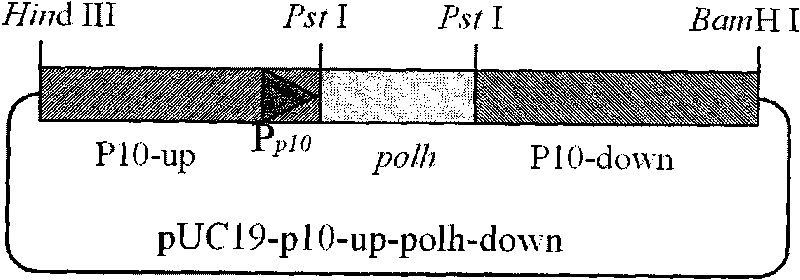Patents
Literature
84 results about "PUC19" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
PUC19 is one of a series of plasmid cloning vectors created by Joachim Messing and co-workers. The designation "pUC" is derived from the classical "p" prefix (denoting "plasmid") and the abbreviation for the University of California, where early work on the plasmid series had been conducted. It is a circular double stranded DNA and has 2686 base pairs. pUC19 is one of the most widely used vector molecules as the recombinants, or the cells into which foreign DNA has been introduced, can be easily distinguished from the non-recombinants based on color differences of colonies on growth media. pUC18 is similar to pUC19, but the MCS region is reversed.
Preparation method of zebrafish notch2 gene mutant
ActiveCN108707628AGenetic stabilityFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch2 gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch2 gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch2-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9 protein into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish through micro-injection, and screening to obtain the notch2 gene mutant stable in inheritance. The preparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene)technology, and by means of selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch2 gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch2 gene is formed, experimental materials are provided for in-depth study on follow-up gene functions, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
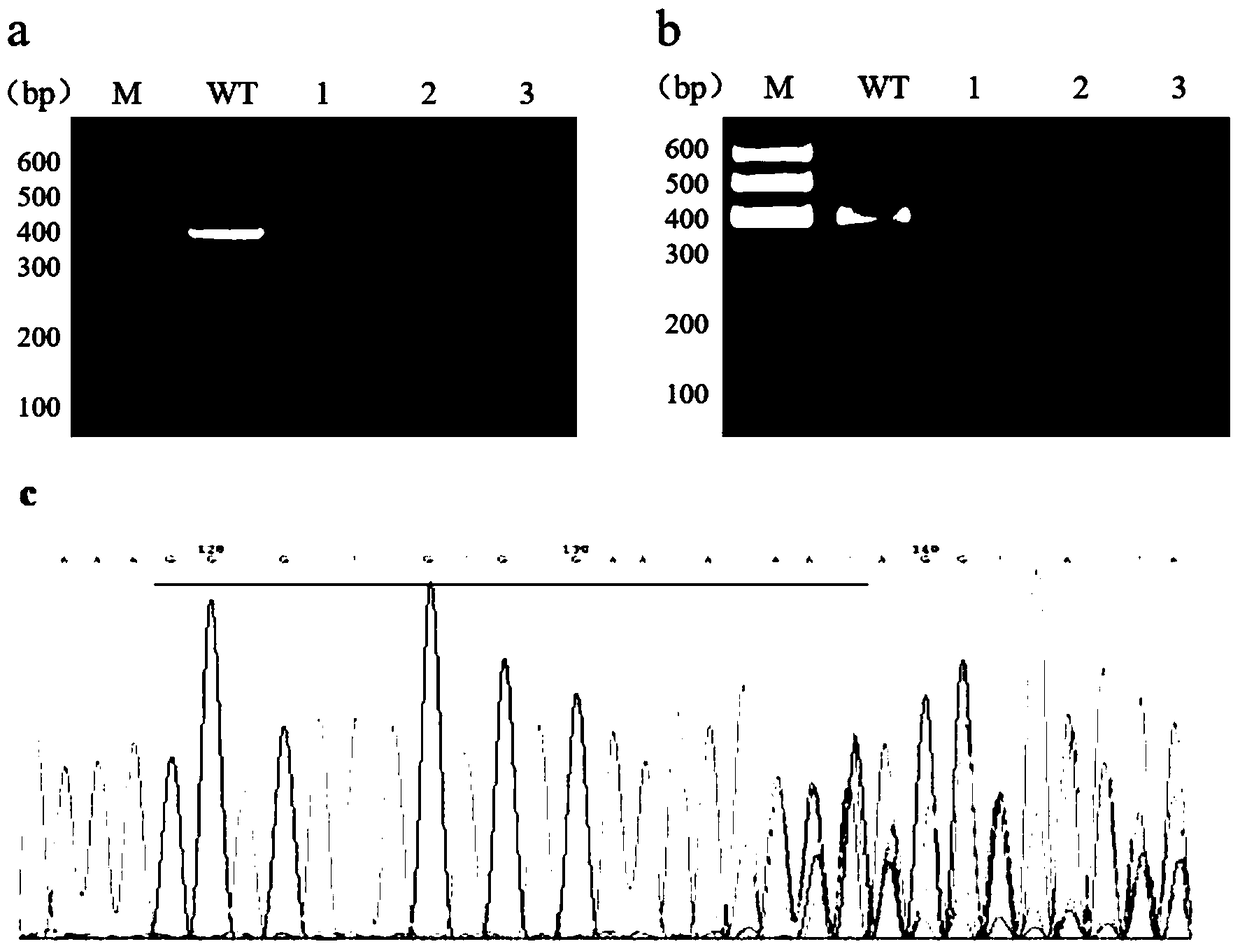
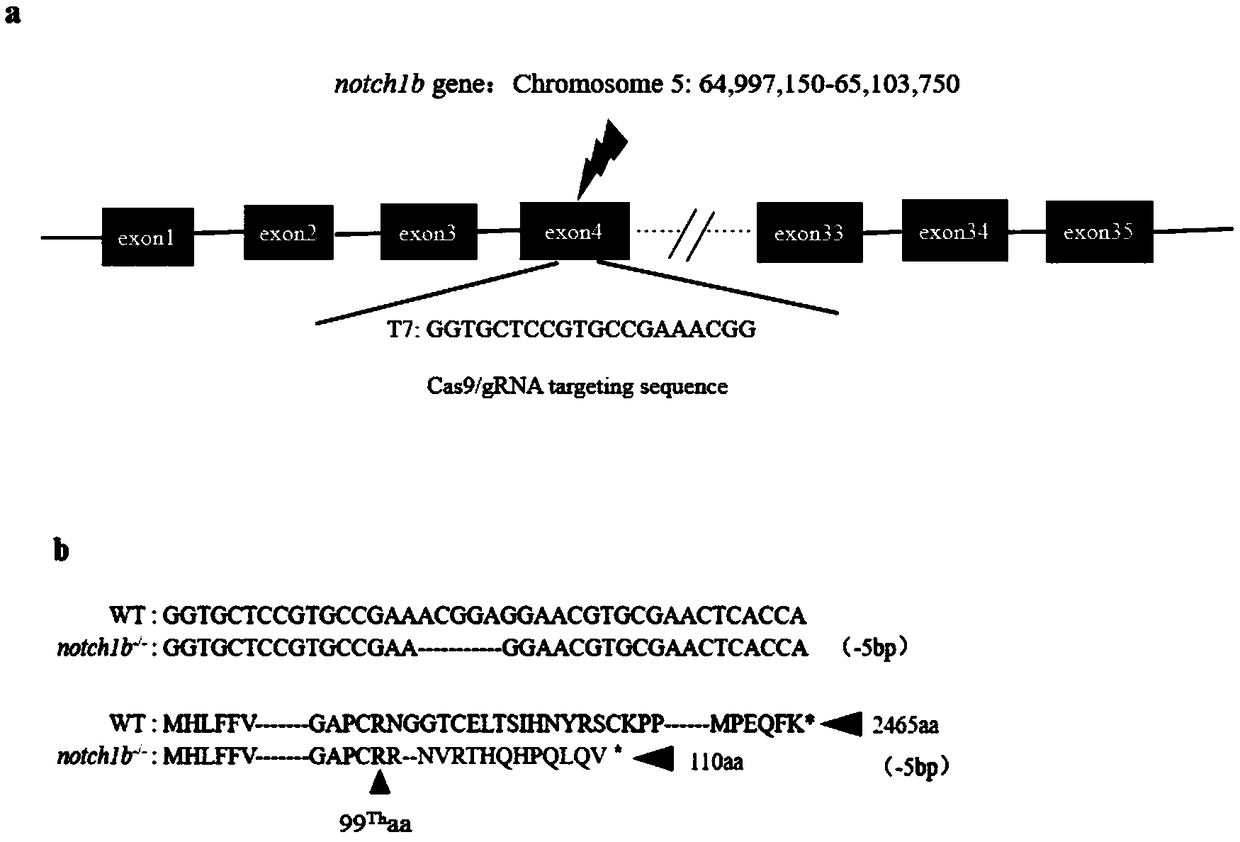
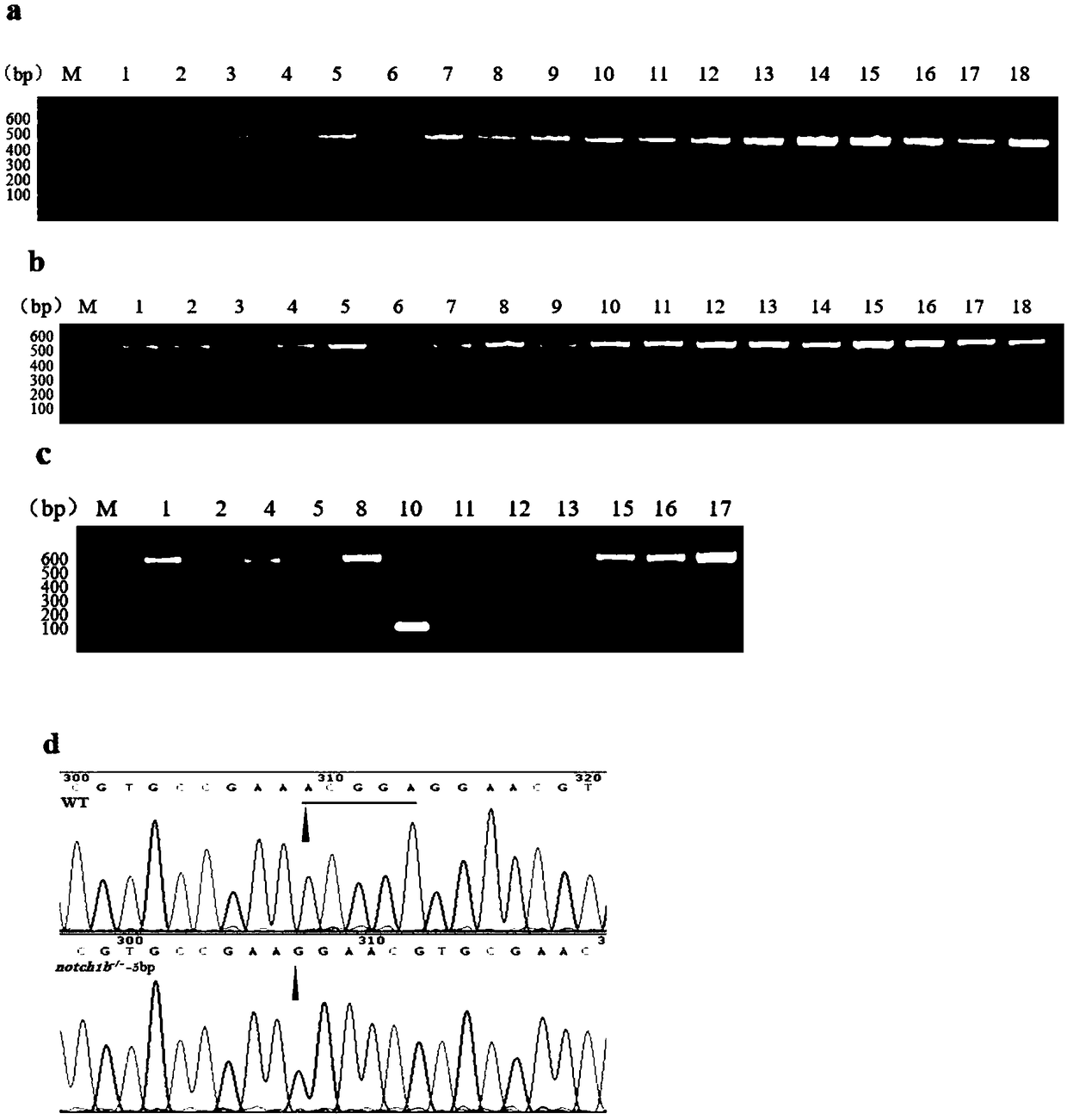
Preparation method of zebrafish notch1b gene mutant
PendingCN108707629AGenetic background is clear and cleanFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch1b gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch1b gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch1b-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9mRNA into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish, and culturing to obtain the notch1b gene mutant stable in inheritance. Thepreparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene) technology, and by meansof selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch1b gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch1b gene is formed, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Extraction of duck enteritis virus genom DNA and sequence thereof
InactiveCN101182526AHigh homologyShort copy cycleFermentationGenetic engineeringPUC19Escherichia coli
The invention discloses a DNA extraction method of Duck Enteritis Virus genome and the genome sequence. Firstly, the pyrolysis of chicken embryo fibroblast which is infected with DEV is processed by hypertonic buffer; then the nuclease is added for the digestion of cell DNA; and the virus genome DNA is obtained through phenol chloroform extracting method. The obtained sample is broken randomly into 2kb to 2.5kb fragments; the pUC19 vector is linked to transform host E. coli and construct genomic library. The positive clones in the library are randomly sequenced; the total sequence length has 6 times coverage rate for the virus genome. The sequence result is assembled and clustered to obtain the whole DEV genome sequence with the length of156512bp. The analysis shows that the genome structure is the same with that of the members of Varicella virus in Alpha- herpesus subfamily, which provides theoretical basis for the classification of DEV.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Preparation method of Trichoderma reesei gene engineering bacterium for highly yielding heat stability xylanase
ActiveCN106676126AIncrease productionFungiVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyPUC19
The invention discloses a preparation method of a Trichoderma reesei gene engineering bacterium for highly yielding heat stability xylanase. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing an expression cassette sequence sequentially comprising a Trichoderma reesei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter, a Trichoderma reesei cbh1 signal peptide sequence, an xylanase xyn-LVK gene sequence and a Trichoderma reesei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase terminator; cloning the expression cassette sequence into pUC19 in order to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid; and lightly uniformly mixing the recombinant expression plasmid with a pAN7-1 vector, co-transforming Trichoderma reesei protoplasts, and screening the Trichoderma reesei protoplasts to obtain the Trichoderma reesei gene engineering bacterium for highly yielding heat stability xylanase xyn-LVK. The content of the xylanase xyn-LVK expressed in the Trichoderma reesei is about 40% higher than the content of the xylanase xyn-LVK expressed in Pichia yeast.
