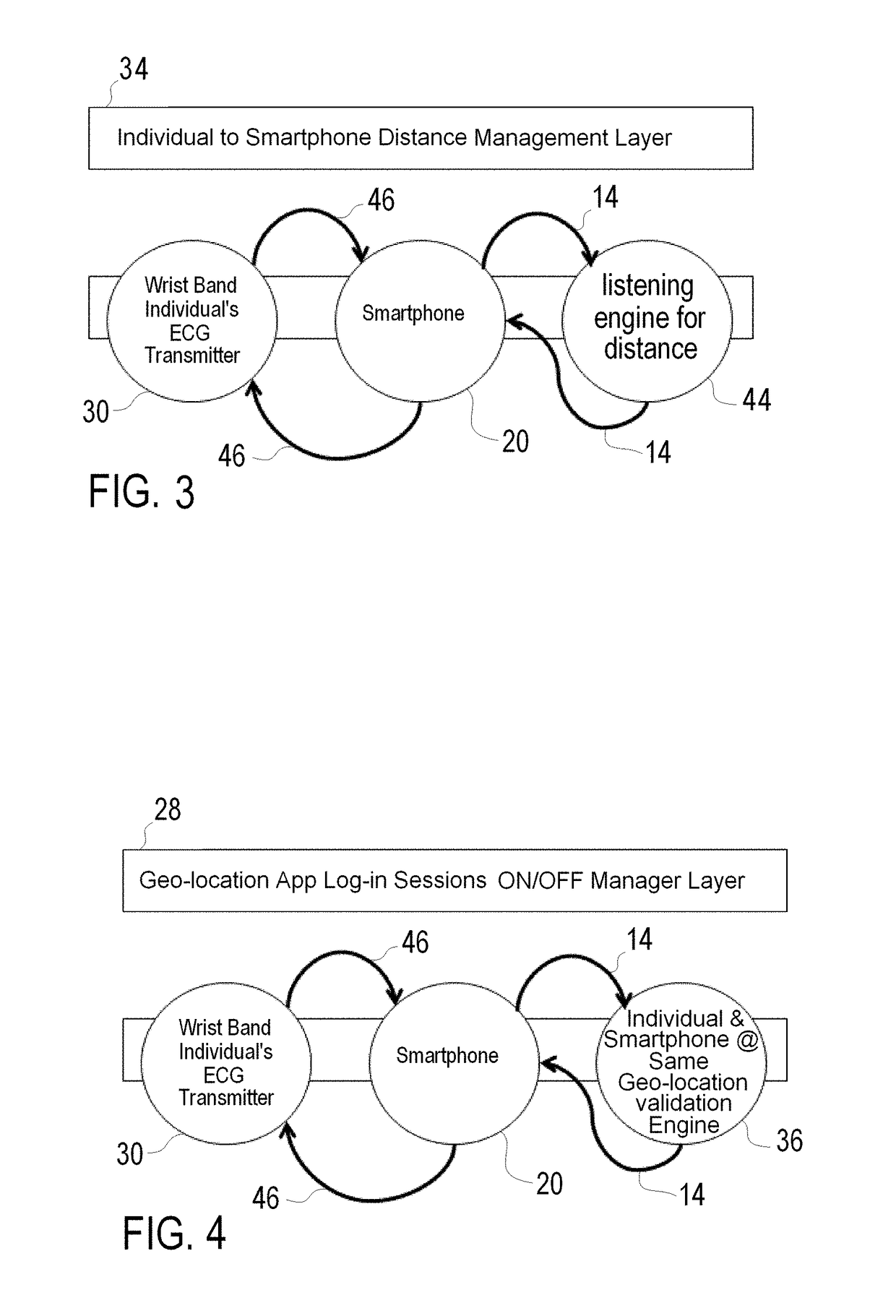
Method and System for Authenticating an Individual's Geo-Location Via a Communication Network and Applications Using the Same
ActiveUS20180049028A1Accurate accessImprove security levelDigital data authenticationTransmissionGeographic siteGeolocation
A method and associated system for authenticating an individual's geo-location via a communication network is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: a) Providing an individual with a smartphone having a GPS receiving unit associated with a communications network; b) Providing the individual with a biometric user identification technology; c) Obtaining via the communications network the geo-location of the smartphone utilizing the GPS receiving unit; d) Identifying the user with the biometric user identification technology by obtaining biometric characteristics that are unique to each human; and e) Verifying the biometric user identification technology is within a preset proximity to the smartphone to authenticate the individual's geo-location
Owner:TALIWARE INC
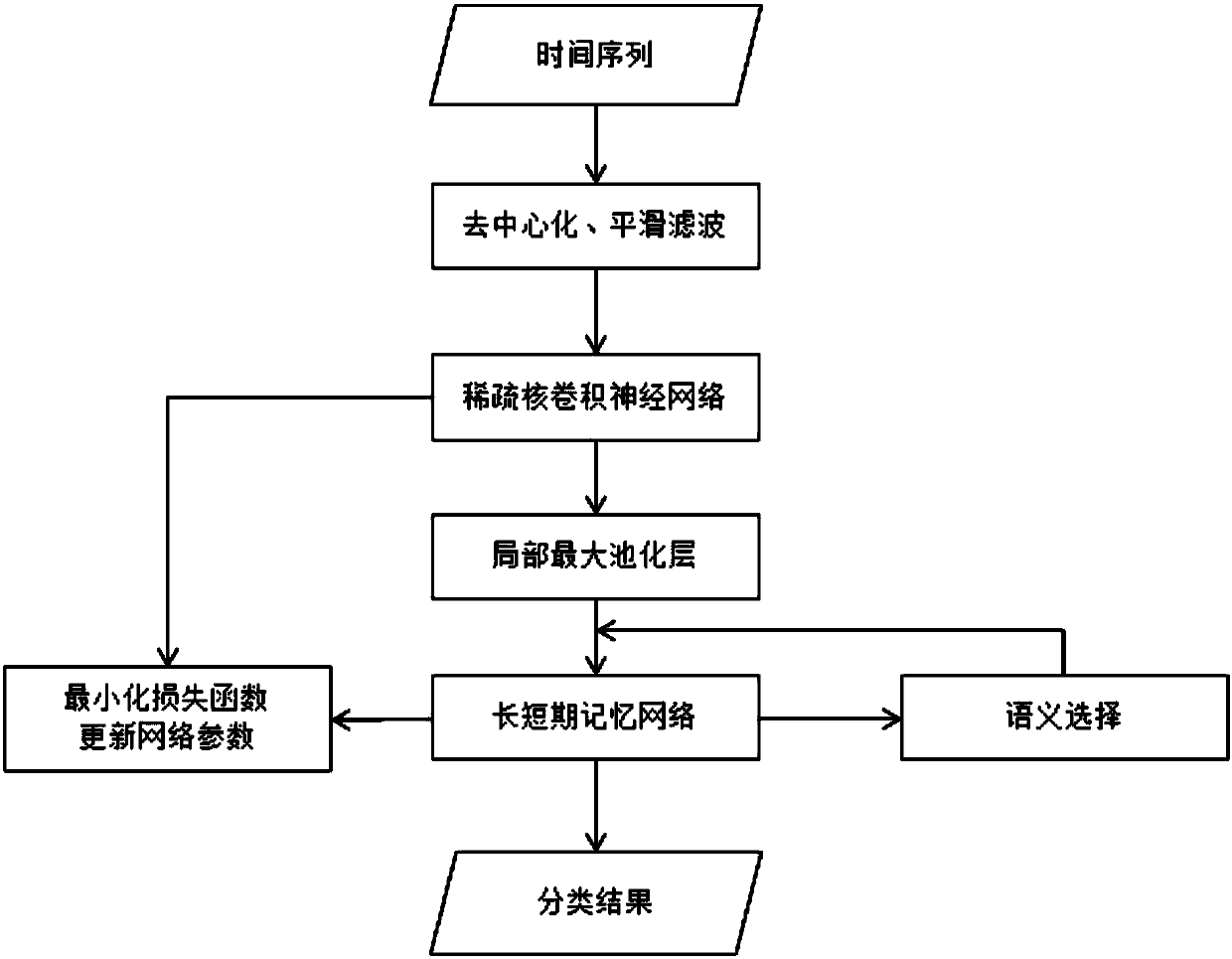
Multi-variable time sequence classifying method based on semantic selection
ActiveCN108182260ACharacter and pattern recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsData setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a multi-variable time sequence classifying method based on semantic selection. Time sequence classification as a machine learning hot research branch has wide application prospects in computer vision, financial analysis, biostatistics and the like. According to a sparse adaptive-semantic learning network (SA-SLN), by means of a sparse convolution kernel, the space semanticconcept and time short-term dependence of multi-variable time sequences are extracted at the same time, an attention diversion method is put forward to be used for selecting the semantic concept, andfinally modeling is conducted on the long-term dependence of the sequences through LSTMs. By means of the SA-SLN, based on the situation that inter-frame properties have correlation, automatic space feature extraction and time-sequence dependence multi-step modeling are realized, the defects of an existing method are overcome, and the currently optimum result is obtained on three public data sets.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Network of biometrically secure devices with enhanced privacy protection
ActiveUS20180108020A1Efficient supplyBroaden the fieldPublic key for secure communicationElectronic credentialsBiometric dataPrivacy protection
This disclosure includes biometrically secured networked devices with enhanced privacy protection. One system includes a first biometrically secured device having a first sensor, and a second biometrically secured device having a second sensor. The first device is programmed to: (i) obtain a first sample of a first biometric using the first sensor; (ii) generate a secret biometrically derived key using the first sample of the first biometric; (iii) encrypt a set of biometric data using the secret biometrically derived key; and (iv) transmit the set of encrypted biometric data to the second biometrically secured device. The second device is programmed to: (i) obtain a second sample of the first biometric using the second sensor; (ii) generate the secret biometrically derived key using the second sample of the first biometric; and (iii) decrypt the set of biometric data using the secret biometrically derived key.
