Method for discriminating microorganism by utilizing Fourier infrared spectrum
A technology of infrared spectroscopy and microorganisms, which is applied in the determination/inspection of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, color/spectral characteristic measurement, etc., can solve problems such as difficult general laboratory promotion, and achieve rapid identification, strong specificity, and low cost low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0086] Step 1 Selection and cultivation of control microorganisms
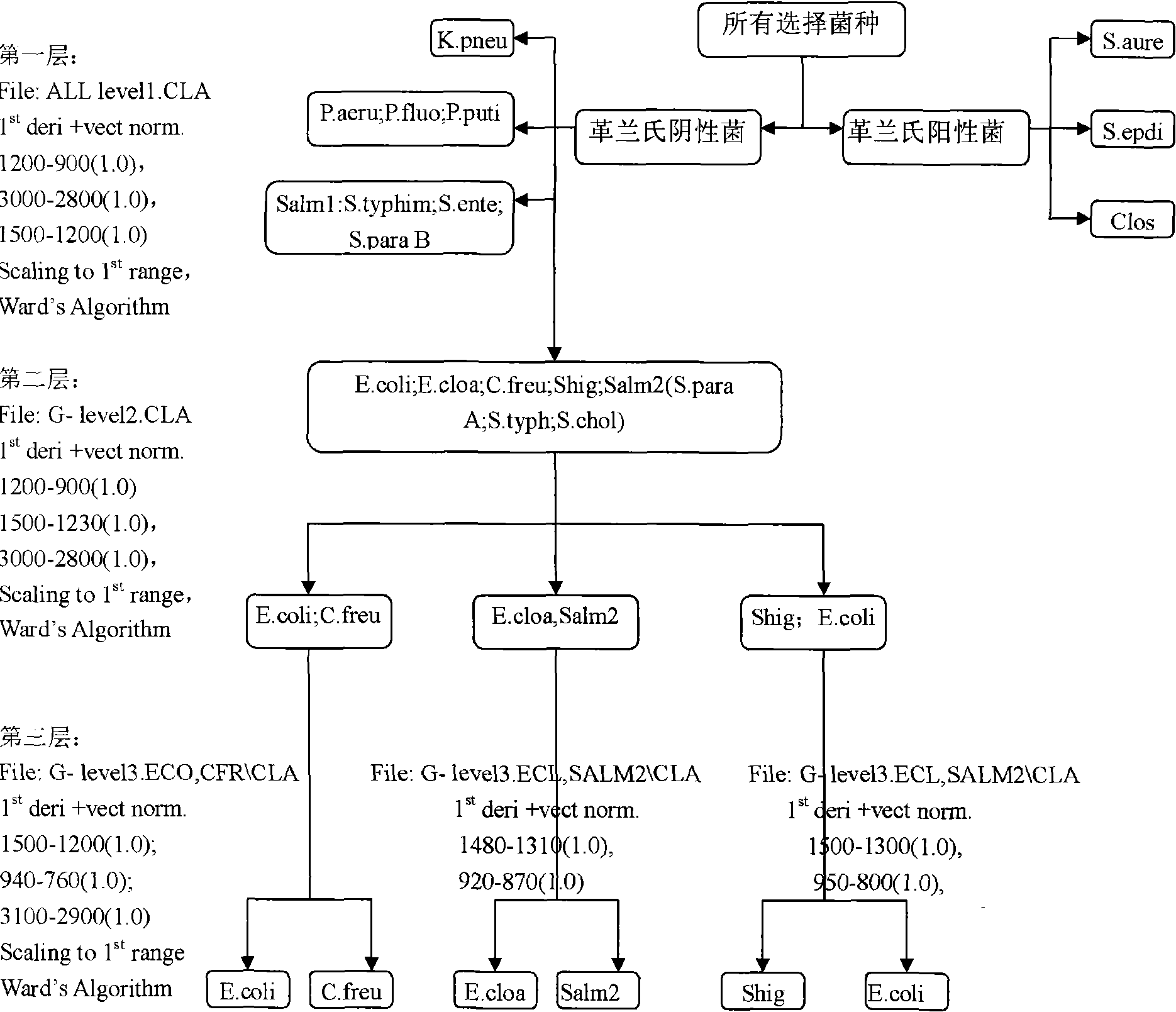
[0087] In order to identify the six control bacteria specified in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, a total of 191 strains of bacteria belonging to 9 genera and 23 species in 4 families were selected as control microorganisms to construct a reference spectrum library. See Table 1 for specific strains and quantities.
