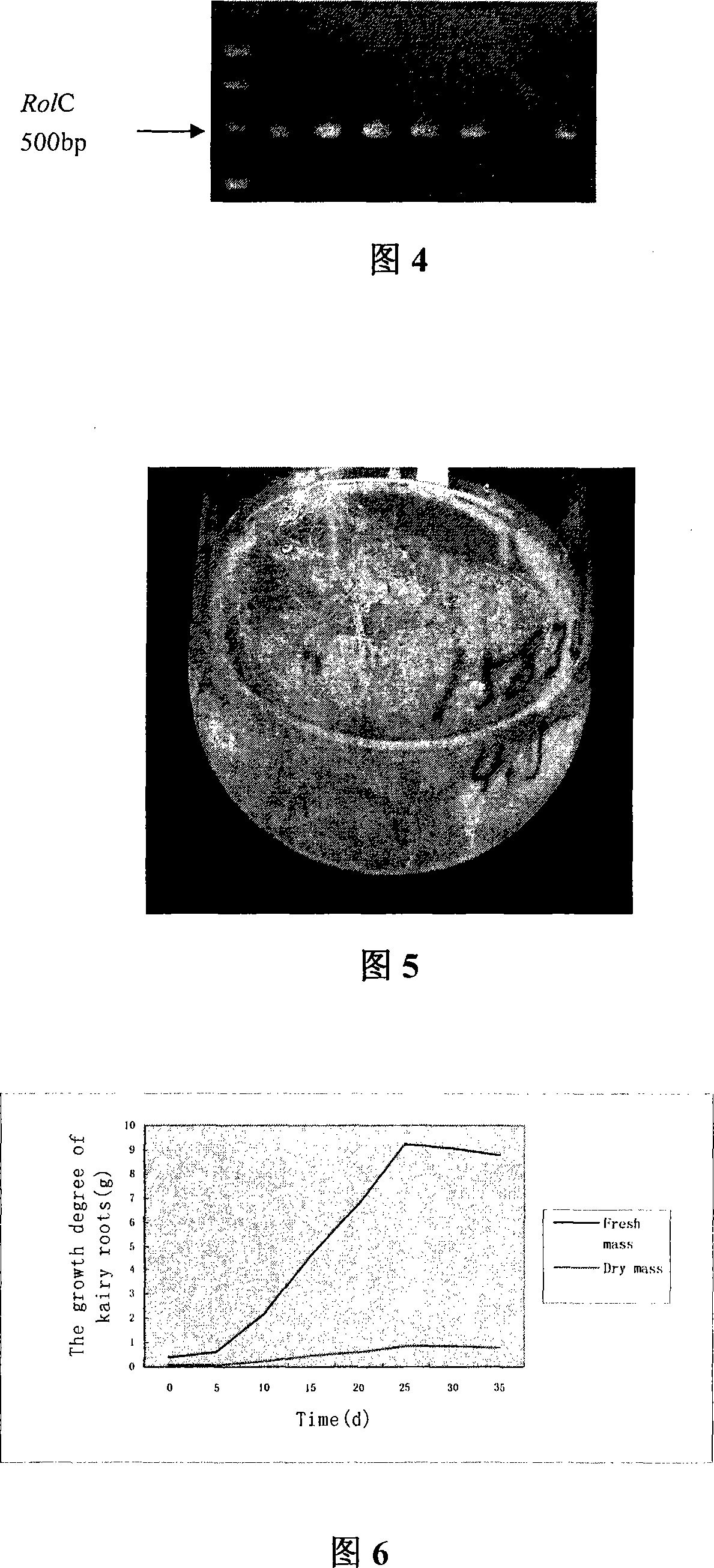
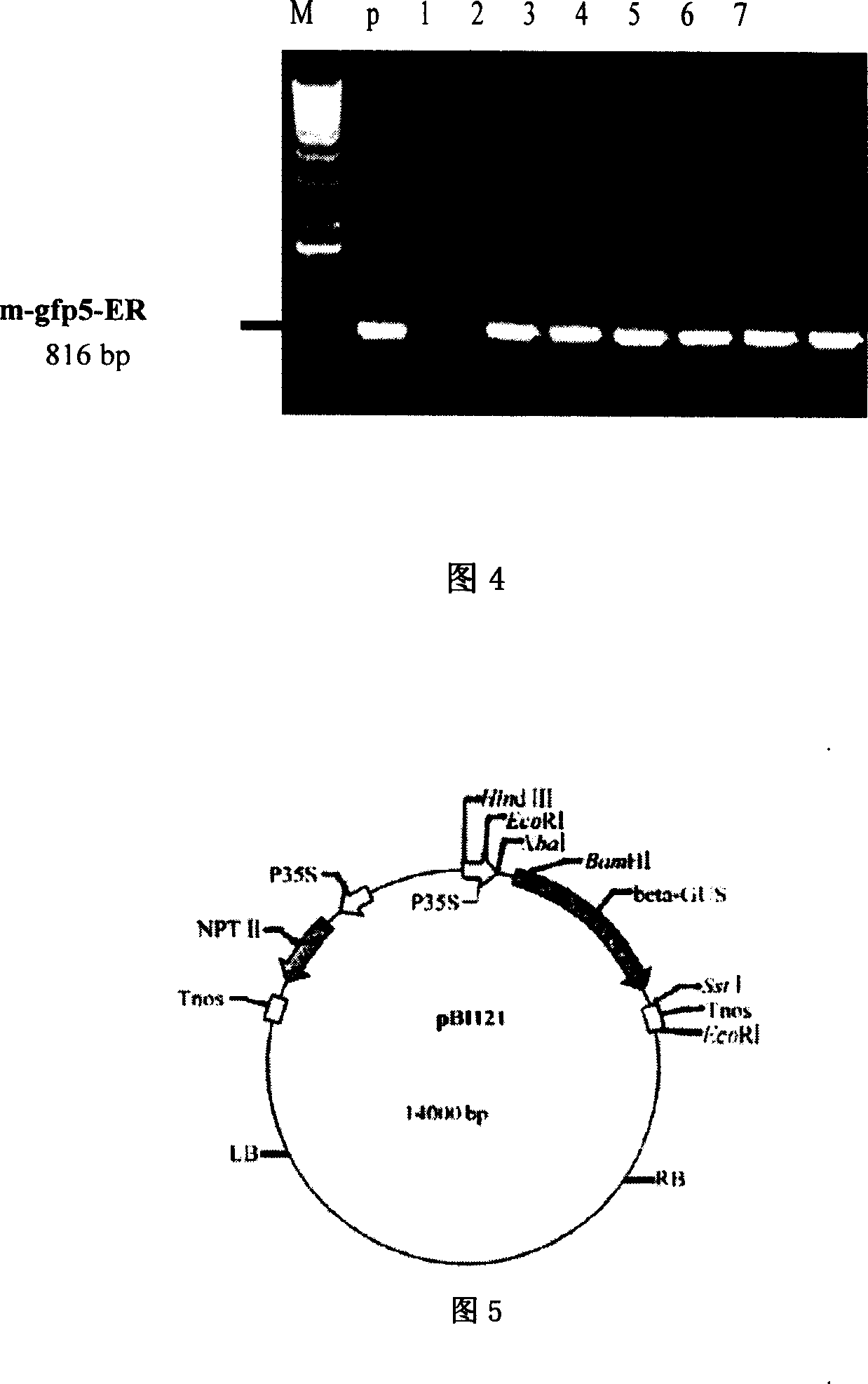
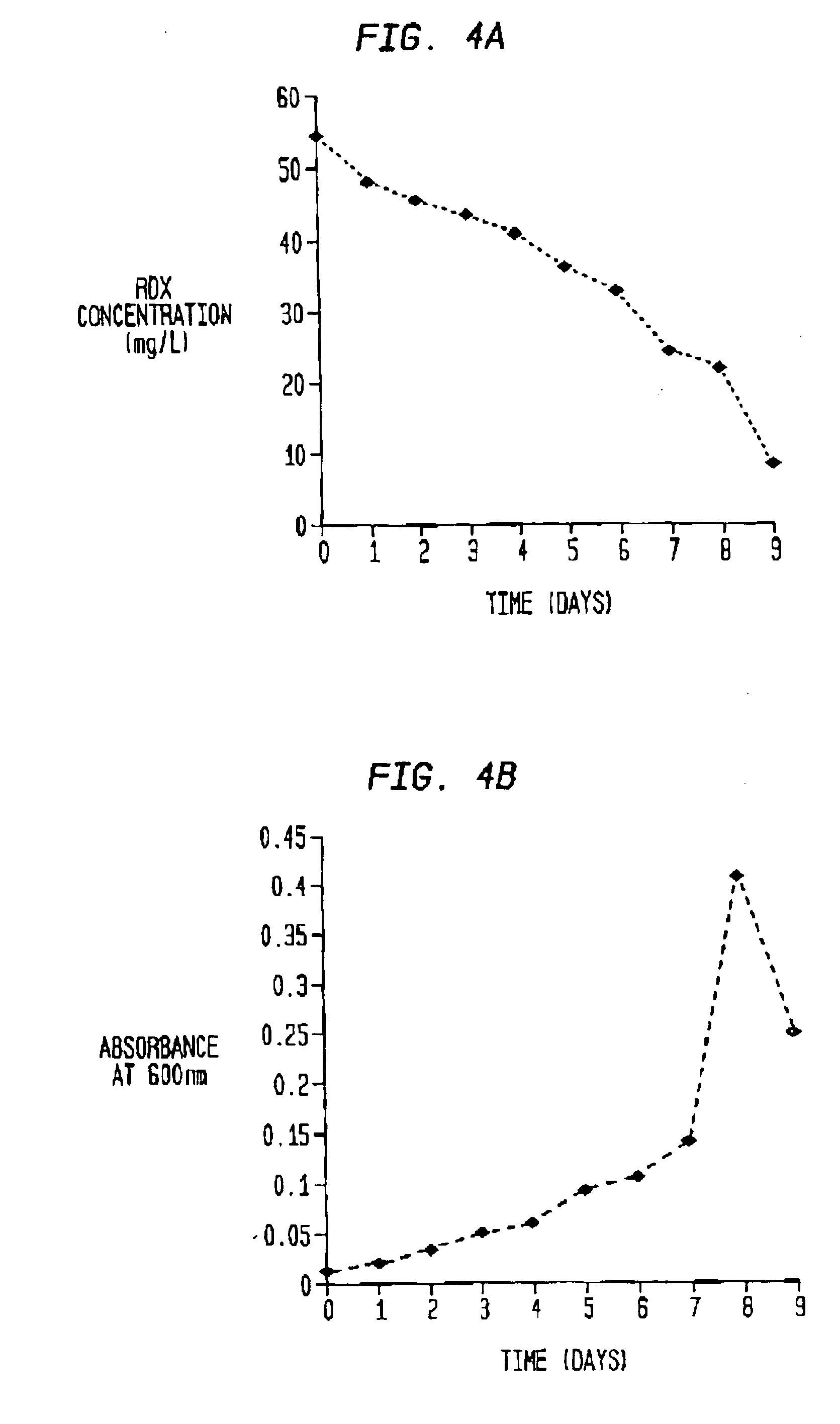Patents
Literature
187 results about "Rhizogene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rhizogene is a genus of fungi in the family Venturiaceae.
