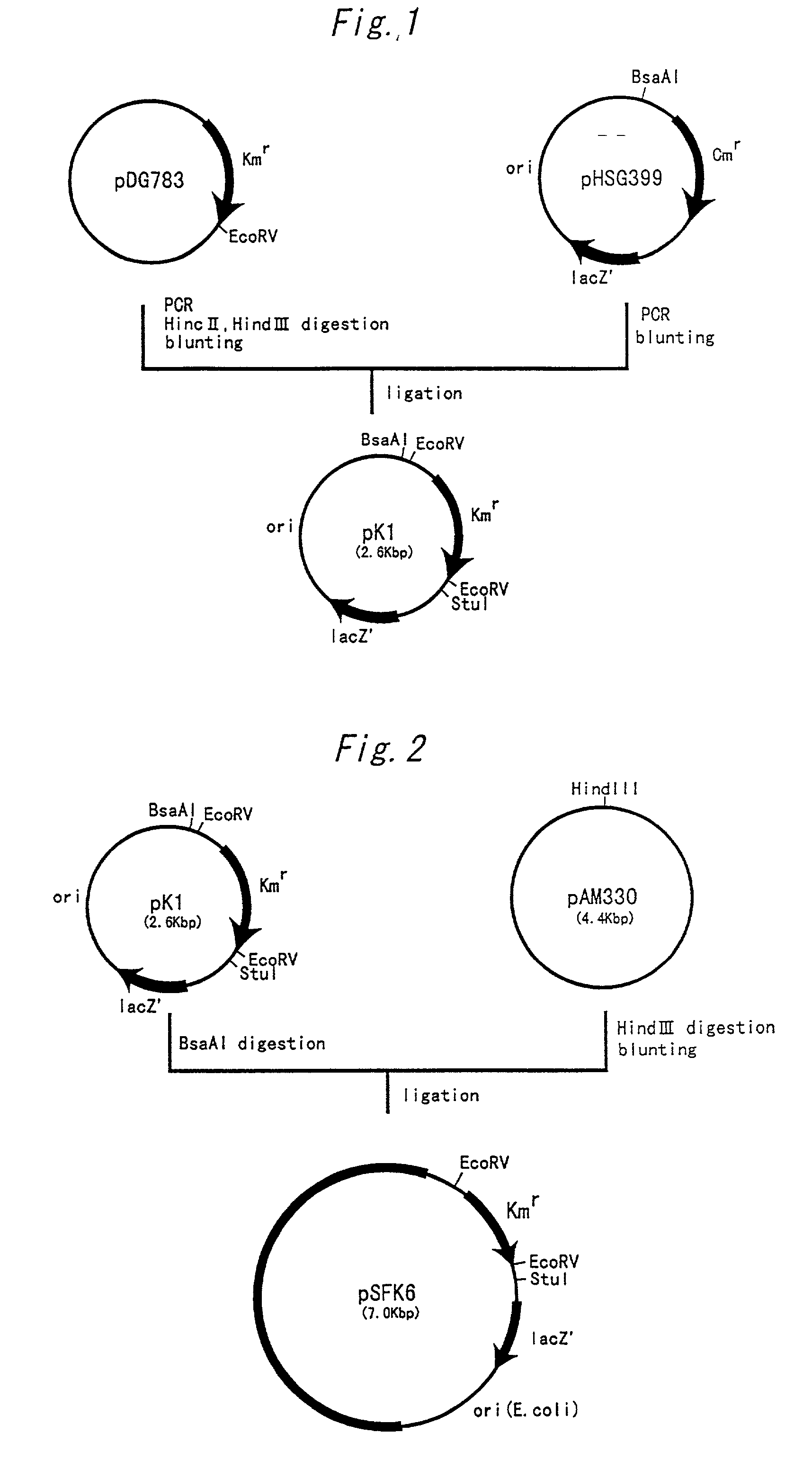
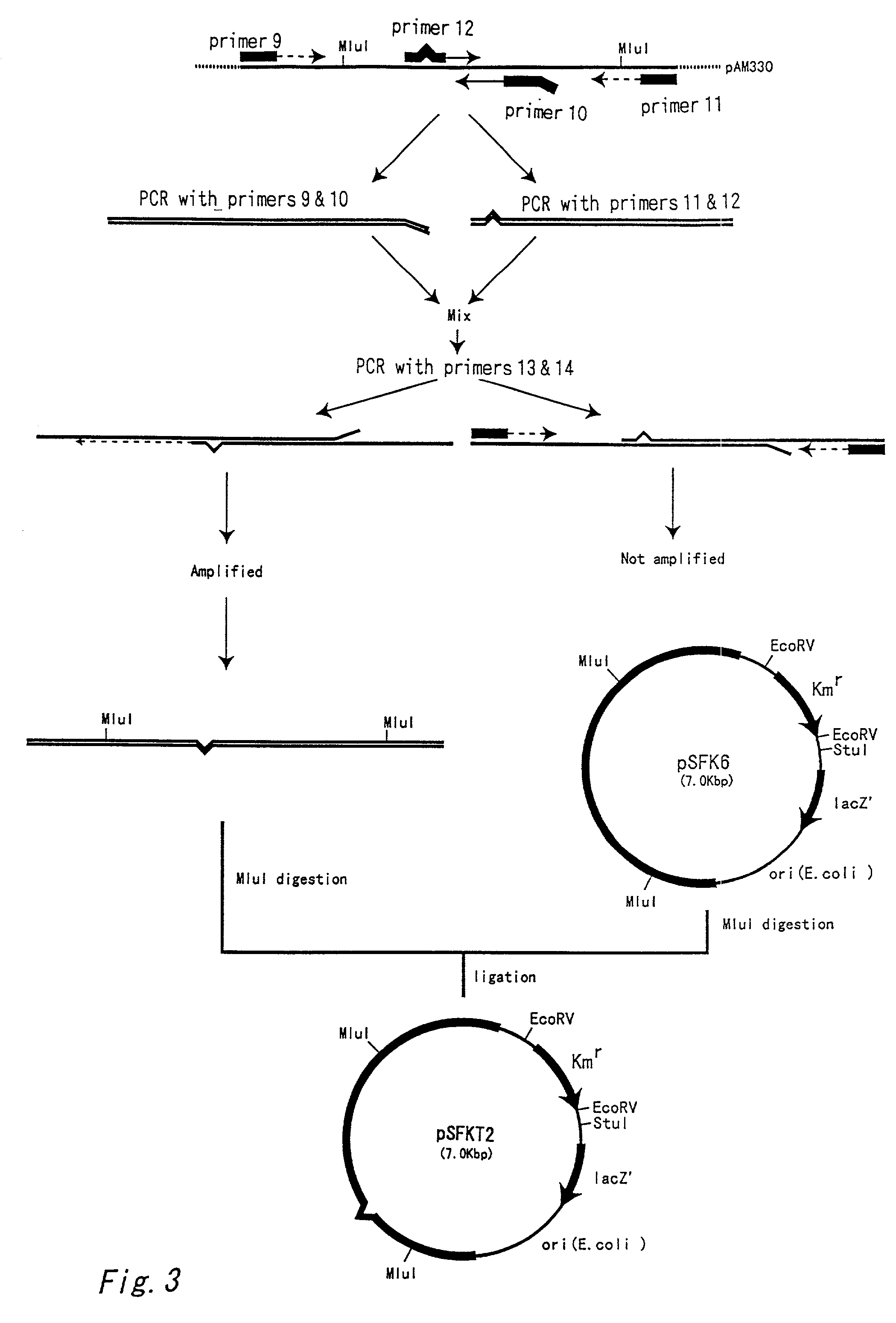
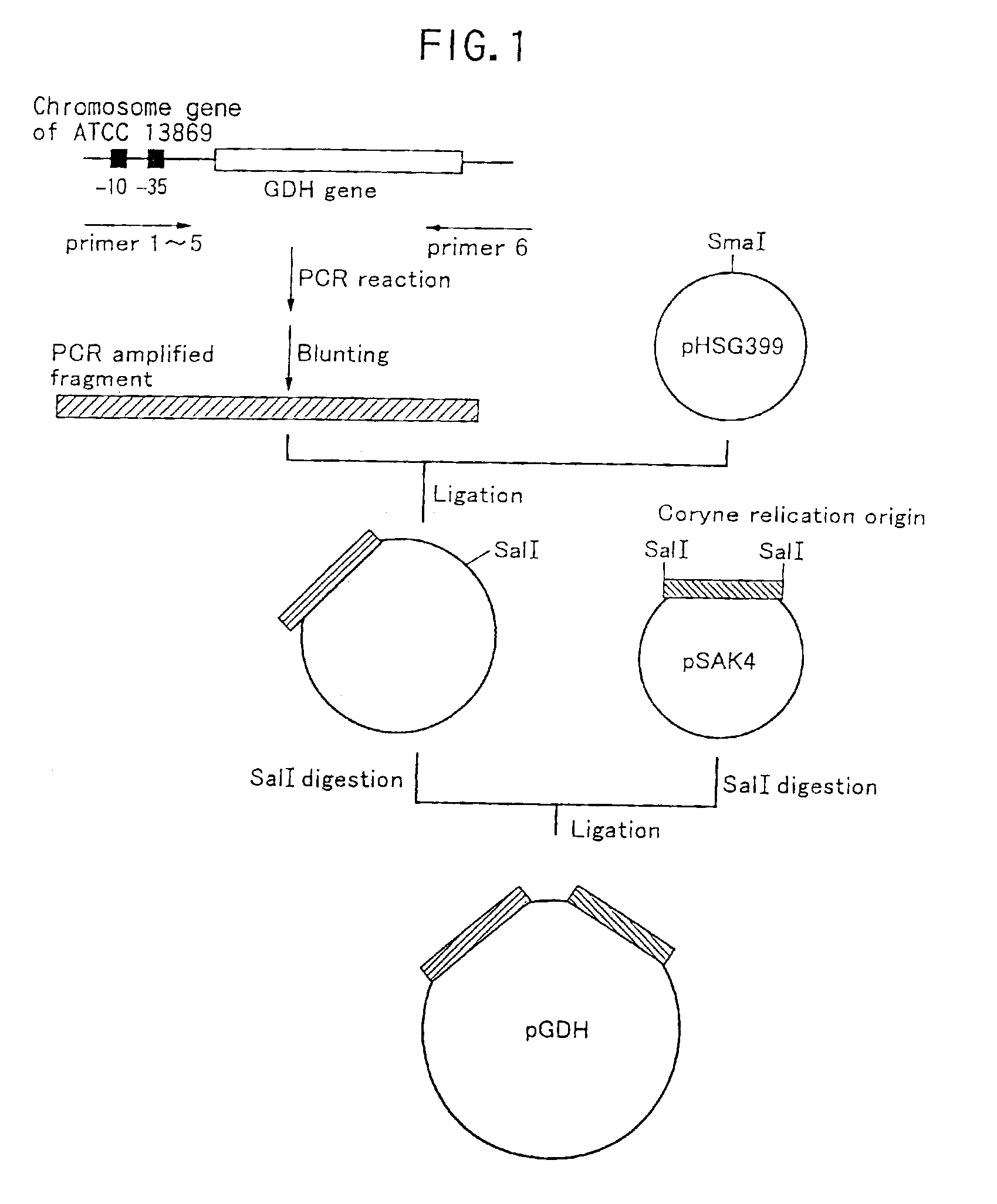
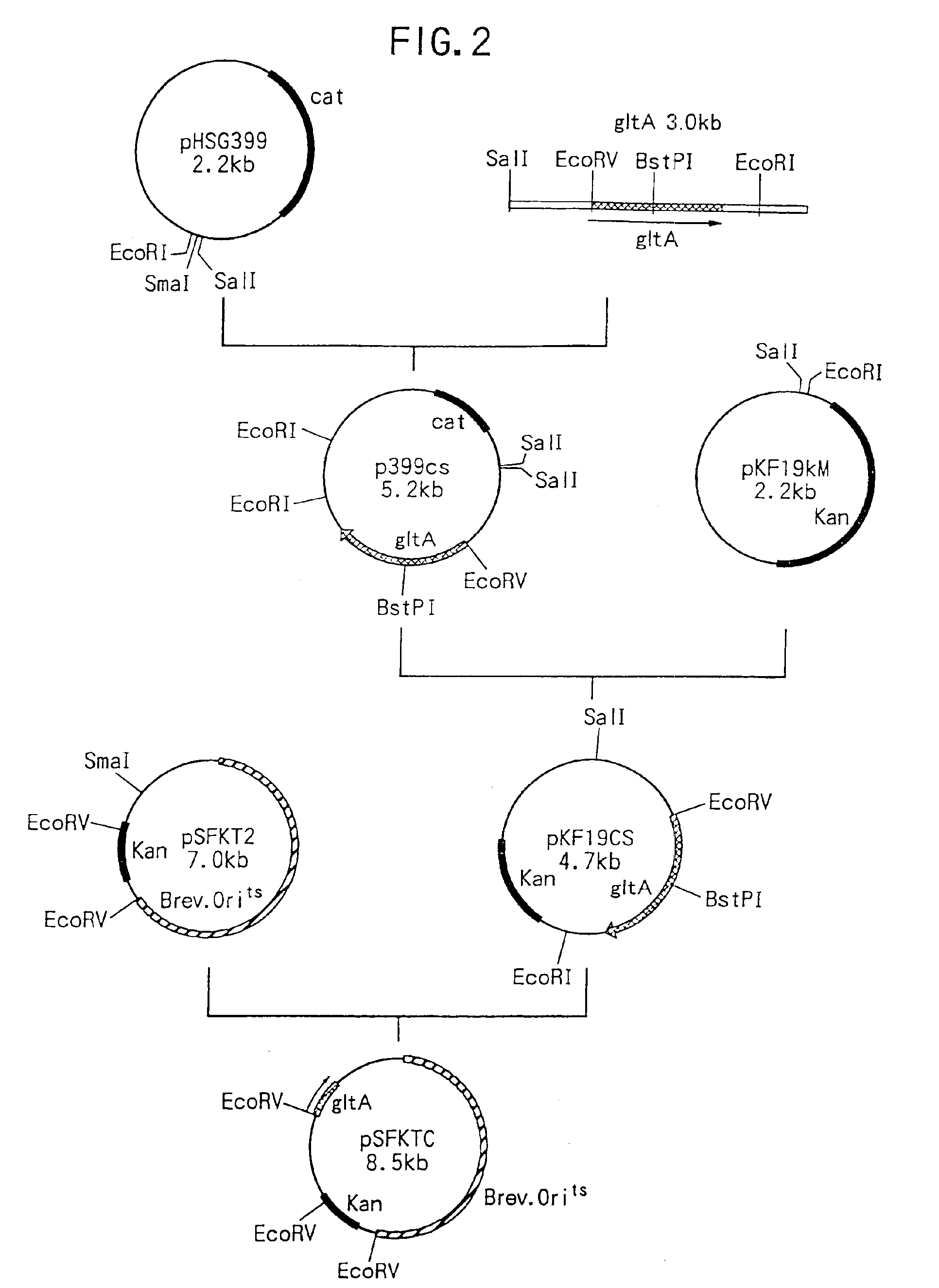
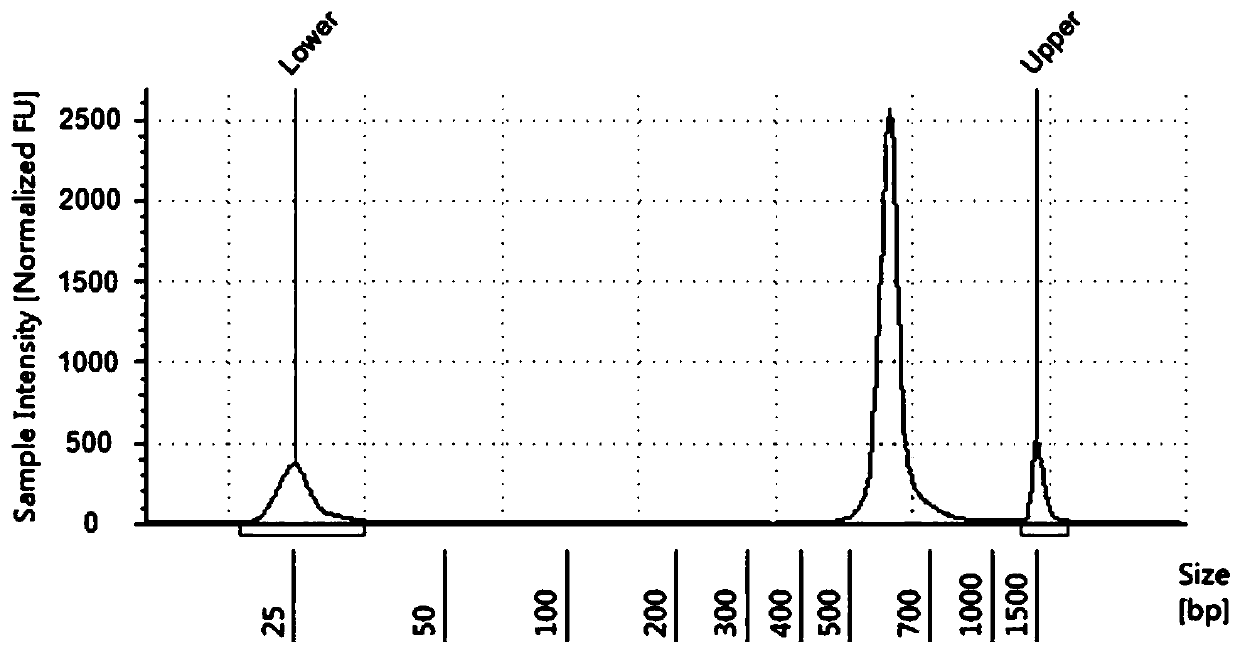
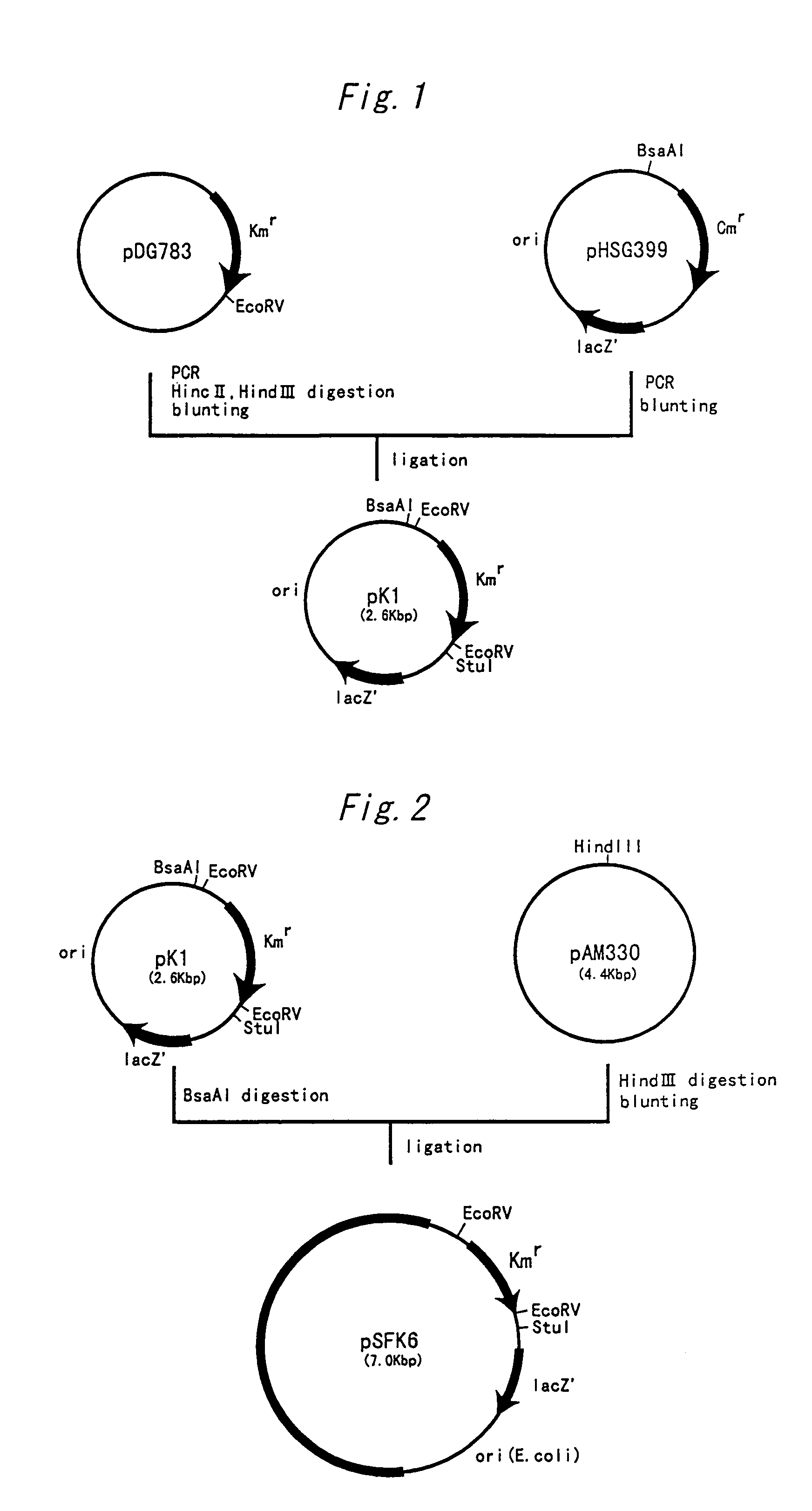
Patents
Literature
175 results about "Corynebacterium amycolatum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Corynebacterium amycolatum is a Gram-positive, non-spore-forming, aerobic or facultatively anaerobic bacillus capable of fermentation with propionic acid as the major end product of its glucose metabolism. One of its best known relatives is Corynebacterium diphtheriae, the causative agent of diphtheria. C. amycolatum is a common component of the natural flora found on human skin and mucous membranes, and as such, is often disregarded by physicians as a contaminant when found in blood cultures. However, C. amycolatum is actually an opportunistic pathogen capable of causing serious human disease such as endocarditis and sepsis.
