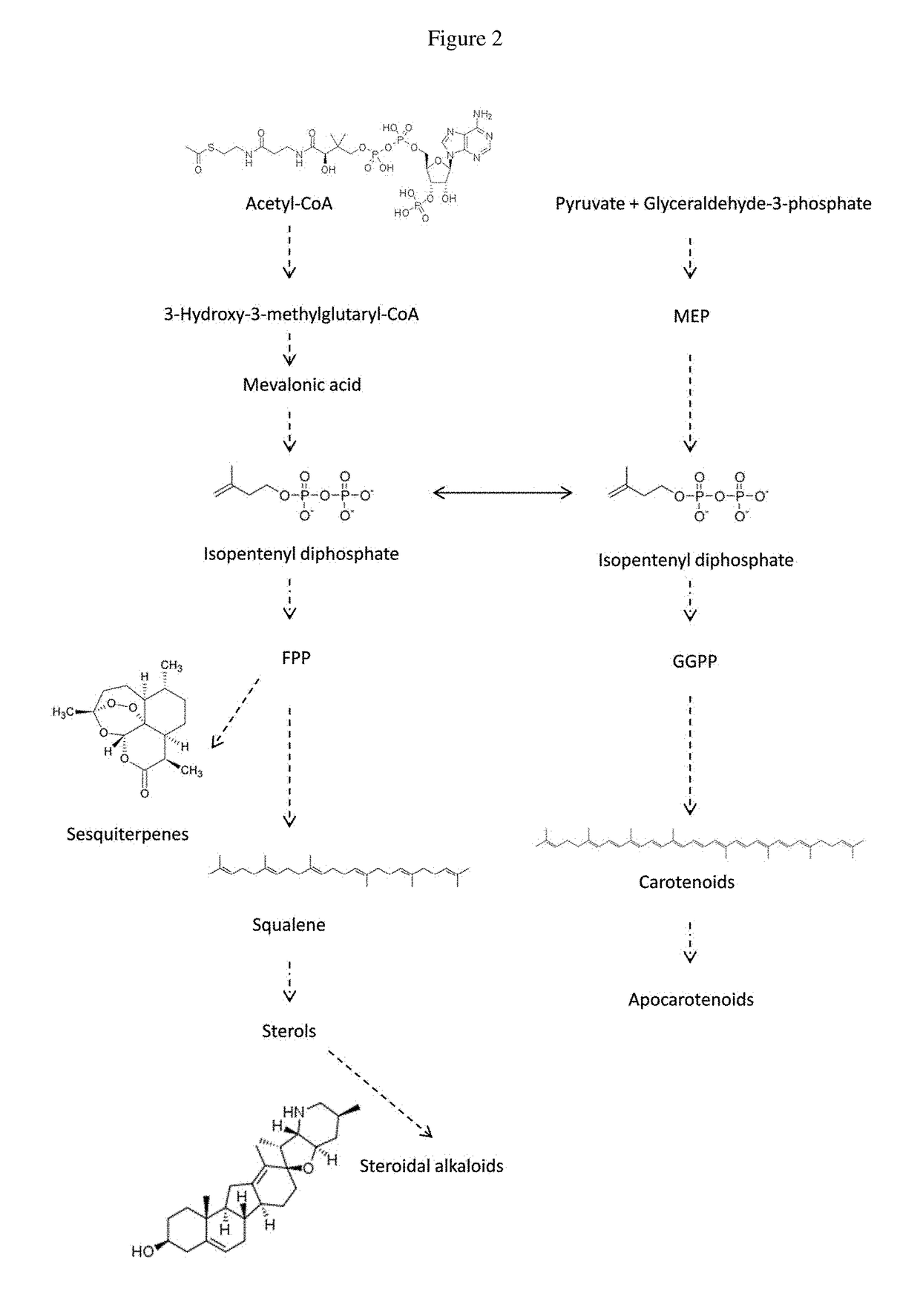
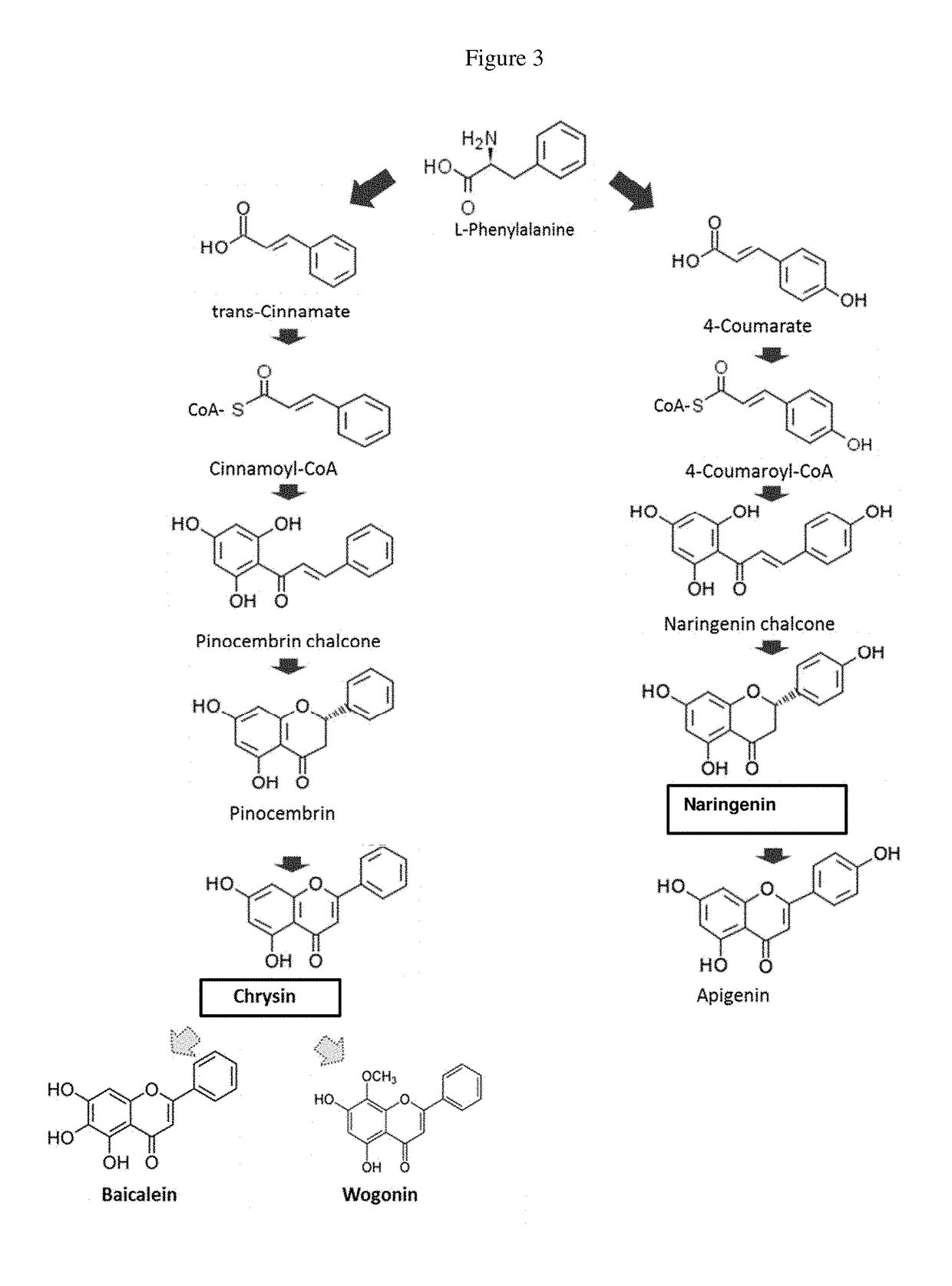
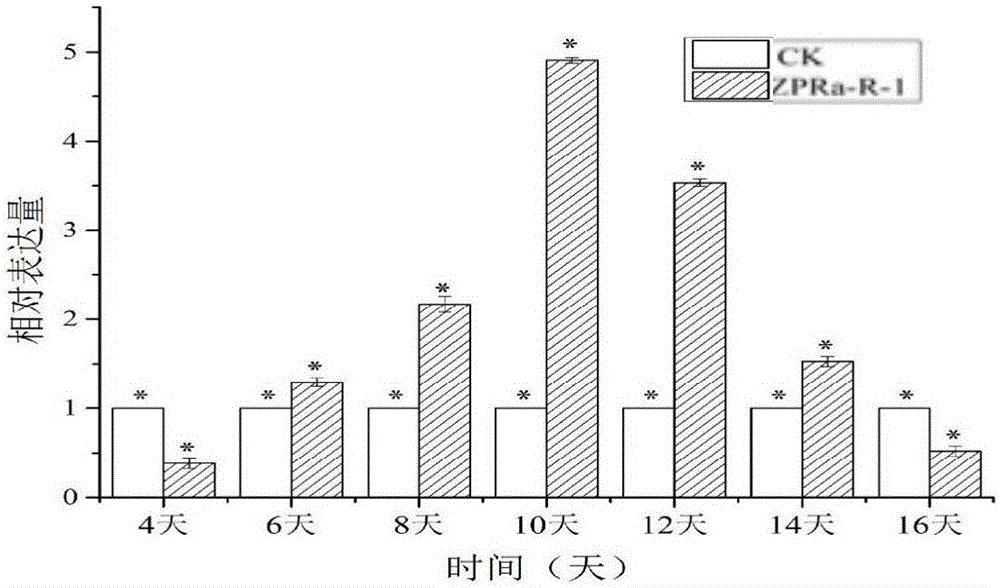
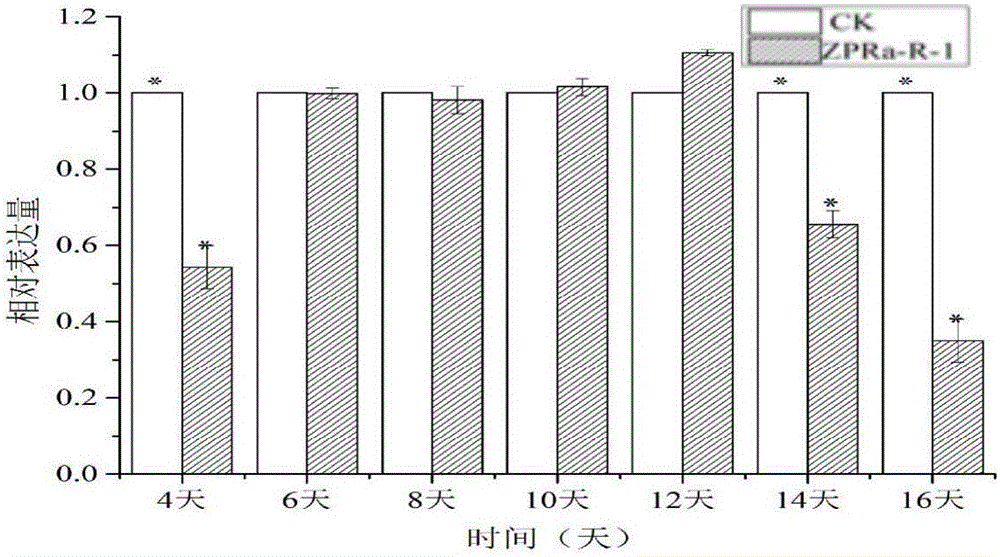
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Hairy root culture" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
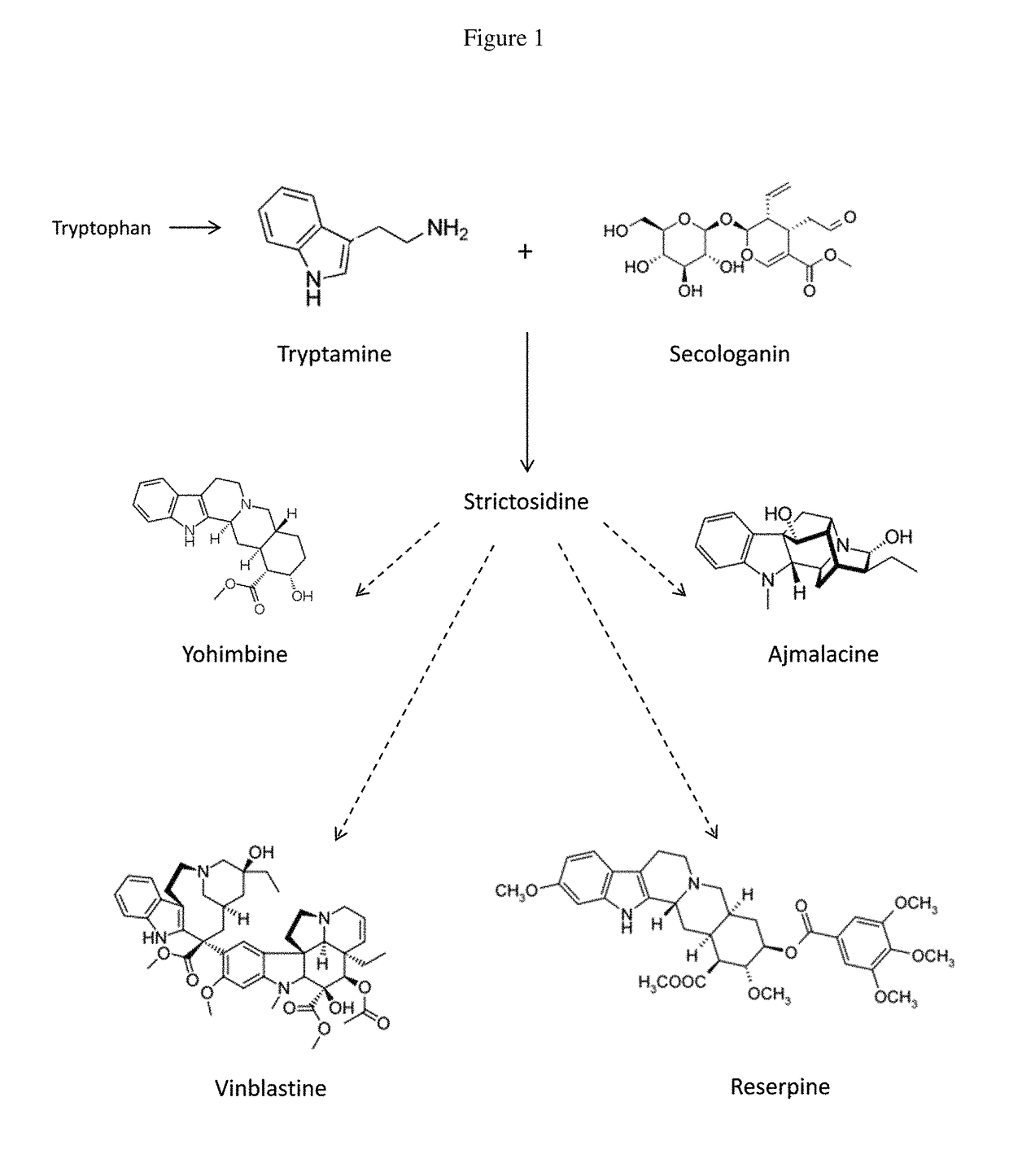
Hairy root culture, also called transformed root culture, is a type of plant tissue culture that is used to study plant metabolic processes or to produce valuable secondary metabolites or recombinant proteins, often with plant genetic engineering.
Method for producing alkannin by utilizing Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root
InactiveCN101869591ANot limited by environmental climateQuality improvementAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiological activationRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention relates to a method for producing alkannin by utilizing Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root. The method includes selection and processing of Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst explant, activation culture of agrobacterium rhizogene, infection of cotyledon explant and induction of hairy root, obtaining of sterile Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root system and liquid culture of Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root as well as alkannin production. The used hairy root has the characteristic of rapid and autonomous growth on culture medium without exogenous hormones, thus the method not only can overcome the defects that cell culture grows slowly and hormone is required to be additionally added to maintain the growth thereof when utilizing cell culture to produce alkannin, and the method has the advantages of stable alkannin throughput, simple operation in cultivation, lower cost and no restriction of climate and land natural conditions. Especially the invention provides a stable and continuable novel medicine source for producing alkannin by utilizing hairy root culture method and provides reliable source and material basis for alkannin mass production by applying bioreactor in the future.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Method for evoking liquorice to generate hairy root
