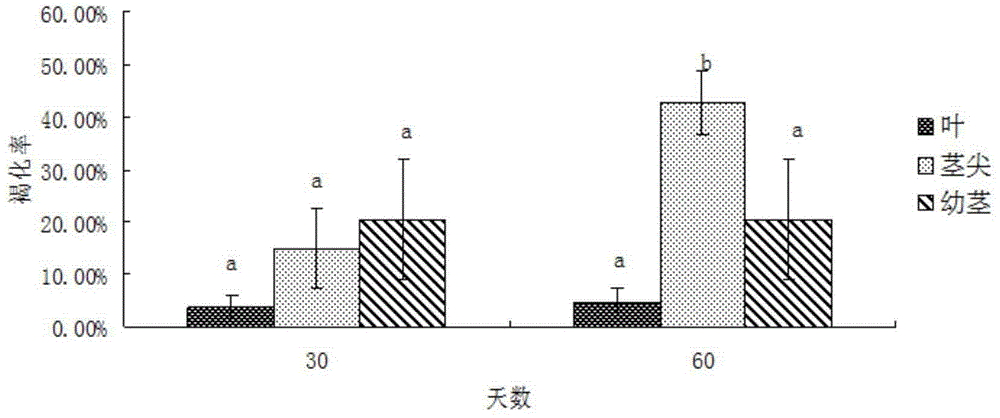
Patents
Literature
665 results about "Cataphyll" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In plant morphology, a cataphyll (sometimes also called a cataphyllum, or cataphyll leaf) is a reduced, small leaf. Many plants have both "true leaves" (euphylls) which perform the majority of photosynthesis, and cataphylls that are modified to perform other specialized functions. Cataphylls include bracts, bracteoles, and bud scales, as well as any small leaves that resemble scales, which are known as scale leaves. Some cataphylls have a primary function other than photosynthesis. The functions of cataphylls such as bud scales may be short-lived and they are often shed after the need for them is past.
Spring dendrobe flowering period control method
InactiveCN1555691AImprove viewing valueNo change in shape and colorPlant phenotype modificationAbscisic acidCataphyll
A method for regulating the blossoming period of spring dendrobium nobile featues that after the blades of its pseudobulb are fully developed, the mixed solution containing paclobutrazol and abscisic acid is sprayed onto the surface of blades for promoting the pseudobulb to become rope, and after 10-15 days, the solution containing thidiazuron is sprayed on the surface of its leaf for inducing the generation of flower buds.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Grow method of pearl guava
InactiveCN101401535AGood sale priceThick fruit shapeFertilising methodsCultivating equipmentsYoung treeCataphyll
Owner:黄国伦
Propagation method of succulent plant leaf cutting secondary rooting
InactiveCN104304005AHigh rooting rateImprove reproductive efficiencyCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsCataphyllPeat
The invention discloses a propagation method of succulent plant leaf cutting secondary rooting, and belongs to the technical field of plant cultivation. On the basis of the existing one-time leaf cutting propagation method, the grown new plants are separated from breeding leaves, existing callus of the new plants are removed, the new plants is coated with a rooting powder and cultured in a mixed matrix of the peat and perlite in the mass ratio of 1:1; and 1-2 months later, finish roots appear on the roots of the new plants, so as to complete the propagation of succulent plant. The method carries out secondary treatment on leaf cutting new plants, so that the leaf cutting succulent plants not easy for rooting can root; the method greatly improves the rooting rate and propagation efficiency of succulent plants leaf cutting; and the propagation method is simple, convenient for implementation and large-scale propagation, does not need much maintenance, and has important economic value.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cultivation method for oriental lily fresh cut-flower
InactiveCN101971757AReduce the impact of developmentGuaranteed supplySeed and root treatmentHorticultureDiseaseCut flowers
The invention relates to a cultivation method for an oriental lily fresh cut-flower, which comprises the following steps of: carrying out different stages of rooting and low-temperature forced germination on handpicked refrigerated seed balls, then planting in a transformed ground substance, strictly controlling the illumination, the temperature, the humidity of each growing stage, and evenly applying all kinds of required fertilizers. In the invention, through low-temperature treatment in a refrigeration house before planting, the roots of the lily seed balls grow to a certain extent, the influence of the harmful factors, such as high temperature and the like, on root system growth in the growth process after planning is reduced, thereby ensuring the supply of the nutrient and the moisture for the plant, and the quality of the cut-flower is improved. By using the cultivation method, the oriental lily has the advantages of fine growth and development, high and robust plant, high cut-flower rate, excellent quality, long childbearing period, bright-coloured flower color, bright lamina, thick and rigid petal character, good insertion-resistance, and little appearing leaf burning; the cultivated lily plant has strong disease resistance and aromatic flavor; and the cultivation method has high use ratio of facility space and can shorten the growth cycle of the fresh cut-flower.
Owner:河南省海芋生物发展有限公司
High-yield cultivation method for sweet potatoes
InactiveCN105027883AMany buried knotsConsistent positionPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsDiseaseCataphyll
The invention discloses a high-yield cultivation method for sweet potatoes. The high-yield cultivation method comprises the following concrete steps: I, choosing an improved variety: the improved variety is the key to produce the sweet potatoes at high yield; according to the use and the sale, the improved variety is chosen in the light of local conditions, and especially, the new variety is particularly obvious in yield-increasing effect; II, cultivating strong seedlings: the roots of the strong seedlings are numerous and developed, after being planted, the seedlings survive quickly, and hair roots bear the sweet potatoes fruitfully, which lay the foundation for full stands, strong plants, numerous potatoes and big potatoes; the standards of the strong seedlings are shown as follows: thick and strong stems, short internodes, fat blades and moderate sizes, with the features of the improved variety, no diseases, plenty latex of cuts, 50cm to 70cm of vine length and more than 0.5cm of stem thickness; III, transplanting in real time; IV, performing scientific management; V, harvesting the sweet potatoes when potato leaves start to turn yellow and the air temperature is below 20 DEG C, wherein the sweet potatoes require to be harvested before the end of October, and potato tubers should be prevented from being damaged by digging during harvesting. The high-yield cultivation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that seeds are saved by more than 1 / 3, the buried section number of seedling vines is large, covering of soil is slight, the soil temperature is high, and after ventilation, the survival rate is high.
