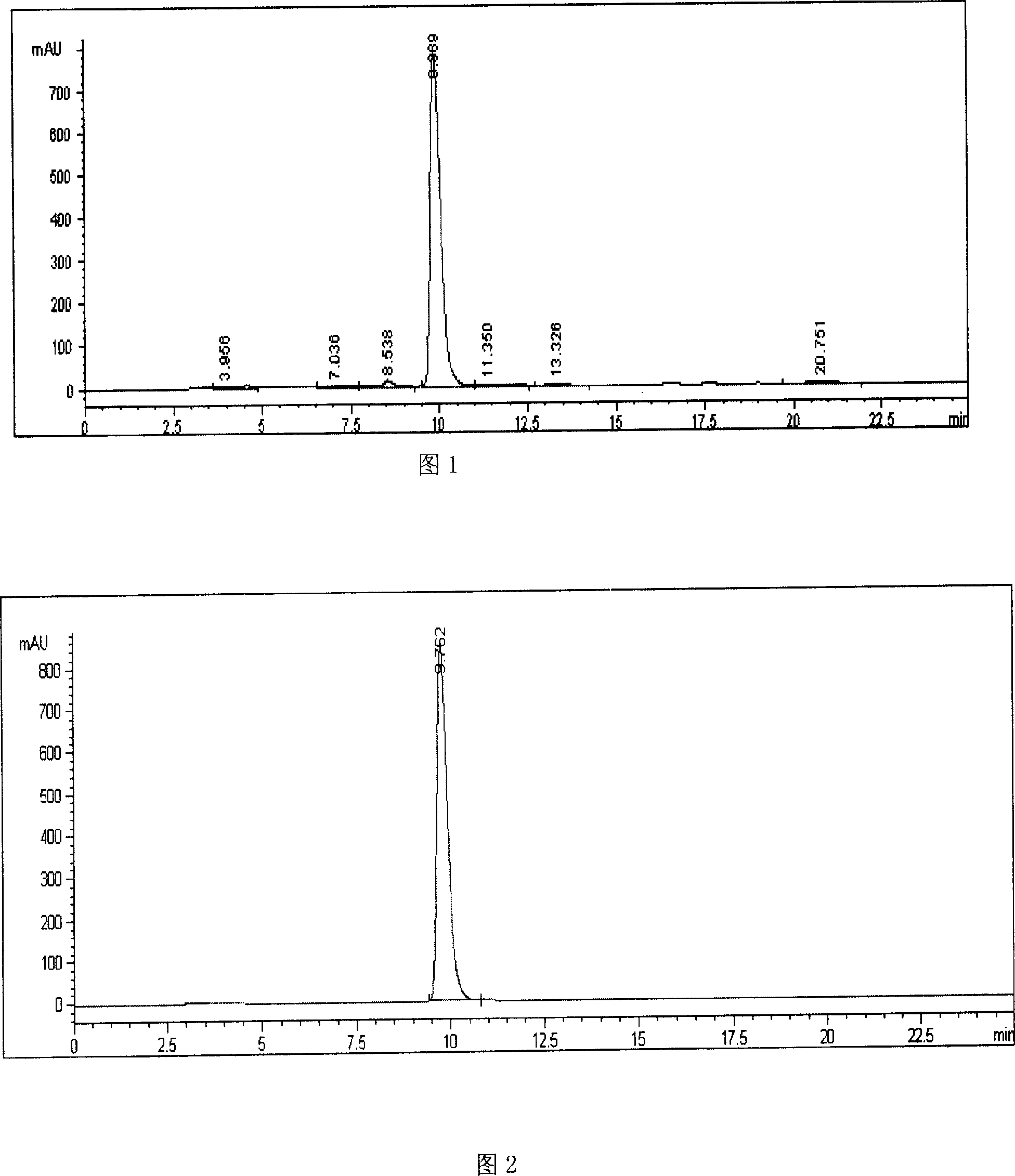
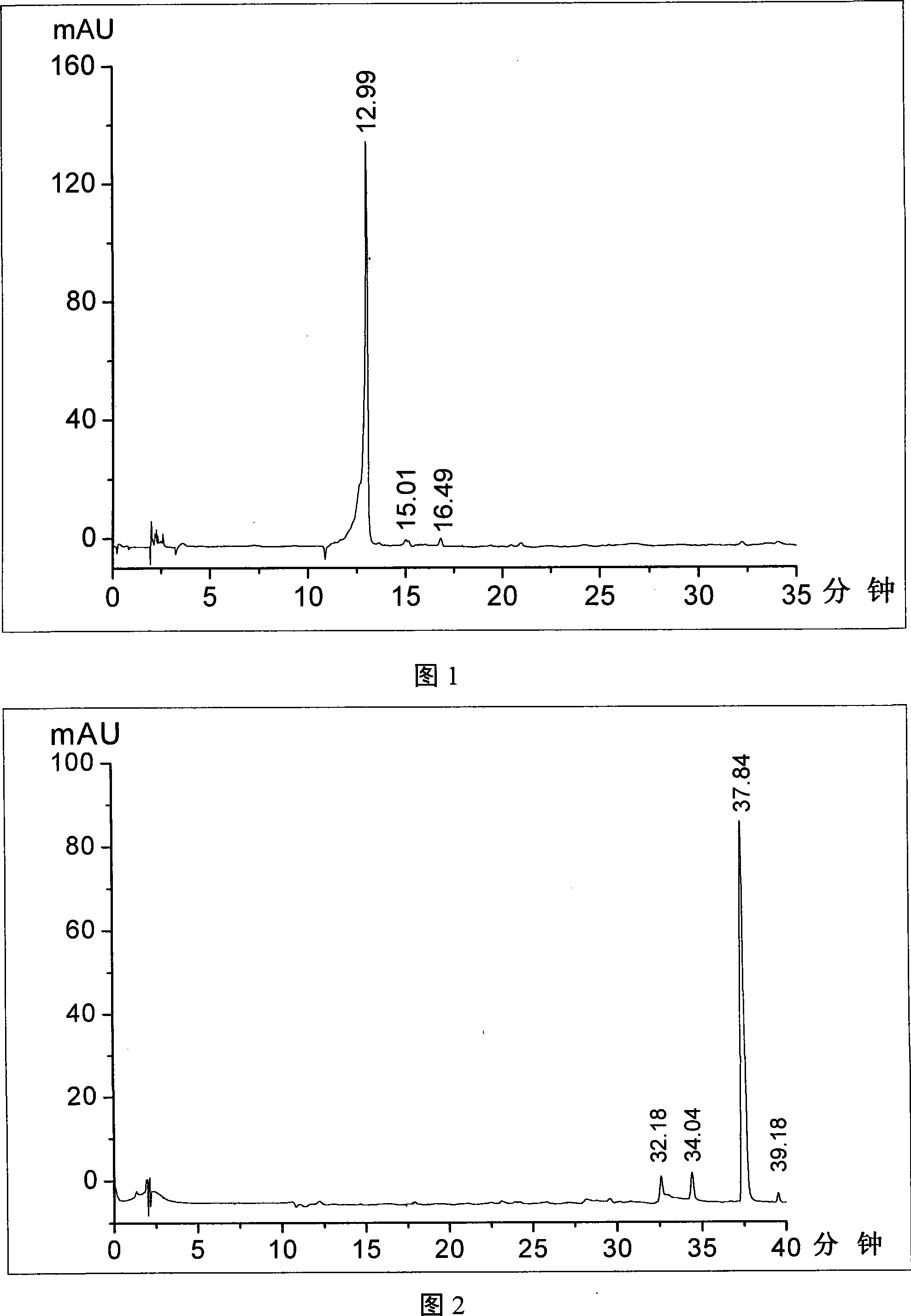
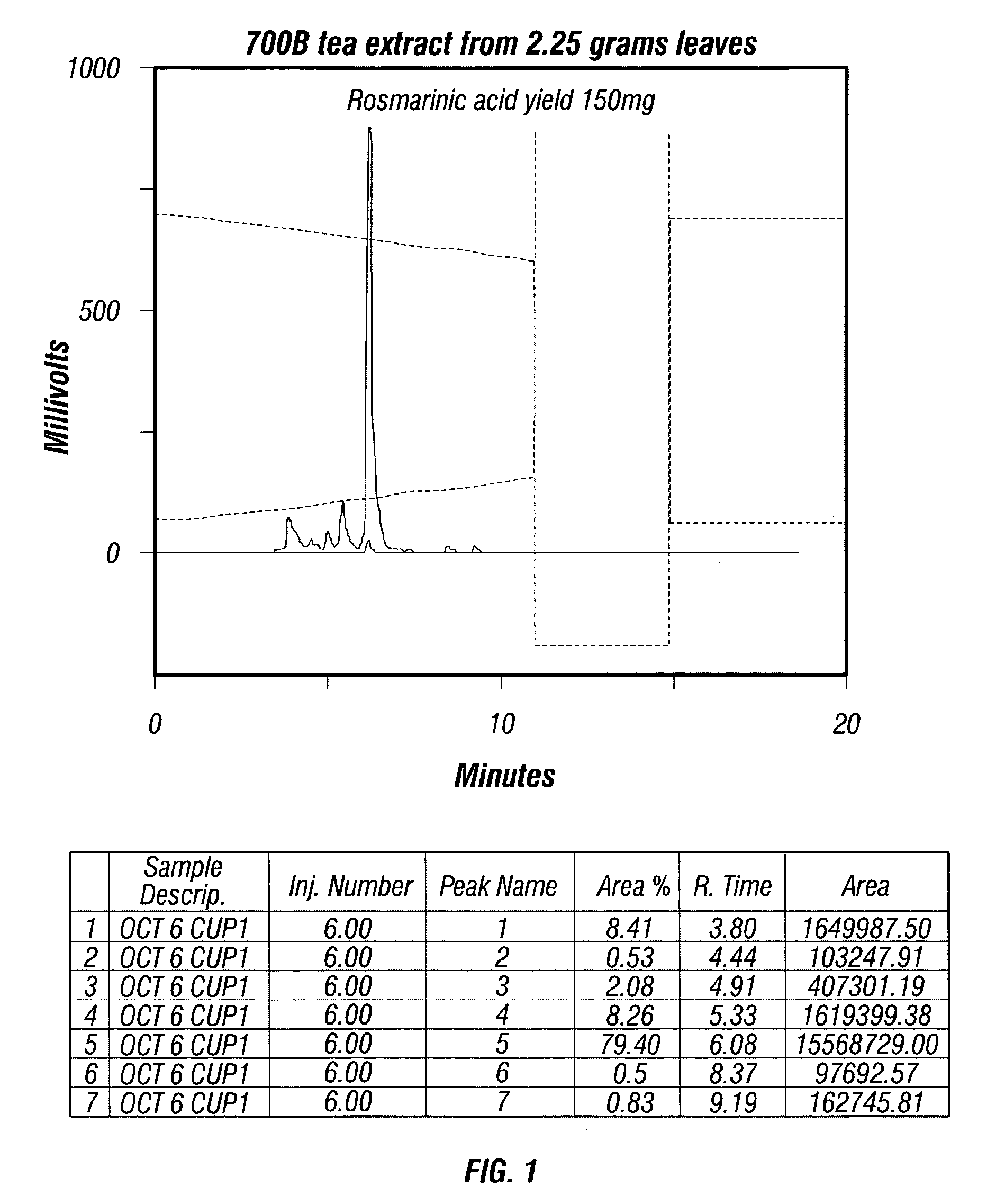
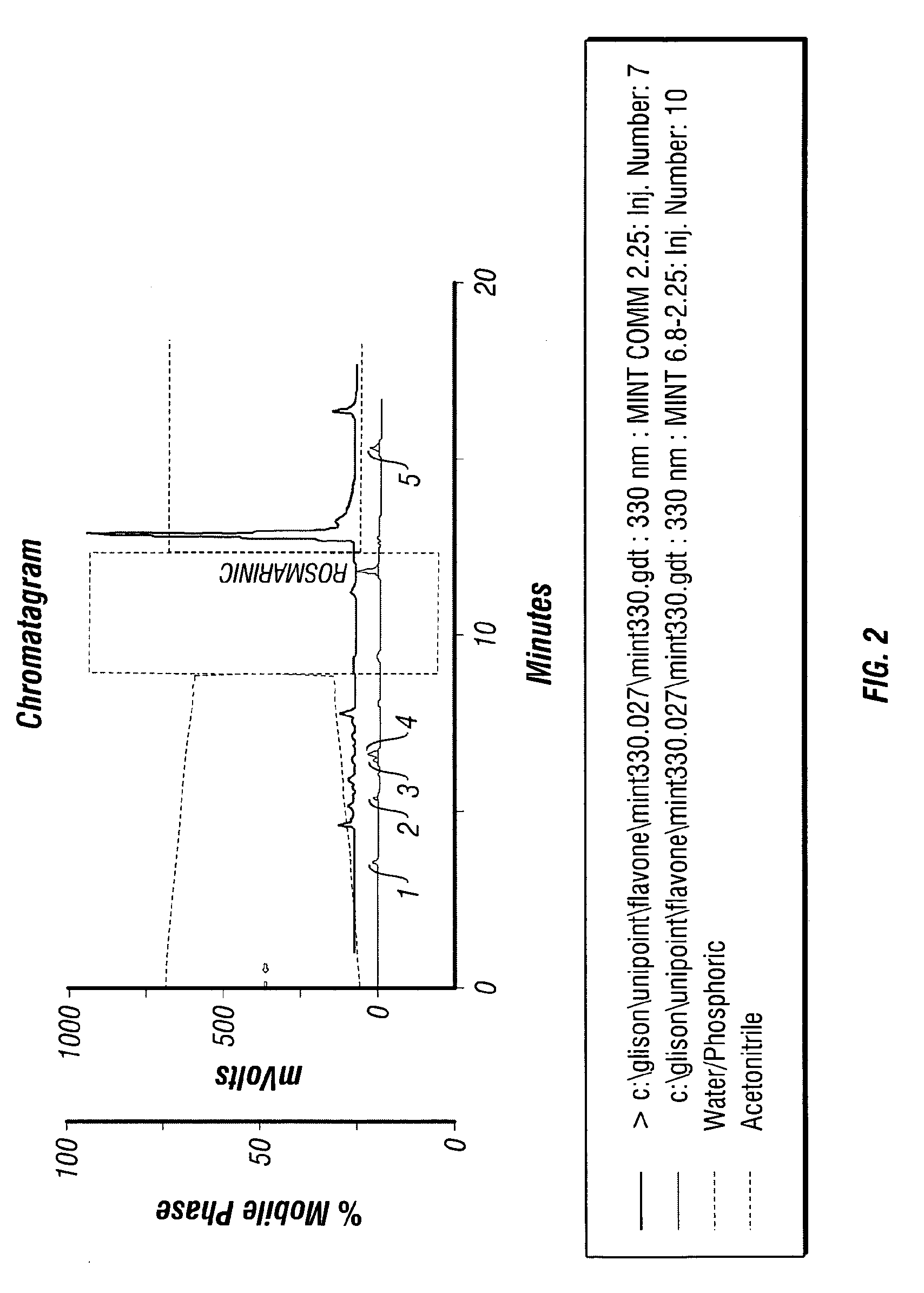
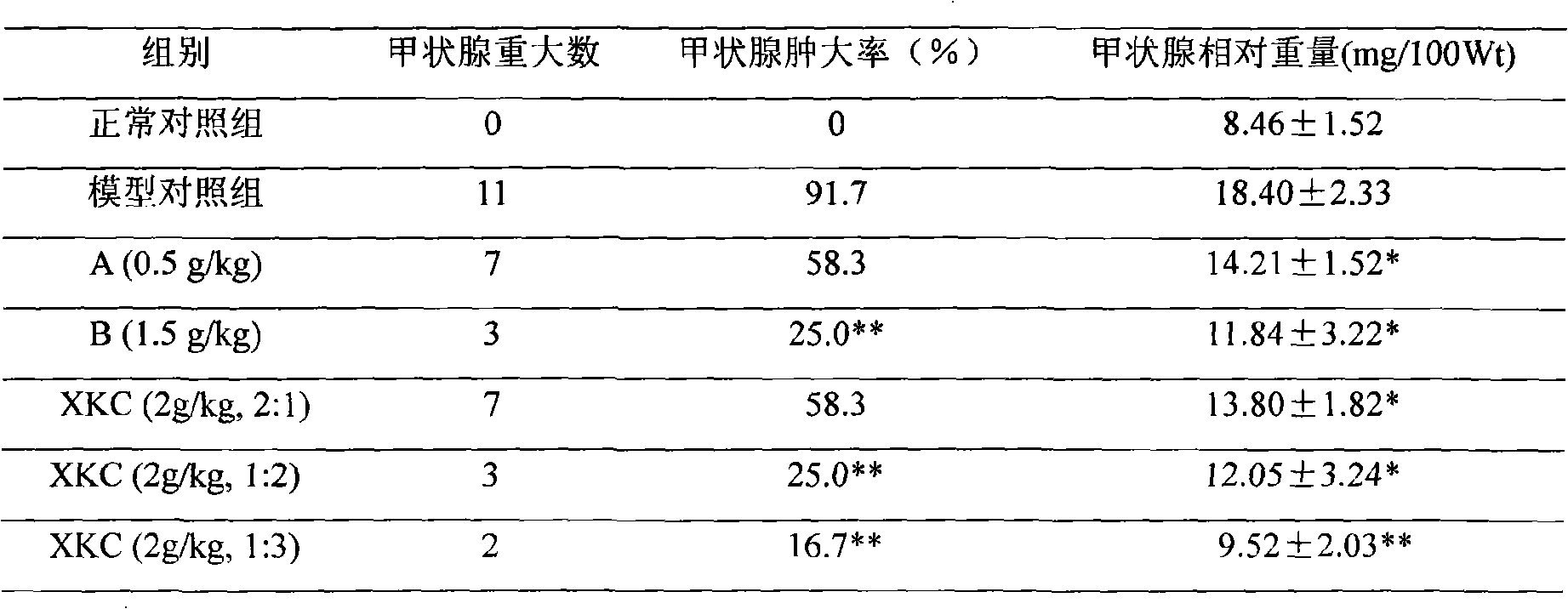
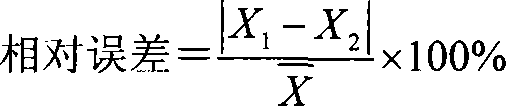Patents
Literature
569 results about "Rosmarinic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
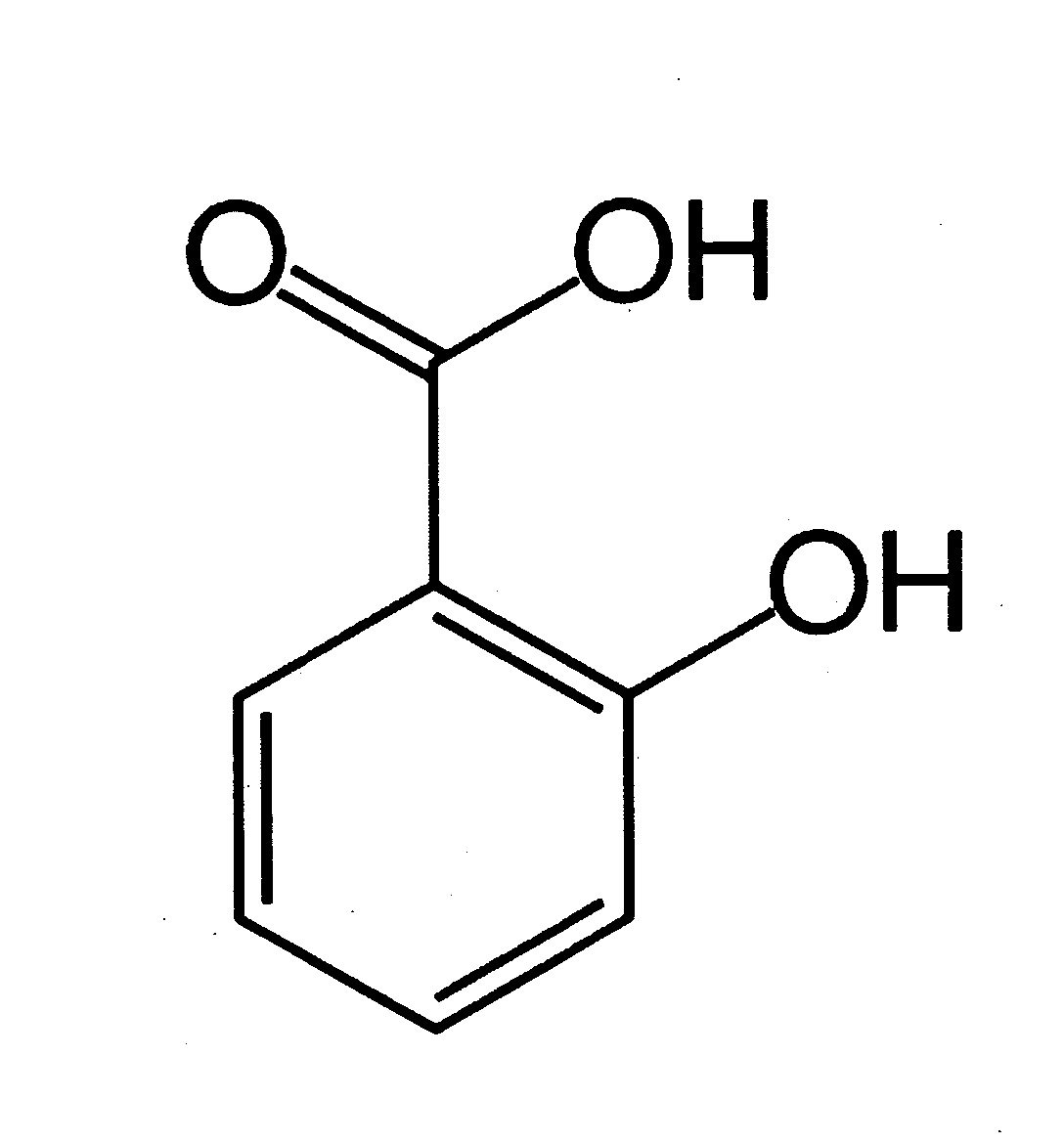
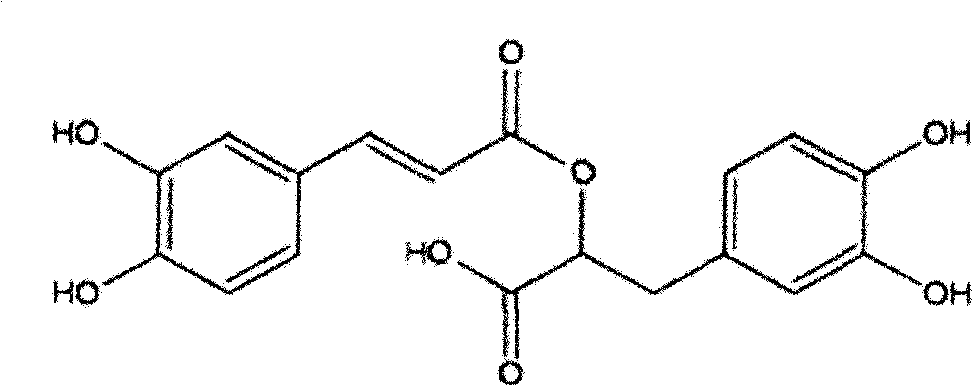
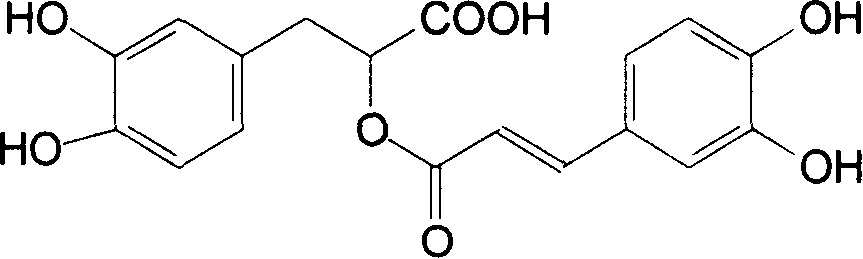
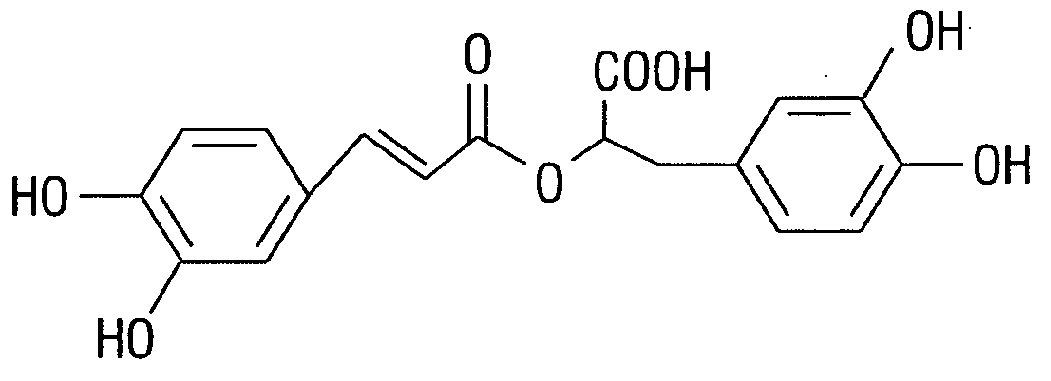
Rosmarinic acid is a chemical compound found in a variety of plants.
Method for preventing off-flavor development and preserving seasoning flavor in irradiated meat and meat products
InactiveUS6099879ASlow onsetReduce developmentMilk preparationDough treatmentAdditive ingredientFood flavor
A method comprising the step of treating meat and meat products, including fish, poultry, fish products, and poultry products, with a stabilizing amount of rosemary extract or rosemary extract in combination singly or collectively with tocopherols, ascorbic acid, citric acid, or sodium tripolyphosphate, prior to exposure of the meat or meat products to ionizing radiation, enhances the flavor and shelf life thereof. In addition, the active antioxidant ingredients of rosemary extract may be used individually or