Patents
Literature
42results about How to "Solve the problem of germplasm degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
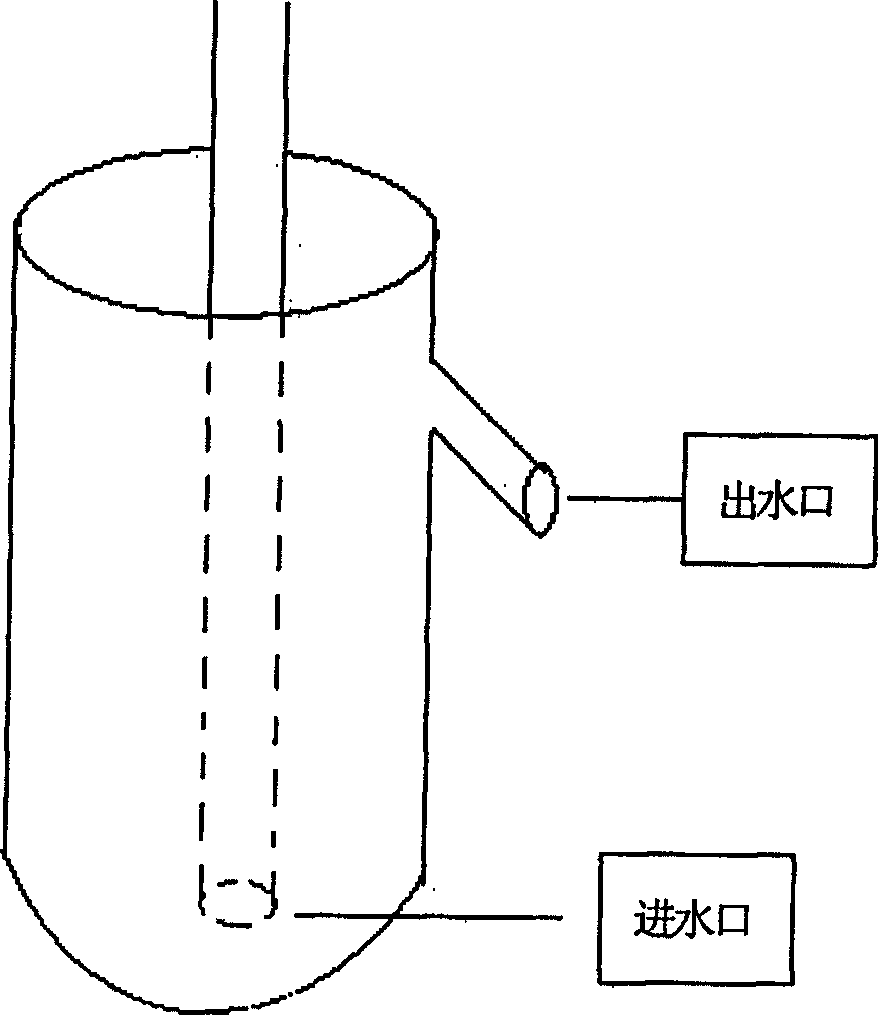
Virus removal and rapid propagation technology of sweet potato variety 'Shangshu 19' and culture material
InactiveCN101611697AImprove immunitySolve the serious sweet potato virus diseaseCultivating equipmentsPlant tissue cultureDiseaseGermplasm
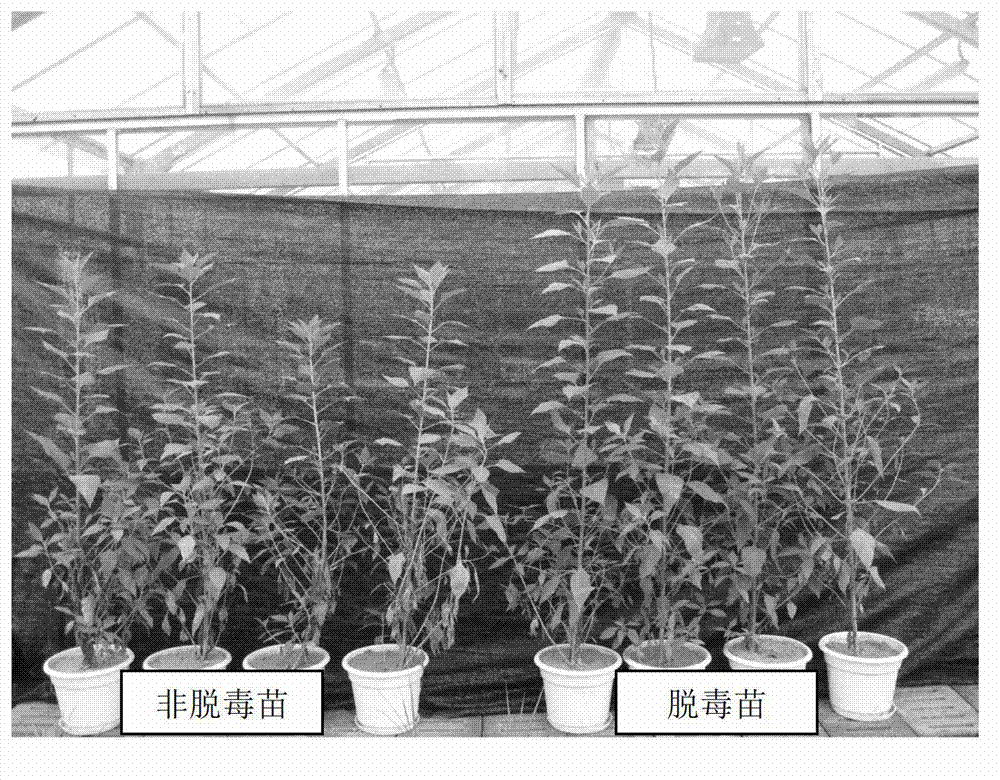
The invention is a virus removal and rapid propagation technology of sweet potato variety 'Shangshu 19', comprising the following steps: selecting plants which are robust without diseases and insect pests and have characteristics of the variety from growing plants; clipping stem with stem tip; removing visible leaves; sterilizing; peeling the stem tip with 1-2 leaf primodia via a dissecting needle; quickly inoculating into a differentiation and induction culture medium; trimming the sterilized seedling into stem segments with 1-2 internode(s) and switching into an enrichment medium after virus detection; selecting sterilized seedling in vigorous growth to cut into small segments with 1-2 internode(s) and switch into a rooting medium; carrying out domestication on seedling after rooting. The invention has stem tip in virus removal and stem segment in rapid propagation, solves the problems of severe virus disease for sweet potato, poor quality of new cultured breed, germplasm degradation, low yield and the like propagated by using sweet potato block and stem. The invention can artificially control the growing conditions, can not be influenced by nature, and has the advantages of small amount of material use, economical culturing materials, short growth cycle, large propagation coefficient and convenient management and is favor of industrial production.
