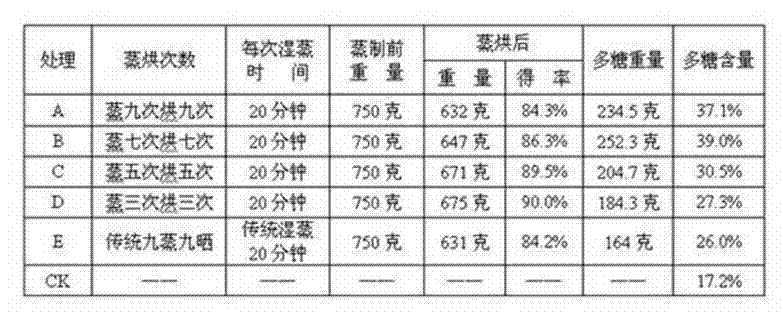
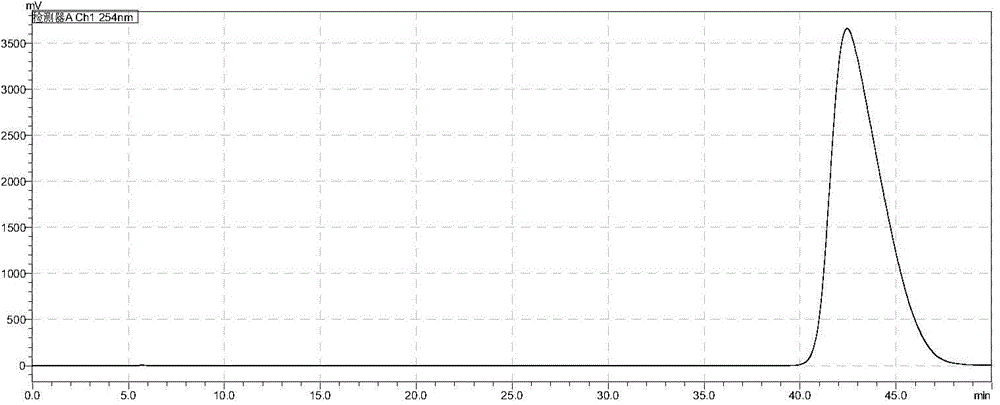
Patents
Literature
517results about How to "High in polysaccharides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dendrobium nobi tissue culturing and planting method
InactiveCN101336605AWith heat retention and fertilityReduce tissue culture time and costSeed and root treatmentHarvestersCulture mediumsAgar
The present invention relates to a tissue culture production technology and a cultivation method of dendrobium nobile, which include the following steps: inserting seeds of dendrobium nobile into a culture medium of N6 + NAA 0.3mg / L + potato juice 20%(V / V) + agar-agar 5g / L to perform cultivation, at 22-25 DEG C, for 10-12 hours of average diurnal light, under 1800-2500lx intensity of illumination, for 15-30 days; transplanting the cultivated seeds to a culture medium of N6 + BA 0.2mg / L + potato juice 20%(V / V) + agar-agar 5g / L to perform cultivation for 25 days; transplanting the cultivated seeds to a culture medium of N6 + NAA 0.2mg / L + banana juice 10%(V / V) + potato juice 20%(V / V) + agar-agar 6g / L for two months to form big seedlings; planting the big seedlings in wood chips which mixed blue stones and decomposed organic fertilizers for hardening-seedling, which begins in every March for one year, and spraying water in time; and transplanting the hardened seedlings to open ground or greenhouse to perform cultivation with a transplanting medium of shale + moss and to fasten the seedlings by cable fasteners, under appropriate humiture and light irradiation, managing with GAP qualitative specification.
Owner:CHISHUI TRUSKY TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE IND DEV
Extracting method for active polysaccharide in higher plant or edible and medicinal fungi
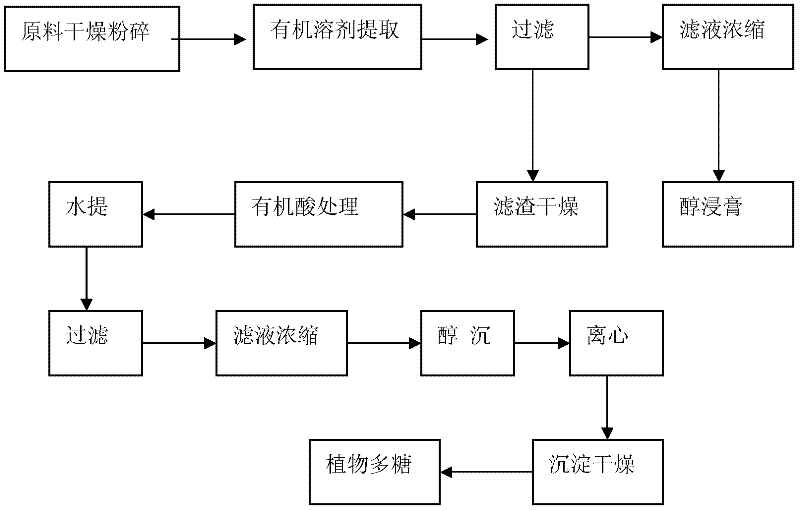
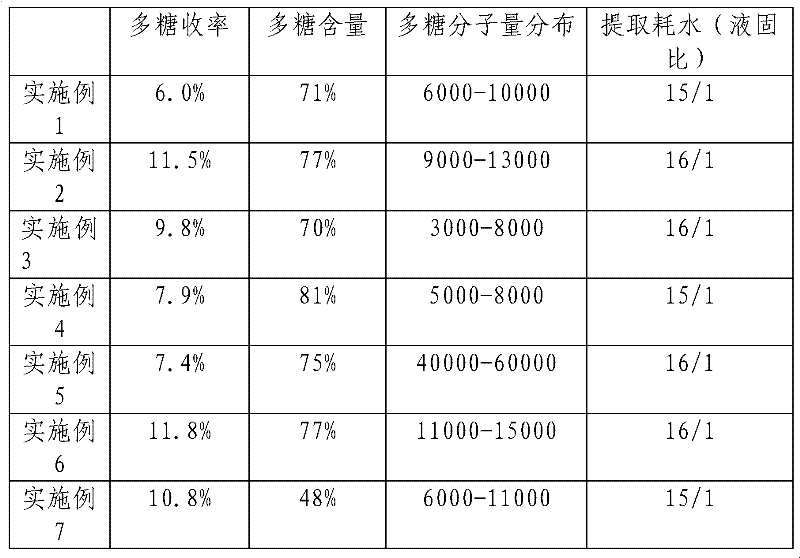
The invention relates to an extracting method for an active polysaccharide in a higher plant or edible and medicinal fungi. The extracting method comprises the following steps: adding an organic acid or an organic or inorganic mixed acid solution in raw materials; heating the raw materials, utilizing the molecules of the organic acid to separate the active polysaccharide from the raw materials, and moderately cutting off glucosidic bonds of macromolecular active polysaccharide of the plant, thereby realizing local degradation; adopting a distilling, filtering or centrifuging method to remove most acid solution in the raw materials, and then washing with an organic solvent, thereby removing few remained acid solutions; extracting by adding water with the volume being 5-15 times that of theraw materials into the raw materials processed with the organic acid, and after concentrating an extracting solution, settling alcohol, thereby obtaining rough active polysaccharide; dissolving the rough active polysaccharide in de-ionized water with the volume being 5-15 times that of the rough active polysaccharide; adjusting pH of the solution to be neutral; and centrifuging, dialyzing or film-separating liquid supernatant, and then concentrating and drying, thereby obtaining an active polysaccharide product with low average molecular weight, narrow molecular weight distribution of the polysaccharide and excellent water solubility. Various defects, such as water consumption and energy consumption caused by technology, low yield of products, and the like, are overcome.
