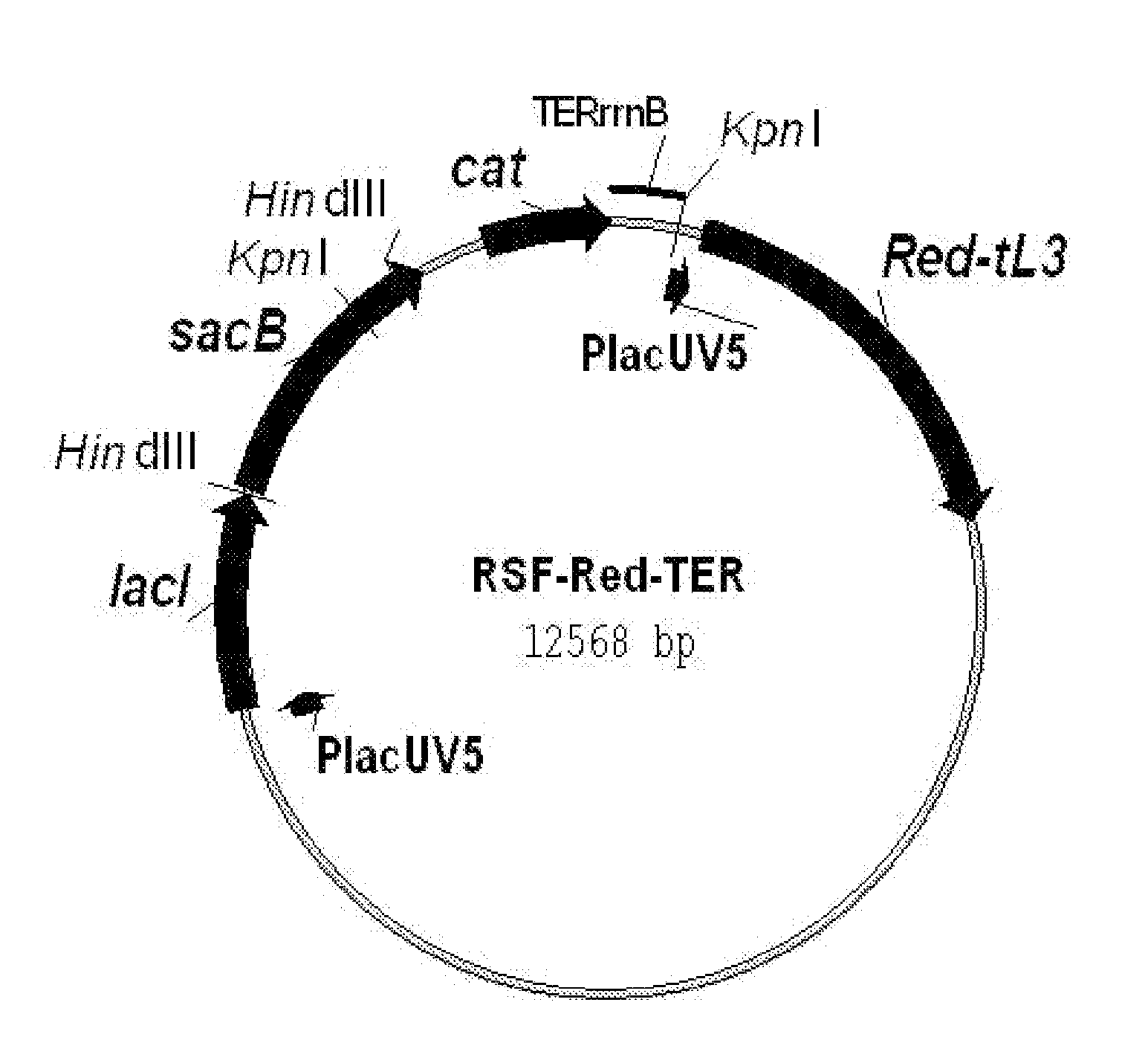
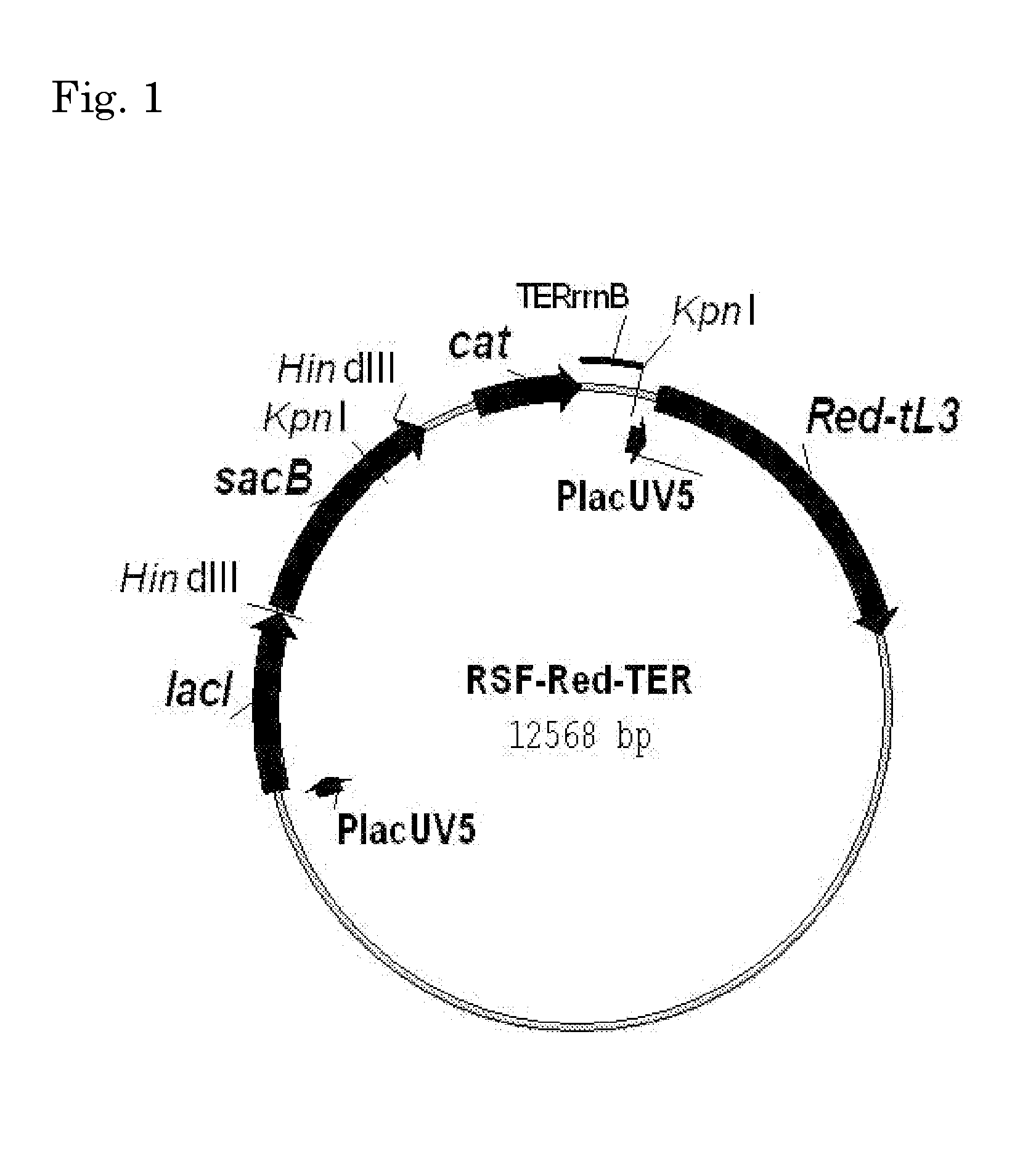
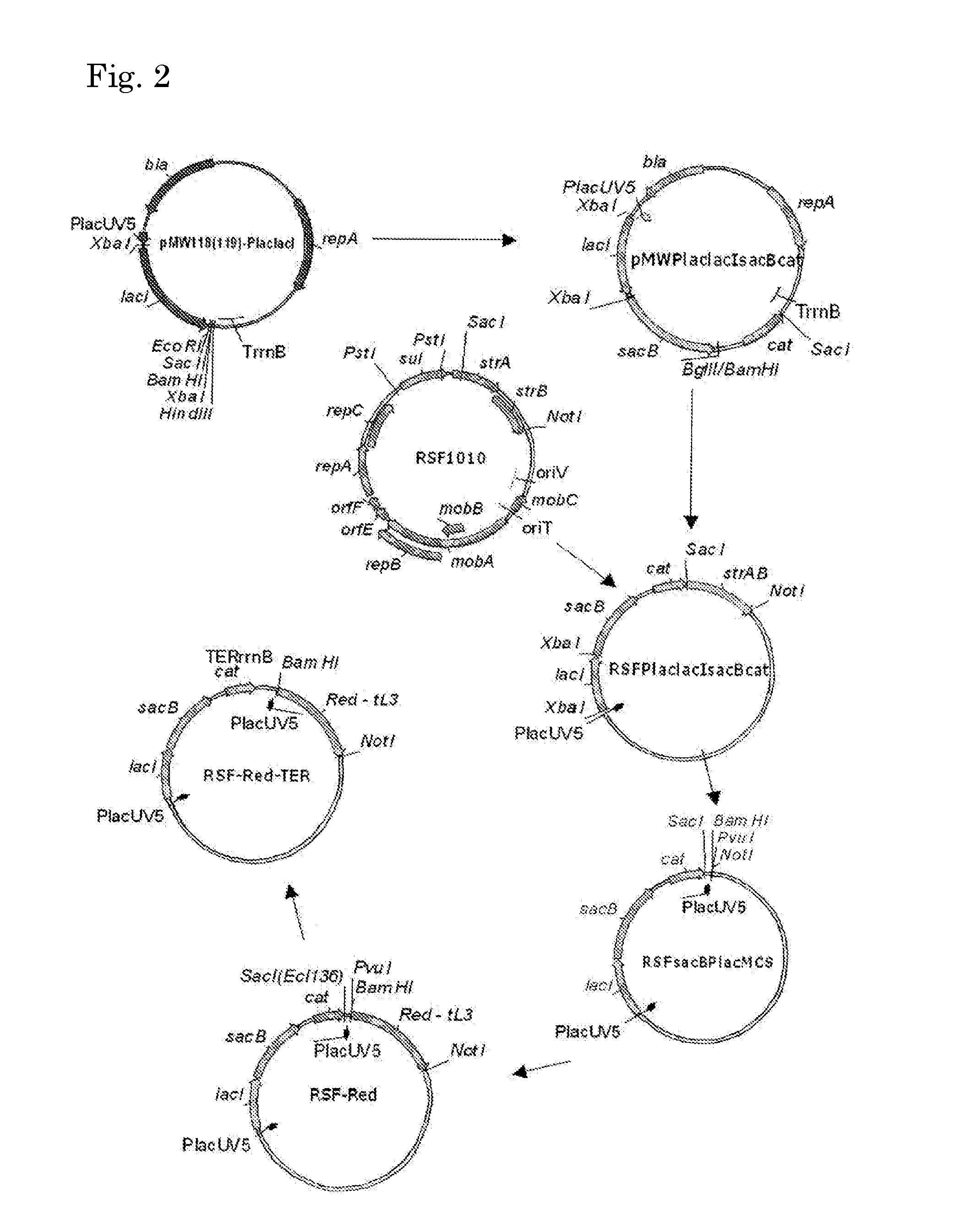
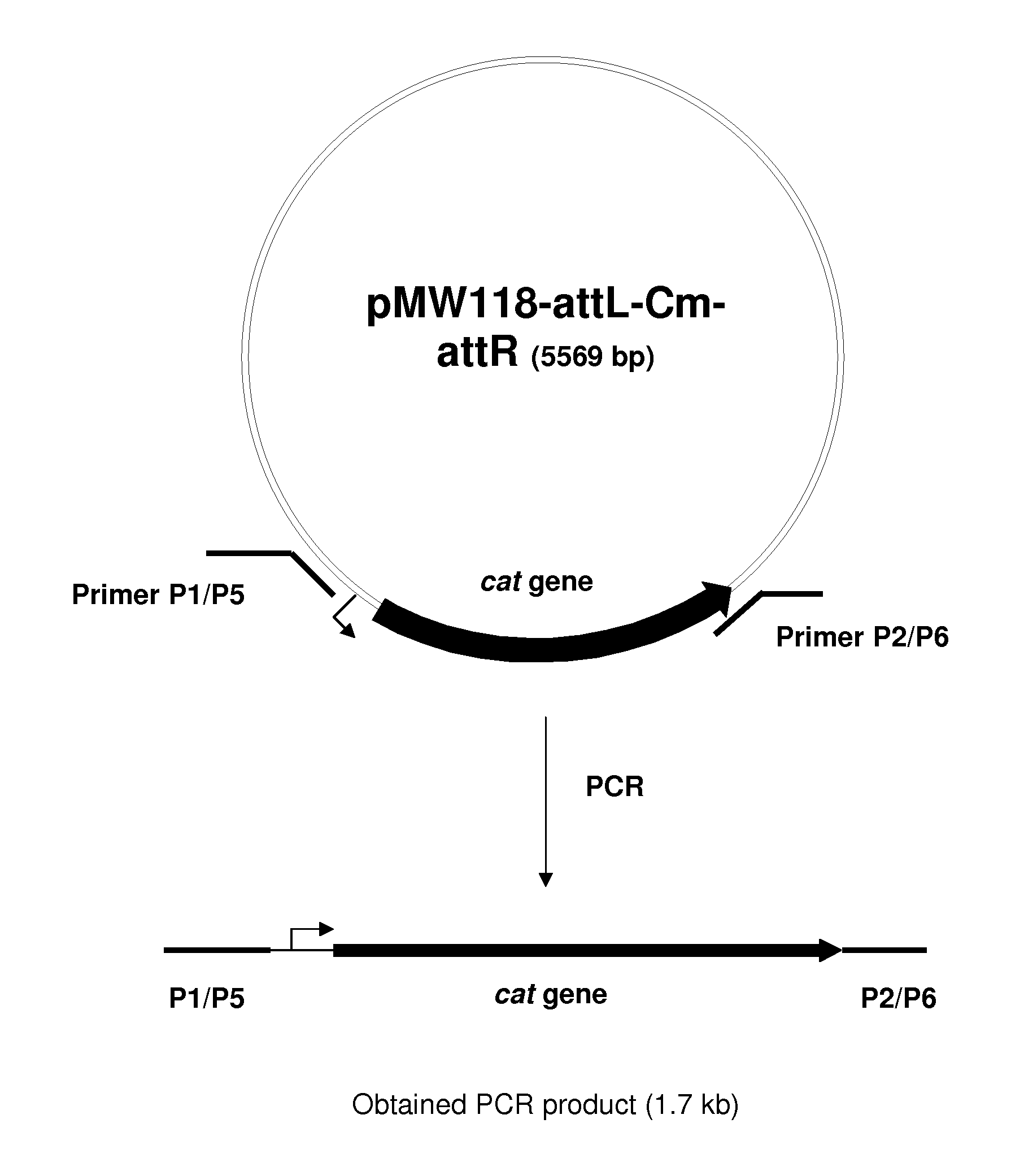
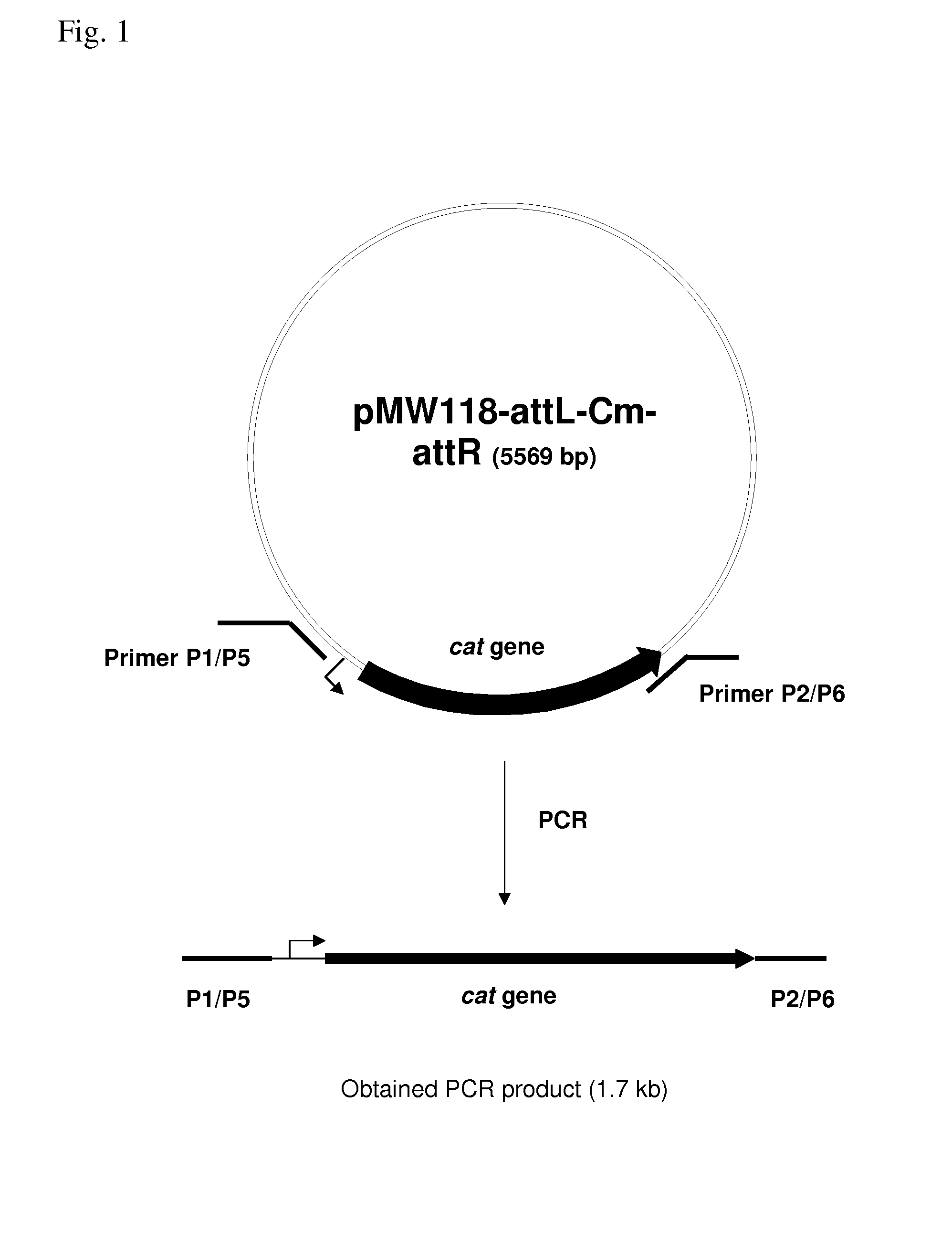
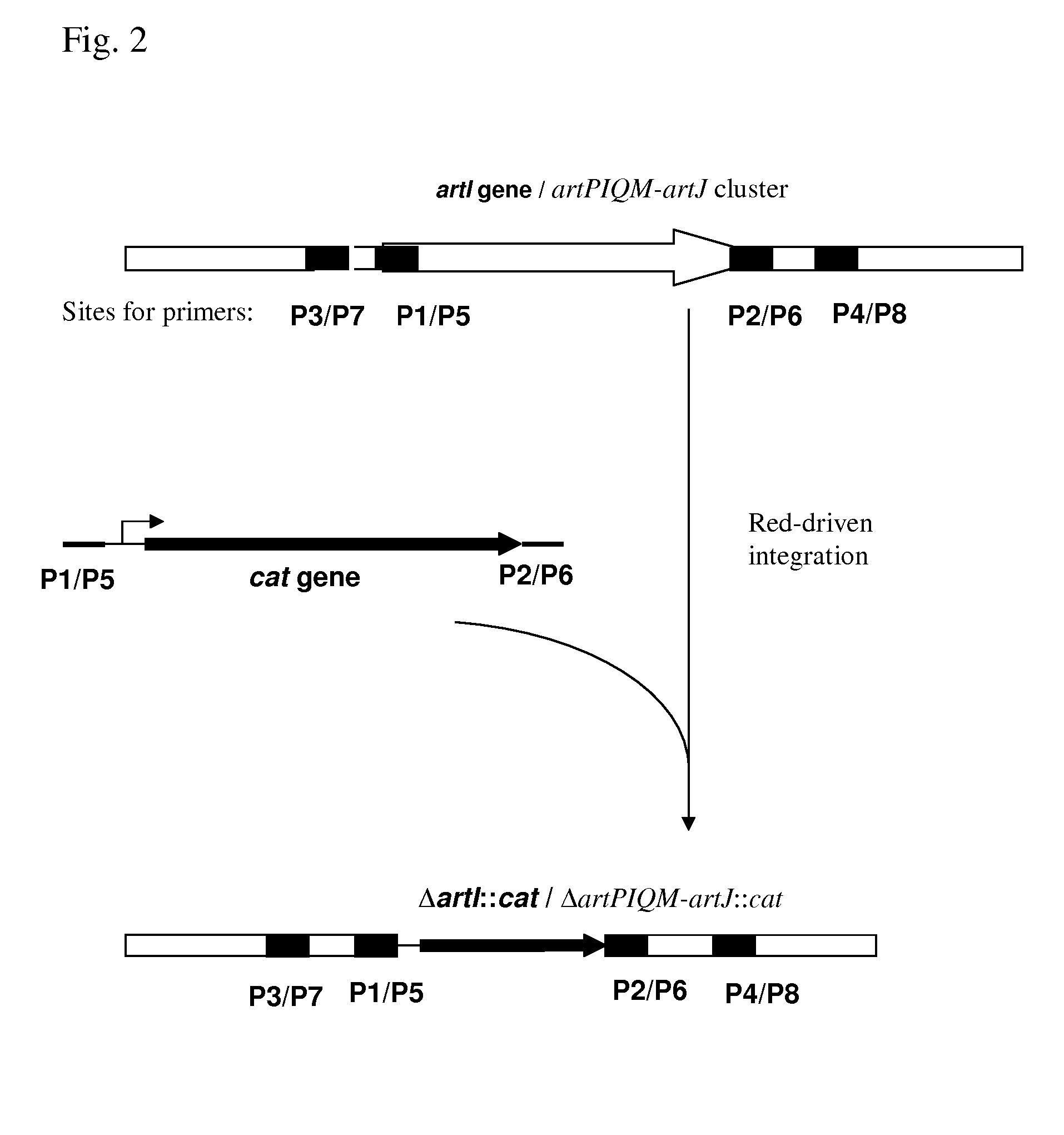
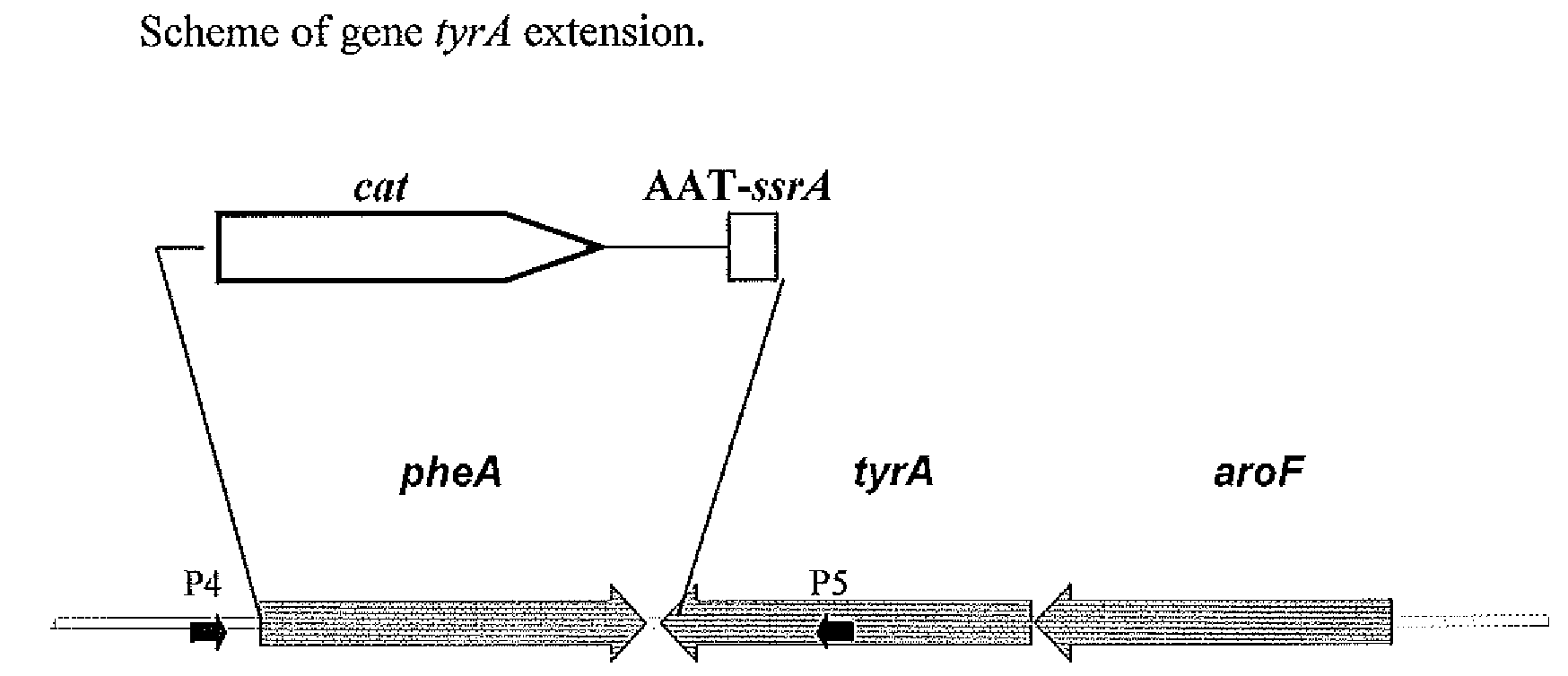
Patents
Literature
145 results about "Enterobacteriaceae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The family Enterobacteriaceae is a large family of Gram-negative bacteria. It was first proposed by Rahn in 1936, and now includes over 30 genera and more than 100 species. Its classification above the level of family is still a subject of debate, but one classification places it in the order Enterobacterales of the class Gammaproteobacteria in the phylum Proteobacteria.