Owner:CLOVER NETWORK INC
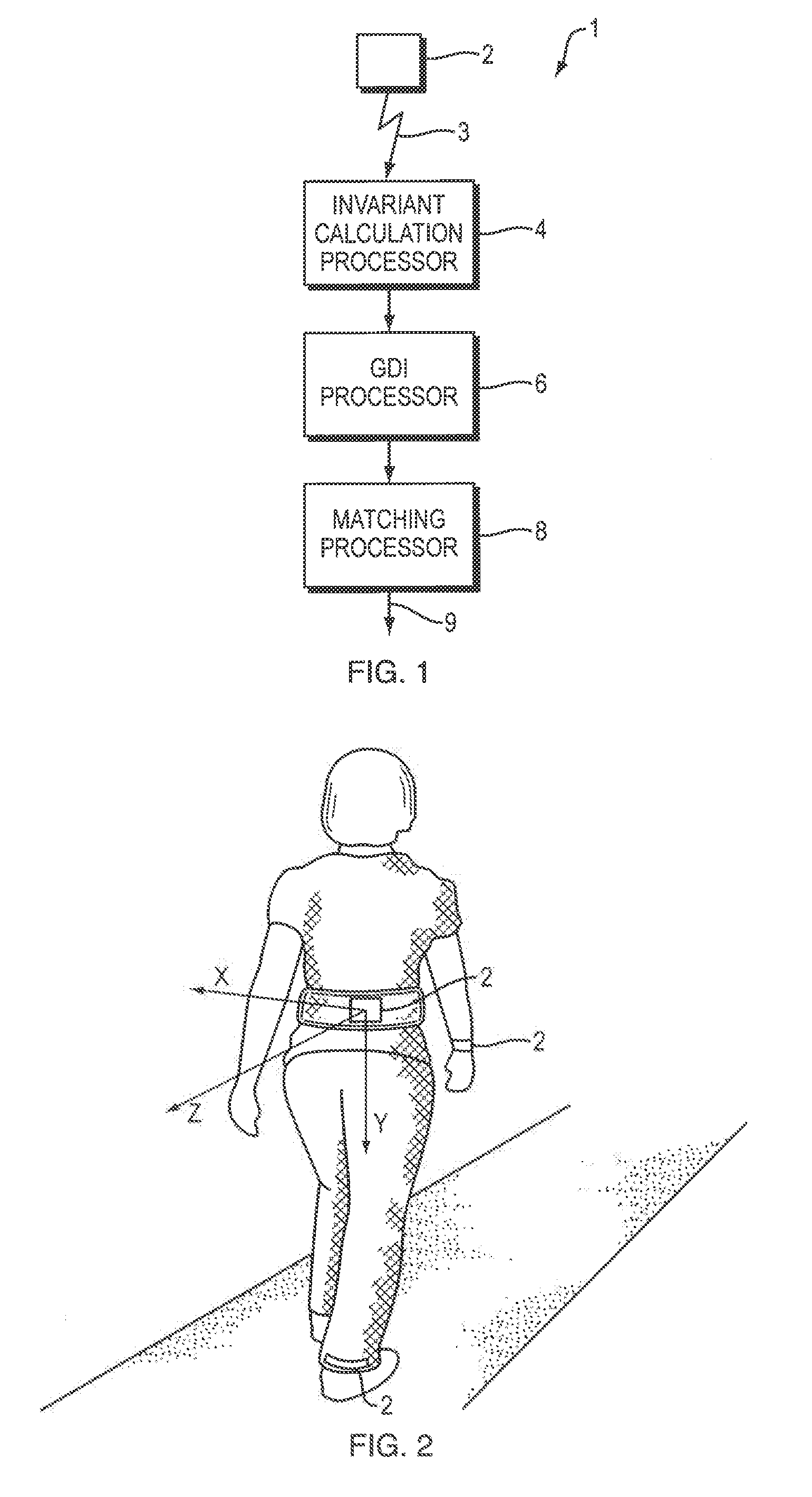
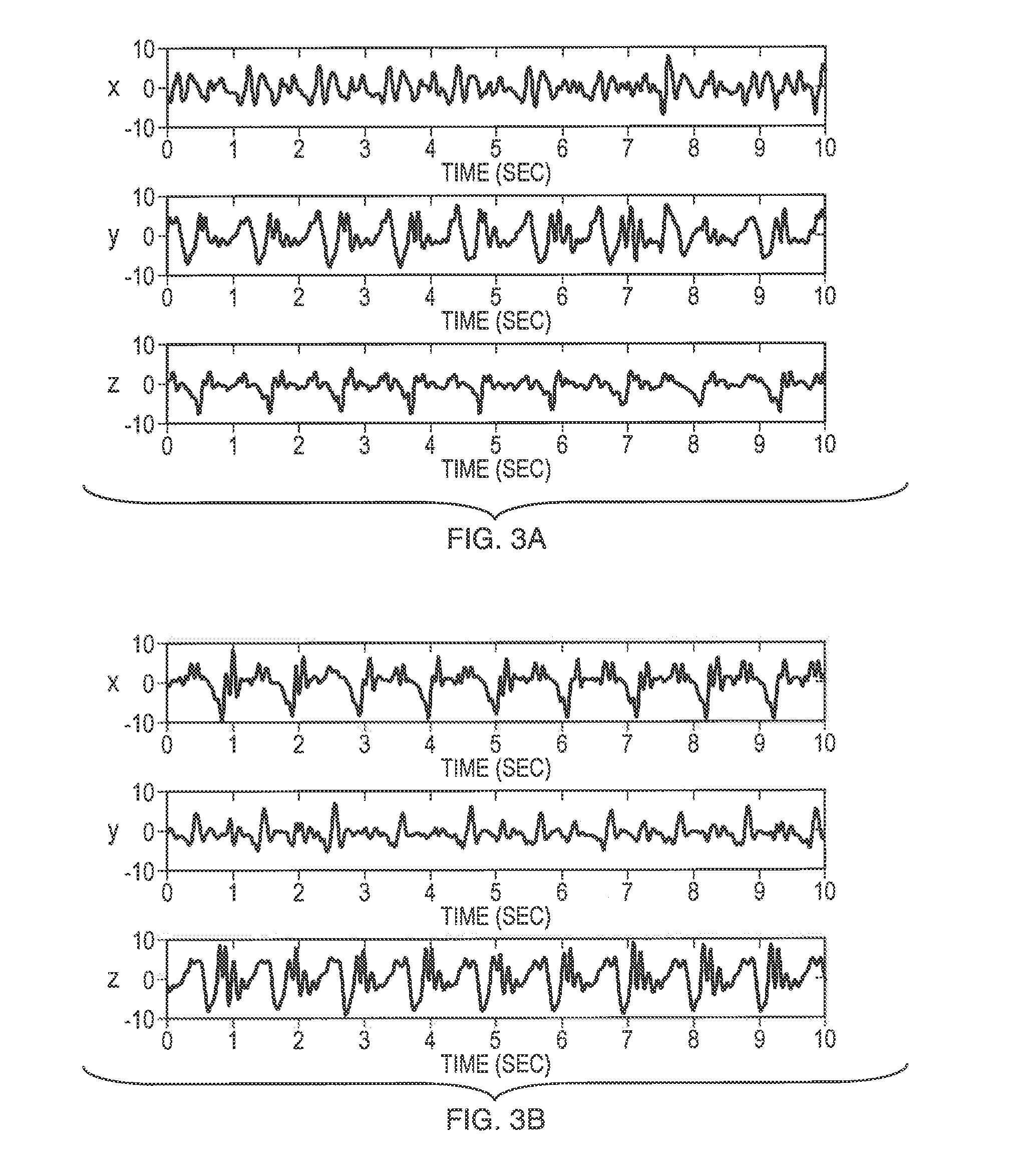
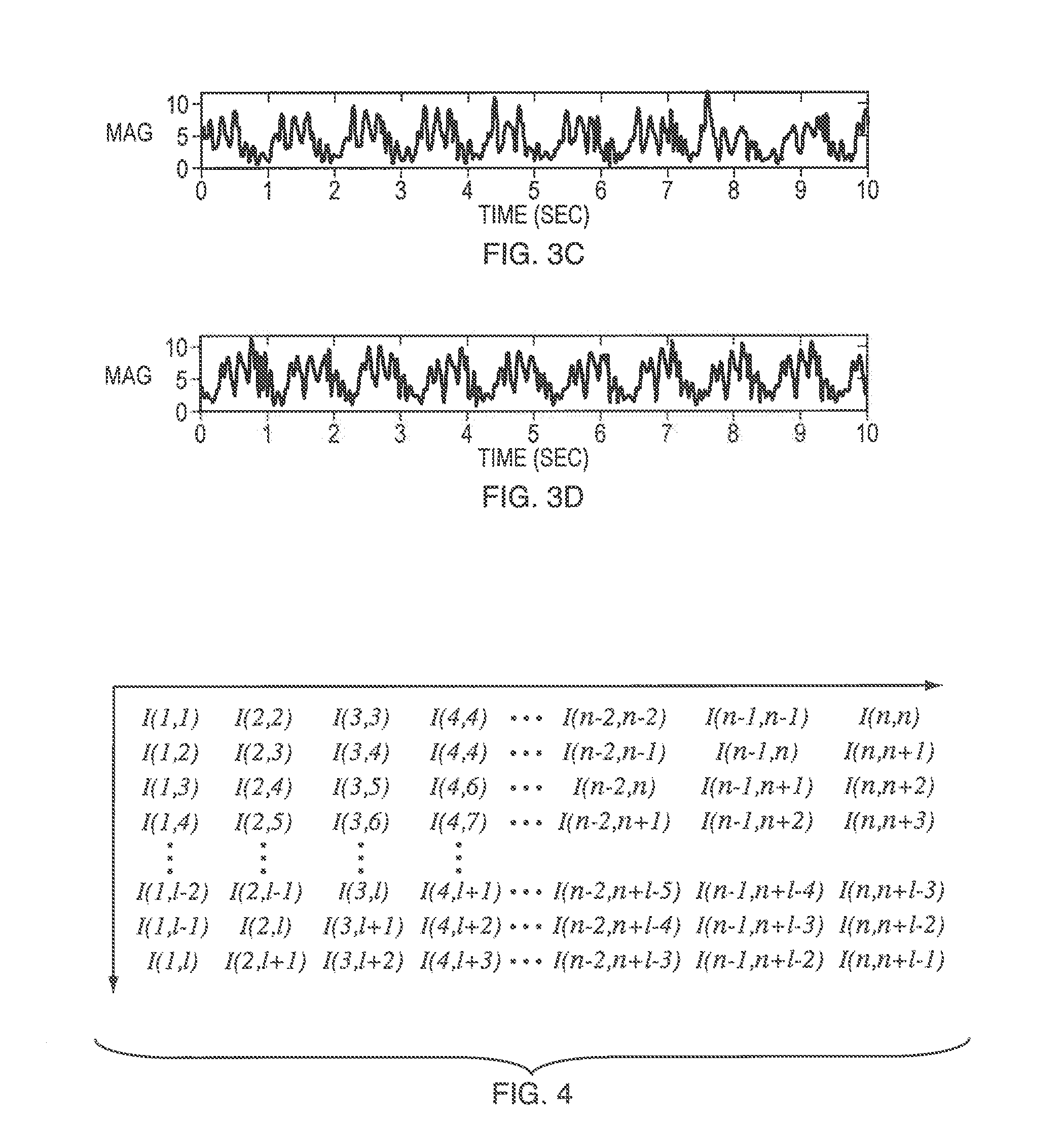
Rotation and pace independent mobile gait analysis
A method for identifying individuals using inertial sensor based gait biometrics. A method for identifying individual persons using orientation and pace invariant gait dynamics images (GDIs). A method of biometric authentication using i-vectors for GDIs.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Living-tissue pattern detecting method, living-tissue pattern detecting device, biometric authentication method, and biometric authentication device
The invention discloses a living tissue mode detection method, a living tissue mode detection device, a biostatistics authentication method and a biostatistics authentication device. The invention allows reliable biometric authentication without risk of forgery or the like. The invention allows biometric authentication and biometric authentication. Detects the concave-convex distribution pattern of deep skin tissue covered by epidermal tissue to extract a unique pattern of living tissue. Biometric authentication is performed based on the detected pattern. The concavo-convex distribution pattern is optically detected by utilizing the difference in optical properties between the epidermis tissue and the deep skin tissue. In this case, long-wavelength light such as near-infrared light is used as illumination light projected onto skin tissue. A branched portion of a subcutaneous blood vessel was used as a portion to be detected. The portion to be examined is determined based on the structure of the bifurcation, in which case subcutaneous blood vessels can be used for biopsy identification.
Owner:SONY CORP
Information processing apparatus, method, and program
InactiveCN101799824AEasy to useDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionInformation processingComputer hardware
An information processing apparatus includes: a biometric information acquirer configured to acquire a user's biometric information; an instructions receiver configured to receive instructions from the user; and an associating unit configured to associate the biometric information with information obtained on the basis of the instructions.
Owner:SONY CORP