Owner:深圳市鼎宏生物科技有限公司
Building method of silkworm BmNPV Polh+Bac-to-Bac rhabdovirus expression system
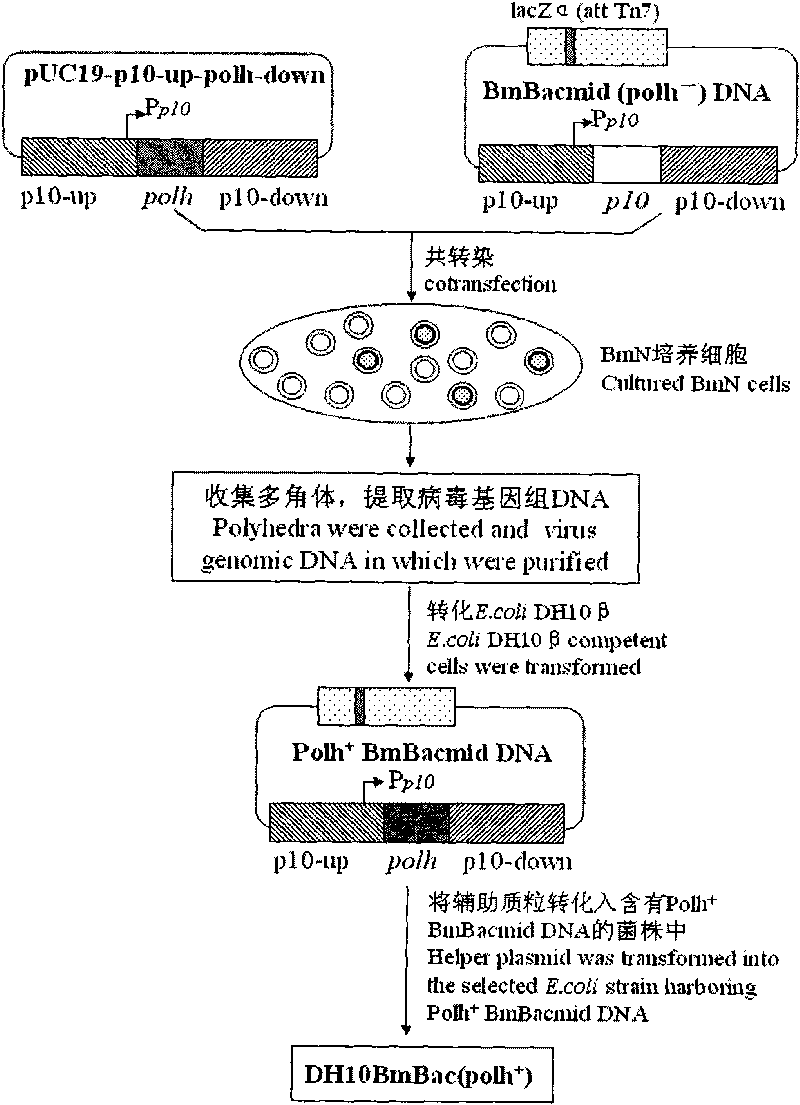
The invention discloses a building method of a silkworm BmNPV Polh+Bac-to-Bac rhabdovirus expression system, comprising: taking silkworm wild type BmNPV genome DNA as the template; respectively taking P10-upF / P10-upB and P10-downF / P10-down B as a primer PCR for amplification to obtain p10-up and p10-down; after processed, inserting into BamHI-PstI-HindIII locus in pUC 19 to obtain recombinant plasmid pUC19-p10-up-down; using pUC-19-p10-up-polh-down, liposome lipofectin and MilliQ H2O to prepare DNA-Lipofectin mixed liquor; adding the mixed liquor into BmN cells for cultivating; collecting transfection cell supernatant; inoculating BmN cells, and recovering a polyhedral body; extracting virus DNA from the polyhedral body and electrically converting DH10 beta competent cells; screening locus ceruleus and cultivating; after cultivating PCR positive bacterial plaque, extracting macro-molecular DNA to transfect to the BmN cells; separating to obtain helper plasmids from DH10Bac culture bacteria of AcMNPV Bac-to-Bac; converting the helper plasmids into E.coli DH10 beta containg Ploh+BmBacmid; and screening the DH10 beta bacterial strain of the helper plasmid containg Ploh+BmBacmid. The invention can produce recombinant virus capable of infecting by eating with mouth, and recombinant virus does not need to infect by intracutaneous inoculation, thus improving the production efficiency of the silkworm rhabdovirus expression system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Double-tagging microbial cell biosensor for detecting N-acyl homoserine lactone
The invention relates to a double-tagging microbial cell biosensor for detecting N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL), and the biosensor is suitable for detection of AHL and characterization of host cells in the environment. The cell biosensor comprises: Escherichia coli used as host cells for carrying recombinant plasmids; recombinant plasmid containing an ahlI promoter responding to AHL, a cherry red fluorescent protein reporter gene mCherry and an AHL regulatory protein gene ahlR; and a neomycin phosphotransferase promoter gene nptII for characterization of host bacteria, a green fluorescent protein reporter gene gfp and a T1-4 pUC19 plasmid of four terminator rrnb tandem sequence. According to the biosensor, constitutive type of expression green fluorescent protein is used to characterize the host bacteria; the response time to AHL is 6 h; and the minimum detectable concentration of AHL is 50 nmol / L. The biosensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, fast response, low cost and simple operation, and can be widely applied to detection of AHL and host characterization in the environment.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aptazyme modified sgRNA carrier with theophylline regulated expression and application
The invention discloses an aptazyme modified sgRNA carrier with theophylline regulated expression. Aptazyme P1-F5 is inserted to tetraloop and stem loop 2 positions of an expressed sgRNA-AZ 2.0 skeleton; by means of Kpn I and EcoR I sites, and EcoR I and Spe I sites, a U6 promoter and the sgRNA-AZ 2.0 skeleton are connected into the carrier pUC19 / EKSHL in order to obtain the carrier pU6-sgRNA-AZ 2.0; using Bsa I for enzyme digestion of the carrier pU6-sgRNA-AZ 2.0, and using cohesive end design and connecting an sgRNA sequence directing at the target gene so as to obtain the pU6-sgRNA-AZ 2.0-target site. The carrier can effectively mediate the genome editing function of Cas9 protein, and bring the editing activity under regulation of theophylline, also can mediate the transcription inhibition of dCas9-KRAB protein to the target gene, and enables regulation of inhibitory activity by theophylline.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
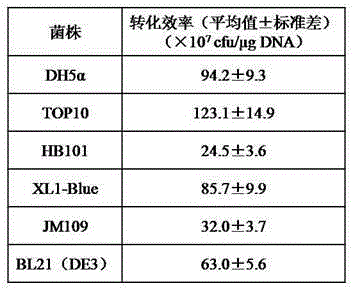
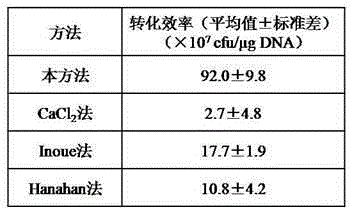
Preparation of escherichia coli competent cells and transformation method of escherichia coli competent cells
InactiveCN105420157ASimplify the manufacturing processSimplify conversion stepsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPUC19
The invention relates to preparation of escherichia coli competent cells and a transformation method of the escherichia coli competent cells. The preparation comprises following the steps of culturing the escherichia coli in a SOB liquid medium, adding a buffer solution I when OD 600 is 0.4 to 0.6, centrifugally collecting cells after ice bath, after a buffer solution II resuspends the cells, respectively putting into pre-cooling sterile centrifuge tubes to obtain the scherichia coli competent cells. In a transformation process, uniformly mixing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) with the competent cells, and directly coating the culture medium with the mixture after heat-shock, wherein ice bath and recovery steps are not needed. The escherichia coli competent cells are prepared by adopting buffer solutions of a special formula, the transformation efficiency can reach 1.23X109 cfu / mug pUC19 DNA. The method is simple in operation, high in transformation efficiency and good in repeatability, the preparation of the escherichia coli competent cells and DNA transforming operation are simplified, and a technological base is provided for high-efficiency and rapid transformation of the DNA.
Owner:SHENZHEN HONGKANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Fused antibacterial peptide and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104448004ASolve the problem of large-scale applicationNo lethalityPeptide preparation methodsHybrid peptidesPUC19Competent cell
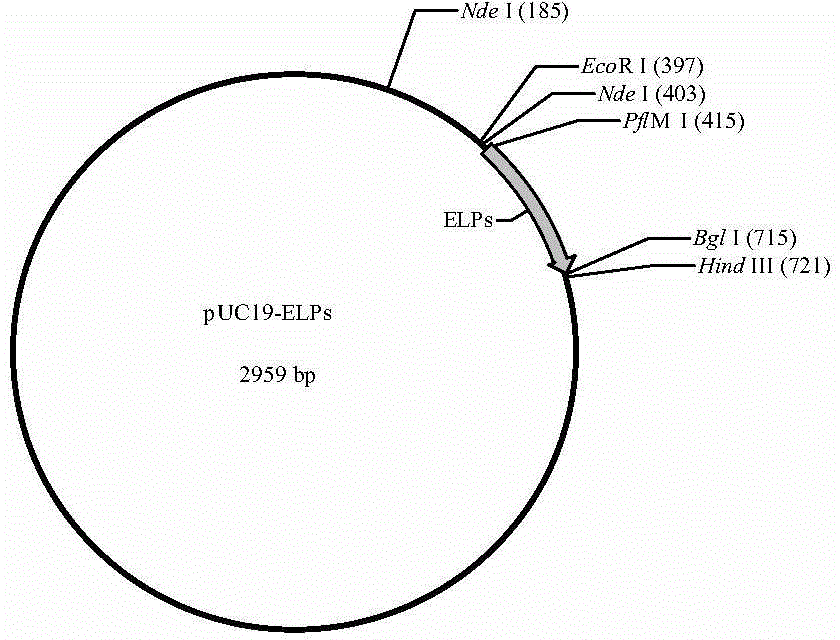
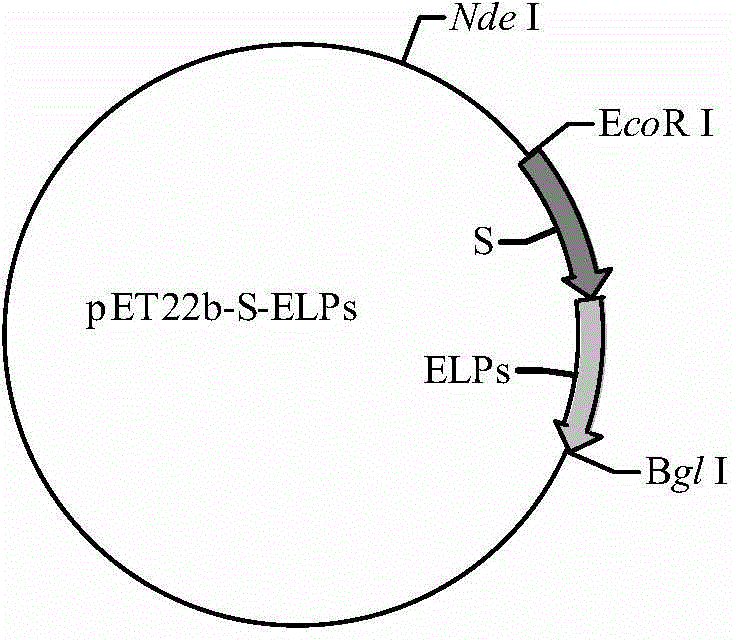
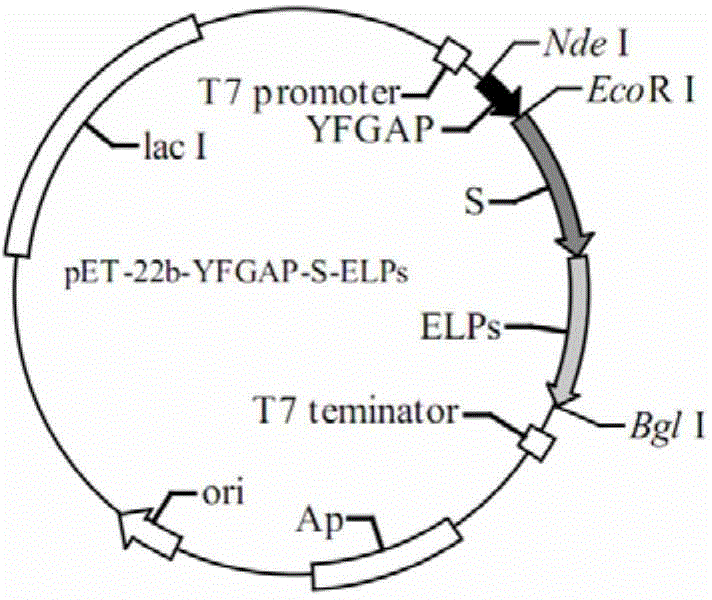
The invention discloses a fused antibacterial peptide and a preparation method thereof. According to the amino acid sequence of the antibacterial peptide YFGAP, the gene sequence of the amino acid sequence is optimally designed and connected to pUC19 to obtain pUC19-YFGAP; the pUC19-YFGAP is connected to pET-22b-S-ELPs to obtain pET-22b-YSELP; the pET-22b-YSELP is transformed to E.coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells to obtain E.coli BL21 (DE3) / pET-22b-YSELP; inoculating and culturing are performed and IPTG is added to induce the expression of the YSELP. The fused antibacterial peptide YSELP has an inhibition effect on a plurality of testing strains without being cut off from the tag protein, and does not kill host bacteria; as a result, the problem of large-scale application of the existing antibacterial peptides is expected to be solved.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Zero-background cloning vector as well as preparation method and application thereof
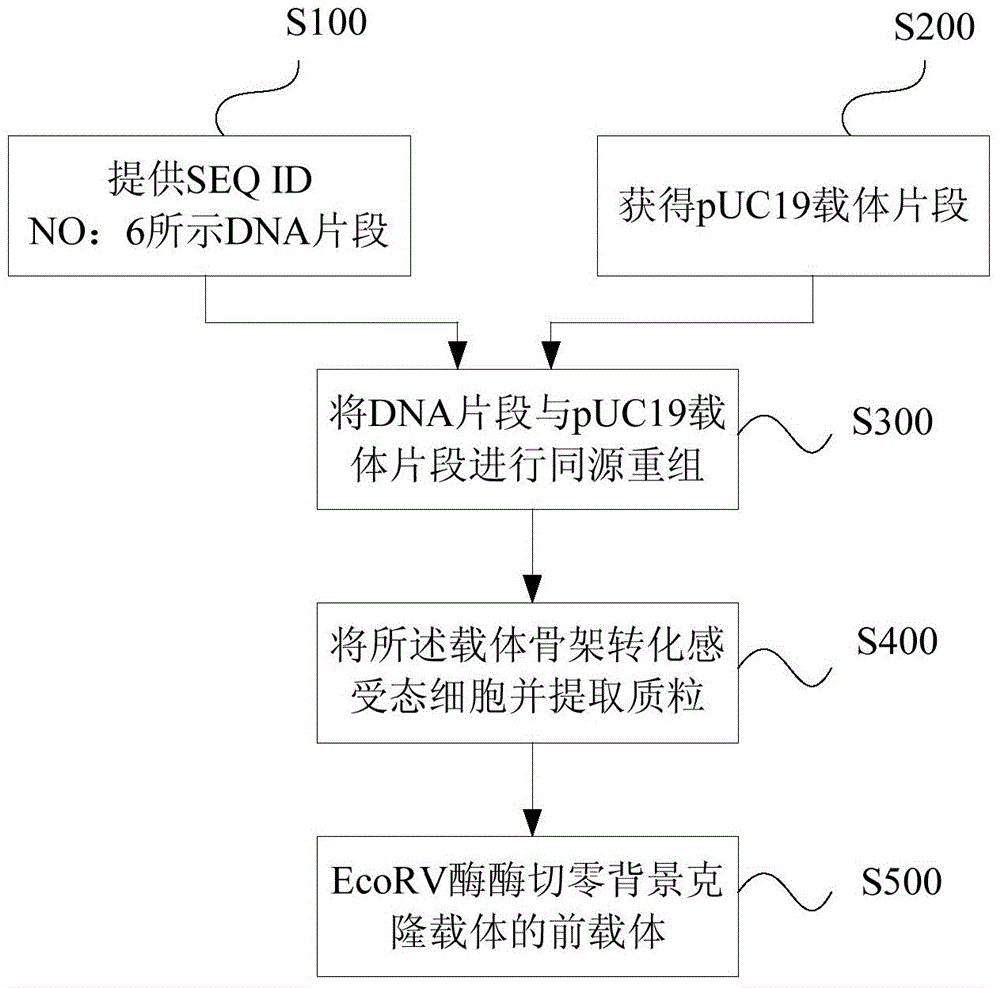
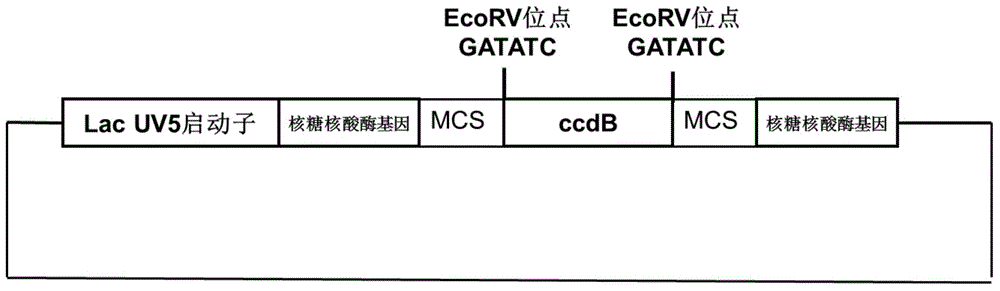
The invention discloses a method for preparing a zero-background cloning vector, and application of the zero-background cloning vector. The method for preparing the zero-background cloning vector comprises the following steps: providing a DNA segment as shown in the sequence SEQ ID NO:6; performing first PCR amplification by taking pUC19 plasmid as a template and utilizing primers as shown in the sequences SEQ ID NO:7-8, thereby obtaining a pUC19 vector segment; performing homologous recombination on the DNA segment and the pUC19 vector segment, thereby obtaining a vector framework; converting the vector framework into competent cells, and extracting the plasmid, thereby obtaining a previous vector of the zero-background cloning vector; and performing enzyme digestion on the previous vector of the zero-background cloning vector by using EcoRV enzyme, thereby obtaining the zero-background cloning vector. The vector obtained by using the method can be directly used for connecting flat tail end products, the vector self-connection background is low, the positive rate of cloning is high, blue and white screening is not needed, rapid and effective cloning can be achieved within a short time, the cloning efficiency is high, and the effect is good.