Owner:周玉玲
Method for rapidly breeding sugarcane stem tip by tissue culture and virus removal
InactiveCN102090340AEasy detoxificationAddress germplasm degradationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiomedical engineeringAxillary bud
The invention relates to a method for rapidly breeding sugarcane stem tip by tissue culture and virus removal, belonging to the technical field of rapid breeding of plant by virus removal. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out disinfection pretreatment on a terminal bud of sugarcane and a cut double-bud stem section, with the terminal bud of the sugarcane and a stem tip tissue ofan axillary bud as explants, and carrying out stem tip initial culture, sprout differentiation culture, crowd sprout strong stock culture, plant root culture and virus checking by adopting a filter paper bridge culture way, thus massive virus-removed tissue culture seedlings are obtained. The invention has the advantages: the stem tip with the length of 1-2mm is taken as the explant, thus the processing operation is easy; the filter paper bridge culture way is adopted during the initial culture, thus the initiating speed is high and the perennial root dwarfing virus removing effect is thorough; and the stem tip is induced and germinated and is rapidly initiated and differentiates massive crowd sprouts, the month breeding coefficient reaches 5-8, and normomorph is realized in a long-term breeding process, thus the method is completely applicable to factory production on a large scale.
Owner:广州甘蔗糖业研究所湛江甘蔗研究中心
Sugarcane detoxication tissue culturing and fast propagating method
InactiveCN101138321AIncrease in sizeEasy to inoculateCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsAxillary budBud
The present invention relates to a method for virus-free tissue culture and rapid propagation of sugarcane belonging to the technical field of plant propagation. The method comprises the following steps that the terminal buds or auxiliary buds of the sugar cane is taken as the explants and the virus-free tissue culture seedlings are propagated in mass after the callus tissue inducement and culture, plant differentiation culture, proliferation culture, radication culture and virus test. The present invention is characterized in that the explants adopted are large and the operation is easy; the inoculation survival rate is high; the detoxification is simple, convenient, fast and thorough; the propagation coefficient per month is 5 to 10 times and the speed is fast which is fit for breeding in factory and commercial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos
InactiveCN102124955ASolve the problem of germplasm degradationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologySomatic embryogenesis
The invention provides an induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos, comprising the following steps: (1) building a regeneration system of a Photinia fraseri asepsis test tube seedling; (2) building a high-frequency rapid-propagation system induced by an in-vitro somatic embryo and an adventitious bud; and (3) rooting, acclimatizing and transplanting for the test tube seedling. The induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos is characterized in that coordinated sets of measures of selecting a proper explant, improving a basic culture medium and ingredients, regulating culture conditions and the like are adopted, and the Photinia fraseri of which the seed is difficult to breed is subjected to path rapid propagation by the somatic embryos; the plant transplantation survival rate is higher than 95%; the germchit grows strongly to solve the problem that an excellent germchit quality degenerates, and a great quantity of purified and rejuvenated detoxification nursery stock with good quality can be provided for production; and in addition, and ideal receptor system is provided for breeding new specimens for Photinia fraseri by genetic transformation or mutation breeding.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
Tilapia oosperm artificial incubation method
InactiveCN101133726AReduce the impactAvoid germplasm degradation in offspringClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSaline waterTilapia
The present invention relates to an artificial incubation method of fertilized egg of tilapia mossambica. It is characterized by that the male and female paired breeding of tilapia mossambica is implemented in net cage, then said invention adopts the following several steps: checking mouth cavity of female fish, if in the mouth cavity of female fish the fertilized eggs are existed, opening mouth cavity of female fish, taking out fertilized eggs and pouring them into a landing net; using saline water to wash said fertilized eggs and placing said fertilized eggs into an incubator; making the fertilized eggs be floated in the water of said incubator and making incubation for 2-7 days so as to obtain the tilapia mossambica fries.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for detoxifying and reproducing helianthus tuberosus quickly
ActiveCN102763594AFor long-term storageShortened growth timeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budBud
The invention relates to a method for detoxifying and reproducing helianthus tuberosus quickly. The method comprises the following steps of: disinfecting young axillary buds or stem tips serving as explants, transferring the young axillary buds or stem tips into a bud induction culture medium, transferring the buds into a rooting culture medium, and performing refining seedlings and transplanting on a complete plant, wherein the bud induction culture medium is improved on the basis of a Murashige and Skoog (MS) culture medium, 0.1 mg.L<-1> of naphthyl acetic acid (NAA) and 0.5 mg.L<-1> of 6-butyl acrylate (BA) are added, so that adventitious buds which are induced are more, callus is small, and the problems of vitrification and water stain are solved; and obtained seedlings are robust and vigorous in growth vigor and can be transferred into the rooting culture medium directly, the rooting rate is 100 percent, and the survival rate of test-tube seedlings is over 90 percent. By the method, the effect of detoxifying the helianthus tuberosus seedlings can be achieved, the reproduction efficiency is improved, the production period is shortened, and an effective path is provided for the large-scale seedling raising of the helianthus tuberosus.