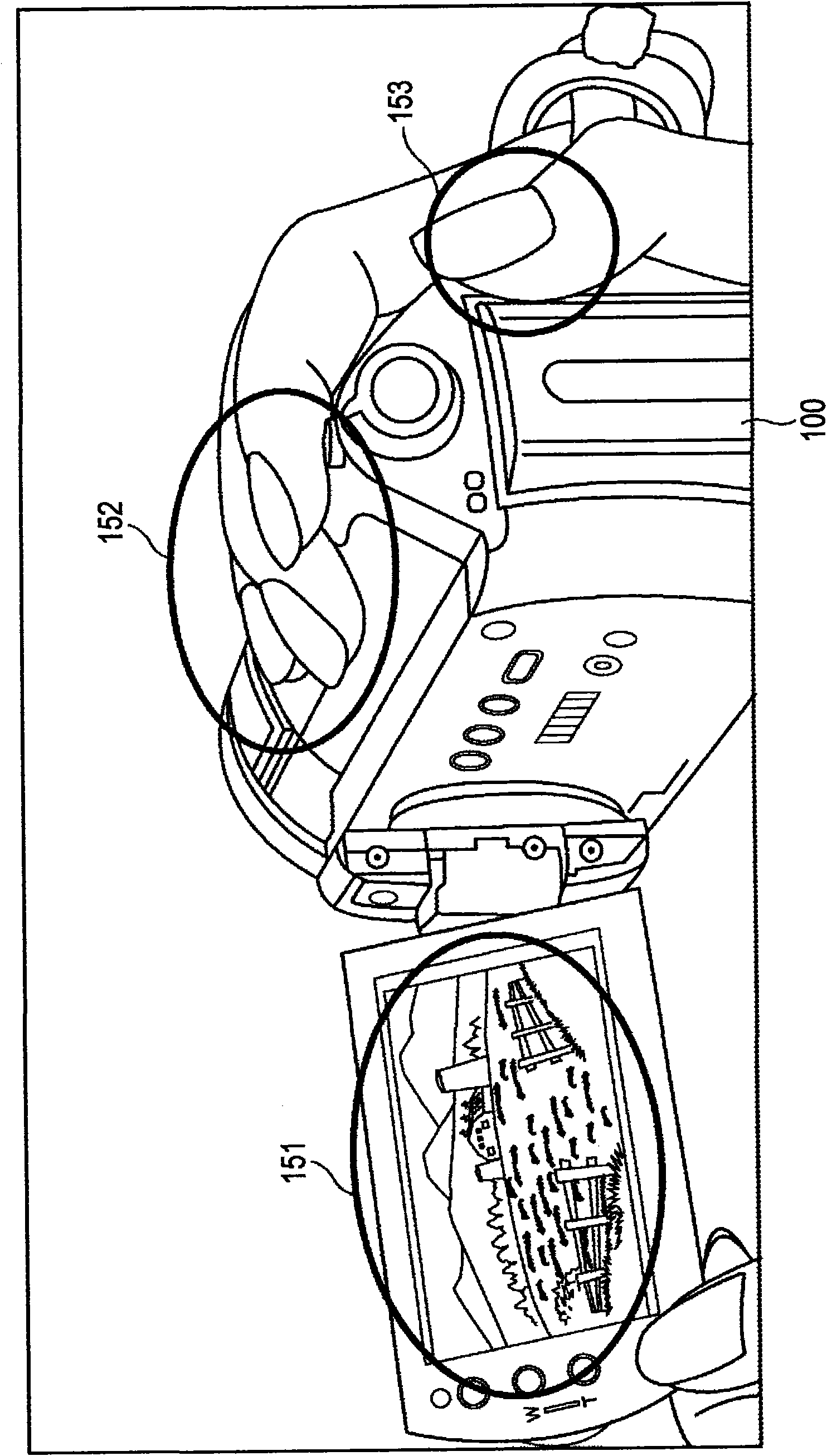
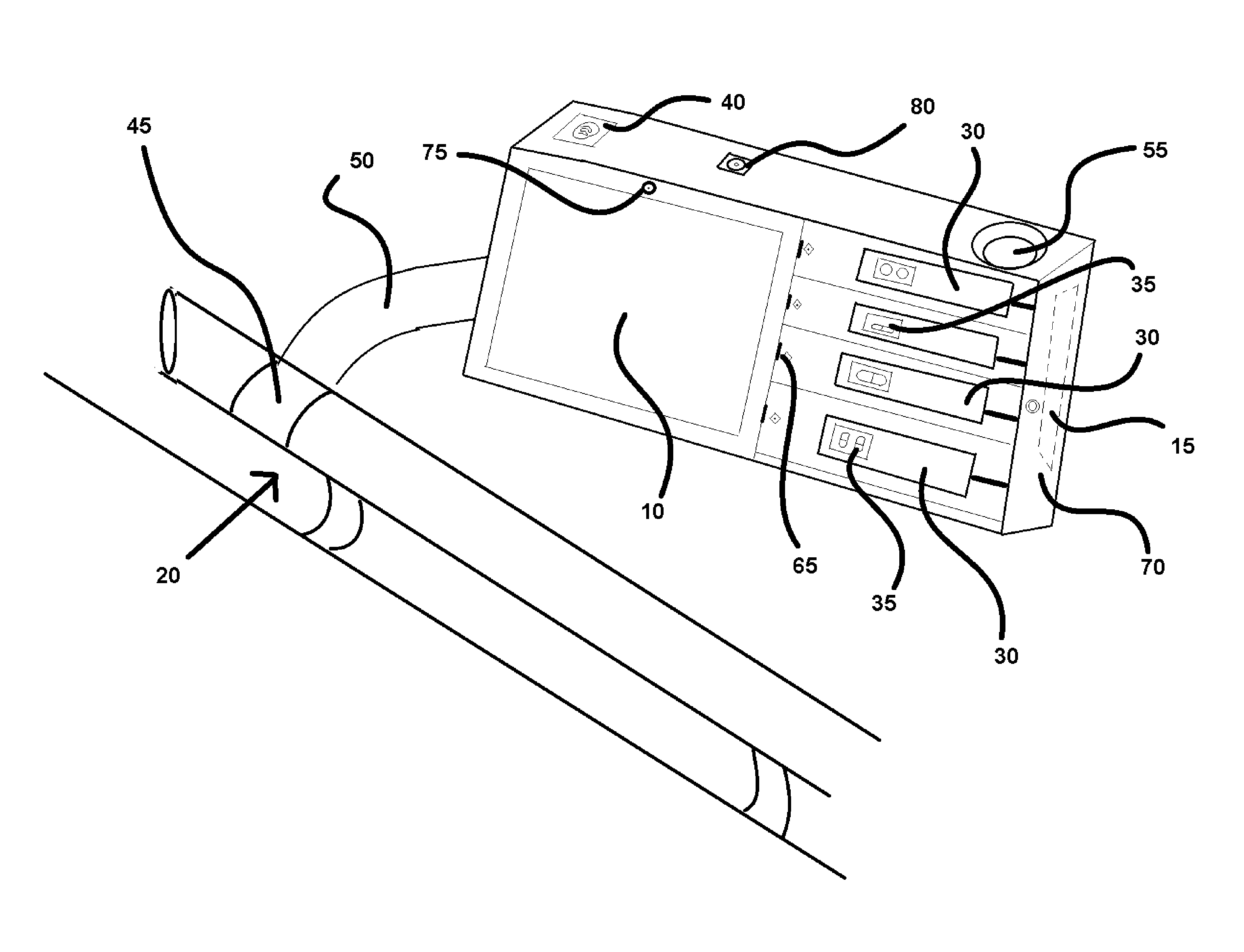
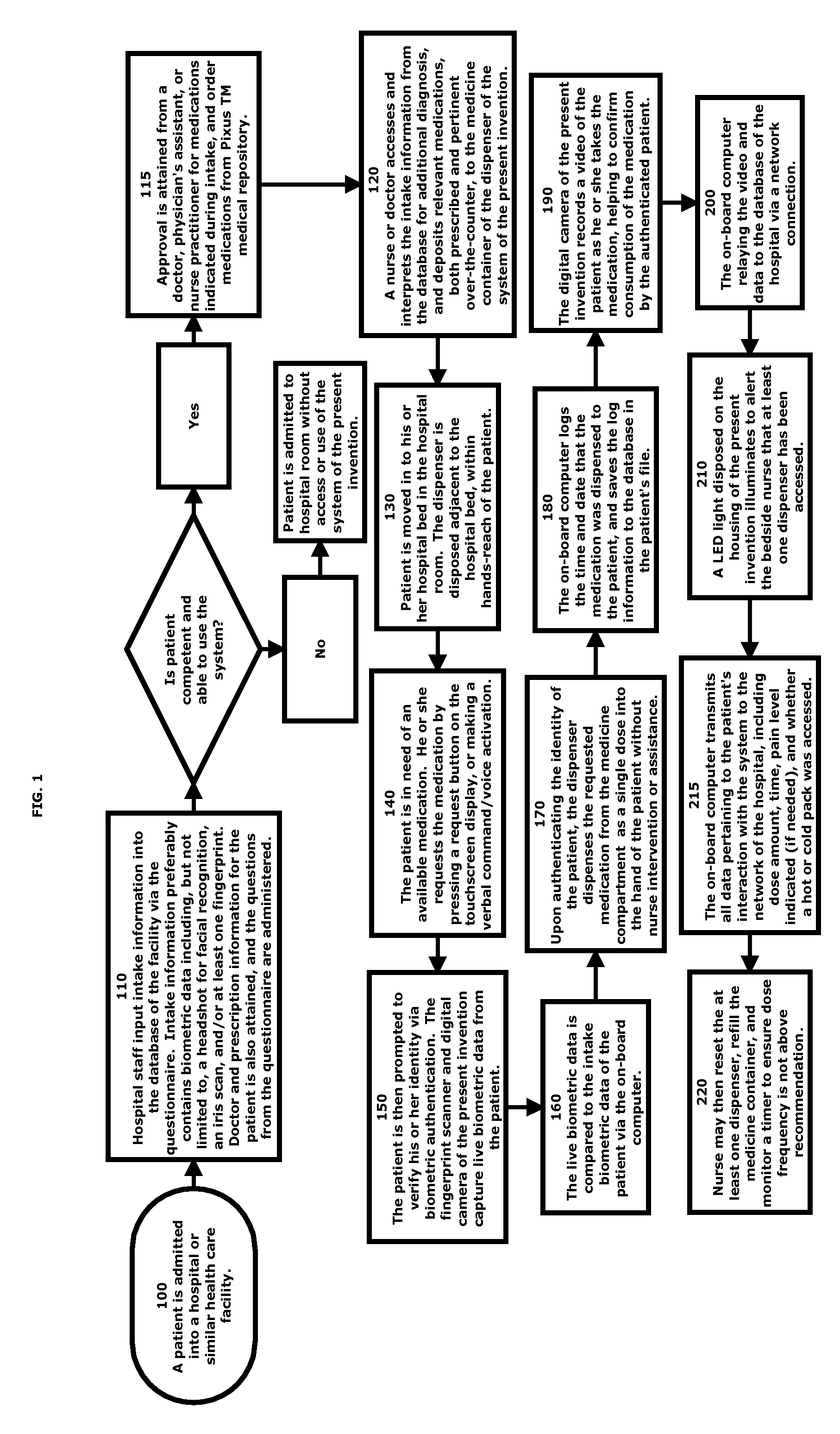
Electronic drug dispenser system
A medication administration and tracking system is described. The system is equipped with an electric medication dispenser configured to administer medication to a patient in a hospital bed without intervention from hospital staff. The dispenser is configured to allocate safe doses of prescribed or over-the-counter medications to a patient upon request by the patient. At least one method of biometric authentication is employed to solely permit access to the medication to the patient upon confirmation of his or her identity. A camera disposed on the dispenser is configured to witness the patient take the medication, and track the time and date of consumption. The medications administered are preferably equipped with a tracking sensor to help track medication levels within the patient, and monitor treatment efficacy.
Owner:LOHMAN CHERYL
Method of validating a biometric capture, notably a body print
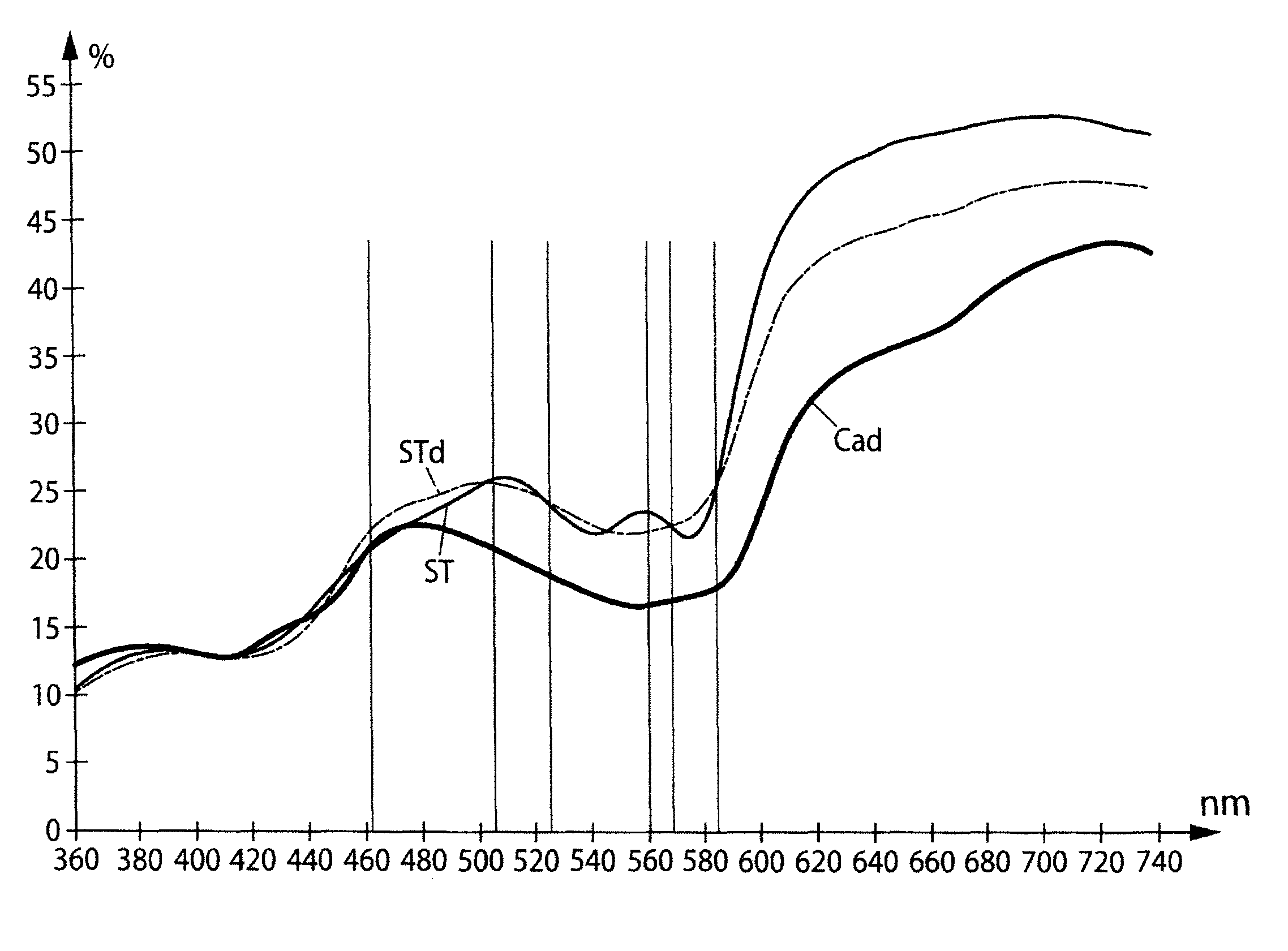
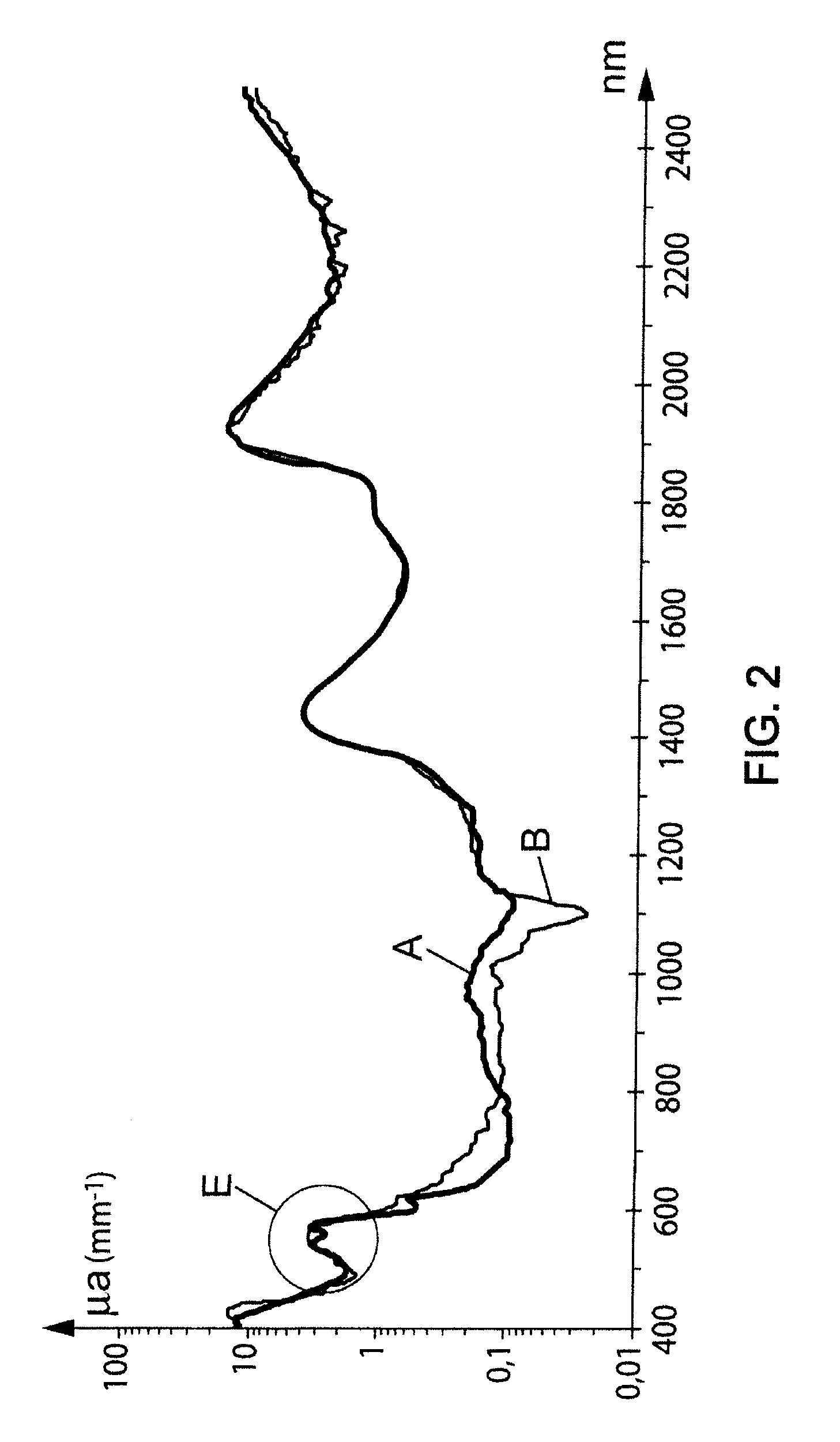
ActiveUS8508337B2Simple and quick to implementElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsFluenceBody area
The invention relates to a method for validating a biometrical acquisition, mainly the acquisition of a body imprint of a body area such as fingerprints or a face imprint, wherein the method involves together with the biometric acquisition: lighting the body area using at least one radiation having at least two respective different wavelengths between approximately 500 nm and 1150 nm; taking at least two reflectometry measurements concerning said and at least two wavelengths for measuring the reflection index of the tissues for these wavelengths; calculating the ratio for two measured indices; and comparing the ratio with a range of reference values characterizing a haemoglobin-containing living tissue in terms of proportions of oxygenated and non-oxygenated forms characteristic of the living states for the wavelengths in question; if the ratio is included in said range, the body area is considered as living and the biometrical acquisition is validated; and conversely, if the body area is considered as not living, the biometrical acquisition cannot be validated.
