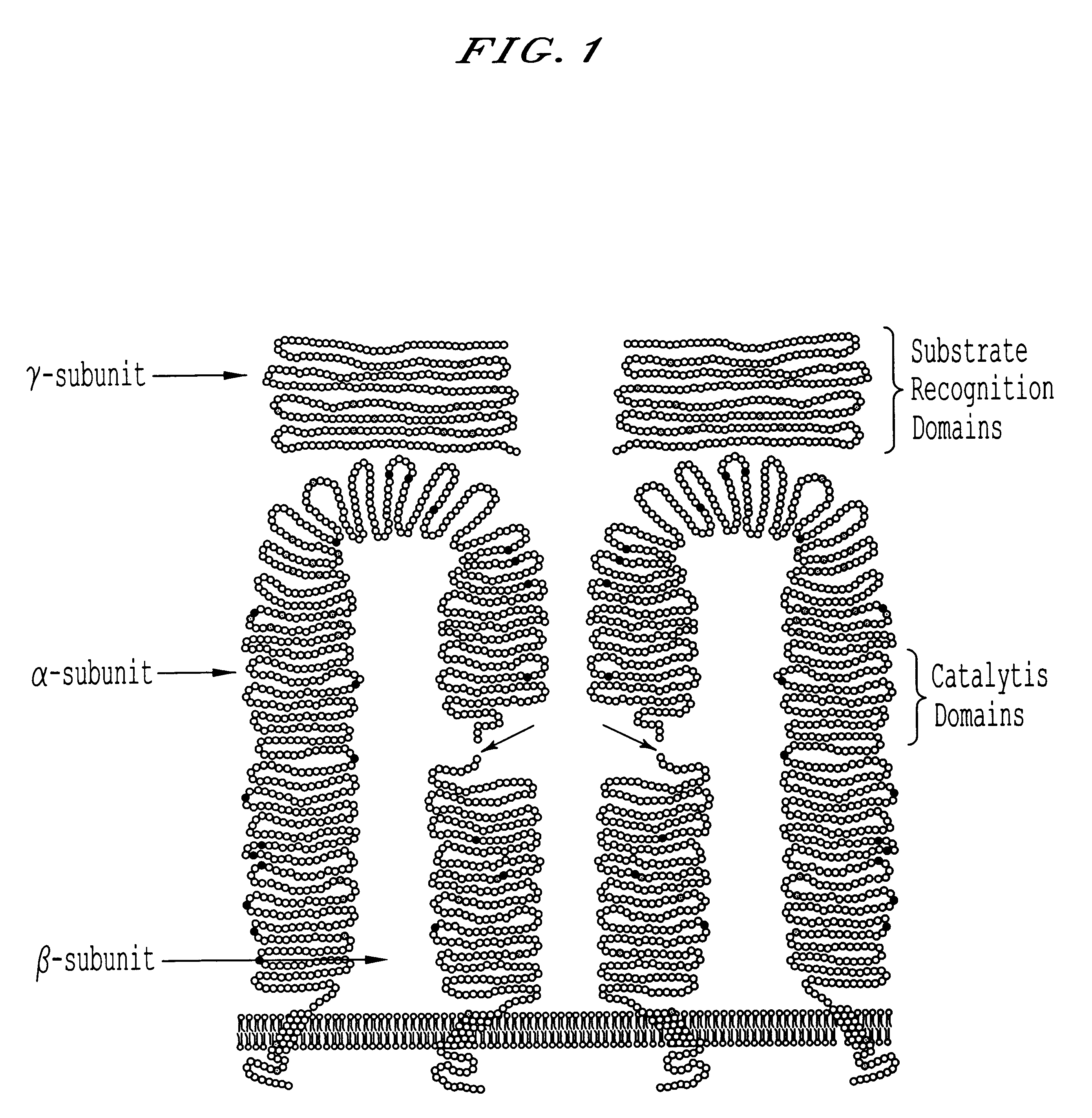
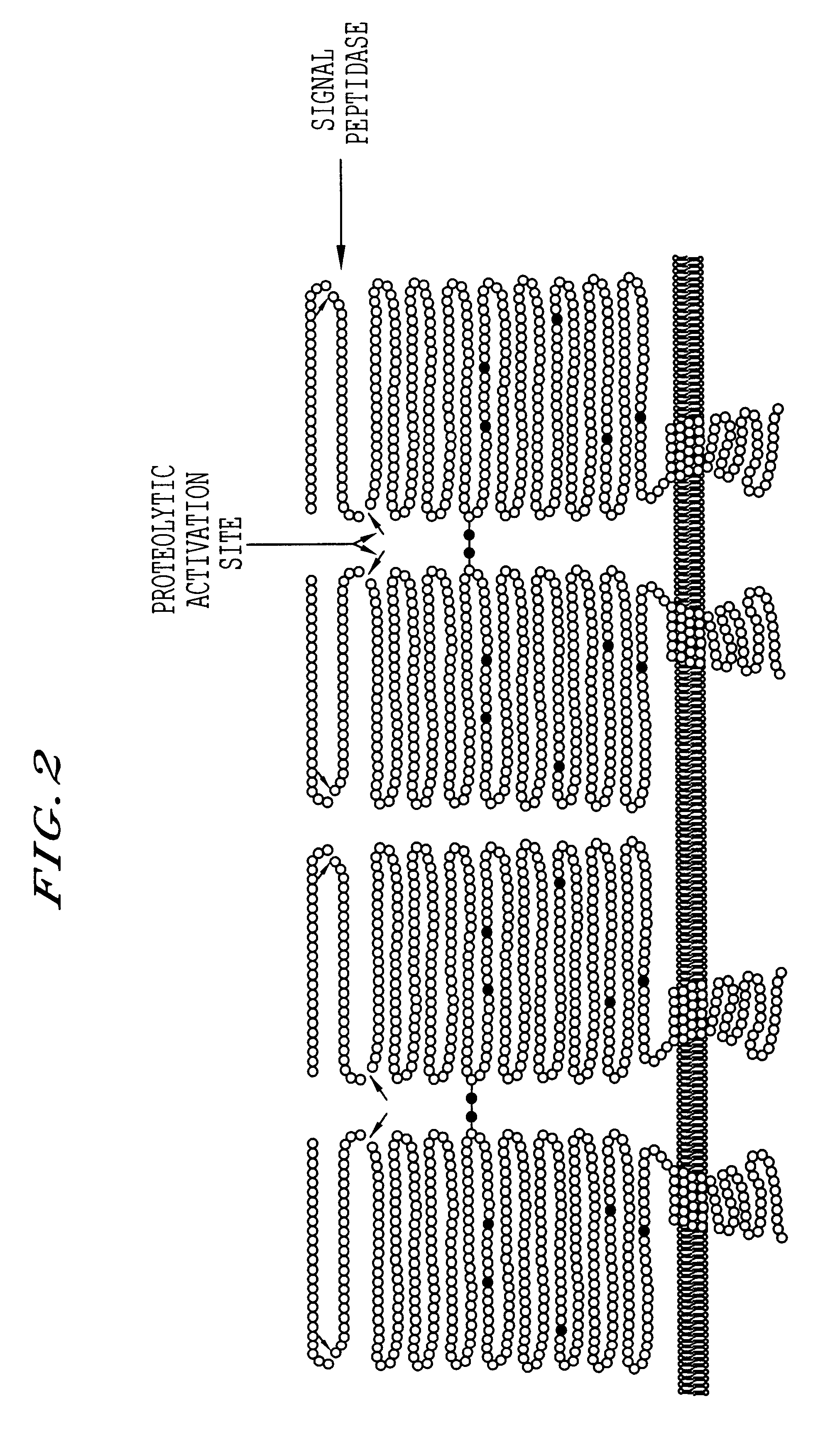
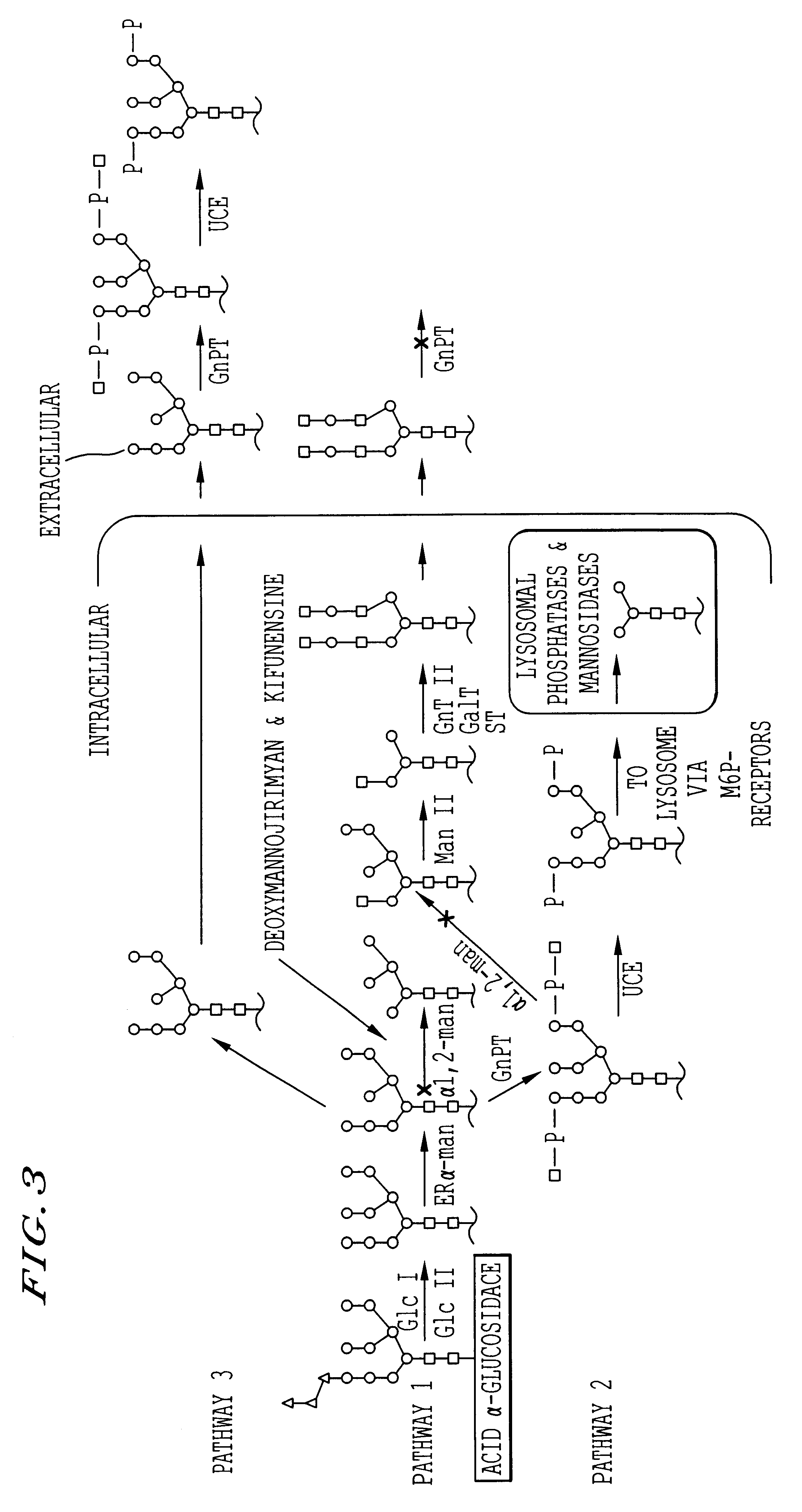
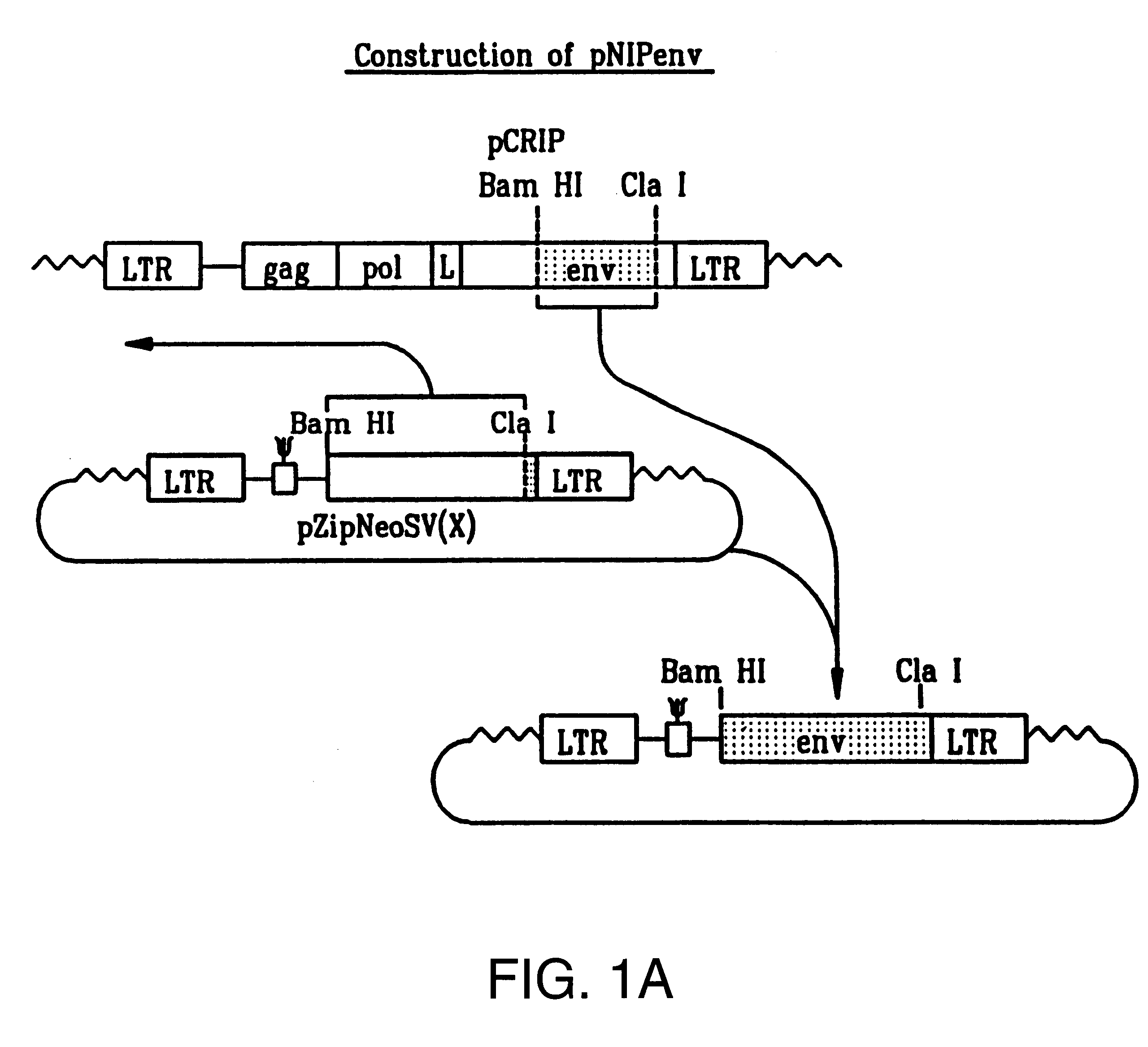
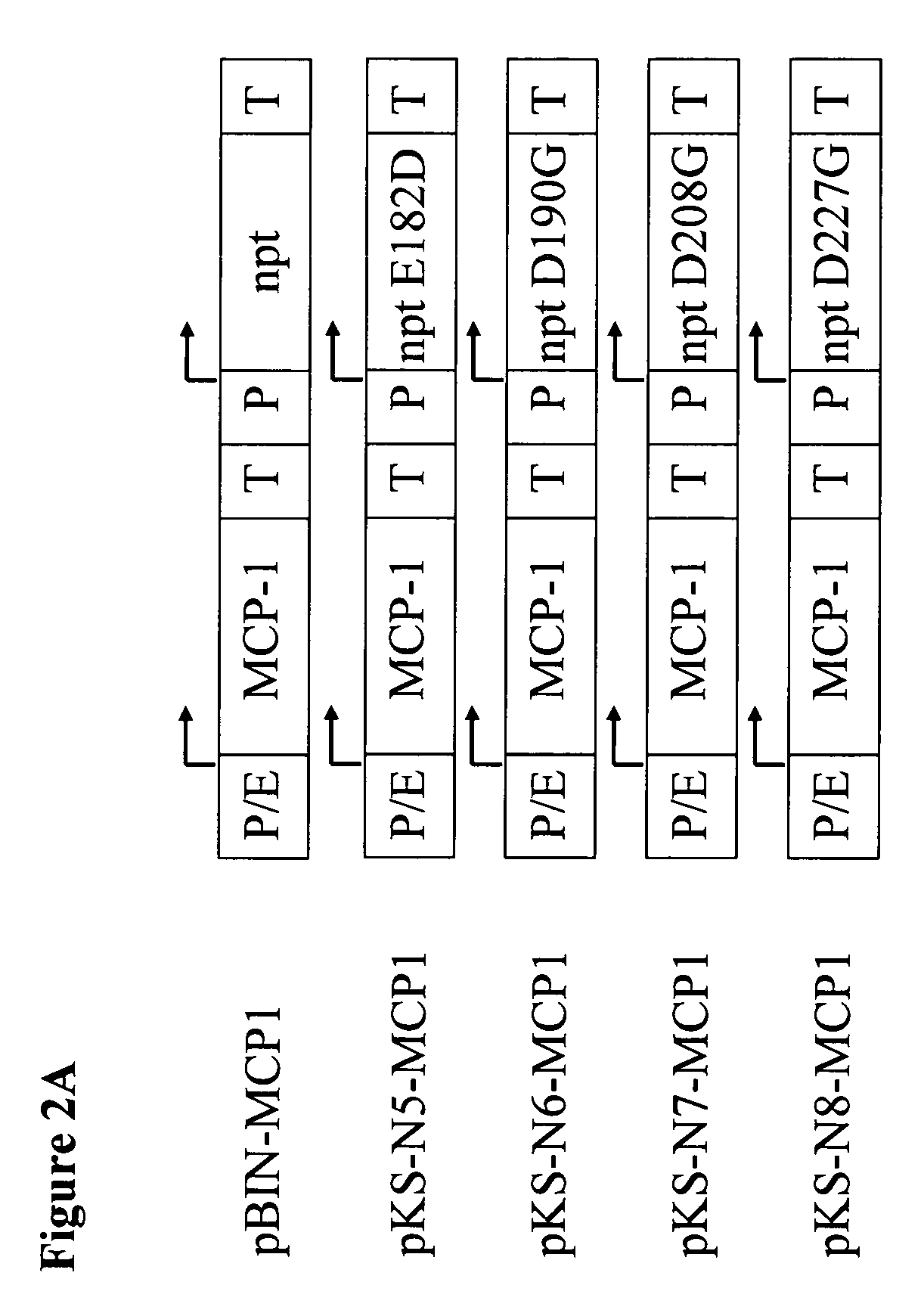
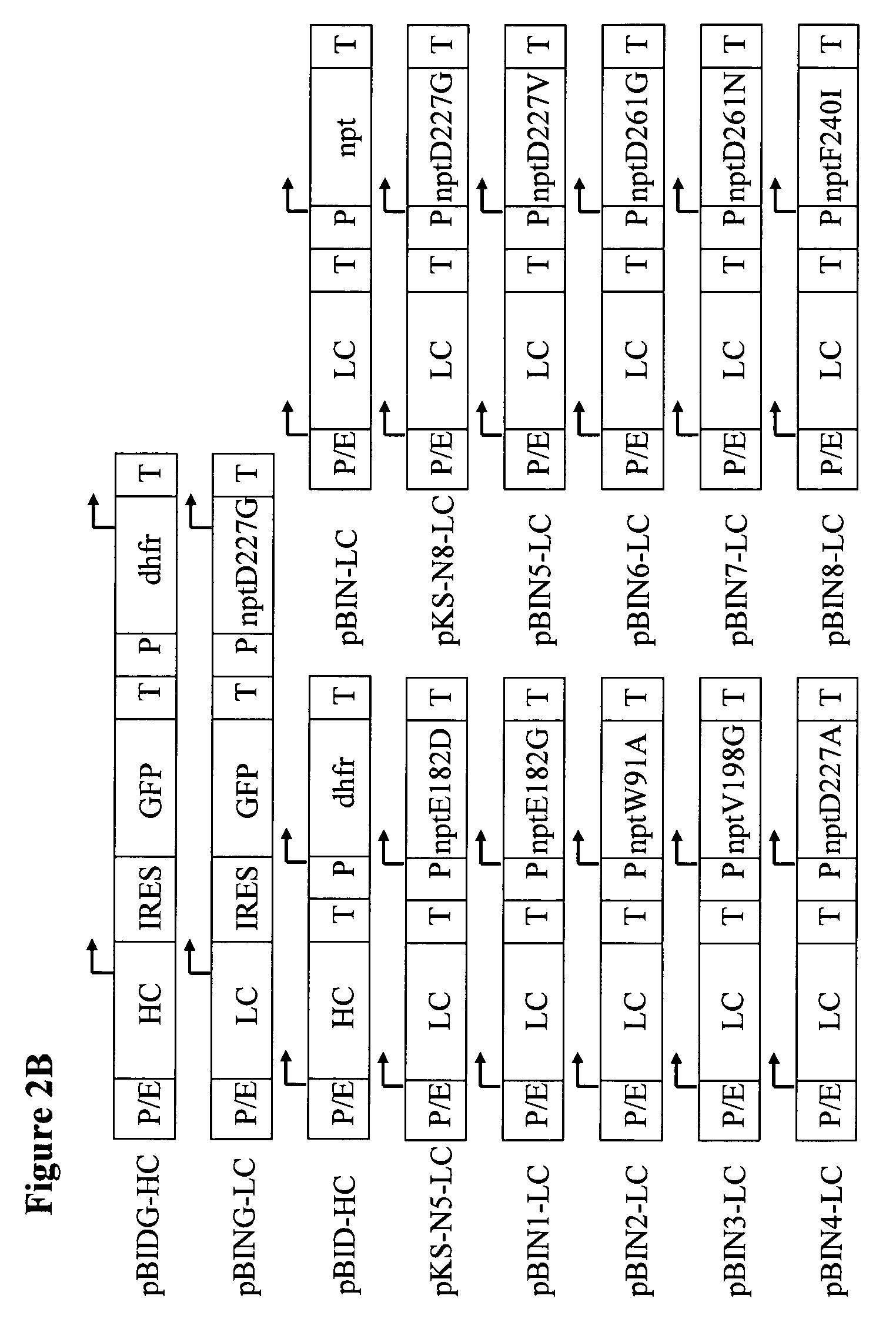
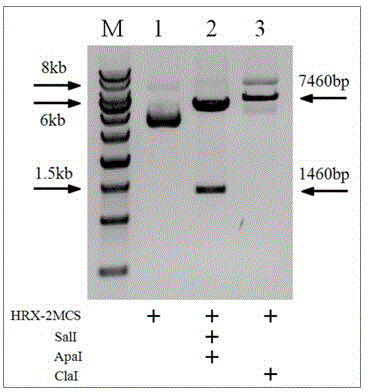
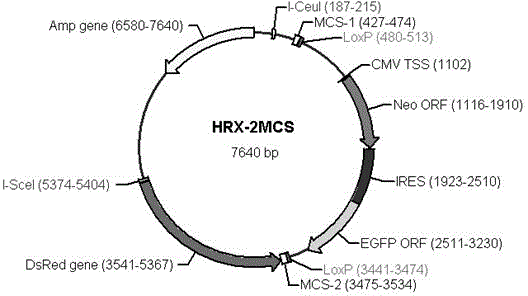
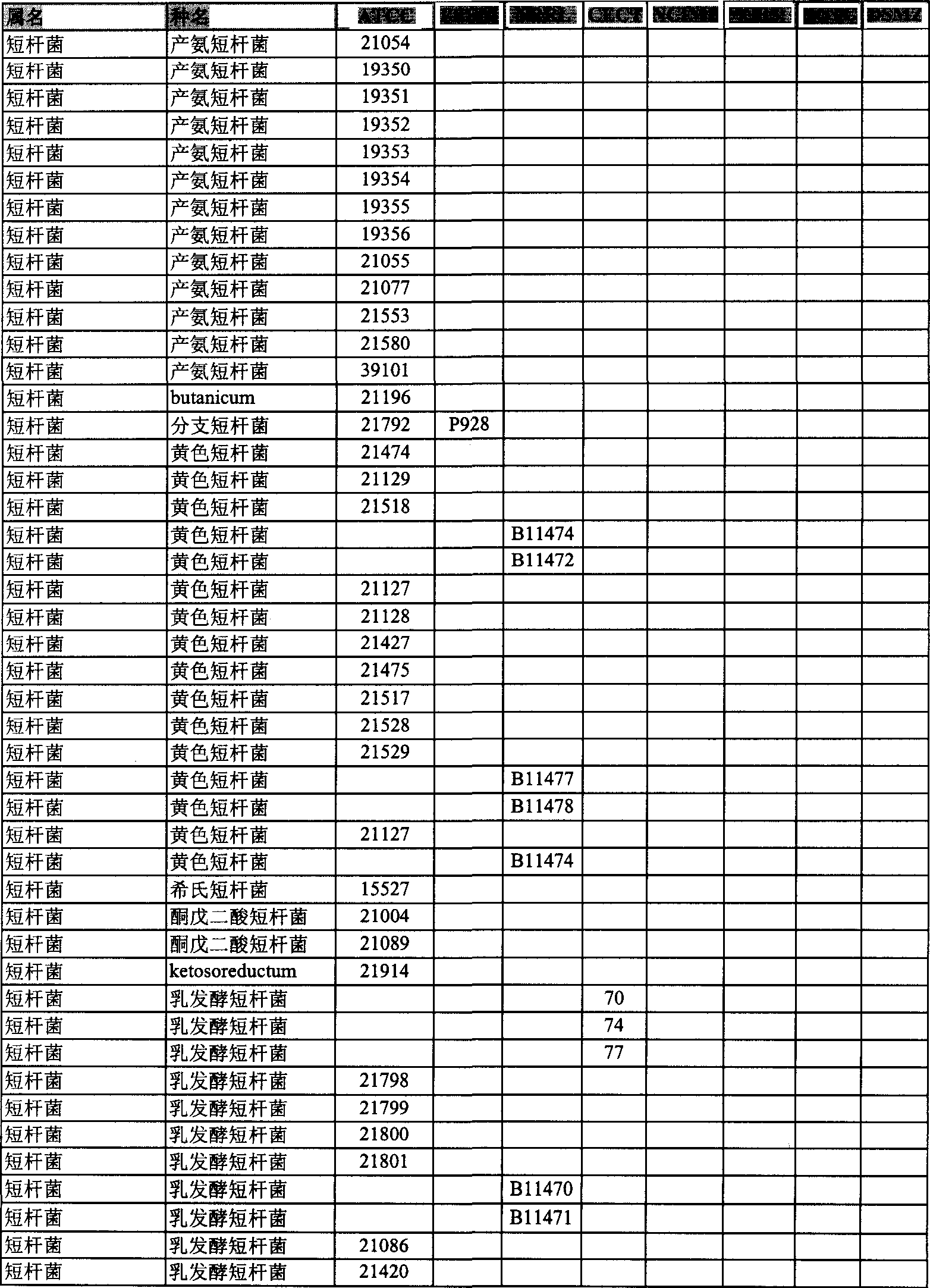
Patents
Literature
75 results about "Phosphotransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
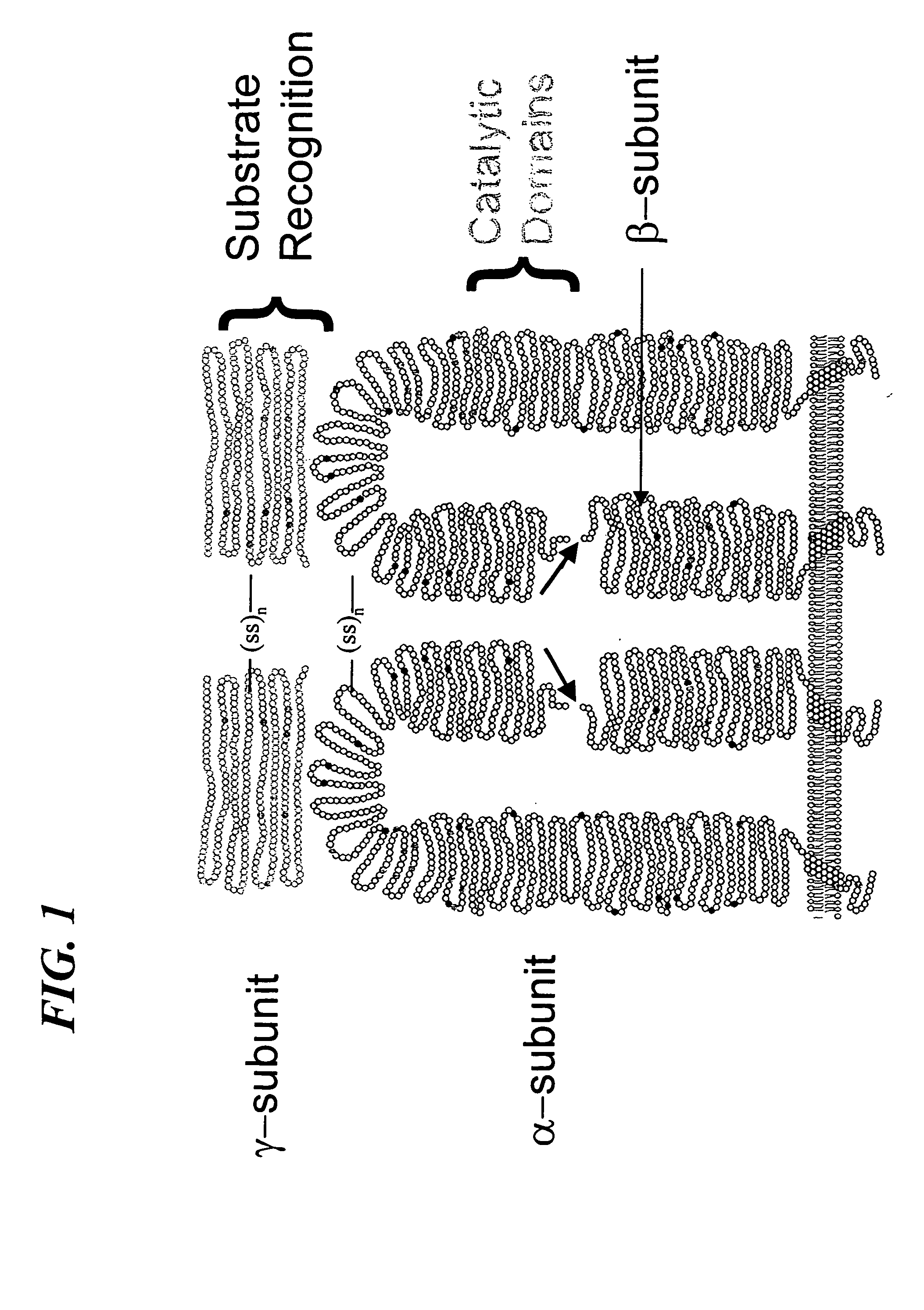
Phosphotransferases are a category of enzymes (EC number 2.7) that catalyze phosphorylation reactions. The general form of the reactions they catalyze is: A-P + B ⇌ B-P + A Where P is a phosphate group and A and B are the donating and accepting molecules, respectively.
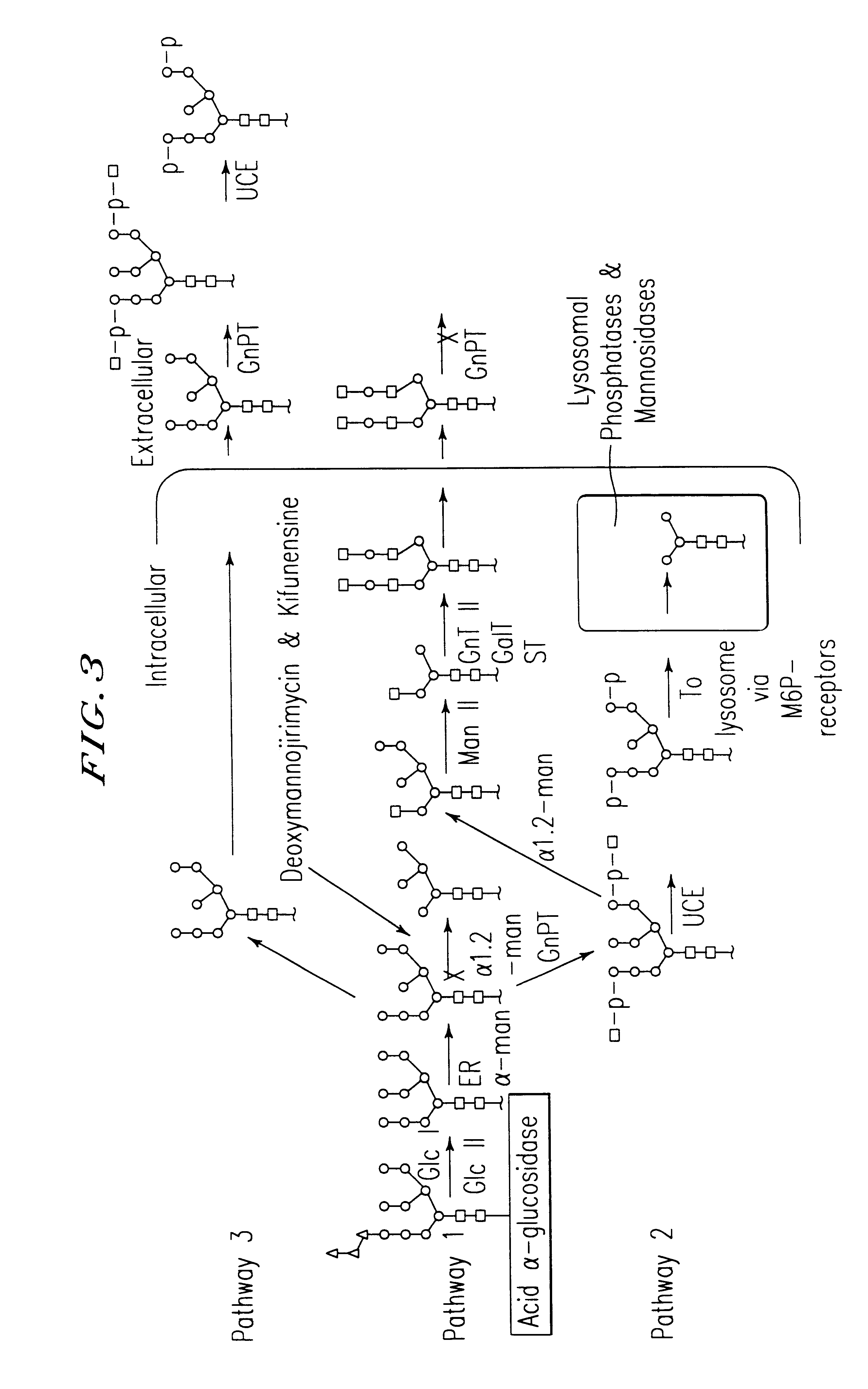
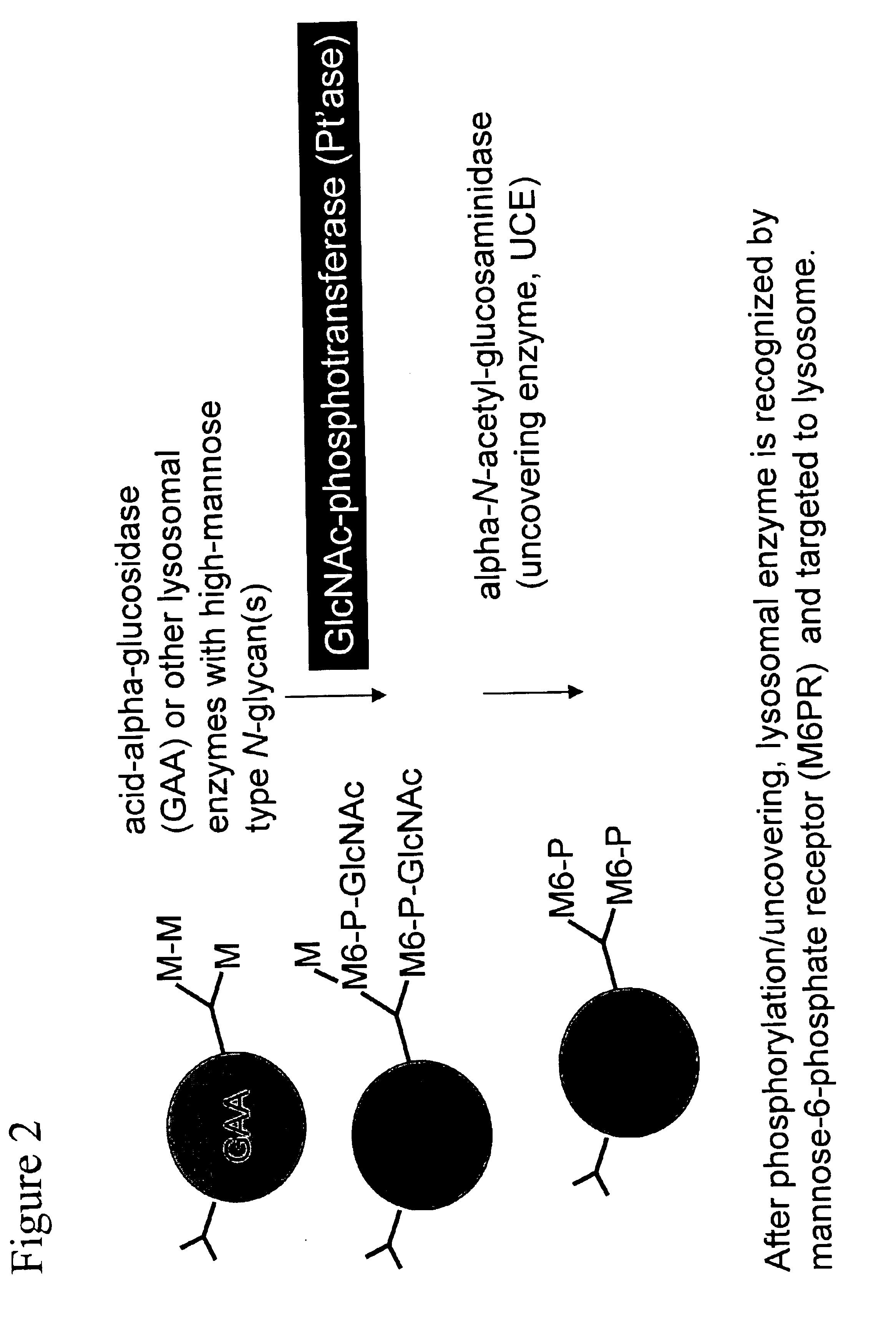
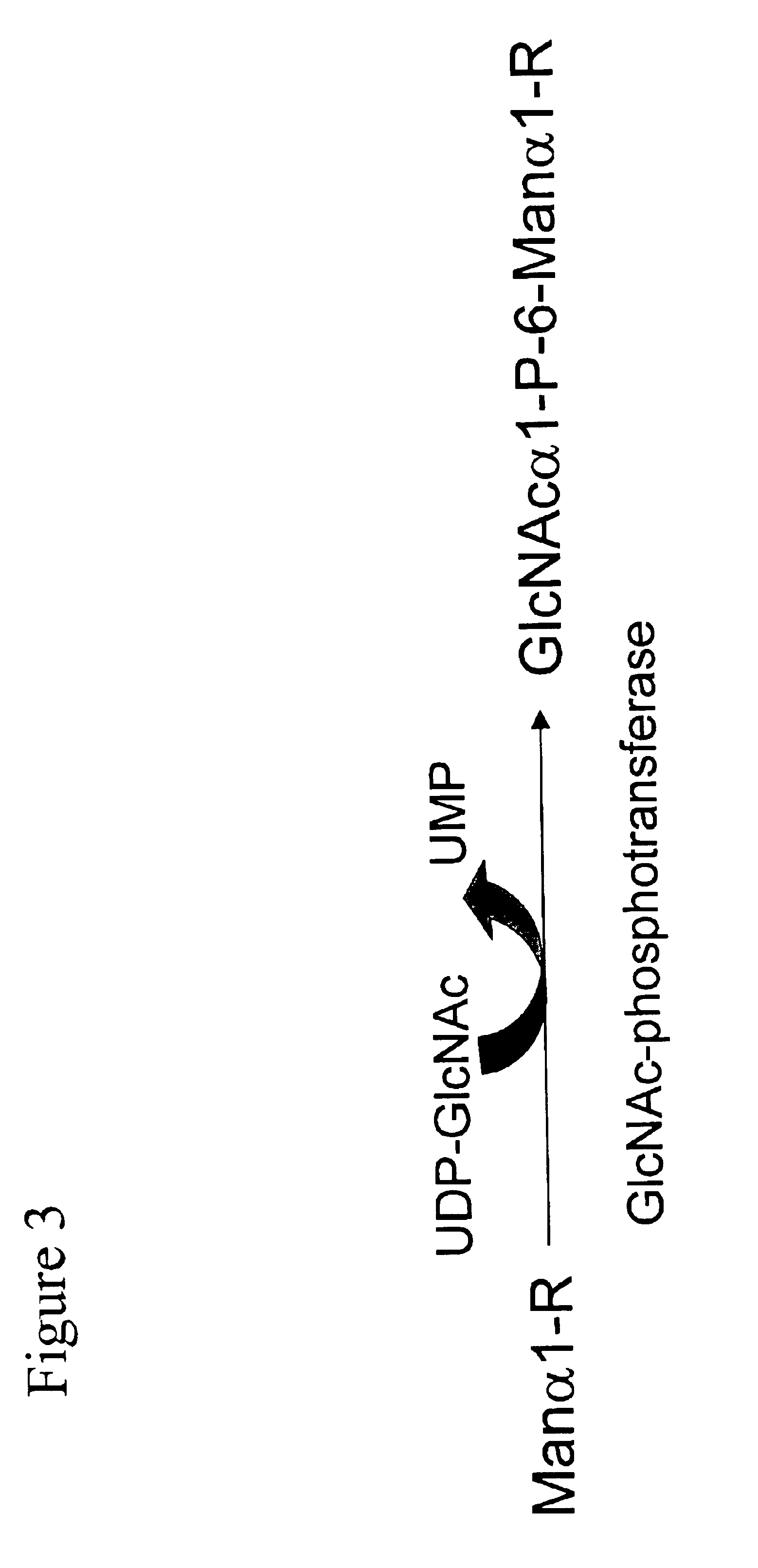
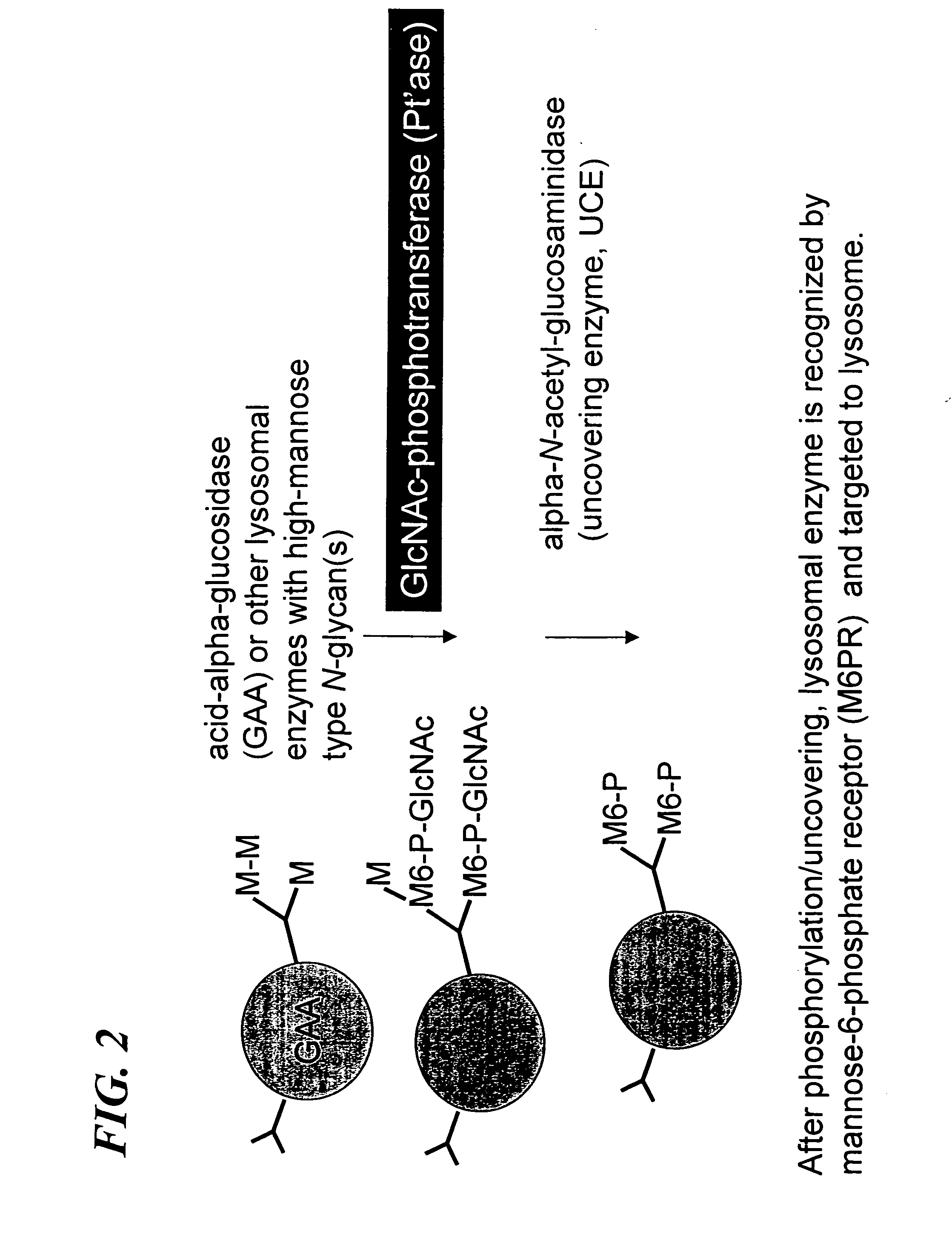
Methods for producing highly phosphorylated lysosomal hydrolases
InactiveUS6534300B1Easy to identifyHigh mannose structureFungiBacteriaLysosomal targetingPhosphorylation
The present invention provides highly phosphorylated lysosomal hydrolases, methods of modifying lysosomal hydrolases with the lysosomal targeting pathway enzymes GlcNAc-phosphotransferase and / or phosphodiester alpha-GlcNAcase.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Recombinant viruses displaying a nonviral polypeptide on their external surface
