Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Solve the problem of rooting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Asexual reproduction method for elaeagnus mollis
ActiveCN101057558AMany spikesEasy to rootFertilising methodsPlant tissue cultureElaeagnus mollisPropagation rate
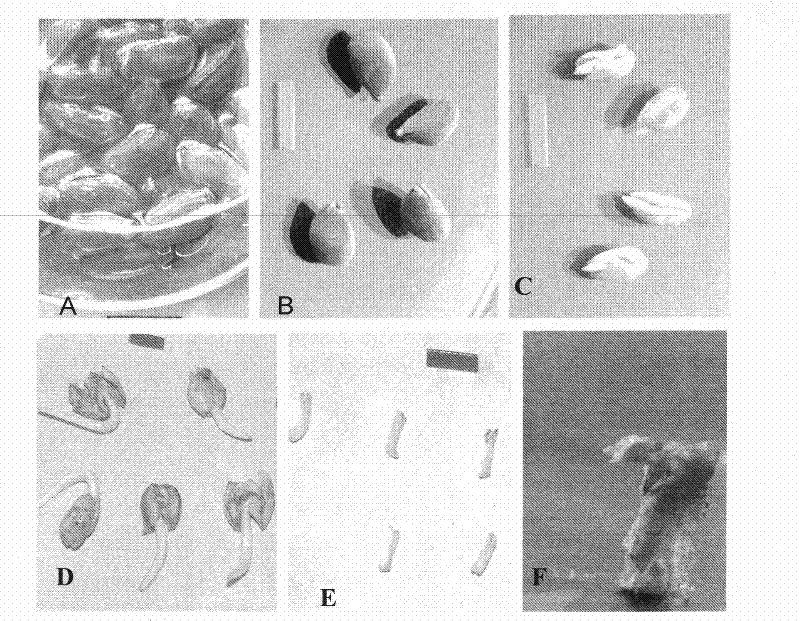
The invention relates to a plant breeding field, which in detail relates to a method of elaeagnus mollis asexual propagation, comprising following steps: building seed bed; collecting ear from parent tree; cutting collected ear in medium on the bed; spraying water on leaves of elaeagnus mollis, the water temperature is 20-30 Deg. C; fertilizing on leaves until ear grows out root. The invention employs technology of asexual propagation to breed more seedling in short time, moderates seedling bed's temperature and humidity to keep physiological balance for cottage ear, disinfects ear and treats it with plant growth hormone to provide bios and nutrition for ear rooting, and treats parent tree to promote formation and growth of adventitious root. It solves problems of difficult rooting of callus and low seedling rate. The invention is characterized by simple and fast propagation technique, low cost and high propagation rate.
Owner:山西琪尔康翅果生物制品有限公司
Method for tender branch cutting propagation of Linze jujube
InactiveCN101699956ASolve the problem of rootingSolve the problem of difficult rooting of seedlingsBiocidePlant growth regulatorsZiziphus jujubaAppropriate technology
The invention relates to a method for tender branch cutting propagation of a Linze jujube, comprising the following steps of: selecting tender branches, wherein the selected tender branches are the tender branches grown from jujube saplings with semi-lignification under high temperature; collecting the tender branches, soaking tender branch cuttings in a well-prepared mixed solution; constructing a seedbed through the steps of sanding, disinfecting, heat preserving, light and moisture regulating and sterilization; and then carrying out cutting propagation and acclimatization. The invention is a duplicating jujube plantlet method by using current-grown tender branches as propagation materials. The duplication process is actually a root getting process, by which rootless branches are grown into rooting plants after being soaked in auxin and an auxin synergist solution. Compared with the most advanced traditional tissue-cultured seedling method, the invention has breakthroughs on two aspects of: 1, capability of directly taking self-rooted seedlings, which solves the problem of hard root-taking of jujube seedlings; and 2, propagation of pure and high-quality plantlets, which solves the bottleneck problem of propagating the pure and high-quality seedlings in the appropriate technology field through the ages.
Owner:甘肃省祁连山水源涵养林研究院
Coptis chinensis planting method
InactiveCN104641850ASolve the problem of rootingReproduce fastSeed and root treatmentPlant cultivationFertilizerCoptis chinensis
The invention discloses a coptis chinensis planting method; the planting method is characterized by comprising the steps: (1) preparation of a planting land; (2) furrowing; (3) seed treatment; (4) planting; (5) cultivation and (6) pest control. The problems of being difficult in rooting and low in reproductive rate are solved effectively by choosing the comprehensive measures such as proper matrixes, proper soaking agent, planting manner and proper temperature and humidity; and the reproduction speed is improved effectively. The coptis chinensis planting method is low in cost; with adoption of an atomizing water and fertilizer management and temperature / humidity control system, the method is simple and practical and is an effective method for large-scale planting of coptis chinensis.
Owner:QINGDAO XINRUNTU NURSERY STOCK SPECIALIZED COOP
Soil-less high stem planting process for Rosa canina
InactiveCN1985581ASolve the problem of rootingImprove efficiencyAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsGreenhouseBud
The soil-less high stem planting process for Rosa canina includes the following steps: selecting cutting wood of 70-150 cm length from annual branch in Feb or March, inserting the lower end of the cutting wood into ABT1 rooting powder solution for 10-30 min, inserting in culture medium comprising perlite, vermiculite and turfy soil in the weight ratio of 2 to 1 to 3 inside greenhouse, maintaining the temperature in 15-30deg.c and air humidity over 80 %, applying 800-1000 times diluted badistan solution once each week to root, transplanting to land, water and fertilizer management, grafting with Chinese rose bud in Aug to Oct, cutting stock in the next spring, and transplanting in the end of the next year. The process has easy operation, high efficiency, and short production period.