Owner:IDEMIA IDENTITY & SECURITY FRANCE +1
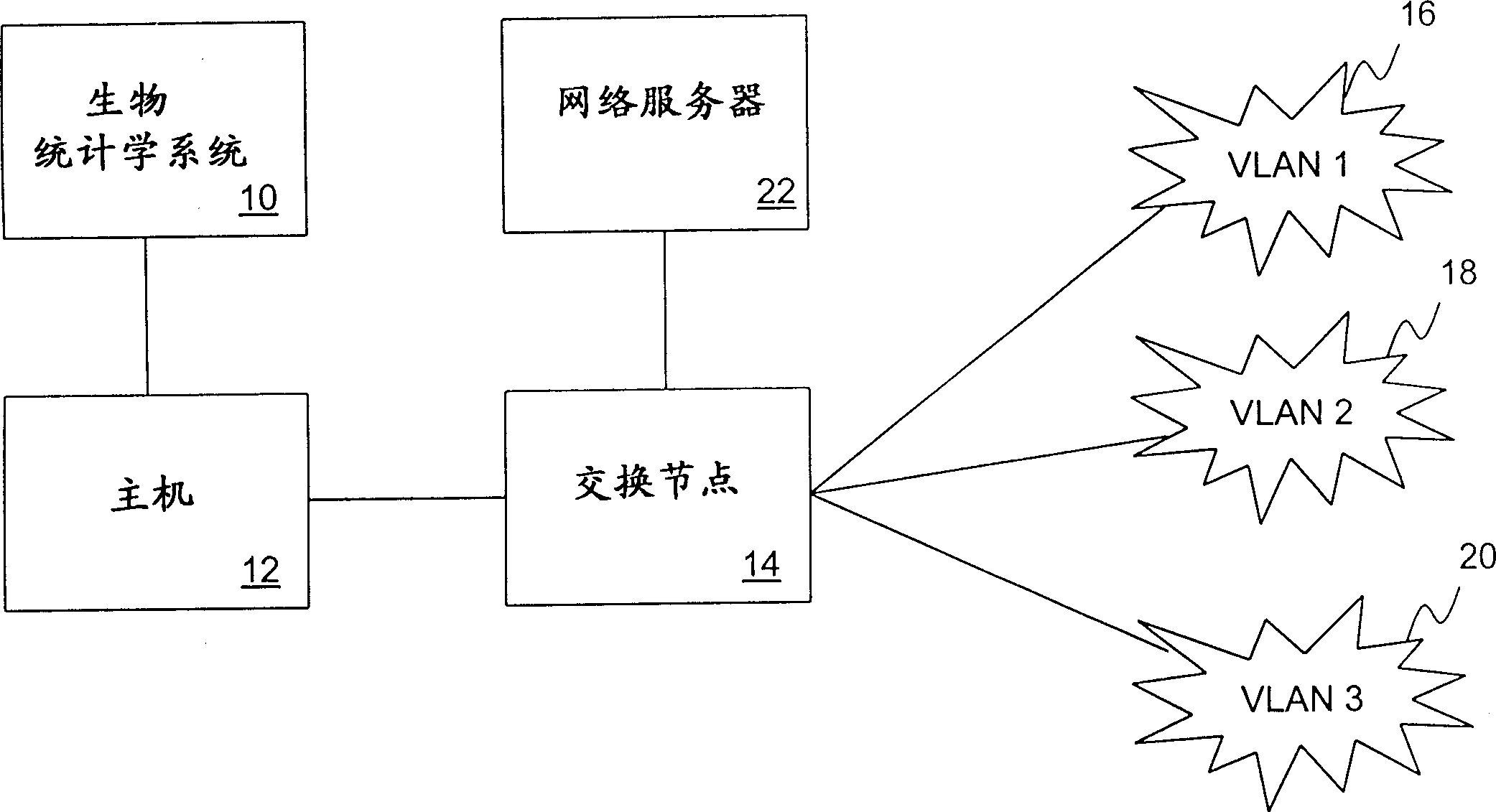
Biostatistically verified VLAN
InactiveCN1400771AReduce usageData taking preventionUser identity/authority verificationInternet privacyUser authentication
A user authentication system and method for a data communication network that helps ensure that a user accessing the network resources is indeed the person having a claimed identity. The user's identity is verified by a biometric system by examining the user's physiological or behavioral characteristic. User identification information needed for accessing the network resources is stored in the biometric system and not released until the user's identity is verified. Upon verification of the user's identity, the user identification data is provided to a switching node for determining the VLANs that the user may access.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
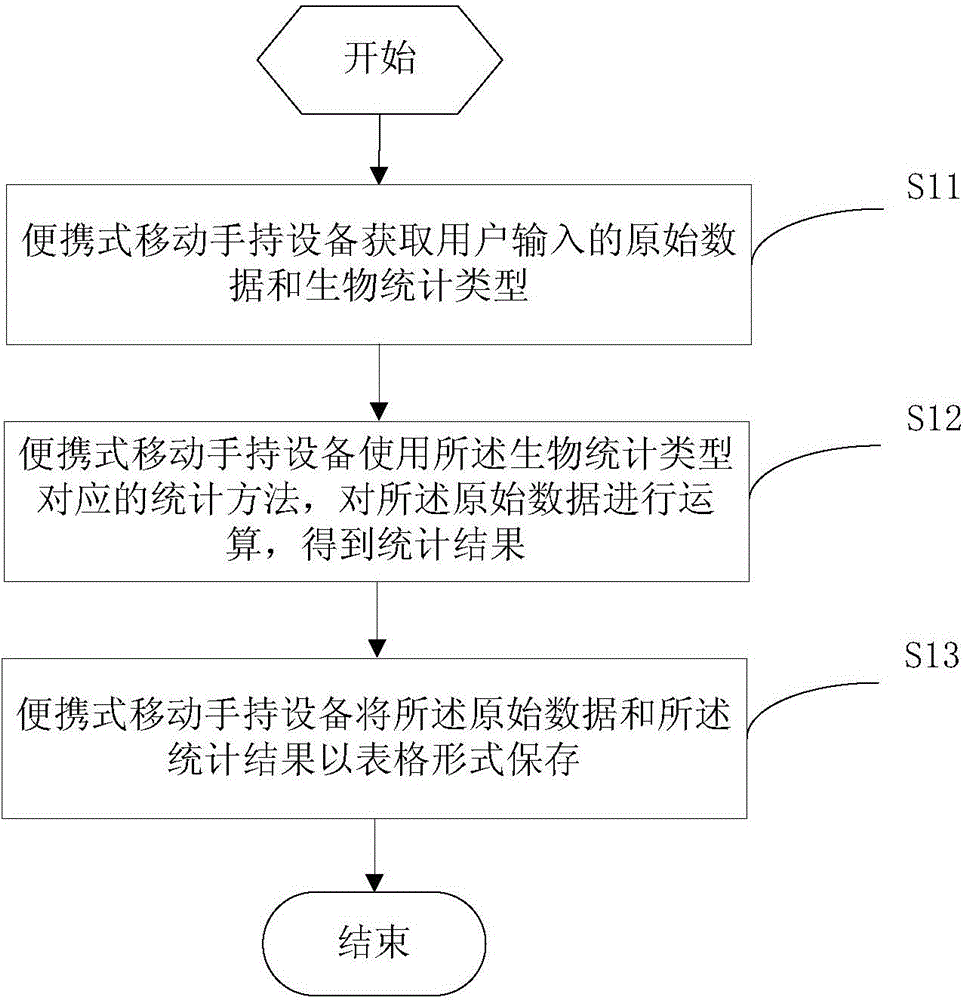
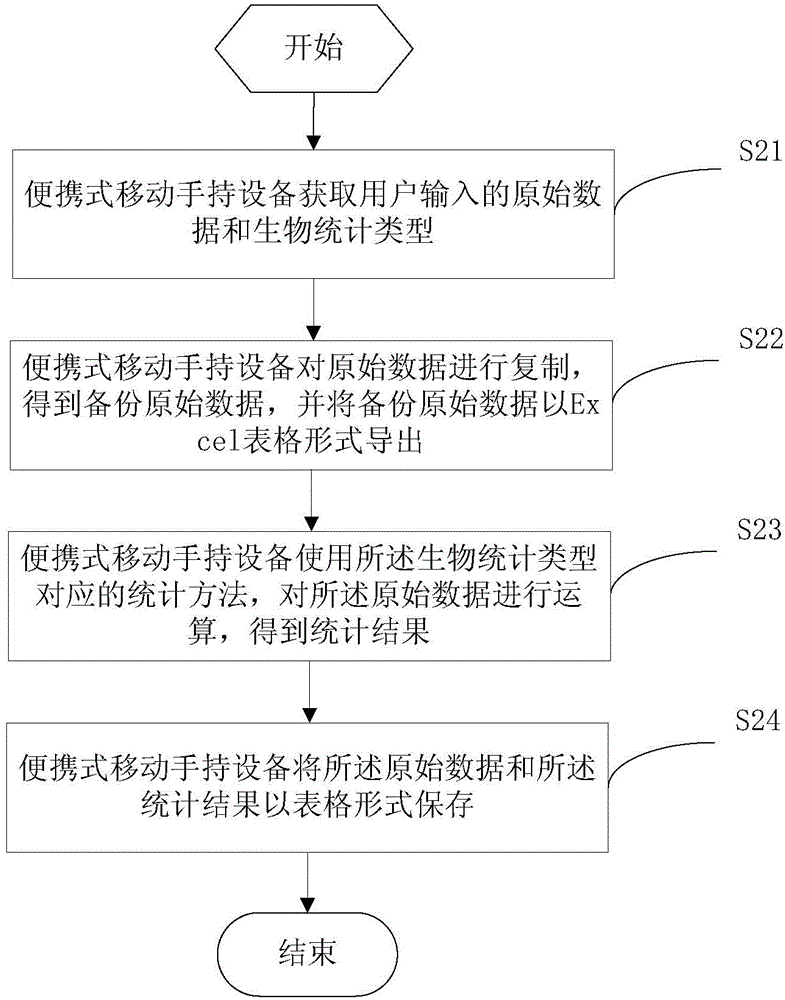
Biological data processing method and device and portable mobile handheld equipment
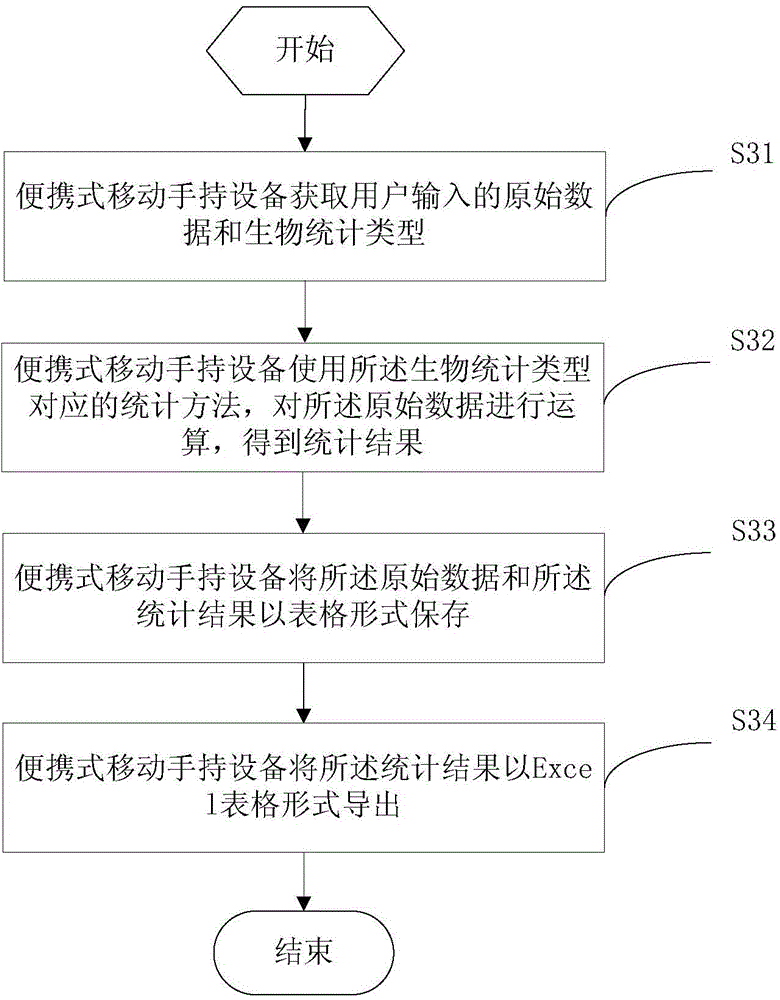
InactiveCN104933329AImprove convenienceImprove experienceSpecial data processing applicationsUser inputOriginal data