collectively as a replacement for rosemary extract, these being carnosic acid, carnosol, and rosmarinic acid, which have been found equivalent to or superior to rosemary extract itself for purposes of the present invention when used in the concentrations set forth herein.
Owner:KALAMAZOO HLDG INC
Acne treatment compositions and methods of use
The present invention relates to a composition for treating acne comprising an antimicrobial / anti-inflammatory polyphenolic molecule(s) including quercetin and rosmarinic acid in combination with salicyclic acid and / or salicylate salts in a topical and / or cosmetic delivery vehicle. The invention further relates to a method for treating acne by topically administering one of the compositions in an amount therapeutically effective to reduce the redness and blemishes associated with acne.
Owner:RESOURCES OF NATURE
Sweetness enhancer, sweetener compositions, methods of making the same and consumables containing the same
InactiveUS20120201935A1High sweetnessFood ingredient as taste affecting agentFood preparationWater basedSweetness
The present invention relates to the use of rosmarinic acid as a sweetness enhancer, to sweetener compositions comprising a sweetener and rosmarinic acid, to methods of making the sweetener compositions and to tabletop sweetener compositions comprising rosmarinic acid. Further, the invention relates to consumables comprising a consumable product and rosmarinic acid. Preferred consumable products are water-based consumables, solid dry consumables, dairy products, dairy-derived products and dairy-alternative products.
Owner:NUTRINOVA NUTRITION SPECIALTIES & FOOD ENGREDIENTS GMBH
Method for extracting ursolic acid, carnosic acid and rosmarinic acid from rosemary
InactiveCN102286059AIncrease profitEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAlcoholRosmarinus
The present invention discloses a method for extracting ursolic acid, carnosic acid and rosmarinic acid from rosemary. Reflux extraction with 95% ethanol solution for 1-2 hours, extract 2-3 times, concentrate the extract under reduced pressure to an alcohol concentration of 30-70%, let stand for crystallization for 3-7 hours, filter out the crystals and dry to obtain ursolic acid; 2) The crystallized mother liquor was concentrated under reduced pressure to no alcohol, centrifuged to obtain the solid and dried to obtain carnosic acid, and the liquid was further concentrated under reduced pressure to obtain rosmarinic acid. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, high raw material utilization rate, low production cost and easy industrial production.