InactiveUS6297004B1Genetic material ingredientsImmunological disordersGene deliveryAntibody fragments
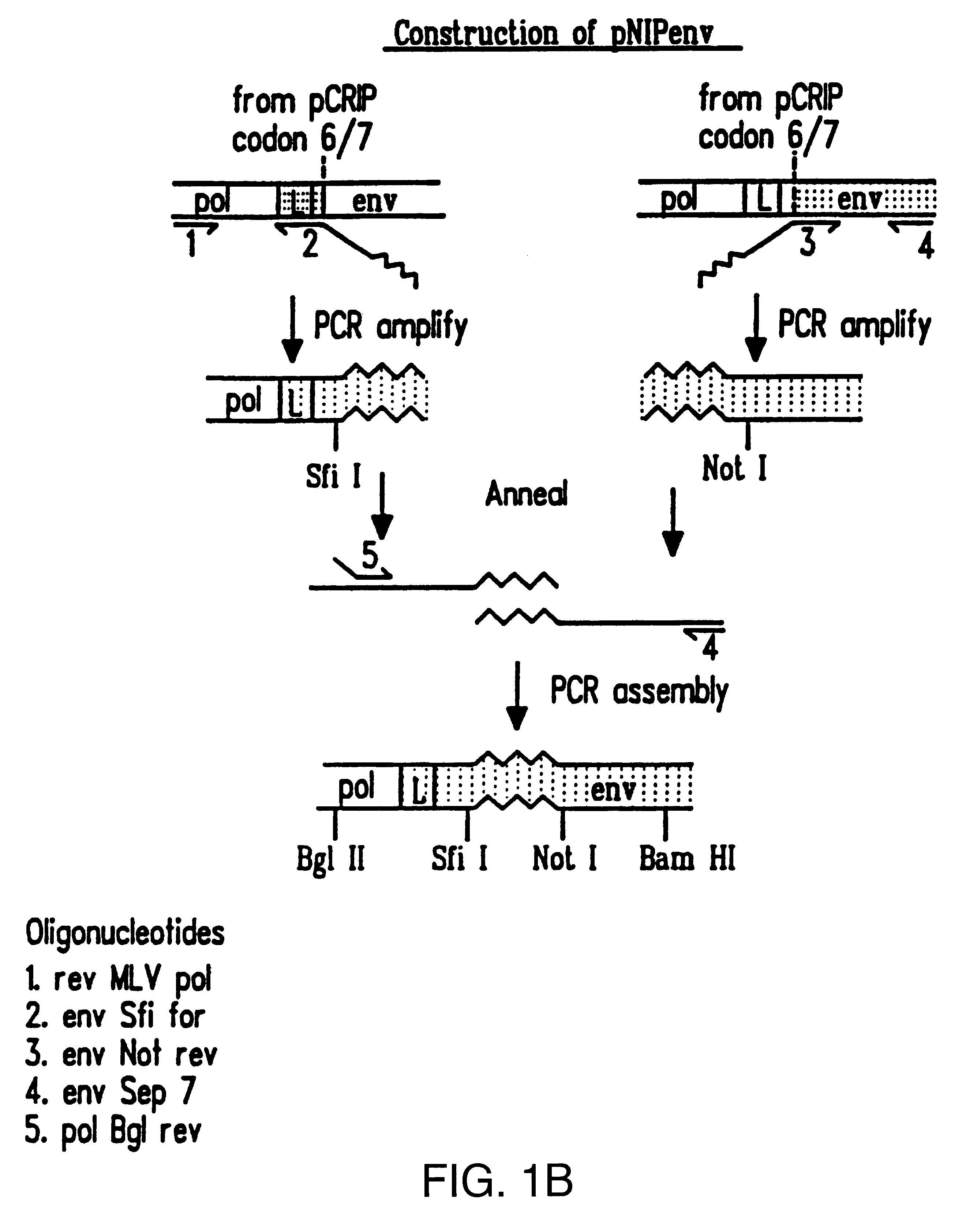
We have made retrovirus particles displaying a functional antibody fragment. We fused the gene encoding an antibody fragment directed against a hapten with that encoding the viral envelope protein (Pr80env) of the ecotropic Moloney murine leukemia virus. The fusion gene was co-expressed in ecotropic retroviral packaging cells with a retroviral plasmid carrying the neomycin phosphotransferase gene (neo), and retroviral particles with specific hapten biding activities were recovered. Furthermore the hapten-binding particles were able to transfer the neo gene and the antibody-envelope fusion gene to mouse fibroblasts. In principle, the display of antibody fragments on the surface of recombinant retroviral particles could be used to target virus to cells for gene delivery, or to retain the virus in target tissues, or for the construction of libraries of viral display packages.
Owner:BIOFOCUS DICOVERY
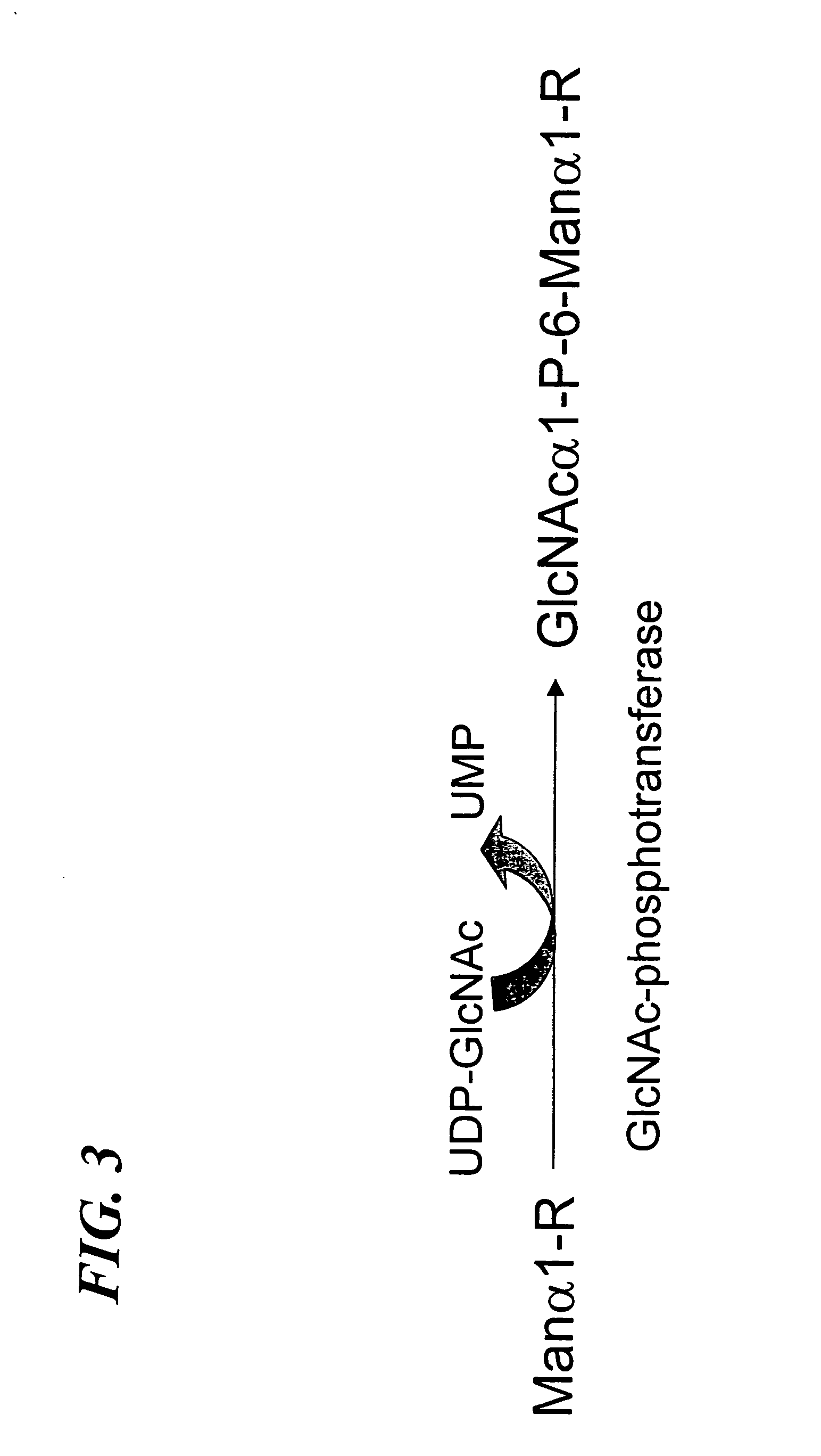
GlcNAc phosphotransferase of the lysosomal targeting pathway
InactiveUS6642038B1Easy to identifyHigh mannose structureFungiSugar derivativesNucleotideLysosomal targeting
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Soluble GlcNAc phosphotransferase