Owner:北京碧青园生态环境科技有限公司
Method for ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and Odontobutis obscura in pond by utilizing artificial ecological base
ActiveCN104285851AThe application operation method is simple and practicalGood and stable water qualityFood processingClimate change adaptationMoenkhausiaWater quality
The invention discloses an application method for ecologically breeding macrobrachium nipponensis and Odontobutis obscura in a pond by utilizing an artificial ecological base. The method comprises the following steps of (1) pond selection; (2) forming of pond artificial ecological base layout and biological film; (3) fry stocking; (4) feedstuff feeding; (5) water quality regulation and control and daily management; (6) fishing of grown macrobrachium nipponensis and grown Odontobutis obscura. Compared with the prior art, according to the method, the water quality of the pond can be kept good and stable, water does not need to be replaced in the whole breeding period except in the season with higher water temperature, new water is added to increase the water level, no breeding wastewater is drained, and the ecological benefits are obvious; the biocenosis such as microorganisms and algae on the ecological base can provide the suitable habitat for shrimp seeds and the Odontobutis obscura; the Odontobutis obscura is utilized for catching and feeding on the weak and sick shrimp seeds and autumn seeds bred in august; the breeding disease rate of the macrobrachium nipponensis is reduced; the out-of-pond specification and yield of the grown macrobrachium nipponensis are improved, and the economic benefits are obvious.
Owner:ZHEJIANG INST OF FRESH WATER FISHERIES
Tilapia male and female pairing propagating method
InactiveCN101138329ASolve the problem of germplasm degradationControl inbreedingClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaGerm plasmTilapia
The present invention relates to a male and female mating propagation method of tilapia, in specific to a mating propagation of tilapia which can adopt the pattern of male mating female; the method belongs to the technical field of aquatic product breeding. The method is characterized in that a net cage is equipped in an outdoor pond or indoor concrete pond; adult male tilapias are selected and people cut the upper jaw of the tilapias and put the tilapias into the net cage after being sterilized; and then adult female tilapias are selected to put in the net cage for mating culture and people can see the zygotes in the mouths of female tilapias after 7 to 10 days. With the present invention, a tilapia family line can be established for the family breeding of tilapias. In addition, people can clearly know the relation between the offspring and parent to control the inbreeding and avoid the germ plasm degeneration of offspring.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for establishing polygonatum sibiricum red high-frequency regeneration system and culture medium
InactiveCN106106187AImprove effective utilizationFast growthPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGermplasmBud
The invention aims at solving the problems that seed propagation adopted in current polygonatum sibiricum red production is difficult, plant diseases and insect pests can easily become more serious and germplasm can be easily degenerated during the conventional rhizome propagation, tissue culture mainly takes terminal buds of rhizome and stem tips as explants for establishing a rapid propagation system, source of the explant is single, test material consumption is high and propagation efficiency is low. According to the method provided by the invention, easily available polygonatum kingianum terminal bud scales are selected as an explant test material, adventitious roots are obtained by inducing bud scale differentiation, and then further induction is carried out on the adventitious roots, so that differentiation bodies of different types such as rhizomes having adventitious roots and terminal buds at the same time, adventitious bud clumps and callus tissues in multiple forms are obtained; and respectively continuously culturing the differentiation bodies of different types, so that new adventitious bud clumps, rhizomes with terminal buds and callus tissues of multiple types can be respectively continuously produced, and an in vitro high-frequency regeneration system for roots, stems and leaves of polygonatum sibiricum red is established; a high-frequency regeneration system for the roots and stems can also be obtained by adopting the same culture medium. The roots, stems, leaves, callus tissues and rhizomes obtained by utilizing the method can be mutually transformed and grow in different culture stages.
Owner:TAISHAN RES INST OF FORESTRY
Seedling-raising method for gracilaria algae
ActiveCN104542237AHigh agar contentGrow fastCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationSporeThree-dimensional space