The application provides a biological data processing method and device and portable mobile handheld equipment. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring original data and a biostatistics type input by a user through the portable mobile handheld equipment; calculating the original data with a statistics method corresponding to the biostatistics type to obtain a statistics result; and saving the original data and the statistics result in a table form. An outdoor biological worker can obtain the statistics result to realize biostatistics by only carrying the portable mobile handheld equipment without carrying any personal computer of a large size and a large weight, so that the convenience in statistics work is enhanced, and the user experience is improved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Serum protein fingerprint spectrum method for nasopharyngeal carcinoma detection
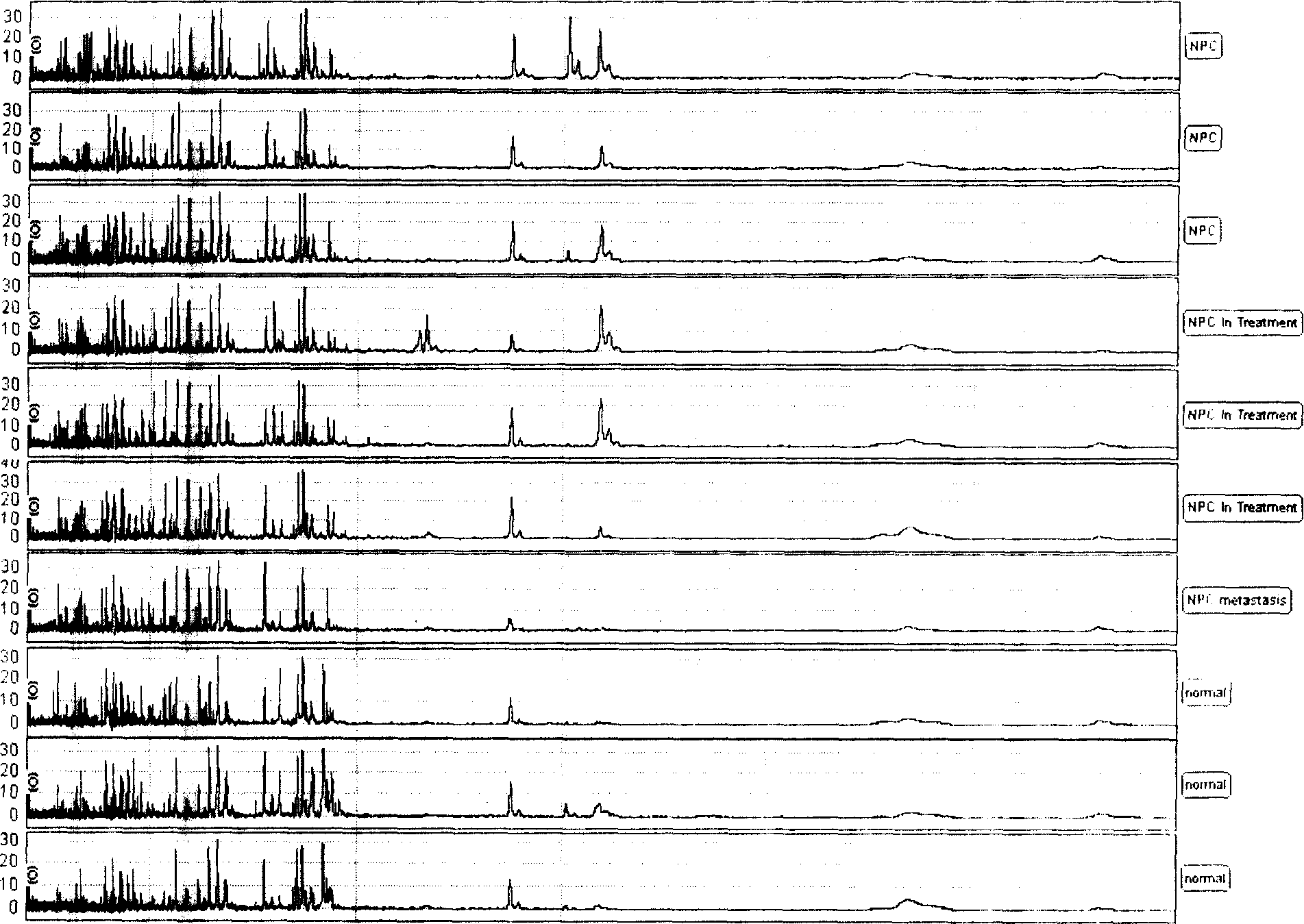
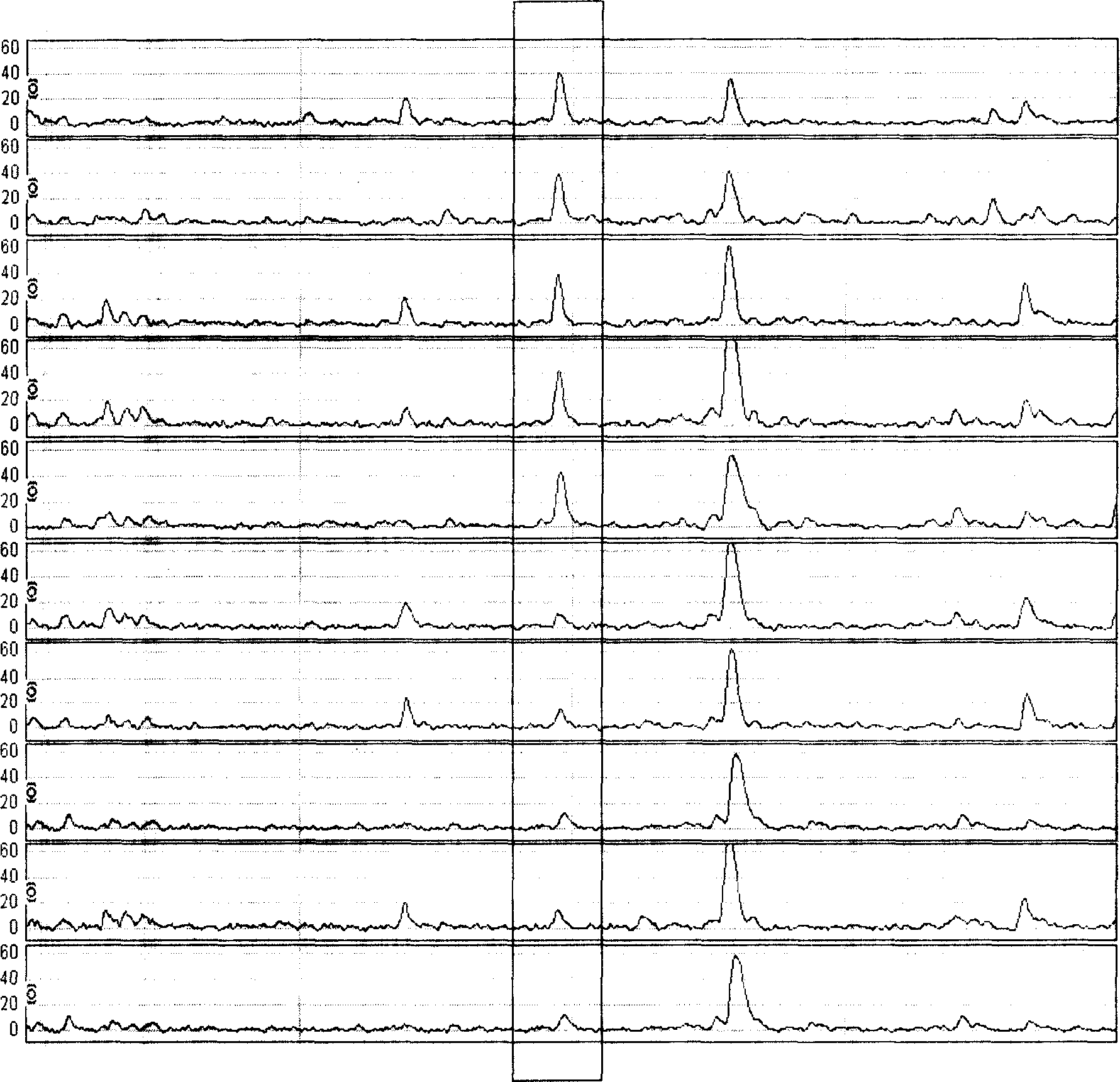
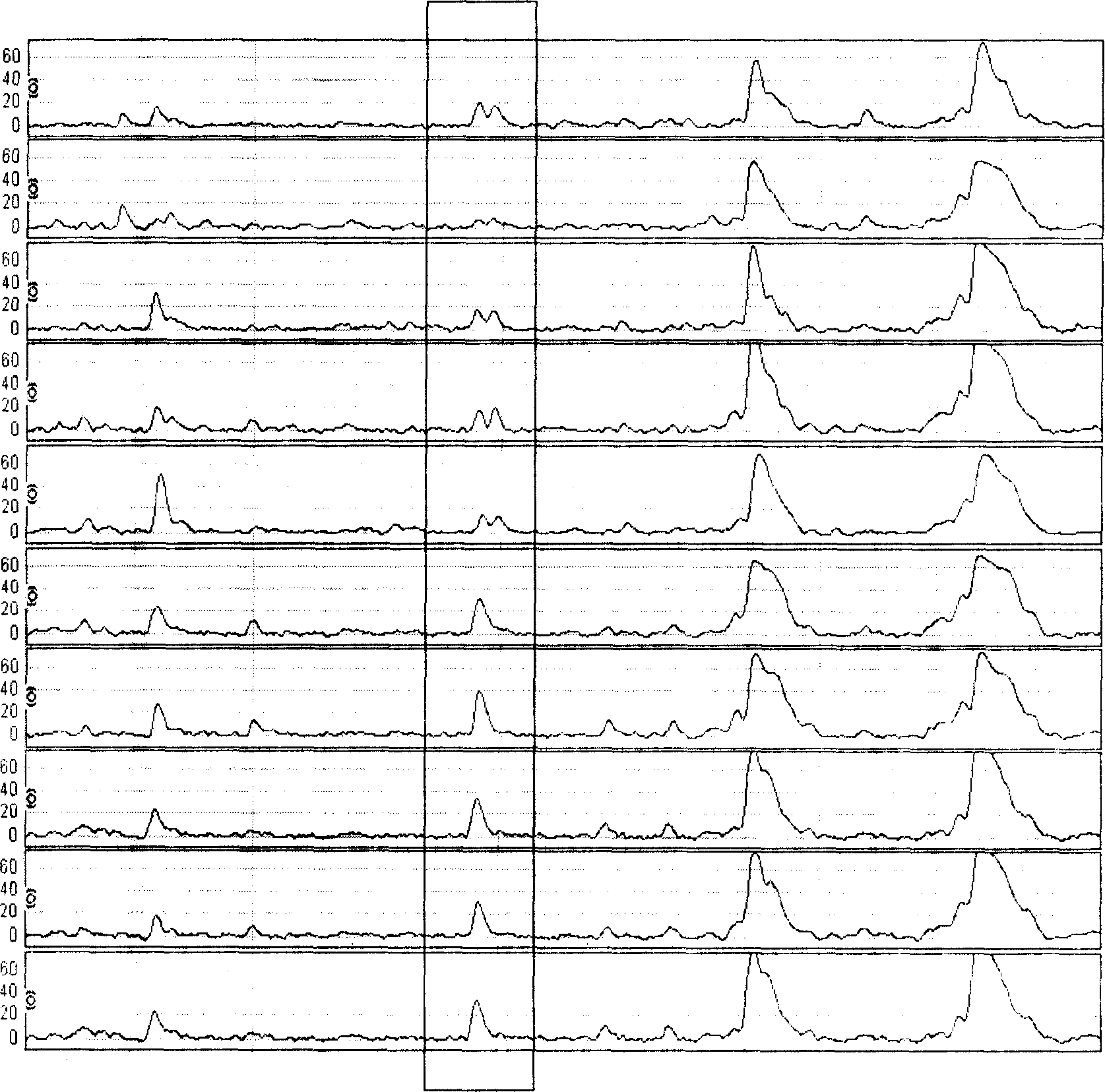
InactiveCN1841069AReduce fatality rateHigh cure rateComponent separationBiological testingNasopharyngeal cancerSerum protein
The serum protein fingerprint pattern method for NPC detection comprises: preparing protein chip with a little serum to generate the fingerprint pattern, building the corresponding database with a great deal of serum samples and fingerprint patterns; detecting sufferer serum in biostatistics to compare by the database and decide the probability of NPC. This invention has sensitivity and specificity more than 80%.