The present invention relates to a soluble GlcNAc phosphotransferase, a method of making the same and a method of phosphorylating with the same.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
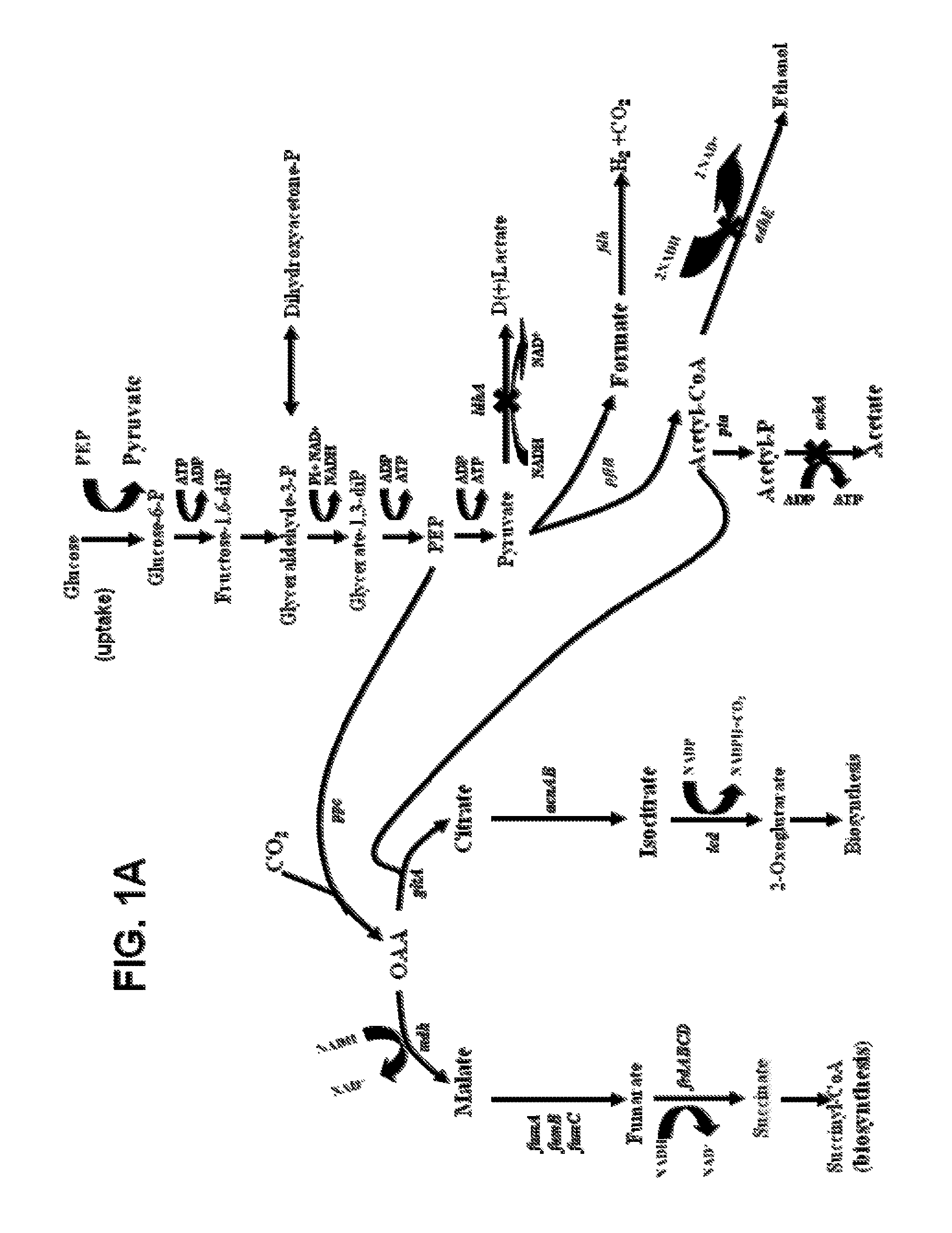
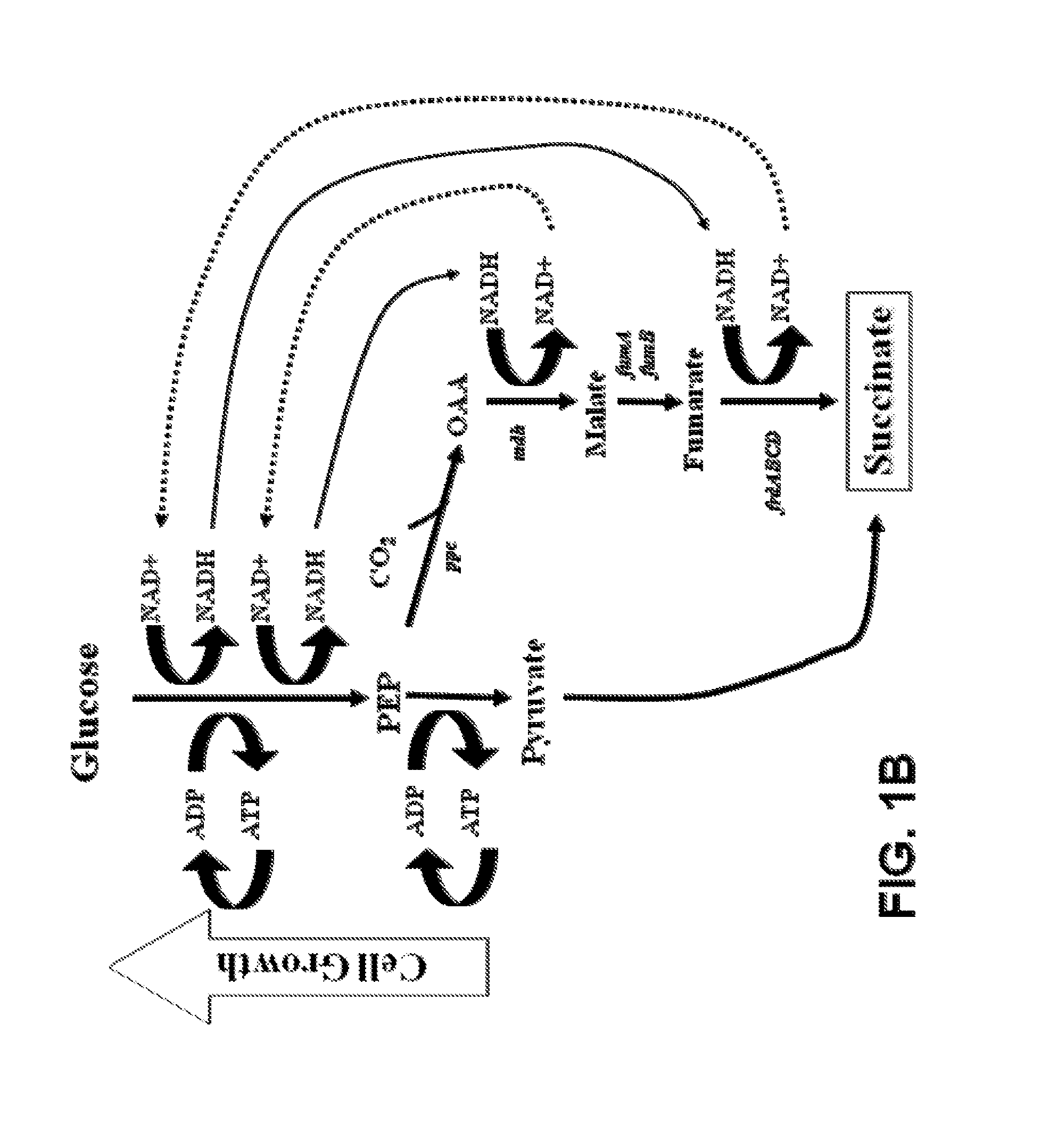
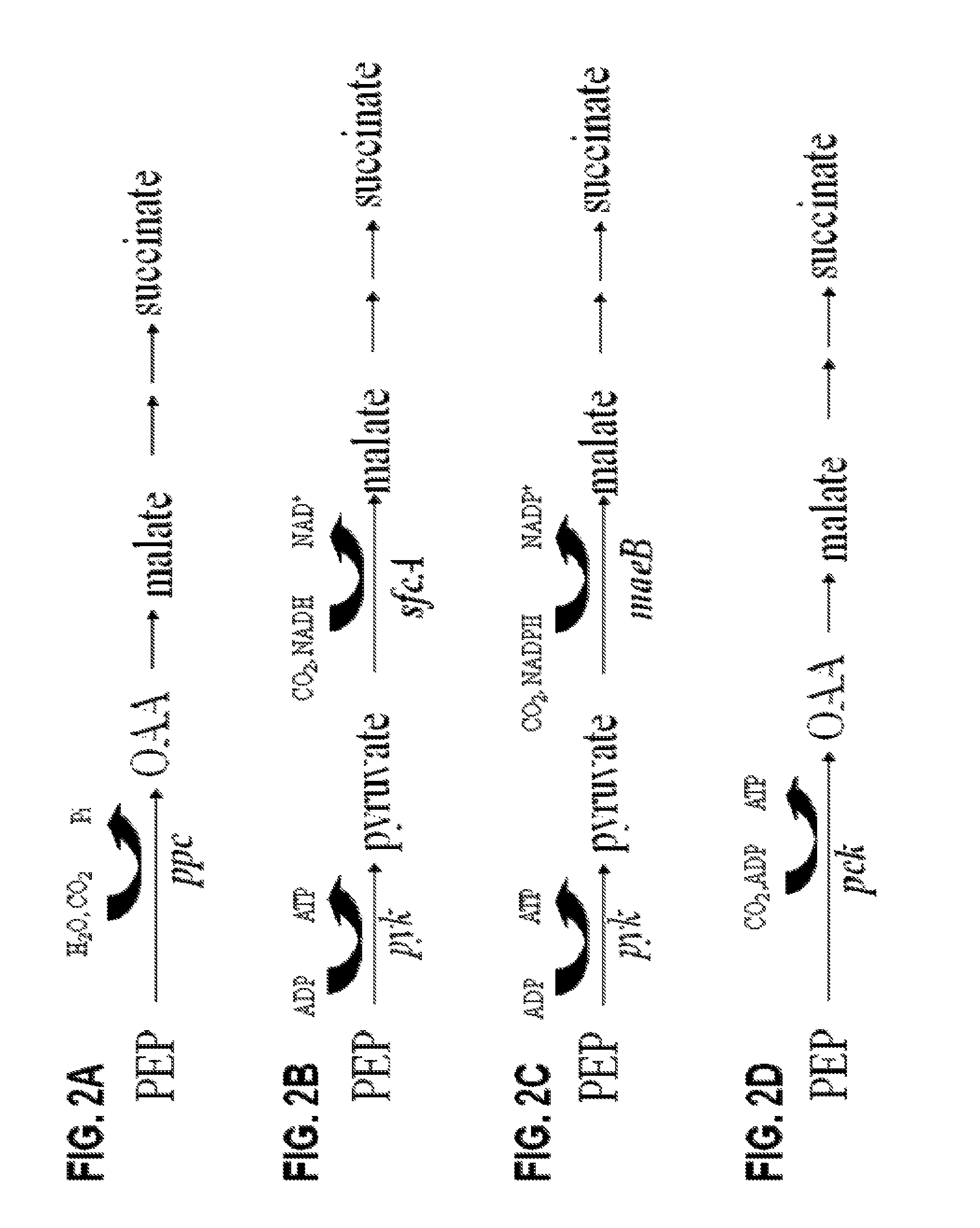
Engineering the pathway for succinate production
InactiveUS20120058530A1Increase overall carbon flowHigh expressionVectorsBacteriaMannheimiaPh control
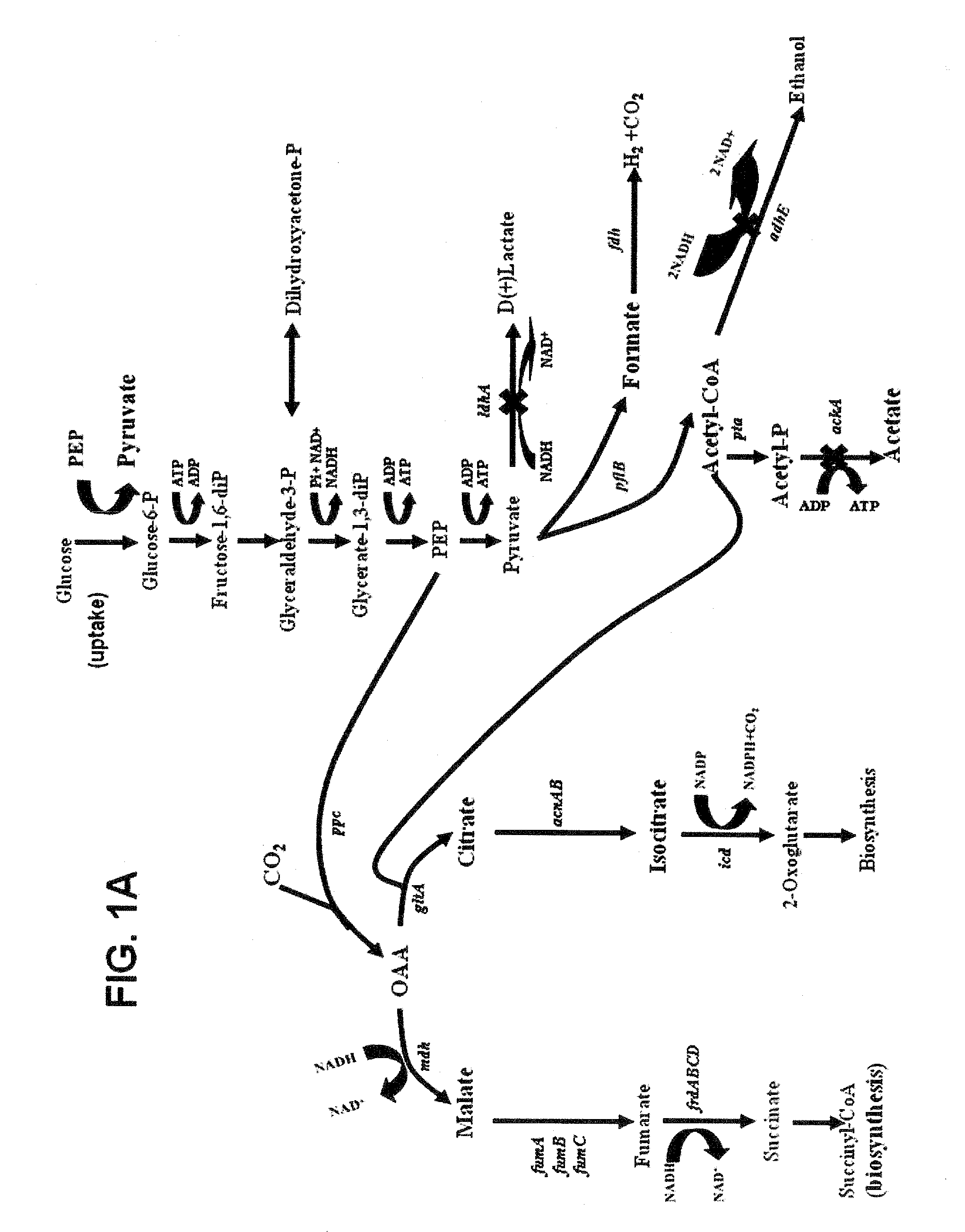
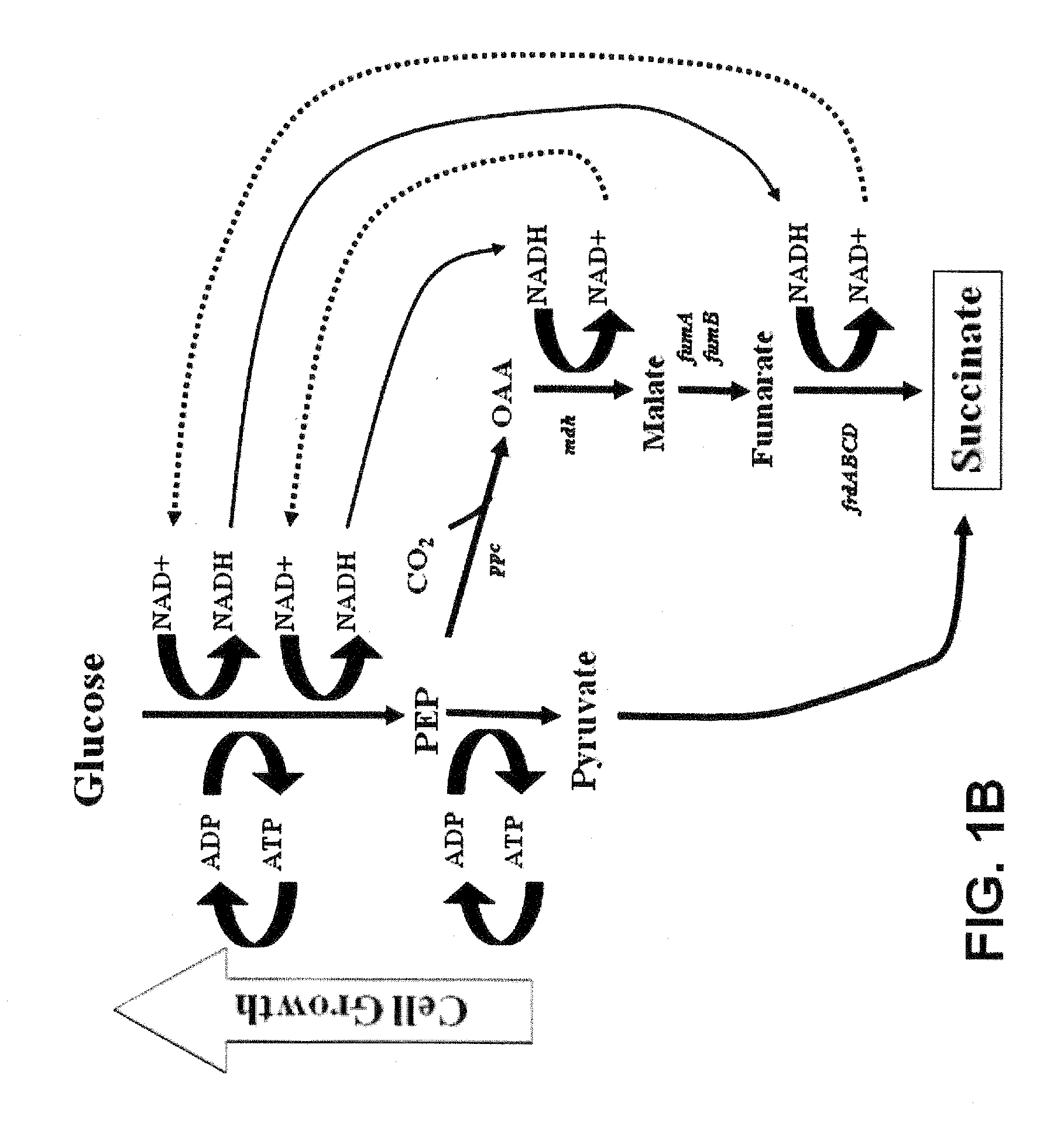
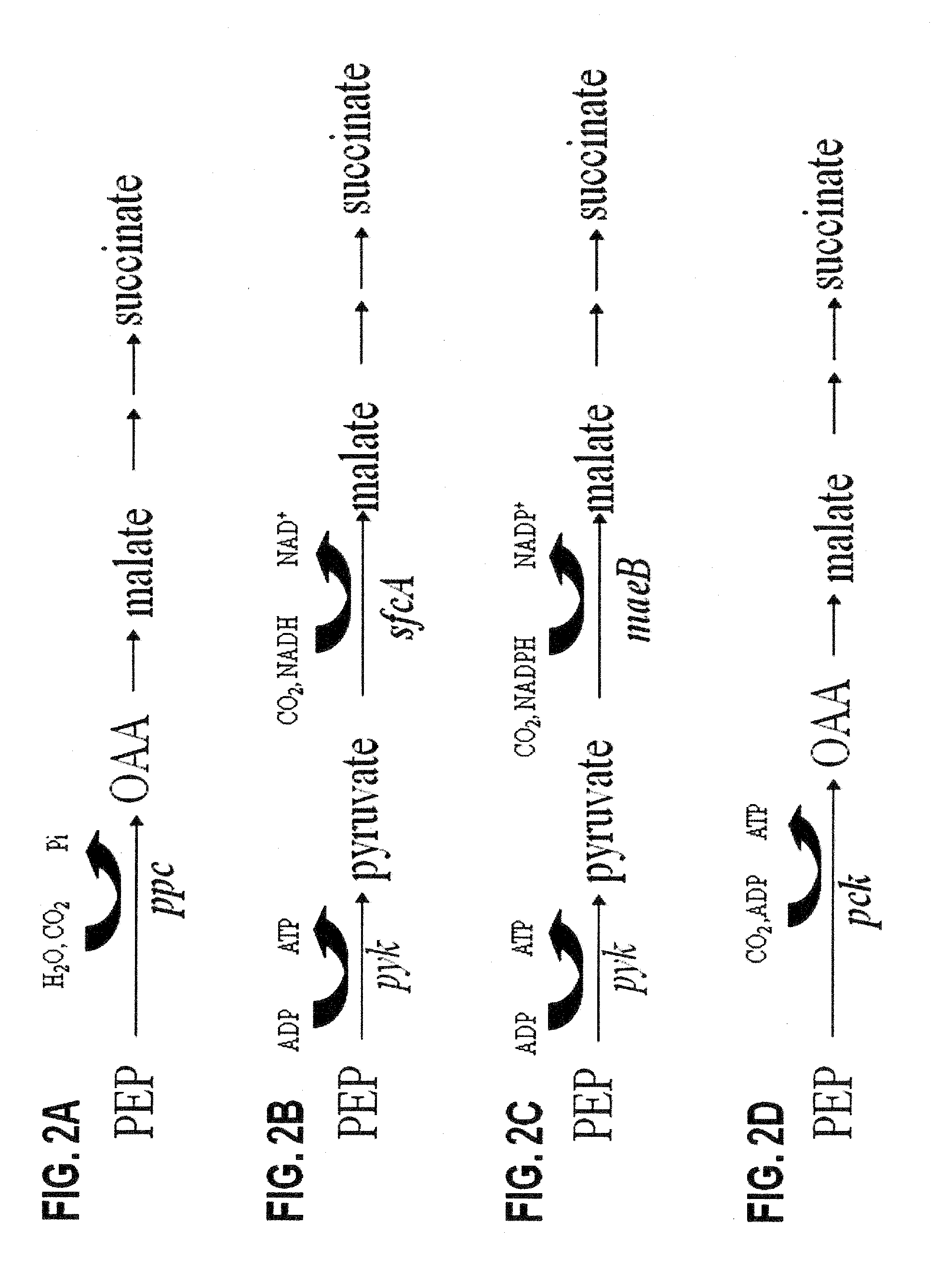
This invention relates to the biocatalysts for the efficient production of succinic acid and / or other products from renewable biological feedstocks. The biocatalysts have a very high efficiency for the growth-coupled production of succinic acid and / or other products from carbohydrate feed stocks as a result of both genetic manipulations and metabolic evolution. More specifically, certain biocatalysts of the present invention produce succinic acid at high titers and yield in mineral salts media during simple pH-controlled, batch fermentation without the addition of any exogenous genetic material. The genetic manipulations of the present invention are concerned with the energy-conserving strategies coupled with the elimination of alternative routes for NADH oxidation other than the routes for succinic acid production. The