Owner:张劲松
Method for extracting polyoses from bagasse
The invention provides a method for extracting polysaccharides from bagasse, the method is: after degreasing the bagasse, using one or more of cellulase, papain and pectinase at pH 4-6, Hydrolyze at 40-80°C for 0.5-1.5 hours, then treat with ultrasonic waves with a frequency of 59KHz for 0.5-1.5 hours, filter, and finally use ethanol to precipitate polysaccharides in the filtrate. The method of the invention adjusts the type and amount of enzymes and the technological conditions of enzyme treatment and ultrasonic extraction on the basis of the process of extracting fungal polysaccharides, and finds a low energy consumption and high-efficiency method for extracting bagasse polysaccharides.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
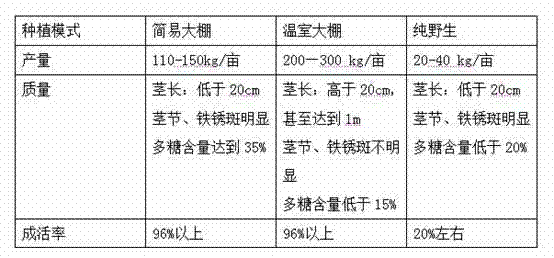
Method for normatively planting dendrobium officinale in simple greenhouse
ActiveCN104322257APure breedGuarantee authenticity of provenanceClimate change adaptationGrowth substratesSeeds sourceGreenhouse
The invention provides a method for normatively planting dendrobium officinale in a simple greenhouse. The method comprises the following steps of selecting and treating a high-quality seed source, selecting a planting foundation, building the simple greenhouse, preparing a planting ground substance, performing fertilization and irrigation management, performing wild-imitating plantation, adjusting and controlling temperature and light illumination, performing scientific harvesting and the like. Due to the fact that a normative planting way is adopted, high-quality dendrobium officinale is obtained while the planting yield is improved, the planted dendrobe is high in quality and stable in yield, and the planting cost is reduced.
Owner:ANHUI MULONGSHAN ECOLOGY TRAVEL DEV
biodegradable polymer composition
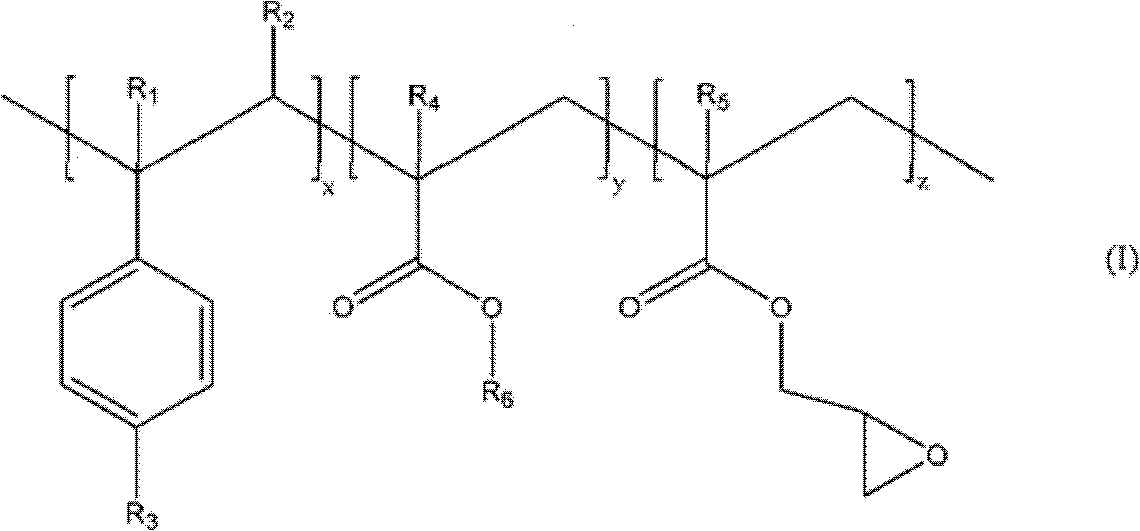
The invention relates to a biodegradable polymer composition comprising the following components (a)-(f) and / or product(s) formed from a reaction between the components: (a) one or more biodegradable polyesters; (b) polysaccharide; (c) polymer having pendant carboxylic acid groups; (d) transesterification catalyst; (e) polyepoxide; and (f) fatty acid sodium salt.
Owner:SETEC
Method for preparing banana juice
InactiveCN102178304AIncrease the juice yieldHigh in polysaccharidesFood scienceAmylaseUltrasonic technology
The invention relates to the field of fruit processing, and discloses a method for preparing banana juice. The method comprises the following steps of: blanching banana fruits, crushing, securing colors, heating to the temperature of between 85 and 95 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 25 to 50 seconds, cooling quickly, and pulping to obtain banana pulp; adding complex enzyme in amount which is 0.05 to 0.09 percent of the mass of the banana pulp, stirring at the temperature of between 42 and 48 DEG C under the condition of ultrasonic waves and under the condition that the pH value is between 4.5 and 4.8, and adding amylase in amount which is 0.002 to 0.02 percent of the mass of the banana pulp, and stirring at the temperature of between 60 and 80 DEG C; and inactivating the enzyme, centrifugating, extracting supernate, and filtering to obtain filter liquor, namely the banana juice. In the preparation method, the banana pulp is subjected to enzymolysis by utilizing the complex enzyme and the amylase and combining the ultrasonic technology, so that the banana juice of which the content of polypeptides and polysaccharides can be obtained, and the juicing rate of the banana juice is improved simultaneously.
Owner:HAINAN STAND BIO TECH
Ganoderma lucidum mycelia powder production process
InactiveCN102835254ARealize automated productionHigh in polysaccharidesHorticulturePlant ingredientsHypsizygusHypha
The invention provides a ganoderma lucidum mycelia powder production process which comprises the following steps of: (1) making grain culture mediums; (2) preparing liquid strains; (3) inoculating the grain culture mediums; (4) sending bottles with inoculated strains into a mycelia growth room; (5) sending the bottles into a bottle digging workshop after the bottles of culture mediums are full of mycelia and digging the mycelia out of the bottles; (7) drying the mycelia in a hot air dryer; (7) grinding the dried corn mycelia, wheat mycelia and soybean mycelia into coarse powder in a proportion of 58-62%: 34-36%: 4-6%; (8) placing the ground coarse powder into a mixing agitator, adding water to agitate evenly and puffing after the water content is up to 10%, wherein the puffing temperature is controlled within 109-111 DEG C; and (9) sending the puffed granular mycelia into an ultra-micro grinder to grind into 150-mesh powder, and packing to obtain finished products. The ganoderma lucidum mycelia powder produced by the method is good in taste and easy to digest and has the advantages of adjusting the immunity and improving the anti-hypoxia capability of organisms.
Owner:YANTAI LONGYU GANODERMA LUCIDUM BIOLOGICAL DEV
Production and cultivation of glossy ganoderma with tea branch, tea, stem material
The invention relates to a production process method for mythic fungus cultivation by tea branches, tea and peduncle-replaced materials. The production process method is characterized in that the proportions are as follows: 33-53% of tea branches, 17-27% of peduncles, 18-48% of wheat bran, 1-2% of brown sugar, 0.5-1% of gypsum and 0.1-0.5% of calcium superphosphate. A plurality of wasted tea branches generated during the cutting process in tea garden, tea and peduncles in the tea making process are sufficiently utilized; furthermore, special inducible factors such as tea polysaccharides, vitamin, trace elements, etc. that are rich in the tea branches and tea peduncles can be utilized to produce the mythic fungus with the 1.5-2.5% of the content of the tea polysaccharides which is higher than that of the current mythic fungus cultivated by the replacing material such as tree sawdust, cotton seed shell, etc. by 24.5-35.8%; meanwhile, the tea can prompt the synthesis of extracellular polysaccharide of mythic fungus, improves the quality and medicinal efficacy of the mythic fungus, cultivates the mythic fungus by the tea branches, tea and peduncle-replaced material, increases new replacing material for the mythic fungus cultivation, prompts the development of Chinese mythic fungus production, and is beneficial to the execution of the Chinese natural forest protection engineering.