Owner:江苏春辉生态农林股份有限公司
Method of utilizing cornus walteri superior-tree twigs for cuttage breeding
ActiveCN109644708ASolve insufficient resourcesHigh rooting rateGrowth substratesCulture mediaDisinfectantGermplasm
The invention discloses a method of utilizing cornus walteri superior-tree twigs for cuttage breeding. The method includes that middle-upper twigs of current-year semi-lignified branches of a cornus walteri superior-tree are utilized as cuttings, three hormone solutions different in mass concentration and a disinfectant are used to treat the cuttings, cuttage facilities are set up, a matrix is prepared, and cuttage and management after cuttage are performed to induce rooting of cornus walteris cuttings and increase cutting rooting rate. The rooting rate reaches 92.7%, the technical problem oflow rooting rate caused by the fact that cornus walteris twigs are utilized for cuttage breeding is solved effectively, and the objective of rapid propagation of cornus walteris high-quality germplasmis achieved. By applying the method, a lot of high-quality cuttage seedlings of cornus walteris can be provided in short time, large-scale seedling culture standards are reached, and domestic demandon high-quality seedlings of cornus walteris can be met.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
Ecological slope protection plant measure method for concrete and rock high steep slope surfaces
ActiveCN109339068ASolve the problem of not being able to enter the soilNot easy to hardenHuman health protectionWatering devicesShotcreteWater storage tank
The invention discloses an ecological slope protection plant measure method for concrete and rock high steep slope surfaces. A concrete water storage tank and a self-flow type micro-irrigation systemare arranged on the concrete and rock slope surfaces to solve the problem that moisture in the steep slope surfaces cannot enter the soil depending on gravity, and reinforced plant planting holes, moisture holes and ventilated topdressing holes are adopted in the slope surfaces to solve the necessary moisture, nutrients and breathability for plant growth. After root hairs of plants are developed,side slopes are greened while a plant reinforcement wall is formed, the improvement of shallow landslides is facilitated, and the purpose of ecological slope protection is achieved. According to the ecological slope protection plant measure method for the concrete and rock high steep slope surfaces, ecological management is carried out on parts such as sprayed concrete, concrete and rocks where the root hairs of the plants are difficult to grow, the rate of survival of the plants is high, planting ranges of the plants are wide, the survival time is long, the landscape effect is good, the environmental influence is small, the wind resistance, water flow corrosion resistance and freezing corrosion resistance capacities are high, the investment is saved, the material expense is less, the labor intensity of workers is low, and the construction period is short.
Owner:郑楚英
Method for strengthening and rooting tissue culture seedlings of transgenic peanuts
ActiveCN102577981AVigorousSolve the difficulty of rooting seedlingsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudCulture mediums
The invention provides a method for strengthening and rooting tissue culture seedlings of transgenic peanuts. The method has a good seedling strengthening effect and is high in rooting rate and rooting quality. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) transferring peanut tissue culture seedlings on which cluster buds are induced and differentiated into a seedling strengthening culture medium A, culturing for 20 days, and replacing the culture medium once every 10 days, wherein a component of the seedling strengthening culture medium A is a Murashige and Skoog (MS) culture medium, and used hormone is cytokinin 6-benzylaminopurine (6-BA); (2) dividing the tissue culture seedlings with the heights of more than 1.5cm into single plants, transferring into a seedling strengthening culture medium B, culturing for 20 to 25 days, and replacing the culture medium once every 10 days, wherein a component of the seedling strengthening culture medium B is the MS culture medium, and used hormone is cytokinin 6-BA at the concentration of 0.4mg / L and auxin naphthyl acetic acid (NAA) at the concentration of 0.1mg / L; and (3) transferring into a rooting culture medium when the seedlings with the heights of 2.5 to 4cm, and rooting, wherein a component of the rooting culture medium is a one / second MS culture medium, and used hormone is auxin indolebutyric acid (IBA) at the concentration of 3mg / L and auxin NAA at the concentration of 0.3mg / L.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Method for culturing rapid propagation seedlings in superior-species chestnut mature embryo tissue
ActiveCN110402818AShorten the breeding cycleSolve the problem of rootingPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGerm plasmGermination
The invention provides a method for culturing rapid propagation seedlings in superior-species chestnut mature embryo tissue. The method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting, cleaning and disinfecting superior-species chestnuts; 2, obtaining and inoculating chestnut mature embryos; 3, culturing an explant; 4, performing acclimation seedling hardening of tissue culture seedlings. Accordingto the method, mature embryos are adopted as explants for performing tissue culture, the germination planting percent of chestnuts is greatly increased, the breeding period is shortened, stock breeding is accelerated, the chestnut germ plasm innovation and new-variety breeding efficiency are improved, and the method is of a great significance in pushing the industrial development of the State Quality Inspection Administration geographic marking product 'Luotian chestnut'.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV
Populus hopeiensis seedling growing method for combining bud grafting and cuttage
InactiveCN106256192APromotes self-rootingSolve the problem of rootingGraftingCultivating equipmentsRootstockGreening
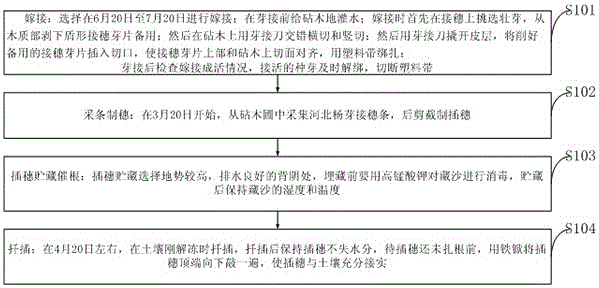
The invention discloses a populus hopeiensis seedling growing method for combining bud grafting and cuttage. Grafting is selected to be carried out from June 20 to July 20; from March 20, populus hopeiensis bud cion seedlings are collected from a stock garden, and then cutting slips are made through shearing; cutting slips are stored at high-terrain shady spots with good drainage performance, burying sand needs to be disinfected with potassium permanganate before burying, and the humidity and temperature of the burying sand are kept after storage; on about April 20, cuttage is carried out when soil is just unfrozen. According to the populus hopeiensis fast grafting seedling growing method, the propagation coefficient of populus hopeiensis hard to propagate can be increased, the problem about hard rooting of the populus hopeiensis is solved, the seedling growth quality is improved, resources are saved, and the method has important significance on land greening and ecological management of mountains, water, forests, land and lakes.