Arginine repressor deficient strain of coryneform bacterium and method for producing L-arginine
InactiveUS20020045223A1Produced in advanceSugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensMicrobiology
L-Arginine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium in which an arginine repressor involved in L-arginine biosynthesis is deleted by disrupting a gene coding for the repressor, and which has L-arginine producing ability in a medium to produce and accumulate L-arginine in the medium, and collecting the L-arginine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method of constructing amino acid producing bacterial strains, and method of preparing amino acids by fermentation with the constructed amino acid producing bacterial strains
A method of producing coryneform bacteria having improved amino acid or nucleic acid productivity comprising the steps of introducing a mutation in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium to make it close to a consensus sequence, or introducing a change in a promoter sequence of amino acid- or nucleic acid-biosynthesizing genes on a chromosome of a coryneform bacterium by gene recombination to make it close to a consensus sequence, to obtain mutants of the coryneform amino acid- or nucleic acid-producing microorganism, culturing the mutants and selecting a mutant capable of producing the intended amino acid or nucleic acid in a large amount. This method allows the construction of a mutant capable of enriching or controlling the expression of an intended gene without using a plasmid and to promote production of amino acids in a high yield by recombination or mutation.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Mutant of homoserine dehydrogenase from Corynebacterium and DNA encoding thereof
Novel polynucleotides derived from microorganisms belonging to coryneform bacteria and fragments thereof, polypeptides encoded by the polynucleotides and fragments thereof, polynucleotide arrays comprising the polynucleotides and fragments thereof, recording media in which the nucleotide sequences of the polynucleotide and fragments thereof have been recorded which are readable in a computer, and use of them.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
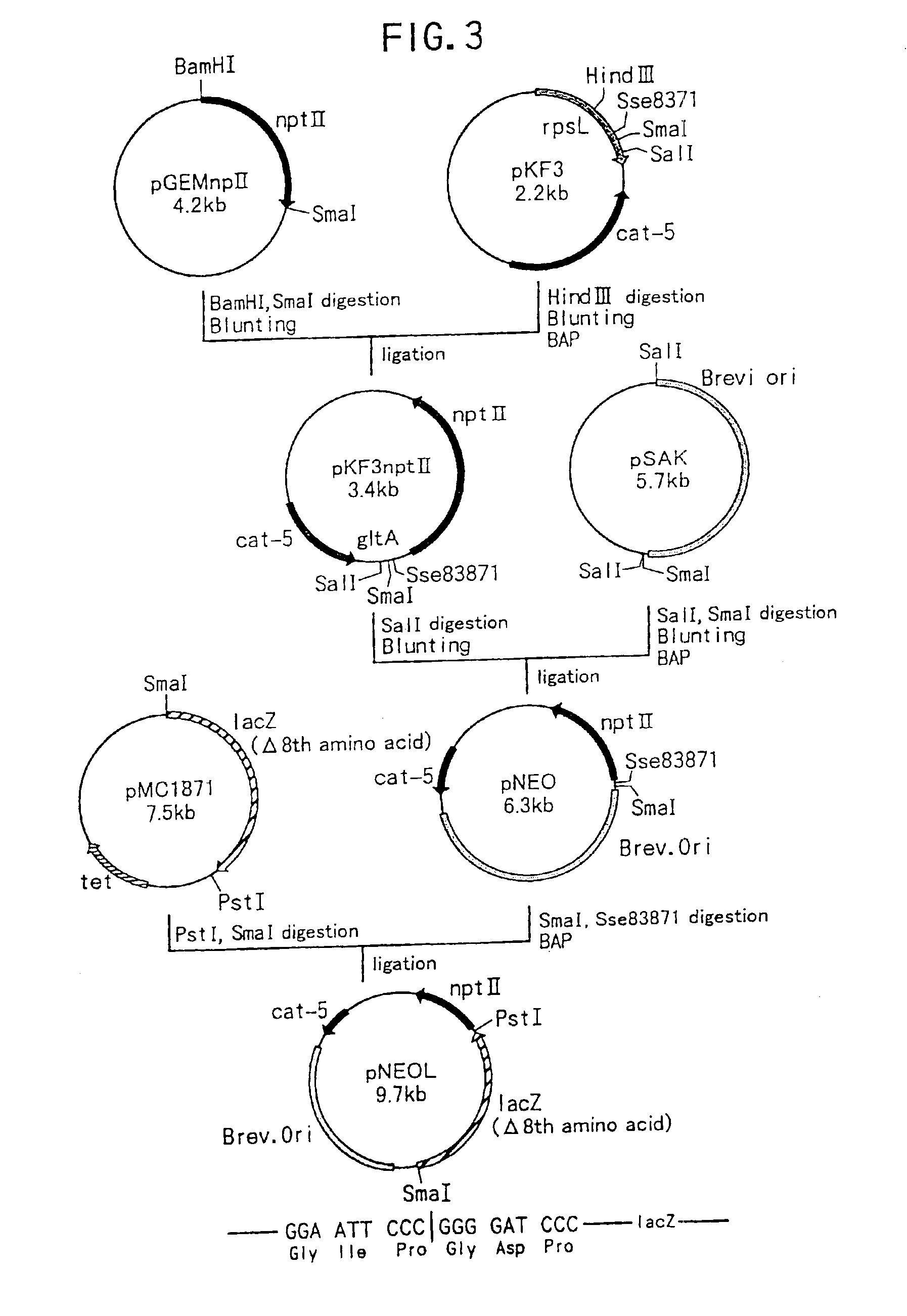
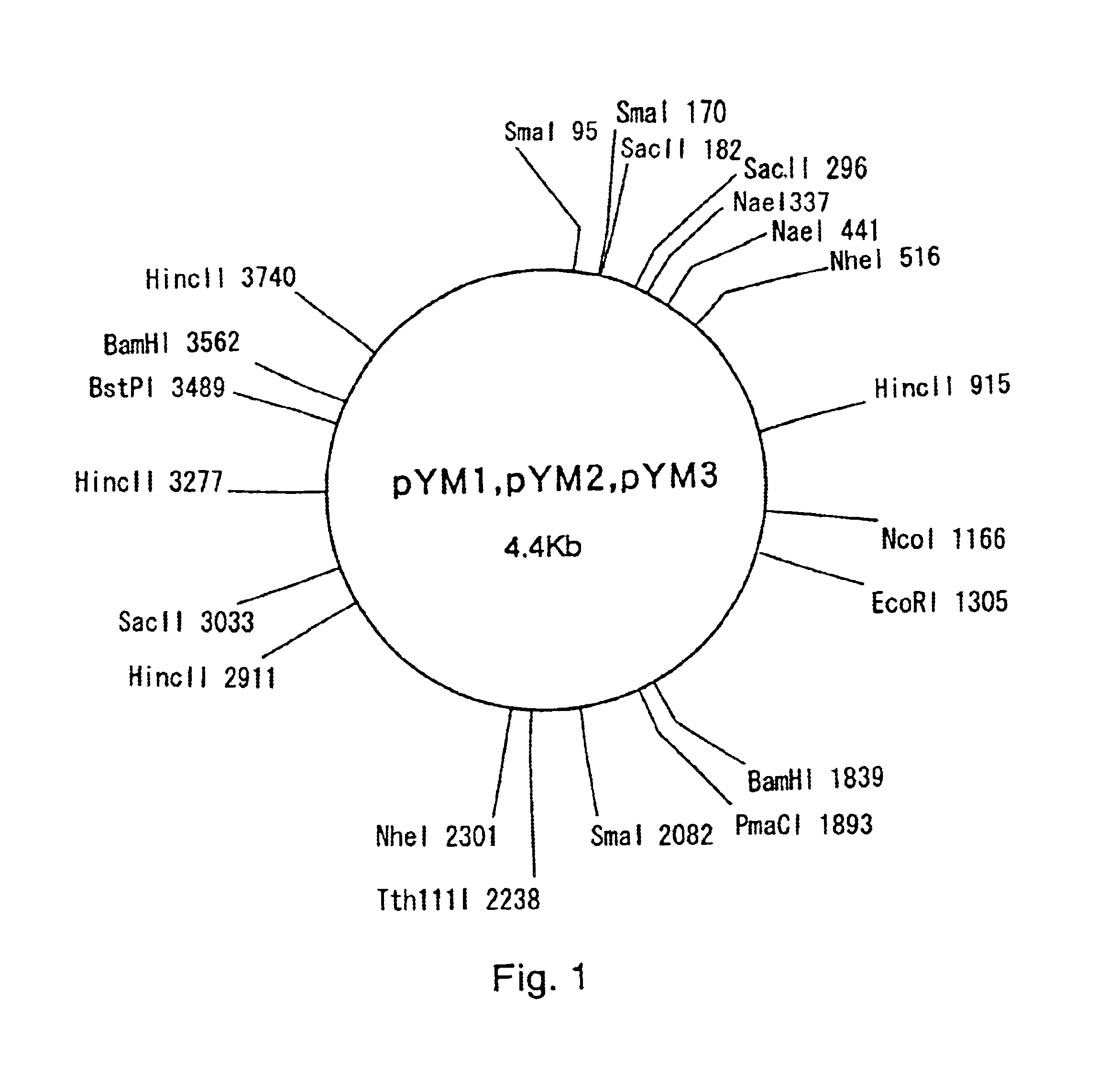
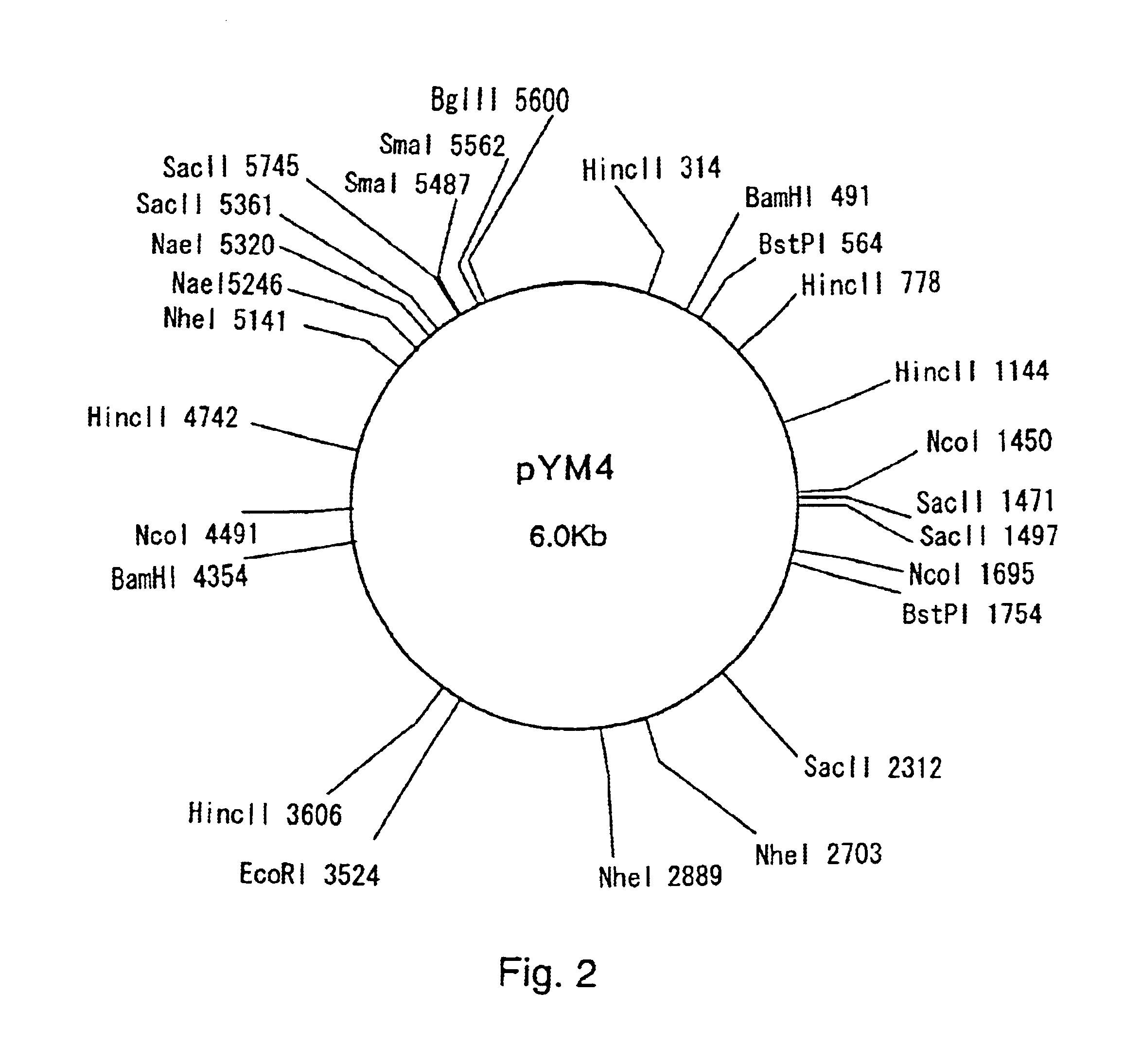
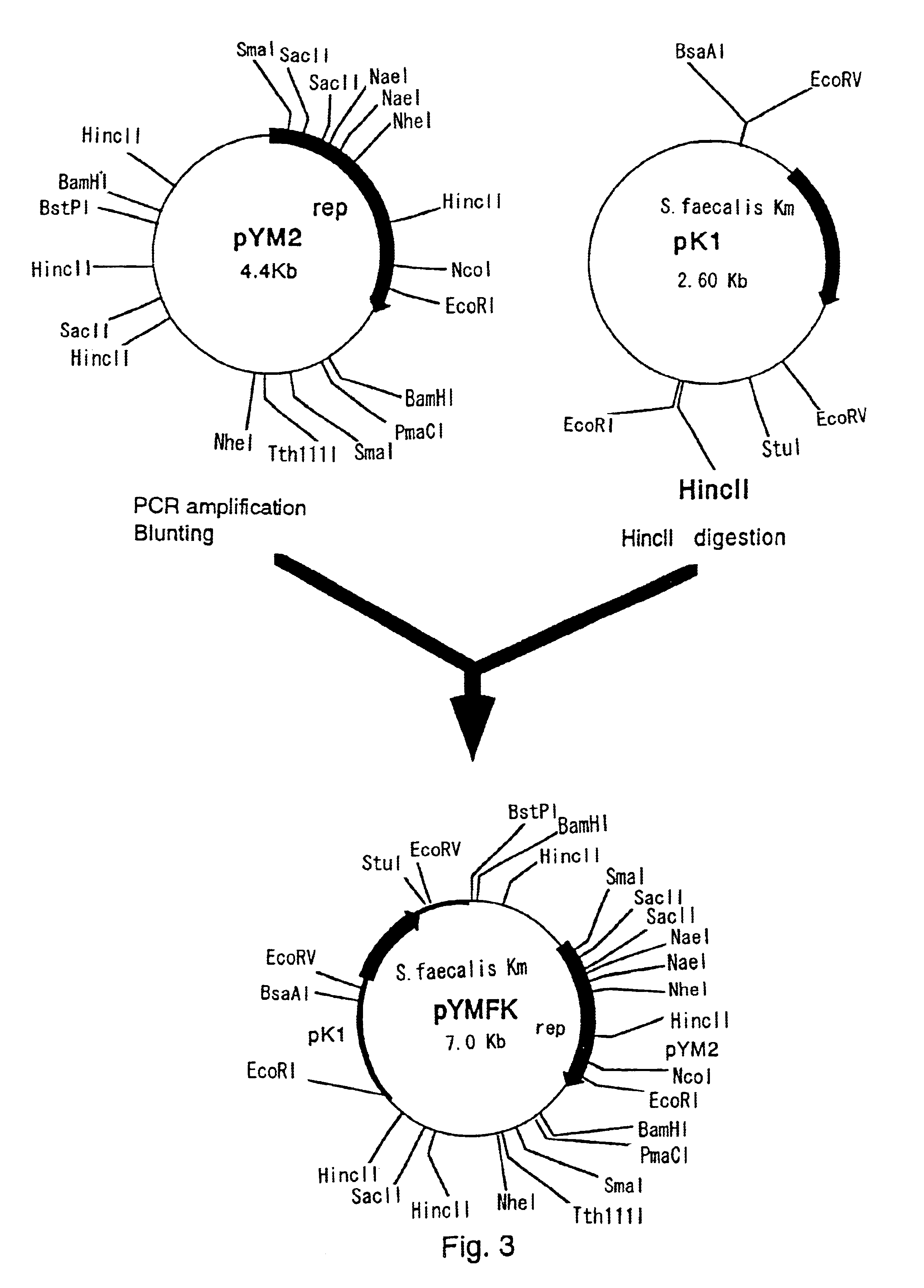
Plasmid autonomously replicable in coryneform bacteria
InactiveUS6905819B1Easy to optimizeImproving a coryneform bacteriumBacteriaSugar derivativesCorynebacterium amycolatumAmino acid
A plasmid which is able to be isolated from Corynebacterium thermoaminogenes, and which comprises a gene coding for a Rep protein having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4 or an amino acid sequence having homology of 90% or more to the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 4. and has a size of about 4.4 kb or about 6 kb, or a derivative thereof.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