Owner:AGRI ECOLOGY INST FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
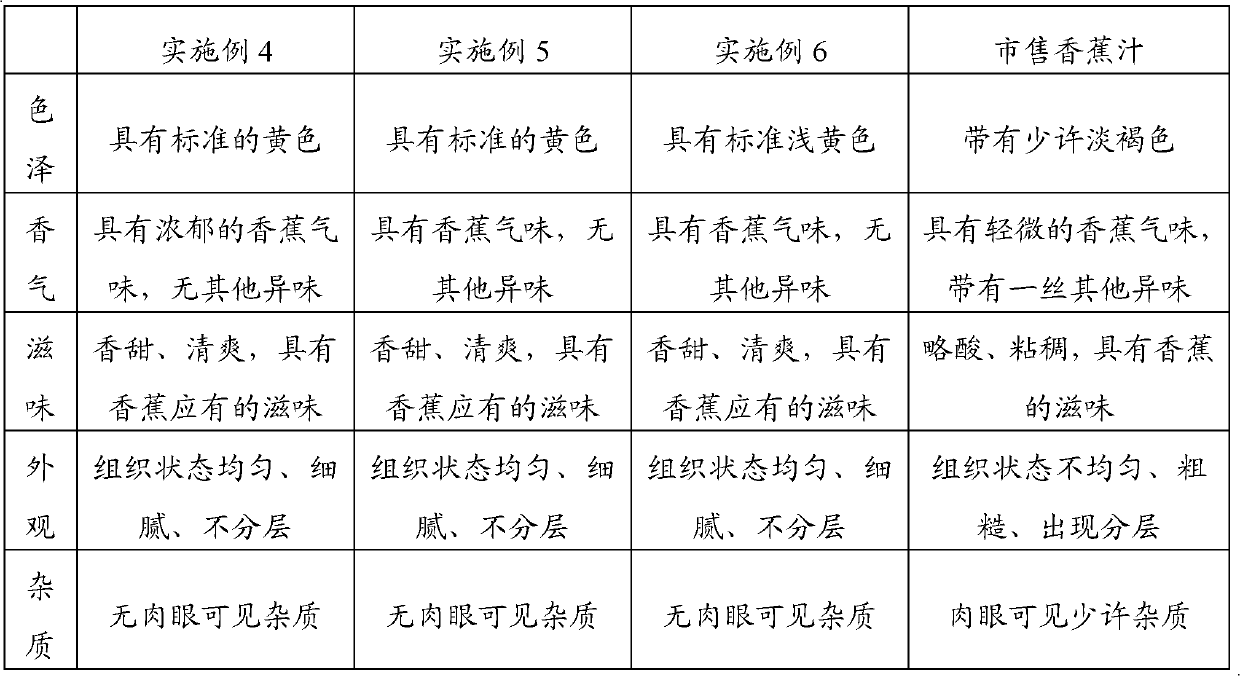
Fresh dendrobium officinale American ginseng particle and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103230538AReduced drying processAvoid breakingNervous disorderMetabolism disorderFiltrationAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a fresh dendrobium officinale American ginseng particle and a preparation method thereof. The weight proportion of dendrobium officinale to American ginseng is (1.5-3.0): (0.8-2.0), wherein the dendrobium officinale is fresh and the American ginseng is dry. The method comprises the following steps of: grinding, filtration, extraction, drying and granulation. The fresh dendrobium officinale American ginseng particle has the beneficial effect that fresh dendrobium officinale is used as raw materials for direct processing, so that the traditional drying process of the dendrobium officinale is saved and the effective constituents are not easy to be destroyed; the obtained product has high polysaccharide content and the yield is higher than that of the traditional process, so that the advantage of the fresh dendrobium officinale American ginseng particle is more obvious. Moreover, as being rich in dendrobium officinale chlorophyll, the product has light green color after brewing; and chlorophyll is taken as a mark to indicate whether the nutritional ingredients are destroyed or not in the product processing process, the product follows the principle of low temperature and quick speed in the whole processing process and then the nutritional ingredients including the dendrobium officinale chlorophyll are completely retained, so that the product has light green color and natural smell after brewing, and to the point, the similar products on the market cannot achieve the effect.
Owner:浙江亚林生物科技股份有限公司
Method for extracting ganoderma lucidum spore polysaccharide
ActiveCN1483743AEasy to pick upHigh in polysaccharidesBulk chemical productionGanoderma pseudoferreumChemistry
The present invention relates to a method for extracting ganoderic spore polysaccharide. It is characterized by that firstly, it uses CO2 supercritical extraction method to extract ganoderic spore oil for another application, and makes the residue obtained after the ganoderic spore oil is extracted undergo the processes of removing fat, water extraction, alcohol precipitation, filtration and drying so as to obtain the invented ganoderic spore polysaccharide.
Owner:NANJING ZHONGKE GRP CORP LTD
Enzymatic extraction method for auricularia auricula polysaccharides
InactiveCN102060934AHigh yieldHigh purityAntibacterial agentsMetabolism disorderAgaricActivated carbon
The invention discloses an enzymatic extraction method for auricularia auricula polysaccharides, which comprises the following steps of: mechanically and coarsely grinding dried auricularia auricula, sieving, mixing according to a material-to-water ratio of 1:(50-200), and extracting at the temperature of between 35 and 50 DEG C and the pH of between 5.0 and 9.0 under the action of chitinase for 60 to 180 minutes, wherein the addition amount of the chitinase is 100 to 600U / g; raising the extraction temperature to be between 80 and 95 DEG C, extracting for 60 to 180 minutes to obtain extract, and centrifuging to obtain supernatant and precipitates; and adding ethanol into the supernatant to precipitate polysaccharides, performing centrifugal separation to obtain precipitates, dissolving the precipitates in water, concentrating to remove residual ethanol, adding a mixture of diatomite and activated carbon into concentrated solution, mixing, fully stirring, filtering, performing membrane filtration on filtrate by using a polysulfone membrane of 30 to 100kD, collecting macromolecular concentrated solution which does not filter through the membrane, and drying the macromolecular concentrated solution to obtain the auricularia auricula polysaccharides. The prepared products have high purity and bioactivity; and the polysaccharide content is over 40 percent.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Dried manyflower solomonseal rhizome and production method thereof
The invention relates to dried manyflower solomonseal rhizome and a production method thereof and belongs to the technical field of food processing. The dried manyflower solomonseal rhizome is characterized by being made of manyflower solomonseal rhizome by cleaning, slicing, repeated steaming and drying, mildew-proof treatment and vacuum-packaging sequentially. Modern processing equipment and advanced technology are applied, and the folk traditional 'multi-steaming and multi-sun-curing' method is optimized. Processing time is shortened, processing cost is reduced, work efficiency is increased, product quality is increased, product storage is prolonged, and a ready-to-eat health food of dried manyflower solomonseal rhizome is provided for modern people.
Owner:LISHUI ACAD OF FORESTRY
Method for extracting polysaccharide of dendrobium officinale
The invention discloses a method for extracting polysaccharide of dendrobium officinale. The method specifically comprises the following steps of uniformly mixing dendrobium officinale powder and a deep eutectic solvent according to a material and liquid ratio of 1g to (30 to 50)mL, wherein the ratio of hydrogen bond receptor to hydrogen bond donor is 3 to (1 to 18)mol / mol; adding 4 to 8mg / mL of at least one of cellulase and pectinase; extracting for 90 to 120min at the temperature of 30 to 60 DEG C; separating and purifying the extracting solution, so as to obtain the polysaccharide of dendrobium officinale. Compared with the traditional enzyme type water extracting method, the method has the advantages that by using the enzyme-assisted deep eutectic solvent to extract, the volatility islow, the stability is high, and the reaction system is mild; the content of impurities in the extracting solution is reduced, the loss of the solvent is reduced, the purifying burden is decreased, theextracting rate of polysaccharide is increased by 10% or above, and the content of polysaccharide is increased by 10% or above.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of cordyceps militaris active polysaccharide
InactiveCN105085704AHigh in polysaccharidesLight colorOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCordycepsDEAE-Sepharose
The invention relates to cordyceps militaris active polysaccharide prepared by a method comprising the following steps: performing ultrafine grinding on cordyceps militaris sporophores, then extracting with boiling water, and collecting supernatant fluid; and concentrating the supernatant fluid, then adding ethanol for deposition, passing a deposited part through a DEAE-sepharose column, desalting a part of 0-0.5N, and then performing freeze-drying. The invention also relates to an application of a cordyceps militaris extract in preparation of an anti-tumor activity product.
