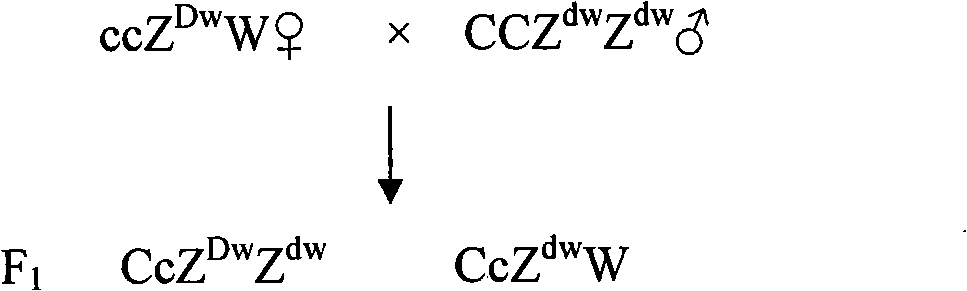Patents
Literature
118 results about "Germ plasm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Germ plasm is August Weismann's 19th century concept (German: Keimplasma) that heritable information is transmitted only by germ cells in the gonads (ovaries and testes), not by somatic cells. The related idea that information cannot pass from somatic cells to the germ line, contrary to Lamarckism, is called the Weismann barrier. The theory to some extent anticipated the development of modern genetics.
Method for nondestructively measuring main fatty acid content of peanut seeds
InactiveCN101887018ANo damageEasy to operateScattering properties measurementsGerm plasmMathematical model
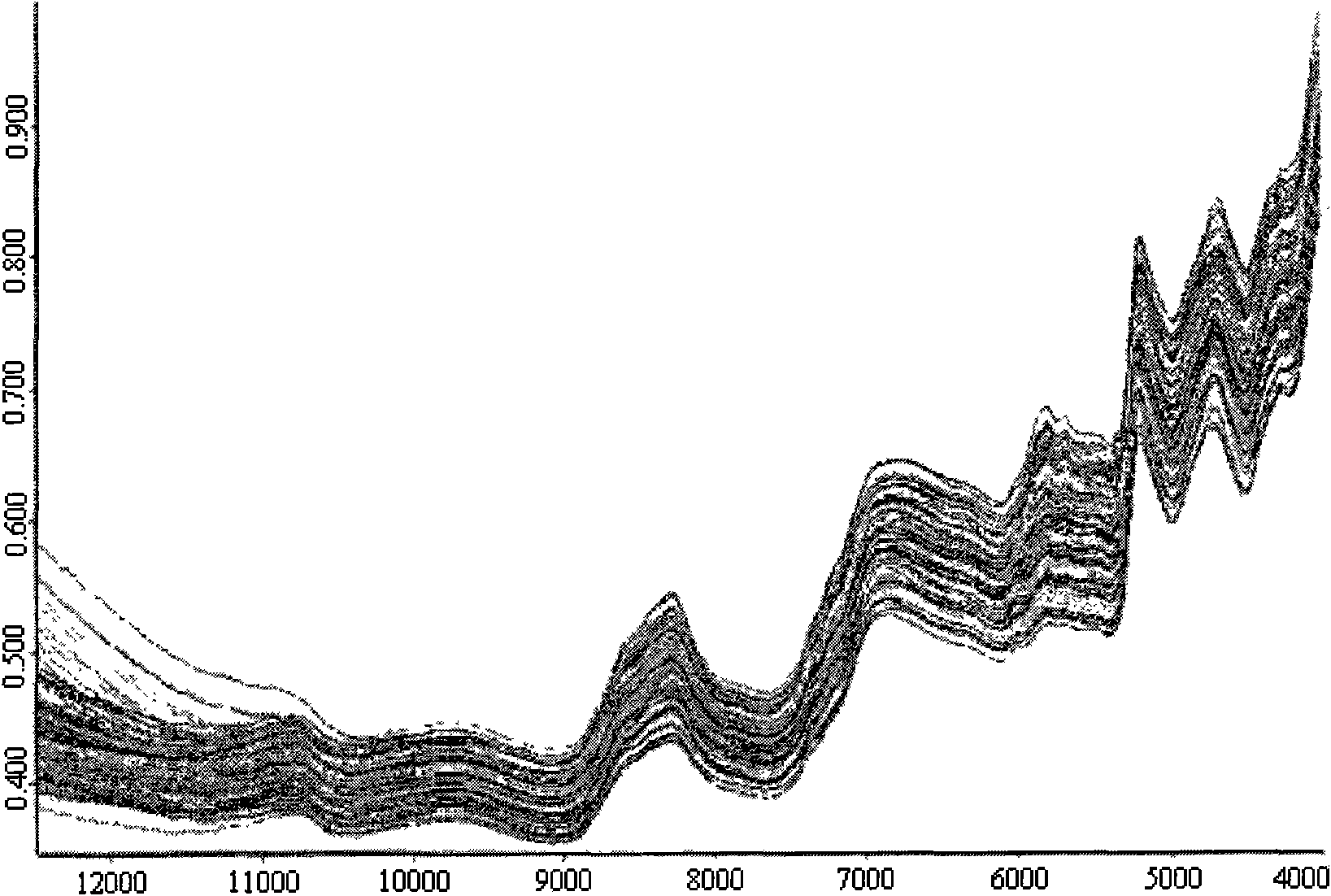
The invention discloses a method for nondestructively measuring main fatty acid content of peanut seeds. The method comprises the following steps of: based on the Fourier transform near-infrared diffuse reflection spectrum technology, scanning spectrums by adopting a best integrating sphere diffuse reflection mode for eliminating solid granule non-uniformity, establishing a multiple regression mathematical model by using full peanut seeds of multiple genotypes as standard sample sets, and predicting the main fatty acid content of an unknown sample through the model. The method is nondestructive, does not need to treat the sample, and does not harm the vitality and tissue structure of the seeds. The method has the advantages of simple operation, high sensitivity, high scanning speed, good signal-to-noise ratio and high measurement speed, and is suitable for high oleic acid quality breeding, germ plasm resource identification and inheritance rule research of peanuts.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Vitrification cryopreservation method of dendrobium wardianum warner protocorm
The invention provides a vitrification cryopreservation method of dendrobium wardianum warner protocorm, relating to the technical field of cryopreservation. The method comprises the following steps of: after preprocessing the protocorm with high permeability at low temperature, transferring the protocorm to a loading liquid; performing dewatering treatment, transferring the protocorm to a freezing tube which is filled with vitrification solution; and rapidly filling with liquid nitrogen for cryopreservation. The method in the invention provides technical guarantee for the preservation of theendangered dendrobium wardianum warner germ plasm resource. The invention provides an effective path for the preservation of the dendrobium plant even the arethusa resource and the cultivation of newspecies by using plant diversity.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
High-flux microorganism identification method
InactiveCN101363056AGood value for moneyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGerm plasmMass spectrometry
The invention discloses a high throughout microbiological assay method which comprises the following steps of sampling; extracting germ plasm; mass spectrometric analysis; data analysis; and microbiological assay. The method has the advantages that thousands of kinds of bacteria, virus, epiphytes and protozoans can be identified at the same time, while other systems only can identify little infective pathogene at the same time, so that the development of the systems are limited by quantity; the method can provide the relative quantity of a plurality of pathogens in a single sample, but most systems do not have the ability currently; the method is rapid and needs not to culture, one sample can be analyzed within less than 4 hours, while a plurality of weeks are spent on culturing, certainly, some samples can not be cultured at all; environmental or clinical samples which range from air to most complex biological samples in all mediums can be analyzed, so that the method is very universal; as no sequence measurement is needed, the method is the proposal with very good cost performance for the identification of infective pathogene.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Amplimer of large yellow croaker mitochondrion complete genome sequence and application thereof
ActiveCN102776183AEasy splicingIncrease success rateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationGerm plasmGene orders
The invention discloses an amplimer of a large yellow croaker mitochondrion complete genome sequence and an application thereof. The 15 pairs of amplimer are applied, a gene order is respectively shown as SEQ ID No: 1-30, the amplimer is further used for obtaining a Tai Qu family large yellow croaker mitochondrion complete genome sequence and a Min-Yue East family large yellow croaker mitochondrion complete genome sequence which are respectively shown as SEQ ID No: 31 and SEQ ID No: 32, and an amplimer of large yellow croakers in a high variation region is obtained. The amplimer and the application have the advantages that the Tai Qu family large yellow croaker and Min-Yue East family large yellow croaker mitochondrion complete genome sequences can be quickly and efficiently obtained respectively through the 15 pairs of amplimers; and the amplimer of the large yellow croakers in the high variation region provides support for the research of species identification, geographical population identification, germ plasm resources and genetic diversity of the large yellow croakers, and further provide the basis for developing an identification technology of Tai Qu family large yellow croakers and Min-Yue East family large yellow croakers.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
New silkworm breed breeding method for mass-production of full-natural pure sericin protein
The invention provides a method for selecting and breeding a novel silkworm breed capable of producing a great number of all natural pure sericin proteins, which introduces a special germ plasm resource from Japan, adopts genetic thremmatology to be combined with bioscience, and utilizes a distant hybridization method to breed a silkworm breed with sturdy, disease prevention, high temperature resistance, short breeding period and excellent economic character. The method leads excellent genes of the silkworm breed in the germ plasm resource to breed into an all natural pure sericin silkworm breed with high purity, and provides a novel approach for non spun silk industries to produce all natural pure siricin materials.