Owner:邵利
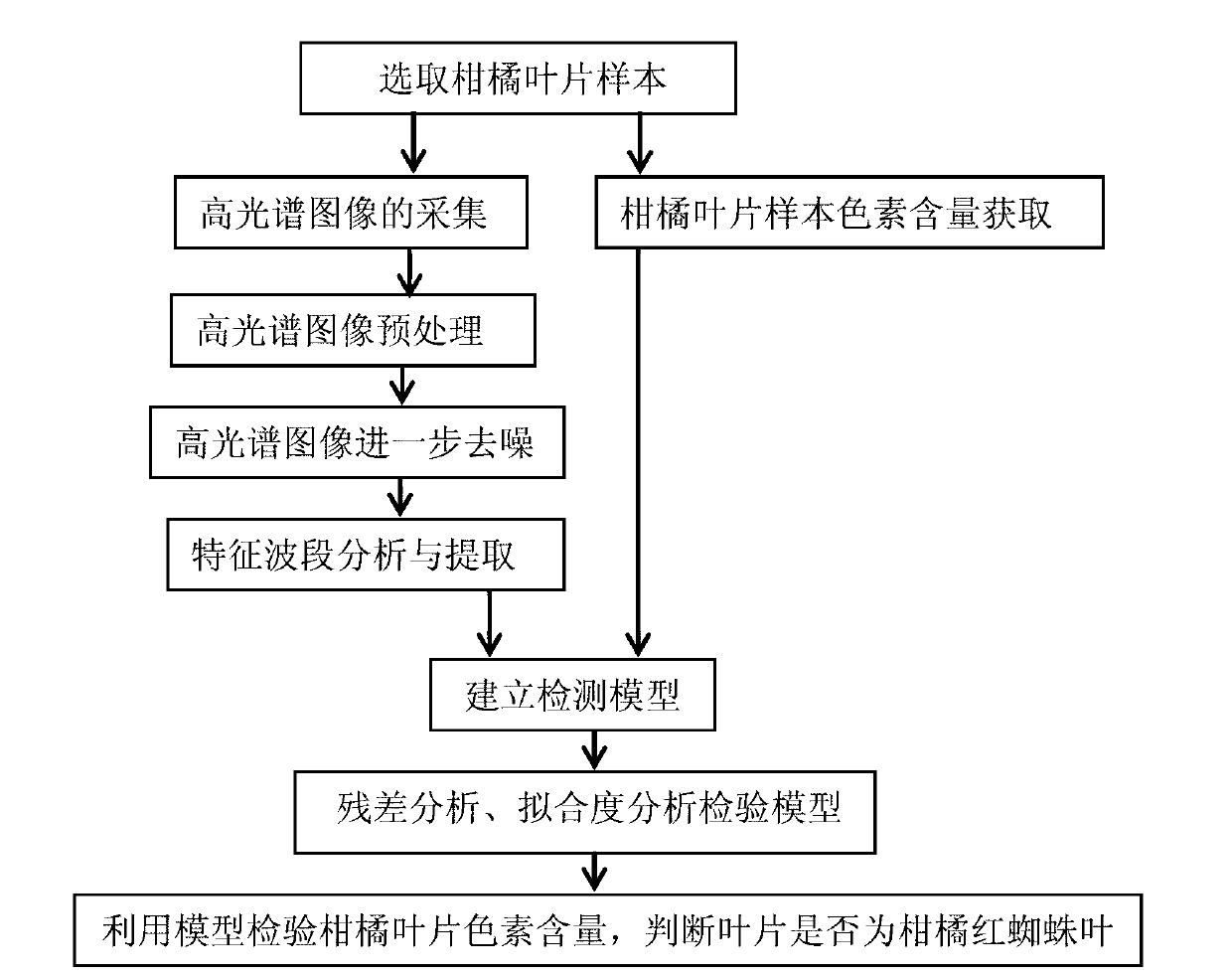
Test and analysis method of red spider insect pest coercion conditions of orange trees
The invention discloses a test and analysis method of red spider insect pest coercion conditions of orange trees. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) selecting a plurality of healthy orange tree leaf samples and orange tree red spider leaf samples; (2) collecting hyperspectral images of the orange tree leaf samples; (3) measuring the chlorophyll and carotenoid contents of the orange tree leaf samples; (4) pre-treating the collected hyperspectral images; (5) further denoising the pretreated hyperspectral images; (6) extracting the characteristic wave bands of the denoised hyperspectral images; (7) creating a detecting model through the extracted characteristic wave bands, picking out the optimal wave band combination by gradual regression analysis, and determining the quantitative relation of the optimal wave band combination and the chlorophyll and carotenoid contents; and (8) detecting the chlorophyll and carotenoid contents of the orange tree leaves through the created model so as to predict the red spider insect pest coercion conditions of the orange tree. The test and analysis method disclosed by the invention is used for predicting the red spider insect pest coercion conditions of the orange tree by creating the model and has the advantages of being unartificial and harmless.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Quick propagating method of blumea riparia(Bl.)DC medicine material
InactiveCN101040602AGenetic stabilityQuality improvementPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShoot apexCataphyll
The invention provides a method for quickly cultivating Blumea riparia medicinal material, which comprises that collecting Blumea riparia explants in wild, which it contains stem sharp, young stem, old stem, blades, bulbs, and seeds, to be washed and disinfected, and using plant organism quick cultivating method and grafting cultivating method to quickly cultivate the Blumea riparia, cultivating seeds, while the obtained seed can be directly used in field. The invention has high cultivate speed, short period as 2-3 months, with high survival rate more than 90%, simple operation, simple device, low cost, and application in whole year. And the product cultivated by the invention has stable gene character, without variation.
Owner:广西桂西制药有限公司
Method for interplanting radix angelicae in ginkgo biloba forest
InactiveCN105409546AHave advantagesWith effectPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsCataphyllEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for interplanting radix angelicae in a ginkgo biloba forest. The method comprises the following steps: sowing after land selection, soil preparation and pretreatment of seeds, pulling out weak seedlings and dense seedlings after the heights of radix angelicae seedlings reach 6 centimeters, applying a humic acid water-soluble fertilizer, applying a compound fertilizer at an interval of 40 days, then alternately applying the humic acid water-soluble fertilizer and the compound fertilizer, and stopping fertilizer application when the heights of the radix angelicae seedlings are 13-16 centimeters; and carrying out protection management on fields, harvesting in the middle to end of September of the current year if seeds of the radix angelicae are sowed in the spring, harvesting in the end of August of the next year when laminas of the radix angelicae are withered, cutting out leaves and stems of the radix angelicae and using the leaves and stems of the radix angelicae as compost, then digging out roots, and drying and ventilating. The radix angelicae is planted in the ginkgo biloba forest, idle blocks in the forest are utilized fully, short-term crops are used for culturing long-term crops, and economic benefit is created. The radix angelicae is interplanted in the ginkgo biloba forest according to the scheme provided by the invention, nutrient transformation rate and soil loosening capability can be improved, so that rhizomes of the radix angelicae can be expanded quickly, and the content of effective substances is greatly increased.
