Patents
Literature
309 results about "Subspecies" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biological classification, the term subspecies refers to one of two or more populations of a species living in different subdivisions of the species' range and varying from one another by morphological characteristics. A single subspecies cannot be recognized independently: a species is either recognized as having no subspecies at all or at least two, including any that are extinct. The term may be abbreviated to subsp. or ssp. The plural is the same as the singular: subspecies.
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
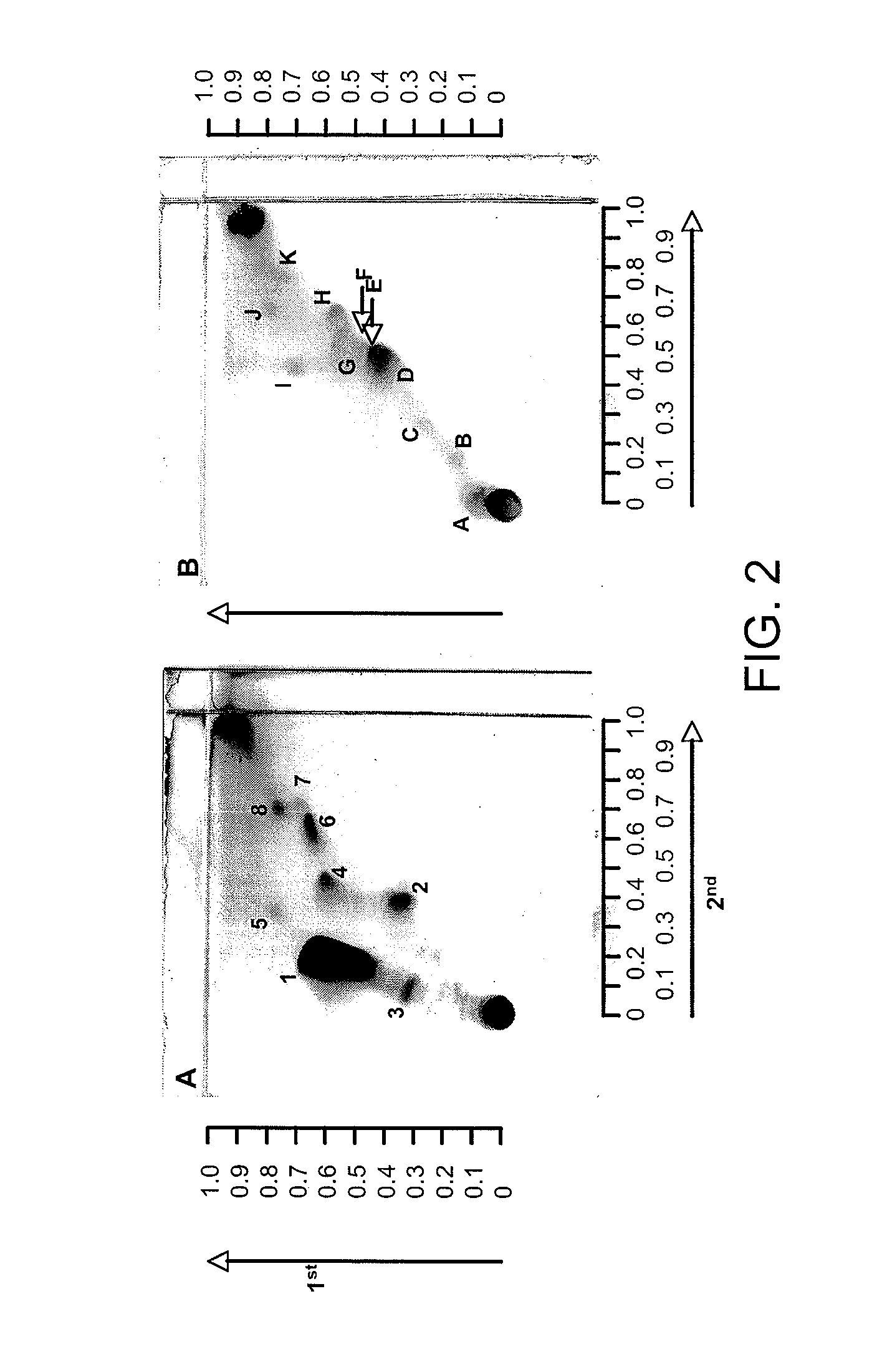
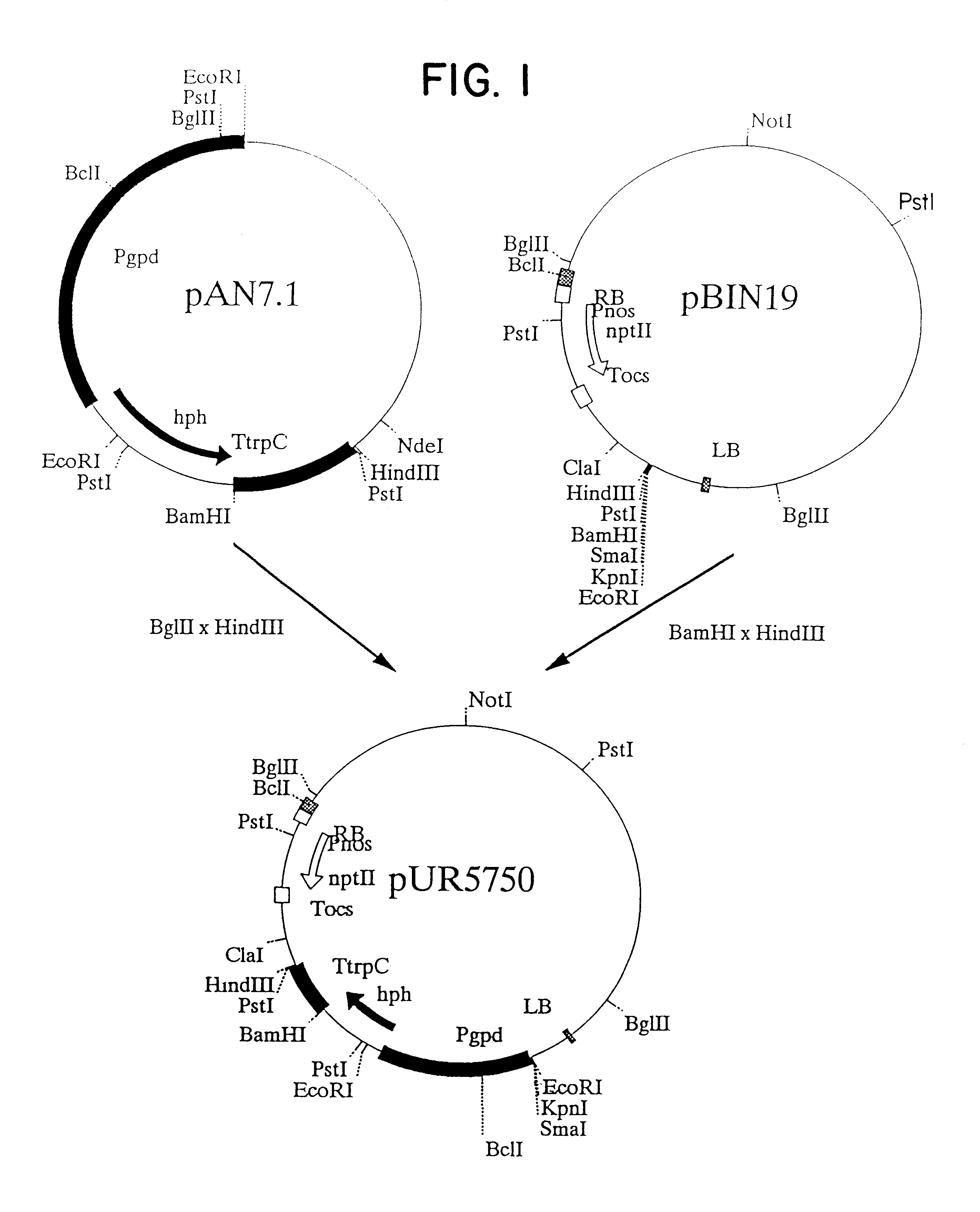
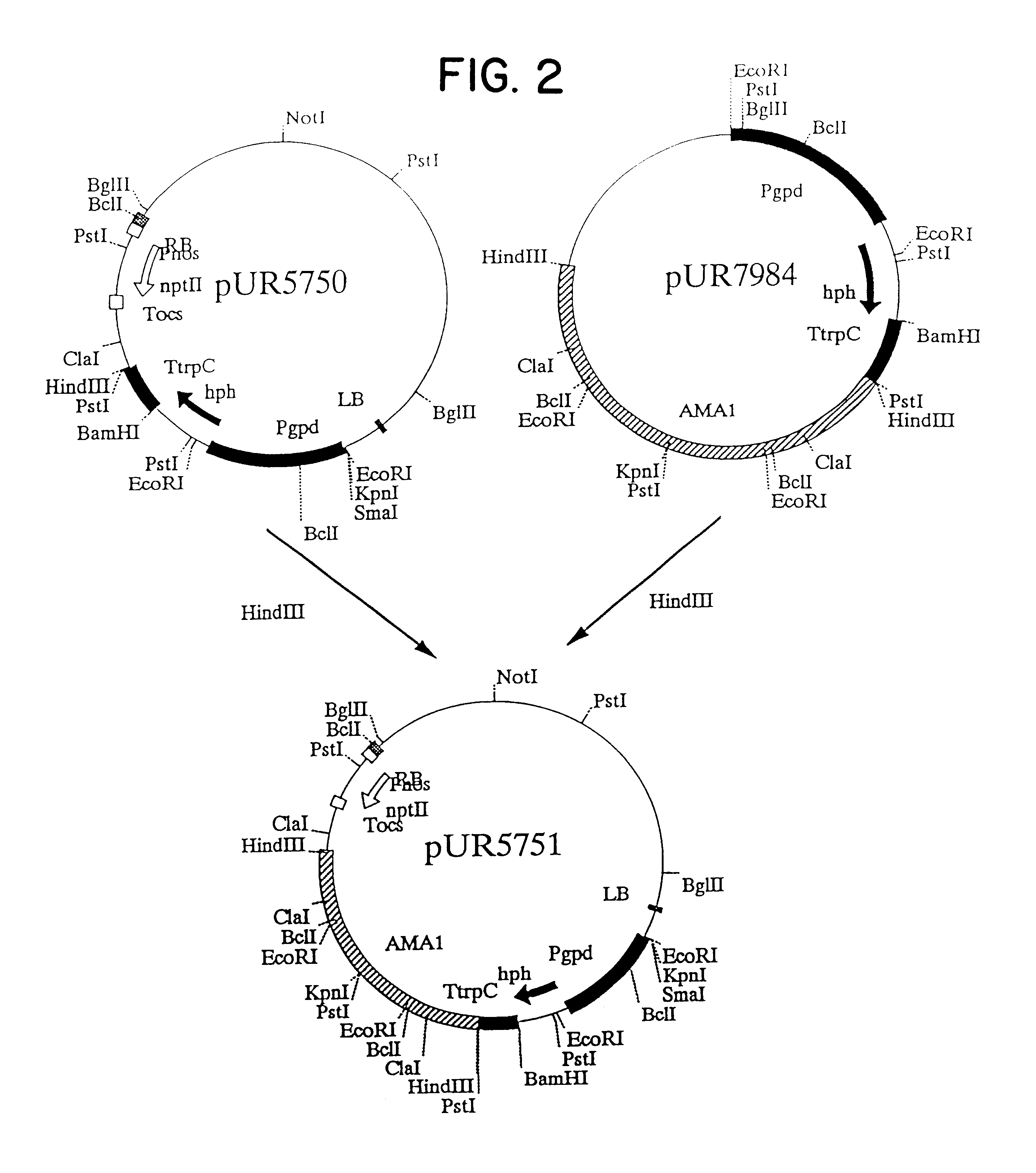
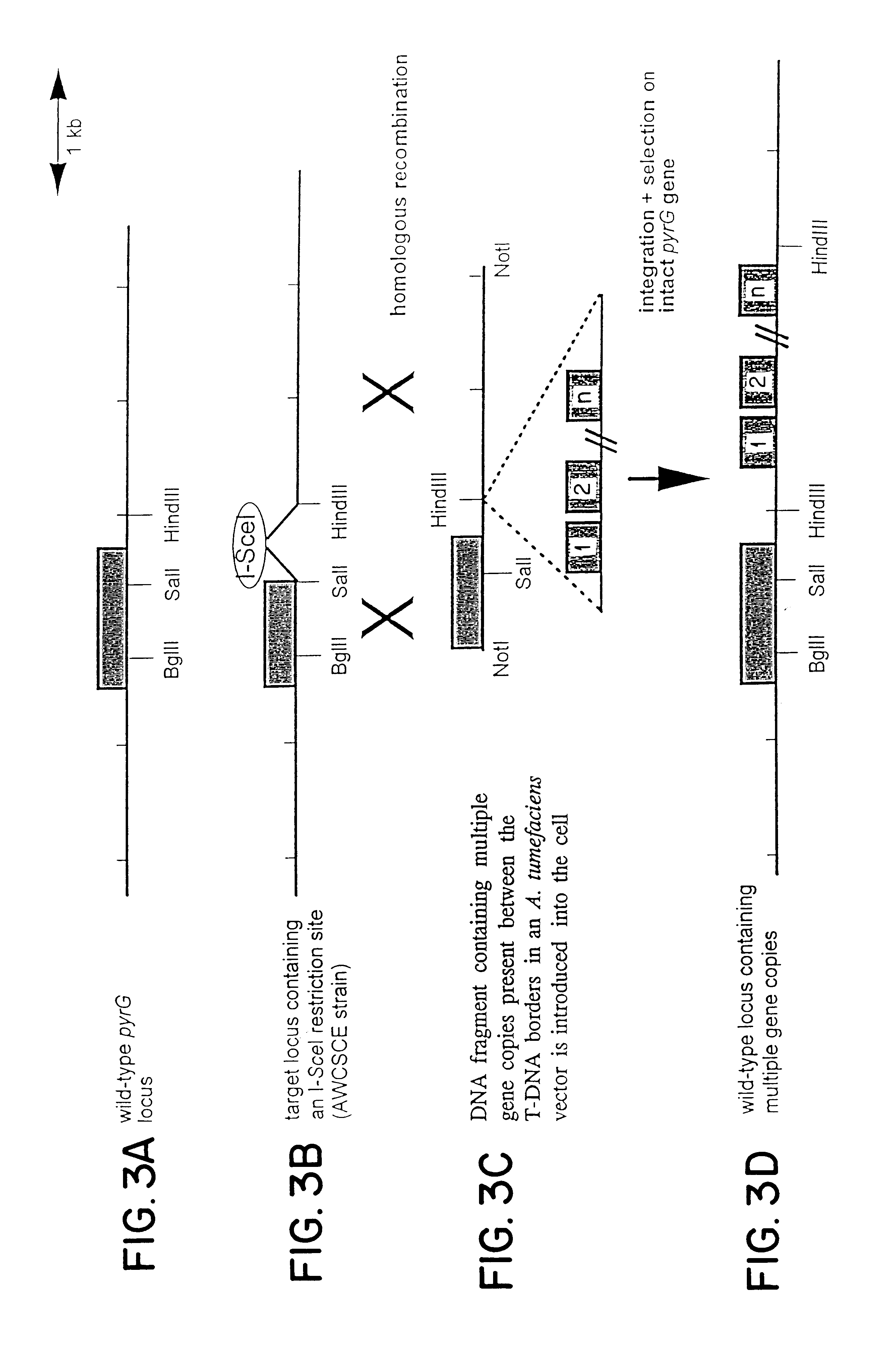
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
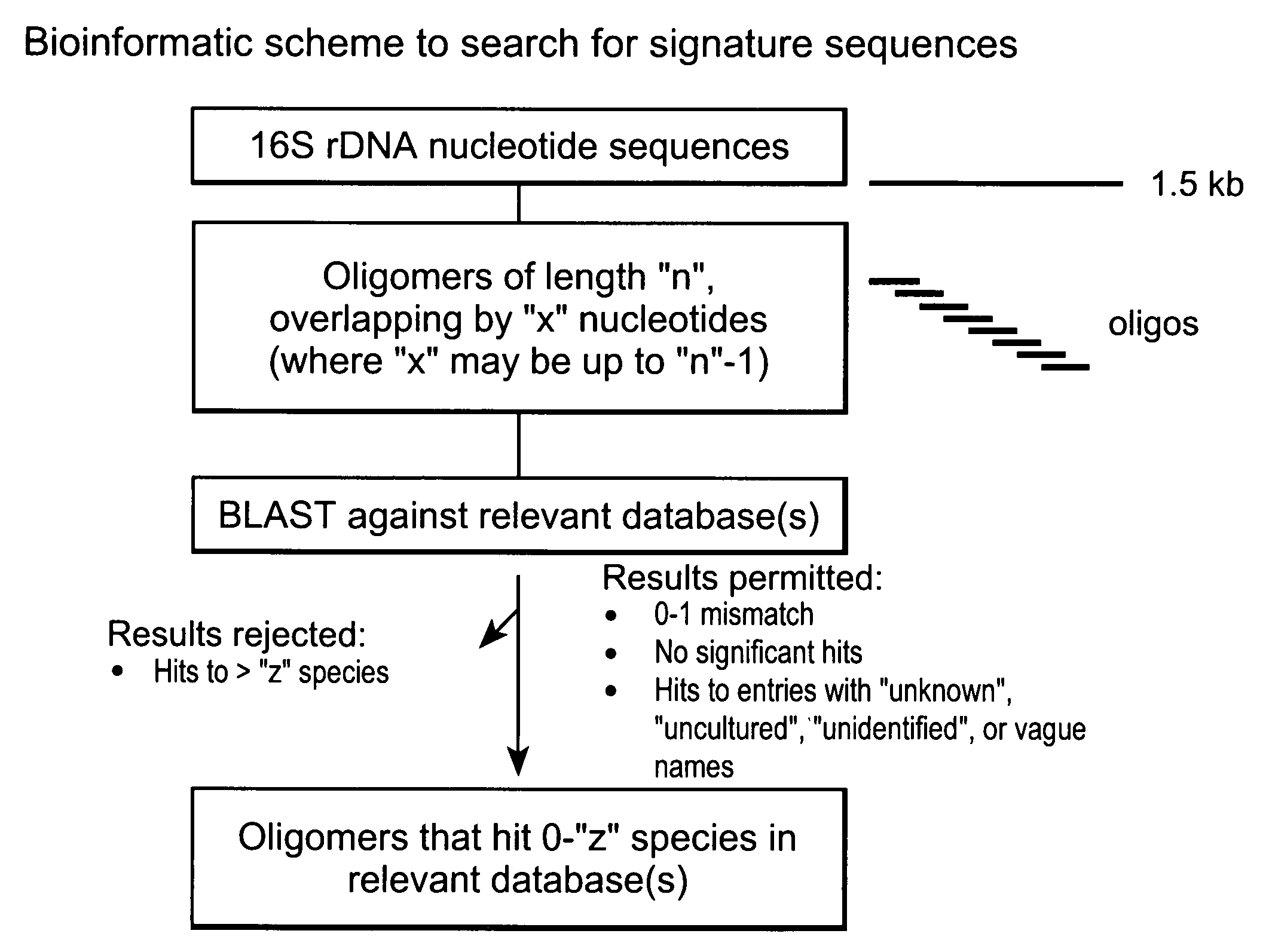
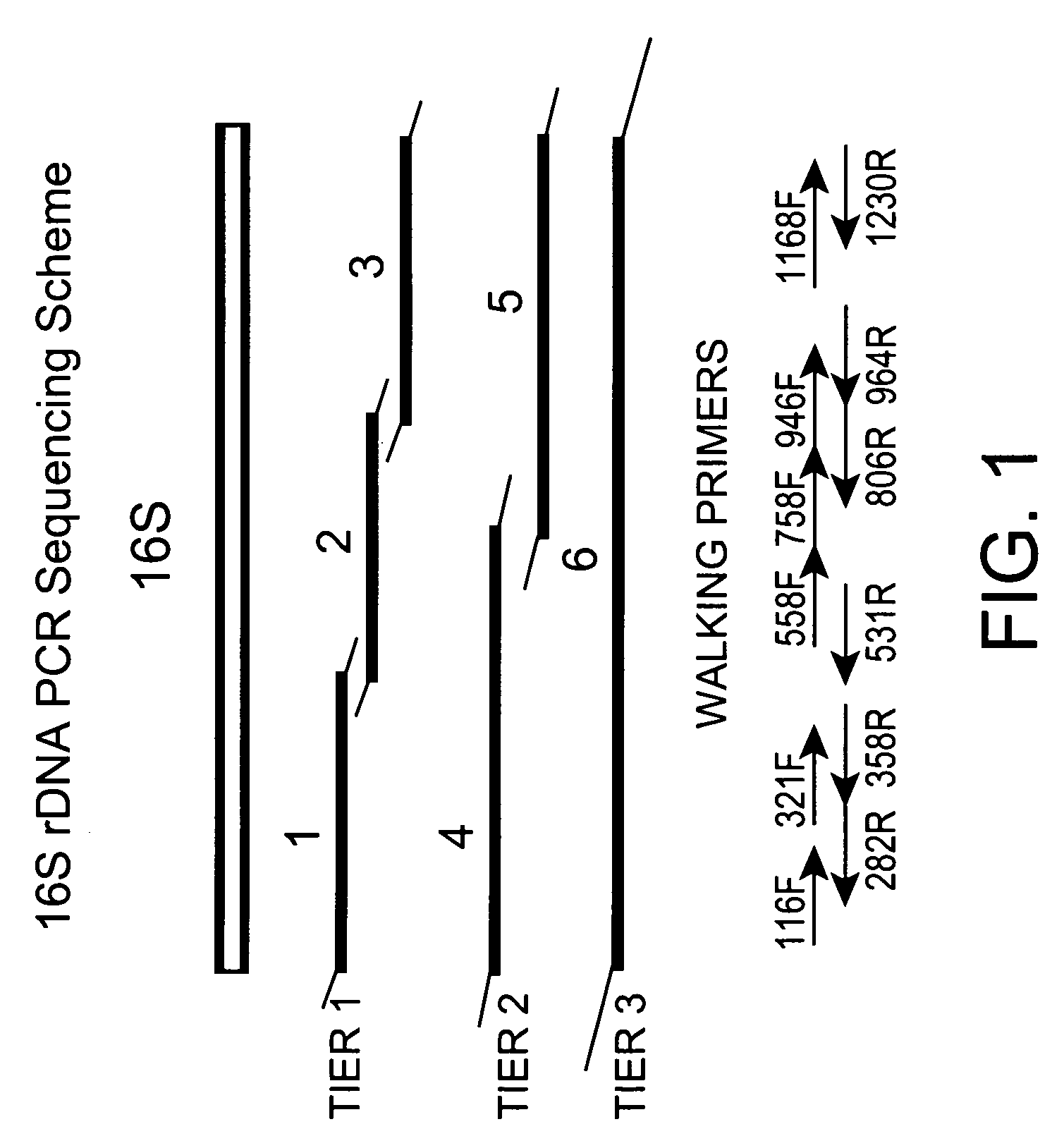
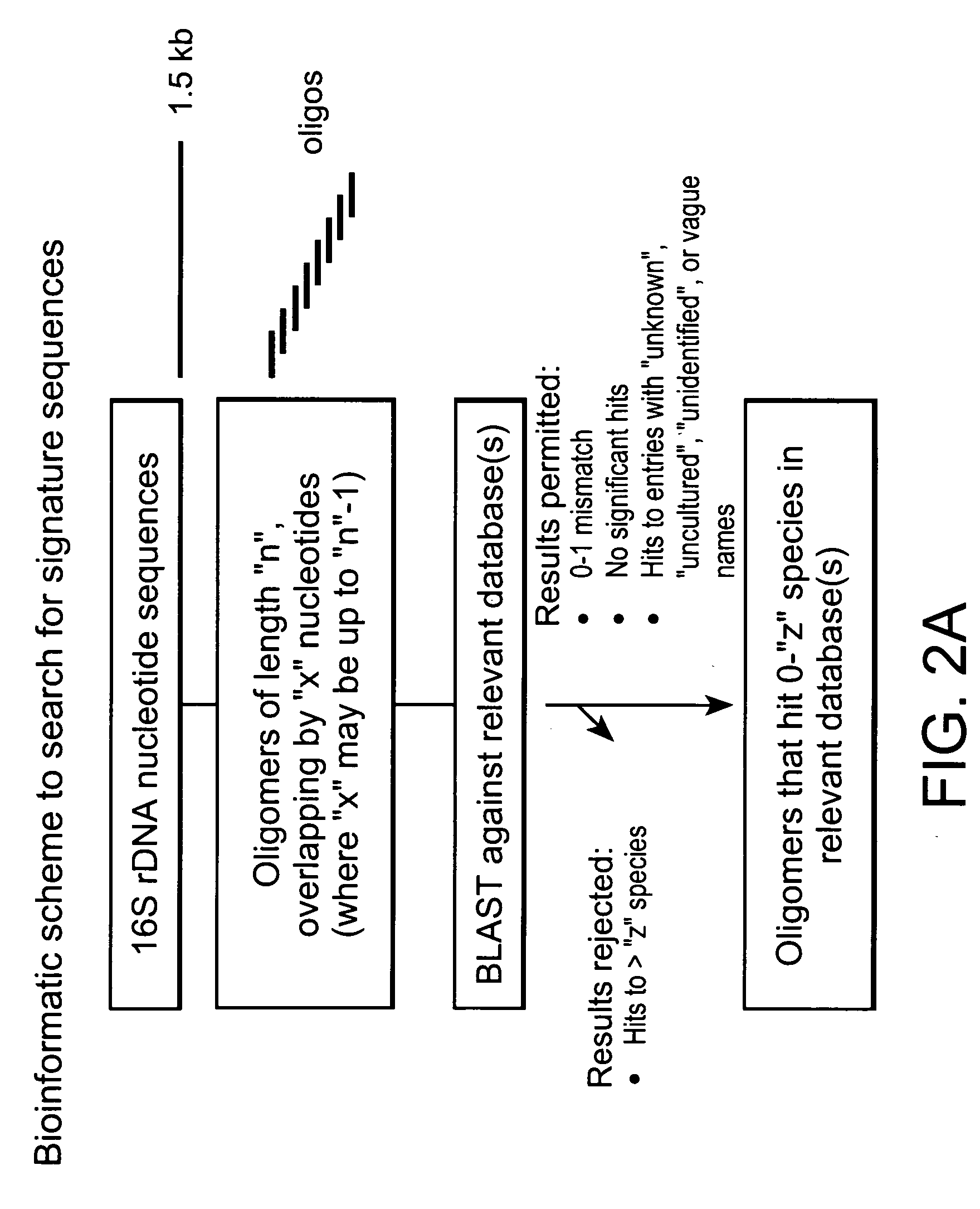
Genus, group, species and/or strain specific 16S rDNA sequences
InactiveUS20060046246A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismStrain specificity
Materials and methods for identifying unique sites in bacterial 16S and 23S rDNA are provided, as well as specific unique sequences of 16S rDNA in select bacteria. The distinguishing moieties will enable rapid differentiation between families, genera, groups, species, strains, subspecies, and isolates of microorganisms. Such differentiation can be performed by using rapid screening kits in combination with in silico analysis for diagnostic, prognastic, epidemiologic, phylogenetic, and other purposes.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC +1