Owner:SERICULTURAL RES INST ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Gene for controlling rice fertility, encoded protein and application thereof
ActiveCN102634522AExpanding the Germplasm BaseSimple methodBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementAnti-Sense RNAGermplasm
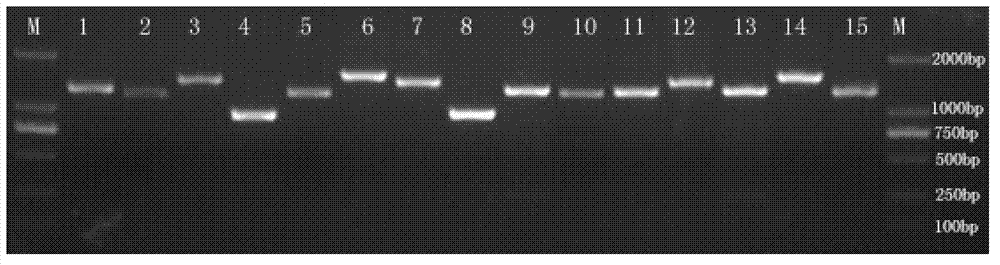
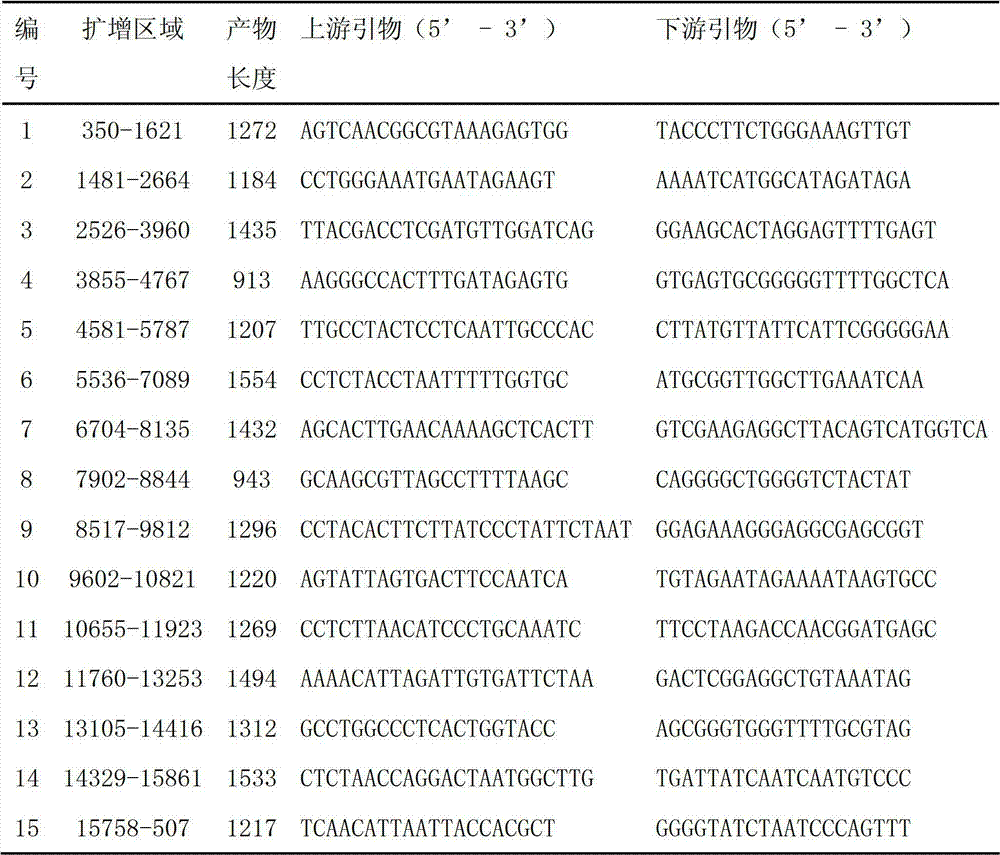
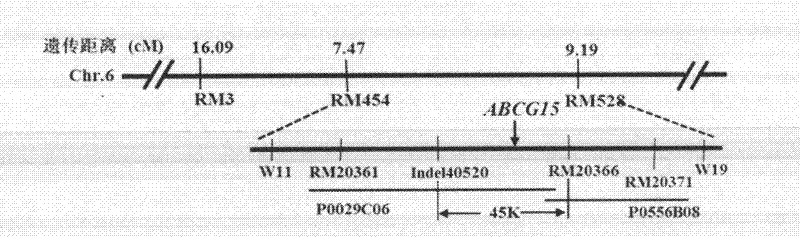
The invention discloses a gene ABCG15 for controlling rice fertility, an encoded protein and the application thereof. The invention also discloses a single recessive nuclear sterile gene, which is generated by mutation caused by deletion of the gene 12bp for controlling the rice fertility. The invention also discloses a method for obtaining a rice sterile line by controlling the expression of the rice fertility gene according to an RNAi technology and the method comprises the following steps of: amplifying a DNA fragment for generating an anti-sense RNA, constructing an expression vector, and transforming the DNA fragment into the normal fertile rice, so as to obtain a new rice nuclear sterile material. The newly found gene for controlling the rice fertility provides a new way for culturing the rice nuclear sterile line. The method for generating the rice nuclear sterile line is convenient and quick. The rice nuclear sterile material can be used for replacing the manual castration during the rice hybridization, labor is saved; the rice nuclear sterile material also can be used for recurrent selective breeding and plays an important role in widening the rice germ plasm basis.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for screening specific molecular markers of rice fertility restorer genes
InactiveCN101717819ASpeed up the breeding processImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGerm plasm
The invention provides a method for screening specific molecular markers of rice fertility restorer genes, which is characterized by applying rice germ plasm resources carrying and not carrying fertility restorer genes and screening the molecular markers, the sterile lines and (or) the restorer lines of which are in specific banding patterns, from the molecular markers closely linked with the rice fertility restorer genes Rf3 and Rf4. With the markers adopted to carry out auxiliary selection on the molecular markers of rice fertility restorer genes, the breeding efficiency of the sterile lines and the restorer lines of indica type rice can be improved.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Method for preparing cabbage type rape BnPABP3 promoter and application thereof
InactiveCN102220325ATissue-specific expression functionHigh biosecurityFermentationPlant genotype modificationGerm plasmEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cabbage type rape BnPABP3 promoter (PBnPABP3) and the application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning PBnPABP3 sequence by utilizing the genome walking method, extracting genome DNA by utilizing the SDS cracking method, carrying out enzyme digestion on DNA by respectively using endonuclease DraI, EcoRV, PvuII and StuI in different systems, carrying out the first round of PCR amplification by adopting the product as a template after joint segments are connected with the product, and carrying out the second round of PCR amplification by adopting the 50 times diluent of PCR products obtained in the first round as a template so as to obtain the PBnPABP3. The PBnPABP3 is applied to anther and pollen grains of plant. The promoter has the function of driving exogenous gene expression, the expression parts of the promoter are in the anther and pollen grains of plant, and the promoter has the application potentiality in the aspects of improving the safety of rape edible oil as well as the quality of crops, artificially creating sterile line and restorer line, enriching germ plasm resources, and the like.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-efficiency screening method for microsatellite marker of Marbled Sand Goby and application of same
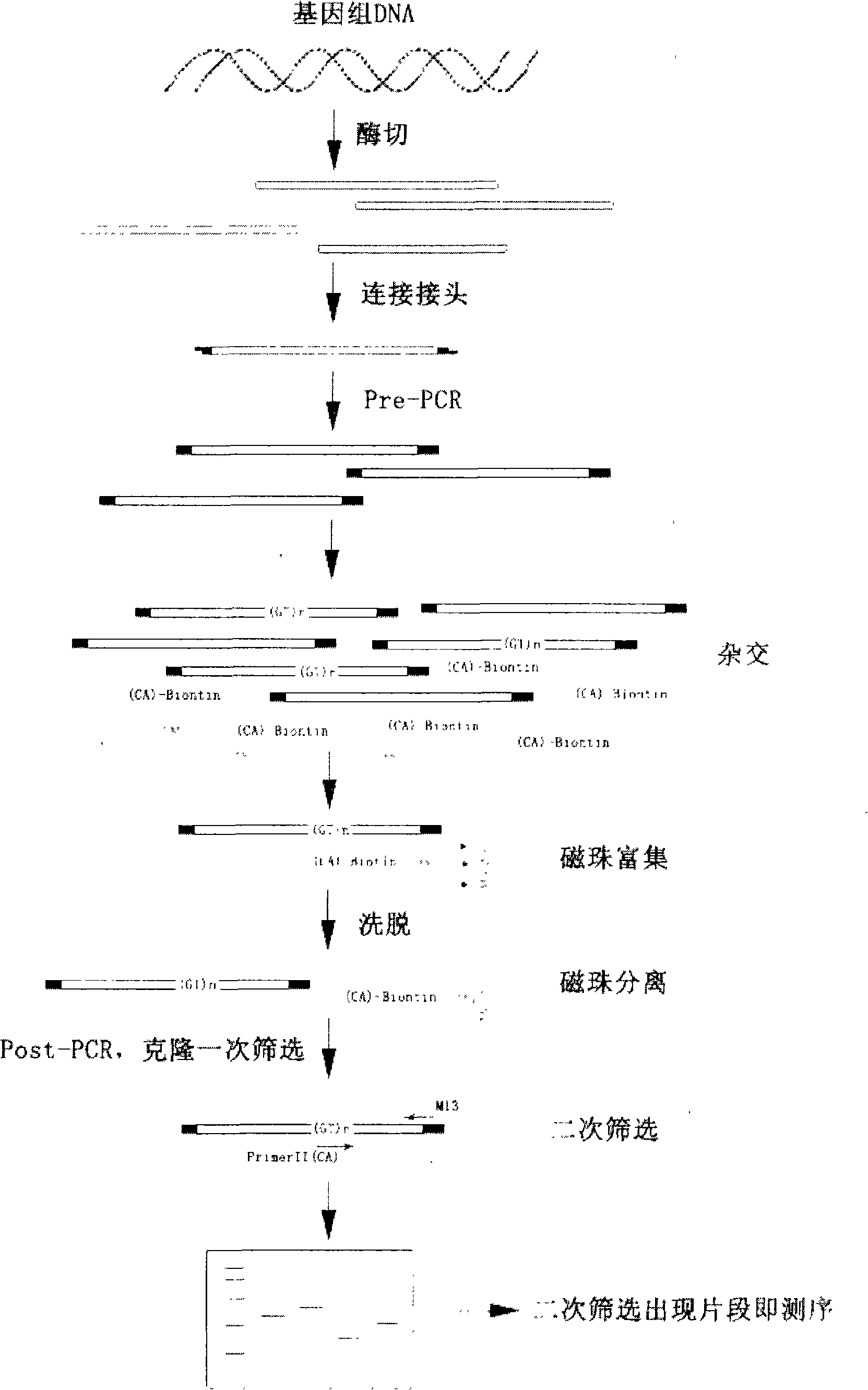