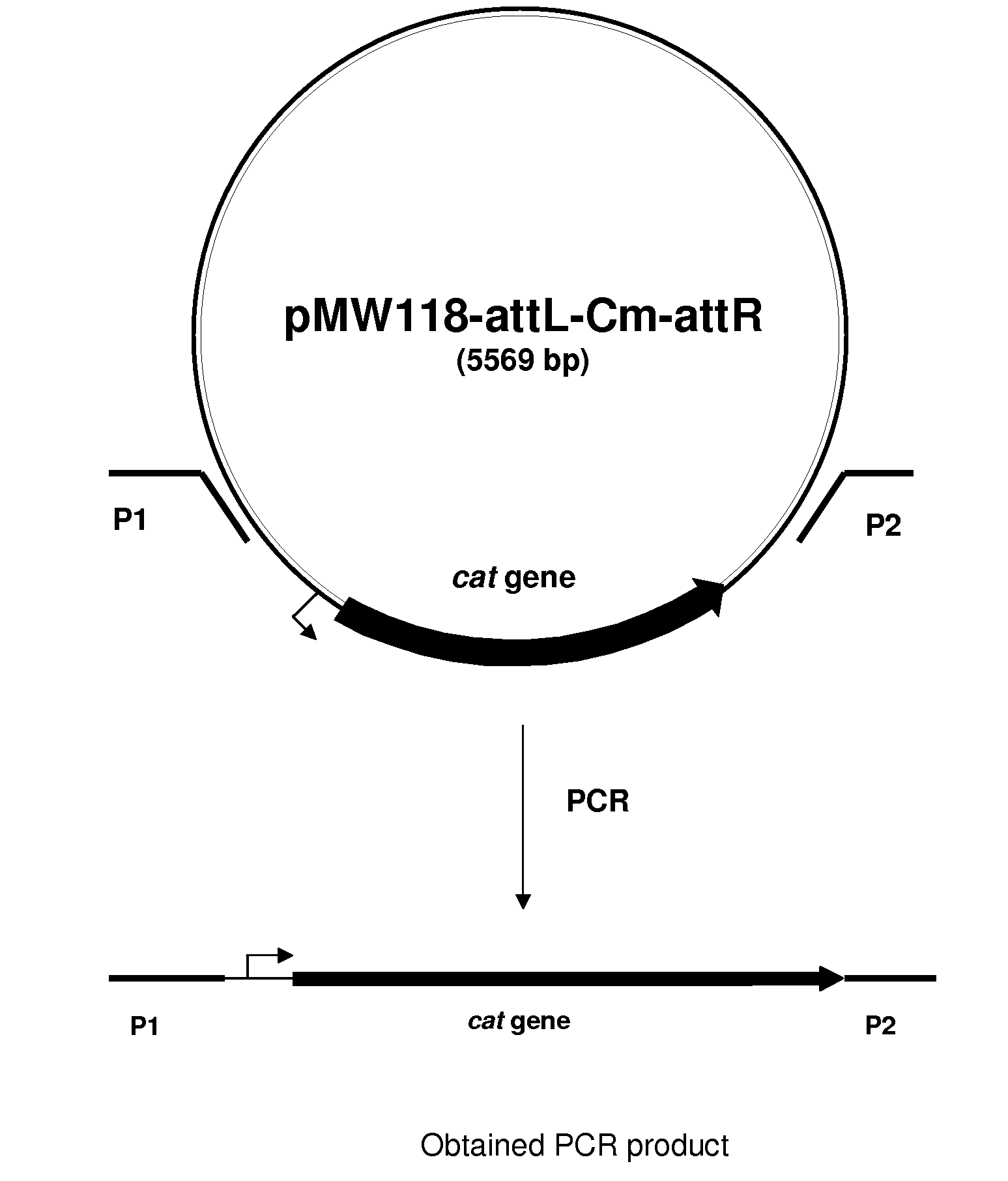
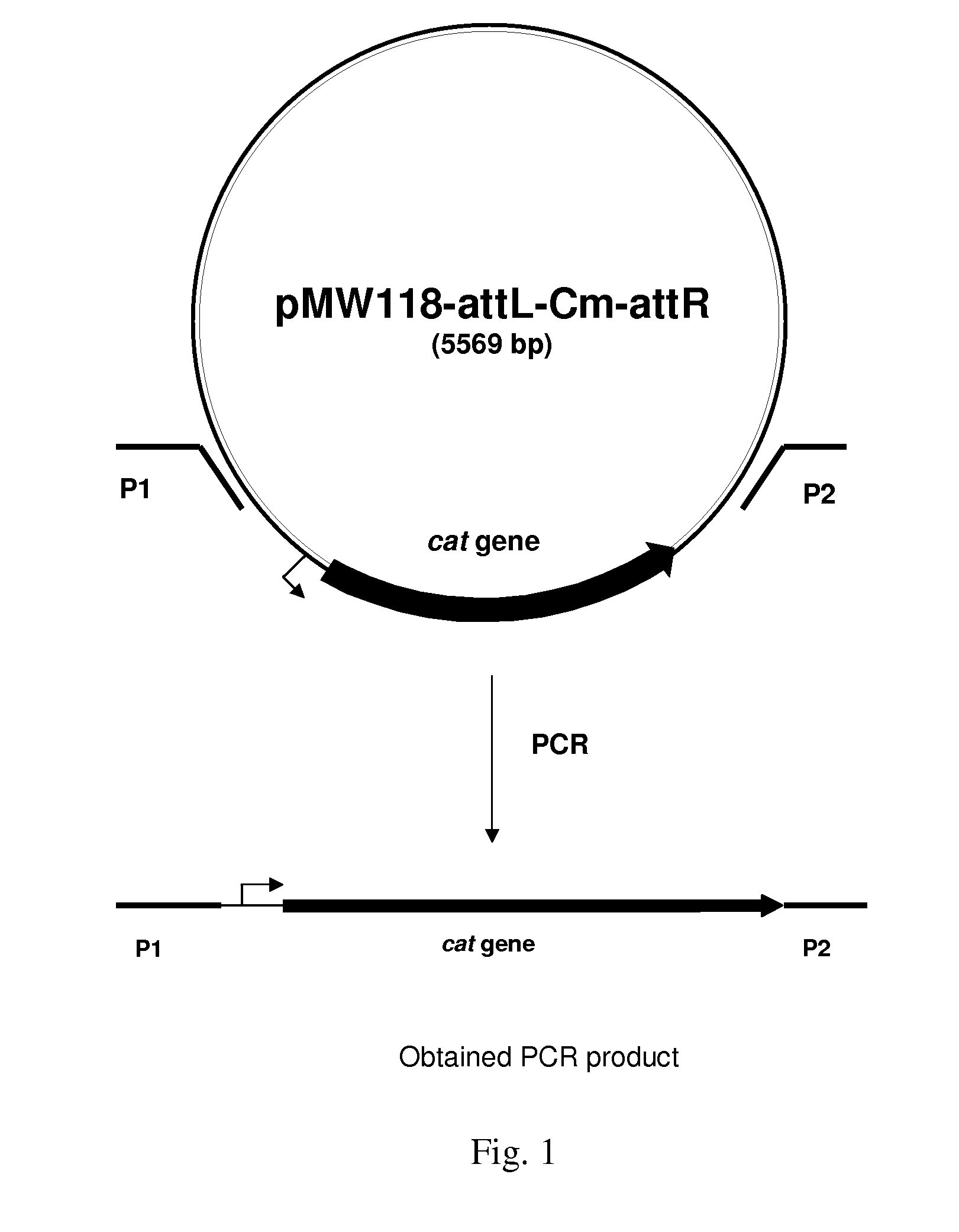
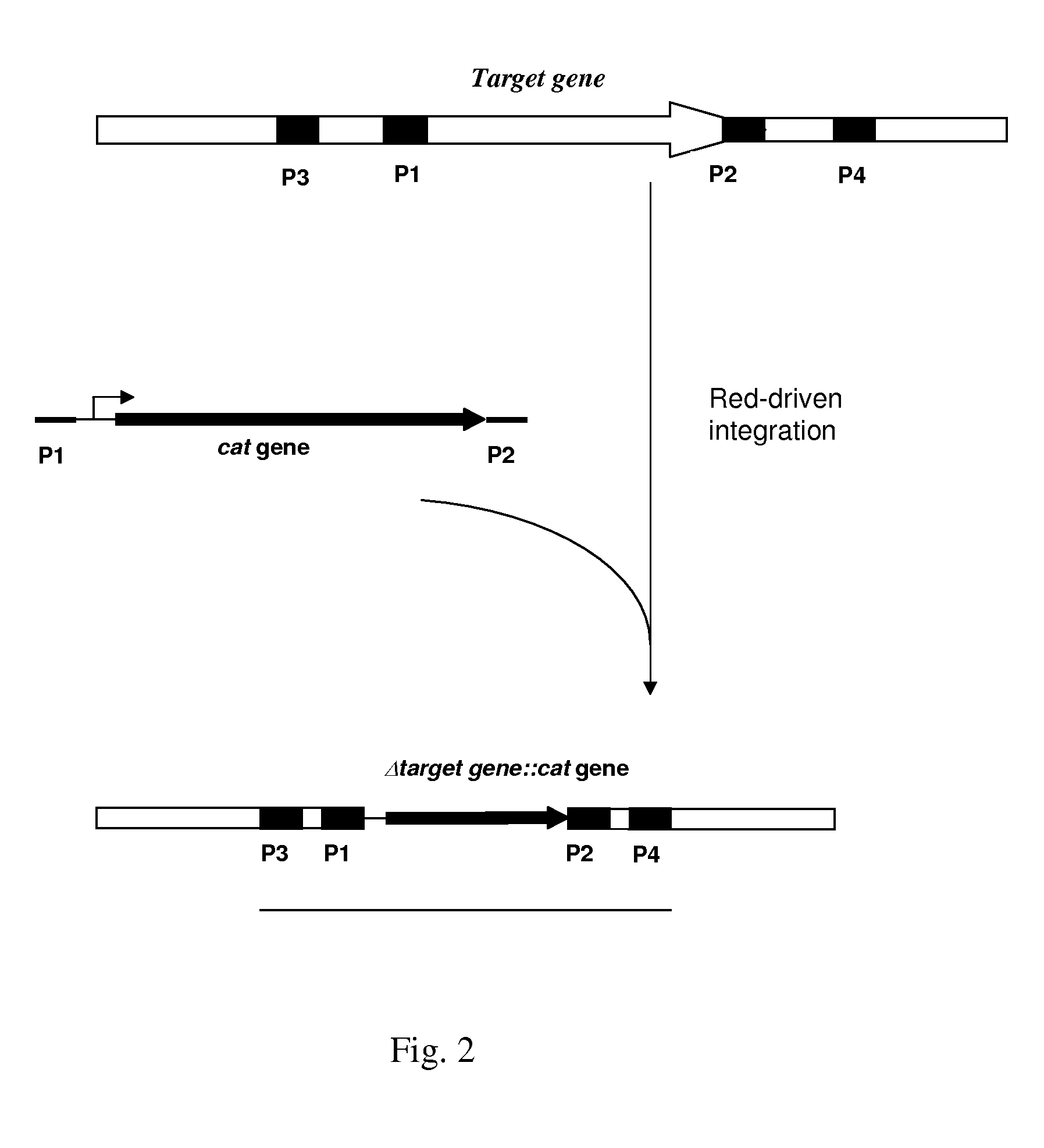
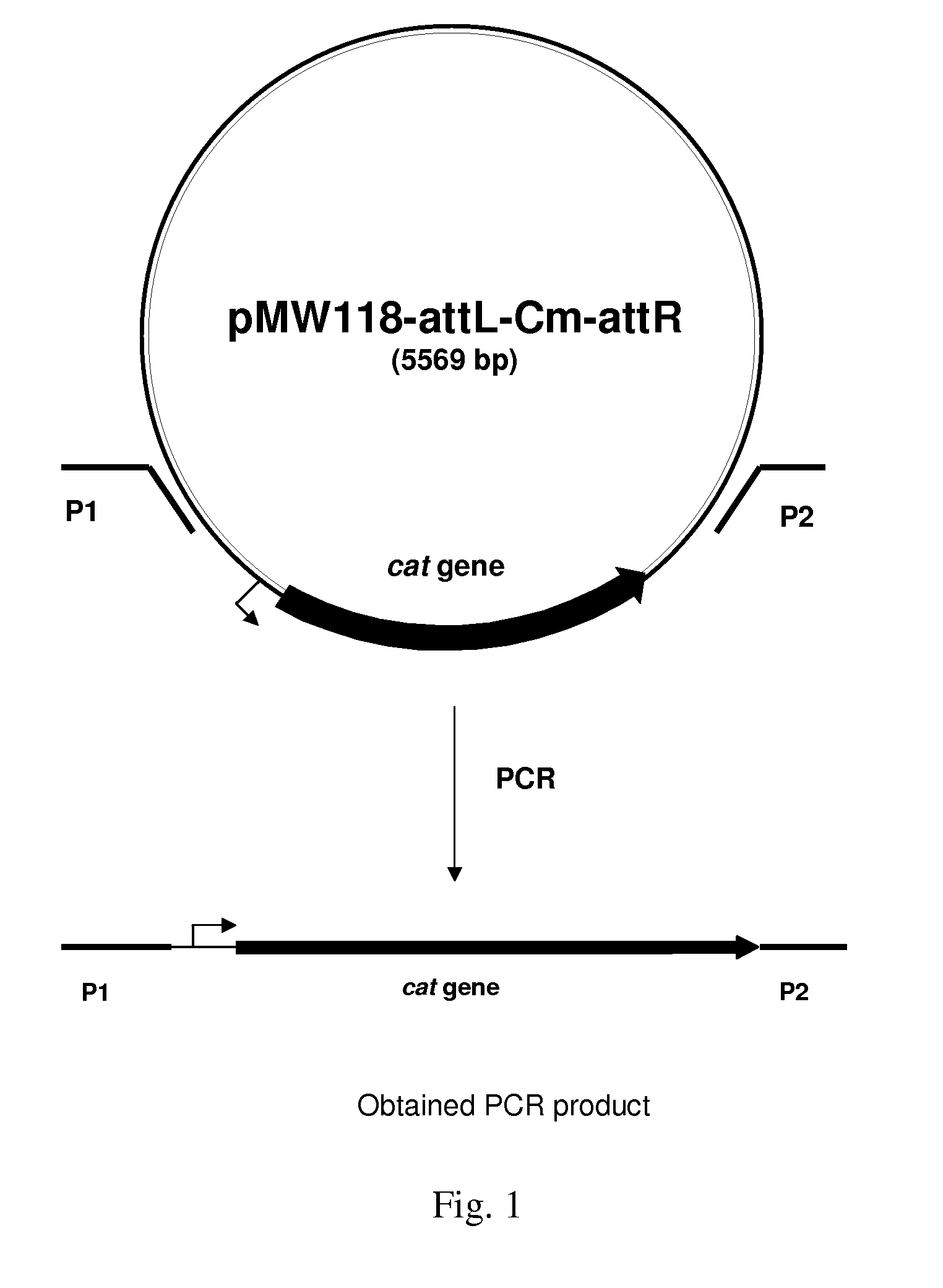
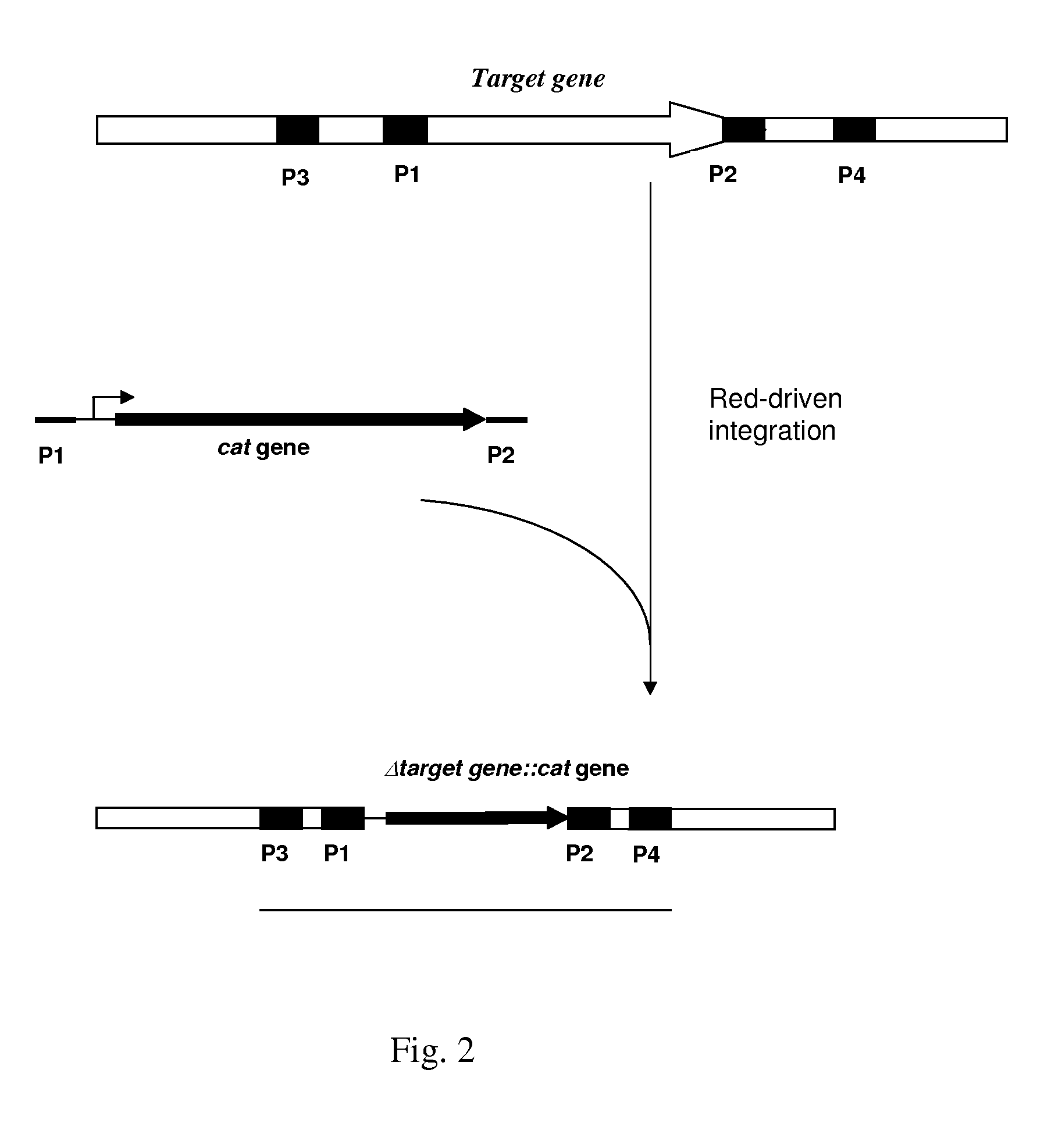
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
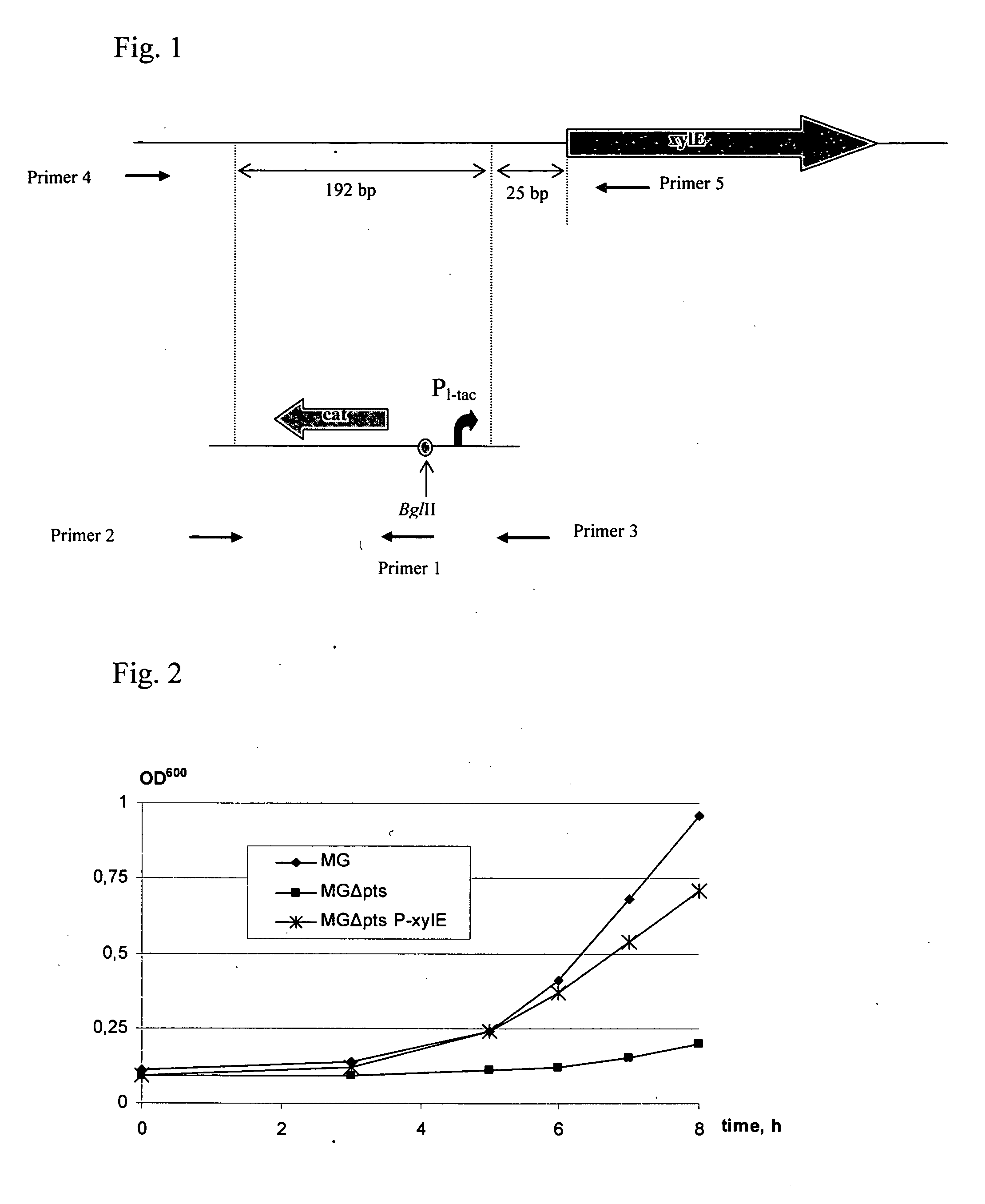
ActiveUS20060088919A1Improve productivityD-xylose permease is enhancedBacteriaDepsipeptidesL-threonineArginine
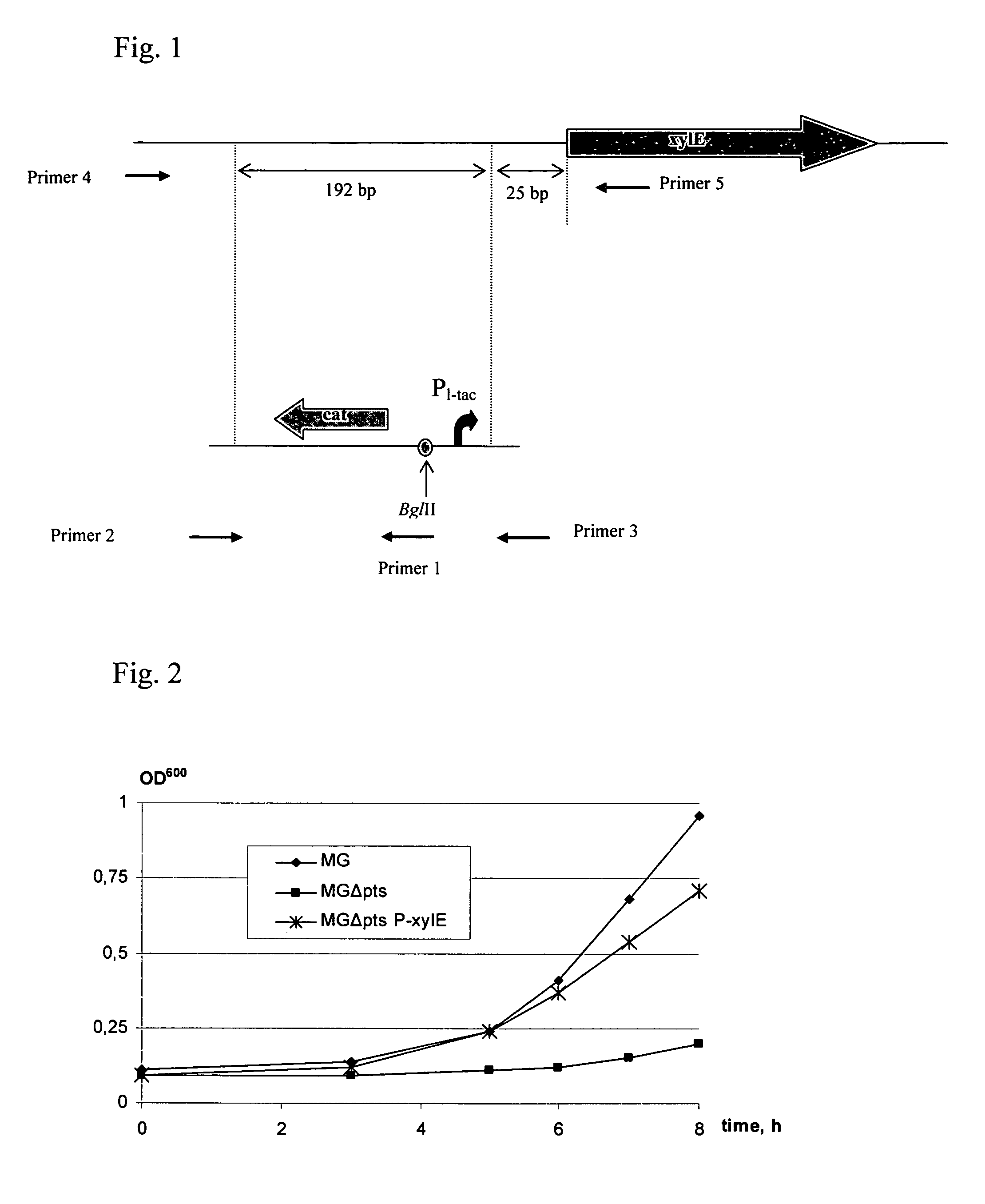
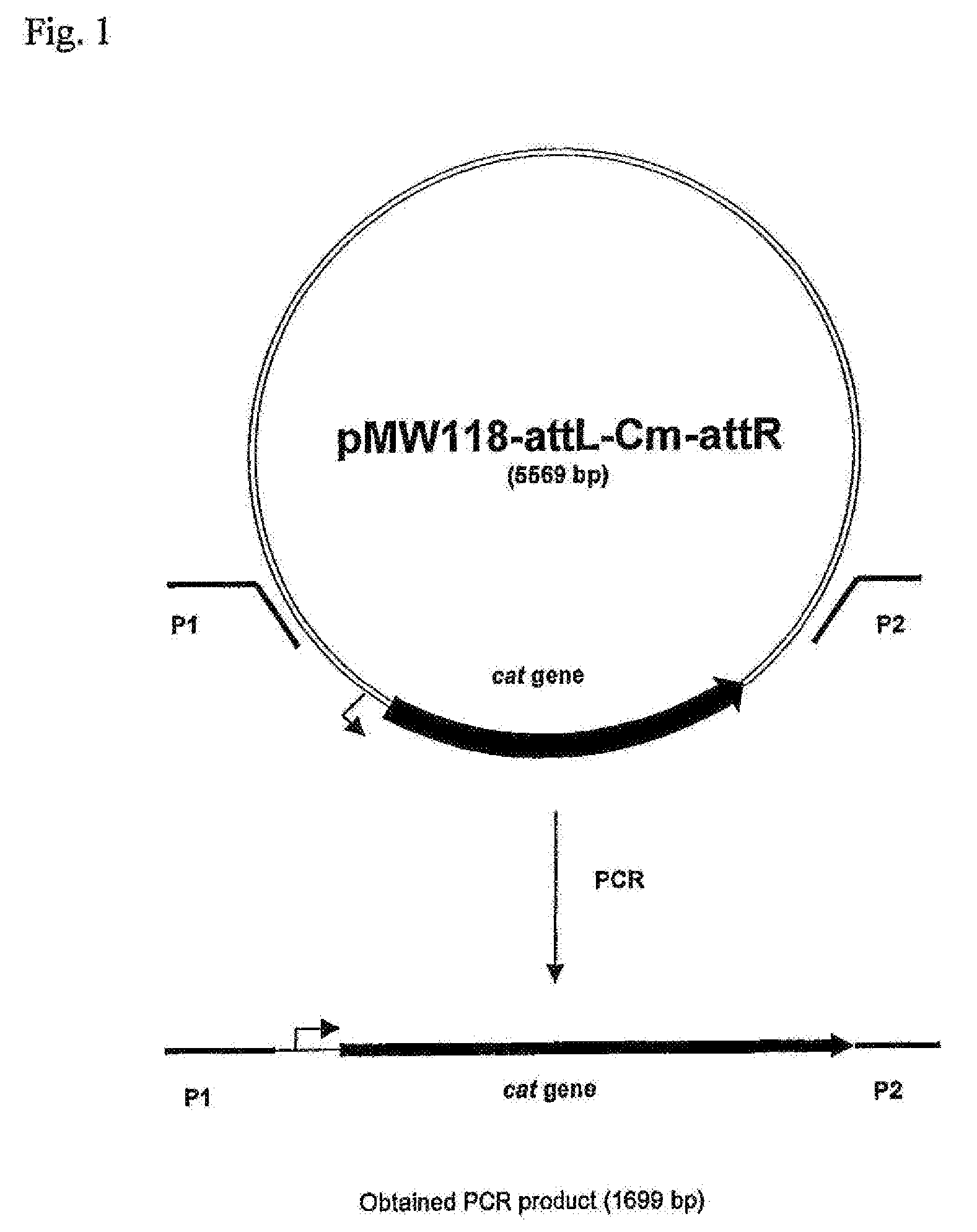
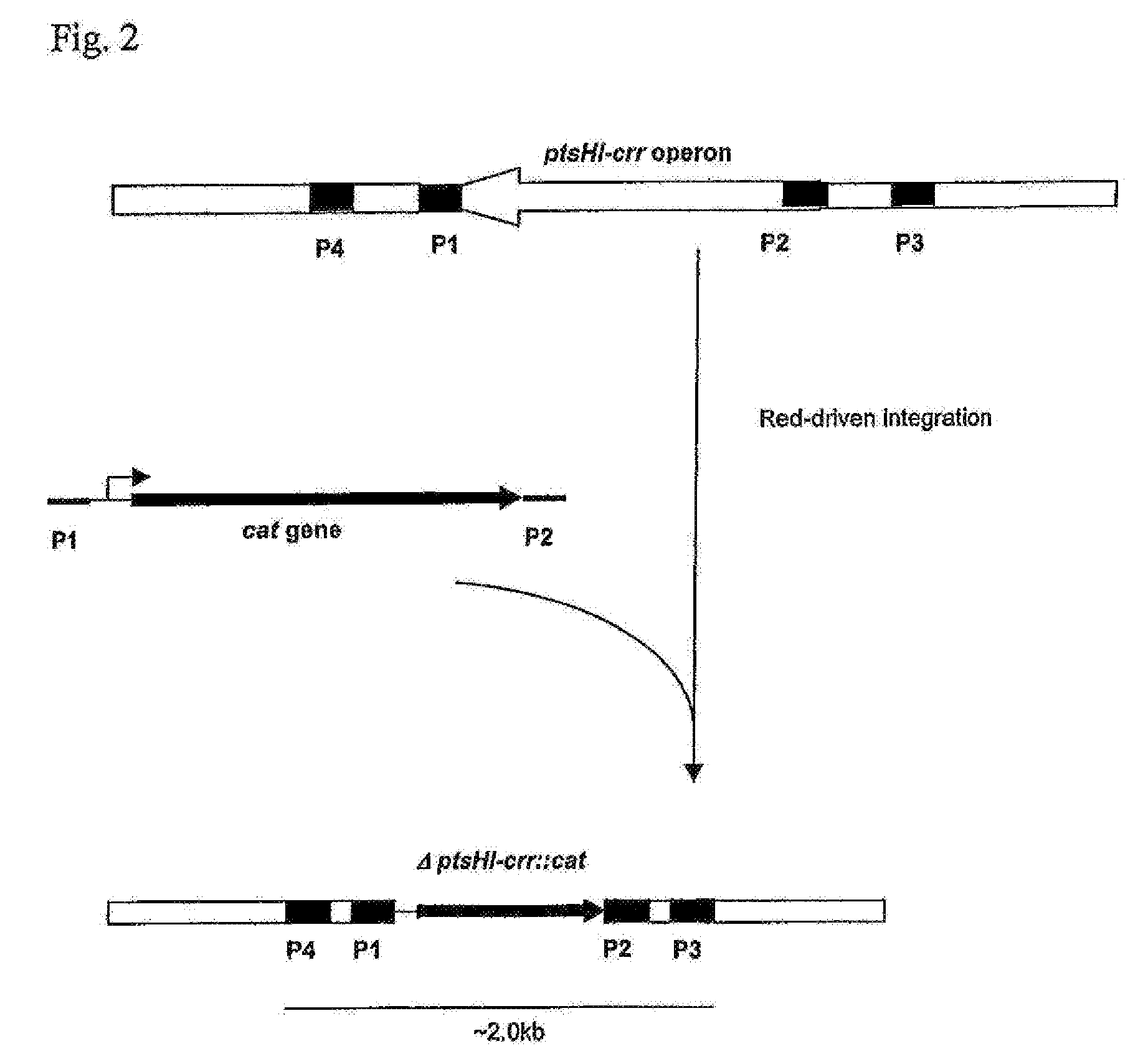
There is disclosed a method for producing L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of D-xylose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid producing microorganism and a method for producing L-amino acid
InactiveUS20060160191A1Improve productivityImprove L-amino acid productivityBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyBacteroides
An L-amino acid producing bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family is described, wherein the bacterium has been modified so as to not produce type I fimbrial adhesin protein is cultured in a medium to produce and excrete said L-amino acid in the medium, and collecting said L-amino acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
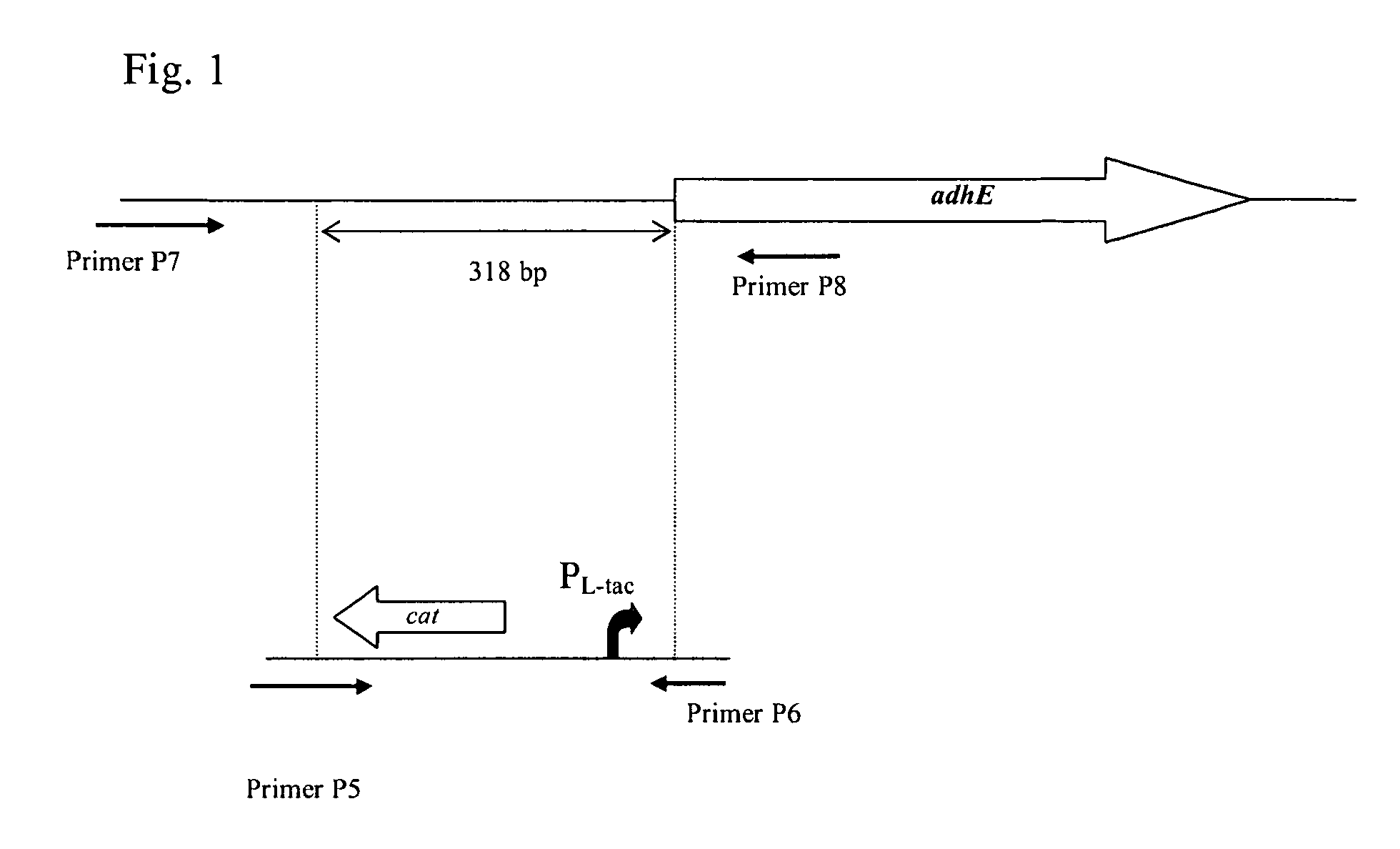
InactiveUS20090203090A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesArginine
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of a wild-type alcohol dehydrogenase encoded by the adhE gene or a mutant alcohol dehydrogenase which is resistant to aerobic inactivation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of administering FimH protein as a vaccine for urinary tract infections