biocatalysts contain glucose-repressed gluconeogenic phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (pck) depressed by genetic modifications and a genetically-inactivated phosphotransferase system. In terms of succinic acid production efficiency, the biocatalysts of the present invention are functionally equivalent to succinate producing rumen bacteria such as Actinobacillus succinogens and Mannheimia succiniproducens with one difference that the biocatalysts are able to achieve this high level of succinic acid production in a minimal salt medium with carbohydrate source as opposed to the requirement for a rich media for succinic acid production by rumen bacteria.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Supply of phosphoenolpyruvic acid in the synthesis pathway of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased by taking bacillus subtilis (bacillus subtilis 168 delta nagP delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nagA delta nagB delta 1dh delta pta::lox72; delta ctc::p43-Gna1, pP43NMK-AGE-NeuB) as an expression host and knocking out ptsG of a glucose specific enzyme EIICBA component of a phosphotransferase system, and therefore the synthesis passway is enhanced; compared with an original strain, the recombinant bacillus subtilis has the advantages that the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased to 660 mg / L from 190 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for improving N-acetylneuraminic acid production from bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
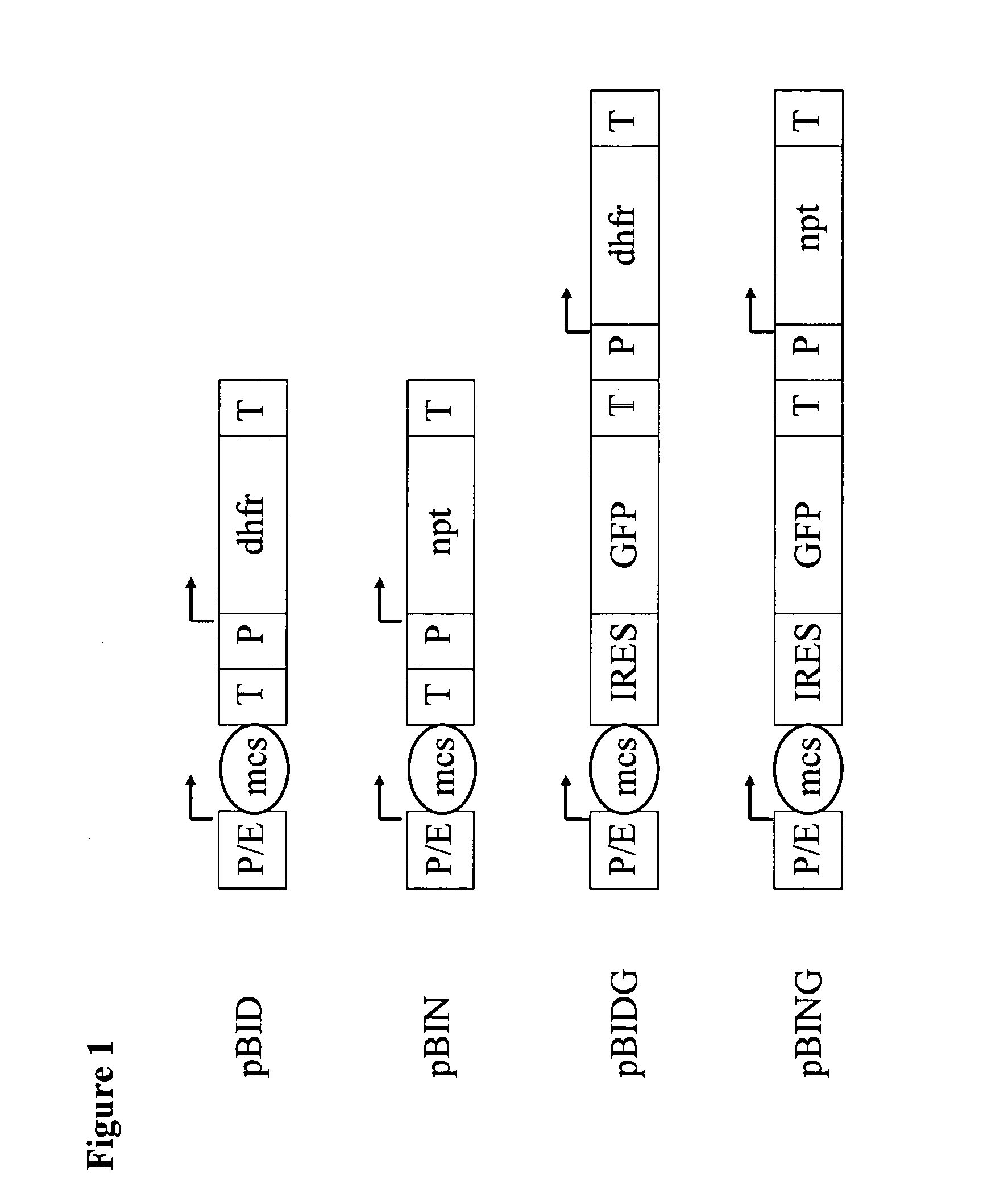
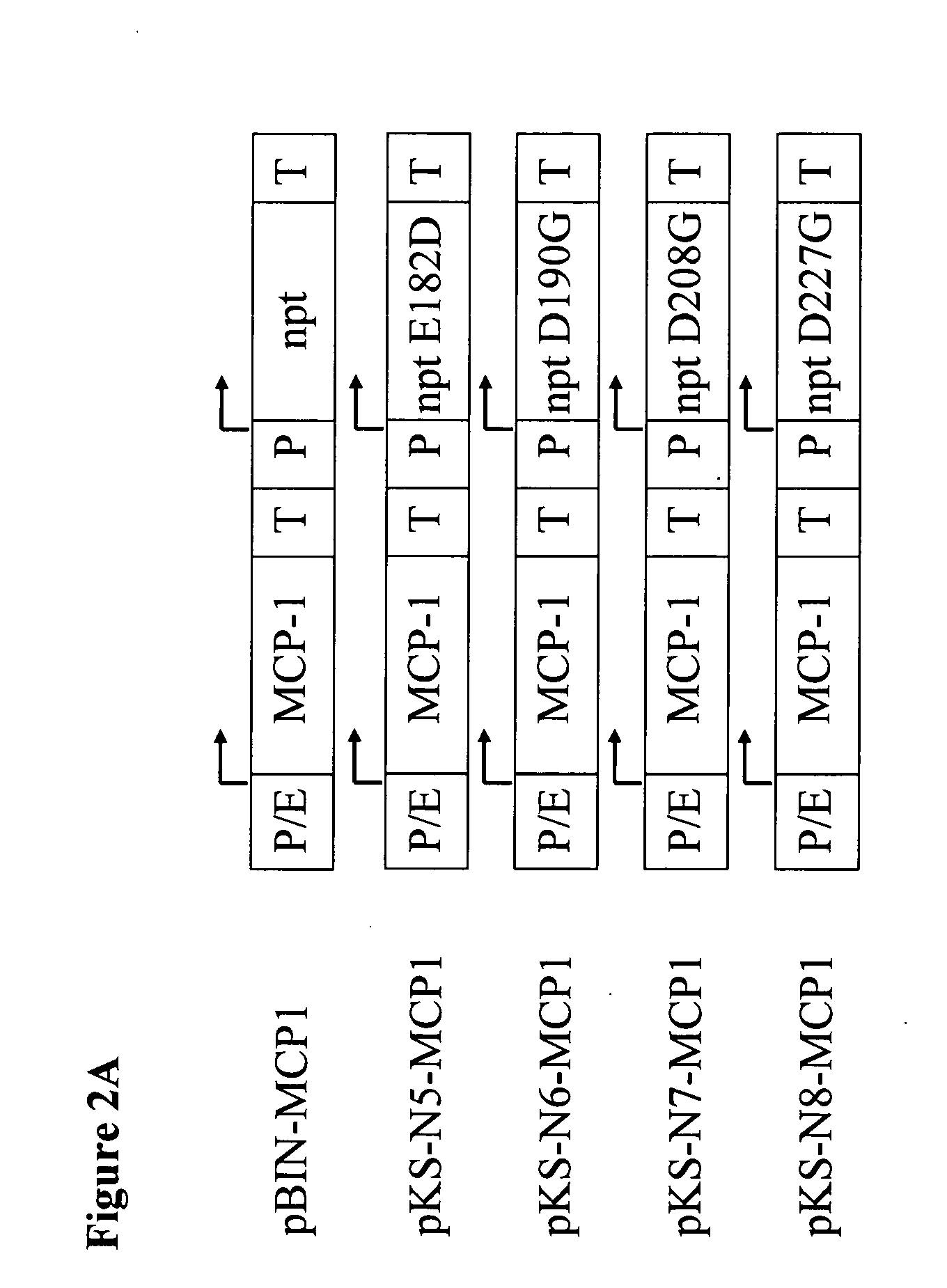
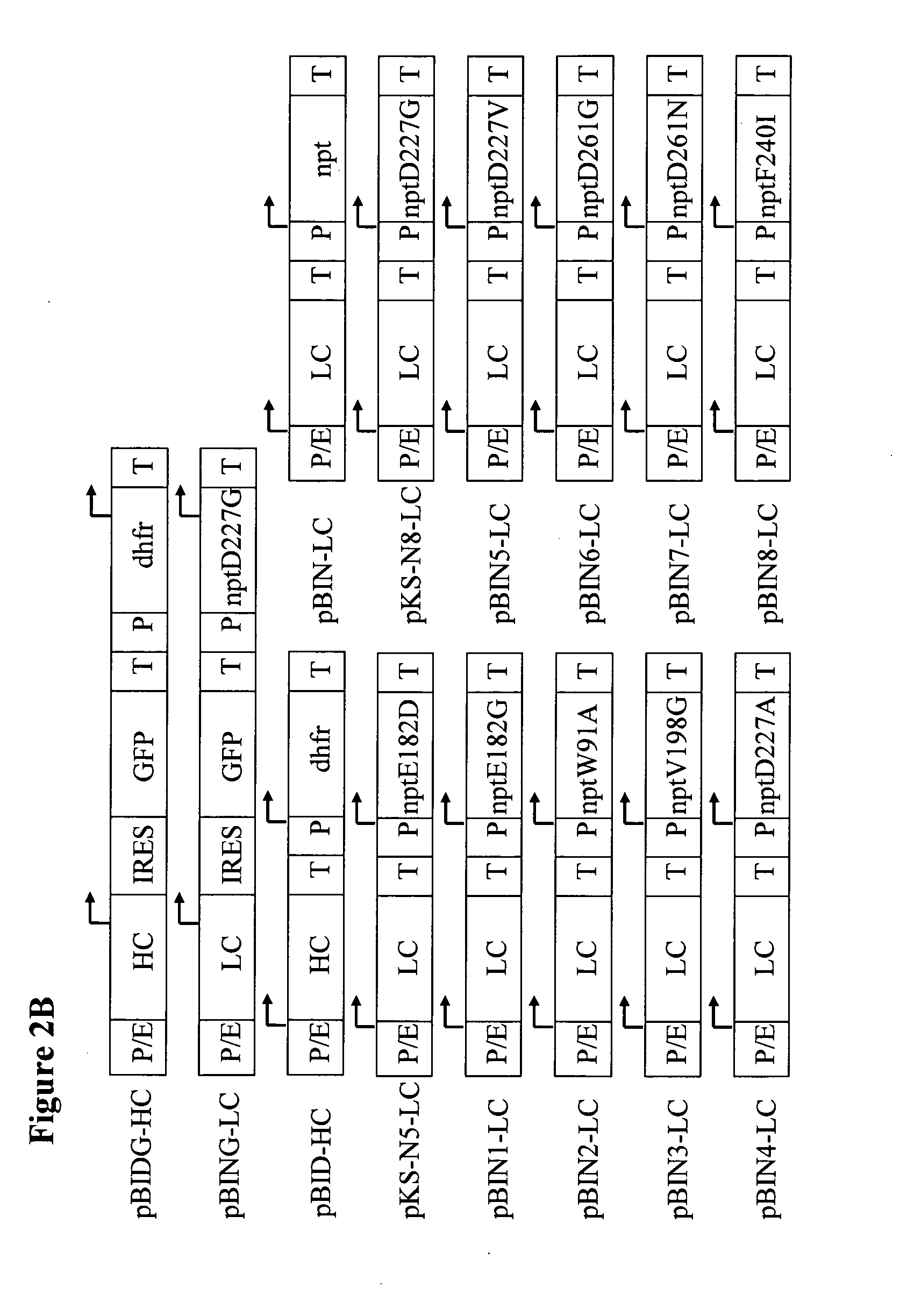
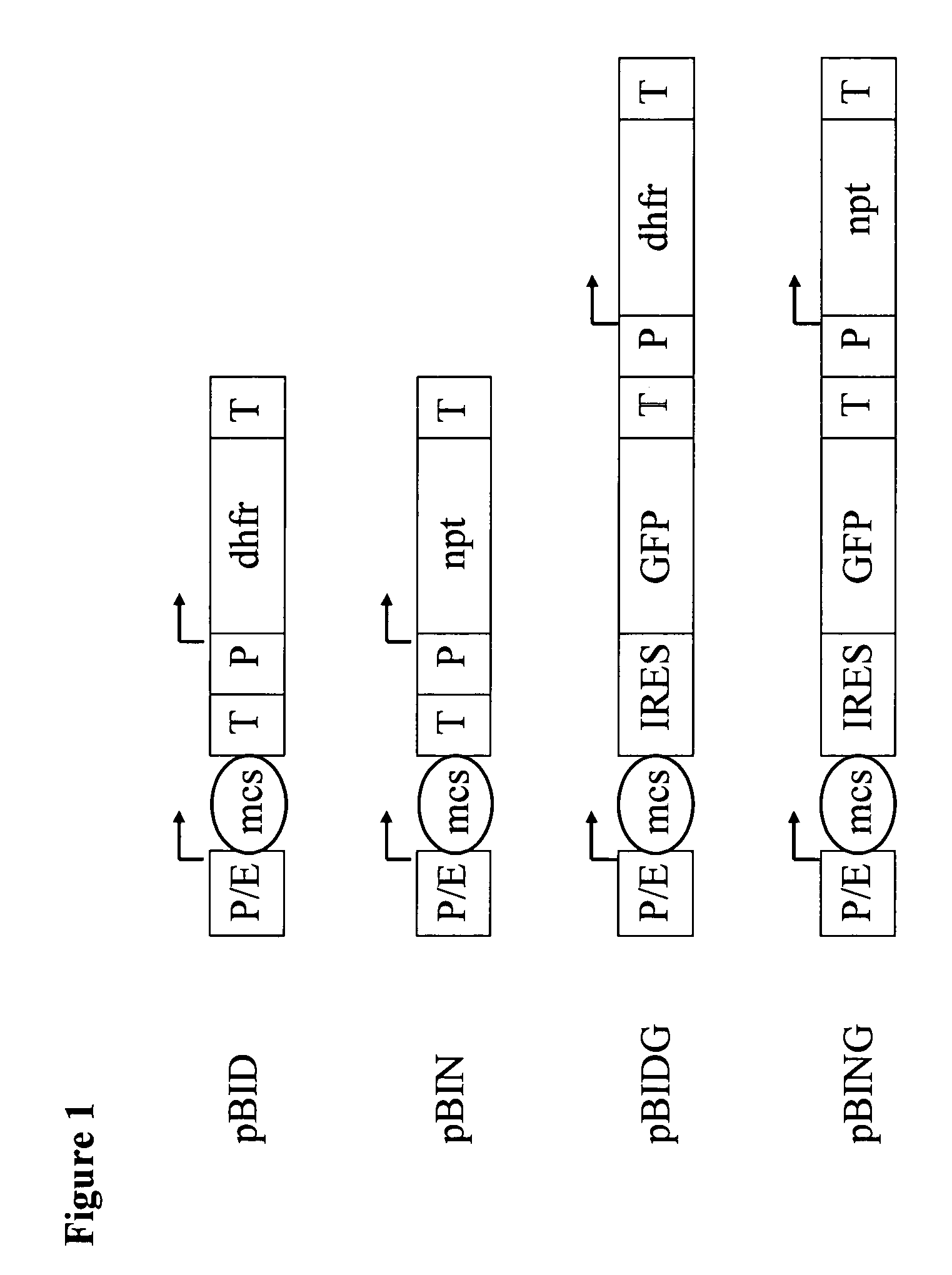
Neomycin-phosphotransferase-genes and methods for the selection for recombinant cells producing high levels of a desired gene product
The invention relates to modified neomycin phosphotransferase genes and their use in a selection method for high-producing recombinant cells. The invention further relates to expression vectors which contain a modified neomycin phosphotransferase gene and a gene of interest functionally linked to a heterologous promoter and a method of preparing heterologous gene products using these expression vectors.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system proteins
InactiveUS6884614B1Increase productionHigh yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesAntisense nucleic acidProtein isolate
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated PTS nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel PTS proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PTS nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated PTS proteins, mutated PTS proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of PTS genes in this organism.
