Method for preparing polygonin through tissue culture and inducement of hairy roots of giant knotweed
A hairy root and polydatin technology, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve the problems of slow cell growth, hormone-dependent maintenance, poor genetic stability, etc., and achieve the effects of simple extraction operation, short production cycle, stable quality and yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
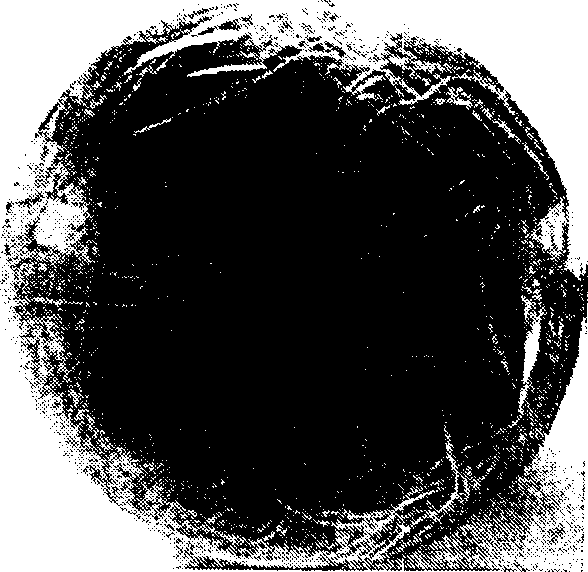
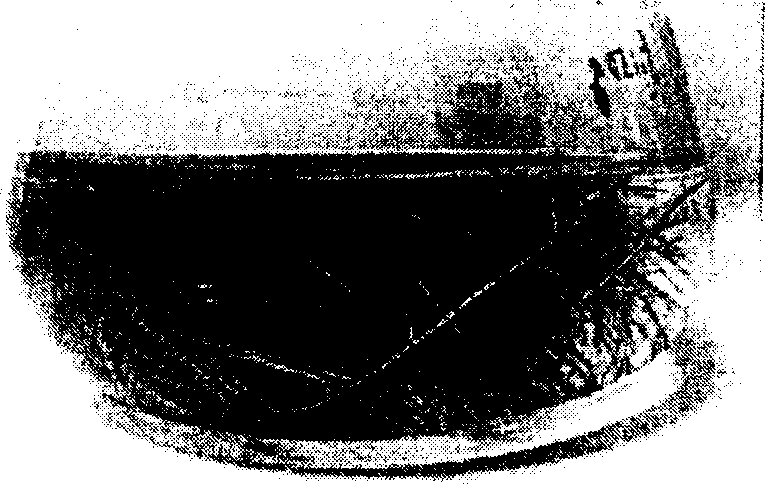
[0039] 1. Select the young buds at the top of the stems of wild Polygonum cuspidatum plants that are healthy, well-developed, free of diseases, insect pests, and fungi. After routine disinfection, place them in a medium that induces clustered bud differentiation: MS+0.05mg / LTDZ+0.5mg / L NAA+0.1mg / L 6-BA. The culture conditions are daytime temperature: 27±1℃, night temperature: 20±1℃; humidity: 60-65%, light intensity: 28μmol / m 2 .s, light time: 14h / d. After 15 days, the clustered seedlings were separated into individual plants, and placed in the growth medium of strong seedlings: MS+0.1mg / L CPPU+1.0mg / LNAA, and the culture conditions were the same as above. One week later, transplant single tissue cultured seedlings into rooting medium: MS+1.0 mg / L NAA+0.5% activated carbon, and the culture conditions are the same as above. The adventitious bud organ proliferation pathway can be used for sustainable rapid propagation, the reproduction coefficient of each bud is 5-7, and a we...
Embodiment 2
[0050] In the step (2), cut the stem section of the aseptic seedling of Polygonum cuspidatum as the infection material. In step (3), at the same time, add 500 μl of Agrobacterium tumefaciens C58 bacterial solution to 100ml YEB culture solution, and Agrobacterium rhizogenes ATCC11325 at 25°C, 140r min -1 , Dark co-cultivation for 22h before use. In step (4), the stem segment explants were soaked in the dual bacteria activation solution for 10min, and placed in MS under dark conditions. 0 CCP cultivated. In step (5), PCR molecular identification is carried out after separating and culturing the hairy roots obtained by stem segment induction; in step (6), the hairy roots obtained by stem segment induction are optimized and cultivated to obtain a large number of proliferating hairy root strains . In step (7), the products of polydatin and resveratrol are extracted, separated and purified from the hairy roots induced by stem segments. In step (8), the contents of polydatin and ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] In the step (2), cut out the sprouts of the aseptic seedlings of Polygonum cuspidatum as infection materials. In step (3), Agrobacterium rhizogenes ATCC11325 was heated at 26°C and 150r min -1 , and used after 24 hours of dark co-cultivation. In step (4), the young shoot explants were soaked in 100ml of activated bacterial liquid, treated in an ultrasonic oscillator for 5-10 sec, and after taking out and absorbing excess bacterial liquid, placed in MS under dark conditions. 0 CCP cultivated. In step (5), PCR molecular identification is carried out after separating and culturing the hairy roots obtained by the sprout induction; in step (6), the hairy roots obtained by the sprout induction are optimized and cultivated to obtain a large amount of proliferating hairy root strains . In step (7), the products of polydatin and resveratrol are extracted, separated and purified from the hairy roots induced by the young shoots. In step (8), the contents of polydatin and resve...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com