Owner:云南康林种植有限公司 +1
Fungus for promoting symbiotic germination of paphiopedilum hirsutissimum seed and application thereof
InactiveCN103087927APromote germinationPromote growthFungiMicroorganism based processesPaphiopedilum hirsutissimumCataphyll
The invention discloses a fungus for promoting the symbiotic germination of paphiopedilum hirsutissimum seeds and application thereof. The strain PhI17 provided by the invention is identified as Epulorhiza sp., the preservation number of the strain PhI17 is CGMCC No.6756. According to the invention, the strain PhI17 and the paphiopedilum hirsutissimum seed are subjected to co-culture, so that the germination of the paphiopedilum hirsutissimum seeds can be successfully promoted, the growth of seedlings can be further promoted, and leaves capable of photosynthesizing are grown; and the seedlings are transplanted to a matrix for culture, and the seedlings can all survive and well grow. The method provided by the invention can promote the germination of the paphiopedilum hirsutissimum seeds or is used for carrying out culture of paphiopedilum hirsutissimum seedlings, is easy to operate and low in cost. The fungus disclosed by the invention has important economic value on the artificial breeding of paphiopedilum hirsutissimum.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for performing regeneration propagation on sterile stalks of butterfly orchids
InactiveCN104082148AReduce manufacturing costStable genetic traitsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budCataphyll
The invention discloses a method for performing regeneration propagation on sterile stalks of butterfly orchids, relates to the technical field of seedling cultivation, mainly relates to a quick butterfly orchid plant reproduction technology, and in particular relates to a plant regeneration method for the butterfly orchid species. The method comprises the steps of cutting a stalk axillary bud stem with a certain length from a robust mother butterfly orchid plant, taking the stalk axillary bud stem as an explant material, wherein an axillary bud is opened and a leaf is in jade green and glossy after the sterile stalk is subjected to primary culture; after the axillary bud is cut down, culturing the stalk on a subculture medium, then continuously forming bud points at an incision of the axillary bud of the stalk to gradually form another axillary bud, continuing to cut down the axillary bud after the axillary bud is opened, and inoculating the stalk on the subculture medium again for subculture, wherein due to the culture, a large number of cluster buds can be obtained from one stalk, and part of the obtained cluster buds can be continued to be subjected to subculture by a bud-propagation-bud method. The method has the advantages that the later generations can keep a stable inheritable character of a maternal line, so that flowering phase control and industrial uniform management are facilitated, and the survival rate is up to 90 percent.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Introduction method for sea-tangle
InactiveCN101120650AHigh ability to withstand harsh environmentsIncrease success rateCultivating equipmentsPlant cellsFrondCataphyll
The present invention provides an introduction method of the laminaria japonica, which can resolve the problems of the prior art that the selected frond section having the mature sporangia is easy to decay and the spore is easy to release, thereby leading to the failure of the introduction. The introduction method adopted by the present invention is to firstly dry and incite the mature sporangia leaf of the laminaria japonica in a temperature-controllable laboratory, then put the mature sporangia leaf of the laminaria japonica into a water tank that is provided with the fresh sterilized sea water and the temperature of the water is controlled between eight cent degrees and twelve cent degrees to release the spores, then cultivate the spore to form the gametophyte, to put the seedling curtain attached with the gametophyte into a low-temperature enclosed bag and finally transport in low-temperature storage to the destination. The shape of all gametophytes on the laminaria japonica seedling curtain is normal, which has high successful rate and the survival rate is nearly one hundred percentages.
Owner:MARICULTURE INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Cuttage propagation method for survived seedlings by tissue culture and transplantation of catalpa bungei
InactiveCN101720618ASpeed up promotionScale upCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationRoot growthCataphyll
The invention discloses a cuttage propagation method for survived seedlings by tissue culture and transplantation of catalpa bungei, and is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1), preparing a cuttage substrate and a root growth promoting agent; 2) scissoring 30 to 50cm of twigs when the survived seedlings obtained through the tissue culture and transplantation of the selected good singleplant tissue grow to a height between 50 and 80cm, shearing the twigs into 5 to 15cm of small segments and reserving 1 / 3 blades, dipping the small segments into the prepared root growth promoting agent for 5 to 8 s, and inserting the dipped small segments into the prepared substrate; and 3) inserting cuttingwood into a potted tray containing the substrate, then totally sealing the potted tray with a plastic film, and keeping the relative humidity between 85 and 95 percent, and the temperature between 20 and 30 DEG C, wherein a cuttingwood base starts generating callus after 10 to 13 days, the callus grows a root system after 18 to 21 days, the root system grows buds after 25 to 30 days, and the seedlings are transplanted after 40 days. The method can keep the original good properties of a catalpa bungei stock plant, and has over 95 percent of cuttage survival rate, low cost and high efficiency.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG FORESTRY TECHN GUIDANCE STATION
In-bottle rooting method for salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling
ActiveCN102726294AHigh rooting rateSolve the problem of rootingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGrowth hormoneCataphyll
The purpose of the present invention is to disclose an in-bottle rooting method for a salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a secondary seedling, wherein a secondary culture salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling is selected, the height of the seedling is 2-3.5 cm, and the robust individual ulmus pumila seedling having extending leaves is selected; and (2) inoculating the selected secondary culture salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling onto a WPM rooting medium, wherein the WPM rooting medium is added with growth hormone, cytokinin and exogenous additives. According to the present invention, a medium formula having a high rooting rate is adopted so as to effectively solve the rooting problem of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling, improve the rooting rate of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling, reduce the cost, accelerate the factory production of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila, provide high quality salt tolerance ulmus pumila seedlings for nursery stock markets, and achieve the purpose of the present invention, wherein the rooting rate of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling can be up to 95%.
Owner:上海菁艺生物科技有限公司
Grafting method for myrica rubra Dongkui and candleberry
The invention relates to a grafting method of myrica rubra Dongkui and candleberry. The grafting method comprises the following steps of: firstly selecting scions and root stocks, wherein the scions are obtained by scissoring strong myrica rubra Dongkui which is 7-15 years old and is excellent and pure in variety, during scion plucking, selecting branches at the middle upper parts of the peripheries of the crowns of seed trees, which are fully mature and robust and have plump bud eyes, after plucking the scions, immediately cutting out leaves, and only leaving leaf stalks; scissoring 1-5cm thick overgrowing branches from candleberry trees serving as the root stocks, wherein the candleberry trees grow in soil with the pH value of 7-11 and are 4-5 years old; grafting after selecting the scions and root stocks, grafting the 1-3cm thick root stocks by adopting a cut-grafting method, and grafting the 3-5cm thick root stocks by adopting a cleft graft method; and the grafting combination of the myrica rubra Dongkui and the candleberry can enable the myrica rubra Dongkui to grow in saline-alkaline soil with the pH value of 7-11, thereby enlarging the planting range of the myrica rubra Dongkui.
Owner:柴春燕
Tissue culture and rapid propagation method for kadsura coccinea
InactiveCN105393919AImprove protectionMeet needsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureShoot apexCataphyll
The invention discloses a tissue culture and rapid propagation method for kadsura coccinea. The method includes the step A of selection and processing of explants, the step B of induction of explants, the step C of browning prevention processing of calluses, the step D of differentiation of calluses, the step E of subculture multiplication culture, the step F of strong seedling culture, the step G of rooting culture and the step H of seedling hardening and transplanting, wherein in the step A, young and tender leaves close to tips of kadsura coccinea stems are taken and disinfected to obtain sterile explants. By means of the method, the browning rate of explants of kadsura coccinea is controlled at 7% or below, the rooting rate reaches 95%, and the seedling formation rate reaches 97% or above.