Owner:TIANGEN BIOTECH BEIJING
Screening non-infective virus recombinant gene SARS-Cov-EGFP for medicine of anti SARS coronavirus
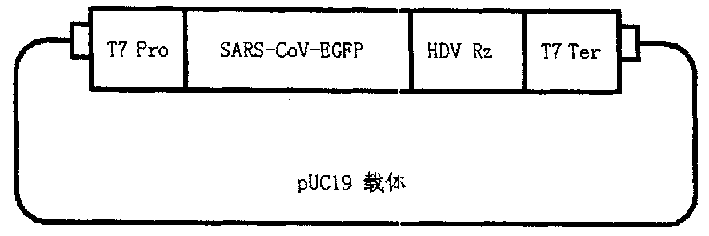
InactiveCN1454996AEasy to filterFacilitate basic research in virologyMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPUC19Virulent characteristics
The present invention relates to a noninfectious virus recombinant gene SARS-CoV-EGFP for screening medicine for resisting SARS virus and making basic research of virology. In 5' end of total genome of SARS coronate virus the promotor sequence T7 Pro. is introduced, the coding sequence of external structural domain related to viral pathogenicity and toxicity in S protein can be sustituted with EGFD gene of code enhanced green fluorescin, and in the 3' end of total genome HDV antisense genome ribozyme sequence HDV R2 and T7 transcription terminator sequence T7 Ter are successively introduced to create recombinant gene SARS-CoV-EGFP, then it is inserted into carrier to construct recombinant plasmid pUC19 / SARS-CoV-EGFP, after cell transfection, through replication, transcription, traslation, processing and packaging to obtain recombinant virus capable of making transfected cell give out green fluorescence under the fluorescent microscope.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
High-molecular-weight T carrier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102304537AQuality improvementImprove stabilityVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Antisense gene
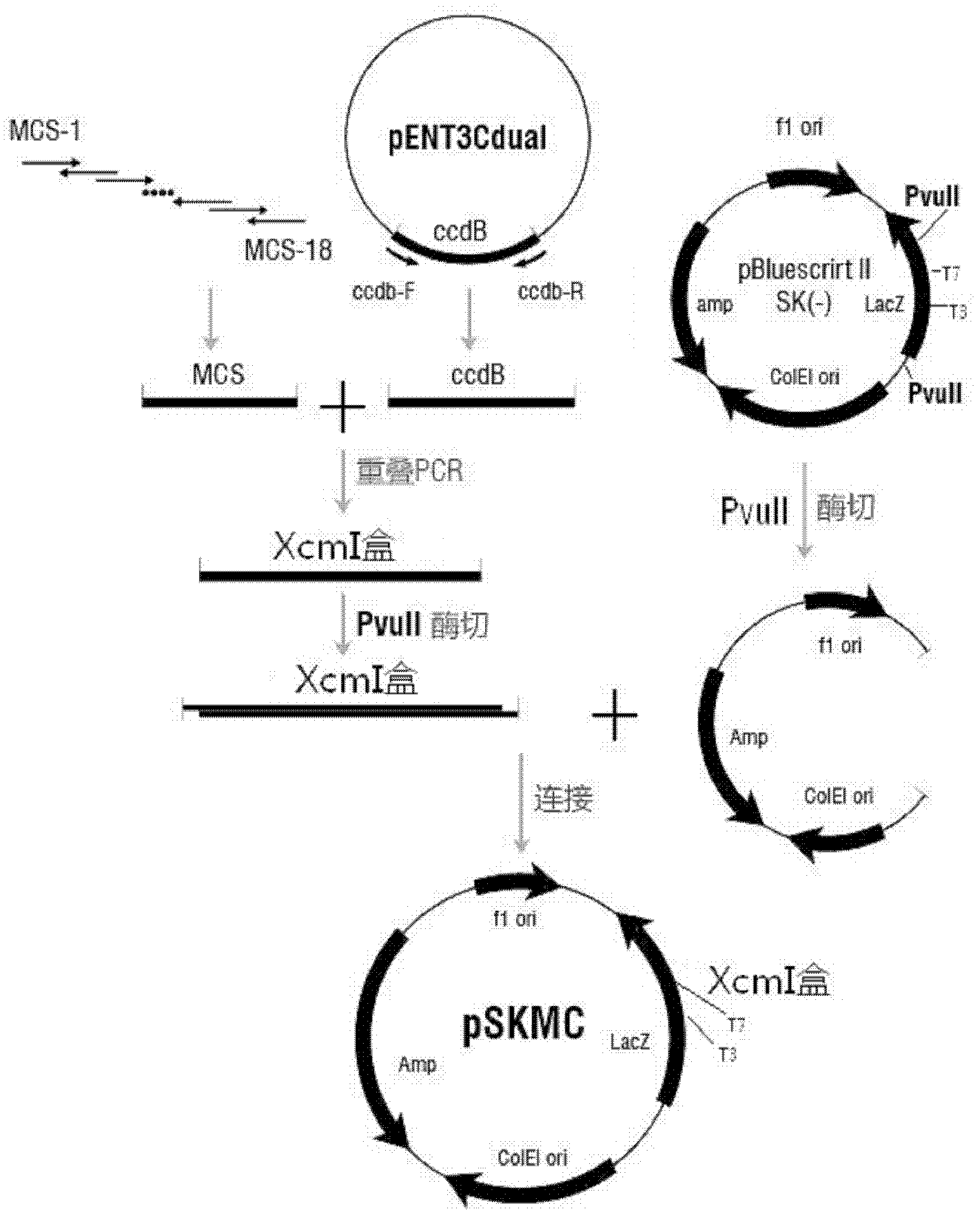
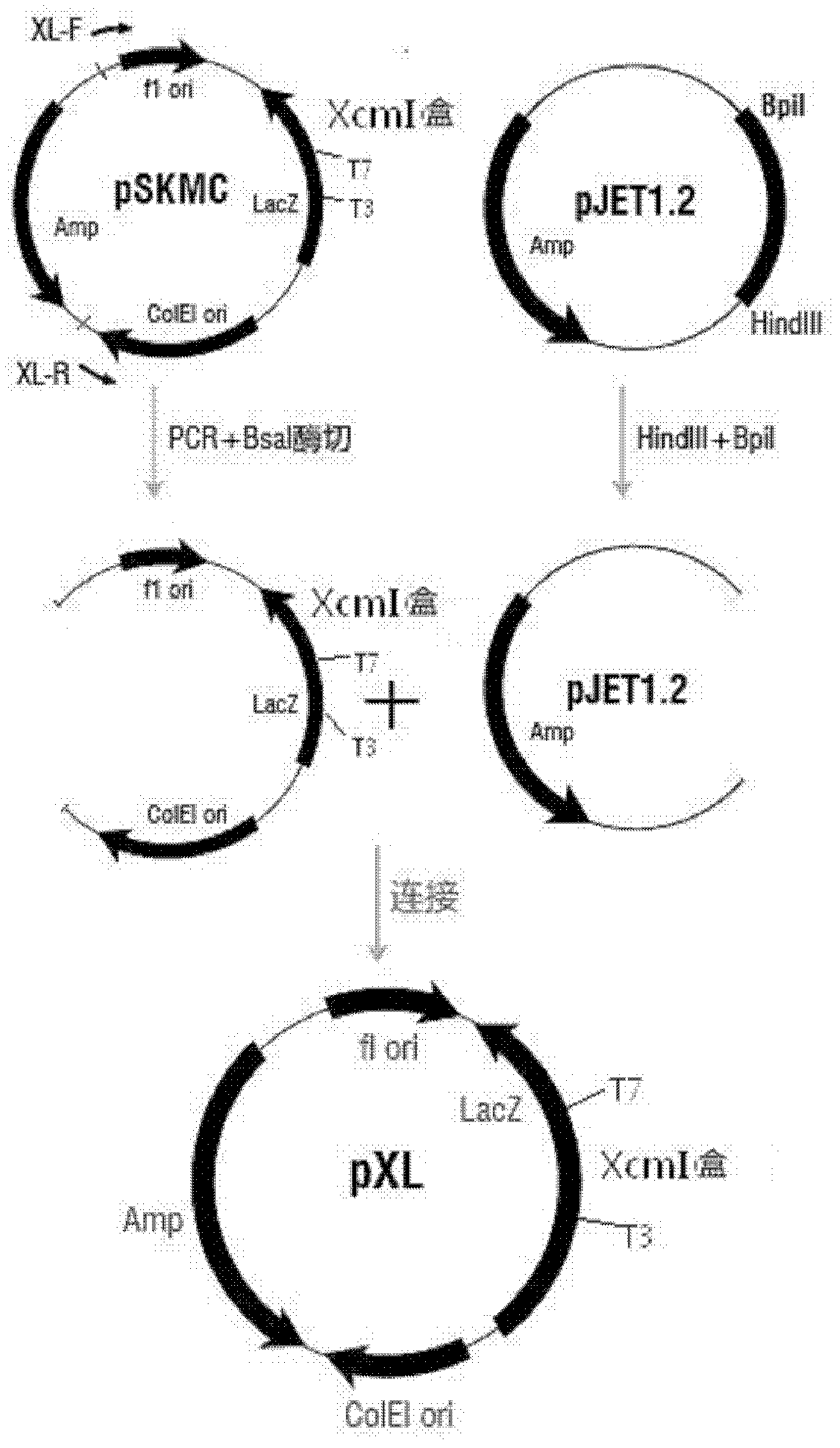
The invention discloses a T carrier and a preparation method thereof. A known carrier is a carrier after an improvement of a starting carrier which is pBlueScript II SK(-), pUC18, pUC19, pUC118, pUC119, pUC19, or pGEM serial carriers the polyclone sites of which are replaced with XcmI cases, wherein the XcmI cases comprise ccdB gene sequences and an XcmI restriction enzyme cutting site sequence which is connected to each of two sides of the ccdB gene sequences, and resistance genes in the starting carrier are lengthened by inserting an antisense gene with the length of 1000-2000bp in front and / or back of the antisense gene. The T carrier provided by the invention has higher TA clone efficiency, the TA clone efficiency can reach 100% especially for fragments which are difficult to distinguish for cloning conventional business clone carriers and have the lengths between 2500bp and 3500bp, and the T carrier plays an important role in the filed of genetic engineering.