Owner:上海瑞丰农业科技有限公司 +2
Method for extracting skunk bush polysaccharide by zymohydrolysis
The invention provides a method for extracting cornel polysaccharide through enzymolysis. The method comprises the following steps that cornel dry flesh is crushed to make cornel dry powder; distilled water is added with the mass being 15 to 60 times than that of the cornel dry powder, and an enzyme are added so as to carry out enzymolysis at a temperature of between 35 and 60 DEG C and a pH value of between 3.5 and 7.0; after the enzymolysis is finished, enzyme inactivation is carried out; an extraction solution is separated and purified so as to obtain a cornel polysaccharide extract; the enzyme is a mixture comprising one sort or more than two sorts of (1) cellulase, (2) papain, (3) pectinase and (4) amylolytic enzyme; and the dose by mass of the enzymes accounts for 0.1 to 24 percent of the mass of the cornel dry powder. The method has the advantages that compared with the prior hot water extraction method, the method can increase the extraction rate of cornel polysaccharide by 10 to 50 percent and the content of cornel polysaccharide by 15 to 80 percent; and due to preventing the influence of the prior hot water extraction, acid extraction or alkaline extraction on the structure of polysaccharide, and adopting enzymolysis treatment to extract cornel polysaccharide, the method has the advantages of moderate conditions, easy removal of impurities, furthest maintained activity of polysaccharide, and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY ACAD
Hericium erinaceus liquid fermented beverage and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104187947AHigh in polysaccharidesHigh exopolysaccharide contentCultivating equipmentsFood preparationMycelial cordCorn flour
The invention discloses a hericium erinaceus liquid fermented mash beverage and a preparation method thereof. A special strain of the hericium erinaceus liquid fermented mash is prepared from a culture medium containing a liquorice matrix, wherein the culture medium of the hericium erinaceus liquid fermented mash contains jujube, malt, chrysanthemum, medlar, corn flour and / or soybean cake powder. Every 100mL of the hericium erinaceus liquid fermented mash contains no less than 25g of fresh hericium erinaceus mycelia. Moreover, the hericium erinaceus liquid fermented mash beverage contains hericium erinaceus fruiting body water extract, wherein a weight ratio of the hericium erinaceus liquid fermented mash to the hericium erinaceus fruiting body water extract is 4: 1. The hericium erinaceus liquid fermented mash beverage disclosed by the invention is rich in nutritional ingredient, and the polysaccharide content in the hericium erinaceus mycelia obtained from fermentation is apparently higher than that in a hericium erinaceus fruiting body. The hericium erinaceus beverage preparation method is short in cycle, high in output and low in cost, and has an actual application value.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Extraction and purification method of bioactive polysaccharides in dendrobium huoshanense
The invention discloses an extraction and purification method of bioactive polysaccharides in dendrobium huoshanense. The method comprises the following steps: crushing the dendrobium huoshanense, then adding water, performing microwave constant-temperature extraction, and performing vacuum concentration on extract solution till the relative density is 110-1.30 so as to get concentrated solution;adding ethanol into the concentrated solution, standing, and further performing centrifugation to get precipitate; adding the water into the precipitate for dissolution, enabling the solution to passthrough an ultrafiltration membrane in the molecular weight of 100KD under the pressure of 0.35MPa, collecting trapped fluid, then enabling the trapped fluid to pass through the ultrafiltration membrane in the molecular weight of 300KD under the pressure of 0.35MPa, and collecting passing fluid; and performing the vacuum concentration on the collected passing fluid, and drying to get a polysaccharide extract from the dendrobium huoshanense. By adopting the method, the extraction time can be shorted, and the yield of a crude extract can be improved from 20% to about 35% under the same extraction times; and the yield of the polysaccharides from the dendrobium huoshanense after purification can be improved from about 5% to 10-15%, and the content of the polysaccharides from the dendrobium huoshanense can be improved from 40% to above 60%.
Owner:JIUXIANZUN HUOSHAN DENDROBIUM CO LTD
Process for half bionic extracting preparing hedgehogt fungus crude polysaccharose
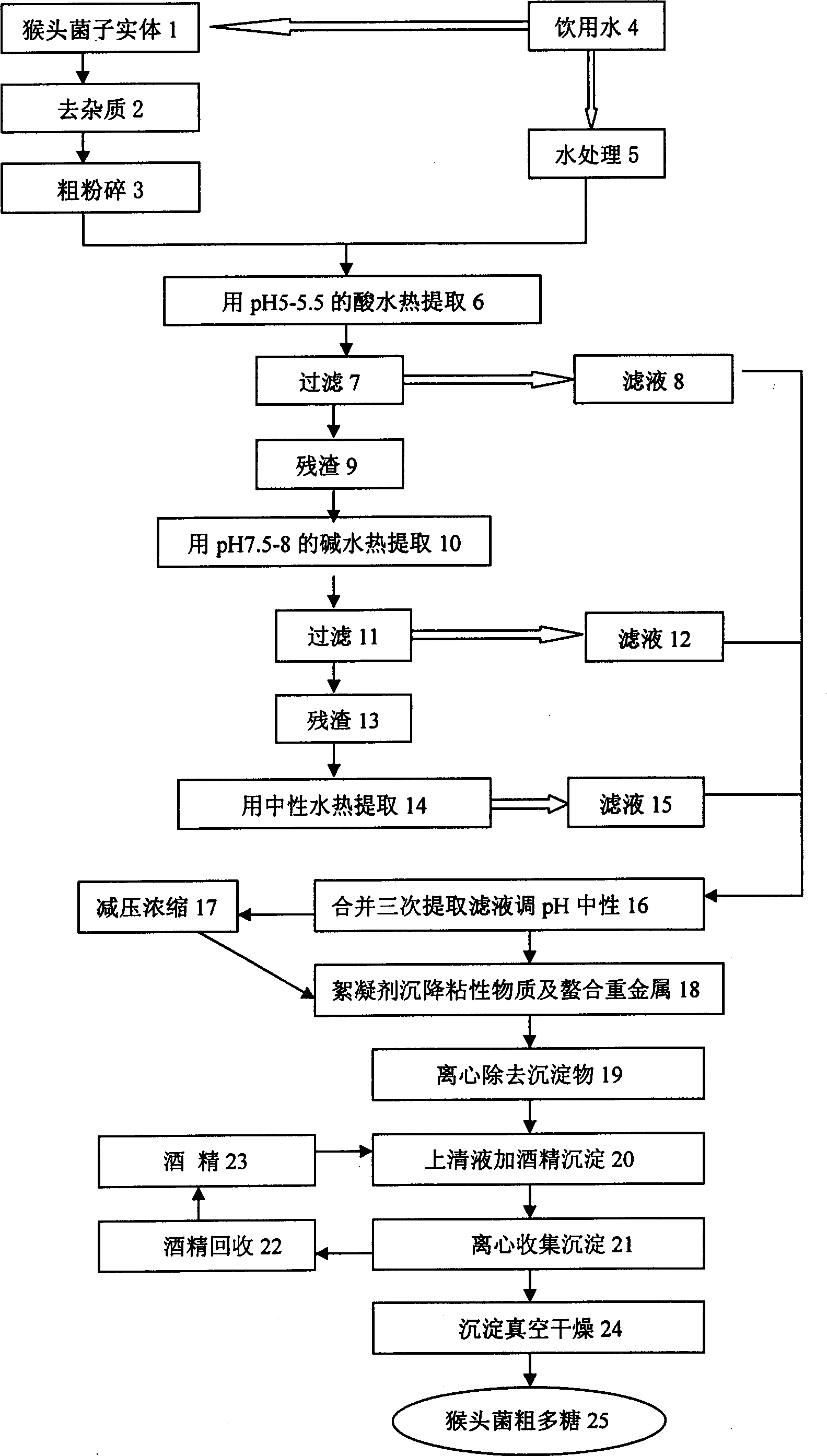
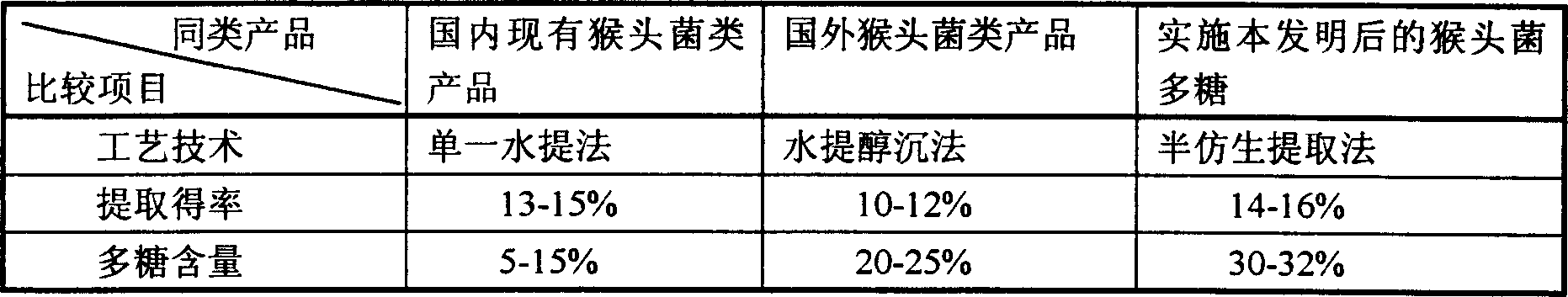
A process for preparing the crude polyose from hedgehog fungus by semi-bionic extracting method features that the semi-bionic extraction instead of water extraction and alcohol deposition is used, and the flocculating deposition is used to remove viscose impurities and residual heavy metal, resulting in higher output rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for processing prepared rehmannia root
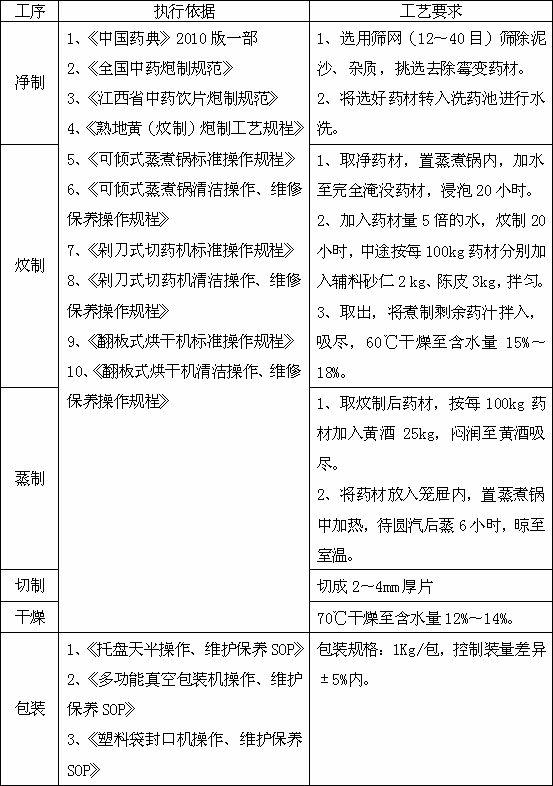
InactiveCN102240340AMoisturizing and softHigh in polysaccharidesNervous disorderMetabolism disorderMedicineRadix Rehmanniae Preparata
