Technique for epicotyl of cotton culturing in vitro regenerated plant, and decapitated epicotyl explant
A technology for in vitro culture and regeneration of plants, applied in plant regeneration, plant cells, botany equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of browning of explants, low rooting efficiency, high deformity rate, etc., and achieve easy survival after transplanting, The regenerated buds are strong and the effect of slowing down browning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
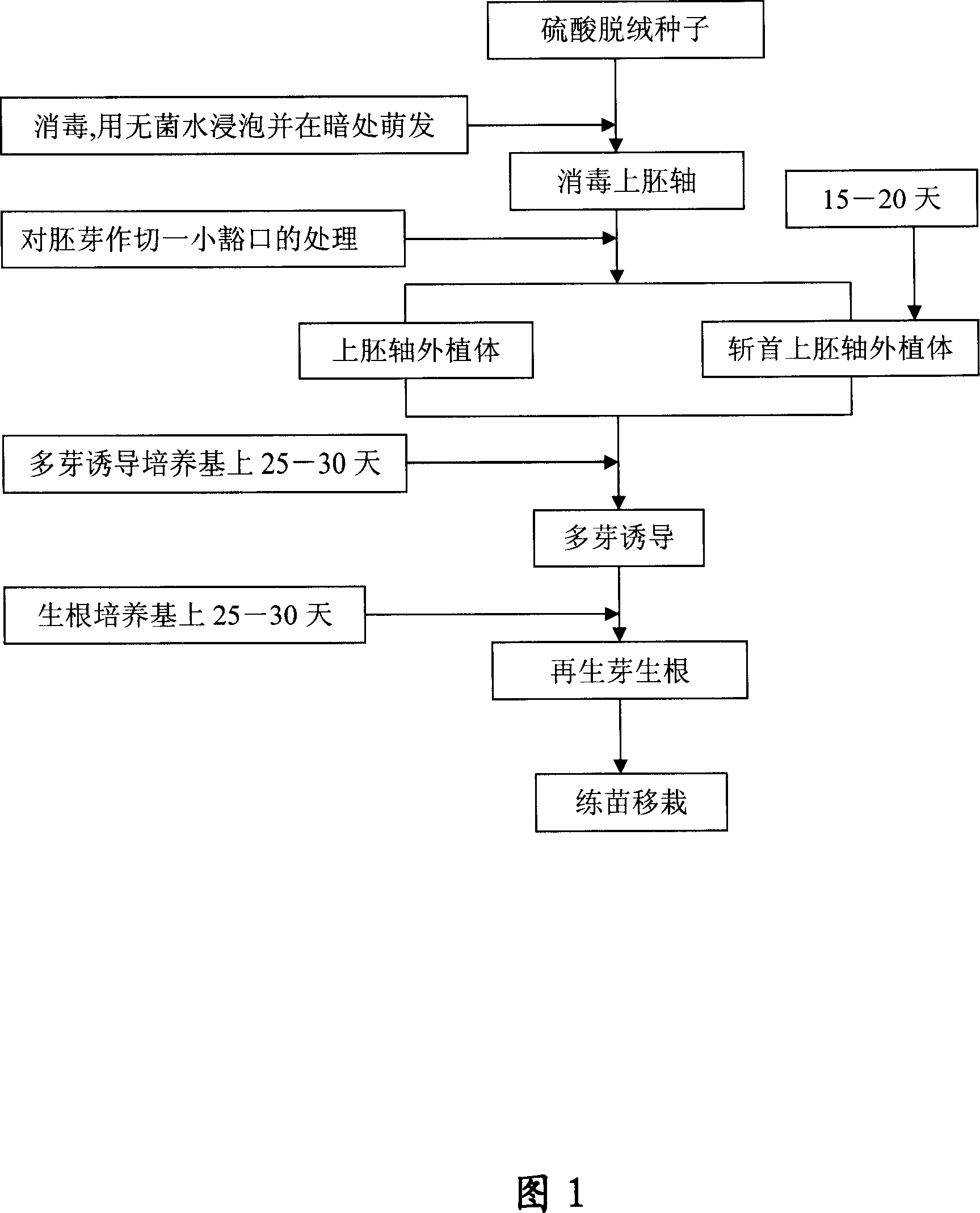
[0047] Example 1: The method of in vitro culture of sea-island cotton epicotyls for direct multi-bud generation and regenerated plants and decapitated epicotyl explants
[0048] The seeds of sea-island cotton variety Xinhai No. 19 were treated with sulfuric acid to obtain light seeds. The seeds were first surface sterilized with 70% ethanol for 30 sec, followed by 15% hydrogen peroxide (H 2 o 2 ) aqueous solution for 2hr., then rinsed with sterilized water for 6 times and soaked in sterilized water, drained after 12-36hr., squeezed out the seed coat, inoculated the seed kernel on 1 / 2MS solid medium and cultured in a dark place On the 1st to 3rd day, the cotyledon and the hypocotyl and radicle 4-6 mm below the cotyledon node were cut off and discarded, and the remaining part was the epicotyl explant. Cut a gap of 0.3-0.7 mm longitudinally at the top of the epicotyl explant, avoid splitting the hypocotyl, and then insert the multi-bud induction medium (MS salt+B) with the 4-6 ...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: The method of in vitro culture of upland cotton epicotyls for direct multi-bud regeneration and decapitated epicotyl explants
[0050] The seeds of Xinluzao 17, an early-maturing upland cotton variety, were treated with sulfuric acid to obtain light seeds. The seeds were first surface sterilized with 70% ethanol for 30 sec, followed by 15% hydrogen peroxide (H 2 o 2 ) aqueous solution for 2hr., then rinse with sterilized water for 5 times and soak in sterilized water. After 36-48hr., drain the water and squeeze out the seed coat, inoculate the seed kernel on 1 / 2MS solid medium and culture in a dark place On 2-5 days, cut off and discard the cotyledons and the hypocotyls and radicles 6-10 mm below the nodes of the cotyledons, and the remaining part is the epicotyl explant. Cut a gap of 0.7-1.3 mm longitudinally at the top of the epicotyl explant, avoid splitting the hypocotyl, and then insert the multi-bud induction medium (MS salt+B) with the 6-10 mm hypoco...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3: The method of in vitro culture of Xintiansi No. 1 epicotyl and direct multi-bud regeneration plant and decapitated epicotyl explant
[0052] Gently crush the seed coat of Xintiansi No. 1 seed to remove the kernel, first sterilize the surface with 70% ethanol for 30 sec, then sterilize with 0.1% mercuric chloride aqueous solution for 10 min., and then rinse with sterilized water for 6 times. Kernels were inoculated on 1 / 2MS solid medium and cultured under light. Cut off the cotyledons and hypocotyls and radicles 6-10mm below the cotyledon nodes from the aseptic seedlings that had been cultured for 5-7 days. For the epicotyl explants, the upper embryo was treated with a small gap, and then transferred to the medium for inducing multiple shoots (MS salt+B 5 Organic +6-BA 0.1~0.5mg / l+NAA 0.5~1.5mg / l+glucose 30g / l), after 20 days of cultivation, multiple buds can be seen. After culturing the epicotyl explants that did not produce multiple buds for 15 days, the bu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com