Production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore
ActiveCN101565689ALow costLow nutritional requirements for growthMicroorganism based processesSpore processesBiotechnologyMicrobial culture technique
The invention discloses a production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore, which belongs to the technical field of microorganism culturing, and comprises the following technical steps of: 1) culturing carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA; 2) culturing the carrot root tissues converted from agrobacterium rhizogenes plasmid DNA and glomus intraradices together in an improved synthetic culture medium; 3) taking a culture containing the root, hypha and spore infected by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and transplanting the culture to a special culture box for culturing; 4) collecting the spore and mycelium; and 5) storing the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore. Compared with the prior art, the production method for high-density pure arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal spore has the advantages that: 1, the culture medium is an asepsis environment with low cost, which not only can meet the growing of a host plant, but also is suitable for the growing of AM epiphyte; 2, the nutrition requirements for the growing of the host plant are low and the host plant can grow and be cultured on the synthetic culture medium; 3, the spore cultured by the method is a non-pollution pure culture; and 4, the produced spore is stored in liquids and the activity can be maintained by above 90 percent.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for producing salidroside by using agrobacterium rhizogenes to inherit and transfer rhodiola sachdlinensis and constructing capillaceous root cultural system
InactiveCN101121941AAddress resource shortagesHas medicinal valueOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationSalidrosideRhodiola sachalinensis
The present invention discloses a method using Agrobacterium rhizogenes (Ar) gene to transform Rhodiola sachalinensis A.Bor to achieve a hairy root system for Salidroside production. By preparation of explant and cultivation in Ar bacteria liquid, Rhodiola sachalinensis A.Bor is induced to grow hairy roots by genetic transformation; the PCR testing proves that hairy roots are generated by transformation; a fermenter is used for massive production of hairy roots, and precursor substances and elicitors are added to improve the Salidroside content. The method is applied to produce Salidroside to substitute the drying-up Rhodiola sachalinensis A.Bor resources.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
Application of method for smearing and transforming agrobacterium rhizogene-mediated hypocotyl to soybean transformation
InactiveCN101705243AEstablish and optimize smear conversion methodsPrecise determination of germination timeMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionHypocotylRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention discloses application of a method for smearing and transforming agrobacterium rhizogene-mediated hypocotyl to soybean transformation. The method for smearing and transforming agrobacterium rhizogen-mediated hypocotyl to is applied to soybeans for the first time, and hairy root transformation of soybean roots is successfully carried out. In this invention, the sprouting time of seeds and the concentration of screening agents are optimized, therefore not only increasing the quantity of transgenic hairy roots induced by each soybean explant, but also obviously enhancing the transformation frequency and growth conditions of hairy roots. A screening marker weed killer usually used for soybean transformation is successfully used for obtaining soybean compound plants in aseptic conditions, wherein each soybean compound plant has a transgenic root and a non-transgenic over-ground part and can be used as the ideal material for studying genes relative to the form of root systems, the symbiotic nitrogen fixation of roots and the formation of fungus roots.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Corn genetic transferring method conducted by agrobacterium rhizogenes
InactiveCN101121942AAvoid chimerasGood for genetic manipulationOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPlantlet
The invention discloses a novel method for Agrobacterium rhizogenes (Ar) mediated corn gene transformation. Ar is adopted to infect corn callus to induce the generation of hairy roots; through differentiation cultivation, the hairy roots regenerate transgene plants. Ri plasmid is taken as a vector to transfer one or a plurality of exogenous genes into the genome of the acceptor. The hairy-root transformation rate of the invention is as high as 78 percent; the hairy-roots regenerate plants (with high frequency) by 55 percent. The survival rate of the transplanted regenerated-plants is as high as 92 percent; objective clone screening is easy, suitable for genetic operation, and practical. During genetic transformation of the exogenous genes, the roots of the plants and drought resistance are very strong due to rol gene action of Ri plasmid. The method can be applied to the production of corn drought-resistant transgene plants.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
Method for producing alkannin by utilizing Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root