Owner:JIERUI BIOENG SHANGHAI
Method for synthesizing protein using expression system in vitro of bombyx mori posterior division of silkgland
InactiveCN101358196APromote generationEasy to separate and purifyVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Protein target
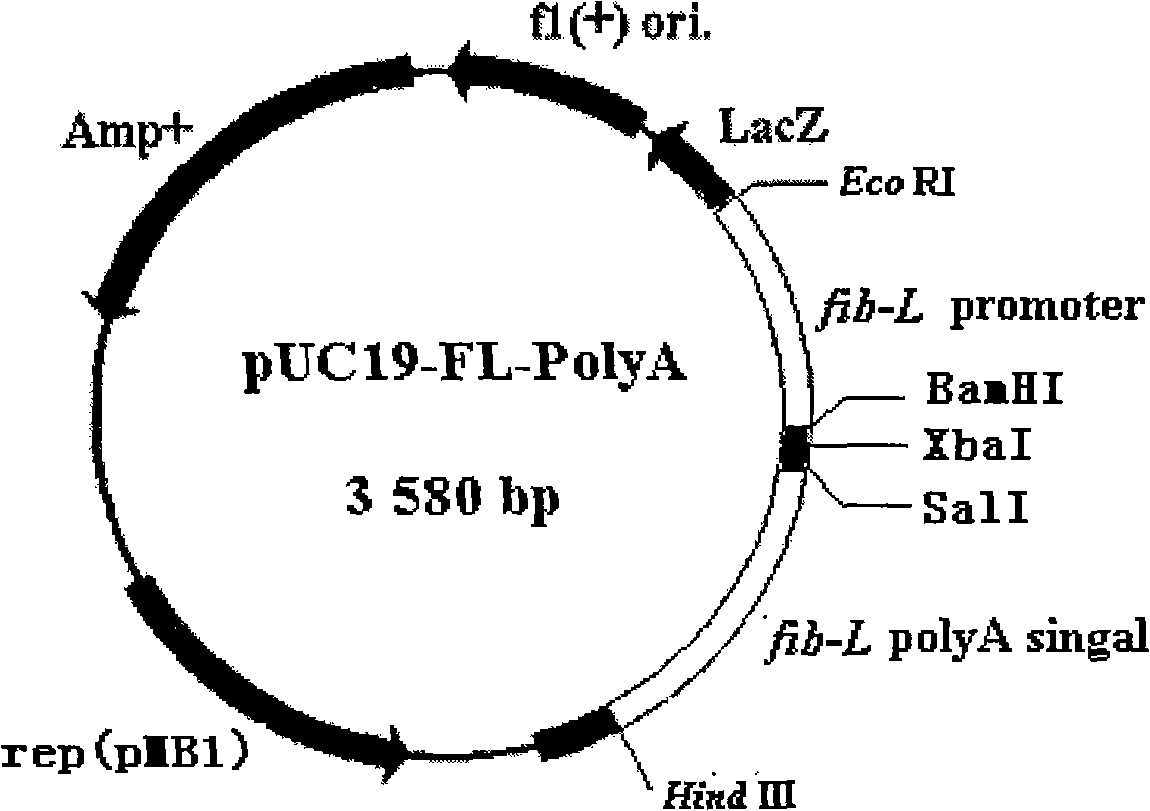
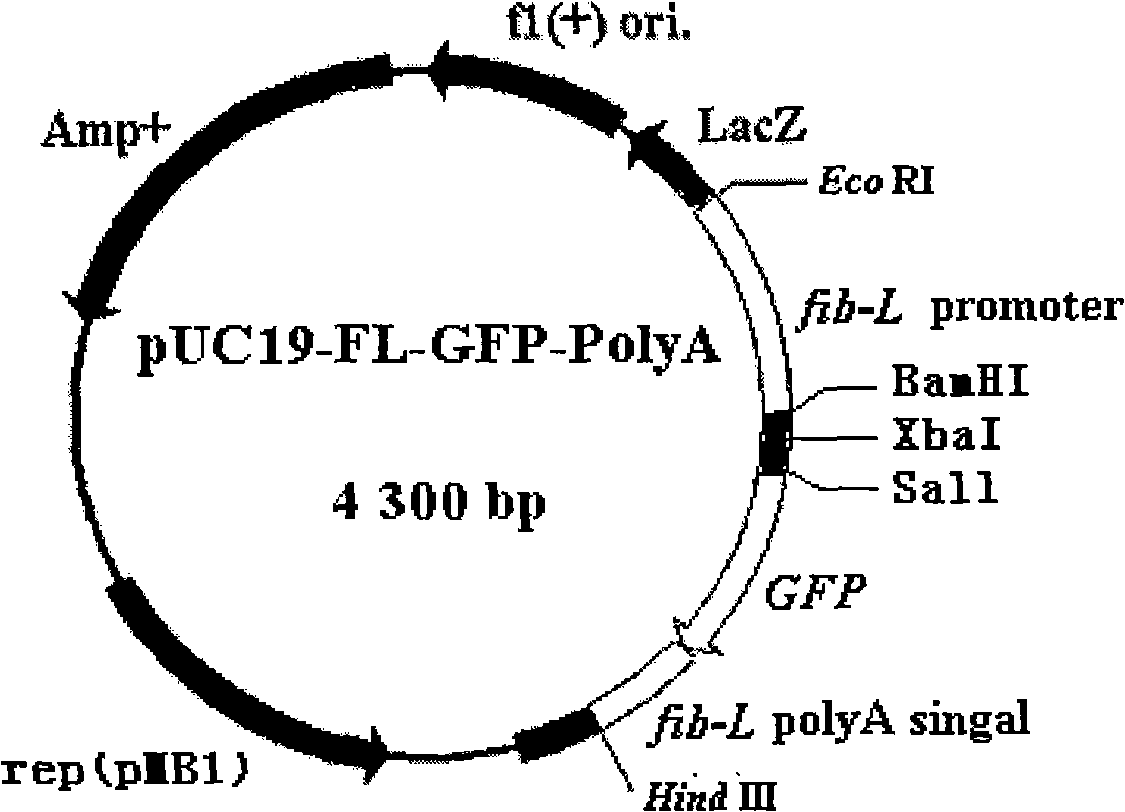
The present invention discloses a method which utilizes the in-vitro expression system of the posterior silkgland of Bombyx mori to synthesize a protein. pUC19-FL-GFP-PolyA recombinant plasmid or pUC19-FL-GFP-PolyA recombinant plasmid with an exogenous gene or a pUC19-FL-PolyA recombinant plasmid or a pUC19-FL-PolyA recombinant plasmid with an exogenous gene and protease inhibitor are added into the tissue extract of the posterior silkgland of Bombyx mori, and after water bathing under the temperature between 25 DEG C and 29 DEG C, the expression of the targeted protein is obtained. The method has the following advantages: since the protein is expressed under a temperature between 25 DEG C and 29 DEG C, the low-temperature condition (normally, 37 DEG C) helps to generate the expressed protein in a dissolved state, and the formation of inclusion bodies is reduced, which is favorable for the separation and purification of the protein. Meanwhile, the method is not limited by cells and can synthesize the protein in a short period.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
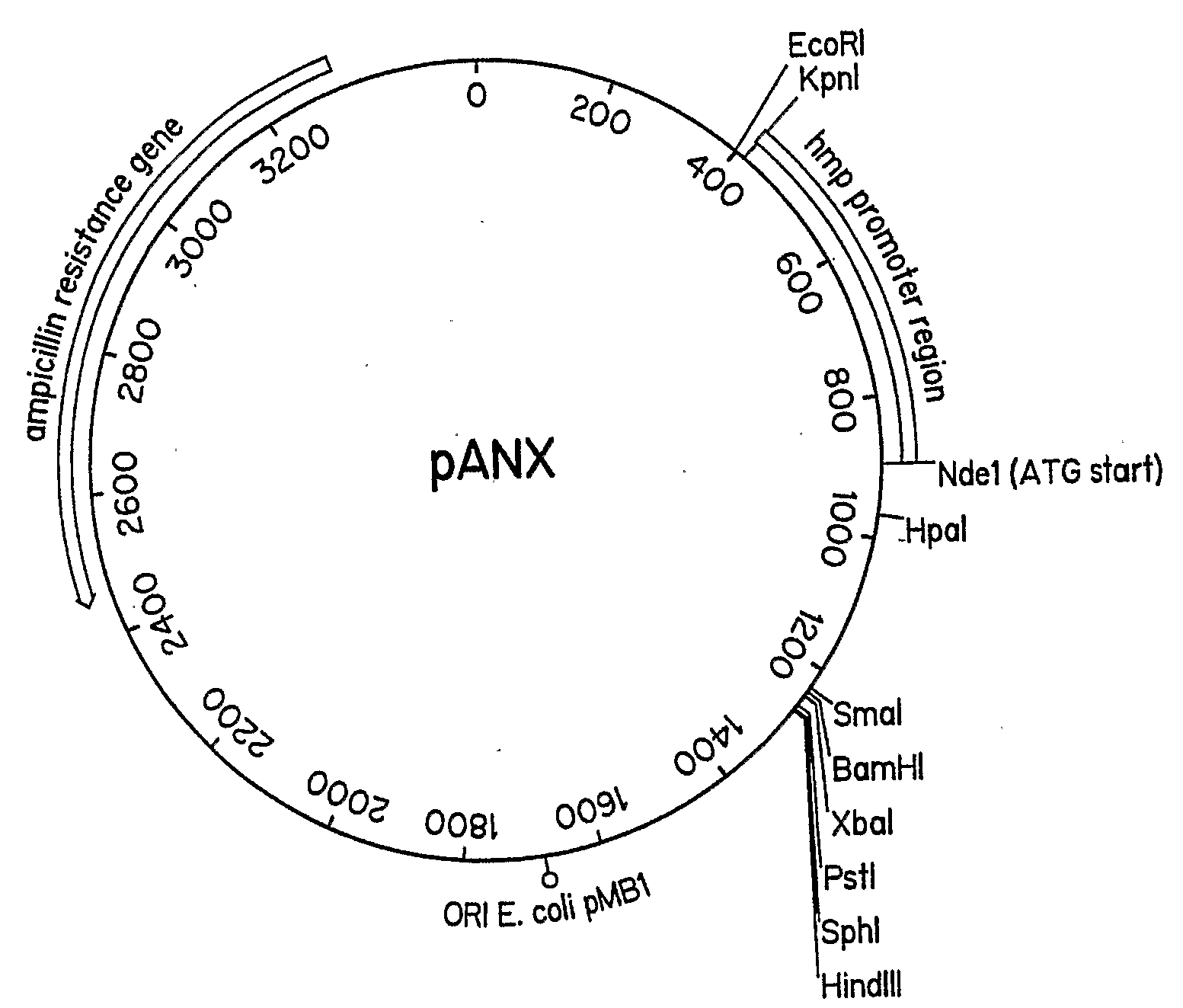
Vector to Induce Expression of Recombinant Proteins under Anoxic or Microaerobic Conditions
InactiveUS20090269801A1Constant aerationSimpler and less-expensiveFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
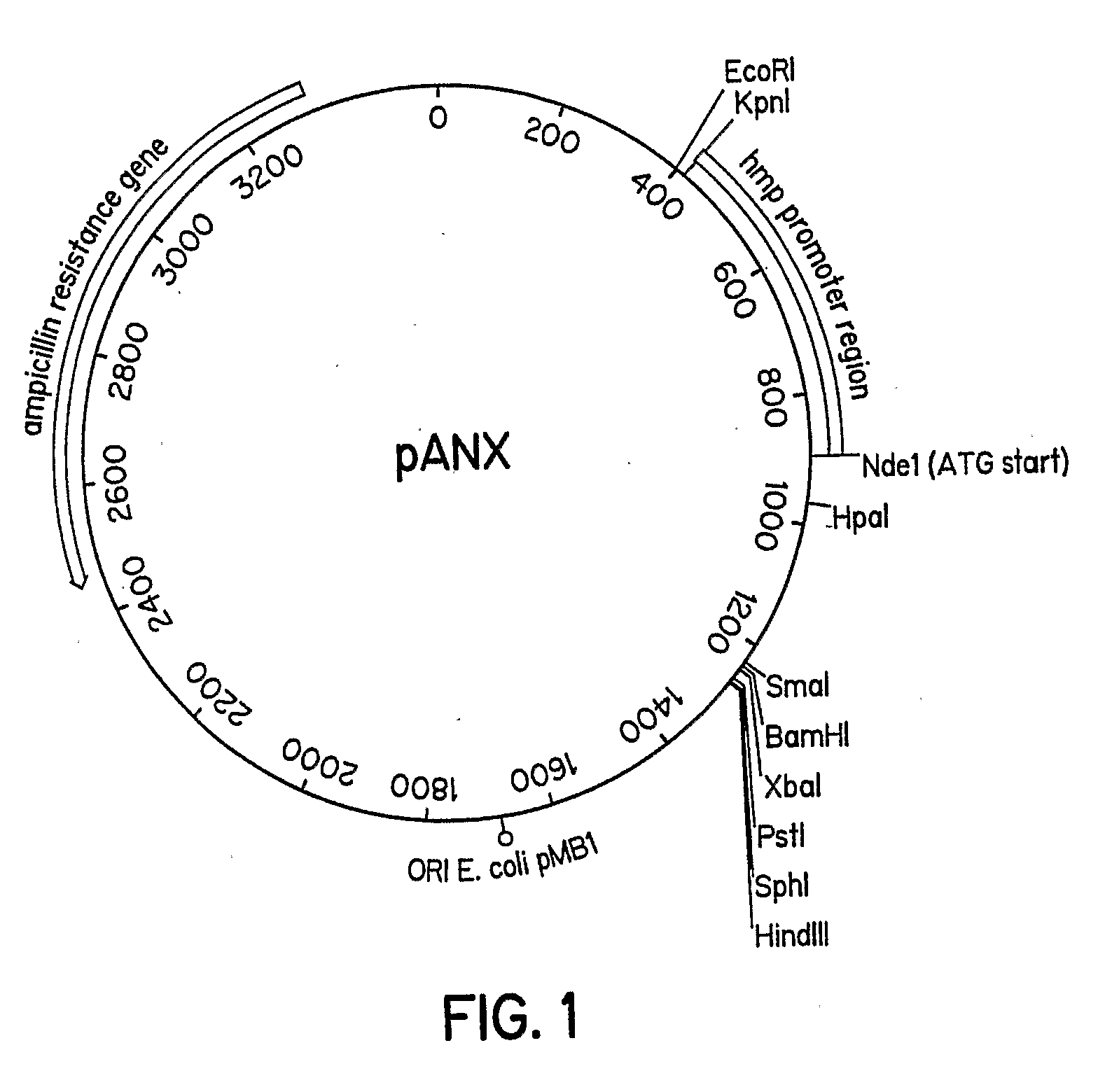
A protein expression vector that expresses large quantities of recombinant proteins under anoxic or microaerobic conditions by inducing expression with nitrate. The vector backbone is pUC19 and protein expression is driven by the E. coli flavohemoglobin promoter, which is inducible by nitrate, nitrite, or nitric oxide under conditions of low oxygen. The Nde1 site of pUC19 has been destroyed by filling in with Klenow fragment and religating the vector. An Nde1 site in the promoter provides an in-frame start methionine and a standard polylinker is available for ease of subcloning. The vector is named pANX for Plasmid ANaerobic eXpression.