InactiveCN102134586ARapid development of germplasm resources protectionImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmEnrichment methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of DNA markers of molecular genetics of fishes, and particularly relates to the fast and highly efficient screening and application of the microsatellite loci of the Marbled Sand Goby. The method comprises the following steps: large mass DNA enzyme ligation, connection; low cycle index Pre-PCR; construction of the enriched library of microsatellite fragments by utilizing a biotinylated probe and streptomycin magnetic beads; screening of positive clones, and further improvement of the detection efficiency of the microsatellite loci through secondary screening; and population genetic analysis by using an obtained microsatellite primer. The invention improves the existing magnetic-bead enrichment method, efficiently and quickly screens the microsatellite loci, reduces the sequencing cost, and simultaneously overcomes the deficiency on safety during secondary screening adopting isotope. The obtained microsatellite marker provides scientific basis and detection means for the germ plasm resource protection, the germ plasm improvement, the genetic breeding, and the like of the Marbled Sand Goby.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Screening method of Muricidae mitochondrion COI gene amplification primer
InactiveCN101942433AEfficient amplificationLow amplification efficiencyDNA preparationGerm plasmScreening method
The invention discloses a screening method of a Muricidae mitochondrion COI gene amplification primer, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: a. a COI general amplification primer is used for amplifying the COI sequence of parts of Muricidae species; b. the sequence of the COI general amplification product is compared with the COI sequence of the obtained parts of Muricidae species to find out all mutation bases of the Muricidae mitochondrion COI sequence on the COI general amplification primer sequence section so as to recombine different Muricidae COI amplification primers; and c. a pair of primers with best Muricidae species amplification effect is obtained by screening the newly-combined different COI amplification primers. The Muricidae mitochondrion COI gene amplification primer of the invention can effectively amplify the COI sequence of different specimens of the Muricidae, and has an important meaning for researching the species taxonomy, system development and systematic geography of Muricidae and protecting Muricidae germ plasm resource.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Detection method for Apostichopus japonicas AjE101 micro-satellite DNA label
InactiveCN102140522AGood polymorphismImprove stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmGenetic diversity
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology DNA labeling technology and application, and in particular relates to Apostichopus japonicas express sequence tag EST micro-satellite label screening development and application. The invention provides Apostichopus japonicas AjE101 micro-satellite specific DNA primers, a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction system by utilizing the primers, and a detection method for an Apostichopus japonicas AjE101 micro-satellite DNA label. The detection method comprises the following steps of: extracting genome of Litopenaeus vannamei Boone; designing the specific primers at two ends of an Apostichopus japonicas AjE101 micro-satellite DNA core sequence; and performing PCR amplification on genome DNA of different groups of the Litopenaeus vannamei Boone or individuals in the group by using the primers, analyzing products, and determining the genome of each individual so as to obtain an Apostichopus japonicas polymorphism genetic variation map. The invention is mainly applied to Apostichopus japonicas germ plasm resource and genetic diversity analysis, cular population genetics, construction of genetic maps and research of functional genes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tilapia male and female pairing propagating method
InactiveCN101138329ASolve the problem of germplasm degradationControl inbreedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGerm plasmTilapia
The present invention relates to a male and female mating propagation method of tilapia, in specific to a mating propagation of tilapia which can adopt the pattern of male mating female; the method belongs to the technical field of aquatic product breeding. The method is characterized in that a net cage is equipped in an outdoor pond or indoor concrete pond; adult male tilapias are selected and people cut the upper jaw of the tilapias and put the tilapias into the net cage after being sterilized; and then adult female tilapias are selected to put in the net cage for mating culture and people can see the zygotes in the mouths of female tilapias after 7 to 10 days. With the present invention, a tilapia family line can be established for the family breeding of tilapias. In addition, people can clearly know the relation between the offspring and parent to control the inbreeding and avoid the germ plasm degeneration of offspring.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Specific primers and screening method for EST-SSR (Express Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeat) marker of torreya grandis transcriptome sequence
