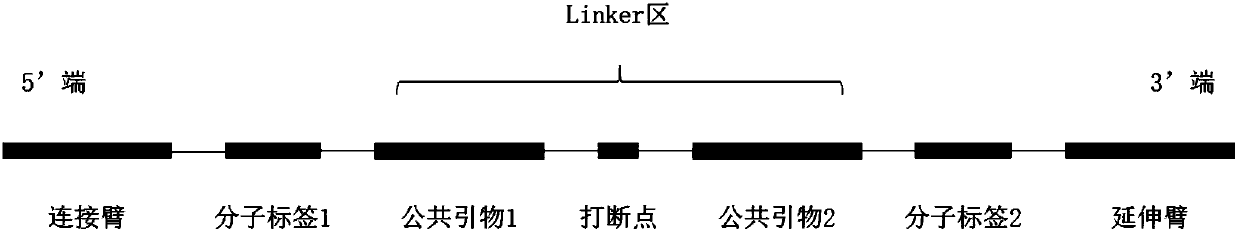
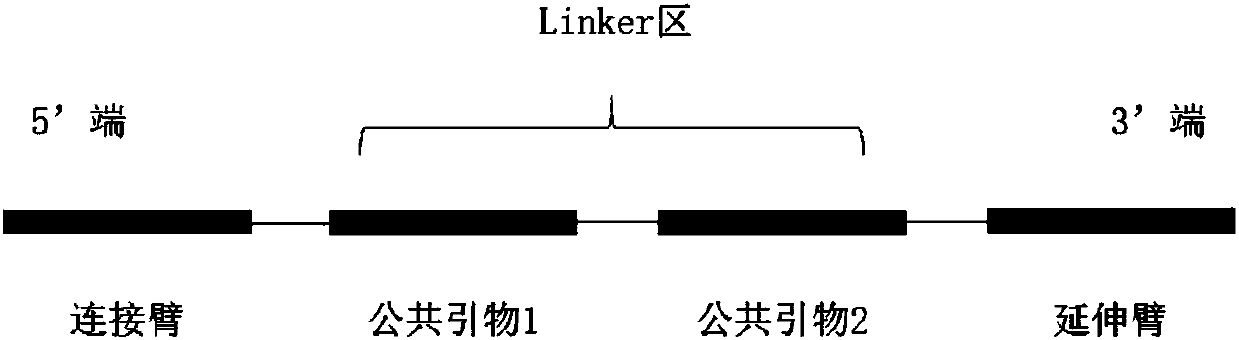
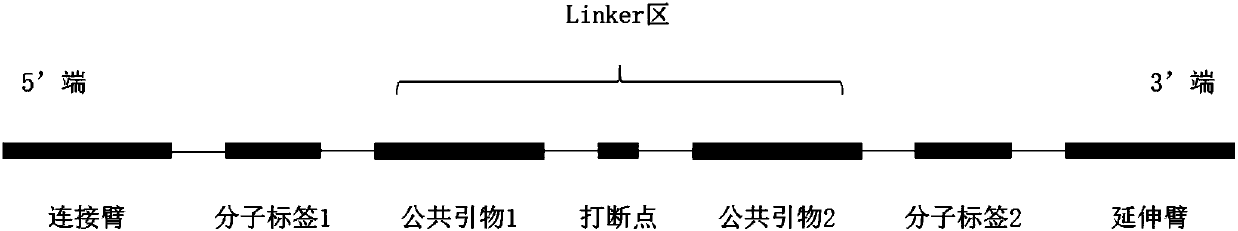
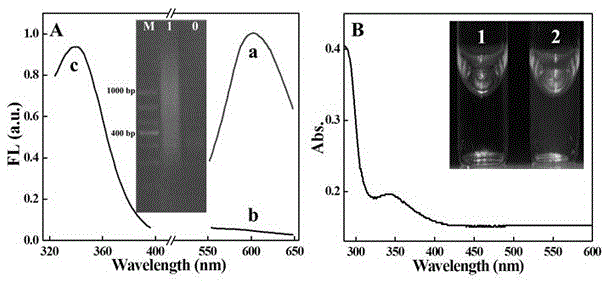
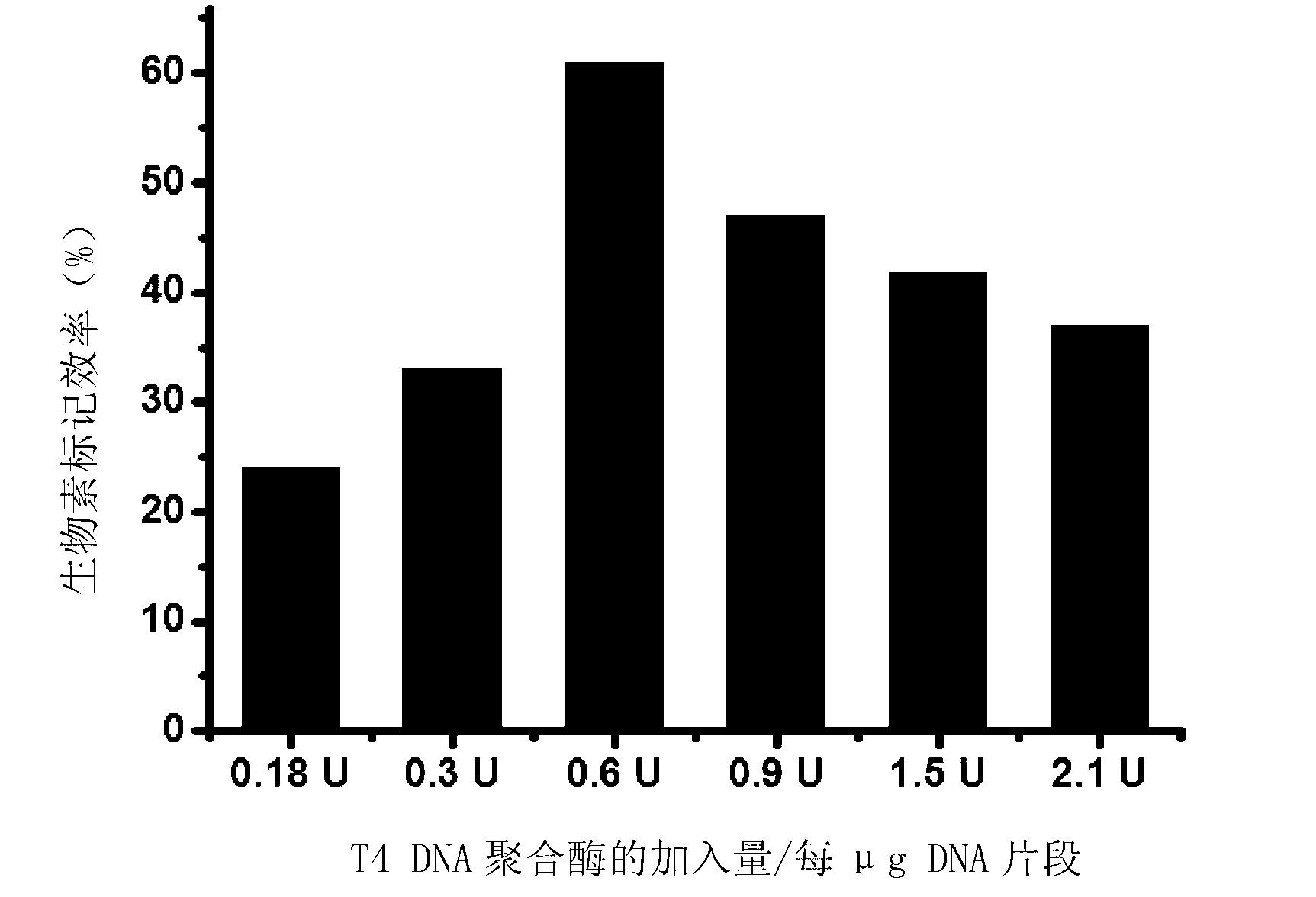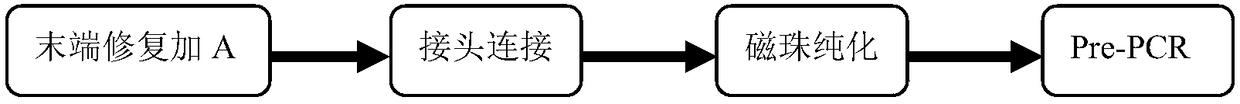Patents
Literature
58 results about "Klenow fragment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Klenow fragment is a large protein fragment produced when DNA polymerase I from E. coli is enzymatically cleaved by the protease subtilisin. First reported in 1970, it retains the 5' → 3' polymerase activity and the 3’ → 5’ exonuclease activity for removal of precoding nucleotides and proofreading, but loses its 5' → 3' exonuclease activity.
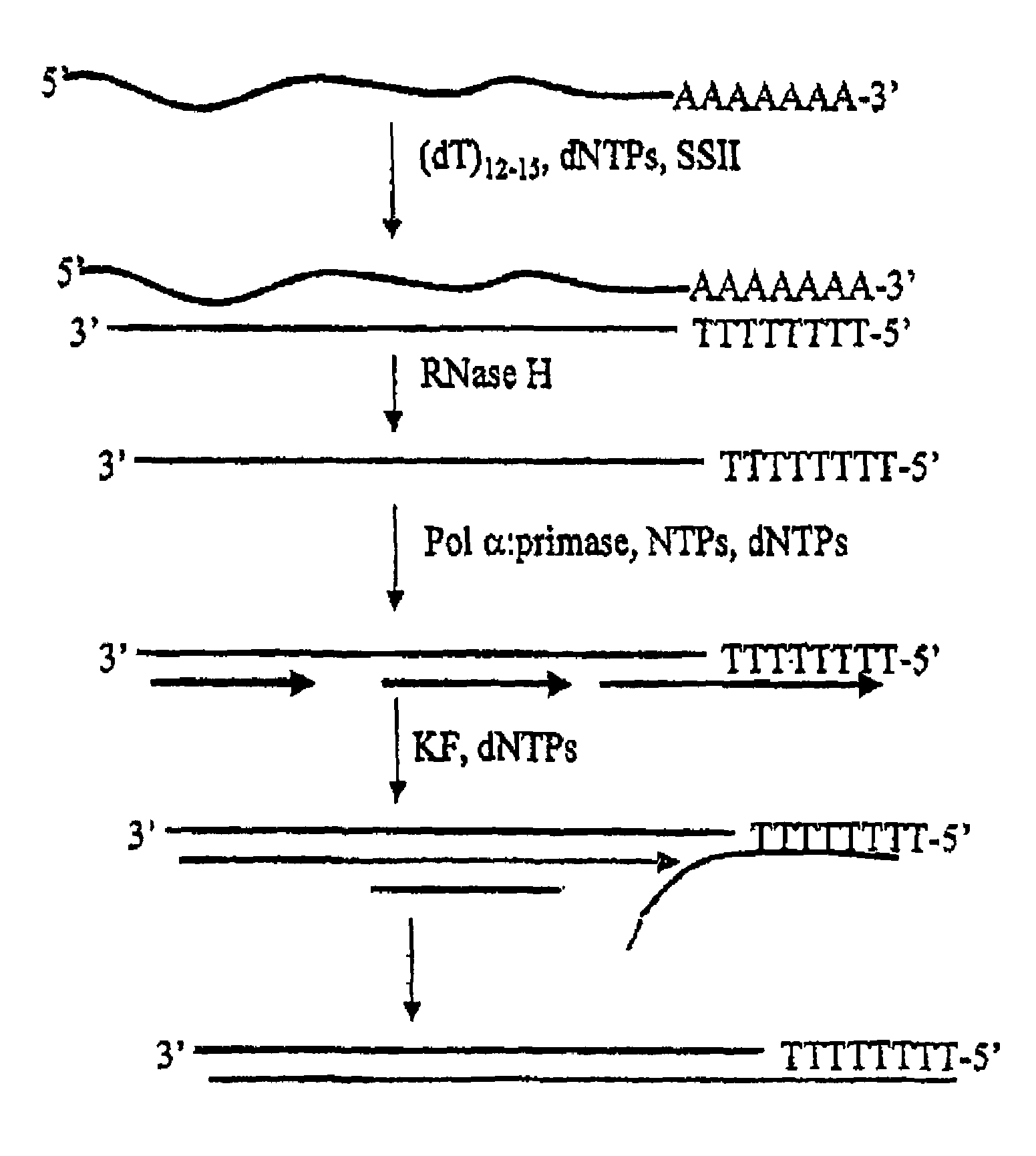
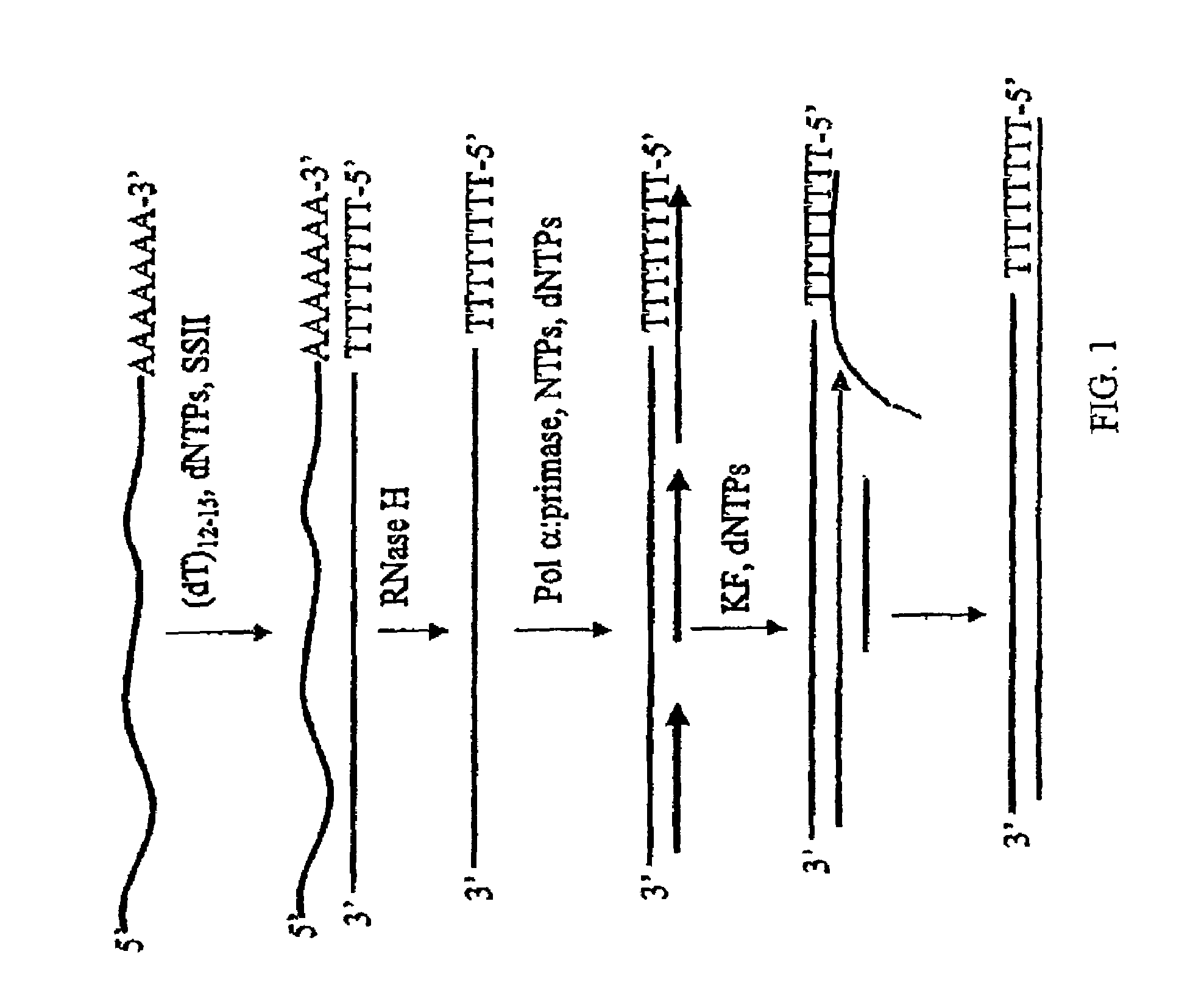
Method for synthesis of the second strand of cDNA
InactiveUS7205128B2Improve synthesis abilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGeneticsPrimase
Synthesis of the second strand of cDNA using pol ∝-primase is provided. Pol ∝-primase is used to initiate primers on a cDNA strand de novo, followed by extension of the primer with pol ∝-primase, a second DNA polymerase or a combination thereof. In a preferred embodiment, pol ∝-primase extends the primer, followed by addition of a second DNA polymerase, preferably Klenow fragment.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
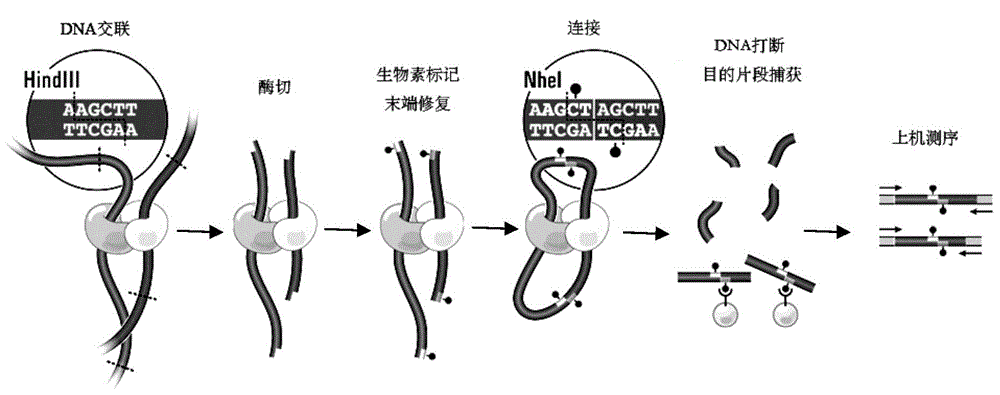
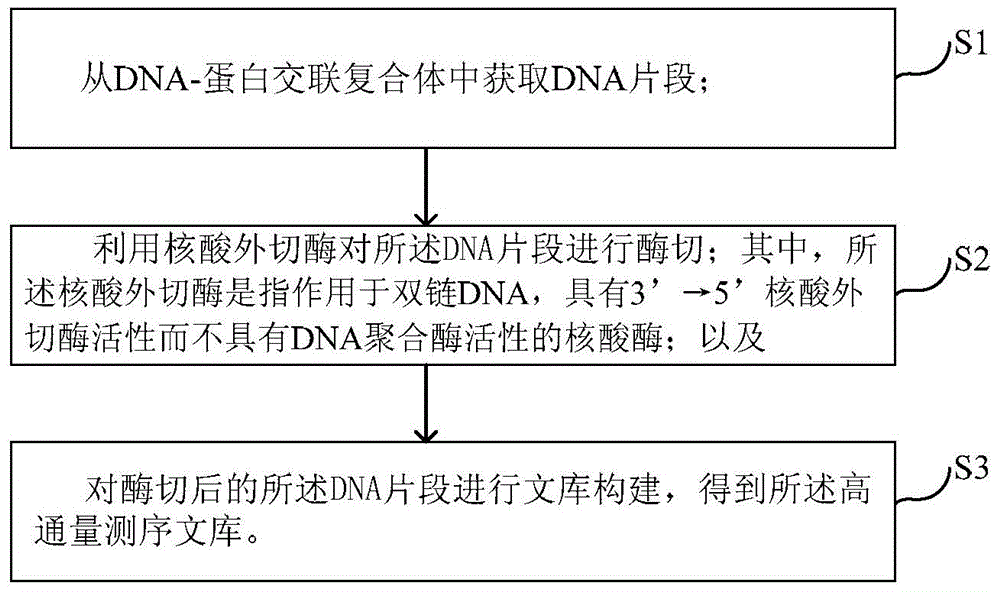
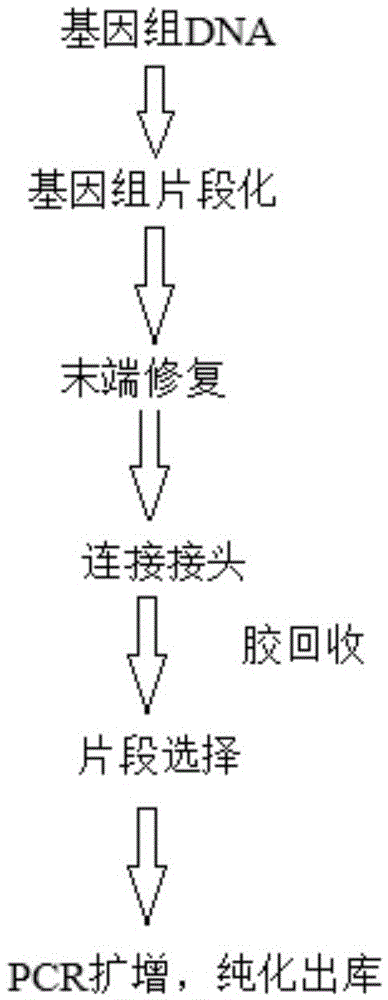
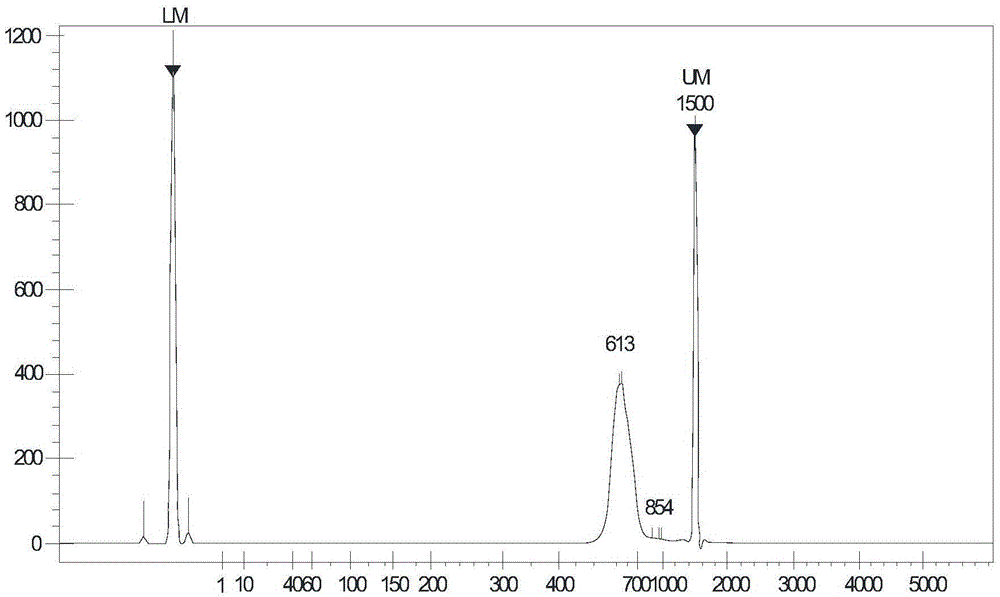
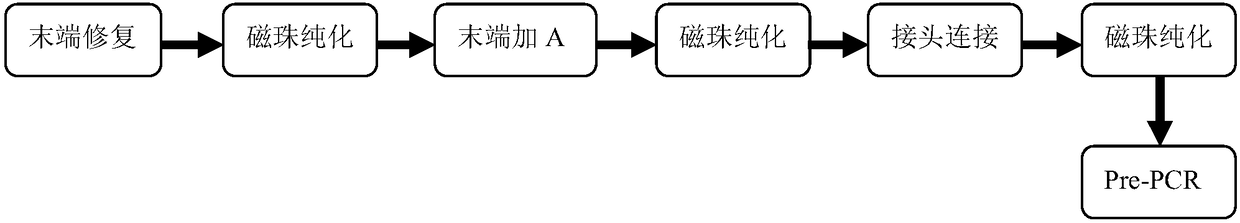
High-throughput sequencing library and construction method thereof
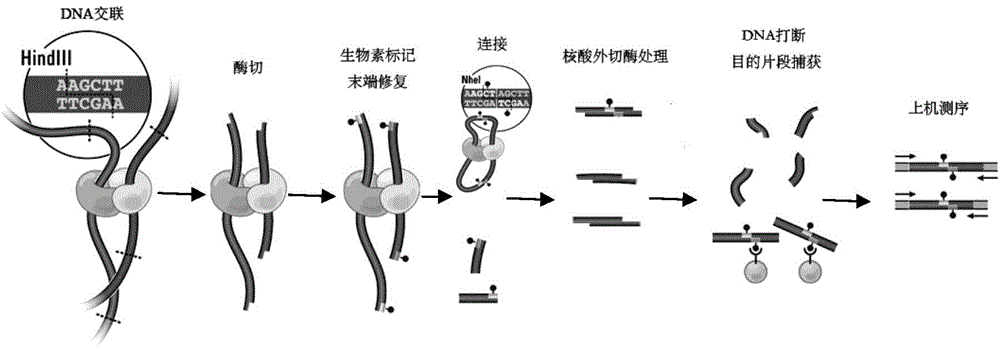
ActiveCN104561362AHigh purityRemove completelyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCross-linkA-DNA