Owner:甘肃金立源科工贸有限公司
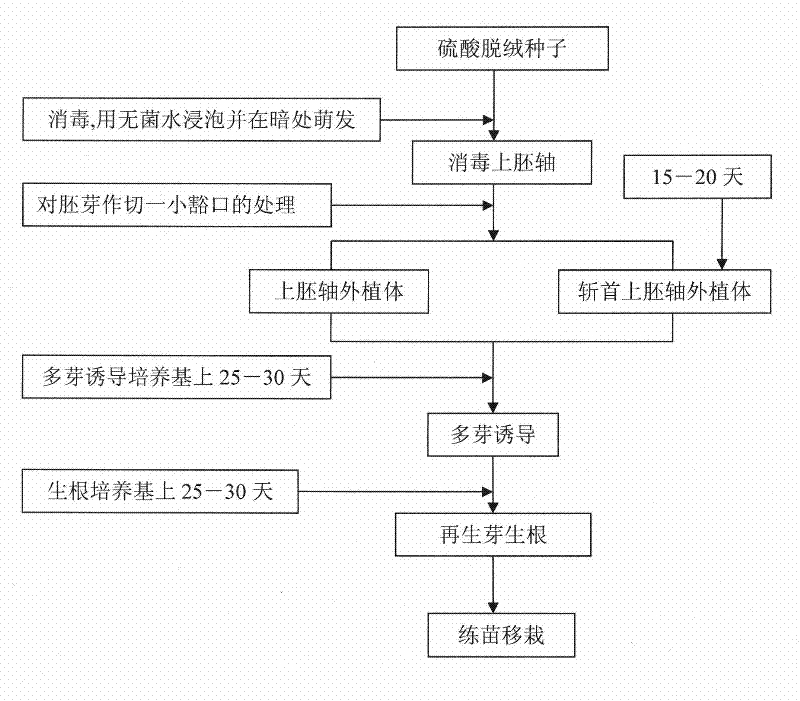
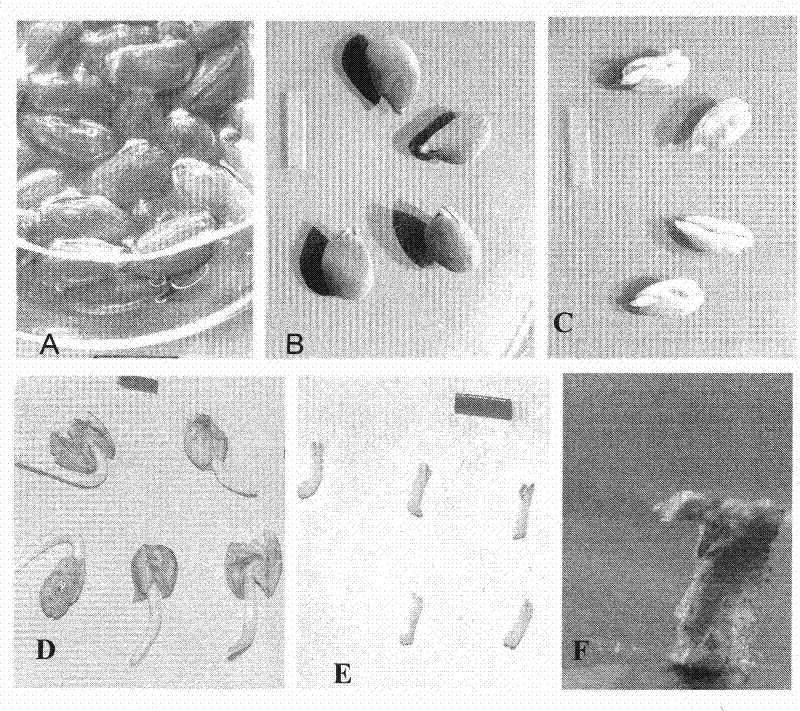
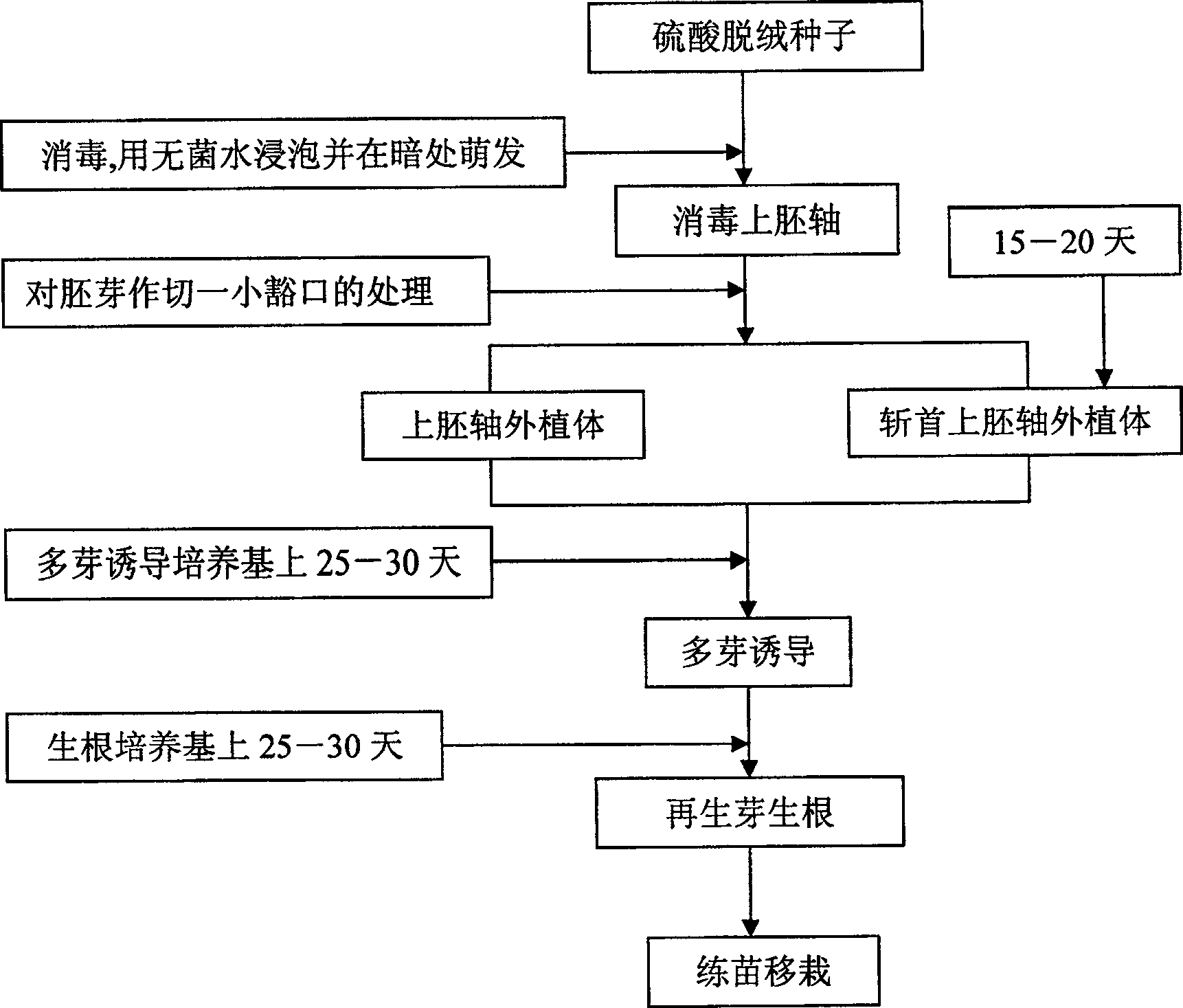
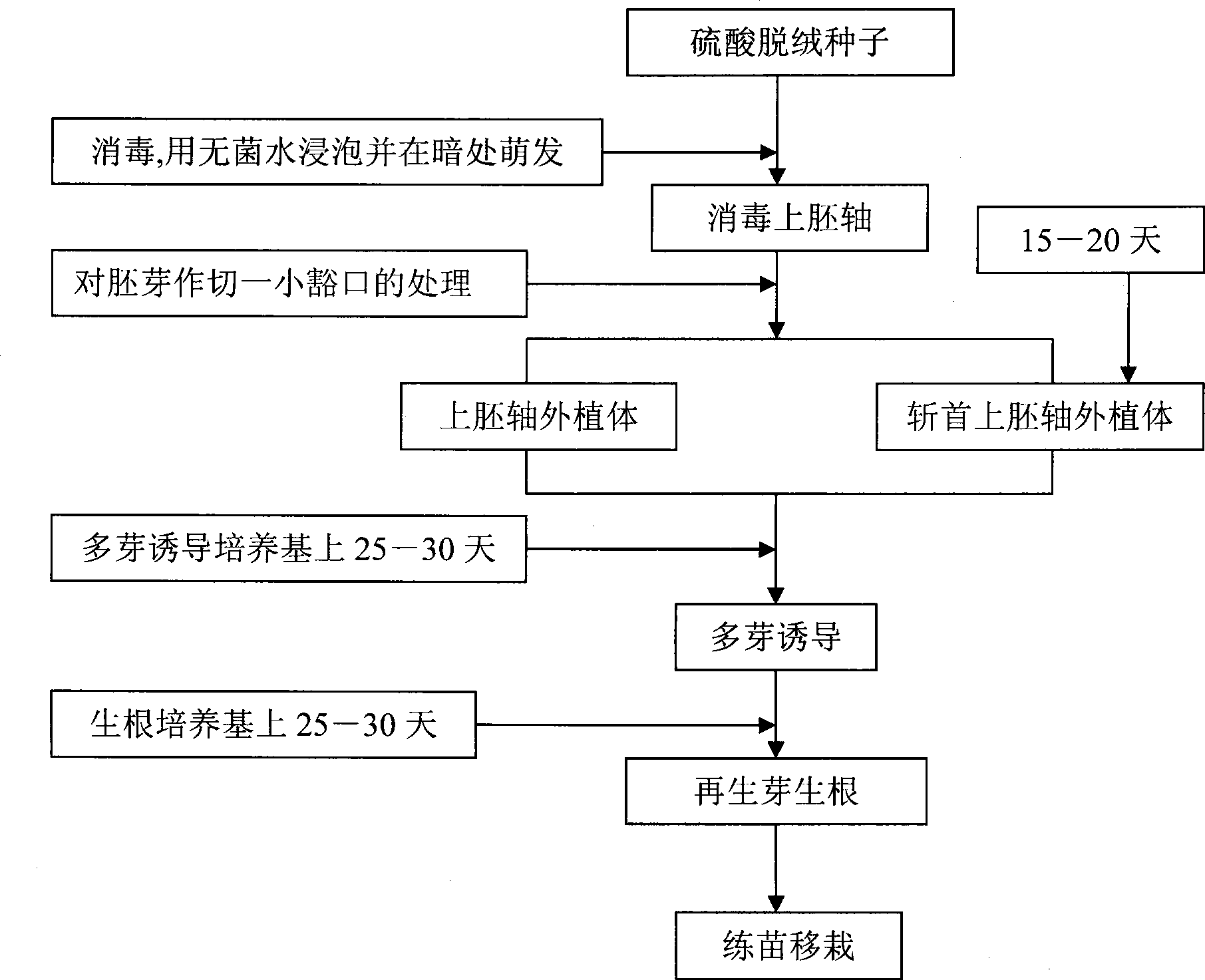
Technique for epicotyl of cotton culturing in vitro regenerated plant, and decapitated epicotyl explant
InactiveCN100998317AReduce deformity rateBreaking the technical bottleneck of genetically transformed cottonHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureEpicotylRhizome
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Rocky barren hill afforestation method
InactiveCN106508577AImprove survival rateGuaranteed survival rateCultivating equipmentsPlantletObserved Survival
The invention provides a rocky hill afforestation method, comprising the steps of digging tree holes in a rocky barren hill land, filling the tree holes with soil and water required by plantlets to grow, transplanting plantlets to the tree holes, and managing the transplanted plantlets. By using the rocky barren hill afforestation method, survival rate of the transplanted plantlets can be effectively increased and may be increased to 95%.
Owner:包头大青山自然保护区天龙生态抗旱植物研究所
Rapid propagation method for excellent Chinese fir family seedlings