ActiveCN101157936AShorten the timeImprove conversion efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsGLYCYRRHIZA EXTRACTRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention discloses a method for inducting hairy root of glycyrrhizae. The procedure of the method is to co-culture glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node and agrobacterium rhizogenes which contains Ri plasmid and then transfer glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node and agrobacterium rhizogenes to an induction medium for induction cultivation after washing of cephamycin-contained sterile water, then glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node yields glycyrrhizae hairy root. The invention takes glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node as acceptor material for the first time and realizes induction of glycyrrhizae hairy root through the mediating of agrobacterium rhizogenes, thus shortening the growing period of glycyrrhizae hairy root to 4 days and raising the transforming efficiency to more than 96 percent. Furthermore, the active component in the hairy root such as licoflavone is as high as 1.6 percent, which settles a good foundation for producing useful glycyrrhizic acid and licoflavone by using glycyrrhizae hairy root culture.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte with danshinolic acid B accumulation inducing effect, and use thereof
The invention relates to a Salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte and its use in the improvement of danshinolic acid B accumulation in the Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root culturing process. The Salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte is Pseudomonas psychrotolerans LG4 concretely, and has a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2015085. The Salvia miltiorrhiza endophytec an promote the accumulation of a phenolic acid substance (danshinolic acid B) in Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for culturing and producing cffeetive ingredients in polyose of saussurca hairy roots of saussurea medusa maxim
InactiveCN1625940ALimited protectionProtect environmentHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureProduction rateAdditive ingredient
A process for culturing the hairy root of medusa saussura to obtain saussura polyose includes providing the aseptic test-tube plantlet of medusa saussura, infecting it with bacterial strain R1000, R1601, or LBA 9402, and suspending culture in the 1 / 2 MS culture medium. Its advantages are high content of polyose (5-10%), and high output rate of polyose (1-2 g / L).