Owner:GARDNER ANNE M +1
Construction of bacillus subtilis integrated vector capable of being cloned by using homologous recombination and application thereof
InactiveCN101948866AAvoid Linked CloningSimple methodVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Bacillus subtilis
The invention discloses construction of a bacillus subtilis integrated vector capable of being cloned by using homologous recombination and application thereof. The construction of the bacillus subtilis integrated vector capable of being cloned by using homologous recombination and the application thereof belong to the technical field of biology. The vector pMLK-BN can transfer an exogenous gene or a promoter cloned on a common cloning vector puc18, puc19 or puc57 to self by a homologous recombination method so as to integrally express exogenous protein in bacillus subtilis or test the promoting effect of the promoter. Compared with a common connecting cloning method, the cloning method of homologous recombination is simple and efficient; and the pMLK-BN can be effectively used as a choice for cloning the exogenous gene or the promoter to the bacillus subtilis to perform integrated expression.
Owner:南宁邦尔克生物技术有限责任公司
Method for targeted knockout of non-essential genes for Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus replication
ActiveCN103589745AEasy accessObtain intuitivelyDsDNA virusesVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Genomic DNA
The present invention relates to a method for targeted knockout of non-essential genes for replication of the Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV. The method is as below: using BmNPV as a material to amplify a homologous sequence at both ends of a non-essential region for replication by PCR and cloning it into a vector pUC19; splicing successively an IE1 early promoter, a marker gene (EGFP) and a termination sequence SV40polyA of BmNPV by an overlapping PCR method and cloning them to the abovementioned vector pUC19 to obtain a recombinant transfer vector pUC19-lef7-IE1-EGFP-SV40polyA-gp64; co-transfecting BmN cells using the vector and the genome of wild BmNPV and carrying out homologous recombination to obtain a recombinant virus RBmNPV-EGFP with a fluorescent marker; and co-transfecting BmN cells using genomic DNA thereof and a transfer vector pUC19-lef7-gp64 without marker gene and carrying out homologous recombination to obtain a recombinant virus RBmNPV without fluorescent marker gene. The present invention solves the problem of the presence of marker genes in recombinant virus genomes and improves the screening efficiency of positive recombinant viruses, and thus the marker genes can be reused.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for synthesizing protein by using cultivated silkworm middle silk gland vitro expression system
InactiveCN101423842APromote generationEasy to separate and purifyVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Water baths
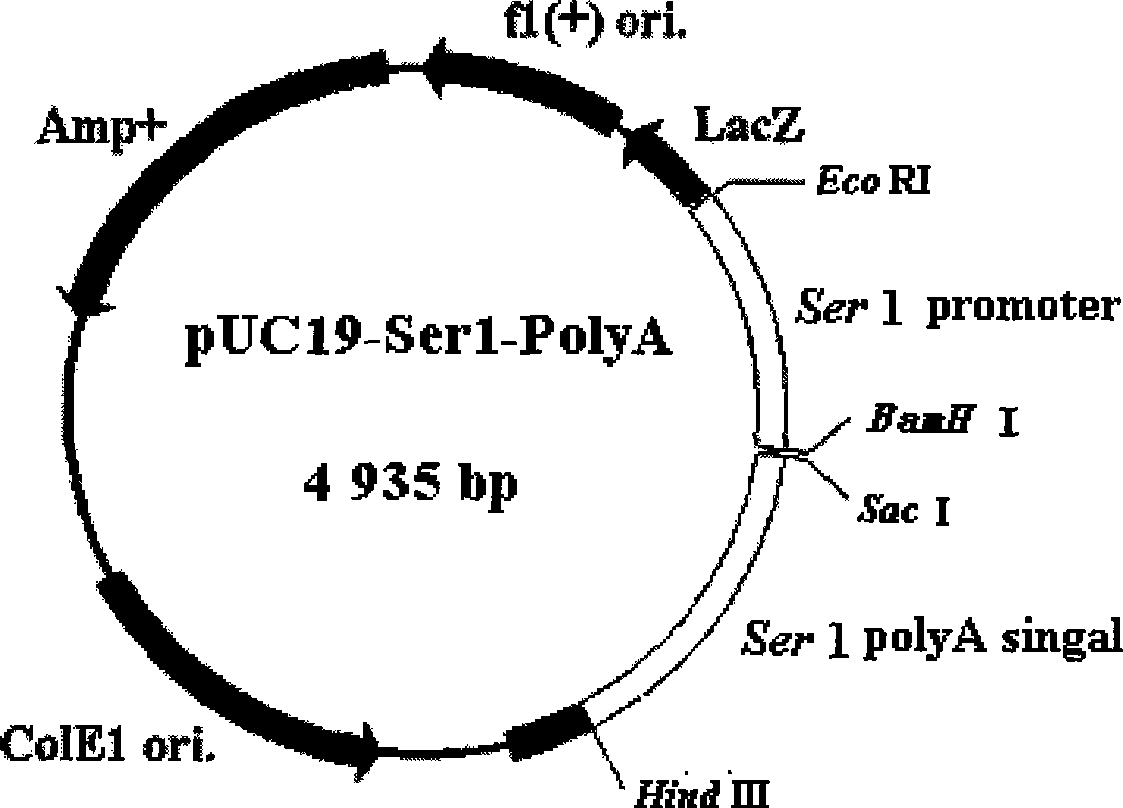
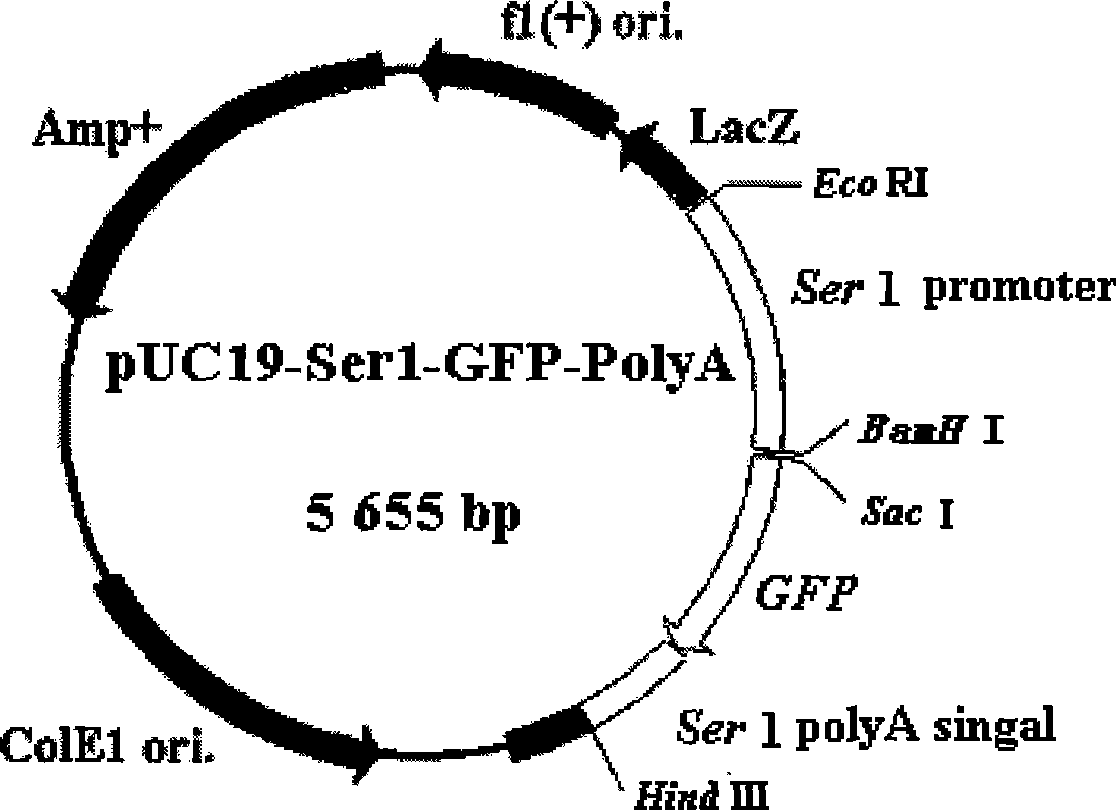
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing protein by using an in-vitro expression system of middle silk glands of silkworms. The method comprises the following steps: adding any one of pUC19-Serl-PolyA recombinant plasmids or pUC19-Serl-GFP-PolyA recombinant plasmids or recombinant plasmids inserted with exogenous genes into tissue extract of the middle silk glands of the silkworms; adding a protease inhibitor into the mixture; and treating the mixture in water bath at a temperature of between 25 and 29 DEG C, so as to obtain expresses of target protein. The method has the following advantages: the protein is expressed under a low temperature condition of between 25 and 29 DEG C, so the method is favorable for generating expression protein in a dissolving state and favorable for separation and purification of the protein. At the same time, the method is not limited by cells, and can synthesize the protein in a short time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
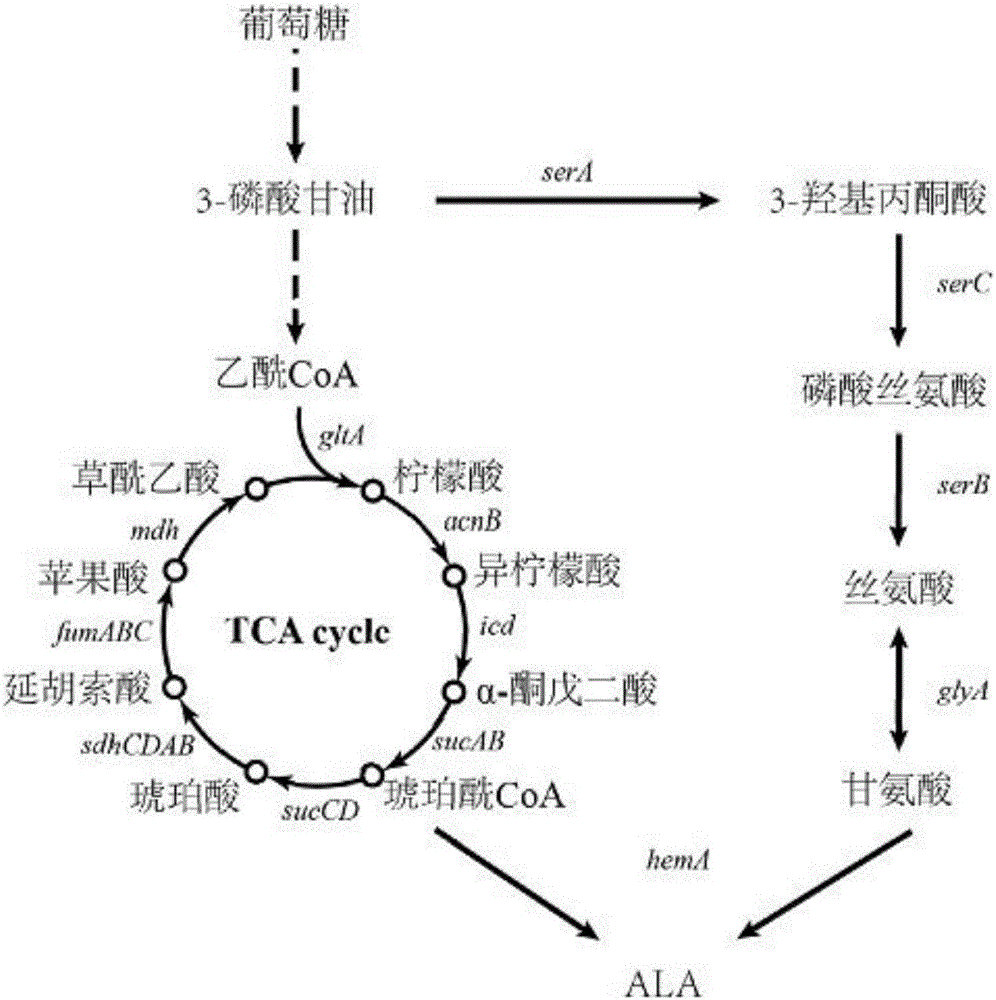
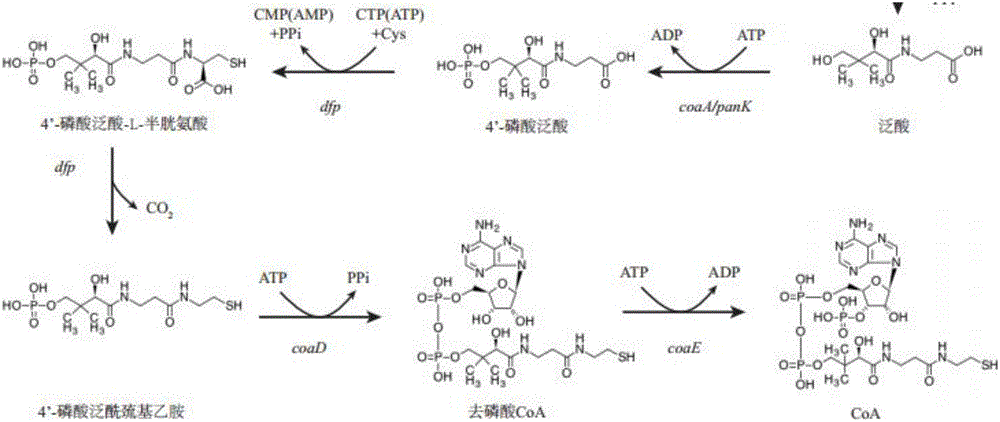
Engineered escherichia coli for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
ActiveCN106497858ASynthesis efficiently utilizes the C4 pathway to promoteEasy to synthesizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPUC19Escherichia coli
The invention discloses engineered escherichia coli for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid and belongs to the fields of metabolic engineering and microbial fermentation. The engineered escherichia coli is characterized by carrying out co-expression of a gene coaA for coding pantothenate kinase, a gene dfp for coding phosphoric acid pantothenylcysteine synthetase and decarboxylase and a gene coaD for coding phosphoric acid CoA pyrophosphorylase from an escherichia coli CoA synthetic pathway by using pUC19 and pETDuet-1 vectors on the basis of excess expression of 5-aminolevulinate synthase hemA which is used as a key enzyme in a synthetic pathway of 5-aminolevulinic acid C4 by using a vector pRSFDuet-1-hemA to build recombination strains. Shake-flask culture proves that the yield of recombinant bacteria ALA for co-expression of CoA pathway genes is obviously improved; the maximum yield reaches 700mg / L and is increased by about 46% in comparison with contrast.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
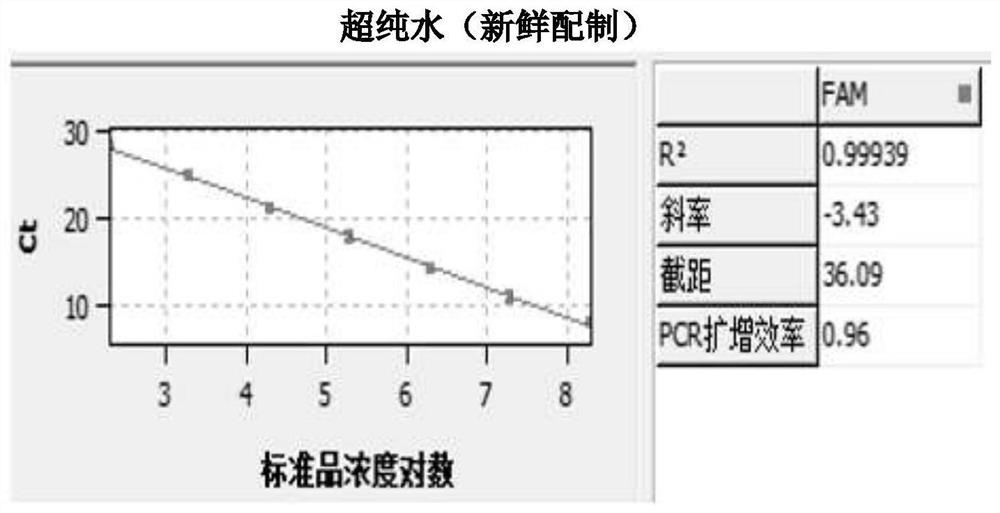
Nucleic acid diluent
The invention relates to a nucleic acid diluent. The nucleic acid diluent comprises 1*TE, F68 and DNA selected from the group consisting of Lambda DNA, pUC19 plasmid DNA, pUC18 plasmid DNA, pBR322 plasmid DNA, denatured protamine DNA, pUC57 plasmid DNA, pTZ19R DNA, Escherichia coli DNA and sssDNA. The nucleic acid diluent provided by the invention can be used for dilution of a standard substance and a sample in quantitative PCR and has the effects of protecting and stabilizing the standard substance and the sample. The invention also relates to a standard substance solution prepared from the nucleic acid diluent and a quantitative PCR method using the standard substance solution.