The invention discloses a high-throughput sequencing library and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the following steps: S1. acquiring a DNA fragment from a DNA-protein cross-linked complex; S2. enzymatically digesting the DNA fragment by virtue of exonuclease; and S3. constructing a library for the enzymatically digested DNA fragment so as to obtain the high-throughput sequencing library, wherein the exonuclease refers to nuclease which acts on double-stranded DNA only and has the activity of 3'->5' exonuclease rather than the activity of DNA polymerase. By replacing a klenow fragment which has the activity of the 3'->5' exonuclease and the activity of the DNA polymerase in the prior art by virtue of the exonuclease which has the activity of 3'->5' exonuclease and does not have the activity of DNA polymerase, the library construction method disclosed by the invention can be used for removing the marker in a non-target fragment more thoroughly, so that the purity of the obtained DNA fragment is greatly improved, and subsequently the effective quantity of subsequent sequencing data is increased.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
Hot start polymerase reaction using a thermolabile blocker
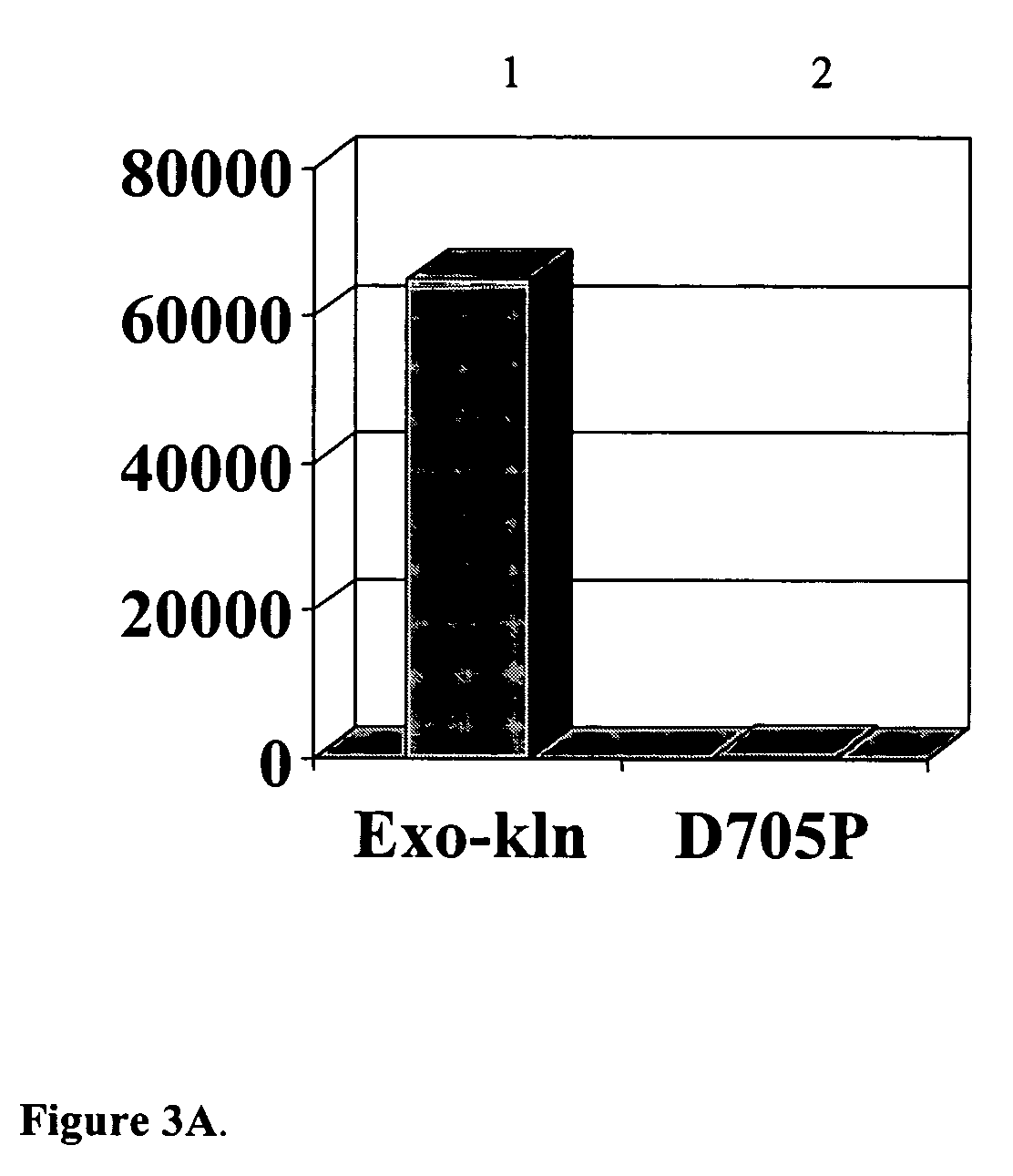
The invention relates to compositions, methods, and kits for hot start polynucleotide synthesis, including extension of primed polynucleotide templates and polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Hot start is provided by a thermally inactivated blocking polymerase protein that binds primed polynucleotide templates and prevents their access to a thermostable nucleic acid polymerase. High temperatures employed in the synthesis reaction cause the blocking polymerase to denature, thereby permitting the action of a thermostable processive polymerase. Compositions of the invention include a specific blocking polymerase protein which is a mutant of the Klenow fragment of E. coli DNA polymerase. The mutant is essentially devoid of polymerase activity, processivity, and 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. Use of the thermally inactivated blocking polymerase together with a thermostable polymerase reduces non-specific priming and accumulation of unwanted amplification products, increasing the specificity and sensitivity of the synthesis reaction.