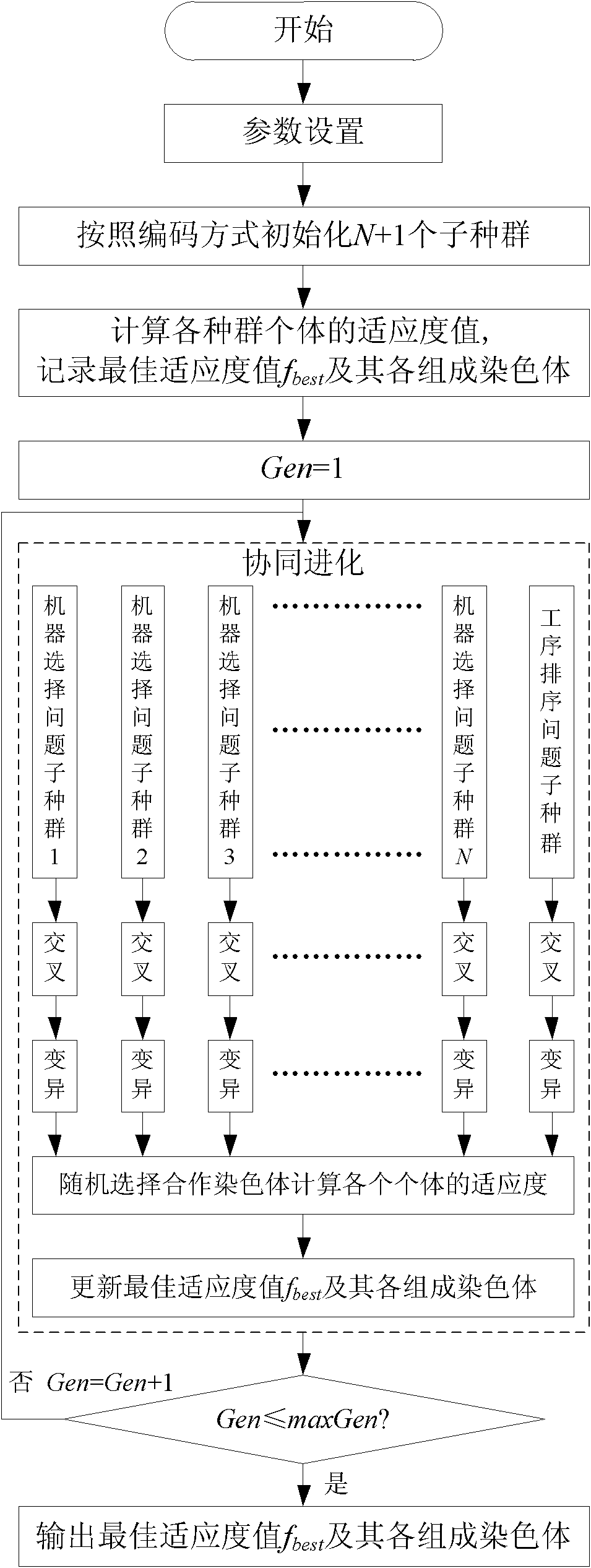
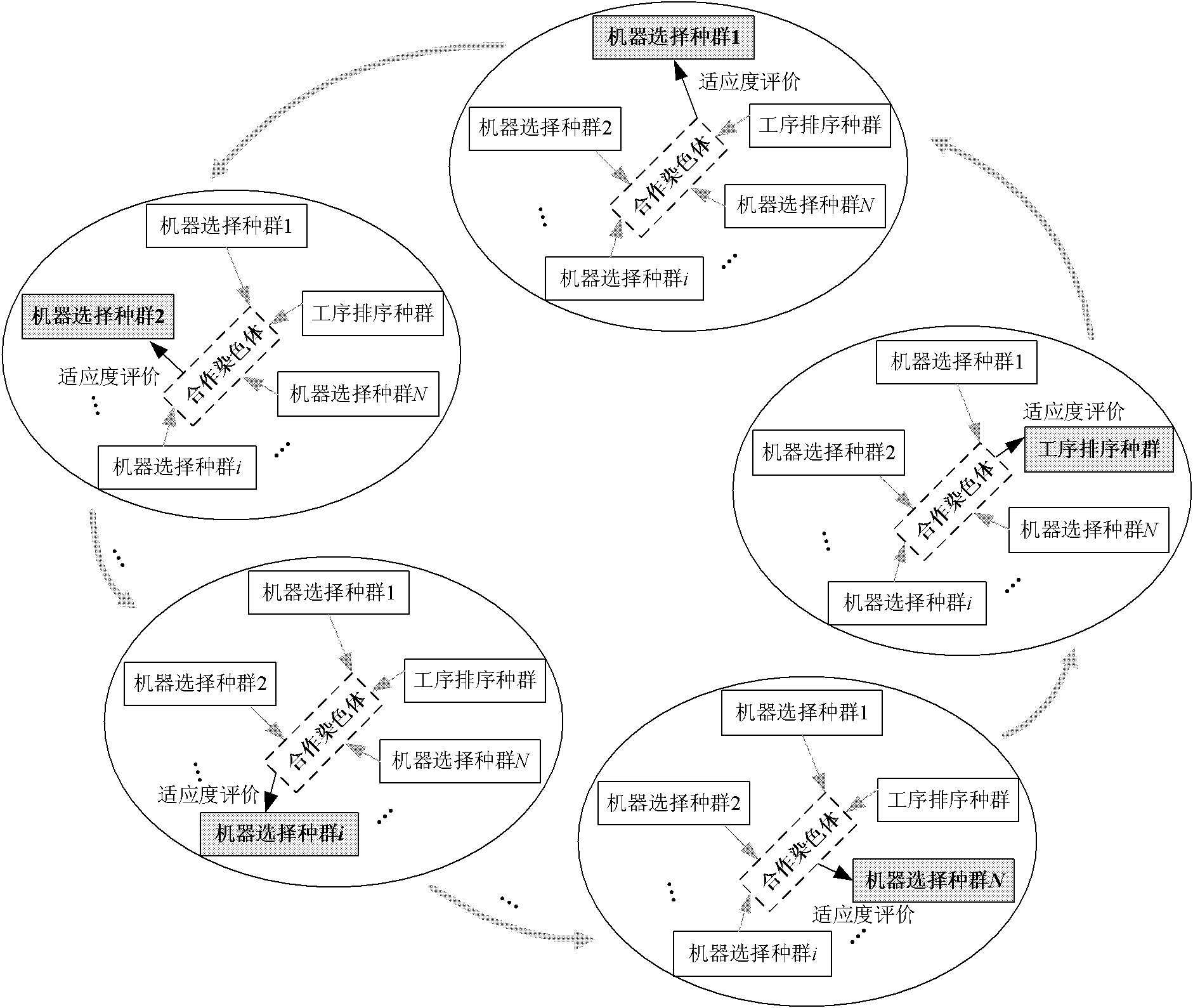
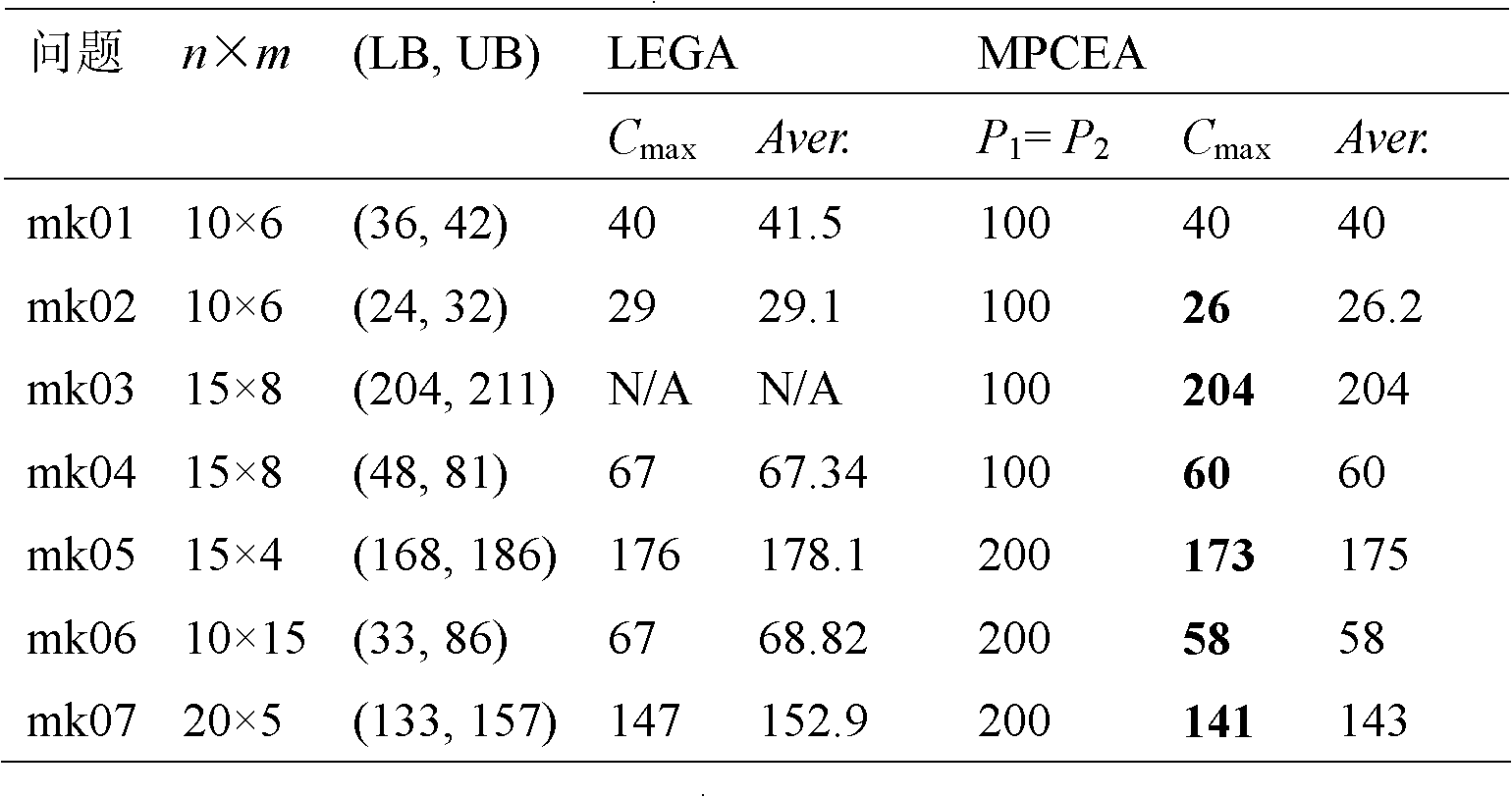
Flexible job shop scheduling method based on multi-species coevolution
InactiveCN101901425AQuality improvementAvoid the disadvantages that the performance cannot be fully utilizedResourcesGuidelineJob shop scheduling
The invention provides a flexible job shop scheduling method based on multi-species coevolution, which belongs to the field of shop scheduling, and mainly overcomes the disadvantage that a flexible job shop scheduling method based on a genetic algorithm can not be exerted fully. The method comprises the main steps of: 1. setting parameters; 2. initializing species according to a set coding method; 3. calculating the fitness value of each chromosome in each species according to a set method, and recording the optimum fitness value and the constitute chromosomes thereof; 4. carrying out multi-species coevolution: carrying out evolution operations, i.e. chiasmata and variation, to chromosomes in each subspecies, and evaluating new chromosomes; and 5. judging whether a method termination criteria is achieved or not: if so, terminating the method and outputting the optimum fitness value and the constitute chromosomes thereof; and otherwise, jumping to the step 4. The invention can be used to obtain a high-quality scheduling scheme suitable for practical production of shops, can shorten production time, and can be used for scheduling management and optimization of the production process of shops.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
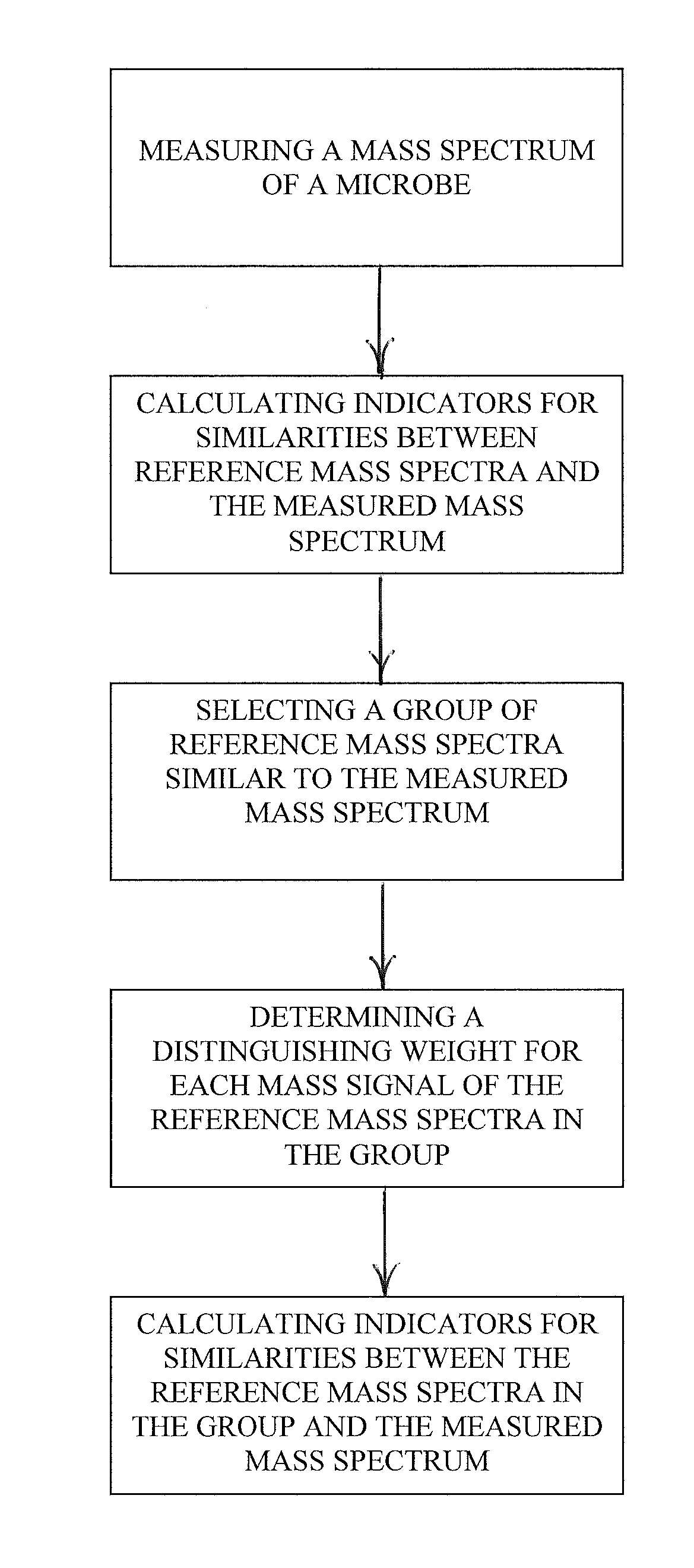