PendingCN113099866ASolve the problem of unstable genetic quality and difficulty in initial bud inductionSolve easy browningGraftingPlant tissue cultureTissue cultureGrafting
The invention discloses a rapid propagation method for excellent Chinese fir family seedlings, and belongs to the technical field of Chinese fir cultivation. The rapid propagation method comprises the following steps: (1) excellent family grafting, (2) explant disinfection, (3) induction culture, (4) multiplication culture, (5) strong seedling culture, (6) ex-vitro rooting seedling transplanting and the like. The rapid propagation method solves the problems that Chinese fir tissue culture seedlings have unstable genetic quality and initial buds are difficult to induce, prone to browning and free of rooting, meanwhile, the procedures of rooting, seedling hardening and transplanting are simplified, so that the culture period is shortened, and the breeding cost is reduced.
Owner:贵州省林业科学研究院
Quick root accelerating method for Tamarix taklamakanensis M. T. Liu cutting slips
InactiveCN107567842AImprove survival ratePromote healingCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationShootZoology
The invention discloses a quick root accelerating method for Tamarix taklamakanensis M. T. Liu cutting slips. The method comprises the steps of collection and cutting of the cutting slips, rooting induction of the cutting slips, root accelerating culture in a hotbed, cuttage of the cutting slips and the like. According to the quick root accelerating method for the Tamarix taklamakanensis M. T. Liucutting slips, the structure of the root accelerating hotbed is reasonably designed, rooting induction and root accelerating in the hotbed are conducted by selecting appropriate rooting powder, and the root accelerating temperature and time are reasonably controlled, so that appropriate environmental conditions are created for the Tamarix taklamakanensis M. T. Liu cutting slips, and the coalescence and rooting of the cutting slip base portions are effectively accelerated; compared with a traditional Tamarix taklamakanensis M. T. Liu cuttage method, the cutting slip surviving rate is increasedby 10%, and the cutting slip breeding efficiency and the cuttage seedling-raising survive rate are obviously improved; the false-growth phenomenon occuring when the Tamarix taklamakanensis M. T. Liucutting slips germinate and grow shoots is effectively controlled, and the problems that the Tamarix taklamakanensis M. T. Liu cutting slip cuttage is difficult in rooting and low in breeding coefficient are solved.