Owner:STRATAGENE INC US
Kit and method for constructing DNA library
ActiveCN105603535AAchieve end repairAchieve plus ALibrary creationT4 polynucleotide kinasePolymerase L
The invention provides a kit and method for constructing a DNA library. The kit comprises an enzymic reagent, a buffer solution and a joint combination, wherein the enzymic reagent comprises a first enzyme mixed liquid, T4DNA ligase and a second enzyme mixed liquid, and the first enzyme mixed liquid is formed by mixing T4 Polynucleotide Kinase, T4DNA polymerase, a Klenow fragment and rTaq enzyme; the second enzyme mixed liquid is a 2X KAPA HiFi HotStart pre-mixed solution; the buffer solution comprises a first buffer solution and a second buffer solution, and the first buffer solution is formed by mixing a 10X T4DNA ligase buffer solution, dNTP mixed liquor and ATP; the second enzyme mixed liquid is formed by mixing ATP, Tris-HCL, MgCl2, PEG8000, Tween 20 and dithiothreitol; the joint combination comprises a joint sequence group and a tag sequence group. According to the kit, the library construction cost can be reduced and the amplification efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING NOVOGENE TECH CO LTD
DNA polymerase, nucleic acid test method and nucleic acid test kit
ActiveCN108588050ALow costShort detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEscherichia coliPolymerase L
The invention provides a DNA polymerase with DNA or RNA as a template. The DNA polymerase is obtained through amino acid replacement, including G198W, V222I, E306K, Q354E, A381E and E582K, of klenow fragments of escherichia coli polymerases I. The invention also provides a primer with a stem loop structure and used for constant-temperature nucleic acid amplification. The invention further providesa nucleic acid test technique and a test kit both based on combination between rapid constant-temperature nucleic acid amplification and a Cas test system. The DNA polymerase, the nucleic acid test technique and the test kit can be used for testing nucleic acid targets in test samples at a constant temperature, have the advantages of low cost, short test time, simplicity and convenience in operation, high specificity, high sensitivity and the like, and are particularly applied to POCT (point-of-care testing).
Owner:BEIJING EXELLON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
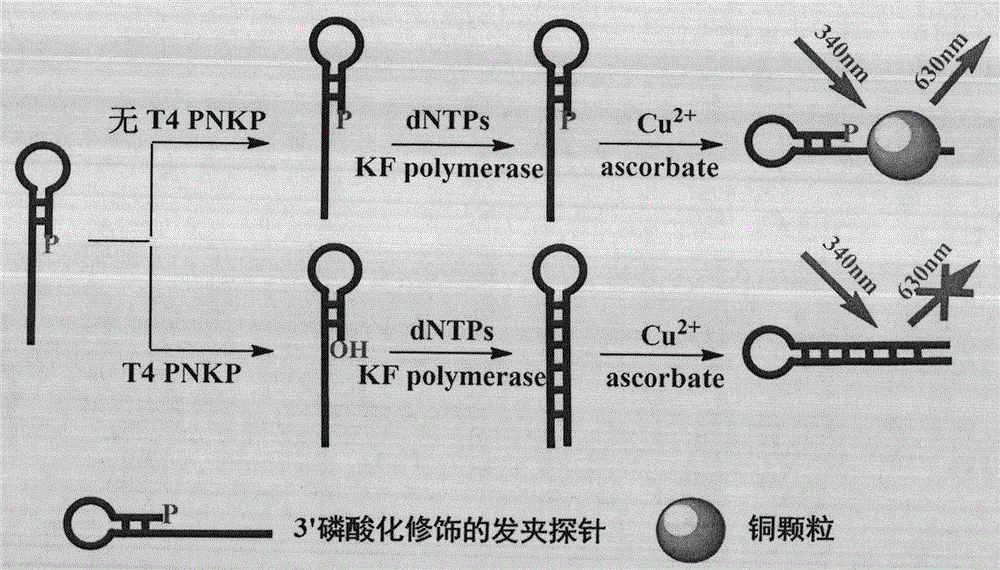
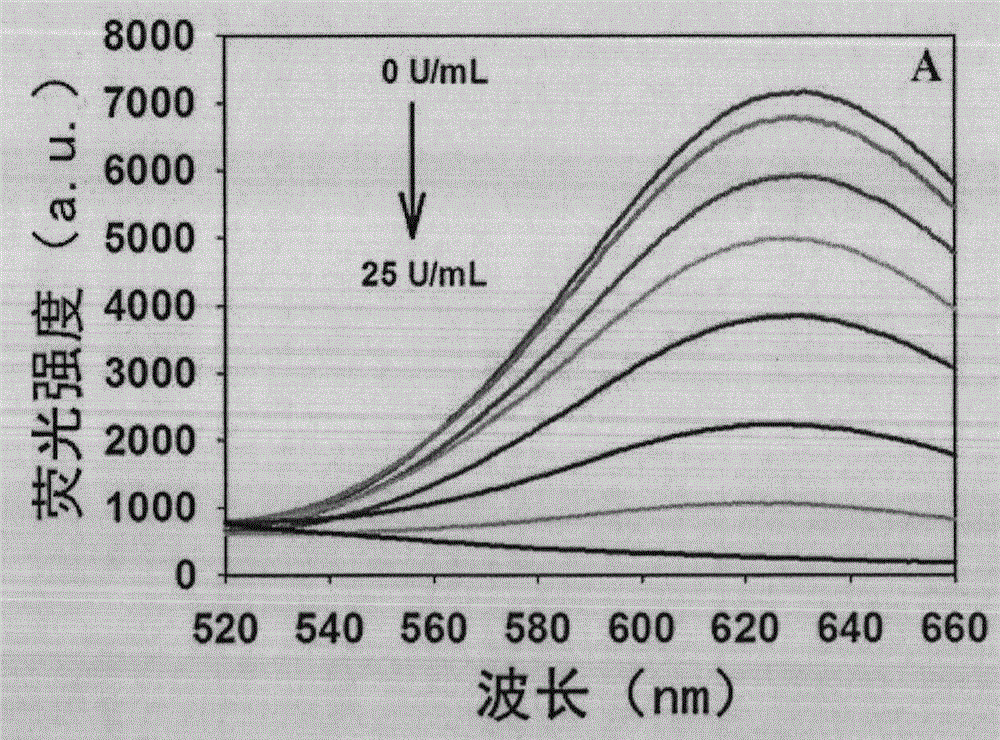
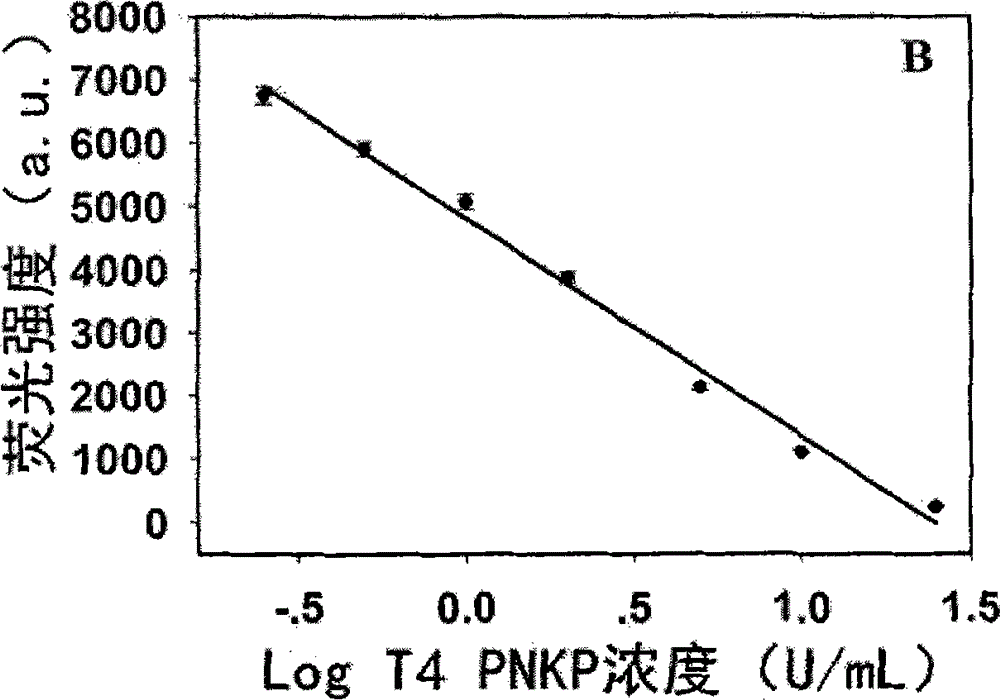
Novel method for beacon-free detection of T4 PNKP (T4 polynucleotide kinase)/phosphatase and inhibitor of T4 PNKP/phosphatase on basis of fluorescent copper nanoparticles
ActiveCN104894222ALow costSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementT4 polynucleotide kinaseSodium ascorbate
The invention discloses a novel method for beacon-free detection of T4 PNKP (T4 polynucleotide kinase) / phosphatase and an inhibitor of T4 PNKP / phosphatase on the basis of fluorescent copper nanoparticles. The method is implemented according to steps as follows: 1), a hairpin probe modified by 3'-terminal phosphorylation is designed, and 5' terminal is a sequence containing a base T; 2), the probe is diluted to the concentration being 100-1,000 nM with a Tris-HCl buffer solution, certain quantities of T4 PNKP, Klenow Fragment and dNTPs are mixed with the probe, and the mixture reacts at the temperature of 37 DEG C for 40-150 minutes; 3), the reaction liquid is diluted to form an MOPS buffer system, and copper sulfate and sodium ascorbate are added and react for 1-30 minutes at the room temperature; 4), the fluorescence strength of the finally obtained reaction liquid is detected with a fluorescence instrument, and a corresponding relation between the fluorescence strength of the system and T4 PNKP concentration is obtained. According to the method, the operation is simple, the cost is low, the sensitivity is high, the selectivity is good, T4 PNKP and the inhibitor can be quantitatively detected and screened, and a potential application value is provided for establishment of other terminal modification enzyme detection methods and molecular biological diagnosis.
Owner:郑州亮点生物技术有限公司
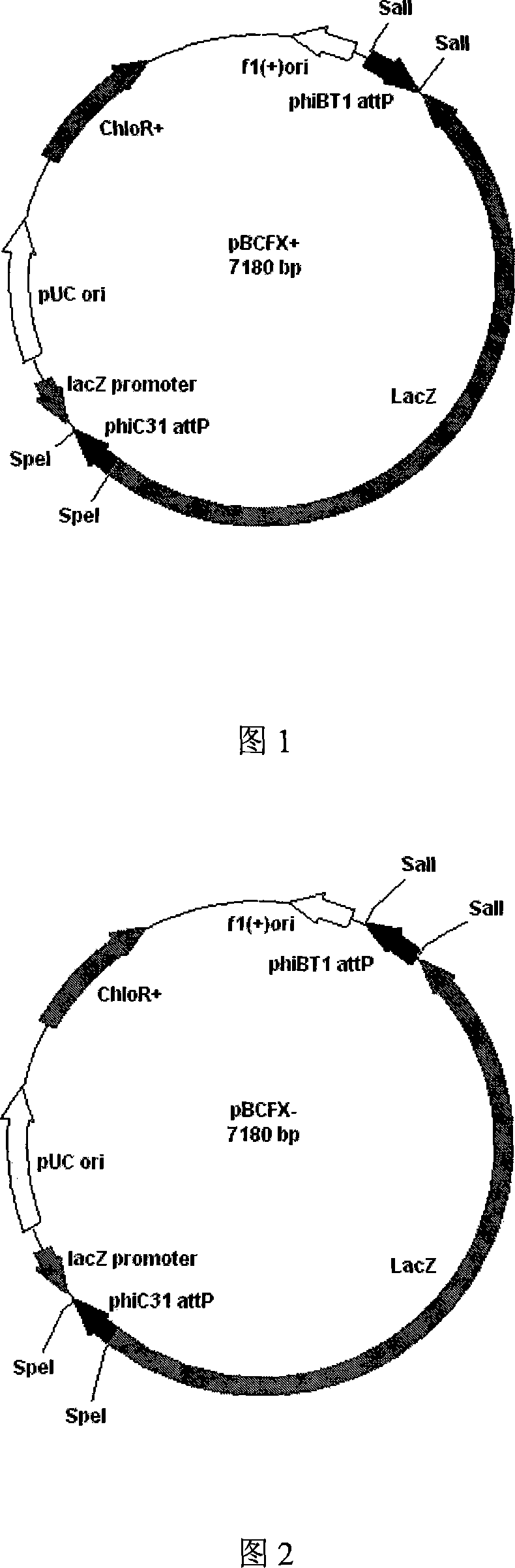
Gene clone plasmid based on Phi BT1 integrase and Phi C31 integrase
InactiveCN101157934AAvoid Interference LimitsVector-based foreign material introductionIntegrasesPlasmid Vector