Owner:NANJING ZELANG MEDICAL TECH
Preparation process of rosmarinic acid
InactiveCN101863767AEasy to operateLow costCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationChromatographic separationAlcohol
The invention relates to a preparation process of rosmarinic acid, which adopts the following steps for preparing the rosmarinic acid: combining aqueous extraction and ethanol extraction, carrying out ion exchange, placing materials on a chromatographic separation medium for gradient elution, and carrying out secondary decolourization, nanofiltration membrane concentration and recrystallization. The method solves the problems of large extraction solvent amount, much chemical residual, poor color intensity and low extraction rate. Products produced by adopting the method have the advantages of good quality, high purity, high extraction rate, simple operation and convenient scale production.
Owner:NANJING ZELANG AGRI DEV
Oregano and mint Anti-inflammatory compositions and methods
InactiveUS20120135094A1Facilitates frameworkReduce painFood ingredient as antioxidantBiocideAdditive ingredientLiquid chromatography mass spectroscopy
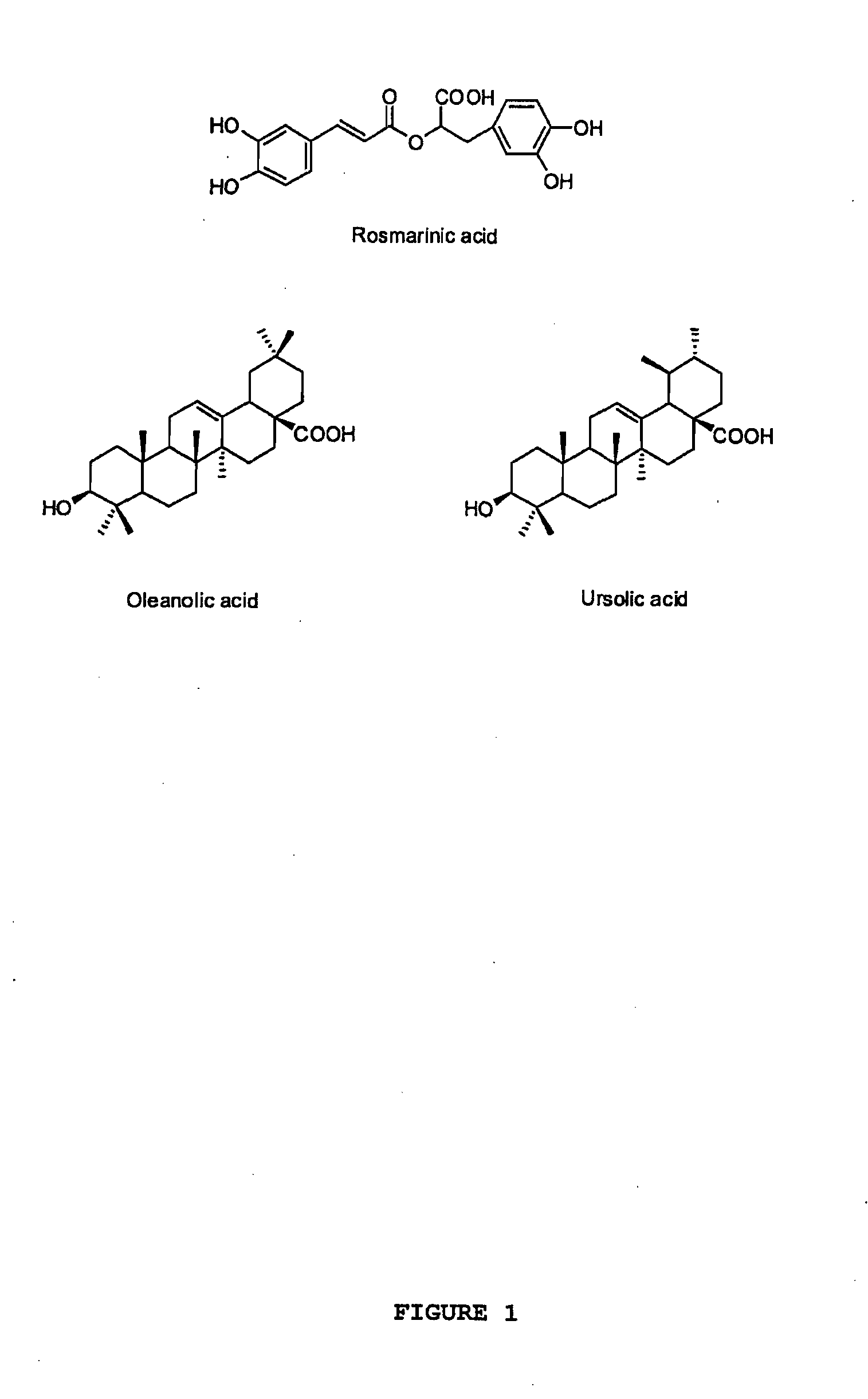
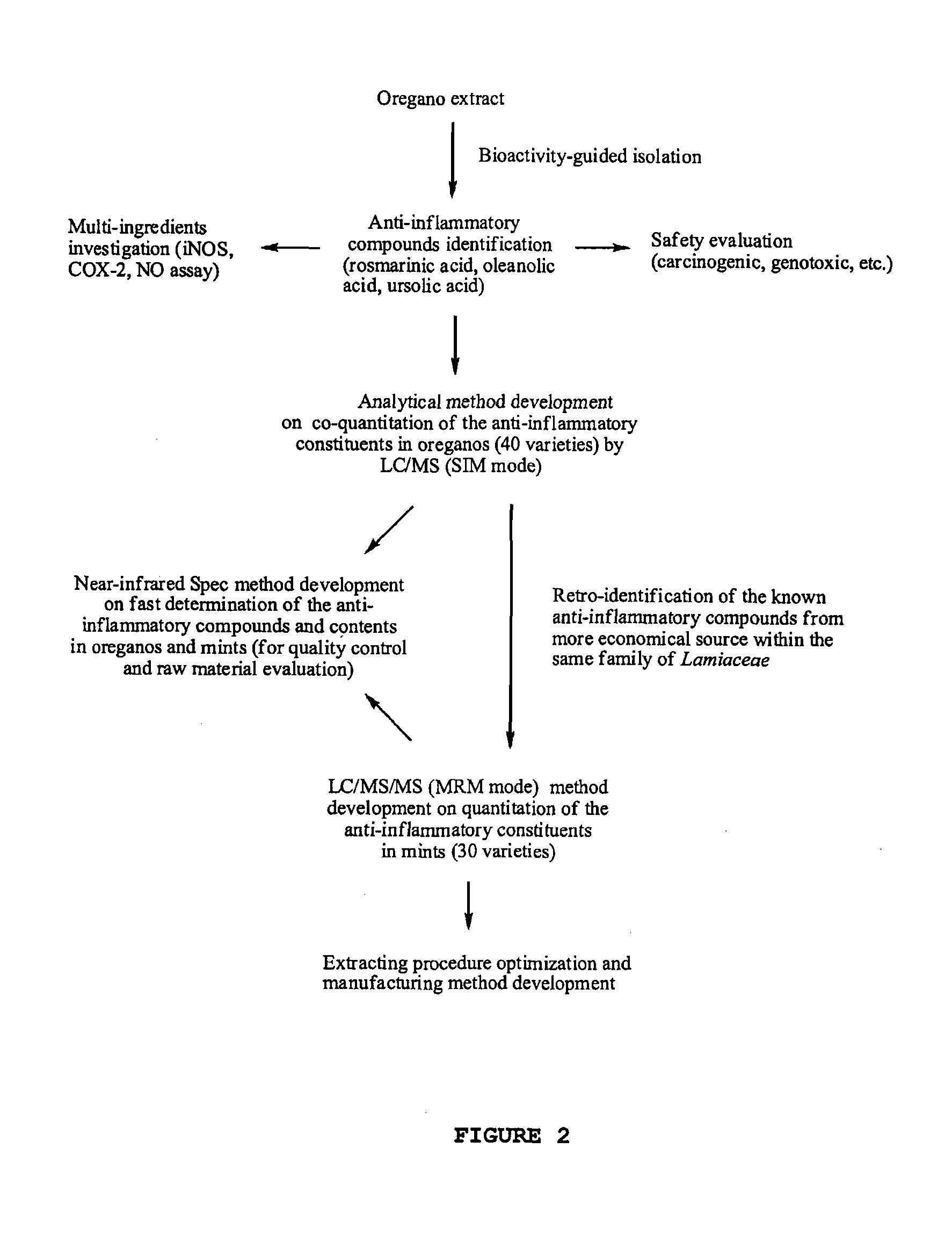
The present invention relates to bioactivity-guided isolation and identification of bioactive compounds from oregano and mint plants, in particular, rosmarinic acid, oleanolic acid and ursolic acid, and use of these compounds or combinations thereof as anti-inflammatory agents for the treatment of conditions related to pain and inflammation and / or as ingredients of dietary supplements. The invention also relates to optimization of the methods for qualitative and quantitative analysis of the bioactive compounds in oregano and mint plants. In particular, this invention introduces an LC / MS (SIM mode) method to achieve co-quantitation of the three organic acids using a unique tandem column system. In addition, the invention also relates to the methods for recovering various water-soluble polyphenols and triterpenes from aromatic plants.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Method of controlling the quality of salvia miltiorrhiza raw material fingerprint in the plant medicine for improving hemorheology
ActiveCN101040907AGuarantee normal implementationHigh sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsComponent separationTanshinone IIAColumn temperature
The invention relates to a DanShen fingerprint spectrum quality control method, comprising that (1), adding 1.0g DanShen powder into carbinol to extract via microwave, (2), washing flow phase gradient that the Alltima C18 column is 4.6mm, 250mm, and 5mum, checking wavelength is 280nm, flow speed is 1.0ml / min, the column temperature is 20-40Deg. C, and the sample amount is 10-20ul, (3), building standard fingerprint spectrum that the first peak is DanShen element, the eighth peak is rosmarinic acid, the ninth peak is alkannic acid, the tenth peak is phenolic acid B, the eleventh peak is phenolic acid B isomer, the fourteenth peak is cryptotanshinone and the fourteenth peak is tanshinone IIA, (4), controlling the quality of fingerprint spectrum that the check peak relative holding times are 0.21 of DanShen element, 0.91 of rosmarinic acid, 0.93 of alkannic acid, 1.00 of phenolic acid B, 1.04 of phenolic acid B isomer, 0.92 of cryptotanshinone and 1.00 of tanshinone IIA, (5), the DanShen planting collecting method. The invention can control the quality of materials to assure the stable quality of product.