The invention belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicines, relating to a process for processing prepared rehmannia root which is Chinese herbal pieces for decoction. The process comprises the following steps of: soaking rehmannia root for 12 to 36 hours, and then taking out and draining; adding water 5 to 8 times more than the rehmannia root, and stewing for 6 to 24 hours; adding 0.5 to 4kg of amomum fruit and 1 to 6kg of tangerine peel into every 100kg of the stewed rehmannia root, continuing to stew for 6 hours, airing till the surfaces of the rehmannia root is slightly dry, and mixing with the remaining decoction; after the decoction is completely absorbed, drying at a temperature within a range of 60-80 DEG C till the moisture content is 12% to 20%, adding 10 to 30g of yellow rice wine into every 100kg of a dried product, moistening until the yellow rice wine is completely absorbed, steaming for 4 to 12 hours, pouring out, and airing to the room temperature; cutting the obtained rehmannia root into slices of 2 to 4mm in thickness, and drying at a temperature within the range of 60 to 80 DEG C till the moisture content is 8% to 15%, thereby obtaining the prepared rehmannia root. The prepared rehmannia root produced in the invention has the characteristics of black and bright surface, moist, soft and flexible texture, brilliantly black section, less smell and sweet taste, and is high in the contents of reducing sugars, polysaccharides and trace elements. The yield of the prepared rehmannia root is 60%-70%.
Owner:胡志方 +1
Special starch syrup for QQ sugar and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103710410AHigh in polysaccharidesSpecial physiological functionFermentationLiquid glucoseFlocculation
The invention discloses a preparation method of special starch syrup for QQ sugar, which comprises the following steps: (1) pulping, and liquefying; (2) performing high-temperature filtration; (3) performing low-temperature filtration; (4) saccharifying; (5) decoloring; (6) performing ion exchange desalination; and (7) concentrating. The special starch syrup for QQ sugar, prepared according to the method, comprises the following sugar components: 0.8-1.2% of glucose, 44-48% of maltobiose, 17-19% of maltotriose and 38-42% of maltotetrose. The invention has the following advantages: (1) fine control is performed on the liquefied liquid glucose components through a special injection and liquefying process, thus obtaining low liquefaction liquid having high DE value; (2) high-temperature deslagging filtration and low-temperature protein flocculation are performed, thereby being more beneficial to impurity removal; (3) a mixed enzyme preparation is added in the saccharifying process, thus regulating and controlling the content of the sugar contents more effectively; and (4) the finished product is high in polysaccharide content, and the content of the sugar components presents a discontinuous ascending ratio, thus having a special physiological function.
Owner:河南飞天生物科技股份有限公司
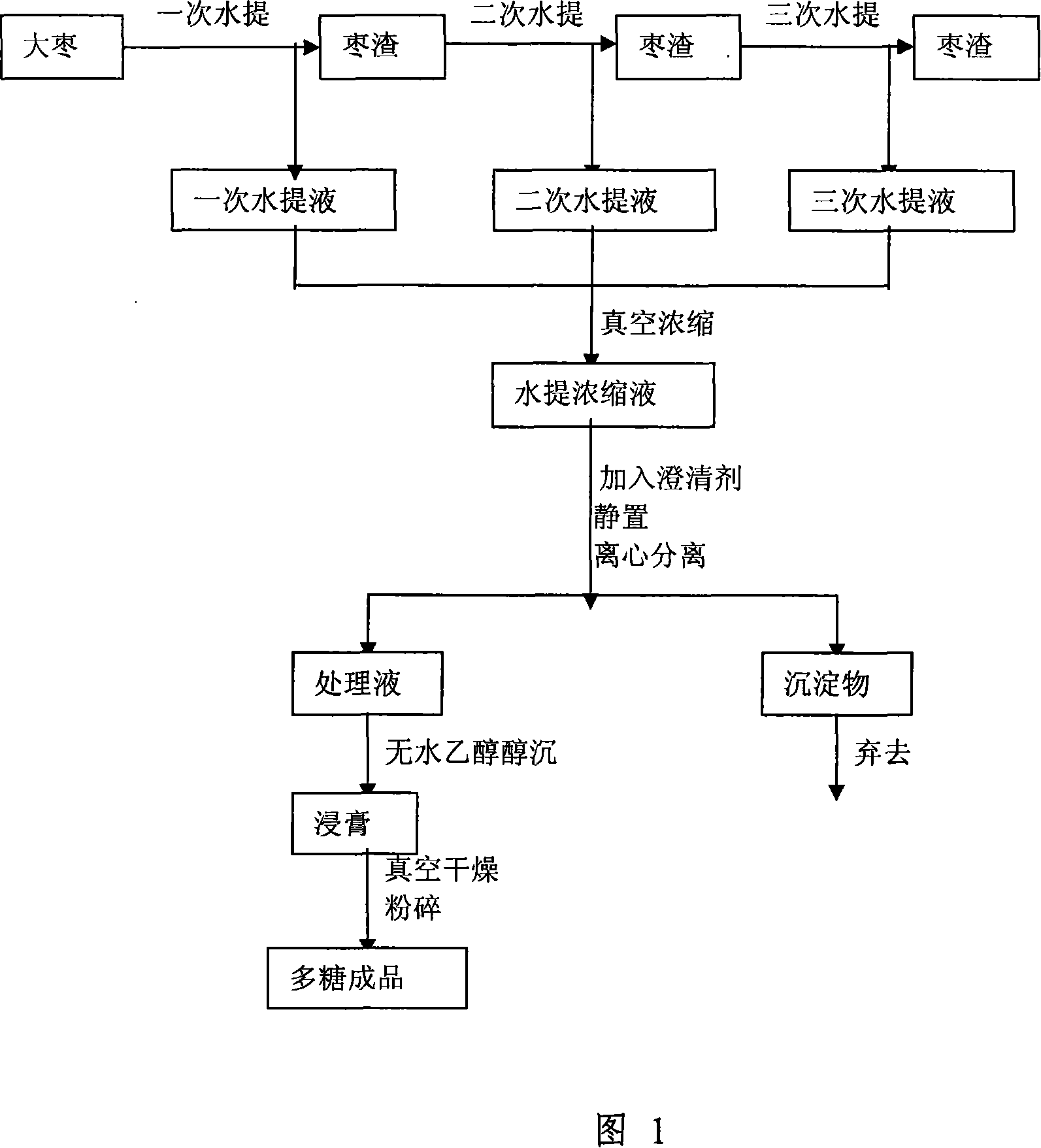
Method for extracting polysaccharide from jujube
The present invention discloses a method tobextract polysaccharide from the jujube. The extraction process is of the following steps: (A) jujube is mixed with water and is extracted for 1 to three times; then the jujube experiences the centrifugal separation and vacuum low-pressure concentration; (B) clarifying agent is added into the jujube mass which is statically placed for centrifugal separation after stirring; (C) the separated sypernatant is added with alcohol, which is more than 70 percent in volume; the alcohol in the sypernatant is deposited overnight, and then the sypernatant experiences centrifugal separation; (D) the solid obtained is dried to get jujube polysaccharides. The jujube polysaccharides obtained through the present invention is more than 40 percent of the original jujube. The whole extraction and separation process involves no toxic and hazardous organic solvents. The present invention is safe and non-toxic. The operation is simple and the consumed time is short. A full green extraction can be achieved through the present invention.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Use of Brassica rapa polysaccharide in preparation of anti-hypoxia drugs
InactiveCN101524389AGood effectPositive and significant anti-hypoxia effectAntinoxious agentsPlant ingredientsBrassica rapaBirdsrape Mustard
The invention relates to a usage of Brassica rapa polysaccharide which is extracted from Brassica rapa plants in the preparation of anti-hypoxia drugs, the average molecular weight of the Brassica rapa polysaccharide is 30,000-80,000, and the total polysaccharide content is 60-95 percent by weight. The Brassica rapa polysaccharide can be prepared into pharmaceutical acceptable formulations, such as granules, oral liquid, capsules, tablets, injections or powder. The Brassica rapa polysaccharide obtained by the method has available raw materials, simple method, low production cost, high polysaccharide content in the product, stable quality and easy control. The Brassica rapa polysaccharide has obvious anti-hypoxia activity. The Brassica rapa polysaccharide can be used for preparing the drugs or health care foods for prevention or / and treatment of low oxygen, hypoxia, hemic hypoxia, circulatory hypoxia and toxic hypoxia.