InactiveUS20030138449A1Reduce morbidityInhibit bindingAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseBacteroides
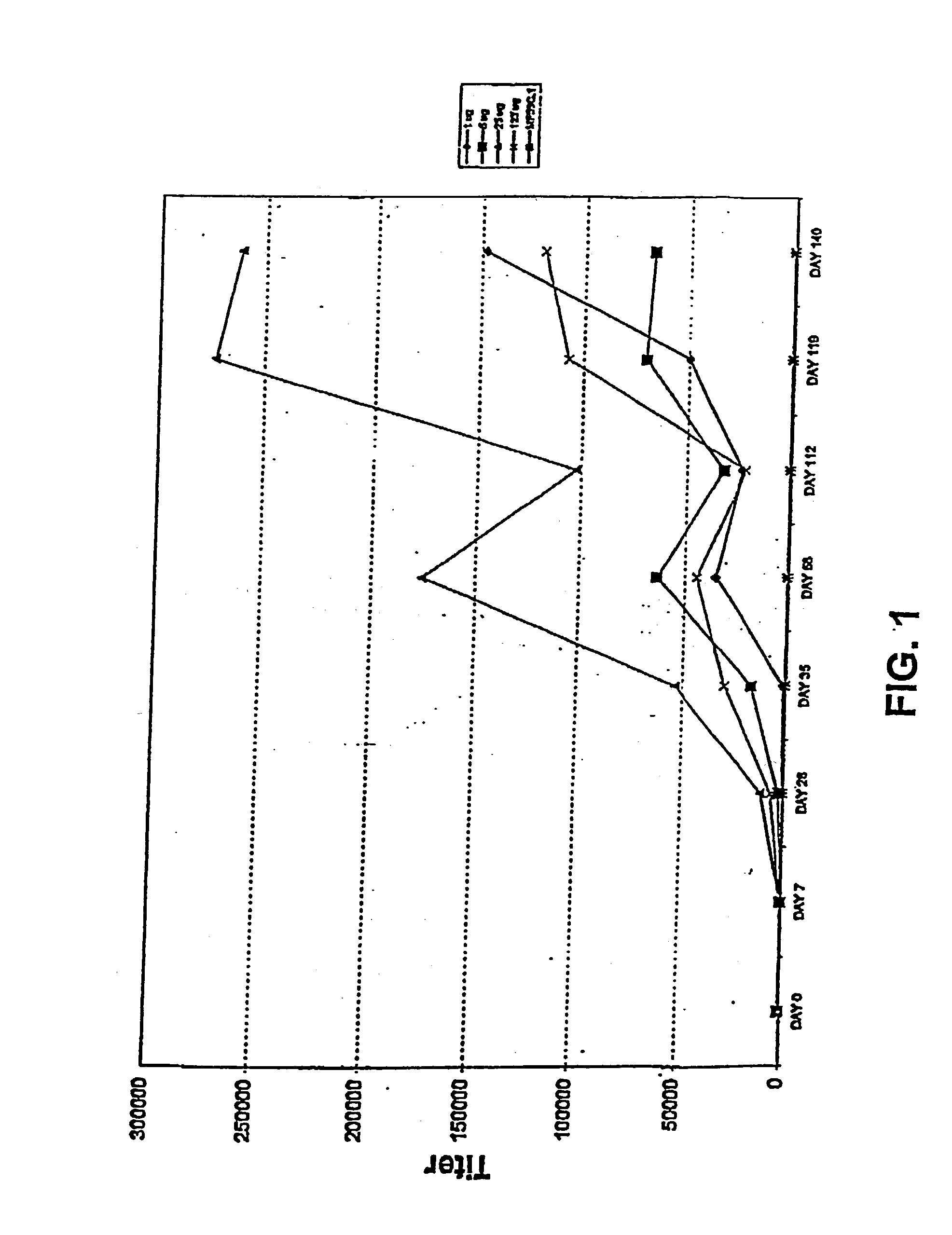
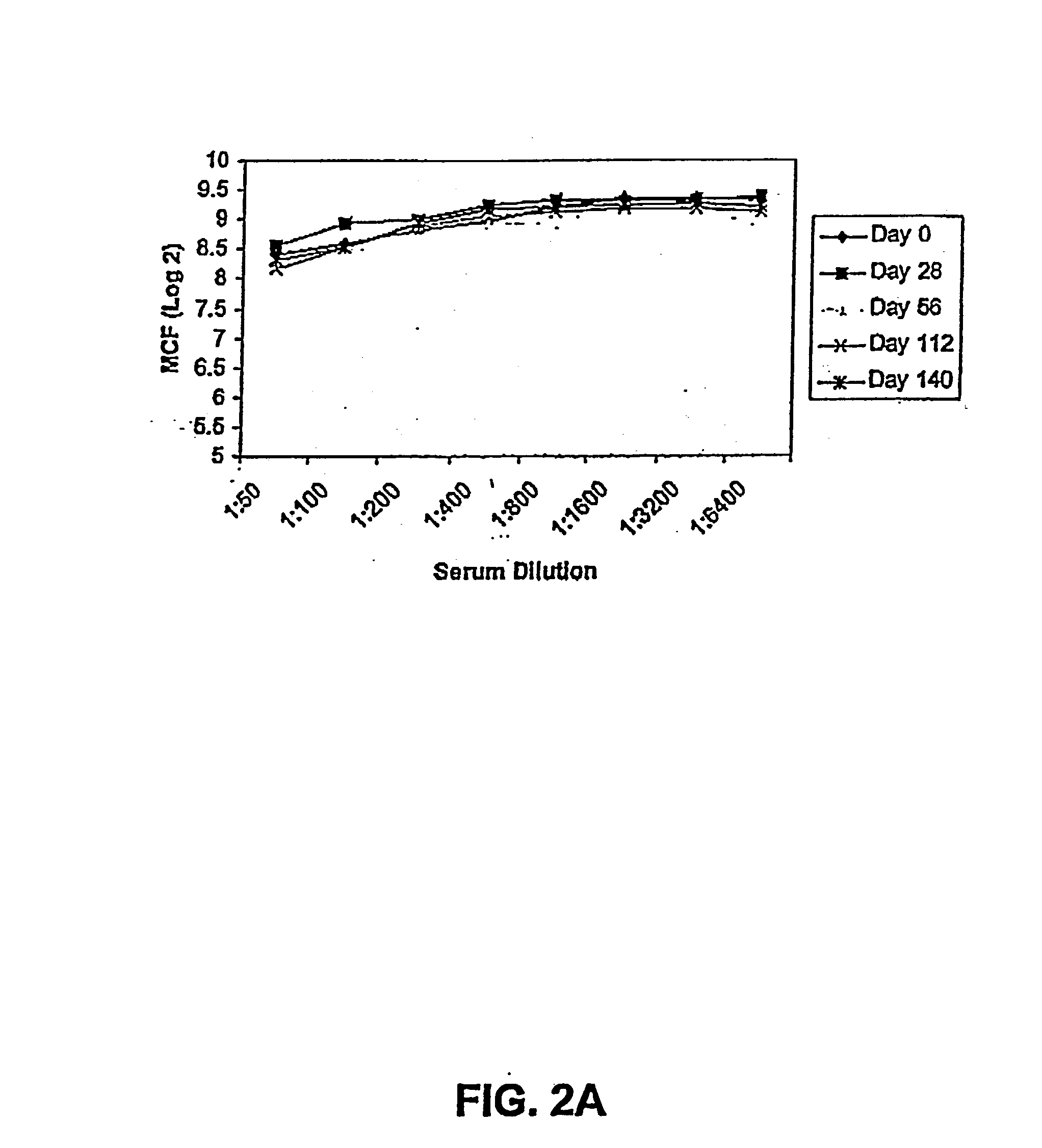
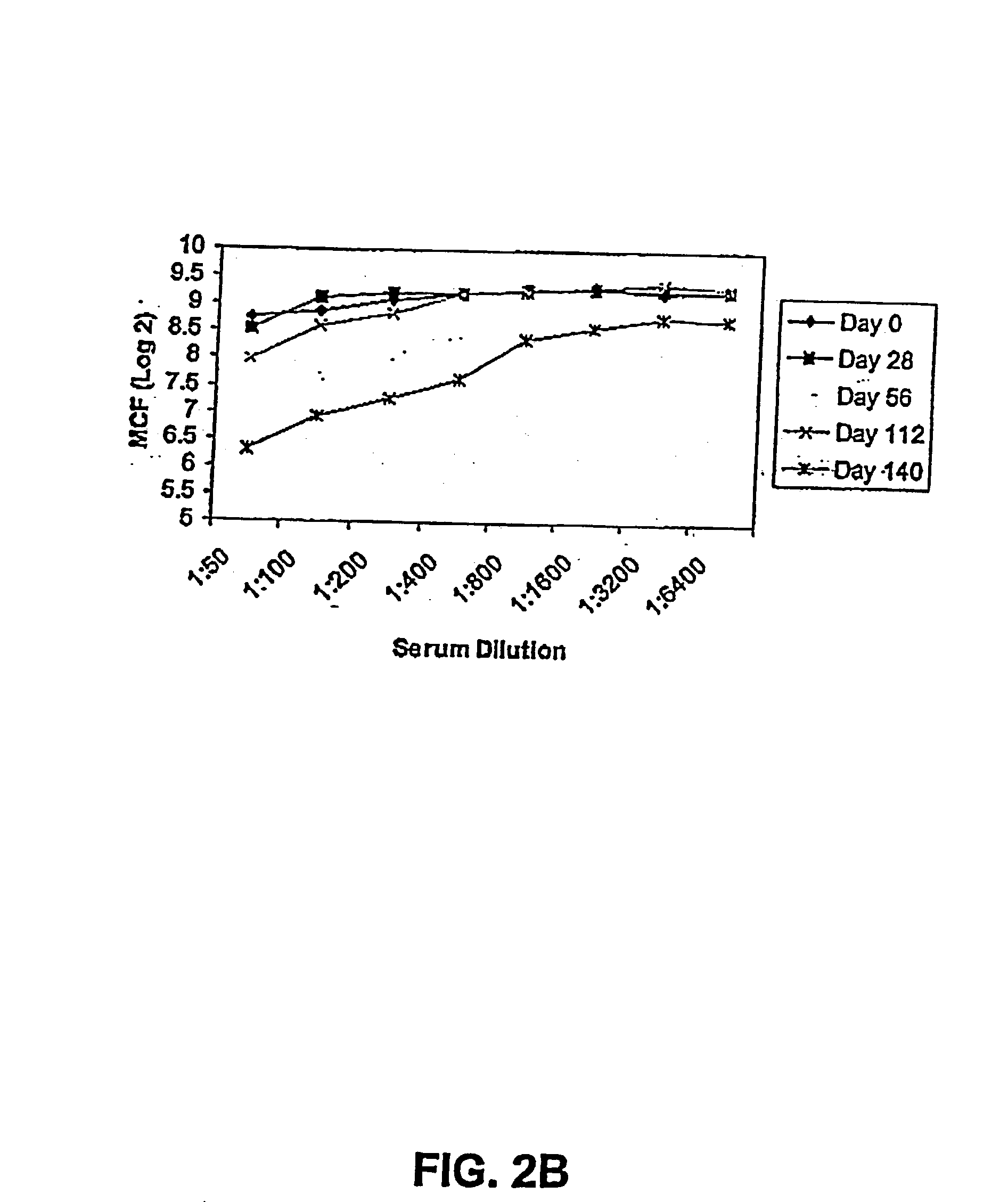
The present invention relates to methods of stimulating an immune response in a primate utilizing compositions comprising bacterial adhesin proteins and / or immunogenic fragments thereof. The compositions are useful for the prevention and treatment of bacterial induced diseases involving bacterial adherence to a target cell, such as diseases of the urinary tract. More specifically, the invention relates to the vaccination of primates, preferably humans, with protein complexes, such as a purified FimH polypeptides, a purified FimC-FimH (FimCH) polypeptide complex, or immunogenic fragments thereof, to stimulate protective immunity in the recipient against infection by pathogenic bacteria, including all types of Enterobacteriaceae, preferably E. coli to produce specific immunoglobin molecules in the serum and urine or mucosal secretions of the subject.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Mutant phosphoribosylpyrophosphate synthetase and method for producing L-histidine
InactiveUS20050176033A1High expressionImprove production yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesPurineEnterobacteriaceae bacterium
The present invention relates to a mutant bacterial PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, and a method for producing L-histidine using the bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family wherein the L-amino acid productivity of said bacterium is enhanced by use of the PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, coded by the mutant prsA gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing l-amino acids using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