Owner:ANHUI ZHIHETANG PHARMACY
Process for preparing rosmarinic acid
InactiveCN1995007AAvoid degradationEasy to maintain stabilityCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationSolventIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a making method of rosmarinic acid, which comprises the following steps: immersing the medicinal material with rosmarinic acid in the fitful quantity of solvent; permeating; extracting through ultrasound; adding anti-oxidant in the extract; adjusting pH value to acid; stewing; filtering; chromatographing the filtrate in the polyamide resin or ion exchange resin or large-hole resin column; fitting for large scale of industrial manufacturing.
Owner:SHANDONG LUYE PHARMA CO LTD
Method for separating and purifying salvianolic acid from red sage root liquid extract by one step
InactiveCN101186572ACarboxylic compound separation/purificationPlant ingredientsProcess dynamicsSalvianolic acid B
The invention relates to a method for furthering separating and purifying salvianolic acid from Danshen extract fluid, which comprises that prepares, breaks and extracts Danshen via water solution, acidifies extract to adjust pH and adds salt to process post-treatment, processes dynamic continuous adsorption and elution on the treated extract at chromatography column stuffed with resin adsorbent, elutes via water, collects and concentrates eluent, elutes via gradient ethanol solution, segmented collects and concentrates eluent, and dries the concentrates solution to obtain product. The invention can simply, effectively and quickly separate and purify various salvianolic acids, wherein test on different salvianolic acid products shows that the highest yields of tanshinol, alkannic acid, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid A and salvianolic acid B are 35. 55%, 70.65%, 99.27%, 82.78%, and 89.34%, and relative highest purities are 95.32%, 65.05%, 29.40%, 33.93%, and 82.35%, which are near or higher than the result of purification on the goal of single component.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparing technique for separating and purifying rosmarinic acid by big-hole adsorption resin
InactiveCN101139291ARealize industrial separation and preparationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAnti plateletDrug biological activity
The present invention relates to a production process of the rosmarinic acid by absorbing the resin with a large hole, separation and purification of the plant containing the rosmarinic acid. The key technical points are: the plant containing the rosmarinic acid is used as the raw material; the extraction liquid is absorbed with a large hole, purified, eluted and vacuum dried to get the refined rosmarinic acid product. The purity of the product can reach above 90 percent. The present invention successfully uses the macroporous absorption technology of the resin in the one-step refinement, separation and purification of the rosmarinic acid. The rosmarinic acid produced in the present invention has the good antioxidant properties; the pharmacological effects of the rosmarinic acid are relatively strong; the effects of the immune inhibition, microbial inhibition, anti-inflammation, anti-thrombotic and anti-platelet aggregation, anti-allergic and other performances are significant. The present invention provides the possibility for the refining production of the large-scale industrialization of the rosmarinic acid product with the high biological activity, and lays the foundation for the further development and the wide application of the active product.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Comprehensive extraction technology of rosmarinic acid, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and carnosic acid
InactiveCN104447334ASimple processEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationSteroidsAlcoholUrsolic acid
The invention discloses a comprehensive extraction technology of rosmarinic acid, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and carnosic acid. The comprehensive extraction technology comprises the steps of (1) preprocessing raw materials; (2) performing reflux alcohol-extraction; (3) carrying out primary separation; (4) separating out rosmarinic acid; (5) separating out ursolic acid; (6) separating out oleanolic acid. According to the comprehensive extraction technology, the process is simple, the operation is convenient, industrial production can be easily carried out, and meanwhile, the purpose of synchronously extracting rosmarinic acid of rosemary, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and carnosic acid is achieved, and the active ingredients of rosemary can be extracted to the maximum; the rosmarinic acid, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid and carnosic acid respectively have the purity exceeding 30%, 25%, 20% and 25%.
Owner:付大亮
Technique for producing purple common perilla rosemary acid
InactiveCN1796362AComplete specificationsSimple production processOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationFood additiveFiltration
This invention relates to a production technique of perilla-derived rosmarinic acid which is accessible for large-scale industrial production. Perilla leaves serving as raw materials are dipped in acidic water and the mixture undergoes filtration with the extracted liquid adsorbed and desorbed in macroporous adsorption resin; the desorbed liquid is vacuum distilled to obtain romarinic acid with a purity of 10%; the 10%-purity rosmarinic acid product is extracted with petroleum ether and the organic phase is vacuum distilled to obtain rosmarinic acid with a purity of 50%; the 50%-purity rosmarinic acid product is gradient eluted with ethanol solutions of different concentrations in adsorption resin and the 95% eluent is vacuum-condensed and crystallized to produce a rosmarinic acid product with a purity of 95%. This invention has the advantages of simple production technique, easy operation, low cost, variable product types, security and reliability and therefore it is applicable in producing food additives, medical intermediates and cosmetics.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Production technology for acquiring two antioxidant agents from Rosmarinus officinalis L.
InactiveCN102199092AReduce conversionPromote dissolutionCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationBulk chemical productionCarnosolCounter current
The invention discloses a production technology employing a ultrasonic countercurrent extraction process and a membrane separation (molecular sieve) process to acquire two antioxidants from Rosmarinus officinalis L. The production technology comprises adding 30 to 85% of edible alcohol into fresh rosemary branches and leaves, carrying out a ultrasonic counter current extraction process for a mixture of the edible alcohol and the fresh rosemary branches and leaves to obtain an extracted liquid with a solid-to-liquid ratio of from 1:10 to 1:30, and carrying out a membrane separation (molecular sieve) process to separate two antioxidant agents consisting of a rosemary fat-soluble antioxidant agent (comprising carnosic acid as a representative) and a rosemary water-soluble antioxidant agent (comprising rosmarinic acid as a representative) from the extracted liquid, wherein a heating time of the extracted liquid can be reduced through the membrane separation (molecular sieve) process thus a conversion ratio of rosmarinic acid to carnosol is reduced. A content of carnosic acid in the rosemary fat-soluble antioxidant agent is increased through a CO2 supercritical extraction process. The rosemary water-soluble antioxidant agent (comprising rosmarinic acid as a representative) is separated from a liquid obtained through a concentration process under reduced pressure and a solid-liquid separation process, and a content of rosmarinic acid in the rosemary water-soluble antioxidant agent is increased through recrystallization from ethanol. The production technology has the advantages of simple processes, low energy consumption, high production efficiency, production safety, and no harmful residual solvent due to single edible alcohol usage during all production processes.
Owner:YUZHOU SENYUAN BENCAO NATURAL PRODS
Production of Rosmarinic Acid from Spearmint and uses Thereof
InactiveUS20100137433A1Enhance memoryReduce in quantityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMentha spicata
The present invention provides plants and plant tissues of spearmint (Mentha spicata) with enhanced rosmarinic acid levels, and extracts derived there from. Methods and compositions for production and use of rosmarinic acid from spearmint as a nutraceutical are also provided. In particular, an edible beverage derived from plant tissues of spearmint that comprise more than 77.5 mg / g rosmarinic acid on a dry weight basis, is provided, as well as methods for making such a beverage and for using it to treat an inflammatory or infectious disease.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Prunella spike extract and its preparation method and use
An extract of prunella spike for treating rheumatoid arthritis and improving immune suppression contains phenolic acid (60-70%) and rosemaric acid (14-21%). Its preparing process is also disclosed.
Owner:JIANGSU KANION PHARMA CO LTD
Composition of Prunella plant extracts, preparation and pharmaceutical use thereof
ActiveCN101274012AThe process steps are simpleHigh yieldAntibacterial agentsMetabolism disorderTriterpeneUrsolic acid
The invention relates to a composition of prunella plant extracts, a preparation method and pharmic use of the composition. The activity components of the composition of the prunella plant extracts are composed of total triterpenes and total phenolic acid, wherein, the extract of the total triterpenes contains 10.0 to 45.0 wt percent of ursolic acid and 50.5 to 98.0 wt percent of the total triterpenes; the extract of the total phenolic acid contains 21.5 to 65.0 wt percent of rosmarinic acid and 70.5 to 99.0 wt percent of the total phenolic acid. The invention also relates to a preparation method and medical application of the composition.