Owner:GUANGXI BOTANICAL GARDEN OF MEDICINAL PLANTS
Cutting-seedling raising method of cyclocarya paliurus branches
InactiveCN104429543AEasy to operateSuitable for large-scale cutting seedlingsCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsCataphyllAsexual reproduction
The invention relates to an asexual reproduction method of cutting-seeding raising cyclocarya paliurus branches to solve the seedling technical problem of cyclocarya paliurus and to efficiently cultivate clone feedings. The method includes the following steps, firstly choosing un-entirely lignification branches from robust cyclocarya paliurus plants and cutting sections with two leaf buds as cuttings, wherein the biology bottom of a cutting is flat and 2 to 3 leaves are left on the upper portion, secondly immersing the lower end of the cuttings in rooting solution for 20 to 100 minutes, thirdly inserting cuttings treated by rooting agent into soil matrix with a depth of 3 to 3.5 cm and spraying with 80% by wt carbendazim until the upper leaves completely wetted after cutting, and fourthly shedding the cut branches with black sunshade nets, sterilizing and moistening the cuttings by spraying carbendazim every two days at the first week and later moistening by spraying water every two days. The cutting-seedling raising method of cyclocarya paliurus branches is simple and practical in operation, short in seedling period and high in cutting rooting rate, and is suitable for large scale cutting seedling.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for grafting and propagating rhododendron hybrids
The invention discloses a method for grafting and propagating rhododendron hybrids. In the method, compact rhododendron hybrids are used as scion, and rhododendron cosmopolitan is used as tree stock. The scion is a current-year semi-lignified strong branch which does not have diseases or insect pests, have full eyes, leaves which turn green and ripe, and terminal bud, and does not sprout or just sprouts; and the tree stock is a current-year lignified strong branch which grows luxuriantly, does not have diseases or insect pests, and has smooth and complete skin. In the method, the rhododendron hybrids are grafted by a cleft grafting method; the scion and the tree stock are covered by a plastic bag to maintain moisture, and water drops are prevented from immersing the grafting joint; and sun is shaded properly after grafting, and the illumination intensity is better to be between 90 and 126mu mol.m<-2>.s<-1>, the temperature is better to be between 25 and 28 DEG C, and the air humidity is better to be between 80 and 90 percent. The method is easy to operate, ensures low cost and high survival rate, is favorable for improving the finished product quality of potted rhododendron hybrids, and can be widely applied to commercial production of the rhododendron hybrid.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
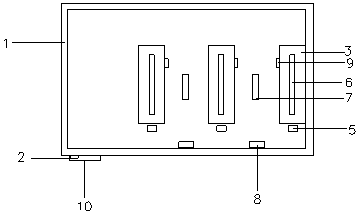
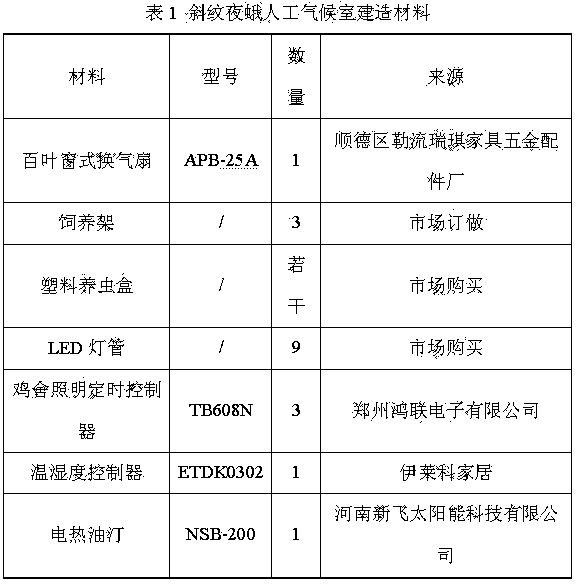
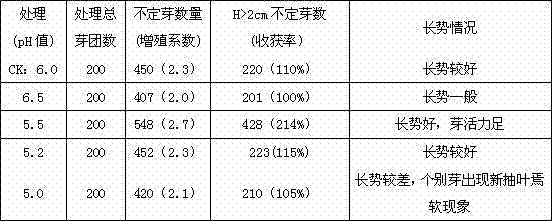
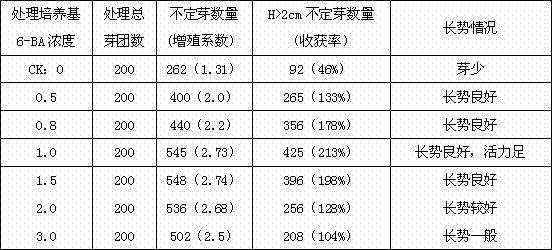
Phytotron for feeding prodenia litura and indoor artificial breeding method
The invention discloses a phytotron for feeding prodenia litura and an indoor artificial breeding method. The method comprises the following steps: putting prodenia litura larvae into the phytotron under a specific condition; selecting natural hosts (tobacco leaf, Chinese cabbage and the like) to feed the prodenia litura larvae; changing fresh hosts everyday and removing faeces and rotten leaves; after the prodenia litura larvae pupate, centrally putting the prodenia litura into an insect rearing box; after adult emergence of the prodenia litura, pairing the prodenia litura according to the female-male ratio of 1 to 1, laying eggs and breeding population. According to the feeding method, the prodenia litura are fed in the manmade phytotron, the feeding technique is simple and easy to operate, low in feeding cost, and high in reproductive rate, and standard health test insects can be obtained in an indoor continuous feeding manner.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Cinnamomum camphora tissue culture method
The invention discloses a cinnamomum camphora tissue culture method. The method comprises the following steps: picking new sprouted semi-lignified branches of cinnamomum camphora in the same year in April to May each year, scissoring branches with 2-3 leaves, removing the leaves, oscillating and washing in sterile water for 3-5 minutes, treating by using 70% alcohol for 1-2 minutes, placing in 0.1% mercury bichloride for 6-10 minutes, and cleaning by using sterile water for 3 times; inoculating the treated semi-lignified branches into an adventitious bud induction medium, thereby obtaining an aseptic explant, culturing under illumination conditions, and thus forming callus and adventitious buds for expanding propagation; culturing in a mulitiplication expanding propagation culture medium and a root induction medium, and cultivating to obtain rooting seedlings; and transplanting the cultured cinnamomum camphora rooting seedlings, wherein the survival rate is over 95 percent.
Owner:江西北辰德天然生物科技有限公司
Method for culturing detoxified seedling by sweet potato stem tip
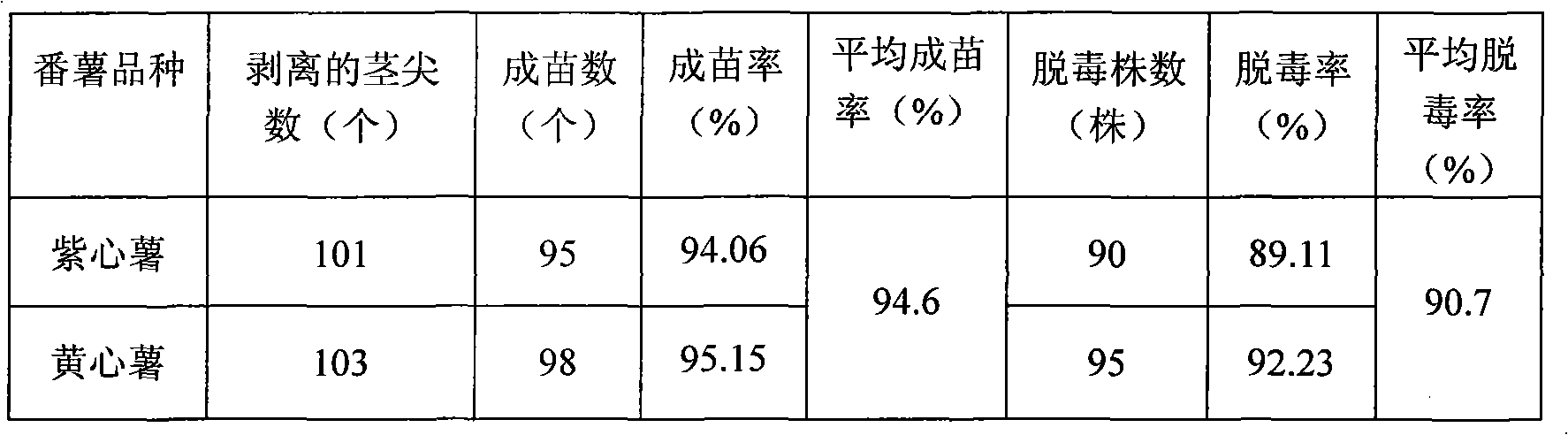
InactiveCN101584301AShort cycleShort qualityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureShoot apexCataphyll
The invention relates to plant cultivation field, particularly a method for culturing the detoxified seedling by the sweet potato stem tip. The method comprises following steps: firstly selecting qualified potato seed for raising seedling, scissoring the photo seedling stem tip, peeling the stem tip meristem for culturing, seedling formation cultivation after the stem tip meristem enlarges and turns green, performing the dwarf shoot cottage cultivation to get the test-tube plantlet, virus detection, taking the detoxified seedling leaves for inducement rapid propagation, domestication and transplantation, obtaining the stem tip seedling of the breeder's seed potato. The invention has simple art, utilizes the detoxified seedling leaves inducement rapid propagation technology to obtain multiple detoxified seedlings of one strain in a short period so as to lower production cost, effectively improve the virus detoxified rate and stem tip establishing percent and rapidly provide the nontoxic seedling for the sweet potato production and resource storage.