The invention relates to a seedling-raising way for algae, in particular to a seedling-raising method for gracilaria algae. The method comprises the following steps: disinfecting cleaned mature gracilaria algae with sodium hypochlorite for 3-5 minutes, flushing the disinfected gracilaria algae with boiled fresh water, and putting the flushed gracilaria algae into boiled seawater for serving as breeding algae in later use; drying the breeding algae in the shade, stimulating, releasing spores, growing a disk-shaped body, performing suspension cultivation after scraping the disk-shaped body, performing enlarged cultivation, inducing the formation of vertical branches, and performing gradual cultivation to prompt growth of seedlings. By adopting the seedling-raising method, the entire spore seedling-raising process is implemented in a relatively small and controllable three-dimensional space, the seedling-raising amount is large, the survival rate is up to 90-100 percent, seedlings grow rapidly, the emergence rate is high, and gracilaria seedlings which are uniform in size and are 5 centimeters in length can be cultivated within 30-60 days.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chinese scholartree detached leaf somatic embryo induction rapid-breeding method
ActiveCN105660396AConvenient inductionInduced fastPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budGermplasm
The invention discloses a Chinese scholartree detached leaf somatic embryo induction rapid-breeding method. The method comprises selecting Chinese scholartree tender twigs, disinfecting the tender twigs, taking stems with axillary buds or terminal buds, inoculating a bud initial medium with the axillary buds or terminal buds, inducing germination of the axillary buds or terminal buds, removing base leaves of the produced young sprouts, carrying out cutting to obtain stem sections with axillary buds or terminal buds, inoculating a test-tube plantlet multiplication medium with the stem sections with axillary buds or terminal buds to obtain sterile test-tube plantlets, taking leaves of the sterile test-tube plantlets, inoculating a somatic embryo inducing medium with the leaves of the sterile test-tube plantlets, carrying out culture to obtain callus, inoculating an adventitious bud induction medium with the callus, carrying out culture to obtain multiple shoots, cutting the multiple shoots to obtain callus blocks, inoculating a test-tube plantlet multiplication medium or an adventitious bud induction medium with the callus blocks, carrying out culture, transferring the cultured multiple shoots into a shoot strengthening medium, carrying out shoot strengthening culture and carrying out seedling hardening and transplanting. The method has a high regeneration rate, a large budding rate, a plant transplanting survival rate of 95% or more, produces strong seedlings and effectively solves the problem of degeneration of excellent seedling germplasm.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
Industrial earthworm breeding method
An industrial earthworm breeding method includes steps: breeding place construction, to be more specific, selecting a shady, cool, ventilated and quiet room as a breeding place, and mounting temperature adjusting equipment and spraying devices in the room; breeding frame manufacturing; breeding box manufacturing, to be more specific, making a plurality of pores in the bottom of and around each breeding box body; earthworm bait preparation; after complete bait fermentation, adding baits into each breeding box, and adding earthworm larvae into each box; putting the breeding boxes with the baits and the earthworm larvae inside on breeding frames; stopping breeding when the breeding boxes are full of wormcast, and collecting earthworms and wormcast; pouring a mixture of the earthworms and the wormcast in each box body into a vibrating screening machine to separate the earthworms from the wormcast. The industrial earthworm breeding method makes full use of the stereo space for stereo multilayer breeding, breeding conditions can be well controlled while disastrous weather influences are avoided, and high and stable yield is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI SHENGRAN AGRI SCI & TECH
Virus-free tissue culture and rapid propagation method of castor oil plants
InactiveCN105746344AEasy to inoculateImprove vaccination success ratePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsWarm waterBud
The invention discloses a virus-free tissue culture and rapid propagation method of castor oil plants. The method comprises the following steps: adopting current year's ripe seeds, mixing castor oil plant seeds with coarse sands according to a ratio of 1:5-8, carrying out medium speed grinding and shelling, screening to remove the coarse sands, cleaning the obtained seeds with warm water 2-3 times, immersing the washed seeds in 75% alcohol for 0.5-1.0min, disinfecting the immersed seeds with an aqueous solution of 2% sodium hypochlorite for 20-30min, and flushing the disinfected seeds with sterile water 3-5 times to obtain the flushed seeds used as explants; and carrying out induction culture, propagation culture, rooting culture, transplanting and virus detection to obtain mass propagated virus-free tissue culture seedlings, virus-free plant buds and virus-free small root tubers. Compared with present castor oil plant seedling growing methods, the method disclosed in the invention has the advantages of low inoculation and pollution rate, high transplanting survival rate and high quality.
Owner:岳兰兰
Method for strong seedling and rooting culture of strawberries
ActiveCN103348915AIncrease productionQuality improvementPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsFragariaShoot
The invention discloses a method for strong seedling and rooting culture of strawberries, which includes the following steps: firstly, strong seedling and rooting culture: a multiple shoot with a prophyll and 0.3-0.5 cm in height and well in growth and development is cut into a single plant and transplanted to a strong seedling and rooting culture medium for rooting culture, and transplanting is carried out after the plant is 3-5 cm in height; secondly, transplantation: the plant is firstly transplanted to a culture room and grows for 30-35 d, then is transplanted in a plastic-covered tunnel with a shading net, after a new root grows and the plant sprouts, watering frequency is gradually reduced, and the plant is transplanted to a flowerpot for ordinary management. The method for strong seedling and rooting culture of strawberries, provided by the invention, improves the survival rate of transplanted plants by 90% above through supporting measures such as improvement on minimal medium and ingredients and adjustment in culture conditions, enables seedlings to grow healthy, effectively solves the problem of genetical characterization decline of fine seedlings, effectively improves yield and quality of strawberries and enhances the economic value of strawberries at the same time.
Owner:句容市春城镇年胜葡萄园
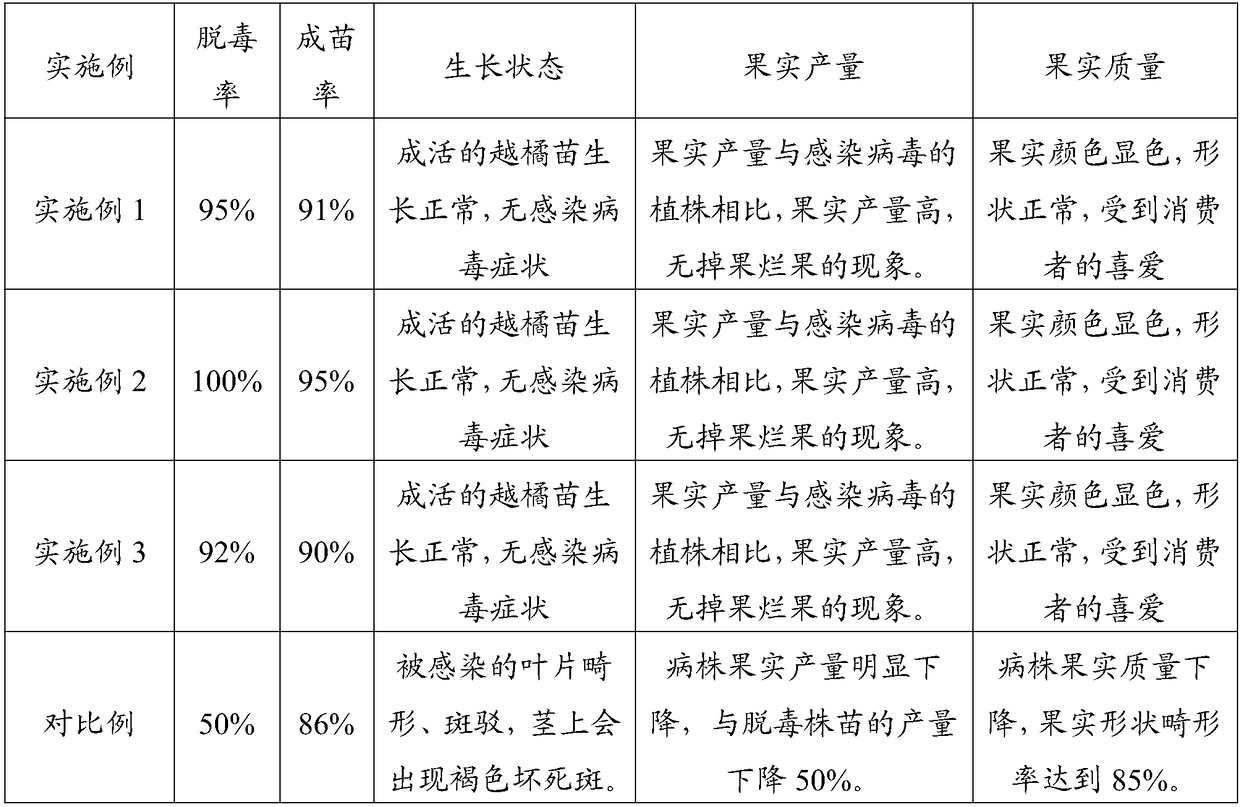
Cowberry detoxification breeding method and detoxification medium
InactiveCN106508681AIncomplete solution to detoxificationPromote germinationHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSterile environmentShoot apex
The invention provides a cowberry detoxification breeding method. The cowberry detoxification breeding method comprises the following steps: accelerating germination of cowberry resting shoots, shearing off a bud when the length of the bud reaches 1-3 cm and carrying out sterilizing treatment; cutting off 0.3-0.8 cm of a stem tip from the sterilized bud, and inoculating the stem tip on a foundational medium, and culturing under the conditions that the temperature is 25-28 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 1,800-2,200 Lx, and the illumination time is 12-16 h / d; after the stem tip grows until the length of the stem tip reaches 1.5-2.0 cm, cutting off 0.03-0.05 cm of a stem tip in a sterile environment and inoculating the stem tip to a detoxification medium, carrying out dark culture for 5-9 days at the temperature of 22-25 DEG C, and continuing culturing in an environment in which the temperature is 23-26 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 1,800-2,200 Lx and the illumination time is 12-16 h / d; and inoculating a detoxification seedling to a medium, carrying out rapid multiplication culture, and then carrying out seedling hardening and rooting after the length of the seedling reaches 2.0-3.0 cm.
Owner:FORESTRY RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE +1
Rapid propagation method of rhizomes of Enshi polygonatum sibiricum
InactiveCN108124766ASolve the problem of germplasm degradationResolution cyclePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsDiseaseShoot apex
The invention relates to a rapid propagation method of rhizomes of Enshi polygonatum sibiricum. Aggravation of disease and insect damage and germplasm degradation easily occur in conventional rhizomepropagation, a rapid propagation system is established with rhizome terminal buds and stem tips used as explants in tissue culture, more available polygonatum sibiricum terminal bud scales are selected as explants test materials in consideration of the current situations of single explants source, large test material consumption and low propagation efficiency, adventitious roots are obtained by inducing bud scale differentiation, the adventitious roots are further induced to produce different types of differentiated bodies such as rhizomes with adventitious roots and terminal buds, adventitious bud clusters and calluses in multiple forms. Those types of differentiated bodies are continuously cultured respectively in Enshi and can continuously produce new adventitious bud clusters, rhizomeswith terminal buds and multiple types of calluses, so that a high-frequency regeneration system of excised roots, stems and leaves of polygonatum sibiricum is established. Roots, stems, leaves, calluses and rhizomes which are obtained with the method can be converted to grow in different culture periods.
Owner:恩施州源惠科技开发有限公司
Bud initiation culture medium of pear tree somatic embryos
InactiveCN105557520ASeedling growthStrong seedlingsHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSucroseSomatic embryogenesis
The invention provides a bud initiation culture medium of pear tree somatic embryos. The bud initiation culture medium comprises 1 / 2 improved SH, 0.5-0.8mgL<-1> of 6-BA, 3-5mgL<-1> of 2,4-D, 0.1-0.2mgL<-1> of NAA, 6.0-7.0gL<-1> of agar, 30gL<-1> of sucrose and 0.1-0.3% of phytagel and has pH value of 5.8-6.0. The bud initiation culture medium has the beneficial effects that pear trees difficult to propagate are rapidly propagated through somatic embryogenesis by improving a basic culture medium and components and adjusting the culture conditions; the plant transplanting survival rate is more than or equal to 96%; seedlings grow robustly, thus the problem of germplasm degeneration of good seedlings can be effectively solved, plenty of high-quality purified and rejuvenated seedlings can be also provided for production and an ideal receptor system can be also provided for breeding new varieties through genetic transformation or mutation breeding of the pear trees.