InactiveUS20070212764A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationL-threonineArginine
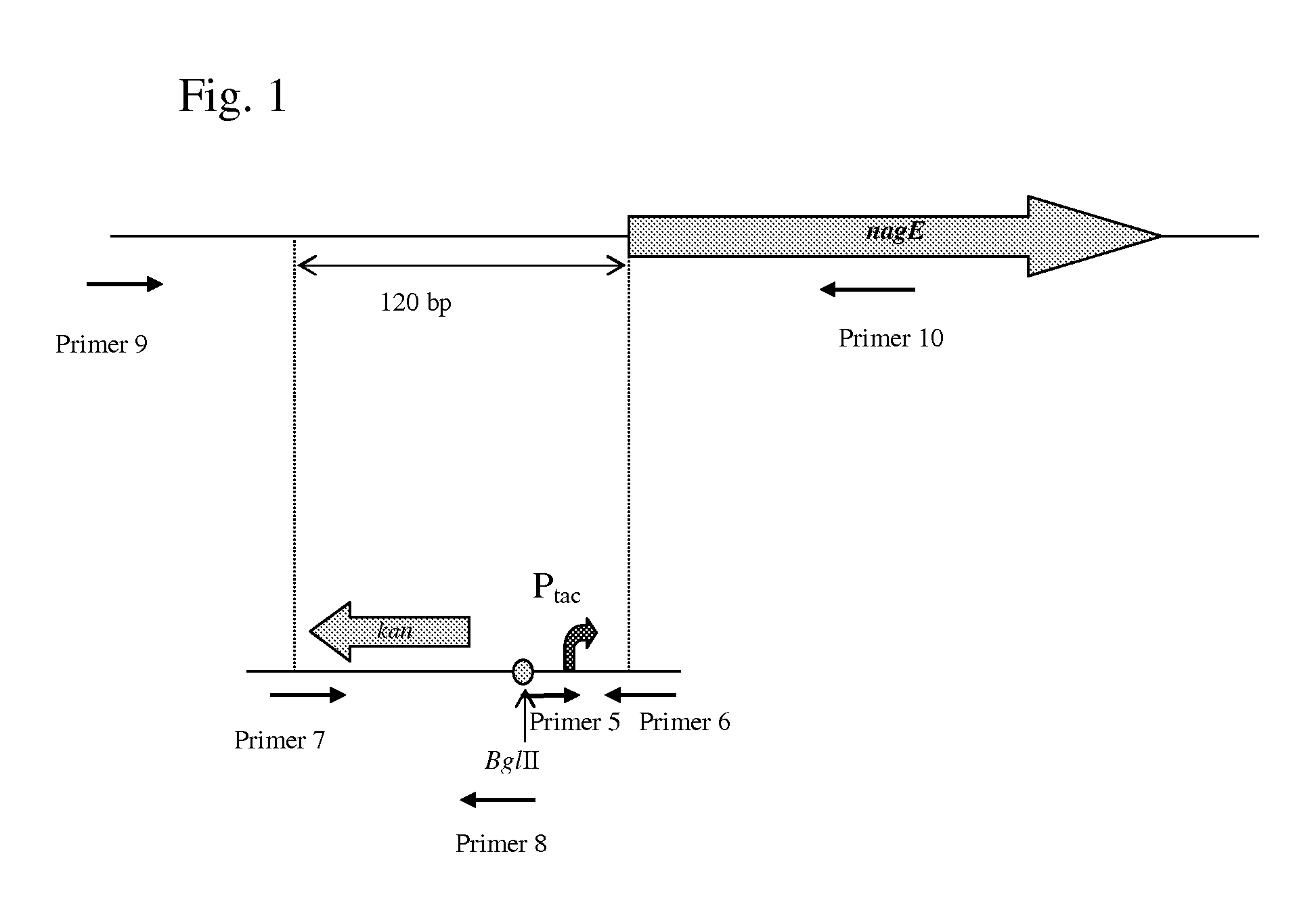
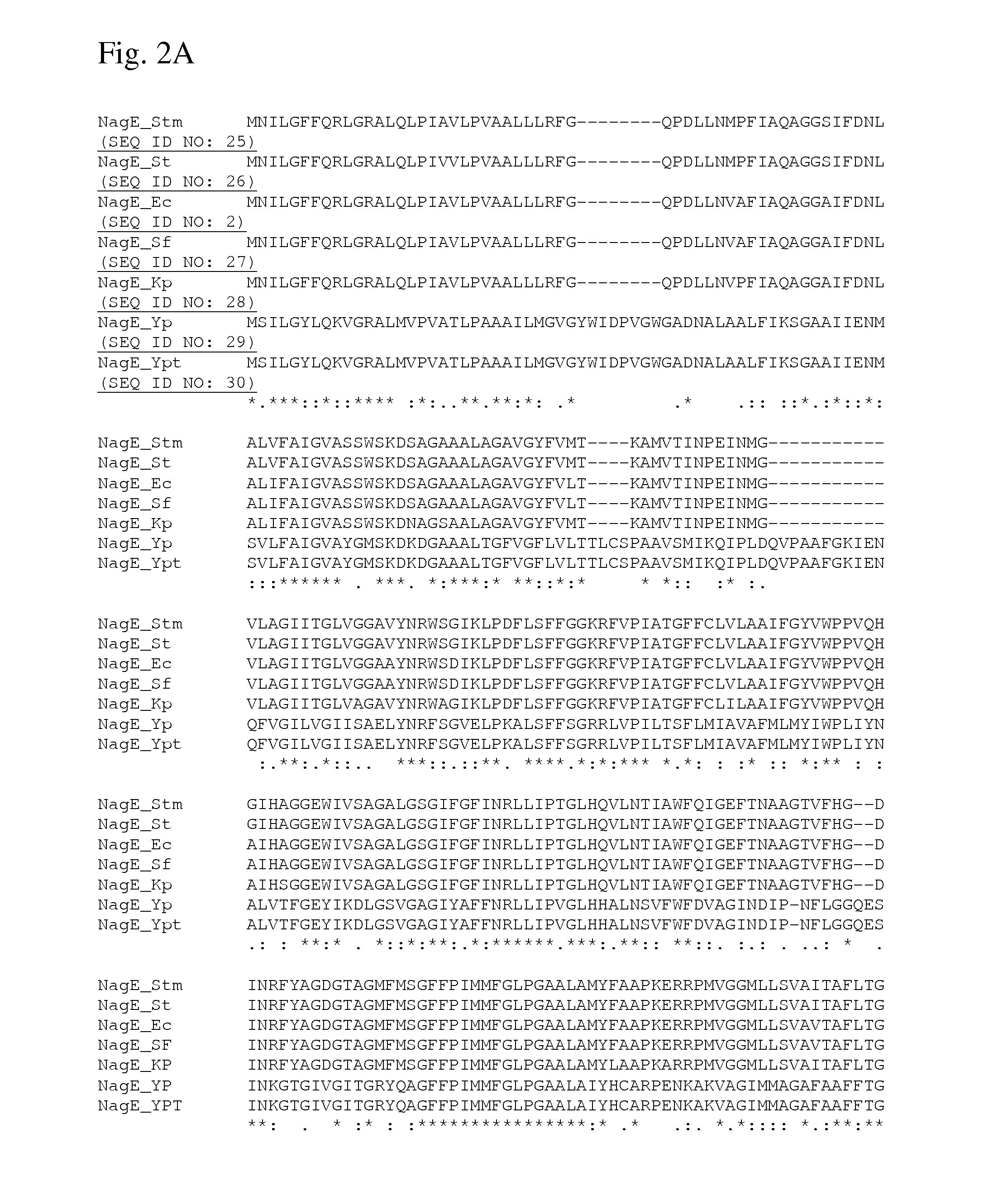
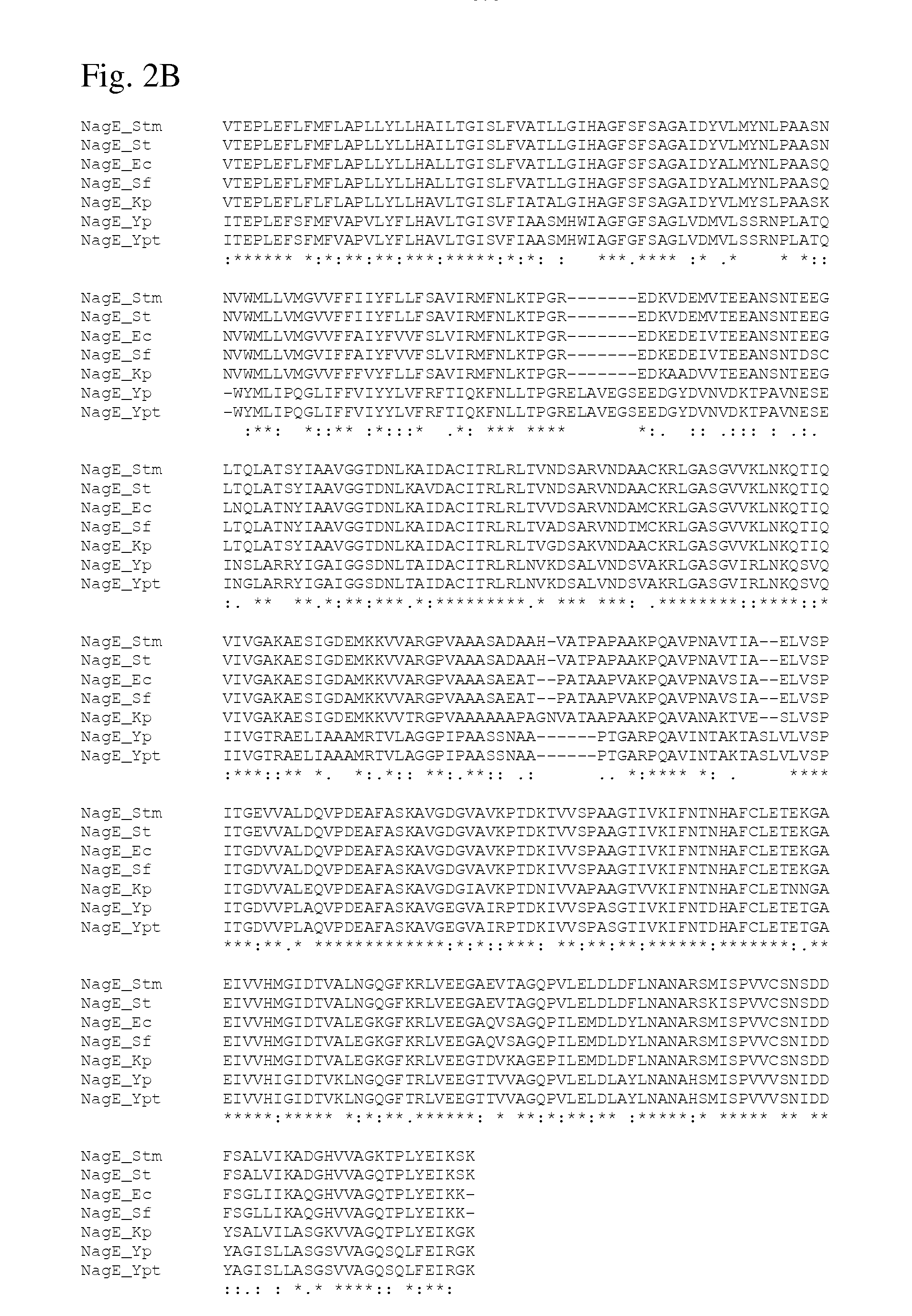
There is disclosed a method for producing an L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of N-acetylglucosamine permease encoded by the nagE gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, kit and detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli
ActiveCN103614465APrecise screeningSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesNucleotideEnterobacteriaceae bacterium
The invention discloses loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) primers, a kit and a detection method for detecting common carbapenemase genes of gram negative bacilli. In the LAMP primers disclosed by the invention, klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) and new delhi metallo-b-lactamase (NDM) primer groups can detect all subtypes except for NDM-10; hypoxanthine nucleotide (IMP) and vimentin (VIM) primer groups can detect common subtypes at home and abroad. The LAMP kit built by the invention is applied to joint detection of KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes, can cover the common carbapenemase genes of non-fermentative bacteria and enterobacteriaceae, can accurately and quickly screen the common carbapenemase genes, and has great clinical significance for timely detecting and further controlling fulminant epidemic caused by propagation of the carbapenemase genes in enterobacteriaceae. The kit disclosed by the invention is high in detection sensitivity and the minimum detection limits of the KPC, NDM, IMP and VIM genes can reach 100 CFU / reaction.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for production of l-amino acid
A bacterium which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family and has an ability to produce an L-amino acid such as L-lysine, L-threonine and L-tryptophan and is modified to enhance glutamic acid decarboxylase activity is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate the L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the bacterium. Then, the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Bacterium for fermenting L-tryptophan from mixed saccharum and fermentation method thereof
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and in particular relates to a bacterium for fermenting L-tryptophan from mixed saccharum and a fermentation method thereof. The Enterobacteriaceae bacterium for producing L-tryptophan can have the capability of simultaneously utilizing hexose and pentose to produce the L-tryptophan because of containing the coding gene of a cAMP receptor protein mutant. The cAMP receptor protein mutant is obtained through mutating one or a plurality of amino acid loci of the cAMP receptor protein. The bacterium provided by the invention consumes glucose and xylose in a culture medium containing the glucose and the xylose at the same time, and the yield and conversion rate of the L-tryptophan are increased.