Owner:INST OF FOOD CROPS HAINAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plant regeneration method by using giant tea rose stem segment as explant
InactiveCN102422815ASolve the problem of breeding difficultiesEasy to collectHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCataphyllBud
The invention provides a plant regeneration method by using a giant tea rose stem segment as an explant. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: cutting the central section of a giant tea rose branch into a segment, sterilizing, carrying out subculture for one month, transversely cutting giant tea rose aseptic seedling blades, inoculating to a callus induction medium until embryogenic callus grows, culturing in a differentiation medium until the embryogenic callus differentiates adventitious buds, inoculating to a strong seedling medium, and inoculating to a rooting medium after growing tall so as to form the complete plant. According to the invention, the explant used is convenient to collect such that propagation of giant tea rose and cell culture can be carried out every year; the obtained embryogenic callus can be used as a good acceptor for genetic transformation, thus providing the acceptor for the establishment of a giant tea rose genetic transformation system; and the established regeneration system can help solve giant tea rose breeding problems so as to better protect and utilize the resource.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tissue cultivating fast reproducing method for pot culturing red palm seedling
InactiveCN1623372AHigh induction rateImprove efficiencyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCataphyllBud
A tissue culture method for quickly reproducing the red cactus includes such steps as disinfecting the tender leaf of red cactus, pretreating in the pretreating liquid containing BA and 2,4-D, cutting to become blocks, inductive culture in the improved MS culture medium to induce calli, differentiating adventitious buds in the improved diferential culture medium, culturing the rooted aseptic seedlings in the improved reproductive culture medium, naturalizing, and transplanting them in pots.
Owner:广东省珠海市园艺研究所 +1
Artificial cultivation method of glenea cantor
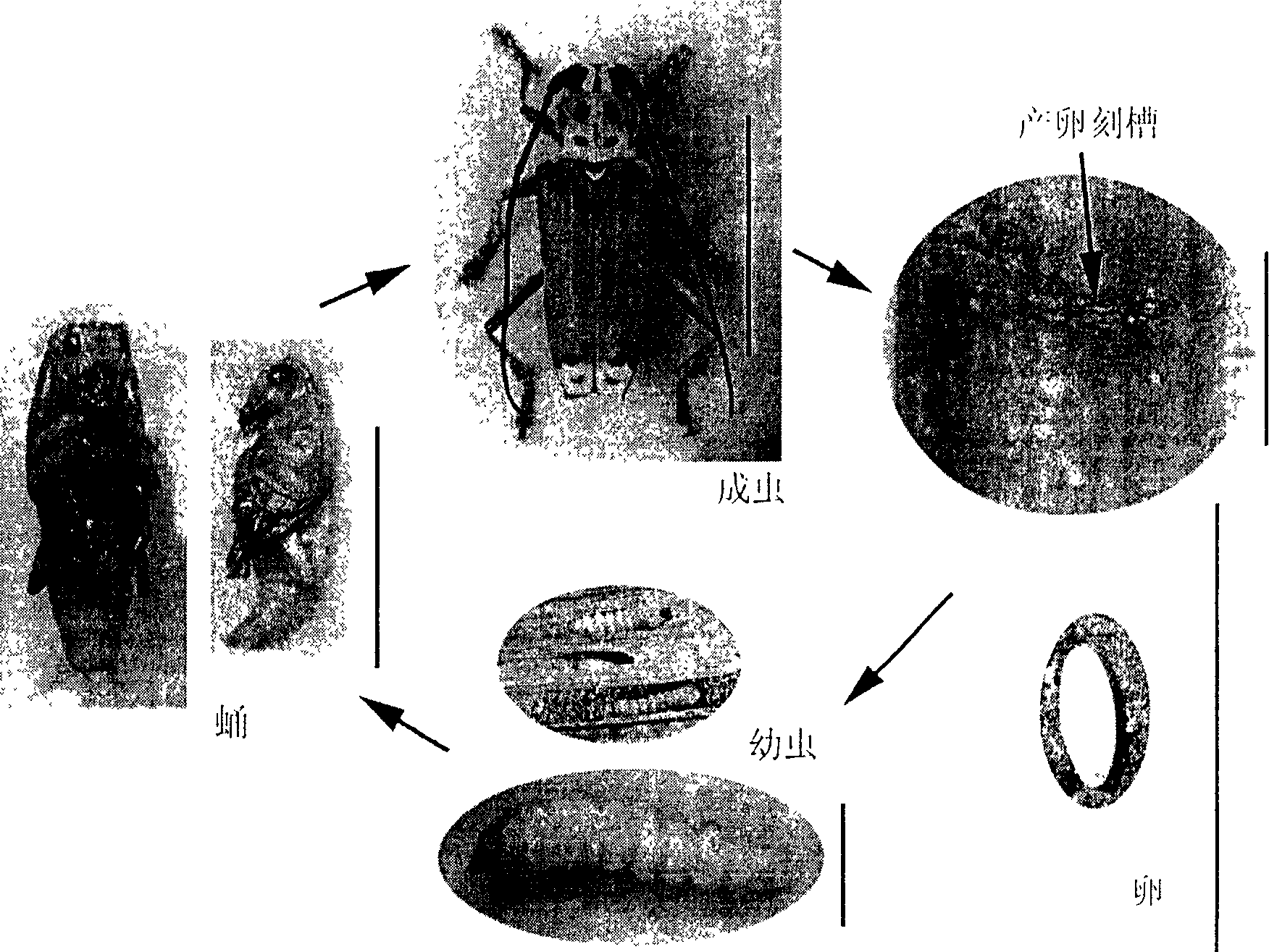
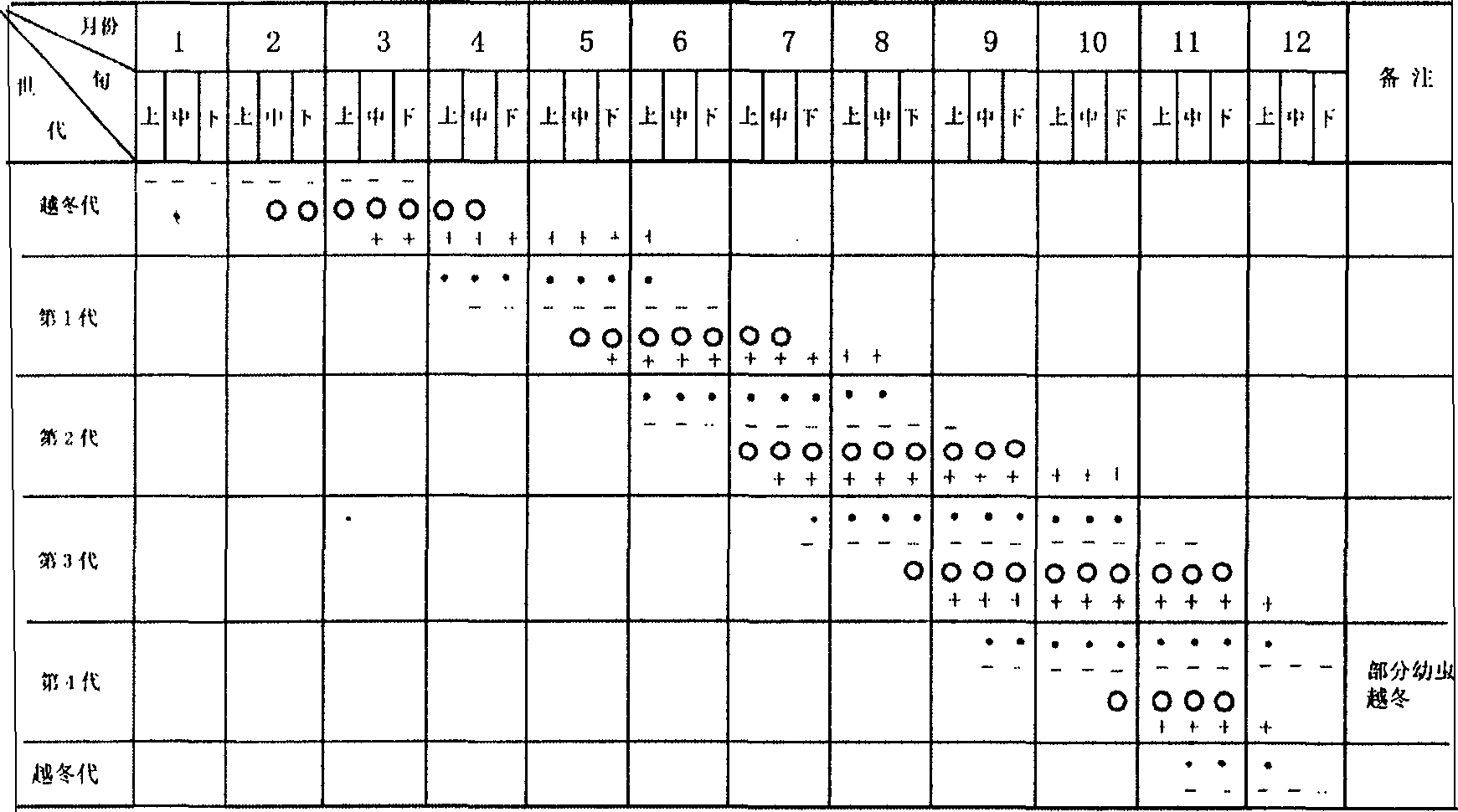
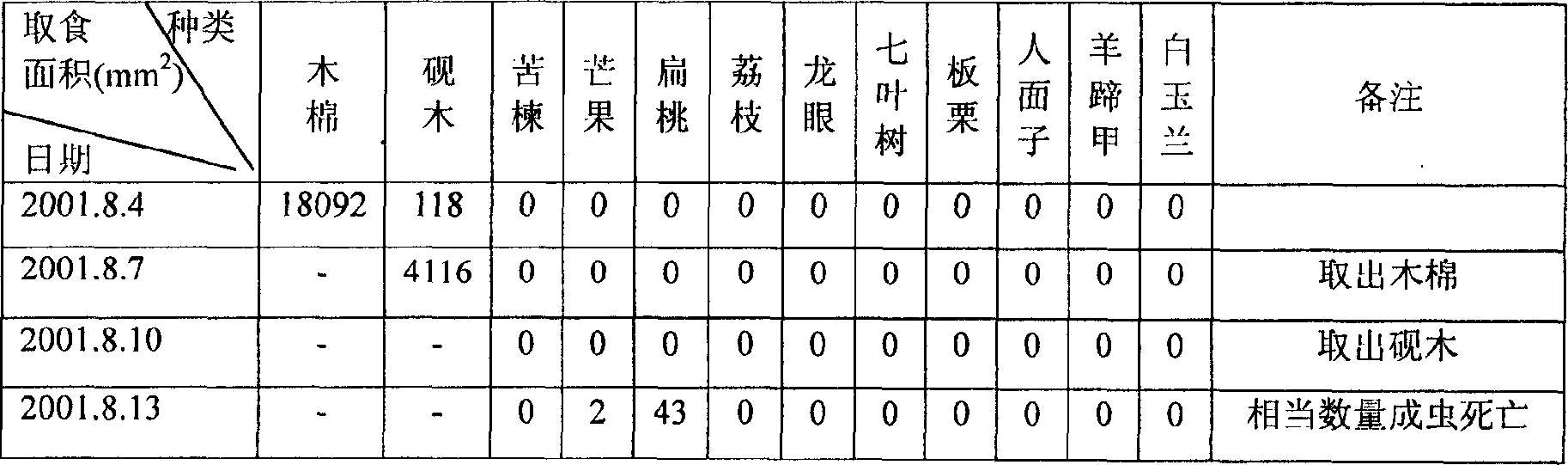