Owner:QINGDAO BAIRUIJI BIOTECH
Rapid propagation method adopting induction of cotyledon somatic embryos of Chinese scholartree
ActiveCN105638472AConvenient inductionInduced fastPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsDiseaseGermplasm
The invention discloses a rapid propagation method adopting induction of cotyledon somatic embryos of Chinese scholartree. The rapid propagation method comprises the following steps: selecting current-year-grown mature seeds without diseases and insect pests of the Chinese scholartree and disinfecting; then taking out cotyledons and cutting; inoculating the cotyledons on a somatic embryo culture medium and culturing to form calluses; transferring the calluses on an adventitious bud induction culture medium and culturing to form cluster bud plantlets; cutting the cluster bud plantlets into callus blocks and transferring the callus blocks to a test-tube plantlet proliferation culture medium or an adventitious bud induction culture medium and culturing; and transferring the cultured cluster buds into a strong seedling culture medium and carrying out strong seedling culture, and then hardening the seedlings and transplanting. The method disclosed by the invention is high in regeneration rate and has more buds; and the transplanting survival rate of plants can reach more than or equal to 90%, germchits grow healthy and the germplasm degeneration problem of the high-quality germchits can be effectively solved.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
Culture medium for multiplying test-tube seedlings based on somatic embryos of pear tree
InactiveCN107787837AImprove survival rateImprove qualityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyDisease
The invention discloses a culture medium for multiplying test-tube seedlings based on somatic embryos of a pear tree. The culture medium is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 14-26 parts of an organosilicone modified starch water emulsion, 10-20 parts of 1 / 2 modified SH, 20-30 parts of sucrose, 20-30 parts of non-ionic polyacrylamide, 5-11 parts of graft modified soybeanprotein, 15-25 parts of alternaria tenuissima protein, 11-19 parts of carbonase, 11-19 parts of sodium p-nitrophenolate, 6-8.4 parts of eugenol, 1.5-6.5 parts of paclobutrazol, 1-3 parts of bacilluscereus, 3-6 parts of a beta-compound detoxification enzyme, 3-5 parts of bacillus natto, 3-5 parts of 6-benzyl aminopurine, 0.5-1.0 part of naphthylacetic acid and 3-6 parts of 2, 4-D. Through optimization of the components of the culture medium, the survival rate of transplanted plants is greatly increased, the incidence of diseases of the seedlings is reduced and the seedlings grow healthily andstrongly.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG POMOLOGY INST OF HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Growth and differentiation culture medium for somatic embryo of pear tree
PendingCN105409777ASolve the problem of germplasm degradationSeedlings grow vigorouslyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySomatic embryogenesis
A growth and differentiation culture medium for a somatic embryo of a pear tree is characterized by comprising 1 / 2 improved MS, 1.0-1.5 mg / L 6-BA, 0.5-1.0 mg / L 2,4-D, 2.0-3.0 mg / L KT, 6.0-7.0 g / L agar, 20 g / L saccharose and 2.0%-2.5% phytagel, wherein the pH (potential of hydrogen) of the culture medium ranges from 5.8 to 6.0. The pear tree difficult to propagate can propagate quickly through somatic embryogenesis on the basis of improvement of a basic culture medium and ingredients and adjustment of a culture condition, the survival rate of transplanted plants can be higher than 96%, seedlings grow robustly, the germplasm degeneration problem of good seedlings can be solved effectively, a large quantity of purified and rejuvenated nursery stocks can be provided for production, and an ideal receptor system is provided for breeding of new varieties during genetic transformation or mutation breeding of the pear tree.
Owner:QINGDAO BAIRUIJI BIOTECH
Application of molecular marker based on TYRP1 gene in giant salamander body color breeding
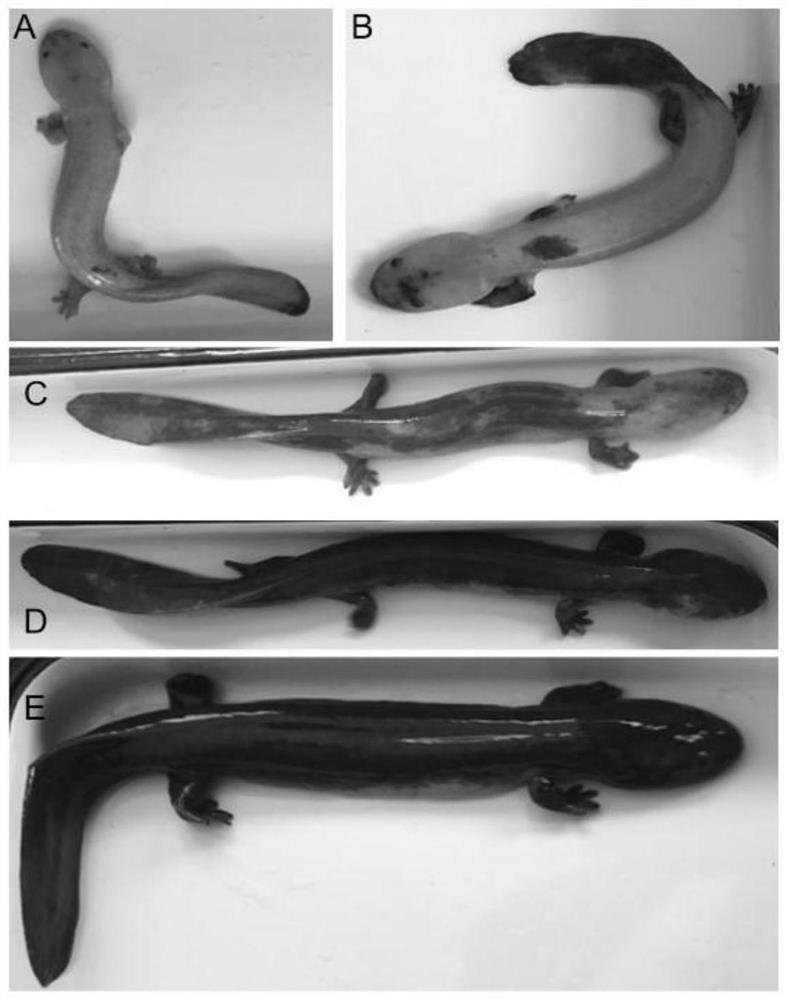
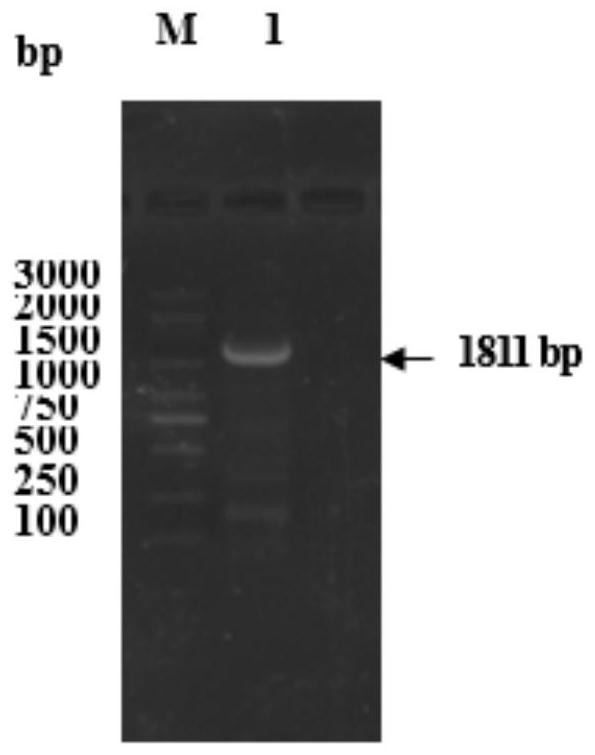
PendingCN114150075AMolecular markers are validSolve the problem of germplasm degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyTYRP1 gene