Owner:新疆梅花氨基酸有限责任公司
Method for producing an l-amino acid using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS20090098621A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesGemella
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of a gene coding for sRNA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid producing bacterium and method of producing l-amino acid
ActiveUS20090258401A1Efficient productionEasy to useSugar derivativesBacteriaBiotechnologyAmino acid
L-amino acid is produced by culturing a bacterium belonging to the Enterobacteriaceae family which has L-amino acid-producing ability and is modified so that expression of the nhaA gene, nhaB gene, nhaR gene, chaA gene, mdfA gene, or combinations thereof is enhanced.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Bacillus subtillus degrading bacterial colony sensing signal and use of bacillus subtillus degrading bacterial colony as antiseptic
InactiveCN101926829AGrowth inhibitionAddressing drug resistanceAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseBacteroides
The invention belongs to the field of hygiene and relates to a bacillus subtillus degrading bacterial colony sensing signal and use of bacillus subtillus degrading bacterial colony as an antiseptic, in particular to bacillus subtillus degrading gram-negative bacterial colony sensing signal and the formation of a bacterial biofilm of the bacillus subtillus degrading gram-negative bacterial colony. In the use of the degrading bacterial colony sensing signal, a proper concentration of the bacillus subtillus is 5*102 to 5*104cfu / ml. The bacillus subtillus is further used as antiseptic to inhibit the bacteria such as pseudomonas, agrobacterium, enterobacteriaceae and vibrionaceae. The antiseptic can be ointment for external use, liquid preparation for external use, oral tablet, oral liquid, disinfectant, clearing agents or water quality improving agent. The consistency of the bacillus subtillus serving as the antiseptic is 105 to 106 cfu / g. The use of the bacillus subtillus provided by the invention and the antiseptic inhibit the formation of biofilm of disease-causing bacteria and the growth of bacteria by using microbial quorum-sensing inhibition instead of preventing and sterilizing bacteria by compound which is adopted by most of the conventional antiseptic; therefore, the problem of drug resistance in the antimicrobial process is avoided.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
There is disclosed a method for producing an L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of L-arabinose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid producing bacterium and method of producing l-amino acid
InactiveUS20090215130A1Effectively producing L-amino acidEasy to useBacteriaFermentationBiotechnologyFepA
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing an L-amino acid-producing bacterium which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family and which has been modified so that the activity of an iron transporter is increased by enhancing expression of one or more genes of the following genes: tonB gene, fepA gene, and fecA.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutant Phosphoribosylpyrophosphate Synthetase and Method for Producing L-Histidine
The present invention relates to a mutant bacterial PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, and a method for producing L-histidine using the bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family wherein the L-amino acid productivity of said bacterium is enhanced by use of the PRPP synthetase which is resistant to feedback by purine nucleotides, coded by the mutant prsA gene.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
L-amino acid producing microorganism and a method for producing an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20100062496A1Efficient productionKdp system is enhancedSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismMicrobiology
A microorganism belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae, which has an L-amino acid-producing ability and has been modified so that the kdp system is enhanced, is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate an L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the microorganism, and the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or cells to produce the L-amino acid.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
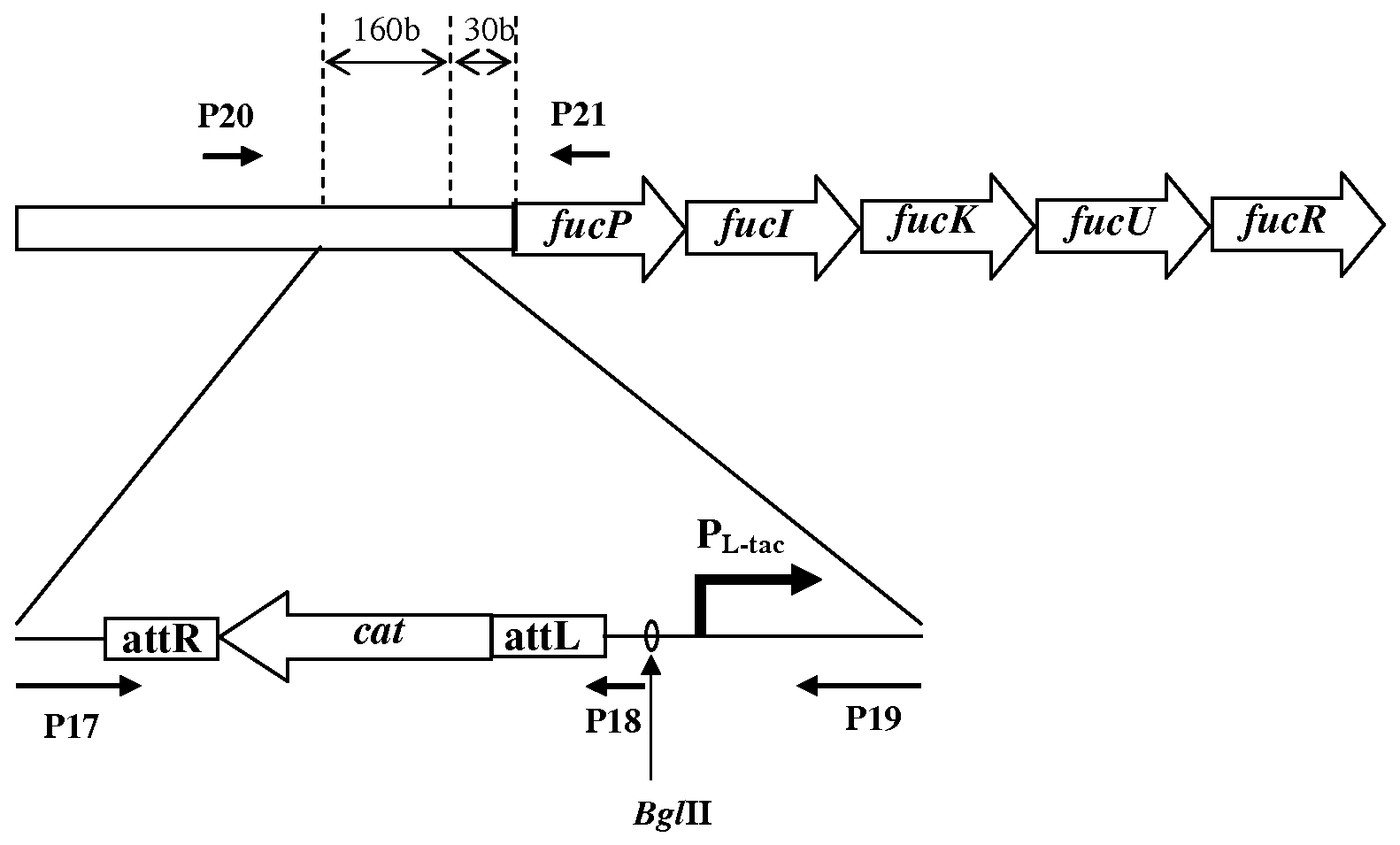
Method for Producing an L-Amino Acid Using a Bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae Family With Enhanced Expression of the fucPIKUR Operon
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to enhance expression of at least one gene of the fucPIKUR operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Process for the preparation of l-amino acids using strains of the enterobacteriaceae family
The invention relates to a process for the preparation of L-amino acids, in particular L-threonine, in which the following steps are carried out: a) fermentation of the microorganisms of the Enterobacteriaceae family which produce the desired L-amino acid and in which the malT gene or nucleotide sequences or alleles which code for it are enhanced, b) concentration of the desired L-amino acid in the medium or in the cells of the microorganisms, and c) isolation of the desired L-amino acid.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
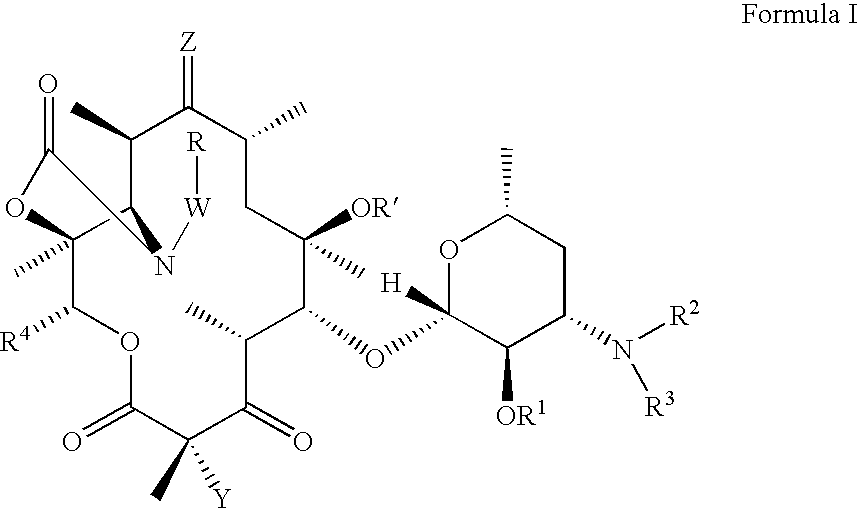
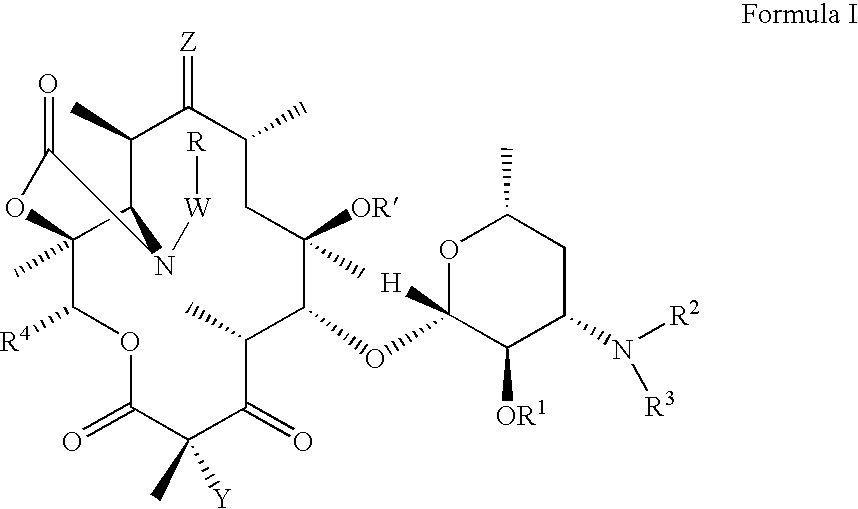
Ketolide derivatives as antibacterial agents
The present invention provides ketolide derivatives, which can be used as anti-bacterial agents. Compounds disclosed herein can be used for the treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed to by gram positive, gram negative or anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla spp., Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasm, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebacterium, Bacillus, Enterobactericeae or any combination thereof. Also provided are processes for preparing compounds disclosed herein, intermediates used in their synthesis, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Method for producing L-amino acid using bacterium of Enterobacteriaceae family, having nir operon inactivated
A method is provided for producing L-amino acid, such as L-arginine using a bacterium of Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging the genus Escherichia, with an inactivated nir operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS7915018B2Improve productivityD-xylose permease is enhancedBacteriaDepsipeptidesBacteroidesArginine
There is disclosed a method for producing L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of D-xylose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid using a bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
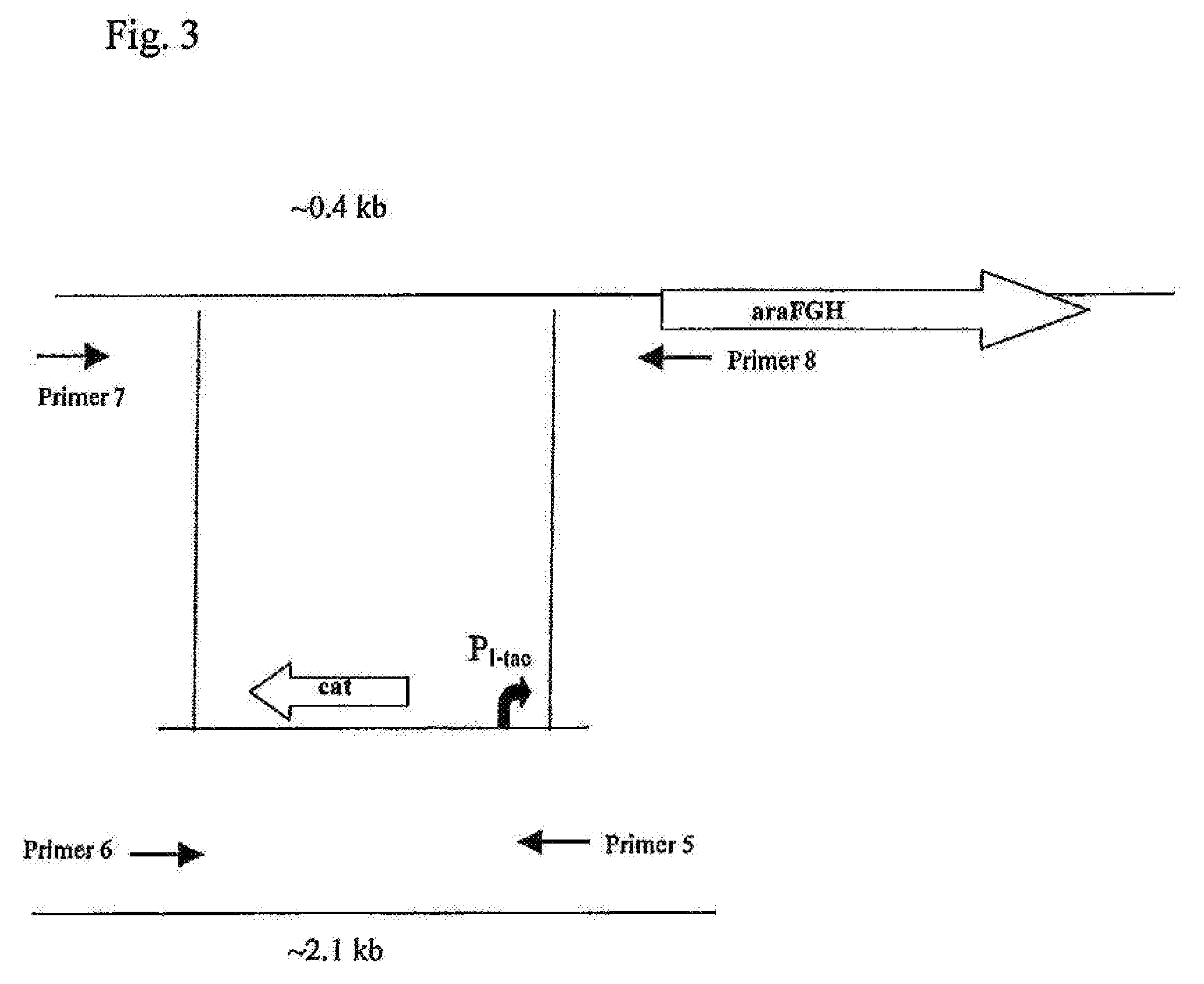
A method is described for producing an L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-leucine, L-histidine, L-cysteine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine, L-tryptophan, L-glutamic acid, L-valine, and L-isoleucine, by fermentation of glucose using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance the activity of the high-affinity arabinose transporter coded by the araFGH operon.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing l-arginine using a bacterium of enterobacteriaceae family, having attenuated expression of a gene encoding an l-arginine transporter