ActiveCN107287288AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGerm plasmGenetic diversity
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) marker technology and application, and particularly relates to specific primers and a screening method for an EST-SSR (Express Sequence Tag-Simple Sequence Repeat) marker of a torreya grandis transcriptome sequence. The screening method comprises the following steps: firstly, assembling fine torreya grandis seed kernel and circular torreya grandis seed kernel transcriptome data by adopting Trinity software to obtain a transcript sequence; secondly, carrying out SSR site research on Unigene with 1kb or above obtained by screening by using an MISA (MIcroSAtellite identification tool) program, and carrying out screening and separating on 2 to 6 base repeat units and repeat times according to microsatellite fragments with repeat times of 9, 8, 5, 5 and 5 in sequence, thereby obtaining an ESTs sequence with microsatellite repeat; thirdly, designing the primers by using a Primer 3 program; finally, comprehensively evaluating repeatability, stability and polymorphism of the EST-SSR marker to obtain the EST-SSR marker. The specific primers disclosed by the invention can be used for conveniently and quickly analyzing germ plasm resources of different types and genetic diversity of interspecific and intraspecific torreya grandis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
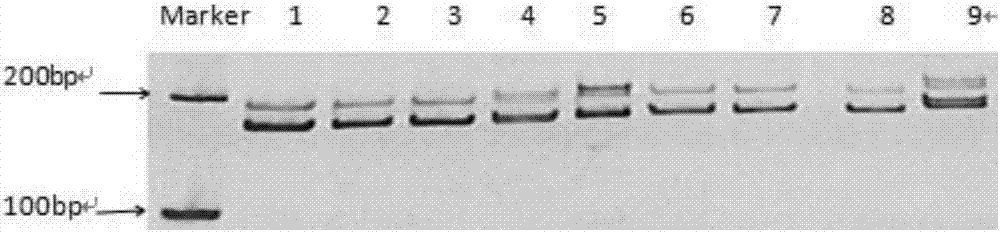
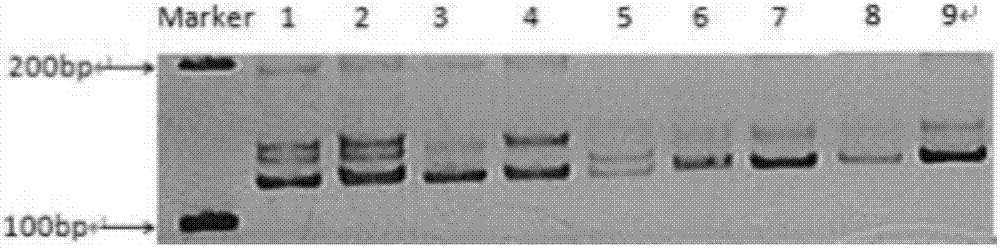
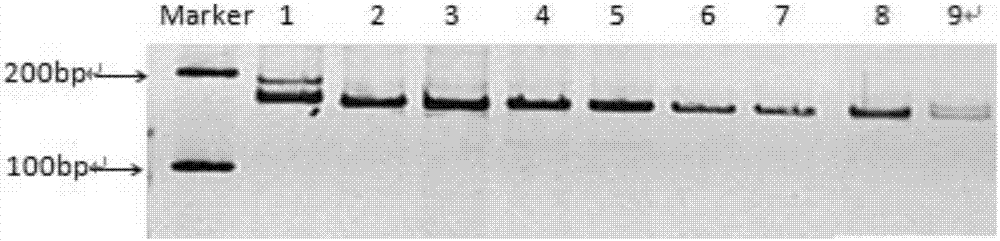
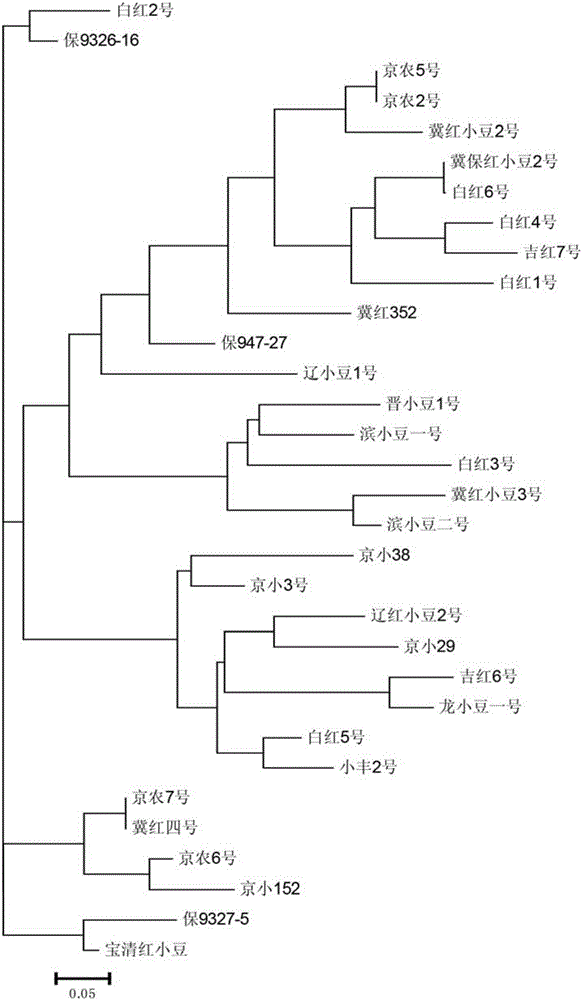
Method for identifying red bean varieties by utilizing genome SSR and EST-SSR fingerprints and application
InactiveCN106191285ASignificant difference in size between band typesSignificant size differenceMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetic diversity
The invention provides a method for identifying red bean varieties by utilizing genome SSR and EST-SSR fingerprints and application and belongs to the technical field of plant variety identification. A mark combination composed of 5 pairs of genome SSRs and 5 pairs of EST-SSR primers is provided, nucleotide sequences of the 5 pairs of genome SSRs and the 5 pairs of EST-SSR primers are respectively as shown in SEQ ID No. 1-20, and fingerprints of 32 kinds of red beans are constructed; according to the fingerprints, red bean seed variety identification and genetic diversity evaluation work can be finished within 4 hours by adopting the mark combination, and the method has the advantages of being efficient, accurate, low in cost and simple and convenient to operate. According to the method, red bean seed authenticity is effectively monitored, variety heritable variation and genetic relationships of varieties are disclosed from the DNA level, crop varieties are protected, forged and fake commodity varieties are prevented from entering the market, technical support is provided for reasonable utilization of excellent germ plasm in the red bean variety breeding process, and the method has good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SNP marker developing and application of rice broad-spectrum rice blast resistance gene Pigm
ActiveCN109628627AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGerm plasm
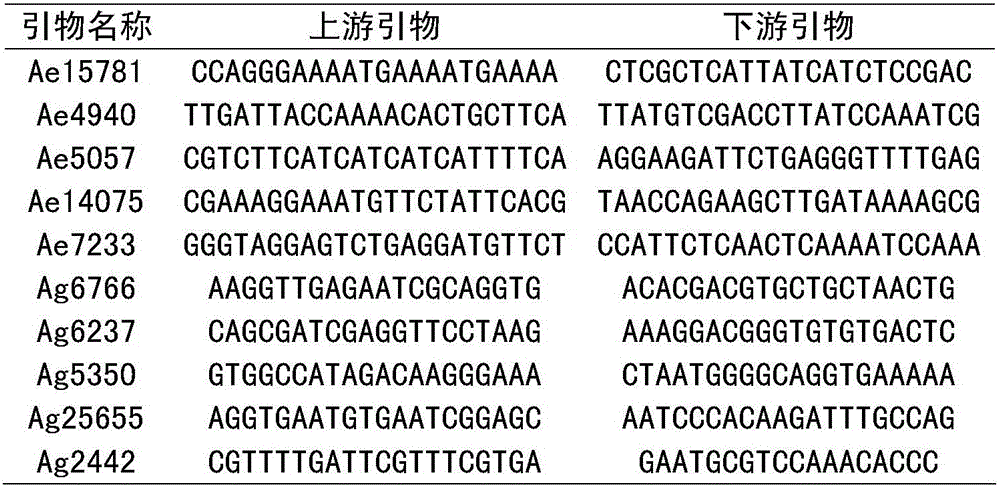
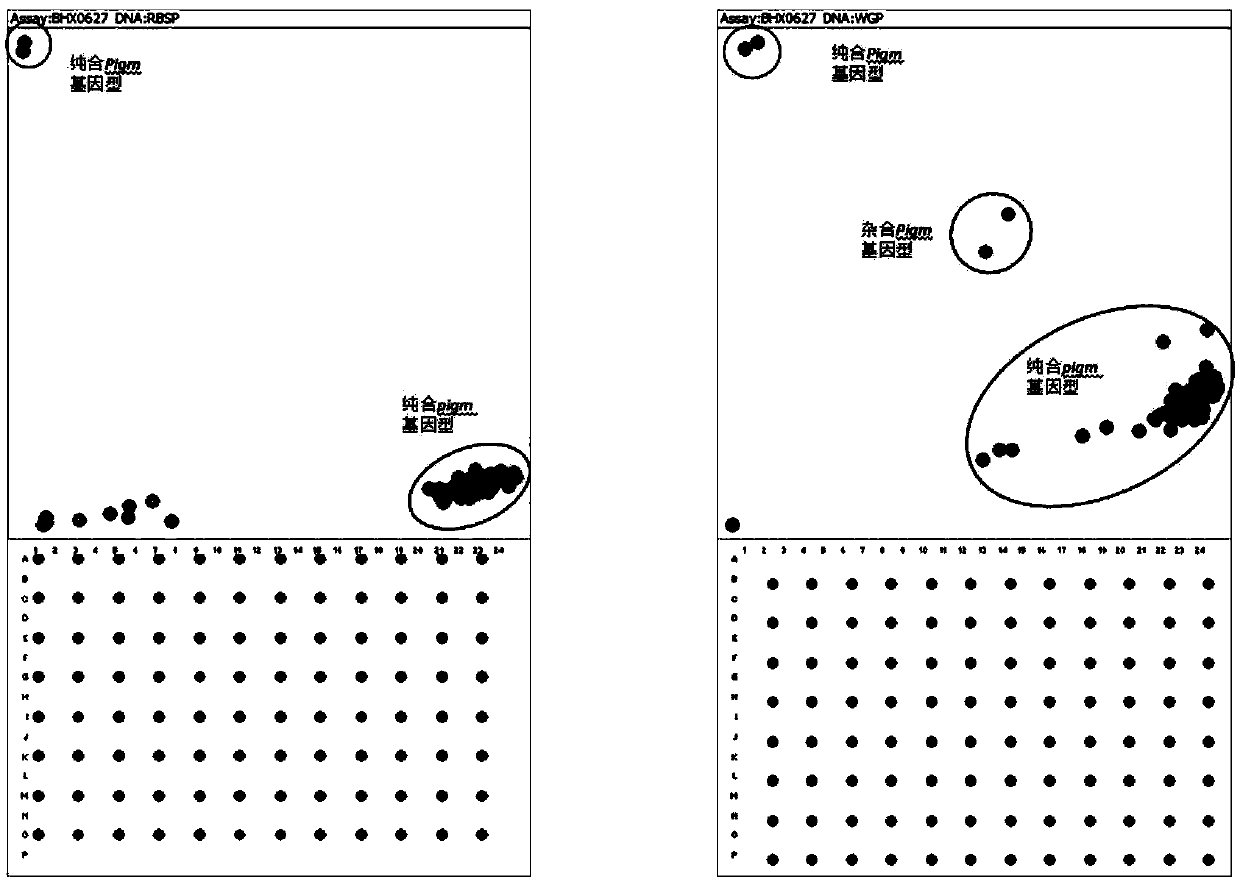
The invention provides an SNP molecular marker K_060508 which is tightly linked to a rice broad-spectrum rice blast resistance gene Pigm. It is detected by the SNP marker that the basic group at the 10421726 site of the 6 chromosome of rice is G or A, and the primer combination of the SNP marker developed based on a KASP technology is Primer X, Primer Y and Primer C. According to the SNP marker, the KASP technology is utilized to perform rapid genotyping on the SNP marker which is tightly linked to the rice blast resistance gene Pigm, the SNP marker can be applied to commercial molecular seedling breeding with high, medium or low through-put, the selectivity efficiency of a developed SNP marker phenotype reaches up to 100%, and therefore the broad-spectrum rice blast resistance gene Pigm can be rapidly and accurately detected in different germ plasm resources of indica rice, japonica rice and the like; the complicated procedures of enzyme digestion, electrophoresis, sequencingand the like are not needed in the detecting process, aerosol contamination is reduced, the use of toxic substances of EB (ethidium bromide) and the like is reduced, outlook molecular marker auxiliaryselection at the early stage of seedling breeding can be conducted to reduce the field planting scale of seedling breeding groups and the seedling breeding cost, and the seedling breeding process isaccelerated.