Owner:西藏自治区高原生物研究所
Method for extracting, separating and purifying Arillus longan polysaccharide
The invention provides a method for extraction, separation and purification of longan pulp polysaccharide. The method comprises the following steps: longan is dried, peeled and decored to obtain longan pulp, the longan pulp is purified by the combination of ultrasound leaching and enzyme hydrolysis. The method has the advantages of high extraction rate of the longan pulp polysaccharide, unnecessary high temperature, low energy consumption, short extraction time, high protein removal efficiency, low loss rate of polysaccharide, and simple operation, reduces the adding amount of chemical reagents, namely chloroform and poisonous reagents of normal butyl alcohol and the like, and reduces extraction and purification cost of the polysaccharide. The yield of the longan pulp polysaccharide is 7.0 percent, the longan pulp polysaccharide content is as high as 64.4 percent, the protein removal rate is 86.7 percent, and the loss rate of the polysaccharide is as low as 4.9 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Novel method for extracting seaweed intermediate by enzyme process
ActiveCN104529570AEfficient decompositionQuick breakdownOrganic fertilisersHas active ingredientAlgal polysaccharides
The invention relates to a novel method for extracting a seaweed intermediate by an enzyme process, which comprises the following steps: sufficiently cleaning and immersing dry Laminaria digitata, adding into an acidic solution, and stirring uniformly to obtain a mixture A; dissolving a composite acidic enzyme in water, and adding into the mixture A to perform primary stirring extraction, thereby obtaining a mixture B; dissolving an inorganic alkaline compound and a composite alkaline enzyme in water, and adding into the mixture B to carry out secondary stirring extraction, thereby obtaining the mixture C; and dissolving a preserving agent in water, adding into the mixture C, and stirring uniformly to obtain the seaweed intermediate. The method for preparing the seaweed intermediate is efficient, quick, mild, comprehensive, safe and harmless. Compared with the traditional acid-alkali extraction technique, the extraction efficiency is enhanced by 50% above, the algal polysaccharides content is enhanced by 50-100%, the alginic acid content is 3.5-4.0, the effect of the seaweed intermediate product is obviously enhanced, and all the effective components in the seaweeds are reserved in the product, thereby implementing complete-effect addition in deed.
Owner:山东筱萤生物科技有限公司
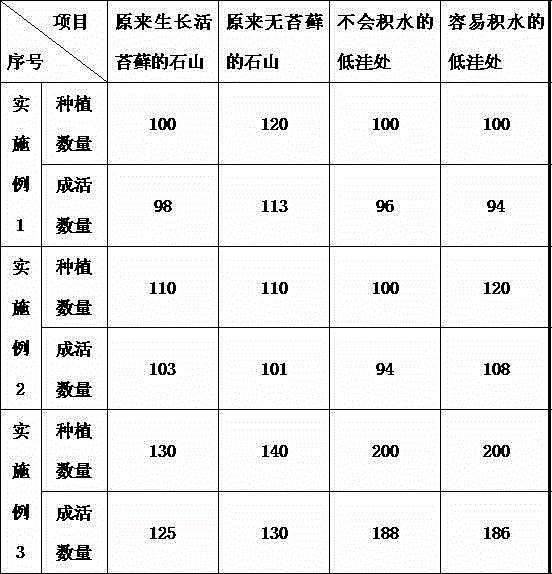
Method for planting dendrobium officinale on rocky desertification land
InactiveCN103999746AImprove survival rateIncrease productionCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationLand resourcesEcological environment
The invention discloses a method for planting dendrobium officinale on rocky desertification land. The method comprises the steps of selecting planting environments on the rocky desertification land, and respectively planting the dendrobium officinale according to the planting environments. 1, for the planting environment of a rocky mountain with live mosses grown originally, the dendrobium officinale seedlings are directly planted in the mosses; 2, for the planting environment of a rocky mountain without mosses originally, the roots of the dendrobium officinale are wrapped with mosses, and the roots of the dendrobium officinale are adhered to rock walls together with the mosses by water-retaining adhesive; 3, for the planting environment of a low-lying area without ponding, a culture substrate which is 8-12cm thick is directly paved, and the dendrobium officinale seedlings are planted into the culture substrate; 4, for the planting environment of a low-lying area easy to water, the low-lying area is filled up or filled to have a depth of 25-35cm by stones as a drainage layer, then a culture substrate is paved, and the dendrobium officinale seedlings are planted into the culture substrate. According to the method, the rocky desertification land resources are fully used, the ecological environment is improved, and the grown dendrobium officinale is high in yield and good in quality.
Owner:湖南崀霞湘斛生物科技有限公司
Method for cultivating triploid dendrobium huoshanense by crossbreeding method of tetraploid plants and diploid plants
ActiveCN104396722AIncrease productionHigh in polysaccharidesPlant genotype modificationBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTProtoplast
The invention discloses a method for cultivating triploid dendrobium huoshanense by a crossbreeding method of tetraploid plants and diploid plants. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dendrobium huoshanense species which are from different producing areas and have characteristics of good stress resistance, rapid growth, thick stalk, long stem, many tillers, low fiber content and high active ingredient content are preferably selected as polyploidy cultivated original plant parents; (2) seeds of the different species of original plants undergo aseptic sowing in a solid medium so as to obtain diploid protocorms; (3) protoplasts of the different species of diploid protocorms are prepared and cell fusion is carried out; (4) detected tetraploid plants undergo asexual tissue culture so as to obtain tetraploid plant seedlings; (5) the tetraploid plant seedlings undergo hardening-seedling acclimatization and cultivation to flowering; (6) the tetraploid plants and diploid plants undergo artificial pollination and crossbreeding, and fructification is completed to obtain triploid dendrobium huoshanense seeds; and (7) the triploid seeds undergo aseptic sowing and culture so as to obtain a lot of triploid seedlings.
Owner:WEST ANHUI UNIV
Wine-making process
InactiveCN102168002AStrong aromaFull bodiedMicroorganism based processesWine preparationBiotechnologyLees
The invention relates to a wine-making process which mainly comprises the steps of squeezing grape materials, inoculating with yeast to carry out alcohol fermentation, inoculating with lactic acid bacteria to carry out malic acid-lactic acid fermentation, aging, cool stabilizing, filtering, sterilizing, filling and the like. In the process, mannoproteins extracted and produced from the fermentation byproduct wine lees are added three times (i.e. after the materials are squeezed, when the lactic acid bacteria are inoculated, and after cool stabilizing and filtering). The method provided by the invention effectively avoids the precipitation and turbidity in the wine-making process and increases the polysaccharide content. The obtained wine is clear and transparent, has intense scent, can send out the typical variety aroma and the unique alcohol aroma, is full-bodied and has a mellow and coordinated mouthfeel.