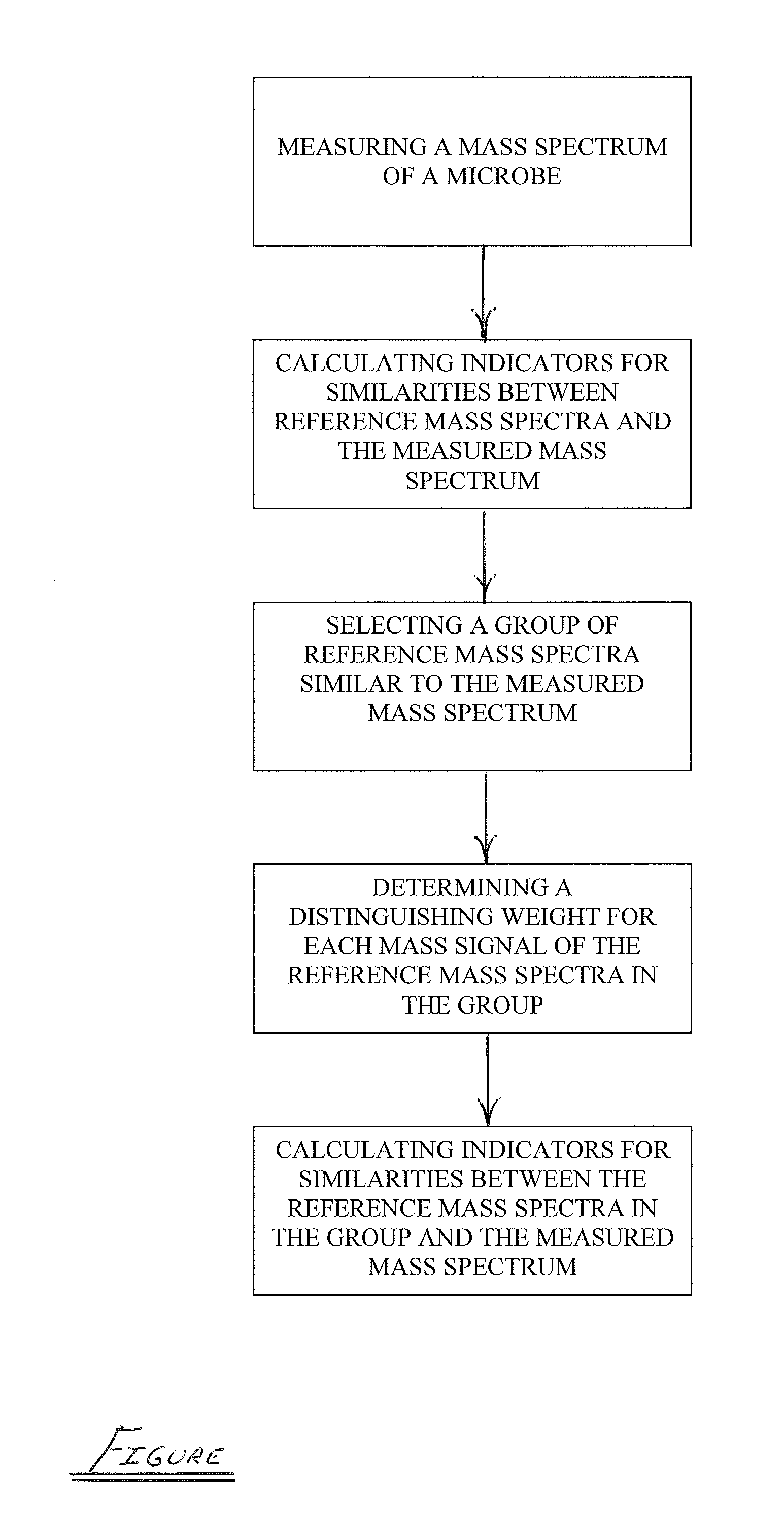
Spectrophotometric identification of microbe subspecies
ActiveUS20110012016A1Particle separator tubesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismDual stage
A dual-stage method is provided for identifying a microbe by, for example, its species or its subspecies. The method includes measuring a mass spectrum of the microbe using a mass spectrometer, calculating indicators for similarities between reference mass spectra in a library and the measured mass spectrum, selecting a group of reference mass spectra similar to the measured mass spectrum, determining a distinguishing weight for each mass signal of the reference mass spectra in the group, where the distinguishing weights emphasize differences between the reference mass spectra in the group, and calculating indicators for similarities between the reference mass spectra in the group and the measured mass spectrum as a function of the distinguishing weights.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Enteral microecological formulation and its preparation process
InactiveCN1843385AIncrease the number ofImprove disease resistanceOrganic active ingredientsBacteriaBifidobacteriumIsomaltooligosaccharide
The invention provides an intestinal tract micro-ecological preparation and its preparing process, wherein each 100g of the product contains bifidobacteria 1.0-20.0g, Lactobacillus acidophilus 1.0-25.0g, Streptococcus thermophilus 1.0-25.0g, Bulgarian subspecies of Lactobacillus fermentum 1.0-25.0g, saccharomycete 1.0-35.0g, and right amount of isomaltose hypgather, fructooligosaccharide, and many kinds of vitamins.