Owner:HUAZHI RICE BIO TECH CO LTD
Method for sifting macrobrachium nipponensis microsatellite mark with magnetic bead concentration method
InactiveCN101403013APolymorphism richImprove reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmEnrichment methods
The invention provides a method for screening microsatellite markers of Macrobrachium nipponensis by a magnetic beads enrichment method, including the following steps: the extraction of the genomic DNA of the Macrobrachium nipponensis; the hybridization of a probe and a target segment; the enrichment of magnetic beads; positive sequencing clone and the amplification of the genomic DNA according to primers which are related to the flanking sequences of the microsatellite. As the invention combines the magnetic beads enrichment and PRC amplification of bacterial liquid to carry out second-time screening, no isotope is needed. The method has the advantages of safety and high efficiency and low cost, short cycle, high reliability and the like. At the same time, in the enrichment process, the magnetic beads are repeatedly washed for a plurality of times, which can clean and remove microsatellite sequences which are not firmly adhered because of less repetition times. Therefore, the obtained microsatellite sequences are longer and are repeated for more times. The microsatellite sequences which are more frequently repeated are considered to have rich diversity at interspecies and intraspecies and can be widely applied to the diversity identification of germ plasm, the building of genetic maps, and QTL. Therefore, the method is one which screens the microsatellite markers of Macrobrachium nipponensis and can be easily popularized.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Vitrifiation freezing preservation method for genine porgy embryo particles
InactiveCN1748494AStrong ability to formGood frost protectionAnimal husbandryVitrificationGerm plasm
The present invention belongs to the field of marine biological technology, and especially the process of granular freezing genuine porgy embryo, preservation in liquid nitrogen, de-freezing and eluting to obtain live embryo. The genuine porgy embryo in cardiopalmus stage is added with antifreeze agent and fast granular vitrification frozen and then treated through preservation in liquid nitrogen, de-freezing and eluting, so as to obtain live embryo. The present invention is significant in germ plasm preservation, genetic diversity, breeding and cultivation of genuine porgy.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
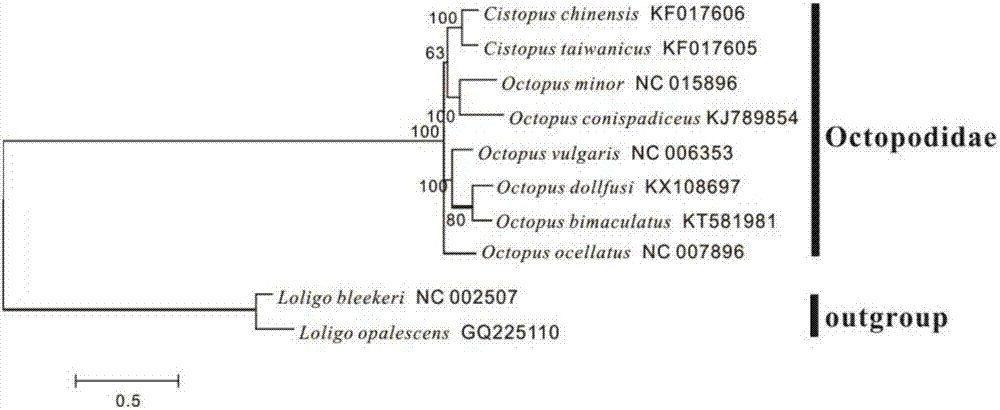
Mitochondrial genome complete sequence primer of octopus dollfusi as well as designing, phylogenetic analysis and amplification methods
InactiveCN107974507APromote amplificationLow number of primersMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsGerm plasmPhylogenetic study
The invention relates to a mitochondrial genome complete sequence primer of octopus dollfusi, which can achieve amplification of mitochondrial genome of the primer in one time and can rapidly acquirea genome complete sequence of the primer via sequencing and assembling and which has the characteristics of being simple, convenient and efficient, as well as designing, phylogenetic analysis and amplification methods; with the application of the primer provided by the invention, the mitochondrial genome of the primer can be amplified in one time and the genome complete sequence of the primer canbe rapidly acquired via sequencing and assembling, and the primer has the characteristics of being convenient and efficient; and the provided phylogenetic analysis of the mitochondrial genome completesequence primer of octopus dollfusi can offer important molecular means and data accumulation for population genetics, germ-plasm conservation and sustainable development and utilization of the octopus dollfusi as well as for phylogenic studies on octopus animals and even on entire cephalopoda.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
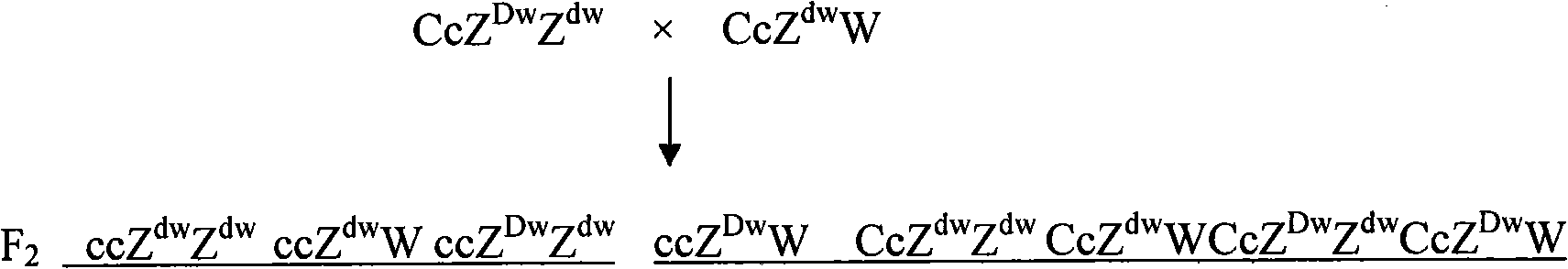
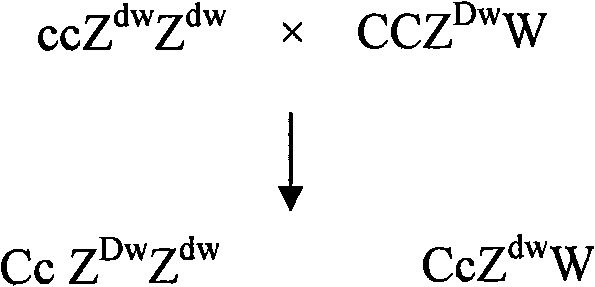
Breeding method of recessive white feather bantam germ plasm resource and supporting application thereof