InactiveUS20100143983A1Improve productivityIncreased ability to produce L-arginineBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesMicrobiology
The present invention provides a method for producing L-arginine using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to the genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to attenuate expression of one or several genes encoding an L-arginine transporter.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing amino acids using bacterium of the enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20090137010A1Improve productivityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesDNA fragmentationA-DNA
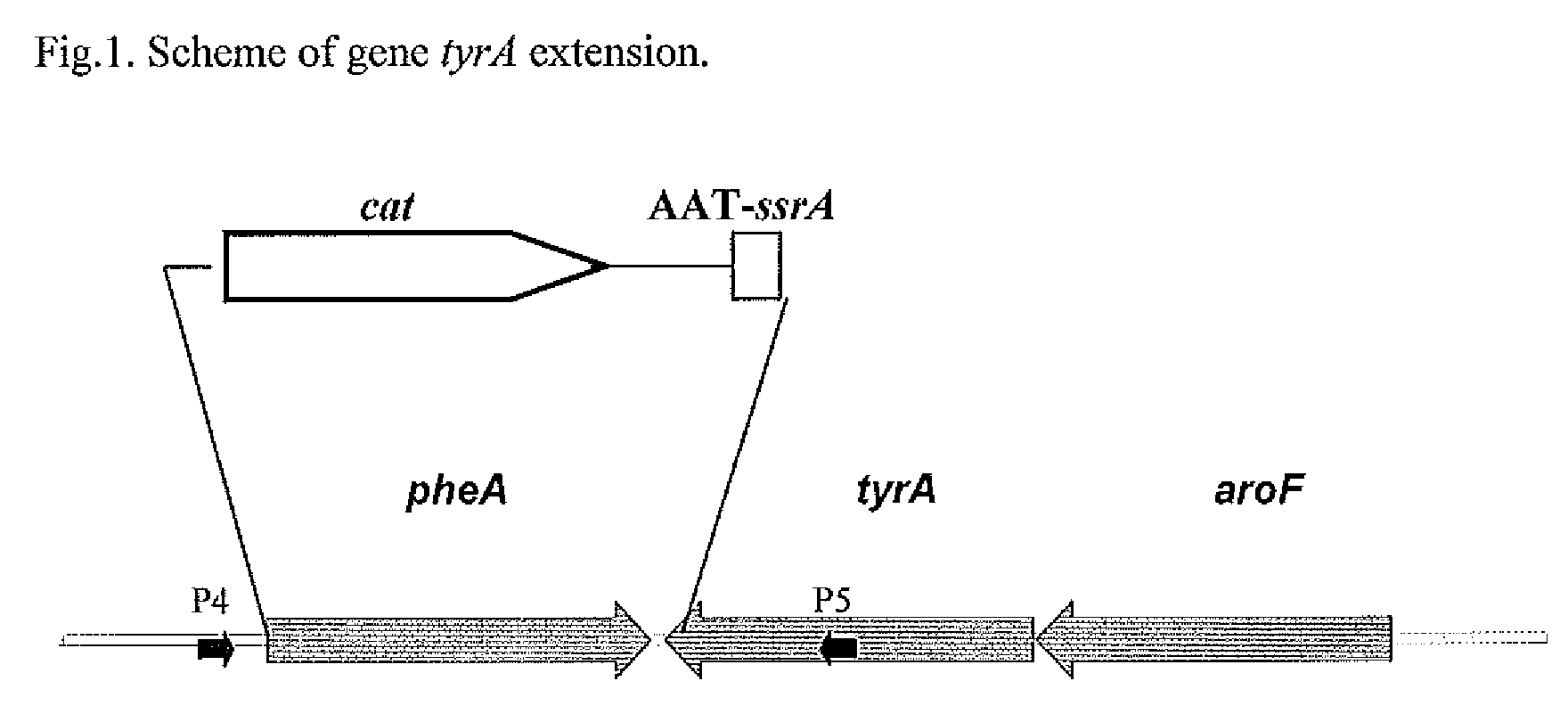
A method for producing an L-amino acid is described, for example, L-phenylalanine and L-histidine, by fermentation using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified by attaching a DNA fragment able to be transcribed encoding the peptide represented in SEQ ID NO: 2, or a variant thereof, particularly a portion of the ssrA gene, to the 3′-end of gene encoding for the bacterial enzyme, which influences on the L-amino acid biosynthesis, such as chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydrogenase or phosphoglucose isomerase.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing an l-amino acid by fermentation using a bacterium having an enhanced ability to utilize glycerol
InactiveUS20090317876A1Improve abilitiesProducing L-aminoBacteriaOxidoreductasesBacteroidesGlycerol kinase
The present invention provides a method for producing an L-amino acid using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, particularly a bacterium belonging to genus Escherichia or Pantoea, which has been modified to have glycerol kinase in which feedback inhibition by fructose-1,6-bisphosphate is desensitized, thereby having enhanced ability to utilize glycerol.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Safe food preservative
InactiveCN105077511AImprove anti-corrosion performanceFruit and vegetables preservationNatural extract food ingredientsHalobacteriumBacilli
The invention belongs to the technical field of food processing, and particularly relates to safe food preservative. The safe food preservative comprises, by mass, 2-7 parts of gingko leaf extractives, 4-9 parts of lysozyme, 12-15 parts of chitosan, 3-7 parts of spice extractives, 4-10 parts of protamines and 80-100 parts of water. According to the safe food preservative, the main inhibiting objects are pseudomonades, micrococcus, bacilli, enterobacteriaceae, vibrios, halobacterium, mycete and the like, and the application range is wide in beverages, seasoning, cooked wheaten food, cakes, sausages, canned fruit, various melons and fruits, vegetables and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN HUIQUAN CANNED FOOD
Novel klebsiella pneumoniae strain as well as isolation method and application thereof
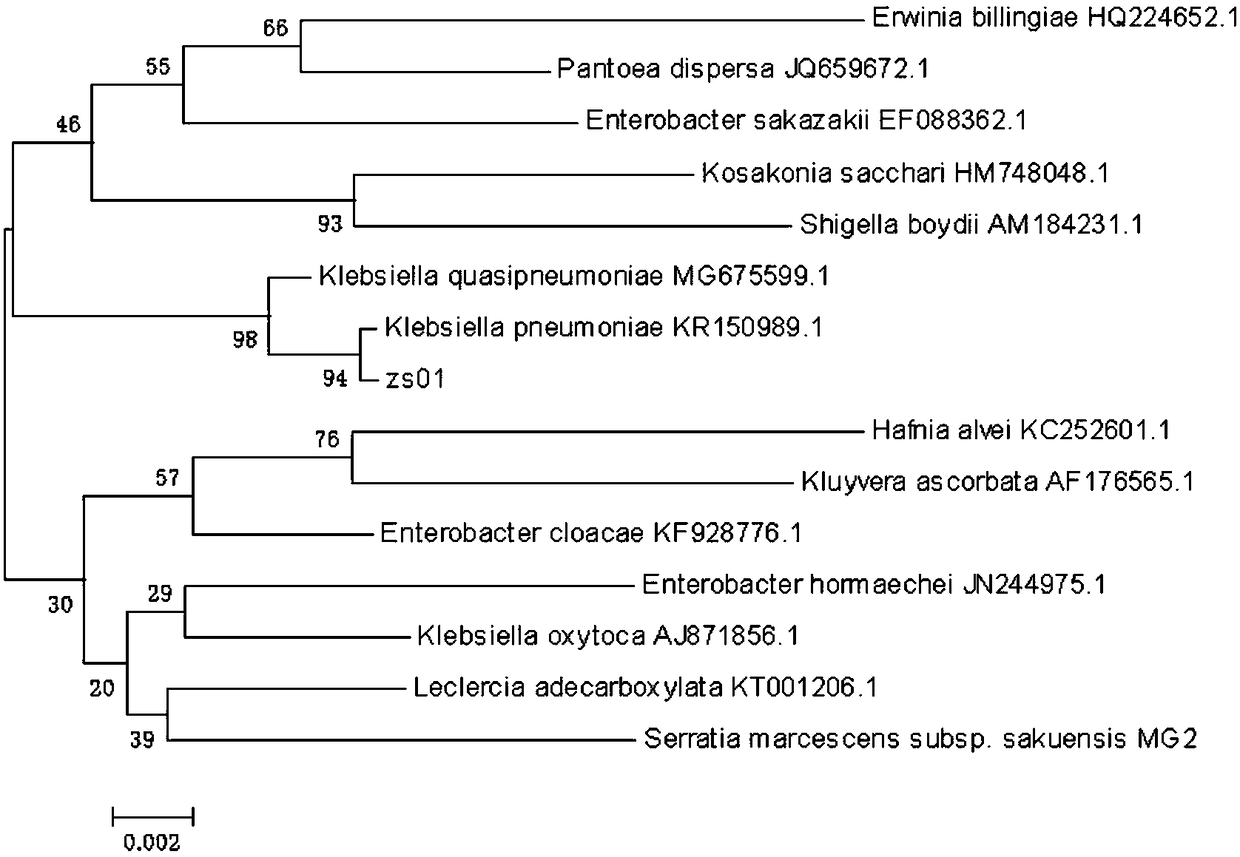
ActiveCN109055282AHas the ability to degradeImprove toleranceBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationK pneumoniae
The invention discloses a novel klebsiella pneumoniae strain as well as an isolation method and application thereof. The novel strain is isolated and screened from activated sludge in an aeration tankof a papermaking sewage treatment plant and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection name is ZS-01, the collection number is 16041, and the collection date is June 30, 2018. The strain has the characteristics and performance as follows: (1), the characteristics are: colonies formed on a phenol MedA solid culture medium are relatively short and thickbacilli, have the sizes of (0.5-0.8)*(1-2)[mu]m, are arranged separately or in pairs, and are pale yellow, uniform in texture and opaque; relatively large gray white sticky colonies are formed on an MPYE solid culture medium, are flagella-free, have capsules, belong to enterobacteriaceae and are Gram-negative short and thick bacilli; (2), the performance is: the strain has certain phenol degradingcapability and has relatively high tolerance to phenol. The strain has the advantages as follows: the strain can degrade the phenol with relatively high concentration, and provides a new bacterial source for effectively treating phenol-containing wastewater with relatively high concentration.
Owner:XIAN LONGHUA ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECHCO LTD
Method of administering FimH protein as a vaccine for urinary tract infections
InactiveUS20050196408A1Reduce morbidityImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsUpper urinary tract infectionPrimate
The present invention relates to methods of stimulating an immune response in a primate utilizing compositions comprising bacterial adhesin proteins and / or immunogenic fragments thereof. The compositions are useful for the prevention and treatment of bacterial induced diseases involving bacterial adherence to a target cell, such as diseases of the urinary tract. More specifically, the invention relates to the vaccination of primates, preferably humans, with protein complexes, such as a purified FimH polypeptides, a purified FimC-FimH (FimCH) polypeptide complex, or immunogenic fragments thereof, to stimulate protective immunity in the recipient against infection by pathogenic bacteria, including all types of Enterobacteriaceae, preferably E. Coli to produce specific immunoglobin molecules in the serum and urine or mucosal secretions of the subject.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
Method for producing an L-amino acid using bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family with attenuated expression of a gene coding for small RNA
InactiveUS7803584B2Improve productivityIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesPantoea
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Antimicrobial agents
Provided herein are substituted aromatic compounds, which are tRNA synthetase inhibitors, and hence can be used as antimicrobial agents. Compounds described herein can be used for the treatment or prevention of a condition caused by or contributed to by gram positive, gram negative, anaerobic bacteria or fungal organisms, more particularly against bacterium, for example, Staphylococci, Enterococci, Streptococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla, Escherichia, Chlamydia, Mycoplasm, Legionella, Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebacterium, Bacillus or Enterobactericeae, and fungal organisms, for example, Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Candida, Coccidiodes, Cryptococcus, Epidermophyton, Hendersonula, Histoplasma, Microsporum, Paecilomyces, Paracoccidiodes, Pneumocystis, Trichophyton, or Trichosporium. Processes for the preparation of these compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating microbial infections are also provided.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com