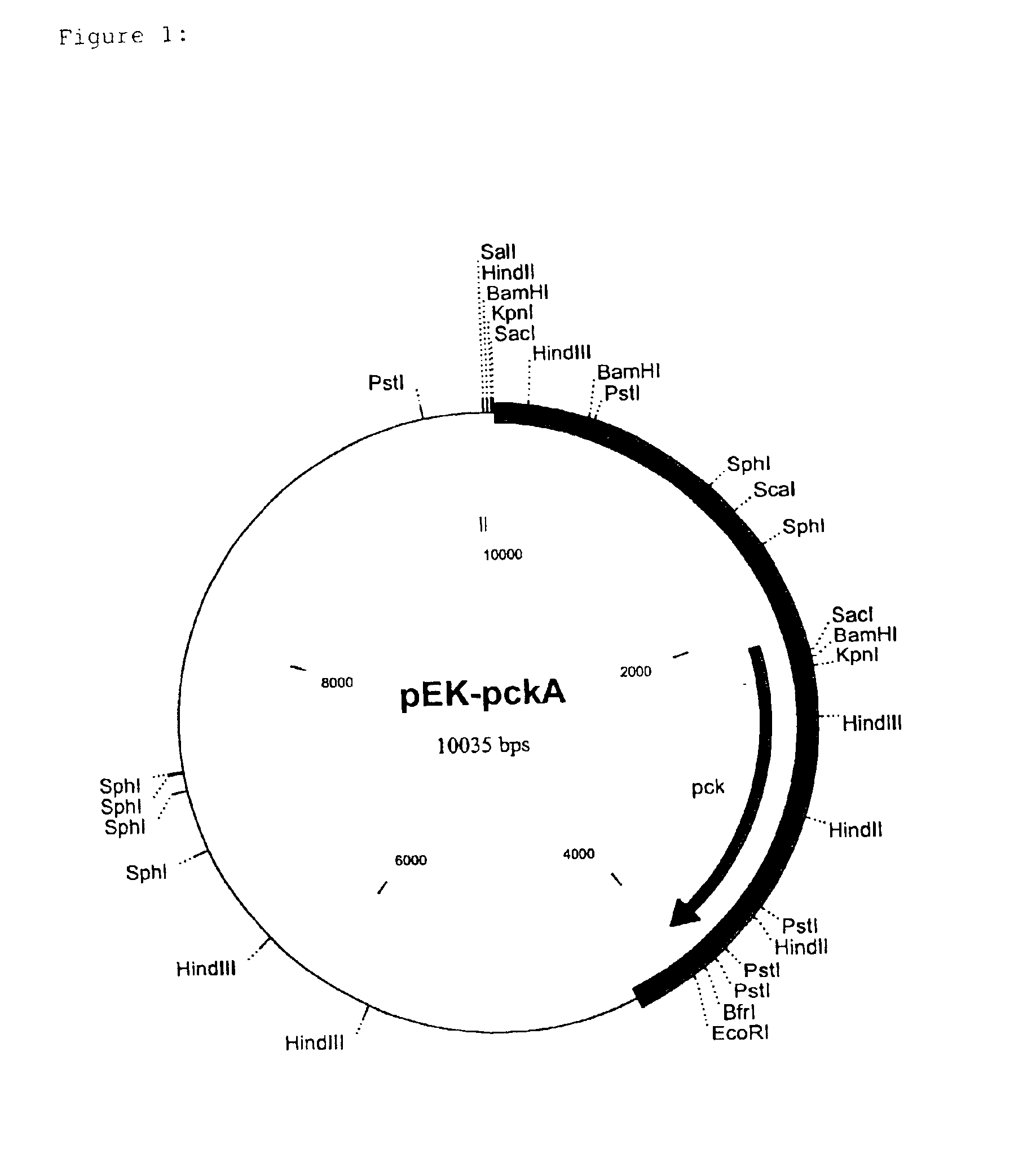
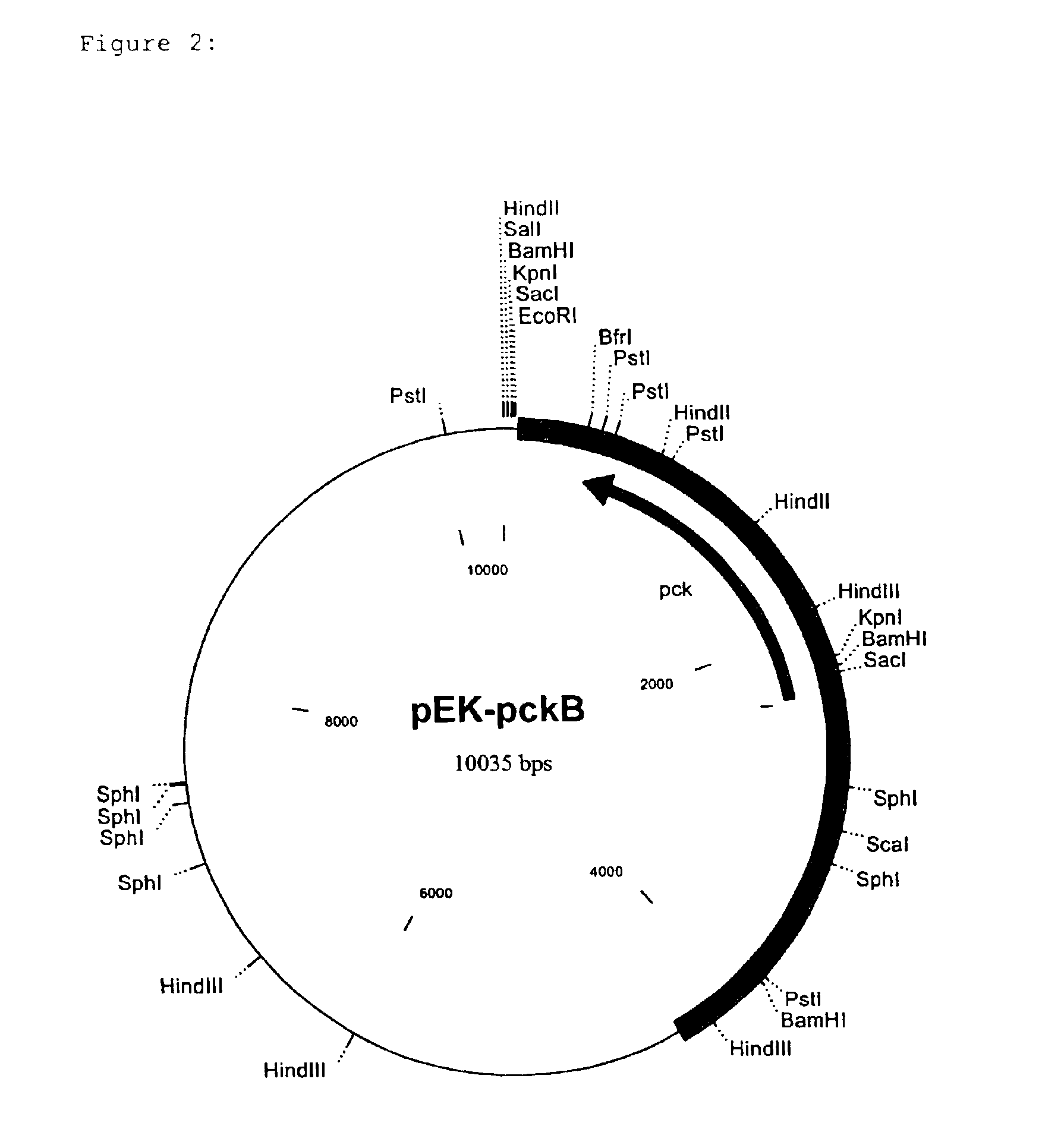
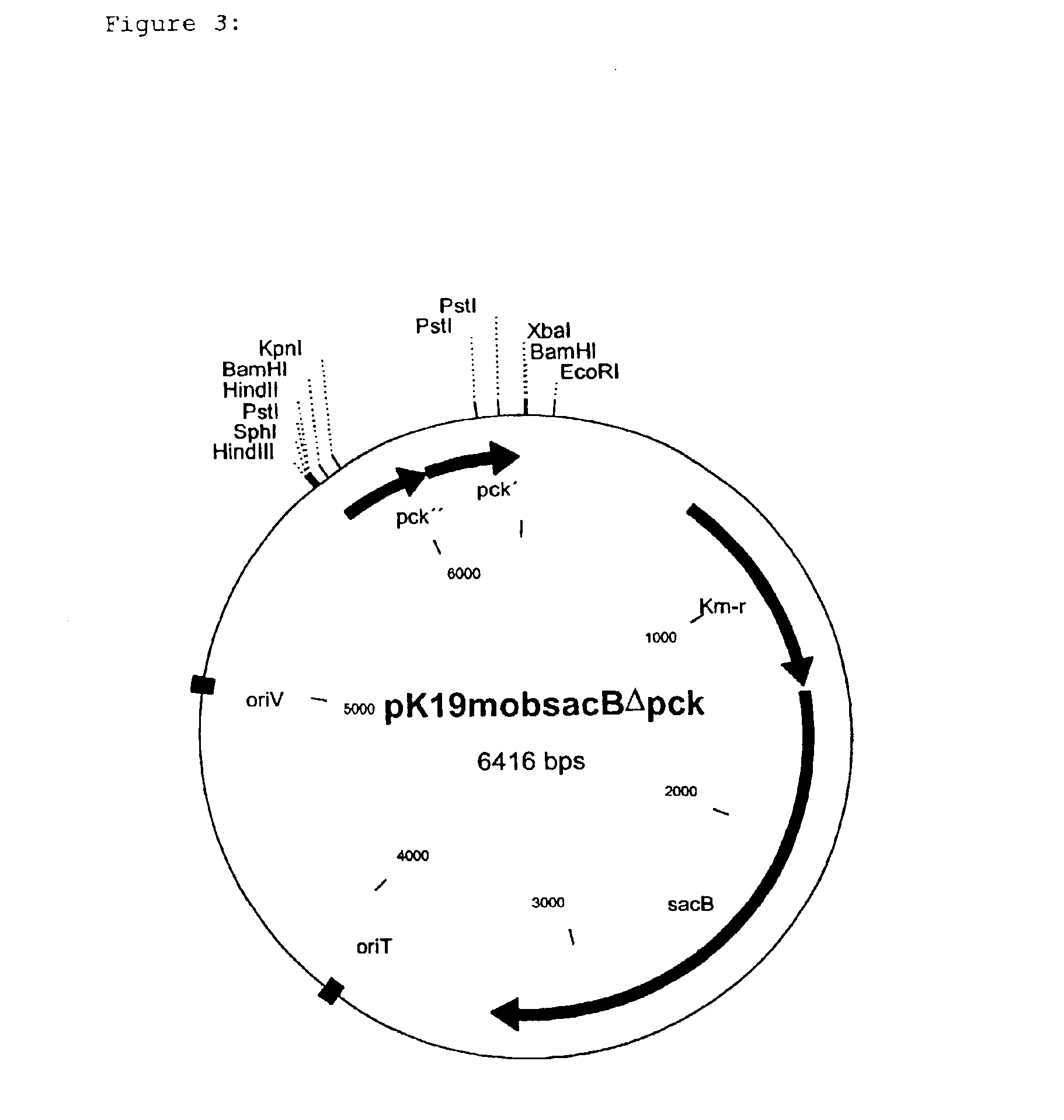
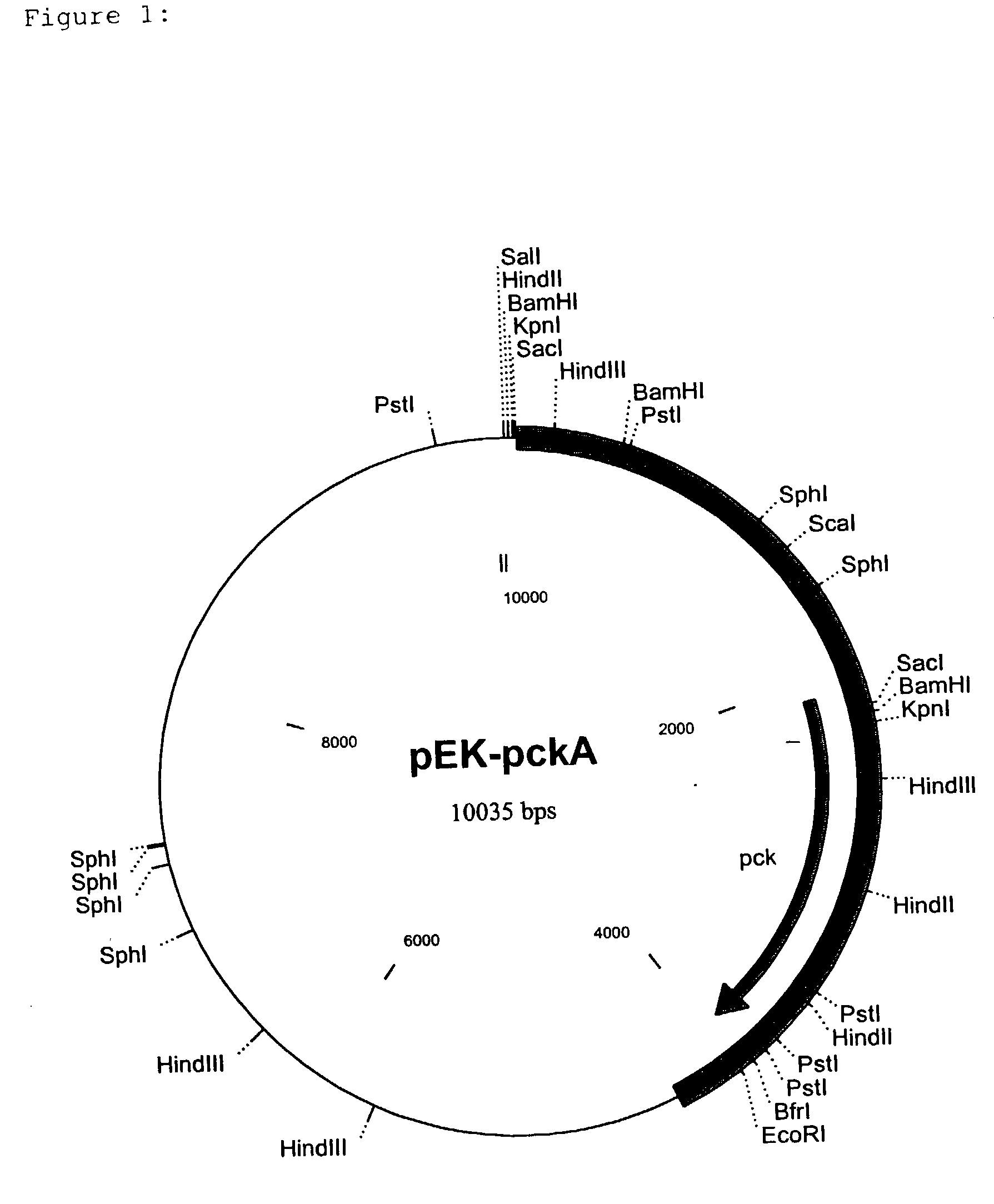
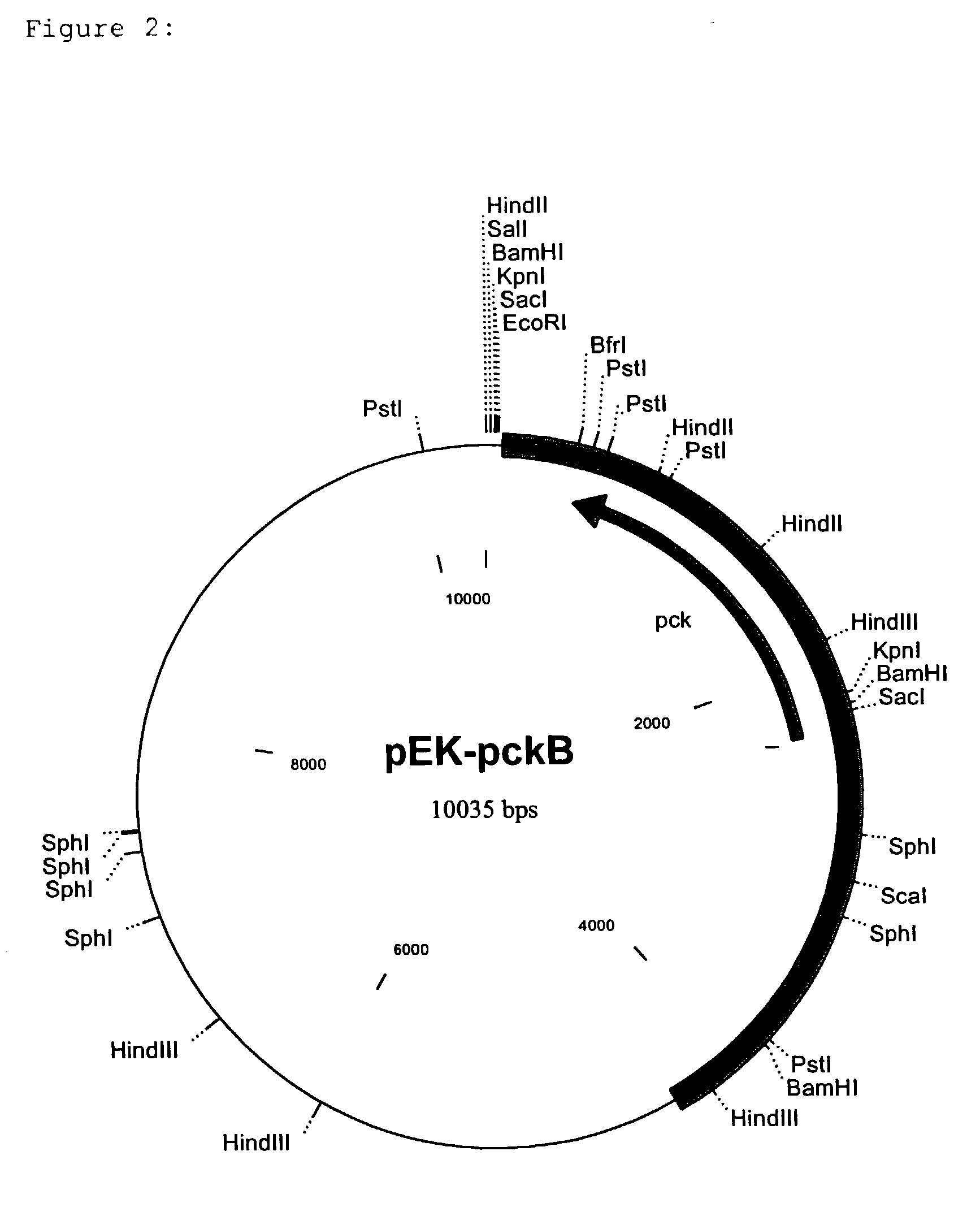
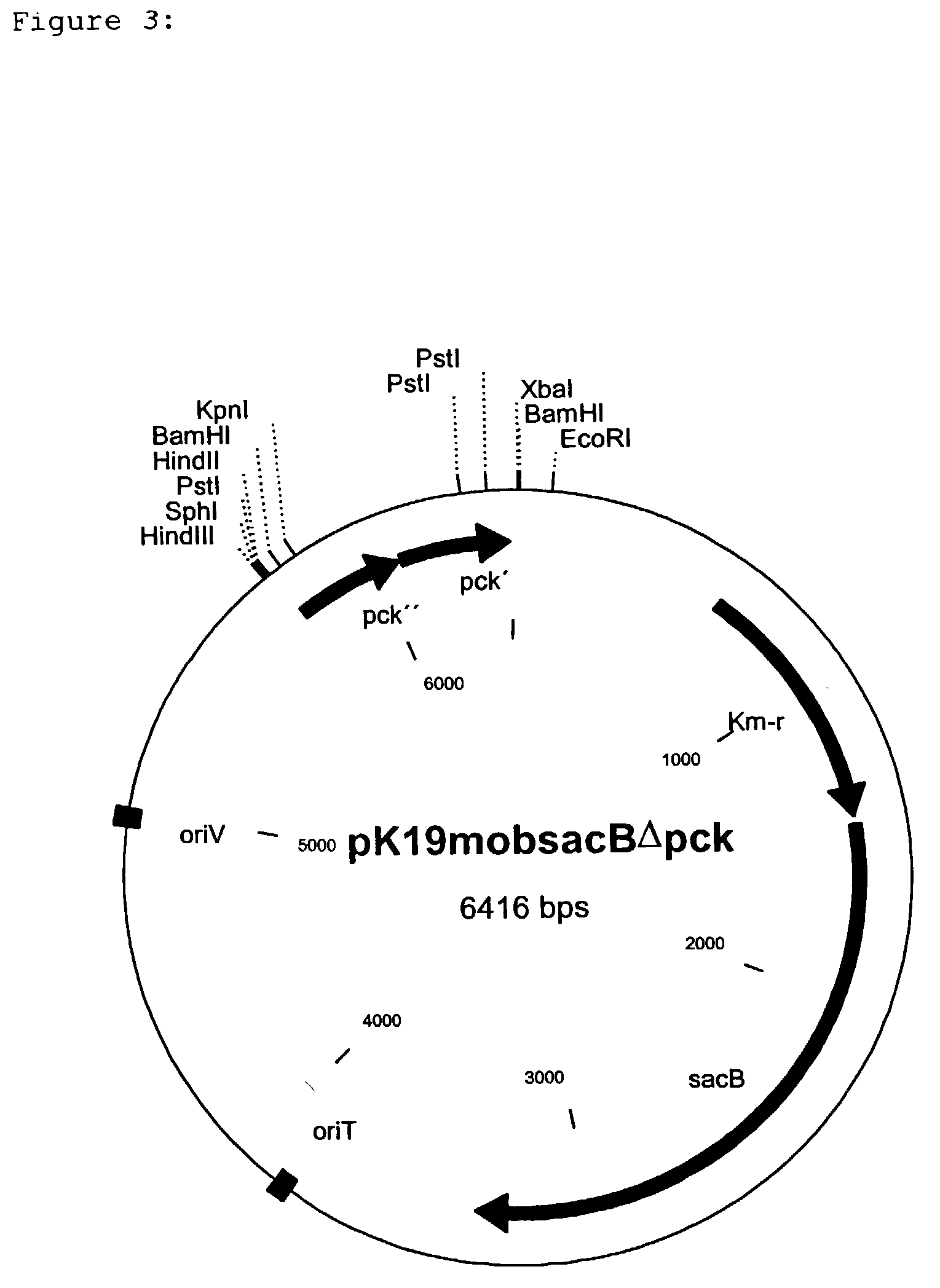
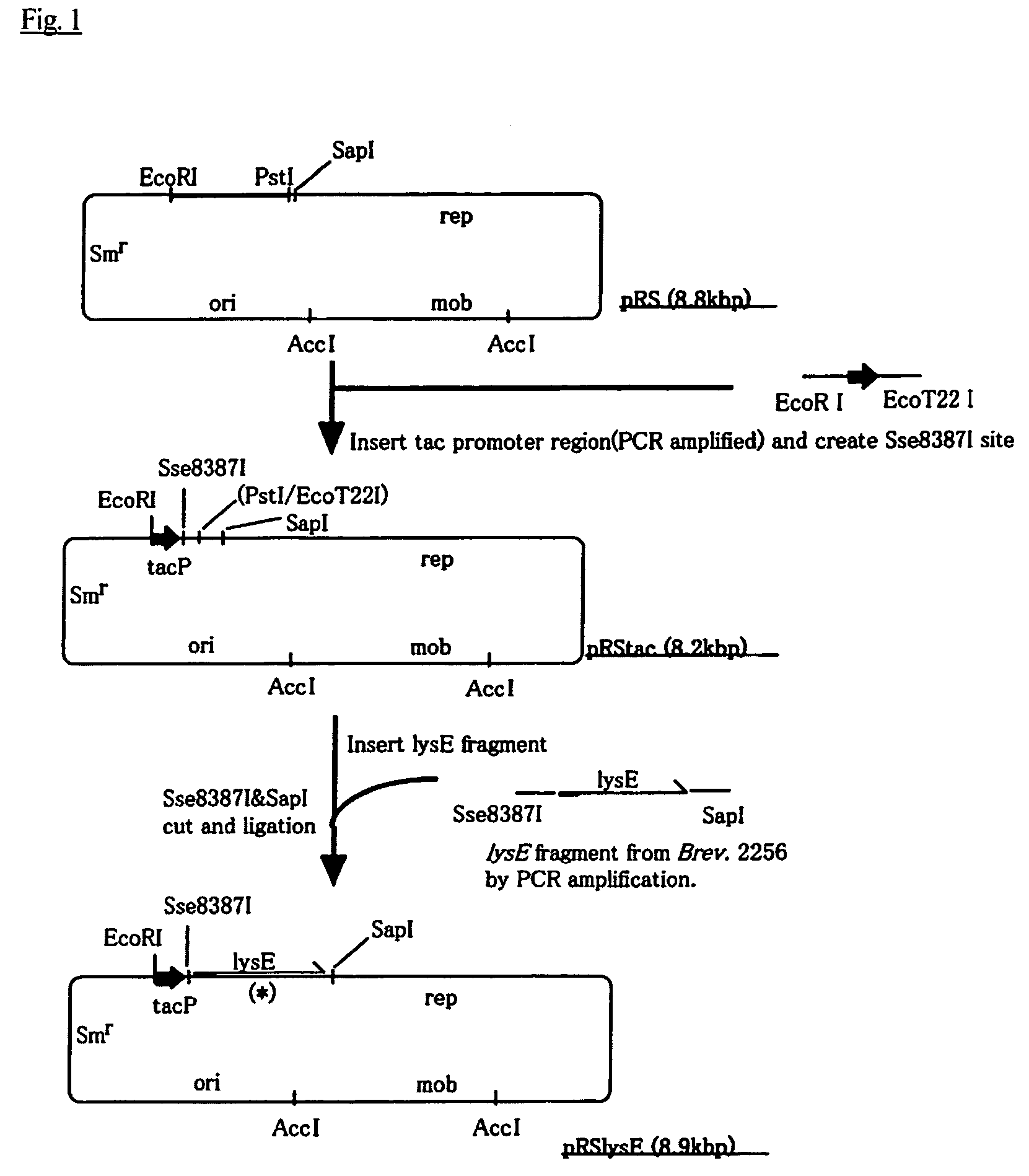
Nucleotide sequences which code for the pck gene
The invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences from Coryneform bacteria which code for the pck gene encoding the enzyme phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEP carboxykinase). The invention also relates a process for the fermentative preparation of L-amino acids, in particular L-lysine, L-threonine, and L-glutamate by attenuation of the pck gene.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
Alleles of the zwf gene from coryneform bacteria
The invention relates to mutants and alleles of the zwf gene of coryneform bacteria, which encode variants of the Zwf subunit of glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC: 1.1.1.49), and to processes for preparing amino acids, in particular L-lysine and L-tryptophan, by using bacteria which harbor said alleles.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
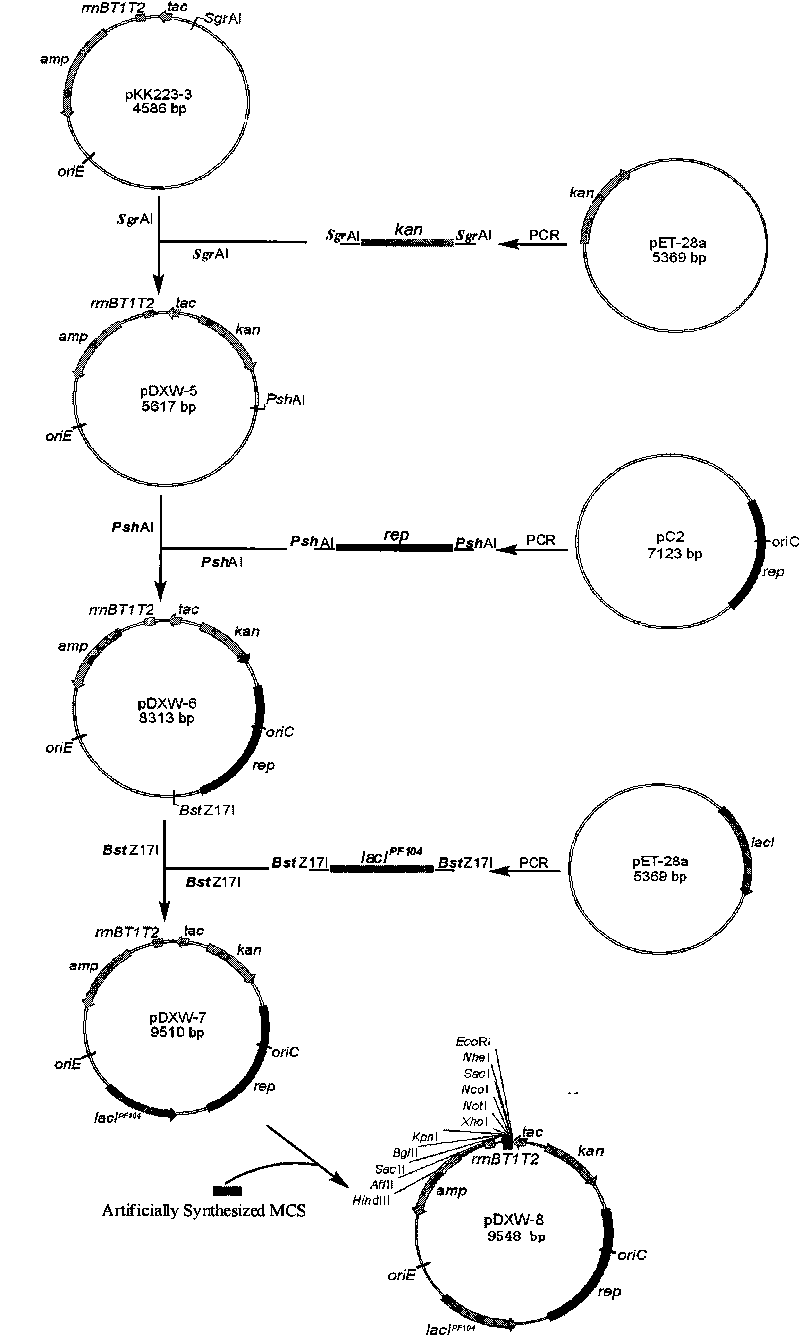
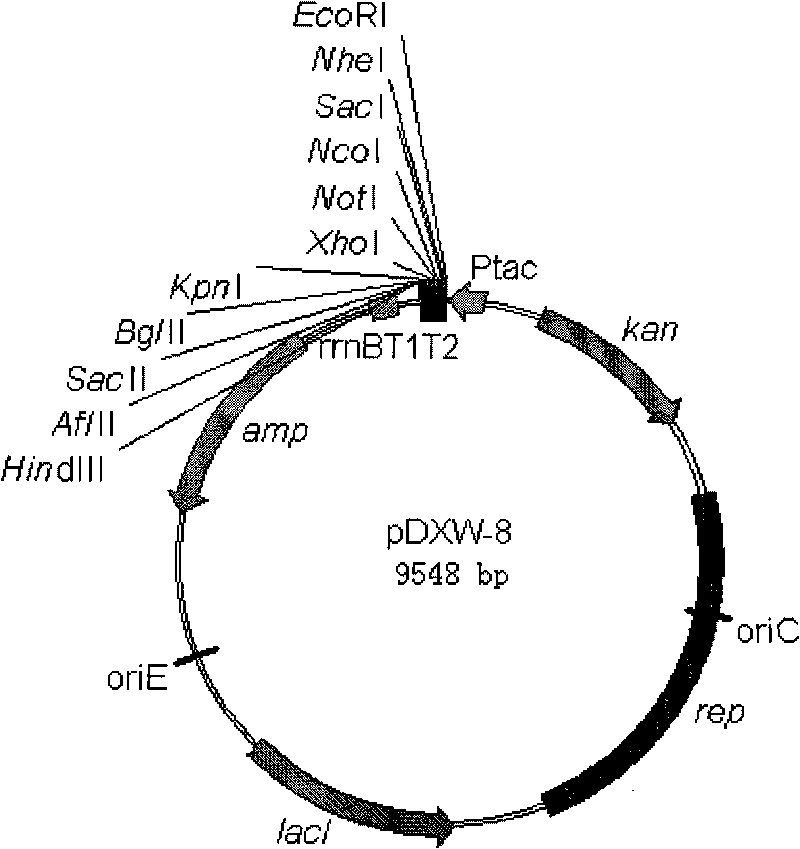
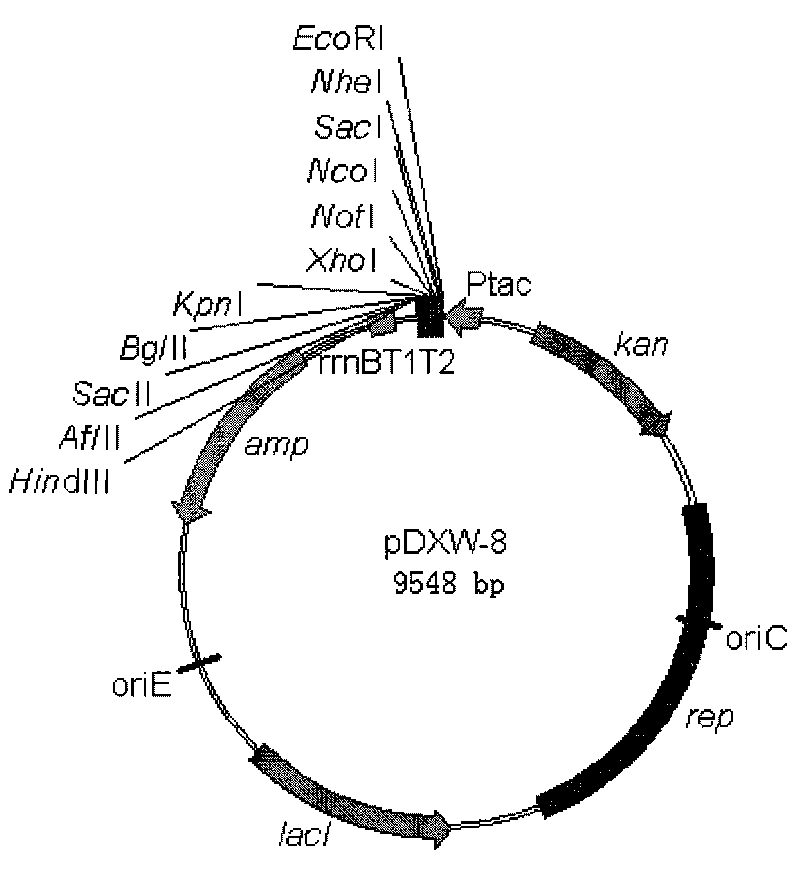
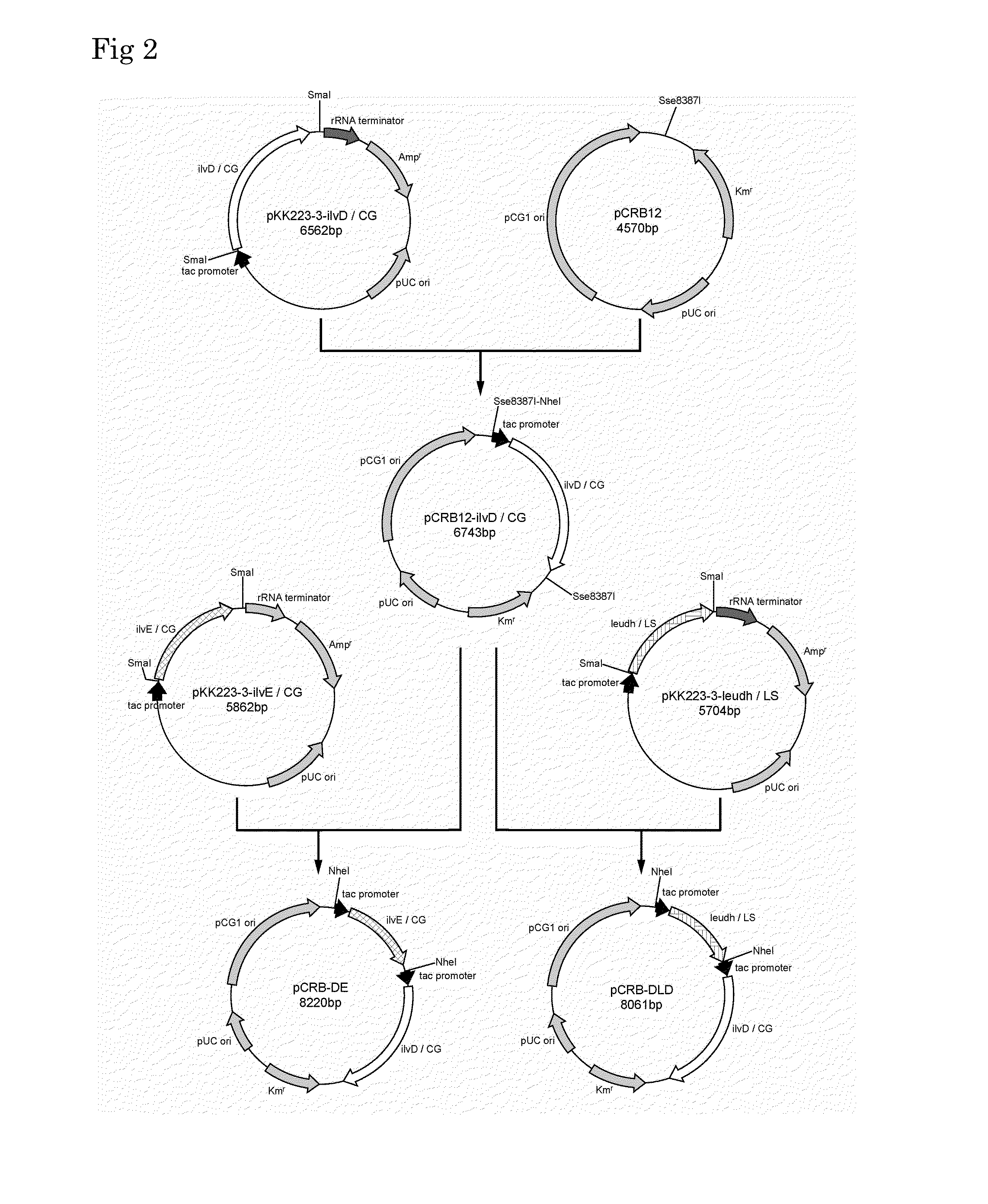
Colibacillus-corynebacterium inducible expression carrier pDXW-8 and building method thereof
ActiveCN101693901AEffective cloningReduced activityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionCorynebacterium efficiensEscherichia coli
A colibacillus-corynebacterium inducible expression carrier pDXW-8 and a building method thereof belong to the technical field of genetic engineering. The inducible expression carrier pDXW-8 can be copied and stably exists in colibacillus and corynebacterium and comprises a tac promoter, a terminator rrnBT1T2, a resistance marker card kanamycin mark resistance gene, a negative regulation gene laclPE104 and a multi-cloning site, wherein the tac promoter plays a transcript promoting function in the colibacillus and the corynebacterium, the terminator rrnBT1T2 has a transcript stopping function, the resistance marker card kanamycin mark resistance gene is used for selecting transformants of the corynebacterium, the negative regulation gene is used for severely controlling expression of the tac promoter, and the multi-cloning site includes 11 signal limited incision enzyme sites. In the corynebacterium, the carrier is moderate in foreign protein expression, and is particularly adaptable to study on corynebacterium metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods for secretory production of proteins