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for inducing production of tripterygium wilfordii hairy root by agrobacterium rhizogenes
InactiveCN102321664AFill in the gapsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsRhizobium rhizogenesTriptolide
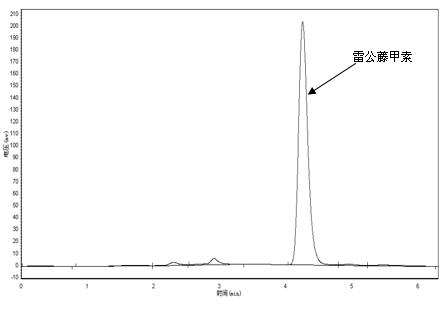
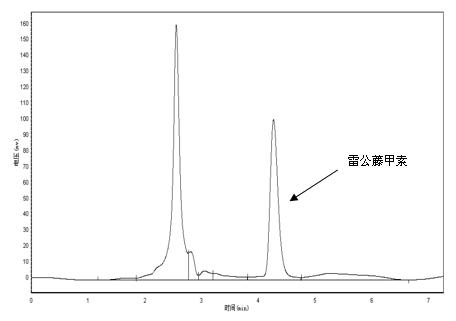
The invention provides a method for inducing the production of tripterygium wilfordii hairy roots by agrobacterium rhizogenes, which comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining aseptic explants; (2) preparing bacterial liquid of agrobacterium rhizogenes; (3) performing agrobacterium rhizogenes infection to induce hairy roots; (4) establishing a hairy root in-vitro culture system, wherein the establishment of the hairy root in-vitro culture system comprises the following steps: culturing hairy roots in a 1 / 2 MS solid medium containing 500 mg / L cefotaxime sodium under a dark culture condition with a temperature of 27 + / -1 DEG C, performing subculture once every 7 days, reducing the using concentration of cefotaxime sodium gradually during subculture till no bacterium is found, finally putting the completely aseptic hairy roots on the 1 / 2 MS solid medium for subculture and preservation. During the detection of the produced aseptic tripterygium wilfordii hairy roots, a considerable amount of triptolide is found to be contained in the hairy roots, and the content is significantly higher than the content of triptolide in traditional tripterygium wilfordii wild roots and tissue culture roots; the method has good prospects for industrial application. The production of triptolide by hairy root culture fills the gap of traditional Chinese medicine.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method to increase the yield of products in plant material
ActiveUS10144913B1Increase productionImprove efficiencyComponent separationCell culture mediaTrappingElicitor
A method or process to increase the production of products of interest in plant material including plant cultures, such as, for example, cell suspension cultures, root cultures, and hairy root cultures is provided. In one embodiment, the method is to contacting the plant material with a precursor or xenobiotic when producing a product of interest from a plant. In another embodiment the plant material is also contacted with a trapping agent. The process may also provide for contacting an elicitor of the product of interest with the plant material. An embodiment provides for contacting an elicitor, precursor and trapping agent with the plant material. The ability to produce novel compounds such as glucosides and glucuronides is provided.
Owner:ARKANSAS STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting salidroside synthetase gene expression activity by using dual reference genes
InactiveCN105886638AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSalidrosideReference genes
The invention provides a method for detecting salidroside synthetase gene expression activity by using dual reference genes. Specifically, a primer which is obtained through design and screening is adopted to amplify to obtain glyceraldehydes phosphate dehydrogenase and phytochelatin synthetase genes, and correct and detect the gene expression activity of three key enzymes, namely, tyrosine decarboxylase, tyrosine transaminase and phenylalanine ammonialyase of synthesized salidroside in rhodiola crenulata tissue culture seedlings by using the gene as the dual reference genes. The method comprises the following steps: extracting total RNA of a rhodiola crenulata plant; synthesizing a cDNA first chain; and by using a fluorescent quantitative PCR technique, amplifying by using a given primer so as to obtain the dual reference genes of GAPDH and PCS, and correcting and detecting the expression activity of synthesized salidroside key enzyme genes TyDC, TAT and PAL in the rhodiola crenulata tissue culture seedlings. The method has the advantages of rapidness, accuracy, practicability, stability and the like in aspects such as production quality control and product activity detection on rhodiola crenulata tissue culture seedlings, cell suspension culture, hairy root culture and the like.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Endophyte having salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root phenolic acid accumulation inducing effect, and uses thereof
ActiveCN104830695APromote accumulationIncrease contentPlant growth regulatorsBiocideRoot weightSalvianolic acid B
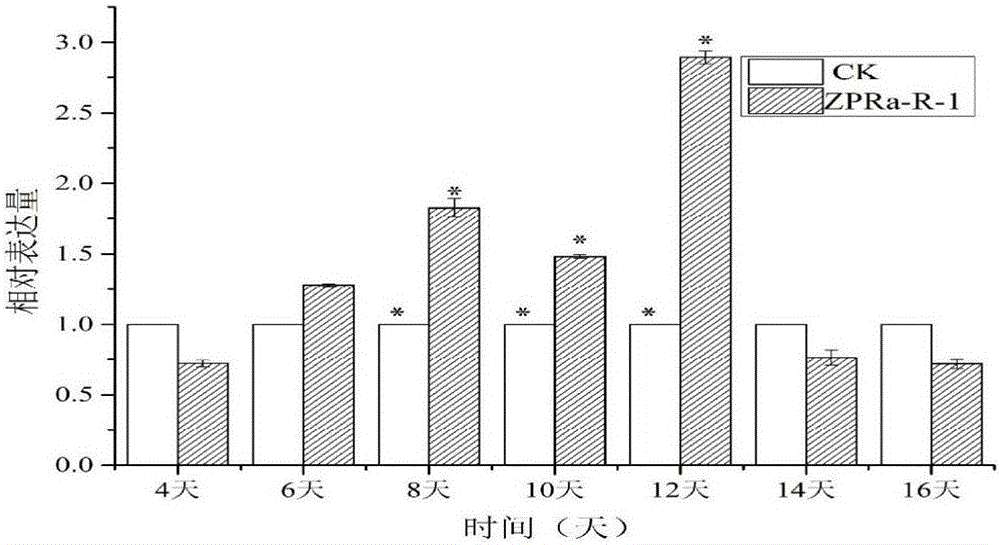
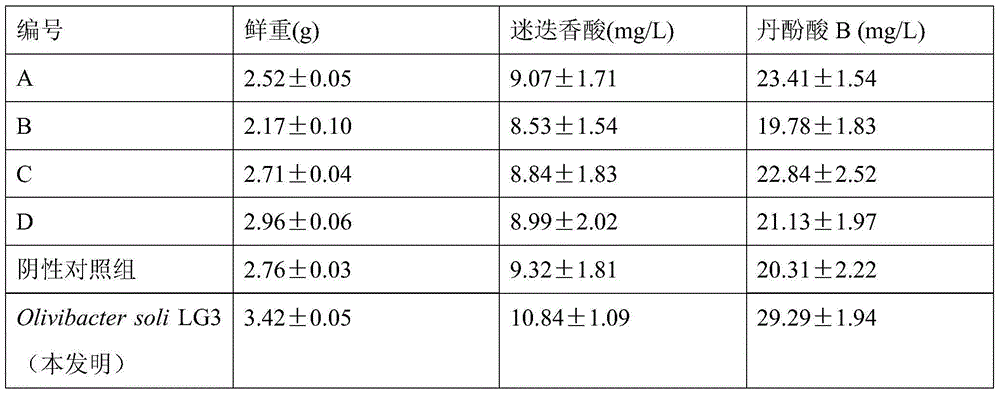