InactiveCN101869591ANot limited by environmental climateQuality improvementAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsBiological activationRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention relates to a method for producing alkannin by utilizing Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root. The method includes selection and processing of Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst explant, activation culture of agrobacterium rhizogene, infection of cotyledon explant and induction of hairy root, obtaining of sterile Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root system and liquid culture of Arnebia euchroma(Royle)Johnst hairy root as well as alkannin production. The used hairy root has the characteristic of rapid and autonomous growth on culture medium without exogenous hormones, thus the method not only can overcome the defects that cell culture grows slowly and hormone is required to be additionally added to maintain the growth thereof when utilizing cell culture to produce alkannin, and the method has the advantages of stable alkannin throughput, simple operation in cultivation, lower cost and no restriction of climate and land natural conditions. Especially the invention provides a stable and continuable novel medicine source for producing alkannin by utilizing hairy root culture method and provides reliable source and material basis for alkannin mass production by applying bioreactor in the future.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Construction method of agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transgenic plants
ActiveCN109679993AOmit the redifferentiation stepOvercoming the long cycle of genetic transformation and other problemsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureStem lengthPlant genetic engineering
The invention provides a construction method of agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transgenic plants, and relates to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The method comprises the steps offirstly, constructing agrobacterium rhizogenes with a target gene, enabling sterile seedlings of plants to take roots and then planting; when the stem lengths of the planted sterile seedling are morethan 3cm from the roots, injecting the bacterial liquid of the agrobacterium rhizogenes with the target gene into the stems of the sterile seedlings of the plants; after the transgenic hairy roots ofthe plants grow out at the injected parts of the stems, culturing until the lengths of the transgenic hairy roots are greater than 3cm and the number of roots is increased to 10, removing the non-hairy roots and extending the hairy roots into the soil to obtain the transgenic plants with the hairy roots. Compared with the conventional plant transgenic system, the method provided by the invention can omit the plant re-differentiation step of callus cells and overcome the problems of long period and the like which are caused by using the callus cells for genetic transformation. The method provided by the invention requires simple equipment and easy in mastering of operation technology, thus having a broad development and application prospects.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for evoking liquorice to generate hairy root
ActiveCN101157936AShorten the timeImprove conversion efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsGLYCYRRHIZA EXTRACTRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention discloses a method for inducting hairy root of glycyrrhizae. The procedure of the method is to co-culture glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node and agrobacterium rhizogenes which contains Ri plasmid and then transfer glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node and agrobacterium rhizogenes to an induction medium for induction cultivation after washing of cephamycin-contained sterile water, then glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node yields glycyrrhizae hairy root. The invention takes glycyrrhizae cotyledonary node as acceptor material for the first time and realizes induction of glycyrrhizae hairy root through the mediating of agrobacterium rhizogenes, thus shortening the growing period of glycyrrhizae hairy root to 4 days and raising the transforming efficiency to more than 96 percent. Furthermore, the active component in the hairy root such as licoflavone is as high as 1.6 percent, which settles a good foundation for producing useful glycyrrhizic acid and licoflavone by using glycyrrhizae hairy root culture.
Owner:BEIJING WEIMING KAITUO CROP DESIGN CENT COMPANYLIMITED
Method for producing medicinal ingredient aucubin by induction and culture of eucommia ulmoides hairly root
InactiveCN101358197AHigh and stableFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyAucubin
The present invention provides a method for producing aucubin used as medicinal ingredient by the induction of Eucommia fairy root, which obtains the Eucommia fairy root by genetic transformation for the production of the aucubin. The method includes the following processes: Agrobacterium rhizogenes are used to genetically transform Eucommia ulmoides Oliv. in order to obtain the Eucommia fairy root, which is determined as the genetically transformed fairy root by molecular detection, and HPLC detection indicates that the Eucommia fairy root obtained by genetic transformation can produce the aucubin. The method can provide novel sustainable medicine source for the production of the aucubin used as medicinal ingredient.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
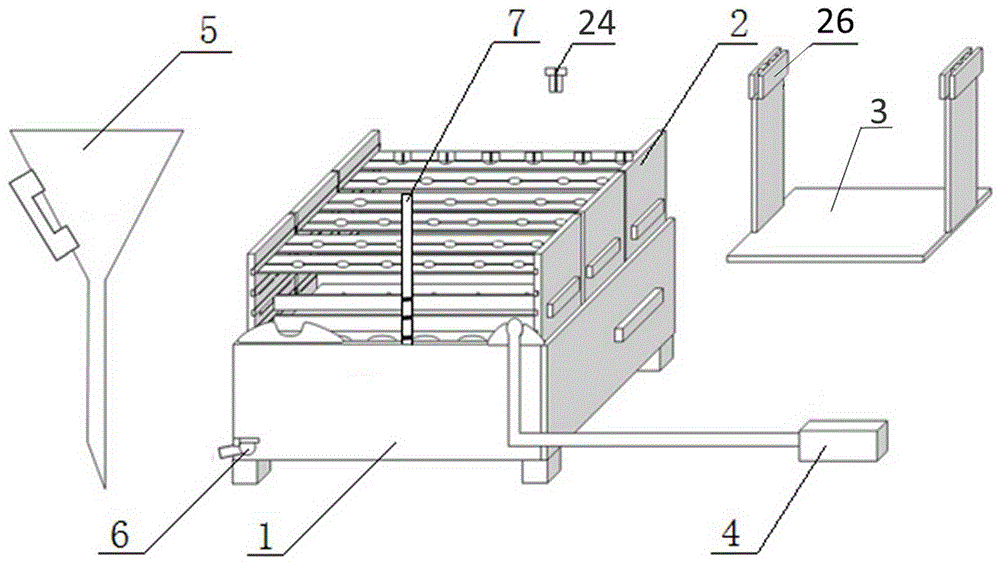
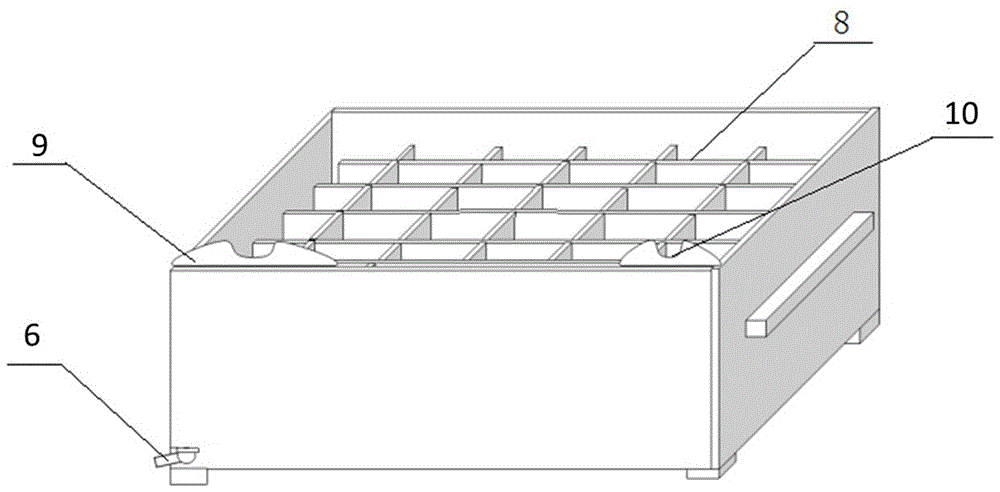
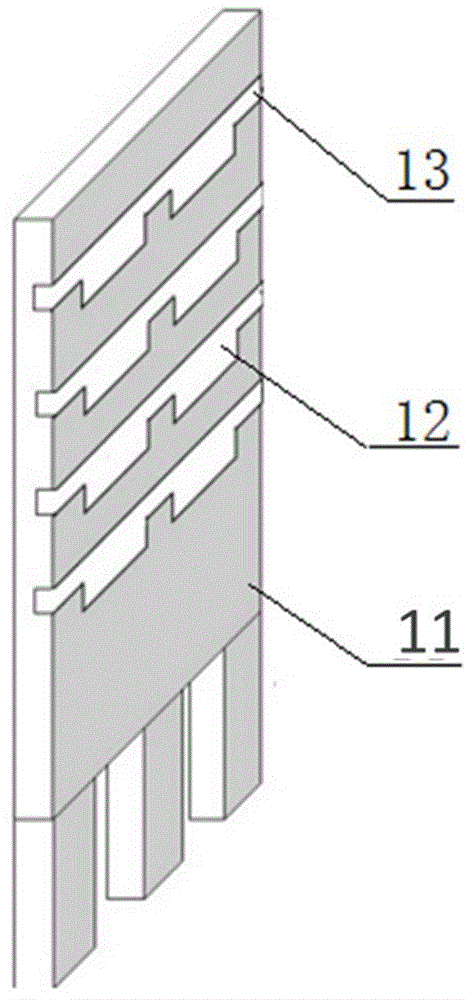
Suitable hydroponic device for root system culture of Agrobacterium rhizogenes transgenic plant
ActiveCN106508654AAvoid breedingQuick and timely replenishmentAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsEngineeringRhizobium rhizogenes
The invention relates to a special hydroponics suitable for root system culture of Agrobacterium rhizogenes and its application, the device comprising a tank, a plant holder, wherein the plant holder comprises a vertical plate support, a clamping plate, and a plate-mounted frame body provided with a height adjustment groove and a chute provided with a combined upper-layer holding plate, a chute sealing strip and a light-shielding plate, the upper deck being provided with a plant gripping hole, the lower holding plate and the shading plate which are provided with corresponding root and stem holes. The tank is a rectangular box with a net length corresponding to the plant holder. The net width is an integral multiple of the width of the plant holder. The box contains an independent root zone corresponding to the root hole separated by a divider. The device configuration also includes an oxygen pump, a root pruning bracket and a pouring funnel. The device can be used for root system culture of Agrobacterium rhizogenes transgenic plants.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cultivation method for inducing scutellaria baicalensis hairy root based on agrobacterium rhizogenes infection