Owner:DAESANG
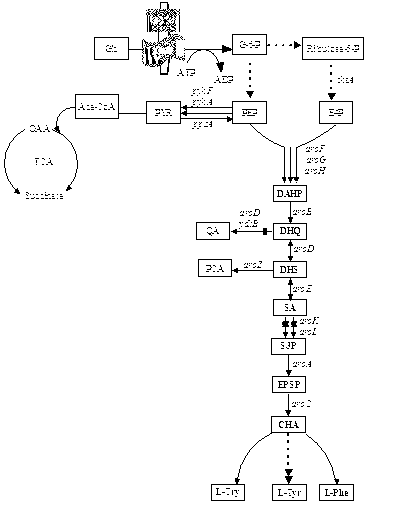
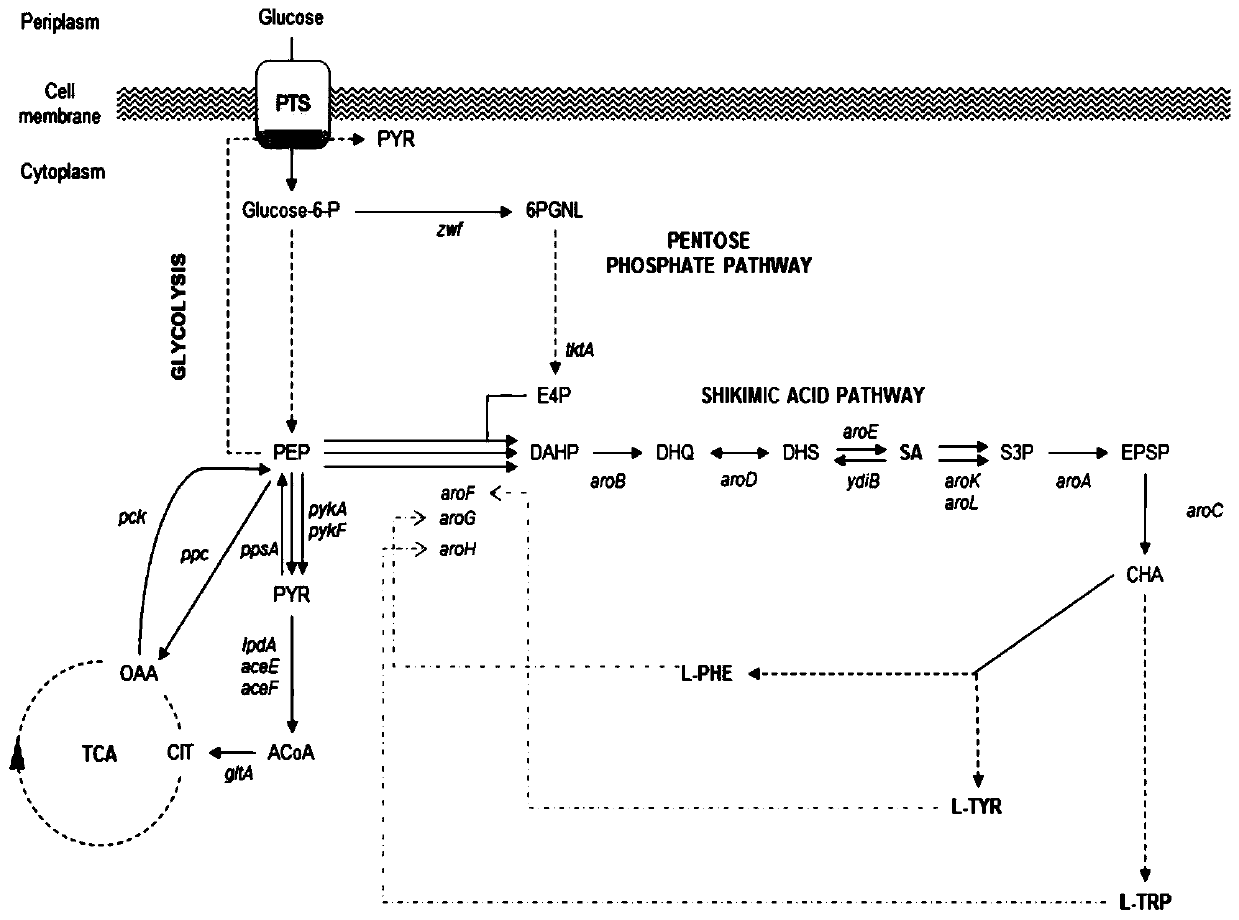
Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102994439AEfficient accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliShikimate kinase
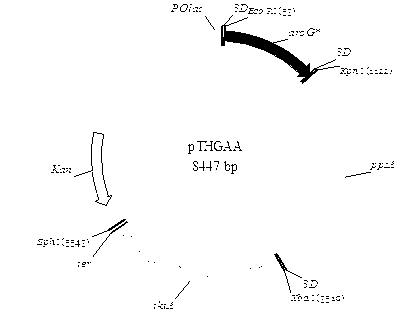
An Escherichia coli recombinant strain producing shikimic acid, and a construction method and application thereof belong to the technical field of microbial gene engineering. The invention firstly utilizes a molecular biology technique to delete shikimic acid kinase I gene (aroK) and shikimic acid kinase II gene (aroL) of Escherichia coli CICIMB0013, and a gene (ptsG) of a key protein EIIBC<Glc> and a quinin acid / shikimic acid dehydrogenase gene (ydiB) of a glucose phosphotransferase system to obtain an Escherichia coli mutant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 (delta aroK, delta aroL, delta ptsG, delta ydiB). The invention also constructs a recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA containing key genes comprising aroG*,ppsA and tktA in a metabolic pathway of shikimic acid; and the recombinant expression plasmid pTHGAA is transferred into the recombinant strain CICIMB0013.SA4 to obtain a recombinant Escherichia coli B0013 (SA4 / pTHGAA) capable of producing shikimic acid efficiently. The Escherichia coli recombinant strain provided by the invention can realize efficient accumulation of shikimic acid in a fermentation process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium and construction method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, and discloses an L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium and a construction method and application thereof. A common pathway of an Escherichia coli central carbon metabolic pathway is modified through a genetic engineering method, a phosphoric enol pyruvic acid-phosphotransferase system with phosphoric enol pyruvic acid as a substrate of escherichia coli is knocked out, a glucose transfer system with non-PEP as a substrate is enhanced, a glucose transfer endocytosis pathway is changed, the L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium is obtained, and consumption of L-tryptophan synthesis precursor phosphoric enol pyruvic acid in the glucose transferring process is avoided, so that the intracellular PEP level is improved, and then the capability of L-tryptophan produced through strain fermentation is improved. An experiment shows that the constructed L-tryptophan production genetically engineered bacterium is an escherichia coli L-tryptophan high-producing strain, L-tryptophan can be effectively accumulated, the yield of the L-tryptophan is improved, and a foundation is laid for industrial production of the L-tryptophan.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
Soluble GlcNAc phosphotransferase
The present invention relates to a soluble GlcNAc phosphotransferase, a method of making the same and a method of phosphorylating with the same.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Neomycin-phosphotransferase-genes and methods for the selection of recombinant cells producing high levels of a desired gene product
The invention relates to modified neomycin phosphotransferase genes and their use in a selection method for high-producing recombinant cells. The invention further relates to expression vectors which contain a modified neomycin phosphotransferase gene and a gene of interest functionally linked to a heterologous promoter and a method of preparing heterologous gene products using these expression vectors.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA KG
General type gene targeting vector
ActiveCN104651402AReduce expressionExpression capacityVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceCloning Site
The invention discloses a general type gene targeting vector, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The general type gene targeting vector uses neomycin phosphotransferase and EGFP as positive selective markers and DsRed as a negative selective marker; two sides of a positive selective marker gene expression frame respectively contain LoxP sites which are arranged in a same direction; and the LoxP sites respectively contain multiple cloning sites which include rare restriction enzyme sites nearby, so that the convenience for the cloning of a gene targeting arm is achieved. The general type gene targeting vector contains two homing restriction enzyme sites, and the two homing restriction enzyme sites are respectively I-CeuI and I-SceI and can be used as general endonuclease sites for linearizing the vector. The general type gene targeting vector provided by the invention not only has the functions of single drug and double fluorescent screening, but also provides a new material for an animal safety transgenic technology because the contained LoxP sites are capable of mediating the high-efficiency deletion reaction of the selective markers, and has significant application prospects.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Double-tagging microbial cell biosensor for detecting N-acyl homoserine lactone
The invention relates to a double-tagging microbial cell biosensor for detecting N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL), and the biosensor is suitable for detection of AHL and characterization of host cells in the environment. The cell biosensor comprises: Escherichia coli used as host cells for carrying recombinant plasmids; recombinant plasmid containing an ahlI promoter responding to AHL, a cherry red fluorescent protein reporter gene mCherry and an AHL regulatory protein gene ahlR; and a neomycin phosphotransferase promoter gene nptII for characterization of host bacteria, a green fluorescent protein reporter gene gfp and a T1-4 pUC19 plasmid of four terminator rrnb tandem sequence. According to the biosensor, constitutive type of expression green fluorescent protein is used to characterize the host bacteria; the response time to AHL is 6 h; and the minimum detectable concentration of AHL is 50 nmol / L. The biosensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, fast response, low cost and simple operation, and can be widely applied to detection of AHL and host characterization in the environment.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
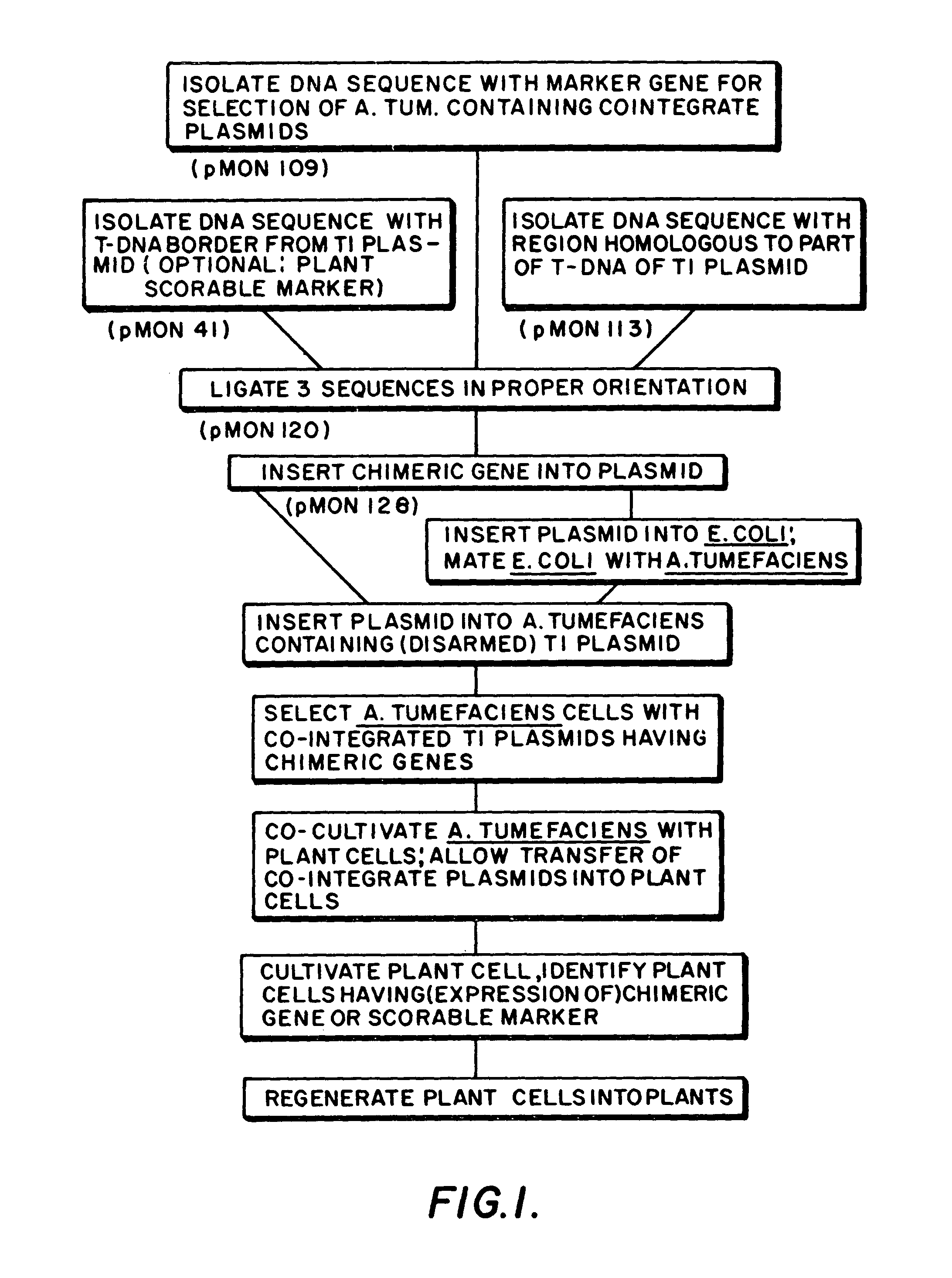
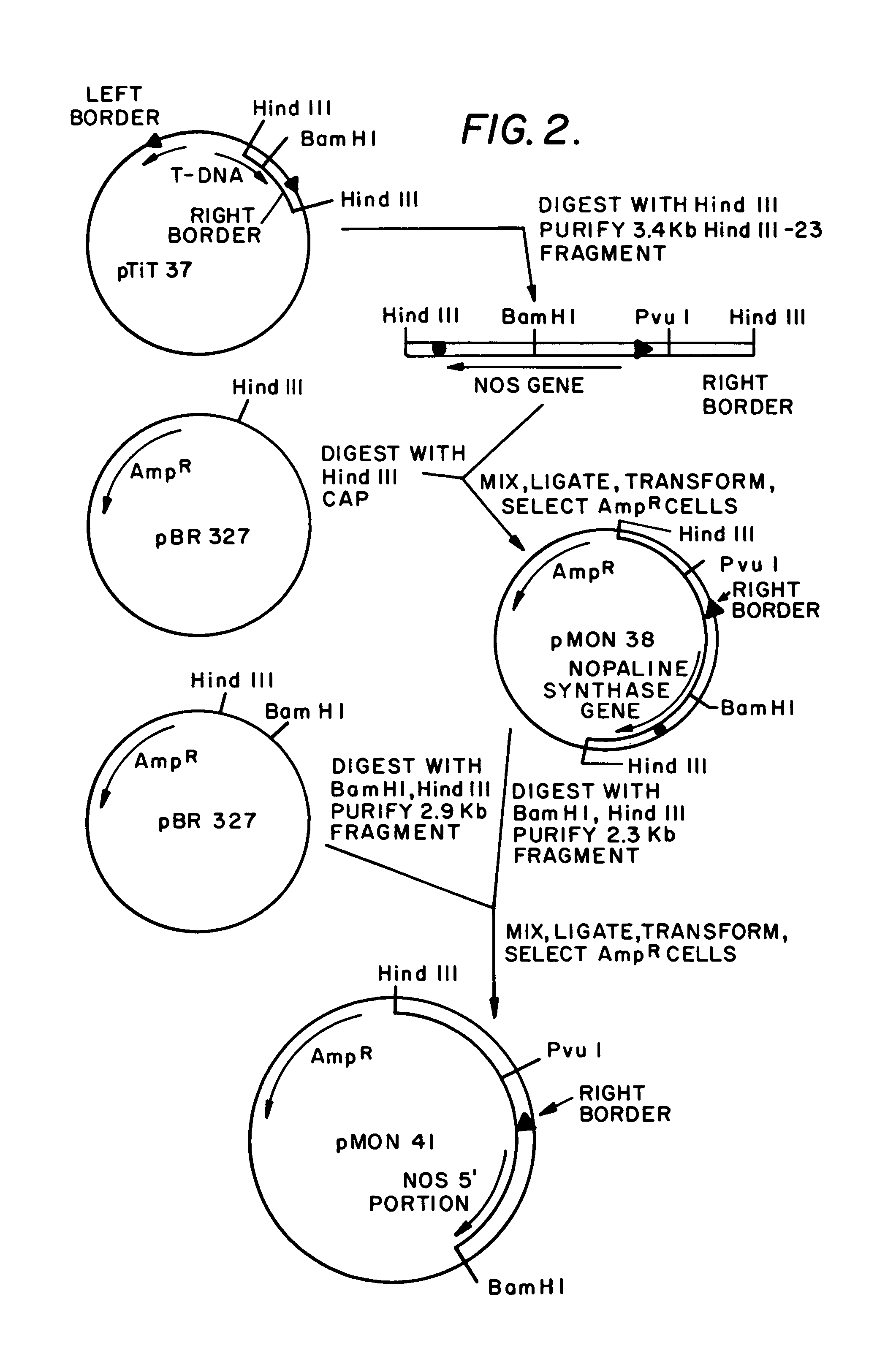
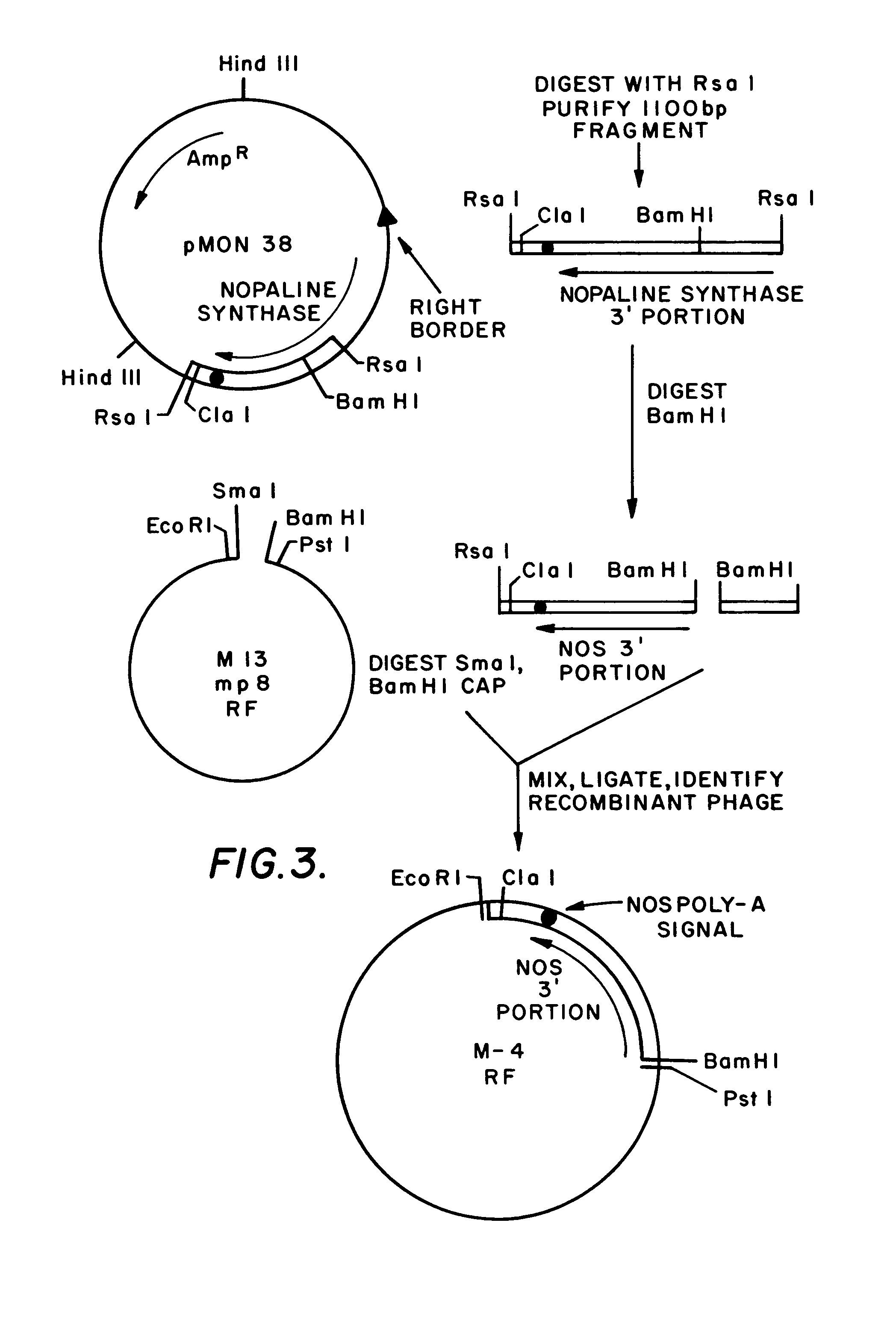
Plasmids for transforming plant cells
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Engineering the pathway for succinate production