A breeding method of recessive white feather bantam germ plasm resource includes: mating a recessive white hen and a mini type cock to produce F1 generation; selecting and mating a hen and a cock which carry recessive white feather gene and mini gene from the F1 generation to produce F2 generation of chicken; and selecting a recessive white feather bantam cock and a recessive white feather bantam hen from the F2 generation to set up a family; or includes: mating a recessive white cock and a mini type hen to produce F1 generation; selecting and mating a cock carrying recessive white gene and a mini type hen from the F1 generation to produce F2 generation; and selecting a recessive white feather bantam cock and a recessive white feather bantam hen from the F2 generation to set up a family. Through family selection and individual selection, the productivity is improved and bantam germ plasm resource with the feature of recessive white feather is bred through propagation and group expanding. The recessive white feather bantam germ plasm resource can be used for breeding high-qaulity laying hens and / or high-quality poulards and producing mini type high-quality indigenous laying hens commodity generation or normal body type high-quality poulards commodity generation.
Owner:湖北欣华生态畜禽开发有限公司
Method for separating and purifying insect pathogenic fungoid thallus from infected insect haemolymph
InactiveCN1807580ANo pollution in the processFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmGenetic Materials
This invention discloses a method for segregation purifying insect pathogenic fungi thalline from suscepted insect bloodlympha. It is prepared through steps as follows: deal with blood cell of suscepted insects with a series of enzymes to destroys and removes their germ plasms; finally seperate and purify to get the products. Adopt the achieved pathogenic fungi thalline to extract DNA and mRNA, which has no insect germ plasm pollution according to PCR and RT-PCR verification. The DNA and mRNA extracted can be used to construct gene library, it also lays solid foundation for further uncovering entomogenous fungi invading mechanism.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
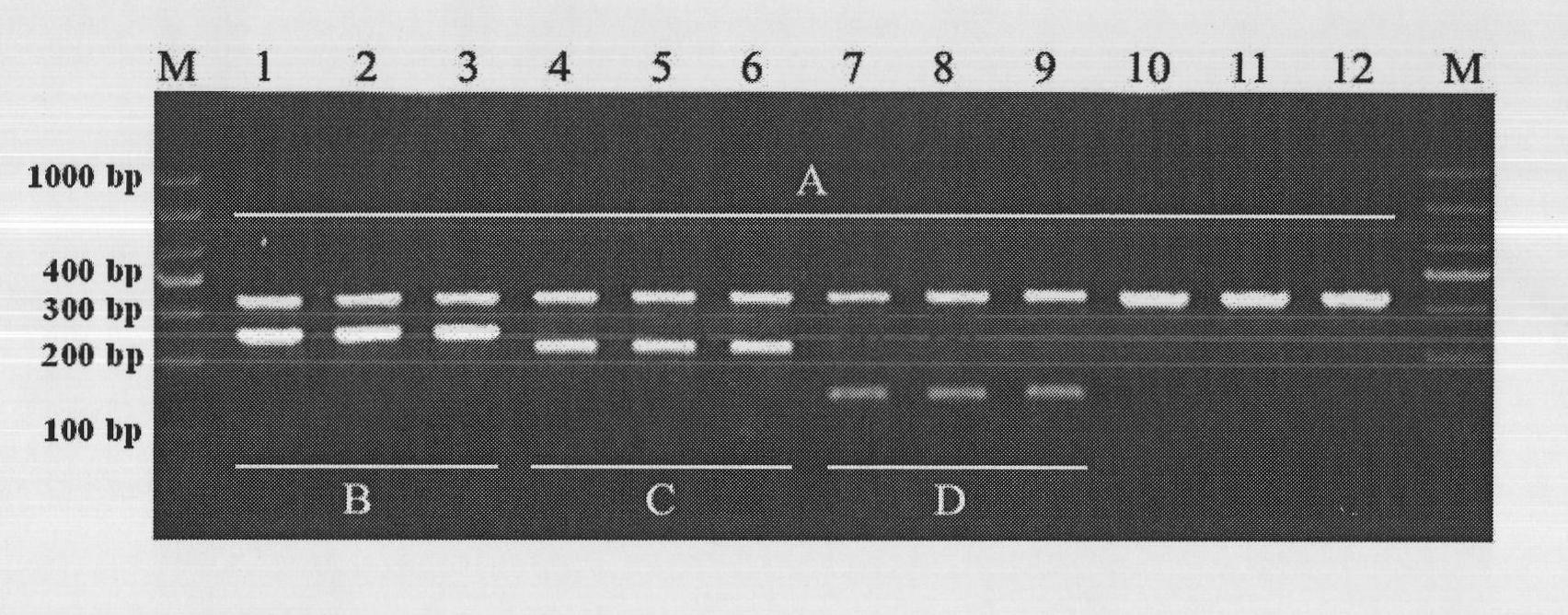
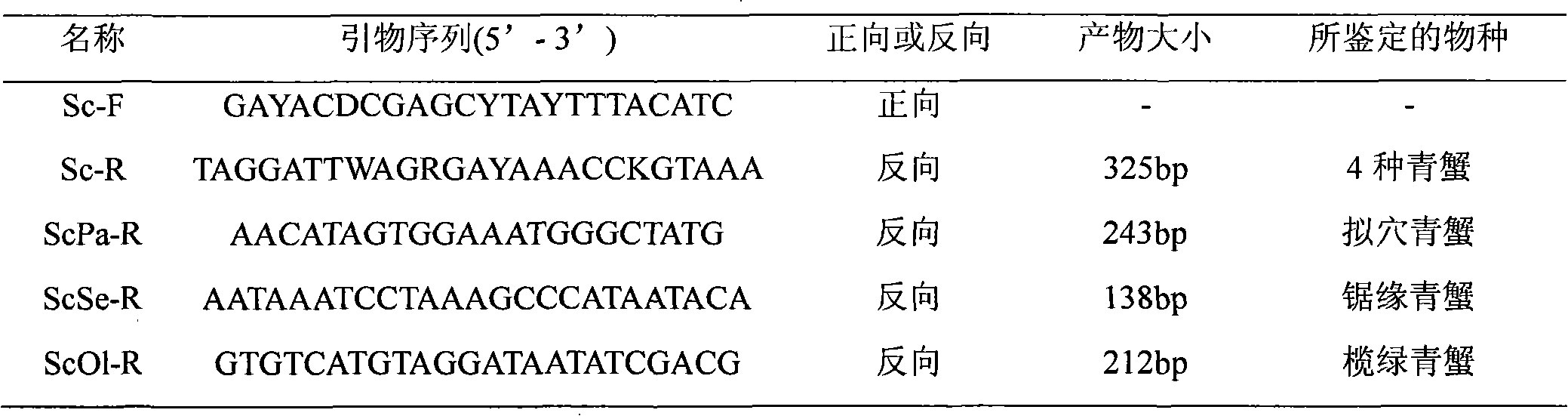
PCR method for rapid identification of four types of blue crabs of scylla
InactiveCN101792809ARapid identificationAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmRapid identification
The invention relates to a PCR method for the rapid identification of four types of blue crabs of Scylla, comprising the following steps: extracting the genome DNA of the four types of the blue crabs; (2) designing a species specific amplification primer according to the nucleotide sequence of the chondriosome (COI) gene of the four types of the blue crabs; (3) carrying out PCR amplification on the genome DNA of the four types of the blue crabs; and (4) utilizing 1.5% of agarose gel electrophoresis to detect PCR products, so as to rapidly identify the four types of the blue crabs according to the different sizes of the products. The method has simple and safe operation, clear amplification stripe and true and reliable results, and can rapidly identify the four types of the blue crabs, thus being widely used in the fileds of protection and management of blue crab germ plasm resources, inheritance breeding and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Tetraploid preparing process suitable for chlamys Farreri
InactiveCN1739343ARich sourcesInduction rate is stableClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGerm plasmArtificial insemination
The present invention discloses tetraploid preparing process suitable for chlamys Farreri. Natural diploid chlamys Farreri with propagation capacity is fertilized artificially to obtain fertilized egg, the fertilized egg is applied with chemical inducing agent to double the chromosome to obtain tetraploid, and the tetraploid is screened in the constant current process. The present invention utilizes special chromosome operating technology to obtain specific germ plasm resource of chlamys Farreri and has rich material source, and stable tetraploid inducing rate over 30 %.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Culturing method for sugarcane germ plasm
InactiveCN1644026AIncrease productionHigh in sugarPlant genotype modificationGerm plasmTrehalose synthase
A method for culturing the new stress-resistant variety of sugar cane includes such steps as transferring the mycose synthetase gene into the enbryonic cells of sugar cane by agrobacterium mediation method and culturing the transgenic plant of sugar cane. Its advantages are short period, high efficiency and high stress-resistant effect.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +1
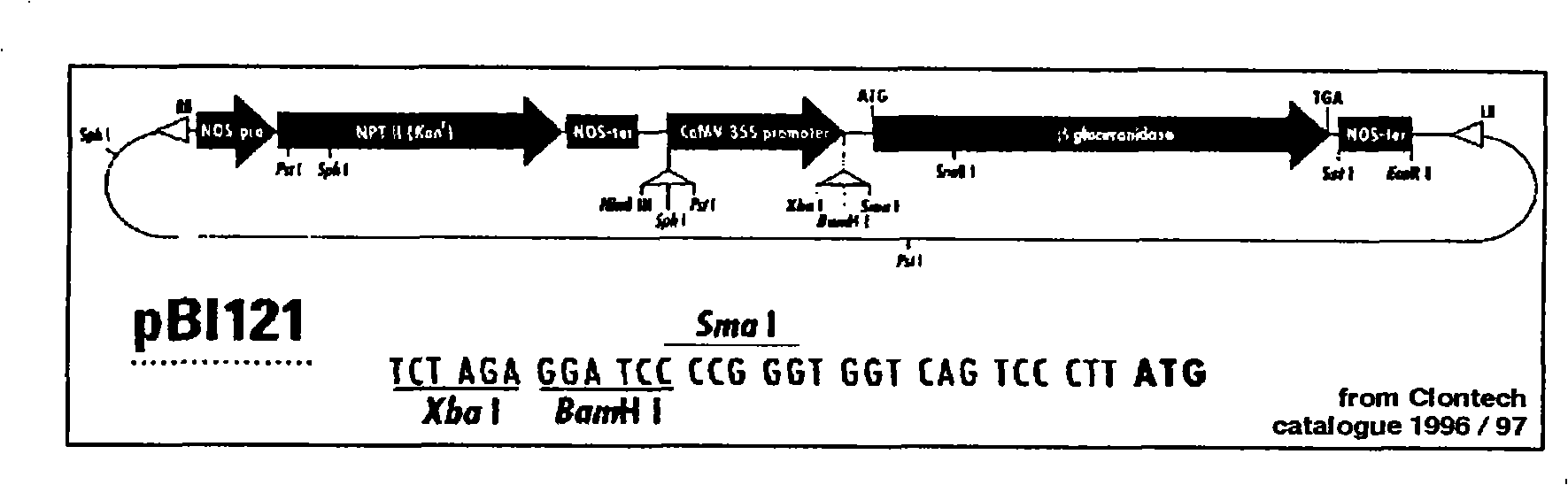
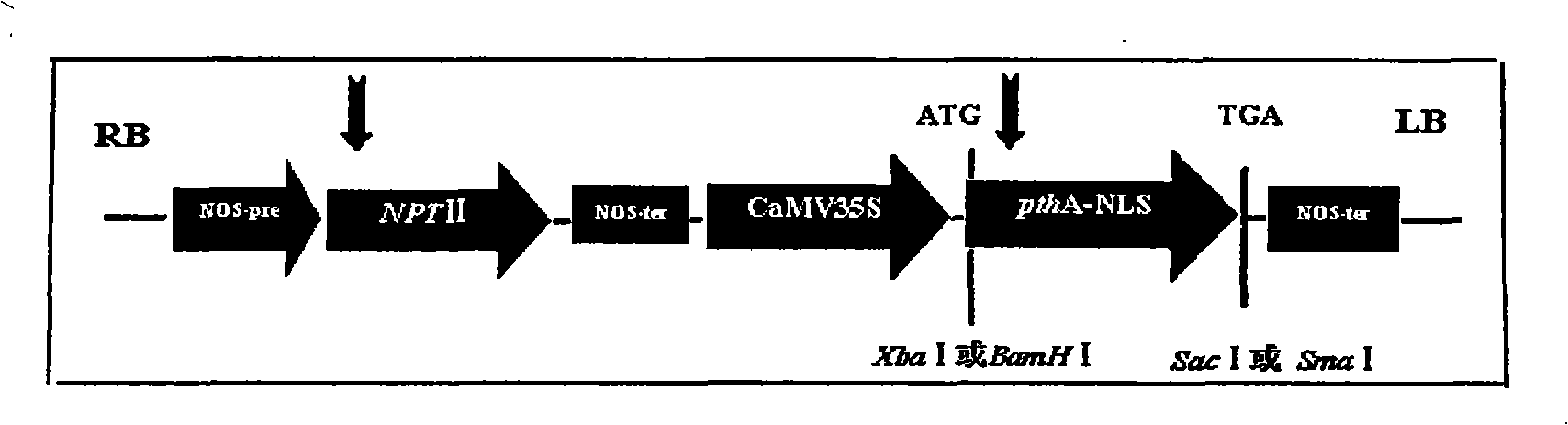
Orange canker resistant pthA-nls gene and its construction method and application