Owner:SHANGHAI MYGT BIOPHARMACEUTICAL LLC
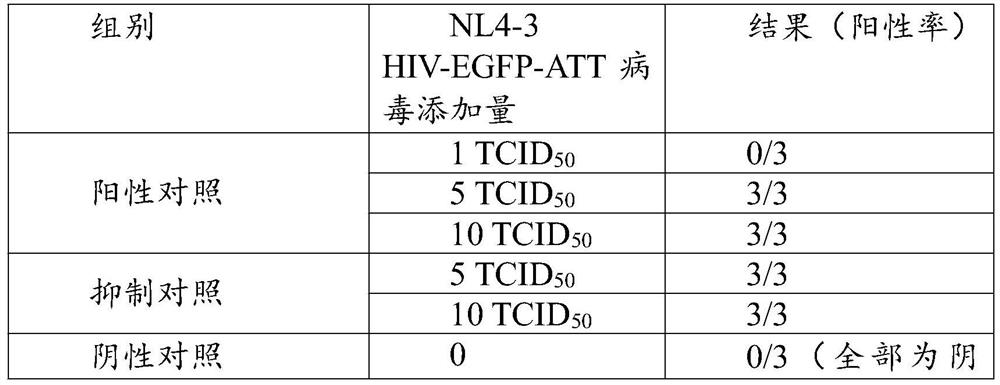
Kit for detecting replicable lentivirus (RCL) and application thereof
PendingCN113789345ALow cytotoxicitySame characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaPUC19Lentivirus
The invention relates to a kit for detecting a replicable lentivirus (RCL) and an application thereof. The kit comprises a recombinant expression vector pUC19-NL4-3HIV-EGFP-ATT or a recombinant bacterium NL4-3HIV-EGFP-ATT, and the recombinant bacterium NL4-3HIV-EGFP-ATT contains the recombinant expression vector pUC19-NL4-3HIV-EGFP-ATT. Compared with the existing method, the kit disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the occurrence of false positive results can be avoided; more detection points are used, the detection result is more reliable, and the safety is higher.
Owner:康美润源(北京)生物技术有限公司
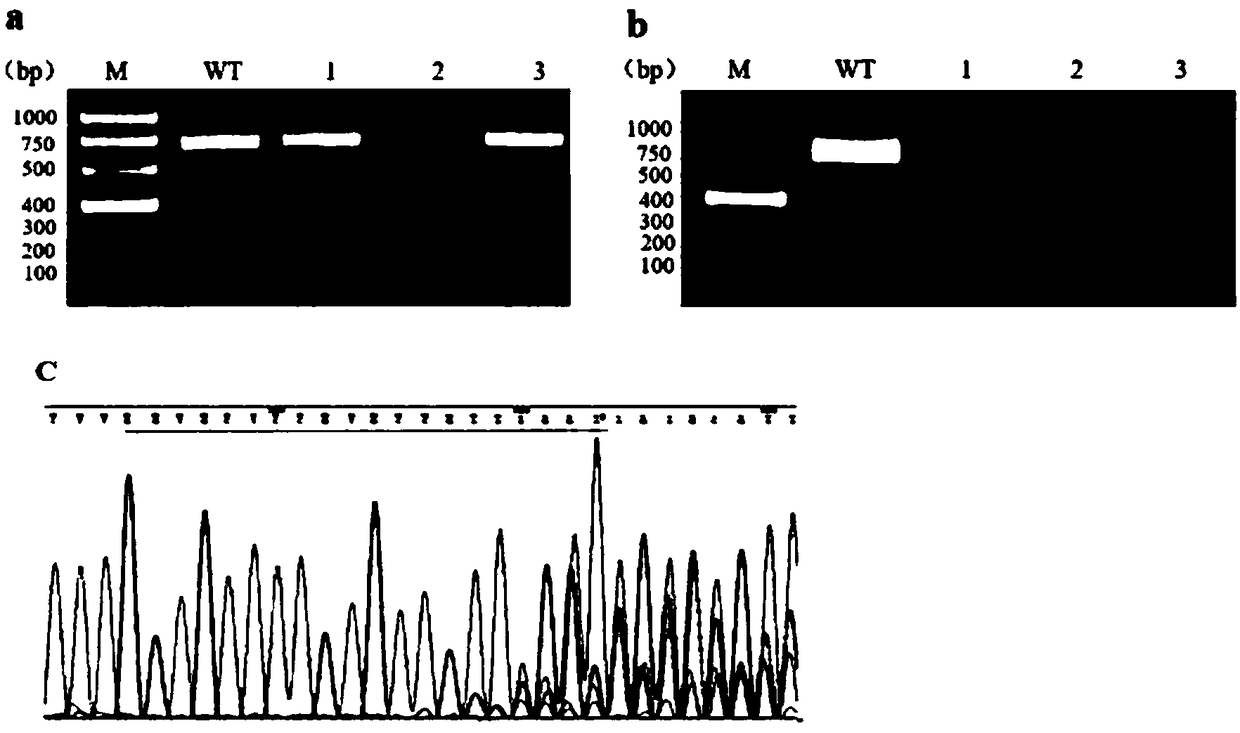
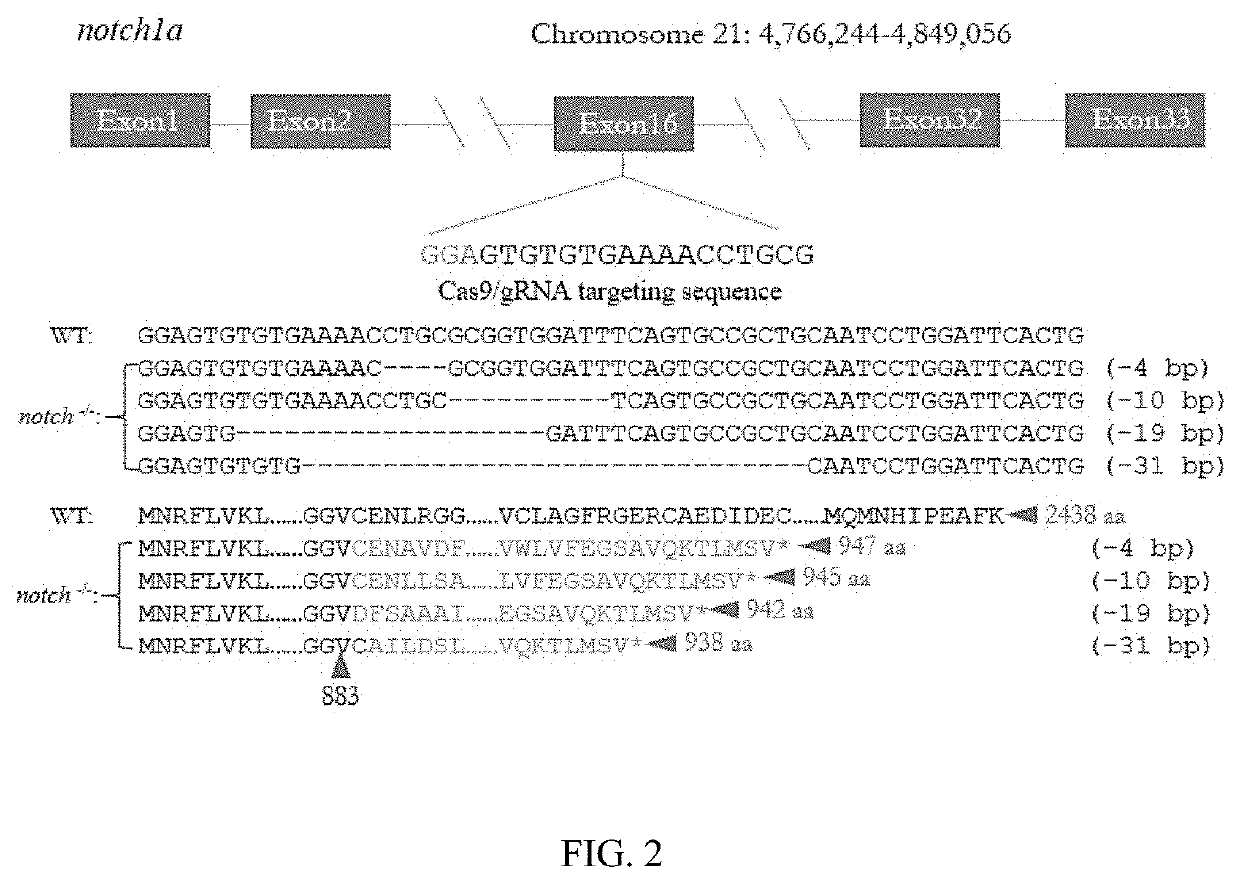
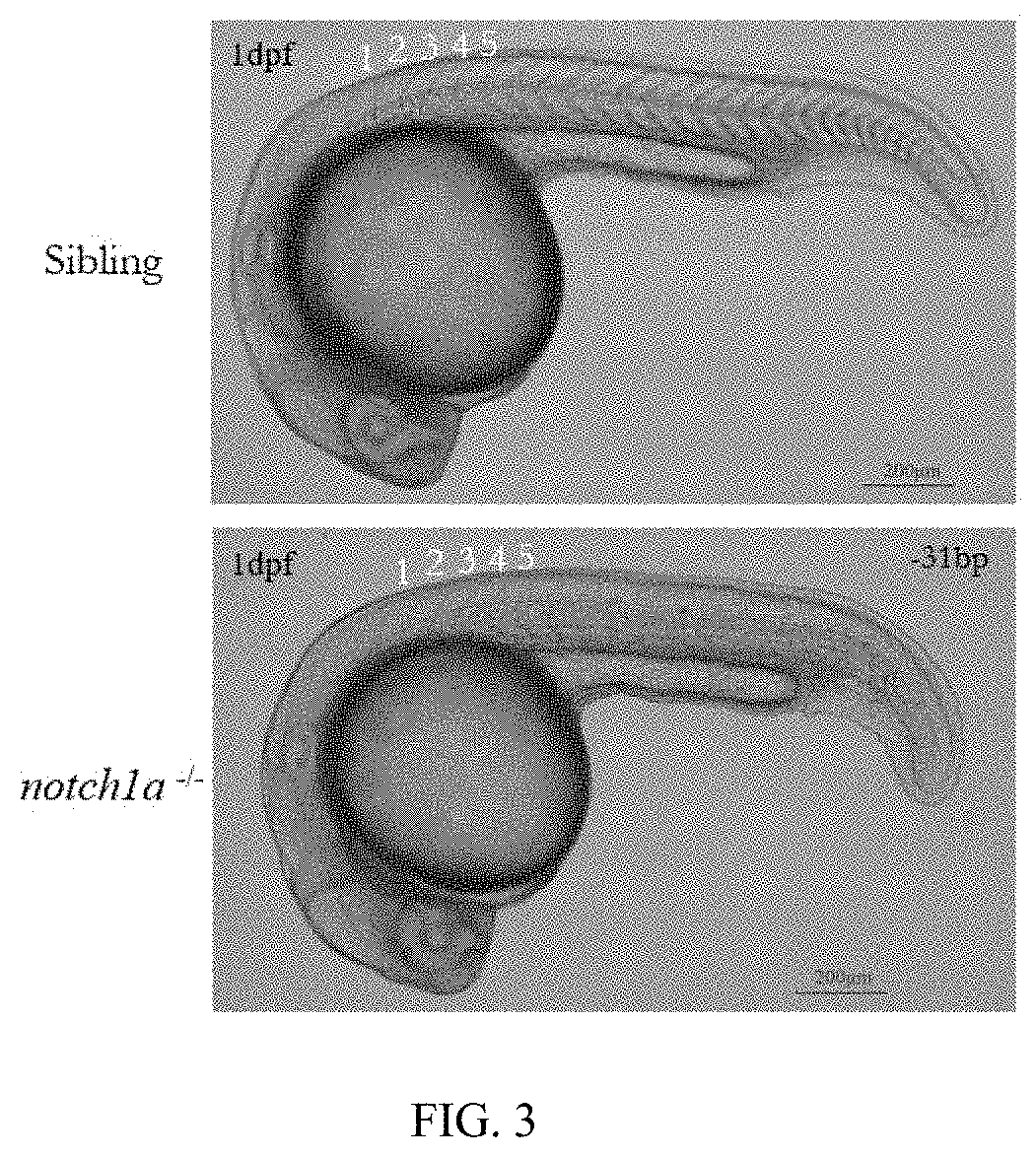
METHOD OF CONSTRUCTING ZEBRAFISH notch1a MUTANTS
ActiveUS20190357507A1Facilitate further studyStably inheritedPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPUC19Notch signalling pathway
A method of constructing a zebrafish notch1a mutant using CRISPR / Cas9 technique. The method includes: determining a target for knocking out notch1a; using primers T7-notch1a-sfd and tracr rev for PCR amplification with a pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template; transcribing PCR product in vitro followed by purification to obtain gRNA; and microinjecting the gRNA and a Cas9 mRNA into a zebrafish embryo followed by culture to obtain an notch1a mutant of stable inheritance. The invention selects a specific target and utilizes CRISPR / Cas9 technique to knock out the notch1a in the zebrafish without destroying other genes, generating the zebrafish notch1a mutant. Moreover, the invention also discloses the phenotype of the zebrafish notch1a mutant, which plays a significant role in studying the effect of the Notch1a receptor in the Notch signaling pathway.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Construction method and application of annular RNA overexpression system of protoplast of moso bamboo
ActiveCN109486856AFast Transient ConversionStable transient conversionVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Host gene
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of an annular RNA overexpression system of protoplast of moso bamboo and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The system constructs an annular RNA overexpression vector and converts the vector to the protoplast of moso bamboo. The construction method comprises the following steps: amplifying an annular RNA host genewith a high fidelity Taq enzyme and constructing an annular RNA overexpressed recombinant plasmid by a Gateway method by taking pUC19-35s-sGPF as a final vector; and extracting the recombinant plasmids massively and converting the plasmids to the protoplast of moso bamboo mediated by PEG to research the influence of annular RNA overexpression to transcription and post-transcription levels of thehost gene.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
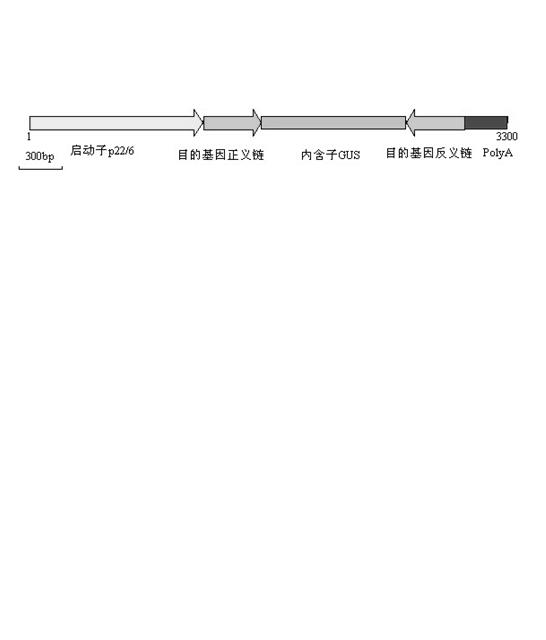
Constructing method of zein gene RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid Interference) carrier
InactiveCN102533847AImprove qualityIncrease contentVector-based foreign material introductionPUC19Partial cdna
The invention discloses a constructing method of a zein gene RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid Interference) carrier. The method comprises the following steps of: constructing a recombinant carrier which is inserted into a forward target fragment and an endospem-specific expression promoter P-zp22 / 6 as well as a recombinant carrier which is inserted into a reverse target fragment and a terminator poly(A) by utilizing pUC19 as a frame carrier, and respectively carrying out digestion and connection on the two recombinant carriers to obtain a recombinant carrier pUC19-p22 / 6-22KD1-22KD2-poly(A); and inserting the GUS gene intron into the recombinant carrier to obtain the zein gene RNAi carrier of which the target fragment is partial cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) fragment of a 22-KD alcohol-soluble protein gene. Another zein gene RNAi carrier is constructed by an identical method, and the target fragment of the zein gene RNAi carrier is partial cDNA fragment of a 19-KD alcohol-soluble protein gene. By adopting the method, the carrier constructing time is shortened and a transgenic plant with high lysine content can be successfully obtained.