The invention discloses application of a molecular marker based on a TYRP1 gene in giant salamander body color breeding, the nucleotide sequence of a giant salamander TYRP1 gene coding region is cloned for the first time, the full length is 1584bp, 527 amino acid residues are coded, and a tyrosinase (177-411 amino acid) functional structure domain is included; detecting the expression profile difference of the TYRP1 gene in tissues with different body colors and skin tissues with different body colors of the wild giant salamander by adopting a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology; complete sequences of CDS regions of TYRP1 genes with different body colors are compared to find that TYRP1 genes of yellow body color individuals have two nucleotide insertion sites, so that a decoding frame is changed, and an amino acid sequence is interrupted. The invention provides an effective molecular marker for directional breeding of giant salamander body color, provides a method for researching a molecular genetic basis and a cell metabolism mechanism formed by body color diversity, is beneficial to breeding of new giant salamander strains, and solves the problem of germplasm degeneration of giant salamanders.
Owner:SHAANXI INST OF ZOOLOGY NORTHWEST INSTOF ENDANGERED ZOOLOGICAL SPECIES
Method for detoxifying and reproducing helianthus tuberosus quickly
ActiveCN102763594BFor long-term storageShortened growth timeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureAxillary budBud
The invention relates to a method for detoxifying and reproducing helianthus tuberosus quickly. The method comprises the following steps of: disinfecting young axillary buds or stem tips serving as explants, transferring the young axillary buds or stem tips into a bud induction culture medium, transferring the buds into a rooting culture medium, and performing refining seedlings and transplanting on a complete plant, wherein the bud induction culture medium is improved on the basis of a Murashige and Skoog (MS) culture medium, 0.1 mg.L<-1> of naphthyl acetic acid (NAA) and 0.5 mg.L<-1> of 6-butyl acrylate (BA) are added, so that adventitious buds which are induced are more, callus is small, and the problems of vitrification and water stain are solved; and obtained seedlings are robust and vigorous in growth vigor and can be transferred into the rooting culture medium directly, the rooting rate is 100 percent, and the survival rate of test-tube seedlings is over 90 percent. By the method, the effect of detoxifying the helianthus tuberosus seedlings can be achieved, the reproduction efficiency is improved, the production period is shortened, and an effective path is provided for the large-scale seedling raising of the helianthus tuberosus.
Owner:北京碧青园生态环境科技有限公司
Complete set culture medium for induction of cotyledon somatic embryos of Chinese scholartree
ActiveCN105638473AShorten the timeConvenient inductionHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudCulture mediums
The invention discloses a complete set culture medium for the induction of cotyledon somatic embryos of Chinese scholartree. The complete set culture medium comprises a somatic embryo induction culture medium, an adventitious bud induction culture medium, a strong seedling culture medium and a rooting culture medium. When the culture medium disclosed by the invention is used for propagating Chinese scholartree seedlings, one step of establishing a Chinese scholartree rapid propagation and regeneration system can be saved, so that time is greatly shortened. The regeneration rate is high, more buds are germinated, and the plant transplanting survival rate can reach more than or equal to 90%; germchits grow healthily; and the germplasm degeneration problem of the high-quality germchits can be effectively solved, and an ideal receptor system also can be provided for genetic transformation or mutation breeding of the Chinese scholartree.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
Method for strong seedling and rooting culture of strawberries
ActiveCN103348915BIncrease productionQuality improvementPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsFragariaShoot
The invention discloses a method for strong seedling and rooting culture of strawberries, which includes the following steps: firstly, strong seedling and rooting culture: a multiple shoot with a prophyll and 0.3-0.5 cm in height and well in growth and development is cut into a single plant and transplanted to a strong seedling and rooting culture medium for rooting culture, and transplanting is carried out after the plant is 3-5 cm in height; secondly, transplantation: the plant is firstly transplanted to a culture room and grows for 30-35 d, then is transplanted in a plastic-covered tunnel with a shading net, after a new root grows and the plant sprouts, watering frequency is gradually reduced, and the plant is transplanted to a flowerpot for ordinary management. The method for strong seedling and rooting culture of strawberries, provided by the invention, improves the survival rate of transplanted plants by 90% above through supporting measures such as improvement on minimal medium and ingredients and adjustment in culture conditions, enables seedlings to grow healthy, effectively solves the problem of genetical characterization decline of fine seedlings, effectively improves yield and quality of strawberries and enhances the economic value of strawberries at the same time.