The object of the present invention is to provide a method of producing a heterologous protein by making a coryneform bacterium to produce and efficiently extracellularly secrete (secreto-production) an industrially useful heterologous protein. According to the present invention, a genetic construct is used where a gene sequence encoding an intended protein which is ligated to the downstream of a sequence encoding the signal peptide derived from a coryneform bacterium, the gene construct is introduced into a mutant coryneform bacterium which has a capacity of secreting the heterologous protein at least 2-fold higher than the wild type Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13869, the mutant coryneform bacterium is cultured and the extracellularly released heterologous protein is recovered.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for the Fermentative Production of L-Amino Acids With the Aid of Coryneform Bacteria Capable of Using Glycerin as the Only Carbon Source
ActiveUS20080293100A1Simple methodInexpensive mannerBacteriaFermentationCorynebacterium amycolatumPolynucleotide
The invention relates to a method for producing L-amino acids in which the following steps are carried out: a) the recombinant coryneform bacteria which produce the desired L-amino acid and in which at least one or several of the heterologous polynucleotides of the glycerol metabolism, selected among the group comprising glpA, glpB, glpC, glpD, glpE, glpF, glpG, glpK, glpQ, glpT, glpX, gldA, dhaK, dhaL, dhaM, dhaR, fsa, and talC, is / are expressed are cultivated in a medium containing glycerol or one or several other optional C sources in conditions in which the desired L-amino acid is enriched in the medium or the cells; and, optionally, b) the desired L-amino acid is isolated, all or fractions (>0 to 100 percent) of the components of the fermentation broth and / or biomass optionally remaining in the final product. In said method, bacteria are used in which other genes of the biosynthesis pathway of the desired L-amino acid are additionally reinforced or in which the metabolism pathways reducing the formation of the desired L-amino acid are eliminated at least in part.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Process for producing useful substance
The present invention provides a process for efficiently producing a useful substance; and a microorganism which belongs to coryneform bacteria and which can be used in the process. The present invention provides a process for producing a useful substance by using a microorganism belonging to coryneform bacteria, the microorganism having an ability to take a sugar, which is taken into a cell via a phosphotransferase system (PTS), into a cell via a system other than the PTS, and having an ability to produce a useful substance.