The present invention relates to salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte and uses thereof, wherein the salvia miltiorrhiza endophyte is used for accumulating phenolic acid substances during salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root culture. Particularly the present invention discloses the endophyte, which is Olivibacter soli LG3 and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M2015084. With the Olivibacter soli LG3, the accumulation of the phenolic acid substances (salvianolic acid B and rosmarinic acid) in the salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root can be promoted, and the salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root weight gain can be promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for cultivating meloidogyne hapla by adopting peanut rooting
ActiveCN105010245AConducive to infection and reproductionHigh reproductive rateAnimal husbandryMeloidogyne incognitaBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for cultivating meloidogyne hapla by adopting peanut rooting. The method comprises the following steps that number 45 seeds are selected, flowered and seeded on an MSB5 culture medium for cultivation; agrobacterium rhizogenes strains A4 are taken for cultivation and activation to achieve a logarithmic growth period; the agrobacterium rhizogenes strains A4 are adopted for infecting the sterile culture 6d flowered number 45 peanut cotyledon for inducing hairy roots; peanut roots with multiple insect galls are selected to be immersed into a NaCLO solution and broken to form a mixed solution; the mixed solution is poured onto combination sieves, wherein the combination sieves are of the types of 40 meshes, 200 meshes, 325 meshes and 500 meshes in sequence from top to bottom, and sterile water is used for spraying and washing, so that the meloidogyne hapla is concentrated to one side; then, a small amount of sterile water is used for washing oversize products from the back faces of the sieves, and liquid is collected into a container to obtain meloidogyne hapla suspension; the meloidogyne hapla suspension is evenly inoculated on a peanut hairy root culture dish, and cultivation is performed to obtain a large number of eggs and second-stage larvae. The method solves the problem that a large amount of purified meloidogyne hapla cannot be obtained easily, and the reproduction rate is high.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Production method for chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid through induction and culture of hairy roots of stevia rebaudiana
ActiveCN103695462AHigh and stable chlorogenic acidHigh and stable dicaffeoylquinic acid contentOrganic chemistryGenetic engineeringDicaffeoylquinic acidRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, specifically to a production method for chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid by establishing a hairy root culture system through genetic transformation of stevia rebaudiana with agrobacterium rhizogenes. The method comprises the following steps: preparation of an explant of stevia rebaudiana, activation and culture of agrobacterium rhizogenes, suspension culture and production of chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid. PCR detection results show that hairy roots of stevia rebaudiana are generated through transformation; HPLC detection results show that the hairy roots of stevia rebaudiana can produce chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid. Since the hairy roots used in the invention have the characteristic of rapid growth on a hormone-free medium, the method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, no restriction by natural conditions like climate and land, etc. A stable and sustainable novel drug source and food function factors are provided for production of chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid through culture of the hairy roots, and a reliable source and a reliable substance base are provided for large scale production of chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid by using a bioreactor in the future.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
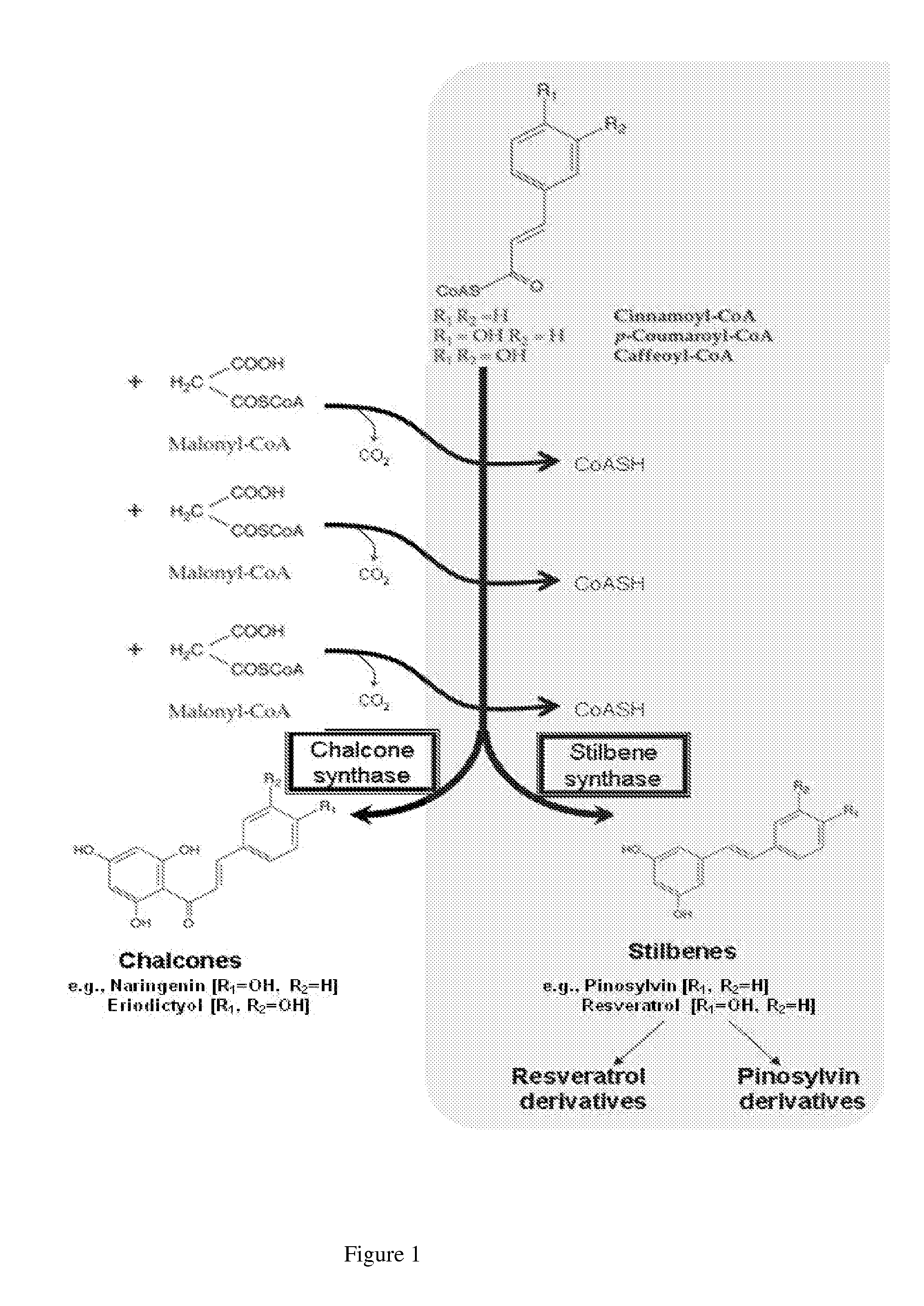
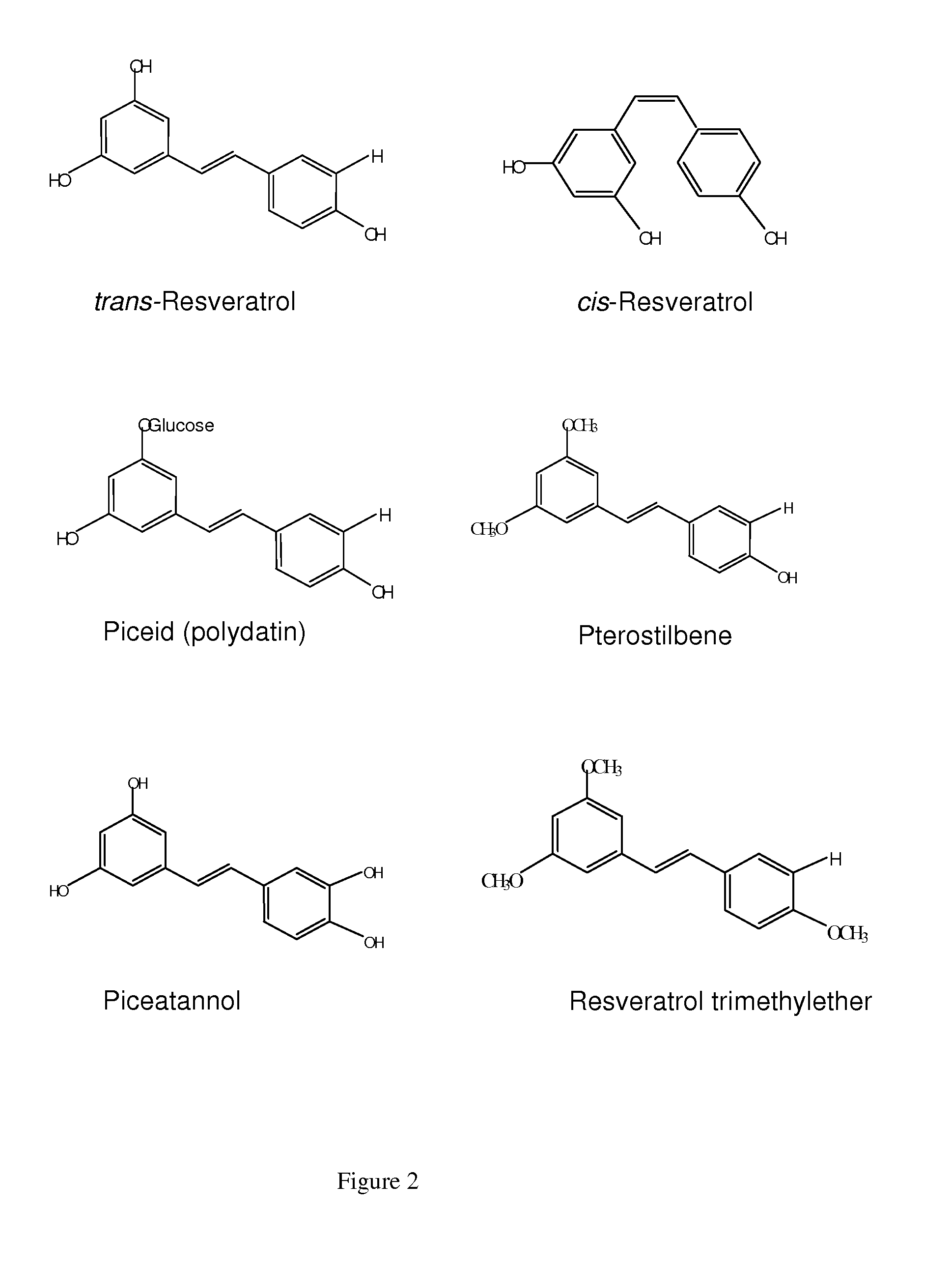
Production of stilbenes in plant hairy root cultures and other root cultures
InactiveUS20100130623A1Increase volumeBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsBiotechnologyPlant cell
Improved methods for production of stilbenoids including resveratrol, pinosylvin and their respective derivatives are provided, including producing root cultures from plant cells and eliciting production of the stilbenes. The plant cells in an embodiment are contacted with substances which elicit production of the stilbenoid compounds.