InactiveCN102229945ASynthetic strongPromote growthVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellsRhizobium rhizogenesActive ingredient
The invention discloses a cultivation method for inducing scutellaria baicalensis hairy root based on agrobacterium rhizogenes infection, which uses an agrobacterium rhizogenes bacteria liquid to infect root of a scutellaria baicalensis explant and induces the scutellaria baicalensis explant to form a hairy root, the scutellaria baicalensis hairy root presents yellow hairy on a MS solid medium, so that scutelloside can be stably synthesized, an ITS sequencing is performed and the hairy root can be identified as the scutellaria baicalensis hairy root of a scutellaria. Then seed selection is performed for further in a seed selection medium and a cultivation condition can be optimized to select lines which raise the content of active ingredient scutelloside used for hairy root traditional Chinese medicines. Hairy root can be obtained through scutellaria of a scutellaria introduced by agrobacterium rhizogenes, wherein the inductivity can reach 10 - 40%, the obtained scutellaria baicalensis hairy root presents yellow hairy which is capable of stably synthesizing scutelloside. According to the invention, the scutellaria baicalensis hairy root of a scutellaria is cultivated on the optimized medium, the growth is rapid and the biomass can be increased for 23 -35 times in 30 - 35 days, and the cultivation is performed under the dark conditions. The invention has the characteristics of low energy consumption and low cost, which is suitable for industrialization production.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fusion gene fragment rolB-FGFs and application thereof
InactiveCN101768597AHigh induction rateHigh protein expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhizobium rhizogenesBiology
The invention discloses a fusion gene fragment rolB-FGFs, which consists of a rolB gene and an FGFs gene that is designed according to the preference of a plant codon, wherein a PIM gene without the antibiotic marker and a human secreted alkaline phosphatase signal peptide (SEAP) gene are introduced; a plant secreted binary expression vector without the antibiotic marker is constructed; the expression vector is transformed into agrobacterium rhizogene; by taking the plant as the host and adopting a hairy root system to express the FGFs, the active FGFs can be purified from a hairy root and culture solution respectively, and the FGFs can be prepared industrially, thereby improving the inductivity, the expressed protein amount, the yield and the stability of the hairy root; and no antibiotic marker exists in the method, thereby protecting the environment. The ginseng hairy root containing the FGFs prepared by taking the ginseng as the host has the double pharmacological effects of the ginseng and the FGFs, thereby being a better health-care product or medicine; in addition, the ginseng hairy root is used for the development and the application of the functional food and medicine and has wide prospect.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for preparing polygonin through tissue culture and inducement of hairy roots of giant knotweed
InactiveCN1759665AShorten the production cycleQuality improvementSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPOLYGONUM CUSPIDATUMRhizobium rhizogenes
A process for preparing the polygonoside from the trichiform root of rhizome polygoni cuspidati by tissue culture and inducing includes such steps as tissue culture of wild rhizome polygoni cuspidati, activating culture of Agrobacterium rhizogene, inducing the trichiform root of rhizome polygoni cuspidati by the T-DNA fragment on rooting plasmide of Agrobacterium rhizogene, optimalizing culture of said trichiform root, and extracting polygonoside from said trichiform root.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for regenerating Chinese rose plant by using immature seed as explant
InactiveCN101946704AGood receptorProliferation effect is goodPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShootSomatic cell
The invention belongs to the technical field of tissue and cell culture of plants and in particular relates to a method for regenerating a plant in Chinese rose somatic embryogenesis. The method comprises the follow three cultivating stages of: (1) cultivating a Chinese rose explant on an induction culture medium and directly inducing somatic embryo from the explant, wherein the explant is an immature zygotic embryo of a Chinese rose; (2) inoculating the somatic embryo to a proliferating culture medium for proliferation and promoting the further differentiation of the somatic embryo; and (3) inoculating the somatic embryo subjected to the proliferating culture to a somatic embryo seedling culture medium so as to regenerate an integrated plant. In the Chinese rose somatic embryo subjected to isolated culture, roots and shoots can grow at the same time during the regeneration of the plant, so that the integrated plant can be formed without rooting culture. The method has the advantages of wide sources of the explant, readily available raw materials and the like. The obtained somatic embryo is a good agrobactrium rhizogenes-mediated and genetically transformed receptor. The method can also be applied to the research of the genetic transformation of Chinese roses.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
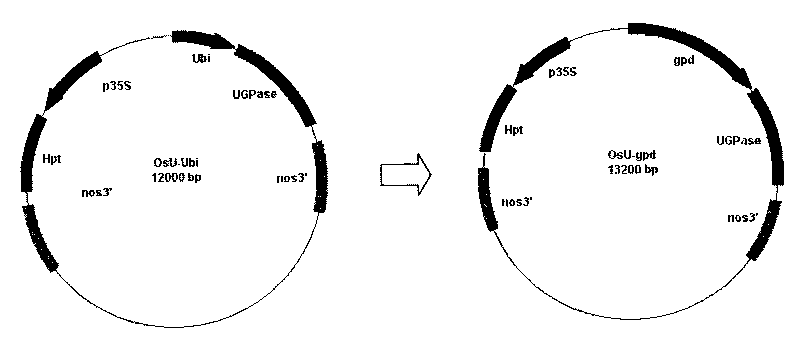
Method for improving biological output and polysaccharide content of lucid ganoderma
InactiveCN101717782AHigh in polysaccharidesLarge biomassVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyUridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase
The invention discloses a method for improving biological output and polysaccharide content of lucid ganoderma. The UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (OsUgp2) gene derived from rice is connected to an overexpression vector and transferred into the lucid ganoderma by a agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated method; in the obtained transgenosis lucid ganoderma strain, the expression of the OsUgp2 gene is strengthened, and the biological output and the intracellular polysaccharide and extracellular polysaccharide content of the ganoderma sinensis are obviously improved. The invention can effectively improve the biological output and the polysaccharide content in edible and medicinal fungi, such as the lucid ganoderma, and the like, provides a new approach for improving the polysaccharide content of the edible and medicinal fungi and has favorable application and development prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
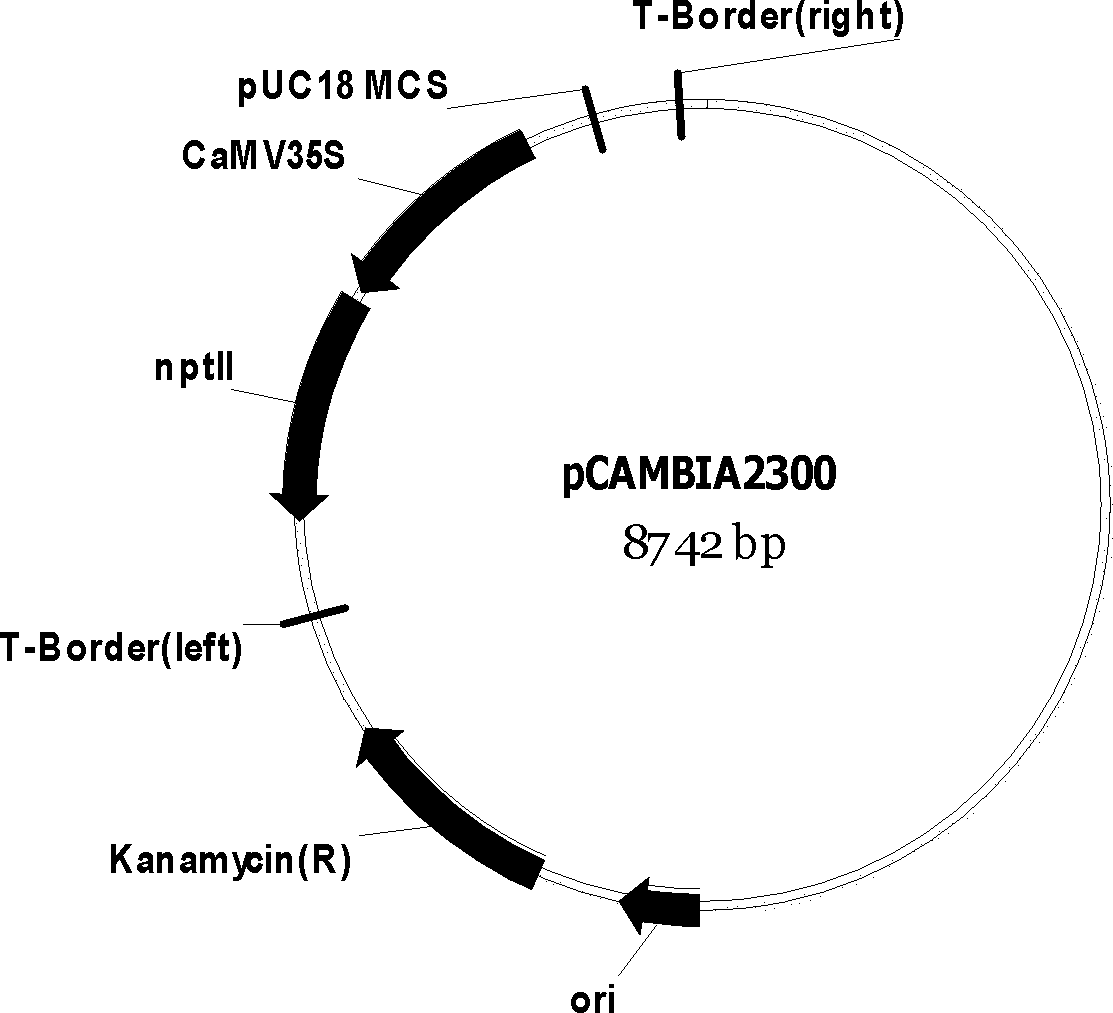
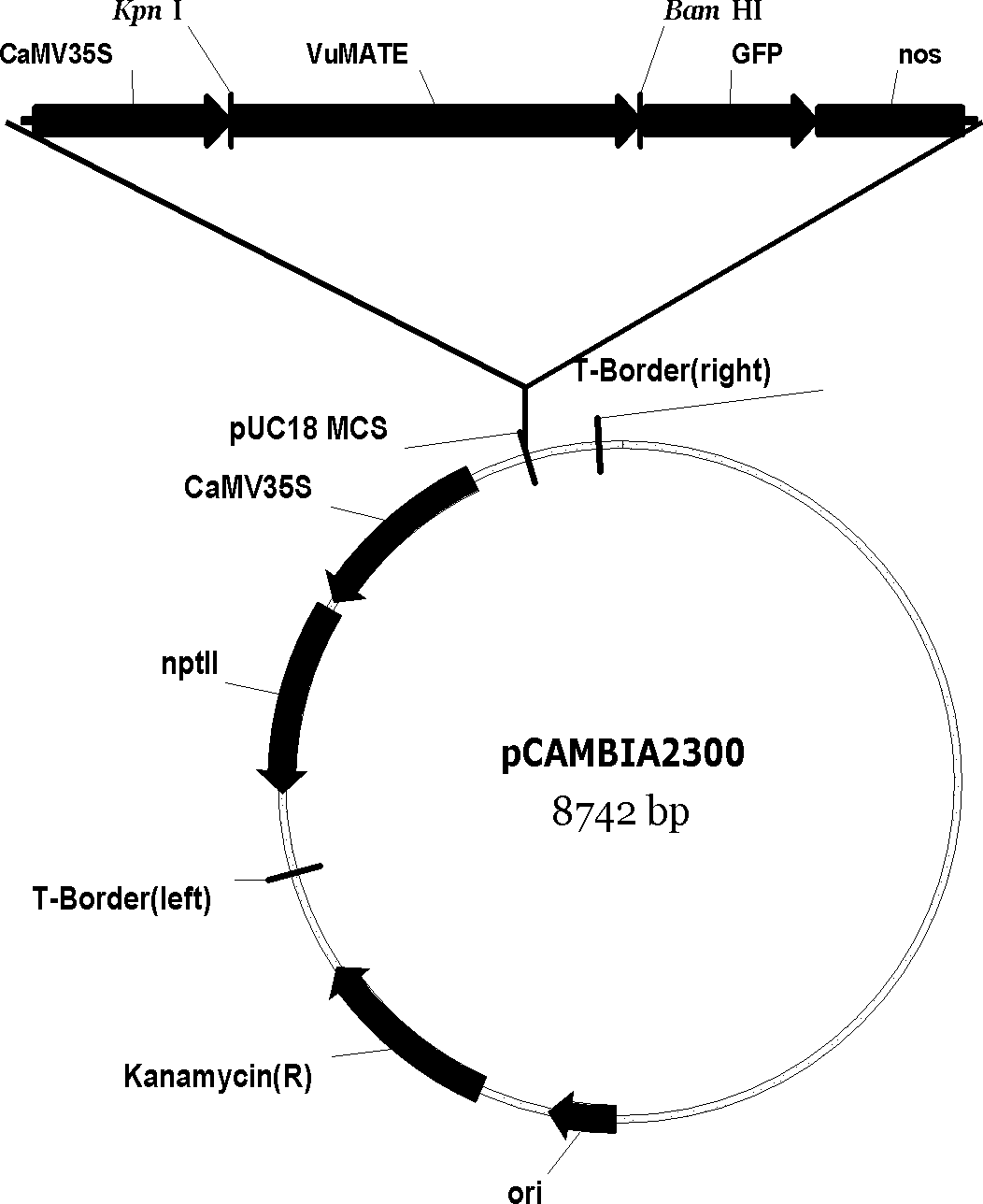
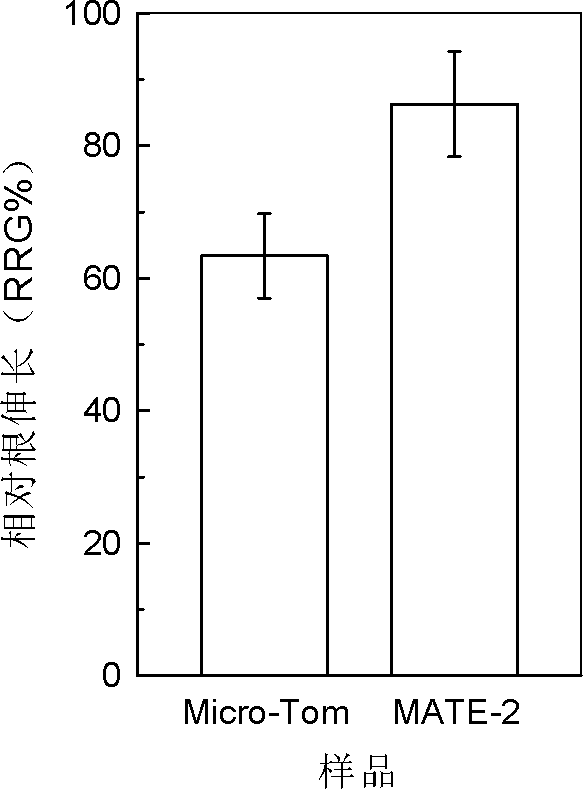
Snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE and use thereof
InactiveCN102154318AIncrease aluminum resistanceImprove secretion capacityFermentationHorticulture methodsNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE, which has a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1. The invention also discloses a method for breeding an aluminum-tolerance transgenic crop, which comprises the following steps: 1) selecting the snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE having the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID No.1; 2) constructing a constitutive type expression transgenic vector; and 3) and breeding the transgenic crop, namely infecting leaf disc of tomatoes Micro-Tom with Agrobacterium rhizogenes EHA105 into which the pseudo-rigid-body model (pRBM) vector is transferred, co-culturing the transgenic plant, selecting, differentiating and rooting to obtain transgenic tomatoes MATE-2. The snailflower citric acid transporter gene VuMATE disclosed by the invention can be used for plant transgenosis for improving the aluminum tolerance of the crop.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
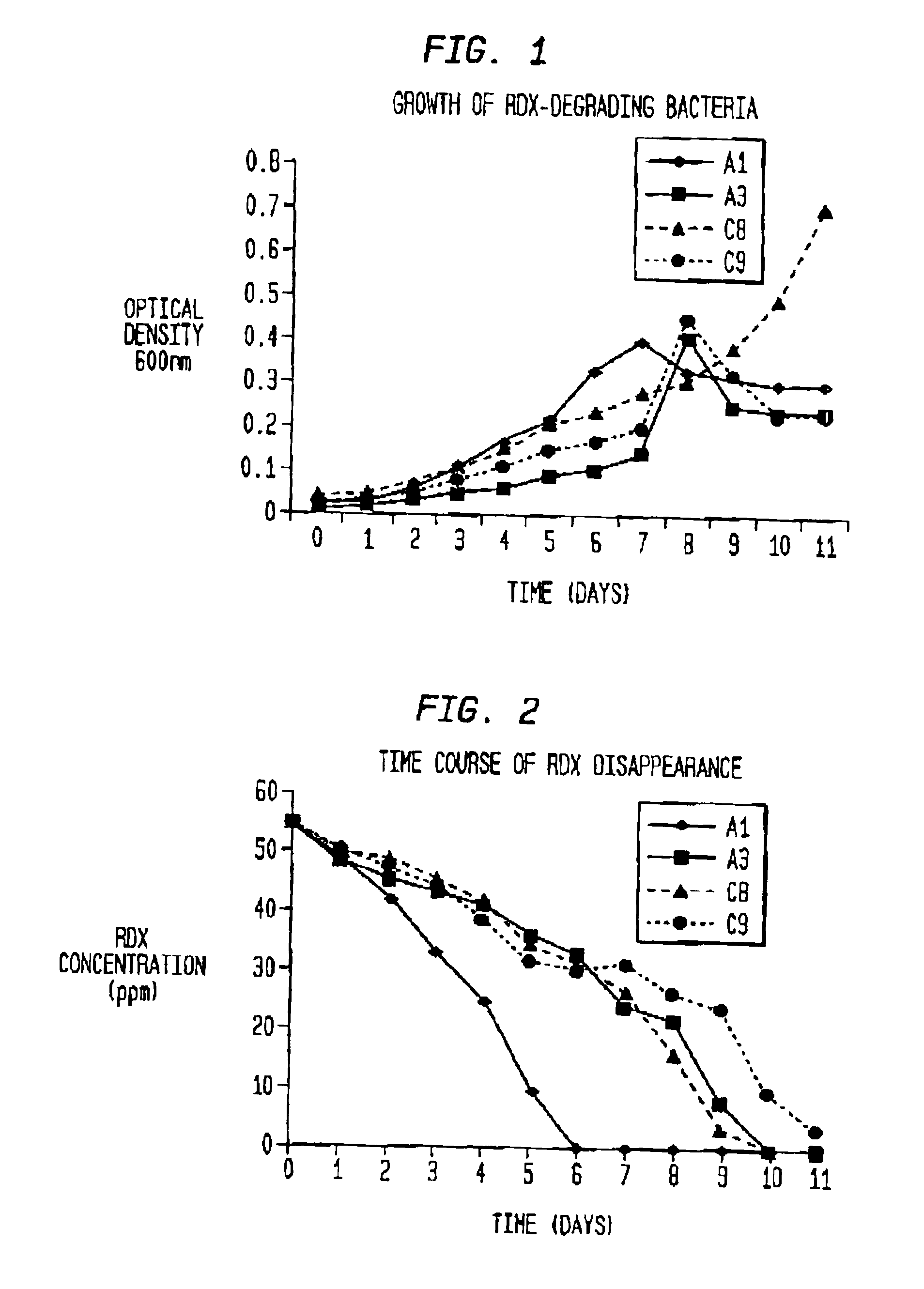
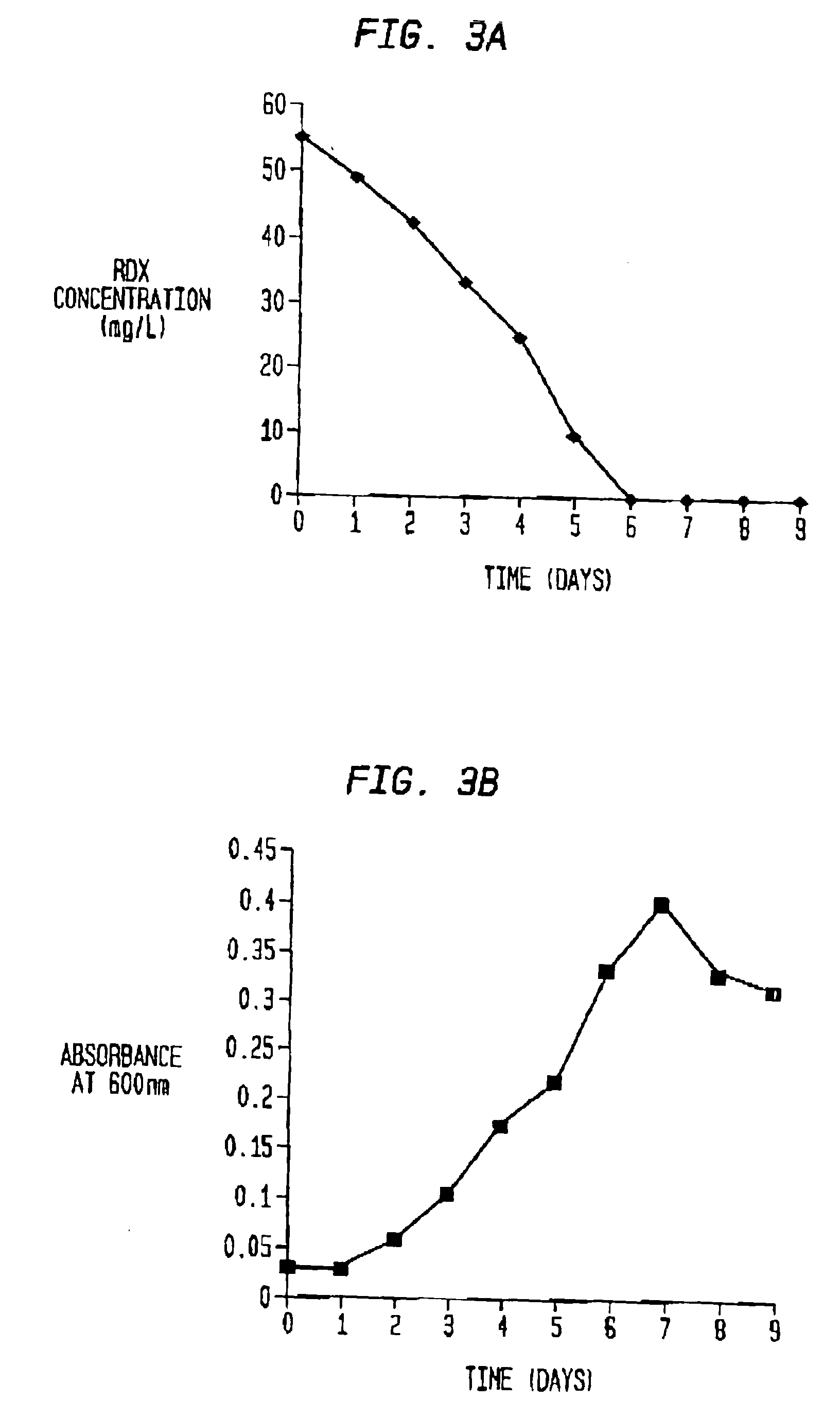
Bioremediation of nitrogenous contaminants
InactiveUS6936456B1Speed up the repair processSpeed up the processBacteriaUnicellular algaeBioremediationRhizobium rhizogenes
A novel process for the remediation of nitrogenous energetic materials such as 1,3,5,-trinitro-1,3,5-triazine (RDX) which can be used in situ on contaminated media is provided. The process comprises the bioremediation by one or more miccroorganisms capable of metabolizing the energetic materials. Examples of such microorganisms include Rhizobium rhizogenes, Burkholderia sp., and Cladosporium cladosporioides (ATCC 66669). Strains of these microorganisms have been deposited. The strain designated A1 has been deposited as Rhizobium rhizogenes BL (ATCC PTA-4110) and the strain designated C8 has been deposited as Burkholderia sp. (ATCC PTA-4111) Additionally, with the addition of a carbon source, such as a sugar, the process can totally degrade the energetic materials in two to three days.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Methods for efficient induction production of Glycyrrihiza uralensisi Fisch hairy roots and production of licorice root secondary metabolites by using Glycyrrihiza uralensisi Fisch hairy roots
InactiveCN103695458AEfficient inductionStable inductionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGlycyrrhiza lepidota
The present invention relates to methods for induction production of hairy roots through infection of Glycyrrihiza uralensisi Fisch seedling stem nodes by using Agrobacterium rhizogenes, and production of medicinal secondary metabolites (such as liquiritin, glycyrrhizic acid and the like) by using the hairy roots, particularly to a method for efficient induction production of Glycyrrihiza uralensisi Fisch hairy roots and a method for production of licorice root secondary metabolites by using the hairy roots. The method is characterized by comprising: (1) obtaining sterile explants, wherein Glycyrrihiza uralensisi Fisch seeds are taken, sterilized, and then inoculated in a seedling culture medium to culture to obtain sterile seedlings with a plant age of 12-15 d, and the roots are cut so as to be adopted as the explants; (2) preparing an Agrobacterium rhizogenes engineering bacteria solution; and (3) inducing production of hairy roots through needling stem nodes. According to the present invention, the method for efficient and stable induction production of the Glycyrrihiza uralensisi Fisch hairy roots is provided, and the obtained Glycyrrihiza uralensisi Fisch hairy roots are subjected to suspension culture through selecting the appropriate liquid culture medium and are used for producing the medicinal secondary metabolites (such as liquiritin, glycyrrhizic acid and the like).
Owner:NINGXIA ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for inducing Polygonum ciliinerve to generate hairy roots
InactiveCN102517322AIncrease the multiplication factorGrow fastVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsCataphyllTransgenic technology