A method for breeding capricorn beetle with speckle in eyebrow, breeding imago bought in market or wild imago with small ceiba fiber branch, putting ceiba fiber when imago enters into laying season for imago laying; cutting down ovum and branch after imago laying and collectively culturing, inoculating laver into ceiba fiber to culture till emergence of imago in laver incubation early period; separating, collecting laver or pupa of young age, middle age or old age; pupa staying in pupa room if for emergence until baiting hole and getting out of pupa room; breeding separately or collectively with fresh ceiba branch or leaves after imago emergence. The capricorn beetle can be produced four generations in one year with method in this invention, and breeding is possible all year around on condition of artificial temperature-control, and parasitics natural enemy of capricorn beetle can be bred and colorful and good shape artwork with high seeing value can be produced according to need of pesticide sift test research and insect diet.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for adjusting flowering time of loquats
InactiveCN102204498AControl pumpingGood ventilation and light transmissionCultivating equipmentsCataphyllLoquat Tree
The invention discloses a method for adjusting the flowering time of loquats. The method for adjusting the flowering time of loquat comprises the steps of: A. after fruit picking, appropriately removing over-dense branches of crowns of loquat trees planted in ecoregions of dry-hot valleys of the Jinsha River, and cutting the side shoots of dense branches with more than 2 shoots on the periphery of the crowns; shearing off cross and overlaid branches and weak branches; back cutting slim and fragile braches to a large extent, and back cutting strong bearing branches slightly; and back cutting the branches with young shoots at the connecting part of the old shoots and young shoots; B. heavily applying organic fertilizer within 5 to 7 days after shearing, and watering in time; and C. applying 25 to 40 kilograms of phosphatic fertilizer, 8 to 12 kilograms of potash fertilizer, 6 to 8 kilograms of nitrogenous fertilizer per 667 square meters of field from June to July, and spraying leaf fertilizer twice or three times in the period when the summer shoots and leaves turn green; and simultaneously, bending or cutting vertical branches, the diameter of which is larger than 1.5 centimeters, in a twisting way. The method for adjusting the flowering time of loquats can be used for delaying the flowering time of loquats planted in the ecoregions of dry-hot valleys of the Jinsha River, preventing the loquats from flowering in June or before June, and enabling the spikes to blossom in July to August concentratedly, the flowering ratio and fruiting rate to be high, the fruit quality to be high, and the fruit to be supplied on the market in a fruit off-season relatively concentratedly.