Owner:HANGZHOU AUBOCAVES WINE
Chinese yam polysaccharides extract and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101628070AImprove production safetyImprove securityMetabolism disorderImmunological disordersCentrifugationColloid
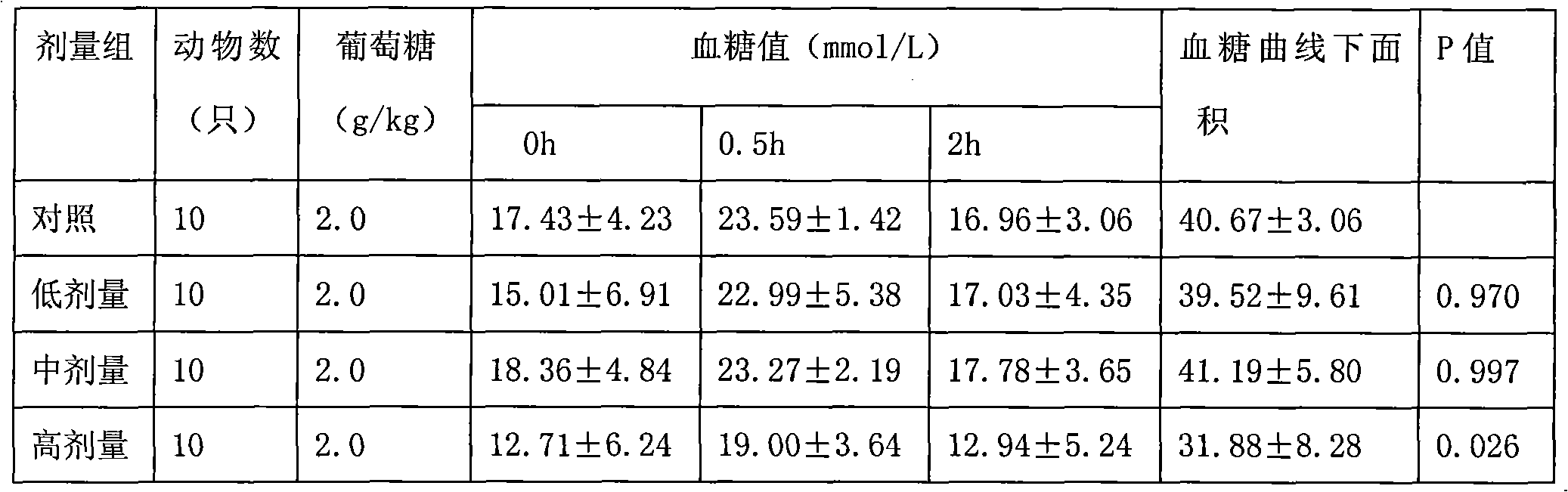
The invention discloses a Chinese yam polysaccharides extract and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: crushing Chinese yam slices, extracting by ethanol, separating by centrifugation, depositing dregs and adding water, stirring, grinding by a colloid grinder, extracting by water, separating by centrifugation, decompressing and concentrating supernatant to prepare liquid extract; depositing the liquid extract by the ethanol, separating by centrifugation, depositing dregs and adding water, stirring and dissolving, separating by centrifugation, and drying liquid extract to prepare the Chinese yam polysaccharides extract, wherein the yield is 10-19 percent. The Chinese yam polysaccharides extract does not contain starch, and the weight percentage content of the Chinese yam polysaccharides extract is 30-61 percent. The Chinese yam polysaccharides extract has the healthcare function of assisting to regulate the blood sugar level and enhancing the immunity, and can be used for preparing medicines or health care products of regulating the blood sugar level and enhancing the immunity.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Dendrobium officinale tissue culture seedling medium
ActiveCN104509438AReasonable collocationNutritional diversityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePhosphateMonopotassium phosphate
Belonging to the technical field of Dendrobium officinale planting, the invention discloses a Dendrobium officinale tissue culture seedling medium, which is composed of the following components: apple puree, banana puree, white sugar, ferrous sulfate, ammonium nitrate, potassium nitrate, magnesium sulfate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, boric acid, glycine, vitamin B1, vitamin B2, sugar amino acid, naphthyl