Owner:SHINSHU UNIVERSITY +1
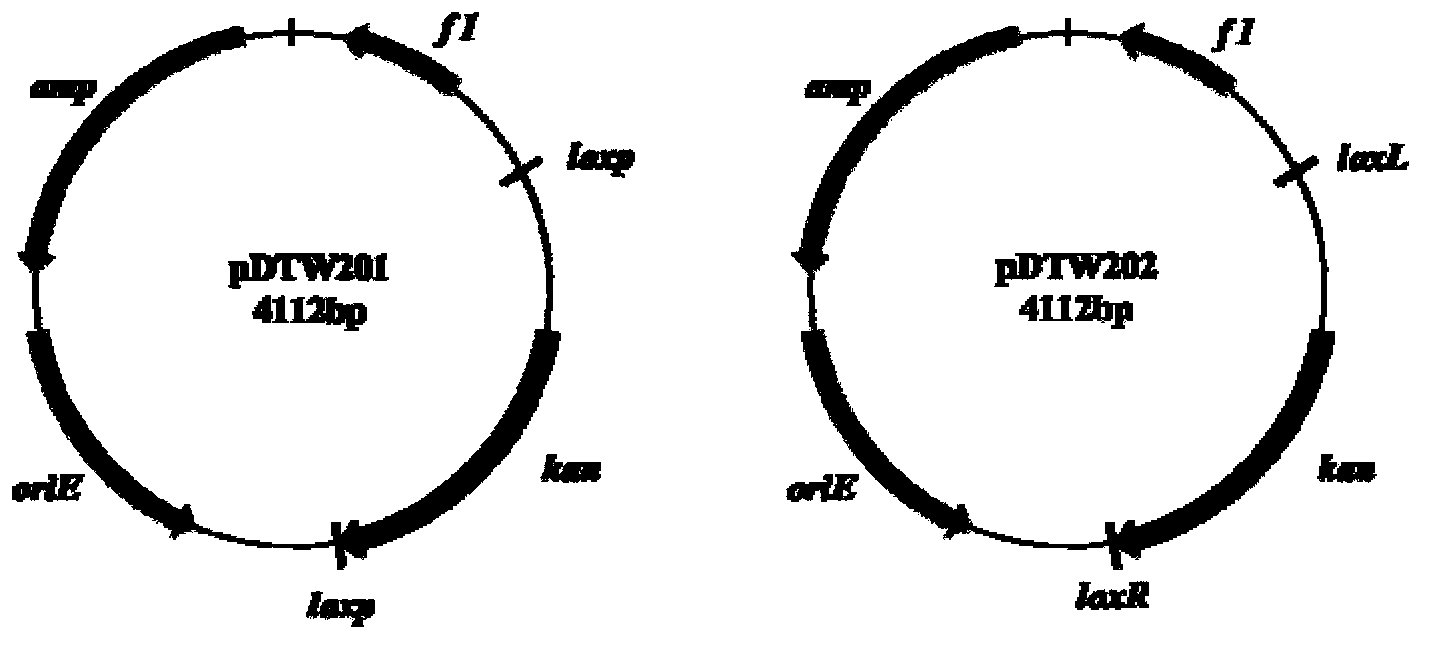
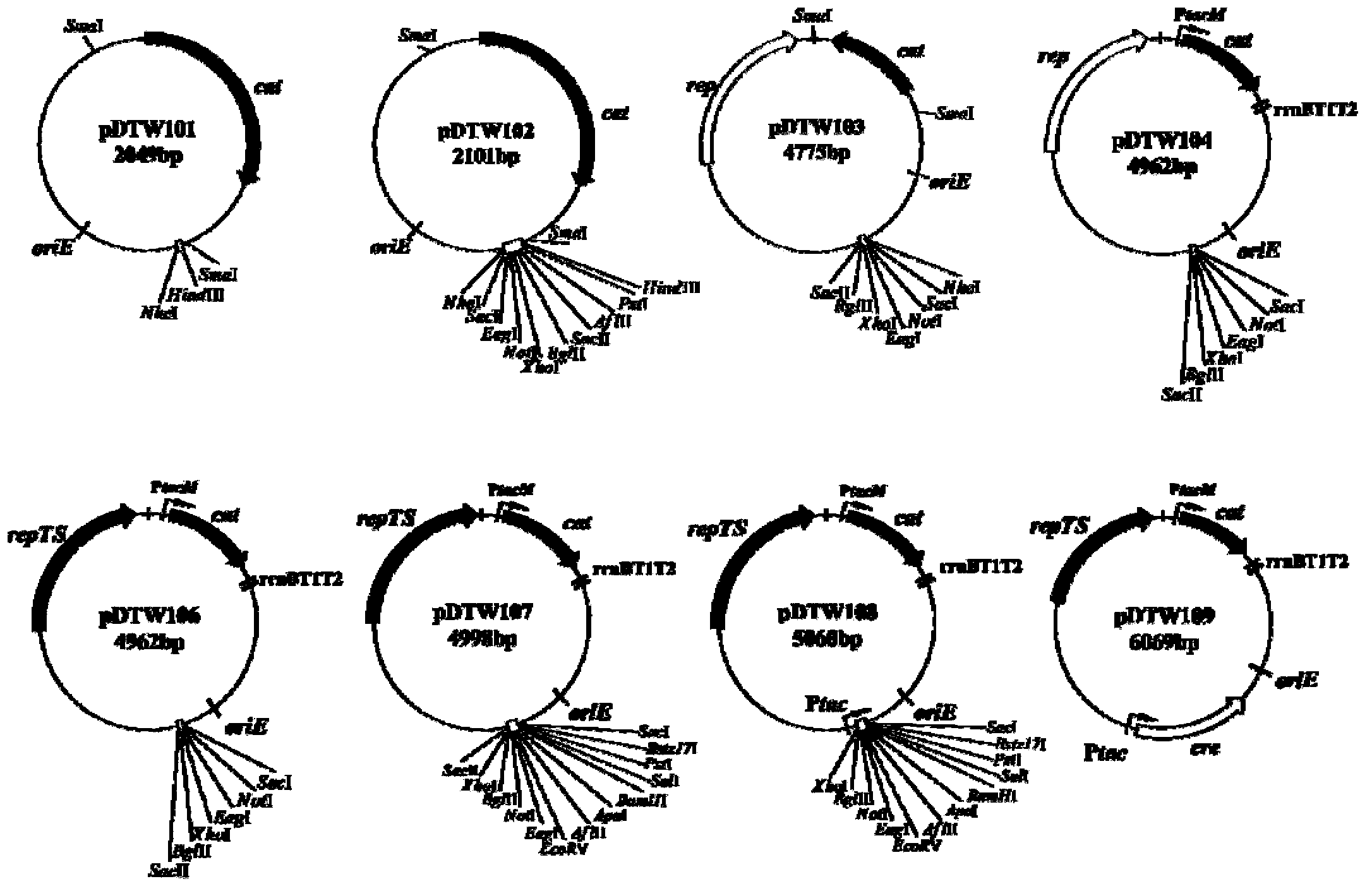
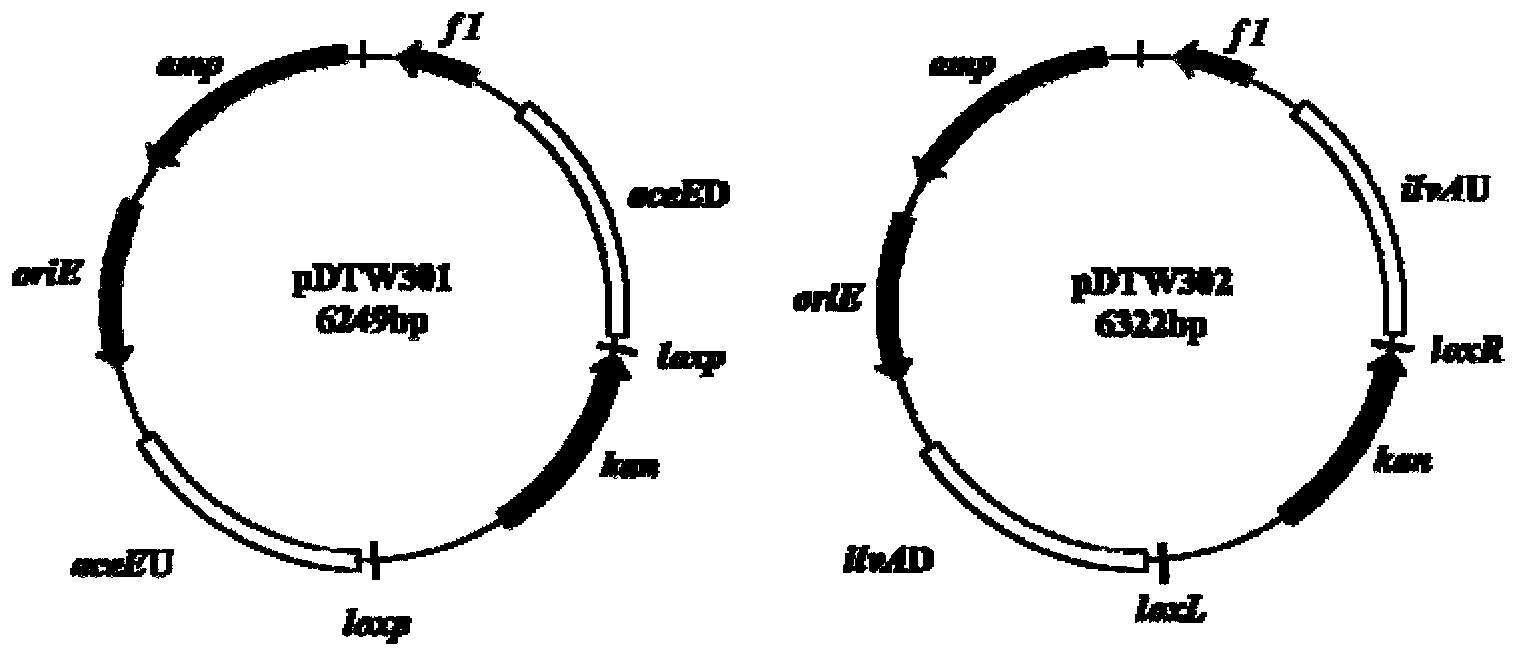
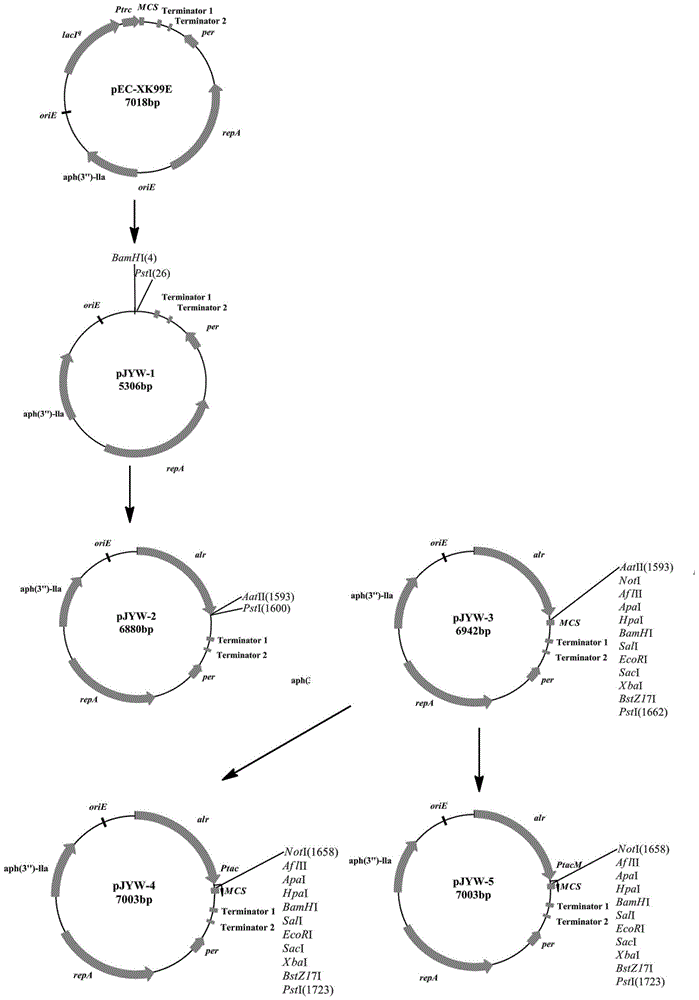
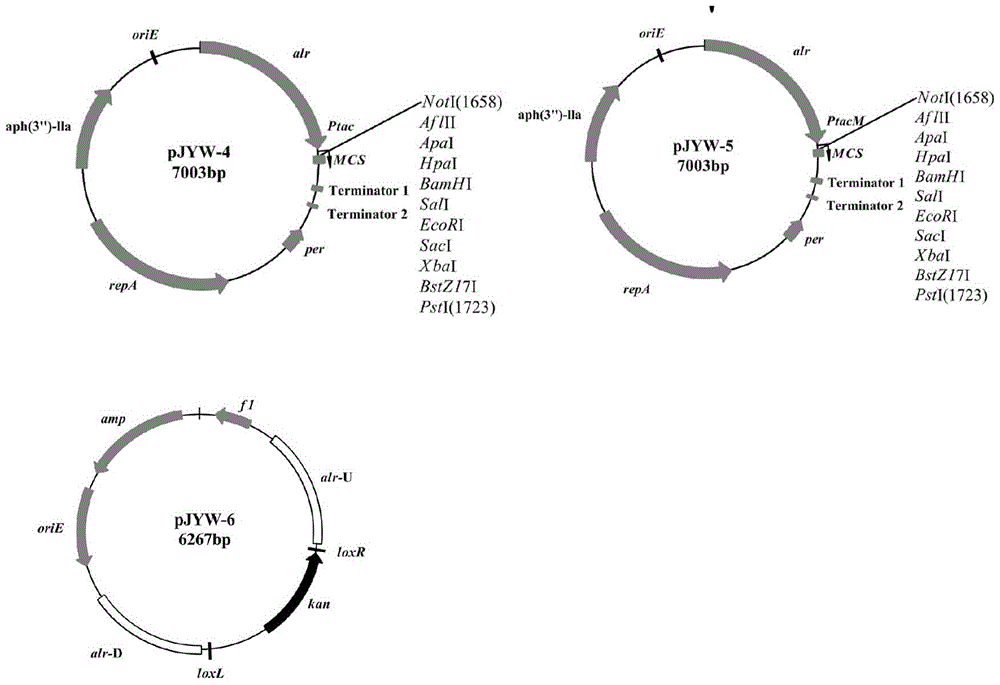
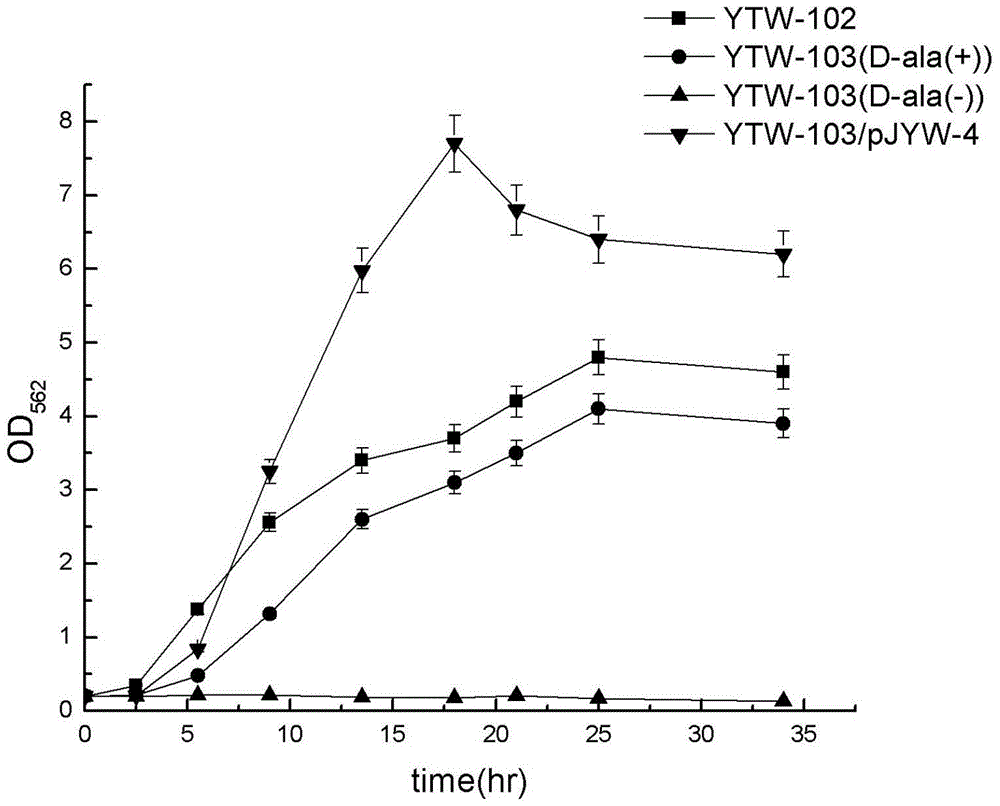
Corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, as well as construction method and application thereof
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of a corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system, belonging to the technical field of genetic engineering. The corynebacterium gene continuous knockout system comprises a template plasmid and a temperature-sensitive expression plasmid, wherein the template plasmid provides a kan fragment (also known as a kan box) with loxp or variant loxL / R sites at two ends; and the temperature-sensitive expression plasmid carries a Cm resistance gene cat and a temperature-sensitive C. glutamicum replicon, expresses a Cre recombinant enzyme and is used for removing a Km resistance gene kan. The corynebacterium continuous knockout system disclosed by the invention can be generally used for continuous gene transformation of corynebacterium and has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation and high efficiency. By utilizing the knockout system, gene (continuous) knockout of three major typical subspecies genomes of the corynebacterium can be successfully completed, and the system is proved to be applicable to research and production of corynebacterium metabolites.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Composition comprising a carrier and a purified mycobacterial lipid cell-wall component and its use in the treatment and diagnosis of disease
InactiveUS7122577B1Improve the immunityReduce sensitivityBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsCorynebacterium amycolatumPharmaceutical preservatives
A composition including a purified lipid cell-wall component or analog or derivative thereof and a suitable pharmaceutical carrier, medium, excipient or adjuvant is described. The composition is useful in prophylactic and therapeutic methods of treating a microbial infection in a subject, typically a mycobacterial infection such as tuberculosis, and immune disorders, inflammatory conditions and allergies in a subject, typically autoimmune diseases. It is also useful in diagnostic methods. The purified lipid cell-wall component is typically a purified mycolic acid or a mixture of purified mycolic acids from a bacterium which produces mycolic acids. The bacterium is from Mycobacterium, Corynebacterium, Nicardia or Rhodococcus.