This invention relates to the biocatalysts for the efficient production of succinic acid and / or other products from renewable biological feedstocks. The biocatalysts have a very high efficiency for the growth-coupled production of succinic acid and / or other products from carbohydrate feed stocks as a result of both genetic manipulations and metabolic evolution. More specifically, certain biocatalysts of the present invention produce succinic acid at high titers and yield in mineral salts media during simple pH-controlled, batch fermentation without the addition of any exogenous genetic material. The genetic manipulations of the present invention are concerned with the energy-conserving strategies coupled with the elimination of alternative routes for NADH oxidation other than the routes for succinic acid production. The biocatalysts contain glucose-repressed gluconeogenic phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase (pck) derepressed by genetic modifications and a genetically-inactivated phosphotransferase system. In terms of succinic acid production efficiency, the biocatalysts of the present invention are functionally equivalent to succinate producing rumen bacteria such as Actinobacillus succinogens and Mannheimia succiniproducens with one difference that the biocatalysts are able to achieve this high level of succinic acid production in a minimal salt medium with carbohydrate source as opposed to the requirement for a rich media for succinic acid production by rumen bacteria.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
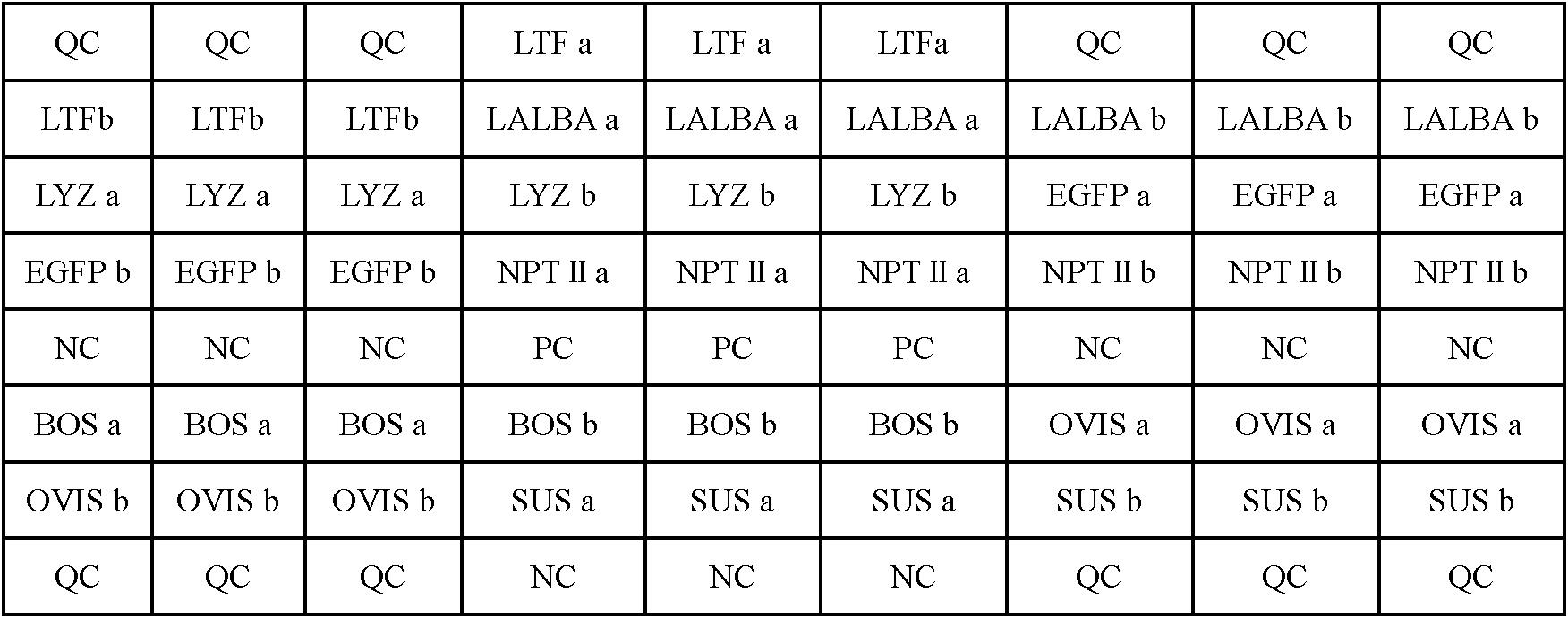
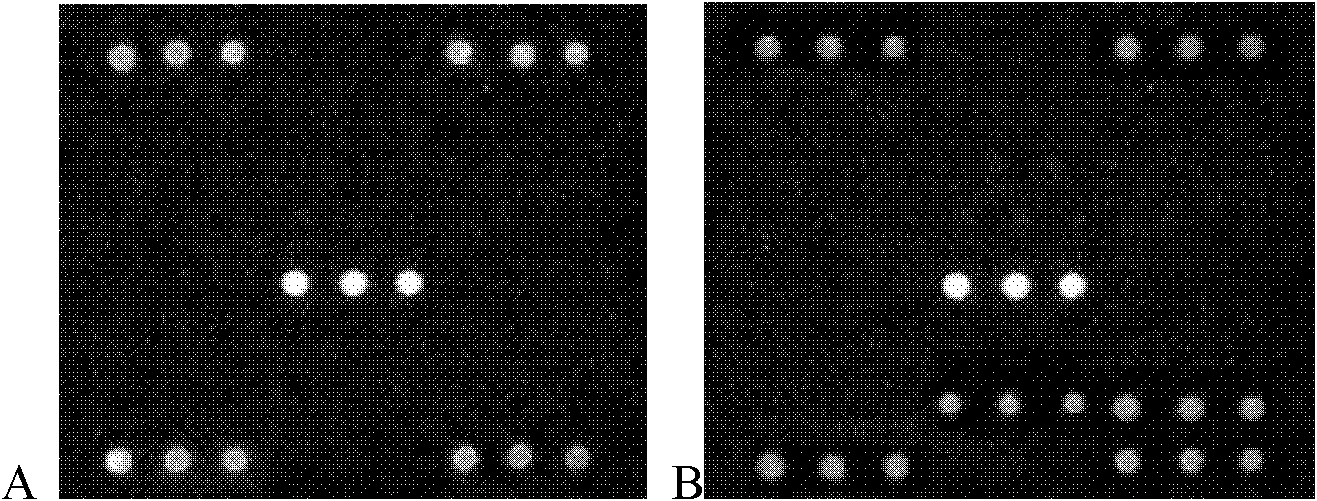
Gene chip for detecting transgenic cattle and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102181553AScreening fitStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementGreen fluorescent proteinLysobacter enzymogenes
The invention discloses a gene chip for detecting transgenic cattle and a preparation method and application thereof. The chip provided by the invention contains solid phase carrier and an oligonucleotide probe fixed on the carrier, wherein the oligonucleotide probe contains a detection probe and a quality control probe; and the detection probe is a specific probe of mitochondrial genes of cattle, sheep and pig, human lactoferrin gene, human lysozyme gene, human-alpha-lactoalbumin gene, green fluorescent protein gene and neomycin phosphotransferase gene. By adopting the gene chip and the construction method to detect transgenic cattle, the accuracy, specificity and sensitivity are all higher; and the gene chip is suitable for the high throughout screening of transgenic cattle.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF INSPECTION & QUARANTINE
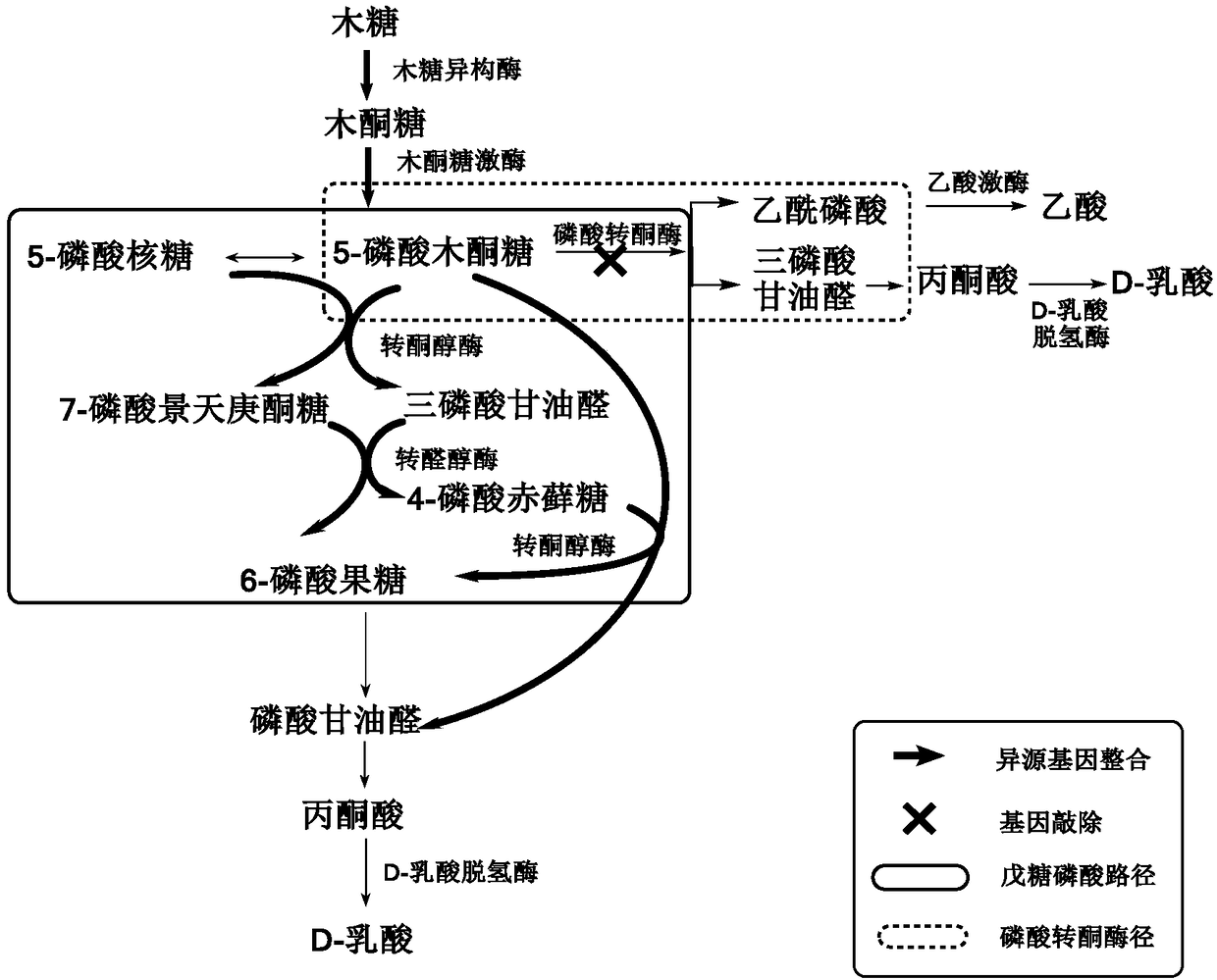
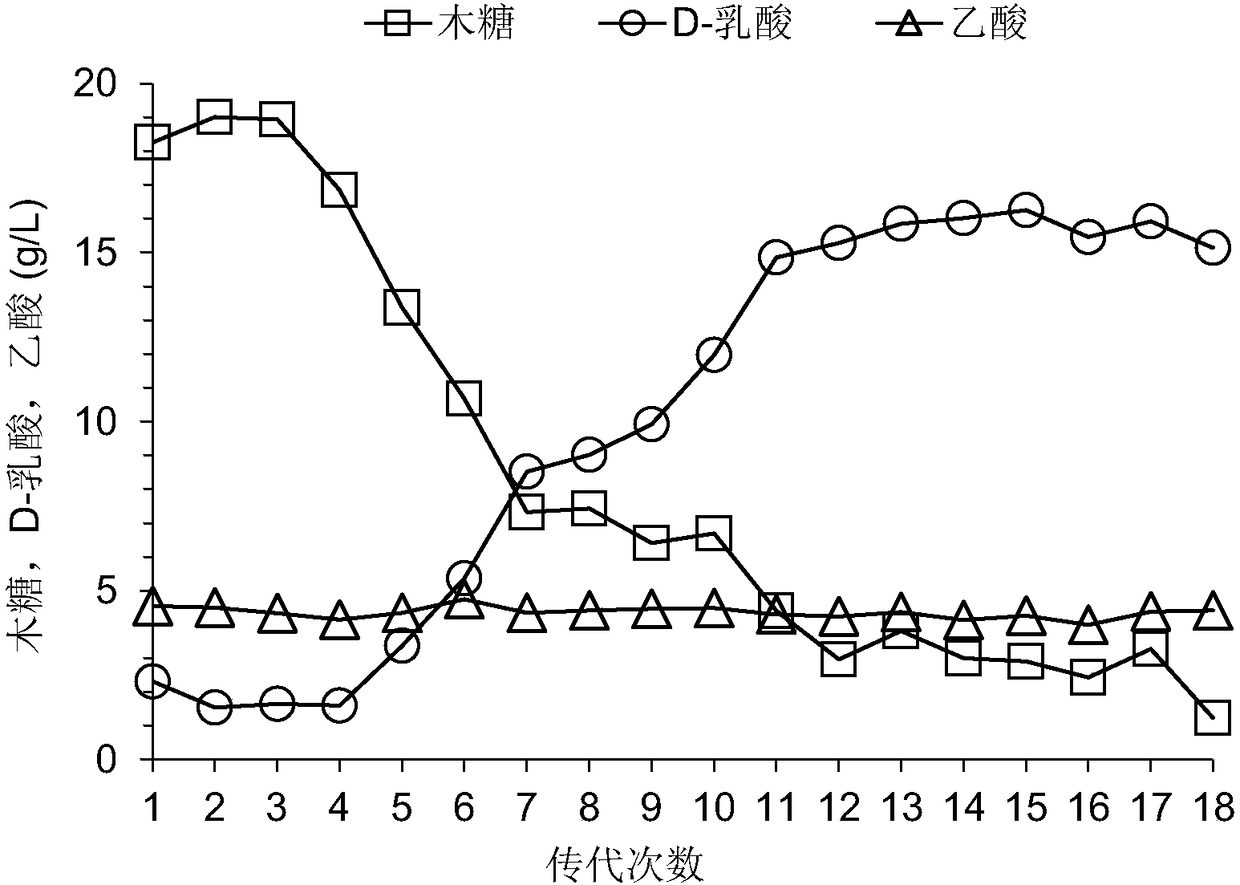
Building method of pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 for producing D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose
The invention discloses a building method of pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 for producing D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following building steps of integrating heterogenous xylose isomerase, xylulokinase, transketolase and transaldolase encoding genes onto pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 (with the preservationnumber being CGMCC NO.8665) genomes by using a thermosensitive knock-out system; knocking out phosphotransferase encoding genes so as to block the generation of byproducts of acetic acids; the capability of the engineering strain for co-fermenting glucose and xylose is obviously improved through an adaptive domestication strategy. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the building of the xylose metabolism path is successfully realized for the first time; the engineering strain for producing optical pure D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose at high efficiency is obtained, is named as P.acidilactici ZY15, and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO.13612.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sensor detecting method for neomycin phosphoric acid transferase gene in transgene plants
ActiveCN101260440AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater bathsPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a sensor detecting method for neomycin phosphotransferase genes in transgene plants, which is characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps that: an amplification reactant namely a double-strand target sequence of neomycin phosphotransferase gene is obtained through loop-mediated isothermal amplification, the double-strand target sequence is pyrolyzed to single-strand target sequences in water bath, the single-strand target sequences are in self assembly fixture on the surface of a gold electrode, and a target sequence modified electrode of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene is obtained, and then nanometer lead sulfide is marked with a probe sequence from the neomycin phosphotransferase gene to obtain a marked probe sequence. The marked probe sequence and the target sequence on the target sequence modified electrode are performed molecular hybridization, and performed electrochemical detection by a coordinate mercury plating anodic stripping method to detect corresponding lead ions. The sensor detecting method for the neomycin phosphotransferase genes in transgene plants has the advantages of rapidness, strong specificity, high sensitivity and convenient use.
Owner:中谱安信(青岛)检测科技有限公司
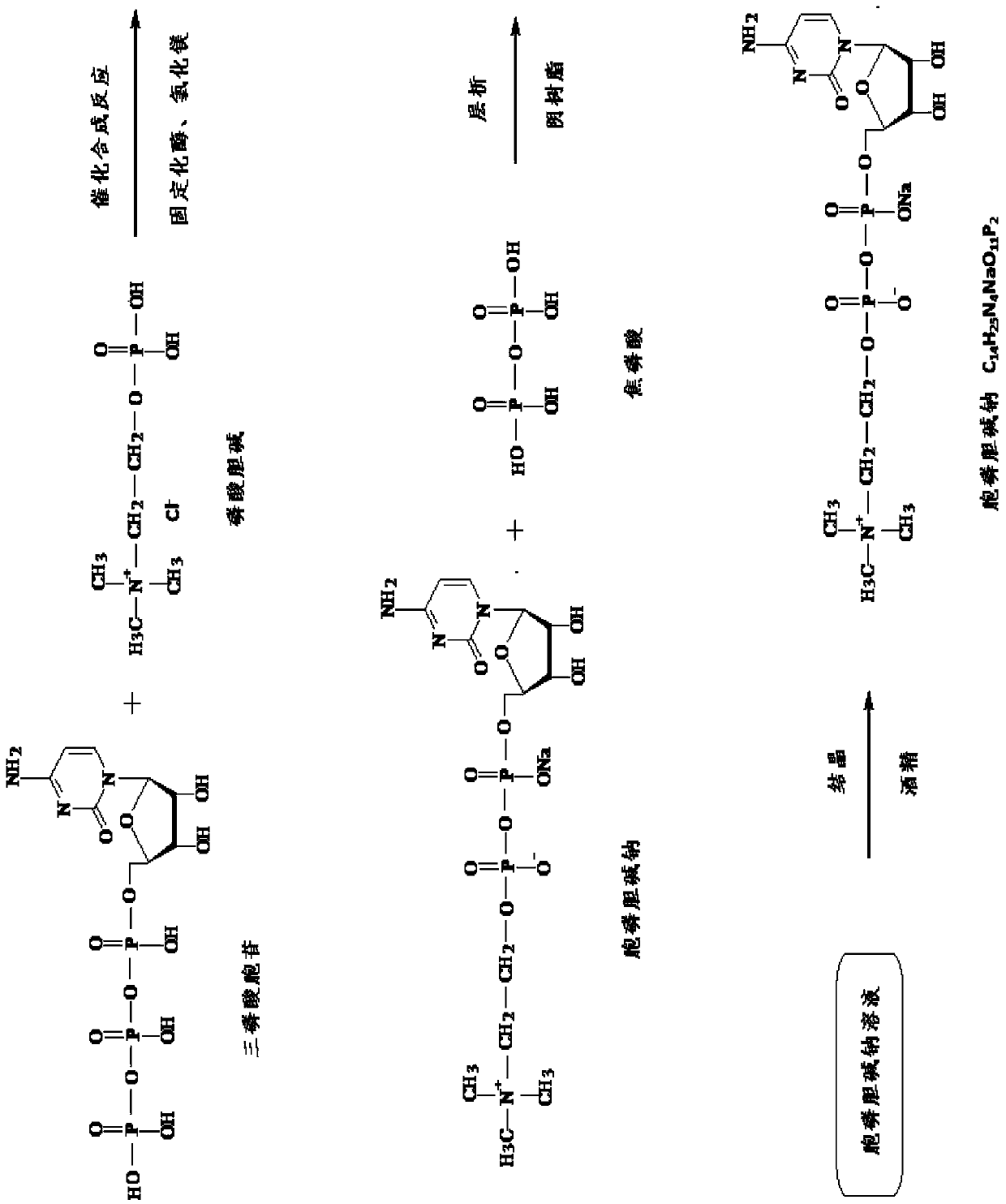
Method for catalytically producing citicoline sodium with immobilized enzyme
ActiveCN103849666AAvoid pollutionAvoid processing powerTransferasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphorylcholine
The invention provides a method for catalytically producing citicoline sodium with an immobilized enzyme. The method comprises the following steps: by utilizing engineered escherichia coli of a molecularly cloned cytidine phosphotransferase gene for fermentation, preparing cytidine phosphotransferase, and preparing cytidine phosphotransferase liquid through purification; immobilizing cytidine phosphotransferase; by using phosphorylcholine and cytidine disodium triphosphate as raw materials, catalytically generating citicoline with immobilized cytidine phosphotransferase. The method is simple in production process, short in production cycle and low in production cost and can be widely applied to industrial production of citicoline.