The invention pertains to biotechnology and gene engineering fields, in particular to a gene cloning plasmid (pBCFX+ and pBCFX-) based on Phi BT1 integrase and Phi C31 integrase and the application thereof. The plasmid uses Phi BT1 integrase and tandem sequence of Phi C31fang integrase corresponding to attP site with interposition of LacZ expression frame as replacement cloning site of a plasmid vector (pBCFX+ and pBCFX-) with insertional inactivation which is used for doing blue-white screening. The cloning method based on the plasmid mainly comprises mixture of Phi BT1 integrase and Phi C31 integrase as site-directed integration kinase and additionally adding corresponding attB sequence to the two sides of inserting DNA fragment by using PCR, etc. according to the purpose to determine the direction of insertion fragment. The cloning system manipulates inserting DNA which contains special incision enzyme sites with convenience and has original predominance in manipulating Klenow fragment. The system simplifies the method of operation on recombinant DNA because of the omitting of manipulation of restricted enzyme, phosphatase and joinase and has extensive application prospect in gene engineering.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Fluorescent biosensor for detecting mercury ions
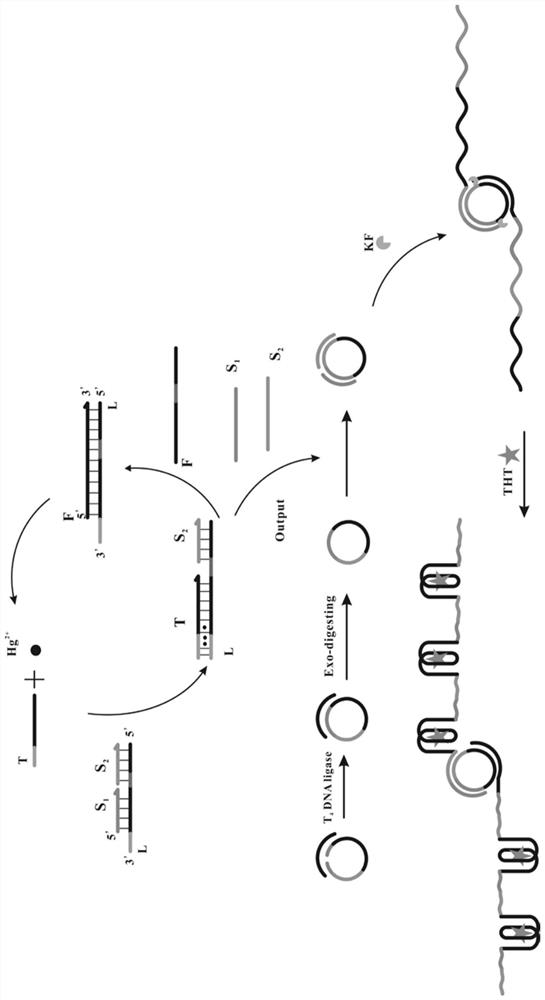
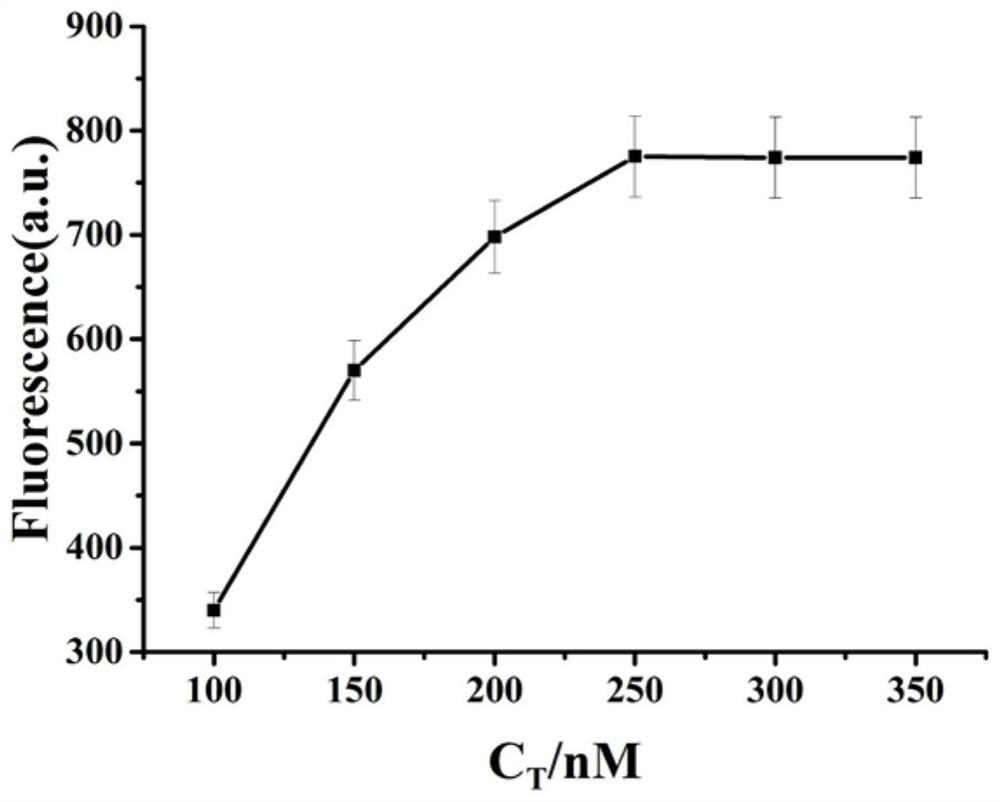
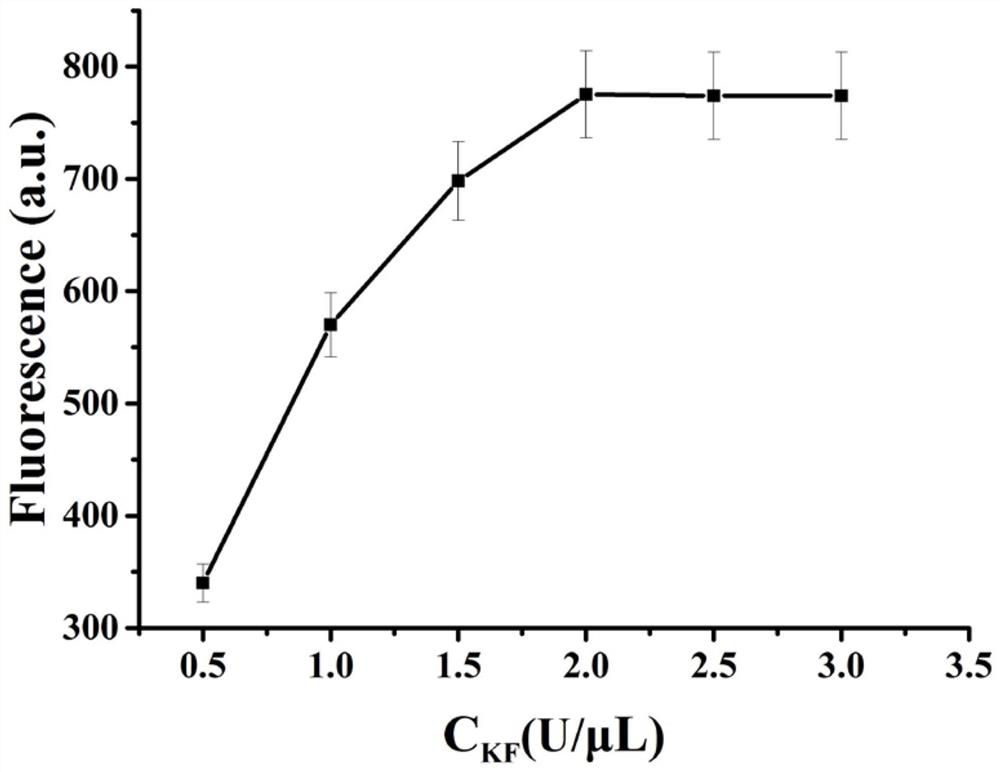
ActiveCN112345506AMild reaction conditionsQuick responseMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMercuric ionFluorescence biosensor
The invention provides a fluorescent biosensor for detecting Hg<2+>. The fluorescent biosensor comprises a composite probe Q, an annular template CP, a trigger chain T, a fuel chain F, a Klenow fragment and thioflavin T; and the trigger chain T, the composite probe Q, the fuel chain F, the annular template CP and the Klenow fragment are uniformly mixed with a mercury ion solution with a series ofconcentrations and a to-be-detected solution respectively, incubating is performed, enzyme is inactivated, the sulfur element T is added, incubating is performed, and the fluorescence intensity is detected. Target cyclic amplification and signal amplification are realized on the basis of the specific binding capacity between basic groups T and Hg<2+> and entropy-driven strand displacement amplification and rolling circle amplification reactions, and the biosensor for sensitive detection of a target object is realized. The sensor has the advantages of high detection speed, low detection limit,high sensitivity and the like, can make up the defects and deficiencies of the existing detection method of Hg<2+>, and realizes rapid and accurate quantitative detection of Hg<2+>.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
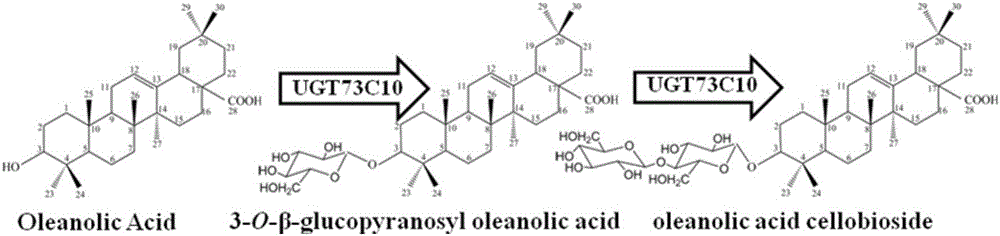
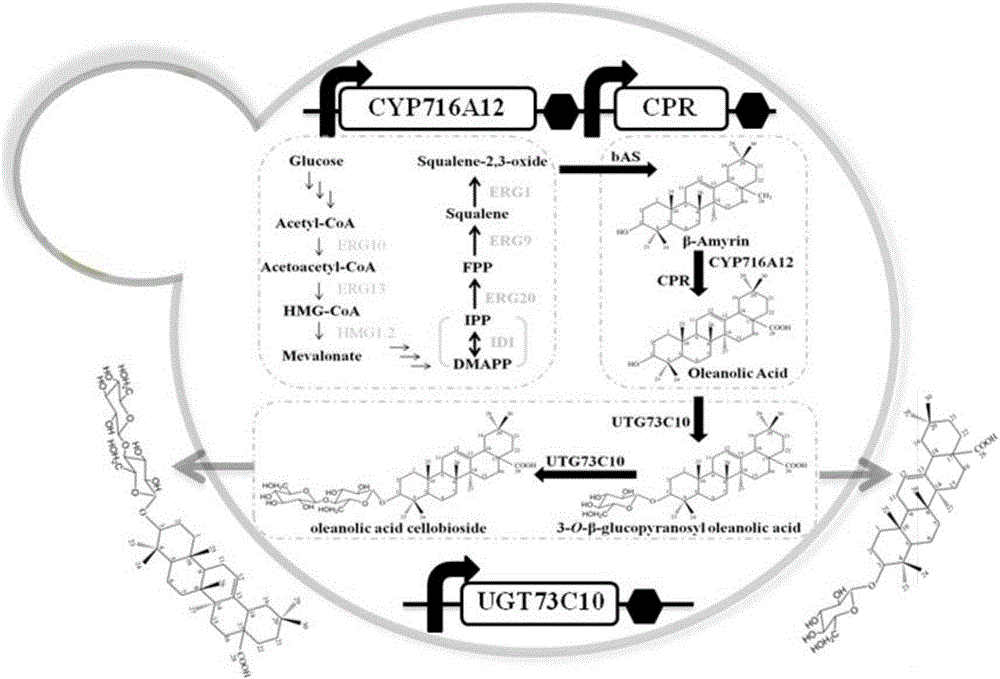
Method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and cellobiose oleanolic acid by using saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN106318966AIncrease productionThe fermentation process is simpleFungiMicroorganism based processesSolubilityUdp glucosyltransferase
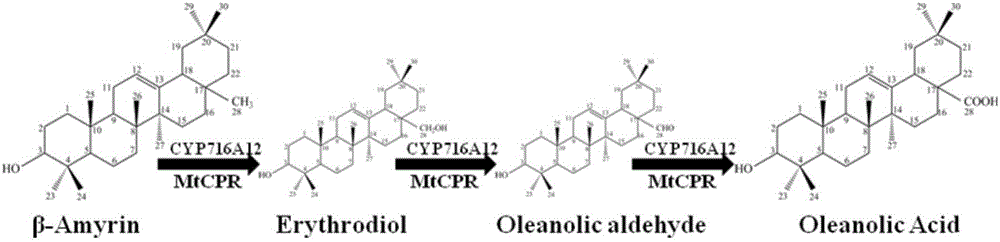
The invention provides a method for synthesizing 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and cellobiose oleanolic acid by using saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a codon optimized P450 cytochrome monooxygenase gene, a cytochrome reductase gene and a UDP-glucosyltransferase gene by a chemical method; constructing corresponding gene expression boxes by combining a saccharomyces cerevisiae promoter with a terminator; constructing gene expression vectors by a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) klenow fragment assembling method, and importing the gene expression vectors into the saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of producing beta-amyrin. Direct synthesis of the 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and the cellobiose oleanolic acid serving as plant secondary metabolites in the saccharomyces cerevisiae is realized for the first time; in addition, two synthesized compounds can span cytomembrane of the saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria, and a downstream separation and extraction process is simplified, so that a new idea is provided for producing pentacyclic triterpene compounds with low water solubility and difficulty in spanning membranes by using the saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method is simple in process and can be used for producing the 3-O-glucose-based oleanolic acid and the cellobiose oleanolic acid by fermenting.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
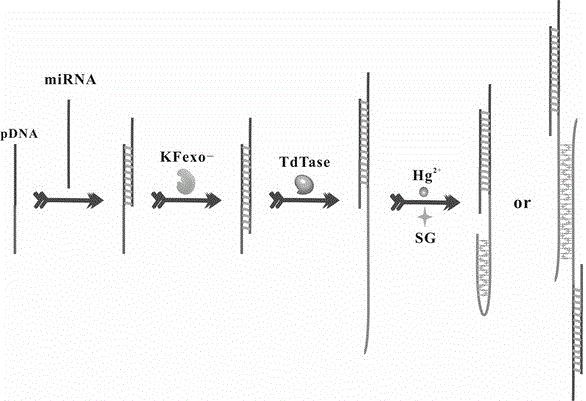
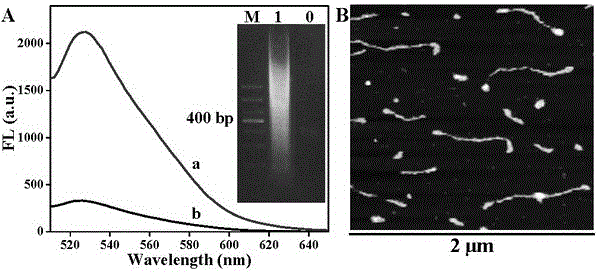
MicroRNA detection method based on Hg<2+> assistance and double-polymerase isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology
ActiveCN106119343AAchieving Sensitive DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid amplification techniqueFluorescence
The invention discloses a microRNA detection method based on Hg<2+> assistance and a double-polymerase isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology, and belongs to the technical field of optical bio-sensing. On the basis of a combined catalytic action of a polymerase Klenow fragment and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, microRNA is effectively extended into a polythymine base sequence which is relatively long; Hg<2+> is added, so that a T-Hg<2+>-T double-stranded structure is formed; an SYBR Green I fluorescent dye is interpolated into the T-Hg<2+>-T double-stranded structure, so that the fluorescence of the SYBR Green I is enhanced; and a fluorescence enhancing degree is positively related to the concentration of the microRNA; therefore, the sensitive detection of the microRNA is achieved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Image visualization method for detecting single molecule DNA duplication