Owner:哈尔滨美华生物技术股份有限公司
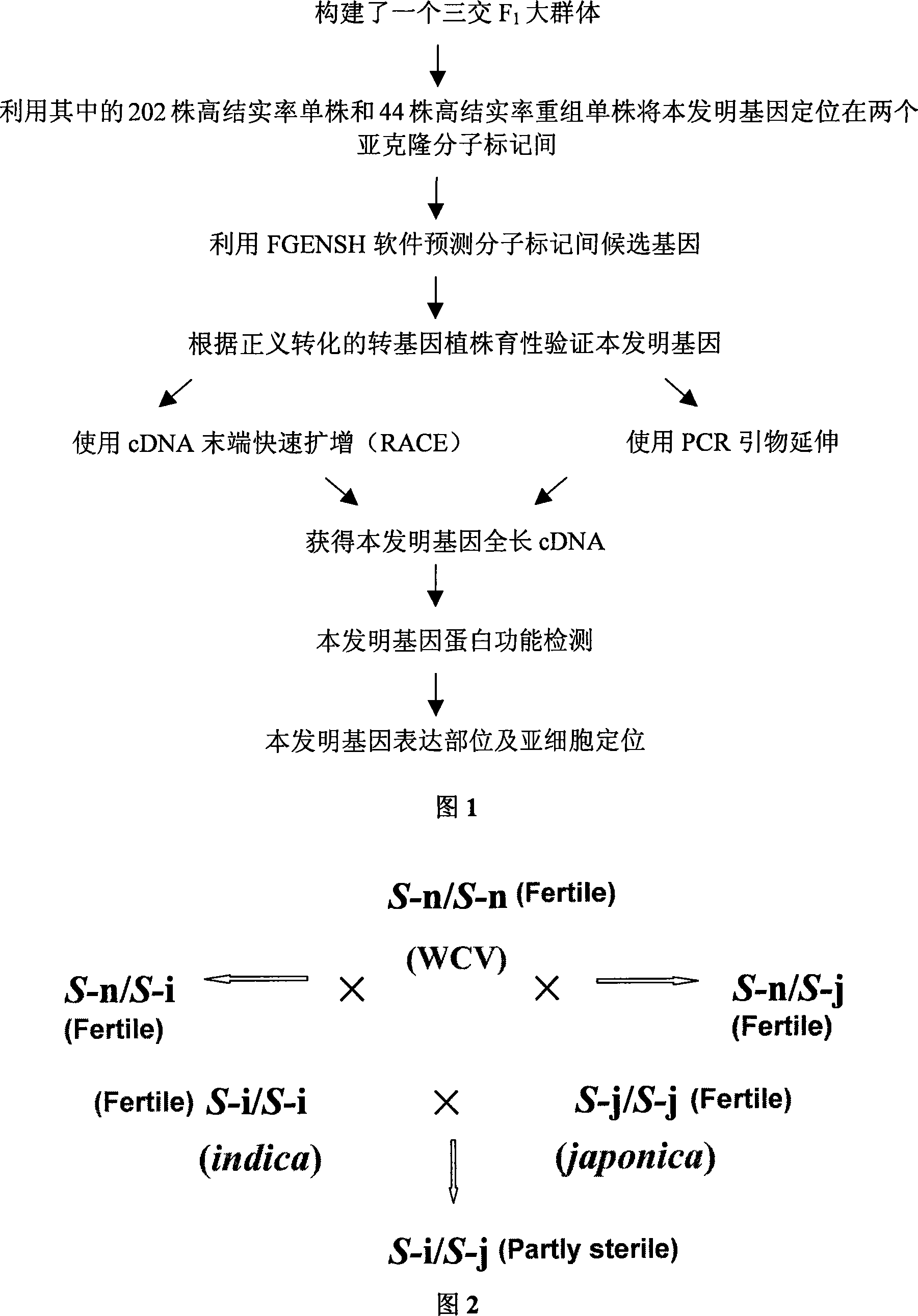
Separating clone of rice wide compatibility gene S5 and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering and concretely relates to the separation clone of paddy wide compatibility gene S5, a function validation and an application thereof for improving the paddy. The segment of the gene contains paddy wide compatibility gene coding aspartic proteinase. Subspecific Indica-Japonica paddy has strong hybrid advantage than varietal paddy, but the sterility of the subspecific Indica-Japonica hybrid restricts using the hybrid advantage thereof. The wide compatibility gene cloned by the present invention can conquer the sterility of the subspecific Indica-Japonica hybrid of the paddy and accordingly uses the strong hybrid advantage of the subspecific Indica-Japonica to further improve the output of the paddy.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
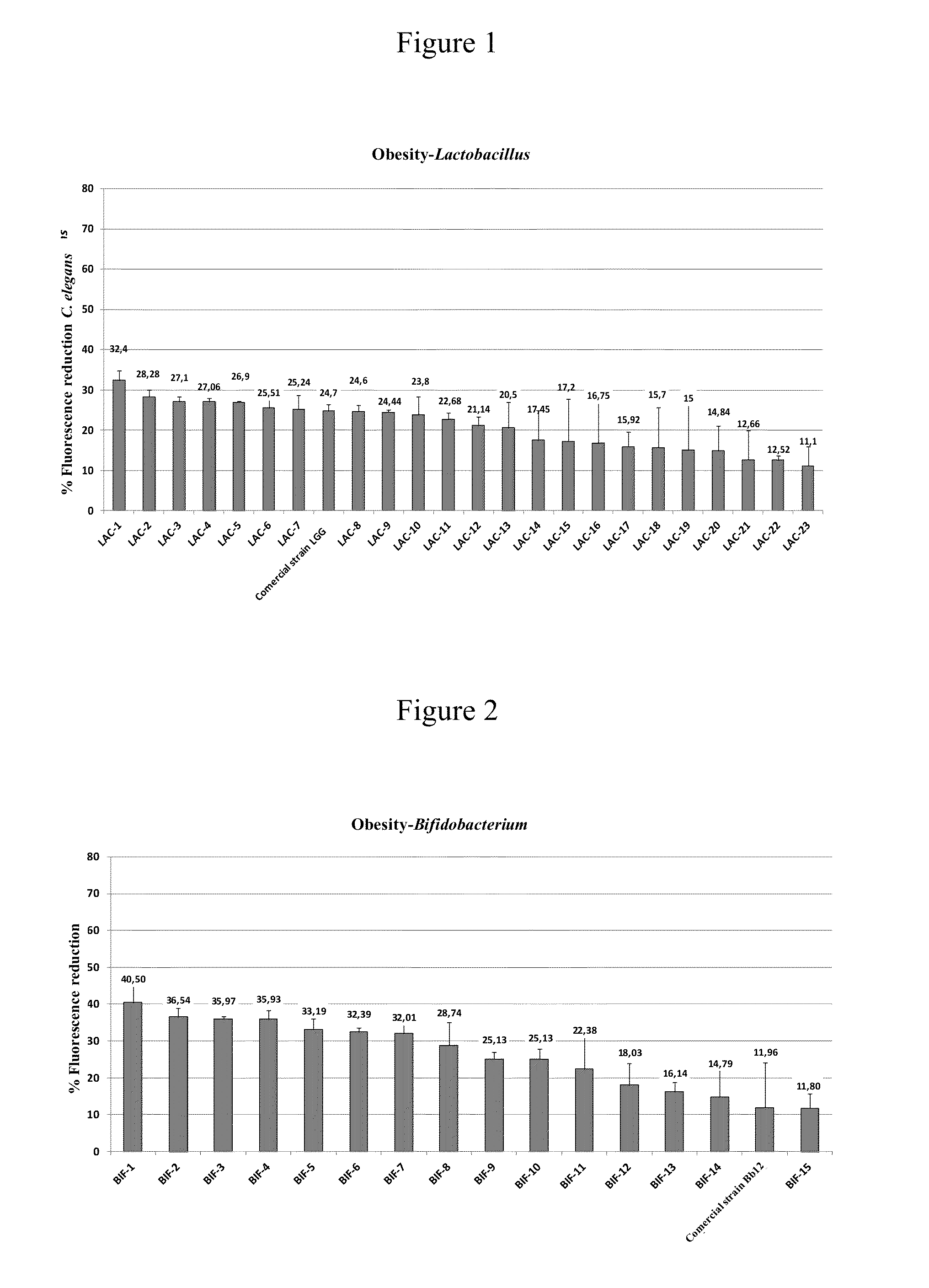
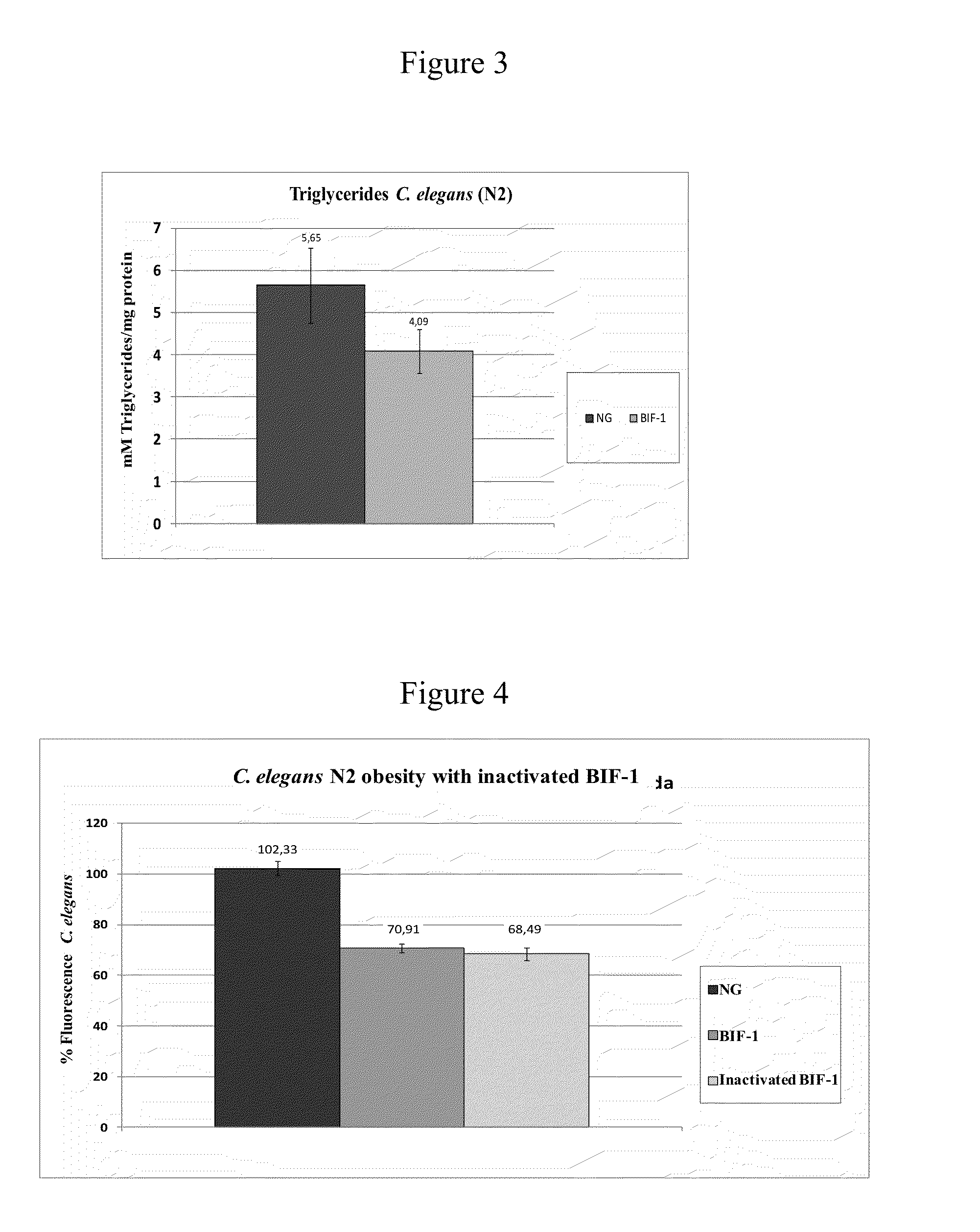
Novel strain of bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis cect 8145 and use thereof for the treatment and/or prevention of excess weight and obesity and associated diseases
ActiveUS20160143963A1Low in fatReduce the impactBiocideMilk preparationMetabolitePharmaceutical formulation
The invention is applicable within the food and pharmaceutical industry. More specifically, it relates to a novel strain of the species Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis CECT 8145, the cell components, metabolites and secreted molecules thereof, which, incorporated into food and / or pharmaceutical formulations, can be used in the treatment and / or prevention of excess weight and obesity and related diseases such as metabolic syndrome, hypertension, glycemia, inflammation, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, hypercholesterolemia, hormonal alterations, infertility, etc.
Owner:BIOPOLIS
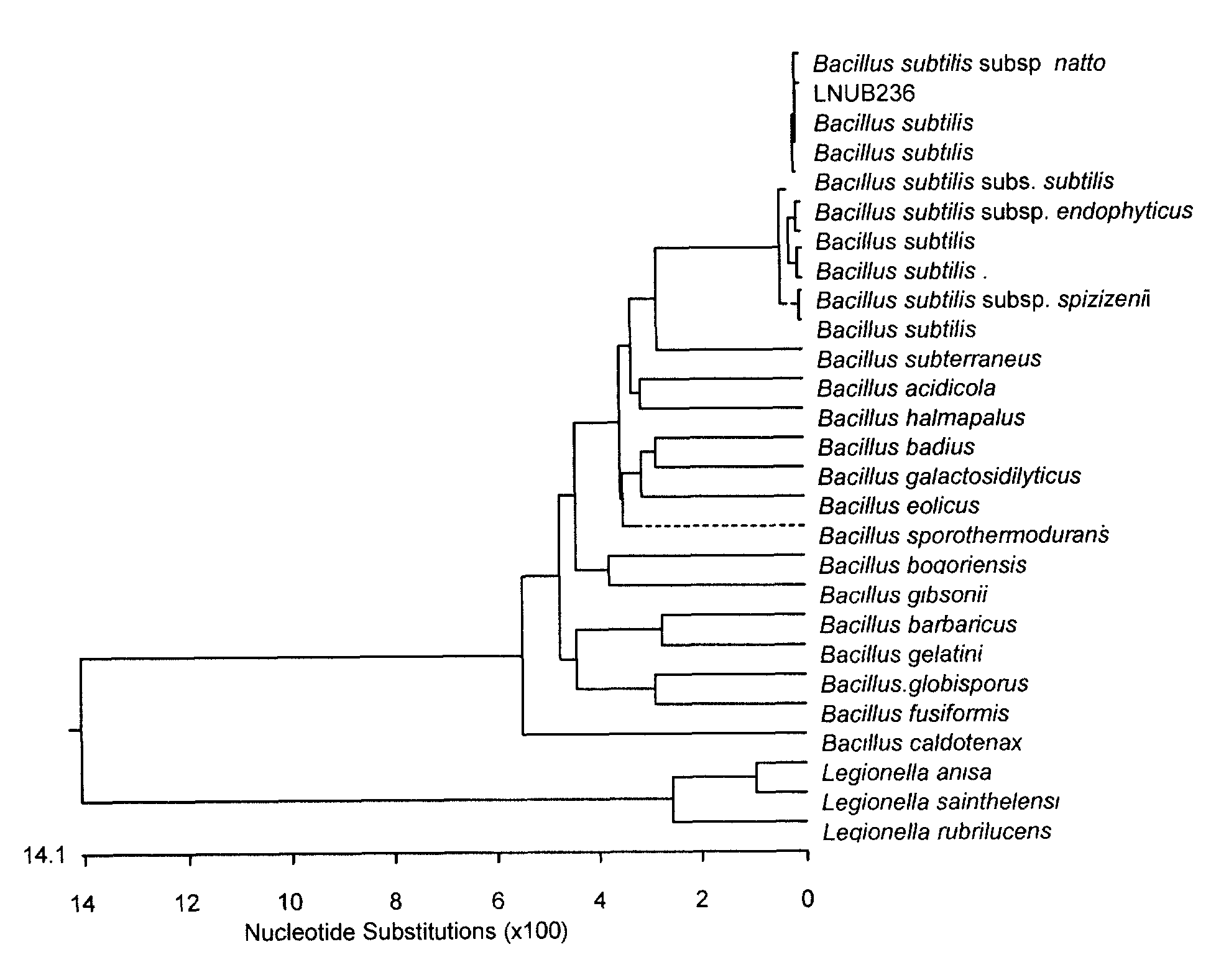
Bacillus subtilis subso natto for producing natto kinase and application thereof
InactiveCN101560478AIncrease enzyme activityGood effectBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCerebral thrombosisSide effect
The invention relates to a bacillus subtilis subso natto for producing natto kinase and application thereof. The bacillus subtilis subso natto (bacillus subtilis subso natto LNUB236), CCTCC No.: M 208156. The bacillus subtilis subso natto is subject to activation of culture, seed liquid and fermentation liquor are prepared, and the natto kinase is extracted. The invention relates to application of the natto kinase to preparing a health product for preventing and treating cerebral thrombosis. Constituents of the health product are proportioned by weight: lyophilized natto powder : natto kinase : natto kinase : evening primrose oil=1:2.0-3.0:1.0-1.5. The bacillus subtilis subso natto LNUB236 has high natto kinase yield, the highest enzyme activity is 431.455IU / ml in the event of production in a 30l fermenter, and the prepared natto kinase-containing health product has the advantages of high enzyme activity, obvious effect and no side effect.