Owner:上海硕方医药科技有限公司
Method for extracting rosmarinic acid from folia perillae acutae
ActiveCN102850219AHigh purityHigh yieldCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationAcid waterDesorption
The invention discloses a method for extracting rosmarinic acid from folia perillae acutae. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a rosmarinic acid product with the purity of more than 98% is prepared by carrying out processes such as cleaning, slicing, ultrasonic extraction, macroporous resin absorption, desorption and concentration, acid water dissolution, extraction and column chromatography on silica gel on a raw material folia perillae acutae at the initial stage of seeding. By utilizing the method disclosed by the invention, a high-purity rosmarinic acid product can be obtained; a rosmarinic acid crude product with the purity of 20-30% and a rosmarinic acid crude product with the purity of 60-75% can be obtained during the production process so as to meet different requirements; and the method provided by the invention is short in extraction time, simple in operation, less in steps, low in production cost and suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:山西金紫苏生物科技股份有限公司
Prepn process and application of resemary acid
InactiveCN101020637ASuitable for industrial productionOrganic active ingredientsCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationThrombocytopenic purpuraMedicine
The present invention discloses preparation process and application of rosemary acid, and features that rosemary acid and its derivative and mixture may be prepared into preparation for antagonizing tumor of digestive tract and other tumor and synergizing and attenuating tumor treating chemotherapeutic medicine and radiotherapy. Medicine preparation of rosemary acid and its derivative and mixture may be used directly in treating primary or secondary thrombocytopenic purpura and leucopenia and thrombocytopenia caused by chemotherapy or radiotherapy. The present invention also provides process of extracting high purity rosemary acid and its derivative and mixture from Sarcandra glabra as the plant material.
Owner:连晓媛 +1
Quality detecting method for traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating hematuresis
ActiveCN105467059AImprove rationalityImprove reliabilityComponent separationAdditive ingredientBerberine hydrochloride
The invention relates to a quality detecting method for a traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation, in particular to a quality detecting method for a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating hematuresis. According to the technical scheme, the quality detecting method for the traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating hematuresis is prepared from cortex phellodendri, lalang grass rhizome, clerodendranthus spicatus and linarin in herba cepbalanoplosis segeti. The invention further provides a method for detecting the content of berberine hydrochloride in cortex phellodendri and the content of rosmarinic acid in clerodendranthus spicatus. High performance liquid chromatography is adopted. According to the method, lalang grass rhizome, cortex phellodendri, clerodendranthus spicatus and herba cepbalanoplosis segeti in the traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating hematuresis are qualitatively detected through thin-layer chromatography, and the method is simple and stable. The high performance liquid chromatography is used for detecting the content of berberine hydrochloride in cortex phellodendri and the content of rosmarinic acid in clerodendranthus spicatus, the method is easy and convenient and high in repeatability and stability, the result is accurate, the method serves as a method for detecting the content of ingredients of the traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation, and the rationality and reliability of the whole quality control method are enhanced.
Owner:云南雷允上理想药业有限公司
Method for extracting and separating rosmarinic acid and ursolic acid from rosemary
InactiveCN102432469AEasy to operateImprove the yield of active ingredientsSteroidsCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationChromatographic separationUrsolic acid
The invention mainly relates to a method for extracting and separating rosmarinic acid and ursolic acid from rosemary. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding the rosemary serving as a raw material, extracting, concentrating, performing column chromatographic separation, extracting, concentrating, crystallizing, recrystallizing, and thus obtaining the rosmarinic acid and the ursolicacid. The whole separation process has low requirements on environmental conditions and equipment, the rosmarinic acid and the ursolic acid have high yield, the shortest separation time, a simple operation method and high purity, and the raw material has the highest comprehensive utilization rate; in addition, the separation materials are readily available and cheap, and the separation operation process is simple and is easy to control; and crystallization and recrystallization are utilized, so that the method is high in purification efficiency and low in cost.