Owner:ARKANSAS STATE UNIV RES & DEV INST
Method for enhanced production of morinda metabolites
ActiveUS20160220625A1Increase productionImprove productivityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemMetaboliteUlcerative colitis
This invention concerns a genetic transformation method to induce hairy root culture of Morinda species, such as Morinda officinalis How, to increase production of therapeutically useful metabolites, related extracts of the roots, and methods to treat ulcerative colitis using extracts of Morinda species, such as Morinda officinalis How.
Owner:CHAN SHAM YUEN
Method for improving content of glycyrrhizae hairy root secondary metabolism production
InactiveCN101263811AHigh in flavonoidsIncrease contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsLiquid mediumSecondary metabolite
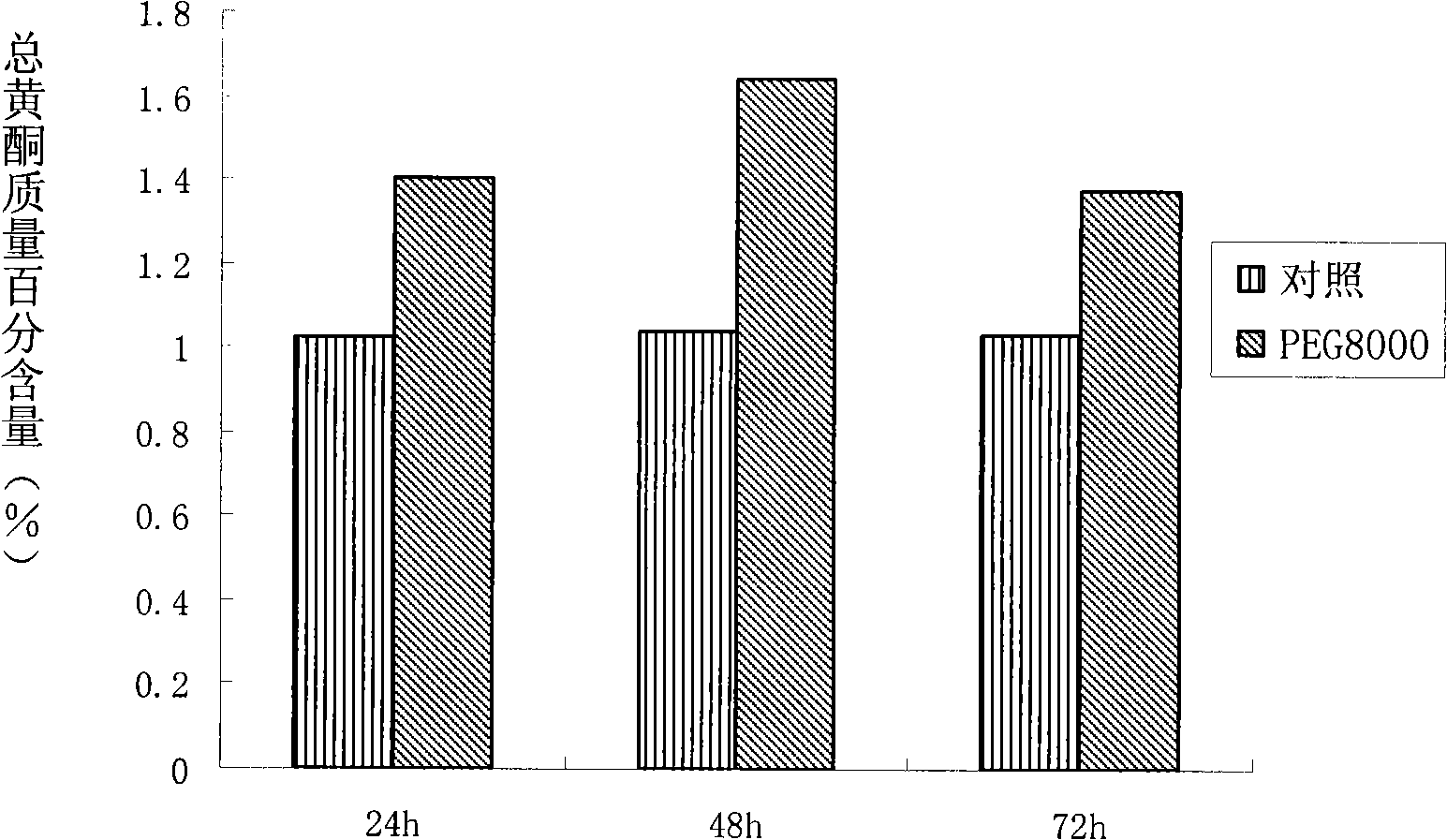
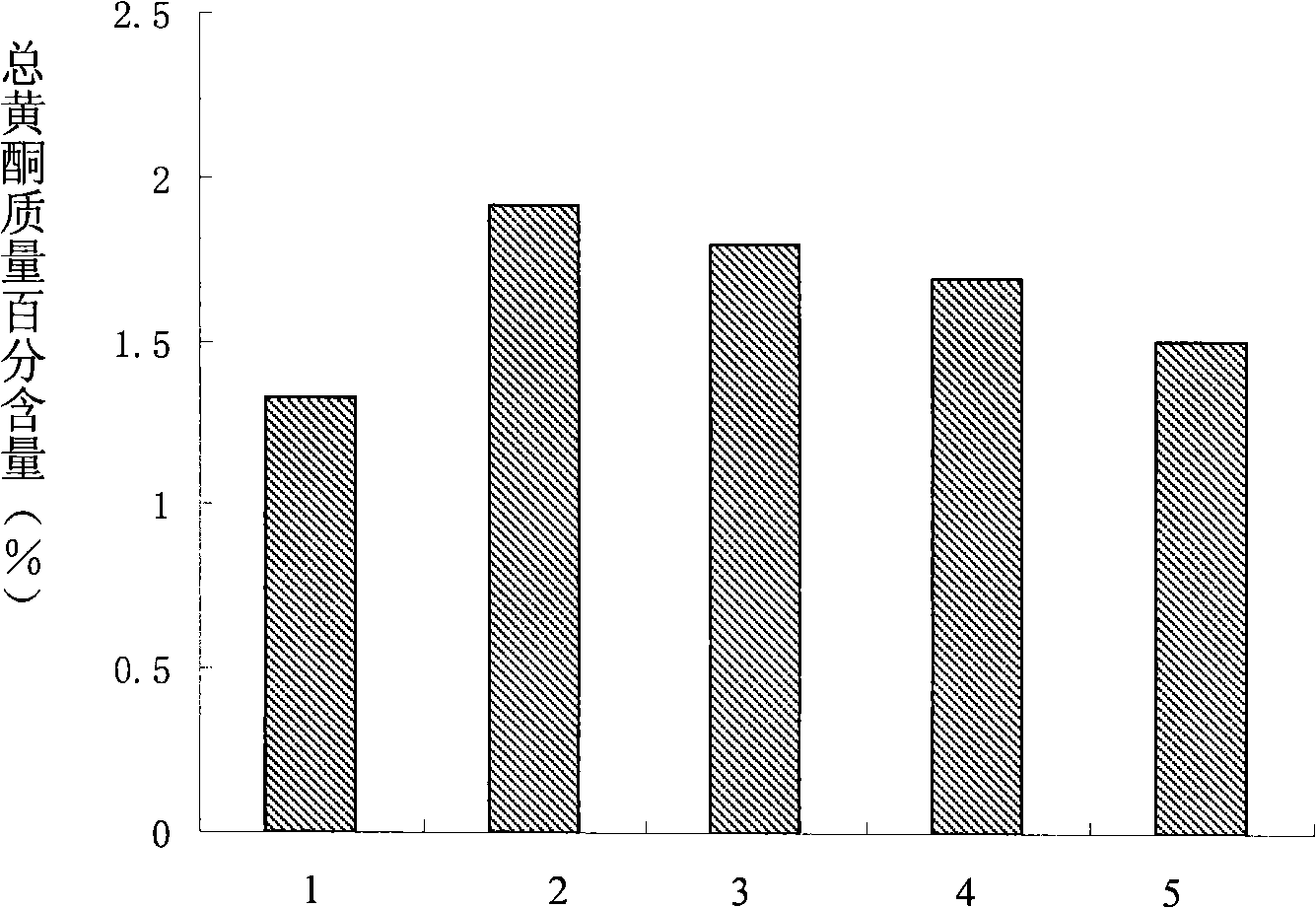
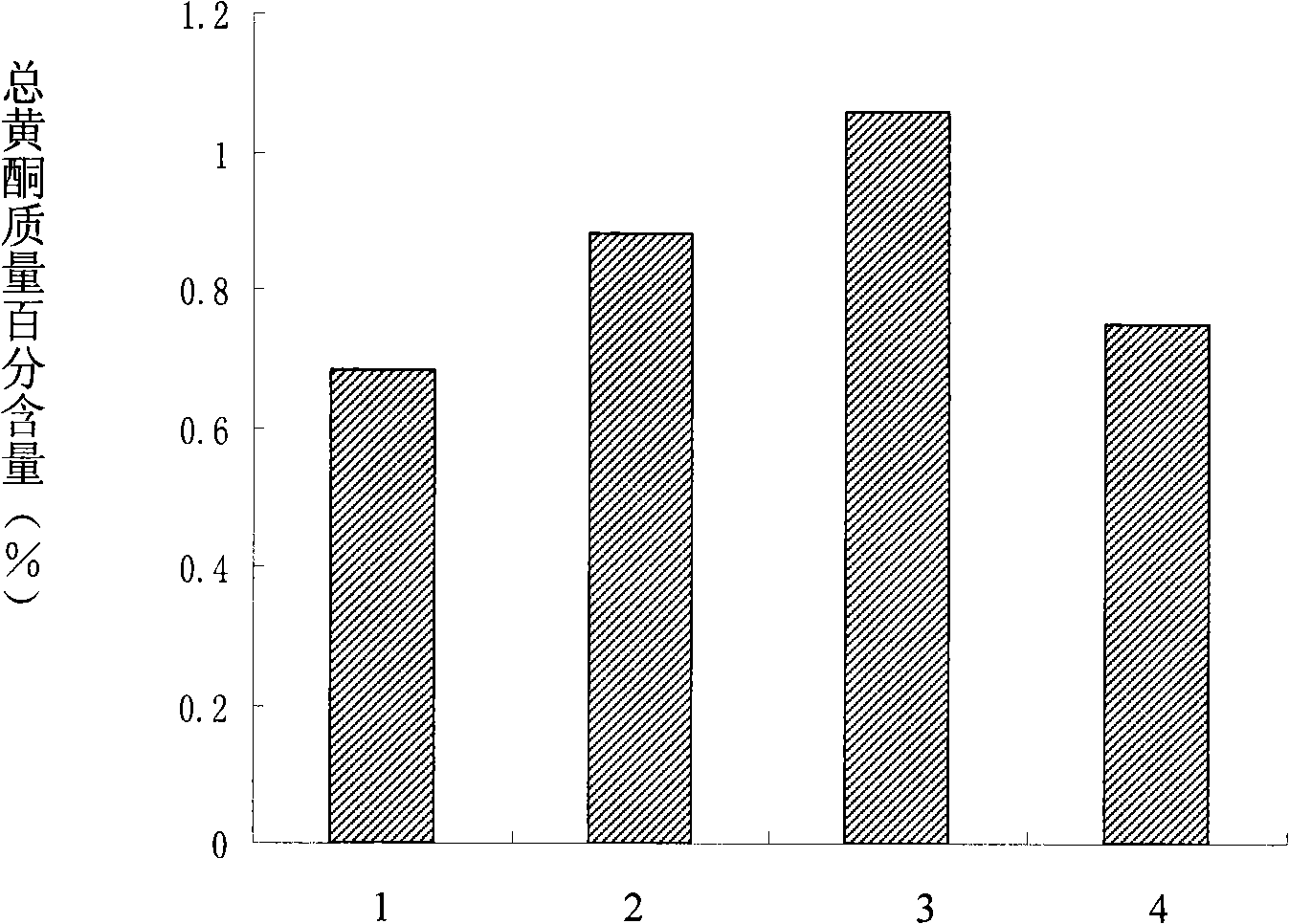
The invention discloses a method to improve the synthetic quantity of secondary metabolites in liquorice hairy roots; the method processes the liquorice hairy roots in a liquid medium by a matter capable of regulating the osmotic pressure of cells to form drought stress, and then liquorice hairy roots with a higher content of secondary metabolites is obtained. The matter capable of regulating the osmotic pressure of cells is PEG or tween. The method of the invention can improve the content of secondary metabolites in liquorice hairy roots by processing the liquorice hairy roots with the matter capable of regulating the osmotic pressure of cells to form drought stress. Experiment showed the method to improve the synthetic quantity of secondary metabolites in liquorice hairy roots has the advantages that, the content of total flavone in the liquorice hairy roots processed by the method is increased to 44% to 55%; the invention provides a new way to rapidly and efficiently obtain high yield liquorice effective secondary metabolites by utilizing liquorice hairy roots culture system.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Preparation and cultivation method of hairy roots of tongkat ali
InactiveCN102754594AFast growthAlleviate market demandPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiological cellRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention discloses a preparation and cultivation method of hairy roots of tongkat ali and belongs to the biological cell engineering technology. The preparation and cultivation method includes: tender stems of tongkat ali are used as explants which subjected