Owner:辽宁储阳生物科技开发有限公司
Identification of bacterial species and subspecies using lipids
InactiveUS20080108104A1Reduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisLipid formationParatuberculosis
The use of free, extractable lipids found in bacteria for identification of bacterial species and subspecies is described. Bacteria have been found to differ sufficiently in their extracted lipid compositions to effect identification using thin layer chromatographic techniques. Burkholderia pseudomallei, Burkholderia thailandensis, and Burkholderia mallei have been distinguished in this manner. Lipopeptides specific to Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis, but not to the closely related bacterium Mycobacterium avium subspecies avium have also been used as a basis for bacterial subspecies identification using mass spectrometry and seroreactivity. Mass spectrometric analysis of total bacterial lipids of Burkholderia pseudomallei, Burkholderia thailandensis, and Burkholderia mallei, and mass spectrometric analysis of total bacterial lipids for Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium subspecies avium, without further lipid separation, has shown that species and subspecies of bacteria may be identified using such analysis.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY
Agricultural chemical composition containing fipronil and bacillus thuringiensis
InactiveCN101248800AOvercome the disadvantage of easy resistanceImprove efficacyBiocideAnimal repellantsFipronilAdditive ingredient
The invention belongs to the pesticide field and particularly relates to a synergic pesticidal composition with active ingredients to be the combinations of fipronil and a series of subspecies of Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt for short), wherein the Bacillus thuringiensis subspecies include six subspecies: Bacillus thuringiensis var.kurstaki, Bacillus thuringiensis var.aizawa, Bacillus thuringiensis var.tianmensis, B.thuringiensis var.israelensis, Bacillus thuringiensis subsp.aizawai and Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kenyae. The main agent thereof includes the following active ingredients by the weight percentages as follows: fipronil 0.1%-80%, Bacillus thuringiensis 100-100000 IU (international unit) / mg, or 10-1000 billion spore / g, or 0.01-20% toxin protein, and the rest is an accessory ingredient. The pesticidal composition can be efficiently used for controlling agricultural pests such as rice leaf rollers, chilo suppressalis walkers, diamondback moths, prodenia lituras, corn borers, and so on, and has particular characteristics of high efficacy, long lasting period and safe usage, so that the pesticidal composition belongs to environment-friendly pesticides and can prolong the generation of resistance, reduce production cost and increase economic benefit.
Owner:JIANGMEN PLANT PROTECTION
Preparation method of (Lactobacillus planetarium subsp. plantarum)Zhang-LL and its listeria monocytogene-resistant bacteriocin
ActiveCN104531562ASource securityStable sourceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood borneListeria murrayi
The invention relates to a preparation method of (Lactobacillus planetarium subsp.plantarum)Zhang-LL and its listeria monocytogene-resistant bacteriocin. The preparation method is suitable for preservation and fresh-keeping of meat and meat products, milk and milk products, fruits and vegetable, and instant foods. The (Lactobacillus planetarium subsp.plantarum)Zhang-LL (CGMCC No.6936) is selected from bacon on the Fujian farmer's market. A bacteriocin production broth is obtained by fermentation of a Zhang-LL strain, and the Zhang-LL strain bacteriocin is extracted and purified by a pH-dependent adsorption-desorption method, a cation exchange chromatography and a reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography so that titer is improved by 32 times and purity is improved by 36.65 times. The bacteriocin can inhibit a plurality of food-borne pathogenic bacteria such as listeria monocytogenes, has high bacteriostatic activity, good heat, acid and base stability, can be degraded by human protease and is a natural and safe biological preservative. The preparation method has the advantages of simple processes, stability, high efficiency, source convenience, low cost and industrial production feasibility.
Owner:BEIJING BEINONG HONGZE BIOTECH CO LTD
High-protein brown yoghourt and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN105724569AHigh nutritional valueDelicate and smooth tasteMilk preparationFood additiveMaillard reaction
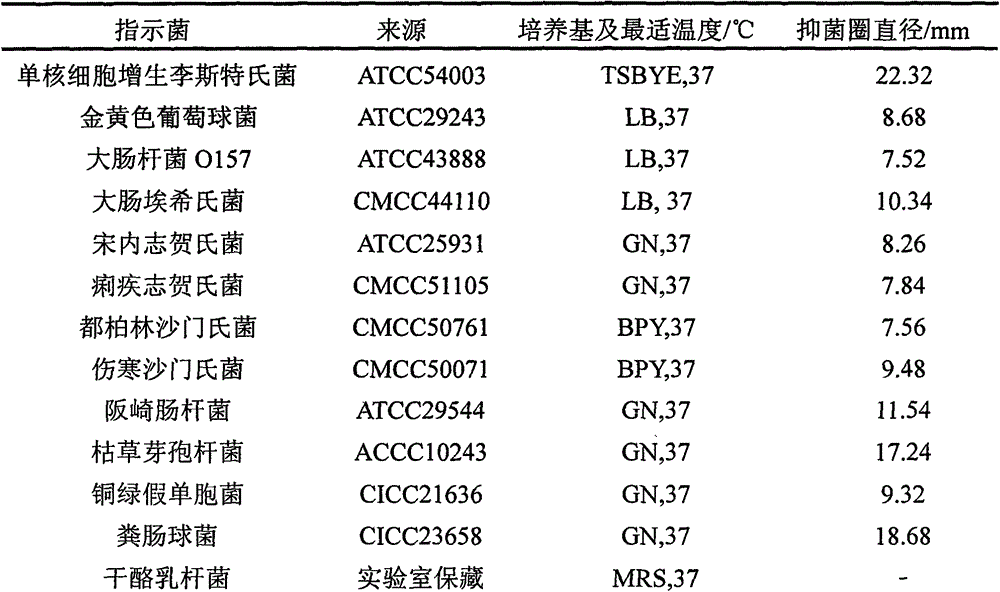
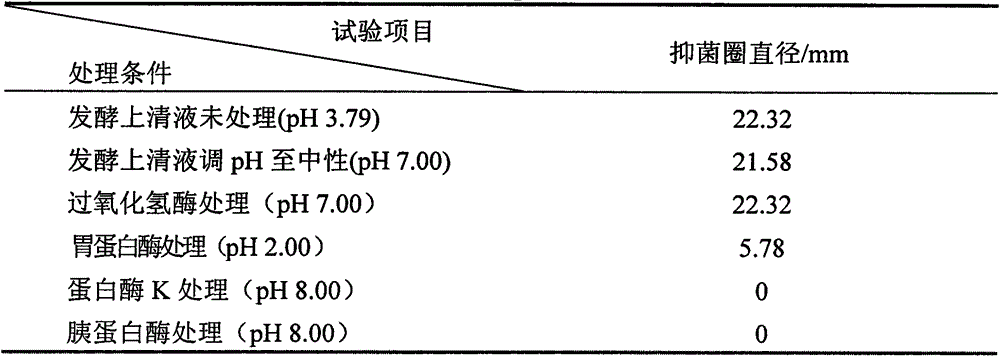
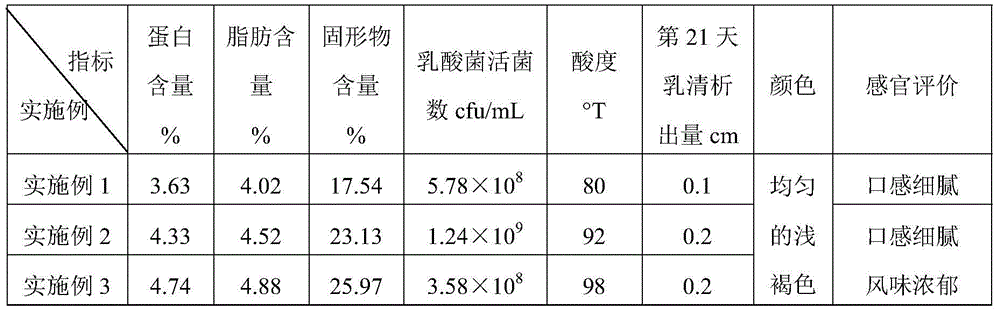
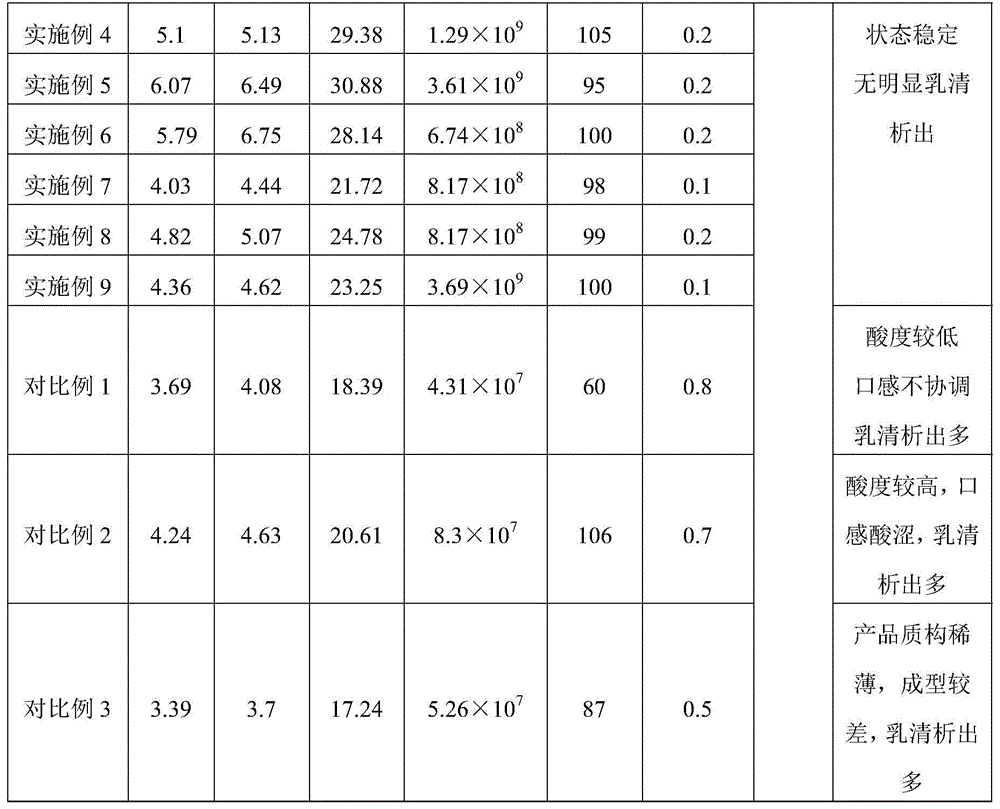
The invention discloses high-protein brown yoghourt and a preparing method thereof.The preparing method includes the steps that 1, processed milk and reducing sugar mixed liquor is homogenized, sterilized, browned and cooled to obtain brown milk; 2, the brown milk is inoculated with starter culture and then fermented to obtain brown yogurt, wherein strains of the starter culture include lactobacillus delbrueckii bulgaricus subspecies, streptococcus thermophilus and lactococcus lactis diacetyl subspecies; 3, the brown yogurt is cooled, passes through a smooth filter, and then is refrigerated and after-cured.The protein content in the high-protein brown yoghourt is 3.63-6.07%, fat content is 4.02-6.75%, solid content is 17.2-30.9%, the amount of active lactobacillus is larger than 5.78*10<8>-3.69*10<9> cfu / mL, and the acidity is 80-100; the yoghourt is light brown, free of food additives and fine and smooth in mouthfeel, has special flavor of a Maillard reaction, can contain dietary fibers and has high nutrition value.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum ZFH-3 and application thereof
ActiveCN104694430AImprove fertilityReduce usageFruit and vegetables preservationBacteriaBiotechnologyBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention discloses a Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum ZFH-3 and application thereof. The classification designation of the strain is Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum, and the collection number is CGMCC No.9884. The strain has obvious inhibiting actions on multiple crop pathogens, especially can effectively control postharvest diseases of fruits, is well used for biological control of contact mold of citrus fruit, olive green mould of ditrus fruit, citrus phomopsis stem end rot, sour rot of citrus, anthracnose of citrus, anthracnose of banana, spike rot of banana, gray mold of strawberry, soft rot of strawberry and other pathogen fungi, obviously lowers the possibility of postharvest diseases of fruits, prolongs the storage life and shelf life, and reduces the consumption of chemical reagents. The strain has the advantages of simple culture conditions and high reproduction speed, can easily implement industrial production, popularization and application, and has favorable development and application prospects.
Owner:珠海真绿色技术有限公司
Antibiosis streptomycete
InactiveCN101463332AHigh activityFunction increaseBiocideBacteriaIntellectual propertyField experiment
The invention relates to an antibiotic streptomyces, fermentation product of which can inhibit broad spectrum fungus and protozoan, and field experiment can control crop fungus plant disease and root-knot nematode. The antibiotic streptomyces has good effect, no pollution nuisance and no residue. The antifungal agent has extremely low hazardness for the people and good performance and development prospect for medical and agricultural use. The invention is named as SIM001 antibiotic streptomyces which is Streptomyces antibioticus subspecies xi an, and is preserved as patent in the depositary institution appointed by patent office of state intellectual property office; the preservation data is April 14th, 2005, the name of the depositary institution is CGMCC, and the number of preservation is CGMCC No.1349. The whole cell hydrolysate of the antibiotic streptomyces contains L, L-DAP (Diaminopimelic acid) and no characteristic glucide; the cytoderm belongs to I type and glucide type C; one of the main antibacterial materials is polyene macrocyclic ketolide which belongs to the broad spectrum antifungal substance.
Owner:刘昶志
Composite bacteria leaven and preparation method thereof
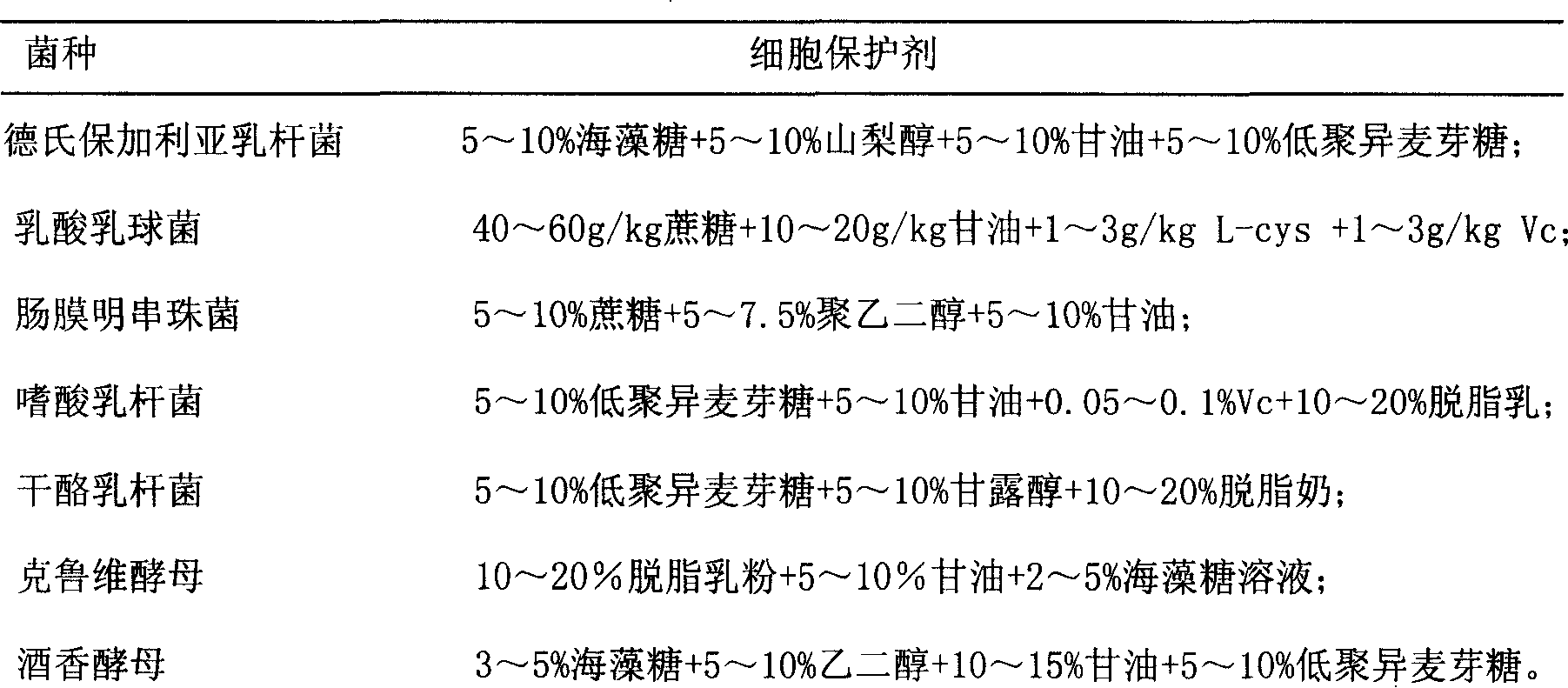
The invention discloses a composite strain starter and the preparation method, belonging to the microorganism fermentation field, which is mainly prepared with equivalent lactobacillus delbrueckii Bulgaria subspecies, lactococcus lactis, Leuconostoc mesenteroide, lactobacillus acidophilus, lactobacillus casei, kluyveromyces and brettanomyces. The preparation method is as follow: the strains are optimized and cultivated, and then are respectively fermented, centrifuge-treated, concentrated, added with cell protective agent, and freezed in vacuum. The invention is compounded with various functional strains; the acidophilus milk made by the omposite strain starter has the advantages of original flavor, which has the function indexes close to kefir particle fermentation acidophilus milk, and can be excellent direct distribution kefir starter; the fermented acidophilus milk has strong inhibition effect to pathogenic microorganism, and has good therapeutic effect to gastrointestinal diseases, metabolic disease, hypertension and heart disease.