Owner:GANSU DESERT CONTROL RES INST
Tissue culture propagation method for helleborus thibetanus
ActiveCN113728921ASolve the problem of low reproduction coefficientSolve the problem of rootingGrowth substratesCulture mediaHelleborus thibetanusSeedling
The invention provides a tissue culture propagation method for helleborus thibetanus. The tissue culture propagation method comprises the following steps of (1), obtaining and treating an explant; (2), carrying out adventitious bud induction culture; (3), carrying out adventitious bud subculture multiplication culture; (4), rooting culture; and (5), hardening seedlings and transplanting to obtain helleborus thibetanus seedlings. According to the method, hormone and a culture environment are comprehensively adjusted, so that the proliferation multiple of the adventitious buds of the helleborus thibetanus reaches 3.5 or above, the rooting rate reaches 90% or above, and the problems that the helleborus thibetanus is low in propagation coefficient, difficult to root and long in production period are solved; and besides, by keeping the excellent characters of the excellent strains, seedlings with stable excellent characters can be produced, standardization and factory operation are easy, and the excellent seedlings with the unified standard are provided for the market.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Nutrition soil for cuttage of European rosa chinensis
InactiveCN110073944AHigh in nutrientsMeets requirementsGrowth substratesCulture mediaWater dischargeAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses nutrition soil for cuttage of European rosa chinensis. The nutrition soil is prepared from the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 40 to 60 percent of acidic peat soil, 5 to 15 percent of perlite, 10 to 20 percent of vermiculite, 1 to 5 percent of rotten chicken manure, 1 to 5 percent of bone meal, 5 to 15 percent of rooting powder and 5 to 10 percent of insecticide sterilizing agents. The nutrition soil is loose and breathable; the nutrition ingredient content is high; through the addition of the bone meal, the seedling strengthening effect is achieved; thenutrition is accumulated for the early-stage flower bud differentiation; while the water is preserved, the water discharge is facilitated; the rooting requirements of the European rosa chinensis are met. The difficult problems of rooting difficulty, weak generated roots, survival difficulty in the later stage and the like of the European rosa chinensis after the cuttage can be solved.
Owner:XUZHOU VOCATIONAL COLLEGE OF BIOENG
A kind of rooting medium of meranti and its application
InactiveCN106359085BWell-growth and strongStrong resistanceClimate change adaptationAfforestationForest industryPlant cell
The invention belongs to the fields of forestry biotechnological seed breeding or plant cell engineering and discloses an E.urophylla*E.saligna rooting culture medium and an application thereof. On the basis of an improved MS culture medium, IBA and 3-AB are supplied to the rooting culture medium. By means of addition of the novel rooting inductive substance 3-AB and the synergistic effect of the rooting-type growth regulator IBA, rooting ratio of the E.urophylla*E.saligna is more than 87% and transplanting survival rate is more than 91%. When rooted seedlings are transplanted on bags, the seedlings grow tidily and robustly, have strong resistance, and completely reach demands of large-scale and commercial seedling production. The rooting culture medium has good repeatability and stable effects, and has no intensive fluctuation on the rooting ratio and transplanting survival rate even after multiple times of usage, thereby completely solving a problem that the E.urophylla*E.saligna is difficult to root during tissue culture induction.
Owner:RES INST OF TROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Direct polygerm-generation regeneration plant culture method by isolated culture of Xinjiang snow locus epicotyl
InactiveCN101518210BReduce deformity rateBreaking the technical bottleneck of genetically transformed cottonPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBudEpicotyl
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Soil-less high stem planting process for Rosa canina
InactiveCN100469239CSolve the problem of rootingImprove efficiencyAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsGreenhouseBud
The soil-less high stem planting process for Rosa canina includes the following steps: selecting cutting wood of 70-150 cm length from annual branch in Feb or March, inserting the lower end of the cutting wood into ABT1 rooting powder solution for 10-30 min, inserting in culture medium comprising perlite, vermiculite and turfy soil in the weight ratio of 2 to 1 to 3 inside greenhouse, maintaining the temperature in 15-30deg.c and air humidity over 80 %, applying 800-1000 times diluted badistan solution once each week to root, transplanting to land, water and fertilizer management, grafting with Chinese rose bud in Aug to Oct, cutting stock in the next spring, and transplanting in the end of the next year. The process has easy operation, high efficiency, and short production period.
Owner:江苏春辉生态农林股份有限公司
Technique for epicotyl of cotton culturing in vitro regenerated plant, and decapitated epicotyl explant
InactiveCN100518498CReduce deformity rateBreaking the technical bottleneck of genetically transformed cottonHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGenotypeEpicotyl
The invention discloses an epicotyl explant (epicotyl explant) of a cotton in vitro culture and direct multi-bud generation regenerated plant and a cultivation method for obtaining a complete regenerated plant by using the explant. The invention also discloses a decapitated epicotyl explant. The present invention utilizes epicotyl explants and fresh epicotyl explants to establish a technique for directly inducing multi-bud generation, elongation and rooting that does not depend on genotype, simple and fast cotton in vitro culture regeneration plant technology, Through the optimal screening of medium formula and carbon source, the degree of browning of explants is reduced to the lightest, the maximum number of buds in one explant is ≥ 3, and the rooting rate of regenerated shoots is above 90%, obtaining a plant with complete roots, stems and leaves. It only takes 3 to 4 months to regenerate plants, and the rate of deformed seedlings is low, which lays the foundation for the genetic improvement of cotton varieties used in production.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Asexual reproduction method for elaeagnus mollis
ActiveCN100571503CIncrease planting areaMaintain physiological balanceFertilising methodsHorticulture methodsTree breedingAsexual reproduction
The invention relates to the technical field of plant propagation, in particular to a method for asexual propagation of Samara oil tree, which solves the problem of low seedling germination rate and emergence rate in the existing propagation method of Samara oil tree, and it is difficult to produce new shoots when cutting twigs. Root and other problems, including building seedbeds; collecting cuttings on the mother tree; cutting the collected cuttings in the seedbed matrix; spraying water on the leaves of Samara oil tree after cuttings, the temperature is 20-30 ° C; fertilizing the leaves , until the spikes take root. The invention utilizes asexual reproduction technology to reproduce more seedlings in a short period of time, adjust the temperature and humidity of the seedbed, maintain the physiological balance of the cuttings, and carry out disinfection and plant growth hormone treatment on the cut cuttings to provide the required growth for the cuttings to take root. At the same time, the mother tree is technically treated to promote the formation and development of adventitious roots of cuttings, effectively solving the problem of difficult callus rooting. The propagation technology is simple and fast, with low cost and high reproduction rate.