to dedifferentiation to obtain fresh callus of tongkat ali, the callus and Agrobacterium rhizogenes containing Ri (root-inducing) plasmid are co-cultured, co-cultured bacteria liquid is transferred to an inductive medium for induced culture after excess bacteria liquid is absorbed with aseptic paper, fairy roots of tongkat ali grow at the callus of tongkat ali; and the explants with hairy roots are laced in an amplification medium for extended culture of the hairy roots after biostatistics culture. The tongkat ali hairy root culture system is established by the biological cell engineering technology and used to prepare the hairy roots of tongkat ali, standard production of tongkat ali is realized, wild resources are replaced, increasing market demands on tongkat ali are eased, and the problem that tongkat ali relies on import is solved. The preparation and cultivation method is important to industrial and commercial development of hairy roots of medicinal plants.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY +1
Method for obtaining raphanin from broccoli hairy root culture system
ActiveCN105713937AFill in the gaps in secretory researchLess investmentOrganic chemistryFermentationLiquid mediumRaphanin
The invention relates to a method for obtaining raphanin from a broccoli hairy root culture system. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inoculating broccoli hairy root to a liquid medium, carrying out proliferation culture and freeze drying, and grinding into powder, thus obtaining lyophilized hairy root powder; (2) grinding newly harvested mustard seeds, carrying out ultrasonic oscillation extraction, and carrying out suction filtration to remove impurities, thus obtaining a crude enzyme; (3) adding the crude enzyme into the lyophilized hairy root powder, carrying out enzymolysis and ultrasonic oscillation extraction, and carrying out vacuum filtration to remove impurities, thus obtaining raphanin crude extraction liquid; (4) concentrating the raphanin crude extraction liquid, and extracting to obtain an ethyl acetate phase A; (5) extracting the liquid medium, thus obtaining an ethyl acetate phase B; (6) mixing the ethyl acetate phase A and the ethyl acetate phase B, and carrying out vacuum concentration and dissolution on the mixture, thus obtaining raphanin methanol solution; (7) carrying out vacuum concentration on the raphanin methanol solution, thus obtaining a raphanin crude extract; and (8) drying the raphanin crude extract to obtain a raphanin crude product with the purity being 5-30%. The method is simple and efficient.