Owner:长沙卫一生物科技有限公司
Rosmarinic acid, rosmarinic acid-containing common selfheal fruit-spike active ingredient and preparation methods and application thereof to prevention and treatment of cancer postoperative metastasis
ActiveCN102018759AOrganic active ingredientsCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationLymphatic SpreadMedicine
The invention discloses rosmarinic acid, a rosmarinic acid-containing common selfheal fruit-spike active ingredient and preparation methods thereof by extraction and separation. Moreover, the invention also discloses the application of the rosmarinic acid or / and the rosmarinic acid-containing common selfheal fruit-spike active ingredient to the preparation of a medicament for preventing or treating cancer postoperative metastasis and discloses a medicinal composition which contains effective doses of the rosmarinic acid or / and the rosmarinic acid-containing common selfheal fruit-spike active ingredient for preventing or treating the cancer postoperative metastasis. The rosmarinic acid and the rosmarinic acid-containing common selfheal fruit-spike active ingredient are obtained by extraction and separation. Pharmacodynamic experiment researches indicate that the rosmarinic acid and the rosmarinic acid-containing common selfheal fruit-spike active ingredient prepared by the method have cancer metastasis resistance and can be used for preparing a medicament for preventing or treating cancer metastasis.
Owner:SHUGUANG HOSPITAL AFFILIATED WITH SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Gynostemma pentaphylla health care tea with antioxidation function and method for preparing the same
InactiveCN1919026APromote development and utilizationKeep active ingredientsTea substituesPlant ingredientsMedicineRosmarinus
The invention discloses a health care tea containing gynostemma pentaphylla with oxidation-resisting actions and preparation process, wherein the tea is prepared from the following raw materials (by weight portion): gynostemma pentaphylla 80-98%, rosmarinic acid 1-10%, wild marjoram 1-10%.
Owner:彭涛
Method for preparing extractive of perilla for killing activity of pine wood nematode
InactiveCN1795724AEnhance killing activitySimple manufacturing methodBiocideAnimal repellantsOrganic solventAdditive ingredient
A process for preparing the extract of perilla with the activity to kill the pine nematode includes such steps as providing fresh perilla leaves, immersing in distilled water, vacuum concentrating, and extracting in organic solvent. Its advantages are high killing activity and no poison.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Method for preparing high-purity danshinolic acid B
InactiveCN101638401AHigh purityEfficient removalOrganic chemistryMicroorganism based processesSalvianolic acid BAqueous solution
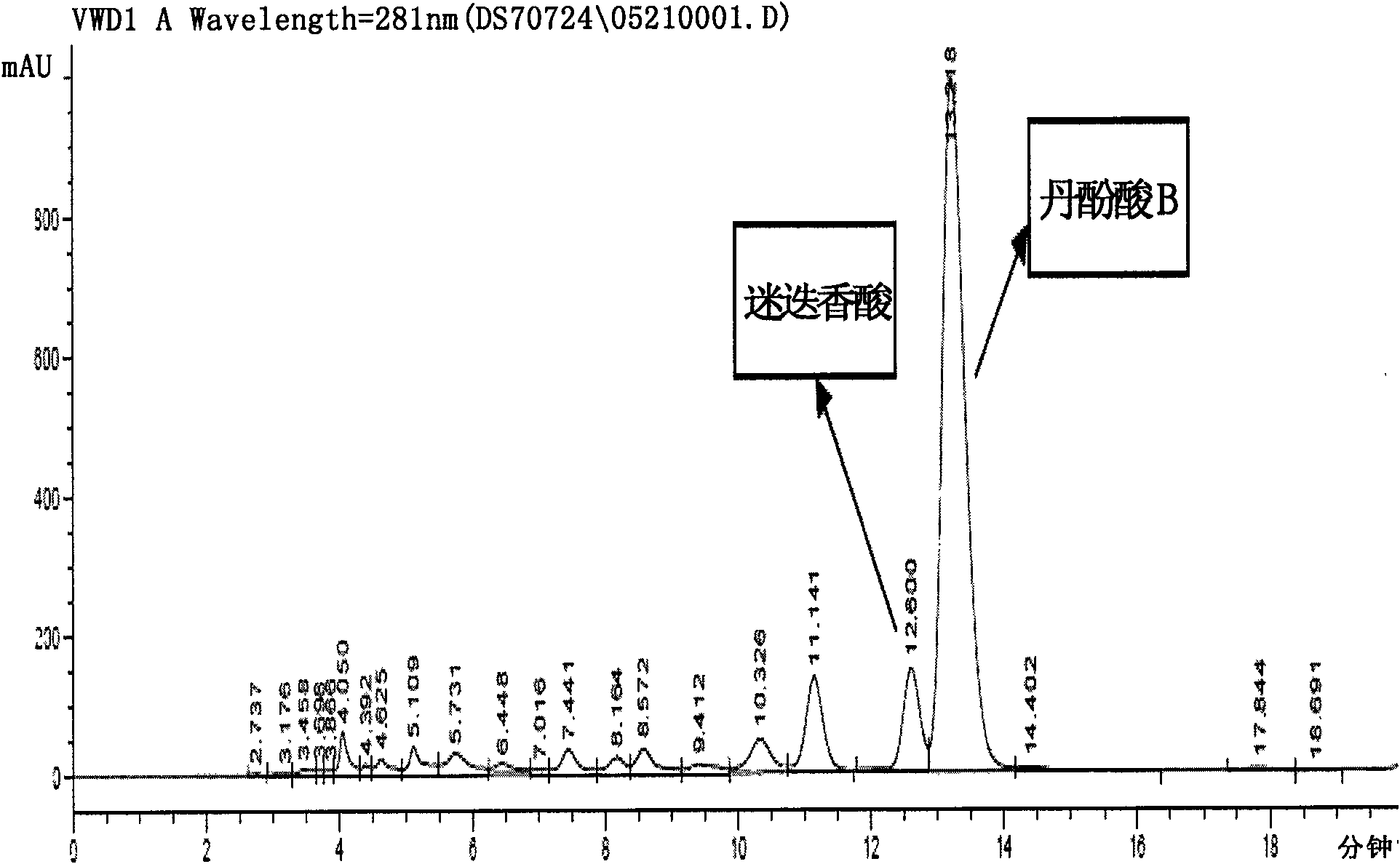
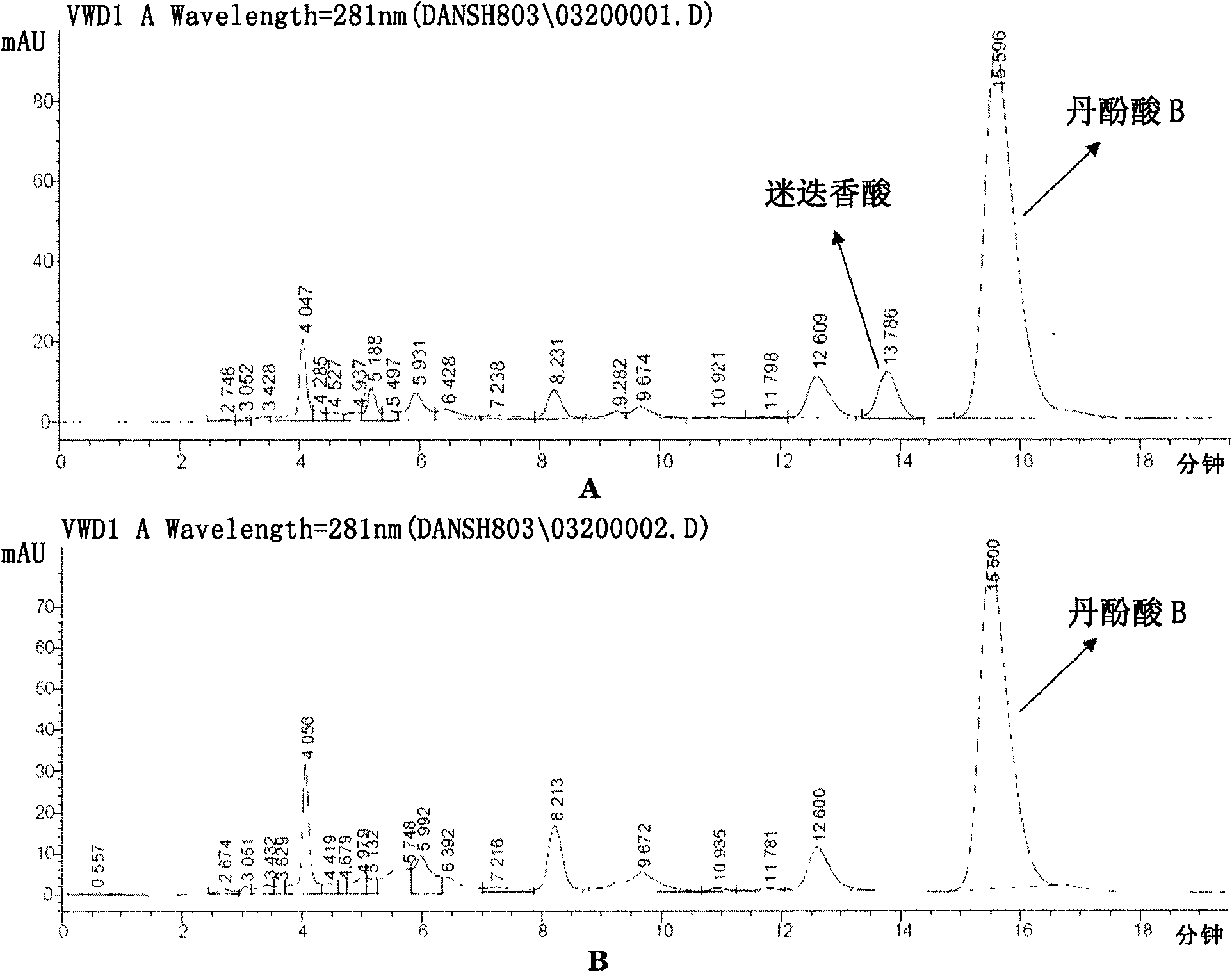
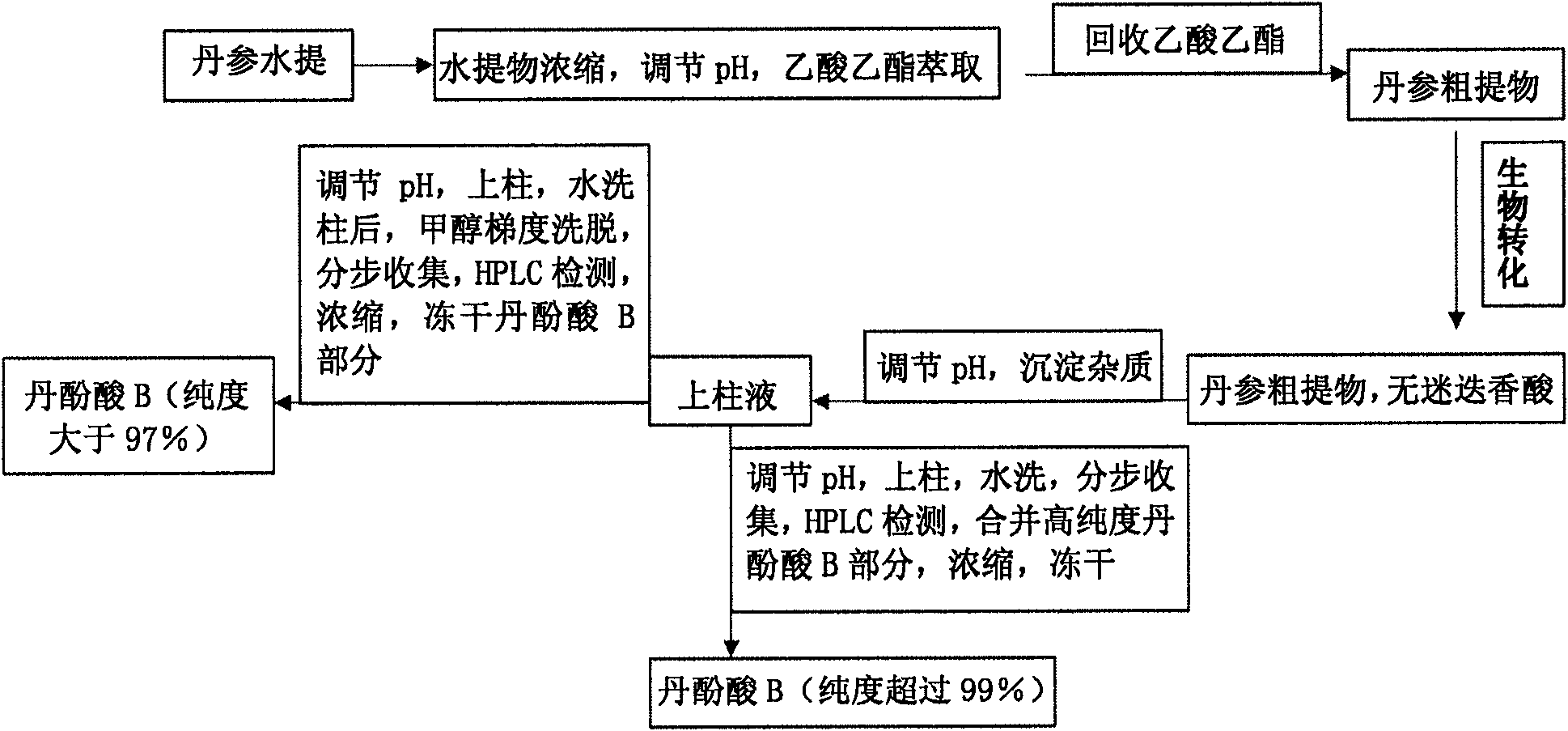
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-purity danshinolic acid B, which comprises the following steps: (1) mixing a red sage root aqueous extract with Fusarium graminearum resting cells,and performing biotransformation at a temperature of between 20 and 35 DEG C for 24 to 90 hours to obtain a red sage root aqueous extract without rosmarinic acid; and (2) adsorbing the red sage root aqueous extract without the rosmarinic acid by anti-phase resin, and eluting the red sage root aqueous extract without the rosmarinic acid to obtain the high-purity danshinolic acid B. The purity of the danshinolic acid B prepared by the method is more than or equal to 99 percent, the recovery percent is over60 percent, the process is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND
Method for detecting traditional Chinese medicine injection for treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
ActiveCN103940929AIncrease limit indexSimple and fast operationComponent separationDiseaseSalvia miltiorrhiza
The invention relates to a method for detecting a traditional Chinese medicine injection for treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The detection method comprises a thin-layer identification method for medicinal materials including radix salviae miltiorrhizae and safflower carthamus, an inspection method for 5-hydroxymethyl furfural, total solids, heavy metals, harmful elements and the like, a high-performance liquid chromatography method of salvianic acid A sodium, protocatechu aldehyde, 4-cumaric acid, rosmarinic acid, danshinolic acid B and danshinolic acid A and an ultraviolet measurement method for measuring total phenols content. The method for detecting the quality of the traditional Chinese medicine injection provided by the invention is good in stability and repeatability, can be used for accurately qualitatively and quantitatively detecting the content of all effective components and impurity components and can be used for comprehensively and objectively evaluating the quality of the traditional Chinese medicine injection so as to finally guarantee the clinical medication safety and curative effect of the traditional Chinese medicine injection.