Owner:山西琪尔康翅果生物制品有限公司
Direct polygerm-generation regeneration plant culture method by isolated culture of Xinjiang snow locus epicotyl
InactiveCN101518210AReduce deformity rateBreaking the technical bottleneck of genetically transformed cottonHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudEpicotyl
The invention discloses a direct polygerm-generation regeneration plant culture method by the isolated culture of Xinjiang snow locus epicotyl. The invention also discloses a decapitated epicotyl exophyte. The invention utilizes an epicotyl exophyte and the decapitated epicotyl exophyte to establish a gene-independent, simple and rapid Xinjiang snow locus isolated culture regeneration plant culture technology which directly induces polygerm generation, elongation and rootage; by the formulation of a culture medium and the optimizing screen of carbon sources, the browning degree of the exophyte is lowered to the lightest degree, an exophyte can have the maximum generation bud number more than or equal to 3 and the regeneration bud rootage rate higher than 90 percent, and a regeneration plant with a full root, a full stalk and full leaves can be obtained by only 3 to 4 months. The invention has low malformed seedling rate and lays a foundation for the hereditary improvement of Xinjiang snow locus breeds applied in production during gene engineering.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A kind of rooting culture medium of Eucalyptus caudatum and its application
InactiveCN106342683BWell-growth and strongStrong resistanceClimate change adaptationAfforestationCuticleLateral root
The invention belongs to the field of forestry biotechnology breeding and discloses a eucalyptus urophylla rooting medium and application. According to the rooting medium, root induction substances, such as IBA, ABT-1, 3-AB and 3-AB, are added on the basis of an improved MS culture medium formula so as to serve as the conventional cytostatics, and by matching with the other two root induction substances, 3-AB achieves an obvious effect of inducing adventitious roots, so that the growth and development directions of cambial cells are changed, a parenchymal cell state is developed into a root primordium form of the adventitious roots, and the cells are decreased and increased, continuously divided along the periclinal direction and finally break through the epidermis to grow into lateral roots. According to use of the rooting medium disclosed by the invention, the rooting rate of eucalyptus urophylla can reach over 85%. The survival rate can be over 90% after transplanting. Moreover, the rooting medium is high in reproducibility and stable in effect, and after repeated use of the medium, the rooting rate and transplanting survival rate do not have great fluctuation.
Owner:RES INST OF TROPICAL FORESTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
In-bottle rooting method for salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling
ActiveCN102726294BHigh rooting rateSolve the problem of rootingPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGrowth hormoneBottle
The purpose of the present invention is to disclose an in-bottle rooting method for a salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting a secondary seedling, wherein a secondary culture salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling is selected, the height of the seedling is 2-3.5 cm, and the robust individual ulmus pumila seedling having extending leaves is selected; and (2) inoculating the selected secondary culture salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling onto a WPM rooting medium, wherein the WPM rooting medium is added with growth hormone, cytokinin and exogenous additives. According to the present invention, a medium formula having a high rooting rate is adopted so as to effectively solve the rooting problem of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling, improve the rooting rate of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling, reduce the cost, accelerate the factory production of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila, provide high quality salt tolerance ulmus pumila seedlings for nursery stock markets, and achieve the purpose of the present invention, wherein the rooting rate of the salt tolerance ulmus pumila tissue culture seedling can be up to 95%.
Owner:上海菁艺生物科技有限公司
A method for fast breeding seedlings by tissue culture of mature embryos of fine chestnut
ActiveCN110402818BImprove germination rateShorten the breeding cyclePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyGermplasm
The present invention provides a method for rapidly growing seedlings by tissue culture of mature mature embryos of Chinese chestnut, comprising the following steps: (1) selecting, cleaning and disinfecting Chinese chestnuts of high quality; (2) obtaining and inoculating mature Chinese chestnut embryos; (3) Cultivation of explants; (4) domestication and hardening of tissue culture seedlings. The method provided by the invention uses mature embryos as explants to carry out tissue culture, which greatly improves the germination and seedling rate of Chinese chestnut, shortens the breeding cycle, accelerates the breeding of improved varieties, improves the efficiency of Chinese chestnut germplasm innovation and new variety selection, and promotes The industrial development of the geographical indication product "Luotian Chestnut" of the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine is of great significance.