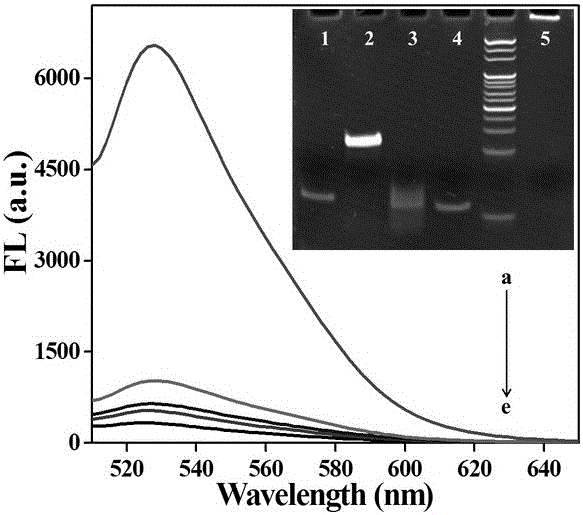
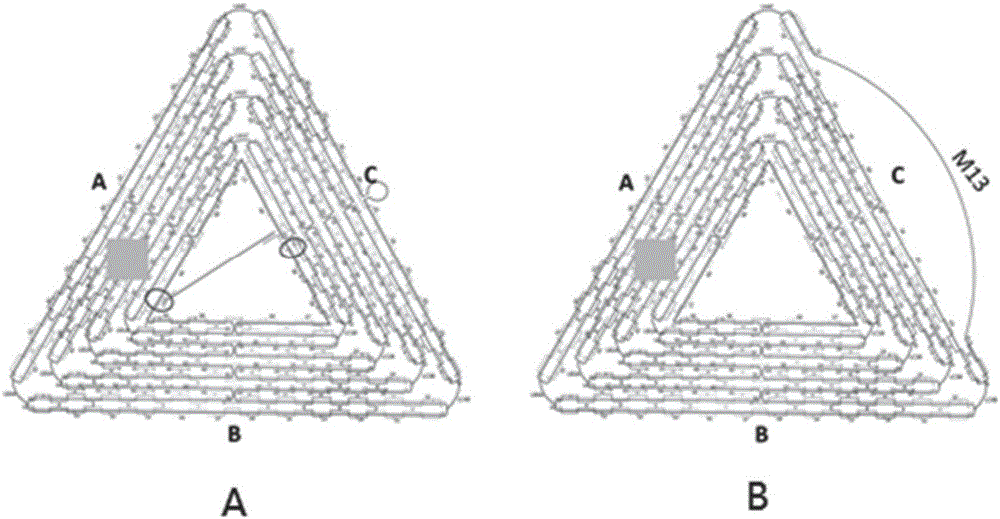
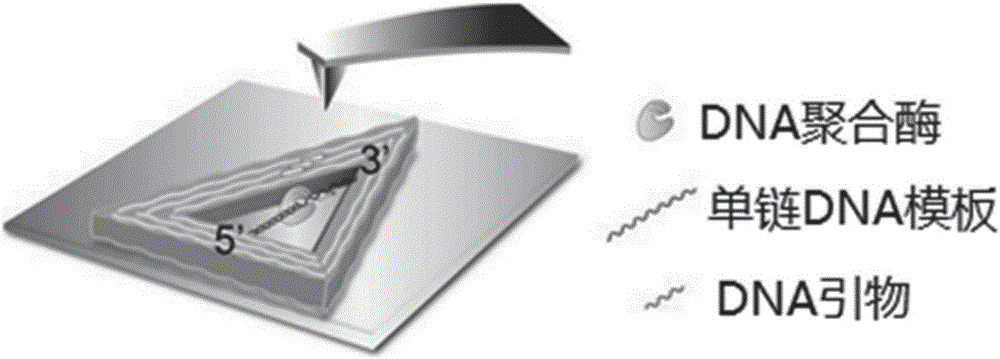
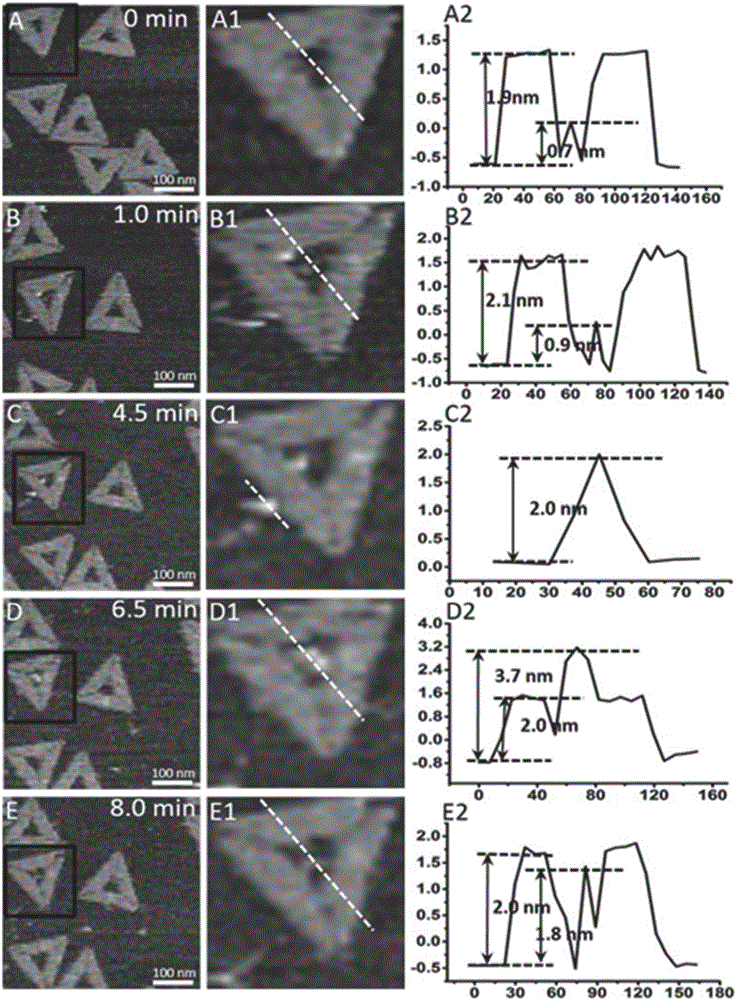
InactiveCN105760715AAids in understanding the mechanism of actionData visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsPolymerase LMolecular level
The invention discloses an image visualization method for detecting single molecule DNA duplication. The method comprises the steps that single-chain DNA and a buffering system of a DNA polymerase Klenow fragment combined with the single-chain DNA are scanned with an atomic force microscope, and DNA duplication is subjected to imaging observation through the atomic force microscope, wherein the single-chain DNA contains dNTP, and the two ends of the single-chain DNA are fixed to two different positions on hollow DNA folded paper respectively. According to the method, the DNA duplication process is tracked on the single molecule level, the whole process of combination of the single-chain DNA and single DNA polymerase, moving between the DNA chain and the DNA polymerase and conversion from the single-chain DNA chain to a double-chain DNA chain is recorded, various forms of state distribution of the DNA chain on the surface of a substrate and the changing situation in the interaction process of DNA and the DNA polymerase can be captured, the biomolecule behavior action mechanism can be understood more easily, and data on the time scale and the space scale in the molecule event obtaining process can be obtained more easily.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Vector to Induce Expression of Recombinant Proteins under Anoxic or Microaerobic Conditions
InactiveUS20090269801A1Constant aerationSimpler and less-expensiveFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
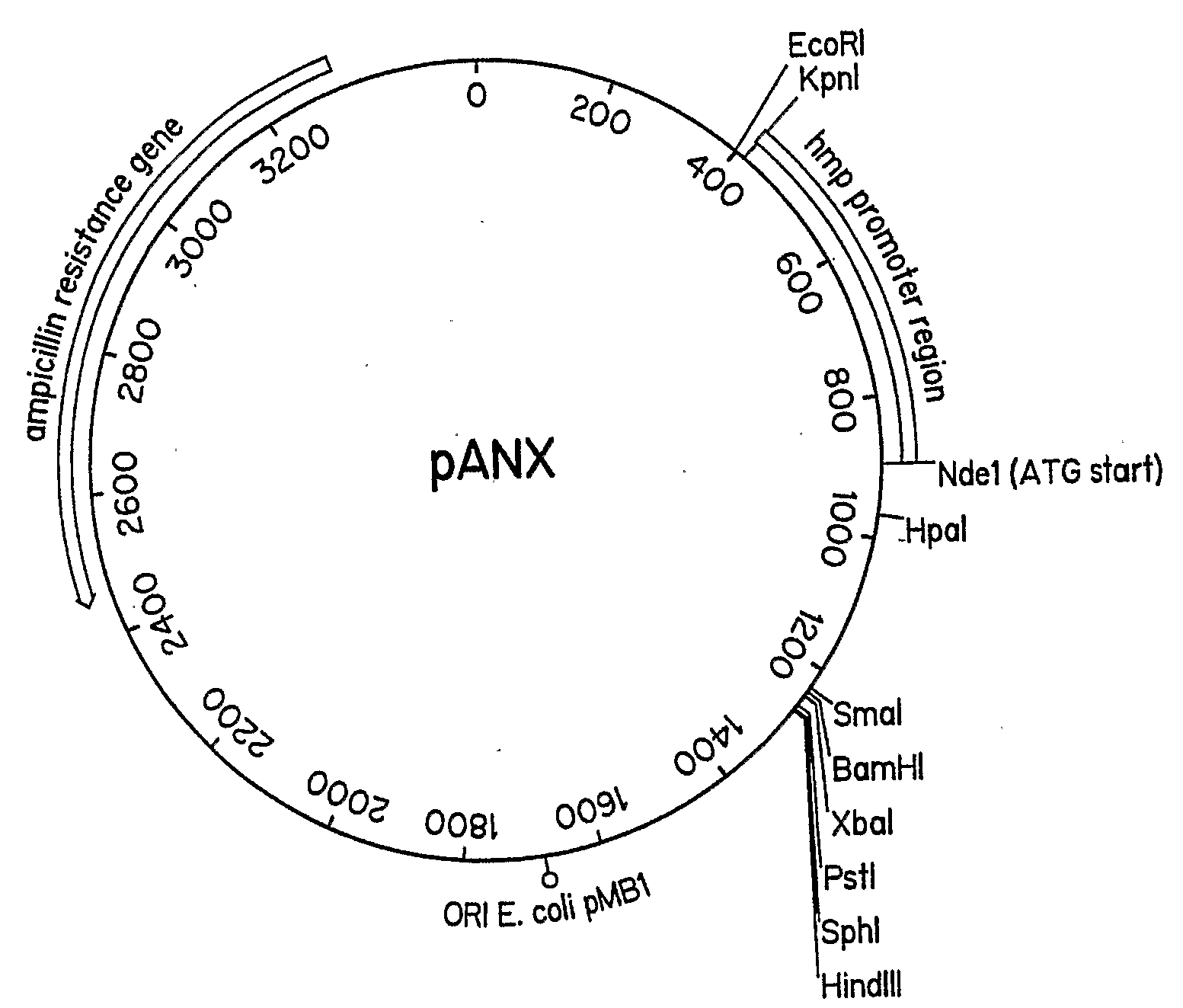
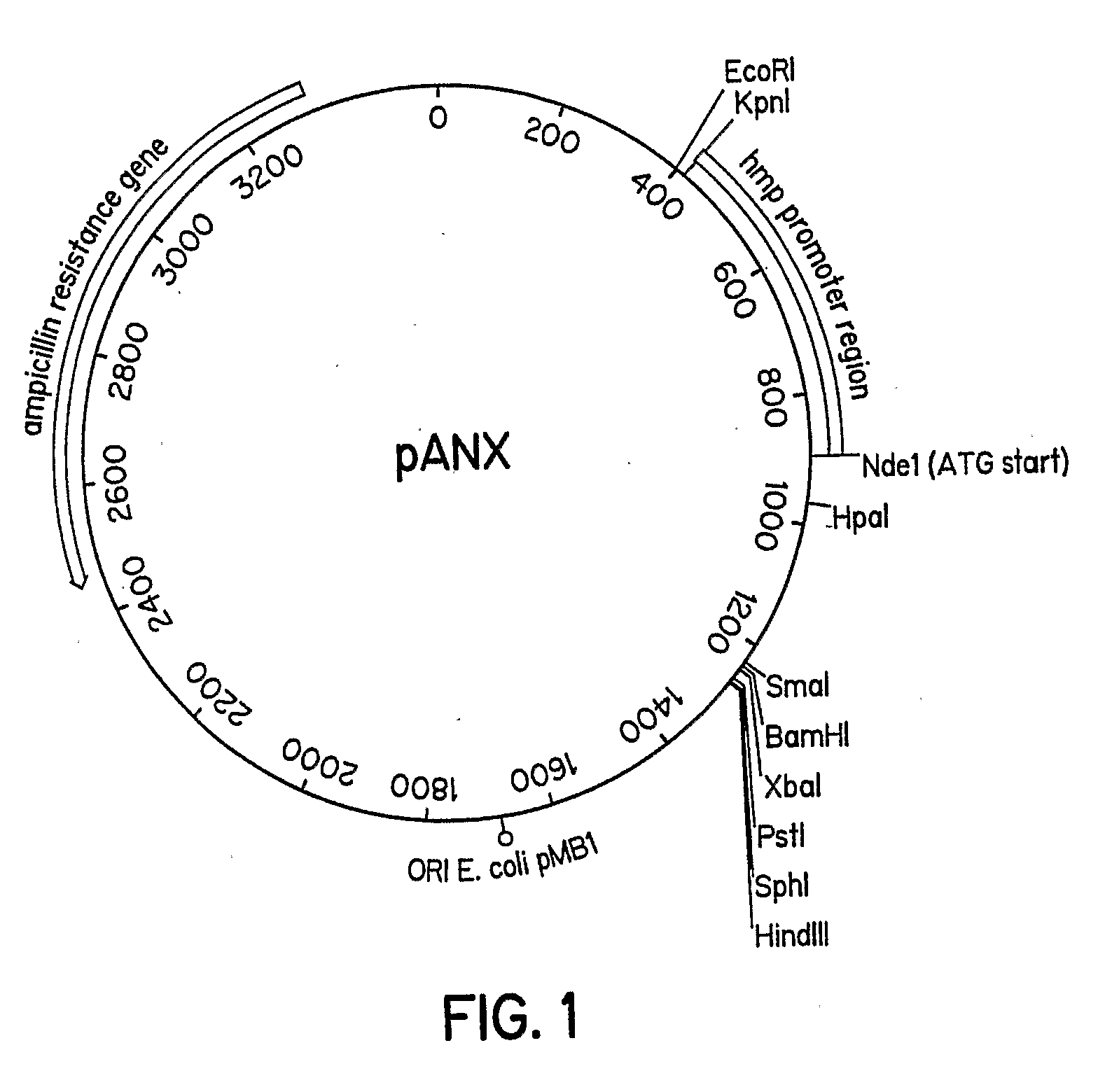
A protein expression vector that expresses large quantities of recombinant proteins under anoxic or microaerobic conditions by inducing expression with nitrate. The vector backbone is pUC19 and protein expression is driven by the E. coli flavohemoglobin promoter, which is inducible by nitrate, nitrite, or nitric oxide under conditions of low oxygen. The Nde1 site of pUC19 has been destroyed by filling in with Klenow fragment and religating the vector. An Nde1 site in the promoter provides an in-frame start methionine and a standard polylinker is available for ease of subcloning. The vector is named pANX for Plasmid ANaerobic eXpression.
Owner:GARDNER ANNE M +1
Method for detecting klenow fragment repetition position in saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome
ActiveCN105624306AQuick checkEfficient detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementYeast chromosomeGenomic sequencing
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to a method for detecting a klenow fragment repetition position in a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome.By combining genomic sequencing with endoreduplication backcrossing, the position of repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the chromosome is confirmed quickly.Through the endoreduplication backcrossing method, the position of the repeated klenow fragment genome DNA in the saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome can be detected efficiently and quickly and repaired, repeated klenow fragment genome DNA is deleted, there is no need to precisely confirm the position of a klenow fragment repetition site or conduct cumbersome experimental data analysis on saccharomyces cerevisiae to be detected, operation is easy, and the experimental period is short.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Non-invasive prenatal detection kit for down syndrome
The invention provides a non-invasive prenatal detection kit for down syndrome, which comprises a T4 DNA ligase buffer solution, a Klenow fragment (5 units / mul), T4 polynucleotide kinase (T4PNK), an linker sequence, a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing primer, a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) component, a DNA sequencing component and the like. Through establishing an in vitro DNA library from peripheral blood of a pregnant woman, the kit can be used for accurate sequencing a genomic sequence of a fetus and screening the down syndrome of the fetus, with accurate results, and without false positive and false negative. Furthermore, the kit can be used for detection of a small number of in vitro peripheral blood samples, so as to greatly reduce the pain and risk of the pregnant woman, and the kit has good application prospects.