The invention provides an anti-citrus bacterial canker disease pthA-nls gene, a construction method and application thereof. The invention uses the pathogenic gene pthA-mediated broad-spectrum disease resistance theory of the citrus bacterial canker disease to construct a new anti-citrus bacterial canker disease gene (pthA-nls). The construction method comprises the following steps of: (1) primer design; (2) clone of NLS sequence; (3) recovery and enzyme digestion of PCR product; (4) double enzyme digestion of a plant expression vector; (5) connection between product of enzyme digestion of pBI121 and corresponding product of PCR enzyme digestion of the NLS sequence by T4 DNA ligase; (6) acquisition of positive cloned gene pthA-nls by converting ligation product into colon bacillus DH5alpha. The gene pthA-nls can further perform genetic transformation on susceptible varieties of orange so as to acquire new anti-citrus bacterial canker disease germ plasm. The anti-citrus bacterial canker disease pthA-nls gene provides an effective tool for breeding of anti-citrus bacterial canker disease.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for preparing promoter of Brassica napus BnPABP2 and application thereof
InactiveCN102226181ATissue-specific expression functionImprove disease resistanceFermentationPlant genotype modificationGerm plasmDisease
The invention discloses a method for preparing a promoter (PBnPABP2) of Brassica napus BnPABP2 and the application thereof. The operation of cloning a PBnPABP2 sequence by using a genome walking method comprises the following steps: extracting genome DNA by using a SDS cracking process; in different systems, carrying out restriction endonuclease reaction on the extracted DNA respectively by using endonucleases DraI, EcoRV, PvuII and StuI; after the obtained DNA is connected with a linker fragment, carrying out first-round PCR amplification by taking the linker fragment as a template; and carrying out second-round PCR amplification by taking a50-time diluent of the obtained first-round PCR product as a template, thereby obtaining the PBnPABP2. The PBnPABP2 is applied in the roots, stems, leaves, flower buds, anthers and peels of plants. The promoter has the function of driving the expression of exogenous genes, and the expression sites thereof are respectively in the roots, stems, leaves, flower buds, anthers and peels of plants; and the promoter has application potentials in the aspect of safety of edible oil of Brassica napus and the aspects of improving the disease resistance, stress resistance and lodging resistance of crops, improving the quality of crops, artificially creating a male sterile line and a restoring line, enriching germ plasm resources, and the like through transgenosis.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method and application method for obtaining novel germ plasm of brassica A genome vegetable
InactiveCN102144560AShort breeding cycleImprove efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGerm plasmBrassica
The invention discloses a method and application method for obtaining a novel germ plasm of brassica A genome vegetable. In the method, free microspore culture is carried out on crossbreeds among vegetables of Chinese cabbage subspecies*pakchoi cabbage subspecies or variety in pakchoi cabbage subspecies*variety of the brassica A genome to obtain a regeneration plant and further to create the novel germ plasm which is used for breeding. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: hybridizing the vegetables of Chinese cabbage subspecies*pakchoi cabbage subspecies or variety in pakchoi cabbage subspecies*variety; inducing free microspore culture embryoids; germinating the embryoids to obtain the regeneration plant; carrying out ploidy identification on the regeneration plant obtainedby microspore culture; reserving seeds of double haploids and polyploids; planting an offspring of the regeneration plant to carry out morphological identification and nutritive index identification;and preparing, hybridizing and combining. The method has the advantages of short cycle and high efficiency, provides a material for efficiently breeding Chinese cabbage vegetables and has broad application prospect.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
TT1 AND TTG1 Control Seed Coat Color In Brassica
InactiveUS20140220564A1Microbiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBrassicaGerm plasm
Seed coat color is a very important trait in oilseed type Brassica crops. Identification of the genes controlling the seed coat color is essential to the manipulation of these genes to develop new yellow-seeded germ plasm for oilseed breeding. The Brassica TTG1 and TT1 genes may be used to control seed color in plants.