Owner:ADCOCK INGRAM LTD
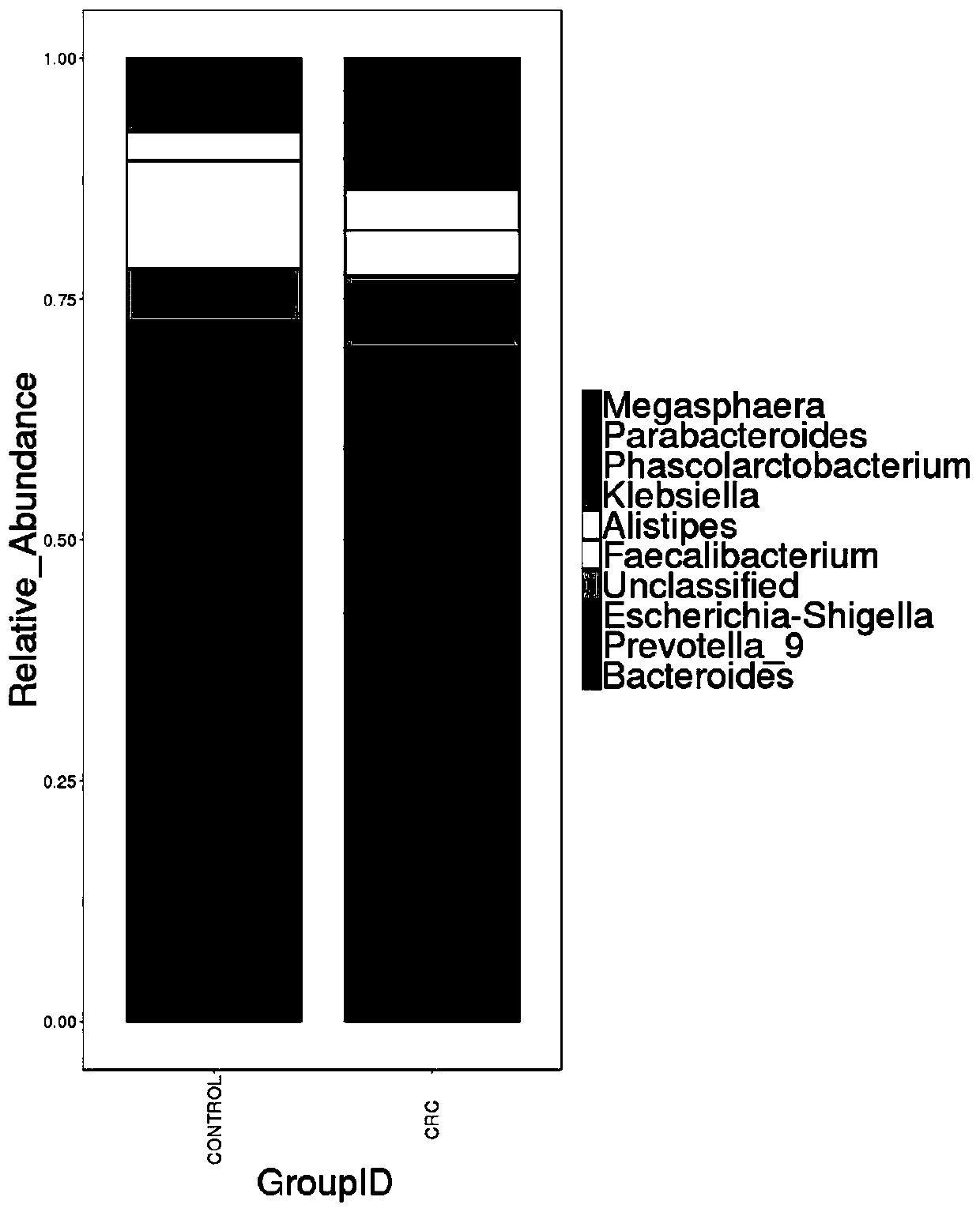
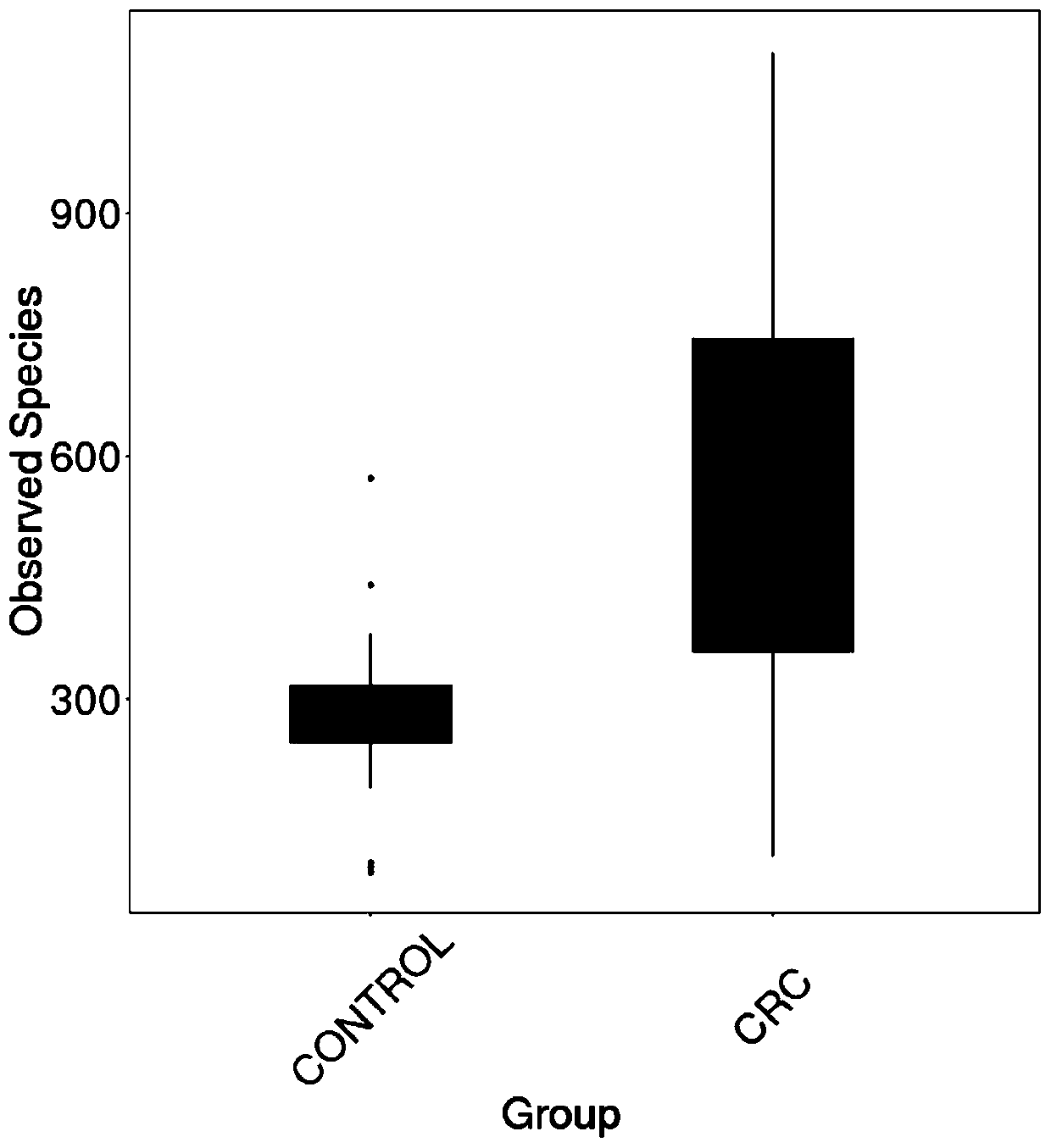
Intestinal flora maker for intestinal cancer and application of intestinal flora maker
InactiveCN110408699AGood forecastMicrobiological testing/measurementGut floraCorynebacterium amycolatum
The invention discloses an intestinal flora maker for intestinal cancer and an application of the intestinal flora maker, and belongs to the technical fields of microorganisms and genetic engineering.The intestinal flora maker comprises megasphaera, veillenella, streptococci, bilophila sp., haemophilus, corynebacterium or Escherichia-Shigella. Through detection by the intestinal flora maker, risks of individuals suffering from intestinal cancer can be assessed, and auxiliary reference can be provided for disease diagnosis and prognosis monitoring.
Owner:FUJIAN HEALTH COLLEGE
Immunomodulator, immunomodulator food
InactiveUS6506388B1Protection from damageLow viscosityOrganic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesDecomposition
An immunomodulator having suppressive activity on IgE antibody production is provided and contains bacterial cells, or their decomposition materials. It can be taken as a food. Bacterial cells such as Corynebacterium, Brevibacterium, Microbacterium, or bacterial cells of mutant strains of these bacteria, or decomposition products of these bacteria are used.
Owner:ASAMA CHEM +2
Arginine repressor deficient strain of coryneform bacterium and method for producing L-arginine
InactiveUS7160705B2Improve L-arginine productivitySugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensMicrobiology
L-Arginine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium in which an arginine repressor involved in L-arginine biosynthesis is deleted by disrupting a gene coding for the repressor, and which has L-arginine producing ability in a medium to produce and accumulate L-arginine in the medium, and collecting the L-arginine from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for producing xanthosine-5'-monophosphate by fermentation using mutant strains of Coryneform bacteria
InactiveUS20020098552A1Increase enzyme activitySuperior in pointBacteriaFermentationBacteroidesCorynebacterium efficiens
Xanthosine-5'-monophosphate is produced by cultivating the bacterium which has a resistance to growth inhibition by an inhibitor selected from the group consisting of inhibitors of cell membrane biosynthesis and / or functioning, phosphorylation inhibitors, uncoupling agents, RNA-polymerase inhibitors and methionine analogs, and has an ability to produce xanthosine-5'-monophosphate according to produce and accumulate xanthosine-5'-monophosphate in the culture, and recovering the xanthosine-5'-monophosphate therefrom.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Process for preparing acellular short corynebacteria preparation
InactiveCN1465401AGuaranteed pollutionBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaPresent methodCentrifugation
The present method of non-cell corynebacterium parvum (NCP) preparation includes the following steps: continuous 2-4 times of passage of corynebacterium parvum (CP) working seed batch strain, then inoculating in large flask or nutrient tank, culturing for 5-7 days in proper culture medium, collecting thallus having no heterobacteria pollution, heating, boiling and inactivating to obtain bacetrialsolution, breaking bacterial solution, centrifugation and collecting precipitate, washing to obtain suspension, heating said suspension and sterilizing so as to obtain the invented NCP. Said invention also provides its application function.
Owner:上海昌润生物科技有限公司
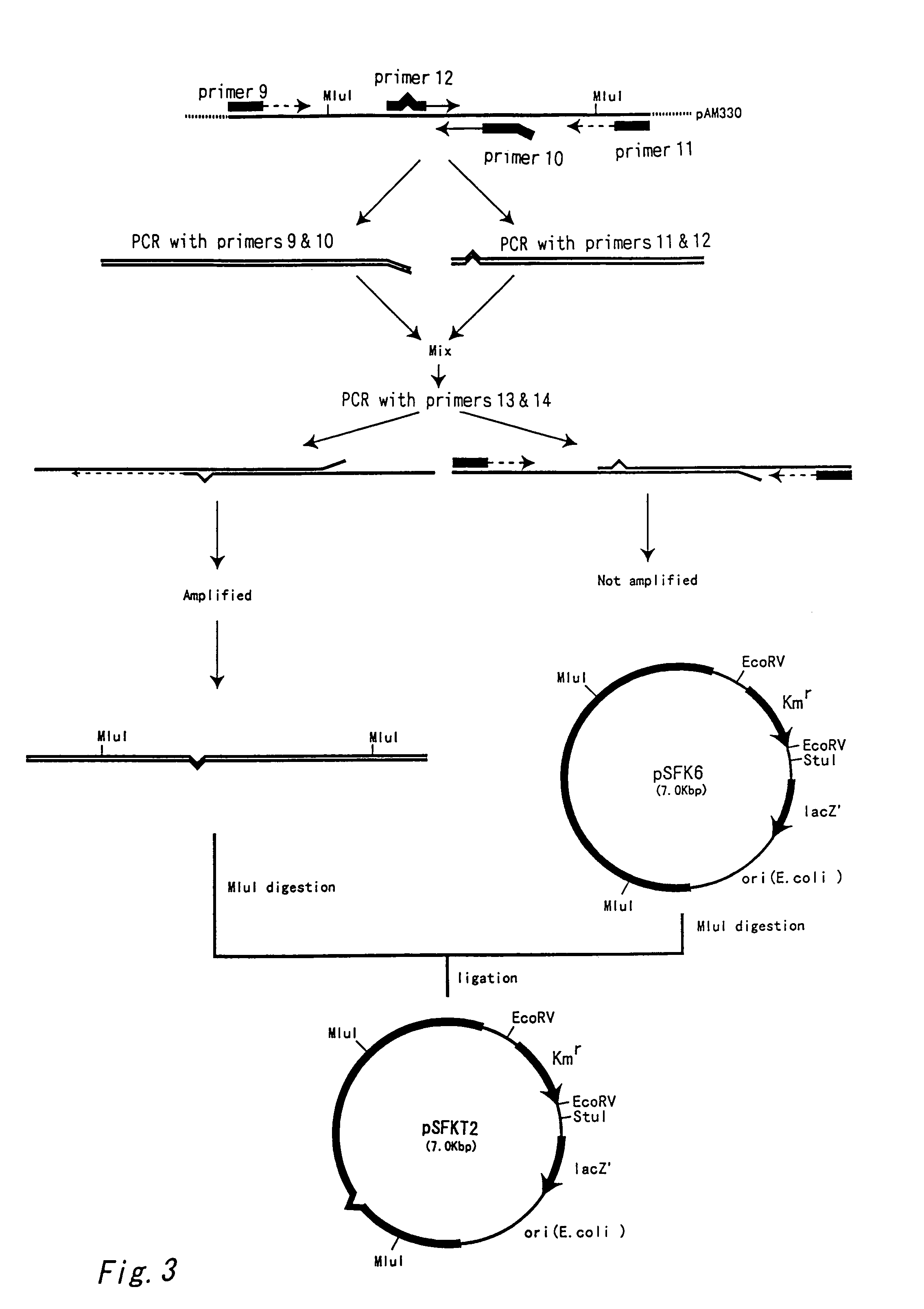
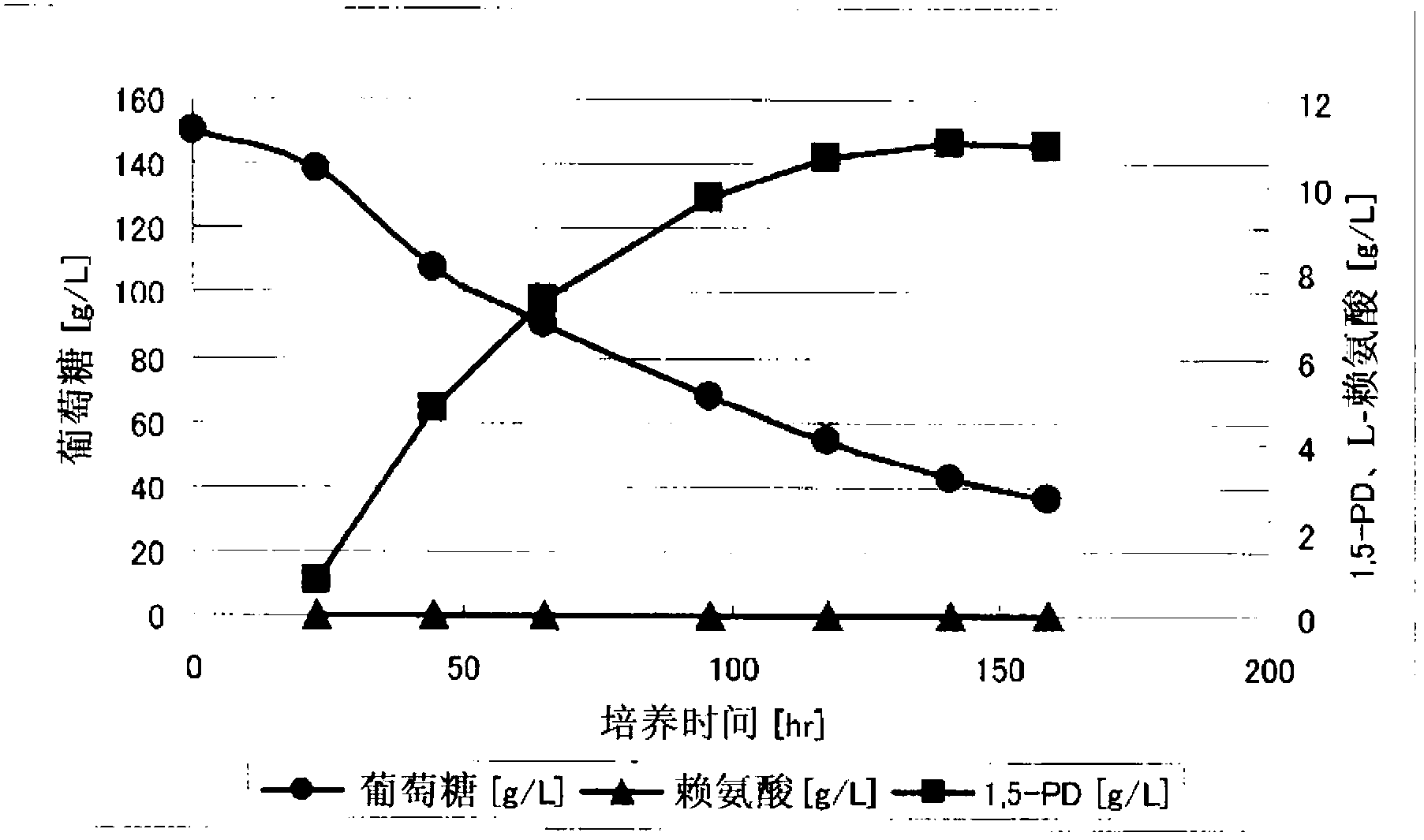
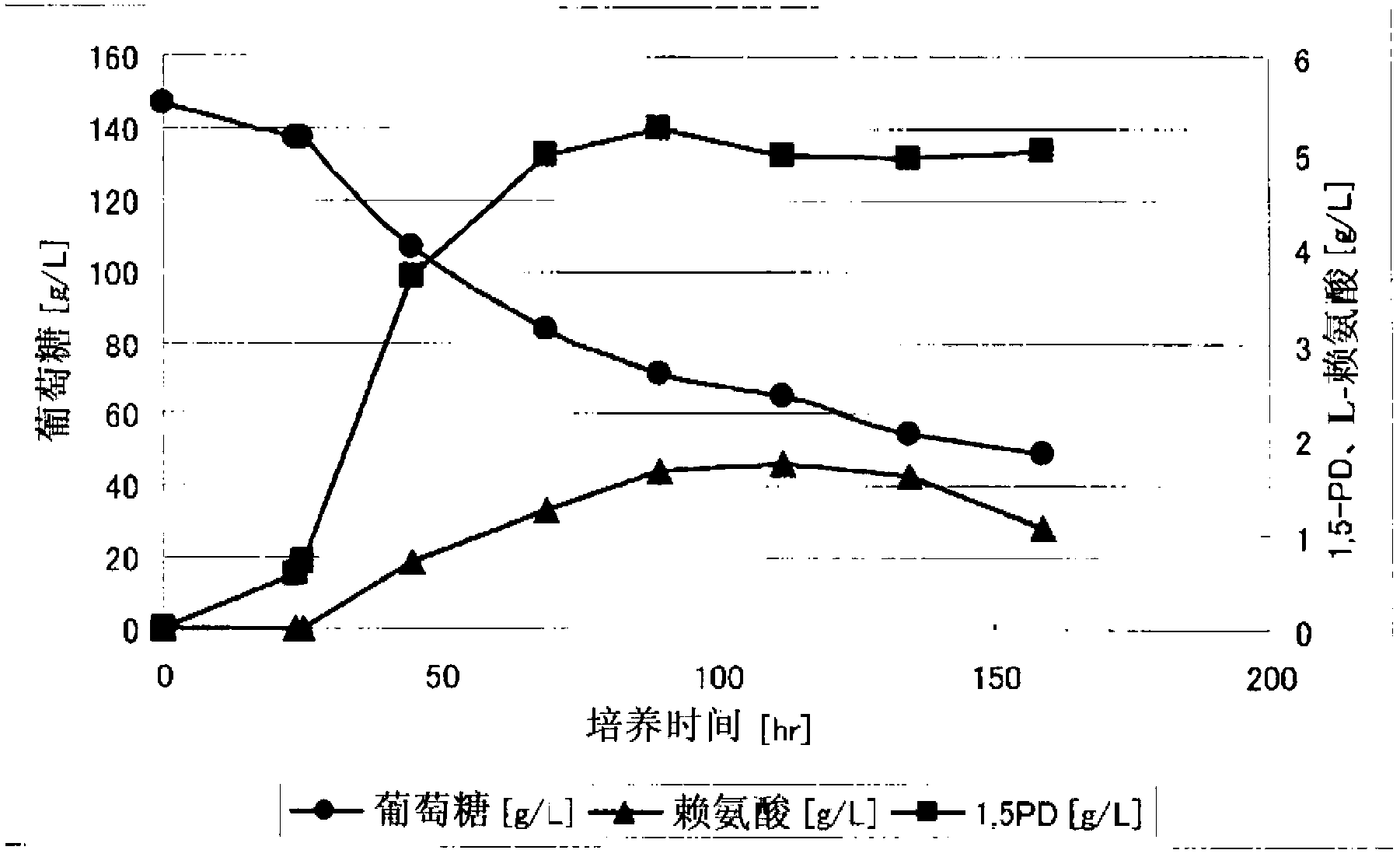
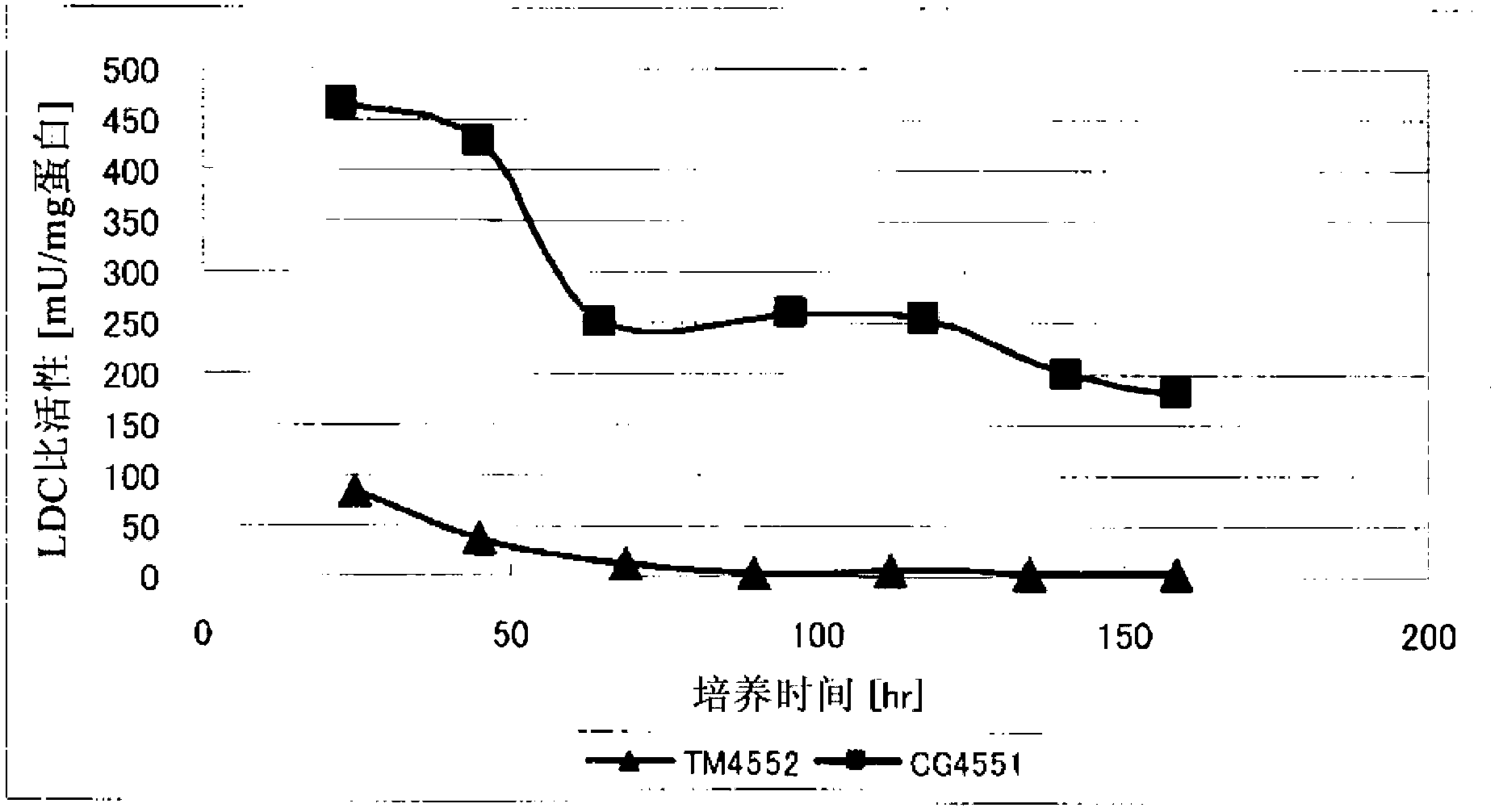
Method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine
Disclosed is a method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine through fermentation using a microorganism, said microorganism having LDC gene in the chromosome and showing regulated secondary production of L-lysine. In the method for producing 1,5-pentanediamine whereby 1,5-pentanediamine is produced by a coryneform bacterium having a gene encoding lysine decarboxylase in the chromosome, said coryneform bacterium continuously maintains a lysine decarboxylase activity of 50 mU / mg protein or greater during the culture.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Nucleotide sequences which code for the pck gene
The invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences from Coryneform bacteria which code for the pck gene encoding the enzyme phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (PEP carboxykinase). The invention also relates a process for the fermentative preparation of L-amino acids, in particular L-lysine, L-threonine, and L-glutamate by attenuation of the pck gene.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSZENTRUM JULICH GMBH
Method of treating cancer
A method of treating cancers by administering to a patient an anti-tumor effective amount ot at least one of a thermostable macromolecular antigen complex or a fragment of such a complex which is interspecific for microorganisms of the Mycobacteria, Nocardia and Corynebacteria group and which exhibits after immunoelectrophoresis an immunoelectrophoretic precipitation pattern corresponding to that of the antigen complex 60 of Mycobacteria bovis Calmette Guerin Bacillus strain. Preferably, the patient is also treated with an additional therapeutic agent which is specific against the patient's cancer such as a tumoral antigen or a non-proliferative tumor cell.
Owner:ANDA BIOLOGICALS
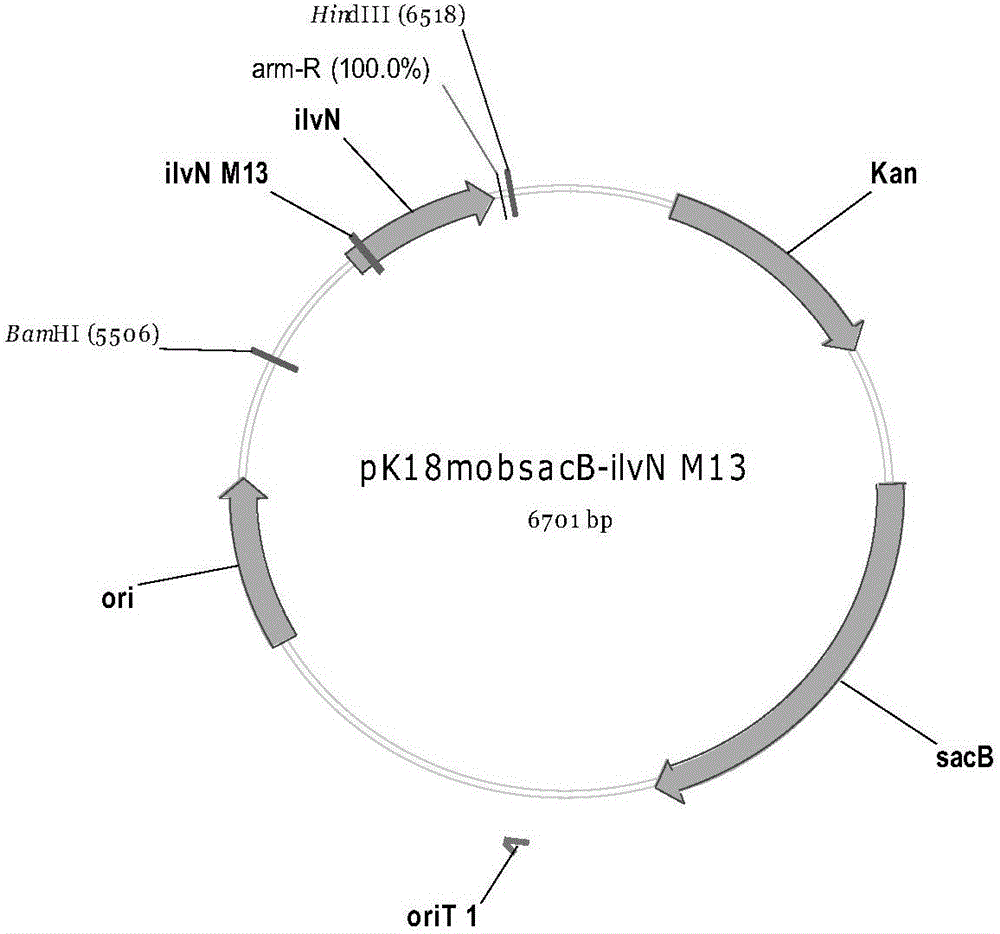
Recombinant strain, method for preparing recombinant strain and method for producing L-valine from recombinant strain
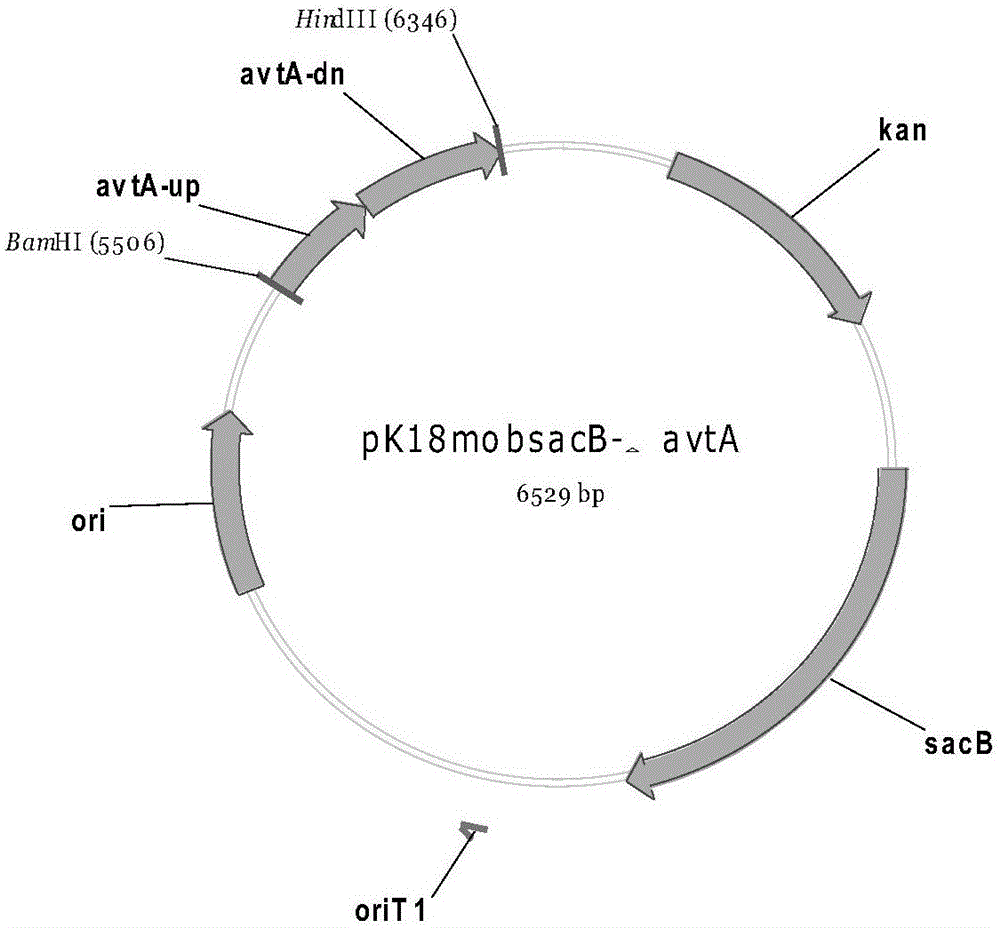
The invention relates to the field of microbial technology, in particular to a recombinant strain, a method for preparing the recombinant strain and a method for producing L-valine from the recombinant strain. According to the recombinant strain, corynebacterium serves as a starting strain for transformation, and the transformation process includes the steps of conducting point mutation on the ilvN gene and knocking out the avtA gene. The recombinant strain is obtained by conducting point mutation on the ilvN in a valine metabolism path and knocking out the avtA gene for transaminase coding; through fermentation culture, the yield of L-valine can reach 12.2 g / L, and generation of the by-product alanine is greatly reduced.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Recombinant bacterial strain for high-yield production of L-lysine, and construction method and application of recombinant bacterial strain
ActiveCN110607313AImprove stabilityEasy to produceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCorynebacterium efficiensOpen reading frame
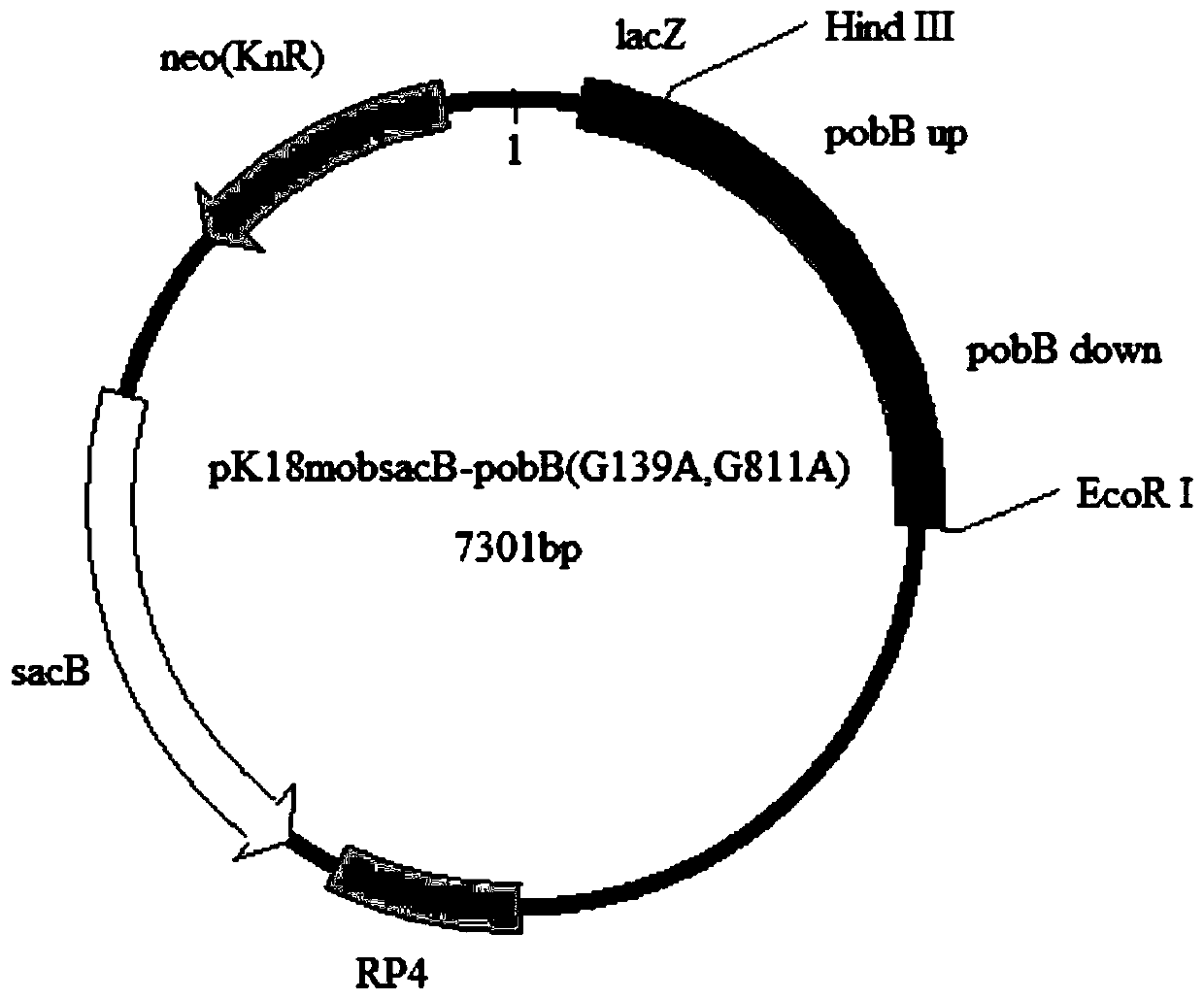
The invention provides a recombinant bacterial strain for high-yield production of L-lysine, and a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterial strain. A polynucleotide sequence comprises a modified pobB gene coding polynucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, and the invention provides a recombinant protein coded by the polynucleotide sequence, the recombinant bacterial strain containing the polynucleotide sequence, a construction method of the recombinant bacterial strain, and an application of the recombinant bacterial strain in fermentation production of L-lysine. According to the recombinant strain disclosed by the invention, point mutation is carried out on the nucleotide sequence of an open reading frame coding region of the pobB gene in wild-type corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain the recombinant strain modified by the coding region of the pobB gene, and the yield of L-lysine is realized compared with the yield of L-lysine by using wild bacterial strains.