Owner:马小明
Functional lactobacillus plantarum and preparation method of compound bacterial powder of functional lactobacillus plantarum
The invention relates to a functional lactobacillus plantarum plant subspecies having a holesterol lowering function and a preparation method of a compound bacterial powder of the plant subspecies, and belongs to the application fields of functional food and microecologics. According to the preparation method, the lactobacillus plantarum plant subspecies Zhang-LL CGMCC No. 6936 is used for preparing Zhang-LL strain freeze-dried powder by virtue of culture activation, fermentation, bacterial sludge collection and freeze-drying, and the viable count of the freeze-dried powder is 3.50*10<11> CFU / g. Bacillus natto BNZ3 CGMCC No. 9146 is used for preparing bacillus natto power by virtue of culture activation, enlarged cultivation, fermentation and drying, and the activity of nattokinase in the bacillus natto power is 2000IU / g; monacus purpureus Zhang-MP CGMCC No. 9221 is used for preparing monacus purpureus powder by virtue of culture activation, enlarged cultivation, solid-state fermentation, drying and grinding; as being tested, the content of the active substance Monacolin K in the monacus purpureus powder is 4.98mg / g. The prepared lactobacillus plantarum plant subspecies powder is thoroughly mixed with the bacillus natto power and the monacus purpureus powder in the ratio of 1:1:1(w / w), thereby obtaining compound bacterial powder having the serum cholesterol lowering effect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
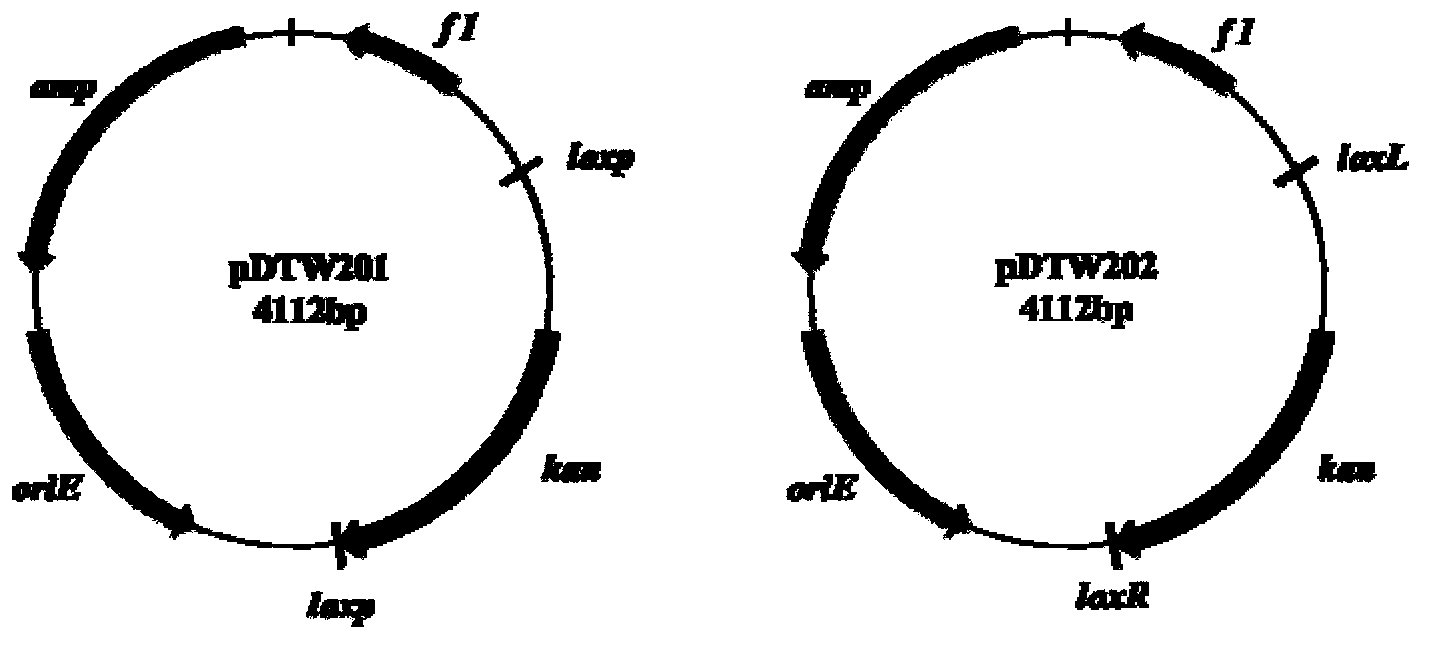
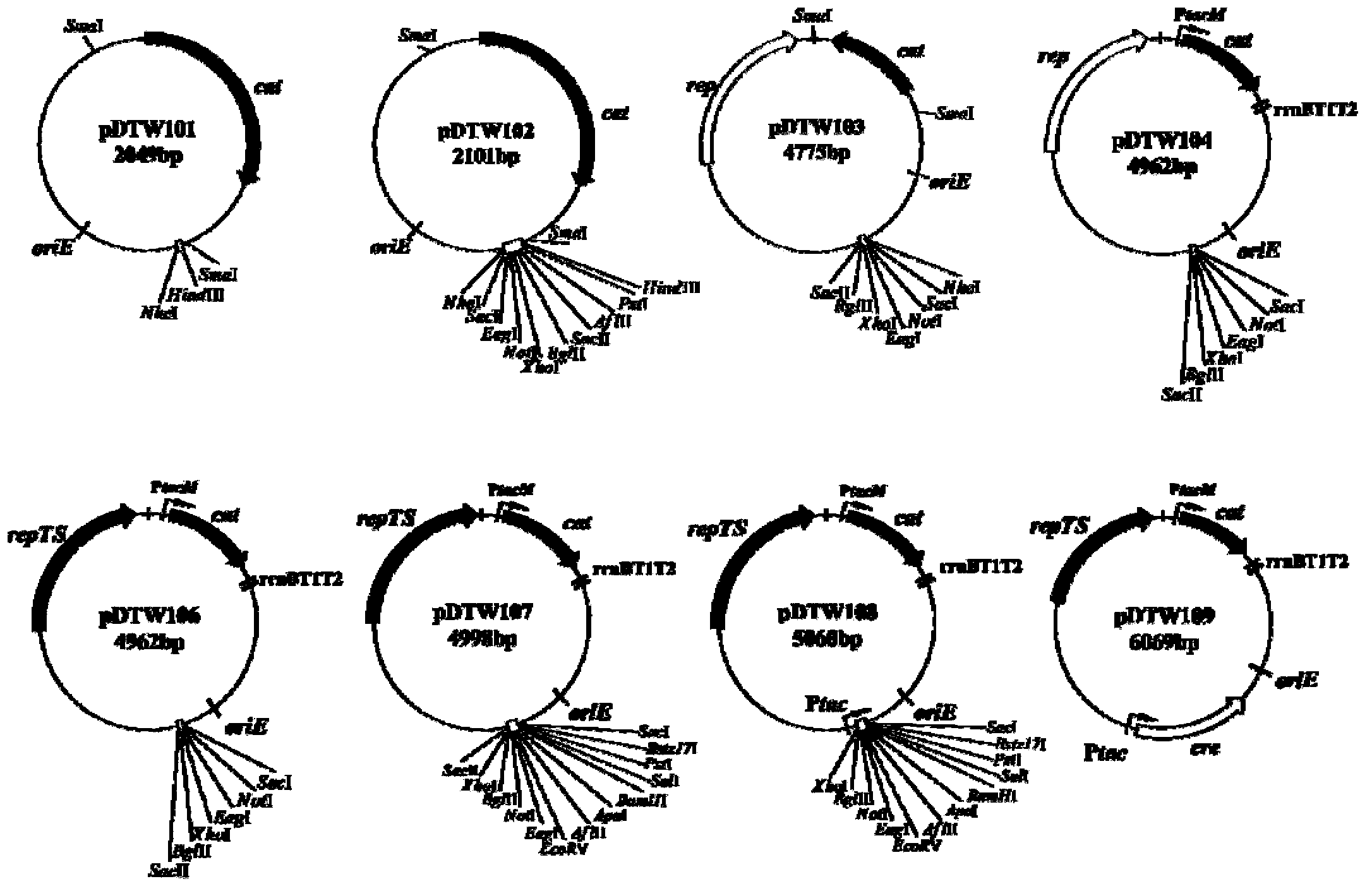
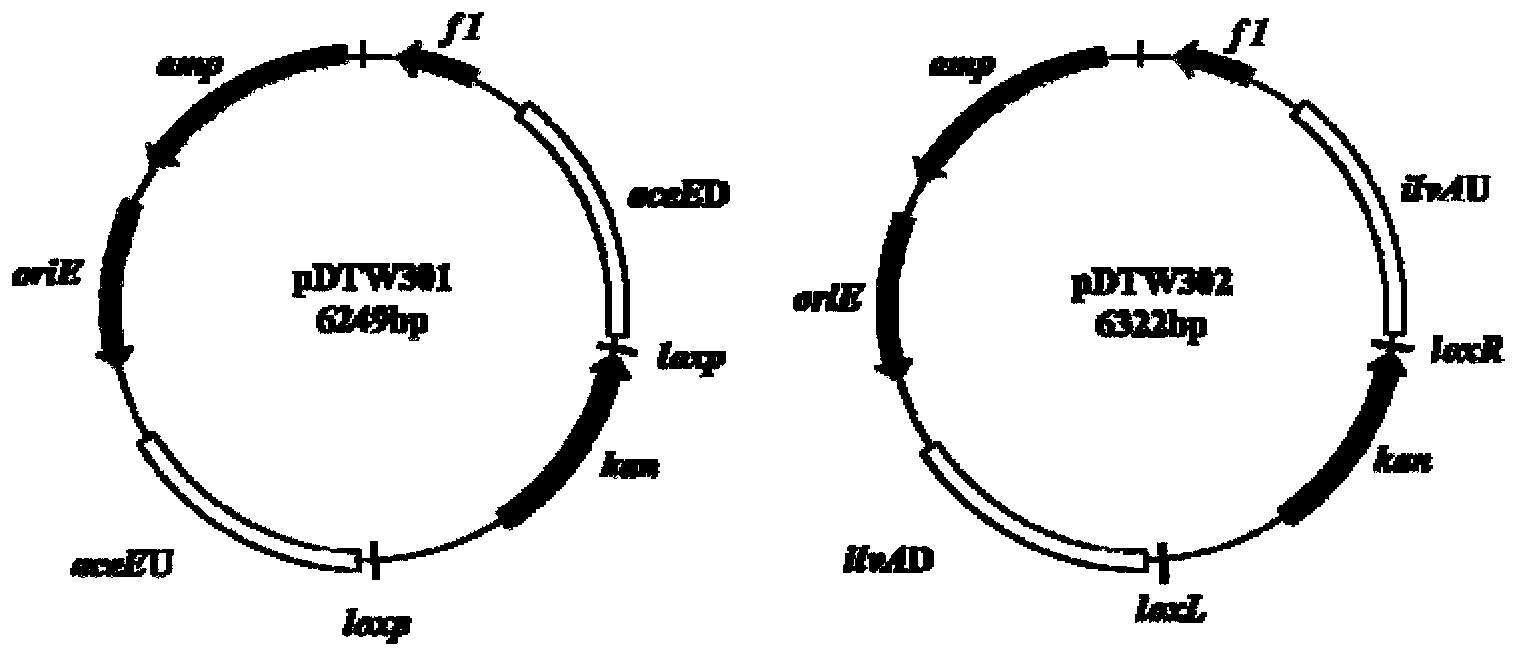
Corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system comprises a template plasmid and a temperature-sensitive expression plasmid, wherein the template plasmid provides a kan fragment (also known as a kan box) with loxp or variant loxL / R sites at two ends; and the temperature-sensitive expression plasmid carries a Cm resistance gene cat and a temperature-sensitive C. glutamicum replicon, expresses a Cre recombinant enzyme and is used for removing a Km resistance gene kan. The corynebacterium continuous knockout system disclosed by the invention can be generally used for continuous gene transformation of corynebacterium and has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation and high efficiency. By utilizing the knockout system, gene (continuous) knockout of three major typical subspecies genomes of the corynebacterium can be successfully completed, and the system is proved to be applicable to research and production of corynebacterium metabolites.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Lactic acid bacterium for prophylaxis or treatment of a stress-included disorder and a composition containing the same
The present invention provides an isolated lactic acid bacterium, Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum PS128 deposited under DSMZ Accession No. DSM 28632. The present invention further provides a composition that comprises Lactobacillus plantarum subsp, plantarum PS128 and a carrier. Moreover, the present invention provides a method for prophylaxis or treatment of a stress-induced disorder in a subject that comprises a step of administering an effective amount of Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum PS128 to the subject. The present invention also provides a method for prophylaxis or treatment of a functional gastrointestinal disorder in a subject that comprises a step of administering an effective amount of Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. plantarum PS128 to the subject.