[0088] Table 1
[0089]
[0090]
[0091] Step 2 Spectral determination of control microorganisms
[0092] The above-mentioned control microorganisms were purified on a TSA medium (BD Company, USA) plate to form a single colony, and then a single colony was selected to be streaked and inoculated on the plate, and cultured at 35°C for 24±2h.
[0093] Use a calibrated vibrating platinum inoculation loop with a diameter of 1 mm (product of Braun, Germany) to take 1-2 rings of bacterial lawn from the place where the colonies converge on the TSA medium, place them in 100 μl of sterilized water, and s...
Embodiment 2
[0116] The test was carried out using the same method and steps as in Example 1, except that the microorganisms to be tested were combined using two identification models to improve the correct rate of identification.
[0117] The specific procedures and results judgment methods are as follows: Figure 5 shown.
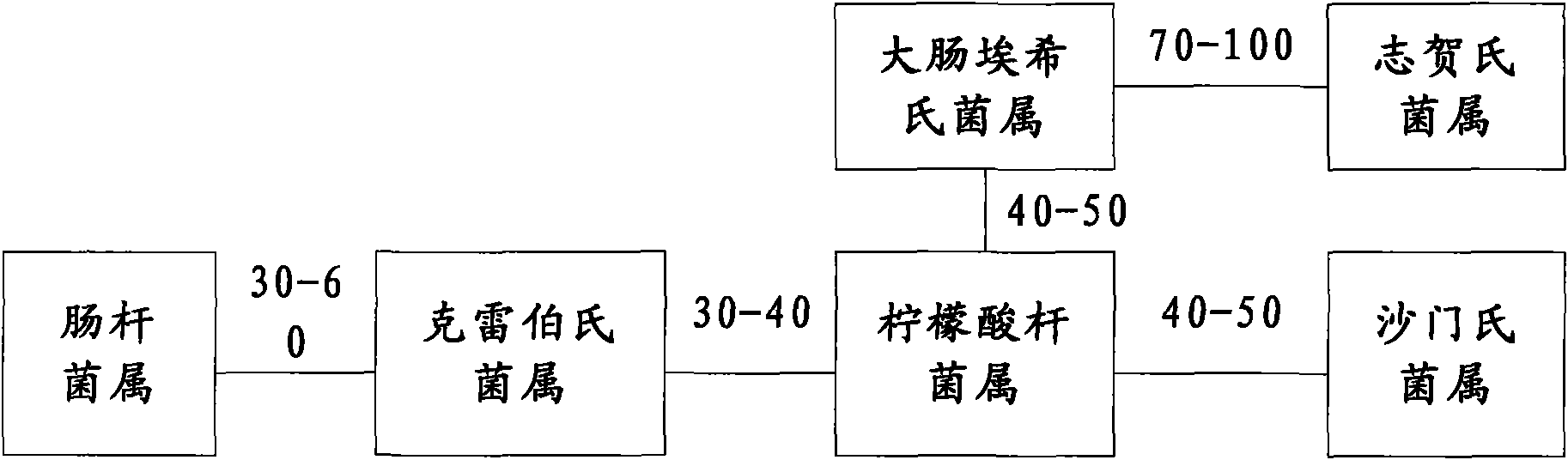
[0118] The original spectrum and the average spectrum of the strains identified correctly in the first step were brought into the second identification method respectively, and the correct identification rate was 92.2% (379 / 411). The strains and results of validation errors are shown in Table 4. It can be seen from Table 4 that identification errors mainly occurred when E. coli was identified as other Enterobacteriaceae microorganisms, that is, false negative results were presented.
[0119] In view of the false negative results caused by the original qualitative analysis identification model, the above spectra that were not correctly identified were added to the mo...
Embodiment 3
[0124] Embodiment 3 differentiates under species
[0125] To distinguish bacterial species below species, such as serotype level. In this embodiment, a series of Salmonella were selected, and their serotypes and IR spectra were determined for cluster analysis. see details Image 6 , where the serum types include O9, O4, and O7, the selected spectral bands are 1202-899, 901-698, and the reproducibility value is 1. The spectrum processing method is First derivative+Vector normalization, and the algorithm is Ward’s algorithm. As can be seen from the figure, the IR patterns are well classified by serotype.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com