Owner:FOOD CROPS RES INST YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
CRISPR/Cas9 system for knocking out dmrt1 gene at double gRNA sites in yellow catfish and application
ActiveCN110923229AHigh knockout efficiencyReduce identification costsMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a CRISPR / Cas9 system for knocking out a dmrt1 gene at double gRNA sites in yellow catfish. The CRISPR / Cas9 system comprises the following steps: (1) designing a target site 1 on a first exon of the dmrt1 gene of the yellow catfish, and designing a target site 2 on a third exon; (2) designing a primer according to a target site sequence in the step (1) to detect the accuracyof the target sites in parent fishes, amplifying the target site 1 and nearby sequences by using dmrt1 E1 F and dmrt1 E1 R, and amplifying the target site 2 and nearby sequences by using dmrt1 E3 F and dmrt1 E3 R; (3) performing PCR amplification on a gRNA1 fragment by using dmrt1 E1 gRNA F and gRNA R by taking pUC19-gRNA-scaffold plasmid as a template, performing PCR amplification on a gRNA2 fragment by using dmrt1 E3 gRNA F and gRNA R, and performing in-vitro transcription and purification by taking the PCR product as a template to obtain gRNA; (4) performing in-vitro transcription synthesis on Cas9 mRNA by taking pXT7-hCas9 linearized plasmid as a template; (5) performing microinjection on the Cas9 mRNA and the two gRNAs into a cell-stage embryo of the yellow catfish; and (6) detectingthe mutation type, and calculating the gene editing rate.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
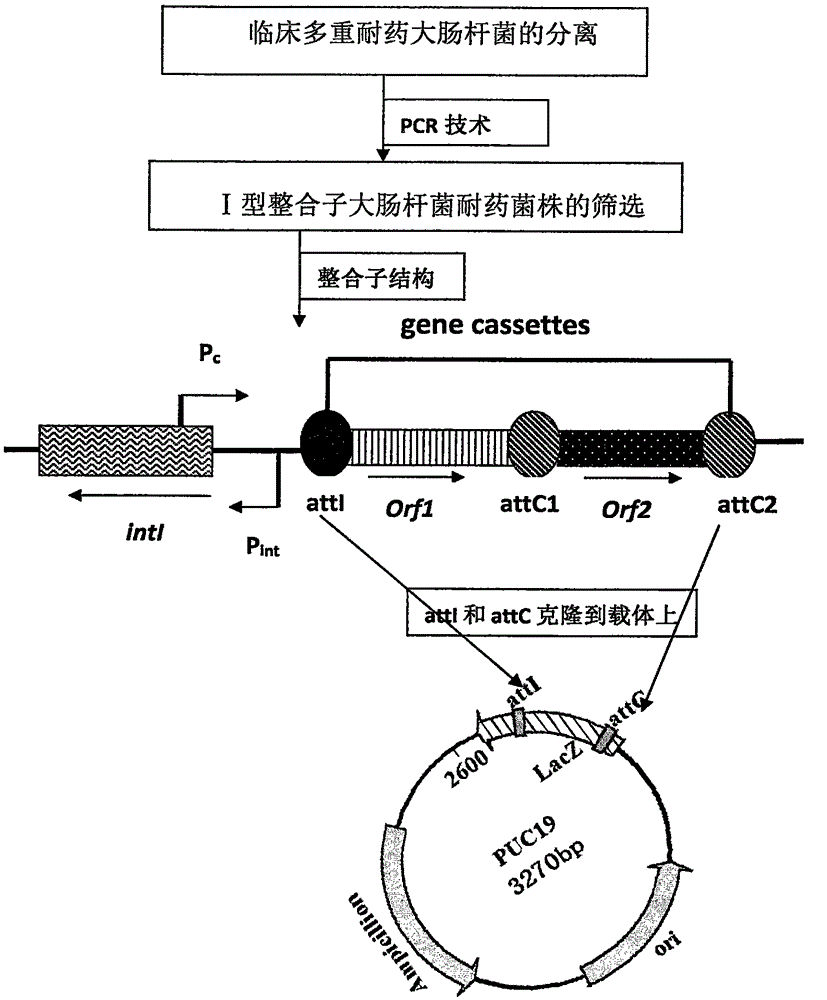
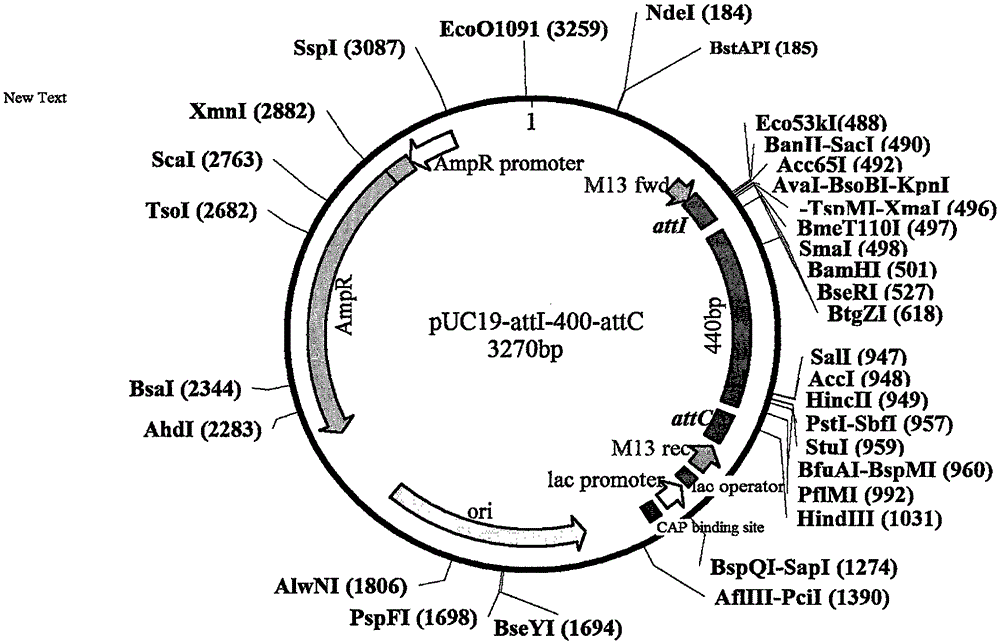
Construction method of drug-resistant Escherichia coli intergrase integration vector pUC19-attI-400-attC
InactiveCN105602974ACarrier smallEasy to filterVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliBacteroides
The invention discloses a construction method of a drug-resistant Escherichia coli intergrase integration vector pUC19-attI-400-attC. The recombinant containing attI and attC recombinant sites is constructed, a 440bp DNA sequence exists between the attI and attC recombinant sites, the vector is small and only contains 3270bp, the attI and attC sites can be simultaneously cut, the attC site also can be individually cut, and the vector also contains more than 10 multiple cloning sites, so a user can conveniently select suitable restrictive endonuclease to research the action site of intergrase; and the vector has aminobenzyl resistance, is convenient to screen, can be used to carry out in vitro detection of the vector model of the integration activity of the drug-resistant bacterial intergrase, and also can be used to explore the integration mechanism of other bacterial integrons.
Owner:河套学院
Universal transfer vector for pseudorabies virus capable of independently expressing dual genes and construction method and application of universal transfer vector
InactiveCN104195156ARecombination is effectiveVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsPUC19Transfer vector
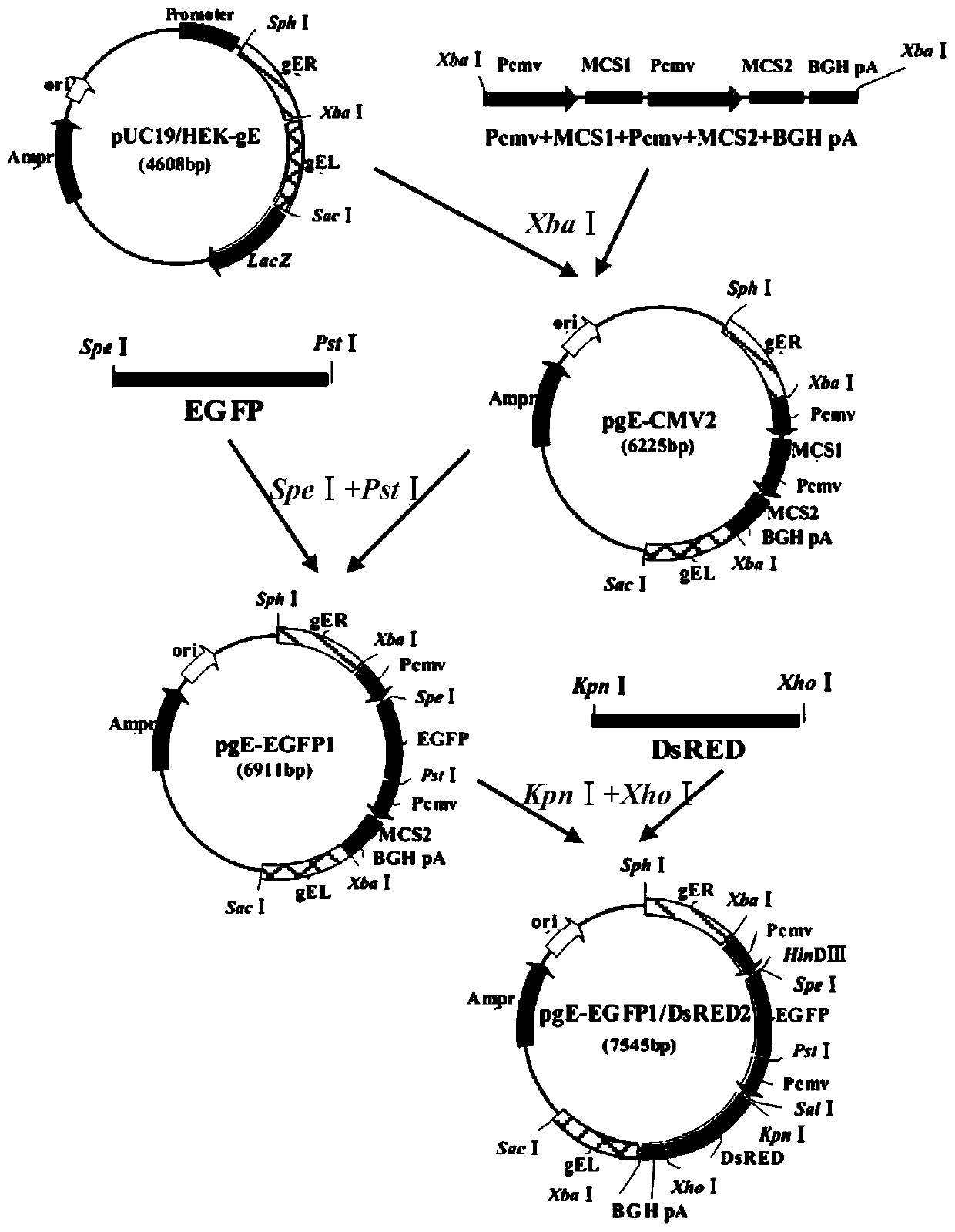
The invention discloses a universal transfer vector for a pseudorabies virus capable of independently expressing dual genes and a construction method of the universal transfer vector. The universal transfer vector is obtained by inserting a dual-gene expression cassette containing two CMV promoters, multiple cloning sites respectively at downstream positions of the two CMV promoters and a BGH pA signal sequence between gEL and gER contained in pUC19 / HEK-gE recombinant plasmids containing gEL and gER. The universal transfer vector is capable of independently expressing two exogenous genes by utilizing two promoters and can be used for constructing a recombinant pseudorabies virus capable of independently expressing two exogenous genes.