Owner:甘肃泽华生物科技有限公司
Microbacterium and uses thereof
ActiveCN104830716AIncreased rosmarinic acid contentIncrease the content of salvianolic acid BBiocidePlant growth regulatorsRoot weightSalvianolic acid B
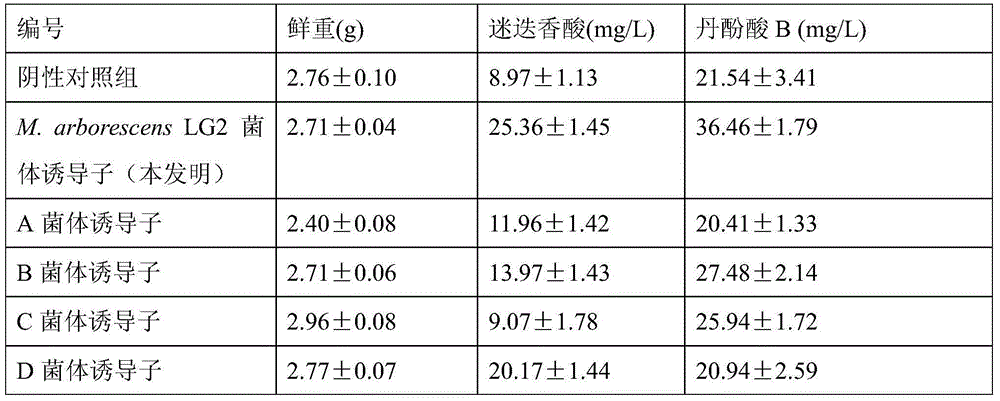
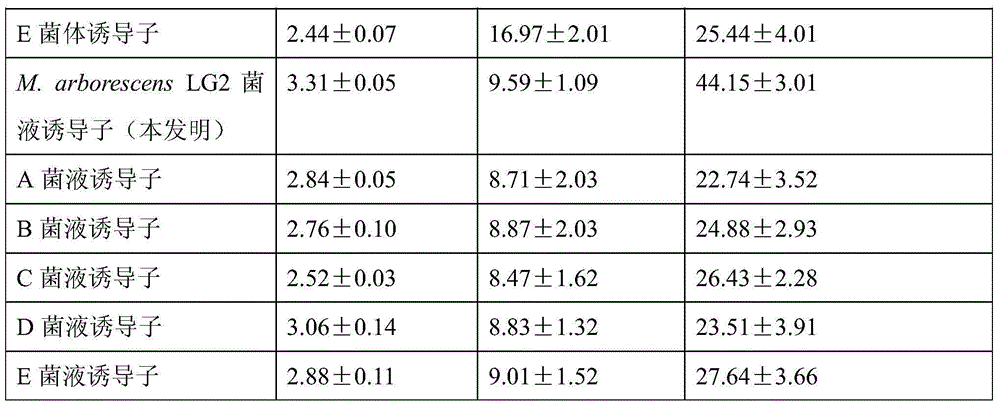
The present invention relates to a strain of Microbacterium and applications of the Microbacterium in a salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy root culture system. Specifically The present invention discloses the Microbacterium, which is Microbacterium arborescens LG2 and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2015083. With the Microbacterium, the accumulation of the salvianolic acid B and the rosmarinic acid in the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy root can be promoted, and the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy root weight gain can be promoted.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte having phenolic acid accumulation inducing effect, and uses thereof
ActiveCN104830714APromote accumulationIncrease contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSalvia miltiorrhizaActive component
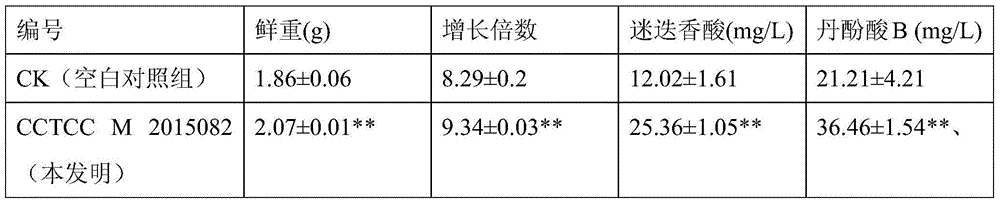
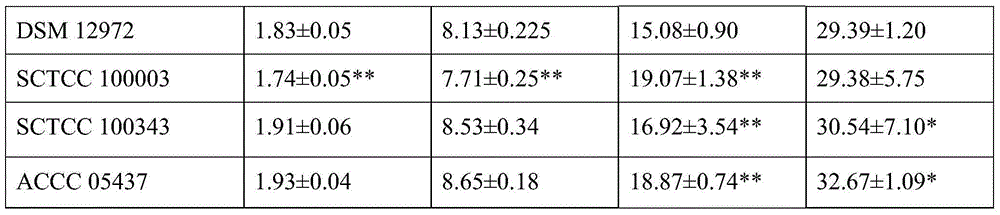
The present invention relates to a nature medicinal plant endophyte salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, and uses thereof, specifically to a salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, which is Pseudomonas chlororaphis LG1, and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2015082. The present invention further discloses the uses of the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, wherein the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte can promote accumulation of phenolic acid substances in salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots. With the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, the problems of low active component content and instable quality during the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy root culture process can be solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Method for producing alkannin by utilizing Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root
InactiveCN101869591BNot limited by environmental climateQuality improvementVector-based foreign material introductionExogenous hormonesBiological activation
The invention relates to a method for producing alkannin by utilizing Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root. The method includes selection and processing of Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst explant, activation culture of agrobacterium rhizogene, infection of cotyledon explant and induction of hairy root, obtaining of sterile Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root system and liquid culture of Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root as well as alkannin production. The used hairy root has the characteristic of rapid and autonomous growth on culture medium without exogenous hormones, thus the method not only can overcome the defects that cell culture grows slowly and hormone is required to be additionally added to maintain the growth thereof when utilizing cell culture to produce alkannin,and the method has the advantages of stable alkannin throughput, simple operation in cultivation, lower cost and no restriction of climate and land natural conditions. Especially the invention provides a stable and continuable novel medicine source for producing alkannin by utilizing hairy root culture method and provides reliable source and material basis for alkannin mass production by applyingbioreactor in the future.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Induced proliferation method for glehnia littoralis hairy roots
InactiveCN103146638AIncrease productionIncrease production capacityPlant cellsGLEHNIA LITTORALIS ROOTMetabolite
The invention provides an induced proliferation method for glehnia littoralis hairy roots. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining glehnia littoralis aseptic seedlings; culturing agrobacterium rhizogenes for infection; performing co-culture on the transformed explant; and inducing hairy root generation and hairy root culture proliferation. The formation of glehnia littoralis hairy roots is induced by utilizing the agrobacterium rhizogenes infection, an in-vitro hairy root culture system is established, the content of medicinal component coumarin is analyzed and measured, the content of medicinal component coumarin is contrasted with the content of coumarin in adventitious root and artificially cultured glehnia littoralis roots, the content of coumarin in the hairy roots is the highest, and the glehnia littoralis hairy roots has the advantages of fast growth, short period, relatively high yield of the secondary metabolite and the like and can be used for industrial production of glehnia littoralis coumarin; and moreover, a novel path is provided for industrial production of the secondary metabolite of the glehnia littoralis by utilizing the hairy roots in the future, the threatened plant is protected, and the ecological balance is maintained.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Induction method of Rabdosia rubescens Hemsl. Hara hairy roots, and induction expression method of oridonin
InactiveCN106167811AOrganic chemistryVector-based foreign material introductionInduction methodCulture mediums
The invention belongs to the biological technology field, and more specifically discloses an induction method of Rabdosia rubescens Hemsl. Hara hairy roots, and an induction expression method of oridonin. According to the induction expression method, Rabdosia rubescens Hemsl. Hara petiole explants are infected with agrobacterium ATCC15834 for 20min, so that induction of generation of hairy roots is realized; the Rabdosia rubescens Hemsl. Hara hairy roots are cultured in B5 culture medium for 45d, and then oridonin is obtained via extraction. The induction method of Rabdosia rubescens Hemsl. Hara hairy roots is disclosed for the first time, high efficiency oridonin production method is established based on method improvement, and foundation of application of hairy root culturing technology in oridonin batch production is provided.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
A method for genetic transformation of transgenic Stevia rebaudiana mediated by Agrobacterium rhizogenes
ActiveCN103667343BEasy to getSimple operation techniqueGenetic engineeringFermentationKanamycinPolyethylene glycol
A method for the genetic transformation of transgenic Stevia rebaudiana mediated by Agrobacterium rhizogenes, in which the stem tip explants of Stevia rebaudiana after precultivation are immersed in the Agrobacterium rhizogenes bacterium liquid carrying the pRI 101-AN DNA plasmid of the gene of interest, After infection, co-cultivation and sterilization treatment, the hairy roots were cultured on the selection medium containing kanamycin, and induced the formation of kanamycin-resistant hairy roots on the explants, and induced the formation of hairy roots The callus differentiates into adventitious buds, and the adventitious buds continue to grow to form test-tube plantlets, and PCR amplification method is used to identify transgenic plants carrying the target gene. By adopting the technical scheme provided by the invention, the target gene can be introduced into Stevia rebaudiana, and compared with the genetic transformation of chemical methods such as polyethylene glycol, the link of isolation and cultivation from protoplasts is reduced; and the genetic transformation of physical methods such as gene guns In contrast, it does not require expensive instruments and equipment, and the operation technique is simple.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Method for enhanced production of morinda metabolites
ActiveUS9968645B2Increase productionImprove productivityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemMetaboliteUlcerative colitis
This invention concerns a genetic transformation method to induce hairy root culture of Morinda species, such as Morinda officinalis How, to increase production of therapeutically useful metabolites, related extracts of the roots, and methods to treat ulcerative colitis using extracts of Morinda species, such as Morinda officinalis How.