The invention discloses a method for inducing Polygonum ciliinerve to generate hairy roots, which comprises the following steps of: inducing laminae of the Polygonum ciliinerve through an Agrobacterium rhizogenes strain W.T15834 to form the hairy roots, and culturing to obtain a great number of hairy roots of the Polygonum ciliinerve, wherein the laminae of the Polygonum ciliinerve serve as explants. According to the method for inducing the Polygonum ciliinerve to generate the hairy roots, the Polygonum ciliinerve is converted by utilizing Agrobacterium rhizogenes on the basis of establishing a sterile rapid propagation system by utilizing isolated culture, thereby, a great number of hairy roots of the Polygonum ciliinerve can be obtained. The method for inducing and culturing the hairy roots of the Polygonum ciliinerve has the characteristics that hormones autonomously and rapidly grow and differentiate, the proliferation coefficient is high, the inheritance is stable, materials can be conveniently fetched without season limitations, and the culture time is short, and has a positive effect on perfecting the Polygonum ciliinerve transgenic technology, performing mass culture on the hairy roots of the Polygonum ciliinerve and utilizing the biotransformation of secondary metabolic products of the hairy roots of the Polygonum ciliinerve in the later period.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Method for acquiring new-type medicine source of camptothecin by adopting genetic co-transformation strategy
InactiveCN103194487AIncrease the content of camptothecinFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant hormoneCancer cell
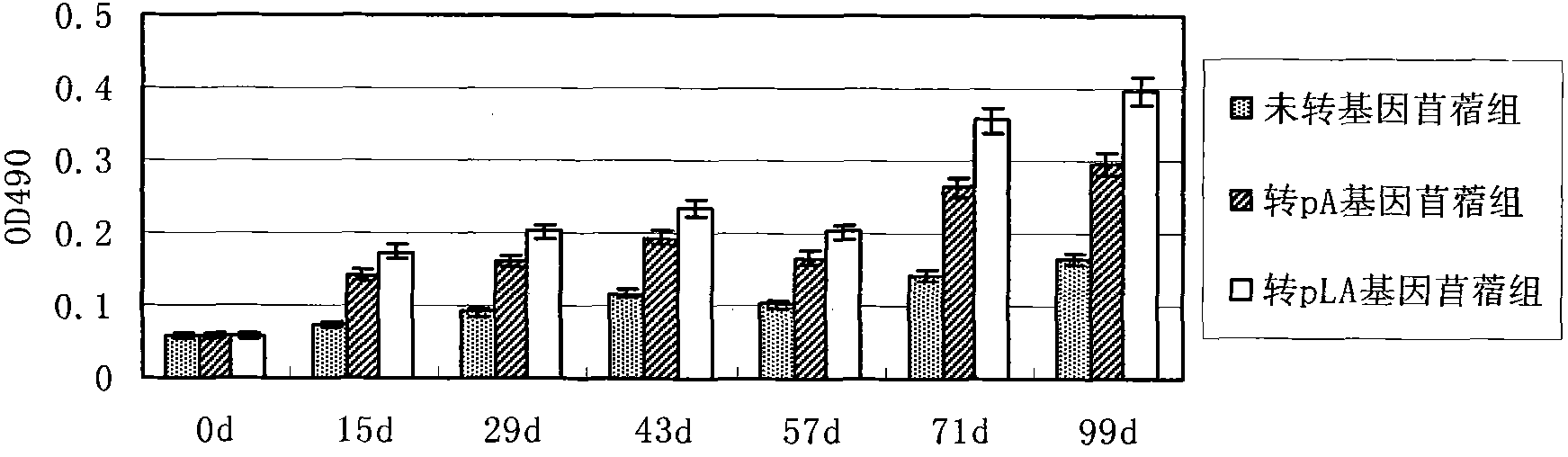
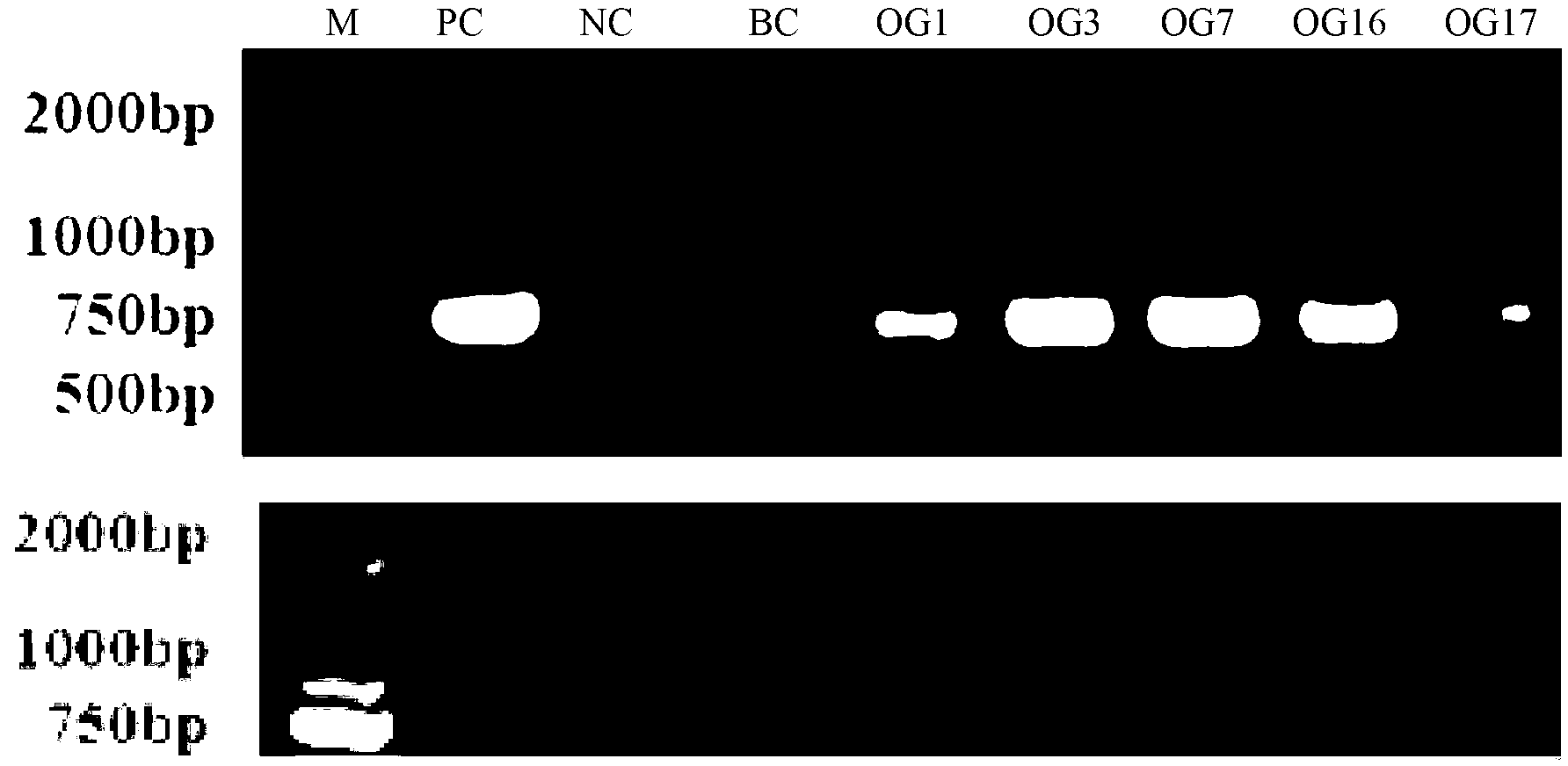
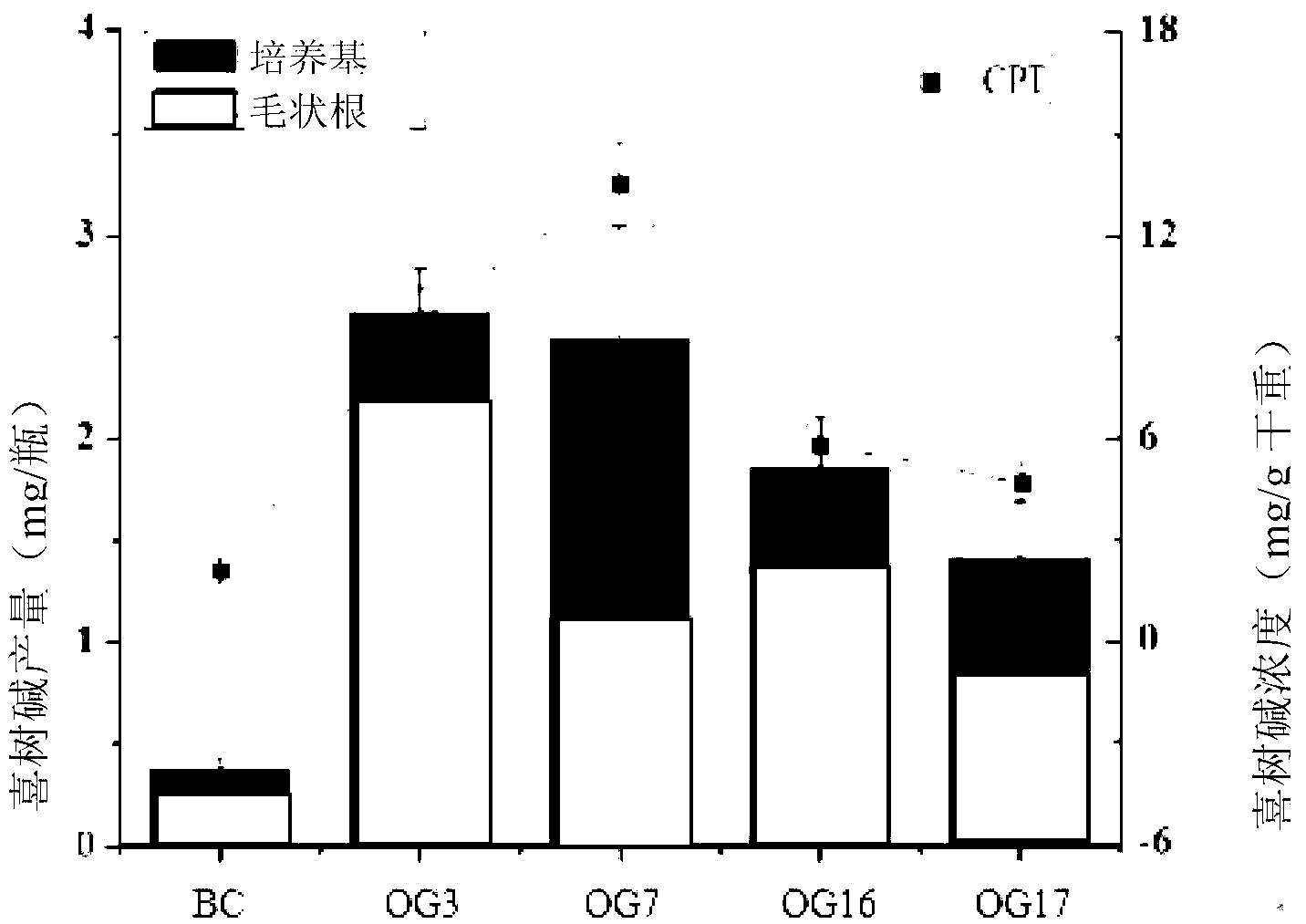
The invention relates to the technical field of bioengineering and discloses a method for improving camptothecin content in hairy roots of the new-type medicine source plant ophiorrhiza pumila of camptothecin. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: cloning coding frame sequences of genes of ophiorrhiza japonica strictosidine synthase and geraniol-10-hydroxylase in catharanthus roseus to build a plant bivalent efficient expression vector containing the genes, carrying out genetic transformation on ophiorrhiza pumila via an agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated method to acquire the hairy roots of the ophiorrhiza pumila for transforming CrSTR and CrG10H genes; and inducing and treating high-yield camptothecin strains by adopting plant hormones to acquire high-yield hairy roots with the camptothecin content of 4.703mg / g DW. The MTT (Methyl Thiazolyl Tetrazolium) detection proves that camptothecin crude extract acquired via a transgenosis manner is good in biological activity and the lethality to cancer cells reaches 35.9%. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, a new medicine source for acquiring the camptothecin is provided and a new method for producing anti-cancer medicine camptothecin in important clinical demand is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving tanshinone content in salvia miltiorrhiza hair roots through methyl jasmonic acid treatment
InactiveCN102577941AIncrease contentReduce manufacturing costPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSalvia miltiorrhizaHair roots
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological culture, in particular to a method for improving the tanshinone content in salvia miltiorrhiza hair roots through methyl jasmonic acid treatment. According to the method, agrobacterium rhizogene is firstly used for infecting salvia miltiorrhiza aseptic seedlings to obtain the salvia miltiorrhiza hair roots, then, the sterilization culture of the salvia miltiorrhiza hair roots is carried out, and next, the salvia miltiorrhiza hair roots are selected to be transferred into a liquid culture medium for carrying out suspension culture; and methyl jasmonic acid is added into the salvia miltiorrhiza hair roots in the time of 4 to 6 days before the salvia miltiorrhiza hair root liquid culture harvesting, then, the harvesting is carried out on time, and the tanshinone content in salvia miltiorrhiza hair roots can be greatly improved. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the tanshinone content in the hair roots can be effectively improved, the operation is simple, the relatively higher front-stage investment required by the utilization of a gene engineering method for improving the tanshinone content is not needed, the production cost of the tanshinone is effectively reduced, and great significance is realized on meeting the large-scale production of the tanshinone.
Owner:开国银
Clostridium welchii disease resistant transgenic plant vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102008720AImprove immunityRich in nutrientsAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliEukaryotic plasmids
The invention discloses a clostridium welchii disease resistant transgenic plant vaccine and a preparation method thereof. At present, the protective ratio on immunization of clostridium welchii disease resistant vaccines is lower. The preparation method of the clostridium welchii disease resistant transgenic plant vaccine comprises the steps of: (1) with a plasmid or disease sample containing coded clostridium welchii toxin as a template, carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) or RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification to obtain a clostridium welchii toxin gene, carrying out enzyme cutting on the obtained clostridium welchii toxin gene or the Ti or Ri plasmid respectively, recycling a target gene and a plant expression vector segment, connecting with and converting escherichia coli, carrying out enzyme cutting, PCR and sequencing identification on the recombinant Ti or Ri plasmid, converting agrobacterium tume faciens or agrobacterium rhizogene with the recombinant plasmid, and screening and identifying positive recombinant agrobacterium; and (2) carrying out vernalization, germination and splicing on plant seeds to obtain explants, infecting the explants respectively with the recombinant agrobacterium in the step (1), carrying out screening, subculturing, rooting and transplanting on the infected explants to obtain transformed plants, and screening and identifying positive transgenic plants.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of novel medicine source raw material of camptothecin
InactiveCN103194488AIncrease the content of camptothecinFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant hormoneFrame sequence