acetic acid, and tap water. The Dendrobium officinale tissue culture seedling medium has the characteristics of reasonable collocation and comprehensive nutrition, can quickly promote rooting and stem growth, increases the Dendrobium officinale polysaccharide content and amino acid content, shortens the culture cycle of Dendrobium officinale, and improves the Dendrobium officinale transplanting survival rate.
Owner:GUANGDONG YIFENG ECOLOGICAL IND CO LTD
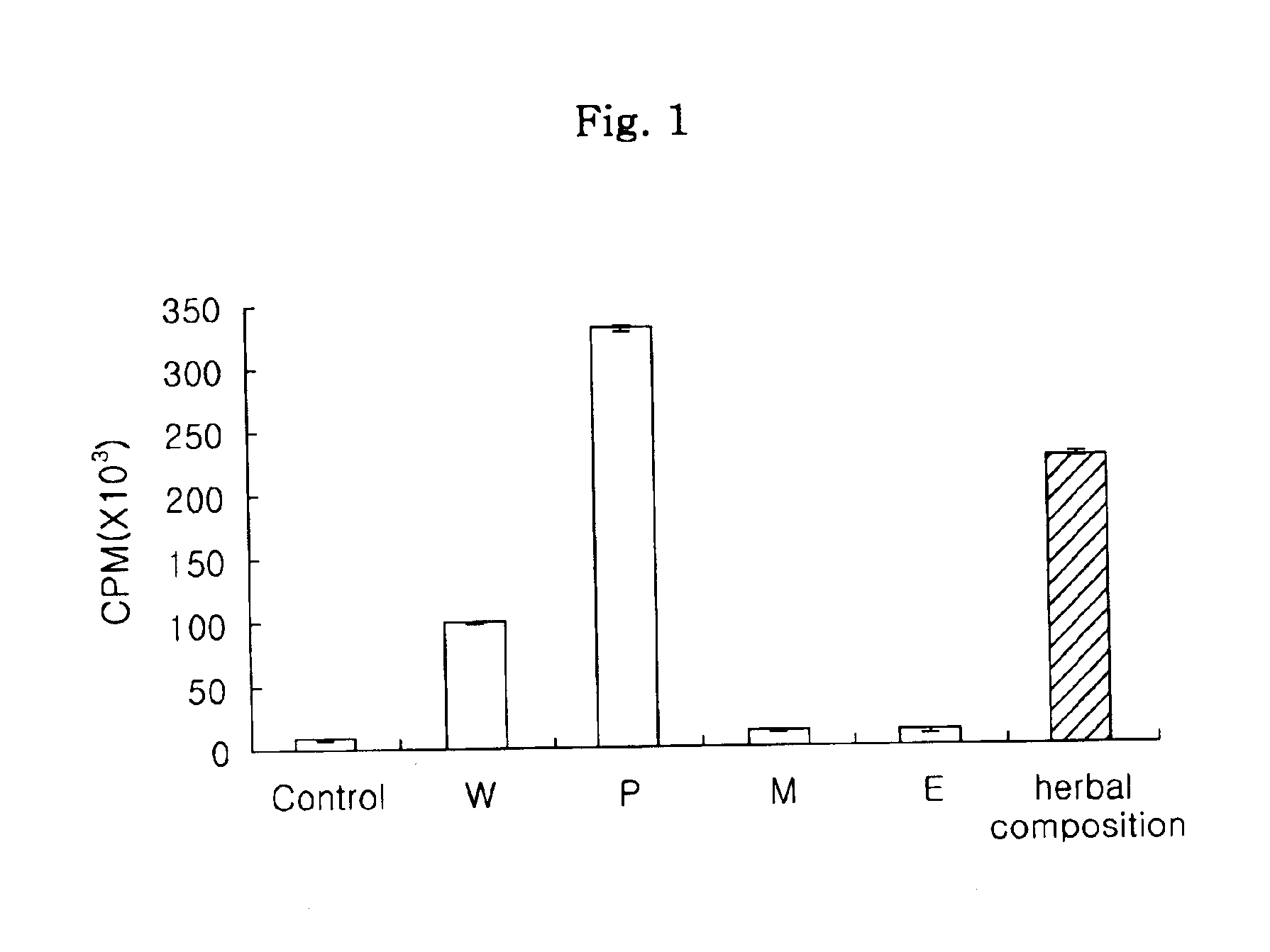
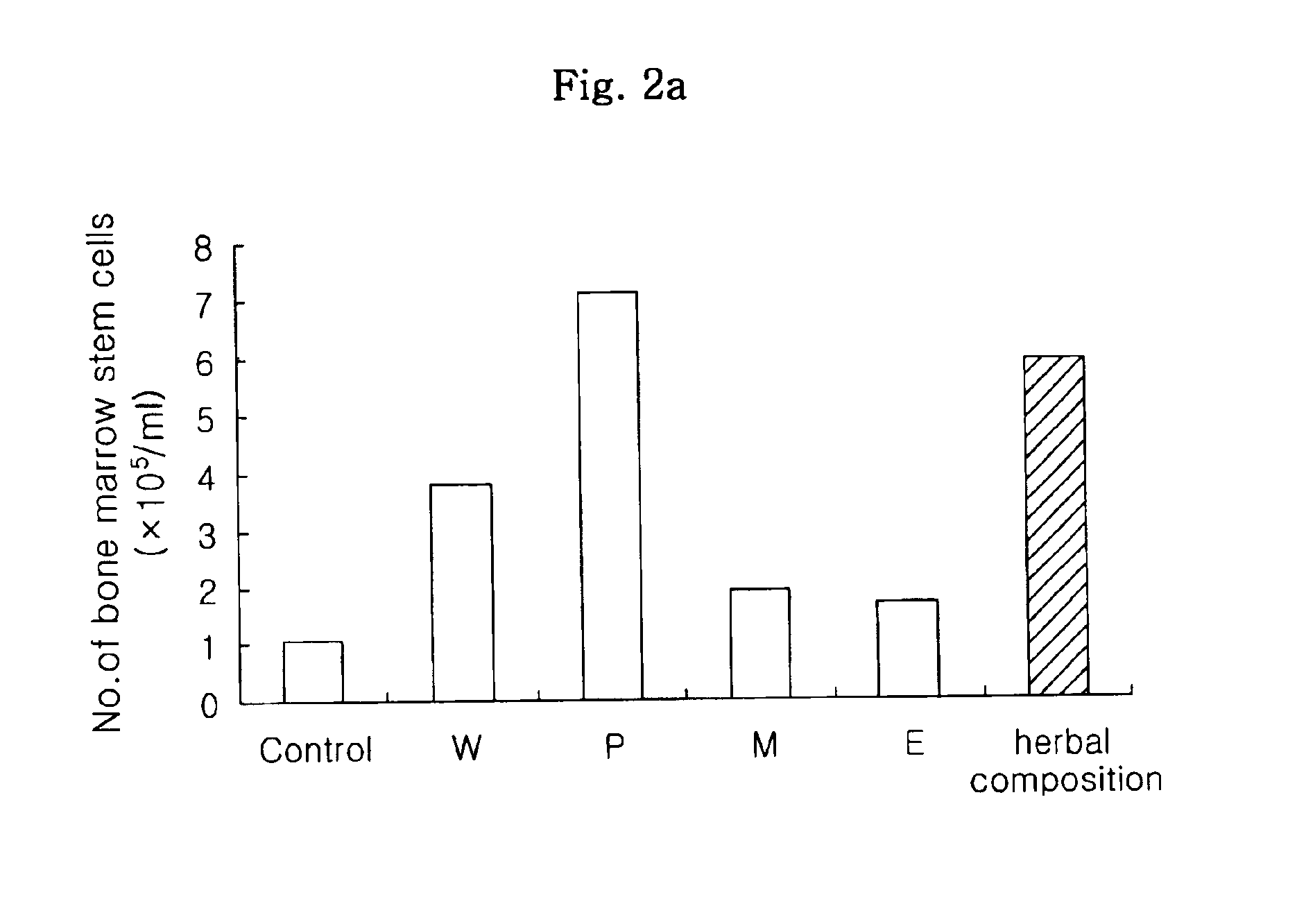
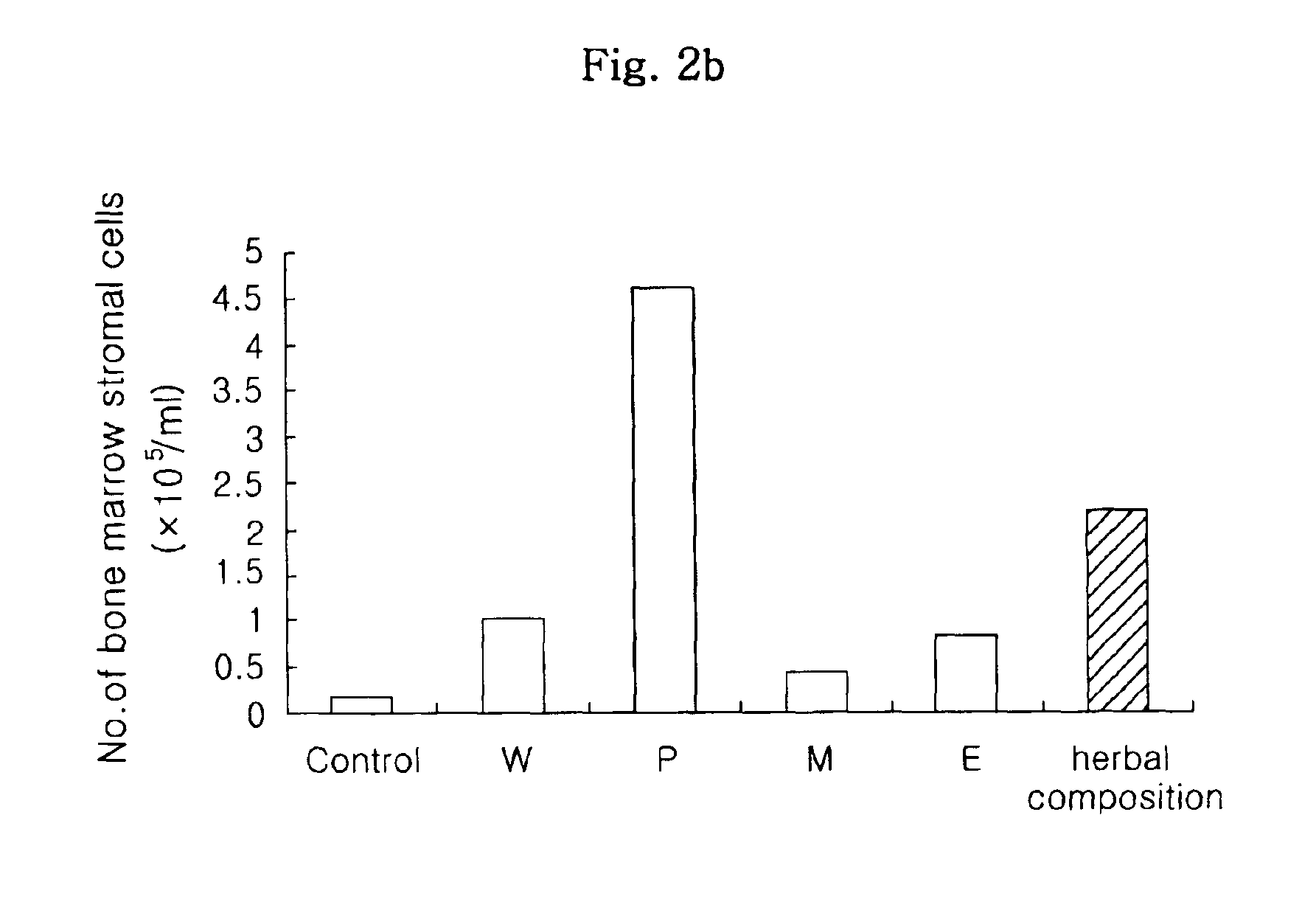
Herbal composition for improving anticancer activity, immune response and hematopoiesis of the body, and protecting the body from oxidative damage, and the method of preparing the same
InactiveUS6964785B2Higher protective effectHigh in polysaccharidesOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCancer preventionSide effect
Disclosed is a herbal composition comprising a first hot-water extract from a mixture of the plants Angelicae gigantis Radix, Cnidium officinale Makino and Paeonia japonica Miyabe et Takeda at an equal weight ratio, and a polysaccharide fraction as a precipitate formed by adding ethanol to a second hot-water extract from a mixture of the plants Angelicae gigantis Radix, Cnidium officinale Makino and Paeonia japonica Miyabe et Takeda at an equal weight ratio. The herbal composition of the present invention is effective in improving the anticancer activity, immune response and hematopoiesis of the body, and protecting the body from oxidative damage. Therefore, by stimulating the recovery from the damage to the immune function and hematopoietic function, often occurring during chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and inhibiting oxidative damage, the herbal composition can be applied for the prevention of the side effects of cancer therapy, as well as for the prevention of various degenerative chronic diseases and the improvement of the health of the weak and the elderly.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com