Owner:SICHUAN AAS HORTICULTURE RES INST
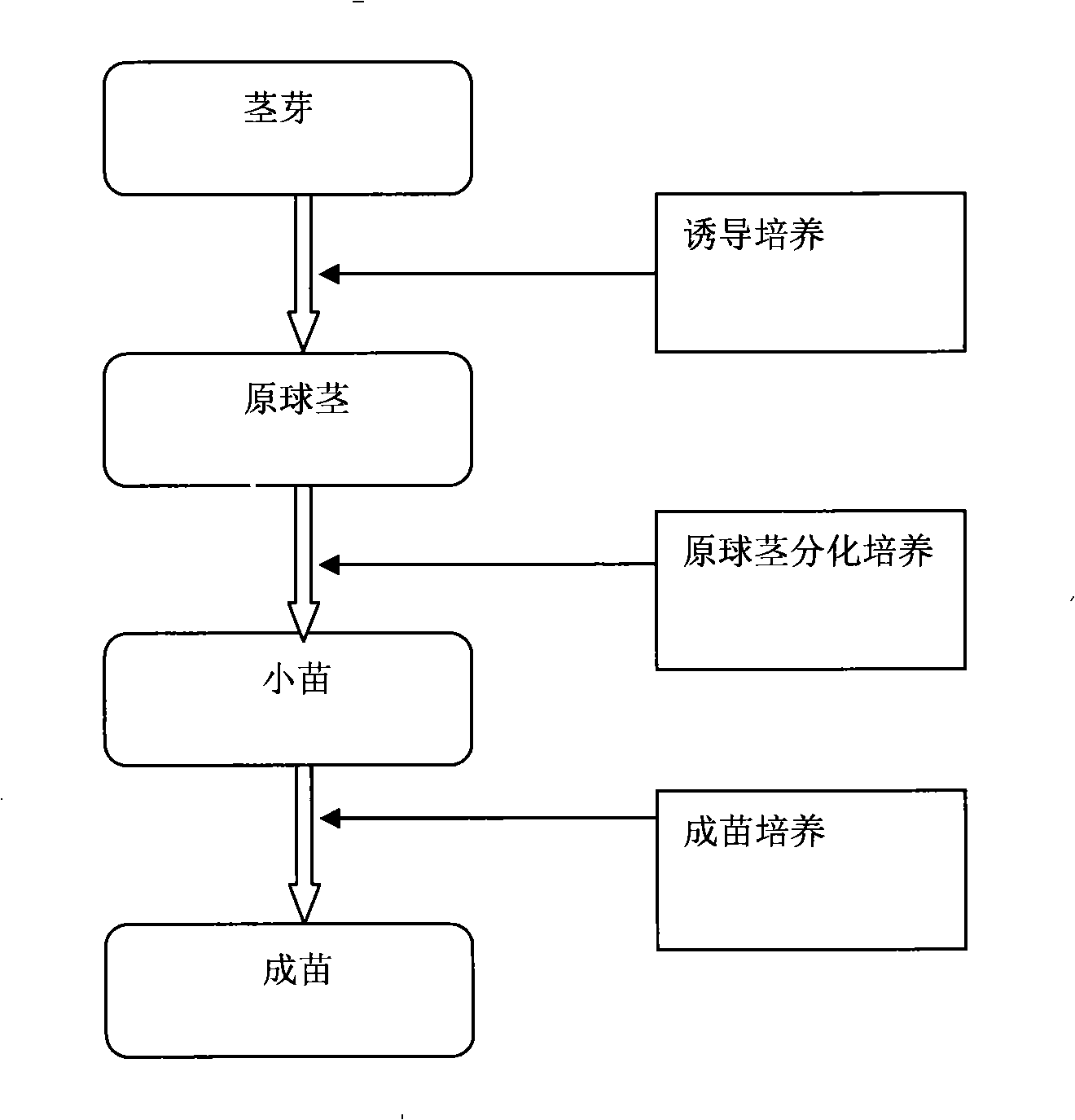
Tissue culture method for rapid propagation of Dendrobium candidum
InactiveCN101273709ATo solve the problem of low natural reproduction rate,Solve problems limited by seasonsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCarrageenanSeeds source
The invention discloses a tissue culture method of dendrobium candidum rapid propagation which relates to the field of biological technique. The stemeye of dendrobiun candidum is first selected for induction culture in a protocorm induction culture medium, after two months, the protocorm can be formed and observed; then the stemeye is put in a differential medium for differentiation culture, after two months, the protocorm in a bottle can be observed to form plantlets with the height of about 1cm by redifferentiation; the differentiated plantlets are connected and put in a mature shoot culture medium for mature shoot culture, after about three months, that the uniformity of the mature seedlings of the dendrobiun candidum is in line, each seedling has at least 2-3 developed and lusty root systems, the height of plants is 3 to 6cm and the vane is relatively green, which can be observed in the bottle. The tissue culture method of the invention can shorten the culture time of dendrobiun candidum, not only effectively solves the source problem of seed source of the dendrobiun candidum, is also not limited by time and places; compared with the traditional germchit enlarging propagation, the speed is improved and the time is shortened to be 7 months and carrageenan is used for substituting for gelose, thus saving cost.
Owner:南京养颐堂生物科技实业有限公司 +1
Tissue culture seedling growing process for trichosanthes
InactiveCN1985582AMeet the requirements of large-scale productionAchieve production scalePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsCataphyllBud
The tissue culture seedling growing process for trichosanthes includes the following steps: 1. taking the bud on tuberous root or stalk of trichosanthes as the explant in summer end or initial summer; 2.cutting bud or stem segment; 3. inoculating the bud or stem segment in culture medium I inside culture bottle; 4. secondary culture in culture medium II inside culture bottle; and 5. rooting culture in culture medium III inside culture bottle for 20-30 days to root. The present invention has short propagation period and high propagation coefficient.