Owner:BENED BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
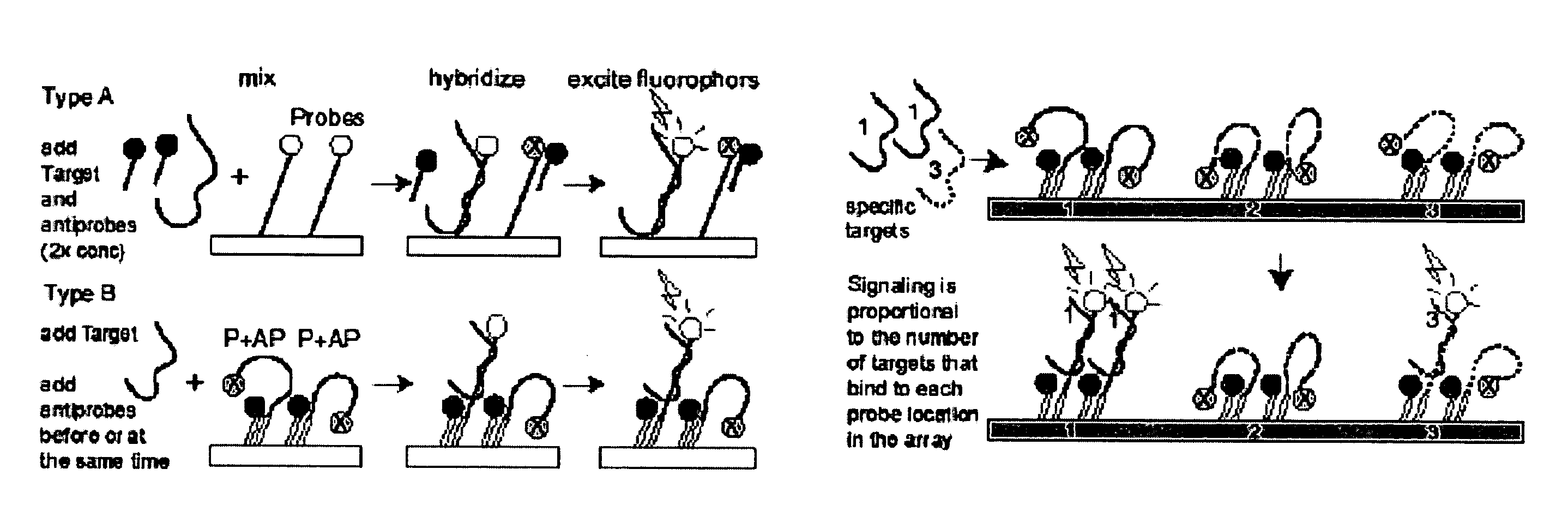
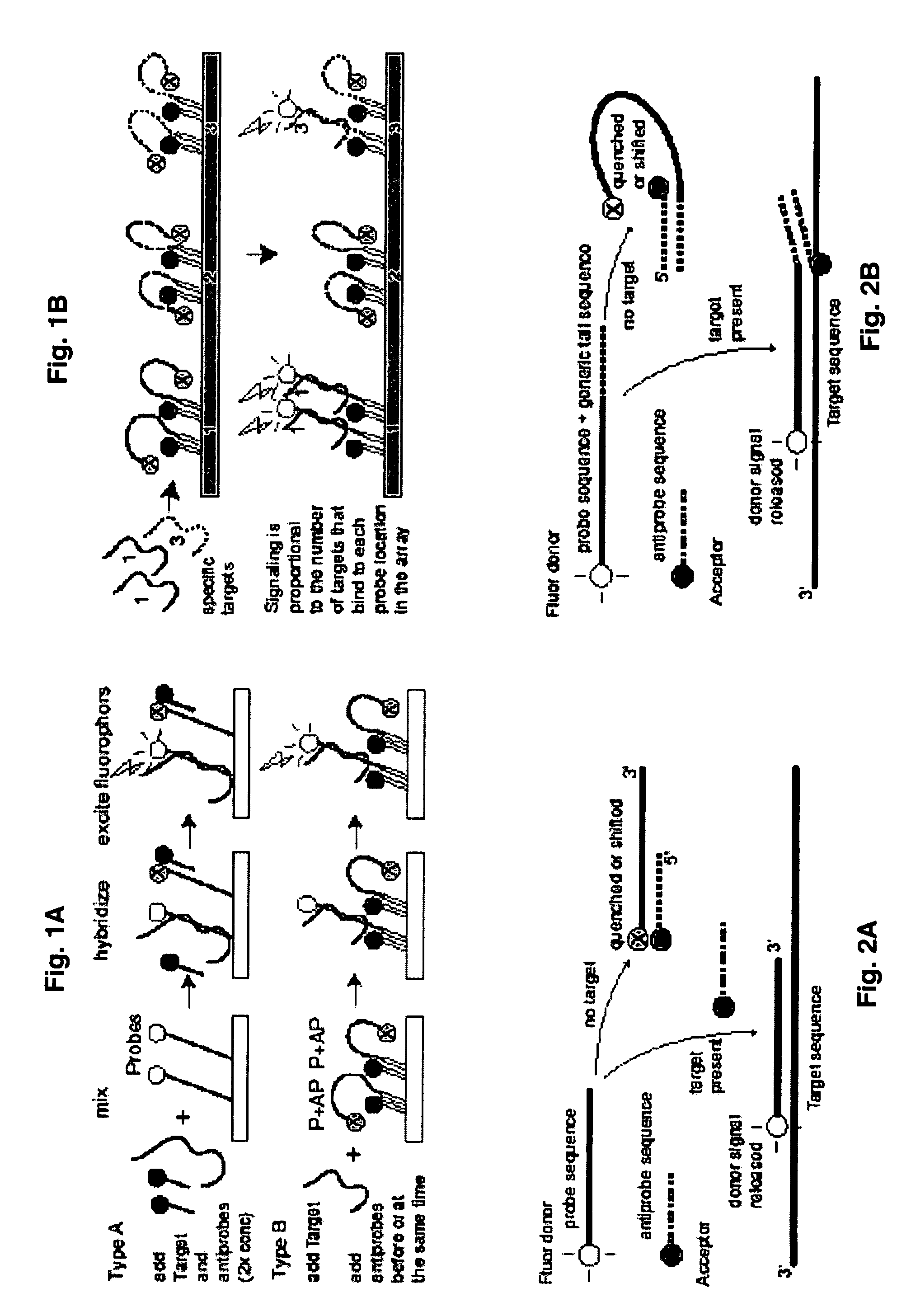
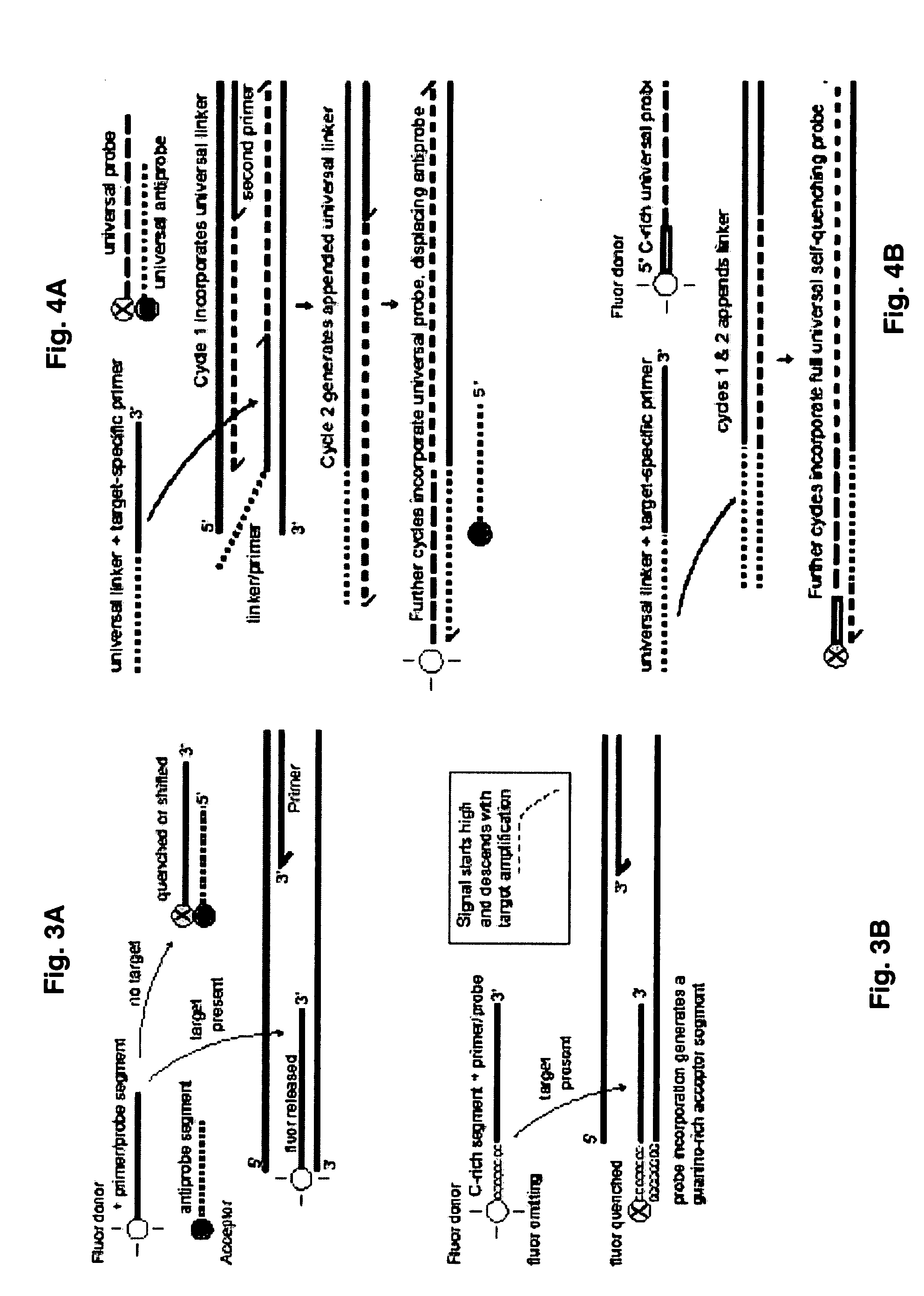
Probe-antiprobe compositions and methods for DNA or RNA detection
ActiveUS20090209434A1Avoiding preventing detectionSimple compositionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSubspeciesDrug resistant mutants
The invention provides novel compositions and methods for detecting unlabeled nucleic acid targets using labeled polynucleotide probes and partially complementary antiprobes. The interaction of probes, antiprobes and targets result in signaling changes that indicate target frequency. This novel detection mechanism is called a DNA detection switch, and it enable end-point detection, microarray detection and real-time PCR detection of a variety of nucleic acid targets including microbial species and subspecies, drug resistant mutants, and pathogenic strains.
Owner:GENETAG TECH
Method for producing gamma-propalanine using saliva chain coccus thermophilous subspecies
InactiveCN1710088AHomoglutamic acid decarboxylase activityImprove securityFermentationHigh pressureGlutamic acid
the invention explains a gamma - amino butyric acid's production method, which uses Streptococcus thermophilus as the bacterial acting on glutaminic acid , glutaminic acid salt , material containing glutaminic acid or glutaminic acid salt to make alpha - he carboxyl of glutaminic acid take decarboxylation reaction , thus turn into gamma - amino butyric acid. This method is a biological synthetic method, does not need high-temperature high pressure reaction condition and harmful raw materials, the uniqueness is high, accessory substances is little and safety is high.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of biopesticide tetramycin in preventing and controlling Magnaporthe grisea
InactiveCN101632367AReduce manufacturing costImprove efficiencyBiocideFungicidesAlbonoursinPositive control
The invention discloses novel application of biopesticide tetramycin generated by Streptomyces ahygroscopicus subsp.Wuzhouensis n.subsp in preventing and controlling Magnaporthe grisea. The tetramycin is compound agricultural antibiotic, comprises tetramycin A1 and A2, albonoursin and flagecidin, and has a rate of preventing and controlling the apple canker of over 95 percent. Indoor and field experiments prove that tetramycin diluent (the ratio of the tetramycin to water is 1: 999) has better effect of preventing and controlling the Magnaporthe grisea than 4 percent kasugamicin waterable powder, 75 percent tricyclazole waterable powder and 25 percent prochloraz missible oil, and has administration lower than positive control remarkably. The tetramycin used can reduce agricultural production cost, improves prevention effect, can be alternately used with other biopesticides, reduces the generation of resistance, has good effect of preventing and controlling the Magnaporthe grisea, and no problems such as environmental pollution, pesticide residue and the like, belongs to the environment-friendly biopesticide, and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:辽宁省微生物科学研究院
Primers for triple PCR of three types of sheep pathogenic mycoplasmas and detection method
InactiveCN106434919AOvercome limitationsQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEpidemiologic surveyMycoplasma pneumonia
The invention provides primers for triple PCR of three types of sheep pathogenic mycoplasmas and a detection method. The three pairs of special primers MO, MCC and MCCP are synthesized respectively according to the designs of sheep mycoplasma pneumoniae, a goat mycoplasma mycoide subspecies and a goat mycoplasma pneumonia subspecies, and a triple PCR optimum reaction system and reaction conditions for the three types of sheep pathogenic mycoplasmas are provided. The simultaneous pathogenic detection of the sheep mycoplasma pneumoniae, the goat mycoplasma mycoide subspecies and the goat mycoplasma pneumonia subspecies can be rapidly carried out without cloning, sequencing and sequence comparison, and the detection method has the advantages of being rapid, accurate, strong in specificity, good in repeatability and the like, suitable for rapid detection of the sheep mycoplasma pneumoniae, the goat mycoplasma mycoide subspecies and the goat mycoplasma pneumonia subspecies and large-scale epidemiological investigation and has great economic and social benefits.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of bacteriocin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. Plantarum Zhang-LL active bacterial preparation
InactiveCN104560799ALow costIncrease the number of live bacteriaBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFreeze-dryingRapeseed
The invention relates to a preparation method of a bacteriocin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. Plantarum Zhang-LL active bacterial preparation, and belongs to the field of microbe application. In the preparation method, by using a bacteriocin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. Plantarum Zhang-LL CGMCC No. 6936 bacterial strain, the active bacterial preparation is prepared through activation, expanding culture, high-density fermentation, centrifugation, freeze-drying protective agent addition, a prefreezing process, a freeze-drying process and other processes. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly, rapeseed peptone is selected as a substituting nitrogen source, so that the culture condition of the lactobacillus plantarum is optimized while the cost of a culture medium is reduced; a 5L of full-automatic fermentation tank is used for performing the high-density fermentation, and under the optimized low-cost culture medium and the optimized culture condition, the viable count of fermented liquid can reach above 1010CFU / mL. In the preparation method, potato pulp is used as a matrix of a freeze-drying protective agent, and an optimal combined formula of the freeze-drying protective agent is determined, so that the survival rate of the Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. Plantarum Zhang-LL reaches above 60% and the viable content can reach above 1011CFU / g. The prepared active bacterial preparation is low in raw material price and relatively high in viable content, can provide a good foundation for developing a novel feed additive for poultry, and can provide a significant economic value.
Owner:BEIJING BEINONG HONGZE BIOTECH CO LTD
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens subsp. plantarum and application thereof
Owner:JIANGSU POLYTECHNIC COLLEGE OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Method for discriminating microorganism by utilizing Fourier infrared spectrum
ActiveCN101556242ALow costRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsMicroorganismSubspecies
The invention relates to a method for discriminating microorganism by utilizing Fourier infrared spectrum, comprising the following steps of: a) culturing control microorganism; b) collecting infraredspectrum of the control microorganism; c) establishing a discriminating model of the microorganism in one or a plurality of spectral sections within the interval between 3000-2800cm<-1> and 1800-700c m<-1>; d) culturing the microorganism to be detected under the same condition with the step a); e) collecting the infrared spectrum of the microorganism to be detected under the same condition with the step b); and f) substituting the infrared spectrum obtained in the step e) into the discriminating model of the microorganism and determining the attribution of the microorganism to be detected. Thediscriminating model of the microorganism can realize fast discrimination and does not need to carry out pre-selection to the classification of the microorganism to be detected by using other taxonom ic methods; the method has strong specificity, can carry out classification according to the units of families, classes, species and the like, and even can discriminate to the level of subspecies and serological types; and once the discriminating model is established, the cost for discriminating microorganism is extremely low.
Owner:NAT INST FOR FOOD & DRUG CONTROL
Lactobacillus rhamnosus derived from human breast milk and application of lactobacillus rhamnosus
InactiveCN106754470AGrowth inhibitionMaintain gut healthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliLactobacillus rhamnosus
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus derived from human breast milk and application of the lactobacillus rhamnosus. The lactobacillus rhamnosus Z5 disclosed by the invention is initially derived from the human breast milk and belongs a new subspecies of the lactobacillus rhamnosus. An experiment proves that the strain has the properties of acid resistance, bile salt resistance, and resistance on a simulated animal gastrointestinal tract environment, capability of inhibiting growth harmful bacteria including escherichia coli and salmonella in intestines and capability of being stuck on epithelial cells of human and animal intestines very well. The lactobacillus rhamnosus can be used for preparing health-care foods, fermented foods, vaccine adjuvants and animal feed so that the balance of intestinal flora of human and animals is easy to adjust and the health of the intestines of the human and animals is increased.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Novel Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei SG96, a Bacteriostatic Composition Containing the same and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20100196341A1Growth inhibitionPromote weight gainBiocideBacteriaEscherichia coliBacteroides
A novel Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei SG96, a bacteriostatic composition containing the same and use thereof, comprise a novel Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei SG96 strain, wherein said strain had been deposited in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, CGMCC, accession number: CGMCC 2697, characterized in that said strain can inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium and the like, and even has an effect of killing bacteria; and a bacteriostatic composition containing said Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei SG96 strain, characterized in that said composition can be used as an additive in animal drinking water, as an additive in animal feed, as an medical composition for animals and humans, as an additive in food products as an additive in beverages, and as a food product, beverage, and health food products, and the like.
Owner:SYNGEN BIOTECH
Selenium-enriched yeast with high biomass, and additive and premix containing the same
ActiveCN103667086AIncrease concentrationImprove conversion abilityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementGramSubspecies
The invention discloses a breeding and production method of selenium-enriched yeast with high biomass. Through screening and domestication on a culture medium containing inorganic selenium, a strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae subspecies Saccharomyces boulardii YBN-2 with high biomass and high content of selenium. Under optimal fermentation conditions, each gram of selenium-enriched yeast enriches as high as 2800-3200 mug / g of organic selenium, has viable count reaching 6.5-8.0*10<10> CFU / g. The selenium-enriched yeast provided by the invention has the advanategs of safety, no toxicity, simple production conditions, low cost and high economic value.