Owner:解码(上海)生物医药科技有限公司
Method for safely producing 1,3-propanediol
InactiveCN103898168AImprove securityMicroorganism based processesFermentationGene clusterBiosecurity
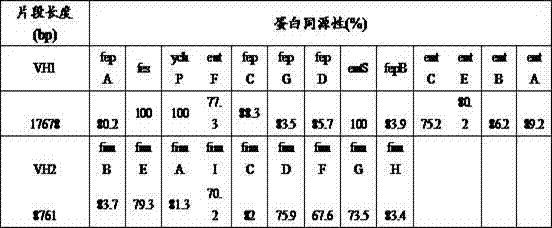
The invention discloses a method for safely producing 1,3-propanediol, namely the safety of 1,3-propanediol fermentation is improved by knocking-out continuous emerging klenow fragment genes in a virus gene cluster VH1 and / or VH2 in klebsiella peneumoniae. Compared with an existing method for producing 1,3-propanediol with converted glycerol, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that latent pathogenic genes in K. peneumoniae are knocked out in klenow fragment and the biosecurity of klebsiella peneumoniae is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
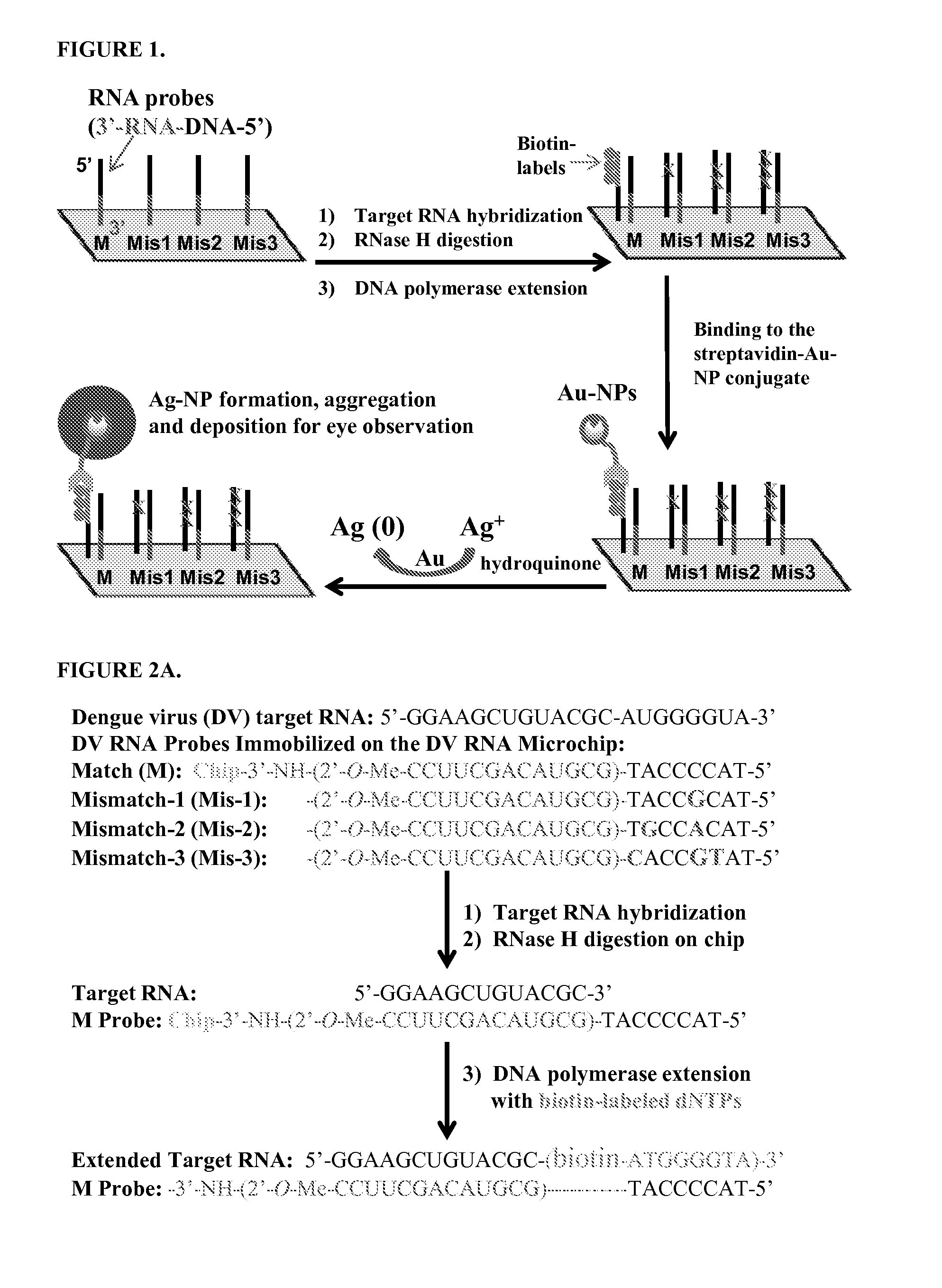
RNA Microchip Detection Using Nanoparticle-Assisted Signal Amplification
InactiveUS20160068894A1High detection sensitivityEasy to detectNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LA-DNA
Disclosed are methods and materials for detecting RNA in a sample. In some forms, the method involves (a) bringing into contact the sample and a probe array, (b) bringing into contact the probe array and a ribonuclease specific for RNA / DNA hybrids (such as RNase H), (c) bringing into contact the probe array, labeled nucleotides, and a nucleic acid polymerase capable of extending a RNA strand using a DNA template and capable of incorporating the labeled nucleotides in the extension from the RNA strand (such as Klenow fragment DNA polymerase), and (d) detecting the labeled nucleotides in the extended nucleic acid strand. The probe array comprises one or more chimeric probes. The chimeric probes comprise a DNA region and a RNA region, where the DNA region and the RNA region are contiguous and where the DNA region is 5′ of the RNA region. The chimeric probe can also include a second DNA region. The second DNA region can also be contiguous with the RNA region and can be 3′ of the RNA region.
Owner:GEORGIA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Constant temperature reaction-based method for detecting microRNA in solution to be detected
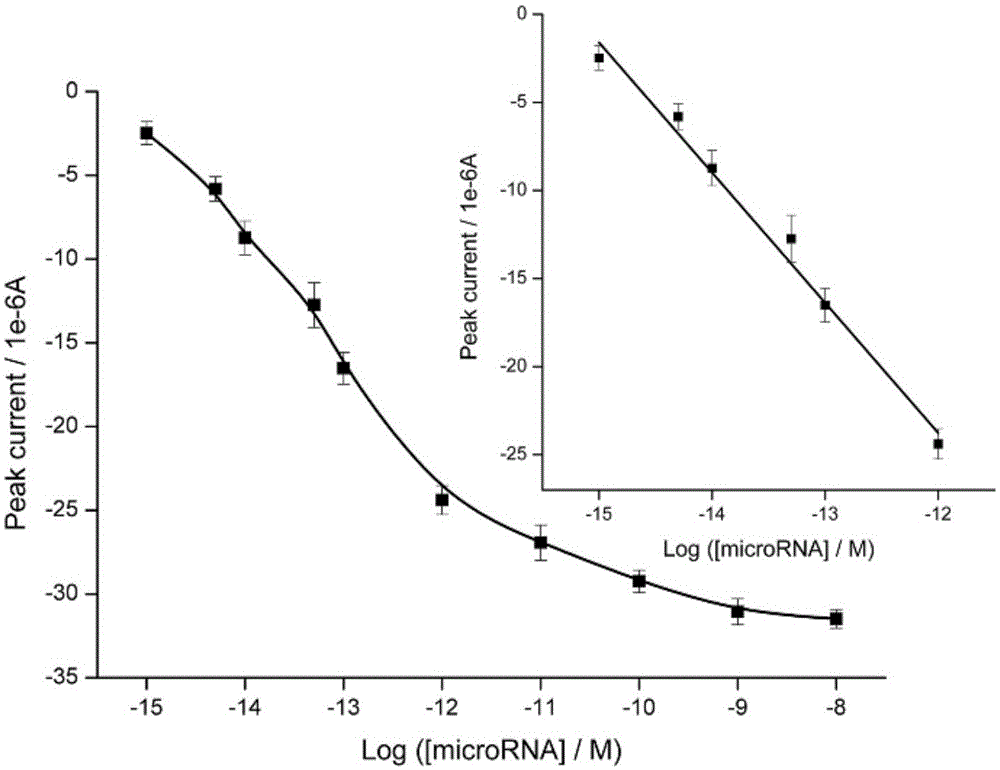
ActiveCN105004780ARealize detectionEasy to operateMaterial electrochemical variablesDNA fragmentationKlenow fragment
The invention relates to a constant temperature reaction-based method for detecting microRNA in a solution to be detected. The method comprises that an electrode is immersed in a first DNA fragment molecular solution, undergoes a reaction at a temperature of 37 DEG C for 6h, then is immersed in a mercapto hexanol solution, undergoes a reaction for 1h, then is immersed in a silver nanoparticle solution, undergoes a reaction for 1h, then is immersed in a second DNA fragment molecular solution and undergoes a reaction for 0.5h, a microRNA standard liquid is prepared, the electrode is immersed in the microRNA standard liquid, a third DNA fragment molecule, a Klenow fragment and dNTPs are added into the microRNA standard liquid, the electrode undergoes a reaction in the mixed liquid at a temperature of 37 DEG C for 1h, then is immersed in a Nt. BbvCI solution and undergoes a reaction for 1h, wherein in the detection, a linear scanning voltammetry method is used, a standard curve graph is drawn, an electrical signal of the liquid to be detected is acquired by the above processes, and the electrical signal and the standard curve graph are compared so that a microRNA concentration of the liquid to be detected is obtained. The constant temperature reaction-based method has the advantages of simple processes, high sensitivity, good specificity, low background signal and wide application range.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
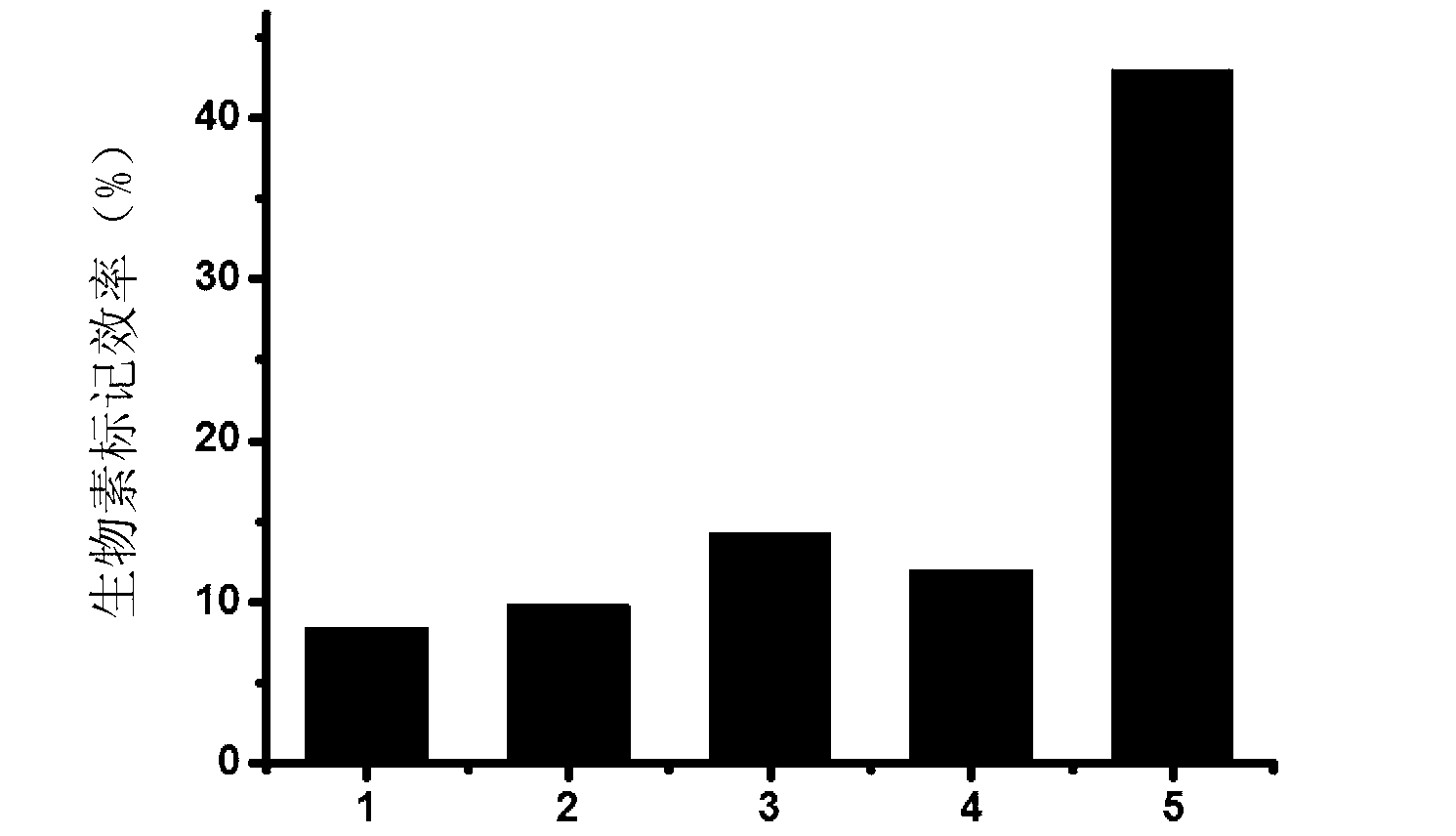
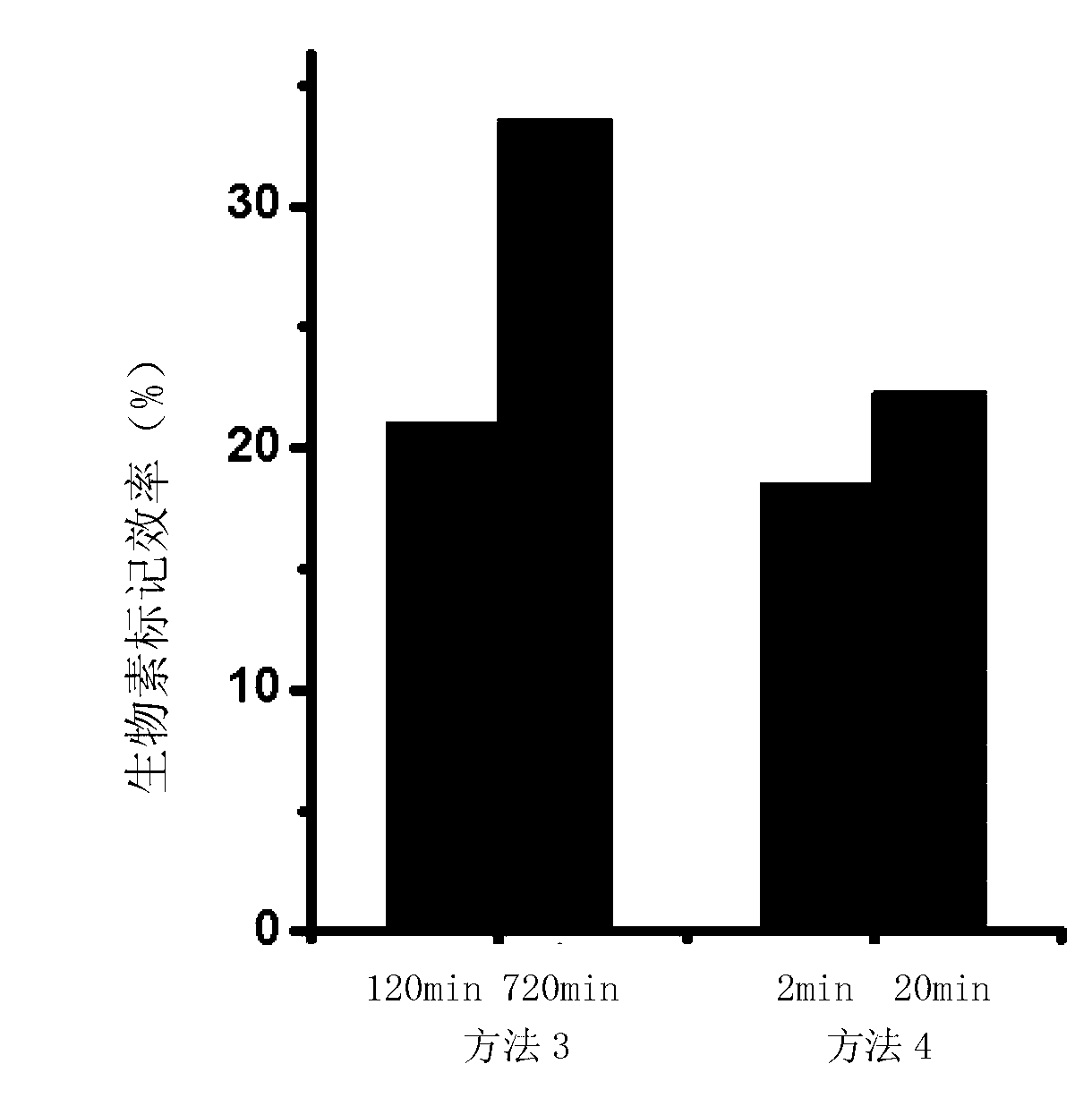
Method for performing 3' end biotin labeling on DNA fragments
ActiveCN103255133AImprove labeling efficiencyLess efficient labelingDNA preparationDNA fragmentationPolymerase L
The invention discloses a method for performing 3' end biotin labeling on DNA fragments obtained through ultrasonication. The method comprises the following steps of: I, adding biotin-labeled dCTP while treating the DNA fragments by Klenow fragments and / or T4DNA polymerase, and then filling in; II, adding biotin-labeled dATP while treating DNA fragments by Klenow fragments and / or T4DNA polymerase, and then filling in; III, adding biotin-labeled dGTP while treating DNA fragments by Klenow fragments and / or T4DNA polymerase, and then filling in; and IV, adding biotin-labeled dTTP while treating DNA fragments by Klenow fragments and / or T4DNA polymerase, and then filling in. The method has the advantages that the labeling efficiency is high; the application range is wide; and the steps of the method are few, and thus the method is simple, convenient and feasible.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Screening method of molecular reverse probes for capturing specific region of enriched genome
ActiveCN110021353AThe experiment process is convenientLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationScreening methodExon
The invention discloses a screening method of molecular reverse probes for capturing a specific region of an enriched genome. The method comprises the steps that firstly the structures of the molecular reverse probes are designed; starting from the 5' end of the target region, the probes with at least 50% of scanned areas falling on the 5' end are selected to serve as a candidate starting set; adjacent probes are scored in pairs, the probes meeting the requirement are combined with the previous selected probes sequentially to form a set of all possible probe combinations, each candidate combination is scored, score calculation is conducted on all possible combinations, and the combination with highest scores or lowest penalty scores is obtained. The method is applicable to linker structures of different sequencing platforms, an obtained molecular reverse probe technique is remarkably improved at the aspects of precision, convenience, detection sensitivity and the like, meanwhile, a coverage target region, especially the number of the probes needed by a klenow fragment exon region is effectively reduced, and the method is convenient and rapid, and saves the cost.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Detection method of microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid)
InactiveCN105648098ARealize detectionLow backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JSodium ascorbate
The invention discloses a detection method of microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid), and belongs to the field of optical biosensing techniques. A to-be-detected sample is mixed with template DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), an obtained first mixture is annealed and hybridized, a buffer solution containing polymerase Klenow fragment, deoxyuracil nucleoside triphosphate and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase is added into a reaction product, an obtained second mixture is caused to react for 4h at 35 DEG C in a water bath, so as to prepare a polyuracil base sequence; sodium ascorbate is added into a polyuracil base sequence solution obtained in the step (4), and then CuCl2 is added into an obtained third mixture, and an obtained fourth mixture is caused to react for 10min at a room temperature, so as to prepare a red-fluorescence copper nano cluster which uses the polyuracil base sequence as a template, thereby obtaining a solution containing the red-fluorescence copper nano cluster. The intensity of the red fluorescence of the solution including the red-fluorescence copper nano cluster is measured by adopting a spectrofluorophotometer; by comparing the result about the intensity of the red fluorescence with a standard relation curve, the concentration of the microRNA is calculated and obtained.