Owner:江苏春辉生态农林股份有限公司
Method for regenerating plants of Chinese rose by using leaves as explants
InactiveCN101946703AGood receptorProliferation effect is goodPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsCataphyllSomatic cell
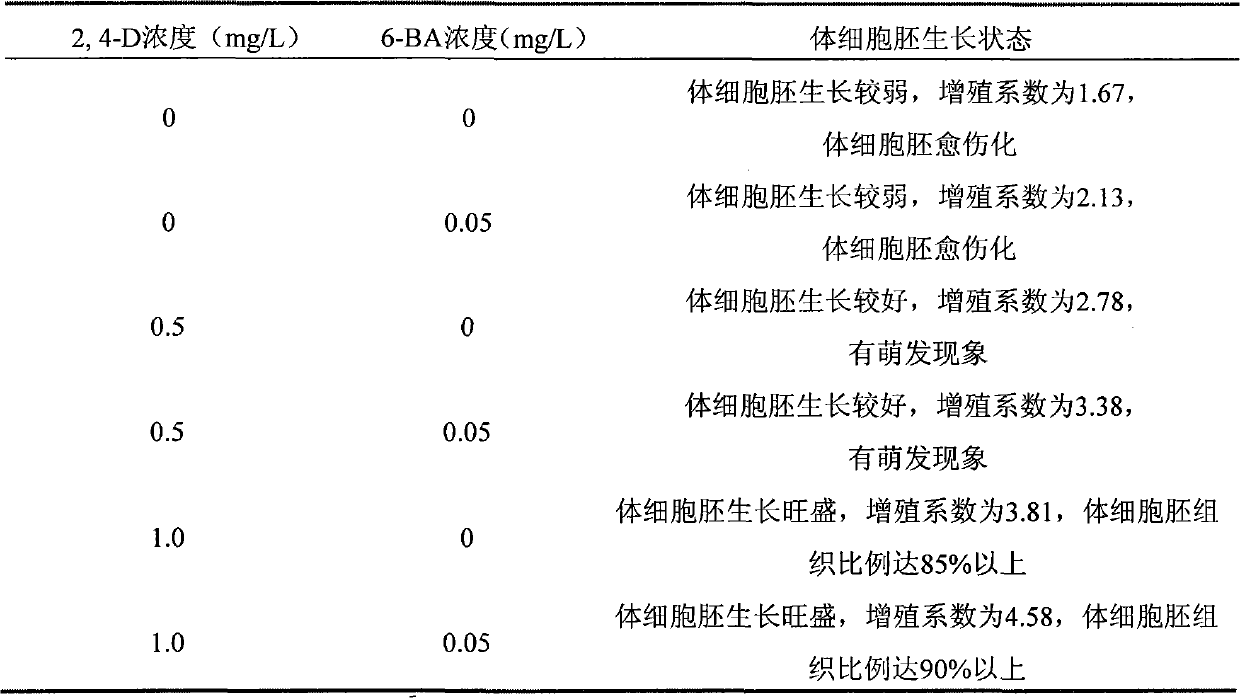
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant tissue and cell culture, and in particular relates to a plant regeneration method by using leaves of Chinese rose as explants through a somatic cell embryogenesis path. The method comprises the following three culture stages: (1) culturing the Chinese rose explants on an induction medium, and directly inducing somatic embryos from the explants, wherein the explants are wrapped leaves of Chinese rose respectively; (2) inoculating the inoculate on a propagation culture medium for propagation and accelerating further differentiation thereof; and (3) inoculating the somatic embryos subjected to propagation culture to a somatic embryo seedling culture medium and a rooting culture medium and regenerating complete plants. The method has the advantages of wide sources of explants, convenient material selection and the like. The prepared somatic embryos are agrobacterium-mediated excellent receptors through genetic transformation and can be used for research on genetic transformation of the Chinese rose. The invention also relates to components of culture media for the method.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for constructing lotus regeneration system
ActiveCN104813939ABuild a regenerative systemOvercoming the defect of easily killing lotus embryosPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShoot apexCataphyll
The invention discloses a method for establishing a lotus regeneration system. The method comprises the following steps: breaking shells of sterilized Guangchang white lotus seeds by using pruning shears; taking out mature lotus nuts (embryos) as explants to culture aseptic seedlings; cutting 2-3mm of stem tips and folded tender leaves (with short petiole) as explants for inducing callus from the aseptic seedlings after 2 months; inducing and differentiating the callus to develop buds after 2 months; after 1 month, cutting off the black callus at the bottom, and proliferating the differentiated seedlings; after 3 months, inducing the differentiated seedlings to develop roots; and strengthening, domesticating and transplanting the rooted tissue culture seedlings after 1 month. By adopting the method, technical basis is provided for transgenic technology of lotus in China, and the inductive callus rate of lotus is increased and the callus is large and stable in size compared with a conventional technique; the propagation coefficients of adventitious buds are increased; as tender leaves of aseptic seedlings of lotus are innovatively taken as explants for inductive callus and are successfully differentiated to obtain seedlings, the material selection of lotus inductive callus is widened, and material guarantee is provided.
Owner:镇江市彩林生态农业观光有限公司
Method for breeding spring cabbage stalk and maintaining springness of inbred line
InactiveCN101473791AGuaranteed survivalKeep springPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSpring cabbageCataphyll
The invention discloses a propagation method for keeping springness of an inbred line of a spring common head cabbage breed. The method comprises the following steps: selecting external-layer green leaves of mature leaf heads of the spring common head cabbage inbred line in spring, inoculating the leaves on an adventitious bud differentiation induction culture medium according to a certain size for culture, and inoculating adventitious buds to an adventitious root differentiation induction culture medium for culture when the adventitious buds grow to 1.5-2.5cm high to obtain complete regenerated seedlings; then transplanting the regenerated seedlings to culture soil for culture, and permanently planting the seedlings in a field (open field) when the seedlings grow to 5-7 true leaves and are adaptively hardened for 7 days, and by which the survival rate of the seedlings reaches over 95%. The method helps improve the breeding effect of the spring common head cabbage, ensure the spring common head cabbage inbred line to complete a heading stage in spring and agronomic character selection of plants of the spring common head cabbage, maintain the characters (springness) of the selected plants unchanged, ensure the inbred line to complete a life cycle, greatly improve the number of the plants with the same genotype of the inbred line, and proliferate the number of the plants over 50 times.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Tissue-culture seedling raising method of rhodiola crenulata
InactiveCN101836585AStart earlyGood synchronizationCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureCataphyllBud
The invention provides a tissue-culture seedling raising method of rhodiola crenulata, which comprises the following steps of: (1) taking the leaves of the rhodiola crenulata as an explant and carrying out budding culture to form adventitious buds; (2) carrying out propagation culture on the adventitious buds to form single seedlings; (3) carrying out rootage culture on the single seedlings obtained after stretching cluster buds to form rootage seedlings; and (4) transplanting the rootage seedlings, wherein a culture medium for the budding culture is an MS culture medium added with 10 to 20mumol / L of 6-benzylaminopurine and 1 to 5mumol / L of gibberellin. The invention reinforces the high-efficiency seedling raising method of the rhodiola crenulata by primary culture dark processing and the combined processing of the addition of active carbon in the rootage process and solves the problem of low propagation coefficient of the rootage seedlings of the rhodiola crenulata, the multiplication coefficient of 20 days of the cluster buds is 2 to 3 times, the rootage rate reaches more than 95 percent, and the transplanting survival rate is as high as more than 90 percent. The method provided by the invention has high differentiation frequency and short growth cycle and is easy for the large-scale production of the rhodiola crenulata.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com