Owner:ZHUHAI BAIYUAN BIOLOGICAL INFORMATION TECH
Rapid chick embryo egg sex identification method
InactiveCN106834460AThe identification steps are simple and feasibleImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAutopsy resultMortality rate
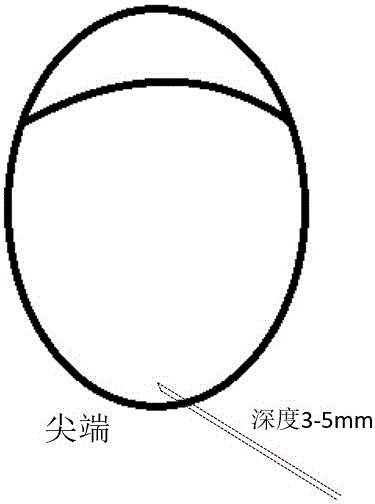
The invention discloses a novel rapid chick embryo egg sex identification method which comprises the following steps: hatching an egg to 16, 17 or 18 days of age, aseptically obtaining allantoic fluid (10 microliters) from the tip of the embryo egg through a 1 ml of injector, sampling and sealing with paraffin wax for normal hatching; taking the obtained allantoic fluid as a template, designing a CDH-W specific primer for PCR amplification, detecting the amplified primer through gel electrophoresis and performing sex identification, wherein double bands (600 bp and 450 bp) are adopted for male amplification, and a single band (450 bp) is adopted for female amplification; after normal hatching, statistically calculating the hatching rate and the death rate, and performing biostatistical analysis with a control group; comparing a sex identification result with an autopsy result of a hatched chick, performing correlation analysis, and statistically calculating the accuracy rate of sex identification (if reaching 99 percent, the accuracy rate is deemed to be 100 percent of effective).
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Coral coverage rate calculation method based on colors
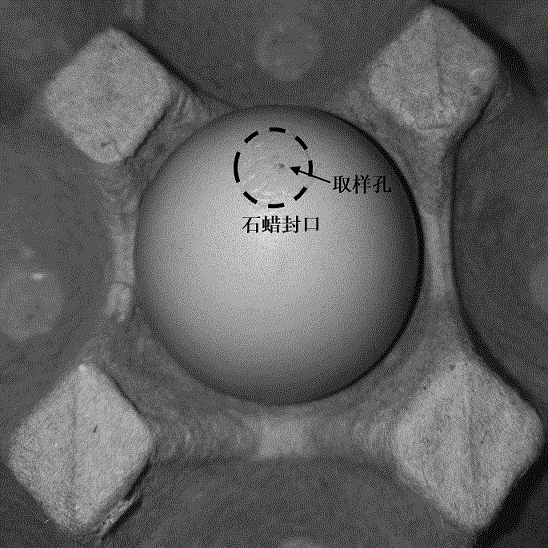
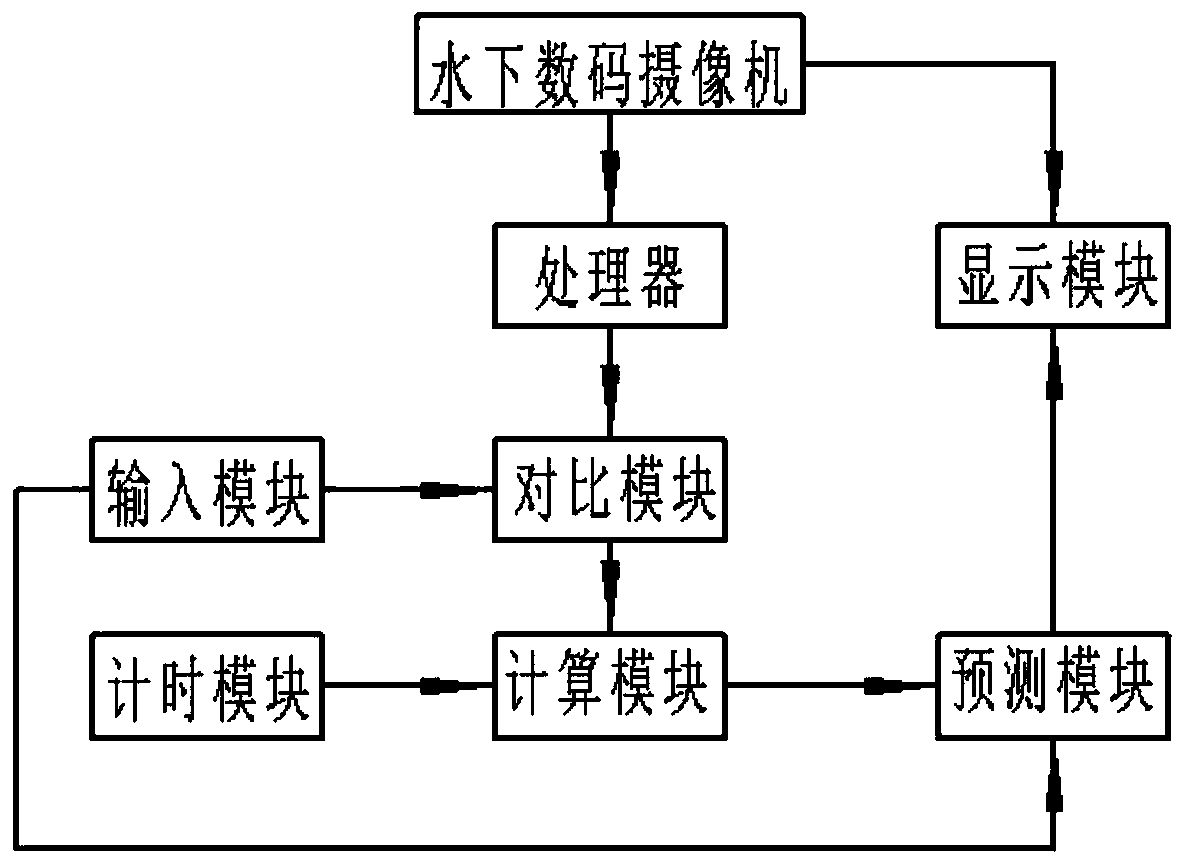
PendingCN110163924ASave time at workEasy to judgeImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceCalculation methods
The invention belongs to the field of biostatistics, and provides a color-based coral coverage rate calculation method aiming at the problem that in the prior art, the coral coverage rate calculationaccuracy is reduced due to the participation of a large amount of manpower, which comprises the following steps: photographing an underwater digital camera on an investigation section to acquire female parent image information; the overwater marine worker checks the female parent image information through the display module and judges coral chromaticity range information; the overwater ocean worker inputs coral chromaticity range information through the input module according to the female parent image; the processor converts the female parent image information into female parent chroma information; the comparison module compares the parent chroma information with the coral chroma range information; the part, meeting the coral chromaticity range information, in the female parent chromaticity information serves as coral chromaticity information, the calculation module calculates proportion information of coral in the female parent image information according to the coral chromaticity information and the female parent chromaticity information, and the proportion information is sent to the display module to be displayed.
Owner:HAINAN ACADEMY OF OCEAN & FISHERIES SCI
Preparation and cultivation method of hairy roots of tongkat ali