Owner:GUANGDONG WENS DAHUANONG BIOTECH +1
Novel bacterial artificial chromosome of turkey herpes virus, construction method and application
PendingCN106350475AImprove stabilityEfficient constructionBacteriaViral antigen ingredientsPUC19Herpes simplex virus DNA
The invention provides a novel bacterial artificial chromosome of a turkey herpes virus, a construction method and application and relates to the field of animal medicine. The bacterial artificial chromosome is obtained by knocking out gC gene in HVT genome and replacing with a mini-F plasmid sequence. The construction method includes: amplifying upstream and downstream homologous arms of the gC gene in the HVT genome, and inserting into a pUC19 vector to obtain a recombinant vector A; inserting a mini-F plasmid segment into the recombinant vector A to obtain a recombinant transfer vector B, performing cotransfection (CEF) with DNA of HTV, and screening to obtain mini-F recombinant HVT; extracting DNA of the mini-F recombinant HVT to convert DH10B cells, adopting chloromycetin for screening to obtain positive recombinant bacteria, culturing, and then extracting plasmid DNA. The bacterial artificial chromosome has high stability, and the construction method is simple, efficiency and applicable to construction of recombinant vector live vaccines.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
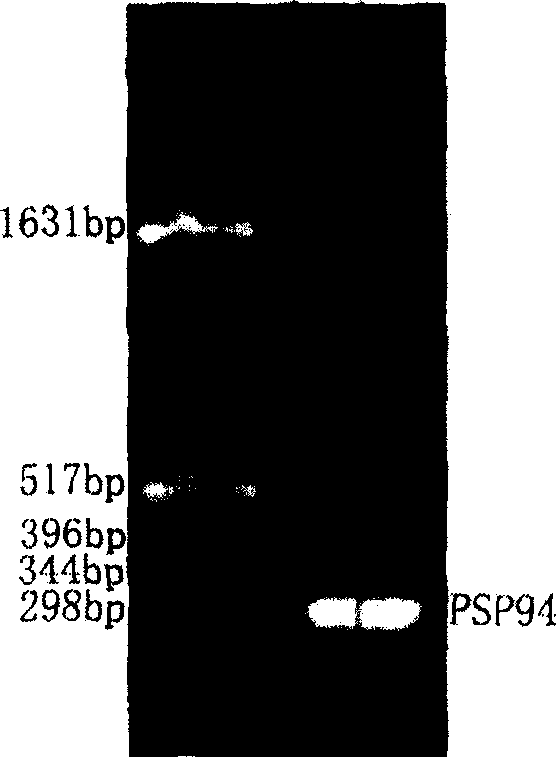
Method for recombining human PSP94 protein secretory expression in colibacillus
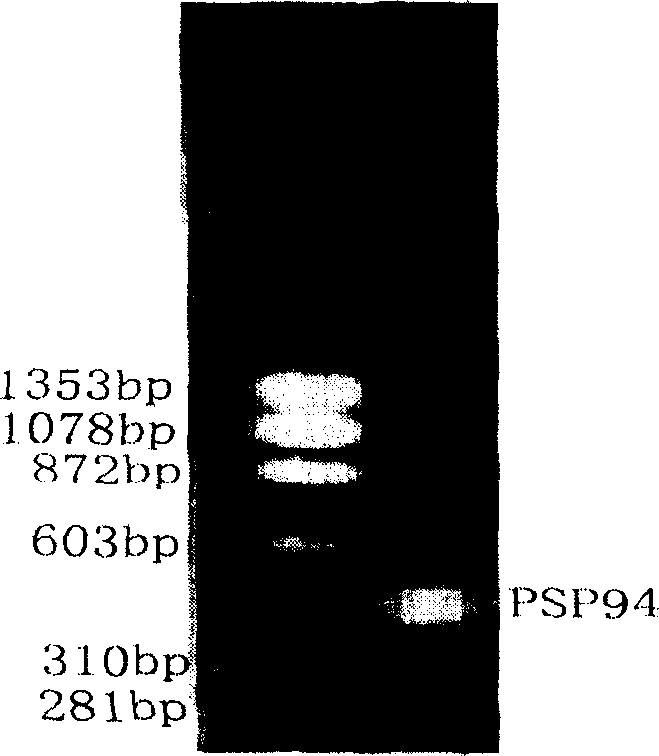
InactiveCN1673377AOvercoming the Problem of Adding Extra Amino AcidsEasy to separate and purifyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliPUC19
The present invention relates to method of secreting and expressing recombinant human PSP94 protein in colibaccillus, and belongs to the field of the expression of bioactive human PSP94 protein. The present invention includes extracting total prostate tissue RNA, obtaining Chinese PSP94 cDNA sequence via RT-PCR process, inserting it into cloned vector pUC19, determining sequence after coarse PCR screening; connecting double restricted PSP94 protein coding gene, signal peptide and pBV220 plasmid to constitute recombinant plasmid pBV-PSP94; transforming colibaccillus strain with the positive recombinant plasmid pBV-PSP94 and protein inducing expression at optimal temperature 40 deg.c for optimal time of 5 hr. The present invention has the beneficial effect of mutating the signal peptide of secreting expression vector and inducing restriction site to the signal peptide superiorly by means of molecular biological technology.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Breeding medium for preparing cells in competence of electric transform in high effectively, and application
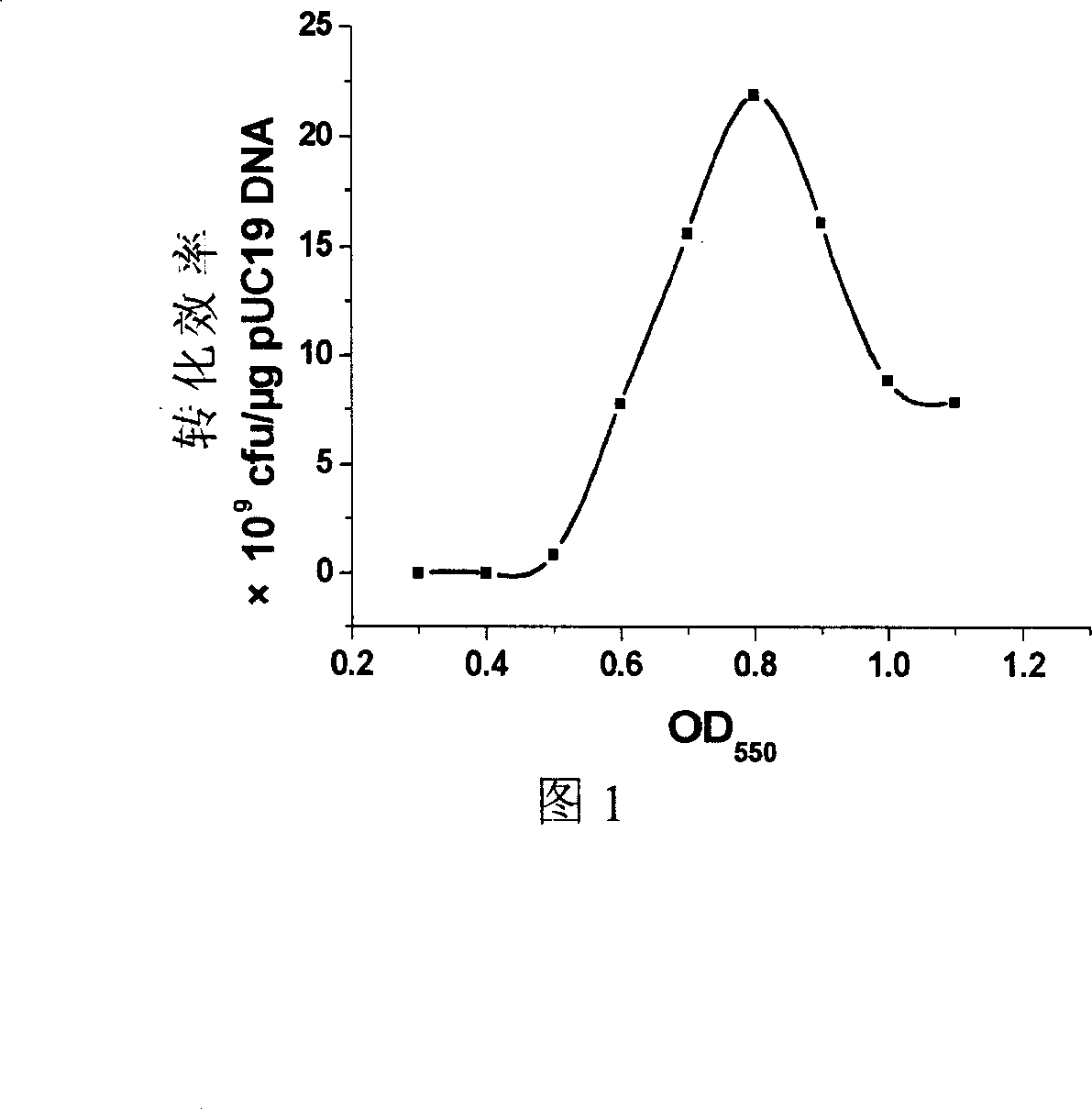
This invention relates to a YENB culture medium for preparing high-efficiency electroporation-competent cells. The YENB culture medium comprises (per liter): yeast extract for cell culture 6-9 g, nutrient broth for cell culture 6-9 g, and water. The YENB culture medium can prepare high-efficiency electroporation-competent cells by controlling cell primary and secondary growth time, centrifugal speed and time. The conversion rate is 2.19X1010 cfu / mu.g pUC19 DNA, which is higher than imported culture medium, while the cost is only 5% that of imported culture medium. The culture medium lays a basis for high-efficiency conversion of large fragment DNA genomic library.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombination bollworm monokaryon capsid polyhedrosis virus for expression polghedrosis and chitinase fusion protein and its preparation method
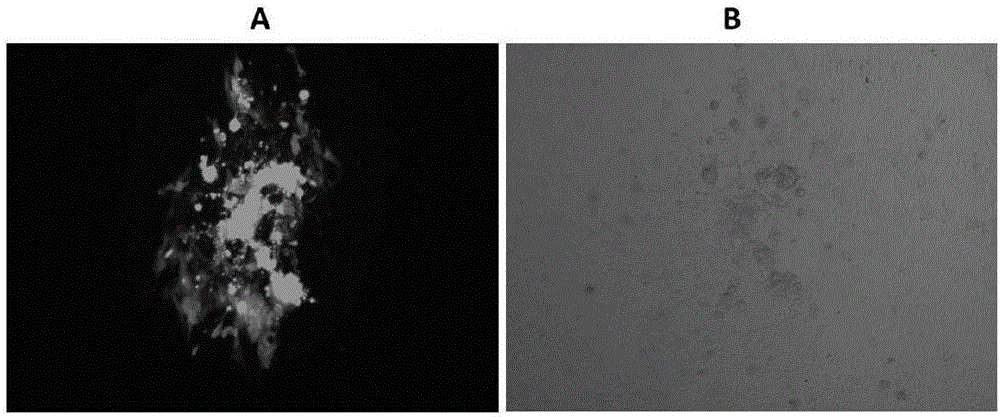
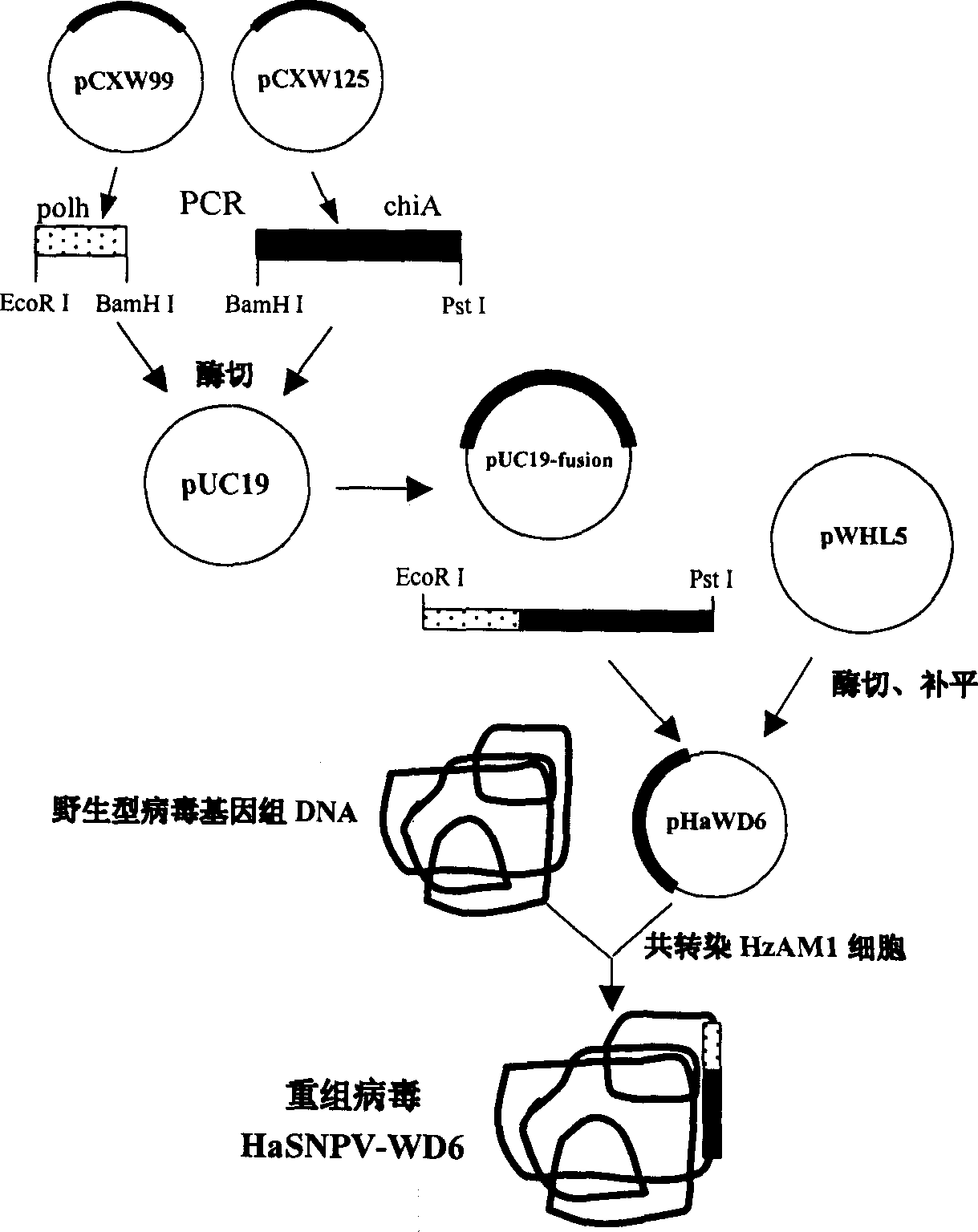
InactiveCN1429902AIncreased efficiency of infecting the midgutSolve the shortcomings of late expression and slow onsetBiocideViruses/bacteriophagesPUC19Wild type
A recombinant mononuclear capsid nucleopolyhedrovirus of bollw orm able to express polyhedron and chitinase fusion protein is prepared through PCR amplification of polyhedron gene HaSNPV and chitinase gene, cloning to carrier pUC19 to configure fusion gene, inserted it in eukaryotic carrier pHaWHL5 to obtain eukaryotic transfer carrier pHaWD6, transfecting insection cell by it along with wild virus DNA, and homologous recombination.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com