Owner:吴滨
Method for detecting influence of mechanical force on interaction of DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) and DNA polymerase
The invention discloses a method for detecting influence of mechanical force on interaction of DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) and DNA polymerase. The method comprises steps as follows: a single-stranded DNA template containing dNTP (deoxyribonucleotide triphosphate) and a buffering system of a DNA polymerase Klenow fragment combined with the single-stranded DNA template are scanned by means of an atomic force microscope, two ends of the single-stranded DNA template are fixed on two different sites on inner edges of hollow DNA origami, the two different sites are not located on the edge of the same straight line, the buffering system is arranged on a newly dissociated mica substrate, and synthesis of double-stranded DNA is observed through imaging of the atomic force microscope. The information about the effect of mechanical force in the non-double-helix direction on the structure and the function of DNA and DNA polymerase is acquired with the detection method, then influence of the mechanical force on DNA synthesis is obtained, accurate positioning on the nano scale can be realized, and a condition is provided for detection of the interaction relation of DNA and DNA polymerase under a certain tension condition is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Amplification primer and amplification method of complete mitochondrial genome sequence of nibea miichthioides chu
InactiveCN106591298AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMarker-assisted selectionConservation genetics
The invention discloses an amplification primer and an amplification method of a complete mitochondrial genome sequence of nibea miichthioides chu. The amplification primer comprises 4 klenow fragment amplification primer pairs and 19 genome walking primers. According to the amplification primer and the amplification method provided by the invention, the complete mitochondrial genome sequence of nibea miichthioides chu, which is obtained by conducting PCR amplification on genome of the nibea miichthioides chu, can provide a material base for conservation genetics and evolutionary genetics of the nibea miichthioides chu and for marker-assisted selection of high-quality breeding varieties.
Owner:MARINE FISHERIES RES INST OF ZHEJIANG
Tobacco root-knot nematode disease pathogen detection kit based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology and application method of tobacco root-knot nematode disease pathogen detection kit
InactiveCN107815490AEasy to operateLow requirements for detection conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseWater baths
The invention discloses a tobacco root-knot nematode disease pathogen detection kit based on a loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology and an application method of the tobacco root-knot nematode disease pathogen detection kit. The tobacco root-knot nematode disease pathogen detection kit based on the loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology comprises a reaction solution I for detecting meloidogyne incognita, a reaction solution A for detecting meloidogyne arenaria, a reaction solution J for detecting meloidogyne javanica, a BstDNA polymerase klenow fragment and a 100*SYBR Green I staining solution. The tobacco root-knot nematode disease pathogen detection kit is based on the loop-mediated isothermal amplification technology, has low requirements on detection conditions,can implement the detection only with a water bath pot or a thermostat and facilitates the popularization and application. Since the kit and the method do not need gel electrophoresis, a detection result can be directly observed by naked eyes, so that the consumed time is short, and the detection can be completed in 1.5h; and the kit comprises an LAMP detection primer for detecting the meloidogyneincognita, the meloidogyne arenaria and the meloidogyne javanica, so that the three common pathogen root-knot nematode of tobacco root-knot nematode disease can be synchronously detected.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Plant-anthocyanin synthesis control gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108018290AImprove detection accuracyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesAgricultural scienceIntein
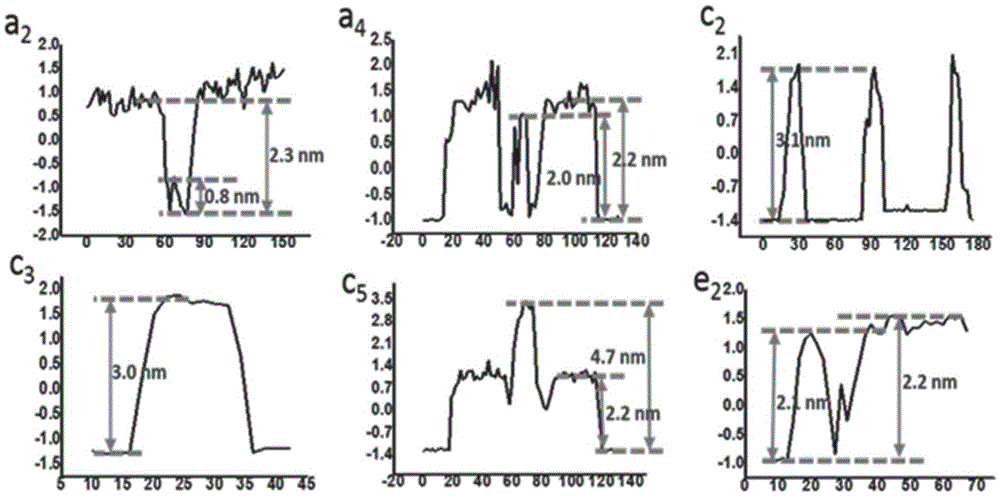
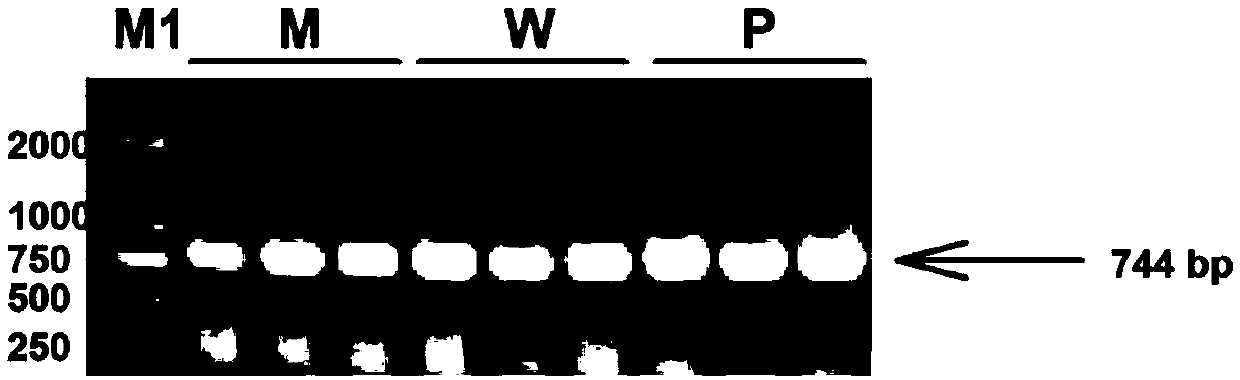
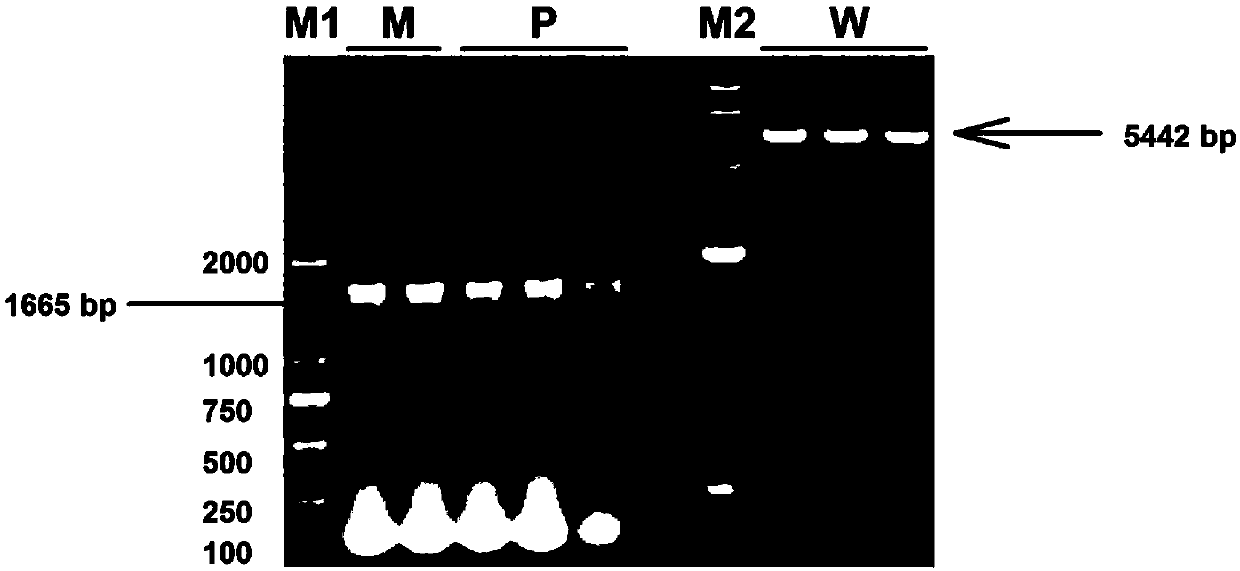
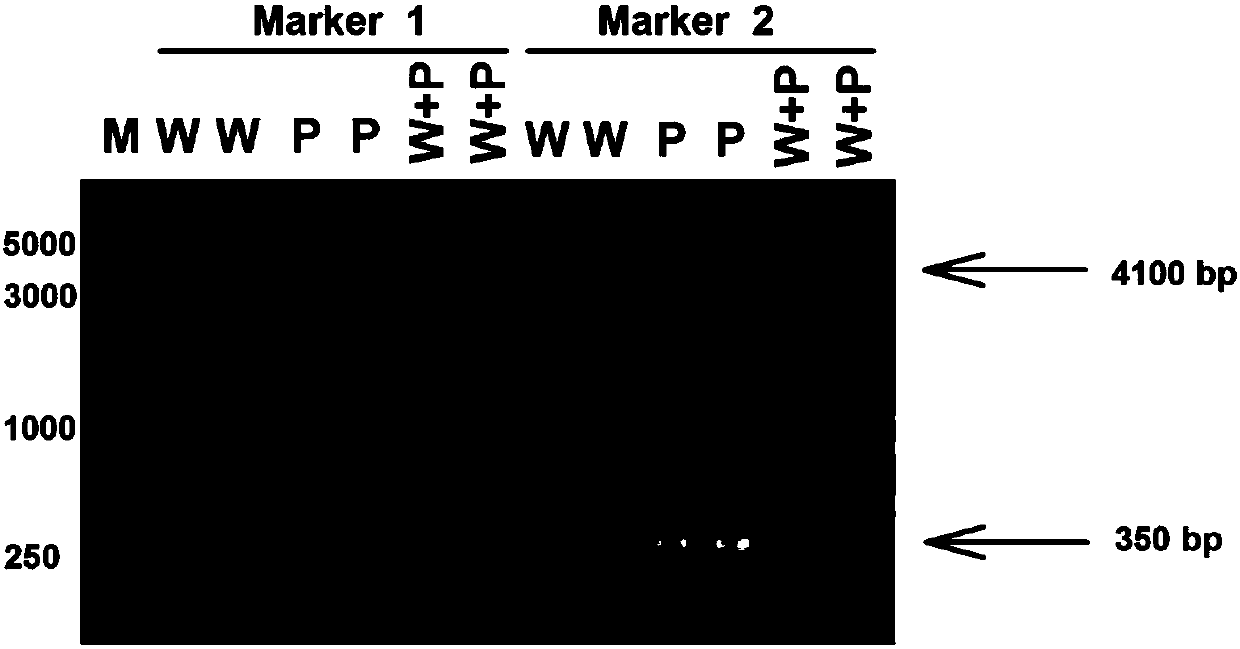
The invention discloses a plant-anthocyanin synthesis control gene and application thereof. The sequence of the disclosed gene is shown in the SEQ ID No.1. A 3,772-bp klenow-fragment insertion mutation of the gene exists in first intron of white heading brassica rapa, and the gDNA sequence of the mutation is shown in the SEQ ID No.5. According to the mutation in the intron in the gDNA nucleotide sequence of the gene, three specificity PCR primers of the Marker 1, the Marker 2 and the Marker 8 are designed, wherein the Marker 1 and the Marker 2 are co-dominant markers, and the Marker 8 is a maternal marker. The DNA of the target brassica rapa is subjected to PCR amplification and identified through agarose gel electrophoresis, drinamyl hybrid strains and homozygous strains in segregation population can be rapidly identified through the Marker 1 and the Marker 2, and the drinamyl hybrid strains and the homozygous strains in the segregation population can also be distinguished through theMarker 8 in cooperation with the heading characteristics.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Kit and method for constructing DNA library
PendingCN112708939AImprove the efficiency of database constructionNucleotide librariesLibrary creationT4 polynucleotide kinaseNucleotide
The invention provides a kit and a method for constructing a DNA library, the kit comprises a mixed enzyme solution, a mixed buffer solution, ligase and a ligation buffer solution, the mixed enzyme solution comprises endonuclease, T4 DNA polymerase, Klenow fragments, Taq DNA polymerase and T4 polynucleotide kinase, the mixed buffer solution and the ligation buffer solution comprise DTT and PEG 8000, the mixed enzyme solution and the mixed buffer solution are used for forming a first reaction system, the ligase and the ligation buffer solution are used for forming a second reaction system, in the first reaction system, the working concentration of the endonuclease is 0.01-0.05 U / mu L, the working concentration of the T4DNA polymerase is 0.04-0.1 U / mu L, the working concentration of the Klenow fragment is 0.005-0.02 U / mu L, the working concentration of the Taq DNA polymerase is 0.025-0.075 U / mu L, the working concentration of the T4 polynucleotide kinase is 0.1-0.5 U / mu L, the working concentration of the DTT is 5-10mM, and the working concentration of the PEG 8000 is 1-10%. According to the invention, the kit and the method for constructing the DNA library, which can improve the library construction efficiency, can be provided.