InactiveCN102754594AFast growthAlleviate market demandPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiological cellRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention discloses a preparation and cultivation method of hairy roots of tongkat ali and belongs to the biological cell engineering technology. The preparation and cultivation method includes: tender stems of tongkat ali are used as explants which subjected to dedifferentiation to obtain fresh callus of tongkat ali, the callus and Agrobacterium rhizogenes containing Ri (root-inducing) plasmid are co-cultured, co-cultured bacteria liquid is transferred to an inductive medium for induced culture after excess bacteria liquid is absorbed with aseptic paper, fairy roots of tongkat ali grow at the callus of tongkat ali; and the explants with hairy roots are laced in an amplification medium for extended culture of the hairy roots after biostatistics culture. The tongkat ali hairy root culture system is established by the biological cell engineering technology and used to prepare the hairy roots of tongkat ali, standard production of tongkat ali is realized, wild resources are replaced, increasing market demands on tongkat ali are eased, and the problem that tongkat ali relies on import is solved. The preparation and cultivation method is important to industrial and commercial development of hairy roots of medicinal plants.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY +1
Method and device for image transformation
InactiveUS7346227B2High sensitivityStably registerTelevision system detailsImage analysisComputer graphics (images)Transducer
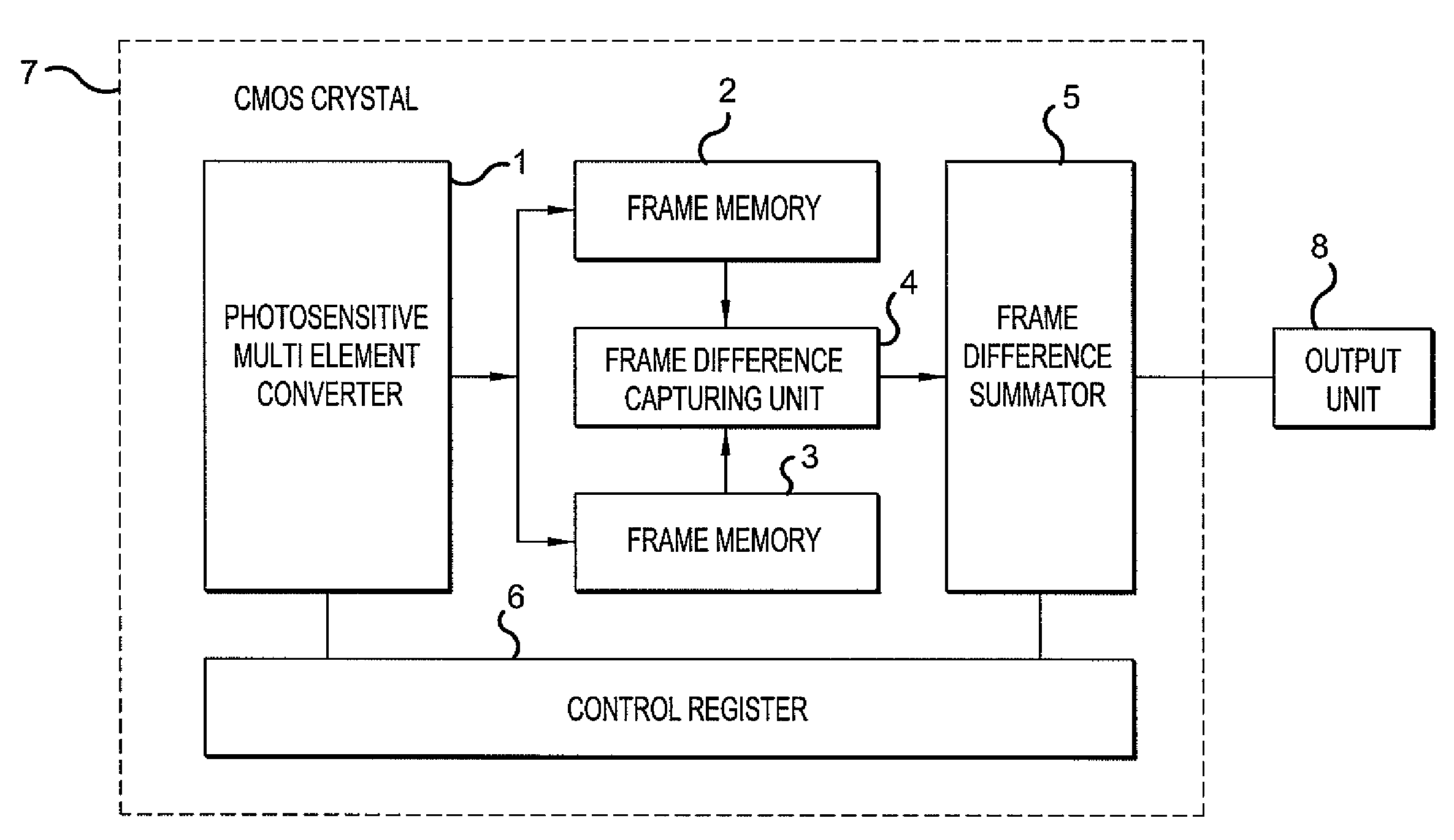
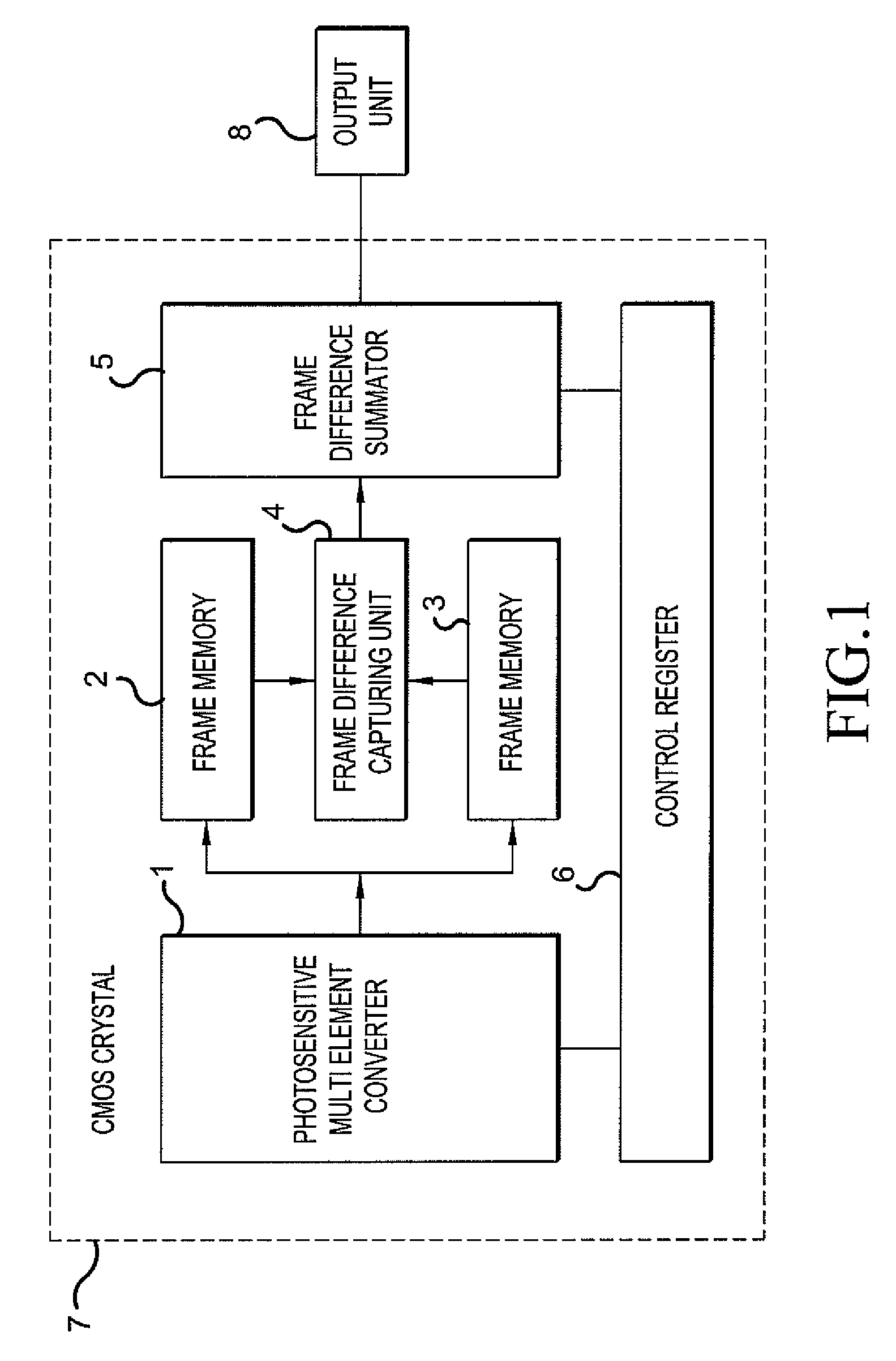
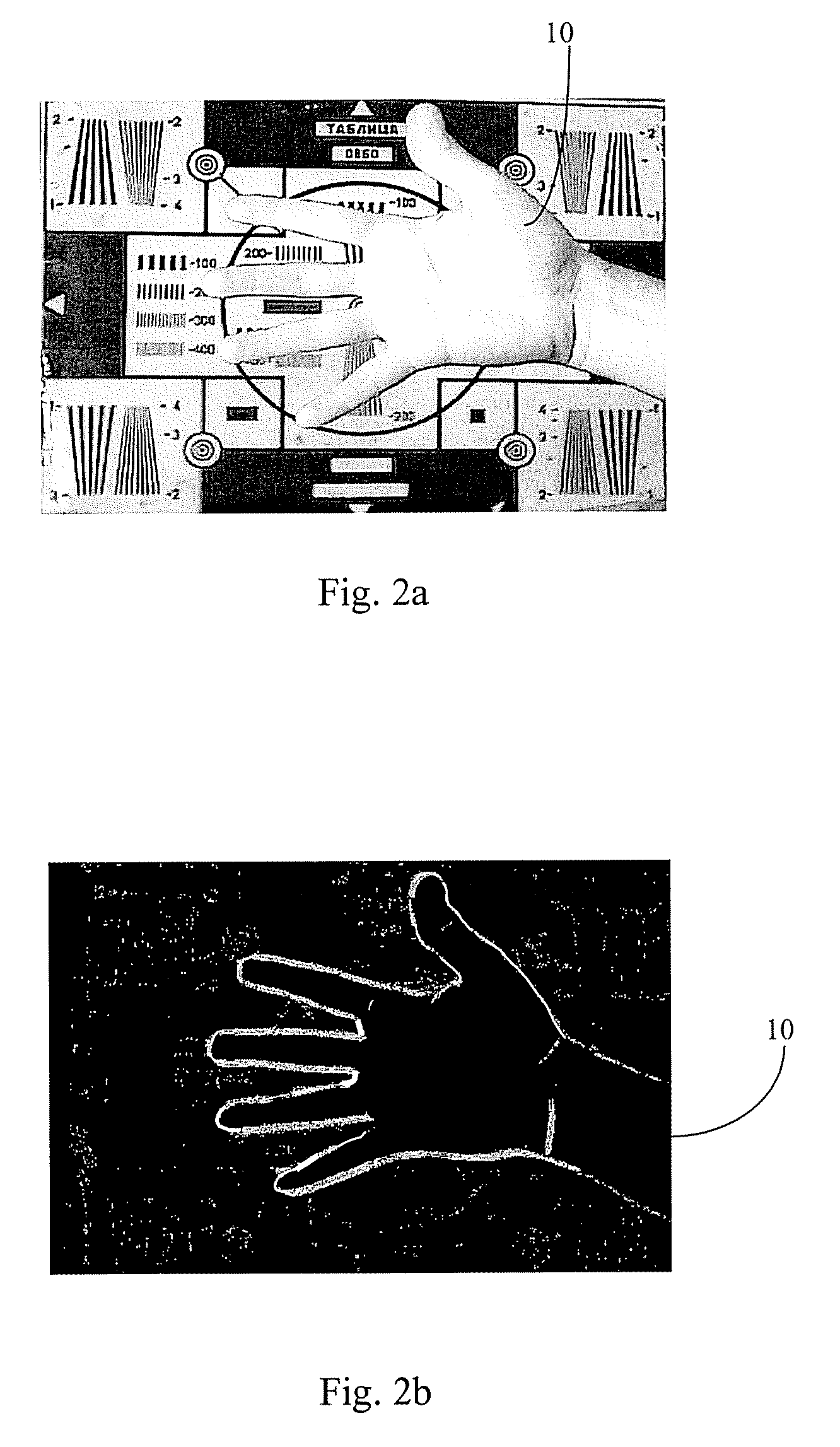
Biometry for transforming, receiving, processing and analyzing electronic images of living biological objects is provided. The Biometry detects the objects, which produce insignificant periodical oscillations thereby making it possible to receive and analyze the images of the objects on a background of stationary and moving objects. Successive exposures of the object's image are received and picture-to-picture differences are evaluated, and a sum of differences of at least two successive exposures during the processing thereof is accumulated. The biometry comprises a photosensitive multielement transducer (1) and means for processing the images of the picture-to-picture difference which contain an exposure memory (2,3), a unit for evaluating the picture-to-picture difference (4), a picture-to-picture difference summator (5) and control registers (6). The device accumulates the sum of the exposure differences detected by the photosensitive multielement transducer.
Owner:OOO MP ELSYS
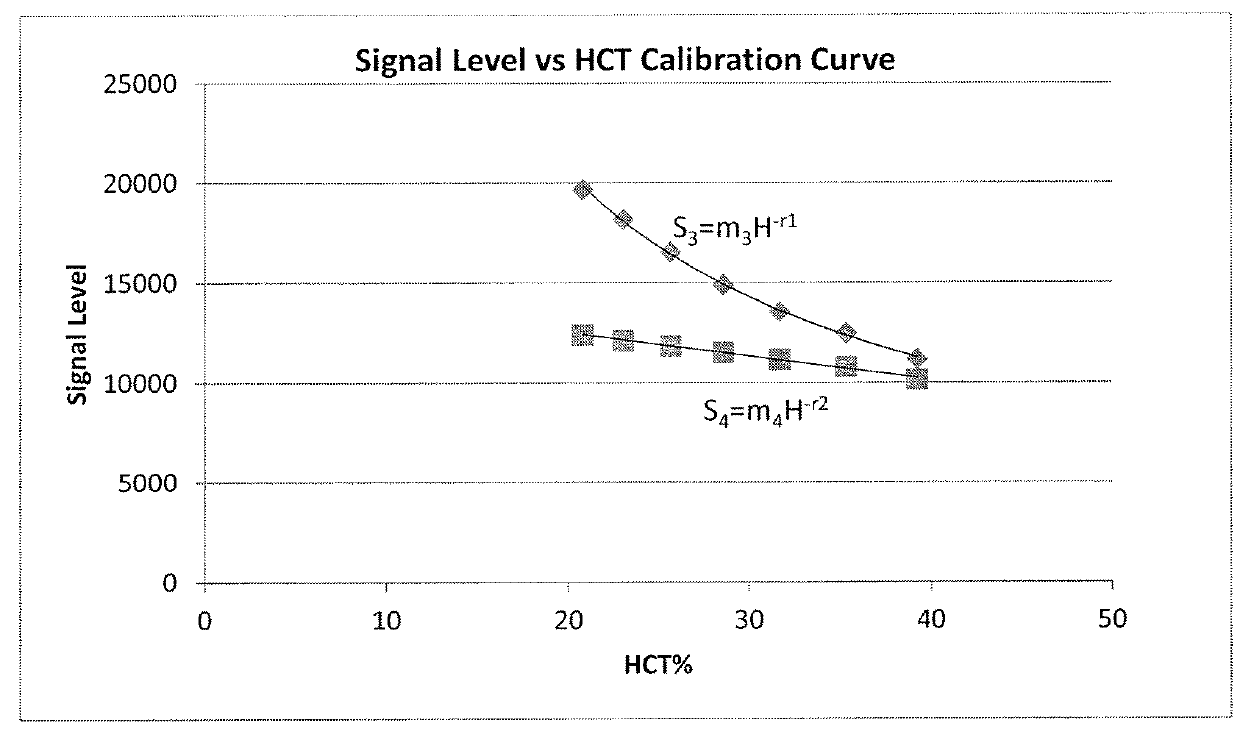
Method and apparatus for determining biometric indicators using multiple fluorescent markers
InactiveUS20180180622A1Accurate predictionShorten test timeDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionCatheterPlasma samplesFiltration
Disclosed are methods for determining biometric indicators such as plasma volume, hematocrit and glomerular filtration rate, in mammalian subjects such as humans. The methods utilize a plurality of fluorescent tags having distinct fluorescent characteristics, which may be associated with a single static molecule, or wherein the static molecule is labeled with a fluorescent tag and a dynamic molecule is labeled with another fluorescent tag. One or more measurements of the intensities of the fluorescent emissions are taken subsequent to introduction of an injectate which contains the fluorescent tags, which can be taken using a probe or via a blood or plasma sample. Compositions and apparatuses for practicing the methods are also disclosed.