Owner:HUANGGANG NORMAL UNIV
Direct multibud-generation regeneration plant culture method by isolated culture of beet epicotyl
InactiveCN101518209BReduce deformity rateBreaking the technical bottleneck of genetically transformed cottonSeed and root treatmentHorticulture methodsBudGene engineering
The invention discloses a direct polygerm-generation regeneration plant culture method by the isolated culture of beet epicotyl. The invention also discloses a decapitated epicotyl exophyte. The invenThe invention discloses a direct polygerm-generation regeneration plant culture method by the isolated culture of beet epicotyl. The invention also discloses a decapitated epicotyl exophyte. The invention utilizes an epicotyl exophyte and the decapitated epicotyl exophyte to establish a gene-independent, simple and rapid beet isolated culture regeneration plant culture technology which directly intion utilizes an epicotyl exophyte and the decapitated epicotyl exophyte to establish a gene-independent, simple and rapid beet isolated culture regeneration plant culture technology which directly induces polygerm generation, elongation and rootage; by the formulation of a culture medium and the optimizing screen of carbon sources, the browning degree of the exophyte is lowered to the lightest deduces polygerm generation, elongation and rootage; by the formulation of a culture medium and the optimizing screen of carbon sources, the browning degree of the exophyte is lowered to the lightest degree, an exophyte can have the maximum generation bud number more than or equal to 3 and the regeneration bud rootage rate higher than 90 percent, and a regeneration plant with a full root, a full stagree, an exophyte can have the maximum generation bud number more than or equal to 3 and the regeneration bud rootage rate higher than 90 percent, and a regeneration plant with a full root, a full stalk and full leaves can be obtained by only 3 to 4 months. The invention has low malformed seedling rate and lays a foundation for the hereditary improvement of beet breeds applied in production duringlk and full leaves can be obtained by only 3 to 4 months. The invention has low malformed seedling rate and lays a foundation for the hereditary improvement of beet breeds applied in production during gene engineering.gene engineering.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
An ecological slope protection plant measure method for high and steep slopes of concrete and rocks
ActiveCN109339068BSolve the problem of not being able to enter the soilNot easy to hardenHuman health protectionWatering devicesShotcreteWater storage
The invention discloses an ecological slope protection plant measure method for high and steep slopes of concrete and rocks. Concrete water storage tanks and self-flowing micro-irrigation systems are used on slopes such as concrete and rocks to solve the problem that water on steep slopes cannot enter the soil by gravity. At the same time, reinforced planting holes, water holes and ventilation holes are used on slopes to solve The water, nutrients and air permeability necessary for plant growth. After the roots of the plants are developed, a plant-reinforced wall is formed while the slope is greening, which is beneficial to the improvement of shallow landslides and achieves the purpose of ecological slope protection. Through the measures and methods of the present invention, ecological control is carried out on the parts where the roots of plants on high and steep slopes such as shotcrete, concrete, and rocks are difficult to grow, and the plant survival rate is high, the planting range is wide, the survival time is long, the landscape effect is good, and the environmental impact is small. Strong wind resistance, water erosion resistance, and freezing erosion resistance, low investment, less material consumption, low labor intensity for workers, and short construction period.
Owner:郑楚英
Artificial efficient propagation method of swertia nervosa (G.Don)Wall.
ActiveCN110506629AOvercome the difficulty of not being able to carry out production on an annual basisSave land resourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsShootBiological materials
The invention discloses an artificial efficient propagation method of swertia nervosa (G.Don)Wall.. According to the method, in the same culture medium, callus induction and basal stem multiple shootgeneration can be conducted simultaneously, basal stem multiple shoot generation and multiplication culture can also be conducted simultaneously, and thus the culture procedure is simplified into three steps; in the whole rapid propagation process, only three kinds of culture mediums are needed to achieve the purposes of callus induction, basal stem multiple shoot generation, and multiplication culture, avoid the phenomena of browning and vitrification and solve the problem of root taking, the inoculation procedures and the culture space are saved, and arrangement of production plans is facilitated; besides, since the inoculation frequency is reduced, the possibility of contamination is lowered; the culture mediums for callus induction and multiplication culture have the function of basalstem multiple shoot generation, so that biological materials better adapt to replacement of the culture mediums, the success rate of tissue culture of the biological materials is increased, and the propagation coefficient is greatly increased.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
A method for rooting in a bottle of tissue cultured seedlings of Xianmai fragrant tea
ActiveCN110972949BSolve the problem of rootingHigh rooting rateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGrowth hormoneSeedling
Owner:WUXI MISHO ECOLOGY LANDSCAPE
A kind of method of black locust hard branch cutting rooting
ActiveCN104705063BImprove permeabilityImproves ability to absorb root powderCultivating equipmentsHorticultureYellow LocustAlcohol
The invention discloses a cutting rooting method for hard branches of robinia pseudoacacia. The method comprises the following steps: selecting one-year shoots of the robinia pseudoacacia as cuttings, and trimming the shoots, so as to enable the shoots to have the mean length being 10-12cm; quickly dipping the trimmed shoots with ethyl alcohol, and soaking with an ABT1 rooting powder solution for 48 hours, and then cutting into a sand substrate of a seedbed; and carrying out cutting, watering thoroughly, and implementing seedling management. The method is low in technical requirements, but the problem of low cutting survival rate of the robinia pseudoacacia caused by secondary metabolites such as tannin is effectively solved; the cutting rooting rate of the robinia pseudoacacia can be up to 95-100%; a technical support is provided for vegetative propagation and seedling of robinia pseudoacacia; and the method has the great application and popularization values.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
Micro-grafting method for tea trees
PendingCN114402824ASolve the problem of rootingHigh reproductive coefficientGraftingCultivating equipmentsSocial benefitsRootstock
The invention provides a micro-grafting method for a tea tree. The micro-grafting method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a stock material; 2, preparing a scion material; 3, micro-grafting; according to the method, 10-December 'Meitan' is selected as a stock, a rootless tissue culture seedling 'plateau green' is selected as a scion, the scion is subjected to a rapid propagation system, explant disinfection, bud and leaf germination culture, multiplication culture, strong seedling culture, seedling hardening and final grafting, and the scion and the stock are healed to form a complete plant. The method can realize industrialized seedling production, solves the problem of supply shortage of improved seedlings in tea garden construction, provides a new way for tea tree propagation, and brings greater economic benefits and social benefits to the society.
Owner:GUIZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com