Owner:SHANDONG DANHONG PHARMA
Scale and corrosion inhibitor and application of scale and corrosion inhibitor in salt draining closed conduit of saline and alkaline land
ActiveCN105016493AReduce corrosion rateGood scale resistanceScale removal and water softeningBenzoic acidPerfluoroacetic Acid
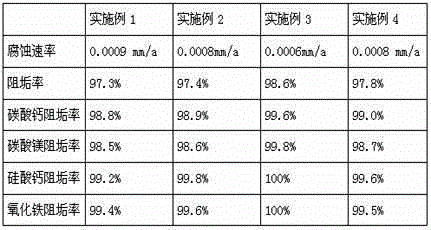
The invention provides a scale and corrosion inhibitor and application of the scale and corrosion inhibitor in a salt draining closed conduit of a saline and alkaline land. The scale and corrosion inhibitor comprises the components in parts by weight: 26-29 parts of ursolic acid, 15-18 parts of rosmarinic acid, 4-6 parts of trifluoroacetic acid, 6-8 parts of bis-1,6-hexylidenetriamine pentamethylene sodium phosphonate, 3-5 parts of thionothiolic acid, 1-3 parts of mannitol, 8-12 parts of polyepoxysuccinic acid, 6-9 parts of sodium benzotriazole, 2-4 parts of propyl hydroxybenzoate and 50-60 parts of water, wherein the purity of ursolic acid is 98%; the purity of rosmarinic acid is 95%; and the solid content of sodium benzotriazole is 40%. By using the scale and corrosion inhibitor provided by the invention, the corrosion rate, which is 0.0006-0.0009 mm / a, of the salt draining closed conduit is obviously reduced, and the service life of the salt draining closed conduit can be prolonged by 10 years.
Owner:WEIFANG YOURONG IND
Method for using near infrared spectroscopy to measure contents of multiple components in radix et rhizoma salviae miltiorrhizae medicinal material
InactiveCN108732126ALow jump chanceLow responseComponent separationMaterial analysis by optical meansQuality assuranceMedicine
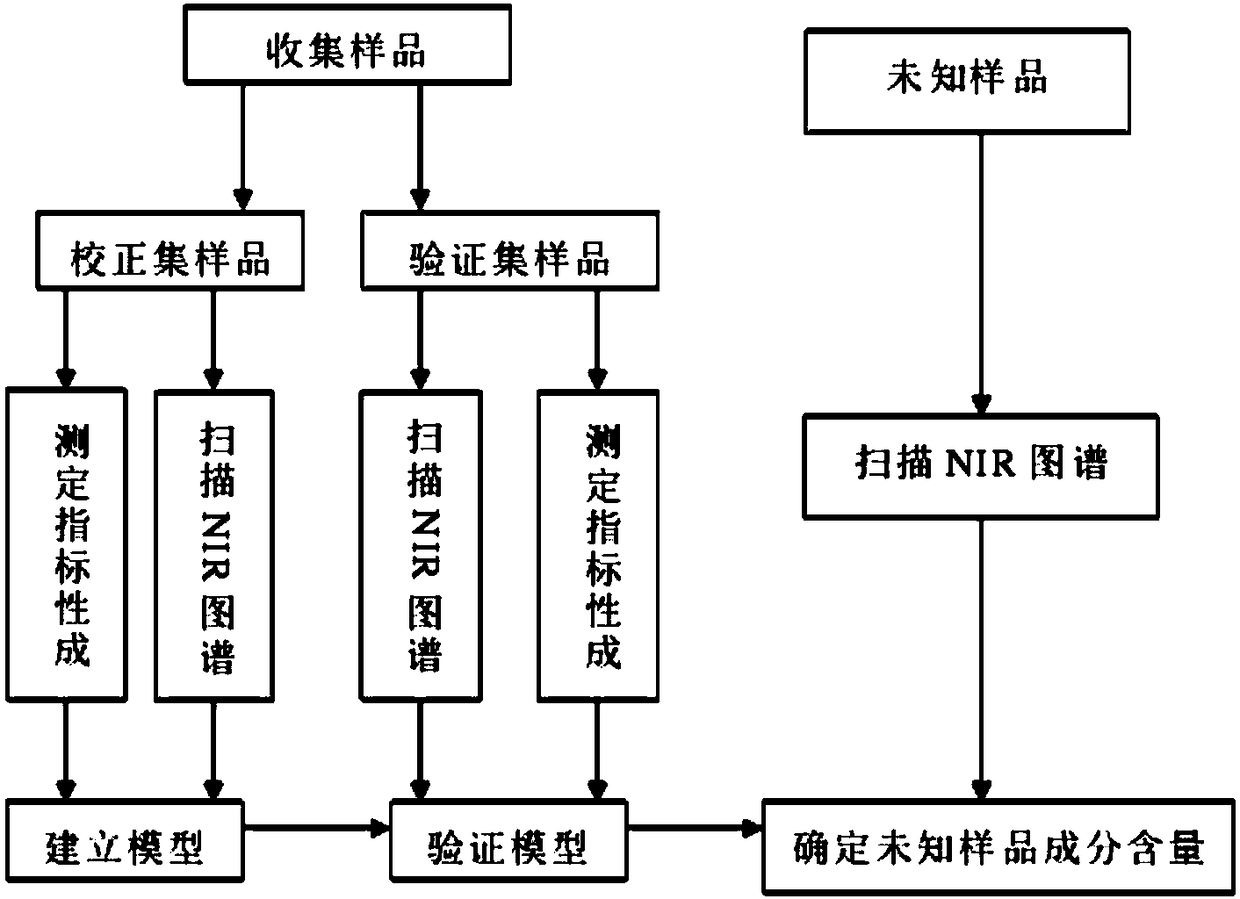
The invention provides a method for using a near infrared spectroscopy to measure contents of multiple components in a radix et rhizoma salviae miltiorrhizae medicinal material and application feasibility of the method in a Chinese patent medicine raw material quality assurance system is discussed. The method comprises the steps: utilizing a high performance liquid chromatography to measure contents of danshinolic acid B, rosmarinic acid, alkannic acid, tanshinone IIA, tanshinone I and cryptotanshinone in radix et rhizoma salviae miltiorrhizae as contrast values; utilizing near infrared diffusion reflection method to collect a sample spectrum, comparing different spectrum pretreating methods and modeling effects of modeling waveband and optimizing modeling parameters; utilizing a partial least squares (PLS) to respectively establish near infrared quantitative analysis models of danshinolic acid B, rosmarinic acid, alkannic acid and tanshinone components (tanshinone IIA plus tanshinoneI plus cryptotanshinone) in the radix et rhizoma salviae miltiorrhizae and evaluating the models. The quantitative analysis models established by the method disclosed by the invention can meet a requirement of quickly obtaining chemical information of massive radix et rhizoma salviae miltiorrhizae medicinal material samples.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
Establishment method of traditional Chinese medicine composite fingerprint
The invention provides an establishment method of a traditional Chinese medicine composite fingerprint, and particularly relates to an establishment method of a Weilikang granule fingerprint. Pure water is added to Weilikang granules, so as to dissolve, and paeoniflorin, naringin, rutin, salvianolic acid B, rosmarinic acid, emodin-8-O-beta-D glucopyranoside and glycyrrhizic acid are used as reference substances, so as to establish the fingerprint by referring to high-performance liquid chromatography. The method is more comprehensive and objective than the current quality standard, and the current quality standard is increased and improved, and more information is provided for the internal quality control of the Weilikang granules.
Owner:SICHUAN LVYE BAO GUANG PHARMA IND
Fibre fabric having antibacterial property
The present invention provides a fiber fabric with antibacterial properties, which is highly safe to the human body, has little impact on the environment, and has washing resistance and excellent antibacterial properties after a long period of time. The fiber fabric with antibacterial property provided by the invention is characterized in that: containing the natural class antibacterial agent that is made of rosemary essential oil or rosmarinic acid, the processing method of the fiber fabric with antibacterial property provided by the invention is characterized in that: utilize A natural antibacterial agent consisting of rosemary essential oil or rosmarinic acid is attached to the fiber material by the padding / dry method or the soaking method using a dyeing machine.
Owner:NISSHINBO IND INC
Frozen minced fillet quality improver and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105309950AMaintain water holding capacityImprove performanceFood ingredientsFood preparationVitamin CSucrose
The invention discloses a frozen minced fillet quality improver which is prepared from, by mass, 0.5-1% of vitamin C, 5-10% of sodium gluconate, 10-20% of sodium caseinate, 1-3% of calcium chloride, 1-3% of kelp polyphenols, 5-10% of trehalose, 5-10% of rosmarinic acid, 3-5% of sucrose ester and the balance soyabean protein. The frozen minced fillet quality improver is scientific and reasonable in formula and high in eating safety, all the components achieve mutual synergistic interaction, and frozen denaturation and oxidation of minced fillet protein can be effectively prevented, so that the jelly strength, the texture, the water holding capacity, the adhesion ability and the like of the frozen minced fillet are greatly improved, the frozen quality of the frozen minced fillet is improved, and the frozen minced fillet quality improved is worthy of being applied and popularized in frozen minced fillet processing. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the frozen minced fillet quality improver. The preparation method comprises the steps of mixing the components according to a ratio so as to obtain the frozen minced fillet quality improver. The technological steps are simple, the requirement for the equipment is low, the operability is high, and the preparation method is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com