Owner:PHARMACOPHOTONICS INC
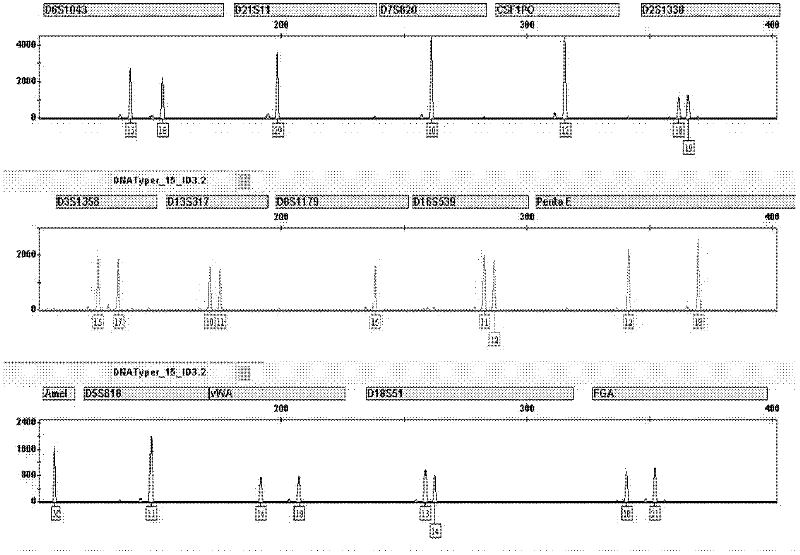
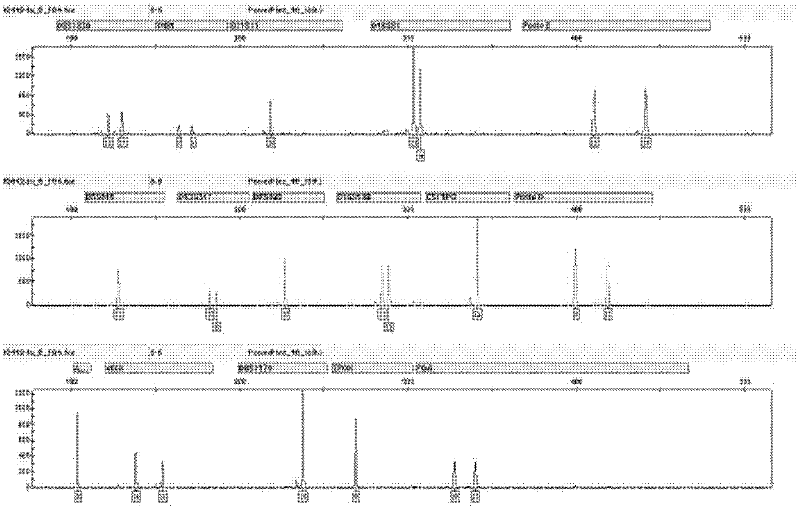
str type standard substance
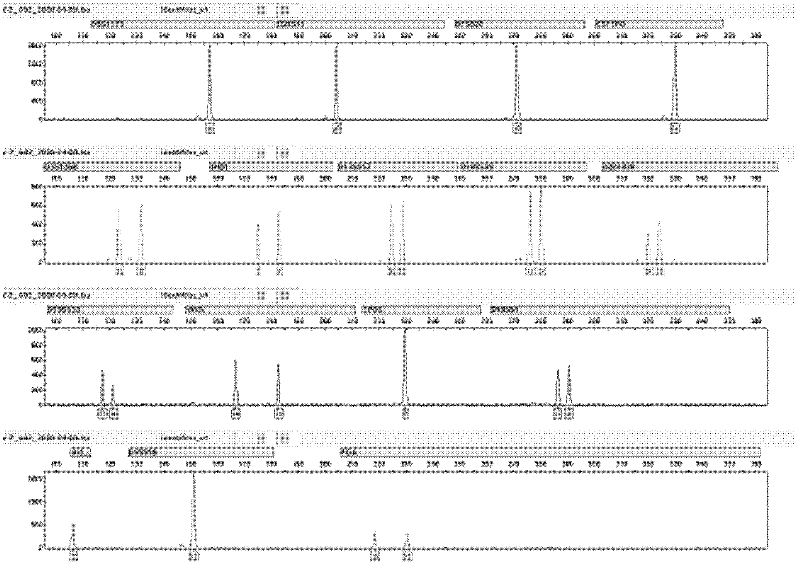
ActiveCN102286476AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a short tandem repeat (STR) parting standard substance, which is a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) mixture and comprises 31 DNA segments with the nucleotide sequences as 1) to 31). In the invention, all allelic genes in the bits of Chinese people groups are researched and studied through focusing on the discovered STR gene bits in the existing forensic molecular genetics, and in addition, the biostatistics technology is used for studying the gene frequency distribution of each allelic gene. On the basis, the experiments techniques such as molecular genetics, molecule biology, cell biology, genetic engineering and the like are integrally utilized, the allelic gene DNA information base is developed and built for the first time, all of the allelic gene DNA segments such as STR bits are included, further, the forensic DNA standard reference system independently developed by China is further built, and the special artificially synthesized STR standard substance is formed.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
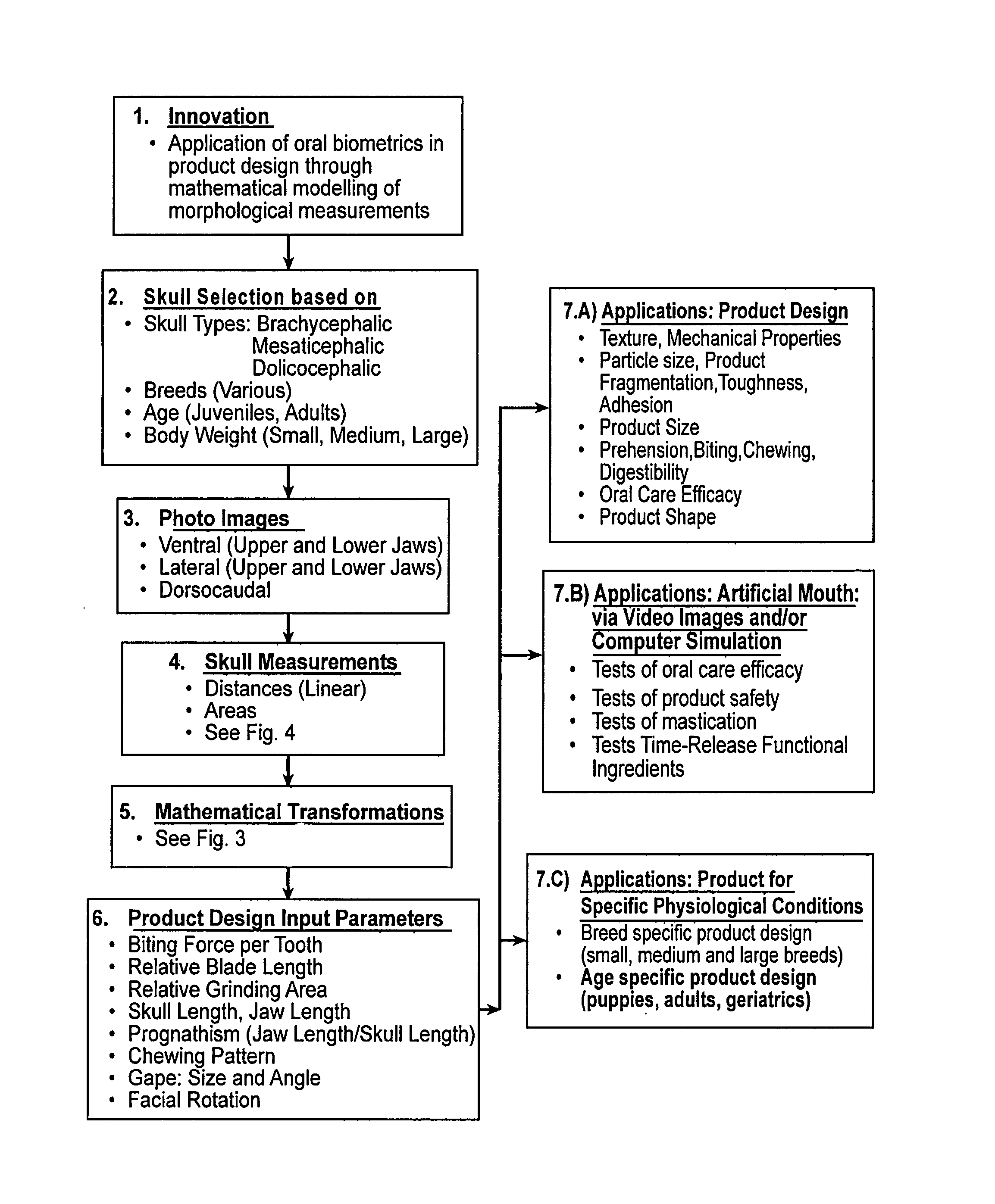
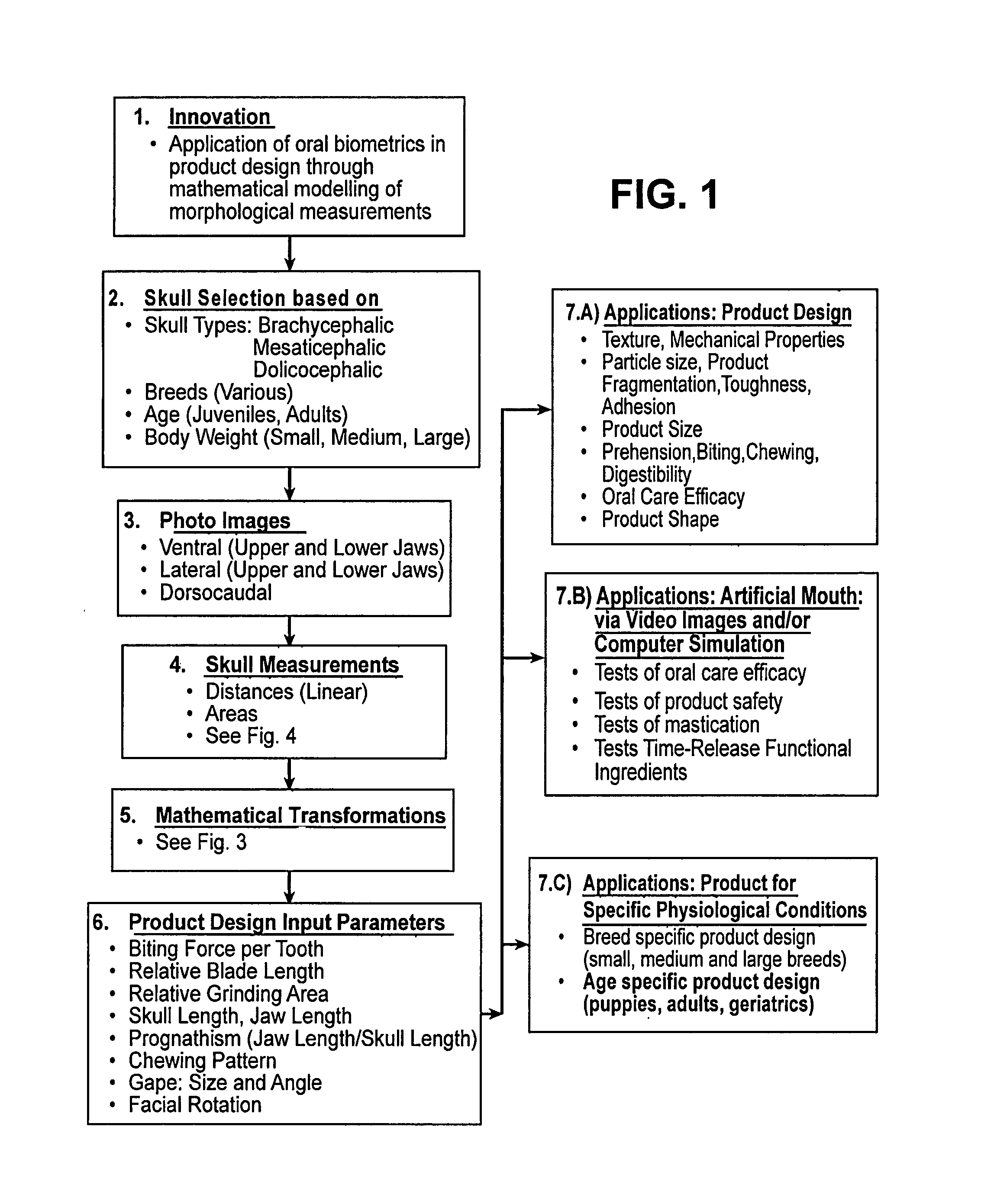
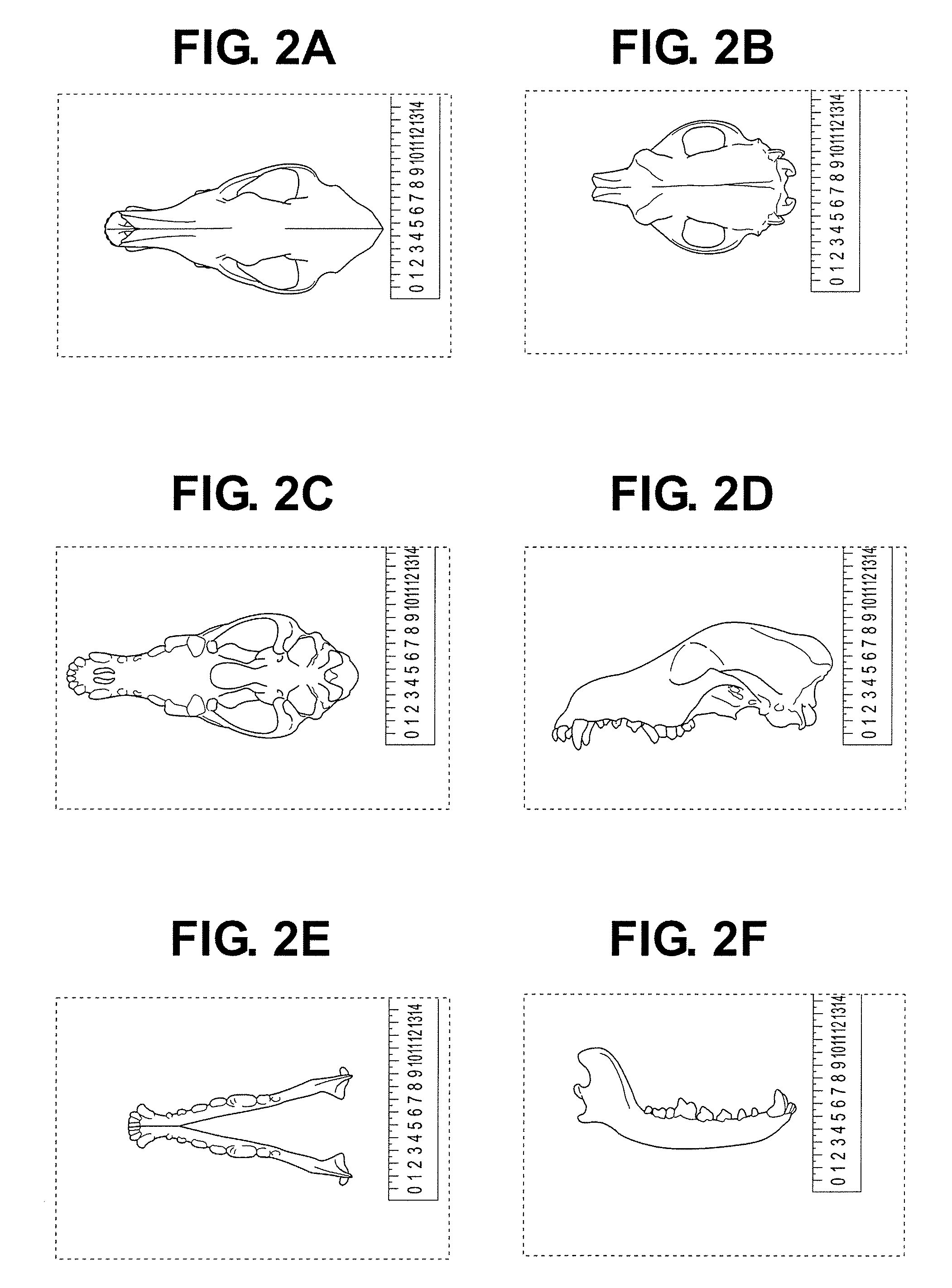
Method for designing an oral pet product using biometric analysis
ActiveUS8548817B2More functionally effectiveFood preservationAnimal feeding stuffCanis lupus familiarisAnalysis method
Owner:MARS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com