Owner:NINGXIA EPPEN BIOTECH
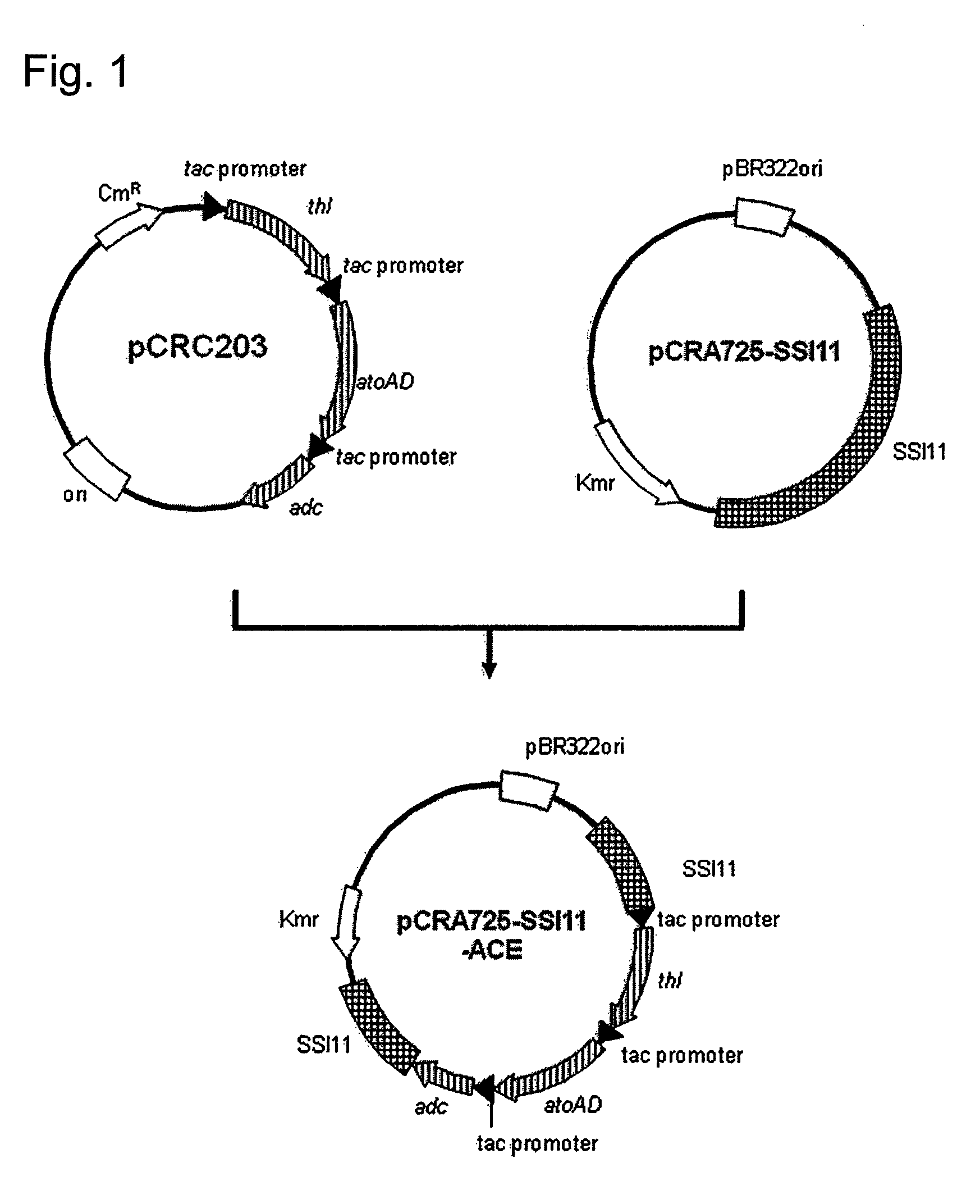
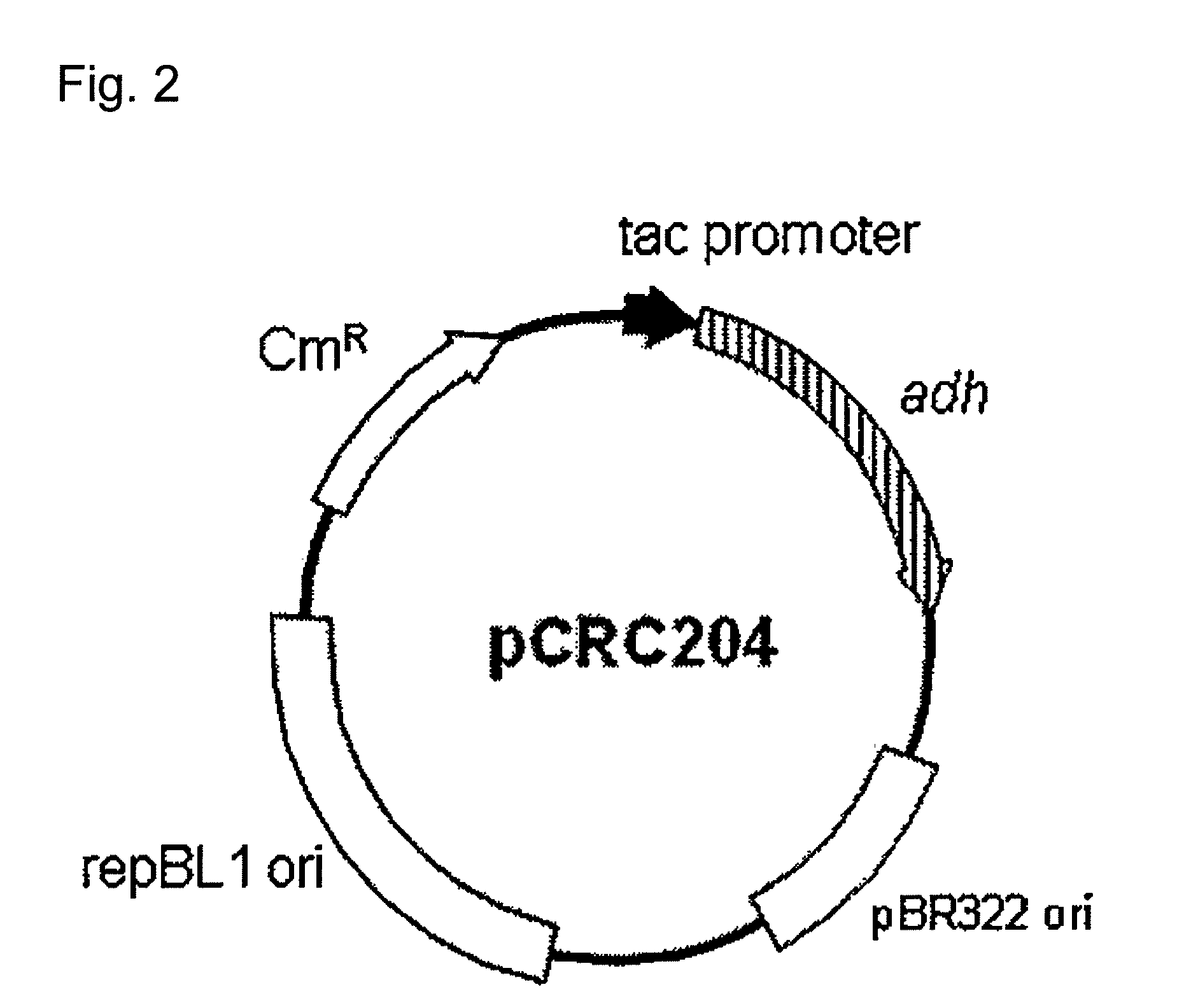
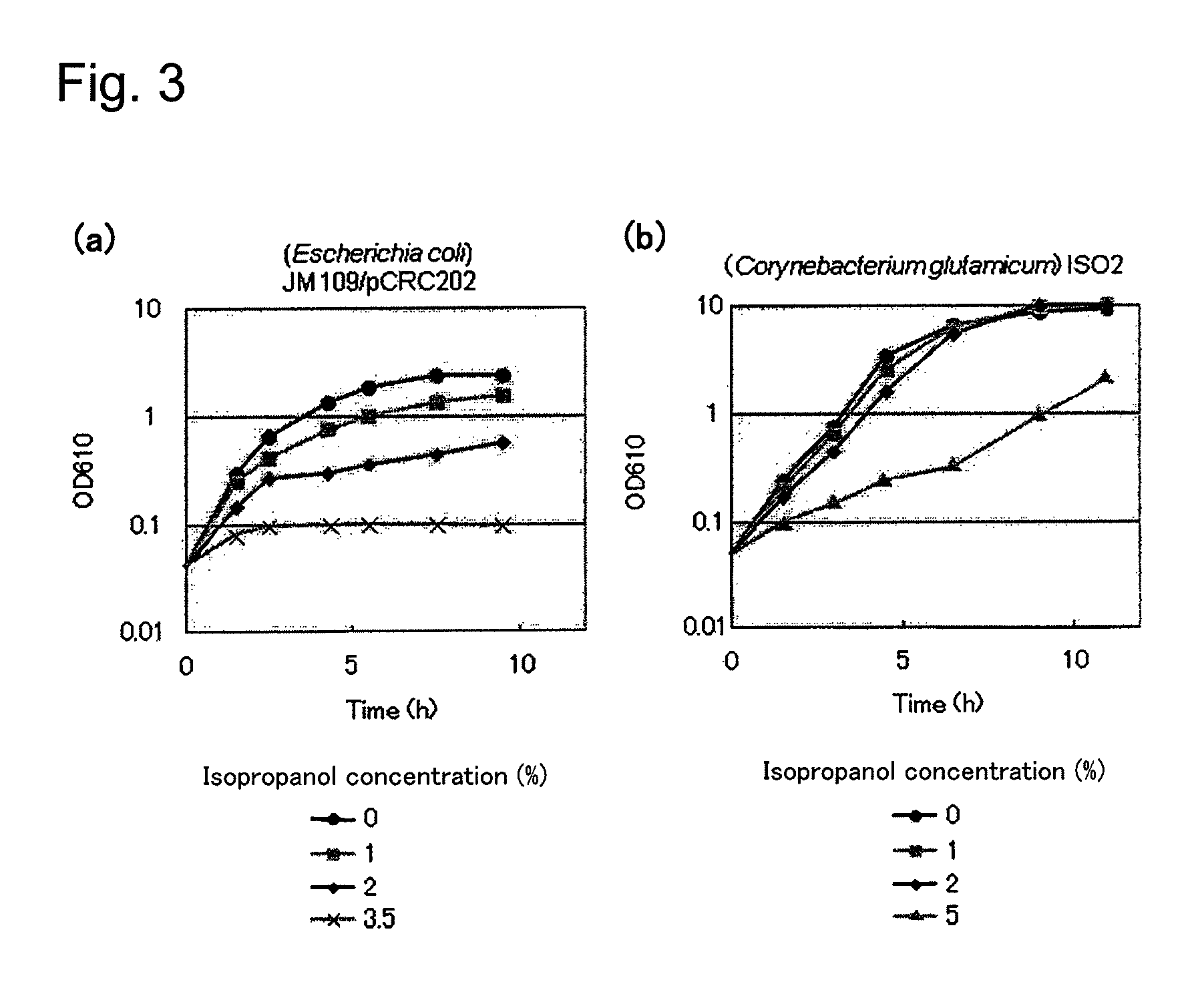
Transformant of coryneform bacteria capable of producing isopropanol
ActiveUS8216820B2Efficient productionBacteriaFermentationCorynebacterium efficiensAcetoacetate decarboxylase activity
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Corynebacterium glutamicum establishment method for increasing yield of L-lysine and improving stability of L-lysine
ActiveCN110106206AIncrease productionImprove stabilityStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesCorynebacterium efficiensNucleotide
The invention relates to a corynebacterium glutamicum establishment method for increasing the yield of L-lysine and improving the stability of the L-lysine. According to the method, after a Tnp7a geneof corynebacterium glutamicum is inactivated, the corynebacterium glutamicum is established, and an amino acid sequence of the Tnp7a gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the corynebacterium glutamicum establishment method for increasing the yield of the L-lysine and improving the stability of the L-lysine, the endogenous gene Tnp7a of the established corynebacterium glutamicum is inactivated, the transposition effect, caused when an insertion sequence is activated due to an environment change, of the corynebacterium glutamicum in the preservation and fermentation process is lowered, thestrain degeneration progress, caused by mutation or frame shift generated by transposition or adjustment on expression of adjacent genes through promoters carried by a genome, of the genome is blocked, and the yield of the L-lysine is increased.
Owner:ZHUCHENG DONGXIAO BIOTECH
Method for producing L-glutamine by fermentation and L-glutamine producing bacterium
InactiveUS7262035B2Avoid by-productsImprove abilitiesSugar derivativesBacteriaCorynebacterium efficiensBacteroides
L-Glutamine is produced by culturing a coryneform bacterium which has L-glutamine producing ability and has been modified so that its intracellular glutamine synthetase activity should be enhanced, preferably which has been further modified so that its intracellular glutamate dehydrogenase activity should be enhanced, in a medium to produce and accumulate L-glutamine in the medium and collecting the L-glutamine.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Use of acellular short corynebacteria preparation in preparation of medicine for treating tuberculosis
InactiveCN1465354AImprove biological activityReduce pollutionAntibacterial agentsBacteria material medical ingredientsTherapeutic effectCorynebacterium amycolatum
The present invention discloses a non-cell corynebacterium parvum preparation (NCP) and its application in preparation of medicine for curing tuberculosis, in which the described NCP is a non-cell preparation prepared by breaking corynebacterium parvum, its grain size is less than 100 nm, and its heat source is less than 160 Eu / ml, protein content is 10-40% (g / g), nucleic acid content is 3-25% (g / g), the rest is polysaccharide. The tests show that it can obtain good therapeutic effect.
Owner:上海昌润生物科技有限公司
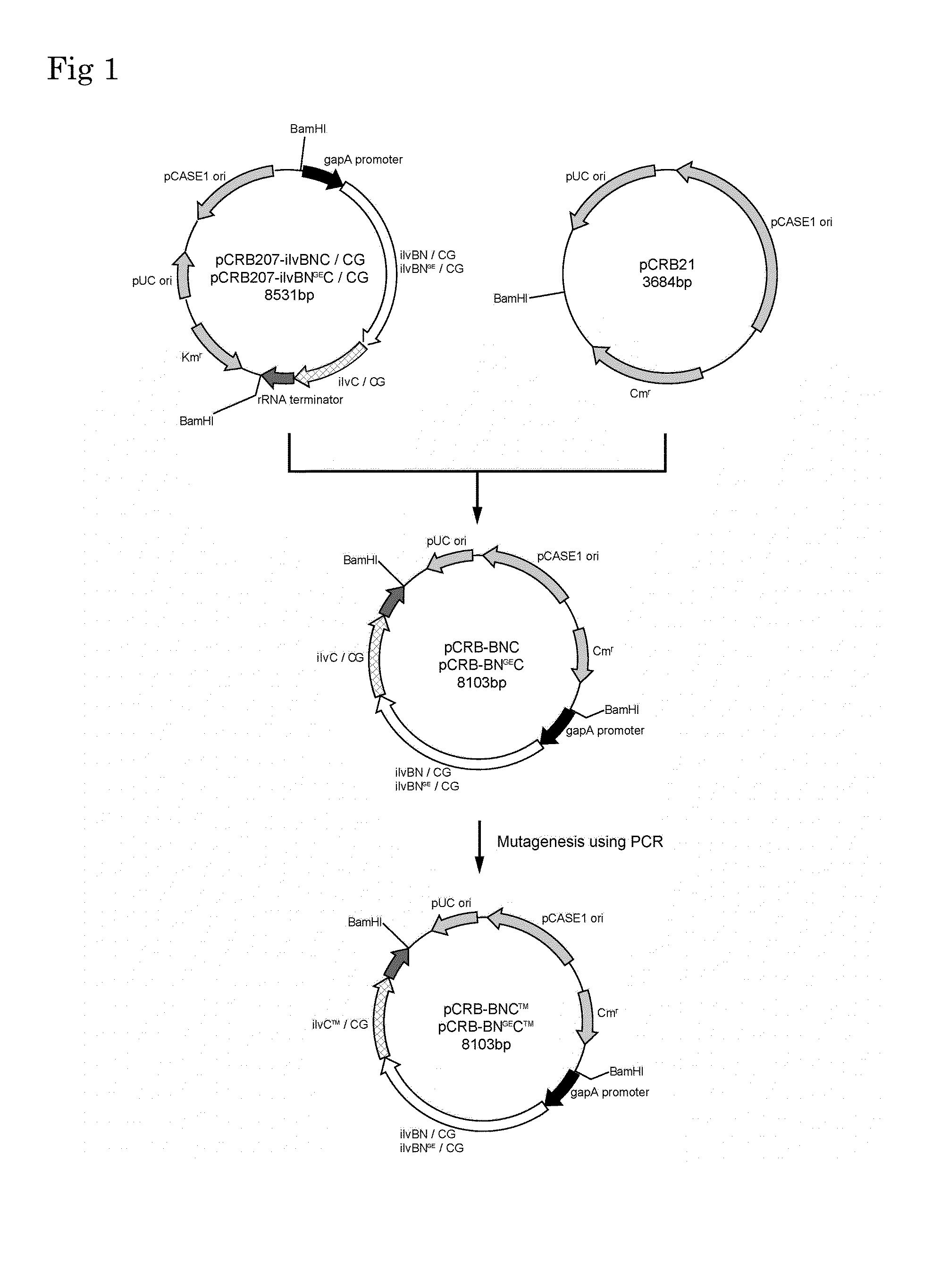
Coryneform Bacterium Transformant and Process for Producing Valine Using the Same
A transformant obtainable by introducing one or more of the following DNAs (a), (b), and (c) into a coryneform bacterium as a host.(a) A DNA which encodes acetohydroxy acid synthase derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum and which has a mutation changing the glycine at position 156 to glutamic acid (G156E) in an amino acid sequence encoded by the DNA, or an analog thereof.(b) A DNA which encodes acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum and which has mutations changing the serine at position 34 to glycine (S34G), the leucine at position 48 to glutamic acid (L48E), and the arginine at position 49 to phenylalanine (R49F) in an amino acid sequence encoded by the DNA, or an analog thereof.(c) A DNA which encodes leucine dehydrogenase derived from Lysinibacillus sphaericus, or an analog thereof.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
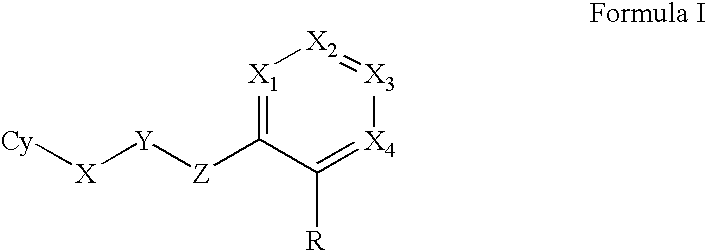
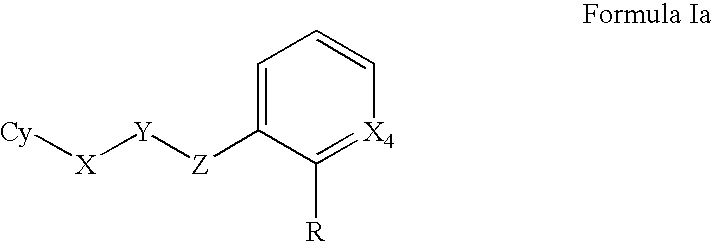
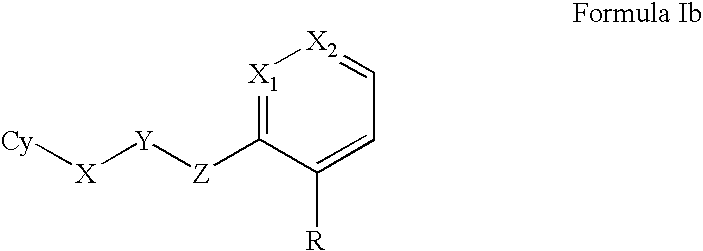
Antimicrobial agents
Provided herein are substituted aromatic compounds, which are tRNA synthetase inhibitors, and hence can be used as antimicrobial agents. Compounds described herein can be used for the treatment or prevention of a condition caused by or contributed to by gram positive, gram negative, anaerobic bacteria or fungal organisms, more particularly against bacterium, for example, Staphylococci, Enterococci, Streptococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla, Escherichia, Chlamydia, Mycoplasm, Legionella, Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebacterium, Bacillus or Enterobactericeae, and fungal organisms, for example, Aspergillus, Blastomyces, Candida, Coccidiodes, Cryptococcus, Epidermophyton, Hendersonula, Histoplasma, Microsporum, Paecilomyces, Paracoccidiodes, Pneumocystis, Trichophyton, or Trichosporium. Processes for the preparation of these compounds, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating microbial infections are also provided.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
A coryneform expression system independent of antibiotics as selection pressure
ActiveCN103834679BFacilitate scientific researchEase of industrial applicationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismGene engineering
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing L-amino acid using methylotroph
InactiveUS7439038B2Improve productivityAbundantly and inexpensively availableSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesMethylotroph
A DNA encoding for a mutant of LysE protein, or a homologous protein thereof, of a coryneform bacterium, wherein the mutant, when introduced into a methanol-assimilating bacterium imparts resistance to L-lysine analogue. The DNA encoding for a mutant of LysE protein, or a homologous protein thereof, is introduced into a methanol-assimilating bacterium to improve L-lysine and L-arginine productivity of the methanol-assimilating bacterium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com