Owner:北京乾胜生物技术有限公司 +1
Mannanase, coding gene and production thereof
ActiveCN103261409AAchieve mass productionGood pH stabilityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBacteriaBiotechnologyYeast
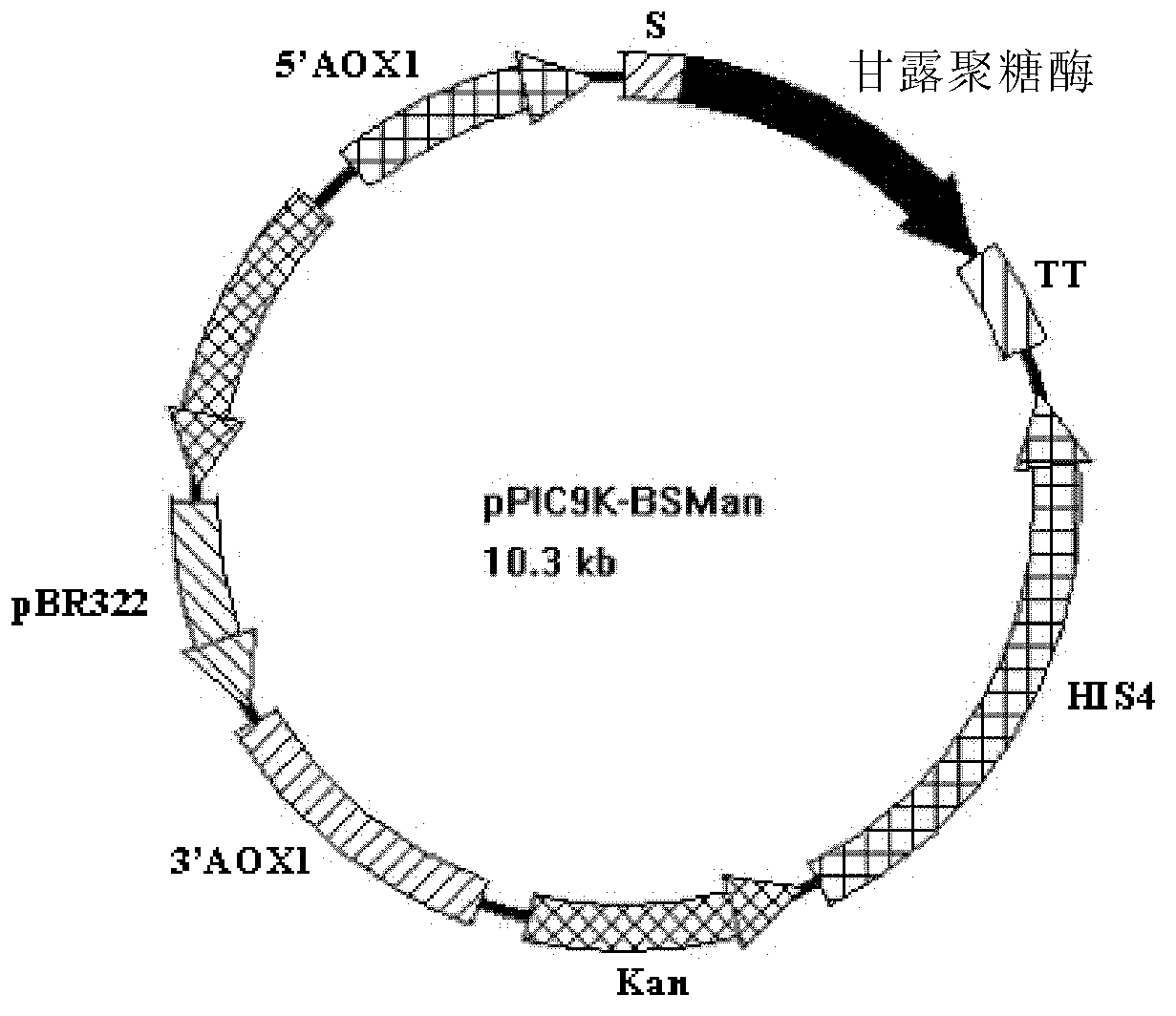
The invention discloses a mannanase and the coding gene, a recombinant vector and a host cell comprising the gene, and expression of the recombinant vector in E.coli and production of the enzyme in yeast cells by using the recombinant vector. The present invention also provides a new wild type subspecies of Bacillus Megaterium, in particular, Bacillus Megaterium FB101.
Owner:FUJIAN FUDA BIOTECH
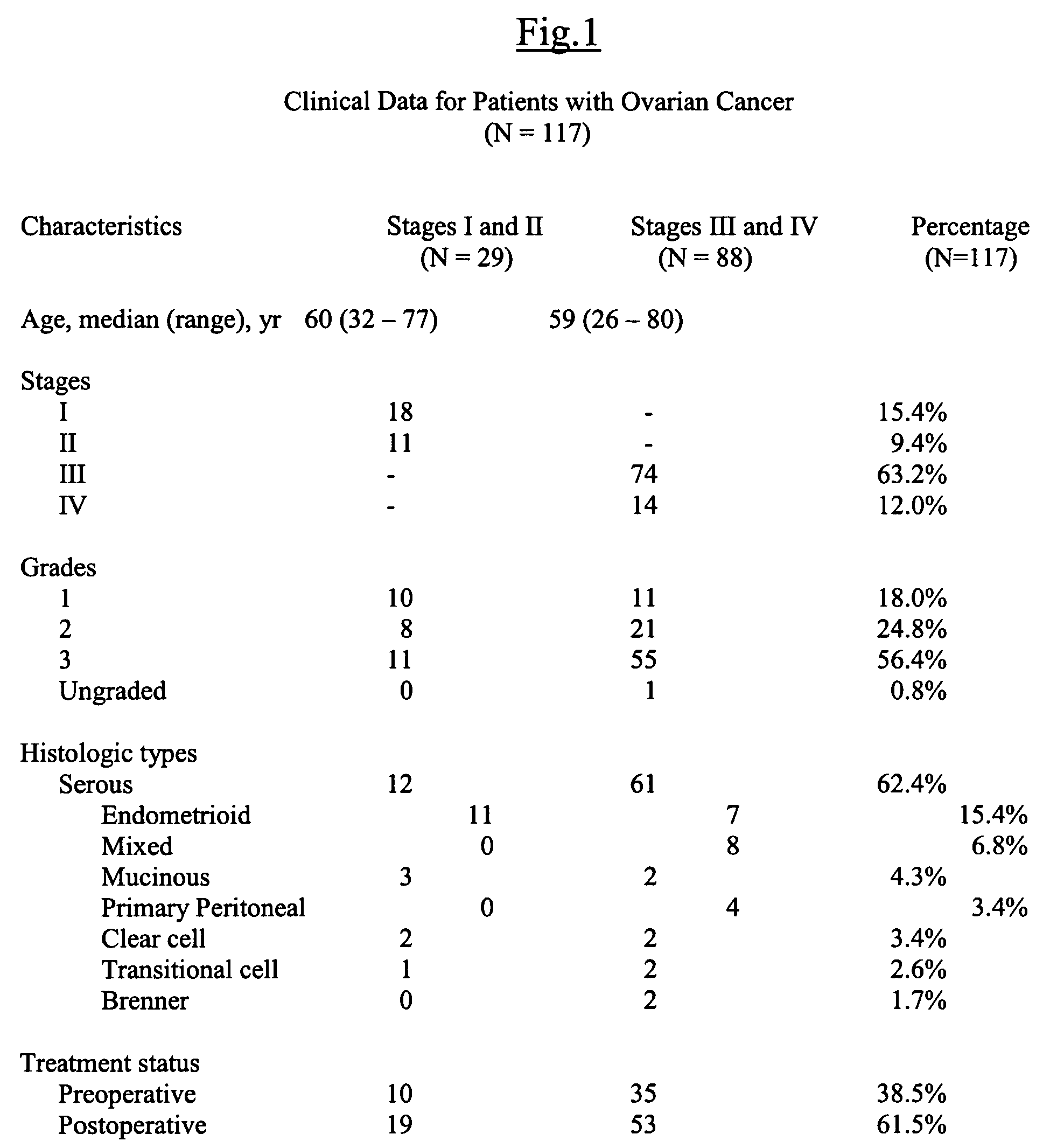
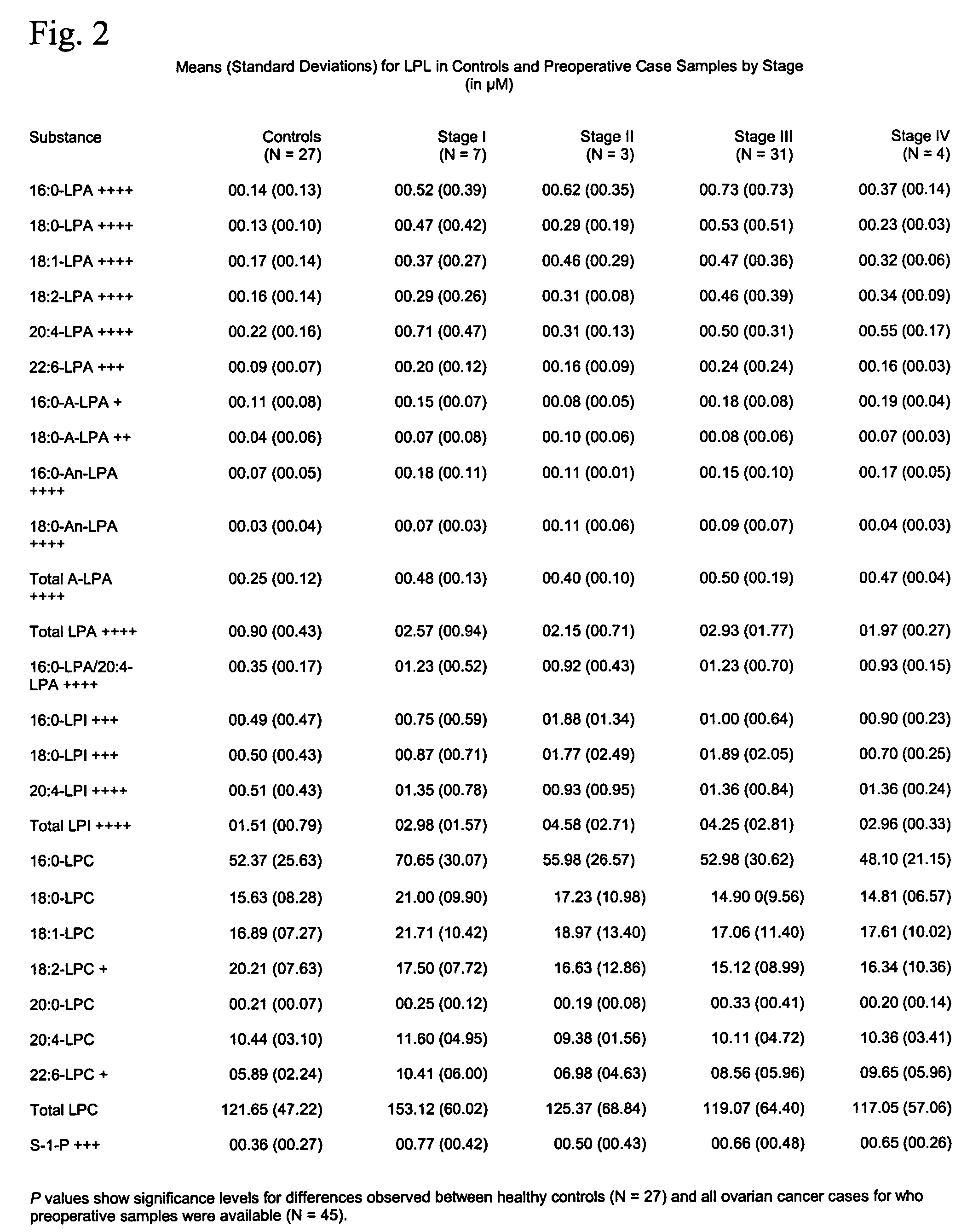
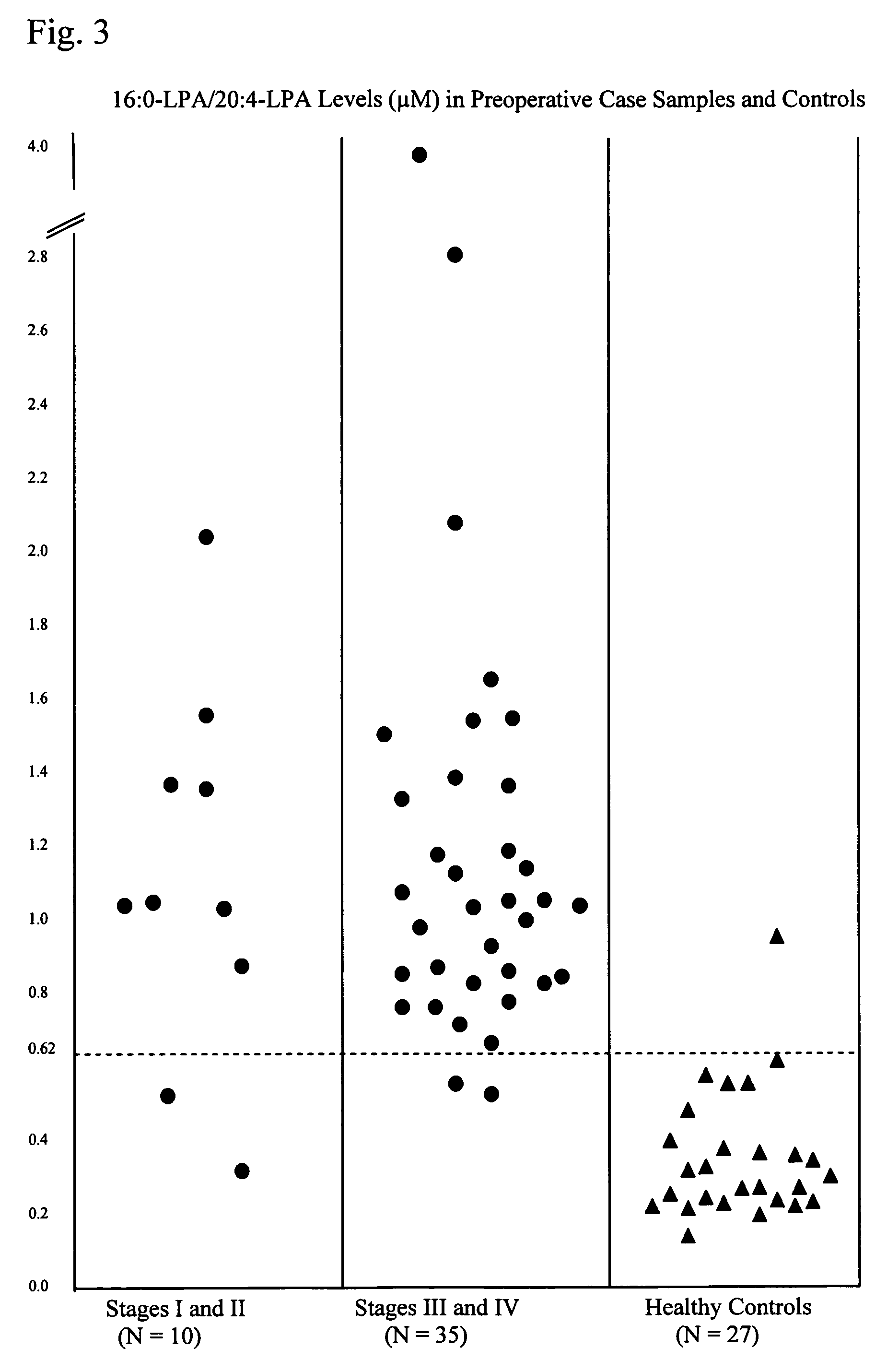
Lysophospholipids as biomarkers of ovarian cancer
InactiveUS7964408B1Improve survivalIncreased mortalityMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisPhosphateSubspecies
A method of using a bioactive lysophospholipid (LL) as a biomarker for detecting the presence and recurrence of ovarian cancer. Subspecies of LL, such as lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), lysophosphatidylinositol (LPI), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and lysosphingolipid sphinsosine-1-phosphate (S1P), are used alone or in conjunction to increase the specificity and sensitivity of the assay.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com