Owner:深圳海普洛斯医学检验实验室
Heredity transformation method of coix seeds mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens
The invention relates to a heredity transformation method of coix seeds mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens. Sprouting treatment is performed on mature coix seeds, and transection is performed untilstem tip meristem is a heredity transformation receptor. The method comprises the following specific operation steps of (1) preparing the heredity transformation receptor; (2) culturing agrobacteriumtumefaciens; (3) performing heredity transformation on coix seeds; and (4) transplanting and managing genetically modified plants. The method does not adopt a tissue culture technique, agrobacteriumtumefaciens are cultured, and a sterile operation is not need. The method which is used has the advantages of being simple to operate and low in cost, capable of transforming klenow fragment DNA, being stable in heredity, and low in copy number and the like, and the method becomes a heredity transformation method which is broad to apply.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Next-generation sequencing library building kit and method for improving library conversion rate
PendingCN112941635AImprove efficiencyReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationT4 polynucleotide kinaseNucleotide
The invention relates to a method and a kit in the technical field of biology, and concretely relates to a next-generation sequencing library building kit and method for improving the library conversion rate. The kit and the method are particularly suitable for next-generation sequencing application of trace samples. The kit comprises: enzyme mixed solutions which comprises a first enzyme mixed solution, a second enzyme solution and a third enzyme mixed solution, wherein the first enzyme mixed solution is formed by mixing T4 polynucleotide kinase, T4 DNA polymerase, a Klenow fragment and Taq enzyme according to a ratio of 3: 1: 2: 1, the second enzyme solution is T4 DNA ligase, and the third enzyme mixed solution is a mixed solution of 2X QuarTaq HiFi HotStart; buffer solutions which comprise a first buffer solution corresponding to the first enzyme mixed solution and a second buffer solution corresponding to the second enzyme mixed solution, wherein the second buffer solution is formed by mixing Tris-HCl with the concentration of 0.1-0.6 M, MgCl2 with the concentration of 0.05-0.1 M, DTT with the concentration of 0.01-0.05 M, ATP with the concentration of 1-10 mM, PEG6000 with the concentration of 30%-50% and 1, 2 propylene glycol with the concentration of 10-20%; and a linker, an index sequence and a universal primer.
Owner:SHANGHAI DYNASTYGENE CO
Kit for DNA library building and application of kit
ActiveCN108660135AReduce usageReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationBlood plasmaKlenow fragment
The invention discloses a kit for DNA library building and an application of the kit, and in particular relates to a kit for peripheral blood cfDNA library building and an application of the kit. According to the invention, the kit for DNA library building is firstly provided, wherein the kit comprises a component A and a component B; the component A consists of the following ingredients at a ratio as follows: 1-3U of T4 PNK to 1-4.5U of Klenow Fragment to 0.25-0.5U of LA Taq DNA Polymerase to 0.3-0.9U of T4 DNA Polymerase to 0.5-2.5 nmol of dNTP to 0.5-2.5nmol of dATP; and the component B consists of the following ingredients at a ratio as follows: 2.5-8nmol of ATP to 26.5 132U of T4 DNA Ligase to 0.213 0.534[mu]L of PEG 8000. According to the kit and the application method provided by the invention, DNA loss in a library building process can be reduced to the greatest extent, the usage amount of plasma can be reduced, library building cost can be reduced, library building time can beshortened, operations can be simplified and more stable and reliable results can be obtained. The kit provided by the invention is significant for improving library building efficiency and reducing labor cost.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL LAB BGI +2
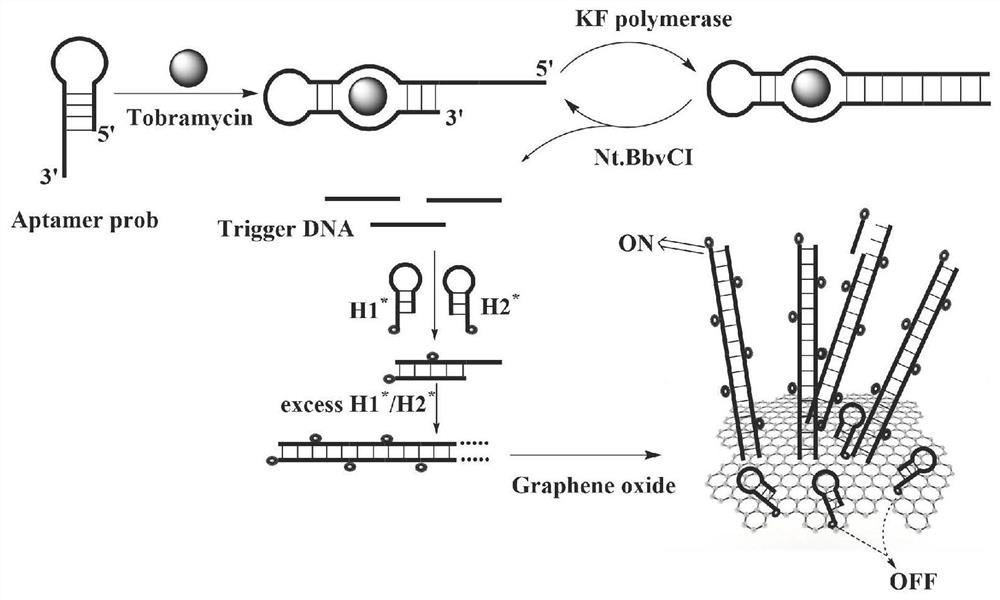
Biosensor for detecting tobramycin and detection method
ActiveCN113341128ADetection adaptationMeet the sensitivity requirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAptamerKlenow fragment
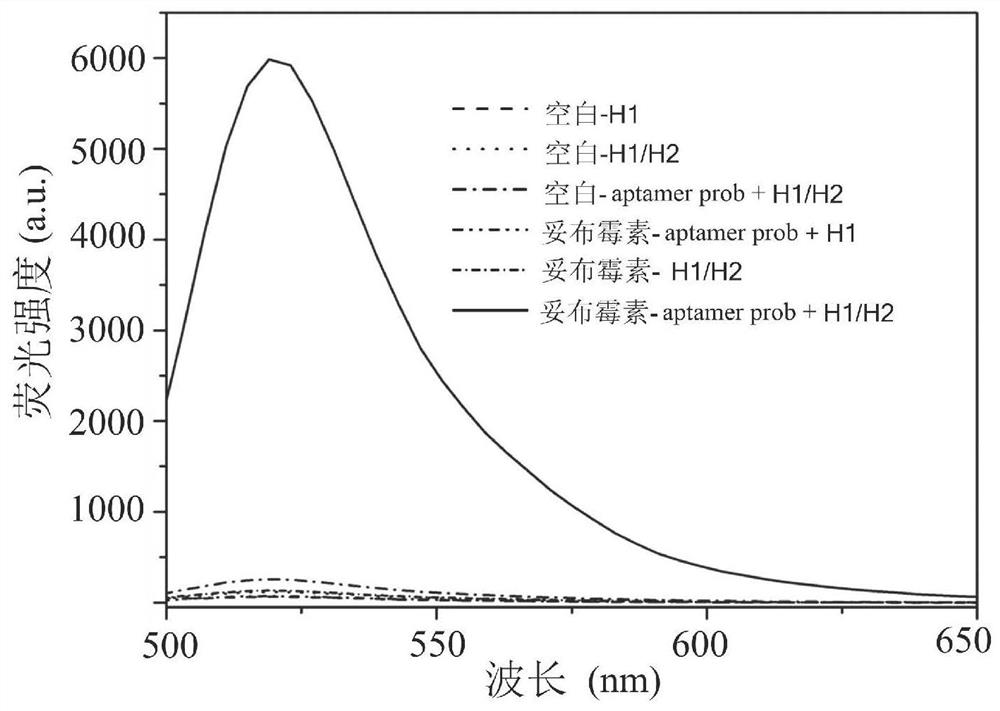
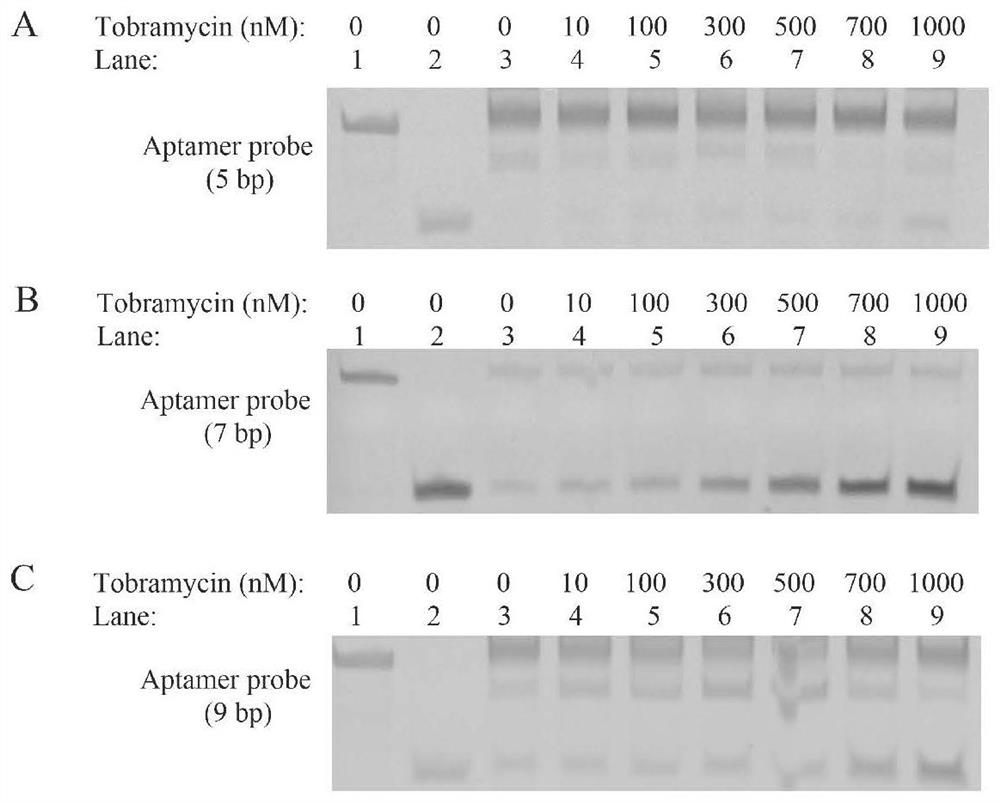
The invention discloses a biosensor for detecting tobramycin. The biosensor comprises an aptamer probe, a hairpin probe H1, a hairpin probe H2, Klenow Fragment polymerase, Nt.BbvCI endonuclease, a buffer solution and graphene oxide. The sequence of the aptamer probe is as shown in SEQ ID No: 1, the aptamer probe is formed by hybridizing an aptamer Aptamer with the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No: 2 and an amplification template T with the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No: 3. The sequence of the hairpin probe H1 is as shown in SEQ ID No: 4, and the sequence of the hairpin probe H2 is as shown in SEQ ID No: 5. When the biosensor is used for detecting tobramycin, the method is simple, the practicability is good, the stability is high, the detection lower limit reaches 0.06 nM and is lower than that of the existing similar sensors, and the biosensor has wide application prospects in the fields of environmental monitoring and food safety.
Owner:JIANGSU INSTITUTE OF EDUCATION
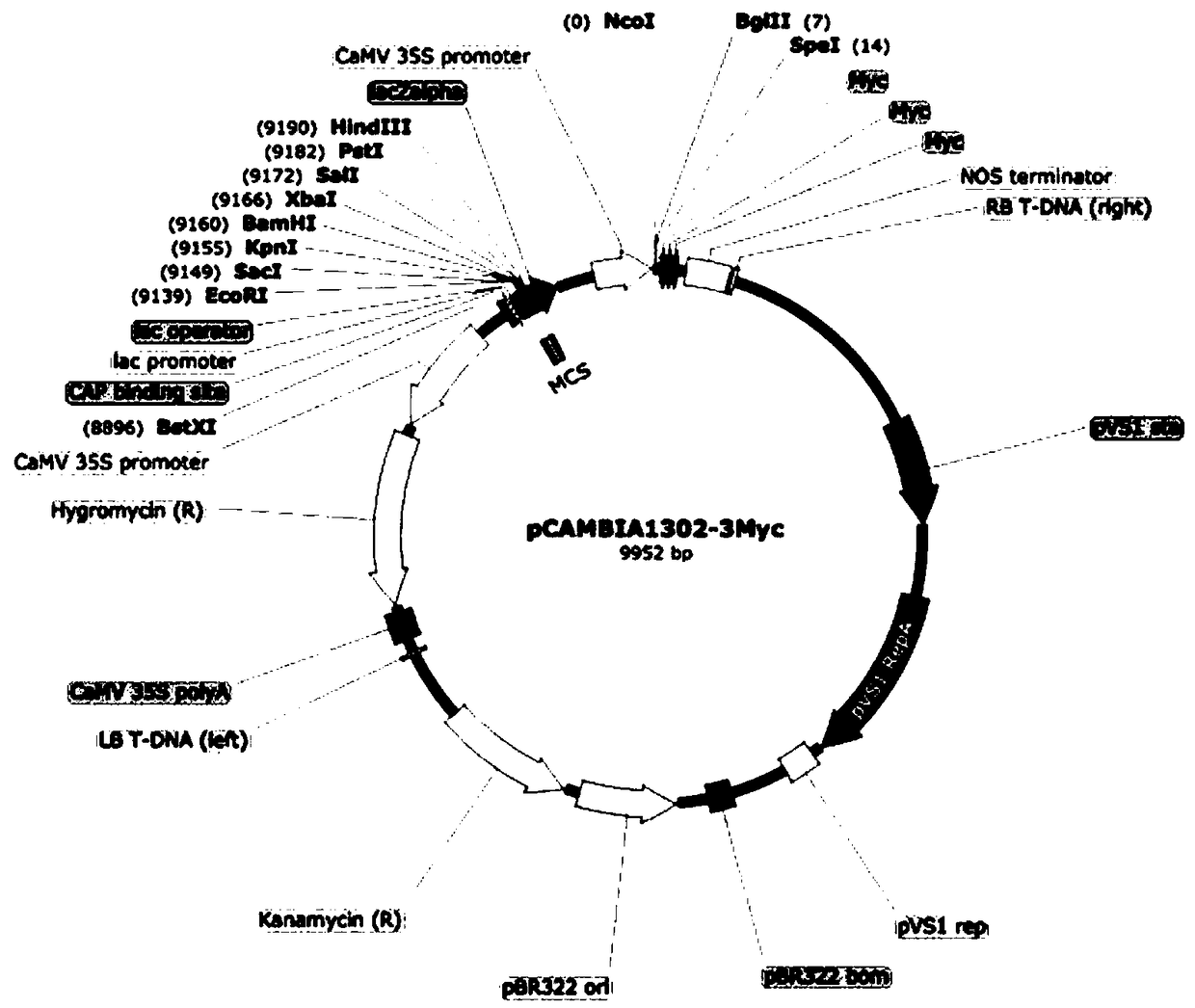
Plant expression plasmid vector containing C-Myc protein fusion label and construction method for vector
InactiveCN108893487AGuaranteed accuracyShort cycle timeVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetRestriction enzyme digestion
The invention discloses a plant expression plasmid vector containing a C-Myc protein fusion label. The plant expression plasmid vector contains the C-Myc protein fusion label at a terminal C of the plant expression plasmid vector. The construction method for the plasmid vector comprises the following steps: (1) taking pCAMBIA1302 as a departing plasmid, carrying out restriction enzyme digestion onthe plasmid by using SpeI and Eco065I, and recycling a klenow fragment through electrophoretic gel cutting; (2) carrying out full-sequence synthesis on a nucleotide sequence encoded with three C-Mycproteins; (3) designing an amplification primer; and (4) adding a SpeI restriction enzyme cutting site at a terminal N, and adding an Eco065I restriction enzyme cutting site at the terminal C; carrying out restriction enzyme digestion on the synthesized fragment by using SpeI and Eco065I; and finally connecting products, transforming DH5 alpha by heat shock, and carrying out PCR identification toobtain positive clone. The plant expression plasmid vector has the advantages that the plant expression plasmid vector of a fusion label of small protein is obtained, a user is assisted to rapidly research functions of the protein, functions of the target protein cannot be interfered, and it ensures that the functions of the protein can be researched accurately.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com