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and provides a method for improving camptothecin content in hairy roots of novel medicine source plant ophiorrhiza pumila of camptothecin. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning coder frame sequences of CrORCA3 and CrG10H genes from catharanthus roseus; constructing a bivalent efficient expression vector of a plant containing such genes; and carrying out genetic transformation to the ophiorrhiza pumila through the agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated transformation method, thus obtaining the hairy roots of the ophiorrhiza pumila containing transformed CrORCA3 and CrG10H genes. The camptothecin content in the obtained hairy roots of the transgenic ophiorrhiza pumila is obviously increased, the camptothecin output in each flask(2.62mg / flask) is averagely increased by 5.52 times in comparison with that in the contrast, and the average content (8.44mg / g DW) is increased by 4.04 times. The total camptothecin output of each flask, induced by plant hormones after culturing one strain for six weeks, is increased by 7.8 times. The preparation method provided by the invention is a novel method for producing an anti-cancer drug that is camptothecin under important clinical demand.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for breeding transgenic tetraena mongolica callus and special culture medium thereof
InactiveCN101974479ASimple and fast operationImprove conversion rateVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellsTetraena mongolicaSkin callus
The invention discloses a method for breeding transgenic tetraena mongolica callus and a special culture medium thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) transplanting a tetraena mongolica stem into the tetraena mongolica callus induction culture medium, and culturing to obtain the callus; (2) and transforming the callus obtained in step (1) by using Agrobacterium rhizogenes containing target gene to obtain the transgenic tetraena mongolica callus. In the method, tetraena mongolica seeds from Wuhai in Inner Mongolia are selected as the initial experimental material; after sterileculture to obtain sterile seedlings, the young stem section is cut off to induce the callus; and by using the callus as the explant, and extraneous gene is integrated into the genome of tetraena mongolica by using the Agrobacterium rhizogenes mediated method. By optimizing the processes of transforming and screening callus, the invention establishes a tetraena mongolica callus transformation system which has the advantages of simple operation, high efficiency and high speed.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chaperonin for enhancing RNP signal communication of plant phloem and application
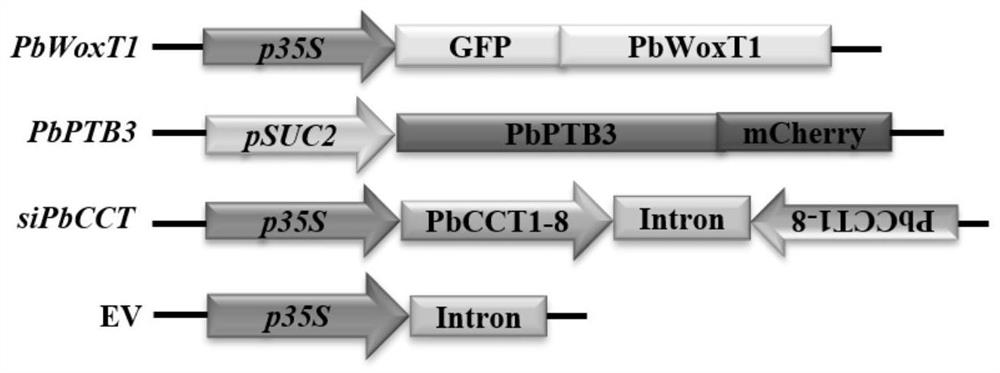
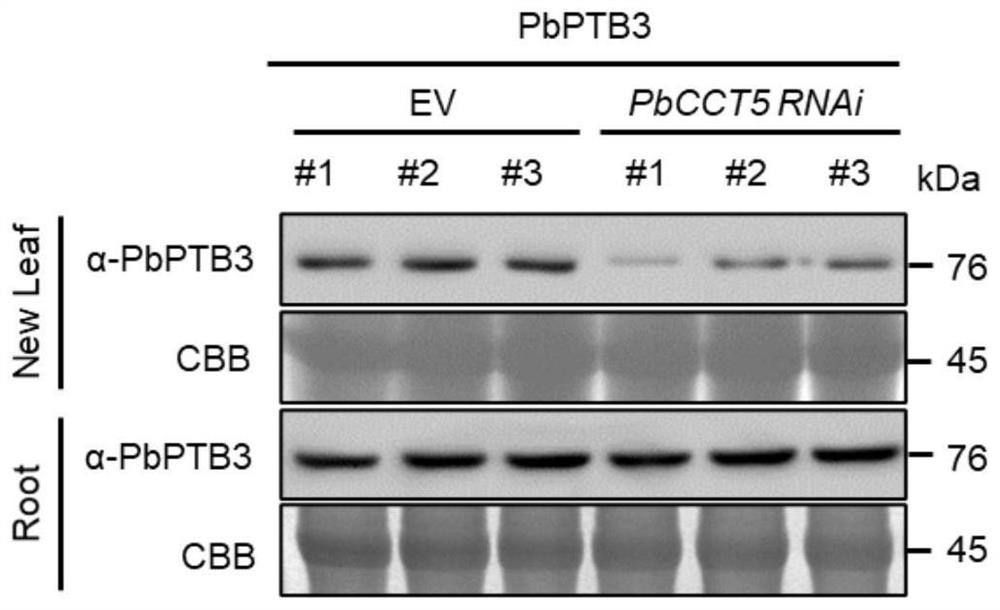
ActiveCN112029774AFacilitate communicationReduce transport efficiencyPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologySignalling molecules
The invention relates to chaperonin for enhancing RNP signal communication of plant phloem and an application. According to the invention, a new phloem RNP signal communication auxiliary factor chaperonin CCT complex is obtained, lack of the chaperonin CCT complex is proved through the transient expression of agrobacterium tumefaciens pear leaves and the transgenic mode of agrobacterium rhizogenes, and the transport efficiency of the RNP complex in phloem is obviously weakened. Through overexpression of the chaperonin CCT complex, communication of the RNP complex in the phloem can be rapidly promoted, besides, long-distance transportation of some signal molecules can be weakened by silencing the chaperonin CCT complex, and long-distance transportation of the RNP complex from a stock to a scion through a grafting opening is promoted by using an auxiliary factor. The scion character is influenced by manually controlling the stock gene, the problem that the transportability of the RNP complex in the phloem cannot be manually regulated is solved, and the method can be universally applied to various types of plants.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
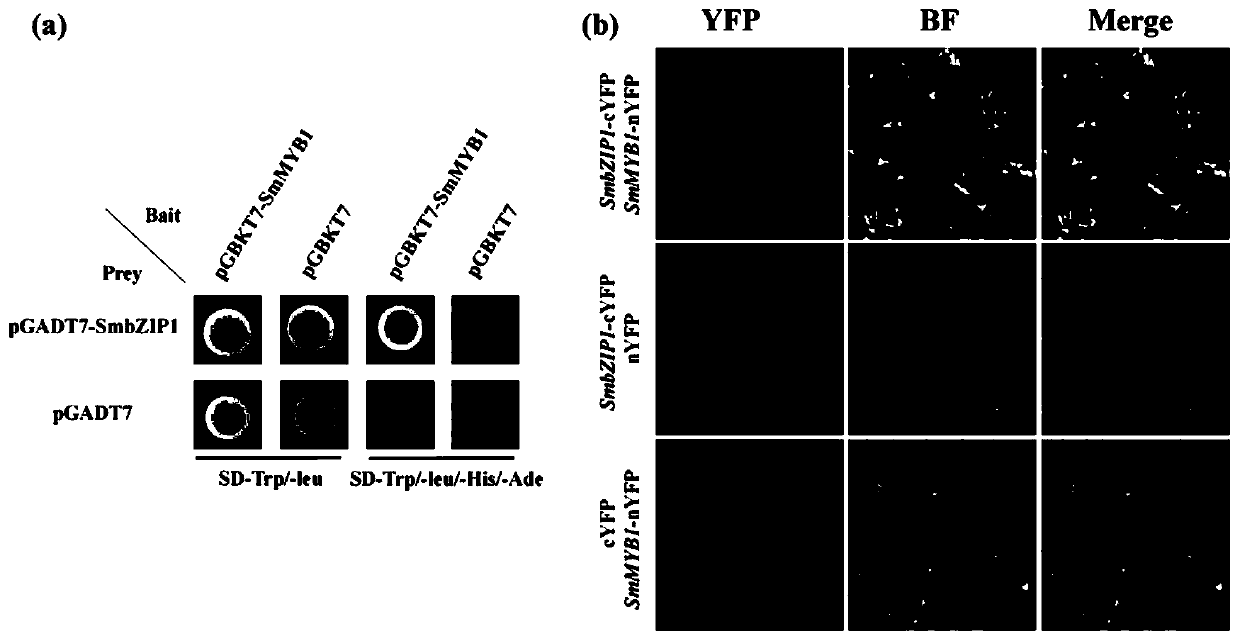
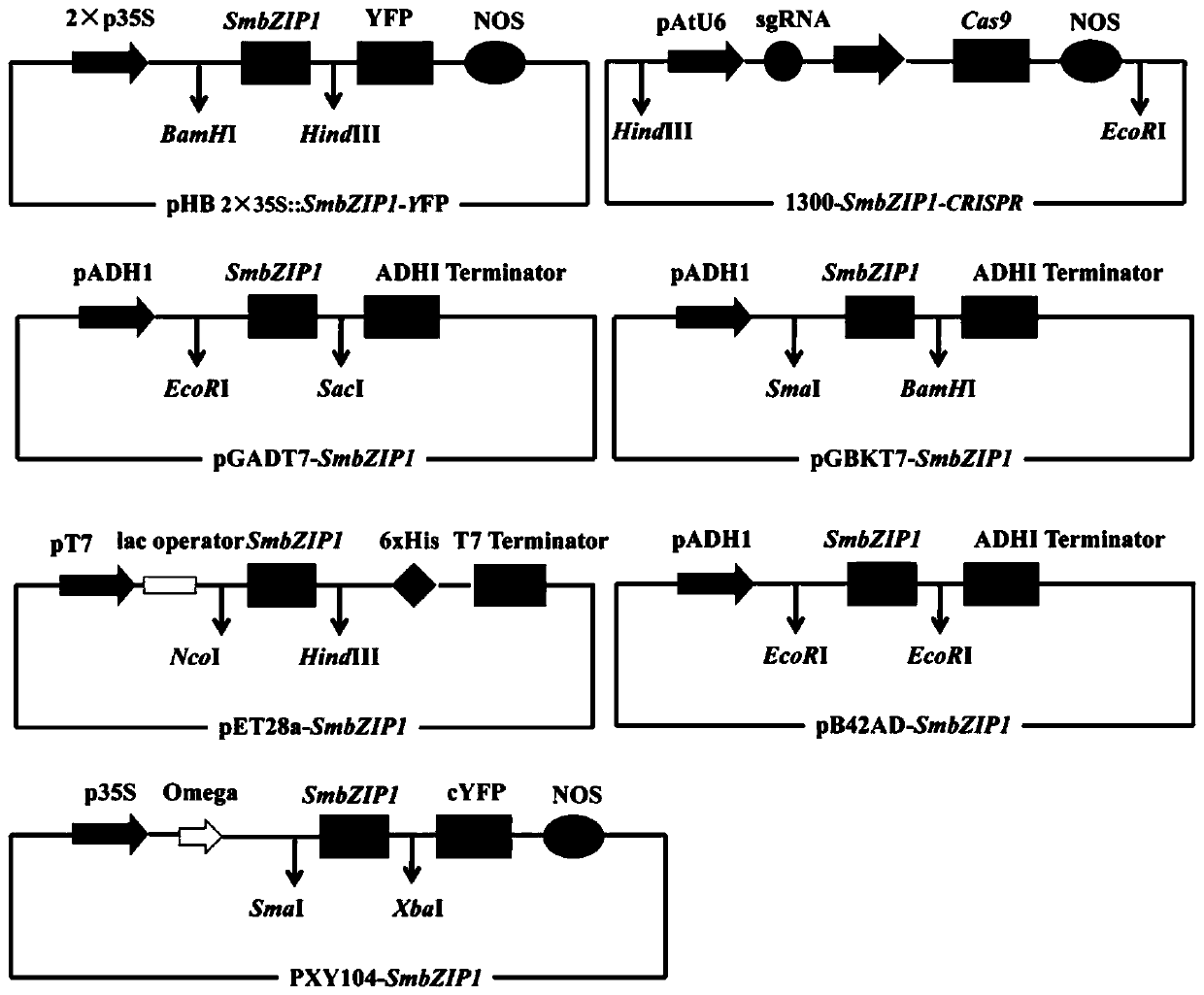
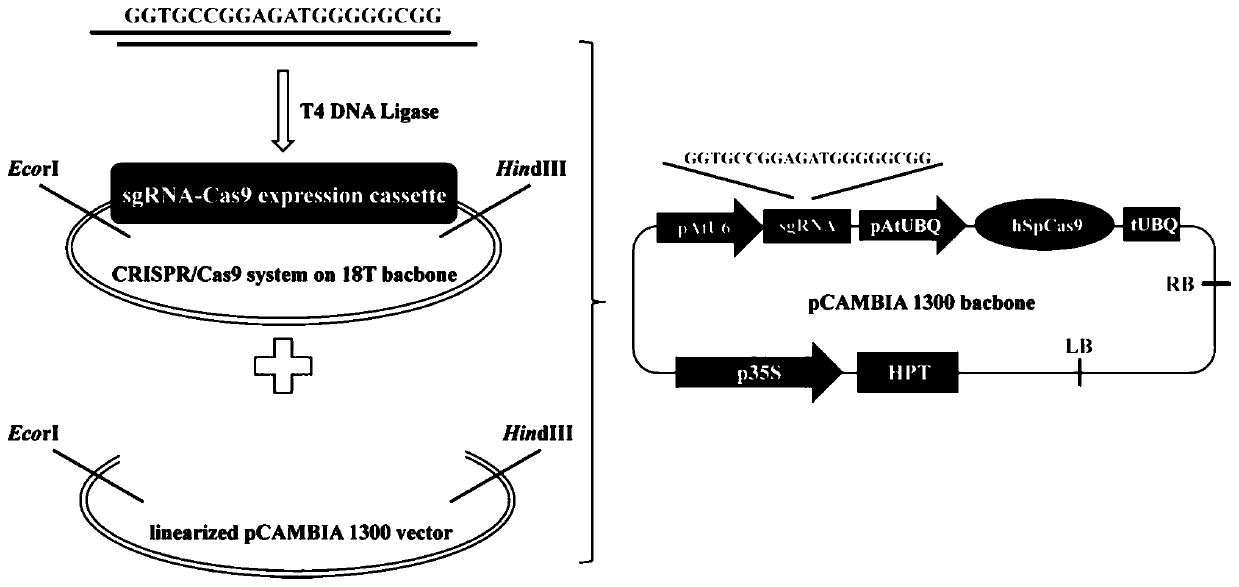
SmbZIP1 gene in increasing content of salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza and application thereof
The invention provides a SmbZIP1 gene of the SmbZIP1 gene in increasing the content of salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza and an application thereof. The SmbZIP1 gene with a full length of 474bpis screened from a salvia miltiorrhiza yeast library by a yeast two-hybrid screening method; the content of salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza can be increased by overexpression of the SmbZIP1 gene in salvia miltiorrhiza, and the specific method comprises the following steps: constructing the SmbZIP1 gene in a plant overexpression regulation sequence according to a salvia miltiorrhiza SmbZIP1gene sequence to form a plant overexpression vector containing the SmbZIP1 gene; converting the obtained plant expression vector containing the SmbZIP1 gene into agrobacterium rhizogenes; using the transformed agrobacterium rhizogenes strain for genetic transformation and infection of the salvia miltiorrhiza aseptic seedling explant, and taking the root system after infection and detecting to bepositive through PCR, namely overexpression; the invention provides a method for increasing the content of salvianolic acid in hairy roots of salviae miltiorrhizae, a new gap can be opened for solvingthe market situation that salvianolic acid supply is short, and the method has high application value and research value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Influence and application method of different strains on hairy roots of ginseng
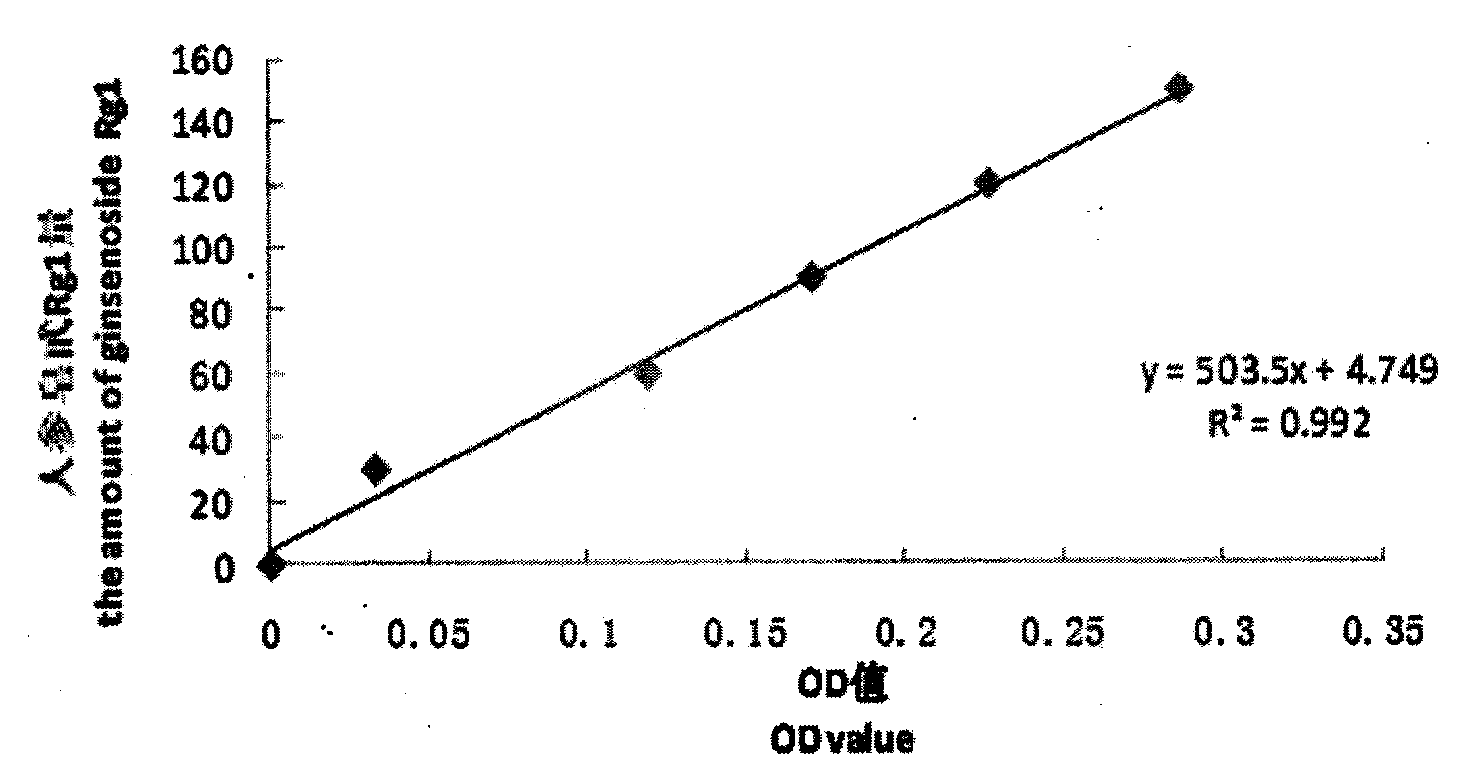
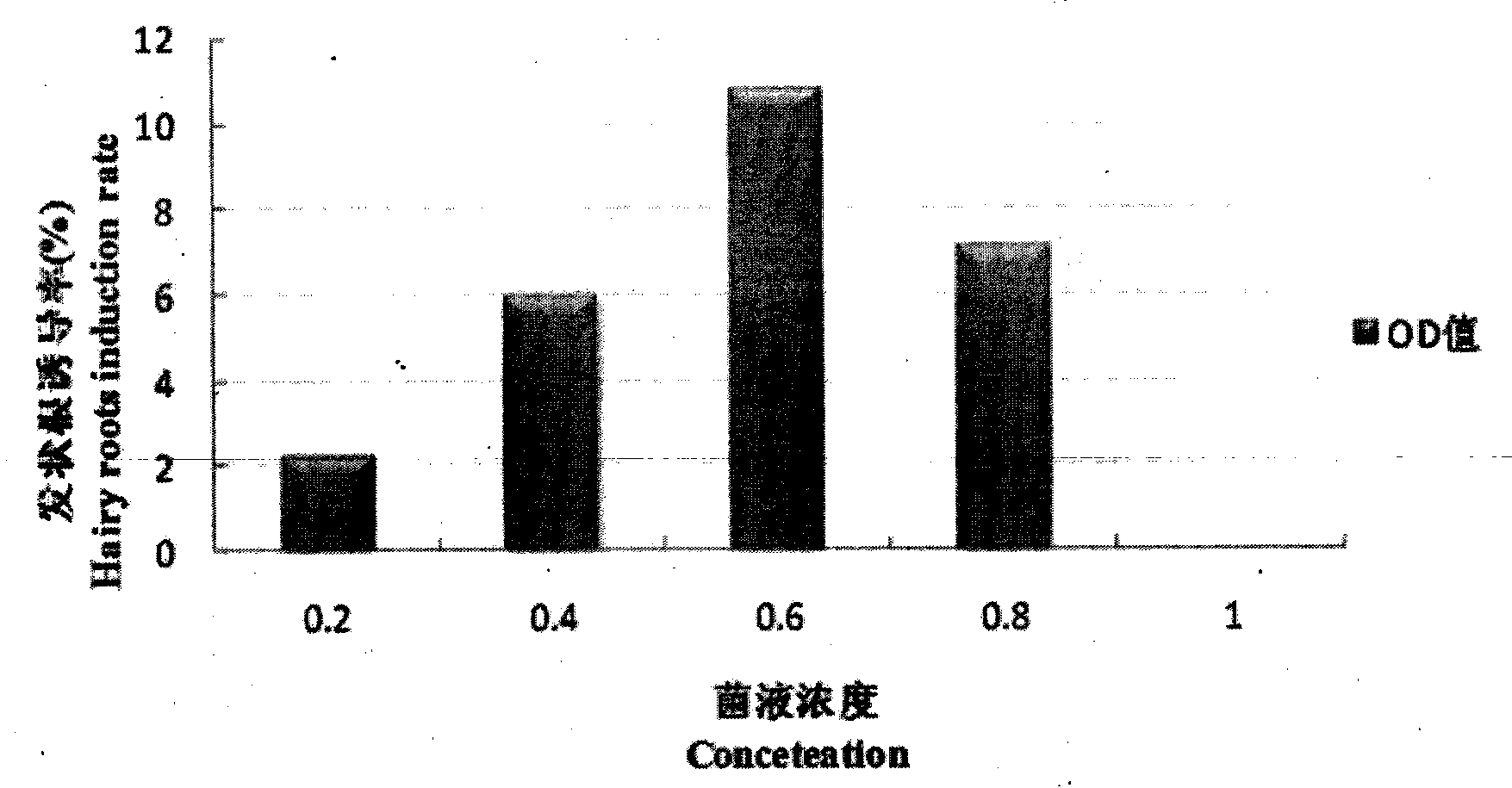