Owner:KAIPING GENUINE BIOCHEM PHARMA
Recombinant bacterium with high biomass and/or high growth speed, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105002105AIncrease biomassFast growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliKinase
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium with high biomass and / or high growth speed, and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant bacterium is characterized in that the recombinant bacterium with higher biomass and / or growth speed than a receptor bacterium is obtained through A1, A2 and A3 reconstruction of the receptor bacterium or A1 and A2 reconstruction of the receptor bacterium; the A1 is characterized by knocking out phosphotransferase Gsubunit gene of the receptor bacterium; the A2 is characterized by knocking out galactose inhibitor gene of the receptor bacterium; the A3 is characterized by inducting glucose kinase gene to the receptor bacterium; and the receptor bacterium is Escherichia coli, lactobacillus, streptococcus or hemophilus. The recombinant bacterium with high biomass and / or high growth speed constructed in the invention and a neurosporene producing recombinant bacterium have high application prospects and exploitation values in the fields of biological researches and medical science.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Orynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding phosphoenolpyruvate sugar phosphotransferase system proteins
The present invention describes isolated nucleic acid molecules encoding novel PTS proteins of Corynebacterium glutamicum, which are referred to as PTS nucleic acid molecules. The present invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PTS nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The present invention also further provides isolated PTS proteins, PTS muteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides, and methods based on Corynebacterium glutamicum PTS genetic engineering to improve the production of desired compounds by this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
Corynebacterium glutamicum genes encoding phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system proteins
InactiveUS20050191733A1High yieldIncrease productionSugar derivativesBacteriaBiological bodyAntisense nucleic acid
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated PTS nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel PTS proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PTS nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated PTS proteins, mutated PTS proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of PTS genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF SE
Specific expression carrier of bec gene in floral organ
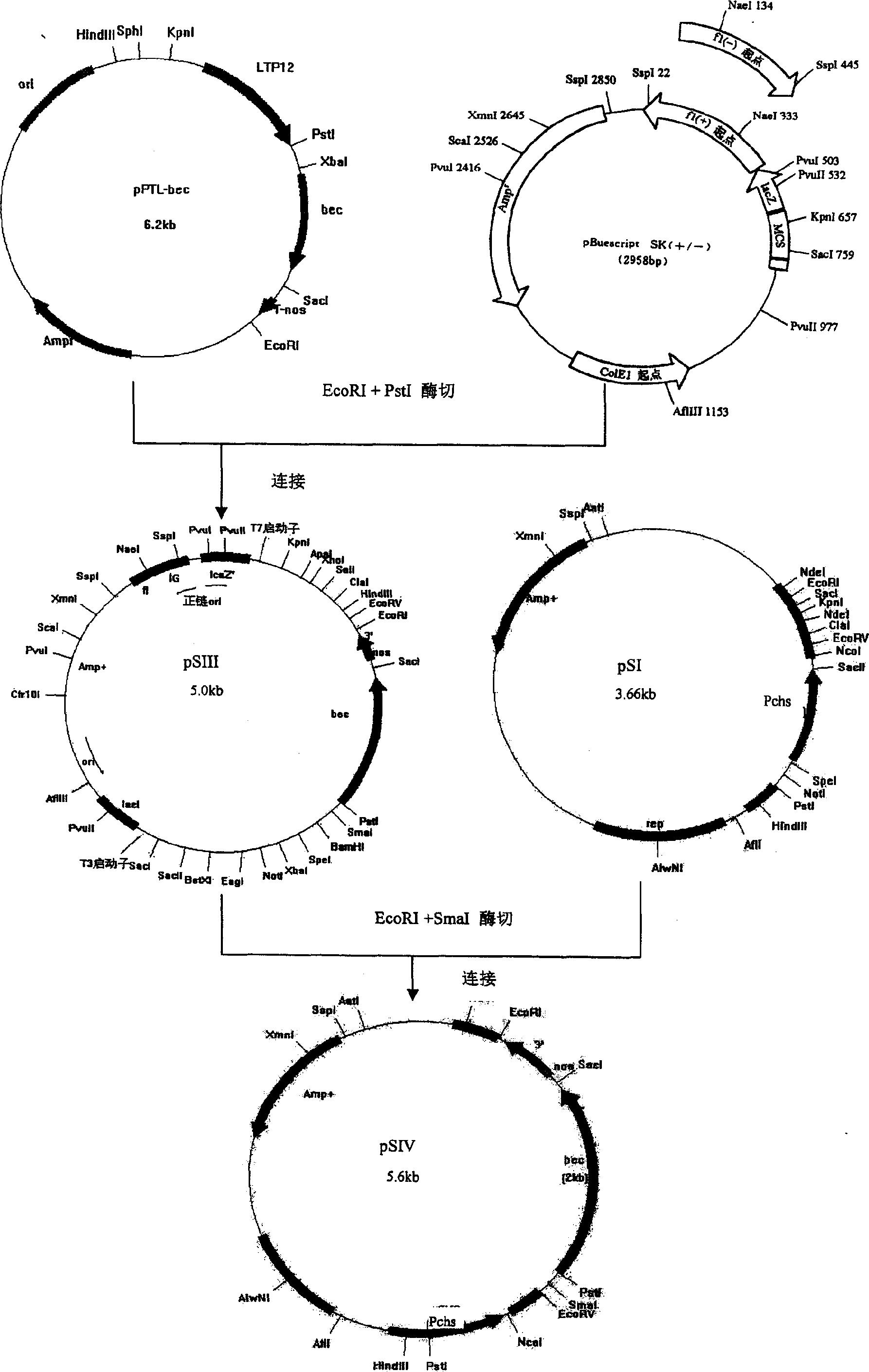
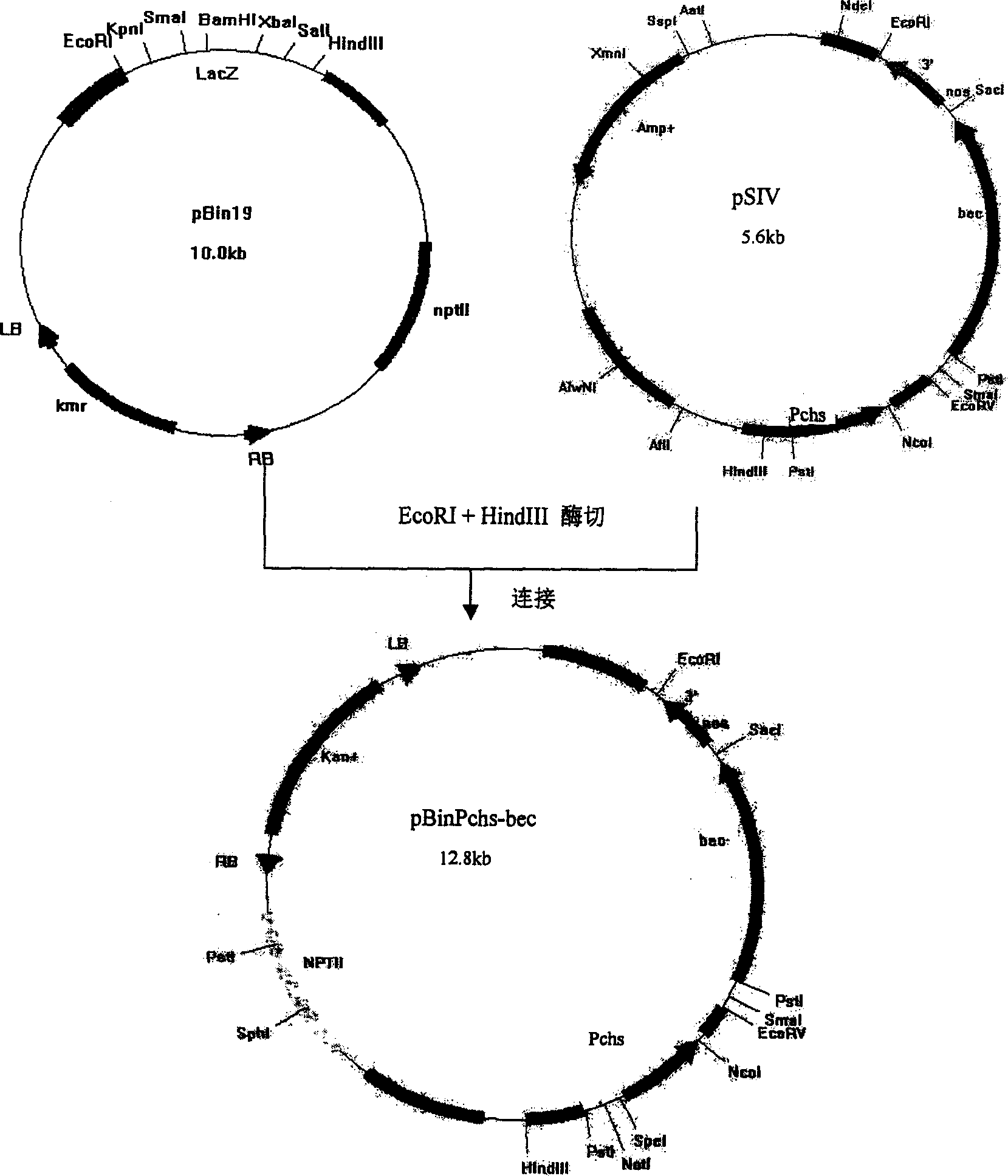
InactiveCN1715415AChange colorEasy to viewFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionIndigoidineDioxygenase
The present invention discloses one specific expression vector of bec gene in floral organ, and the vector contains promoter chalcone synthetase gene chs promoter Pchs, indole dioxygenase gene bec, terminator nos, screening marker gene NPTII and LB sequence and RB sequence expressed specifically in floral organ. The vector features that the bec gene is set under the regulation of floral organ specifically expressing promoter Pchs. Loading the vector into flower can create indigoidine specifically in floral organ to alter the color of flower and raise the enjoying value of flower.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
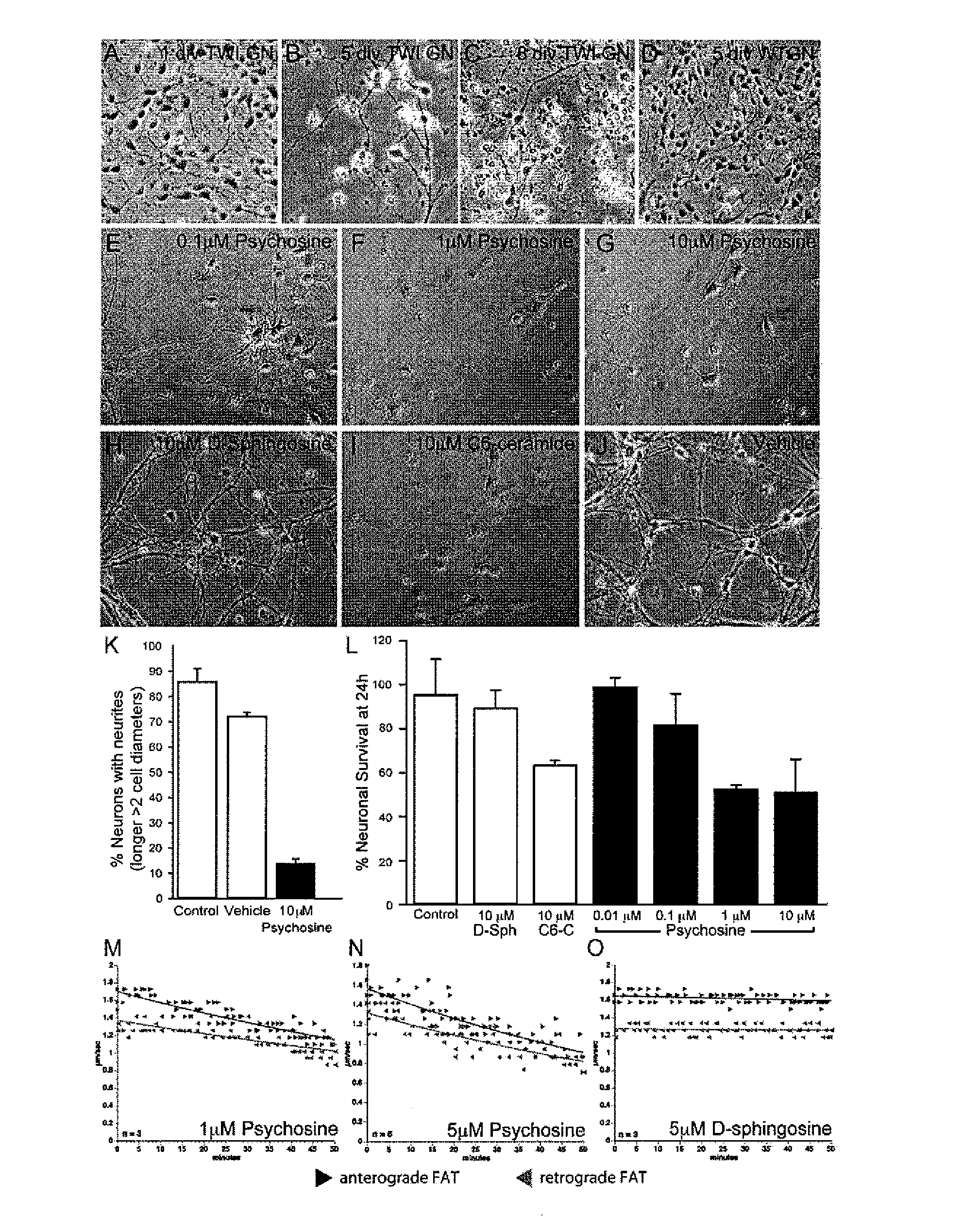
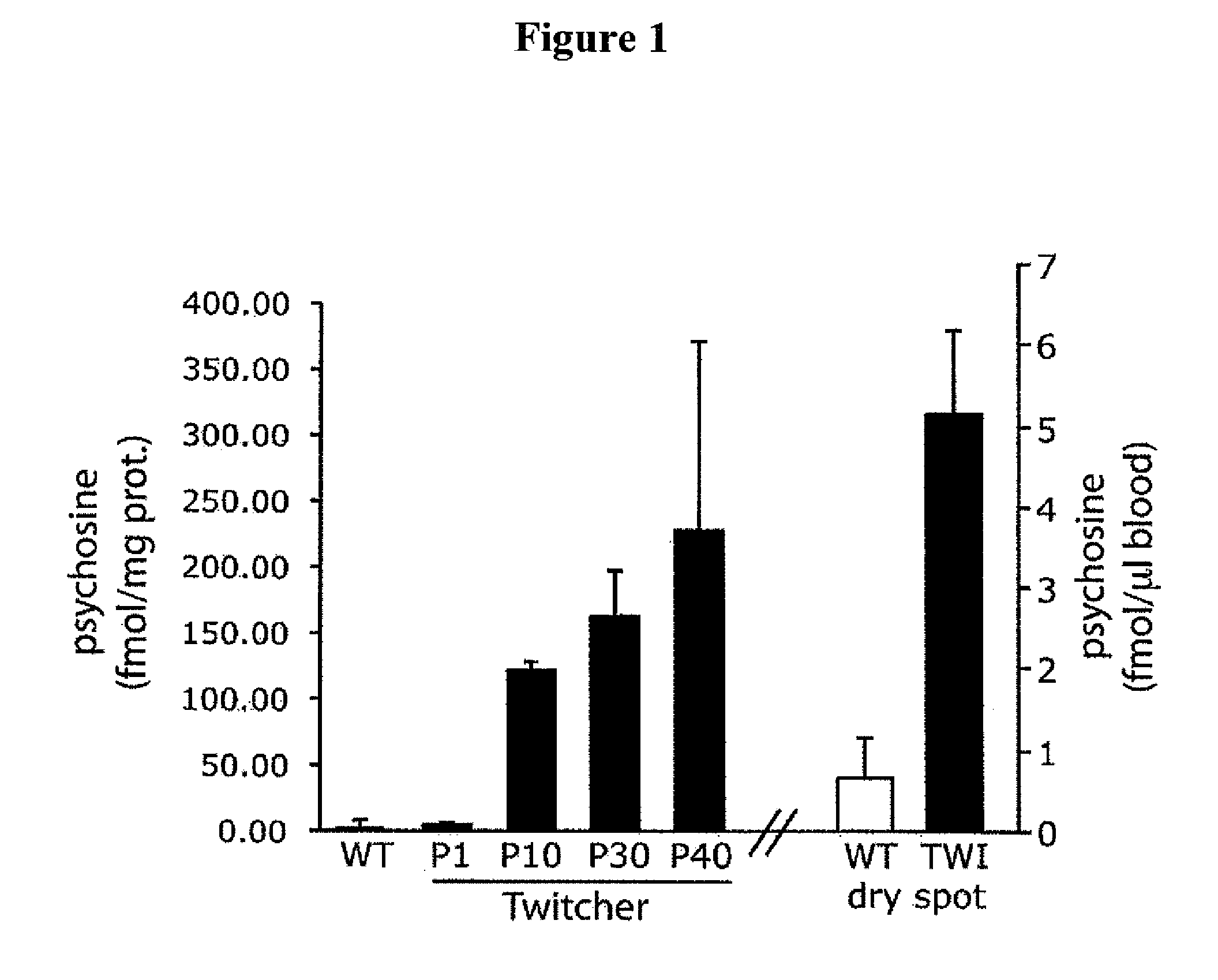
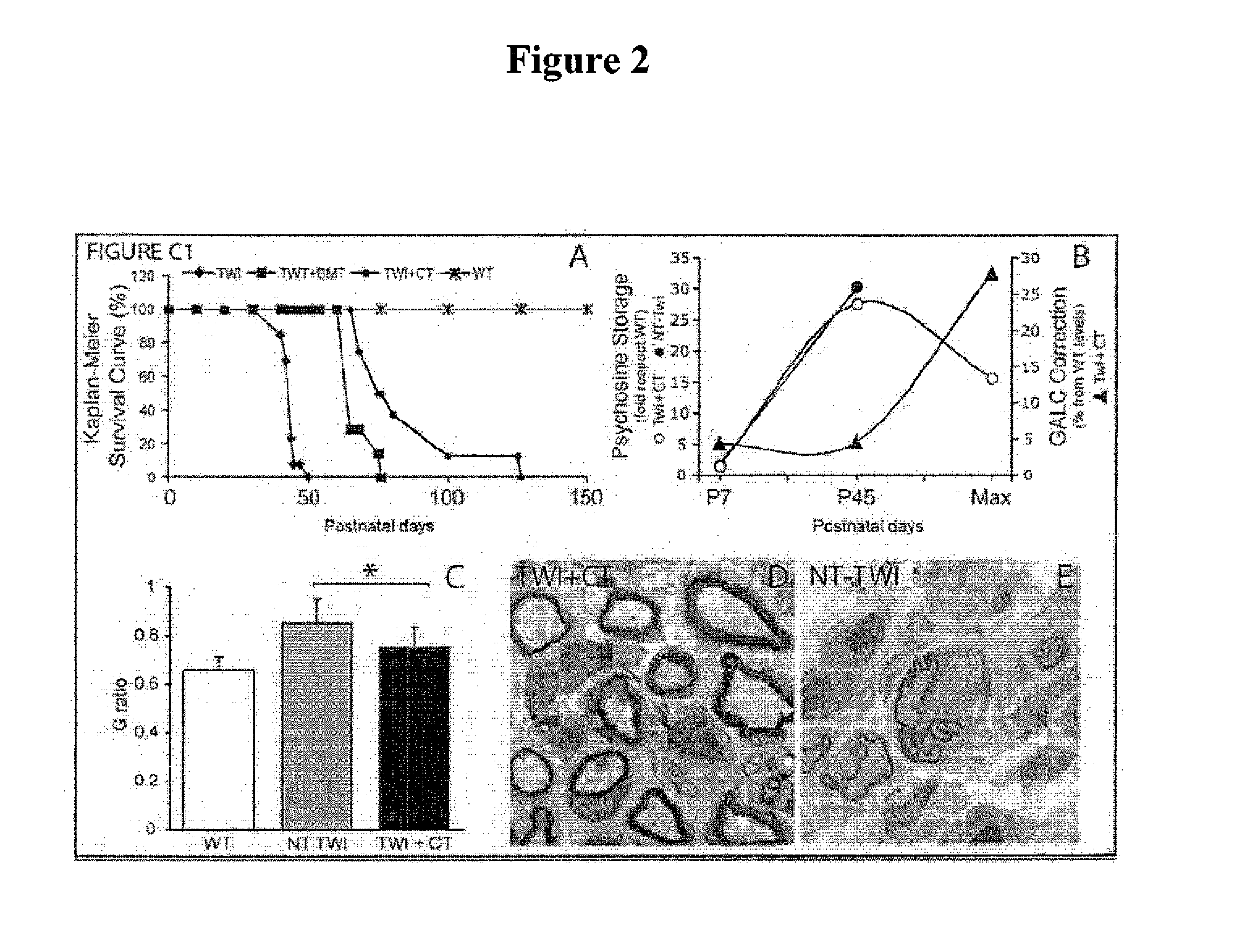
Compositions and methods for the treatment of krabbe and other neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20120156180A1Toxicity is reduced and eliminatedReducing psychosine-induced axonopathyBiocideNervous disorderMetachromatic leukodystrophyGm1 ganglioside
Provided are compositions and methods for the treatment of Krabbe and other neurodegenerative diseases, including storage diseases such as GM1 gangliosidosis, Niemann-Pick disease, Tay-Sachs disease, Sandhoff disease, metachromatic leukodystrophy, Canavan disease, Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease, and storage conditions facilitated by aging of lysosomal functions, which are associated with psychosine (and / or other storage material)-mediated axonal degeneration. Compositions and methods employ (1) one or more inhibitor of a phos-photransferase activity of one or more kinase(s) such as, for example, CDK5, P38, jnk, src, CK2, PKC, GSK3α and β; (2) one or more inhibitor of a phosphotransferase activity of one or more phosphatase(s) such as, for example, the Ser / Thr protein phosphatase PP1 and Tyr protein phosphatase PP2; one or more inhibitor of a caspase / calpain activity of one or more caspases such as caspase 3 and calpains such as calpain 1 and 2; and (4) one or more inhibitor of a sodium / calcium exchange protein such as, for example, NCX1. Inhibitors include small molecules, including the GSK3β inhibitor L803 and the NCX1 inhibitor flecainide, and siRNA molecules that downmodulate cellular levels of one or more mRNA, including siRNA that are capable of downmodulating the cellular expression of PP1. Inhibitors disclosed can cross the blood-brain barrier and, thus, are available to the central nervous system (CNS) and effective in reducing psychosine-mediated axonal degeneration.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Microorganism Which Produces L-Amino Acid and Method for Producing L-Amino Acid Using the Same
The present invention relates to a microorganism belonging to the genus Escherichia sp. and a method for producing L-amino acid using the same. The microorganism belonging to the genus Escherichia sp. has a sucrose assimilability and L-amino acid producing ability, which is obtained by introducing a gene encoding a sucrose assimilative microorganism-derived sucrose metabolic enzyme to sucrose non-assimilative microorganism belonging to the genus Escherichia sp. having an L-amino acid producing ability and sucrose PTS (phosphoenolpyruvate dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system) activity.
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Recombinant strain and application thereof
The invention provides a recombinant strain. The recombinant strains aroK, aroL and phosphoenolpyruvic acid-glucose phosphotransferase system operon (ptsHIcrr) gene are down-regulated, and aroB, aroD,aroE, aroF, tktA, ppsA genes are up-regulated. Among them, ptsHIcrr includes ptsH gene, ptsI gene and crr gene. The recombinant strain according to an embodiment of the invention is an industrial recombinant strain with high yield of shikimic acid.
Owner:HEC PHARM
High biomass and/or high growth rate recombinant bacteria and its construction method and application
ActiveCN105002105BIncrease biomassFast growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium with high biomass and / or high growth speed, and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the recombinant bacterium is characterized in that the recombinant bacterium with higher biomass and / or growth speed than a receptor bacterium is obtained through A1, A2 and A3 reconstruction of the receptor bacterium or A1 and A2 reconstruction of the receptor bacterium; the A1 is characterized by knocking out phosphotransferase Gsubunit gene of the receptor bacterium; the A2 is characterized by knocking out galactose inhibitor gene of the receptor bacterium; the A3 is characterized by inducting glucose kinase gene to the receptor bacterium; and the receptor bacterium is Escherichia coli, lactobacillus, streptococcus or hemophilus. The recombinant bacterium with high biomass and / or high growth speed constructed in the invention and a neurosporene producing recombinant bacterium have high application prospects and exploitation values in the fields of biological researches and medical science.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Corynebacterium glutamicum gene encoding hpr of phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system
Isolated nucleic acid molecules, designated PTS nucleic acid molecules, which encode novel PTS proteins from Corynebacterium glutamicum are described. The invention also provides antisense nucleic acid molecules, recombinant expression vectors containing PTS nucleic acid molecules, and host cells into which the expression vectors have been introduced. The invention still further provides isolated PTS proteins, mutated PTS proteins, fusion proteins, antigenic peptides and methods for the improvement of production of a desired compound from C. glutamicum based on genetic engineering of PTS genes in this organism.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for synthesizing fludarabine phosphate through biological catalysis
PendingCN113584104AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldTransferasesOxidoreductasesReaction temperaturePhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing fludarabine phosphate by an enzyme method. Fludarabine phosphate is prepared by taking fludarabine as a raw material through an enzyme catalytic reaction in the presence of inorganic salt and coenzyme; an enzyme used in the enzyme catalysis reaction is selected from at least one of phosphotransferase, aldoketoreductase, alcohol oxidase or alcohol dehydrogenase; the pH value of the enzyme catalytic reaction is 7.3-7.6, the reaction temperature is 37 DEG C, and the reaction time is 1-4 hours; the coenzyme is ATP. According to the invention, fludarabine phosphate is prepared by adopting a novel enzymatic process, so that the technical problems existing in some existing chemical processes are solved, and the process is improved compared with the existing enzymatic preparation process; the production cost is reduced; the process is environment-friendly and reaction conditions are mild.
Owner:JIANGSU OCEAN UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com