Owner:句容市春城镇年胜葡萄园
A virus-free breeding method and virus-free culture medium for cranberry
InactiveCN106508681BSolve the problem of germplasm degradationImprove qualityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSterile environmentShoot apex
The invention provides a cowberry detoxification breeding method. The cowberry detoxification breeding method comprises the following steps: accelerating germination of cowberry resting shoots, shearing off a bud when the length of the bud reaches 1-3 cm and carrying out sterilizing treatment; cutting off 0.3-0.8 cm of a stem tip from the sterilized bud, and inoculating the stem tip on a foundational medium, and culturing under the conditions that the temperature is 25-28 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 1,800-2,200 Lx, and the illumination time is 12-16 h / d; after the stem tip grows until the length of the stem tip reaches 1.5-2.0 cm, cutting off 0.03-0.05 cm of a stem tip in a sterile environment and inoculating the stem tip to a detoxification medium, carrying out dark culture for 5-9 days at the temperature of 22-25 DEG C, and continuing culturing in an environment in which the temperature is 23-26 DEG C, the illumination intensity is 1,800-2,200 Lx and the illumination time is 12-16 h / d; and inoculating a detoxification seedling to a medium, carrying out rapid multiplication culture, and then carrying out seedling hardening and rooting after the length of the seedling reaches 2.0-3.0 cm.
Owner:FORESTRY RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG PROVINCE +1
Artificial planting method for Vernonia anthelmintica
InactiveCN111631088AAddress resource shortagesReduce planting costsSeed and root treatmentPlant cultivationBiotechnologyVernonia anthelmintica
The invention relates to an artificial planting method for Vernonia anthelmintica. The artificial planting method comprises the following steps: seed selection, selection of proper lands, soil preparation, sowing, final singling, field management and fruit harvesting. The method is simple and convenient, the planting cost is lowered, the method is easily grasped by planters, the yield of fruits (seeds) of the Vernonia anthelmintica is increased, the method is suitable for industrialized cultivation of the Vernonia anthelmintica, and a foundation is laid for breeding and intermediate propagation of fine varieties of the Vernonia anthelmintica. According to the method, the key problems of variety breeding, large-scale artificial planting and seed-breeding of the Vernonia anthelmintica whichis suitable for Hetian Prefecture and high in biomass, fruit yield and contents of effective components, real-time evaluation criterions of the quality of a planting process, development of high-value-added products, comprehensive utilization of resources and the like are emphatically solved.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos
InactiveCN102124955BSolve the problem of germplasm degradationPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySomatic embryogenesis
The invention provides an induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos, comprising the following steps: (1) building a regeneration system of a Photinia fraseri asepsis test tube seedling; (2) building a high-frequency rapid-propagation system induced by an in-vitro somatic embryo and an adventitious bud; and (3) rooting, acclimatizing and transplanting for the test tube seedling. The induction rapid-propagation culture method for Photinia fraseri in-vitro leaf somatic embryos is characterized in that coordinated sets of measures of selecting aproper explant, improving a basic culture medium and ingredients, regulating culture conditions and the like are adopted, and the Photinia fraseri of which the seed is difficult to breed is subjectedto path rapid propagation by the somatic embryos; the plant transplantation survival rate is higher than 95%; the germchit grows strongly to solve the problem that an excellent germchit quality degenerates, and a great quantity of purified and rejuvenated detoxification nursery stock with good quality can be provided for production; and in addition, and ideal receptor system is provided for breeding new specimens for Photinia fraseri by genetic transformation or mutation breeding.
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY +1
Tilapia oosperm artificial incubation method
InactiveCN100518500CReduce the effects of feedingSolve the problem of germplasm degradationClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaSaline waterTilapia
The present invention relates to an artificial incubation method of fertilized egg of tilapia mossambica. It is characterized by that the male and female paired breeding of tilapia mossambica is implemented in net cage, then said invention adopts the following several steps: checking mouth cavity of female fish, if in the mouth cavity of female fish the fertilized eggs are existed, opening mouth cavity of female fish, taking out fertilized eggs and pouring them into a landing net; using saline water to wash said fertilized eggs and placing said fertilized eggs into an incubator; making the fertilized eggs be floated in the water of said incubator and making incubation for 2-7 days so as to obtain the tilapia mossambica fries.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
A complete medium for inducing rapid propagation of somatic embryos from isolated leaves of Sophora japonica
ActiveCN105519441BConvenient inductionInduced fastPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBuddingGermplasm
The invention discloses a kit culture medium for detached-leaf-somatic-embryo induced rapid propagation of sophora japonica. The kit culture medium comprises a bud starting culture medium, a test-tube plantlet propagation culture medium, a somatic embryo induction culture medium, an adventitious bud induction culture medium, a sound seedling culture medium and a rooting culture medium. Through propagating sophora japonica seedlings by using the culture medium disclosed by the invention, the regeneration rate is high, the budding is good, the survival rate of plant transplanting can reach 95% or more, and the seed seedlings are robust in growth, so that the problem of germ plasm degeneration of excellent seed seedlings can be effectively solved, and an ideal acceptor system can be provided for the genetic transformation and induced breeding of the sophora japonica.
Owner:SHANDONG FOREST SCI RES INST
A method for cultivating fuchsia high temperature resistant hybrid seedlings
ActiveCN109496931BRich germplasm resourcesImprove toleranceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaHybrid seedMicrobiology
The invention relates to a method for cultivating a high temperature-resistant amaranthine hybrid seed, and the hybrid seed. The method comprises the following steps: S1, scallop population hybridization of Bohai Sea Red scallop parents with fully-developed sexual glands, and high temperature-resistant natural selection of hybridization progenies in a southern sea area to obtain a first-generationBohai Sea Red scallop high temperature-resistant breeding line; S2, obtaining of a hybridization progeny with mature A.i. concentricus Say and the high temperature-resistant breeding line in step S1as parents; S3, backcrossing of the high temperature-resistant breeding line used as a male parent and the hybridizaiton progeny obtained in step S2, used as a female parent, to obtain a backcrossed progeny; and S4, continuous population self-crossing purification breeding of the backcrossed progeny, obtained in step S3 and used as the parent, with amaranthine shell color and shell height as breeding indexes to obtain the high temperature-resistant amaranthine hybrid seed. The method utilizes the hybridization and backcrossing processes to genetically improve the scallop Bohai Sea Red and A.i.concentricus Say, so the obtained hybrid scallop has the advantages of large size, high growth speed and good high temperature resistance.
Owner:GUANGDONG OCEAN UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com