Owner:CHAN SHAM YUEN
Induced proliferation method for glehnia littoralis hairy roots
InactiveCN103146638BIncrease productionIncrease production capacityPlant cellsGLEHNIA LITTORALIS ROOTMetabolite
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
A method for inducing and cultivating stevia hairy roots to produce chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid
ActiveCN103695462BQuality improvementStable outputOrganic chemistryGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyDicaffeoylquinic acid
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and specifically relates to a method for producing chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid by using Agrobacterium rhizogenes to genetically transform stevia rebaudiana to establish a hairy root culture system. The content includes the preparation of stevia rebaudiana explants, the activation culture of Agrobacterium rhizogenes, the suspension culture and the production of chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid. The detection by PCR proved that the hairy root of Stevia rebaudiana was produced by transformation, and the detection by HPLC showed that the hairy root of Stevia rebaudiana could produce chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid. Since the hairy roots used have the characteristics of rapid growth on the hormone-free medium, the method has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, and not being restricted by natural conditions such as climate and land. It provides a stable and sustainable new drug source and food functional factor for the production of chlorogenic acid and dicaffeoylquinic acid by using hairy root culture. The large-scale production of acid provides a reliable source and material basis.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for inducing production of tripterygium wilfordii hairy root by agrobacterium rhizogenes
InactiveCN102321664BFill in the gapsVector-based foreign material introductionRhizobium rhizogenesTriptolide
The invention provides a method for inducing the production of tripterygium wilfordii hairy roots by agrobacterium rhizogenes, which comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining aseptic explants; (2) preparing bacterial liquid of agrobacterium rhizogenes; (3) performing agrobacterium rhizogenes infection to induce hairy roots; (4) establishing a hairy root in-vitro culture system, wherein the establishment of the hairy root in-vitro culture system comprises the following steps: culturing hairy roots in a 1 / 2 MS solid medium containing 500 mg / L cefotaxime sodium under a dark culture condition with a temperature of 27 + / -1 DEG C, performing subculture once every 7 days, reducing the using concentration of cefotaxime sodium gradually during subculture till no bacterium is found, finally putting the completely aseptic hairy roots on the 1 / 2 MS solid medium for subculture and preservation. During the detection of the produced aseptic tripterygium wilfordii hairy roots, a considerable amount of triptolide is found to be contained in the hairy roots, and the content is significantly higher than the content of triptolide in traditional tripterygium wilfordii wild roots and tissue culture roots; the method has good prospects for industrial application. The production of triptolide by hairy root culture fills the gap of traditional Chinese medicine.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Aquilaria sinensis hairy root induction and genetic transformation method
ActiveCN108841856AOptimal induction conditionEfficient selectionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureMetaboliteGreen fluorescent protein
The invention provides an aquilaria sinensis hairy root induction and genetic transformation method. According to the method, on the basis of research on conditions such as explant types, infection modes, infection times and hairy root culture temperatures, conditions applicable to aquilaria sinensis hairy root induction and culture are tested and screened, and most appropriate infection conditions for different explants of aquilaria sinensis are obtained. In addition, optimal induction conditions for inducing hairy roots from different parts (cotyledon, stems, roots and leaves) of SW101 aquilaria sinensis are provided. The invention provides a method for improving aquilaria sinensis hairy root genetic transformation efficiency. A green fluorescent protein (fgp) is introduced into aquilaria sinensis hairy roots, whether aquilaria sinensis hairy root genetic transformation succeeds or not can be visibly identified, and meanwhile, the effectiveness of a transformation system can be doubly verified in a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection mode. Good, efficient and simple options are provided for aquilaria sinensis function gene study and / or industrialization of aquilaria sinensis hairy root metabolite.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Preparation method of catharanthus roseus high-content anticancer alkaloid
InactiveCN102464670APromote growthHigh and stable anticancer alkaloid contentAlkaloids chemistryAlkaloidsVentilation statusCatharanthus
The invention relates to a preparation method of catharanthus roseus high-content anticancer alkaloid. According to the invention, hairy roots obtained through agrobacterium rhizogenes mediation are subject to several times of subculture; an excellent clone with high growth speed and high and stable alkaloid content are screened according to the growth rate and the alkaloid content; the hairy root excellent clone is cultured by using a miniature fermenting machine (10-30L); through adjustments upon conditions such as medium components, ventilation status, illumination, temperature, exogenous hormone and culture mode, technology indexes and process flow of hairy root culturing are obtained; a hairy root clonal propagation system is established, and alkaloid is extracted, separated and purified from the hairy root.
Owner:廖龙
Method for culturing and producing cffeetive ingredients in polyose of saussurca hairy roots of saussurea medusa maxim
InactiveCN1331388CLimited protectionProtect environmentHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAdditive ingredientSaussurea medusa
A process for culturing the hairy root of medusa saussura to obtain saussura polyose includes providing the aseptic test-tube plantlet of medusa saussura, infecting it with bacterial strain R1000, R1601, or LBA 9402, and suspending culture in the 1 / 2 MS culture medium. Its advantages are high content of polyose (5-10%), and high output rate of polyose (1-2 g / L).
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for increasing the content of flavonoids in Scutellaria baicalensis
InactiveCN104186318BOriginalityIncrease productionSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorXanthonoidElicitor
Owner:雷桅
A kind of tissue culture method for the induction and proliferation of bovine vigorous hairy roots
InactiveCN104372020BSimple and fast operationReduce manufacturing costGenetic engineeringFermentationChemical compositionCotyledon plant
The invention discloses a tissue culture method for inducing and proliferating bovine vigorous hairy roots. In the method, the cotyledons of the boulders are used as explants to induce hairy roots, and the method includes explant sterilization, Agrobacterium activation culture, hairy root induction culture, proliferation culture and the like. Advantages of the present invention: (1) adopt the cotyledons of Bovine vigor to transform as explants; (2) Establish the pre-culture time, bacterium concentration, infection time and co-cultivation time suitable for the induction of bovine vigor hairy roots; (3 ) determined the best bacteriostatic agent for explant bacteriostatic culture; (4) determined the best pre-cultivation, co-cultivation, bacteriostatic culture and subculture medium; (5) the whole set of method operation provided by the present invention It is simple, low in production cost, high in induction success rate, and fast in proliferation, and can sustainably obtain the hairy root of the plant, which can be used for large-scale cultivation of the hairy root of the plant to extract the main chemical components such as the polysaccharide of the plant, and has a good application prospect .
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com