The invention relates to influence and an application method of different strains on hairy roots of ginseng, and belongs to the technical field of crop biology. The process comprises the following aspects: (1) explant treatment; (2) storage and activation of strains; (3) optimization of ginseng hairy root induction conditions; (4) acquisition and identification of ginseng hairy roots; (5) determination of the ginseng hairy root liquid, the solid culture growth amount and the content of total saponins; (6) establishment and condition optimization of a ginseng hairy root regeneration system; (7) study of physiological-biochemical characteristics in the hairy root regenerating plant pathway; and (8) histological observation and karyotype analysis on ginseng hairy roots and culture thereof. According to the influence and application method, ginseng is infected by agrobacterium rhizogene to induce hairy roots, a plurality of influence factors of hairy root induction and the hairy root regenerating plant process can be provided, a novel path is provided to germplasm resource storage and creative storage of ginseng, and a basis is established for ginseng breeding.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for obtaining hairy roots of broccoli
InactiveCN105063084AShort infection timeHigh induction rateVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsBiotechnologyBroccoli raab
The invention relates to a method for obtaining hairy roots of broccoli. The method comprises the step (1) of clipping explants of aseptic seedlings of rapid propagation of the same batch, putting the explants on sterile filter paper, using a sterile needle head to prick 2-8 wounds on the surfaces of the explants, inoculating the explants in an MS culture medium and performing preincubate in the dark to obtain the oreincubate sterile seedling explants; step (2) of using agrobacterium rhizogenes to infect the sterile seedling explants to be cultured, using the sterile filter paper to soak up residual bacterial liquid on the surfaces, inoculating the explants to an MS culture medium adding acetosyringone to culture the explants together in the dark to obtain receptor explants cultured together; and step (3) of transferring the receptor explants cultured together to an MS culture medium adding Carbencillin Disodium to be cultured in the dark, transferring the receptor explants once every 5 days and obtaining the aseptic hairy roots after the explants are transferred from 2 to 5 times. The method is simple and efficient and suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Agrobacterium rhizogenes transformation method for living body growth cone of woody plant
InactiveCN101935672ASuitable for environmental risks such as flutteringAvoid environmental risks such as floatingVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsWoody plantTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses an agrobacterium rhizogenes transformation method for a living body growth cone of a woody plant, which comprises multiple steps of preparing agrobacterium rhizogenes engineering bacterium osmosis transformation liquid, converting and inoculating the living body growth cone, coculturing the growth cone and agrobacterium rhizogenes engineering bacteria, screening resistant sprouts, culturing resistant branches, identifying a transgenic plant, and the like. The invention breaks through two technical bottlenecks of difficult gene transformation and difficult regeneration of the woody plant, is independent of plant genotype and tissue culture, has the advantages of high transformation efficiency, simple operation, low cost, and the like and is suitable for most of woody plants, such as tea trees, and the like, especially the woody plant with full terminal buds.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for cultivating meloidogyne hapla by adopting peanut rooting
ActiveCN105010245AConducive to infection and reproductionHigh reproductive rateAnimal husbandryMeloidogyne incognitaBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for cultivating meloidogyne hapla by adopting peanut rooting. The method comprises the following steps that number 45 seeds are selected, flowered and seeded on an MSB5 culture medium for cultivation; agrobacterium rhizogenes strains A4 are taken for cultivation and activation to achieve a logarithmic growth period; the agrobacterium rhizogenes strains A4 are adopted for infecting the sterile culture 6d flowered number 45 peanut cotyledon for inducing hairy roots; peanut roots with multiple insect galls are selected to be immersed into a NaCLO solution and broken to form a mixed solution; the mixed solution is poured onto combination sieves, wherein the combination sieves are of the types of 40 meshes, 200 meshes, 325 meshes and 500 meshes in sequence from top to bottom, and sterile water is used for spraying and washing, so that the meloidogyne hapla is concentrated to one side; then, a small amount of sterile water is used for washing oversize products from the back faces of the sieves, and liquid is collected into a container to obtain meloidogyne hapla suspension; the meloidogyne hapla suspension is evenly inoculated on a peanut hairy root culture dish, and cultivation is performed to obtain a large number of eggs and second-stage larvae. The method solves the problem that a large amount of purified meloidogyne hapla cannot be obtained easily, and the reproduction rate is high.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Method for preparing polygonin through tissue culture and inducement of hairy roots of giant knotweed
InactiveCN100338083CShorten the production cycleQuality improvementSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationPOLYGONUM CUSPIDATUMRhizobium rhizogenes
A process for preparing the polygonoside from the trichiform root of rhizome polygoni cuspidati by tissue culture and inducing includes such steps as tissue culture of wild rhizome polygoni cuspidati, activating culture of Agrobacterium rhizogene, inducing the trichiform root of rhizome polygoni cuspidati by the T-DNA fragment on rooting plasmide of Agrobacterium rhizogene, optimalizing culture of said trichiform root, and extracting polygonoside from said trichiform root.
Owner:HEBEI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com