Owner:ZHANG JIEFU +5
Method for identifying Y excellent series hybrid rice germ plasm
InactiveCN101408528AReduce the risk of mass productionAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGerm plasmAgricultural science
The invention relates to a method for identifying the germ plasm of Y-superior serial hybrid rice, comprising the following steps: (1) a primer which can be used for identifying the germ plasm of Y-superior serial hybrid rice is selected; (2) the PCR augmentation on rice samples to be identified is carried out by the obtained primer; (3) the electrophoresis detection for a DNA special marker is carried out; (4) the molecule id card number which is corresponding to the rice samples to be identified is manufactured according to the obtained DNA special marker scattergram, when the first digit of the number is '1', only one digit '1' can appear from the second digit to the fifth digit, and the rice samples to be indentified is Y-superior serial hybrid rice, otherwise the identifying conclusion is contrary. By making use of the method, the varieties and the parent-strain germ plasm of the Y-superior serial hybrid rice can be indentified. The invention has the advantages of short detecting time, large quantity, high efficiency and accurate seed purity identification, thereby the risk of the large-area production of the hybrid rice can be greatly reduced.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Quick detection method for Scylla paramamosain by microsatellite markers from functional genes
InactiveCN101787395AFast detection methodThe detection method is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGerm plasmScylla paramamosain
The invention relates to a quick detection method for Scylla paramamosain by microsatellite markers from functional genes, which comprises the following steps: (1) extracting genomic DNA of the Scylla paramamosain; (2) acquiring a gene sequence containing microsatellite repeats according to a functional gene sequence of the Scylla paramamosain in a GeneBank database; (3) designing microsatellite marker primers; (4) performing PCR amplification on the genomic DNA of different geographic population or different individuals in the population of the Scylla paramamosain; and (5) detecting a PCR product by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The detection method has the advantages of quickness, accuracy, sensitivity and the like, and can intuitively detect genotypes of different individuals of the Scylla paramamosain so as to quickly acquire a polymorphic map for hereditary variation at functional gene microsatellite loci of the Scylla paramamosain; and the microsatellite markers can be applied to the fields such as hereditary variation analysis of the Scylla paramamosain, germ plasm resource protection and management, genetic linkage map construction and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
SNP marker developing and application of rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5
InactiveCN109628629AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzyme digestionAgricultural science
The invention provides an SNP molecular marker K_050527 which is tightly linked to a rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5. It is detected by the SNP marker that the basic group at the 437500site of the 5 chromosome of rice is C or G, and the primer combination of the SNP marker developed based on a KASP technology is Primer X, Primer Y and Primer C. According to the SNP marker, the KASP technology is utilized to perform rapid genotyping on the SNP marker which is tightly linked to the rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5, the SNP marker can be applied to commercial molecularseedling breeding with high, medium or low through-put, the selectivity efficiency of a developed SNP marker phenotype reaches up to 100%, and therefore the rice bacterial blight resistance gene xa5can be rapidly and accurately detected in different germ plasm resources of indica rice, japonica rice and the like; the complicated procedures of enzyme digestion, electrophoresis, sequencing and thelike are not needed in the detecting process, aerosol contamination is reduced, the use of toxic substances of ethidium bromide EB (ethidium bromide) and the like is reduced, outlook molecular markerauxiliary selection at the early stage of seedling breeding can be conducted to reduce the field planting scale of seedling breeding groups and the seedling breeding cost, and the seedling breeding process is accelerated.
Owner:HUAZHI RICE BIO TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com